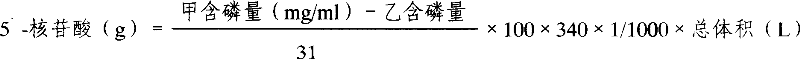Patents
Literature
211 results about "Sporophyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A sporophyte (/spɔːroʊˌfaɪt/) is the diploid multicellular stage in the life cycle of a plant or alga. It develops from the zygote produced when a haploid egg cell is fertilized by a haploid sperm and each sporophyte cell therefore has a double set of chromosomes, one set from each parent. All land plants, and most multicellular algae, have life cycles in which a multicellular diploid sporophyte phase alternates with a multicellular haploid gametophyte phase. In the seed plants, (gymnosperms) and flowering plants (angiosperms), the sporophyte phase is more prominent than the gametophyte, and is the familiar green plant with its roots, stem, leaves and cones or flowers. In flowering plants the gametophytes are very reduced in size, and are represented by the germinated pollen and the embryo sac.
Method for culturing rhizome drynariae
InactiveCN1726760AImprove germinationEarly germinationHorticulture methodsSpore germinationSporophyte
An artificial reproduction method for drynaria includes asexual production and spore reproduction. Said asexual reproduction includes such steps as taking its rhizome segment with 3-5 bud points and 3-5 sporophyllary leaves, fixing it to tree or mountain rock, covering it by bryophyte, spraying water and management. Said spore reproduction includes such steps as sterilizing the burnt earth, immersing in cold boiled water, loading the sporanges in bag, drying in air, preparing the suspension of sporanges, spraying it onto said burnt earth, optical culture to obtain gametophytes, transplanting, culturing to obtain sporophytes, and transplanting them on tree or mountain rock.
Owner:WUHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Sterilized spore germination of platycerium wallichii and test tube seedling cultivating method
The present invention relates to a method for propagation and cultivation of platycerium. It is characterized by that said invention adopts sterile spore germination technique and makes it be combined with test-tube seedling-cultivating technique to implement propagation and cultivation of platycerium. Said method includes the following several steps: collecting storing, health and mature spore, making sterile spore germination, gametophyte growth culture, insemination to form zygoite, sporophyte enrichment culture, rooting culture and transplantation, etc.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Gulfweed transplanting method based on juvenile sporophyte adhesion function
ActiveCN104663419ASolve the problem of not successfully attaching to the substrateImprove transplant survivalCultivating equipmentsSeaweed cultivationSporophyteOrganism
The invention discloses a gulfweed transplanting method based on a juvenile sporophyte adhesion function. The method includes the steps of firstly, collecting fertilized gulfweed archegoniophore; secondly, crushing the gulfweed archegoniophore, adding sea water, well mixing, filtering impurities, and collecting the filtered liquid mixture; thirdly, concentrating the liquid mixture with a centrifuge to prepare concentrated mucus; fourthly, well mixing juvenile sporophyte and the concentrated mucus to obtain juvenile sporophyte concentrated mucus; fifthly, diving to reach the seabed, removing organisms and sediments adhering to a seabed ledge matrix, and smearing the juvenile sporophyte concentrated mucus on the surface of the seabed ledge matrix. By the method, the problems that gulfweed juvenile sporophyte adhesion success probability is reduced due to the actions of waves and sea currents, and the juvenile sporophyte cannot be adhered successfully are solved.
Owner:MARINE FISHERIES RES INST OF ZHEJIANG
Summering cultivation method for seedlings of Hizikia fusiform (Harv)Okamura juvenile sporophytes
InactiveCN102224800AOvercoming adverse sea conditionsReduce energy consumptionAlgae productsCultivating equipmentsLow latitudeSporophyte
The invention discloses a summering cultivation method for seedlings of Hizikia fusiform (Harv)Okamura juvenile sporophytes, comprising the following steps: raising seedlings in a north sea area at a high latitude during the high temperature stage; and transferring the cultivated seedlings to a south cultivation sea area at a low latitude after summering for cultivation. In the invention, seedling raising and cultivation are performed in different levels and sea areas, thus overcoming the disadvantageous sea conditions in cultivation sea areas, and avoiding high energy consumption in an indoor temperature-reduction cultivation mode.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MARICULTURE RES INST
Propagation method of cyrtomium fortunei
ActiveCN102860262AMake up cycleCover costsHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologySporeling
The invention discloses a propagation method of cyrtomium fortune. The propagation method comprises the following processing steps of: 1, preparing a culture medium; 2, sterilizing cyrtomium fortune spores; 3, inoculating and cultivating; and 4, reculturing seedling and transplanting cyrtomium fortune sporophyte seedling. The propagation method has the following advantages that: deficiencies of long culture period, high cost and low efficiency of the conventional cyrtomium fortune propagation technology are made up, and a new way for artificial propagation of the cyrtomium fortune is developed. Few spore materials are utilized, so that a large amount of sporophytes can be quickly propagated, the seedling is formed in 65 days, and the planting percent is about 97%, so that large-scale industrial production of the cyrtomium fortune becomes possible, thus requirements of the market on the cyrtomium fortune are satisfied, and meanwhile, damage on the wild resources and the environment canbe reduced. Furthermore, the invention further provides a good testing system for developing researches about genetic breeding of species and conservation biology, and wide application prospect is provided.
Owner:江苏蕨美植物科技有限公司
Tissue culturing method, culturing method of ferns and explant obtained therefrom
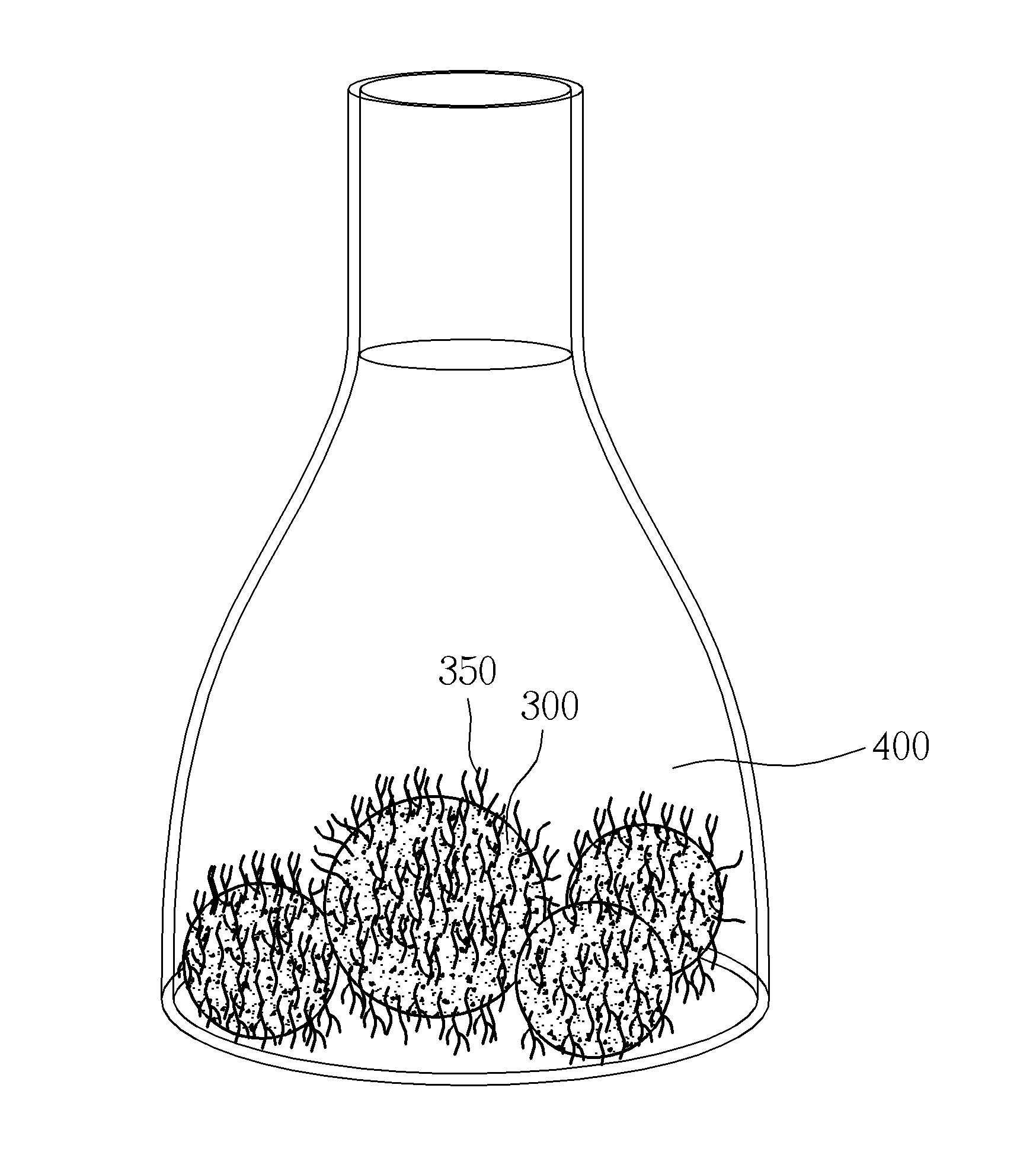
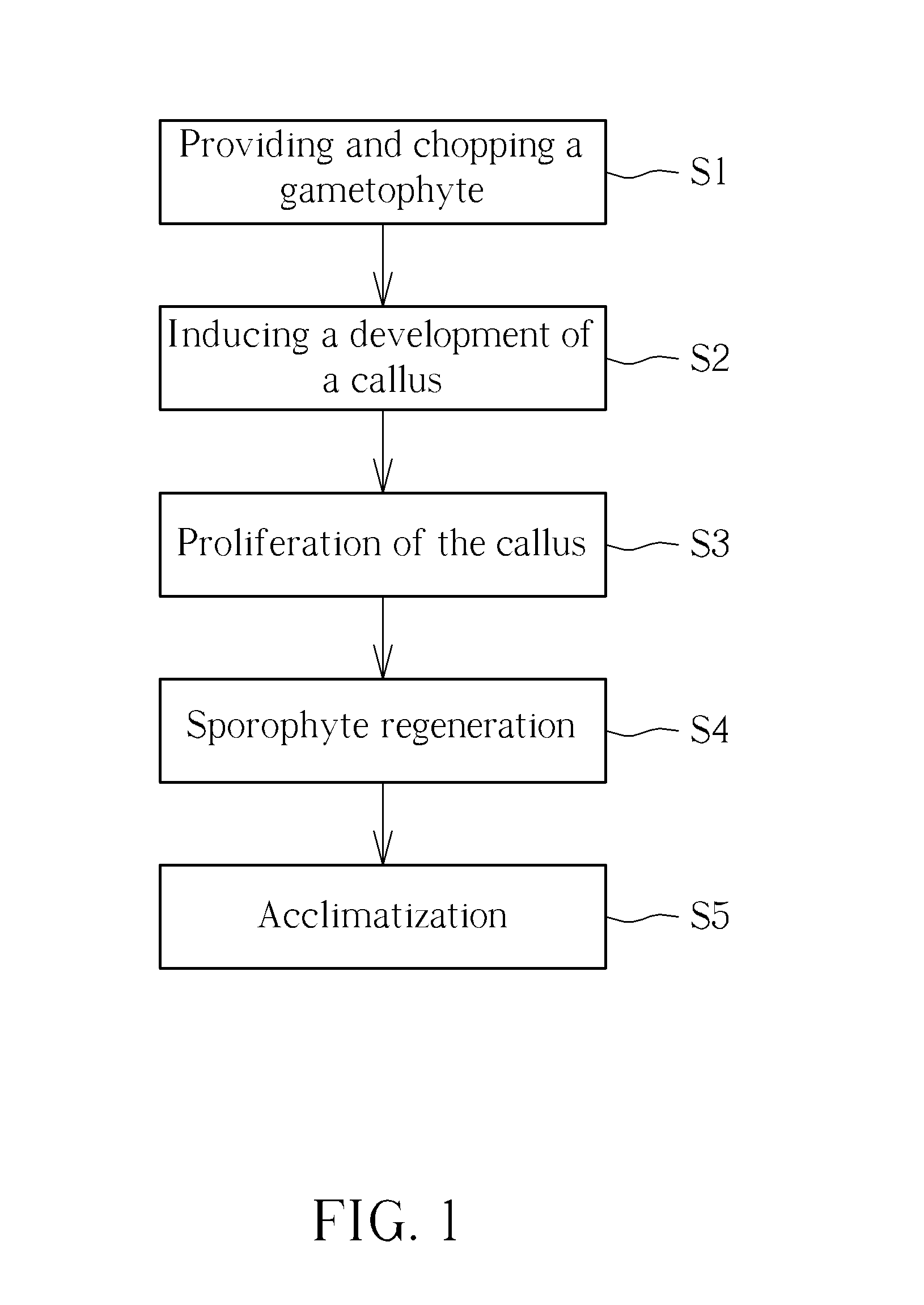
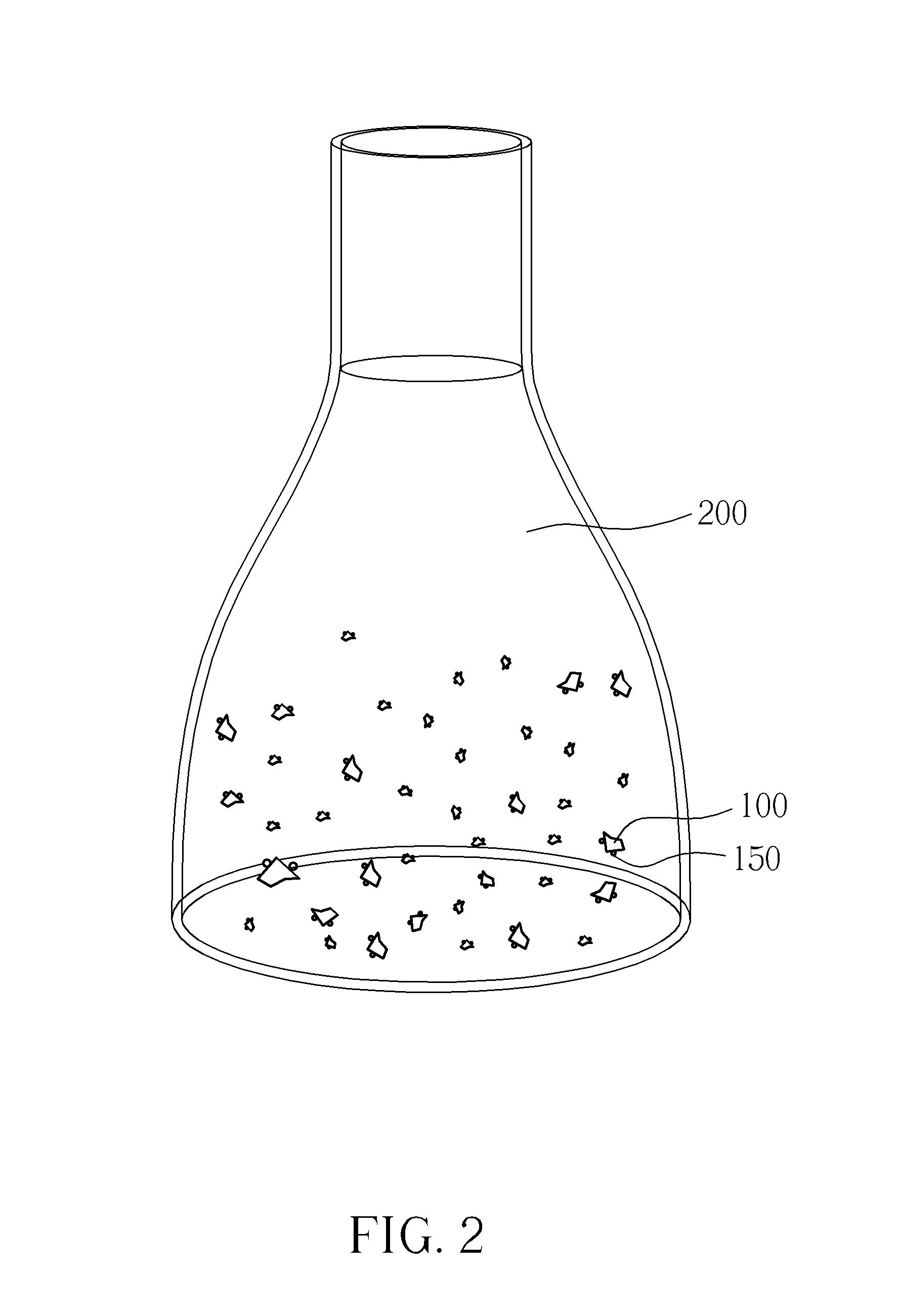
InactiveUS20150132852A1Promote reproductionEfficient regenerationCulture processCell culture mediaSporophyteCulture fluid
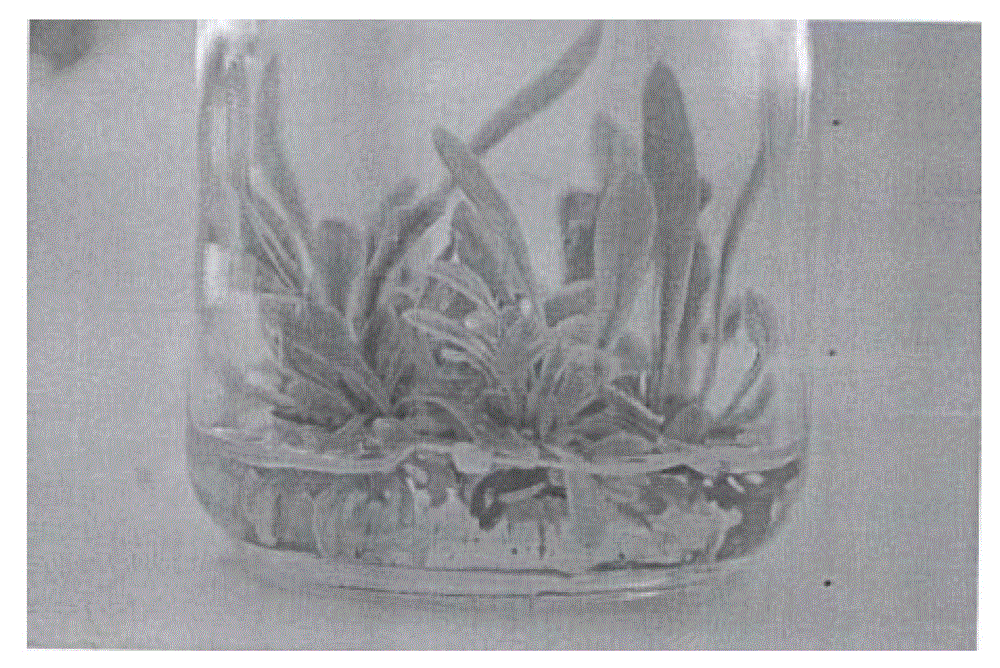
A tissue culturing method includes following steps: providing a chopped gametophyte, generating calluses by culturing the chopped gametophyte, and performing apogamic regeneration of sporophytes, by culturing the calluses in a culture fluid to develop the sporophytes from the calluses. The present invention also provides a tissue culturing method of ferns and an explant.
Owner:CHUNGHWA PICTURE TUBES LTD
Seedling cultivation method for sea-tangle
InactiveCN101502232AGuaranteed healthy growthImprove simplicityCultivating equipmentsSeaweed cultivationSporophyteIrradiation
The present invention discloses a seedling cultivation method of sea tangle, wherein the method comprises the following steps: a. cultivating the collected zoospores under the white radiation irradiation with a certain illumination intensity for forming gametophyte; b. cultivating the gametophyte with the blue light illumination with a certain illumination intensity for converting the gametophyte to micro sporinite; c. growing the micro sporinite under the red light illumination with a certain illumination intensity for a certain period of time; and d. cultivating the sporinite under blue light illumination with a certain illumination intensity so that the sporinite obtains the dimension required for stored cargo delivery. The healthy growing of sporinite can be guaranteed under a higher temperature through adopting the combination irradiation with various light qualities for executing seedling cultivation of sea tangle. The method is simple for applying and the seedling cultivation cost is low.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Plug-in artificial algal reef and method for constructing algal field by using same
InactiveCN102150608AImprove reliabilityComplex and reasonableClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaRough surfaceSporophyte
The invention discloses a plug-in artificial algal reef and a method for constructing an algal field by using the same. The algal reef comprises a solid base and an attached block movably connected to the solid base through a connecting rod, wherein the attached block is semispherical and has a rough surface, thereby meeting the requirement for the attachment of algae germ cells; and both the solid base and the attached block can be formed by one-step concrete pouring. When the algal field is constructed, the solid base is put into the sea and is soaked for a period of time; meanwhile, the attached block is dipped into seawater containing algae germ cells, and the attached block subjected to species introduction is movably connected to the solid base through the connecting rod after the algae germ cells are attached to the attached block. The plug-in artificial algal reef is convenient to use and is firm and durable, and algae can be prepositively fixed on the attached block so that germ cells diffused by algae sporophytes continue growing on the solid base; the germ cells is prevented from being swallowed by natural enemies, and the success rate of algae introduction is increased; the rehabilitation of the algal field can be realized, and a foundation is laid for building a new algal field.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method for rapidly reproducing new pteris fern seedlings by using prothallium reproduction approaches
ActiveCN102715092ASame biological ageGrow neatlyCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsSporophyteSeedling
The invention belongs to the field of agricultural biotechnology and relates to a method for rapidly reproducing new pteris fern seedlings by using prothallium reproduction approaches. The method comprises the steps of prothallium culture process, multiplication culture process, sporophyte induction process, rooting induction process, and transplant and manage process. The technological process is simple; by reproduction in the form of prothallium, a great amount of prothallium can be obtained; by the processes of multiplication, sporophyte induction, sporophyte rooting and transplant, a great number of seedlings capable of being used for production and culture can be obtained; the obtained seedlings are at the same physiological age and grow uniformly; and the method is suitable for industrial seedling raising and scale culture.
Owner:TROPICAL CORP STRAIN RESOURCE INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Dryopteris erythrosora spore propagation method
InactiveCN102283090AConducive to rapid breedingIncrease production capacityCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationSpore germinationPeat
A conventional Dryopteris erythrosora spore propagation method is mainly characterized in that Dryopteris erythrosora spores are prepared into suspension and the suspension is evenly poured onto mediums contained in an earthen pot by using a syringe; sowing mediums are mixtures of sand, peat and pearlite which are mixed by volume ratio of 1:1:1; the earthen pot into which the spores are sown is put into a transfer case, the height of the water-soaked bottom of the transfer case is 1.5cm and the water-soaked bottom of the transfer case is covered by plate glass; the spores are cultured in the sunshade position of a greenhouse at 25 DEG C to 35 DEG C under the condition that direct sunlight is avoided; juvenile sporophytes are obtained after culture and are respectively transplanted into transplanting mediums I which are formed by leaf mould, peat and sand in an evenly mixing way by volume ratio of 1:1:1, transplanting mediums II which are formed by sand, pearlite and peat in an evenly mixing way by volume ratio of 1:1:1, transplanting mediums III which are formed by peat and garden mould in a mixing way by volume ratio of 1:1, and reference mediums which are formed by garden mould; and the juvenile sporophytes are cultured under the same conditions. By using the characteristic that the germination and the fertilization of the spores need water and by applying pot planting, water soaking and moisture preservation to Dryopteris erythrosora spore propagation, the germination rate of the Dryopteris erythrosora spores, the seedling rate and the survival rate of the transplant sporophytes are effectively improved; in the propagation process, any sterilization process is not required, the processes are reduced, the pollution is reduced, the cost is saved, the operation is simple and convenient and the rapid propagation and the mass production of seedlings are facilitated; the survival rate of the transplanted juvenile spore seedlings reaches more than 85 percent.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
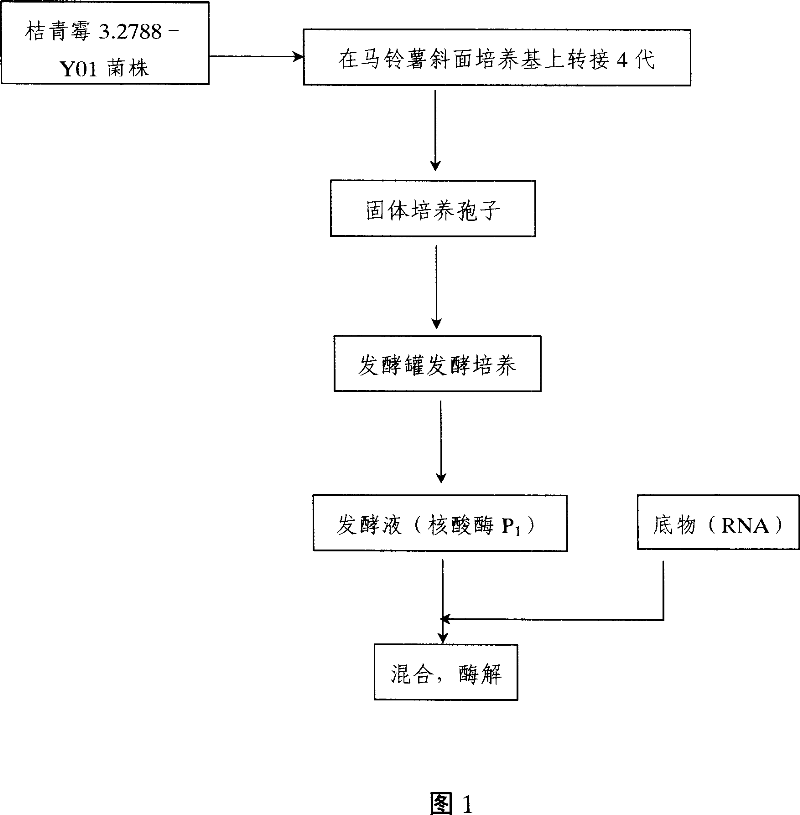
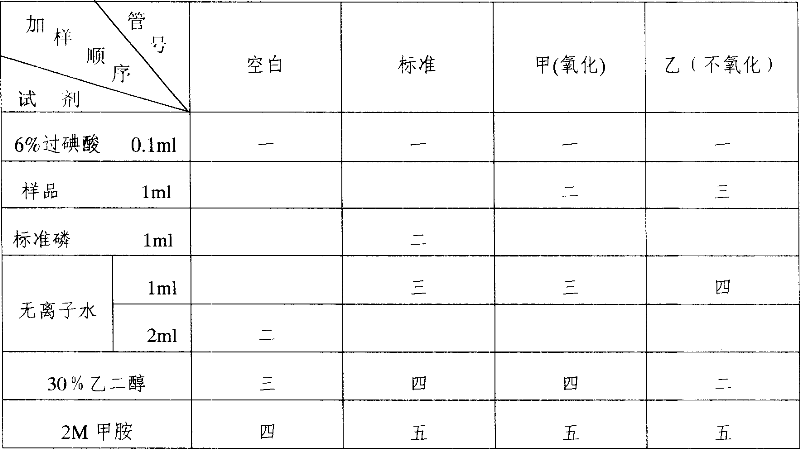
Method for preparing nuclease P1 by ferment process
The invention provides a fermentation method for preparing nuclease P1, which using directly penicillium citrinum sporogon as seed, fermenting by means of fed-batch sugar supplement to improve activity of the nuclease P1, the mehod without first and second order seed culture shorts production cycle greatly and raises efficiency. The invetion also uses obtained enzyme for preparing 5'-mononucleotide with 85-90% rate of enzymatichydrolysis and 15 mg / ml of producing rate of nucleotide. The invention also provides a penicillium citrinum 3.2788-Y01 of nuclease P1, which fungus stroing number is CGMCC NO.1943, the stem can raise one times active unit of the nuclease P1.
Owner:北京燕京中科生物技术有限公司
Technique for producing sargassum thunbeergii kuntze offspring
The invention discloses a seedling producing technique for rat-tailed algae, applying to seedling breed in-door according to sexual reproduction law, including: selecting and collecting the seed algae, stimulating and diffusing the seed algae, collecting the juvenile sporophyte, culturing and catadromousing seedlings, provided an artificial seedling producing technique for rat-tailed algae, dissolving the current shortcoming problem of the rat-tailed algae seedlings.
Owner:YANTAI UNIV
Method for extracting astaxanthin from haematococcus pluvialis
The invention discloses a method for extracting astaxanthin from haematococcus pluvialis. The method comprises the steps of (1) breaking walls of sporophore: taking fresh wet algae mud, adding 3 mol / L HCl with an amount of two times by mass of the fresh wet algae mud, stirring uniformly, stirring for 3 min at a temperature of 50 DEG C with a stirring speed of 180 times per minute, cooling rapidly, centrifuging and washing and taking the algae bodies; and (2) extracting astaxanthin: adding ethanol into the wall-broken sporophore with an amount of two times of the sporophore, oscillating for 5 min at a low temperature of 10 DEG C, centrifuging, recovering ethanol, repeating for 2 times, merging the recovered ethanol; concentrating at a low temperature and in vacuum; and recovering ethanol by evaporation, and thus the left material being astaxanthin. The method is simple and can be easily understood, is reasonable in operation, enables the haematococcus pluvialis to perform nutritive growth relatively well, is relatively fast in transformation from nutritive growth to non-nutritive growth, and accumulates relatively much haematococcus pluvialis, thereby increasing efficiency and stability of culture, transformation and accumulation and effectively preventing contamination of miscellaneous algae during a culture process. The manufactured astaxanthin is relatively low in cost.
Owner:QINGDAO ZHONGREN PHARMA
Undariapinnatifida seedling cultivation method through parthenogenesis
ActiveCN103651094AResistant to washingFirmly attachedClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsPuccinia xanthiiSporeling
The invention relates to an undariapinnatifida cultivation method, in particular to an undariapinnatifida seedling cultivation method through parthenogenesis. The method comprises the steps that induction culture is conducted on female gametophytes until juvenile sporophytes reach more than 1mm, aerated feeding culture is conducted on the female gametophytes, then the life history of parthenogenesis sporophytes is completed, and mature sporophytes are obtained; sporophyls of the sporophytes are placed into sea water to be released to obtain planospores, after the color of the sea water where the planospores are obtained through releasing is changed into yellowish-brown, the planospores are attached to a seedling curtain, and then the seedling curtain is put into fresh sea water; after all the germinal planospores develop into the female gametophytes and are sufficiently grown, light intensity is lowered, the development of the gametophytes is delayed to enable the gametophytes to pull through the high-water-temperature summer; the male gametophytes and the female gametophytes attached to the seedling curtain are simultaneously cultured, and the development and fertilization processes are completed; after reaching about 200 micrometers, the juvenile sporophytes are moved to sea to be cultivated, and then undariapinnatifida cultivation is achieved. According to the undariapinnatifida seedling cultivation method through parthenogenesis, female gametophyte clonal update and enlarged cultivation can be achieved through the parthenogernesis life history, and it is of great significance in clonal preservation and crossbreeding.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
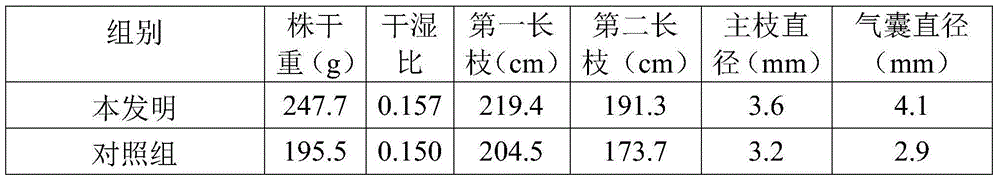
Rapid breeding method of Sargassum fusiforme
ActiveCN104620969ARich in colloidDark colorCultivating equipmentsSeaweed cultivationFemale to maleDry weight
The invention discloses a rapid breeding method of Sargassum fusiforme. The method includes the steps of selecting parents, performing isolation cultivation to single plants, promoting maturity, allowing fertilization, screening juvenile sporophytes, cultivating the juvenile sporophytes and the like. During isolation cultivation of the single plants, the weight ratio of the parents to cultivation water is 1:100; maturity promoting liquid is natural seawater added monopotassium phosphate, calcium chloride and sodium ethylene diamine tetracetate, under salinity of 27%. to 28%.; during fertilization, the ratio of females to males is 5:1. The method has the advantages that the technical defect of germplasm degeneration in the prior art is overcome, high-quality seedlings of Sargassum fusiforme can be obtained, plant dry weight of Sargassum fusiforme bred by the method is up to 247.7g, sac diameter is up to 4.1mm, and by the use of the method compared to the traditional methods, yield per mu of the plant dry weight is increased by 26.1%, the sac diameter is increased by 41.1%, and economic benefit is increased by 37.8%.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Breeding method for alsophila spinulosa
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Sargassum fusiform line differentiation and classification method
A method provided by the present invention is applicable to the aspects such as sargassum fusiform germplasm resource analysis, artificially cultured sargassum fusiform group line classification, elite seed and pedigree seed near-source genetic relationship analysis and manual seedling screening by using sexual reproduction of sargassum fusiform. The method mainly comprises the operating steps of sargassum fusiform history feature and sargassum fusiform mature sporophyte morphological feature main component morphological measurement, sargassum fusiform mature sporophyte morphological feature correlation mathematical model analysis, sargassum fusiform mature sporophyte morphological feature main component mathematical model analysis, sargassum fusiform mature sporophyte morphological feature main component cluster mathematical model analysis, and sargassum fusiform mature sporophyte line differentiation and classification determination and the like. The present invention may provide a scientific differentiation and classification method for the aspects such as sargassum fusiform germplasm resource investigation, sargassum fusiform mature sporophyte group diversity analysis, sargassum basic scientific research and experimental sample screening, sargassum fusiform introduced seed morphological feature stability analysis, manual elite seed differentiation and screening by using sexual reproduction of sargassum fusiform and asexual reproduction excellent plant rhizoid storage.
Owner:温州市洞头区水产科学技术研究所 +1
Method for breeding spore of Dryopteris varia
InactiveCN101297635AShort reproductive cycleReduce investmentCultivating equipmentsPlant tissue cultureSporophore formationSporophyte
The invention relates to a spore reproducing method for Dryopteris varia (L.) Ktunze which can be reproduced fast and is characterized in that the disinfected Dryopteris varia (L.) Ktunze spore is cultured in the culture medium of spore germination and grows into laminar prothallium which is then cultured in multiplication medium for 30 days, in sporophyte inductive medium for 40 days and in sporophyte subculture medium for 20 days in sequence; after forming juvenile sporophyte and grows two to three pieces of juvenile sporophyte leaf, the prothallium is cultured in sporophyte rooting medium for 30 days, is transplanted out of bottle after the base part grows brown fine roots with scales and is transplanted to the soil matrix for culturing after seedling is trained. The spore reproducing method of the invention has little investment and simple equipment, only needs 110 days from the spore germination to the forming of the juvenile sporophyte, obtains large quantities of Dryopteris varia (L.) Ktunze seedlings in short time with the survival rate of the juvenile sporophyte of 90 percent, and leads the Dryopteris varia (L.) Ktunze to become an excellent foliage plant and perform the medical value thereof.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
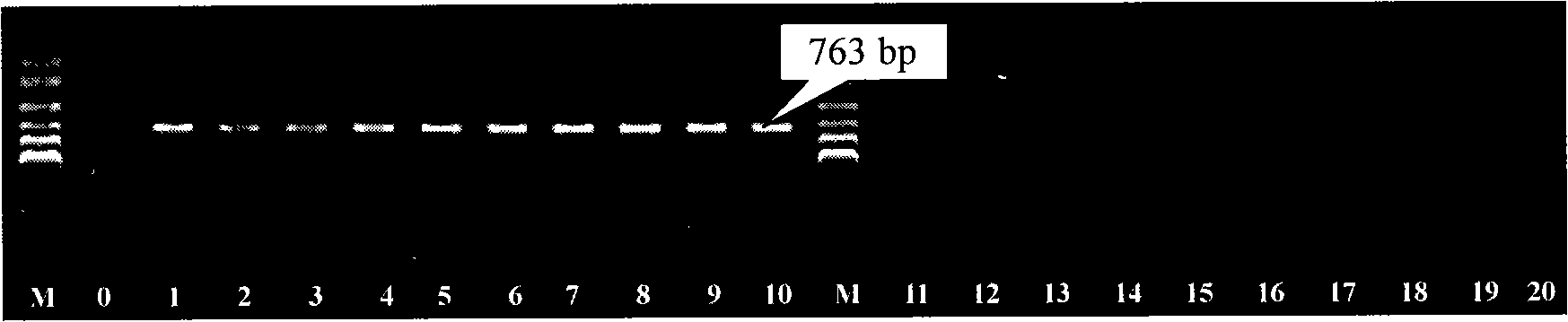
Specific molecular marker capable of identifying sea-tangle female and male gametophytes
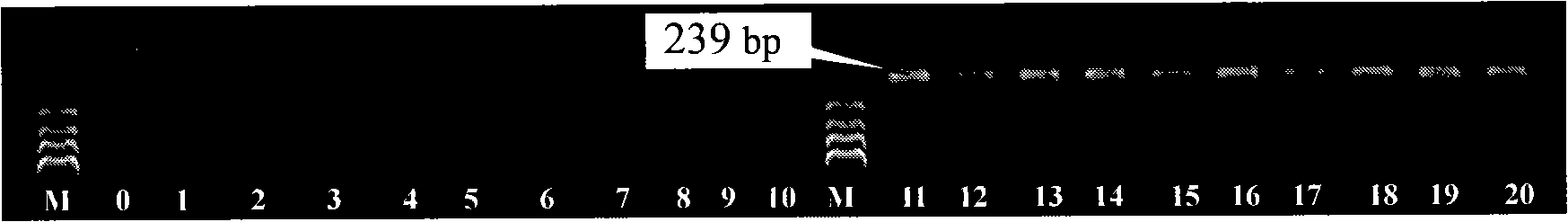
The invention belongs to the technology field of the gene engineering, in particular relates to a specificity molecule marker which can distinguish laminaria female and male gametophyte. The specificity molecule marker is obtained through the following method: two pairs of primers of SEQ ID No1and SEQ ID No2 are designed according to 5'end flanking sequence of the laminaria female and female gametophyte gene groups, polymerase chain reaction amplification is performed to the deoxyribonucleic acid of the laminaria female and female gametophyte gene groups, and the deoxyribonucleic acid of specificity amplification fragment are reclaimed; large intestine rod competent strain JM109 is cloned through pMD19-T vector to obtain a laminaria female gametophyte specificity molecule marker Rf-763 and a laminaria male gametophyte specificity molecule marker Rm-239, and the sequences thereof are SEQ ID No3 and SEQ ID No4. The genders of the laminaria gametophyte, parthenogenesis laminaria sporophyte parental source and the genders of the offspring thereof can identified through utilizing the specificity molecule marker, and the laminaria gender differentiation in basis of the cell and molecule level can be studied.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Method for generating macrogametocyte by somatic cell of inducing undaria pinnatifida gynecogenic juvenile sporophyte
The invention discloses a method for generating macrogametocytes by somatic cells of inducing undaria pinnatifida parthenogenesis juvenile sporophytes, which has easy operation, low cost and high maturation rate of the generated macrogametocytes and can provide a large quantity of the macrogametocytes for the large-scale seedling production of undaria pinnatifida. The method comprises the following steps of: cutting undaria pinnatifida macrogametocytes stored and cultured in a room into pieces and then culturing under the conditions of temperature suitable for the undaria pinnatifida macrogametocytes to grow to be mature, illumination and nutritive salt, wherein when the undaria pinnatifida macrogametocytes grow to be mature, form oocysts in large quantities and ovulate with ovums, a small quantity of the fertilized ovums are germinated to seedlings through parthenogenesis because unfertilized ovums are died by being unfertilized by spermatozoa; and when the somatic cells of the parthenogenesis seedlings are grown to 0.4-0.6 cm, adopting a rhizoid cutting method to enable fronds to lose polarity and constraint on the somatic cells, and inducing the somatic cells of the seedlings to generate the macrogametocytes.
Owner:DALIAN FISHERIES UNIVERSITY
Mass pteridophyta reproduction method
The invention discloses a mass pteridophyta reproduction method. The mass pteridophyta reproduction method includes the steps of (1), harvesting pteridophyta spores; (2), sowing, namely, mixing collected spores with a hormone solution, spraying the mixture into a sowing medium, and reproducing by keeping relative air humidity above 85% and temperature ranging from 25 DEG C to 27 DEG C, wherein the hormone solution consists of 1 / 2 MS (Murashige and Skoog) culture medium, NAA (naphthalene acetic acid) and GA3; (3), performing 'two-time transplant', namely, transplanting gametocytes on the culture medium after the gametophytes mature and before sporophytes arise, and transplanting seedlings into yellow soil when the sporophytes have 2-3 leaves. By the aid of the mass pteridophyta reproduction method, spore germination rate can be increased, and prothallus development can be promoted; production sowing quantity is guided effectively, and sporophyte growth and transplant management are benefitted; gametophyte fertilization is further benefited by 'two-time transplant', and seedling growth uniformity can be improved while seedling survival rate can be increased.
Owner:SHENZHEN TECHAND ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT CO LTD +1
Method for collecting seedlings from scytosiphon filaments
InactiveCN101946683ASolve the limitation of algae breeding seasonResolution timeClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsSporangiumBiology
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV
Method for wall-breaking leaching ganoderma spore powder
A process for breaking the wall of ganoderma sporophyte and extracting includex mixing the ganoderma sporephytes with solvent, ultrasonic pretreating and high-pressure treating under 250-550 MPa for 5-20 min.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
KMethod for carrying out germchit production for brown alga sargassum through breeding induction and controlled fertilization
InactiveCN1726764AControl culture conditionsDevelopmental synchronizationClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsSporophyteSARGASSUM FUSIFORME
A process for culturing the seedlings of Sargassum fusiforme by inducing reproduction and controlling fertilization includes such steps as providing seawater tank, choosing the seed sargassum fusiforme with male and female receptacles, controlling circulating time, illumination intensity and temp for synchronous mature and discharge of sperm and egg, fertilization, collecting fertilized eggs, inoculating the young sporophytes to attachment, and culturing in seawater at 20-25 deg.C for 1-2 months.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Potted ornamental Stenoloma Chusanum Ching spore propagation and maintenance method
The invention discloses a potted ornamental Stenoloma Chusanum Ching spore propagation and maintenance method, which relates to a spore propagation method for ferns. The method is to propagate sporophytes by using spores of Stenoloma Chusanum Ching and maintain the sporophytes. The method comprises: adding 100 to 200 milligrams of spores into 100 to 200 milliliters of cold boiled water, exhausting air for 1 hour, removing floating matters and water fluid, adding 500 to 1,000 milliliters of cold boiled water to prepare spore suspension, spraying each 500 milliliters of suspension onto 1 to 2 square meters of substrate, covering with a thin film after the substrate is completely wetted by the cold boiled water, and culturing under conditions of a temperature of 20 to 28 DEG C, a light intensity of 5,000 to 20,000Lx and a light period of 10 to 12 h / d till light intensity comes out. For maintaining the sporophytes, bamboo leaf humus soil is used as a substrate, the temperature is kept above 10 DEG C, the light intensity is kept between 10,000 to 50,000Lx, the water content in the substrate is 85 to 90 percent, the ventilation is high, and the bamboo leaf humus soil or tea leaf residueis sprayed every 15 to 30 days. The propagated Stenoloma Chusanum Ching sporophytes can be used as an ornamental and medicinal plant resource.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
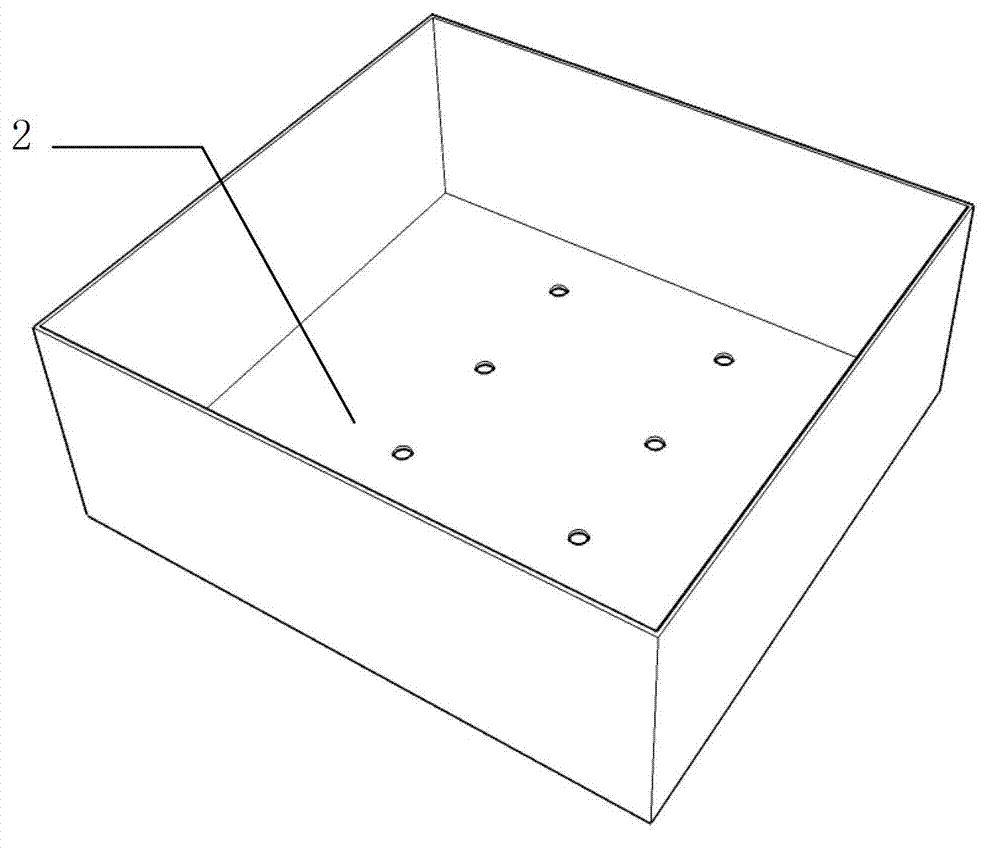
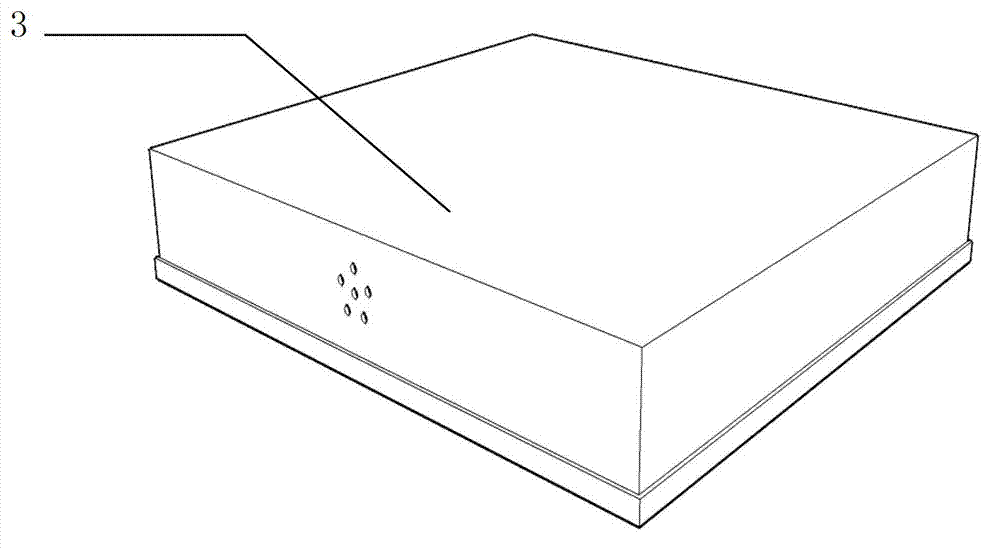
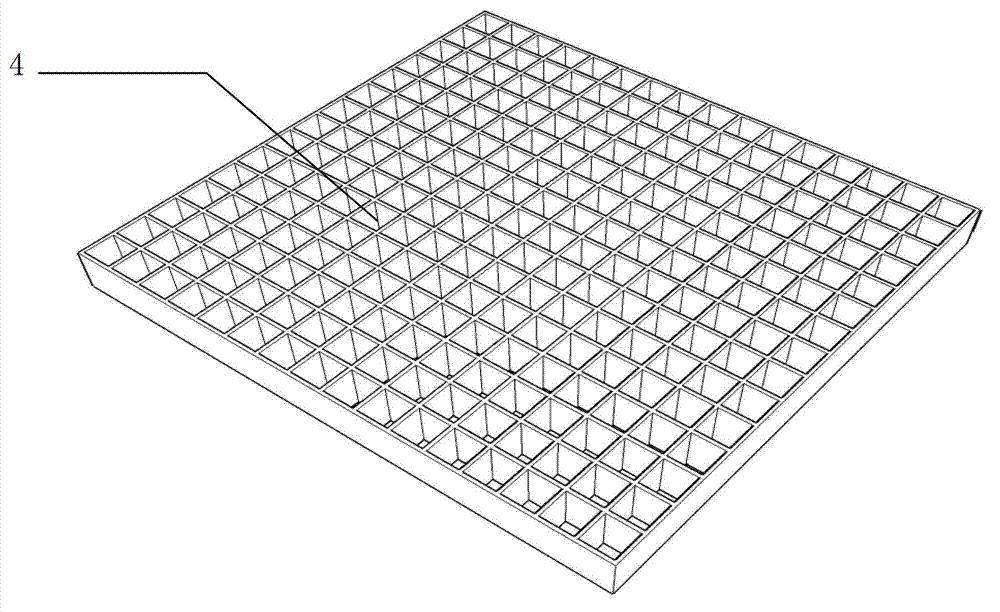
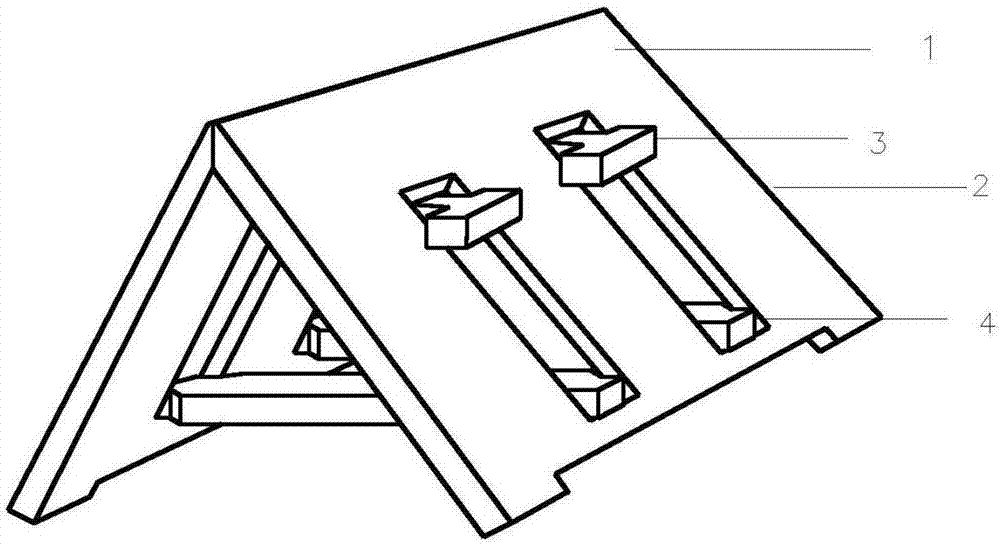
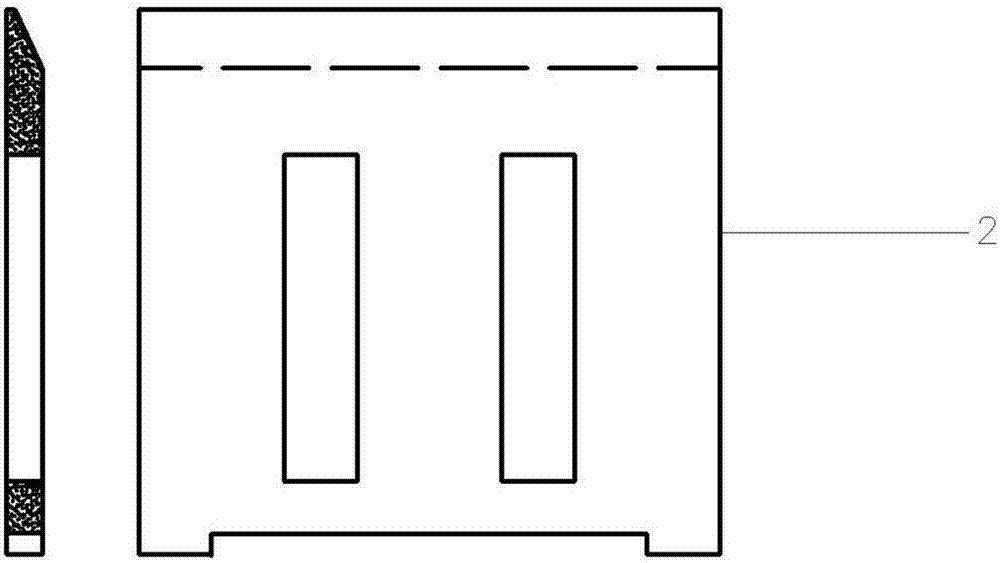
Pteridophyte seedling raising device
ActiveCN103081745AReasonable size designMake full use of spaceReceptacle cultivationSporePteridophyte
The invention discloses a pteridophyte seedling raising device. The pteridophyte seedling raising device comprises a seedling raising basin, a sowing clapboard, and a culture medium pushout constructional element. The seedling raising basin comprises a basin body (2) and a cover body (3) which is matched with the basin body. The basin body is composed of a bottom wall and side walls. Through-holes are formed in the bottom wall. The cover body is composed of a top wall and side walls. Convection holes are formed in the side wall of the cover body. The sowing clapboard (4) is arranged in the basin body and is composed of clapboard side walls and side walls of griddings arranged inside the clapboard side walls. The culture medium pushout constructional element (5) comprises a base seat and a convex circular cylinder which is arranged on the base seat and matched with the shape of gridding cavities. The pteridophyte seedling raising device can improve efficiency of seedling and transplanting, reduce cross infection probability between sporophytes, reduce damage of gametophytes and sporophytes in transplanting process, and has the advantages that cultivating room is made full use of, stability of development environment of spores and seeding transplanting process standardization are guaranteed, management cost is reduced and the pteridophyte seedling raising device is suitable for pteridophyte seedling standardization and large-scale production.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Green globular body (GGB) pathway drynaria roosii seedling tissue culture rapid propagation method
ActiveCN111406652AFast growthShort reproductive cyclePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyDrynaria roosii
The invention provides a green globular body (GGB) pathway drynaria roosii seedling tissue culture rapid propagation method. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of disinfection of explant; induction of GGB; proliferation culture of GGB; differentiation culture of GGB; bud cluster segmentation; and juvenile sporophyte culture. After the drynaria roosii GGB is obtained, inthe proliferation culture of GGB, the use of cytokinin is reduced, and a dark condition is adopted, so that the reduction of the proliferation efficiency of GGB due to differentiation under illumination conditions is obviously improved, the proliferation speed of GGB is increased, and the use cost of light energy is reduced. After the drynaria roosii GGB is differentiated to generate the bud clusters, the root-shaped stem of the tender juvenile sporophyte obtained by segmenting the bud clusters is extremely small, and the time required for culturing the root-shaped stem to reach the volume which can come out of a bottle can be relatively long. By adding the relatively high-concentration of sucrose to treat the juvenile sporophyte in the culture medium, the growth speed of the late root-shaped stem is greatly increased, and then the propagation period of the seedlings is shortened.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Assembling multifunctional artificial algal reef
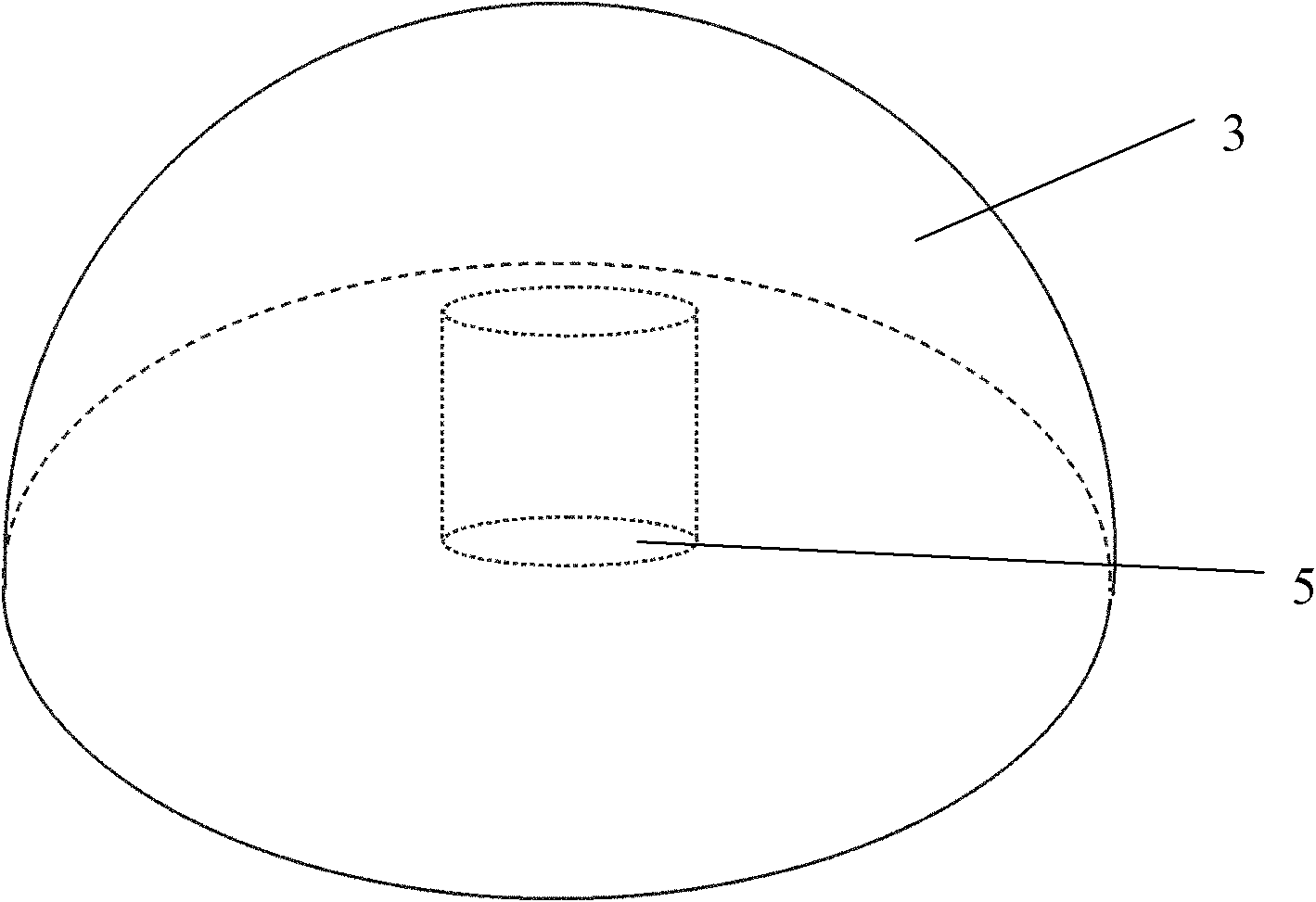
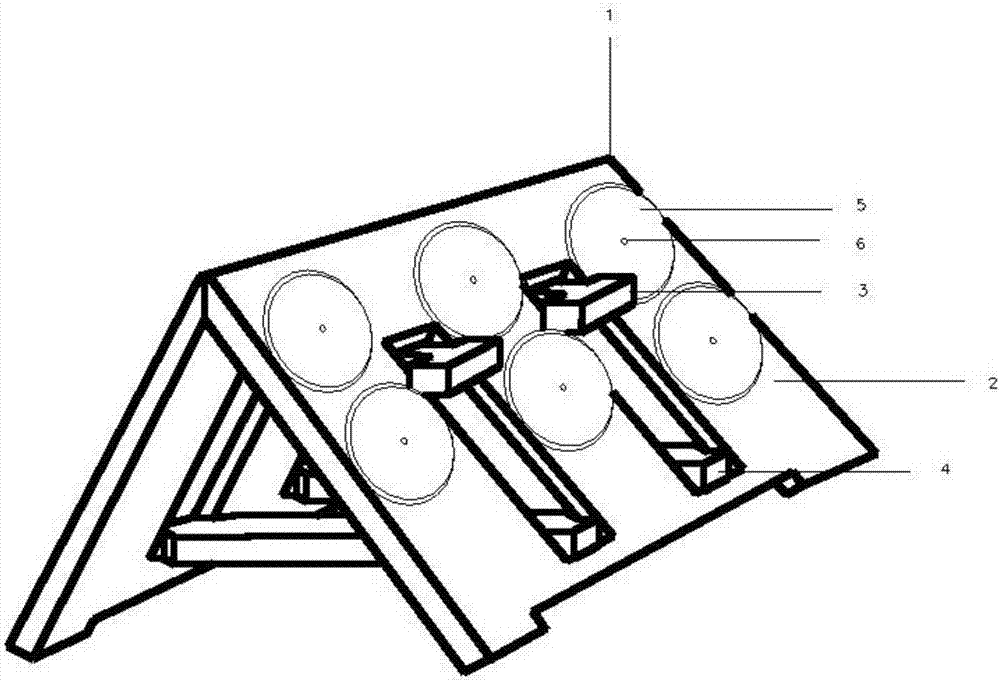
PendingCN107018889AEasy to manufactureSimplify the shipping processClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaSporophyteReinforced concrete
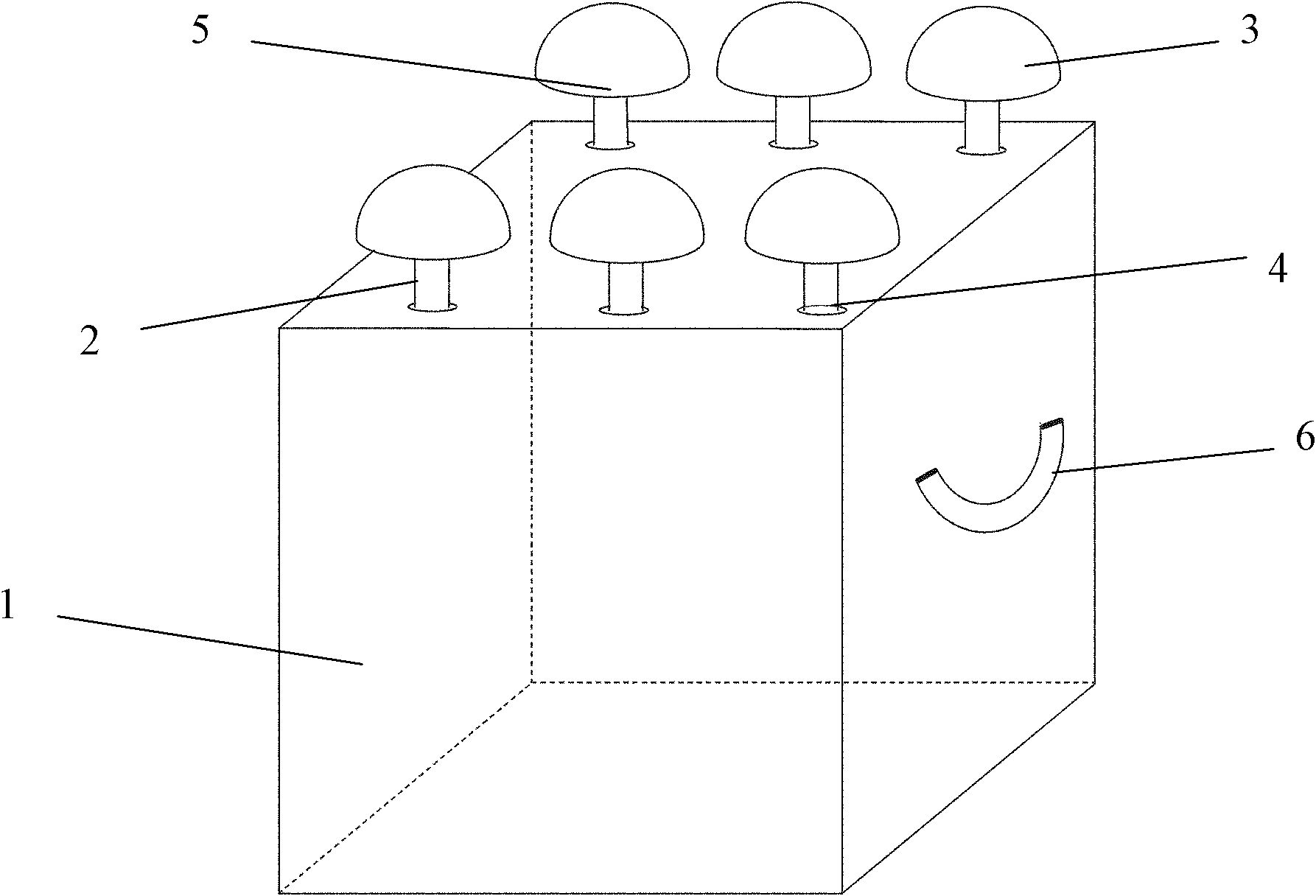
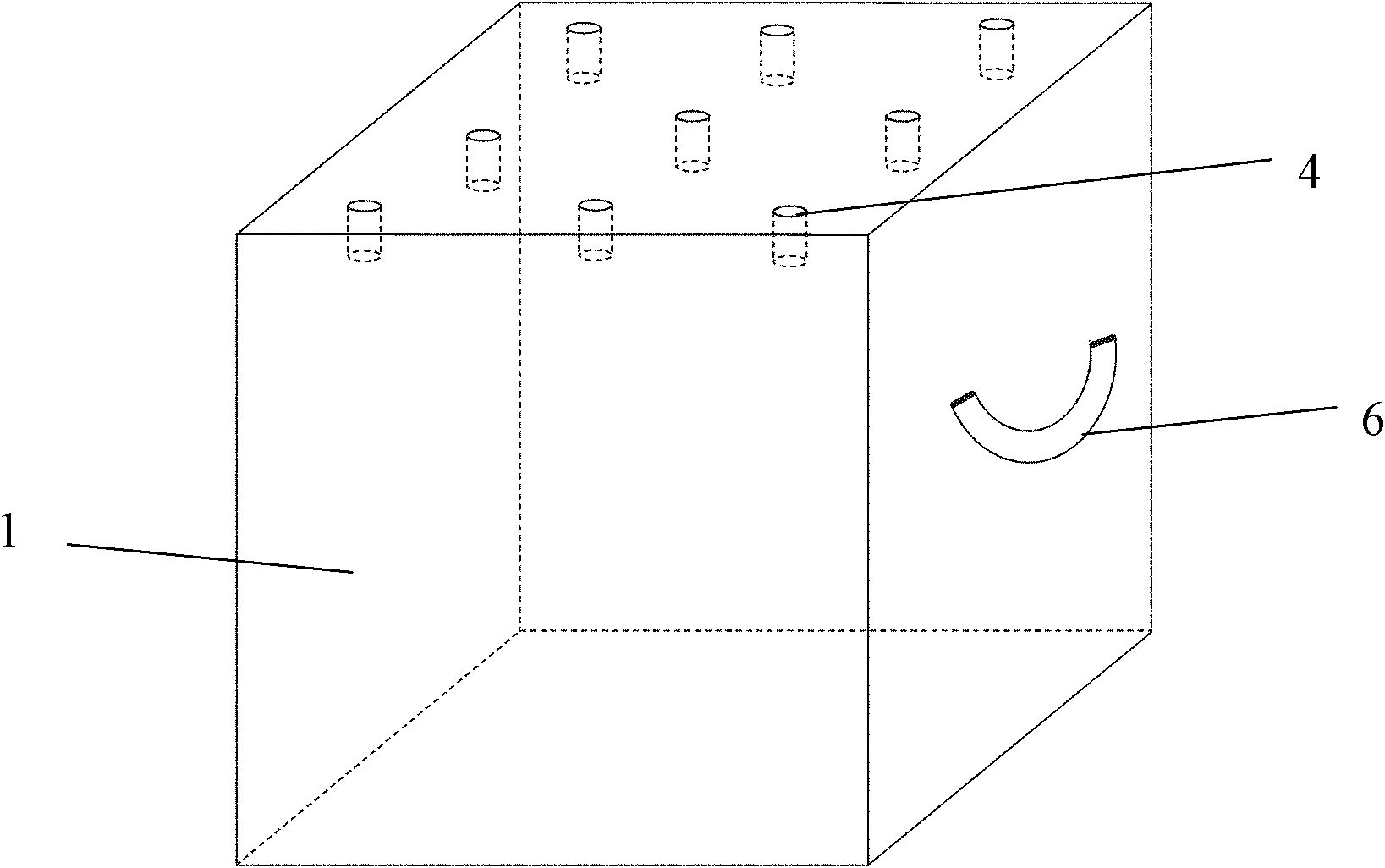
The invention discloses an assembling multifunctional artificial algal reef which comprises a parent reef (1) and a plurality of sub-reefs (5) arranged on the surface of the parent reef (1), wherein the parent reef (1) and the sub-reefs (5) are in reinforced concrete structures; the surfaces of the parent reef (1) and the sub-reefs (5) are in porous structures to facilitate adhesion of macroscopic algae; the parent reef (1) is connected with the sub-reefs (5) by stainless steel screws (6) with diameters of 10mm; no gap exists between the parent reef (1) and the sub-reefs (5); the parent reef (1) comprises two main body adhesion components (2), two drawing components (3) and two supporting components (4); the components are mutually supported to form a triangular structure. The assembling multifunctional artificial algal reef can be completely manually assembled and disassembled, has good wind wave resistance, can avoid silting of deposits on the surface of the algal reef, is available for adhesion of juvenile sporophytes of natural algae, and is also available for adhesion and wind wave sheltering of trepang, abalone, viscous roes and the like.
Owner:MARINE BIOLOGY INST OF SHANDONG PROVINCE
Propagation method of stenoloma chusana spores
InactiveCN102144490AAvoid bacterial contaminationPrevent the growth of other unrelated organismsSeed and root treatmentCultivating equipmentsBiologyGametophyte
The invention relates to a propagation method of stenoloma chusana spores, which comprises the following steps of: mature stenoloma chusana spore collecting, ground substance disinfecting, spore sterilizing, spore germinating, zygote forming, gametophyte growing, antiphyte growing, seedling transplanting and the like. The method can be used for fast propagating the stenoloma chusana, is simple in the preparation of the cultivation ground substance, is simple and convenient in operation method, is high in operability, and has the advantages of being small in investment and high in yield, so that the transplanting survival rate of the spore seedlings reaches more than 85%.
Owner:李红 +2
Method for culturing fern in lime stone area
The present invention relates to a pteridophyte propagation method in limestone district, belonging to the field of flowers, plants and Chinese medicinal herbs cultivation technology. Said method includes the following steps: collecting spores in spore ripening season of pteridophyte, placing the collected spores into a clean container, placing said container in a ventilating shade place and making it be naturally dried; in 2-3 month of spring sowing the spores into the moss cluster grown on the nightside limestone, after the sporophyte is grown for 20-30 days, transplanting the sporophyte together with moss cluster into green-house or flowers nursery garden to make cultivation.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com