Liquid microbial agent and preparation method and application thereof
A liquid bacterial agent and microorganism technology, applied in the field of microbial liquid bacterial agent and its preparation, can solve the problems of low content of effective bacteria and easy inactivation, and achieve the effects of improving nutrient absorption, promoting rapid proliferation and solving soil acidification.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
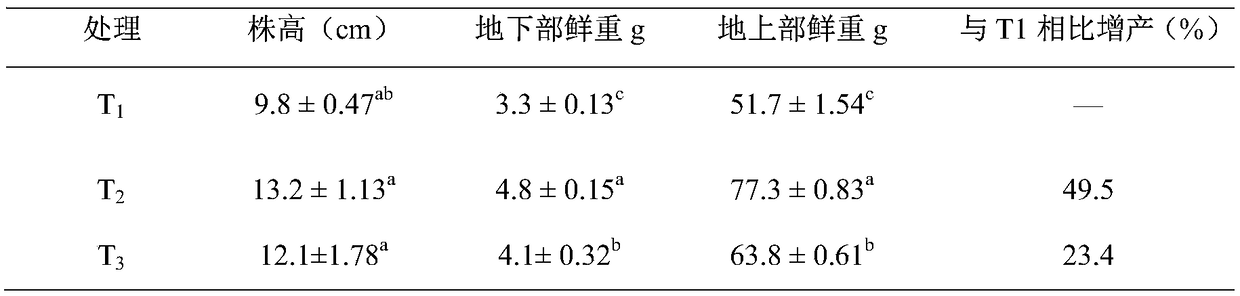
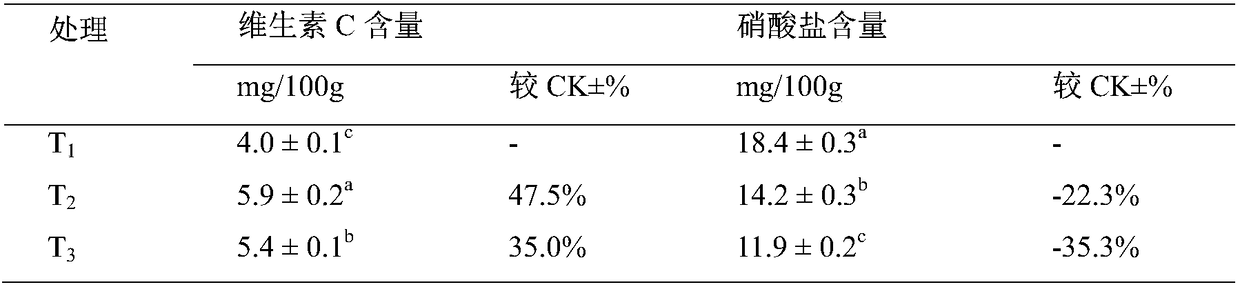
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] The fermentation of embodiment 1 growth-promoting bacteria
[0039] Prepare the growth-promoting bacteria liquid according to the following steps:
[0040] Activate the Bacillus subtilis CCTCC NO:M 2016264, Bacillus jelly-like CCTCC NO:M 2016265, and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens CCTCC NO:M 2016266 stored on a slant at 4°C, and inoculate them in eggplant-shaped culture flask medium (i.e., activation culture Base), cultured at 32°C for 18h. Transfer the activated strains to the fermentation medium, culture at 30°C for 24h, place the fermented liquid in a cold storage at 4°C for 48h at low temperature, and measure by plate coating, the number of viable bacteria in each microbial fermentation liquid can reach 8 ×10 9 CFU / mL or more, the three microbial fermentation liquids are mixed according to the volume ratio of 1:1:1 to obtain the growth-promoting bacteria liquid.
[0041] The medium in the described eggplant-shaped culture bottle is LB medium, and the fermentation med...
Embodiment 2
[0043] The preparation of embodiment 2 compound microbial liquid inoculum
[0044] Prepare the composite microbial liquid bacterial agent containing polyglutamic acid, biological organic matter, growth-promoting bacterial liquid according to the following method:
[0045] (1) Polyglutamic acid was prepared by fermentation (reference Xu Z, Feng X, Dan Z, et al. Enhanced poly(γ-glutamic acid) fermentation by Bacillus subtilis, NX-2 immobilized in anaerobic plant fibrous-bed bioreactor[J ].Bioresour Technol, 2014,155:8-14), the polyglutamic acid content of the fermented liquid is 15% after concentration;
[0046] (2) The molasses is purchased by the sugar factory;
[0047] (3) Mix the composite growth-promoting bacteria liquid obtained in Example 1 with the polyglutamic acid fermentation concentrate and molasses according to the mass ratio of 1:2.5:6.5 to obtain a composite microbial liquid bacterial agent. After testing, the mass percentage of polyglutamic acid content is 3.5%...
Embodiment 3
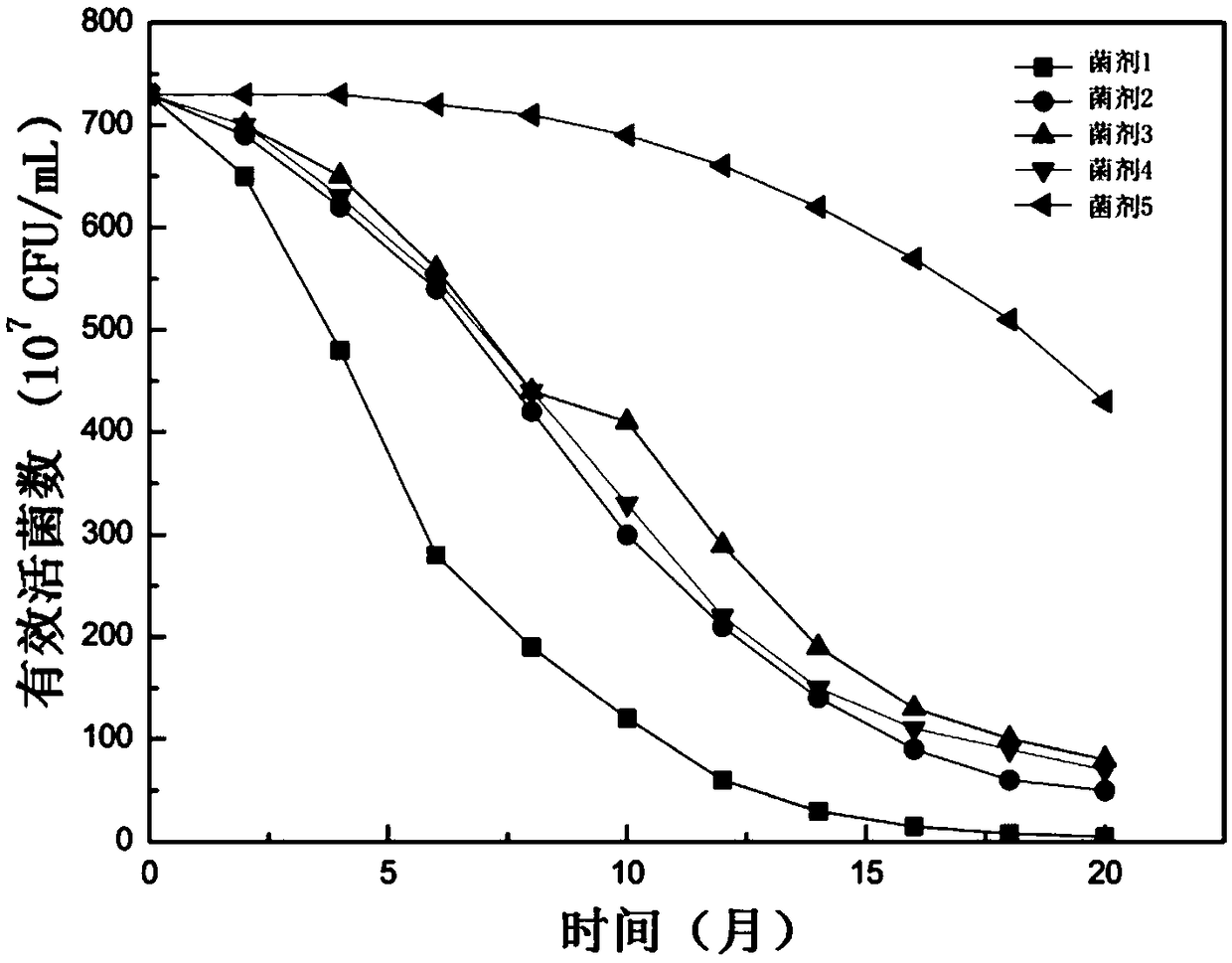
[0048] Embodiment 3 Composite microbial liquid inoculum can be kept open for up to 18 months
[0049] The bacterial agent used in the present embodiment is as follows:
[0050] (1) The mixed bacterial agent prepared in Example 1 is diluted to an effective viable count of 7.3 × 10 9 CFU / mL, as bacterial agent 1.
[0051] (2) The mixed bacterial agent prepared in Example 1 is mixed in proportion with the polyglutamic acid fermentation concentrate, so that the polyglutamic acid content is 3.5%, and the effective viable count is 7.3×10 9 CFU / mL, as bacterial agent 2.
[0052] (3) The mixed bacterial agent prepared in Example 1 is mixed uniformly with molasses in proportion, so that the organic matter content is 67%, and the effective viable count is 7.3×10 9 CFU / mL, as bacterial agent 3.
[0053] (4) The mixed bacterial agent prepared in Example 1 is mixed uniformly with polyglutamic acid and molasses in proportion, so that the polyglutamic acid content is 3.5%, the organic ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com