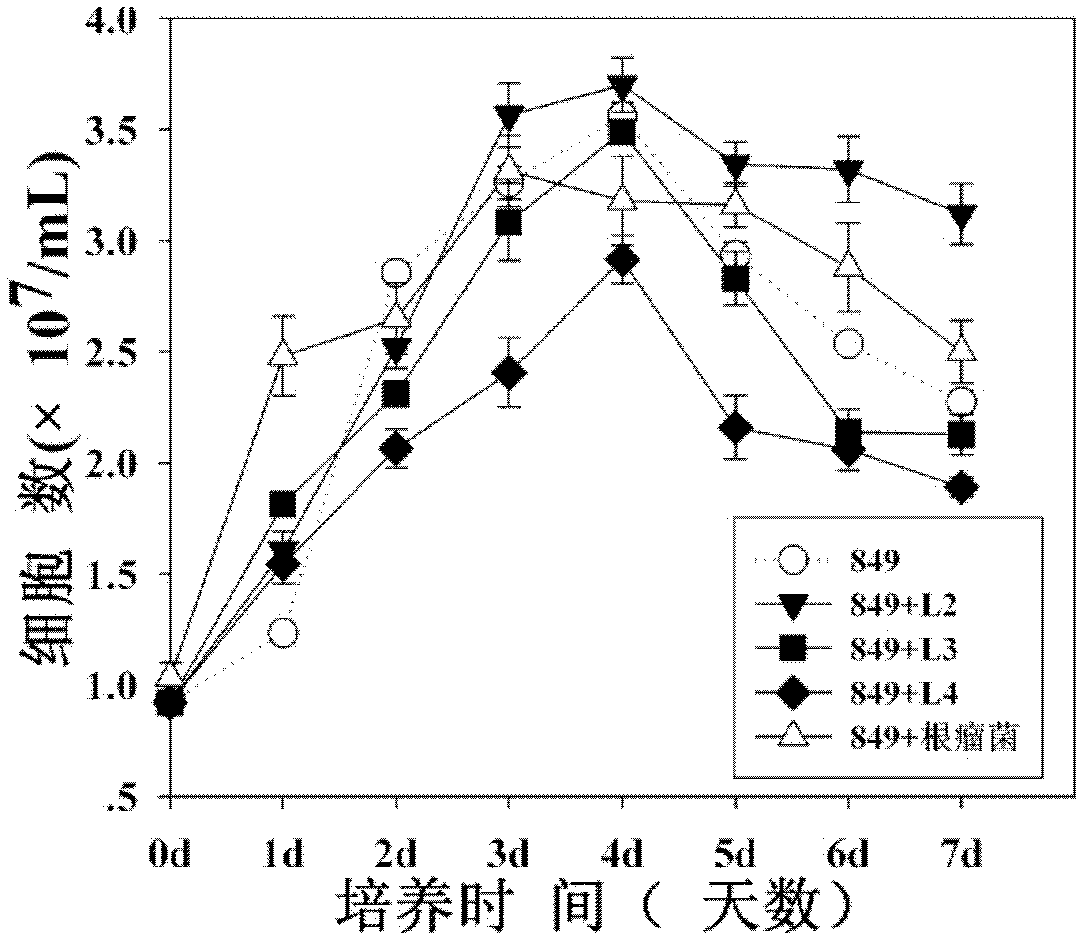
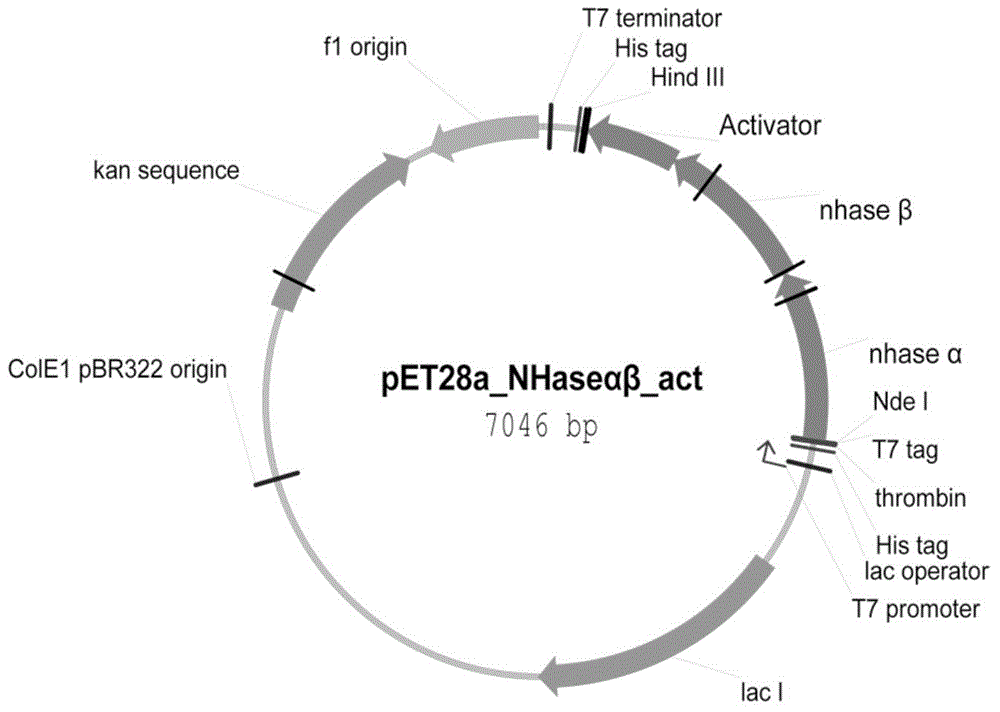
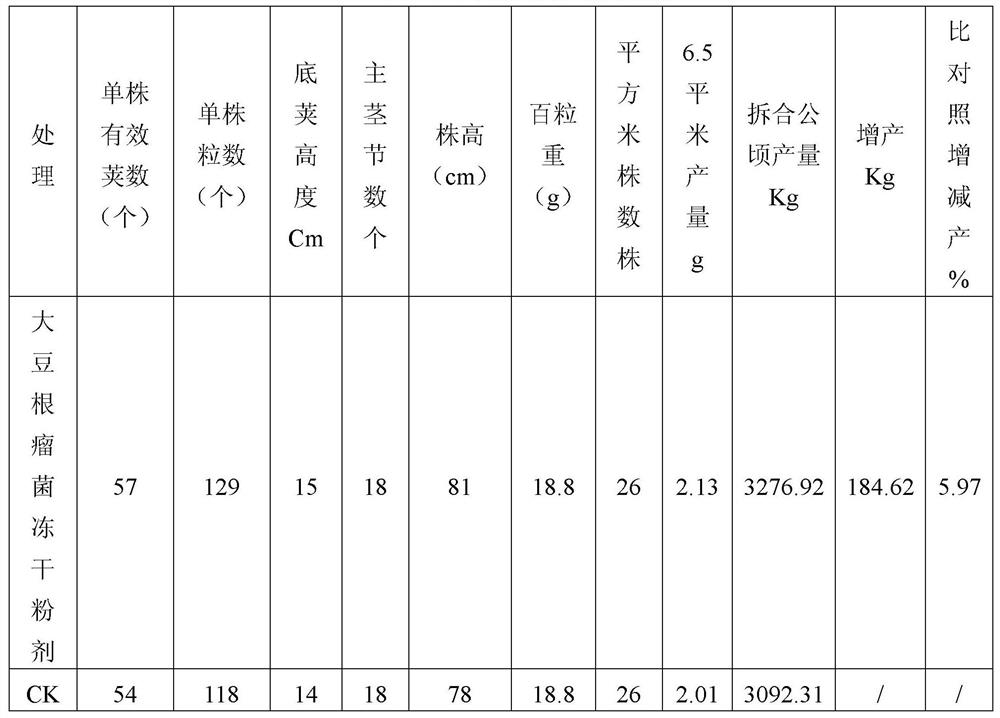
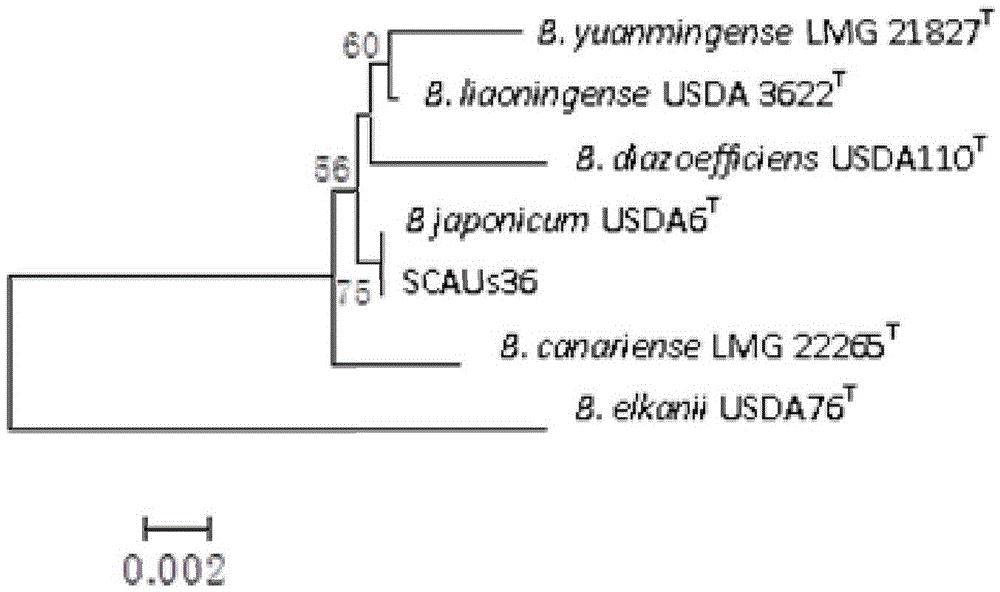
Patents
Literature
36 results about "Bradyrhizobium japonicum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bradyrhizobium japonicum is a species of legume-root nodulating, microsymbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria. The species is one of many Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacteria commonly referred to as rhizobia. Within that broad classification, which has three groups, taxonomy studies using DNA sequencing indicate that B. japonicum belongs within homology group II.
Methods and compositions for production of lipo-chito oligosaccharides by rhizobacteria
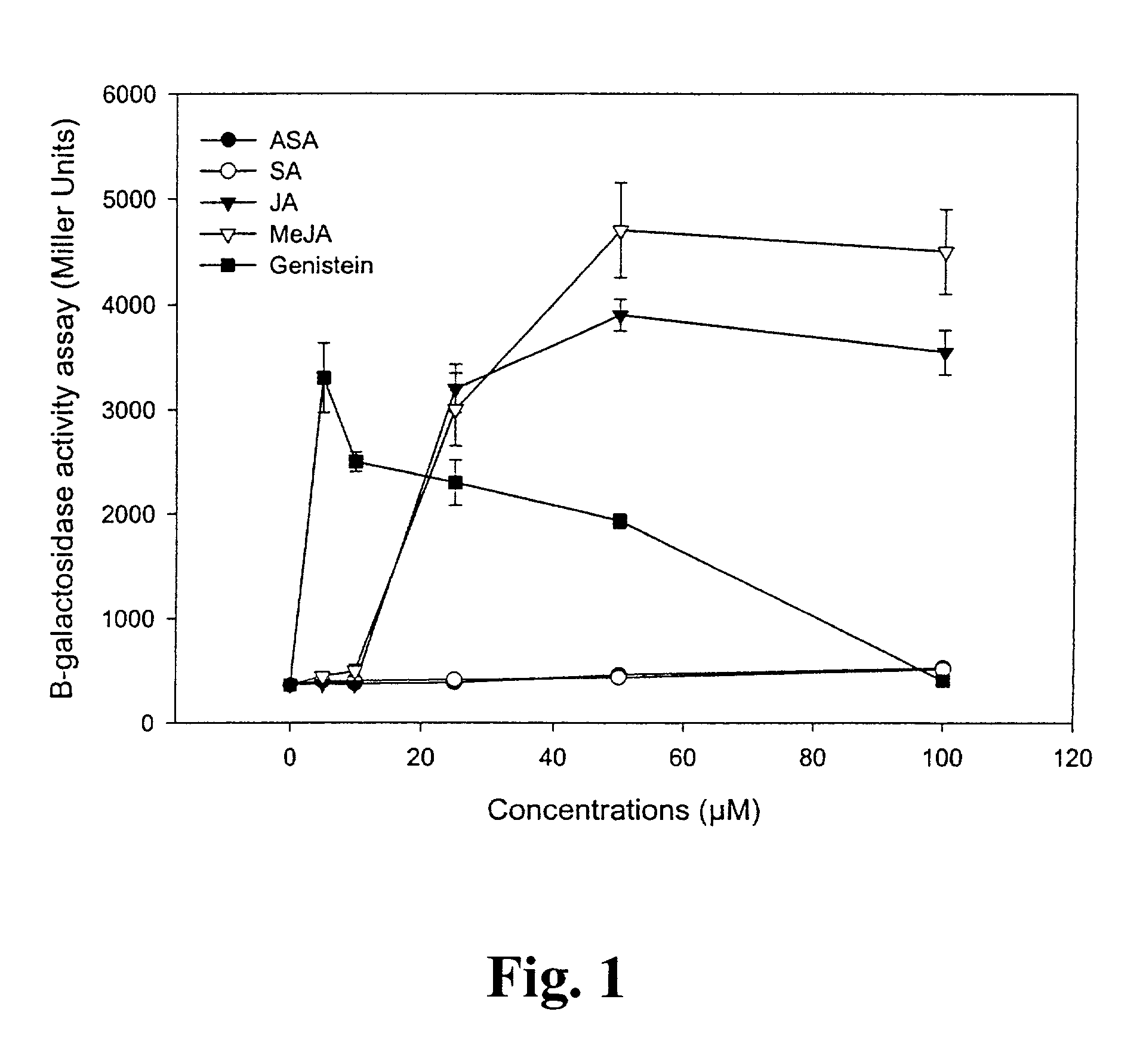
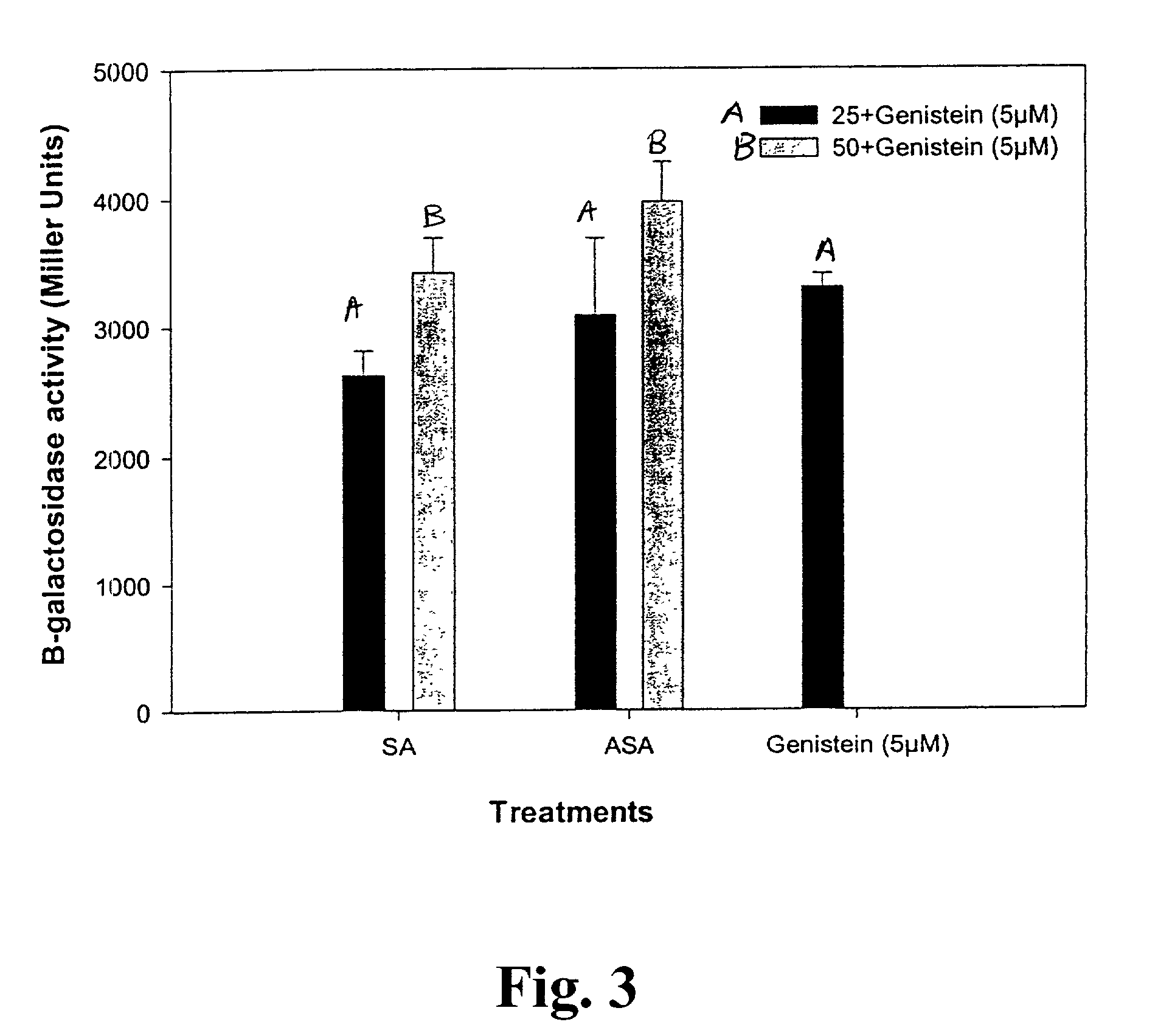
Lipo-chito oligosaccharides (LCOs) are produced by culturing rhizobacteria cells in or on a culture medium comprising at least one of: jasmonic acid or a derivative thereof; linoleic acid or a derivative thereof; or linolenic acid or a derivative thereof. Preferably, the rhizobacteria cells are Bradyrhizobium japonicum cells having the identifying characteristics of B. japonicum strain USDA 3. Preferably, the derivative of jasmonic acid is an ester thereof, preferably methyl jasmonate. Also provided are methods for improving LCO production at low temperatures, particularly temperatures below 25° C.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Composition for accelerating seed germination and plant growth
InactiveUS6979664B1Promote plant growthIncrease productionBiocideAnimal repellantsBrassicaceaeMyriophyllum
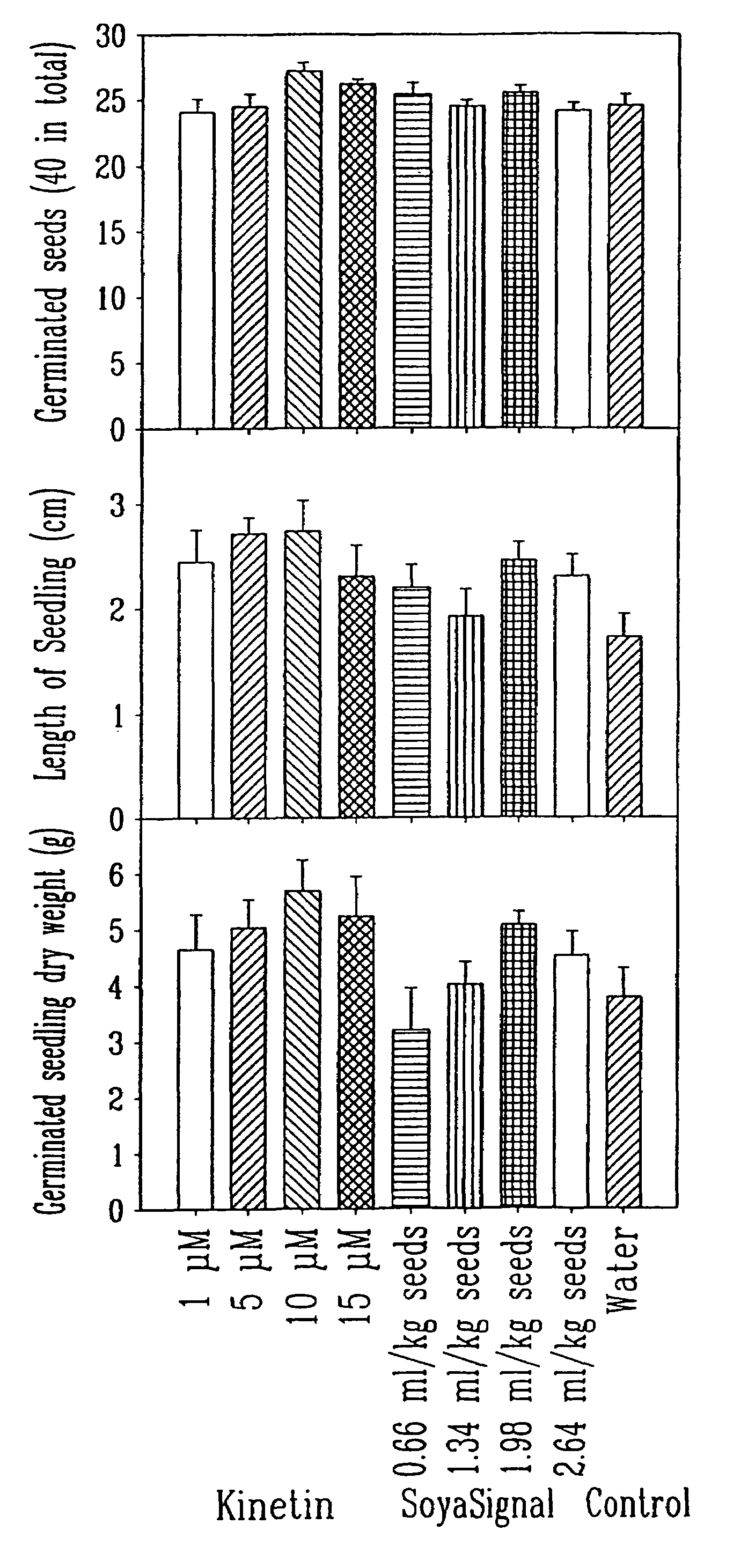
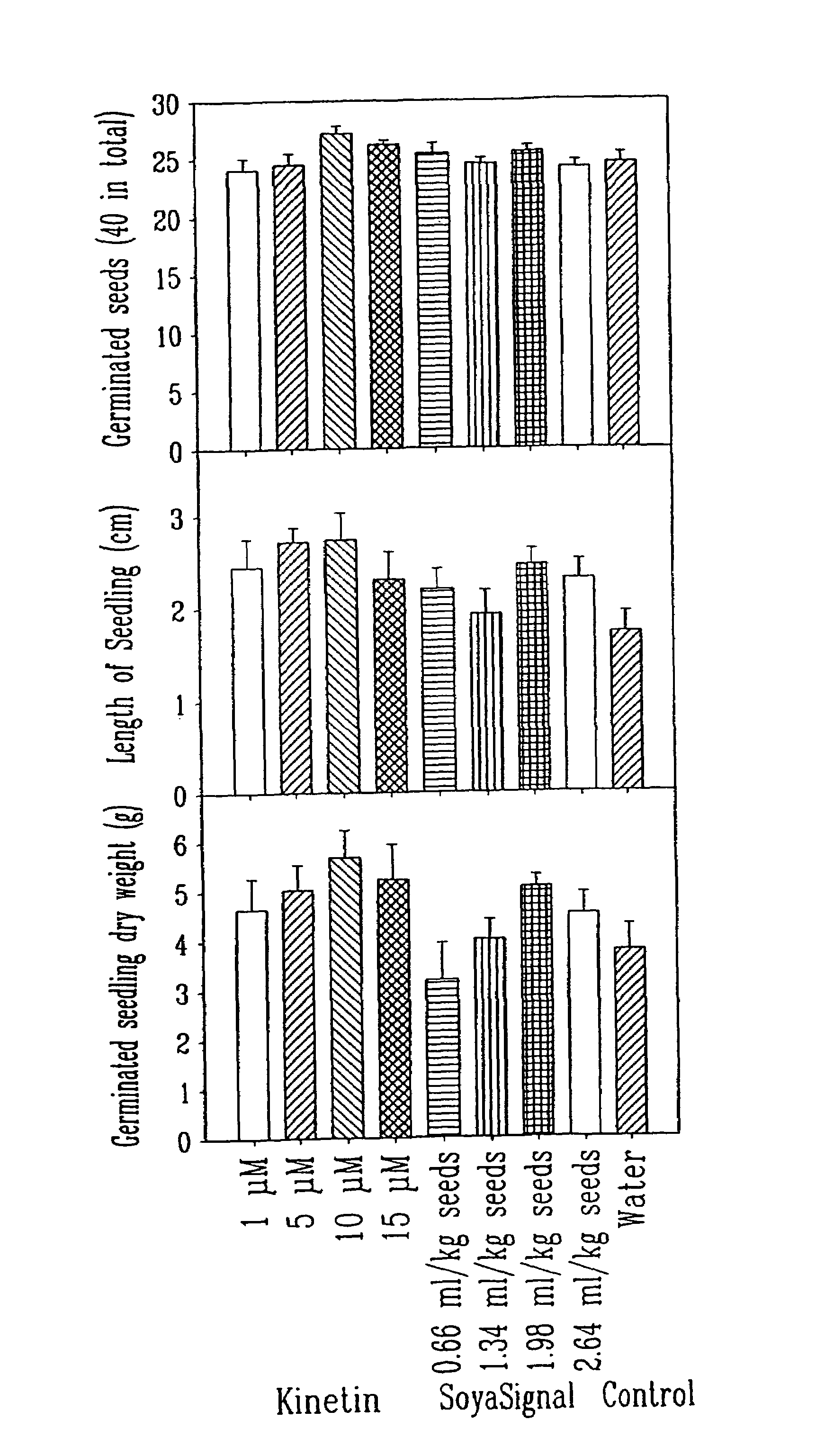
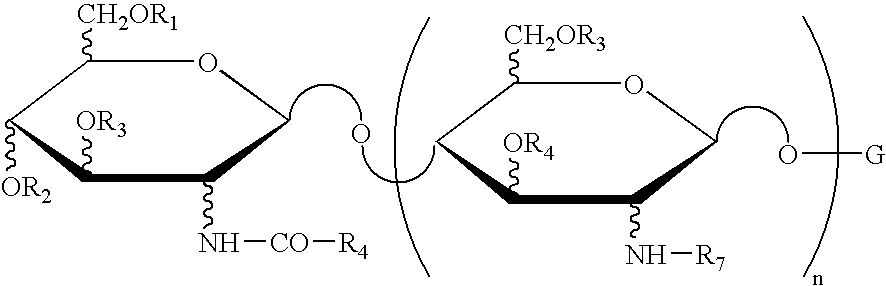
Lipo Chitooligosaccharide (LCO) [NodBj-V(C18:1,Mefuc)] isolated from Bradyrhizobium japonicum strain 532C was able to stimulate seed germination / seedling emergence, or in the case of potato, sprouting, of a number of crop plants representing eight distantly related plant families (Poaceae, Fabaceae, Brassicaceae, Cucurbitaceac, Malvaceae, Asteraceae, Chenopodiaceae and Solanaceae) of plants, at 25 and / or at 15° C. It also promoted sprouting potato minitubers. Other LCOs [NodRM-V(C16:2,5) and LCO from R. leguminosarum] were also shown to also display growth-promoting effects on the tested crop plants. The compositions comprising at least one LCO are shown to be effective in promoting growth under both laboratory and field conditions. The invention thus also relates to methods for promoting seed germination and / or seedling emergence and / or growth of plants comprising subjecting the seeds and / or plants to an effective amount of an agricultural composition comprising at least one LCO.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV +1
Composite microbial fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102199050AImprove the preservation effectImprove sexual functionOrganic fertilisersBacillus megateriumNutrient solution
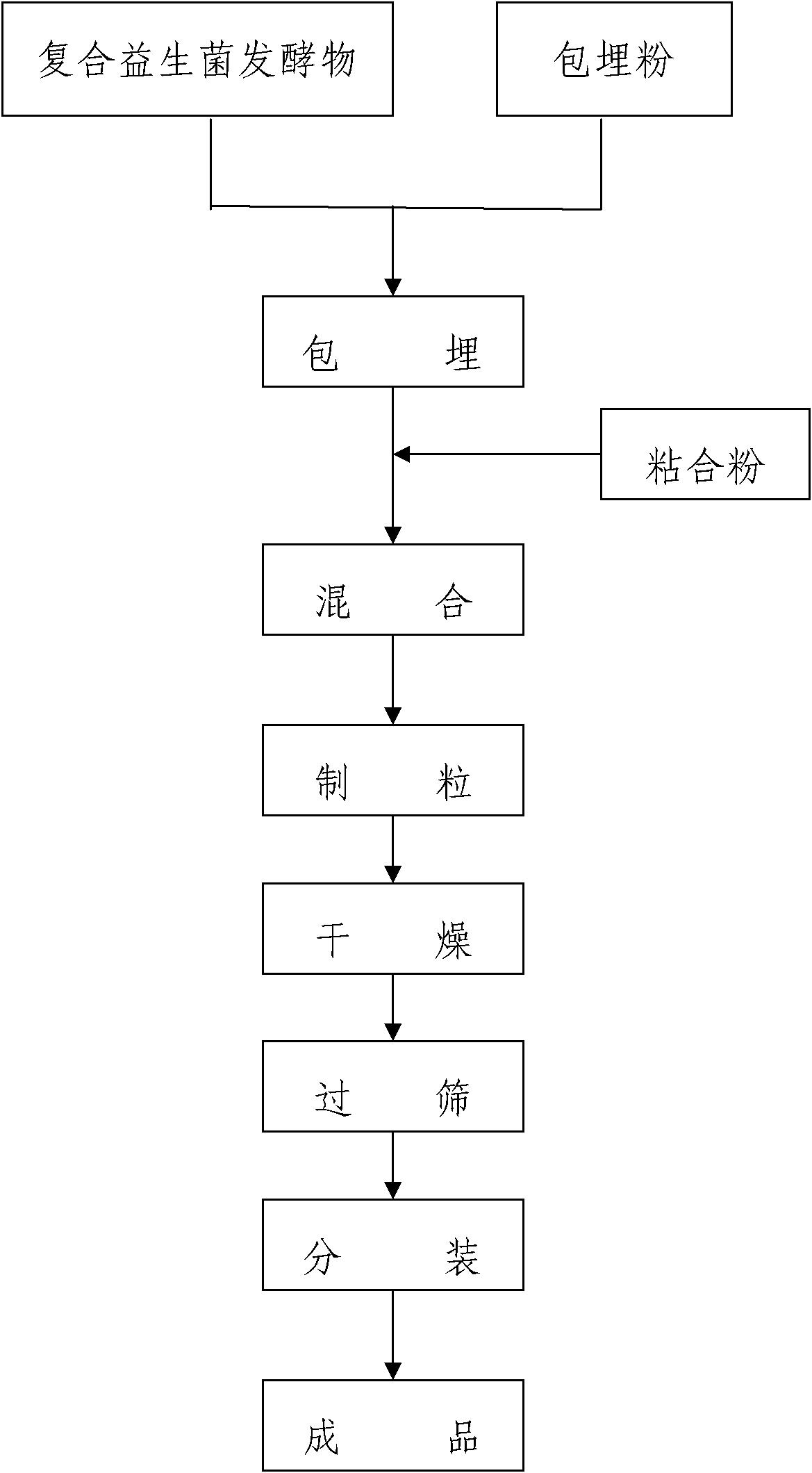
The invention relates to the field of microbiology, and specifically relates to a composite microbial fertilizer and a preparation method thereof. The composite microbial fertilizer is composed of a composite microbial fermentation broth and an embedding medium, wherein a volume ratio of the composite microbial fermentation broth to the embedding medium are in a range of 1:5 to 1:4. The compositemicrobial fermentation broth is compounded of a co-culture comprising Candida utilis, lactic streptococci, lactobacillus acidophilus and bacillus subtilis, and a single nutrient solution comprising Bradyrhizobium japonicum, Azospirillum lipoferum, Rhodopseudomonas palustris, Bacillus megaterium, Bacillus mucilaginosus and Azotobacter chrococcum. In the invention, composite microbes processed by embedding can be stored stably for more than 60 days and a count of the composite microbes is always more than 2 billion per gram, thus the composite microbial fertilizer comprising the composite microbes has a long effective time and can improve a planting capacity of soil.
Owner:沈阳科丰牧业科技有限公司
Bradyrhizobium japonicum capable of effectively fixing nitrogen and culture method and application thereof
ActiveCN102174436AWide variety of sourcesLow pricePlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyEthylene glycol toxicity
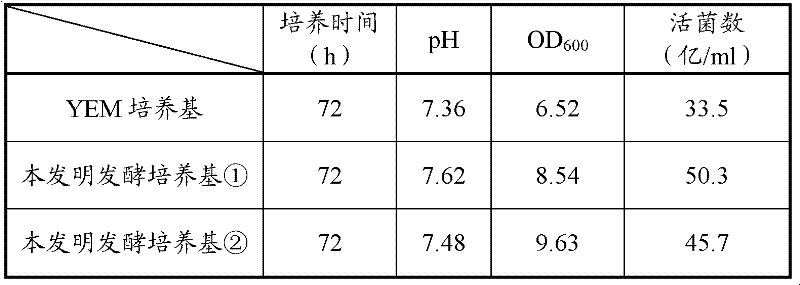
The invention relates to bradyrhizobium japonicum capable of effectively fixing nitrogen and a culture method and application thereof. The bradyrhizobium japonicum CGMCC No.4346 is cultured by the steps of strain activation, seed culture, fermentation culture and the like. The invention has the following beneficial effects: sorbitol and diethylene glycol are utilized to replace the carbon source, mannitol in the traditional YEM (yeast extract mannitol) culture medium, and when the improved fermentation culture medium is adopted for culturing, the viable count of the fermentation liquor is higher than that of the YEM culture medium; compared with the rhizobium inoculants which are not inoculated on the soy beans, the bradyrhizobium japonicum agent ensures the theoretical yield of the soy beans to be increased by 16.7-17.2%, the crude fat content to be increased by 0.65-1.21% and the protein content to be increased by 1.29-1.60% after being inoculated on the soy beans, thus being an excellent strain for production of rhizobium japonicum and inoculation of the soy beans; and the culture method is simple and practical, and the raw materials have wide sources and low price and are suitable for large-scale industrialized production.
Owner:领先生物农业股份有限公司
Materials and methods for the enhancement of effective root nodulation in legumes
InactiveUS6855536B2Reduced nodY-lacZ inductionReduced nodulation efficiencyBiocideBacteriaBacteroidesPlant nodule
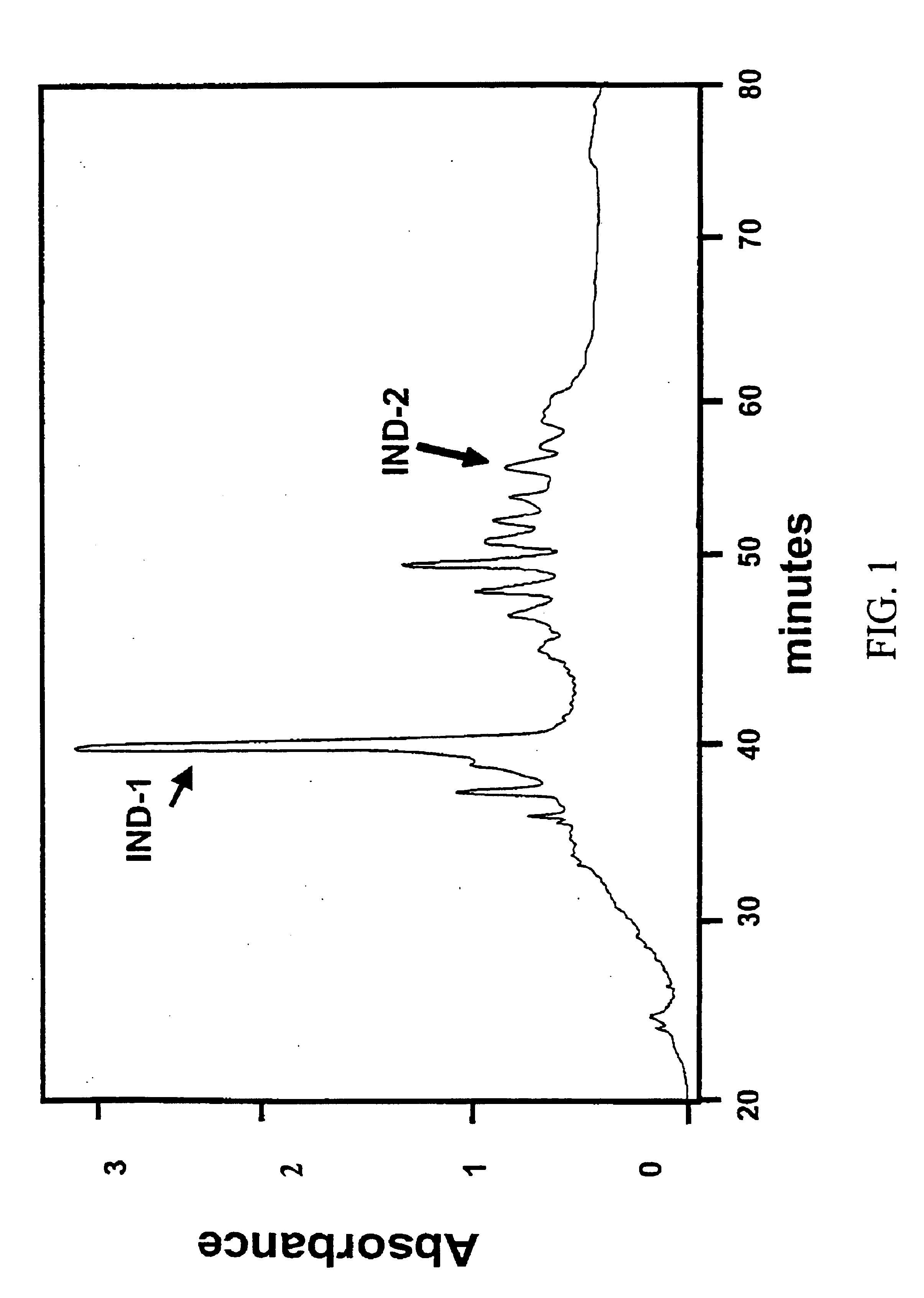
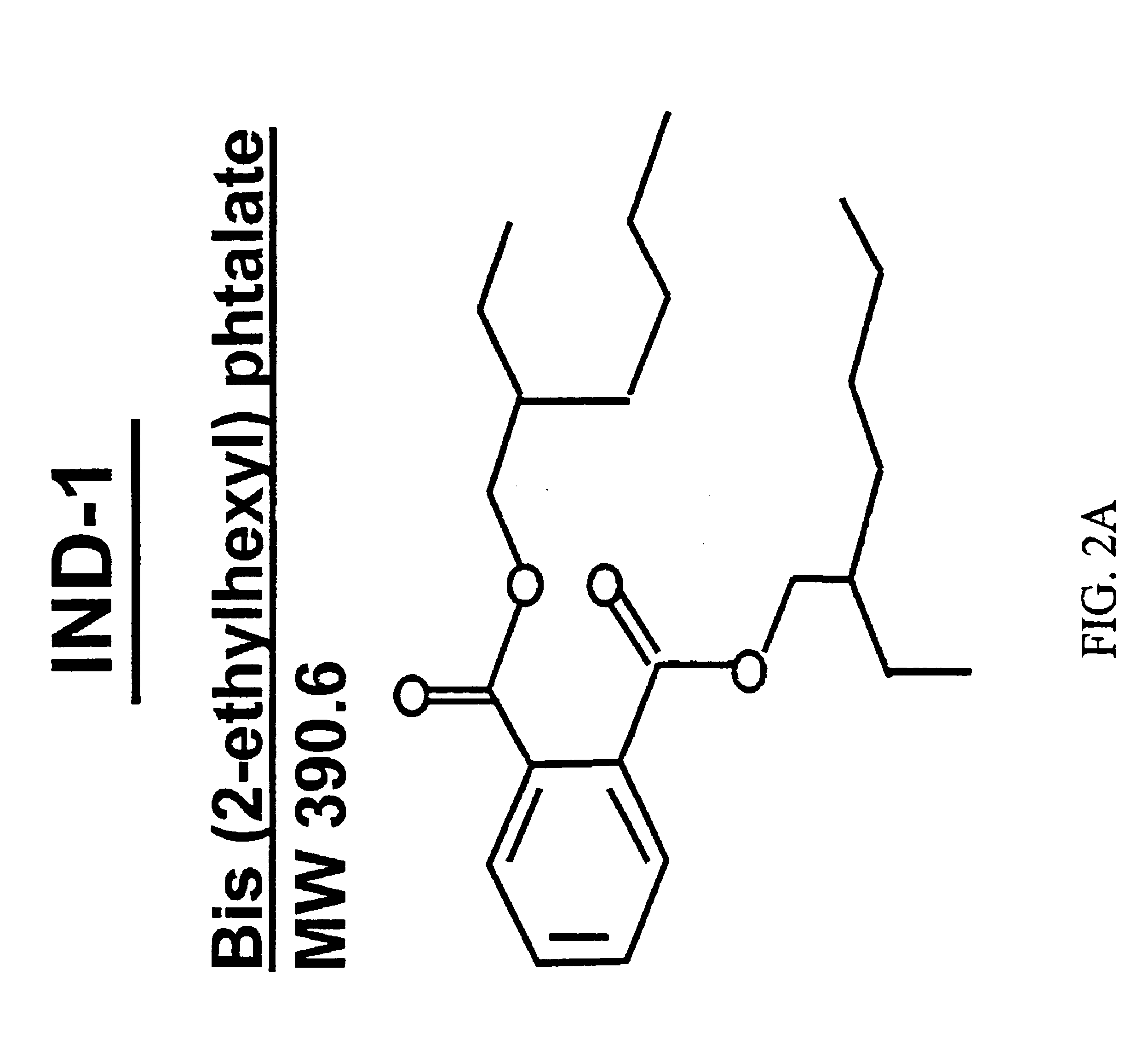
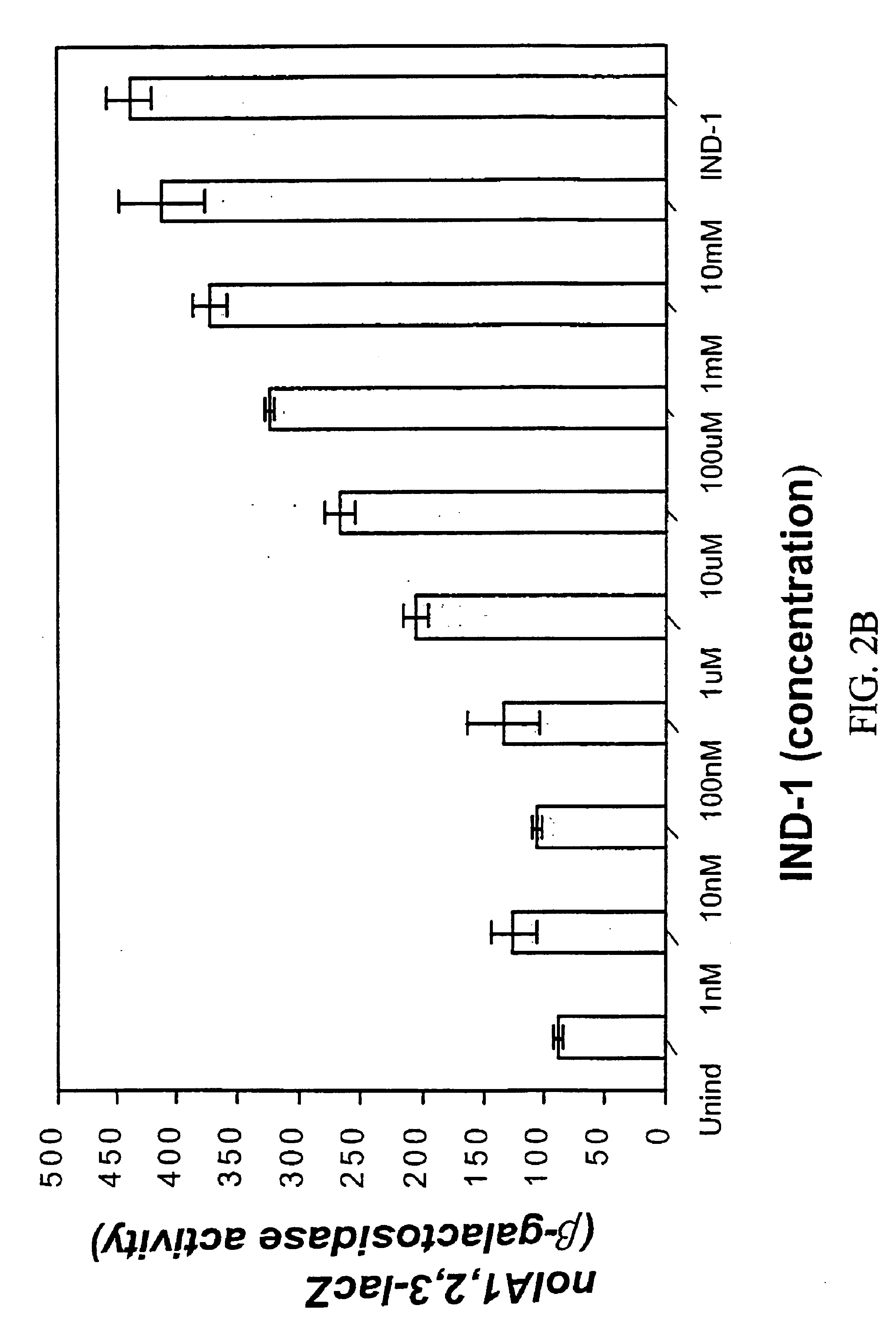
The subject invention relates to compounds and compositions which induce transcripts of the nolA gene in nitrogen-fixing bacteria, such as Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Novel bacterial strains which are insensitive too NolA, soil inoculants comprising NolA insensitive bacteria and / or nolA inducers, and methods of increasing nitrogen fixation in legumes are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Composite microbial fertilizer and low temperature embedding preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102153381AEnsure the original functionRealization of low temperature granulationOrganic fertilisersStaphylococcus lactisBacillus megaterium
The invention relates to the field of bio-fertilizer, in particular to a composite microbial fertilizer and a low temperature embedding preparation method thereof. The composite microbial fertilizer contains a leavening of a composite microbe, an embedding medium and bonding powder; and the leavening, the embedding medium and the bonding powder are embedded in a low temperature plasmid and dried to obtain the composite microbial fertilizer; the composite microbial fertilizer contains the following components in percentage by weight: 50-70% of the leavening of the composite microbe, 25-45% of the embedding medium and 3-8% of the bonding powder, wherein the raw materials are pelletized at a low temperature of 8-20 DEG C and dried at a low temperature of 10-20 DEG C; and the leavening of thecomposite microbe is obtained by compounding a coculturing material of Candida utilis, Lactococcus lactis, Lactobacillus acidophilus and bacillus subtilis with a single culture solution of Bradyrhizobium japonicum, Azospirillum lipoferum, Rhodopseudomonas palustris, Bacillus megaterium, Bacillus mucilaginosus and Azotobocter chroococcum. The fertilizer provided by the invention is prepared in a dry state so that the activity of the microbe can be kept at more than 90% and the quality guarantee period reaches more than 18 months.
Owner:沈阳科丰牧业科技有限公司
(+)gamma-lactamase with racemate gamma-lactam resolution activity and its application
The invention provides a (+)gamma-lactamase with racemate gamma-lactam resolution activity and application of its coding gene in chiral compounds, as well as a method for production of (-)gamma-lactam with bradyrhizobium japonicum. The method comprises: extracting the genomic DNA of the bradyrhizobium japonicum, constructing a recombinant thallus for recombinant protein extraction, then conducting expression to obtain the (+)gamma-lactamase; and adding a gamma-lactam substrate into a phosphate buffer solution in which the recombinant thallus for recombinant protein extraction or the (+)gamma-lactamase suspends, and then carrying out reaction and extraction so as to obtain the (-)gamma-lactam. Or the method can be performed as the following: extracting the genomic DNA of the bradyrhizobium japonicum, constructing the recombinant thallus for recombinant protein extraction, then conducting expression to obtain the (+)gamma-lactamase, adding the substrate, and implementing reaction and extraction, thus obtaining the (-)gamma-lactam. The (+)gamma-lactamase provided in the invention derives from the bradyrhizobium japonicum and has high catalytic efficiency. The obtained (-)gamma-lactam has high purity.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Microorganisms for the treatment of soil and process for obtaining them
The present invention relates to product(s) containing living microorganism(s) suitable for soil treatment, microorganisms multiplying under different climatic and natural circumstances, as well as procedures for the production of the products, and procedures for the treatment of the soil and plants with the products. More particularly, the invention relates to a procedure for preparing the products from any of the microorganisms specified below, or from the mixture thereof. Furthermore, the invention relates to a procedure for the creation of the cultures of the microorganisms to be used. The subject invention also pertains to the microorganisms themselves. More particularly, the invention relates to a procedure for the treatment of the soil and the plants with a product containing at least one of the microorganisms selected from Azospirillum brasilense ssp. SW51 (NCAIM / P / B 001293), Azotobacter vinelandii ssp. M657 (NCAIM / P / B 001292), Pseudomonas fluorescens var. SW11 (NCAIM / P / B 001296), Bacillus polymyxa var. SW17 (NCAIM / P / B 001295), Bacillus megaterium var. M326 (NCAIM / P / B 001291), Micrococcus roseus ssp. A21 (NCAIM / P / B 001294), Bradyrhizobium japonicum var. PH25 (NCAIM / P / B 001302), and Streptomyces albus var. 0003 LP (NCAIM / P / B 001301), and furthermore the products multiplying and existing in the environment of the plant in question, containing the listed microorganisms and their production.
Owner:AGRO BIO HUNGARY KFT
Method for com-culturing and improving hydrogen output by utilizing bacteria and chlamydomonas reinhardtii
InactiveCN102559832AIncrease hydrogen productionReduce the greenhouse effectMicroorganism based processesFermentationChlamydomonas reinhardtiiBradyrhizobium japonicum
The invention relates to a biological hydrogen production technology, in particular to a method for com-culturing and improving hydrogen output by utilizing bacteria and chlamyodomonas reinhardtii. Through mixing aerobic bacteria represented by bradyrhizobium japonicum with the chlamydomonas reinhardtii according to a certain proportion for culture, the hydrogen output can be remarkably improved. The invention provides a new method for further improving the hydrogen output in a chlamydomonas reinhardtii twp-step-method hydrogen production technology.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
Heat-resistant recombinant nitrile hydratase gene, encoded enzyme, engineering bacterium and application of gene engineering bacterium
InactiveCN104561065AHigh expressionHigh activityBacteriaFermentationEscherichia coliBiological activation
The invention discloses a heat-resistant recombinant nitrile hydratase gene, an encoded enzyme, a vector, an engineering bacterium and an application of the gene engineering bacterium to catalysis of a nitrile compound to produce amide and a biodegradation herbicide, that is, dichlobenil. The functional expression of the tentative nitrile hydratase gene from bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA 110 is realized, and the crucial role of an activation element of the nitrile hydratase in the expression process is proved. Meanwhile, the invention provides a method for constructing the nitrile hydratase gene engineering bacterium in Escherichia coli, and the nitrile hydratase with the high expression quantity and the high activity is obtained from the nitrile hydratase gene with the participation of the activation element.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
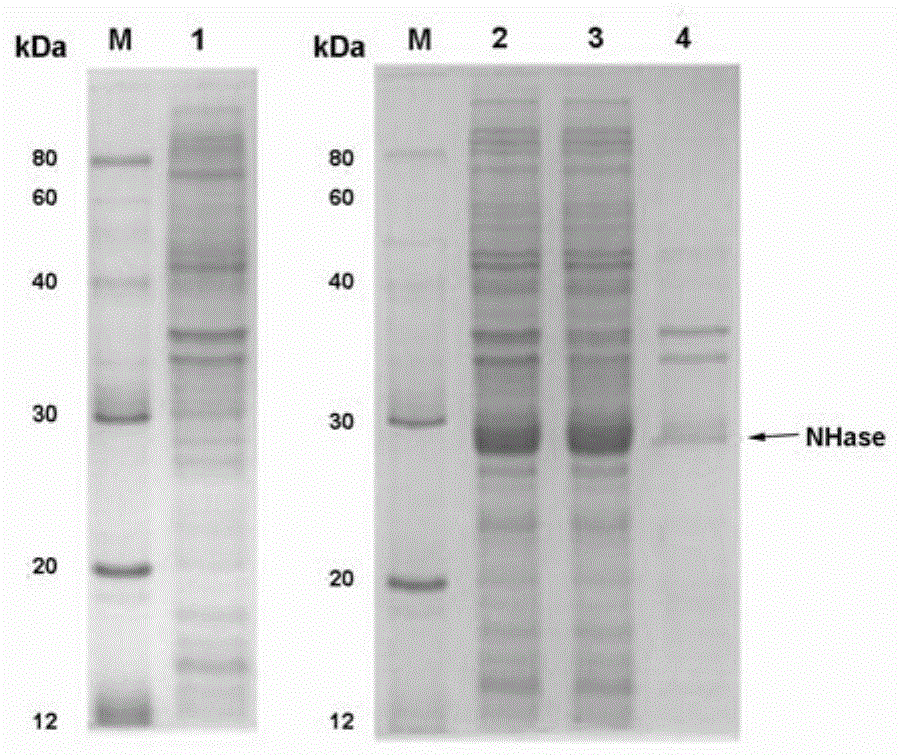
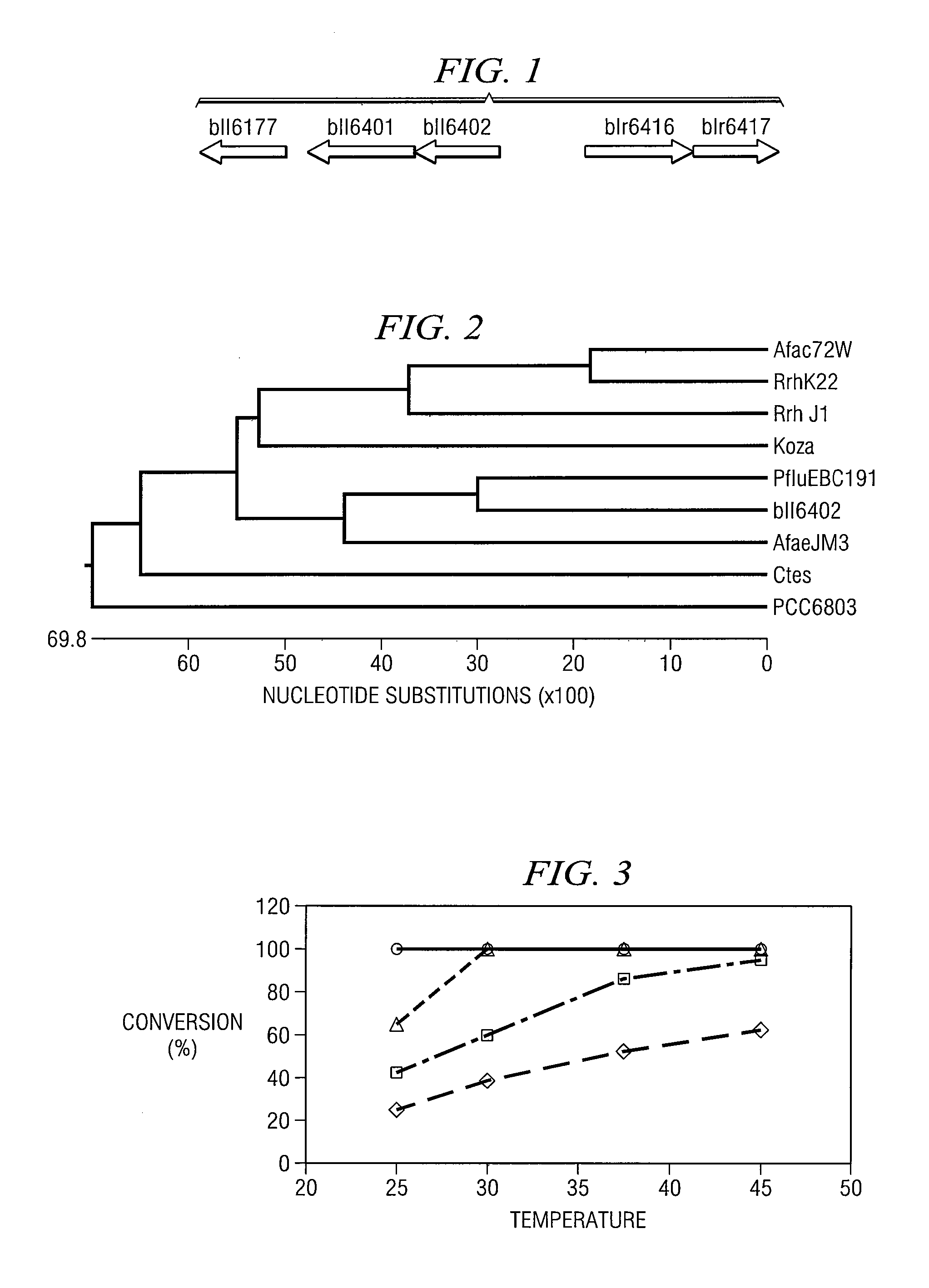
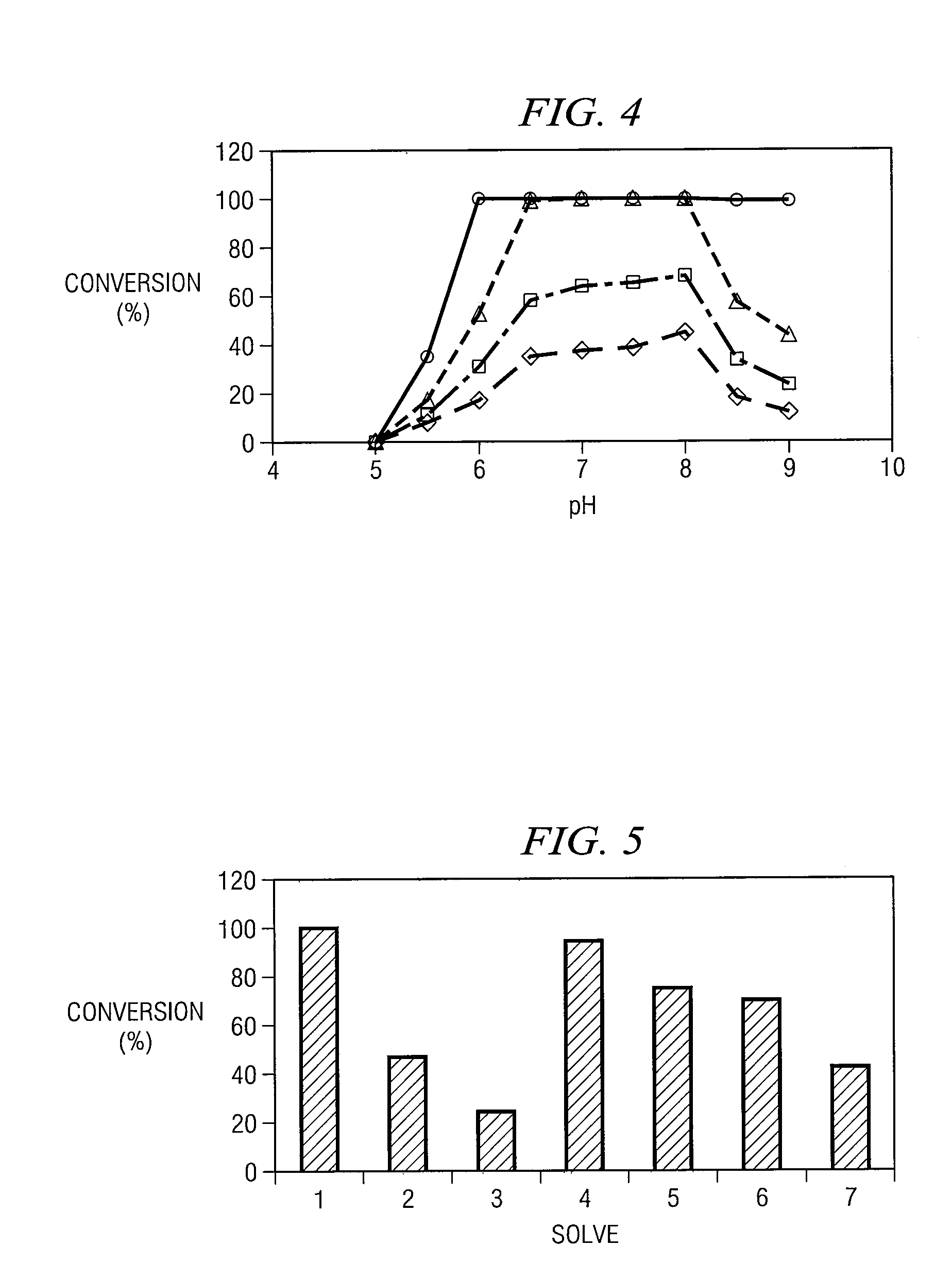
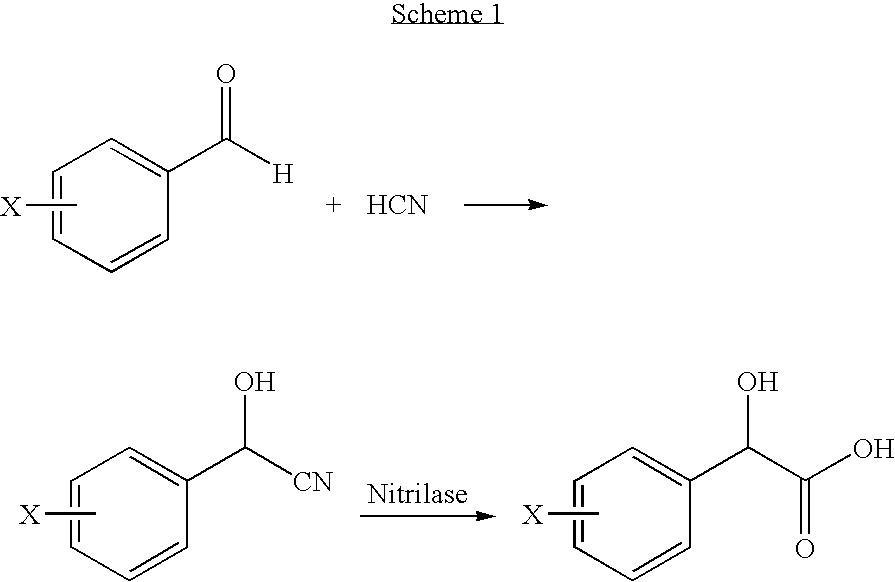
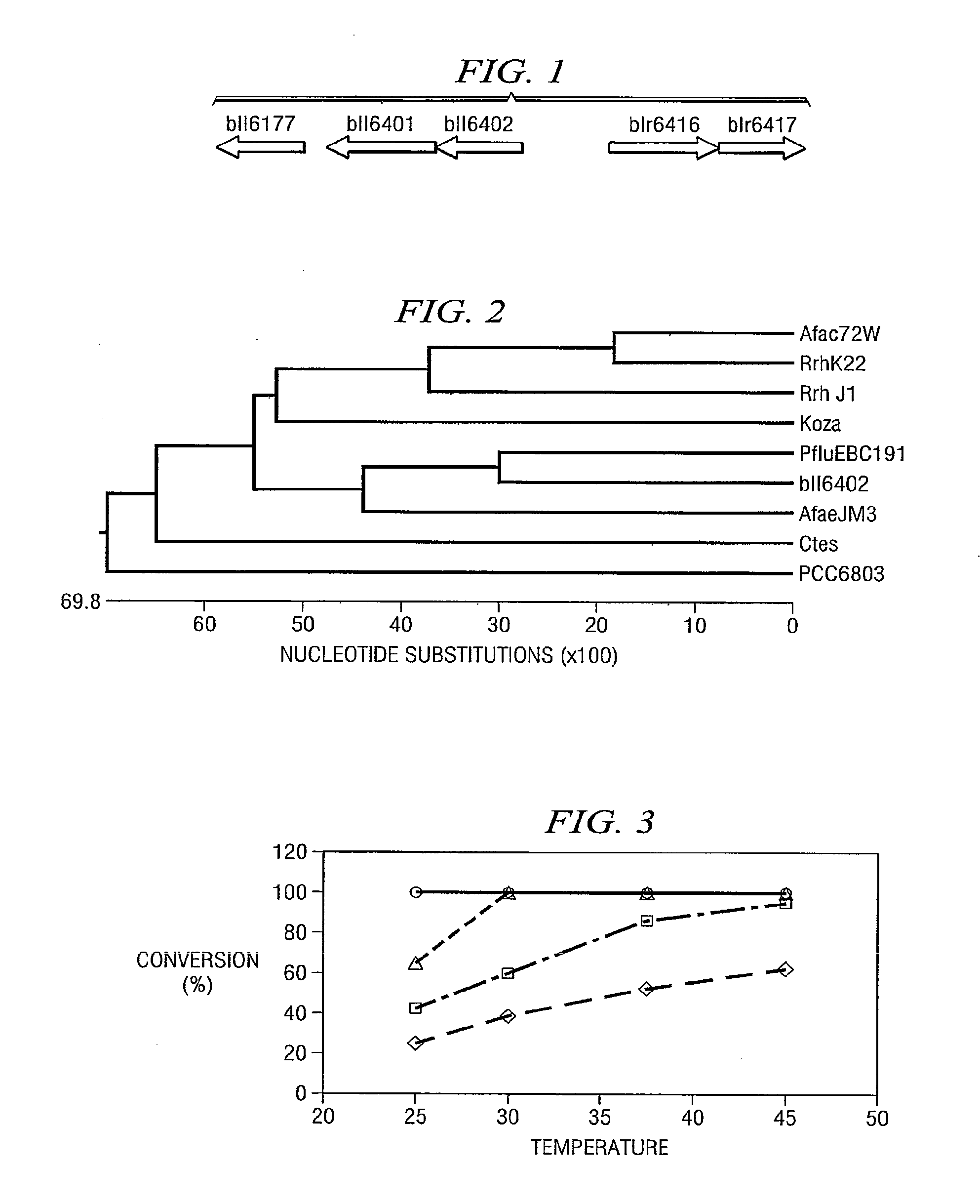
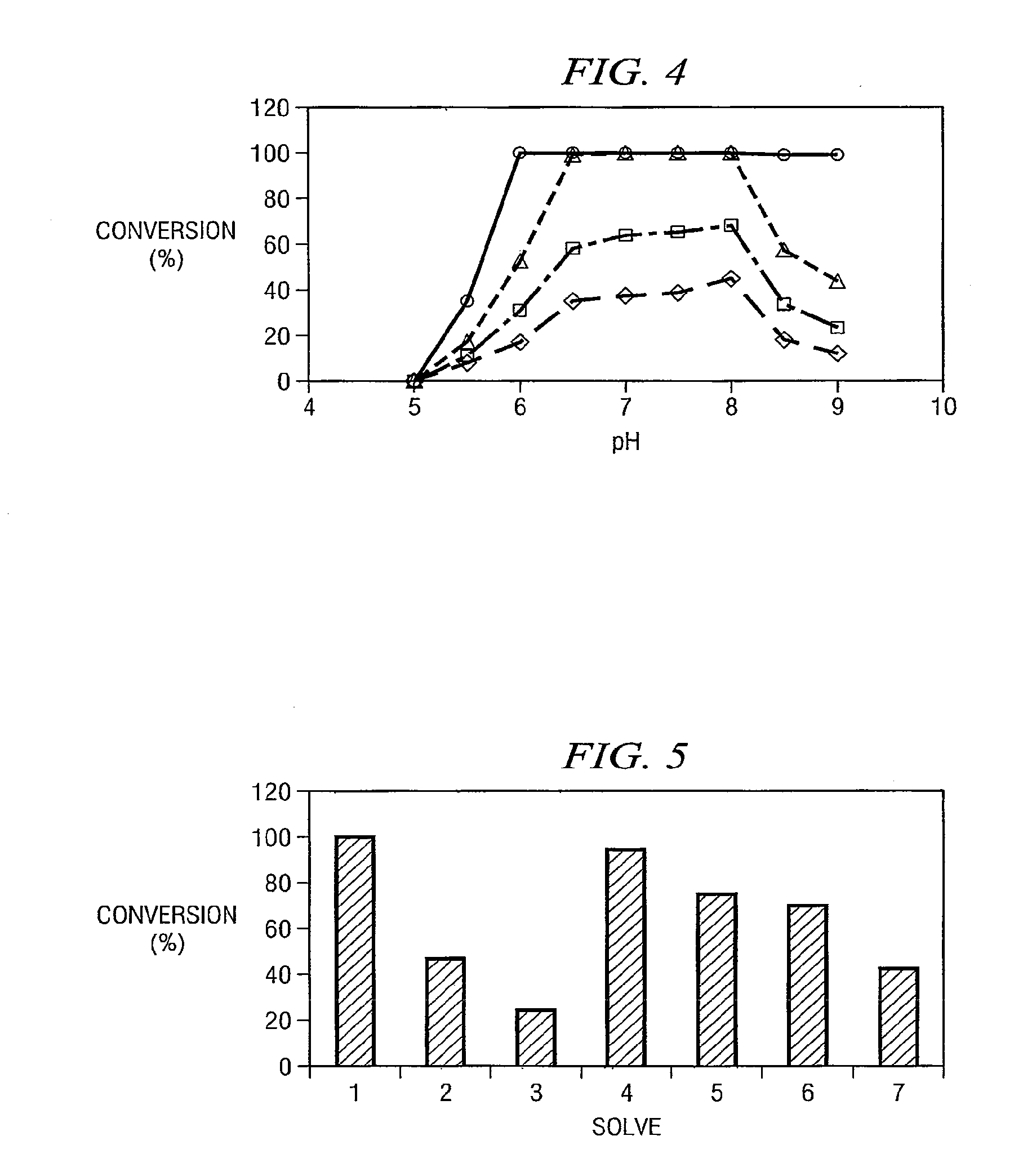
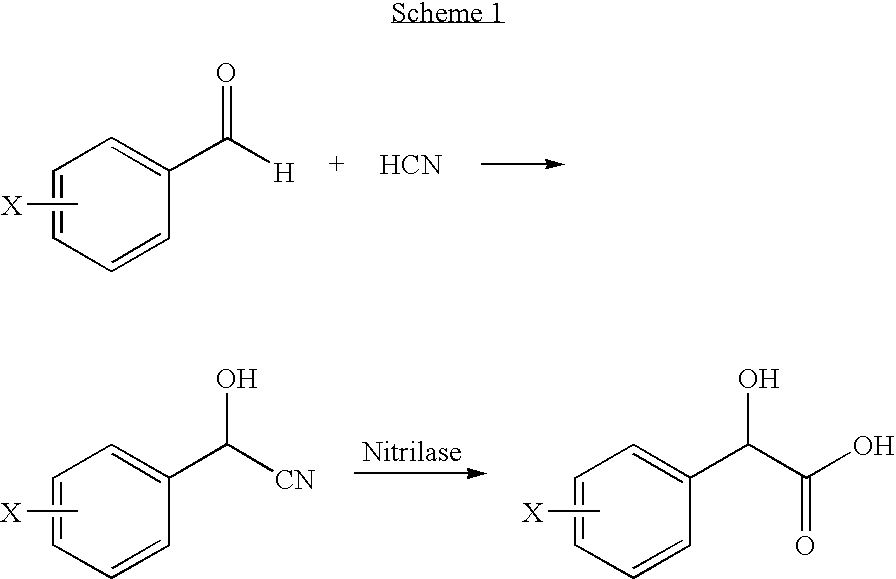
Identification Of A Nitrilase From B. Japonicum By Rational Genome Mining And Methods Of Use
InactiveUS20070178575A1Improve reaction speedWide rangeHydrolasesFermentationCarboxylic acidBradyrhizobium japonicum
The present disclosure relates to methods of rational genome mining. A method may include narrowing the number of clones that would otherwise need to be screened and / or identifying a gene with a desired catalytic activity. The disclosure also relates to a nitrile hydrolase from Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110 first identified by rational genome mining. In addition, the disclosure relates to nitrilase bll6402 and catalytically active variants capable of converting an α-hydroxy nitriles, a β-hydroxy nitrile and / or an α,ω-dinitrile to a carboxylic acid.
Owner:SOUTHERN METHODIST UNIVERSITY
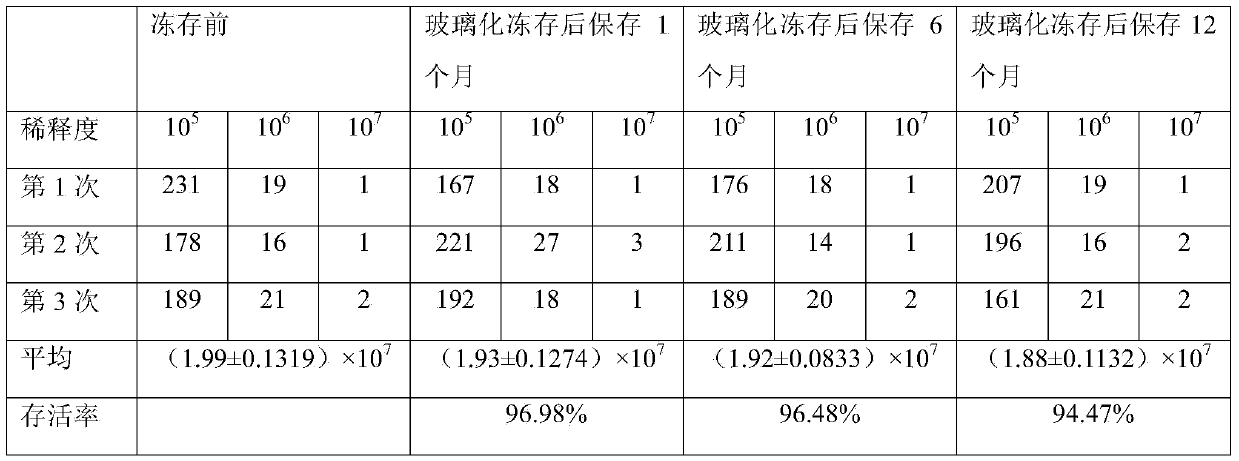
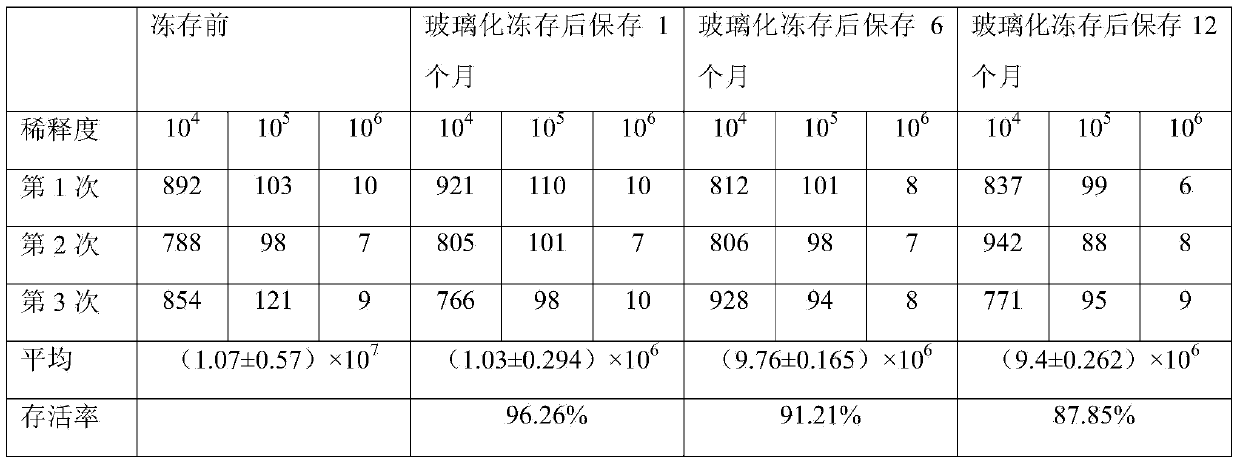
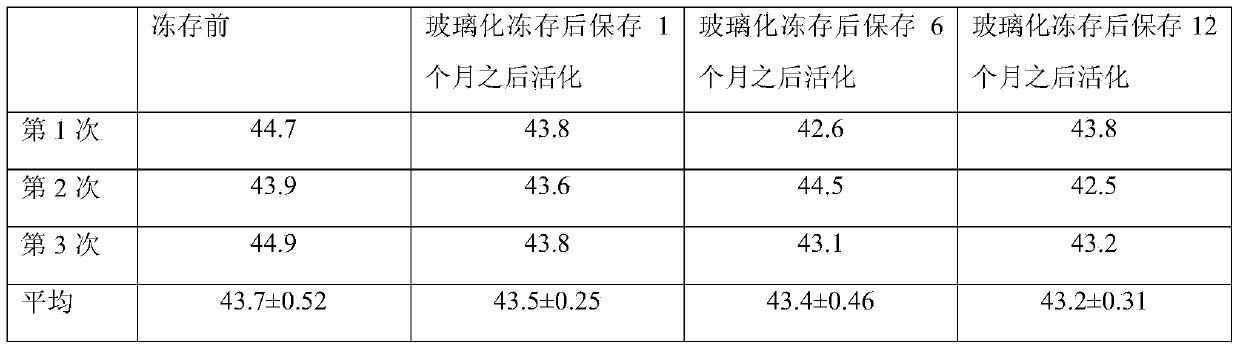
Bradyrhizobium japonicum vitrified cryopreservation liquid and method for vitrified cryopreservation of bradyrhizobium japonicum
ActiveCN103421693AImprove the preservation effectNo adverse effectsMicroorganism based processesMicroorganism preservationMicroorganism preservationMicroorganism
The invention discloses bradyrhizobium japonicum vitrified cryopreservation liquid and a method for vitrified cryopreservation of bradyrhizobium japonicum and relates to microorganism vitrified cryopreservation liquid and a method for vitrified cryopreservation of microorganisms. The bradyrhizobium japonicum vitrified cryopreservation liquid contains ethanediol and is simple in compound composition. The bradyrhizobium japonicum vitrified cryopreservation liquid is composed of glycerinum, ethanediol, DMSO and distilled water. According to the method for vitrified cryopreservation of the bradyrhizobium japonicum, bradyrhizobium japonicum liquid is added into the bradyrhizobium japonicum vitrified cryopreservation liquid, and then the bradyrhizobium japonicum vitrified cryopreservation liquid is put into liquid nitrogen for fast vitrified cryopreservation. The bradyrhizobium japonicum vitrified cryopreservation liquid and the method for vitrified cryopreservation of the bradyrhizobium japonicum are used in the field of microorganism preservation.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY HEILONGJIANG ACADEMY OF SCI
Gamma-lactamase with racemate gamma-lactam resolution activity as well as encoding gene and applications thereof
InactiveCN103966192AWith absolute selectivityBacteriaHydrolasesGamma-lactamaseBradyrhizobium japonicum
The invention discloses gamma-lactamase with racemate gamma-lactam resolution activity as well as an encoding gene and applications thereof, namely, bradyrhizobium japonicum (Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA6) derived gamma-lactamase as well as an encoding gene and applications thereof, and provides an application of the gamma-lactamase in the hydrolytic resolution of racemate gamma-lactam. The gamma-lactamase disclosed by the invention is a protein as the following (a) or (b): (a) a protein consisting of amino acid residue sequences shown in SEQ ID No:1 in a sequence table; and (b) a protein formed by that amino acid residue sequences shown in SEQ ID No:1 in a sequence table are replaced and / or deleted and / or added by one or more amino acid residues, with racemate gamma-lactam resolution activity, and derived from SEQ ID No:1. Racemate gamma-lactam is subjected to hydrolytic resolution by using the gamma-lactamase, the resolution activity of the gamma-lactamase is close to 100%, and then gamma-lactam is prepared by using a catalytic product amino acid.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
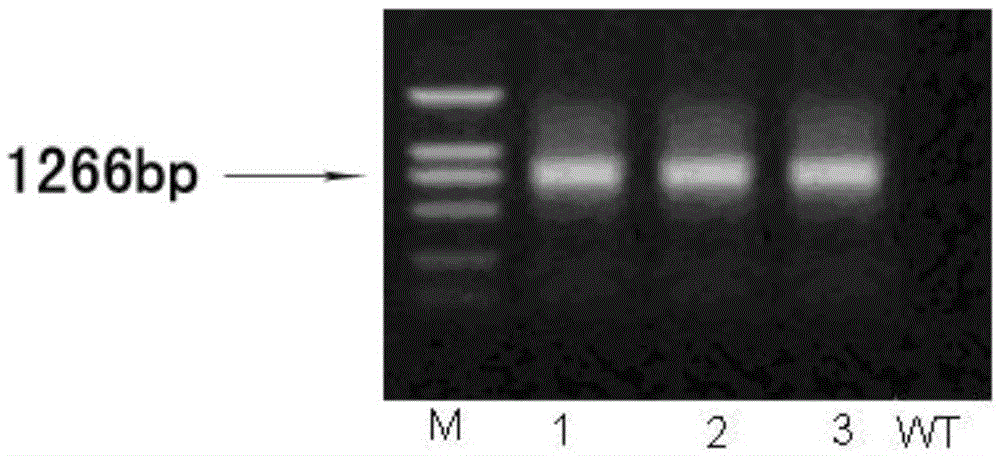
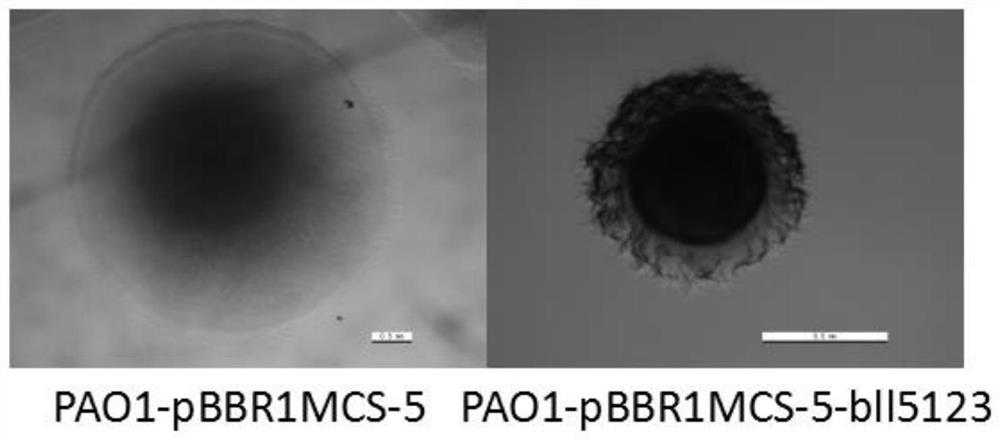
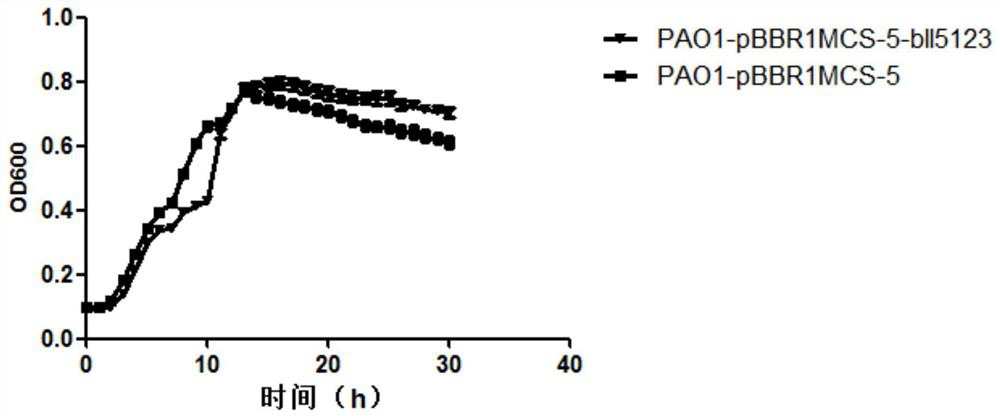
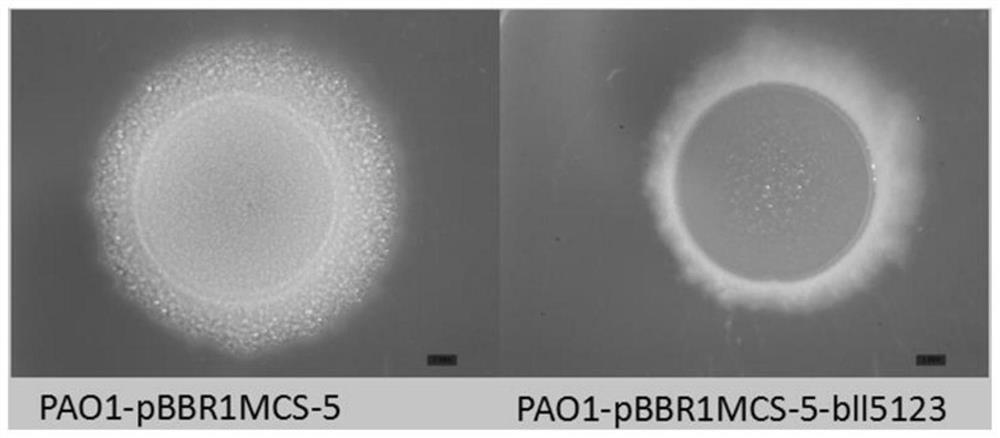
Method of researching gene function of Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110
ActiveCN108611306AConvenient primary screeningQuick ScreeningBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBradyrhizobium speciesProkaryotic expression
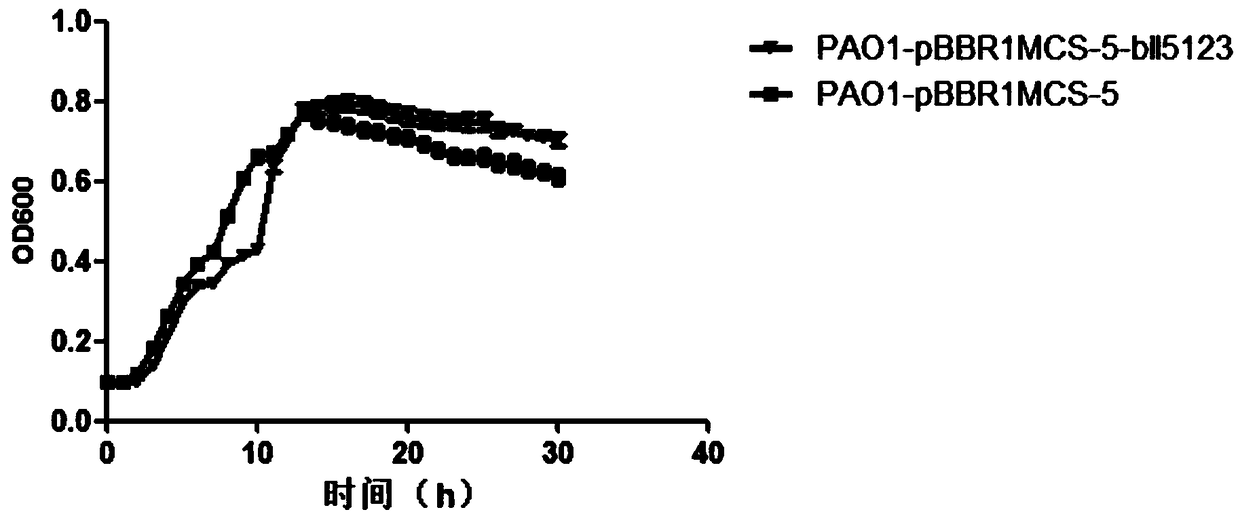
The invention discloses a method of researching functions of genes of Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110, and provides a prokaryotic expression system which utilizes pseudomonas aeruginosa as host bacteria; the pseudomonas aeruginosa is Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. In the invention, phenotype research related to gene synthesis and degradation functions of intracellular messenger cyclic di-guanosinemonophosphate (c-di-GMP) in the Bradyrhizobium japonicum is directly carried out in the pseudomonas aeruginosa of which the background mechanism research is definite; by observing the character changes of the pseudomonas aeruginosa, functions of the target gene is initially obtained. The invention provides the novel prokaryotic expression system in which the gene of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum isexpressed and colonial morphology, moveability, generation of exopolysaccharide and generation quantity of biomembrane are inspected, thereby initially obtaining the function of the gene of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum. The method saves time and consumable costs, accelerates researching process and is beneficial to research on the gene function of Bradyrhizobium japonicum.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Saline-alkali soil resistant nitrogen fixation rhizobium japonicum and application thereof
ActiveCN114456981AHigh nitrogen contentIncrease productionPlant growth regulatorsBiocidePlant noduleEcological environment
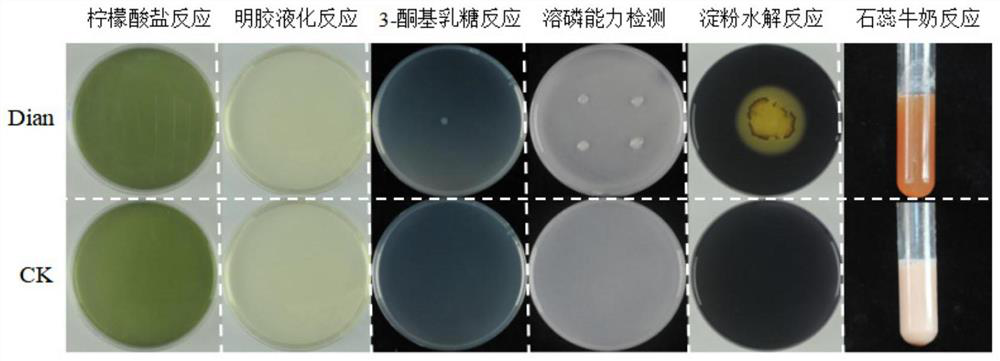
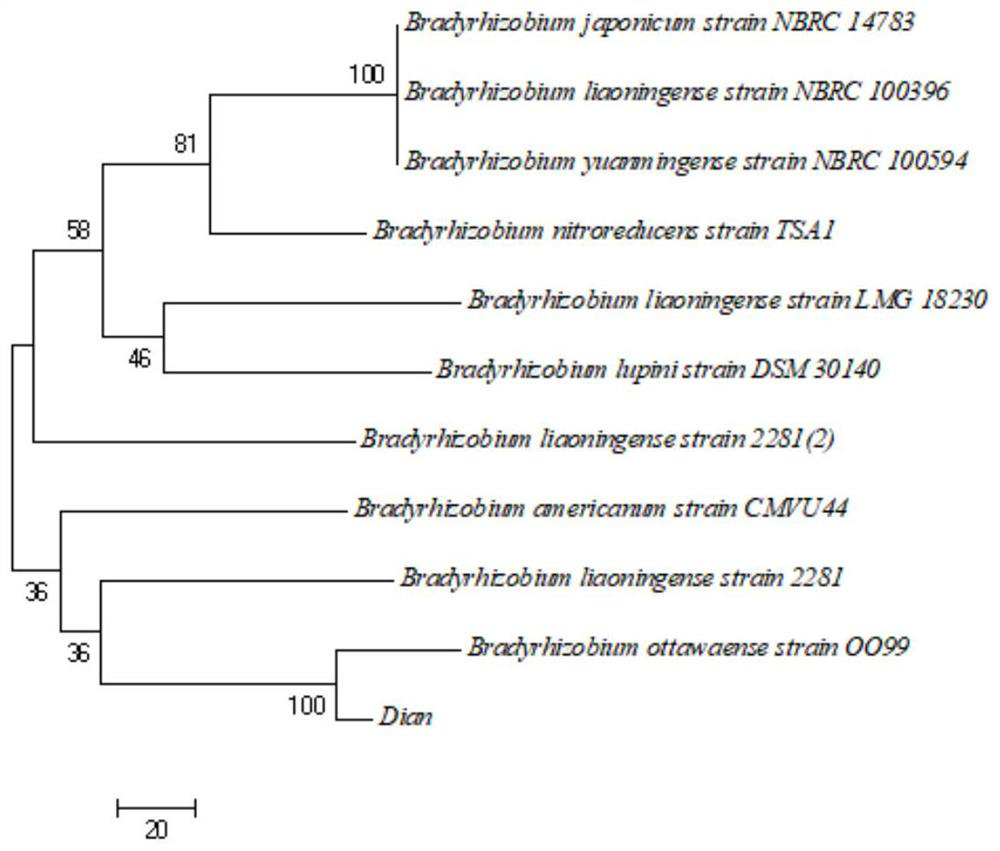
The invention discloses a nitrogen-fixing bradyrhizobium japonicum strain resistant to saline-alkali soil and application of the bradyrhizobium japonicum strain. According to the invention, a strain of bradyrhizobium taihuae Dian strain is obtained through separation and is preserved in Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center on January 11, 2022, and the preservation number is GDMCC No: 62202. Researches show that the strain has the characteristics of high nodulation rate and strong nitrogen fixation capability, and can optimize the micro-ecological environment of alkaline soil crop root growth; the Dian strain is adopted to treat plants, soybean nodulation and nitrogen fixation can be effectively promoted, plant nitrogen nutrition is increased, plant growth is promoted, and the biomass, root nodule number and nitrogen content of soybean plants can be remarkably improved. The strain is especially suitable for cultivation and production of soybeans in stony desertification areas, expands a strain resource library of nitrogen-fixing rhizobium, is beneficial to promoting nodulation and nitrogen fixation of plants, and increases nitrogen nutrition of the plants.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Identification of a nitrilase from b. japonicum by rational genome mining and methods of use
InactiveUS20100137636A1Reduce in quantityOrganic chemistryHydrolasesCarboxylic acidBradyrhizobium japonicum
The present disclosure relates to methods of rational genome mining. A method may include narrowing the number of clones that would otherwise need to be screened and / or identifying a gene with a desired catalytic activity. The disclosure also relates to a nitrile hydrolase from Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110 first identified by rational genome mining. In addition, the disclosure relates to nitrilase bll6402 and catalytically active variants capable of converting an α-hydroxy nitriles, a β-hydroxy nitrile and / or an α,ω-dinitrile to a carboxylic acid.
Owner:SOUTHERN METHODIST UNIVERSITY
Method for com-culturing and improving hydrogen output by utilizing bacteria and chlamydomonas reinhardtii
InactiveCN102559832BIncrease hydrogen productionReduce the greenhouse effectMicroorganism based processesFermentationChlamydomonas reinhardtiiOxygen
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
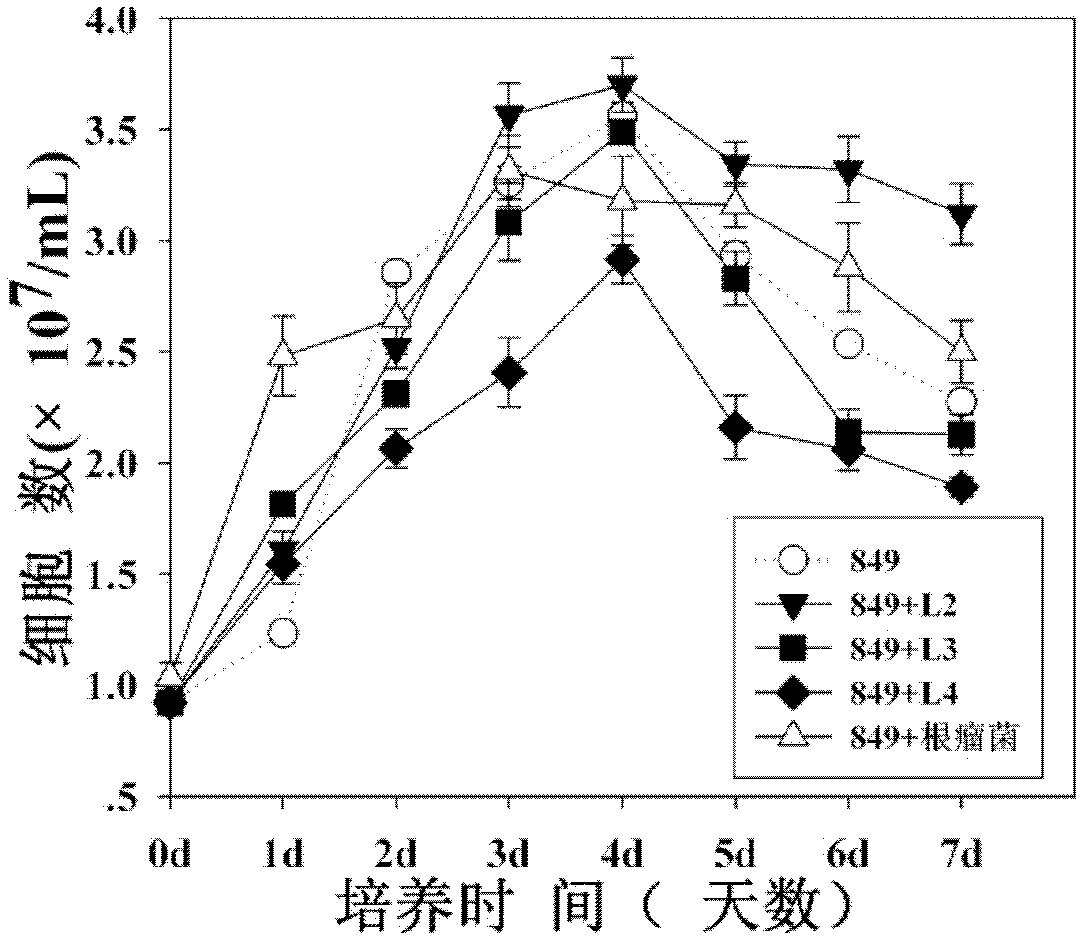
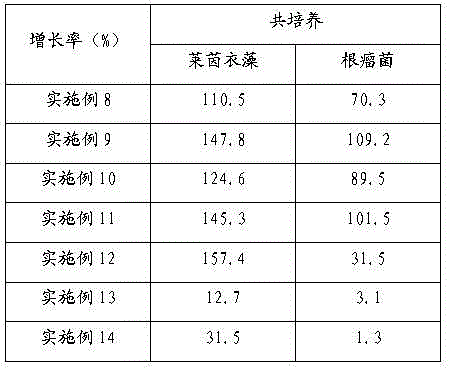
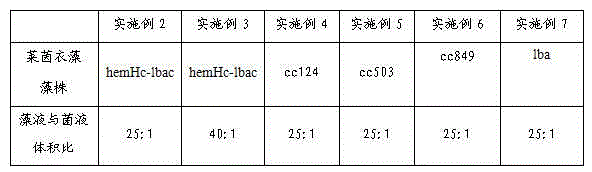
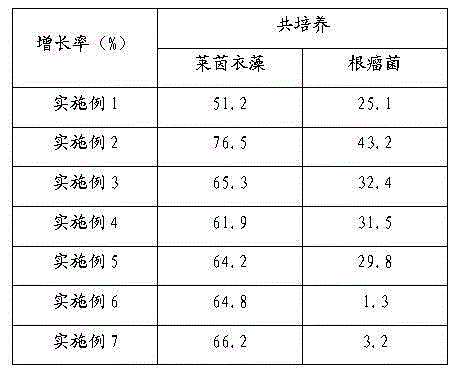
Method for mutually promoting growth of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
InactiveCN104017763AIncrease productionBacteriaUnicellular algaeChlamydomonas reinhardtiiEcological environment
The invention relates to the technical field of biological hydrogen production and particularly relates to a method for mutually promoting growth of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.. The method comprises the following steps: respectively co-culturing Bradyrhizobium japonicum (hereinafter referred to as rhizobia) and another three strains, namely Chlamydomonas reinhardtii strain cc124 (hereinafter referred to as 124), algal strains cc503 (hereinafter referred to as 503) and transgenic Chlamydomonas reinhardtii hemHc-lbac (hereinafter referred to as hemHc-lbac) in a normal culture medium and a sulfur-deficient culture medium, the results show that the growth of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and Bradyrhizobium japonicum can be promoted and the Bradyrhizobium japonicum gathers around the Chlamydomonas cell and grows prior to the hydrogen production decrescence, which indicates that a phenomenon of a periodical reciprocal symbiosis exists between Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and rhizobia. The method disclosed by the invention provides an experimental basis and a new idea for further broadening the host range of rhizobia, promoting the biomass accumulation of large-scale cultivation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, producing a renewable biological energy source and improving the ecological environment.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
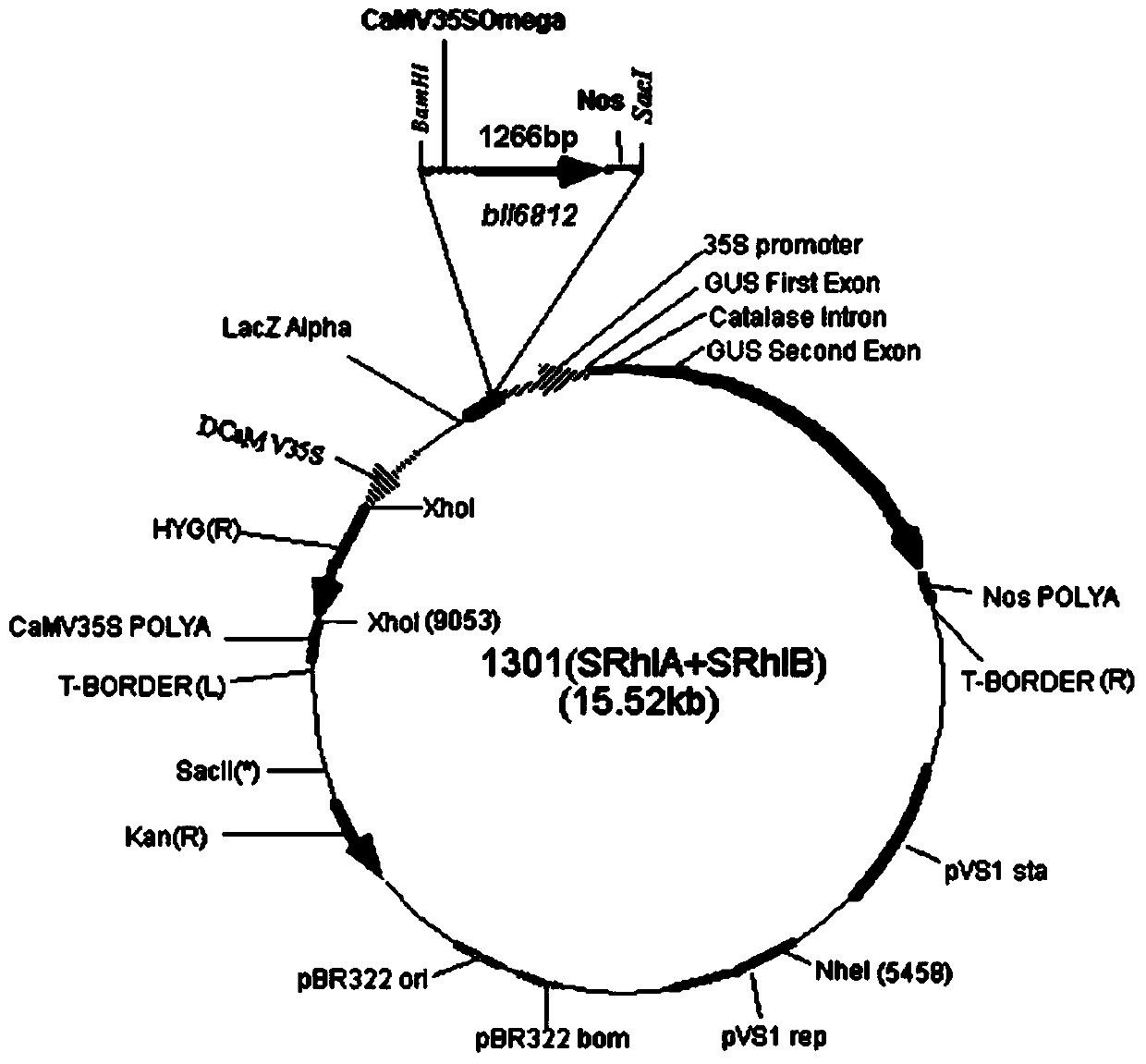
D-lactate dehydrogenase gene b116812S as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103740737AObvious resistance to glyphosateImproved resistance to glyphosateMicroorganism based processesFermentationNucleotideGlyphosate
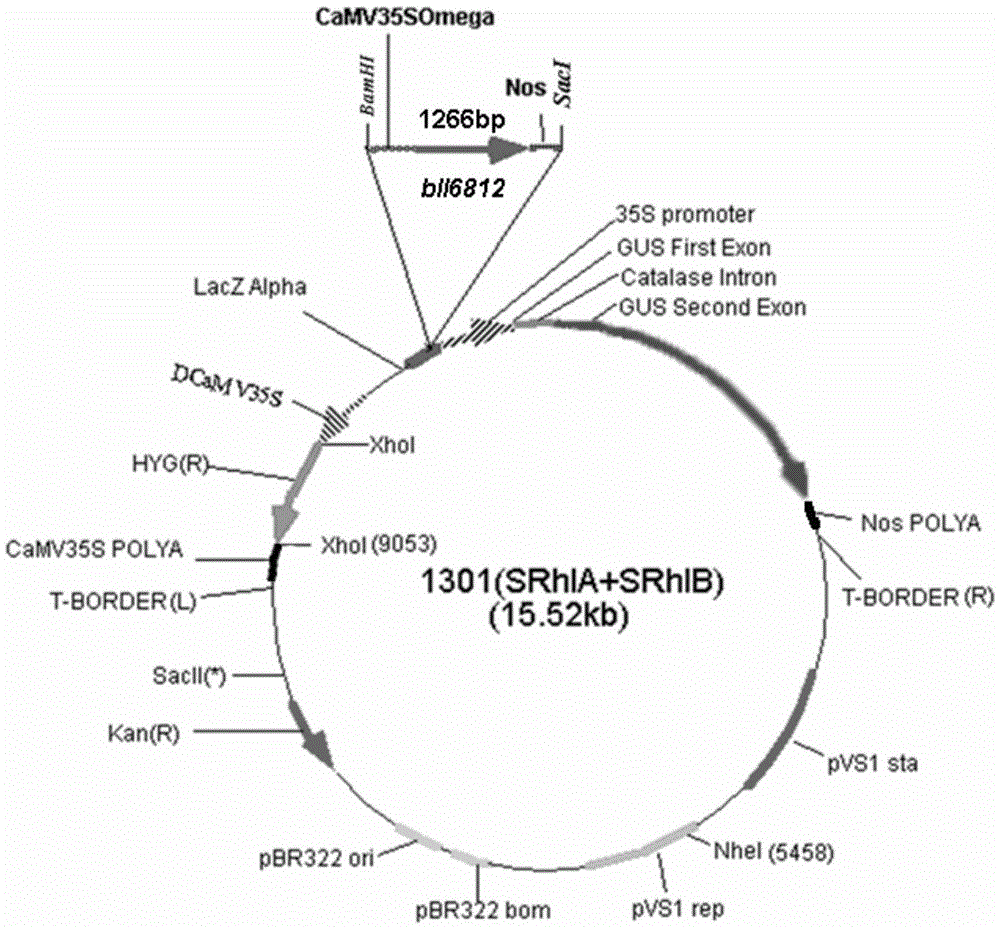
The invention discloses a D-lactate dehydrogenase gene b116812S derived from a high-efficiency nitrogen fixation bradyrhizobium japonicum as well as a preparation method and application of the D-lactate dehydrogenase gene b116812S. A nucleotide sequence of the D-lactate dehydrogenase gene b116812S is shown in SEQ ID No.1, and an amino acid sequence coded by the D-lactate dehydrogenase gene b116812S is shown in SEQ ID No.2. The D-lactate dehydrogenase gene b116812S is prepared by reconstructing a D-lactate dehydrogenase gene b116812 derived from the high-efficiency nitrogen fixation bradyrhizobium japonicum according to a plant preferred codon and by using a gene synthesis method. The D-lactate dehydrogenase gene b116812S is converted into arabidopsis thaliana to obtain a transgenosis arabidopsis thaliana, and the performance of the transgenosis arabidopsis thaliana resisting glyphosate is remarkably superior to that of wild type arabidopsis thaliana, and can be applied to glyphosate-resisting crop breeding.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
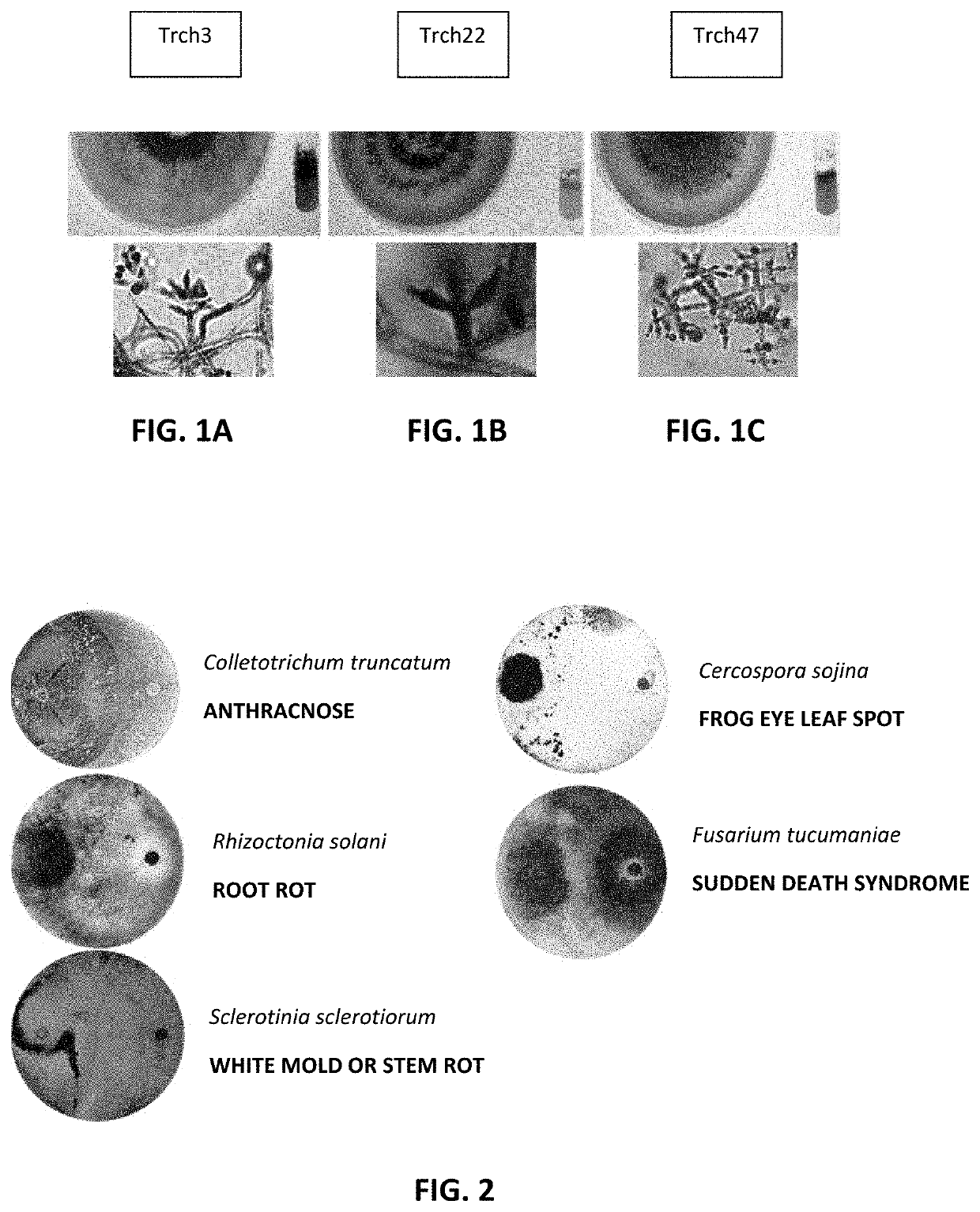
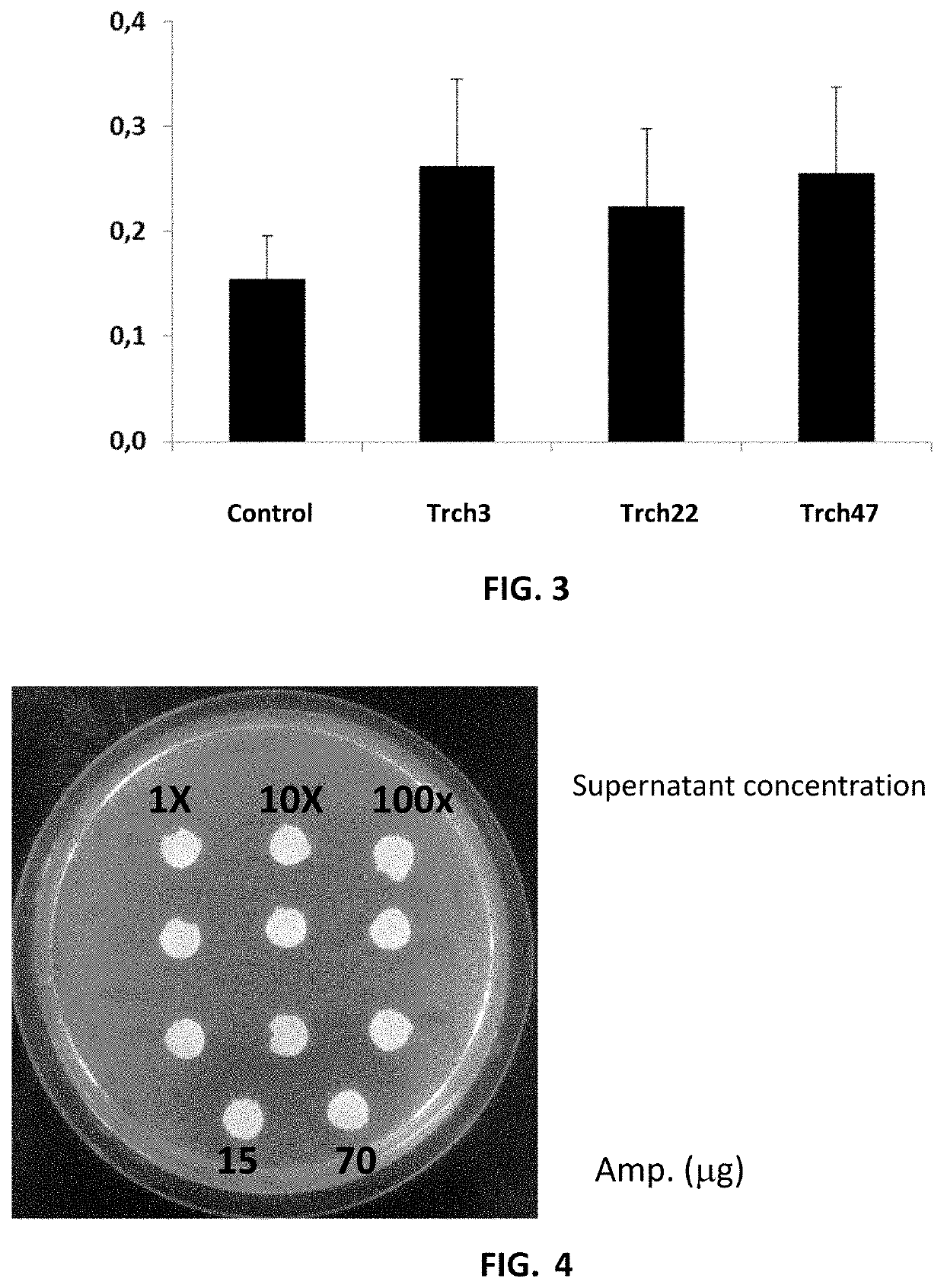
Biological inoculant having enhanced fertilizing and fungicidal activity
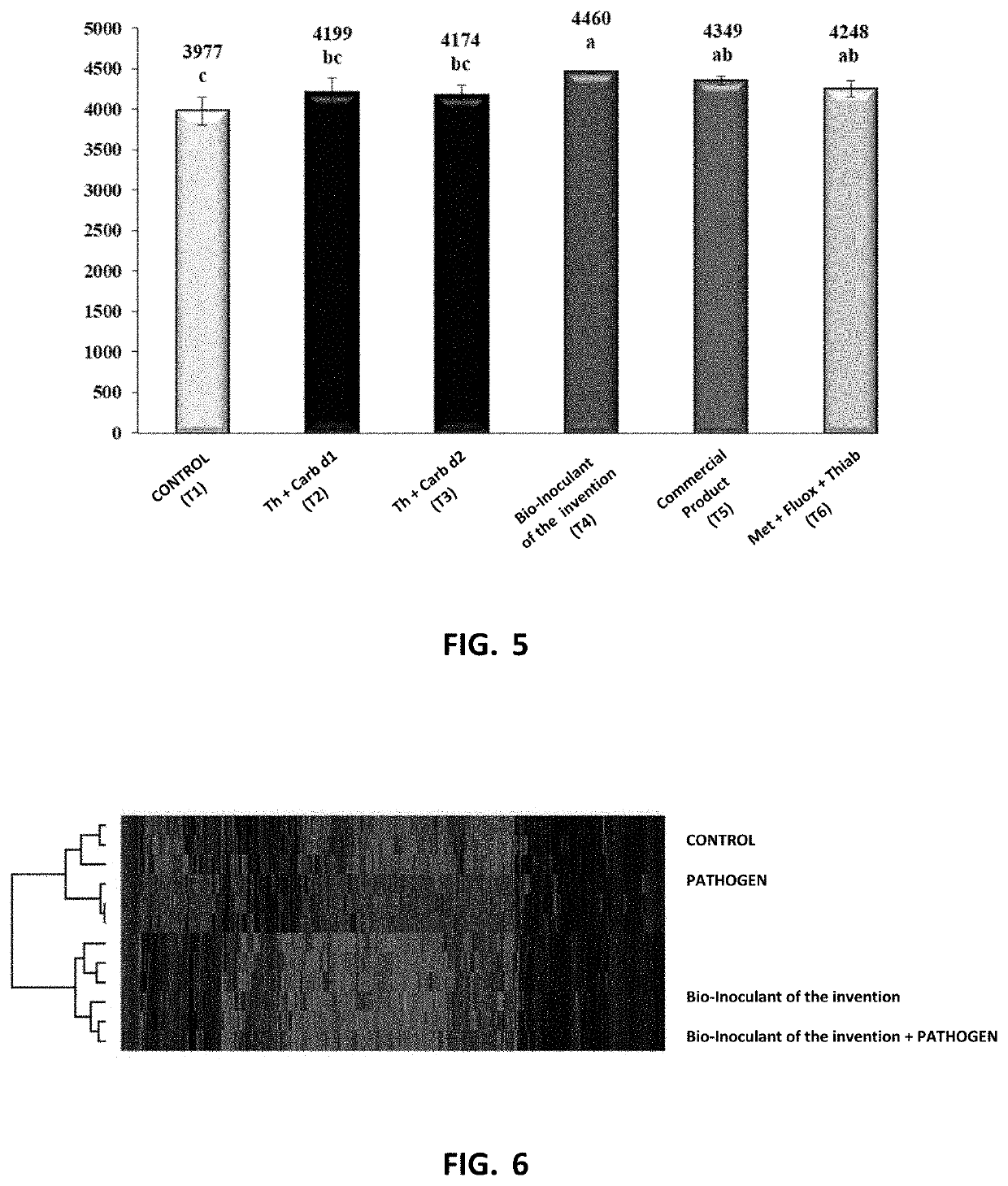
A biological inoculant having both fertilizing and fungicidal activity is disclosed. More particularly, a bio-inoculant having the said combined effects, comprising Bradyrhizobium japonicum and specific isolates from the Trichoderma genus is disclosed. The bio-inoculant is applied to soybean crops for preventing fungi borne diseases. More particularly, the bio-inoculant of the invention is useful for protecting soybean crops against infection by Fusarium sp., Colletotrichum sp., Cercospora sp., Sclerotinia sp. and Rhizoctonia sp.
Owner:YPF TECHA
Environment-friendly biological agent for treating fruit and vegetable organic garbage
PendingCN114058540ALow working conditionsShort processing cycleFungiBio-organic fraction processingBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention relates to an environment-friendly biological agent for treating fruit and vegetable organic garbage. The microbial agent comprises 4-8 parts of white rot fungus powder, 3-6 parts of streptomyces powder, 6-9 parts of bacillus licheniformis powder, 6-9 parts of bacillus pumilus powder, 4-8 parts of nitrobacteria powder, 8-10 parts of lactic acid bacteria powder, 7-10 parts of bacillus megatherium powder, 8-12 parts of bacillus subtilis powder, 8-12 parts of bacillus amyloliquefaciens powder and 5-8 parts of saccharomyces cerevisiae powder, 1-5 parts of bacillus mucilaginosus powder, 1-5 parts of Bradyrhizobium japonicum powder, 4-8 parts of azotobacter chroococcum powder, 3-7 parts of Thermomonospora fusca powder, 1-3 parts of lactobacillus delbrueckii, 1-5 parts of cellulase, 0.5-2 parts of ligninase, 0.01-0.05 part of 90% amino-oligosaccharin and 0.05-1 part of brassinolide. The environment-friendly biological agent can be applied to treatment of different fruit and vegetable organic solid wastes, the treatment period is greatly shortened to 24 hours to one week, the process is environmentally friendly and harmless, the final treatment product is the biological bacterial fertilizer, and waste is turned into wealth.
Owner:上海玖霖环保科技有限公司
Microbial agent suitable for planting of corn in saline-alkali soil and preparation method of microbial agent
ActiveCN109988017AMeet the nutritional needs of growthIncrease productionFungiBio-organic fraction processingActivated sludgeAlkali soil
The invention provides a microbial agent suitable for planting of corn in saline-alkali soil. The microbial agent is prepared by the following steps: firstly preparing composite microbial powder fromtrichosporon cutaneum, bradyrhizobium japonicum, trichoderma viride, bacillus coagulans, pseudomonas cepacia, and azotobacter chroococcum, mixing the composite microbial powder and a pre-mixed material prepared from corn straw powder, mushroom residues, cottonseed meal and other materials, performing anaerobic fermentation to obtain a fermented material, pouring the fermented material into a covering material prepared from polyaspartic acid and a polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution to obtain a pre-prepared material, finally adding polycaprolactone into the pre-prepared material, performing uniform stirring to obtain a mixture, adding activated sludge into the mixture, and performing aerobic fermentation to obtain the the microbial agent. After the microbial agent provided by the invention is applied into the saline-alkali soil, the physical and chemical properties of the soil can be improved, the nutrient requirements of growth of the corn can be met, and the yield of the corn can be improved.
Owner:MAIZE RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Composite microbial fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102199050BImprove the preservation effectImprove sexual functionOrganic fertilisersBacillus megateriumNutrient solution
The invention relates to the field of microbiology, and specifically relates to a composite microbial fertilizer and a preparation method thereof. The composite microbial fertilizer is composed of a composite microbial fermentation broth and an embedding medium, wherein a volume ratio of the composite microbial fermentation broth to the embedding medium are in a range of 1:5 to 1:4. The compositemicrobial fermentation broth is compounded of a co-culture comprising Candida utilis, lactic streptococci, lactobacillus acidophilus and bacillus subtilis, and a single nutrient solution comprising Bradyrhizobium japonicum, Azospirillum lipoferum, Rhodopseudomonas palustris, Bacillus megaterium, Bacillus mucilaginosus and Azotobacter chrococcum. In the invention, composite microbes processed by embedding can be stored stably for more than 60 days and a count of the composite microbes is always more than 2 billion per gram, thus the composite microbial fertilizer comprising the composite microbes has a long effective time and can improve a planting capacity of soil.
Owner:沈阳科丰牧业科技有限公司
Method for whole-cell splitting of racemate beta-lactam by using Bradyrhizobium japonicum
ActiveCN103937867AReduce pollutionImprove reaction efficiencyMicroorganism based processesFermentationBradyrhizobium japonicumRelative yield
The invention relates to a method for whole-cell splitting of a racemate beta-lactam by using Bradyrhizobium japonicum, and belongs to the technical field of separation. According to the present invention, the whole-cell transformation splitting of 3-hydroxy-4-phenyl-2-azetidinone and 3-acetoxy-4-phenyl-2-azetidinone with Bradyrhizobium japonicum has high catalysis efficiency, and the high purity single configuration compound can be obtained, wherein the (3R,4S)3-hydroxy-4-phenyl-2-azetidinone e.e value is 99.99%, the target product relative yield is 99%, the total yield is 49.5%, the (3R,4S)3-acetoxy-4-phenyl-2-azetidinone e e.e value is 99.88%, the target product relative yield is 93.58%, and the total yield is 46.79%.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
A kind of soybean rhizobia suitable for making freeze-dried powder and its application
ActiveCN109880759BImprove low temperature resistanceEasy to processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyRhizobium japonicum
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY HEILONGJIANG ACADEMY OF SCI
A Soybean Bradyrhizobium scaus36 and Its Application
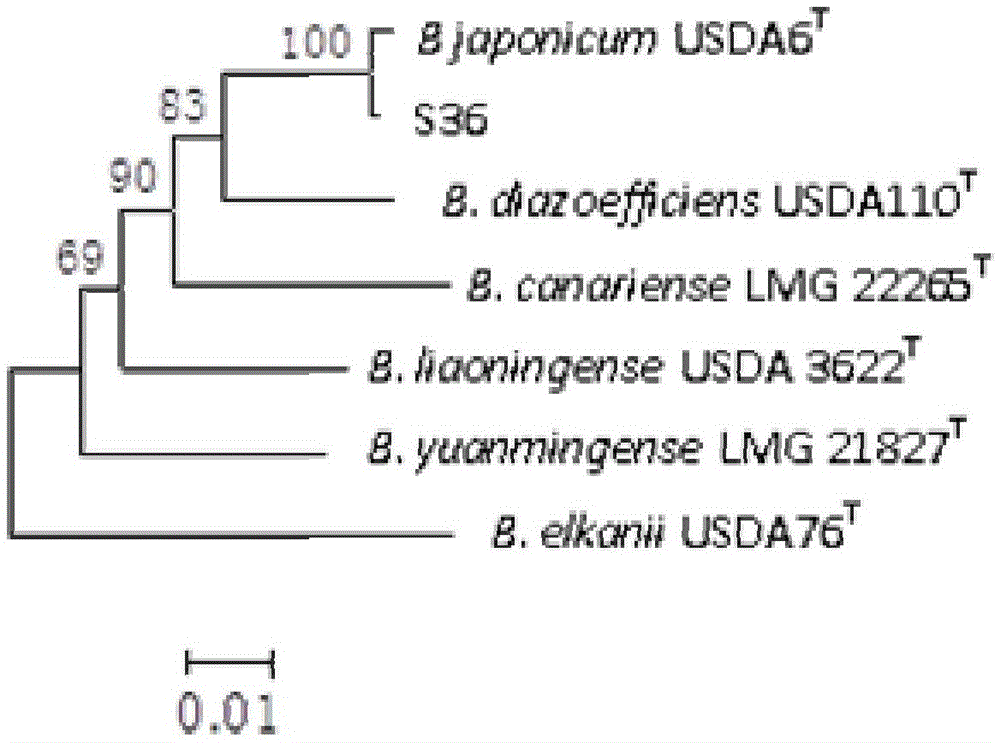
InactiveCN103952343BStrong stress resistanceHas the ability to secrete IAABiocidePlant growth regulatorsPlant noduleRhizobium japonicum
The invention discloses a Bradyrhizobium japonicum SCAUs36 and application thereof. The strain is separated and purified from fresh soybean root nodules. The strain is collected to China Center for Type Culture Collection of Wuhan University on March 14th, 2014, the collection number is CCTCC NO.M2014082, and the classification designation is Bradyrhizobium japonicum. The strain is applied to production of Sichuan soybeans. The Bradyrhizobium japonicum SCAUs36 is a favorable broad-spectrum Rhizobium japonicum strain with high symbiotic fixation capacity, wide application range for Sichuan soybean species, IAA (indoleacetic acid) secretion capacity, capacities for dissolving inorganic phosphorus and organic phosphorus and high stress tolerance. The strain has favorable matching affinity with Sichuan dominant bean species, and can enhance the soybean yield by more than 31% in different ecological regions where no nitrogen fertilizer is applied and the SCAUs36 is inoculated, which is much different from the regions where the SCAUs36 is not inoculated.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
High-density culture method for slow-growing rhizobium japonicum
PendingCN112940973AAchieve high density cultureHigh viable countBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMetabolite
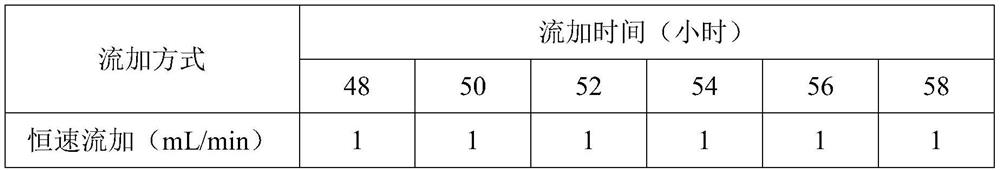
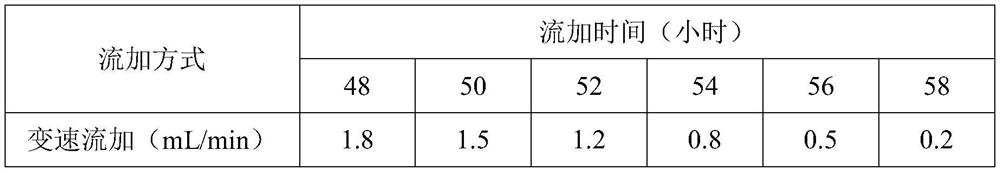
The invention discloses a high-density culture method for slow-growing rhizobium japonicum, and belongs to the technical field of heterotrophic culture fermentation processes. The method solves the problems that the carbon nitrogen ratio in the logarithmic phase is unbalanced, the growth of thalli is poor due to the increase of metabolites, and the high-density culture of the slow-growing rhizobium japonicum cannot be realized in the conventional method for culturing the rhizobium japonicum in a fermentation tank. According to the method, a constant-speed fed-batch feeding mode is adopted, the ratio and concentration of carbon and nitrogen in fermentation liquor are effectively maintained, the viable count of the slow-growing rhizobium japonicum in the logarithmic phase is effectively increased, the final effective viable count of fermentation is stabilized at 6.8 * 10 < 9 > cfu / mL, and high-density culture of the rhizobium japonicum is achieved. In addition, the adopted constant-speed fed-batch feeding mode is easy to operate, amplification culture is easier, and the method is more suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY HEILONGJIANG ACADEMY OF SCI
A d-amino acid dehydrogenase gene bll6812s and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN103740737BObvious resistance to glyphosateImproved resistance to glyphosateMicroorganism based processesFermentationNucleotideWild type
The invention discloses a D-lactate dehydrogenase gene b116812S derived from a high-efficiency nitrogen fixation bradyrhizobium japonicum as well as a preparation method and application of the D-lactate dehydrogenase gene b116812S. A nucleotide sequence of the D-lactate dehydrogenase gene b116812S is shown in SEQ ID No.1, and an amino acid sequence coded by the D-lactate dehydrogenase gene b116812S is shown in SEQ ID No.2. The D-lactate dehydrogenase gene b116812S is prepared by reconstructing a D-lactate dehydrogenase gene b116812 derived from the high-efficiency nitrogen fixation bradyrhizobium japonicum according to a plant preferred codon and by using a gene synthesis method. The D-lactate dehydrogenase gene b116812S is converted into arabidopsis thaliana to obtain a transgenosis arabidopsis thaliana, and the performance of the transgenosis arabidopsis thaliana resisting glyphosate is remarkably superior to that of wild type arabidopsis thaliana, and can be applied to glyphosate-resisting crop breeding.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A method for studying the gene function of Bradyrhizobium
ActiveCN108611306BSave time and costAccelerate the progress of experimental researchBacteriaMicroorganism based processesColony morphologyBradyrhizobium
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
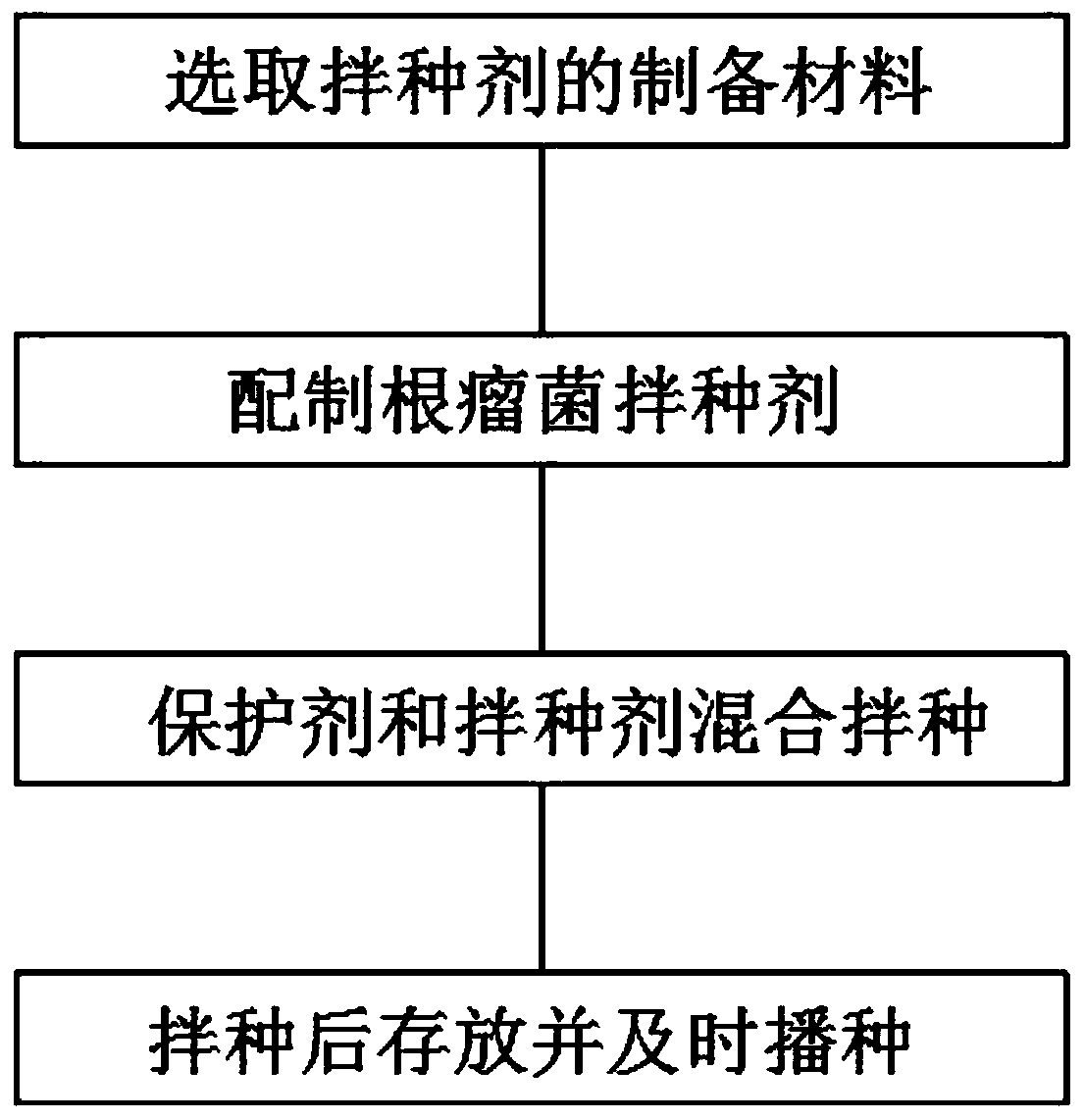
Bradyrhizobium japonicum seed dressing agent
InactiveCN110959631AImprove disease resistanceImprove stress resistanceBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyMedicinal herbs
The embodiment of the invention discloses a bradyrhizobium japonicum seed dressing agent, which is a class of microorganisms capable of being symbiotic with leguminous crops and meeting nitrogen required by crop growth by fixing nitrogen in the atmosphere. The method comprises the following steps: 1, selecting raw materials for preparing a bradyrhizobium japonicum seed dressing agent, wherein theraw materials comprise: sanguisorba officinalis, folium artemisiae argyi, cacumen biotae, nutmeg, fennel, myrrh and juncus effuses; 2, mixing the components according to the formula ratio, crushing, adding 20 times by weight of water, decocting and extracting for 2 h twice, combining and concentrating the filtrates until every 1 mL of the filtrate contains 1 g of the raw medicinal material to obtain a medicament concentrated solution, and diluting the medicament concentrated solution with water by 250 times; 3, during seed dressing, uniformly mixing a protective agent in a small bag and the bradyrhizobium japonicum agent in a plastic bag, and carrying out seed dressing; and 4, after seed dressing, storing in a shady, cool and dark environment, and sowing the seeds in time within three days. The bradyrhizobium japonicum seed dressing agent can also induce plants to generate systematic resistance, so that the probability of diseases of crops is reduced.
Owner:黑龙江黑土加速度生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com