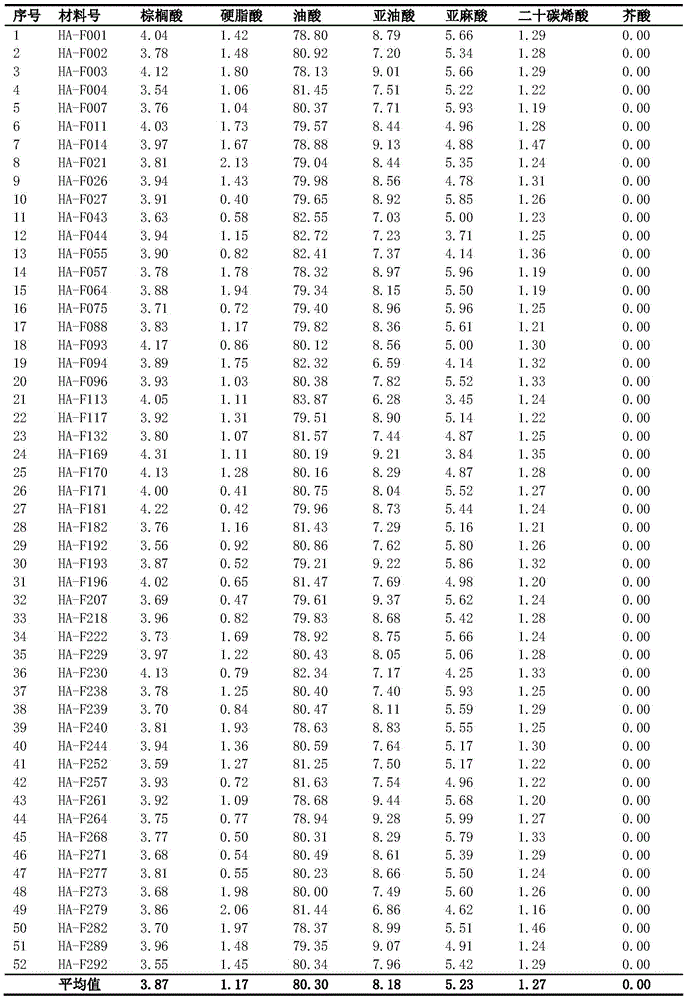
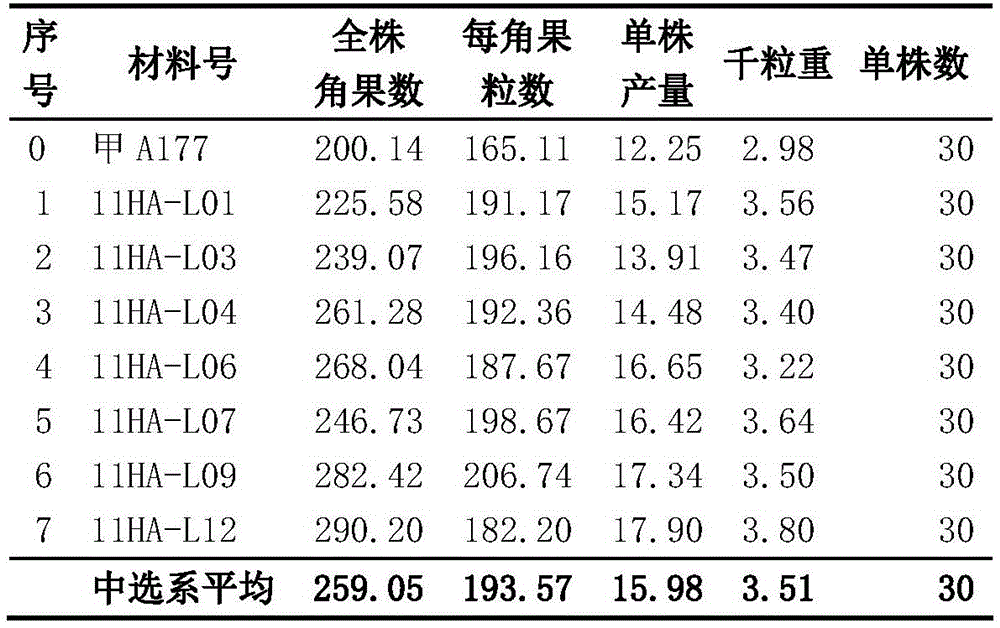
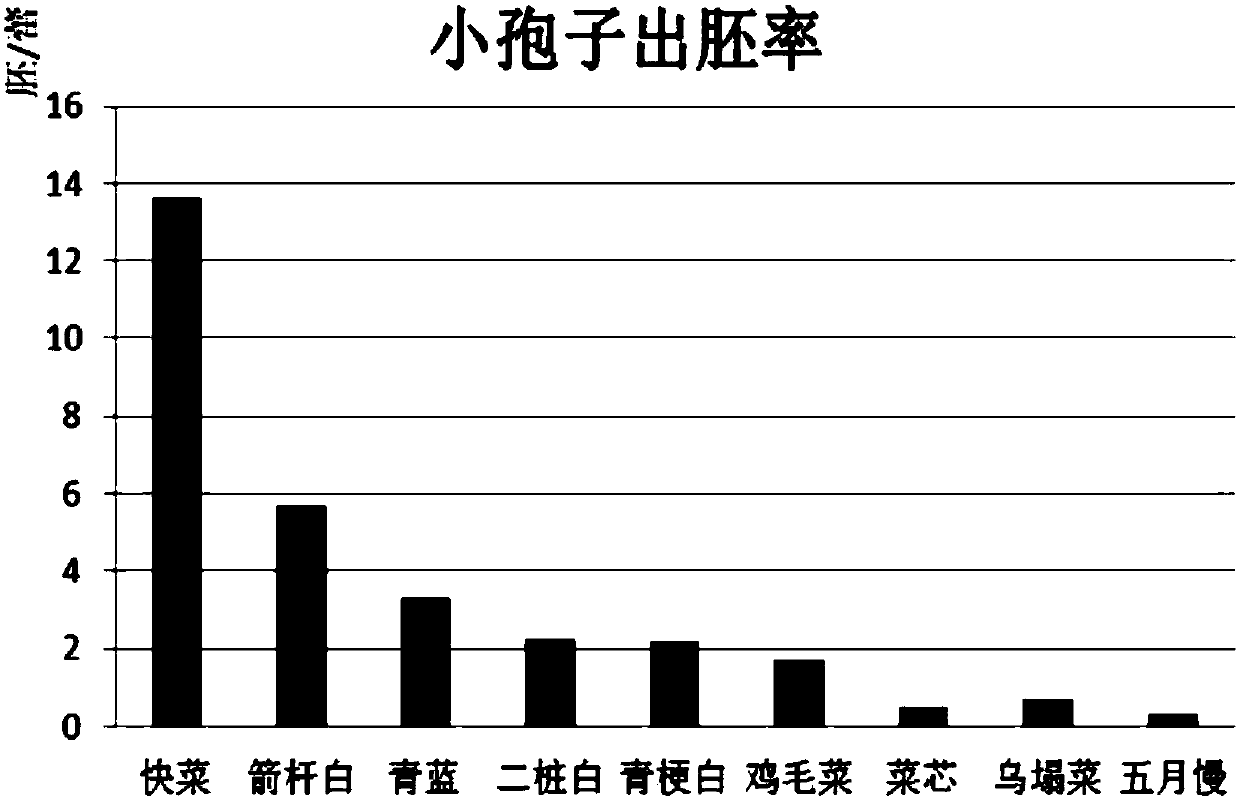
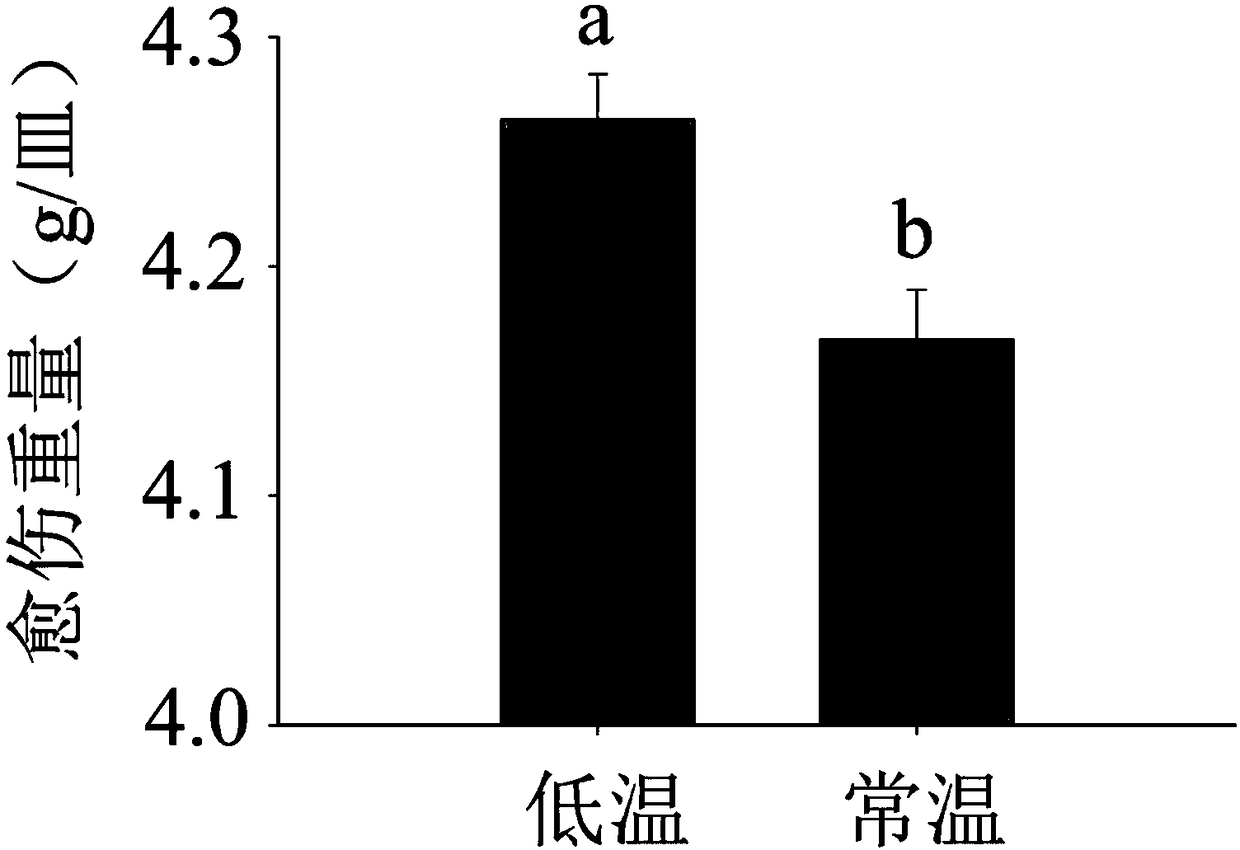
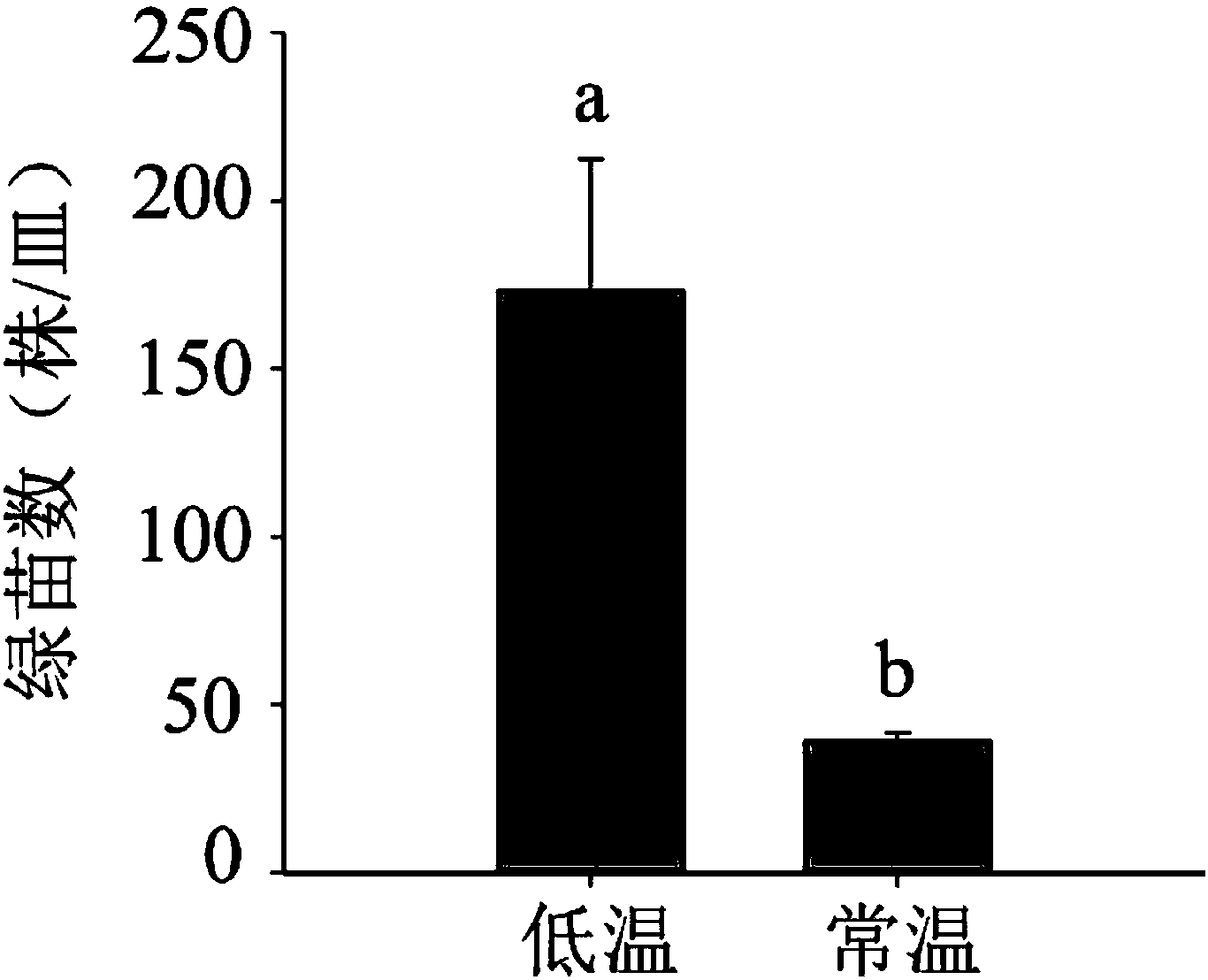
Patents
Literature
182 results about "Microspore" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microspores are land plant spores that develop into male gametophytes, whereas megaspores develop into female gametophytes. The male gametophyte gives rise to sperm cells, which are used for fertilization of an egg cell to form a zygote. Megaspores are structures that are part of the alternation of generations in many seedless vascular cryptogams, all gymnosperms and all angiosperms. Plants with heterosporous life cycles using microspores and megaspores arose independently in several plant groups during the Devonian period. Microspores are haploid, and are produced from diploid microsporocytes by meiosis.
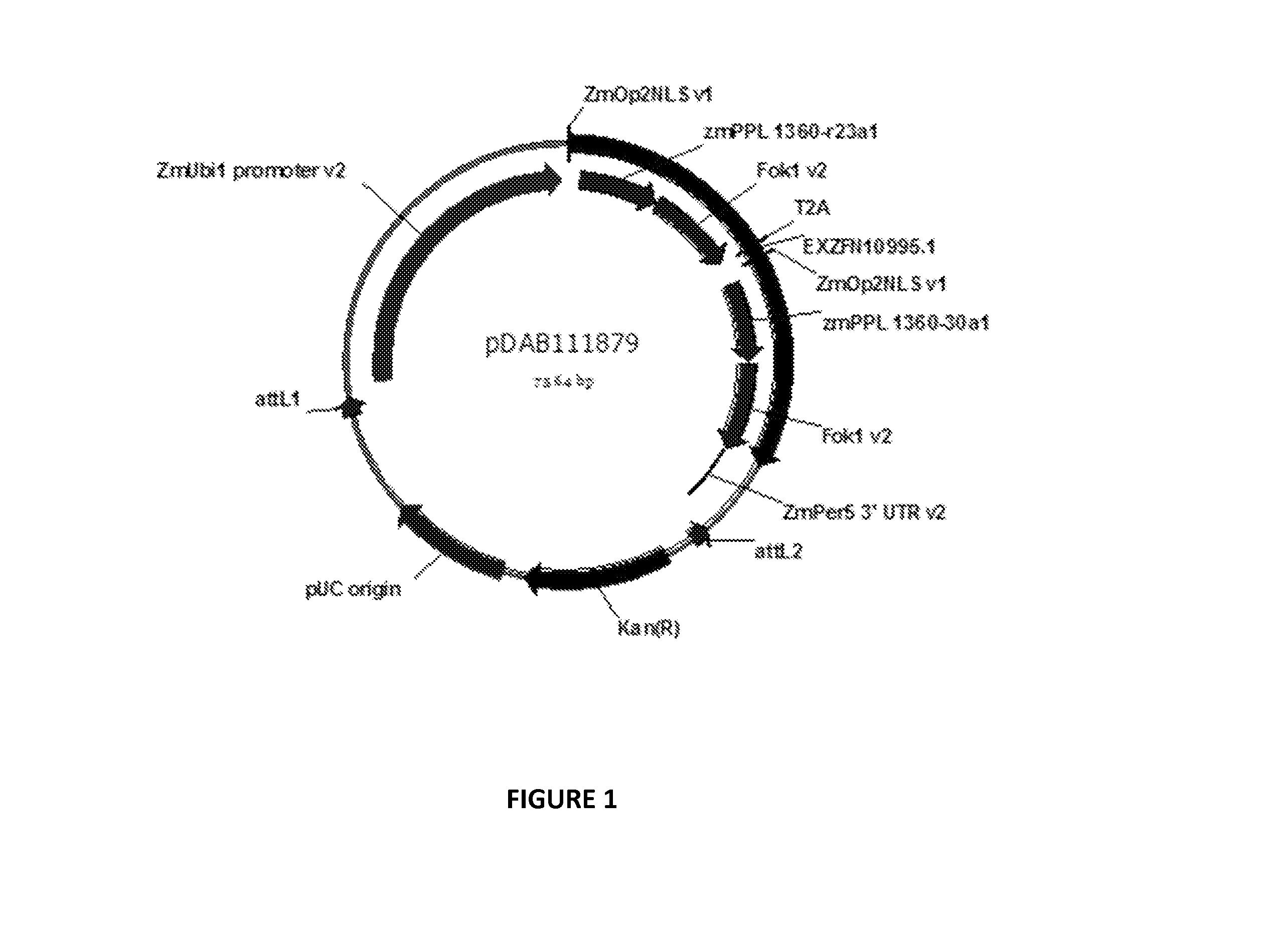
Haploid maize transformation
PendingUS20150307889A1Stably integratedModified stabilizationMicrobiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyAndrogen
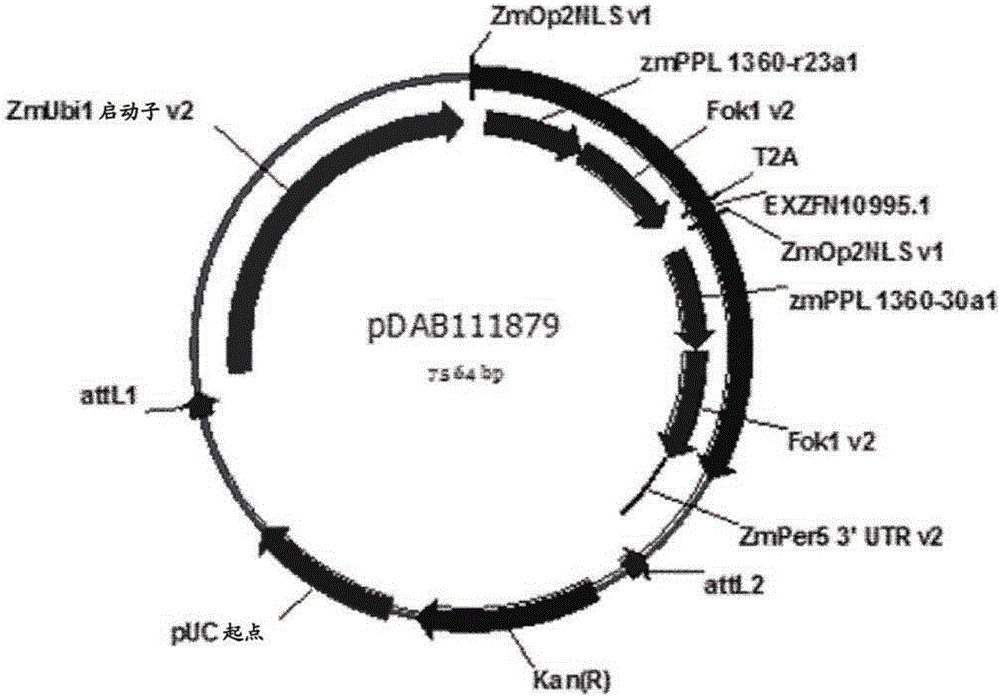
Disclosed are methods for transformation of an androgenic-derived, haploid cell line with a site-specific nuclease. In some embodiments, the androgenic-derived, haploid cell line is a maize microspore-derived plant tissue culture. In addition, the disclosure provides a method for modifying, e.g., by mutating or targeting and integrating donor DNA into, a specific locus of a haploid or dihaploid tissue genome. The disclosure further provides methods for regenerating a whole plant from the haploid or dihaploid tissue that contains either the mutation at a specific genomic locus or a donor DNA integrated within a specific genomic locus may be obtained from the subject disclosure.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
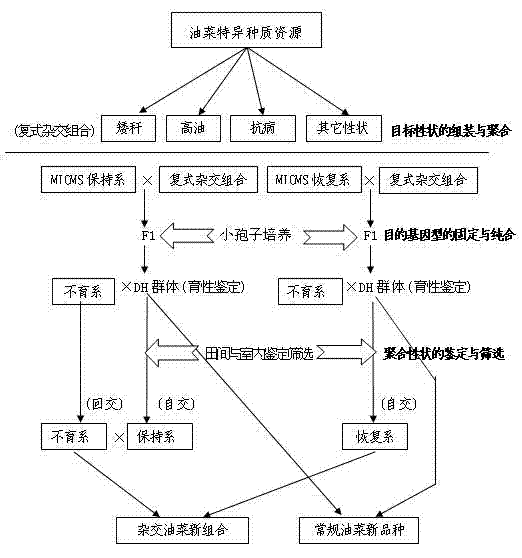
Rapid multi-target property polymerization breeding method for rape
InactiveCN102224801AImprove breeding levelShorten the breeding cyclePlant genotype modificationSporeGreenhouse
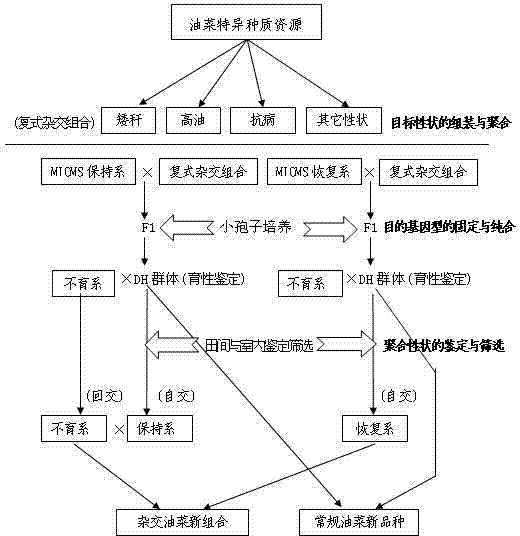
The invention provides a rapid multi-target property polymerization breeding method for rape, belonging to a plant breeding method, and comprising the following steps of: selecting excellent breeding target properties requiring to be polymerized, preparing single-cross combinations at room temperature in winter locally, preparing multi-parent complicated cross combinations in summer at different places, and assembling and polymerizing the multiple parents with excellent target properties based on the breeding requirements; performing microspore seedling cultivation on the complex filial generation for which multi-target property breeding restructuring polymerization is already realized, constructing a dihaploid (DH) breeding group, and realizing rapid fixation and homozygosis of the target genotypes of the generation of the multi-target property polymerization; and performing effective field and indoor identification and screening on the target genotypes of the generation for which the multi-target property polymerization is realized based on the property characteristics, performing molecular marker assistant selection on important target properties, and breeding new materials conforming to the breeding targets.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Rice pollen-preferential promoters and uses thereof
The present invention relates to rice genomic promoter sequences which promote transcription preferentially in microspores and / or pollen of plants. Also provided are chimeric genes comprising these promoter sequences, and plant transformation vectors comprising these chimeric genes. The present invention also discloses plant cells, plant tissues, plants, seeds and grains comprising these chimeric genes. The invention further discloses methods for expressing foreign nucleic acid sequences preferentially in pollen and for producing plants with modified pollen fertility.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCIENCE NV
SSR molecular marker method of brassica allohexaploid and primers thereof
ActiveCN104059971AReduce concentrationReduce generationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBrassicaAgricultural science
The invention discloses an SSR molecular marker method of a brassica allohexaploid and primers thereof. The SSR molecular marker method of the brassica allohexaploid comprises the steps: hybridizing a brassica allohexaploid parent, and performing microspore culture on the obtained filial generation to obtain a DH colony; extracting genome DNAs of the brassica allohexaploid parent and the DH colony, and performing PCR amplification with all genome DNAs as a template by using the primers; constructing a genetic map of the brassica allohexaploid parent according to a PCR amplification result, wherein 217 pairs of primers are included, with base sequences respectively shown in SEQ ID No. 1 / 2-433 / 434. According to the SSR molecular marker method, a first genetic map of the brassica allohexaploid is constructed, and the basis is provided for further performing QTL location and molecular marker assistant breeding.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for obtaining dihaploid plants of sweet peppers
InactiveCN102047843AImprove cultivation efficiencyIncrease DH Strain RatioPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsGenotypeCapsicum baccatum
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for rapidly obtaining pure line of hybrid wheat
InactiveCN101946629AEasy to optimizeInduction frequency is highAspharagus cultivationPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologySporeling
The invention relates to a method for rapidly obtaining a pure line of hybrid wheat, comprising the following steps: (1) preparing a hybridized combination; (2) planting a hybrid material; (3) determining an appropriate ear fetching period; (4) pre-treating anther; (5) dissociating and purifying microspores: (6) adjusting the density of the microspores; (7) forming microspore embryos by induction; (8) forming regenerated plants by differentiation culture; (9) allowing regenerated seedlings to pass the summer at low temperature; (10) culturing the strong seedlings; (11) hardening the seedlings; (12) transplanting the seedlings; (13) managing the transplanted seedlings; and (14) harvesting after the seedlings become mature. In the method, a test material is directly planted in a field and the microspores are dissociated from the anther for culture to eliminate the disturbance of an anther wall, thus being beneficial to optimization of various culture factors, improving the induction frequency of the microspore embryos, overcoming limitation on a genotype, promoting more hybrid combined materials to obtain the regenerated plants, providing more abundant base materials for variety breeding, and playing an important role in enhancing the breeding efficiency of a haploid.
Owner:甘肃省农业科学院生物技术研究所
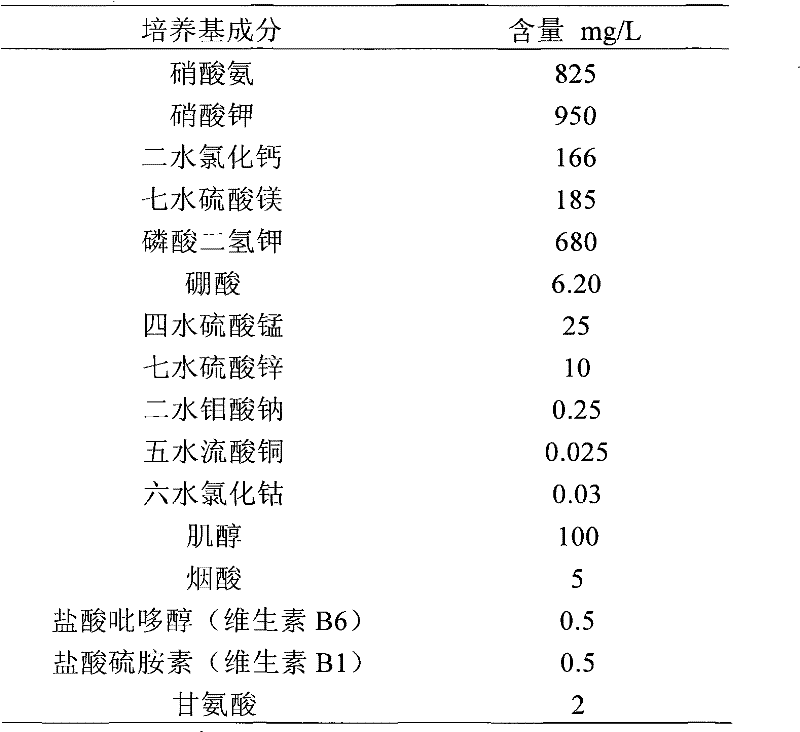
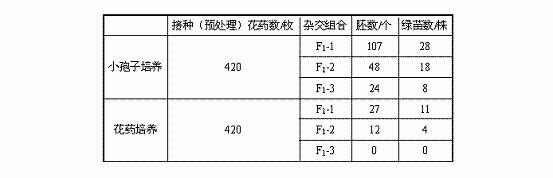
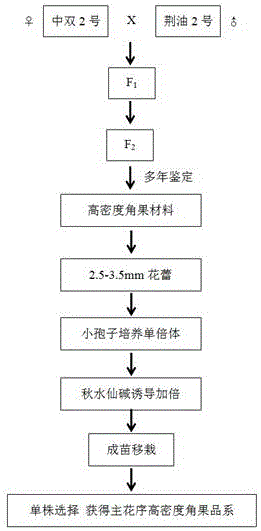
Breeding method of rape with high-density siliques on main inflorescence and application
The invention discloses a breeding method of rape with high-density siliques on a main inflorescence and application. The breeding method comprises the following steps: adopting double-2 in the variety of cabbage type rape and nepeta oil-2 in the variety of cabbage type rape as parents for hybridization to obtain F1, and conducting bagged selfing propagation to obtain a segregated population; selecting single plants in the segregated population to conduct identification on phenotypic characteristics in the field continuously for 4 years, selecting single plants with high-density siliques on the main inflorescence (number of effective siliques on the main influorescence / main-inflorescence length being greater than 2 pieces / cm); in a flowering period, selecting flower buds 2.5-3.5mm in length on the main inflorescence, using colchicine to double chromosomes, using microspores for culture to obtain a double-haploid population, and selecting single plants to breed into strain with high-density siliques on the main inflorescence and stable characters; using the strain and double 11 in the variety of cabbage type rape (the density of siliques on the main inflorescence is about 1.7 pieces / cm) to conduct hybridization, utilizing F2:3 populations to conduct genetic segregation analysis and finding that the characters of the high-density siliques are controlled by 2 pairs of additive-dominant-epistatic main genes. The breeding method and the application disclosed by the invention have the advantages that the variety of rape with high-density siliques on the main inflorescence can be bred by utilizing hybridization of the high-density silique materials on the main inflorscence and common rape, and the yield per unit of the rape can be greatly increased.
Owner:贵州省油菜研究所
Method for obtaining haploid regenerated plant by chilli anther culturing
InactiveCN104041414AStrong differentiation abilityInduction frequency is highHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureHeat shockSpore
The invention relates to a method for obtaining a haploid plant by chilli anther culturing, which belongs to the technical field of agriculture. The method comprises the steps of sterilizing selected flower bud, grafting anther, pretreating, culturing anther, and inducing callus tissue to be subjected to redifferentiation to form the haploid plant. According to the method, a microspore and an anther wall are co-cultured by virtue of a solid culturing medium, low temperature and heat shock pretreatment is performed, and callus induction, culturing medium component differentiation and culturing conditions are adjusted, so that the callus rate and the differentiating capability of the callus tissue are enhanced. When the method is used for culturing chilli anther, the callus inductivity reaches over 60%, the emergence rate reaches over 80% and the problem of low inductivity in chilli anther culturing is solved. By virtue of the method, the haploid regenerated plant can be obtained rapidly and the emergence rate is high; a powerful approach is provided for new variety breeding.
Owner:NANJING INST OF VEGETABLE SCI
Anther development control gene and use thereof in realizing male sterility in Arabidopsis thaliana
ActiveCN102140131AAccording to Mendelian inheritanceIn line with the law of inheritancePlant peptidesFermentationNucleotideWild type
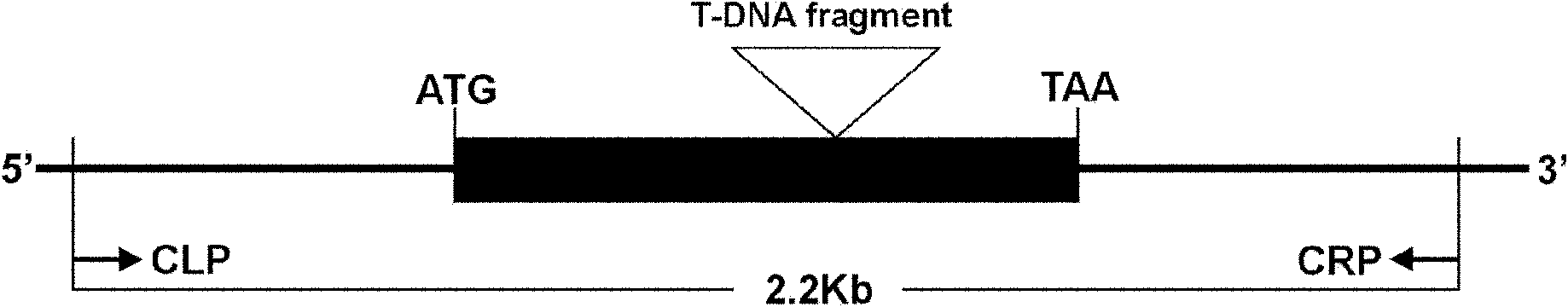
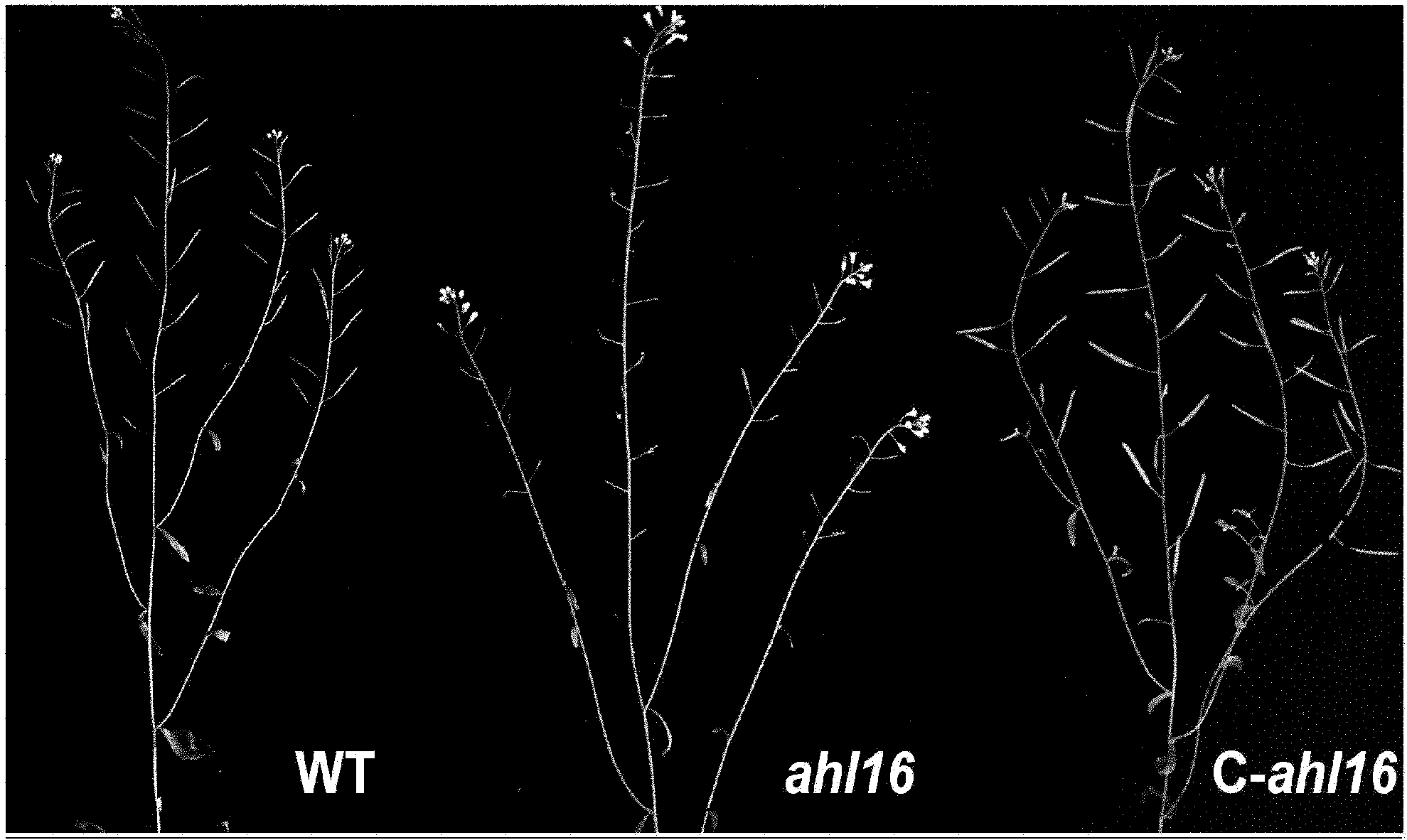
The invention relates to an anther development control gene and use thereof in realizing male sterility in Arabidopsis thaliana. An Arabidopsis thaliana male sterile mutant ahl16 is screened out from T-DNA-inserted mutant population, a gene AHL16 controlling the fertility of Arabidopsis thaliana is cloned and identified, the nucleotide sequence of the gene AHL16 is represented by SEQ ID N0.1, and genetic complement experiments prove that the AHL16 gene in a wild type can restore the male sterile phenotype. Amino acid sequence analysis and subcellular localization experiments indicate that the AHL16 gene codes proteins of an AT-hookmotif nuclear localized protein family and is located in the nucleus. In Arabidopsis thaliana, the mutation of the gene leads to complete male sterility. The gene has a very important application value in aspects of explanation of influences of the growth of the inner layers of the outer walls of microspores and the structures of the inner walls on the fertility of plants and improvement on yield by hybrid seed production.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for continuously culturing high frequency regeneration plants through cereal crop single plant source microspores
ActiveCN105340755AReduce incubation timeAchieve trainingHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSporeSkin callus
The invention relates to a method for continuously culturing high frequency regeneration plants through cereal crop single plant source microspores, particularly to a culture method of the cereal crop single plant source microspores and the method for culturing and obtaining the regeneration plants through the cereal crop single plant source microspores. The method comprises the following steps: separating the microspores from young spikes of a single plant of the cereal crop; carrying out callus induction and differentiation steps on the separated microspores, wherein the step of separating the microspores from the young spikes of the cereal crop comprises the steps of continuously obtaining young spikes of which the middle floret microspores are in the mononuclear early-middle period from the same cereal crop plant which is planted indoors and continuously tillers and ears; carrying out the separation, callus induction and differentiation steps on the young spike obtained each time.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for screening anti-fusarium graminearum toxin of wheat crops
The invention provides a method for screening anti-fusarium graminearum crude toxin of wheat crops. The method comprises the steps of: giving the fusarium graminearum crude toxin to the anther before microspore is cultivated in a stressing way, separating out the microspore from the anther which is stressed by the crude toxin, putting the microspore into a fusarium graminearum crude toxin-adding inductive medium to cultivate, and putting the microspore into a NaCl-adding differential medium to cultivate after the embryoid is obtained to obtain a regeneration plant. The whole screening processof the method is performed under a laboratory controllable condition, so that a screening result is real and reliable; and the resistance genes carried by the screened regeneration plant is homozygous with the other genes for once, and the controllable genetic stability of the genes is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Culture method for brassica oleracea L. var. acephala microspore regeneration plant
InactiveCN102228003AImprove embryo emergence rateImprove utilization efficiencyHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSporeHeat shock
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
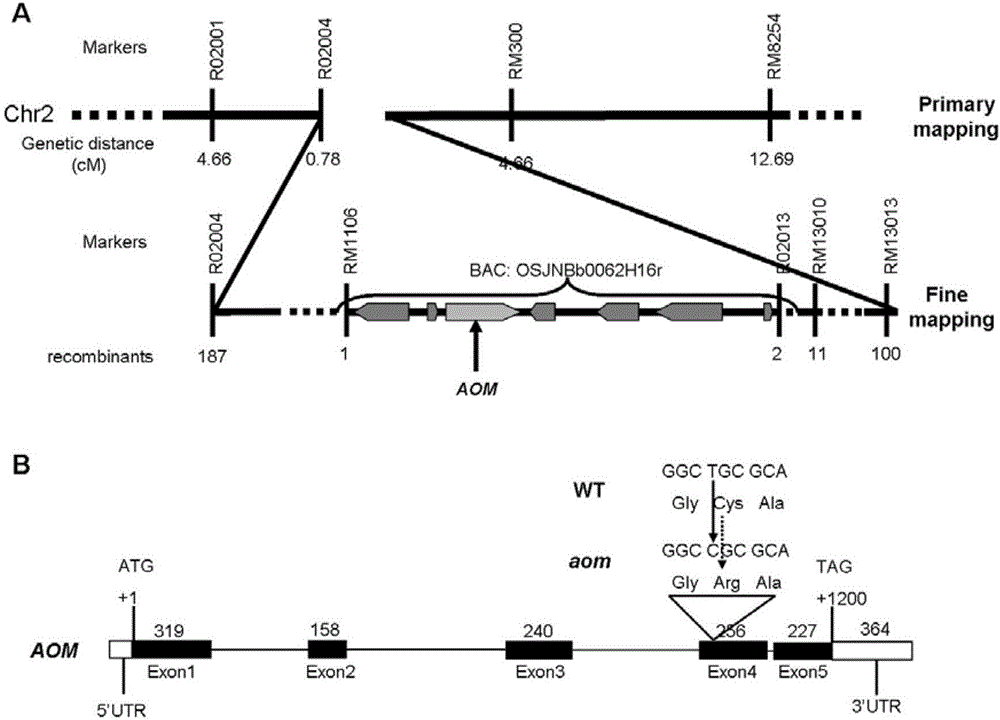
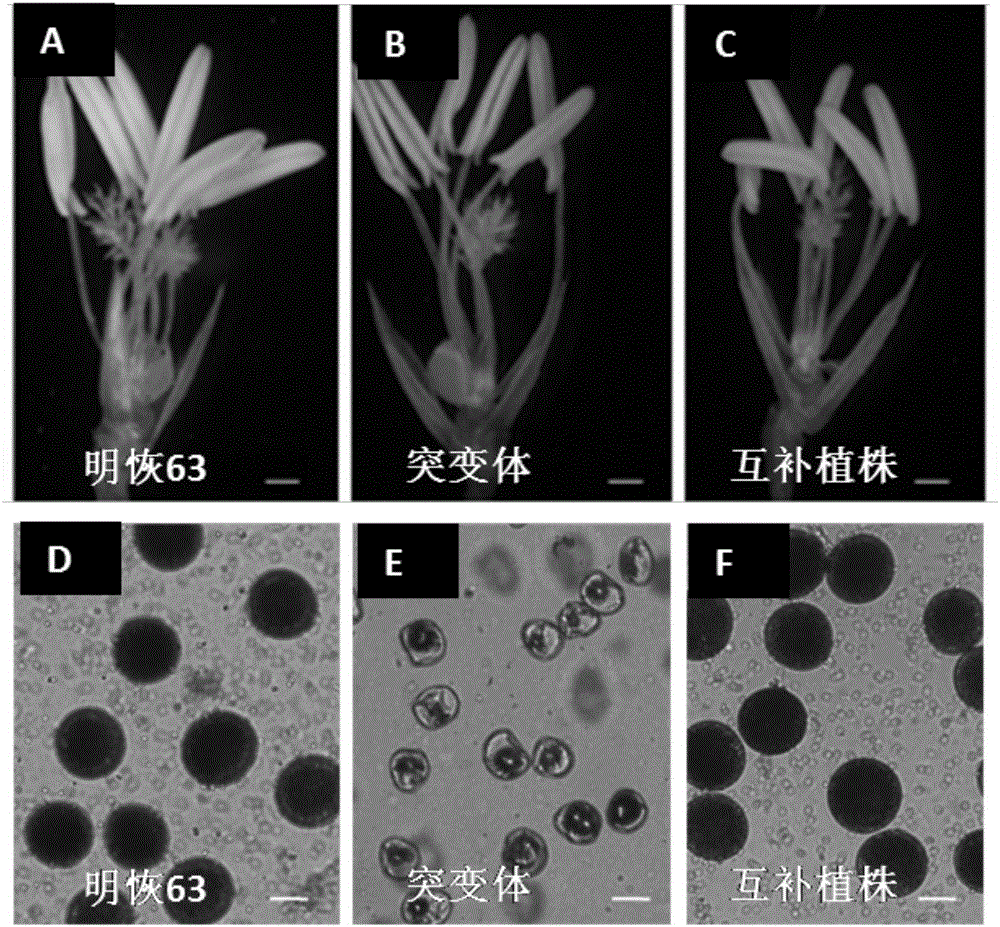
Oryza sativa pollen germination aperture development and pollen fertility gene OsAOM, mutant gene, and recombinant expression vector and application thereof
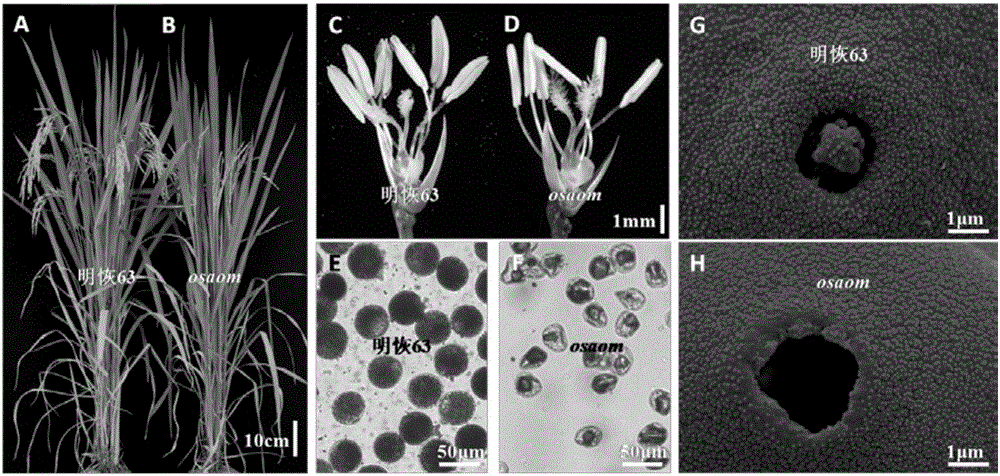
The invention relates to an oryza sativa pollen germination aperture development and pollen fertility gene OsAOM, a mutant gene, and a recombinant expression vector and application thereof. The gene encoded protein is protein with the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1, or protein which is obtained by substituting, missing or adding at least one amino acid and has the same function as the OsAOM; the protein formed by the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1 has the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The invention also discloses the recombinant expression vector of the OsAOM gene. The OsAOM gene disclosed by the invention encodes one piece of GDSL lipase; the functions of regulating and controlling the pollen germination aperture growth, the microspore cell membrane expansion and the pollen inner wall and cytoplasm development are realized; the gene is a necessary gene for developing microspores into fertile pollen; the gene function deficiency can cause germination aperture structure disorder, microspore cell membrane and cytoplasm degradation, pollen inner wall formation incapability and oryza sativa male sterility.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Method for efficiently obtaining regeneration plant by cultivating isolated microspores of brassica oleracea L.var.capitata L.
ActiveCN104429952AIncrease incidenceQuality improvementHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSporeGermplasm
The invention discloses a method for efficiently obtaining a regeneration plant by cultivating isolated microspores of brassica oleracea L.var.capitata L.. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing embryogenesis; and (2) performing embryo germination, thereby obtaining the regeneration plant, wherein the separated microspores are subjected to dark culture in a culture box at the temperature of 18+ / -0.5 DEG C until an embryoid visible to the naked eyes is generated in the step (1) of performing embryogenesis; and then the small embryoid is transferred to a dark shaking table at a speed of 50-55 revolutions per minute at the temperature of 25+ / -0.5 DEG C to perform shake culture until the cotyledonous embryoid is formed. According to the method, the genetically homogenous double-haploid plant materials can be obtained in batches, the germplasm resource innovation is accelerated, and the breeding progress is shortened. The method disclosed by the invention can be popularized and applied in the research field of molecular marker assisted breeding, mutant screening and cell totipotency mode systems of the brassica oleracea L.var.capitata L..
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Method for culturing regeneration plants of Brassica oleracea microspores
InactiveCN102239803AImprove embryo emergence rateImprove utilization efficiencyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBudPloidy
The invention discloses a method for culturing regeneration plants of Brassica oleracea microspores, which comprises the following steps of: taking flower buds from inflorescences of Brassica oleracea and Brassica napus directly or taking the flower buds from the inflorescences of the Brassica oleracea and the Brassica napus after inducing; sterilizing, adding an induced culture medium NLN-13 to prepare a suspension, filtering to obtain filter liquor, and centrifuging to obtain precipitates; adding the induced culture medium NLN-13 and mixed solution of active carbon sequentially to obtain a microspore suspension; performing heat activation, and culturing to obtain embryoid in the cotyledon stage; inoculating to an embryoid differential medium until the embryoid is differentiated to germinate; cutting regenerated sprouts, inoculating to a rooting culture medium to perform rooting culture, and hardening seedlings and transplanting to obtain the regeneration plants; and taking tender leaves of the regeneration plants to detect the ploidy of the regeneration plants, and identifying regenerated seedlings of the Brassica napus and regenerated seedlings of the Brassica oleracea from a regeneration plant colony. In the method, the Brassica napus of which the embryos are easy to germinate and the Brassica oleracea of which the embryos are difficult to germinate are mixed to be cultured, and materials of which the embryos are easy to germinate drives materials of which the embryos are difficult to germinate to germinate the embryos, so that the embryo growth rate of the Brassica oleracea is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Cultivation method for barley microspores
InactiveCN109105258APromote productionPromote formationPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSporeCentrifugation
The invention discloses a cultivation method for barley microspores. The cultivation method comprises the following steps of selecting young spikes, performing pretreatment, taking florets on the young spikes, performing disinfection, washing the florets with sterile water, performing inoculation to an extracting solution, and performing treatment for 1-2 d at 1-10 DEG C; performing rotary cuttingon the florets after inoculation, performing filtering and centrifugation, and collecting microspores; putting the collected microspores in the extracting solution for 1-3 d in the dark at 24-26 DEGC, and purifying the microspores with maltose; and washing the purified microspores with an induction medium, performing suspension, regulating the density of the microspores, performing inoculation to a culture dish, performing sealing, and performing cultivation for 15-24 d in the dark at 24-26 DEG C. In the cultivation method, by performing low temperature treatment on the florets in vitro, thecallus yield and the seedling formation amount in cultivation of the barley microspores are increased, the regeneration capacity is greatly improved, the problem of less amount of a donor material issolved, the operation is simple and feasible, and the cost is saved.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Haploid maize transformation
InactiveCN106455512AOther foreign material introduction processesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyNuclease
Disclosed are methods for transformation of an androgenic-derived, haploid cell line with a site-specific nuclease. In some embodiments, the androgenic-derived, haploid cell line is a maize microspore-derived plant tissue culture. In addition, the disclosure provides a method for modifying, e.g., by mutating or targeting and integrating donor DNA into, a specific locus of a haploid or dihaploid tissue genome. The disclosure further provides methods for regenerating a whole plant from the haploid or dihaploid tissue that contains either the mutation at a specific genomic locus or a donor DNA integrated within a specific genomic locus may be obtained from the subject disclosure.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
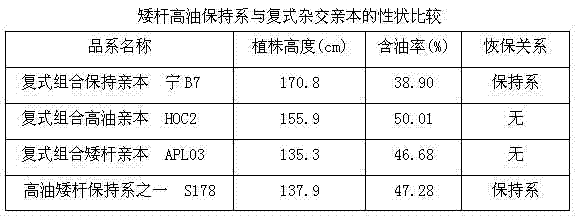
Cultivating method for high-oleic acid rapeseed variety
InactiveCN105613258AReduce workloadImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationBrassicaSpore
The invention belongs to the field of rapeseed breeding, and particularly relates to a cultivating method for a high-oleic acid rapeseed variety. The cultivating method is characterized by comprising the following steps: performing hybridization by taking first Brassica napus L. A177 with the oleic acid content of 65 percent or below as a female parent and taking first high-oleic acid Brassica napus L. H003 which has the preservation number of CCTCC NO:P201604 and has the oleic acid content of at least 78 percent as a male parent, and obtaining F1 through artificial emasculation; planting the F1, obtaining a separated DH line through microspores culture; performing high-oleic acid molecular marker identification on strain seedling stage of a DH line group, and determining the genotype of each strain; measuring the content of oleic acid of each single plant by utilizing a gas chromatograph, and determining the content of the oleic acid of the each primarily selected line; selecting the parent strains of which the characters, such as the whole plant pod number, the seed number per pod, the thousand seed weight and the yield per plant, are superior to the parent strain with the oleic acid content lower than 69 percent from the DH strain with the oleic acid content of greater than 75 percent to obtain the high-oleic acid rapeseed selected line and variety of which the oleic acid is greater than 78 percent.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Wheat anti-gibberellic in-vitro directional selection breeding method
InactiveCN104969856ASelection inefficiencySmall chance of selectionPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceDirectional selection
The invention belongs to the technical field of crop disease-resistance genetic breeding, and provides a wheat anti-gibberellic in-vitro directional selection breeding method, which comprises: (1) Fusarium graminearum strain separation and culture; (2) crude toxin obtaining; (3) hybridization F1 generation seed obtaining; (4) resistant microspore arrhenokaryon development; (5) resistant callus differentiation; (6) haploid seedling obtaining; (7) anti-gibberellic strain obtaining; and (8) anti-gibberellic characteristic identification on the doubled haploid individual so as to screen the stable anti-gibberellic strain line. According to the present invention, the toxin is used to stress the wide microspore genotype variation and massive microspore cell populations due to gene recombination in the F1 generation anther tissue, the sensitivity difference of the resistant genotype microspore and the non-resistant genotype microspore on toxin is used to screen the resistant genotype, the selection characteristic is directional, the selected groups are large, and the selection efficiency is high.
Owner:平顶山市平丰种业有限责任公司
Method for improving embryogenesis efficiency and plant regeneration efficiency of stem nodule mustard microspore embryo
ActiveCN103329804AImprove regeneration efficiencyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBiotechnologySporeling
The invention discloses a method for improving the embryogenesis efficiency and the plant regeneration efficiency of a stem nodule mustard microspore embryo. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) selecting materials, namely observing flower buds by a microscope, and selecting the flower buds with the diameters of 2-3 mm; (2) performing sterilization, namely performing sterilization by adopting 0.1 percent of mercury bichloride for 12 min, and washing the flower buds by germfree water for three times; (3) extracting pollens, namely adding a B5-13 liquid culture medium for grinding and filtration, and performing centrifugation; (4) performing heat-activation treatment, namely transferring sedimented pollens into an NLN-16 liquid culture medium containing a colchicine solution, culturing the pollens in the dark at the temperature of 32 DEG C for 48-52 hours; (5) performing induction to obtain the embryo, namely performing centrifugation, adding the NLN-13 liquid culture medium, packaging the pollens into a culture dish according to a unit of 1.5 flower buds per culture dish, and culturing the flower buds in the dark at the temperature of 25 DEG C; and (6) performing induction to obtain seedlings, namely after the embryo is formed, transferring the embryo into a B5-3 solid culture medium for culture. The invention creates a novel method of a stem nodule mustard free microspore culture technology and has a wide application prospect in breeding of stem nodule mustards.
Owner:NINGBO ACAD OF AGRI SCI
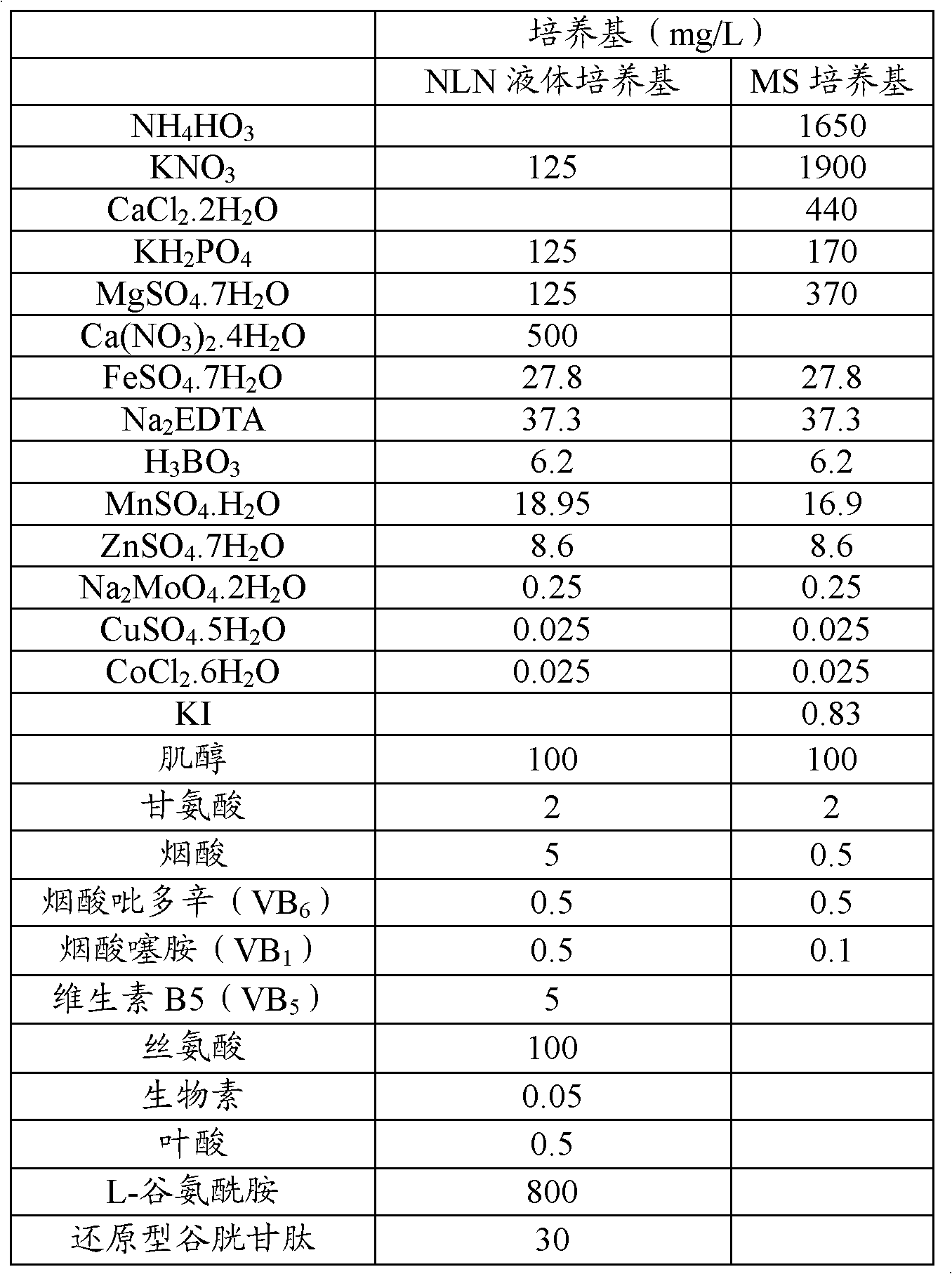
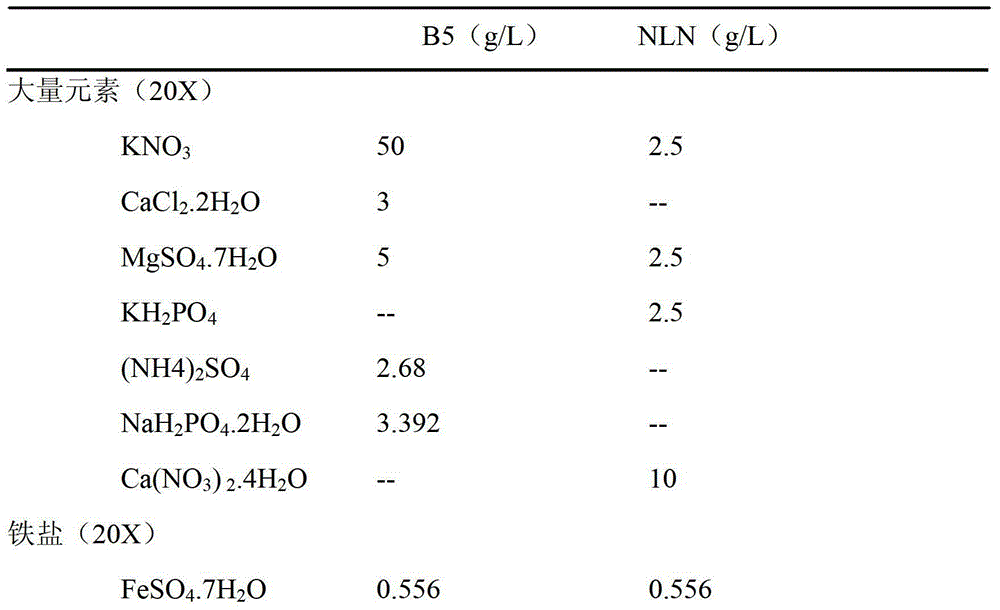
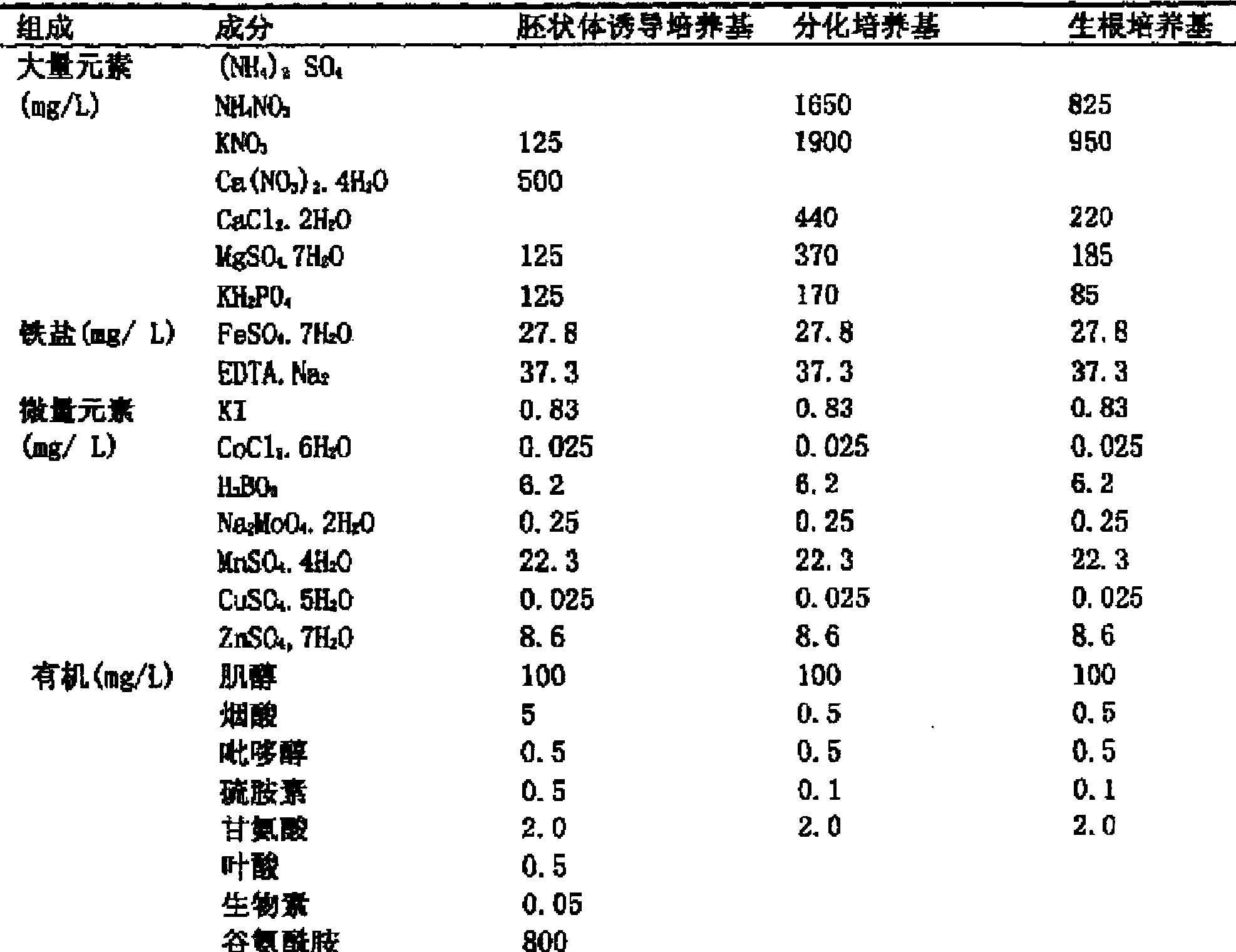
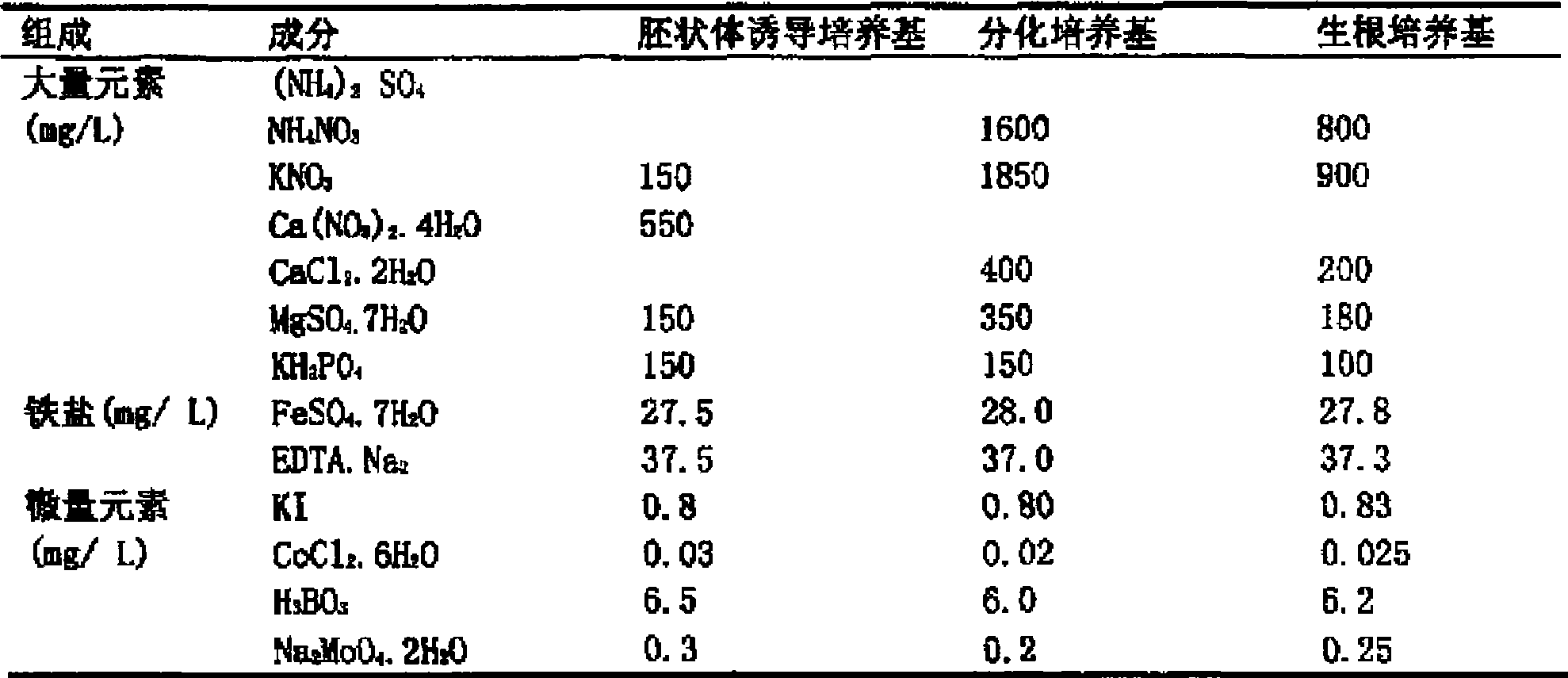
Culture medium prescription of regenerated plant from isolated microspore of brassica
InactiveCN101433184AWide adaptabilityRich breeding resourcesPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSporeBrassica
The invention provides a culture medium formulation for regenerated plantlets of Brassica isolated microspores, which relates to improvement of a culture medium formulation for regenerated plantlets of Brassica microspores as horticultural crops, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The invention provides the culture medium formulation for regenerated plantlets of Brassica isolated microspores, which is high in induced embryo formation rate and differentiation rate. A culture medium of the invention comprises an embryoid induction culture medium, a differentiation culture medium and a rooting culture medium, wherein the embryoid induction culture medium, the differentiation culture medium and the rooting culture medium all comprise macroelements, trace elements and organic elements. The formulation has the advantages of providing a large number of new genotype pure lines for breeding and greatly enriching breeding resources of Brassica.
Owner:刘祥军
Method for breeding and cultivating early ripening disease-resistant stem broccoli
ActiveCN103988775ANormal developmentGood flowering and fruitingPlant genotype modificationSporeSource material
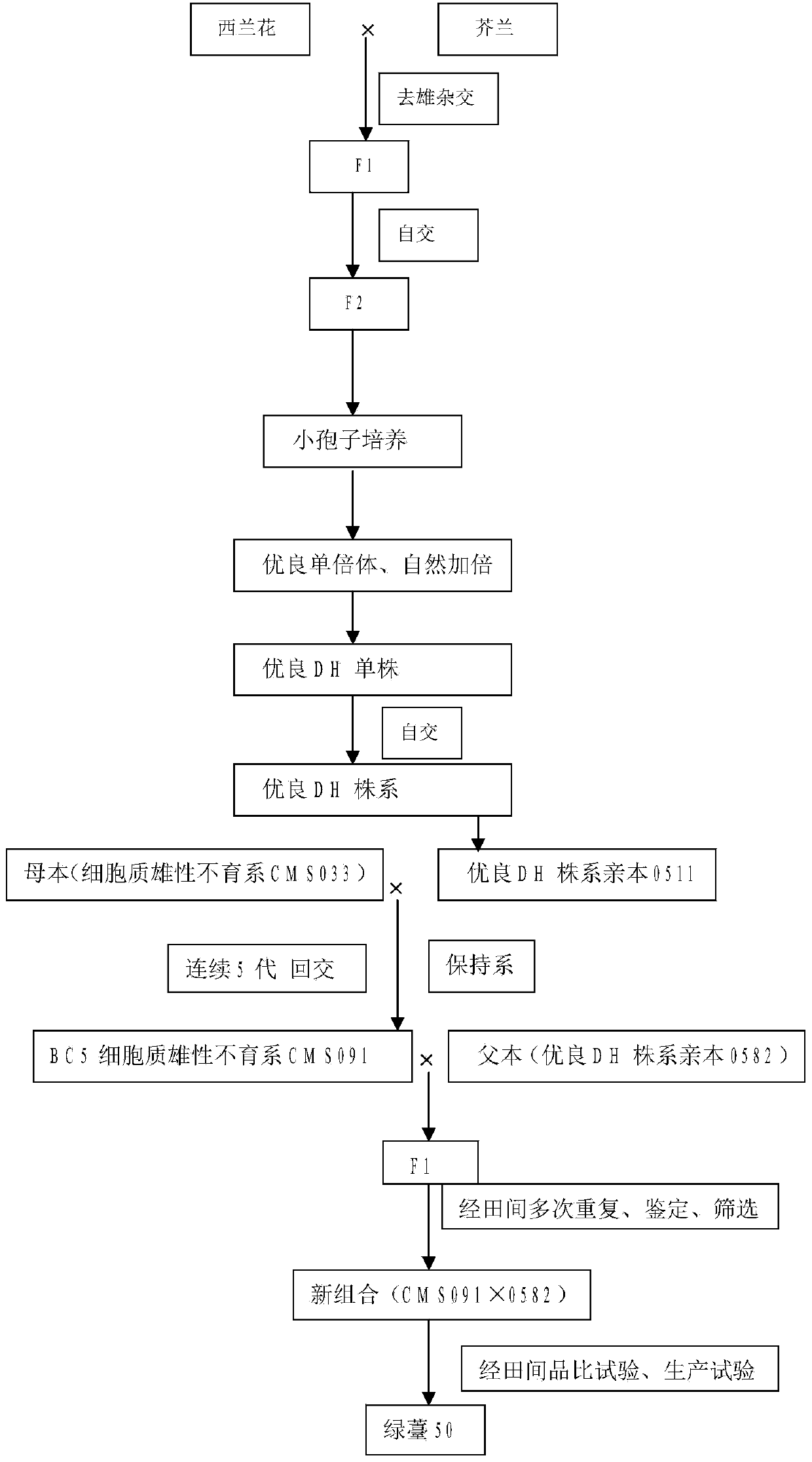
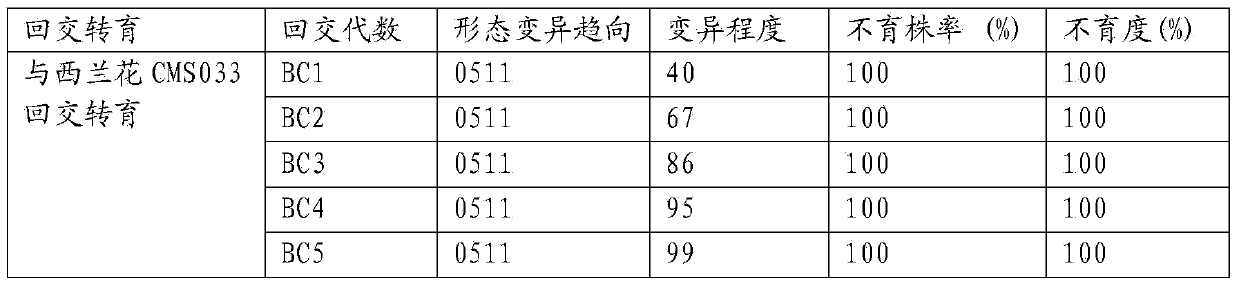
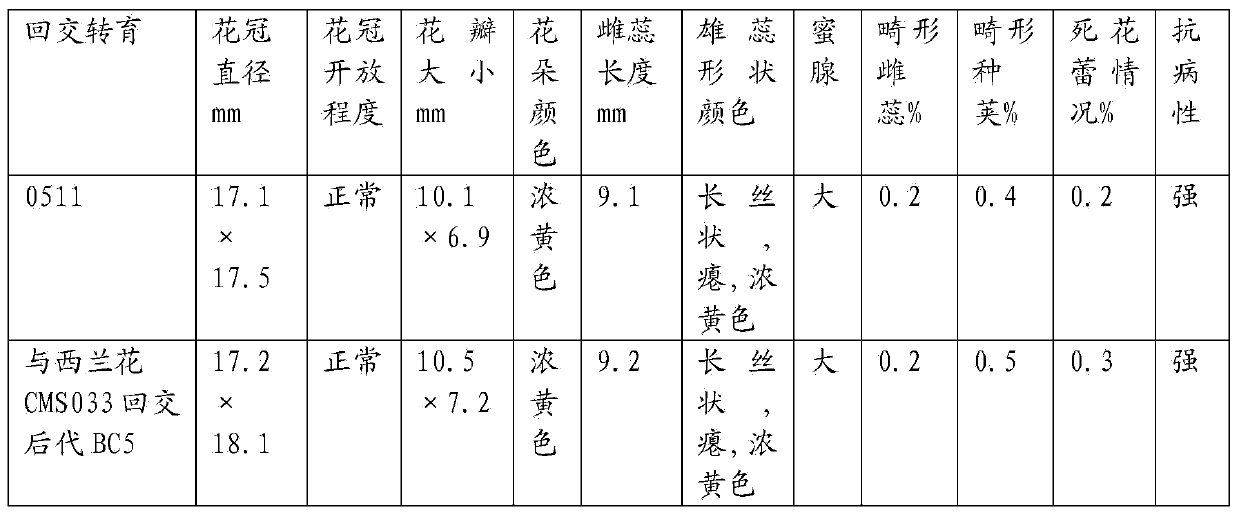
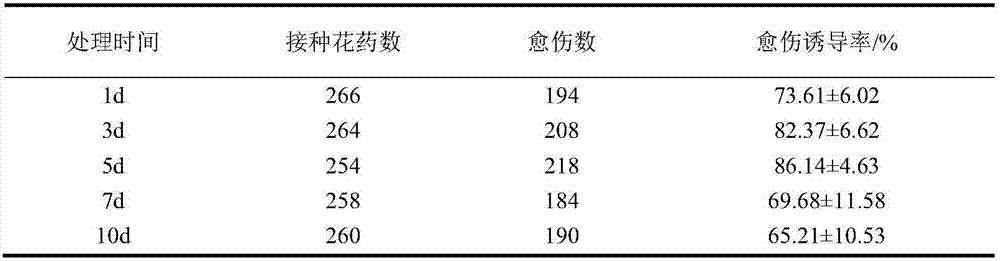
The invention relates to a plant breeding and cultivating method and in particular relates to a stem broccoli breeding and cultivating method, belonging to the technical field of plant cultivation. The method comprises the following steps: performing artificial emasculation to prepare hybrid first generation seeds F1 during flowering phase by utilizing a broccoli breeding material and a cabbage mustard breeding material, and performing selfing on a selected individual plant with excellent comprehensive agronomic traits to obtain F2; screening excellent individual plants, performing microspore culture on flower buds suitable for microspore culture from the late uninucleate stage to early dikaryophase stage, creating lots of normal regeneration plants, screening excellent DH plants for performing selfing, obtaining lots of DH strains with stable botanical traits, high combining ability and large pollen quantity, hybridizing one DH strain serving as a recurrent parent with a cytoplasmic male-sterile source material, breeding to obtain a cytoplasmic male-sterile line CMS091 with excellent comprehensive characters through five-generation backcross transformation, performing trial hybridized combination on the DH strain serving as a male parent and the cytoplasmic male-sterile line CMS091, and obtaining the early ripening disease-resistant stem broccoli.
Owner:安徽三掌柜田园休闲服务有限公司
Method for cultivating actinidia arguta anther into haplobiont
ActiveCN107306793ASimple and fast operationHigh selectivityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureActinidiaBud
The invention provides a method for cultivating actinidia arguta anther into haplobiont. The method comprises the following steps: (A) collecting flower buds developed by actinidia arguta microspores, carrying out low-temperature refrigeration treatment for 1-10 days, and peeling anther; and (B) putting the anther in a callus tissue induction medium for carrying out dark culture for 20 days or more, culturing the anther for 40 days or more in a plant differentiation medium, and finally transferring the anther into a rooting medium for culturing and rooting to obtain the haplobiont. Through the method for cultivating actinidia arguta anther into haplobiont of the embodiment, multiple homozygous breeding materials are provided for breeding of actinidia arguta; selection and breeding materials are provided; meanwhile, an ideal receptor material is provided for the basic theoretical research; compared with the manners such as an in-vitro microspore culturing manner and a somatic chromosome eliminating manner, the anther culturing method is simple and convenient to operate; a method of artificially culturing in-vitro anther is an effective method for obtaining haplobiont of actinidia arguta; the method is extremely worthy of extensive popularization and application.
Owner:INST OF SPECIAL ANIMAL & PLANT SCI OF CAAS
Method for separating and purifying plant tapetum tissue
ActiveCN105602885AResearch organization characteristicsLess impuritiesPlant cellsFiltrationCentrifugation
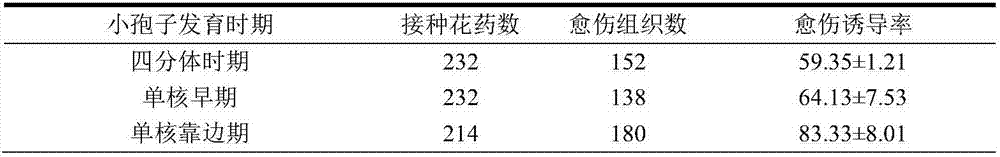
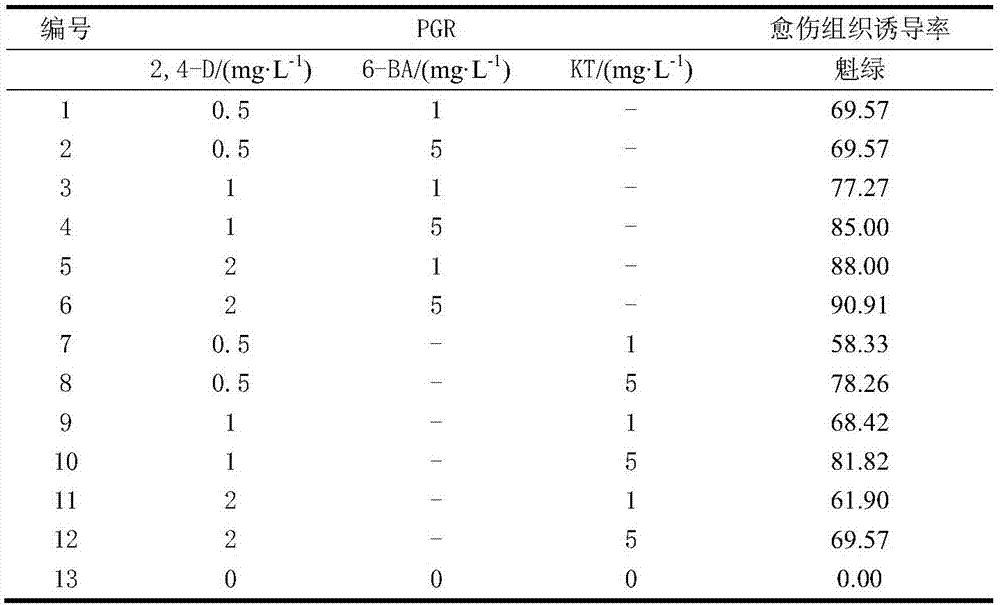
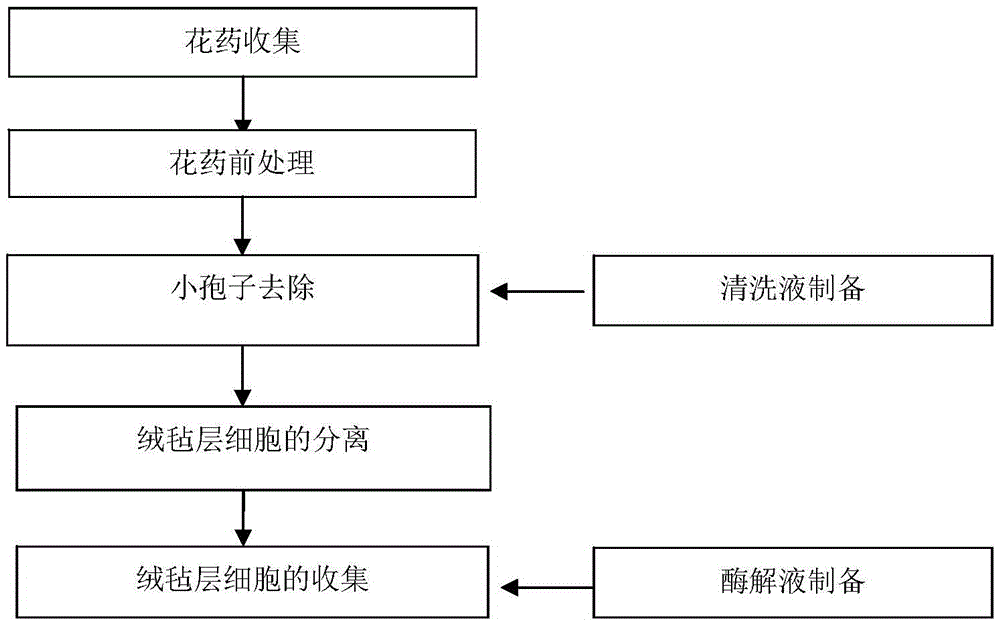
The invention relates to a method for separating and purifying a plant tapetum tissue, and belongs to the fields of developmental biology and cell biology. The method comprises the steps of collection of anthers, preparation of a cleaning liquid, preparation of an enzymolysis liquid, pretreatment of the anthers, removal of anther microspores, and separation and collection of tapetum cells. Suitable enzyme species and concentration are used for enzymolysis separation of a tapetum tissue, and then the tapetum is collected through filtration, centrifugation and purification. The method has the advantages of simple steps, convenient operation, shorter consumed time and the like, the separation efficiency is good, and the obtained tapetum tissue can be used for subsequent experiments.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Method for identifying haploid regenerated by brassica napus microspores simply, conveniently and quickly
InactiveCN102304561AImprove application efficiencyUse impactMicrobiological testing/measurementCuticlePlant cell
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant cytology, and particularly relates to a method for identifying haploid regenerated by brassica napus microspores simply, conveniently and quickly in batch in the early stage in a method of chloroplast counting. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: inoculating an embryoid cultured by in-vitro microspores onto a B5 culture medium; when the embryoid is grown into a complete plant, cutting the fifth even leaf sterilely; dyeing the lower epidermis tissue in the middle of the leaf by using iodine-potassium iodide; observing chloroplasts of guard cells of air vents by using an optical microscope; and recording the number of the chloroplasts of 10 air vents on each prepared leaf (namely the same leaf), wherein more than 7 air vents have 6 to 8 chloroplasts, and the plants of the chloroplasts are the haploid. By the method, the problem of long-time subculture of the haploid is solved, and in ten thousands of plants, the cost of reagents, lands and labors can be saved by 19,083 RMB. The method has a simple process, is easy to operate and low in cost and can be used for identifying the ploidy of a large number of plants, and one plant of seedling is identified only for 5 minutes, so the application efficiency of the double haploid (DH) technology is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Complex breeding method of high-chlorophyll multi-tiller barley
The invention provides a complex breeding method of barley with high chlorophyll content and / or large tiller number, a method for preparing barley green products and a method for improving the chlorophyll content and / or the tiller number of the barley. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: selecting spikelets with barley microspores in development single-nuclear early stage and / or middle stage, and performing treatment at the temperature of 2-10 DEG C for 10-30 days; harvesting the microspores, culturing the microspores and regenerating to obtain a homozygous doubled haploid; culturing the homozygous doubled haploid; and further screening to obtain the barley with the high chlorophyll content and / or the large tiller number, and preparing the barley into the required barley green products. According to the method, a plurality of excellent traits are polymerized through a hybridization technology, a microspore culture technology is utilized to perform fast homozygous stabilization on target traits, multi-index screening is performed under an artificial controllable environment, and a barley germplasm material with high chlorophyll content and multiple tillers is finally obtained. The material can be used as the excellent germplasm material for producing the barley green and other nutritional and health care products in a field planting or water culture way.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for restoring new germplasm by rapidly creating male sterility of processing type hot pepper
InactiveCN106718895AGuaranteed cultivation efficiencyEffectively expandPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsProcessing typeGermplasm
The invention discloses a method for restoring a new germplasm by rapidly creating male sterility of processing type hot pepper. The method comprises the following steps: placing a processing type hot pepper donor parent plant at the temperature of 26.4+ / -0.4 DEG C; performing anther culture and selecting small microspores which are in a mid-late uninucleate stage for inducing the generation of embryoid bodies; taking flower buds before 9 am every day, and performing low-temperature pre-treament on the flower buds for 1 to 3 days in a refrigerator at 4 DEG C; soaking in alcohol under an aseptic condition, then sterilizing, washing with sterile water, and taking anther out from the flower buds and inoculating to an induced culture medium by using tweezers; inoculating weight flower buds in a culture vessel; after the anther is taken out from the flower buds under the sterile condition, uniformly dispersing the anther on the induced culture medium; transferring the induced embryoid bodies to an MS culture medium; when the root length reaches 4 to 5 cm, transplanting, wherein seedling hardening is required to be performed before transplanting. According to the method, the anther culture work is carried out more effectively and conveniently; morphological indexes of sampling flower buds are mastered; operation links are reduced; the anther culture induction efficiency is ensured.
Owner:CHONGQING ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for culturing non-heading Chinese cabbage microspore plantlets
ActiveCN110089426AExtended production timeReduce pollutionHorticulture methodsPlant tissue culturePetalCulture mediums
The invention discloses a method for culturing non-heading Chinese cabbage microspore plantlets. The method comprises the following specific steps of (1) flower bud selection, wherein flower buds withthe number ratio of 1:1 between petals and anthers are selected; (2) culture of microspore derived embryos, wherein the flower buds collected in the step (1) are disinfected by a sodium hypochloritesolution for 10-15 minutes, washed with sterilization water and rinsed by an NLN-13 culture medium; the rinsed flower buds are completely ground, filtered, centrifuged, diluted by the NLN-13 culture medium containing 10-30 mg / L of a boron substance and subpackaged in culture dishes, activated carbon is added, heat shock treatment is conducted, dark culture is conducted at 24-26 DEG C for 14-16 days, and the embryoids are formed; (3) germination into the plantlets from mature embryos, wherein the embryoids are subjected to shake culture, mature embryos turning to green are transferred into a solid MS culture medium for culture, and after 38-42 days of culture, acclimatization and transplant can be directly conducted. According to the method, on the premise of ensuring the embryo formation rate, the operation steps are simplified, the operation time is greatly shortened, and the plantlet production efficiency is improved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for increasing barley microspore culture callus yield and green seedling yield
InactiveCN108401903AIncrease productionEasy to trainHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSporeHordeum vulgare
The invention relates to the technical field of bioengineering, in particular to a method for increasing barley microspore culture callus yield and green seedling yield. The method includes steps: planting barley, and subjecting to low-temperature treatment when seedlings grow to a two-leaf period, namely transplanting in a phytotron after culture at 3-5 DEG C for 28-32 days. The method has advantages that improvement is performed aiming at seedling management in a barley microspore technique, barley seedlings are subjected to low-temperature treatment for a period of time and then transplanted in the phytotron, and accordingly barley microspore culture callus yield and green seedling yield are remarkably increased, and high efficiency in operation of the barley microspore technique is realized. The improvement technique can be applied to barley haploid breeding and haploid transformation.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Culture method for directly obtaining plant by pepper anther and culture medium
ActiveCN103444542APromote formationIncrease release ratePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsPlant cellEmbryo
The invention relates to a culture method for directly obtaining a plant by a pepper anther and a culture medium, and belongs to the field of plant cell engineering. The culture method comprises the steps: (1), selecting a flower bud with microspores in a mid-late uninucleate stage; (2), soaking the flower bud by alcohol with the concentration being 70 percent for 0.5-1min and mercuric chloride with the concentration being1.2 percent for 8-15min, washing for 3-5 times by using sterile water, sucking water to be dry by using sterile filter paper to obtain a sterile anther in the mid-late uninucleate stage; (3), floating the sterile anther in the mid-late uninucleate stage in the liquid culture medium, carrying out dark shake culture for 20-25 days, and then carrying out illumination shake culture; (4), after carrying out illumination shake culture for 10-20 days, transferring a formed cytoledon-stage embryo to an MSO solid culture medium for being cultured, and growing into a normal plant. The culture method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that (1), the induction frequency of a normal embryo is greatly increased, the regeneration frequency of the normal plant is remarkably increased; (2), the operation process is simple, and the plant can be directly obtained from microspores freely dispersing in the liquid culture medium; (3), the culture method is suitable for multiple types of peppers such as cow-horn peppers, capsicum, line peppers and sweetbell redpeppers.
Owner:北京海花生物科技有限公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com