Patents
Literature
81 results about "Single mutation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Single gene Mutations. (a) Mutations are random changes in the genome that can result in no protein or an altered protein being expressed. (b) Single gene mutations involve the alteration of a DNA nucleotide sequence as a result of the substitution, insertion or deletion of nucleotides.
Stabilized interleukin 2
InactiveUS6689353B1Reduce ionic strengthFast rebuildPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsGlycineSucrose
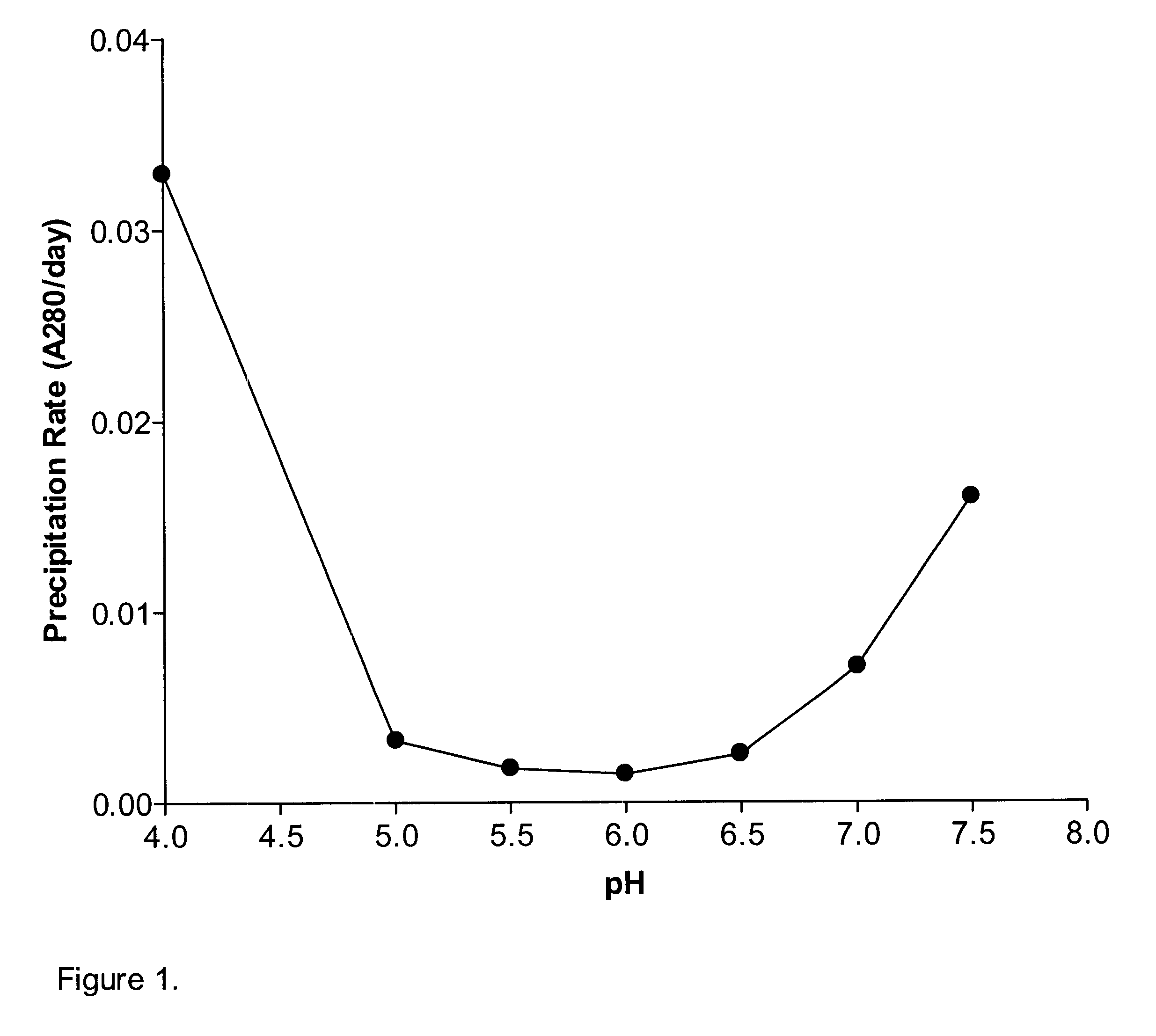
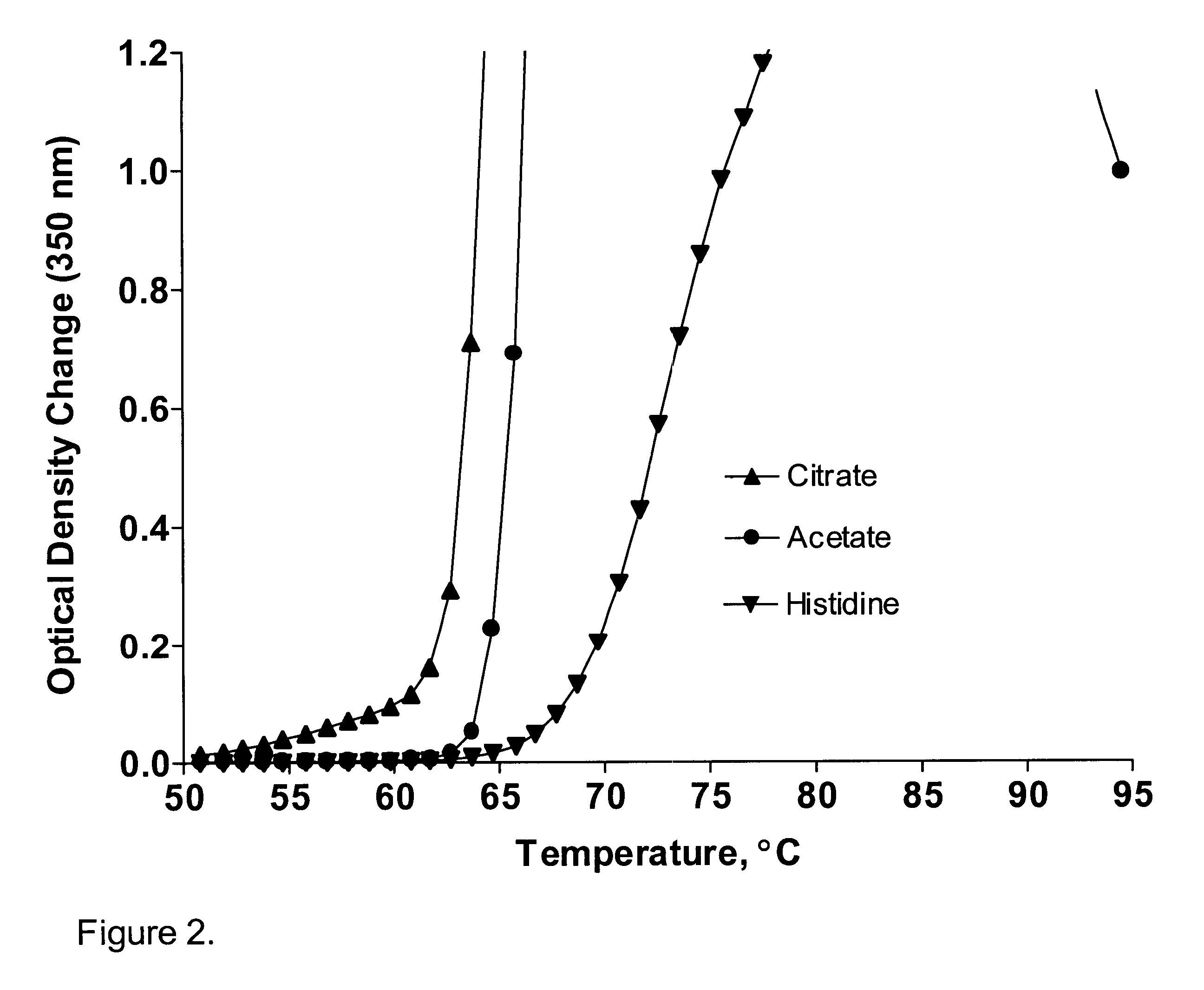
A stable pharmaceutical preparation comprising Human interleukin-2 or a variant thereof and a stabilizing amount of histidine. A preferred formulation includes glycine and sucrose and a variant of IL-2 having a single mutation, N88R. The preferred formulation is in lyophilized form which, on reconstitution with an aqueous diluent, results in a solution having a pH ranging from about 5.0 to 6.5.
Owner:AICURIS GMBH & CO KG
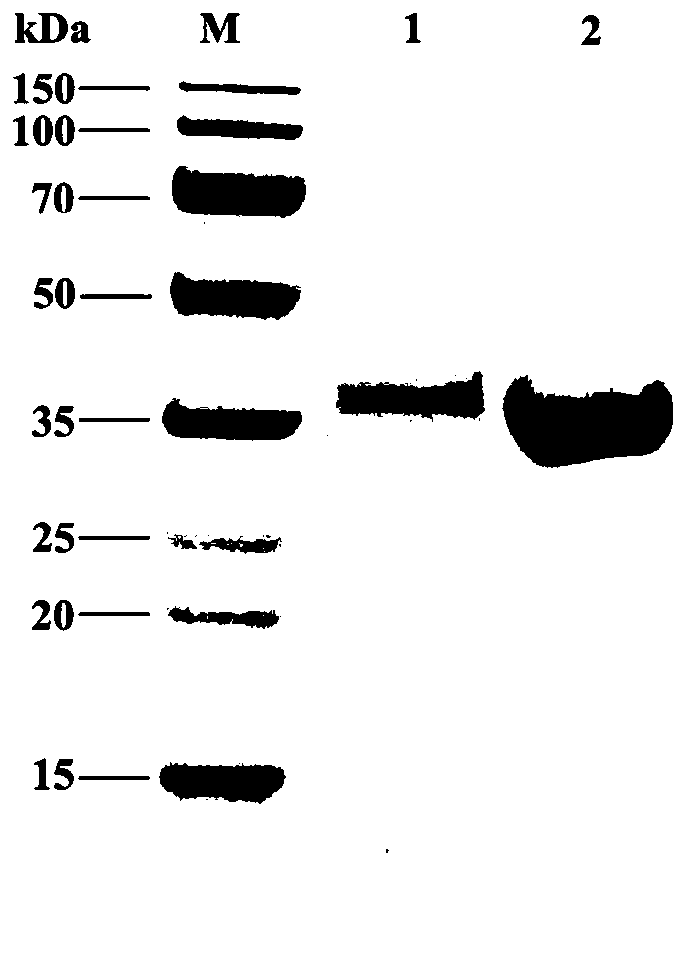
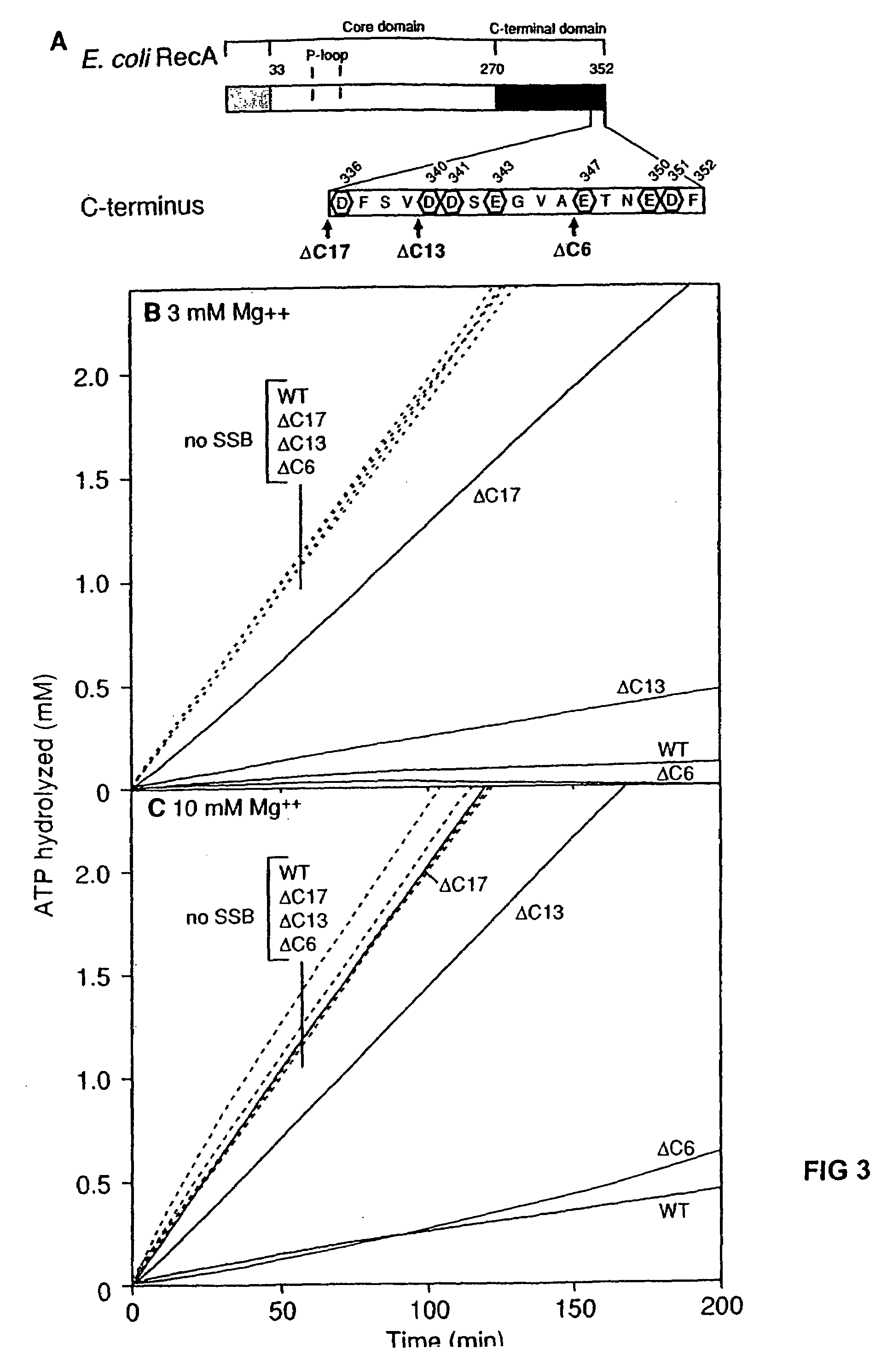
RecA mutants
InactiveUS7176007B2Improve concentrationEliminate requirementsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMutated proteinDouble mutation
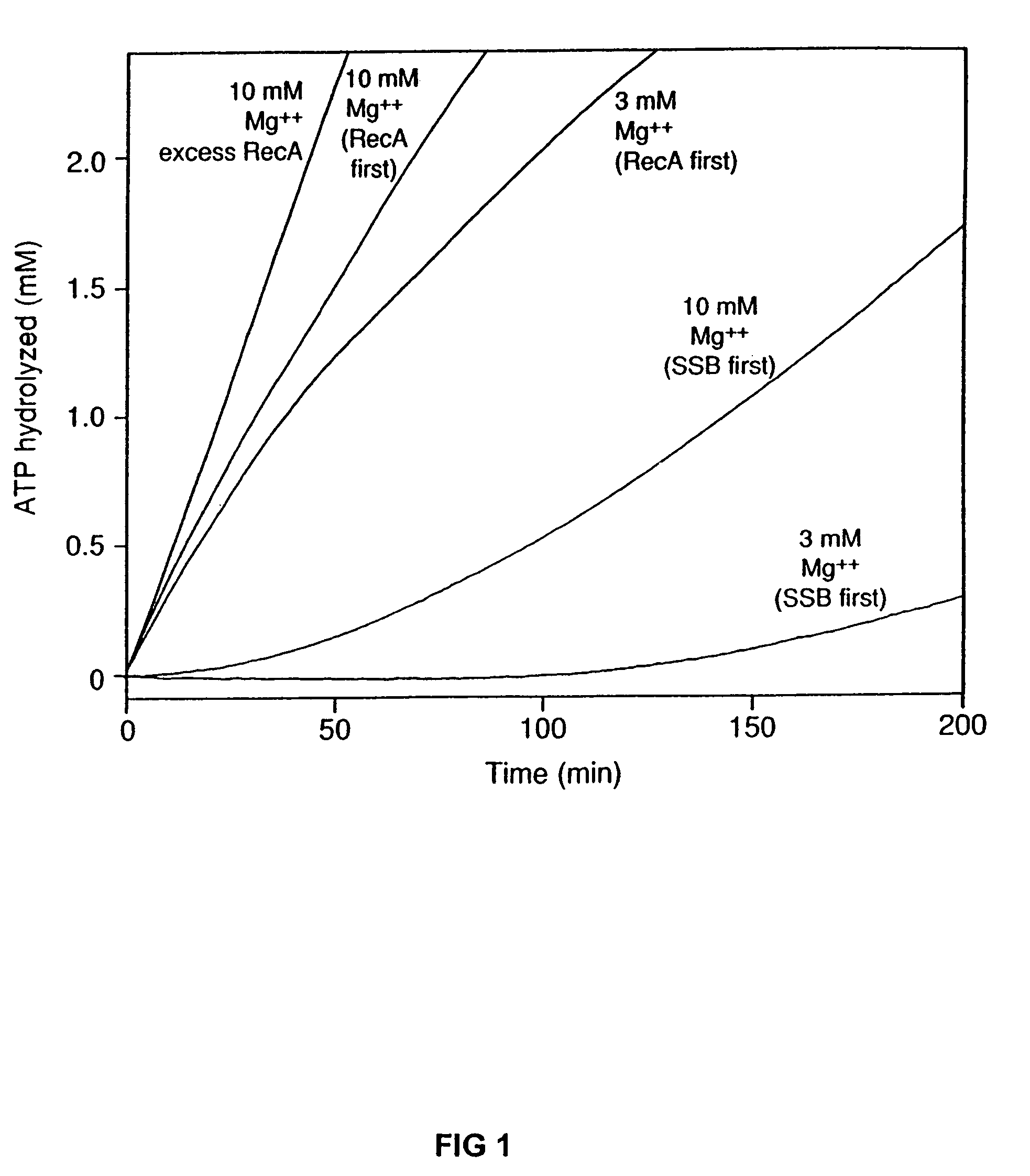
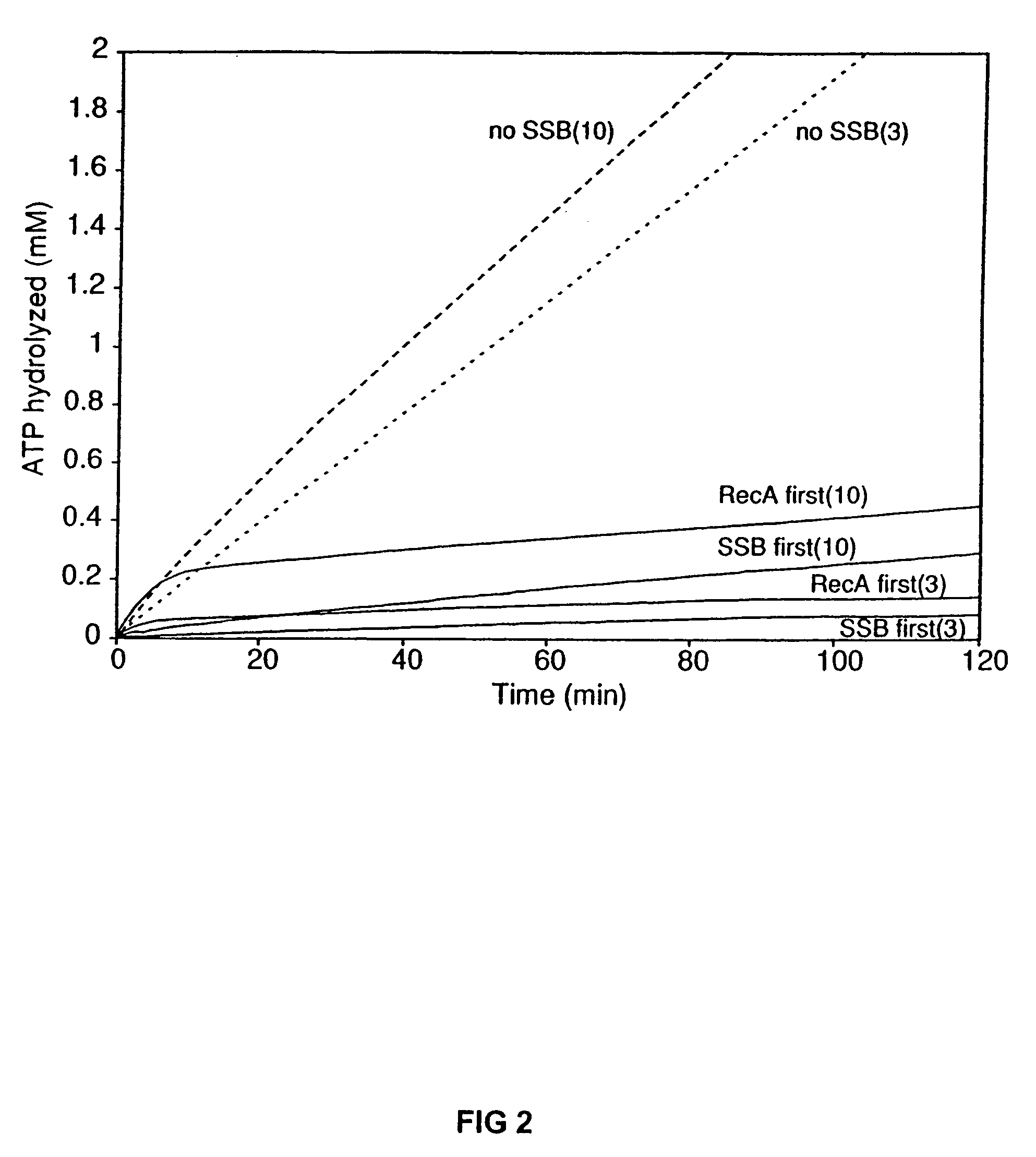
The present invention provides RecA mutant proteins, having either a single mutation or a double mutation. The RecA mutant proteins are highly proficient in both SSB displacement and steady state binding of DNA in the presence or absence of SSB as compared to the wild-type protein. The single RecA mutant, RecAΔC17, has 17 amino acid residues removed from the carboxyl terminus. The double mutant RecA, RecAΔC17 / E38K, combines the 17 amino acid residue C-terminal deletion of RecAΔC17, with a single amino acid change from Glutamate to Lysine at position 38. These RecA mutant proteins are pH sensitive allowing control over formation of products. Hence, methods of using the novel RecA mutants and kits having the RecA mutants as components thereof are also contemplated by the present invention.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Nicotinamide ribokinase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN110373398AMild reaction conditionsStable energy cycle systemTransferasesFermentationSingle mutationNicotinamide mononucleotide
Owner:JIANGSU CHENGXIN PHARMA
D-amino acid oxidase mutant and application thereof
The invention discloses a D-amino acid oxidase mutant and application thereof. The mutant is obtained by carrying out single mutagenesis or multiple mutagenesis on a 52nd site, a 54th site, a 58th site, a 213rd site and a 335th site of amino acid with an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1, wherein glycine at the 52nd site is mutated into leucine, asparagine at the 54th site is mutated into valine, phenylalanine at the 58th site is mutated into glutamine, methionine at the 213rd site is mutated into serine, and serine at the 335th site is mutated into glycine. According to the D-amino acid oxidase mutant and the application thereof, a D-amino acid oxidase gene with an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.2 is mutated by utilizing a site-saturation mutagenesis technology, so thatthe enzyme activity and the product conversion rate are far higher than those of a wild type, and therefore the product yield in a 4-(hydroxymethylphosphoryl)-2-carbonyl-butanoic acid production process is increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
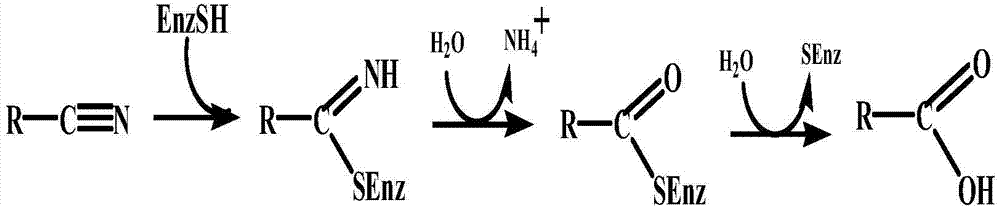
Nitrilase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN104774825AIncreased specific enzyme activityBacteriaHydrolasesDouble mutationSingle mutation
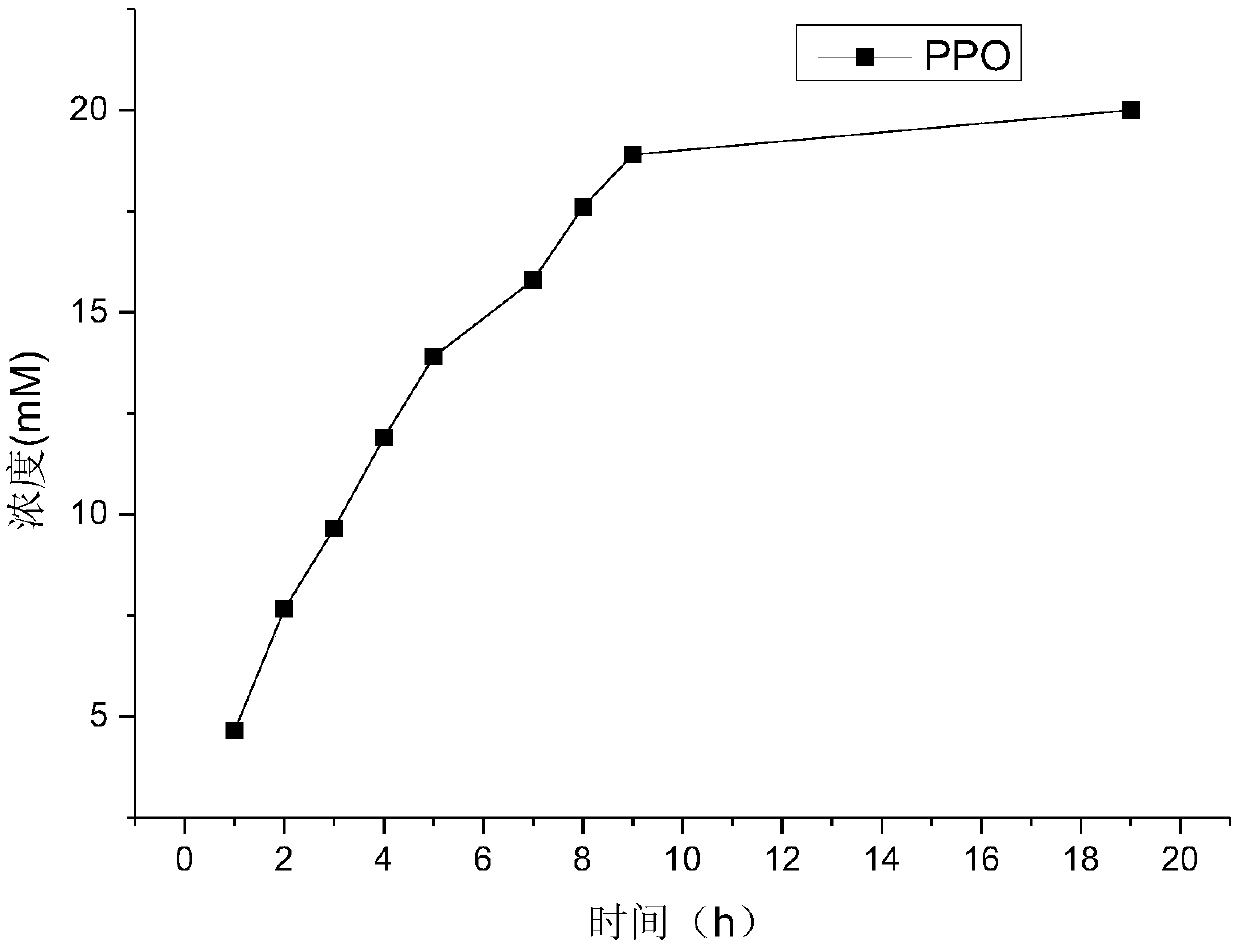
The invention discloses a nitrilase mutant and its application in R-o-chloromandelic acid synthesis. The mutant is obtained by single mutation or double mutation of the 132nd threonine or 189th phenylalanine on the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2. Compared with non-mutant nitrilase, the enzyme activity is increased by 3.70 times and reaches 1.08U / mg, and the enantioselectivity is up to 99%. Also, the result shows that in a two-phase system (with ratio of toluene to water being 2:8) the nitrilase mutant can catalyze 300mM o-chloromandelonitrile, and the yield is 90.8%. Through fed batch of the substrate, a maximum of 500mM o-chloromandelonitrile can be catalyzed, the yield is 90%, and the enantioselectivity is greater than 99%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Omega-transaminase mutant and application thereof in preparation of sitagliptin intermediate
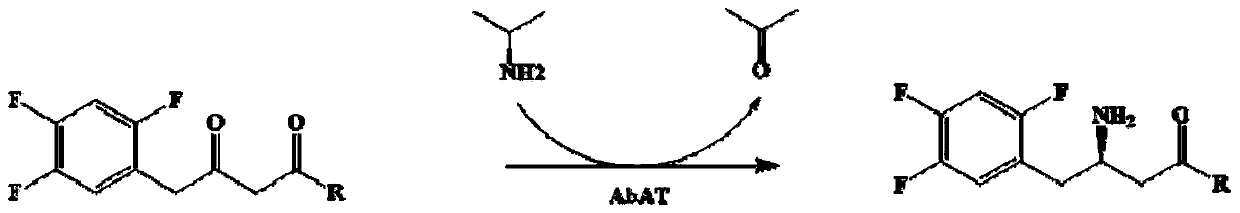
The invention discloses an omega-transaminase mutant and application thereof in preparation of sitagliptin intermediate. The omega-transaminase mutant is obtained by performing single mutation on the56 position or the 134 position of an amino acid sequence as shown in a SEQ ID No.2; the 56 phenylalanine is substituted by valine, histidine or tyrosine; and the 134 threonine is substituted by glycine. The omega-transaminase mutant has relatively high enzyme activity which is higher than 300U / g and is at least 2.7 times that of a wild type since the omega-transaminase mutant is subjected to site-specific mutagenesis by acquiring certain sites possibly influencing the catalytic activity of the omega-transaminase mutant through molecular docking, homologous modeling and other modes, can be used for efficiently catalyzing precursor ketone 1-piperidine-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)-1,3-dibutanone of the sitagliptin intermediate to synthesize the sitagliptin intermediate (R)-3-amino-1-piperidine-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)-1-butanone, and has a conversion rate of 85 percent.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +2
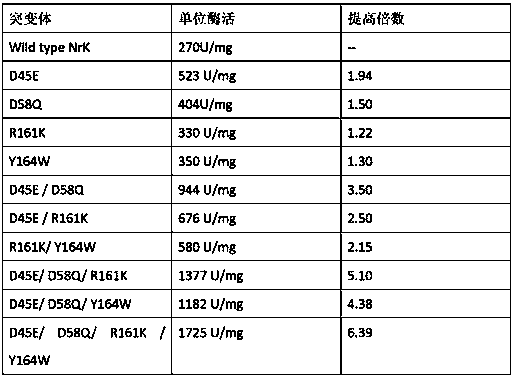
Glufosinate dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN109750009AIncreased specific enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGlycineSpecific enzyme
The invention discloses a glufosinate dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof. The glufosinate dehydrogenase mutant is obtained by single mutation or multiple mutation of the 90th, 91st and 376thamino acid shown in SEQ ID No.2; the 90th lysine is mutated to serine; the 91th glycine is mutated to serine or valine; the 376th serine is mutated into arginine. The mutant utilizes a site-directedsaturation mutation technique for mutation of the glufosinate dehydrogenase gene shown in SEQ ID No.1, and finds that the 90th, 91st, and 376th positions are key sites affecting the enzyme activity, the obtained specific enzyme activity is much higher than the mutant of the parental glufosinate dehydrogenase, the specific enzyme activity of the mutant lvPDH-K90S-G91P-S376R is 8.4 times higher thanthat of the parental glufosinate dehydrogenase, and the mutant has industrial application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN110373397AMild reaction conditionsStable energy cycle systemMicroorganism based processesFermentationNicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferaseSingle mutation
The invention provides a nicotinamide ribosyltransferase mutant and application thereof. Compared with an amino acid sequence SEQID NO. 2, the difference of the amino acid sequence of the mutant is that the R189th, S232th and R302th sites in the amino acid sequence SEQID NO. 2 are subjected to single mutation or in-pair combined mutation or three combined mutation. Novel nicotinamide ribosyltransferase mutant enzyme is used for synthesis and preparation of beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide. The constructed nicotinamide ribosyltransferase mutant enzyme has the advantages that the enzyme cost islow, the transformation time is short, and the process operation is simple, and has a broad large-scale industrial application prospect.
Owner:KINGDOMWAY BIOTECH (JIANGSU) CO LTD +1
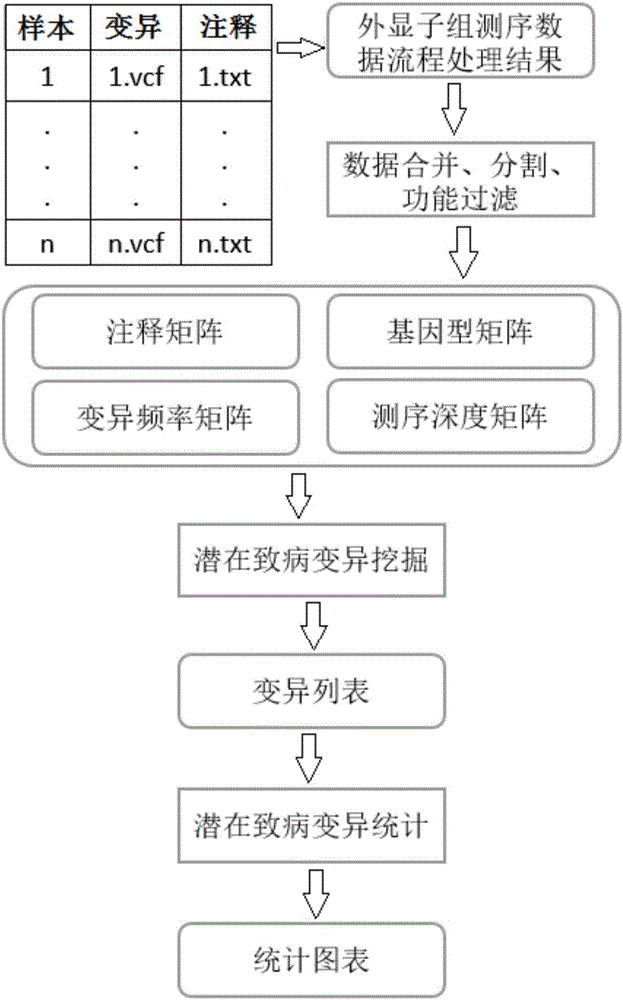
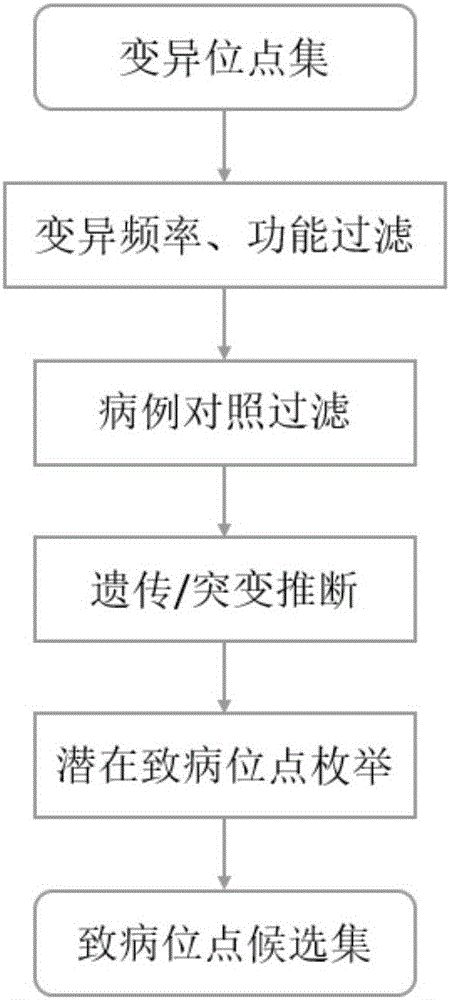
Exome potential pathogenic mutation detection method based on family line
InactiveCN105925685ASolve the problem of mining potential pathogenic variantsImprove heterogeneityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsFiltrationSingle mutation
The invention provides an exome potential pathogenic mutation detection method based on a family line. The detection method comprises the following steps: 1) reading a result file of an exome sequencing data processing flow, and conducting function filtering; 2) reading the file obtained in the last step, extracting mutations in all samples, calculating a union set, and then combining all samples, so that a matrix is constituted; 3) extracting mutation information in the matrix obtained in the last step, enumerating and assessing pathogenicity of single mutation and pathogenicity of combined dual-site mutation, so that a potential pathogenic mutation list is obtained; and 4) in accordance with the list obtained in the last step, calculating the appearance situations of sites in various samples and target genes. According to the method disclosed by the invention, data integration and basic filtration are completed by taking an output result of the common exome sequencing processing flow as an input condition; by virtue of a special mutation screening algorithm, a candidate set of the potential pathogenic mutations is provided; and the method focuses on solving a problem on potential pathogenic mutation mining of sequencing data with high heterogeneity, high mutation rate and high noise.
Owner:WANKANGYUAN TIANJIN GENE TECH CO LTD
Thermal stability improved mutant enzyme of D-psicose 3-epimerase and application thereof
InactiveCN103849613AImprove thermal stabilityMicroorganism based processesIsomerasesIsomerasePsicose
The invention provides thermal stability improved mutant enzyme of D-psicose 3-epimerase and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of enzyme genetic engineering. The mutant enzyme is characterized in that D-psicose 3-epimerase (DPE enzyme for short) sourced from clostridium ((i) Clostridium bolteae ( / i)) ATCC BAA-613 is used as a parent, and glycine Gly at the position 109 is replaced by proline Pro through the gene mutagenesis technique so as to obtain single mutant enzyme G109P; the stability of the mutant enzyme is improved; high industrial application value is brought.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
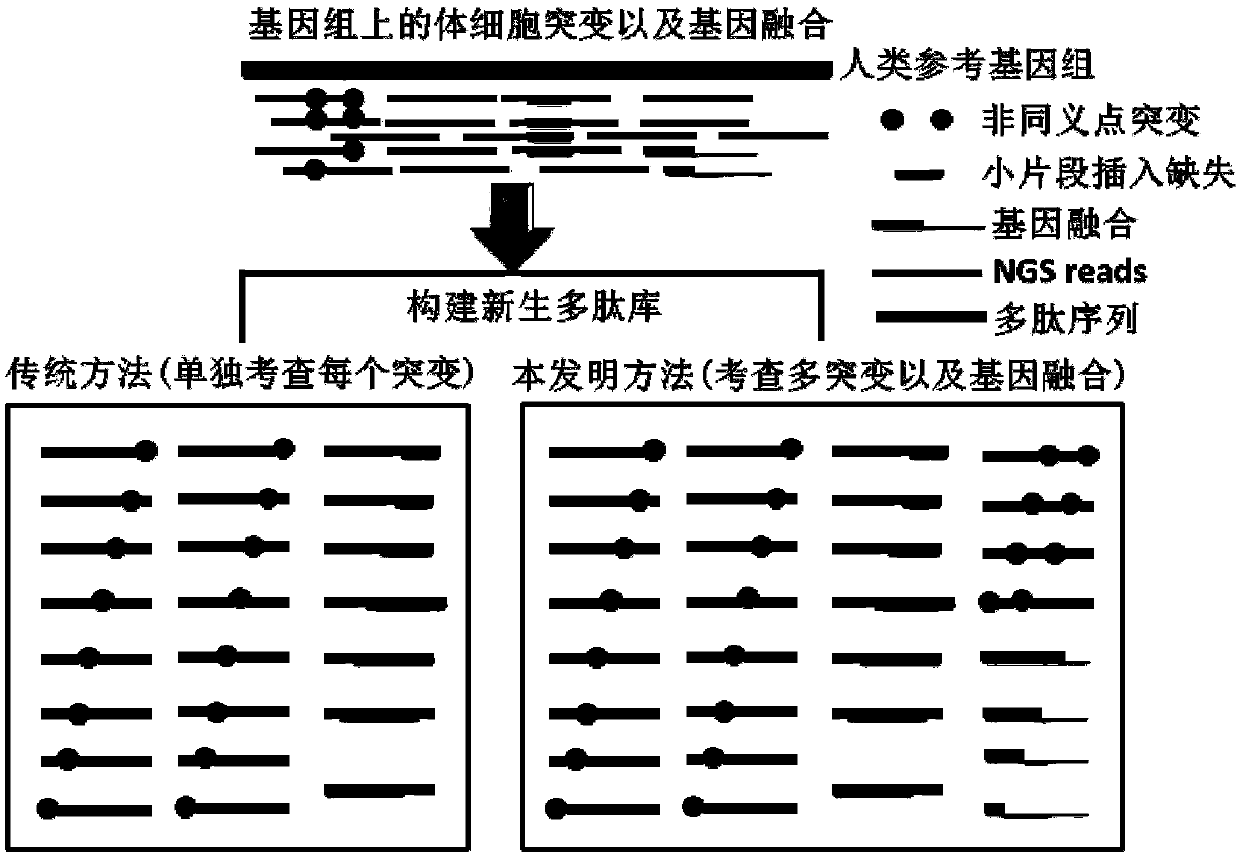
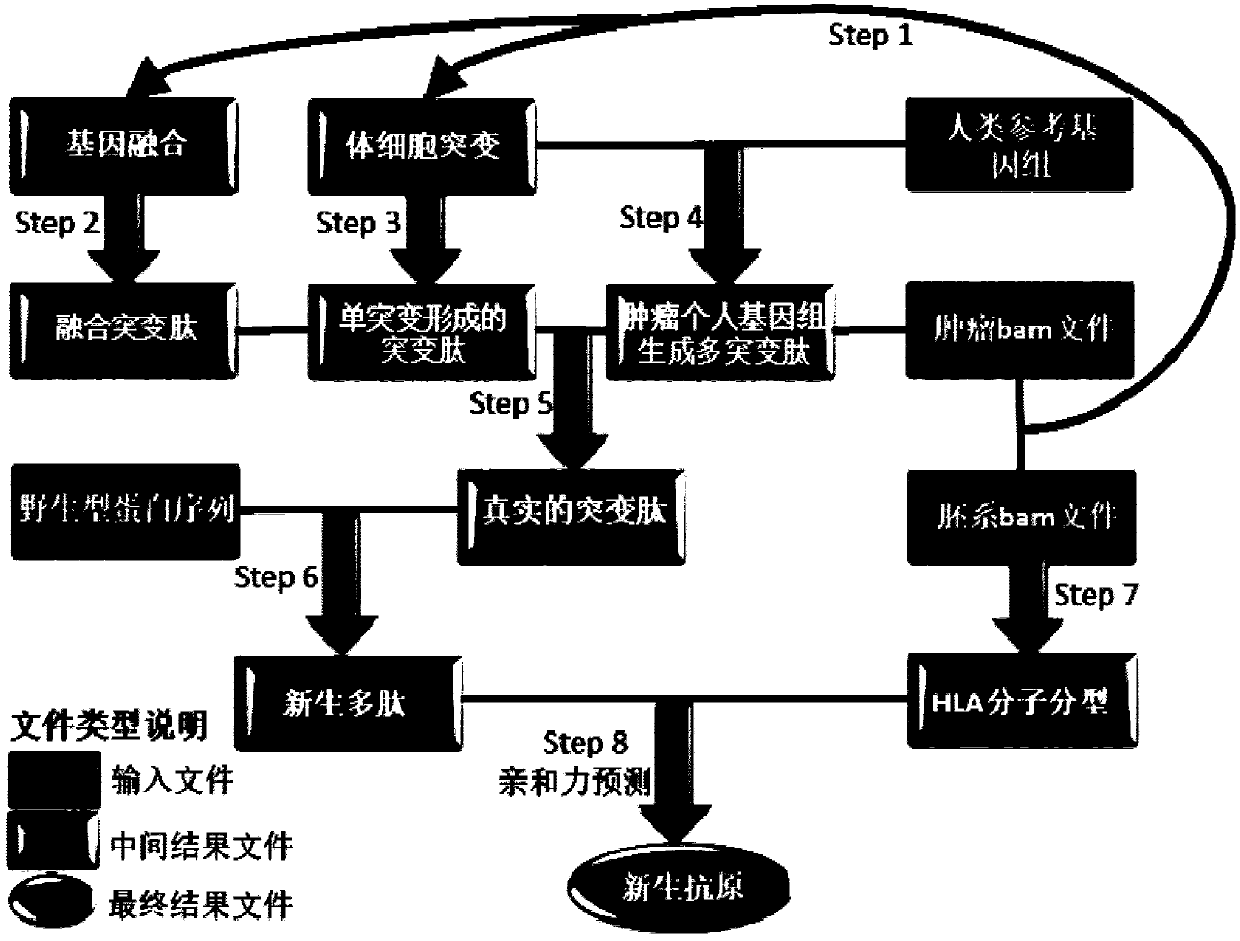
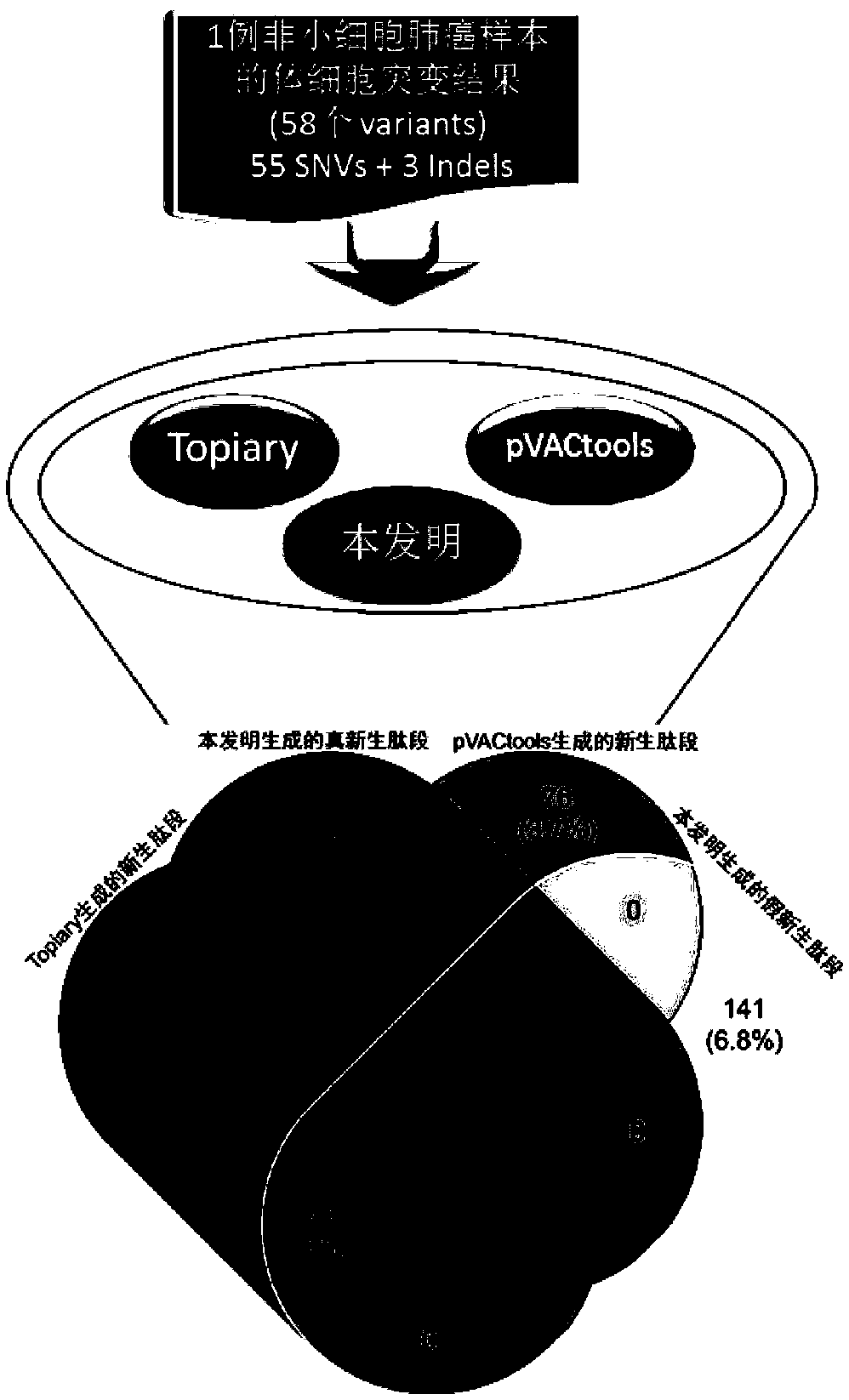
Method and device for predicting tumor newly-born antigen and storage medium
ActiveCN109584960AComprehensive forecasting methodAccurate responseProteomicsGenomicsBiomarker (petroleum)Wilms' tumor
The invention relates to a method for predicting a tumor newly-born antigen. The method comprises the steps that 1, according to a tumor-embryonal system contrast sample, somatic mutation and gene fusion detection are conducted; 2, for each pair of fusion genes, fusion mutation peptide and corresponding wild peptide are generated; 3, based on each somatic mutation, mutation peptide and corresponding wild peptide are generated; 4, a specific individual genome of a tumor sample is established, and mutation peptide containing multiple mutations is generated; 5, the true and false of mutation peptide of single-mutation and multi-mutation are judged; 6, mutation peptide completely identical to wild protein in other position sequence is removed; 7, HLA molecular subtyping detection is conducted,the appetency of newly-born peptide and HLA molecules is predicted, and newly-born peptide with high appetency is used as a candidate tumor newly-born antigen. The invention further provides a corresponding device and a computer storage medium. By adopting the method and device and the storage medium, the biomarker assessment can be effectively responded to through tumor treatment, and the precise candidate peptide fragment is provided for design of a tumor vaccine.
Owner:XUKANG MEDICAL SCI & TECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD
High-activity glutathion peroxidase GPX 1 mutant and its preparation method
ActiveCN103320406AIncrease vitalityImprove protectionOxidoreductasesVector-based foreign material introductionGenes mutationNatural source
A high-activity glutathion peroxidase GPX 1 mutant and its preparation method belong to the field of biotechnology. A mutant gene is obtained by a gene mutation or synthesis method, and then a catalytic group SeCys of GPX is introduced into a substrate binding part of the mutant through an auxotroph prokaryotic expression system or an auxotroph and SPP low-temperature combined expression system so as to endow the mutant with high GPX activity; or a target gene, along with a SeCys insertion sequence, is firstly assembled onto a secreting type mammalia cellular expression vector, and then a binding protein 2 of the SeCys insertion sequence is assembled onto an intracellular mammalia cellular expression vector, contransfection of the same lactation cell strain is carried out by the two vectors, and GPX is synthesized by the lactation cell in the presence of sodium selenite. The method provided by the invention is simple. The mutant provided by the invention has advantages of high activity, high yield and good stability. Yield decreasing and inactivation caused by renaturation of an inclusion body are avoided. Thus, natural GPX source limitation and unstable properties are solved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Mutant of cyclodextrin glucosyl transferase having highly alpha-cyclodextrin yielding property and mutation method
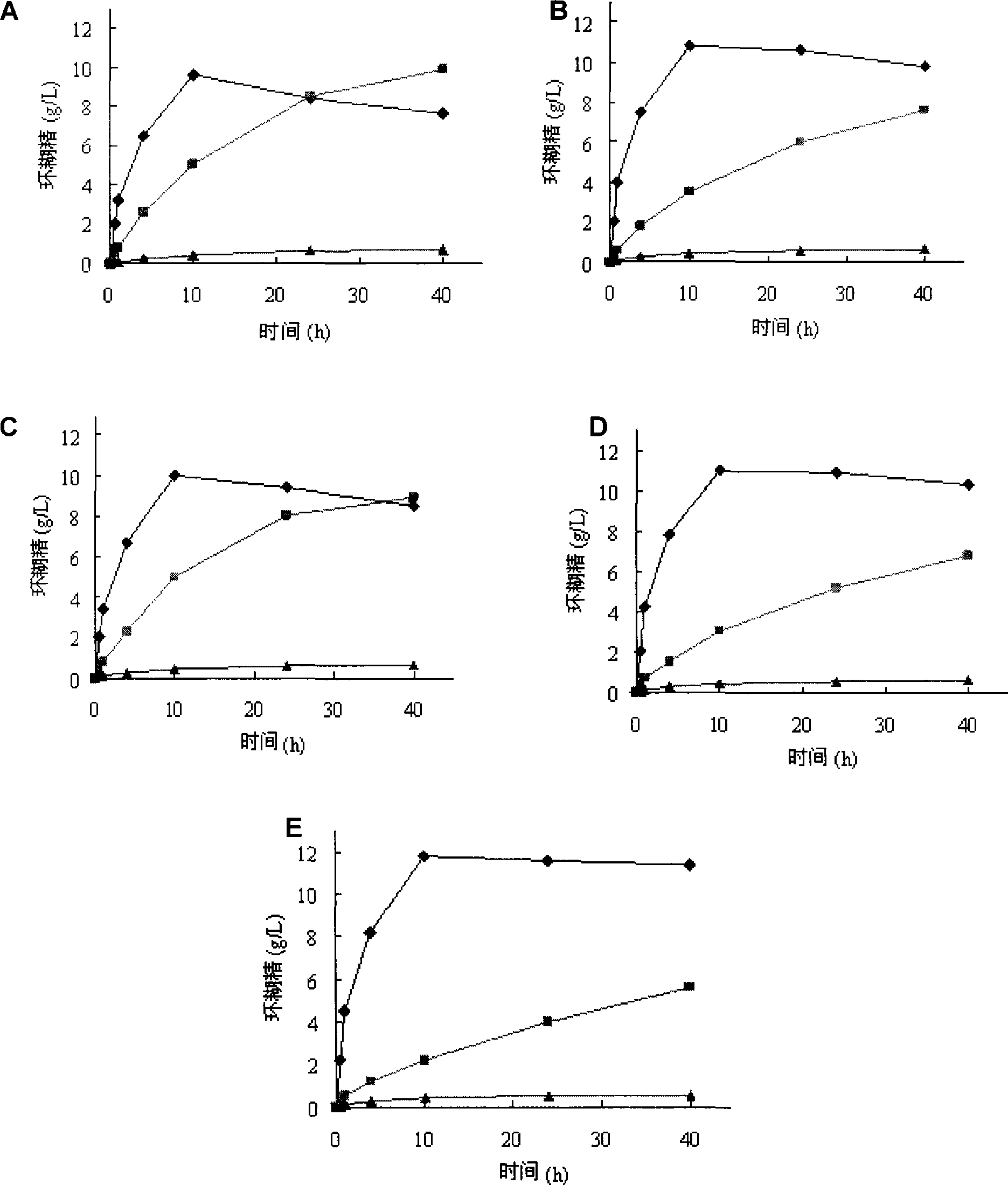
InactiveCN101503681AEase of industrial productionStrong specificityTransferasesMicroorganism based processesWild typeGene engineering
The invention relates to a mutant of a cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase with the capability of highly yielding alpha-cyclodextrin and a mutation method, which belong to the fields of gene engineering and enzyme engineering. The invention improves the specificity of products of the cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase (CGT enzyme for short), provides a mutant proposal for improving the capability of CGT enzyme from Peanibacillus macerans JFB05-01 (CCTCC NO: M 208063) for producing the alpha-cyclodextrin, and substitutes Asp on the 372 position of the CGT enzyme for Lys, and Tyr on the 89 position as Asp and Arg to respectively obtain single mutant enzyme D372K, Y89D and Y89R; the alpha-cyclodextrin production capacity of the obtained mutant enzyme is improved compared with wild type CGT enzymes; genetic fragments of the CGT enzyme with Lys 372 are substituted by corresponding genetic fragments of Y89R so as to obtain double mutant enzyme D372K / Y89R; and the yield of the alpha-cyclodextrin of the ouble mutant enzyme D372K / Y89R is improved by 1.5 times compared with the wild type CGT enzyme, while the yield of the beta-cyclodextrin is reduced by 57 percent. The mutants are more favorable for industrial production of the beta-cyclodextrin than the wild type CGT enzymes.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Genetic engineering strain high in yield of phenazine-1-formamide and construction method thereof
PendingCN106635937AIncrease productionEffective biological controlBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPseudomonas tolaasiiSingle mutation
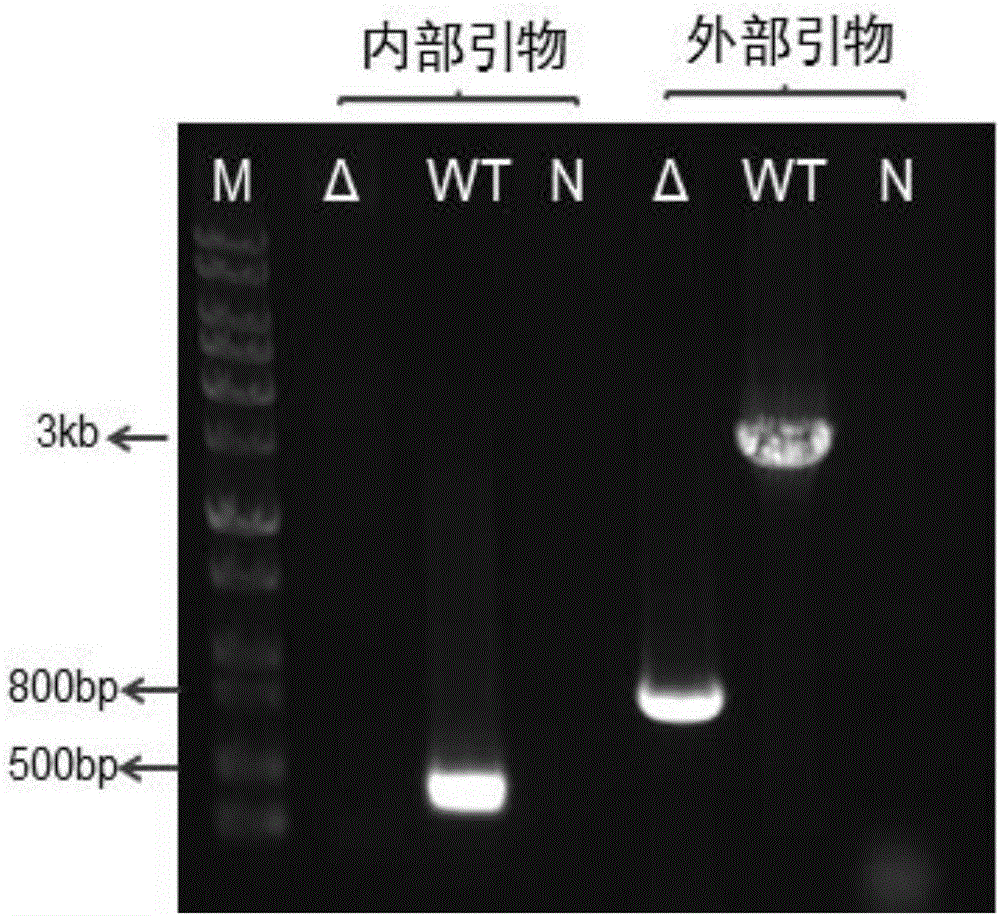
The invention discloses a genetic engineering strain high in yield of phenazine-1-formamide and a construction method thereof. The genetic engineering strain is a genetic engineering strain obtained by knocking out one or two of lon gene and parS gene of HT66CCTCC NO: M 2013467 genome of Pseudomonas chlororaphis, or a genetic engineering strain obtained by knocking out one or two of lon gene and parS gene of HT66CCTCC NO: M 2013467 rpeA and psrA single mutation strain or amphimutation strain genome of Pseudomonas chlororaphis, wherein single mutation strain is HT66 Delta rpeA and HT66 Delta psrA, and amphimutation strain is HT66 Delta rpeA Delta psrA. Compared with the prior art, the genetic engineering strain has the advantages that after lon and parS genes are delected from the genome of Pseudomonas chlororaphis, fermentation yield of phenazine-1-formamide is up to 2425mg / L, and the genetic engineering strain can be used for industrial production and agricultural application of phenazine-1-formamide.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Amylosucrase mutant and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109402081AIncrease hydrolysis rateGenetic engineeringFermentationGenetic engineeringChemistry
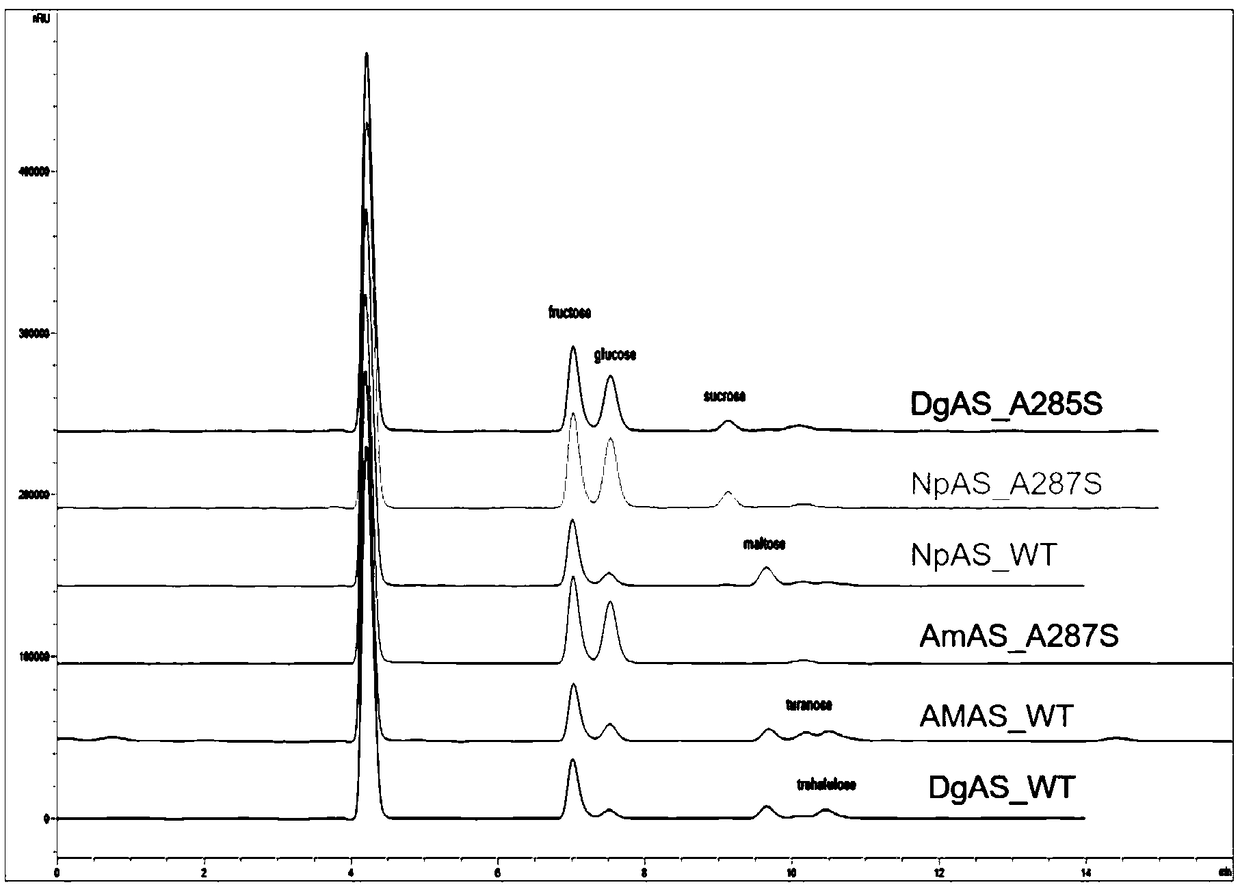
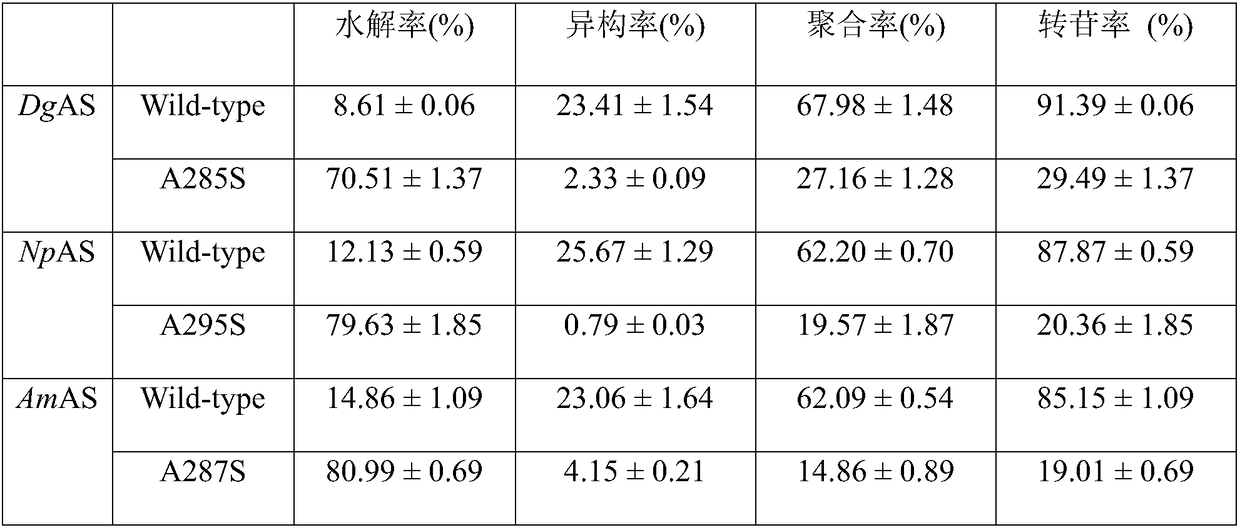
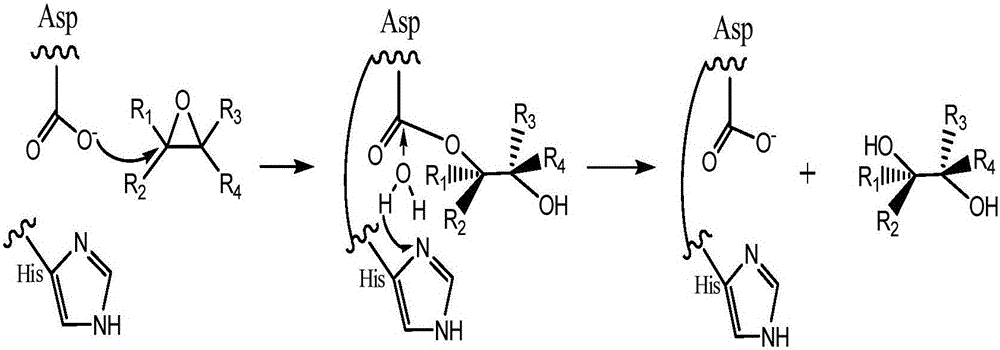
The invention discloses amylosucrase and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. Site-directed mutation is performed on alanine residue 285 of amylosucrase from Deinococcusgeothermalis, site-directed mutation is performed on alanine residue 287 of amylosucrase from Alteromonas macleodii, and site-directed mutation is performed on alanine residue 295 of amylosucrase from Neisseria polysaccharea; a single mutant enzyme acquired has higher hydrolytic activity than wild amylosucrase. The amylosucrase herein is helpful for the research on glucoside hydrolase glucoside conversion and hydrolytic mechanisms, and is also applicable to industrial production of polysaccharides from glucoside hydrolase.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Epoxide hydrolase mutant and application thereof
InactiveCN105734028AImprove selectivity E valueIncrease enzyme activityHydrolasesFermentationDouble mutationHalf-life
The invention discloses an epoxide hydrolase mutant and its application. The mutant is the 108th isoleucine or the 131st aspartic acid or the 247th aspartic acid in the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2. Threonine is obtained by carrying out single mutation, double mutation or triple mutation; compared with the unmutated epoxide hydrolase mutant, the enzymatic activity, stereoselectivity and stability of the epoxide hydrolase mutant according to the present invention Significantly improved; Among them, the specific enzyme activity of the mutant was improved by 5.4 times compared with the original enzyme, reaching 315.2U / mg, the half-life was improved by 12.8 times, the enantioselective E value was improved by 2.1 times, and the epoxide hydrolase mutant was In the two-phase system, 800mM racemic epichlorohydrin can be catalytically resolved, and the yield of R-epichlorohydrin reaches more than 90% of the theoretical yield, and the enantioselectivity is greater than 99%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Recombinant aldo-keto reductase mutant and application thereof
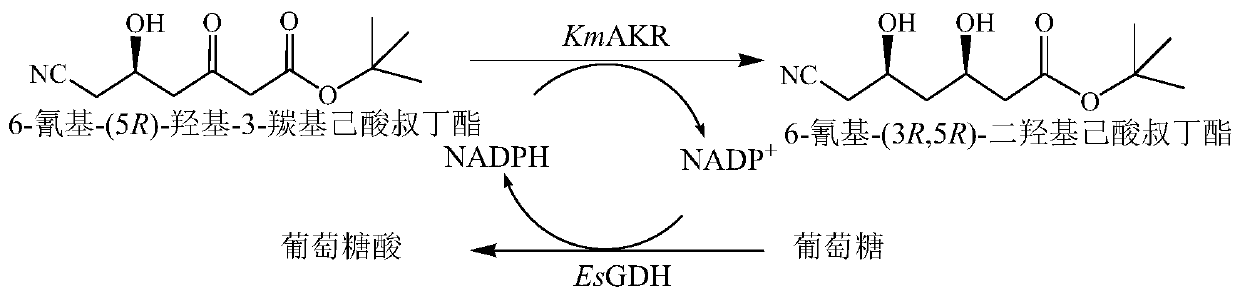
The invention discloses a recombinant aldo-keto reductase mutant and an application thereof in asymmetric reduction of 6-cyano-(5R)-hydroxy-3-tertiary butyl carbonyl hexanoate to prepare 6-cyano-(3R,5R)-tertiary butyl dihydroxycaproate. The recombinant aldo-keto reductase mutant is obtained by single or multiple mutations of 29th and 28th amino acids shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The specific enzyme activity of the prepared aldo-keto reductase mutant KmAKR-Y296W / W297H / K29H / Y28A is 1.15 times higher than that of a control group KmAKR-Y296W / W297, and the feeding amount of the maximum substrate 6-cyano-(5R)-hydroxy-3-tertiary butyl carbonyl hexanoate is up to 200 g / L, the conversion rate of the substrate is more than 99%, and the dep value of the product is remained at 99.5% or more. The concentration of the product is 549 mM and the space-time yield reaches 670.5 g / L d.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Preparation and application of homologous recombination repair detection reference substance
PendingCN112210553AStable sourceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSingle mutationGenetic Materials
The invention aims to provide a preparation method of a homologous recombination repair detection reference substance, which comprises the following steps: carrying out gene editing on a tumor cell line, modifying 117 sites of 25 homologous recombination repair related genes to obtain embryonic system mutations of the homologous recombination repair related genes, and screening cells meeting the requirements through detection of a spectrophotometer and ddPCR (droplet digital PCR) to serve as the homologous recombination repair gene detection reference substance. The reference substance is derived from cytogenetic materials obtained after gene editing, is stable in source and has reproducible and stable performance; and in addition, the reference substance comprises a single mutation site and a combined mutation site, so that somatic mutation and embryonic system mutation can be detected, and the HRR detection range is comprehensively covered.
Owner:菁良科技(深圳)有限公司
Preparation method of gene mutation and fusion gene positive reference
The invention aims to provides a preparation method of a gene mutation and fusion gene positive reference. The preparation method comprises the following steps: with a lentivirus or a retrovirus, usedfor integrating a foreign gene in a cell genome, as a vector, preparing a sequence meeting different gene mutations or fusion genes, and after the sequencing validation is error-free, embedding in the cell genome through the virus, screening out a monoclonal cell line with gene mutation or fusion gene from a drug, thereby obtaining the continual positive reference. The cell line is preferably 293T cell line, the mutation can be conducted at a single mutation site of a single gene, multiple site mutations of a single gene and multiple site mutations of multiple genes, and the fusion gene canbe a single fusion gene,and can also be multiple fusion genes connected in series. The preparation method has the advantages of being rapid, accurate, simple, low in cost, high in sensitivity, and capable of realizing mass production, and application and popularization in the markets are facilitated.
Owner:辽宁琦润生物科技有限公司
N-linked glycosylation alteration in E0 and E2 glycoprotein of classical swine fever virus and novel classical swine fever virus vaccine
InactiveUS20100104597A1Slow onsetDelaying severitySsRNA viruses positive-senseSugar derivativesVirulent characteristicsWild type
E2 is one of the three envelope glycoproteins of Classical Swine Fever Virus (CSFV). E2 is involved in several functions including virus attachment and entry to target cells, production of antibodies, induction of protective immune response in swine, and virulence. Seven putative glycosylation sites in E2 were modified by site directed mutagenesis of a CSFV Brescia infectious clone (BICv). A panel of virus mutants was obtained and used to investigate whether the removal of putative glycosylation sites in the E2 glycoprotein would affect viral virulence / pathogenesis in swine. We observed that rescue of viable virus was completely impaired by removal of all putative glycosylation sites in E2, but restored when mutation N185A reverted to wild-type asparagine produced viable virus that was attenuated in swine. Single mutations of each of the E2 glycosylation sites showed that amino acid N116 (N1v virus) was responsible for BICv attenuation. N1v efficiently protected swine from challenge with virulent BICv at 3 and 28 days post-infection suggesting that glycosylation of E2 could be modified for development of CSF live-attenuated vaccines. Additionally, a new developed virus, contained deletions of putative glycosylation sites N1 in E2 and N1 in E0 (6b), called N1E0 / 2v, induce a solid protection against the challenge at 3 and 28 days post-inoculation.
Owner:BORCA MANUEL +1
L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN109735522AHigh activityImprove catalytic stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-AspartateSingle mutation
The invention discloses an L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase mutant and application to converting L-aspartic acid to produce beta-alanine. The mutant is obtained in a manner that the 98th site, the305th site, the 451th site, the 111th site, the 139th site, the 403th site, the 469th site, the 372th site and the 325th site of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1 are subjected to single mutation or multi-mutation. According to the L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase mutant, the catalytic capacities of mutant enzymes PanDR98H-K305E and PanDR98H-K305E-I451V and non-mutated enzymes underthe partial neutrality condition are compared, the result discovers that under the condition of pH7.0, the conversion rates obtained when the mutant enzymes PanDR98H-K305E and PanDR98H-K305E-I451V catalyze the L-aspartic acid to generate the beta-alanine are 3.33 times and 2.76 times that of the non-mutated enzymes respectively.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Nitrilase mutant with improved nitrile hydration activity specificity and application thereof
The invention discloses a nitrilase mutant with improved nitrilase hydration activity specificity and application thereof. The mutant is obtained by carrying out single mutation or multiple mutation on the 87th site, the 136th site, the 224th site and the 226th site of an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1. When the mutant R224S / V226R / I136Q / A87M constructed in the invention is used for catalyzing phenylacetonitrile, a reaction main product is phenylacetamide, the content of amide reaches 91.2%, and the nitrile hydration activity is 113.3% of that of OsNIT. When the phenylacetonitrile is catalyzed by the wild nitrilase OsNIT, the content of the phenylacetamide is 50.6%, and meanwhile, the nitrile hydration activity of the OsNIT is 100%. The amide content and the hydration activity of the R224S / V226R / I136Q / A87M are 1.53 times and 1.13 times of those of the wild nitrilase respectively. The reaction specificity of the nitrilase is regulated and controlled, so that the nitrilase can be applied to amide green industrial catalytic synthesis, and important significance is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
1,3-1,4-beta-glucanase mutant
ActiveCN105671022AImprove thermal stabilityMaintain catalytic activityBacteriaWort preparationGlucanaseMutase
The invention discloses a 1,3-1,4-beta-glucanase mutant and belongs to the field of gene engineering and enzyme engineering.40-bit serine and 43-bit serine, 46-bit glutamic acid and 205-bit histidine of 1,3-1,4-beta-glucanase from bacillus terquilensis CGX 5-1 are mutated into glutamic acid, glutamic acid, praline and praline respectively through an iterative saturation mutation method, and finally four strains of single mutants and three strains of compound mutants are obtained.Seven strains of mutate enzyme all represent better heat stability, and particularly S40E / S43E / E46P / H205P mutate enzyme has extremely good heat stability.Compared with wild enzyme, the mutate enzyme can be used in the industry more easily.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Reliable and Secure Detection Techniques for Processing Genome Data in Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Genetic samples are obtained from separate people, and at least a portion of each are purposefully combined before testing to form a pooled genetic sample. The pooled genetic sample is tested for the presence of a signature for a given known ailment. DNA identification uses discovered InDels in a region of InDel variation in a genetic sample. A pair-wise comparison is performed to reference InDels, and a distance is measured between the first InDel and the reference Indel. Reference kmers are identified in a reference genome, and in a test sample. The plurality of sample kmers are filtered to those which have a 1 edit distance from a corresponding one of the plurality of reference kmers. Reads that have kmers that do not have a 1 edit distance from the corresponding one of the plurality of reference kmers are identified, and multiple single-mutations are eliminated from candidate InDel reads.
Owner:CRYSTAL GENETICS INC
N-Linked Glycosylation Alteration in E1 Glycoprotein of Classical Swine Fever Virus And Novel Classical Swine Fever Virus Vaccine
ActiveUS20120014992A1Reduce severityAltered glycosylation patternSsRNA viruses positive-senseSugar derivativesPost infectionEnv Glycoproteins
E1, along with Erns and E2 is one of the three envelope glycoproteins of Classical Swine Fever Virus (CSFV). Our previous studies indicated that glycosylation status of either E2 or Erns strongly influence viral virulence in swine. Here, we have investigated the role of E1 glycosylation of highly virulent CSFV strain Brescia during infection in the natural host. The three putative glycosylation sites in E1 were modified by site directed mutagenesis of a CSFV Brescia infectious clone (BICv). A panel of virus mutants was obtained and used to investigate whether the removal of putative glycosylation sites in the E1 glycoprotein would affect viral virulence / pathogenesis in swine. We observed that rescue of viable virus was completely impaired by removal of all three putative glycosylation sites in E1. Single mutations of each of the E1 glycosylation sites showed that CSFV amino acid N594 (E1.N3 virus), as well the combined mutation of N500 and N513 (E1.N1N2 virus) resulted in BICv attenuation. Infection of either E1.N1N2 or E1.N3 viruses were able to efficiently protected swine from challenge with virulent BICv at 3 and 28 days post-infection. These results, along with those demonstrating the role of glycosylation of Erns and E2, suggest that manipulation of the pattern of glycosylation could be a useful tool for development of CSF live-attenuated vaccines.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Methods and apparatus for screening and detecting multiple genetic mutations
InactiveUS7601493B2Avoid reactionEffective strategyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDiscriminatorSingle mutation
An assay system and methods are described where patient samples containing genomic DNA are analyzed for the presence of known genetic polymorphisms using a universal reporter strategy. In a preferred embodiment, the amplified DNA is localized at test sites in an array of sites on a microchip followed by a series of hybridization reactions that screen for the presence of a single mutation from among a number of mutations, and allow the identification of specific mutations. In addition to universal reporters, the assay may use blockers and discriminators for screening and identification of known polymorphisms.
Owner:GAMIDA FOR LIFE
7beta-HSDH enzyme mutant as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN113832122AReduce usageIncreased enzyme activity per unitBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCholic acidSingle mutation
The invention discloses a 7beta-HSDH enzyme mutant as well as a coding gene and application thereof. Compared with a wild type 7beta-HSDH enzyme with an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 2, the amino acid sequence of the 7beta-HSDH enzyme mutant has the advantage that any one of single mutation or pairwise combined mutation is carried out on the 237th site and the 240th site of the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. The 7beta-HSDH enzyme mutant can be used for synthesis and preparation of 24-nor ursodeoxycholic acid, the 7beta-HSDH enzyme mutant is used as a biocatalyst to convert a substrate 24-nor-7-ketocholic acid to generate 24-nor ursodeoxycholic acid, and HPLC verifies that the reaction conversion rate is greater than 90%. Compared with a wild enzyme, the 7beta-HSDH enzyme mutant constructed by the invention has the advantages that the catalytic activity is obviously improved, the use amount of the enzyme can be obviously reduced, and the 7beta-HSDH enzyme mutant has a wide prospect of large-scale industrial application.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN BAILING BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Recombinant lipase mutant, coding gene, recombinant engineering bacterium and application
The invention discloses a recombinant lipase mutant, a gene, a vector, an engineering bacterium and application of the mutant. The mutant is obtained in the mode that sporisorium reilianum SRZ2lipase(SRL) as a start is mutated. The lipase mutant is obtained in the mode that the 145 and 194 loci of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2 are subjected to single mutation or combined mutation. Compared with a wild enzyme, the catalytic activity and substrate tolerance of the mutant during reaction conversion are greatly improved, and the consumed time in the reaction process is obviously shortened. Compared with (S,S)-2,8-diazabicyclo[4,3,0]nonane prepared through a chemical method, the product obtained through the technology is high in stereoselectivity, the reaction conditionsare milder, the requirements for the equipment are low, the reaction cost is lowered, and the product is environmentally friendly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Amine transaminase AcATA mutant and application thereof in preparation of sitagliptin intermediate
ActiveCN111549008AIncrease enzyme activityImprove conversion rateBacteriaTransferasesKetonePhenylalanine
The invention discloses an amine transaminase AcATA mutant and application of the amine transaminase AcATA mutant in preparation of a sitagliptin intermediate. The amine transaminase AcATA mutant is obtained by single mutation at the 122th site of an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No.2. The amino acid sequence of the amine transaminase AcATA mutant is shown in SEQ ID No.2. The amino acid sequence of the amine transaminase AcATA mutant is shown in the description, wherein methionine at the 122 position is mutated into histidine, valine or phenylalanine. According to the invention, sites possibly influencing the catalytic activity are obtained through molecular docking, homologous modeling and other methods, and site-specific mutagenesis is carried out, so that the finally obtained aminotransferase AcATA mutant has high enzyme activity, and the enzyme activity is higher than 460U / g and is more than 4 times of that of a wild type; the catalyst can efficiently catalyze the sitagliptin intermediate precursor ketone 1-piperidine-4-(2, 4, 5-trifluorophenyl)-1, 3-dibutanone to synthesize the sitagliptin intermediate (R)-3-amino-1-piperidine-4-(2, 4, 5-trifluorophenyl)-1-butanone, and the 24-hour conversion rate is up to 90%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +2
Pantoea amidase mutant, gene, engineering bacterium and application thereof
ActiveCN107937376AIncreased parental vitalityReduce inhibitionBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologySingle mutation
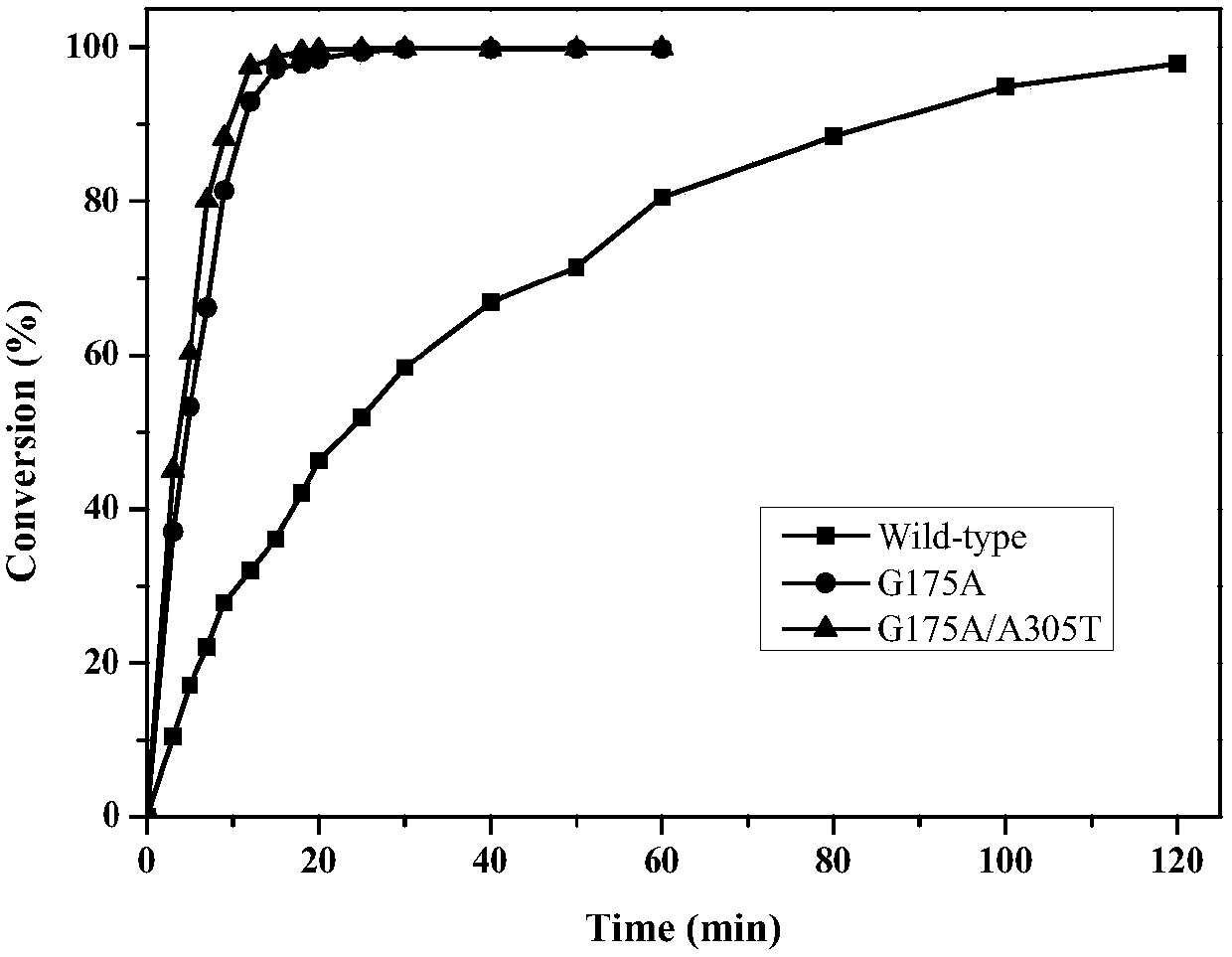
The invention discloses a pantoea amidase mutant, a gene, an engineering bacterium and an application thereof. The amidase mutant is obtained by conducting single mutation or multiple mutation on the105th, 175th, 301st, 305th or 309th site of an amino acid sequence of pantoea amidase shown as SEQ ID No.2. The activity of the pantoea amidase mutant provided by the invention, in comparison with a parent, is improved by 2-3 times; a tolerance capacity to a substrate, namely 2-chloronicotinamide, exceeds 200mM, and the tolerance capacity can even exceed 1M by virtue of a material supplementing method; and a conversion rate can be still kept above 95%. With the application of the material supplementing method provided by the invention, an inhibitory effect of 2-chloronicotinic acid to an amidase product or bacterium product can be effectively relieved, catalysis efficiency can be kept at relatively high level, and meanwhile, the separation-out of the finished product, namely the 2-chloronicotinic acid, can be promoted to the greatest extent, so that the extraction and purification of the finished product are facilitated. Therefore, the amidase mutant provided by the invention is applicable to the enzymatic industrial production of the 2-chloronicotinic acid.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com