Patents
Literature
119 results about "Parafilm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Parafilm is a semi-transparent, flexible film composed of a proprietary blend of waxes and polyolefins. It is a ductile, malleable, non-toxic, tasteless & odorless self-sealing thermoplastic. The name Parafilm is a registered trademark of Bemis Company, Inc, headquartered in Neenah, WI (United States).
Organically modified silica sol and preparation method thereof
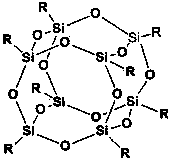
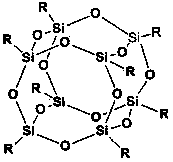
The invention relates to an organically modified silica sol and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps: under stirring, adding organic silicon into an organic solvent to obtain a mixed solution A, wherein the molar ratio of organic silicon to the organic solvent is 1:7-12; under stirring, adding a silane coupling agent, POSS or a hyperbranched polymer, deionized water and a catalyst into the organic solvent, to obtain a mixed solution B, wherein the molar ratio of the modification agent (the hyperbranched polymer, the silane coupling agent or POSS), deionized water, the organic solvent and the catalyst is 1-10:45-55:150-170:0.01-1; under stirring, slowly dropwise adding the mixed solution A into the mixed solution B, transferring the mixed solution into a beaker, sealing a mouth with a parafilm, pricking a plurality of small holes on the parafilm, storing at the room temperature for 1-15 days, and thus obtaining the modified organic silicon sol. The organically modified silica sol and the preparation method thereof have the advantages of simple production process and lower manufacturing cost, the used solvent is the organic solvent, and the field of silica sol application is expanded.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Preparation method of hollow tube filling type heating non-combustible fuming product with sealing film and application
InactiveCN109512022ASimplify the manufacturing processReduce turnoverCigar manufactureTobacco devicesEngineeringFog
The invention provides a preparation method of a hollow tube filling type heating non-combustible fuming product with a sealing film and application. The hollow tube filling type heating non-combustible fuming product with the sealing film is composed of a circular hollow tube, a filter section, a supporting section, an obstruction piece, a fuming section and the sealing film, wherein the circularhollow tube is filled with the filter section, the supporting section, the obstruction piece, the fuming section and the sealing film which are sequentially connected, and the method comprises the steps that the sealing film torn by an easily-heated piece or needle is used for sealing one end of the circular hollow tube at first, then, the circular hollow tube is filled with the fuming section, and then filled with the obstruction piece axially provided with a plurality of through holes, a cavity is reserved behind the obstruction piece as the supporting section, the supporting section is filled with the filter section for sealing, and the fuming product is prepared. The sealing film torn by the easily-heated piece or needle is adopted for being inserted into the fuming section of the fuming product for heating to generate aerial fog, and a consumer sucks heated aerial fog at the near-lip filter section.
Owner:陈征
Aluminium foil sealing film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102700819ADoes not affect ease of peelingImprove cooking temperatureSynthetic resin layered productsSealingPolymer sciencePolyethylene terephthalate glycol
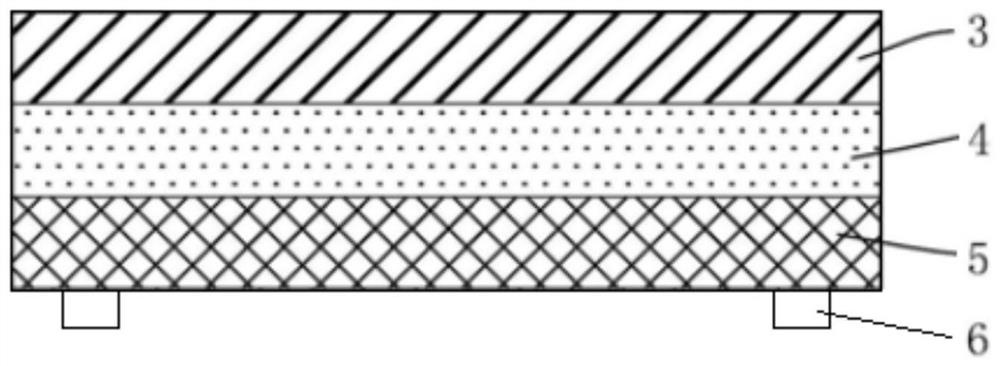
The invention provides an aluminium foil sealing film and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of plastic packaging. The aluminium foil sealing film comprises a protective layer, a separation layer and a heat-seal layer, wherein the protective layer is a gloss oil layer or a PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) film layer; the separation layer is an aluminium foil layer; and the heat-seal layer comprises the materials as follows: 15 to 25 wt% of polybutene, 25 to 35 wt% of ethylene-propylene copolymer and 40 to 60 wt% of HDPE (high-density polyethylene). As a sealing film for the bottle mouth of a polypropylene plastic bottle, the aluminium foil sealing film provided by the invention has the excellent properties of cooking resistance and easiness for uncovering, and when the cooking-resistant temperature is 121 DEG C, the sealing film is unchanged in color and is not stratified. The opening force is 5 to 25 N after the sealing film and the polypropylene bottle are heat-sealed at 200 DEG C, and the heat-seal strength of a heat-seal strip with the width of 15 mm is 5 to 25 N, which shows that the aluminium foil sealing film has the excellent properties of cooking resistance and easiness for uncovering at the same time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GOLDSTONE PACKING
Rice fresh-keeping method
InactiveCN101336743AEasy to eatEnsure hygieneClimate change adaptationFood preservationNitrogenProduct gas
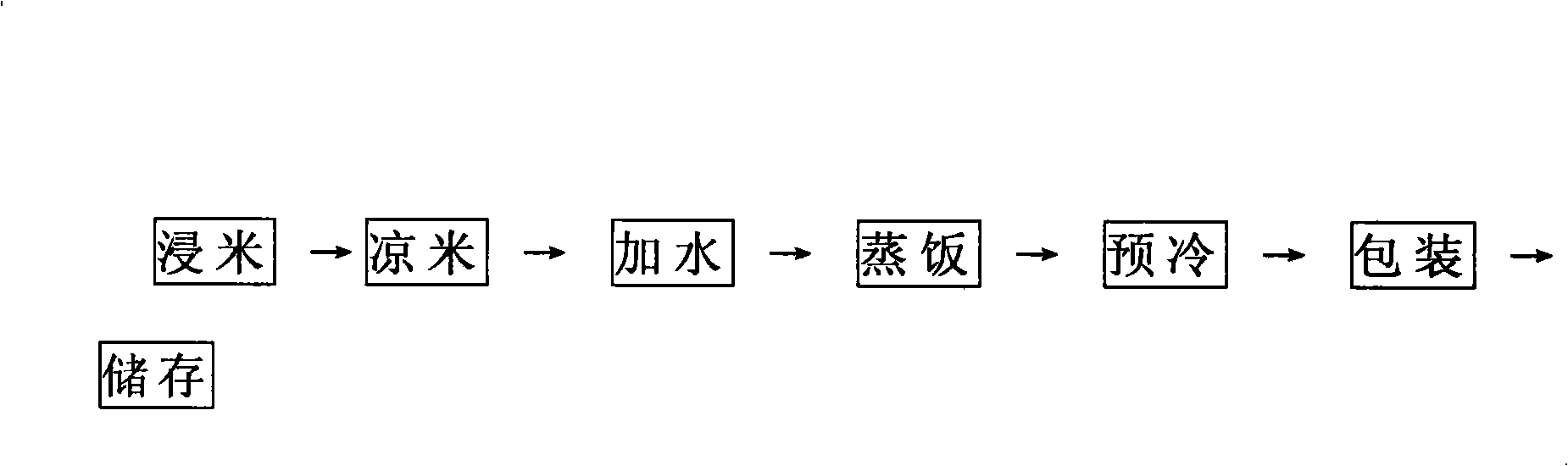
A fresh-keeping method for rice, which belongs to the field of the preservation technology for food, comprising: (1) soaking the rice with water; (2) draining the soaked rice, mixing and stirring evenly the white vinegar of 0.5% density which has 2-4 wt% of the dry rice, and the white sugar of 3-5 wt% of the dry rice[0.5% white vinegar and white sugar, wherein the weight of 0.5% white vinegar is 2-4% of that of the dry rice, the weight of white sugar is 3-5% of that of the dry rice ];(3) mixing the stirred rice with water according to the ratio of 1:1, and putting the rice into a box made of the PP material;(4) steaming the rice under normal pressure.(5) reducing the temperature of the rice to about 6-10 DEG C by vacuum precooling machine in a cleanroom;(6) putting the box onto the atmosphere adjusting machine, vacuumizing, and filling the interval with a mixed gas consisting of nitrogen and carbon dioxide to perform the fresh-keeping packaging, with the PP parafilm wrap as preservative film;(7) storing in the environment at the temperature of 4-8 DEG C. Using the method, the bento produced may be sanitary and convenient, while maintaining the original taste and aroma during a longer storage period.
Owner:杨声盛
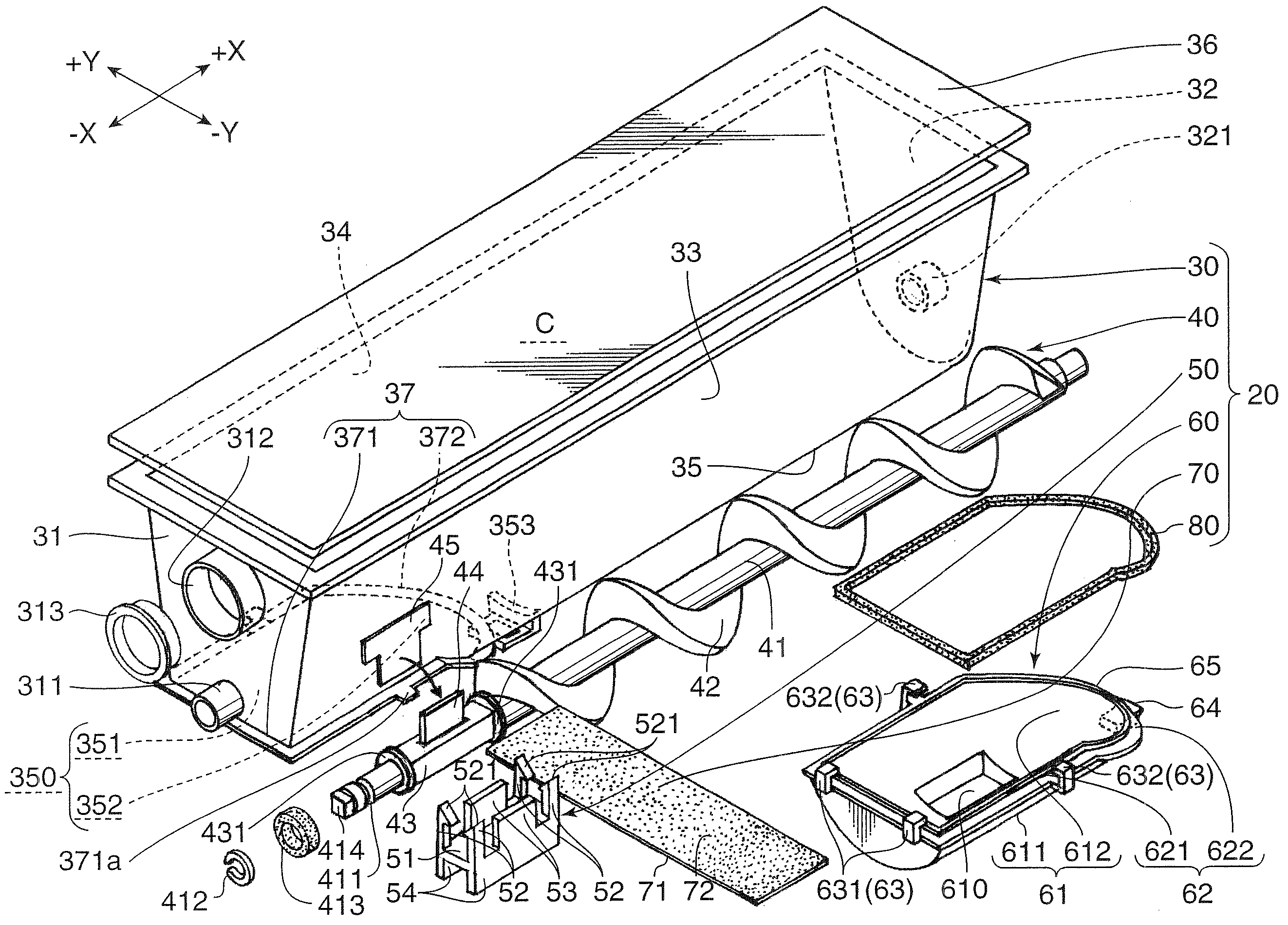
Toner cartridge, toner refilling method and image forming apparatus using the toner cartridge
InactiveUS20080240772A1Easy to reassemblePermit recyclingElectrographic process apparatusToner refillMechanical engineering
A toner cartridge (20) includes a main cartridge body (30) having a housing formed with an opening (350) and also having a rotary shaft (41) supported by the housing for rotation about an axis thereof, a detachable member (60) mounted to the opening (350) and having a toner outlet (610) through which the toner (T) is discharged and a sealing film (70) having a first end so attached to the detachable member (60) as to close the toner outlet (610) and a second end attached to a part of the main cartridge body (30), the first end of the sealing film (70) being peeled off from the detachable member (60) by the rotation of the rotary shaft (41).
Owner:KYOCERA DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS INC
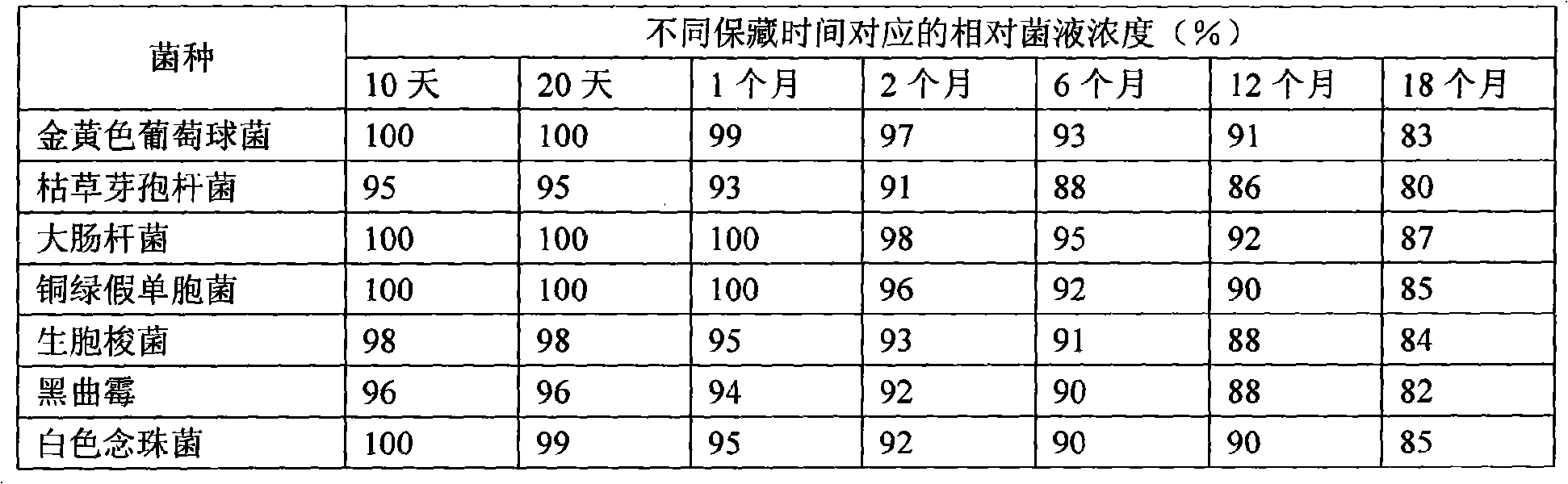
Culture collection process
InactiveCN101307293ALong storage timeStable concentrationMicroorganism based processesMicroorganism preservationRefrigerated temperatureAspergillus niger
The invention provides a spawn preservation method adopting semisolid low-temperature air-tight culture. A spawn is inoculated in an aseptic semisolid culture medium which is vertically stored at an ambient temperature of between 6 and 8 DEG C after aseptic liquid paraffin is added into the culture medium. The spawn is staphylococcus aureus, escherichia coli, pseudomonas aeruginosa, bacillus subtilis, clostridium orogenes, aspergillus niger or candida albicans. The specific process is as follows: preparing the semisolid culture medium, carrying out sub-package and sterilization, and then culturing for 2 to 3 days, inoculating the spawn into the semisolid culture medium in a mode of stab inoculation after asepsis is ensured, with the number of stab inoculation points parallel with the plane of the culture medium being no less than 3; pouring the aseptic liquid paraffin with a height of 1 to 2 cm into the culture medium which is sealed by a sealing film and is stored in a refrigerator at a temperature of between 6 and 8 DEG C. The method can not only prolong the spawn preservation time but also keep a relatively stable spawn concentration, thereby saving much cost for production and test, reducing the treatment and discharge of rejected material after spawn use, and reducing environmental hazard.
Owner:药大制药有限公司
Grafting breeding method for plukenetia volubilis
The invention discloses a grafting breeding method for plukenetia volubilis. Mature plukenetia volubilis seeds are sown in a nutritious cup filled with flower soil to carry out seedling raising; after the seeds sprout and before hypocotyls grow to 5cm and seed leaves completely expand, seedlings are disinfected and the hypocotyls are cut off and are used as rootstocks for later use; plukenetia volubilis sprouts to be grafted are collected to be used as scions and are inserted into notches of the rootstocks and then the junctions of the scions and the rootstocks are wrapped tightly and bundled solidly by Parafilm sealing films; and grafted nursery stocks are moved into a greenhouse and after the wounds at the junctions of the scions and the rootstocks are healed, the seedlings are exercised for one week and then can be moved into the land to be planted. The grafting breeding method has the characteristics that the grafting breeding method is simple to operate, needs a small number of scion materials, has high survival rate, low cost and high growth speed and can be applied to rapid propagation of superior individual plants and fine varieties; a great amount of high-quality nursery stocks can be propagated in short time; and the grafting breeding method has good market application prospect.
Owner:XISHUANGBANNA TROPICAL BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for simple and rapid high-throughout extraction of plant genome DNA
The present invention provides a method for simple and rapid high-throughput extraction of plant genome DNA, and relates to the technical field of a plant complete gene DNA extraction method. A purpose of the present invention is to solve technical problems of high cost, complex operation, low throughput, long time consuming, low purity, easy pollution, and the like in the traditional and existing (2011) plant genome DNA extraction method. According to the present invention, self-preparing reagent formulas are adopted, and an enzyme reagent is not adopted, such that cost is low; liquid nitrogen grinding is not required, such that operation is simple; 384 samples can be performed in one time, such that throughout is high; an extraction process requires only 2.5 hours, such that a consumed time is short; only 0.5 mul of the extracted DNA is required to be adopted as a PCR template, such that purity is high; and a Parafilm film is adopted for sealing, such that characteristics of sealing, leakage resistance, cleaning, and no pollution are provided. In addition, the extracted plant complete genome DNA can be applicable for plant population genetics, phyletic evolution, molecular marker-assisted breeding, deep sequencing, and other researches, and suitable for industrial production and ordinary biological laboratory science researches.
Owner:匡贤彦 +2
Method for separating single fungus spore
The invention discloses a method for separating a single fungus spore. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the method comprises the following steps of: inserting a glass capillary tube into a Pasteur pipet from a tip; enclosing the tip pipe orifice of the Pasteur pipet with a Parafilm sealing film; picking a fungus material to be separated by using a dissecting needle; positioning the center of the pipe orifice of the capillary tube over against and close to the spore; and transferring the spore to be upper side of a culture medium to finish fungus and spore separation, wherein the culture medium is a PDA (Potato Dextrose Agar) culture medium or SDA (Sahli Dextrose Agar) or MEA (Malt Extract Agar) culture medium. The Pasteur pipet is combined with glass capillary tubes of different specifications, so that sucking and transferring operation of various fungus spores is realized. The method has the characteristics of low preparation cost, easiness of manufacturing and operation, convenience for detaching and sterilizing, reusability and the like. Meanwhile, the defect that various conventional methods are unsuitable for separating fungus spores from a liquid environment is made up.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Aluminum box packing machine
InactiveCN101691141AWrapper twisting/gatheringPackaging automatic controlEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses an aluminum box packing machine, which comprises a machine frame, a container conveying belt, an aluminum box feeding device, a filling device, a parafilm holding device and a sealing device. The aluminum box feeding device, the filling device, the parafilm holding device and the sealing device are sequentially arranged along the container conveying belt. The sealing device comprises a box ejecting mechanism for moving an aluminum box away from the container conveying belt, a heat sealing mechanism for sealing the aluminum box and a box moving mechanism for moving the aluminum box moved away by the box ejecting mechanism to the heat sealing mechanism. The heat sealing mechanism comprises a heat sealing device and a heat sealing lower die, wherein the heat sealing lower die is provided with an aluminum box holding hole and a heating device; and the heat sealing device is positioned above the aluminum box holding hole. In the aluminum box packing machine, the aluminum box is placed on the container conveying belt by the aluminum box feeding device, the filling and the parafilm placing are sequentially performed when the aluminum box is conveyed by the container conveying belt, the aluminum box is moved away from the container conveying belt by the box ejecting mechanism in the sealing device and then moved to the heat sealing mechanism by the box moving mechanism to be heated and sealed, the sealed aluminum box is taken out by an aluminum lifting mechanism, and thus, the filling and sealing of the aluminum box are completed.
Owner:GUANGDONG YUEDONG MECHANICAL IND
Grafting survival method of walnut test tube seedlings outside test tube
InactiveCN101911900AReduce pollutionPromote healingHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureOperabilityVertical incision
The invention relates to a walnut seedling cultivating method, in particular to a grafting survival method of walnut test tube seedlings outside a test tube, solving the problems of low propagation coefficient, long seedling growing time, unstable survival rate, and the like of the traditional walnut propagation method. The grafting survival method of the walnut test tube seedlings outside the test tube comprises the following steps of: (1) cultivation of the rootstock seedlings; (2) cultivation of cions, which comprises the obtaining of rootless test tube seedlings and the acclimatization of the rootless test tube seedlings; (3) selection of cortex salicis and preparation and treatment of a growth regulator solution; and (4) grafting comprising the treatment of the cions and the rootstock seedlings: inserting the wedge-shaped parts of the cions into the vertical incisions of the rootstock seedlings during the grafting, then taking out the cortex salicis soaked in the growth regulator solution to wrap the split parts of the rootstock seedlings, and binding from bottom to top by using strip-shaped parafilms. The grafting survival method of the walnut test tube seedlings outside the test tube has fast propagation, can grow the seedlings for one year and enhance the grafting survival rate from 45 percent to more than 85 percent and has the advantages of fast and firm healing of wounds, high operability, simplicity, practicability, low cost, fast propagation, extensive application prospect and obvious economic benefit.
Owner:POMOLOGY INST SHANXI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Aluminium foil sealing film and preparation method thereof
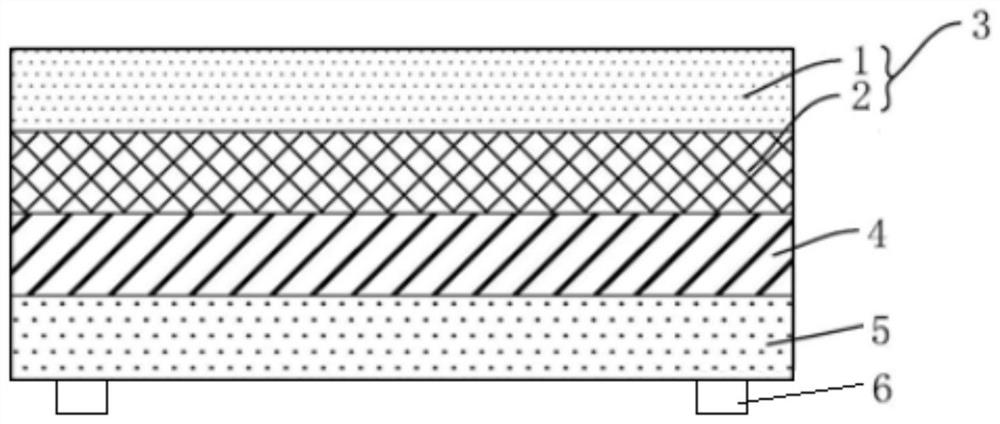
ActiveCN105059707AImprove qualityImprove uniformitySealingMetal layered productsPolypropyleneAluminum foil
The invention provides an aluminium foil sealing film and a preparation method thereof. The aluminium foil sealing film comprises a protective layer, a barrier layer and a heat-sealing layer which are sequentially combined from top to bottom, the protective layer is a gloss oil layer or PET film, the barrier layer is an aluminium foil layer, and the heat-sealing layer is formed by 15-25wt% of polybutylene, 25-50wt% of metallocene LLDPE and 25-60wt% of HDPE. When the aluminium foil sealing film is combined with an opening of a polypropylene plastic bottle, the bonding force is moderate and uniform, the aluminium foil sealing film can be removed easily, the problem that during the transportation process, articles in the polypropylene plastic bottle strike the sealing film, the portion where the bonding force is relatively small can generate an opening easily, and the sealing is failed is avoided, and therefore the quality of the aluminium foil sealing film is greatly improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GOLDSTONE PACKING
A method for establishing a single-plant cloning system of Erythrodonticus through asexual reproduction
The invention discloses a method for establishing a syntrichia caninervis mitt. individual plant cloning system through asexual propagation. The method comprises the following steps: a syntrichia caninervis mitt. pure group is selected, a robustly growing plant is selected and the pure group and the plant are washed and sterilized, then sterilized fine-pointed forceps are used to take the stem tips, stems and stem leaf pieces with strong regeneration capabilities of the treated syntrichia caninervis mitt. individual plant, the stem tips, stems and stem leaf pieces are inoculated to a sterilized BBM solid culture medium and then a culture dish is sealed with a parafilm; the culture dish is put in an illuminating incubator for culture under the conditions that the temperature is 25 DEG C, the illumination intensity is 36mu mol.m<-2>.s<-1> and the light / dark time is 14h / 10h, after culture for 2-3 weeks, new branches will appear on the stem tips, spores and leaf blade bases of the mosses through induction; the protonemata will appear on the stem leaf pieces and new branches will appear when the protonemata are developed to a certain stage; and 2 weeks later, the new branches are takenoff, the stem tips and stems of the new branches are re-transferred to a new solid culture medium and repeated transfer and progressive amplification culture are carried out to form the individual plant cloning system.
Owner:XINJIANG INST OF ECOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cicadellidae insect indoor breeding method and bionic breeding box
The invention relates to the technical field of biological control of insects, and provides a cicadellidae insect indoor breeding method and a bionic breeding box. The bionic breeding box for cicadellidae insect indoor breeding includes a box cover and an opaque box body; air holes are formed in the bottom of the box body; supporting blocks are arranged on an upper inner wall of the box body; a first partition plate is arranged on the supporting blocks; an opening sealing film is arranged on an upper end surface of the first partition plate; a second partition plate is arranged on the opening sealing film; a food holding cavity is formed among the sealing film, the inner wall of the box body, and the second partition plate; leaf-shaped openings are formed in opposite positions of the first partition plate and the second partition plate; and the box cover is arranged on the box body. The breeding method includes: adding a liquid fodder into the bionic breeding box; putting insects in the bionic breeding box; and adjusting the temperature and the humidity. The beneficial effects of the invention are that: the bionic breeding box facilitates leafhopper inhabiting, can induce the leafhopper to eat food, can separate the food from the insects, can simplify operations, and can achieve large-scale breeding.
Owner:TEA RES INST OF FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Processing technology of adhesive tape
InactiveCN104559818AEasy to tearIncrease stickinessNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesLamination ancillary operationsPolymer scienceAdhesive glue
The invention discloses a processing technology of an adhesive tape and relates to the field of chemical technologies. The processing technology of the adhesive tape comprises processes of cutting and polishing, cleaning, fixed-length stitching, punching and preparation and smearing of a pressure-sensitive adhesive. During the fixed-length stitching process, a teflon sealing film is taken and cut into a tape which has equal width as a BOPP original tape, and the tape is placed onto a conveyor; after heated and softened at 60-68 DEG C, the tape is pressed onto the BOPP original tape at the pressure of 1-2 MPa; and BOPP original tapes are pressed at the interval of 10-15 cm on the tape-shaped teflon sealing film so as to obtain a composite film. The technology is simple. A fixed quantity of the tape can be torn. After the BOPP original tape and the sealing film are pressed together, characteristics of the BOPP transparent original tape such as good viscidity, lightness and thinness, etc. can be maintained, and the problem that an opening is not easy to find when in use and fingers easily touch glue so as to influence viscidity can be solved by the use of the sealing film. After the transparent adhesive tape is pasted, the sealing film is stretched, and on the basis of the transparent adhesive tape, the sealing film is coated. Thus, the problem that the sealing film is easy to break is solved, and sealing waterproofness of the transparent adhesive tape is also enhanced. Advantages of both the sealing film and the transparent adhesive tape are combined.
Owner:丹阳恒安化学科技研究所有限公司
Novel culture dish
InactiveCN103436438ASolve problems that require parafilm sealingNo pollution problemBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPetri dishStructural engineering
The invention proposes a novel culture dish which comprises a lower cover equipped with an anti-sliding edge and an upper cover which can be sleeved with the lower cover, wherein a circular groove is formed in the periphery in the inner top surface of the upper cover; a seal ring is arranged in the circular groove; a central step hole is formed in the center of the upper cover; a circular ventilation membrane is arranged on the surface of the central step hole; a membrane pressing piece is arranged on the circular ventilation membrane, and is used for tightly pressing the circular ventilation membrane; ventilation holes are formed in the membrane pressing piece. Through the scheme, the circular groove is formed in the periphery in the inner top surface of the upper cover, the seal ring is arranged in the circular groove, and the ventilation holes and the ventilation membrane are arranged on the upper cover, so that the air inside the culture dish can exchange with the outer air, the culture dish has sufficient air, no pollution is caused, and the long-term problem that a sealing film is needed for the culture dish can be solved.
Owner:海南科晶生物技术有限公司
Transparent easily-torn sealing film and manufacturing method thereof
PendingCN107415382AEasy accessEasy to tearSynthetic resin layered productsDomestic containersPolyethylene terephthalate glycolAdhesive
The invention discloses a transparent easily-torn sealing film and a manufacturing method thereof. The transparent easily-torn sealing film comprises a matrix, wherein the matrix comprises a printing layer, an adhesive layer, a blocking layer and a heat seal layer which are sequentially connected; the printing layer is a polyethylene glycol terephthalate film layer, and the blocking layer is a polyethylene glycol terephthalate film layer. The manufacturing method of the transparent easily-torn sealing film comprises the following steps: (1) manufacturing a blank film; and (2) carrying out ripening. After being subjected to hot seal with a metal cover, the transparent easily-torn sealing film is easy to tear, safe, sanitary, transparent and visual, and packaged objects are conveniently taken out; and safety hazards in the prior art that aluminum scraps fall into mill powder and fingers are scratched by aluminum foils are eliminated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GOLDSTONE PACKING
Method for improving embryogenesis rate of Raphanus sativus L. sinoruber makino
ActiveCN104186309ASolve the problem of low frequencyImprove embryo emergence rateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureActivated carbonSpore
The invention discloses a method for improving the embryogenesis rate of Raphanus sativus L. sinoruber makino. The method comprises the following steps: sterilizing Raphanus sativus L. sinoruber makino flower buds, then adding B5 wash medium to prepare a suspension liquid, filtering to obtain a filtrate, and centrifuging to obtain precipitate; sequentially adding NLN-13 induction medium and an activated carbon mixed solution to obtain microspore suspension liquid; subpackaging into a sterile culture dish, then adding sterile broccoli anther, performing Parafilm sealing and then conducting heat-shock treatment; performing routine culture to obtain cotyledonous embryoid; inoculating to an embryoid differentiation medium until differentiation is performed, and regenerating buds; cutting and inoculating regenerated buds to a rooting medium for rooting culture, and hardening seedling and transplanting, to obtain regenerated plants. According to the method, the broccoli anther easy to form embryos and the Raphanus sativus L. sinoruber makino isolated microspore difficult to form embryos are mixed for culture according to certain proportion, so that the embryonic development of the Raphanus sativus L. sinoruber makino can be promoted to obtain a great amount of regenerated plants, and the culture efficiency can be improved.
Owner:南京利华农业科技有限公司
Device suitable for sogatella furcifera feeding method RNA interference experiment and using method thereof
PendingCN106942162AEasy to takeEasy to observeAccessory food factorsBiotechnologyArthropod mouthparts
The invention discloses a device suitable for a sogatella furcifera feeding method RNA interference experiment. The device comprises a hollow and transparent glass tube, opening sealing layers and a light-proof sleeve, wherein the light-proof sleeve is arranged in the middle of the outer surface of the glass tube in a sleeving mode, the opening sealing layers are arranged at the two ends of the glass tube, fodder layers are arranged on the opening sealing layers, dsRNA and artificial fodder are arranged in the fodder layers, and the dsRNA is double-stranded RNA of a specific gene of sogatella furcifera. A characteristic that insects utilize optical driving is utilized, the sogatella furcifera moves to the two ends of the glass tube and reaches the opening sealing layers, the artificial fodder and the dsRNA are fixed in the opening sealing layers through two layers of films, the sogatella furcifera can pierce thinned Parafilm opening sealing films through mouthparts, and convenience is brought to the sogatella furcifera to take fodder and corresponding dsRNA. In addition, research specialist staff can conveniently observe sogatella furcifera phenotypic change such as death rate, malformation and the like by arranging the transparent glass tube after some gene expression is silenced by a feeding method RNA interference technology, and a sogatella furcifera gene function researching technology can be further obtained.
Owner:ZUNYI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Food automatic packaging film sealing device
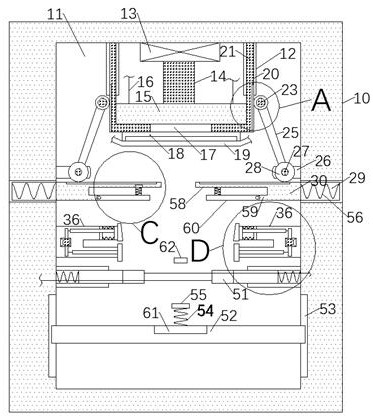
InactiveCN111924171AControl outputEqual quantityPackaging foodstuffsProcess engineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to the field of food processing, in particular to a food automatic packaging film sealing device. The technical problem is to provide the food automatic packaging film sealing device. According to the technical scheme, the food automatic packaging film sealing device includes a machine plate, a box feeding mechanism, a food adding mechanism, an auxiliary mechanism and the like, the auxiliary mechanism and a conveying belt are fixedly connected with the upper end of the machine plate, the conveying belt is located at the bottom of the auxiliary mechanism, and a sealing mechanism is fixedly connected with another side of the upper end of the machine plate. The device replaces the manpower to package food, so that the working efficiency can be effectively improved, meanwhile the device can control the outputting amount of the food, so that the quantity of the food filling food boxes is even, and the device further has the effect that sealing films after being used are recycled so that resources can be saved.
Owner:杜学涵
Device for cyclic spreading of tray sealing film in sealing machines
ActiveUS20150107191A1Reduce consumptionMajor functioning reliabilityWrapper twisting/gatheringStopper pretreatmentElectrical and Electronics engineeringMachine
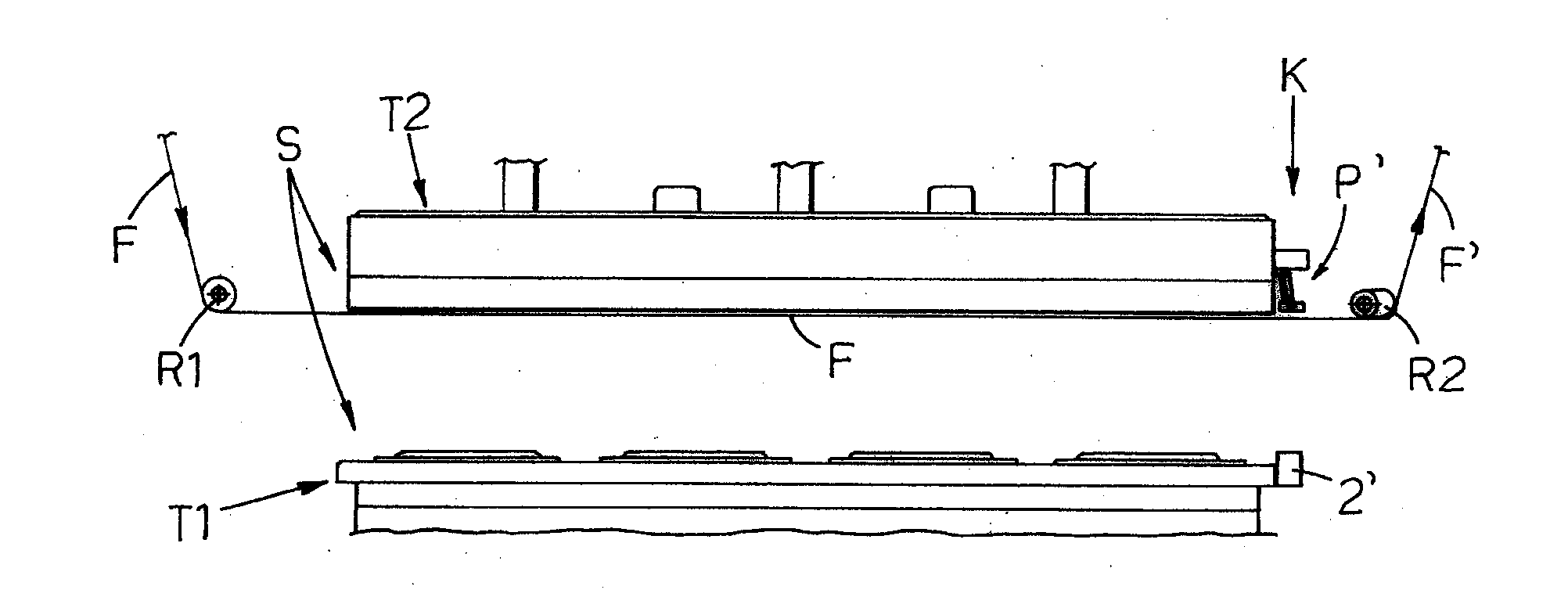
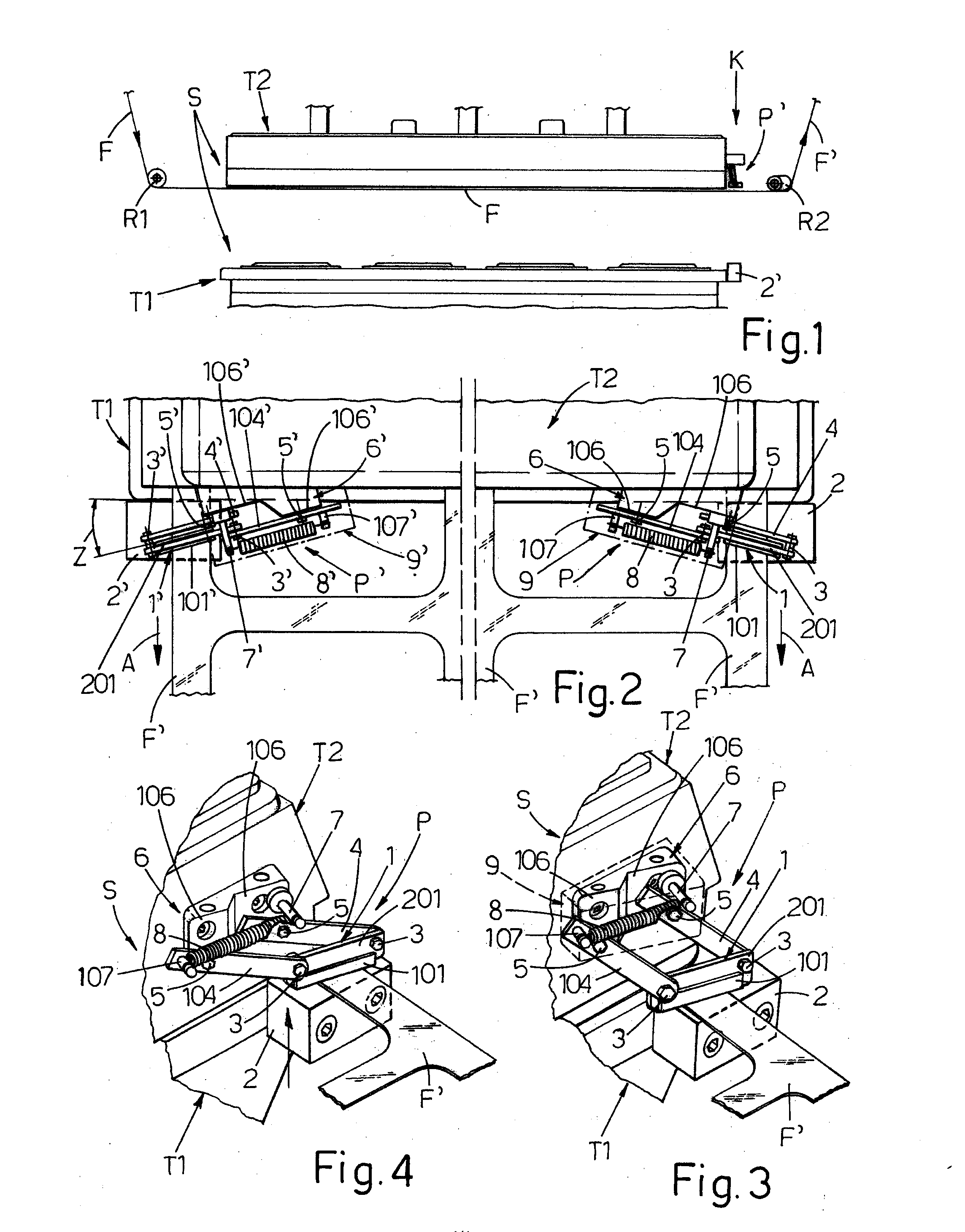
A device for spreading the tray sealing film in so-called tray sealers, in order to avoid the formation of folds in said film (F) which, with the trays, is inserted in a sealing and cutting station (S), between a pair of opposing bells (T1, T2) provided with a relative reciprocal approaching and distancing movement, where downstream of said station (S) means are provided to subject the off-cut of film which exits to a transversal stretching action which ensures correct spreading of said film between said bells, characterized by comprising means for braking the film upstream of said station (S) and comprising pincer means (P, P′) with a jaw (1, 1′) mounted on the side of the upper bell (T2) from which the film exits, turned downwards and vertically opposing a corresponding jaw (2, 2′) mounted on the lower bell (T1), all being envisaged to ensure that in the reciprocal approach and closure step of the two bells (T1, T2), before the film is gripped and blocked between them, longitudinal and lateral portions of the film (F, F′) which are close to the bells are pincered between said opposing pairs of jaws (1, 2, 1′, 2′) of said pincers (P, P′), which firmly grip the film, also due to the presence of counter springs (8, 8′) and friction sliding blocks (101, 101′) and which, due to an inclines and divergent position of them with respect to the direction (A) of advance of the film, subject said film to transversal or preferably transversal and longitudinal stretching, in the same direction of advance (A) indicated above, to spread the film between the bells before their closure on said film.
Owner:GRUPPO FABBRI VIGNOLA
A kind of aluminum foil sealing film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105059707BImprove qualityImprove uniformitySealingMetal layered productsAluminum foilPolypropylene
The invention provides an aluminum foil sealing film and a preparation method thereof, comprising a protective layer, a barrier layer and a heat-sealing layer compounded sequentially from top to bottom, the protective layer is a varnish layer or a PET film, the barrier layer is an aluminum foil layer, The heat-sealing layer is composed of 15-25wt% polybutene, 25-50wt% metallocene LLDPE and 25-60wt% HDPE. When the aluminum foil sealing film of the present invention is combined with the mouth of a polypropylene plastic bottle, the bonding strength is moderate and uniform, and it is easy to unravel, and it will not occur that the items in the polypropylene plastic bottle hit the sealing film during transportation, and the bonding force is relatively high. Small parts are easy to open, leading to the problem of sealing failure, which greatly improves the quality of aluminum foil sealing film.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GOLDSTONE PACKING
Cassava tender stem greenhouse grafting method
The invention provides a cassava tender stem greenhouse grafting method. A stem grafting method is adopted. The grafting method comprises the following steps of (1) stock selection, wherein cassava branches from fields are selected, lignified, inserted into a small basin with sandy soil and used as stocks, and grafting begin to be carried out when the tender branches come out; (2) scion treatment, wherein tender stems with intact and robust bud eyes without damage are selected as scions, and soaked through 0.2 mM / L of naphthalene acetic acid for 15-30 minutes; (3) stock peeling, wherein the tender stock branches with the thickness and the maturity of the scions being basically identical are selected, the opposite side of each bud eye is peeled into a slope which inclines by about 30 degrees and is about 1 cm long; (4) scion peeling, wherein the opposite side of each bud eye is peeled into a slope with the inclination and the length being basically identical with the inclination and the length of the peeled face of each stock; (5) jointing, wherein the stocks are aligned to the scions, after the slopes of the stocks and the scions closely fit, Parafilm opening sealing films are used for binding grafting openings firmly, and fractures of the upper ends of the scions are well sealed to the greatest extent. The method has the advantages that the low is low, the operation is easy, healing time is short, and the survival rate is high.
Owner:TROPICAL CORP STRAIN RESOURCE INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Liquid sealing film for injection molding cup and film coated paper cup and preparation method of liquid sealing film
PendingCN112852335AGood matching of heat sealGood compatibilityHeat-activated film/foil adhesivesLow-density polyethyleneLinear low-density polyethylene
The invention provides a liquid sealing film for an injection molding cup and a film coated paper cup. The liquid sealing film comprises a printing layer, a blocking layer and a heat sealing layer which are sequentially arranged from top to bottom and are fixed in a mutual co-extrusion manner, wherein the heat sealing layer is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 10 to 20 parts of high-density polyethylene, 8 to 15 parts of low-density polyethylene, 25 to 30 parts of linear low-density polyethylene, 5 to 8 parts of ethylene-methacrylic acid copolymer, 8 to 12 parts of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer and 10 to 15 parts of polyolefin plastomer. When the sealing film is combined with cup openings of an injection molding cup and a film coated paper cup, the heat sealing matching performance is good, the combination strength is moderate, the easy-to-tear effect is good, puncture is easily achieved, and impact resistance is good. The sealing film disclosed by the invention can seal two materials, namely a PP injection molding cup and a PE film coated paper cup at the same time, and has certain sealing strength and a certain easy-to-uncover effect at the same time.
Owner:JIANGSU LEATER GREEN PACKAGING CORP LTD
Dyeing method of tetranychid digestion system
InactiveCN106975084AEasy to operateLuminescence/biological staining preparationFluorescenceDigestion
The invention relates to a dyeing method of a tetranychid digestion system. The dyeing method is characterized in that under the conditions of the temperature being 20 to 35 DEG C and the humidity being 75 to 90 percent, 0.05 to 5 percent sodium fluorescein or fuchsine solution is poured into a culture dish; then, the stretched parafilm is sheared into a round shape with the diameter being smaller than that of the culture dish; then, the sheared parafilm is flatly put onto the surface layer of the sodium fluorescein or fuchsine solution contained in the culture dish so that the parafilm floats on the solution in the culture disc; finally, tetranychid after the hungry treatment for 24 to 48 hours is put onto the parafilm; after 2 to 4 hours, the tetranychid digestion system can be observed under fluorescence or microscope. The dyeing method has the advantages that the operation is simple; the practical technical reference can be provided for observing the alimentary tract and the whole digestion system of the tetranychid.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Reaction tube and test kit
PendingCN111876319AAvoid destructionThe connection structure is stableBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStructural engineeringReaction tube
The invention provides a reaction tube and a test kit. The reaction tube comprises a tube body, an upper cover and a first liquid storage cavity, wherein an external thread , a first height indicationpart and a second height indication part are formed in the outer surface of the side wall of the tube body,. The test kit comprises a reaction tube, and a second liquid storage cavity, a sealing film, test paper and a piercing assembly which are sequentially arranged in a shell from bottom to top, an opening is formed in the upper surface of the second liquid storage cavity, and the opening is sealed by the sealing film. After detection is completed, the test paper can be continuously screwed into the reaction tube and pierces the sealing film, the test paper can react with a nucleic acid destroying reagent, and residual nucleic acid in the test kit is completely removed. Therefore, even if the reaction tube accidentally falls off or the test kit is damaged to cause internal exposure in the subsequent process, no pollution is caused.
Owner:象山县第一人民医院医疗健康集团 +3
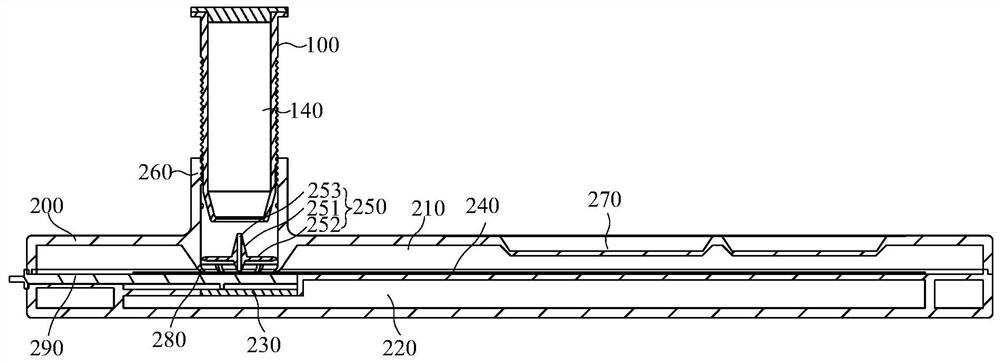
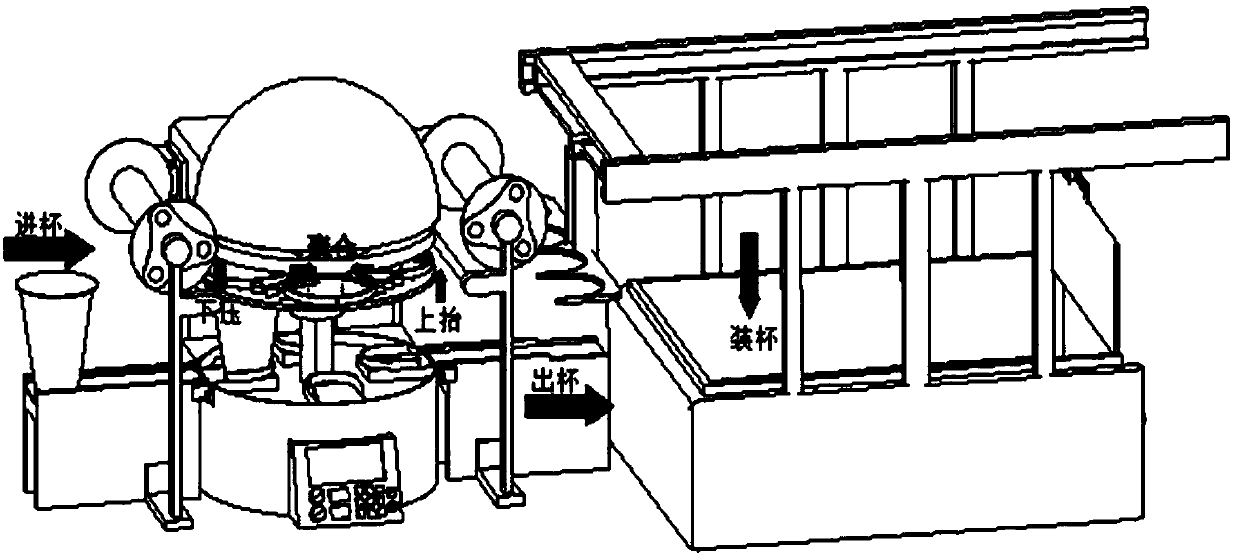
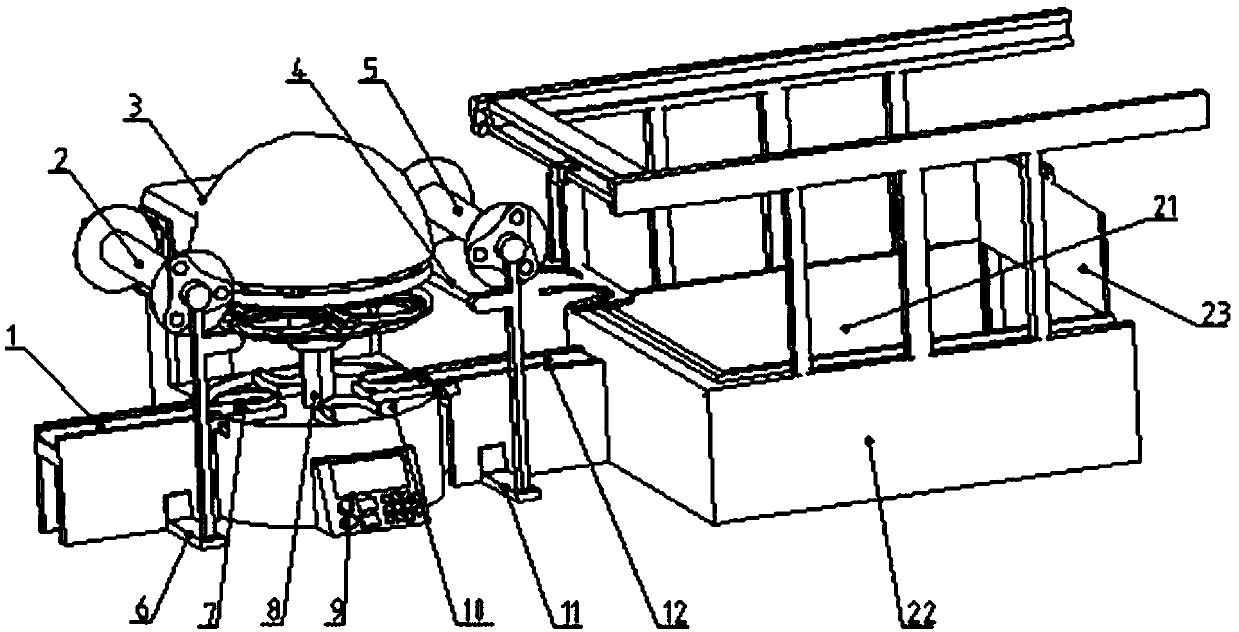
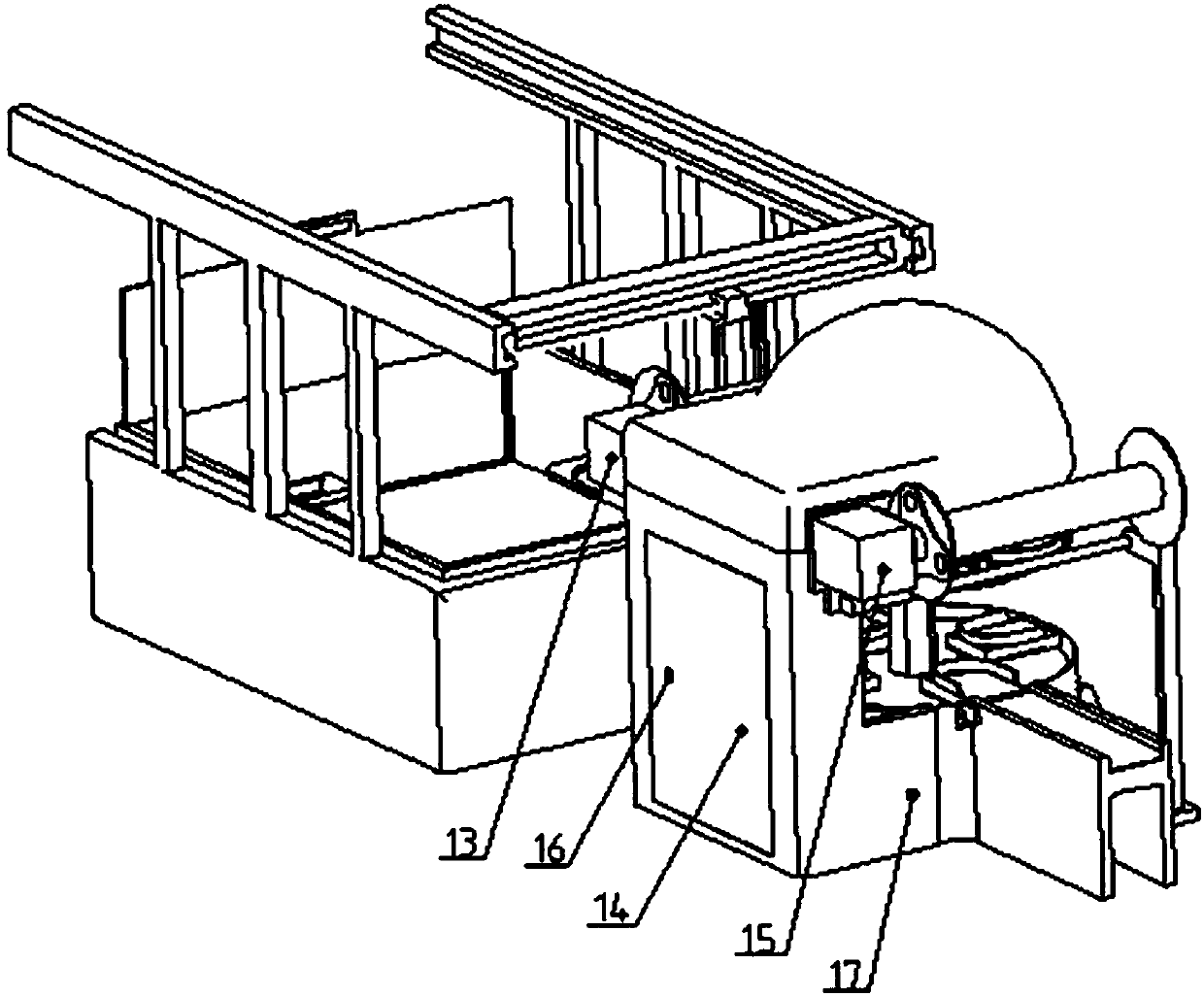
Full-automatic sealing machine and application thereof
ActiveCN107776980AIngenious structural designReduce volumeWrapping material feeding apparatusWrapper twisting/gatheringEngineeringManipulator
The invention relates to a full-automatic sealing machine and application thereof. The full-automatic sealing machine comprises a cup sending portion, a film sending portion, a film pressing portion,a cup discharging portion and a boxing portion. An inlet conveying belt of the cup sending portion conveys cups to the film pressing portion; the film sending portion is used for providing sealing films for the film pressing portion; the film pressing portion comprises a rotary worktable component, a clamping portion component and a film sealing component, and after cups on the rotary worktable component are in position, the clamping port component descends to clamp cup rims; the film sealing component descends to perform hot-pressing sealing and cutting of the sealing films; an outlet conveying belt of the cup discharging portion sends out the cups subjected to hot-pressing sealing; the boxing portion comprises a storage box and a cup taking manipulator, and the cup taking manipulator stacks the cups sent by the outlet conveying belt into the storage box. The full-automatic sealing machine is structurally ingenious, small in size, low in cost, widely applicable to small enterprises ormerchants and high in automation degree, functions of automatic cup sending, film sending, film pressing, hot sealing, cutting, cup discharging, stacking and the like can be realized, and labor saving and high operating efficiency are realized.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for observing and identifying filamentous fungi
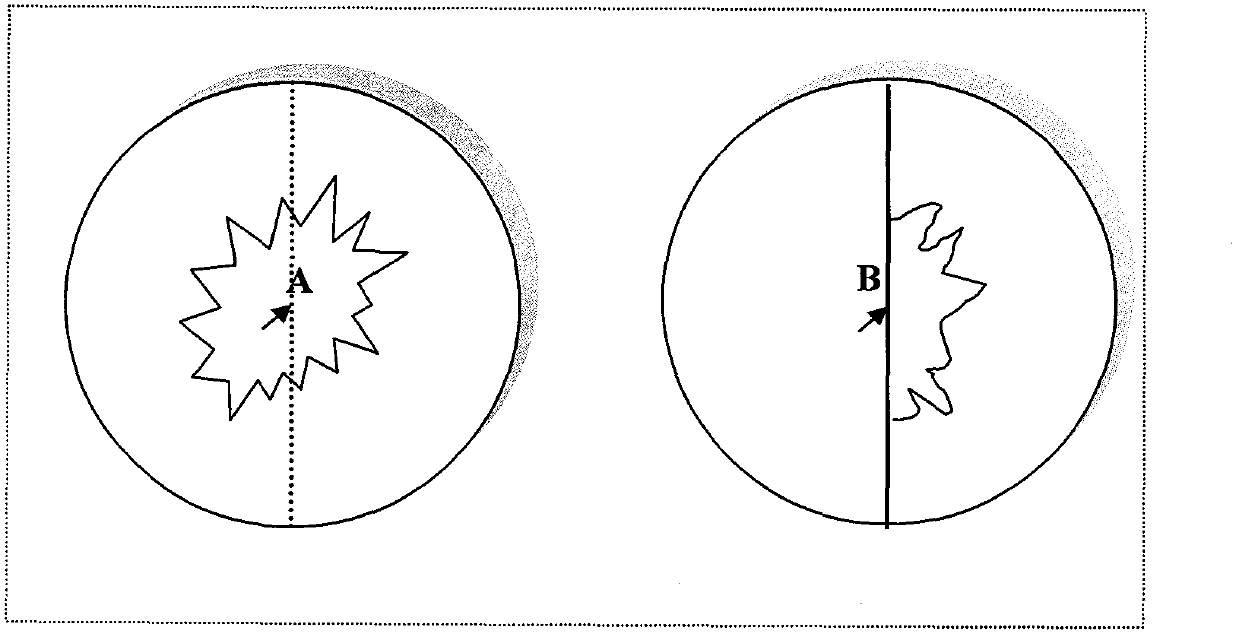
Disclosed is a method for observing and identifying filamentous fungi. The method includes the steps of adding a potato dextrose agar (PDA) culture medium into a culture dish first, cutting the PDA culture medium by using an operating knife along the diameter of the culture medium and perpendicular to the bottom of the culture dish after the PDA culture medium condenses, removing half of the culture medium, selecting to-be-identified fungus culture and inoculating the to-be-identified fungus culture to the middle of the connection portion of the culture medium and the bottom of the culture dish, covering the culture dish with a culture dish lid, carrying out marking after sealing the culture dish through a parafilm, and culturing the culture medium in dark at the temperature of 28 DEG C. After culturing is finished, the fungi grow into half of a normal bacterial colony in half of the culture dish with the culture medium, and bacterial colony characteristics can be observed; and hyphae grow sparsely in the other half of the culture dish without the culture medium, and the hyphae can be micro-observed when the culture dish is inversely placed. The method for observing and identifying the filamentous fungi has the advantages that flaking is not needed, fungus individual form observation and colony form observation are combined, operation is simple, convenience and quickness are achieved, the hyphae and the bacterial colony, in a naturally-growing state, of strain can be observed in real time at the same time, accuracy of identifying work for the filamentous fungi can be guaranteed, cost is saved, and workload is reduced.
Owner:FARMING & CULTIVATION RES INST OF HEILONGJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +2
Tea cup sealing leakage detection and secondary sealing device
InactiveCN112124662ASolve the problem of not being able to seal againSolve the problem of negligently forgetting to replace the steel ringMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateWrapper twisting/gatheringThin membraneMaterials science
The invention discloses a tea cup sealing leakage detection and secondary sealing device. The device comprises a sealing machine and a working cavity, wherein the working cavity is formed in the sealing machine, a sealing mechanism is fixedly arranged on the top wall of the working cavity. According to the tea cup sealing leakage detection and secondary sealing device, a mechanism for detecting whether a cup opening is firmly sealed or not is arranged in a traditional sealing machine, and the bulging height of a sealing film is detected through extruding a cup body; if the cup body bulges, noair leakage occurs on the cup body, and if not, sealing fails and re-sealing is needed, and at the moment, a secondary heating signal is triggered, and a film on the sealed cup opening is heated underthe condition that a new film is not sealed, so that the film is heated again to be melted and softened, the cup opening is firmly sealed, and therefore the problem that re-sealing cannot be performed after sealing failure is solved; and meanwhile, when different cups are sealed, steel rings do not need to be replaced, the device can automatically identify the types of the cups and pushes out thecorresponding steel rings, and thus the problem that the steel rings are forgotten to be replaced due to negligence in the sealing process is solved.
Owner:慈溪市纵深包装有限公司
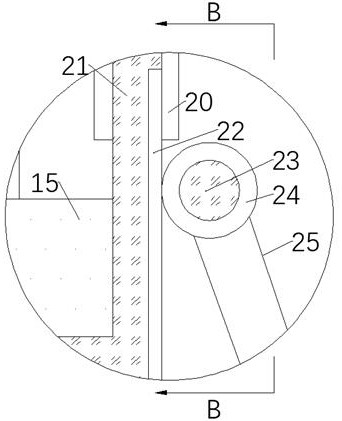
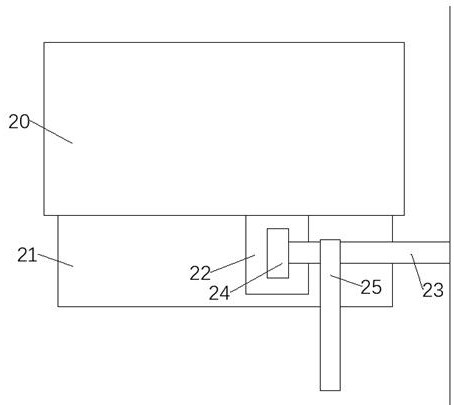
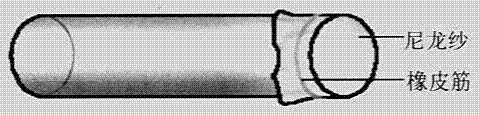
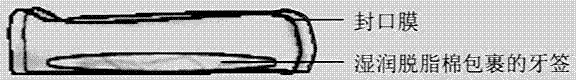
Spawning device for small brown planthoppers and application method thereof
The invention relates to a spawning device for small brown planthoppers, which is used for detecting the reproductive capacity of the small brown planthoppers in an RNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid) interference test. The device is concretely composed of: a glass tube with openings at two ends, 80-mesh nylon yarn, a rubber band, sterile toothpicks, wetting sterile degreasing cotton and a sealing film (Parafilm). During use, use the 80-mesh nylon yarn to seal one end of the glass tube; then take a toothpick wound by the wetting sterile degreasing cotton, use the sealing film to seal the degreasing cotton, and imitate rice seedlings; put in adult small brown planthoppers to lay eggs, use a layer of sealing film to seal the other end of the glass tube; add artificial feed in the center of the film, then reuse a layer of sealing film to seal the feed; after completion, use a humidifier to conduct mist spray for preserving moisture. The device can solve the problem that the small brown planthoppers do not have a spawning site in the RNAi study of a feeding method, and provides guarantee for successfully carrying out the gene function study.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com