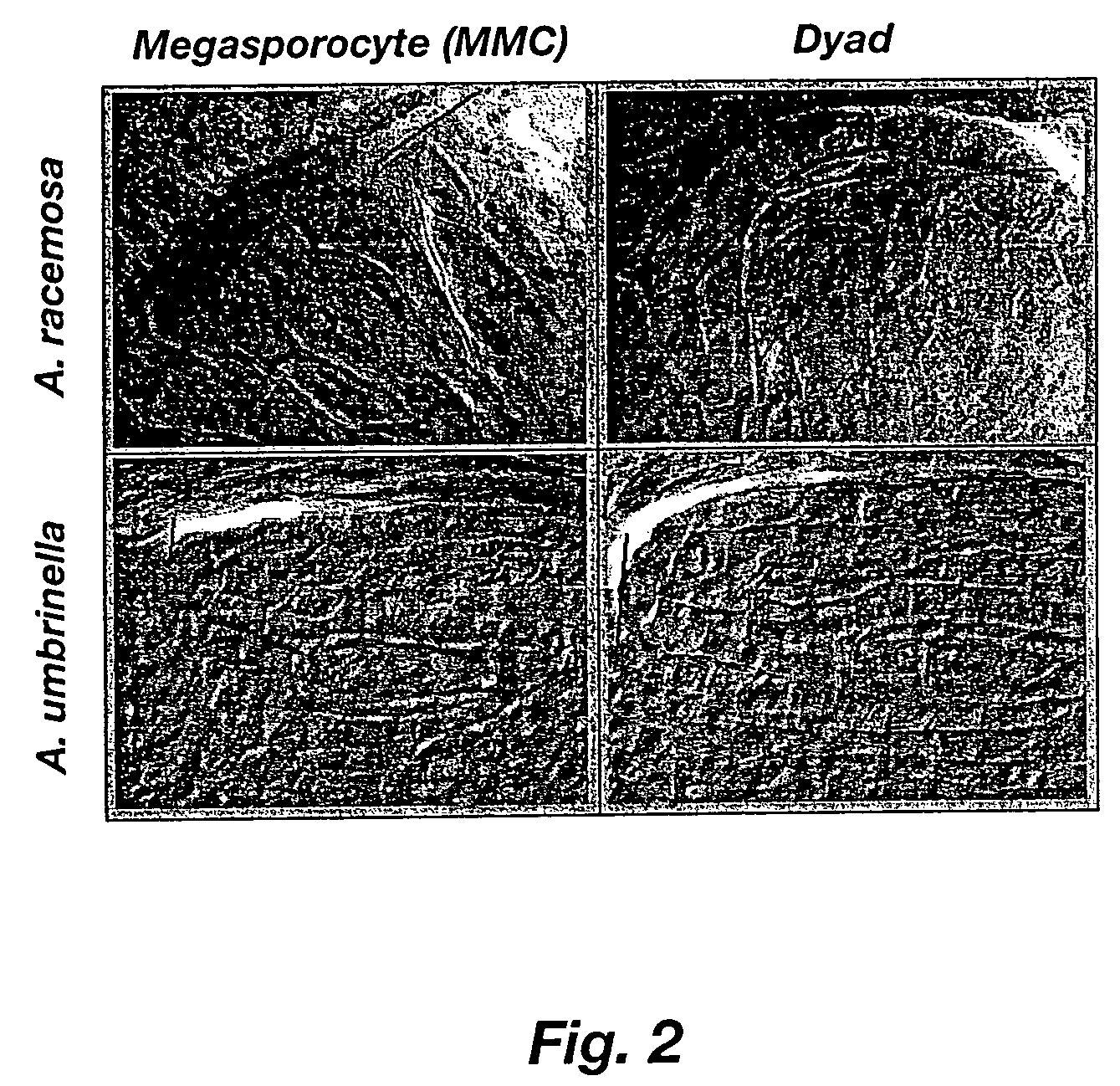
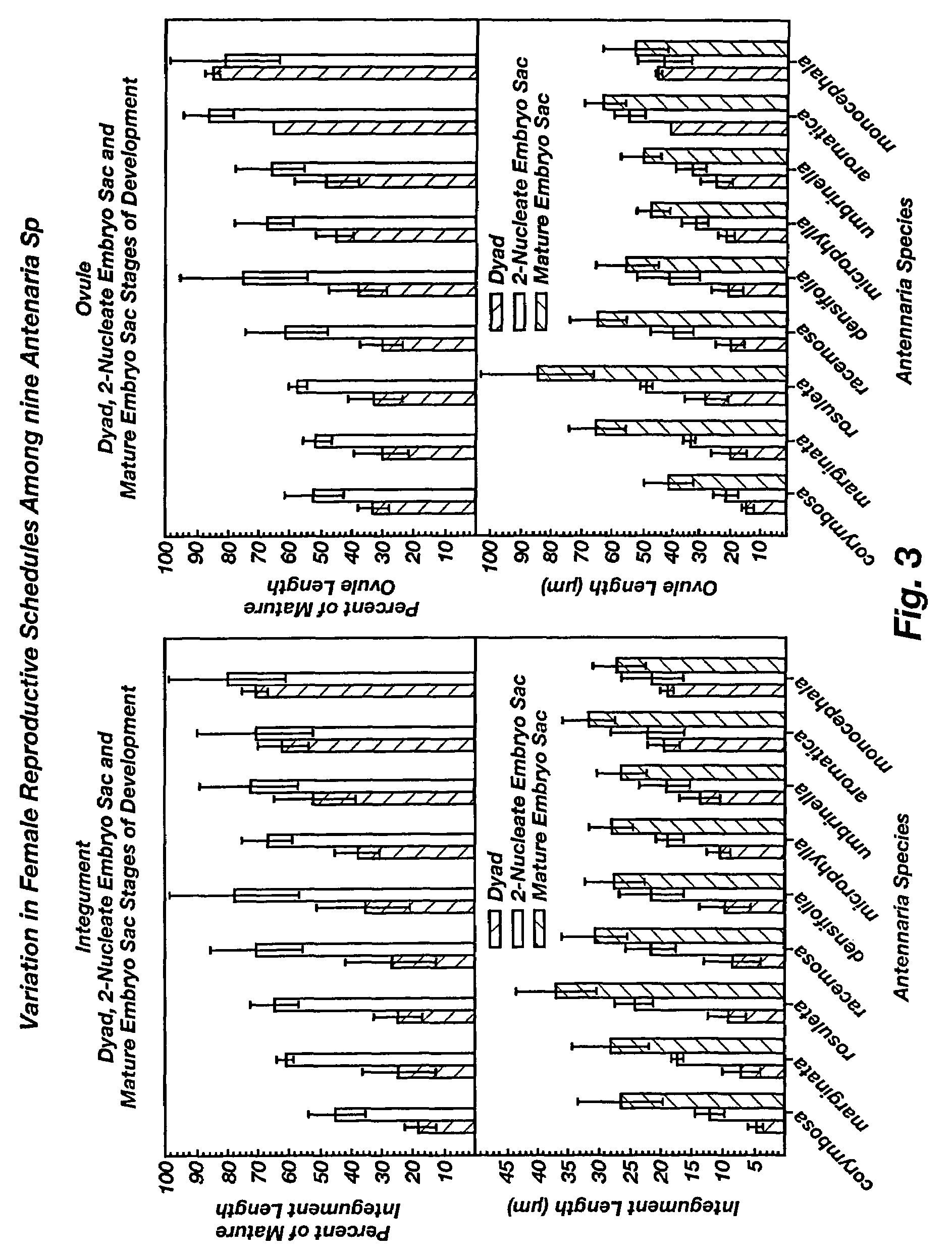
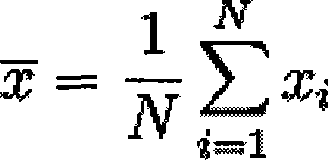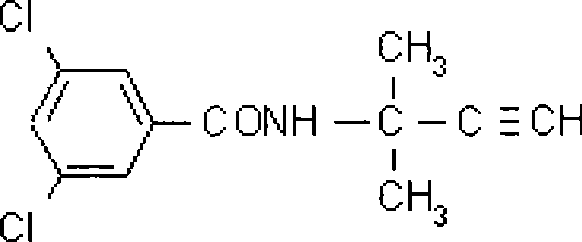Patents
Literature
82 results about "Parthenogenesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Parthenogenesis (/ˌpɑːrθɪnoʊˈdʒɛnɪsɪs, -θɪnə-/; from the Greek παρθένος, parthenos, 'virgin' + γένεσις, genesis, 'creation') is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which growth and development of embryos occur without fertilization. In animals, parthenogenesis means development of an embryo from an unfertilized egg cell. In plants parthenogenesis is a component process of apomixis.
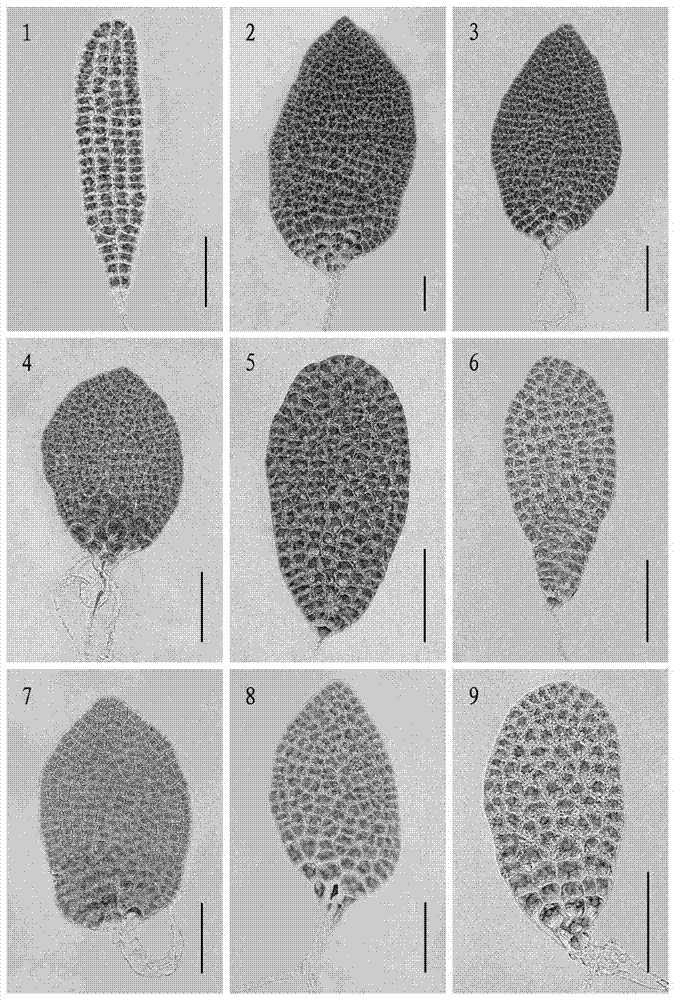
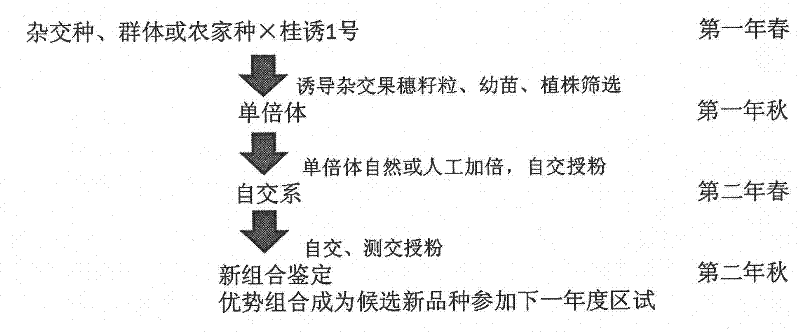
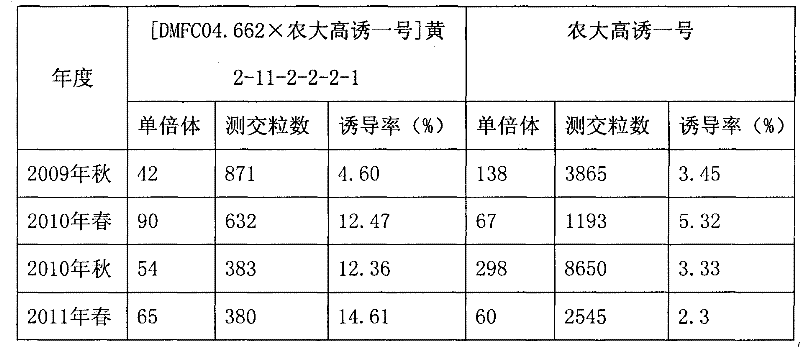
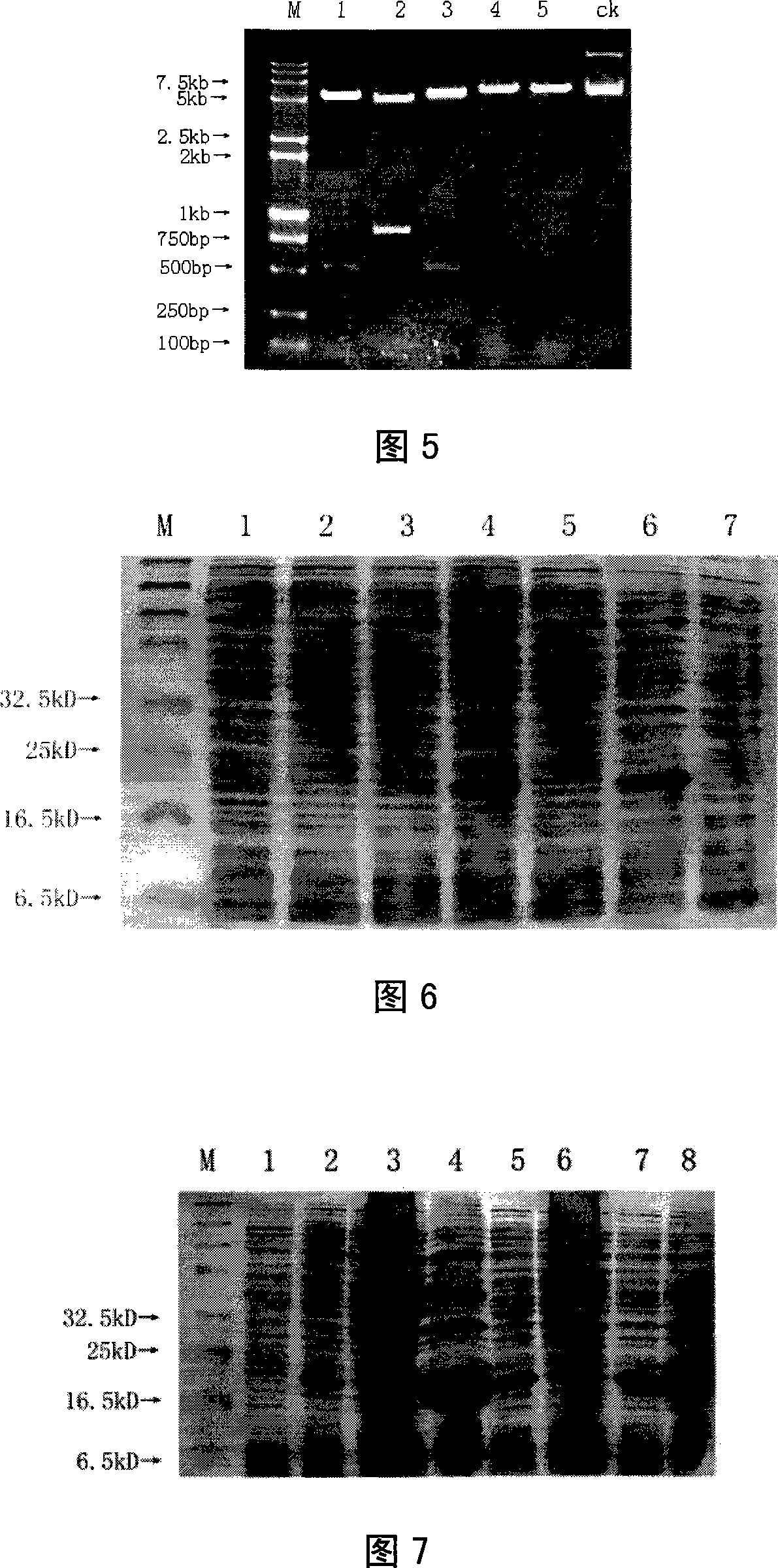
Breeding method of maize parthenogenesis inducer and its application in maize inbred line breeding
InactiveCN102440179AShorten breeding timeSimple procedurePlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceParthenogenesis
The invention discloses a breeding method of a maize parthenogenesis inducer and its application in maize inbred line breeding. Employment of a maize parthenogenesis inducer can induce a female parent material to perform parthenogenesis and generate a female parent haploid, thus realizing a method able to rapidly breed a highly homozygous maize inbred line in a large-scale through simple process and create a lot of new maize breeding resources. And the application of a maize parthenogenesis inducer consists of: using a high frequency parthenogenesis inducer Guiyou No.1 as a male parent to hybridize with an excellent maize breeding germplasm resource, making use of an obvious seed purple marker to pick out a haploid grain, and utilizing the purple marker of a plant to distinguish a non-haploid plant, subjecting a haploid plant to chromosome doubling so as to become a normal diploid, then conducting inbreeding so as to generate a new highly homozygous maize inbred line, which can be applied in maize hybrid combination preparation for breeding new maize varieties. Compared with a traditional pedigree breeding method, the method provided in the invention can shorten the breeding time of an inbred line by 3-4 years, thus shortening the breeding period of new maize varieties.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION CORN RES INST
Production of parthenogenetic stem cells and patient-specific human embryonic stem cells using somatic cell nuclear transfer
ActiveUS20140234968A1Reduced feature requirementsNew breed animal cellsHybrid cell preparationPatient specificParthenogenesis
Immunocompatible pluripotent stem cells (pSCs), which include cells compatible with different patient populations or patient-specific cells, find wide application in regenerative medicine therapies. Described herein are immunocompatible pSCs generated using techniques such as parthenogenesis resulting in cells possessing desired haplotypes of reduced zygosity, antigenically compatible with multiple patient populations, or nuclear transfer allowing generation of patient-specific cells. Methods described herein related to parthenogenesis, nuclear transfer, or pSC cell line generation. Also described herein are compositions of immunocompatible pSCs and cell lines generated by the aforementioned techniques.
Owner:SUNG KWANG MEDICAL FOUND
Breeding method for inducing parthenogenesis of corn by trifluralin
InactiveCN102550399AHigh chance of parthenogenesisThere is no difficulty in identifyingPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyParthenogenesis
The invention discloses a breeding method for inducing parthenogenesis of corn by trifluralin. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: selecting 48 percent trifluralin missible oil as an inducer, and diluting the trifluralin missible oil into 200-1,000-fold solution by using water; inducing, namely spraying or coating trifluralin diluent on thrums after the thrums on clusters come out; harvesting to obtain diploid seeds with homozygous genotype when seeds are mature; seeding in the next season, identifying truth according to phenotype and weeding out inferior plants,namely seeding the harvested clusters for the next generation, selectively harvesting rows according with a breeding goal, and thus obtaining a homozygous self-bred line of the corn. The invention has the advantages that: the trifluralin has low toxicity, can be used in the field under open conditions, and is safe to people, livestock and the environment; the inductivity is about 1.0 to 3.0 percent, pollination is not required, and the method is simple, easy to operate, low in cost and high in efficiency and can be used in a large scale; the diploid seeds are directly formed, and the process of doubling chromosomes is not required; and moreover, compared with that of the conventional seed selection method and a Stock 6 genetic induction method, the seed selection period is shortened by more than six generations and is shortened by more than one generation.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
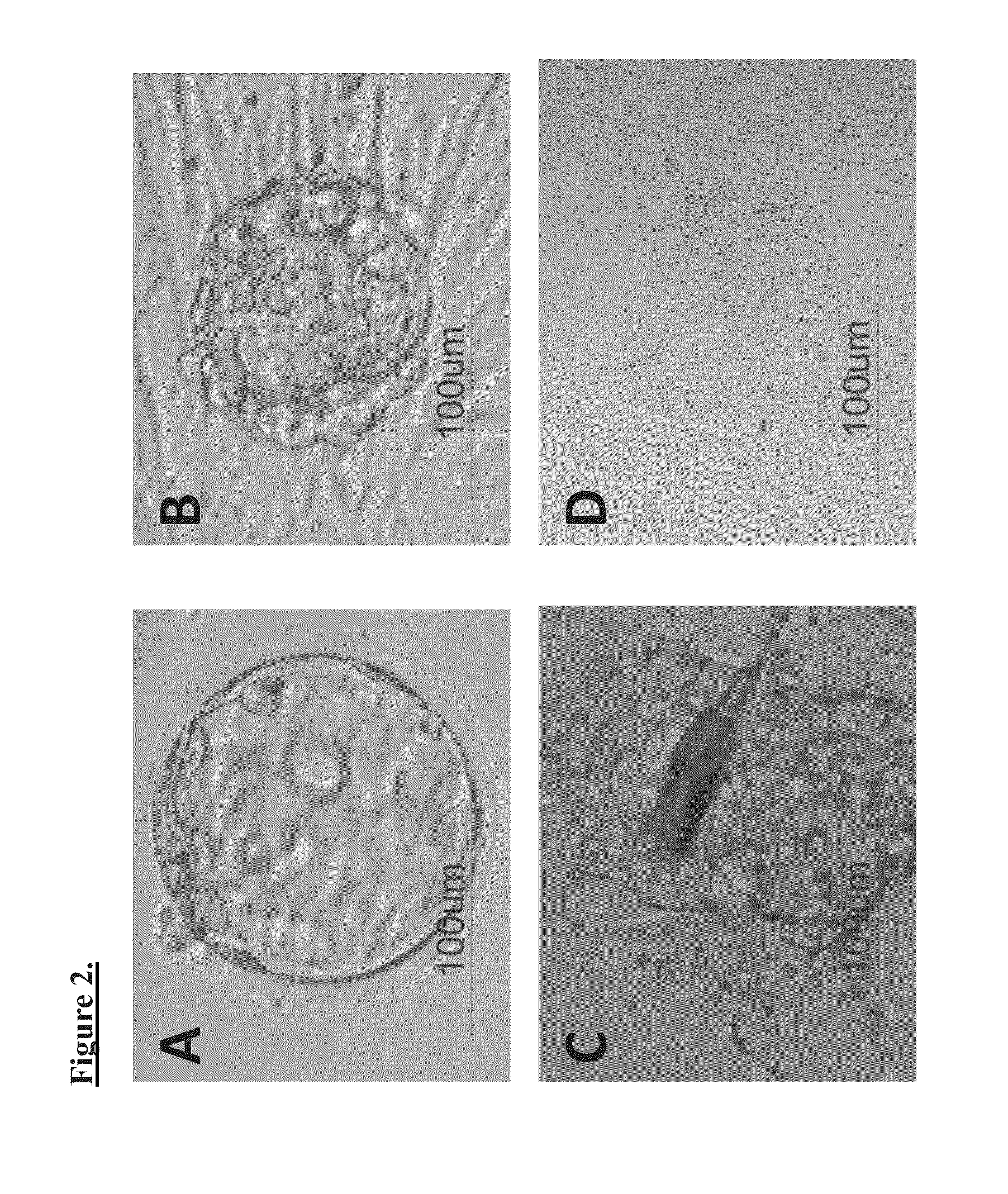
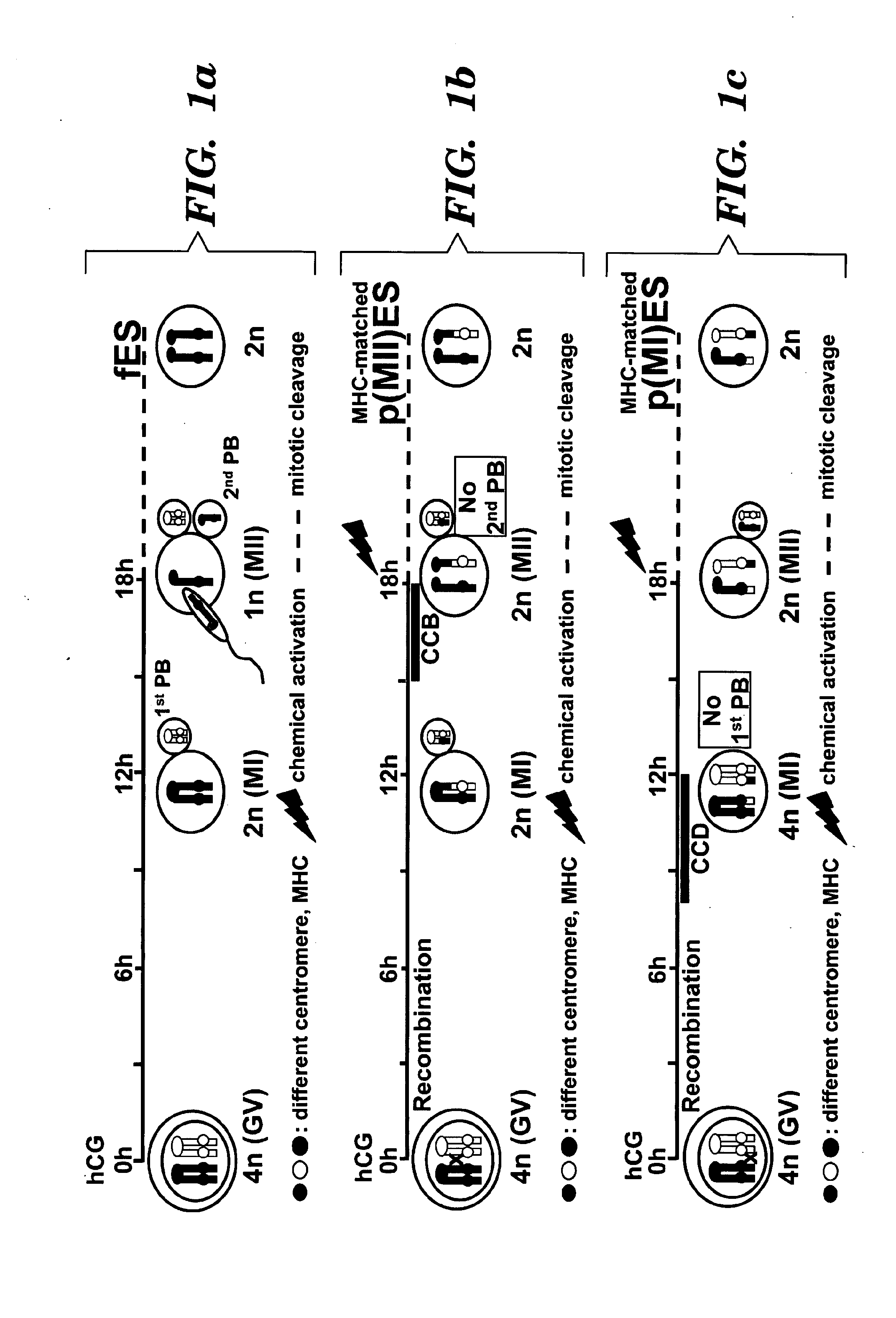
Methods for producing embryonic stem cells from parthenogenetic embryos
InactiveUS20100069251A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningOocyte donorParthenogenesis
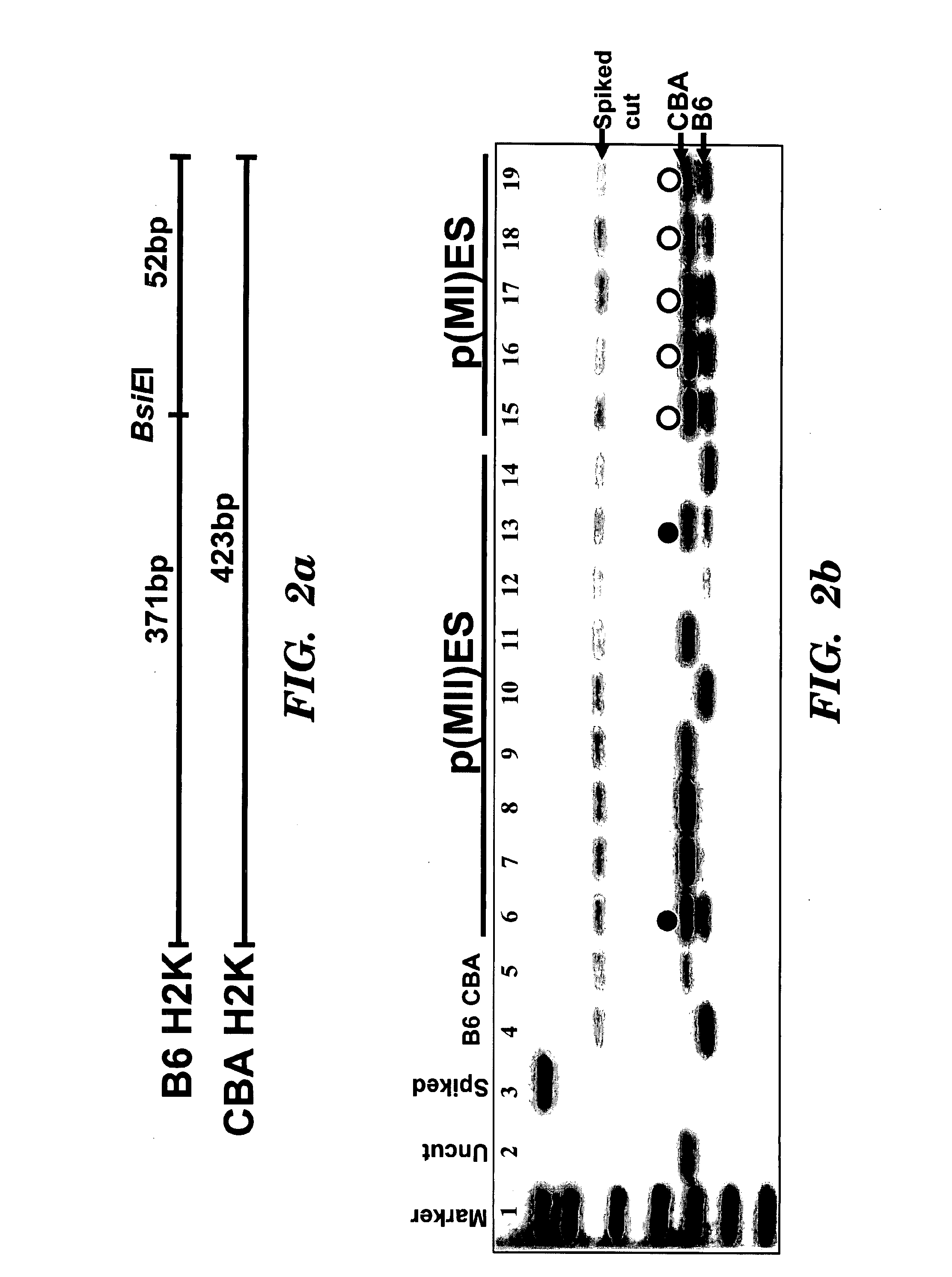
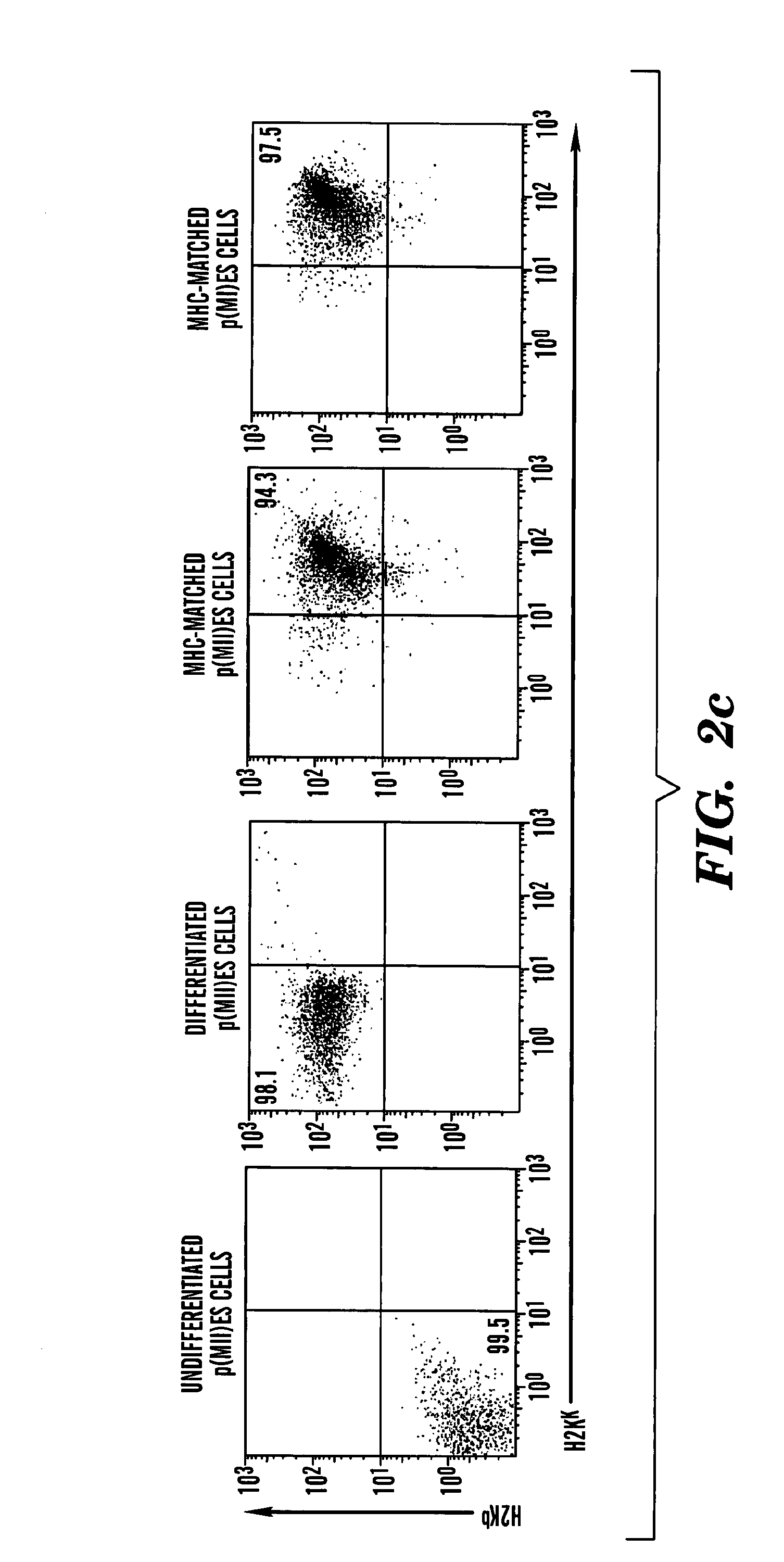
Means for producing embryonic stem (pES) cells which have a heterozygous genome that is matched to an individual donor are provided. In one embodiment, a means for the generation and isolation of parthenogenetic embryonic stem (pES) cells which have regions of heterozygosity that are fully matched to the oocyte donor at the MHC loci (e.g. (h-)p(MI)ES cells is provided. This is in contrast to the traditional methods of parthenogenesis that generate parthenogenetic embryonic stem (pES) cells having a substantially homozygous haploidentical set of chromosomes that are homozygous at the MHC loci.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Parthenogenic activation of human oocytes for the production of human embryonic stem cells
Methods of producing human stem cells by parthenogenetically activating human oocytes by manipulation of oxygen tension, including manipulation of Ca2+ under high 02 tension using anionophore and contacting oocytes with serine threonine kinase inhibitors (DMAP) under low 02 tension, isolating inner cell masses (ICMs) from the activated oocytes, and culturing the cells of the isolated ICMs under high 02 tension. Moreover, methods are described for the production of stems cells from activated oocytes in the absence of non-human animal products, including the use of human feeder cells / products for culturing ICM / stem cells. Stem cells produced by the disclosed methods are also described.
Owner:INT STEM CELL CORP
Undariapinnatifida seedling cultivation method through parthenogenesis
ActiveCN103651094AResistant to washingFirmly attachedClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsPuccinia xanthiiSporeling
The invention relates to an undariapinnatifida cultivation method, in particular to an undariapinnatifida seedling cultivation method through parthenogenesis. The method comprises the steps that induction culture is conducted on female gametophytes until juvenile sporophytes reach more than 1mm, aerated feeding culture is conducted on the female gametophytes, then the life history of parthenogenesis sporophytes is completed, and mature sporophytes are obtained; sporophyls of the sporophytes are placed into sea water to be released to obtain planospores, after the color of the sea water where the planospores are obtained through releasing is changed into yellowish-brown, the planospores are attached to a seedling curtain, and then the seedling curtain is put into fresh sea water; after all the germinal planospores develop into the female gametophytes and are sufficiently grown, light intensity is lowered, the development of the gametophytes is delayed to enable the gametophytes to pull through the high-water-temperature summer; the male gametophytes and the female gametophytes attached to the seedling curtain are simultaneously cultured, and the development and fertilization processes are completed; after reaching about 200 micrometers, the juvenile sporophytes are moved to sea to be cultivated, and then undariapinnatifida cultivation is achieved. According to the undariapinnatifida seedling cultivation method through parthenogenesis, female gametophyte clonal update and enlarged cultivation can be achieved through the parthenogernesis life history, and it is of great significance in clonal preservation and crossbreeding.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
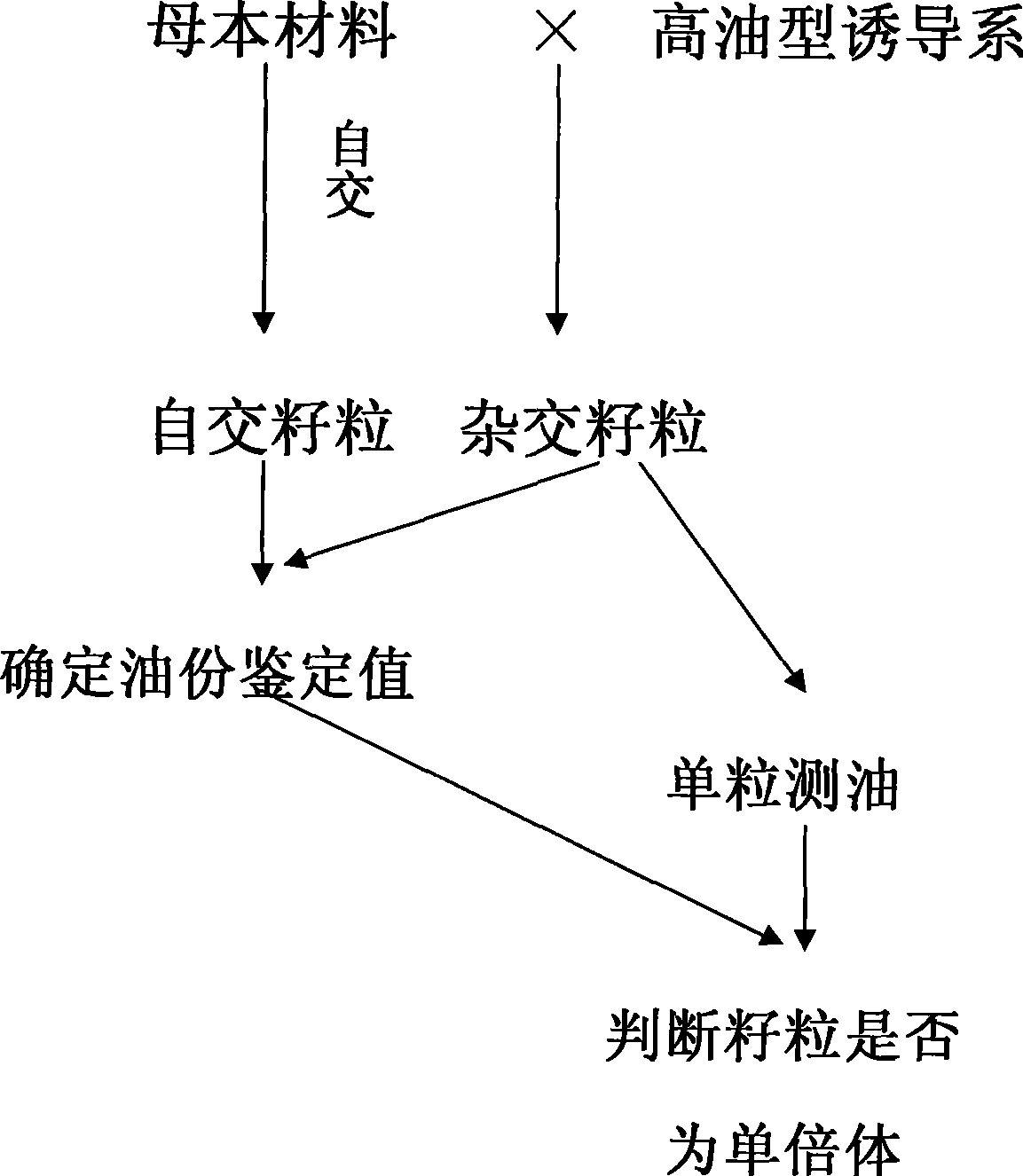
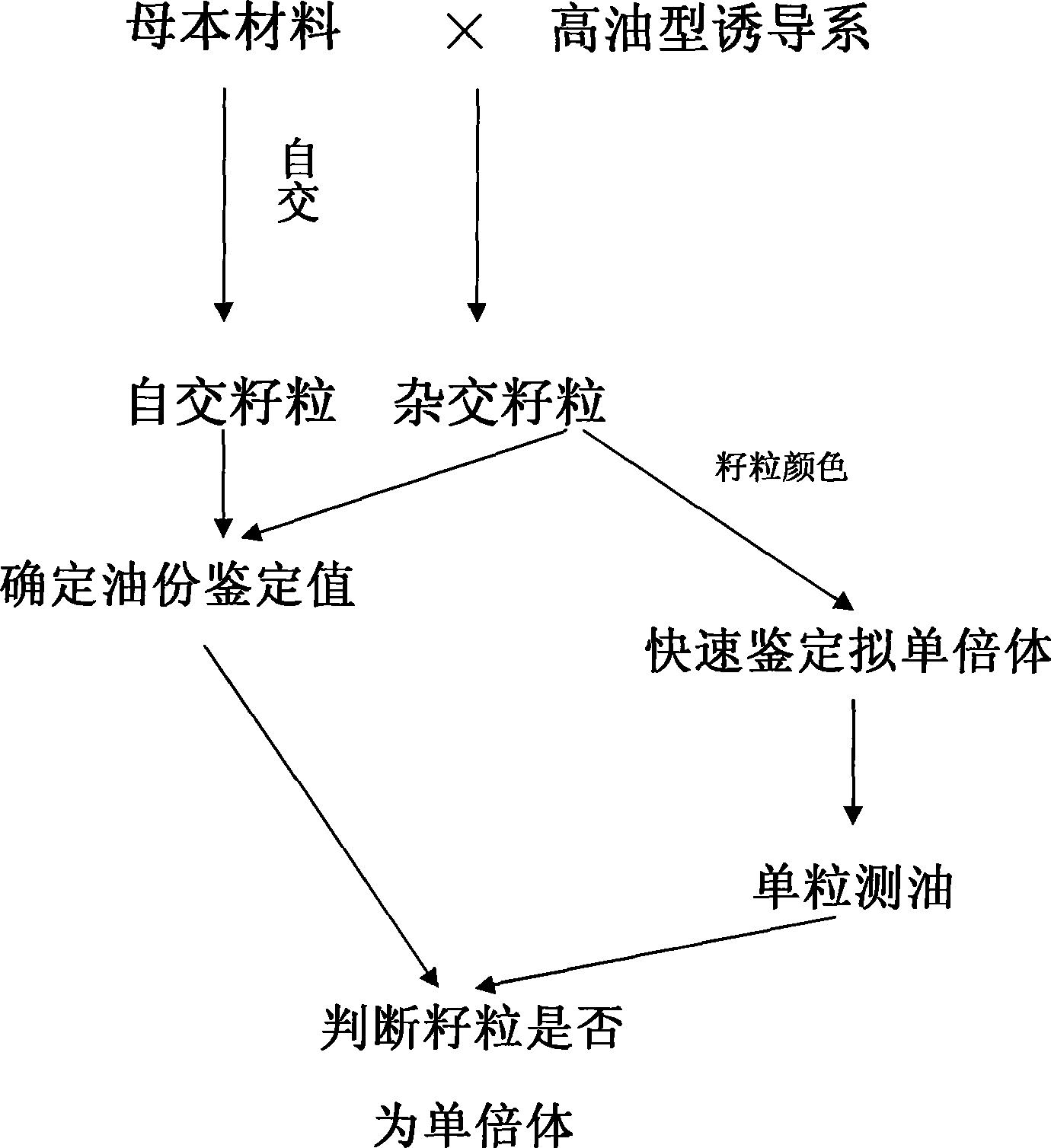
Method for identifying corn parthenogenesis haploidy
InactiveCN101377481AImprove breeding efficiencyFlexible operationTesting foodAgricultural scienceParthenogenesis
The invention discloses a method for identifying a core parthenogenesis haploid. The method for identifying the core parthenogenesis haploid comprises the following steps: (1) a corn haploid derived line is used to be taken as a male parent to carry out hybridization with a female parent corn, and hybrid present kernals are harvested; (2) an identification standard value is ensured; (3) the oil content of a single hybrid present kernal to be tested is tested, if the oil content of the single hybrid present kernal to be tested is bigger than or equal to the identification standard value, the single hybrid present kernal to be tested is the haploid. Compared with the traditional method, the identification method has the characteristics of convenient operation, time conservation, labor conservation and high identification efficiency. The identification method opens up a new way for the identification of the haploid, can carry out large scale operation, and provides the possibility for carrying out haploid picking in a mechanized way, thereby enhancing the breeding efficiency.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for generating macrogametocyte by somatic cell of inducing undaria pinnatifida gynecogenic juvenile sporophyte
The invention discloses a method for generating macrogametocytes by somatic cells of inducing undaria pinnatifida parthenogenesis juvenile sporophytes, which has easy operation, low cost and high maturation rate of the generated macrogametocytes and can provide a large quantity of the macrogametocytes for the large-scale seedling production of undaria pinnatifida. The method comprises the following steps of: cutting undaria pinnatifida macrogametocytes stored and cultured in a room into pieces and then culturing under the conditions of temperature suitable for the undaria pinnatifida macrogametocytes to grow to be mature, illumination and nutritive salt, wherein when the undaria pinnatifida macrogametocytes grow to be mature, form oocysts in large quantities and ovulate with ovums, a small quantity of the fertilized ovums are germinated to seedlings through parthenogenesis because unfertilized ovums are died by being unfertilized by spermatozoa; and when the somatic cells of the parthenogenesis seedlings are grown to 0.4-0.6 cm, adopting a rhizoid cutting method to enable fronds to lose polarity and constraint on the somatic cells, and inducing the somatic cells of the seedlings to generate the macrogametocytes.
Owner:DALIAN FISHERIES UNIVERSITY
Method for collecting seedlings from scytosiphon filaments
InactiveCN101946683ASolve the limitation of algae breeding seasonResolution timeClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsSporangiumBiology
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV
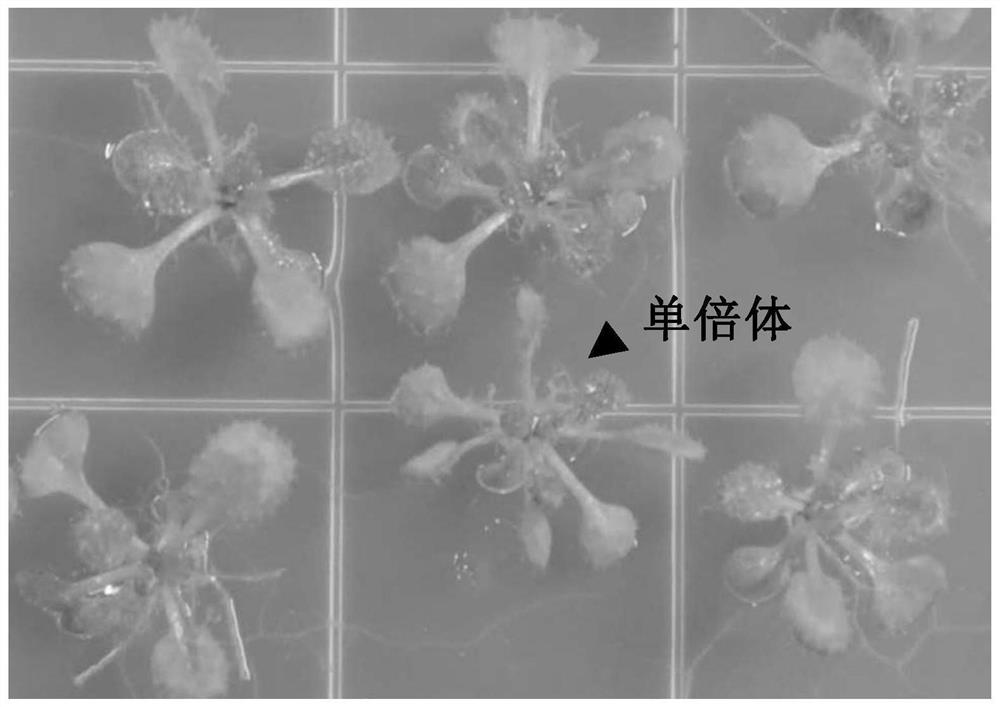
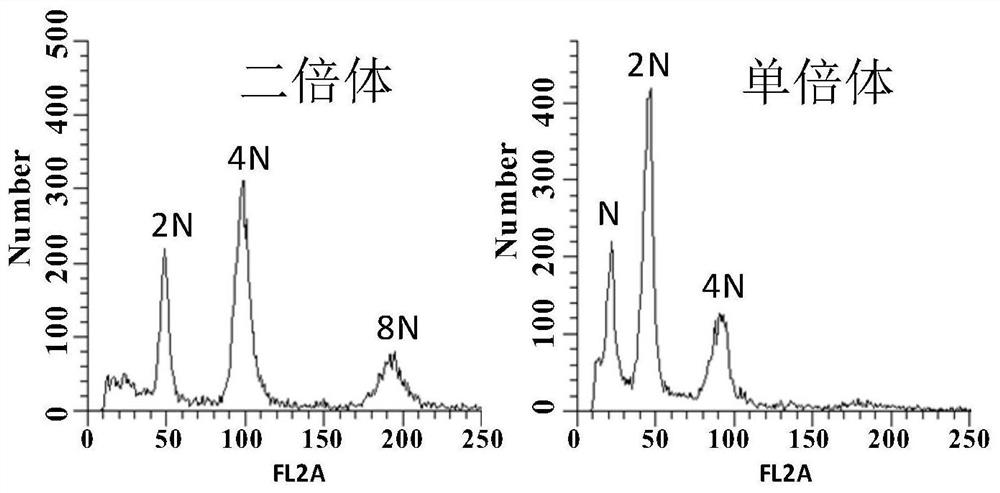
Parthenogenetic haploid induced gene DMP and application thereof
The invention discloses a parthenogenesis haploid induced gene DMP and application thereof. According to the invention, parthenogenesis haploid induced genes AtDMP8 and AtDMP9 are cloned from arabidopsis thaliana. Experiments prove that mutation of the AtDMP8 and the AtDMP9 can generate parthenogenesis haploid inducibility, so that the application of parthenogenesis induced haploid extends to dicotyledonous crops. Verification is further carried out in tomatoes, and the invention also finds that mutation of SlDMP can generate parthenogenesis haploid inducibility in tomatoes. The invention laysan important foundation for widening the application of haploid breeding technology in dicotyledons and revealing the biological mechanism of parthenogenetic haploid production. In view of the universality of haploid breeding technology utilization in the current breeding industry, the DMP has very wide application space and market prospect.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method to Screen Plants for Genetic Elements Inducing Parthenogenesis in Plants
InactiveUS20130180005A1Fertilization of will not be preventedPromote generationOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationNucleotideMutant allele
Compositions and methods for producing a plant population lacking sexually derived embryos are provided. Compositions include suppression cassettes encoding polynucleotides and promoters resulting in parthenogenesis. Further provided are parthenogenesis genetic elements used to prevent sexual reproduction in self-reproducing plants.Methods include: utilizing maternal embryo defective recessive mutations which are maintained as a sterile inbred maintenance system, allowing generation of populations that are homozygous for recessive mutant alleles, but transgenically complemented. Methods include utilizing a toxin genes expressed via egg-cell specific promoters, creating a dominant, embryo-less phenotypes, non-transmittable through female gametes. Resultant hemizygous plants are transformed with egg-cell promoters driving the antidote, a pollen ablation PTU and a seed color marker for identification of transgenic seed. The generation of a plants 50% female fertile, having seed which when grown in the next generation will yield plants with 50% viable transgenic seed, and 50% non-viable embryo-less seed.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Treatment method for inducing maize parthenogenesis with colchicine
ActiveCN104604673ASolve pollutionFreedom of operationPlant genotype modificationRetention timePollen contamination
The invention relates to a treatment method for inducing maize parthenogenesis with colchicine. The method is characterized in that when female ear filaments are completely exposed, a paper bag is removed; the upper-portion of a flower bud is cut transversely from a female ear flower bud at a place from the top and close to the female ear young ear downward; a part of filaments is cut at the section with a curved graver, such that a cavity with a depth of 5-15mm is formed; an inducing agent which is colchicine treatment liquid is injected into the cavity with a pipette or a syringe, such that the cavity is filled with the liquid and the entire cut surface is wetted by the liquid; and the female ear is sleeved with the paper bag. During the treatment process, no pollen contamination prevention measure such as sealing, blocking, spatial and temporal isolation, and the like is needed. The method has the following advantages: harm to human health caused by treatment liquid dropping, spilling and scratching are avoided; a hard-to-solve pollen contamination problem is thoroughly solved; all filaments can contact the treatment liquid, and treatment liquid retention time is long, such that an induction rate is improved; the treatment liquid is saved by approximately 50%; and compared to a conventional inbred line breeding method, a breeding period is shortened by more than 5 generations.
Owner:SHENYANG TEYIJIA CORN TECH
Specific molecular marker capable of identifying sea-tangle female and male gametophytes
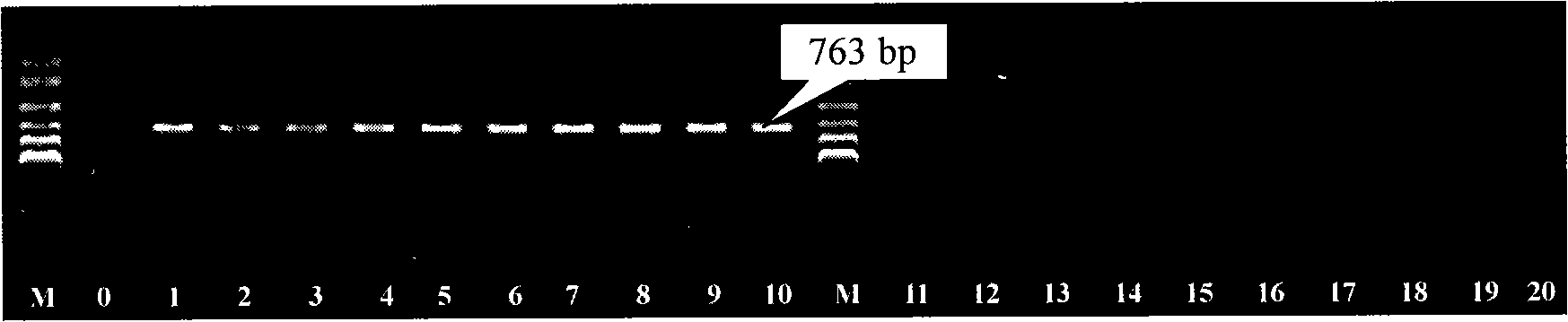
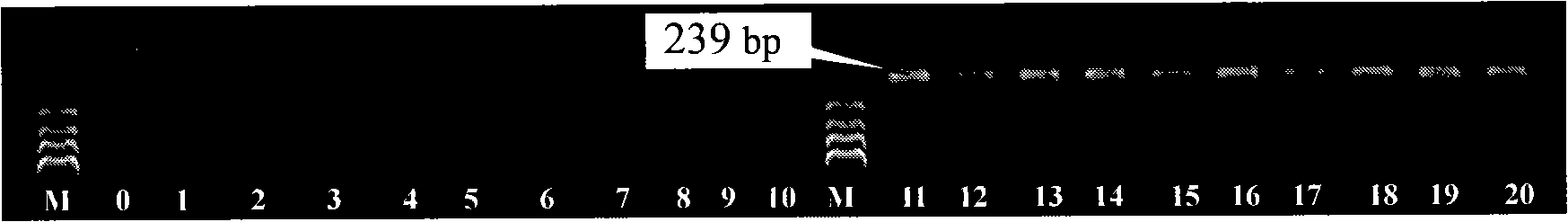
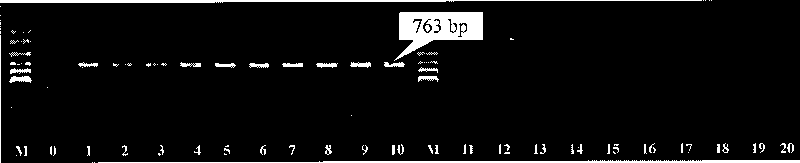
The invention belongs to the technology field of the gene engineering, in particular relates to a specificity molecule marker which can distinguish laminaria female and male gametophyte. The specificity molecule marker is obtained through the following method: two pairs of primers of SEQ ID No1and SEQ ID No2 are designed according to 5'end flanking sequence of the laminaria female and female gametophyte gene groups, polymerase chain reaction amplification is performed to the deoxyribonucleic acid of the laminaria female and female gametophyte gene groups, and the deoxyribonucleic acid of specificity amplification fragment are reclaimed; large intestine rod competent strain JM109 is cloned through pMD19-T vector to obtain a laminaria female gametophyte specificity molecule marker Rf-763 and a laminaria male gametophyte specificity molecule marker Rm-239, and the sequences thereof are SEQ ID No3 and SEQ ID No4. The genders of the laminaria gametophyte, parthenogenesis laminaria sporophyte parental source and the genders of the offspring thereof can identified through utilizing the specificity molecule marker, and the laminaria gender differentiation in basis of the cell and molecule level can be studied.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Cultivating method for obligate parthenogenesis rotifera population
InactiveCN103053476AIncrease culture densityIncrease productivityAnimal husbandryCulture fluidNutrient solution
The invention discloses a cultivating method for an obligate parthenogenesis rotifera population by using chemical drug induction, microwave irradiation mutation, ultraviolet radiation mutation and manual breeding. In a breeding process of the cultivated rotifera population, even if in a nutrient solution with density of 800-1000 / milliliter, parthenogenesis is conducted, and sexual propagation is not conducted, so that rotifera cultivating density can be greatly increased, rotifera production efficiency is improved, cultivation water volume is reduced, production cost is reduced, the cultivating method can be applied to indoor rotifera high-density cultivation, is also suitable for outdoor open pool cultivation propagation of rotifera, and can provide sufficient live food organism for cultivating of offspring seeds and larva of aquatic product economical cultivation animals.
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV
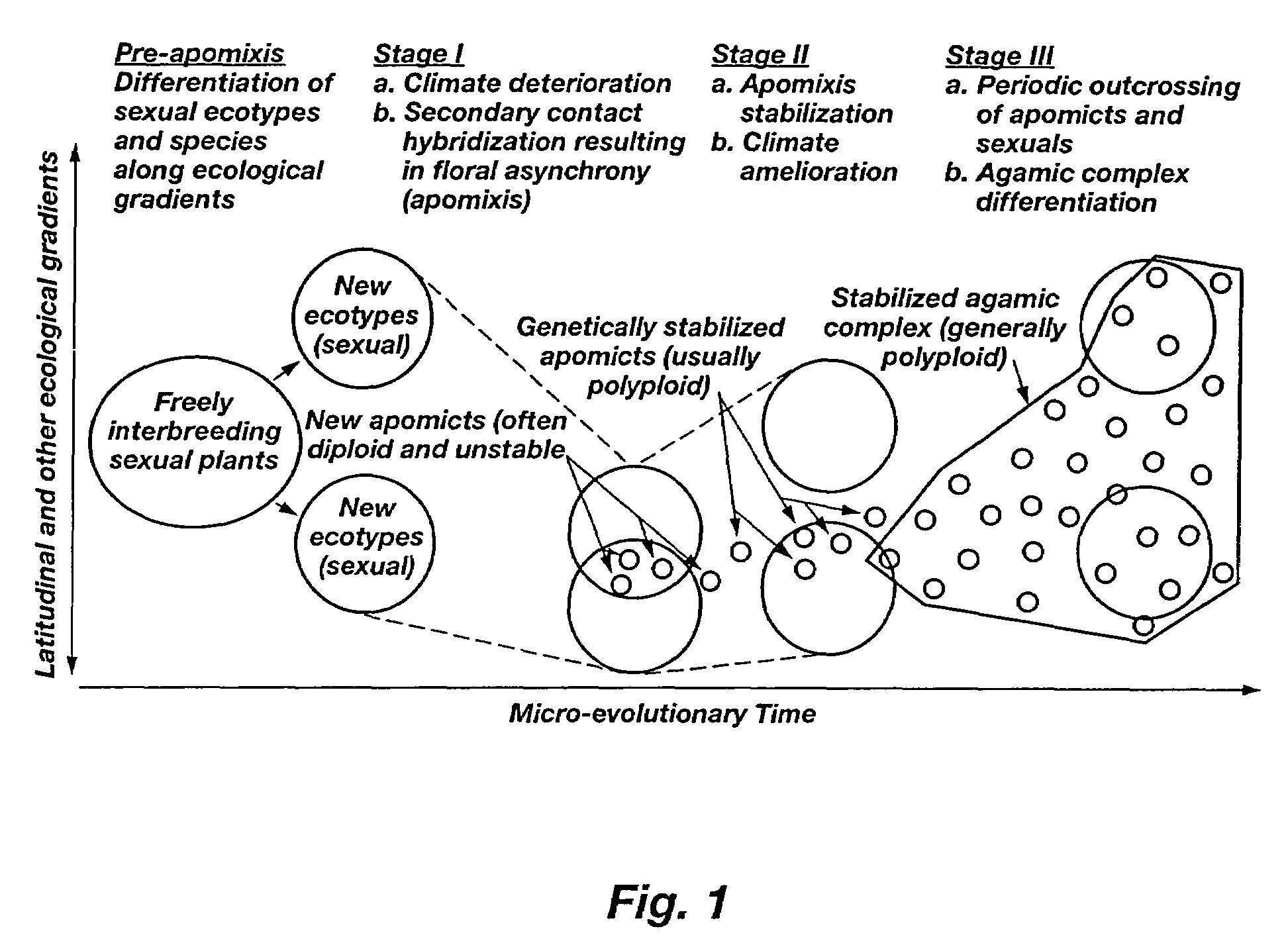
Methods for stabilizing and controlling apomixis
InactiveUS7638680B2Simplifying hybrid seed productionSolve the complicated productionVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationApomixisFacultative
Methods are disclosed for detecting genetic instability for apomixis in angiospermous plant, and for enhancing, genetically stabilizing, and controlling apomixis expression in such plants. Enhanced expression, stabilization, and control are achieved by converting a facultative apomict to obligate apomixis. Enhanced expression of apomixis is further achieved by increasing frequencies of unreduced egg formation and / or parthenogenesis. Genetic stabilization of apomixis is alternatively achieved by conferring mechanisms to a facultative apomict that, during facultative sexual seed formation, prevent the segregational loss of unique alleles at multiple loci, which cause apomixis, such that progeny produced sexually from the facultative apomict inherit the unique allelic combinations required to maintain apomixis. The disclosed methods are used in various combinations to produce apomictic plants that possess improved yield, quality, and / or seed production characteristics.
Owner:UTAH STATE UNIVERSITY
Breeding method for inducing parthenogenesis of corn by propyzamide
InactiveCN102960242ALow toxicityThere is no difficulty in identifyingPlant genotype modificationParthenogenesisPollination
The invention relates to a breeding method for inducing parthenogenesis of corn by propyzamide, belonging to the field of polyploid breeding of plants. The breeding method specifically comprises the following steps of: preparing an inducer with the content of 5 mu mol / L-200mu mol / L by the propyzamide and water; performing induction treatment on filaments, wherein the inducer is sprayed or smeared onto the filaments which grow to about 2.5cm long after emerging, and mature seeds are harvested to get genotype homozygous diploid seeds; and selecting and identifying the seeds according to a conventional method, and selecting a head progeny row which conforms to a breeding goal, thus finally getting a homozygous corn inbred line. The breeding method disclosed by the invention has the positive effects of omitting artificial pollination, being simple, being easy to implement, low in cost, high in efficiency and suitable for large-scale use.
Owner:SHENYANG JINSEGU SPECIAL CORN
Treating method for chemically inducing parthenogenesis of corn
ActiveCN104604674AStrong moisturizing abilitySolve pollutionPlant genotype modificationComing outPollen
The invention provides a treating method for chemically inducing parthenogenesis of corn. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: adding roll paper into an inductive agent and carrying out stirring so as to prepare paper paste; sleeving a female ear with a paper bag before filament emergence; picking off the paper bag when filaments come out and transversely cutting off a basal part at the top of the bud of the female ear with a blade so as to form a circular cross section which has filaments at the center and husk leaves at the periphery; picking up the paper paste with dressing pliers, placing the paper paste on the cross section and allowing the paper paste to closely contact with the cross section and fill in space formed after the cutting; restoring pulled-open husk leaves to original positions so as to allow the paper paste to be packed in the husk leaves; and finally, sleeving the treated ear with the paper bag again. The invention has the following beneficial effects: the problem of pollen pollution difficult to overcome in a conventional chemical-induction treatment method is thoroughly overcome; threat to human health is avoided; induction operation is carried out under completely open conditions; an induction rate is improved; loss of the liquid of the inductive agent is small; and compared with a conventional selfing line breeding method, the breeding period in the method provided by the invention is shortened by more than 5 generations.
Owner:SHENYANG TEYIJIA CORN TECH
Chemical induction corn parthenogenesis operation method
The invention provides a chemical induction corn parthenogenesis operation method. The chemical induction corn parthenogenesis operation method is characterized by comprising strictly bagging female ears before filaments are protruded, dropping off paper bags in 4-5 days after the filaments of the female ears are protruded, pinching the filaments under bract isolation conditions by the aid of improved long-nose pliers, pulling out the filaments by hands and reserving a hole after each filament is pulled out; injecting preferably 2-5 ml of inductive agents into each hole by the aid of a syringe; sleeving the female ears with the paper bags to complete treatment procedures. The chemical induction corn parthenogenesis operation method has the advantages that the problems in the aspect of safe use of poisonous reagents can be solved, the problem of existing pollen pollution can be thoroughly solved, and operation procedures are carried out under completely open conditions; good chemical application effects can be realized, operation can be carried out in all seasons, and the chemical induction corn parthenogenesis operation method is easy to implement, high in treatment speed and suitable for large-scale application.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV +1
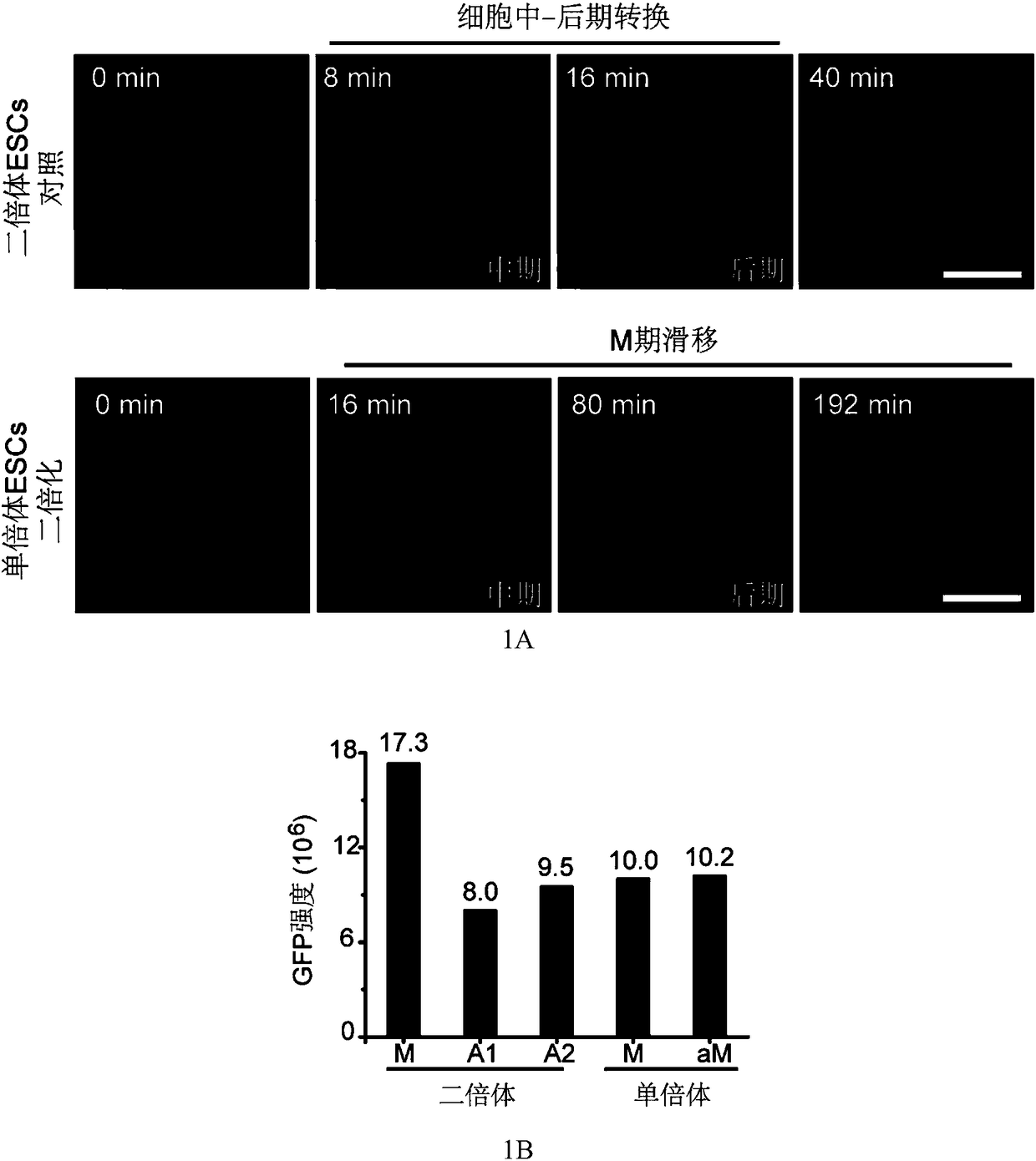
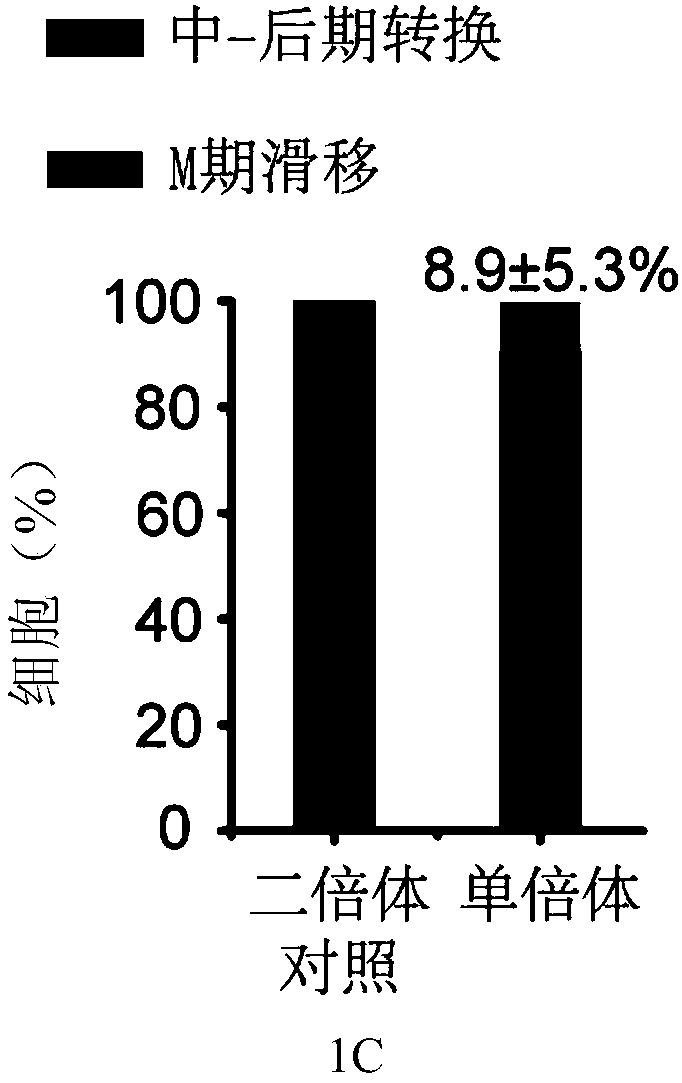
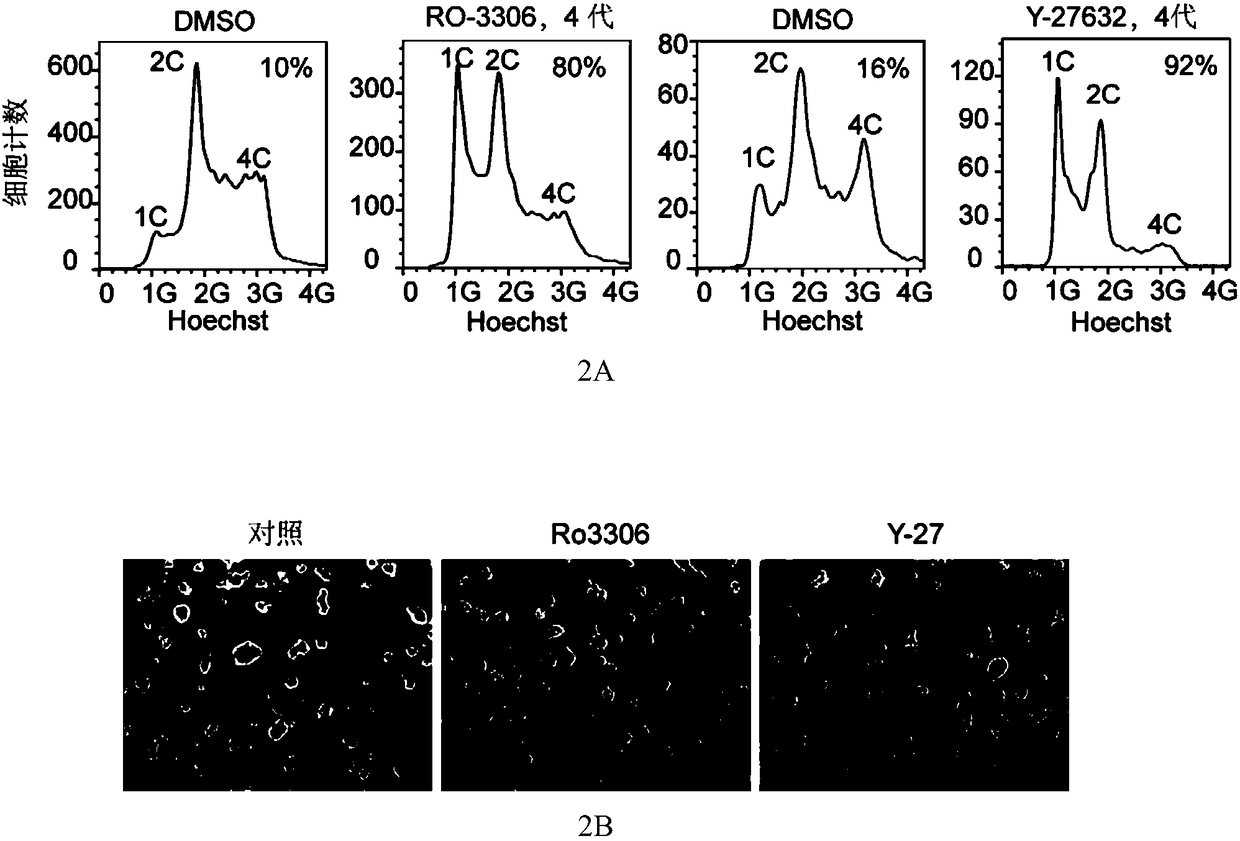
Use of protein kinase inhibitor for inhibiting diploidization of haploid cells
ActiveCN108998410AInhibition of diploidationAids in amplificationNervous system cellsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPTK InhibitorsTyrosine-kinase inhibitor
The invention provides the use of a CDK1 protein kinase inhibitor and / or a Rock protein kinase inhibitor for inhibiting the diploidization of haploid cells. The screened CDK1 protein kinase inhibitorand Rock protein kinase inhibitor can be utilized to widely culture and differentiate patrogenesis and parthenogenesis haploid embryonic stem cells. A technical scheme of the invention provides a basis for research and application based on haploid genome.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Seed sorting method for fixing plant heterosis
ActiveCN110093354AEfficient sortingEliminate complex seed production proceduresPlant peptidesFermentationHybrid seedHeterosis
Provided is a seed sorting method for fixing plant heterosis. The invention provides a method for controlling and screening marker genes by a pollen specific genetic switching system and then sortingand cloning seeds so as to realizing the application of a hybrid seed non-fusion system. Three closely linked gene expression cassettes and a MiMe knockout vector are simultaneously transferred into ahybrid plant. The three gene expression cassettes include: 1) an embryonic autonomous gene expression cassette E1 driven by an oocyte specific expression promoter; 2) a screening marker gene expression cassette E2 regulated by E3; and 3) an expression cassette E3 for pollen-specific control of E2. In selfing fruiting seeds of hybrid transgenic plants, besides asexual embryo seeds which are fixedwith heterosis and are generated through parthenogenesis, zygotic embryo seeds formed by pollination and fertilization are also included; the two kinds of seeds are sorted by screening markers controlled by a pollen-specific gene switch, cloned seeds retain heterosis and can be used for production, and the remaining seeds can be used for commercial purposes.
Owner:HUNAN HYBRID RICE RES CENT
Low-cost interlinear silkworm hybrid breeding method
The interlinear silkworm hybrid breeding method includes high hatchability non-meiotic female parthenogenesis to propagate the female parent as hologynic filial generation for silkworm hybrid, egg color limiting process to propagate the male parent as holandric filial generation for silkworm hybrid ,and hybridization with the two parents to produce interlinear silkworm hybrid. The present invention has low hybrid breeding cost to raise high-quality new silkworm hybrid with high feed efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Method for inducing gynogenesis of Chinese sturgeons through homologous sperms
ActiveCN106614116AGuarantee authenticityPrevent infiltrationClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaGenomic sequencingGenetic Materials
The invention belongs to the field of artificial induction to parthenogenesis of Chinese sturgeons and particularly relates to a method for inducing Chinese sturgeon ova to perform gynogenesis through genetically inactivated Chinese sturgeon homologous sperms. The method comprises the steps of genetic material inactivation of Chinese sturgeon sperms, Chinese sturgeon ovum collection, insemination operation of the Chinese sturgeon sperms, chromosome doubling processing of Chinese sturgeon fertilized ova, breeding of gynogenesis inducing ova and identification of gynogenesis fry. High-homozygous-degree Chinese sturgeon fry can be produced by utilizing the method, an experiment material is provided for research on whole genome sequencing of the Chinese sturgeons, a fry source is provided for production of single-gender Chinese sturgeon fry, information is provided for disclosure of Chinese sturgeon gender determining mechanism, and technical support is provided for further research on parthenogenetic reproduction production.
Owner:CHINESE STURGEON RES INST CHINA THREE GOR
Porphyra yezoensis mutation breeding method based on pigment mutant selection
The invention discloses a porphyra yezoensis mutation breeding method based on pigment mutant selection. The porphyra yezoensis mutation breeding method comprises the steps of: carrying out induced mutation, carrying out enzymolysis and separation on differentiated cells, selecting good regenerated thallus according to an improved variety selection target for carrying out single-strain culture, qualitatively and quantitatively determining the selected good pigment mutant regenerated thallus; carrying out enzymolysis, culturing into regenerated thallus to obtain diploid pure-line protonema through a parthenogenesis technology, and culturing into F1-generation thallus; and crushing the good pure-line protonema and then carrying out a shell seedling culturing test, picking seedlings from shell protonema on a culture web curtain, and carrying out a thallus pigment mutant good strain culturing test in a sea area. According to the invention, the breeding of the large cultivation algae porphyra yezoensis is switched into early-stage prediction and judgment in a laboratory from the later-stage sea cultivation test detection, stable inheritance of the porphyra yezoensis pigment mutant is obtained by using ray radiation treatment, and mutants relevant to the breeding target trait are selected to be used as breeding targets for carrying out breeding.
Owner:吕峰
Specific molecular marker capable of identifying sea-tangle female and male gametophytes
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
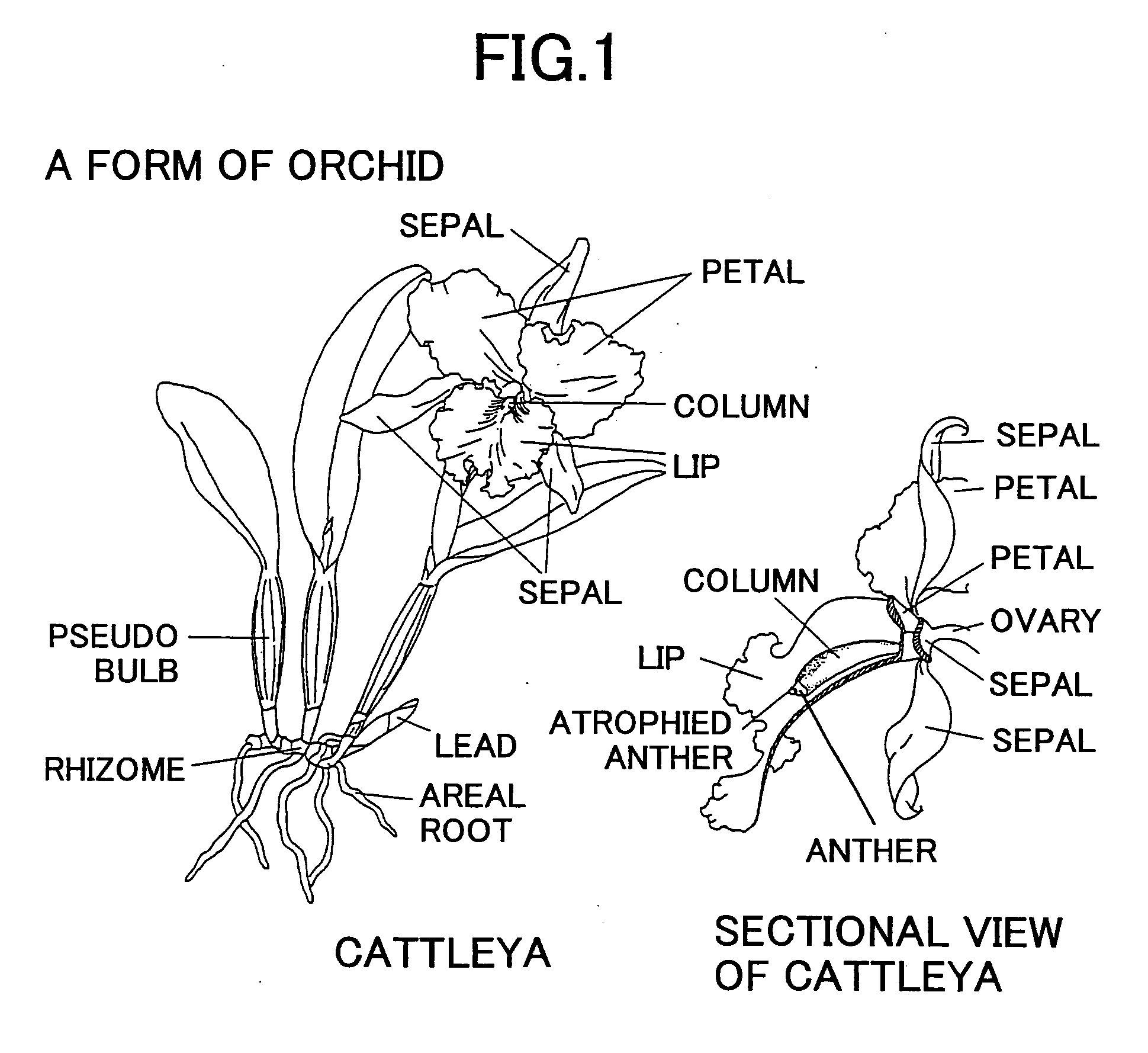
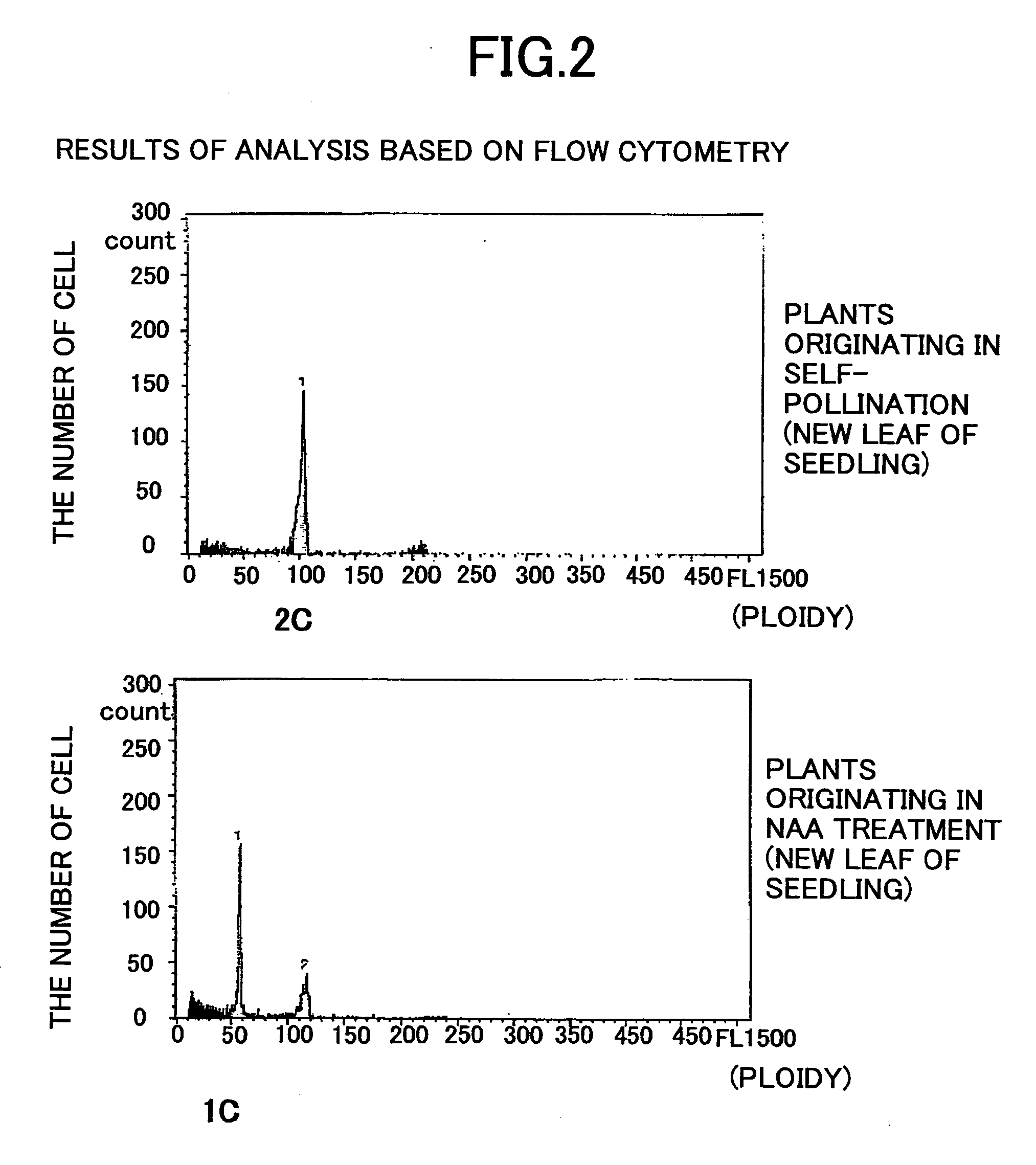
Method of constructing orchid haploid by treating unfertilized orchid flower with auxin and method of growing orchid
It is intended to provide a pure line plant which is required in constructing a seed propagation variety of orchid. An auxin solution is dropped to unfertilized orchid flowers so as to form seeds based on parthenogenesis. Then these seeds are germinated and haploid plants are selected from orchid plants thus grown. The germinating seeds judges as haploid plants are grown to give pure line plants having doubled chromosomes. Thus, a seed propagation variety of orchid is obtained.
Owner:SAPPORO BREWERIES
Double-screening and double-inducing technology system for building disease-resistant grass carp pure line
The invention discloses a double-screening and double-inducing technology system for building a disease-resistant grass carp pure line, comprising the following steps of (1) performing artificial infection in a first stage and a second stage to screen out heterozygous grass carps with excellent disease-resistant gene combination; (2) selecting carp sperms which are dead after being hybridized with grass carp ova, activating the growth of disease-resistant heterozygous grass carp ova after a genetic complete inactivation process, and doubling the chromosomes by a cold shock process so as to obtain the grass carps with high homozygous gene combination; (3) performing artificial infection for the obtained female parthenogenesis homozygote grass carps in the first stage and the second stage so as to screen out homozygous grass carps inherited with the excellent disease-resistant gene combination; (4) after the obtained disease-resistant homozygous grass carps are mature in groups, selecting the grass carps which are good in bodily form and fast in growth speed to perform artificial inducing to obtain ova, activating the growth of the genetically inactivated carp sperms and performing chromosome artificial doubling process, and preparing the disease-resistant grass carp pure line with excellent growth performance. Practice proves that the average survival rate of the pure line disease-resistant grass carps reaches above 70 percent.
Owner:湖南海博水产种业科技有限公司
Universal expression vector for large transgenic green alga and transformation expression method thereof
ActiveCN101717783AReduce osmotic pressurePromote growthAlgae productsVector-based foreign material introductionMacrocystis pyriferaParthenogenesis
The invention discloses a universal expression vector for a large transgenic green alga and a transformation expression method thereof. Through studying the universality of a resistant screening marker and a resistant screening marker gene of large transgenic green algae, such as Enteromorpha prolifera, long Ulva, sea lettuce, and the like, corresponding resistant screening marker gene is cloned,the traditional carrier of the higher plant is adequately used on the basis or a homologous recombination technology is utilized to reconstruct the vector, and a universal carrier pSVB suitable for the large transgenic green alga is constructed. In the invention, on the basis of a cell regeneration system and a gametic parthenogenesis system, the efficiently transformed and stably expressed universal carrier is utilized to finally establish a large alga transformation and expression system so that the exogenous gene can be efficiently and stably expressed in the large algae, and the foundation for establishing an alga reactor and producing an important medicament and the alga energy sources in future is established.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Method for improving the embryo transplantation pregnancy rate for cattle and sheep
InactiveCN101116640AImprove the level ofImprove pregnancy rateAnimal reproductionParthenogenesisEmbryo transfer
The invention provides a method for increasing embryo transplantation pregnancy rate of cattle and sheep, which increases embryo transplantation pregnancy rate through improving IFN-tau level inside maternal uterus. The invention also provides a plurality of feasible methods for improving IFN-tau level, which comprise adding IFN-tau into transplantation liquid during embryo transplantation and transplanting parthenogenesis embryo or living tissue fragments together with normal embryo. Through the method provided by the invention, embryo transplantation pregnancy rate of cattle and sheep can be substantially increased by 15 percent to 20 percent as compared with the control group; meanwhile, the invention has a simple operation, low application cost, outstanding effect without any harmful influence on animal, thereby being suitable for extensive application in cattle and sheep embryo transplantation industry and embryo engineering and having huge market potential.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Methods for making and using reprogrammed human somatic cell nuclei and autologous and isogenic human stem cells
Activated human embryos produced by therapeutic cloning can give rise to human totipotent and pluripotent stem cells from which autologous cells for transplantation therapy are derived. The present invention provides methods for producing activated human embryos that can be used to generate totipotent and pluripotent stem cells from which autologous cells and tissues suitable for transplantation can be derived. In one embodiment, the invention provides methods for producing activated human embryos by parthenogenesis; in another embodiment, the invention provides methods for producing activated human embryos by somatic cell nuclear transfer whereby the genetic material of a differentiated human donor cell is reprogrammed to form a diploid human pronucleus capable of directing a cell to generate the stem cells from which autologous, isogenic cells for transplantation therapy are derived. The ability to create autologous human embryos represents a critical step towards generating immune-compatible stem cells that can be used to overcome the problem of immune rejection in regenerative medicine. The activated human embryos produced by the present invention also provide model systems for identifying and analyzing the molecular mechanisms of epigenetic imprinting and the genetic regulation of embryogenesis and development.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
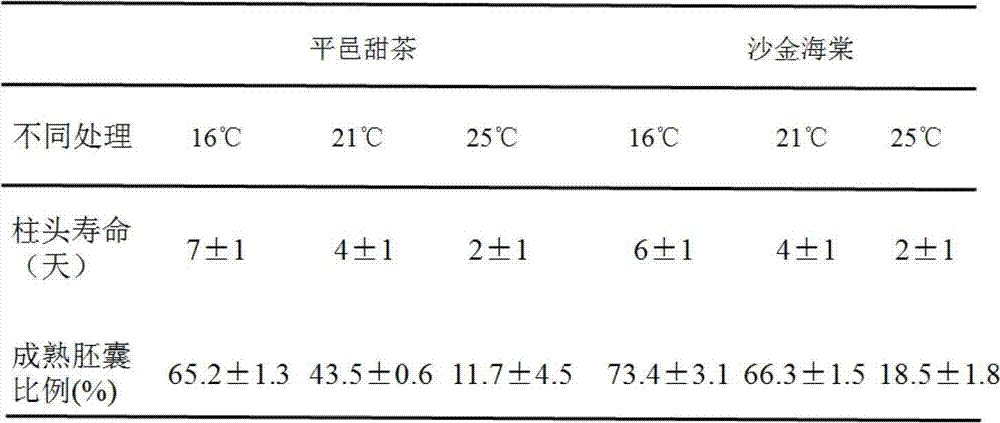
Method for increasing apomixis ratio of apple rootstocks and trimming degree of nursery stocks
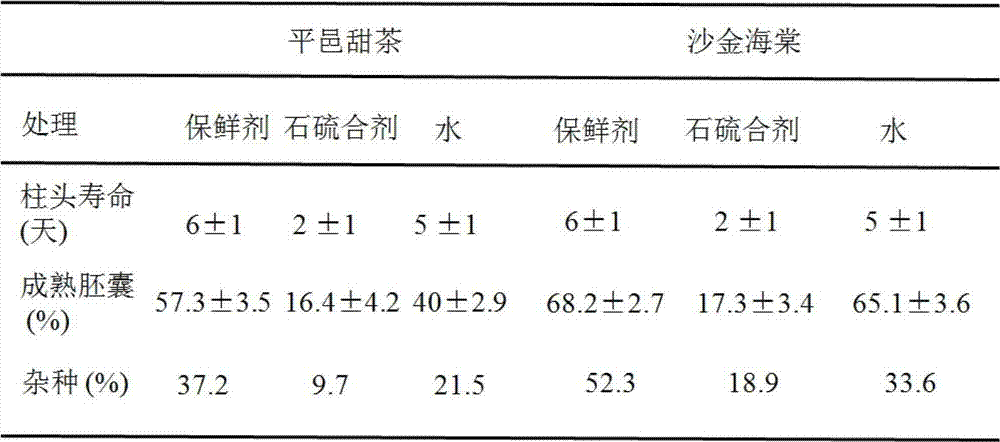
The invention provides a method for increasing the apomixis ratio of apple rootstocks and the trimming degree of nursery stocks. According to the method, before pollination and fertilization of apple flowers are finished, lime sulfur at the concentration of 1.0 baume degree is sprayed on the apple flowers at the full-blossom stage for one time in the morning or in the evening every day (the flowers are sprayed uniformly until the petals are wet and liquid does not drop off), continuously for three days. When the lime sulfur is sprayed on the apple flowers, the stigma activity is reduced, seriously, the stigma is wilted and the life of the stigma is shortened, so that the effective time of pollination and fertilization is shortened, the fertilization of the embryo sac is limited, the fertilization process of the 2N embryo sac of the apples with the apomictic feature is avoided, and the unfertilized 2N embryo sac forms clonal seeds through the apomixis way. By adoption of the lime sulfur, the life of the stigma is shortened and the pollination time is shortened, so that the apomixis ratio of the apple rootstock seeds with the apomictic feature and the trimming degree of the nursery stocks are increased.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com