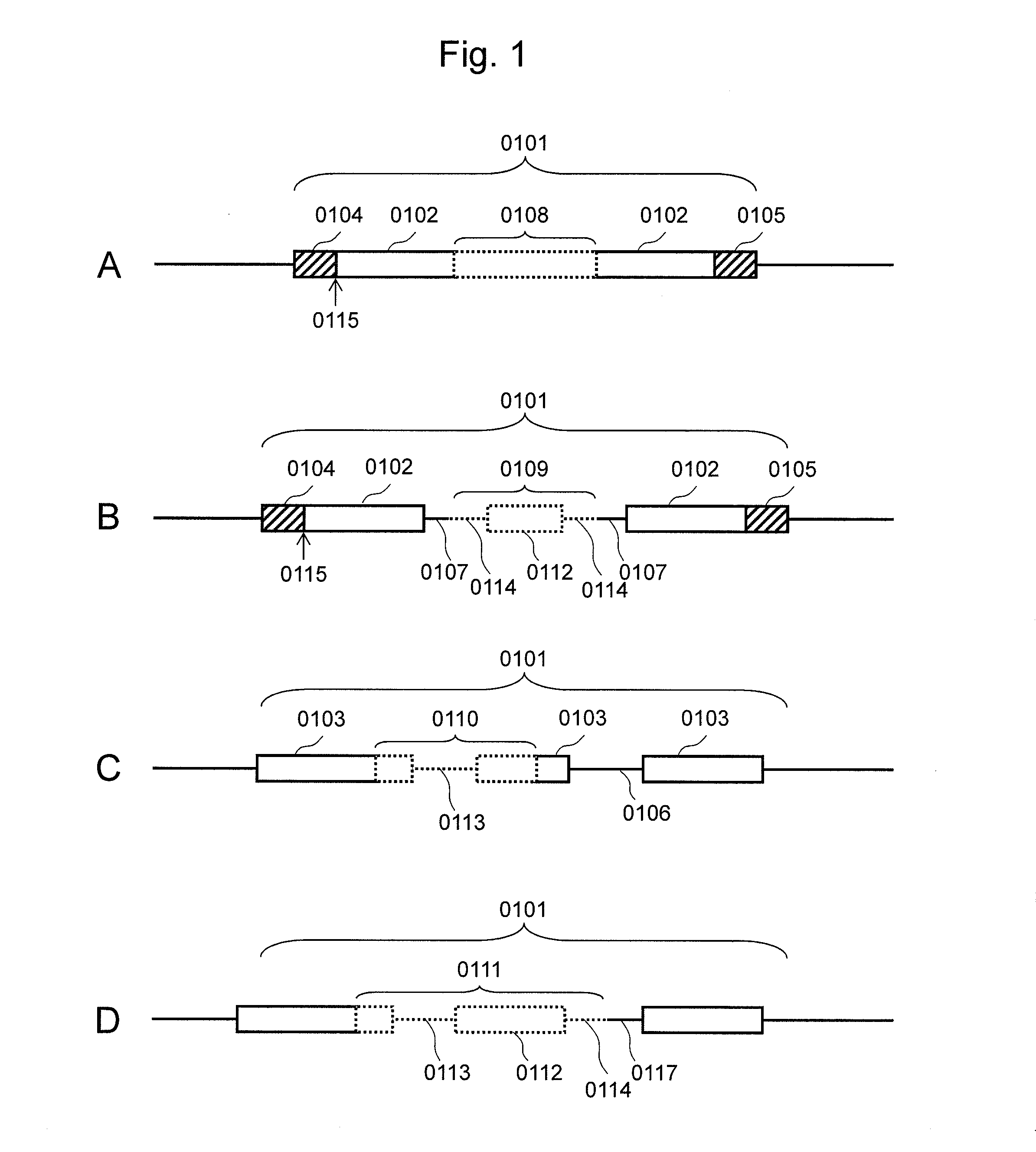
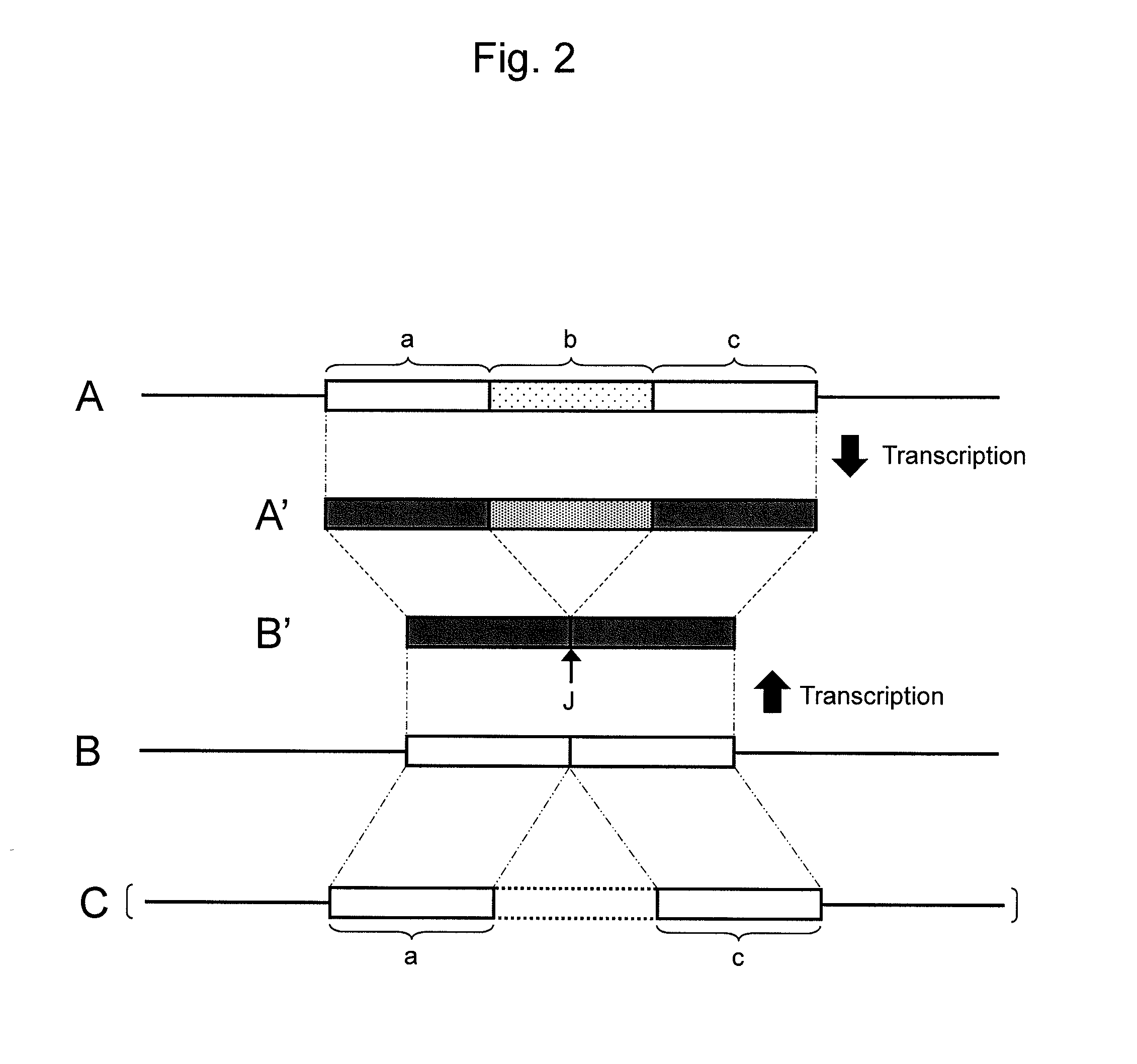
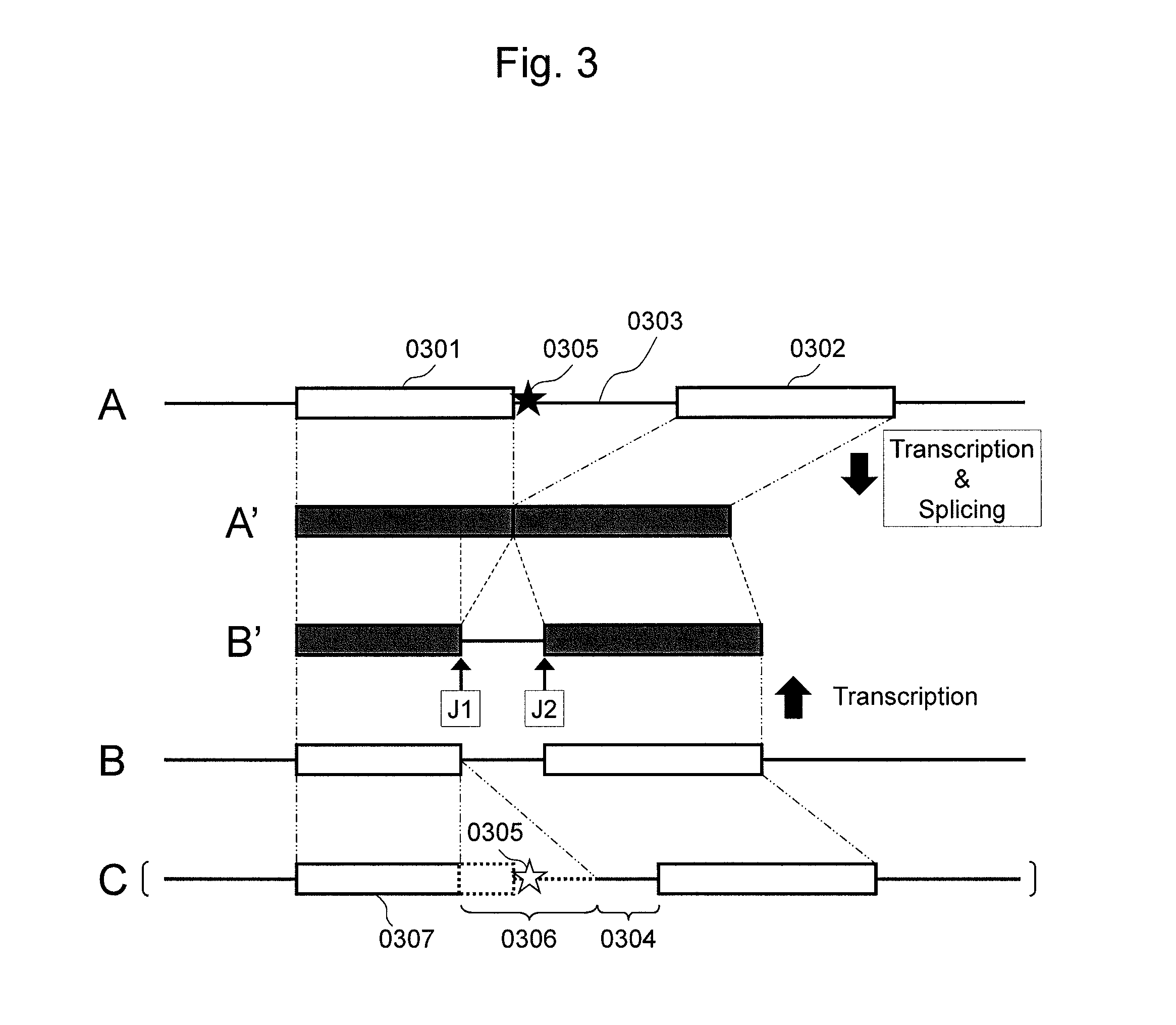
Patents
Literature
1356 results about "Mutant gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mutant gene. n. A gene that has lost, gained, or exchanged some of the material it received from its parent, resulting in a permanent transmissible change in its function.
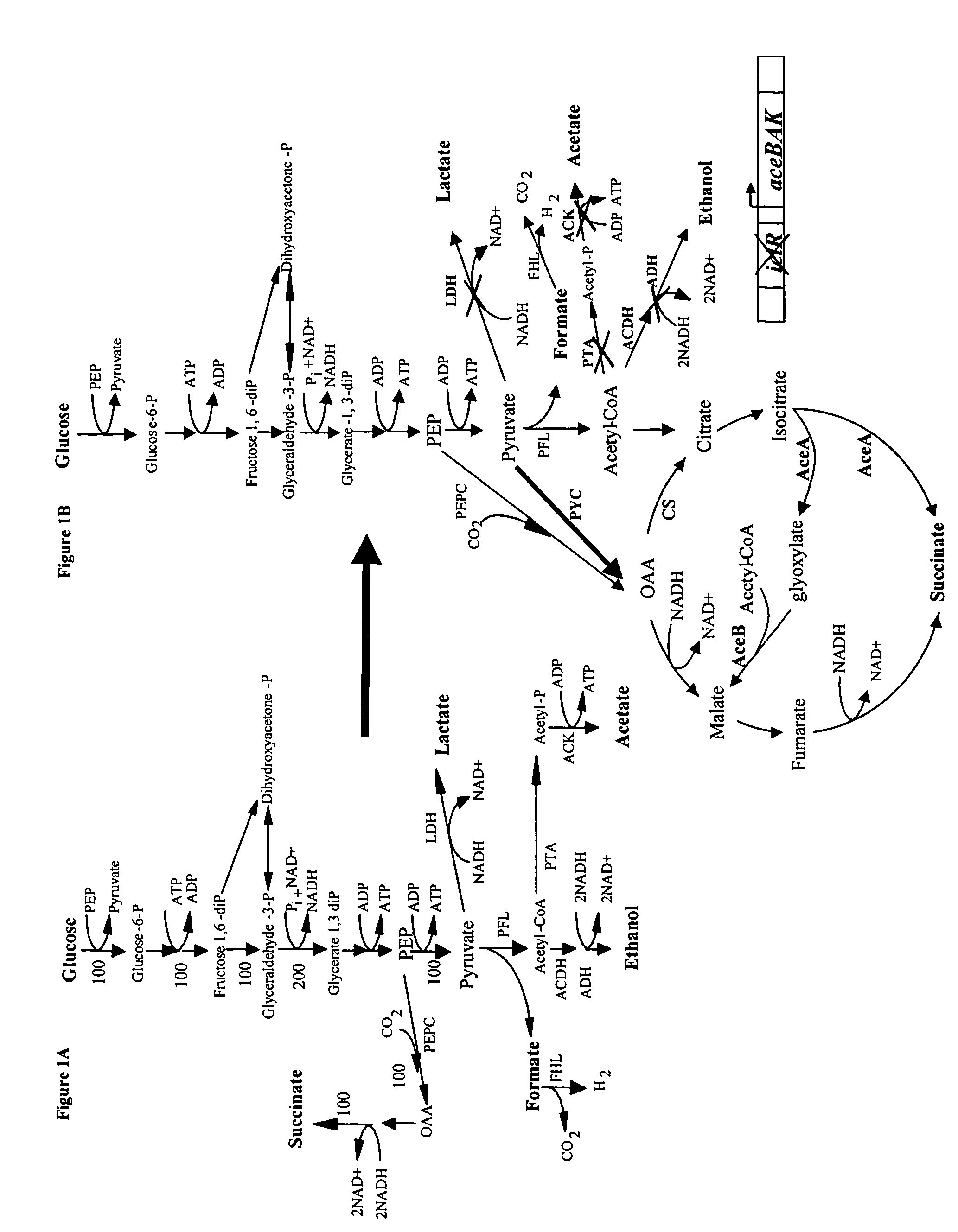
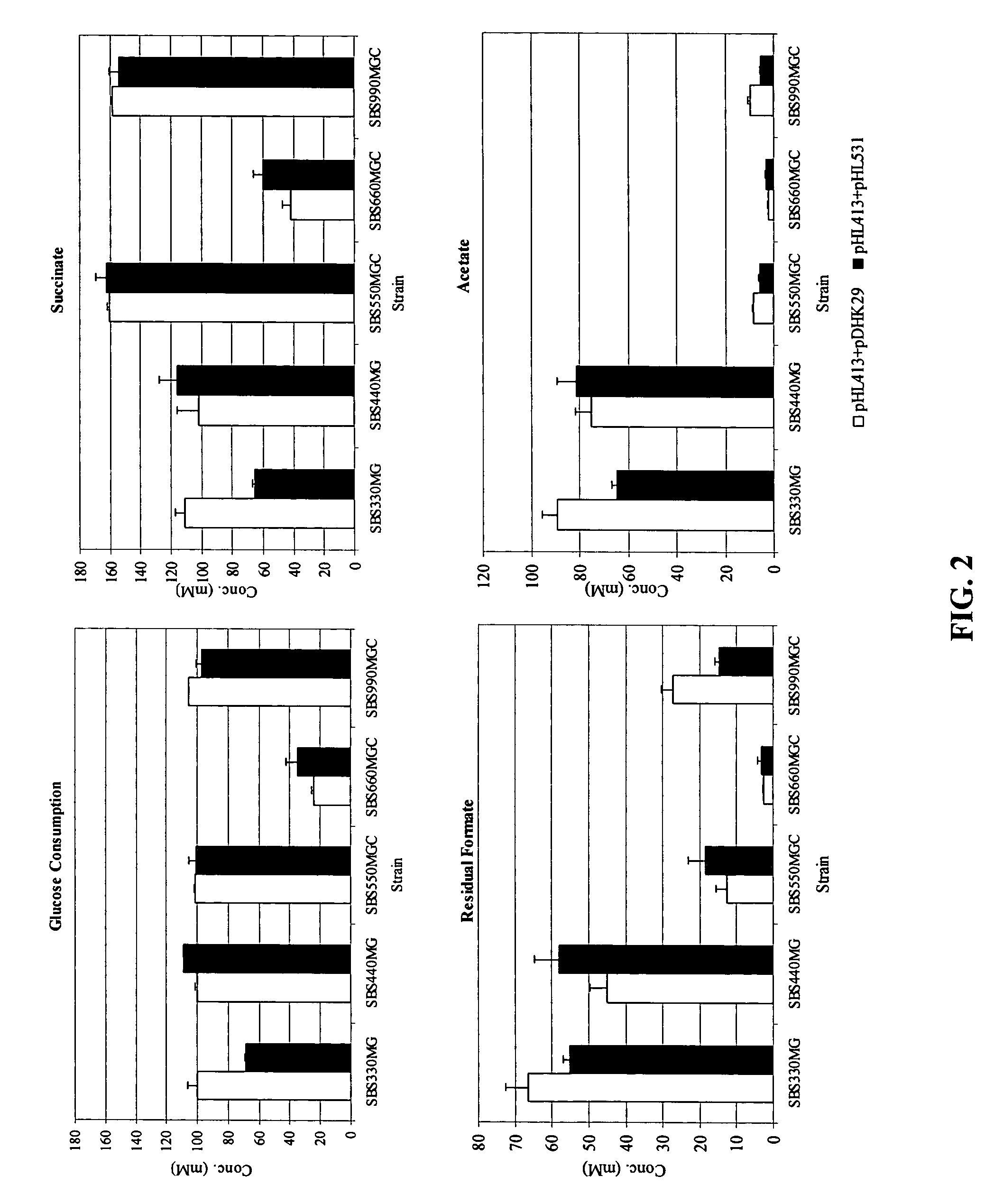
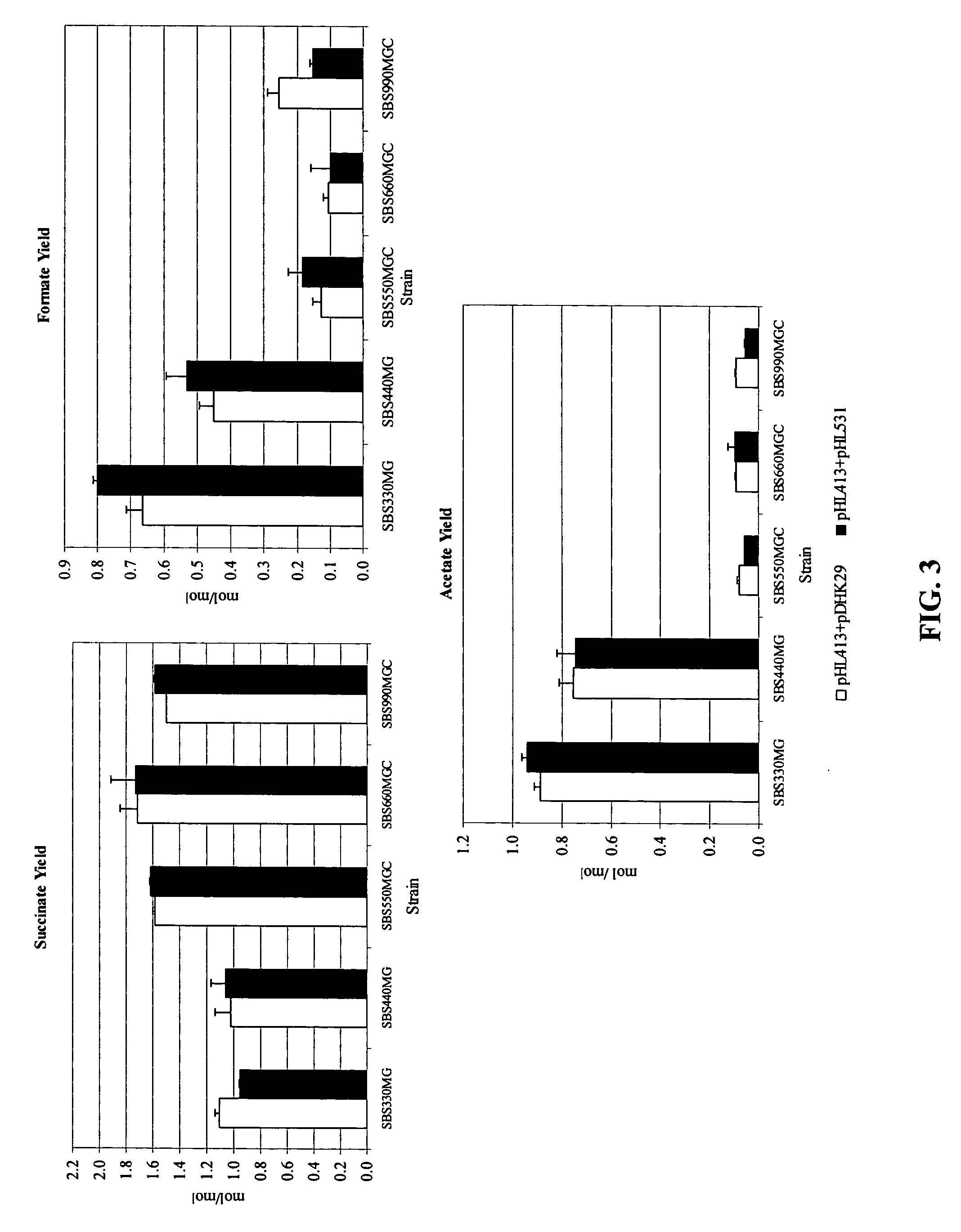
Mutant E. coli strain with increased succinic acid production
The invention relates to a mutant strain of bacteria, which either lacks or contains mutant genes for several key metabolic enzymes, and which produces high amounts of succinic acid under anaerobic conditions.
Owner:RICE UNIV
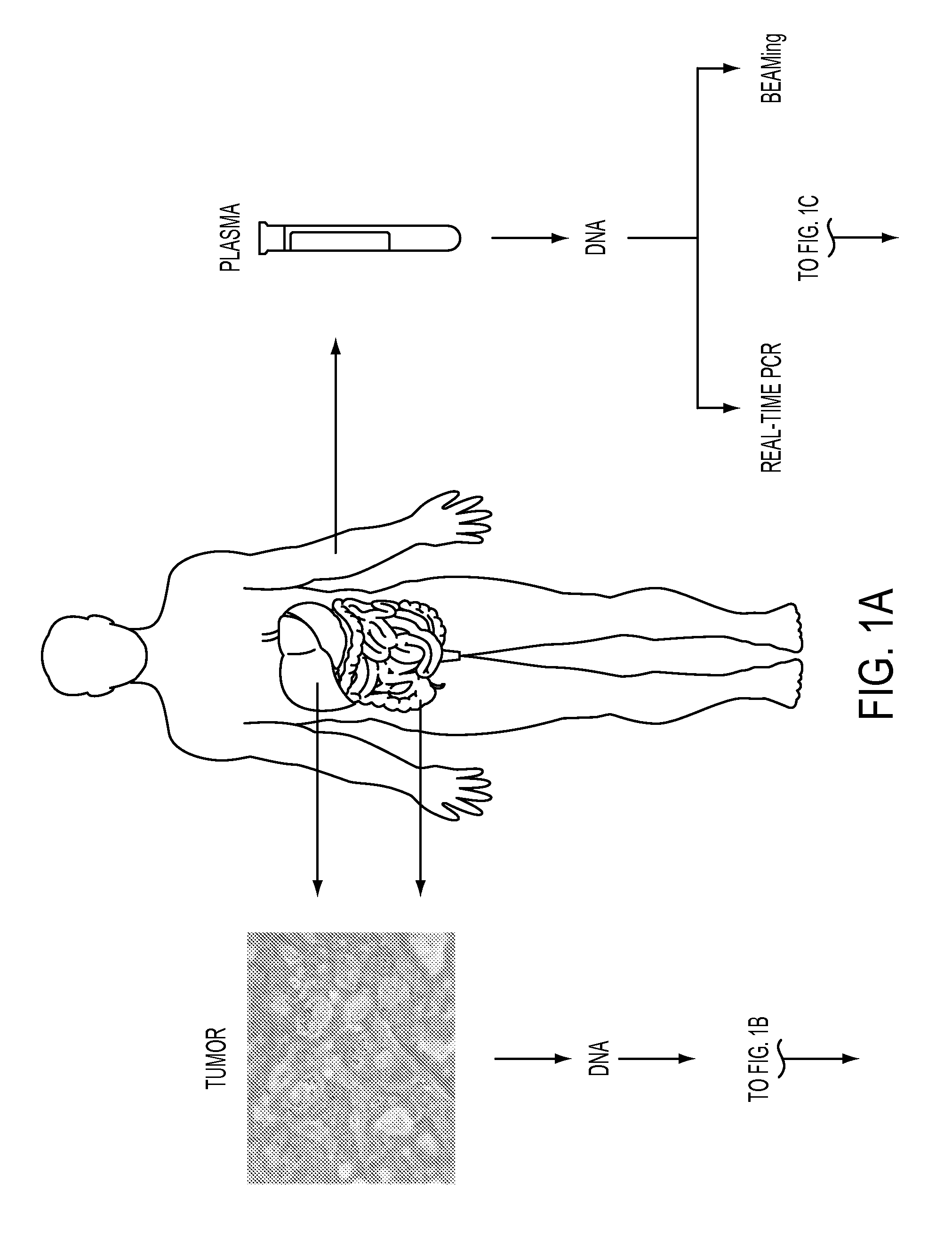
Circulating Mutant DNA to Assess Tumor Dynamics
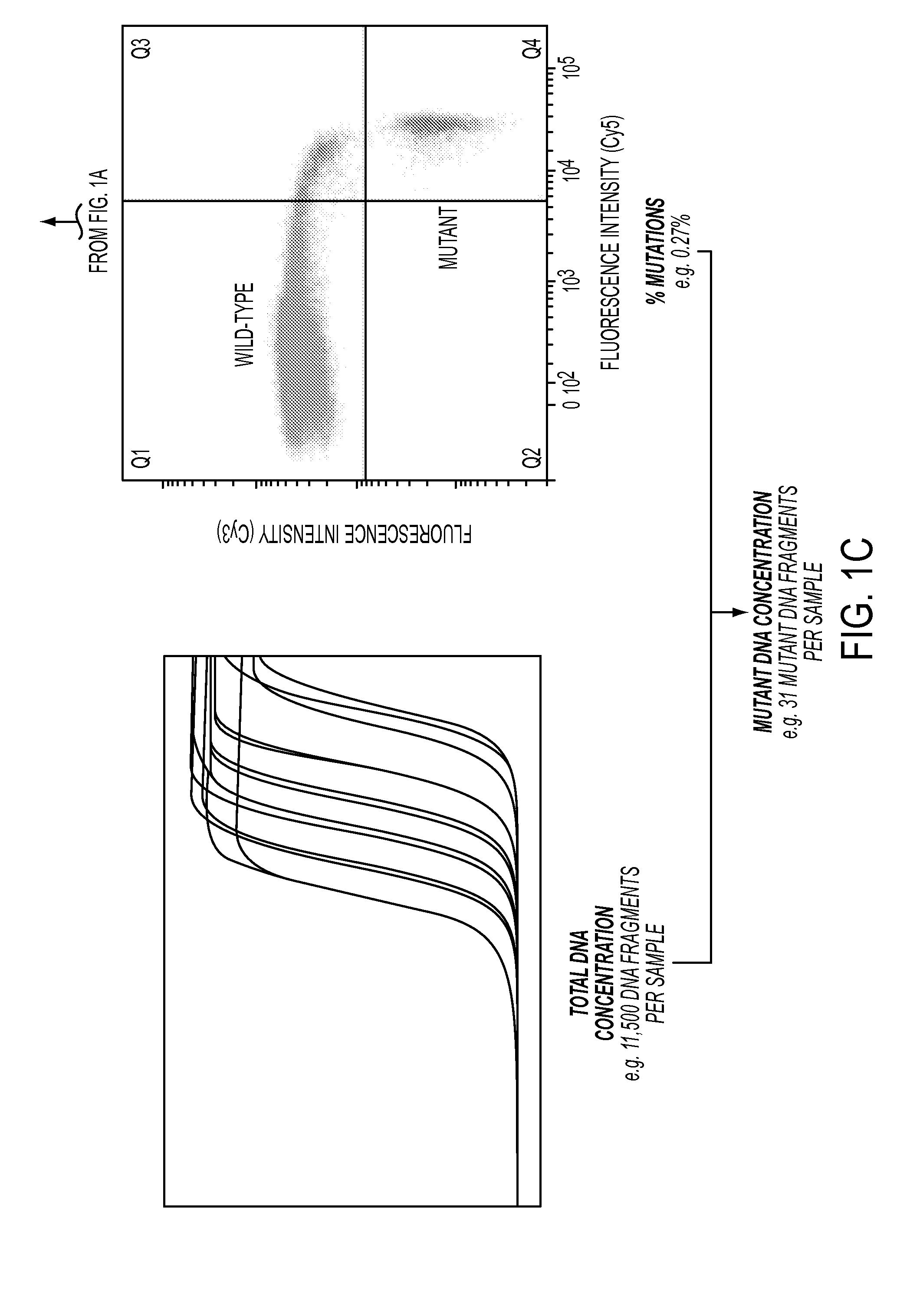
DNA containing somatic mutations is highly tumor specific and thus, in theory, can provide optimum markers. However, the number of circulating mutant gene fragments is small compared to the number of normal circulating DNA fragments, making it difficult to detect and quantify them with the sensitivity required for meaningful clinical use. We apply a highly sensitive approach to quantify circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in body samples of patients. Measurements of ctDNA can be used to reliably monitor tumor dynamics in subjects with cancer, especially those who are undergoing surgery or chemotherapy. This personalized genetic approach can be generally applied.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Dual functional oligonucleotides for use in repressing mutant gene expression
InactiveUS20050256072A1Improve in vivo stabilityNervous disorderSugar derivativesHuntingtons choreaHuntington's disease
The present invention is based, in part, on the discovery that endogenous mRNAs can be recruited for translational repression of target mRNAs. The RNA-silencing agents and the methods described herein, thereby provide a means by which to treat genetic (e.g., genetic neurodegenerative diseases such as Huntington's Disease) or non-genetic diseases by, for example, blocking the synthesis of proteins that contribute to the diseases. Accordingly the RNA-silencing agents of the present invention have an mRNA targeting moiety, a linking moiety, and an mRNA recruiting moiety.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
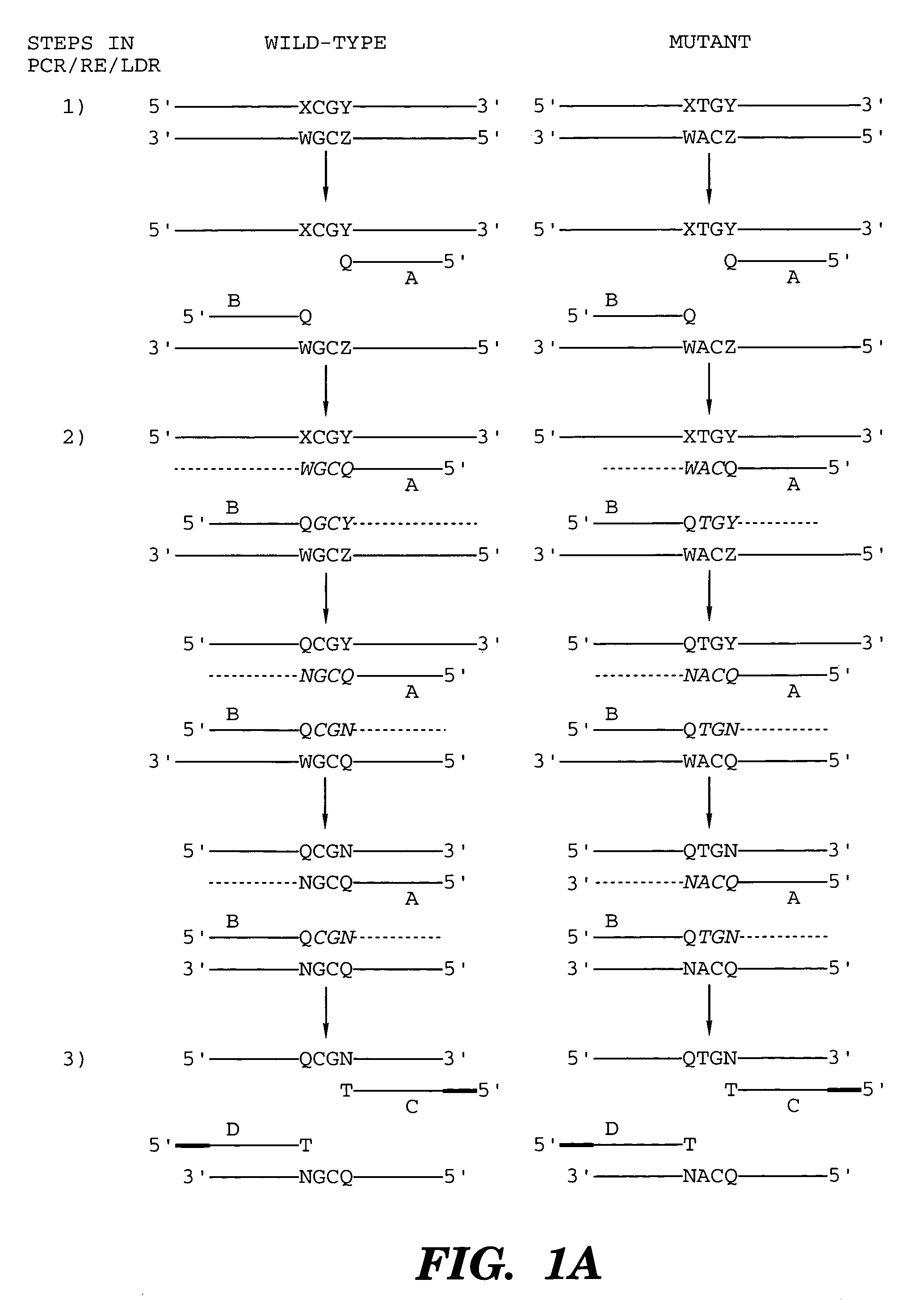
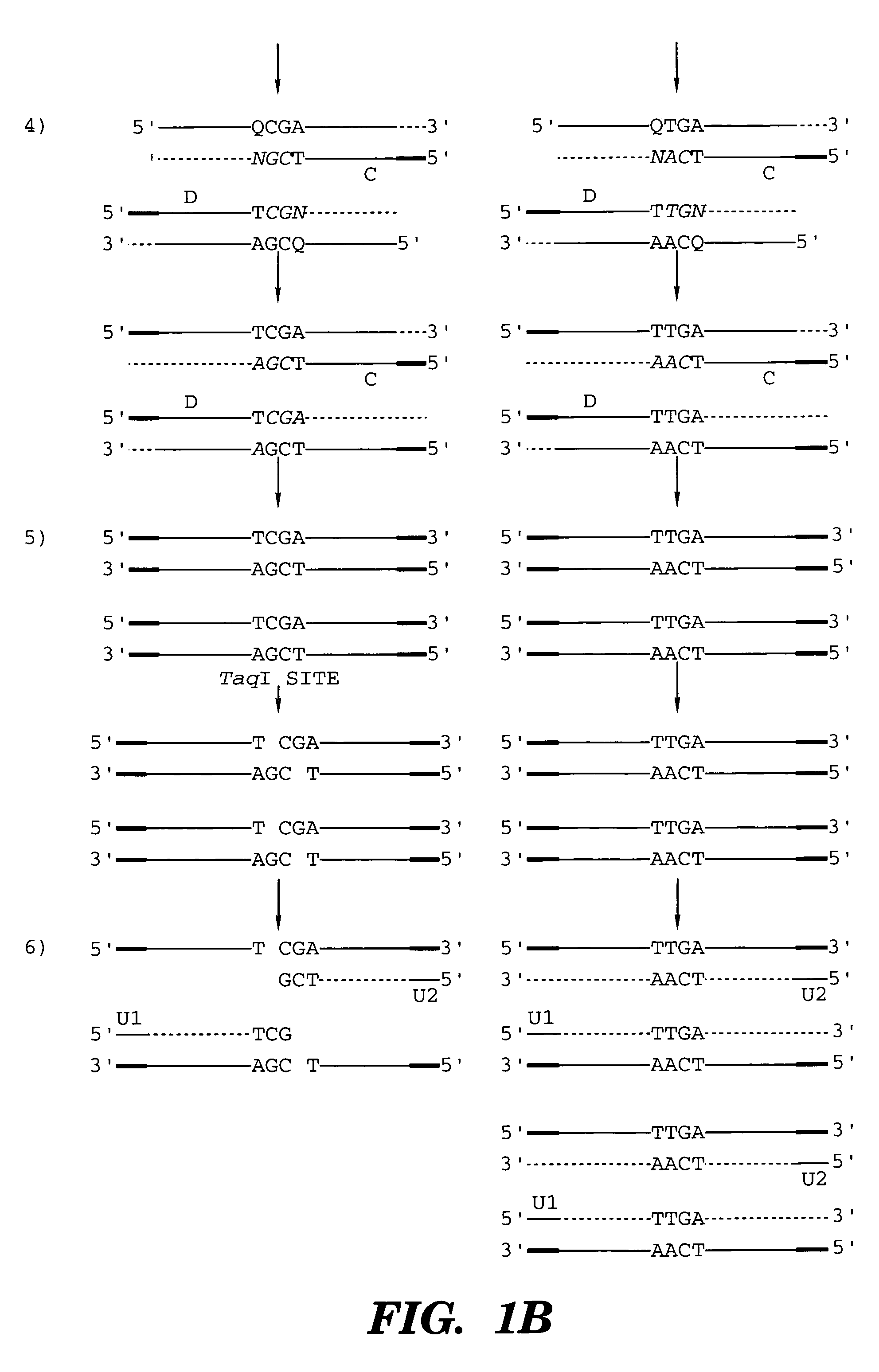
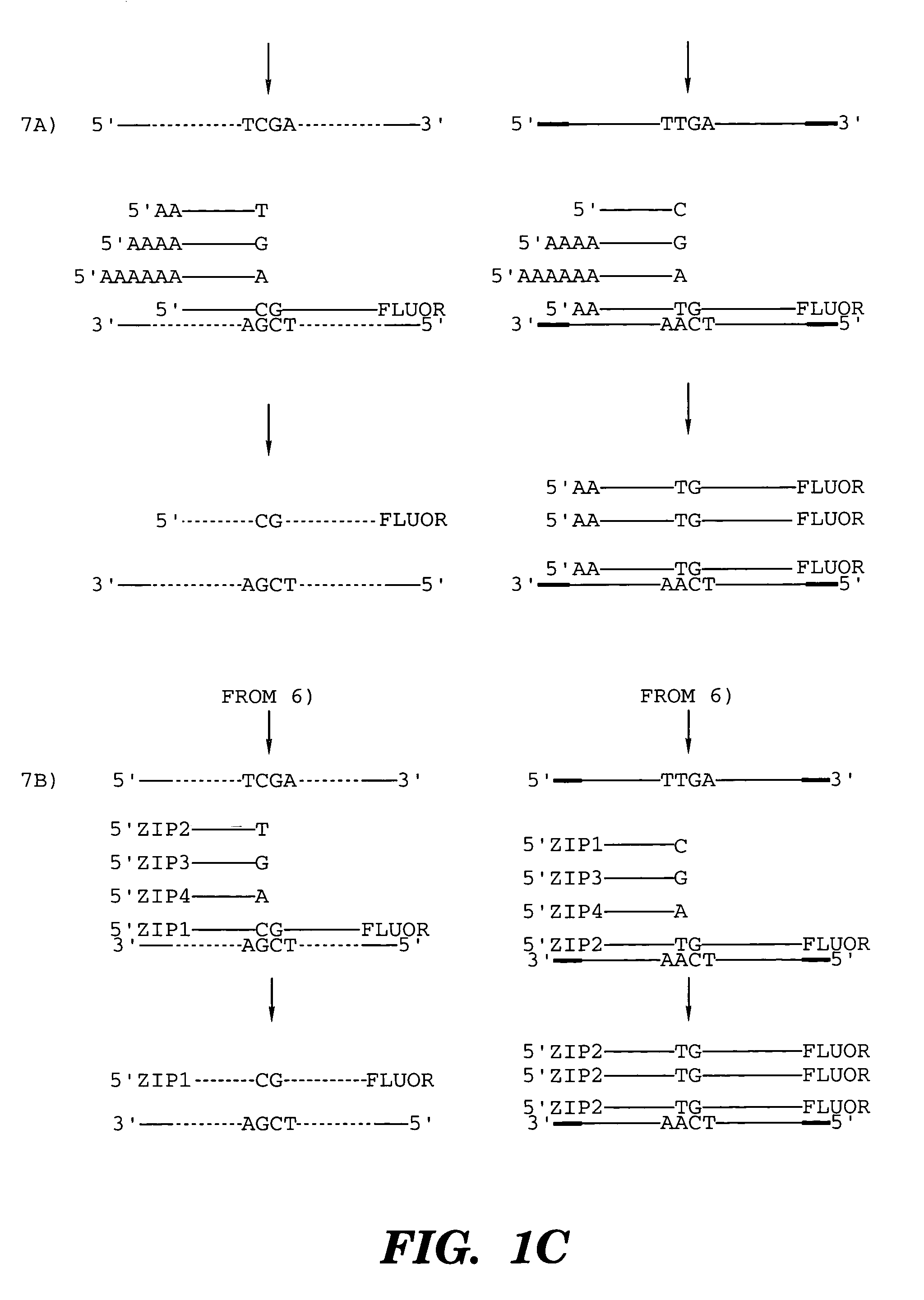
Coupled polymerase chain reaction-restriction-endonuclease digestion-ligase detection reaction process
InactiveUS7014994B1Sensitive highOptimizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideWild type
The present invention provides a method for identifying one or more low abundance sequences differing by one or more single-base changes, insertions, or deletions, from a high abundance sequence in a plurality of target nucleotide sequences. The high abundance wild-type sequence is selectively removed using high fidelity polymerase chain reaction analog conversion, facilitated by optimal buffer conditions, to create a restriction endonuclease site in the high abundance wild-type gene, but not in the low abundance mutant gene. This allows for digestion of the high abundance DNA. Subsequently the low abundant mutant DNA is amplified and detected by the ligase detection reaction assay. The present invention also relates to a kit for carrying out this procedure.
Owner:LOUISIANA STATE UNIV +1
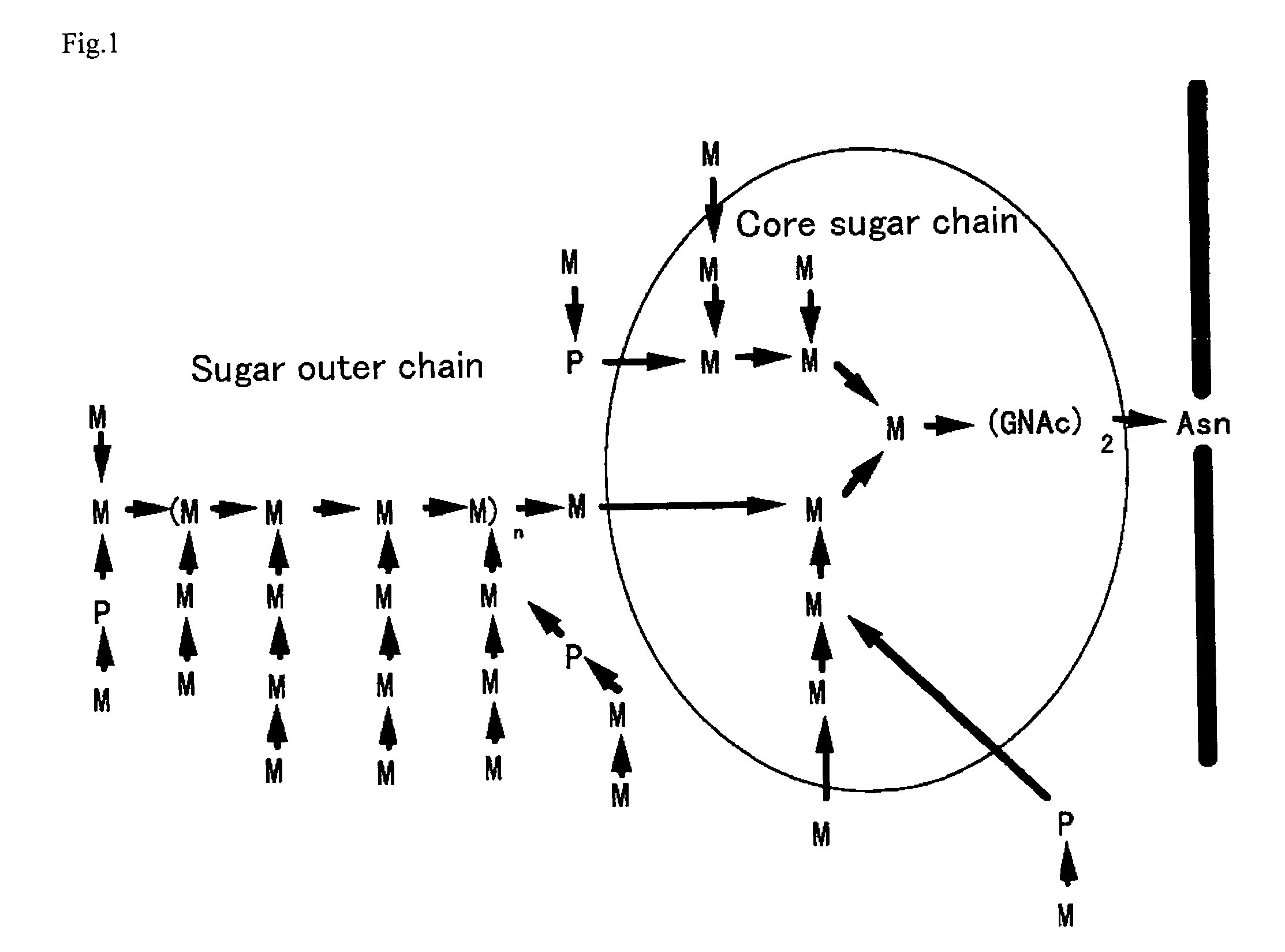
Process for producing protein with reduction of acidic sugar chain and glycoprotein produced thereby
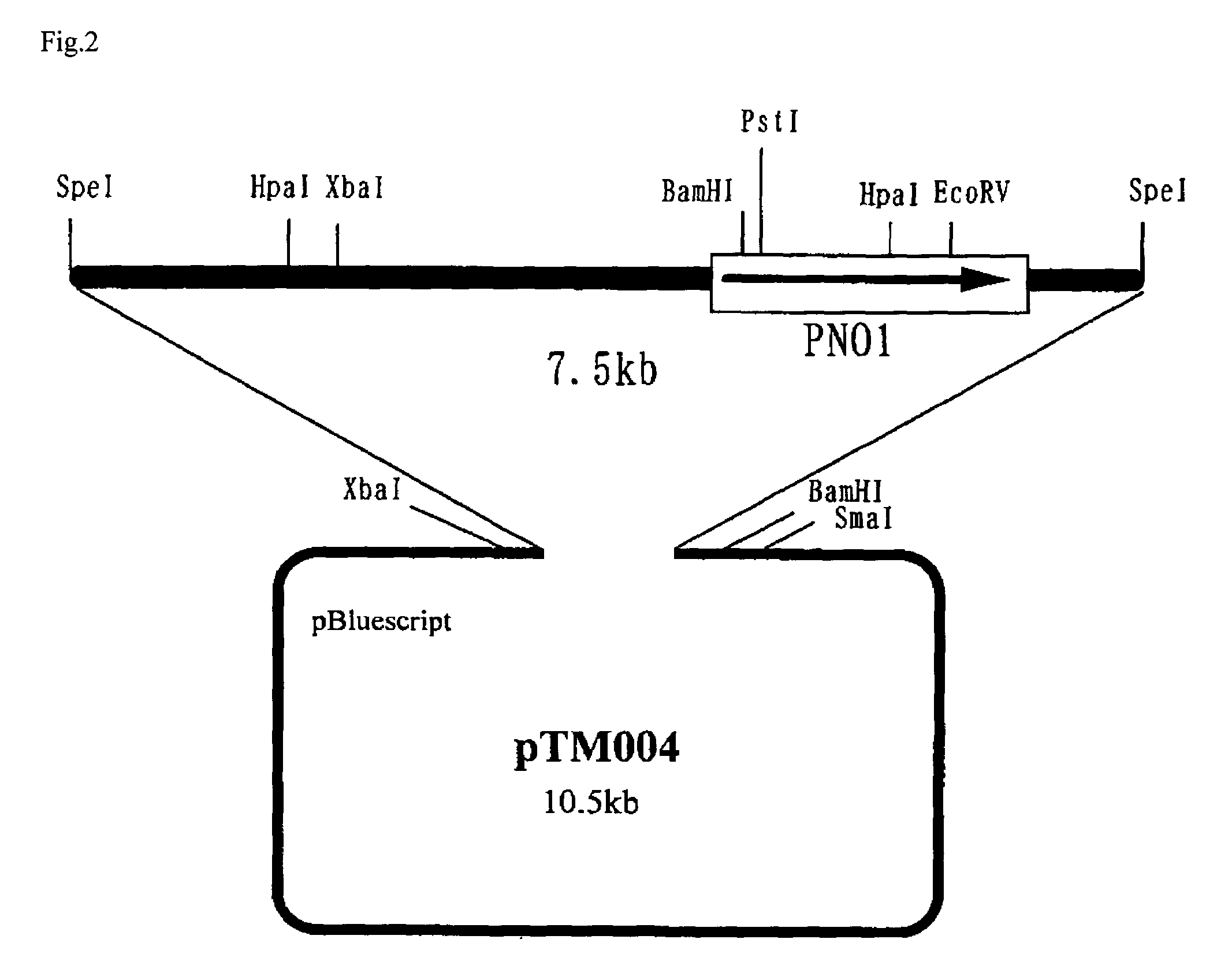
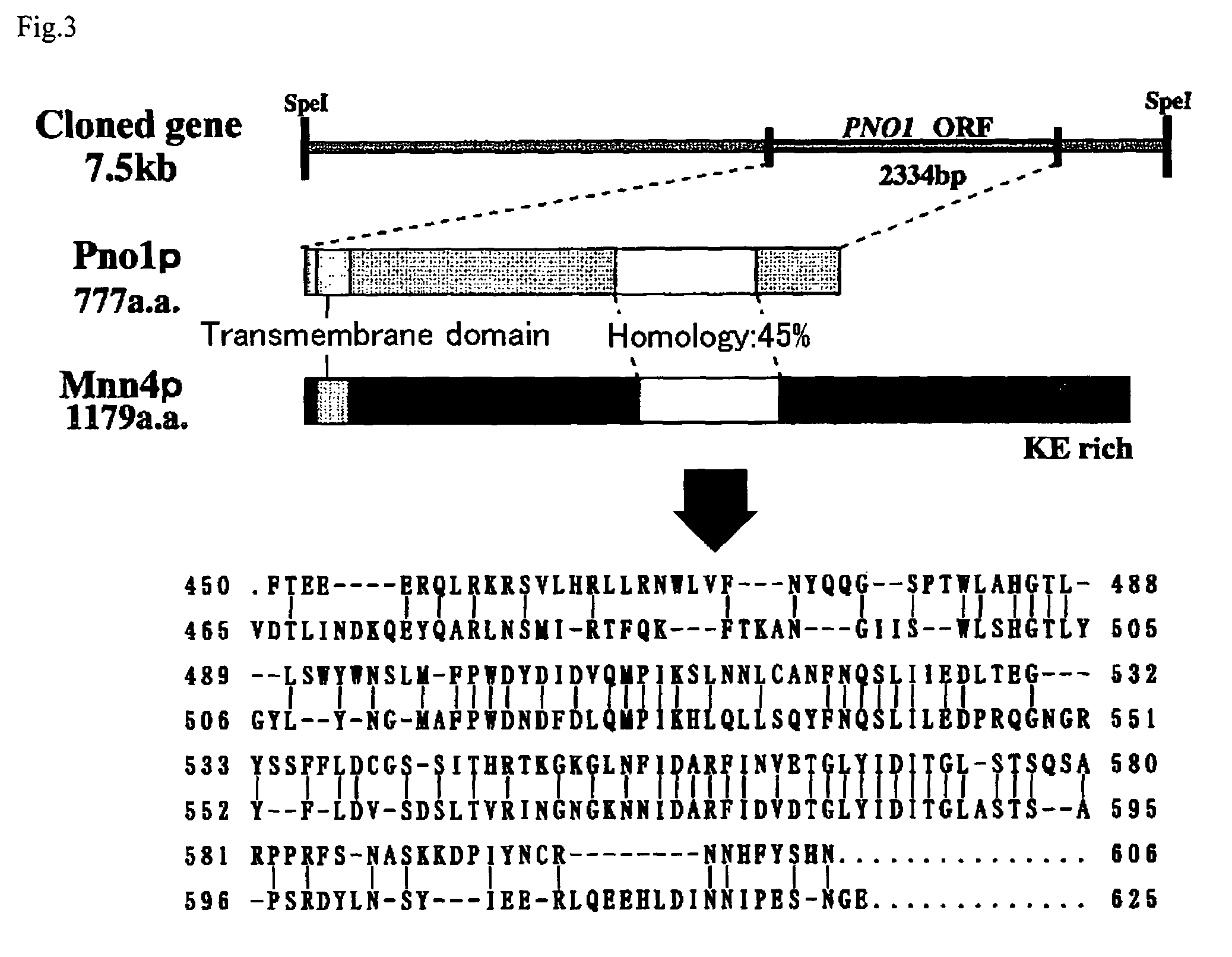
The present invention intends to find out a gene participating in addition of mannose phosphate to a sugar chain of a glycoprotein originating in a yeast belonging to the genus Pichia and provide a means of controlling the same. The present invention also intends to provide a process for producing a protein with reduction of an acidic sugar chain by using the thus controlled yeast strain belonging to the genus Pichia. Namely, the present invention includes a protein participating in the addition of mannose phosphate to a sugar chain of a glycoprotein; a gene encoding this protein; a mutant of this gene; a vector carrying the mutant gene; a yeast strain belonging to the genus Pichia having been transformed by this vector; a process for producing a protein with reduction of an acidic sugar chain by using the transformed yeast strain; and a glycoprotein thus produced.
Owner:MITSUBISHI TANABE PHARMA CORP
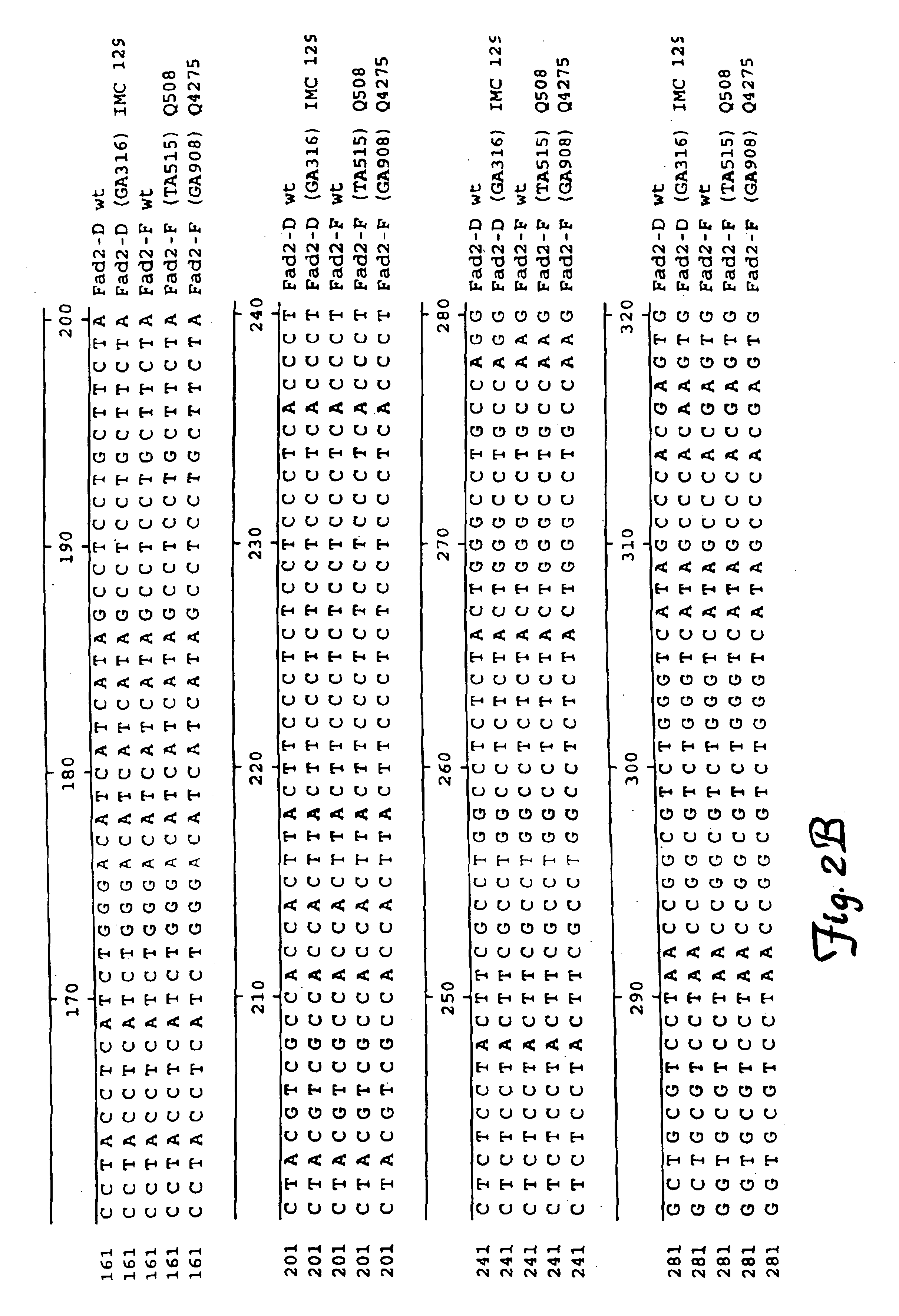
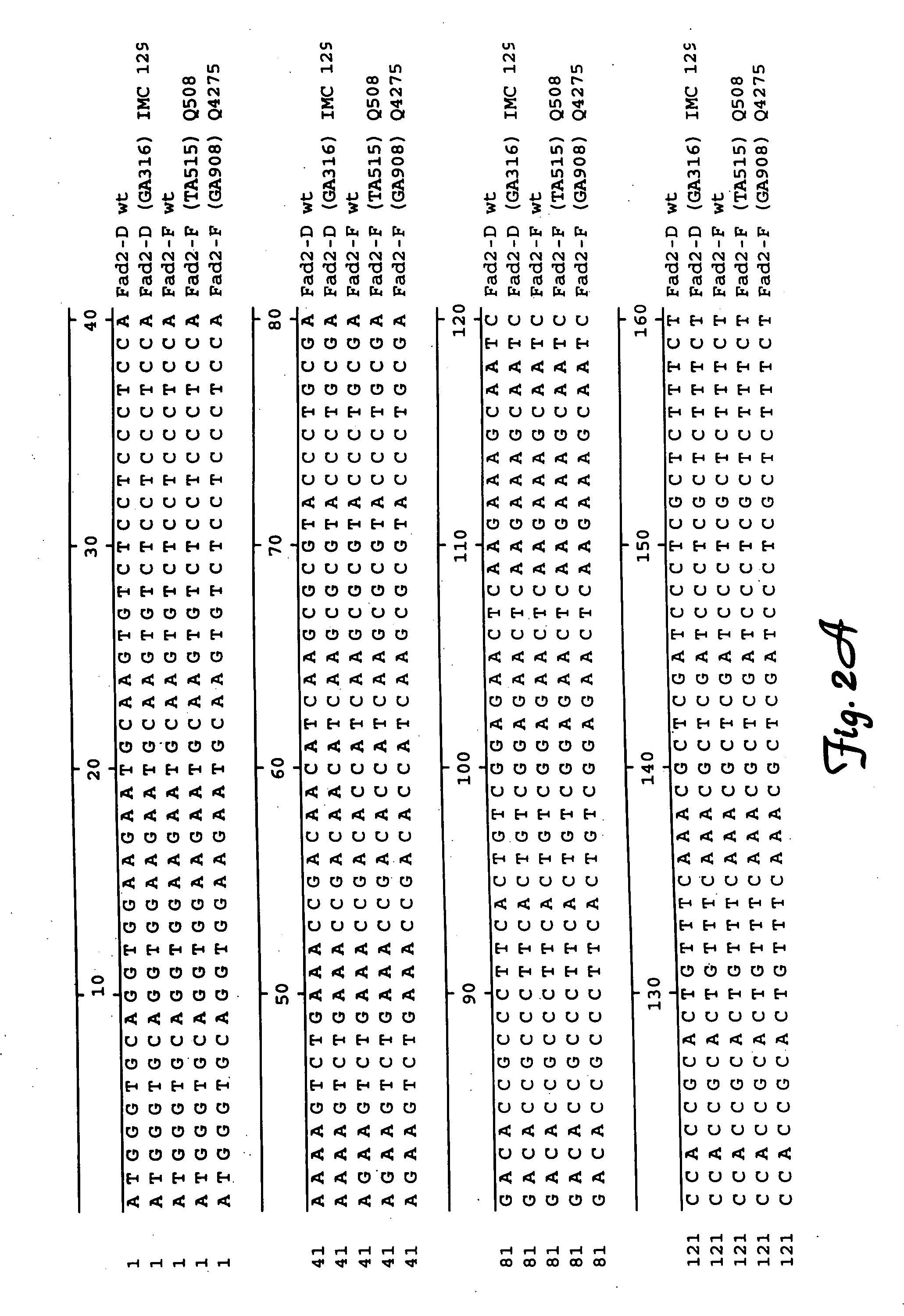
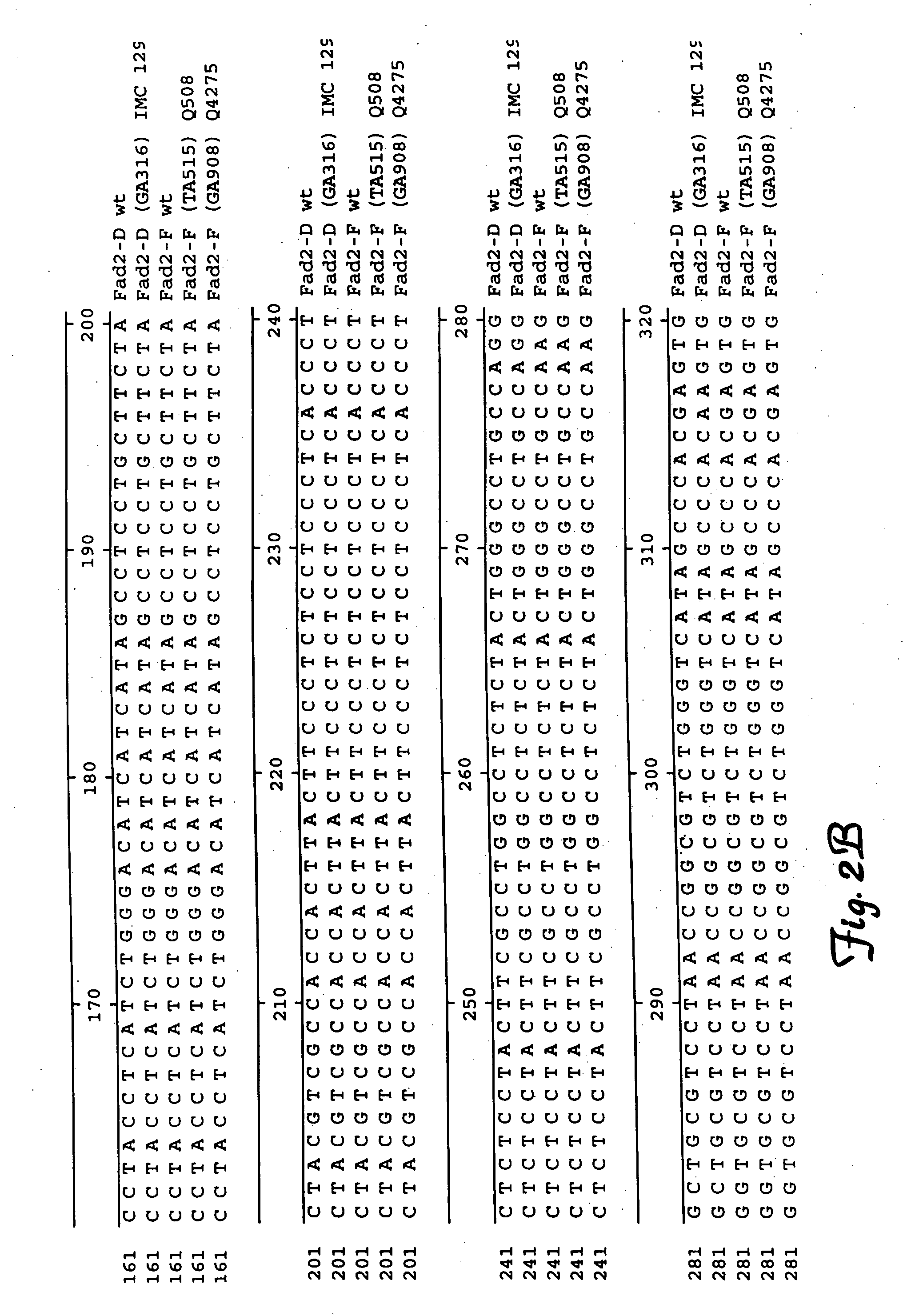
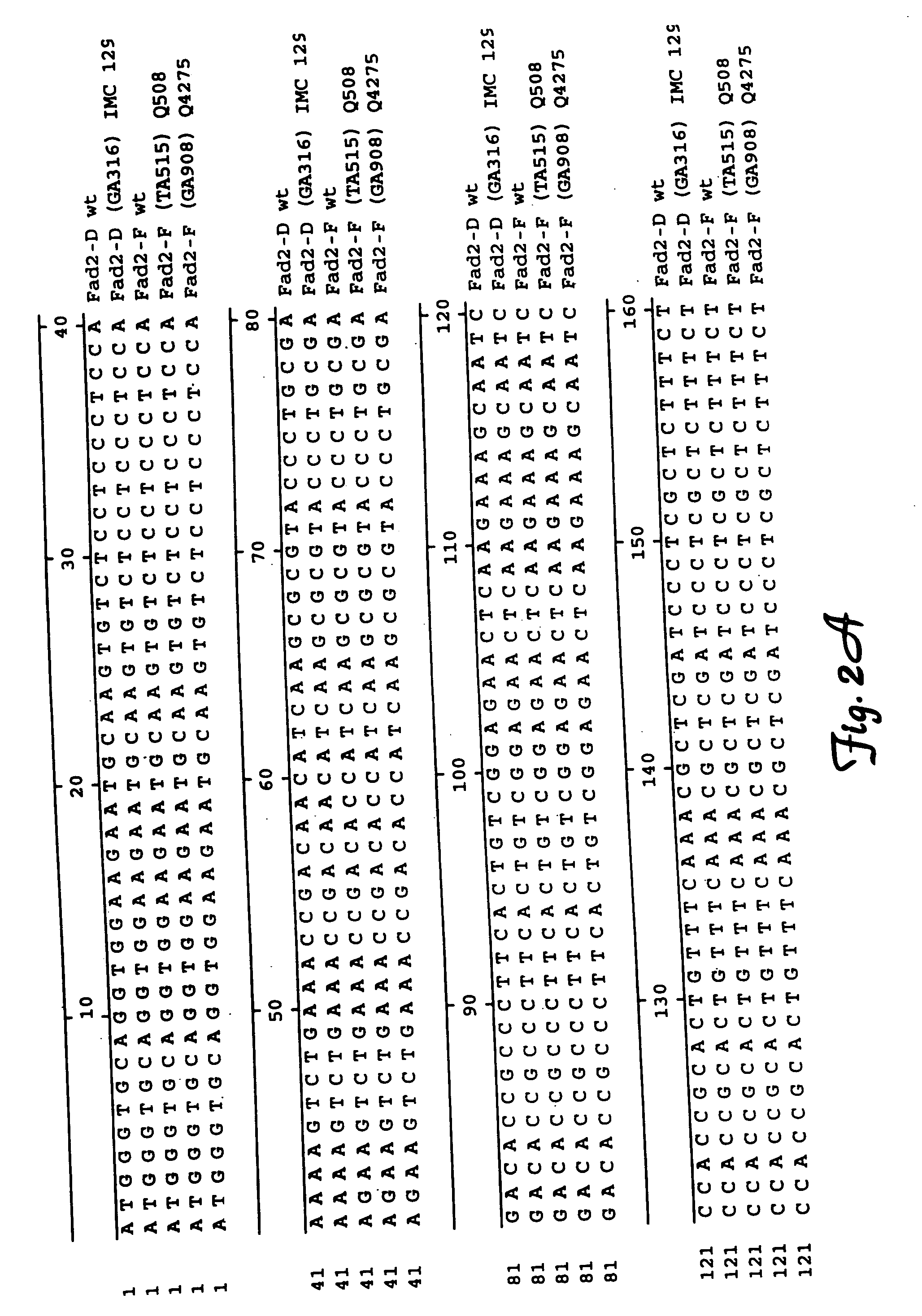
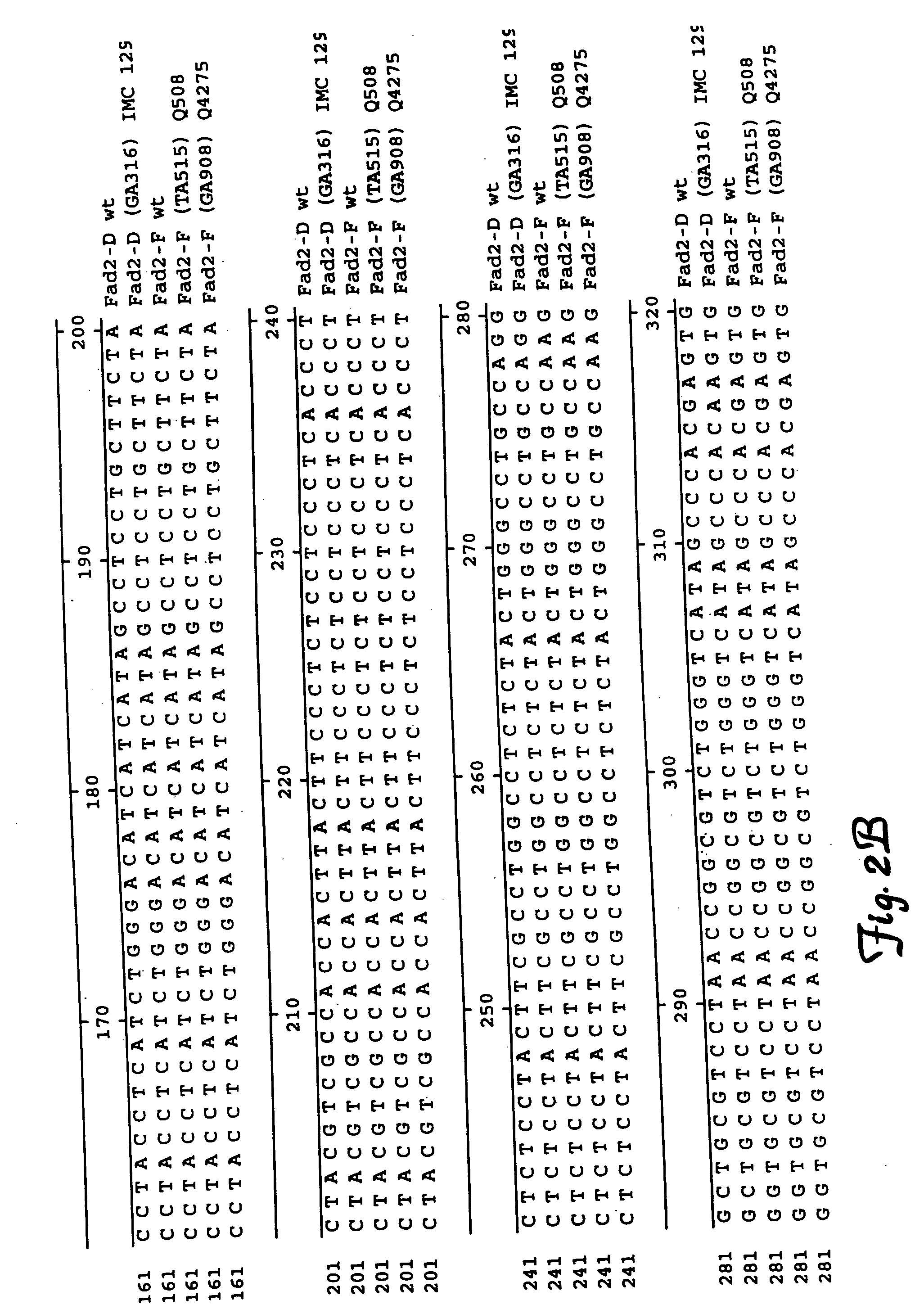
Fatty acid desaturases and mutant sequences thereof
InactiveUS6967243B2Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesHigh oleic acidRapeseed
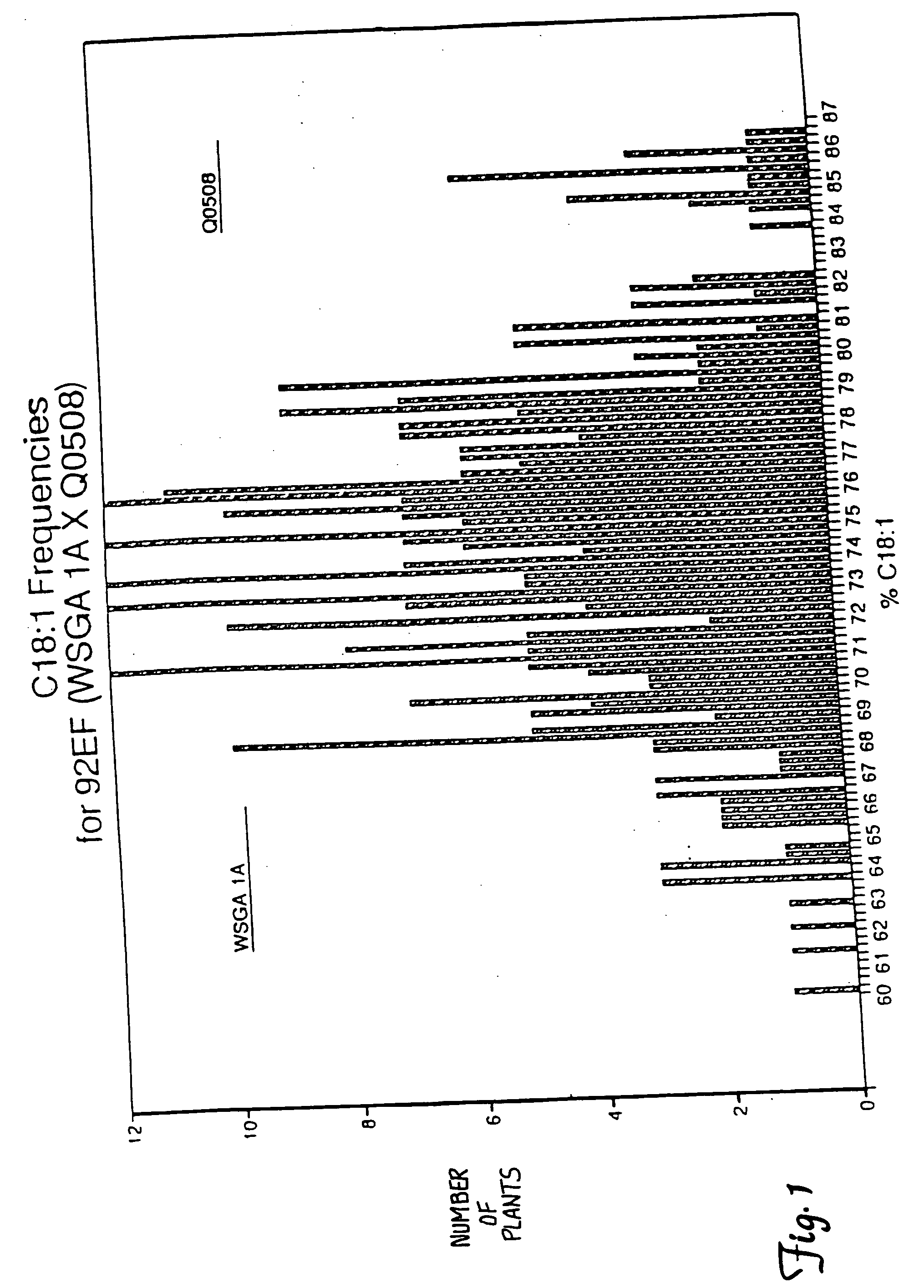
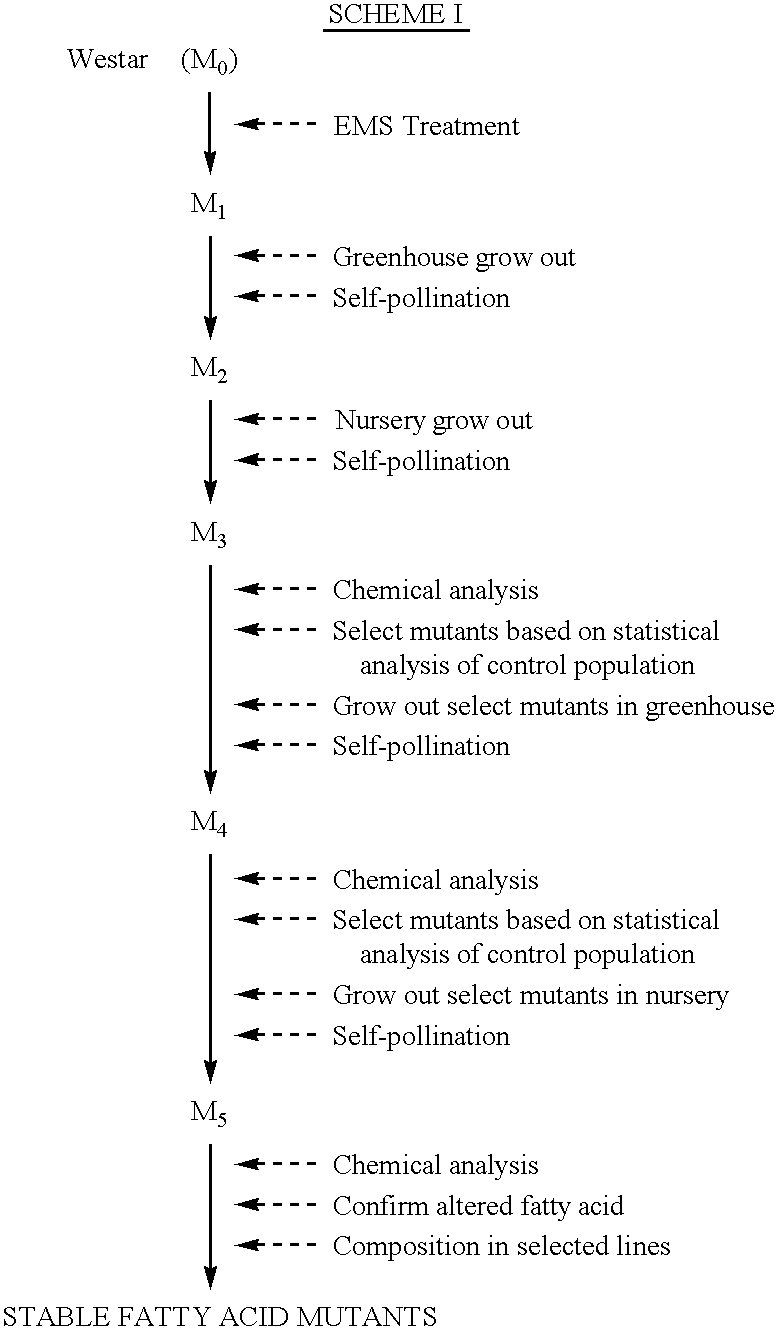
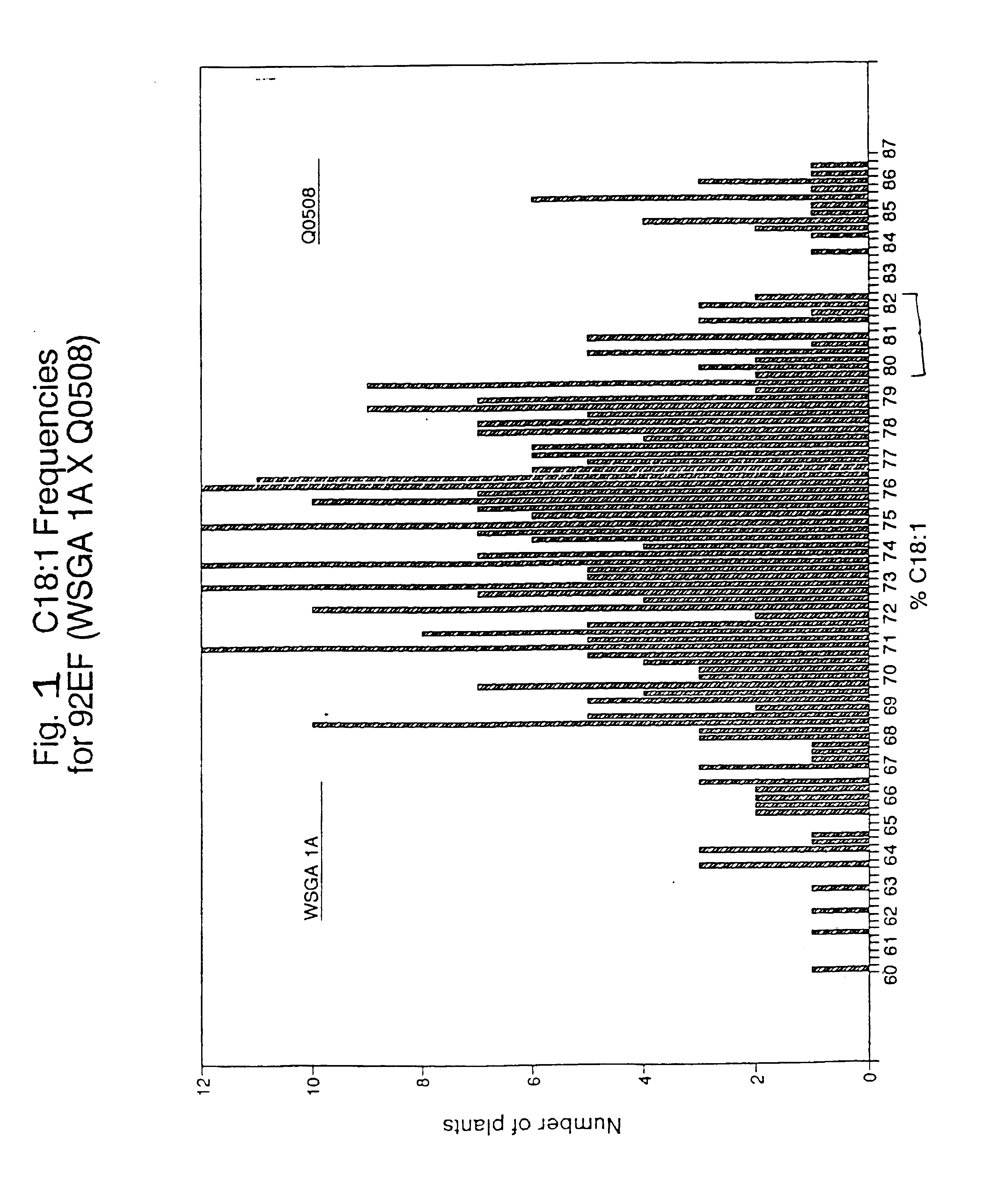
Seeds, plants and oils are provided having high oleic acid; low linoleic acid; and low linoleic acid plus linolenic acid; and advantageous functional or nutritional properties. Plants are disclosed that contain a mutation in a delta-12 or delta-15 fatty acid desaturase gene. Preferred plants are rapeseed and sunflower plants. Plants carrying such mutant genes have altered fatty acid composition in seeds. In one embodiment, a plant contains a mutation in a region having the conserved motif His-Xaa-Xaa-Xaa-His, found in delta-12 and delta-15 fatty acid desaturases. A preferred motif has the sequence His-Glu-Cys-Gly-His. A preferred mutation in this motif has the amino acid sequence His-Lys-Cys-Gly-His. Nucleic acid fragments are disclosed that comprise a mutant delta-12 or delta-15 fatty acid desaturase gene sequence.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Hepatocellular chimeraplasty
InactiveUS6524613B1Decrease in levelReduce riskOrganic active ingredientsBiocideGenetic ChangeFhit gene
The present invention concerns compositions and methods for the introduction of specific genetic changes in endogenous genes of the cells of an animal. The genetic changes are effected by oligonucleotides or oligonucleotide derivatives and analogs, which are generally less than about 100 nucleotides in length. The invention provides for macromolecular carriers, optionally incorporating ligands for clathrin coated pit receptors. In one embodiment the ligand is a lactose or galactose and the genetic changes are made in hepatocytes. By means of the invention up to 40% of the copies of a target gene have been changed in vitro. Repair of mutant genes having a Crigler-Najjar like phenotype and Hemophilia B phenotype were observed.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV +1
Fatty acid desaturases and mutant sequences thereof
InactiveUS20070163002A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesHigh oleic acidRapeseed
Seeds, plants and oils are provided having high oleic acid; low linoleic acid; and low linoleic acid plus linolenic acid; and advantageous functional or nutritional properties. Plants are disclosed that contain a mutation in a delta-12 or delta-15 fatty acid desaturase gene. Preferred plants are rapeseed and sunflower plants. Plants carrying such mutant genes have altered fatty acid composition in seeds. In one embodiment, a plant contains a mutation in a region having the conserved motif His-Xaa-Xaa-Xaa-His, found in delta-12 and delta-15 fatty acid desaturases. A preferred motif has the sequence His-Glu-Cys-Gly-His. A preferred mutation in this motif has the amino acid sequence His-Lys-Cys-Gly-His. Nucleic acid fragments are disclosed that comprise a mutant delta-12 or delta-15 fatty acid desaturase gene sequence.
Owner:DEBONTE LORIN R +2
Fatty acid desaturases and mutant sequences thereof
InactiveUS20050262591A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesHigh oleic acidRapeseed
Seeds, plants and oils are provided having high oleic acid; low linoleic acid; and low linoleic acid plus linolenic acid; and advantageous functional or nutritional properties. Plants are disclosed that contain a mutation in a delta-12 or delta-15 fatty acid desaturase gene. Preferred plants are rapeseed and sunflower plants. Plants carrying such mutant genes have altered fatty acid composition in seeds. In one embodiment, a plant contains a mutation in a region having the conserved motif His-Xaa-Xaa-Xaa-His, found in delta-12 and delta-15 fatty acid desaturases. A preferred motif has the sequence His-Glu-Cys-Gly-His. A preferred mutation in this motif has the amino acid sequence His-Lys-Cys-Gly-His. Nucleic acid fragments are disclosed that comprise a mutant delta-12 or delta-15 fatty acid desaturase gene sequence.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Brassica or helianthus plants having mutant delta-12 or delta-15 sequences
InactiveUS7135614B1Improve the level ofSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBrassicaNucleotide
Plants are disclosed that contain a mutation in a delta-12 or delta-15 fatty acid desaturase gene. Preferred plants are rapeseed and sunflower plants. Plants carrying such mutant genes have altered fatty acid composition in seeds. In one embodiment, a plant contains a mutation in a region having the conserved motif His-Xaa-Xaa-His, found in delta-12 and delta-15 fatty acid desaturases. A preferred motif has the sequence His-Glu-Cys-Gly-His. A preferred mutation in this motif has the amino acid sequence His-Lys-Cys-Gly-His. Nucleic acid fragments are disclosed that comprise a sequence of at least 20 nucleotides from a mutant delta-12 or delta-15 fatty acid desaturase gene.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Enrichment and analysis method for circulating tumor cells
ActiveCN104178454AEnrichment cannot be effectiveEnrichmentApparatus sterilizationTumor/cancer cellsLysisWhite blood cell
The invention provides an enrichment and analysis method for circulating tumor cells. The method mainly comprises the following steps: subjecting a biological fluid sample to red blood cell lysis treatment; adding immune beads specifically bonding with white cells, red cells and / or platelets for incubation; and filtering cell suspension by using a filter membrane and enriching circulating tumor cells. According to the invention, through integration and optimization of CTCs enrichment methods such as red blood cell lysis treatment, an immune bead method and membrane filtration, the enrichment effect of the circulating tumor cells is greatly improved; with the method, the removal rate of leukocytes is greater than 99.9%, and the enrichment rate of tumor cells is greater than 80%. Meanwhile, the invention also provides a kit using the enrichment method for the circulating tumor cells and discloses a device for enrichment of the circulating tumor cells. The invention also provides an analysis method for the enriched circulating tumor cells. With the analysis method, analysis of dynamic changes like the amount of tumor cells, gene mutation and gene expression profiles can be realized.
Owner:SUREXAM BIO TECH
Agent for suppressing expression of dominant mutant gene
InactiveUS20130197061A1Inhibit expressionMaintain expressionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesWild typeGene
Owner:LSIP
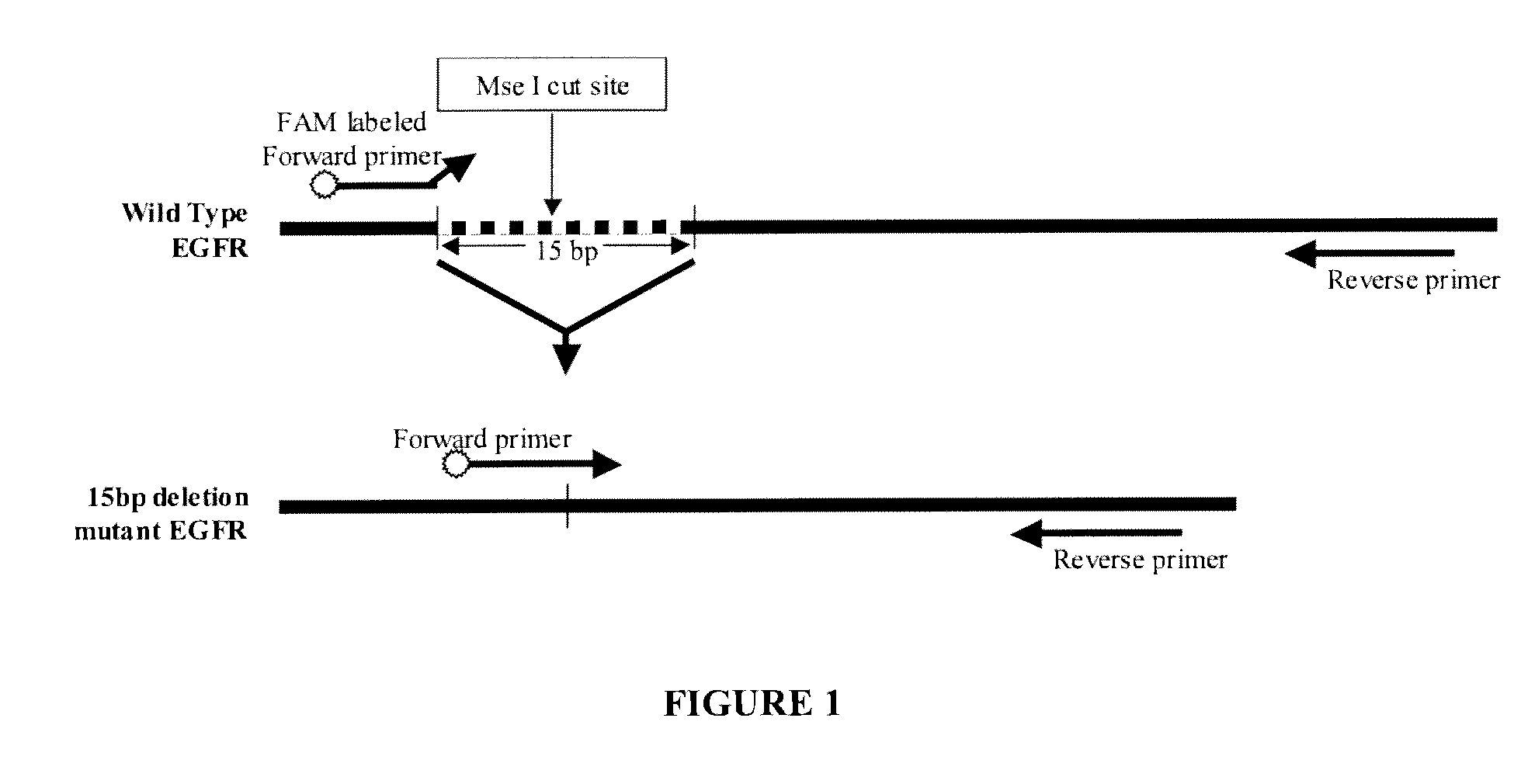
Primers, probes, kit and method for detecting human EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) gene mutations
ActiveCN102747157AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEGFR Gene MutationWild type
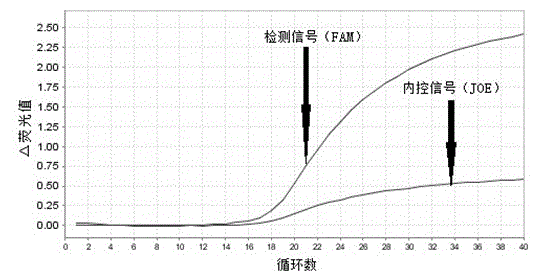
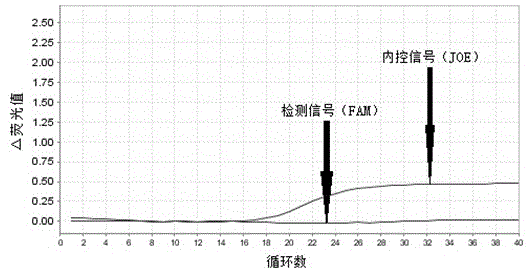
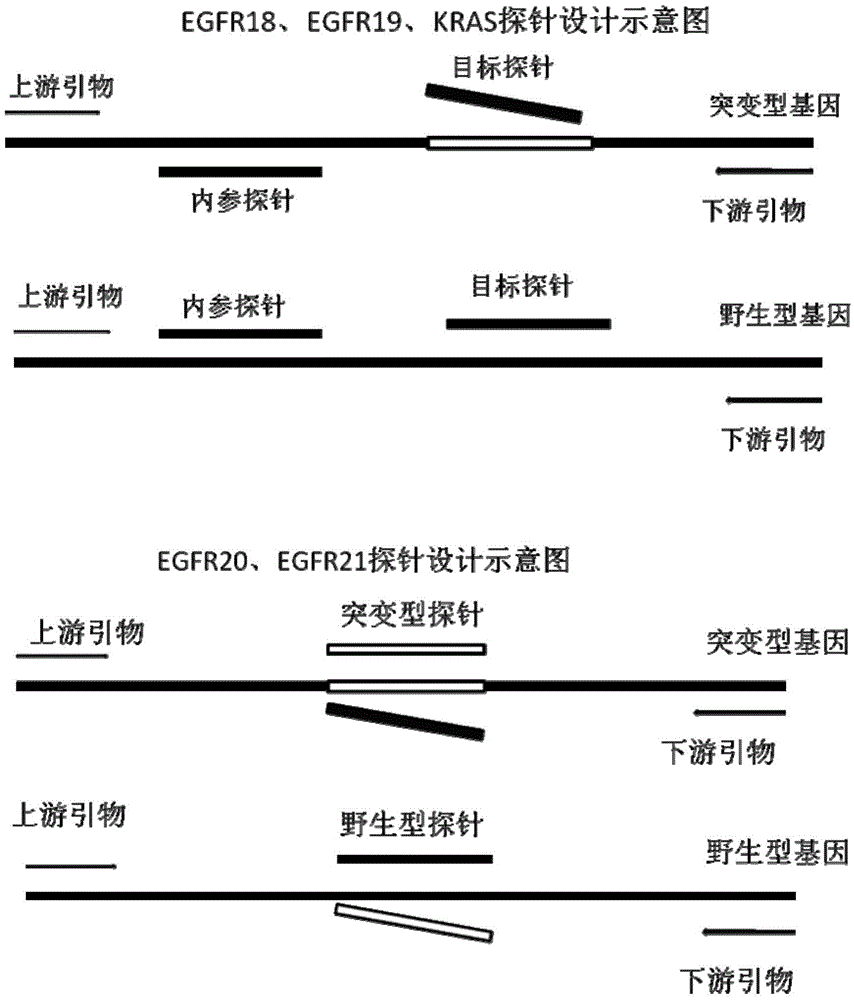
The invention provides primers, probes, kit and method for detecting human EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) gene mutations. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) providing the primers and the probes; (2) processing detected samples and extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid); (3) carrying out fluorescent quantitation on components of a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) system; (4) amplifying target sequences of an EGFR gene mutation to be detected; and (5) distinguishing wild type genes and mutant type genes by utilizing ARMS (amplification refractory mutation system) primers and judging results via the fluorescence intensity of an FAM and a JOE. The primers, probes and method provided by the invention have the beneficial effects that 29 kinds of mutations on the EGFR genes can be simultaneously detected, so that the sensitivity is high, the specificity is strong and the detection speed is high; and the whole detection process only takes 60 minutes.
Owner:武汉海吉力生物科技有限公司
Primer, probe and kit for detecting EGFR and/or K-ras genetic mutation
ActiveCN105624309AEasy to optimizeMeet the requirements of rapid detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationK-ras GenesFluorescence
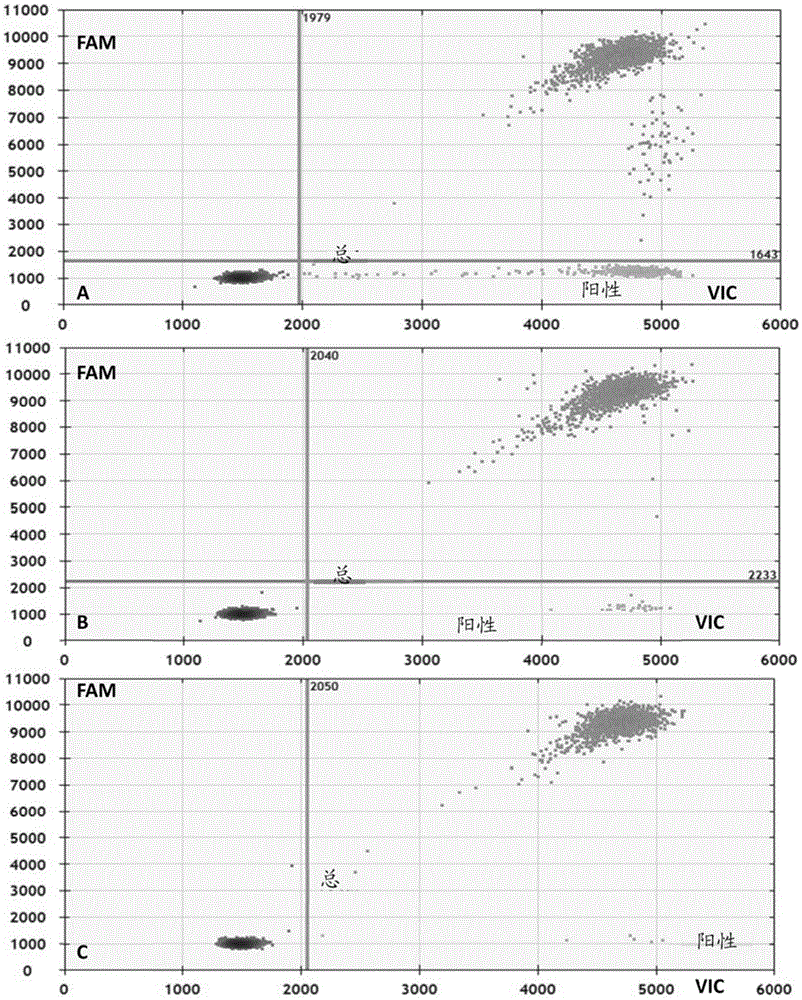
The invention discloses a primer and probe for detecting a human epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene and / or a K-ras gene, a kit containing the primer and the probe and a device for detecting genetic mutation on the basis of a digital PCR platform.The method for detecting the genetic mutation by means of the primer and the probe comprises the steps that the prime and the probe are provided; DNA of a sample to be detected is extracted; a fluorescent PCR reaction system capable of amplifying a mutant gene sequence is prepared; a target probe and an internal reference probe are utilized to be hybridized with amplified products respectively, and fluorescent signals of corresponding fluorescent groups are detected; existence of the genetic mutation is judged and / or the mutation rate is calculated according to the strength and proportion of the fluorescent signals of the target probe and the internal reference probe.According to the method for detecting the genetic mutation, the needed primers and probes are small in number, the optimization procedure is simple, related mutation of EGFR and / or K-ras gene can be qualitatively or quantitatively detected, and the detection sensitivity is high; a DNA sample with low initial amount can also be detected stably.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST
Genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently producing N-acetylglucosamine
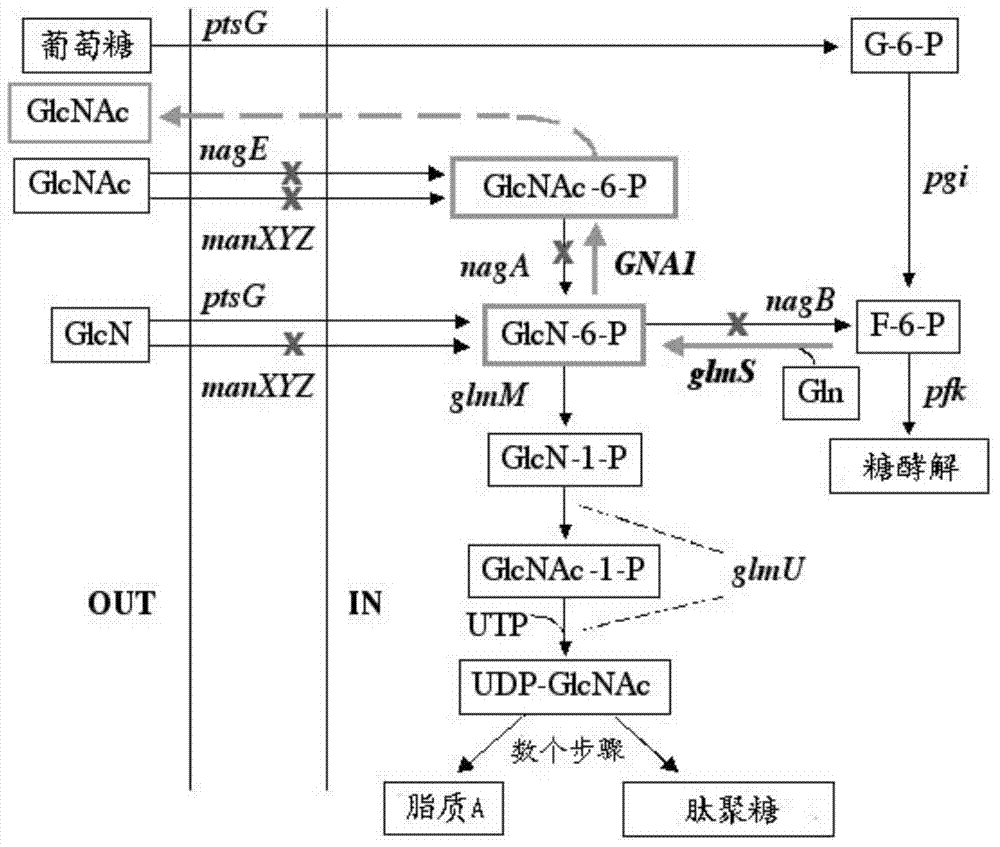
InactiveCN104293724AImprove fermentation yieldImprove stabilityBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention provides genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently producing N-acetylglucosamine. The genetically engineered bacteria are prepared by the following steps: integrating chromosome deficiency nag DCABE gene clusters of Escherichia coli, respectively connecting 6-glucosamine phosphate synthetase mutant genes and N-acetylglucosamine transferase genes which are respectively mediated by a T7 promoter and a Trc promoter with a gene expression cassette in series, wherein the 6-glucosamine phosphate synthetase mutant genes are obtained by mutating wild 6-glucosamine phosphate synthetase genes from an Escherichia coli W3110 strain source into A38T / R249C / G471S mutants. The genetically engineered bacteria constructed by the invention have the advantages of high N-acetylglucosamine fermentation yield and high strain stability and have wide industrial application prospects.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES & DEV CENT OF INDAL BIOTECH +1
SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) locus related to maize plant high character
ActiveCN102373278ASpeed up the breeding processMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyExon
The invention discloses an SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) locus related to a maize plant high character, which is the nucleotide 5248 from the 5' tail end in SEQ ID NO:1, the nucleotide 5248 from the 5' tail end in SEQ ID NO:1 is positioned in the 5th exon of a maize dwarf mutant gene br2 in a maize genome, and the nucleotide 5248 is T. Molecular markers of the invention can be used for maize breeding in different genetic backgrounds, can be used for the genetic improvement of maize; and the method and the marks have wide application prospects in the field of maize breeding.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Compositions and methods for inhibiting expression of a mutant gene
InactiveUS20050074757A1Inhibit expressionSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsWild typeDouble stranded
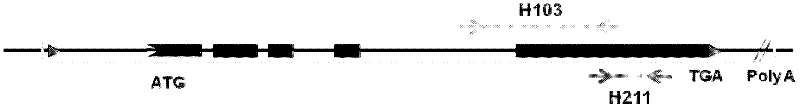
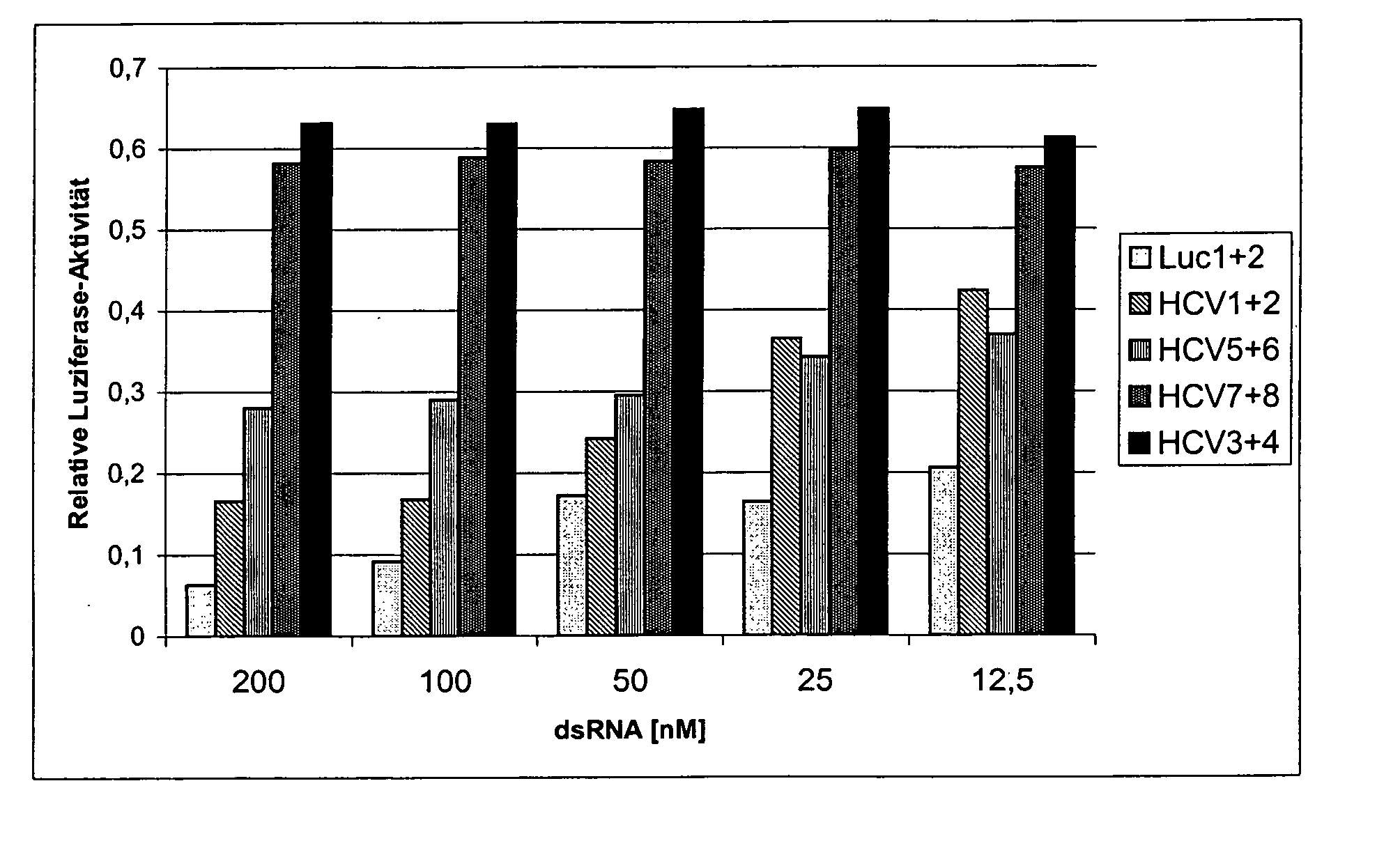
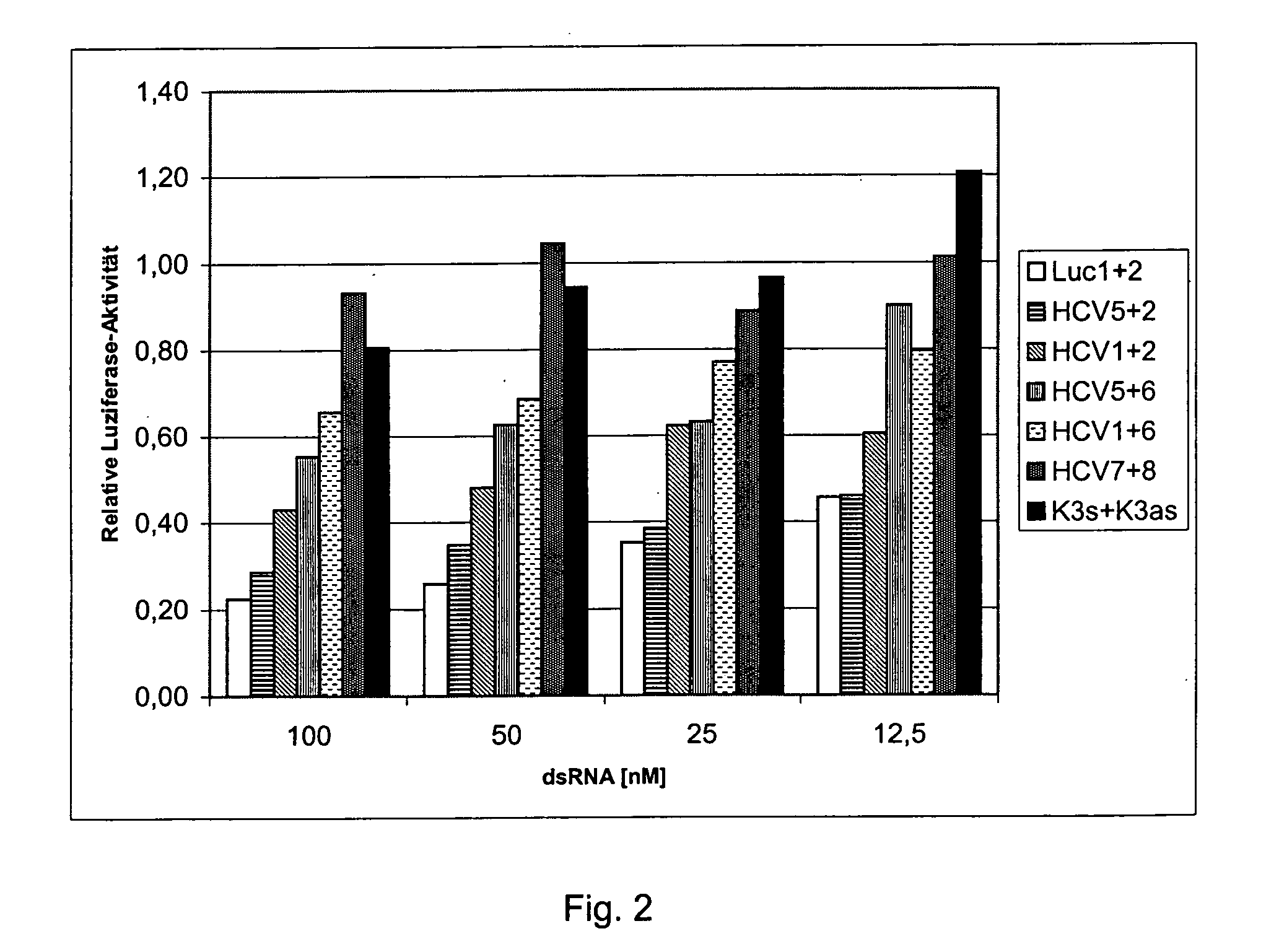
The present invention relates to a double-stranded ribonucleic acid (dsRNA) for inhibiting the expression of a mutant gene, comprising a complementary RNA strand having a complementary region that is substantially complementary to a portion of the mutant gene, and which is partially complementary to the corresponding wild-type gene. The invention further relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the dsRNA and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The pharmaceutical compositions are useful for inhibiting the expression of a target mutant gene, as well as for treating diseases caused by expression of the target gene. The invention also relates to methods for inhibiting the expression of a target mutant gene, as well as methods for treating diseases caused by the expression of the target gene.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
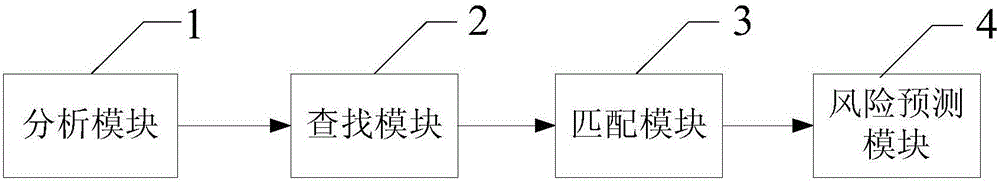
Disease risk predication method and disease risk predication system
InactiveCN106202936AReduce disease riskKnow Your RisksMedical simulationForecastingDisease riskSusceptibility gene
The invention relates to a disease risk predication method and system. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, receiving input gene sequencing result information; analyzing the input gene sequencing result information to obtain all mutant gene information; S2, looking up disease gene mutant information of corresponding gene sites from a precision medical knowledge base according to the gene sites corresponding to the mutant gene information, so as to obtain at least one piece of disease gene mutant information; S3, matching each piece of the disease gene mutant information with all the disease gene mutant information to obtain the similarity of each piece of the mutant gene information, and all the disease gene mutant information; and S4, obtaining a risk predication table aiming at the gene sequencing result information according to the similarity of each piece of the mutant gene information, and all the disease gene mutant information. By analyzing an association relation of susceptibility genes, mutation sites, mutation types and diseases, disease risk predication is carried out on healthy people and general disease risk grade predication is provided; disease risks in the future are reduced.
Owner:为朔医学数据科技(北京)有限公司
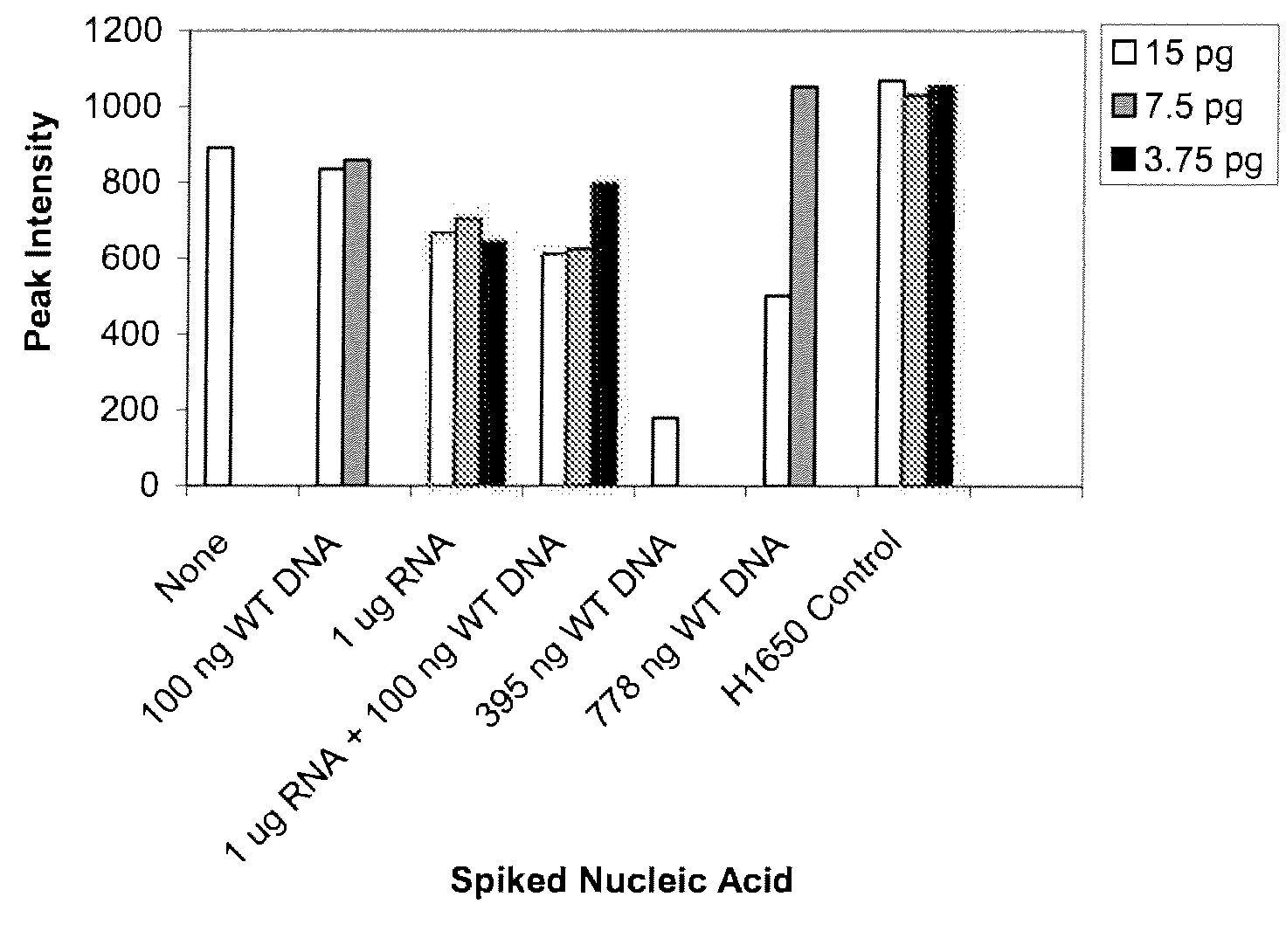
Nucleic acid detection combining amplification with fragmentation
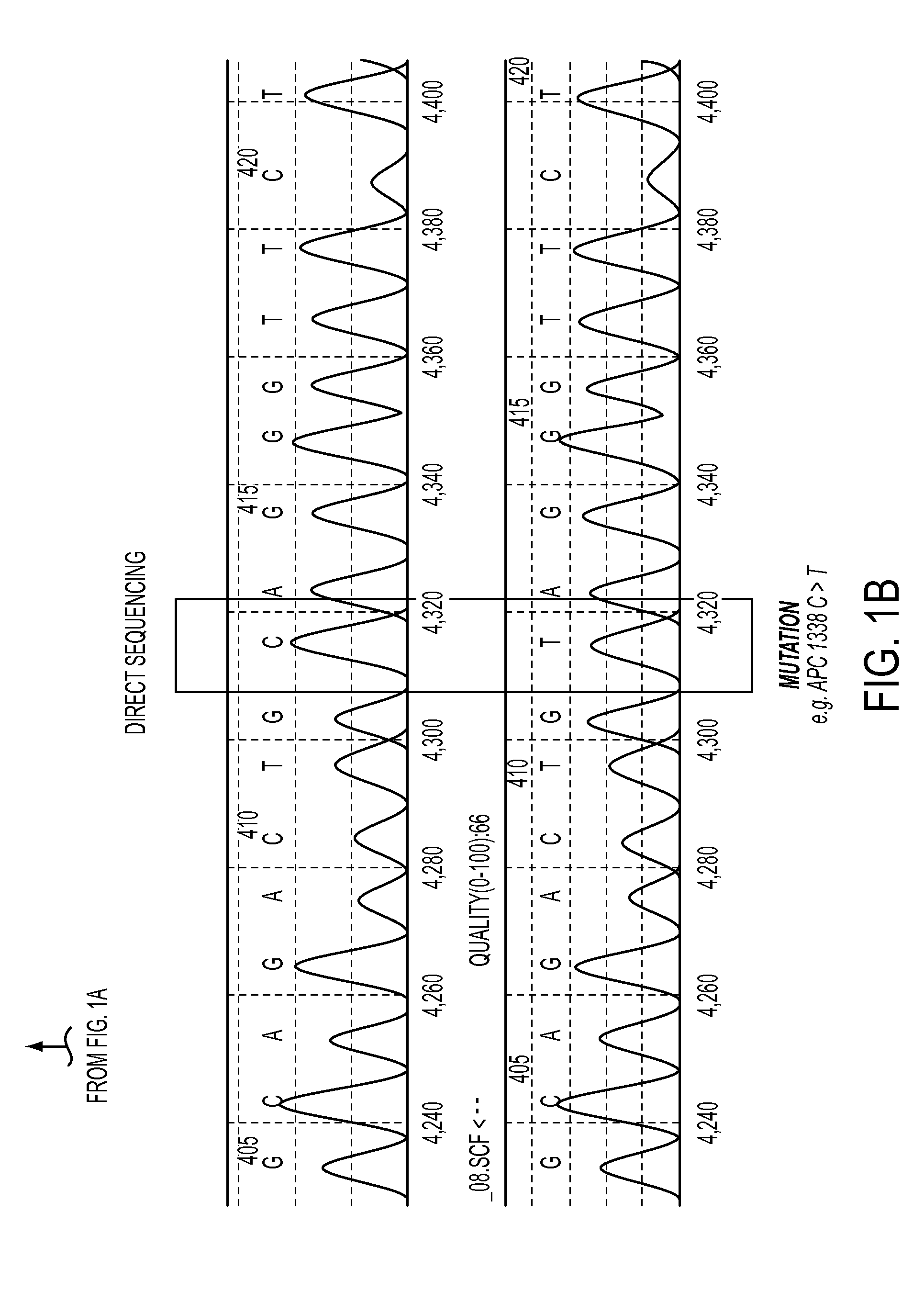
Provided herein are methods and compositions for detection of a nucleic acid target in a sample. The methods and compositions use primer directed amplification in conjunction with nucleic acid fragmentation. The methods have high sensitivity even in the presence of a large amount of non-target nucleic acid. Also provided are oligonucleotides and kits useful in the method. Exemplary nucleic acid targets are those with mutant gene sequence such as mutant sequence of the EGFR, APC, TMPRSS2, ERG and ETV1 genes.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
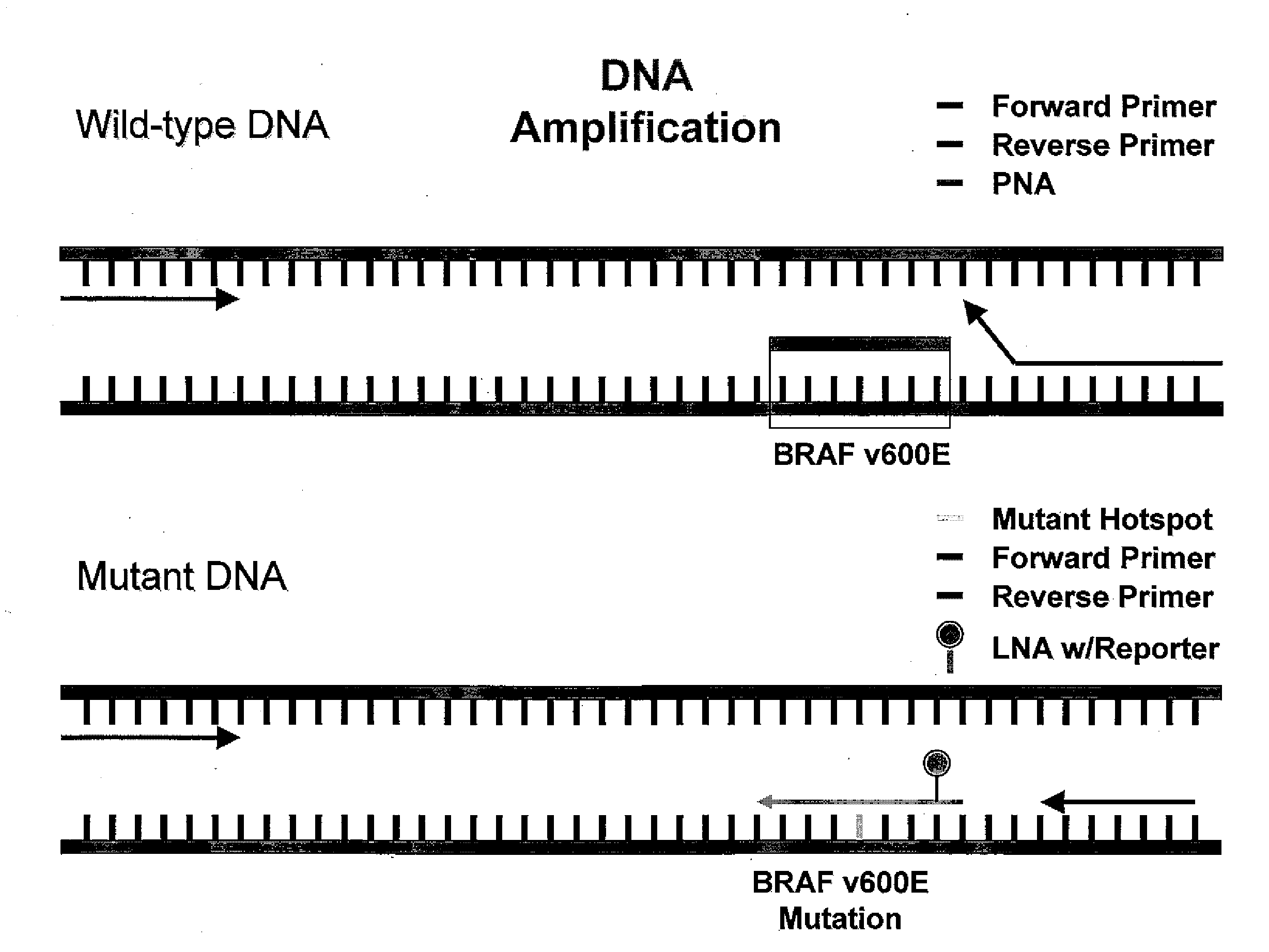
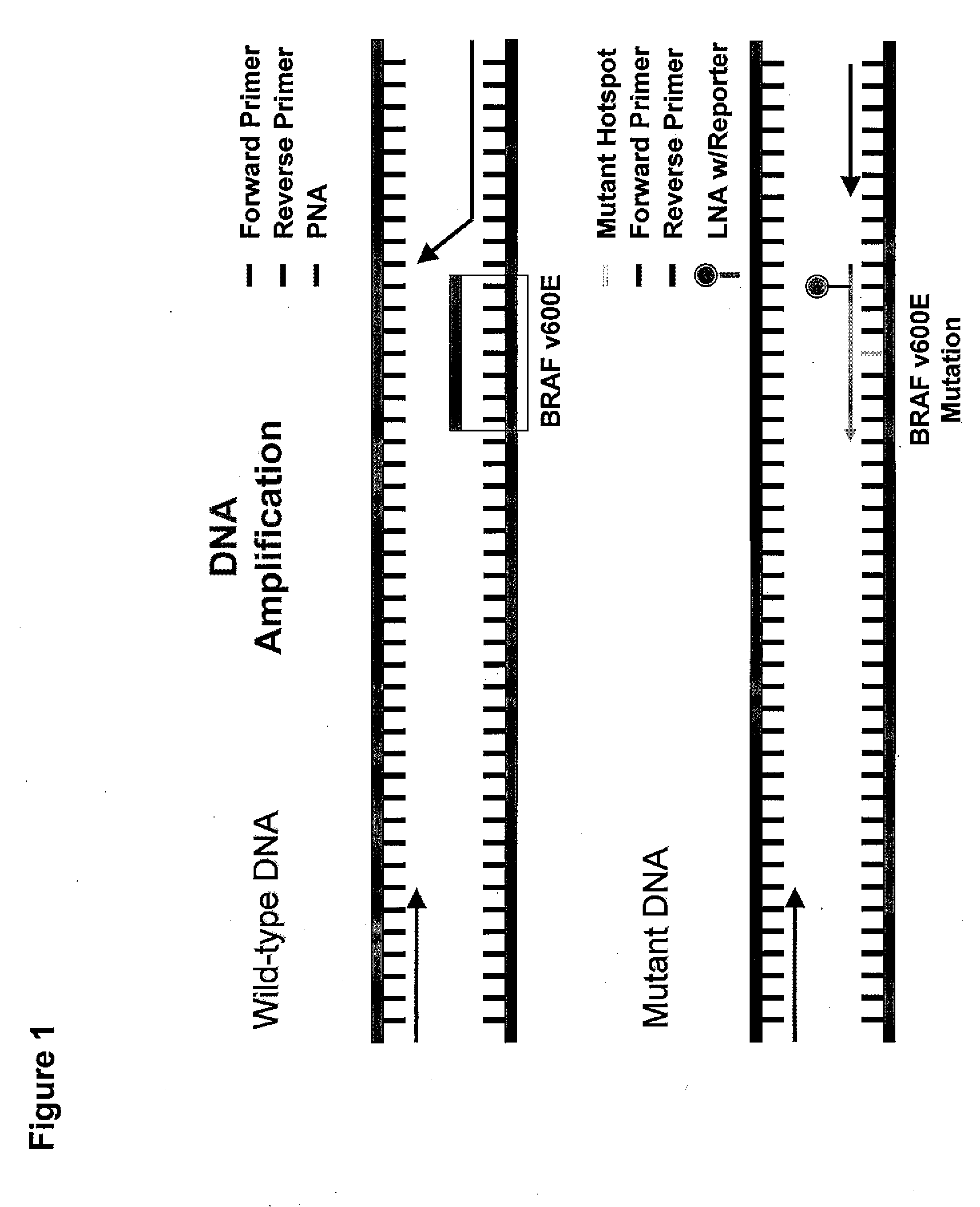
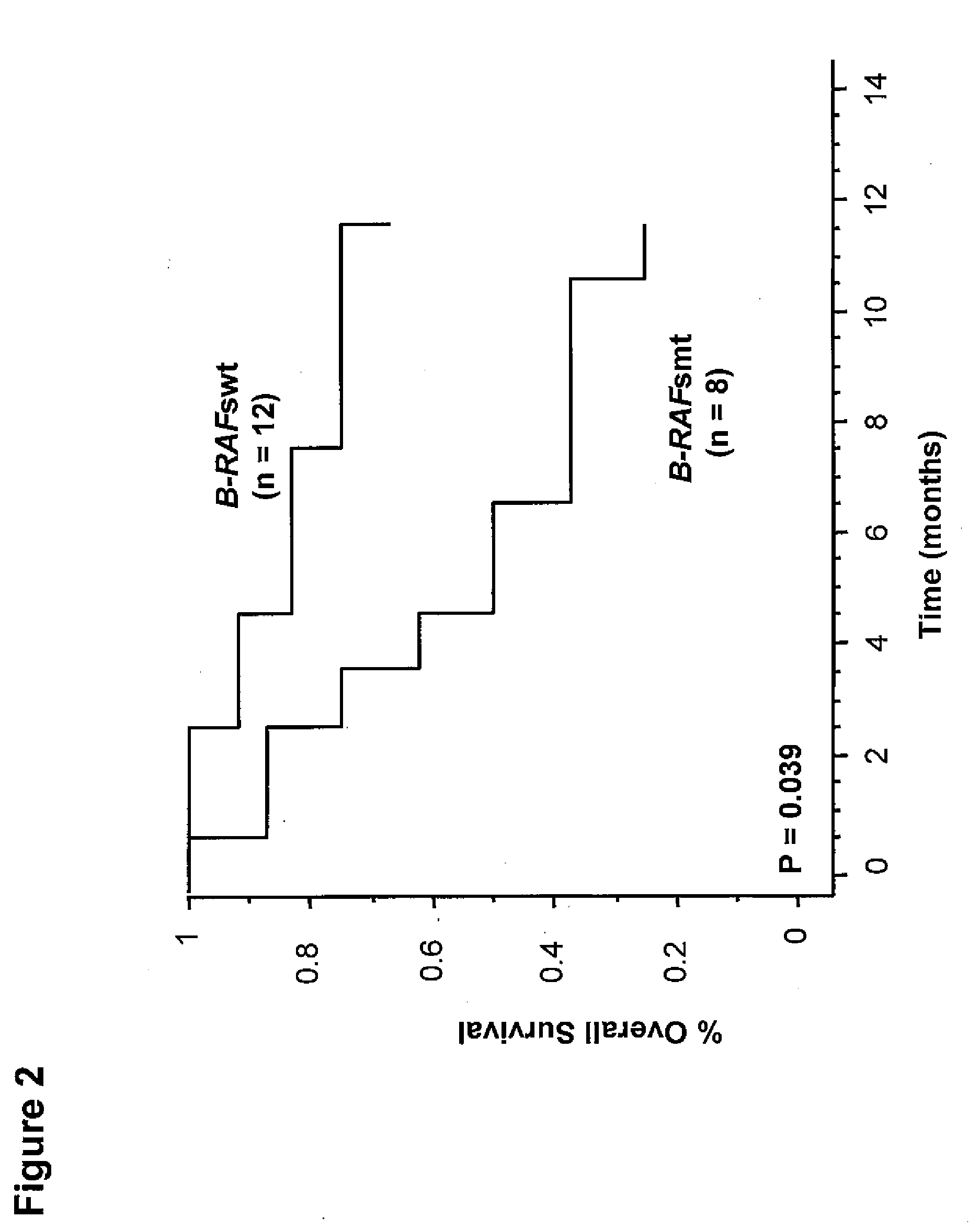
Utility of b-raf DNA mutation in diagnosis and treatment of cancer
The present invention discloses a method of detecting a wild-type or mutant B-RAF gene in a body fluid sample from a subject. Also disclosed are methods of using B-RAF as a biomarker for detecting cancer, predicting the outcome of cancer, and monitoring the treatment of cancer or the status of cancer. Furthermore, the invention discloses methods and compositions for detecting a mutant gene with a peptide nucleic acid clamp capable of hybridizing to a wild-type gene and a locked nucleic acid probe capable of hybridizing to a mutant of the gene.
Owner:JOHN WAYNE CANCER INST
Glucose oxidase mutant gene, expression and application thereof
InactiveCN101955953AIncrease secreted expressionIncrease enzyme activityFungiBacteriaYeastGlucose polymers
The invention discloses a glucose oxidase mutant gene, expression and application thereof. In the invention, 272 basic groups are changed through codon optimization and GC content change and the content of GC is reduced to 48.44% from 55.54% so as to obtain the glucose oxidase mutant gene, wherein the basic group is represented by SEQ ID NO.2. The glucose oxidase mutant gene is transferred into pichia yeast to express; the experimental result shows that the secretory expression level of the glucose oxidase mutant gene in the pichia yeast is significantly improved by comparing with the same before mutation; compared with partial research at home and abroad, the final secretory expression of the glucose oxidase mutant gene achieves high expression level, thereby building the foundation for further expansion of industrial production. The determination of enzymatic properties of the glucose oxidase mutant gene shows that the recombinant glucose oxidase protein expressed by the glucose oxidase mutant gene has good thermal stability and high enzyme activity.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Omega-aminotransferase mutant gene and application thereof
InactiveCN104894148AHigh enzyme productionHigh catalytic efficiencyTransferasesGenetic engineeringPropylamineNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses an omega-aminotransferase mutant gene and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of the molecular biological technology. The nucleotide sequence of the omega-aminotransferase mutant gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The omega-aminotransferase amino acid sequence embodied by the code of the omega-aminotransferase mutant gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The omega-aminotransferase mutant gene is firstly provided, and the omega- aminotransferase corresponding to the code of the omega-aminotransferase mutant gene has a high enzyme amount, so that the biological catalysis and conversion efficiency is improved in industrial production. The invention further provides the application of the omega-aminotransferase embodied by the code of the omega-aminotransferase mutant gene in preparation of trifluoro-propylamine. The trifluoro-propylamine is added to a buffer solution to serve as the substrate for the reaction, and then products of trifluoromethyl amine compounds are collected from the reaction liquid. The method for preparing the trifluoro-propylamine has the obvious advantages that the reaction conditions are mild, no pollution is caused, and the process is simple.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Bacterial laccase mutant protein, recombinant expression plasmid, transformed engineered strain and fermentation preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104087560AImprove stabilityIncrease temperatureBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMutated proteinGenetic engineering
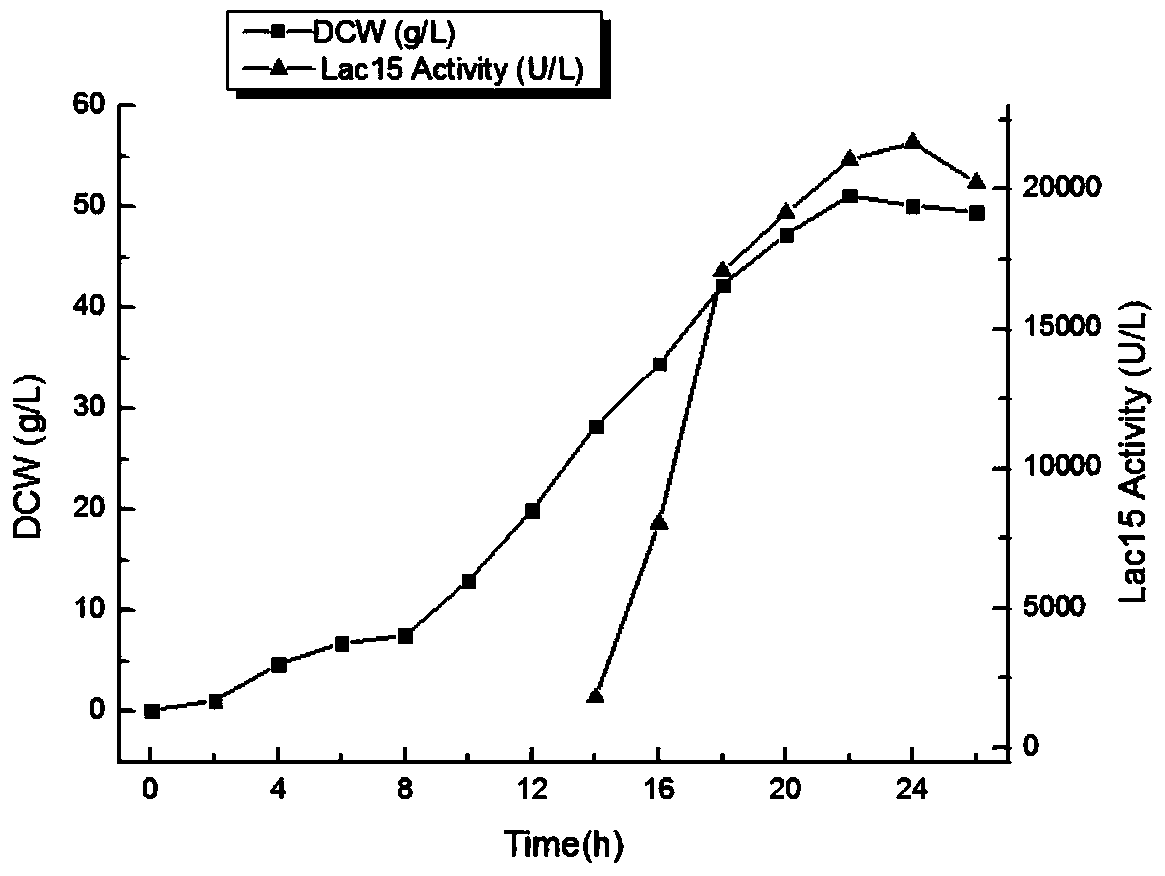
The invention discloses a bacterial laccase mutant protein, which is characterized in that the mutant protein amino acid sequence is obtained by deletion mutation of the 323rd glycine residue to the 332rd glycine residue in the bacterial laccase amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1. Through a genetic engineering reconstruction method, a stability improved bacterial laccase protein coding gene, its expression plasmid and engineered bacteria can be obtained, and after large-scale fermentation and induced expression of the engineered bacteria, the stability improved bacterial laccase protein can be obtained. According to the invention, the marine uncultured microorganism source bacterial laccase Lac15 is taken as the foundation, and by means of genetic engineering reconstruction, mutant gene can be obtained. At the same time, a recombinant escherichia coli is employed to conduct high-density culture for high-efficiency expression of the bacterial laccase mutant protein. According to the invention, the stability and yield of the bacterial laccase are greatly improved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
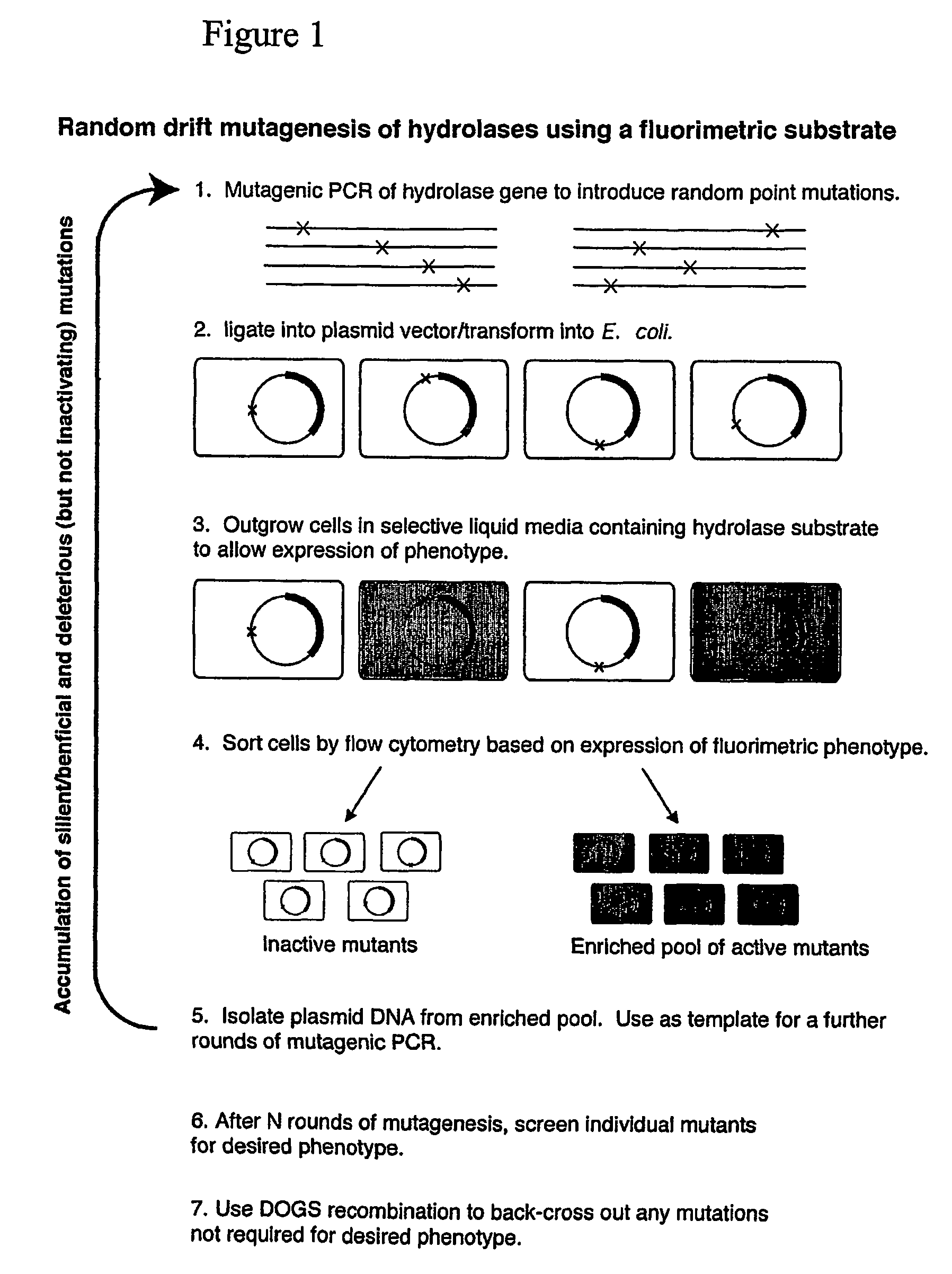
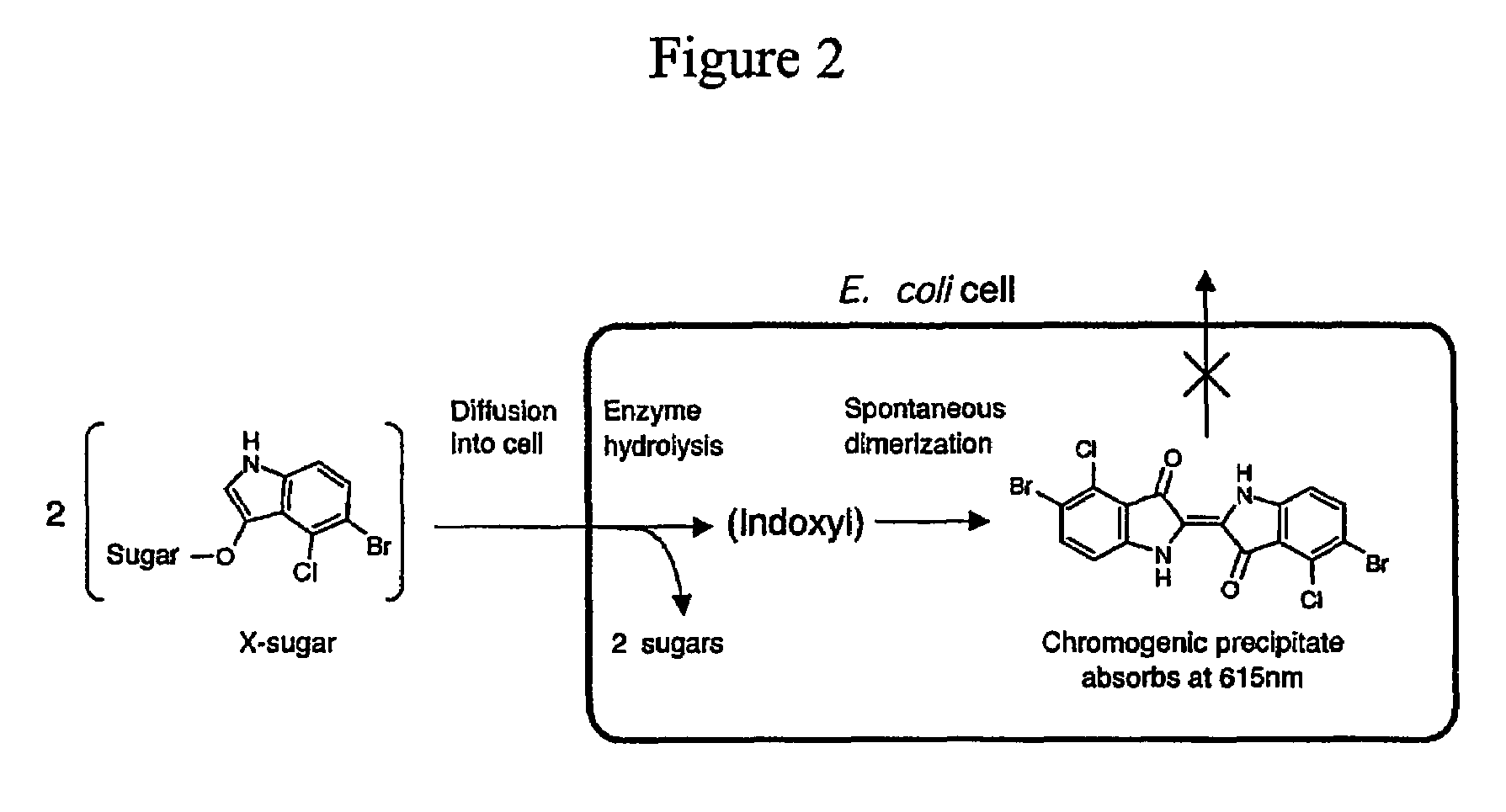
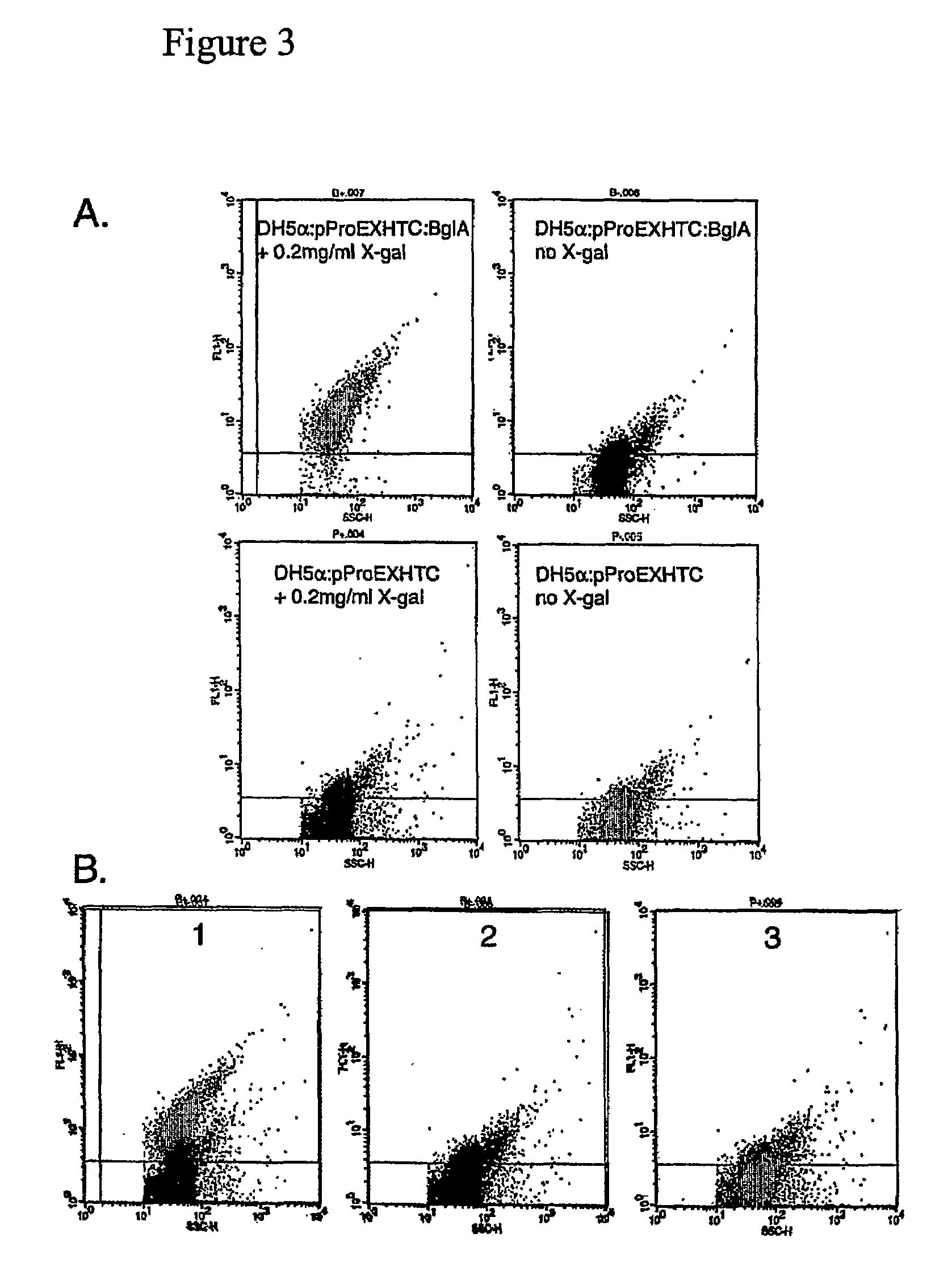
Random drift mutagenesis
A method for producing a mutant gene encoding a functional gene product comprising: (a) introducing one or more mutations into a gene to form a mutated gene; (b) providing the mutated gene to a host microorganism; (c) culturing the host microorganism containing the mutated gene under conditions which allow expression of the mutant gene product; and (d) selecting a host microorganism capable of producing a functional gene production from the mutated gene.
Owner:MACQUARIE UNIV
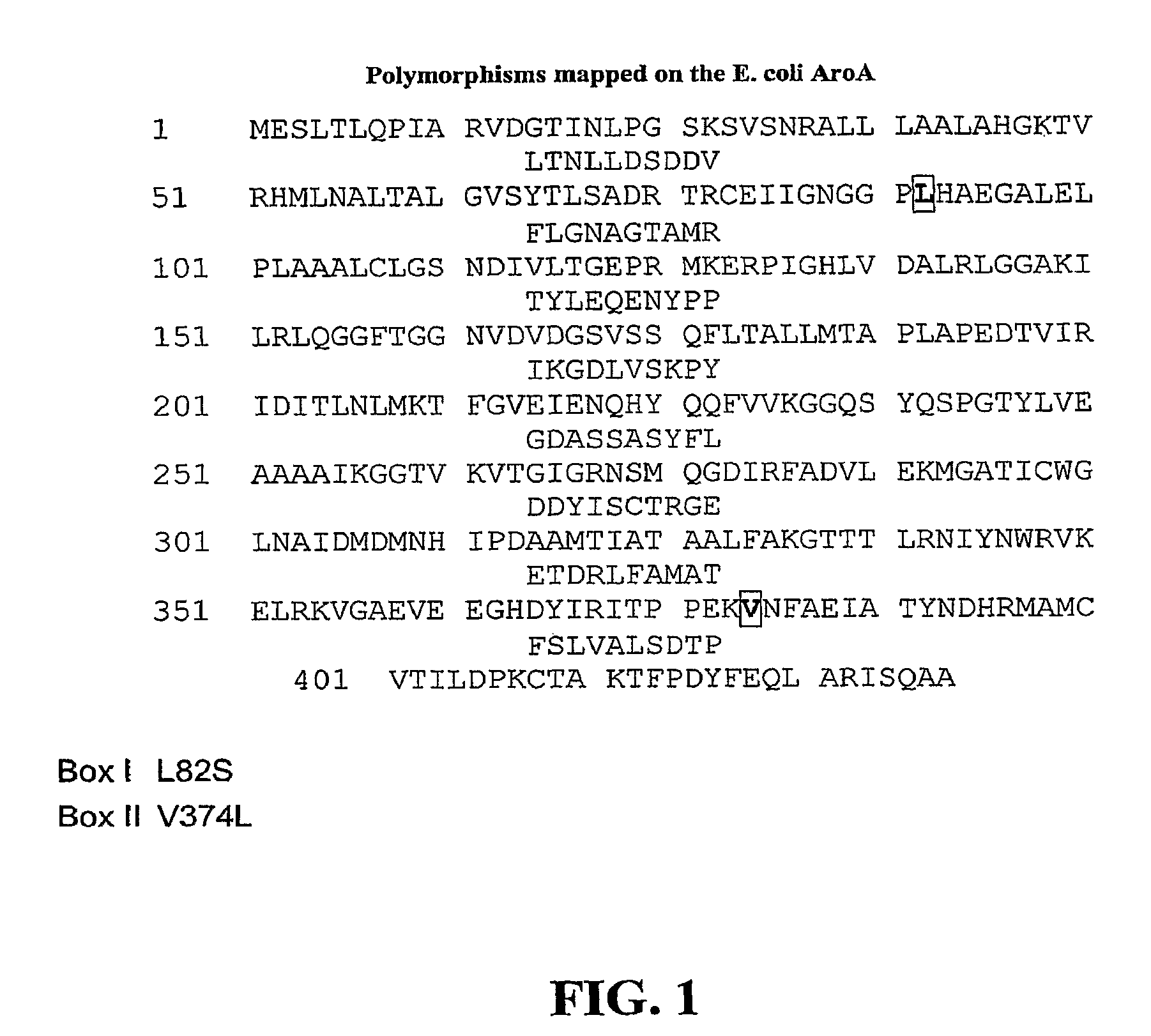
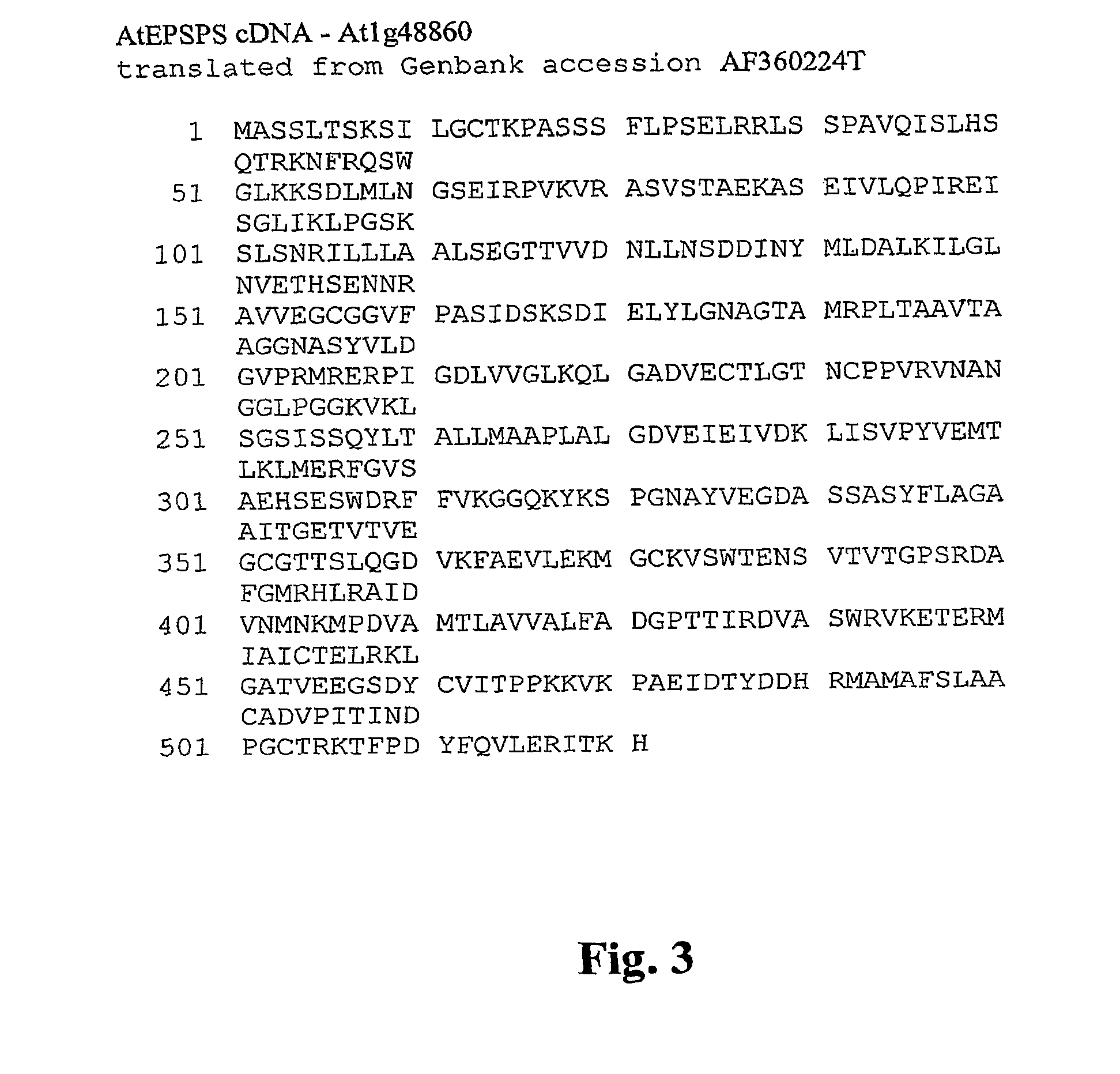
EPSPS mutants
The present invention relates to the production of a non-transgenic plant resistant or tolerant to a herbicide of the phosphonomethylglycine family, e.g., glyphosate. The present invention also relates to the use of a recombinagenic oligonucleobase to make a desired mutation in the chromosomal or episomal sequences of a plant in the gene encoding for 5-enol pyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS). The mutated protein, which substantially maintains the catalytic activity of the wild-type protein, allows for increased resistance or tolerance of the plant to a herbicide of the phosphonomethylglycine family, and allows for the substantially normal growth or development of the plant, its organs, tissues or cells as compared to the wild-type plant irrespective of the presence or absence of the herbicide. Additionally the present invention relates to mutant E. coli cells that contain mutated EPSPS genes.
Owner:CIBUS
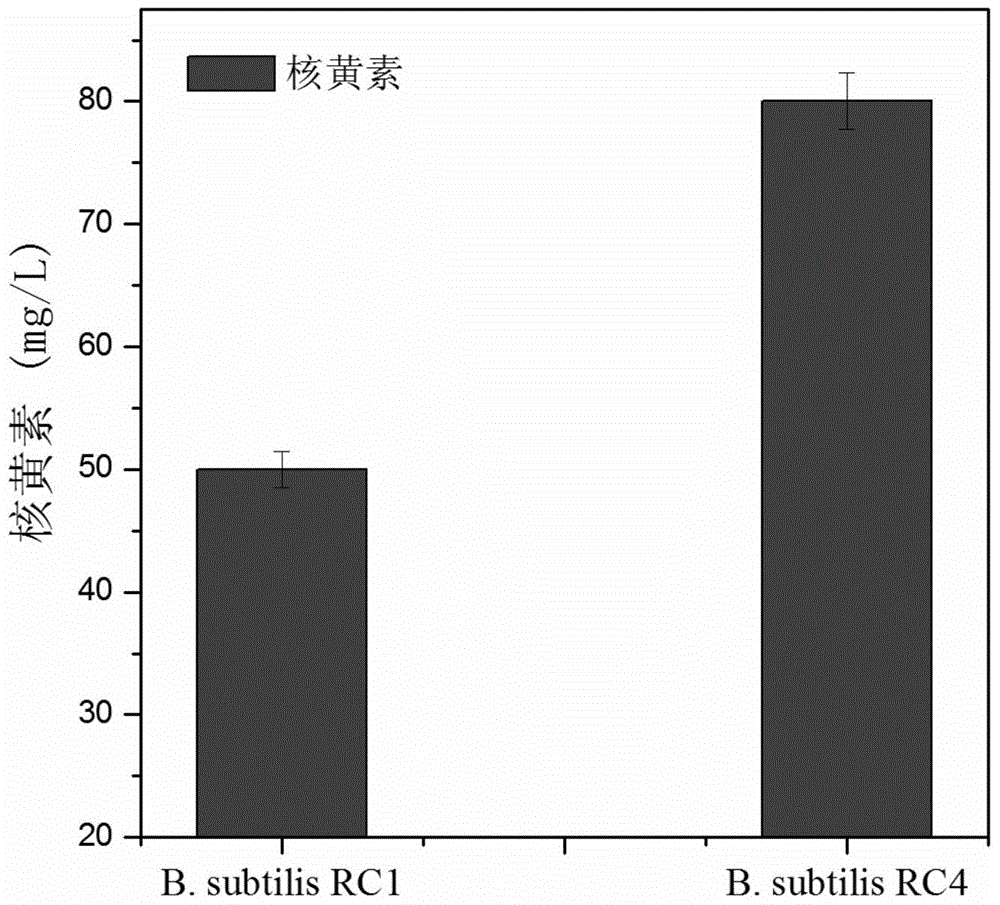
Bacillus subtilis adenylosuccinate synthetase mutant gene purA and applications thereof
ActiveCN103952419AImprove the ability to synthesize riboflavinClear genetic backgroundBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAdenylosuccinateMicrobiology
The invention discloses a Bacillus subtilis adenylosuccinate synthetase mutant gene purA and applications thereof. The sequence of the Bacillus subtilis adenylosuccinate synthetase mutant gene purA is shown in SEQ ID No.1. Engineering bacteria containing the Bacillus subtilis adenylosuccinate synthetase mutant gene purA (C725T) and built according to the invention are good in bio-safety and clear in genetic background, and the contained mutant gene purA (C725T) can significantly improve the riboflavin synthesis capacity of Bacillus subtilis, and under the condition of fermentation in a shaking flask, the level of riboflavin accumulation is increased by over 40%.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Screening method for new tumor antigen
ActiveCN109021062AReduce the number of experimentsSave moneyPeptide preparation methodsEnzyme digestionMajor histocompatibility
The invention provides a screening method for a tumor new antigen, and the method comprises: A, obtaining polypeptide sequences encoded corresponding to mutant genes of a tumor tissue cell; B, performing predicting on the affinity of each polypeptide sequence with a major histocompatibility complex MHCI, and screening a polypeptide sequence having the affinity exceeding a specified threshold; andC, predicting polypeptide enzyme digestion sites of the polypeptide sequences encoded corresponding to the mutant genes, and retaining the polypeptide sequences in which the enzyme digestion sites arenot in the polypeptide sequence having the affinity exceeding the specified threshold and which can be separated into segments and cannot be enzyme-digested, as candidate polypeptide sequences of thetumor new antigen. The screening method for the tumor new antigen facilitates subsequent further targeted experiments based on the screening for the tumor new antigen, can greatly reduce the number of the experiments, and saves time, labors and expenditures.
Owner:BETA PHARM SUZHOU LTD
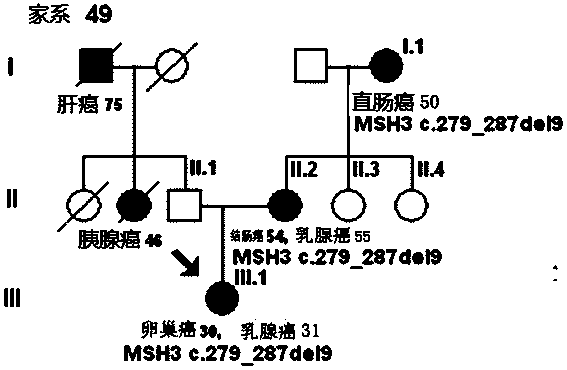
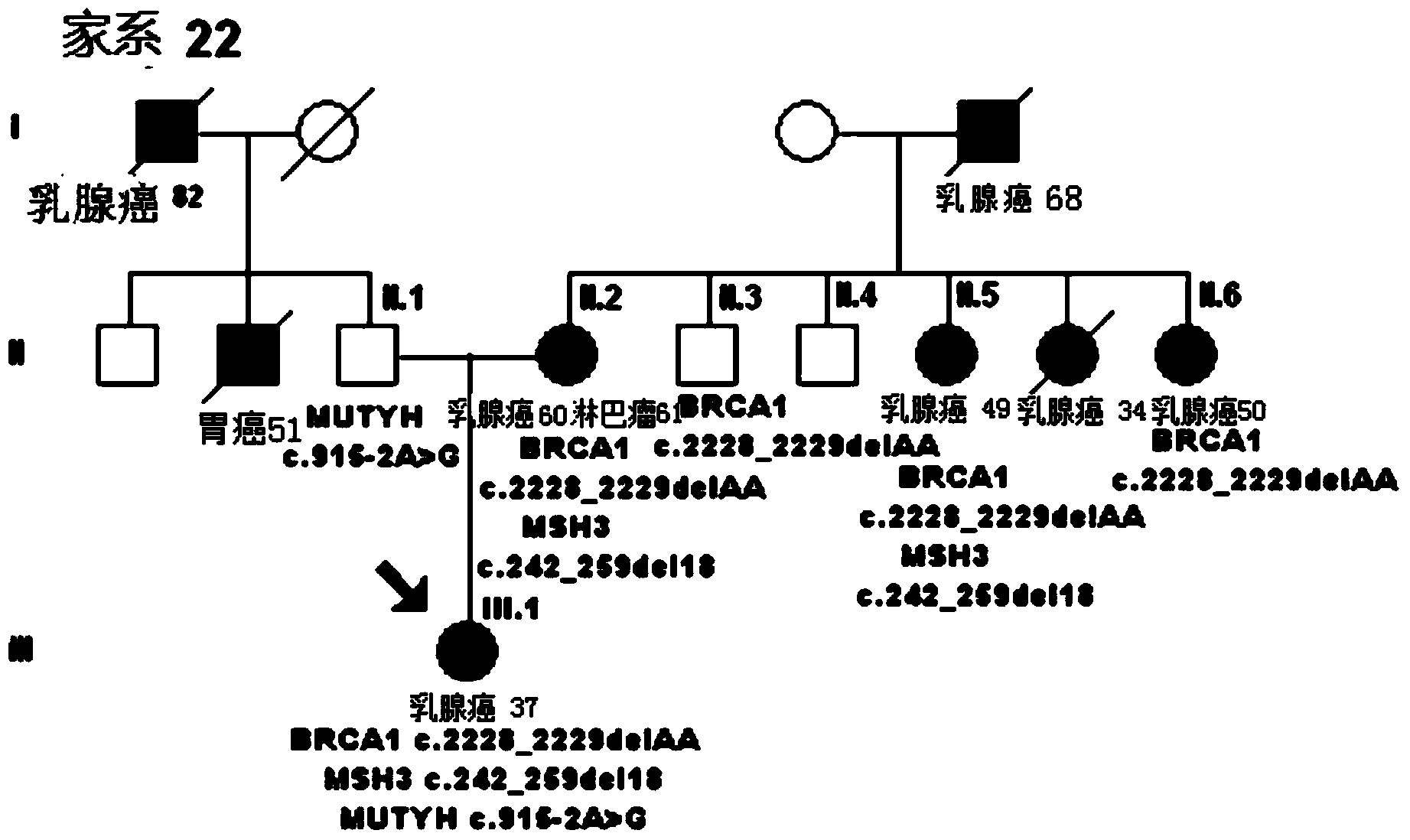
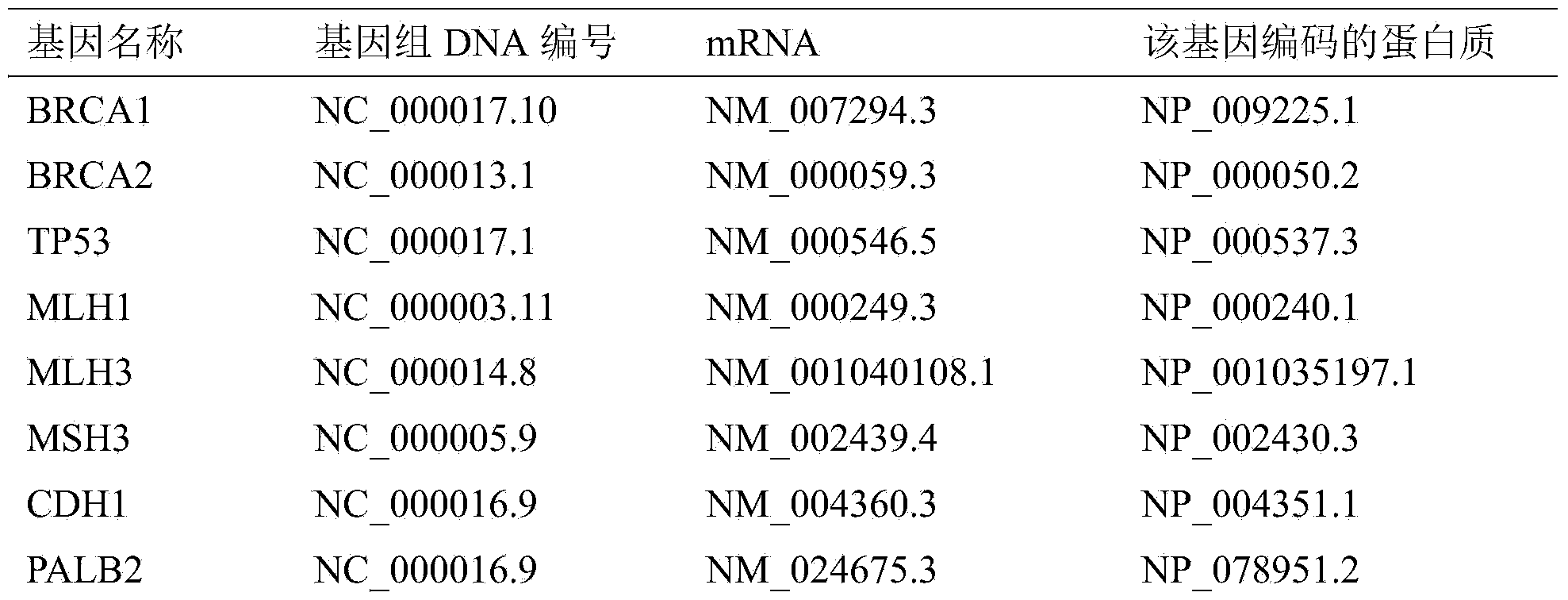
Mutant gene group for mammary cancer risk assessment and detection kit thereof
InactiveCN103981273AImprove detection efficiencyImprove the detection rateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBrca1 geneCvd risk
The invention discloses a mutant gene group for mammary cancer risk assessment and a detection kit thereof. The mutant gene group is a mutant gene set comprising the following seven genes: BRCA1 gene, BRCA2 gene, TP53 gene, MLH1 gene, MLH3 gene, MSH3 gene and CDH1 gene. The mutant gene group of the seven genes totally carries 25 mutant sites disclosed as Table 3. The invention also discloses a detection kit of the mutant gene group for mammary cancer risk assessment, which comprises probes or primers for detecting the mutant genes in the mutant gene group. The detection kit disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high detection efficiency, high detection speed, high detectable rate and the like.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV SHANGHAI CANCER CENT
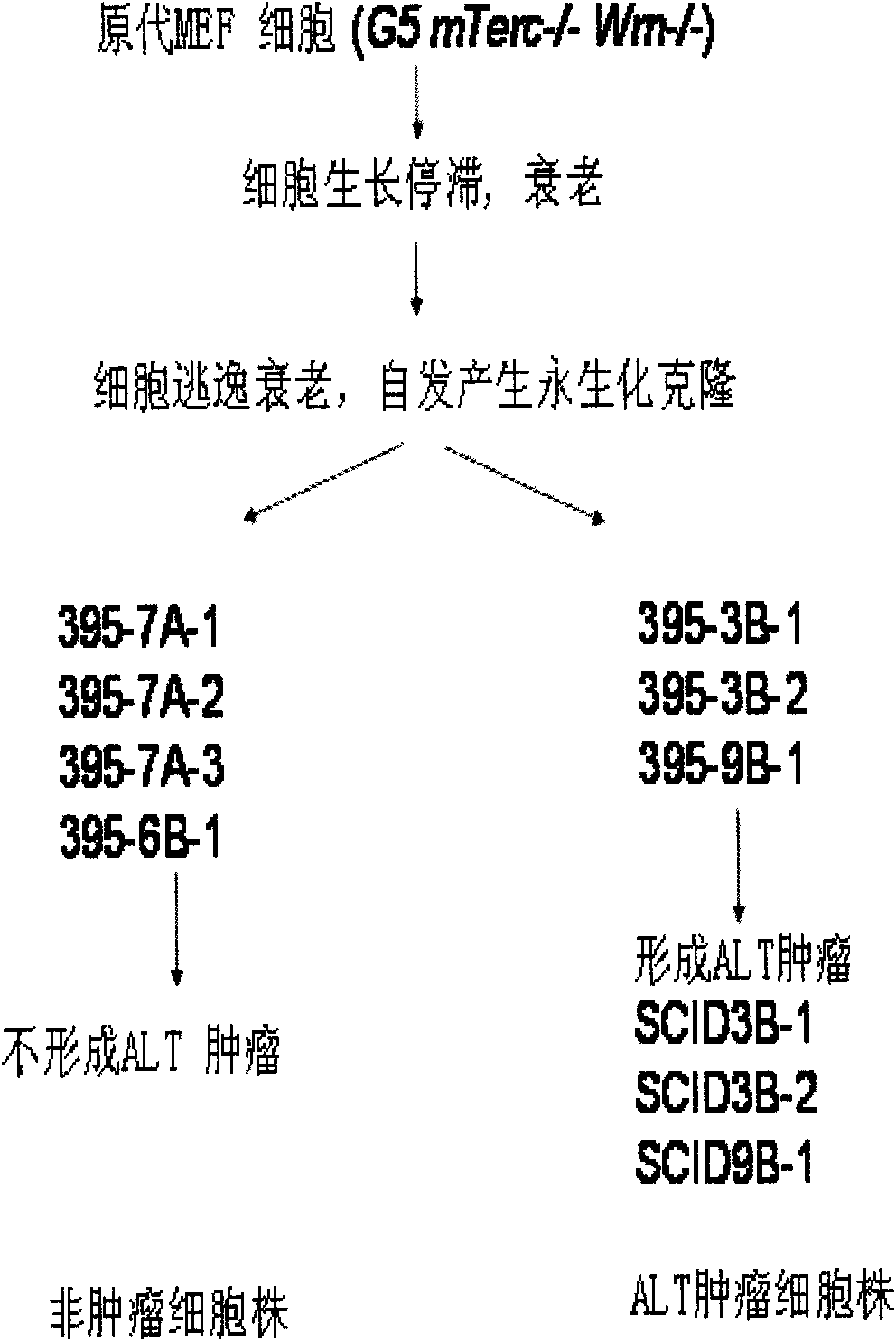
Peculiar p53 mutated protein-p53N236S of ALT tumor caused by progeria syndrome and application thereof
InactiveCN101805738APeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthMutated protein
The invention relates to a mutant gene p53A1243G caused by the point mutation of a tumor suppressor gene p53, encoded protein p53N236S and functions thereof, and application thereof to tumor diagnosis. First, the important functions of p53N236S in an ALT tumor caused by progeria syndrome are disclosed. The invention can be applied to the tumor diagnosis with p53N236S as the target molecule, the screening of anticancer medicine and cancer treatment strategies, and has important significance in preventing tumors caused by aging.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com