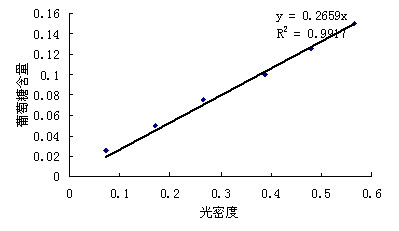
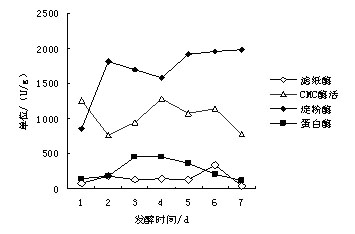
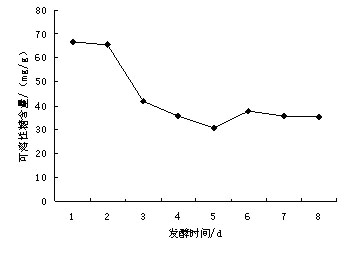
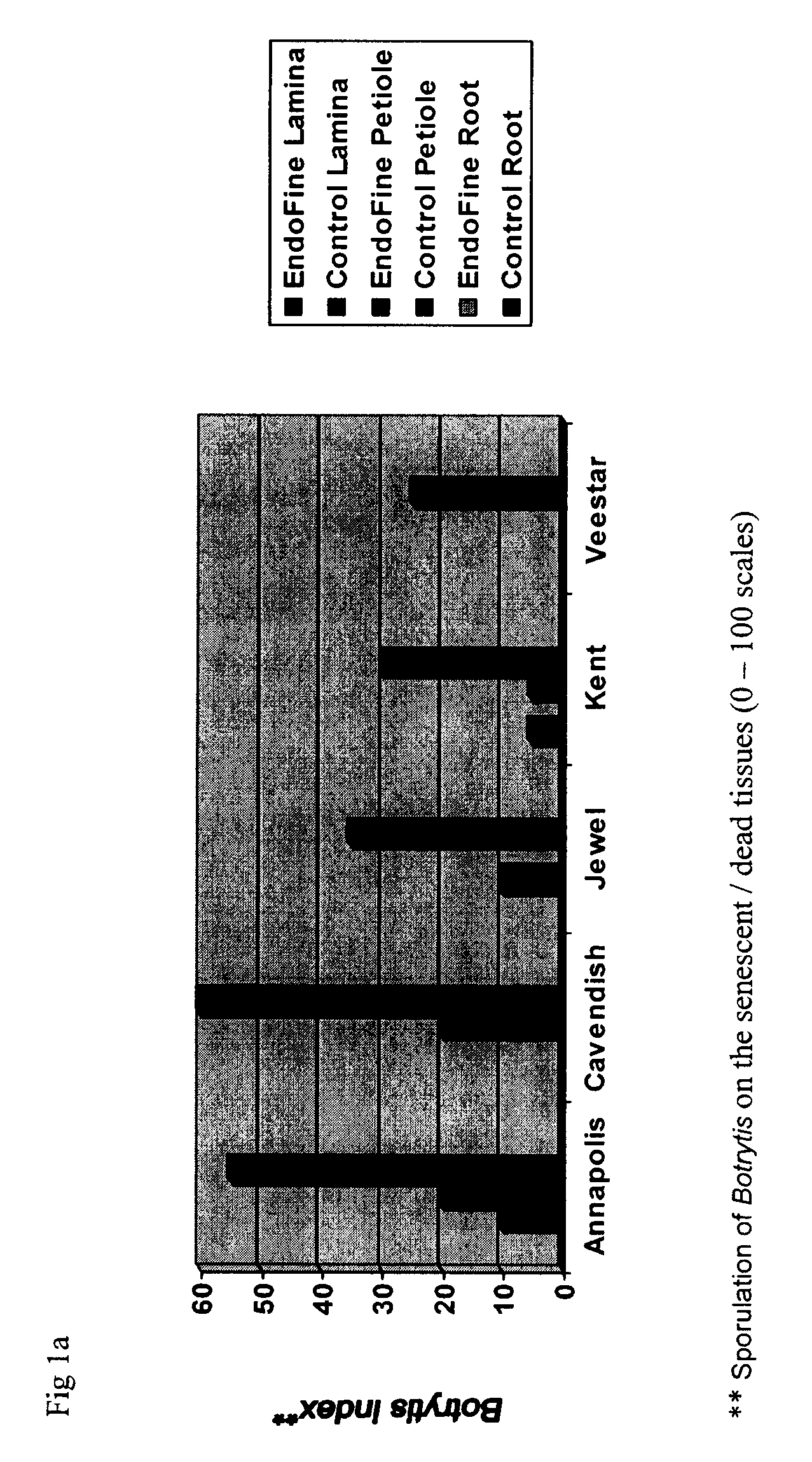
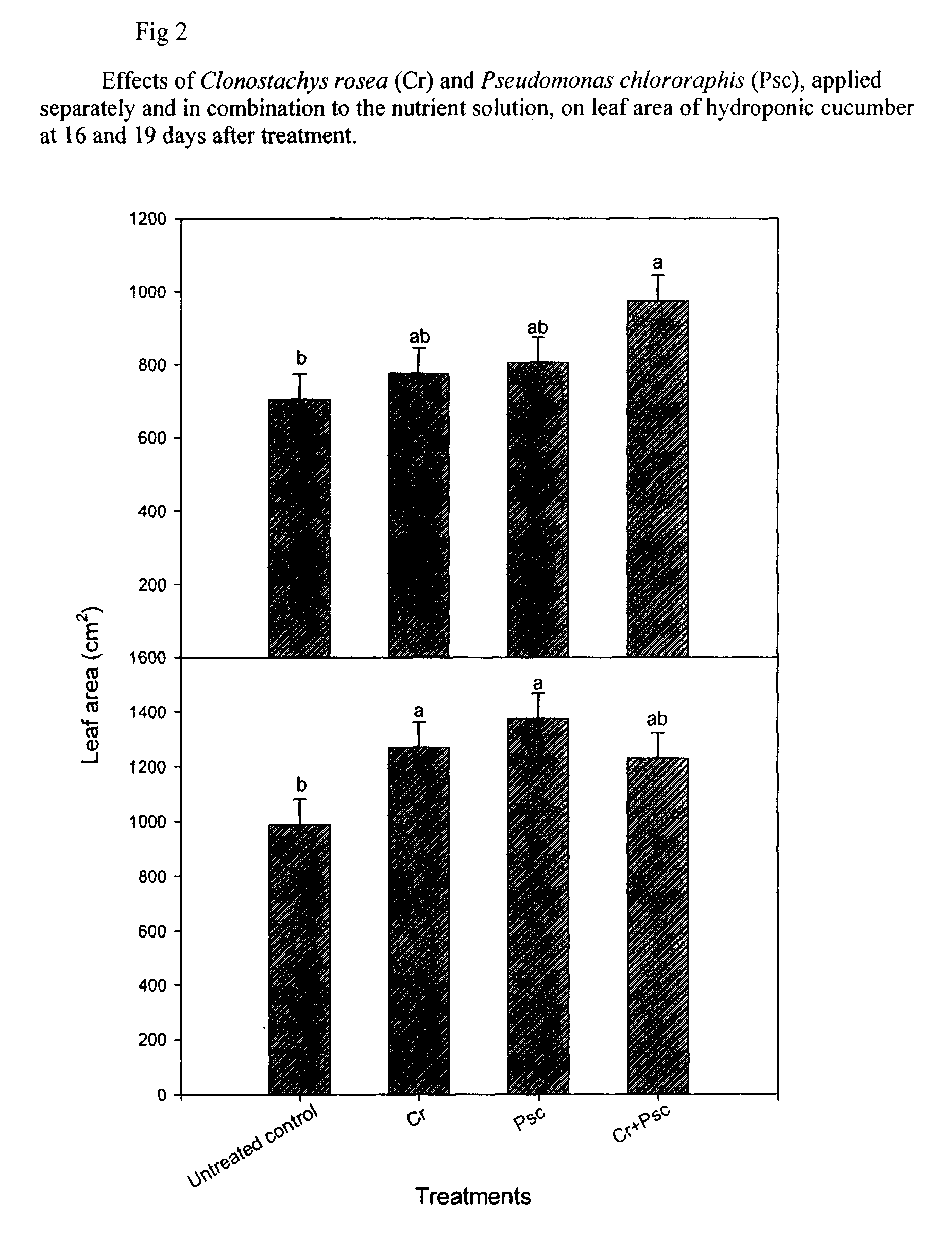
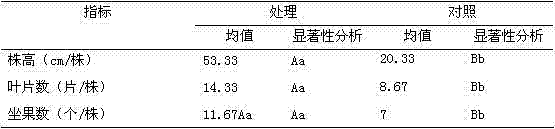
Patents
Literature
326 results about "Potato dextrose agar" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Potato dextrose agar (BAM Media M127) and potato dextrose broth are common microbiological growth media made from potato infusion, and dextrose. Potato dextrose agar (abbreviated "PDA") is the most widely used medium for growing fungi and bacteria.
Selenium-rich cordyceps culturing method
The invention relates to a selenium-rich cordyceps culturing method belonging to the technical field of cordyceps culturing methods. The selenium-rich cordyceps culturing method comprises the following process steps of: (1) activating strains in a PDA (Potato Dextrose Agar) solid culture medium; and (2) culturing liquid strains. The selenium-rich cordyceps culturing method is characterized by also comprising the following step of: (3) carrying out sporocarp selenium-rich culture, wherein a sporocarp selenium-rich culture medium is formed by rice, selenate and a glutelin hydrolyzing solution, and the selenate is one of sodium selenate, potassium selenate and ammonium selenate; then inoculating the liquid strains cultured by a fermentation liquid medium into the sporocarp selenium-rich culture medium with the formula, and culturing for 40-50 days according to fermentation management requirements. The cultured cordyceps can greatly increase the content of selenium contained in cordyceps sporocarps to 3.83-81.95Mug / g; the cordyceps sporocarps have high growth vigour, higher output and bright colors, therefore the nutritive and medical value of the cordyceps is enhanced; and besides, the invention has implementing conditions which are easy to achieve, thereby being popularized in a whole industry.
Owner:YIWU DANXI MEDECINAL BIOLOGY DEV RESINST +1
Method for jointly treating stalks by steam explosion and microorganism fermentation
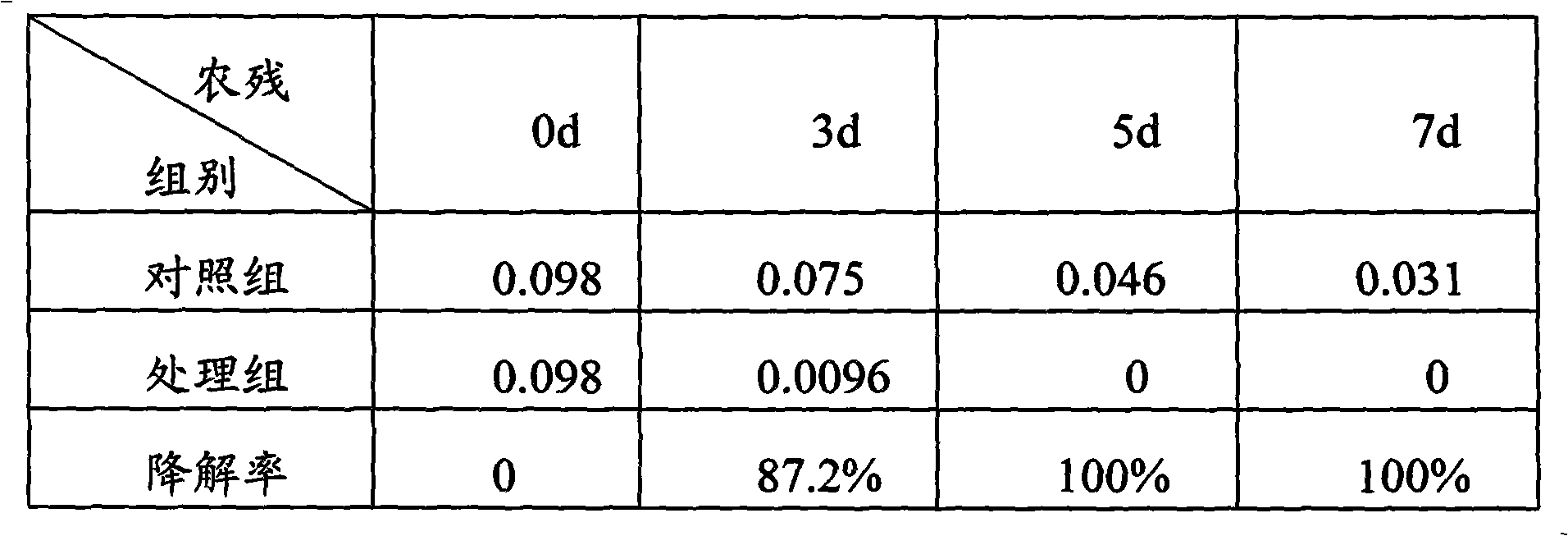
ActiveCN102077903ACompletely degradedSolve the problem of human-animal competition for foodFood processingAnimal feeding stuffSporelingNutrient solution
The invention relates to a method for jointly treating stalks by steam explosion and microorganism fermentation, comprising the following steps of: firstly, carrying out steam explosion pretreatment on the stalks to obtain exploded stalks; then preparing spore seed liquid: inoculating aspergillus oryzae or trichoderma Koningi to a PDA (Potato Dextrose Agar) culture medium, standing and culturing for 3-5 days at the temperature of 28-32 DEG C, and preparing the spore seed liquid with the concentration of 106-108 per mL; and finally carrying out microorganism fermentation: uniformly mixing 18g of exploded stalks, 2g of bran and 30mL of mineral element nutrient solution, adjusting pH to be 7.0 with Ca(OH)2, sterilizing for 15min at the temperature of 121 DEG C and the pressure of 0.15MPa to obtain a solid fermentation medium a, inoculating the spore seed liquid according to 2-4% of inoculum size, and culturing the spore seed liquid for 5-7 days at the temperature of 28-32 DEG C. The fermentation stalks obtained by utilizing the method have low content of lignose, cellulose and hemicellulose and high activity of filter paper carbohydrase, CMC (carboxymethyl cellulose) enzyme, amylase and protease.
Owner:河南德邻生物制品有限公司
Production and use of endophytes as novel inoculants for promoting enhanced plant vigor, health, growth, yield reducing environmental stress and for reducing dependency on chemical pesticides for pest control
InactiveUS20090105076A1Improve scalabilityPrevent degradationBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyFungal endophyte
A process and method for the production of endophytes as plant inoculant products, specifically Clonostachys rosea strain 88-710, for the promotion of plant vigor, health, growth and yield are disclosed. The endophyte, Clonostachys rosea strain 88-710 produces a fungal conidial preparation by utilizing a discrete solid substrate fermentation system, namely Potato Dextrose Agar or Malt Extract Agar. Additionally, the endophyte, Clonostachys rosea strain 88-710, can act as an inoculant to stimulate and have an additive effect with rhizobium bacteria on the production of nitrogen fixing nodules on legumes and growth enhancement e.g. beans, soybeans, peas and alfalfa. As well, Clonostachys rosea strain 88-710, can combine with rooting hormones, e.g. indole-3-butyric acid (IBA) to provide inoculant and rooting benefits to cuttings / transplants of plants.
Owner:ADJUVANTS PLUS INC
Preparation method of trichoderma multifunctional soil modifying agents
InactiveCN102505010APromote growthReduce manufacturing costBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologySporeling
The invention relates to a preparation method of trichoderma multifunctional soil modifying agents. The preparation method comprises the steps that: trichoderma harzianum SH2303 with the CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) NO. 4963 is cultured on a potato dextrose agar (PDA) culture medium for 2 to 3 days, a bacterial cake is punched by a hole puncher with the diameter being 5mm, the bacterial cake is inoculated into a seed culture medium for 5 to 7 days at the bacterium inoculation quantity of three tablets per bottle and is then inoculated into a spore production culture medium, the fermentation is carried out for 5 to 7 days under the optimized culture condition in a 300 L fermentation tank, and the number of thick-wall spores is (6 to 7)*10<8> / mL; and fermenting liquid and carriers are mixed according to the weight ratio of 1:1, the secondary open type solid fermentation is carried out for 5 to 7 days at the normal temperature, and the number of trichoderma conidiospores and chlamydospores is 200 to 500 million / g. The soil modifying agents prepared by the method have the main purposes of improving the primary and secondary salinization of vegetable planting soil and degrading the organic phosphorus pesticide residue soil, and have the effects of treating soil-borne diseases, promoting the crop growth and improving the crop yield. Because only one trichoderma strain is utilized, the fermentation process is easy to optimize, the microbial inoculum preparation cost is low, the commercial large-scale popularization is easy to realize, and high field general use values are reached.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Chaetomium globosum and application thereof
ActiveCN104694397AField disease preventionHave a growth-promoting effectBiocideFungiBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a chaetomium globosum FSR-74. The collection unit of the chaetomium globosum FSR-74 is China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the collection date of the chaetomium globosum FSR-74 is September 19, 2014 and the collection number of the chaetomium globosum FSR-74 is CGMCC No. 9690. The strain is relatively slow in growth and has light brown colonies and an irregular wave-like edge when subjected to plate culture at 25 DEG C in a potato dextrose agar (PDA) culture medium. FSR-74 ascocarps are supergene and fixed on the surface of a matrix by rhizoids; top hair is wavy, brown and has intervals, and dense wart points are arranged on the surface; 8 ascospores are arranged in an ascus; the ascospores are shaped like lemons and have single apical bud holes. The chaetomium globosum FSR-74 has an efficient broad-spectrum bacteriostatic effect against main pathogenic bacteria causing ginseng rust rot, blight, sclerotinia rot, rust rot, blackspot, sheath blight and gray mold. The invention further provides a biological control mechanism and application of the chaetomium globosum FSR-74 in prevention and treatment of plant fungal diseases, as well as application in preparation of a microbial agent for preventing and treating the plant fungal diseases.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Edible mushroom culturing method
InactiveCN102550284ANot easy to inactivateInoculum size can be adjustedHorticultureFertilizer mixturesBiotechnologyEdible mushroom
The invention discloses an edible mushroom culturing method which comprises the following steps: inoculating edible mushroom strains to a solid medium and culturing for 25-40 days at the temperature of 20-26 DEG C, thus obtaining solid strains; adding a stabilizing agent into water or a PDA Potato Dextrose Agar fluid nutrient medium and mixing, thus obtaining a liquefying agent; adding the solid strains into the liquefying agent, stirring, filtering and taking filtrate, thus obtaining liquid strains; and inoculating the liquid strains into the production culture medium for production and cultivation, thus obtaining the edible mushroom. During the edible mushroom culturing process, the liquefying agent is utilized for liquefying the solid strains which are then inoculated for production and cultivation, the edible mushroom is produced for use, the operation is simple and convenient, the labor intensity can be lightened, the strain quantity can be well controlled, and standardized production is benefited; the product quality of scattered growers is stable, and regional scaled production can be formed; and simultaneously pollution can be effectively controlled, labor and material wastes can be reduced, and the product benefit and the product quality can be improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Polysporus trichoderma and application thereof
The invention discloses a polysporus trichoderma (Hypocrea pachybasioide) FSR-97 strain, wherein the preservation unit is China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the preservation date is 19, September, 2014 and the preservation number is CGMCC No.9691. The strain is cultured on a potato dextrose agar culture medium (PDA) plate at 25 DEG C and rapidly grows, and a monospore is germinated to form a white bacterial colony; the colour on the back surface of the bacterial colony is transited from colourless to yellow. The polysporus trichoderma (Hypocrea pachybasioide) FSR-97 has an effective broad-spectrum antibacterial effect on the main pathogenic bacteria causing the panaxginsen fusarium rot, epidemic disease, sclerotiniose, root rust rot, black spot, rhizoctonia solani, and botrytis. The invention further discloses a plurality of biocontrol mechanisms of the polysporus trichoderma (Hypocrea pachybasioide) FSR-97 for preventing and controlling the plant fungous disease, and an application for preparing a microbial preparation to prevent and control the plant fungous disease.
Owner:四川臻润农业科技有限公司
A kind of artificial cultivation method of Brown Ganoderma lucidum fruiting body
The invention relates to an artificial cultivation method for Ganoderma brownii (Murrill) Gilb. fruiting bodies, which is characterized in that tissue isolation or spore isolation is conducted to fresh Ganoderma brownii (Murrill) Gilb. fruiting bodies, the isolated tissues or spores are cultured on a potato dextrose agar (PDA) inclined-surface slant culture medium and a slant comprehensive PDA culture medium to obtain stock culture for production, the stock culture for production is inoculated and cultured in a pre-culture spawn culture medium to obtain pre-culture spawns, the pre-culture spawns are cultured in a production spawn culture medium to obtain production spawns, and finally the production spawns are inoculated in a culture medium for production and are cultured till mature fruiting bodies grow. The artificial cultivation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the biological efficiency of the Ganoderma brownii (Murrill) Gilb. fruiting bodies can reach 30 percent to 90 percent, i.e. 30g to 90g fresh Ganoderma brownii (Murrill) Gilb. fruiting bodies can be obtained per 100g culture medium, and the fresh Ganoderma brownii (Murrill) Gilb. fruiting bodies can be used as raw materials or materials for researches.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Method for preparing edible mushroom liquefied strains
The invention discloses a method for preparing edible mushroom liquefied strains. The method comprises three steps, i.e. the purification and culture of primary strains, the preparation of sterilized water and the preparation and liquefaction of secondary strains. According to the method, the primary strains are cultured in a PDA (Potato Dextrose Agar)-enriched culture medium so as to obtain purified primary strains; the purified primary strains are segmented and are then inoculated into a water-soluble culture medium so as to obtain the secondary strains; and hyphae of the secondary strains are broken into pieces by using a high-speed strain crusher, and then, the secondary strains are added to the sterilized water and diluted, thereby obtaining the liquefied strains. The method has the advantages of simple process, simplicity and convenience in inoculation, quickness in strain growth, earliness in mushroom growing, good quality, high yield, high efficiency, low pollution risk, low investment and operating cost and good economic benefit. After the edible mushroom liquefied strains prepared by using the method are inoculated, the permeation of the strains is strong, and the strain growth is quick. Furthermore, the culturing and mushroom growing time of the edible mushroom liquefied strains is greatly shortened, the mushroom growing is orderly, the growing speed is high, and the yield is obviously increased.
Owner:TIANSHUI ZHONGXING BIO TECH
Degelatinized enzyme made from Aspergillus niger and its use in degumming of fiberflax
InactiveCN101074433AHigh enzyme productionEnzyme richFungiMicroorganism based processesPectinaseAspergillus wentii
A de-bonding enzyme produced by Aspergillus niger HYA4 and its use in flax de-gumming are disclosed. The process is carried out by taking potato glucose agar culturing medium as tapered-land preservative culturing medium, taking solid fermenting culture medium as bran, bean dregs, ammonia sulfate and ammonium nitrate, putting ferment under room temperature, leaching by natural water stilly, filtering to obtain coarse enzyme liquid, diluting, and determining pectase and xylanase activity. It's cheap and non-toxic; has more enzyme yield, complete varieties, shorter production period, various raw material sources, more yielding rate and combing rate and less water-source pollution.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
Method for improving submerged fermentation level of trichoderma reesei cellulase liquid
InactiveCN102229920AIncrease the level of submerged fermentationProlong growth periodMicroorganism based processesEnzymesBiotechnologySpore
The invention provides a method for improving a submerged fermentation level of trichoderma reesei cellulase liquid. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: first-grade seed culturing: preparing a spore suspension solution from activated trichoderma reesei CICC 13052 bacterial strain on a PDA (Potato-Dextrose-Agar) slant culture medium and inoculating the spore suspension solution into a fresh seed culture medium according to the inoculating amount of 3% to be cultured; and fermenting and culturing: inoculating the first-grade seeds in a logarithm growing periodinto a fresh fermenting culture medium to be cultured and controlling the pH values and dissolved oxygen in a pot of the fermenting process by sections to maintain the pH values and dissolved oxygen of the different periods at the different levels, and carrying out feed supplement and controlled culturing. By utilizing the method provided by the invention, the liquid is fermented for 168 hours; the enzyme activity of the fermenting liquid is measured by utilizing an international standard method which is recommended by the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry); and the enzyme activity of filter paper is 14.2 IU / mL and is improved by 67.1% compared with the interval fermenting enzyme activity level (8.5 IU / mL) before the process is optimized.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for rejuvenating cordyceps militaris strains
The invention relates to rejuvenation of degenerated edible bacterial strains, in particular to a method for rejuvenating cordyceps militaris strains, which mainly comprises steps of cordyceps militaris strain activated culture, cordyceps militaris strain rejuvenation, and cordyceps militaris strain conservation. The method is characterized in that: the rejuvenation culture is that: the activatedcordyceps militaris strain is inoculated to a potato dextrose agar (PDA) plate which is compounded with one or more kinds of antibiotics for first rejuvenation culture, and the strain which is subject to first rejuvenation culture is inoculated to a PDA plating culture medium which is compounded with one or more kinds of antibiotics for second rejuvenation culture. The invention breaks through the traditional strain rejuvenation method, and rejuvenates the strain by an antibiotic method which is easy to operate, simple and practical, and has remarkable effect. The strain which is rejuvenated by the method has robust and compact hypha, and the growing speed of the strain is improved by about 8 times compared with that of the strain which is not rejuvenated.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Separation and cultivation method for isaria fumosorosea
InactiveCN103451113APrevent ejectionLarge diameter areaFungiMicroorganism based processesSporeIsaria fumosorosea
The invention discloses a separation and cultivation method for isaria fumosorosea. The method comprises the following steps of collecting bemisia tabaci bodies infected with entomogenous fungus from vegetable leaves, separating the entomogenous fungus from the bodies, putting the entomogenous fungus on a PDA (potato dextrose agar) culture medium for cultivating to obtain spore suspension which is sprayed on two-year-old nymphs of bemisia tabaci, then separating the entomogenous fungus from the bodies again after cultivation, storing the entomogenous fungus on a slope of a test tube and storing the test tube in a refrigerator; taking the entomogenous fungus out of the refrigerator, preparing the spore suspension, dipping the spore suspension through filtration paper, inoculating the spore suspension onto the culture medium, cultivating in a mildew incubator, picking up hypha, inoculating the hypha into germfree water, then stirring and filtering; putting the spore suspension at the center of a culture dish, perforating a hole in the center of a bacterial colony, dispersing tween-80, stirring and filtering again, and calculating the sporulation quantity and the diameter of the bacterial colony. The method is used for screening an optimal culture medium formula, the optimal temperature, an optimal pH, a lighting condition and a ventilating condition. The method has the advantages that the diameter area of the bacterial colony is large and the sporulation yield is large.
Owner:SHANXI AGRI UNIV
Production method of liquid phagostimulant for fattening pigs
InactiveCN102224885AReduce investmentSimple production processFungiBacteriaPotato dextrose agarFermentation broth
The invention provides a production method of a liquid phagostimulant for fattening pigs. The production method is characterized by comprising the following specific steps of: performing streak culture of Saccharomyces boulardii and Lactococcus lactis; inoculating Saccharomyces boulardii and Lactococcus lactis into a potato dextrose agar (PDA) culture medium and an M17 liquid culture medium for culturing to obtain Saccharomyces boulardii liquid and Lactococcus lactis liquid; inoculating the Saccharomyces boulardii liquid into a Saccharomyces boulardii fermentation broth culture medium for aerobic culture to obtain Saccharomyces boulardii fermentation broth, and inoculating the Lactococcus lactis liquid into a Lactococcus lactis fermentation broth culture medium for anaerobic culture to obtain Lactococcus lactis fermentation broth; and mixing the Saccharomyces boulardii fermentation broth and the Lactococcus lactis fermentation broth to obtain the liquid phagostimulant. The raw materials used in the liquid phagostimulant provided by the invention are all natural agricultural products and food raw materials. The liquid phagostimulant is prepared by a simple production method, has good phagostimulant effect and functions of increasing feed intake and saving the investment in high-price feed.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHUANGBO MODERN NATURAL AGRI GRP
Method for artificially cultivating Ganoderma guinanense fruiting bodies
The invention relates to a method for artificially cultivating Ganoderma guinanense fruiting bodies, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: carrying out a tissue separation or a spore separation on fresh Ganoderma guinanense (Ganoderma guinanense J.D.Zhao et Z.Q.Zhang) fruiting bodies; then culturing on a PDA (Potato Dextrose Agar) slant culture medium and a slant comprehensive PDA culture medium to obtain a stock spawn for production; then inoculating the cultured sporophores into a stock culture medium to be cultured; culturing until mature fruiting bodies grow. According to the artificially cultivating method provided by the invention, the biological efficiency of the Ganoderma guinanense fruiting bodies can reach 35-75%, namely 35-75 g of fresh Ganoderma guinanense fruiting bodies can be obtained by utilizing 100 g of culture materials for production; and the fresh Ganoderma guinanense fruiting bodies can be used as raw materials or materials for researching.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Preparation method of Phellinus linteus mycelium
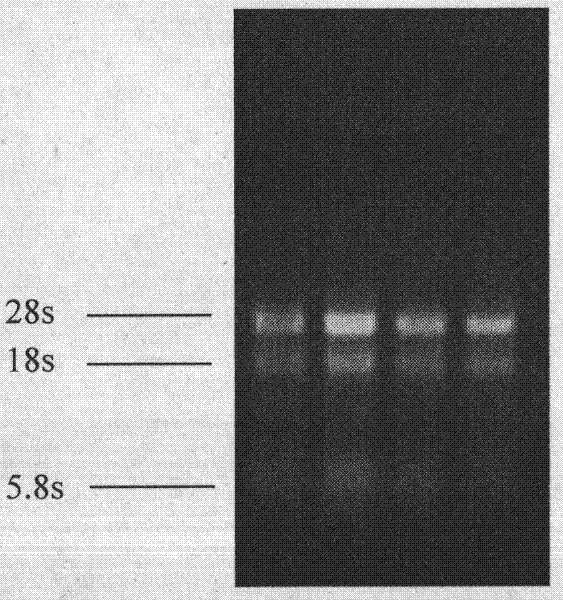
InactiveCN102363749AHigh purityQuality improvementFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyTotal rna
The invention aims at providing a preparation method of a Phellinus linteus mycelium. The method comprises the following steps of: activating Phellinus linteus spawn; executing plate cultivation of potato dextrose agar culture medium; scraping the Phellinus linteus mycelium to inoculate the scraped Phellinus linteus mycelium to the potato dextrose agar culture medium for shake cultivation; collecting the Phellinus linteus mycelium; extracting Phellinus linteus mycelium total RNA; and observing result via agarose gel electrophoresis. The spawn used in the preparation method is the Phellinus linteus spawn (Phellinus baumii Pilate) collected in the CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection), and the collection number is Phellinus linteus DL101 CCTCC M 2011137. The preparation method is simple to operate and has straightforward principle, and a simple and convenient method for obtaining large-scale high-purity Phellinus linteus mycelium and high-quality Phellinus linteus total RNA in the future is provided, and the basis for fundamental research and application development of the Phellinus linteus is also provided.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for producing enoki mushrooms rich in selenium and zinc
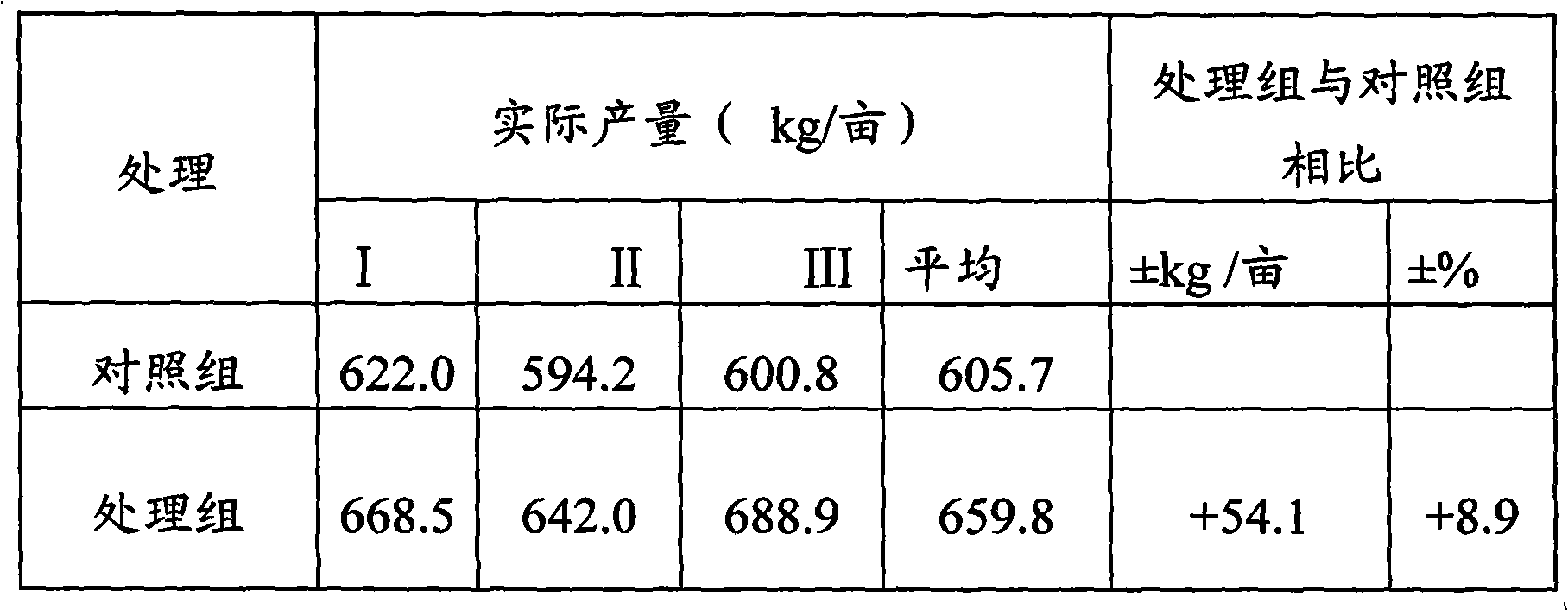
InactiveCN103229665APromote absorptionIncrease productionHorticultureFertilizer mixturesBiotechnologySulfate zinc
The invention discloses a method for producing enoki mushrooms rich in selenium and zinc and belongs to the field of edible fungi cultivation. The method comprises stock preparation, original strain preparation and enoki mushroom cultivation. Sodium selenite and zinc sulfate are added in a stock preparation culture medium and an original strain preparation culture medium and enoki mushroom culture compost. The stock preparation culture medium is composed of, by weight, 200g of potatoes, 25g of glucose, 30g of agar, 3g of peptone, 0.5g to 1g of monopotassium phosphate, 0.5g to 1.5g of magnesium sulfate, 11mg to 13mg of sodium selenite, 0.2g to 0.4g of heptahydrate and 1000g of water. The enoki mushrooms are high in selenium and zinc absorption in the growth process, and the yield is high.
Owner:汤阴县食用菌协会
Method for producing cordycepin through semi-continuous liquid fermentation of cordyceps militaris
InactiveCN102965416AEasy to separateIncrease fermentation intensityChemical recyclingFermentationBiotechnologyBatch fermentation
The invention discloses a method for producing cordycepin through semi-continuous liquid fermentation of cordyceps militaris, and the method comprises the following concrete operating steps of: (1) putting hyphae of the Cordyceps militaris on a PDA (Potato Dextrose Agar) solid culture medium and activating to generate a bacterial lawn with a plenty of dense mycelia; (2) putting the bacterial lawn on a seed culture medium, carrying out shake cultivation, and forming a plenty of mycelium pellets after 5 days, thereby obtaining seed liquid; (3) transferring the seed liquid into a seed liquid fermentation tank to carry out expanding culture; (4) transferring the seed liquid after being subjected into the expanding culture in a 500L tank to carry out first-batch fermentation; and (5) carrying out semi-continuous fermentation in 10 batches in the 500L tank under the same conditions. In the fermentation process, a method of adjusting the culture medium composition and the fermentation conditions is adopted to control the cordyceps militaris to form the mycelium pellets with regular shape and uniform size and the average diameter of the mycelium pellets is 3-5mm, so that the separation of fermentation broth and thalli is easy; the carbon and nitrogen source and other inorganic salts needed in the growth of mycelium pellets are saved by utilizing the repeated fermentation of the mycelium pellets of the cordyceps militaris, so that the cost is saved; and the fermentation cycle is shortened and the fermentation intensity is increased, so that the method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for asexual propagation of wild aweto fungi
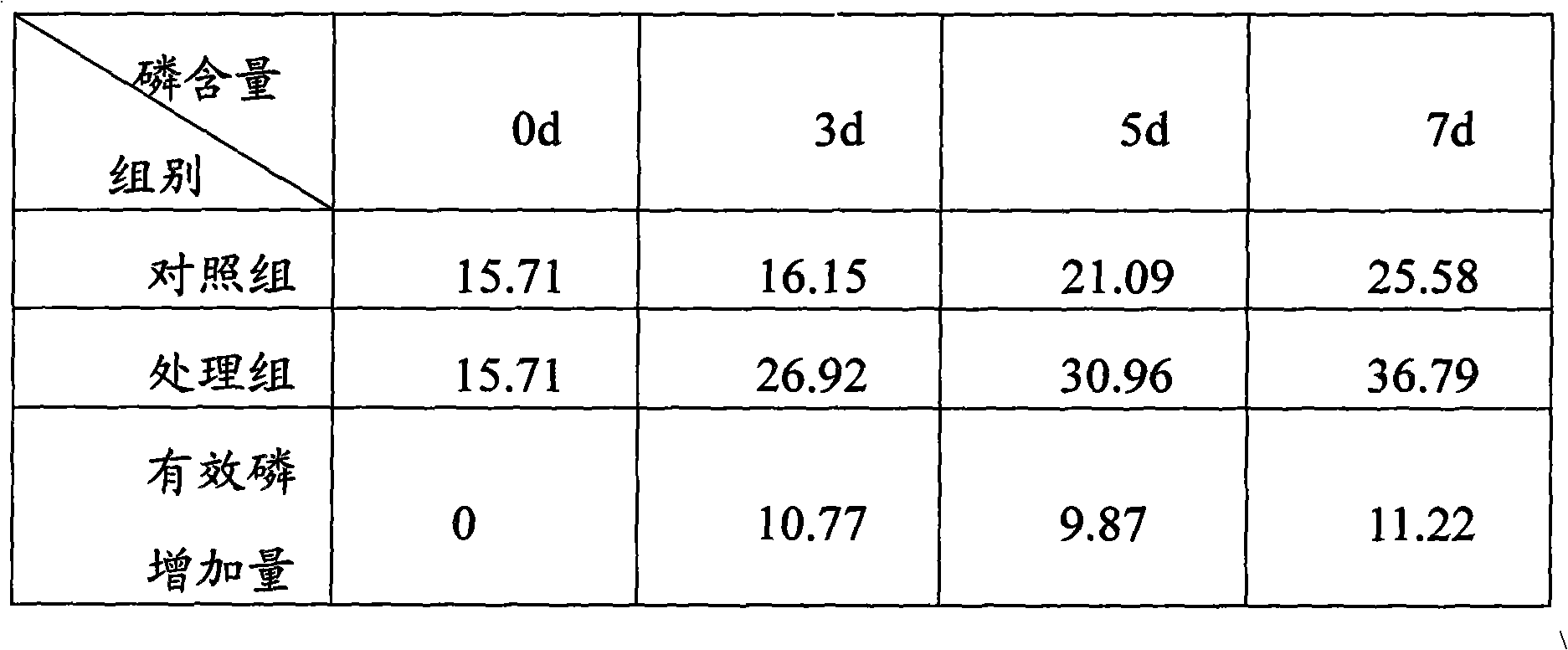
InactiveCN102187786AReasonable nutritional contentHigh strain activityHorticultureFertilizer mixturesPhosphateMonopotassium phosphate
The invention provides a method for asexual propagation of wild aweto fungi and belongs to the technical field of biology. In the method, living cells of wild aweto are used as strains, and the aweto fungi suitable for artificial culture are obtained in a special potato dextrose agar (PDA) culture medium by a cloning technology; and the PDA culture medium comprises the following components by mass: 950 to 1,050 grams of water, 280 to 320 grams of potatoes, 4 to 8 grams of peptone, 3 to 5 grams of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 1 to 2 grams of magnesium sulfate, 15 to 20 grams of agar and 18 to 23 grams of glucose, and the pH value is between 6.0 and 7.0. The method comprises the following steps: 1, selection of living cells; 2, domestication of strains; 3, purification; and 4, rejuvenation and obtaining of excellent mother seeds of aweto. The method has the advantages of reasonable nutrients of the PDA strain culture medium, high strain activity, no pollution by molds and bacteria, stable quality of fungi and no mutation of fungi. In addition, the content of effective nutrients of the aweto is high, and the good-quality and high-yield fruit body is obtained.
Owner:杜保华
Preparation method for multifunctional soil remediation microbial inoculum
InactiveCN102911875ALarge biomassStrong stress resistanceFungiContaminated soil reclamationSpore germinationOrganophosphorus pesticides
The invention provides a preparation method for multifunctional soil remediation microbial inoculum. The preparation method comprises the following steps: A. cultivating slope culture aspergillus niger strains J6 through a PDA (potato dextrose agar) culture medium until spores are mature, inoculating in a seed culture medium to obtain spore seed liquid after spore germination; and B. inoculating the spore seed liquid in a solid fermentation medium according to mass percent of 5-10%, conducting shallow pan cultivation for 4-7 days at the temperature of 25-35 DEG C, and turning over for 2-3 times to obtain the multifunctional soil remediation microbial inoculum. With the adoption of the multifunctional soil remediation microbial inoculum prepared by the method, organophosphorus pesticide in soil can be efficiently degraded, and heavy metal such as chromium and lead and the like in the soil can be efficiently adsorbed, so that the purpose of multiple remediation of the soil is achieved.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF SCI INST OF BIOLOGY LIABILITY
Morchella esculenta bacterial strain and culture method thereof
ActiveCN103710271AIncrease biomassStrong generative abilityFungiMicroorganism based processesContamination rateBacterial strain
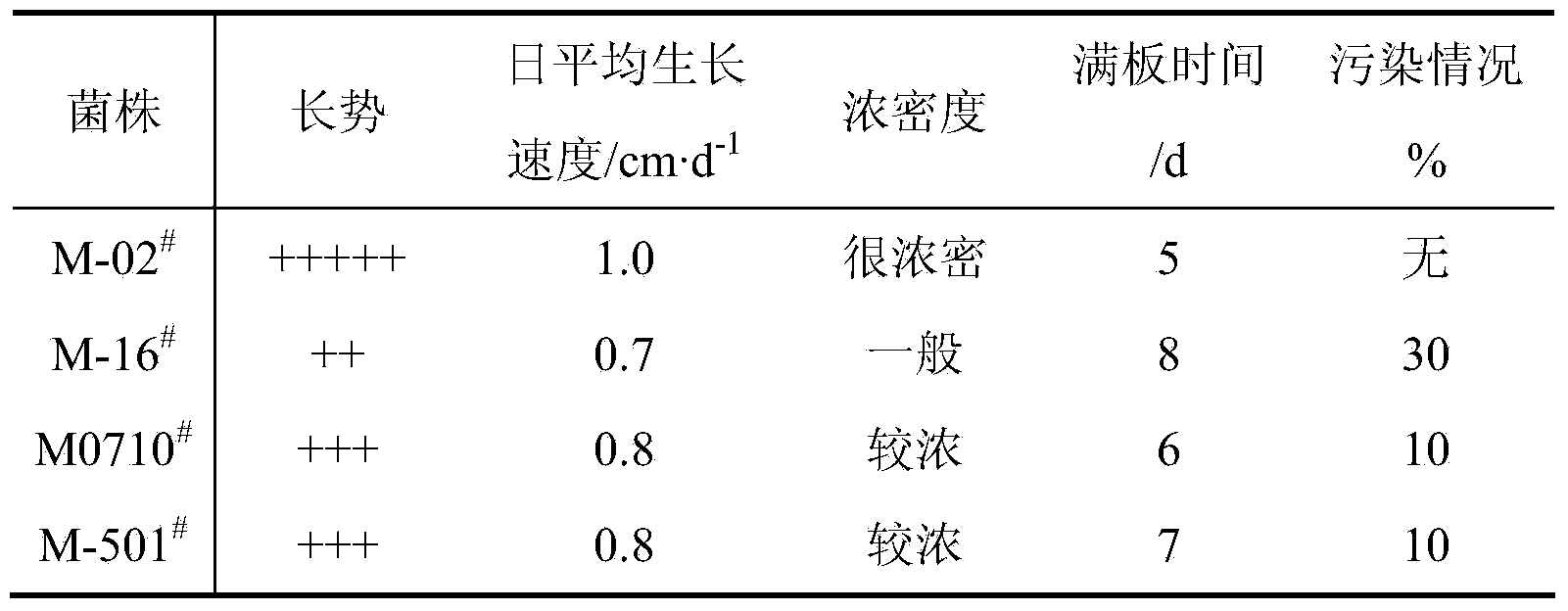
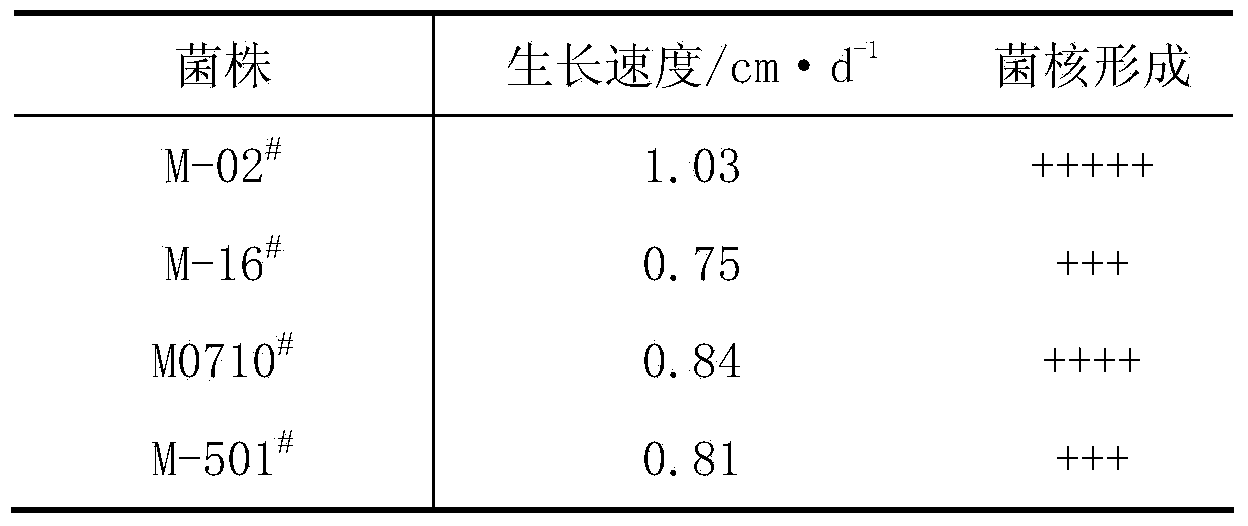
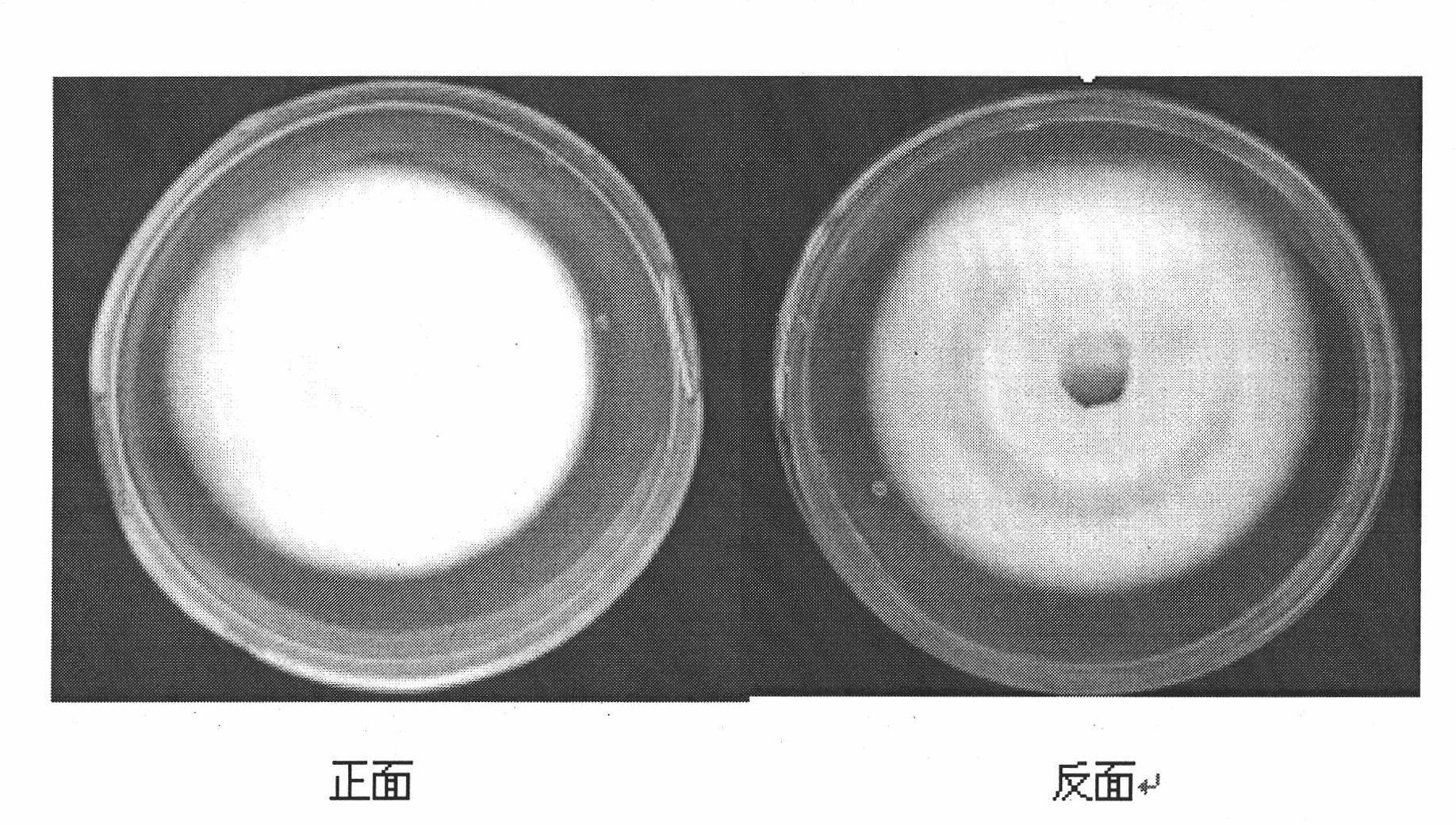
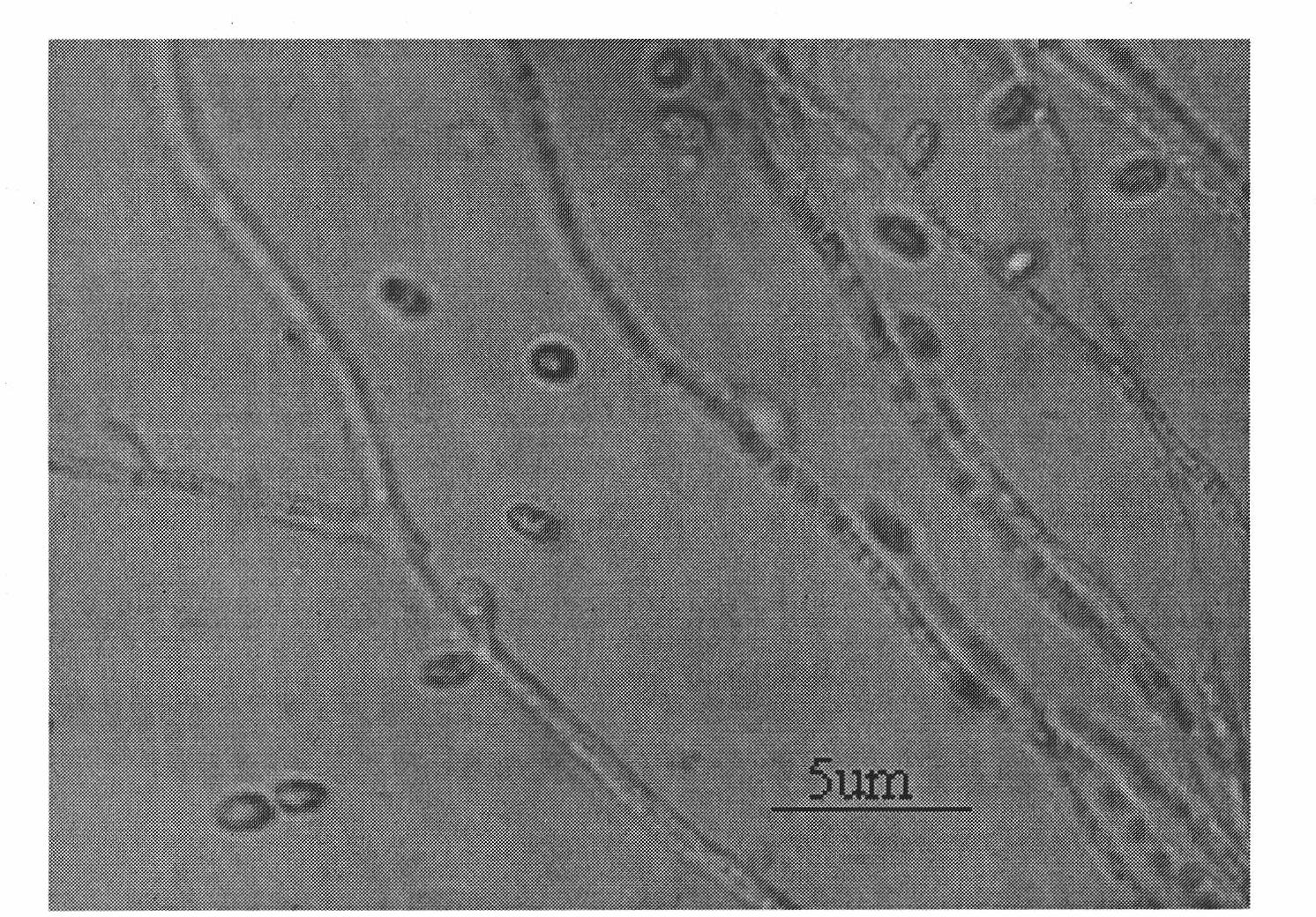
The invention discloses a morchella esculenta bacterial strain and a culture method thereof. The culture method of the morchella esculenta M-02# bacterial strain with a preservation number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center ) No.7058 is as follows: inoculating a mycelium of the morchella esculenta bacterial strain into a test tube culture medium inclined surface which contains an improved PDA (Potato Dextrose Agar) culture medium for culturing for 5 days-7 days under 18 DEG C-24 DEG C to obtain a test tube strain; inoculating the test tube strain into a triangular flask which contains a liquid culture medium for culturing on a shaking bed at 20 DEG C-26 DEG C, and culturing for 5 days-7days at rotation speed of 120 r / minute-160r / minute to obtain a primary liquid strain; and inoculating the primary liquid strain into a fermentation tank, ventilating for culturing for 72 hours-96 hours to obtain a liquid strain of the bacterial strain. The bacterial strain disclosed by the invention has mycelium biomass live-weight as high as 25g / kg, strong sclerotium generating capacity, pollution resistance, a low culturing contamination rate not greater than 2%, and short liquid fermentation time of 72 hours-96 hours, so that an excellent strain is provided for morchella esculenta wild resource protection and reproduction promotion.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF EDIBLE FUNGI CHINA NAT SUPPLY & MARKETING GENERAL COOP +2
Preparation method and application of zearalenone biodegradation agent
The invention relates to a preparation method of a zearalenone biodegradation agent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: culturing through beer yeast, namely, firstly culturing in a PDA (potato dextrose agar) solid culture medium for 48hours, then taking single colony, inoculating the single colony into a PDB (potato dextrose broth) liquid culture medium for performing shaking culture for 3-5 days, adding 1-10% by weight of yeast fermentation broth by using wine lees protein feed as a carrier to prepare a crude enzyme preparation of the zearalenone biodegradation agent; extracting a zearalenone degradation enzyme of a beer yeast fermentation product, culturing through the beer yeast at the temperature of 37 DEG C for 3-5 days, taking the fermentation broth, performing freezing centrifugation under the condition of 8000r / min at the temperature of 4 DEG C for 20minutes, or separating supernatant liquid from bacterial cells by adopting a suction filtration method; and taking the supernatant liquid which is separated out, thereby obtaining an extracellular crude extraction solution, precipitating with 30-90% of ammonium sulfate, and performing the freezing centrifugation under the condition of 8000r / min at the temperature of 4 DEG C for 20minutes to obtain the zearalenone degradation enzyme which is finely extracted. The zearalenone degradation agent disclosed by the invention has the advantages that yeast can not only degrade toxins, but also adsorb the toxins.
Owner:赵刚绩
High-selenium liquid culture method for pleurotus eryngii
InactiveCN102511303AImproving the Tolerant Selenium Concentration in Liquid CultureHigh content of organic seleniumHorticulturePotato dextrose agarPleurotus eryngii
The invention discloses a high-selenium liquid culture method for pleurotus eryngii. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) inoculating pleurotus eryngii strains into a PDA (Potato Dextrose Agar) comprehensive culture medium to perform test tube strain culture to obtain initial flora suspension; (2) mixing a selenium source and the PDA comprehensive culture medium to prepare selenium-containing culture mediums with gradient selenium concentrations respectively; sterilizing the selenium-containing culture mediums; inoculating the pleurotus eryngii strains into the sterilized selenium-containing culture mediums in a flora suspension inoculation mode to perform selenium-tolerant culture at the selenium concentrations one by one in the conventional pleurotus eryngii strain culture mode in an order from low to high of the selenium concentration, wherein the flora suspension used in the primary selenium-tolerant culture is initial flora suspension, the flora suspension adopted by the subsequent selenium-tolerant culture is the flora suspension used for performing the selenium-tolerant culture at the current selenium concentration, and the like; and the best selenium tolerance concentration of the pleurotus eryngii and the highly selenium-tolerant pleurotus eryngii strains are obtained; and (3) performing fermentative culture on the highly selenium-tolerant pleurotus eryngii strains obtained by the step (2). After the highly selenium-tolerant culture of the pleurotus eryngii strains, the tolerance against selenium content in a culture medium is greatly improved in the state of liquid submerged culture.
Owner:SUZHOU SETEK
Efficient stable indoor inoculation method for Ustilaginoidea virens and special strain
InactiveCN102599031AStable and efficient inoculation effectOptimizing the inoculation methodFungiMicroorganism based processesSporeInoculation methods
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant protection, and particularly relates to an efficient stable indoor inoculation method for Ustilaginoidea virens and a special strain. The method includes: subjecting a hyphal mass (6mm) cultivated for 7 days on PSA (potato dextrose agar) to shake cultivation through PSB (photosynthetic bacteria) for 7-10 days so as to prepare hypha and spore mixed liquor, and filtering the mixed liquor with four layers of filter cloth to obtain spore liquor inoculants 106 / ml; inoculating rice ear bracts by injecting at the seventh stage of rice young ear differentiation; and keeping moist for three days at 25 DEG C and under 95%RH (relative humidity), and placing in a spray irrigation net chamber for cultivation at 25-32 DEG C and under 90%-98%RH. By the method, the rate of diseased ears under artificial inoculation of Ustilaginoidea virens can reach more than 90%. By the method compared with the outdoor artificial inoculation techniques, efficientstable incidence of Ustilaginoidea virens can be obtained under controllable conditions.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for preparing fibrilia by using epicoccum nigrum DB3 strains
InactiveCN102409411AShorten the growth cycleImprove heat resistanceFungiMicroorganism based processesFiberBuffer solution
The invention relates to a method for preparing fibrilia by using epicoccum nigrum DB3 strains. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preserving the epicoccum nigrum DB3 strains in a potato dextrose agar medium for cultivation, and adding a freezing buffer solution; (2) inoculating bacteria the amount of which equals to the pick-up amount of an inoculating ring, obtained in the step (1) into the potato dextrose agar medium, and carrying out shaking culture; (3) inoculating the culture medium obtained in the step (2) into a flax lignin fermentation medium, and carrying out shaking culture to obtain a fermentation bacteria liquid; (4) mixing sterilized fiber raw material with the fermentation bacteria liquid obtain in the step (3), carrying out table shaking and removing fermentation liquid to obtain the fibrilia; and (5) mixing the fibrilia with degumming liquid, processing and then rinsing, oiling and drying to obtain the fibrilia. The method in the invention has simple technology, short degumming time and high degumming efficiency, thus being suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:YANCHENG XUER TEXTILE
Bacillus pumilus as well as culture method and application thereof
InactiveCN101942403AGrowth inhibitionGood control effectBiocideBacteriaPotato dextrose agarCulture mediums
The invention discloses bacillus pumilus with a collection name of Bacillus pumilus 223, a collection unit of Chinese Type Culture Collection Center, a collection address of Wuhan University in Wuhan China, a collection date of April 8, 2010 and a collection number of CCTCC NO: M2010075. The invention also discloses a culture method of the bacillus pumilus and a method for preparing an antibiotic active substance by using the bacillus pumilus, comprising the following steps of: (1), carrying out streak culture on bacterial strains on a PDA (Potato Dextrose Agar) culture medium; (2), culturing a single colony in an SMA (Standard Methods Agar) fluid culture medium; (3), culturing bacterial liquid after being coated on an SMA solid culture medium; (4), soaking an obtained substance of the step (3) by using phosphate buffer and centrifuging; and (5) adding (NH4)2SO4 into supernatant liquid, centrifuging after standing and redissolving obtained precipitates by using the phosphate buffer. In the invention, the bacillus pumilus and the antibiotic active substance can be used for preventing and treating rice sheath blight diseases.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Fungus strain for degrading polyurethane plastic and culture method and application of fungus strain
The invention provides a fungus strain A. flavus G10 for degrading polyurethane plastic. The microorganism preservation number of the fungus strain A. flavus G10 is GDMCC 60537. The invention also provides a method for culturing the fungus strain A. flavus G10. The method includes the steps of isolating the fungus strain from the intestinal tract of a cricket; adopting PU as a unique carbon sourcefor culturing the fungus strain in a liquid culture medium to obtain a culture solution; diluting the culture solution and coating a solidified nutrient agar culture medium containing tetracycline antibiotics and a potato glucose agar culture medium with the culture solution to obtain cultured growing products. The cultured growing products are subcultured on fresh plates at 30 DEG C until a single fungus strain is obtained on each plate. The fungus strain A. flavus G10 can degrade the polyurethane plastic quickly.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing active phenolic compounds through rosin-induced bioconversion
InactiveCN102181488AAchieve antibacterialAchieve antiviralMicroorganism based processesFermentationSilica gelEthyl acetate
The invention provides a method for preparing active phenolic compounds through rosin-induced bioconversion. The method comprises the following steps: performing the routine culture of the microbial strain A5<+> in potato dextrose agar (PDA) culture medium to obtain the activated strain, inoculating the activated strain in the PDA culture medium to ferment for 48-72 hours; adding the inducer in the fermented strain to perform bioconversion; filtering and concentrating the conversion fluid to obtain conversion product crude extract; performing gradient alcohol precipitation on the conversion product crude extract, extracting with petroleum ether and ethyl acetate, finally separating and purifying the product through thin layer chromatography, silica gel column chromatography LH-20 gel chromatography and high performance liquid chromatography to obtain O,O-1,1'-di(2-hydroxyl-3,4,5-trimethyl)phenyl oxo bridge and 4,5,6-trimethyl-1,2-pyrocatechol. The bioconversion method has the advantages of high efficiency and selectivity and mild reaction conditions, and can hardly cause environmental pollution; the cost of the method is lower than the extraction method, thus the cost can be saved; and the obtained phenolic compounds have the functions of antioxidant property, antibacterial property, antiviral property, anticancer property, radiation resistance and antiallergic property.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Conventional low-temperature preservation method of volvariella volvacea strain
ActiveCN105238693AAchieve preservationLow equipment requirementsMicroorganism based processesMicroorganism preservationMannitol solutionHypha
The invention relates to a conventional low-temperature preservation method of a volvariella volvacea strain. The preservation method comprises the following steps: (1) transferring the volvariella volvacea strain onto a PDA (potato dextrose agar) plate, performing static culturing in an incubator at 30-32 DEG C, then transferring the strain to a PDA test tube slant after mycelia permeate the plate, performing static culturing at 30-32 DEG C for 3-7d; (2) preparing a mannitol solution which is 5-20% in mass fraction, and then filtering and sterilizing; and (3) transferring the mannitol solution in the step (2) to the test tube slant which is full of the mycelia in the step (1) by virtue of a sterile injector, and preserving the test tube slant at conventional low temperature. The preservation method disclosed by the invention can prolong a preservation duration of the volvariella volvacea mycelia in a low-temperature environment of 3-6 DEG C; the preservation method has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, low cost, long preservation duration of the strain, rapid recovery and growth, good stability and the like; and the preservation method is especially suitable for small and medium-sized enterprises and farmers planting the volvariella volvacea.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Liquid fermentation method for producing laccase by using marine endogenous pestalotia
The invention discloses a liquid fermentation method for producing laccase by using marine endogenous pestalotia, which comprises the following steps of: (1) screening a strain: screening soil in the depth of 10-20m on the offshore of the East China Sea to obtain a novel marine fungi; (2) preserving the strain: inoculating the strain in a modified potato dextrose agar (PDA) medium for culture, and preserving on a slope at the temperature of 4DEG C; (3) activating and propagating the strain: inoculating a spore of the strain in a PDA medium added with special components, and inoculating the activated spore in a seed culture medium for propagation; (4) preparing a marine endogenous pestalotia liquid fermentation medium; and (5) fermenting: performing liquid fermentation and enzyme production by using the newly prepared medium, and determining the optimized enzyme production condition. In the method for producing the laccase, the novel marine endogenous pestalotia is taken as a production strain; and the method has the characteristic that the media are coarse, wide in sources, low in prices and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com