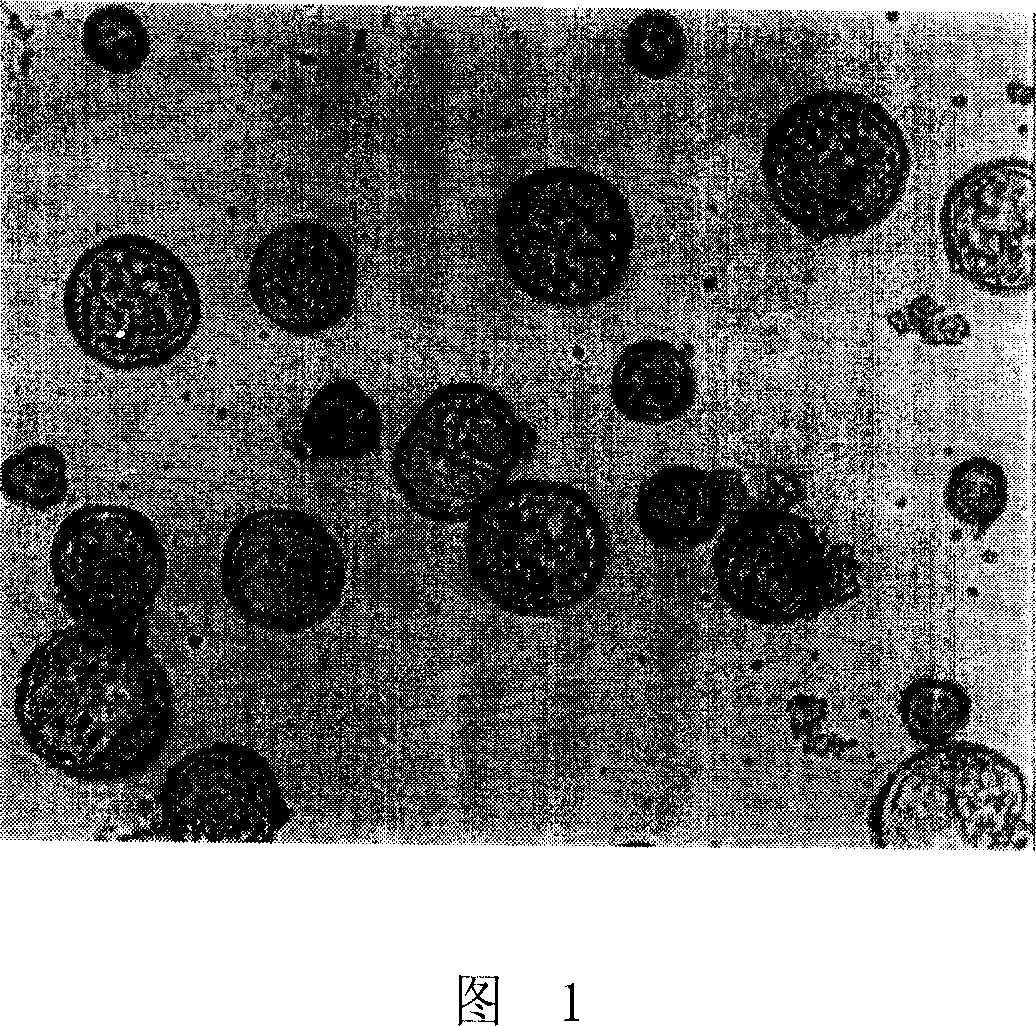
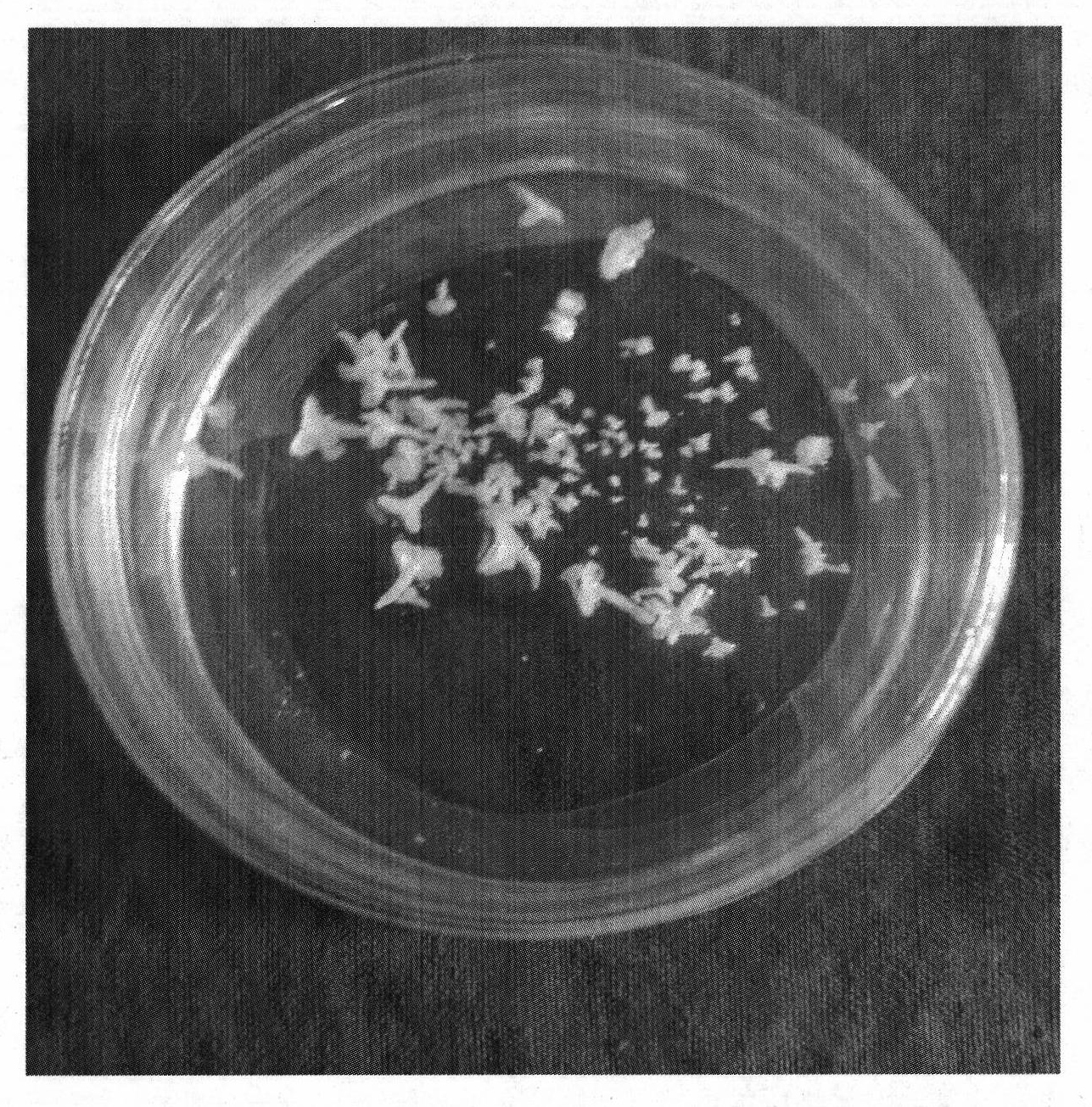
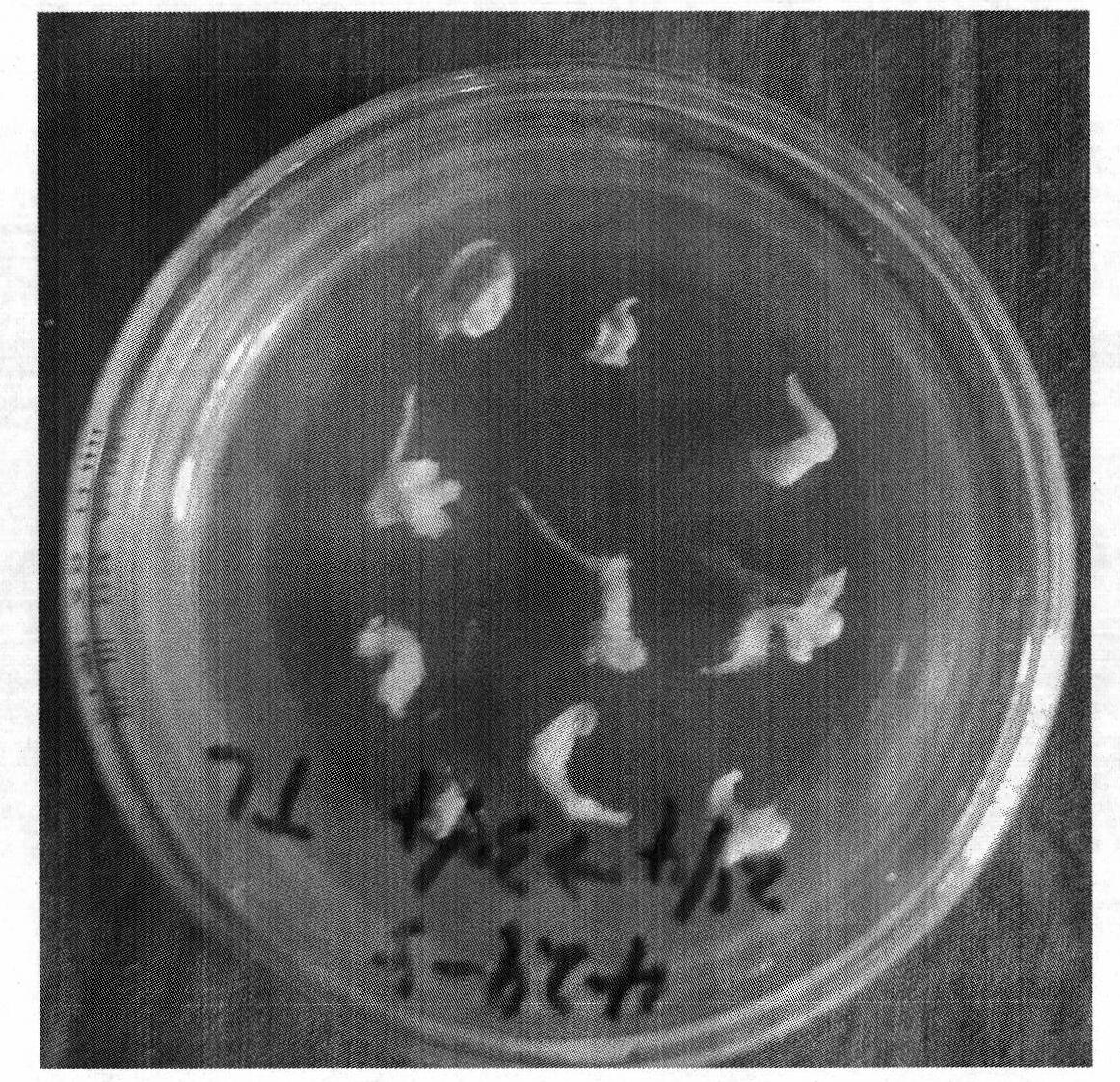
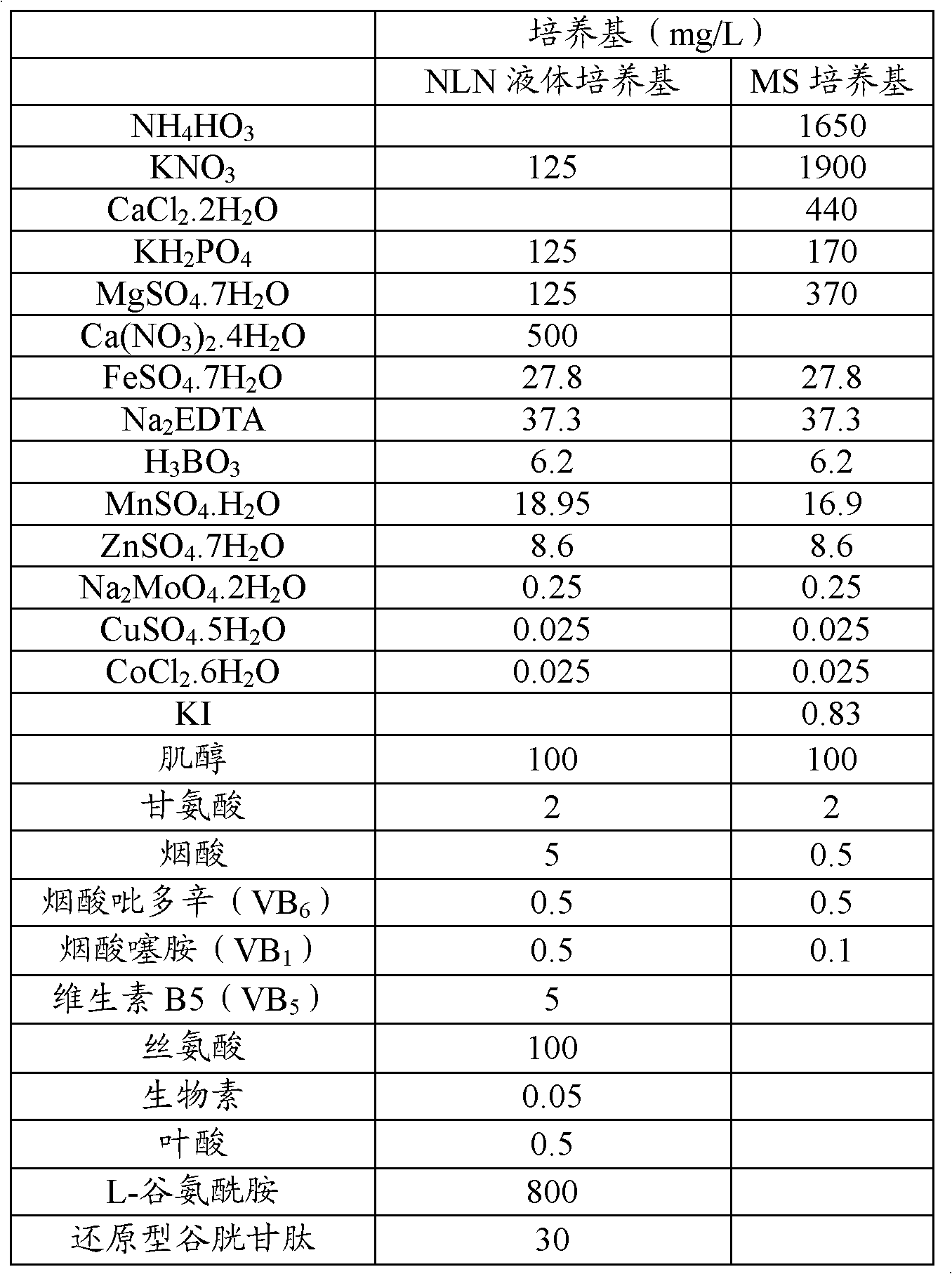
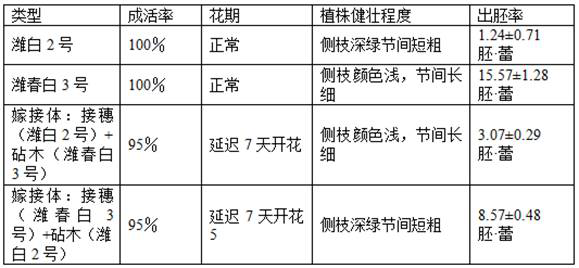
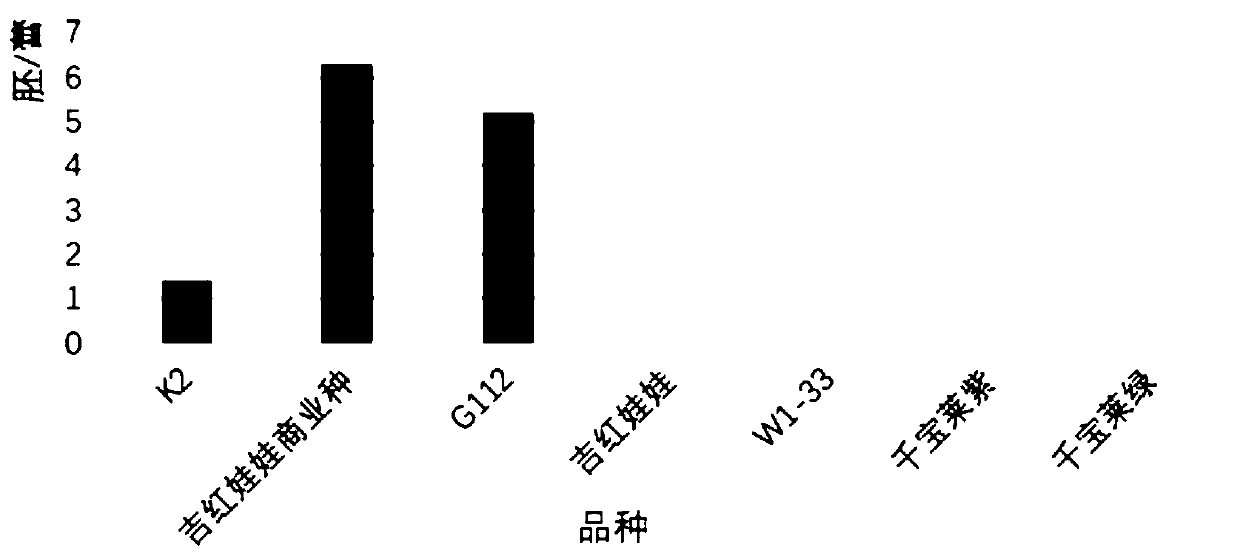
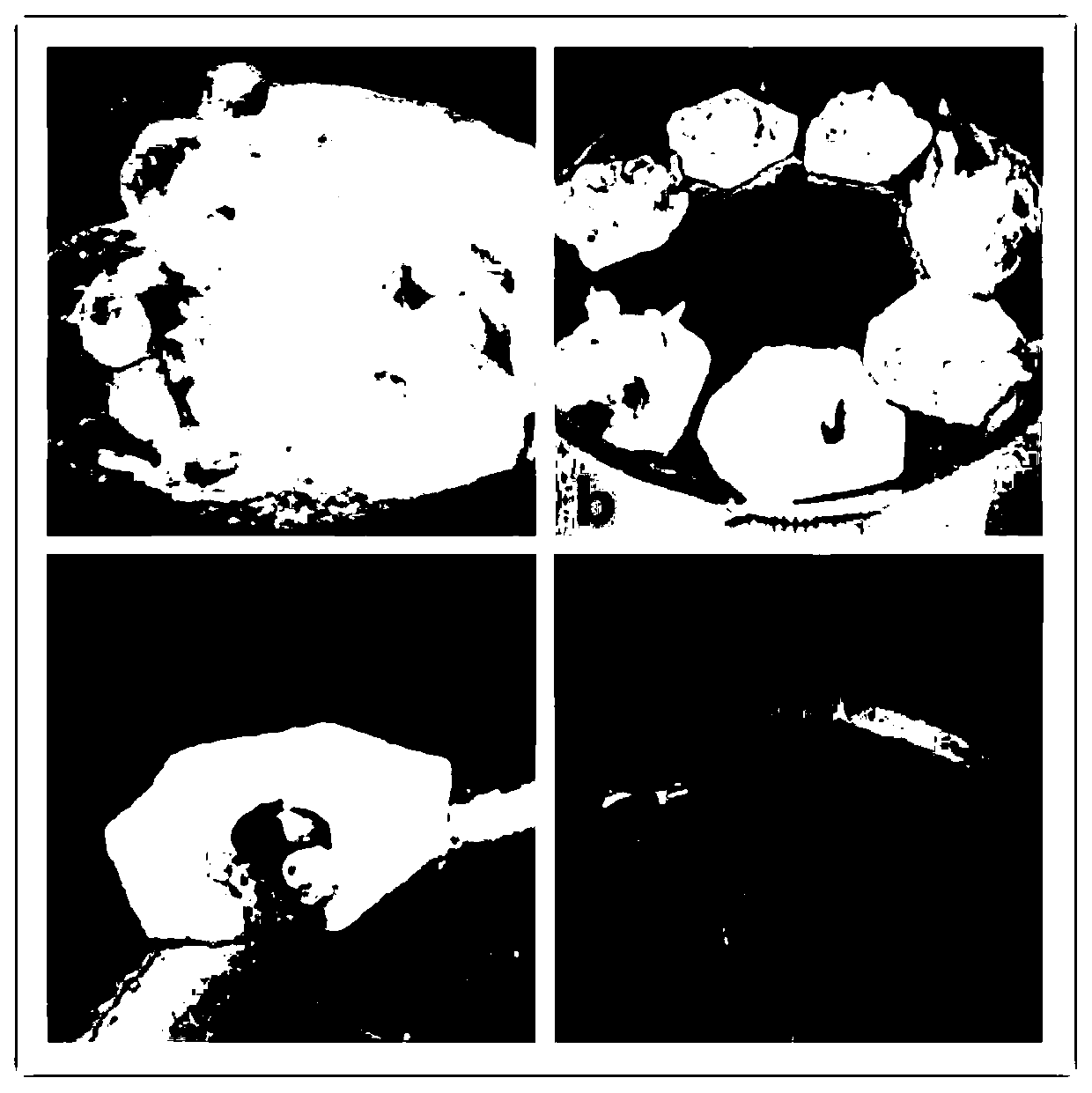
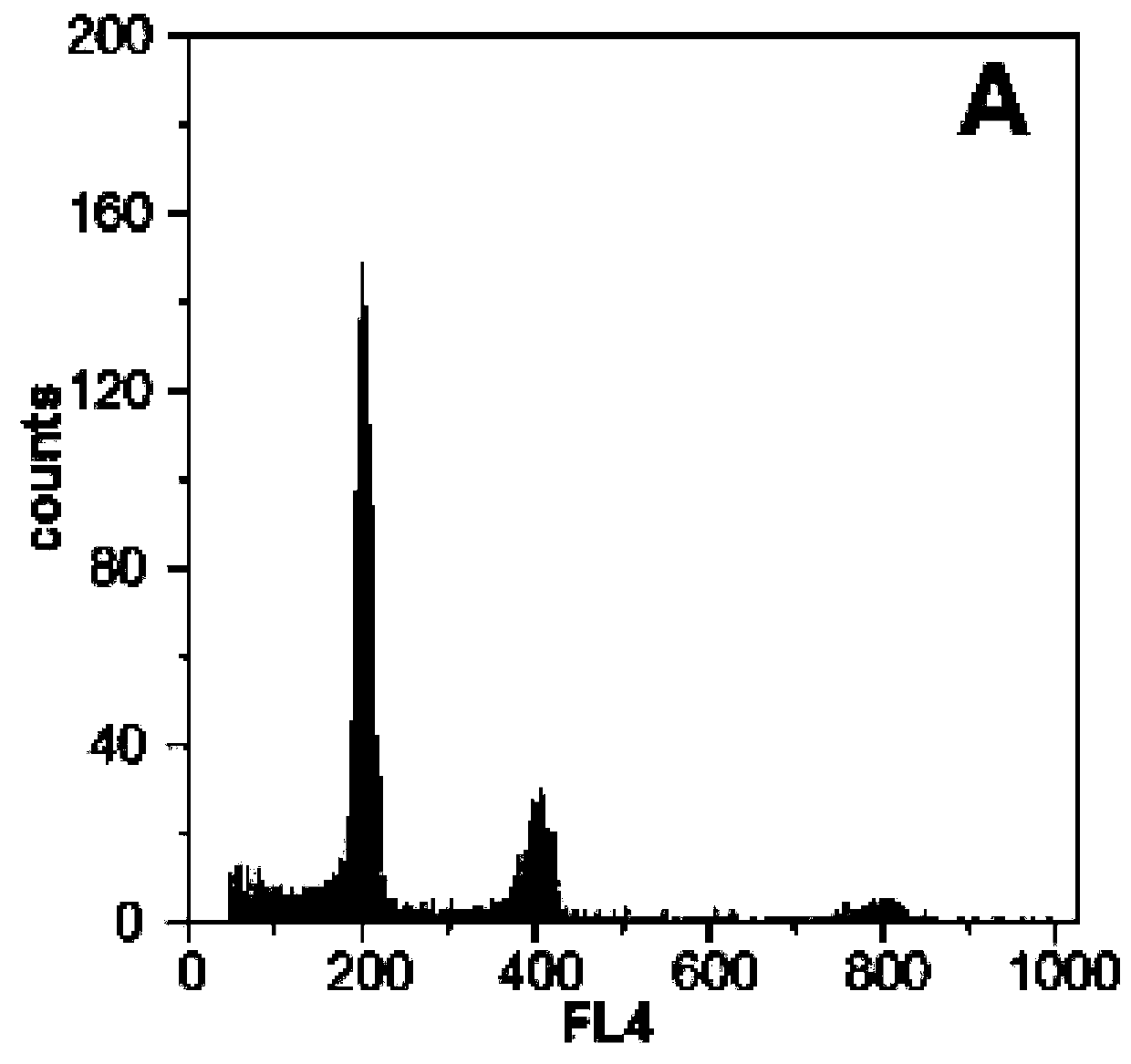
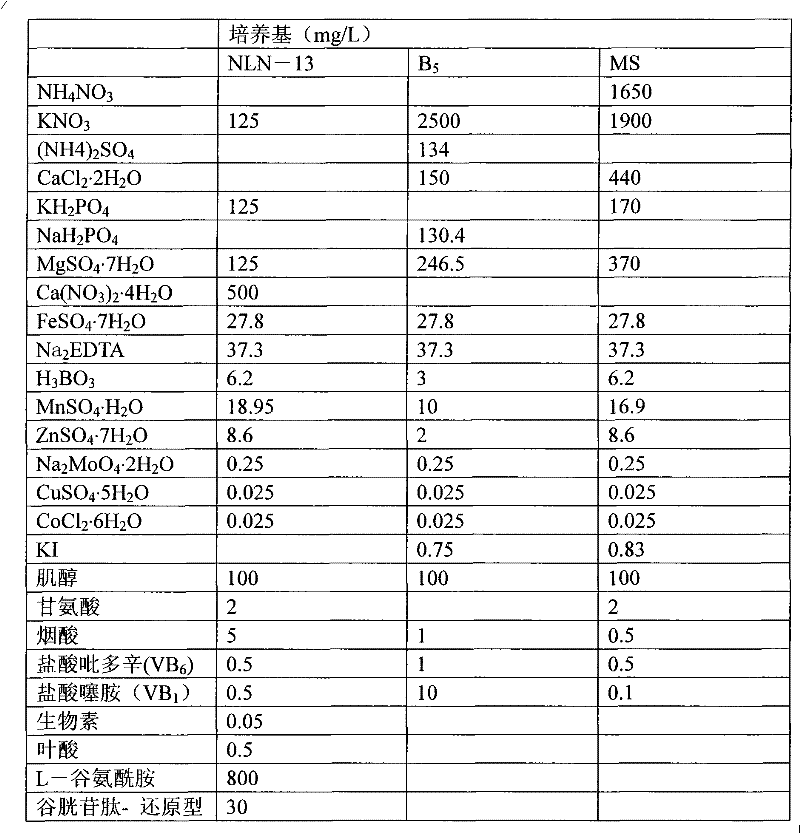
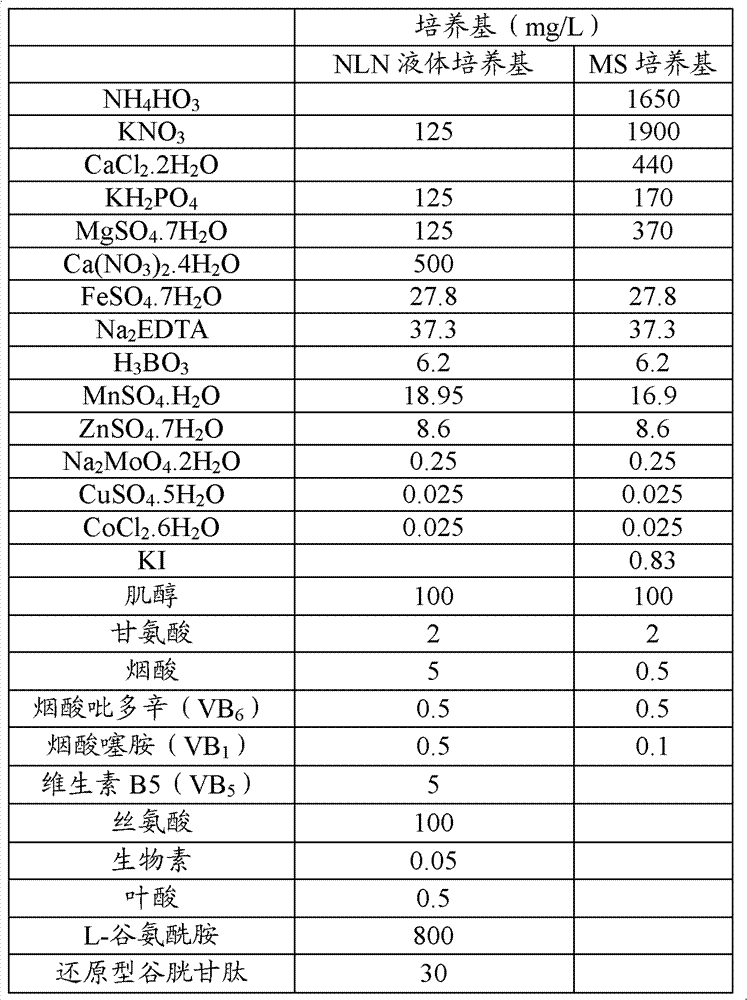
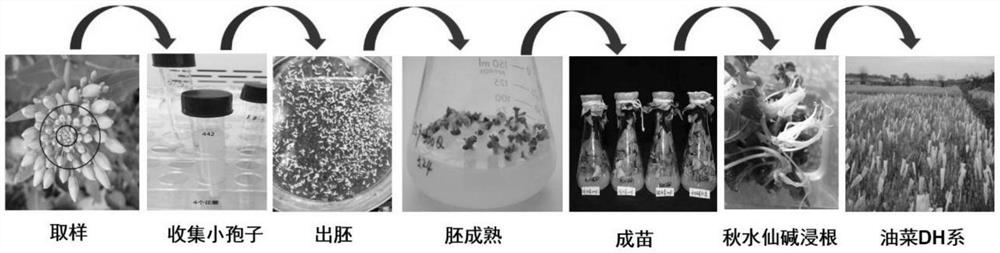
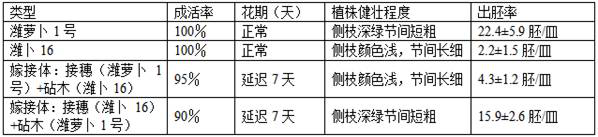
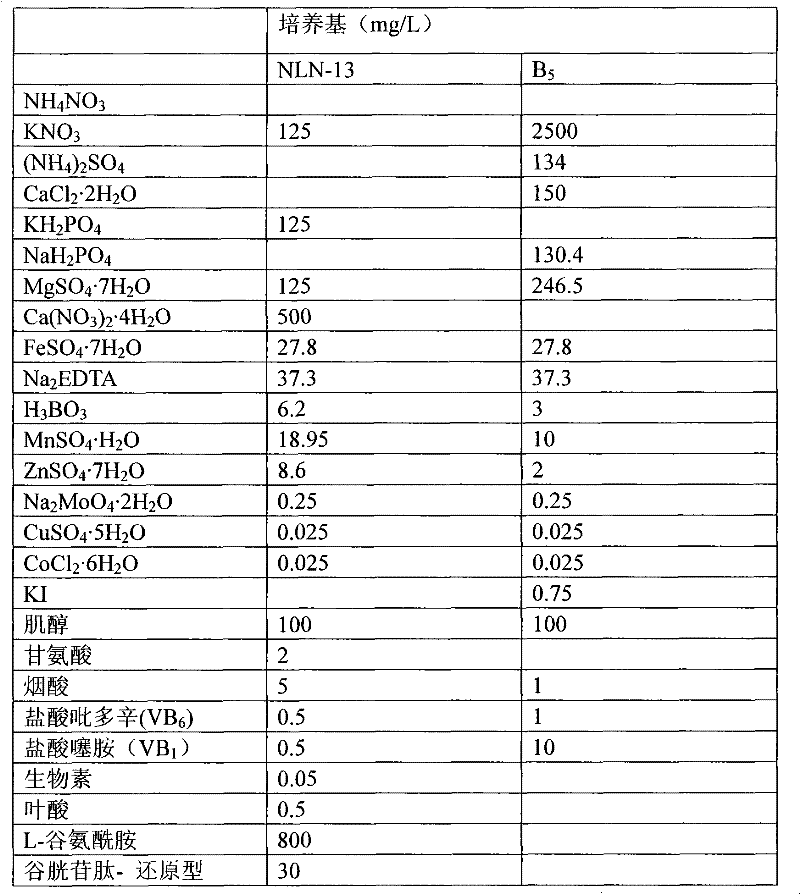
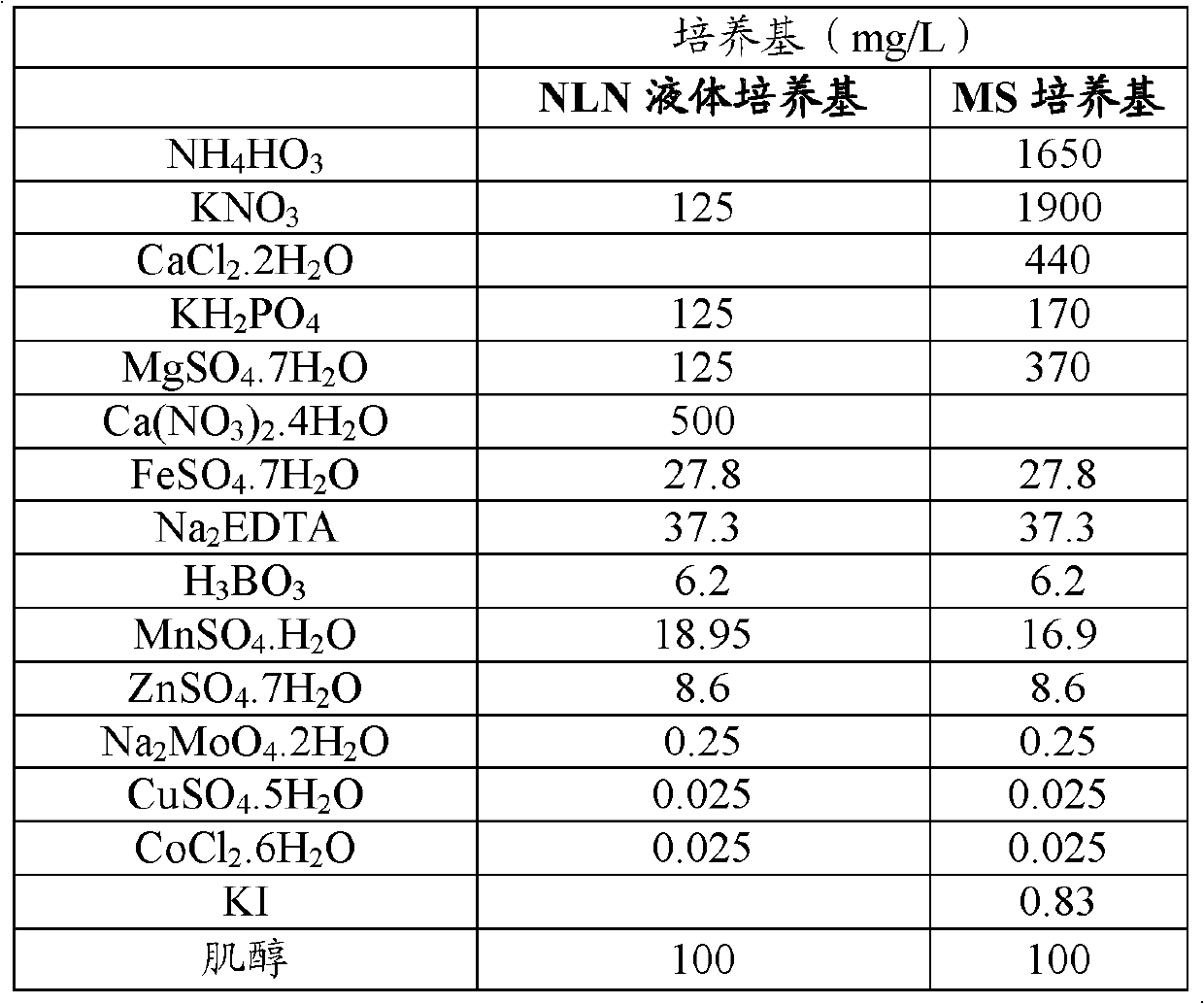
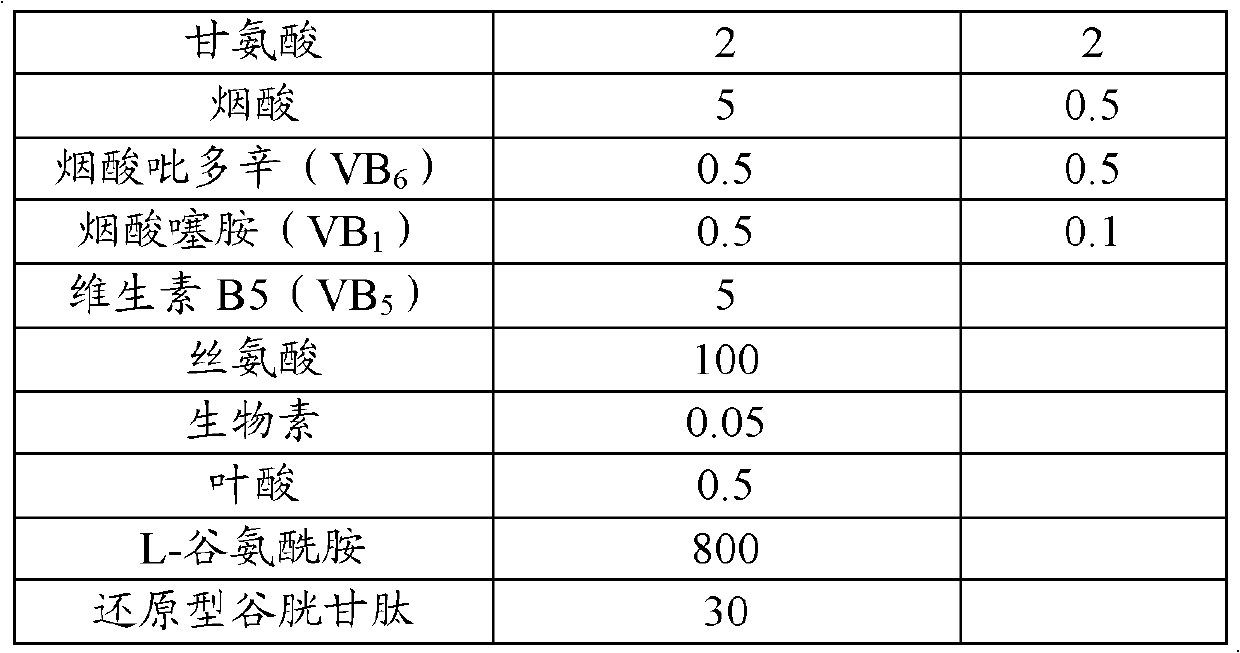
Patents
Literature
30results about How to "Improve embryo emergence rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for obtaining Brassica oleracea var. acephala DC. small spore regenerated plants and special culture medium
InactiveCN1922986AWide adaptabilityImprove embryo emergence rateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSporePlantlet
The invention relates to a method for obtaining collard regenerated plant and special cultivation base. Wherein, said method comprises (1), planting the collard into induced cultivation base, until the density is 5*10<4-5*10<5n / mL, at 30-35Deg.C and in dark, treating it at high temperature for 24-72hours, and under 24-26Deg. C and in dark, inducing idiosome; (2), when the idiosome has been formed, under 24-26Deg. C, 1500-2500Lux, cultivating for 5-10days while each day lights 14-18hours; then grafting the seed into differentiation cultivation base, to be cultivated in same conditions; (3) when grows out branch and leaf, transplanting it into rooting cultivation base, under 24-26Deg. C, 1500-2500Lux, lighting 14-18hours each day, to root, to obtain the collard regenerated plant.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for culturing isolated microspore of common head cabbage to obtain regeneration plant
InactiveCN101773072AImprove embryo emergence rateHigh induction ratePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBudBottle
The invention discloses a method for culturing isolated microspore of a common head cabbage to obtain a regeneration plant, which belongs to the field of biotechnology. The method comprises the following steps: choosing a flower bud of appropriate length, pre-treating the flower bud under the low temperature of 4 DEG C for 24 hours, using the squeezing and pressing method to make the microspore isolated after sterilization, filtering and centrifuging the microspore, suspending the purified microspore in a liquid culture medium, and thermally pre-treating the microspore under the high temperature of 32.5 DEG C for 24 hours and transferring to dark cultivation under the temperature of 25 DEG C for 15-20 days; when a macroscopic embryoid emerges, placing in the sunshine for cultivation for 5-7 days until the emergence of a leaf type embryoid, after the greening of the embryoid, switching to a secondary culture medium for germination and transferring to a root culture medium to root, and obtaining the integrated regeneration plant; and then opening the bottle for hardening off, and hardening and transplanting into a culture pan with sterilization matrix. In case of using the method for cultivation, the embryoid with high frequency can be obtained, the obtained haploid regeneration plant is not only a good breeding material, but also an excellent material for research on molecular markers, genetic mapping, gene clone, trans gene and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Method for culturing regeneration plants of Brassica oleracea microspores
InactiveCN102239803AImprove embryo emergence rateImprove utilization efficiencyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBudPloidy
The invention discloses a method for culturing regeneration plants of Brassica oleracea microspores, which comprises the following steps of: taking flower buds from inflorescences of Brassica oleracea and Brassica napus directly or taking the flower buds from the inflorescences of the Brassica oleracea and the Brassica napus after inducing; sterilizing, adding an induced culture medium NLN-13 to prepare a suspension, filtering to obtain filter liquor, and centrifuging to obtain precipitates; adding the induced culture medium NLN-13 and mixed solution of active carbon sequentially to obtain a microspore suspension; performing heat activation, and culturing to obtain embryoid in the cotyledon stage; inoculating to an embryoid differential medium until the embryoid is differentiated to germinate; cutting regenerated sprouts, inoculating to a rooting culture medium to perform rooting culture, and hardening seedlings and transplanting to obtain the regeneration plants; and taking tender leaves of the regeneration plants to detect the ploidy of the regeneration plants, and identifying regenerated seedlings of the Brassica napus and regenerated seedlings of the Brassica oleracea from a regeneration plant colony. In the method, the Brassica napus of which the embryos are easy to germinate and the Brassica oleracea of which the embryos are difficult to germinate are mixed to be cultured, and materials of which the embryos are easy to germinate drives materials of which the embryos are difficult to germinate to germinate the embryos, so that the embryo growth rate of the Brassica oleracea is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Method for obtaining distant hybridization offspring of common head cabbage and cabbage type rape
InactiveCN108308020ARestore fertilityShorten the rescue induction timeHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureGermplasmBud
The invention provides a method for obtaining a distant hybridization offspring of a common head cabbage and a cabbage type rape, and belongs to the field of biotechnological breeding. The method comprises the steps that (1) a common head cabbage cytoplasmic male sterility is selected to serve as a female parent, a cabbage type rape restorer serves as a male parent, and the female parent and the male parent are isolated after hand pollination is conducted; (2) an ovary after being pollinated for 18-25 days is cut and disinfected; (3) in-vitro culture is conducted for 18-25 days; (4) an ovule in the ovary which is subjected to in-vitro culture is peeled off, and then subjected to induction culture to germinate; (5) differentiation culture is conducted, and a F1 generation seedling is obtained; and (6) a lateral bud of the F1 generation seedling is separated and transplanted onto a rooting medium, and a complete hybridization seedling is obtained. The method utilizes an embryo rescue technique to overcome the problem that the hybridization seedling cannot be obtained due to abortion of a young embryo is prone to occurring in the distant hybridization process of the common head cabbage and the cabbage type rape, an excellent recovery gene of the rape is transferred into a common head cabbage cytoplasmic male sterile cultivated species, the fertility of cabbage is recovered, and the technical evidences are provided for innovation and application of germplasm resources of cabbage.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
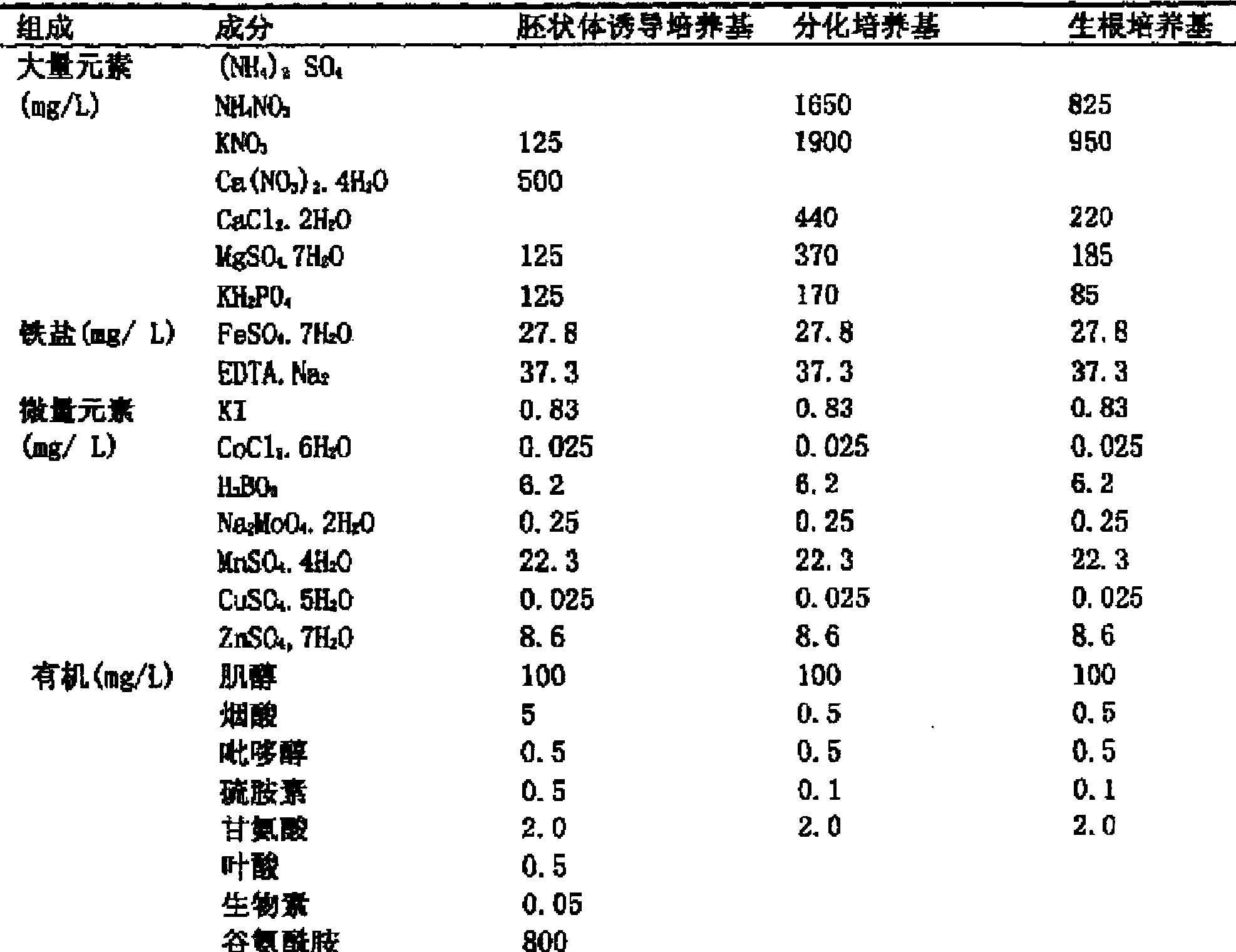
Culture medium prescription of regenerated plant from isolated microspore of brassica
InactiveCN101433184AWide adaptabilityRich breeding resourcesPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSporeBrassica
The invention provides a culture medium formulation for regenerated plantlets of Brassica isolated microspores, which relates to improvement of a culture medium formulation for regenerated plantlets of Brassica microspores as horticultural crops, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The invention provides the culture medium formulation for regenerated plantlets of Brassica isolated microspores, which is high in induced embryo formation rate and differentiation rate. A culture medium of the invention comprises an embryoid induction culture medium, a differentiation culture medium and a rooting culture medium, wherein the embryoid induction culture medium, the differentiation culture medium and the rooting culture medium all comprise macroelements, trace elements and organic elements. The formulation has the advantages of providing a large number of new genotype pure lines for breeding and greatly enriching breeding resources of Brassica.
Owner:刘祥军
Method for improving embryogenesis rate of Raphanus sativus L. sinoruber makino
ActiveCN104186309ASolve the problem of low frequencyImprove embryo emergence rateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureActivated carbonSpore
The invention discloses a method for improving the embryogenesis rate of Raphanus sativus L. sinoruber makino. The method comprises the following steps: sterilizing Raphanus sativus L. sinoruber makino flower buds, then adding B5 wash medium to prepare a suspension liquid, filtering to obtain a filtrate, and centrifuging to obtain precipitate; sequentially adding NLN-13 induction medium and an activated carbon mixed solution to obtain microspore suspension liquid; subpackaging into a sterile culture dish, then adding sterile broccoli anther, performing Parafilm sealing and then conducting heat-shock treatment; performing routine culture to obtain cotyledonous embryoid; inoculating to an embryoid differentiation medium until differentiation is performed, and regenerating buds; cutting and inoculating regenerated buds to a rooting medium for rooting culture, and hardening seedling and transplanting, to obtain regenerated plants. According to the method, the broccoli anther easy to form embryos and the Raphanus sativus L. sinoruber makino isolated microspore difficult to form embryos are mixed for culture according to certain proportion, so that the embryonic development of the Raphanus sativus L. sinoruber makino can be promoted to obtain a great amount of regenerated plants, and the culture efficiency can be improved.
Owner:南京利华农业科技有限公司
Rape microspore culture method utilizing mannitol as osmotic regulator
InactiveCN106718904AImprove solubilityIncrease the doubling ratePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsLiquid mediumBud
The invention discloses a rape microspore culture method utilizing mannitol as an osmotic regulator, belonging to the technical field of plant tissue culture. The method comprises the following steps: fetching cabbage type rape as a donor plant for microspore culture; fetching the flower bud on the donor plant; sterilizing and adding an NLN-13 liquid medium to obtain a suspension; filtering to obtain filtrate, and centrifuging to obtain precipitate; adding a mannitol-containing NLN liquid medium, a colchicine solution and active carbon mixed liquid to obtain a microspore mixed suspension; performing heat shock treatment or direct culture to obtain a cotyledon-stage embryoid; inoculating into a regeneration medium till bud regeneration; cutting the regenerated bud and inoculating to a rooting medium for rooting culture; performing seedling hardening and transplanting to obtain a regenerated plant; and fetching the tender leaves of the regenerated plant and detecting the ploidy of each regenerated plant. Through the method disclosed by the invention, the microspore quality, regeneration rate and doubling rate are remarkably improved.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF BIOENG
Distant hybridization method of common head cabbage and cabbage type rape
InactiveCN108450322ARestore fertilityImprove embryo emergence rateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureFertilityPollination
The invention provides a distant hybridization method of common head cabbage and cabbage type rape and belongs to the field of biotechnological breeding. The method comprises the following steps: (1)selecting cytoplasmic male sterile line cultivated species of common head cabbage as female parents, taking restorer line cultivated species of cabbage type rape as male parents, carrying out artificial pollination and then isolating the female parents and the male parents; (2) cutting ovaries which are pollinated before 15-18 days, and disinfecting the ovaries; (3) peeling ovules of the disinfected ovaries and carrying out induction culture until the ovules are germinated; (4) carrying out differentiation culture of the germinated ovules to obtain an F1 generation of seedlings; and (5) separating lateral buds of the F1 generation of seedlings and inoculating a rooting culture medium with the lateral buds to obtain complete hybridized seedlings. According to the distant hybridization method, an embryo rescue technique is used, the problem that the hybrid plants cannot be obtained because of high possibility of abortion of young embryos when the cultivated species of common head cabbageand cabbage type rape are distantly hybridized can be overcome; excellent restoration genes of the rape are transferred into cytoplasmic male sterile line cultivated species of common head cabbage, so that the fertility of the cabbage can be restored; the technical basis is provided for innovation and application of genetic resources of the cabbage.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
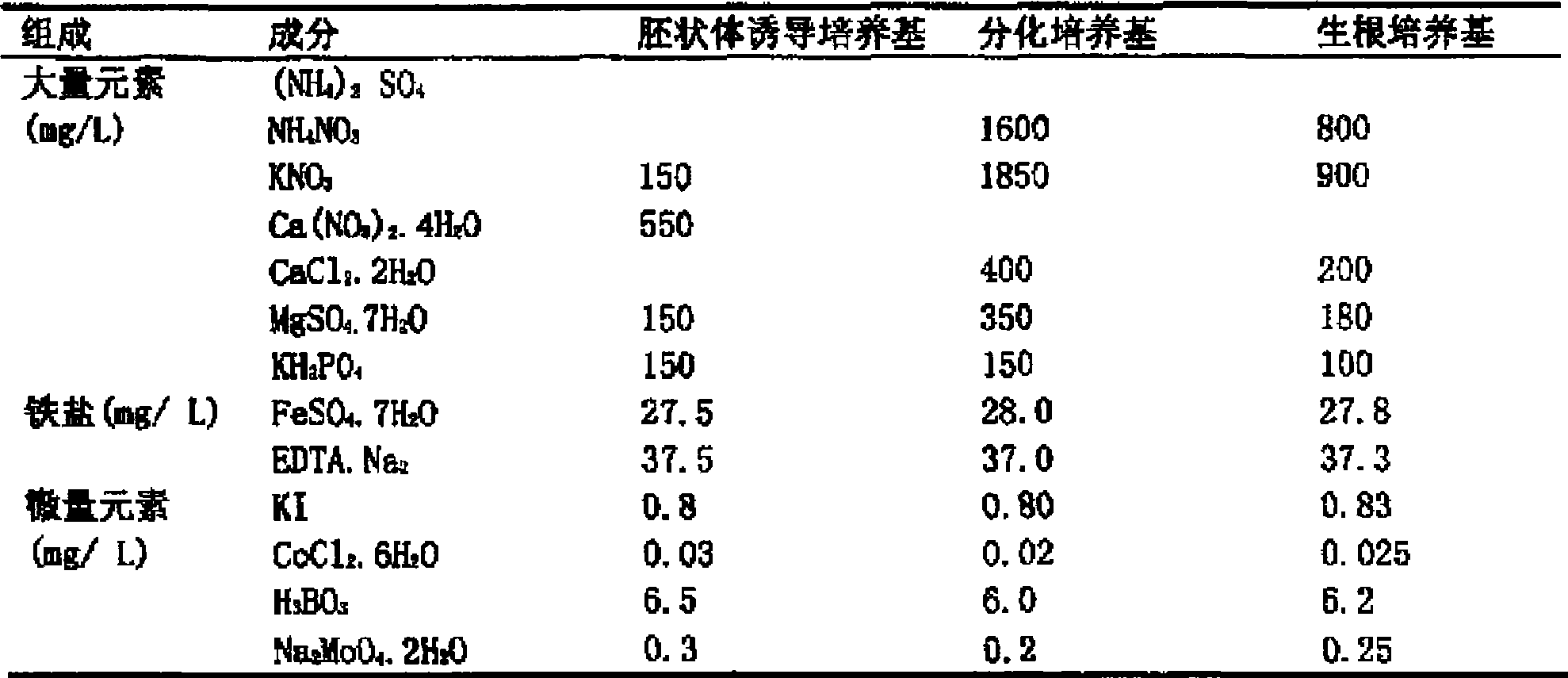
Method for cultivating regenerated plant from isolated microspore of brassica
InactiveCN101433183AWide adaptabilityImprove embryo emergence rateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureHorticultural cropsPlant Microspores
The invention provides a culture method for regenerated plantlets of Brassica isolated microspores, which relates to improvement of a culture technique for regenerated plantlets of Brassica isolated microspores as horticultural crops, and belongs to the field of biological breeding techniques. The invention provides the culture method applicable to regenerated microspore plantlets of Brassica crops. The culture method comprises the following steps: (1) culturing microspores; (2) performing differentiation culture; and (3) performing rooting culture. The culture method has the advantages of providing a large number of new genotype pure lines for breeding, greatly enriching breeding resources of Brassica, accelerating breeding pace, greatly shortening breeding time and having broad application prospects.
Owner:刘祥军
Method for increasing non-heading Chinese cabbage microspore embryo induction rate
InactiveCN109937876AThe effect of high embryo rateImprove embryo emergence ratePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsHeat shockActivated carbon
The invention discloses a method for increasing non-heading Chinese cabbage microspore embryo induction rate. The method includes the steps: (1) flower bud collection; (2) microspore embryo culture: sterilizing, cleaning and rinsing the flower buds collected in the step (1), grinding the rinsed flower buds, filtering and centrifuging the grinded flower buds, diluting yellow-green precipitation bya first culture medium, performing heat shock treatment, and performing dark culture for 14-16 days at the temperature of 24-26 DEG C to form an embryoid; (3) enabling the embryoid to sprout to form aplant. The first culture medium is an NLN-13 culture medium added 0.04-0.08mg / L 6-BA, 10-20mg / L ascorbic acid and 1mg / L activated carbon. According to the method, operation steps are simplified whengerm extraction rate can be ensured, operation time is greatly shortened, and the production efficiency of plants is improved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for improving germplasm creation efficiency of Chinese cabbage
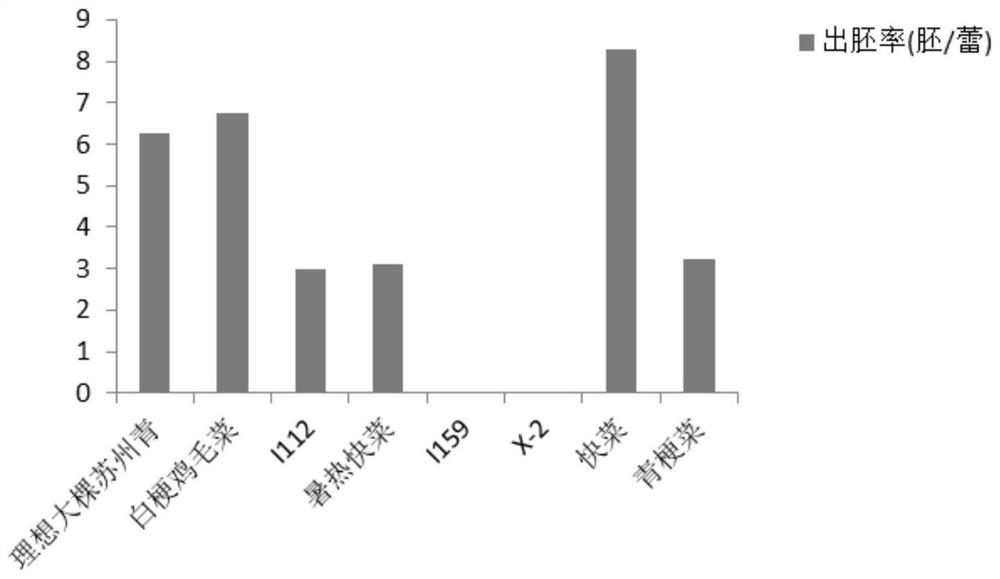
The invention discloses a method for improving the germplasm creation efficiency of Chinese cabbage. The method specifically comprises the following steps: S1, preparation of stocks and scions: selecting a hybrid variety with a large root as a stock material, selecting a bolting-resistant spring Chinese cabbage hybrid variety as a scion material, and sowing and vernalizing stock and scion seeds; S2, field planting; S3, grafting environment management: enabling plants to grow by controlling the environment temperature to be 15-20 DEG C, and irrigating roots with a chlormequat chloride diluent when the plants sprout for 20 cm; S4, grafting condition selection: taking second primary branches of the stocks as grafting parts, and selecting primary branches with the length of 6-10 cm as the scion; S5, grafting: grafting scion buds on the stock plants; and S6, management after grafting: after grafting is completed, managing grafted plants by controlling the growth environment temperature. The method can effectively improve the embryogenesis rate of free microspores of the material difficult to embryogenesis, accelerate the purification speed of the Chinese cabbage material and improve the germplasm creation efficiency.
Owner:SHANDONG WEIFANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Method for cultivating non-heading Chinese cabbage microspore plants
InactiveCN110547193AEmbryo effectExtended production timePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsEthylmethane SulfonateEmbryo
The invention discloses a method for cultivating non-heading Chinese cabbage microspore plants. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting flower buds; (2) cultivating microspore derivedembryos, wherein the flower buds are sterilized and washed and rinsed with a 1 / 2NLN-13 culture medium; the rinsed flower buds are added into the 1 / 2NLN-13 culture medium and fully ground, filtered andcentrifuged, a yellow-green precipitate is diluted with a NLN-13 culture medium and split-charged into a culture dish after treatment with ethylmethane sulfonate, activated carbon is added into the culture dish to enable the concentration of the activated carbon to be 1 mg / mL, heat shock treatment is carried out, and then dark culture is carried out for 14 days to form embryoid bodies; (3) germinating mature embryos into plants, wherein the embryoid bodies undergo shaking culture, the mature embryos becoming green are transferred to an improved solid 1 / 2MS culture medium for 40 days, and thenacclimatization and transplanting are directly carried out. According to the method, under the condition that the embryo yield can be guaranteed, the operation steps are simplified, the operation time is greatly shortened, and the plant production efficiency is improved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for inducing pumpkin haplobiont and culture medium using induction method
PendingCN109874671AEasy to operateImprove embryo emergence ratePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsMurashige and Skoog mediumAgronomy
The invention discloses a method for inducing a pumpkin haplobiont. The method comprises the following steps that surface disinfection is carried out on an unfertilized ovary of a pumpkin, the parts,without ovule, at two longitudinal ends of the ovary and skin of the ovary are cut off and then the remaining ovary is transversely cut into ovary slices with the thickness of 1-2 mm, and the ovary slices are inoculated into an induction culture medium for induction culture after being sterilized; when an obtained embryo has an obvious morphological upper end and a morphological lower end, the embryo is transplanted into a seedling culture medium for seedling culture until a regenerated plant is obtained; the pumpkin haplobiont is screened out through ploidy identification. The method is easyto operate, the haplobiont can be obtained within 60 days, the embryo yield and the plant regeneration rate are relatively high, the breeding period is shortened, the breeding efficiency is greatly improved, and the haploid rate is high. The invention also provides the induction culture medium. Only one hormone is added on the basis of an MS culture medium, preparation is convenient, the price islow, and the induction culture medium can be effectively applied to unfertilized ovary isolated culture of the pumpkin.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Dihaploid induction method of head cabbage with high efficiency
InactiveCN102204511AWide adaptabilityImprove embryo emergence ratePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBudCell budding
The invention discloses a dihaploid induction method of head cabbage with high efficiency, which belongs to the filed of biological breeding. The method relates to a regeneration of microspore plant of the horticultural plant head cabbage and an improvement of dihaploid induction technology thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting bud and separating microspore; (2) doubling inducing and culturing formed embryo; (3) differencing seedlings and subculturing; (4) cultivating strong seedling rooting. According to the invention, the dihaploid of head cabbage can be applied in a mass production with a large scale, a plurality of novel genetype pure lines can be provided for breeding. The method is affected slightly of the growth environment and genotype, and has the advantages of high embryo generation and embryo formation, good doubling effect, strong growth of seedlings plant, less subculture frequency, strong root and seedings after rooting and high survival rate of the field transplanting.
Owner:陕西省杂交油菜研究中心
Method for cultivating non-heading Chinese cabbage microspore plants
InactiveCN113080065AEasy to operateShorten test timeHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSporelingActivated carbon
The invention discloses a method for cultivating non-heading Chinese cabbage microspore plants. The method for cultivating the non-heading Chinese cabbage microspore plants comprises the following steps of (1) sampling and selecting flower buds; (2) carrying out microspore cultivation, specifically, disinfecting the flower buds with sodium hypochlorite, cleaning the flower buds twice with sterilized water, and rinsing the flower buds with a 1 / 2NLN-13 culture medium; grinding, filtering and centrifuging the rinsed flower buds, diluting yellow-green precipitates with an NLN-13 culture medium, adding activated carbon, adding melatonin, sub-packaging the yellow-green precipitates into 35mm culture dishes, carrying out heat shock at 33 DEG C for 24 hours, and carrying out dark culture for 10 days to form embryoids; and (3) carrying out plant regeneration, specifically, carrying out light-supplementing shaking culture on the embryoids, then transferring the embryoids into an improved solid 1 / 2MS culture medium to be cultured for 50 days, and carrying out acclimatization and transplantation. According to the method for cultivating the non-heading Chinese cabbage microspore plants a part of varieties difficult to germinate can be induced to germinate, the germination rate of varieties easy to germinate is improved, the operation steps are simplified, the test time is shortened, and the survival rate of regenerated plants is improved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Culture method of high diplont rate sporule regeneration plant of broccoli
ActiveCN101617630BImprove embryo emergence rateImprove germination rateCultivating equipmentsPlant tissue cultureSporeEmbryo
The invention discloses a culture method of high diplont rate sporule regeneration plant of broccoli, which belongs to the technical field of plant tissue culture and comprises the following steps: (1), preparing a culture medium; (2), culturing the high diplont rate sporule regeneration plant of broccoli: 1), selecting a donor plant and a bud, 2), sterilizing the bud, 3), pre-treating and culturing the bud, 4), separating, mixing and subpackaging of bud sporule, 5), culturing sporule embryoid, 6), differentiating and culturing a regeneration plant, 7), rooting and transplanting the regeneration plant and 8), detecting ploidy of the regeneration plant. The invention obviously increases the germ extraction rate and the rate of emergence of the sporule culture of the broccoli and the diplont rate of the regeneration plant respectively to 120 embryos / bud, 70 percent and more than 70 percent from common 80 embryos / bud, 50 percent and about 50 percent, thereby improving the breeding efficiency of the broccoli. The method can be popularized and applied to a vegetable breeding department or company.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Method for culturing regeneration plants of Brassica oleracea microspores
InactiveCN102239803BImprove embryo emergence rateImprove utilization efficiencyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsEmbryoPloidy
The invention discloses a method for culturing regeneration plants of Brassica oleracea microspores, which comprises the following steps of: taking flower buds from inflorescences of Brassica oleracea and Brassica napus directly or taking the flower buds from the inflorescences of the Brassica oleracea and the Brassica napus after inducing; sterilizing, adding an induced culture medium NLN-13 to prepare a suspension, filtering to obtain filter liquor, and centrifuging to obtain precipitates; adding the induced culture medium NLN-13 and mixed solution of active carbon sequentially to obtain a microspore suspension; performing heat activation, and culturing to obtain embryoid in the cotyledon stage; inoculating to an embryoid differential medium until the embryoid is differentiated to germinate; cutting regenerated sprouts, inoculating to a rooting culture medium to perform rooting culture, and hardening seedlings and transplanting to obtain the regeneration plants; and taking tender leaves of the regeneration plants to detect the ploidy of the regeneration plants, and identifying regenerated seedlings of the Brassica napus and regenerated seedlings of the Brassica oleracea from a regeneration plant colony. In the method, the Brassica napus of which the embryos are easy to germinate and the Brassica oleracea of which the embryos are difficult to germinate are mixed to be cultured, and materials of which the embryos are easy to germinate drives materials of which the embryos are difficult to germinate to germinate the embryos, so that the embryo growth rate of the Brassica oleracea is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
A kind of high-efficiency cultivation method of rapeseed microspores
InactiveCN108770686BIncrease the doubling rateImprove embryo emergence rateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologySporeling
The invention relates to a method for efficiently cultivating microspores of oilseed rape, comprising the following steps: S1, material selection and bud selection; S2, double culture: pollen is diluted with a NLN-16 liquid medium containing 14-16 mg / L of colchicines for dark culture; S3, embryo induced culture: a uncontaminated NLN-16 pollen suspension obtained after double culture is centrifuged, and the precipitated pollen is diluted with a NLN-13 medium containing 7-8 mg / L of colchicine for dark culture; S4, regeneration seedling cultivation; and S5, seedling transplanting. A high-efficiency technical system for cultivation of oilseed rape microspores is established. By the technique, the embryogenic efficiency, the primary seedling rate and the doubling rate of existing genotype materials which are difficult in embryogenesis can be improved effectively.
Owner:WUHAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
A method for improving the germination rate of free microspores of alfalfa
ActiveCN108633736BImprove embryo emergence rateImprove selection efficiencyHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologySporeling
The invention discloses a method for increasing the germination rate of free microspores of alfalfa, which comprises selecting healthy and pest-free flower buds from donor plants at the full-blooming stage of alfalfa, and selecting flower buds with free microspores in the uninucleated middle stage for cultivation. The invention has the advantages that microspore embryos of alfalfa can be obtained quickly and efficiently, and the embryo emergence rate reaches 44.22 per bud, and the obtained regenerated plants can be used for haploid breeding of alfalfa.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Dihaploid induction method of head cabbage with high efficiency
InactiveCN102204511BHigh expansion rateReduce deadweight lossHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureEmbryoGenotype
The invention discloses a dihaploid induction method of head cabbage with high efficiency, which belongs to the filed of biological breeding. The method relates to a regeneration of microspore plant of the horticultural plant head cabbage and an improvement of dihaploid induction technology thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting bud and separating microspore; (2) doubling inducing and culturing formed embryo; (3) differencing seedlings and subculturing; (4) cultivating strong seedling rooting. According to the invention, the dihaploid of head cabbage can be applied in a mass production with a large scale, a plurality of novel genetype pure lines can be provided for breeding. The method is affected slightly of the growth environment and genotype, and has the advantages of high embryo generation and embryo formation, good doubling effect, strong growth of seedlings plant, less subculture frequency, strong root and seedings after rooting and high survival rate of the field transplanting.
Owner:陕西省杂交油菜研究中心
Method for creating diploid germplasm resources by using tetraploid Chinese cabbages
ActiveCN113940276AImprove embryo emergence rateImprove seedling rateCell culture mediaPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologySporeling
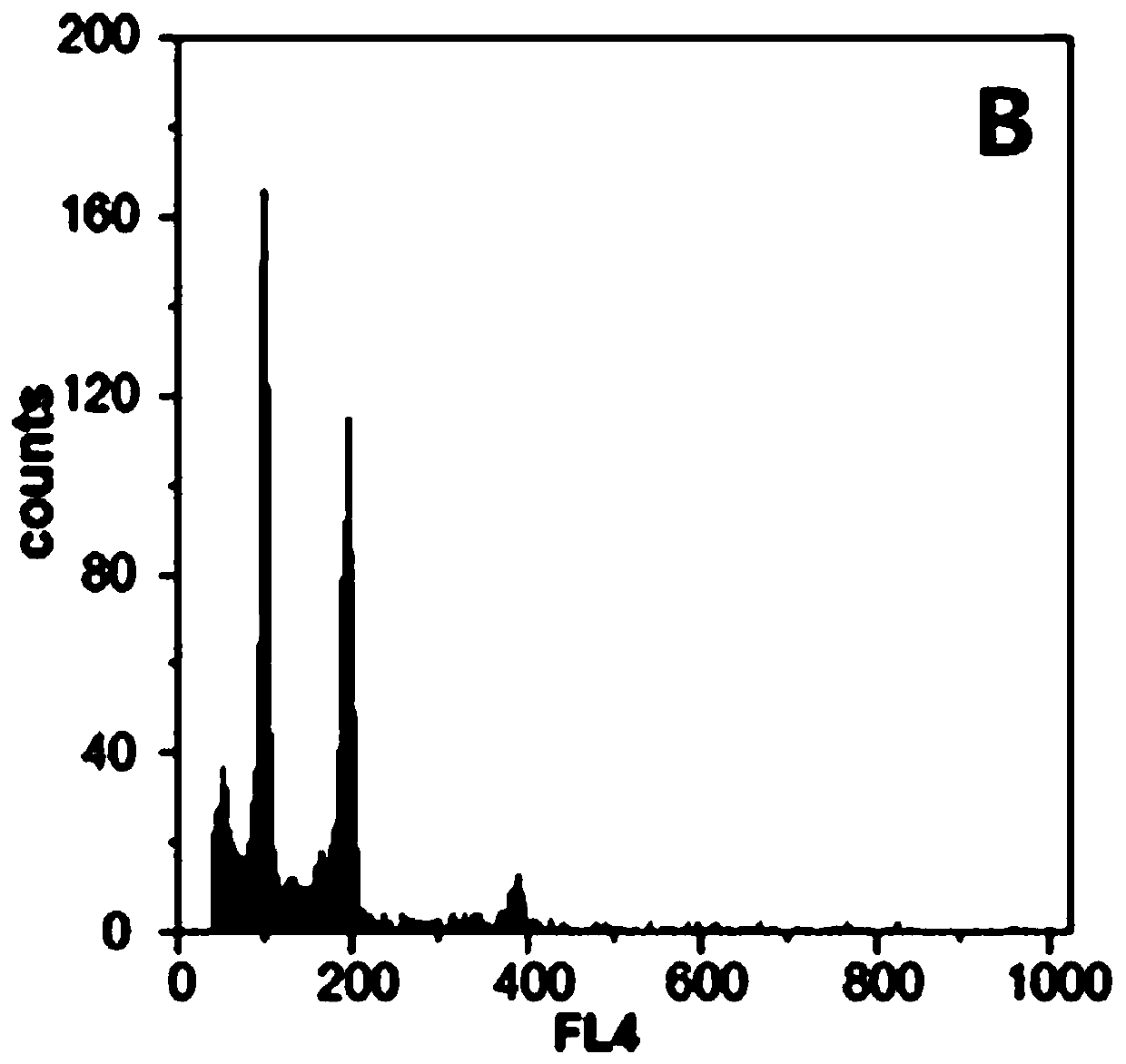
The invention relates to the technical field of Chinese cabbage breeding, and particularly relates to a method for creating diploid germplasm resources by using tetraploid Chinese cabbages. The tetraploid Chinese cabbages are subjected to isolated microspore culture, the obtained tetraploid isolated microspores are subjected to heat shock treatment and dark culture temperature regulation culture to obtain embryoids, and the embryoids are subjected to tissue culture and acclimatization and transplantation to obtain regenerated plants and germplasm resources. According to the method, the advantage that the number of chromosomes of the tetraploid Chinese cabbages is multiplied is utilized, the frequency of interchromosomal gene interchanges is significantly higher than the frequency of diploid intergenic interchanges, and the formed microspore genotypes are richer, so that a new diploid material with more variant characters can be obtained.
Owner:河北省农林科学院经济作物研究所
Simplified efficient culture method for brassica napus microspores
InactiveCN102217532BImprove utilization efficiencyReduce in quantityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBrassicaSpore
The invention relates to a rape microspore culture method and discloses a simplified efficient culture method for brassica napus microspores, belonging to a new plant variety breeding method. Aiming at the problems in conventional brassica napus microspore culture, the technical aspects of sampling period, time and mode, an extracting solution, a culture method, a doubling method, long-distance sterile transportation and the like are respectively improved, so that the efficiency of the brassica napus microspore culture is greatly improved, the culture method and the culture program are simplified, the culture cost is reduced, and the method disclosed by the invention is convenient for popularization and application.
Owner:INST OF IND CROPS HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A method for rapidly obtaining menuploid plants of Violet japonica
ActiveCN104186310BImprove application efficiencyQuality improvementPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSporeHeat shock
The invention discloses a method for rapidly obtaining ploidy plants of Viola japonica, comprising: taking purple cauliflower flower buds, adding B5 washing medium after sterilization to make a suspension, filtering the obtained filtrate to obtain precipitates through centrifugation; adding NLN-13 in sequence The mixture of induction medium and activated carbon was obtained to obtain microspore suspension; it was divided into sterile petri dishes, and sterile cabbage anthers were added, and then heat-shocked after Parafilm sealing; after conventional culture, cotyledon-type embryoid bodies were obtained; inoculated into The embryoid body is kept in the differentiation medium until it is differentiated, and sprouts are regenerated; the regenerated shoots are cut and inoculated on the rooting medium for rooting culture, and the regenerated plants are obtained through hardening and transplanting. In the method, the cabbage anthers which are easy to germinate and the free microspores of purple cauliflower which are difficult to germinate are mixed and cultivated in a certain proportion, thereby promoting the development of the embryos of the violet cauliflower which is difficult to germinate, obtaining a large number of regenerated plants, and improving the culture efficiency.
Owner:天津天隆在田农业科技有限公司
Method for improving embryonic induction rate of free microspores of medicago sativa l
ActiveCN108633736AImprove embryo emergence rateImprove selection efficiencyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBudDisease free
The invention discloses a method for improving the embryonic induction rate of free microspores of medicago sativa l., wherein the method includes the steps: selecting robust disease-free and insect-free flower buds from a donor plant at a full-blossom period of medicago sativa l., selecting flower buds of the free microspores in a mononuclear metaphase, and cultivating. The method has the advantages that the microspore embryos of the medicago sativa l. can be obtained quickly and efficiently, the embryonic induction rate reaches 44.22 per bud, and obtained regenerated plants can be used for haploid breeding of medicago sativa l.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI CAAS
Method for improving germplasm creation efficiency of radish
The invention discloses a method for improving germplasm creation efficiency of radish, which comprises the following steps: S1, preparation of rootstocks and scions: selecting a hybrid variety easy to generate embryos as a rootstock material, selecting a hybrid variety with brittle green skin color and flesh color as a scion material, and sowing and vernalizing rootstock and scion seeds; S2, field planting; S3, grafting environment management: controlling the environment temperature to enable plants to grow, and irrigating roots with a chlormequat chloride diluent; S4, grafting time selection: taking the second and later primary branches of the rootstocks as grafting parts, and selecting primary branches with the length of 6-10 cm as the scions; S5, grafting: grafting the scion buds on rootstock plants; and S6, management after grafting: after grafting is completed, managing grafted plants by controlling the growth environment temperature. The method can effectively improve the embryogenesis rate of free microspores of the material difficult to embryogenesis, accelerate the purification speed of the radish material and improve the germplasm creation efficiency.
Owner:SHANDONG WEIFANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Method for rapidly obtaining haplobiont of Brassica oleracea var. botrytis
ActiveCN104186310AImprove application efficiencyQuality improvementPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAgronomyPlant Microspores
The invention discloses a method for rapidly obtaining haplobiont of Brassica oleracea var. botrytis. The method comprises the following steps: sterilizing Brassica oleracea var. botrytis flower buds, then adding B5 wash medium to prepare a suspension liquid, filtering to obtain a filtrate, and centrifuging to obtain precipitate; sequentially adding an NLN-13 induction medium and activated carbon mixed solution to obtain microspore suspension liquid; subpackaging into a sterile culture dish, then adding sterile brassica oleracea anthers, performing Parafilm sealing and then conducting heat-shock treatment; performing routine culture to obtain cotyledonous embryoid; inoculating to an embryoid differentiation medium until differentiation is performed, and regenerating buds; cutting and inoculating regenerated buds to a rooting medium for rooting culture, hardening seedlings and transplanting, to obtain regenerated plants. According to the method, the brassica oleracea anthers easy to form embryos and the Brassica oleracea var. botrytis isolated microspores difficult to form embryos are mixed for culture according to certain proportion, so that the embryonic development of the Brassica oleracea var. botrytis can be promoted to obtain a great amount of regenerated plants, and the culture efficiency can be improved.
Owner:天津天隆在田农业科技有限公司
Method for obtaining Brassica oleracea var. acephala DC. small spore regenerated plants and special culture medium
InactiveCN100422314CWide adaptabilityImprove embryo emergence ratePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSporeCulture mediums
The invention relates to a method for obtaining collard regenerated plant and special cultivation base. Wherein, said method comprises (1), planting the collard into induced cultivation base, until the density is 5*10<4-5*10<5n / mL, at 30-35Deg.C and in dark, treating it at high temperature for 24-72hours, and under 24-26Deg. C and in dark, inducing idiosome; (2), when the idiosome has been formed, under 24-26Deg. C, 1500-2500Lux, cultivating for 5-10days while each day lights 14-18hours; then grafting the seed into differentiation cultivation base, to be cultivated in same conditions; (3) when grows out branch and leaf, transplanting it into rooting cultivation base, under 24-26Deg. C, 1500-2500Lux, lighting 14-18hours each day, to root, to obtain the collard regenerated plant.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Culture method of high diplont rate sporule regeneration plant of broccoli
InactiveCN101617631BImprove embryo emergence rateImprove germination rateCultivating equipmentsPlant tissue cultureSporePloidy
The invention discloses a culture method of high diplont rate sporule regeneration plant of broccoli, which belongs to the technical field of plant tissue culture and comprises the following steps: (1), preparing a culture medium; (2), culturing the high diplont rate sporule regeneration plant of broccoli: 1), selecting a donor plant and a bud, 2), sterilizing the bud, 3), pre-treating and culturing the bud, 4), separating, mixing and subpackaging of bud sporule, 5), culturing sporule embryoid, 6), differentiating and germinating and culturing a regeneration plant, 7), rooting and transplanting the regeneration plant and 8), detecting ploidy of the regeneration plant. The invention obviously increases the germ extraction rate and the rate of emergence of the sporule culture of the broccoli and the diplont rate of the regeneration plant respectively to 80 embryos / bud, 70 percent and more than 70 percent from common 60 embryos / bud, 50 percent and about 50 percent, thereby improving the breeding efficiency of the broccoli. The method can be popularized and applied to a vegetable breeding department or company.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
A method for improving the embryogenesis rate of rouge radish
ActiveCN104186309BSolve the problem of low frequencyImprove embryo emergence rateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBudCulture mediums
The invention discloses a method for improving the embryogenesis rate of Raphanus sativus L. sinoruber makino. The method comprises the following steps: sterilizing Raphanus sativus L. sinoruber makino flower buds, then adding B5 wash medium to prepare a suspension liquid, filtering to obtain a filtrate, and centrifuging to obtain precipitate; sequentially adding NLN-13 induction medium and an activated carbon mixed solution to obtain microspore suspension liquid; subpackaging into a sterile culture dish, then adding sterile broccoli anther, performing Parafilm sealing and then conducting heat-shock treatment; performing routine culture to obtain cotyledonous embryoid; inoculating to an embryoid differentiation medium until differentiation is performed, and regenerating buds; cutting and inoculating regenerated buds to a rooting medium for rooting culture, and hardening seedling and transplanting, to obtain regenerated plants. According to the method, the broccoli anther easy to form embryos and the Raphanus sativus L. sinoruber makino isolated microspore difficult to form embryos are mixed for culture according to certain proportion, so that the embryonic development of the Raphanus sativus L. sinoruber makino can be promoted to obtain a great amount of regenerated plants, and the culture efficiency can be improved.
Owner:南京利华农业科技有限公司
Culture method for brassica oleracea L. var. acephala microspore regeneration plant
InactiveCN102228003BImprove embryo emergence rateImprove utilization efficiencyHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBudPloidy
The invention discloses a culture method for a brassica oleracea L. var. acephala microspore regeneration plant. The method comprises the following steps: taking inflorescences of brassica oleracea L. var. acephala and rape, directly taking or taking after induction alabastrum of the inflorescences, adding the alabastrum into NLN-13 induced medium after disinfection to form fluid suspension, carrying out filtering, and centrifuging the filtrate to obtain a precipitate; adding NLN-13 induced medium and active carbon mixed liquor in order so as to obtain a microspore fluid suspension; carrying out a heat shock treatment, followed by culturing so as to obtain embryoids in cotyledon stage; inoculating the embryoids to embryoid differential medium until the embryoids are differentiated and regenerates into buds; cutting the regenerated buds to a rooting medium for rooting culture, and hardening and transplanting seedlings to obtain regenerated plants; taking young leaves of the regeneratedplants for the detection of ploidy of corresponding regenerated plants and determining regenerated seedlings of rape and brassica oleracea L. var. acephala in the regenerated plants. According to themethod provided in the invention, rape which is easy to generate embryos and brassica oleracea L. var. acephala which is difficult to generate embryos are mixedly cultured; the material which is easyto generate embryos is used to spur the material which is difficult to generate embryos; therefore the ratio of embryos of brassica oleracea L. var. acephala is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com