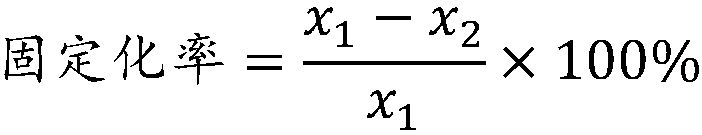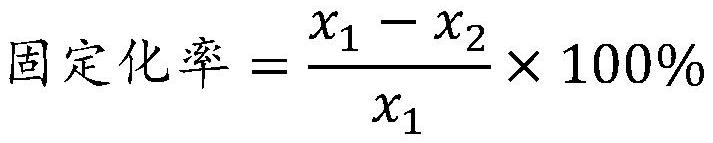Patents
Literature
35 results about "Immobilized DNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Use of immobilized PCR primers to generate covalently immobilized DNAs for in vitro ... Bead-immobilized DNA templates would provide a convenient way to circumvent these problems by enabling the bead-bound DNA templates to be collected and recycled after each transcription reaction. ... permits the synthesis of large proteins not ...
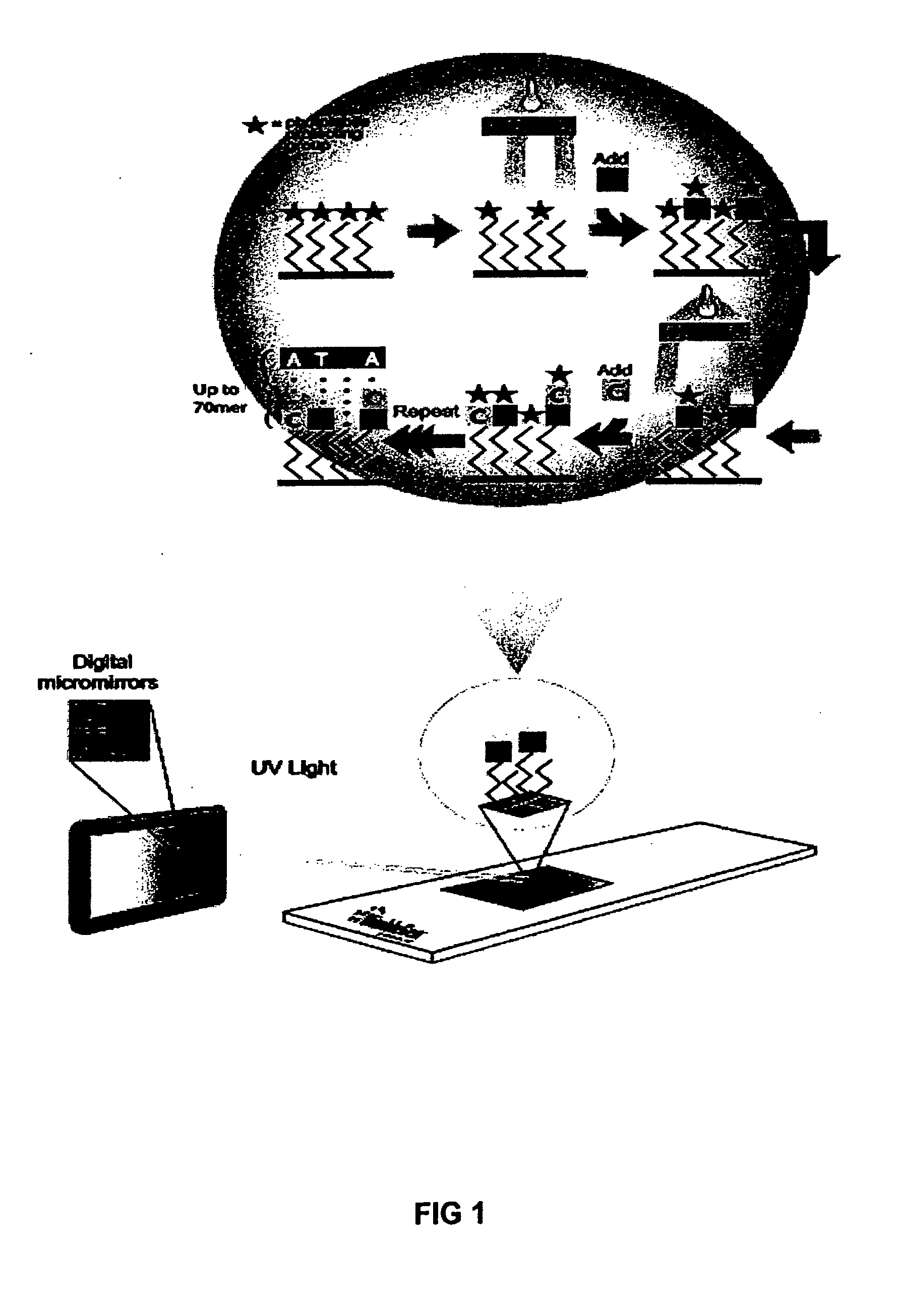
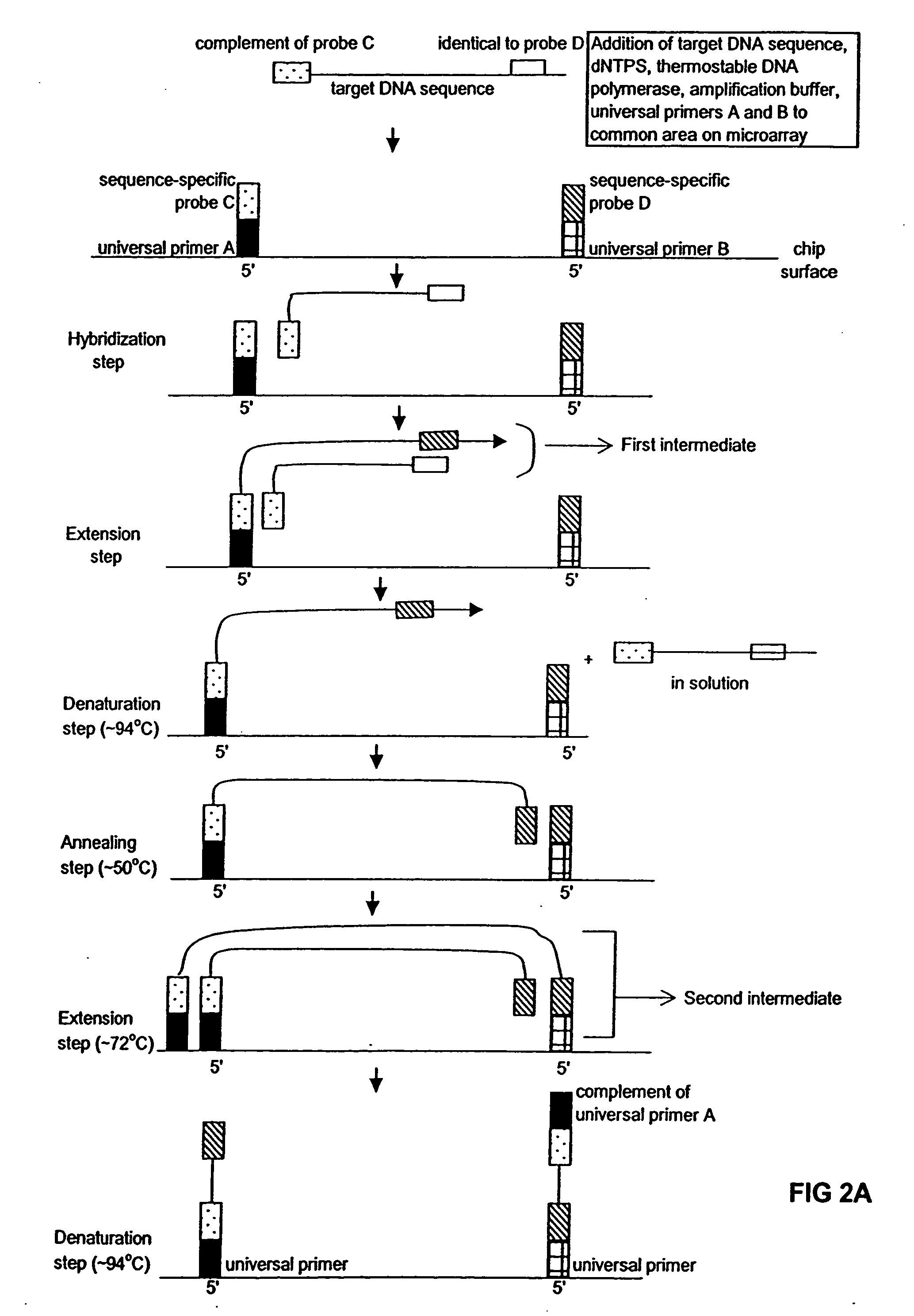
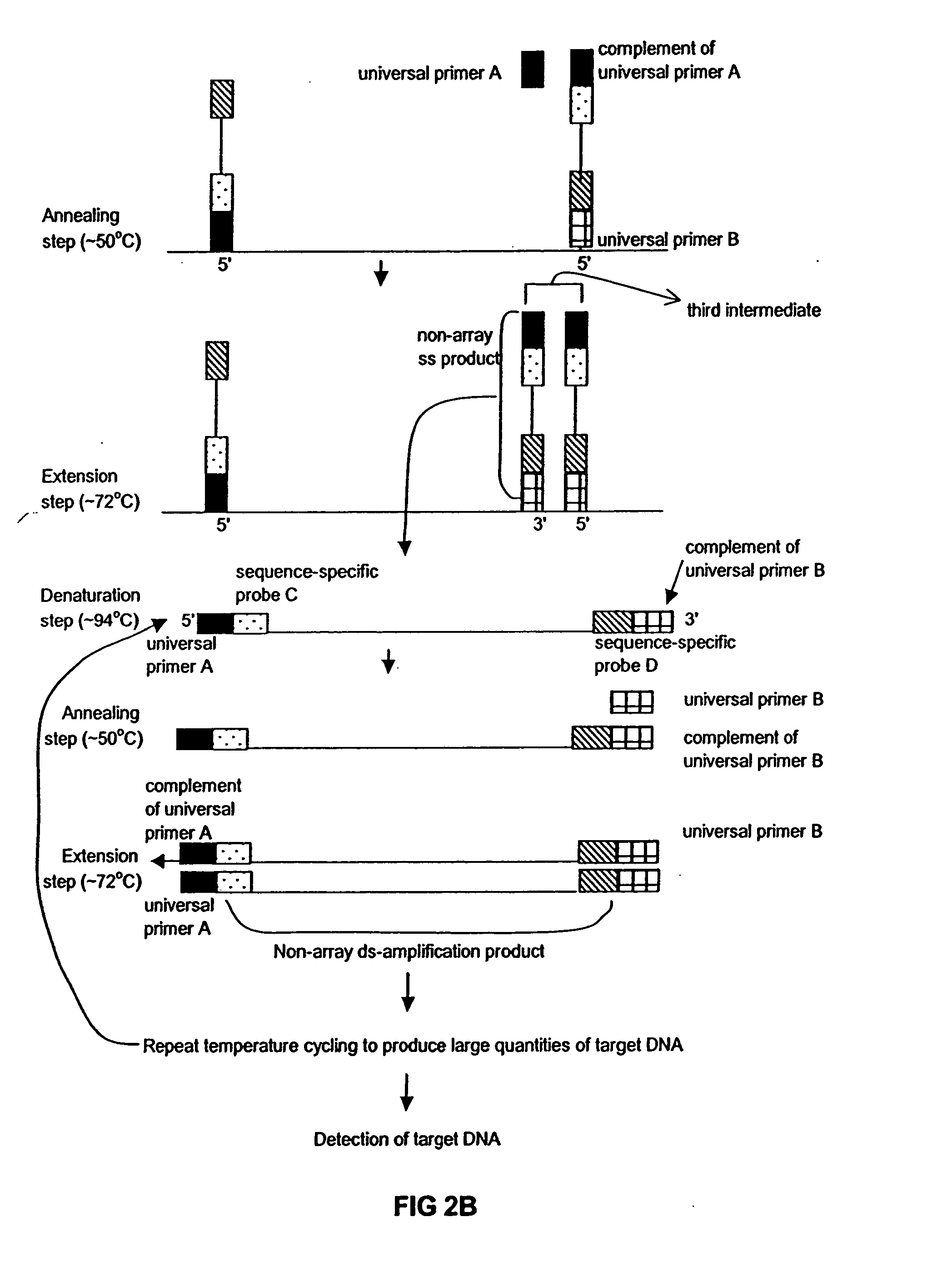
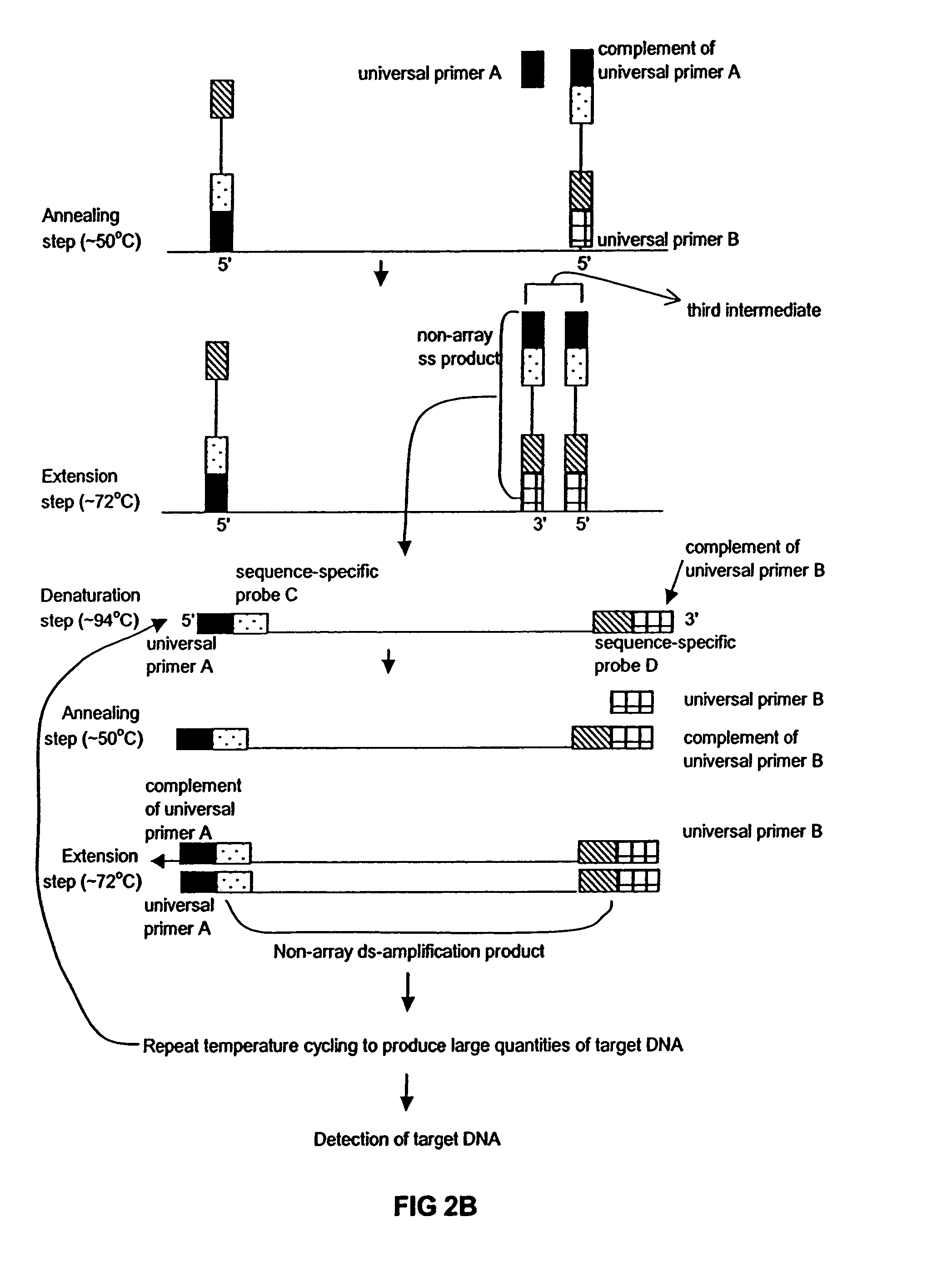
Method of performing PCR amplification on a microarray
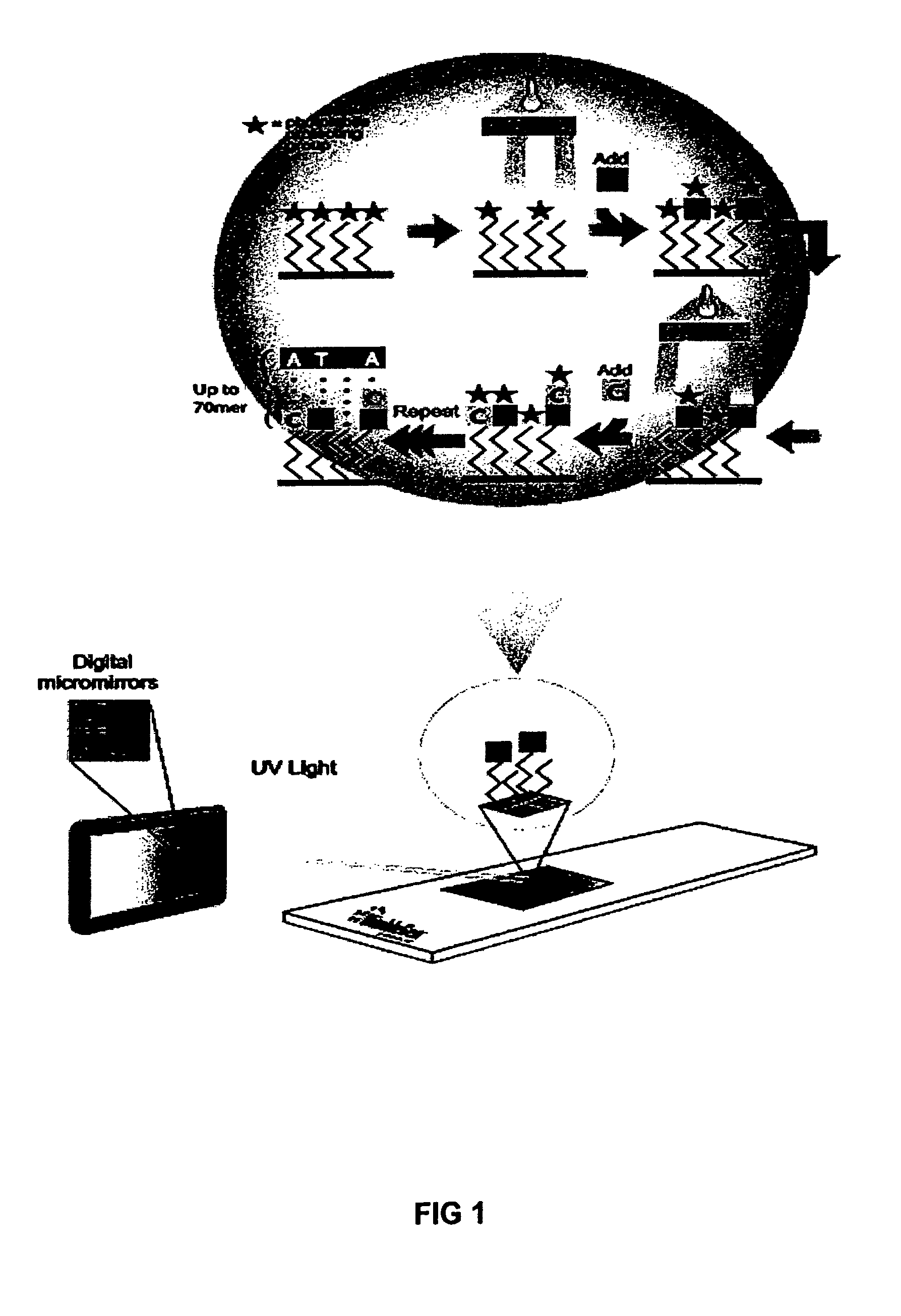
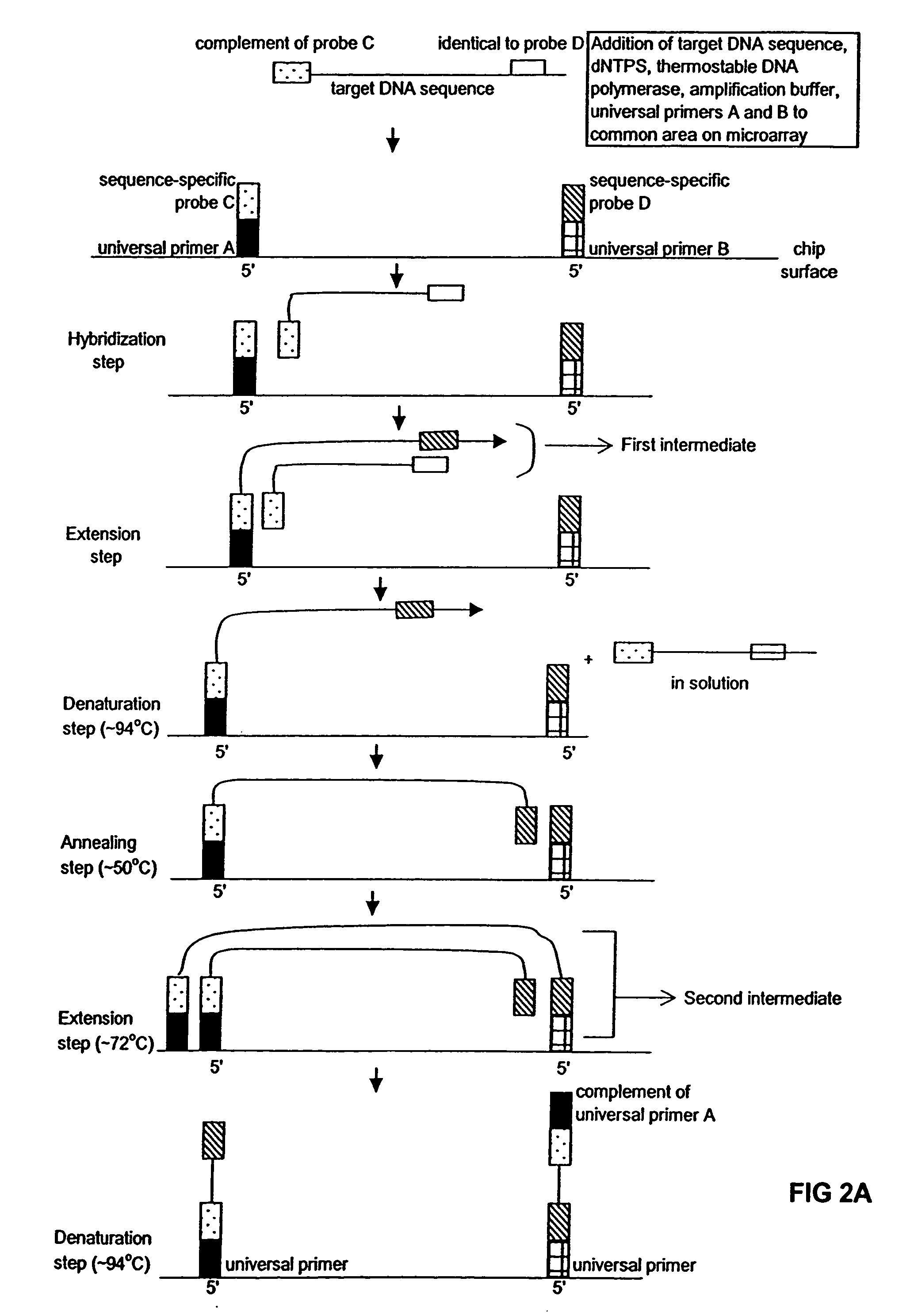
The present invention provides a method of amplifying target DNA by PCR or multiplex PCR on a microarray using array-immobilized DNA probes synthesized in a common area on the microarray by a maskless array synthesizer (MAS). The MAS constructed array-immobilized DNA probes include a universal primer linked to a sequence-specific probe, and optionally a calibrated probe for use in quantifying amplified target DNA.
Owner:ROCHE NIMBLEGEN
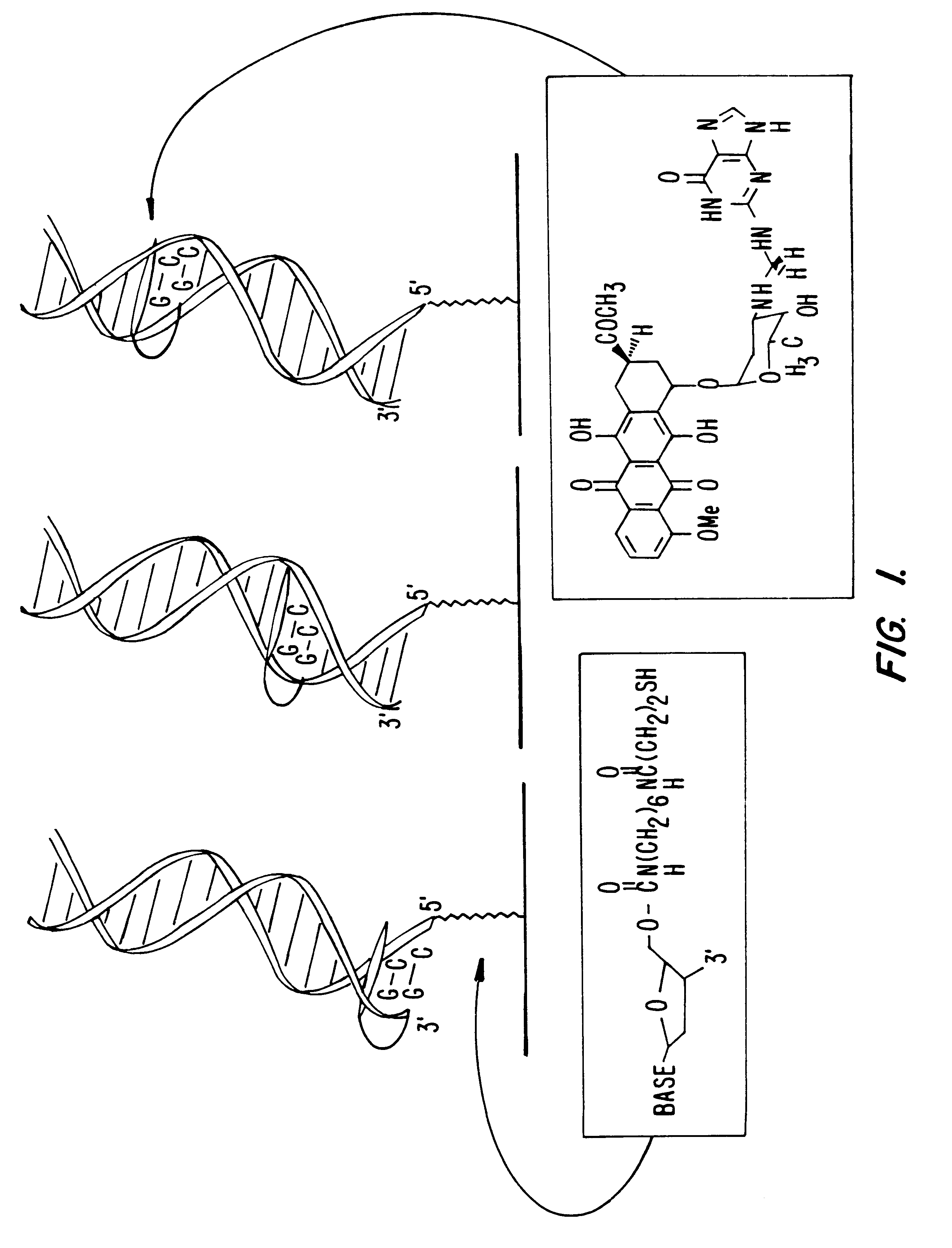
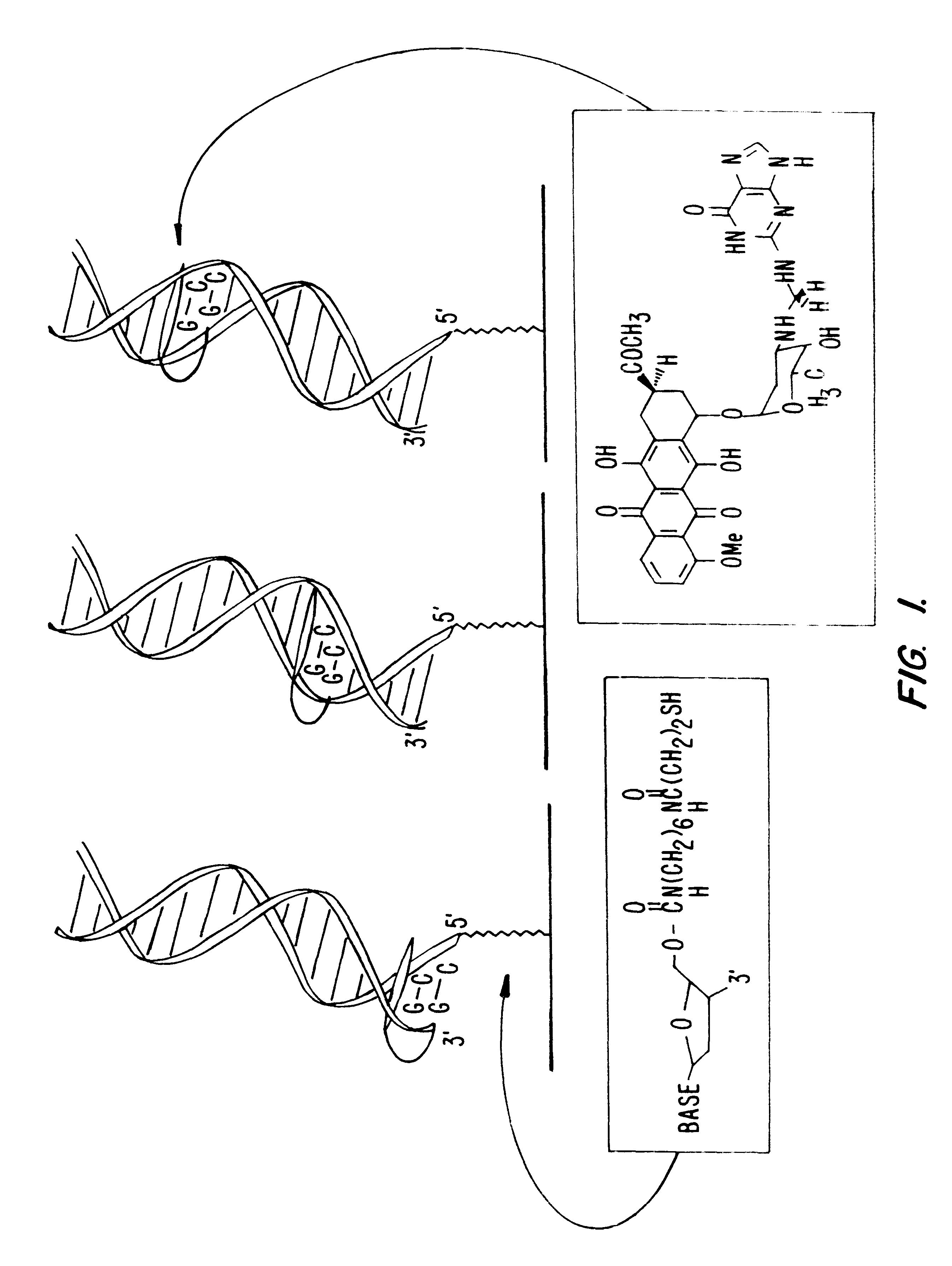
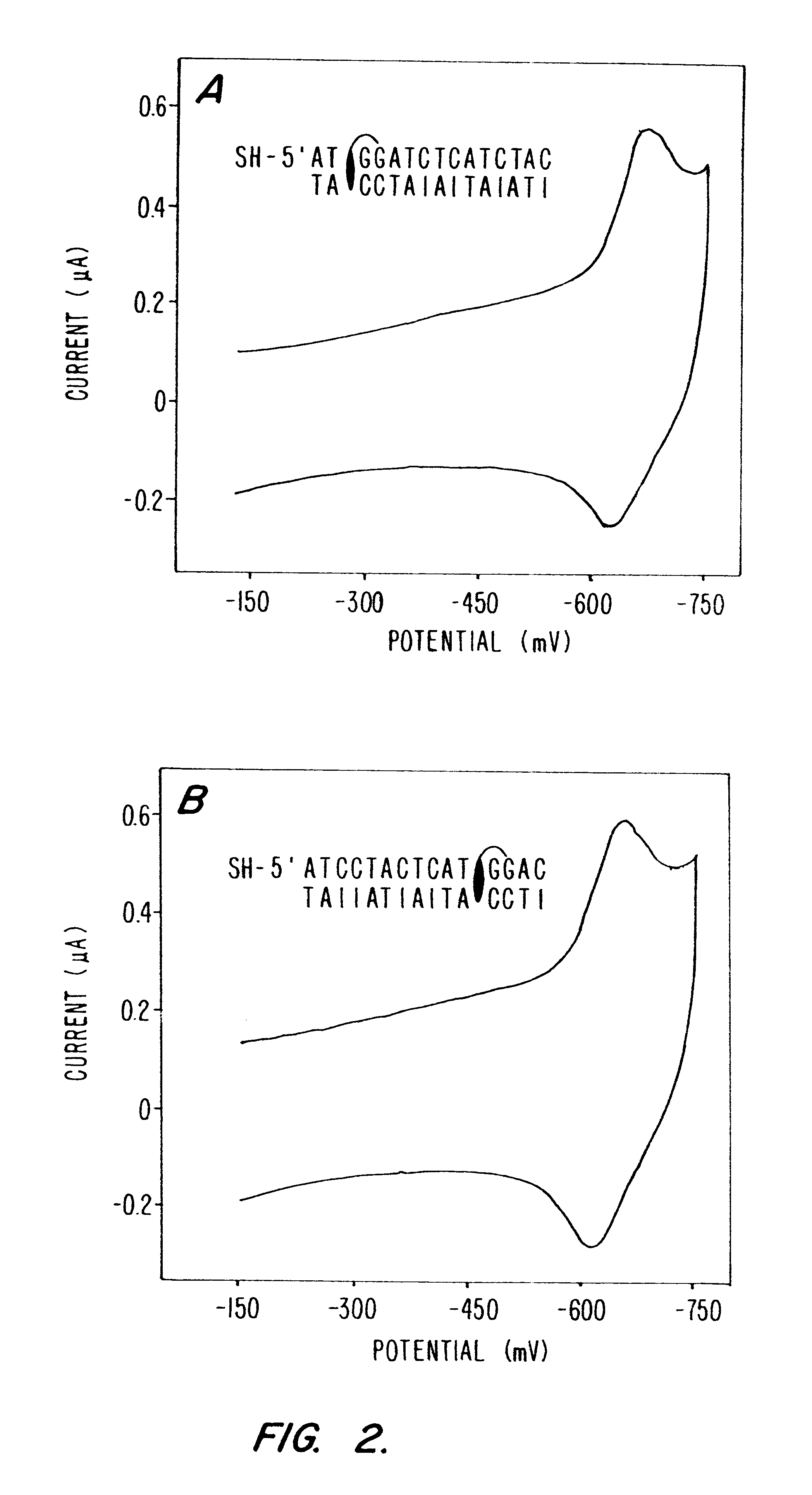
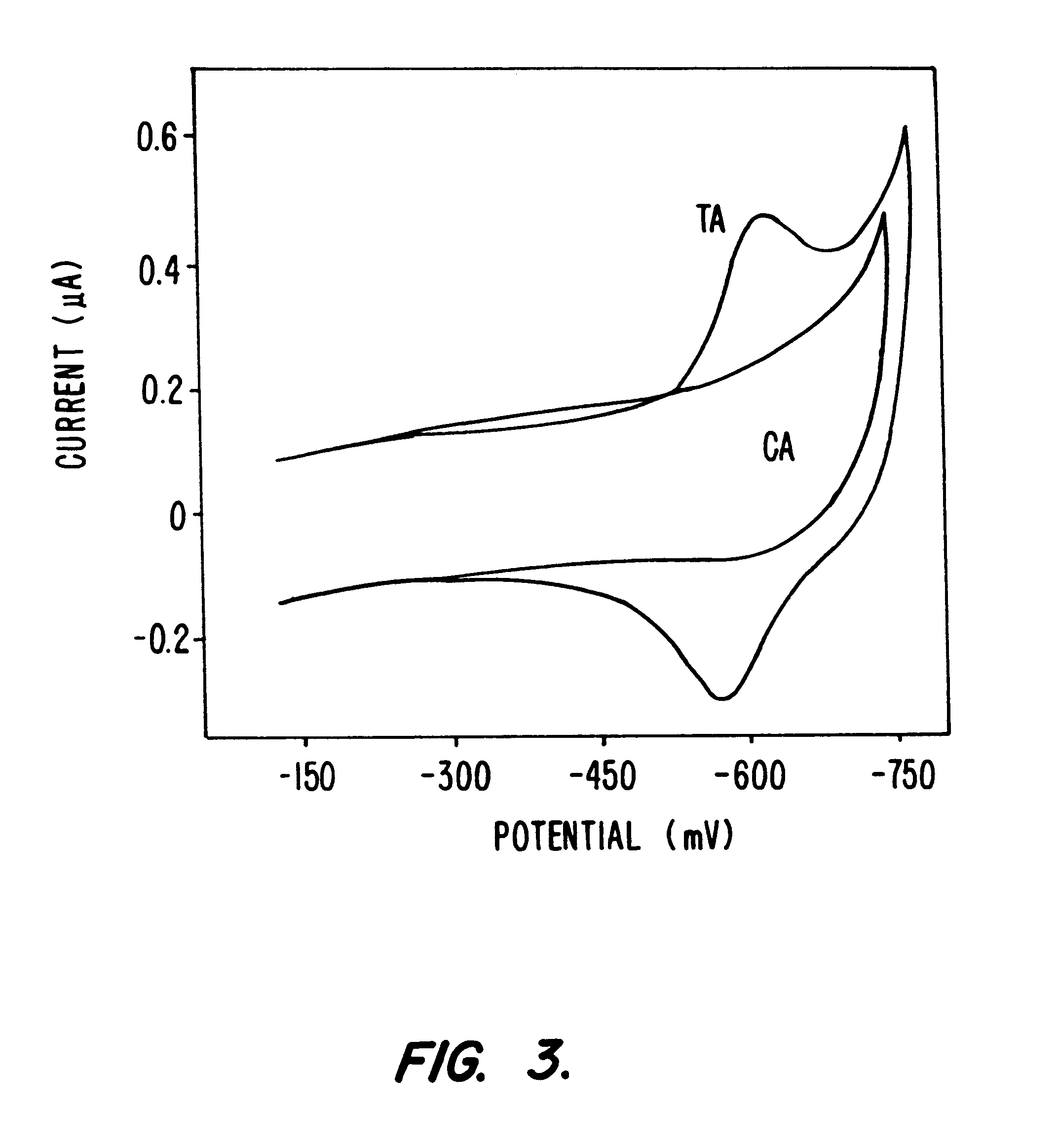
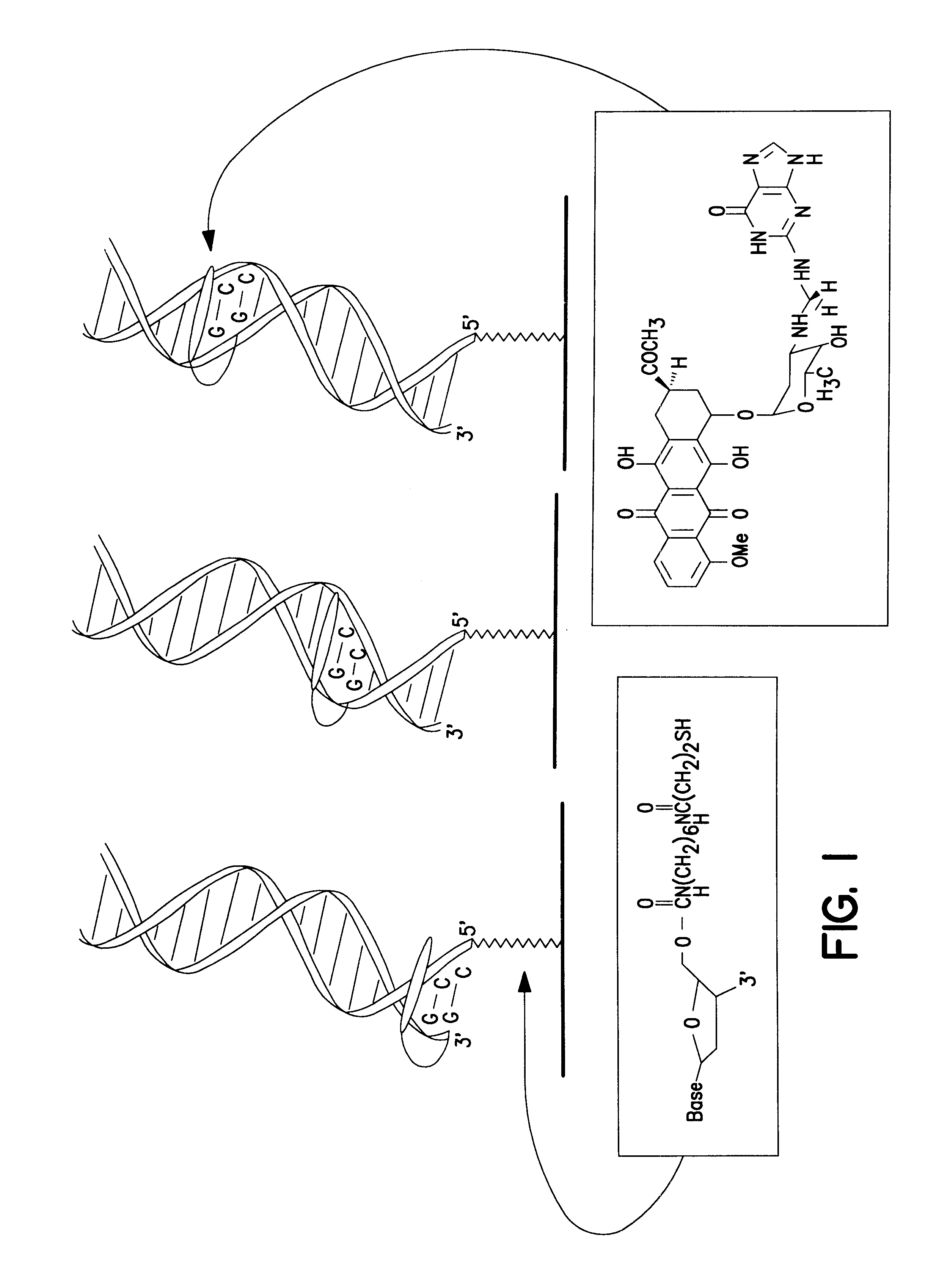
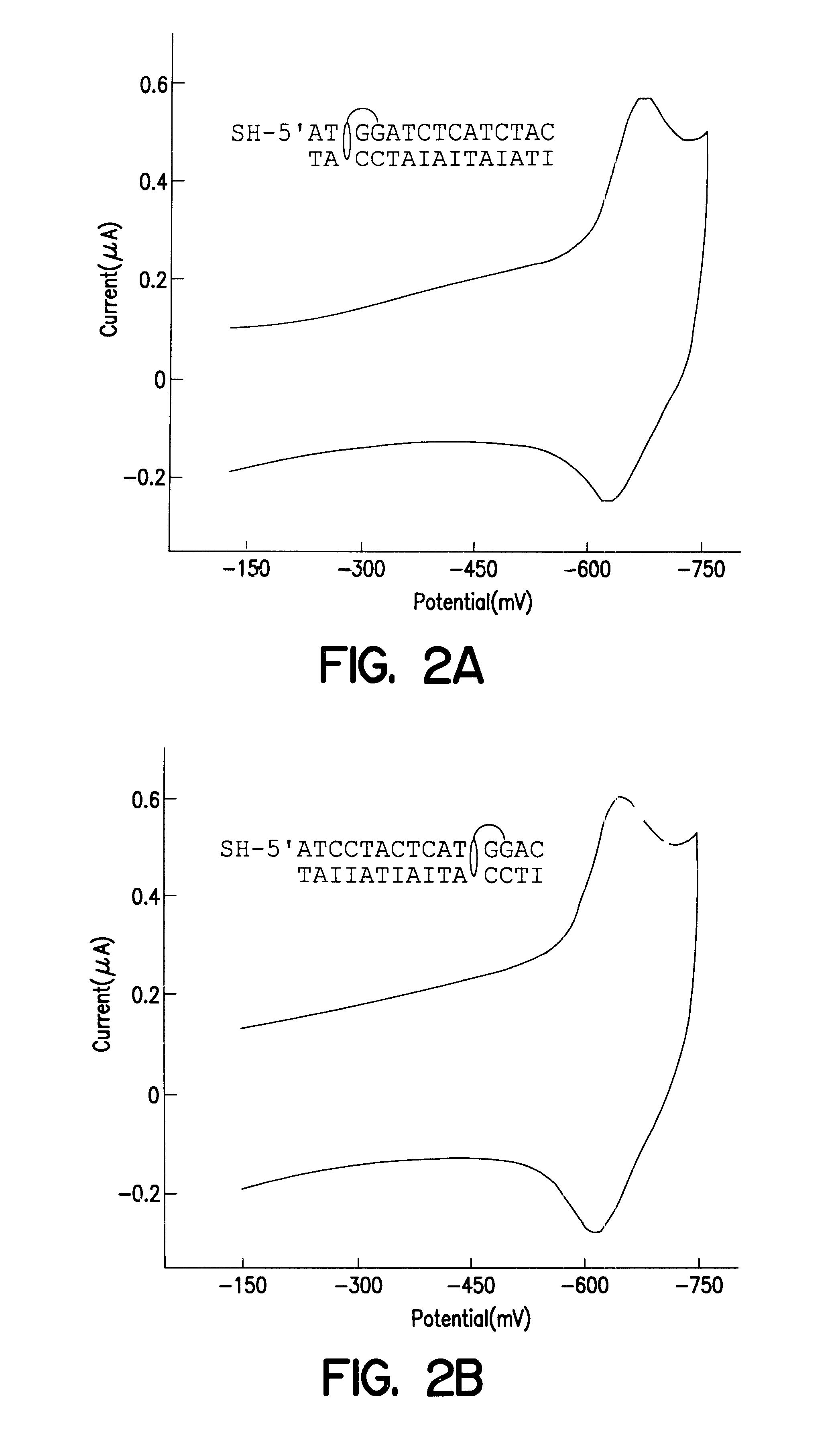
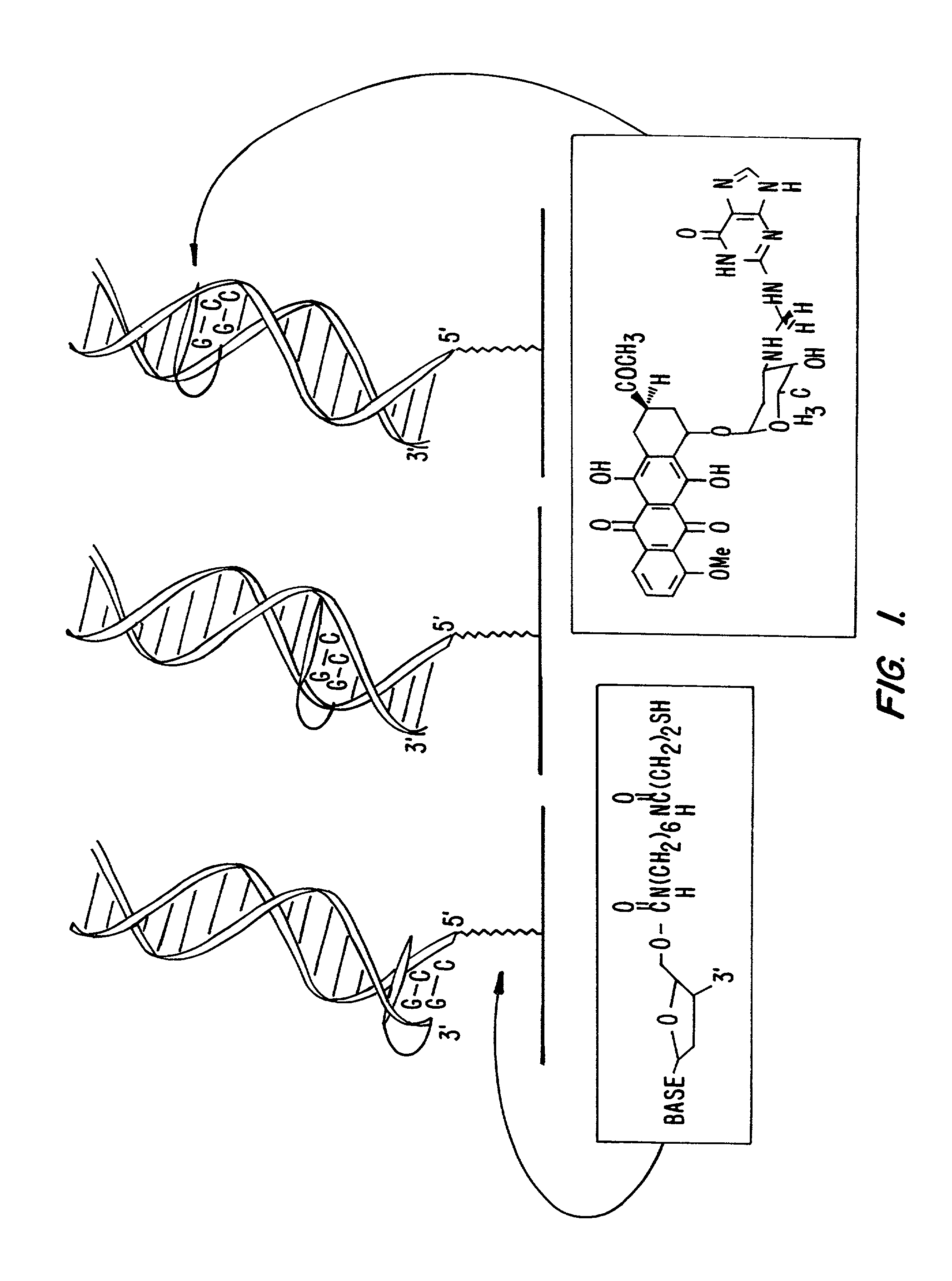
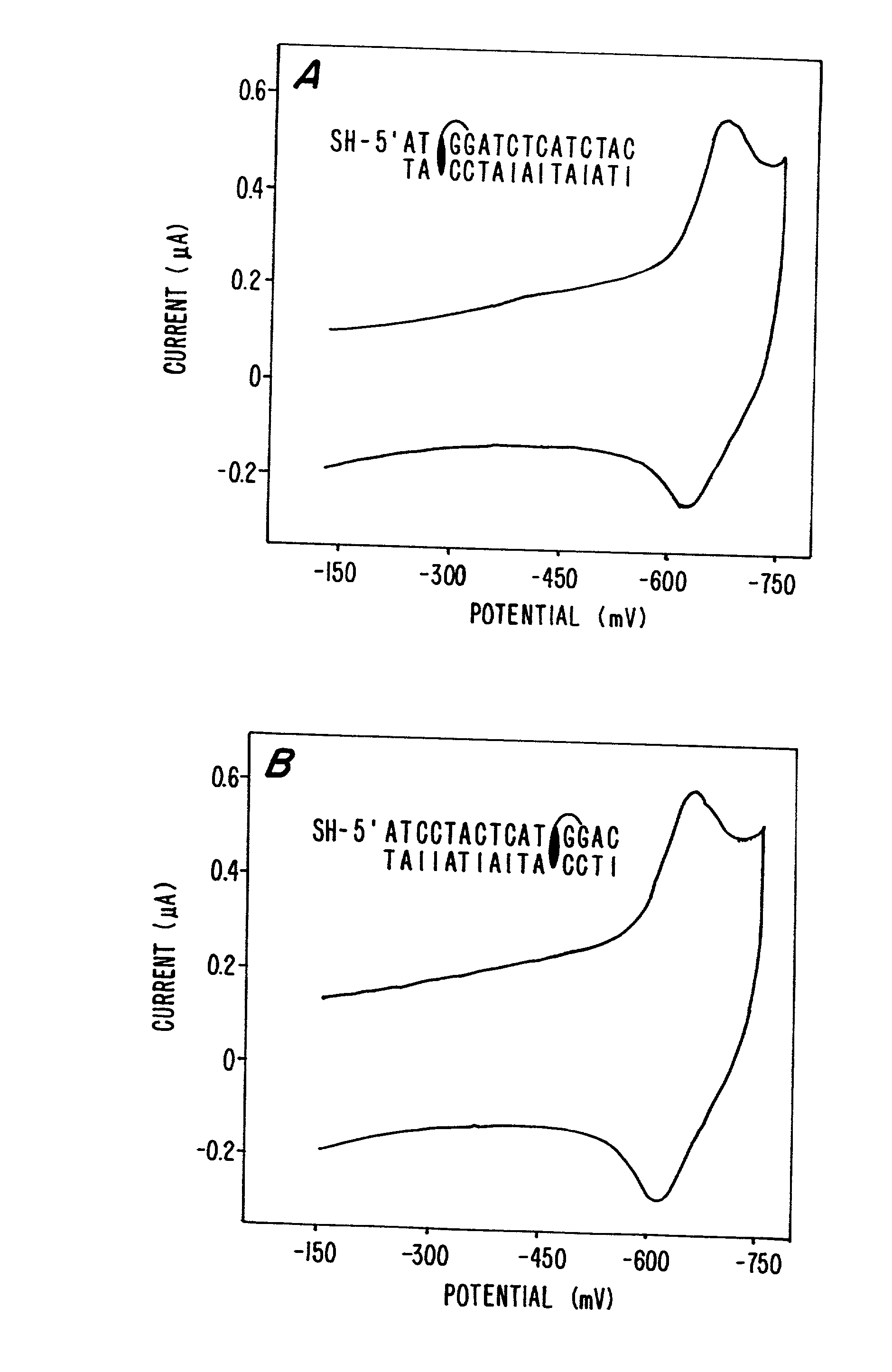
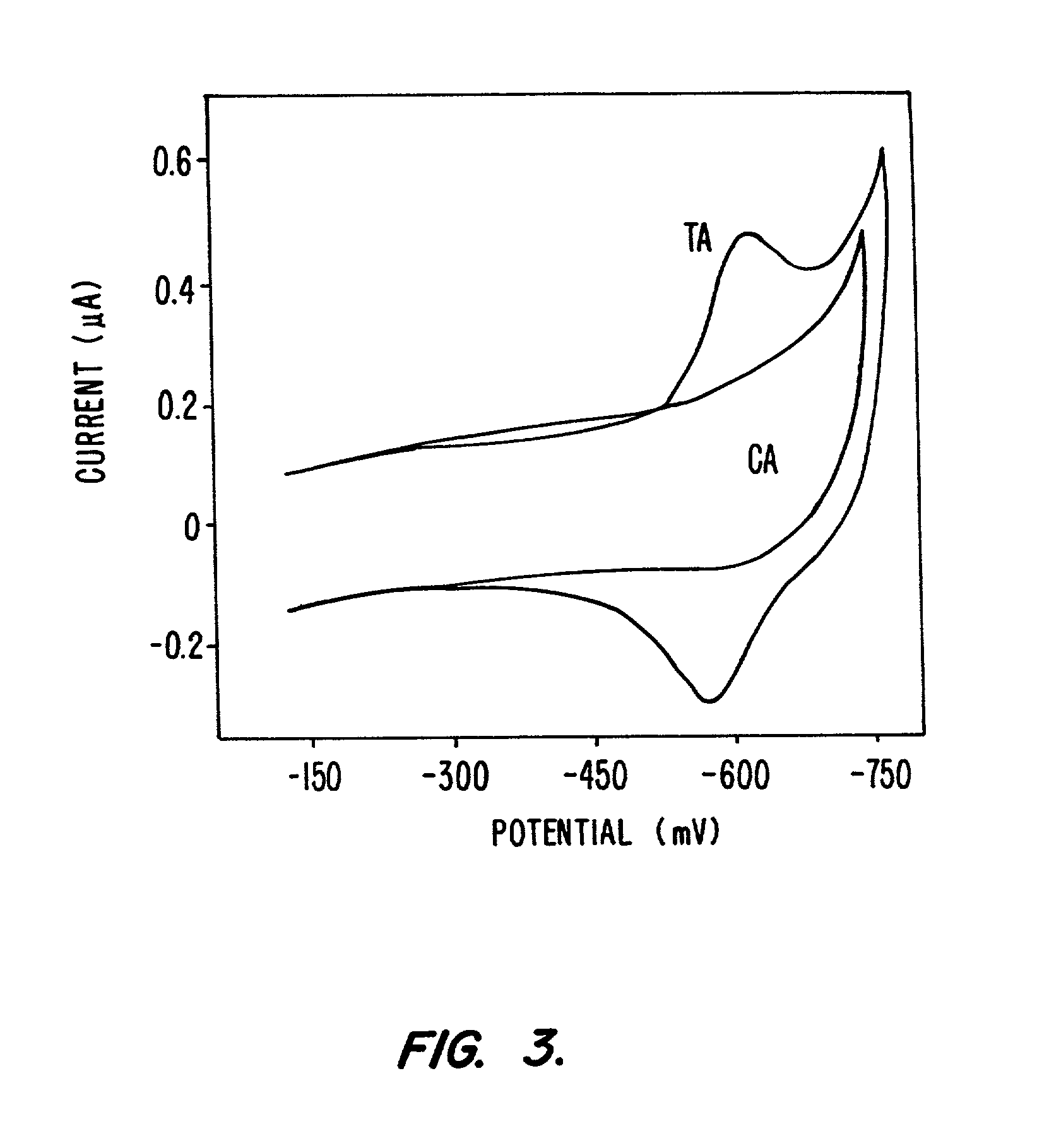
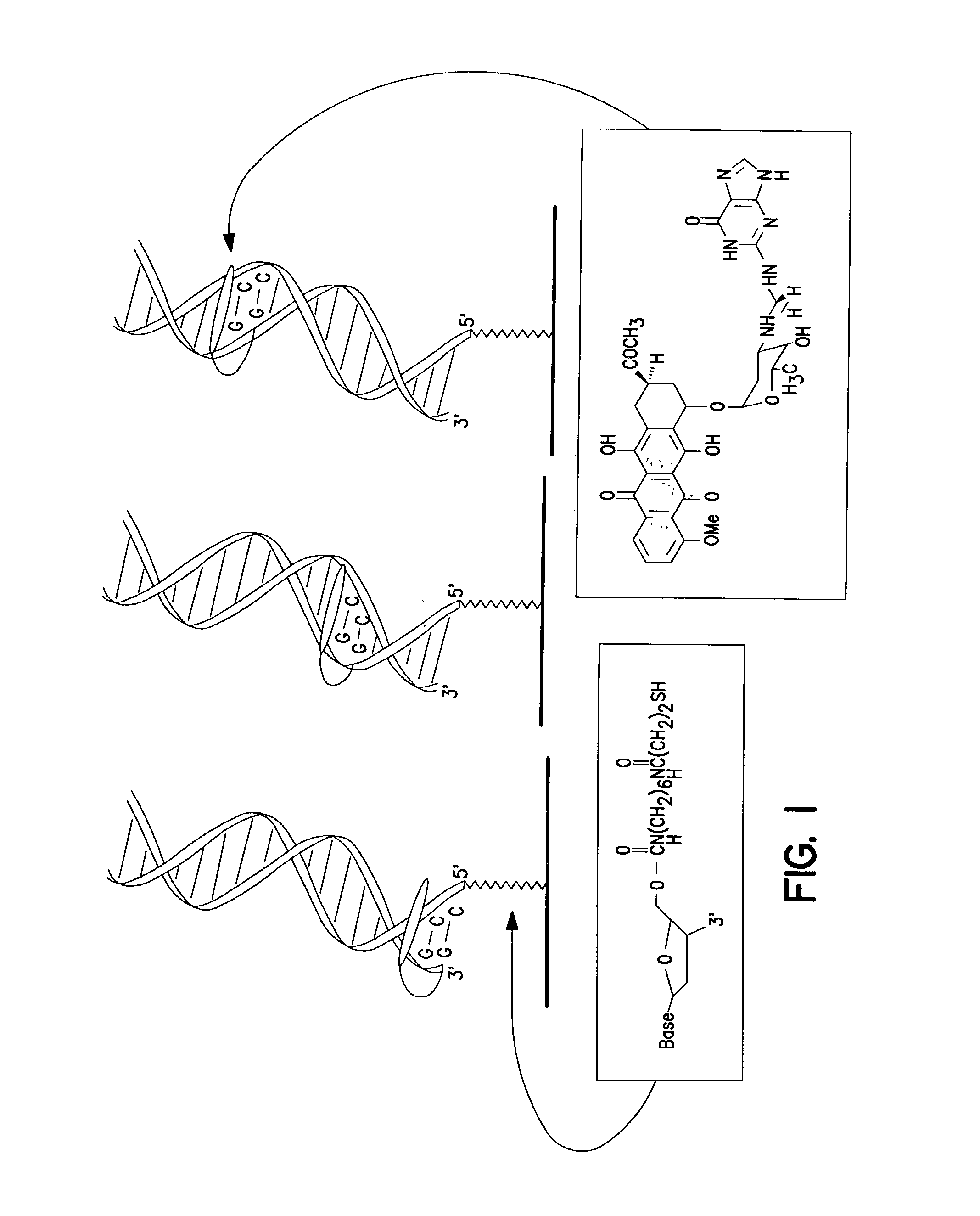
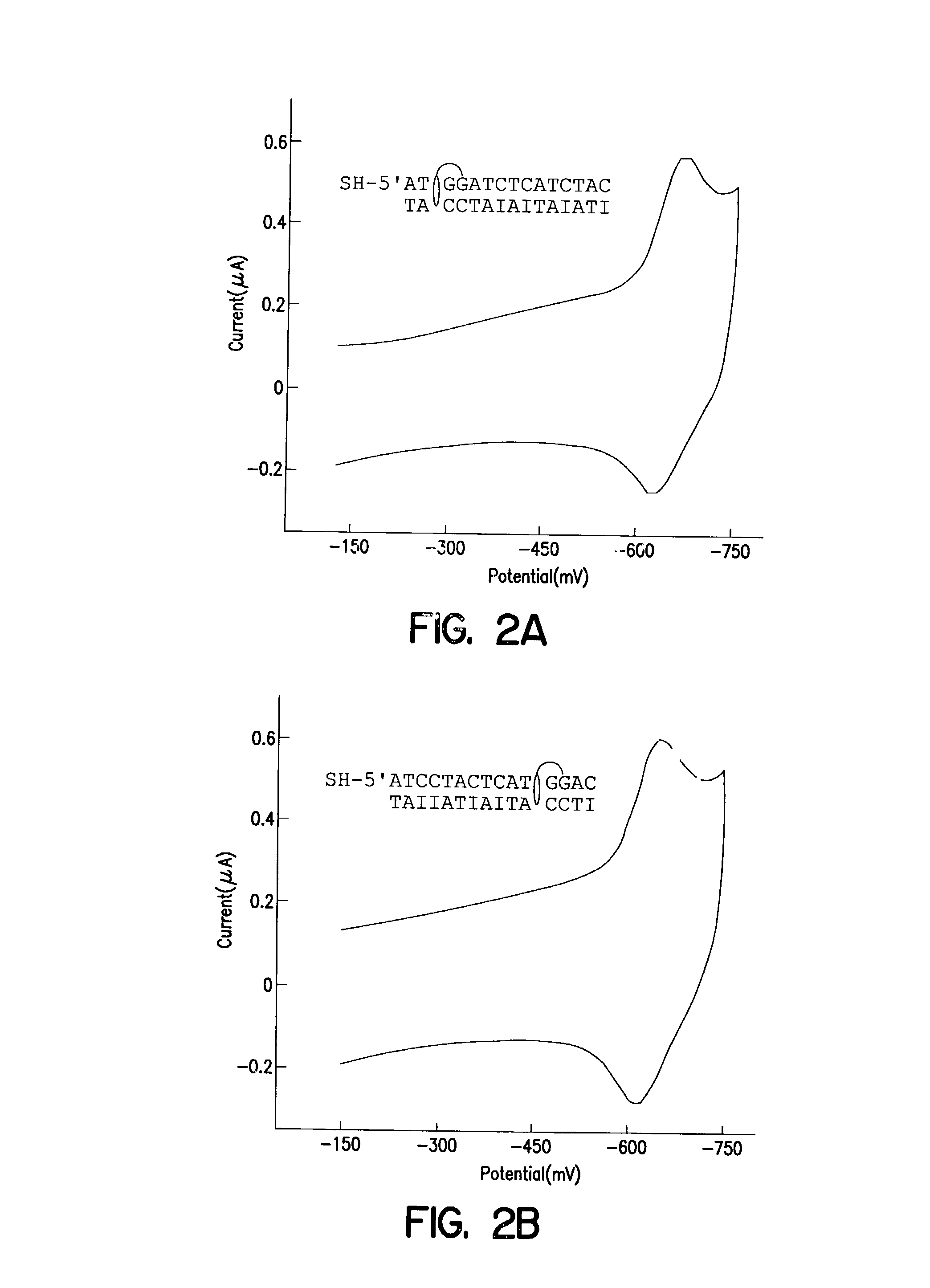
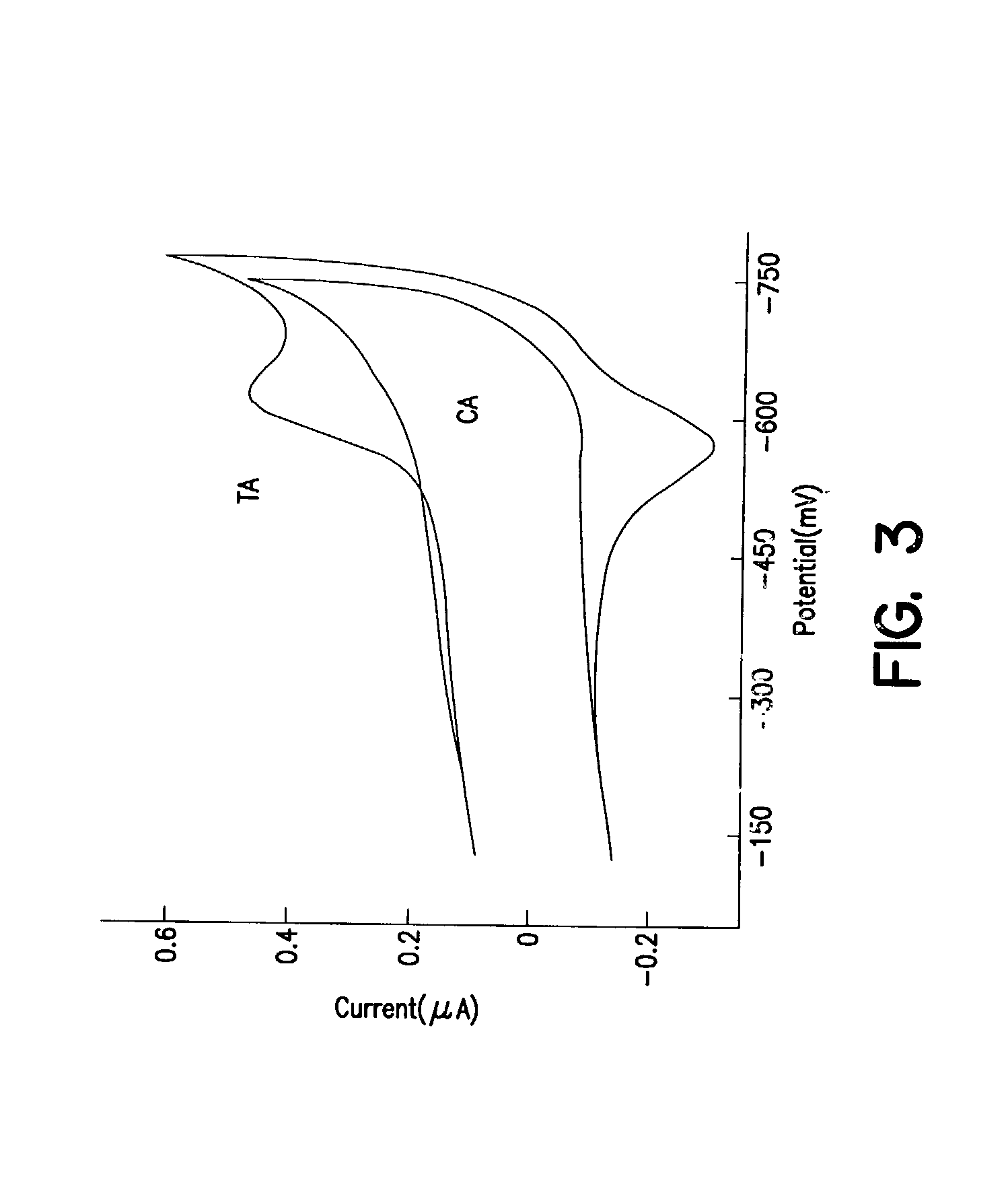
Electrochemical sensor using intercalative, redox-active moieties
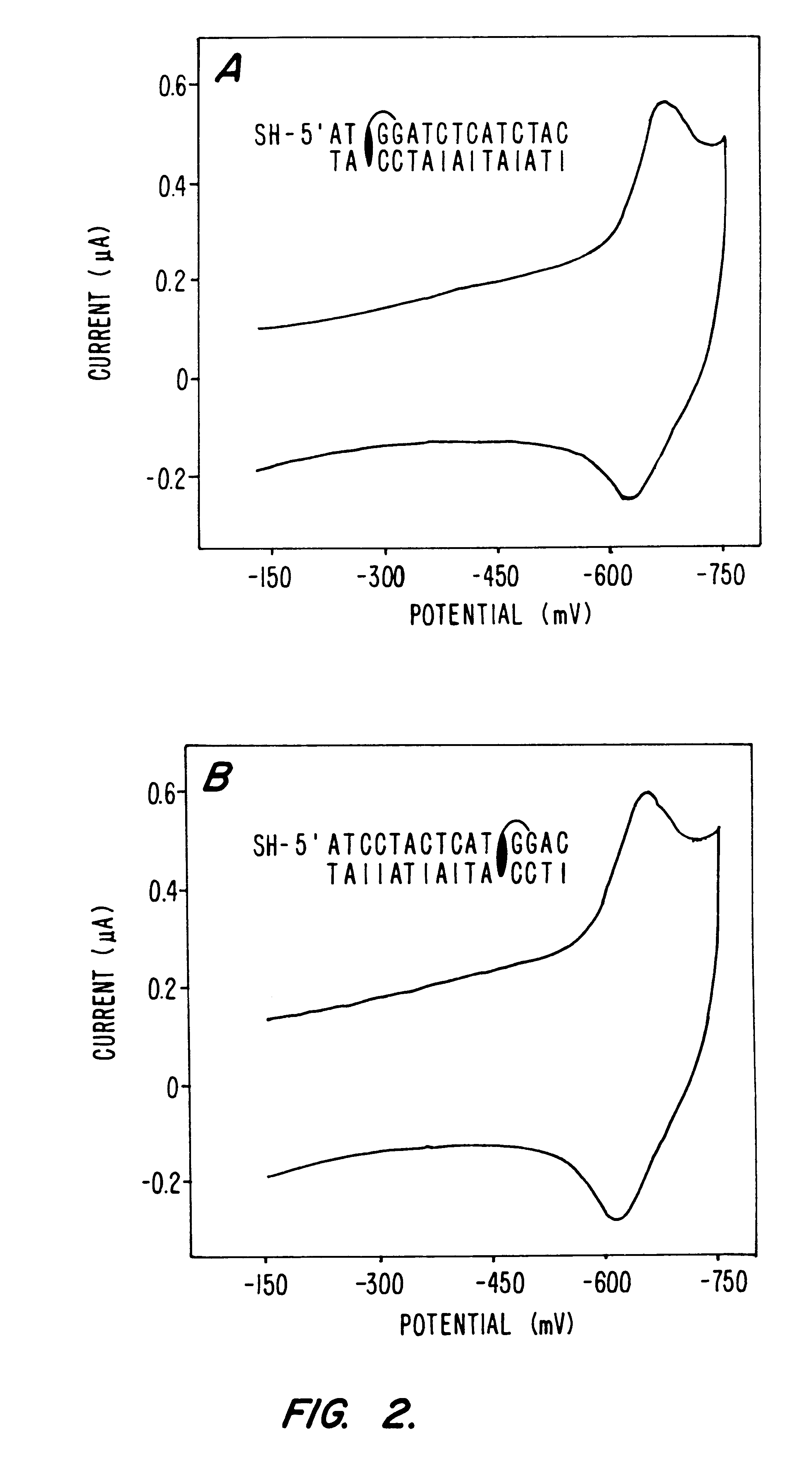
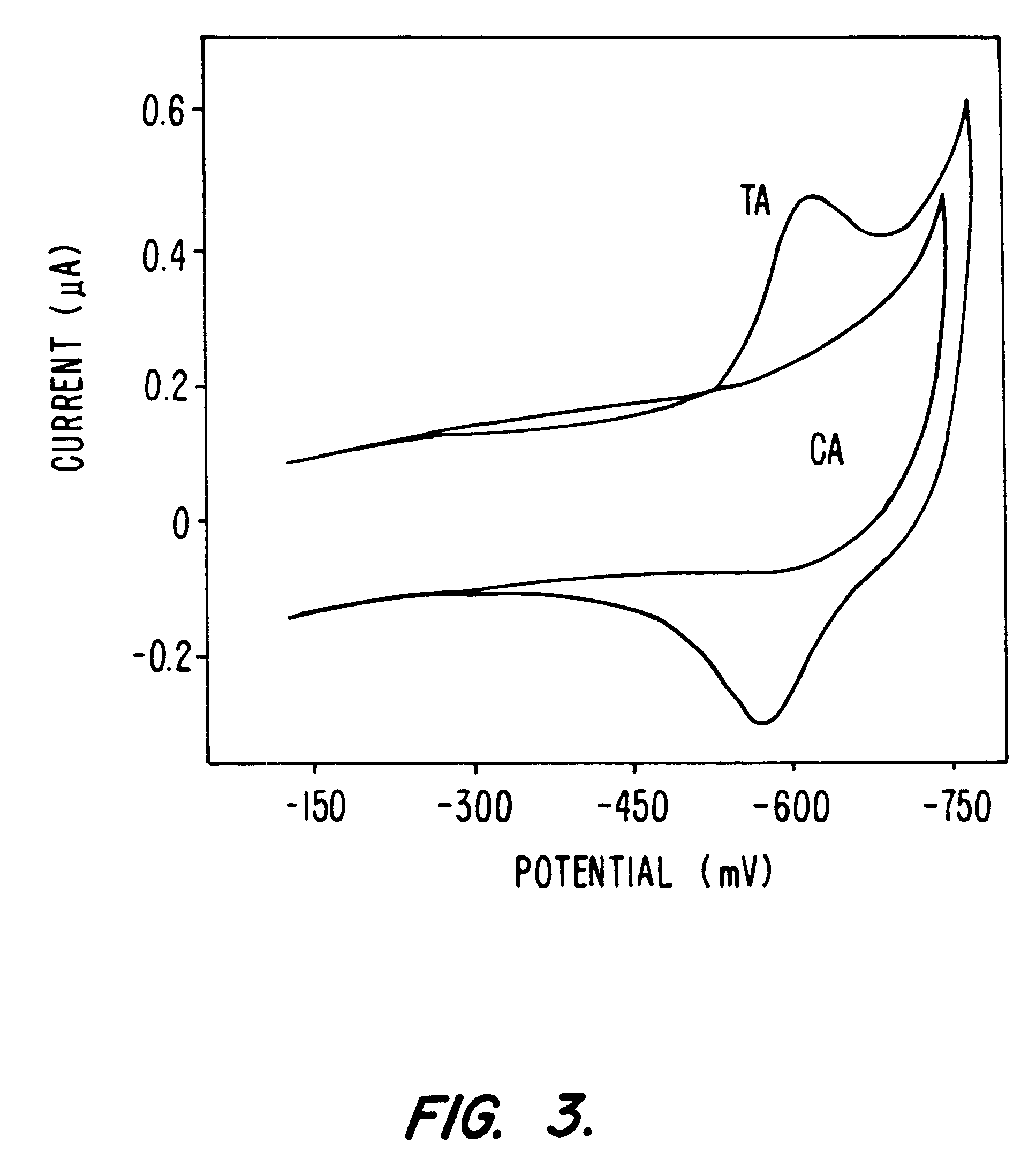
Compositions and methods for electrochemical detection and localization of genetic point mutations and other base-stacking perturbations within oligonucleotide duplexes adsorbed onto electrodes and their use in biosensing technologies are described. An intercalative, redox-active moiety (such as an intercalator or nucleic acid-binding protein) is adhered and / or crosslinked to immobilized DNA duplexes at different separations from an electrode and probed electrochemically in the presence or absence of a non-intercalative, redox-active moiety. Interruptions in DNA-mediated electron-transfer caused by base-stacking perturbations, such as mutations or binding of a protein to its recognition site are reflected in a difference in electrical current, charge and / or potential.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
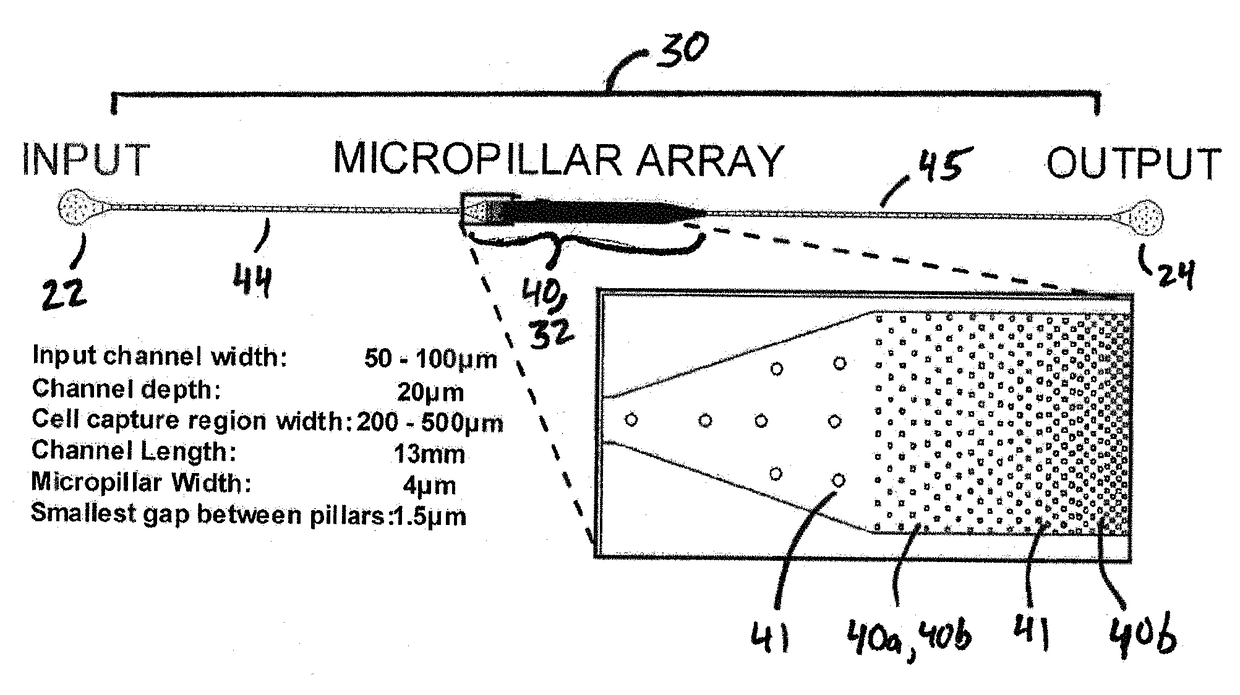
Microfluidic device for extracting, isolating, and analyzing DNA from cells
ActiveUS20140194313A1Facilitates single-molecule analysisReducing background fluorescenceVolume/mass flow measurementLibrary screeningAnalysis dnaCell separation
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Chip preparation method, DNA or protein immobilization method and chip
InactiveCN109610006AQuality improvementImprove efficiencyPeptide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein chipRepeatability
The invention discloses a chip preparation method, a DNA or protein immobilization method, and a chip. The chip preparation method of the invention comprises performing weak passivation treatment after immobilization treatment, wherein the weak passivation treatment comprises contacting a weak passivation reaction solution containing a catalyst with a chip subjected to immobilization treatment, soas to promote binding of DNA or protein to the surface of a substrate, and to enable the DNA or protein to be sufficiently immobilized on the surface of the substrate. The preparation method of the invention increases the weak passivation treatment step after the immobilization treatment, so that the DNA or protein can be more fully immobilized on the surface of the substrate, the quality and efficiency of DNA or protein immobilization are improved, also DNA or protein is more fully immobilized, the relationship between the amount of the DNA or protein immobilized on the chip and the concentration of the DNA or protein initially added is more closely, and thus the immobilization amount of the DNA or protein is highly controllable, the repeatability is good, and a foundation is laid for preparing high-quality DNA or protein chips.
Owner:GENEMIND BIOSCIENCES CO LTD
Electrochemical sensor using intercalative, redox-active moieties
InactiveUS6461820B1Material nanotechnologySugar derivativesNucleic acid binding proteinElectron transfer
Compositions and methods for electrochemical detection and localization of genetic point mutations and other base-stacking perturbations within oligonucleotide duplexes adsorbed onto electrodes and their use in biosensing technologies are described. An intercalative, redox-active moiety (such as an intercalator or nucleic acid-binding protein) is adhered and / or crosslinked to immobilized DNA duplexes at different separations from an electrode and probed electrochemically in the presence or absence of a non-intercalative, redox-active moiety. Interruptions in DNA-mediated electron-transfer caused by base-stacking perturbations, such as mutations or binding of a protein to its recognition site are reflected in a difference in electrical current, charge and / or potential.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
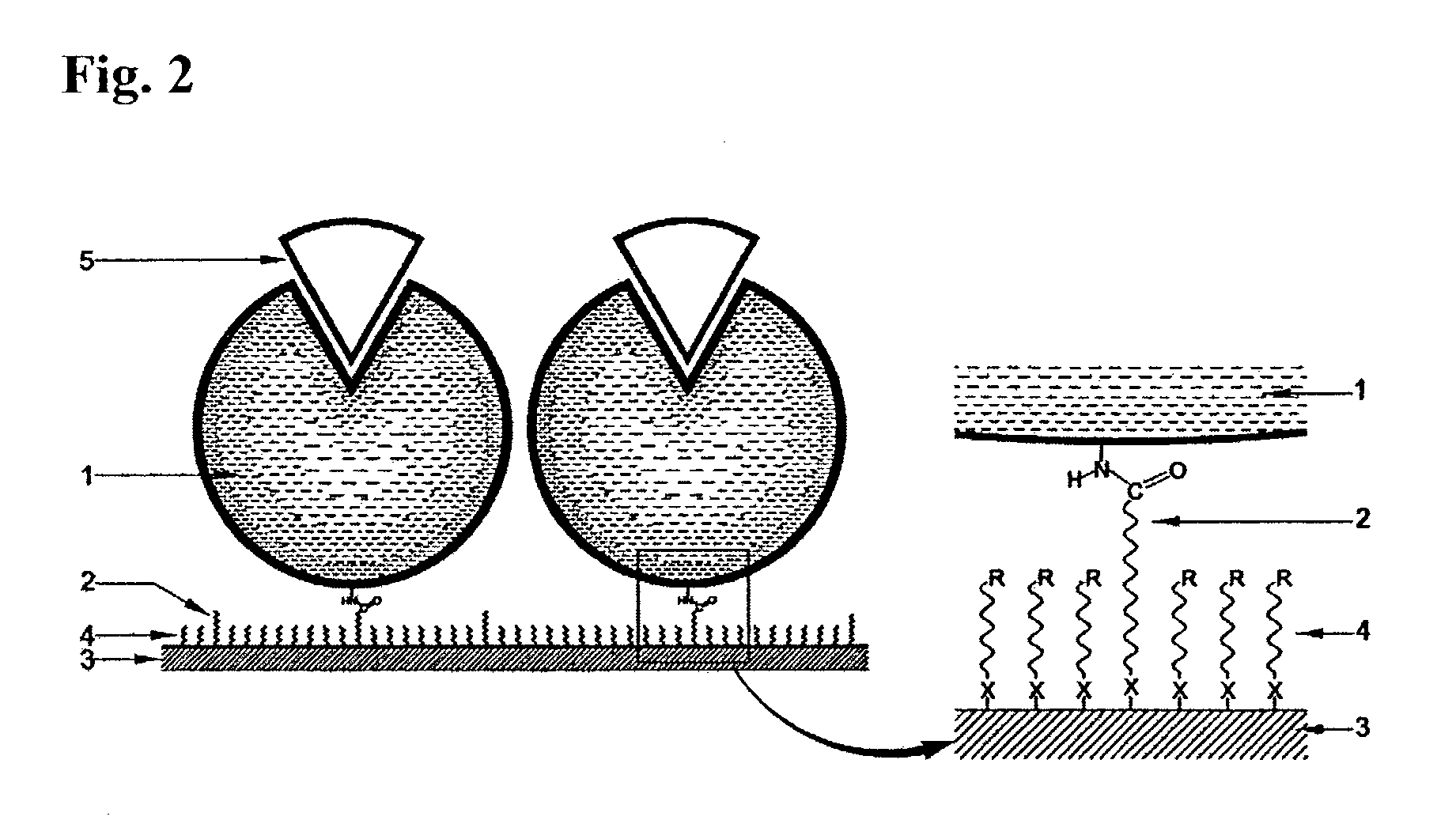
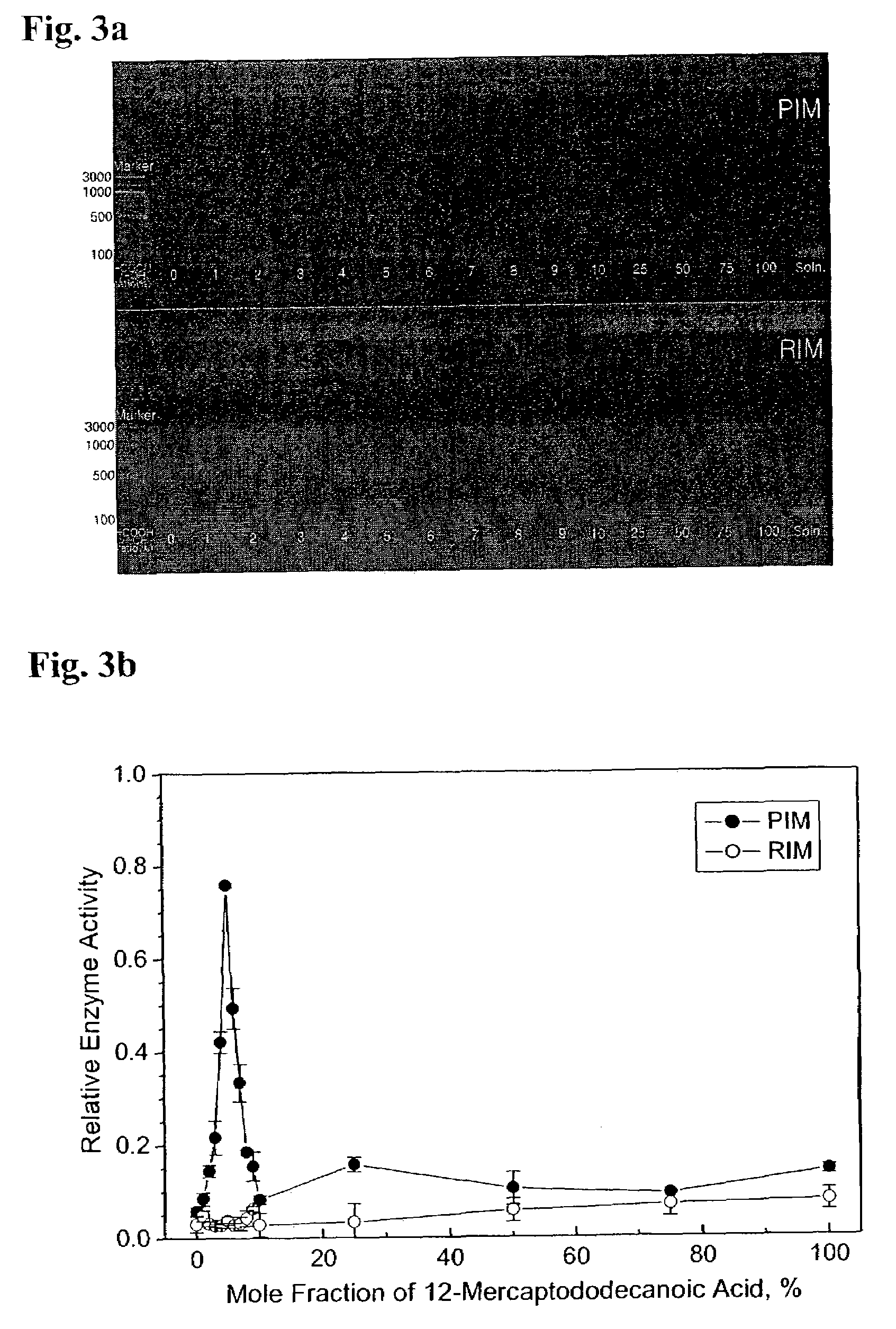
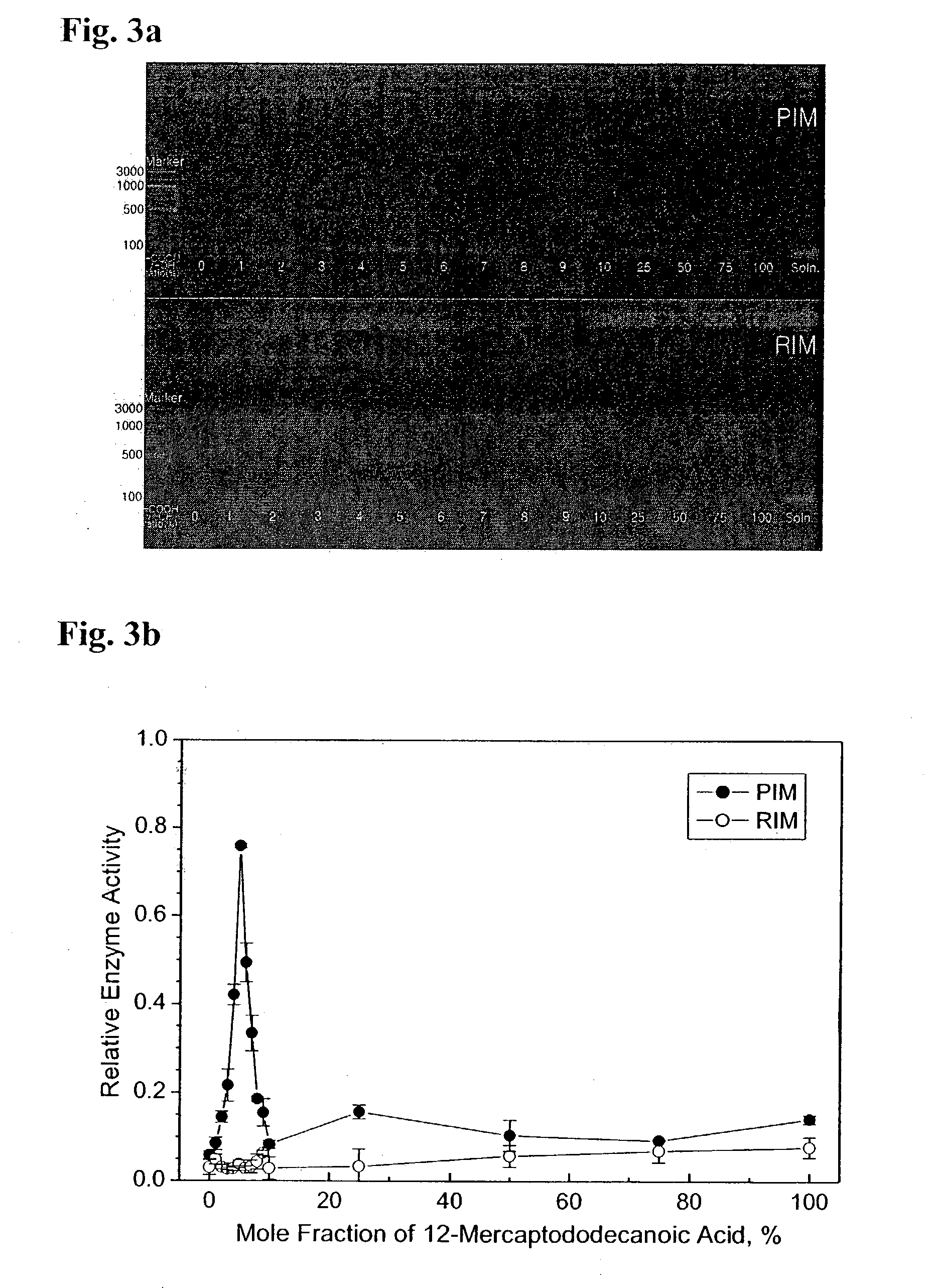
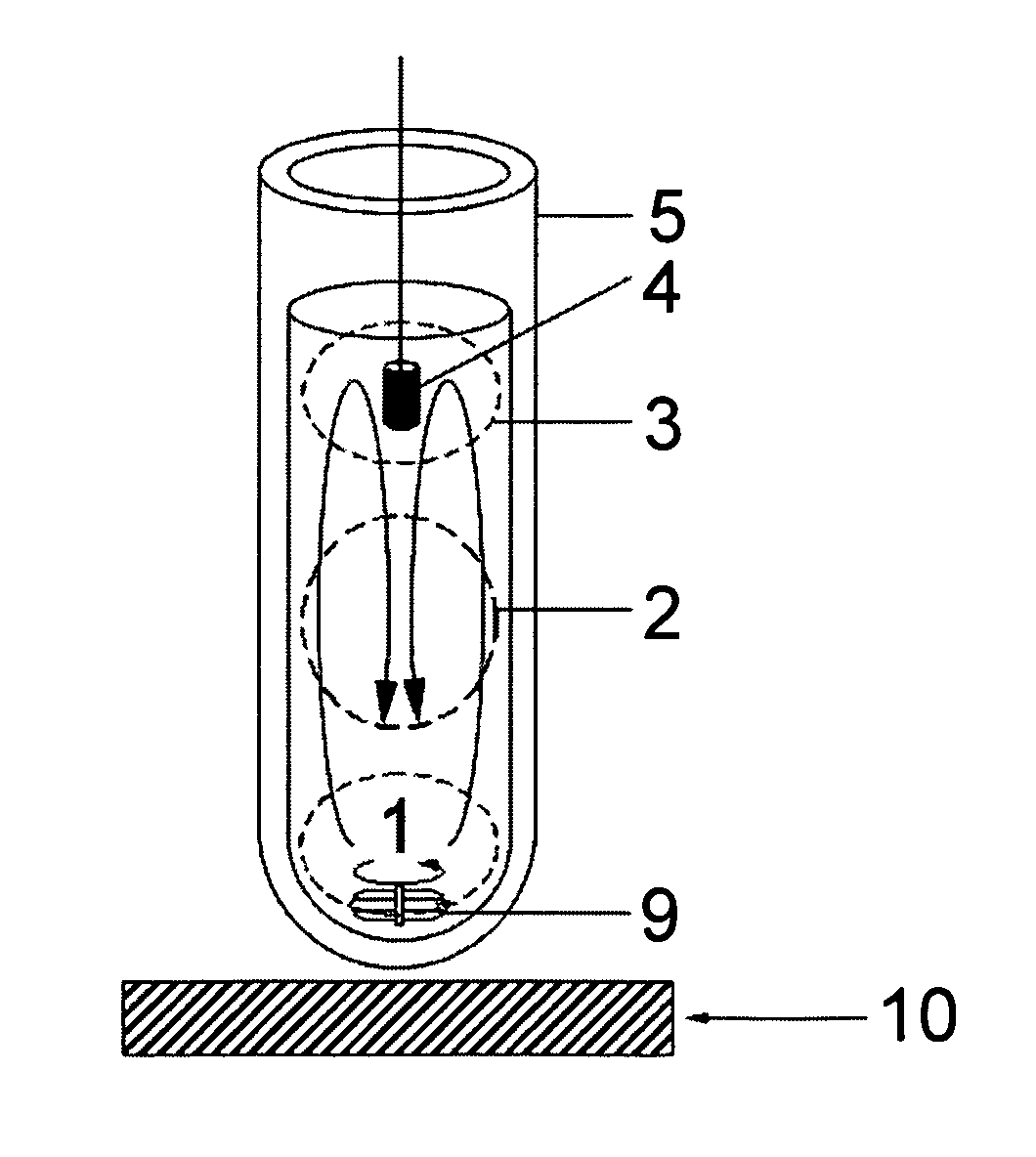
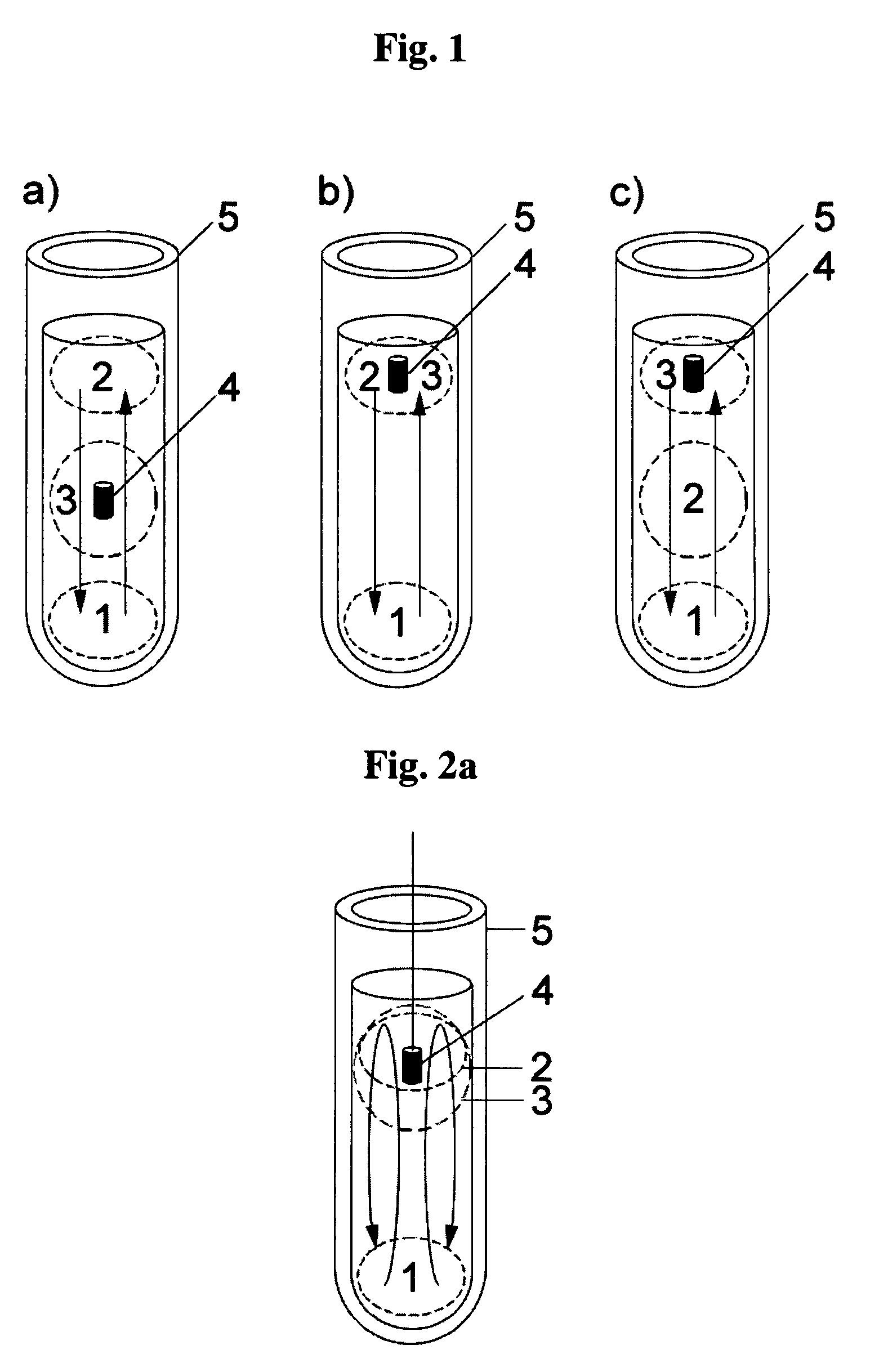
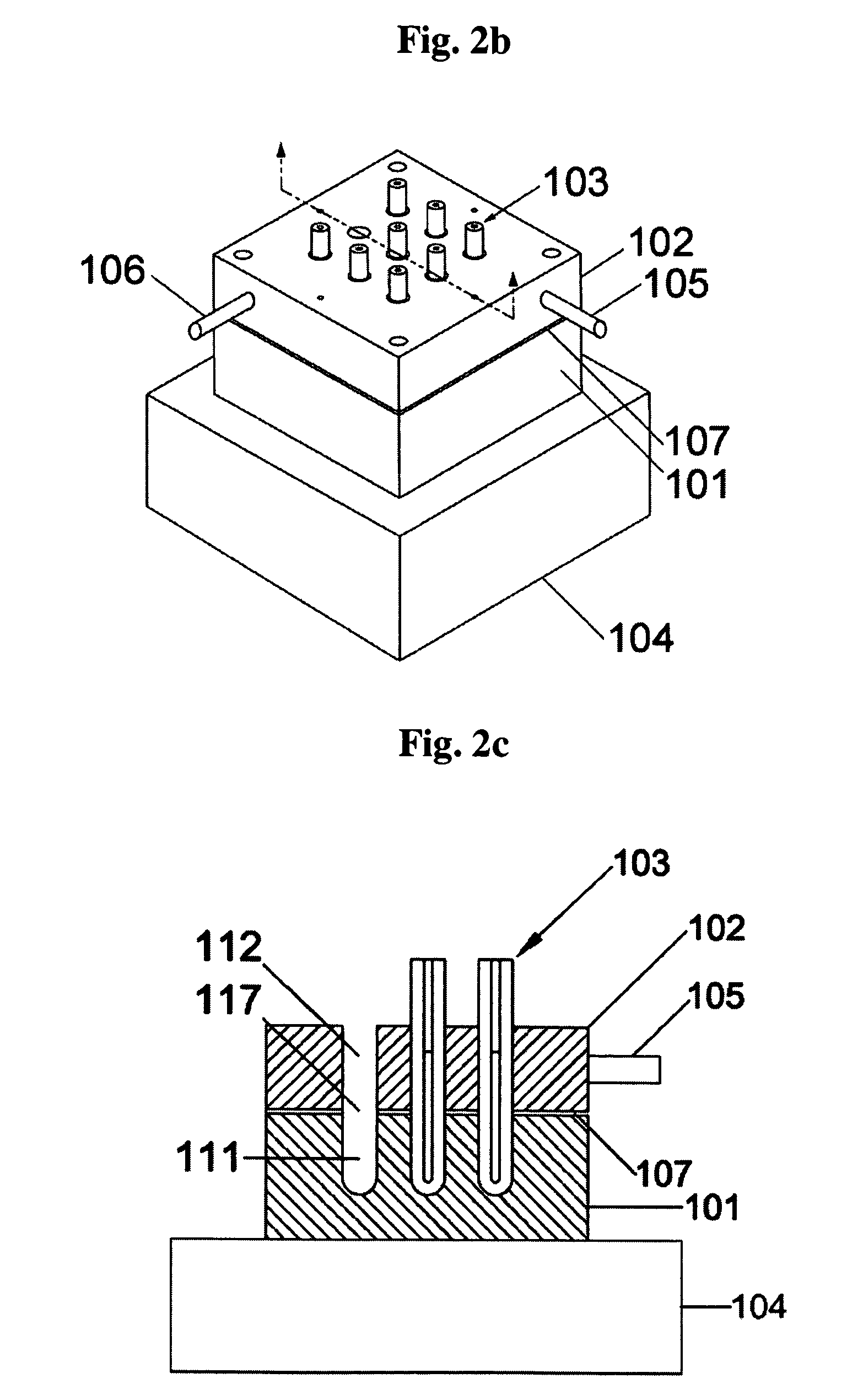
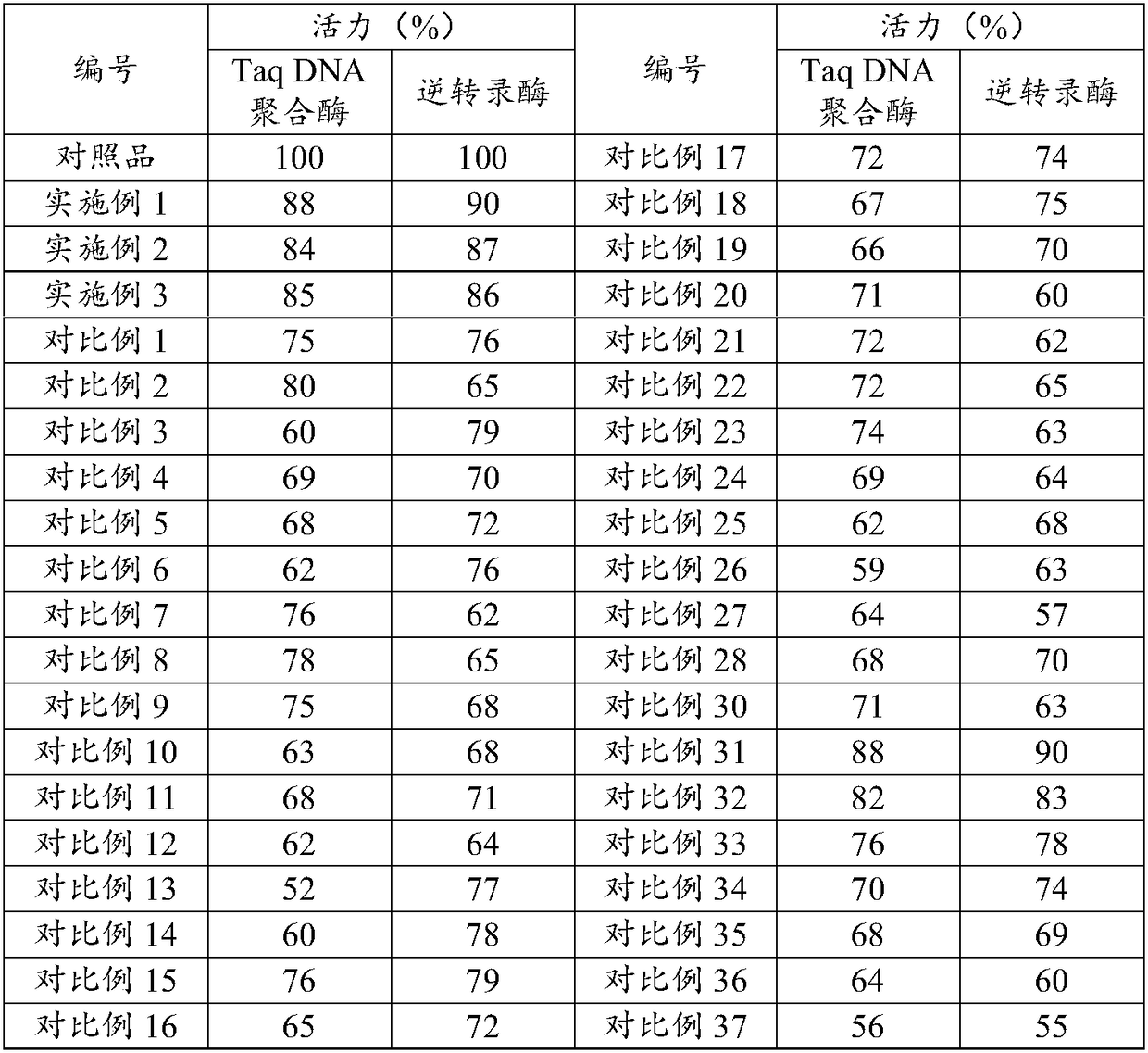
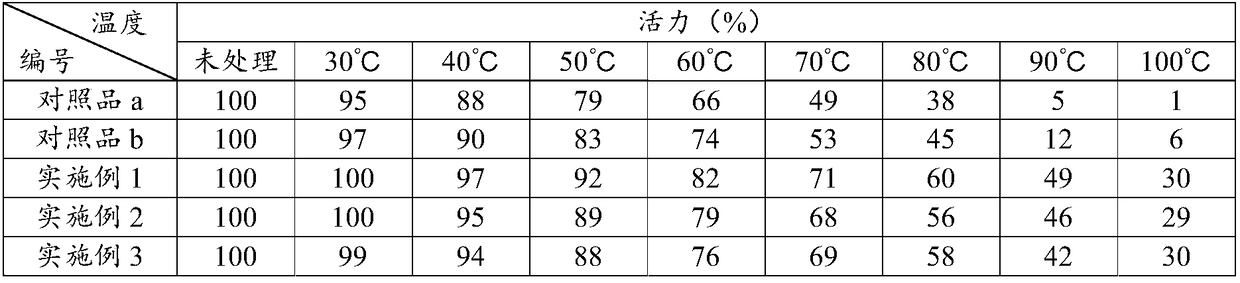
Immobilized DNA polymerase
The present invention relates to a DNA polymerase immobilized by covalent bonding. More particularly, the present invention relates to an immobilized DNA polymerase whose activity is maximally preserved by masking the active site of the DNA polymerase and optimizing interaction of the masked molecule to the substrate material. In one embodiment, the average activity of the immobilized DNA polymerase is more than about 10% relative to that of the solution phase DNA polymerase. Further provided by the invention are methods and kits for performing polymerase chain reactions (PCR).
Owner:AHRAM BIOSYST INC
Electrochemical sensor using intercalative, redox-active moieties
InactiveUS6649350B2Highly accurateSensitive highBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyNucleic acid binding proteinElectron transfer
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method for measuring 9-hydroxy fluorine based on electrochemistry hairpin DNA biosensor
InactiveCN102680549AHigh affinityHighly ordered structureMaterial electrochemical variablesSulfurImmobilized DNA
The invention belongs to the technical field of electrochemistry detection and chemical sensors for detecting 9-hydroxy fluorine based on a hairpin DNA modified gold electrode sensor, and relates to preparation of a hairpin DNA modified gold electrode capble of having electrochemical response to 9-hydroxy fluorine and detection on the 9-hydroxy fluorine with the electrode. Specifically, the synthetic sulfhydryl modified hairpin DNA is used as a raw material, the hairpin DNA is self-assembled to the surface of the gold electrode by the Au-S bond interaction to prepare the DNA modified electrode. The immobilized DNA electrode has high response to the 9-hydroxy fluorine, and the detection on the 9-hydroxy fluorine can be carried out according to the change of response of the electrochemistry to the impedance. The DNA sensor has the advantages of mild preparation condition, simplicity in operation, good stability and high sensitivity.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Electrochemical sensor using intercalative, redox-active moieties
Compositions and methods for electrochemical detection and localization of genetic point mutations and other base-stacking perturbations within oligonucleotide duplexes adsorbed onto electrodes and their use in biosensing technologies are described. An intercalative, redox-active moiety (such as an intercalator or nucleic acid-binding protein) is adhered and / or crosslinked to immobilized DNA duplexes at different separations from an electrode and probed electrochemically in the presence or absence of a non-intercalative, redox-active moiety. Interruptions in DNA-mediated electron-transfer caused by base-stacking perturbations, such as mutations or binding of a protein to its recognition site are reflected in a difference in electrical current, charge and / or potential.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
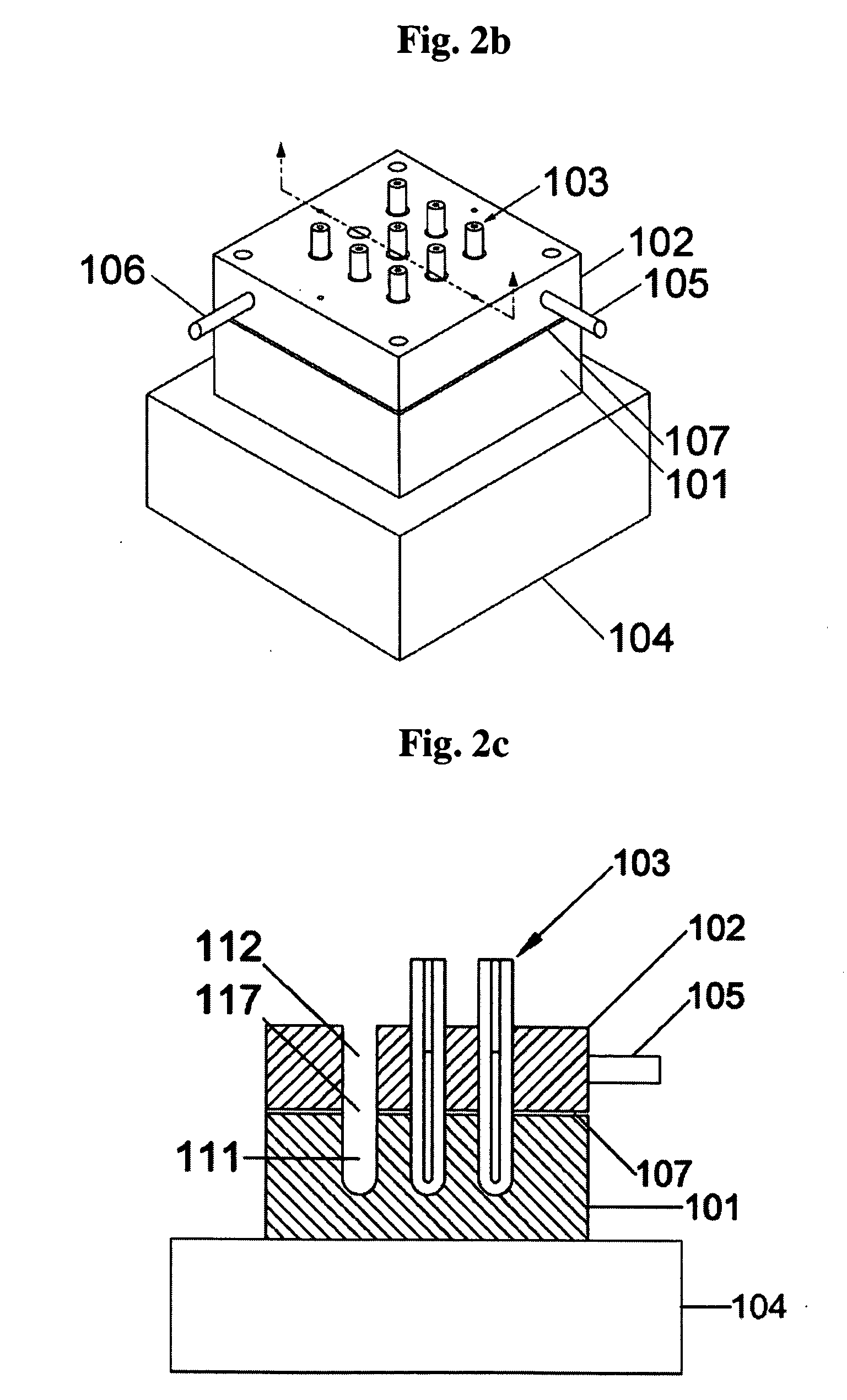
Method and apparatus for amplification of nucleic acid sequences using immobilized DNA polymerase
InactiveUS20040191830A1Easy to separatePromote recoveryBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLab-on-a-chipPolymerase L
The present invention generally relates to methods and apparatuses for amplifying nucleic acid sequences using immobilized DNA polymerase. More particularly, it relates to methods and apparatuses useful for amplifying target nucleic acid sequences by forming a plurality of reaction regions in which polymerase chain reaction (PCR) can occur, positioning immobilized DNA polymerase in a specific reaction region, and circulating DNA through the reaction regions. The present invention provides those methods and apparatuses that allow simple separation and recovery of the DNA polymerase after the amplification, that can be operated not only with thermostable DNA polymerases but also with non-thermostable DNA polymerases, and that are simpler in their designs and processes so that they can be readily integrated into complex devices such as Lab-on-a-chip.
Owner:AHRAM BIOSYST
Immobilized DNA polymerase
The present invention relates to a DNA polymerase immobilized by covalent bonding. More particularly, the present invention relates to an immobilized DNA polymerase whose activity is maximally preserved by masking the active site of the DNA polymerase and optimizing interaction of the masked molecule to the substrate material. In one embodiment, the average activity of the immobilized DNA polymerase is more than about 10% relative to that of the solution phase DNA polymerase. Further provided by the invention are methods and kits for performing polymerase chain reactions (PCR).
Owner:AHRAM BIOSYST
Method and apparatus for amplification of nucleic acid sequences using immobilized DNA polymerase
InactiveUS7488595B2Readily separated and recoveredImprove purification effectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusPolymerase LLab-on-a-chip
Owner:AHRAM BIOSYST INC
Electrochemical sensor using intercalative, redox-active moieties
InactiveUS20020146716A1Highly accurateSensitive highMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsProtein insertionElectron transfer
Compositions and methods for electrochemical detection and localization of genetic point mutations, common DNA lesions and other base-stacking perturbations within oligonucleotide duplexes adsorbed onto electrodes and their use in biosensing technologies are described. An intercalative, redox-active moiety (such as an intercalator or nucleic acid-binding protein) is adhered and / or crosslinked to immobilized DNA duplexes at different separations from an electrode and probed electrochemically in the presence or absence of a non-intercalative, redox-active moiety. Interruptions in DNA-mediated electron-transfer caused by base-stacking perturbations, such as mutations or binding of a protein to its recognition site are reflected in a difference in electrical current, charge and / or potential.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Microfluidic device for extracting, isolating, and analyzing DNA from cells
ActiveUS9926552B2Small sizeEasy to analyzeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalysis dnaCell separation
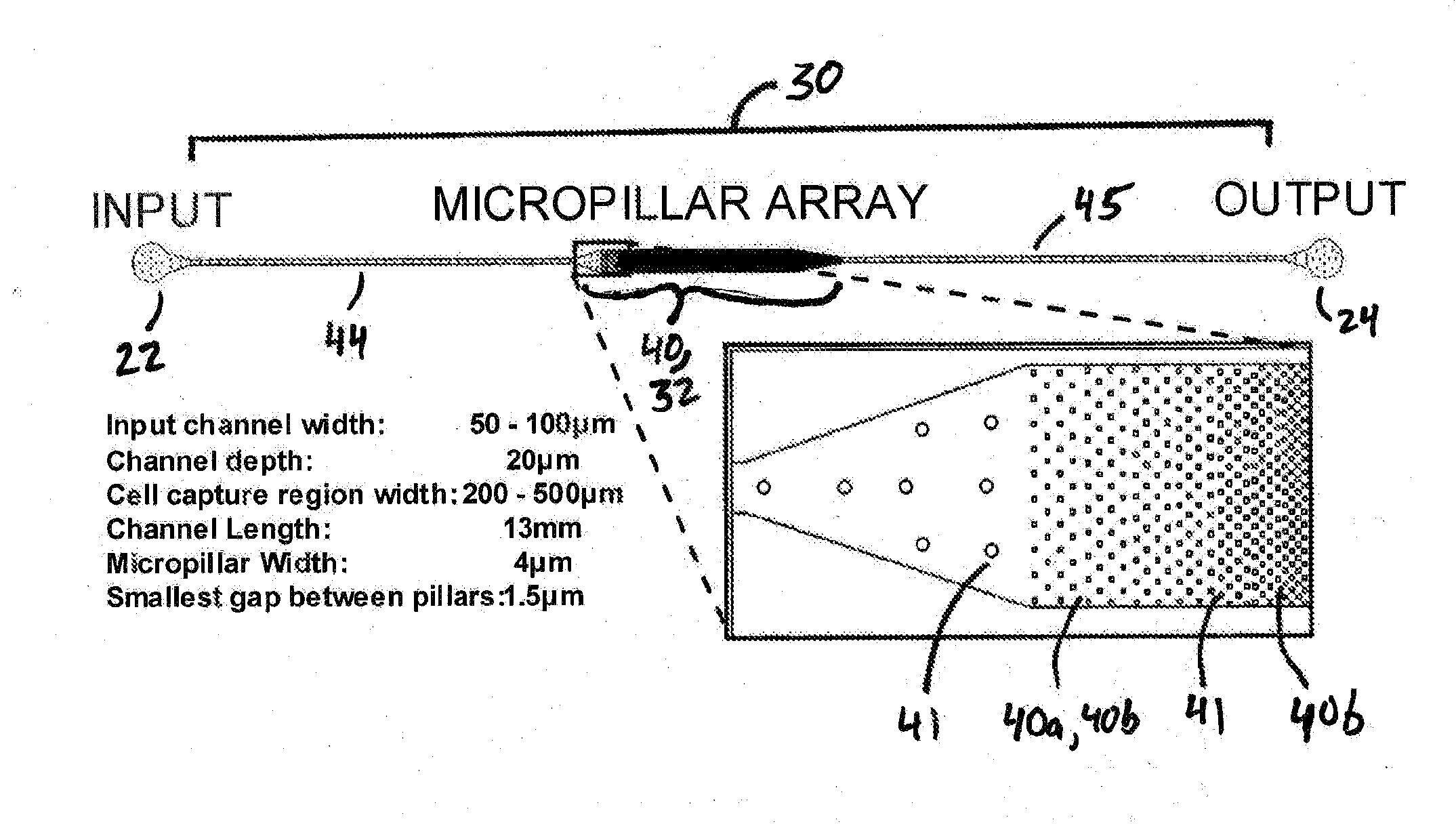
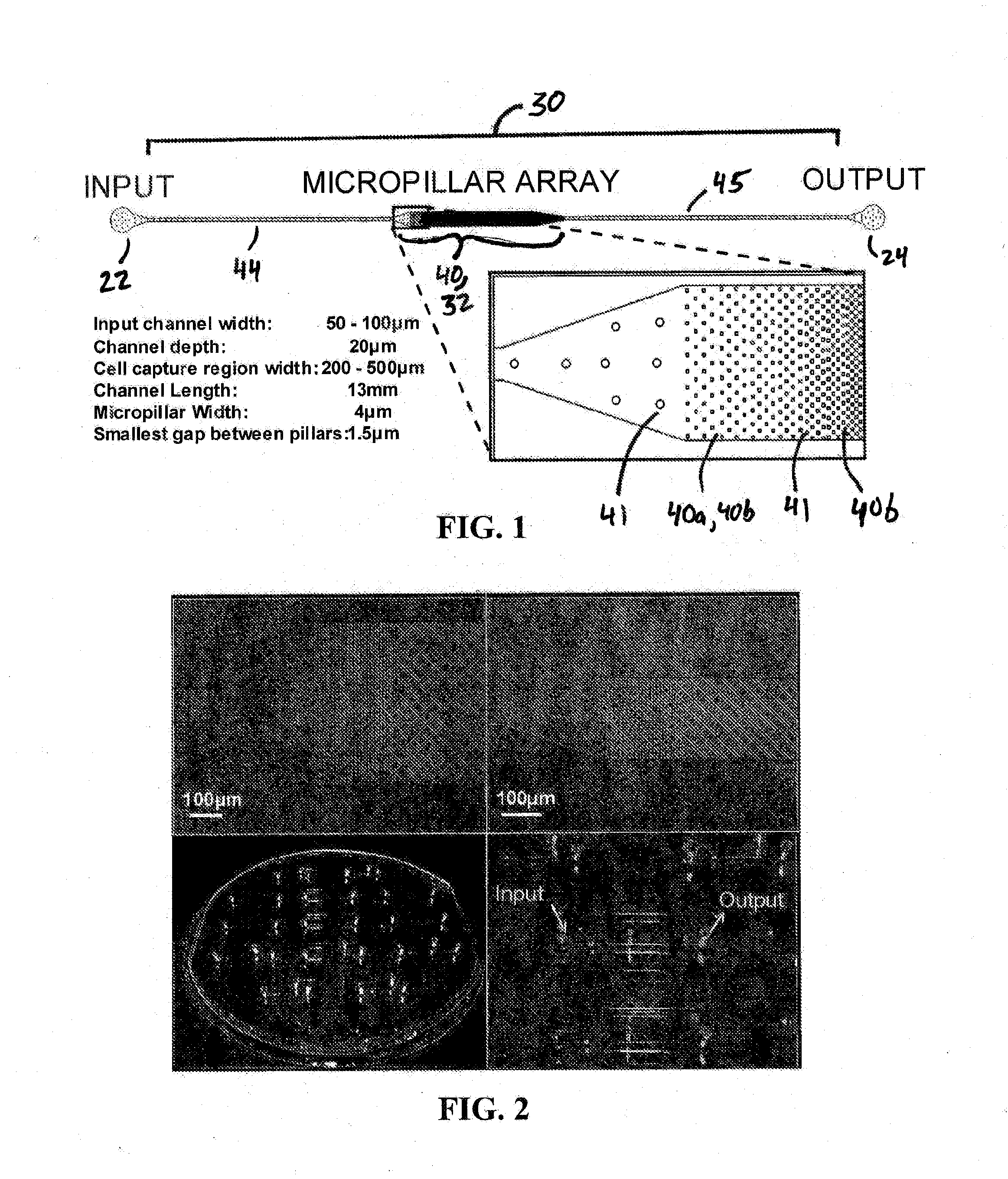
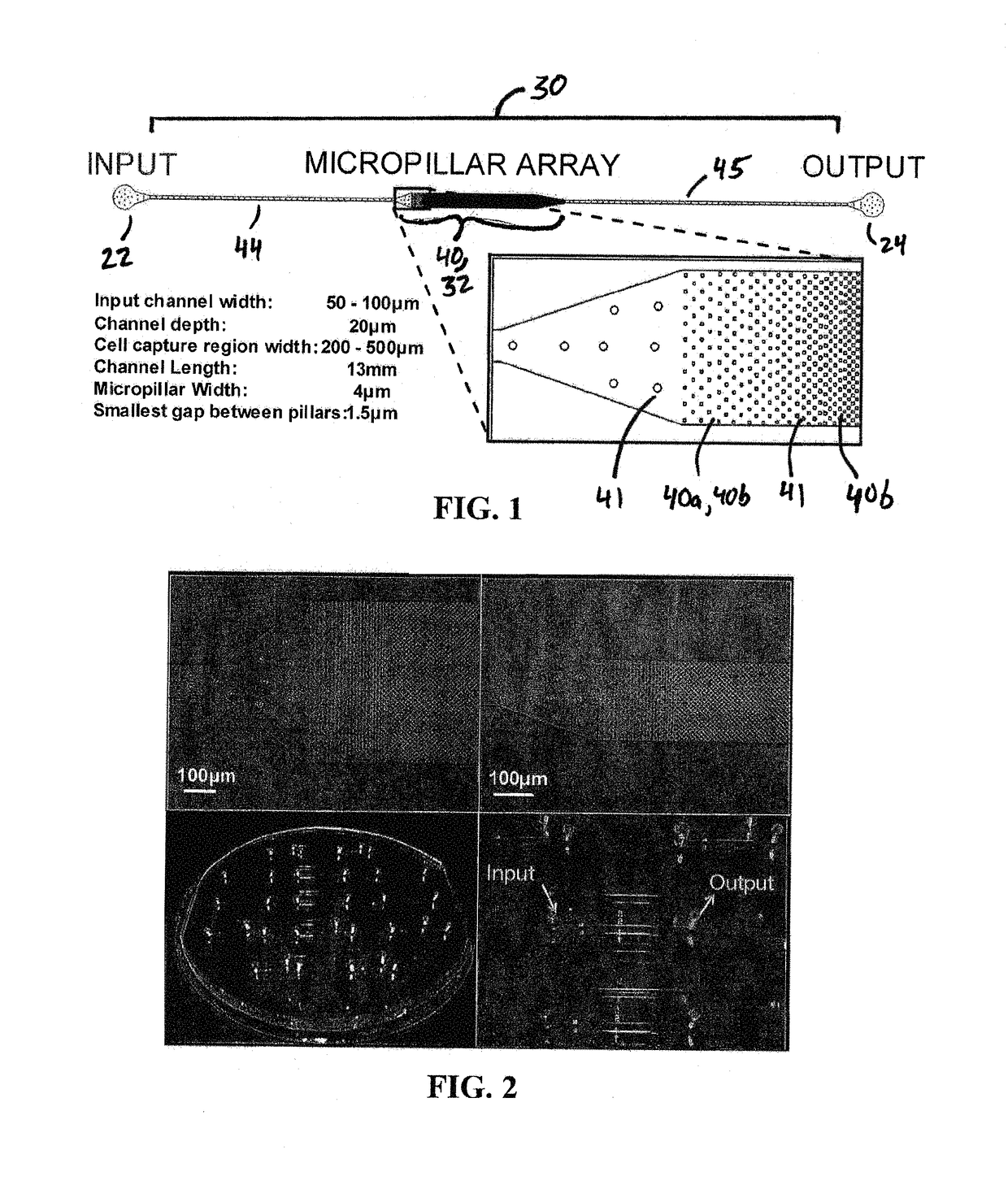
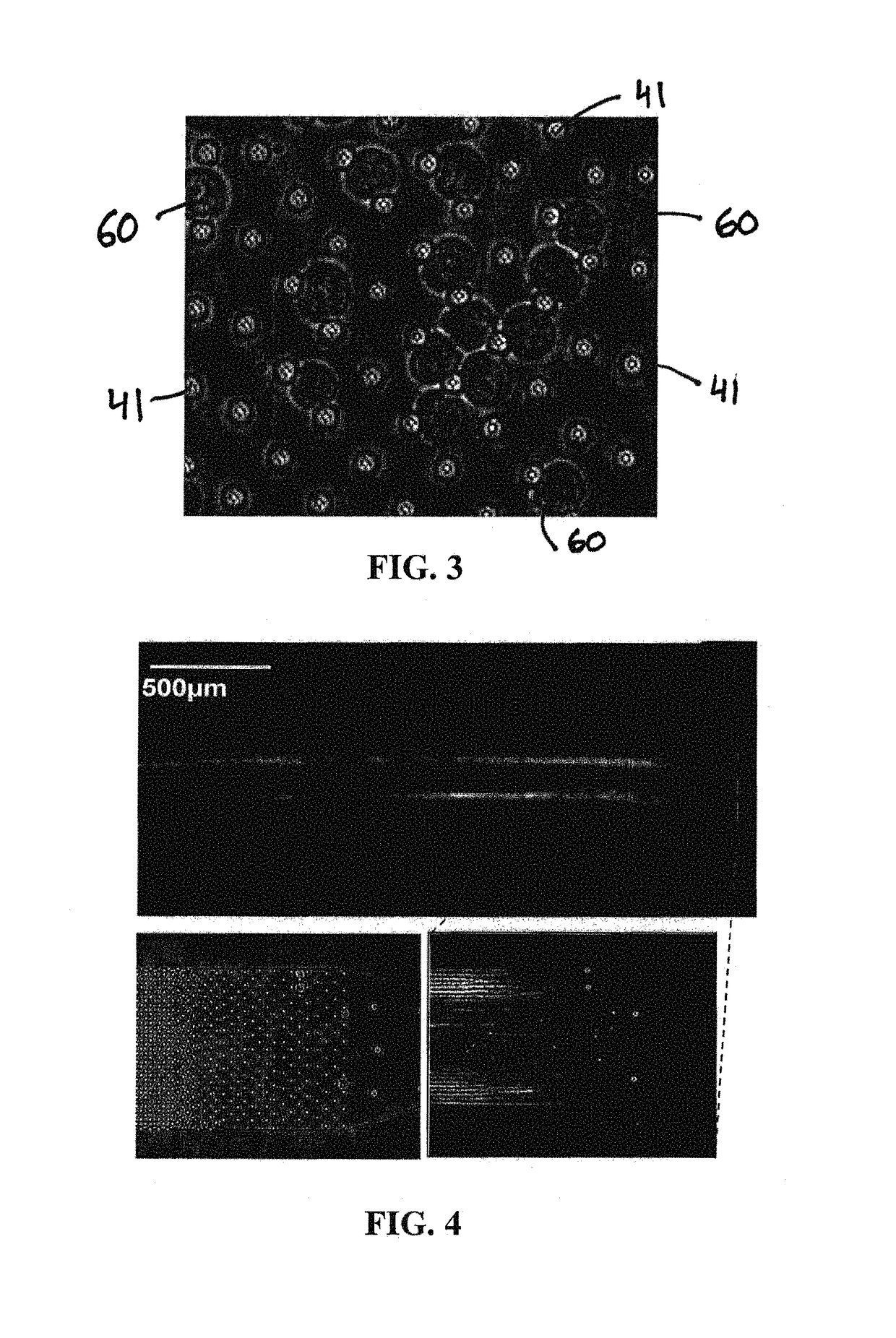
The present invention relates to a microfluidic device for extracting and isolating DNA from cells. The device includes a support having an inlet port for receiving a sample containing a cell, an outlet port for dispensing DNA isolated from the cell, and a microfluidic channel disposed within the support and extending from the inlet port to the outlet port. The microfluidic channel includes a micropillar array, an inflow channel disposed between the inlet port and the micropillar array, and an outflow channel disposed between the micropillar array and the outlet port. The micropillar array includes micropillars spatially configured to entrap, by size exclusion, the cell, to immobilize DNA released from the cell, and to maintain the immobilized DNA in elongated or non-elongated form when hydrodynamic force is applied to the microfluidic channel. Systems and methods of making and using the device are also provided herein.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for amplification of nucleic acid sequences using immobilized DNA polymerase
InactiveUS20100086975A1Readily separated and recoveredImprove purification effectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusPolymerase LLab-on-a-chip
The present invention generally relates to methods and apparatuses for amplifying nucleic acid sequences using immobilized DNA polymerase. More particularly, it relates to methods and apparatuses useful for amplifying target nucleic acid sequences by forming a plurality of reaction regions in which polymerase chain reaction (PCR) can occur, positioning immobilized DNA polymerase in a specific reaction region, and circulating DNA through the reaction regions. The present invention provides those methods and apparatuses that allow simple separation and recovery of the DNA polymerase after the amplification, that can be operated not only with thermostable DNA polymerases but also with non-thermostable DNA polymerases, and that are simpler in their designs and processes so that they can be readily integrated into complex devices such as Lab-on-a-chip.
Owner:AHRAM BIOSYST INC
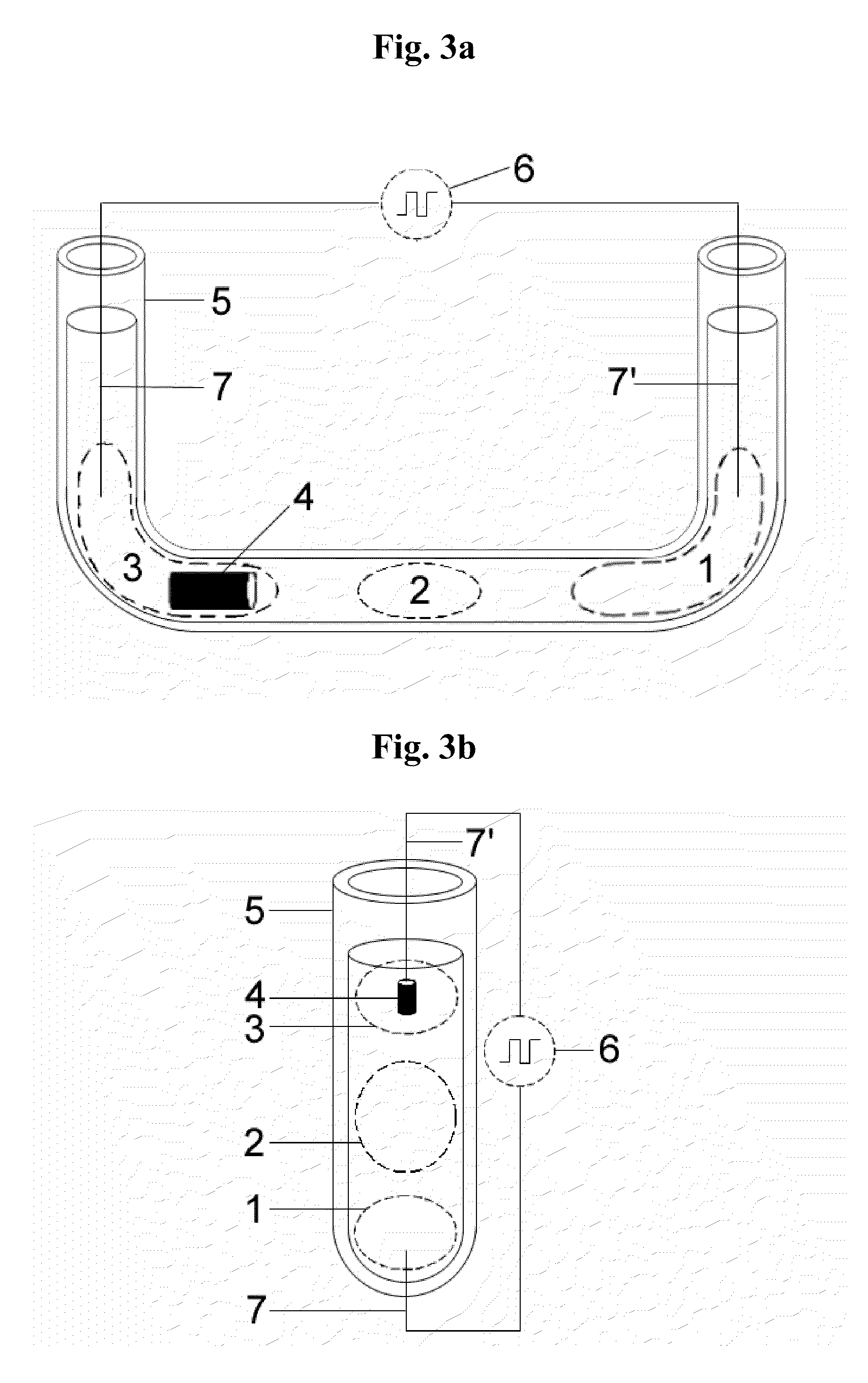
Method for biochemical analysis of dna and arrangement associated therewith
InactiveUS20050164199A1Reduces and even eliminates disadvantageSimplify complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementScavengerPolymer network
A system with immobilized DNA is used in the fields of medicine, environmentology or criminology as an analytical tool in the analysis of nucleic acid. The immobilized DNA is provided with a biocatalytically active marker, such as an enzyme, an with an inhibitor substance which reversibly inhibits catalytic activity, or in addition to the immobilized biocatalytic marker, the immobilized DNA is provided with a substance which can reversibly inhibit the catalytic activity of the marker. Alternatively, an immobilized biocatalytically active marker can be provided with DNA as a scavenger which includes a substance as an inhibitor which can reversibly inhibit the activity of the marker. In another alternative, it is possible to use a complex including a molecule binding double-stranded DNA and a substance as an inhibitor which can reversibly inhibit the activity of the marker by interacting with the immobilized biocatalytically active marker. In all cases, the inhibitor or compound including an inhibitor and a molecule which can bind double-stranded DNA interacts with the biocatalytically active marker and defines the inactive state of the system. When the DNA, which is to be analyzed, is bonded, especially hybridized, to the DNA scavengers, the interaction between the biocatalytically active marker and the inhibitor is cancelled as a result of the formation of the double strand. The system is thus shifted from a first state into a second state defining the active state. A carrier with integrated microelectrodes is provided in the associated device, whereby the enzyme is either immobilized therein or is contained in a polymer network in the vicinity of the microelectrodes.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method for preparing immobilized DNA guiding substrate surface nano-titanium dioxide film growth
InactiveCN101314525ANo pollution in the processRealize immobilizationCoatingsSolar batteryCalcination
The invention discloses a preparation method for leading the growth of a nanometer titanium dioxide film on the surface of a substrate by DNA immobilization. The method comprises the following steps that: (1) the substrate is cleaned and dried; (2) DNA molecules on the surface of the substrate are immobilized; and (3) the substrate treated by the step (2) is immersed into a 2 to 20 mM of TiCl4 aqueous solution containing hydrochloric acid and subject to the sedimentation of the nanometer titanium dioxide film. The method has no environmental pollution, realizes the immobilization and the ordered assembly of DNA and leads the assembly and growth of the nanometer titanium dioxide film at a low temperature with the substrate as a template. The nanometer titanium dioxide film prepared on the substrate surface by the method needs no high-temperature calcination, has a certain crystal structure, even film surface and strong adhesive force with the substrate surface and can be used for preparing a transparent conductive film and a self-cleaning surface of a solar battery and other functional devices.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Colorimetric method for simultaneously detecting multiple miRNA (micro-ribonucleic acid) sequences based on competitive hybridization reaction
InactiveCN103529200AHigh sensitivitySimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsModified dnaHybridization reaction
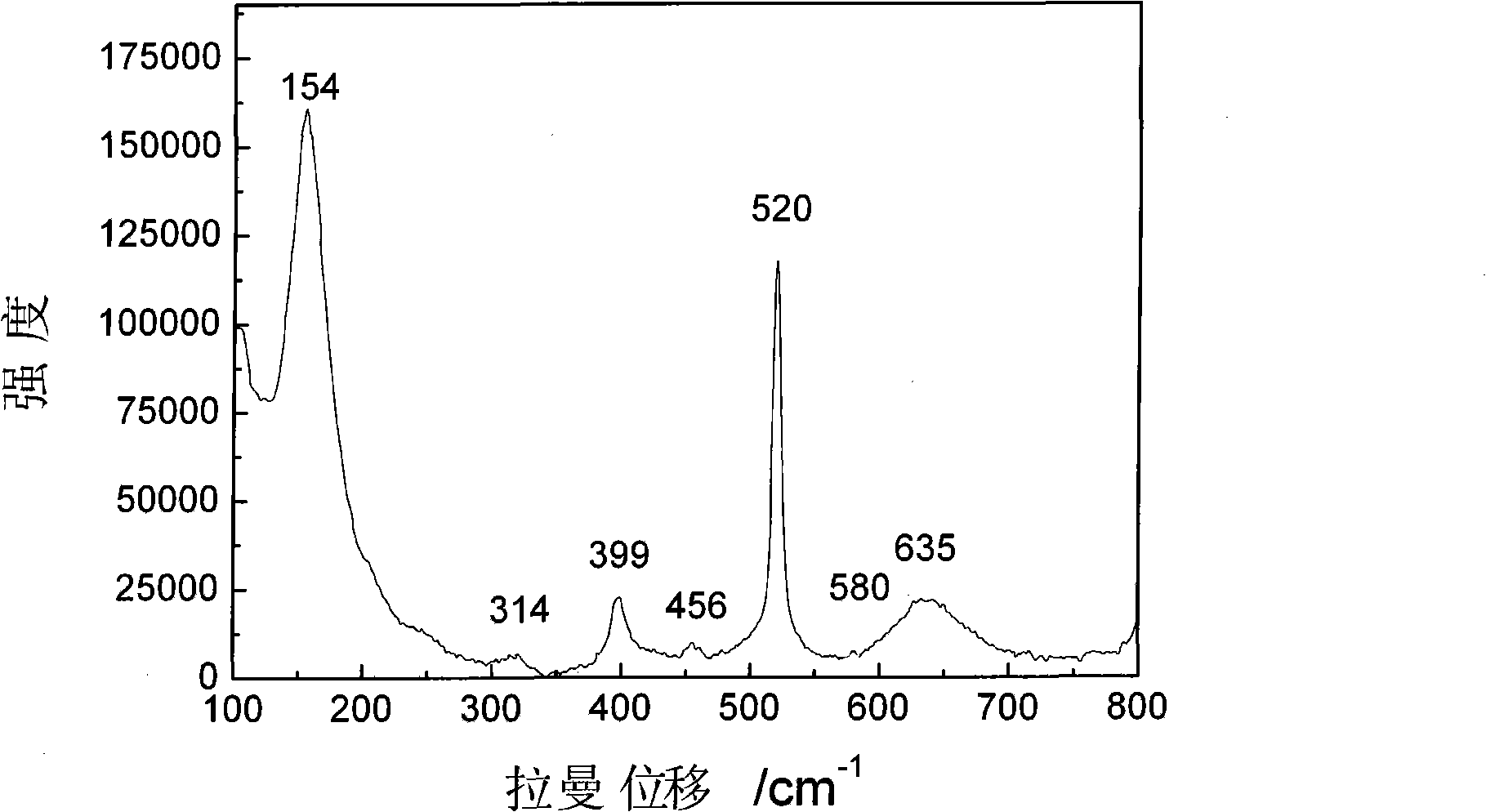
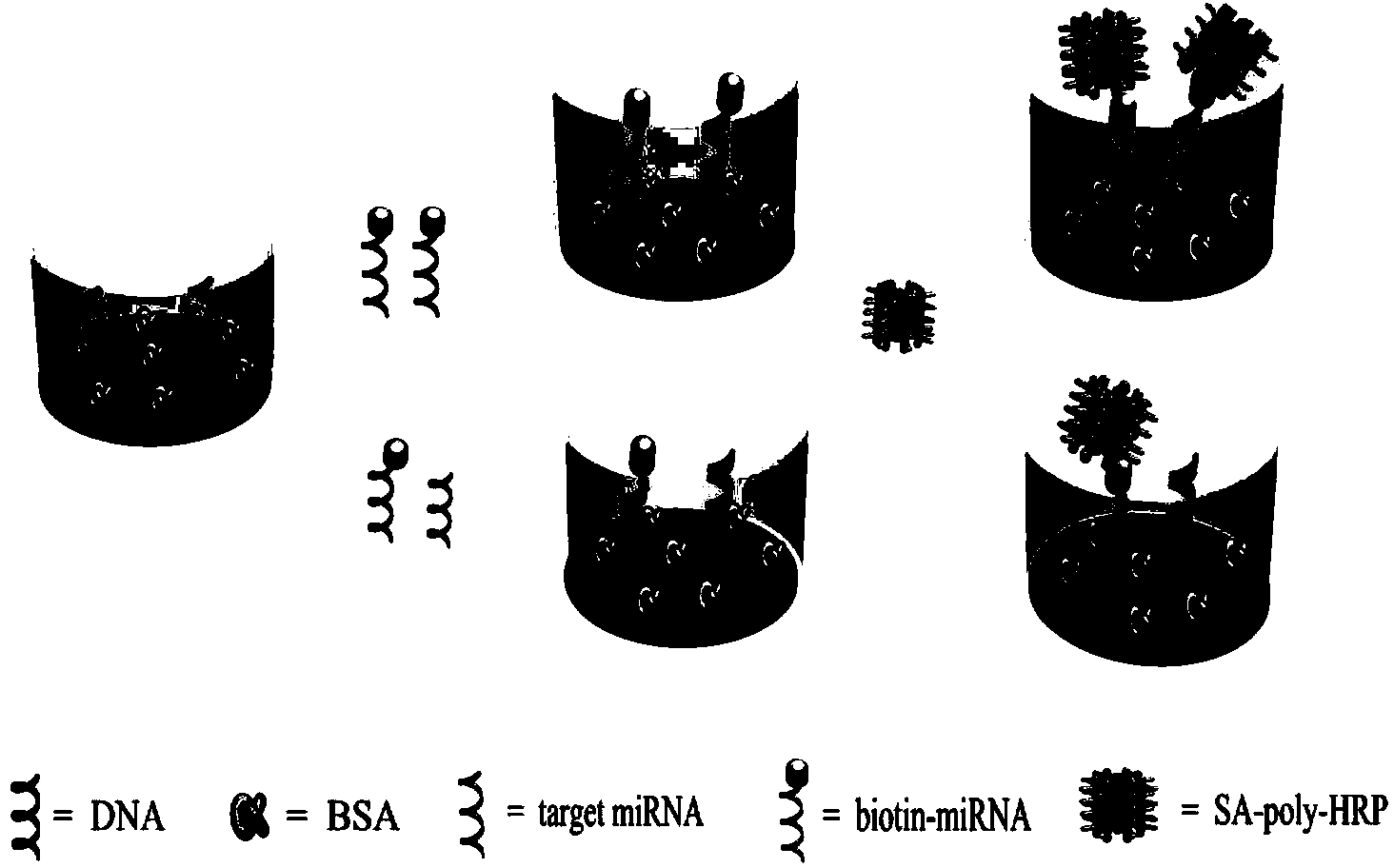
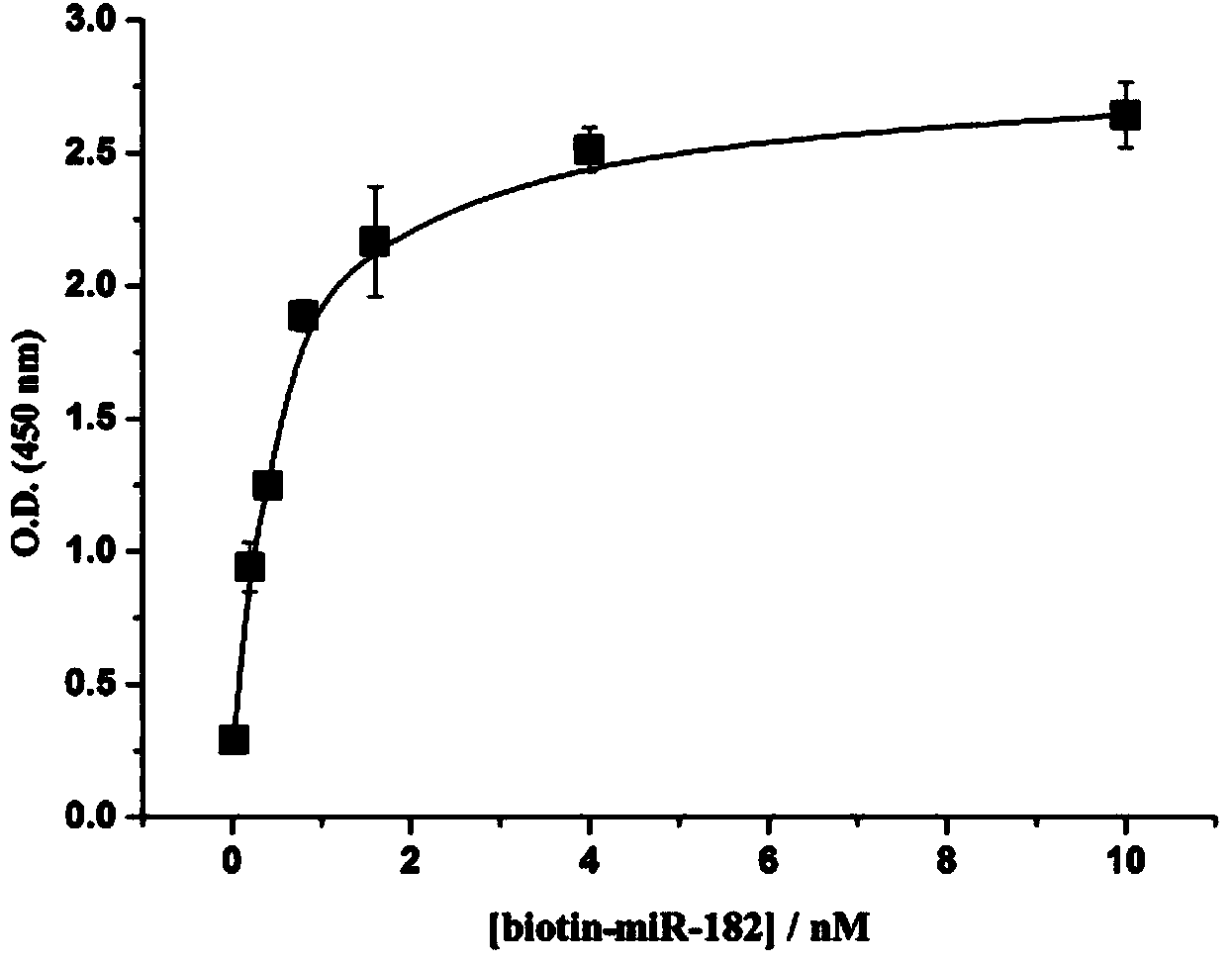
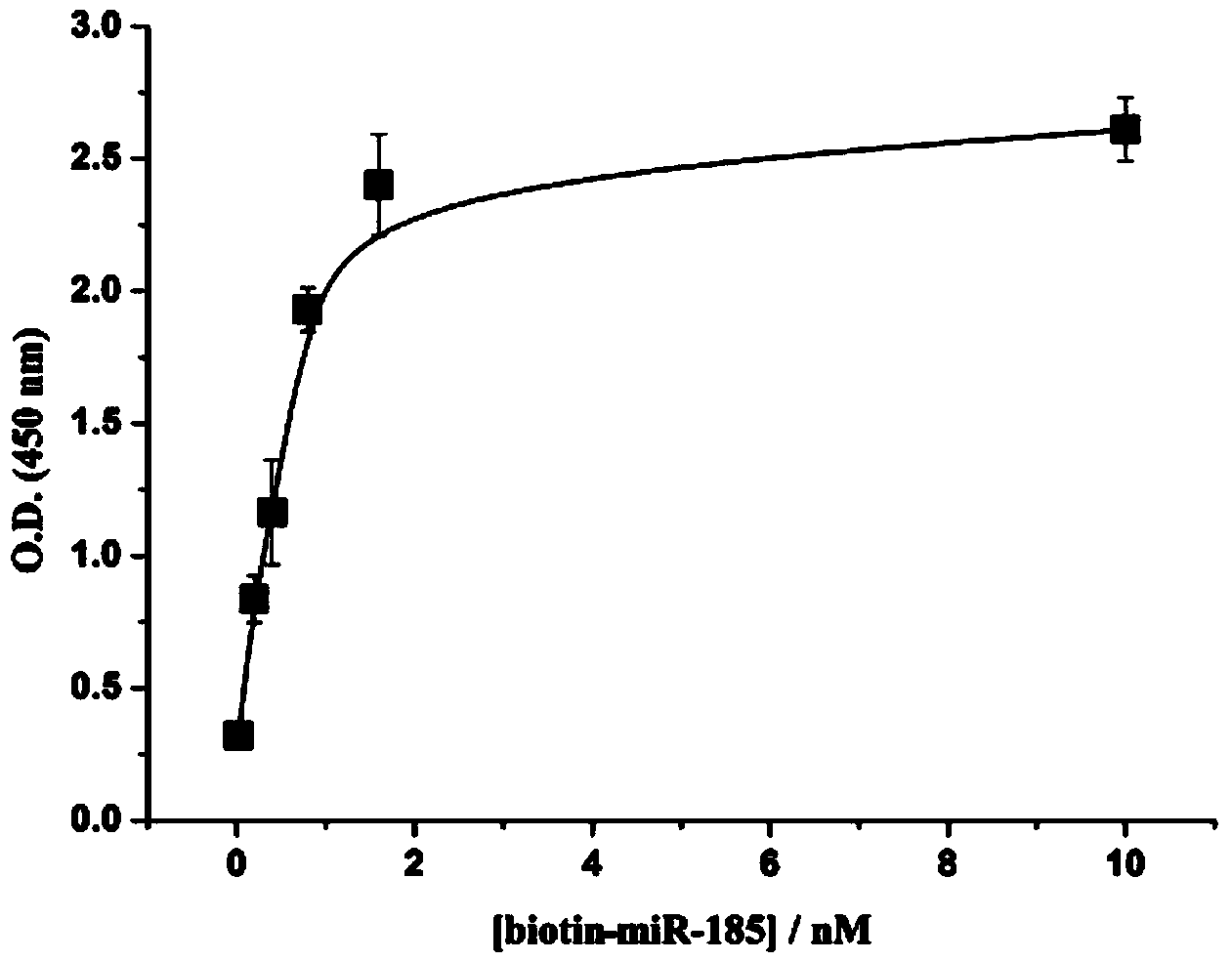
The invention discloses a colorimetric method for simultaneously detecting multiple miRNA (micro-ribonucleic acid) sequences based on a competitive hybridization reaction. The method comprises the following steps: assembling amino modified DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) on the surface of a micropore plate, and closing micropores; performing a competitive hybridization reaction on biotin modified miRNA and a target miRNA sequence with a fixed DNA probe on the surface of the micropores; deriving avidin marked poly-horseradish peroxidase to the surface of the micropores, and catalyzing a chromogenic reaction between TMB (tetramethylbenzidine) and hydrogen peroxide by the poly-horseradish peroxidase. The target miRNA sequence is detected by determining the absorbance of a colored solution. The method is simple, quick, high in sensitivity and good in selectivity, does not need to mark an actual sample, and can be directly used for detecting multiple miRNA sequences.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
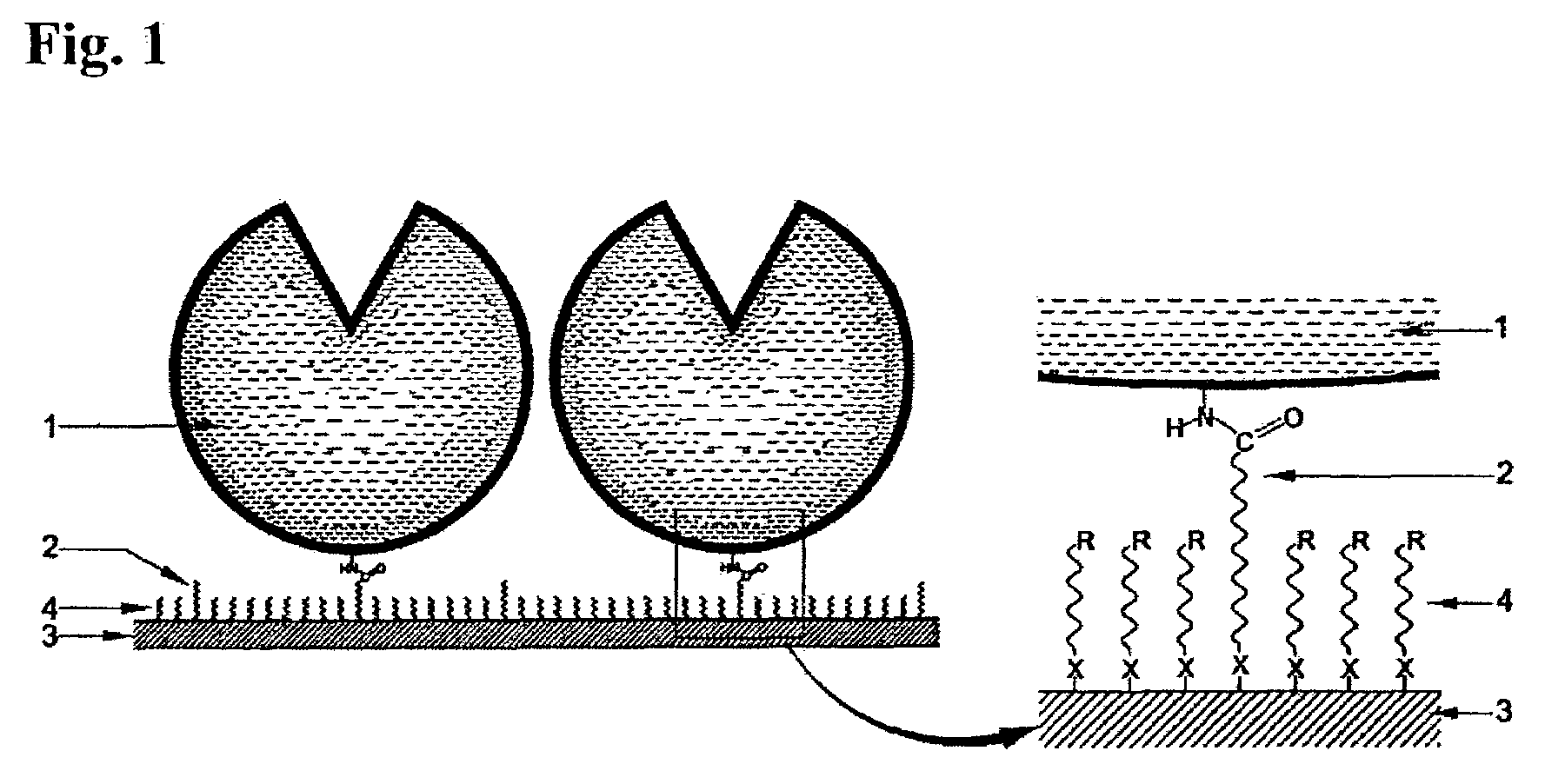
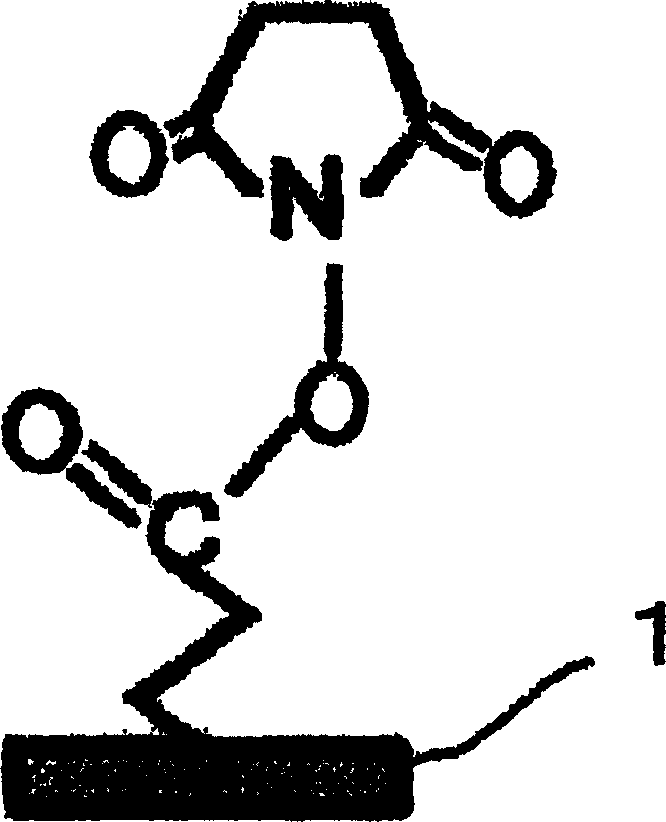
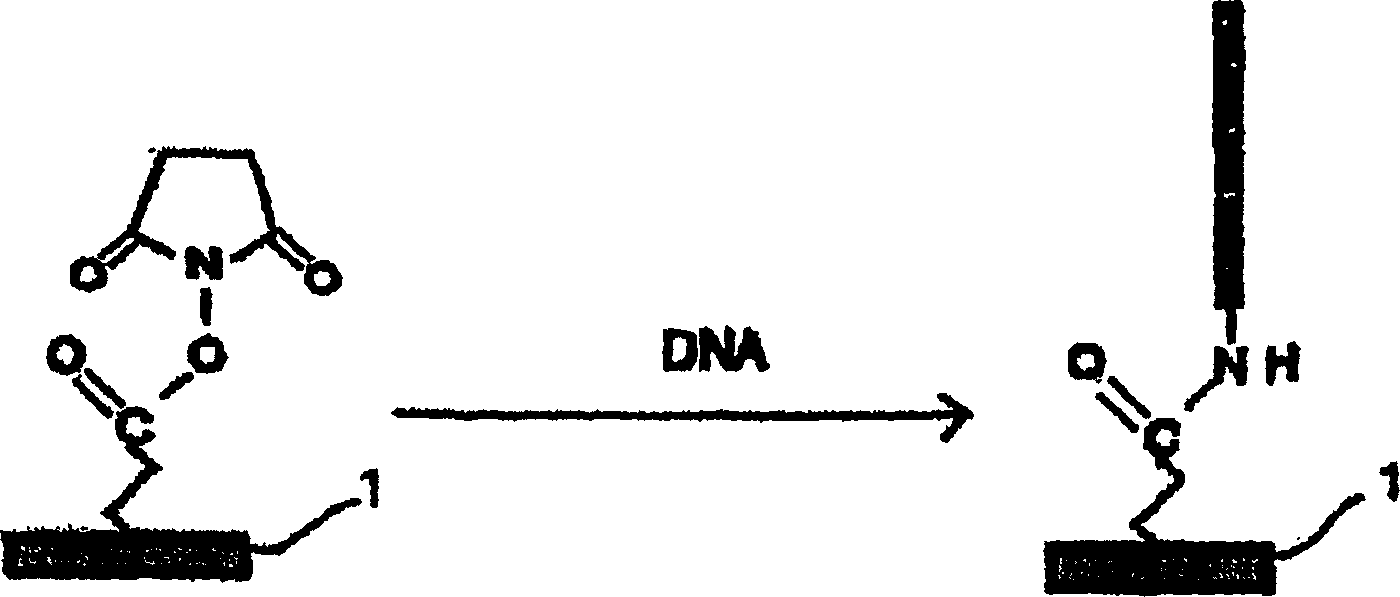
Substrate activation kit and method of detecting DNA or the like by using the same
InactiveCN1606693AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingPhosphateBiological activation
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a convenient and fast method for immobilizing DNA on a substrate and a method for accurately detecting DNA, and the density of DNA immobilized by the method is as high as that of the traditional method. A substrate activation kit is provided, which includes phosphate buffered saline at pH 6, solution A (aqueous) of N-hydroxysuccinimide and 1-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]3-ethylcarbodi Solution B of imine (dioxane solution); a method for detecting DNA is provided, which is characterized in that the DNA is spotted onto the substrate activated with the above-mentioned activation kit, and then hybridized with fluorescently labeled DNA with the spotted DNA.
Owner:TOYO KOHAN CO LTD
Method for efficiently screening out DNA chain scission injury protective drugs
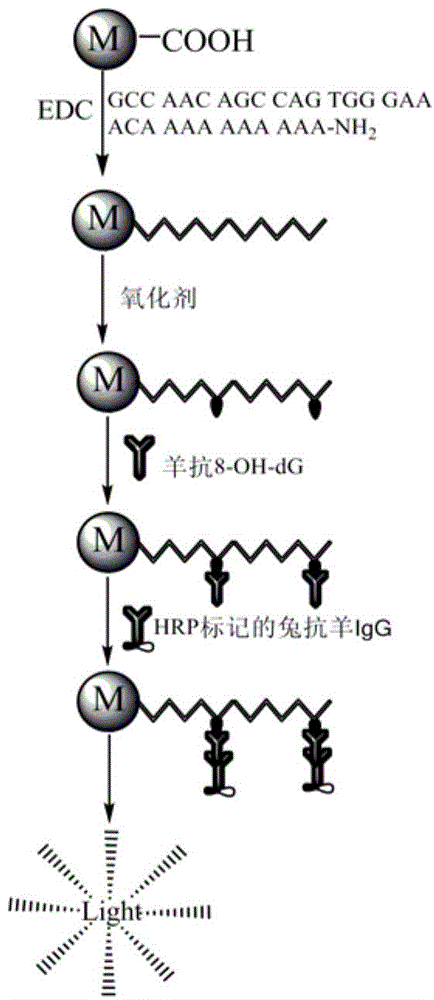
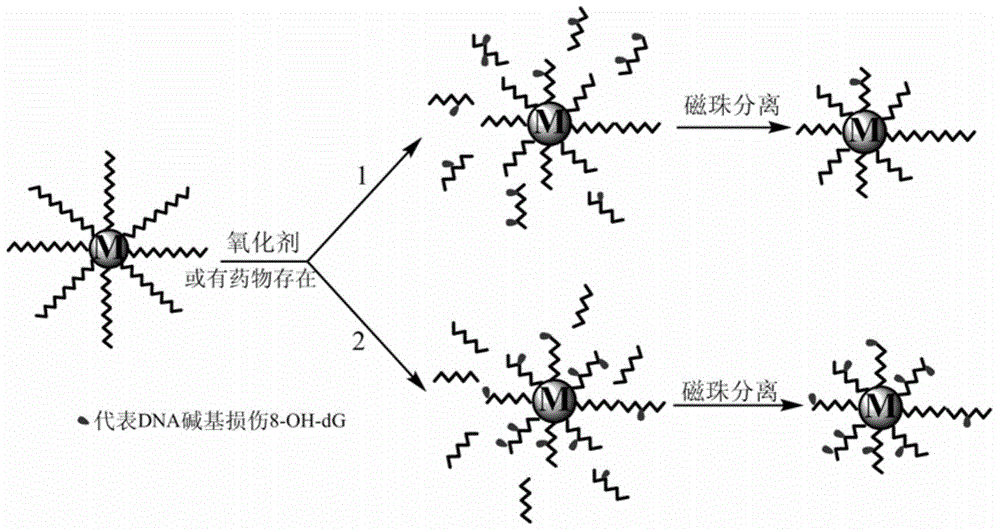
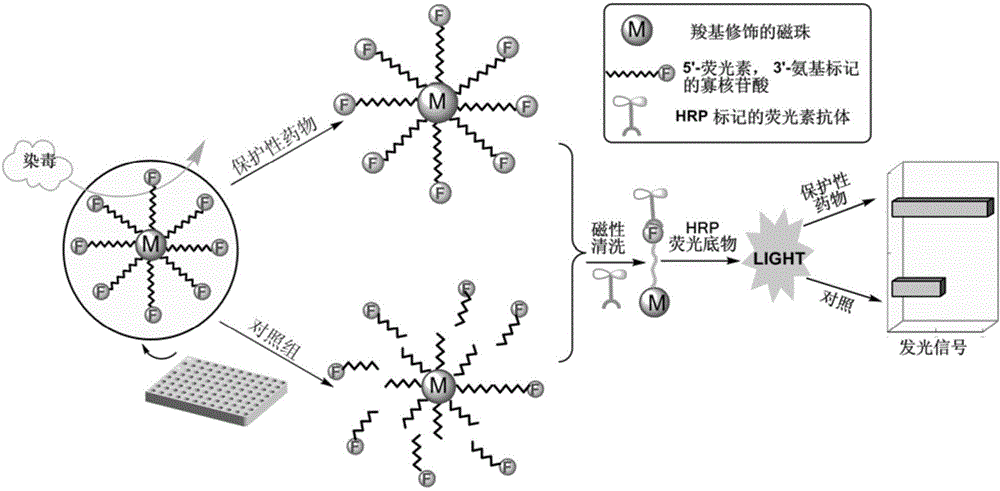
The invention relates to a method for efficiently screening out DNA chain scission injury protective drugs. The method is characterized by comprising the steps that DNA with one end modified by FAM and the other end modified by amino is fixed to a magnetic microsphere surface through a covalent bond, and immobilized DNA is obtained; a drug solution is added into the immobilized DNA, and DNA with drugs is obtained; in vitro exposure is carried out on the DNA with the drugs, and exposure DNA is obtained; magnetic separation is carried out on the exposure DNA, exposure ingredients and reaction impurities are separated away, and DNA free of chain scission is retained; an enzyme-labeled FAM antibody is added into the DNA free of chain scission, the enzyme-labeled FAM antibody and the FAM at the free end of the DNA free of chain scission have an immunoreaction, and DNA is obtained after the immunoreaction; an enhanced chemiluminescent is added into the DNA obtained after the immunoreaction, the high-sensitivity chemiluminiscence method is adopted for detecting the DNA obtained after the immunoreaction, and detection signals are obtained; the detection signals are compared with comparison group signals, and whether the drugs protect the DNA or not is judged. The method can reduce false positives, and has the practical value.
Owner:SHANGHAI YANGPU CENT HOSPITAL
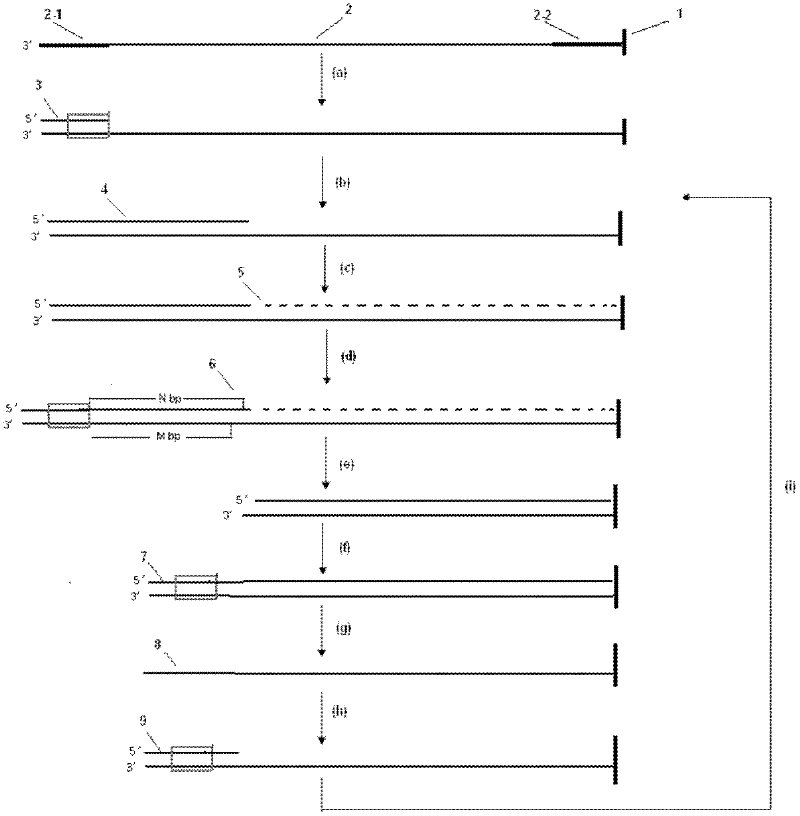
Method for shortening deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) sequencing of DNA template and application thereof
InactiveCN102344967AImprove accuracyIncrease read lengthMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesA-DNARecognition sequence
The invention relates to a method for shortening DNA sequencing of a DNA template and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) determining a small segment of sequence which is fixed in the DNA template by synthesizing or adopting a connecting sequencing method; (2) stopping the sequencing of sequencing primers, adding four kinds of dNTPs monomer extension sequencing primer strands, and making the DNA template become double strands; (3) shortening the DNA template: processing by using restriction enzyme to preset a connexon with an enzyme recognition sequence; and fracturing a small segment of sequence in the determined DNA template; (4) connecting the sequencing primer and a double stranded oligonucleotide segment with the enzyme recognition sequence on the cut and shortened DNA template; (5) denaturing, removing unfixed DNA strands, and obtaining the DNA template again; (6) hybridizing the sequencing primer, and continuously determining the small segment of sequence fixed in the DNA template; and (7) repeating the step (2) to the step (6) until the sequencing of the undermined DNA template is completed.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
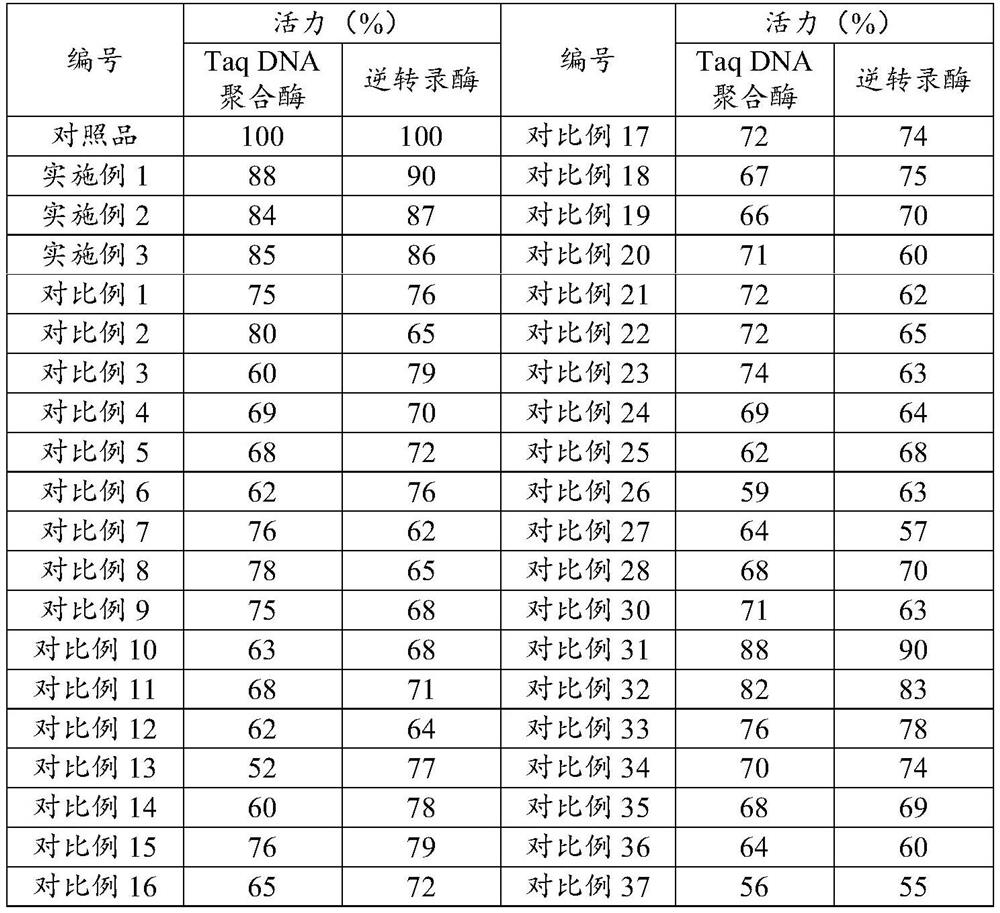
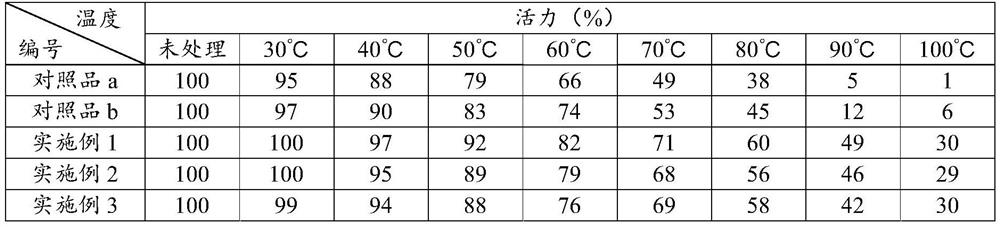
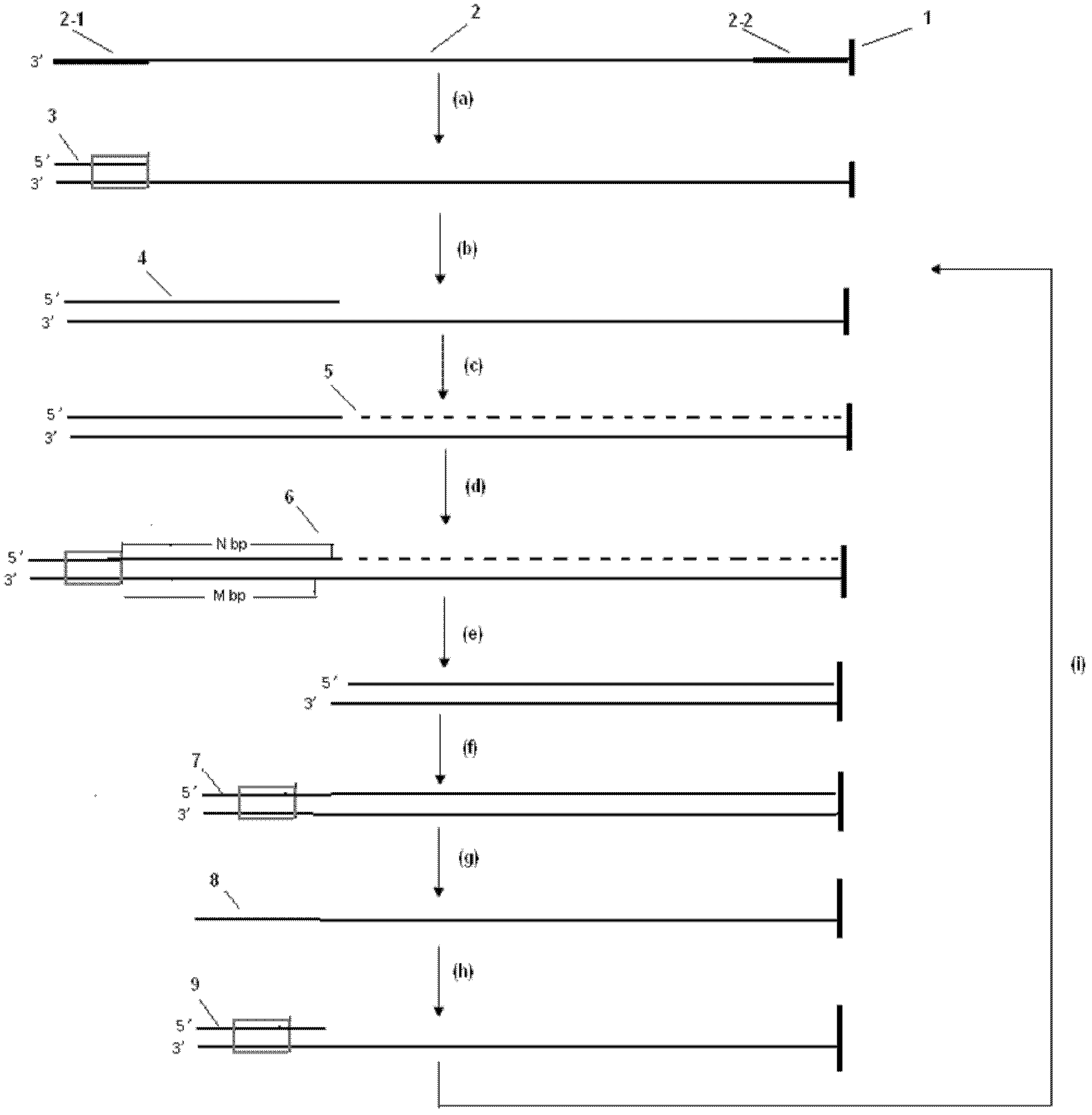
DNA polymerase immobilization method and application thereof
ActiveCN108130317AIncrease vitalityImprove thermal stabilityTransferasesOn/in organic carrierFreeze-dryingPolymerase L
The invention belongs to the field of enzyme engineering and particularly relates to a DNA polymerase immobilization method and an application thereof. The immobilization method comprises steps as follows: a modified chitosan water solution is prepared firstly, an adsorption reaction solution of DNA polymerase is prepared, a crosslinking reaction solution of the DNA polymerase is prepared, the crosslinking reaction solution and wood pulp sponge are mixed, a carrageenin water solution is added, the mixture is centrifuged and washed and finally freeze-dried, and the immobilized DNA polymerase isobtained, and the prepared immobilized DNA polymerase has higher activity and better thermal stability; the prepared immobilized DNA polymerase has the highest activity and the best thermal stabilityby selecting a specific protein flocculant, specific adsorption reaction conditions, specific crosslinking reaction conditions, a specific crosslinking agent, a specific buffer solution, specific carriers, a specific PCR accelerator and specific freeze-drying conditions.
Owner:SUZHOU BAIYUAN GENT CO LTD
Gene chip for detecting tumour chemotherapy drug susceptibility
InactiveCN1966722AIncreased sensitivityShorten detection timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular levelWilms' tumor
The invention discloses a gene chip for detecting the sensitivity of tumor chemotherapeutics. The gene chip is to immobilized DNA probes for detecting the sensitivity of drugs on slide glass, silicon chip or polymer material. The said DNA probes comprise at least five nucleotide sequences of SEQ ID No.1 to SEQ ID No.59. The expression level of Tumor chemotherapeutics sensitivity-related gene selected in the invention relates to the sensitivity of organism on drugs. The gene chip is characterized in: detecting the sensitivity or drug fast of organism on drugs on molecular level, high detection flux, high sensitivity, short time, low cost, and simple operation.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
Method of performing PCR amplification on a microarray
Owner:ROCHE NIMBLEGEN
Co-immobilization method for DNA polymerase and reverse transcriptase, and application of co-immobilized DNA polymerase and reverse transcriptase
ActiveCN108342380AAchieve one-step conversionHigh catalytic efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesBiotechnologyReverse transcriptase
The invention specifically relates to a co-immobilization method for DNA polymerase and reverse transcriptase, belonging to the field of enzyme engineering. The method comprises the following steps: adding sodium alginate into a first buffer, then adding DNA polymerase, carrying out mixing and immobilizing, and then carrying out vacuum drying so as to obtain immobilized DNA polymerase; adding a second buffer and reverse transcriptase into the immobilized DNA polymerase, carrying out mixing and immobilizing, then carrying out vacuum drying and then carrying out washing with the second buffer; and then carrying out lyophilization so as to obtain the co-immobilized DNA polymerase and reverse transcriptase. According to the invention, DNA polymerase and reverse transcriptase are co-immobilizedon a same carrier, so one-step conversion of a RT-PCR reaction is realized, and the catalytic properties of DNA polymerase and reverse transcriptase are integrated to eliminate certain interference factors, and thus, the overall catalytic efficiency of DNA polymerase and reverse transcriptase to RT-PCR reactions is improved.
Owner:SUZHOU BAIYUAN GENT CO LTD
A kind of co-immobilization method and application of dna polymerase and reverse transcriptase
ActiveCN108342380BAchieve one-step conversionHigh catalytic efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesReverse transcriptaseImmobilized DNA
The invention belongs to the field of enzyme engineering, in particular to a co-immobilization method of DNA polymerase and reverse transcriptase. The method comprises the following steps: adding sodium alginate to the first buffer solution, then adding DNA polymerase, mixing, fixing, and vacuum-drying to obtain immobilized DNA polymerase; adding the second DNA polymerase to the immobilized DNA polymerase The second buffer solution and the reverse transcriptase are mixed, fixed, vacuum-dried, and then washed with the second buffer solution; freeze-dried to obtain co-immobilized DNA polymerase and reverse transcriptase. By co-immobilizing DNA polymerase and reverse transcriptase on the same carrier, the present invention can not only realize the one-step conversion of RT-PCR reaction, but also can combine the catalytic properties of the two, and can eliminate some interference factors, thereby improving The overall catalytic efficiency of the two on the RT-PCR reaction.
Owner:SUZHOU BAIYUAN GENT CO LTD
A dna sequencing method for shortening dna template and its application
InactiveCN102344967BImprove accuracyIncrease read lengthMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesA-DNARecognition sequence
The invention relates to a method for shortening DNA sequencing of a DNA template and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) determining a small segment of sequence which is fixed in the DNA template by synthesizing or adopting a connecting sequencing method; (2) stopping the sequencing of sequencing primers, adding four kinds of dNTPs monomer extension sequencing primer strands, and making the DNA template become double strands; (3) shortening the DNA template: processing by using restriction enzyme to preset a connexon with an enzyme recognition sequence; and fracturing a small segment of sequence in the determined DNA template; (4) connecting the sequencing primer and a double stranded oligonucleotide segment with the enzyme recognition sequence on the cut and shortened DNA template; (5) denaturing, removing unfixed DNA strands, and obtaining the DNA template again; (6) hybridizing the sequencing primer, and continuously determining the small segment of sequence fixed in the DNA template; and (7) repeating the step (2) to the step (6) until the sequencing of the undermined DNA template is completed.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
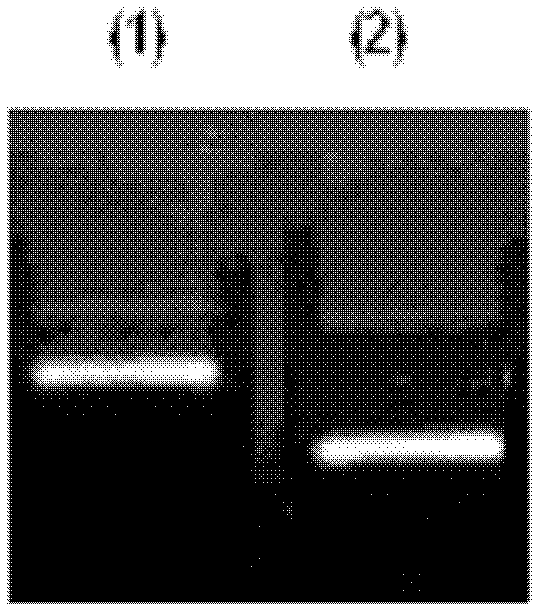
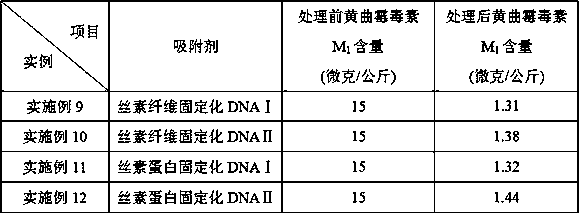
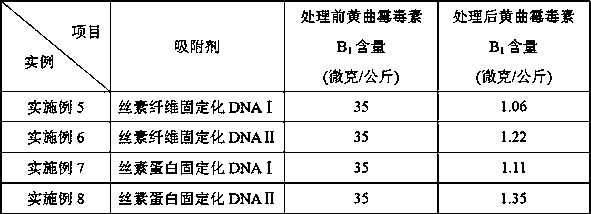
Preparation method of fibroin-immobilized DNA adsorbent based on glutaraldehyde crosslinking action and application thereof in aflatoxin elimination
InactiveCN109569524AImprove mechanical propertiesAvoid defectsOther chemical processesFatty-oils/fats refiningFiberSorbent
The invention provides a method for preparing novel fibroin-immobilized DNA through chemical crosslinking, especially crosslinking of glutaraldehyde molecule and amino and a method for capturing and eliminating aflatoxin by allowing DNA on the fibroin-immobilized DNA and aflatoxin to be in chelation action and separating and removing the fibroin-immobilized DNA. The adsorbent is especially suitable for eliminating aflatoxin in grease like peanut oil, maize oil and cow's milk and dairy products. The DNA is hydrophilic and soluble in water, thereby being insupportive of separation from water-soluble media or reaction systems and lack of mechanical performance like proper strength, hardness, toughness and plasticity; fibroin fiber is hydrophilic and insoluble in water and is good in mechanical performance, bio-safe and degradable, so that the fibroin-immobilized DNA can avoid original defects of DNA and can fully display and give play to performance of the DNA in capturing and eliminatingaflatoxin.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
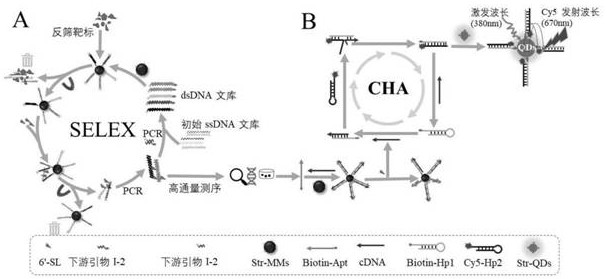
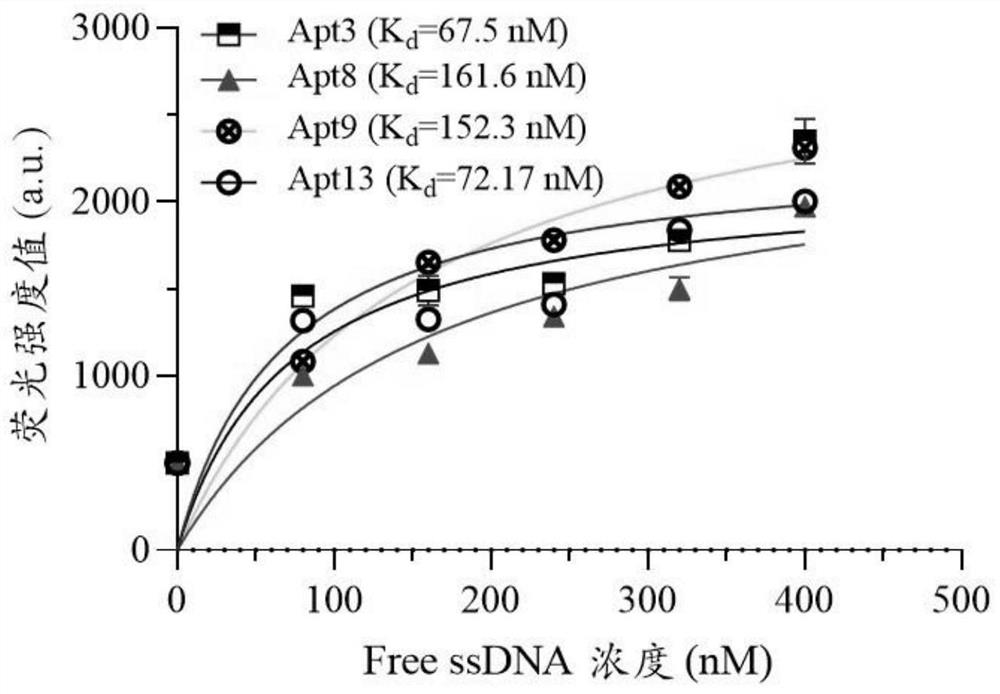
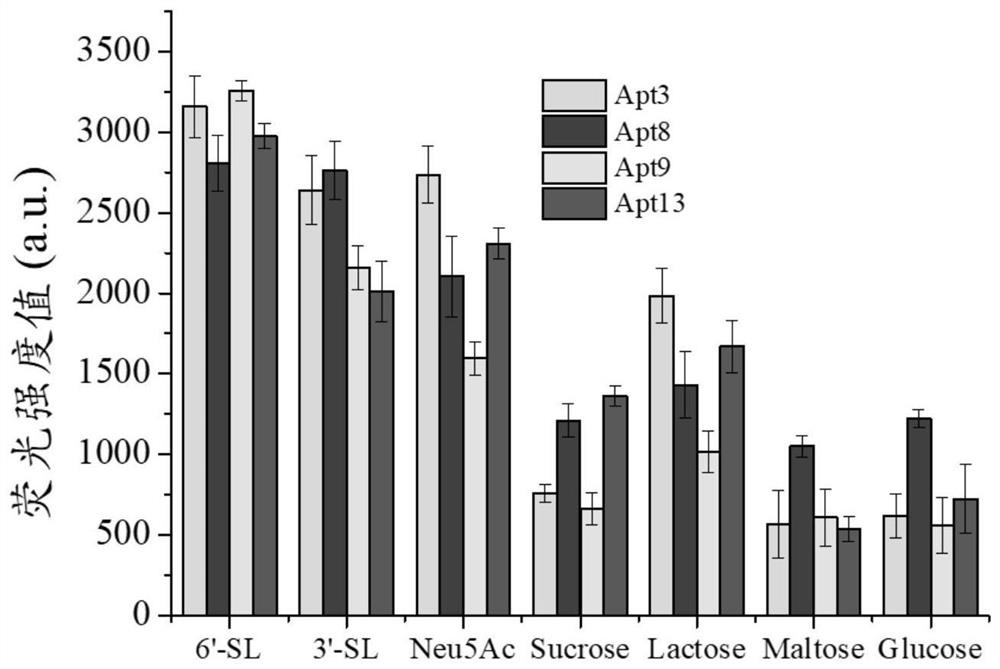
ssDNA aptamer specifically recognizing 6'-sialyllactose and its screening method and application
ActiveCN113943736BShort operation processEfficient operation processMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingAptamerStreptavidin
The present invention uses streptavidin-modified magnetic beads-SELEX technology to screen through the immobilized DNA library method, and obtains 4 ssDNA adaptations with high affinity and specificity to 6'-sialyllactose from 3187 sequencing results Using ssDNA aptamer as 6'-sialyllactose biorecognition element, catalytic hairpin self-assembly as signal amplification unit, and quantum dots as signal label, a fluorescent biosensor based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer was constructed to detect6 '‑sialyllactose. The invention provides a recognition element and a detection method with high affinity, high specificity, easy modification and labeling for the detection of 6'-sialyllactose.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
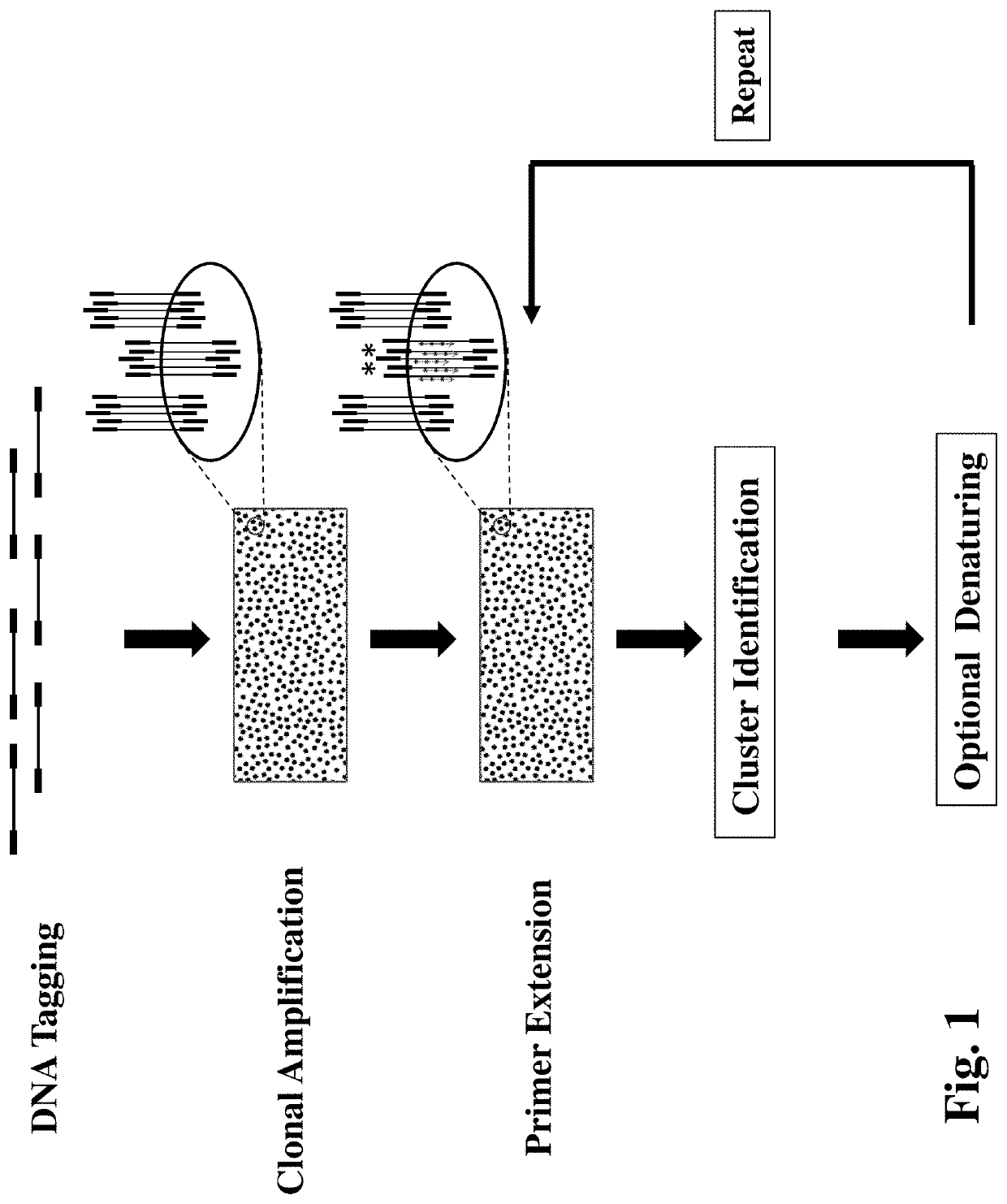
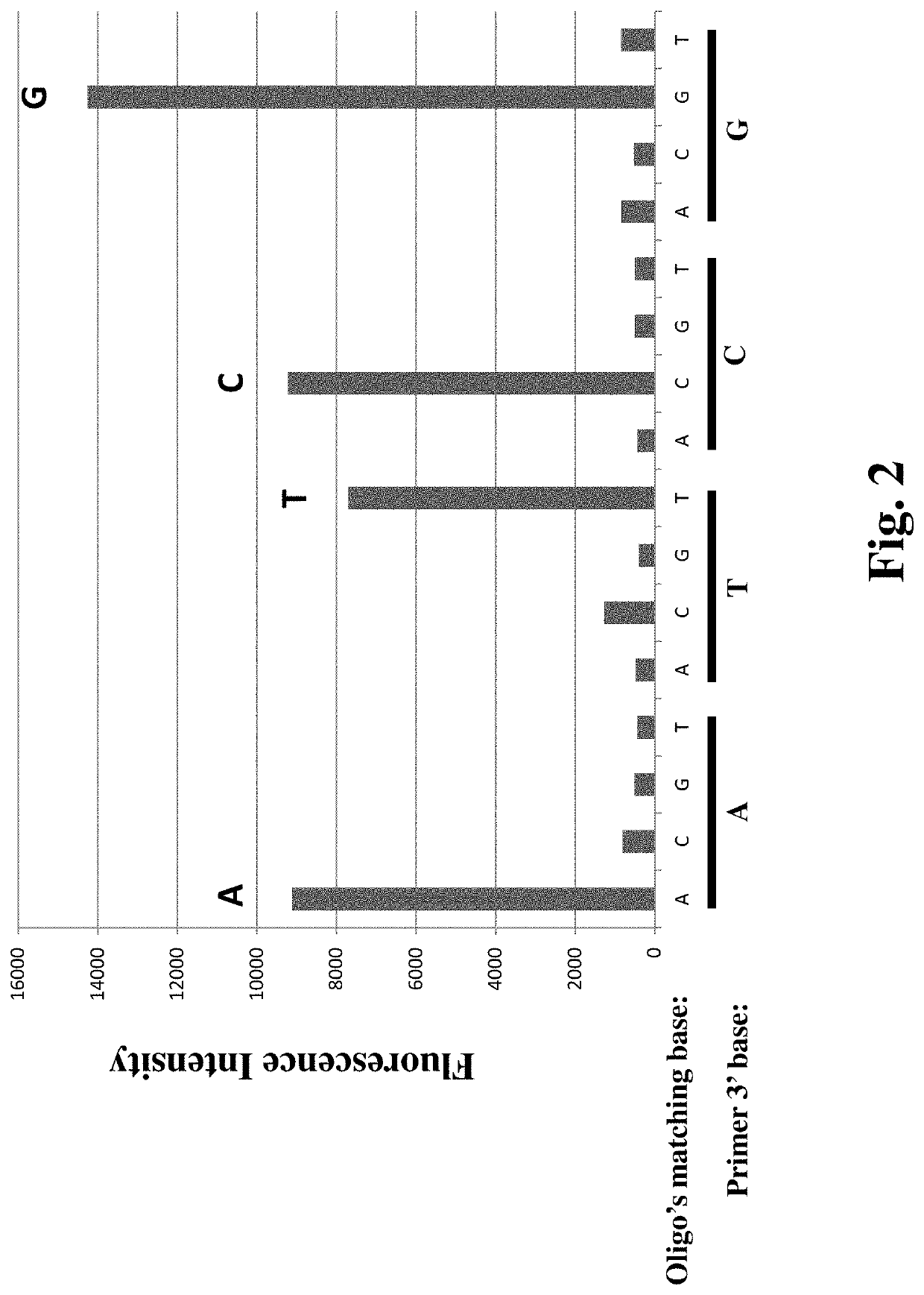
Method for Detecting multiple DNA Mutations and Copy Number Variations
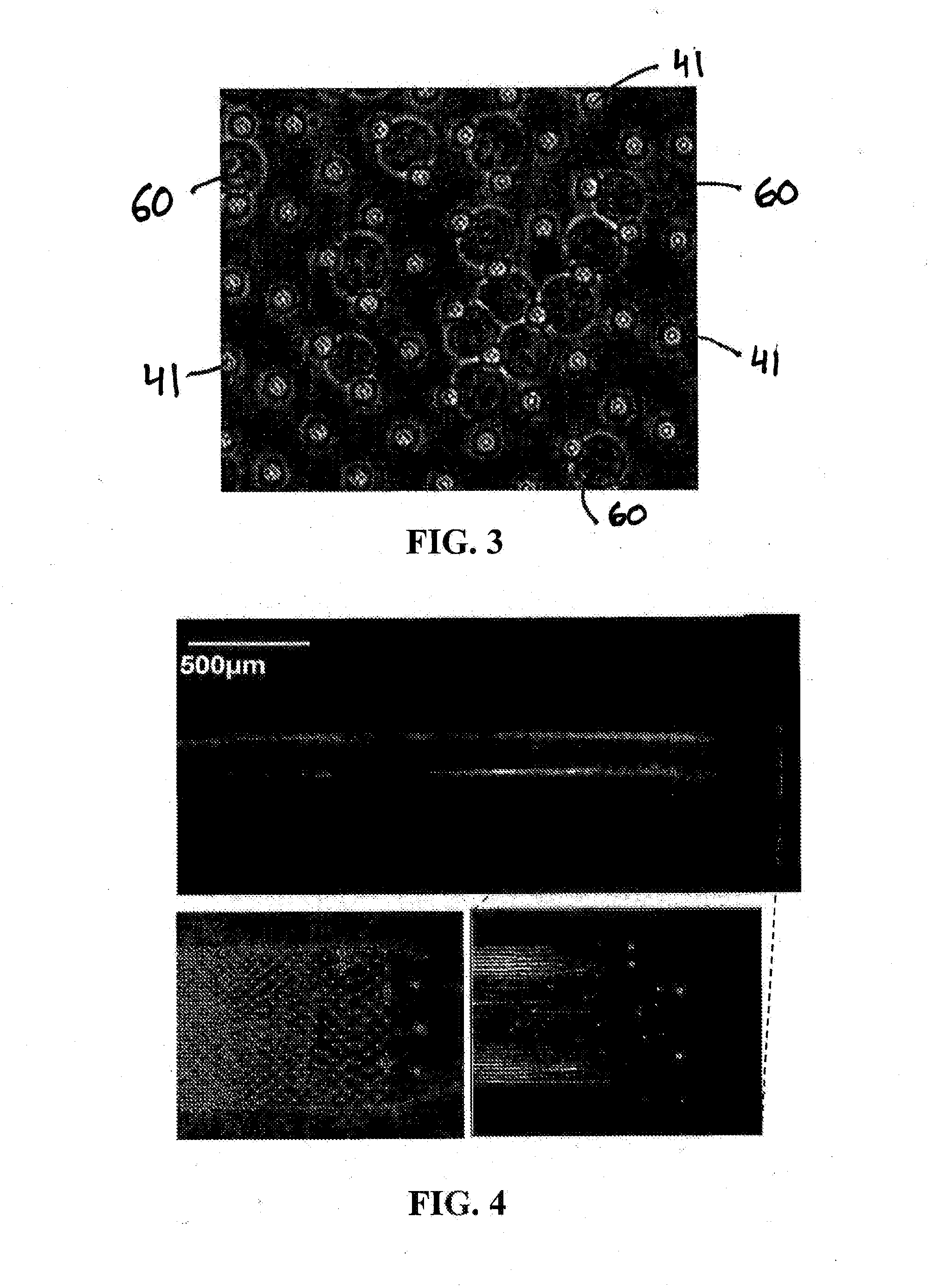
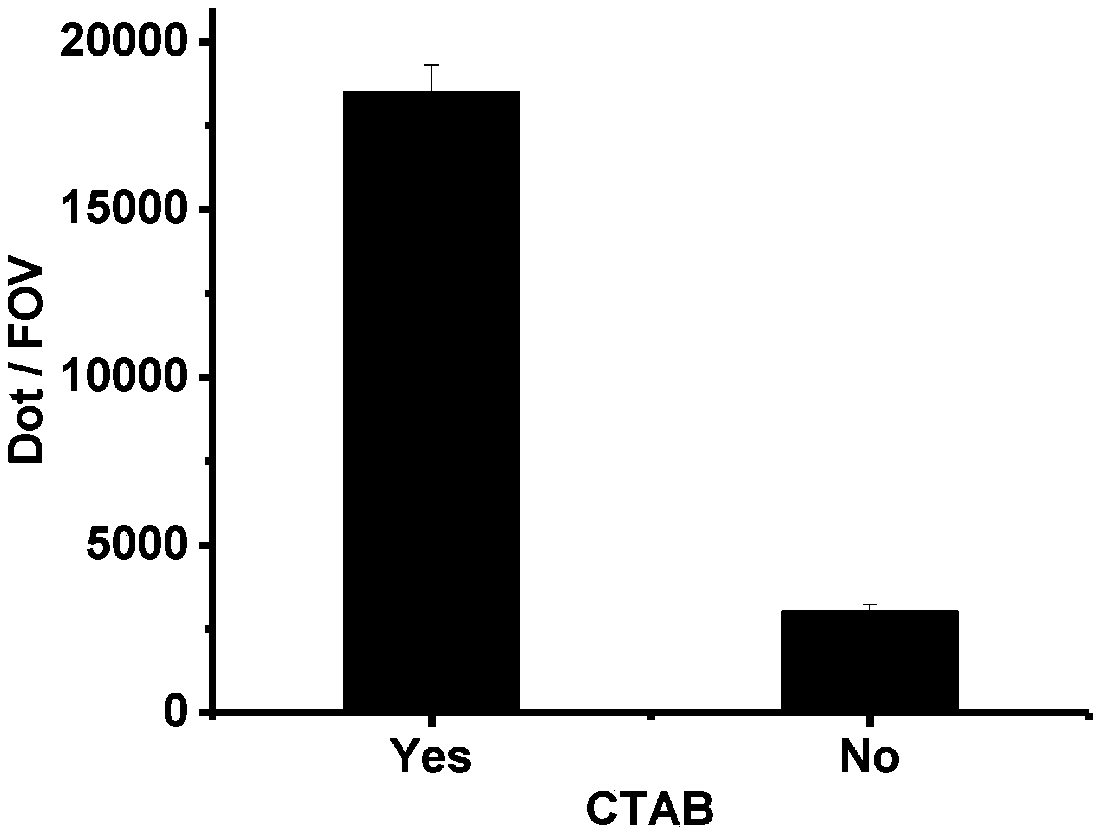
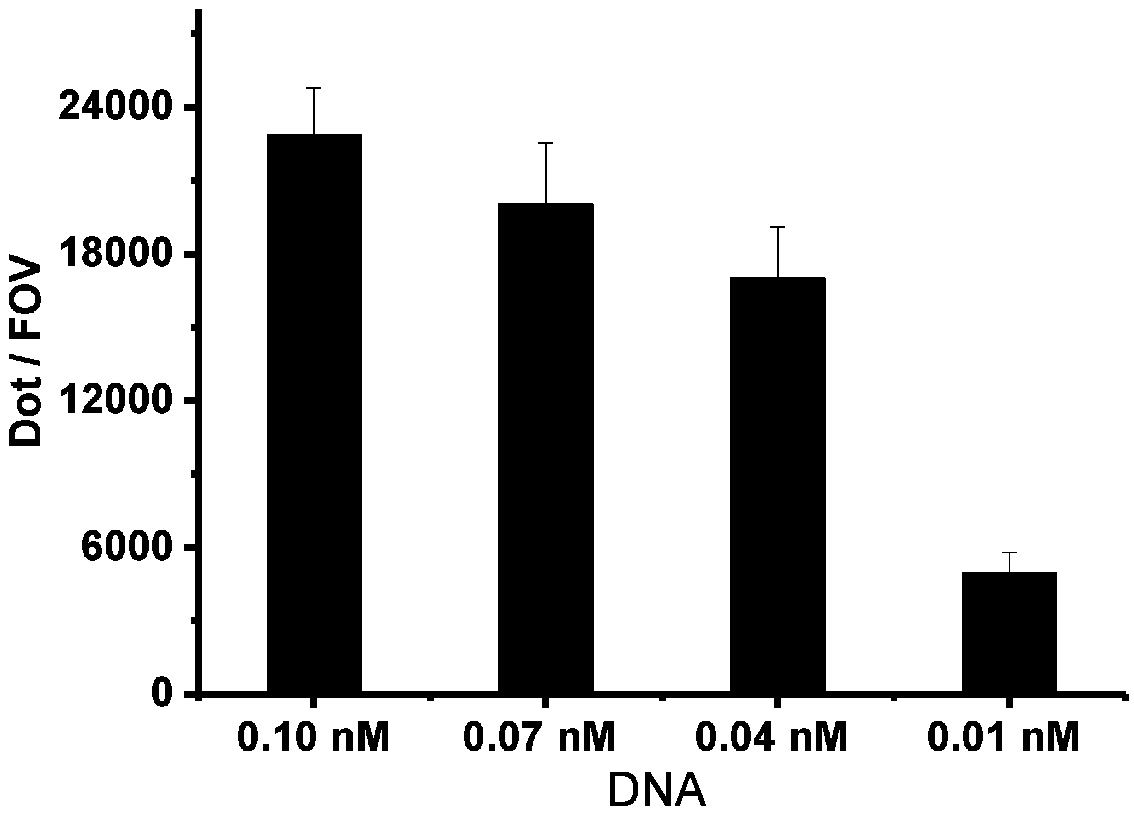
PendingUS20200277654A1Detection procedure simpleReduce material costsNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementA-DNATarget gene
Disclosed are methods for detecting DNA mutations of target genes in a DNA sample by combining single-molecule clonal amplification and mutant primer specific extension detection. In the method, thousands and millions of DNA molecules are locally amplified to form immobilized DNA clusters of identical sequences. Mutation specific primers are used to anneal to the mutant sequences in the DNA clusters and are extended by DNA polymerase to make labeled DNA strands. The labeled DNA clusters are detected to identify the DNA clusters of mutant sequences. This method enables detection of single mutation molecule and direct enumeration of mutation molecules in the sample. Once generated from a DNA sample, the immobilized DNA clusters can be reused many times for detection of different mutations or sequences of interest. Methods for determining differential gene expression and chromosome copy number variation are also disclosed.
Owner:WANG YAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com