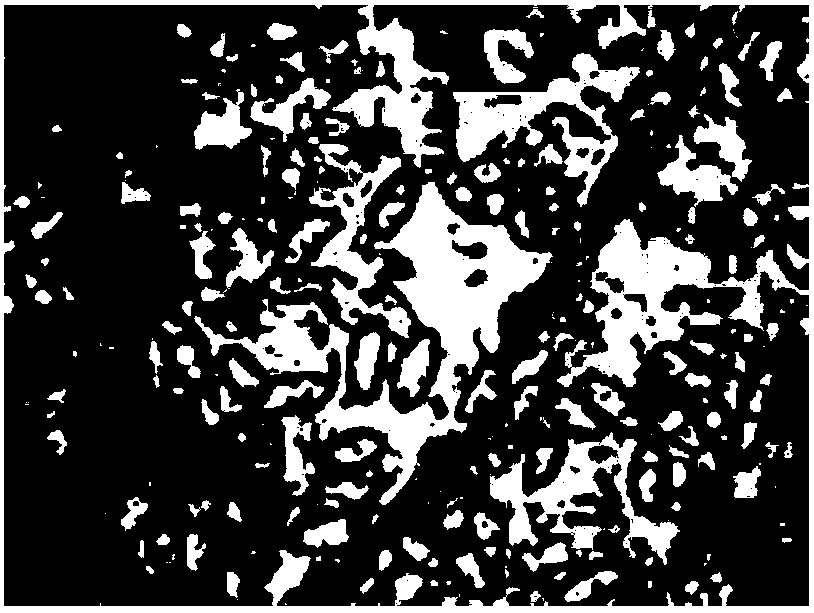Patents
Literature
1479 results about "Sporeling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A sporeling is a young plant or fungus produced by a germinated spore, similar to a seedling derived from a germinated seed. They occur in algae, fungi, lichens, bryophytes and seedless vascular plants.
Stable aqueous spore-containing formulation
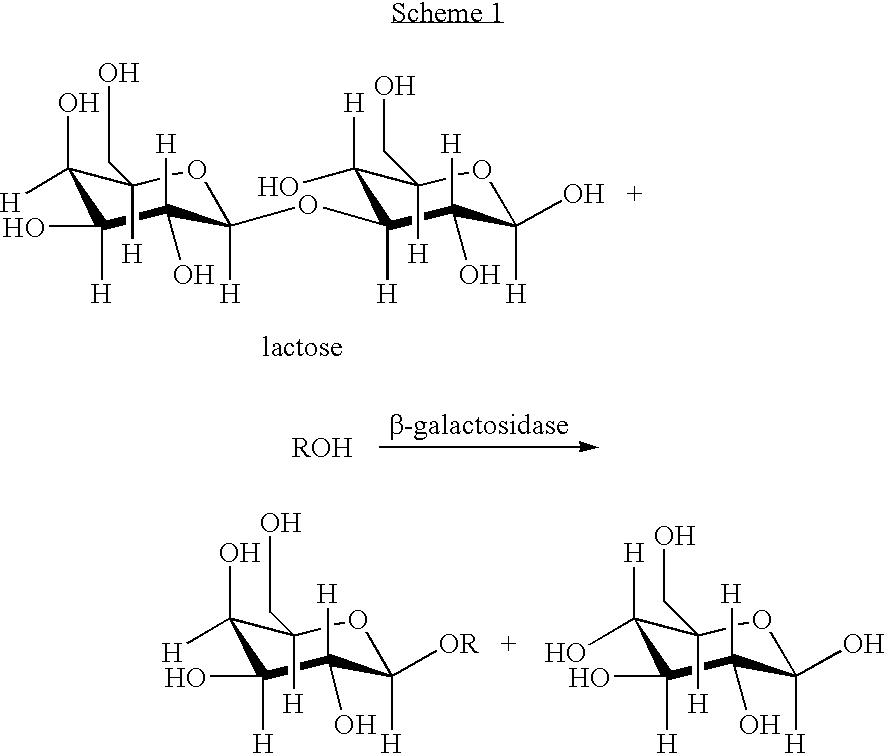
Stable aqueous spore-containing chemical formulations having a low to medium viscosity profile are provided. The formulations comprise at least one spore in a mixture of water and at least one water miscible solvent, optionally at least one surfactant, optionally at least one stabilizer such as a metal salt, optionally at least one biocide, optionally at least one buffer, and optionally at least one chemical insecticide or fungicide or a mixture thereof. The formulations are particularly suitable as a seed coating and foliar spray. Methods of preparation as well as methods of treating a plant are also provided.
Owner:BASF CORP
Fertilizer compositions and methods of making and using same
Fertilizer compositions for plant production are described, comprised of decontaminated manure and Bacillus spores, preferably a humic acid derived from lignite and, optionally, one or more of N compounds, P compounds, K compounds, and combinations of two or more of these compounds. Preferred compositions are those wherein the ingredients are blended into an admixture resulting in a granular product. Other preferred compositions are those blended into an admixture resulting in a powdered product. Preferably, the ingredients are formed into hardened prills or pellets. Processes for production and use are also presented.
Owner:MICROBES
Antimicrobial and sporicidal composition
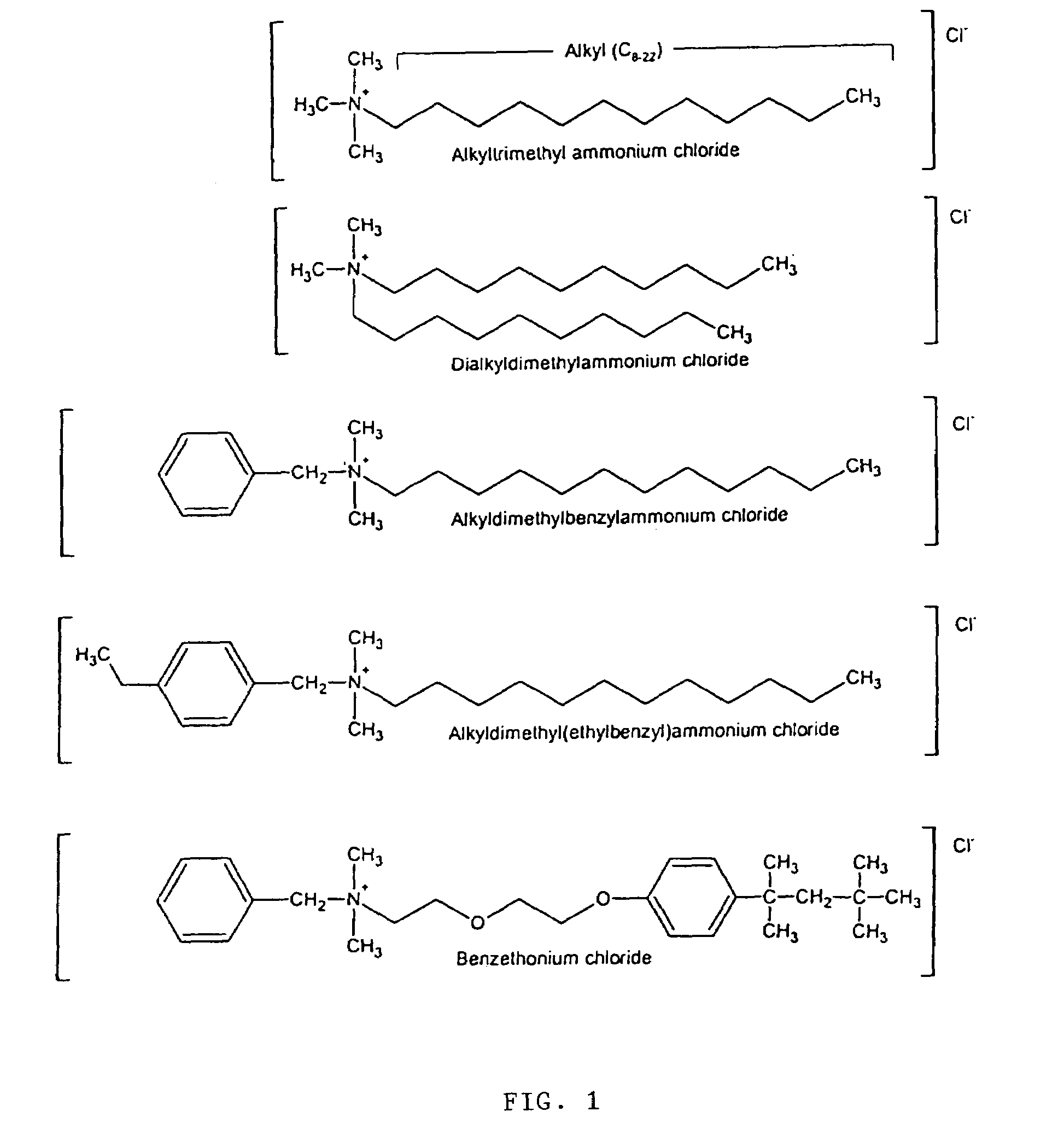
InactiveUS7192601B2High bactericidal activityAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsBacteroidesAmmonium compounds
Germicidal compositions with enhanced activity towards killing microbiological spores and vetgetative cells comprising certain quaternary ammonium compounds (QACs), phenolic compounds, monohydric alcohols, hydrogen peroxide, iodine, triclocarban, triclosan or combinations thereof with one or more spore coat opening agents. The invention also provides for the application of the germicidal compositions to animate and inanimate surfaces to help kill germs and protect against the risk of infection from bacteria, molds, yeasts, fungi, viruses, and microbiological spores.
Owner:PURE IP LC
Method and composition for reducing E. coli disease and enhancing performance
Bacillus strains that inhibit pathogenic swine E. coli and / or improve performance are provided. Inhibition of pathogenic swine E. coli decreases E. coli disease. At least one strain enhanced swine performance by improving average daily gain, feed efficiency, and feed intake. Preferred Bacillus strains are of species that are included on the GRAS list. Bacillus species are sporeformers and therefore are highly stable and can be fed to swine.
Owner:AGTECH PRODS
Application method of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in large-scale tobacco cultivation
InactiveCN103125251AImprove qualityImprove mineral nutritionHorticulture methodsBiotechnologySporeling
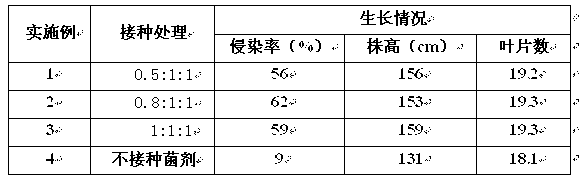
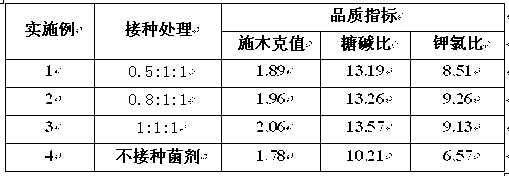
The invention relates to an application method of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in large-scale tobacco cultivation. A primary arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi fungicide is inoculated and propagated separately, and propagule spore density of an arbuscular mycorrhiza of each fungi after the propagation is 30 pieces per gram of dry soil. A float breeding method is adopted to conduct arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi fungicide combinedinoculation to tobacco, mycorrhization tobacco seedlings are obtained, and the mycorrhization tobacco seedlings are directly applied to field production. When being transplanted, the mycorrhization tobacco seedlings are conducted with a two-step inoculation, and the mixed fungicide is mixed by propagated acaulospora mellea, glomus mosseae and glomus intraradices at a proportion of 0.5-1: 1:1. A colony formed by the propagation of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus is close to a natural state, and fungus cooperate and play a better role of growth promoting and quality improving. According to the application method of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in the large-scale tobacco cultivation, by means of the two times of inoculations of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus, the proportion of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and the tobacco in a symbiotic system built during a seedling stage of the tobacco is guaranteed, and the beneficial effects of the symbiotic system to the development of the tobacco seedlings are ensured. The application method of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in the large-scale tobacco cultivation is simple and practical in method and environment friendly.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Aspergillus flavus producing no aflatoxin and application thereof
ActiveCN103509723AReduce pollutionAvoid infectionFungiMicroorganism based processesSporeMicroorganism
The invention discloses an aspergillus flavus strain producing no aflatoxin. The aspergillus flavus strain producing no aflatoxin, provided by the invention, is specifically aspergillus flavus GZ-17; the preservation number of the aspergillus flavus strain in the general microbiology center of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms is CGMCC No.8050. Experimental results show that the aspergillus flavus strain GZ-17 provided by the invention plays a role in restraining the poison production of the aspergillus flavus strain producing the aflatoxin; when the concentration ratio of the strain to a toxic producing fungus spore is 105: 105, the poison production restrained ratio of bacterium producing no poison to the bacterium producing poison is nearly 96%. The strain has important significance for restraining the infection of the aspergillus flavus producing poison to agricultural products and reducing the aflatoxin pollution in the agricultural products.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for jointly treating stalks by steam explosion and microorganism fermentation
ActiveCN102077903ACompletely degradedSolve the problem of human-animal competition for foodFood processingAnimal feeding stuffSporelingNutrient solution
The invention relates to a method for jointly treating stalks by steam explosion and microorganism fermentation, comprising the following steps of: firstly, carrying out steam explosion pretreatment on the stalks to obtain exploded stalks; then preparing spore seed liquid: inoculating aspergillus oryzae or trichoderma Koningi to a PDA (Potato Dextrose Agar) culture medium, standing and culturing for 3-5 days at the temperature of 28-32 DEG C, and preparing the spore seed liquid with the concentration of 106-108 per mL; and finally carrying out microorganism fermentation: uniformly mixing 18g of exploded stalks, 2g of bran and 30mL of mineral element nutrient solution, adjusting pH to be 7.0 with Ca(OH)2, sterilizing for 15min at the temperature of 121 DEG C and the pressure of 0.15MPa to obtain a solid fermentation medium a, inoculating the spore seed liquid according to 2-4% of inoculum size, and culturing the spore seed liquid for 5-7 days at the temperature of 28-32 DEG C. The fermentation stalks obtained by utilizing the method have low content of lignose, cellulose and hemicellulose and high activity of filter paper carbohydrase, CMC (carboxymethyl cellulose) enzyme, amylase and protease.
Owner:河南德邻生物制品有限公司
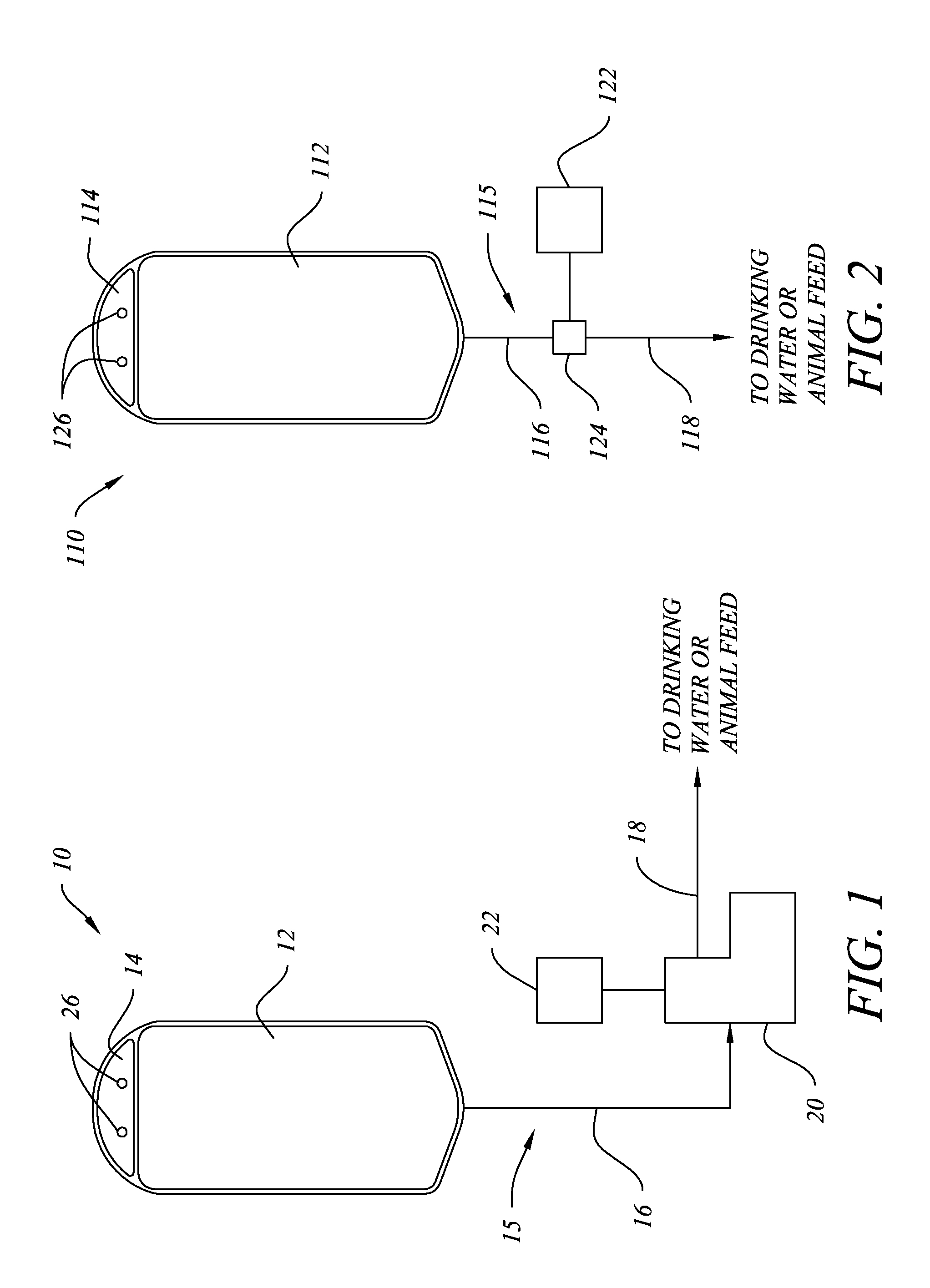
Delivery System and Probiotic Composition for Animals and Plants
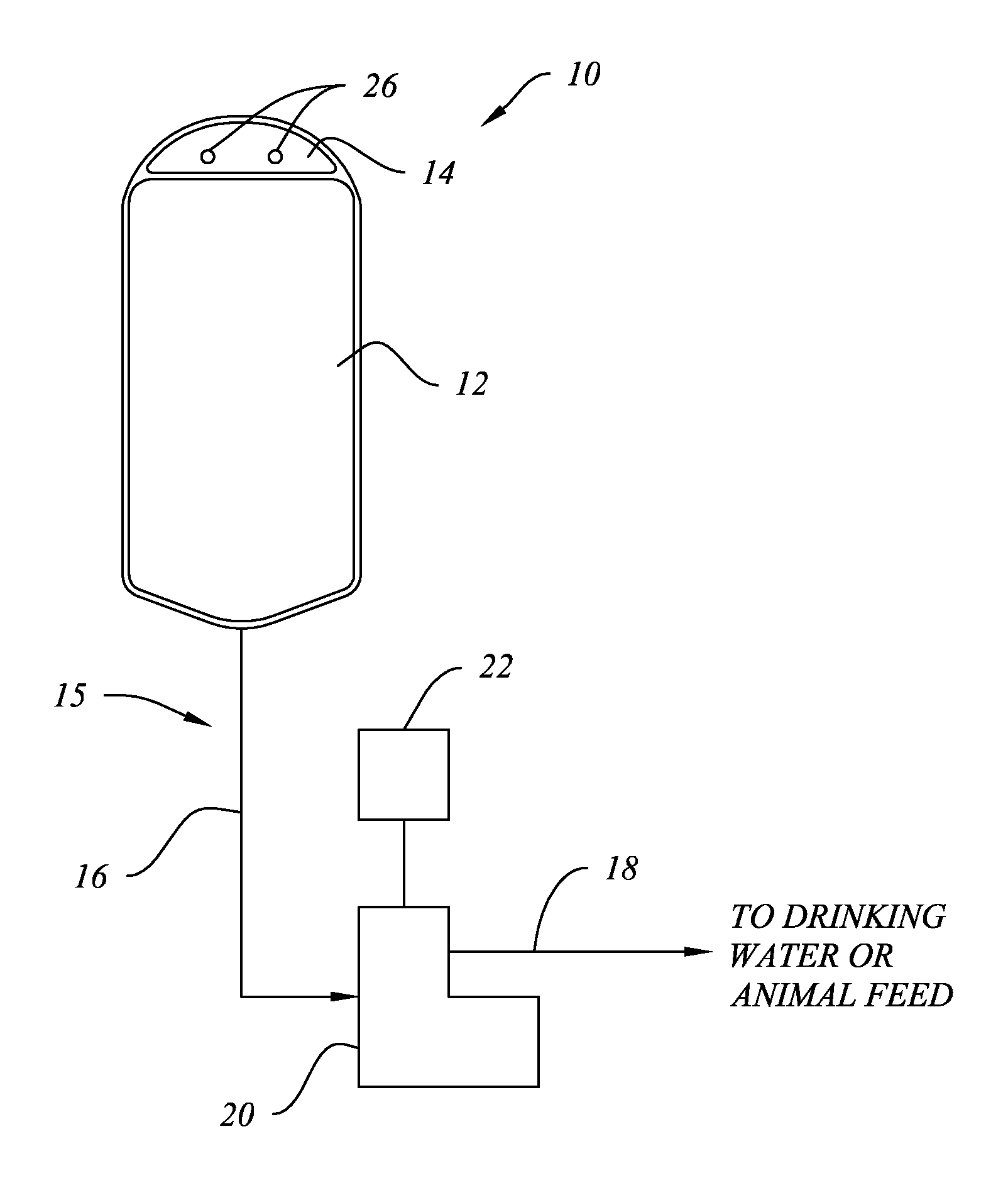
ActiveUS20150118203A1Improve efficiencyAvoid pollutionBiocideAnimal watering devicesMotion detectorFluid level
Probiotic compositions that comprise one or more bacteria species in spore form, a thickener to form a stabilized suspension and to preferably act as a prebiotic, one or more acids or salts of acids, and optionally a water activity reducer. A system for delivering probiotic compositions by gravity feed or non-contact pump to a point of consumption by a plant or animal, preferably in conjunction with acidified drinking water, comprising a collapsible container with attachable tubing that prevent contamination of the probiotic composition within the container. Delivery may be actuated in response to a timer, motion detector, fluid level sensor, RFID tag, or other mechanism to periodically or continuously dispense a dosage of probiotic composition directly to the soil surrounding a plant or to the water or feed for an animal. A method for increasing beneficial bacteria in an animal's GIT comprises adding probiotics to acidified drinking water.
Owner:NCH CORP
Detection of biological warfare agents
InactiveUS6838292B1High sensitivity and selectivityHigh specificity and selectivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOrganic moleculesTerbium
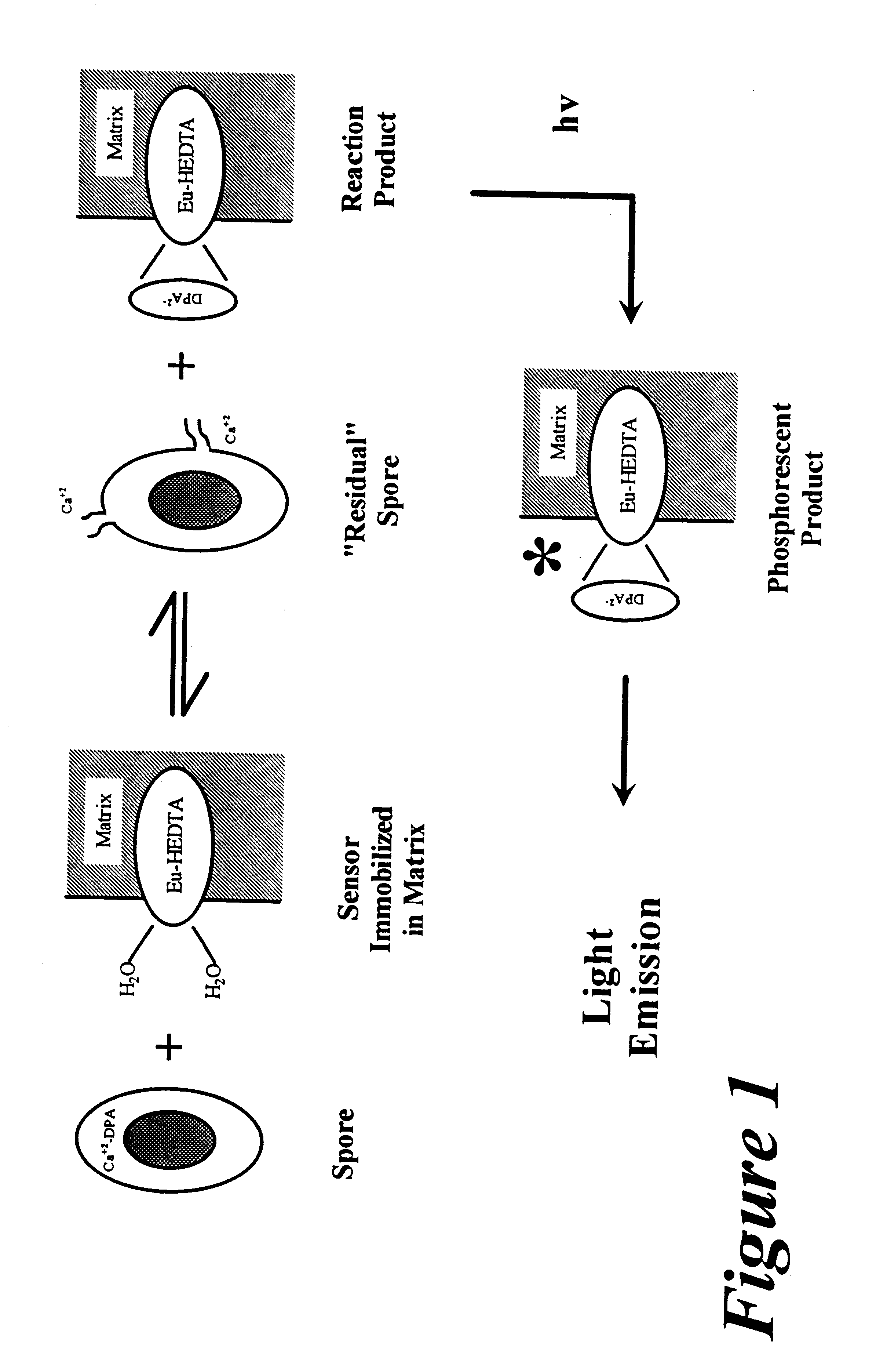
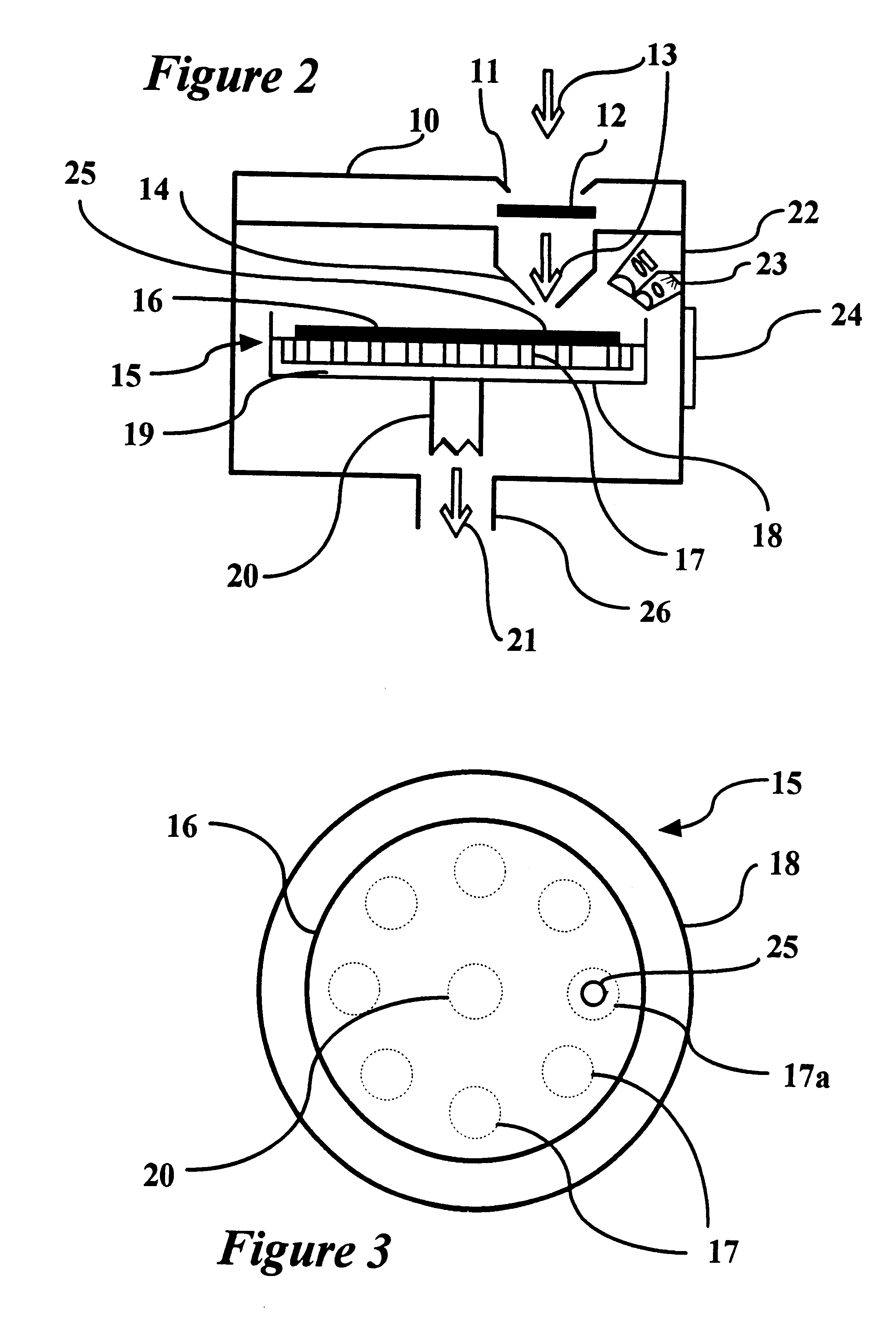
Methods and devices are provided for the detection of bacterial agents such agents as Bacillus anthracis and Clostridium botulinum with high sensitivity and selectivity. More specifically, methods and devices are based on a phosphorescence-emission detection system using chelate-stabilized lanthanides (e.g, Eu(III), Tb(III), and Sm(III)) to detect various spore-specific small organic molecules (e.g., dipicolinic acid, diaminopimelic acid, n-acetlymuramic acid, and the like). By careful selection of the chelating agent or ligand coordinated to the lanthanide, both high specificity and selectivity can be obtained. Examples of suitable and preferred sensor systems include N-(2-hydroxyethyl)ethylenediaminetriacetic acid (HEDTA) and N-(2-hydroxyethyl)iminodiacetic acid (HEIDA) combined with europium (III) and / or terbium (III). The chelate-stabilized lanthanides react with the spore-specific “target” molecules to form a characteristically phosphorescent product which can then be detected.
Owner:ALION SEIENCE & TECH CORP +1
Microscopic image detection and recognition method for rice blast fungus spore based on support vector machine
InactiveCN108564124ASolve the detection accuracyResolving Analysis ResultsCharacter and pattern recognitionMicroscopic imageDisease
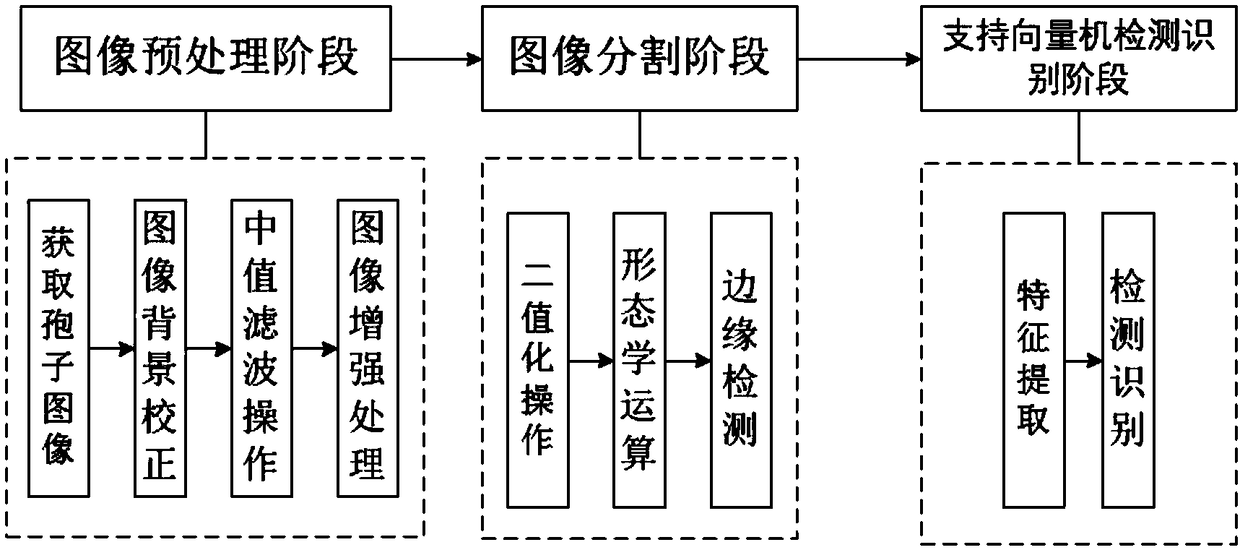
The invention discloses a microscopic image detection and recognition method for a rice blast fungus spore based on a support vector machine. The method comprises the steps of (1) image preprocessingincluding image background correction, median filtering processing and image enhancement processing, (2) image segmentation including binarization operation, morphological operation and edge detectionof a preprocessed image and the obtainment of a graph contour of a suspected rice blast fungus spore, and (3) support vector machine detection and identification including the extraction of most representative shape feature parameters and texture feature parameters from the graph contour of a suspected rice blast fungus spore, the training of a support vector machine classifier model with the shape feature parameters and texture feature parameters as input vectors, and the detection and identification of the rice blast fungus spore by using the trained support vector machine classifier model.According to the method, the rapid and accurate identification of the rice blast fungus spore can be achieved, and a technical support can be provided for the early detection and the discrimination of a disease degree of a rice blast disease.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Sporicidal composition for clostridium difficile spores
A cleaning medium or formulation that contains a sporicidal composition is described. The composition includes about 0.1-20% weight / weight of a germinant agent, about 0.01-75% w / w of an antimicrobial agent, in terms of dry or wet total weight, and which is admixed with water to generate a solution with a pH of 3.5-9.5. The composition can help trigger the germination of spores, in particular C. difficile, and subsequently deactivate or kill the spores. A means of applying the cleaning formulation in a medium and process for cleaning are also described.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Lentinula edodes strain and application thereof in lentinula edodes cultivation method
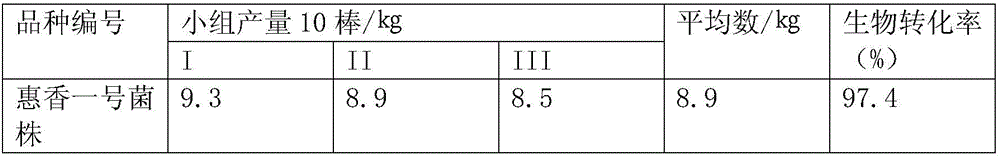
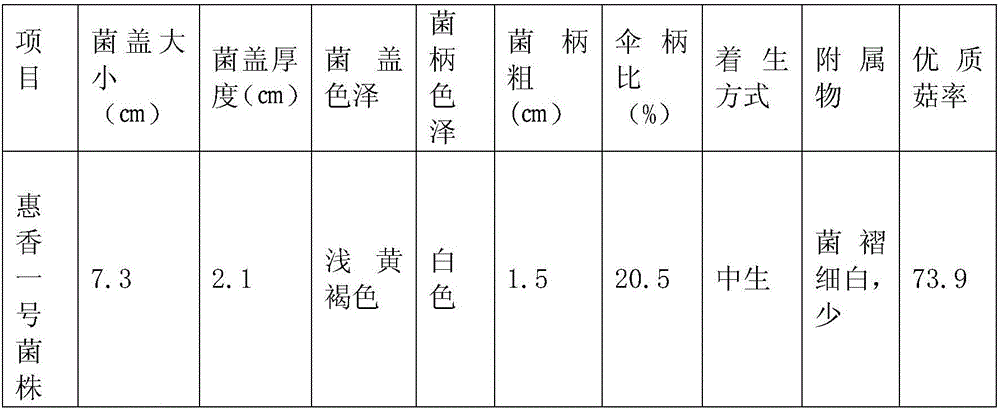
The invention belongs to the technical field of fungus cultivation, and in particular relates to a lentinula edodes strain and an application thereof in a lentinula edodes cultivation method. The biological preservation number of the lentinula edodes strain is CGMCC No:12501. The application of the lentinula edodes strain in the lentinula edodes cultivation method is characterized by specifically comprising the following steps: (1) preparing nutrients; (2) conducting bagging and sterilizing; (3) conducting inoculating; (4) culturing fungus bags; and (5) conducting fruiting management. Stipes are white and grow from the middle, the stipes are 2-4.5cm long and 1.4-1.9cm in diameter; and gills are thin and white, with lightly white spore prints. Lentinula edodes is high in yield, and 5-6 turns of lentinula edodes can be produced. A biological efficiency can reach 93.2% or above, which is 9.6% above that of control lentinula edodes SD-1.
Owner:SHANDONG HUIMINCHUNSHENG EDIBLE FUNGUS TECH DEV CO LTD +1
Method for preparing pleurotus geesteranus compost
InactiveCN103416224AQuality improvementIncrease productionHorticultureFertilizer mixturesSporelingNutrition
Disclosed is a method for preparing pleurorus geesteranus compost. The method for preparing the pleurorus geesteranus compost comprises the steps that sieving, impurity removing and heap building are conducted on mulberry saw dust; quick lime powder is scattered on the surface of the saw dust and a thin film covers the quick lime powder for warming; other raw materials are weighed and mixed with the mulberry saw dust, and the compost are placed into plastic bags; sterilization is conducted after bagging, then inoculation is conducted, the plastic bags are placed back into a room to be cultured for fungus sprouting, and after fungi grow everywhere inside the bags, the fruiting stage starts; picking is conducted before the color of mushroom caps fades and spores shoot off. According to the method for preparing the pleurorus geesteranus compost, the mulberry saw dust is used as the main component of the pleurorus geesteranus compost, the prepared compost has the advantages that nutrition is sufficient, fungus spouting speed is high, the number of fungi is large, the pleurorus geesteranus quality is good, the pleurorus geesteranus growing density is large, pleurorus geesteranus growing power is strong, the yield is high and the disease-prevention performance is good. In addition, the compost is low in price, materials are easy to obtain, prescription and the preparation method are simple, and the compost is applicable to mass production.
Owner:刘万顺
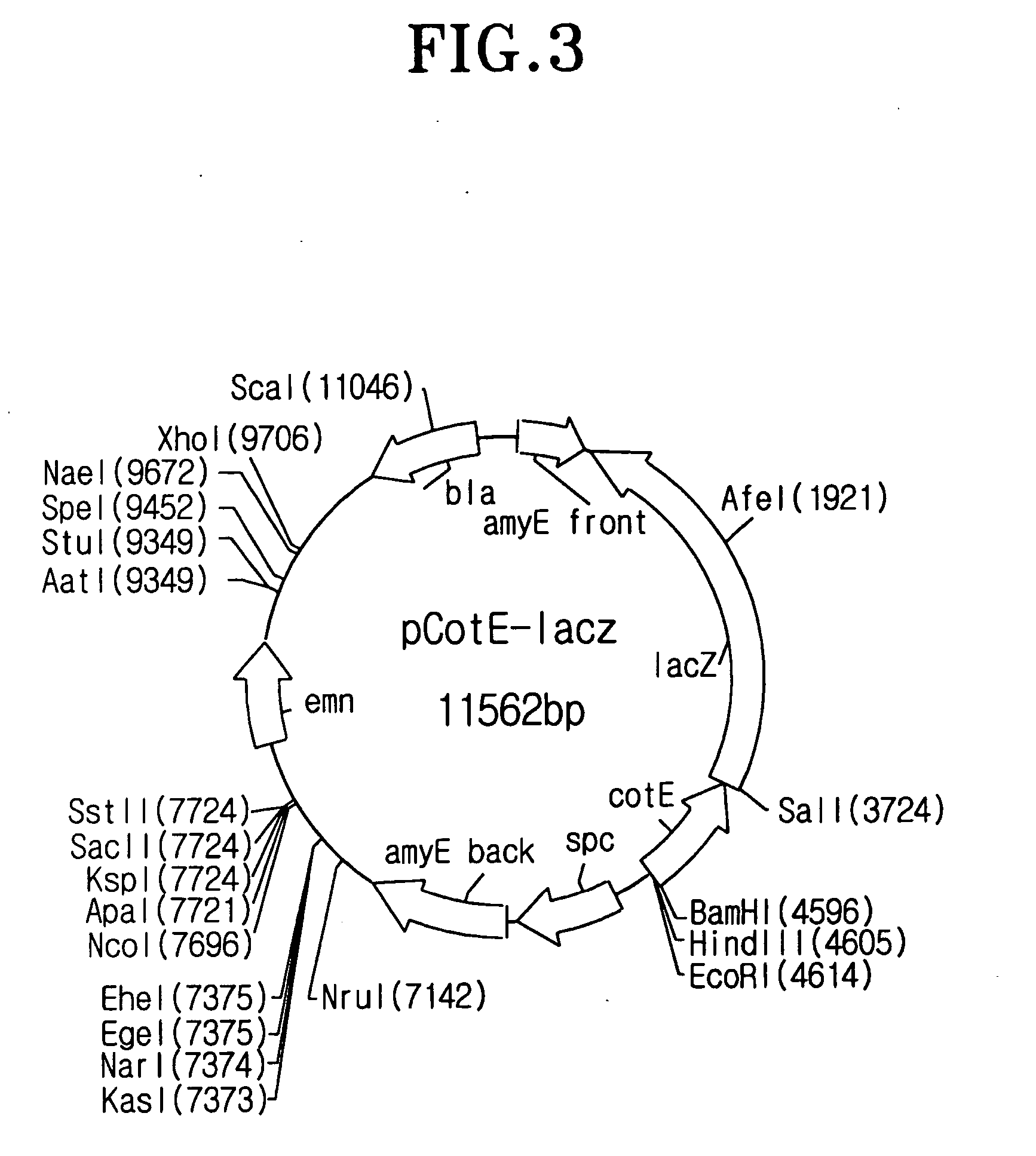
Method for expression of proteins on spore surface
The present invention relates to a method for display of proteinson spore surface and a method for improving protein with rapidity using the same, which comprises the steps of (i) preparing a vector for spore surface display comprising a gene construct containing a gene encoding spore coat protein and a gene encoding a protein of interest, wherein, when expressed, the gene construct expresses a fusion protein between the spore coat protein and the protein of interest, (ii) transforming a host cell with the vector for spore surface display; (iii) displaying the protein of interest on a surface of a spore of the host cell; and (iv) recovering the spore displaying on its surface the protein of interest.
Owner:GENOFOCUS
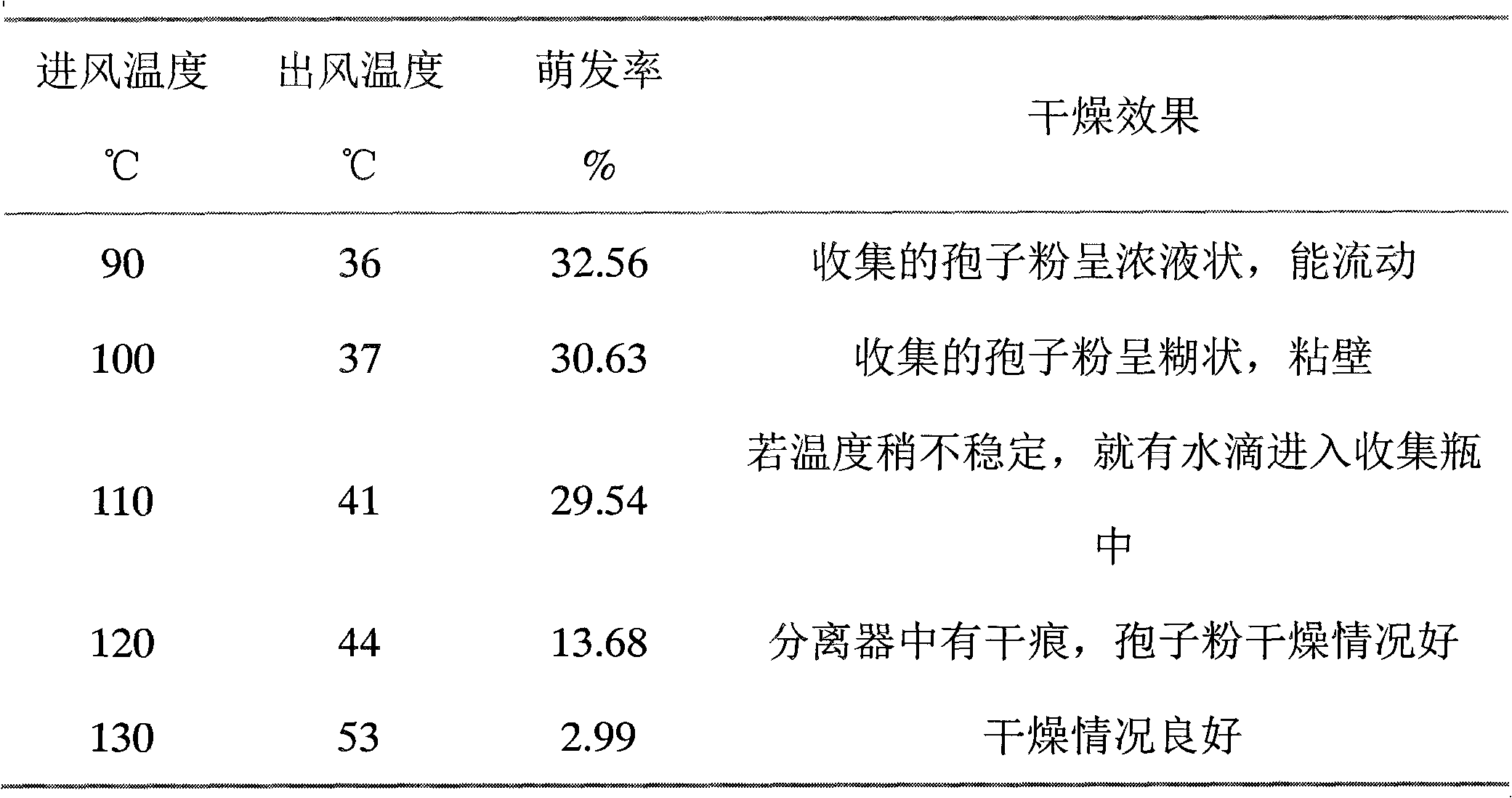
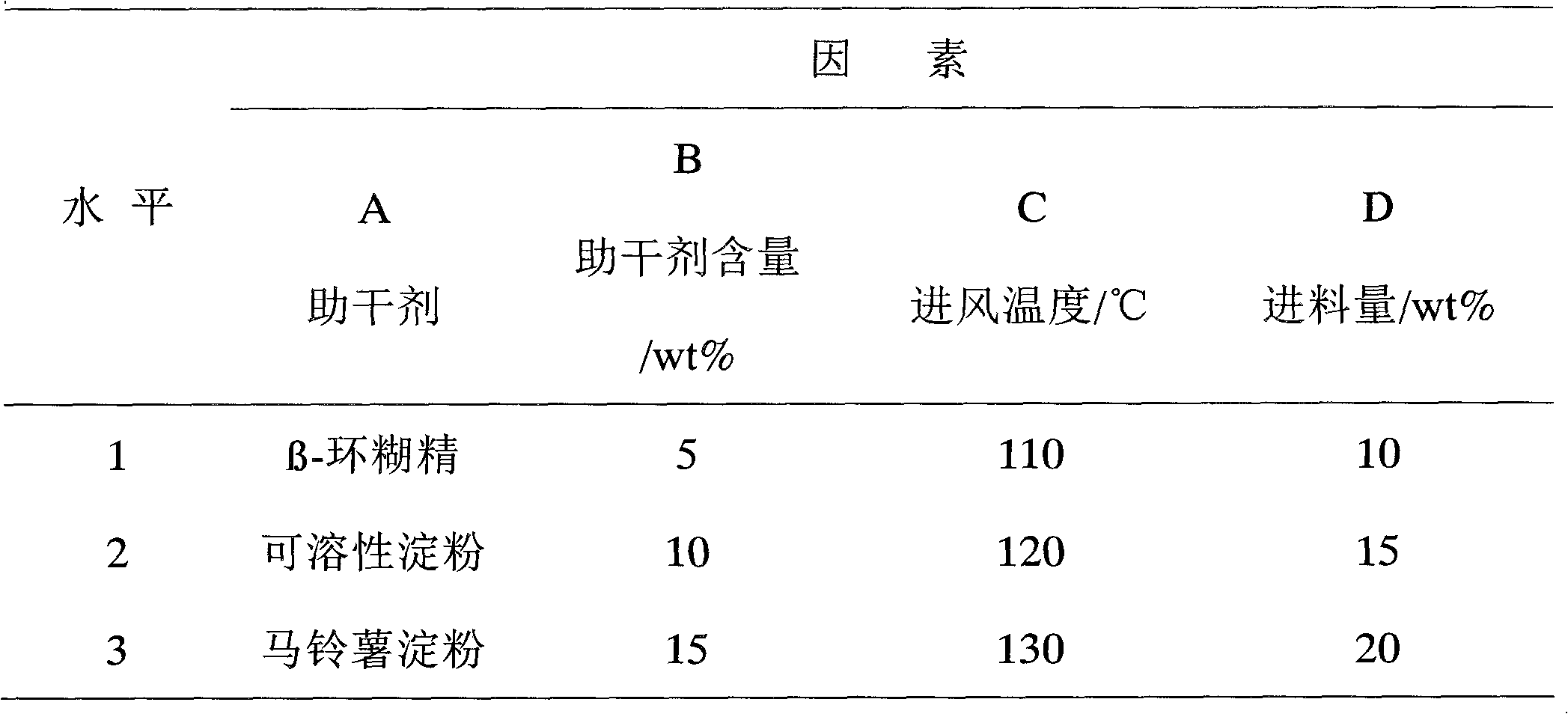
Trichoderma spore powder as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102067885AInhibitionTo achieve the effect of preventionBiocideFungicidesMicroorganismSpore
The invention discloses a trichoderma spore powder as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The trichoderma spore powder contains trichoderma spore powder and a drying aid, wherein the trichoderma spore powder is the spore powder of Trichoderma sperellum T1 which is preserved in the general microorganism center of CCCCM (China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms) and has the preservation number of CGMCC NO: 3531 and a rDNA ITS region segment sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1; the drying aid is one or more of beta-cyclodextrin, potato starch and soluble starch. The trichoderma spore powder has an effective prevention and control effect on banana vasicular wilt, and has a remarkable antagonism effect on various pathogenic funguses, especially on soil-borne funguses. The preparation time is saved with the preparation method of the trichoderma spore powder, which can be used for preparing the trichoderma spore powder which has high density, high germination rateand high drying efficiency and is easy to store, transport and use.
Owner:惠州市南天生物科技有限公司 +2
A kind of yellow basket fungus and its application in the prevention and treatment of plant pathogenic bacteria
The invention provides a talaromyces flavus, and also relates to the application of the talaromyces flavus in the inhibition of a variety of plant pathogens. The preservation number of the talaromyces flavus qw12 is CGMCC5067, the talaromyces flavus colony is round, the texture is flocculent and fluffy or flocculent, and the front of the colony is yellow; the conidiophores have penicilli, and the spore is spherical; the primordium is nearly cylindrical, big and curved; the gymnothecium is spherical or nearly spherical, the ascus is spherical, and the ascospore is spherical or nearly sphericaland unicellular. The antagonistic bacterium provided by the invention can effectively inhibit the growth of valsa sordida, rhizoctonia solani, corn sheath blight fungi, curvularia lunata, colletotrichum gloeosporioides, fusarium graminearum, alternaria alternate, cryphonetria parasitica, colletotrichum nicotianae and other plant pathogens, effectively prevent plant diseases, reduce the dosage of chemical pesticide and the accumulation of the chemical pesticide in soil and help to increase the quality and yield of economic crops in China, and therefore economic and social benefits are remarkable.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV +1
Paecilomyces lilacinus and application
The invention discloses Paecilomyces lilacinus FZ07-9F-5 CGMCC No.2780, microbial inoculum and application thereof. The microbial inoculum is wireworm killing biological microbial inoculum with slow application function, which is prepared by the following steps: using a macromolecular material, namely sodium alginate as basic skeleton, using mycelium and spore mixture of P. lilacinus FZ07-9F-5 CGMCC No.2780 as active components, using infusorial earth as a carrier, and adopting a method of sodium alginate-calcium chloride reaction according to the characteristic of forming gel by the sodium alginate and polyvalent cations to be prepared into the microbial inoculum. Proved by experiments, the microbial inoculum has better wireworm killing efficacy, has control ratio up to between 50 and 60 percent, is comparatively stable, has no noxious chemical residues (innocuous and non-residue), does not pollute agricultural products and environment (does not react with other substances in the environment), and has the characteristics of high cost performance and convenient application. The microbial inoculum plays an important role in control of wireworm diseases of plant roots and knots, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:中农绿康(北京)生物技术有限公司
Method for production of C30-aldehyde carotenoids
The present invention provides methods to engineer microorganisms for the production of C30-aldehyde carotenoids. Specifically, various combinations of crtM, sqs, crtN and crtN2 genes from Staphylococcus aureus and Methylomonas sp. 16a can be co-expressed in transformant hosts, leading to the production of diaponeurosporene monoaldehyde, diapocarotene monoaldehyde, and / or diapocarotene dialdehyde. In a preferred embodiment, the genetically engineered pathway is introduced into a strain of Escherichia coli that has been engineered for the expression of carotenoids, and the C30-carotenoid product is diapocarotene dialdehyde.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Lactobacillus buchneri strain LN1326 and its use to improve aerobic stability of silage
InactiveUS20090028993A1Improving animal performanceImprove performanceMilk preparationBacteriaBacteroidesMicroorganism
A method for treating silage to enhance aerobic stability by inhibiting growth of microorganisms selected from yeasts, molds and spore-forming bacteria is disclosed. The method comprises treating silage or feed with a composition comprising Lactobacillus buchneri, LN 1326, or the antimicrobial components produced thereby. The strain of Lactobacillus buchneri disclosed in the invention has been purified and isolated and has been found to be nontoxic, safe and able to improve aerobic stability of silage.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Paecilomyces lilacinus and application thereof
A (P.lilacinus)YES-2 CGMCC No. 2012, its bacterial agent and use are disclosed. The process is carried out by taking polymer sodium alginate as base skeleton, taking (P.lilacinus)YES-2 CGMCC No. 2012 mycelium and spore mixture as active ingredients, taking diatomite as carrier, forming sodium alginate and polyvalent positive ion into gel and sodium alginate-calcium chloride reacting to obtain final product. The prevention rate reaches to 50-60%. It's stable, cheap and convenient. It has no chemical residual and pollution for agricultural product and environment. It can be used to prevent plant root nematode.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Rapid multi-target property polymerization breeding method for rape
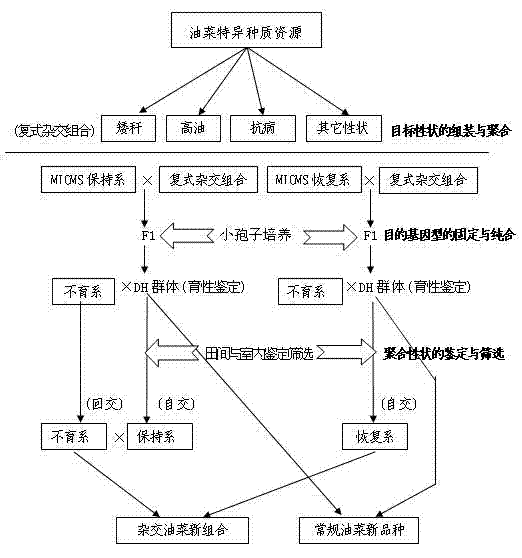
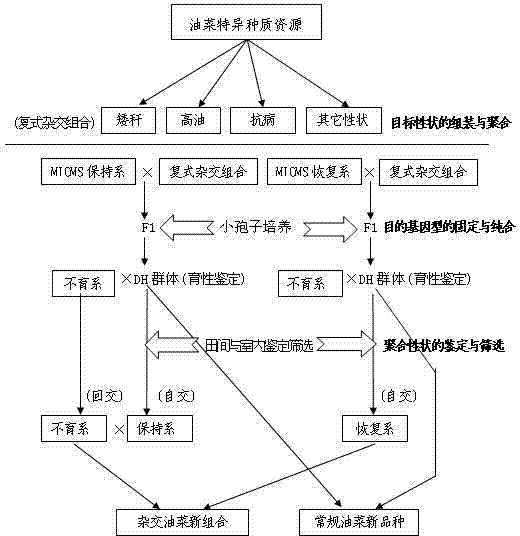
InactiveCN102224801AImprove breeding levelShorten the breeding cyclePlant genotype modificationSporeGreenhouse
The invention provides a rapid multi-target property polymerization breeding method for rape, belonging to a plant breeding method, and comprising the following steps of: selecting excellent breeding target properties requiring to be polymerized, preparing single-cross combinations at room temperature in winter locally, preparing multi-parent complicated cross combinations in summer at different places, and assembling and polymerizing the multiple parents with excellent target properties based on the breeding requirements; performing microspore seedling cultivation on the complex filial generation for which multi-target property breeding restructuring polymerization is already realized, constructing a dihaploid (DH) breeding group, and realizing rapid fixation and homozygosis of the target genotypes of the generation of the multi-target property polymerization; and performing effective field and indoor identification and screening on the target genotypes of the generation for which the multi-target property polymerization is realized based on the property characteristics, performing molecular marker assistant selection on important target properties, and breeding new materials conforming to the breeding targets.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Metarhiziumanisopliae compound insecticide composition and use thereof
The invention relates to a metarhiziumanisopliae compound insecticide composition and use thereof. The metarhiziumanisopliae compound insecticide composition is characterized in that: the active ingredients of the composition include metarhiziumanisopliae and a new neonicotinoid insecticide; the density of the metarhiziumanisopliae in the composition is 1 to 10 billion spores per gram; and the new neonicotinoid insecticide content of the composition is 20 mass percent; and the rest content of the composite are pesticide auxiliary ingredients. The composition has an obvious synergistic effect on grubs and is suitable for preventing and controlling plant pests, particularly grubs. The composition can be used on various crops such as lawns, peanut, sweet potatoes and vegetables or in various places and has the advantages of stable insecticide effect, high quick-acting performance, long efficacy duration, safety and environmental protection.
Owner:SHENZHEN NOPOSION AGROCHEM
Preparation method of trichoderma multifunctional soil modifying agents
InactiveCN102505010APromote growthReduce manufacturing costBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologySporeling
The invention relates to a preparation method of trichoderma multifunctional soil modifying agents. The preparation method comprises the steps that: trichoderma harzianum SH2303 with the CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) NO. 4963 is cultured on a potato dextrose agar (PDA) culture medium for 2 to 3 days, a bacterial cake is punched by a hole puncher with the diameter being 5mm, the bacterial cake is inoculated into a seed culture medium for 5 to 7 days at the bacterium inoculation quantity of three tablets per bottle and is then inoculated into a spore production culture medium, the fermentation is carried out for 5 to 7 days under the optimized culture condition in a 300 L fermentation tank, and the number of thick-wall spores is (6 to 7)*10<8> / mL; and fermenting liquid and carriers are mixed according to the weight ratio of 1:1, the secondary open type solid fermentation is carried out for 5 to 7 days at the normal temperature, and the number of trichoderma conidiospores and chlamydospores is 200 to 500 million / g. The soil modifying agents prepared by the method have the main purposes of improving the primary and secondary salinization of vegetable planting soil and degrading the organic phosphorus pesticide residue soil, and have the effects of treating soil-borne diseases, promoting the crop growth and improving the crop yield. Because only one trichoderma strain is utilized, the fermentation process is easy to optimize, the microbial inoculum preparation cost is low, the commercial large-scale popularization is easy to realize, and high field general use values are reached.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Isaria fumosorosea oil suspending agent and preparation method as well as application thereof
InactiveCN102246750ALower resistanceEffective controlBiocideAnimal repellantsSpore germinationCabbage moth
The invention discloses an isaria fumosorosea oil suspending agent and a preparation method as well as application thereof. The oil suspending agent is prepared from the following components in mass percent: 1-40% of isaria fumosorosea spore suspension, 1-20% of vegetable oil, 3-8% of emulsifying agent, 0.1-5% of dispersing agent, 1-5% of stabilizing agent, 1-5% of anti-freezing agent and the balance of inert mineral oil or aromatic hydrocarbon solvent. The spore of the isaria fumosorosea oil suspending agent disclosed by the invention has long survival time, and the germination rate of the spore which is stored for 2 years is 80%; the isaria fumosorosea oil suspending agent has good ageing stability and is safe to crops and environments; and the isaria fumosorosea oil suspending agent is mainly used for pest control of crops including fruit trees, vegetables, wheat, rice, flowers and the like, and especially has an obvious effect on controlling myzus persicae, whiteflies, cabbage caterpillars, cabbage moths and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Rice pollen-preferential promoters and uses thereof
The present invention relates to rice genomic promoter sequences which promote transcription preferentially in microspores and / or pollen of plants. Also provided are chimeric genes comprising these promoter sequences, and plant transformation vectors comprising these chimeric genes. The present invention also discloses plant cells, plant tissues, plants, seeds and grains comprising these chimeric genes. The invention further discloses methods for expressing foreign nucleic acid sequences preferentially in pollen and for producing plants with modified pollen fertility.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCIENCE NV
Biological soil remediation agent and method for remediating soil
InactiveCN105618478AImprove the growing environmentEffective passivationContaminated soil reclamationSoil remediationBiology
The invention discloses a biological soil remediation agent which is prepared by mixing a solid passivator and a microbic solution according to the volume-weight ratio of 1:(15-30) (L / kg). The solid passivator comprises the following ingredients in percent by mass: 50-60 percent of clay carrier, 15-30 percent of diatomite, 10-15 percent of humic acid and 10-20 percent of charcoal. The microbic solution comprises a non-spore forming bacterium and streptomyces microflavus. The biological soil remediation agent can be used for remediating a soil ecosystem, improving the crop growth environment, effectively passivating heavy metal pollutants, such as lead, and reducing the availability for plants.
Owner:NANJING GAIA BIOLOGICAL ENG CO LTD
Glossy ganoderma spore oil and its preparing method and use
ActiveCN1586295AImprove product qualitySimple processUnknown materialsFood preparationSporeTriterpene
The present invention relates to a kind of active component extracted from glossy ganoderma spore as material and its preparation and use. The glossy ganoderma spore oil contains total triterpene in 24-35 %, has density of 0.88-0.92, refractive index 1.45-1.48 and acid number 14-35. The preparation process with wall breaking glossy ganoderma spore as material includes mixing with alcohol solution, pelletizing, drying, supercritical CO2 extraction in extracting reactor, two-stage separation, and extraction to obtain oily matter, and eccentric separation to obtain yellow oil. The glossy ganoderma spore oil product is used in preparing medicine and food for raising body's immunity. The process of the present invention is simple, stable in product quality, convenient and high in product yield, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HANFANG PHARMA
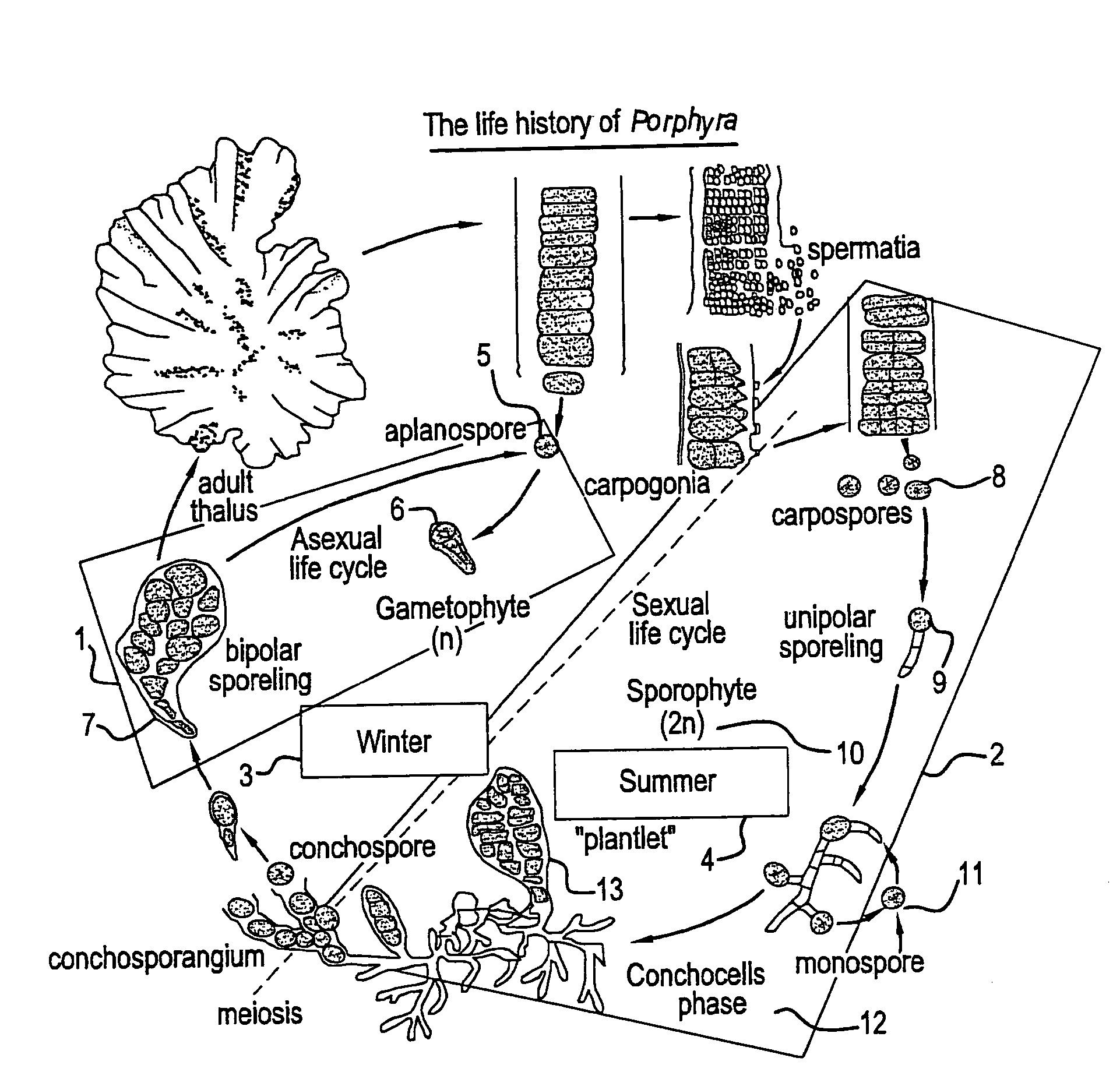
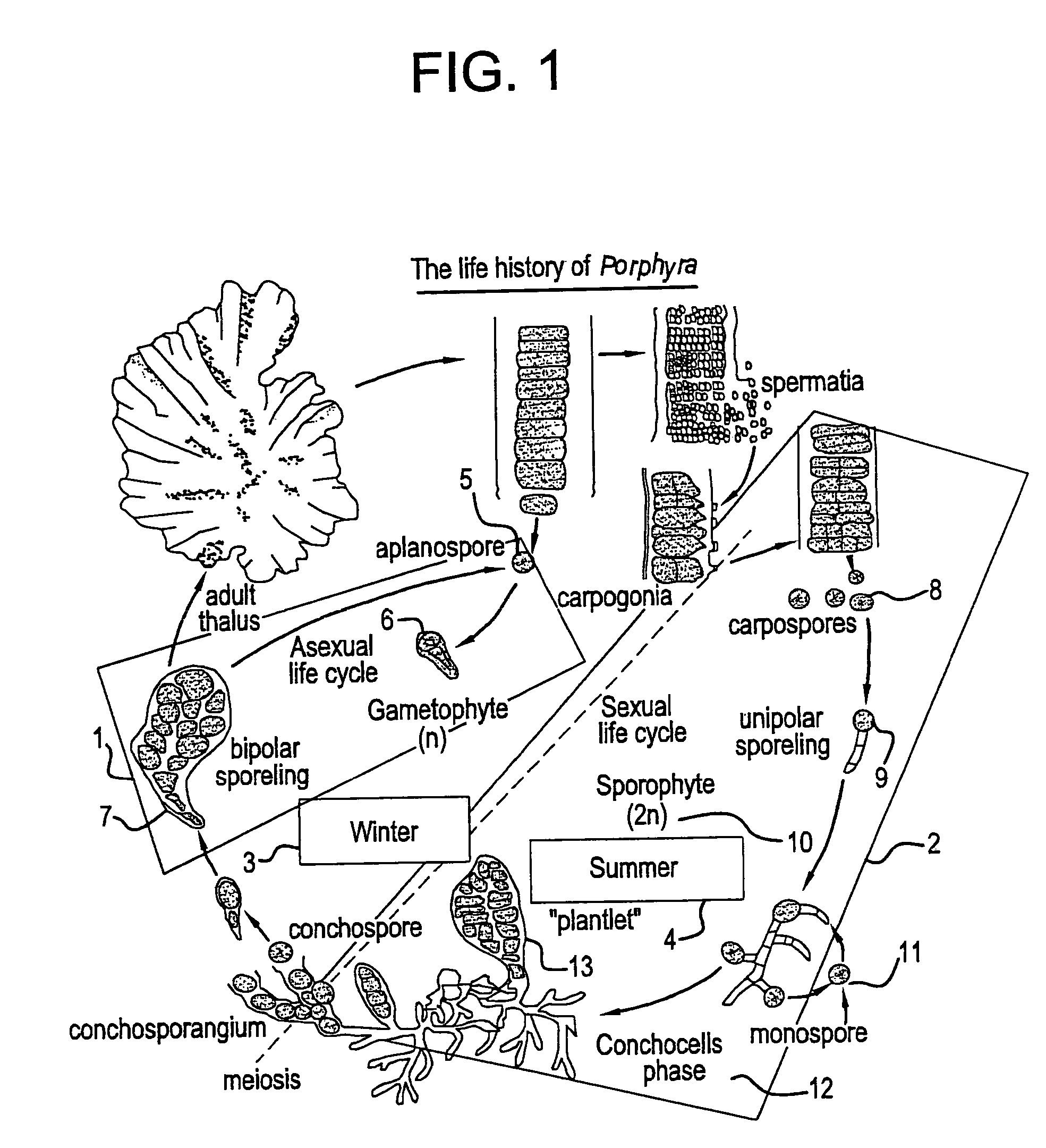
Technology for cultivation of Porphyra and other seaweeds in land-based sea water ponds
InactiveUS7484329B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSporelingAscophyllum
Owner:SEAWEED BIO TECH
Preparation method of natamycin
The preparation method of natamycin belongs to a technique for producing and extracting natamycin by using luteofuscus spore streptomycete as strain and adopting fermentation process. It includes the following steps: adopting luteofuscus spore streptomycete, preparing spore suspension liquor, culturing seed, making femrentation, extracting, controlling pH value and dissolved oxygen level, and adopting glucose-feeding mode in batches in the period of fermentation to prepare natamycin. In order to raise its yield, adopting low-temp. evaporation methanol-removing process to extract natamycin.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Polysporus trichoderma and application thereof
The invention discloses a polysporus trichoderma (Hypocrea pachybasioide) FSR-97 strain, wherein the preservation unit is China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the preservation date is 19, September, 2014 and the preservation number is CGMCC No.9691. The strain is cultured on a potato dextrose agar culture medium (PDA) plate at 25 DEG C and rapidly grows, and a monospore is germinated to form a white bacterial colony; the colour on the back surface of the bacterial colony is transited from colourless to yellow. The polysporus trichoderma (Hypocrea pachybasioide) FSR-97 has an effective broad-spectrum antibacterial effect on the main pathogenic bacteria causing the panaxginsen fusarium rot, epidemic disease, sclerotiniose, root rust rot, black spot, rhizoctonia solani, and botrytis. The invention further discloses a plurality of biocontrol mechanisms of the polysporus trichoderma (Hypocrea pachybasioide) FSR-97 for preventing and controlling the plant fungous disease, and an application for preparing a microbial preparation to prevent and control the plant fungous disease.
Owner:四川臻润农业科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com