Patents
Literature
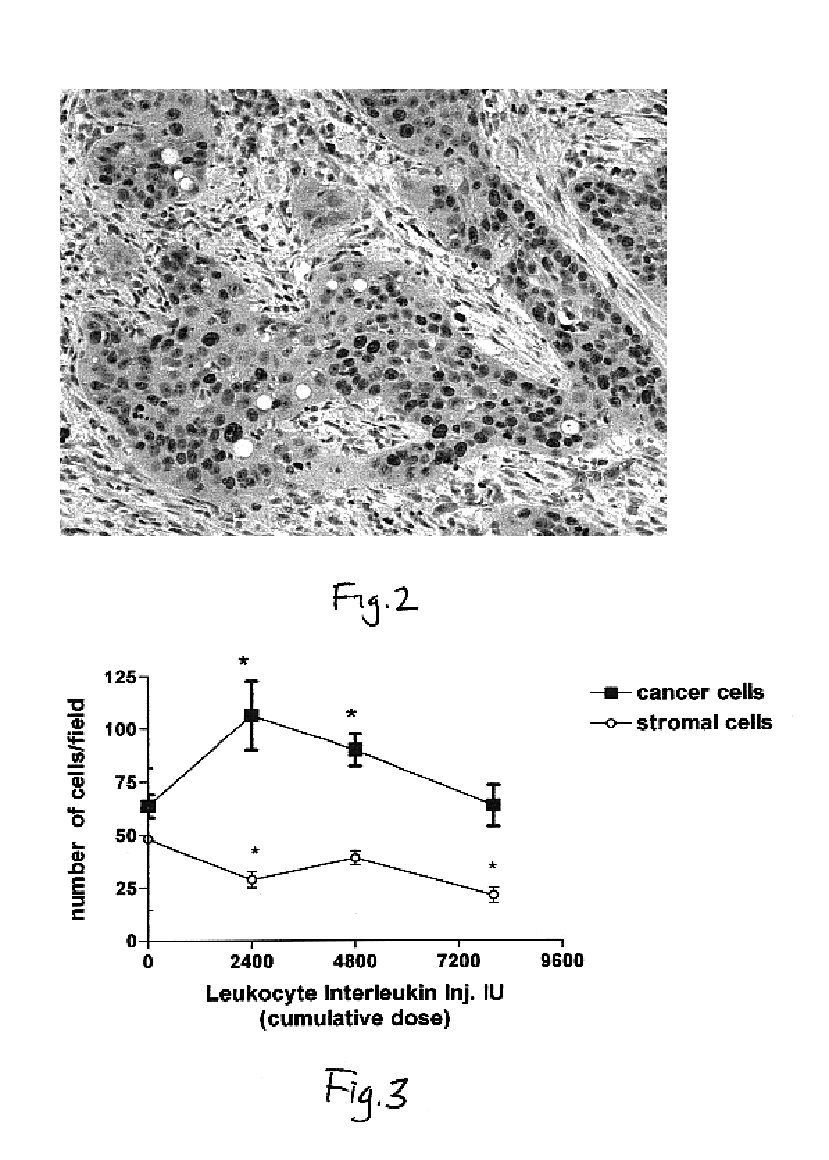
459 results about "Interleukin II" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
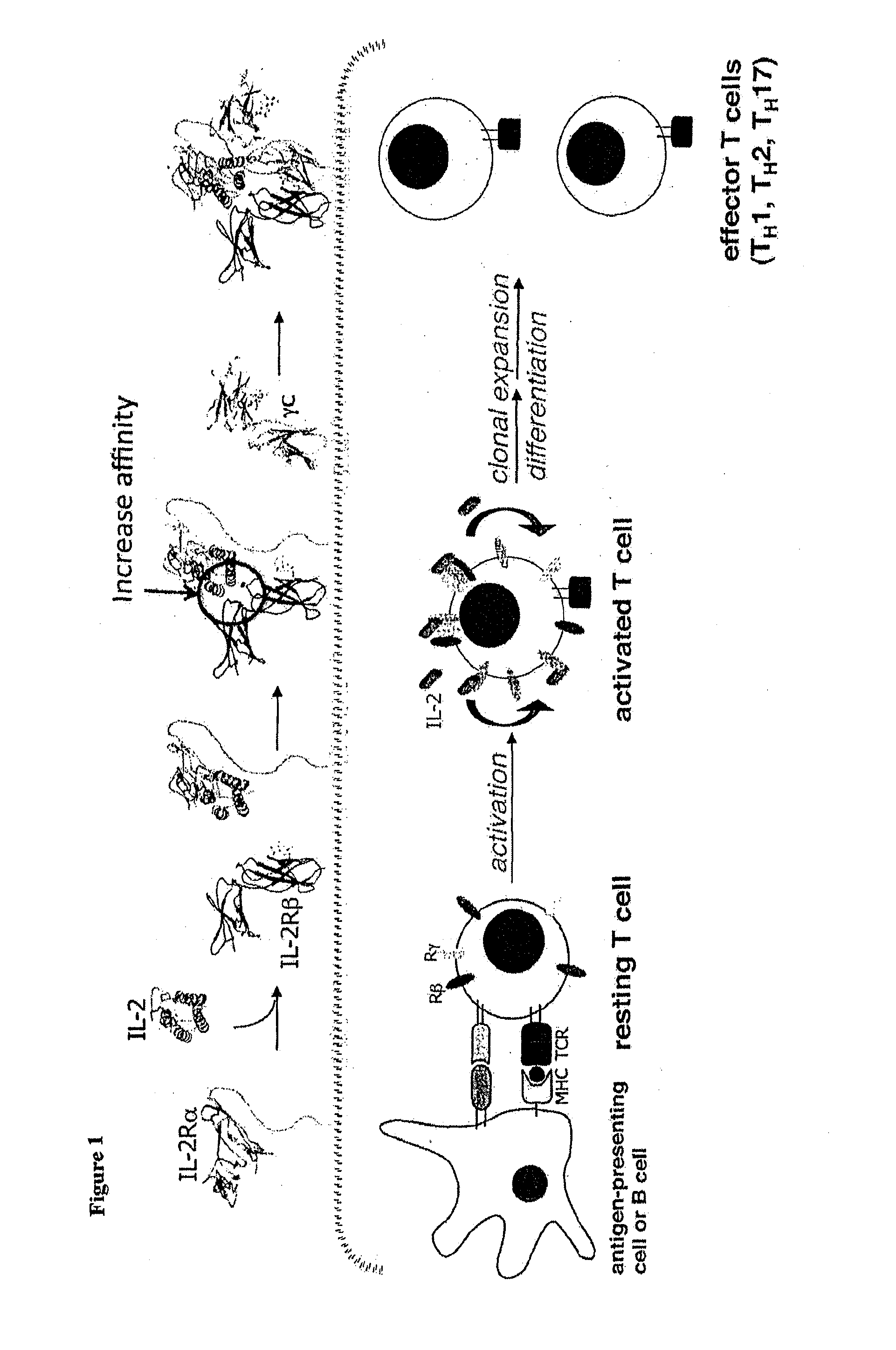
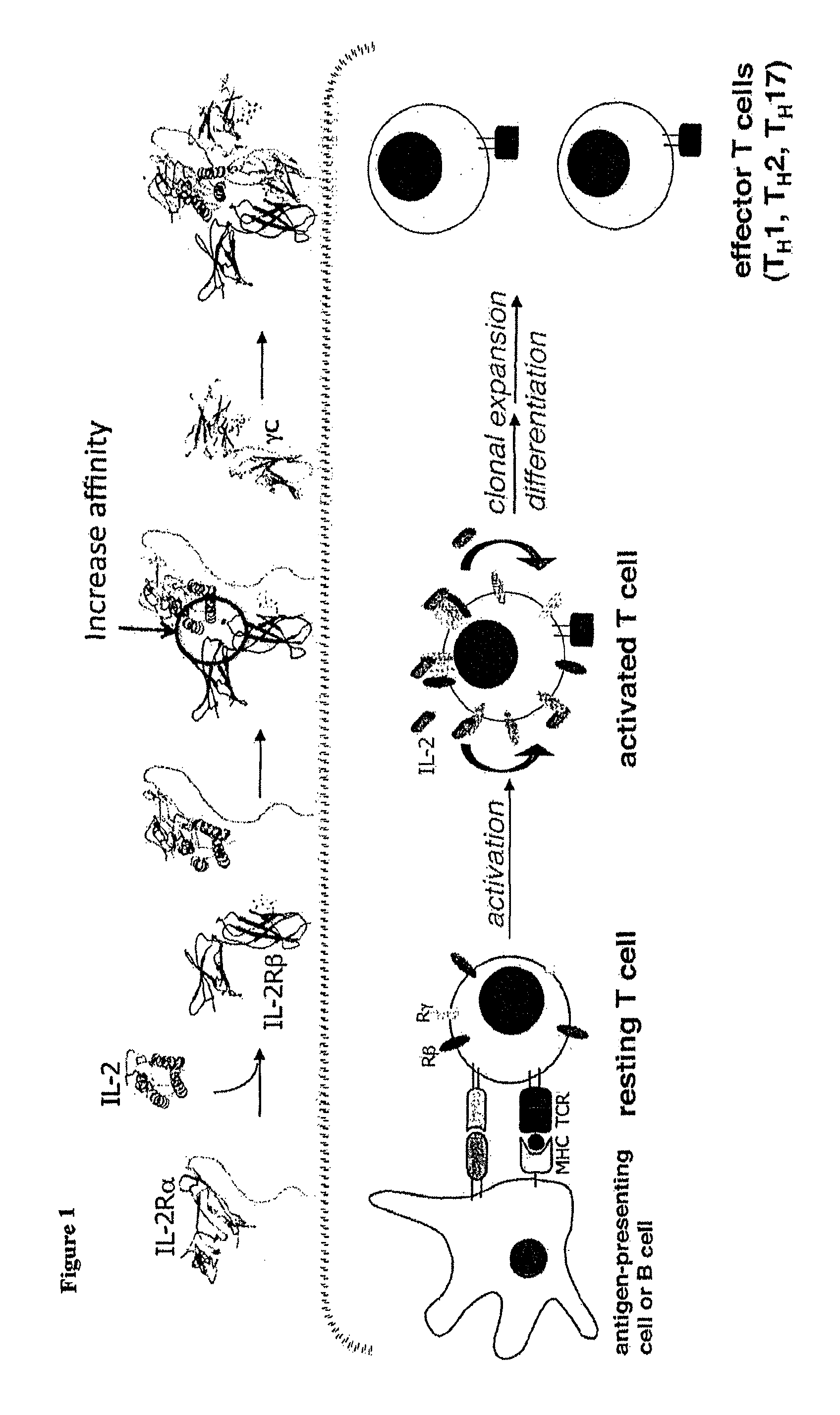
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is an interleukin, a type of cytokine signaling molecule in the immune system. It is a protein that regulates the activities of white blood cells (leukocytes, often lymphocytes) that are responsible for immunity.
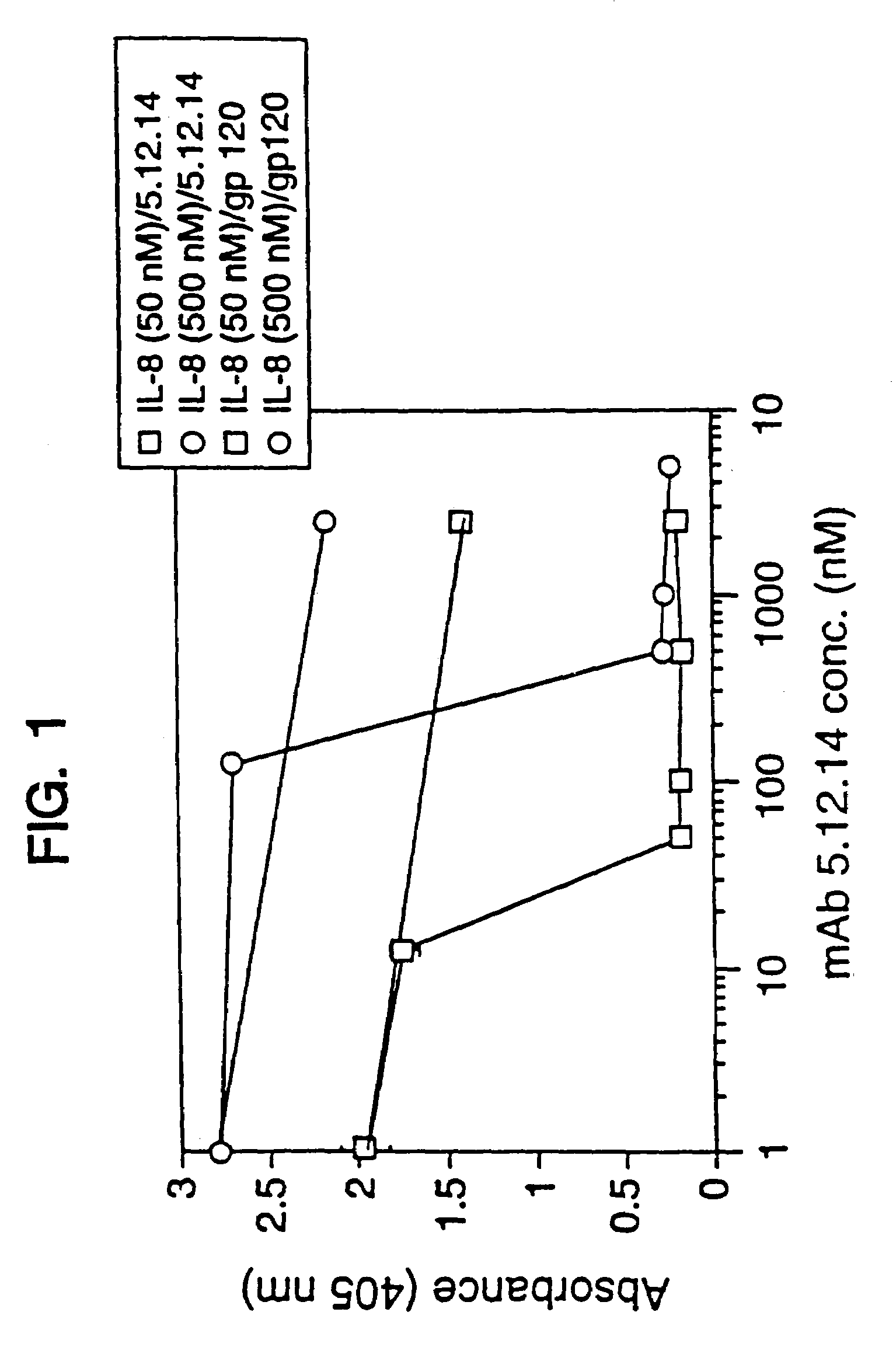
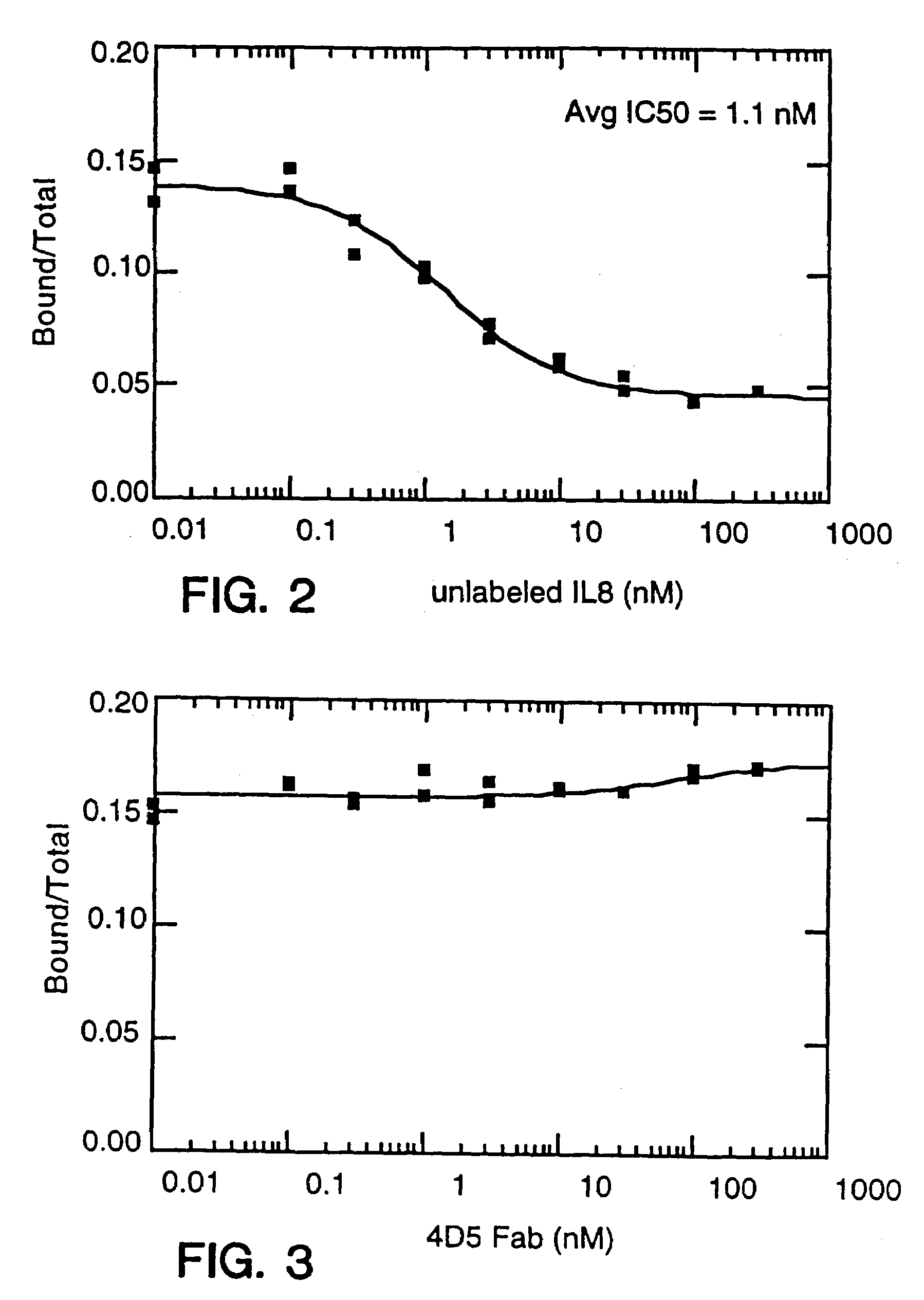
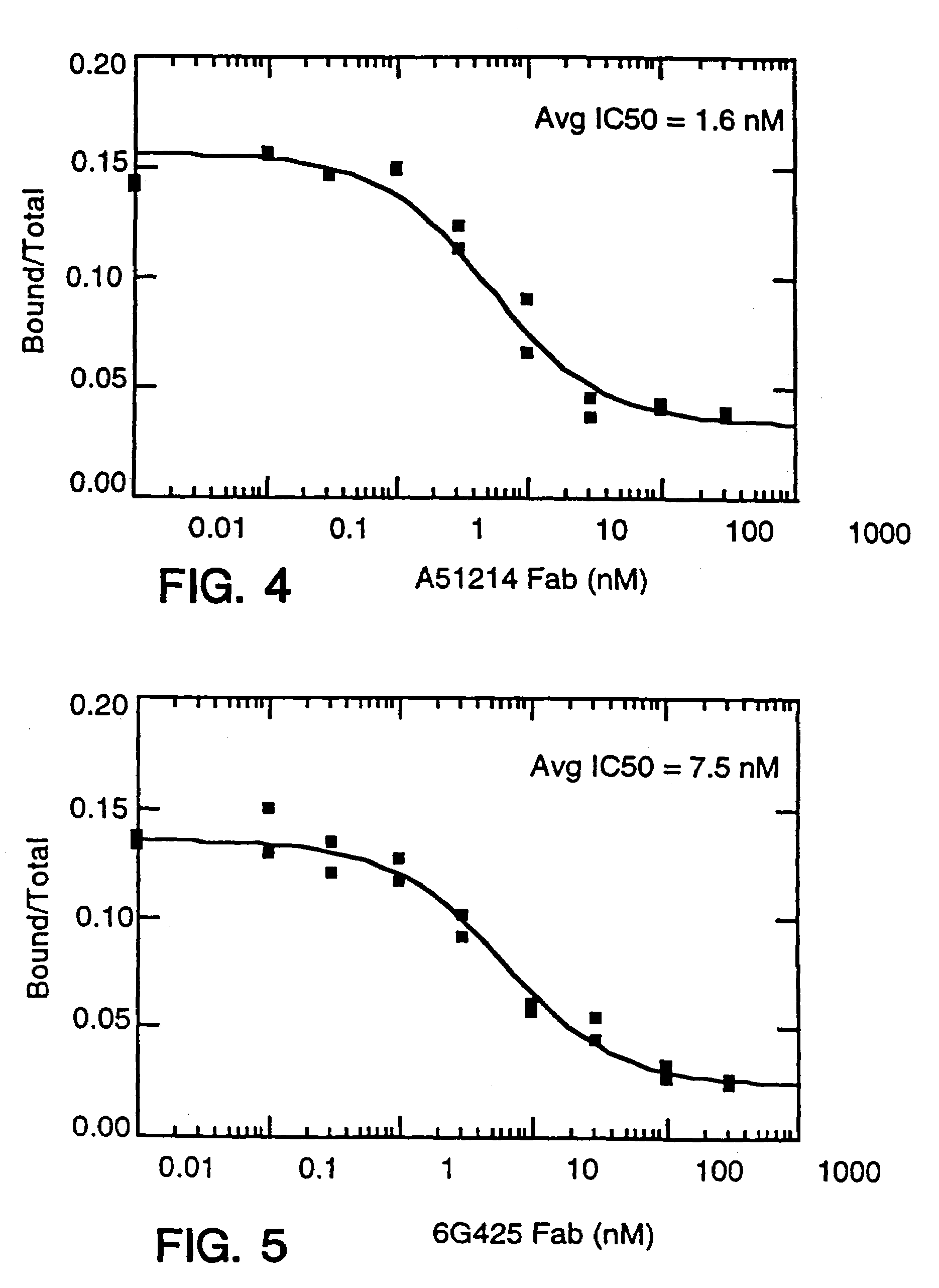
Antibody fragment-polymer conjugates and uses of same
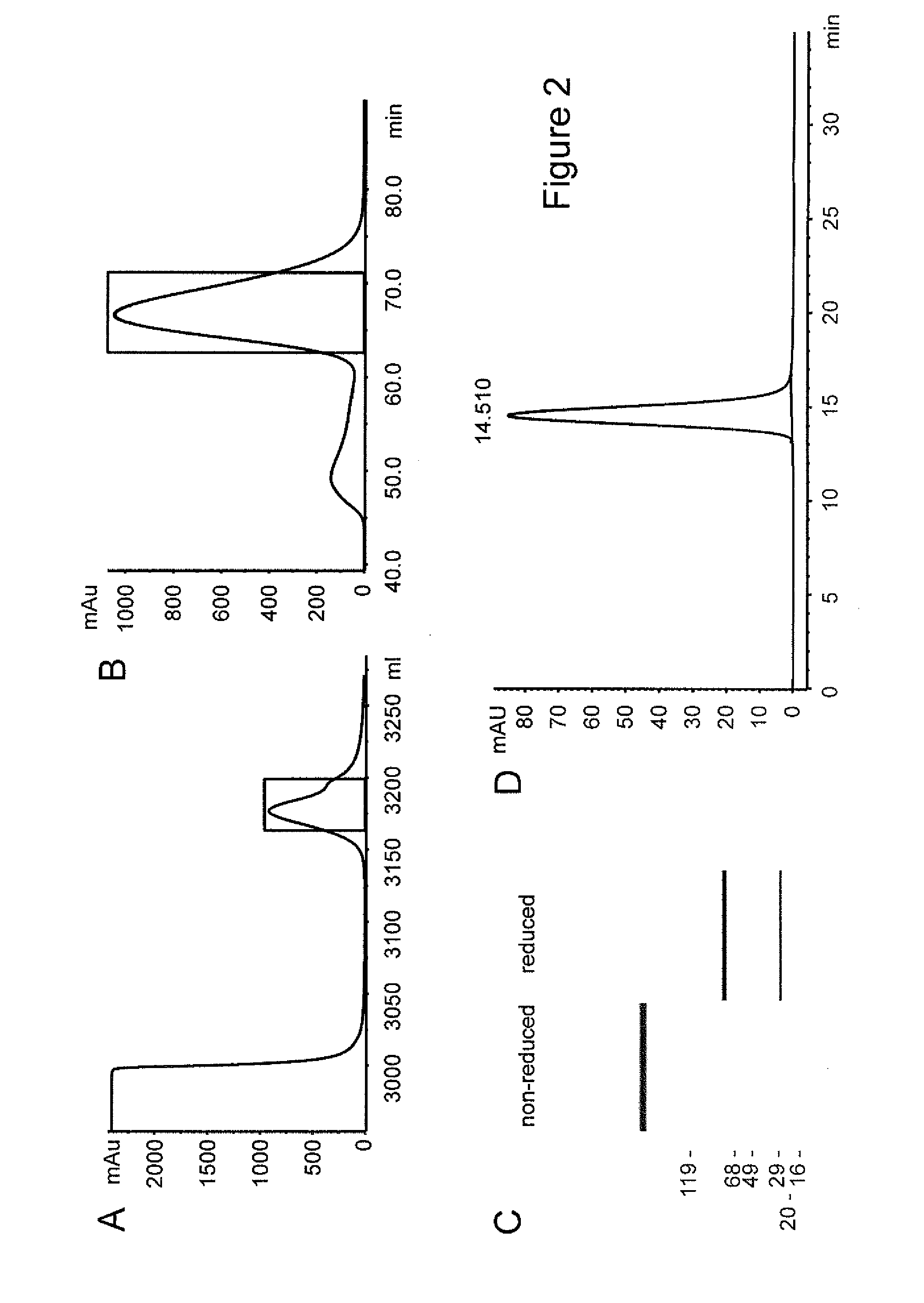
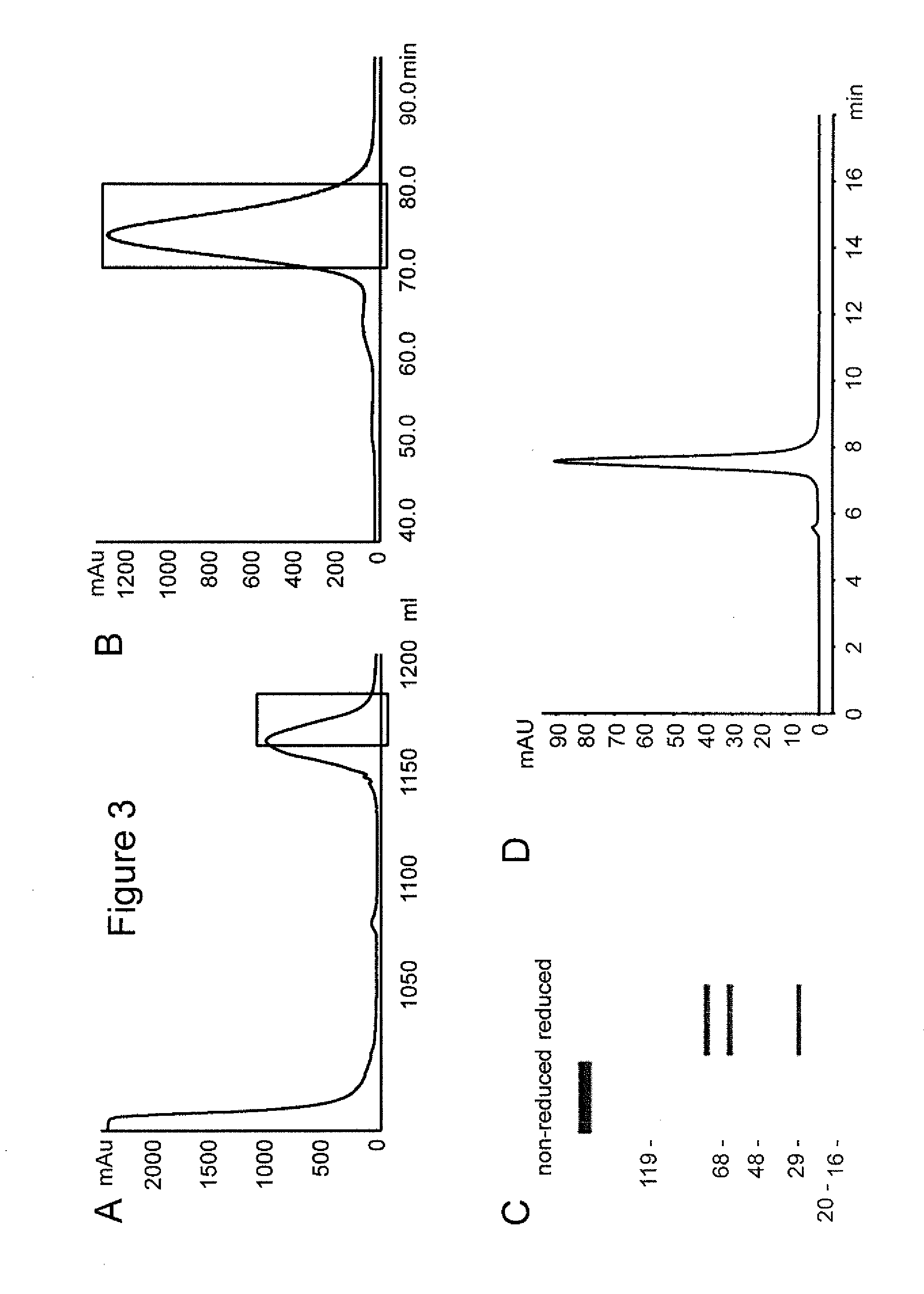
Described are conjugates formed by an antibody fragment covalently attached to a non-proteinaceous polymer, wherein the apparent size of the conjugate is at least about 500 kD. The conjugates exhibit substantially improved half-life, mean residence time, and / or clearance rate in circulation as compared to the underivatized parental antibody fragment. Also described are conjugates directed against human vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), human p185 receptor-like tyrosine kinase (HER2), human CD20, human CD18, human CD11a, human IgE, human apoptosis receptor-2 (Apo-2), human tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), human tissue factor (TF), human α4β7 integrin, human GPIIb-IIIa integrin, human epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), human CD3, and human interleukin-2 receptor α-chain (TAC) for diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Expansion of lymphocytes with a cytokine composition for active cellular immunotherapy
PendingUS20170107490A1Increase stimulationImprove scalabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological material analysisTissue sampleLymphocyte
The present invention relates to a composition for expanding lymphocytes comprising at least two types of cytokines selected from interleukin 2 (IL-2), interleukin 15 (IL-15) and interleukin 21 (IL-21). It further relates to a Method of preparing a population of clinically relevant lymphocytes, comprising the steps of: obtaining a body sample from a mammal in particular a tissue sample or body liquid sample, comprising at least one lymphocyte and optionally separating the cells in the body sample, culturing the body sample in-vitro to expand and / or stimulate lymphocytes in the sample wherein the culturing comprises using IL-2, IL-15 and / or IL-21, and optionally determining the presence of clinically relevant lymphocyte in the cultured sample. The present invention also relates to an immunotherapy and the population of clinically relevant lymphocytes.
Owner:POLYBIOCEPT GMBH
Genetically modified human natural killer cell lines
ActiveUS8313943B2Increase rangeHelp studyDrug screeningImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFc(alpha) receptorFc receptor
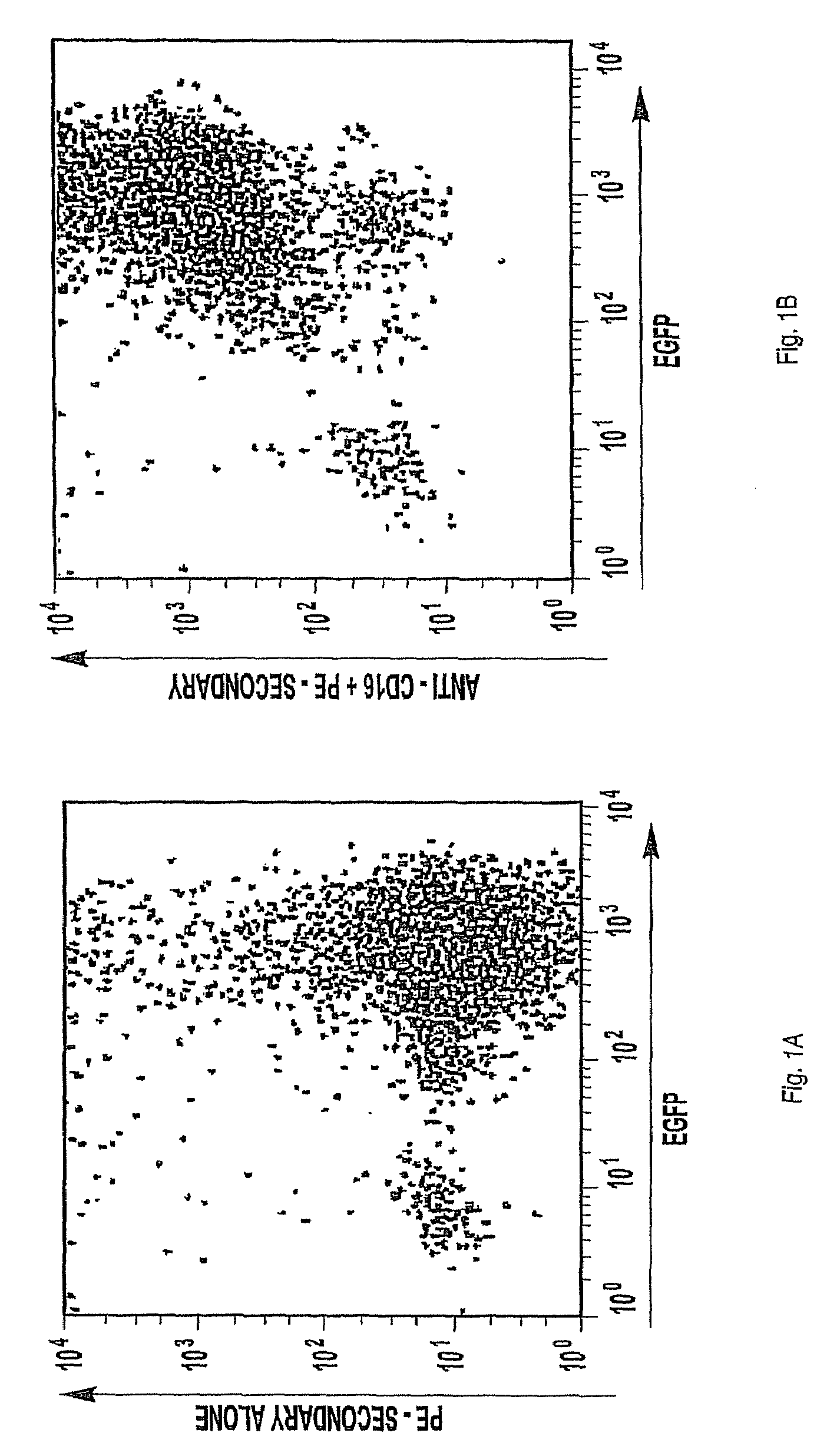
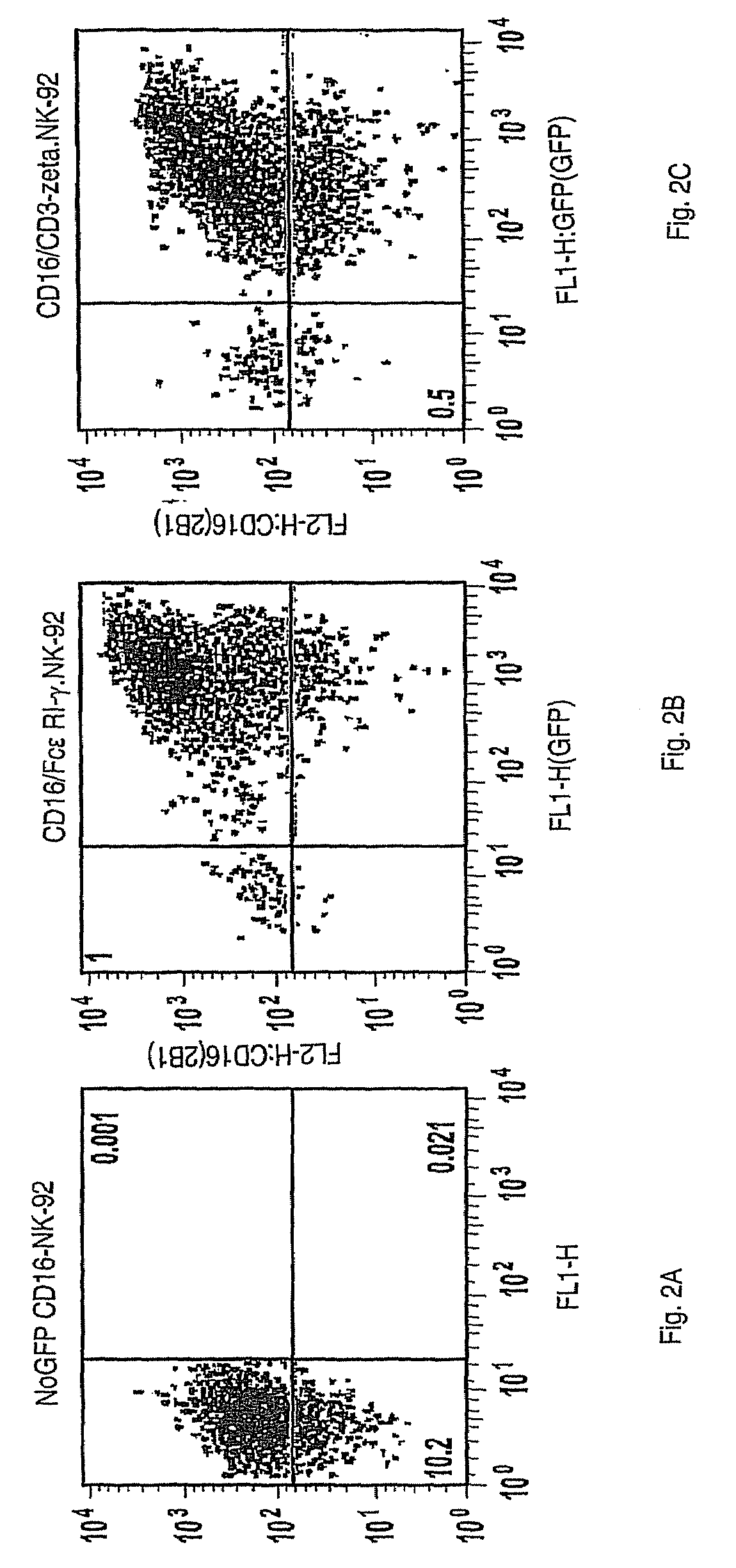
The invention provides a natural killer cell, NK-92, modified to express an Fc receptor on the surface of the cell, such as CD16 (FcγRIII-A), or other Fcγ or Fc receptors. The modified NK-92 cell can be further modified to concurrently express an associated accessory signaling protein, such as FcεRI-γ, TCR-ζ, or to concurrently express interleukin-2 (IL-2) or other cytokines. Additional methods are disclosed for various assays, assessments, and therapeutic treatments with the modified NK-92 cells.
Owner:INST FOR CANCER RES
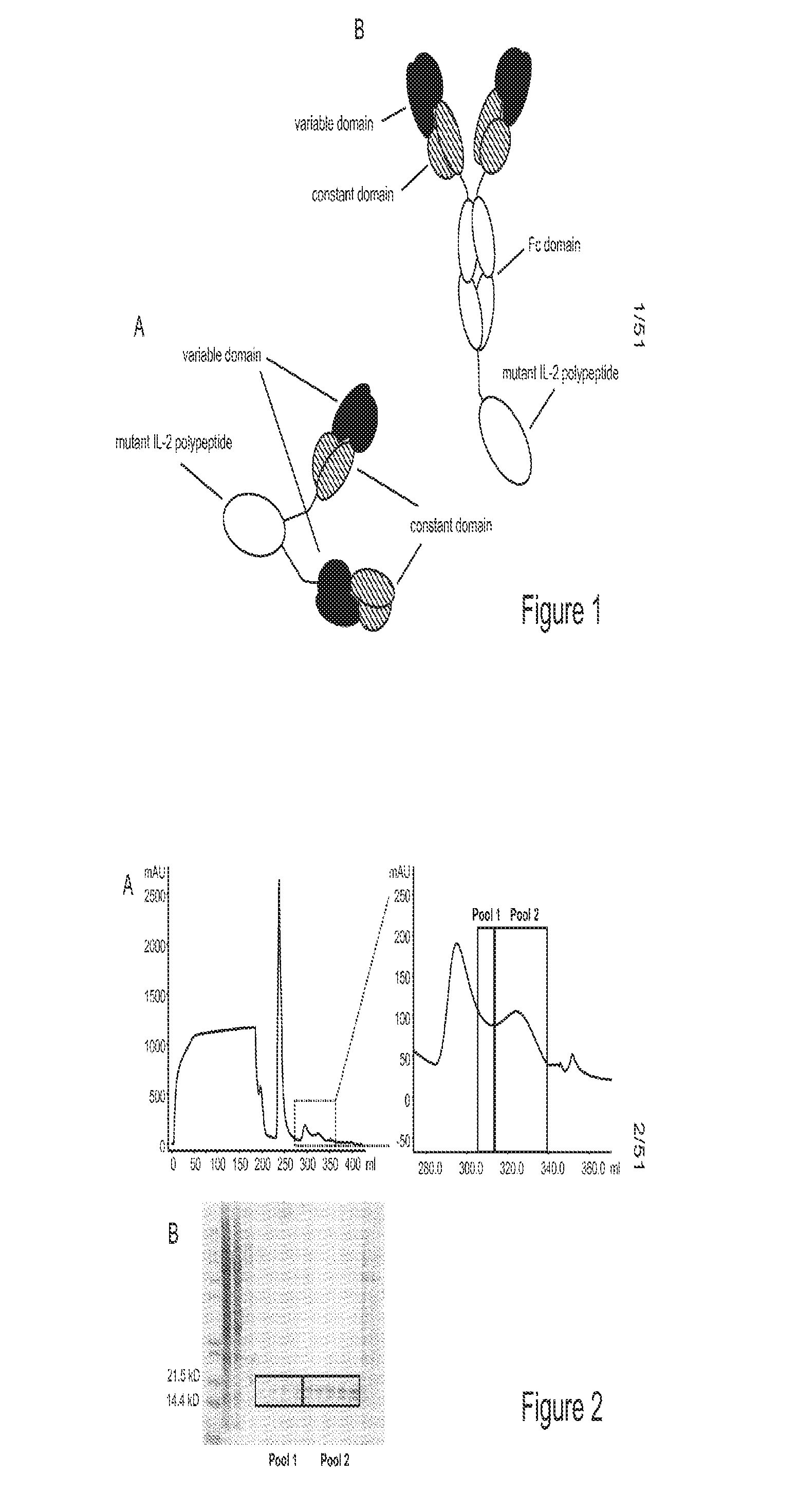
Mutant interleukin-2 polypeptides
ActiveUS9266938B2Eliminates and decrease and delayEliminates and decrease and and and effectPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunotherapeutic agentNucleotide
The present invention generally relates to mutant interleukin-2 polypeptides that exhibit reduced affinity to the α-subunit of the IL-2 receptor, for use as immunotherapeutic agents. In addition, the invention relates to immunoconjugates comprising said mutant IL-2 polypeptides, polynucleotide molecules encoding the mutant IL-2 polypeptides or immunoconjugates, and vectors and host cells comprising such polynucleotide molecules. The invention further relates to methods for producing the mutant IL-2 polypeptides or immunoconjugates, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same, and uses thereof.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
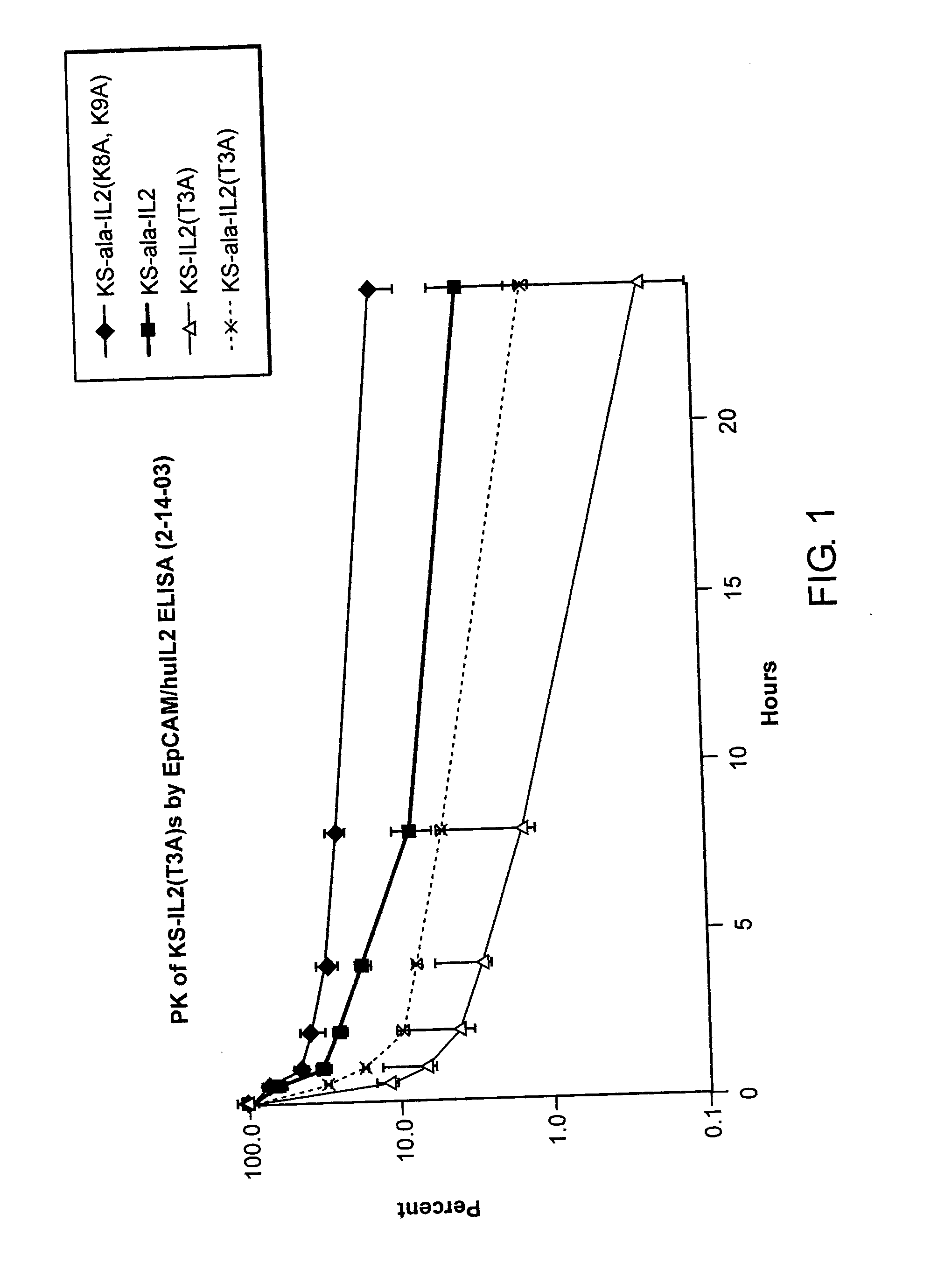
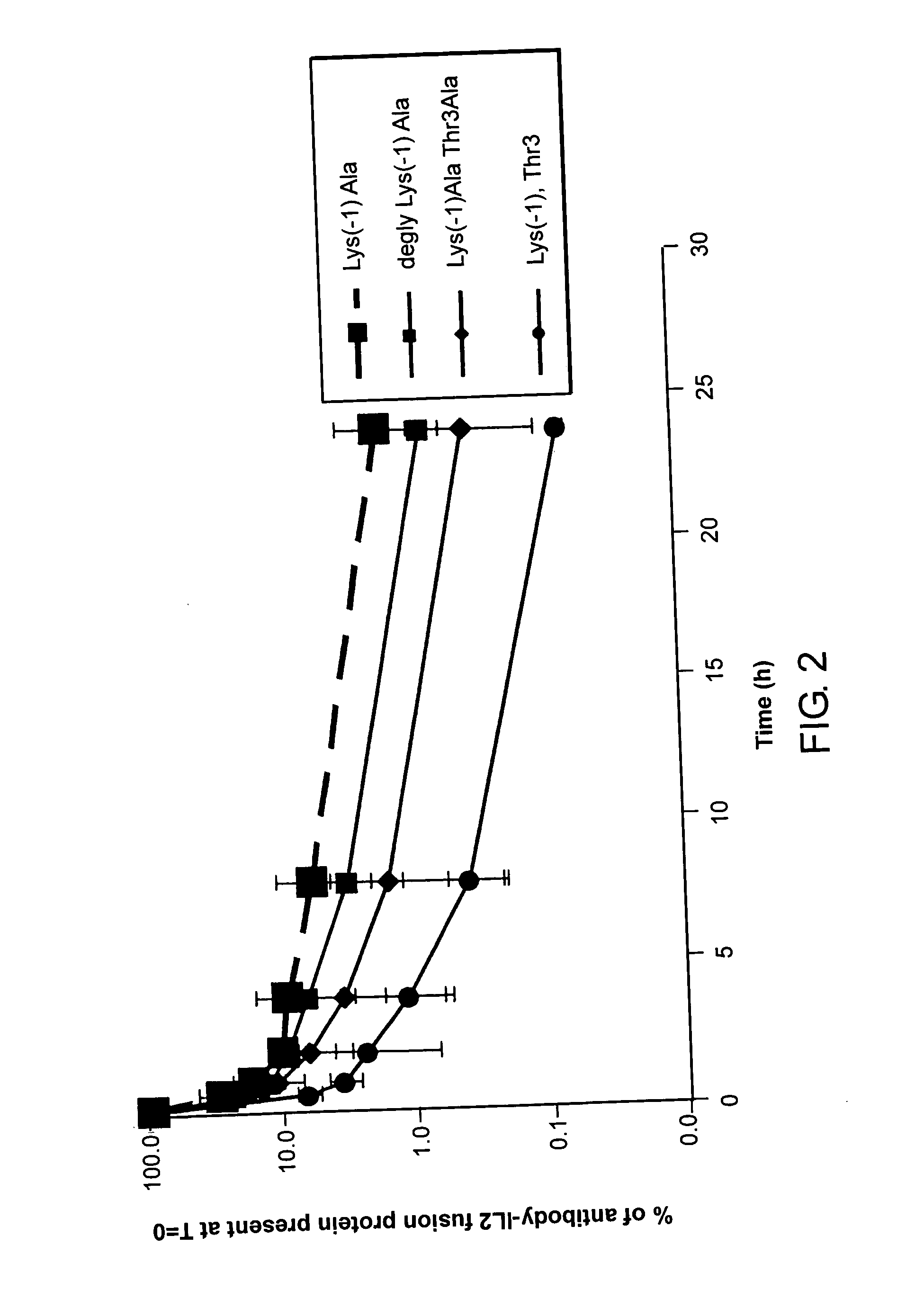
Enhancing the circulating half-life of interleukin-2 proteins
InactiveUS20050069521A1Enhance growth (and proliferation)Increased serum half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHalf-lifeInterleukin II
Disclosed are compositions and methods for enhancing the circulating half-life of interleukin-2 proteins.
Owner:EMD SERONO RES CENT
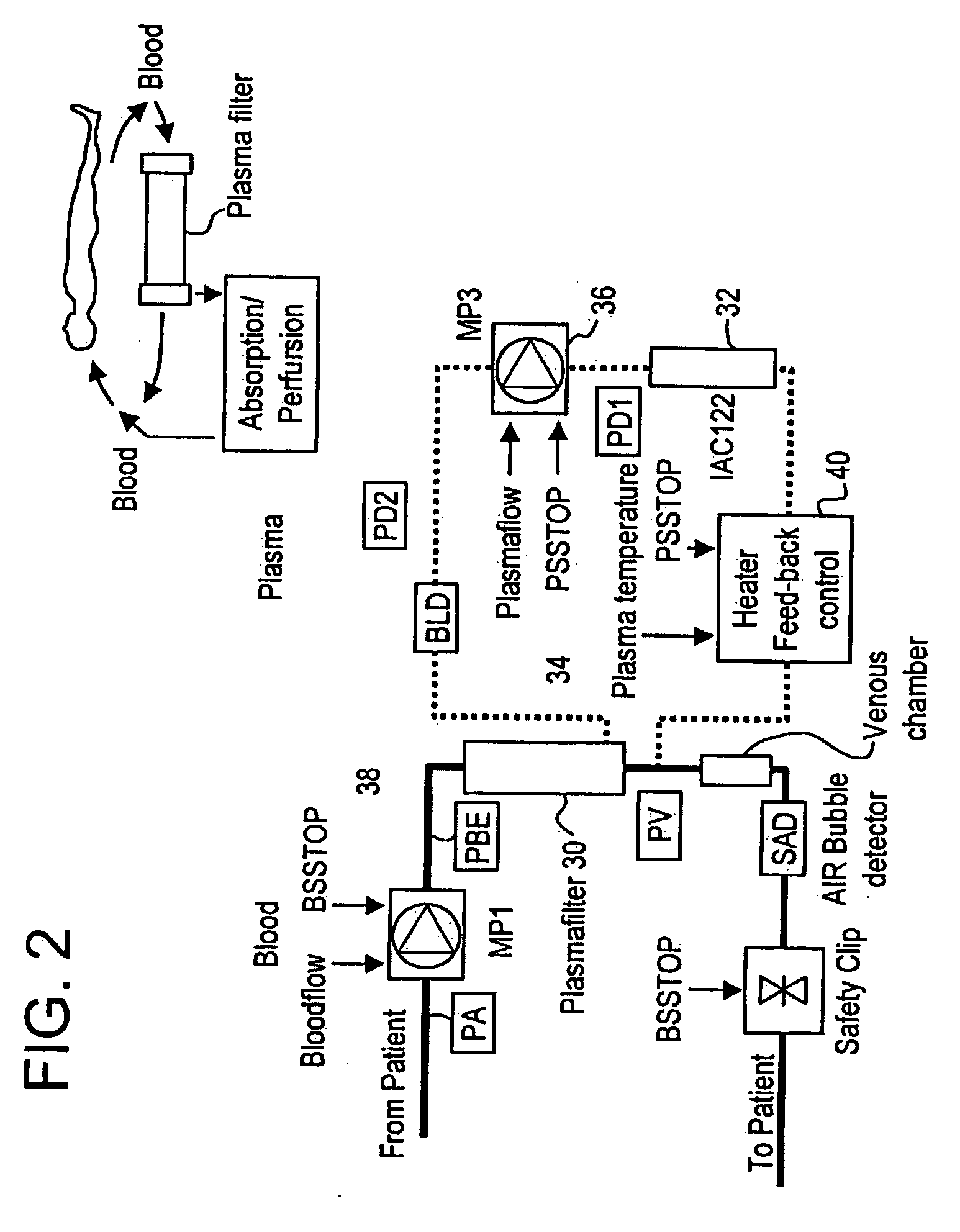
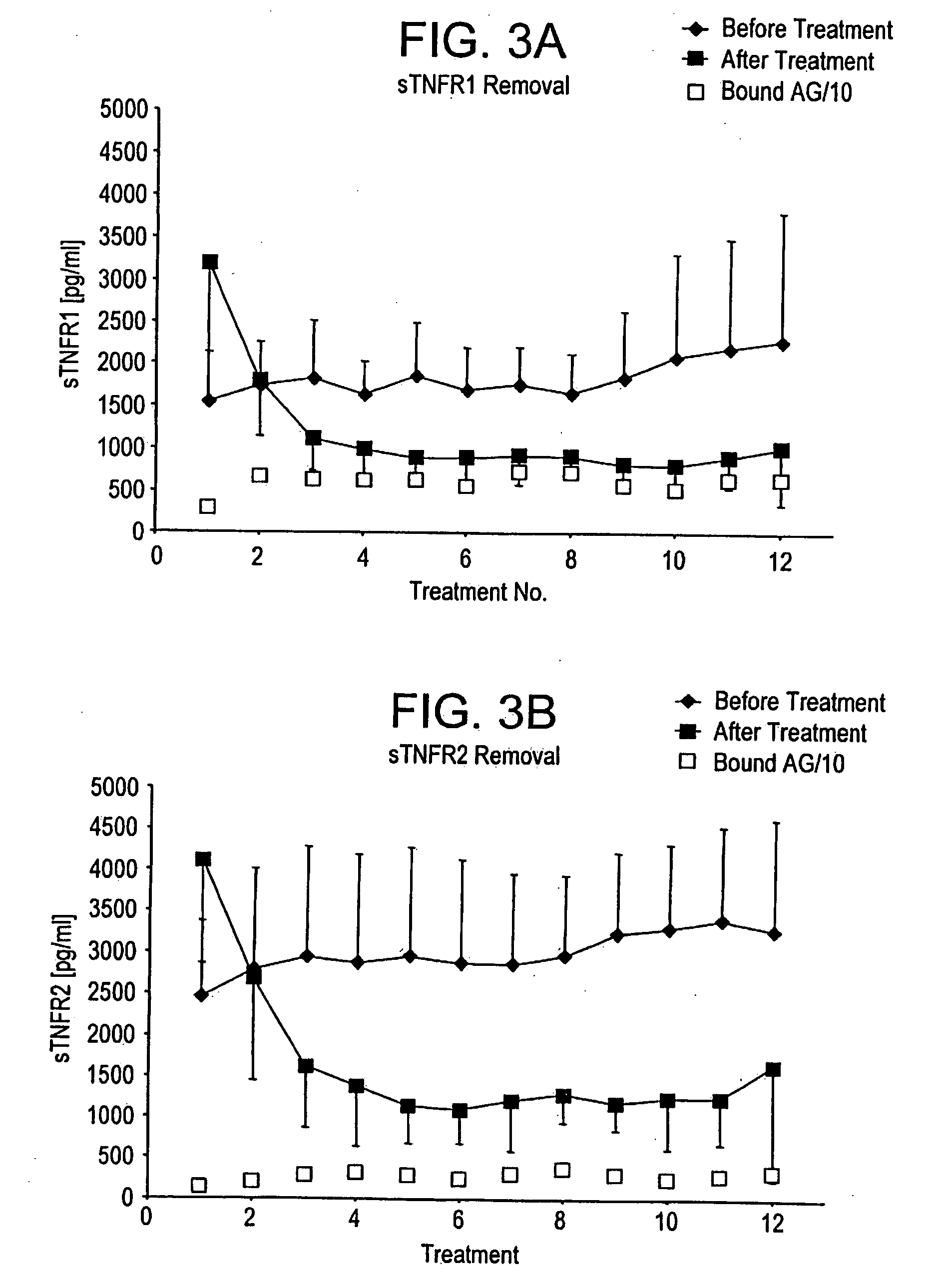
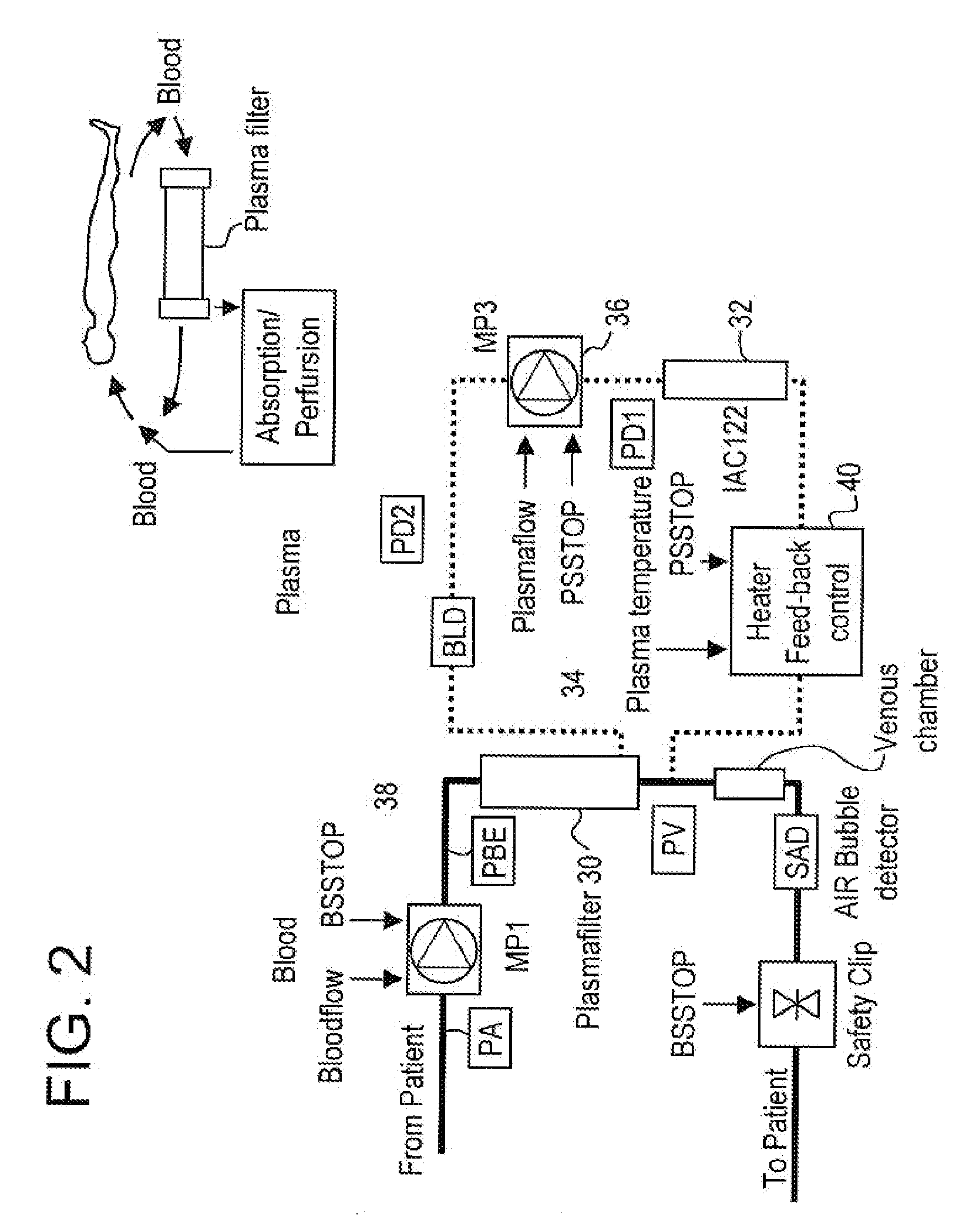
Method and system to remove soluble TNFR1, TNFR2, and IL2 in patients
InactiveUS20050265996A1Induce remissionPeptide/protein ingredientsHaemofiltrationDiseaseAntiendomysial antibodies
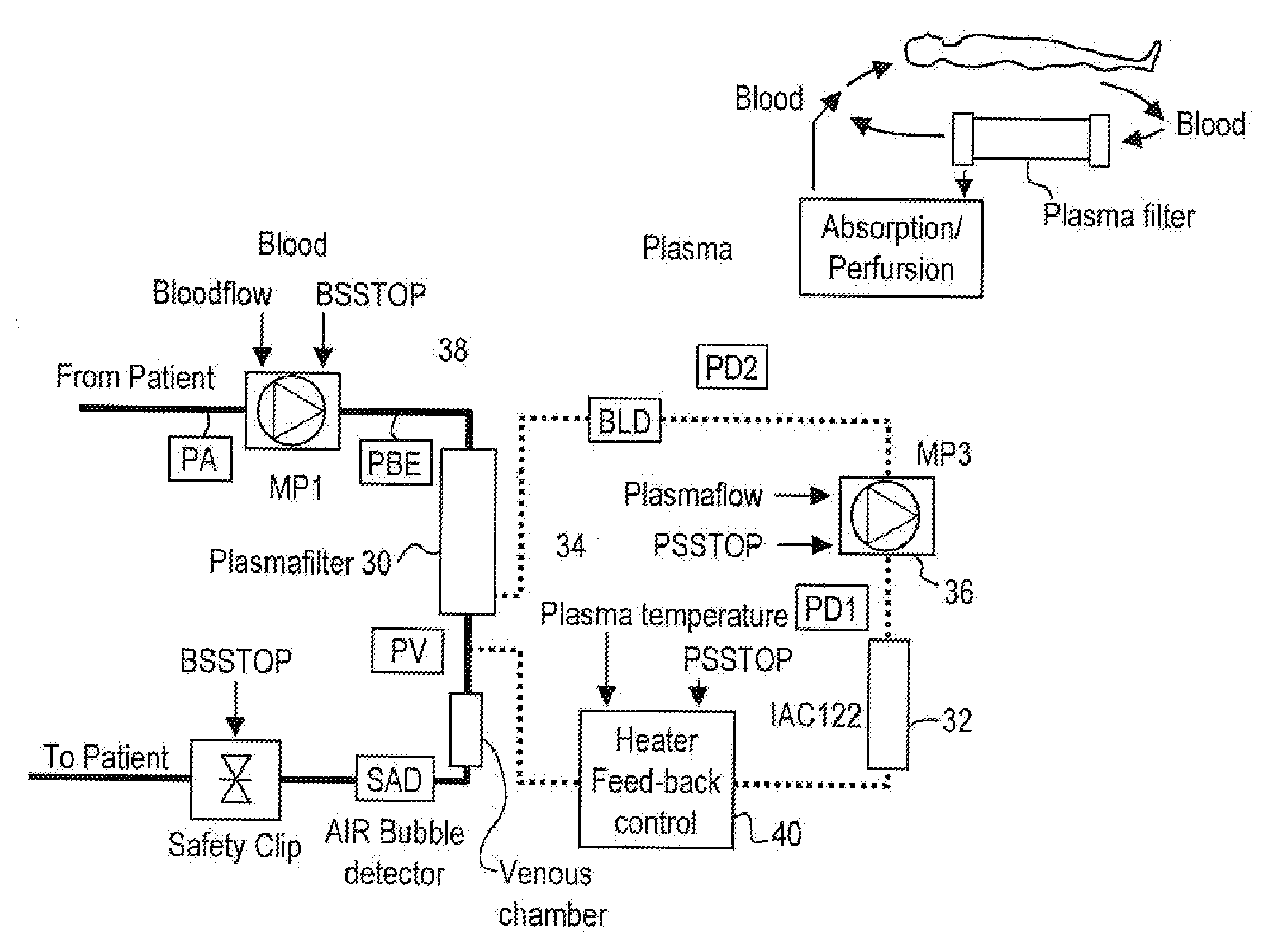
A method, and system, to induce remission in diseases characterized by excess production of sTNR and interleukin 2 has been developed. In the most preferred embodiment, the system consists of antibodies to sTNFR1, sTNFR2 and sIL2R immobilized in a column containing a material such as SEPHAROSE™. The patient is connected to a pheresis machine which separates the blood into the plasma and red cells, and the plasma is circulated through the column until the desired reduction in levels of sTNFR1, sTNFR2, and IL2 is achieved, preferably to less than normal levels. In the preferred method, patients are treated three times a week for four weeks. This process can be repeated after a period of time. Clinical studies showed reduction in tumor burden in patients having failed conventional chemotherapy and radiation treatments.
Owner:INNATUS CORP
Mutant interleukin-2 polypeptides
ActiveUS20160208017A1Eliminates and decrease and delayEliminates and decrease and and and effectPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunotherapeutic agentNucleotide
The present invention generally relates to mutant interleukin-2 polypeptides that exhibit reduced affinity to the α-subunit of the IL-2 receptor, for use as immunotherapeutic agents. In addition, the invention relates to immunoconjugates comprising said mutant IL-2 polypeptides, polynucleotide molecules encoding the mutant IL-2 polypeptides or immunoconjugates, and vectors and host cells comprising such polynucleotide molecules. The invention further relates to methods for producing the mutant IL-2 polypeptides or immunoconjugates, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same, and uses thereof.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
Adoptive immunotherapy using macrophages sensitized with heat shock protein-epitope complexes
InactiveUS6156302AEnhancing host 's immunocompetenceHigh activityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseInterleukin 6
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for enhancing immunological responses and for the prevention and treatment of infectious diseases or primary and metastatic neoplastic diseases based on the administration of macrophages and / or other antigen presenting cells (APC) sensitized with heat shock proteins non-covalently bound to peptide complexes and / or antigenic components. APC are incubated in the presence of hsp-peptide complexes and / or antigenic components in vitro. The sensitized cells are reinfused into the patient with or without treatment with cytokines including but not limited to interferon- alpha , interferon- alpha , interleukin-2, interleukin-4, interleukin-6 and tumor neurosis factor.
Owner:FORDHAM UNIVERSITY
Stabilized interleukin 2
InactiveUS6689353B1Reduce ionic strengthFast rebuildPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsGlycineSucrose
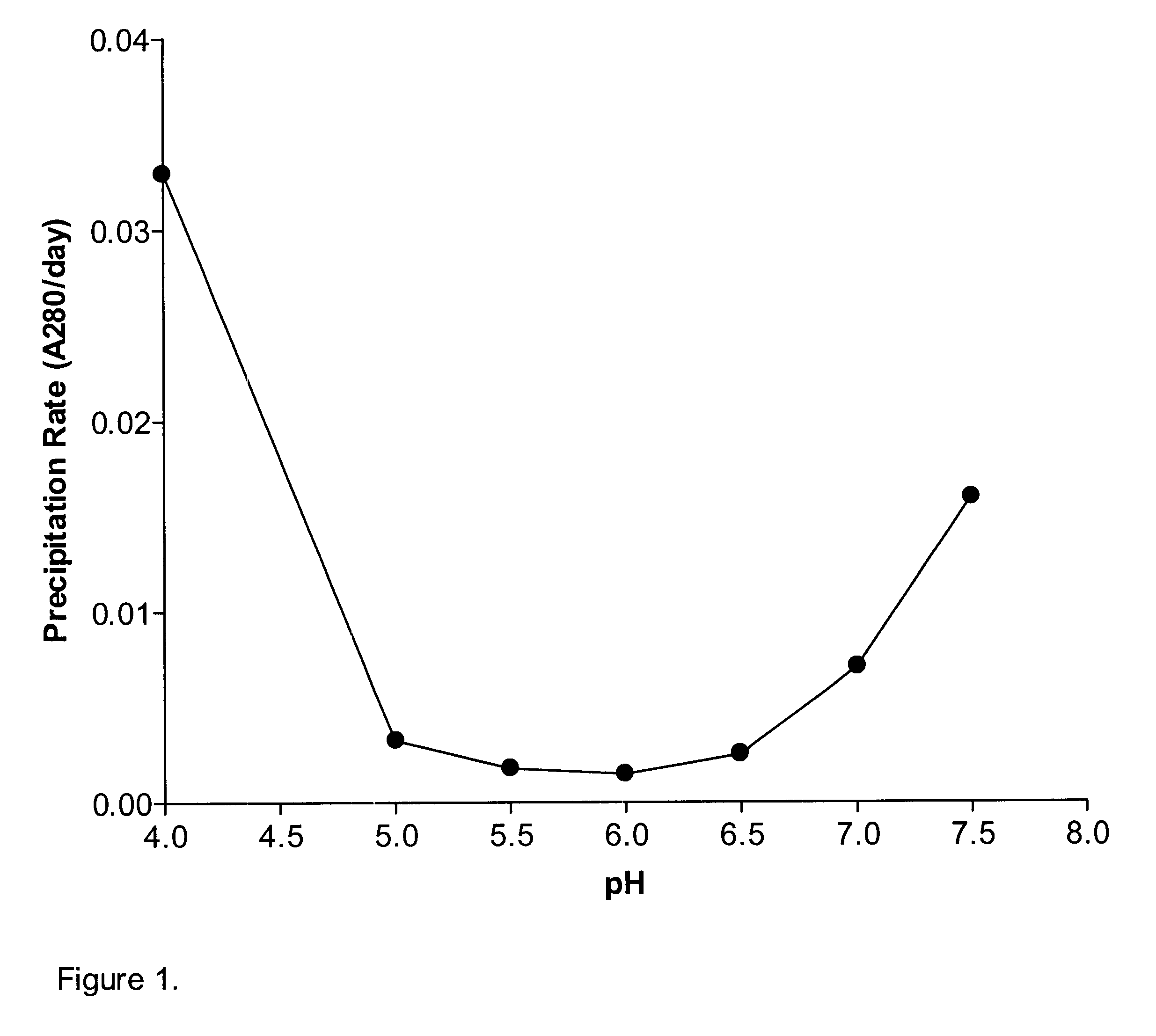
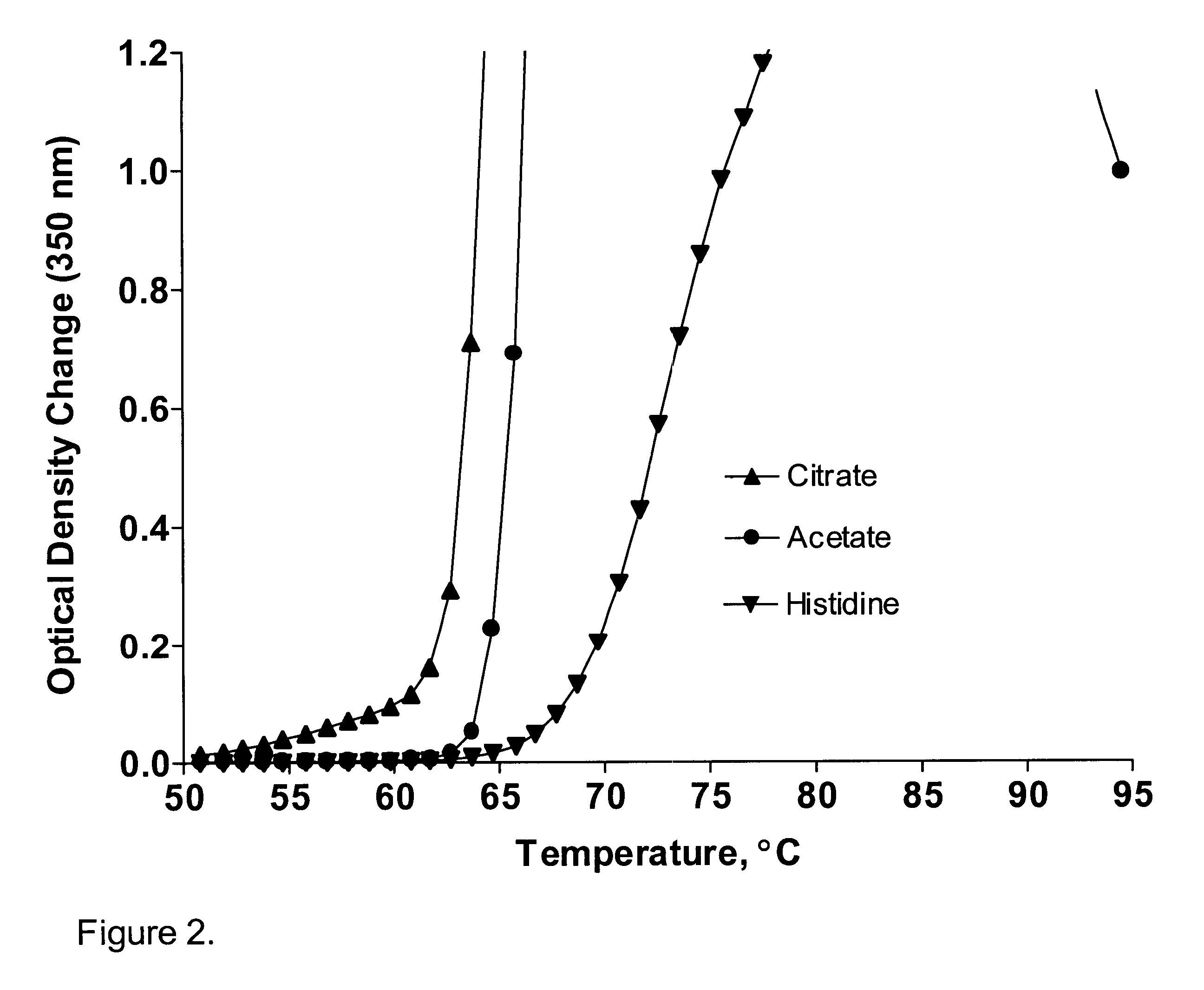
A stable pharmaceutical preparation comprising Human interleukin-2 or a variant thereof and a stabilizing amount of histidine. A preferred formulation includes glycine and sucrose and a variant of IL-2 having a single mutation, N88R. The preferred formulation is in lyophilized form which, on reconstitution with an aqueous diluent, results in a solution having a pH ranging from about 5.0 to 6.5.
Owner:AICURIS GMBH & CO KG
Methods of therapy for cancers characterized by overexpression of the HER2 receptor protein
InactiveUS7306801B2Promotes therapeutic responseImproved therapeutic responsePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDosing regimenAnti her2
Methods for treating a subject with a cancer that is characterized by overexpression of HER2 receptor protein using a combination of interleukin-2 (IL-2) or variant thereof and at least one anti-HER2 antibody or fragment thereof are provided. These anti-tumor agents are administered as two separate pharmaceutical compositions, one containing IL-2 (or variant thereof), the other containing at least one anti-HER2 antibody (or fragment thereof), according to a dosing regimen. Administering of these two agents together potentiates the effectiveness of the anti-HER2 antibody alone, resulting in a positive therapeutic response that is improved with respect to that observed with this anti-tumor agent.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC +1
Nucleic acids encoding interleukin-1 inhibitors and processes for preparing interleukin-1 inhibitors
Compounds are disclosed having the general formula R1—X—R2, wherein R1 and R2 are biologically active groups, at least one of which is polypeptidic. X is a non-peptidic polymeric group. R1 and R2 may be the same or different. Preferred R1 and R2 groups are interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, 30 kDa TNF inhibitor, interleukin-2 receptors and CR1 and muteins thereof. Also included are site selectively modified interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and 30 kDa TNF inhibitor.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Superagonists and antagonists of interleukin-2
ActiveUS20140046026A1Reduce interactionPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesAgonistInterleukin II
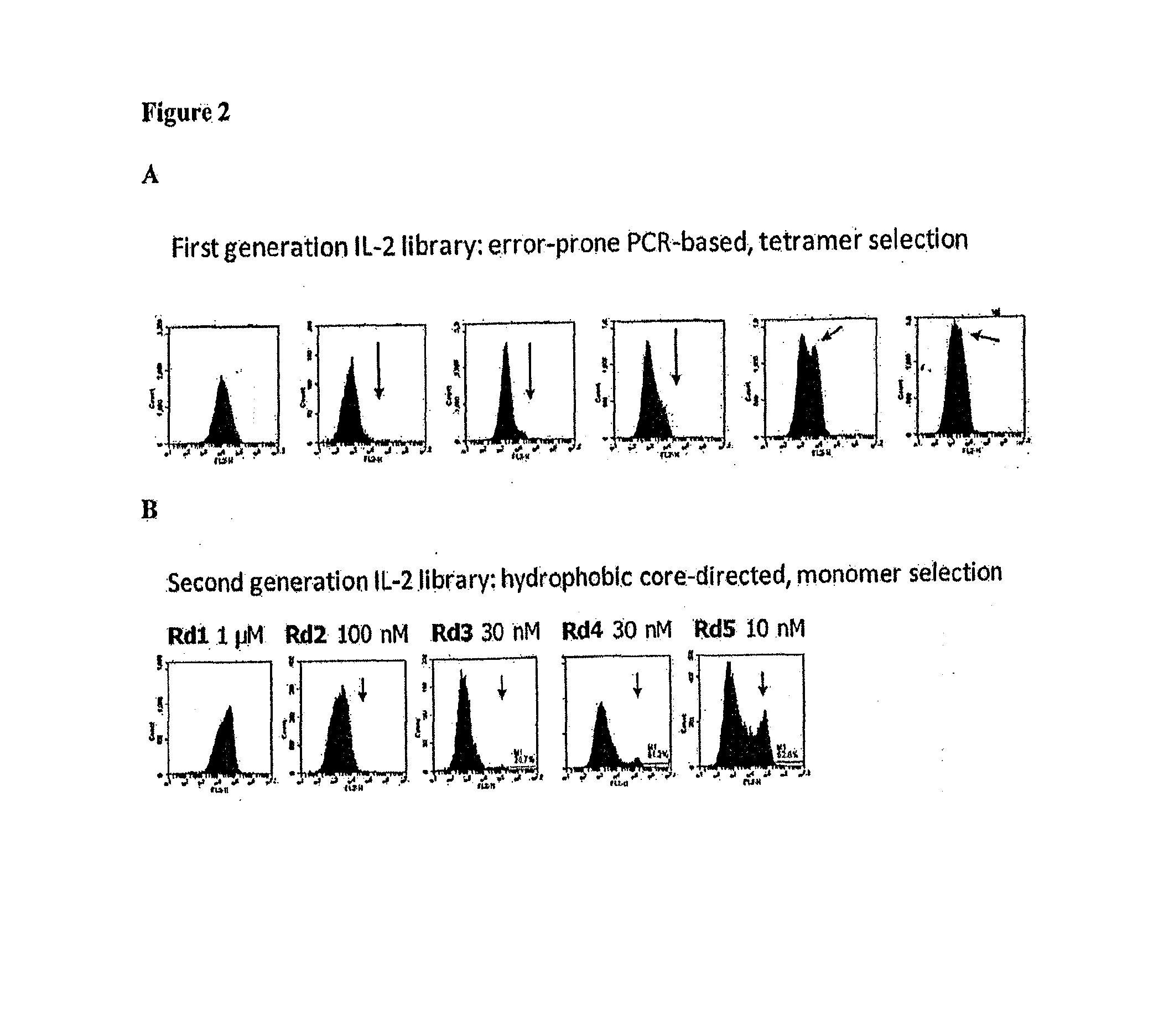
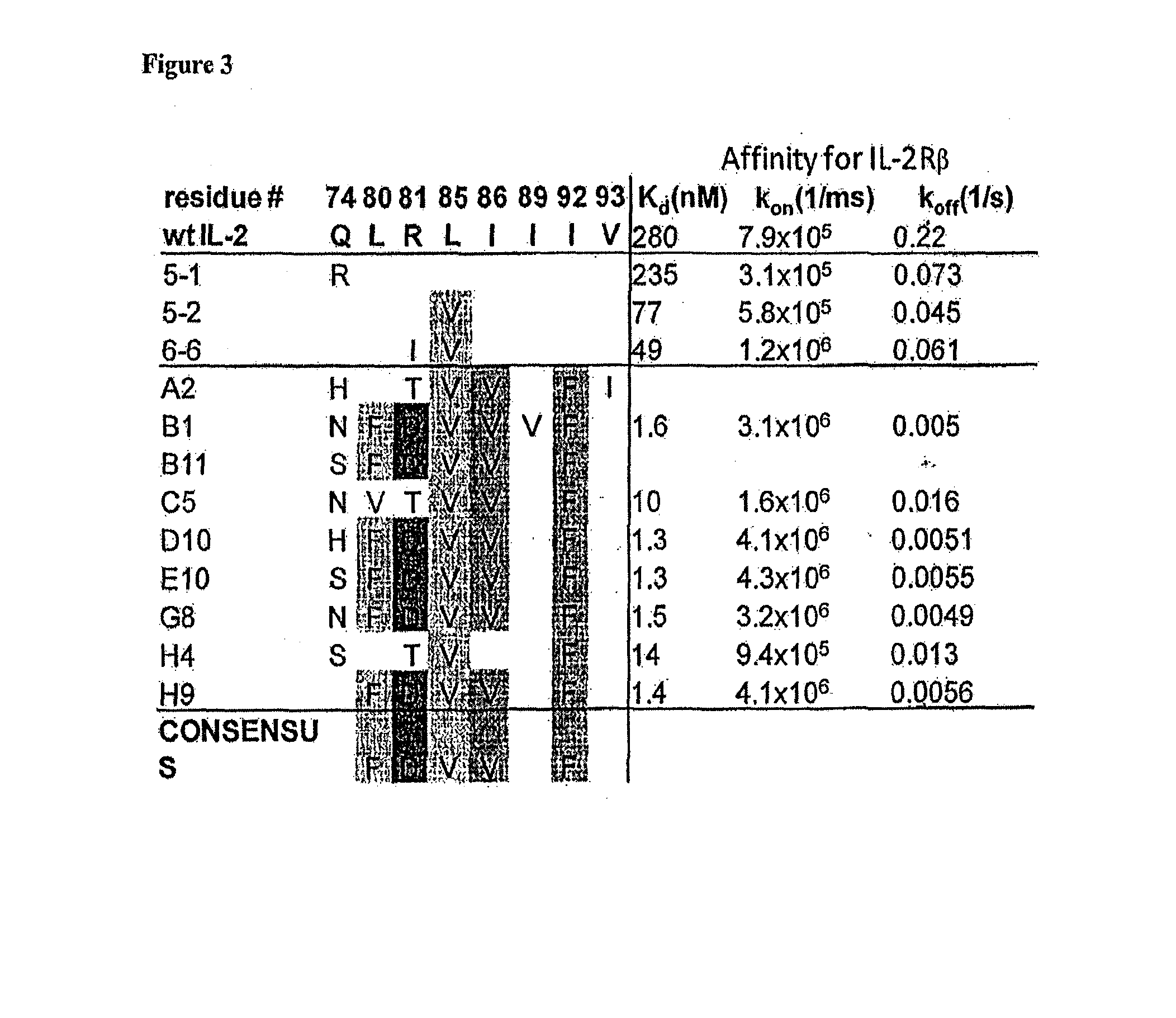
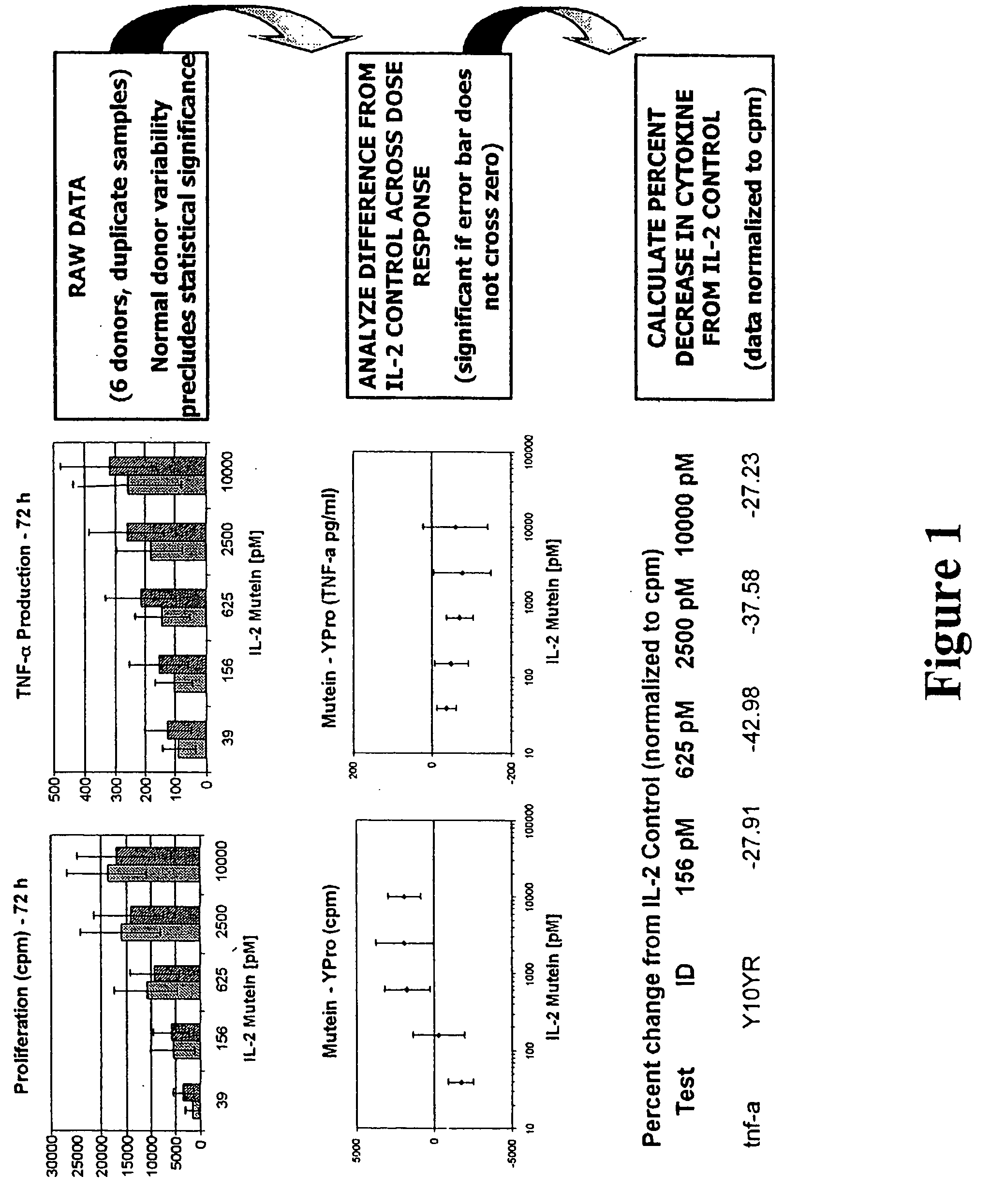
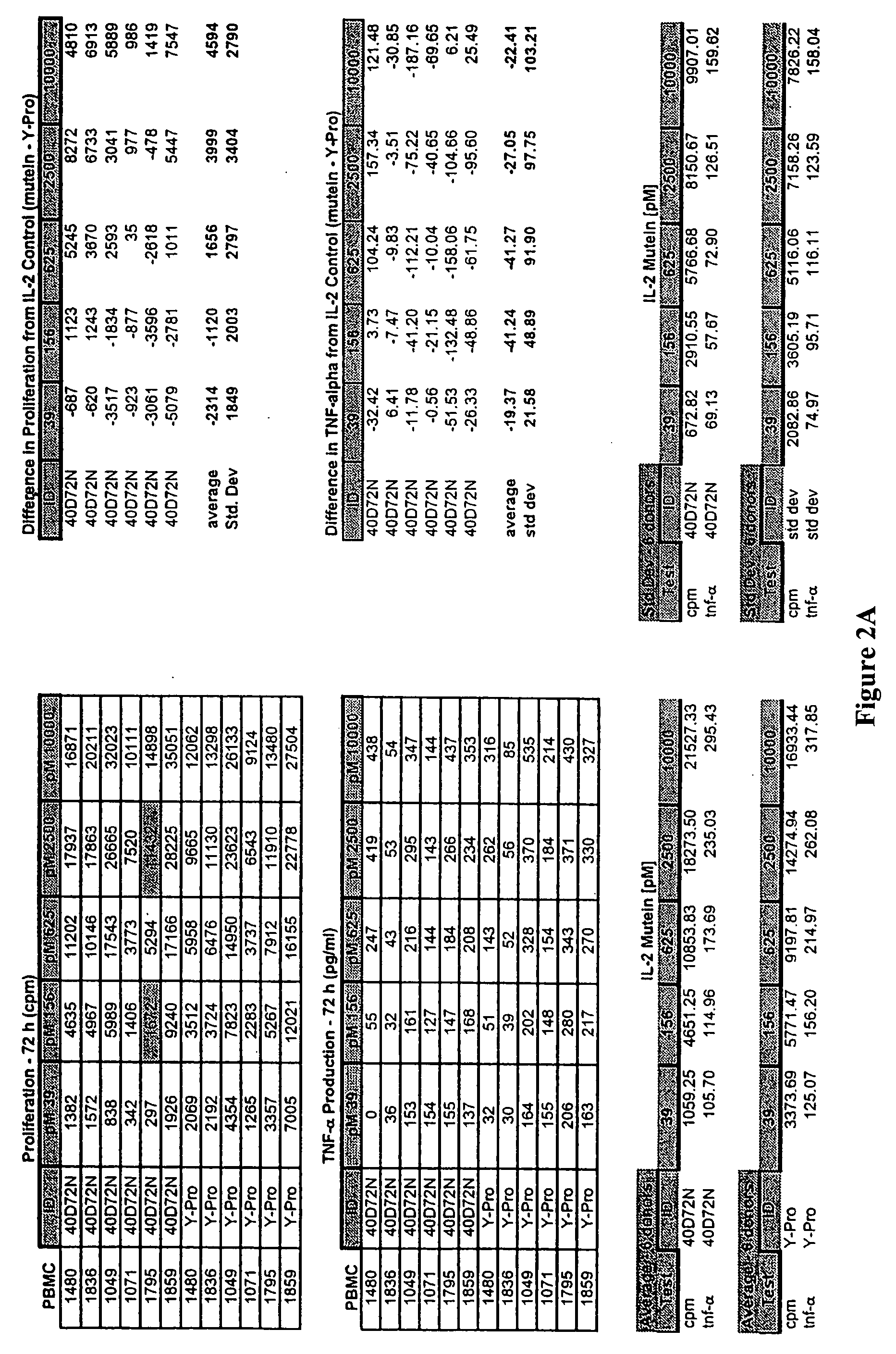
Novel human interleukin-2 (IL-2) muteins or variants thereof, and nucleic acid molecules and variants thereof are provided. Methods for producing these muteins as well as methods for stimulating the immune system of an animal are also disclosed. In addition, the invention provides recombinant expression vectors comprising the nucleic acid molecules of this invention and host cells into which expression vectors have been introduced. Pharmaceutical compositions are included comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a human IL-2 mutein of the invention and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The IL-2 muteins can be used in pharmaceutical compositions for use in treatment of cancer and in stimulating the immune response.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Combinatorial interleukin-2 muteins
InactiveUS20060160187A1Maintaining and enhancing proliferationLower Level RequirementsPeptide/protein ingredientsTissue cultureNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory ReceptorsInterleukin II
Novel human interleukin-2 (IL-2) muteins or variants thereof, and nucleic acid molecules and variants thereof are provided. Methods for producing these muteins as well as methods for stimulating the immune system of an animal are also disclosed. In addition, the invention provides recombinant expression vectors comprising the nucleic acid molecules of this invention and host cells into which expression vectors have been introduced. Pharmaceutical compositions are included comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a human IL-2 mutein of the invention and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The IL-2 muteins have lower toxicity than native IL-2 or Proleukin® IL-2, while maintaining or enhancing NK cell-mediated effects, and can be used in pharmaceutical compositions for use in treatment of cancer, and in stimulating the immune response.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
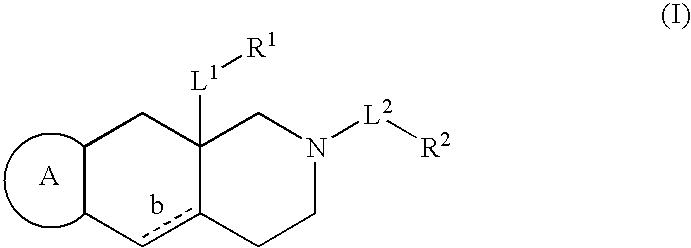
Composition for topical administration
InactiveUS7033604B2Inhibit inflammationAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsMicrobial agentInterleukin II
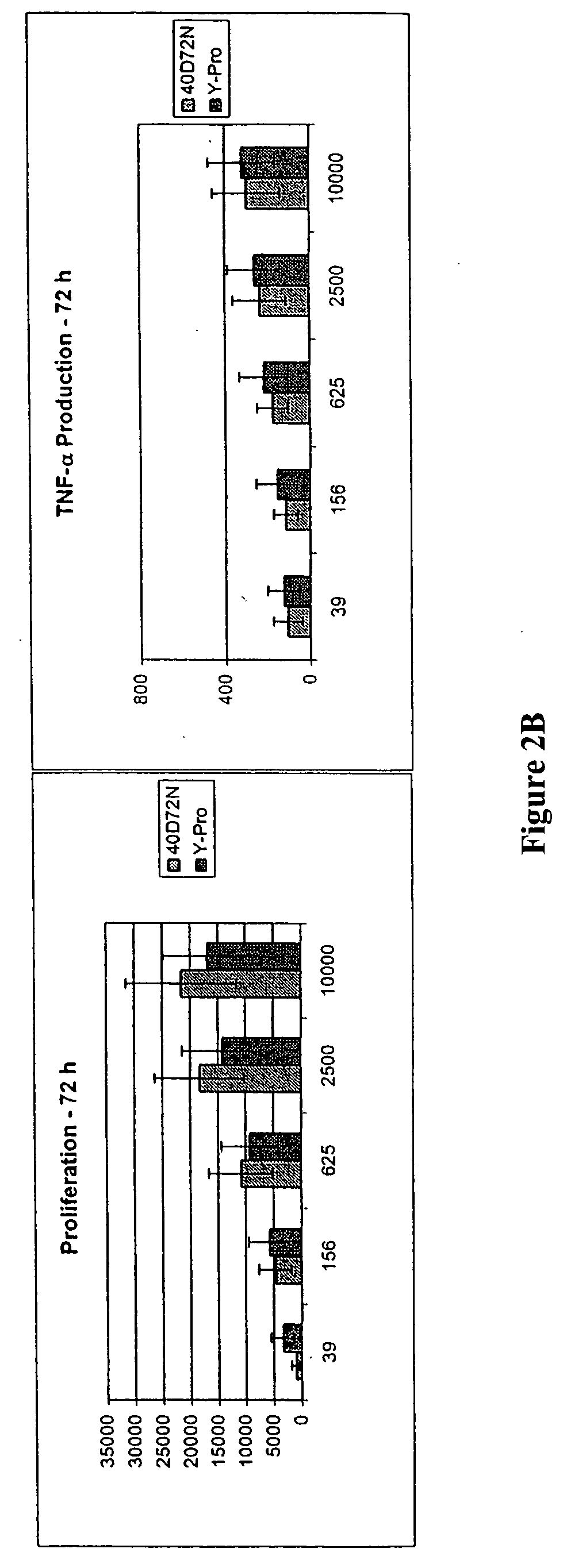
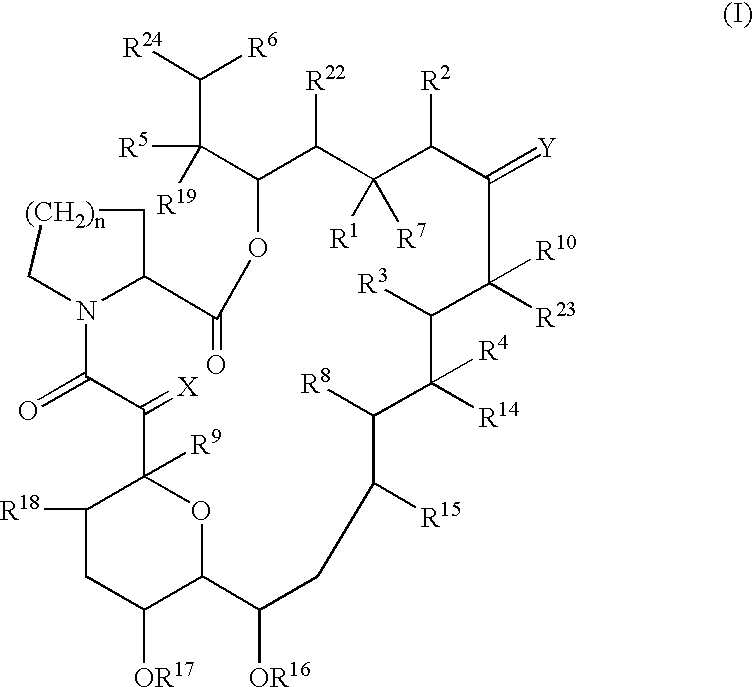
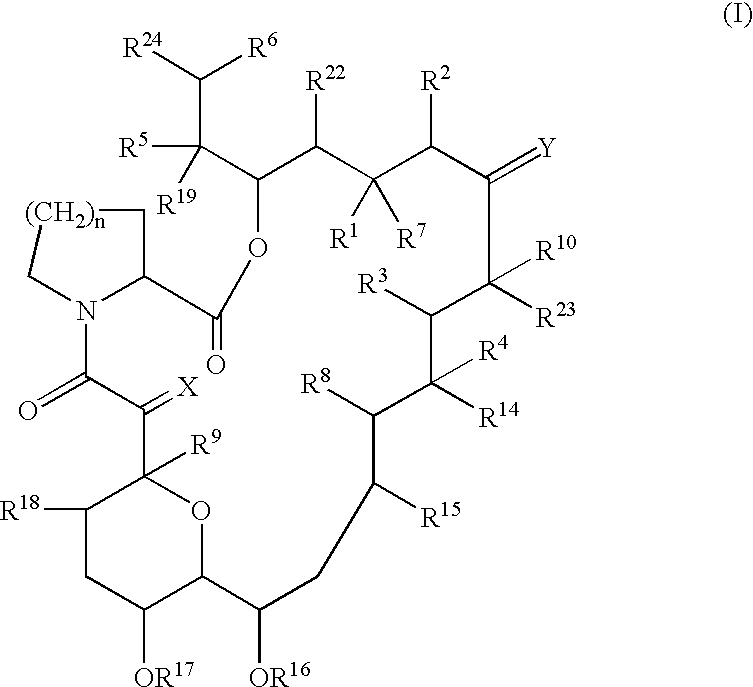
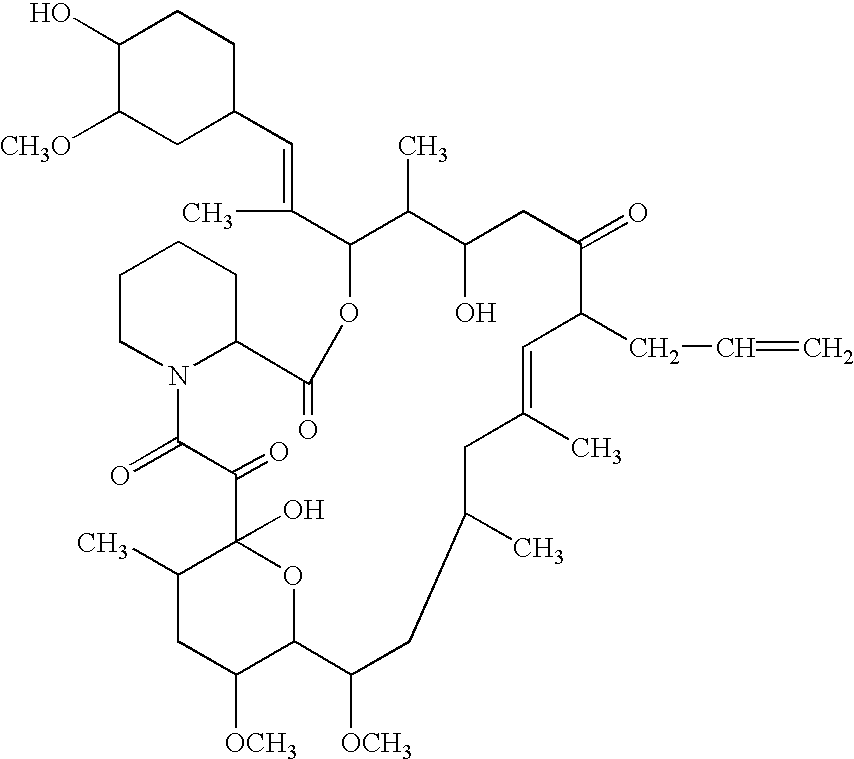
The present invention provides a composition for topical administration comprising an interleukin 2 inhibitor and an antimicrobial agent as active ingredients thereof, wherein said interleukin 2 inhibitor contains a tricyclo compound as shown by the general formula (I) or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. The present invention further provides a method for treating inflammations and / or infections comprising topical administration of an effective amount of an interleukin 2 inhibitor and an antimicrobial agent to a subject in need of the treatment of inflammations and / or infections.
Owner:SUCAMPO
Antagonists of interleukin-2 receptor
ActiveUS9428567B2Reduce interactionPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesInterleukin IIMutant protein
Novel human interleukin-2 (IL-2) muteins or variants thereof, and nucleic acid molecules and variants thereof are provided. Methods for producing these muteins as well as methods for stimulating the immune system of an animal are also disclosed. In addition, the invention provides recombinant expression vectors comprising the nucleic acid molecules of this invention and host cells into which expression vectors have been introduced. Pharmaceutical compositions are included comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a human IL-2 mutein of the invention and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The IL-2 muteins can be used in pharmaceutical compositions for use in treatment of cancer and in stimulating the immune response.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method for efficiently multiplying gamma delta T cells by stimulating peripheral blood in vitro and application of method
ActiveCN105112370AIntact Antitumor CytotoxicityMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsWhite blood cellAntigen receptors
The invention belongs to the field of medical biology engineering, and particularly relates to a method for effectively multiplying gamma delta T cells by stimulating peripheral blood in vitro and application of the method. The method comprises the step of using feeder cells, an OKT3 (ornithine ketoacid transaminase) antibody, interleukin-2 and zoledronic acid. The feeder cells are formed by specifically inserting CD64, CD86 and CD137L genes in a target site of a genome of the feeder cells. After the zoledronic acid and the nterleukin-2 are used for increasing the proportion of the gamma delta T cells of the peripheral blood, protein products of genes, the OKT3 antibody and the interleukin-2 act in a combined manner, and the gamma delta T cells can be stimulated so that a large amount of gamma delta T cells can be multiplied. The multiplied gamma delta T cells can be used for killing tumor cells which are pretreated by the zoledronic acid, or the tumor cells can be directly killed by modifying and expressing chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) via a genetic engineering means. The gamma delta T cells which are obtained by the method have complete anti-tumor cytotoxicity, and can kill solid tumor cells and non-solid tumor cells.
Owner:杭州朔溪生物医药有限公司
Conjugates of an IL-2 moiety and a polymer
Conjugates of an interleukin-2 (“IL-2”) moiety and one or more nonpeptidic, water-soluble polymers are provided. Typically, the nonpeptidic, water-soluble polymer is poly(ethylene glycol) or a derivative thereof. Also provided, among other things, are compositions comprising conjugates, methods of making conjugates, methods of administering compositions to an individual, nucleic acid sequences, expression systems, host cells, and methods for preparing IL-moieties.
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
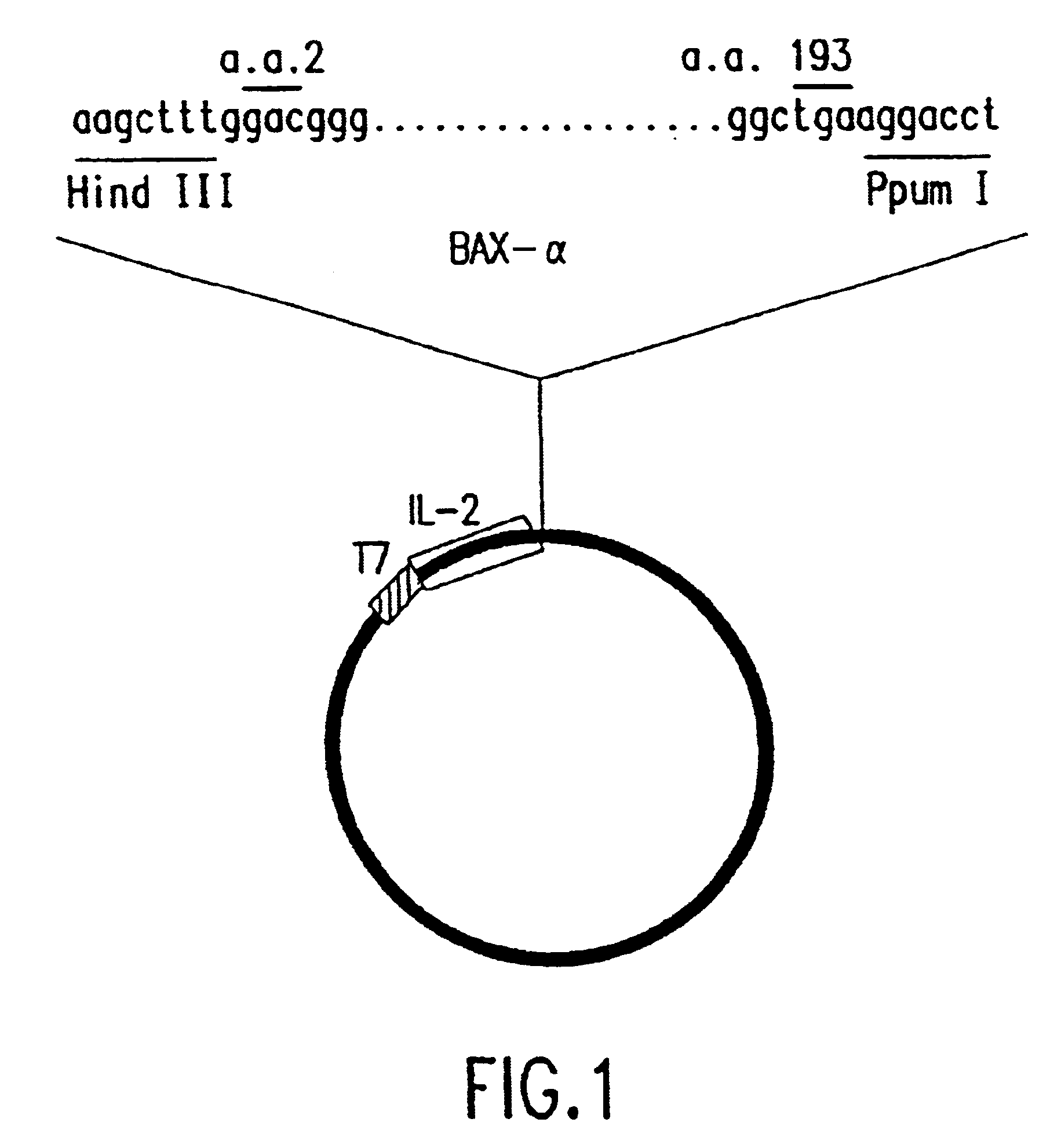
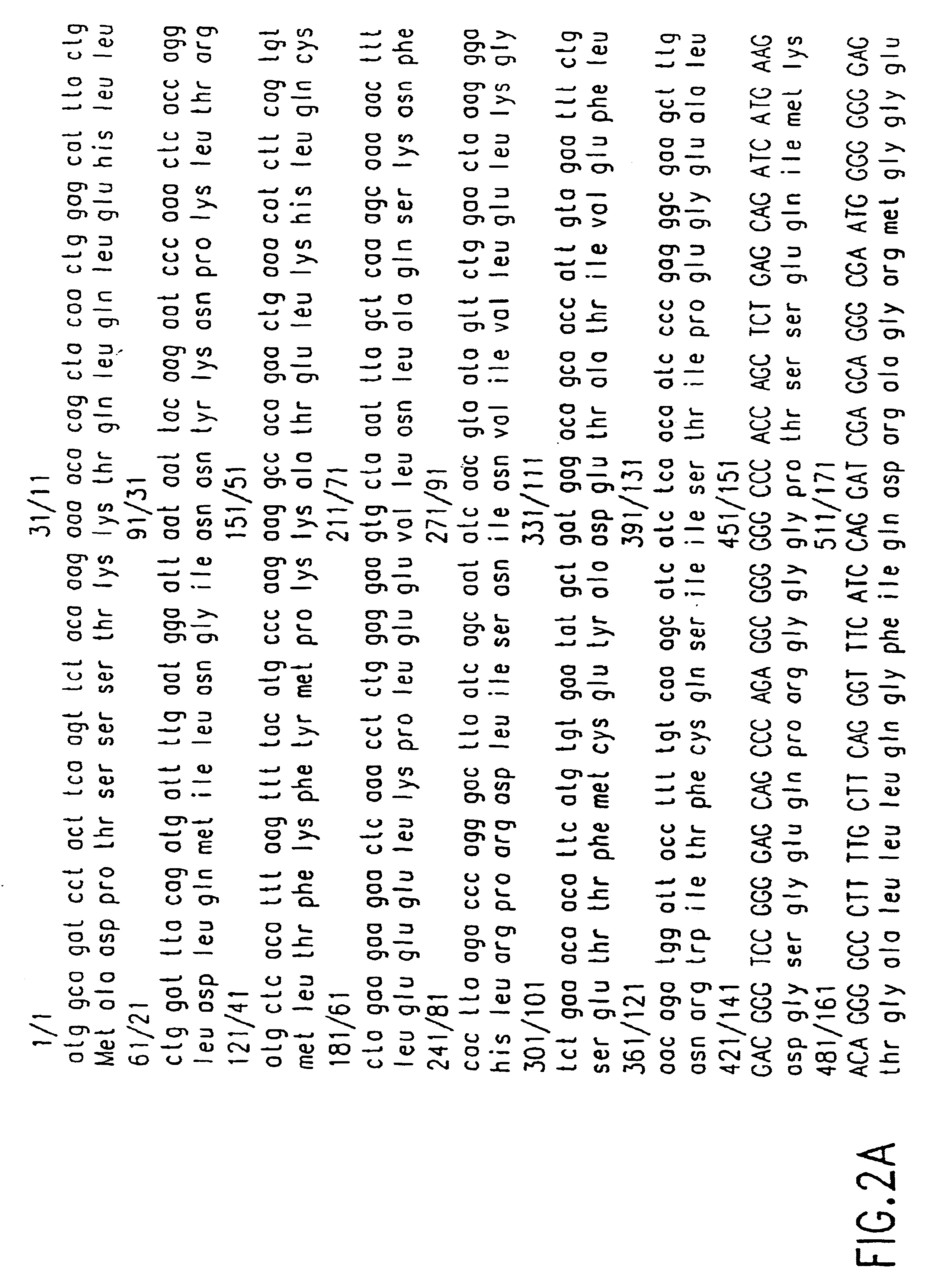
Chimeric proteins with cell-targeting specificity and apoptosis-inducing activities
InactiveUS20020090374A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsApoptosisInterleukin II
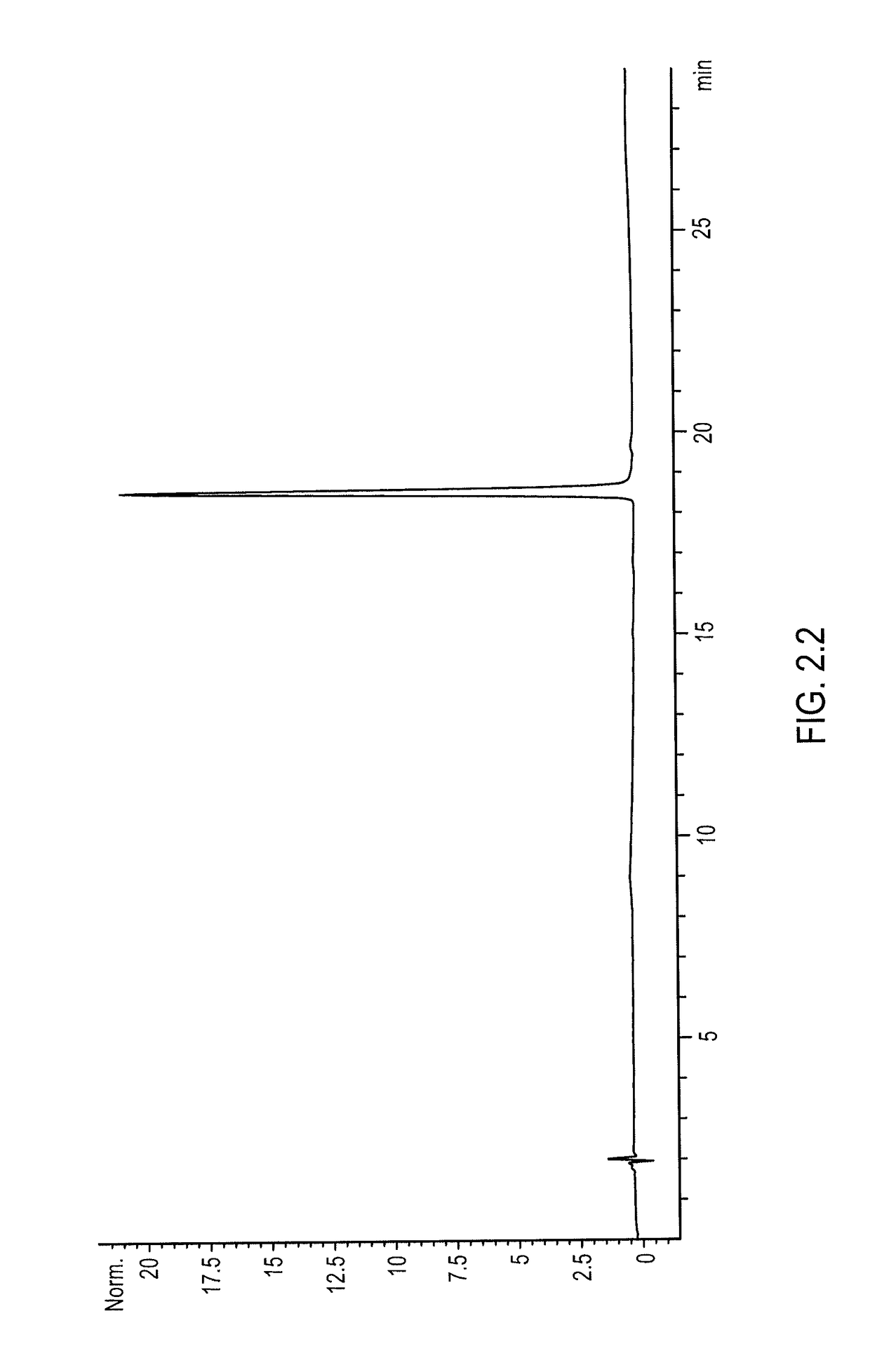
The present invention relates to chimeric proteins with cell-targeting specificity and apoptosis-inducing activities. In particular, the invention is illustrated by a recombinant chimeric protein between human interleukin-2 (IL2) and Bax. The chimeric protein specifically targets IL2 receptor (IL2R)-expressing cells and induces cell-specific apoptosis.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Method of producing a mouse suitable for engraftment, differentiation and proliferation of heterologous cells, mouse produced by this method and use of the mouse
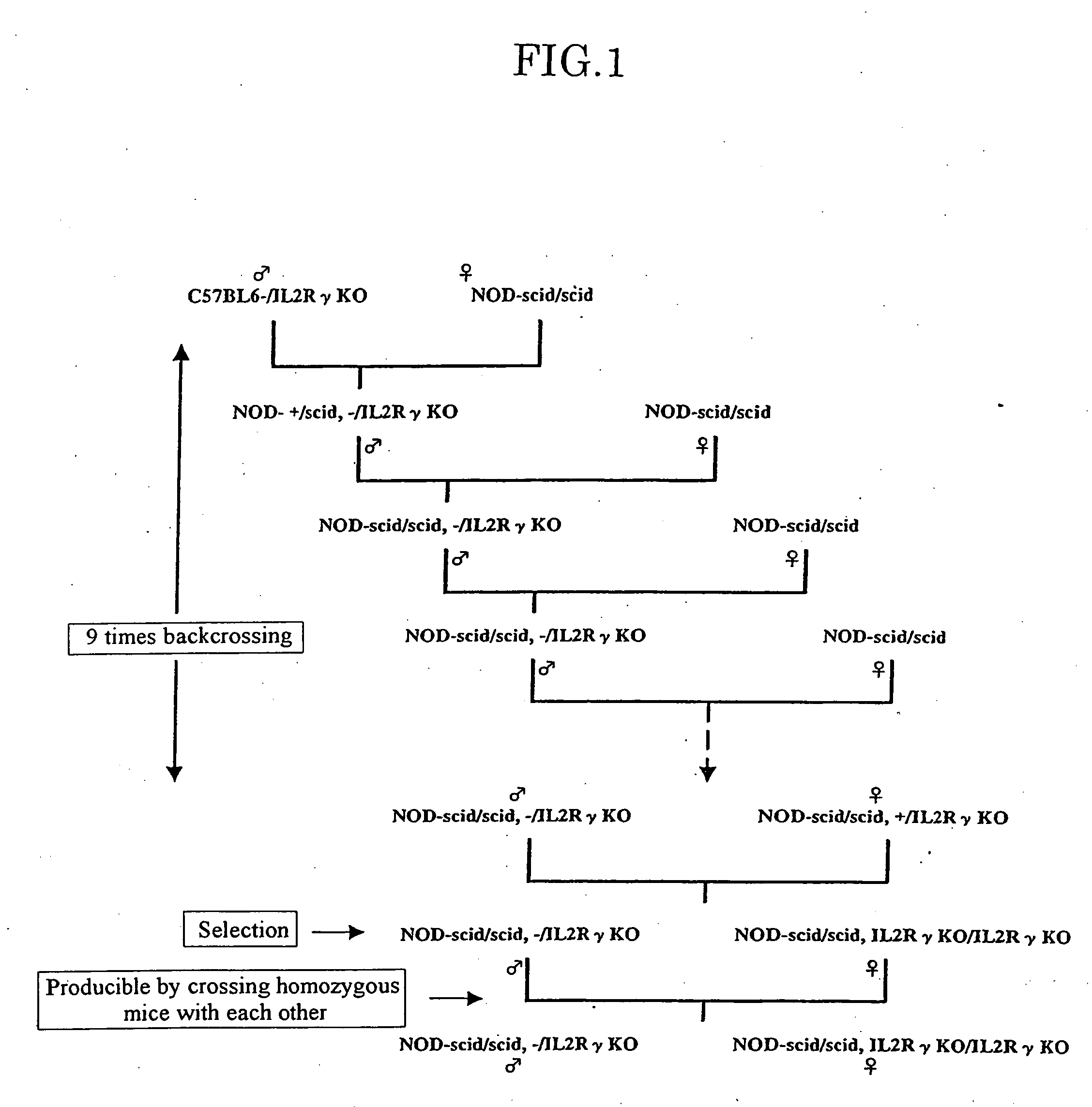
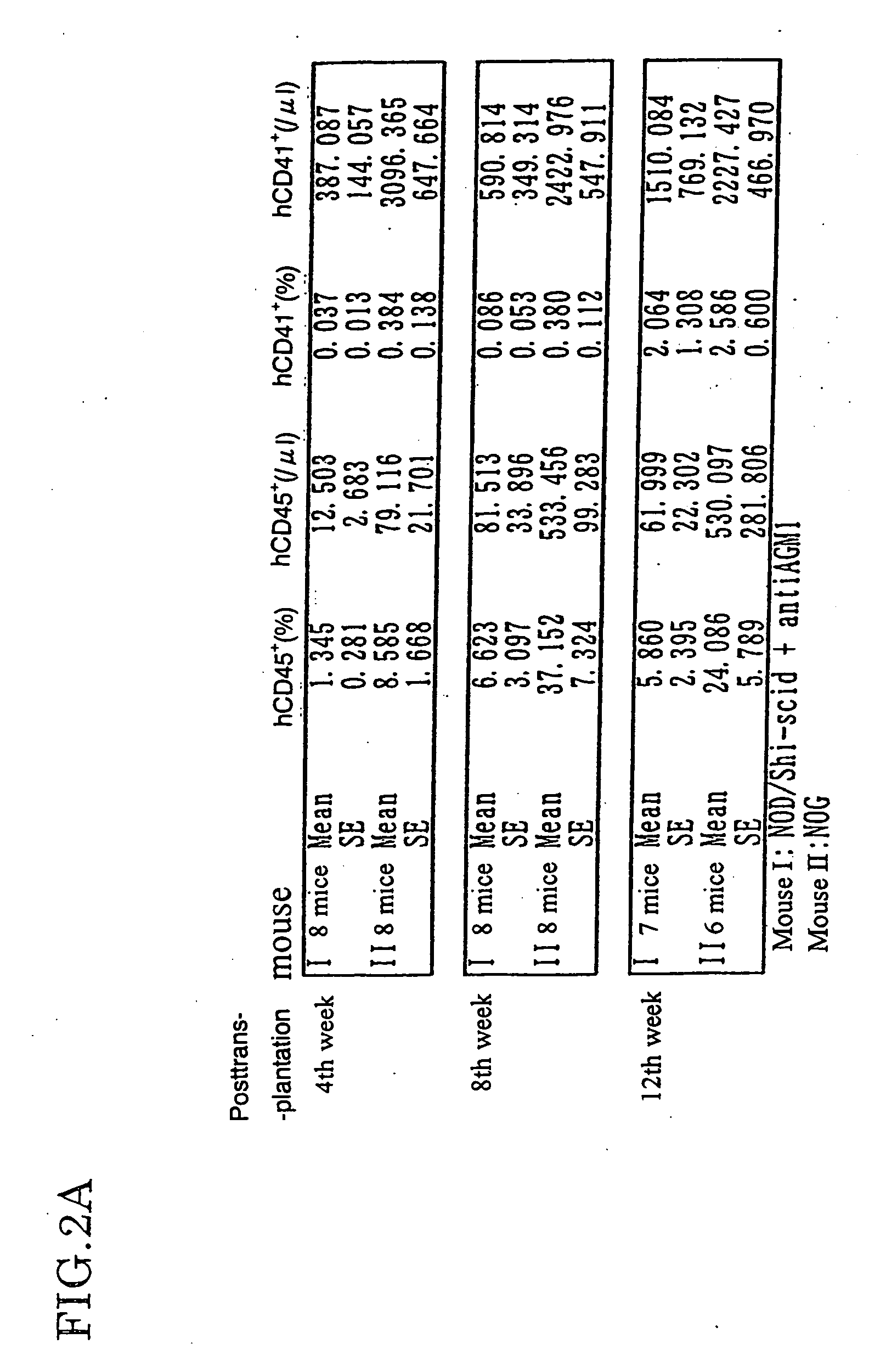
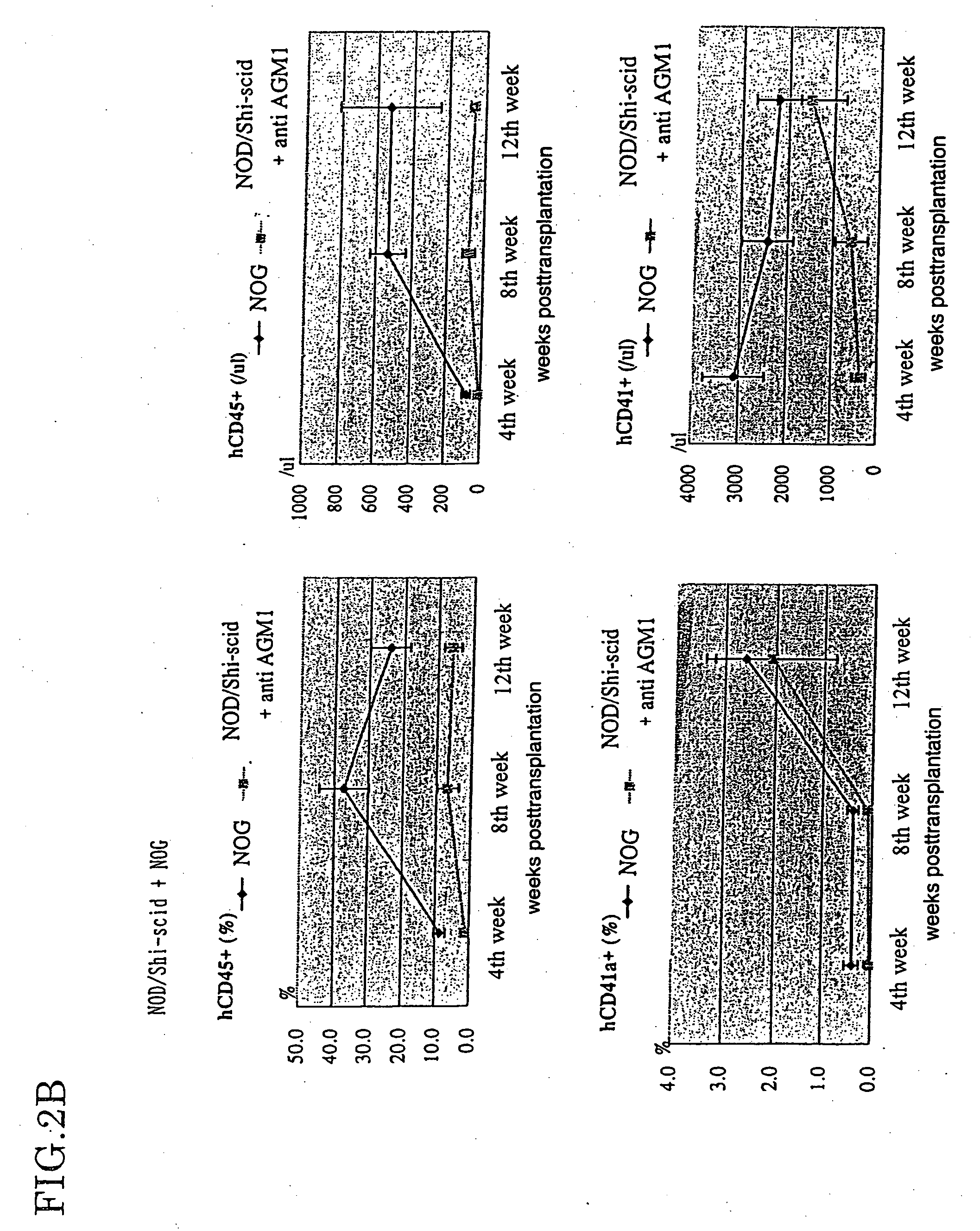
InactiveUS20070011753A1Excellent heterologous cell engraftment capacityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansArtificially induced pluripotent cellsHeterologousAbnormal tissue growth
The present invention provides an immunodeficient mouse (NOG mouse) suitable for engraftment, differentiation and proliferation of heterologous cells, and a method of producing such a mouse. This mouse is obtained by backcrossing a C.B-17-scid mouse with an NOD / Shi mouse, and further backcrossing an interleukin 2-receptor γ-chain gene-knockout mouse with the thus backcrossed mouse. It is usable for producing a human antibody and establishing a stem cell assay system, a tumor model and a virus-infection model.
Owner:ITO MAMORU +9
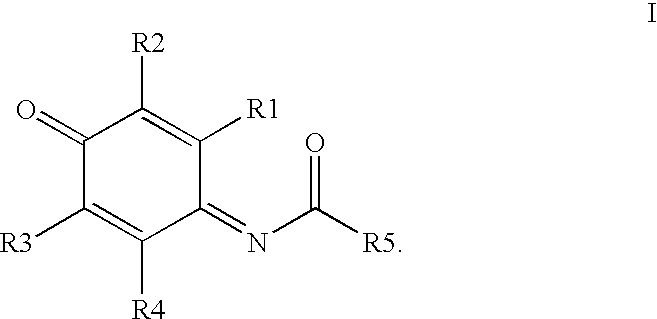
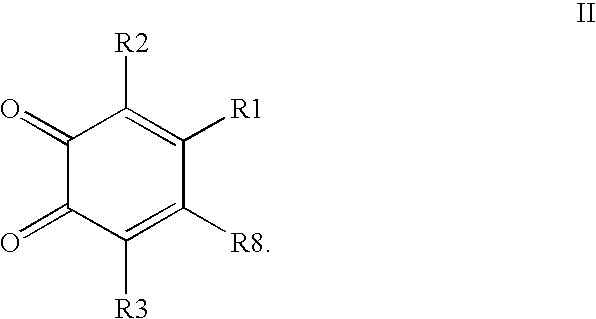
Compounds having MIF antagonist activity
There are disclosed methods of use and pharmaceutical compositions for two related genera of low molecular weight compounds comprising optionally substituted iminoquinone or orthoquinone ring systems. The compounds have MIF (macrophage migration inhibitory factor) antagonist activity and find utility as such. For example, the compounds are useful for treating a variety of diseases involving inflammatory activity or pro-inflammatory cytokine responses, such as autoimmune diseases (including rheumatiod arthritis, insulin-dependent diabetes, multiple sclerosis, graft versus host disease, lupus syndromes), asthma, arthritis, EAE, ARDS, psoriasis, interleukin-2 toxicity, proliferative vascular disease, and various forms of sepsis and septic shock, and other conditions characterized by underlying MIF responses including, for instance, tumor growth and neovascularization (angiogenesis).
Owner:CYTOKINE PHARMASCI
Immunomodulatory interleukin-2 polypeptides and methods of treating melanoma
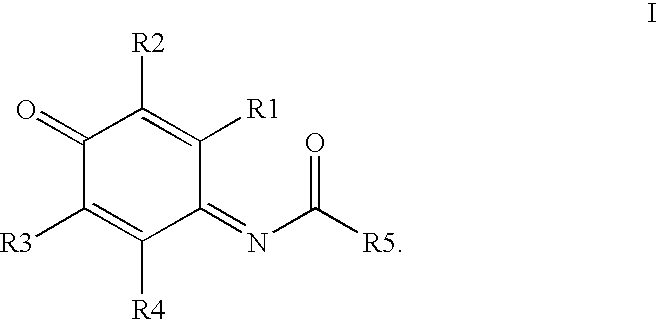
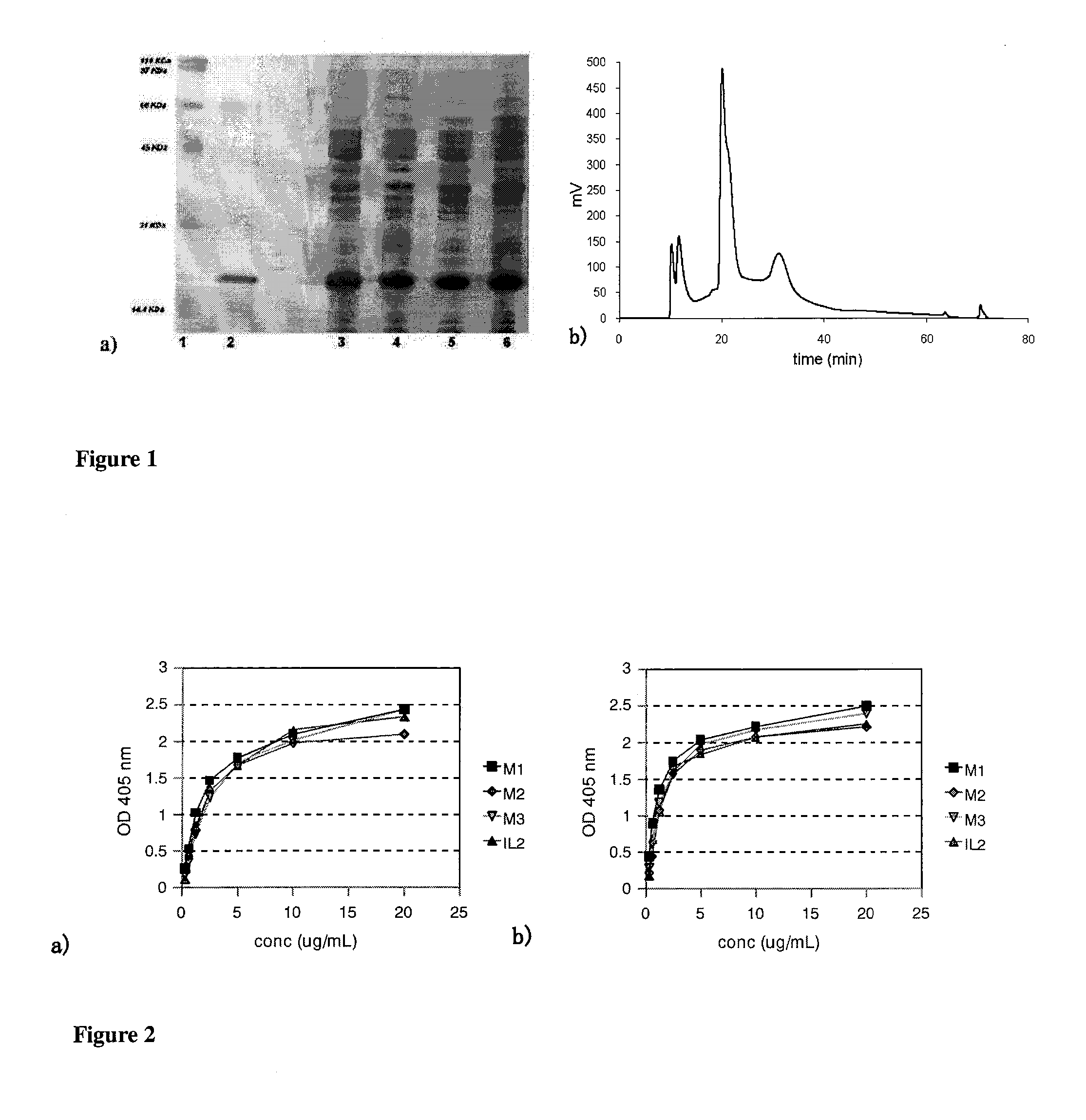
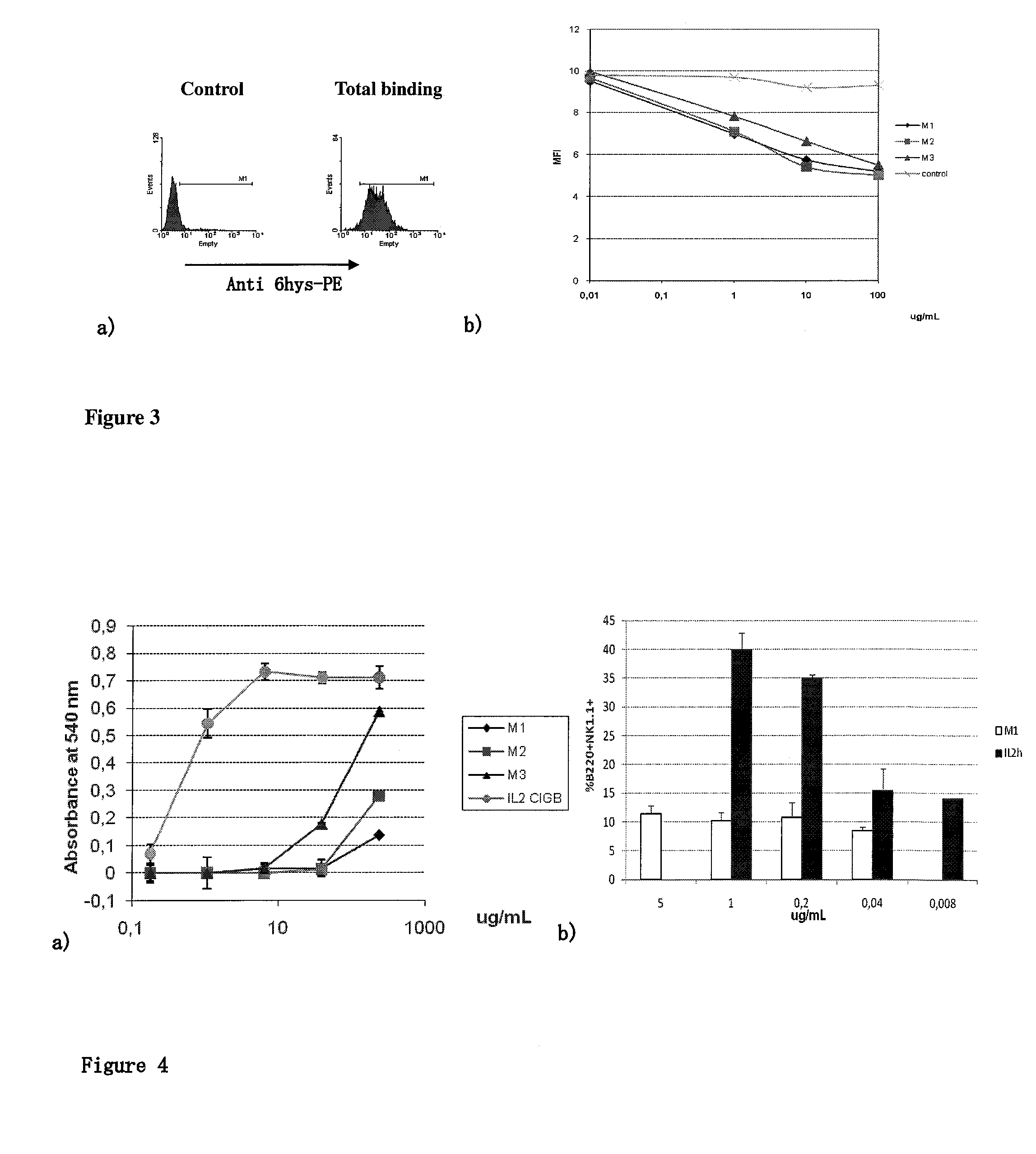
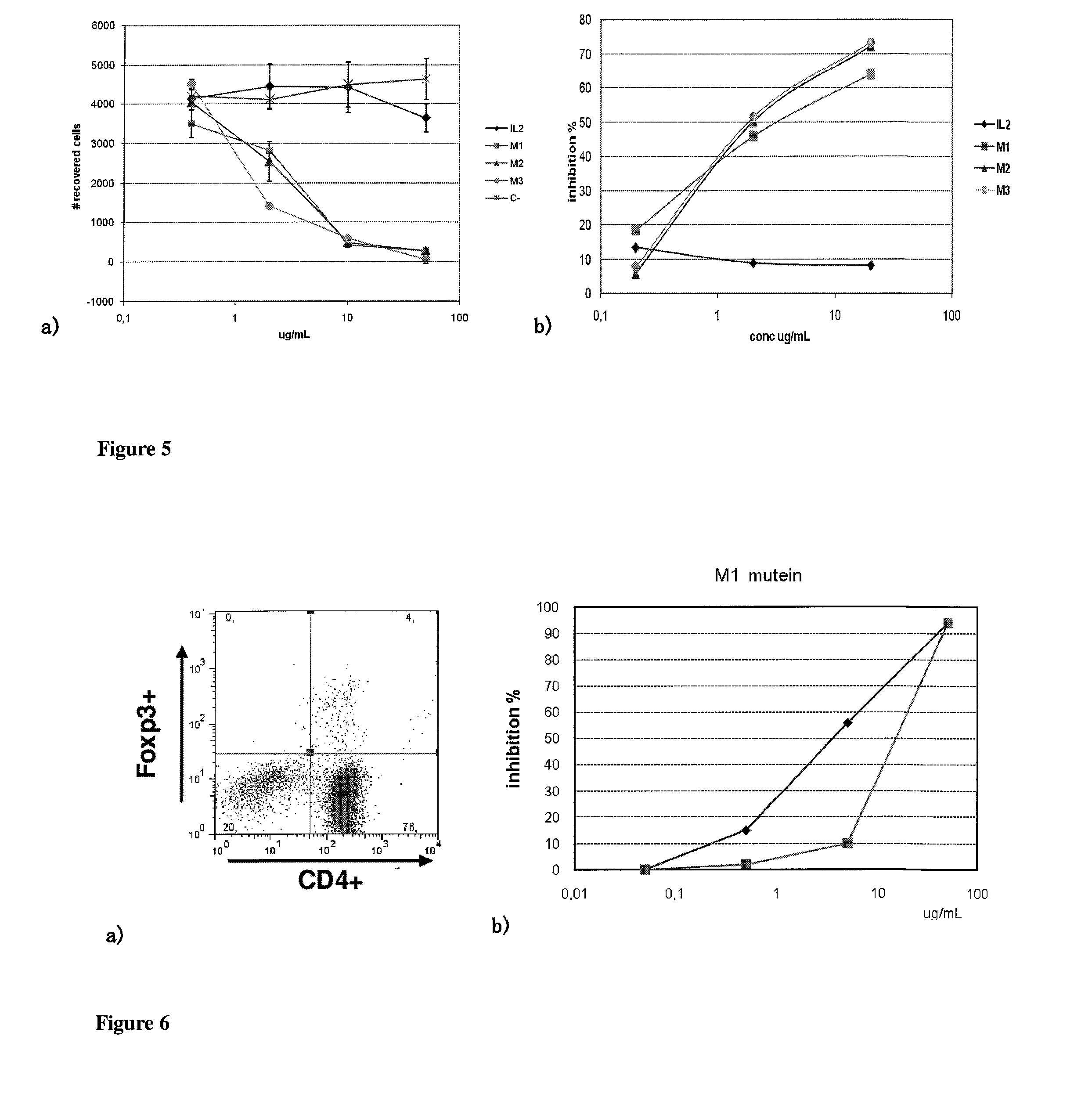
The present invention relates generally to polypeptides whose primary sequence has high sequence homology with human interleukin 2 (IL-2) with some punctual mutations in the sequence of native IL-2. The polypeptides of the present invention have an immunomodulatory effect on the immune system, which is selective / preferential on regulatory T cells. The present invention also relates to specific polypeptides whose amino acid sequence is disclosed herein. In another aspect the present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising as active ingredient the polypeptides disclosed. Finally, the present invention relates to the therapeutic use of the polypeptides and pharmaceutical compositions disclosed due to their immune modulating effect on diseases such as cancer and chronic infectious diseases.
Owner:CENT DE INMUNOLOGIA MOLECULAR CENT DE INMUNOLO
Method for amplification and activation of NK cells by K562 cells
ActiveCN103232973AHelp identify and killHelp activate recognition and killMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory ReceptorsCD86
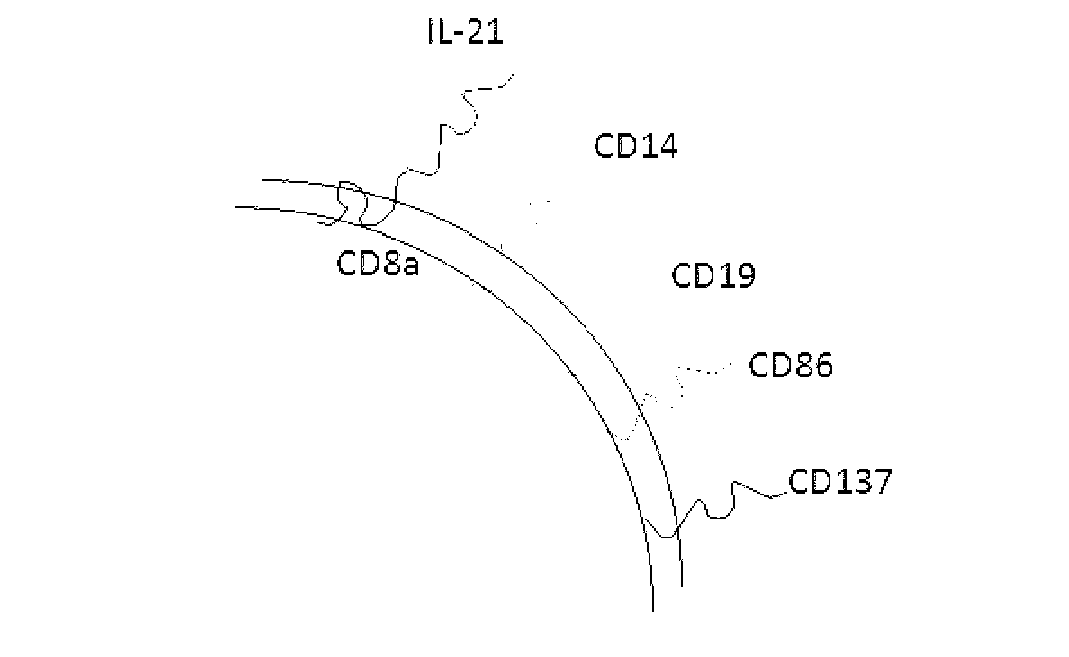
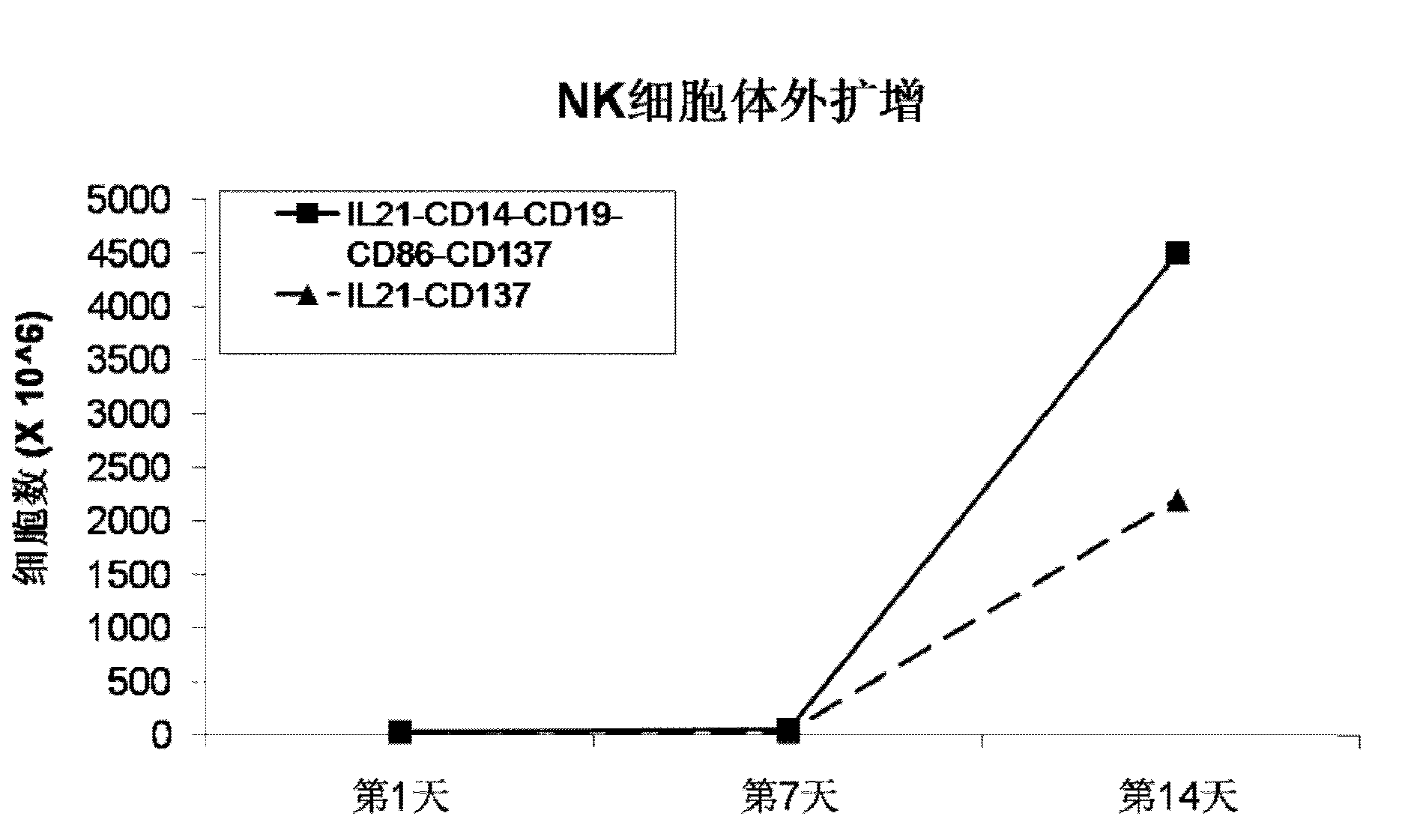
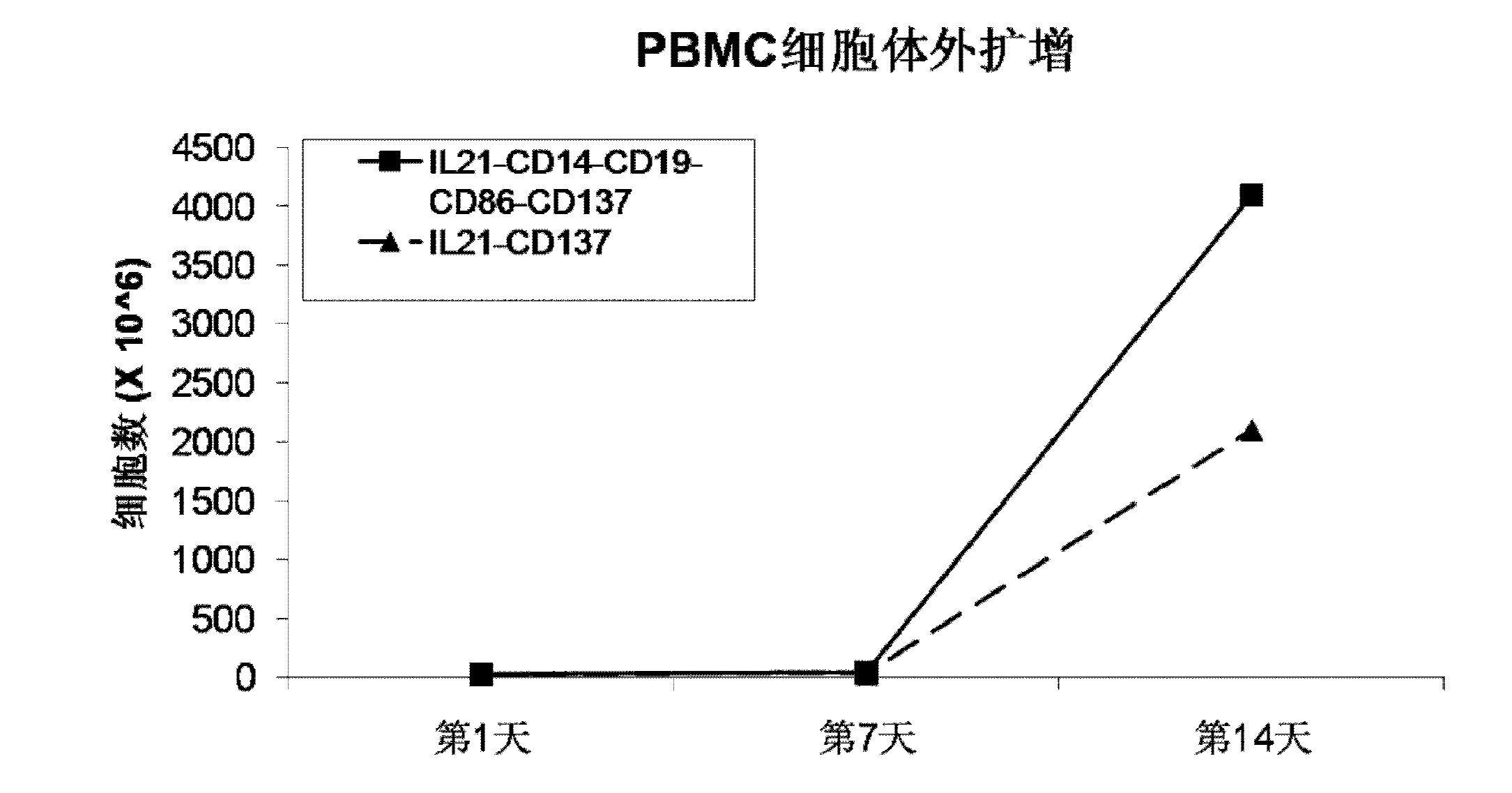
The invention discloses a method for amplification and activation of NK cells by K562 cells. The method comprises that through synergism of K562 cells transfected by transmembrane interleukin 21, CD14, CD19, CD86 and CD137, and low-concentration interleukin 2, NK cells are subjected to directed amplification and activation. Compared with the existing similar compounds, the compound provided by the invention has a stronger lymphocyte amplification and activation capability and higher efficiency. The method has wide prospects in immunological therapy.
Owner:杭州中赢生物医疗科技有限公司
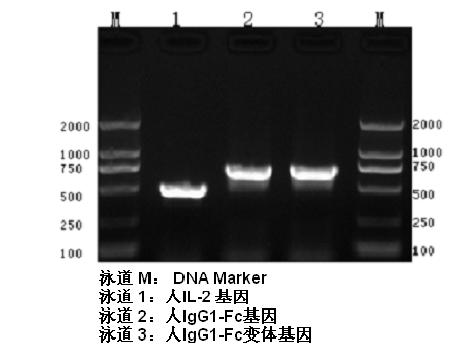
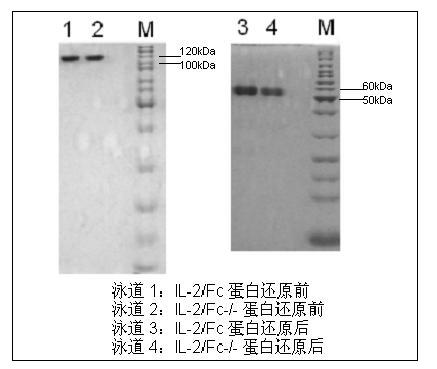
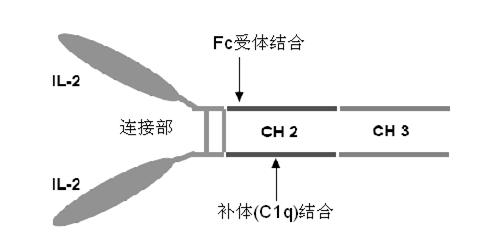
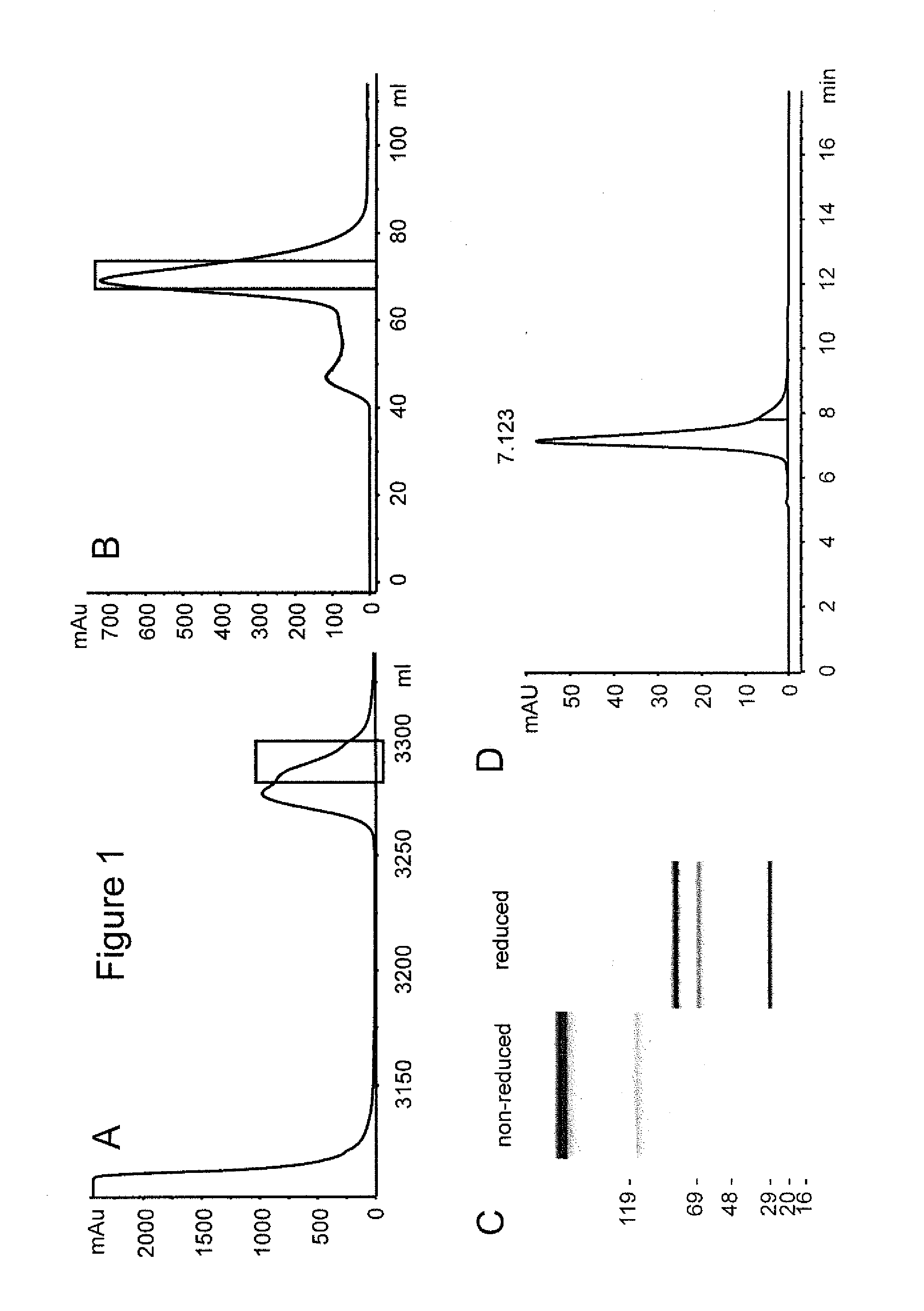
Human interleukin-2 (IL-2)/Fc fusion protein
ActiveCN102174111AEnhance humoral immune responseImprove immunityPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemRegulatory T cellHalf-life
The invention provides human interleukin interleukin-2 (IL-2) / Fc fusion protein. The human IL-2 of the fusion protein comprises all sequences of a human IL-2 extracellular region; the Fc fragments comprise a hinge region, a CH2 region and a CH3 region; the human IL-2 / Fc sequences are fused directly or through a connection sequence; and the Fc fragments are human or animal IgG, IgM, IgD and IgA orsubtypes thereof. The ADCC and CDC effective factor action can be eliminated, and in addition, the human IL-2 / Fc fusion protein has the compatibility with a recombinant IL-2 receptor so that the half-life period is obviously prolonged and also has all the biological activity of the IL-2 receptor. The IL-2 / Fc obviously improves the humoral immune response stimulated by the hepatitis B vaccine and the immunity of the CD8+T cells targeted to the hepatitis B vaccine. Moreover, the balance immune (suppression) of the effective T cells and the regulatory t cells can be adjusted under the action of the cyclosporine A so that the pancreatic islet transplantation immune tolerance is induced.
Owner:上海百英生物科技股份有限公司
Interleukin-2 fusion proteins and uses thereof
The present invention generally relates to fusion proteins of immunoglobulins and interleukin-2 (IL-2). More particularly, the invention concerns fusion proteins of immunoglobulins and mutant IL-2 that exhibit improved properties for use as therapeutic agents, e.g. in the treatment of autoimmune diseases and immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. In addition, the present invention relates to polynucleotides encoding such fusion proteins, and vectors and host cells comprising such polynucleotides. The invention further relates to methods for producing the fusion proteins of the invention, and to methods of using them in the treatment of disease.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG +1
Method and system to remove soluble tnfr1, tnfr2, and il2 in patients
A method, and system, to induce remission in diseases characterized by excess production of sTNR and interleukin 2 has been developed. In the most preferred embodiment, the system consists of antibodies to sTNFR1, sTNFR2 and sIL2R immobilized in a column containing a material such as SEPHAROSE™. The patient is connected to a pheresis machine which separates the blood into the plasma and red cells, and the plasma is circulated through the column until the desired reduction in levels of sTNFR1, sTNFR2, and IL2 is achieved, preferably to less than normal levels. In the preferred method, patients are treated three times a week for four weeks. This process can be repeated after a period of time. Clinical studies showed reduction in tumor burden in patients having failed conventional chemotherapy and radiation treatments.
Owner:INNATUS CORP
Chimeric proteins with cell-targeting specificity and apoptosis-inducing activities
The present invention relates to chimeric proteins with cell-targeting specificity and apoptosis-inducing activities. In particular, the invention is illustrated by a recombinant chimeric protein between human interleukin-2 (IL2) and Bax. The chimeric protein specifically targets IL2 receptor (IL2R)-expressing cells and induces cell-specific apoptosis.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
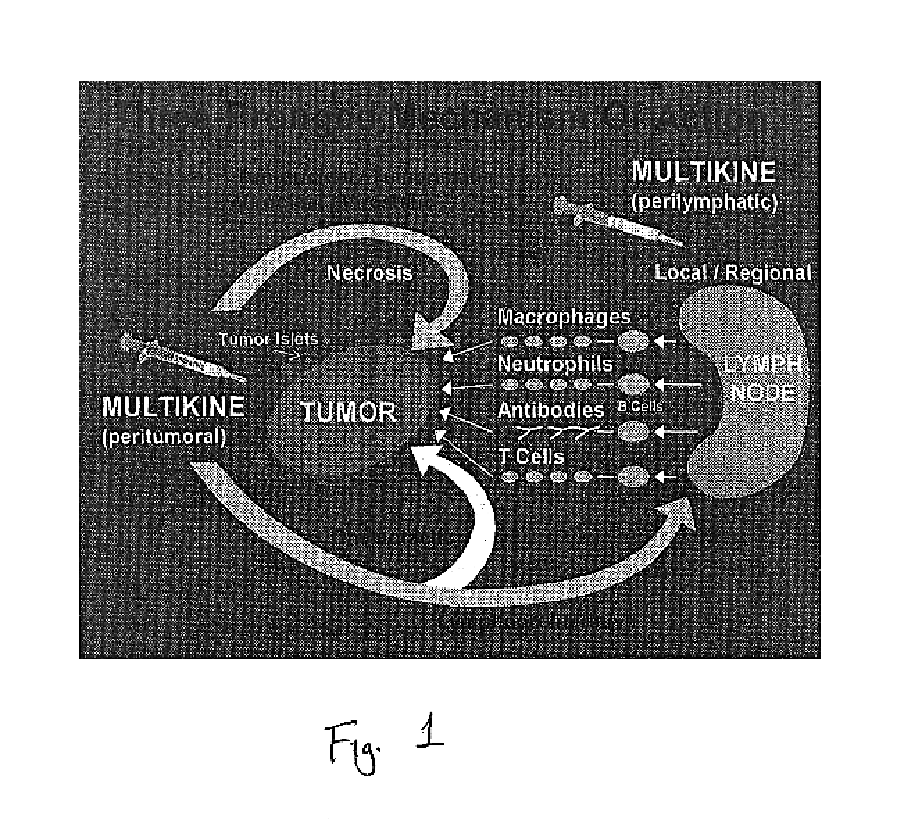
Method of pre-sensitizing cancer prior to treatment with radiation and/or chemotherapy and a novel cytokine mixture
This invention relates to a breakthrough method for pre-sensitizing cancer prior to a therapeutic treatment such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy or immuno-therapy and a novel cytokine mixture used in the method thereof. The cytokine mixture is a serum-free and mitogen-free mixture comprised of specific ratios of cytokines such as IL-1β, TNF-α, IFN-γ and GM-CSF to Interleukin 2 (IL-2), which is effective in inducing cancerous cells to enter a proliferative cell cycle phase thereby increasing their vulnerability to chemotherapy, radiation therapy and immuno-therapy. One such novel cytokine mixture is Multikine®, which can be used alone or in combination with other drugs for the treatment of cancer thereby increasing the success of cancer treatment and the disease free survival of cancer patients.
Owner:CEL SCI CORP
Interleukin-2 stimulated T lymphocyte cell death for the treatment of autoimmune diseases, allergic responses, and graft rejection
A method for the treatment or prevention of autoimmune diseases, allergic or atopic disorders, and graft rejection is provided, comprising inducing the death by apoptosis of a subpopulation of T lymphocytes that is capable of causing such diseases, while leaving substantially unaffected the majority of other T lymphocytes. Cell death is achieved by cycle(s) comprising challenging via immunization these T cells with antigenic substance at short time intervals, or by immunization followed by administering interleukin-2 (IL-2) when these T cells are expressing high levels of IL-2 receptor so as to cause these T cells to undergo apoptosis upon re-immunization with the antigenic peptide or protein. These methods are applicable to the treatment of autoimmune diseases such as, for example, multiple sclerosis, uveitis, arthritis, Type I insulin-dependent diabetes, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, Grave's thyroiditis, autoimmune myocarditis, etc., allergic disorders such as hay fever, extrinsic asthma, or insect bite and sting allergies, food and drug allergies, as well as for the treatment or prevention of graft rejection.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Antibody fragment-polymer conjugates and uses of same
Described are conjugates formed by an antibody fragment covalently attached to a non-proteinaceous polymer, wherein the apparent size of the conjugate is at least about 500 kD. The conjugates exhibit substantially improved half-life, mean residence time, and / or clearance rate in circulation as compared to the underivatized parental antibody fragment. Also described are conjugates directed against human vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), human p185 receptor-like tyrosine kinase (HER2), human CD20, human CD18, human CD11a, human IgE, human apoptosis receptor-2 (Apo-2), human tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), human tissue factor (TF), human α4β7 integrin, human GPIIb-IIIa integrin, human epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), human CD3, and human interleukin-2 receptor α-chain (TAC) for diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Use of a glucocorticoid receptor ii antagonist to treat depression in patients taking il-2
The invention pertains to the discovery that type II glucocorticoid receptor antagonists can be used in methods for reversing or inhibiting the symptoms of depression in patients receiving interleukin-2 treatment.
Owner:CORCEPT THERAPEUTICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com