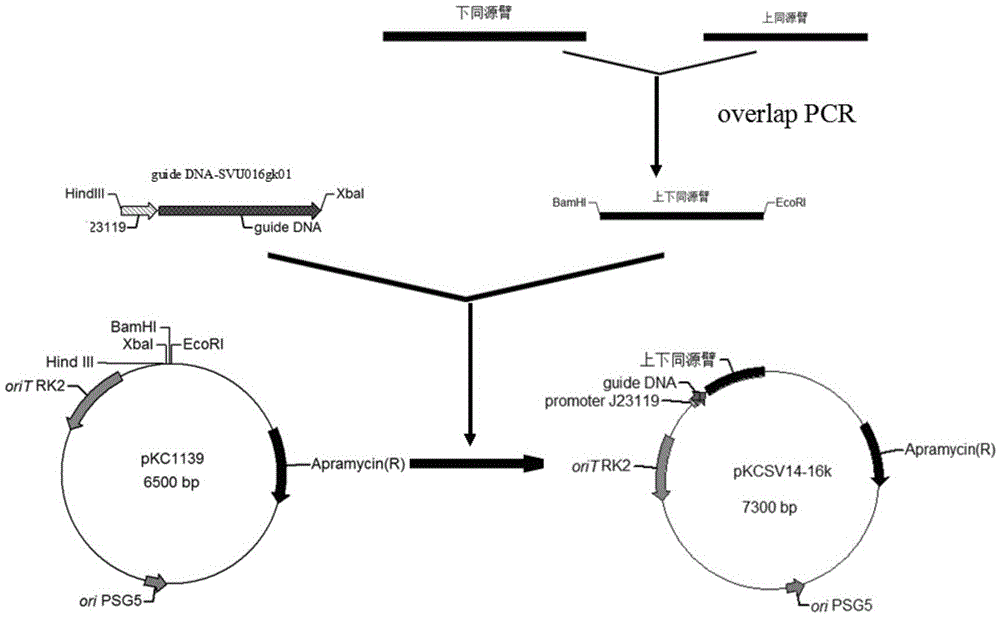
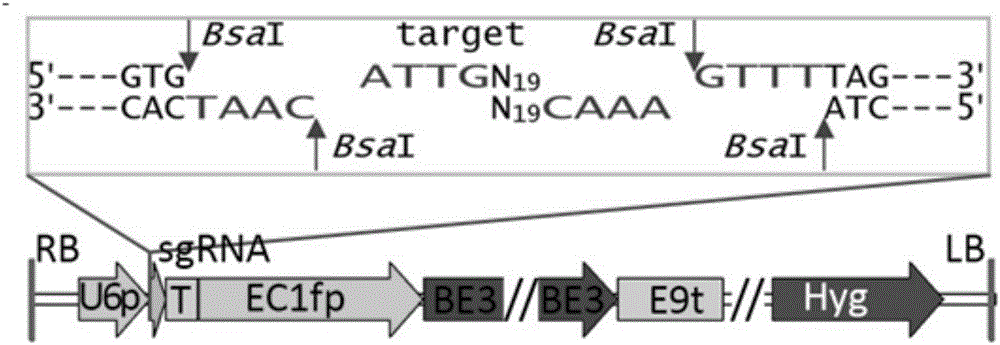
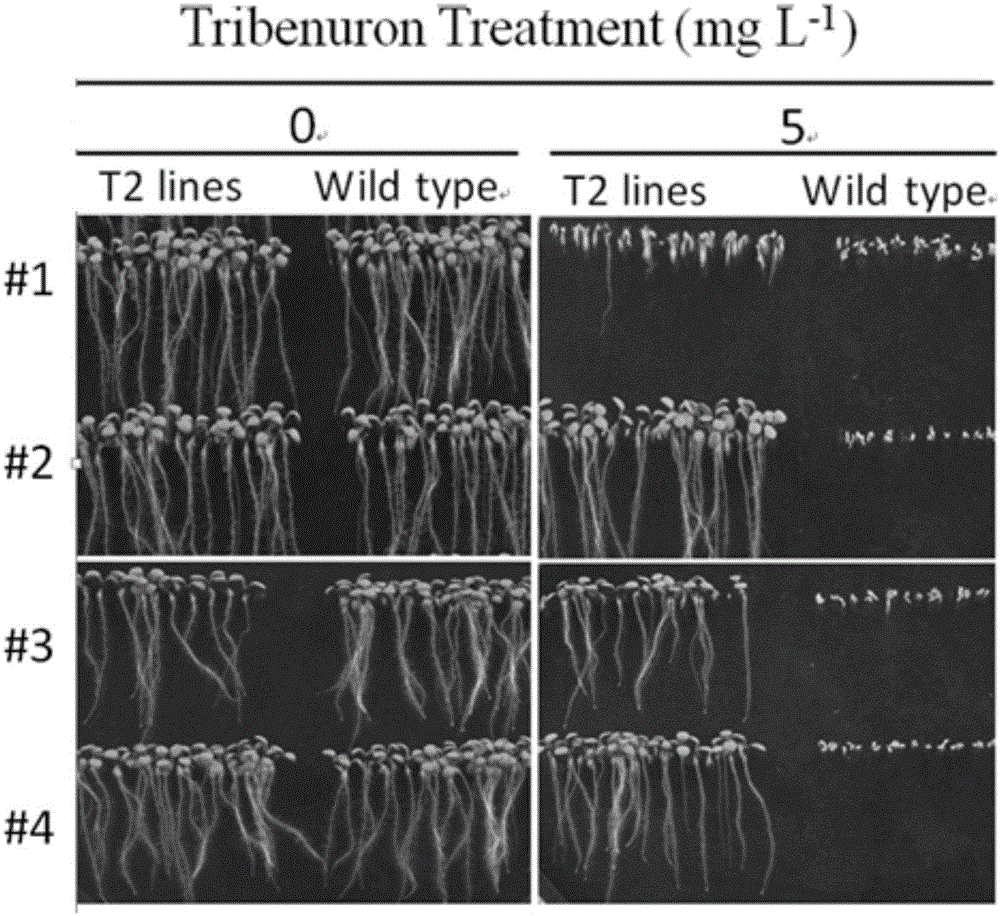
Patents
Literature
1405 results about "Point mutation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A point mutation or substitution is a genetic mutation where a single nucleotide base is changed, inserted or deleted from a sequence of DNA or RNA. Point mutations have a variety of effects on the downstream protein product—consequences that are moderately predictable based upon the specifics of the mutation. These consequences can range from benign (e.g. synonymous mutations) to catastrophic (e.g. frameshift mutations), with regard to protein production, composition, and function.
Analying polynucleotide sequences
InactiveUS6054270AStable duplexReduce impactSequential/parallel process reactionsSugar derivativesHybridization reactionSequence determination
This invention provides an apparatus and method for analyzing a polynucleotide sequence; either an unknown sequence or a known sequence. A support, e.g. a glass plate, carries an array of the whole or a chosen part of a complete set of oligonucleotides which are capable of taking part in hybridization reactions. The array may comprise one or more pair of oligonucleotides of chosen lengths. The polynucleotide sequence, or fragments thereof, are labelled and applied to the array under hybridizing conditions. Applications include analyses of known point mutations, genomic fingerprinting, linkage analysis, characterization of mRNAs, mRNA populations, and sequence determination.
Owner:OXFORD GENE TECH
Systems for in vivo site-directed mutagenesis using oligonucleotides
InactiveUS20040171154A1Large deletionImprove applicabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousSite-directed mutagenesis
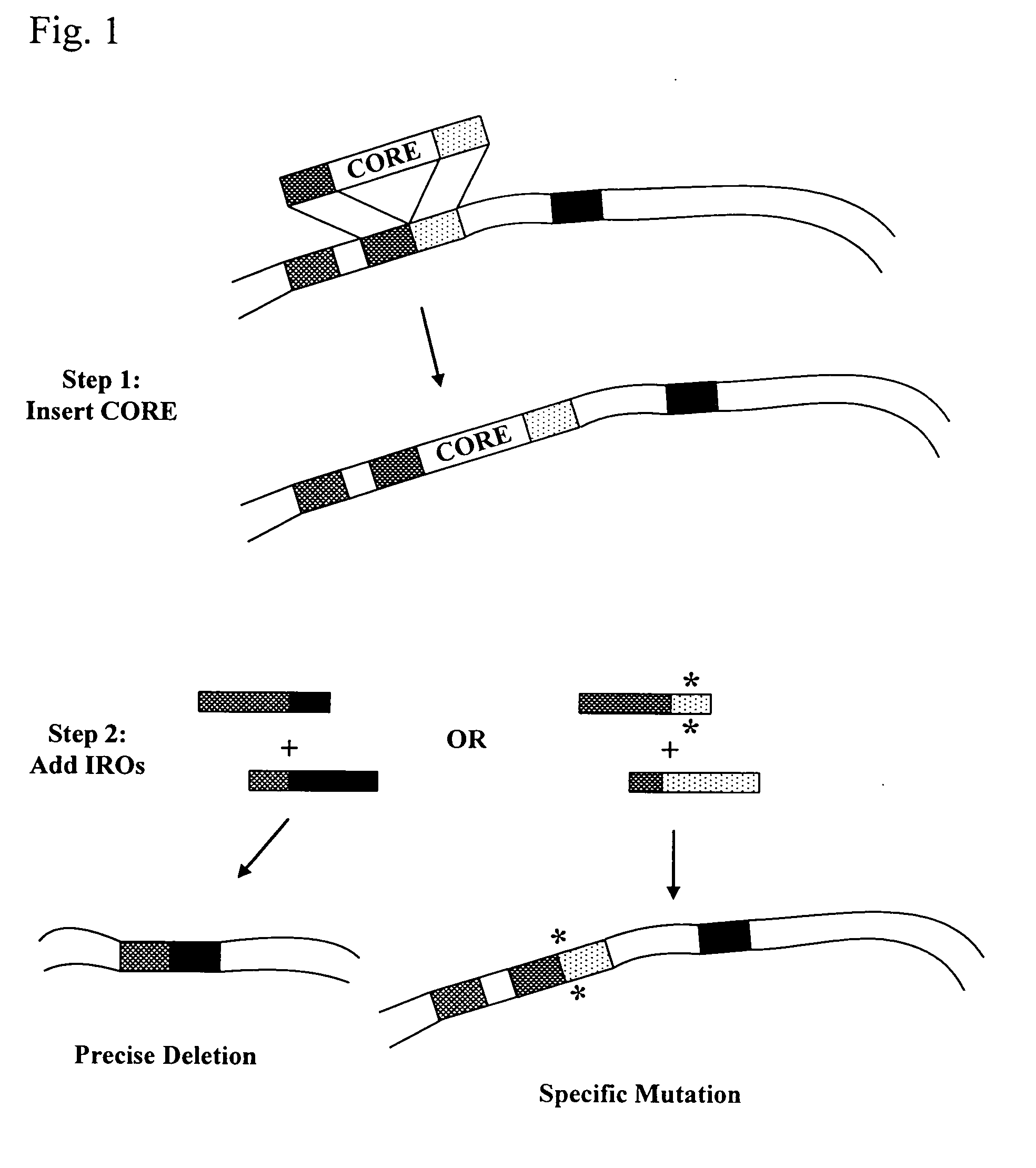
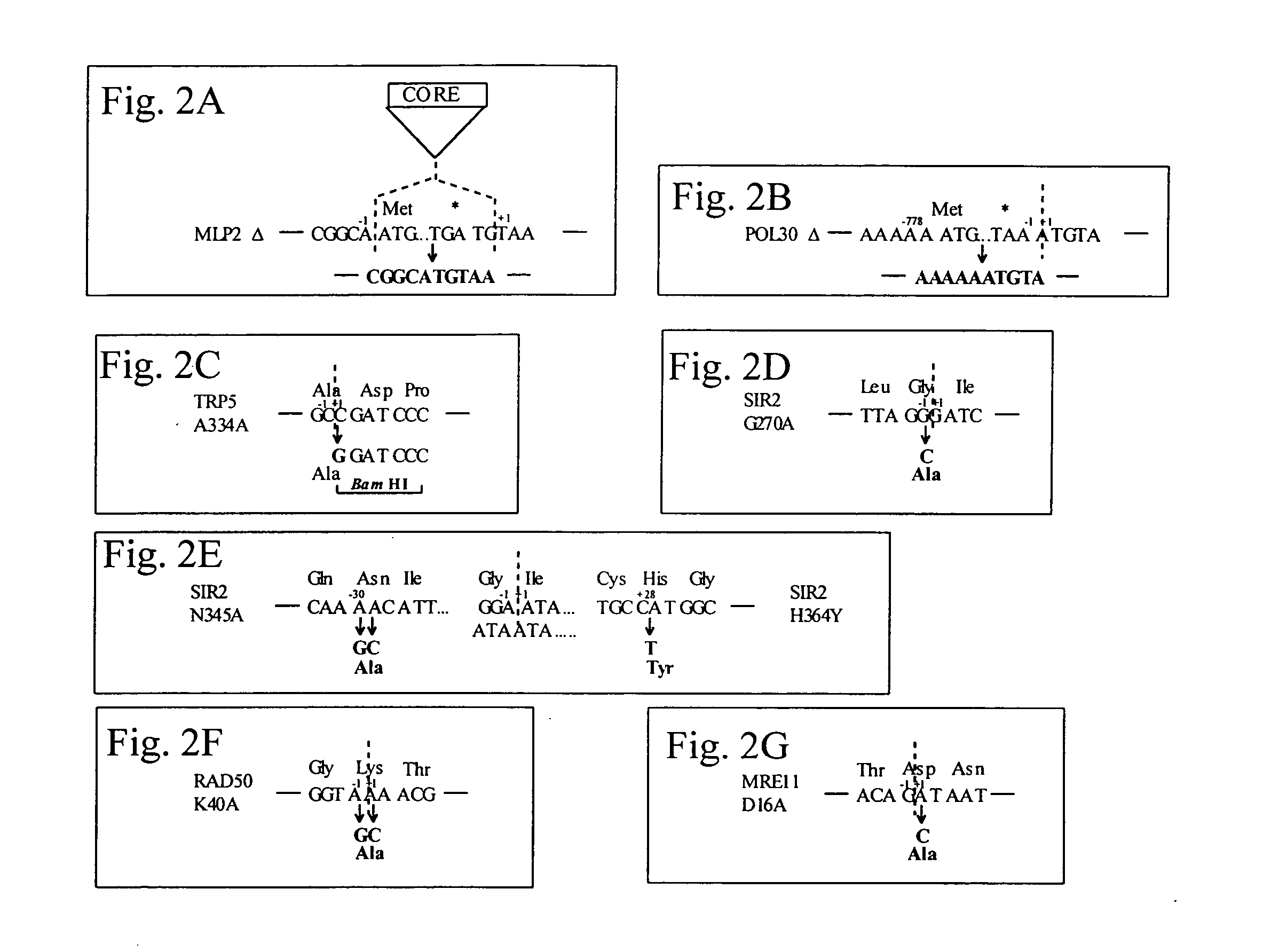
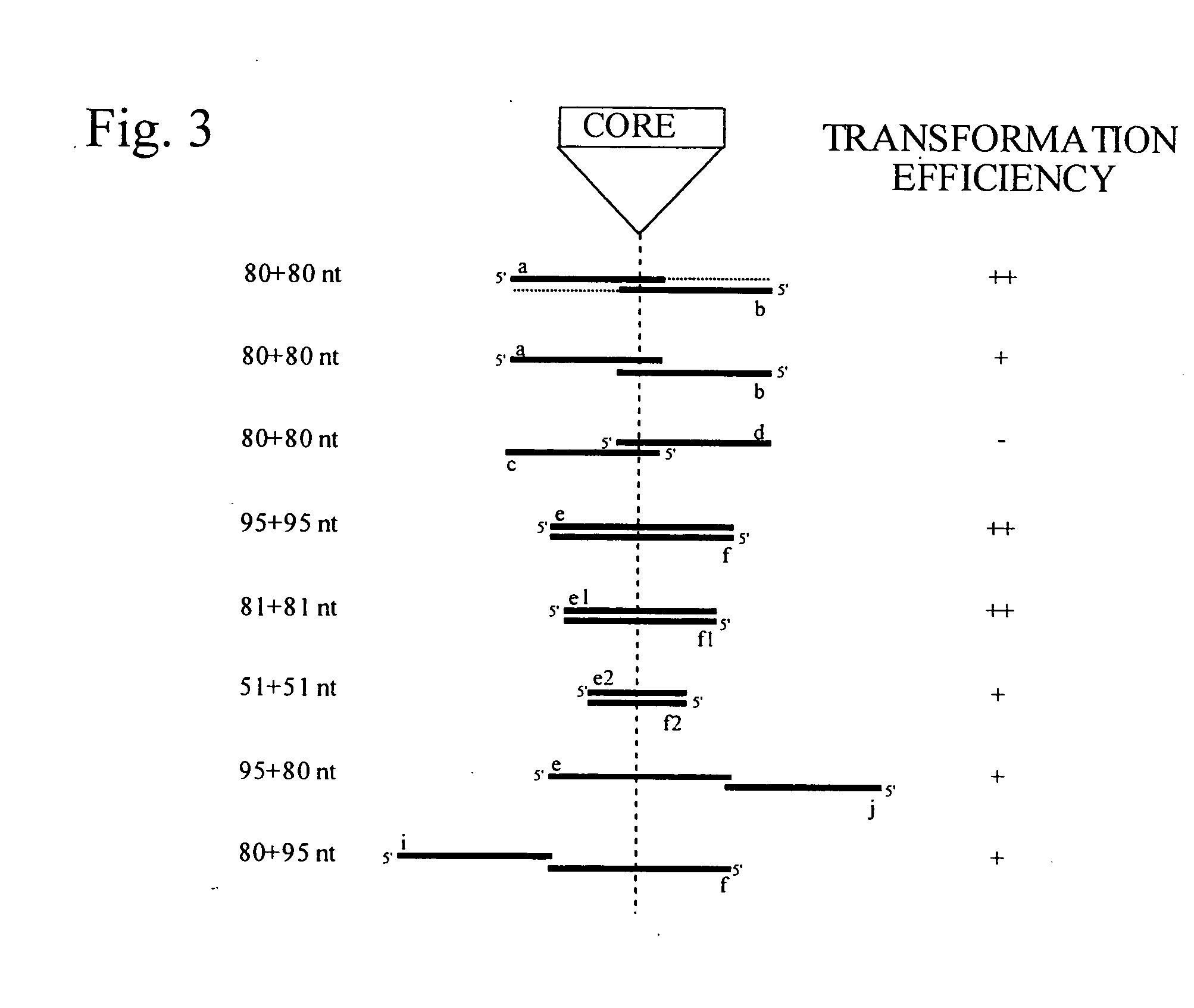
This disclosure provides several methods to generate nucleic acid mutations in vivo, for instance in such a way that no heterologous sequence is retained after the mutagenesis is complete. The methods employ integrative recombinant oligonucleotides (IROs). Specific examples of the described mutagenesis methods enable site-specific point mutations, deletions, and insertions. Also provided are methods that enable multiple rounds of mutation and random mutagenesis in a localized region. The described methods are applicable to any organism that has a homologous recombination system.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES DEPT OF THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE
Methods and compositions for flow cytometric determination of DNA sequences
InactiveUS6057107AReduce fluorescenceReduce intensityMicrobiological testing/measurementIndividual particle analysisAnalysis dnaTest sample
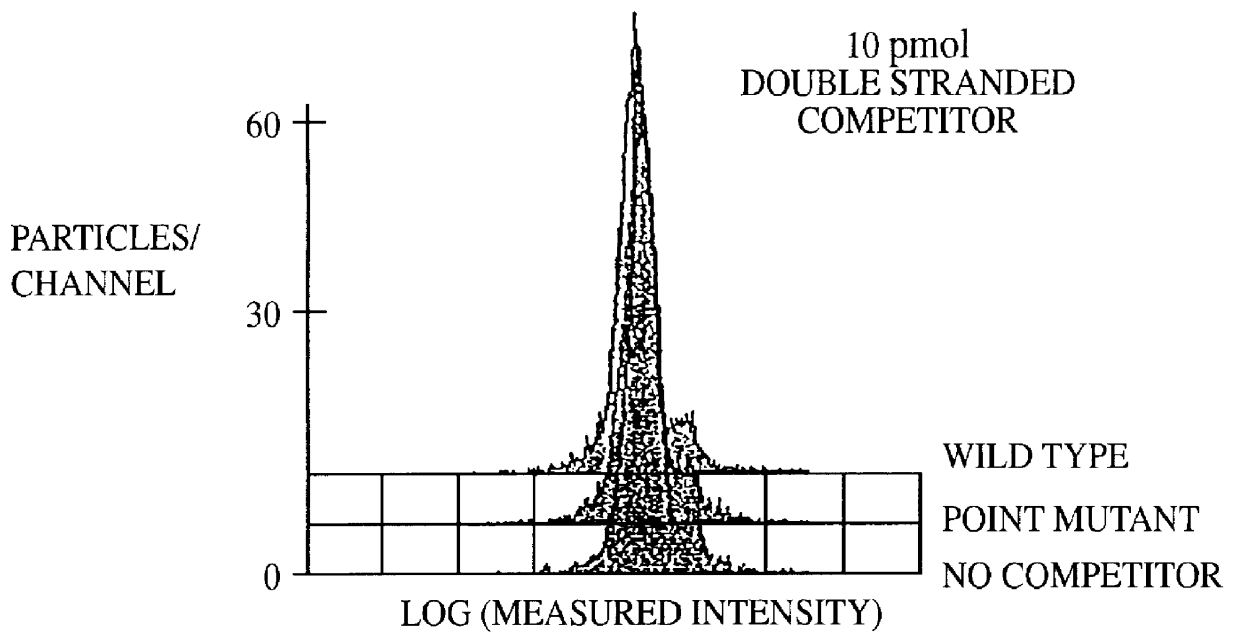
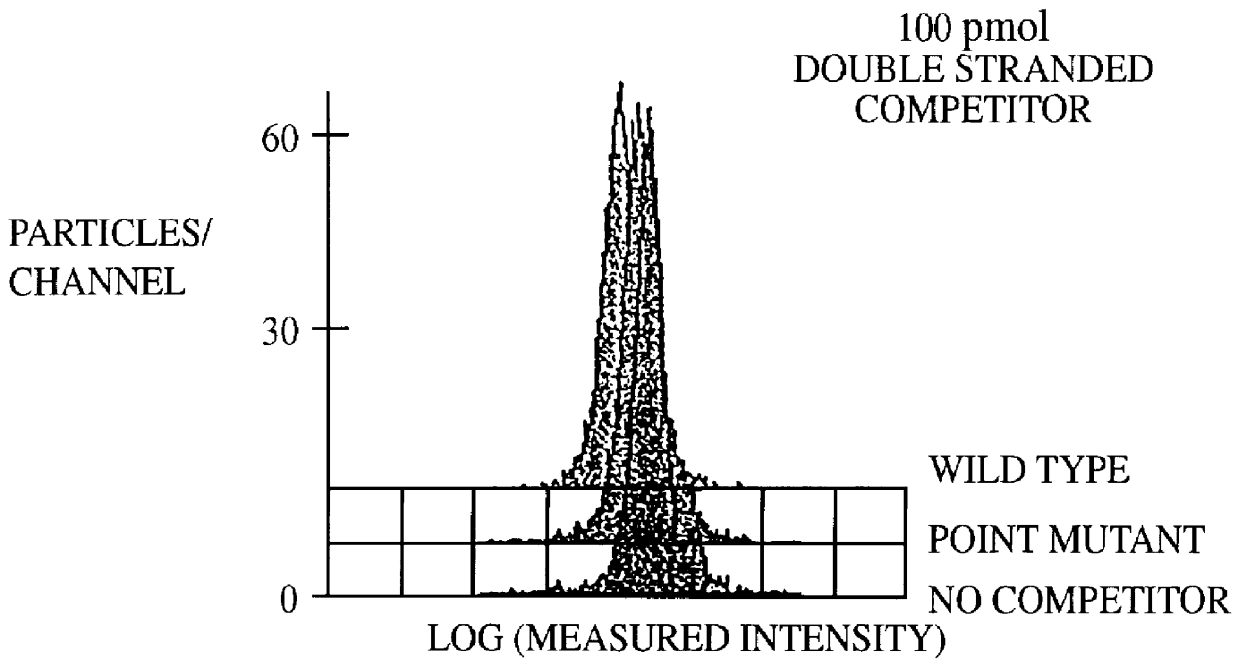
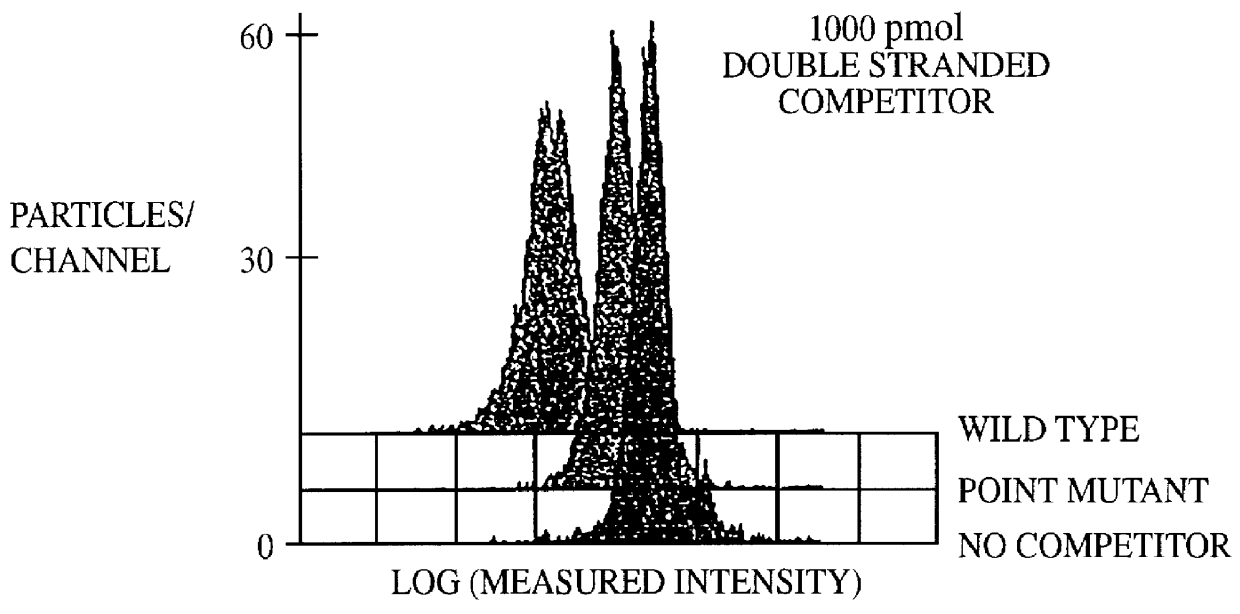
A method for the analysis of DNA sequences and PCR products comprises the steps of constructing an oligonucleotide-labeled beadset, and labeled complementary probe, and exposing the beadset and probe to a DNA fragment or PCR product under hybridizing conditions and analyzing the combined sample / beadset by flow cytometry. Flow cytometric measurements are used to classify beads within an exposed beadset to determine the presence of identical or nonidentical sequences within the test sample. The inventive technology enables the rapid analysis of DNA sequences and detection of point mutations, deletions and / or inversions while also reducing the cost and time for performing genetic assays.
Owner:LUMINEX
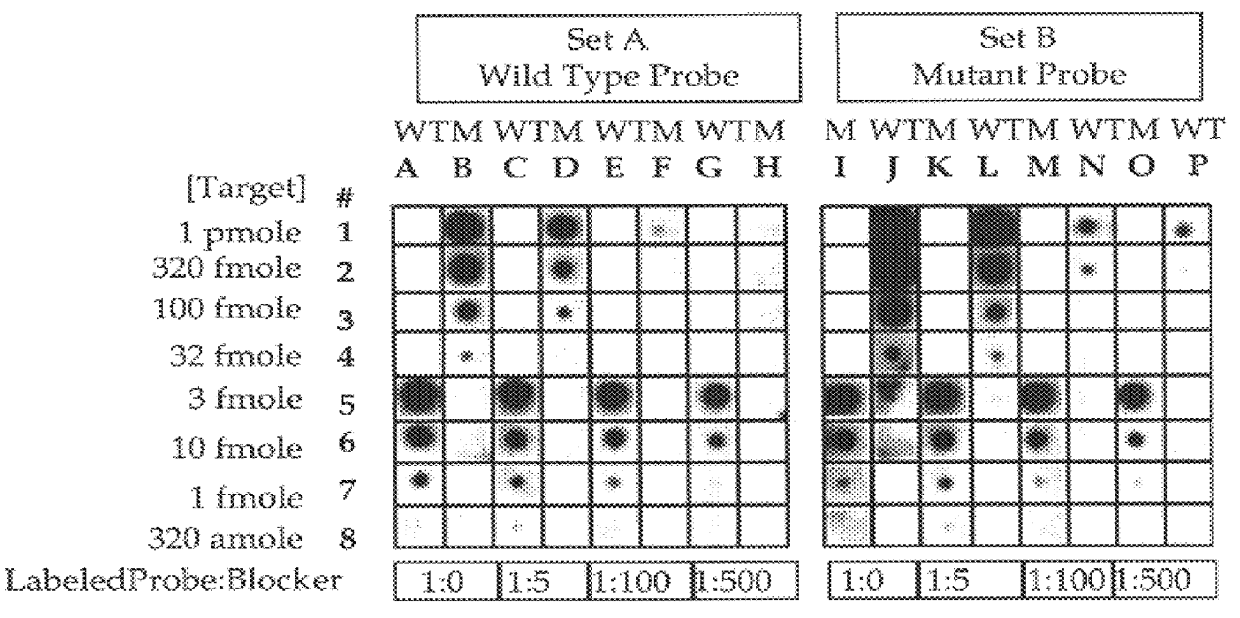
Methods for suppressing the binding of detectable probes to non-target sequences in hybridization assays
InactiveUS6110676AIncrease assayEasy to addSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleic Acid ProbesTrue positive rate
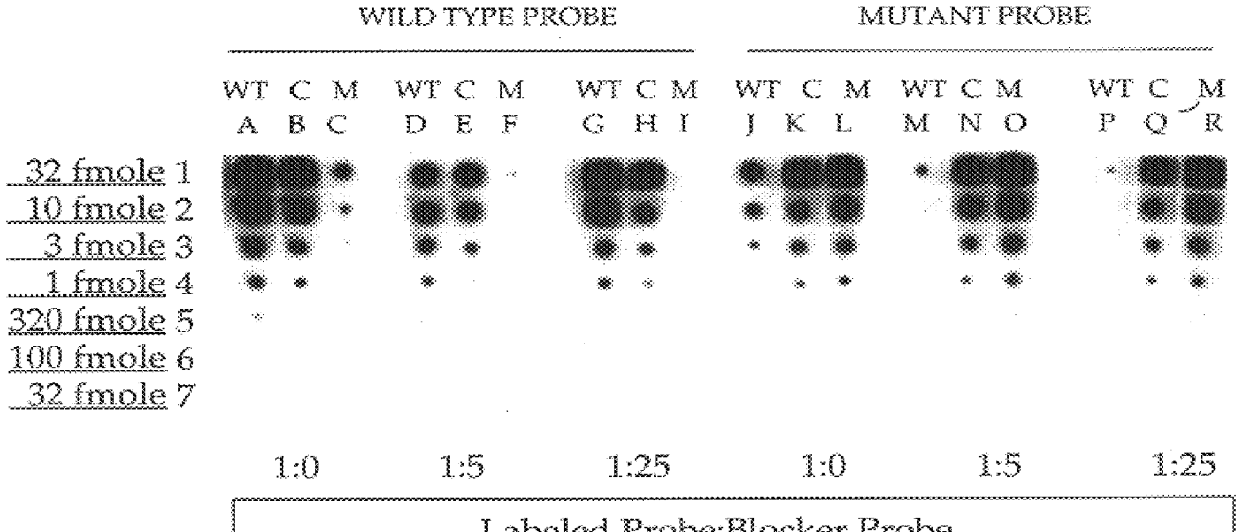
This invention relates to methods, kits and compositions suitable for the improved detection, analysis and quantitation of nucleic acid target sequences using probe based hybridization assays. The invention is more specifically directed to methods, kits and compositions suitable for suppressing the binding of detectable nucleic acid probes or detectable PNA probes to non-target nucleic acid sequences in an assay for a target nucleic acid sequence to thereby improve the reliability, sensitivity and specificity of the assay. The methods, kits and compositions of this invention are particularly well suited to the detection and analysis of nucleic acid point mutations.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC +1
Bispecific Antibody Point Mutations for Enhancing Rate of Clearance
A mutant bispecific antibody that includes (a) a human hinge constant region from IgG having one or more amino acid mutations in the CH2 domain, (b) two scFvs; and (c) two Fvs has been constructed. This type of antibody displays enhanced clearance, which has been found to be particularly useful in the context of pre-targeting methods.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
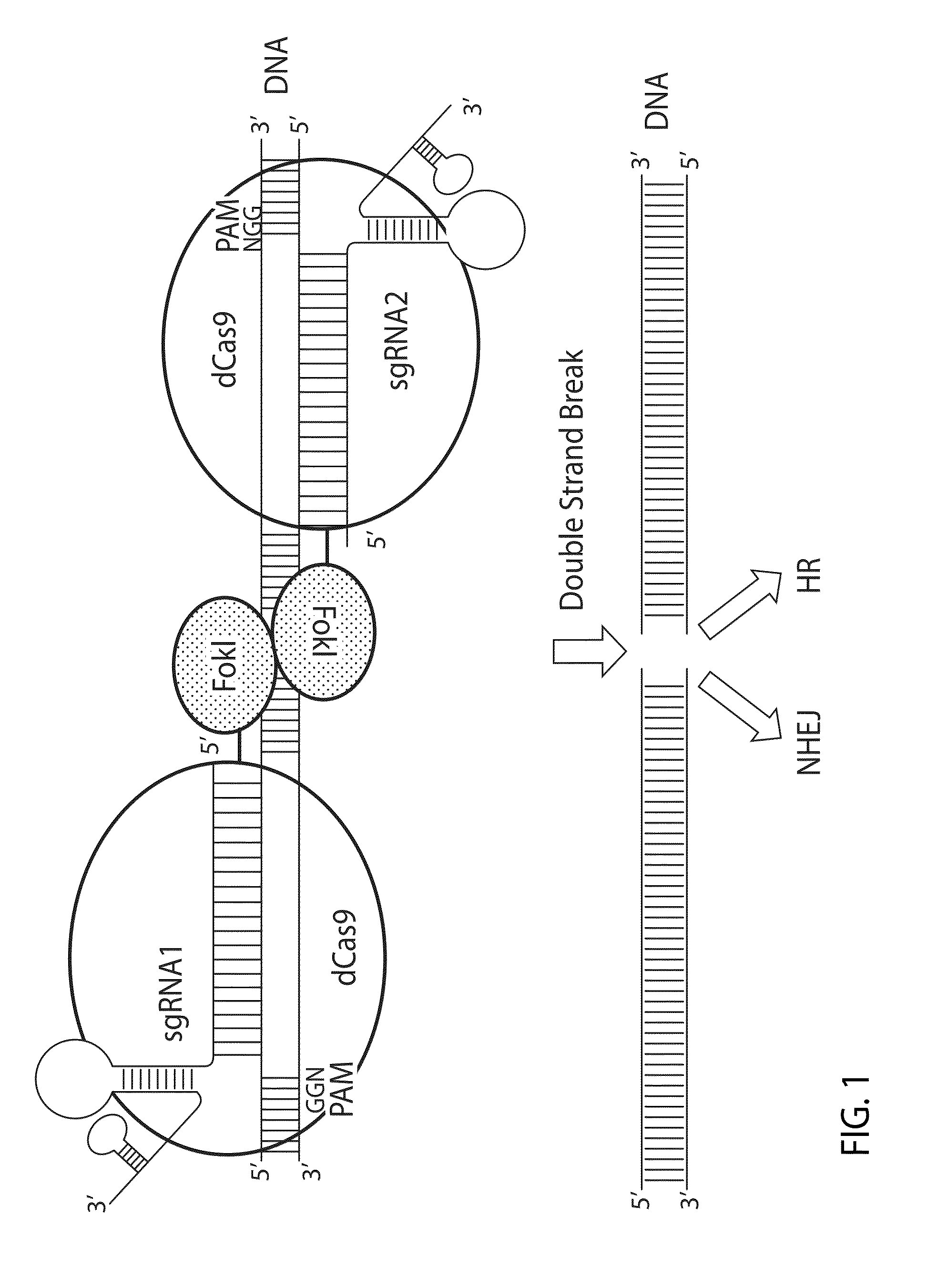
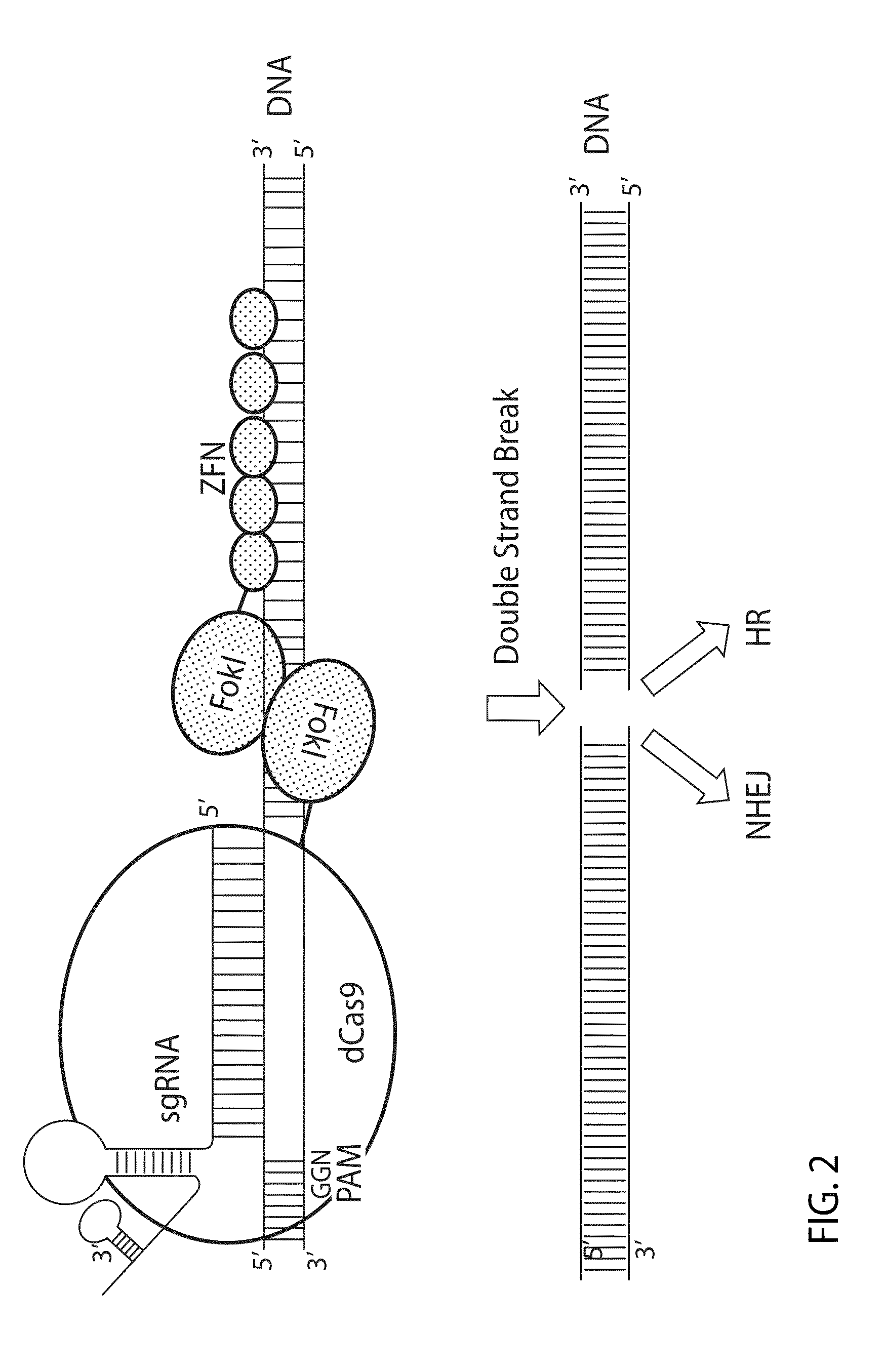
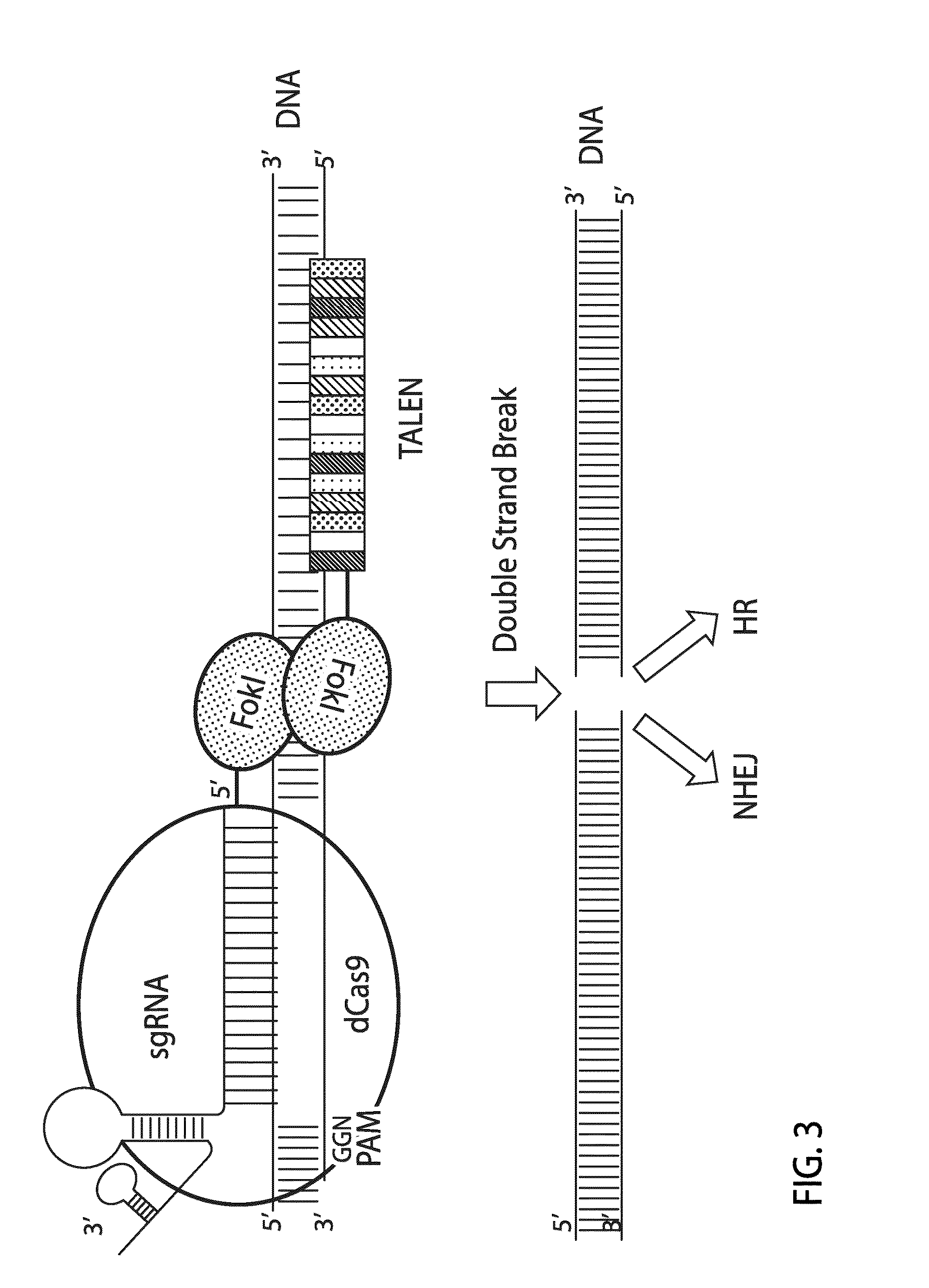
Crispr/cas system-based novel fusion protein and its applications in genome editing
An inactive CRISPR / Cas system-based fusion protein and its applications in gene editing are disclosed. More particularly, chimeric fusion proteins including an inCas fused to a DNA modifying enzyme and methods of using the chimeric fusion proteins in gene editing are disclosed. The methods can be used to induce double-strand breaks and single-strand nicks in target DNAs, to generate gene disruptions, deletions, point mutations, gene replacements, insertions, inversions and other modifications of a genomic DNA within cells and organisms.
Owner:SAGE LABS
Methods of identifying point mutations in a genome
InactiveUS6994962B1Improve performanceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsDeleterious mutation
The invention relates to a method for identifying inherited point mutations in a targeted region of the genome in a large population of individuals and determining which inherited point mutations are deleterious, harmful or beneficial. Deleterious mutation are identified directly by a method of recognition using the set of point mutations observed in a large population of juveniles. Harmful mutations are identified by comparison of the set of point mutation observed in a large set of juveniles and a large set of aged individuals of the same population. Beneficial mutations are similarly identified.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Mutant cholera holotoxin as an adjuvant
InactiveUS7384640B1Low toxicityEnhance immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseBacteriaAntigenAdjuvant
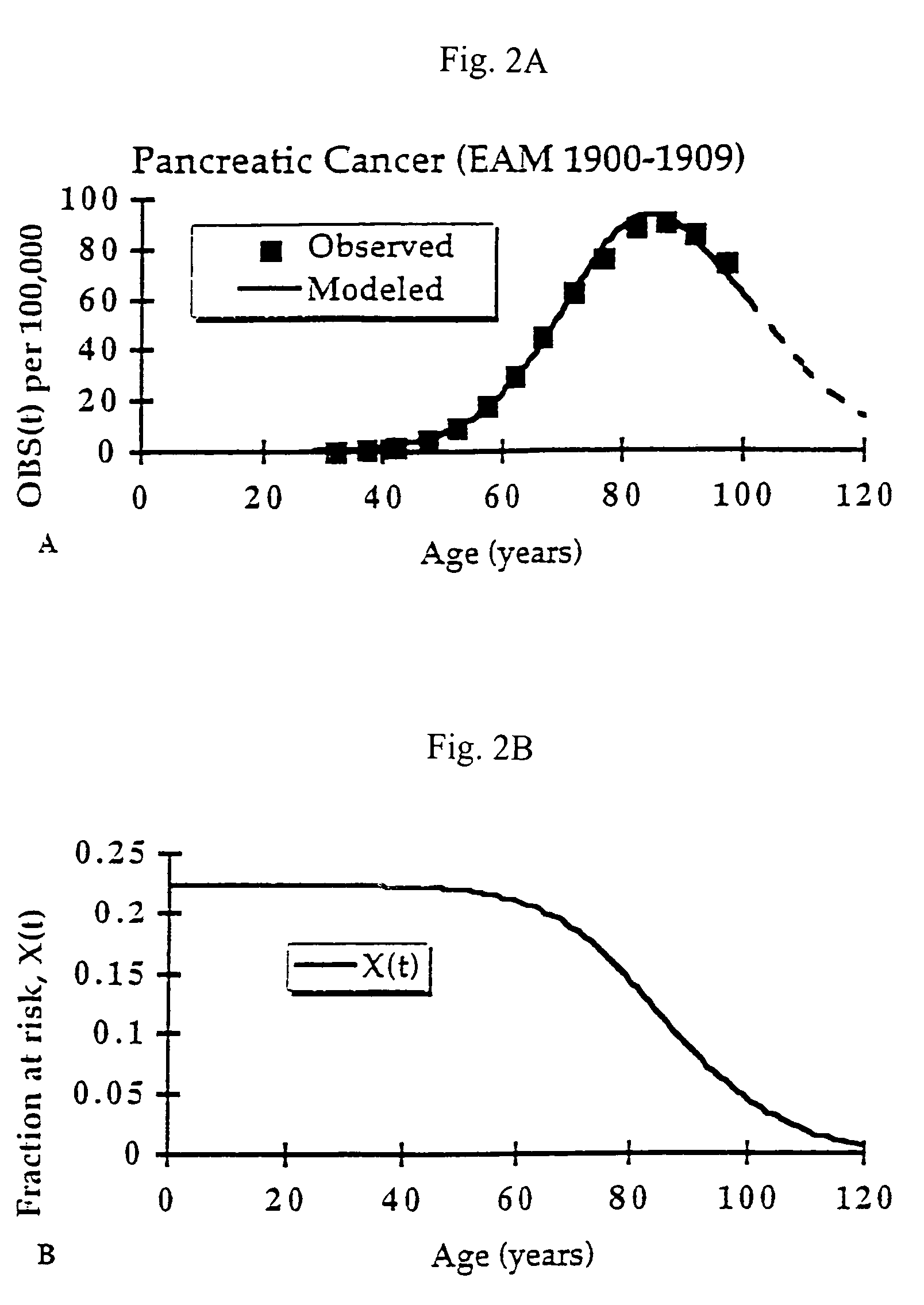
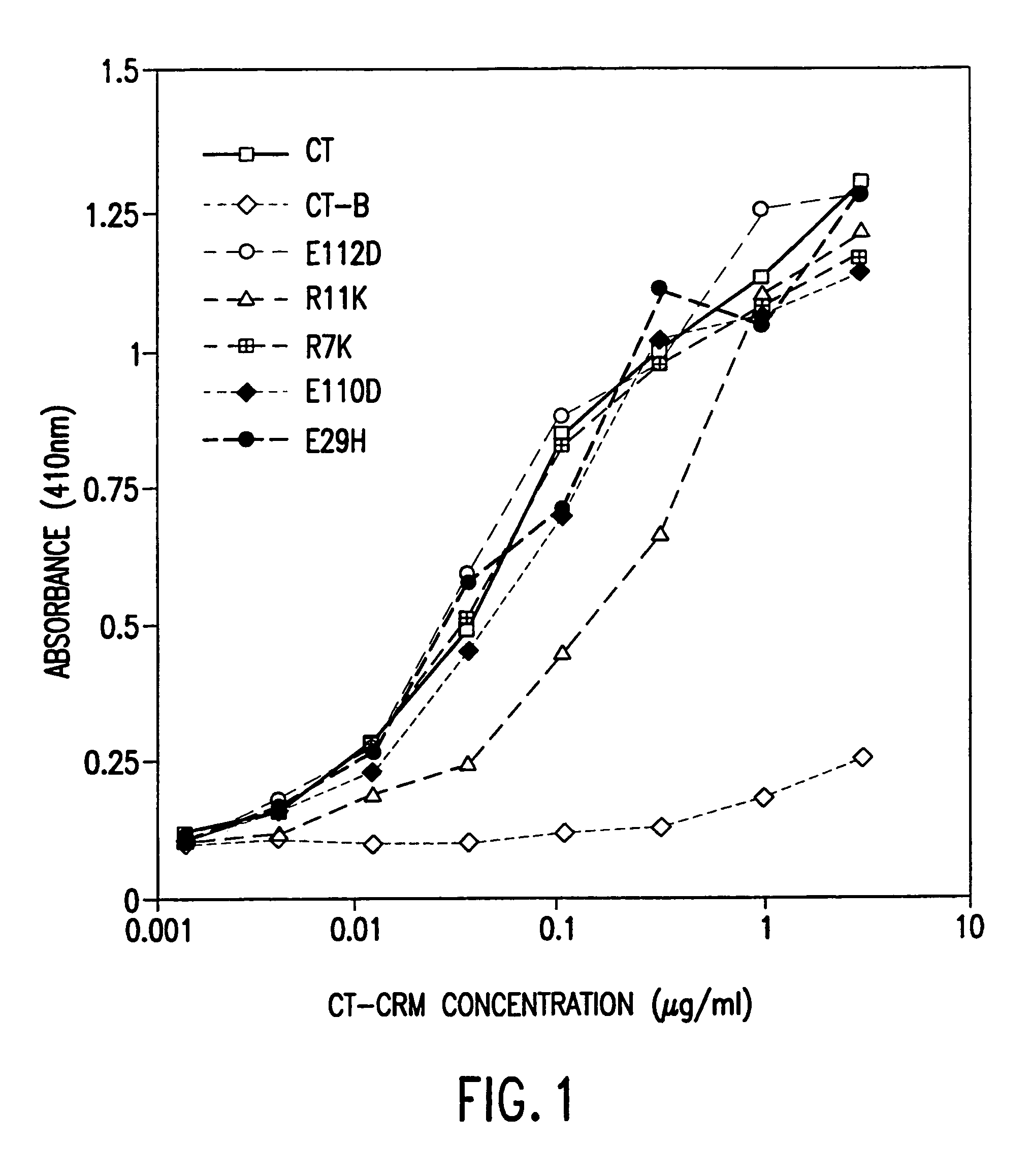
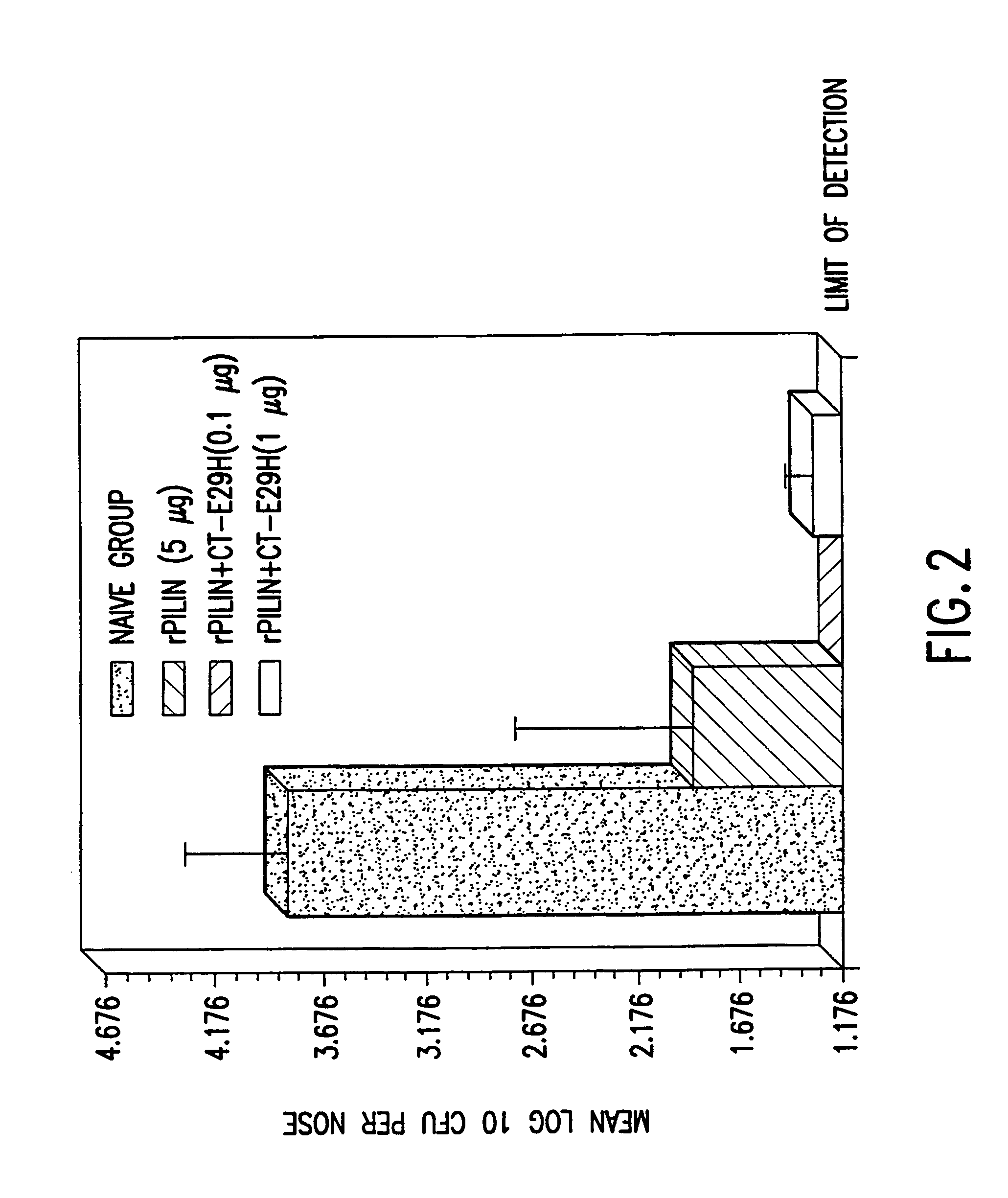
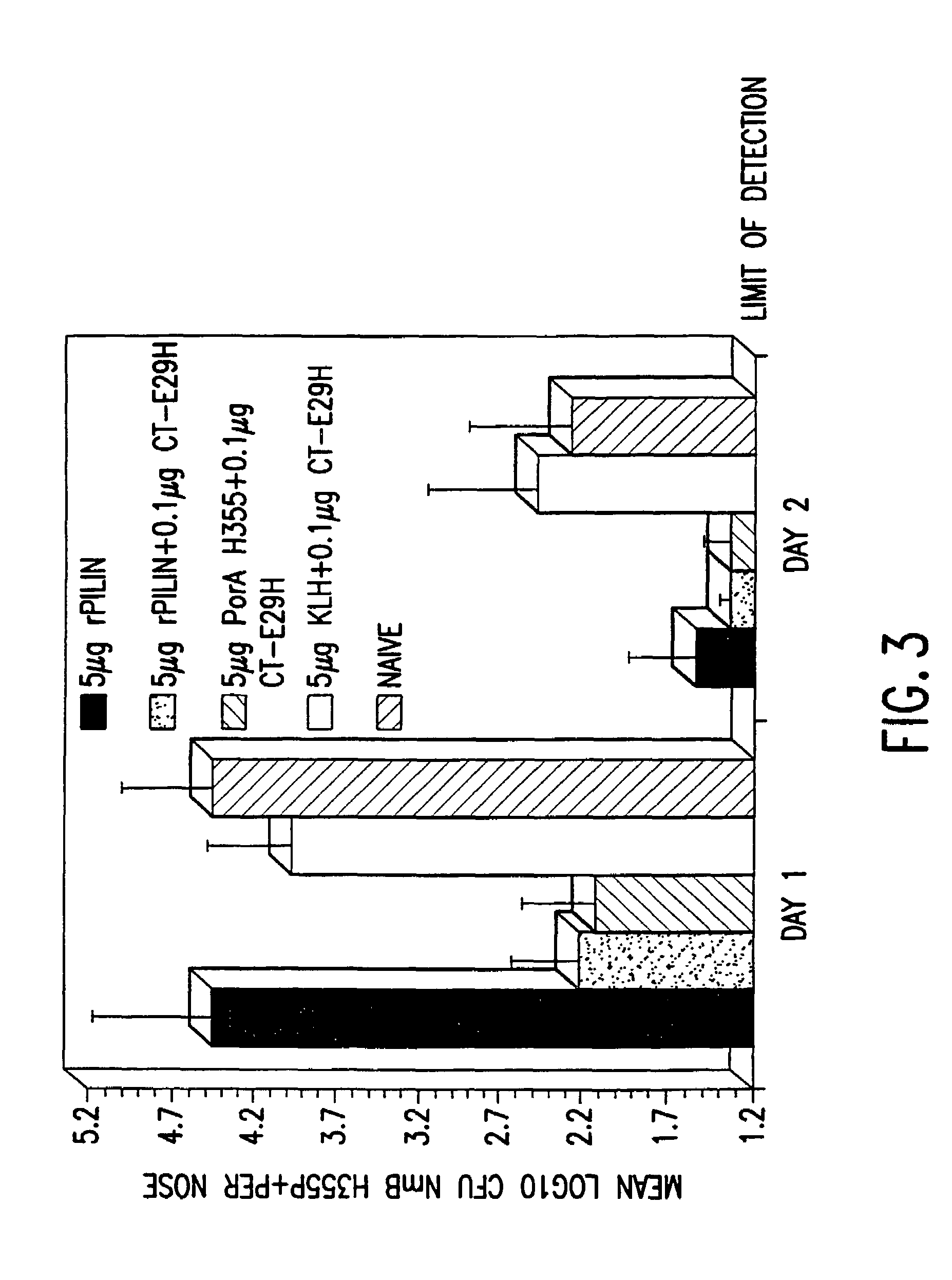
A mutant cholera holotoxin featuring a point mutation at amino acid 29 of the A subunit, wherein the glutamic acid residue is replaced by an amino acid other than aspartic acid, is useful as an adjuvant in an antigenic composition to enhance the immune response in a vertebrate host to a selected antigen from a pathogenic bacterium, virus, fungus or parasite. In a particular embodiment, the amino acid 29 is histidine. The mutant cholera holotoxin may contain at least one additional mutation in the A subunit at a position other than amino acid 29. The antigenic composition may include a second adjuvant in addition to the mutant cholera holotoxin.
Owner:UNIFORMED SERVICES UNIV OF HEALTH SCI UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE +1
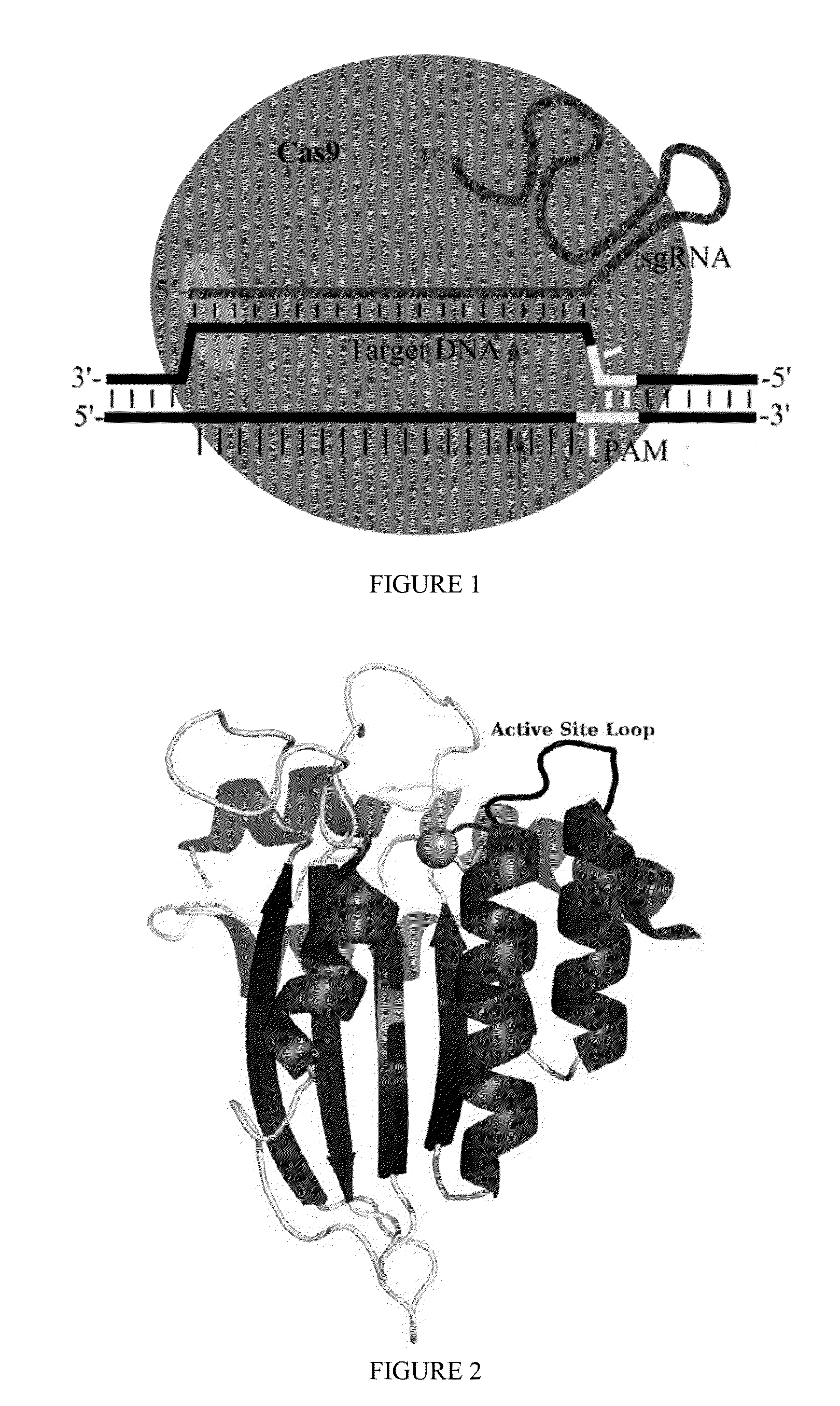
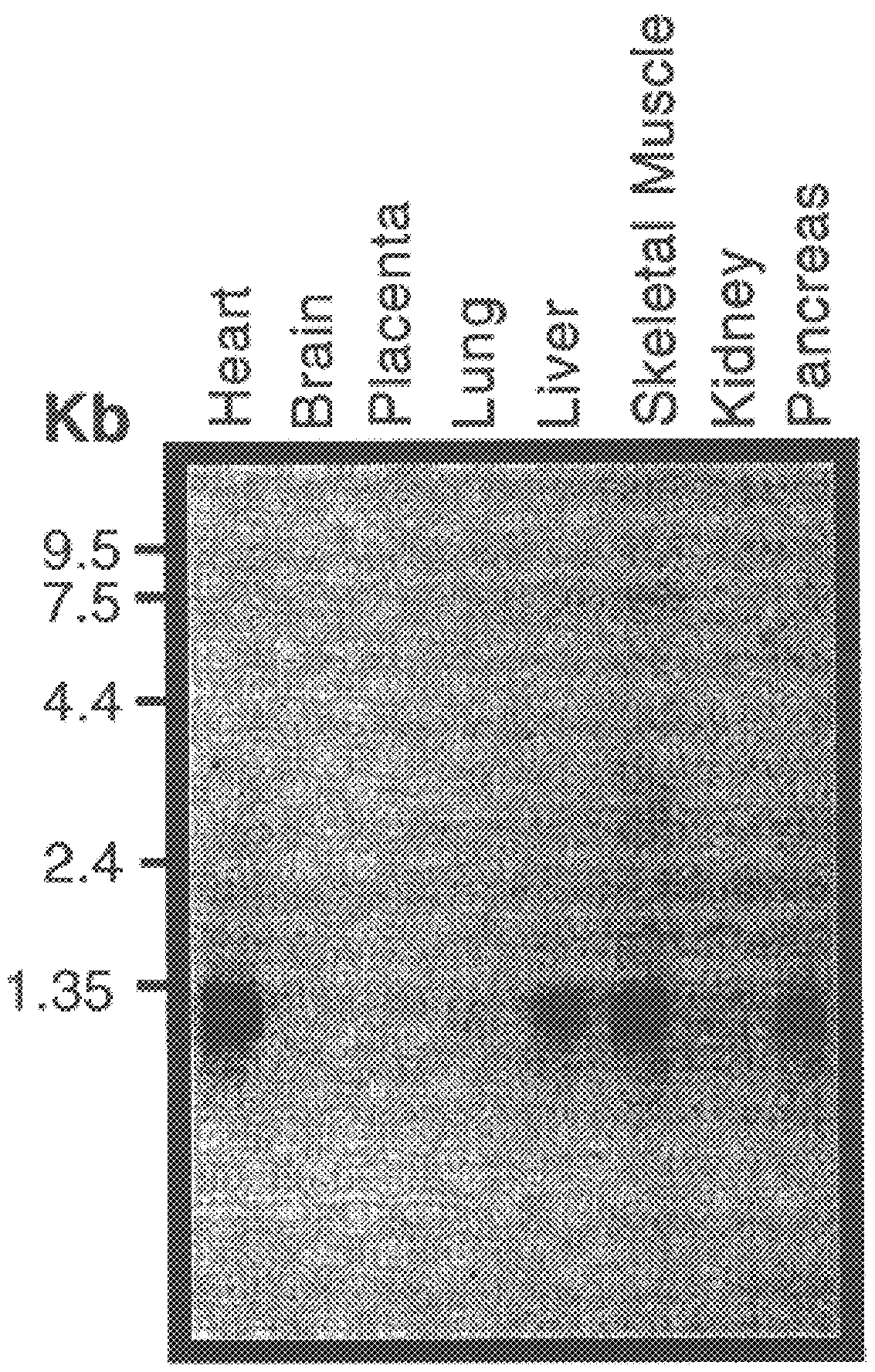
Methods for correcting caspase-9 point mutations
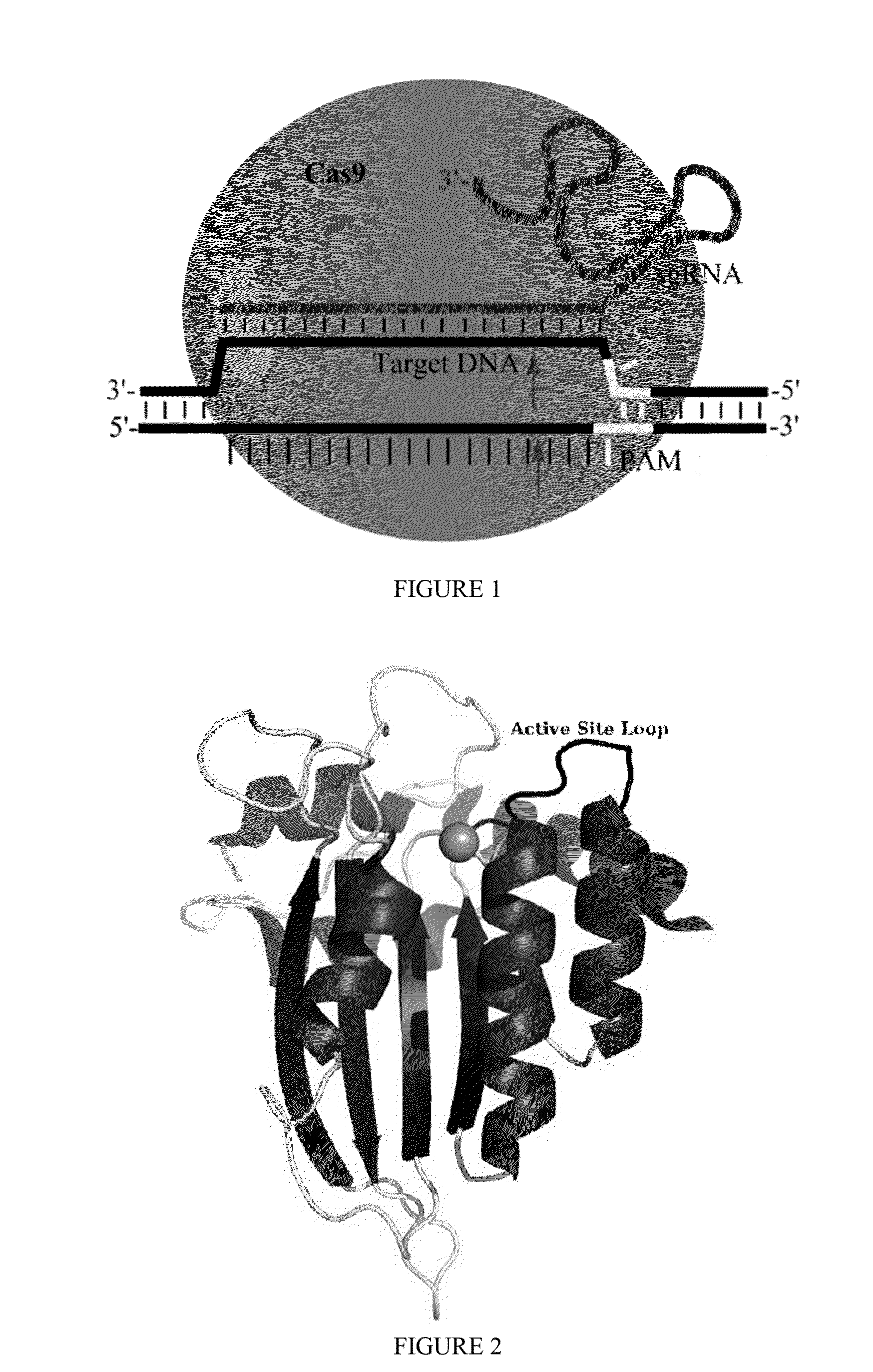
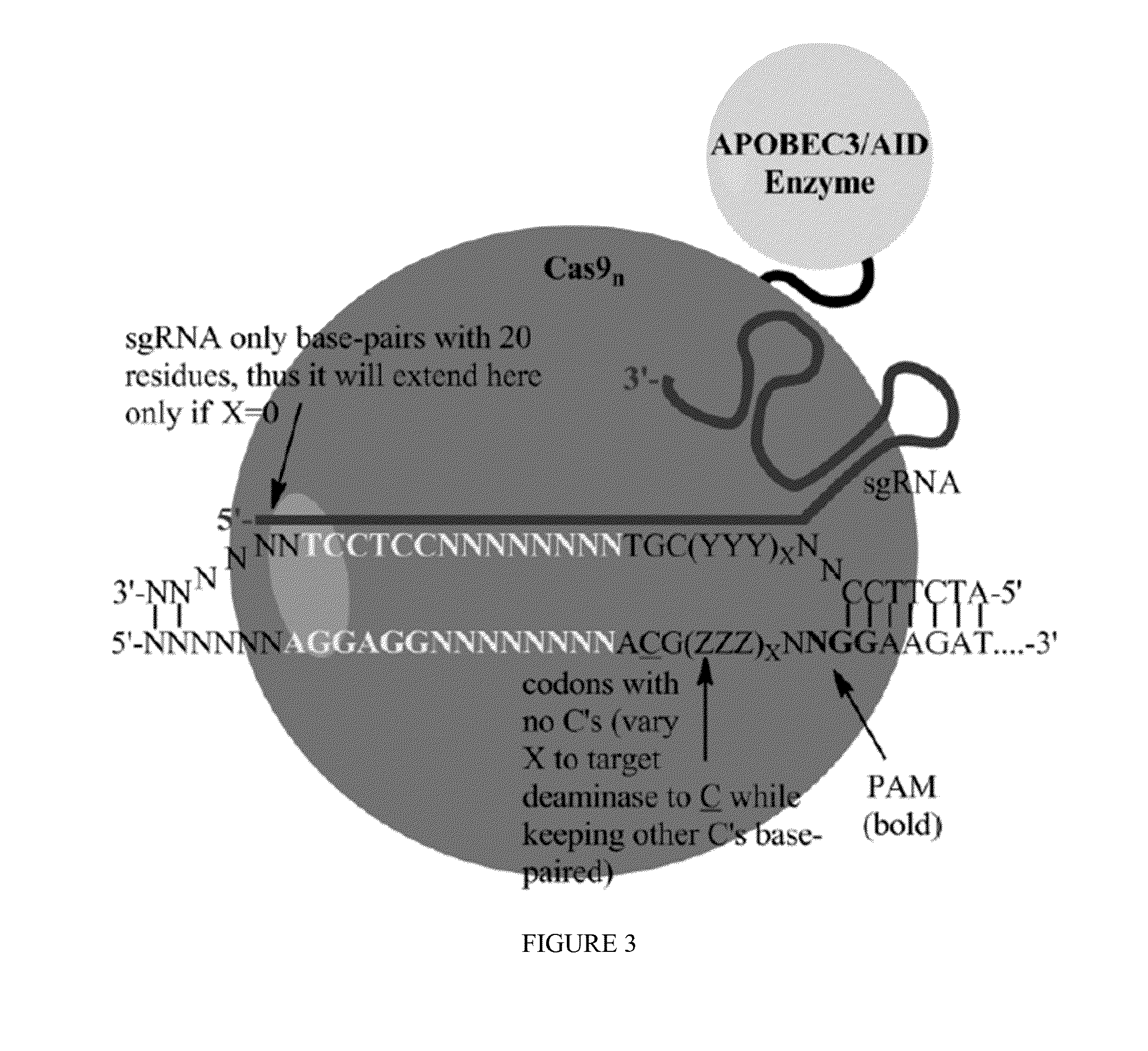
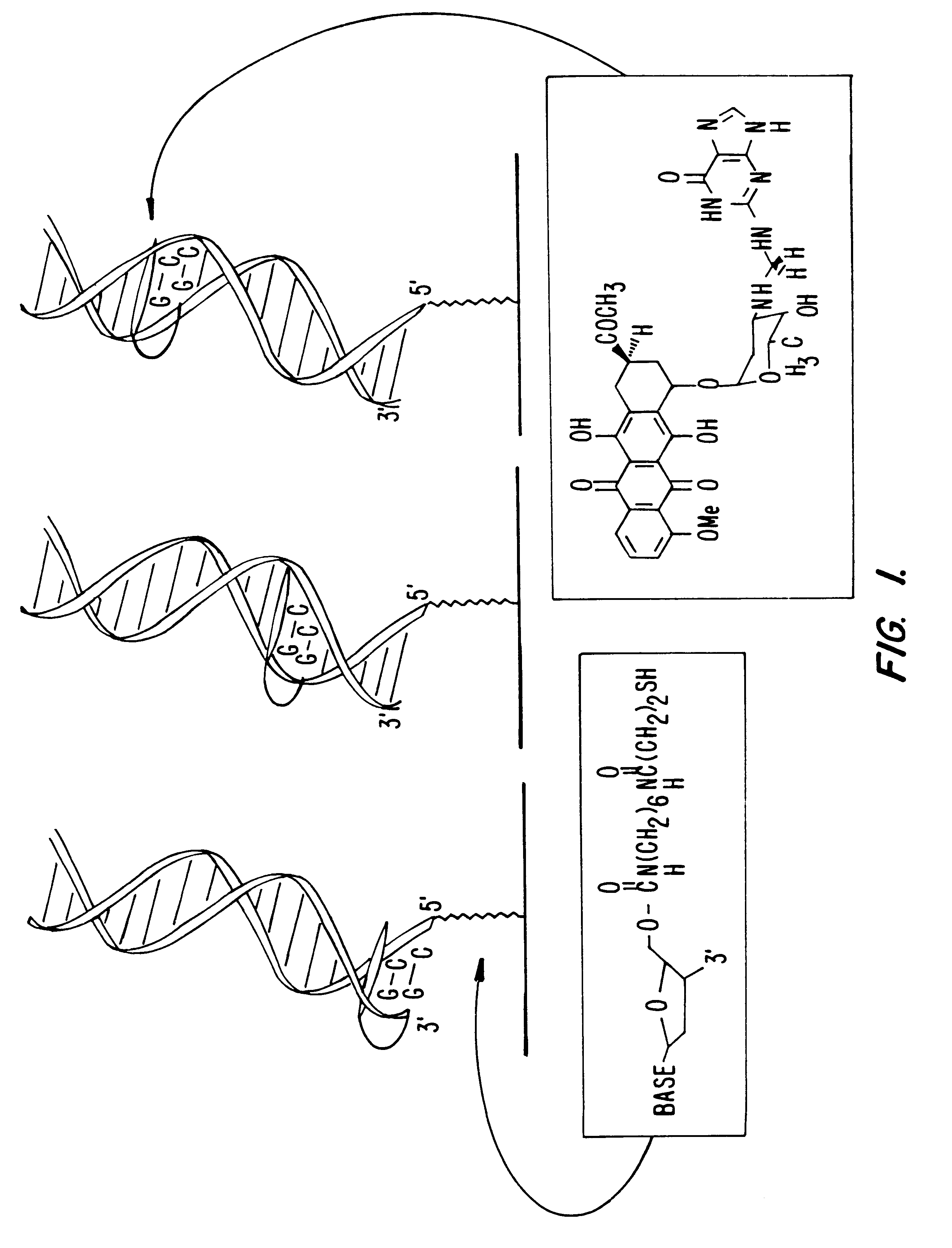
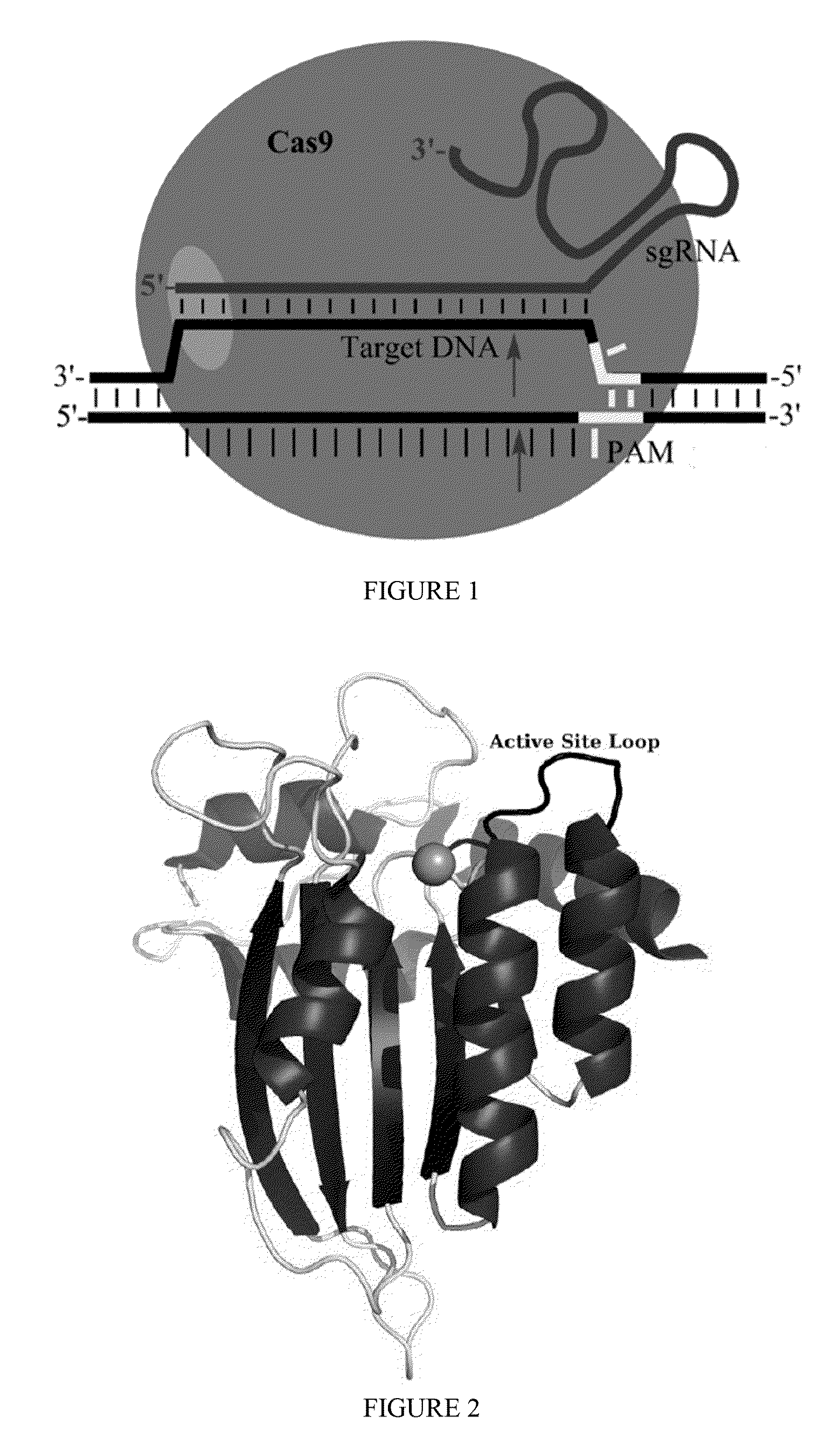
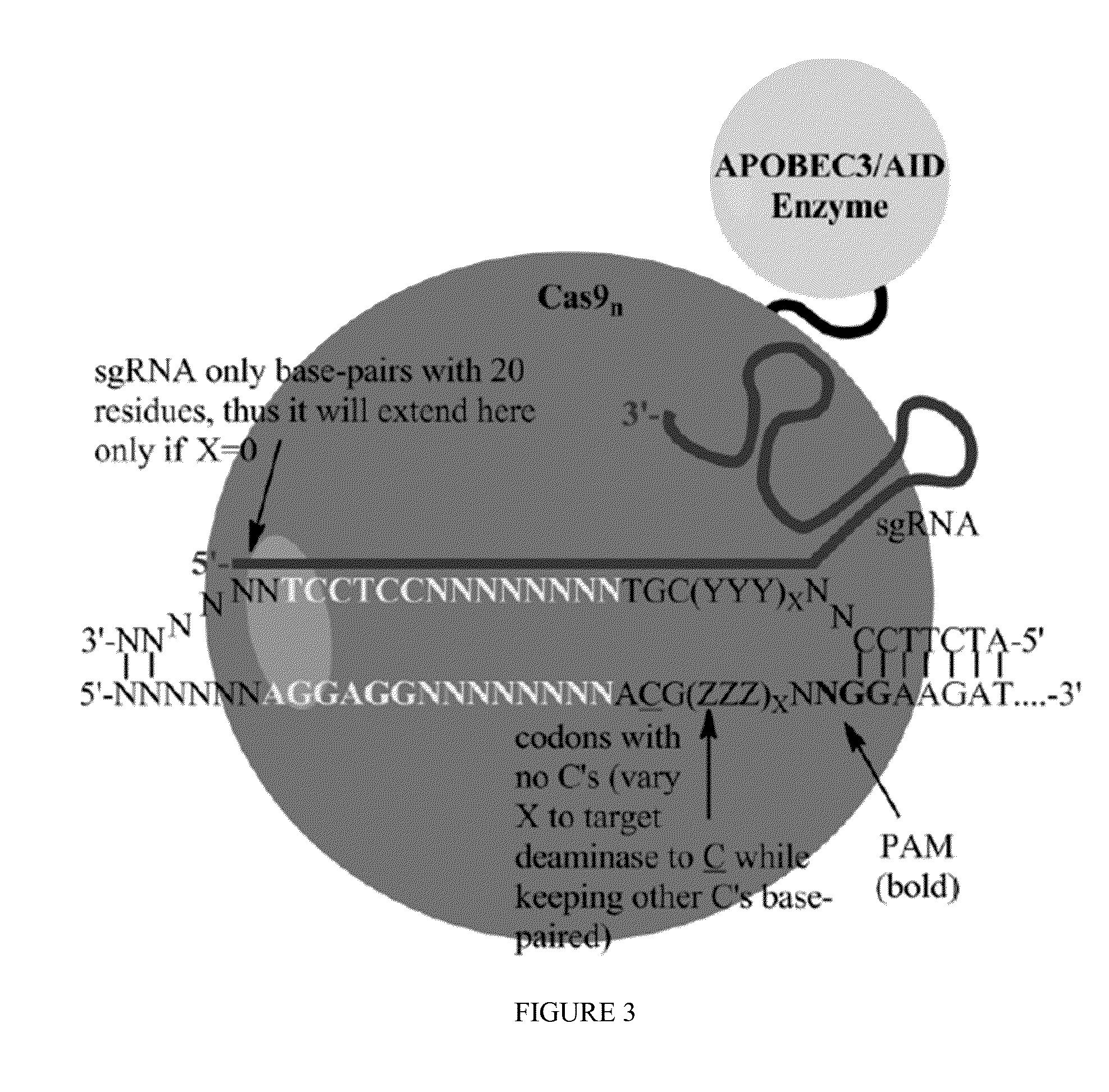
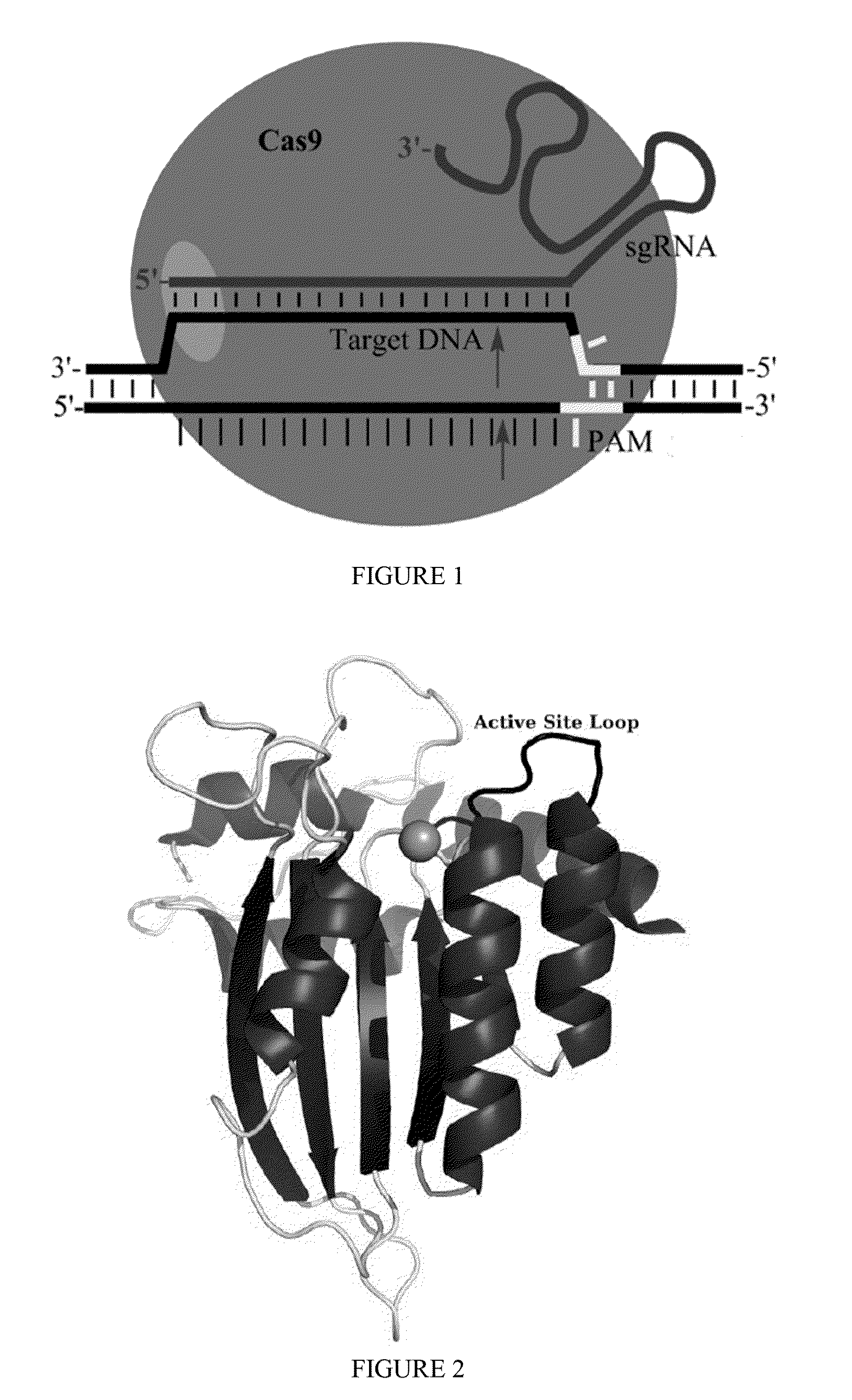
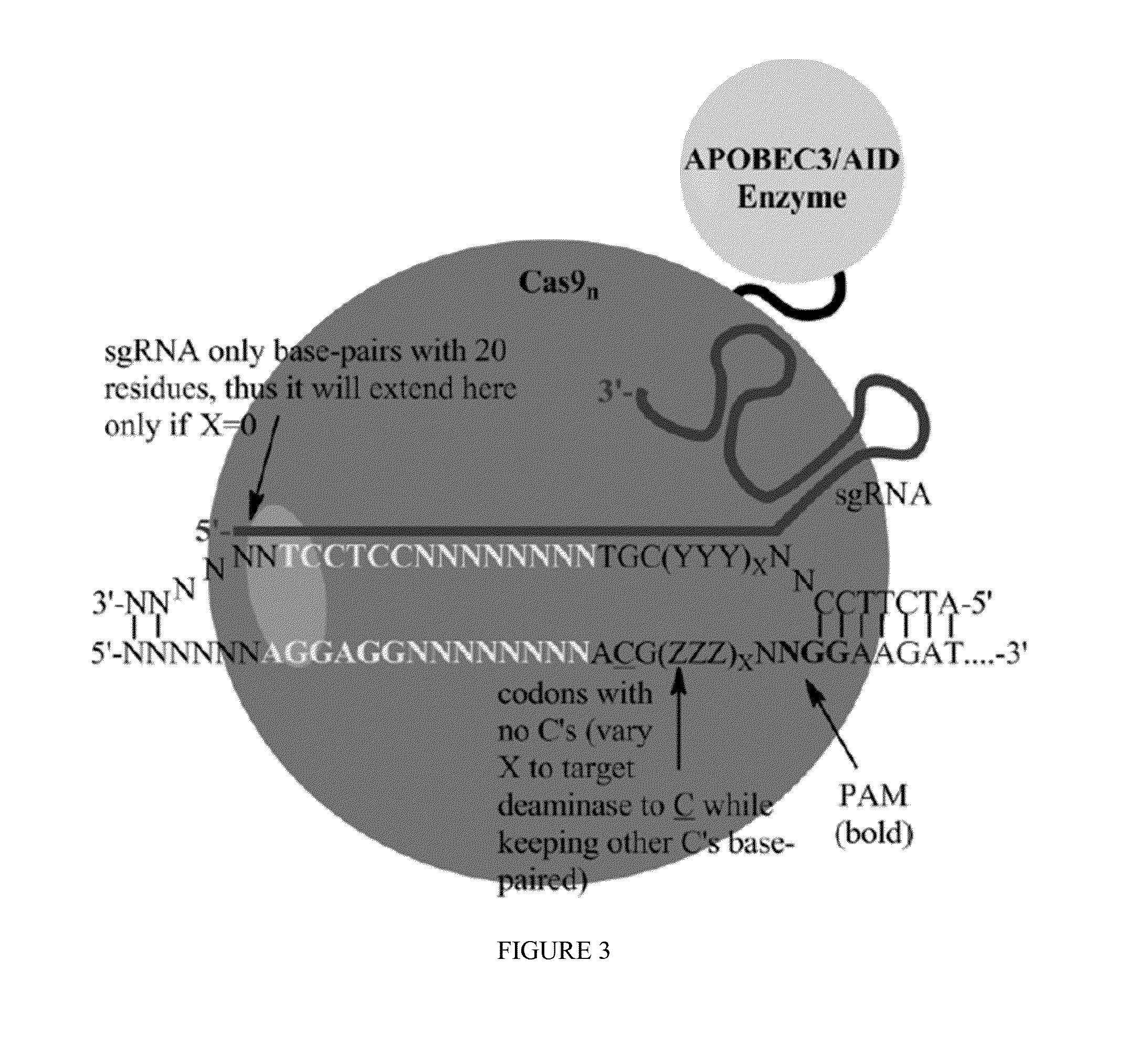
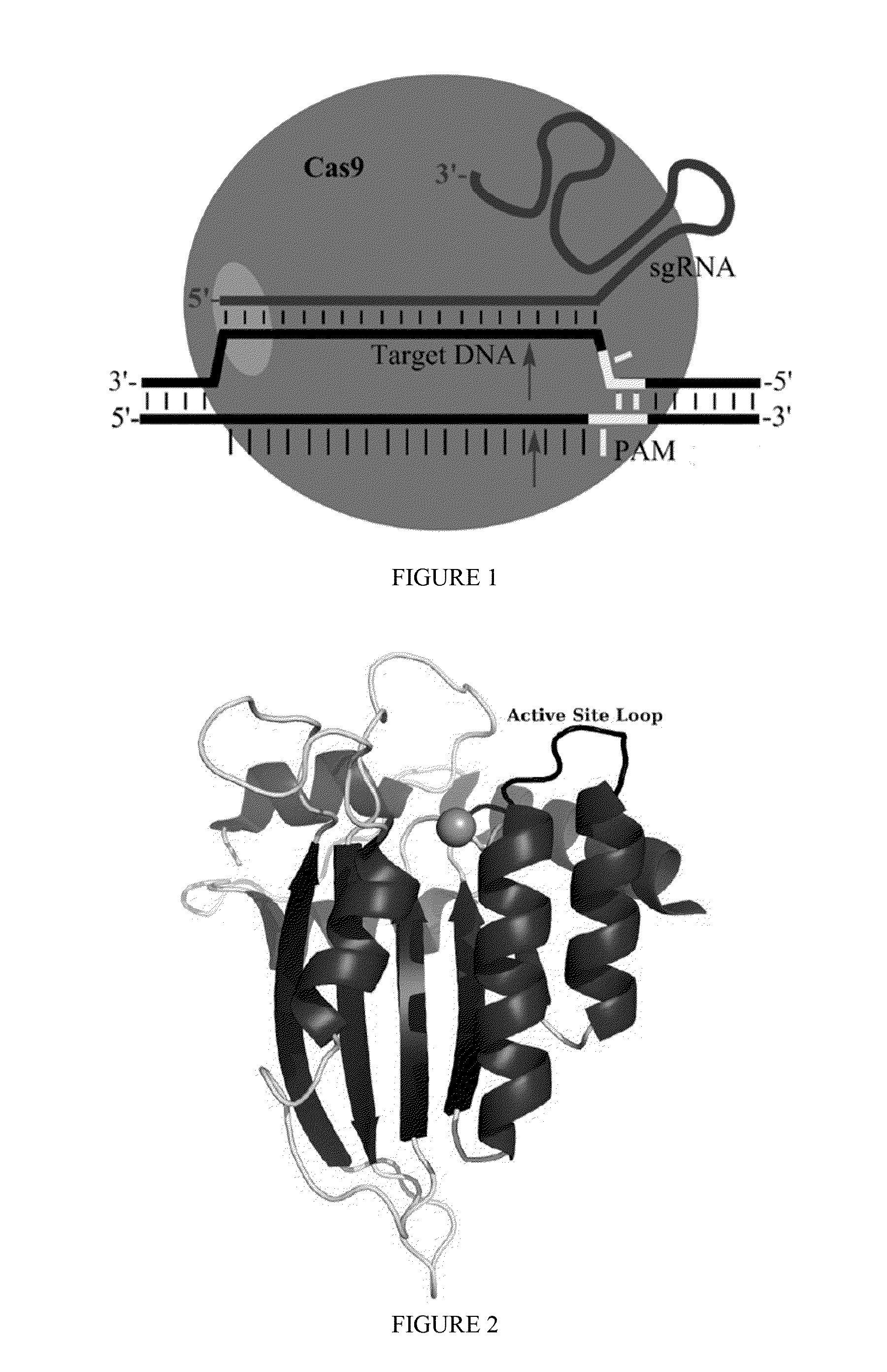
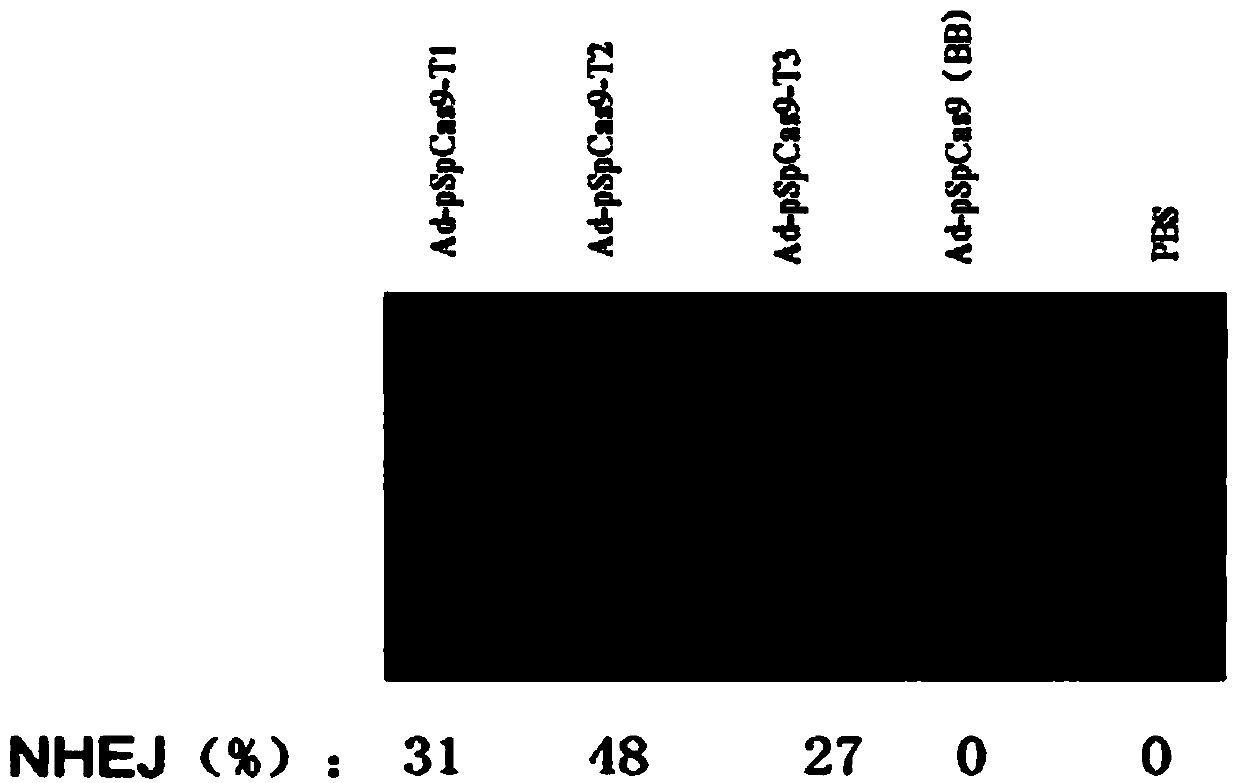
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a nucleic acid encoding a mutant Caspase-9 protein to correct a point mutation associated with a disease or disorder, e.g., with neuroblastoma. The methods provided are useful for correcting a Caspase-9 point mutation within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
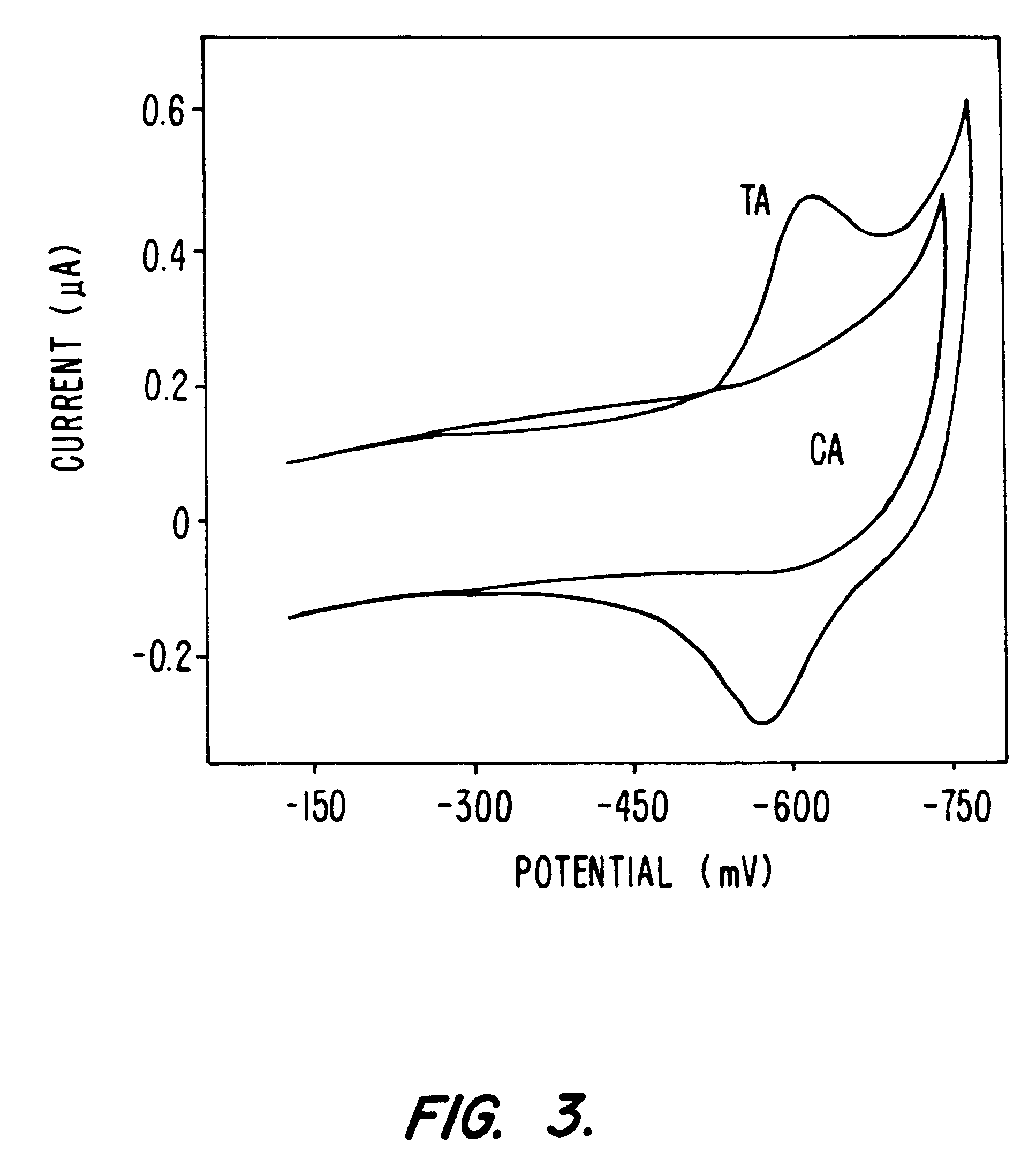
Electrochemical sensor using intercalative, redox-active moieties
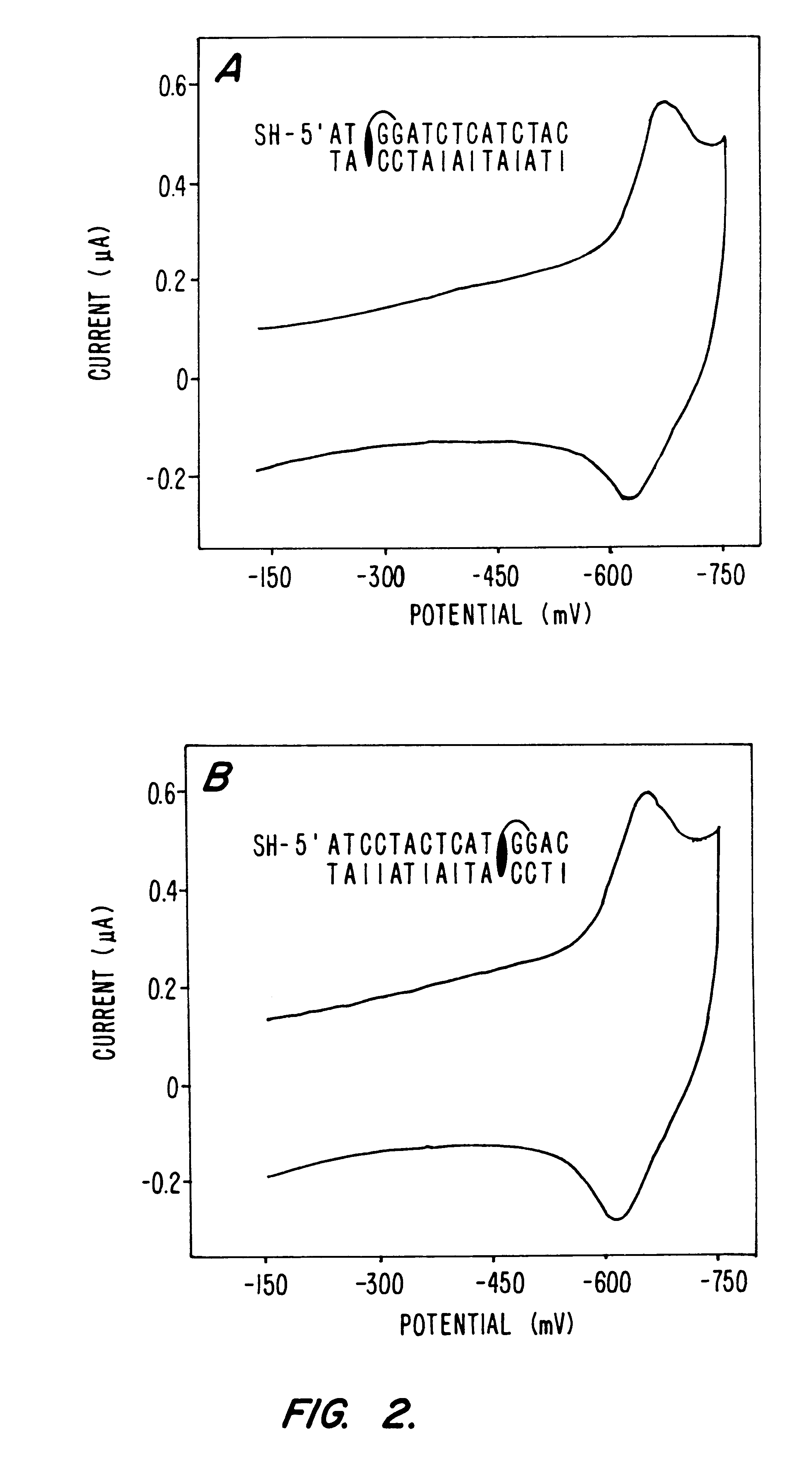
Compositions and methods for electrochemical detection and localization of genetic point mutations and other base-stacking perturbations within oligonucleotide duplexes adsorbed onto electrodes and their use in biosensing technologies are described. An intercalative, redox-active moiety (such as an intercalator or nucleic acid-binding protein) is adhered and / or crosslinked to immobilized DNA duplexes at different separations from an electrode and probed electrochemically in the presence or absence of a non-intercalative, redox-active moiety. Interruptions in DNA-mediated electron-transfer caused by base-stacking perturbations, such as mutations or binding of a protein to its recognition site are reflected in a difference in electrical current, charge and / or potential.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
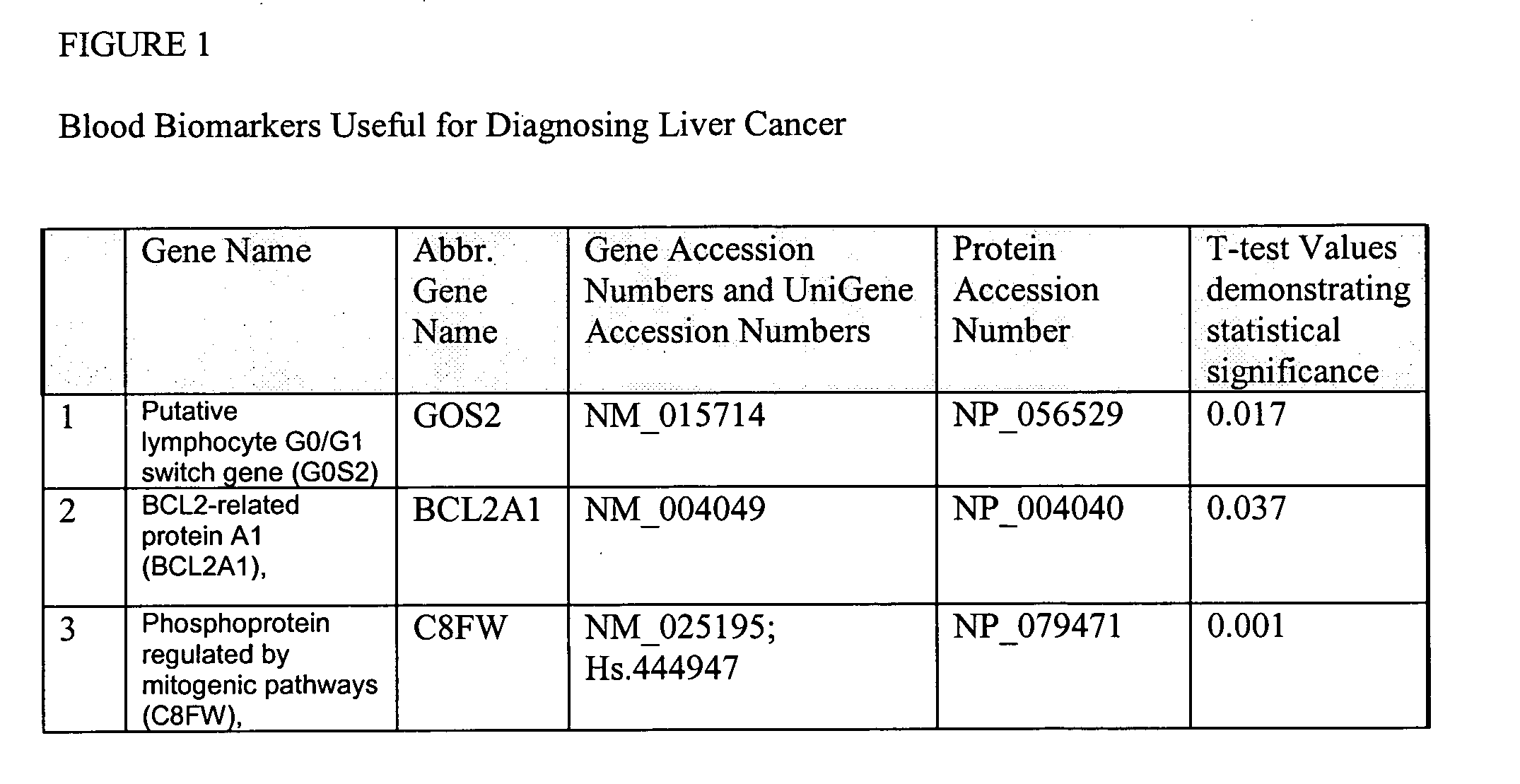
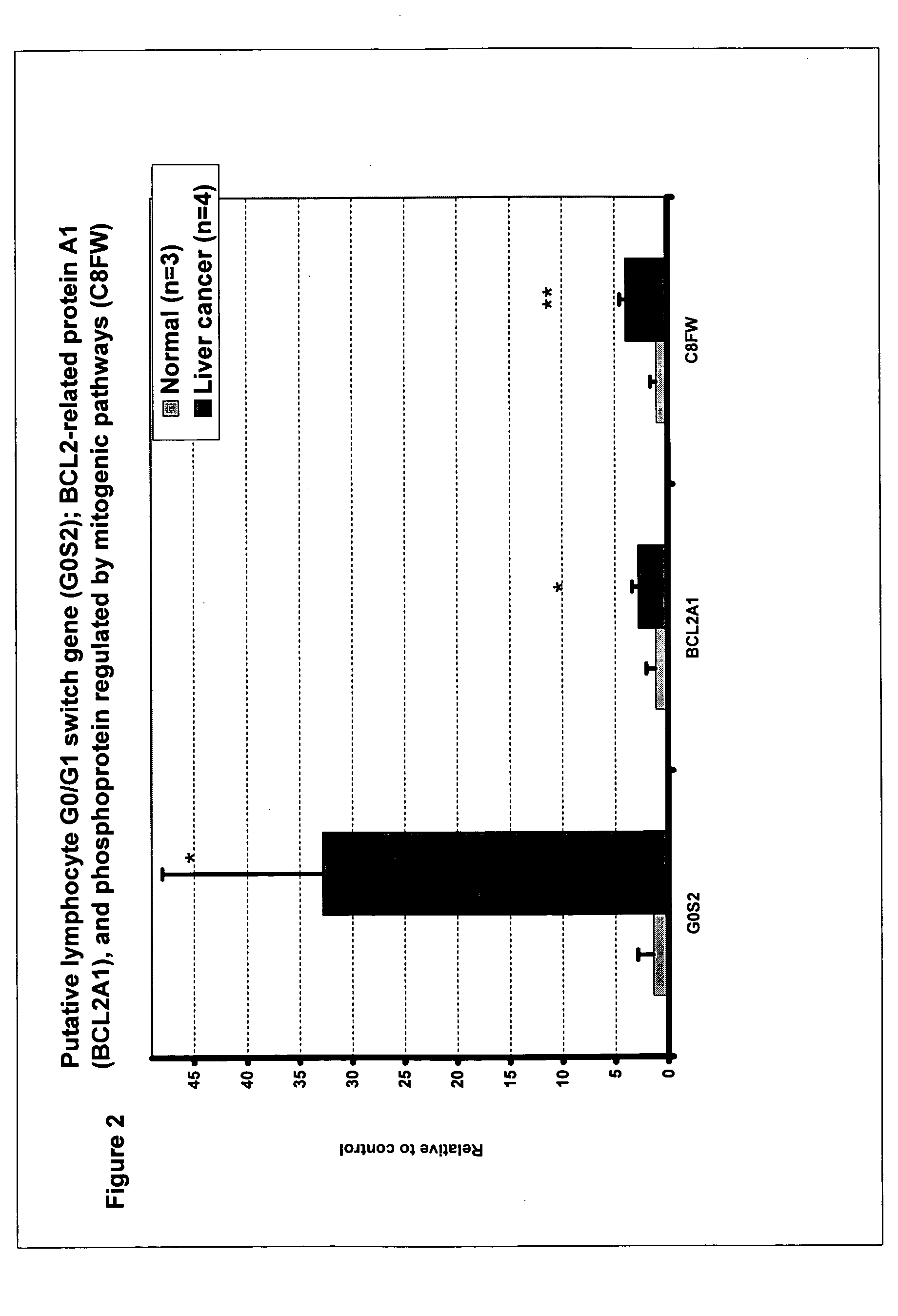
Liver cancer biomarkers
InactiveUS20050152908A1Small amountSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRegimenScreening method
The invention relates to the identification and selection of biomarkers which demonstrate particular advantage in identifying individuals having liver cancer. The invention further relates to useful combinations of biomarkers for diagnosing liver cancer. The invention further provides for the polynucleotides and polypeptides and kits thereof for use as a tool to diagnose disease and to monitor the efficacy of therapeutic regimens. The invention further provides a method of selecting biomarker combinations and the combinations thus identified for diagnosis of liver cancer. Also encompassed by the invention are screening methods to identify therapeutic targets for treating liver cancer, and identify single nucleotide point mutations related to liver cancer.
Owner:GENENEWS
Methods for correcting alpha-antitrypsin point mutations
InactiveUS20150166984A1Nervous disorderFusion with DNA-binding domainHuman DNA sequencingObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a nucleic acid encoding a mutant α-antitrypsin protein to correct a point mutation associated with a disease or disorder, e.g., with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) disease. The methods provided are useful for correcting an α-antitrypsin point mutation within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Methods for correcting presenilin point mutations
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Methods for correcting pi3k point mutations
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a nucleic acid encoding a mutant PI3KCA protein to correct a point mutation associated with a disease or disorder, e.g., with a neoplastic disorder. The methods provided are useful for correcting a PI3KCA point mutation within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Direct molecular diagnosis of Friedreich ataxia
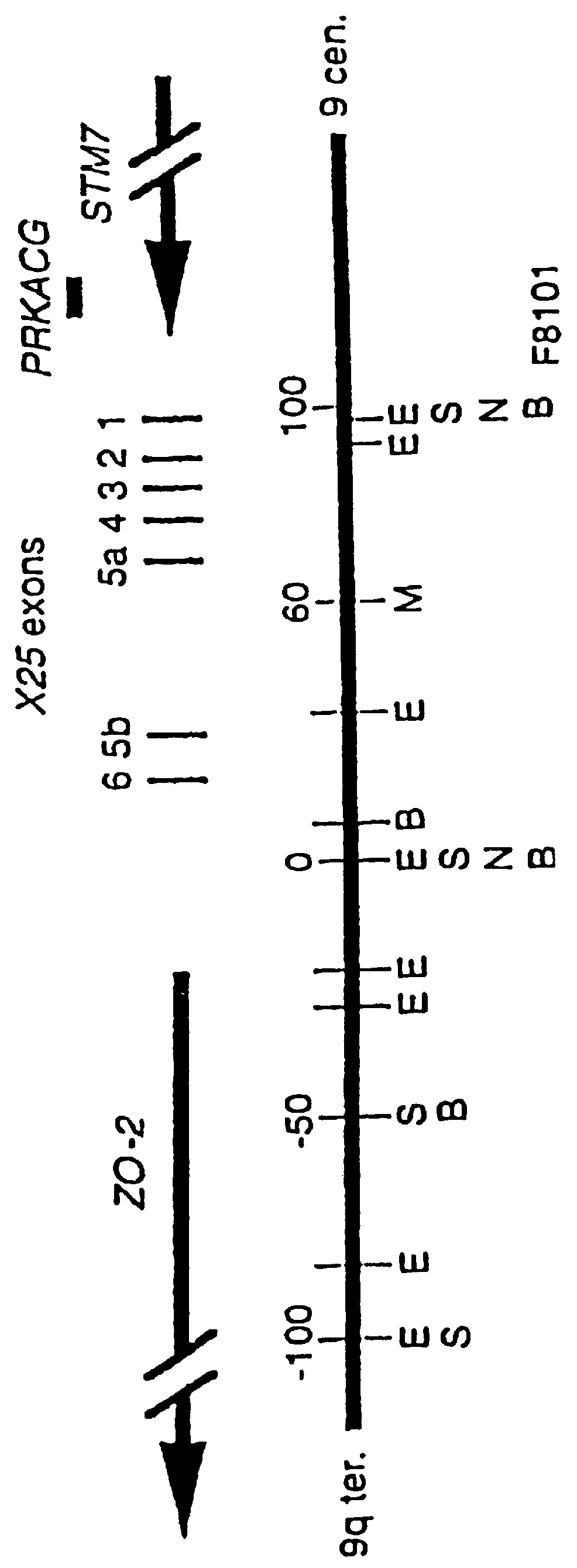
This invention relates generally to methods for the diagnosis and therapeutic treatment of Friedreich Ataxia. Friedreich ataxia (FRDA) is an autosomal recessive, degenerative disease that involves the central and peripheral nervous system and the heart. A gene, X25, was identified in the critical region for the FRDA locus on chromosome 9q13. The gene encodes a 210 amino acid protein, frataxin, that has homologues in distant species such as C. elegans and yeast. A few FRDA patients have been found to have point mutations in X25, but the vast majority are homozygous for a variable, unstable GAA trinucleotide expansion in the first X25 intron. Mature X25 mRNA was severely reduced in abundance in individuals with FRDA. Carriers and individuals at risk for developing FRDA can be ascertained by the methods of the present invention. Further, the methods of the present invention provide treatment to those individuals having FRDA.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE +1
Methods for correcting von willebrand factor point mutations
InactiveUS20150166985A1Nervous disorderFusion with DNA-binding domainHuman DNA sequencingFactor VIII vWF
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a nucleic acid encoding a mutant von Willebrand Factor protein to correct a point mutation associated with a disease or disorder, e.g., with von Willebrand disease. The methods provided are useful for correcting a vWF point mutation within the genome of a cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or enzyme domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing enzymes or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
CRISPR/Cas9 system-containing targeted knockout vector and adenovirus and applications thereof
InactiveCN104004778AHigh knockout rateGenetic material ingredientsViruses/bacteriophagesBiotechnologyEnzyme digestion
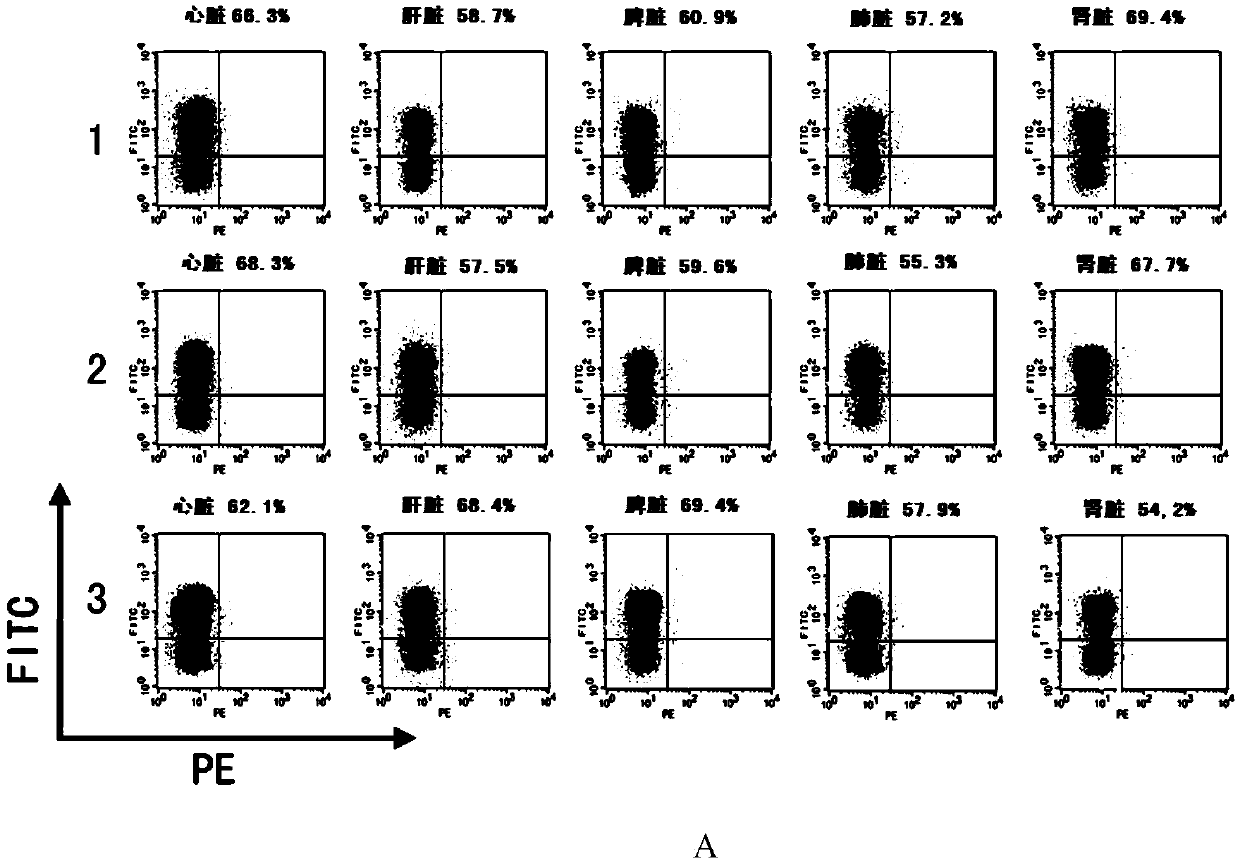
The invention discloses a CRISPR / Cas9 system-containing targeted knockout vector and adenovirus and applications thereof. The targeted knockout vector is prepared through the following steps: after a pX330 U6-Chimeric_BB-CBh-hSpCas9 plasmid is subjected to enzyme digestion and filling-in by using EcoRI and SacII, connecting the pX330 U6-Chimeric_BB-CBh-hSpCas9 plasmid with a pAdTrack-CMV plasmid subjected to enzyme digestion and filling-in by using BstXI; after the obtained product is linearized by using BbsI, connecting the obtained product to a specific target sequence of a desired gene; and after the obtained object is linearized by using PmeI and dephosphorylated by using CIAP alkaline phosphatase, recombining the obtained product with a pAdEasy-1 plasmid. The targeted knockout vector can mutate gene sequences in target sequence areas, and the mutation rate is high, up to 30.6-45.8%, therefore, the targeted knockout vector can be used for gene site-directed mutation, and lays a foundation for gene therapy.
Owner:重庆高圣生物医药有限责任公司
Application of CRISPR/nCas9 mediated site-directed base substitution in plant
ActiveCN107043779ARapid improvement of agronomic traitsImproved agronomic traitsVectorsVector-based foreign material introductionUracil-DNA glycosylaseSubstitution method
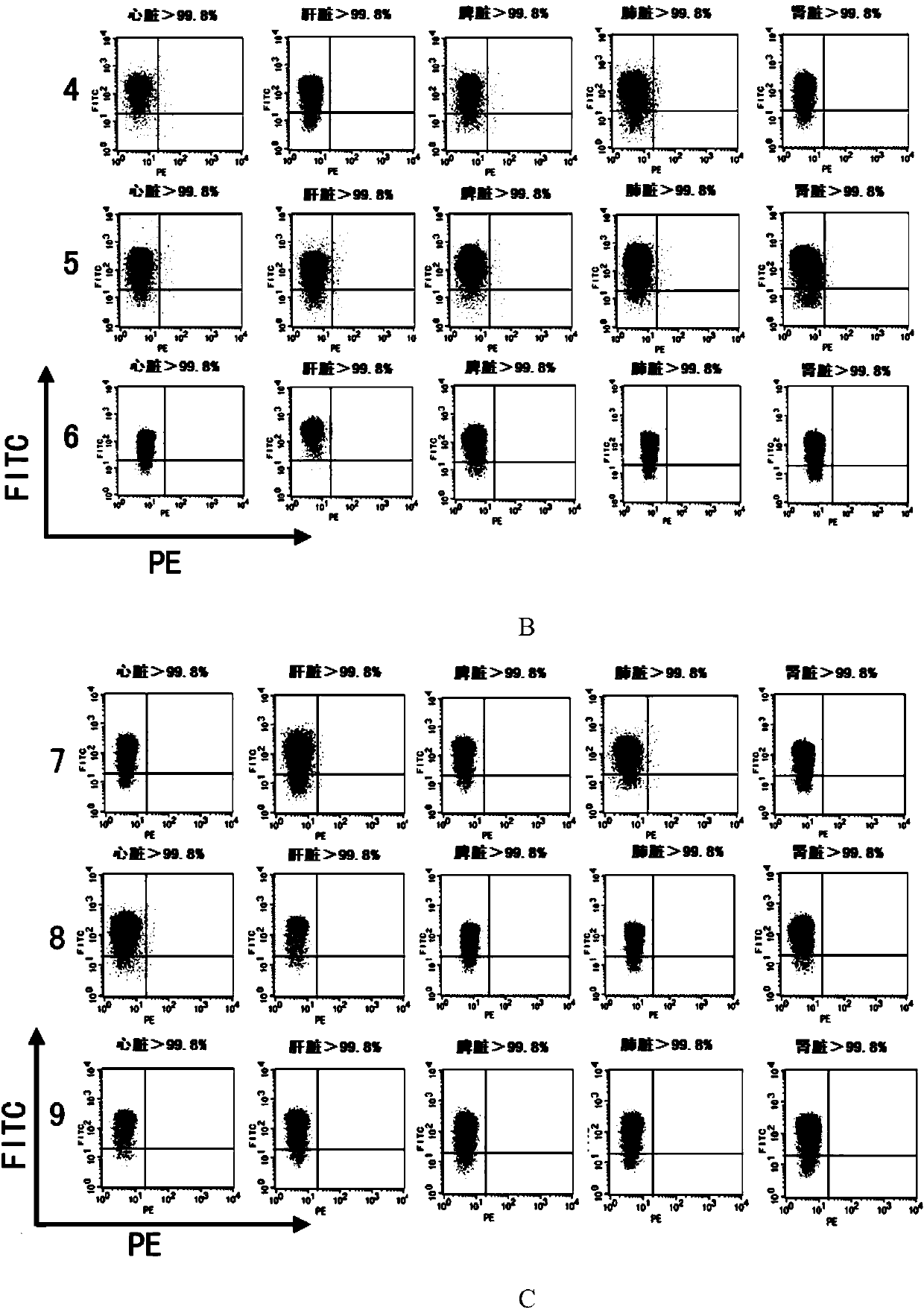
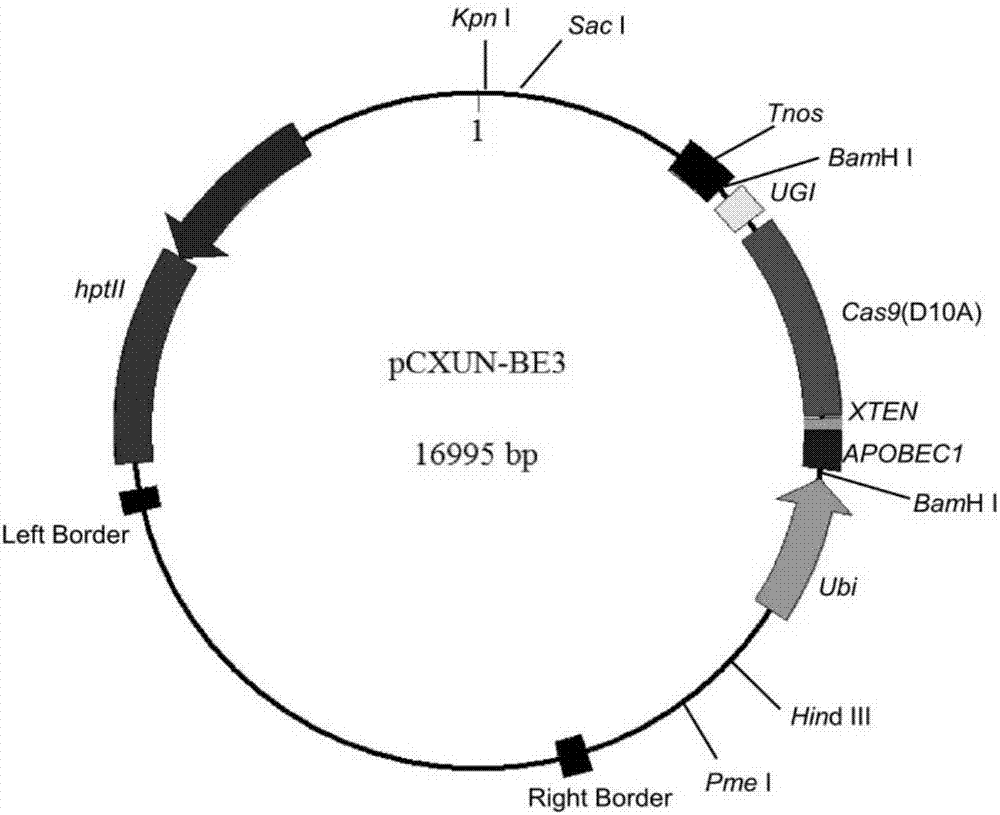
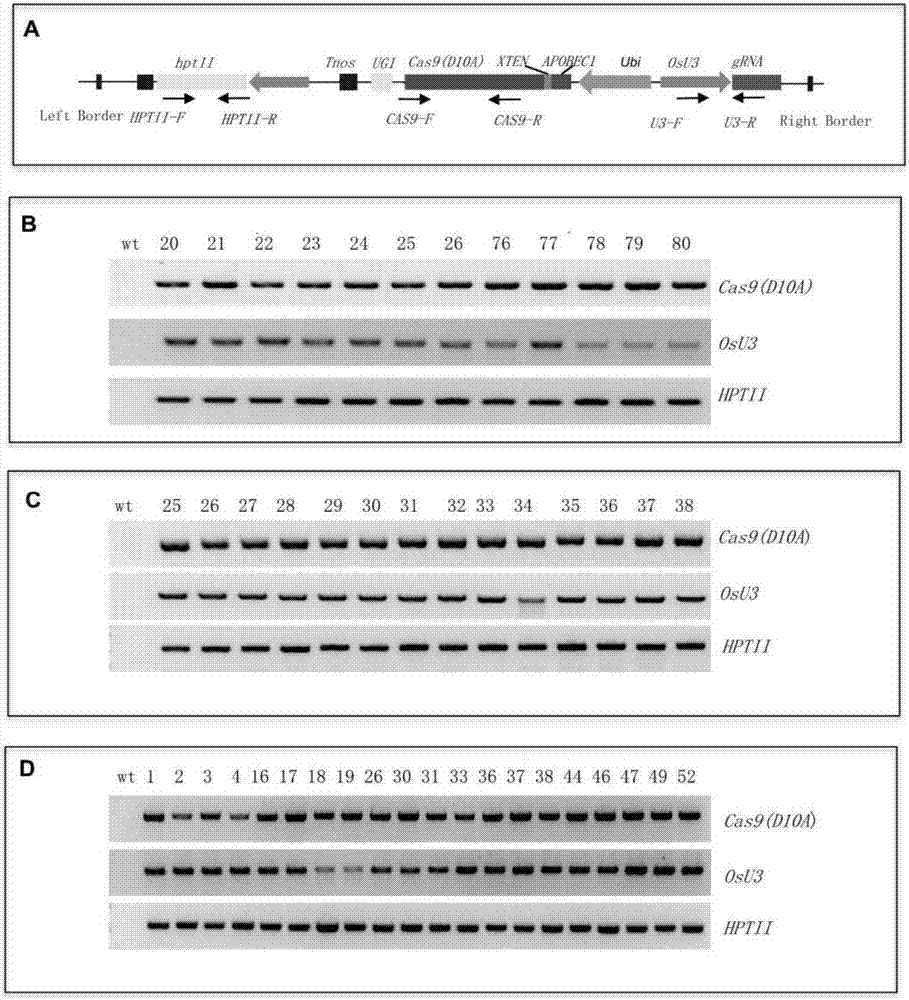
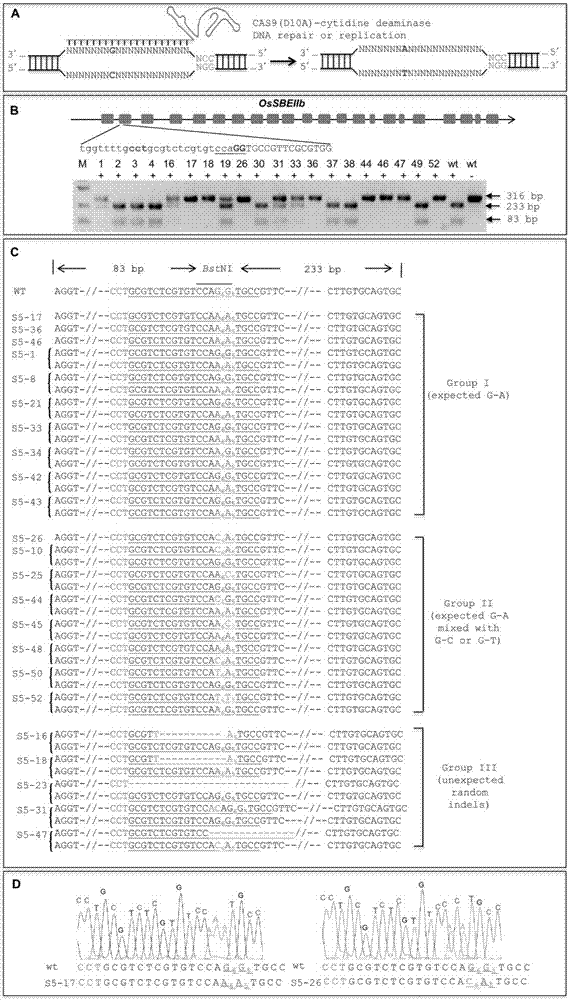
The invention discloses application of CRISPR / nCas9 mediated site-directed base substitution in a plant. The invention provides a plant genome site-directed edition system. The system comprises a BE3 plant expression carrier (expressing a fusion protein composed of nCas9(D10A), deaminase and a uracil DNA glycosylase inhibitory protein), and rice OsPDS and OsSBEIIb are taken as target genes for verifying the system. Results show that an expected site-directed mutant plant is respectively obtained in the three selected target spots, accurate site mutation of a base is realized in rice, and the highest efficiency reaches about 20%, so that a feasible and effective base substitution method is provided for crop breeding, the method has strong application potential in the aspect of agricultural breeding, and a foundation is provided for rapidly improving important agronomic traits of crops.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
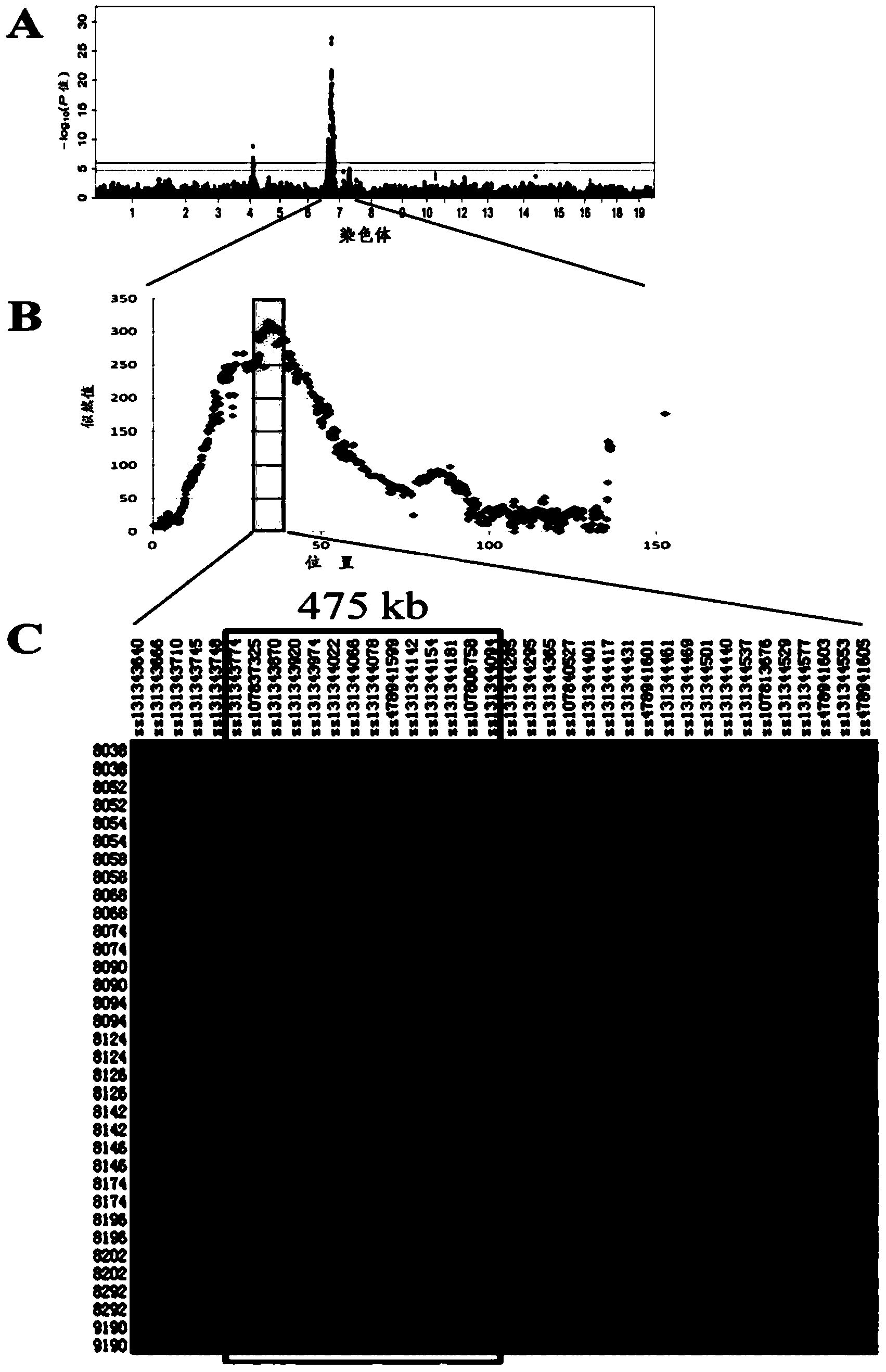
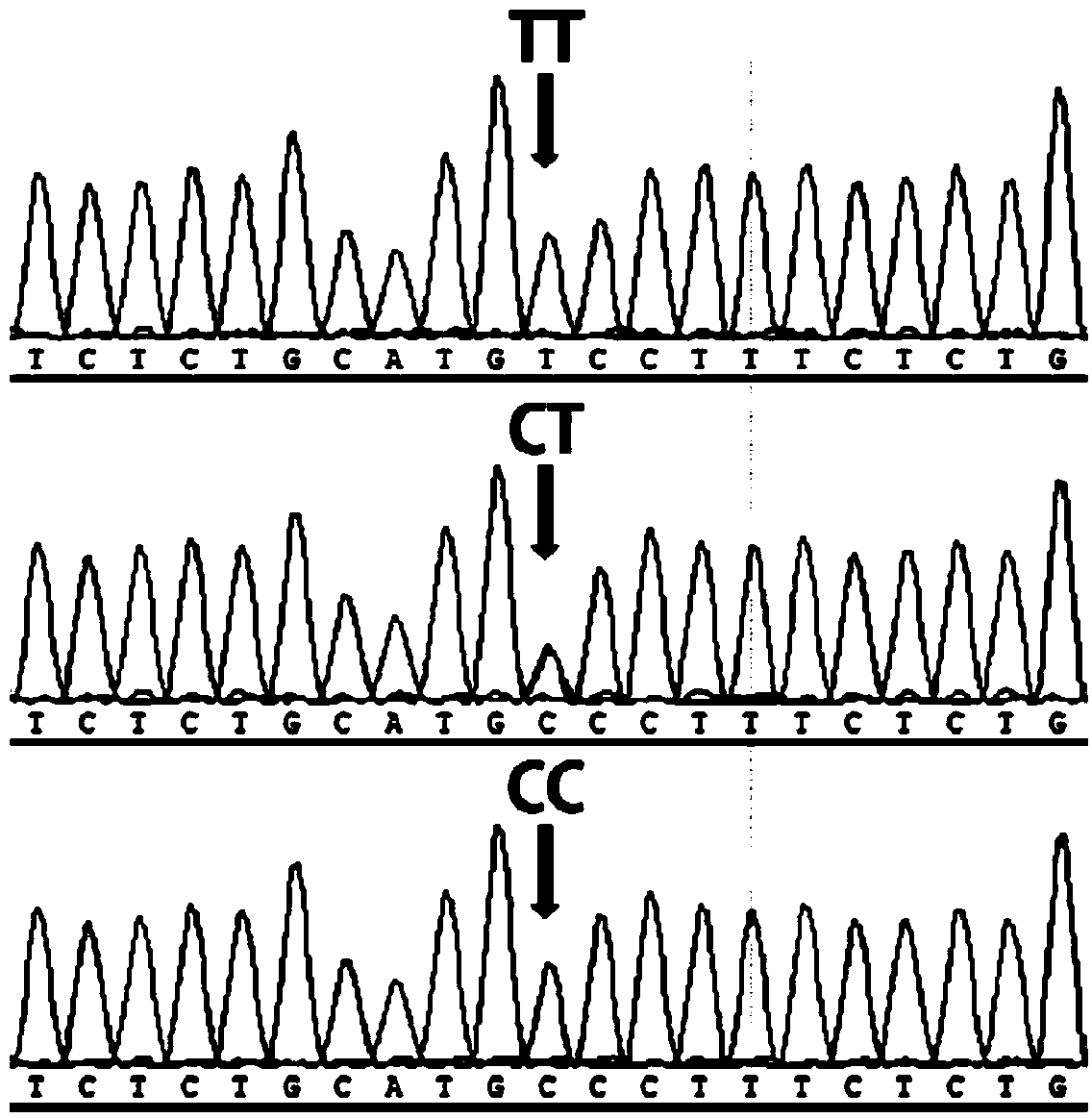
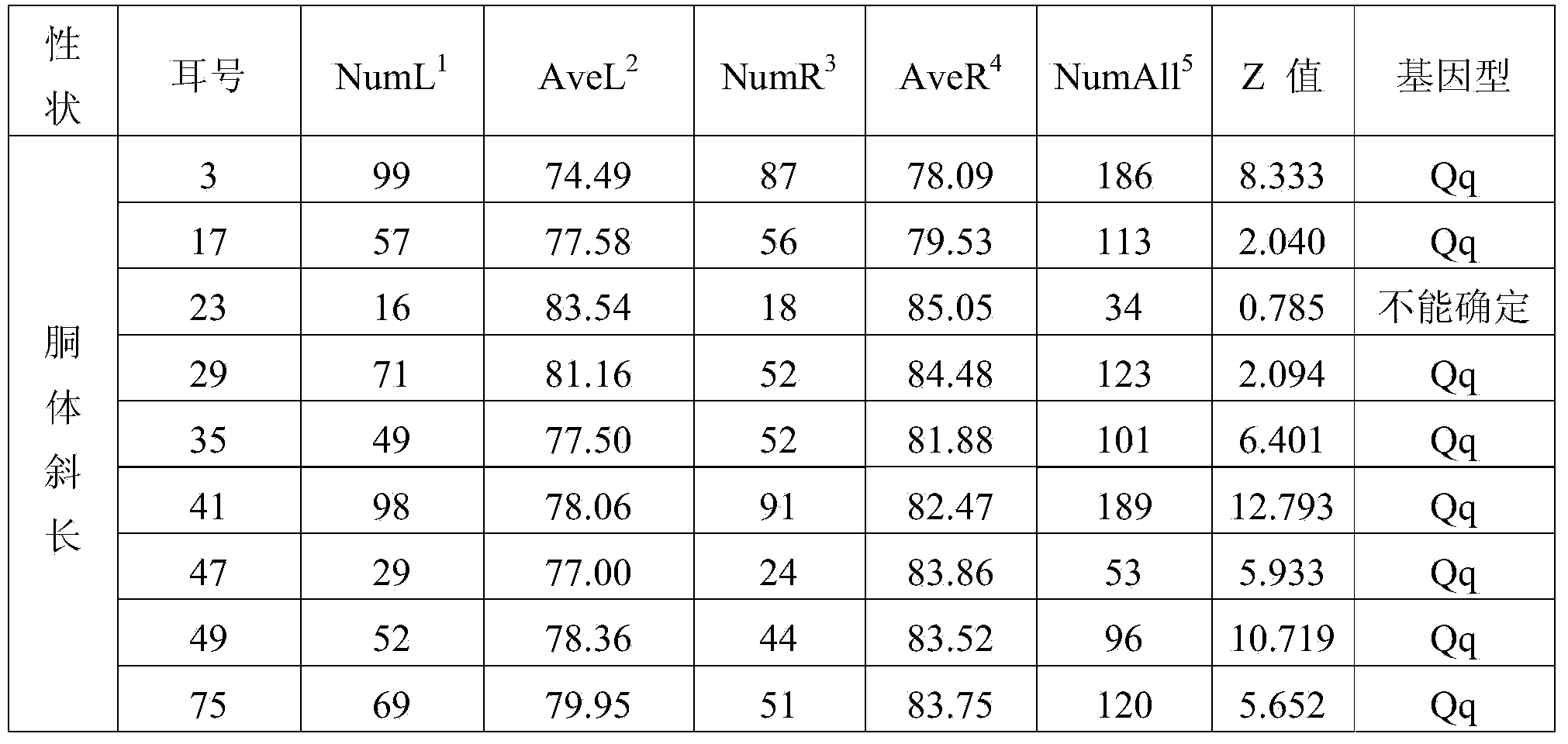
Major SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) marker influencing growth traits of pigs and application thereof in genetic improvement of productivity of breeding pigs
The invention provides a major SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) marker influencing the growth traits of pigs. The SNP marker is located at a nucleotide sequence of an HMGA1 gene of a pig chromosome 7, a locus of the SNP marker is the nucleotide mutation of C857-G857 with an SEQ ID NO:1 sequence labeling position of 857, corresponding to a 34983991st nucleotide locus C> on chromosome 7 in a reference sequence in an international pig genome version 10.2, G mutation, or one of seven other loci completely linked with the locus. The invention also provides the application of the SNP marker in the genetic improvement of growth traits of breeding pigs, and provides the application of an SNP molecular marker with a linkage disequilibrium degree (r2) with the SNP marker of greater than 0.8 in the genetic improvement of growth traits of breeding pigs. The growth traits include one or more of the length and height of a living body of a pig, carcass length, carcass weight, daily gain and head weight. According to the invention, the breeding process of breeding pigs can be accelerated, the productivity of breeding pigs can be effectively improved, and remarkable economic benefits can be obtained.
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
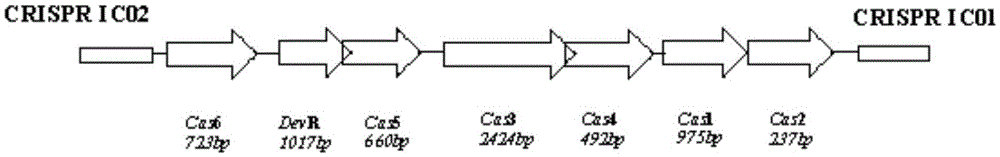
CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat sequences)-Cas (CRISPR-associated proteins) system in Streptomyces virginiae IBL14 and method for carrying out gene editing by using CRISPR-Cas system
InactiveCN105543266AChange genetic traitsIncrease production levelsNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionOrganismPlasmid
The invention discloses a CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat sequences)-Cas (CRISPR-associated proteins) system in Streptomyces virginiae IBL14 and a gene editing operation method using the CRISPR-Cas system. The method comprises the processes of carrying out design and plasmid construction on features, targeted genes and gene editing templates of a CRISPR-Cas I-B type gene editing system and carrying out gene editing operation in the Streptomyces by a targeted gene and gene editing template recombinant plasmid. Through carrying out knockout, insertion, traceless point mutation and RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) level regulation and control on genetic genes by using the CRISPR-Cas I-B type gene editing system in the Streptomyces virginiae IBL14, the hereditary features of organisms can be conveniently changed; according to the CRISPR-Cas system and the method for carrying out gene editing by using the CRISPR-Cas system, novel technologies and methods are provided for improving the production level of products of medicine, food and other industries and improving the quality of the products.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Gene site-directed mutation vector as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN106834341ANucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionCytosine deaminaseCytosine
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering and in particular relates to a gene site-directed mutation vector as well as a construction method and application thereof. The invention provides the gene site-directed mutation vector due to lots of optimizations, cytosine deaminase is guided to be close to cytosine through a CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) system, the cytosine is changed into uracil, then uracil is changed into thymine through self-repair in plant cells, and finally, site-specific mutagenesis from C to T is realized in plants so as to generate resistance to herbicides. In addition, point mutation can be produced in a non-sgRNA targeted area, and novel herbicide-resistant great agronomic traits are brought.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Use of mixed duplex oligonucleotides to effect localized genetic changes in plants
InactiveUS7094606B2Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationACC oxidaseGenetic Change
Owner:CIBUS
Method for editing prokaryotic genomes using endogenic CRISPR-Cas (CRISPR-associated) system
ActiveCN105331627AReduce workloadWide range of application hostsBacteriaVector-based foreign material introductionGenome editingWorkload
The invention relates to a method for editing prokaryotic genomes using an endogenic CRISPR-Cas (CRISPR-associated) system. An editor plasmid carrying both an artificial CRISPR cluster and a donor DNA is required to be established for the genome editing of a prokaryote containing the endogenic CRISPR-Cas system, after NDA interference is caused by the endogenic CRISPR-Cas to the genome, and the genome is edited through homologous recombination. The method has the advantages that a range of applicable hosts is wide, all bacteria and archaea containing the endogenic CRISPR-Cas being available for operation; the method is applicable to operations in various editing manners, such as deletion, insertion and point mutation; the editing efficiency is higher, screening positive rage is high, and the background is low; a flow is simple, a short period of time is required, and the workload of prokaryotic genome editing is greatly reduced.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Methods of performing homologous recombination based modification of nucleic acids in recombination deficient cells and use of the modified nucleic acid products thereof
A simple method for modifying genes in a recombination deficient host cell is disclosed. Such modifications include generating insertion, deletions, substitutions, and / or point mutations at any chosen site in the independent origin based cloning vector. The modified gene can be contained in an independent origin based cloning vector that is used to introduce a modified heterologous gene into a cell. Such a modified vector may be used in the production of a germline transmitted transgenic animal, or in gene targeting protocols in eukaryotic cells.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Method for site-directed mutation of maize gene by means of CRISPR/Cas9 system
ActiveCN107022562AGood characterSite-directed mutagenesisPeptidesNucleic acid vectorDNA fragmentationA-DNA
The invention provides a method for site-directed mutation of a maize gene by means of a CRISPR / Cas9 system. An sgRNA sequence based on CRISPR / Cas9 is designed aiming at a target gene in maize, a DNA fragment for encoding the sgRNA sequence is connected to a vector carrying CRISPR / Cas9, and then maize transformation is conducted, so that site-directed mutation of a specific gene in maize is realized. Further, the vector containing CRISPR / Cas9 is transferred to an acceptor material carrying the target gene by means of a genetic transformation method, so as to obtain a site-directed mutation regeneration plant of the target gene. By the adoption of the method, site-directed mutation of a maize genome can be achieved. The method has the advantages that the experimental period is short, and operation is easy. Different target genes can be transformed in a site-directed mode by means of CRISPR / Cas9 systems with different targeting directions, a novel method is provided for improved breeding of maize, and the method is of great practical significance for maize trait improvement.
Owner:先正达集团股份有限公司
Stabilized proteins
InactiveUS7037894B2Prevent undesired cross-linkControl cross-link reactionHormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsTyrosineProtein retention
Isolated polypeptides or polypeptide chains are modified by di-tyrosine cross-linking such that the retain at least one functional activity. In one embodiment, the isolated polypeptide or polypeptide chains comprise at least one di-tyrosine cross-link, wherein at least one tyrosine of the di-tyrosine cross-link originates from a point mutation to tyrosine, and wherein the di-tyrosine cross-linked protein retains at least one function displayed by the protein in the absence of di-tyrosine cross-linking. In another embodiment, the di-tyrosine cross-linked polypeptide or polypeptide chain has enhanced stability compared to the same polypeptide or polypeptide chain in the absence of di-tyrosine cross-linking. A method for stabilization of a polypeptide or polypeptide complex, by the introduction of intra-polypeptide and / or inter-polypeptide di-tyrosine bonds, which simultaneously maintains the structure and function of the polypeptide or polypeptide complex is also described.
Owner:CALDER BIOSCI INC
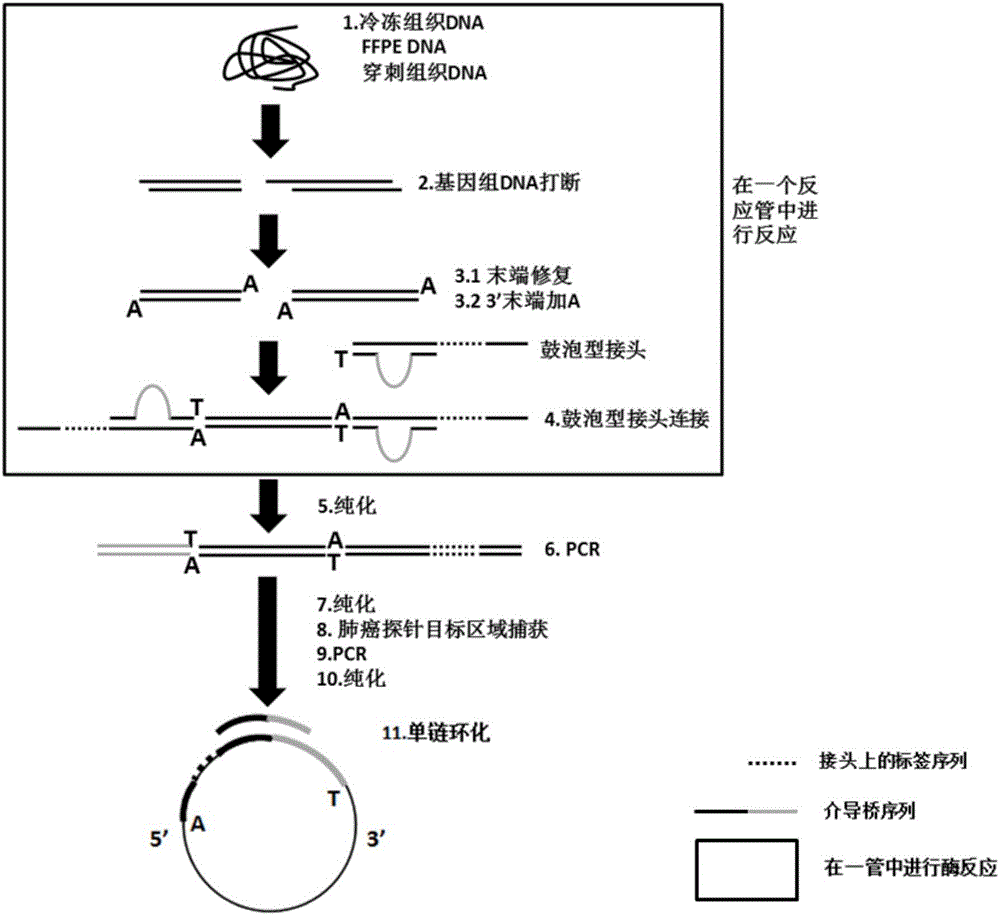
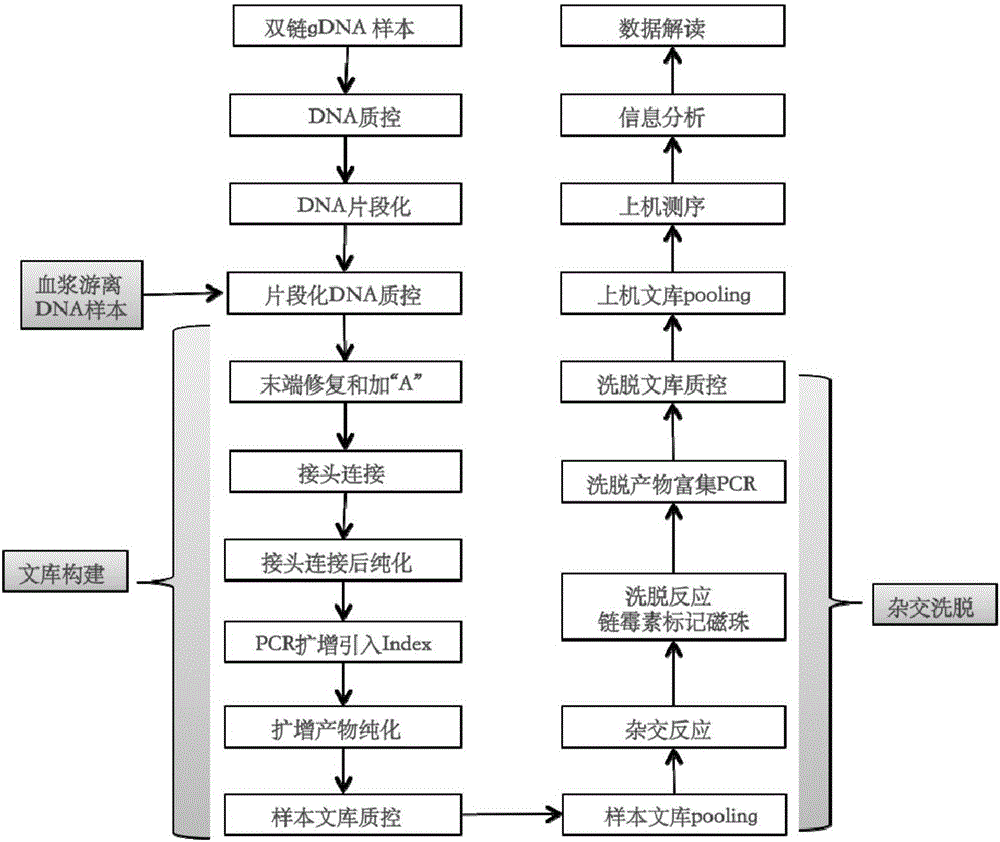
Building method of library for detecting non-small cell lung cancer gene mutation and kit
PendingCN106497920AImprove recycling efficiencyImprove utilization efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationGene targetingGene mutation
The invention discloses a building method of a library for detecting non-small cell lung cancer gene mutation and a kit. The method includes: using tubular reaction to complete genome DNA breaking and connector connection, performing hybrid capture on connection products after amplification and non-small cell lung cancer related gene target area probes, and performing BGISEQ-500 / 1000 platform sequencing and data analysis to obtain mutation conditions. The method has the advantages that the experiment flow is optimized greatly by the tubular reaction, operation complexity and time are reduced, and the requirements on clinical sample initial amount are lowered; multiple genes and multiple sites can be detected in one step, point mutation, insertion and deletion, structural variation and copy number variation are covered, the detecting result is accurate and overcomes the defect that a PCR capture method cannot detect the structural variation in one step, and the effectiveness of the high-throughput sequencing applied to the detection of the non-small cell lung cancer gene mutation; the method is wide in coverage, high in cost performance, capable of providing a reference basis for the diagnosing, treatment and drug use performed by doctors, and the method is suitable for being popularized and used in a large-scale manner.
Owner:BGI BIOTECH WUHAN CO LTD
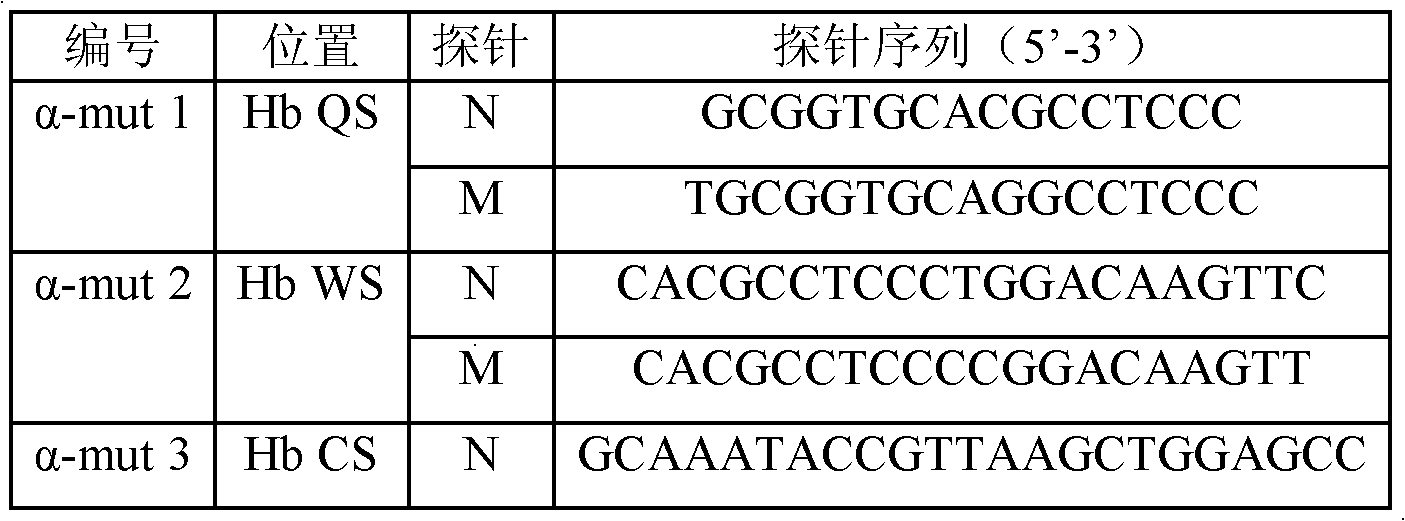
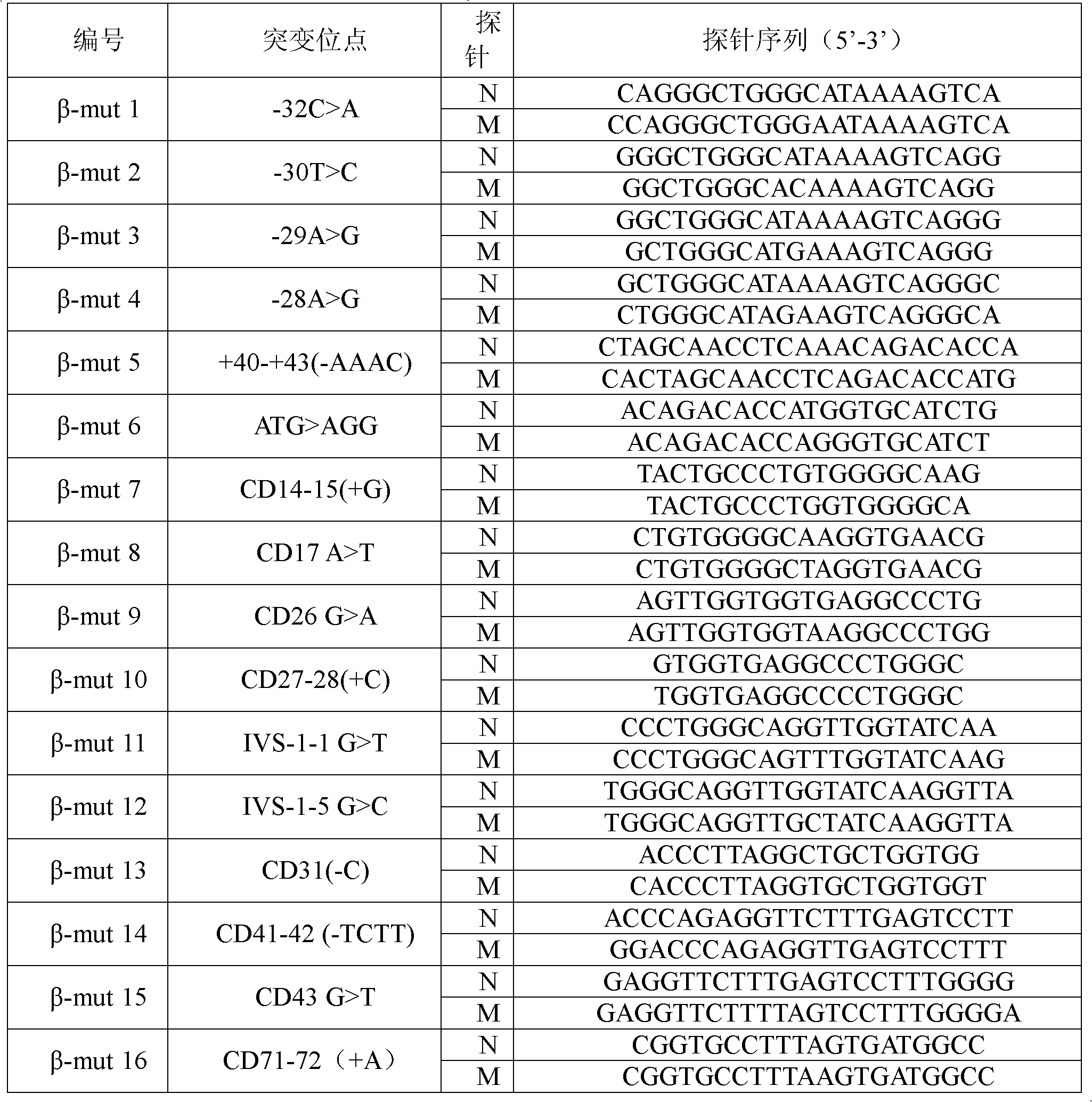
Nucleic acid film tape and kit for diagnosing alpha mediterranean anemia
ActiveCN101092647AReduce financial burdenRich reference informationMicrobiological testing/measurementPrenatal diagnosisThalassemia
This invention relates to test kit and test paper with oligonucleotide probes for diagnosing alpha-thalassemia. The test paper comprises a base, and specific oligonucleotide probes immobilized on the base. The oligonucleotide probes comprise: specific oligonucleotide probes for detecting mutation of alpha-globin gene, specific oligonucleotide probes for detecting deletion of alpha-globin gene, and base sequence complementary with the above sequences. The test kit comprises specific primer for amplifying alpha-globin gene or transcript, and specific oligonucleotide probes for detecting mutation / deletion of alpha-globin gene. The test kit and the test paper have such advantages as low cost, rapid detection, and stable results. The test kit and the test paper can be used in detection of mutation / deletion of alpha-globin gene, and prenatal diagnosis of severe thalassemia (alphaTalpha) caused by point mutation, and do not have error diagnosis.
Owner:亚能生物技术(深圳)有限公司
Probe and sequence combination for simultaneous detection of various mutation types
InactiveCN106480205ARealize multiple comprehensive detectionAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHydrothoraxTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses a probe and a sequence combination for simultaneous detection of various mutation types and particularly provides a kit, a method, a gene chip, a probe and a sequence combination which are high in sensitivity and specificity and used for simultaneous detection of point mutation, short segment insertion and deletion, copy number variation and fusion genes of 57 tumor driver genes listed in a detection list. The invention further discloses a sequence combination and probe associated gene chip and kit and a method for simultaneous detection of various mutation types. By detection of body fluid including blood, hydrothorax, abdominal dropsy and the like and tumor frozen tissues or paraffin sections, comprehensive tumor driver gene mutation information can be acquired, sensitivity and accuracy in tumor gene detection are improved, and accordingly clinicians can be assisted in making of individualized medication schemes to achieve best accurate treatment effects.
Owner:BEIJING GENEPLUS TECH +1
Method, kit and application for diagnosing thalassemia based on liquid chip system
ActiveCN102277419ADetection time is shortEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceMicrosphere
Disclosed are a method for diagnosing thalassemia based on a liquid chip system, and a kit and an application. The present invention designs probes for detecting a, ß thalassemia genetic defect types. These probes are respectively cross-linked and mixed with fluorescent encoding microspheres of different colors to obtain liquid chips for diagnosing a, ß thalassemia. After PCR amplification is performed, by using a specific primer of the present invention, on a sample to be detected, a biotin-labeled PCR product is obtained, which is then hybridized with the liquid chip of the present invention, and further undergoes fluorescence labeling by use of phycoerythrin. Finally, a detection result is read out through a liquid chip detector. The kit of the present invention comprises PCR primers and specific probes, and can detect deletion or non-deletion point mutation a, ß thalassemia.
Owner:GUANGDONG WOMEN & CHILDREN HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com