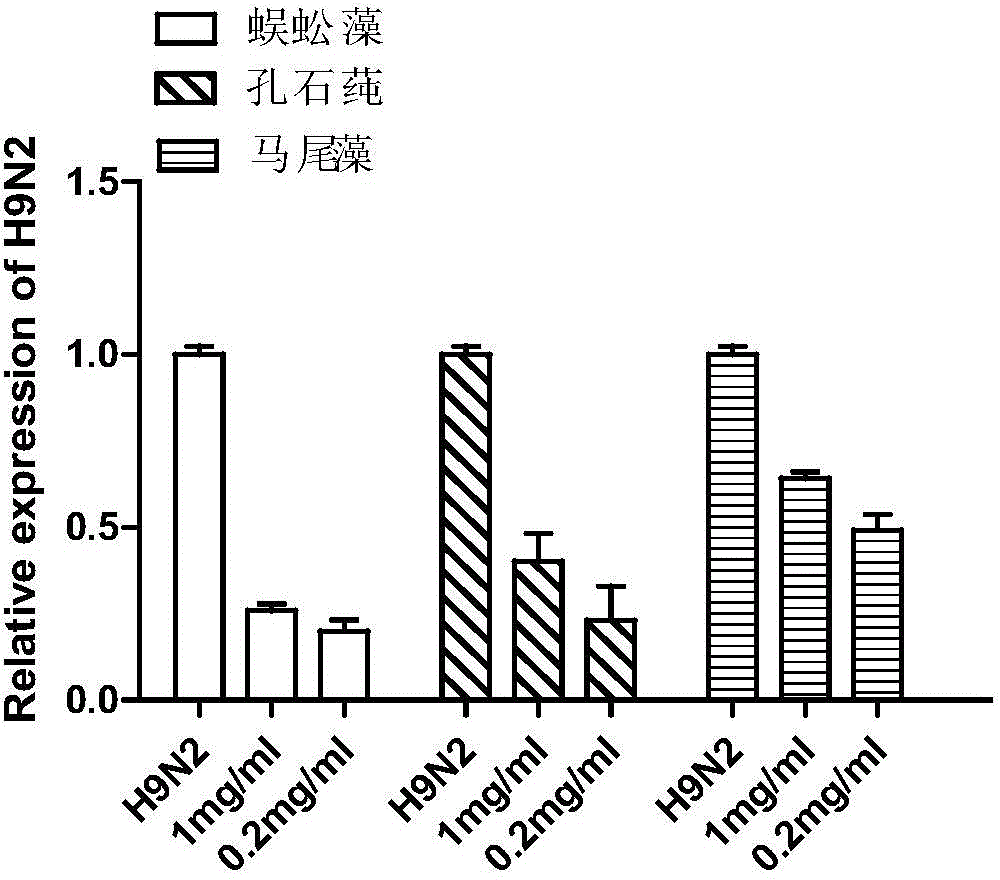
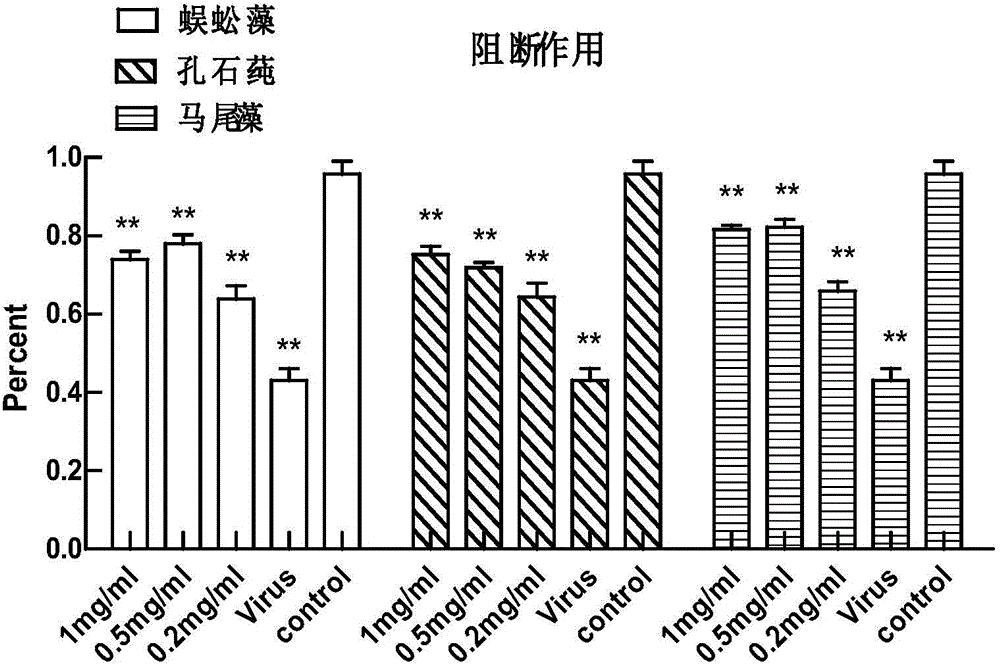
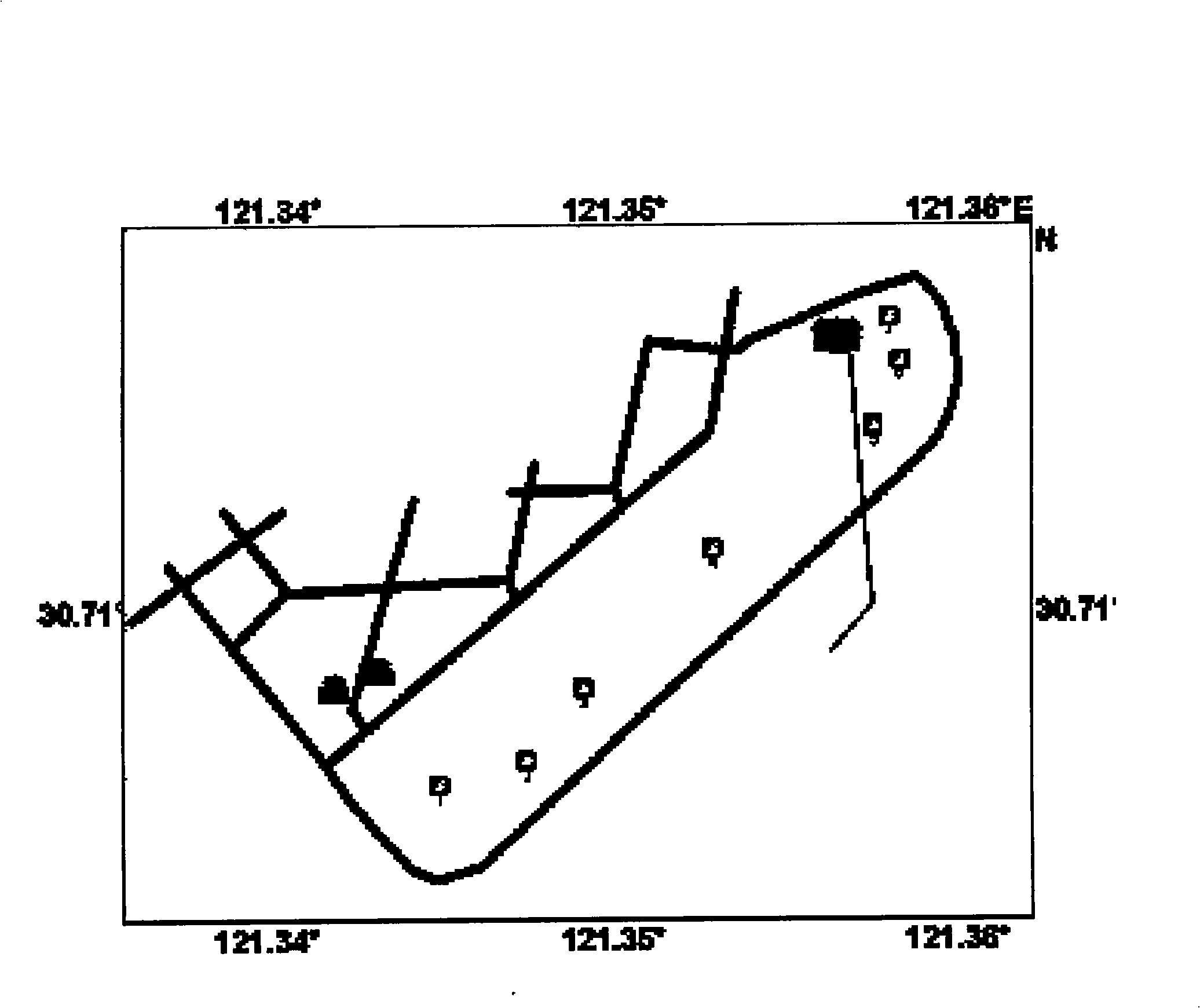
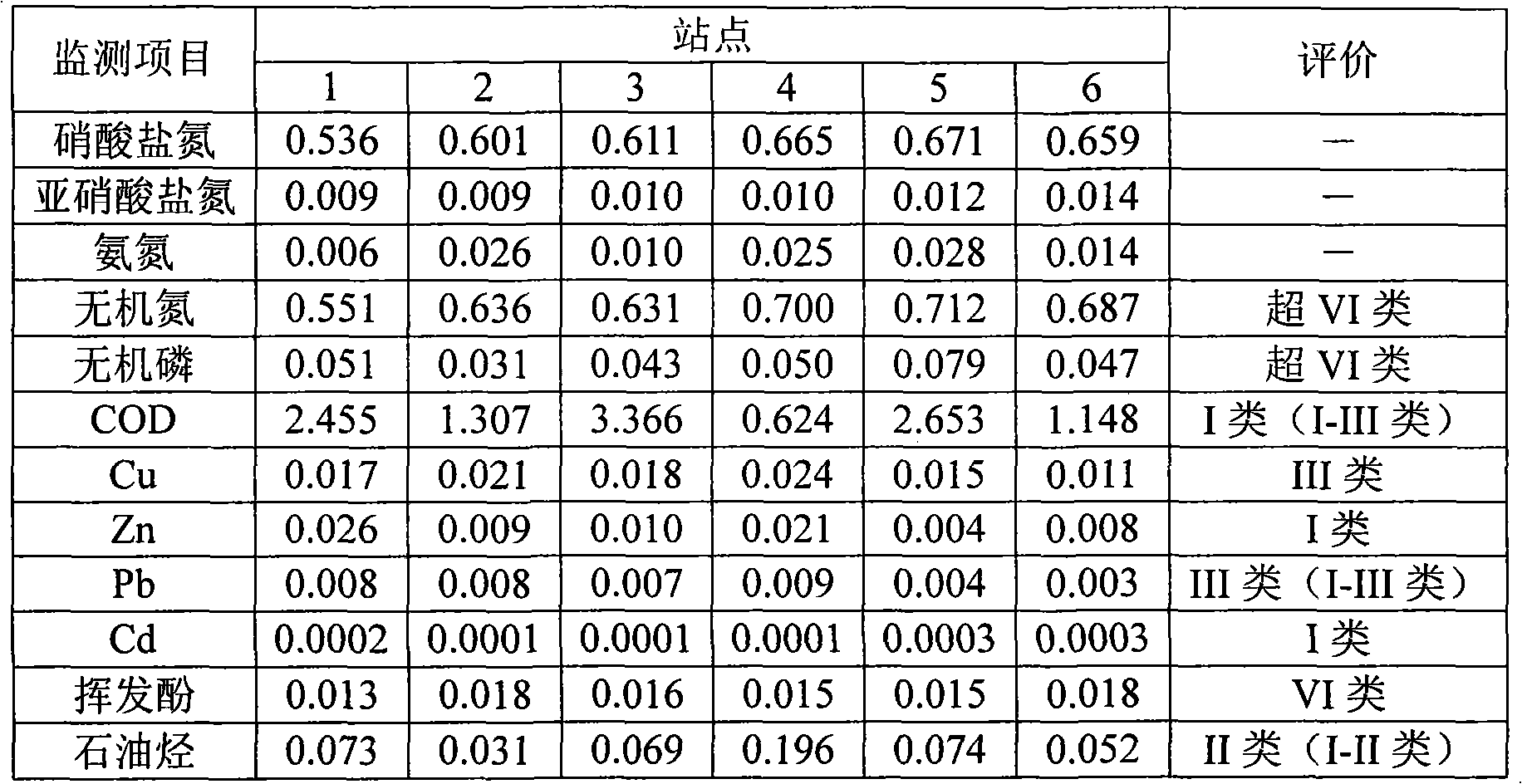
Patents
Literature
62 results about "Macrocystis pyrifera" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
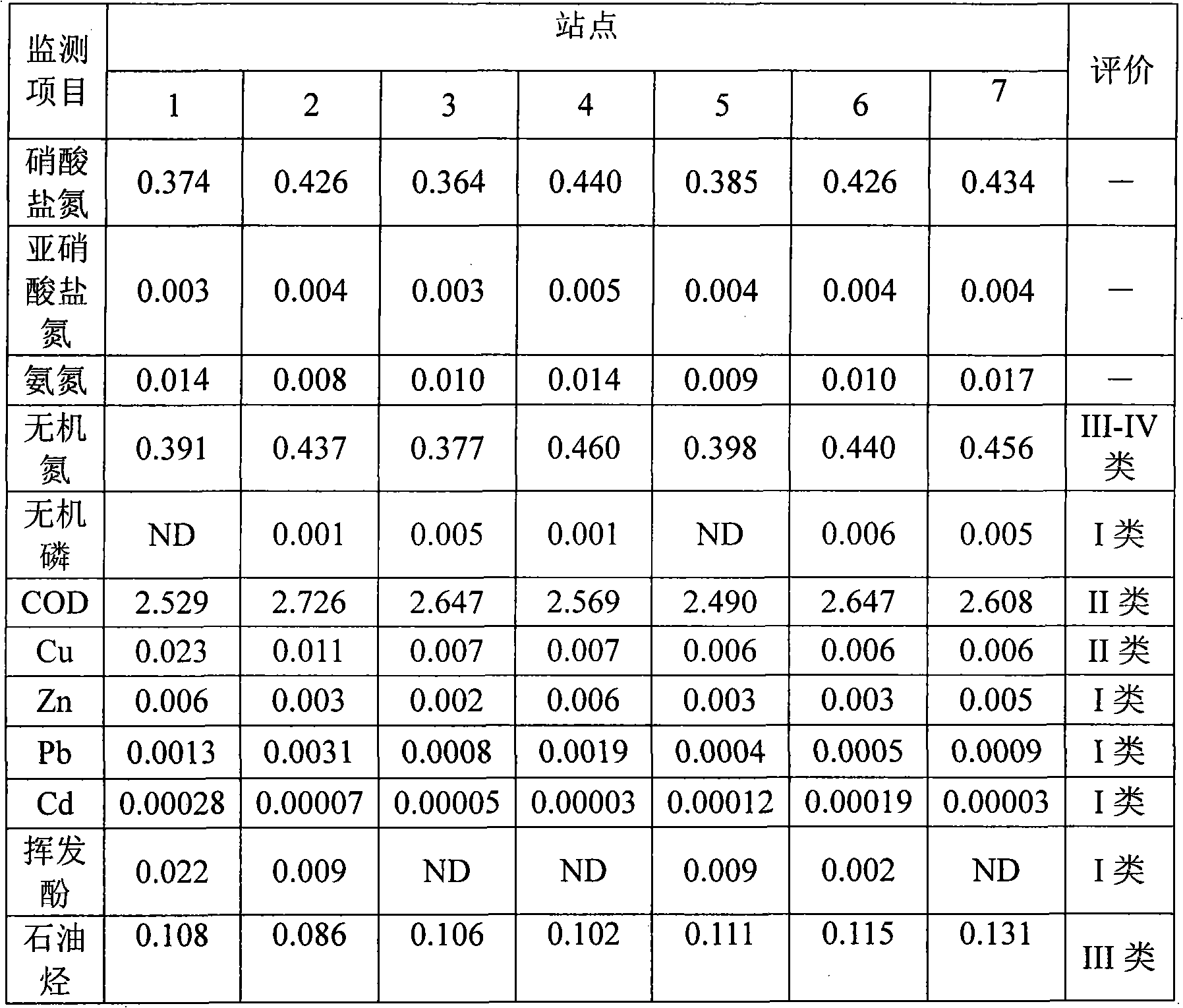
Macrocystis pyrifera, commonly known as giant kelp or giant bladder kelp, is a species of kelp (large brown algae), and one of four species in the genus Macrocystis. Giant kelp is common along the coast of the eastern Pacific Ocean, from Baja California north to southeast Alaska, and is also found in the southern oceans near South America, South Africa, Australia, and New Zealand. Individual algae may grow to more than 45 metres (150 feet) long at a rate of as much as 60 cm (2 ft) per day. Giant kelp grows in dense stands known as kelp forests, which are home to many marine animals that depend on the algae for food or shelter. The primary commercial product obtained from giant kelp is alginate, but humans also harvest this species on a limited basis for use directly as food, as it is rich in iodine, potassium, and other minerals. It can be used in cooking in many of the ways other sea vegetables are used, and particularly serves to add flavor to bean dishes.
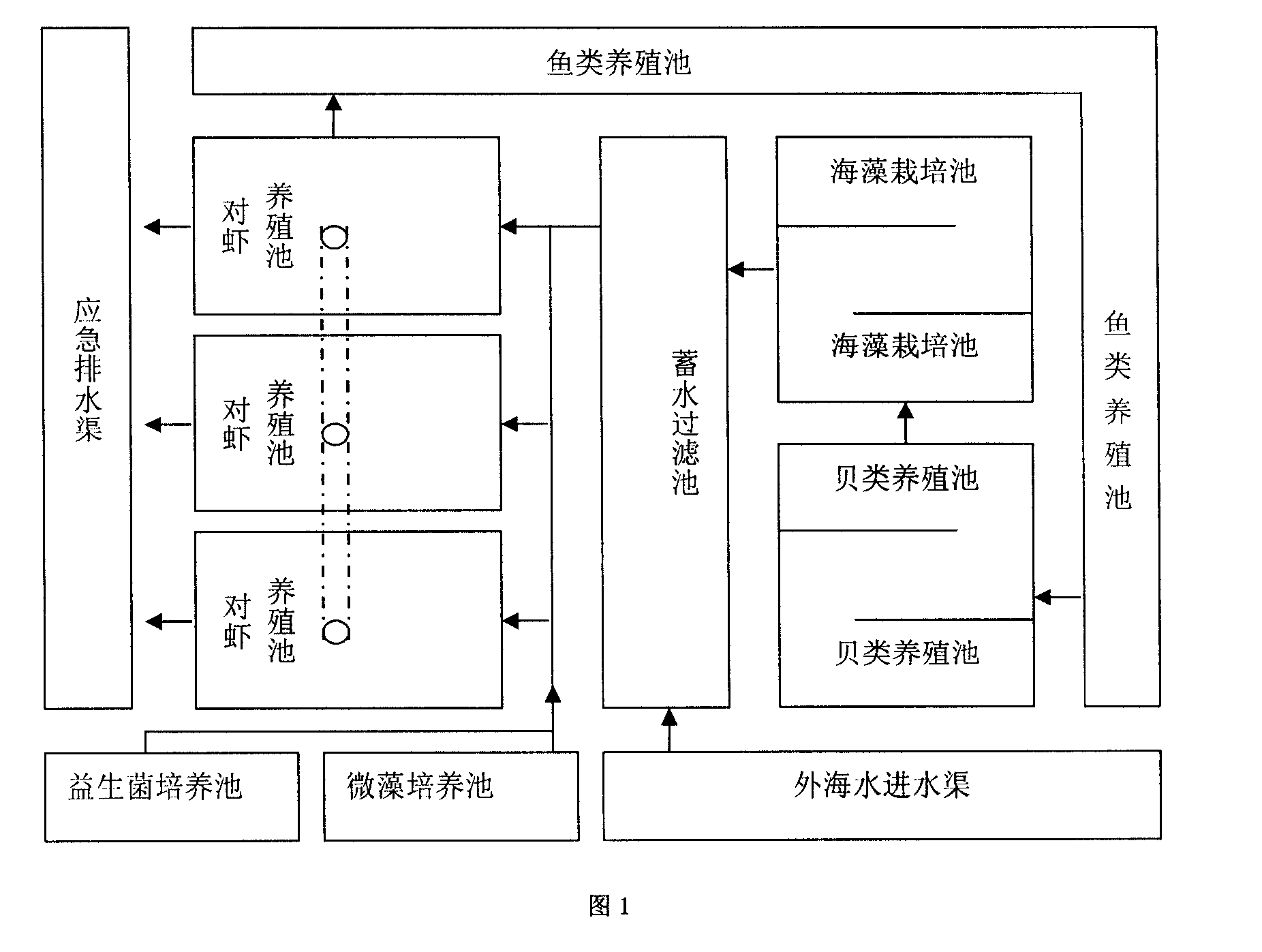
Shrimp-fish-shellfish-algae multiple cultivation and water quality biological regulate and control system thereof
InactiveCN101248766AAvoid direct competitionReduce mutual harmClimate change adaptationMultistage water/sewage treatmentMacrocystis pyriferaWater quality
The invention provides a shrimp-fish-shellfish-alga multi-unit culture and aquatic organism regulation system thereof. A shrimp culture zone, a fish culture zone, a shellfish culture zone, a large scale alga cultivation zone, a probiotics and microalga culture zone, a water processing zone and an emergency drainage system are arranged in a closed water circulation culture system, wherein the culture water circulates in different culture and water processing units. As the water circulates in different culture units and is utilized in multiple levels by various aquatic organisms of different trophic level and ecological niche, the system gives the various aquatic organisms full play to the positive bait resource complementarity, prevents the aquatic organisms from directly competing on living space and dissolved oxygen and reduces the mutual damage caused by organic remains and metabolic waste, achieves the 'self-modification' and 'biomanipulation' of the culture environment, enables the environment itself to recover from the pollution in culture process, and decontaminates the seawater culture environment.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
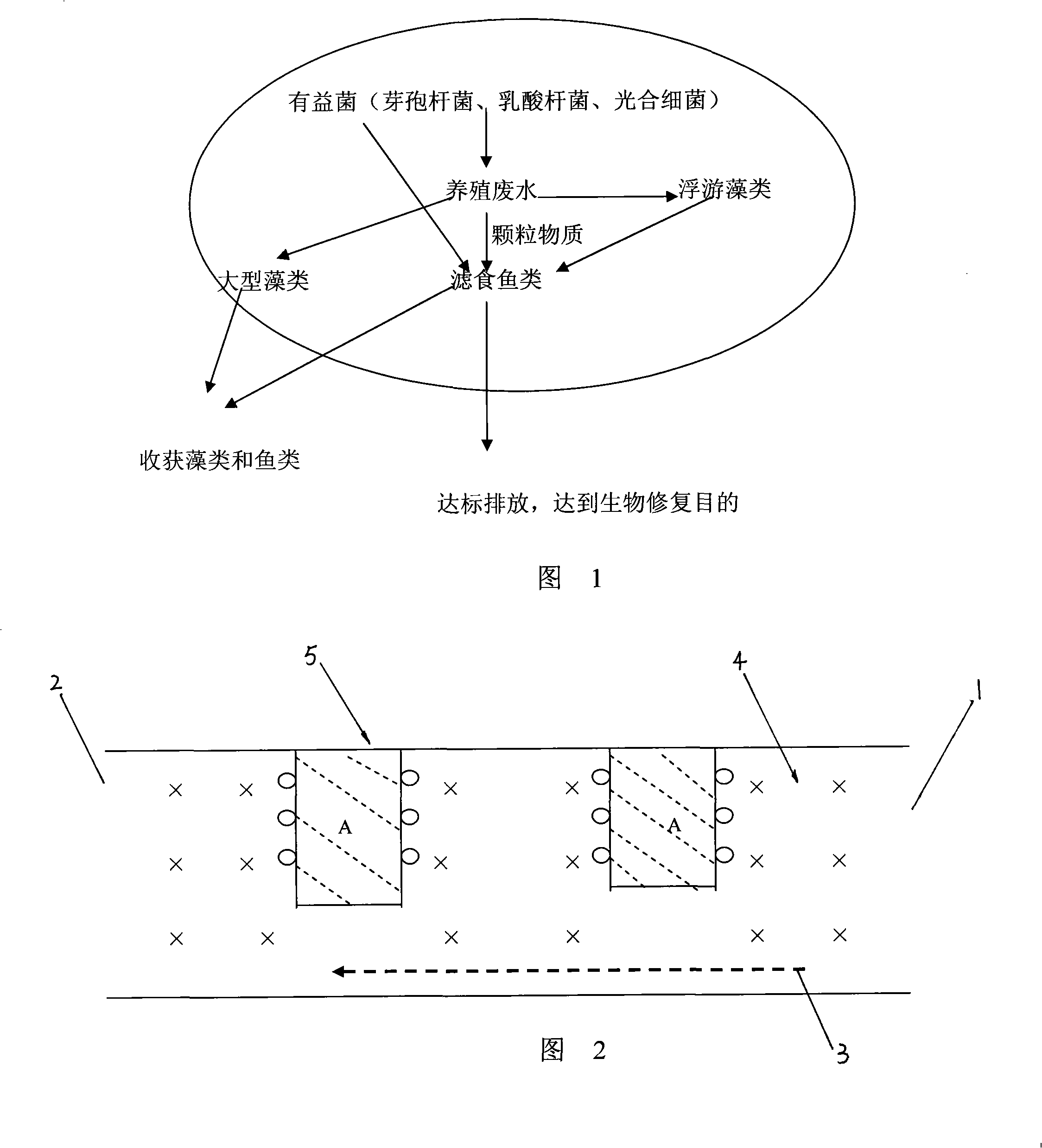
Sea water culture environment multiple state position biological restoring method
InactiveCN101264980AAchieve sustainable developmentReduce pollutionBiological water/sewage treatmentMarine aquacultureMacrocystis pyrifera
The invention discloses a multi-ecological niche bioremediation method of seawater aquiculture environment, which comprises the steps of draining aquiculture wastewater into an aquiculture trench, adding beneficial bacteria to remove nitrogen and phosphorous and convert organic matters on the first stage, culturing filter-feeding fishes and large-scale seaweed to form a multi-ecological niche biosphere coexisting microalgae, filter-feeding fishes and large-scale seaweed in the second stage, and allowing bioremediation of seawater aquiculture environment by utilizing different ecological niches of beneficial bacteria, microalgae, filter-feeding fishes and large-scale seaweed through synergic action of organisms. The inventive method can clean aquiculture wastewater to meet discharge standards, remediate aquiculture environment, and obtain fishes and large-scale seaweed, thereby bringing environmental, economic and ecological benefits.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
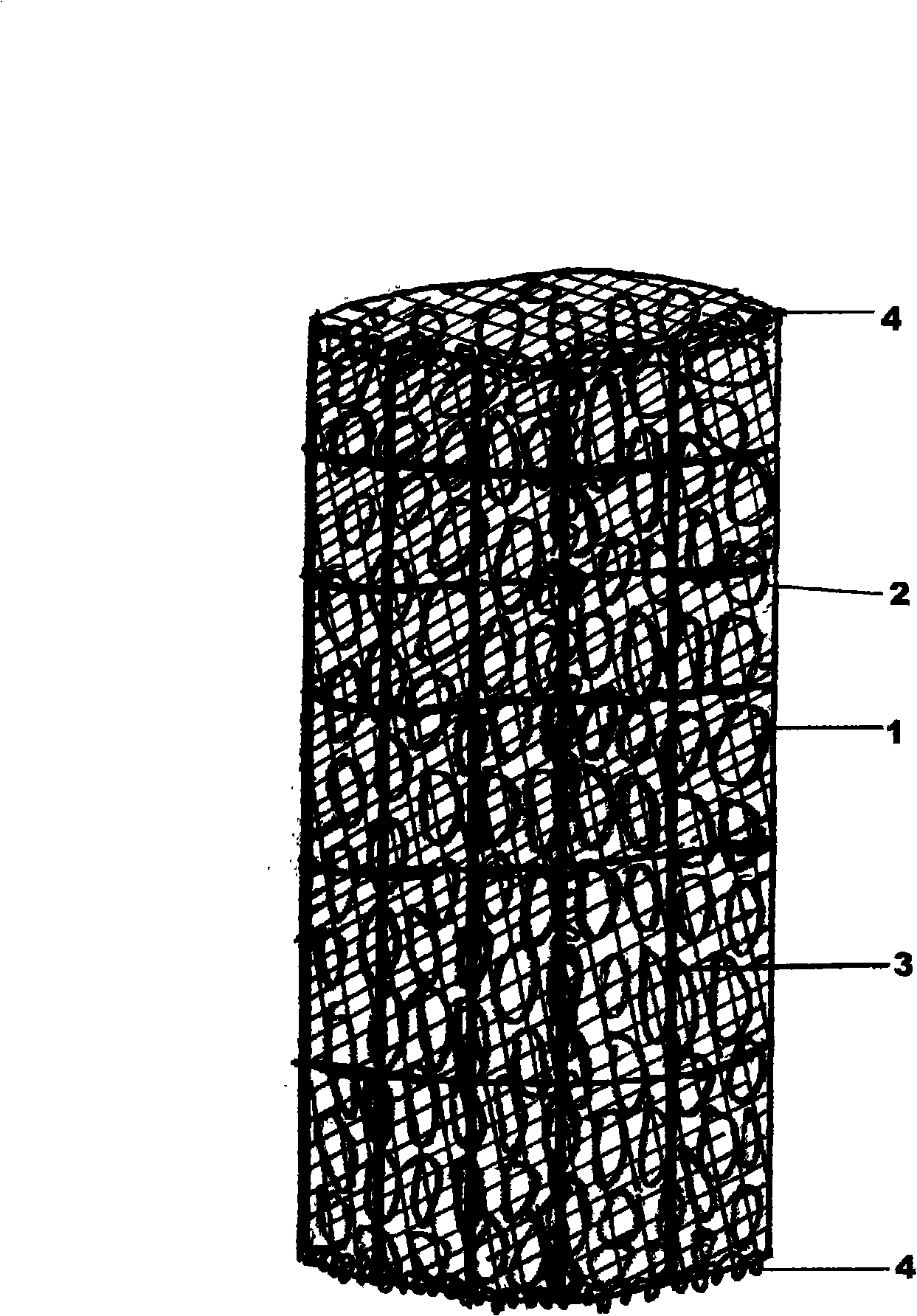
Artificial algae field and construction method
InactiveCN101341851ALow priceRaw materials are easy to getClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaMacrocystis pyriferaEutrophication
The invention relates to an artificial sea-grass field which is characterized by comprising a net cage; the net cage is provided with a seashell; an iron mesh is wrapped on the net cage; a fixed cable is arranged outside the iron mesh. During construction, sea-grass seeds are introduced to the seashell or a PE rope and wound on the net cage; the cable is used to levelly lay the net cage and fix the net in the depth of the sea. The price of the construction materials used by the invention is low, the raw materials are easily available, the operation is convenient, and the depth of the prior sea which is not suitable for the sea-grass to grow is improved, so that the depth of the sea is suitable for the sea-grass to be attached and grow. In the construction method, large sea-grass seedlings are introduced artificially, so that the construction success rate of the sea-grass field is high. The artificial sea-grass field can effectively prevent the eutrophication of sea areas, improve the water quality and restore the ecological environment of the sea areas; meanwhile, the sea-grass itself is the bait of marine organisms and the place of activities and egg laying, which can improve the biological diversity index of the sea areas.
Owner:MARICULTURE INST OF SHANDONG PROVINCE
Application of seaweed polysaccharides
ActiveCN104814985AObvious antiviral effectSignificant immune enhancementAlgae medical ingredientsAntiviralsAscophyllumMacrocystis pyrifera
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedicines, and in particular relates to application of seaweed polysaccharides. The seaweed polysaccharides can be taken as preparations for preparing anti-viral or immune medicines. Cell models and in-vivo animal experiments show that the seaweed polysaccharides can be used for significantly enhancing the animal immunity, and can also be used for promoting the generation of cell factors, the typing of T lymphocytes and the proliferation of mouse spleen cells so as to ensure that cellular immune reaction can be activated. The functional seaweed polysaccharides disclosed by the invention are natural polysaccharides which are extracted from seaweeds such as large seaweeds and kelps, gulfweeds, grateloupia sparsa, eucheuma muricatum, ulva pertusa kjellm, enteromorpha, gracilaria, ascophyllum nodosum and scytosiphon lomentaria, and can also be low-molecular-weight seaweed polysaccharides or seaweed oligosaccharides which are prepared by degrading the seaweed polysaccharides by virtue of different preparation methods. According to the application disclosed by the invention, a polysaccharide extract of single seaweed or a polysaccharide extract mixture of a variety of seaweeds can be taken as a novel anti-viral and immune enhancing agent to be applied to feeds of livestock, poultry, fish, shrimps and shellfish, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ecology reparation method of eutrophication barricaded sea area using gracilaria marine macroalgae
ActiveCN101331849AHigh transparencyAvoid elevationClimate change adaptationEnergy based wastewater treatmentOpen seaMacrocystis pyrifera
The invention relates to an ecological method for restoring eutrophication enclosure sea area by Gracilaria Greville macrophyte. The ecological method for restoring eutrophication enclosure sea area mainly comprises the following steps: collecting the seedlings of Gracilaria, Gracilaria seedling transportation, domestication in sea area, building a dam and enclosing sea in eutrophication sea area, cutting off the tide of the open sea and carrying out ecological restoration. After the Gracilaria which is cultivated in a large scale in the eutrophication sea area is introduced and cultivated, the Gracilaria can absorb the superfluous dissolution-typed nutrient salt with a great deal for supplying for self-growth, can restrain the explosible growth of monoplast algae meanwhile and can also absorb mud and sand; the Gracilaria can be gained again so as to transfer the nutrient matters in water body out of a pollution system, improve the water quantity and restore the ecology of the sea area; the water body after ecological restoration is exchanged with the environment again, thus achieving the purpose of relieving and eliminating eutrophication of the sea area, eliminating eutrophication can be realized gradually, meanwhile higher economic value can be produced. The method is applicable to carrying out ecological restoration for the eutrophication enclosure sea area.
Owner:SHANGHAI FISHERIES UNIV
Feed with addition of enteromorpha algae and asparagus for siganids and method for preparing same
The present invention relates to a feed with addition of enteromorpha algae and asparagus for siganids and a method for preparing the same. The feed for siganids includes fish meal, soybean meal, seaweed powder, fish oil, soybean oil, tapioca starch and excipients. According to the feed for siganids, the algae-eating character of the siganids is fully taken advantage of, and based on the feeding preference for large algae and digestion and the utilization rate for algae of the siganids, the enteromorpha algae and the asparagus are selected to be used as raw materials for the seaweed powder. The invention also provides the method for preparing the feed for the siganids. By using algae feed in the feed of the present invention, the usage amount of fish meal can be reduced by 10%, the protein level required by fingerlings is reduced by 2-3%, so the feed with addition of enteromorpha algae and asparagus for siganids is an efficient, low-cost feed with great promotional value.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV
Method for adsorbing heavy metal ions in environment by utilizing macroalgae
InactiveCN104370324AHigh adsorption rateShorten the timeSeawater treatmentWater contaminantsMacrocystis pyriferaPhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a method for adsorbing heavy metals, and concretely relates to a method for adsorbing heavy metal ions in environment by utilizing macroalgae. The method comprises: pouring macroalgae into a to-be determined sample, and utilizing cytomembrane of macroalgae and a nutrient-element ion channel on the cytomembrane to enable heavy metal ions to be adhered to cytomembrane and enter macroalgae cells through the ion channel, so as to further remove heavy metal ions in the to-be determined sample. By employing macroalgae for adsorbing the heavy metal ions, the adsorption scope is 30-90% and the highest adsorption rate is 90% or more.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for implanting and cultivating Gracilaria bursa-pastoris in north pond
InactiveCN101779595AHigh economic valueGood purification effectClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsMacrocystis pyriferaEutrophication
The invention provides a method for implanting and cultivating Gracilaria bursa-pastoris in a north pond. By using the method, the problems of water eutrophication and the like, caused by the ecological imbalance owning to using the prior art for signal animal breeding in the north pond, can be solved. The cultivation process of the invention can be divided to a sprout proliferation phase, a bottom sowing propagation phase, an increasing interharvesting phase and an overwintering seedling protection phase. By using the invention, the problem that owning to the change of factors such as climate, growing environment and the like in the north, the transplanting of south macrophyte fails, can be solved; the method has effects of low input and high output, and the ratio of the fresh weight input to fresh weight output of the algae is 1:1500. The yield per mu is 1500kg. The method of the invention can be used to fill the gap of cultivating macrophyte in aestival pond of northern areas and the diversity of algae resources in northern China is enriched.
Owner:MARICULTURE INST OF SHANDONG PROVINCE
Integrated ecology renovation method for extratropical eutrophication marine site
InactiveCN1990394AImprove self-cleaning abilityRestoring eutrophic environmentsSeawater treatmentClimate change adaptationTemperate climateParticulates
The invention relates to a technique for treating polluted environment, which in detail is a comprehensive ecological restore method especially for etrophication waters in temperate zone in part of China. It combines the cultivation of large scale of algae and culture filter feeding animal of in etrophication waters to build a biological filter device and then restore polluted environment. The invention makes full use of ecological function of large scale algae absorbing dissolved nitrogen and phosphorus in large amount and ecological function of filter feeding animal filtering suspended particle and nutrient matter from water, to restore etrophication waters. The applied algae and filter feeding animal are important economical varieties, thus they can also bring economical benefit. The invention is characterized by both ecological benefit and economical benefit and suitability for etrophication waters in temperate zone in north of China.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Comprehensive organism repairing method of eutrophication seawater cage culture zone
InactiveCN101817592AHigh economic valueSeawater treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentMacrocystis pyriferaEutrophication
The invention discloses a comprehensive organism repairing method of an eutrophication seawater cage culture zone, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: hanging large-scale seaweeds on the upper part of a water body in a cage culture zone by using immobilized microorganisms, the large-scale seaweeds and filter-feeding bivalves as a combined repairing organism; putting the filter-feeding bivalves capable of rapidly absorbing and converting inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus eutrophication substances in the water body to the bottom of the culture zone; putting the immobilized microorganisms partially depositing to the surface layer of a bottom material of a culture field; and intensifying the degradation of organic matters and the nitrification velocity of nitrogen in the water body or substrate sludge through the oxidization and the nitrification. The method has the characteristics that firstly, the comprehensive organism repairing method which uses the large-scale seaweeds, the filter-feeding bivalves and immobilized nitrobacteria as a main organism can eliminate the eutrophication substances and organic pollutants in the water body and the bottom material; and secondly, the large-scale seaweeds and the filter-feeding bivalves with higher economic value can be obtained while eliminating the pollutants, thereby great environment and economic benefits are achieved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Shrimp-pool marine macroalgae grass composite space cultivation method
InactiveCN101422126ASolve the current situation that it is difficult to carry out macroalgae farmingStabilize seafloor vegetationClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaMacrocystis pyriferaShrimp
The invention relates to a compound culturing system in a shrimp pool, in particular to a compound space culturing method for large varech in the shrimp pool; Sargassum thunbergii is cultured on the surface layer of the water body of the shrimp pool; gardon asparagus and / or gulfweed are cultured in the middle layer of the water body; Zosteraceae is transplanted in the bottom layer of the water body; and the surface layer of water body refers to the location of 0 to 30cm under water surface and the bottom layer of water body refers to the location of 50 to 150cm below the water surface. The method fully utilizes the limited space in the shrimp pool, not only has remarkable economic benefits, but also plays remarkable role of improvement on the environment of the shrimp pool.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Method for efficiently purifying heavy metals in bodies of cultured oysters
InactiveCN107125173AWide variety of sourcesLow priceWater contaminantsClimate change adaptationMacrocystis pyriferaOyster
The invention relates to a method for efficiently purifying heavy metals in bodies of cultured oysters. The method comprises the steps of utilizing fresh macroalgae such as gracilaria lemaneiformis, gracilaria and ulva to be combined with chitosan and the oysters for carrying out mixed cultivation for 7-14 days, wherein the ratio of the algae to seawater is equal to (1-5)kg to 1m<3>, the ratio of the oysters to the seawater is equal to (10-20)kg to 1m<3>, and the concentration of the chitosan is 1-10mg / L; feeding the oysters with a right amount of platymonas subcordiformis, periodically replacing the seawater and supplementing the chitosan, carrying out continuous air inflation, and the like; the method can efficiently purify heavy metal ions in the bodies of the oysters; the heavy metal content of the purified oysters is significantly lower than the safety limit of first class or second class GB18421-2001 of the standard of China; the Cu<2+> purification efficiency and the Pb<2+> purification efficiency of the method are respectively 87.63-93.73% and 78.21-96.11%. The method is high in efficiency, short in period, high in practicality, environment-friendly and safe; a new method is provided for the purification of the heavy metal ions in the bodies of the oysters, and a new idea is provided for the purification of heavy metal ions in the bodies of marine shells.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV
Epinephelus coioicles ecological feed formula and preparation method
InactiveCN105995183AReduce morbidityEasy to feedFood processingClimate change adaptationMacrocystis pyriferaPhytase
The invention discloses an epinephelus coioicles ecological feed formula and a preparation method. The epinephelus coioicles ecological feed is prepared from fish meal, tenebrio molitor powder, nereis powder, earthworm powder, silkworm chrysalis meal, shrimp head meal, blood meal, squid visceral powder, beer yeast, bean pulp, soybean phospholipid, alpha-starch, flour, alfalfa meal, moringa powder, macroalgae mixed powder, fish oil, shell mixed powder, dry ginger powder, choline chloride, composite multiple vitamin powder and a phytase preparation. The raw materials are weighed according the proportions, cleaned, dried, smashed and put into a vessel to be stirred to be uniform, granulation is conducted through fluidized bed spray, feed particles are cooled, subpackaged and sealed, and the target product is obtained. According to the epinephelus coioicles ecological feed, feeding is convenient, storing is convenient, the feed quality is high, the nutritional requirement of epinephelus coioicles is met, preparation is dry and thorough, long-term storing is convenient, the feed is not prone to deterioration, active substances in tenebrio molitor, nereides, silkworm chrysalises and fresh ginger can not be subjected to inactivation, the utilization rate of the epinephelus coioicles to the feed is increased, and the growth performance of the epinephelus coioicles is improved.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
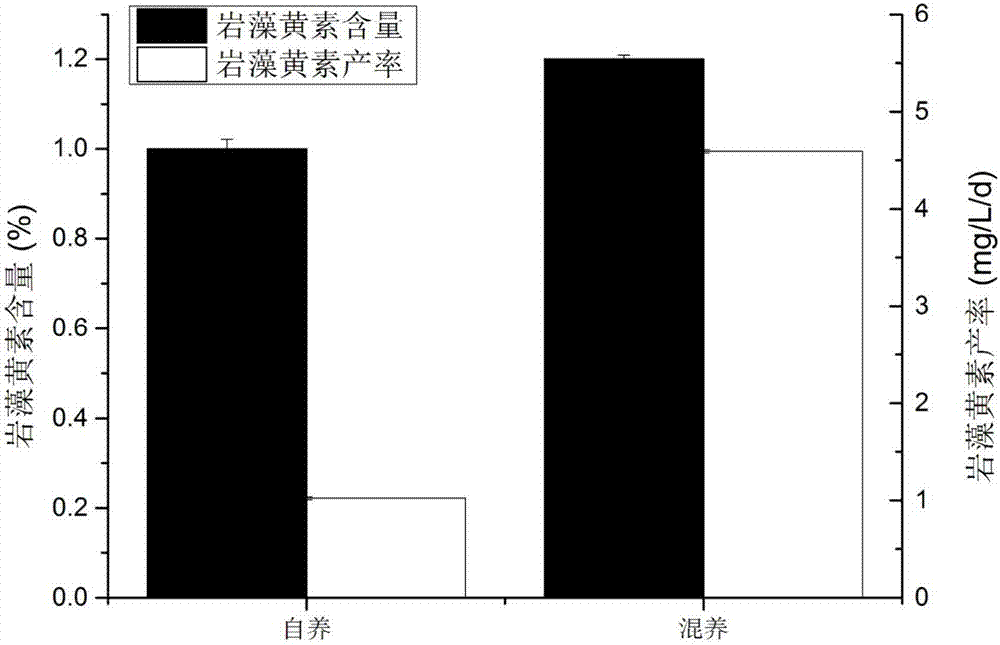
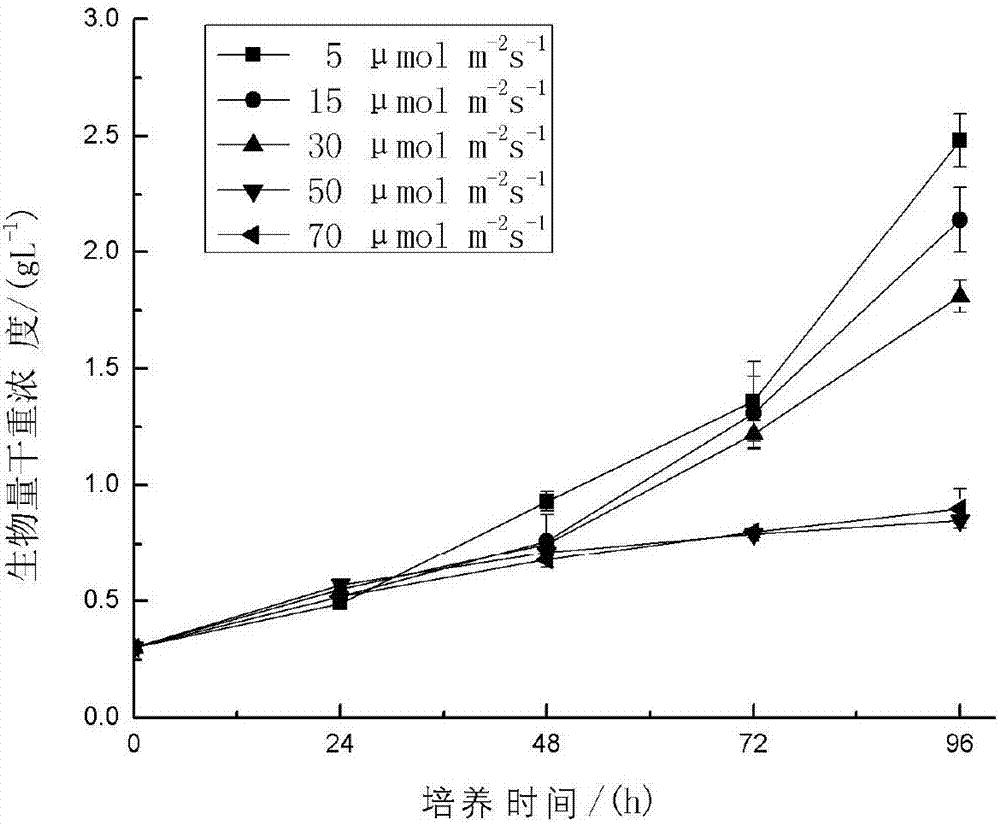
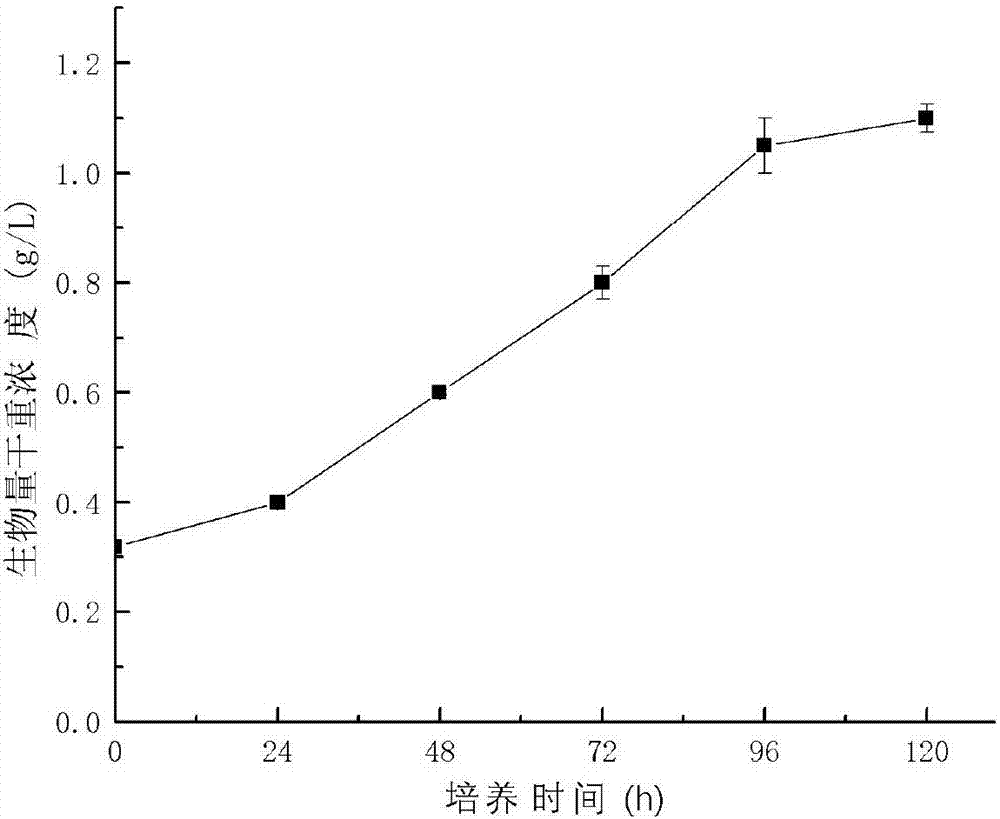
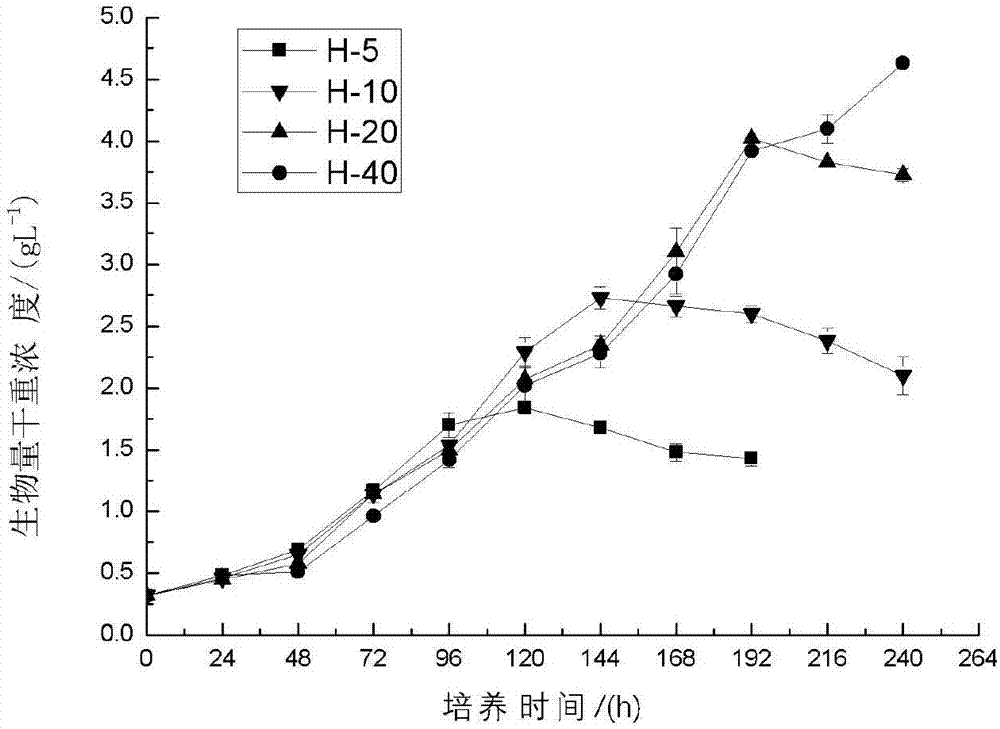
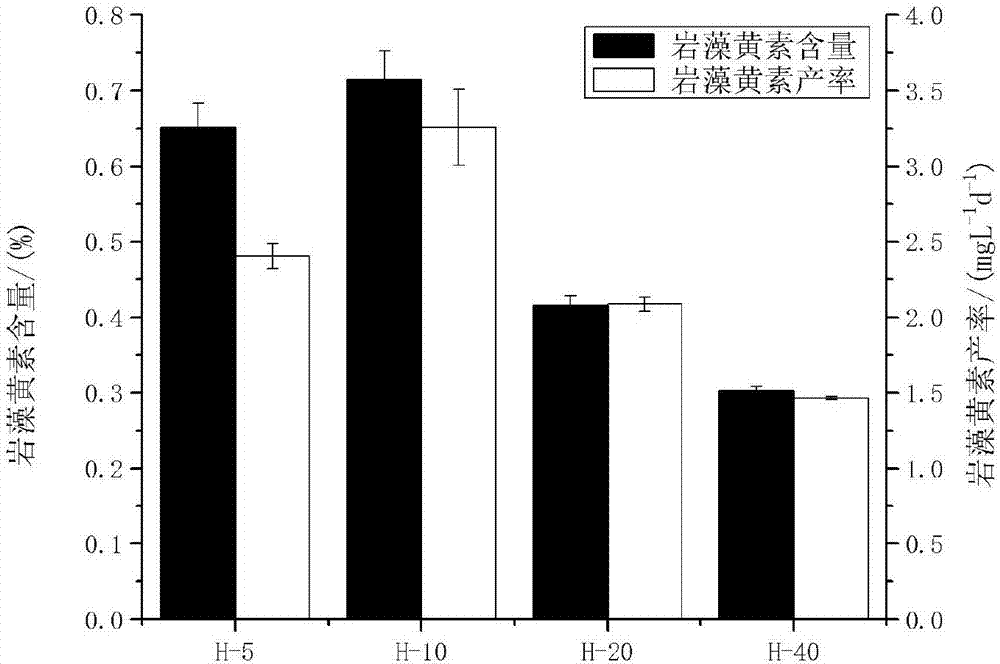
Method for producing fucoxanthin through light culture of nitzchia laevis
ActiveCN107119099AIncrease contentHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesFermentationMacrocystis pyriferaMicroorganism
The invention belongs to culture of microorganisms, in particular to a method for producing fucoxanthin through light culture of nitzchia laevis. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a seed solution; performing fermentation culture; extracting the fucoxanthin from fermentation liquor obtained after fermentation. By adopting the method, the problems of low biomass concentration, low fucoxanthin yield, low fucoxanthin content and the like of the nitzchia laevis under a phototrophic condition in the prior art are solved. Prepared nitzchia laevis dry powder has high fucoxanthin content and high fucoxanthin yield, the fucoxanthin produced by the method is safer than fucoxanthin derived from a large-sized seaweed source, the production efficiency is increased, the production cost is lowered, and meanwhile the pollution risk in a culturing process is lowered greatly.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for repairing polluted seawater by shellfish-alga composite ecologic system
InactiveCN101462799AGood removal effectGood economic valueBiological water/sewage treatmentMacrocystis pyriferaEngineering
The invention provides a method for restoring the polluted seawater by a shellfish-seaweed complex ecological system, and relates to a method for restoring the polluted seawater. The organism arrangement of the shellfish-seaweed complex ecological system comprises: at least one macrophyte restoration area and at least one shellfish restoration area are arranged, wherein the macrophyte restoration area and the shellfish restoration area are arranged at intervals, the shellfish and the macrophyte are in laminated distribution in parallel, and the direction of each lamination is vertical to the flowing direction of seawater of a drainage system; the design of a suspended culturing raft comprise: the shellfish and the microphyte are in suspended cultivation by a raft, and the suspended culturing raft can be of pile fixed type and anchor fixed type; the biological density in the shellfish-seaweed complex ecological system comprises: the initial density of the macrophyte is between 300 and 1,000kg / mu, and the initial density of the shellfish is between 100 and 500kg / mu; and management of the shellfish-seaweed complex ecological system comprises that the macrophyte is harvested every other month, while the shellfish is partially harvested after 6 to 7 months, and the density of the shellfish is maintained not more than 1.5 times of the density of the macrophyte.
Owner:DONGSHAN INST OF ECOLOGY ENVIRONMENT SCI
Method for controlling macroalgaes in stichopus japonicas culture pond
InactiveCN103598080AOptimize and improve the environmentReduce the chance of diseaseClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsStichopusMacrocystis pyrifera
The invention relates to a method for controlling macroalgaes in a stichopus japonicas culture pond. The method comprises the following steps: applying an inorganic fertilizer and a low-temperature resistant beneficial bacteria preparation inside a stichopus japonicas culture pond, so that the density of monodus subterraneus in the pond achieves 500,000-1,000,000 cell / ml; the filament length achieves 30cm and the macroalgaes inside the pond are manually fished out when the cover area of the macroalgaes on the bottom of the pond achieves 25%; basket fish fries and stichopus japonicas are cultivated in a mixing manner and 3-5ml of beneficial bacteria preparation is applied to each mu when the water temperature of the pond is 17-20 DEG C; the macroalgaes close to death are manually fished out, the basket fish fries are fed with 500-600g of macroalgaes everyday, and the cover area of the macroalgae on the bottom of the pond is controlled at 8-10% when the water temperature of the pond achieves 26-30 DEG C; the basket fish fries are captured when the water temperature of the pond is 13-14 DEG C. The method is simple in technology, easy to operate, low in cost, low in labor intensity, and high in work efficiency; the quantity of the macroalgaes in the stichopus japonicas culture pond can be eliminated and controlled; the yield and the quality of stichopus japonicas cultivation are improved.
Owner:WENDENG AQUATIC PROD TECH PROMOTION STATION
Method for restoring degenerated algae field by using gracilaria macro-algae namely gracilaria salicornia
InactiveCN106035050ASeed qualityReduce seedling costClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsMacrocystis pyriferaSpore
The invention relates to a method for restoring a degenerated algae field by using gracilaria macro-algae namely gracilaria salicornia, and belongs to the technical field of marine ecological environment restoration. According to the method, a natural gracilaria salicornia algae field with high-quality growth vigor is selected in the period when gracilaria salicornia are mature and release generative cells, a mesh with a specification of 5*20m<2> is laid at the bottom of the algae field to provide an appropriate adhering substrate for spores, and after collection of the spores and when the spores grow naturally to have discoidal bodies or in the stage of formation of erect branches, and the mesh with gracilaria salicornia seedlings is transplanted to an algae restoration area to ensure that gracilaria salicornia populations can be enlarged in a partially degenerated algae field or stable gracilaria salicornia populations can be reestablished in a completely degenerated algae field, thereby achieving ecological restoration of a gracilaria algae field. By adoption of the method, a germplasm source is provided for a restored area, and a degenerated algae field can be effectively restored.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
Moss prevention method for sea cucumber pond based on construction of alga floating bed
PendingCN109197705AGrowth inhibitionSolve the problem of WangfaClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaMacrocystis pyriferaAquaculture of sea cucumbers
The invention discloses a moss prevention method for a sea cucumber pond based on a construction of alga floating bed. According to characteristics of the living history of moss in the pond, the algafloating bed with a vinylon net screen as a matrix and green alga in the ulva family is constructed in the surface layer of a water body of the sea cucumber pond in the larva phase of moss in the midmonth of March to the midmonth of April, a natural sunlight barrier layer is established with growth of alga, the intensity of incident light to the pond bottom is reduced, growth of moss is inhibited,and biological prevention against moss in the sea cucumber pond is realized.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Large yellow croaker-asparagus integrated culture matching mode
ActiveCN105165680AEasy to getShort breeding cycleClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaMacrocystis pyriferaEutrophication
The invention discloses a large yellow croaker-asparagus integrated culture matching mode. Asparagus is cultured in large yellow croaker culturing cages in a hung mode, and a whole cage culturing area serves as an integrated system; the reasonable matching culturing quantities of large yellow croakers and the asparagus are calculated by taking dissolved inorganic nitrogen and dissolved inorganic phosphorus as balance indexes and monitoring the net flux of input and output nutrient salt pollution loads flowing through the system according to the nitrogen and phosphorus nutrient salt circulation path and the nutrient salt absorbing capacity of the asparagus. According to the large yellow croaker-asparagus integrated culture matching mode, the water eutrophication condition of the culturing area can be effectively improved, the nutrient salt released by cage culturing is quickly absorbed by large kelp, and therefore the kelp yield is increased; the dissolved oxygen content in water is increased through the photosynthesis of the large kelp, better living environment and habitat environment are supplied to fishes, the fish harvesting yield is increased, disease occurrence is reduced, and therefore the good ecological benefits and economic benefits are achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
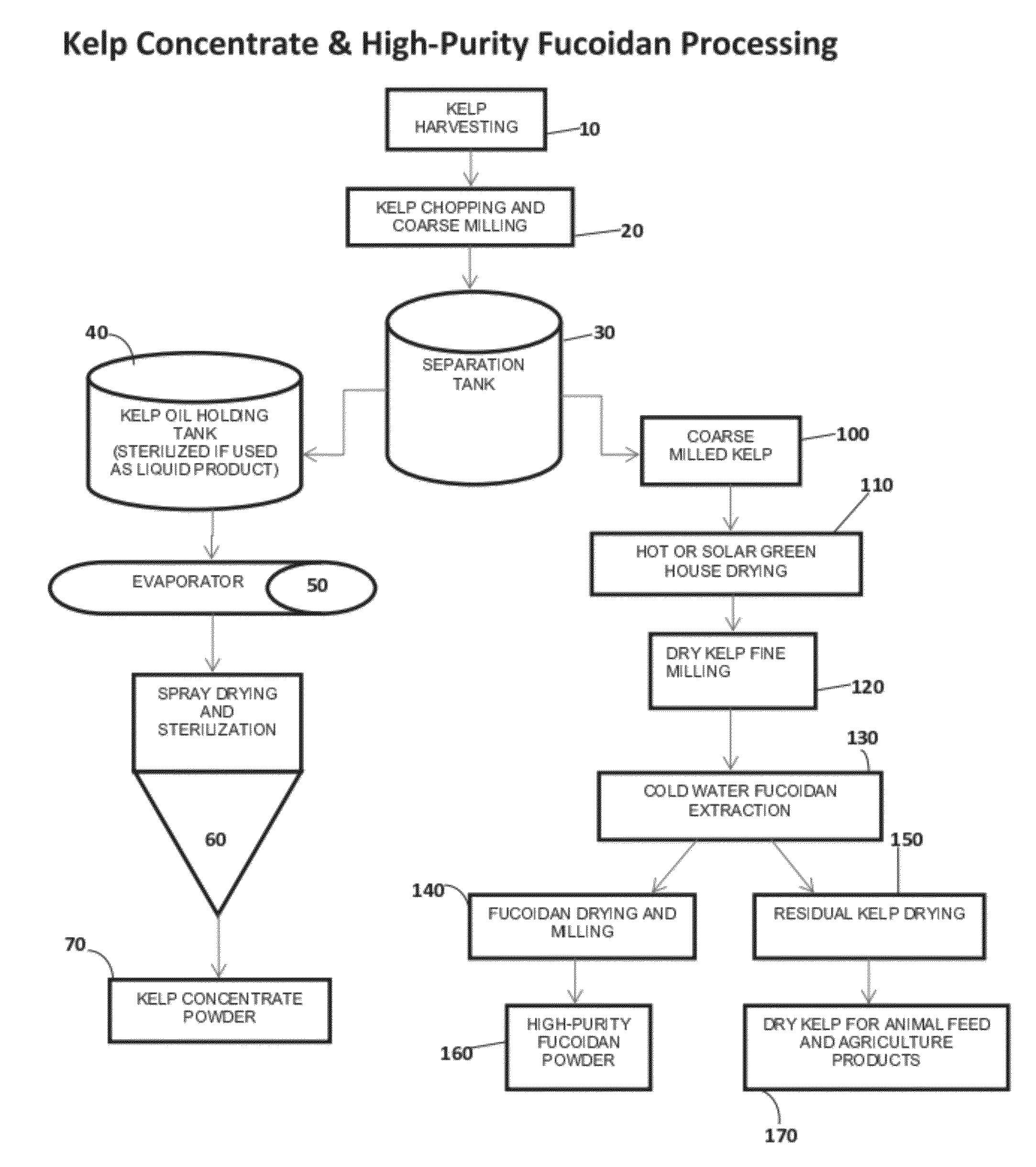
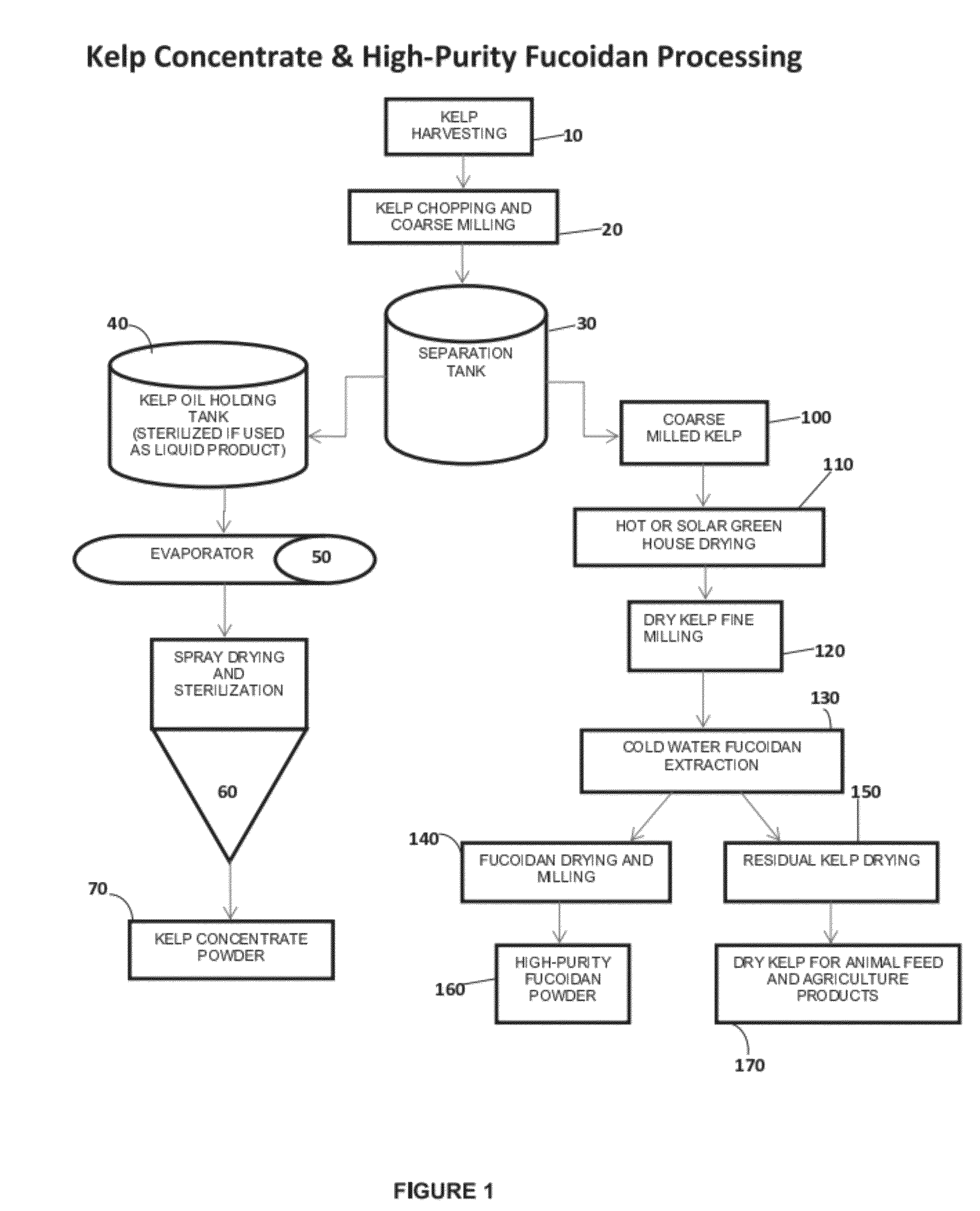
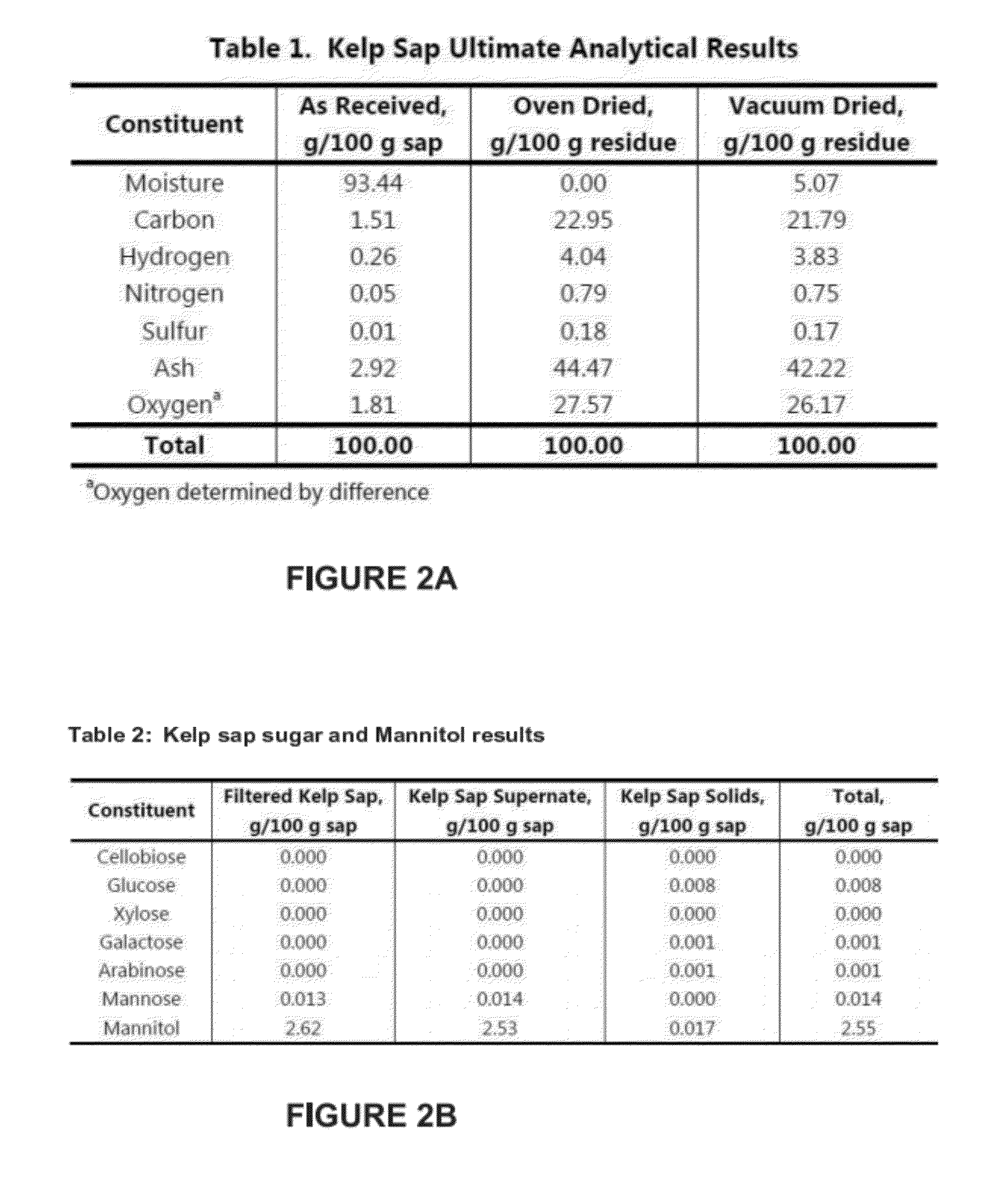
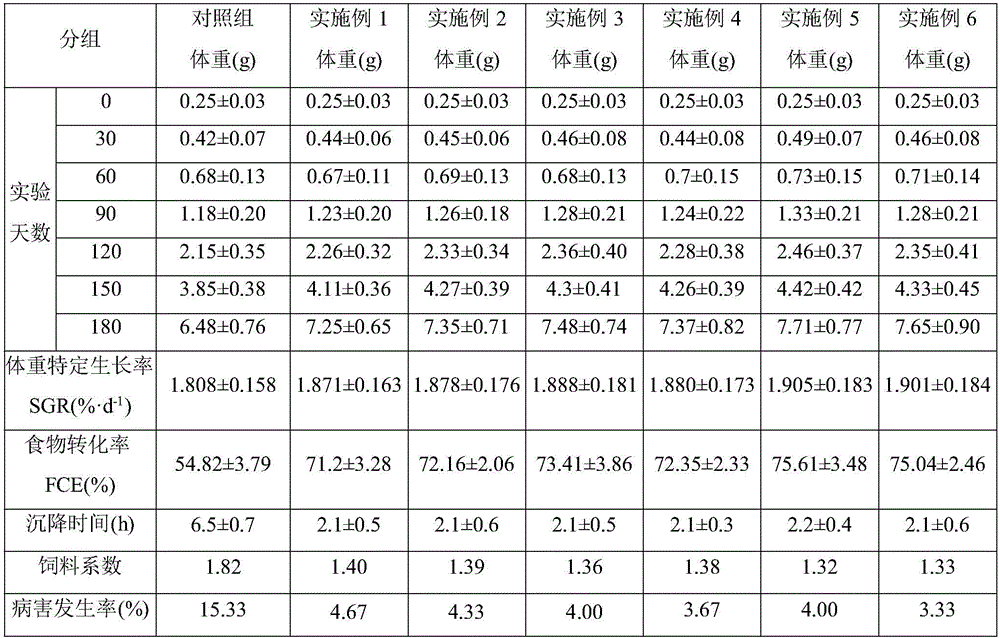
Macrocystis Pyrifera Derived Health and Wellness Products and Methods of Using the Same
The exudate of macroalage is collected and selectively dried to produce a health supplement capable of oral, topical, or transdermal delivery to benefit the health of user. The macroalage is preferably brown macroalage of the species Macrocystis pyrifera and the exudate preferably collected within 12 to 24 hours of harvest. High purity Fucoidan derived from Macrocystis pyrifera is administered in an effective amount to benefit the health of a user. Collected exudate, dried exudate or High Purity Fucoidan may be combined with other materials such as krill oil to create a synergistic boost to Antioxidant power and health benefits.
Owner:KNOCEAN SCI
Complete formula feed for young apostichopus japonicas and preparation method of complete formula feed
PendingCN105815609AReduce the amount of applicationReduce dependencyClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffMacrocystis pyriferaYeast
The invention discloses a complete formula feed for young apostichopus japonicas and a preparation method of the complete formula feed. The complete formula feed is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 15 to 25 parts of sweet potato root tuber powder, 10 to 15 parts of sargassum thunbergii powder, 15 to 25 parts of sargassum powder, 25 to 35 parts of degummed kelp powder, 2 to 5 parts of spirulina platensis powder, 8 to 12 parts of yeast powder, 1 to 2 parts of enzymed soy albumen, 1 to 3 parts of composite vitamins, 1 to 2 parts of composite mineral salt, and 0.5 to 1 part of compound enzyme. According to the complete formula feed for the young apostichopus japonicas, sweet potatoes are used as formula components of a feed of the young apostichopus japonicas, so that the application amount of macroalgae such as sargassum thunbergii is effectively reduced, the dependency on the macroalgae is reduced, and excessive development and utilization of macroalgae resources are avoided.
Owner:山东省海洋科学研究院青岛国家海洋科学研究中心
Method for constructing transgene kelp
InactiveCN1524955AVerify validityReliable source of materialAlgae productsOther foreign material introduction processesMacrocystis pyriferaSpore
The invention relates to a method for preparing transgenic large scale sea weed, wherein the reportedly exogenesis gene or functional exogenesis gene and antibiotic or weedicide genes are recombined to the promotor downstream originated from advanced plant or algae for constructing carrier for transportation, the large-scale sea weed spores are used as transportation receptor, and gene guns are used to direct the recombined plasmid DNA into the spores of large-scale sea weed, new plants can be grown through the approach of natural growth. The invention can realize the stabilized expression of exogenesis genes.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing fucoxanthin by heterotrophic culture of smooth nitzschia
InactiveCN107099564AIncrease contentHigh yieldUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesMacrocystis pyriferaFucoxanthin
The invention belongs to culture of microorganisms, and particularly relates to a method for producing fucoxanthin by heterotrophic culture of smooth nitzschia. The method comprises the following steps: preparation of a seed solution, fermental cultivation, extraction of the fucoxanthin from fermentation liquor after fermentation is finished and the like. The problem that the biomass concentration of the smooth nitzschia, the yield of the fucoxanthin and the content of the fucoxanthin are low under the condition of heterotrophic culture in the prior art is solved. The method has the advantages that the content of fucoxanthin in prepared dry smooth nitzschia powder is high, the yield of the fucoxanthin is high, the fucoxanthin is safer than fucoxanthin from large seaweeds, and while the production efficiency is improved and the production cost is reduced, pollution risks in a culture process is greatly reduced.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Preparation of Gymnodinium breve inhibitor
The invention relates to a method for preparing a Gymnodinium breve inhibitor and belongs to the field of treatment of marine red tide. The method comprises the following preparation steps: firstly, a large-scale alga ulva pertusa material is pulverized and leached through anhydrous ethanol, usually, each kilogram of the ulva pertusa material uses 2 to 5 liters of the anhydrous ethanol to obtain an extract; secondly, cream obtained through condensation of the extract is dissolved in water; a supernatant fluid is taken out, is extracted through petroleum ether and is delaminated to obtain a water phase substance; and the water phase substance is extracted with n-butyl alcohol and is delaminated to obtain a water phase substance; and finally, the water phase substance is extracted with acetic ether; and the obtained acetic ether phase is the Gymnodinium breve inhibitor. The inhibitor with the concentration of between 8 and 10 milligram / litre has optimal inhibition ratio on Gymnodinium breve. The preparation method has a simple process, low preparation cost and no organic pollution; and the used reagent has low price and lower toxicity.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
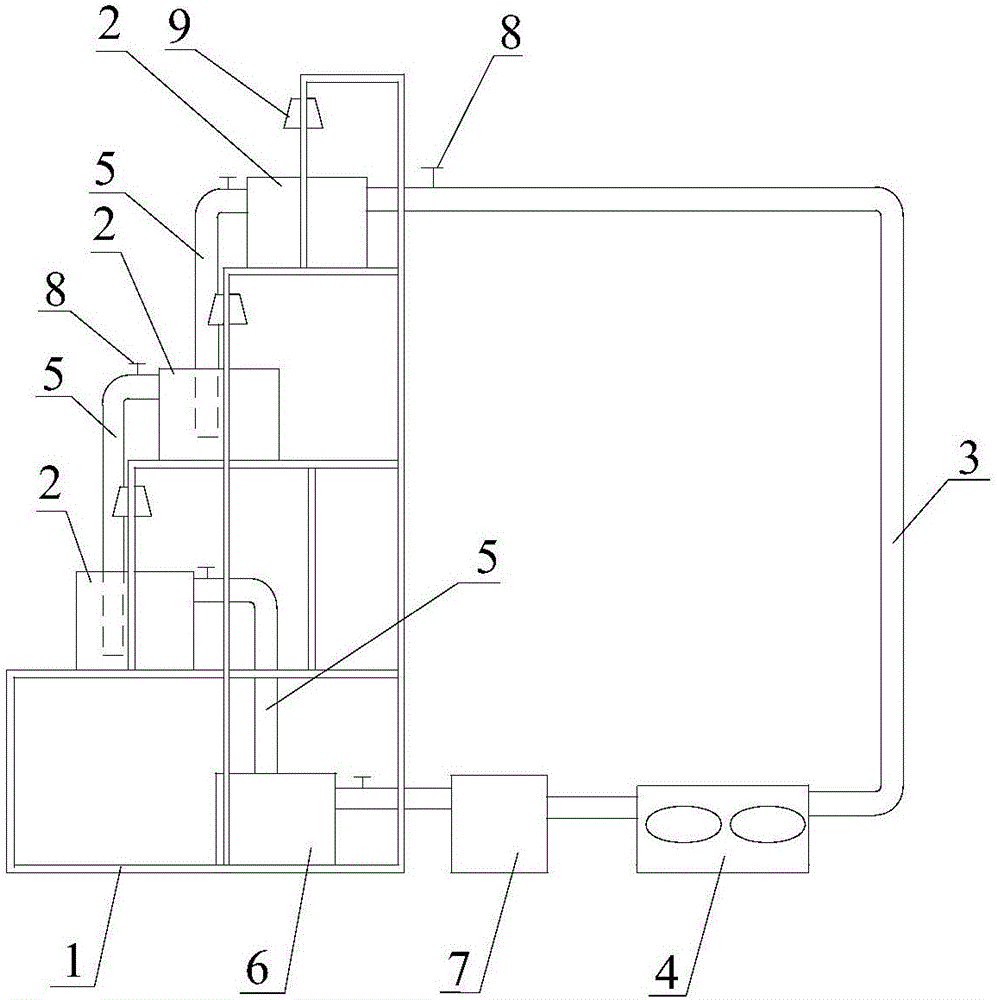
Indoor rapid multiplication cultivation system for seaweed Gracilaria lemaneiformis
InactiveCN106258922ASuitable for amplificationSuitable for trainingClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsMacrocystis pyriferaSea waves
The invention discloses an indoor rapid multiplication cultivation system for seaweed Gracilaria lemaneiformis, comprising a multi-stair support; a plurality of cultivation boxes are arranged on the multi-stair support side by side from bottom to top, a water inlet of each top cultivation box is connected with a heat changer through a water delivery pipe, an outflow pipe arranged on the upper portion of each cultivation box is extended down to the bottom of one lower cultivation box, an outflow pipe of each bottom cultivation box is connected sequentially with an inflating device, a circulating pump and the heat exchanger, and a circulating water loop is formed; support cross rods are fitted with solar lamps each above one cultivation box. The stereoscopic multi-tier multi-passage connected cultivation box structure is utilized, a flow of water is controlled to flow out from bottom to top, waves of natural sea areas are simulated, space and light are maximally utilized, and the true natural growth state of Gracilaria lemaneiformis is simulated; different cultivation interfaces can be provided, the growth environment is optimized, the system is suitable for multiplication and cultivation of Gracilaria lemaneiformis under different biomasses, and all-weather indoor large-scale multiplication cultivation of Gracilaria lemaneiformis is thus achieved.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Sinkable floating alga ecological restoration device
ActiveCN109832185APurify waterRealize the anti-storm functionClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsMacrocystis pyriferaSporophyte
The invention discloses a sinkable floating alga ecological restoration device which can purify water, supplement alga population through sporophyte diffusion during macroalga reproduction and achievea wind and wave preventing function through manual sinking. The sinkable floating alga ecological restoration device comprises a base, a support floating rack, an alga culture device and a connectionand sinking triggering mechanism and is characterized in that the support floating rack is connected with the base through first connecting ropes; the alga culture device comprises a floating platform floating below the support floating rack, an alga rack arranged on the floating platform and pre-connection ropes connecting the alga rack and the support floating rack; the connection and sinking triggering mechanism comprises a slide sleeve slidably arranged in a vertical guide sleeve, a lower connector arranged in the slide sleeve, a triggering rope connecting a floating ball and an upper piston, a second connecting rope connecting a bottom touch release mechanism and a lower connector and a third connecting rope connecting a counterweight and the base.
Owner:MARINE FISHERIES RES INST OF ZHEJIANG
Preparation method of special biological selenium-rich nutrition solution for plants
InactiveCN109251088AImprove balanceGuaranteed healthy growthBio-organic fraction processingNitrogenous fertilisersDiseaseGlycerol
The invention relates to a preparation method of a special biological selenium-rich nutrition solution for plants, wherein the components of the formula comprises (by weight): 0.3-1.3% of cystine, 0.5-1.5% of a methionine-copper complex, 0.7-1.7% of Clostridium butyricum, 1-2% of a common yam rhizome extract, 1.2-2.1% of an amino acid-iron complex, 1.3-2.2% of a Sterculia lychnophora Hance extraction liquid, 1.9-2.9% of folic acid, 2.5-3.5% of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, 2.9-3.9% of a Fritillaria ussuriensis Maxim extract, 2.3-3.3% of acetohydroxamic acid, 2.7-3.7% of sorbitol, 2.8-3.8% of a fructus momordicae extract, 1.1-2.1% of Bifidobacterium bifidum, 0.5-1.5% of Trisodium hydrogen diphosphate, 0.1-1% of Glycerol, 0.8-1.8% of a Cassia nomame extract, 0.2-1% of Avocado oil, 0.9-1.9% of Macrocystis pyrifera powder, 2.7-3.7% of probiotics, 1.7-2.7% of yeast selenium, and 71.9-52.4% of water. According to the present invention, the special biological selenium-rich nutrition solution canwell supplement nutrition elements required in plant growth, strengthening and enlarge seedlings, promote the robust growth of plants, enhance the stress resistance, the cold resistance and the disease resistance of plants, achieve the strong stems and the green leaves of plants, fundamentally reduce the occurrence of diseases, balance the plant nutrition, ensure the healthy growth of plants, andprolong the flowering period of plants.
Owner:CHANGSHA XIEHAOJI BIOENG CO LTD
Method for increasing content of fucoxanthin in heterotrophic cultured smooth nitzschia fermentation liquid by utilizing illumination
ActiveCN108841887AIncrease contentRealize continuous industrial productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationMacrocystis pyriferaFucoxanthin
The invention belongs to post-treatment of fermentation liquid, and particularly relates to a method for increasing the content of fucoxanthin in heterotrophic cultured smooth nitzschia fermentation liquid by utilizing illumination. The method comprises process processing steps of preparing smooth nitzschia fermentation liquid by adopting a heterotrophic culture method; transferring the prepared smooth nitzschia fermentation liquid into a photobioreactor under the illumination of single-colored light or hybrid light, performing ventilation for induced culture under the illumination condition and the like. The method solves the technical problem that the content of the fucoxanthin in the smooth nitzschia fermentation liquid prepared by heterotrophic culture is low in the prior art. The method has the advantages that the content of the fucoxanthin in prepared dry smooth nitzschia powder is high, continuous industrial production can be stably realized, general pollutants in the ocean suchas heavy metals and polychlorinated biphenyl can be controlled from the source of a culture medium, and the fucoxanthin from relatively large-sized alga is safer.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for efficiently removing epibiotic microorganisms on surfaces of large seaweed
InactiveCN105274033ALow costEasy to prepare in large batchesFungiBacteriaMacrocystis pyriferaNatural product
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnologies of seaweed, and relates to a method for efficiently removing epibiotic microorganisms on the surfaces of large seaweed. The method particularly includes removing the epibiotic microorganisms on the surfaces of the to-be-treated large seaweed under the resonance actions of quartz sand and the to-be-treated large seaweed. The method has the advantages that the epibiotic microorganisms on the surfaces of the large seaweed can be efficiently and thoroughly removed by the aid of the method, and the method is free of interference on endophytic microorganisms; the method can be used for separating and purifying endosymbiotic microorganisms of the seaweed and studying active natural products of the seaweed.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Planting method for iodine-containing strawberries
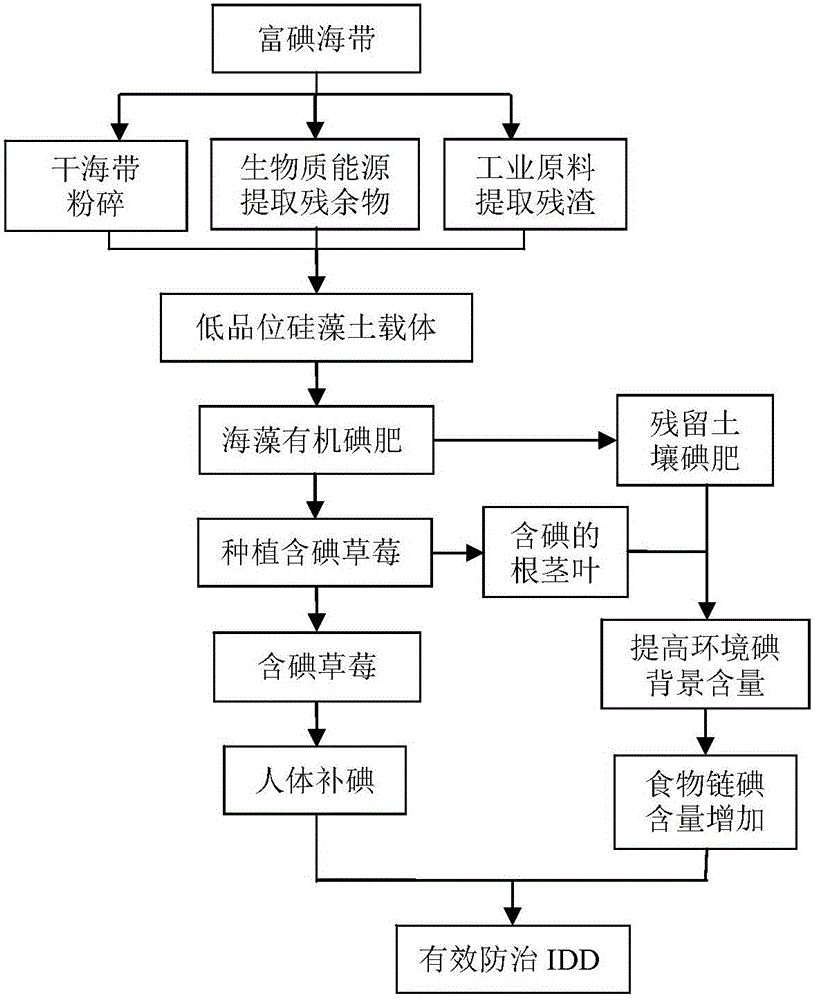
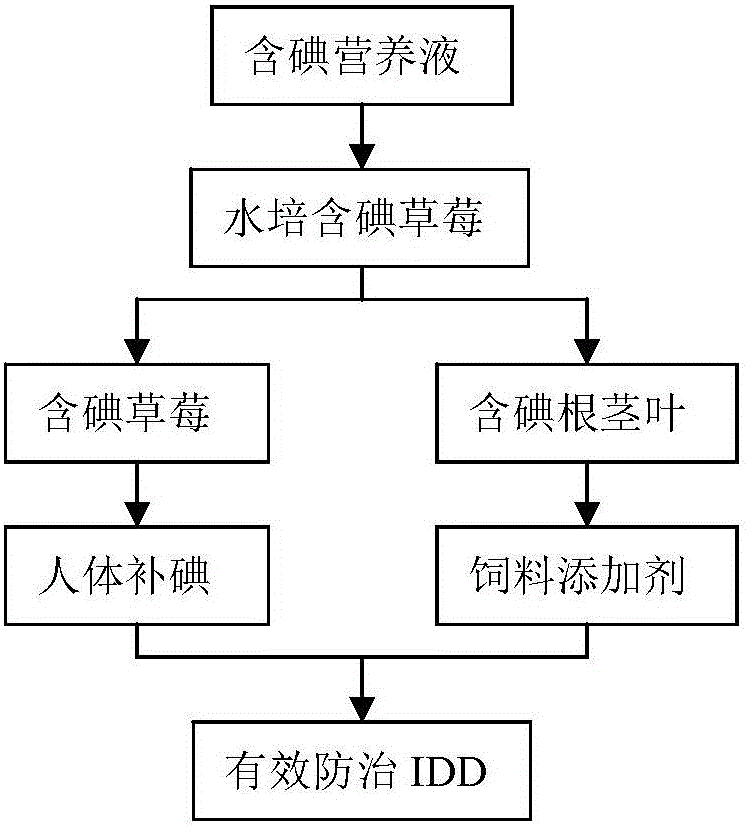
InactiveCN105724021APromote absorptionIncreased iodine backgroundSeed and root treatmentBioloigcal waste fertilisersMacrocystis pyriferaFragaria
The invention discloses a planting method for iodine-containing strawberries.The method comprises the following steps that 1, germination accelerating is performed on strawberry seeds; 2, the strawberry seeds treated through germination accelerating are sown on a ridged field, and transplanting and planting are performed after strawberry seedlings grow out 3-5 true leaves; 3, organic alga iodine fertilizer is applied to surface soil at a time while base fertilizer is sufficiently applied to transplanting soil, and then strawberry seedling transplanting and planting are performed.The strawberry seedlings also can be transplanted into a container containing a solution in the step 3, the root systems are suspended in the solution, and continuous ventilation is kept; after being cultured for 3 days with tap water, 3 days with a 1 / 2 nutrient solution and 3 days with a complete nutrient solution separately, the strawberry seedlings are cultured with a nutrition solution with the iodine containing concentration of 0.25-1.0 mg / L and the pH of 5.5+ / -0.1, and the nutrition solution is replaced for once every five days.According to the planting method, the organic algae iodine fertilizer is prepared from large algae and kelps which are rich in iodine by taking low-grade diatomaceous earth as a carrier, or the iodine-containing nutrition solution is prepared by dissolving KI into a nutrition solution, and therefore the iodine-containing strawberries are planted for effective natural iodine supplementary.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com