Patents
Literature
30 results about "Bradyrhizobium species" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
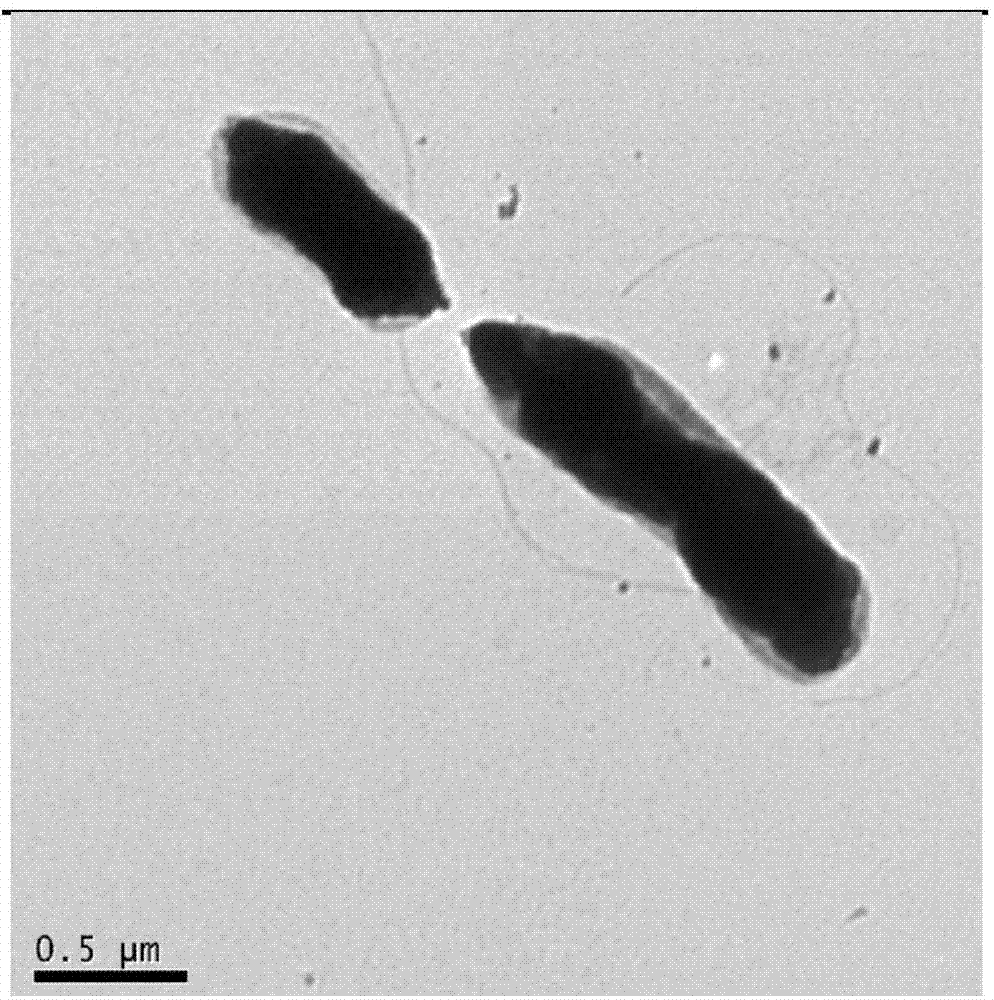
Bradyrhizobium species are Gram-negative bacilli (rod-shaped) with a single subpolar or polar flagellum. They are common soil-dwelling micro-organisms that can form symbiotic relationships with leguminous plant species where they fix nitrogen in exchange for carbohydrates from the plant.
Bradyrhizobium strains
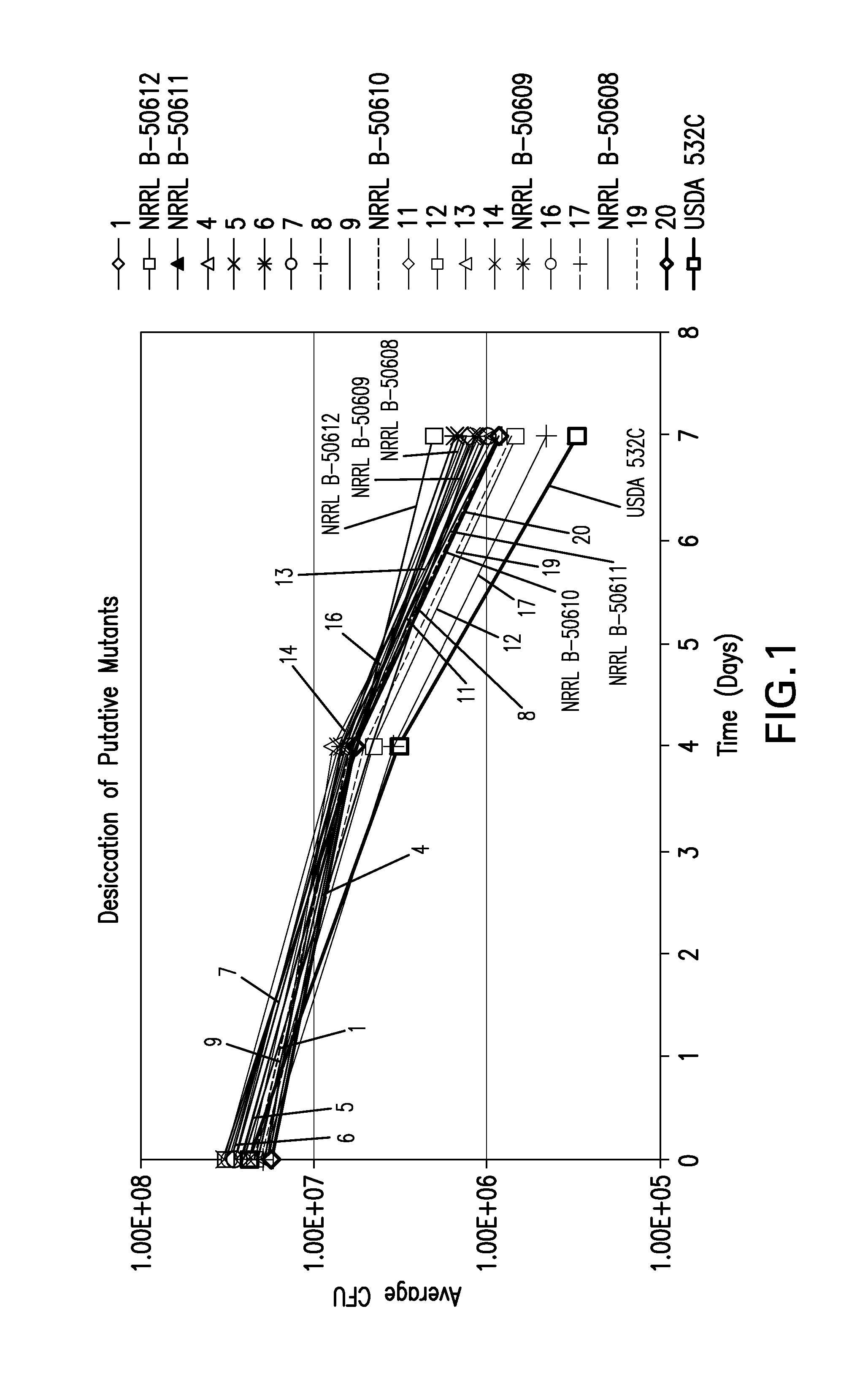
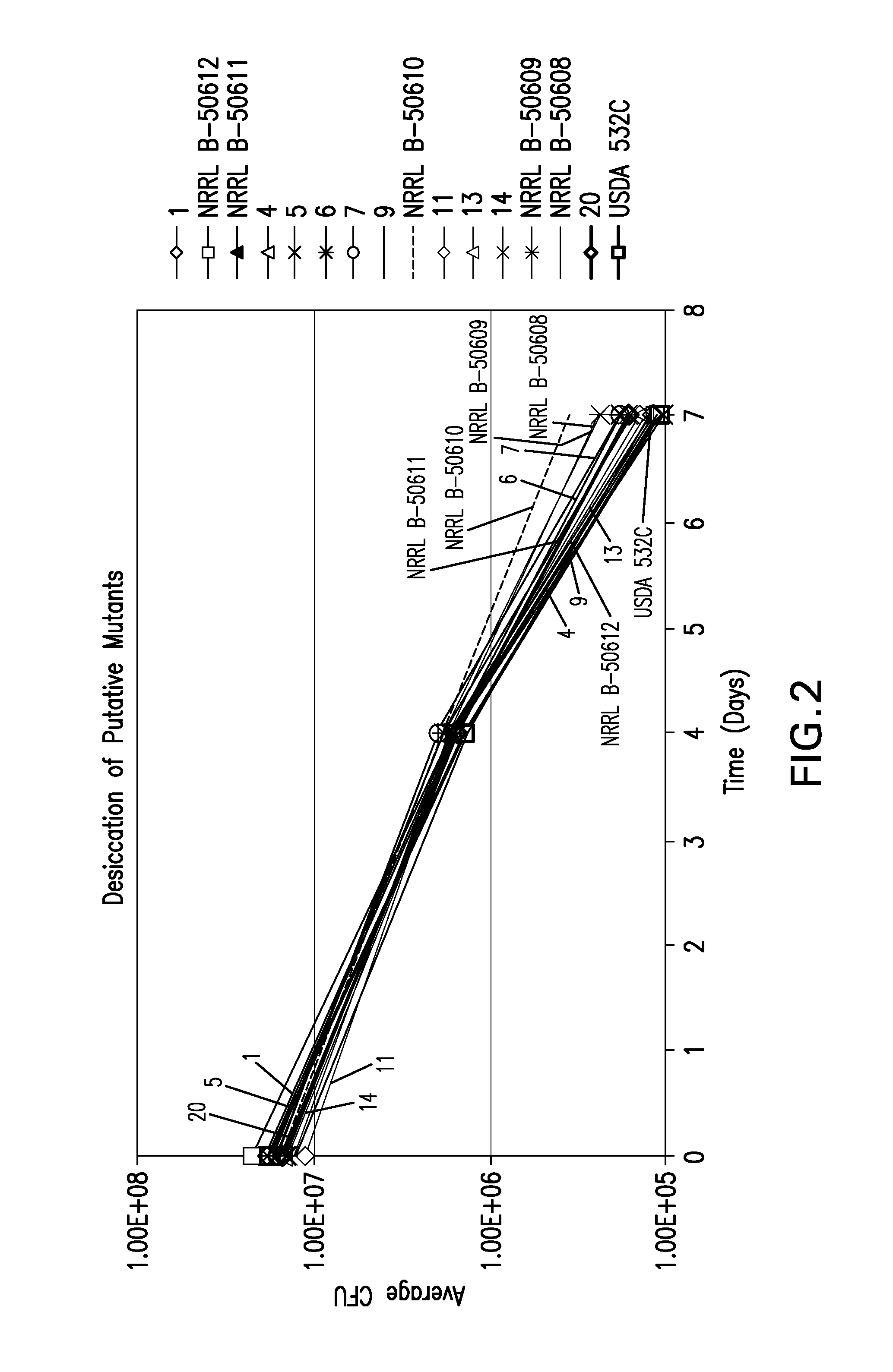
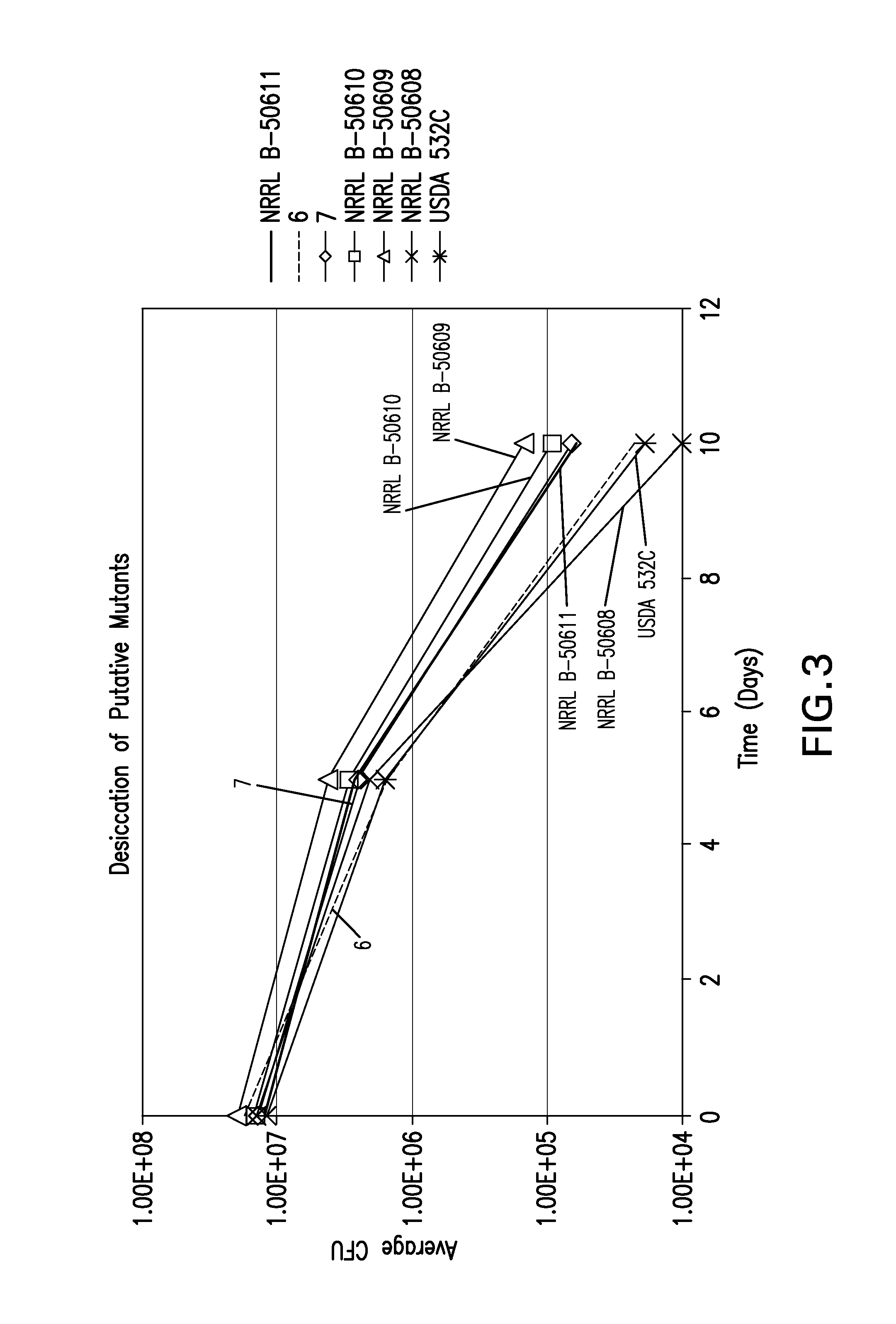
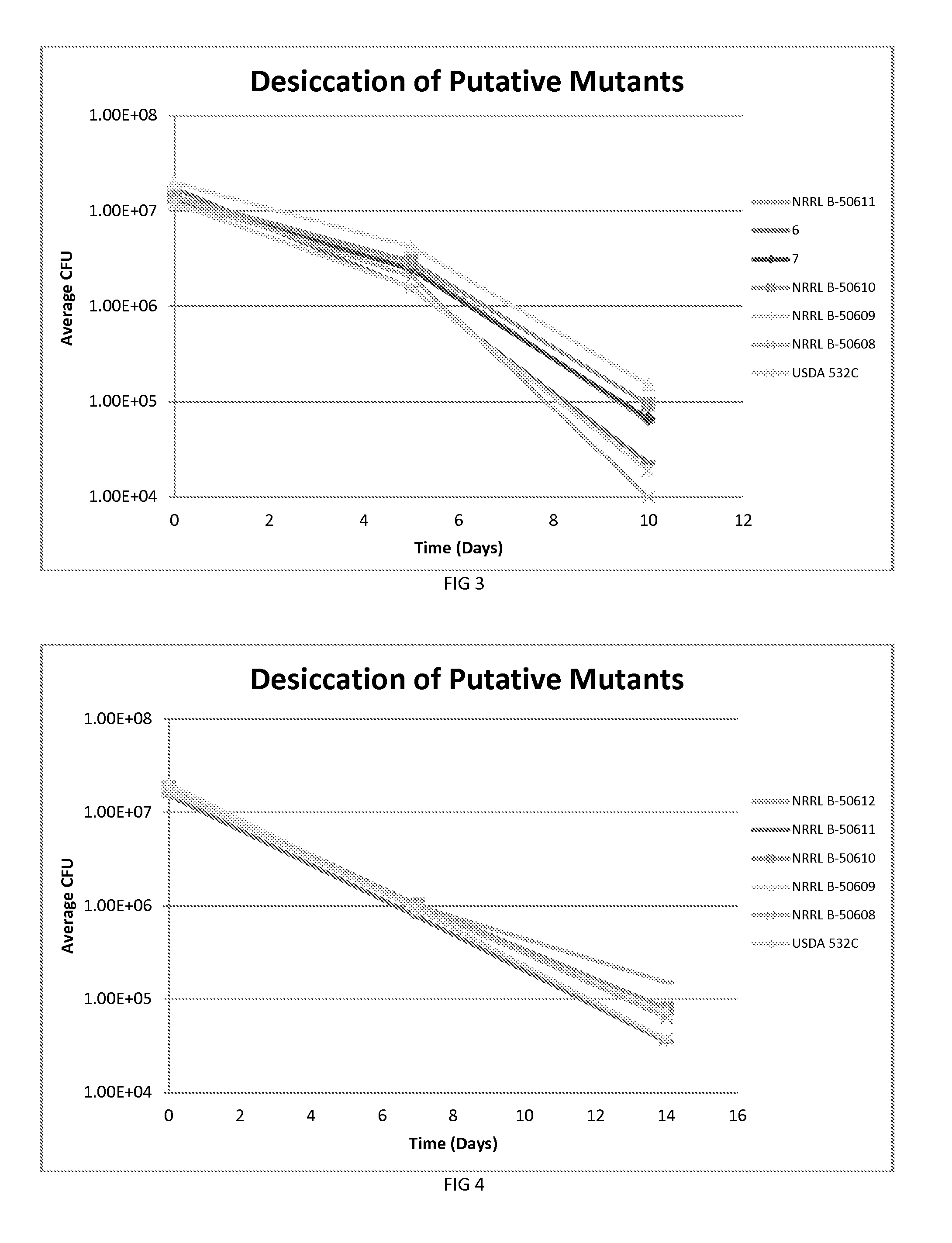
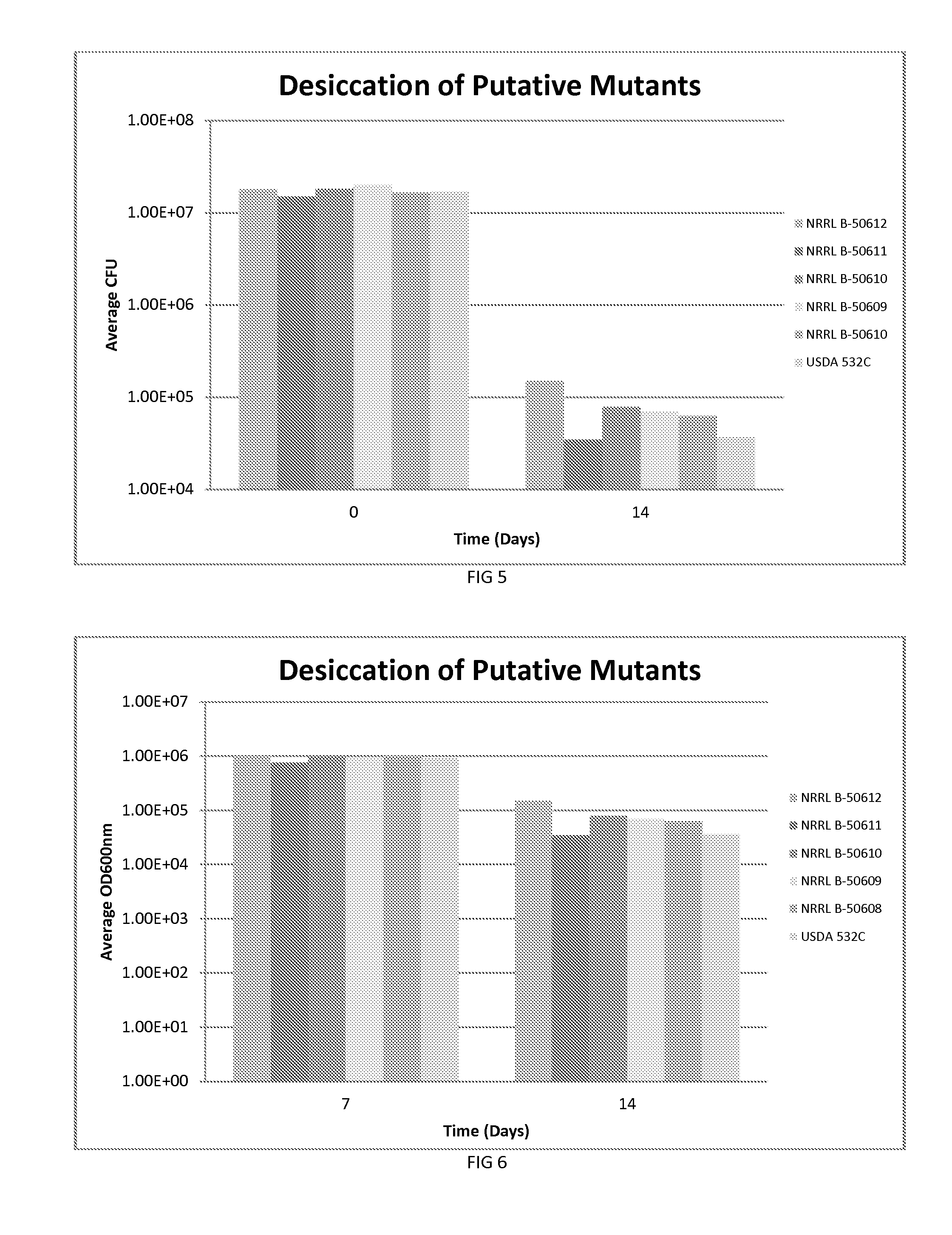
According to the present invention new isolates of Bradyrhizobium japonicum have been isolated and possess unique properties. These Bradyrhizobia are plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium (PGPR), possess superior tolerance / resistance to desiccation, and enhance the overall performance of leguminous plant growth.
Owner:NOVOZYMES BIOAG AS
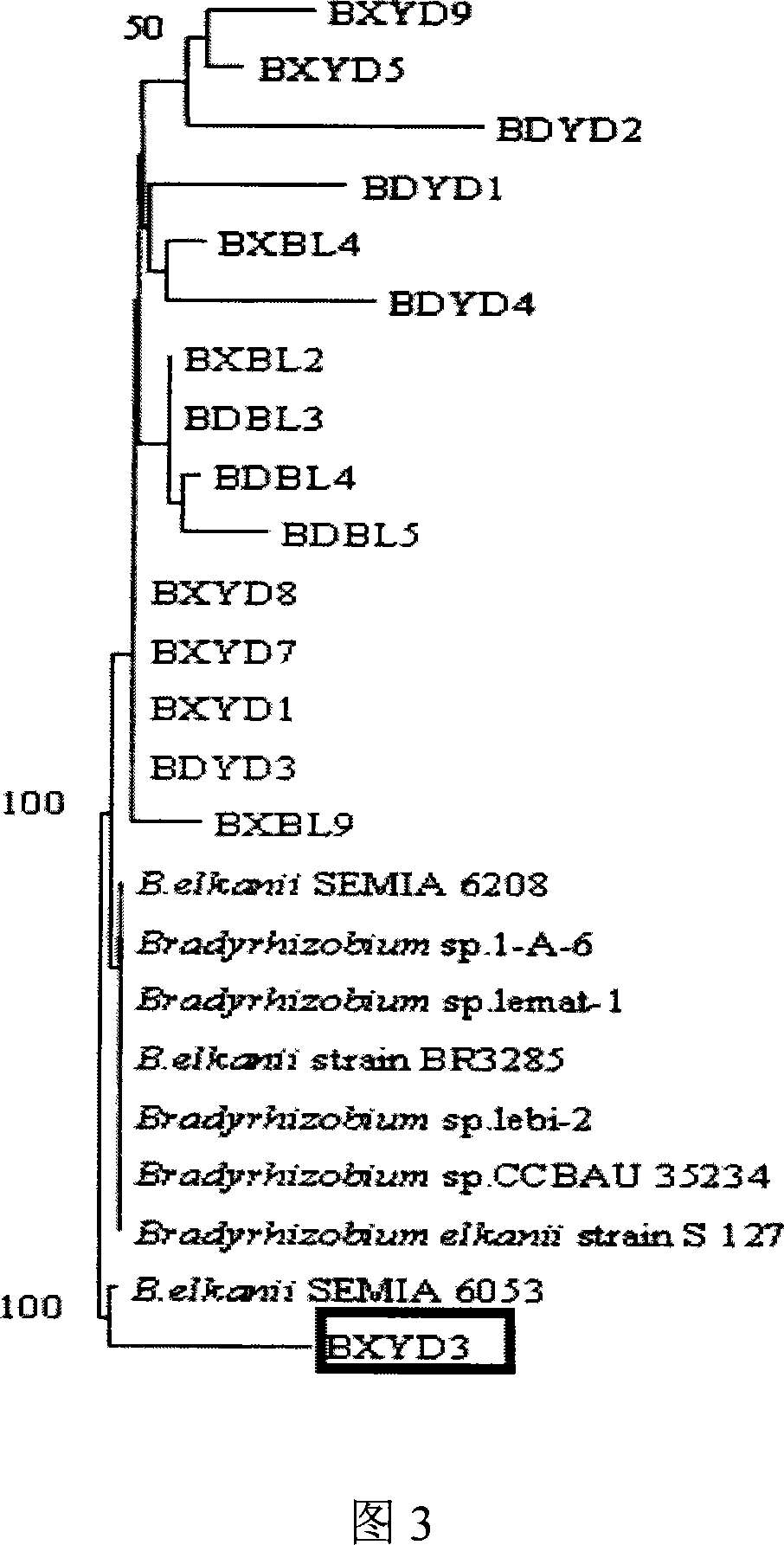
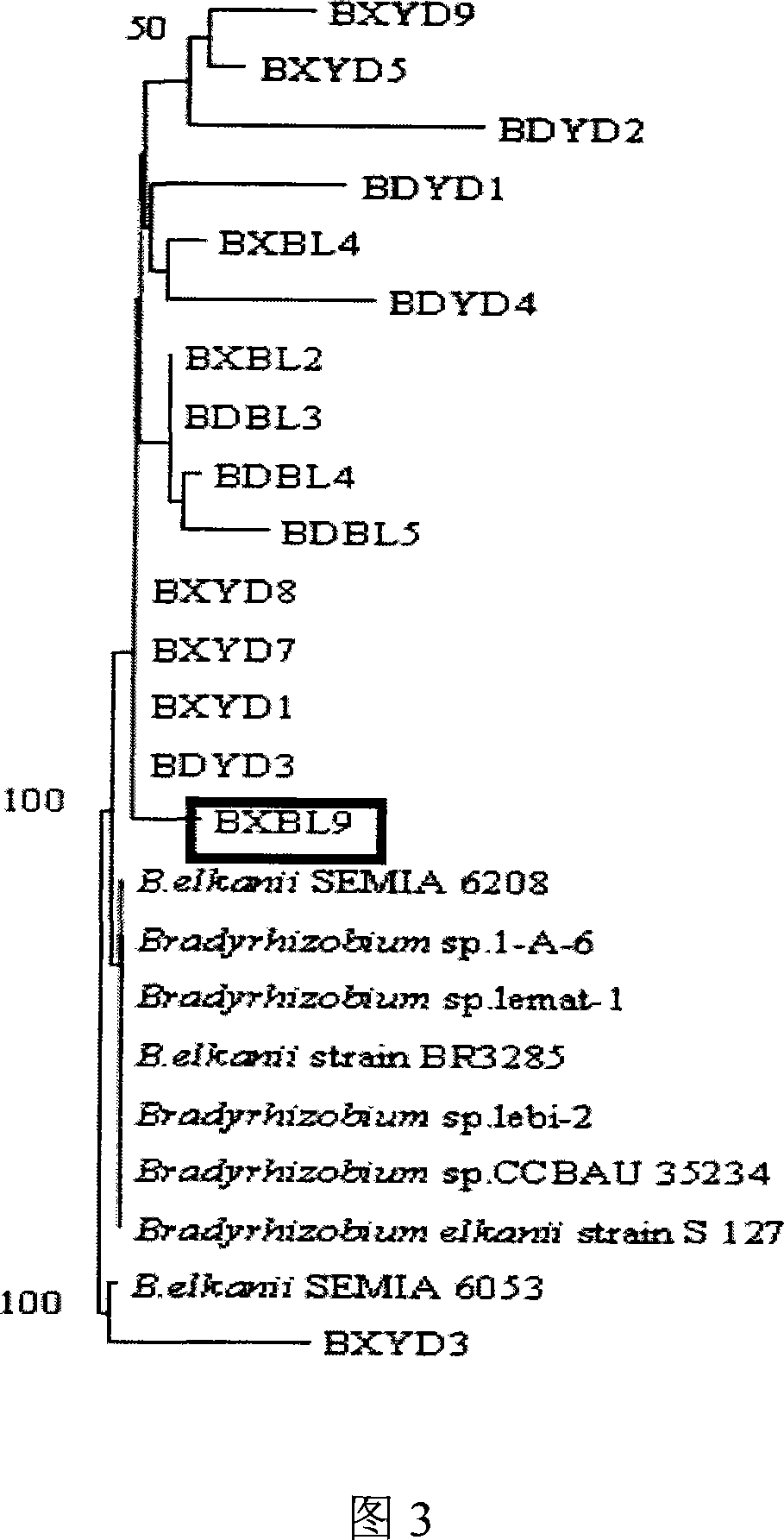
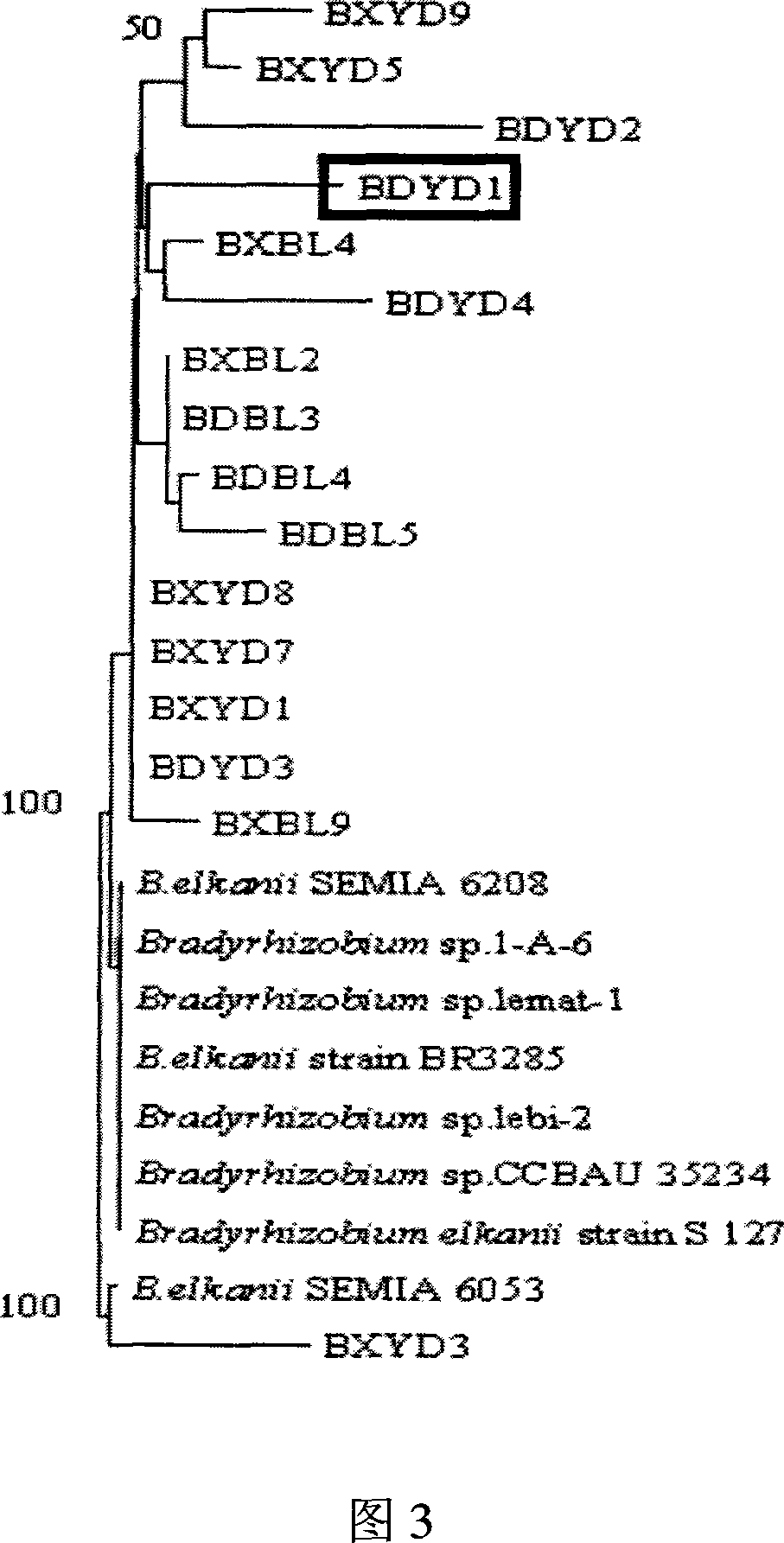
Root nodule azotobacter strain BXYD3 and uses thereof
The invention discloses a Nodule Azotobacter strain BXYD3 and the application. The strain is obtained by a way that the Rhizobia strains in the soil are respectively captured through different soybean varieties; the Rhizobia strains are separated and purified in fresh root nodules; part 16S rDNA of the strain is sequenced; the phylogenetic analysis determines that the strain is a novel Bradyrhizobium strain, which is named as Huagu 3. The Nodule Azotobacter strain BXYD3 of the invention has the characteristics of acid and aluminum tolerance and high level of nodules, which are proved by laboratory pot culture and field experiment. The inoculation of the Rhizobia strain can improve the yield of soybean more than 20 percent to 30 percent. The invention suits for the acid soil area in South China, which can be used as one of the measures for the conventional cultivation of soybean.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Root nodule azotobacter strain BXBL9 and uses thereof
The invention discloses a Nodule Azotobacter strain BXBL9 and the application. The strain is obtained by a way that the Rhizobia strains in the soil are respectively captured through different soybean varieties; the Rhizobia strains are separated and purified in fresh root nodules; part 16S rDNA of the strain is sequenced; the phylogenetic analysis determines that the strain is a novel Bradyrhizobium strain, which is named as Huagu 2. The Nodule Azotobacter strain BXBL9 of the invention has the characteristics of acid and aluminum tolerance and high level of nodules, which are proved by laboratory pot culture and field experiment. The inoculation of the Rhizobia strain can improve the yield of soybean more than 20 percent to 30 percent. The invention suits for the acid soil area in South China, which can be used as one of the measures for the conventional cultivation of soybean.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
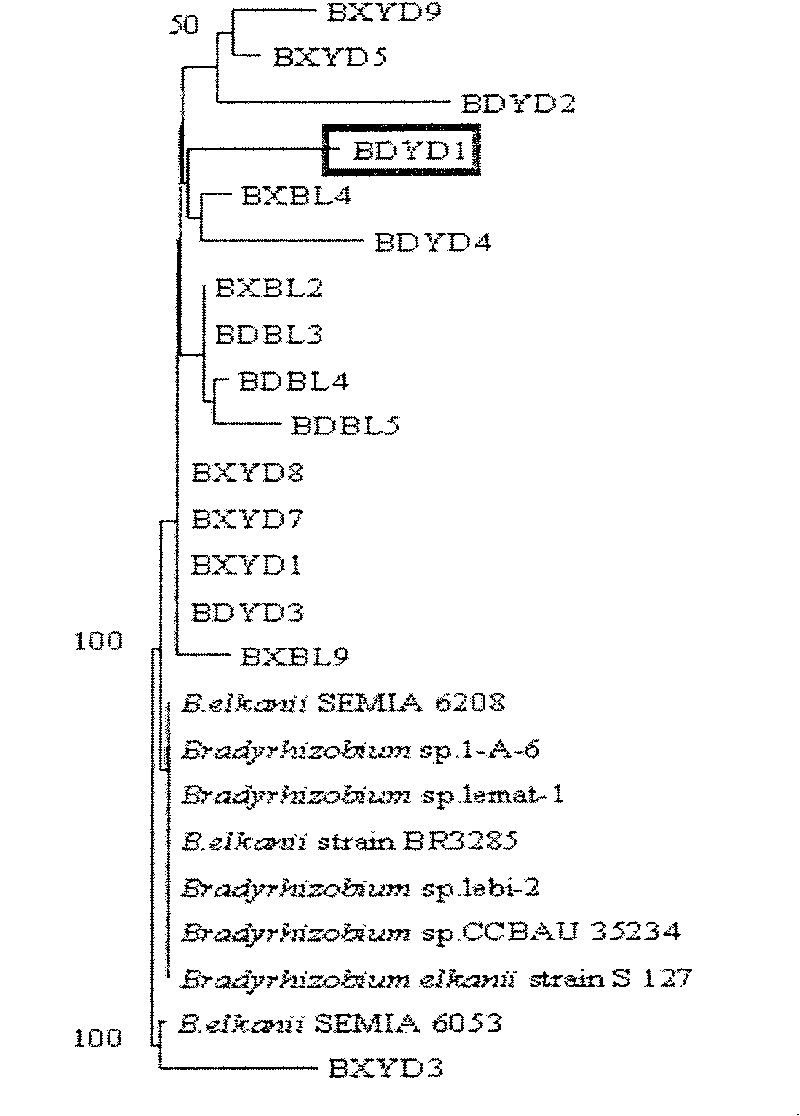
Root nodule azotobacter strain BDYD1 and uses thereof
InactiveCN101182478AIncrease useWith anodized aluminumBiocideBacteriaPlant noduleBradyrhizobium species
The invention discloses a nitrogen-fixing bacterial strain BDYD1 and its application. The bacterial strain captures the rhizobia in the soil through different soybean varieties, separates and purifies the rhizobia from fresh nodules, and extracts the 16S rDNA part of the strain. The sequence was determined, and through phylogenetic analysis, it was determined to be a new strain of Bradyrhizobium (Bradyrhizobium), and it was named Huagu No. 1. The nitrogen-fixing bacterium strain BDYD1 of the present invention has been proved by laboratory potting and field back-inoculation tests that it has the characteristics of acid-resistant aluminum and high-efficiency nodulation. Inoculation of the rhizobia can increase soybean yield by more than 20-30%, and it can be applied to acid soil regions in South China , as one of the measures of conventional soybean cultivation.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Root nodule azotobacter strain RY1 bacterial strain and application thereof
InactiveCN101781630AWide applicabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlant noduleBradyrhizobium species
The invention discloses a root nodule azotobacter strain RY1 bacterial strain and an application thereof. The bacterial strain (Bradyhizobium sp.RY1) is obtained from gathering fresh root nodules in main Stylosanthes guianensis planting areas in China and separating and purifying in a laboratory, the partial sequence of 16S rDNA of the bacterial strain is measured, and the bacterial strain is determined to be a new bacterial strain of Bradyrhizobium by the phylogenesis analysis and is named as Re Yan 1 (RY1). By the potted planting and the inoculation test in the laboratory, the nodule azotobacter strain RY1 bacterial strain is proven to have the characteristic of enabling the two main Stylosanthes guianensis varieties (TPRC2 and TPRC5) in China to realize the high-efficiency nodulation and achieve the high yield. Compared with the inoculation-free process, the inoculation with the root nodule can improve the yield of the Stylosanthes guianensis by more than 2 times, and can be used as one of conventional Stylosanthes guianensis culturing measures for planting the Stylosanthes guianensis.
Owner:TROPICAL CORP STRAIN RESOURCE INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI +2
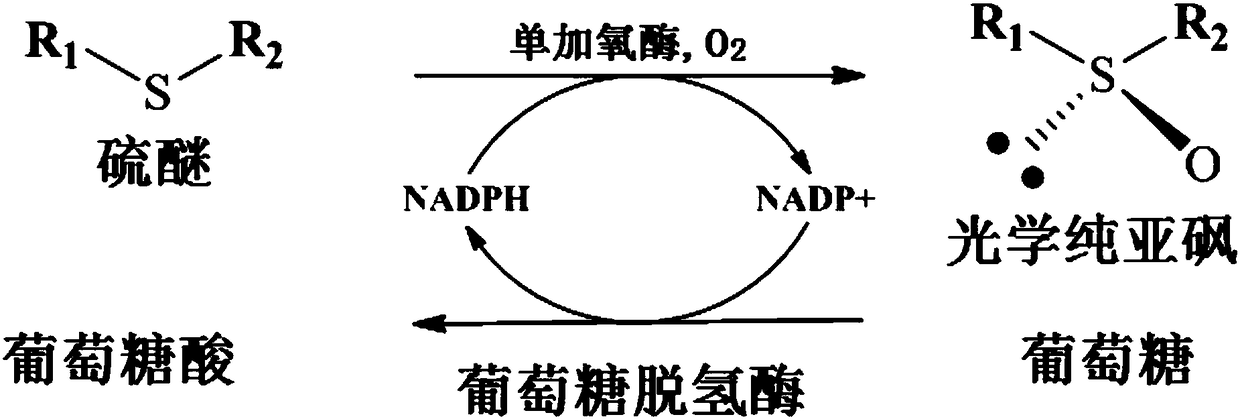
Bradyrhizobium monooxygenase and application thereof to preparation of chiral sulfoxide
ActiveCN108570425AIncrease concentrationHigh optical purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSulfur EthersDexlansoprazole
The invention discloses bradyrhizobium monooxygenase, a gene for encoding the monooxygenase, a recombinant expression vector comprising the gene, a recombinant expression transformant, a method for preparing the monooxygenase by the recombinant expression transformant and an application of the monooxygenase to preparation of optical pure chiral sulfoxide, and particularly relates to a method for preparing a razole medicine by asymmetric oxidation of catalytic razole precursor sulfur ether. Compared with other methods for preparing optical pure sulfoxide, a product prepared by the monooxygenaseserving as a catalyst is high in optical purity, avoids generation of sulphone serving as a by-product and has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, simplicity and convenience in operation, easiness in amplification and the like. Therefore, the monooxygenase has an excellent industrial application prospect in synthesis of a series of medicine intermediates and razole medicines, particularlyright-handed rotation lansoprazole.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
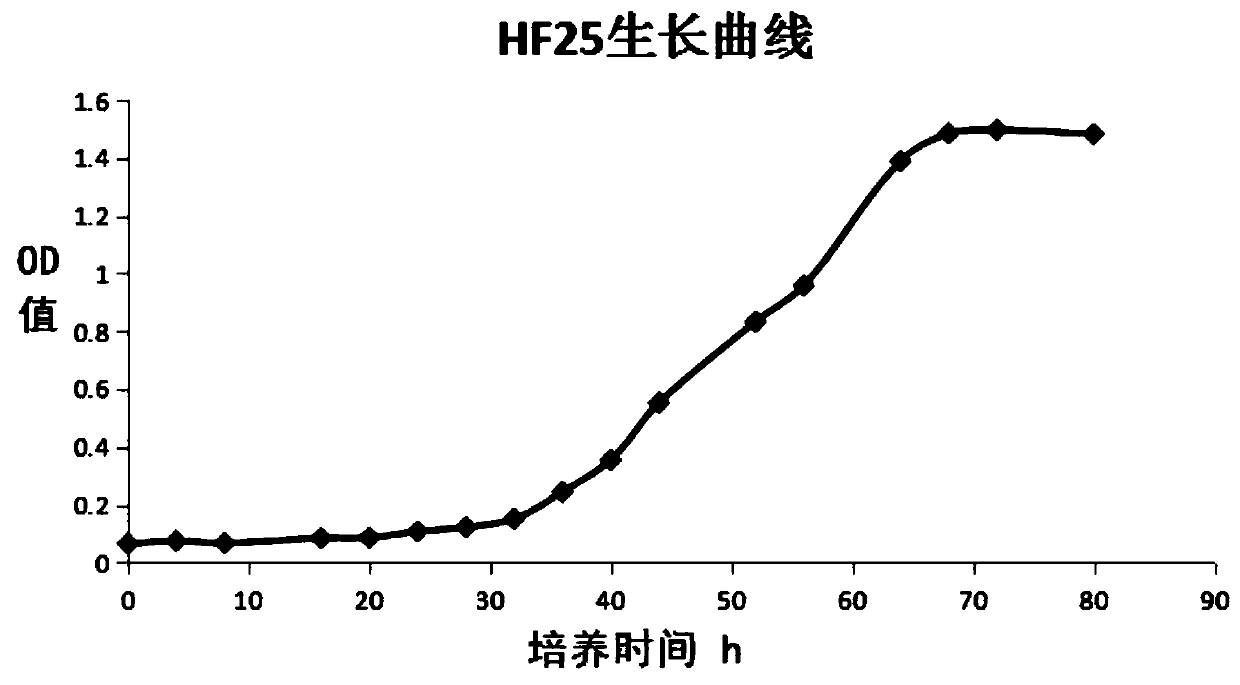
Soybean slower-growing rhizobium with broad-spectrum nodulation characteristics, application thereof and composite rhizobium agent prepared from same
InactiveCN109735468AHas broad-spectrum nodulation propertiesGood matching affinityBacteriaFabaceae cultivationMicrobial agentKlebsiella oxytoca
The invention relates to a soybean slower-growing rhizobium with broad-spectrum nodulation characteristics, application thereof and a composite rhizobium agent prepared from the same, and belongs to the technical field of agricultural microorganisms. In order to solve the problems that the soybean nodule bacteria are low in nodulation rate and poor in nitrogen fixing effect, the invention providesa Japanese Bradyrhizobium japonicum HF25, the preservation number is CGMCC No.14857, the bacterial strain has high matching affinity, nodulation competitiveness and nodulation and nitrogen fixation capacity. The invention further provides the composite rhizobium agent which is prepared from Japanese Bradyrhizobium japonicum HF25 and Klebsiella oxytoca ASP-15, two kinds of bacteria are compounded,and the nodulation and nitrogen fixation capacity is significantly improved; the composite rhizobium agent is applied to soybean planting, compared with soybeans which are not applied with a microbial agent, the number of soybean nodules is increased by 170%, the number of pods per plant is increased by 37.3%, and the hundred-grain weight of soybeans is increased by 5.5%.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY HEILONGJIANG ACADEMY OF SCI
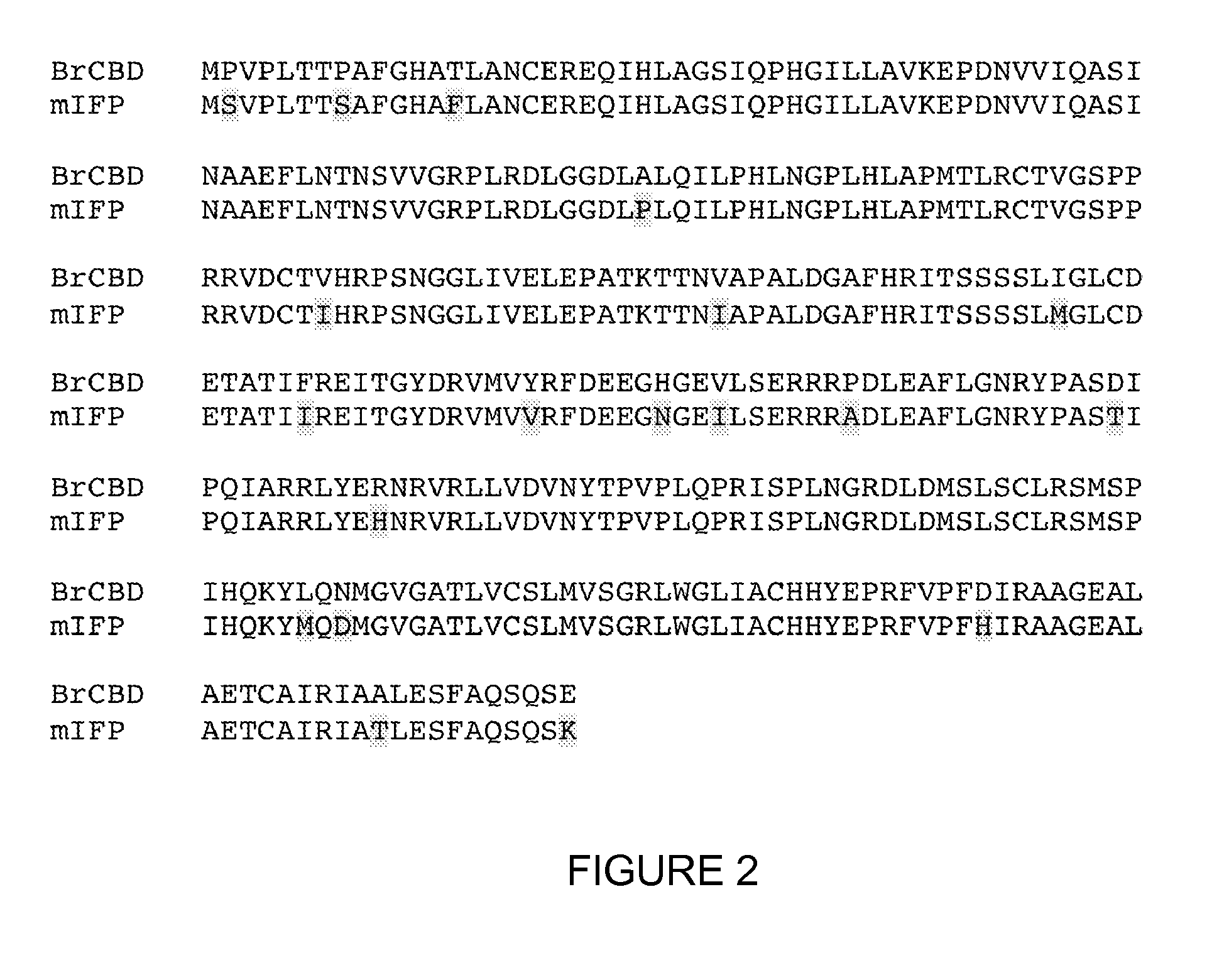
Monomeric and bright infrared fluorescent proteins
The invention described herein features variants related to infrared fluorescent proteins, in particular to mutants of a phytochrome from the bacterium Bradyrhizobium sp. ORS278. The variants show approximately a ten-fold increase in brightness compared to other known infrared fluorescent proteins. The variants are monomeric, allowing them to be used as a protein tag without disrupting the function of the tagged protein of interest.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
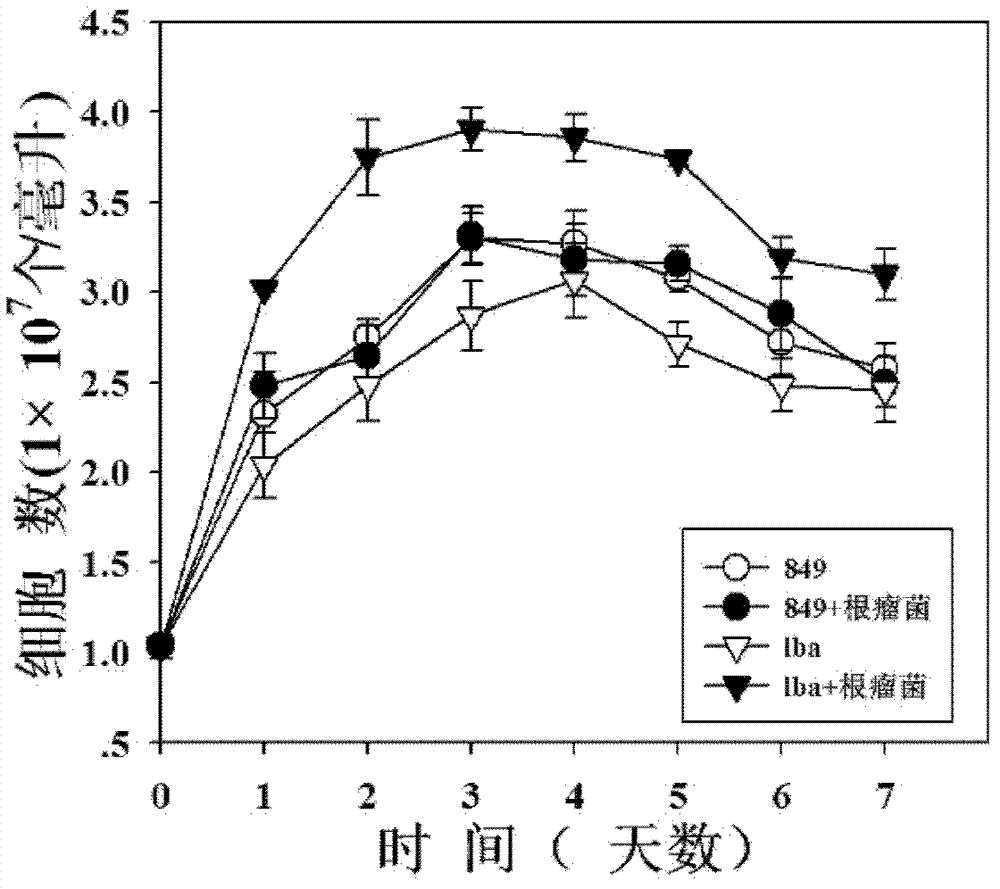
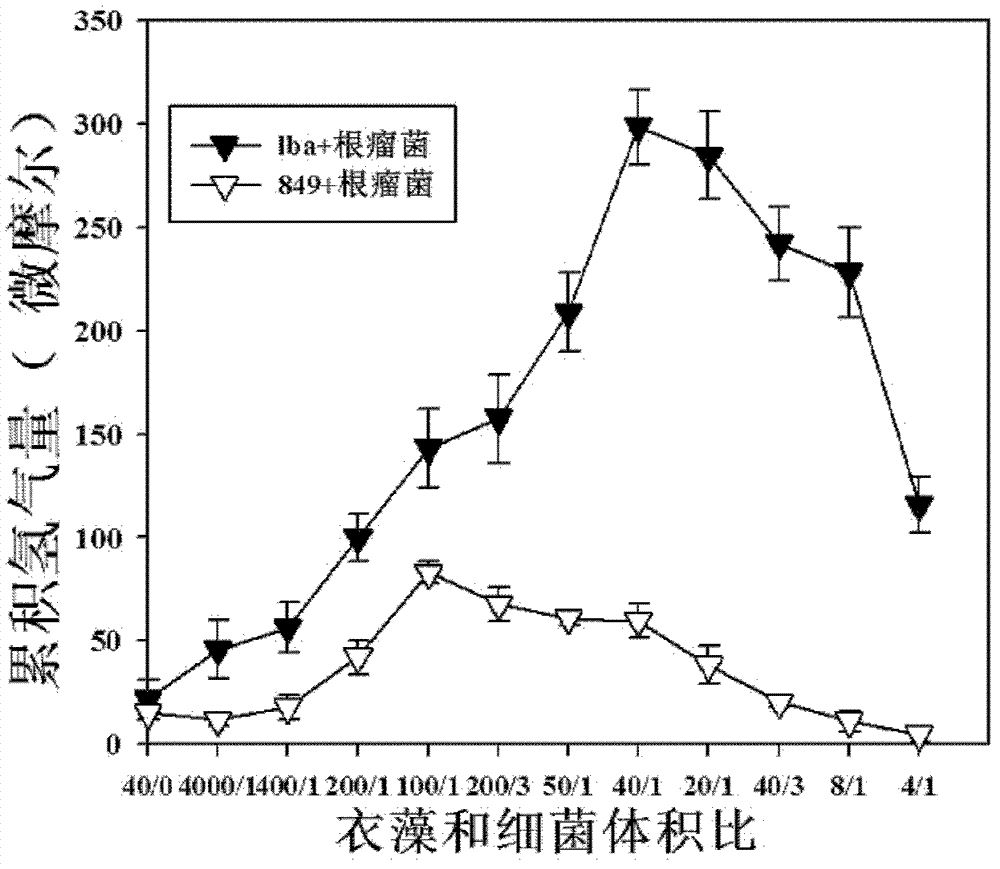
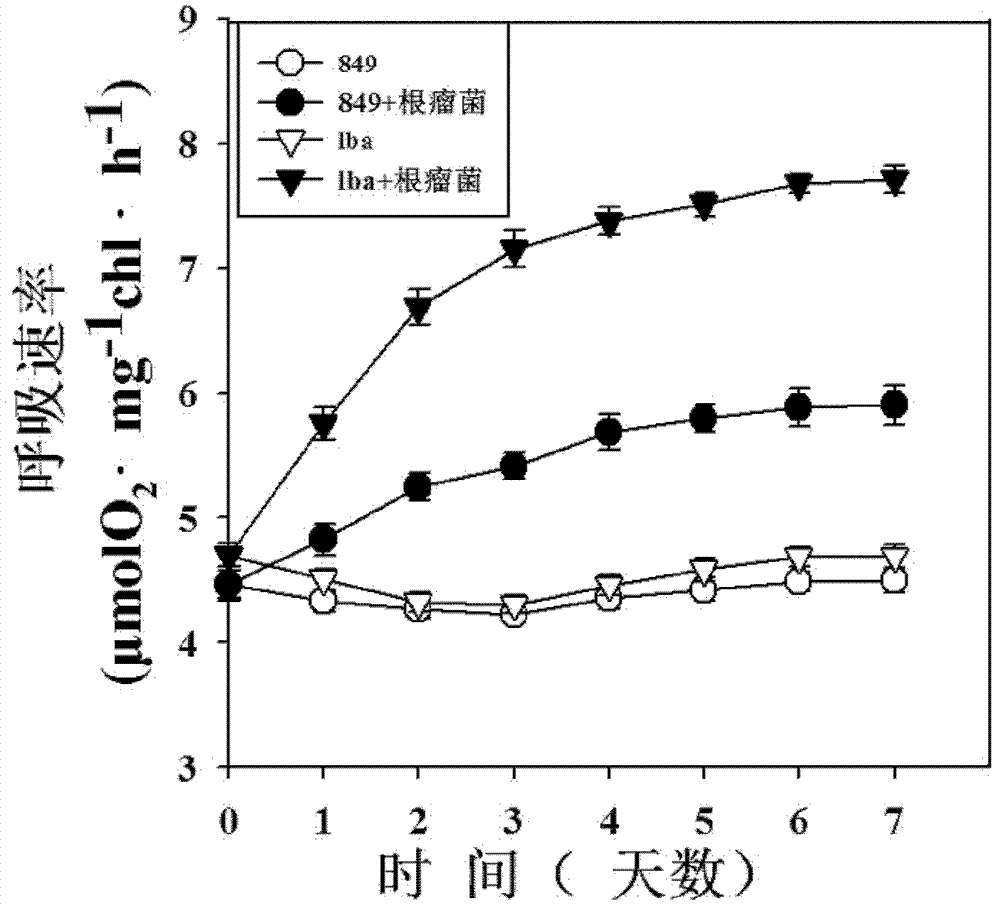
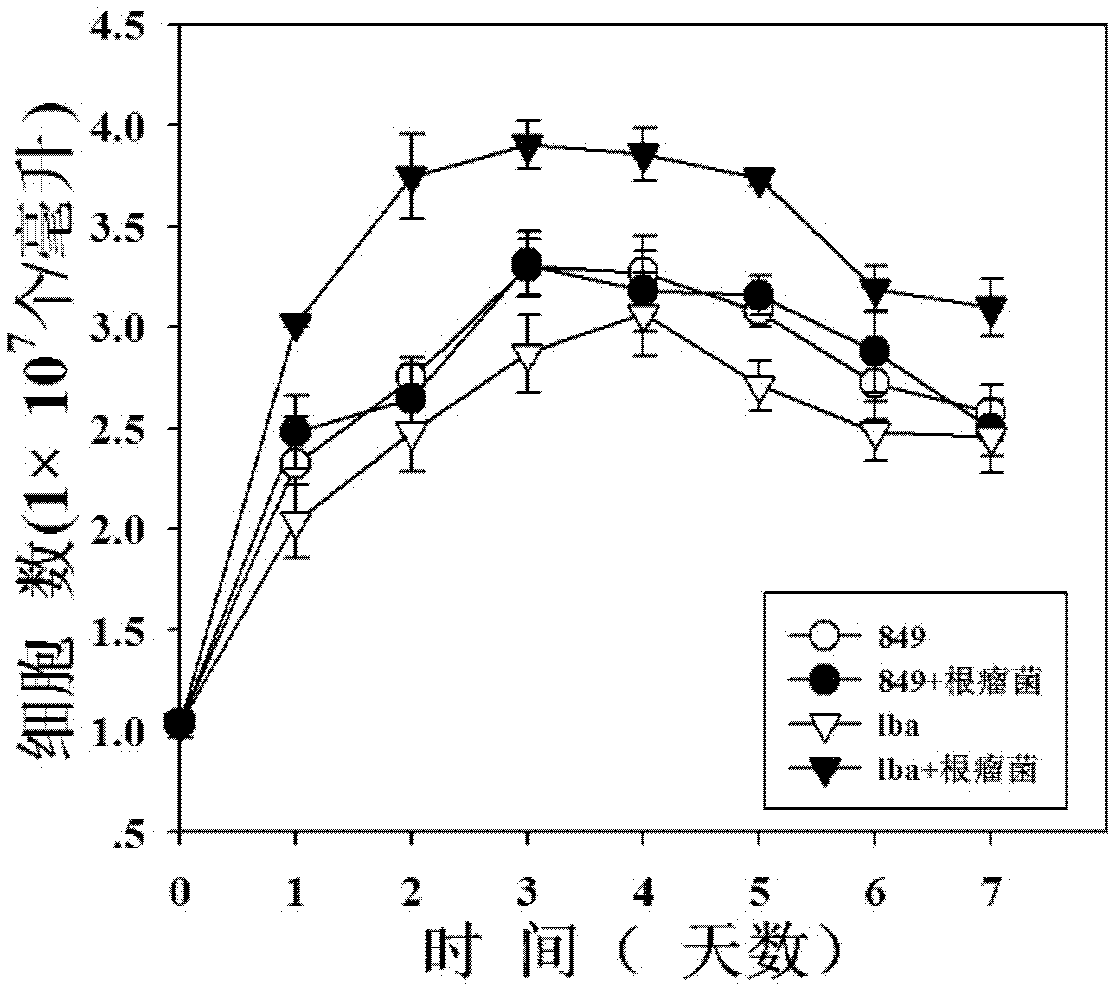
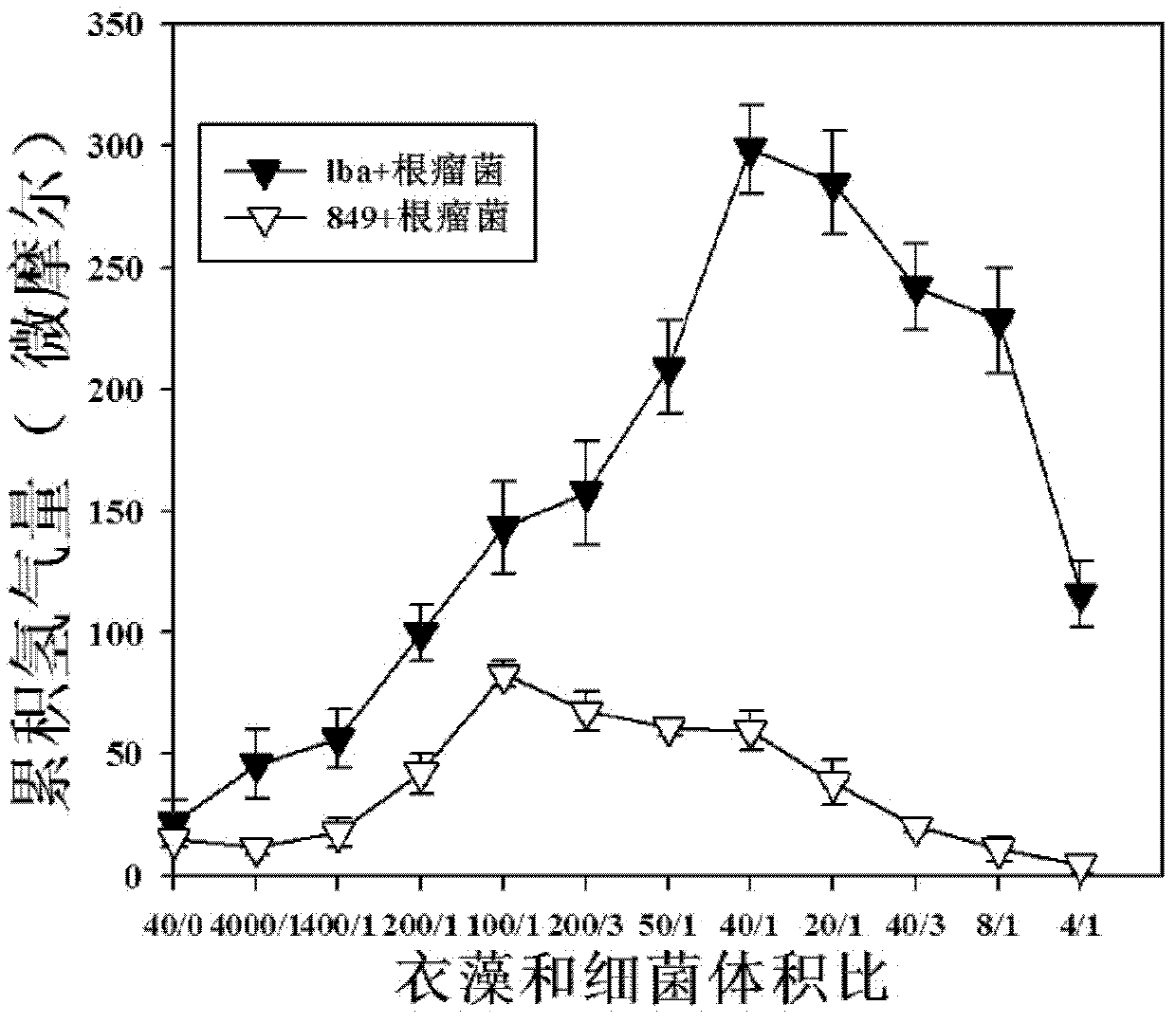
Method for increasing hydrogen yield of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by using slow-growing Bradyrhizobium japomcum
InactiveCN102732563AIncrease hydrogen productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationChlamydomonas reinhardtiiBradyrhizobium species
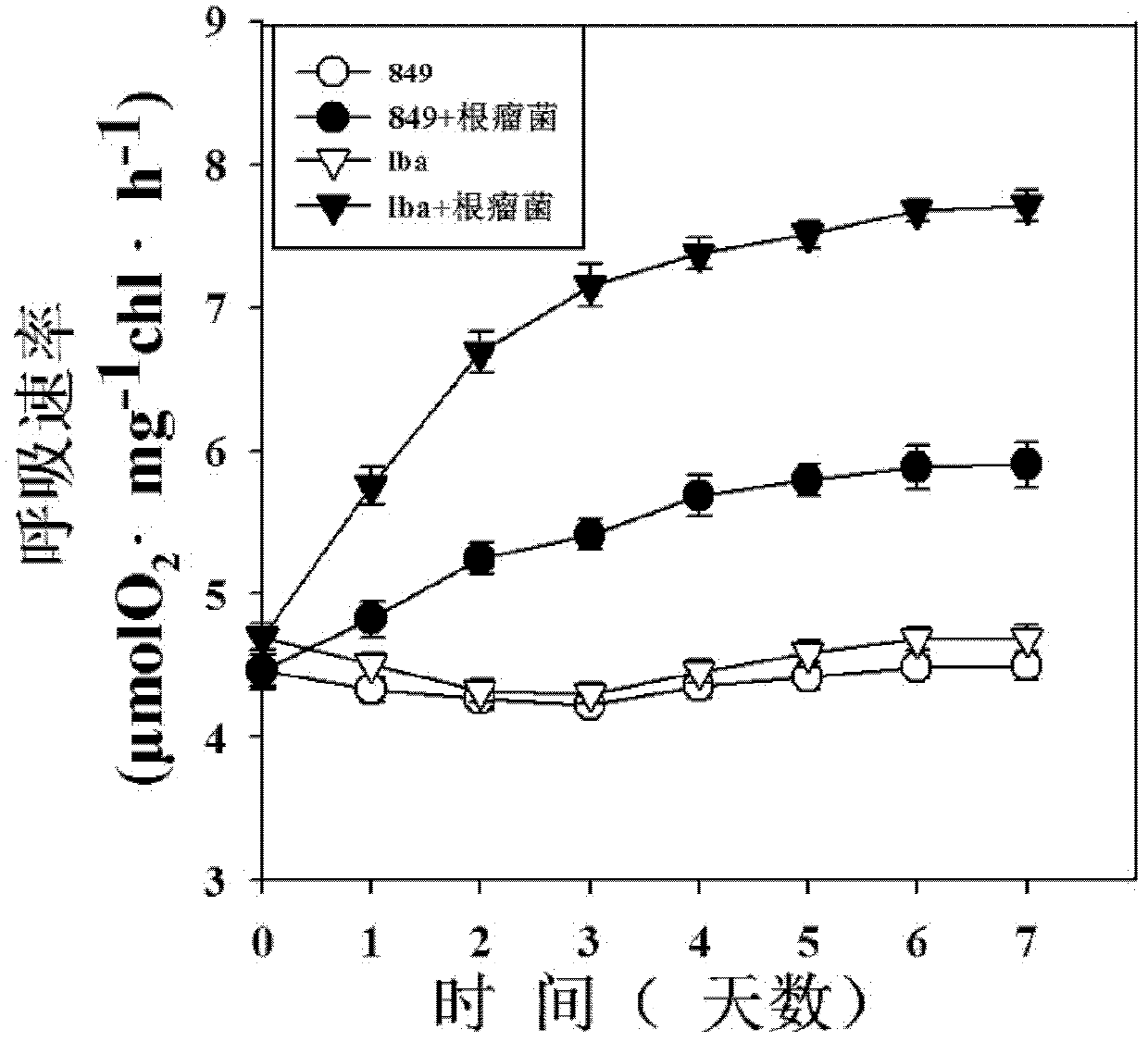
The invention, relating to the technique of biological hydrogen production, particularly relates to a method for increasing hydrogen yield of genetically modified Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by using rhizobium. The method is characterized by respectively mixing slow-growing Bradyrhizobium japomcum with genetically modified Chlamydomonas reinhardtii strain lba in the first stage and second stage of a two-step hydrogen producing method according to certain volume ratios to co-culture, wherein the genetically modified Chlamydomonas reinhardtii strain lba transforms leghemoglobin globulin subunit lba gene in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii strain cc849 and chloroplast. The results show that the slow-growing Bradyrhizobium japomcum promotes the growth of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii strain lba in thefirst stage, and significantly increases the hydrogen yield of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii strain lba 17 times over.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
Rhizobium and application thereof
InactiveCN103898009AIncrease biomassAchieve high yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesContinuous croppingRoot nodule
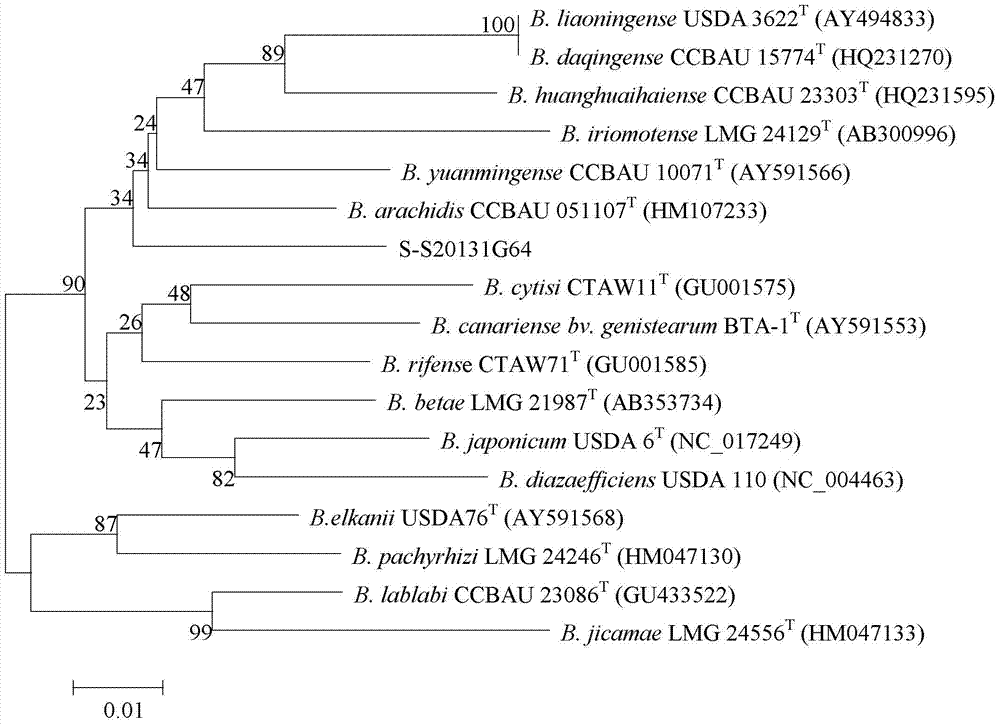
The invention discloses rhizobium and application thereof. The invention aims to solve the problem that the conventional rhizobium inoculated by soybean is low in competitive nodulation capacity and nitrogenase activity under long-term continuous cropping conditions. The rhizobium refers to bradyrhizobium hailunense (Bradyrhizobium hailunense) S-S20131G64 and is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the collection address is 3#, courtyard No.1, Beichen west road in Chaoyang District in Beijing, the collection date is 10th, January in 2014, and the collection number is CGMCC No.8693. The application refers to application in long-term soybean continuous cropping soil. The rhizobium has the high-efficiency nodulation characteristic, the soybean biomass can be improved, the nitrogen nutrition of soybeans is improved, and the rhizobium is applied to long-term soybean continuous cropping soil districts in Heilongjiang Province. The invention is applied to the field of agriculture.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Strain A56WU capable of raising anti-drought and anti-heat ability of leguminous trees and culture method of root nodule seedlings thereof
InactiveCN102206594AImprove rapid growthImprove drought resistanceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRevegetationPlant nodule
The invention relates to a biological strain resource, in particular to a strain capable of raising fast-growing, anti-drought and anti-heat ability of leguminous trees in dry-hot valley areas, and a culture method of root nodule seedlings thereof. Strain A56 WU disclosed in the invention is Bradyrhizobium eikanii, CGMCC No: 4591. The culture method comprises isolation and purification, microscopic examination, back grafting and inoculation of the strain. The strain disclosed in the invention is a good strain selected from the strains in dry-hot valley areas and capable of effectively raising fast-growing, anti-drought ability of leguminous trees in dry-hot valley areas, so that the strain has important utilization value for vegetation restoration of dry-hot valley areas, allowing leguminous trees to live through the crisis securely under the threat of dry-hot environment, and ensuring the survival rate of large area afforestation in dry-hot valley areas.
Owner:SOUTHWEST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method of researching gene function of Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110
ActiveCN108611306AConvenient primary screeningQuick ScreeningBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBradyrhizobium speciesProkaryotic expression
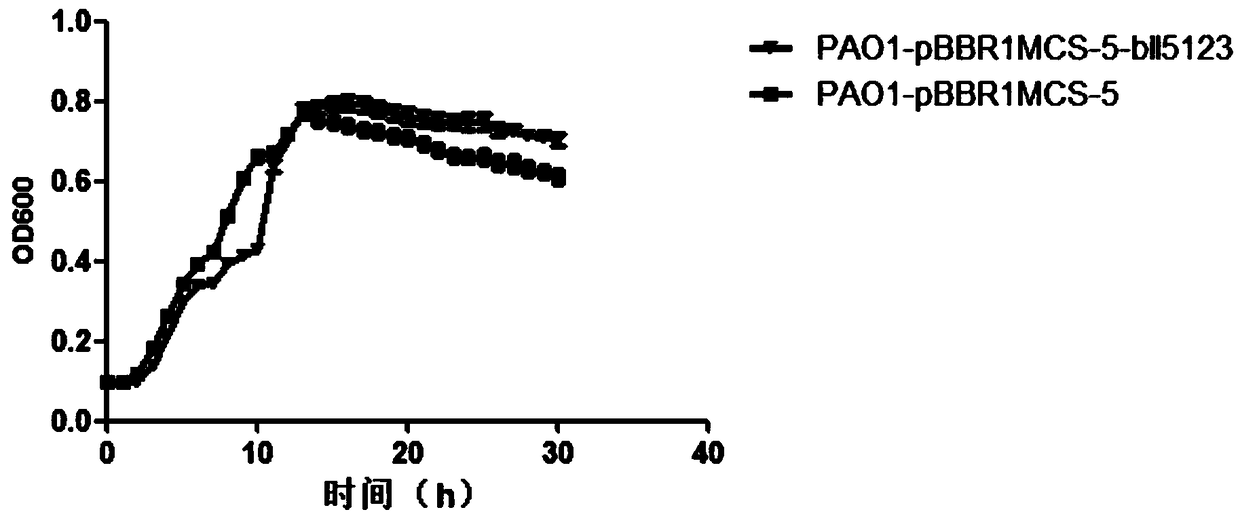
The invention discloses a method of researching functions of genes of Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110, and provides a prokaryotic expression system which utilizes pseudomonas aeruginosa as host bacteria; the pseudomonas aeruginosa is Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. In the invention, phenotype research related to gene synthesis and degradation functions of intracellular messenger cyclic di-guanosinemonophosphate (c-di-GMP) in the Bradyrhizobium japonicum is directly carried out in the pseudomonas aeruginosa of which the background mechanism research is definite; by observing the character changes of the pseudomonas aeruginosa, functions of the target gene is initially obtained. The invention provides the novel prokaryotic expression system in which the gene of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum isexpressed and colonial morphology, moveability, generation of exopolysaccharide and generation quantity of biomembrane are inspected, thereby initially obtaining the function of the gene of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum. The method saves time and consumable costs, accelerates researching process and is beneficial to research on the gene function of Bradyrhizobium japonicum.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Mesorhizobium huizhouense and application thereof
ActiveCN104498381AStrong ACC deaminase activityStrong stress resistanceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlant noduleMicrobial agent
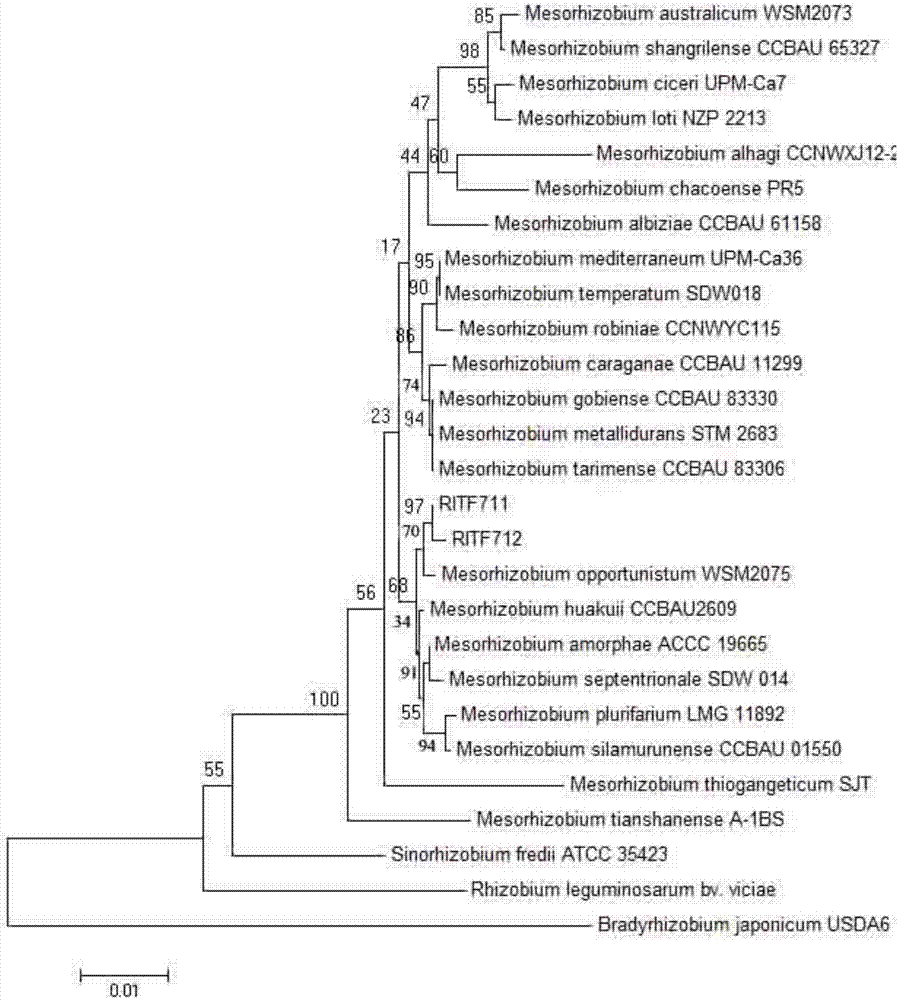
The invention discloses a Mesorhizobium huizhouense and application thereof. The Mesorhizobium huizhouense RITF711 is preserved in China Center For Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on July 23, 2014, the address is: Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M2014354. The Mesorhizobium huizhouense provided by the invention is separated and screened out from Acacia melanoxylon root nodule, the strain can achieve nodulation and symbiosis with Acacia melanoxylon, Acacia aneura, Acacia implexa and other hosts, and has strong ACC deaminase activity, can effectively improve the growth and stress resistance of Acacia trees, and has broad application prospects in production of nitrogen-fixing microbial agents and bio-organic fertilizers.
Owner:RES INST OF TROPICAL FORESTRY CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Bradyrhizobium strains
According to the present invention new isolates of Bradyrhizobium japonicum have been isolated and possess unique properties. These Bradyrhizobia are plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium (PGPR), possess superior tolerance / resistance to desiccation, and enhance the overall performance of leguminous plant growth.
Owner:NOVOZYMES BIOAG AS
Bradyrhizobium sp. suitable for drug resistance, stress resistance and nitrogen fixation in Huanghuai region and application of Bradyrhizobium sp.
The invention discloses a Bradyrhizobium sp. suitable for drug resistance, stress resistance and nitrogen fixation in Huanghuai region and an application of the Bradyrhizobium sp.. The invention provides Bradyrhizobium sp. HHPB1, with the preservation number of CGMCC No.17501 in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center. The Bradyrhizobium sp. HHPB1 has wide adaptability, such as drought resistance, pesticide resistance, acid resistance and the like, and is a biosafety strain. In Huanghuai region, fresh weight, nodule number and needle number of peanut in different development stages can be significantly increased, and the fruit saturation rate can be increased to a certain extent, with the highest peanut yield increased by 27.6%. The Bradyrhizobium sp. HHPB1 is a stable and efficient microbial fertilizer strain resource for reducing weight and increasing efficiency.
Owner:安徽微壤生物科技有限公司
Monomeric and bright infrared fluorescent proteins
The invention described herein features variants related to infrared fluorescent proteins, in particular to mutants of a phytochrome from the bacterium Bradyrhizobium sp. ORS278. The variants show approximately a ten-fold increase in brightness compared to other known infrared fluorescent proteins. The variants are monomeric, allowing them to be used as a protein tag without disrupting the function of the tagged protein of interest.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
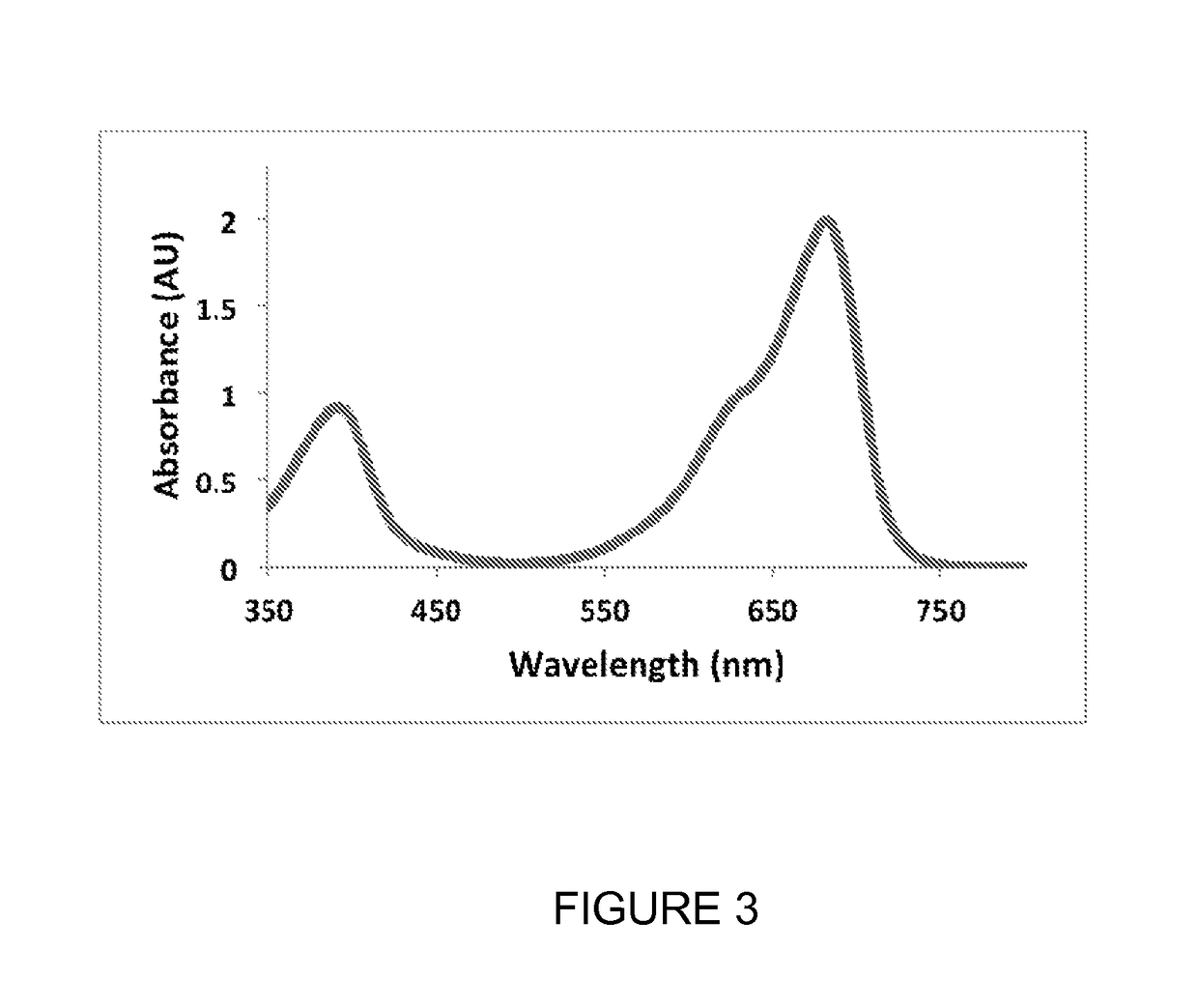
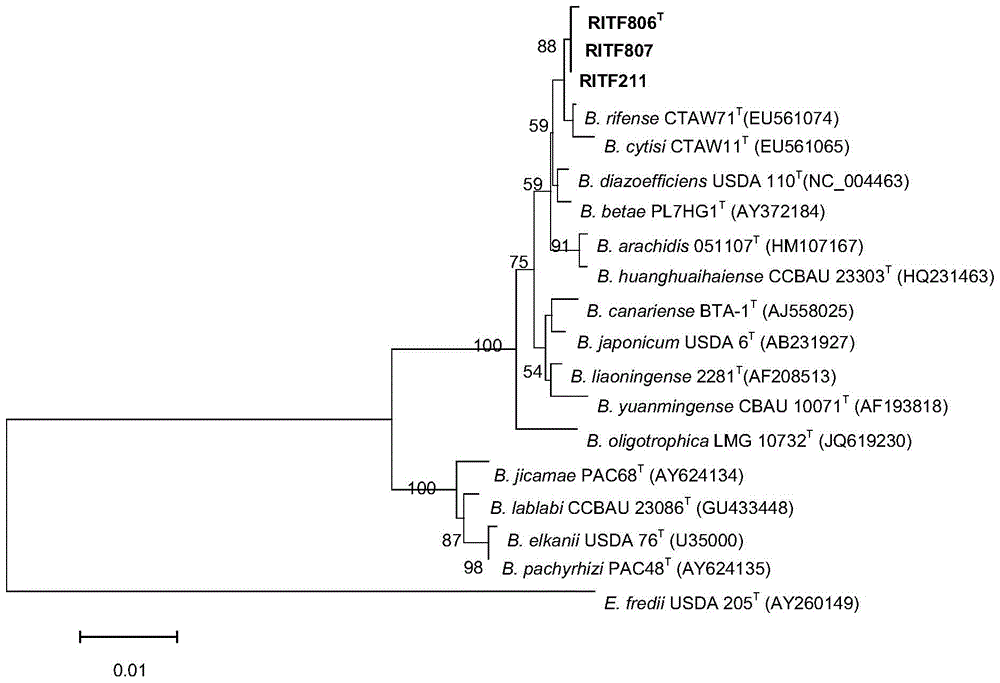
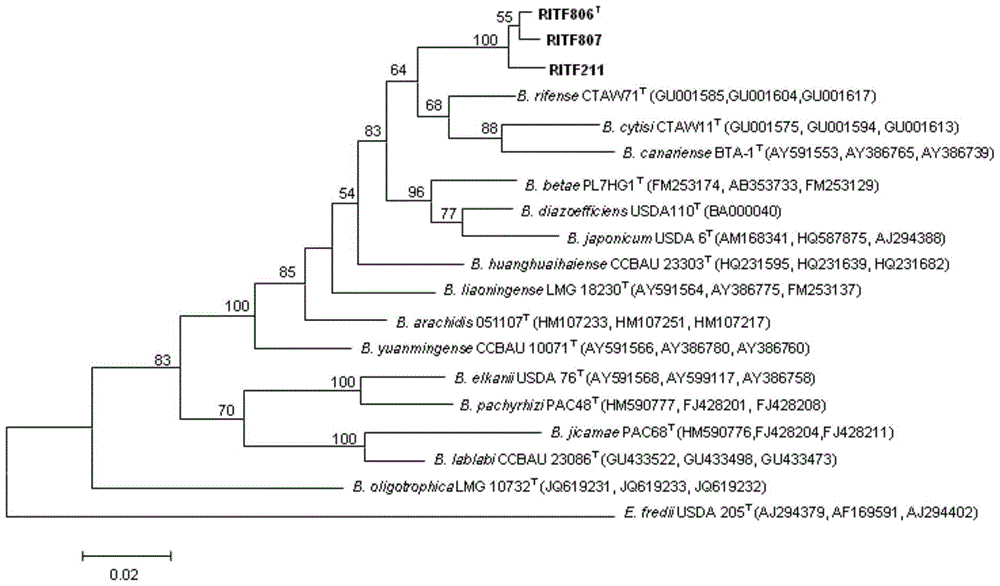
A kind of Ganzhou bradyrhizobium and its application
The invention discloses bradyrhizobium ganzhouense sp.nov. and application thereof. Bradyrhizobium ganzhouense sp.nov. RITF806 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), Wuhan University, Wuhan, China since 26th Feburary, 2014, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M2014044. Bradyrhizobium ganzhouense sp.nov. is separated and screened out from acacia melanoxylon rootnodule, is capable of realizing nodulation symbiosis with acacia melanoxylon, acacia aneura, acacia implexa and the like, has high stress resistance, and has wide application prospect for azotification microbe inocula and bio-organic fertilizers.
Owner:RES INST OF TROPICAL FORESTRY CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
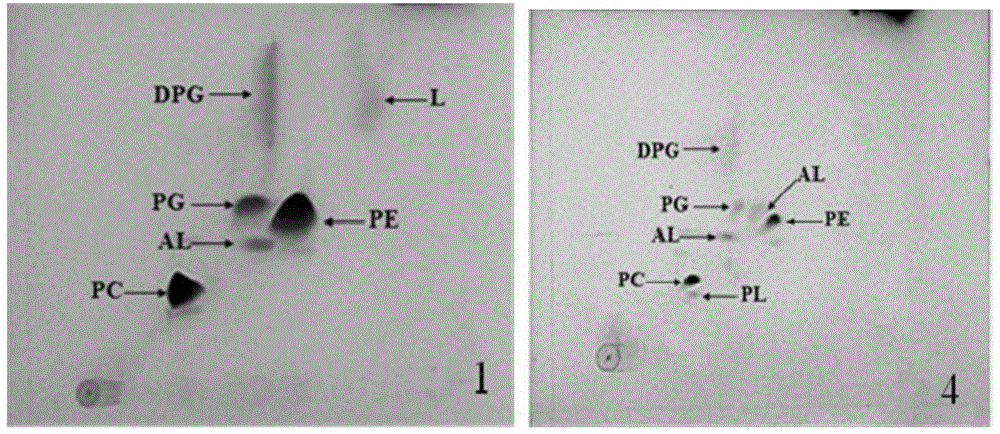
Extraction method for bradyrhizobium extract and application of bradyrhizobium extraction in mango grafting
ActiveCN109121778APromote growthRapid scab healingBacteriaGraftingCulture fluidBradyrhizobium species
The invention discloses an extraction method for bradyrhizobium extract and application of the bradyrhizobium extract in mango grafting. The extraction method comprises the steps of selective culturing of bradyrhizobium: specifically selecting bradyrhizobium from peanut roots, drying the peanut roots, conducting crushing, conducting crude extraction with ethanol to obtain a crude extract, then putting the crude extract in a supercritical extraction kettle to conduct supercritical carbon dioxide extraction on the crude extract, so as to obtain a bradyrhizobium extraction substance; (2) puttingselected bradyrhizobium in a culture medium for culturing to obtain a culture solution, filtering the culture solution by a gauze for sterilization, so as to obtain a bradyrhizobium fermentation solution; and (3) mixing the bradyrhizobium extraction substance and the bradyrhizobium fermentation solution to obtain the bradyrhizobium extract. According to the invention, an agent for promoting graftwound to heal is prepared by mixing the bradyrhizobium extraction substance and the bradyrhizobium fermentation solution, is capable of promoting healing of grafting wounds of mangoes, and guaranteesa short healing time for the grafting wounds and a high grafting successful rate.
Owner:云南元江大有为食品有限公司
Method for increasing hydrogen yield of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by using slow-growing Bradyrhizobium japomcum
InactiveCN102732563BIncrease hydrogen productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationChlamydomonas reinhardtiiBradyrhizobium species
The invention, relating to the technique of biological hydrogen production, particularly relates to a method for increasing hydrogen yield of genetically modified Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by using rhizobium. The method is characterized by respectively mixing slow-growing Bradyrhizobium japomcum with genetically modified Chlamydomonas reinhardtii strain lba in the first stage and second stage of a two-step hydrogen producing method according to certain volume ratios to co-culture, wherein the genetically modified Chlamydomonas reinhardtii strain lba transforms leghemoglobin globulin subunit lba gene in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii strain cc849 and chloroplast. The results show that the slow-growing Bradyrhizobium japomcum promotes the growth of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii strain lba in the first stage, and significantly increases the hydrogen yield of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii strain lba 17 times over.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
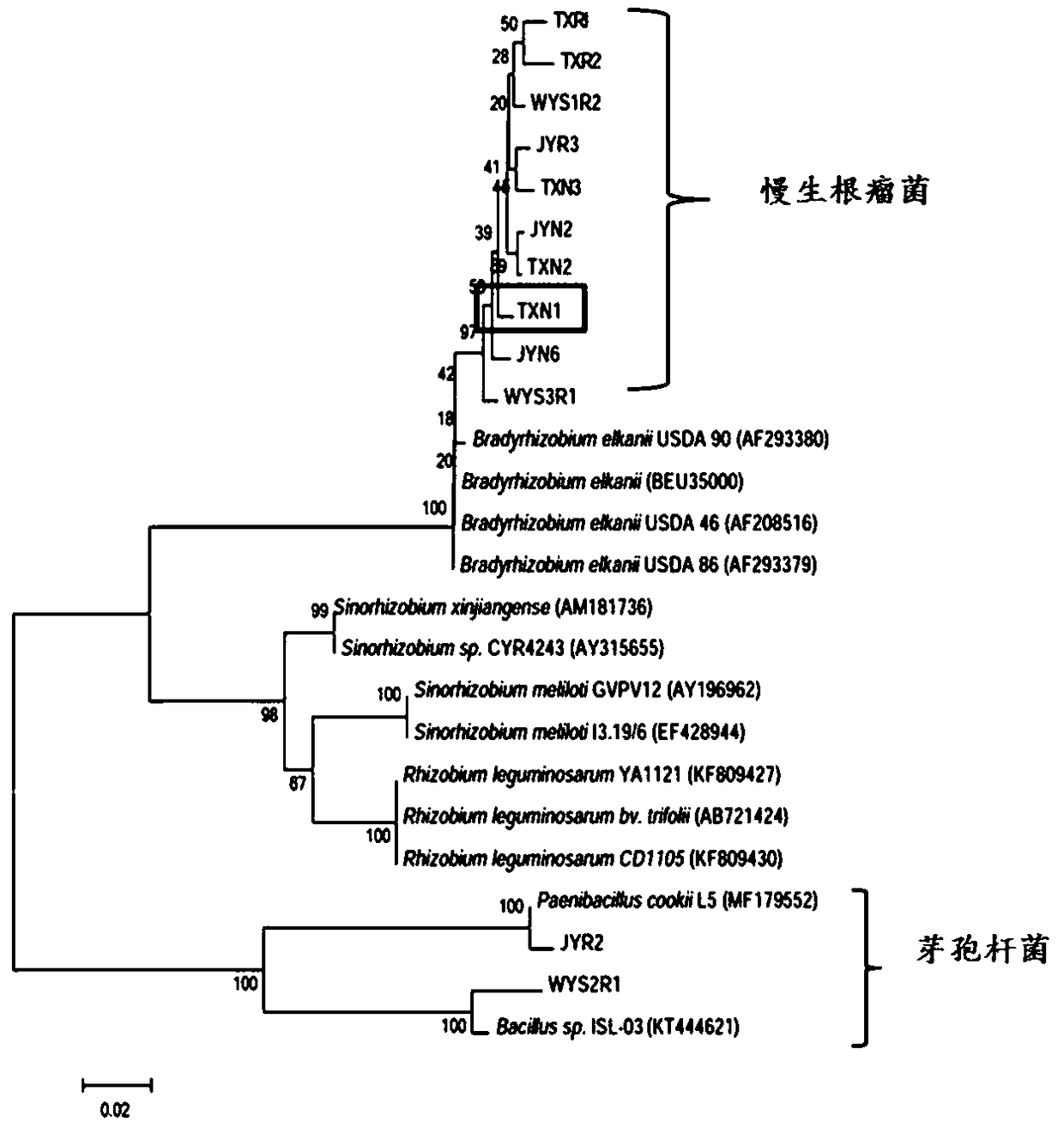
Cassia rhizobium strain TXN1 and application thereof
InactiveCN109294962ANodulation rate is highStrong nitrogen fixation abilityPlant growth regulatorsBiocidePlant noduleEcological environment
The invention discloses a cassia rhizobium strain TXN1 and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of microorganism. The cassia rhizobium strain TXN1 is obtained by being separated andpurified from fresh nodules of cassia grasses and performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection on nodA (nodulation protein A) gene as well as 16S rDNA (ribosomal deoxyribonucleic acid identification) molecular biological detection, determined to be a new strain of Bradyrhizobium and named as Tianyu-1. The cassia rhizobium strain TXN1 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collectionin April 10, 2018 with a preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2018191. Laboratory pot culture inoculation experiments prove that the cassia rhizobium strain TXN1 has the advantages of efficient nodulation and large nitrogen fixing capacity; inoculation of the cassia rhizobium strain TXN1 can significantly increase the number of root nodules, the root nitrogen fixing efficiency, the biomass and the plant nitrogen content of cassia grasses and further achieve the effects of increasing soil fertility and improving the ecological environment.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
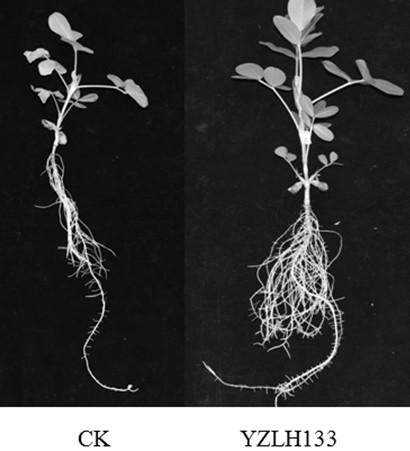
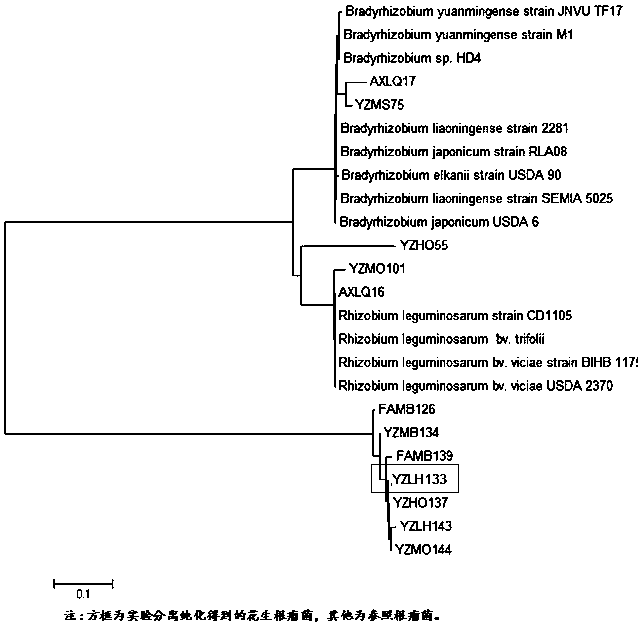
Rhizobium YZLH133 and application thereof
InactiveCN109439589ANodulation rate is highStrong nitrogen fixation abilityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsRoot nodulePhylogenetic profiling
The invention discloses a rhizobium YZLH133 and application thereof. The strain is a new strain which is captured from the soil in Youxi District, Fujian Province through Longhua peanut variety, is separated and purified from fresh nodules, is determined to be Bradyrhizobium through phylogenetic analysis by testing part sequences of 16s rDNA of the strain, and is named Funong 3#. A laboratory hydroponic tieback test and a large field tieback experiment prove that the rhizobium YZLH133 disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of efficient nodulation and strong nitrogen fixing capacity; the biomass and the yield of peanuts can be improved by inoculating the rhizobium; and the rhizobium is applicable to acid soil in South China to serve as one of the measures for conventional cultivation of the peanuts.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Root nodule azotobacter strain BXYD3 and uses thereof
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
A kind of compound rhizobia agent and its preparation and application
Owner:BIOTECH CENT OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI +1
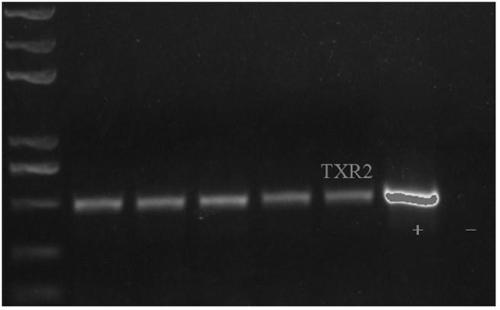
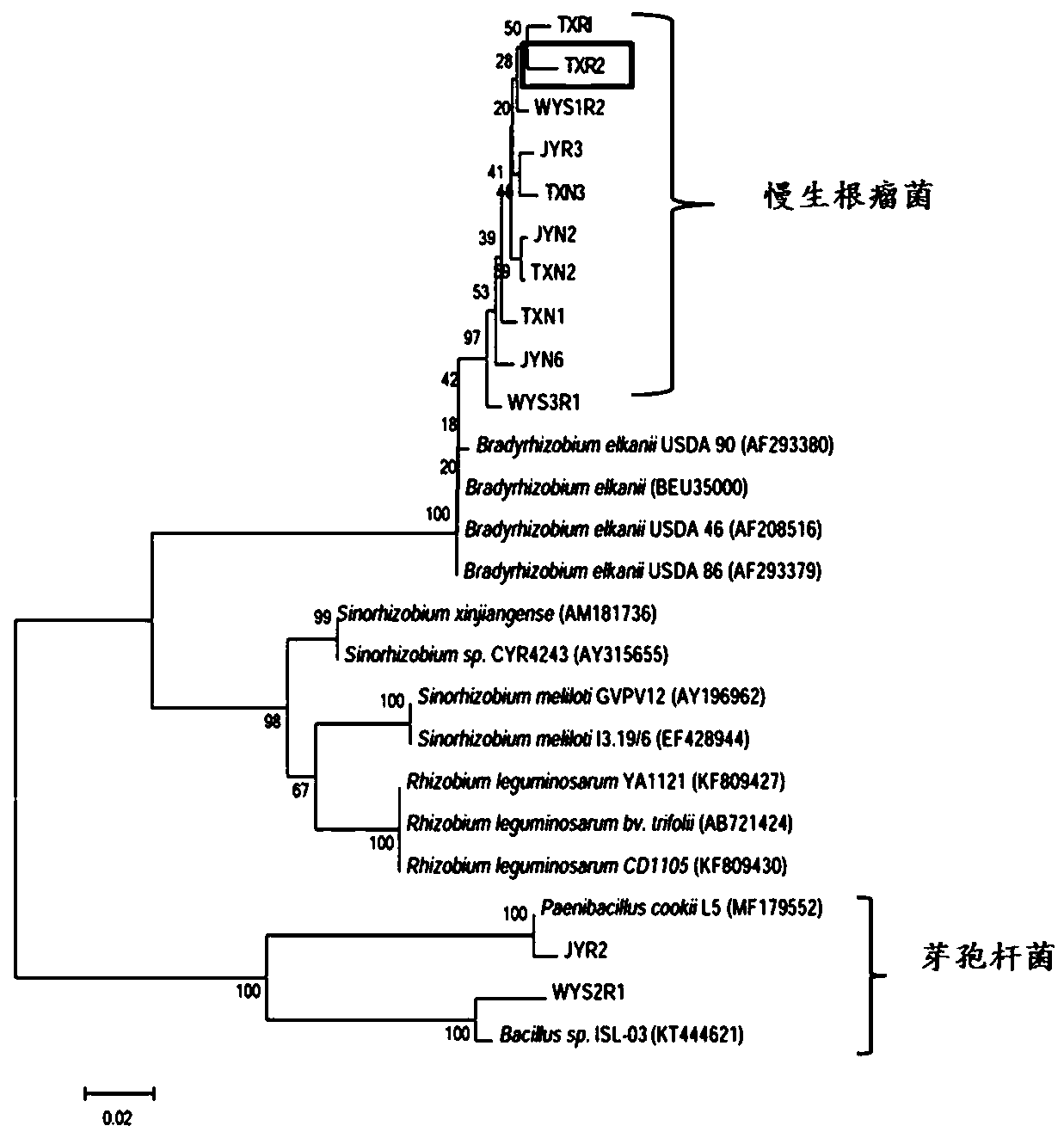
Chamaecrista rhizobium TXR2 and application thereof
InactiveCN109337847ANodulation rate is highStrong nitrogen fixation abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlant noduleEcological environment
The invention discloses rhizobium TXR2 and the application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of microbes. The strain is isolated and purified from fresh root nodules of chamaecrista pasture;through PCR detection of a nodA gene as well as 16S rDNA molecular biological identification, the rhizobium TXR2 is determined to be a novel strain of bradyrhizobium, and is named as Tianyuan No.2. The rhizobium TXR2 is collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection on April 10, 2018, with the collection number of CCTCC NO: M2018193. A pot culture tie-back test in a laboratory proves thatthe rhizobium TXR2 has the characteristics of high-efficiency nodulation and strong nitrogen-fixing ability; inoculation with the rhizobium can significantly increase the number of the root nodules ofthe chamaecrista pasture, the nitrogen nitrogen-fixing efficiency of the root nodules, the biomass and the nitrogen content of plants, and the effects of improving the soil fertility and improving the ecological environment are achieved.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
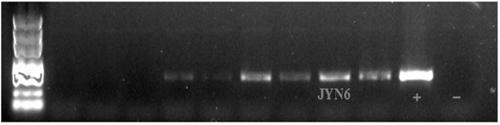
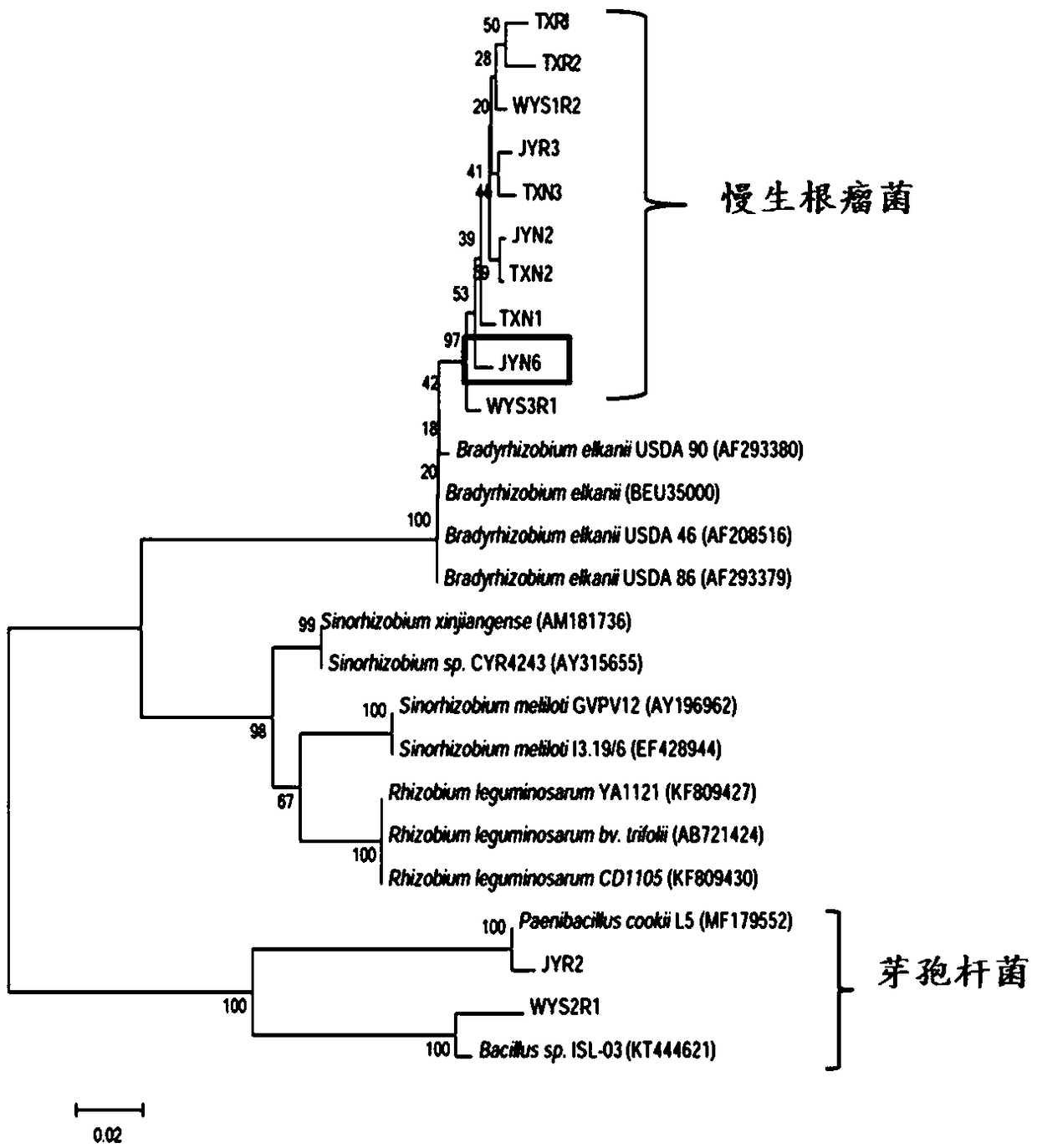
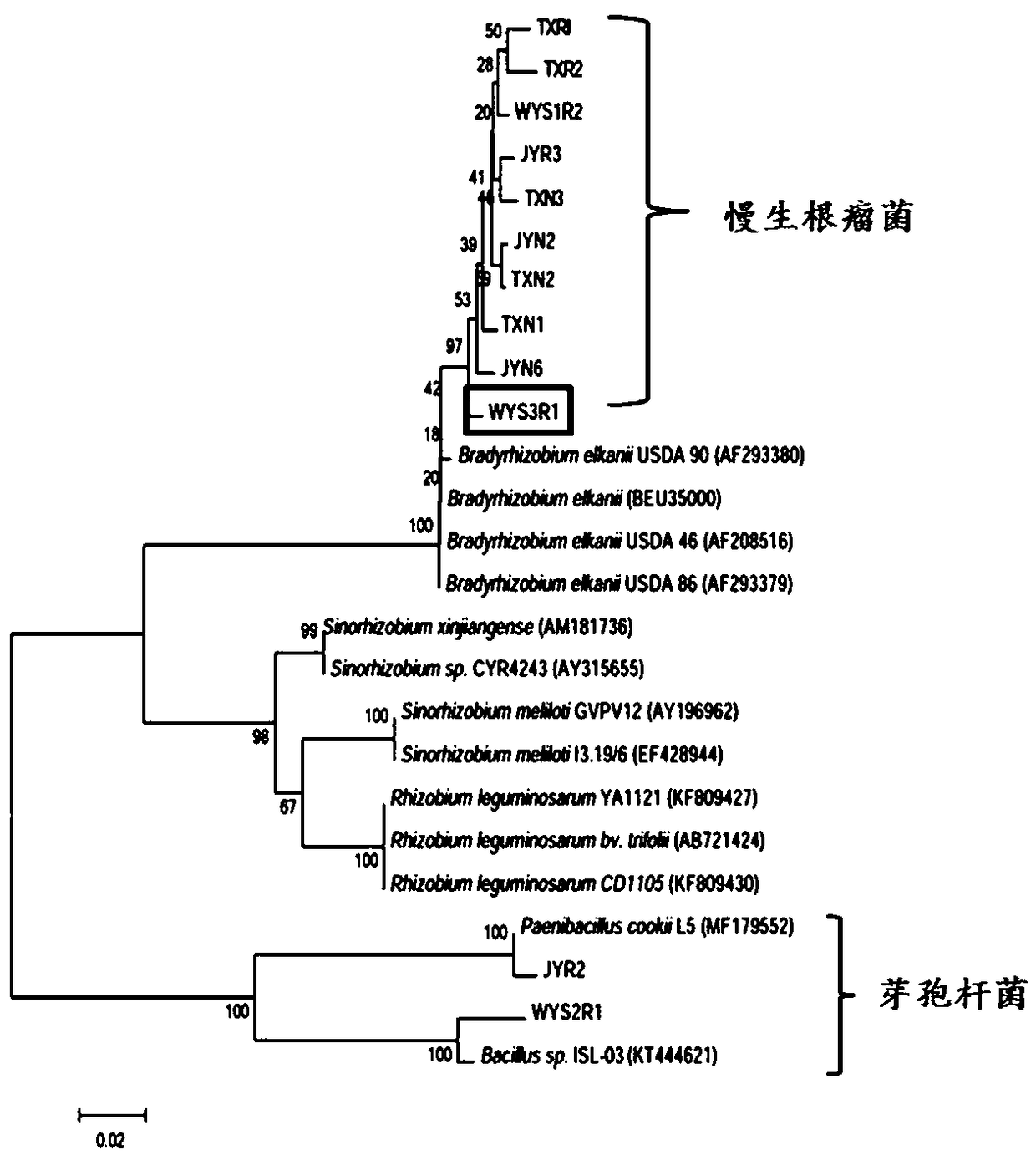
Chamaecrista Bradyrhizobium sp. JYN6 and application thereof
InactiveCN109370953ANodulation rate is highStrong nitrogen fixation abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPlant nodule
The invention discloses Chamaecrista Bradyrhizobium sp. JYN6 and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The strain is obtained by being separated and purified froma Chamaecrista chamaecrista forage fresh root nodule, and subjected to nodA gene detecting through a PCR and 16S rDNA molecular biological identification, and the strain is determined to be a new strain system of Bradyrhizobium and named as Anyu No.1; and the strain is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on April 10, 2018, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M2018192. Itproves that the Bradyrhizobium sp. JYN6 has the characteristics of efficient nodulation and high nitrogen fixation capacity through a laboratory potting tie-back test, by being inoculated with the Bradyrhizobium, the number of root nodules of Chamaecrista forage can be remarkably increased, the root nodule nitrogen fixation efficiency of the Chamaecrista forage can be remarkably improved, and thebiomass and the plant nitrogen content of the Chamaecrista forage can be remarkably increased, and thus the effect of soil fertility culturefertility improving and ecological environment improving are achieved.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Chamaecrista bradyrhizobiumsp. WYS3R1 and application thereof
InactiveCN109439590ANodulation rate is highStrong nitrogen fixation abilityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMicroorganismRoot nodule
The invention discloses chamaecrista bradyrhizobiumsp. WYS3R1 and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. A strain line is separated and purified from fresh chamaecrista grass nodule; nodA gene is detected by PCR; a novel strain line of Bradyrhizobium is determined by biological assay of 16S rDNA molecule and is named as Wuyuan 1. The chamaecrista bradyrhizobiumsp. WYS3R1 was preserved in China Center for Type CultureCollection on April 10th, 2018, with a preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2018190. The bonsai tieback test in a laboratory proves that the bradyrhizobiumsp. WYS3R1 disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of efficient nodulation and nitrogen fixation capabilities; by inoculating the bradyrhizobiumsp., nodule number, nodule nitrogen fixation efficiency and the biomass of chamaecrista grass and nitrogen content of plants can be obviously improved, and further the effects of culturing soil fertility and improving ecological environment are realized.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Rhizobium YZM0144 and application thereof
InactiveCN109355234ANodulation rate is highStrong nitrogen fixation abilityPlant growth regulatorsBiocidePlant noduleBradyrhizobium species
The invention discloses rhizobium YZM0144 and application thereof. The rhizobium YZM0144 is obtained by collecting rhizobium in soil of Youxi area of Fujian Province through a MO peanut novel variety,the rhizobium is separated and purified from fresh nodules, a 16s rDNA partial sequence of a strain is determined and identified as a novel strain of Bradyrhizobium by a phylogenetic analysis, and the rhizobium is named as Funong No. 4. The rhizobium YZM0144 proves that the rhizobium has the advantages of high-efficiency nodulation and strong nitrogen-fixing ability through laboratory hydroponicreturning experiments and field returning experiments, inoculation of the rhizobium can increase peanut biomass and yield, and the rhizobium can be applied to acid soil in South China as one of the measures for the routine cultivation of peanuts.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Bradyrhizobium liquid culture medium and preparation and culture methods thereof
InactiveCN109988737AWide variety of sourcesLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMyceliumBradyrhizobium species
The invention discloses a bradyrhizobium liquid culture medium and preparation and culture methods thereof. The bradyrhizobium liquid culture medium is prepared from fulvic acid, mannitol, a yeast extract, K2HPO4, KH2PO4, MgSO4, NaCl, CaCl2, FeCl3, H3BO3, Na2MnO4 and biotin. The preparation method includes the step that the raw materials and water are mixed and prepared into a solution. The raw materials of the prepared culture medium for culturing bradyrhizobium have wide sources; the preparation method is easy to implement, fermentation only needs to be conducted once, and no materials needto be added halfway; on this basis, the effect of adopting the prepared culture medium to culture bradyrhizobium is better than that of adopting an ordinary culture medium for culturing, and the culture method includes the steps of activating strains, culturing seeds and conducting fermentation culture. The mycelium density of bradyrhizobium cultured by the culture medium in the same period of time is greater; on the premise of meeting a certain quantity of mycelia, the fermentation time can be shortened; therefore, the effect of the prepared culture medium on the bradyrhizobium growth efficiency is obviously improved.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Strain A56WU capable of raising anti-drought and anti-heat ability of leguminous trees and culture method of root nodule seedlings thereof
InactiveCN102206594BImprove drought resistanceGuaranteed survival rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRevegetationPlant nodule
The invention relates to a biological strain resource, in particular to a strain capable of raising fast-growing, anti-drought and anti-heat ability of leguminous trees in dry-hot valley areas, and a culture method of root nodule seedlings thereof. Strain A56 WU disclosed in the invention is Bradyrhizobium eikanii, CGMCC No: 4591. The culture method comprises isolation and purification, microscopic examination, back grafting and inoculation of the strain. The strain disclosed in the invention is a good strain selected from the strains in dry-hot valley areas and capable of effectively raisingfast-growing, anti-drought ability of leguminous trees in dry-hot valley areas, so that the strain has important utilization value for vegetation restoration of dry-hot valley areas, allowing leguminous trees to live through the crisis securely under the threat of dry-hot environment, and ensuring the survival rate of large area afforestation in dry-hot valley areas.
Owner:SOUTHWEST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Root nodule azotobacter strain BDYD1 and uses thereof
The invention discloses a Nodule Azotobacter strain BDYD1 and the application. The strain is obtained by a way that the Rhizobia strains in the soil are respectively captured through different soybeanvarieties; the Rhizobia strains are separated and purified in fresh root nodules; part 16S rDNA of the strain is sequenced; the phylogenetic analysis determines that the strain is a novel Bradyrhizobium strain, which is named as Huagu 1. The Nodule Azotobacter strain BDYD1 of the invention has the characteristics of acid and aluminum tolerance and high level of nodules, which are proved by laboratory pot culture and field experiment. The inoculation of the Rhizobia strain can improve the yield of soybean more than 20 percent to 30 percent. The invention suits for the acid soil area in South China, which can be used as one of the measures for the conventional cultivation of soybean.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com