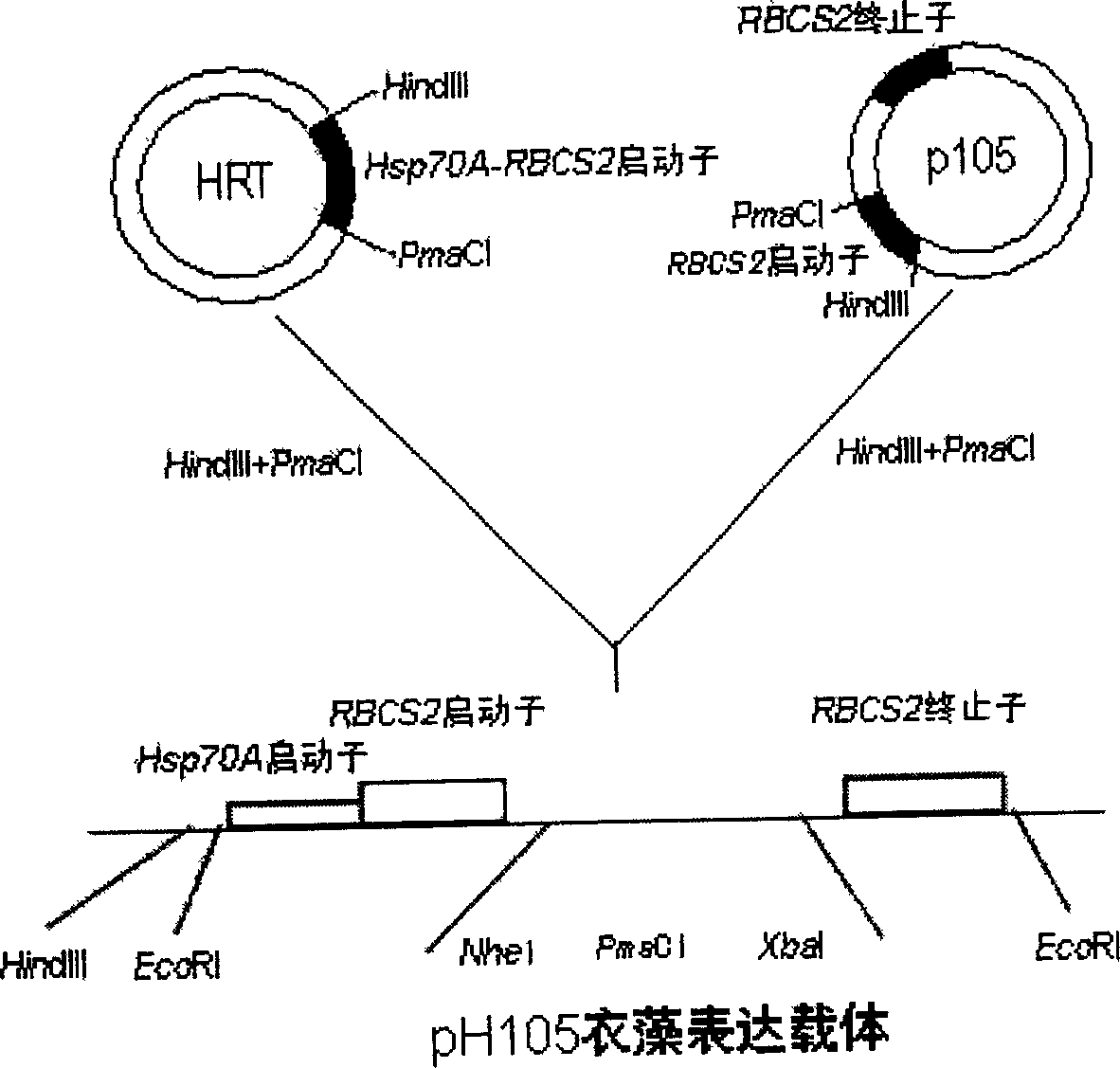
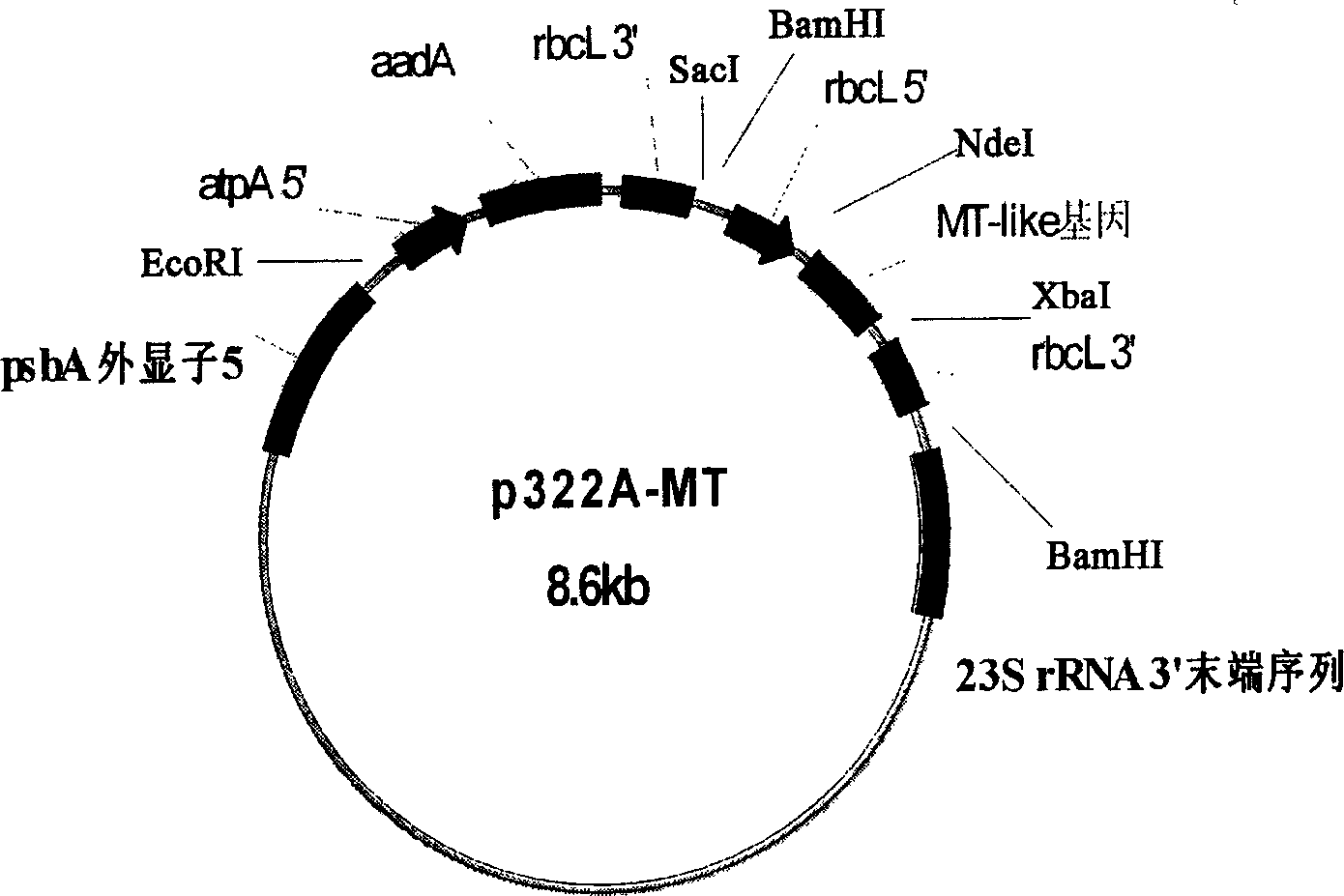
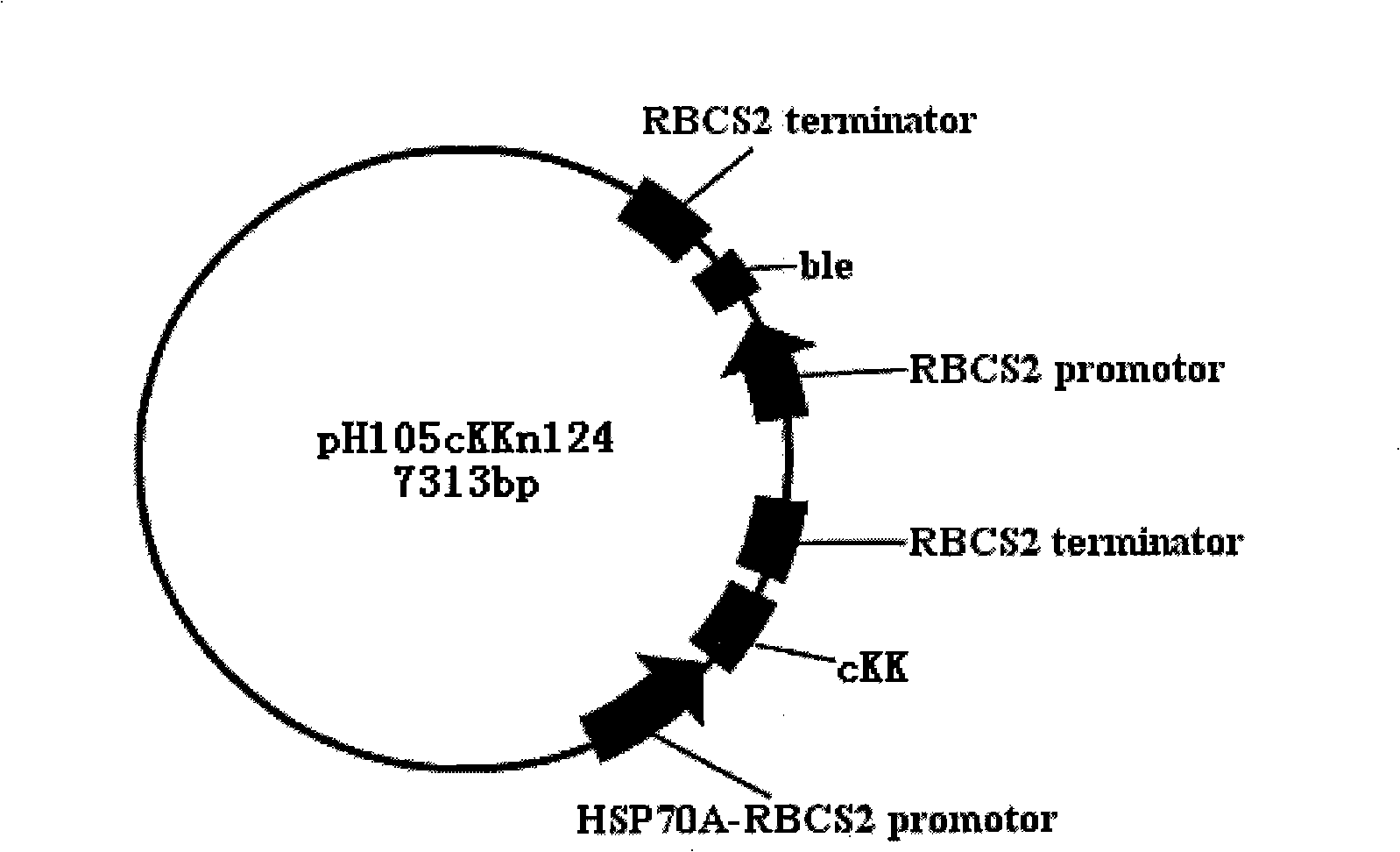
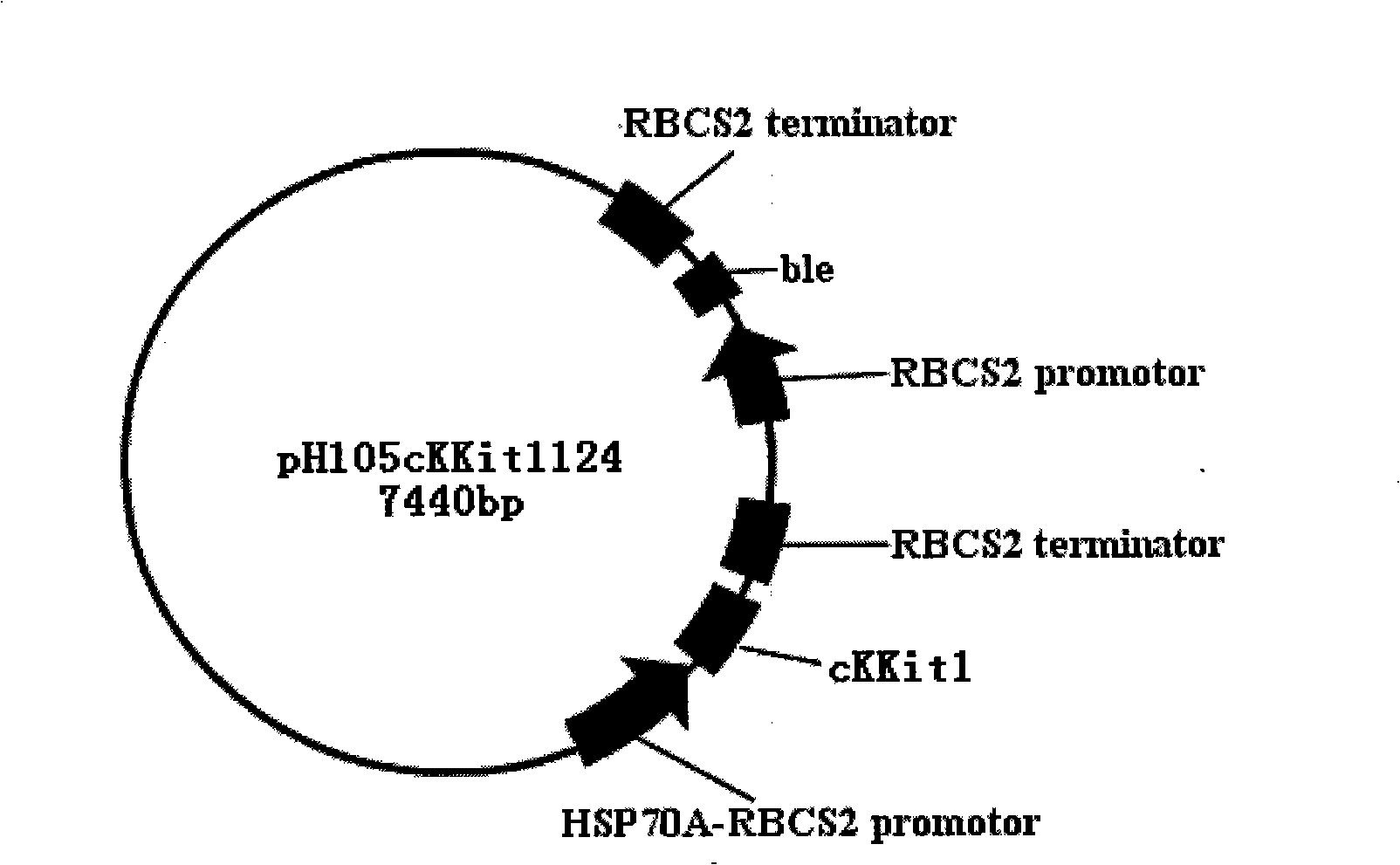
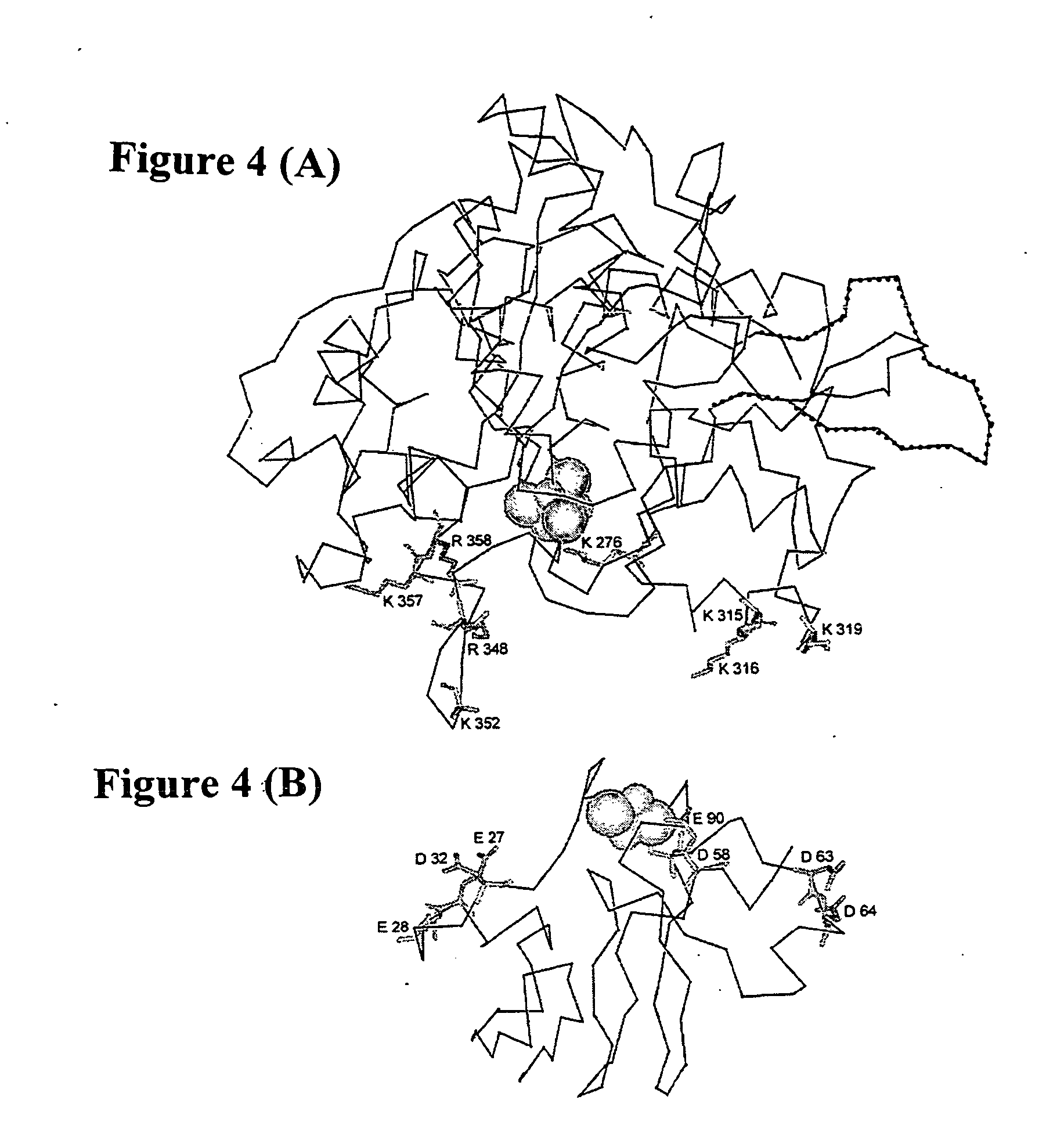
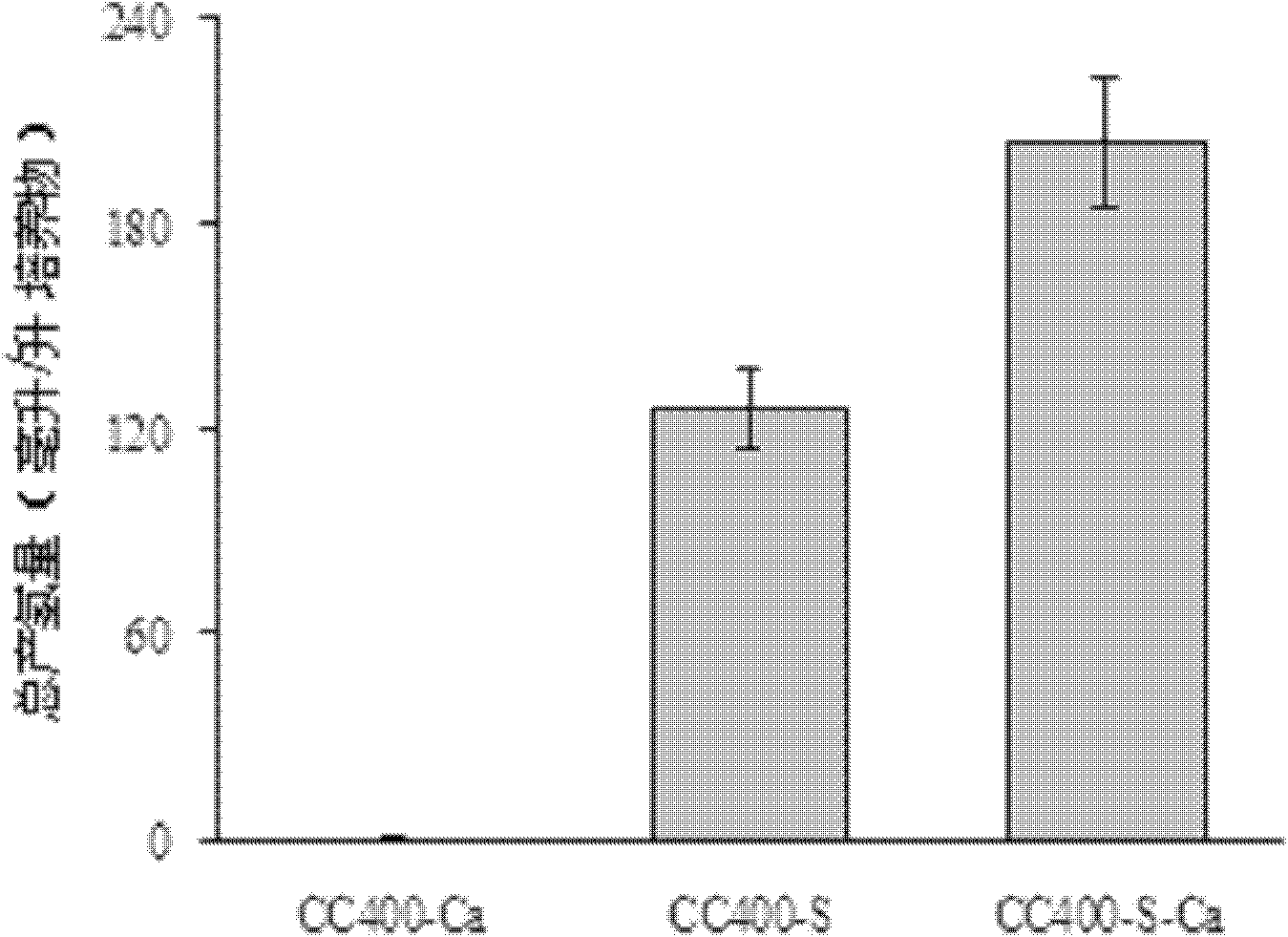Patents
Literature
135 results about "Chlamydomonas reinhardtii" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is a single-cell green alga about 10 micrometres in diameter that swims with two flagella. It has a cell wall made of hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins, a large cup-shaped chloroplast, a large pyrenoid, and an eyespot that senses light.
Regulatory Factors Controlling Oil Biosynthesis In Microalgae And Their Use
The production of transgenic plant oils is described by transfecting plant host cells with heterologous transcription inducers. Such inducers are specific for endogenous biosynthetic plant oil genes, such that the inducers induce an overexpression of the plant oil genes. The overexpressed gene product (i.e., for example, diacylglycerol transferase) thereby results in a increased intracellular production of a plant oil (i.e., for example, triacylglycerol). In one embodiment, the transfected plant host cell can be a plant algae species (i.e., for example, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii).
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
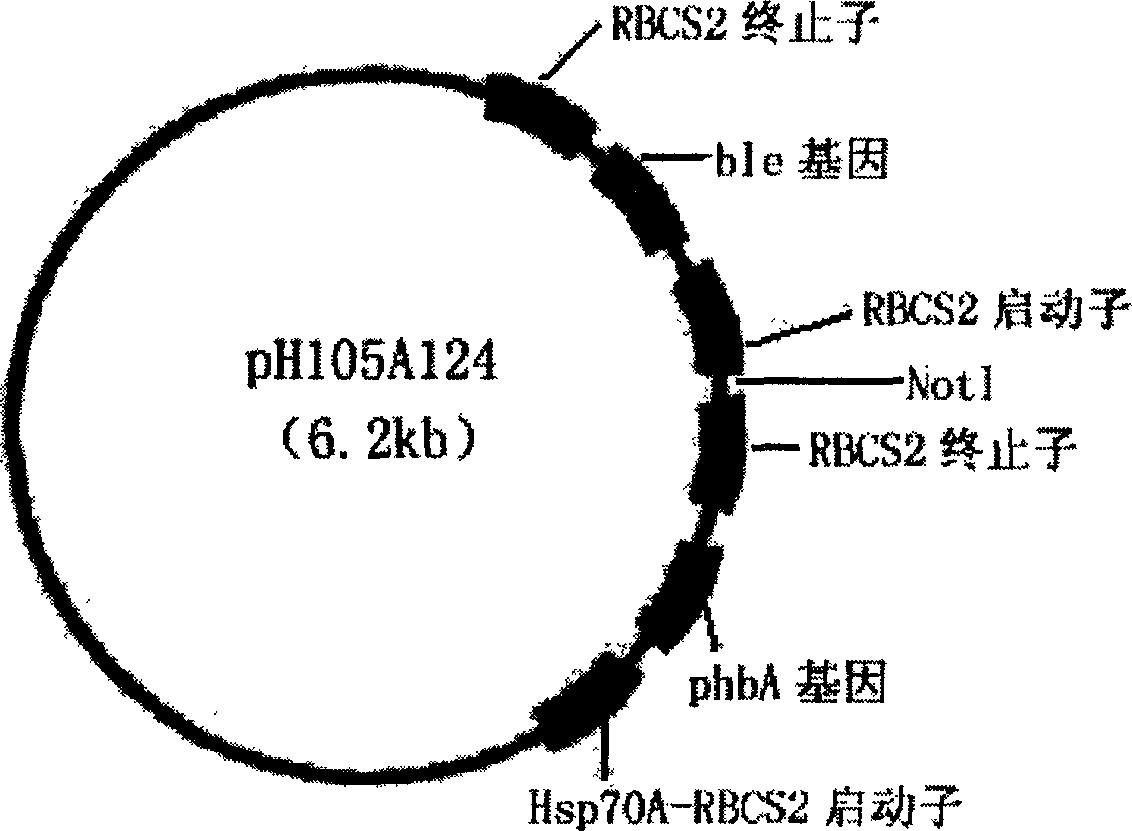
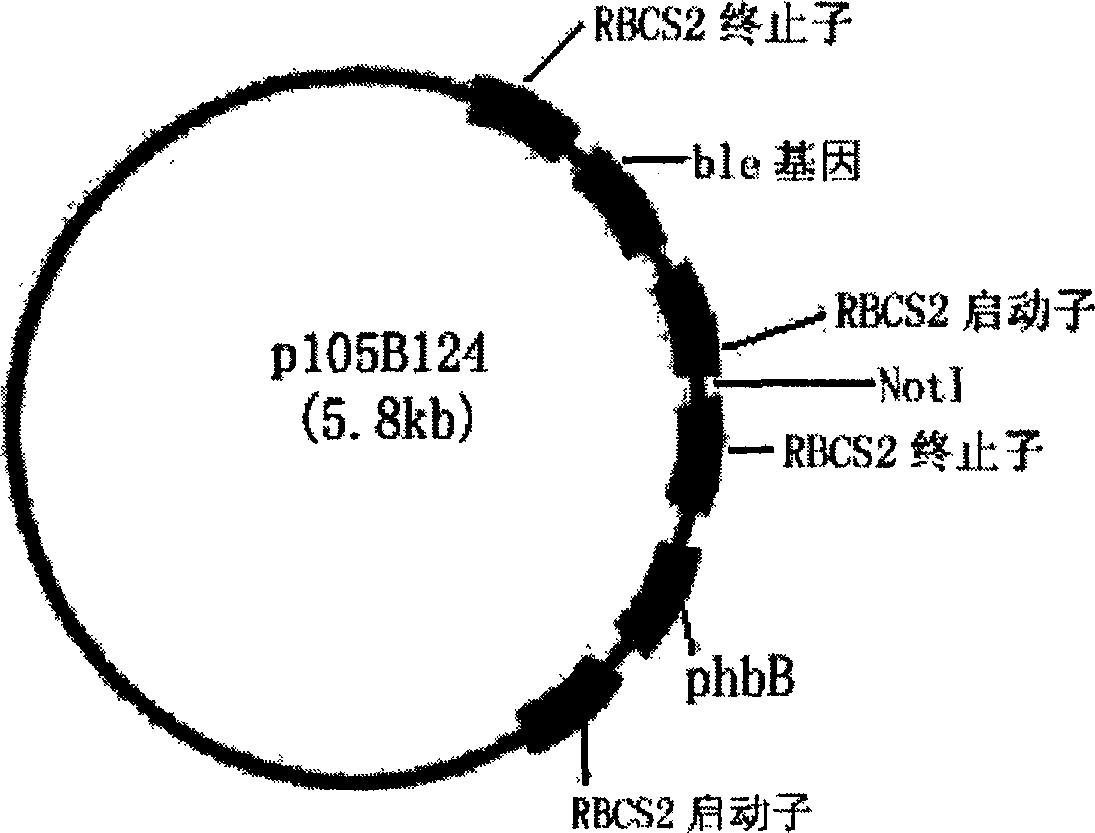
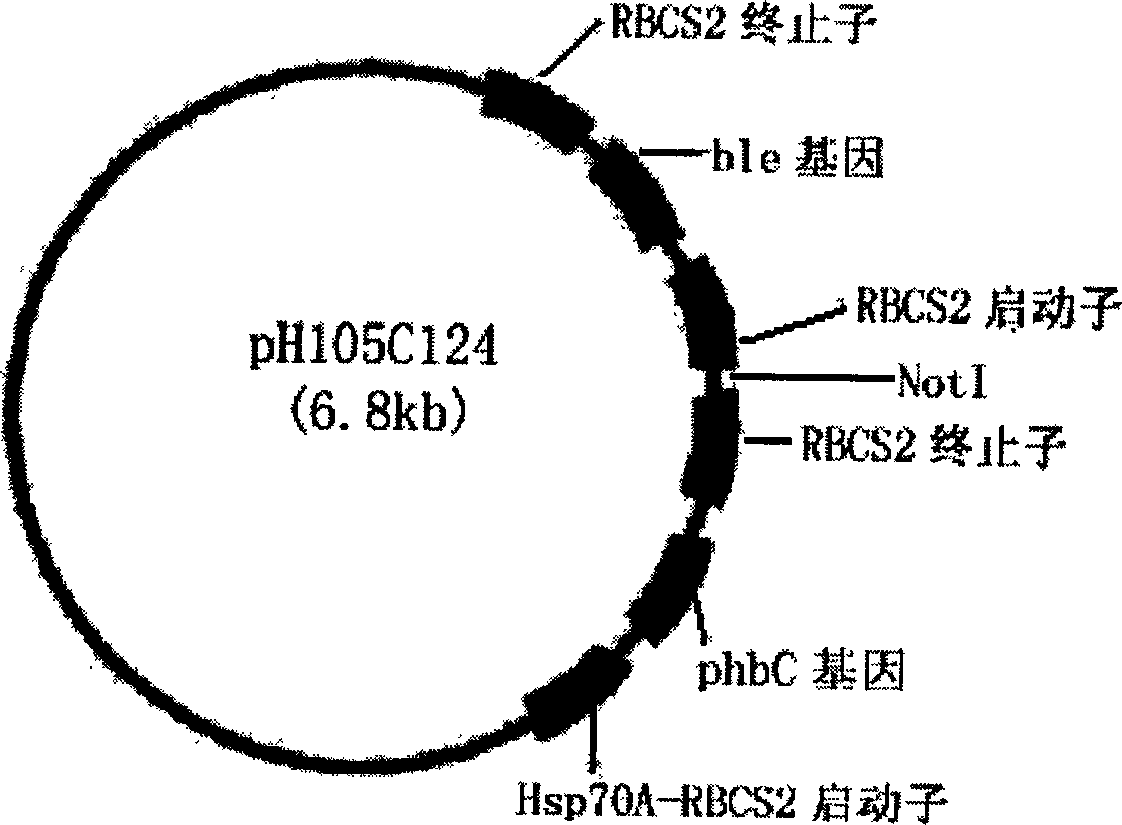
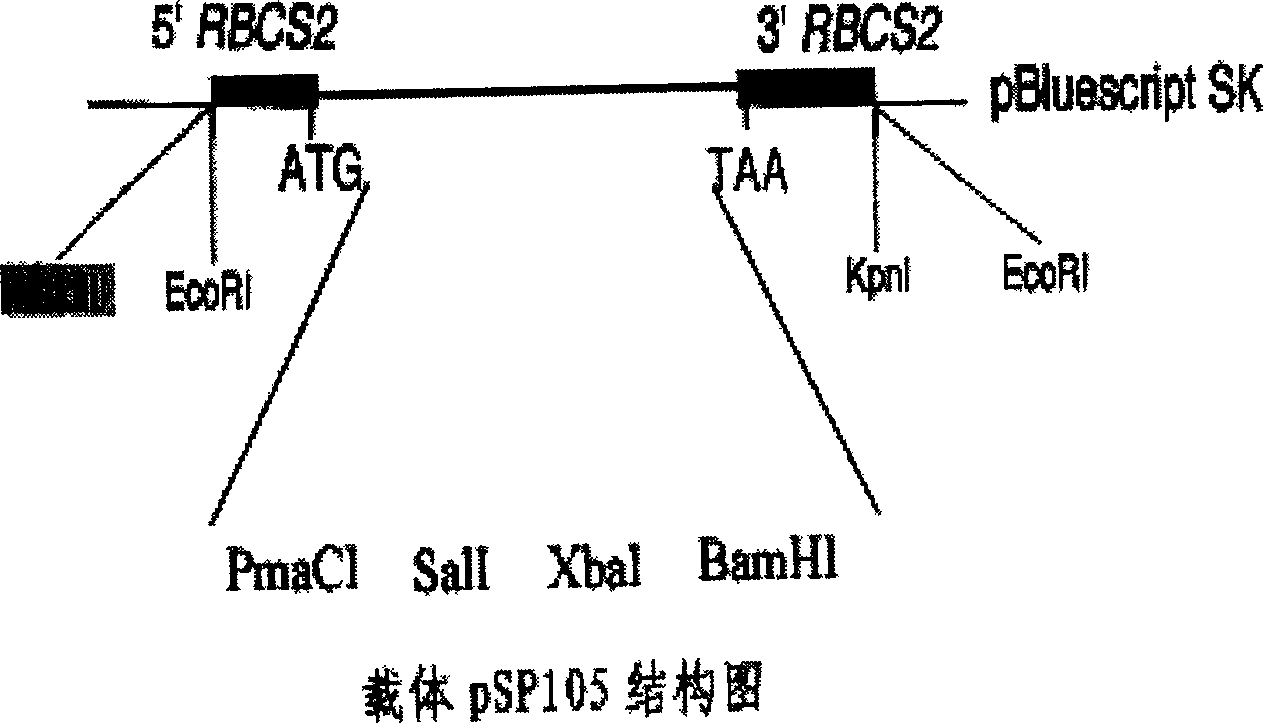
Exogenous gene expression system of Chlamydomonasreinhardtii and method for constructing and producing PHB transgenic algae
ActiveCN1807649AImprove expression efficiencyIncrease productionUnicellular algaeFermentationHydroxybutyric acidChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention discloses an expression system and constructing PHB transgene algae method of rhine chlamydomonas exogenesis gene, which comprises the following parts: promotor, exogenesis-goal gene, screening badge and rhine chlamydomonas acceptor algae strain, wherein the method comprises the following: A, selecting and cultivating acceptor algae strain; B, cloning key enzyme gene by PHB biosynthesizing; C, expressing carrier of PHB biosynthesizing key enzyme rhine chlamydomonas; D, using PHB biosynthesizing key enzyme to lead in rhine chlamydomonas from fungus Bacillus alcaligenes with bead-milling method, gene-gun method or electrization; obtaining bivalence or transgene Chlamydomonas of producing PHB by screen selecting and molecule detecting. The poly-hydroxybutyric acid is compounded by acting in conjunction of PHB compounding key enzyme of phbA, phbB and phbC gene coding, which uses acetylcoenzyme A as substrate by photosynthesis. The method simplifies the operating, which reduces cost.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Constructing method for transgene Chlamydomonas reinhardtii bioreactor
InactiveCN1827769AEasy point-to-point integrationSolve training difficultiesUnicellular algaeMicrobiological testing/measurementChlamydomonas reinhardtiiVaccination
The invention relates the construct method for transgenosis rhinestone algae bioreactor. The method comprises the following steps: using the rhinestone algae as transgenosis receptor biology, highly effective expressing the carrier construct by constructing the exogenesis gene containing screening mark expression frame, leading the destination genes in rhinestone algae with bead milling method, electric punching method and other methods, integrating them into nucleus genome or chloroplast genome, and adopting a series of gene expression regulate and control technology to construct the transgenosis rhinestone algae bioreactor. The transgenosis rhinestone algae bioreactor possesses the characters of fast growth rate, short breeding cycle, easy segregation, photoautotroph and large scale culture, fast and cheap producing medicinal protein, industrial raw materials, and feeding vaccination, and possessing the bioactivity secondary metabolite.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Construction method of transgenic chlamydomonas reinhardtii for expressing human tissue kallikrein
ActiveCN101255438ARich in nutrientsReasonable structureUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesDiseaseChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention is a constructing method of a genetic modified chlamydomonas reinhardtii to express kallikrein of human tissue. Firstly kallikrein gene sequence suitable for expression of chlamydomonas reinhardtii kernel genome or expression of chloroplast genome or expression of mitochondrial is designed according to kallikrein gene sequence of human tissue and preferred codon table of chlamydomonas reinhardtii, the gene sequence is synthesized by artificial synthesis, kallikrein gene of human tissue containing non-coded sequence is artificially synthesized, then expression vector of chlamydomonas reinhardtii kernel genome or expression vector of chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast genome or expression vetor of chlamydomonas reinhardtii mitochondrial with mention foreign gene is constructed, then transformed into chlamydomonas reinhardtii by genetic transformation, and genetic modified algal strains capable of expressing kallikrein of human tissue is obtained after screening. The invention lays foundation of treating and preventing some diseases such as hypertention, glomerulonephritis with human original kallikrein gene chlamydomonas reinhardtii and products there.
Owner:深圳市微宇生物科技有限公司
Method for constructing secretory expression carrier and secretory expression system of Chlammydomonas reinhardtii
ActiveCN102181471AEasy to separate and purifyHigh recovery rateMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionSequence signalChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention discloses a method for constructing a secretory expression carrier and secretory expression system of Chlammydomonas reinhardtii. In the invention, the method comprises the steps of predicating a signal peptide gene sequence by using an amino acid sequence from a secretory protein of the Chlammydomonas reinhardtii through signal peptide predicating software; artificially synthesizing a signal peptide gene obtained by predicating; and inserting the signal peptide gene between a promoter and a cloning site of the Chlammydomonas reinhardtii expression carrier to construct the secretory expression carrier of the Chlammydomonas reinhardtii; meanwhile, detecting the expression efficiency of the constructed secretory expression carrier of the Chlammydomonas reinhardtii by using an exogenous gene; converting the secretory expression carrier of the Chlammydomonas reinhardtii, containing the exogenous gene, to the Chlammydomonas reinhardtii by using a Chlammydomonas reinhardtii genetic conversion method; and screening the Chlammydomonas reinhardtii to obtain a transgene engineering strain capable of expressing the exogenous gene in a secretory way. By using the invention, the basis is laid for using the Chlammydomonas reinhardtii as the secretory expression exogenous gene of a bioreactor.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
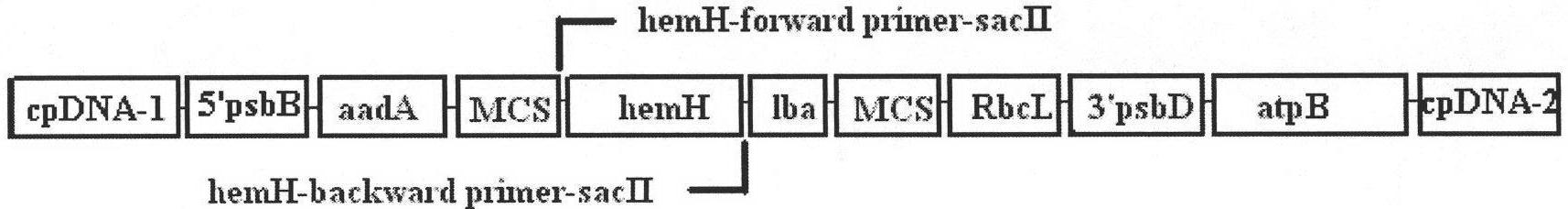
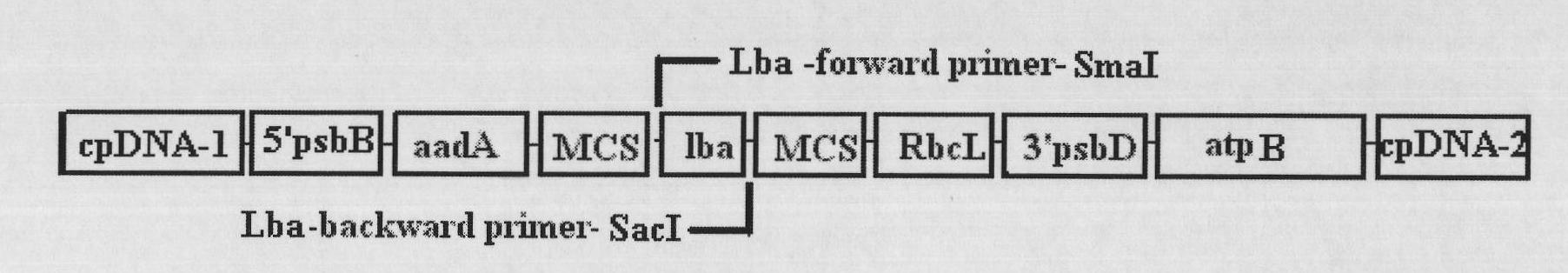
Method for improving chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production amount of leghemoglobin ferrous chelate enzyme gene
InactiveCN101775407ALower oxygen levelsIncrease hydrogen productionUnicellular algaeFermentationEnzyme GeneChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention relates to a biological hydrogen production technology, in particular to a method for improving the chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production amount of a leghemoglobin ferrous chelate enzyme gene. The traditional chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production method has the defects that chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen enzymes are sensitive to oxygen and easily restricted by the oxygen to lose activity, and the chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production effect is limited. The invention discloses an application of a leghemoglobin ferrous chelate enzyme gene and a globulin subunit gene to hydrogen production by constructing the leghemoglobin ferrous chelate enzyme gene hemH and the globulin subunit gene lba in a chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast expression vector, transferring the expression vector in the chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast and expressing the hemH-lba gene in the chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast. The invention has the advantages that the content of oxygen in a closed culture system of the transformed chlamydomonas reinhardtii is reduced obviously faster than that of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii of an un-transformed gene, the oxygen content is kept at a lower level, and the hydrogen production amount is obviously increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
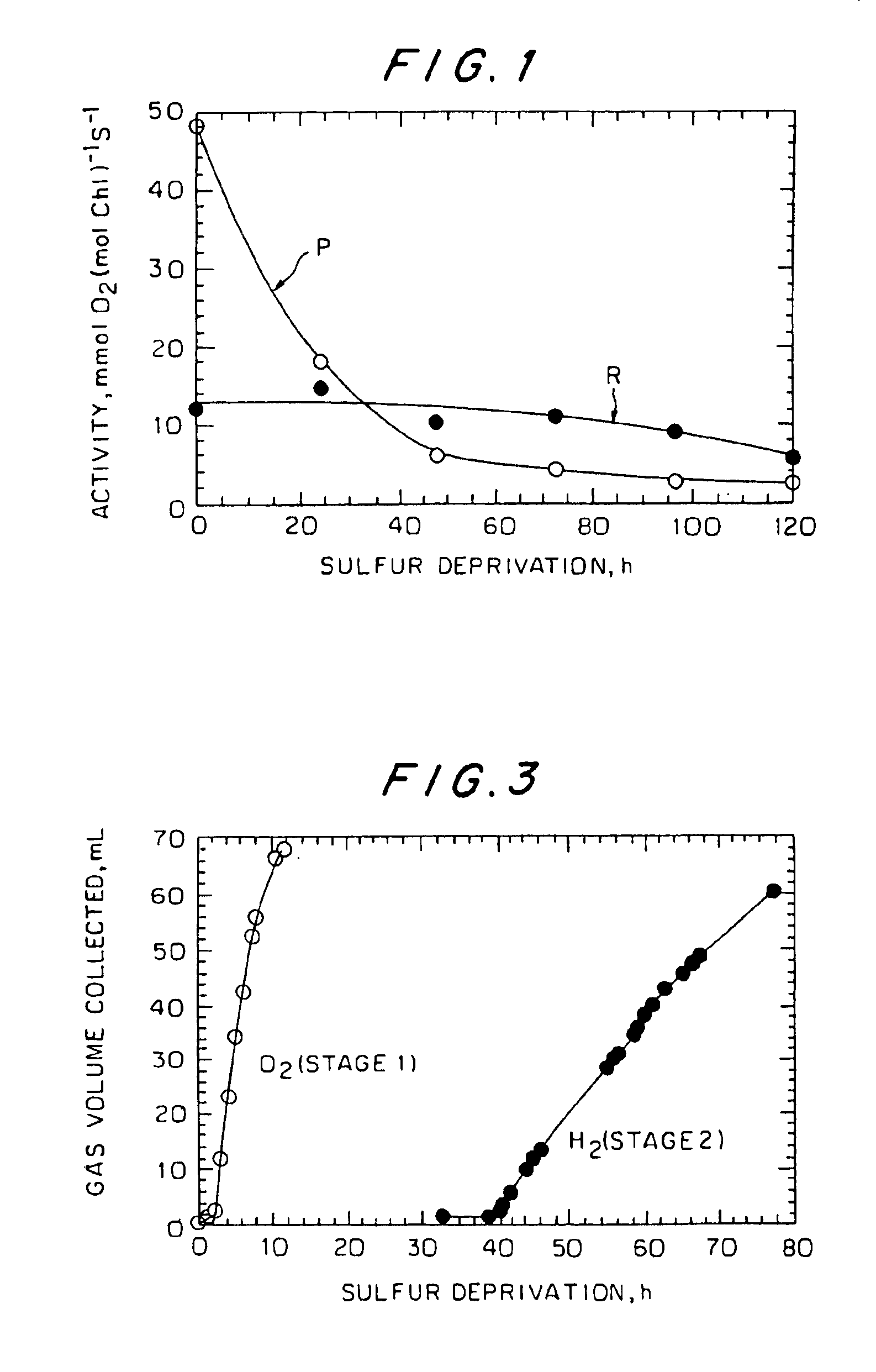
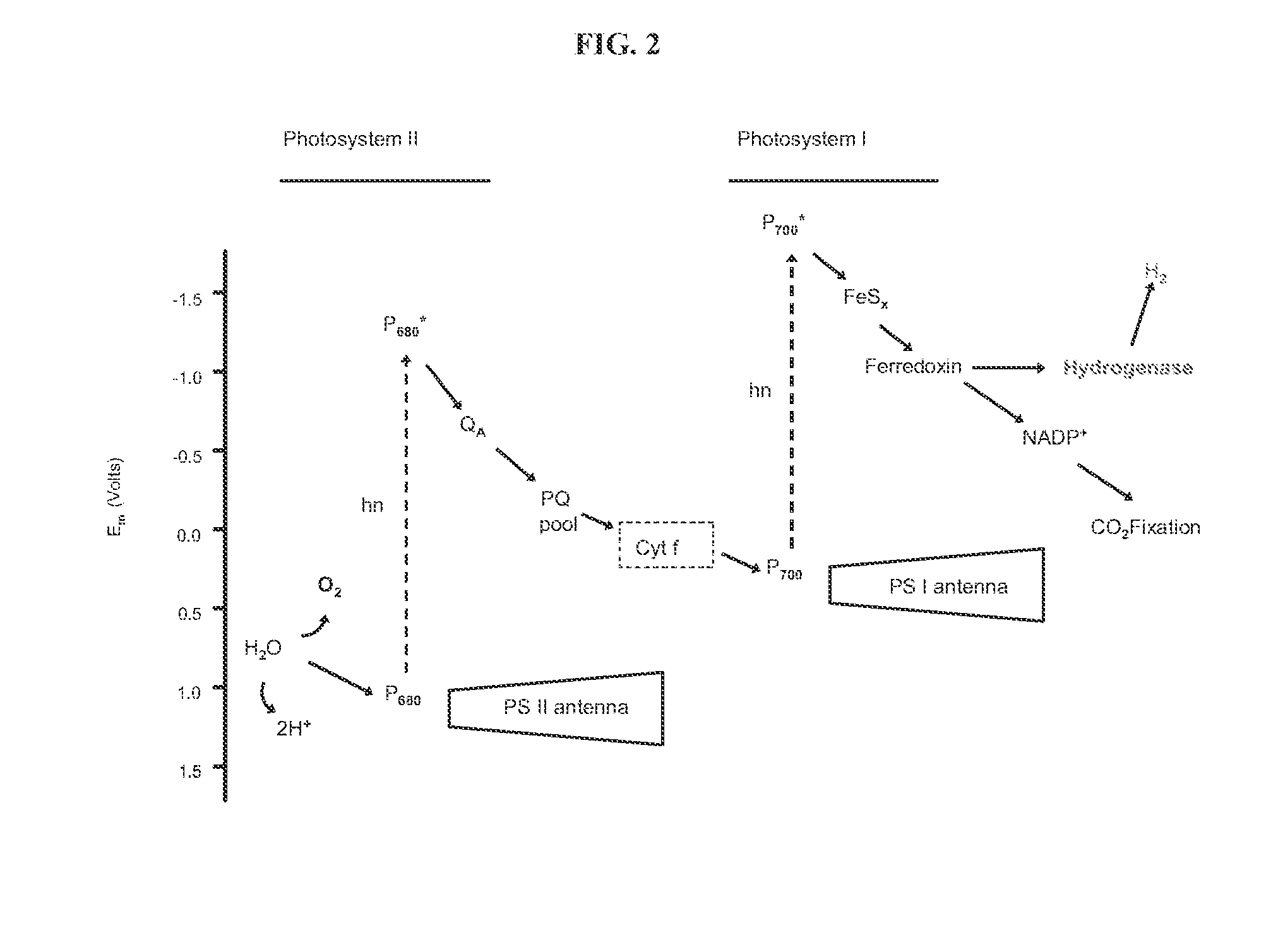
Hydrogen production using hydrogenase-containing oxygenic photosynthetic organisms
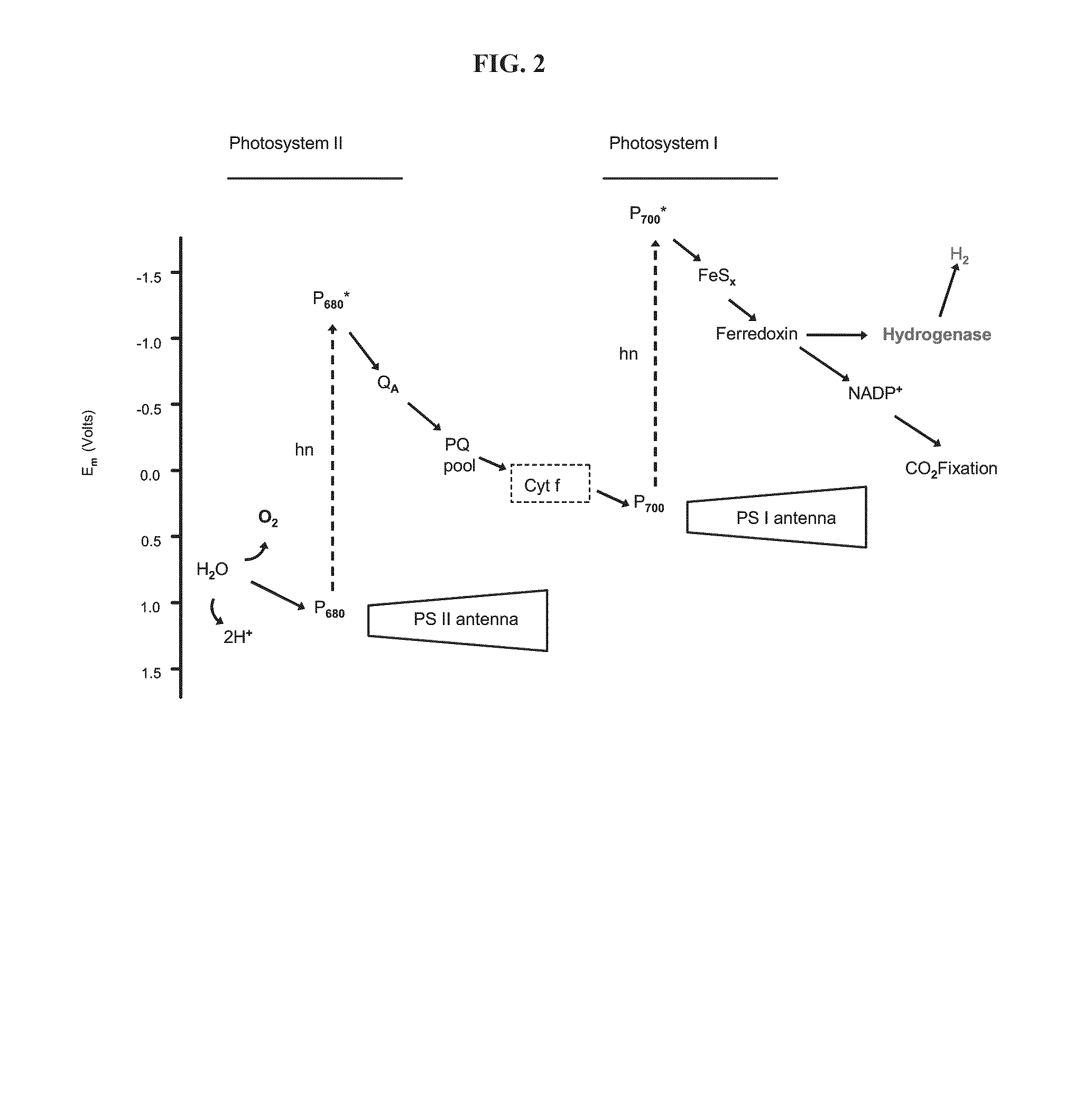
A reversible physiological process provides for the temporal separation of oxygen evolution and hydrogen production in a microorganism, which includes the steps of growing a culture of the microorganism in medium under illuminated conditions to accumulate an endogenous substrate, depleting from the medium a nutrient selected from the group consisting of sulfur, iron, and / or manganese, sealing the culture from atmospheric oxygen, incubating the culture in light whereby a rate of light-induced oxygen production is equal to or less than a rate of respiration, and collecting an evolved gas. The process is particularly useful to accomplish a sustained photobiological hydrogen gas production in cultures of microorganisms, such as Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Method for resourceful treatment of cadmium polluted wastewater
InactiveCN101367575AWaste water treatment from animal husbandryEnergy based wastewater treatmentEnvironmental energyChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention discloses a method of generating hydrogen for twice at the same time that the waste water containing cadmium heavy metal is treated by harmless biological absorption by using an algae and fungi synergistic system, and belongs to the technical field of the environmental energy source. The method is mainly characterized in that algae cell wall and fungi cell wall are cooperated to absorb the cadmium; at the same time of removing the cadmium, Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii can generate hydrogen by using the characteristic that the stress effect of the heavy metal of the Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii is similar to the deficiency effect of sulfur element during cultivation; furthermore, butyric acid clostridium is used to ferment the biomass cumulated by the photosynthesis of the Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii to re-generate hydrogen; the fungi used during cadmium absorption and hydrogen generation is treated in an immobilized way. The method has high efficiency, is easy for downstream treatment, can get clean water and a great deal of hydrogen finally with qualified cadmium concentration, and can be widely used for the clean treatment and energy recovery utilization to industrial waste water containing the cadmium.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
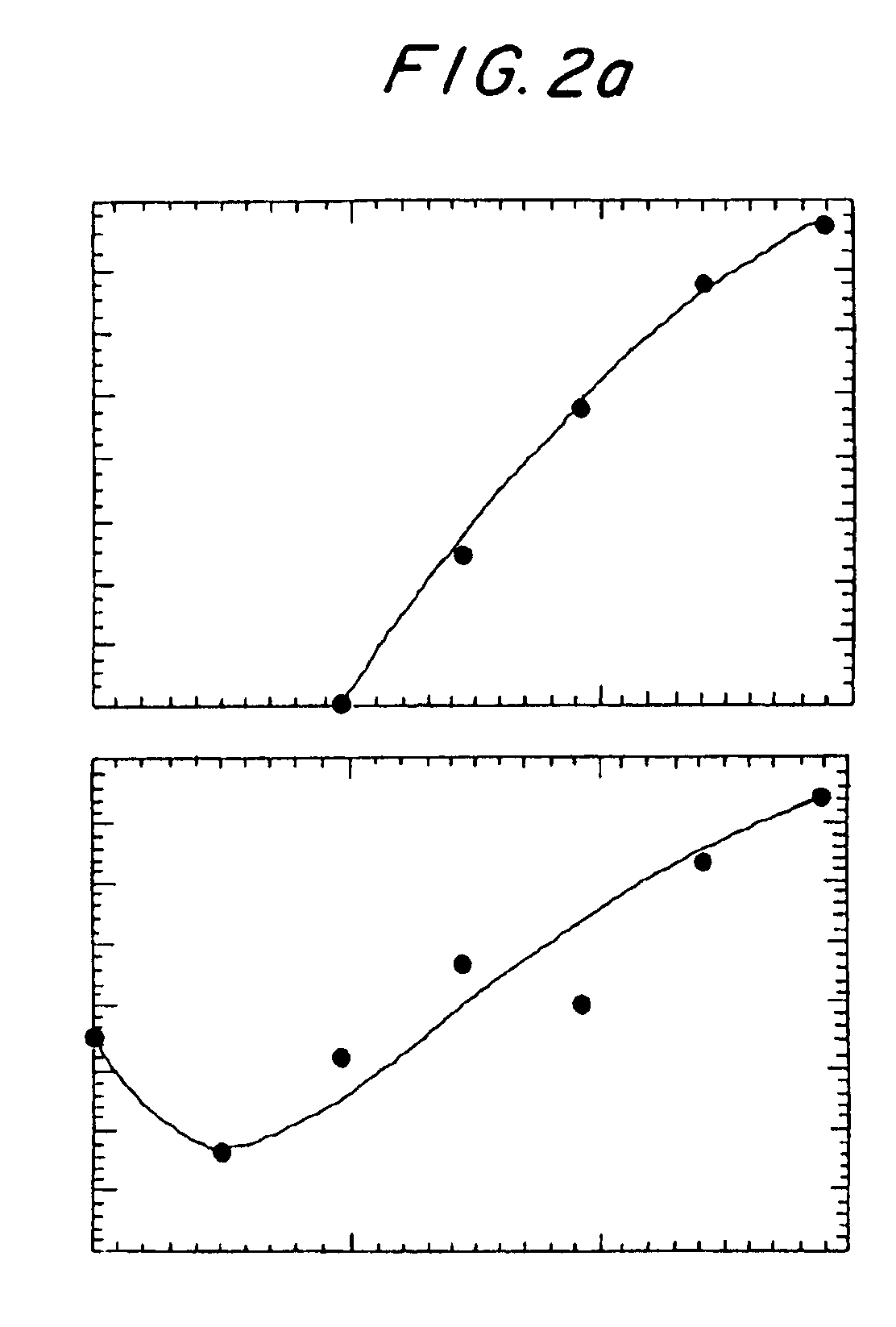
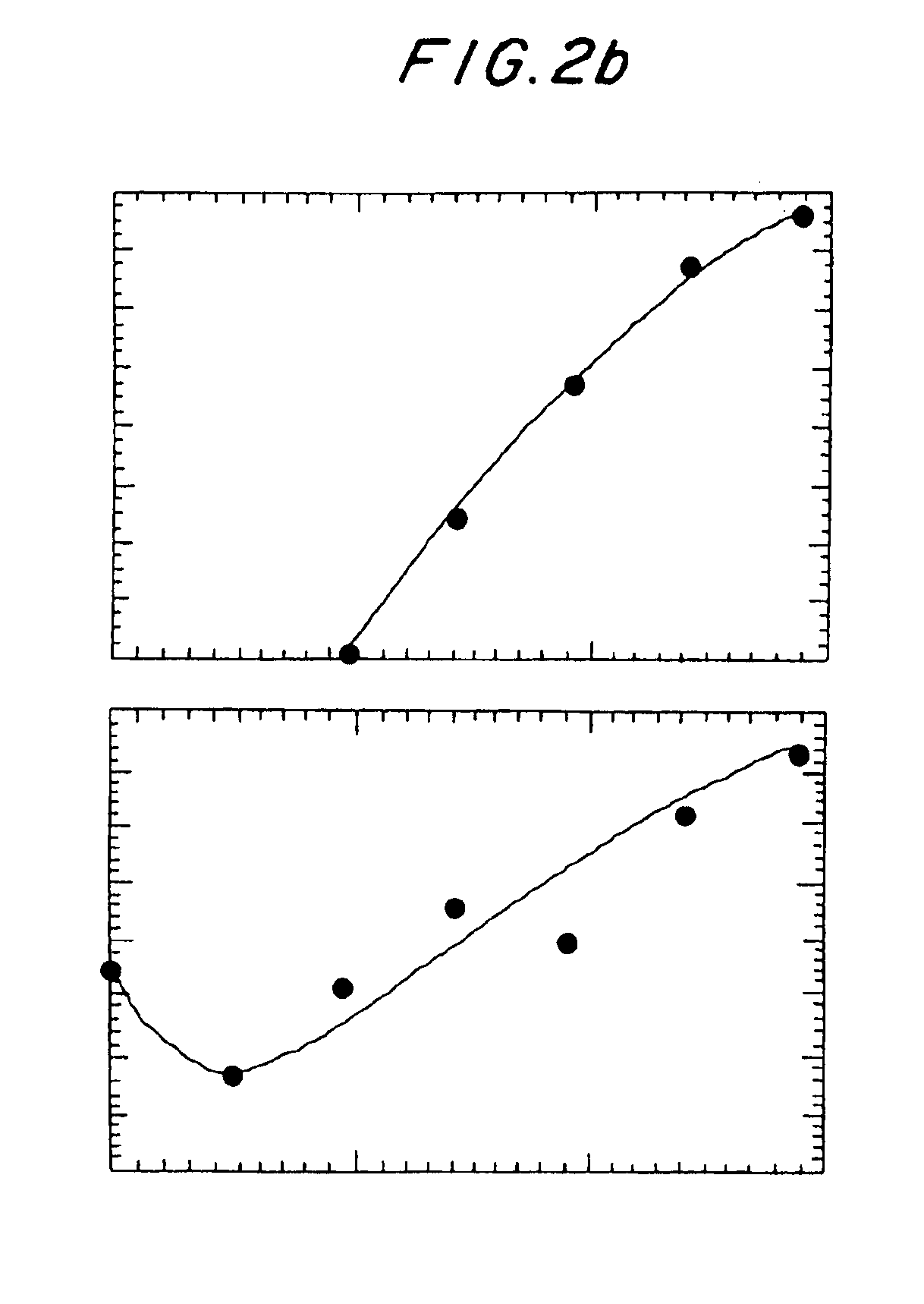
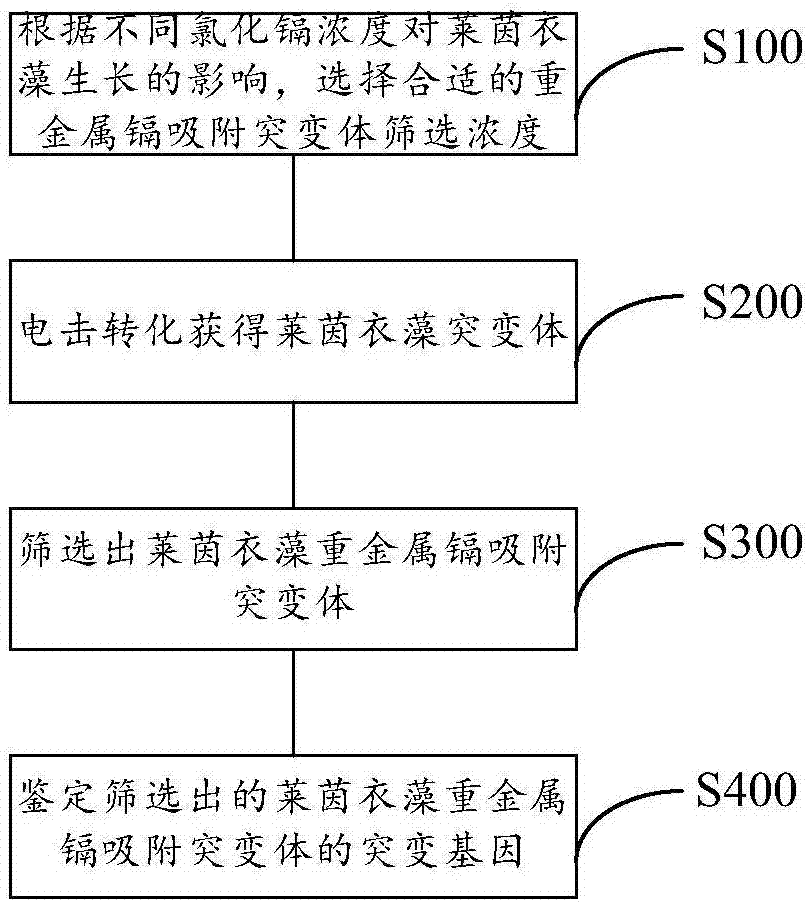
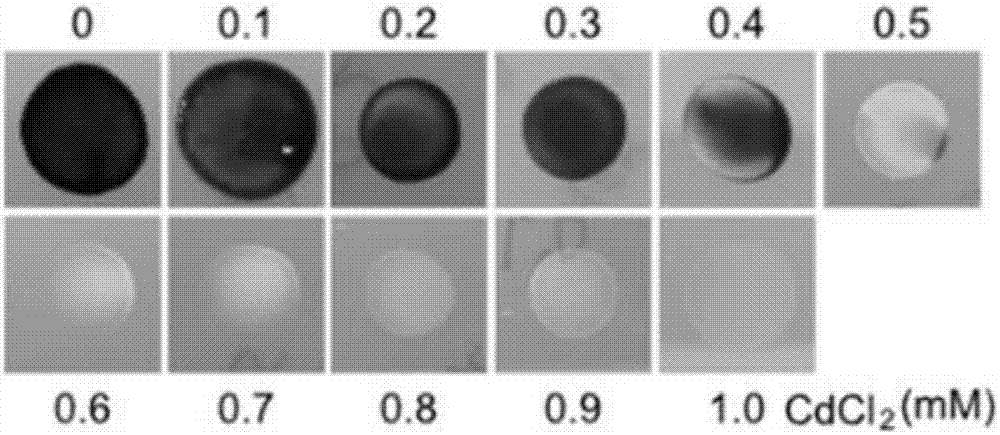
Screening method of chlamydomonas reinhardtii heavy metal cadmium adsorption mutants
InactiveCN106967749ASimple stepsImprove screening efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesCadmium adsorptionChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention discloses a screening method for heavy metal cadmium adsorption mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. The screening method comprises: selecting a suitable screening concentration for heavy metal cadmium adsorption mutants according to the influence of different cadmium chloride concentrations on the growth of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii; Transformation to obtain Chlamydomonas reinhardtii mutants; screening out heavy metal cadmium adsorption mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, the screening of heavy metal cadmium adsorption mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii includes screening heavy metal cadmium sensitive mutants and screening heavy metal cadmium resistant mutants; identification screening Mutant genes of heavy metal cadmium adsorption mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. The invention achieves the technical effect of being able to obtain a large amount of Chlamydomonas heavy metal cadmium adsorption mutants simply and efficiently.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
Method for increasing exogenous gene expression quantity and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production quantity by codon optimization
InactiveCN102146344AHigh expressionLower oxygen levelsUnicellular algaeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention relates to exogenous gene expression and biological hydrogen production technologies, in particular to a method for increasing exogenous gene expression quantity and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production quantity by codon optimization. In the prior art, the expression efficiencies of exogenous leghemoglobin genes hemH and lba in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast are low, thus influencing the increase of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production quantity. The invention discloses a method for respectively optimizing the codon bias of the leghemoglobin genes hemH and lba. The codon-optimized hemHc and lbac genes are transferred into the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast to be expressed. The invention obviously increases the expression quantity of the exogenous recombinant protein; the expression quantity of the exogenous leghemoglobin hemH and Lba in the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast is increased by 6.8 times; and compared with the non-codon-optimized hemH and lba transgenic Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production quantity is increased by 22%. The invention is applicable to regulating and controlling the exogenous gene expression of more species having codon bias.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
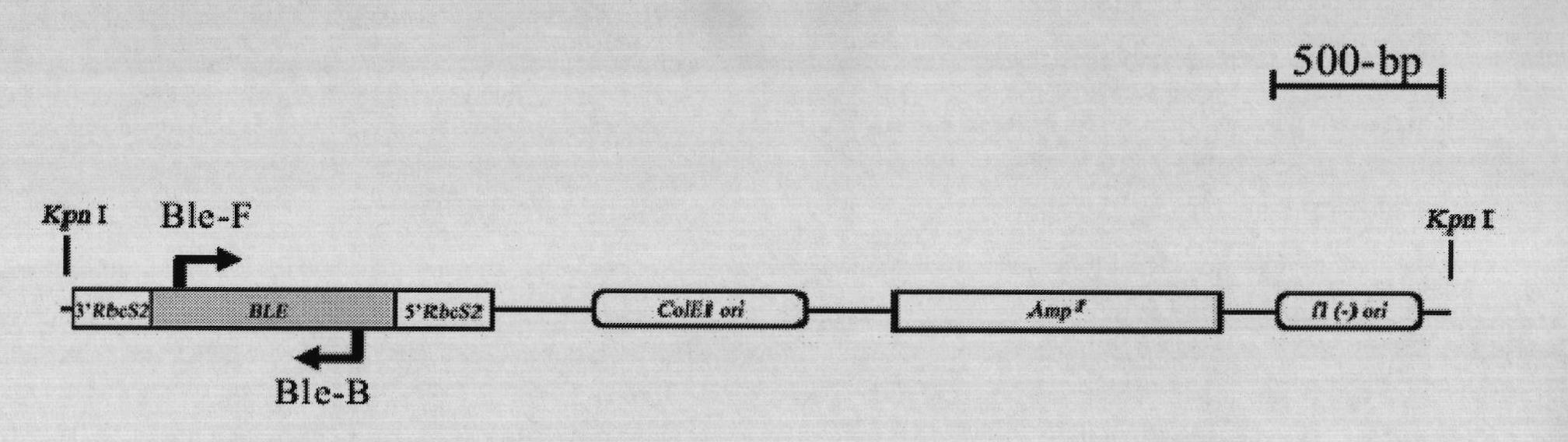
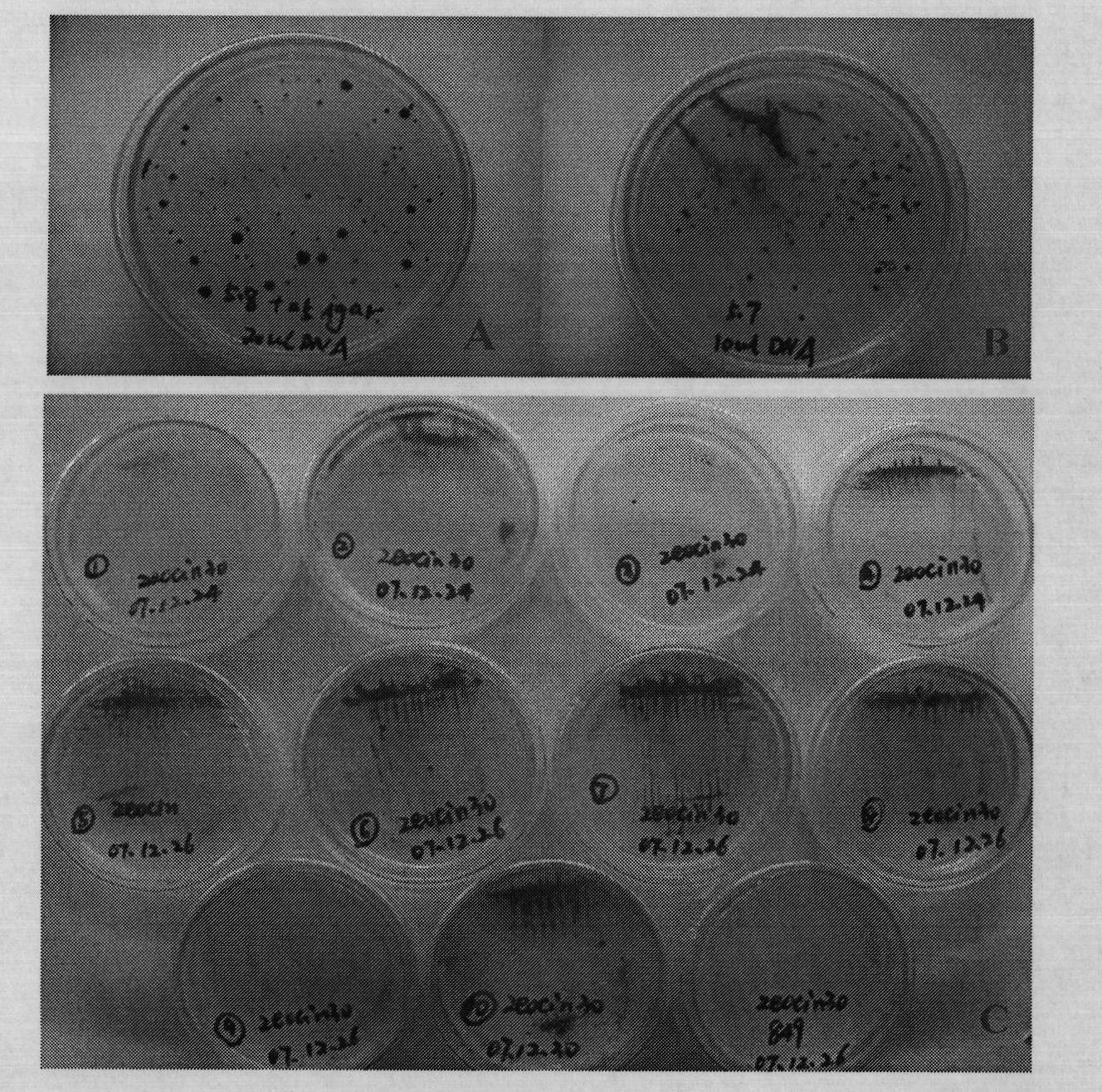
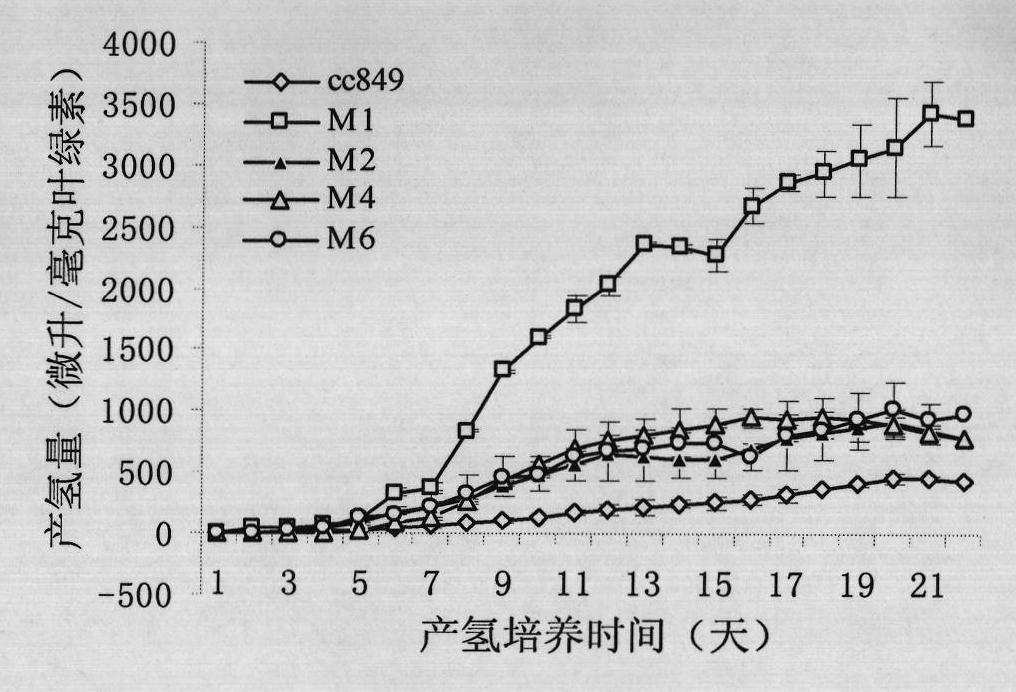
Method for breeding high-yield photosynthetic-hydrogen-production chlamydomonas reinhardtii through cell nucleus insertion mutagenesis
InactiveCN101864365AHigh biohydrogen productionGood experimental materialUnicellular algaeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention relates to a biological hydrogen production technology, in particular to a method for breeding high-yield photosynthetic-hydrogen-production chlamydomonas reinhardtii through cell nucleus insertion mutagenesis. The traditional chlamydomonas reinhardtii has low hydrogen production rate and limits the application and the development of a biological and photosynthetic hydrogen production technology. The method for obtaining a high-hydrogen-production mutant strain through the random insertion mutagenesis of chlamydomonas reinhardtii cell nuclei comprises the following steps: cultivation of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii; preparation of a chlamydomonas reinhardtii cell nucleus transformation vector and a glass bead; chlamydomonas reinhardtii cell nucleus transformation and transformant screening; analysis of the hydrogen yield and the oxygen consumption of chlamydomonas reinhardtii transformant hydrogen-production cultivation; analysis of the integration and the expression thereof of ble genes in a chlamydomonas reinhardtii mutant strain; and analysis of the influence of recombinant leghemoglobin hemH-1ba on the growth of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii. The invention has the advantages that the biological hydrogen production yield of the obtained high-hydrogen-production chlamydomonas reinhardtii is 7 times of the original yield; the method provides a good experimental material and a good basic condition for deeply researching the hydrogen-production metabolic mechanism of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
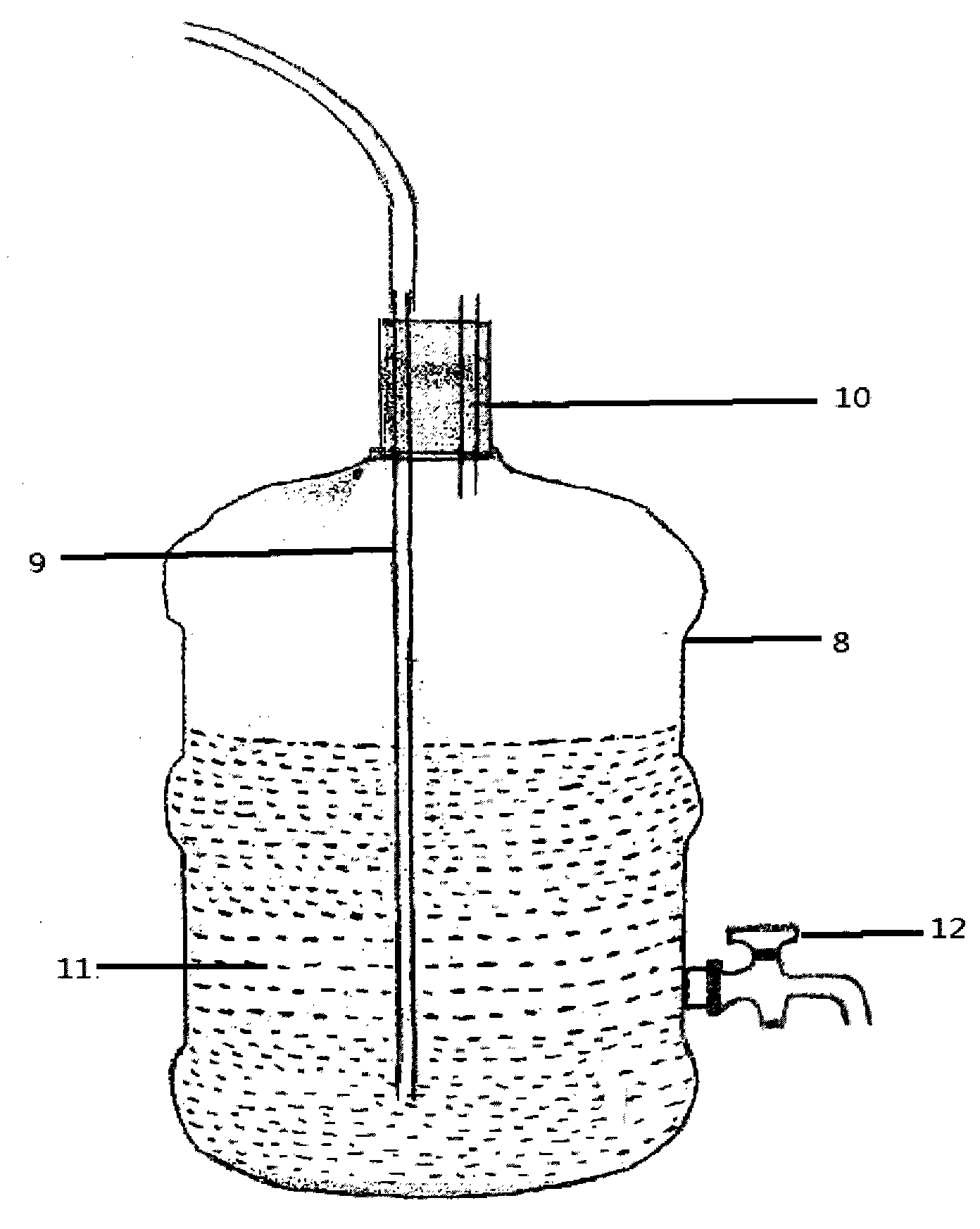
Culture medium for culturing Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by urea plant wastewater and culture method of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
ActiveCN103966102AReduce outputIncrease productionUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesChlamydomonas reinhardtiiArginine
The invention discloses a method for culturing Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by urea plant wastewater. According to the method, urea plant wastewater can be treated in low cost, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with important economic value can also be obtained, the waste is changed into treasures, harm is turned into a good and many things are achieved at one stroke. A traditional method for culturing Chlamydomonas reinhardtii comprises the step of culturing Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in an open concrete runway pool by virtue of a TAP culture medium, and has the disadvantages of low growth speed, low output, great investment, easy pollution and low efficiency. According to the invention, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is cultured in a household mineral water bucket to achieve the advantages of low cost, small possibility of pollution, convenience in cleaning, reutilization and convenience in operation; since nutritional ingredients, such as urea plant wastewater, yeast extract powder, sodium deoxycholate, sorbitol, mannitol, sodium thioglycolate, soil extract liquid, sheep manure leachate, chicken manure leachate, L-arginine, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, yeast extract, and diatomite powder are added into the culture medium, and an organic fertilizer is used in combination with an inorganic fertilizer, nutrition is more comprehensive and balanced, the growth rate and yield of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are substantially increased and the yield is increased by 280%.
Owner:江西赣兴气体有限公司
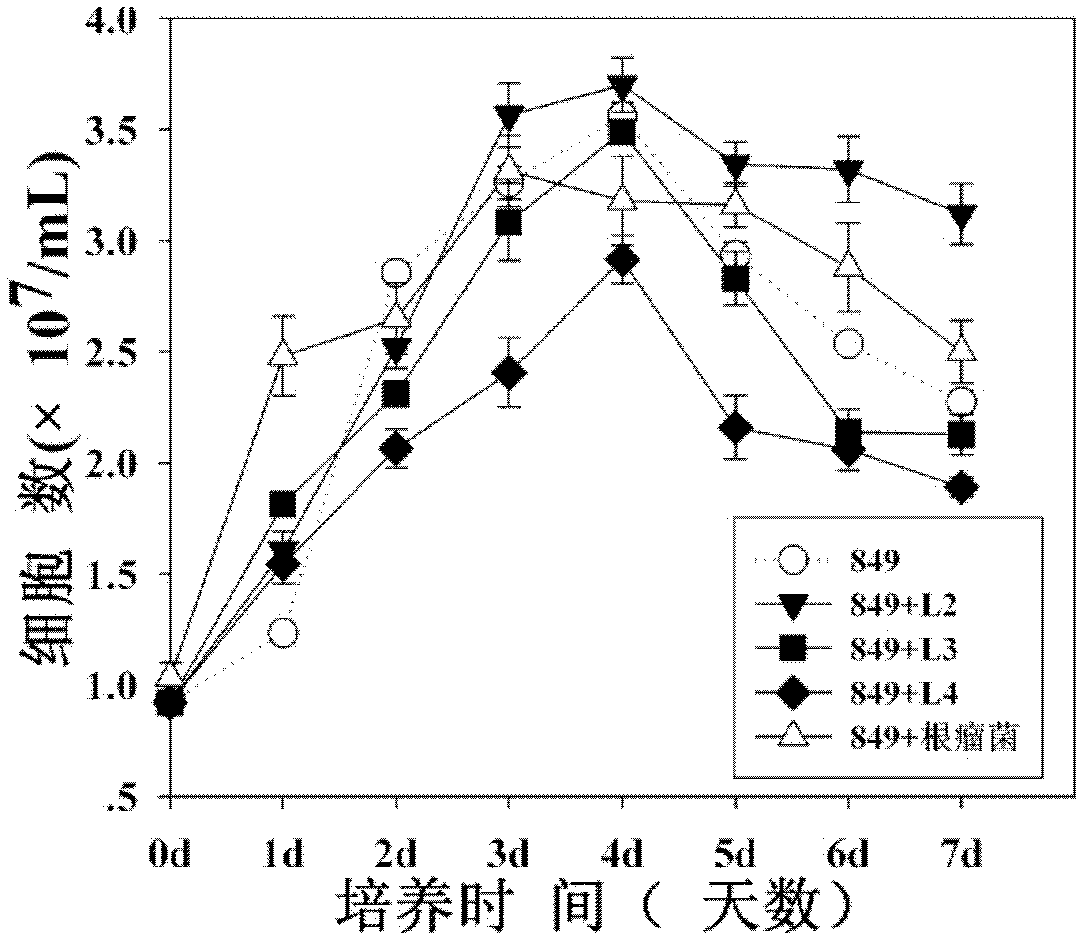
Method for com-culturing and improving hydrogen output by utilizing bacteria and chlamydomonas reinhardtii
InactiveCN102559832AIncrease hydrogen productionReduce the greenhouse effectMicroorganism based processesFermentationChlamydomonas reinhardtiiBradyrhizobium japonicum
The invention relates to a biological hydrogen production technology, in particular to a method for com-culturing and improving hydrogen output by utilizing bacteria and chlamyodomonas reinhardtii. Through mixing aerobic bacteria represented by bradyrhizobium japonicum with the chlamydomonas reinhardtii according to a certain proportion for culture, the hydrogen output can be remarkably improved. The invention provides a new method for further improving the hydrogen output in a chlamydomonas reinhardtii twp-step-method hydrogen production technology.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
Method for improving yield of chlamydomonas reinhardtii biological hydrogen production through soybean hemoglobin genes
InactiveCN101845461AIncrease hydrogen productionUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesChlamydomonas reinhardtiiChloroplast
The invention belongs to a biological hydrogen production technology, particularly to a method for improving the yield of chlamydomonas reinhardtii biological hydrogen production through soybean hemoglobin genes. Traditional chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production has the disadvantages that chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogenase is sensitive to oxygen and is easily inhabited by the oxygen to inactivate; and the hydrogen production effect of chlamydomonas is limited. The invention discloses application of soybean hemoglobin globulin subunit genes in chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production, the soybean hemoglobin globulin subunit genes lba are constructed in a chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast expression vector, and the expression vector is transformed into chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast, so that the lba genes are expressed in the chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast. The decrease of the oxygen content in a closed culture system of the transformed chlamydomonas reinhardtii is markedly quicker than that of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii of the untransformed genes, the oxygen content can be kept at a lower level, and the hydrogen yield is markedly increased; the method is applicable for all microalgae for hydrogen production.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
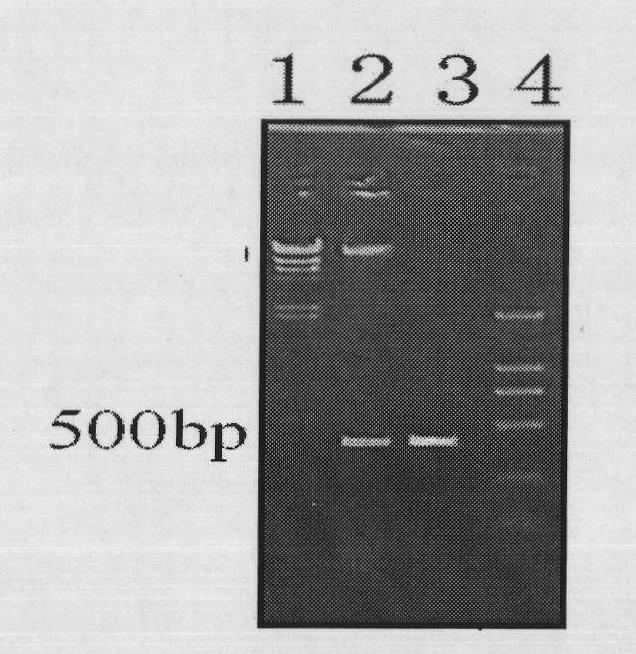
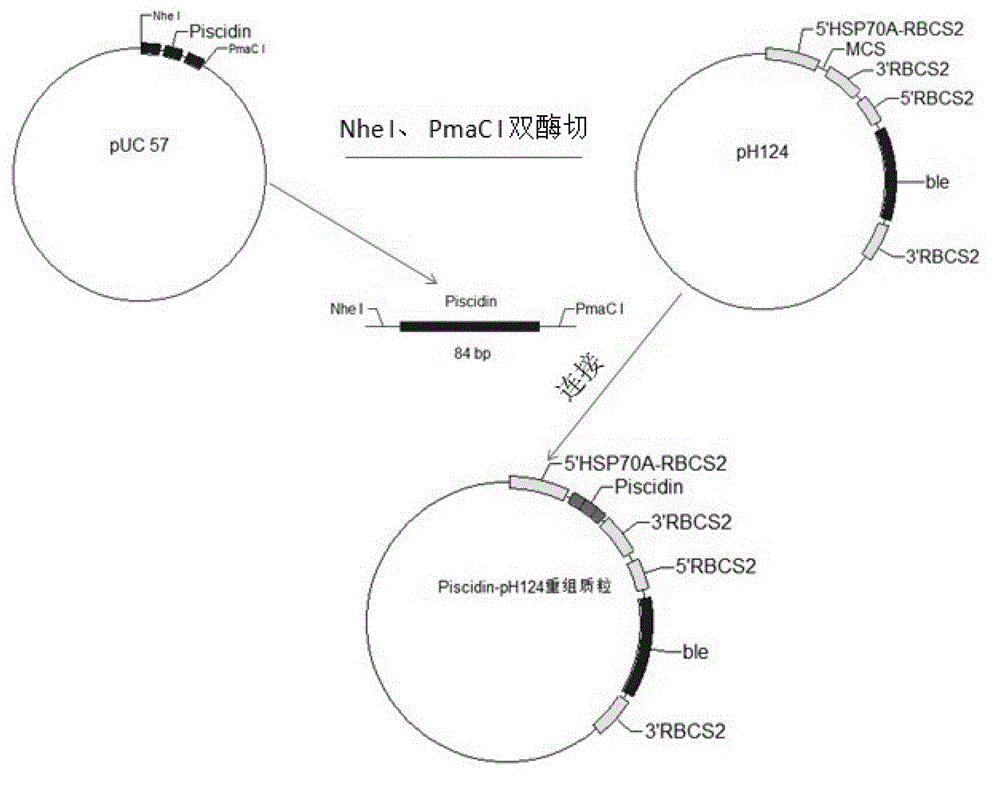
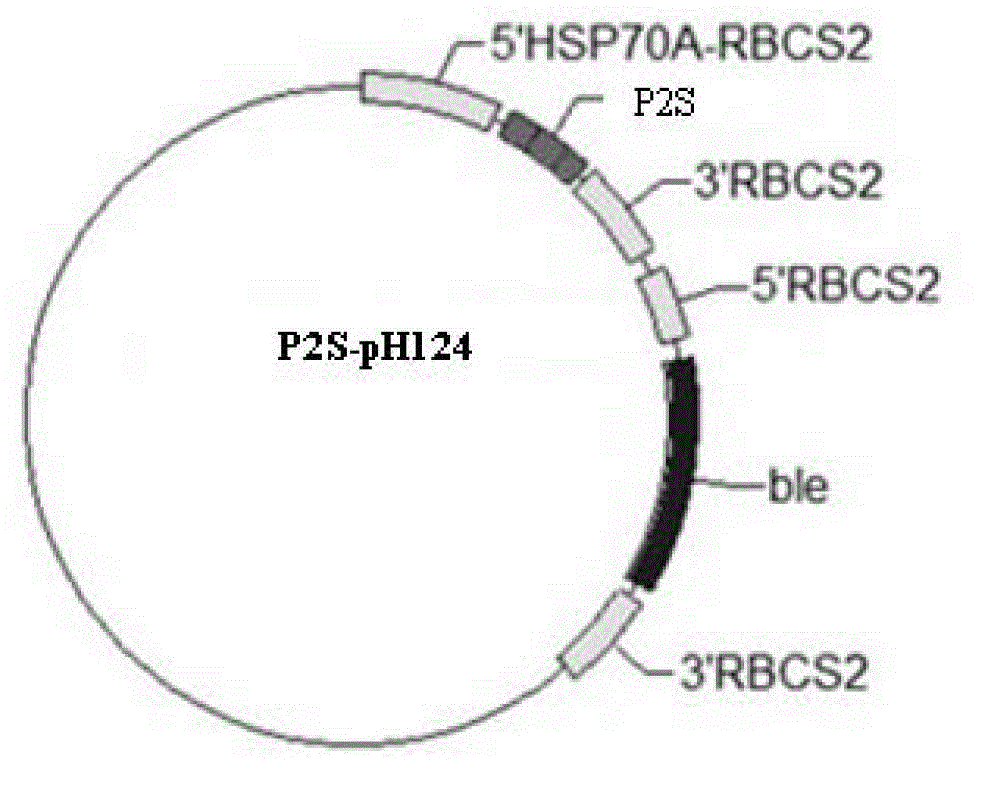
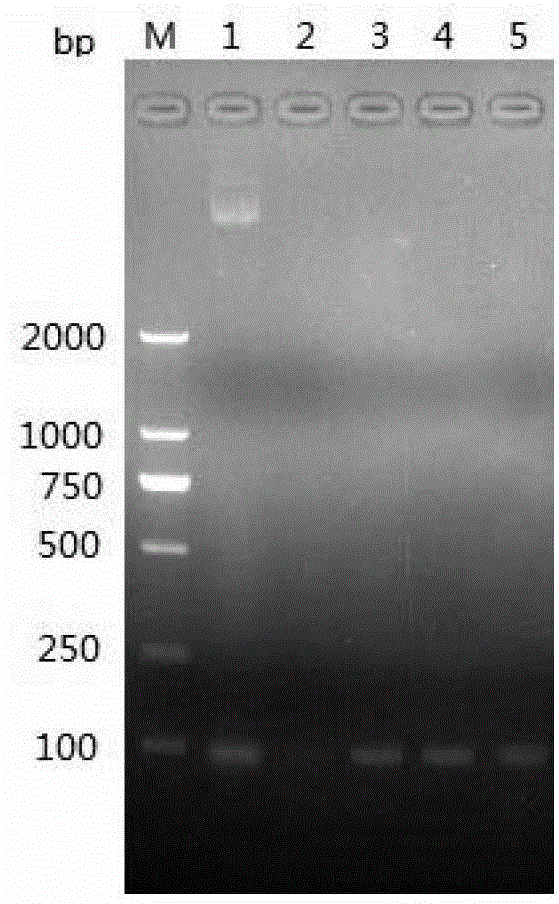
Constructing method and application of transgenic chlamydomonas reinhardtii for expressing epinephelus antibacterial peptide piscidin
The invention provides a constructing method and application of transgenic chlamydomonas reinhardtii for expressing epinephelus antibacterial peptide piscidin, provides an epinephelus antibacterial peptide piscidin gene with an optimized chlamydomonas reinhardtii codon, a carrier with the gene and a transformant and also provides an application of the epinephelus antibacterial peptide piscidin gene with the optimized chlamydomonas reinhardtii codon in the preparation of the transgenic chlamydomonas reinhardtii.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii efficient library building method using square wave electroporation
ActiveCN105543281AIncrease the number ofSuitable for buildUnicellular algaeStable introduction of DNASquare waveformChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention discloses a chlamydomonas reinhardtii efficient library building method using square wave electroporation. The method includes the following steps that chlamydomonas reinhardtii is continuously illuminated at 23+ / -0.5 DEG C in a TAP fluid medium, subjected to aerobic culture at 8000 Lx light intensity and then cultured and treated after being transferred, resistance DNA fragments are transformed through square wave electroporation, resistance DNA is randomly integrated into chlamydomonas reinhardtii chromosomes, a resistance screening plate is coated with a product obtained after overnight low light recovery, and a mutant library causing random insertion mutation is obtained after culture of a light period lasting 7 days. The method has the advantage that a large number of randomly-inserted transformants can be efficiently obtained to build the chlamydomonas reinhardtii mutant library.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for improving hydrogen production of chlamydomonas
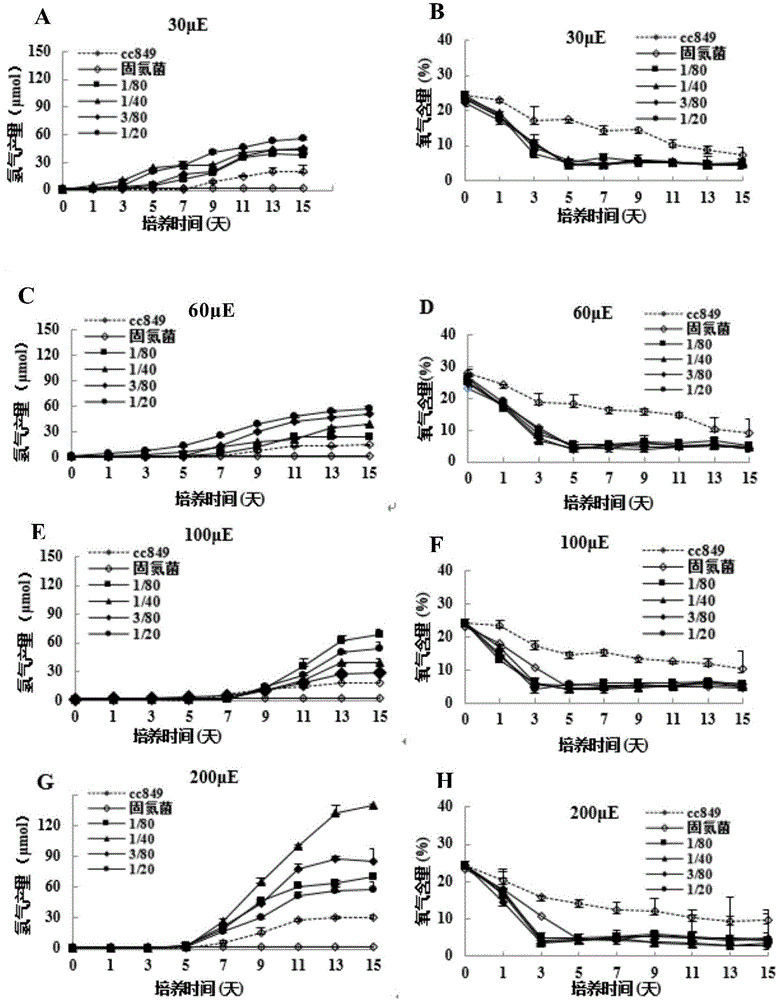
ActiveCN106520897ABroaden the range of symbiotic objectsPromote growthMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention discloses a method for improving hydrogen production of chlamydomonas. The method includes steps of commonly cultivating chlamydomonas and nitrogen-fixing bacteria; before commonly cultivating, cultivating chlamydomonas to a saturated period and cultivating nitrogen-fixing bacteria to a logarithmic phase, wherein the nitrogen-fixing bacteria is round brown nitrogen-fixing bacteria; the chlamydomonas is Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cc849 (with cell wall type) and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cc124 (cell wall defective type). The method can effectively improve the hydrogen production of chlamydomonas; in relative to the hydrogen production of independent chlamydomonas, the maximum hydrogen production can be improved by 16 times.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
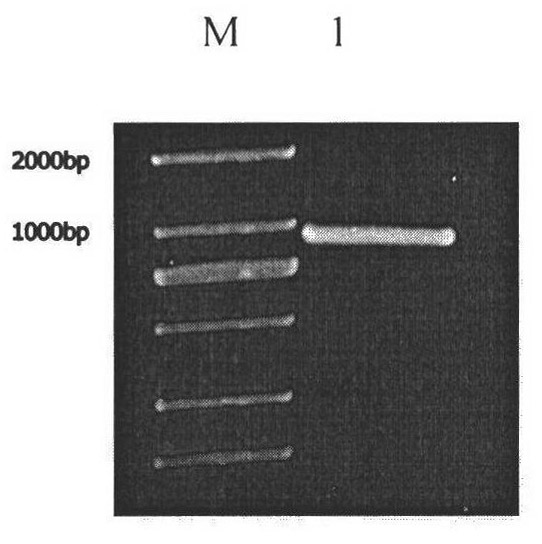
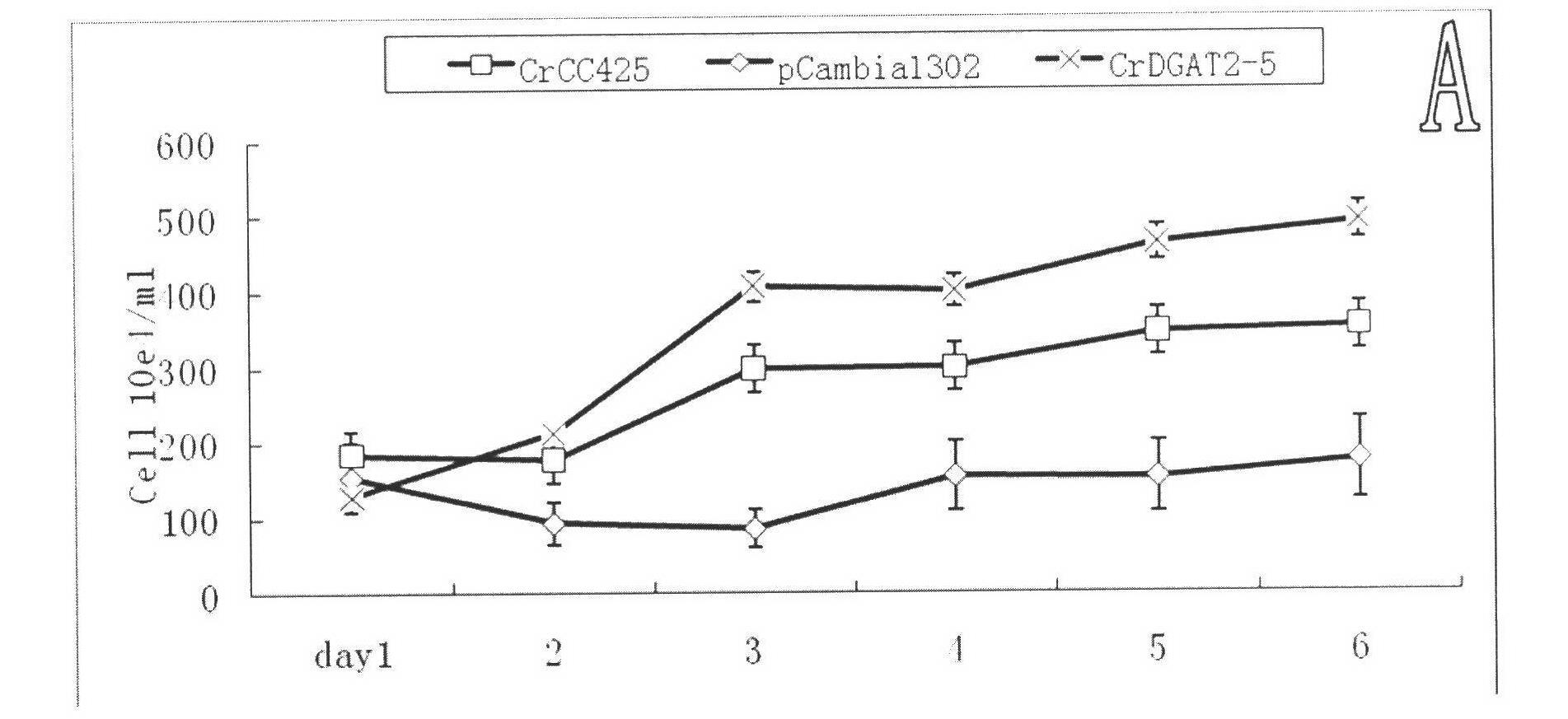
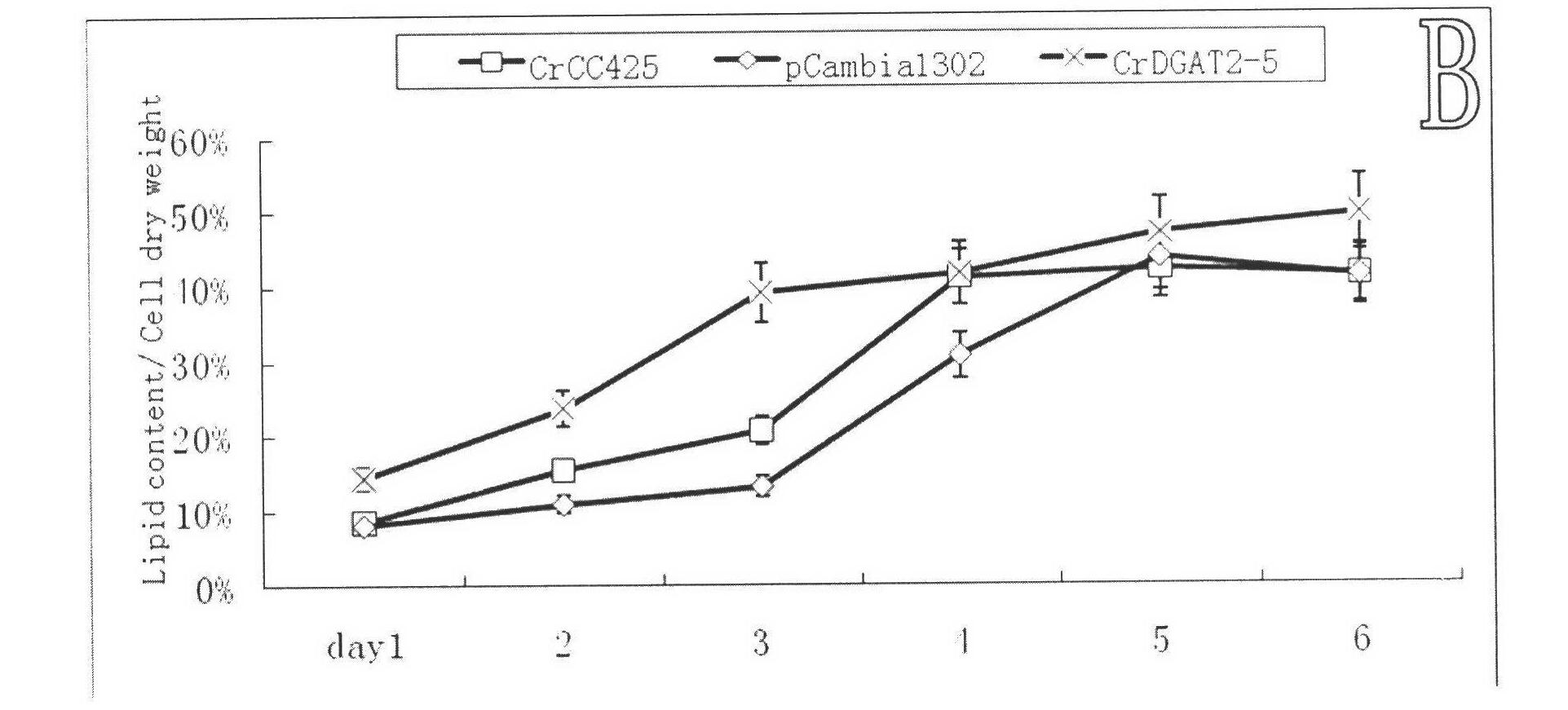
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii lipid metabolism gene CrDGAT2-5, encoding protein thereof, and application thereof
InactiveCN102321642AHigh oil contentImprove qualityTransferasesFermentationChlamydomonas reinhardtiiNucleotide
The invention relates to a chlamydomonas reinhardtii lipid metabolism gene CrDGAT2-5 (Chlamydomonas reinhardtii diacylgycerol acyltransferase2-5), an encoding protein thereof, and an application thereof. The chlamydomonas reinhardtii lipid metabolism gene CrDGAT2-5 is obtained from cDNA amplification with an au.g4218_t1 gene disclosed by JGI chlamydomonas reinhardtii gene database as a template. The sequence of the nucleotide is represented by SEQ ID NO:1. The protein sequence of CrDGAT2-5 encoding protein is conjectured from the base sequence of CrDGAT2-5, and the protein has an amino acid residue sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:2. The gene can be used in chlamydomonas reinhardtii plant expression, and assists in substantially improving the neutral lipid content and the biomass of chlamydomonas reinhardtii. According to the invention, the au.g4218_t1 gene disclosed by JGI chlamydomonas reinhardtii gene database is adopted as the template, and cDNA amplification is carried out, such that the chlamydomonas reinhardtii lipid metabolism gene CrDGAT2-5 is obtained. When used in chlamydomonas reinhardtii plant expression, the gene assists in substantially improving the neutral lipid content and the biomass of chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Therefore, the invention has a great significance in the improving of microalgae oil content and quality.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
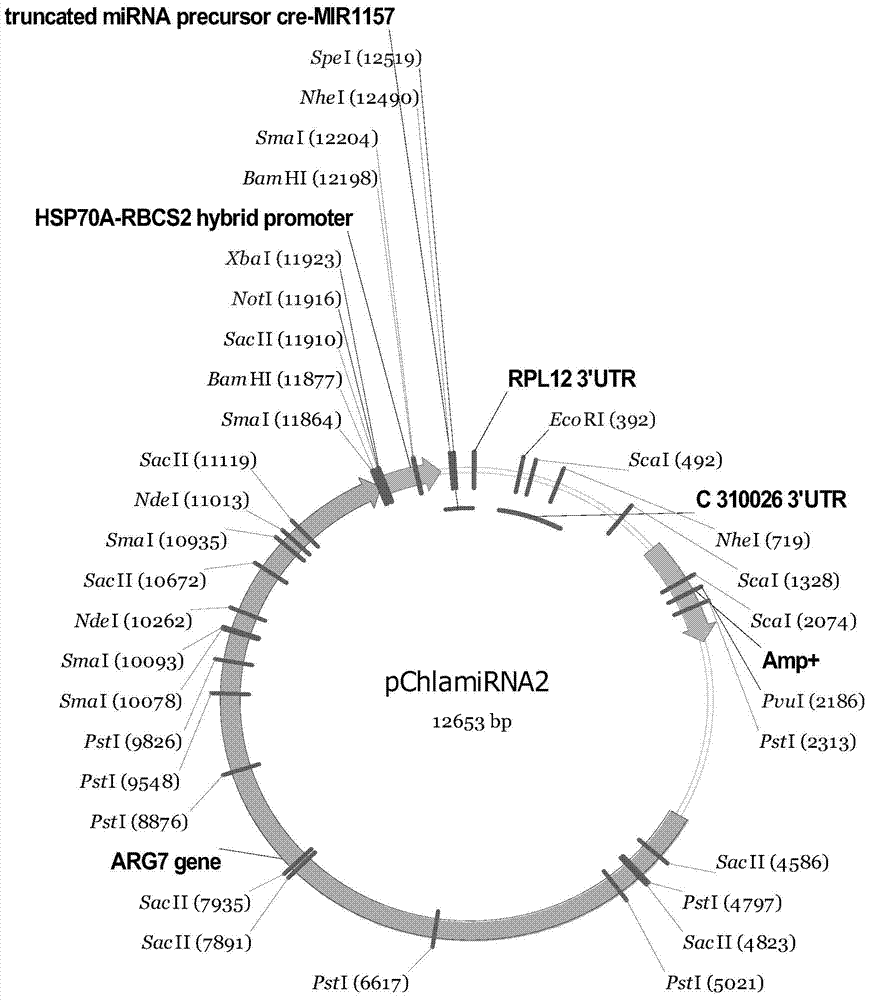
Gene and protein related to lipid metabolism pathway of chlamydomonas reinhardtii, protein, gene mutation strains and applications thereof
The invention discloses gene and protein related to lipid metabolism pathway of chlamydomonas reinhardtii, protein, gene mutation strains and applications thereof. According to the invention, silent treatment is carried out respectively on the two genes by designing microRNA(AT-mic and TAGLP-mic) corresponding to the two genes AT and TAGLP, and silent mutation strains (AT-CR and TAGLP-CR) of the AT and TAGLP genes of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii are obtained; by determination on the contents of neutral lipids and the total contents of lipids of the mutation strains, the contents of the neutral lipids of the mutation strains AT-CR and TAGLP-CR are respectively increased by 14.73% and 13.18% as compared with the wild type, and the contents of the total lipids of the mutation strains AT-CR and TAGLP-CR are respectively increased by 76.97% and 102.03% as compared with the wild type; the invention plays an important role in extracting the contents of the lipids from the chlamydomonas reinhardtii, and is wide in application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
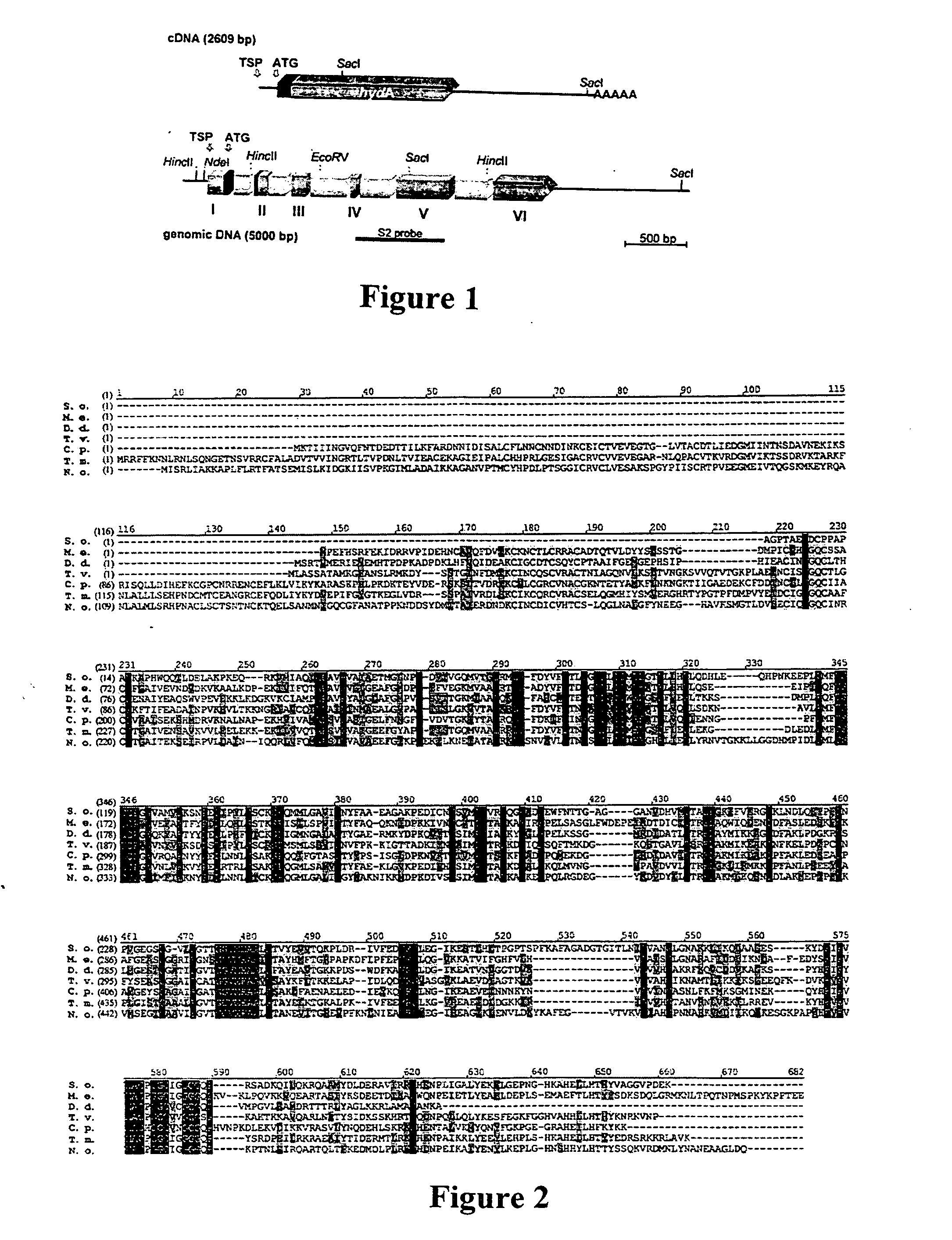
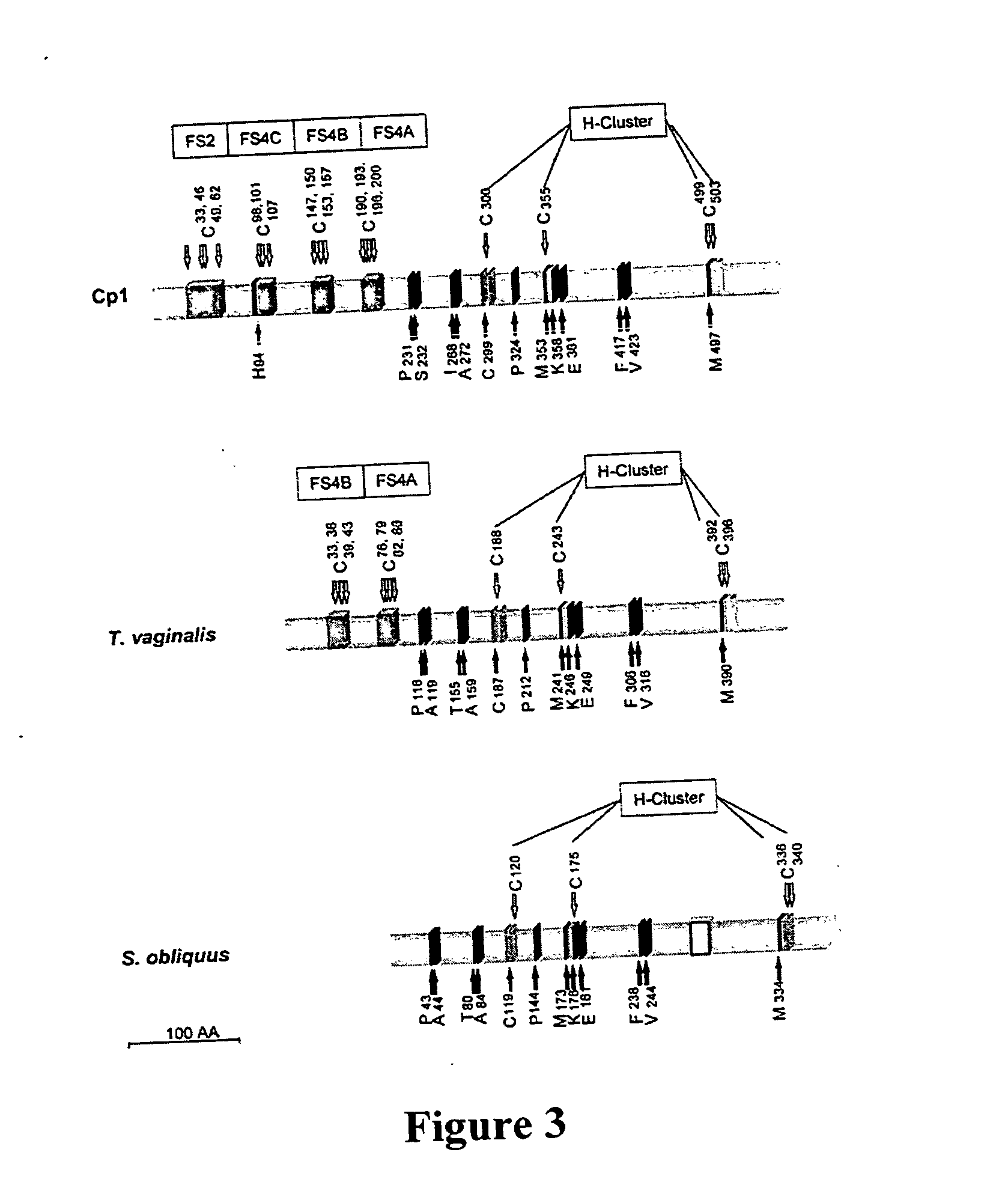
Hydrogen production
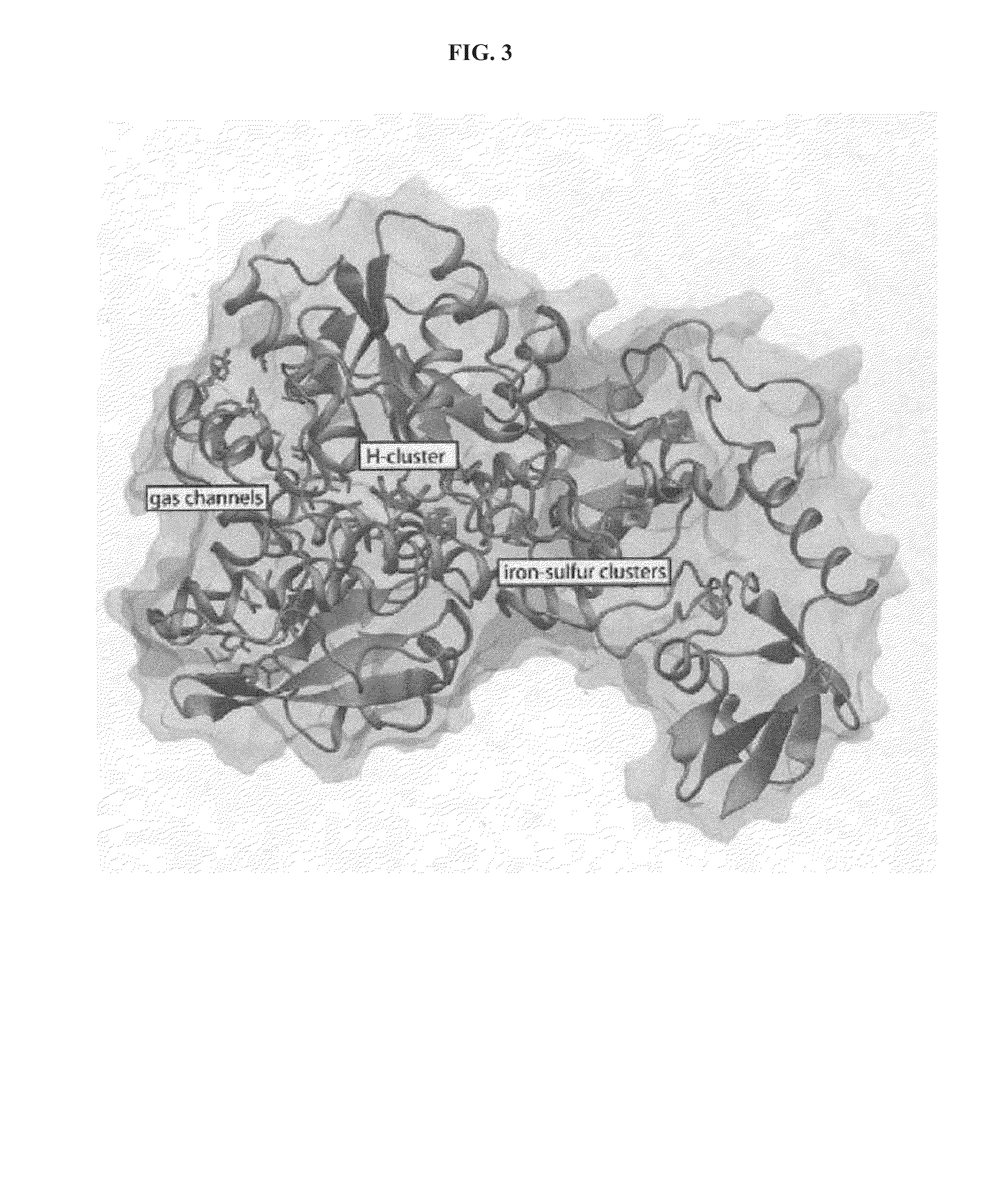
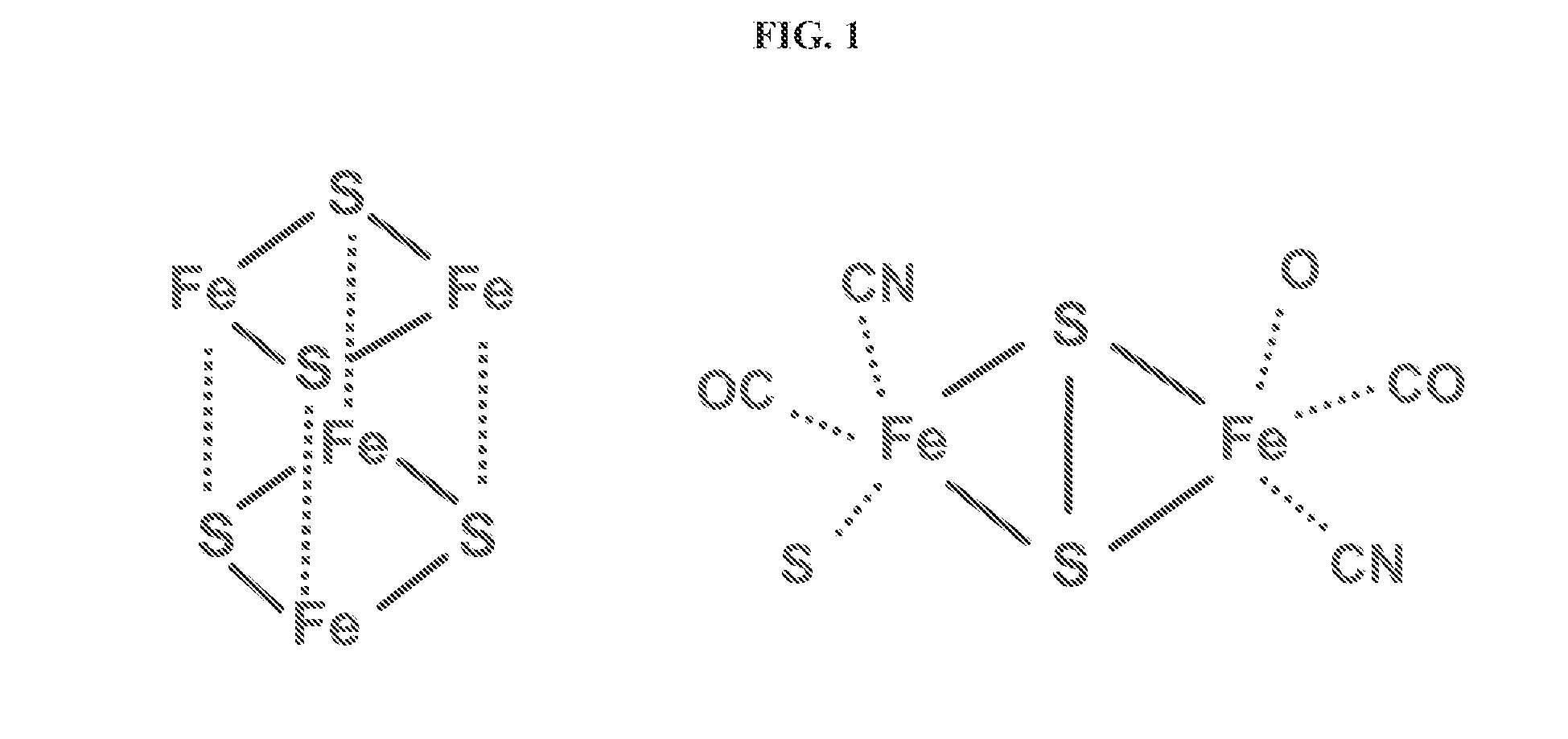
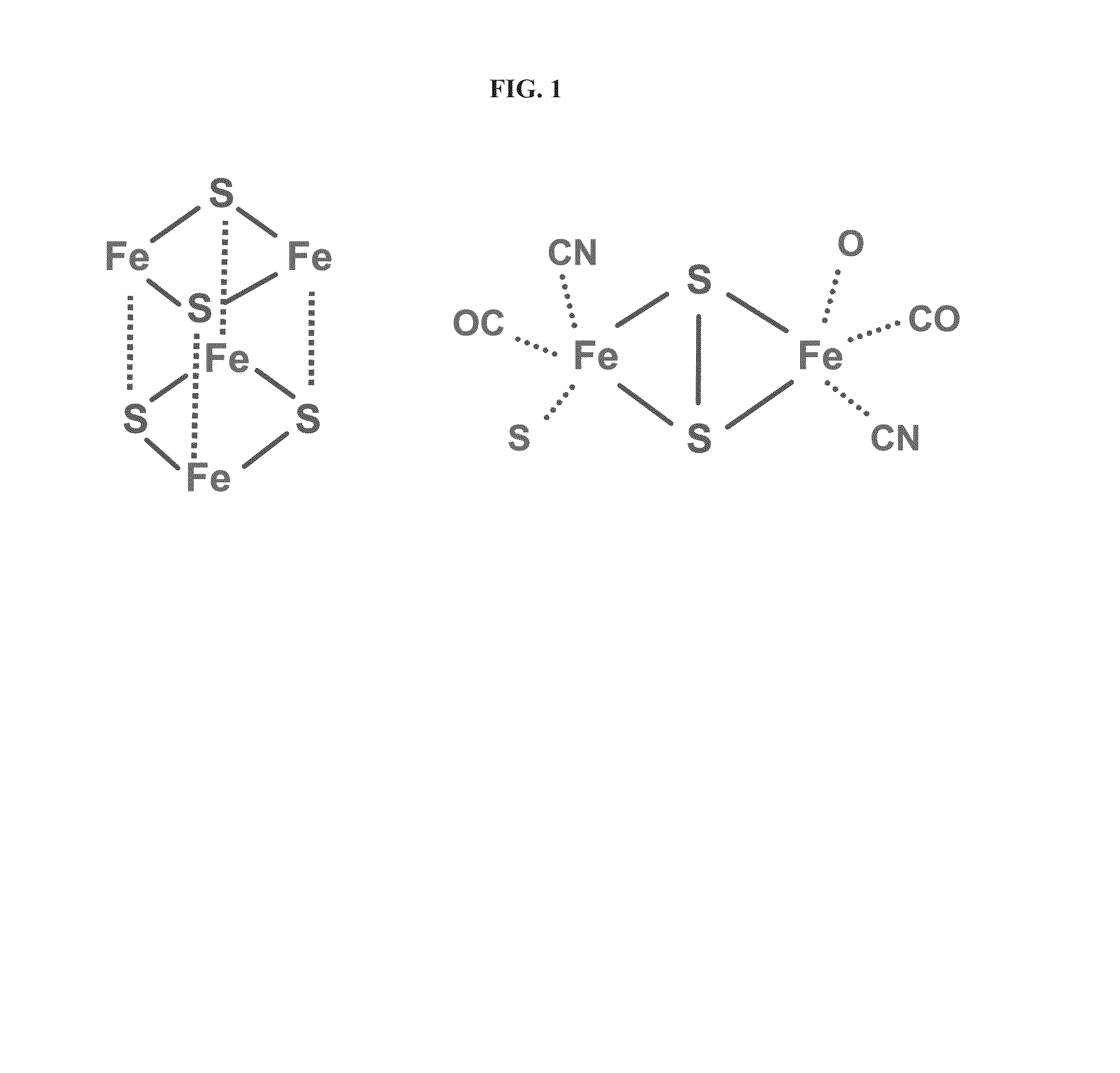
The enzyme, iron hydrogenase (HydA), has industrial applications for the production of hydrogen, specifically, for catalyzing the reversible reduction of protons to molecular hydrogen. The present invention relates to the isolation of a nucleic acid sequence from the algae Scenedesmus obliquus, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and Chlorella fusca that encodes iron hydrogenase. The invention further discloses the genomic nucleic acid, c-DNA and the protein sequences for HydA. The genes and gene products may be used in a photosynthetic process for hydrogen production which includes growing a microorganism containing the gene coding for HydA in a culture medium under illuminated conditions sufficient to accumulate an endogenous substrate; depleting a nutrient selected from the group consisting of sulfur, iron, and manganese from the medium; then allowing the culture to become anaerobic by consumption of an endogenous or exogenous substrate in the light.
Owner:HAPPE THOMAS
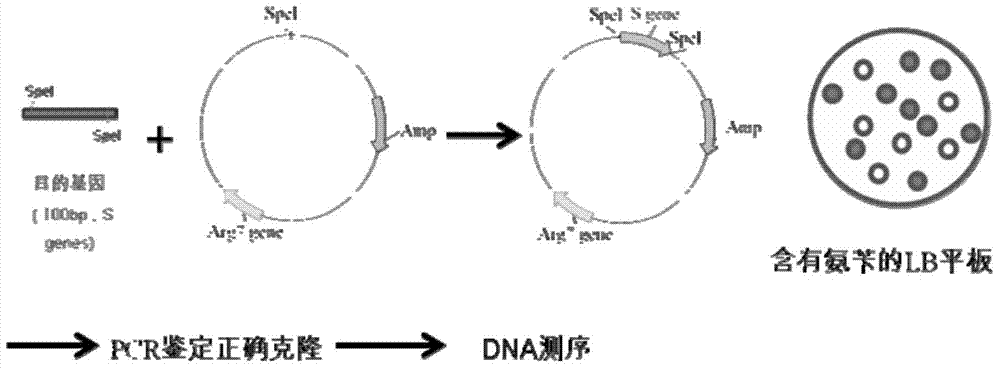
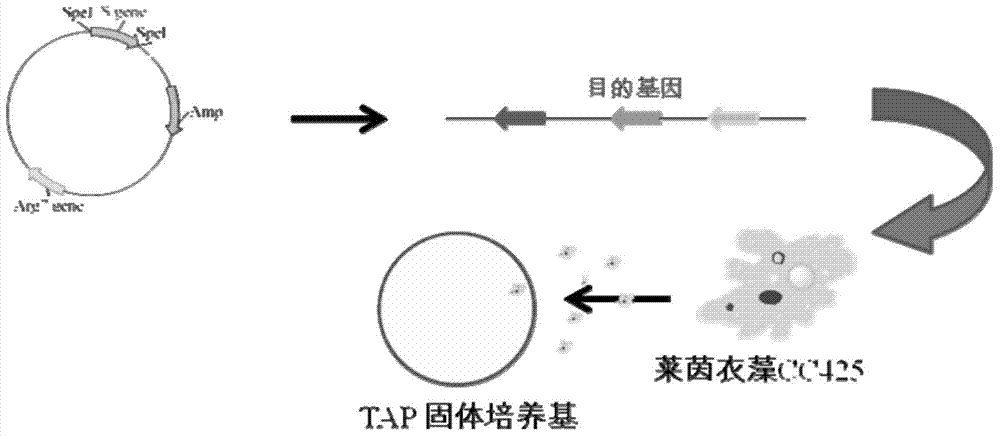
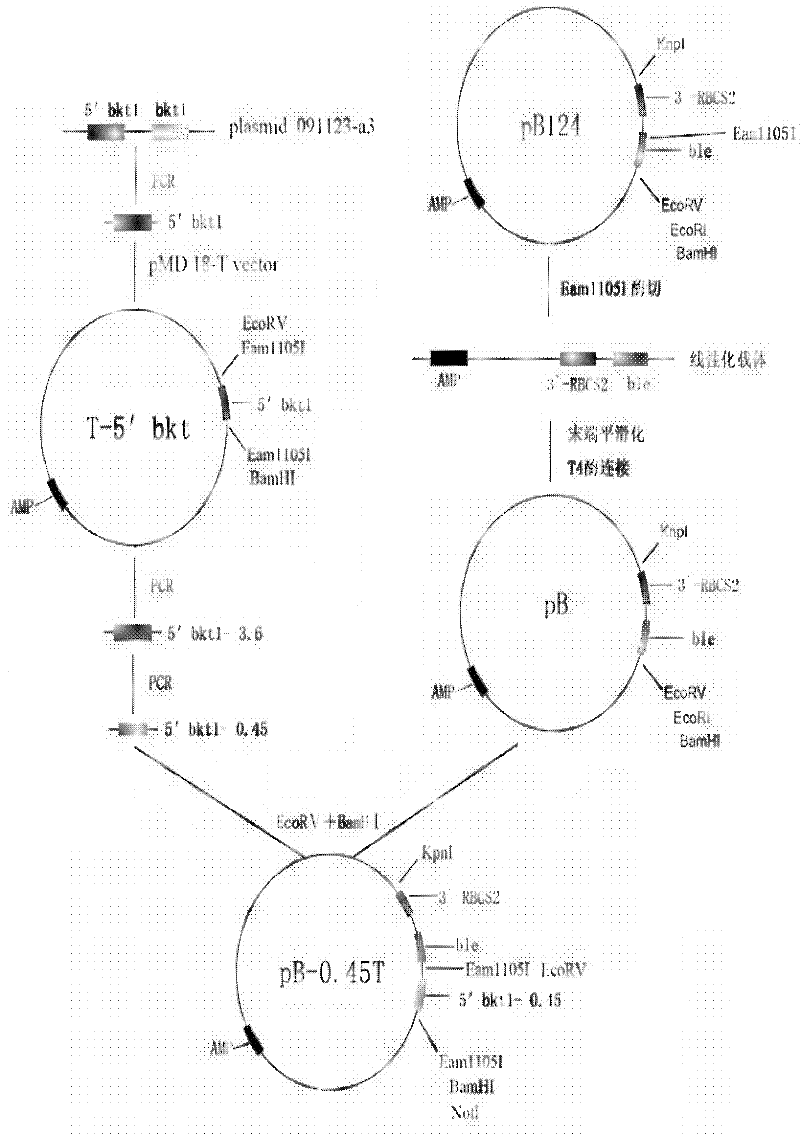
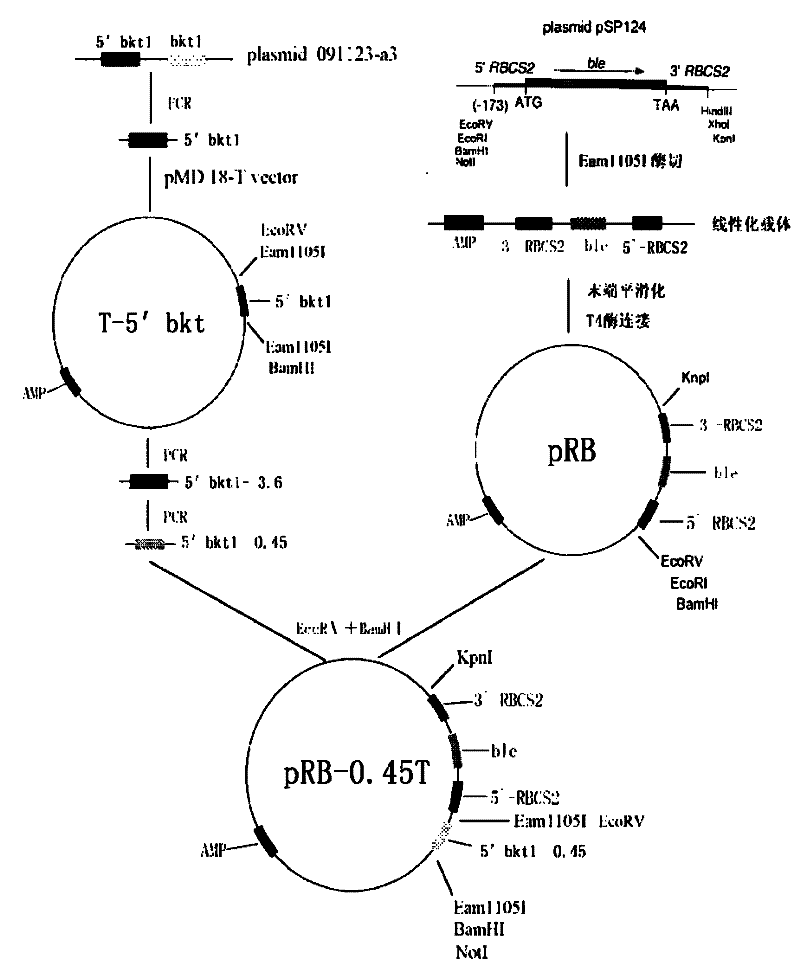
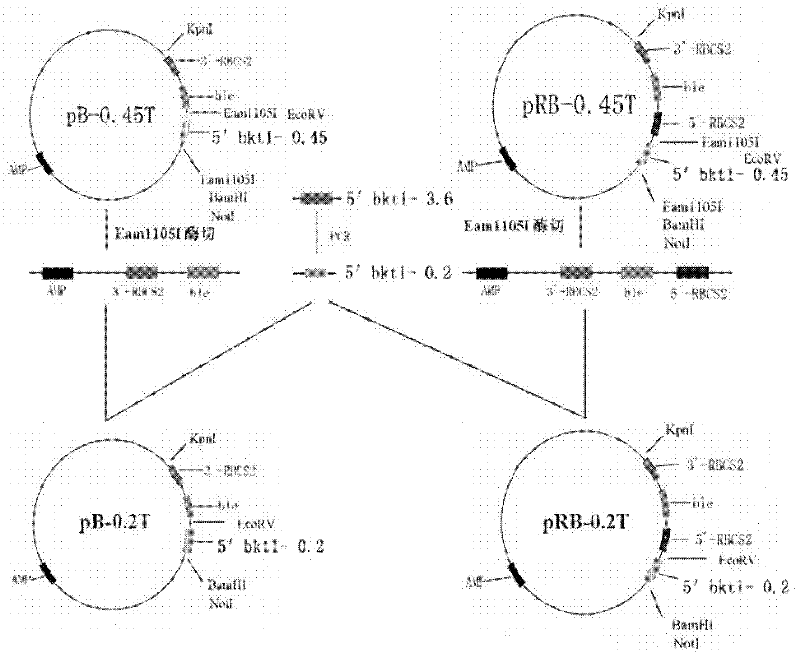
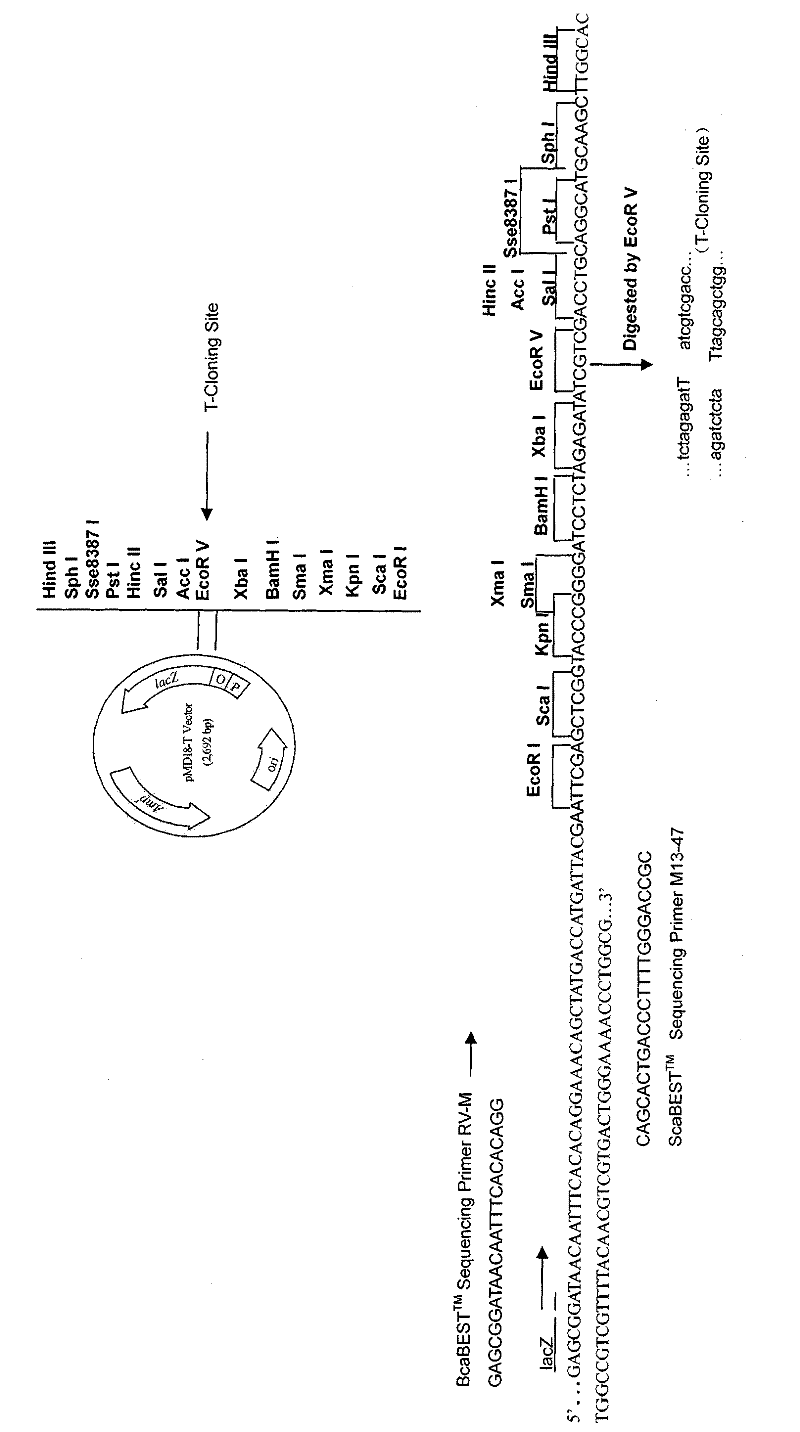
Preparation method of T vector capable of cloning microalgae promoter and application thereof
InactiveCN102399811AMature construction technologySimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingEnzyme digestionAgricultural science
The invention discloses a preparation method of a T vector capable of cloning a microalgae promoter and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: obtaining a spacer sequence by undergoing a PCR (polymerase chain reaction), and introducing a restriction enzyme recognition site; connecting the spacer sequence to a pSP124 vector with a mutated Eam1105I site, and constructing a pre-T vector respectively; introducing a ble gene to be served as a screening gene; performing enzyme digestion, electrophoretic separation and rubber cutting recovering to obtain a T vector, connecting a microalgae promoter fragment to an Eam1105I enzyme digestion site; and connecting the microalgae promoter to obtain a complete expression cassette, wherein the expression cassette consists of a promoter, an expression gene and a terminator. The invention further discloses application of the T vector capable of cloning the microalgae promoter to detecting the function of the microalgae promoter. The method is easy, and the technology is mature and reliable. The microalgae promoter is cloned rapidly by using the vector, and the function of the promoter is verified in chlamydomonas reinhardtii; and the T vector becomes a beneficial tool for research personnel of microalgae gene engineering.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Culture medium for improving hydrogen production amount of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, and its preparation method
ActiveCN102925490AReduce compositionEasy to removeMicroorganism based processesFermentationAcetic acidChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention discloses a culture medium for improving the hydrogen production amount of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, and its preparation method. The culture medium provided by the invention is composed of NH4Cl, MgCl2.6H2O, K2HPO4, KH2PO4, a Tris base, H3BO4, ZnCl2, MnCl2.4H2O, CoCl2.6H2O, CuCl2.2H2O, (NH4)6Mo7O24.4H2O, FeCl2.4H2O and glacial acetic acid. Experiments in the invention prove that the hydrogen production amount of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in the sulfur-lack and calcium-lack TAP culture solution is about 2 / 3 higher than the hydrogen production amount of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in present sulfur-lack systems after optimizing the formulas of present hydrogen desorption culture mediums (sulfur-lack TAP culture solutions), and a culture medium component is omitted, so the cost is reduced.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
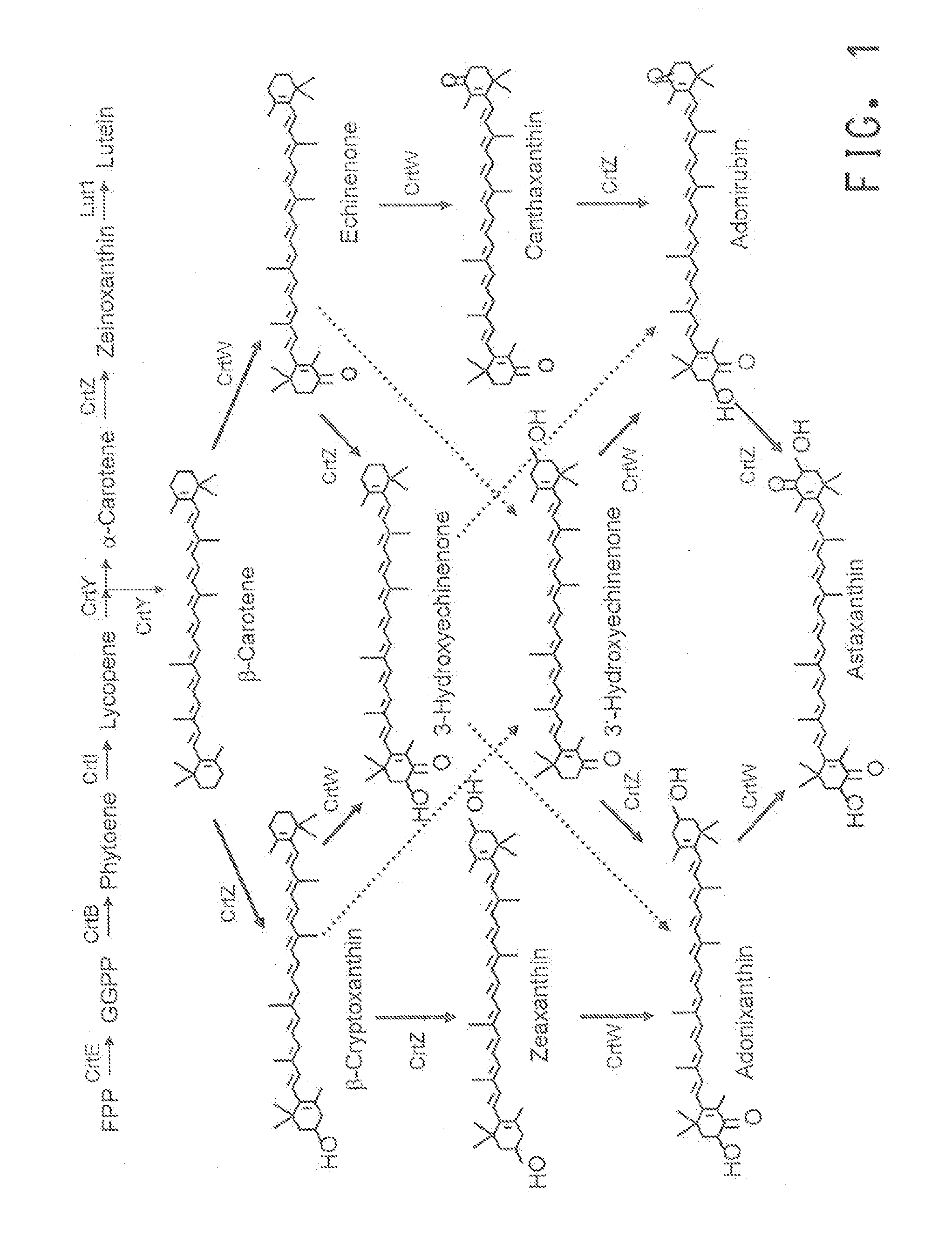
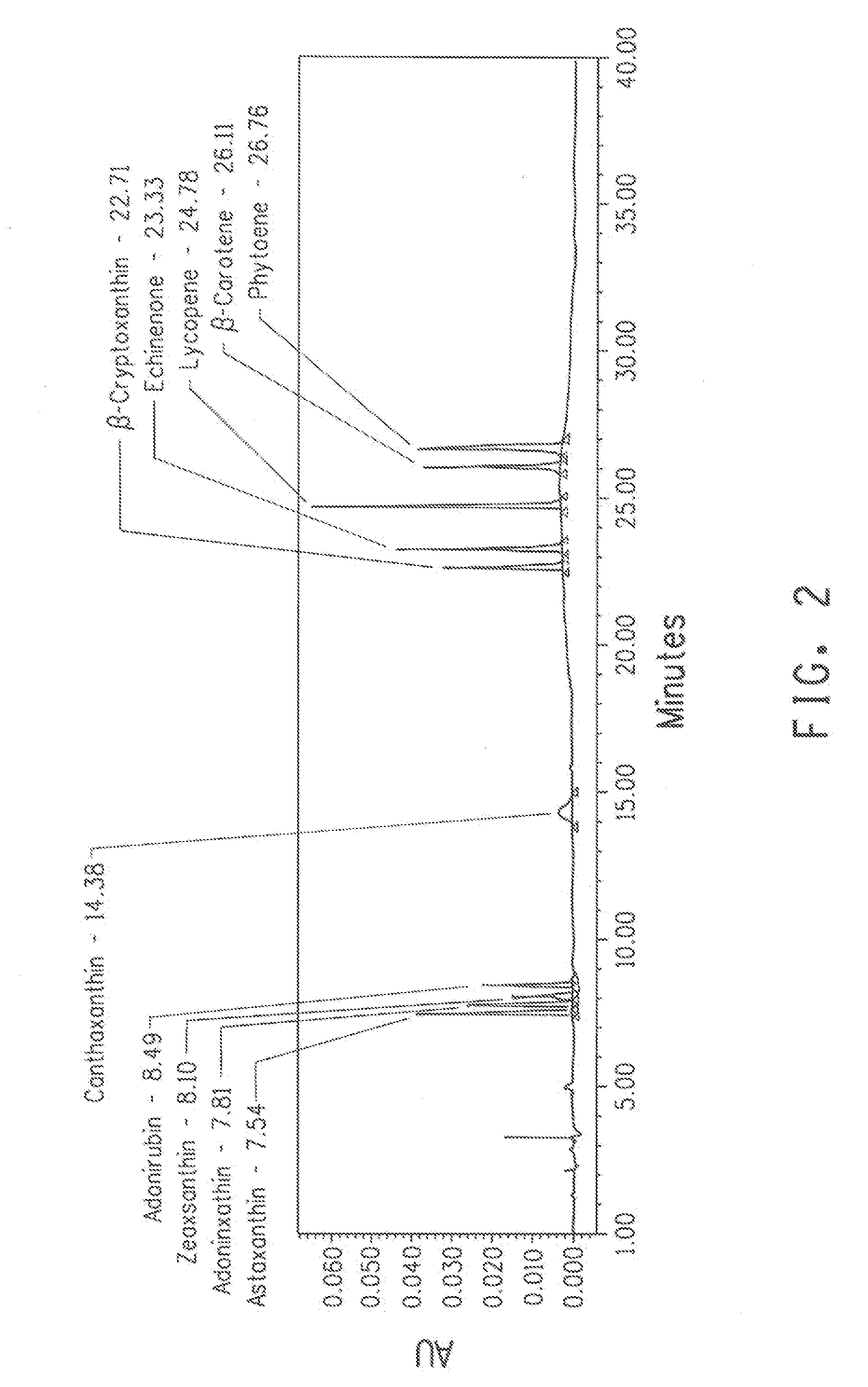
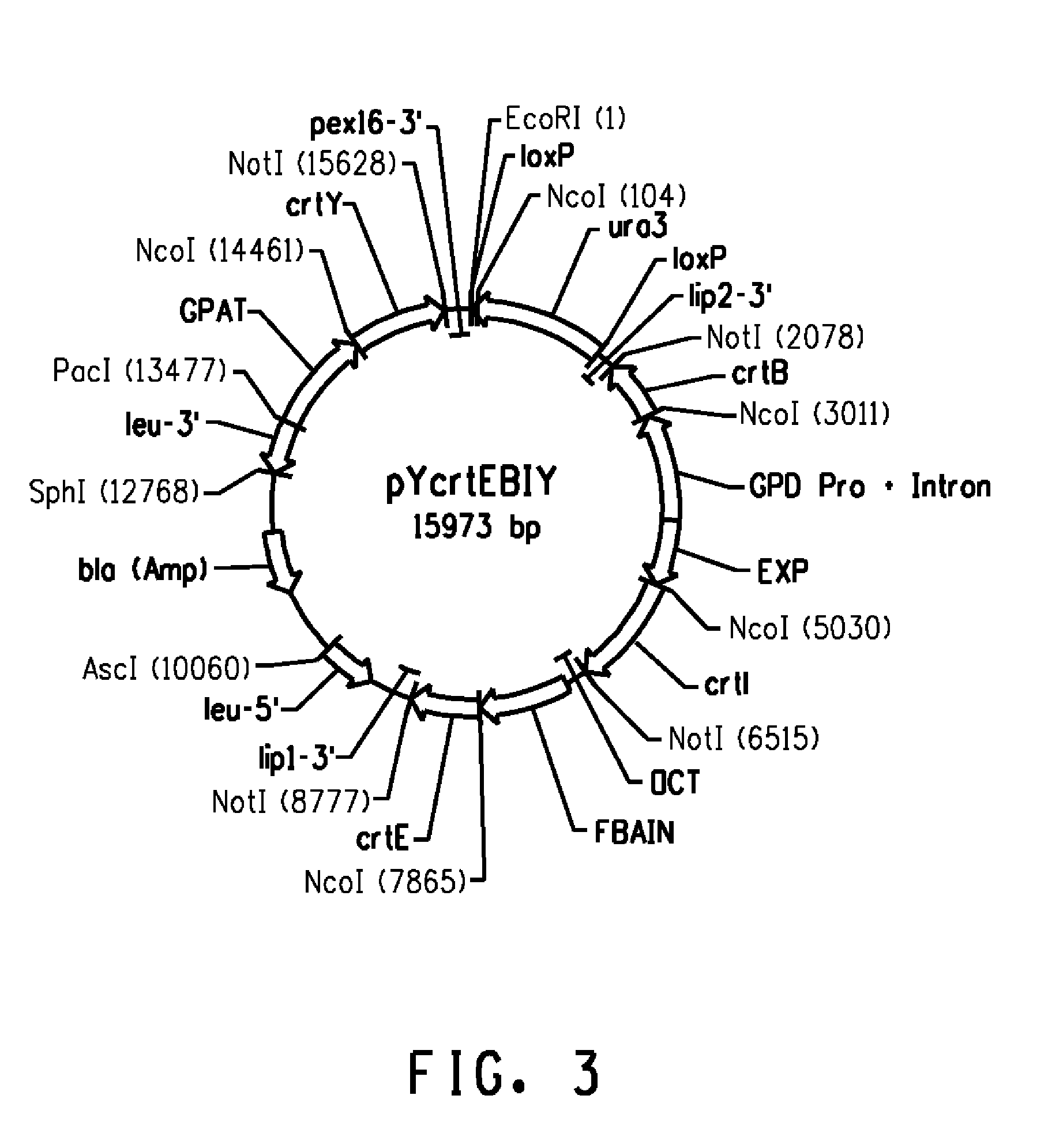
Astaxanthin production using a recombinant microbial host cell
A recombinant microbial host cell is provided capable of producing astaxanthin from β-carotene without a measurable concomitant accumulation of ketolated or hydroxylated intermediates such as adonixanthin, zeaxanthin, adonirubin, echinenone, 3-hydroxyechinenone, 3′-hydroxyechinenone, canthaxanthin, and β-cryptoxanthin. Specifically, a β-carotene producing microbial host cell was engineered to express two heterologous genes, a β-carotene ketolase from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in combination with a carotenoid hydroxylase from Brevundimonas vesicularis or Arabidopsis thaliana.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for knocking out target gene of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
InactiveCN102229940AFirmly connectedQuick connectionVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationRestriction Enzyme Cut SiteChlamydomonas reinhardtii
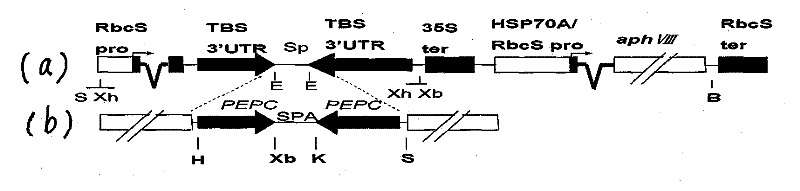
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering and in particular relates to a method for knocking out a target gene of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. The method comprises the following step of constructing a vector pMCS-SPA-MCS and a vector pTSBIR-XIR. According to the invention, the purpose of silencing the target gene of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is achieved by screening a transformant which exerts a silencing effect on the candidate gene, utilizing the restriction enzyme cutting sites of the vector pMCS-SPA-MCS and constructing a vector pXF-SPA-XR to construct the vector pTSBIR-XIR for the target gene RNAi. The method has the characteristics of increasing the efficiency of knocking out the target gene and being convenient to operate and rapid.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
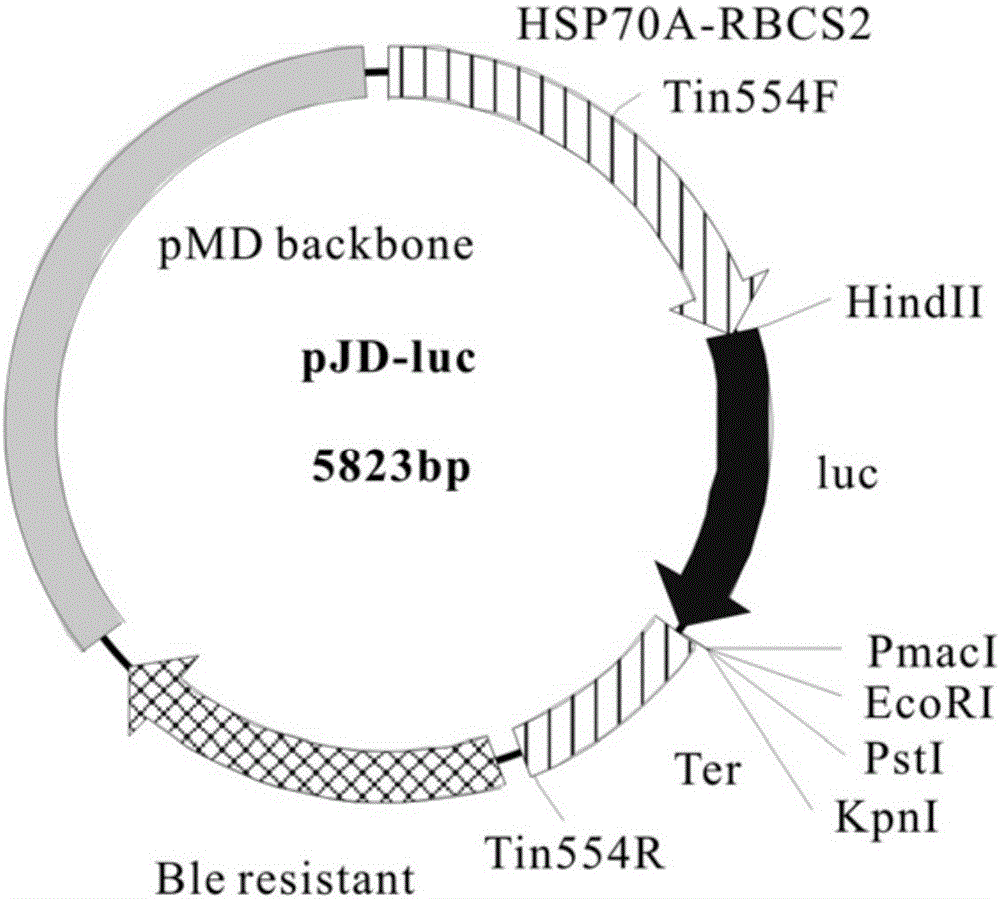
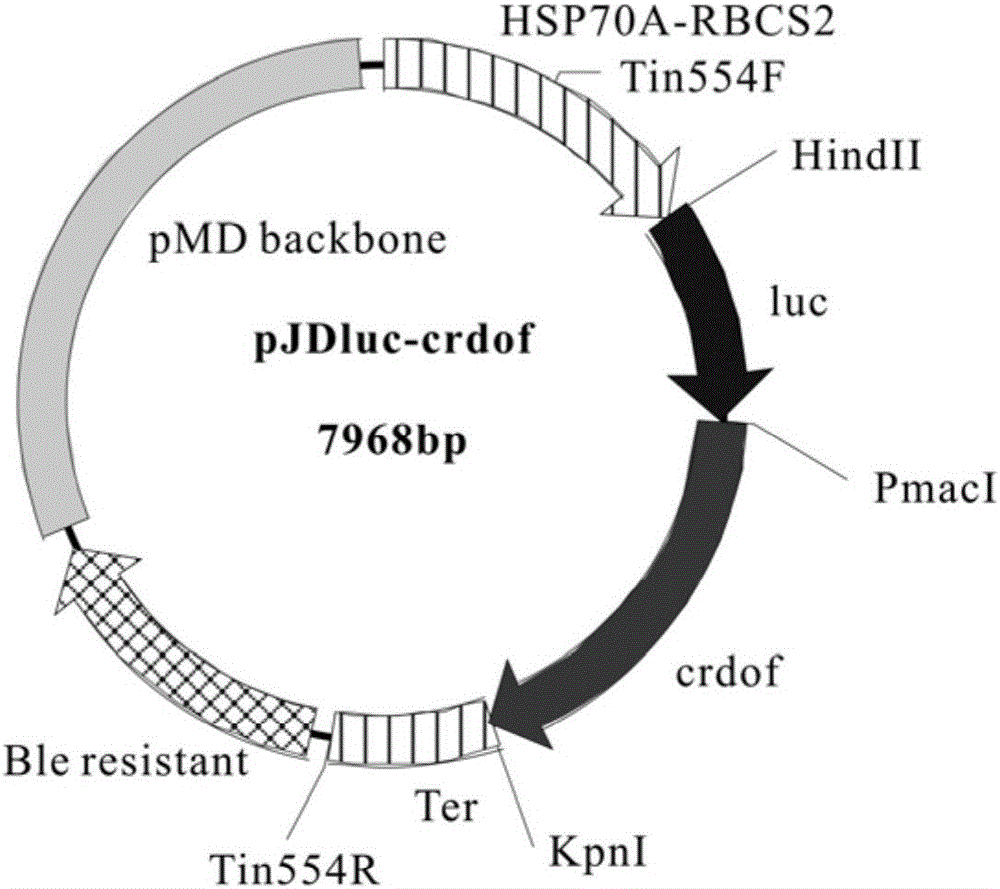
Recombinant expression vector of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Dof (DNA binding with one finger) gene as well as construction method and application of recombinant expression vector
InactiveCN105755034AHarm reductionEasy to findUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesChlamydomonas reinhardtiiTransgenesis
The invention discloses a recombinant expression vector of a Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Dof (DNA binding with one finger) gene as well as a construction method and an application of the recombinant expression vector. The recombinant expression vector suitable for overexpressing the Dof gene in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is constructed and is transferred into a host, namely, a Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cell, and genetically modified Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is obtained. The expression quantity of CrDof in the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is remarkably increased; the overexpressed CrDof regulates the expression quantity of lipid metabolism related genes, and the lipid content of genetically modified Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cells is remarkably increased. The recombinant expression vector of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Dof gene as well as the construction method and the application of the recombinant expression vector has great significance in enhancement of lipid metabolism gene regulation and increase of microalgae lipid content, and has greater application value and prospect in the technical field of genetic engineering.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Photosynthetic hydrogen production from the green alga chlamydomonas reinhardtii
The present invention relates generally to hydrogen production for use in fuel cells, foodstuffs and chemical production, and more particularly, to biologically and photosynthetically produced hydrogen. Specifically, disclosed is a method for producing bacteria and green alga that can produce hydrogen in quantities that exceed four hundred percent of the hydrogen produced by green alga in nature; thus, producing organisms which can serve as hydrogen generators for fuel cells, chemical production and numerous other applications.
Owner:H2OPE BIOFUELS LLC
Screening method of chlamydomonas reinhardtii selenium-rich mutant
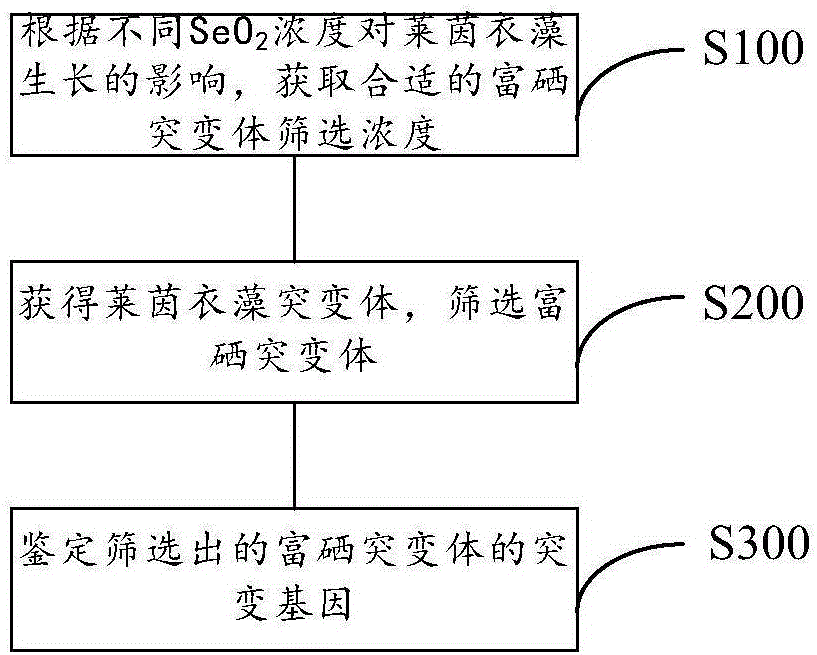
InactiveCN106520756ASolving the technical problem of lack of screening methods for selenium-enriched mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtiiSimple stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementMutant preparationChlamydomonas reinhardtiiScreening method
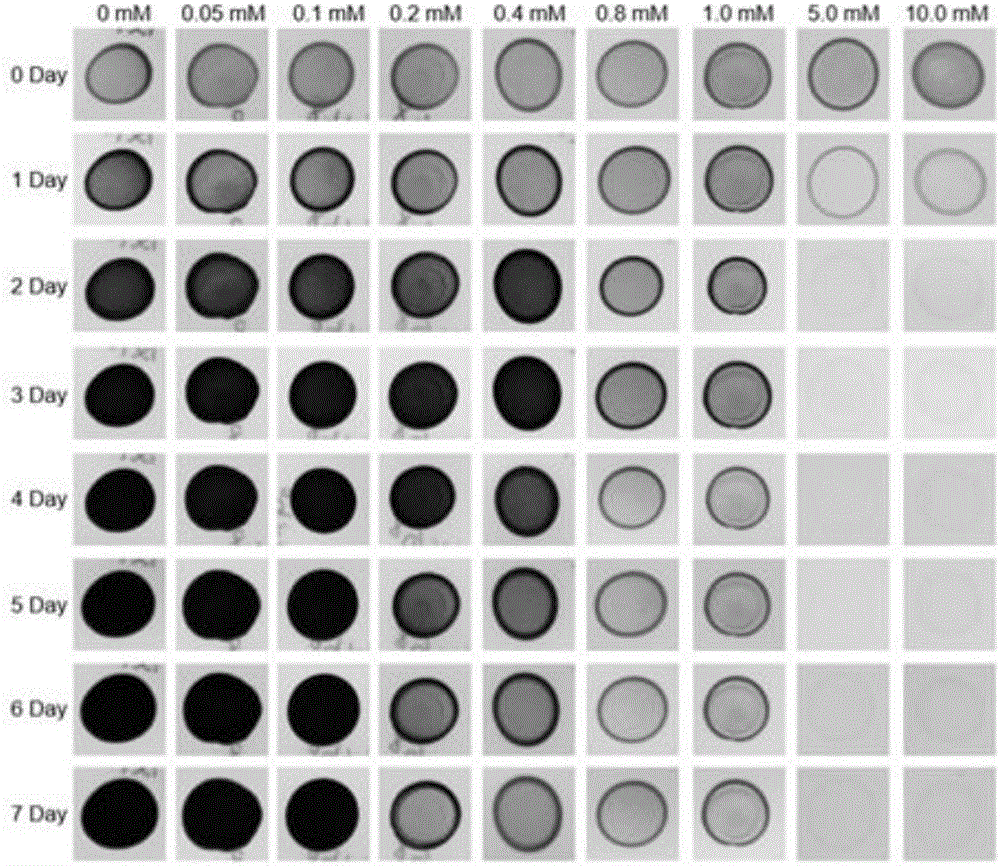
The invention discloses a screening method of a chlamydomonas reinhardtii selenium-rich mutant. The screening method comprises selecting an appropriate screening concentration of a selenium-rich mutant according to influence produced by different concentrations of SeO2 on the growth of chlamydomonas reinhardtii, acquiring a chlamydomonas reinhardtii mutant, screening a selenium-rich mutant, and identifying a mutant gene of the screened selenium-rich mutant. The screening method has simple processes and high screening efficiency, and realizes fast and accurate screening of a chlamydomonas reinhardtii mutant capable of growing at a high selenium concentration. Through RESDA-PCR, the mutant gene and the inserted mutation site can be identified.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Se1K expression vector as well as construction method and expression method thereof
InactiveCN104561078AImprove singlenessGood orientationMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionChlamydomonas reinhardtiiPlasmid Vector
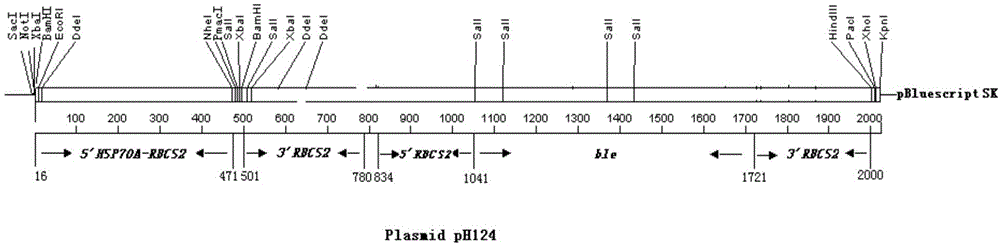
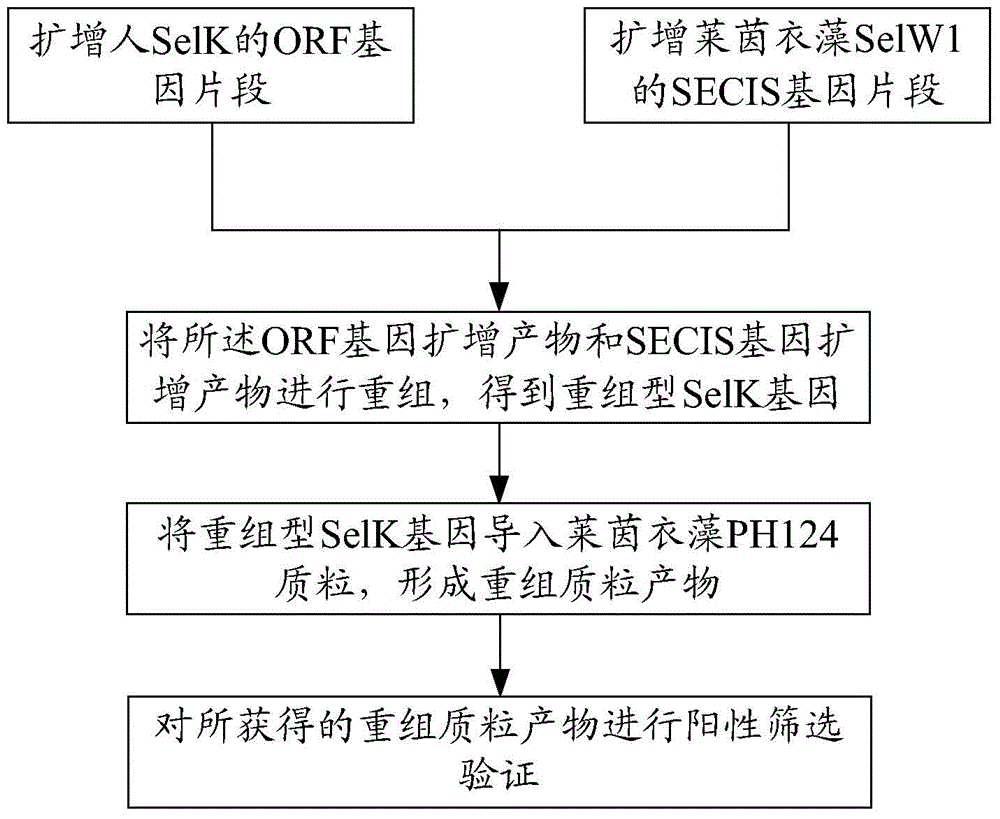
The invention provides a construction method of a chlamydomonas reinhardtii Se1K expression vector. The construction method comprises the following steps: amplifying an ORF gene segment of human Se1K to obtain an ORF gene amplification product; amplifying an SECIS gene segment of chlamydomonas reinhardtii Se1W1 to obtain an SECIS gene amplification product; recombining the ORF gene amplification product with the SECIS gene amplification product to obtain a recombinant Se1K gene; and introducing the recombinant Se1K gene into a plasmid vector which can be expressed in the chlamydomonas reinhardtii to form a recombinant plasmid product. According to the chlamydomonas reinhardtii Se1K expression vector constructed by the method, a novel plasmid vector capable of expressing an exogenous target selenoprotein K in the chlamydomonas reinhardtii is constructed; compared with the existing in-vitro expression vectors such as a prokaryotic expression system, and a method, the product is generated by a similar expression mechanism, so that the product has good monotonicity and directionality; the efficiency is greatly improved; the chlamydomonas reinhardtii can be adopted as a reactor for producing selenoprotein during expression; and the construction method is portable and efficient, and can completely meet the bases of research on structure functions of the selenoprotein and development of selenoprotein anti-cancer drugs.
Owner:SHENZHEN CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Photosynthetic hydrogen production from the green alga chlamydomonas reinhardtii
The present invention relates generally to hydrogen production for use in fuel cells, foodstuffs and chemical production, and more particularly, to biologically and photosynthetically produced hydrogen. Specifically, disclosed is a method for producing bacteria and green alga that can produce hydrogen in quantities that exceed four hundred percent of the hydrogen produced by green alga in nature; thus, producing organisms which can serve as hydrogen generators for fuel cells, chemical production and numerous other applications.
Owner:H2OPE BIOFUELS LLC
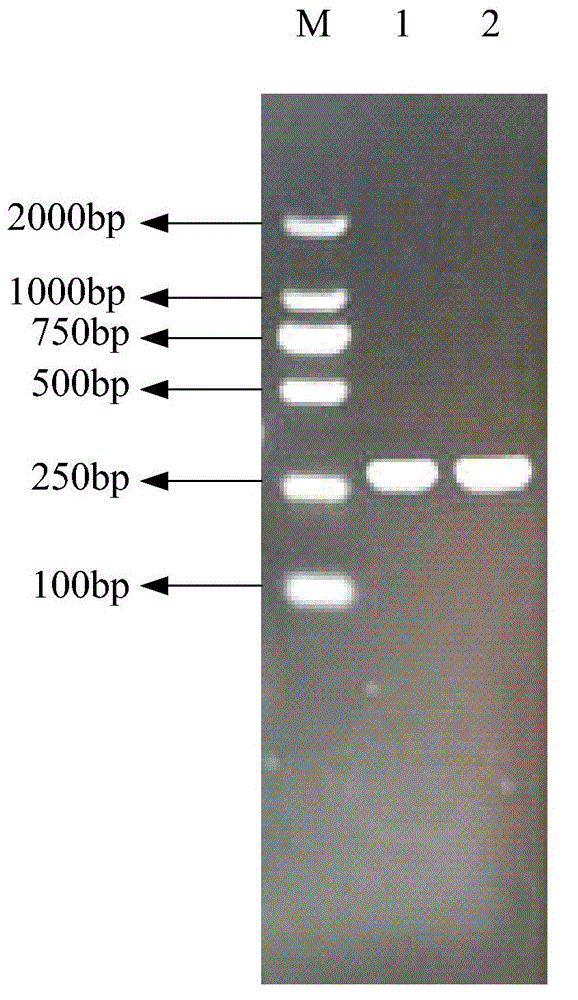
Application of chlamydomonas reinhardtii LRR (Leucine Rich Repeat) gene in regulating and controlling cadmium resistance of chlamydomonas reinhardtii
InactiveCN107760693ASimple methodImprove efficiencyUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention discloses application of a chlamydomonas reinhardtii LRR (Leucine Rich Repeat) gene in regulating and controlling cadmium resistance of chlamydomonas reinhardtii, and belongs to the technical field of biologics and the field of environmental pollution improvement. According to the application, an aphVIII fragment with a paromomycin resistance gene is randomly inserted into chlamydomonas, then a chlamydomonas reinhardtii mutant alga strain which is remarkable in cadmium chloride resistance is cultured, and further identification shows that the cadmium sensitivity of the mutant alga strain is caused since the aphVIII (SEQ ID NO:3) fragment is inserted into an LRR gene (a CDS (Cadmium Sulfide) sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:1 in the specification). By reducing expression of thechlamydomonas reinhardtii LRR gene, deactivating the LRR gene or by deleting the LRR gene, the cadmium resistance of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii can be improved; a cadmium resistance improved chlamydomonas reinhardtii strain obtained by means of genetic engineering can be applied to monitoring and improvement of cadmium polluted water areas, cadmium polluted water environments can be treated with the cadmium resistance improved chlamydomonas reinhardtii strain, the operation is simple and feasible, and the cost is low.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com