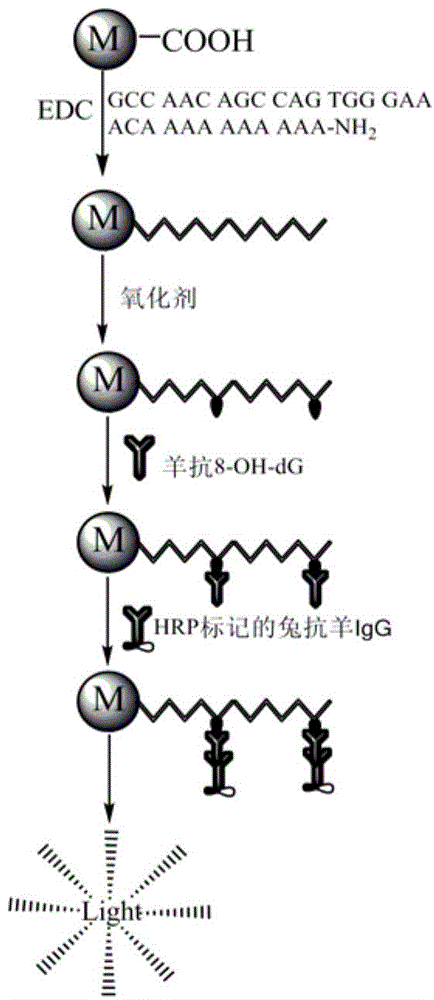
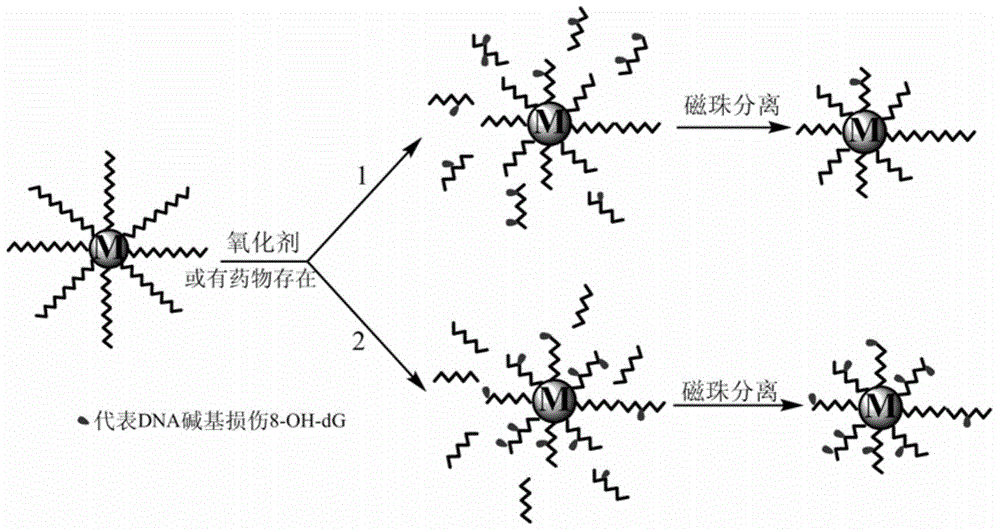
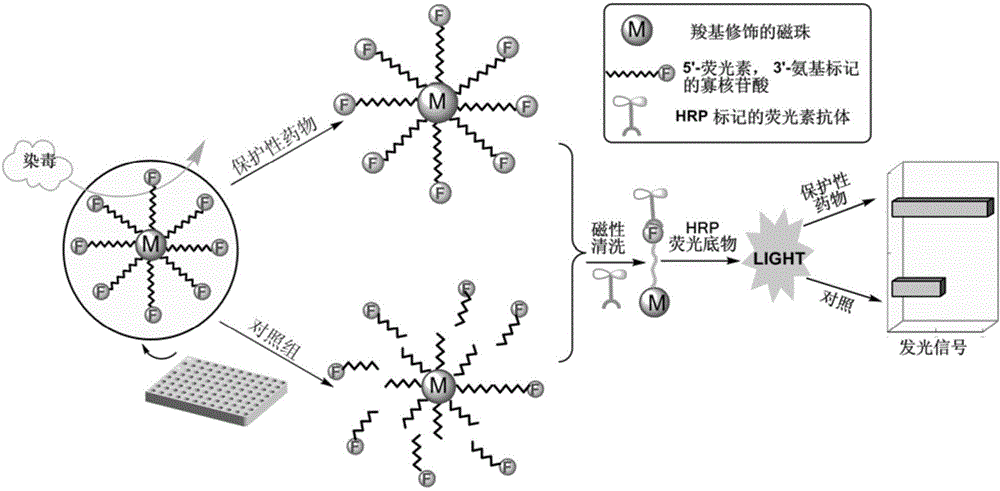
Method for efficiently screening out DNA chain scission injury protective drugs
A protective and chain-breaking technology, applied in the field of pharmacy, can solve the problems of large signal difference, chain-like structure breakage, false positives, etc., and achieve the effect of simplifying the screening process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1 Detection of DNA chain scission damage caused by Fenton reagent
[0037] 1.1 Reagents and instruments
[0038] All reagents were of analytical grade. N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N'-ethyl-carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) was purchased from Sigma; HRP-labeled rabbit anti-FAM was from Invitrogen.Molecular probe; HRP CL kit Purchased from Milipore Company; Plus carboxylated magnetic microspheres (MB, 1.5 μm, 20 mg / mL) were purchased from Polyscience; BSA was purchased from Huamei Biotechnology Company; DNA (5′-FAM-AAAGGGGAAA-NH2-3′) was purchased from Shanghai Sangon Biotechnology Ltd; Fenton's reagent: (NH 4 ) 2 Fe(SO 4 ) 2 Prepare a fresh aqueous solution stock solution with EDTA at a molar ratio of 1:3 every day, dilute before use, and use 30% H2 o 2 The solution is stored in the refrigerator in the refrigerated layer, protected from light, and diluted before use.
[0039] The ultrapure water used in the test was prepared by a Milli-XQ instrument, and al...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The selection of embodiment 2 DNA charging amount
[0049] The amount of DNA input determines the density of the DNA immobilized on the magnetic microspheres and the probability of subsequent chain scission reactions. Therefore, it is necessary to investigate the influence of the amount of DNA input on the detection signal in order to select the appropriate amount of DNA input while saving costs. figure 2 The detection signal of negative control and positive control is shown by the amount of DNA input
[0050] Intensity of influence. The experimental conditions are: Fe 2+ The concentration is 0.9Mm, H 2 o 2 54mM, HRP-labeled rabbit anti-
[0051] The FAM antibody was diluted 1 / 10000. Such as figure 2 It can be seen that along with the gradual increase of the amount of DNA feeding, the signals of the negative control and the positive control are all gradually enhanced and tend to be saturated, and the degree of DNA chain scission represented by the difference bet...
Embodiment 3
[0052] The influence of the concentration of embodiment 3 Fenton's reagents on the intensity of chemiluminescence
[0053] Fenton's reagent that can generate hydroxyl radicals (ie Fe 2+ Mediated H 2 o 2 Reaction :) It is a relatively classic poisoning system that can cause DNA strand breakage damage. The Fenton reaction system that the present invention adopts: (NH 4 ) 2 Fe(SO 4 ) 2 / EDTA / H 2 o 2 The molar ratio is 1:3:60. Of which (NH 4 ) 2 Fe(SO 4 ) 2 Configured with EDTA, it can significantly reduce Fe 2+ The rate of autoxidation in solution increases with H 2 o 2 Reaction efficiency of post-exposure DNA infection step. image 3 The effect of Fenton's reagent concentration on the chemiluminescent signal produced after exposure is shown. As the concentration of Fenton's reagent increases, the number of broken chains of immobilized DNA gradually increases, resulting in a gradual decrease in the signal detected by chemiluminescence enzyme-linked immunoassay of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com