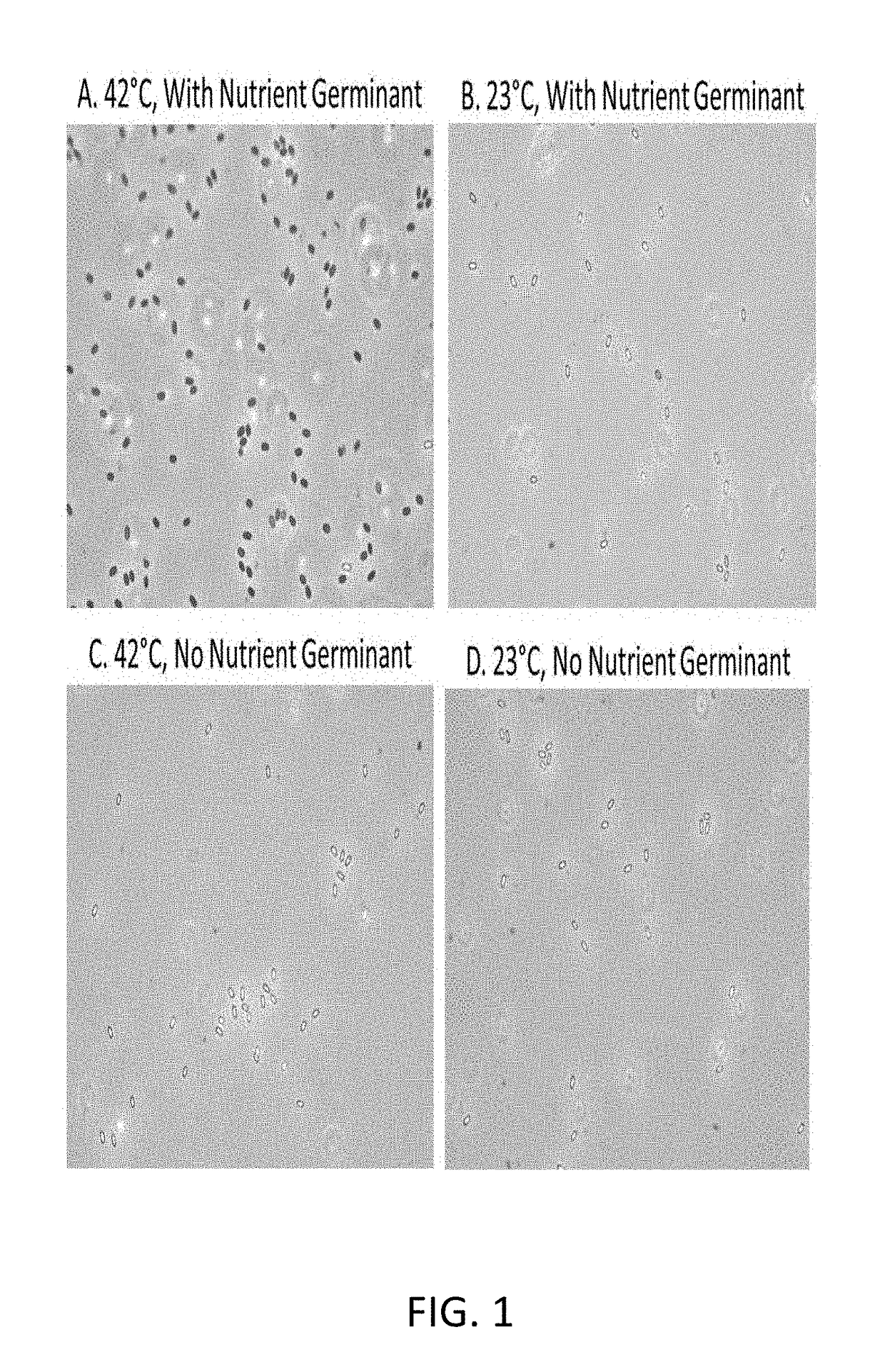
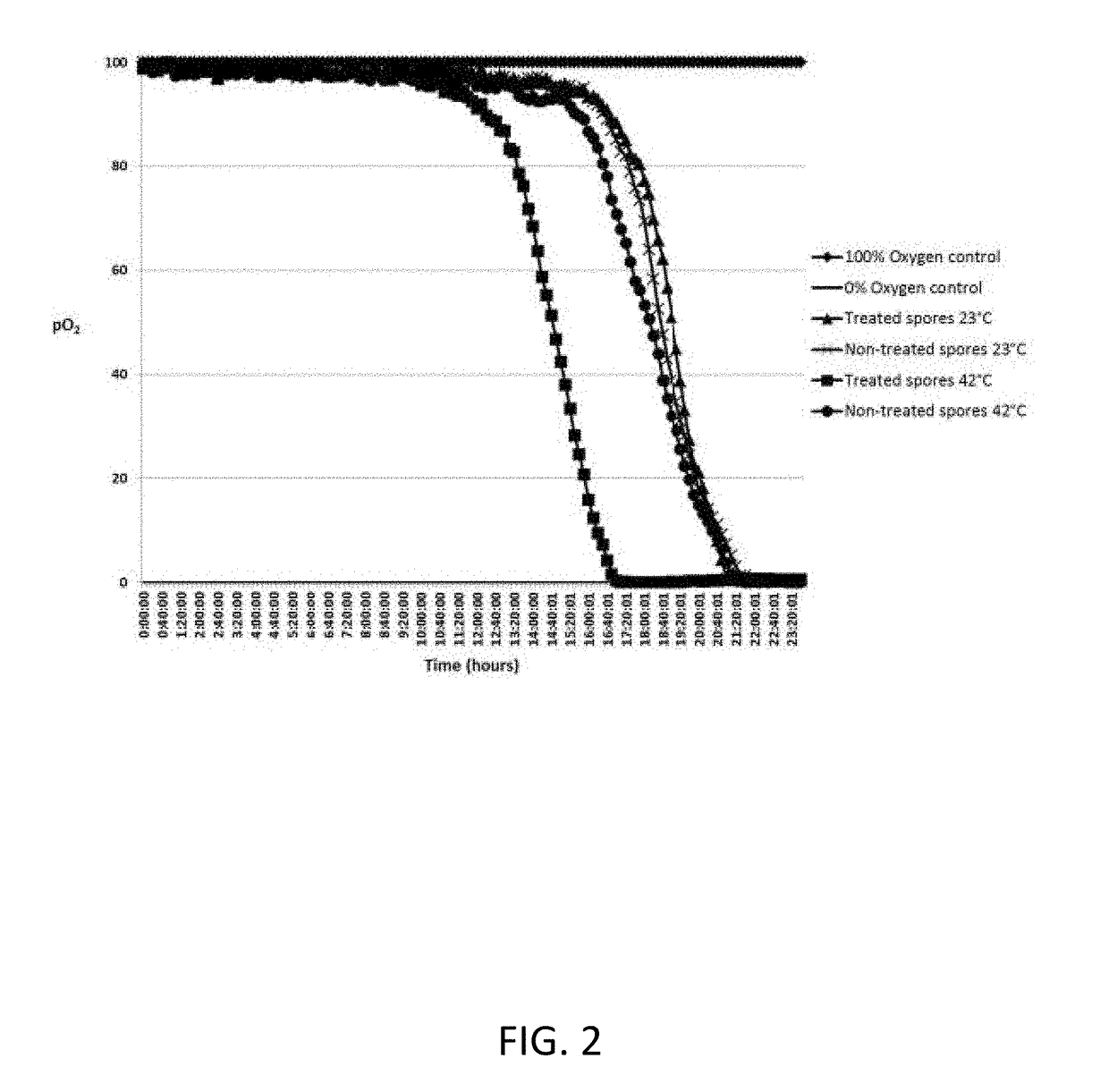
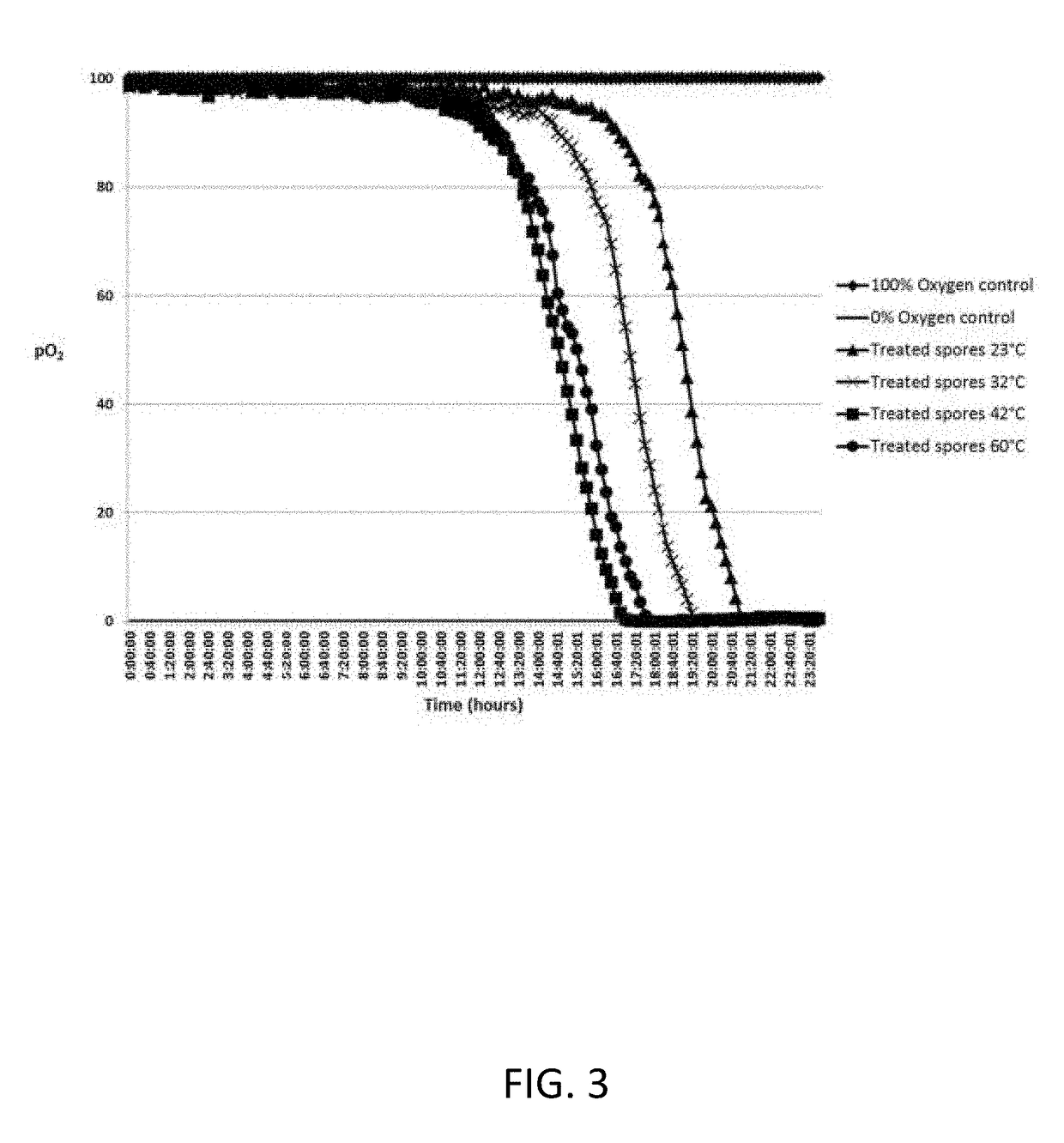
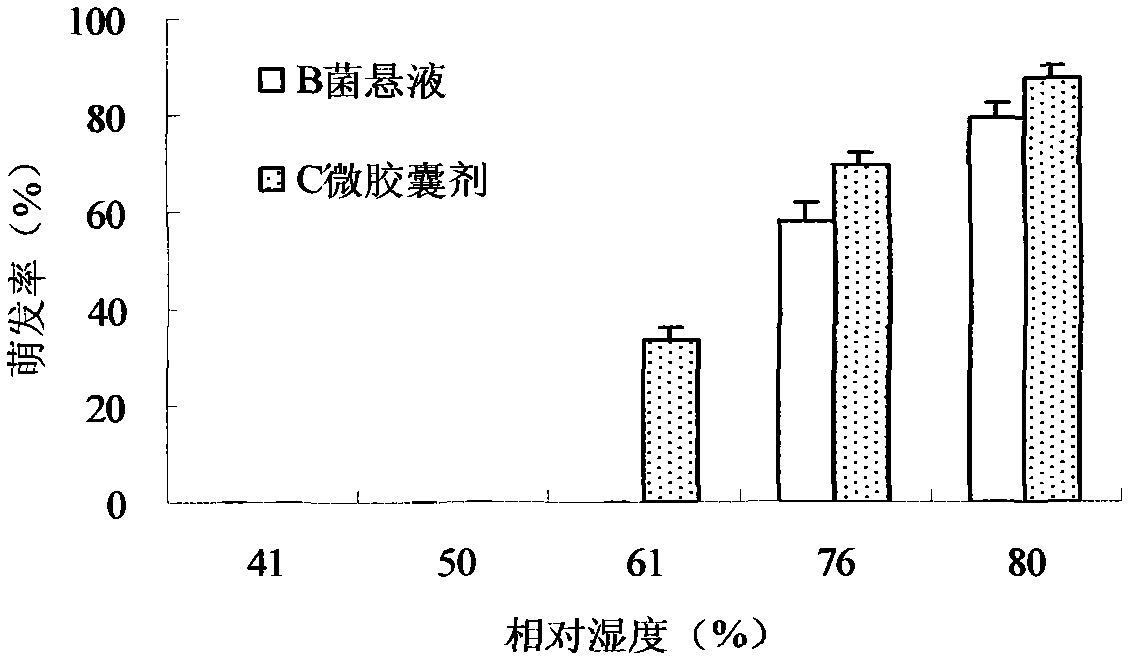
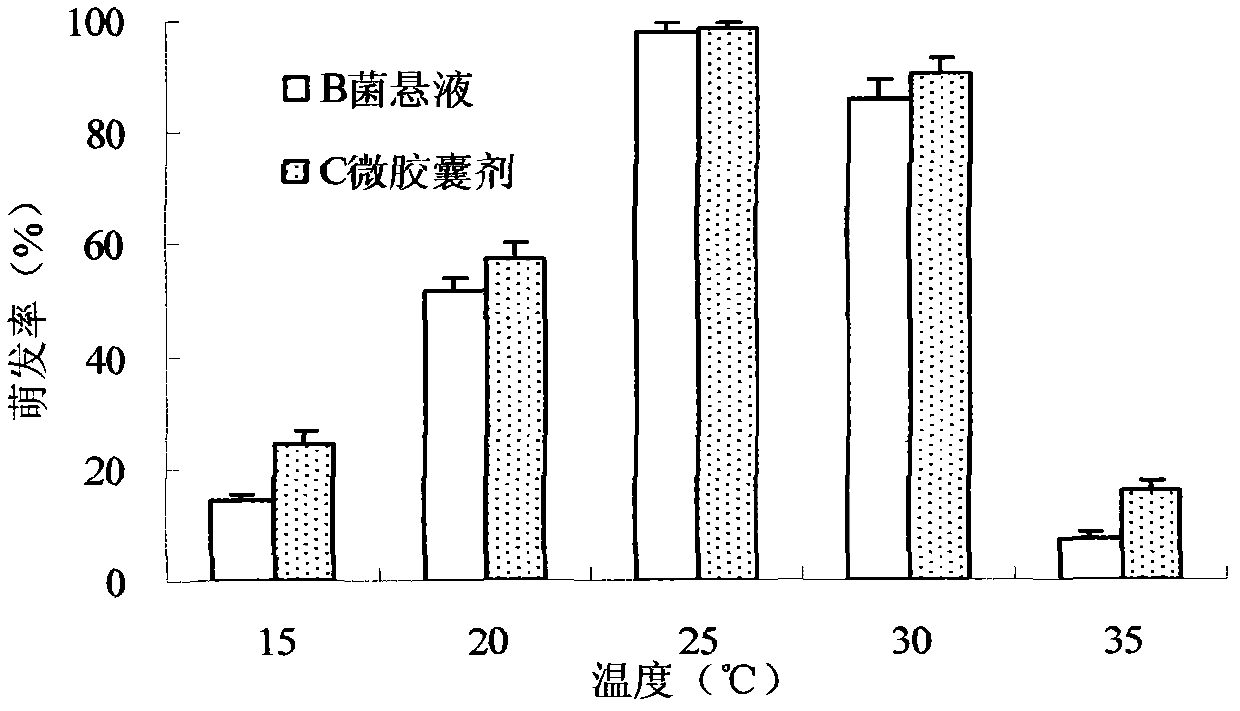
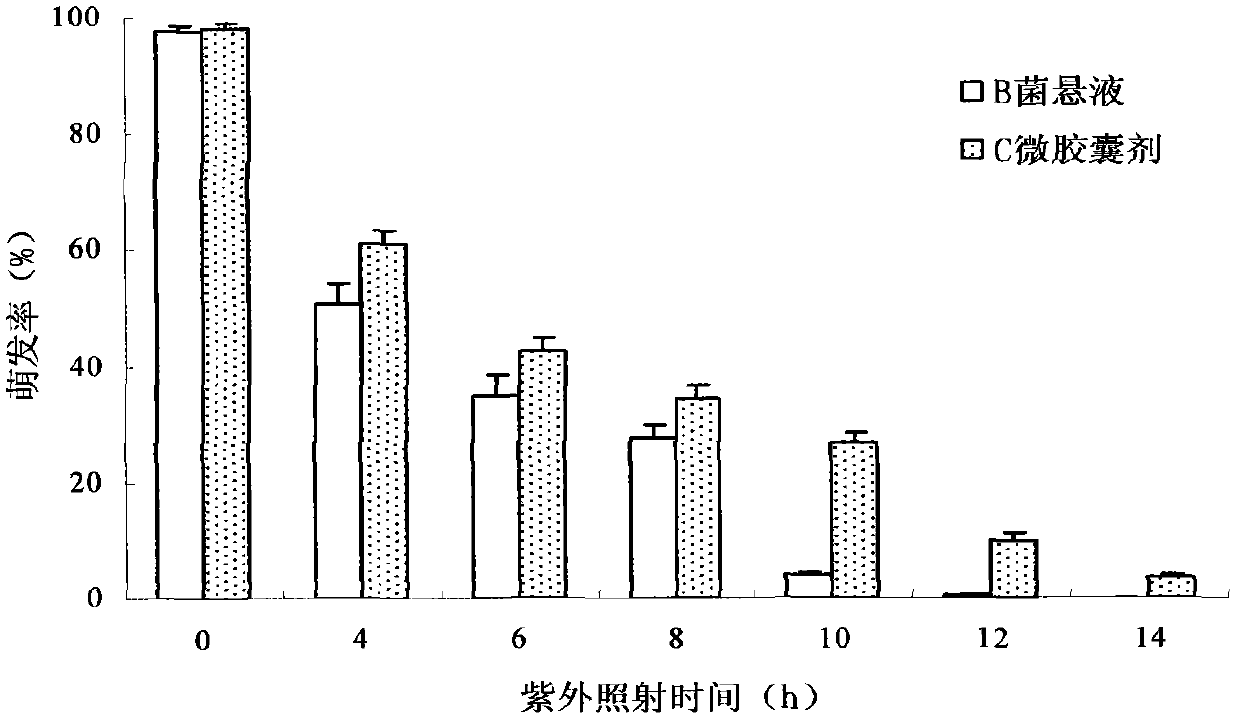
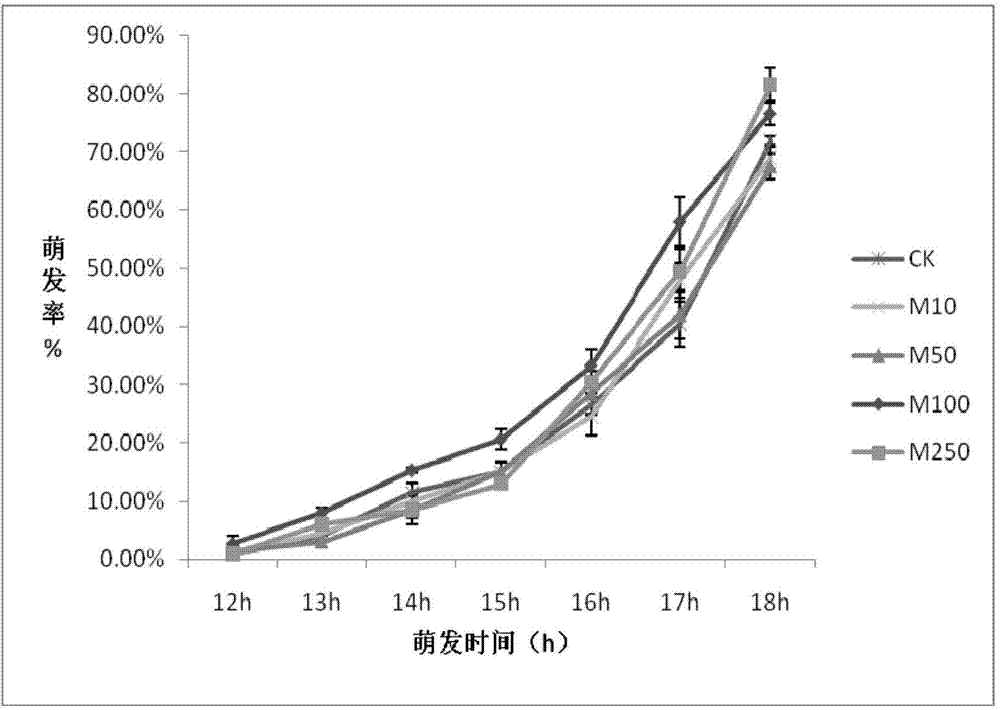
Patents
Literature
658 results about "Spore germination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Spore germination is a process whereby spores exit dormancy to become competent for mitotic cell division.
Composition for accelerating seed germination and plant growth
InactiveUS6979664B1Promote plant growthIncrease productionBiocideAnimal repellantsBrassicaceaeMyriophyllum
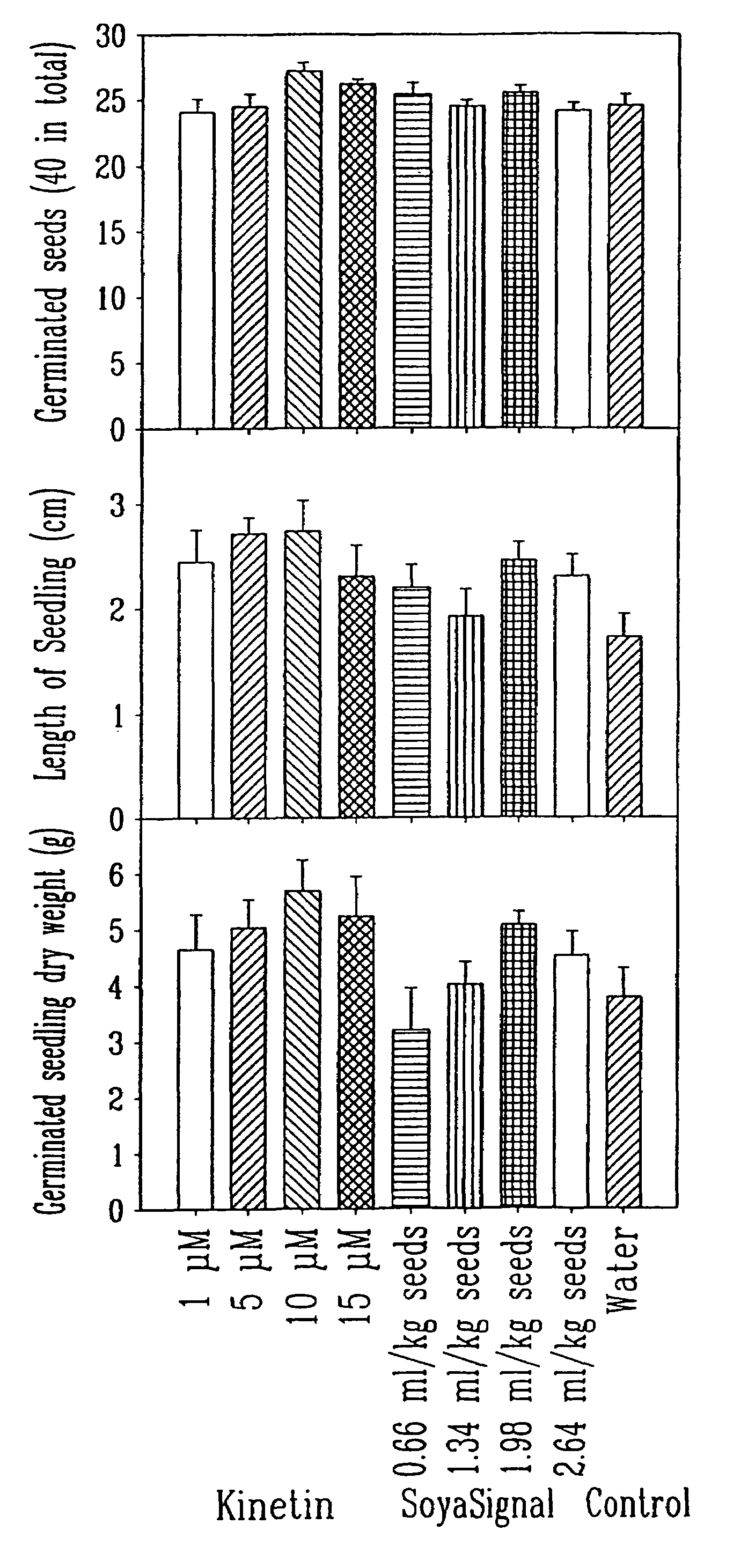
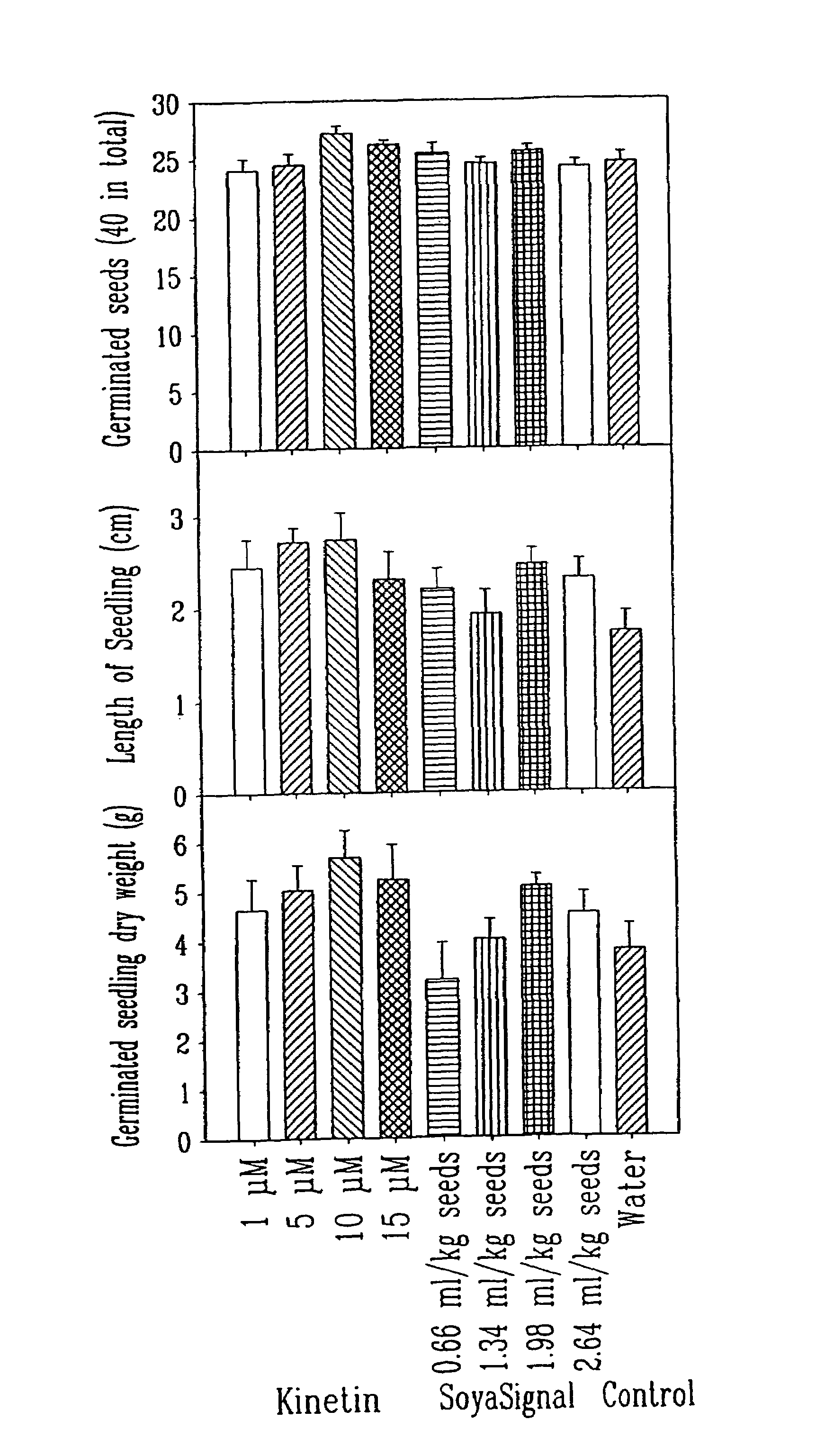
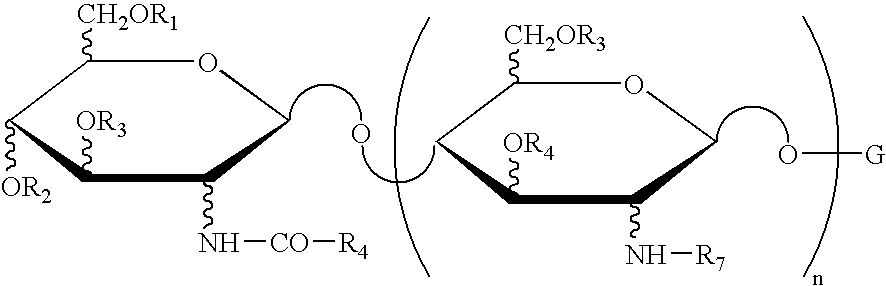
Lipo Chitooligosaccharide (LCO) [NodBj-V(C18:1,Mefuc)] isolated from Bradyrhizobium japonicum strain 532C was able to stimulate seed germination / seedling emergence, or in the case of potato, sprouting, of a number of crop plants representing eight distantly related plant families (Poaceae, Fabaceae, Brassicaceae, Cucurbitaceac, Malvaceae, Asteraceae, Chenopodiaceae and Solanaceae) of plants, at 25 and / or at 15° C. It also promoted sprouting potato minitubers. Other LCOs [NodRM-V(C16:2,5) and LCO from R. leguminosarum] were also shown to also display growth-promoting effects on the tested crop plants. The compositions comprising at least one LCO are shown to be effective in promoting growth under both laboratory and field conditions. The invention thus also relates to methods for promoting seed germination and / or seedling emergence and / or growth of plants comprising subjecting the seeds and / or plants to an effective amount of an agricultural composition comprising at least one LCO.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV +1
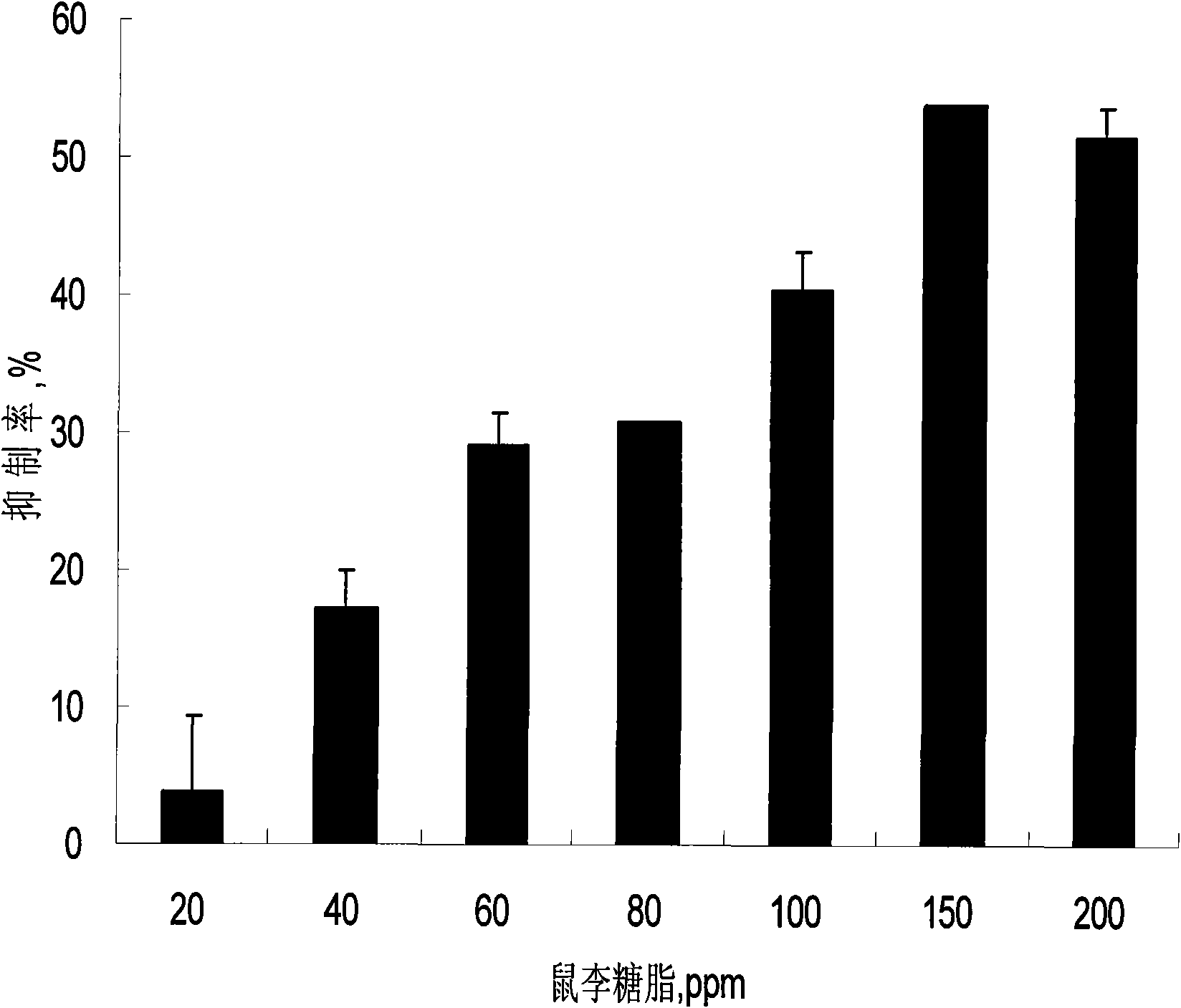
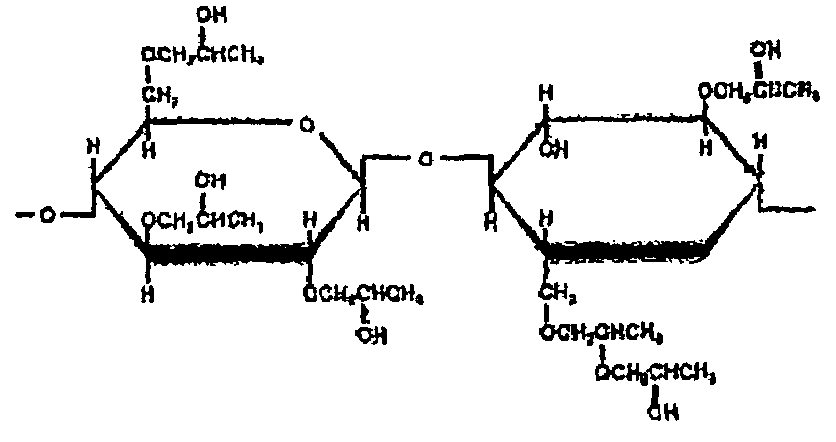
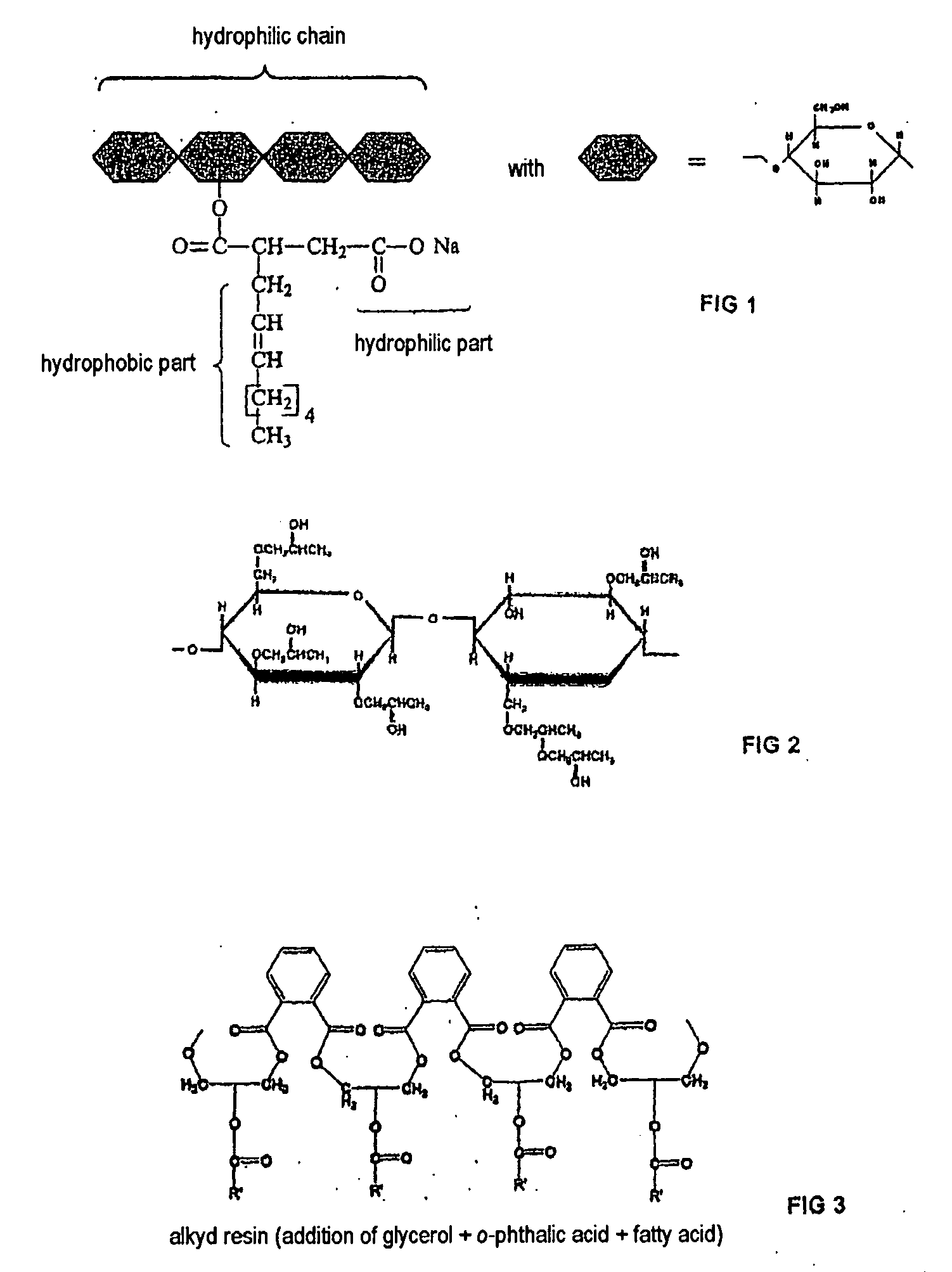
Preparation method and application of rhamnolipid
ActiveCN101845468AReduce manufacturing costLow costBiocideSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningDiseaseSpore germination
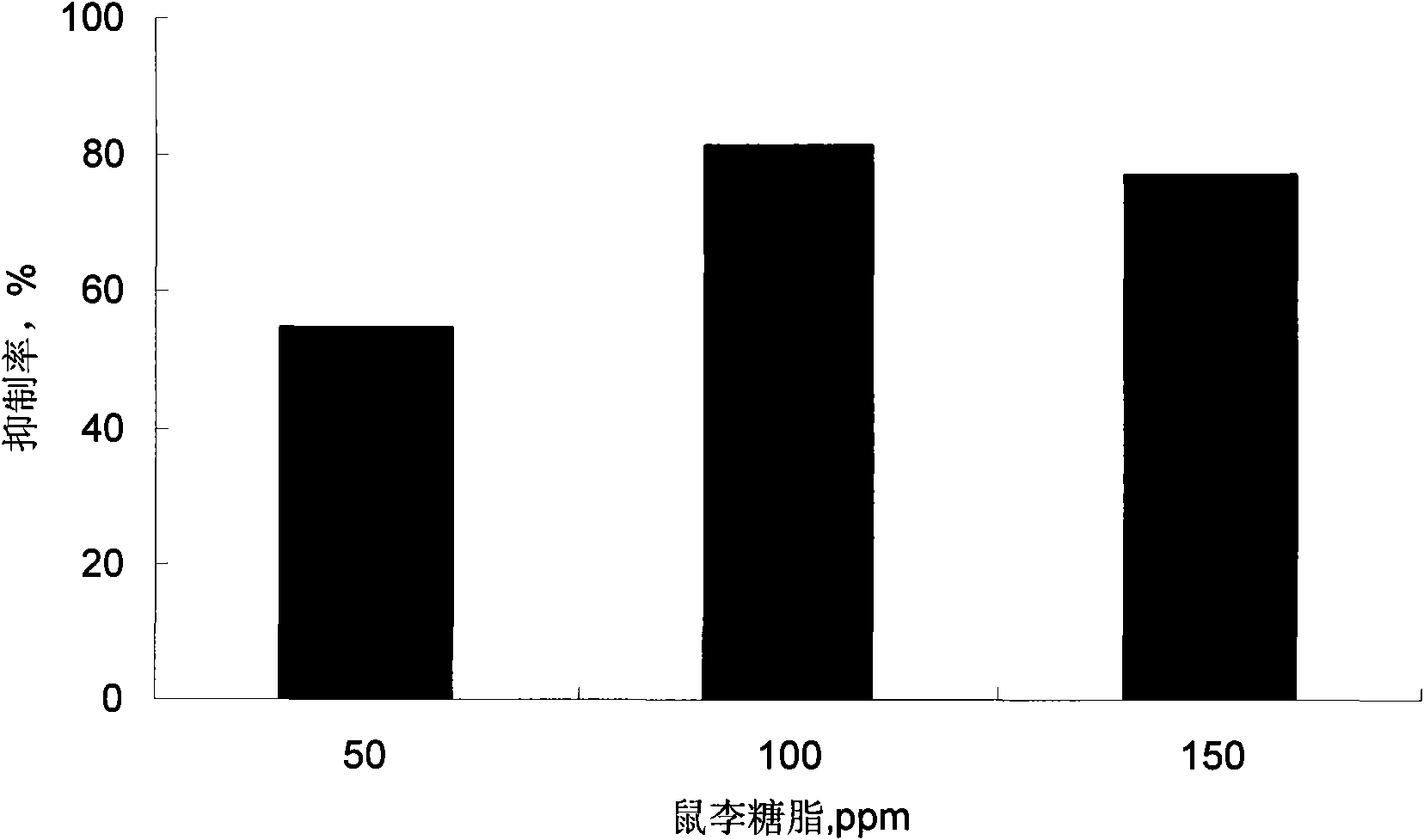
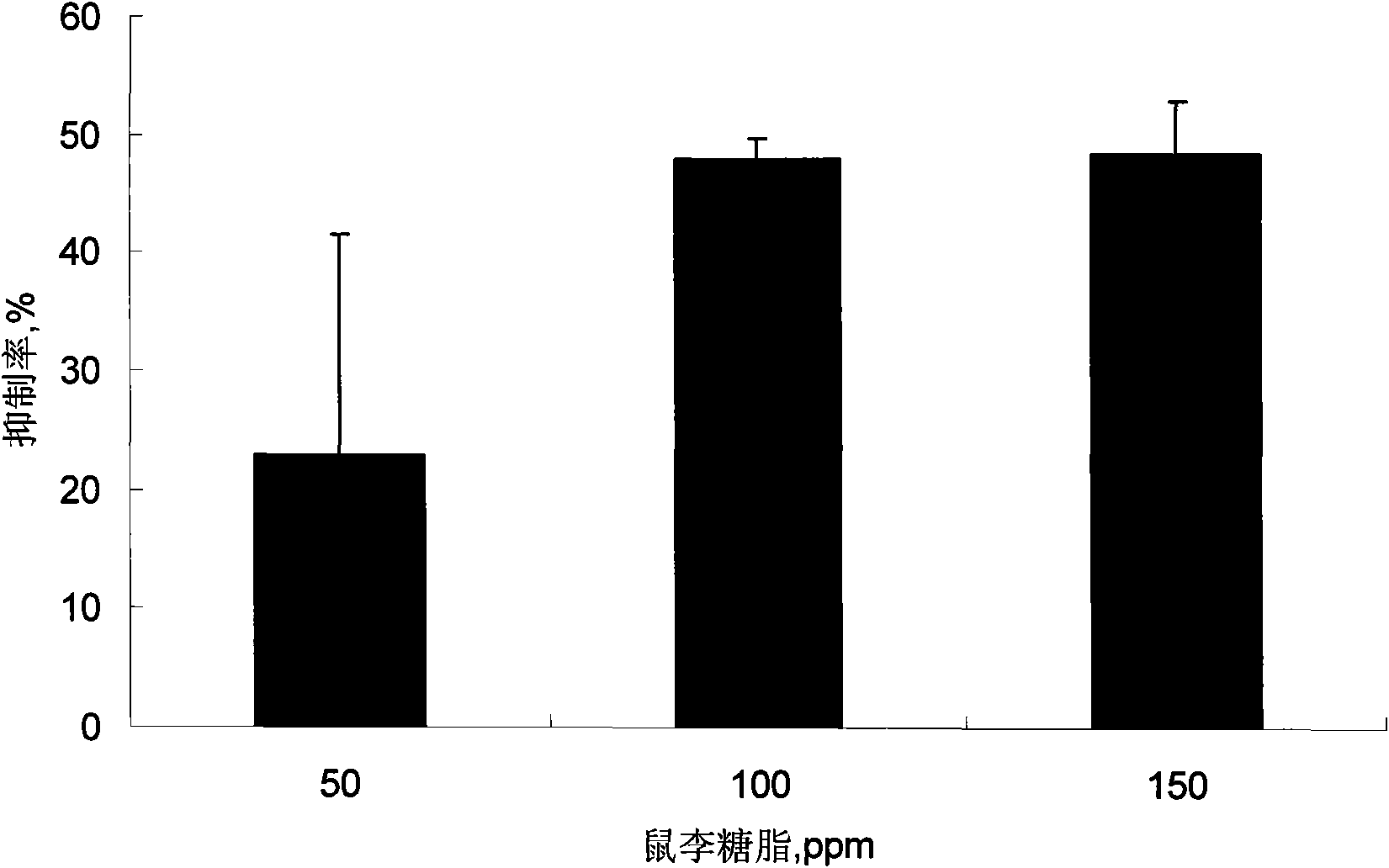
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of rhamnolipid. In the method, the rhamnolipid is produced by using waste grease as carbon source, and utilizing the fermentation of pseudomonas aeruginosa; and with the combination of the defoaming effect of ethanol, the yield of the rhamnolipid can reach 35 to 50 g / L and the cost is about 25 to 40 percent lower than that of the conventional method. When the solution containing 20 to 500 mg / L of rhamnolipid is used for processing plant disease fungus, the ratio of inhibiting disease fungal mycelium growth and spore germination can reach 40 to 90 percent and the plant fungal diseases can be effectively inhibited; the solution containing 20 to 500 mg / L of rhamnolipid has an obvious effect of killing cockroaches and aphids; and in addition, when the rhamnolipid is used as an aid of pesticide, fertilizer and feed and a dehydrating agent of oil-contained sludge by replacing a chemical surface active agent, the effect is obvious.
Owner:浙江圣达紫金生物科技有限公司
Delayed-effect agronomic treatment agent, in particular for seed germination and plant development
ActiveUS20090199314A1Promote growthImprove the immunityBiocidePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSeparated stateHydrophilic polymers
Agent for the agronomic treatment of a living plant supported by a moist substrate, for example a soil, wherein said agent is in the solid and divided state, and comprises solid particles containing at least one active entity for the agronomic treatment, characterized in that each particle comprises: —a nucleus consisting of a grain of a solid material which is inert with respect to the substrate, comprising an inner developed surface area which is greater than its apparent surface area and, as a result, suitable for adsorption and / or absorption, —the active entity for agronomic treatment, absorbed into the grain and / or adsorbed at the surface of said grain, —a membrane encapsulating the nucleus comprising the active entity, consisting of at least one hydrophilic polymer which is permeable to the outside with respect to the active entity, when it is in direct or indirect contact with the moist substrate.
Owner:HM CLAUSE
Isaria fumosorosea oil suspending agent and preparation method as well as application thereof
InactiveCN102246750ALower resistanceEffective controlBiocideAnimal repellantsSpore germinationCabbage moth
The invention discloses an isaria fumosorosea oil suspending agent and a preparation method as well as application thereof. The oil suspending agent is prepared from the following components in mass percent: 1-40% of isaria fumosorosea spore suspension, 1-20% of vegetable oil, 3-8% of emulsifying agent, 0.1-5% of dispersing agent, 1-5% of stabilizing agent, 1-5% of anti-freezing agent and the balance of inert mineral oil or aromatic hydrocarbon solvent. The spore of the isaria fumosorosea oil suspending agent disclosed by the invention has long survival time, and the germination rate of the spore which is stored for 2 years is 80%; the isaria fumosorosea oil suspending agent has good ageing stability and is safe to crops and environments; and the isaria fumosorosea oil suspending agent is mainly used for pest control of crops including fruit trees, vegetables, wheat, rice, flowers and the like, and especially has an obvious effect on controlling myzus persicae, whiteflies, cabbage caterpillars, cabbage moths and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
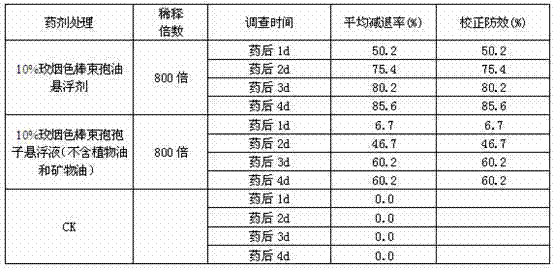
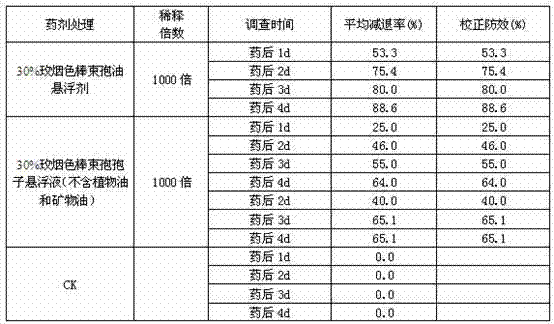
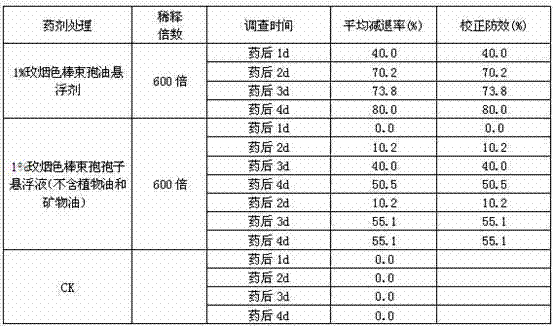
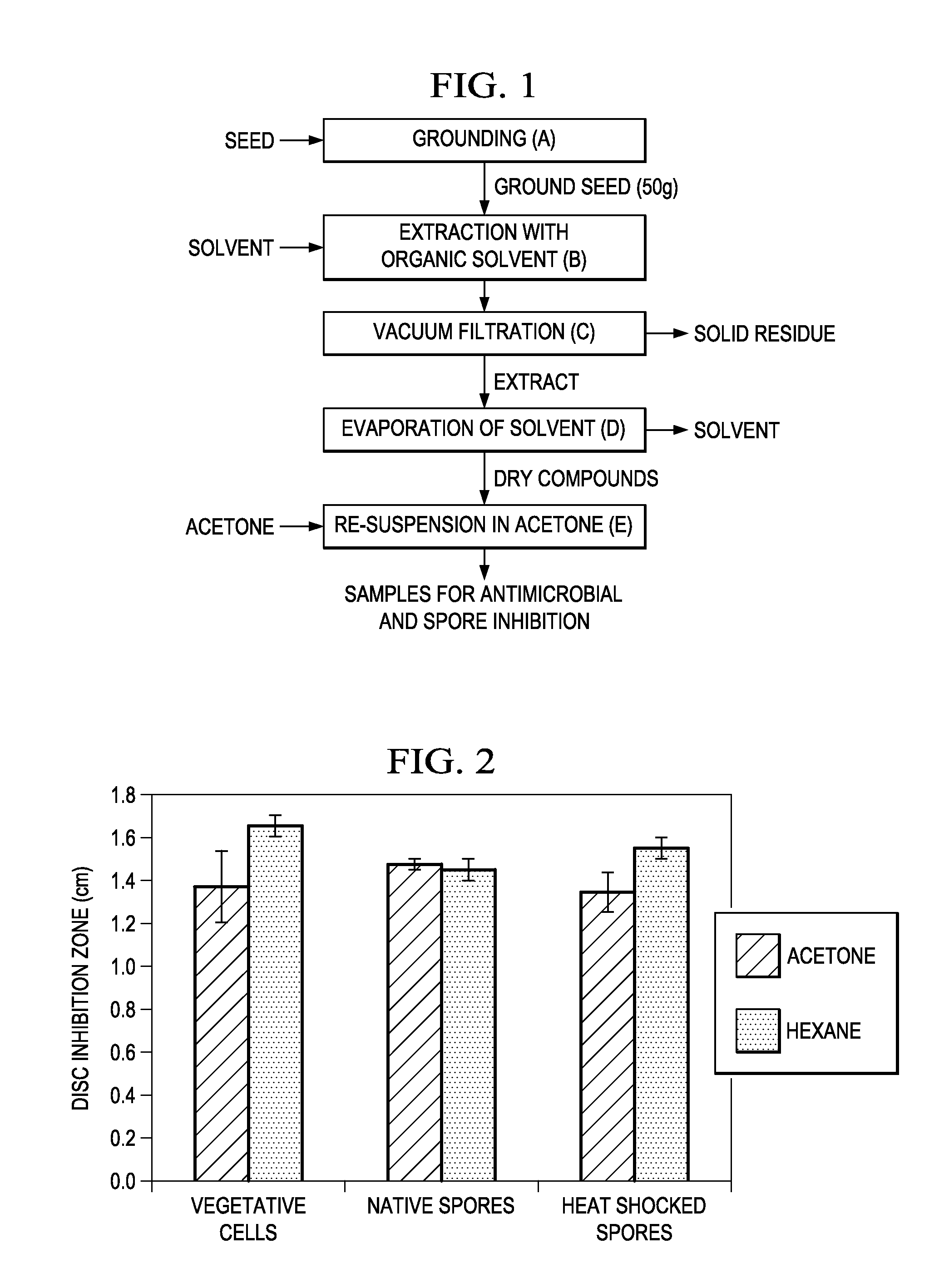
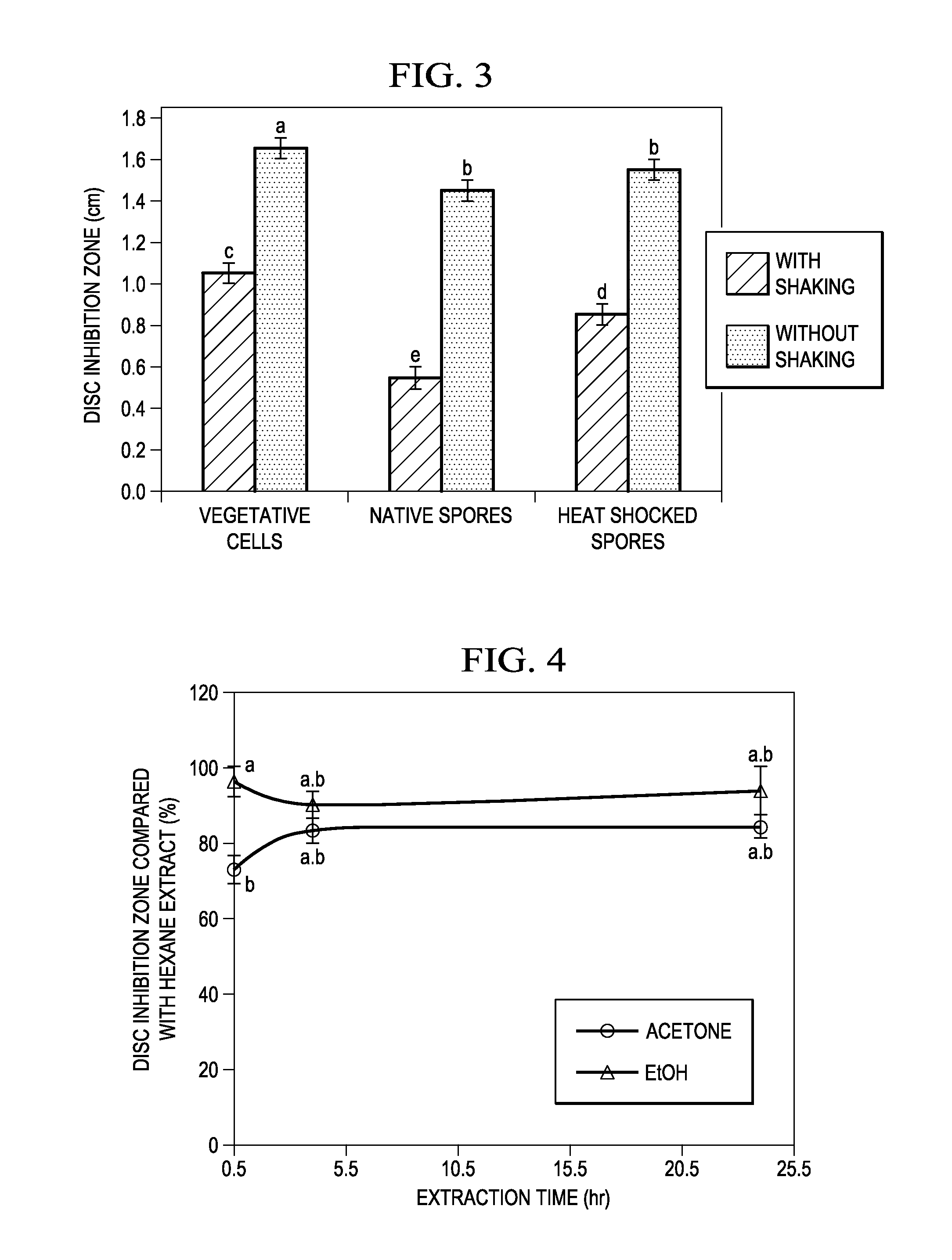
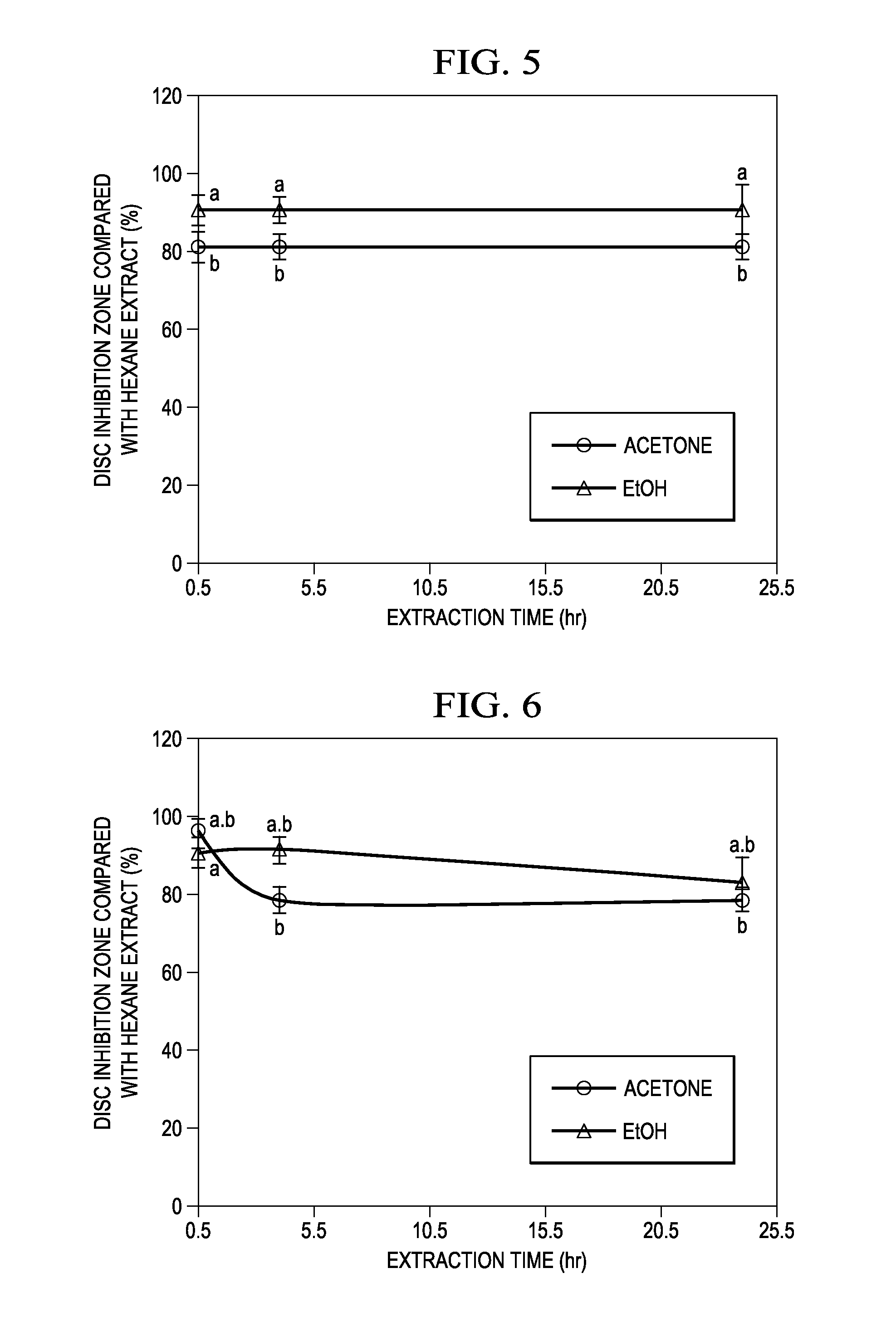
Antimicrobial, antibacterial and spore germination inhibiting activity from an avocado extract enriched in bioactive compounds
InactiveUS20130216488A1Inhibit growth of viableInhibition of spore germinationAntibacterial agentsBiocideSpore germinationCompound (substance)
The present disclosure relates to extracts from Persea sp. (avocado) enriched in bioactive compounds which can be used as antimicrobial, antibacterial or spore germination inhibiting agents, the process for obtaining the extracts, acetogenins and isolated molecules and methods for using the extracts enriched in bioactive compounds for providing antimicrobial, antibacterial or spore germination inhibiting effect.
Owner:INST TECHNOLOGICO & DE ESTUDIOS SUPERIORES DE MONTERREY +1
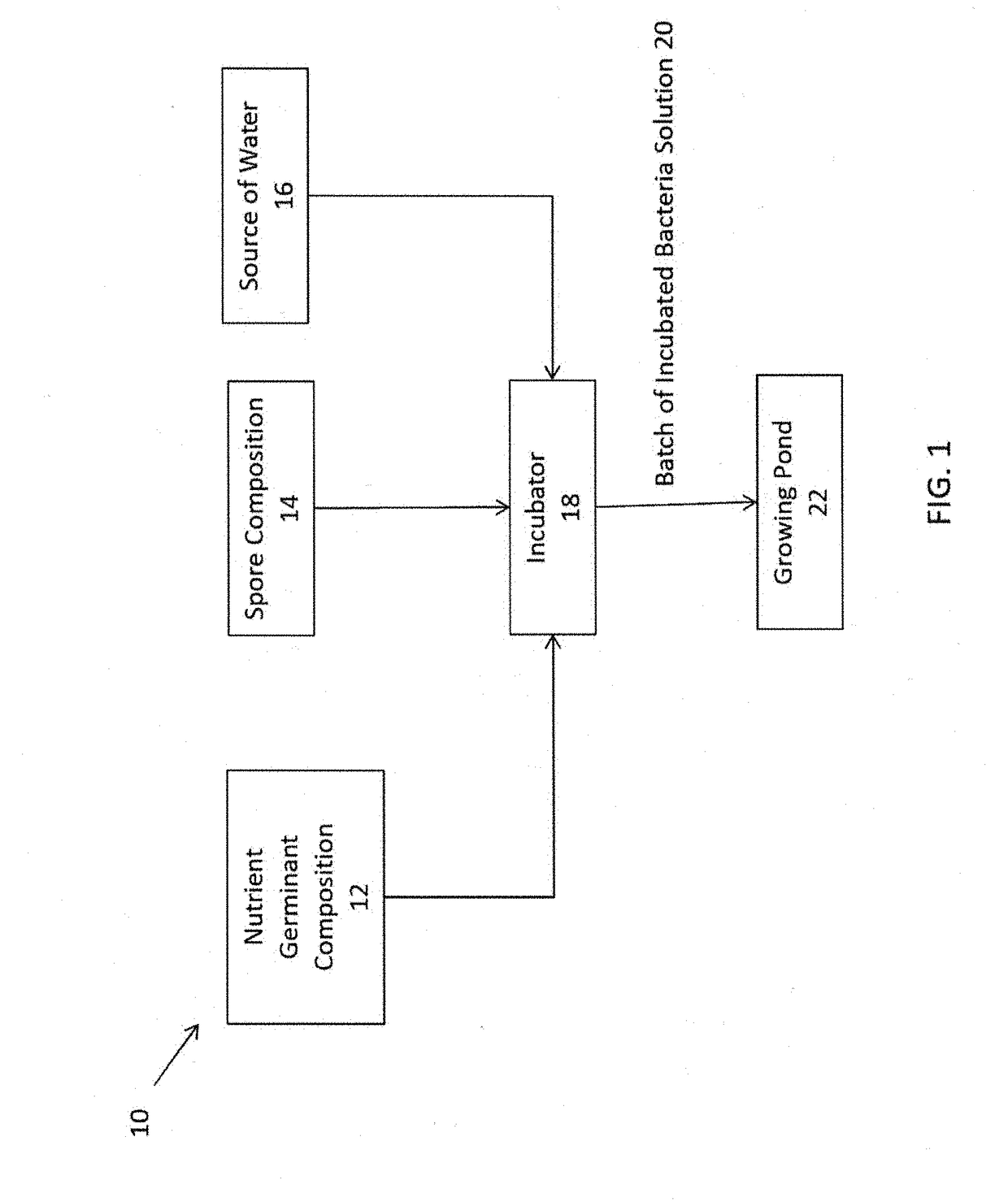
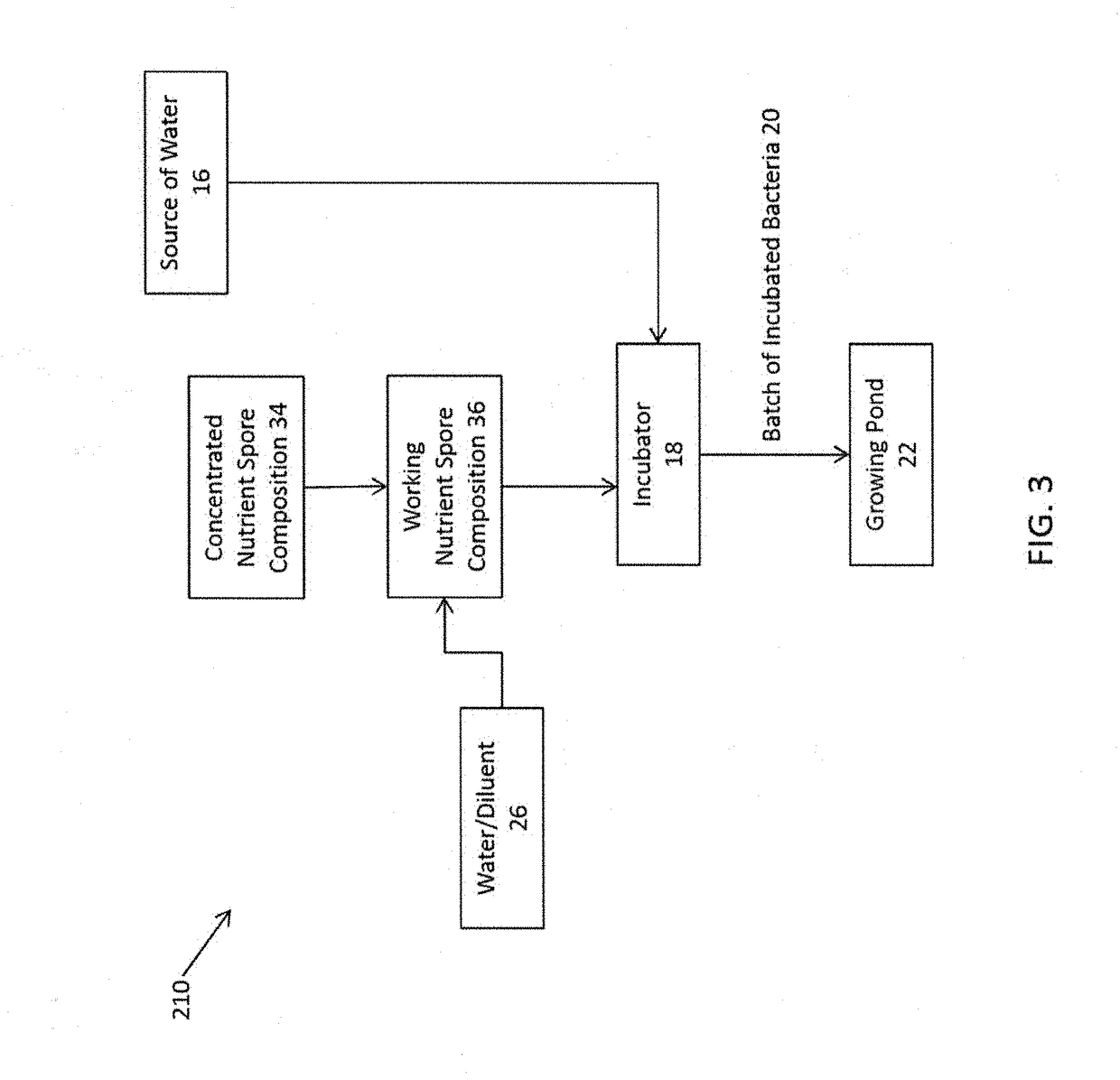
Method for Improving Quality of Aquaculture Pond Water Using a Nutrient Germinant Composition and Spore Incubation Method
ActiveUS20190071336A1Reduces disease pressureIncrease harvestWater contaminantsWaste water treatment from animal husbandrySpore germinationMetal particle
A method for improving the quality of pond water used in aquaculture applications by adding to the pond water active bacteria that are preferably germinated from spores on site using a nutrient-germinant composition and an incubation method for increased spore germination efficiency, in combination with a nitrification enhancement agent such as calcium carbonate or calcified seaweed, and an optional reaction surface area modifier such as calcified seaweed or plastic or metal particles or fragments. The nutrient-germinant composition comprises L-amino acids, D-glucose and / or D-fructose, a phosphate buffer, an industrial preservative, and may include bacteria spores (preferably of one or more Bacillus species) or they may be separately combined for germination. The incubation method comprises heating a nutrient germinant composition and bacteria spores, to a temperature range of 35° C. to 60° C. for around 2 to 60 minutes to produce an incubated bacteria solution that is discharged to the aquaculture application.
Owner:NCH CORP
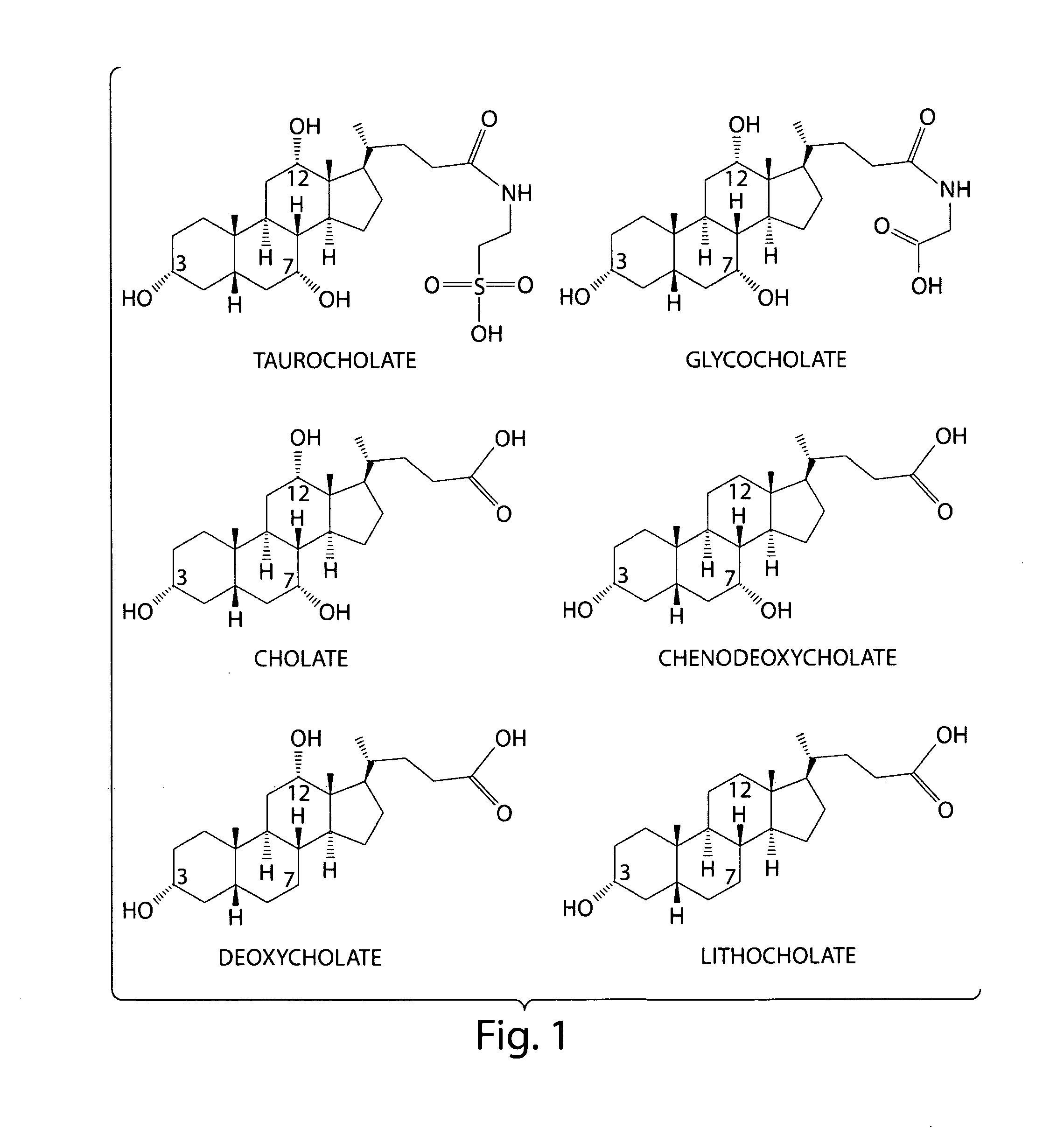
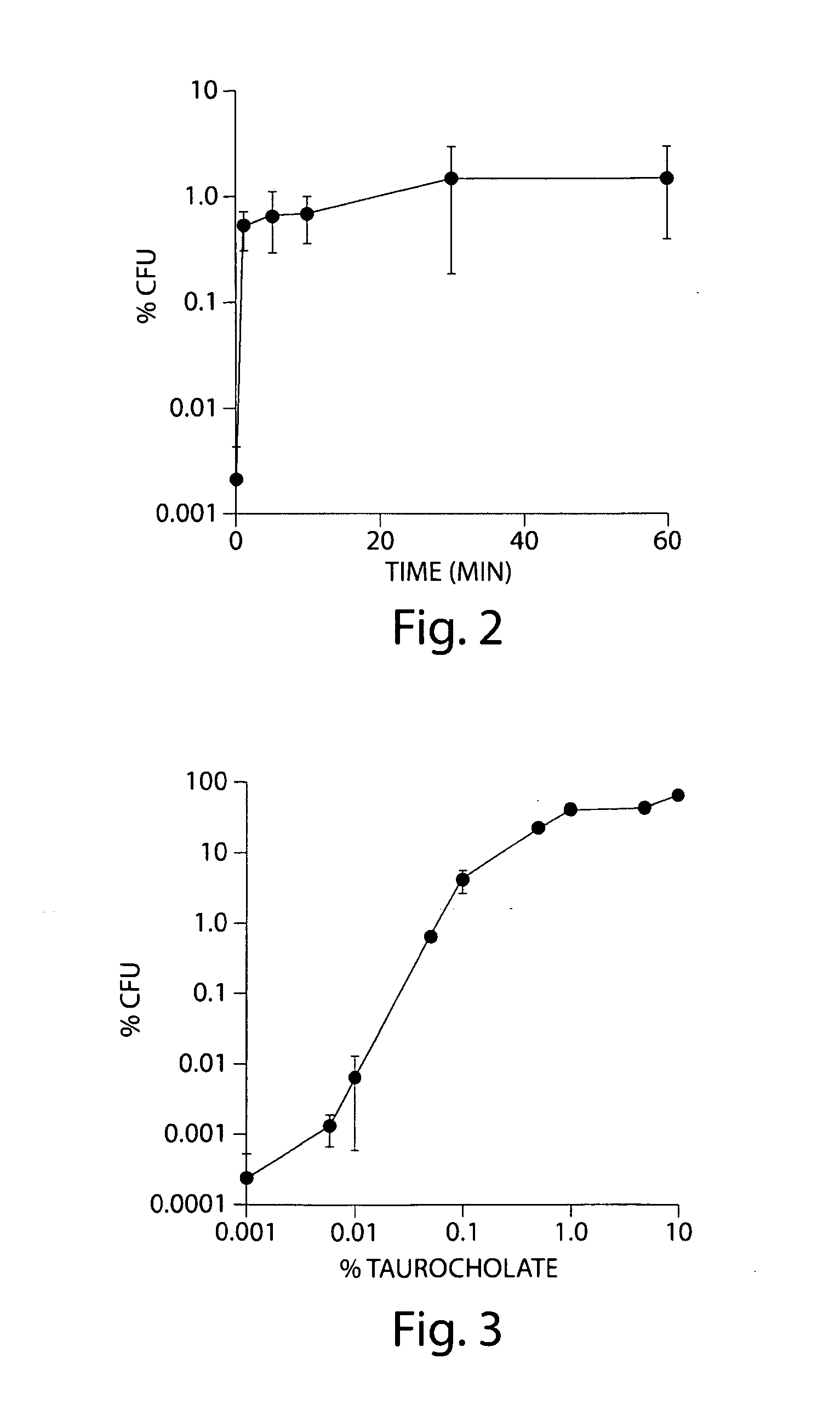
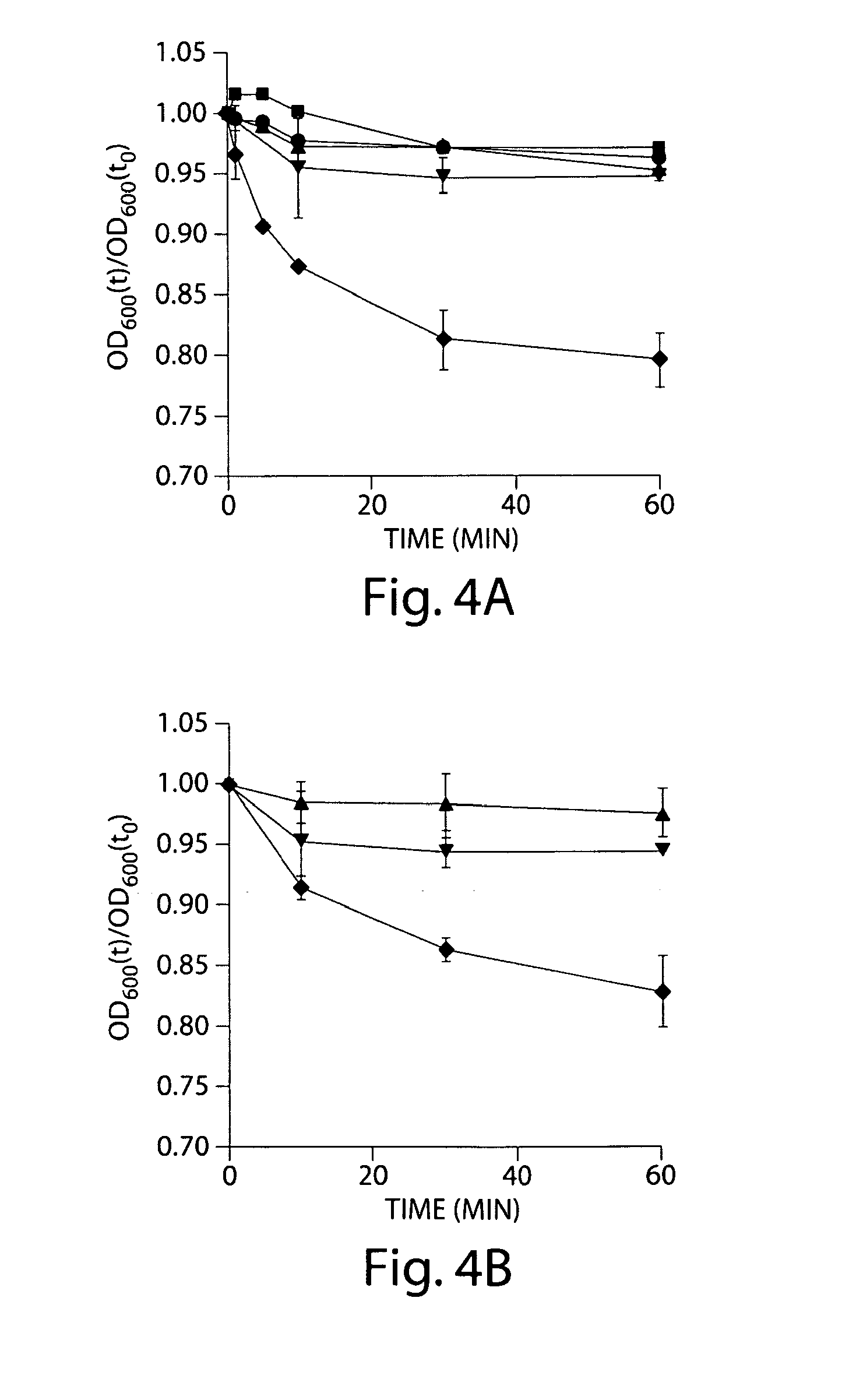
Methods and compositions for inhibiting clostridium difficile spore germination and outgrowth
ActiveUS20110280847A1Preventing Clostridium difficile-associated diseaseGrowth inhibitionAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseSpore germination
Certain bile acids, including novel bile acids, and derivatives thereof can be used to inhibit the germination of C. difficile spores and / or the growth of C. difficile cells. The methods and compositions of the invention are useful for preventing and treating C. difficile-associated diseases, including but not limited to C. difficile colitis.
Owner:TUFTS UNIV
Paecilomyceslilacinus strain having strong pathogenicity for diaphorina citri
ActiveCN103160442AStrong pathogenicityStrong action and effectBiocideFungiSpore germinationMicrobiological culture
The invention relates to a paecilomyceslilacinus strain having strong pathogenicity for diaphorina citri and belongs to the technical field of the microorganism. The strain is paecilomyceslilacinus ZJPL08 which is registered and conserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on March 15, 2013, and the conservation number of the strain is CGMCC No. 7318. The paecilomyceslilacinus ZJPL08 provided by the invention has stronger pathogenicity for diaphorina citri and can be developed into a biocontrol agent for biological prevention and treatment of diaphorina citri; and compared with the present chemical agent for preventing and treating diaphorina citri, the paecilomyceslilacinus ZJPL08 has the characteristics of high efficiency, low toxicity, low residue, no pollution and not easy creation of resistance to drugs. The strain ZJPL08 has stronger acting effect on diaphorina citri than other paecilomyceslilacinus strains; the strain ZJPL08 is quick to cultivation, high in sporulation quantity, high in germination rate of spores and easy for preparation, and has excellent market application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CITRUS RES INST
Novel targets and compositions for use in decontamination, immunoprophylaxis, and post-exposure therapy against anthrax
InactiveUS20050271689A1Precise positioningEfficient methodBacterial antigen ingredientsDepsipeptidesEpitopeSpore germination
The present invention relates to the decontamination of anthrax spores, prophylaxis and treatment of anthrax infections and, more particularly, to compounds that act as specific inhibitors of B. anthracis germination / outgrowth-associated proteins, methods and means for making such inhibitors and their use as pharmaceuticals and / or vaccines. The invention also relates to the prophylaxis and treatment of anthrax infections and, more particularly, to vaccines and compositions that comprise B. anthracis antigens, epitopes, proteins, or nucleic acid molecules, including anthrax protective antigen, anthrax lethal factor, anthrax edema factor and anthrax proteins associated with spore germination and outgrowth, as well as methods and means for making such compositions and their use pharmaceuticals and / or vaccines.
Owner:ALTIMMUNE INC
Method for culturing rhizome drynariae
InactiveCN1726760AImprove germinationEarly germinationHorticulture methodsSpore germinationSporophyte
An artificial reproduction method for drynaria includes asexual production and spore reproduction. Said asexual reproduction includes such steps as taking its rhizome segment with 3-5 bud points and 3-5 sporophyllary leaves, fixing it to tree or mountain rock, covering it by bryophyte, spraying water and management. Said spore reproduction includes such steps as sterilizing the burnt earth, immersing in cold boiled water, loading the sporanges in bag, drying in air, preparing the suspension of sporanges, spraying it onto said burnt earth, optical culture to obtain gametophytes, transplanting, culturing to obtain sporophytes, and transplanting them on tree or mountain rock.
Owner:WUHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
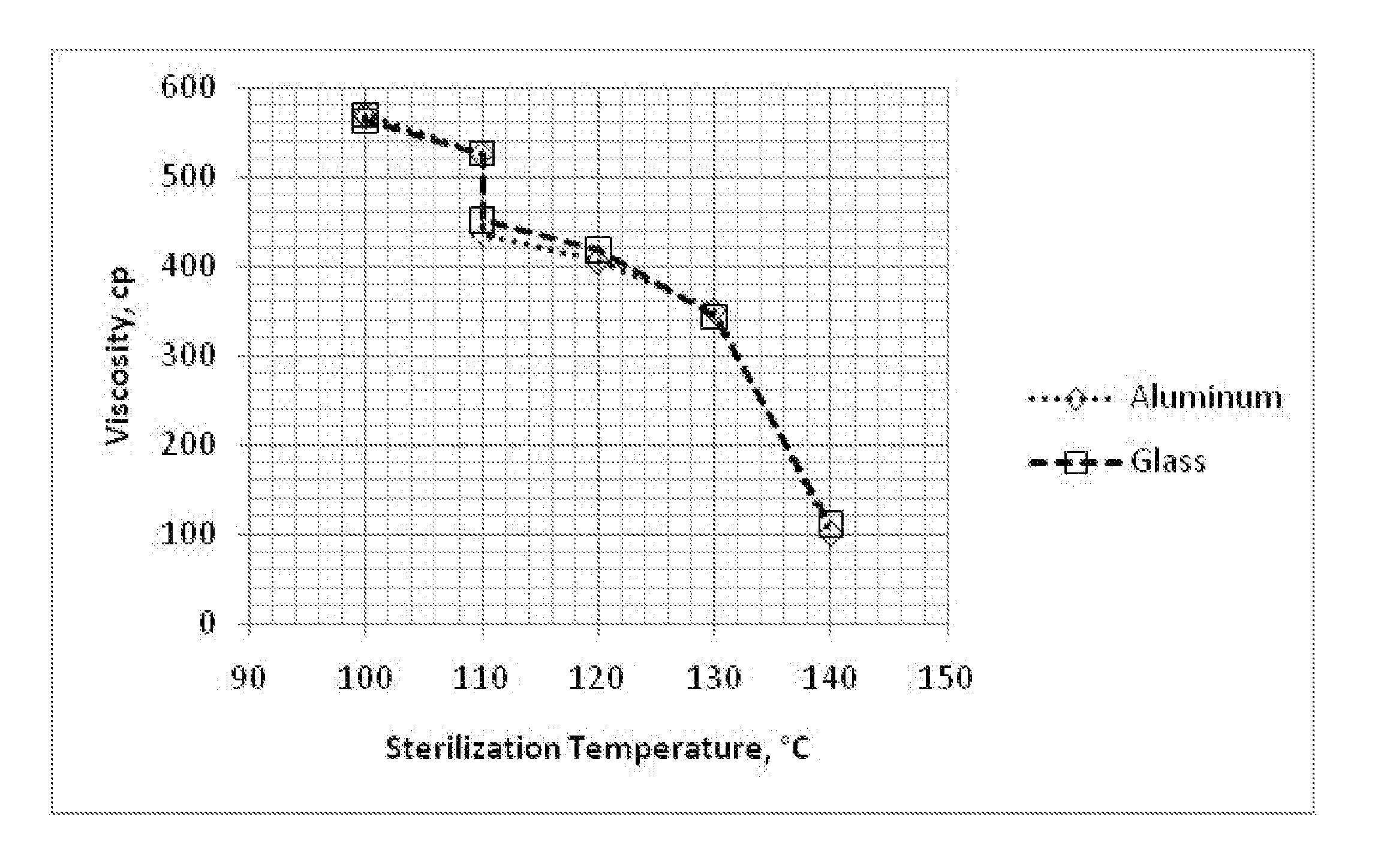
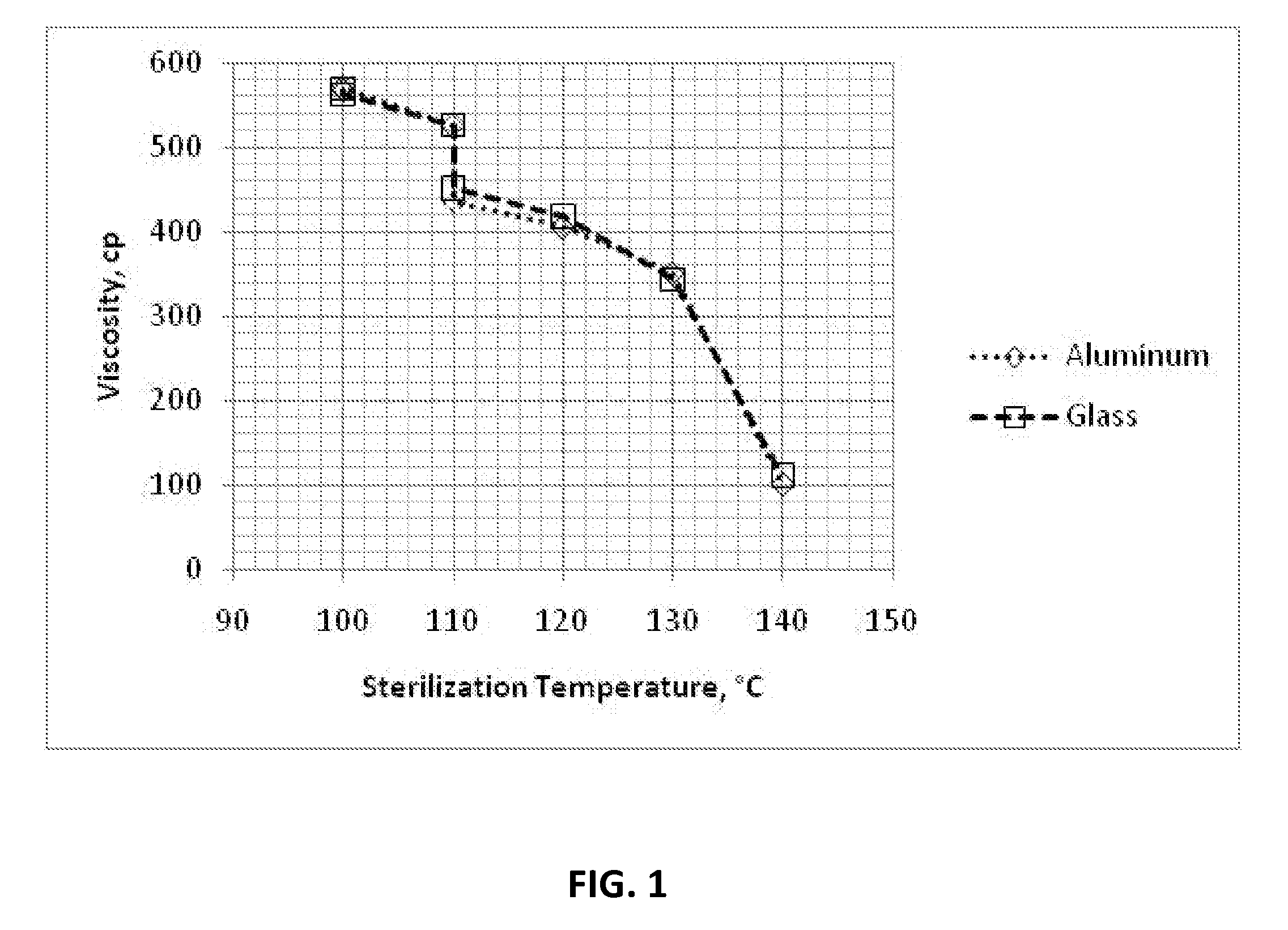
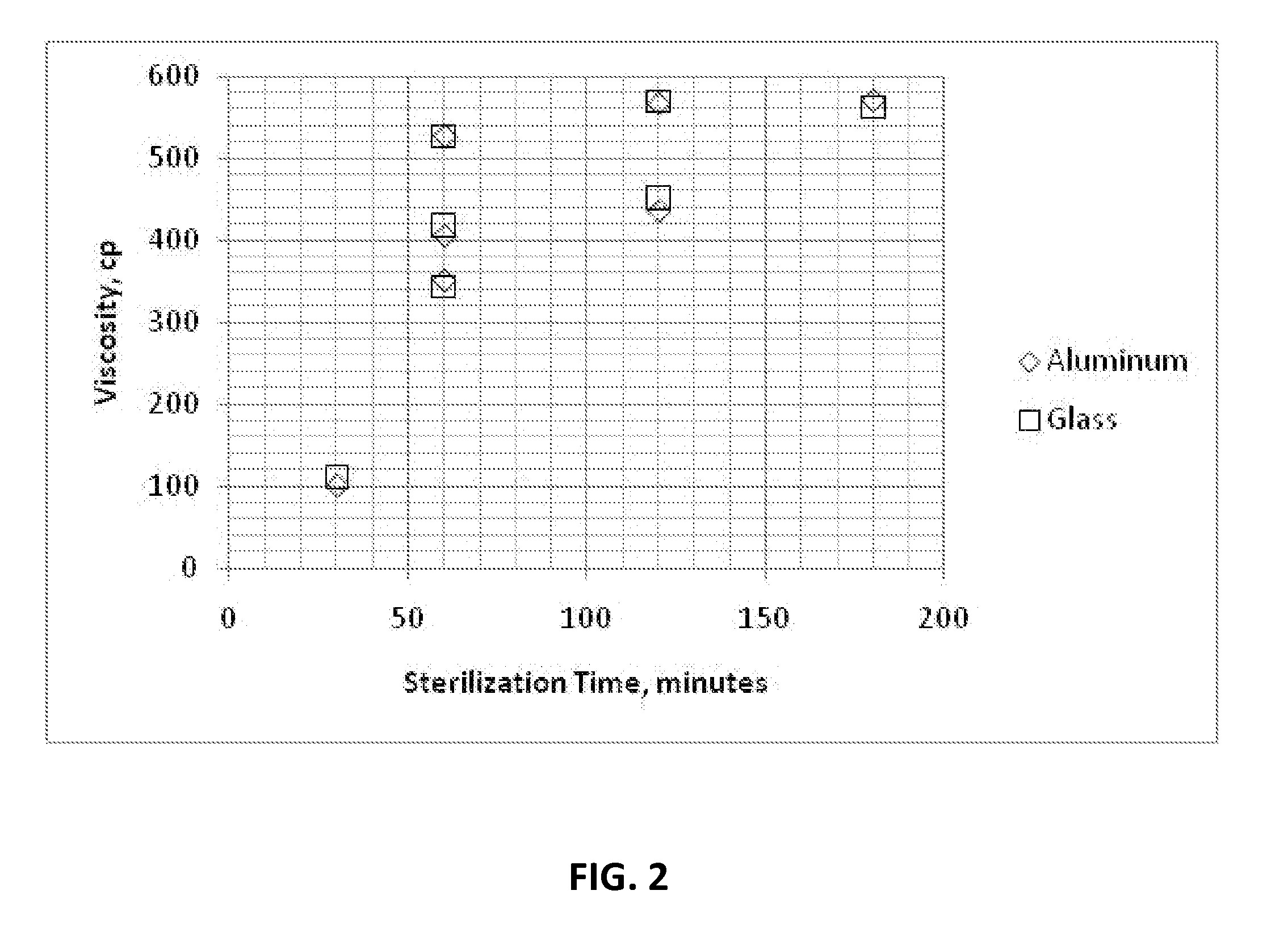
Cyanoacrylate Adhesive Compositions and Devices and Process for Sterilization Thereof
The viscosity of 2-cyanoacrylate monomer based adhesives is increased by combining the monomers with suitable thickeners according to a certain process. The resulting formulations may be heat sterilized without degrading the viscosity or causing premature polymerization. The effectiveness of the sterilization process is assayed by disposing bacterial spores in the formulation, exposing it to a dry heat sterilization process, transferring it to a sterile aldose solution, transferring and exposing the sample to a nutrient medium which supports germination and growth of viable spores, incubating the samples, and determining the presence or absence of growth.
Owner:CLAST TRADING
Dried spore germinative compound mixtures
ActiveUS20140220662A1Improved germination and growthHigh activityBacteriaUnknown materialsSpore germinationBacteria
In one aspect, the present invention is directed to a dried intimate mixture comprising a bacteria spore and a germinative compound, and methods for preparing the intimate mixture. In another aspect, this invention is directed to a composition comprising such an intimate mixture. The invention also relates to methods for increasing the germination, growth, metabolism, and / or enzyme activity of a bacteria spore comprising preparing an intimate mixture of a bacteria spore and a germinative compound.
Owner:ENVERA LLC
Preparation method of bacillus subtilis wettable powder
ActiveCN105432667AReduce exposureReduce the chance of germinationBiocideDead animal preservationSpore germinationPlant disease
The invention relates to the fields of biological pesticide and microbial fertilizer, and specifically discloses a bacillus subtilis wettable powder containing spore germinator and a preparation method thereof. The wettable powder is composed of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 40 to 70 parts of bacillus subtilis fermentation broth, 20 to 30 parts of filling material (diatomite), 1 to 4 parts of wetting agent (Morwet EFW), 0.2 to 1 part of dispersant (CMC-Na), spore germinator: 0.1 to 0.5 part of L-alanine, 0.1 to 0.5 part of inosine, and 0.5 to 1.5 parts of fructose; UV protector: 0.5 to 2 parts of ascorbic acid, and 0.2 to 1 part of lecithin; dryness protector: 1 to 4 parts of maltose and 0.2 to 1 part of methylcellulose, and 1 to 2 parts of synergist (amino oligosaccharin). After the prepared bacillus subtilis wettable powder is applied to the fields, the spore germination speed is accelerated, the germination rate is high, the fertilizing effect and the plant disease control effect are both prominently improved, the using amount of spores is reduced, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:广西南宁晴空万里环保科技有限公司
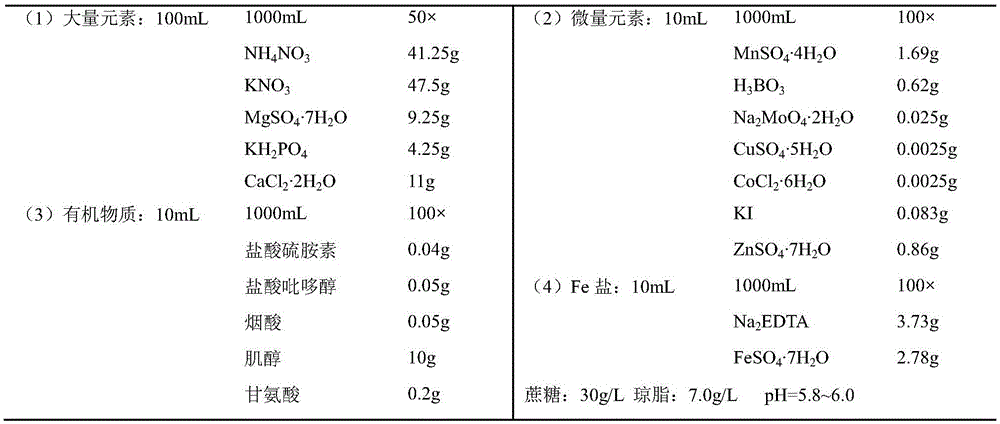
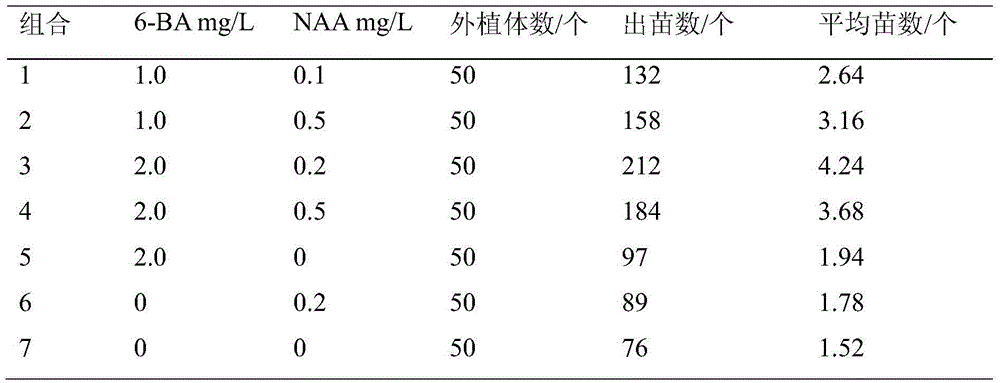
Culture medium composition suitable for germ-free germination of orchid seeds and method thereof
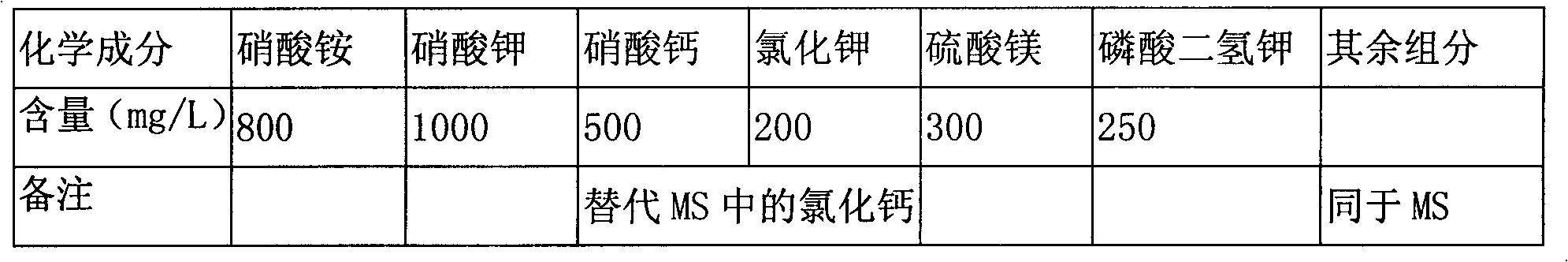
InactiveCN101622955AStrong targetingImprove applicabilitySeed and root treatmentCultivating equipmentsSucroseSpore germination
The invention mainly relates to a culture medium composition suitable for germ-free germination of orchid seeds and a method thereof. Various components of a basic culture medium and a seed germination culture medium are as follows: 500mg / L of calcium nitrate, 200mg / L of potassium chloride, 20-30g / L of sucrose or white sugar and 5-7g / L of agar, wherein the basic culture medium is selected from self-improved MS, i.e. on the basis of the original MS culture medium, 440mg / L of calcium chloride in the MS basic culture medium is replaced into 500mg / L of calcium nitrate and 200mg / L of potassium chloride; and the pH value is 5.0-5.6. The seed germination culture medium comprises the basic culture medium, 0.5-1.0mg / L of 6-BA, 0.5-1.0mg / L of NAA, 1.0g / l of active carbon and 50-100m / L of coconut milk. The invention has the advantages that: (1) the orchid group-cultured optimized culture medium has strong pertinence, good adaptability and high seed germination rate; (2) the method greatly shortens the breeding period of orchid so as to rapidly obtain new genetic improvement; and (3) the method is convenient for operation and reduces the pollution to the minimum extent.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
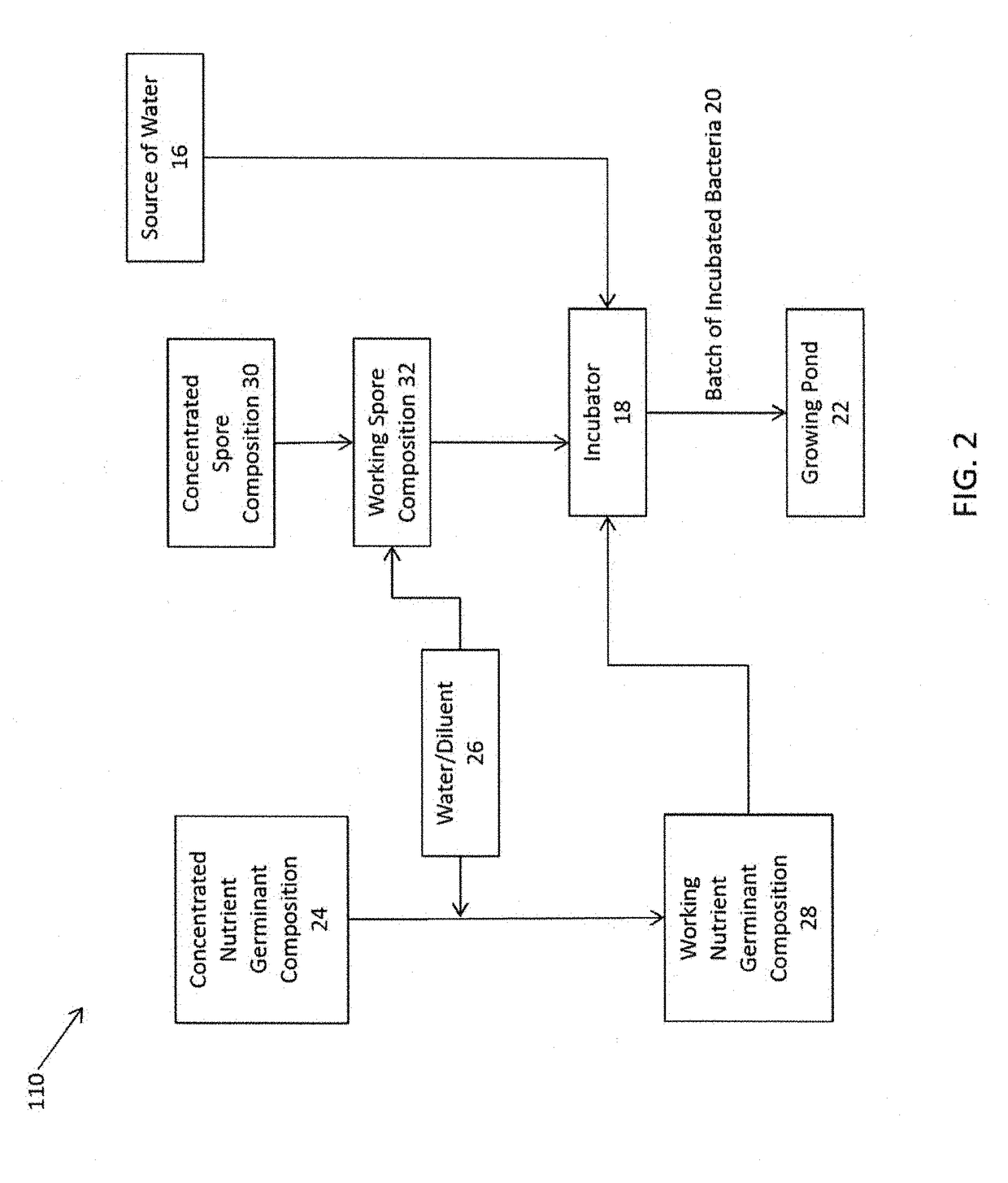
Nutrient Rich Germinant Composition and Spore Incubation Method
ActiveUS20170281696A1Easy and fast mixingLow costBacteriaInorganic non-active ingredientsSpore germinationD-Glucose
A nutrient-germinant composition to aid in spore germination and a method for increased spore germination efficiency. The composition comprises L-amino acids, D-glucose and / or D-fructose, a phosphate buffer, an industrial preservative, and may include bacteria spores or they may be separately combined for germination. The method comprises providing a nutrient-germinant composition and bacteria spores, preferably of one or more Bacillus species, and heating to a preferred elevated temperature range of 41° C. to 44° C. for an incubation period of around 2 to 60 minutes. The nutrient-germinant composition is preferably in a concentrated liquid form that is diluted just prior to initiating the germination / incubation method at the point of use. The method may also include dispensing a germinated spore solution to a point-of-use / consumption, such as animal feed, water, or bedding, or a wastewater system or drain.
Owner:NCH CORP
Biocontrol bacterium and application of biocontrol bacterium to preventing and controlling cotton blight and cotton greensickness
The invention discloses Streptomyces rochei 42561 which is preserved in the general microorganism center of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms (CCCCM), with the preservation number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) NO.6556. The bacteriostatic and prophylactic actions of the biocontrol bacterium 42561 are comprehensively tested according to a cup-plate method, a mycelial growth rate inhibition method, a spore germination inhibition method, greenhouse pot culture and field tests; and the testing results show that the strain has a remarkable prevention effect on cotton blight and cotton greensickness, can be used as an effective biological pesticide preparation agent and has excellent application and development prospects.
Owner:TARIM UNIV
Rapid propagation method for dendrobium hancockii seeds
ActiveCN105638477AMeeting nutritional needsEffectively regulate growthHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSpore germinationSeedling
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant tissue culture and discloses a rapid propagation method for dendrobium hancockii seeds. The rapid propagation method comprises a pretreatment stage, a seed germination culture stage, a protocorm differentiation culture stage and a rooting and seedling strengthening culture stage. According to the rapid propagation method for the dendrobium hancockii seeds, at the seed germination stage, a large number of protocorms can appear after 45 d, and the germination rate of the seeds reaches up to 95%; at the protocorm differentiation stage, time for seedlings to be differentiated is controlled within 60 d, optimally 50 d; at the rooting and seedling strengthening culture stage, tissue culture seedlings grow to 3 cm or above after about 45 d, and the number of branches of one root is 2 or above. The period from seed germination to aseptic seedling rooting to acclimatization and transplanting requirement satisfaction is within 150 d, the propagation speed of the dendrobium hancockii seeds is greatly increased, and convenience is brought to rapid production of dendrobium hancockii.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Sterile sowing and seedling raising method for hybrid orchid and Cymbidium tracyanum hybrid seeds
ActiveCN105706900AGerminate fastImprove germination ratePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSpore germinationBiology
The invention provides a sterile sowing and seedling raising method for hybrid orchid and Cymbidium tracyanum hybrid seeds. The sterile sowing and seedling raising method comprises the following steps: taking hybrid orchid 'Miss Taipei' as a female parent and Cymbidium tracyanum as a male parent; carrying out artificial pollination to obtain hybrid capsular fruits; and carrying out reproduction steps such as capsule pretreatment, seed sowing, seed germination, synchronous rhizome proliferation and differentiation, rooting and transplantation and acclimatization and transplant to obtain hybrid offspring population. The sterile sowing and seedling raising method for hybrid orchid and Cymbidium tracyanum hybrid seeds has the advantages of high seed germination percentage, large numbers of survived seedlings, short seedling development time, good seedling quality and the like; and the rate of survival reaches 97.8% after the seedlings are transplanted for 60 days, a large number of obtained progeny plants lay a material base for breeding of excellent new species (series) of the hybrid orchid, and meanwhile, an effective new path is provided for production of seedlings of the hybrid orchid.
Owner:CROP RES INST OF FUJIAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Gastrodia elata sexual propagation technology
InactiveCN102771287AImprove germination rateShorten the production cycleHorticulture methodsSpore germinationLoment
The invention belongs to agriculture planting, and in particular relates to a gastrodia elata cultivation technology which specifically comprises the following steps of: selecting gastrodia elata, covering the gastrodia elata by fine soil with adequate water, and putting the gastrodia elata at a constant temperature of 18-28 DEG C to grow until flower; pollinating after the maturation of pollen; after the maturation of fruits, picking seeds, and mixing the seeds with germination bacteria; sawing broad leaf tree twigs into 30-40 centimeters of small segments, chipping 4-6 scaly small holes on the small segments, and putting armillaria mellea into the scaly small holes to be used as bacteria; selecting sandy loam field with gradient, digging ridges, uniformly spreading the seeds over ridge bottoms, laying the bacteria in the ridges which is spread with the seeds, and laying 2-3 centimeters of fin soil over the bacteria; covering with sandy soil, and ridging for ranks; digging out the seeds in October of the next year to obtain poacynum pictum bail; during beginning of the winter to the fresh green of the next year, seeding the poacynum pictum bail according to step 5; and after the winter begins, picking the gastrodia elata. Compared with the conventional method, the cultivation period of the method is obviously shortened, and sufficient labor is provided for farmland; the cultivation process is simplified, and the probability of various crop failures is reduced; and the added additive is contributed to increasing the seed germination, and furthermore, the yield is increased.
Owner:CHONGQING FUXINYANG EDIBLE FUNGUS
Application of rhamnolipid as biological pesticide and biological insecticide
The invention discloses application of rhamnolipid as a biological pesticide and a biological insecticide. A solution containing 20 to 500 mg / L of rhamnolipid has an inhibition rate of 40 to 90% on mycelial growth and spore germination of a plant pathogenic fungus when used for treating the plant pathogenic fungus, so the solution can effectively inhibit plant fungal diseases. And the solution containing 20 to 500 mg / L of rhamnolipid has striking insecticidal effects on cockroach and aphid.
Owner:浙江圣达紫金生物科技有限公司
Beauveria bassiana microcapsule formulation
InactiveCN102578154ABarrier effectImprove the immunityBiocideAnimal repellantsSpore germinationBeauveria caledonica
The invention discloses a beauveria bassiana microcapsule formulation which is prepared by taking suspension prepared from beauveria bassiana conidia, kaolin and water as a capsule core, taking sodium alginate as a capsule wall, dispersing in a dispersing agent of n-hexadecane, corn oil and lecithin with different proportions, crosslinking through calcium ions, and solidifying microcapsules to enveloped fine particles with partical diameter being smaller than 100 Mu m. In the germination process of the beauveria bassiana conidia, a germ tube can perforate through the envelop of the capsule wall. The microcapsule formulation is also added with a conidium germination nutrient solution which increases the germination percentage and the germination speed of the conidia. The beauveria bassiana microcapsule formulation can effectively prevent the influences bad environments such as external ultraviolet rays and drying from the conidia, achieves high germination percentage under the influences of the same temperature, humidity and ultraviolet rays, and has good control effect to agriculture and forestry pests; and meanwhile the beauveria bassiana microcapsule formulation has simple production process and is easy for mass production.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
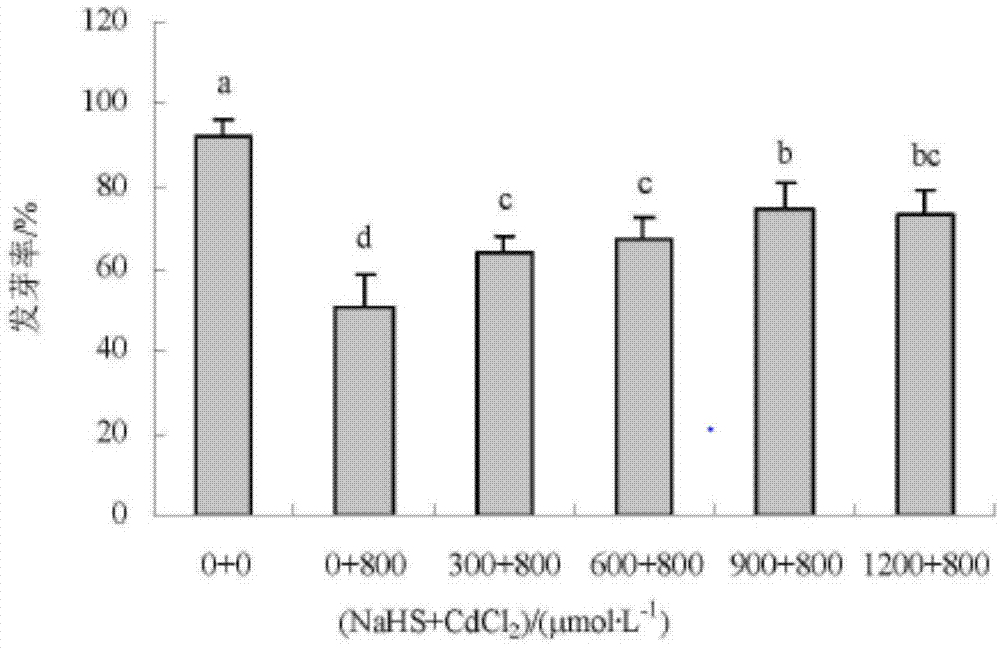
Method for promoting plant seed germination under cadmium stress
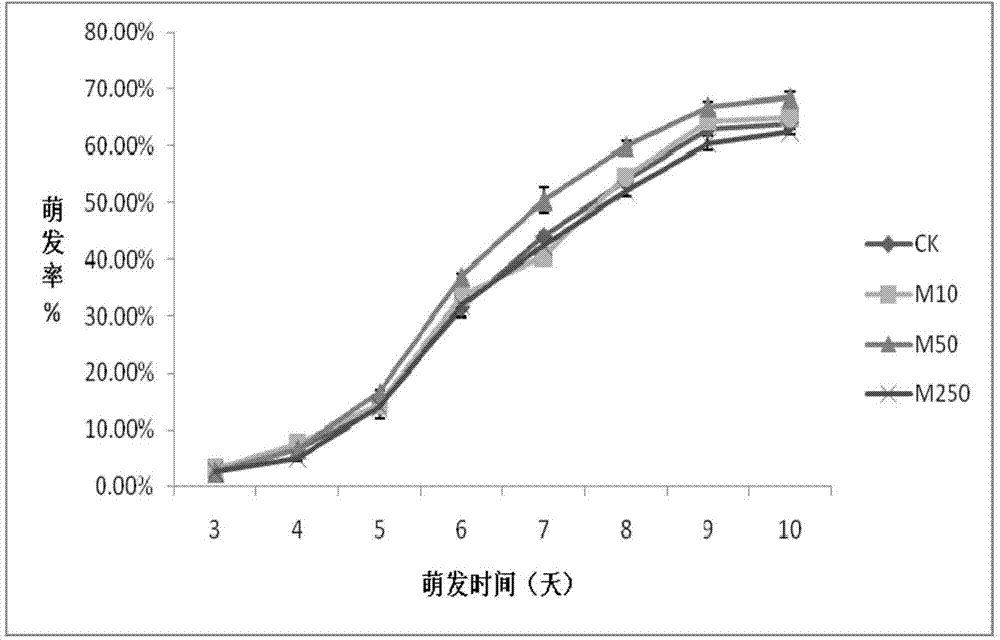
InactiveCN104718840APromote germinationNeat germinationBiocidePlant growth regulatorsSpore germinationPlanting seed
The invention relates to a method for promoting plant seed germination under cadmium stress. The method comprises the treatment of plant seeds through melatonin before germination. The method comprises the following step: enabling the plant seeds to contact with 10 to 250 micron mol / L by concentration of melatonin. With the adoption of the method, the germination potential of the plant seeds, in particular cucumber seeds and switchgrass seeds under the cadmium stress, can be effectively increased; the germination rate can be increased; the seeds can rapidly germinate uniformly; the important topic on the way of enabling normal germination of the seeds in the soil polluted by cadmium in the agricultural production is solved; the method has an important application value in production; melatonin is utilized to pre-treat, so that the expression of antioxidant enzyme activities can be induced, a large amount of free radicals produced under the cadmium stress can be removed, the oxidation stress is relieved, the oxidation damage is reduced, the seeds can be kept in a relatively small membrane lipid peroxidation level, and as a result, the seeds can germinate normally.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Preparation method for multifunctional soil remediation microbial inoculum
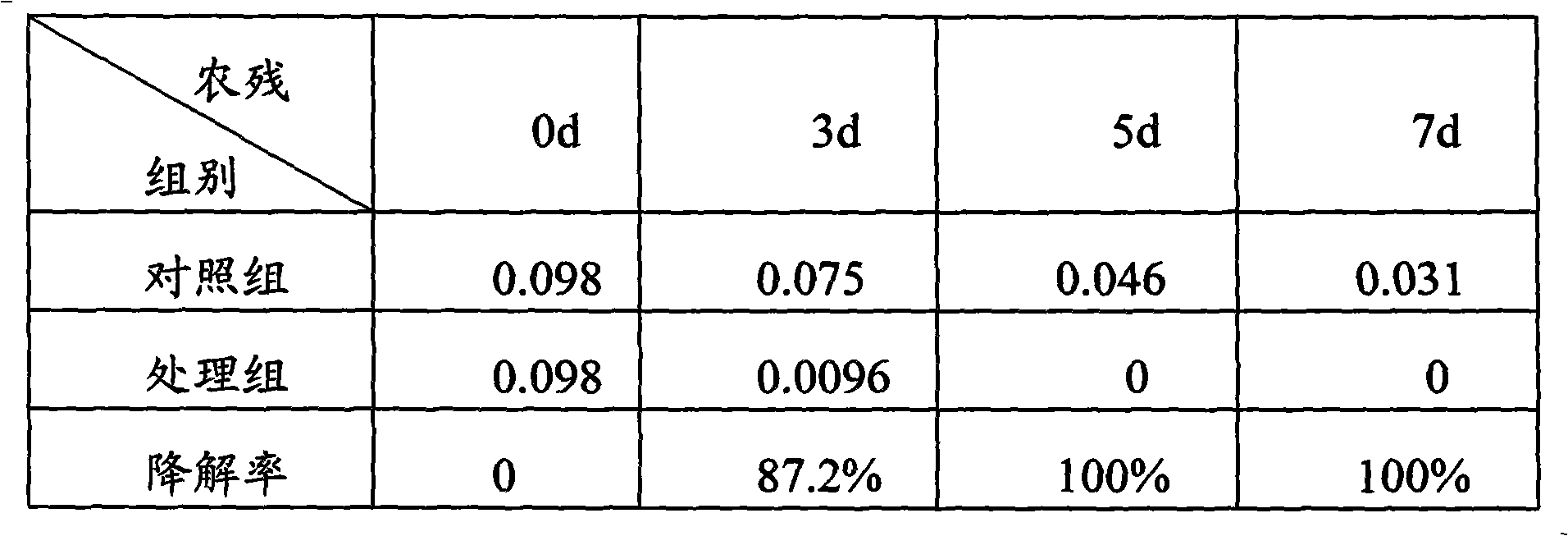
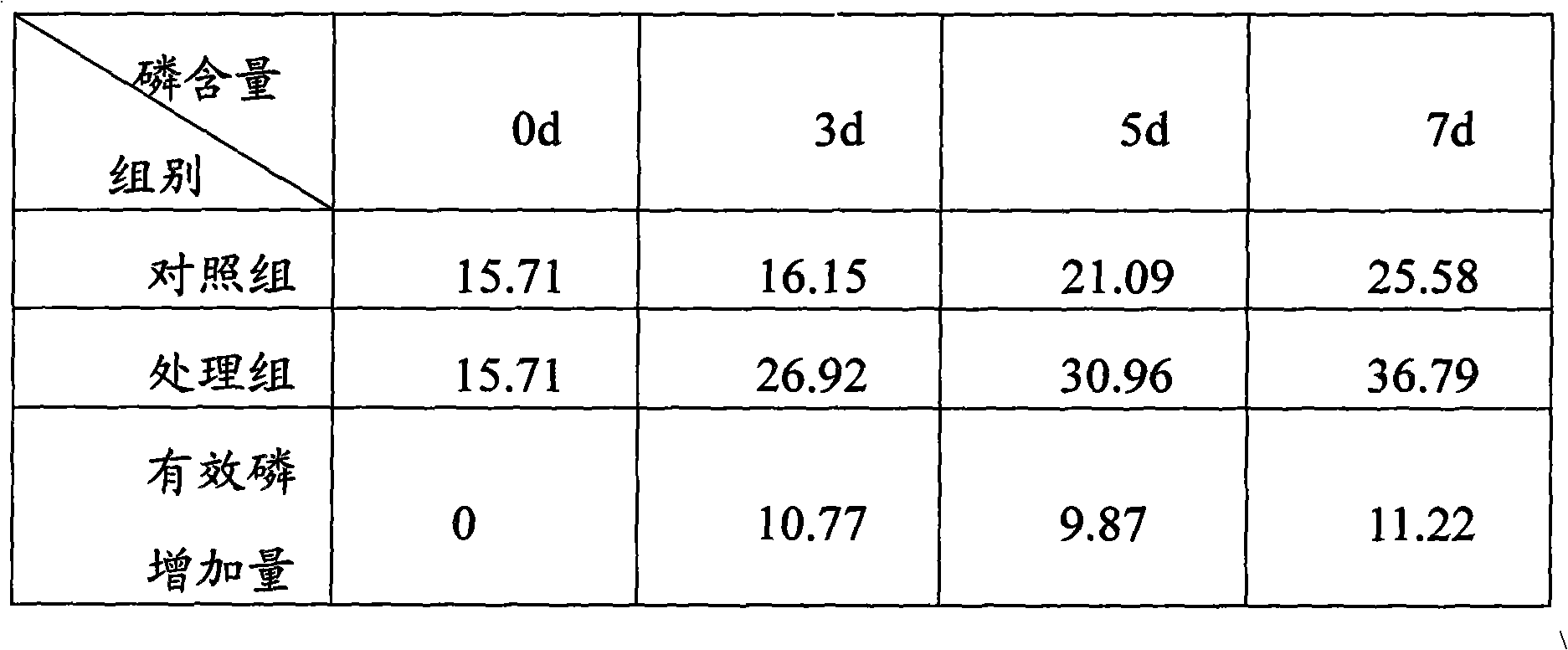
InactiveCN102911875ALarge biomassStrong stress resistanceFungiContaminated soil reclamationSpore germinationOrganophosphorus pesticides
The invention provides a preparation method for multifunctional soil remediation microbial inoculum. The preparation method comprises the following steps: A. cultivating slope culture aspergillus niger strains J6 through a PDA (potato dextrose agar) culture medium until spores are mature, inoculating in a seed culture medium to obtain spore seed liquid after spore germination; and B. inoculating the spore seed liquid in a solid fermentation medium according to mass percent of 5-10%, conducting shallow pan cultivation for 4-7 days at the temperature of 25-35 DEG C, and turning over for 2-3 times to obtain the multifunctional soil remediation microbial inoculum. With the adoption of the multifunctional soil remediation microbial inoculum prepared by the method, organophosphorus pesticide in soil can be efficiently degraded, and heavy metal such as chromium and lead and the like in the soil can be efficiently adsorbed, so that the purpose of multiple remediation of the soil is achieved.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF SCI INST OF BIOLOGY LIABILITY
Construction method of in-vitro regeneration system of adiantum reniforme var.sinense
InactiveCN104663443AProtect and ease commercial production needsHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureAdiantum reniformeSpore germination
The invention discloses a construction method of an in-vitro regeneration system of adiantum reniforme var.sinense, and relates to a method for regenerating the adiantum reniforme var.sinense through the plant tissue culture technology by the GGB manner. The method is that a mature spore of adiantum reniforme var.sinense is used as an explant, and the steps of disinfecting of the explant, germination cultivating of the spore, propagation and differentiation and the like are performed to build the regeneration system of adiantum reniforme var.sinense. The method is of important significance on the protection of endangered plants and relieving of commercial production demand.
Owner:李军
Hypsizigus marmoreus dreg culture medium and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103864527AHigh fruiting densityPromote growthBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationLivestock manureSpore germination
The invention discloses Hypsizigus marmoreus dreg culture medium and a preparation method thereof. The Hypsizigus marmoreus dreg culture medium is prepared by carrying out building piles and turning piles for four times on the following components by weight part: 35-65 parts of Hypsizigus marmoreus dregs, 30-40 parts of livestock manure, 0.5-1 part of wheat bran, 0.5-1.5 parts of potassium chloride, 1-2 parts of ammonium nitrate, 1-1.5 parts of lime, 1-1.5 parts of plaster, 2 parts of superphosphate, 0.5-1 part of sawdust, 1.5-2.5 parts of corn stalks, 0.5-1.5 parts of cotton seed hulls and 1-1.5 parts of humic acids. The fruiting period of grass mushrooms can be anticipated for 6-10 days if straw mushrooms are cultivated by the culture medium, the mushroom harvesting period is extended by 10-15 days, the yield of straw mushroom is increased by 34%-38%, spore germination speed is 6-1.18cm / day, spore germination period is 20 days, the environmental pollution due to Hypsizigus marmoreus dreg is reduced and the bio-conversion of cultivation raw materials and economic benefit of straw mushroom cultivation are improved.
Owner:泗阳县农业科学研究所
Pilot scale production method for gliocladium roseum chlamydospore by liquid fermentation
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbes, and provides a pilot scale production method for gliocladium roseum chlamydospore by liquid fermentation, and the method comprises medium formula and fermentation parameter control. The liquid medium is composed of 40-50 g / L of cane sugar, 20-25 g / L of bean cake powder, 0.5-2 g / L of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.2-1 g / L of magnesium sulfate and water, and the liquid medium is used for fermentation production of gliocladium roseum HLD-1 chlamydospore, wherein the inoculation amount is 0.2%-2% (volume ratio), the culture condition comprises that: pH is 4-6, the temperature is 26 DEG C-30 DEG C, the stirring speed is 180-250 r / min and the ventilatory capacity is 1:0.2-0.8. The culture time is calculated from inoculation, the spore is germinated when 8 hours pass by, and a large amount of chlamydospore is formed when the culture is 24-40 hours. When the time of liquid fermentation is 3-5 days, the concentration of chlamydospore is 1.5*108 per milliliter. The invention aims at providing a cheaper medium formula with abundant raw material source and an efficient easily-controllable liquid fermentation technology; and by using the method, the large-scale production of gliocladium roseum HLD-1 chlamydospore can be realized, and the method provides guarantee for large-area biocontrol application of gliocladium roseum HLD-1 chlamydospore.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Liquid microbial agent and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108794187AReduce compaction rateReduce knot rateBacteriaBioloigcal waste fertilisersSpore germinationMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a liquid microbial agent. The liquid microbial agent is prepared from the following components in percentage by mass: 1-10% of a growth-promoting bacterium solution, 0.1-10% ofpolyglutamic acid and 50-70% of a biological organic matter. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the liquid microbial agent. The invention further discloses application of the liquid microbial agent in one or any of improving the crop yield, improving the crop quality and enhancing the crop stress resistance. When the agent is in a packaged state, by providing an high organicmatter environment and a high osmotic pressure environment, growth-promoting bacterium spore germination is inhibited, so that growth-promoting bacteria are in a spore state; when the liquid microbialagent is diluted for application, the organic matter can provide nutrition for spore germination to promote fast proliferation of the growth-promoting bacteria; when the biological organic matter isused in cooperation with the polyglutamic acid, through a synergistic effect, the activity of the growth-promoting bacteria in the liquid microbial agent is maintained, so that the shelf life of the liquid microbial agent is greatly prolonged.
Owner:NANJING SHINEKING BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for removing 226Ra in uranium tail sand and radioactive contaminated soil by plants
ActiveCN102303039ASolve
<sup>226</sup>
Ra removal puzzleSolve removal puzzlesContaminated soil reclamationSpore germinationUranium mine
The invention relates to a method for removing 226Ra in uranium tail sand and radioactive contaminated soil by plants. The method mainly uses an accumulation plant of the 226Ra, namely a Pieris multifida, to accumulate the 226Ra in the uranium tail sand and the radioactive contaminated soil and simultaneously convey the 226Ra to the overground part of the plant, thereby removing the 226Ra in the uranium tail sand and the radioactive contaminated soil. The method has the following specific steps of: (1) spore germination cultivation; (2) potting seedling; (3) planting the plant in the uranium tail sand or the radioactive contaminated soil; (4) harvesting the overground part of the plant and executing centralized treatment on the harvested plant. The method has the advantages of being convenient to obtain materials, low in cost, high in remediation efficiency, easy to management, simple and convenient in steps, less in environmental risk, and the like, thereby being suitable for removing the 226Ra in the uranium tail sand and the radioactive contaminated soil in uranium mines, uranium water treatment factories, tailings pools and the like.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
Artificial domestication and planting method for wild binwang mushroom
The invention provides an artificial domestication and planting method for wild binwang mushroom, wherein the bacterial cultivating process comprises, (1) purifying the mycelium of spore germination in the field, or incising fruiting body of the fresh mushroom under the asepsis condition, culturing a hyphostroma on the culture medium, culturing the mother bacterial again, making original breed after generation addition breeding, finally conducting the routine culture of the original breed based on the culture medium. The mushroom manual cultivating method comprises the steps of culturing on purpose-made cultivation material, mixing the culture material with turfy soil, sterilizing and culturing the mushroom in culture chambers with the temperature of 22+-2 deg. C.
Owner:杨军
Dryopteris erythrosora spore propagation method
InactiveCN102283090AConducive to rapid breedingIncrease production capacityCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationSpore germinationPeat
A conventional Dryopteris erythrosora spore propagation method is mainly characterized in that Dryopteris erythrosora spores are prepared into suspension and the suspension is evenly poured onto mediums contained in an earthen pot by using a syringe; sowing mediums are mixtures of sand, peat and pearlite which are mixed by volume ratio of 1:1:1; the earthen pot into which the spores are sown is put into a transfer case, the height of the water-soaked bottom of the transfer case is 1.5cm and the water-soaked bottom of the transfer case is covered by plate glass; the spores are cultured in the sunshade position of a greenhouse at 25 DEG C to 35 DEG C under the condition that direct sunlight is avoided; juvenile sporophytes are obtained after culture and are respectively transplanted into transplanting mediums I which are formed by leaf mould, peat and sand in an evenly mixing way by volume ratio of 1:1:1, transplanting mediums II which are formed by sand, pearlite and peat in an evenly mixing way by volume ratio of 1:1:1, transplanting mediums III which are formed by peat and garden mould in a mixing way by volume ratio of 1:1, and reference mediums which are formed by garden mould; and the juvenile sporophytes are cultured under the same conditions. By using the characteristic that the germination and the fertilization of the spores need water and by applying pot planting, water soaking and moisture preservation to Dryopteris erythrosora spore propagation, the germination rate of the Dryopteris erythrosora spores, the seedling rate and the survival rate of the transplant sporophytes are effectively improved; in the propagation process, any sterilization process is not required, the processes are reduced, the pollution is reduced, the cost is saved, the operation is simple and convenient and the rapid propagation and the mass production of seedlings are facilitated; the survival rate of the transplanted juvenile spore seedlings reaches more than 85 percent.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com