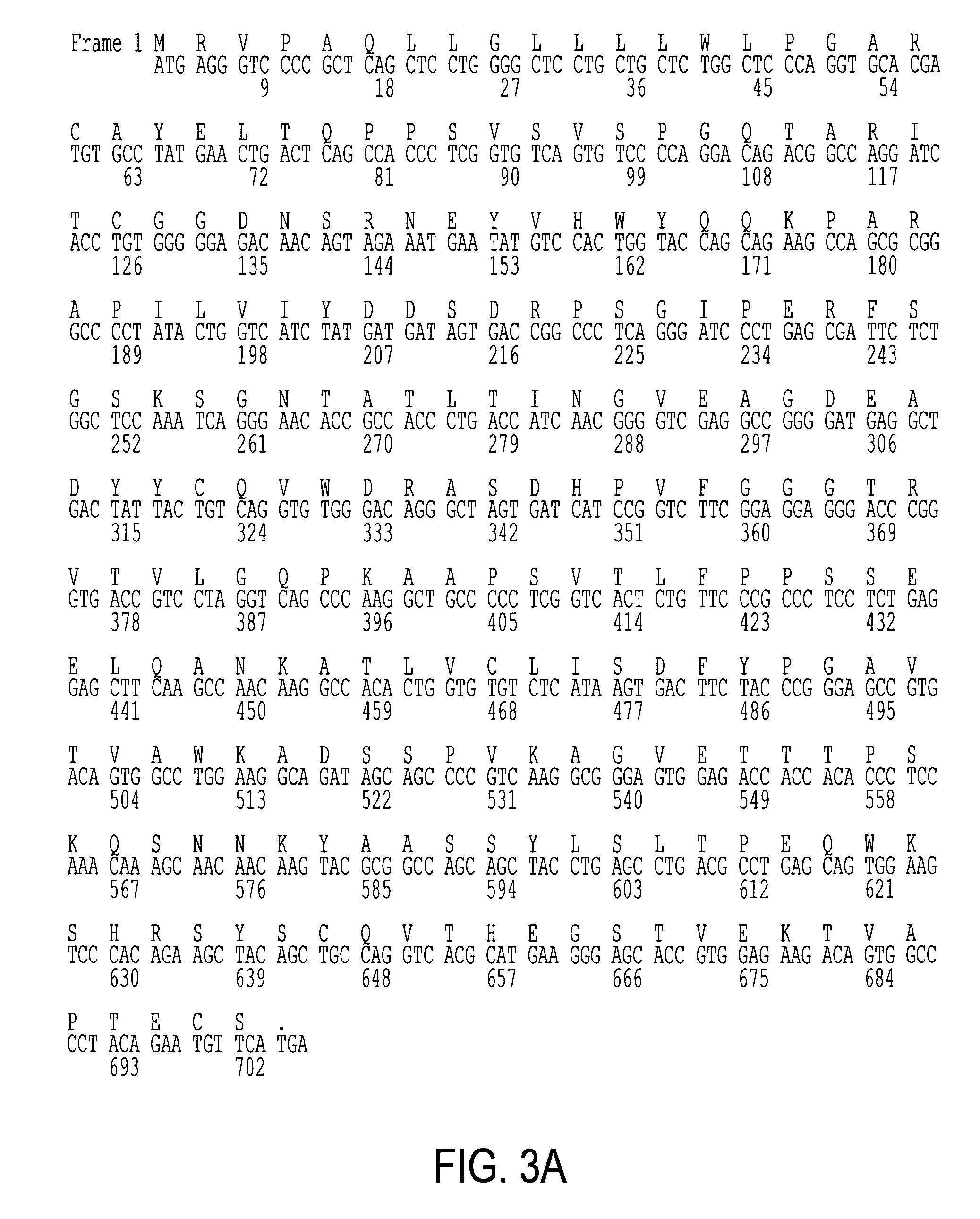Patents
Literature
127 results about "CD86" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cluster of Differentiation 86 (also known as CD86 and B7-2) is a protein expressed on antigen-presenting cells that provides costimulatory signals necessary for T cell activation and survival. It is the ligand for two different proteins on the T cell surface: CD28 (for autoregulation and intercellular association) and CTLA-4 (for attenuation of regulation and cellular disassociation). CD86 works in tandem with CD80 to prime T cells.
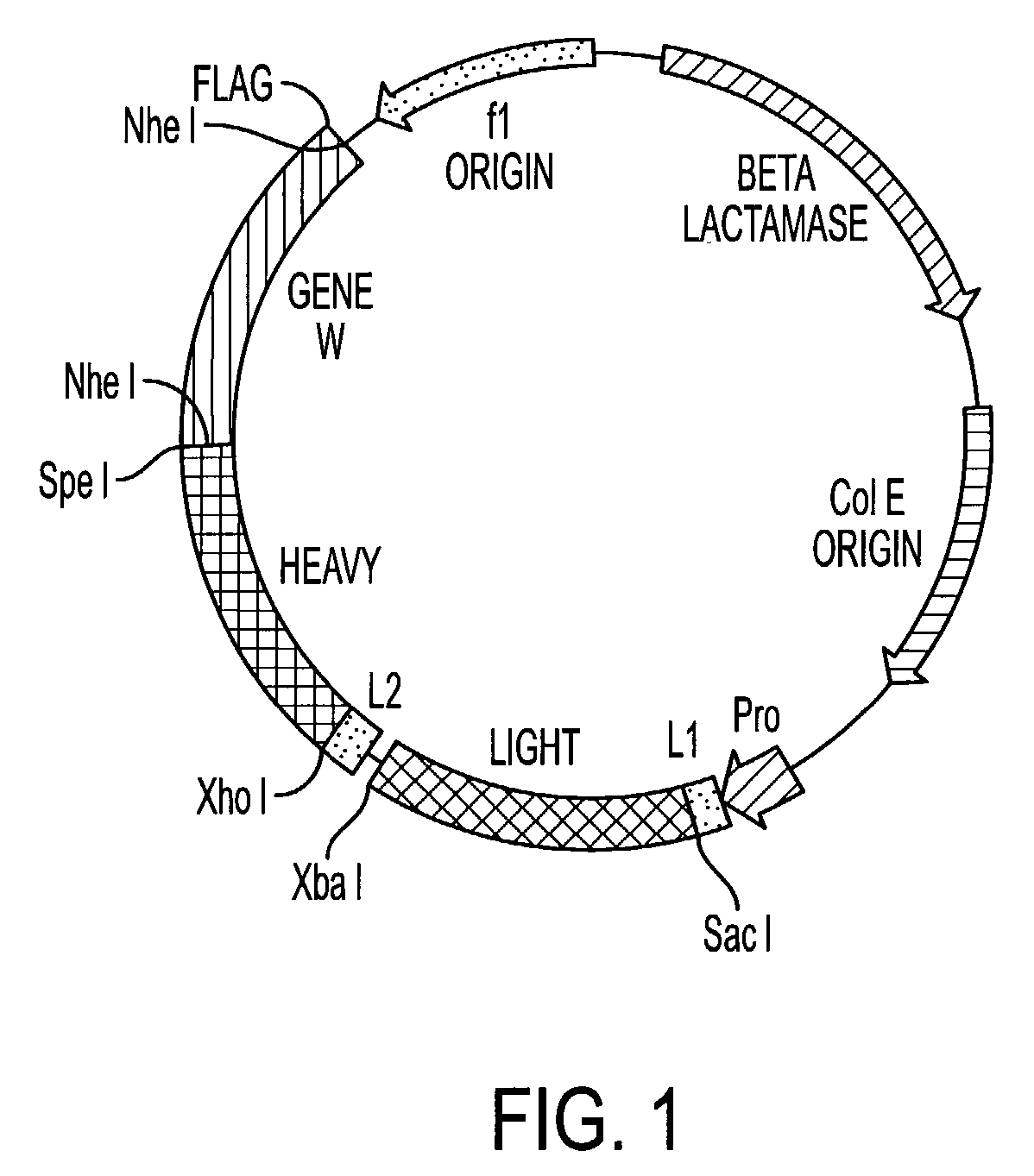
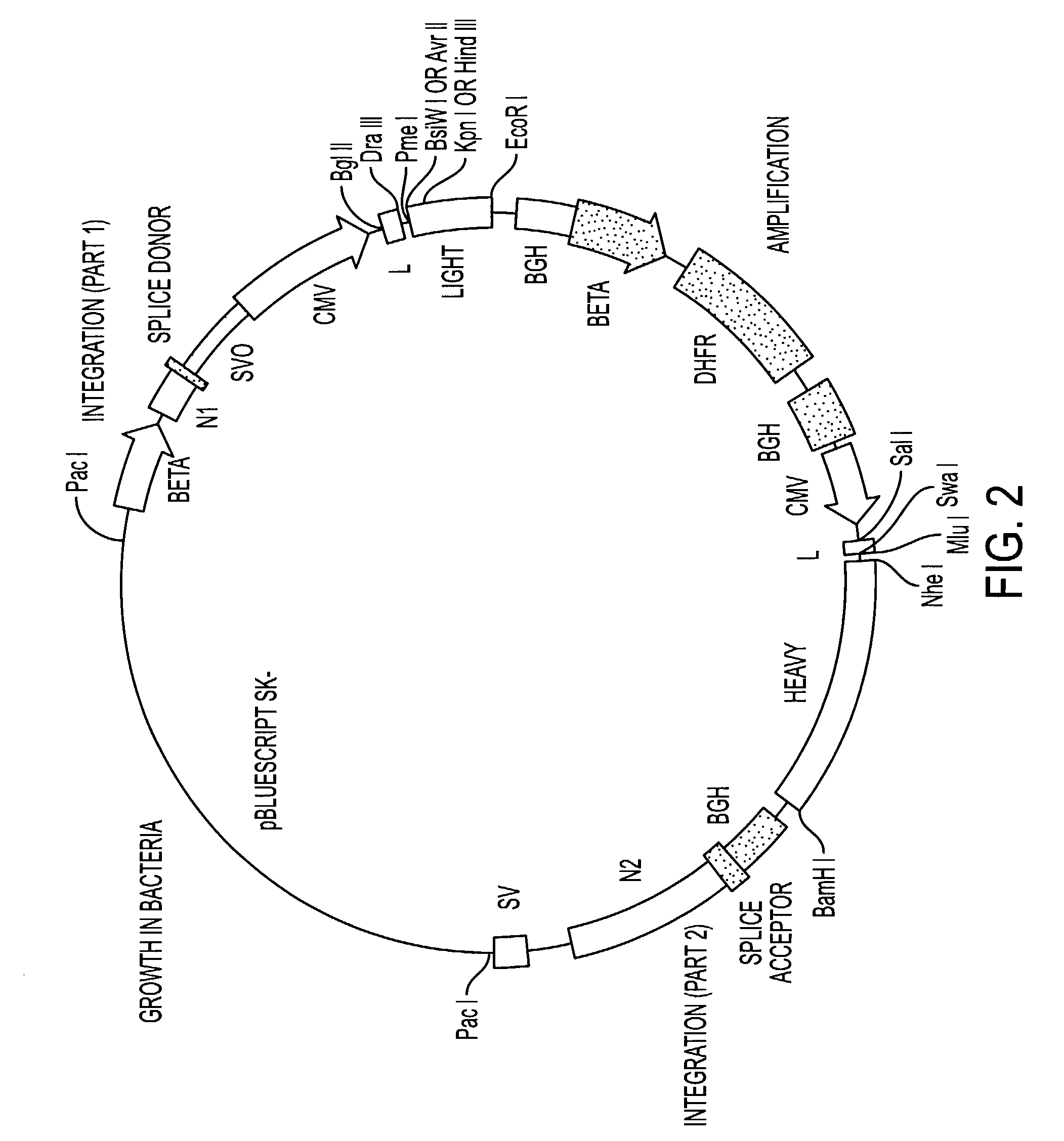
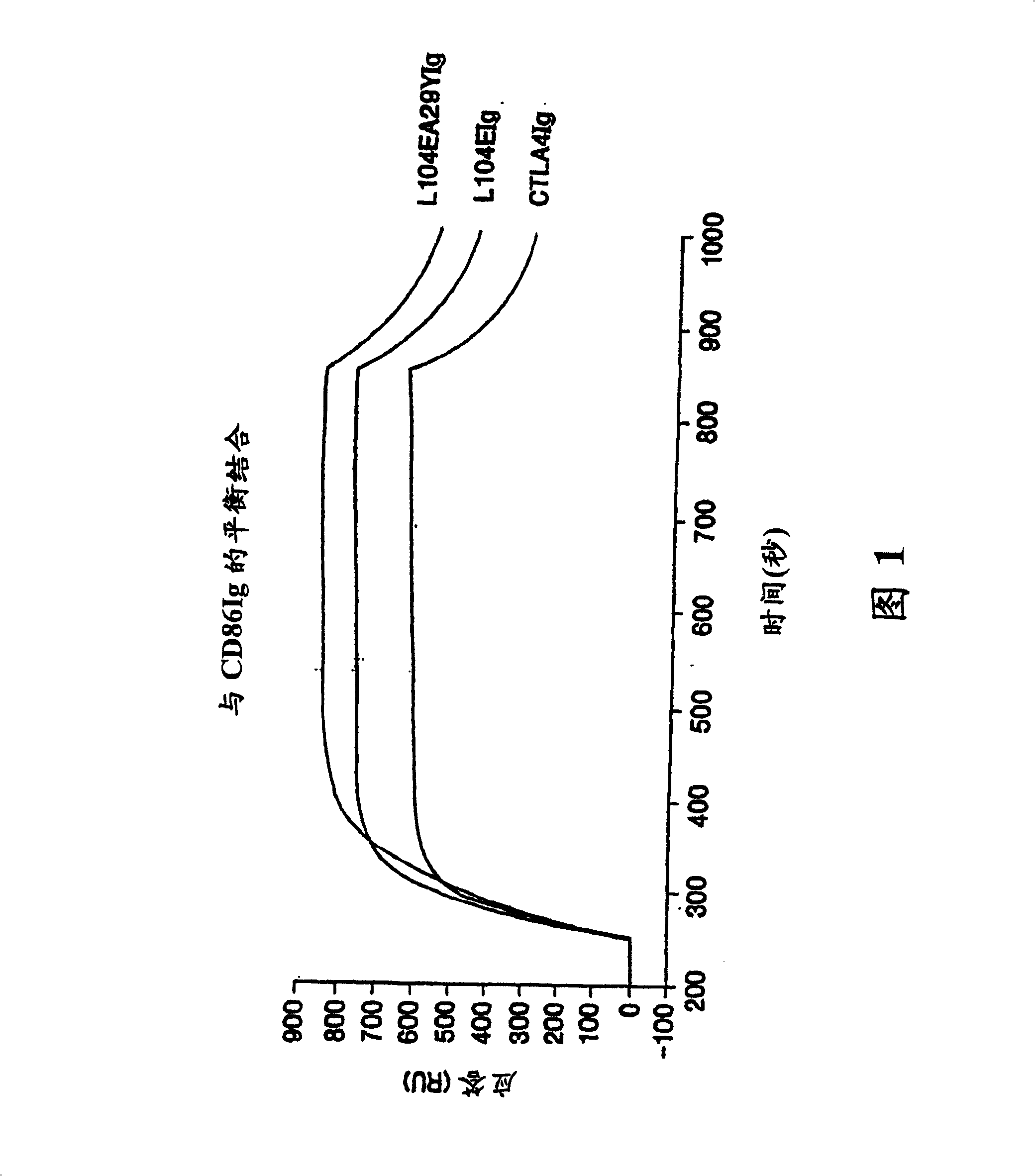
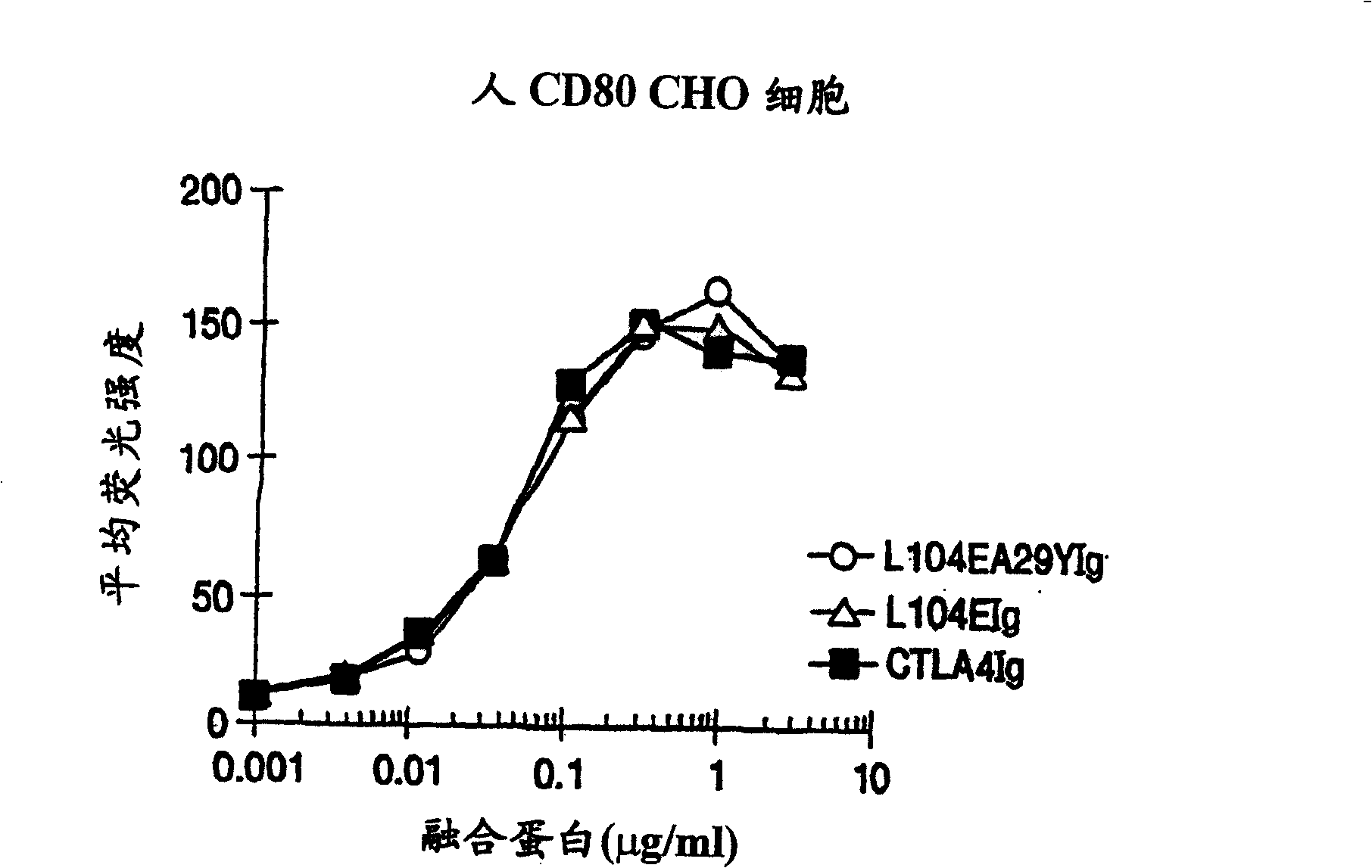
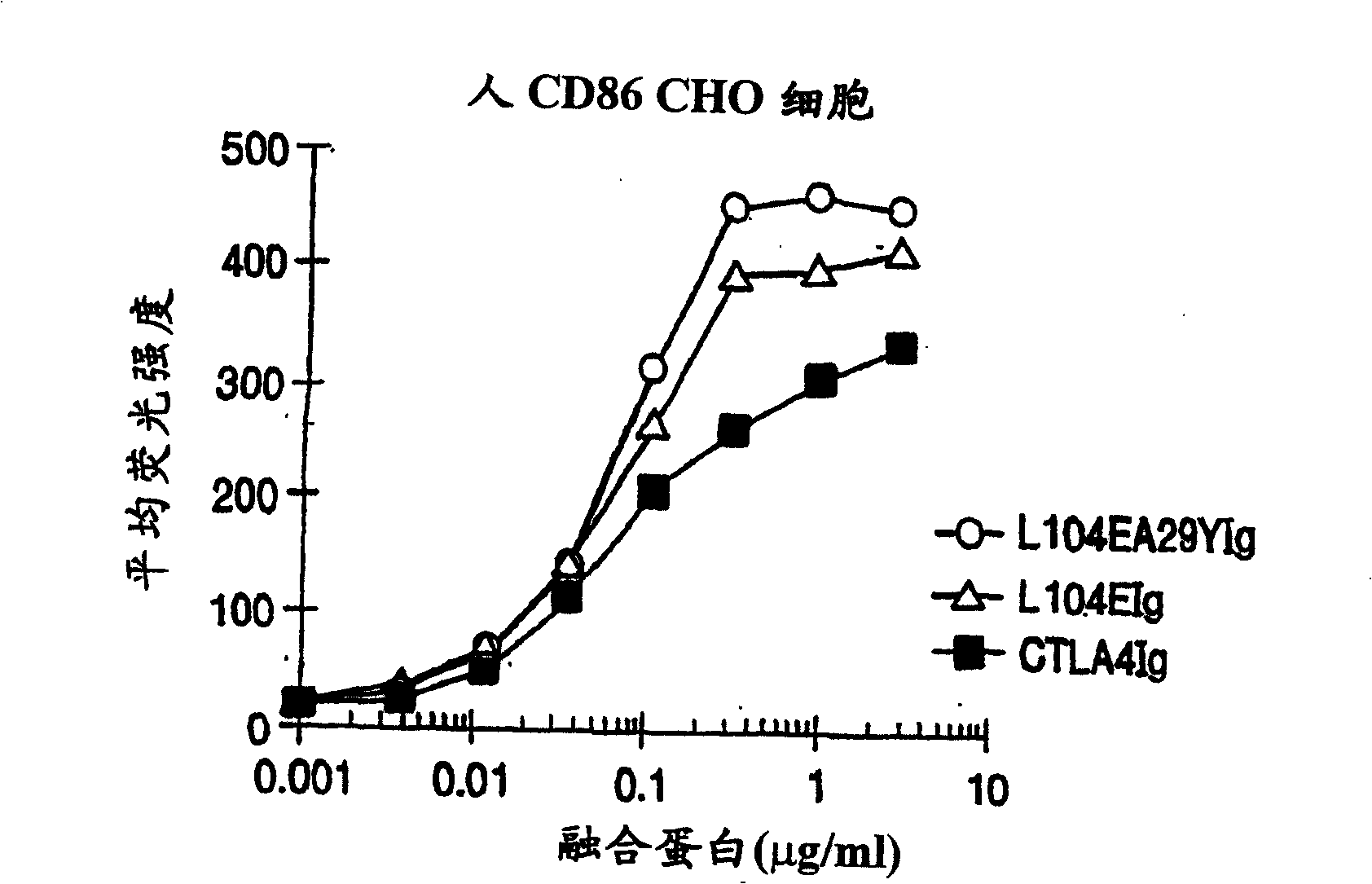
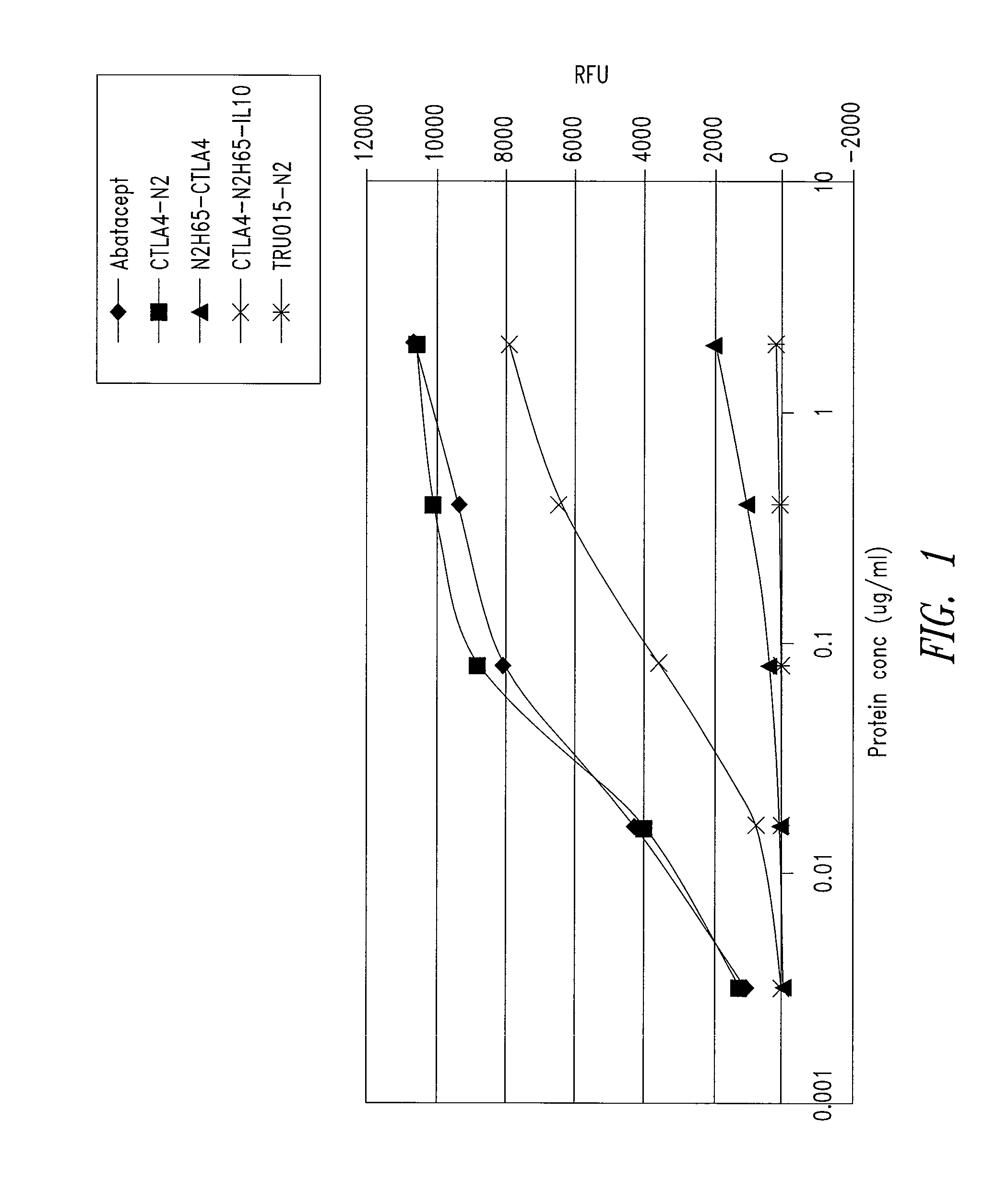
Soluble CTLA4 mutant molecules
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
RNAi-based therapeutics for allergic rhinitis and asthma
InactiveUS20060058255A1Suppress gene expressionGood curative effectAntibacterial agentsSpecial deliveryTLR8Disease
The present invention provides compositions comprising one or more RNAi agents (e.g., siRNAs, shRNAs, or RNAi vectors) for the treatment of conditions and diseases mediated by (e.g., featuring IgE-mediated hypersensitivity), as well as systems for identifying RNAi agents effective for this purpose. The compositions are suitable for the treatment of allergic rhinitis and / or asthma. In certain embodiments of the invention the RNAi agent is targeted to a transcript that encodes a protein selected from the group consisisting of the FCεRIα chain, the FCεRIβ chain, c-Kit, Lyn, Syk, ICOS, OX40L, CD40, CD80, CD86, Re1A, Re1B, 4-1BB ligand, TLR1, TLR2, TLR3, TLR4, TLR5, TLR6, TLR7, TLR8, TLR9, CD83, SLAM, common γ chain, and COX-2. In addition, the invention provides RNAi agent / delivery agent compositions and methods of use. In certain embodiments of the invention compositions comprising an RNAi agent are delivered by the respiratory route.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Novel ctla4-ig immunoadhesins
Owner:XENCOR
Antisense oligomers and methods for inducing immune tolerance and immunosuppression
ActiveUS20060276425A1Reduce capacityIncrease productionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsExtracellularDendritic cell
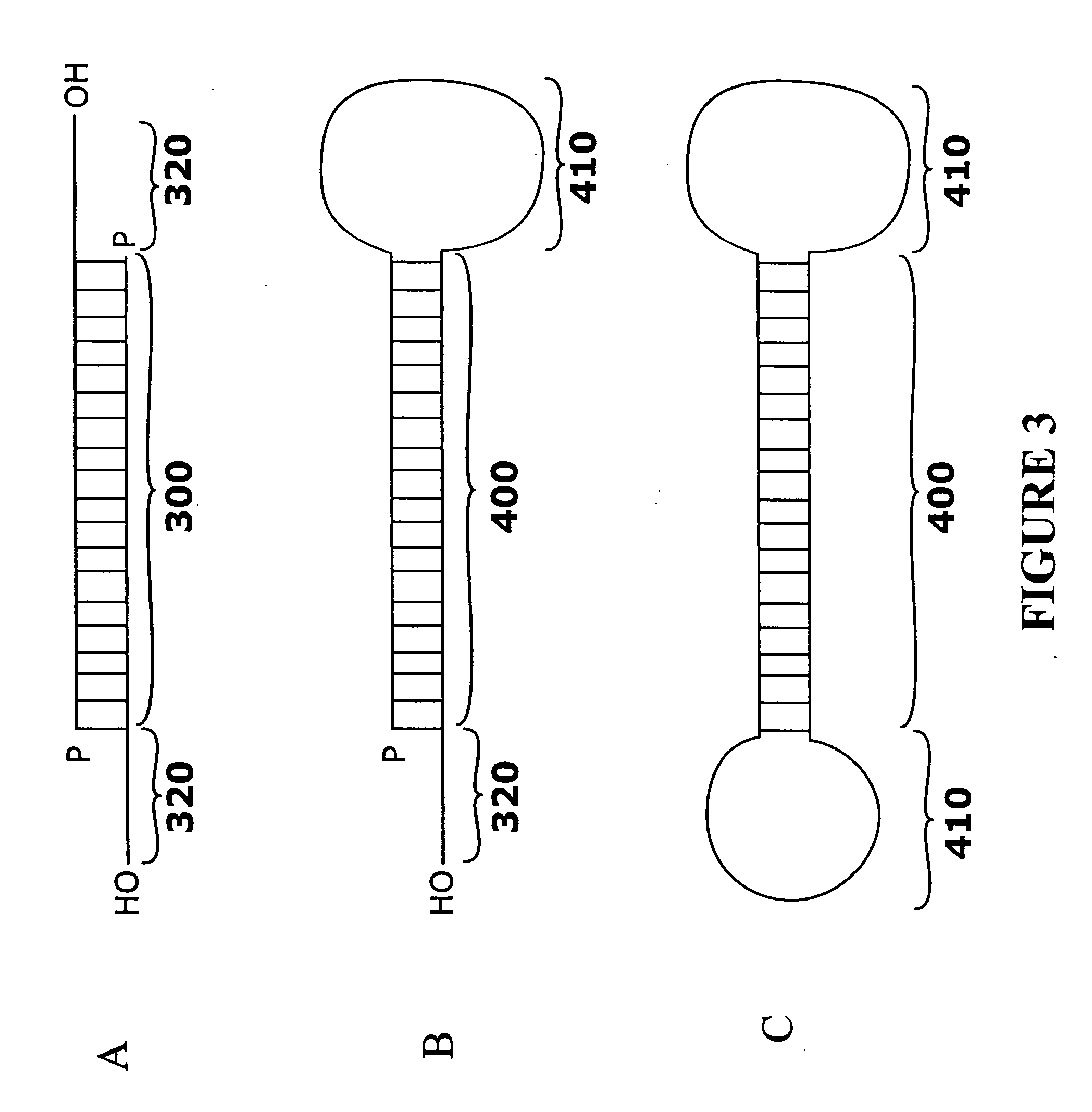
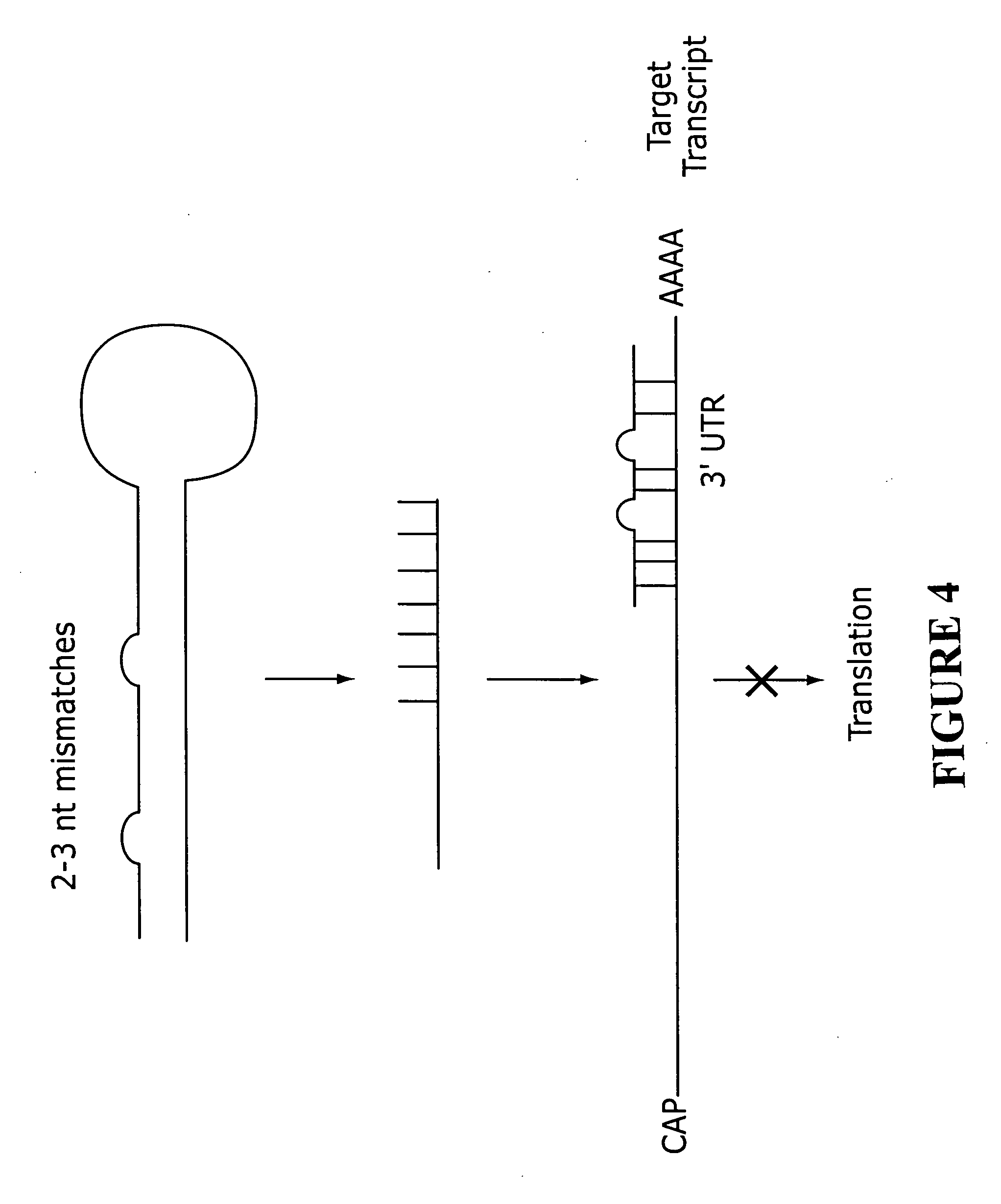
A method and composition for inducing human dendritic cells to a condition of reduced capacity for antigen-specific activation of T cells, and, in mature dendritic cells, increased production of extracellular IL-10 is disclosed. A population of dendritic cells is exposed to a substantially uncharged antisense compound, including partially positively charged, containing 12-40 subunits and a base sequence effective to hybridize to an expression-sensitive region of a preprocessed or processed human CD86 transcript identified, in its processed form, by SEQ ID NO:33, to form a duplex structure between said compound and transcript having a Tm of at least 45° C. Formation of the duplex blocks expression of full-length CD86 in said cells, which in turn leads to reduced capacity for antigen-specific activation of T cells, and, in mature dendritic cells, increased production of extracellular IL-10.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
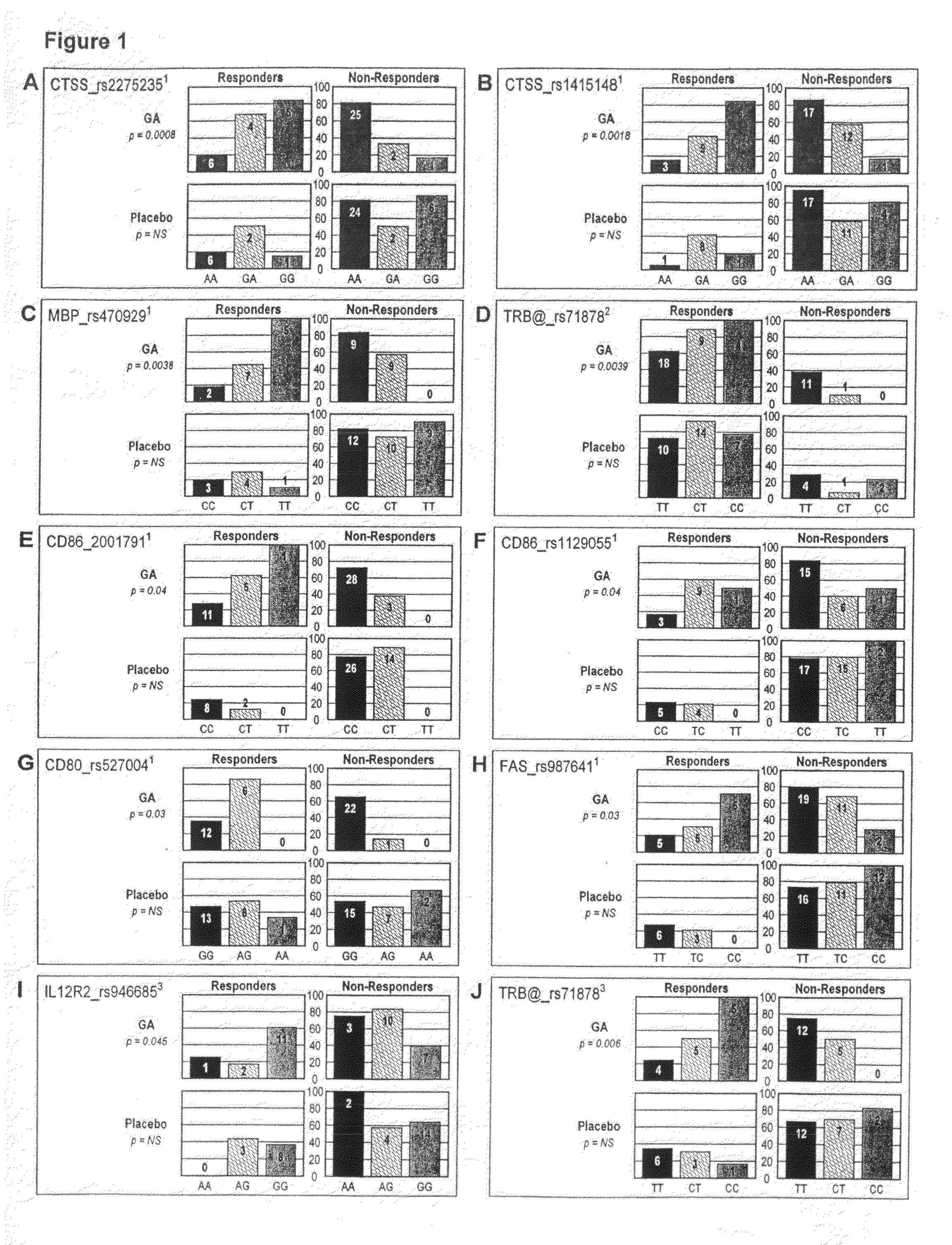
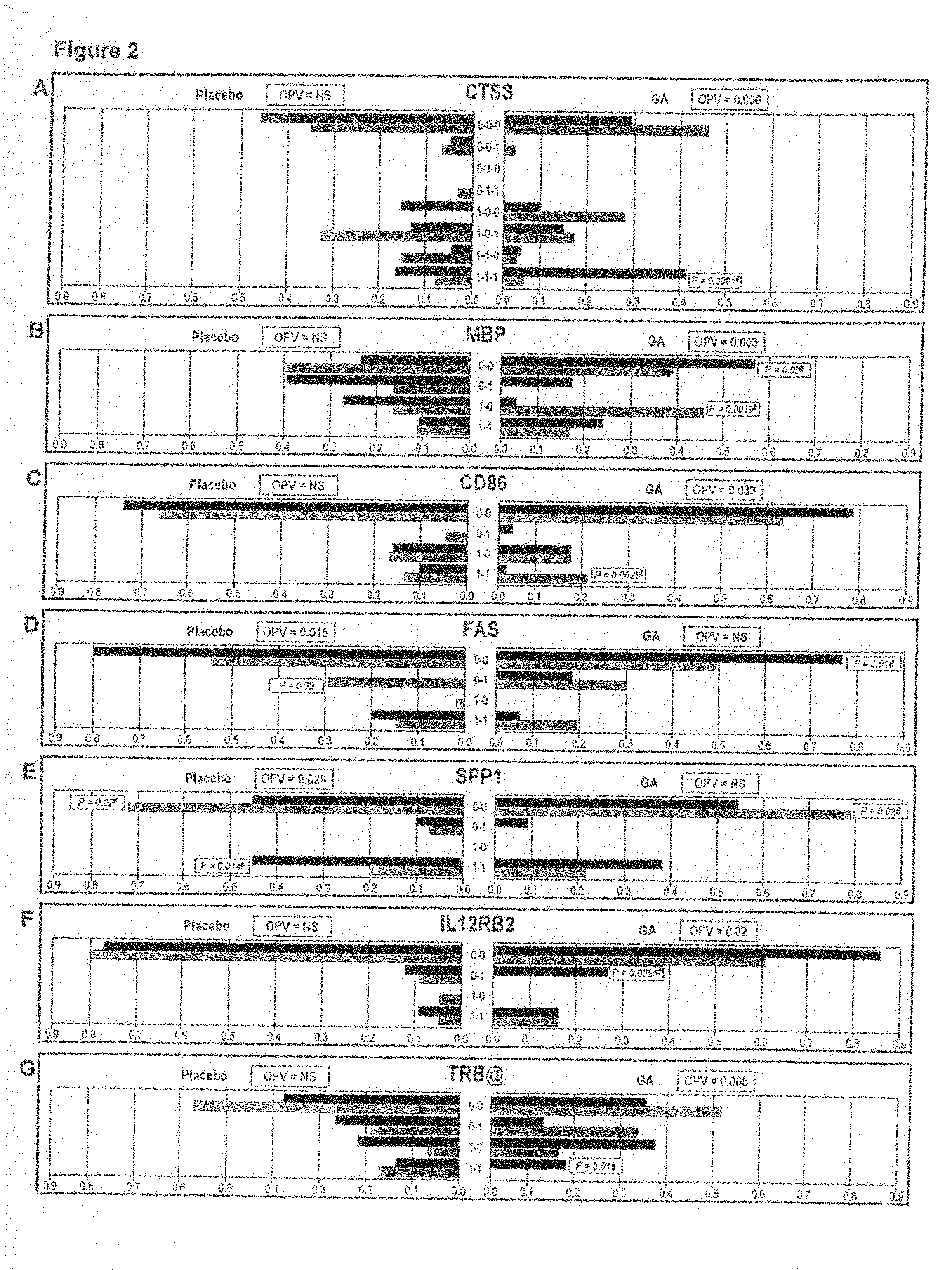
Markers associated with the therapeutic efficacy of glatiramer acetate
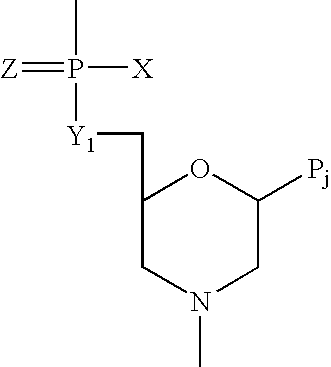
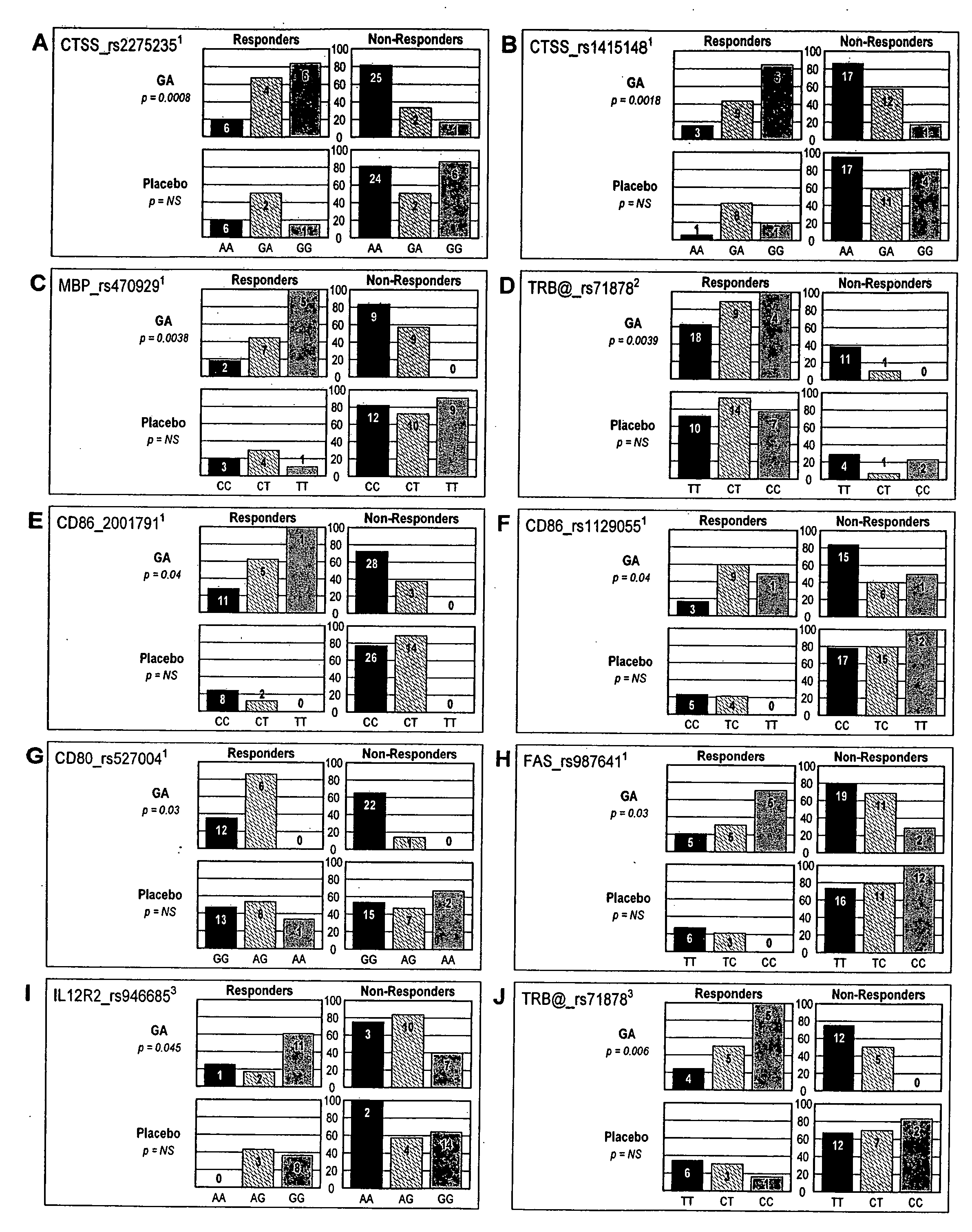
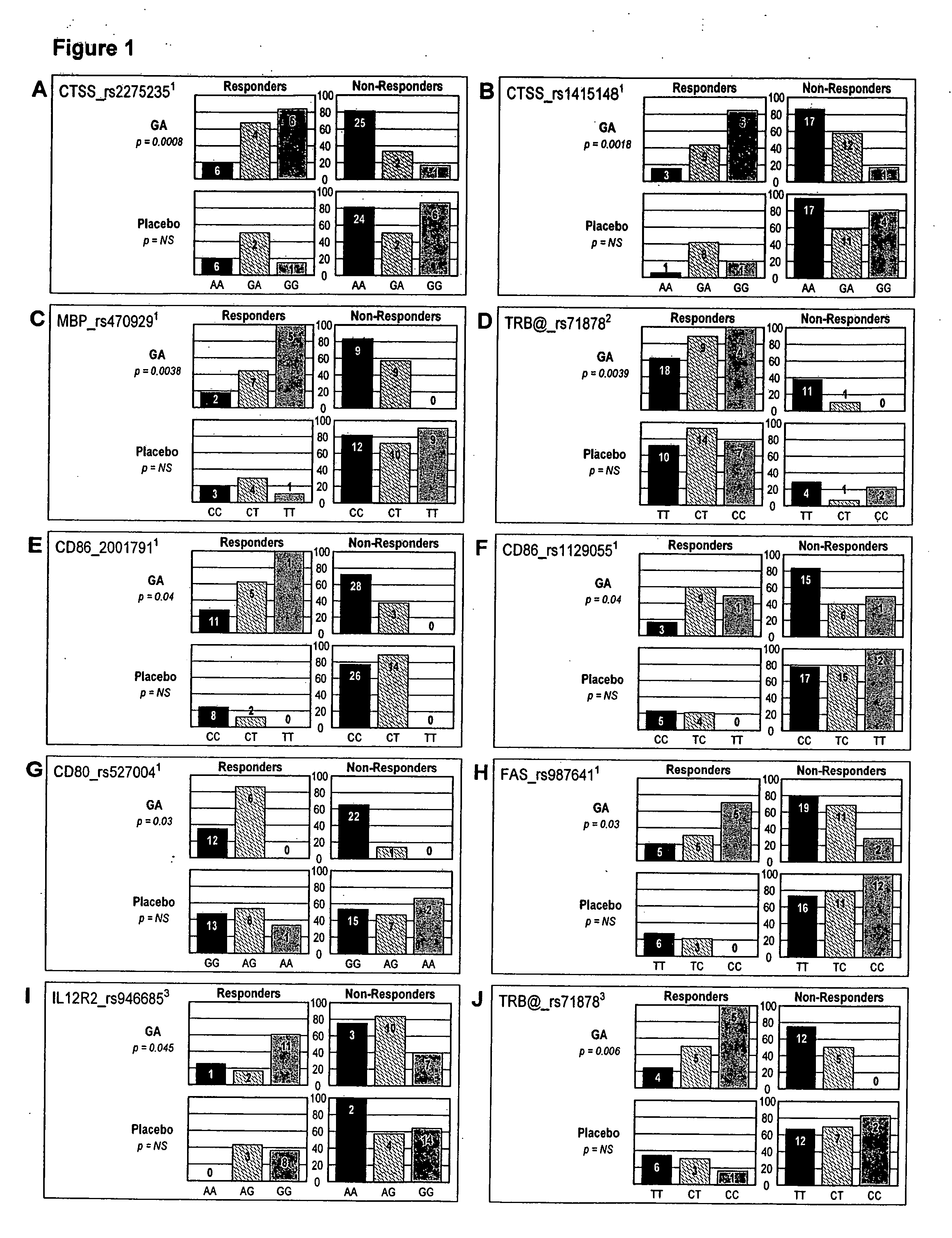
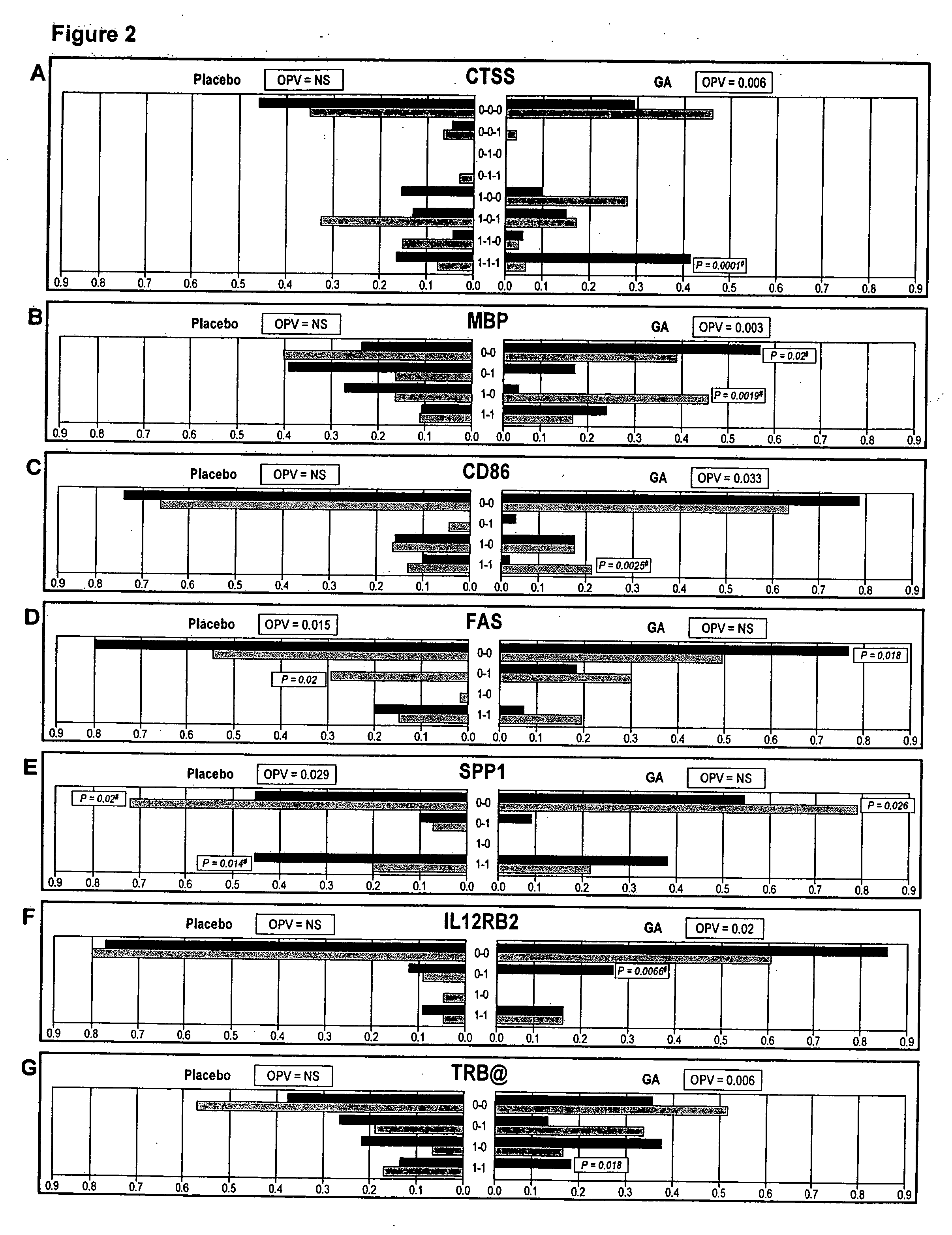
The present invention is directed to methods and kits based, at least in part, on the identification of allele-specific responsiveness or non-responsiveness to glatiramer acetate for the treatment of immune disorders, such as relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. The allele-specific responsiveness or non-responsiveness is based on polymorphisms in the following genes, CTSS, MBP, TCRB, CD95, CD86, IL-1R1, CD80, SCYA5, MMP9, MOG, SPP1 and IL-12RB2.
Owner:RAPPAPORT FAMILY INSTITUTE FOR RESEACH IN THE MEDICAL SCIENCES +2
Tolerogenic antigen-presenting cells
InactiveUS20060147432A1Conveniently achievedFavorable antigen presentationBiocideGenetic material ingredientsDendritic cellCD80
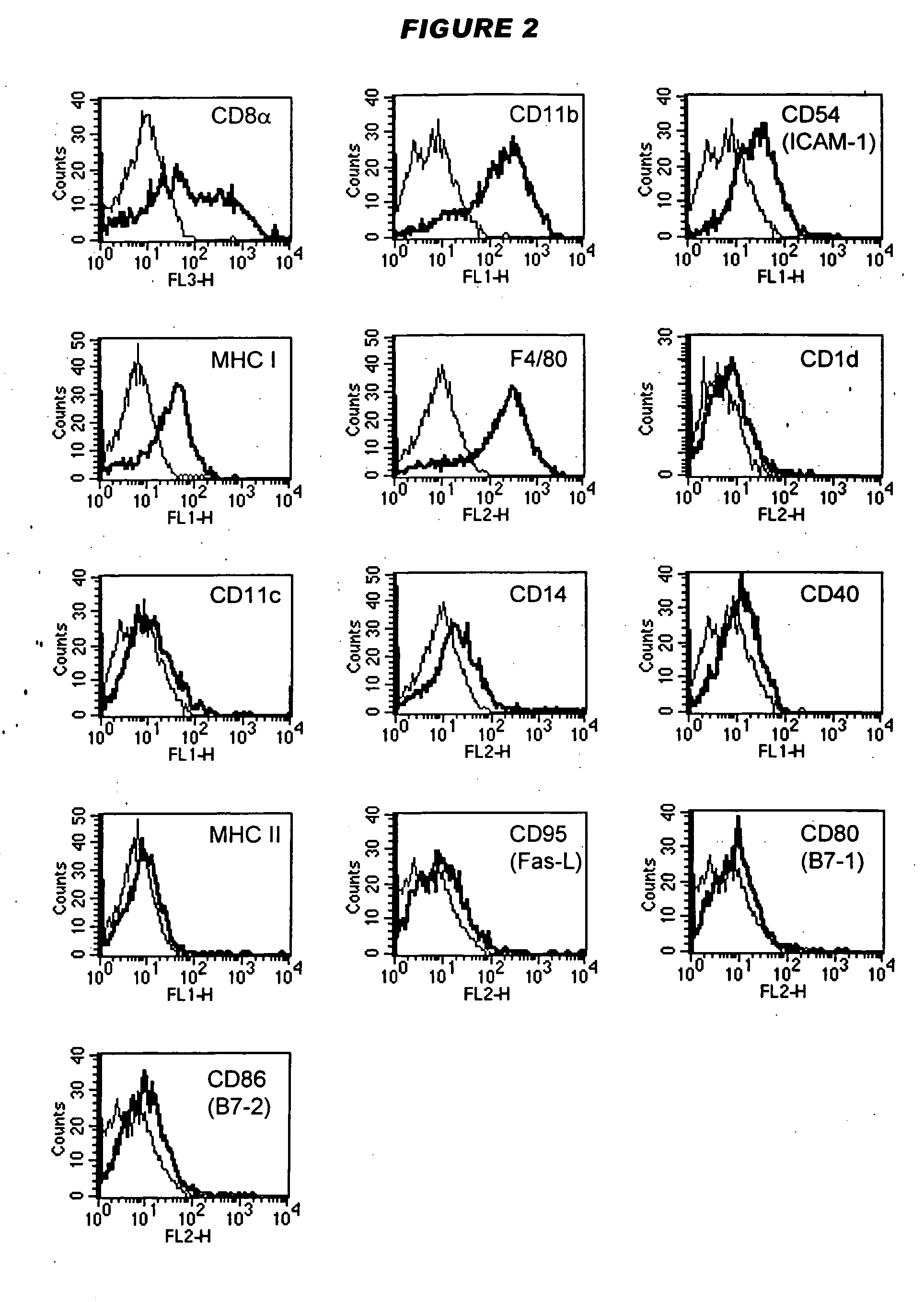
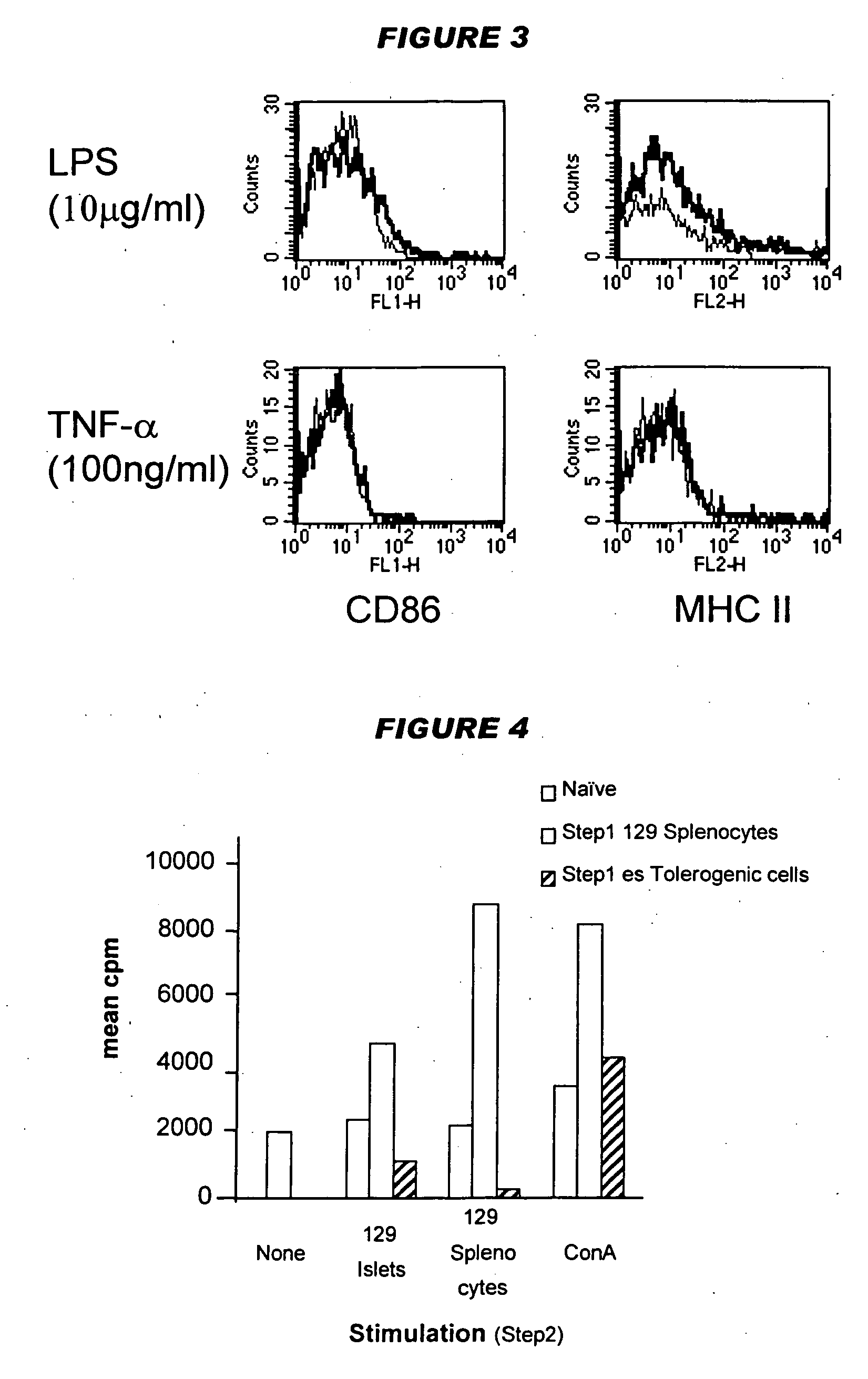
It has been found that dendritic cells can be prepared which cannot mature. These cells can provide signal 1 to T cells but cannot provide co-stimulatory signal 2. T cells which are stimulated by the permanently immature dendritic cells therefore anergise, so the dendritic cells are tolerogenic rather than immunogenic. The cells are generally CD40−ve, CD80−ve and CD86−ve, and remain so when stimulated by inflammatory mediators such as lipopolysaccharide. The cells can be prepared conveniently by the culturing adherent embryonic stem cells in the presence of GM-CSF.
Owner:REVIVICOR INC
Molecule which binds cd80 and cd86
InactiveUS20070148162A1Prevent rejectionAvoid immune responseAnimal cellsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenT cell mediated immunity
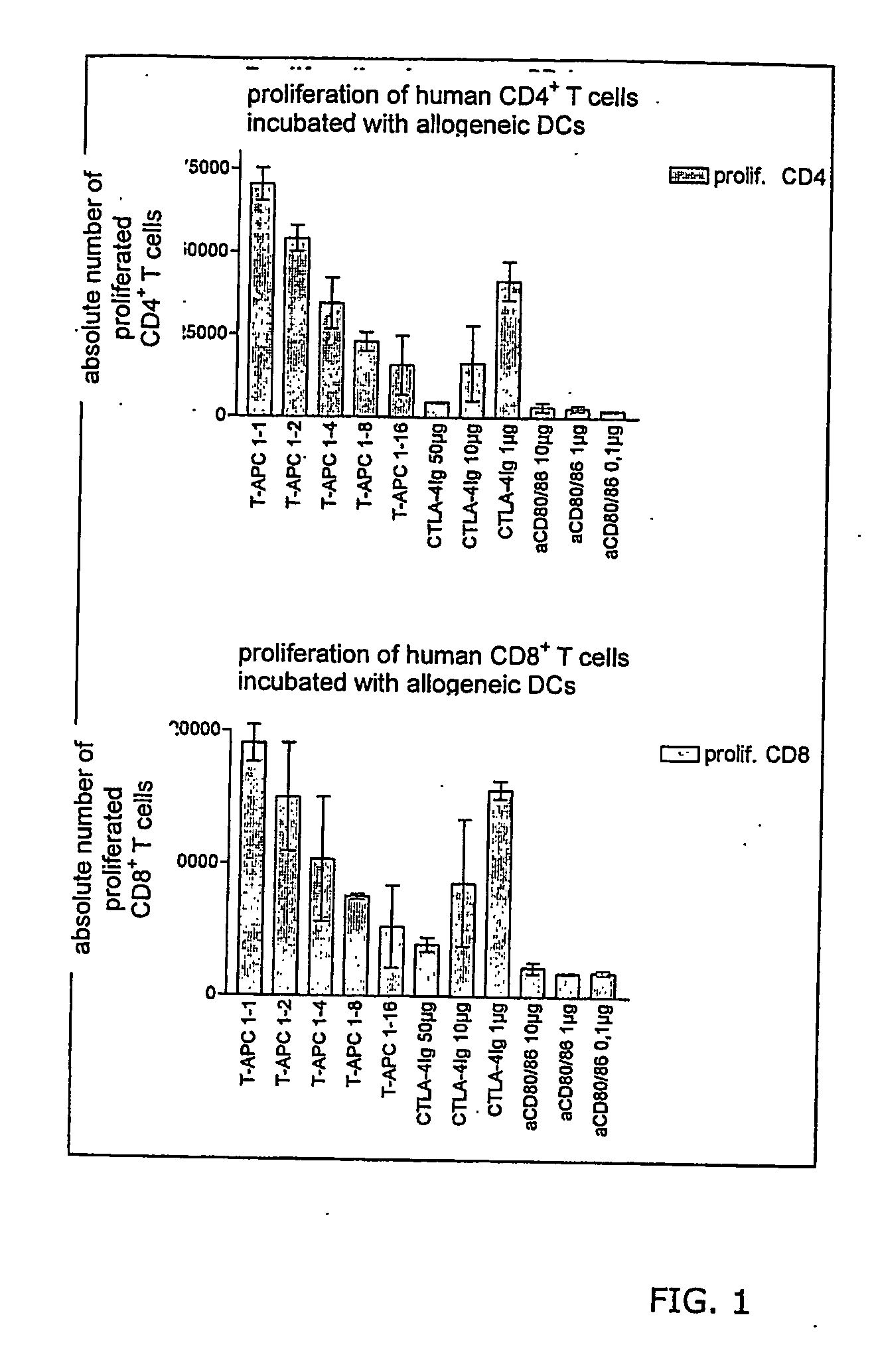
The present invention relates to the identification of molecules, which are specific to CD80 and CD86 antigens. Also preferably, such antibodies are capable of inhibiting the binding of CD28 and CTLA4 to those receptors. Those molecules are able to inhibit T cell mediated immune reactions.
Owner:THERAVISION
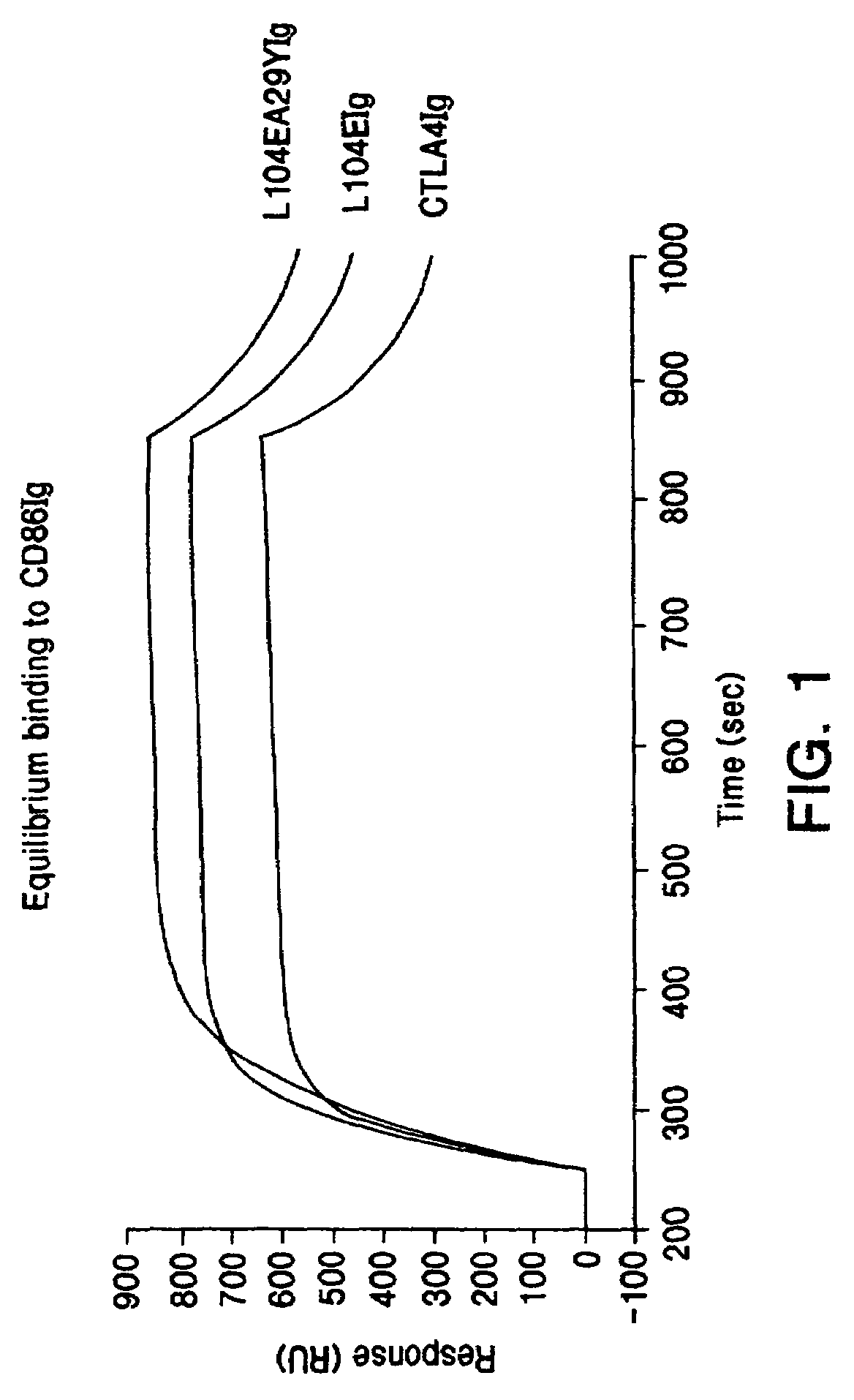
Soluble CTLA4 mutant molecules and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050214313A1Faster rateHigh affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSolubilityCD80
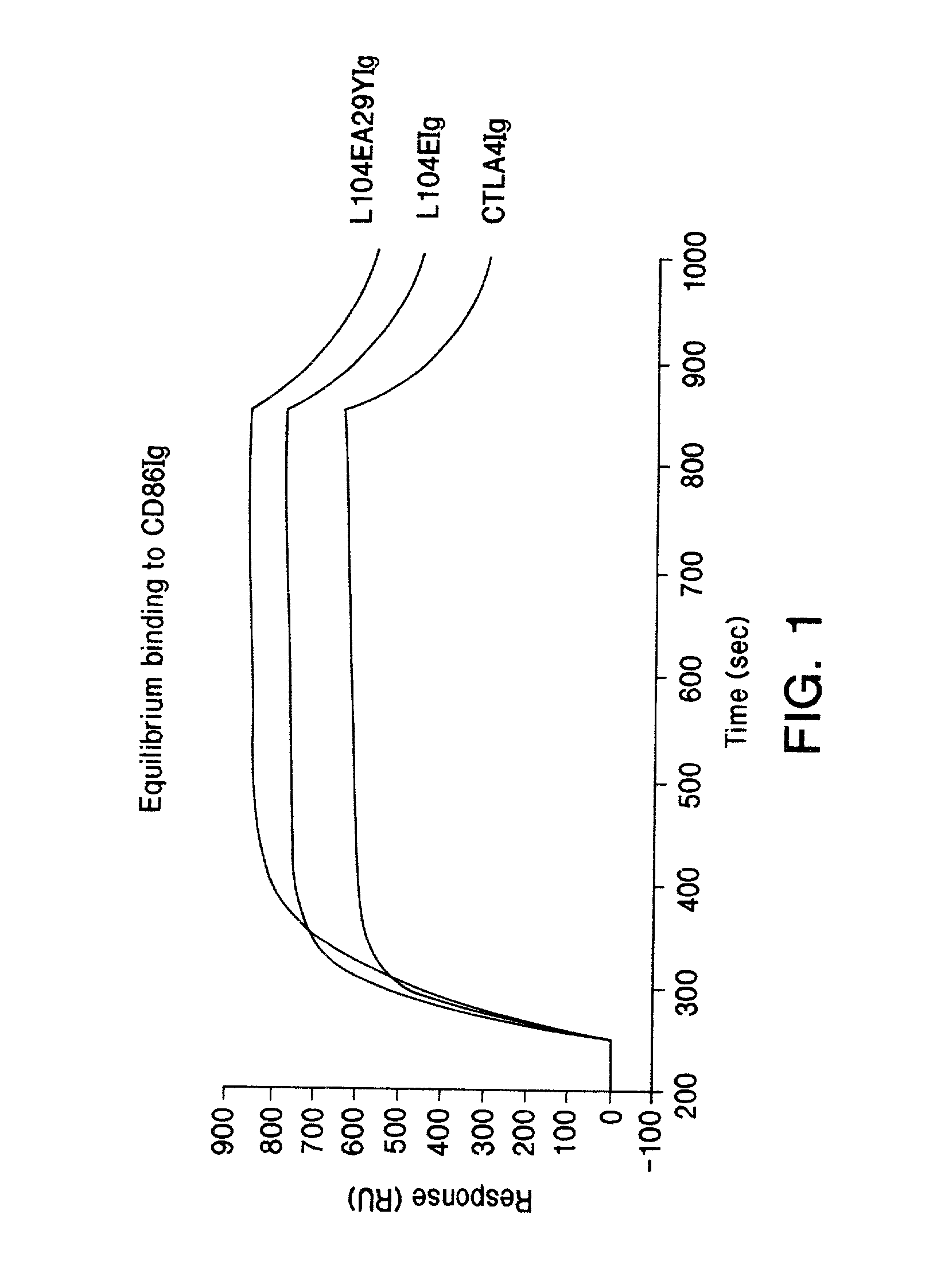
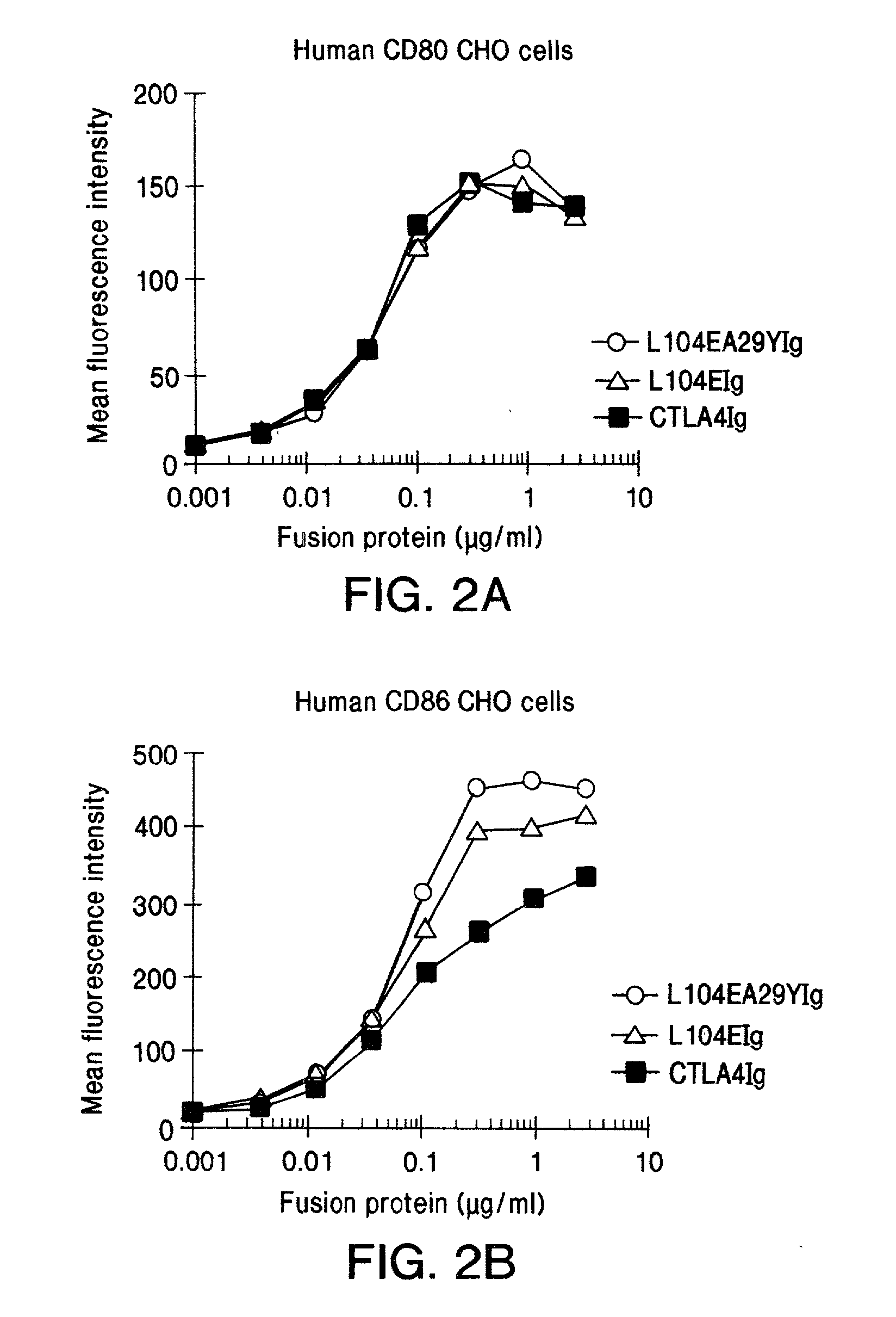
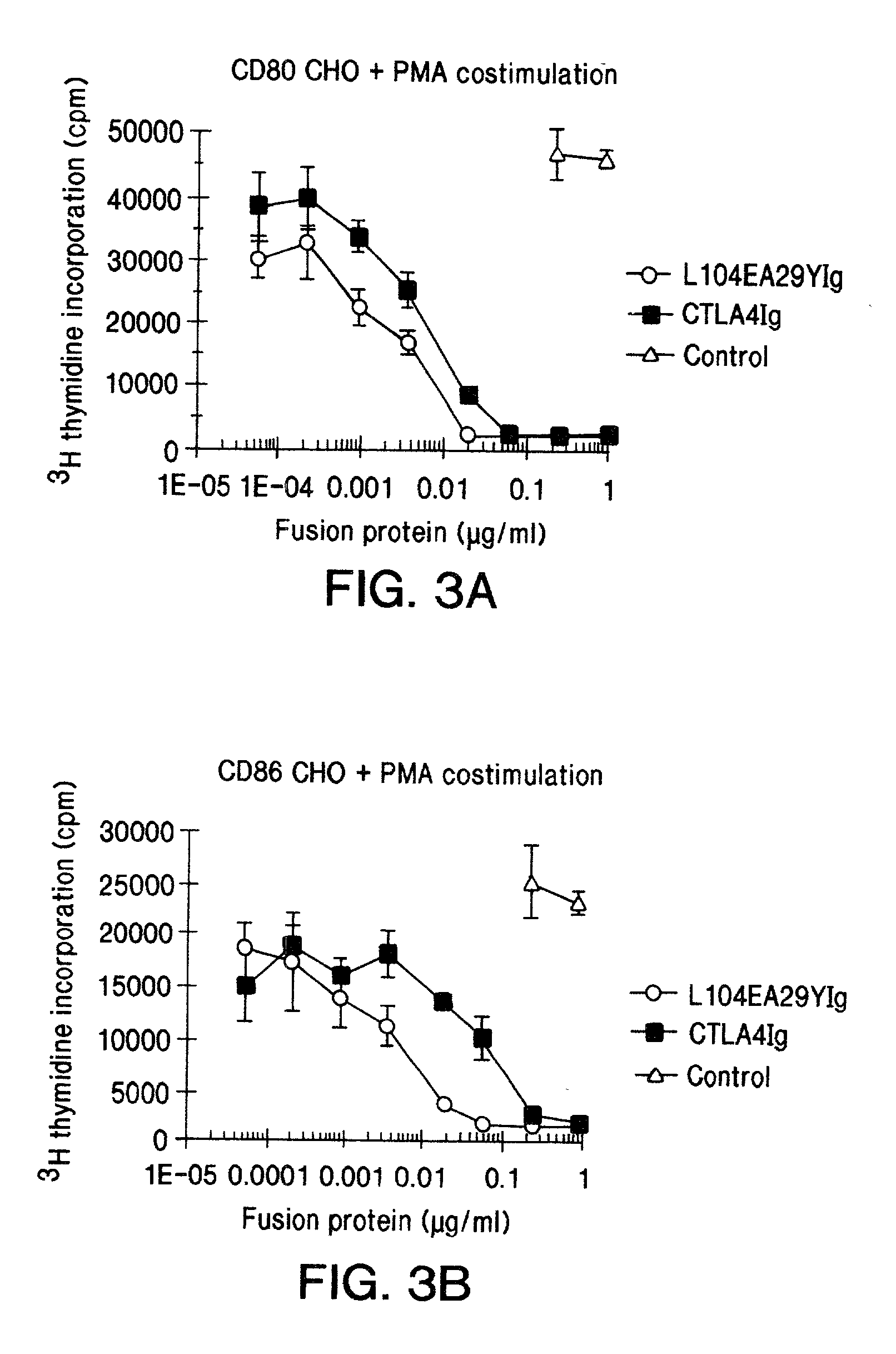
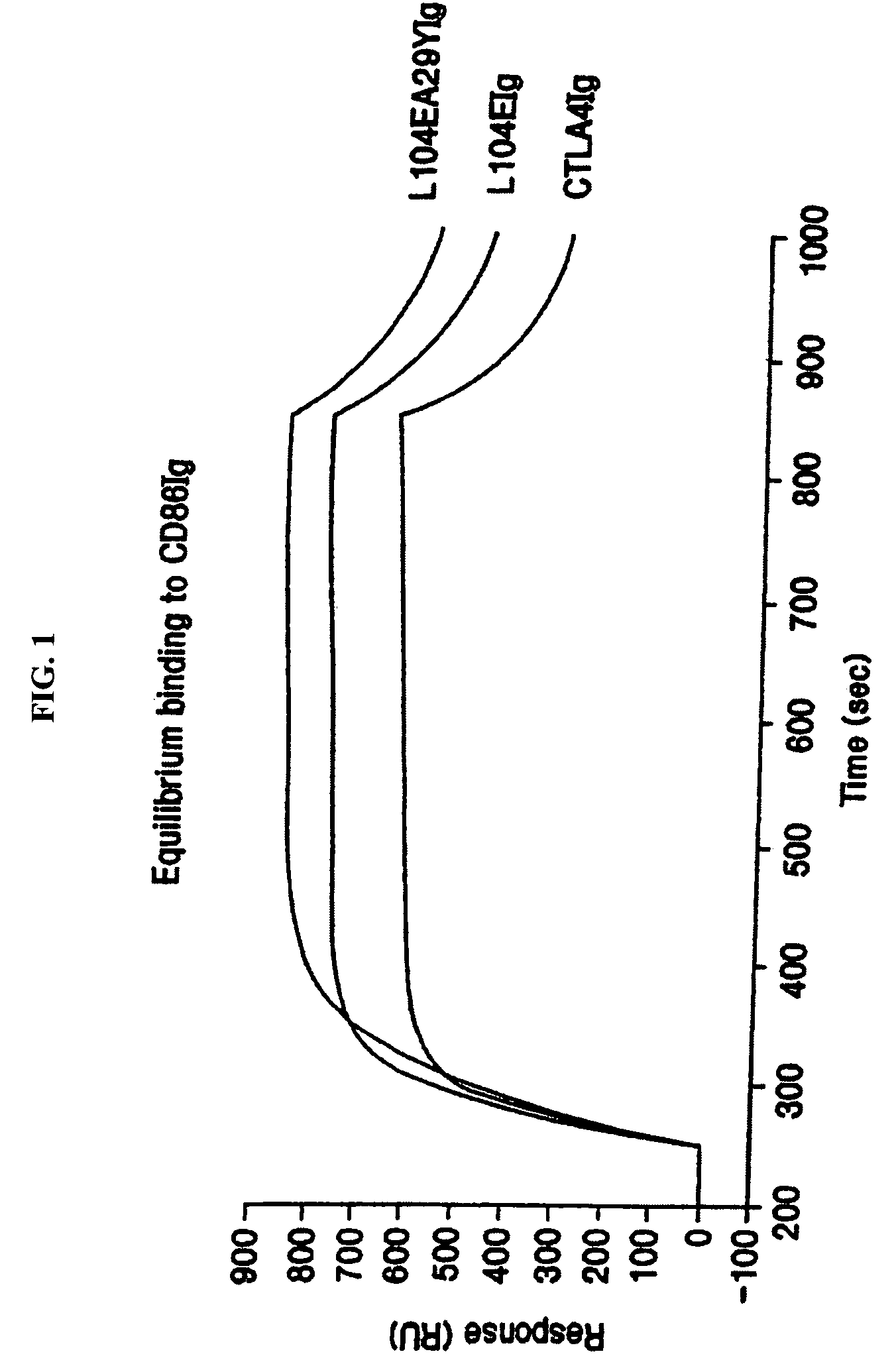
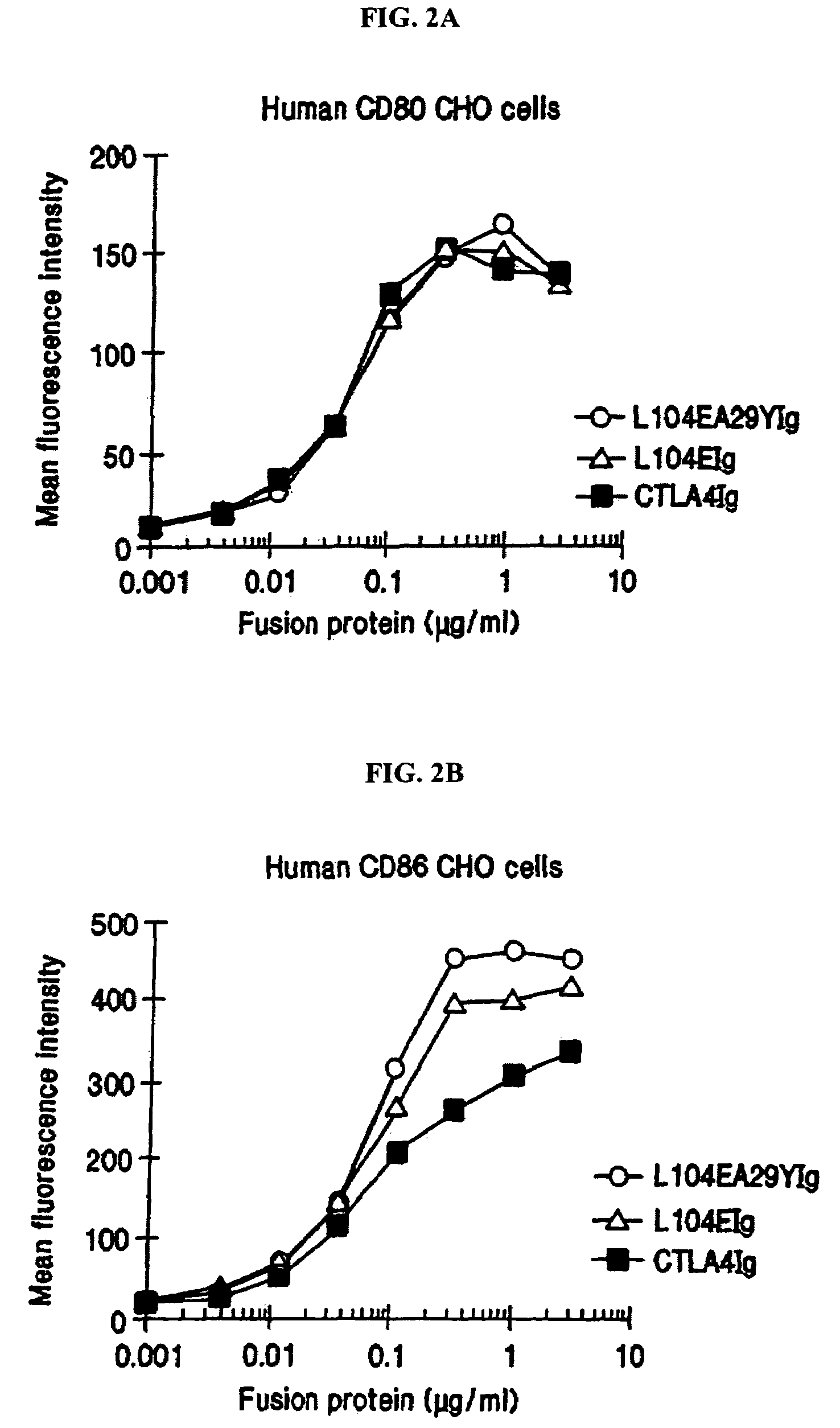
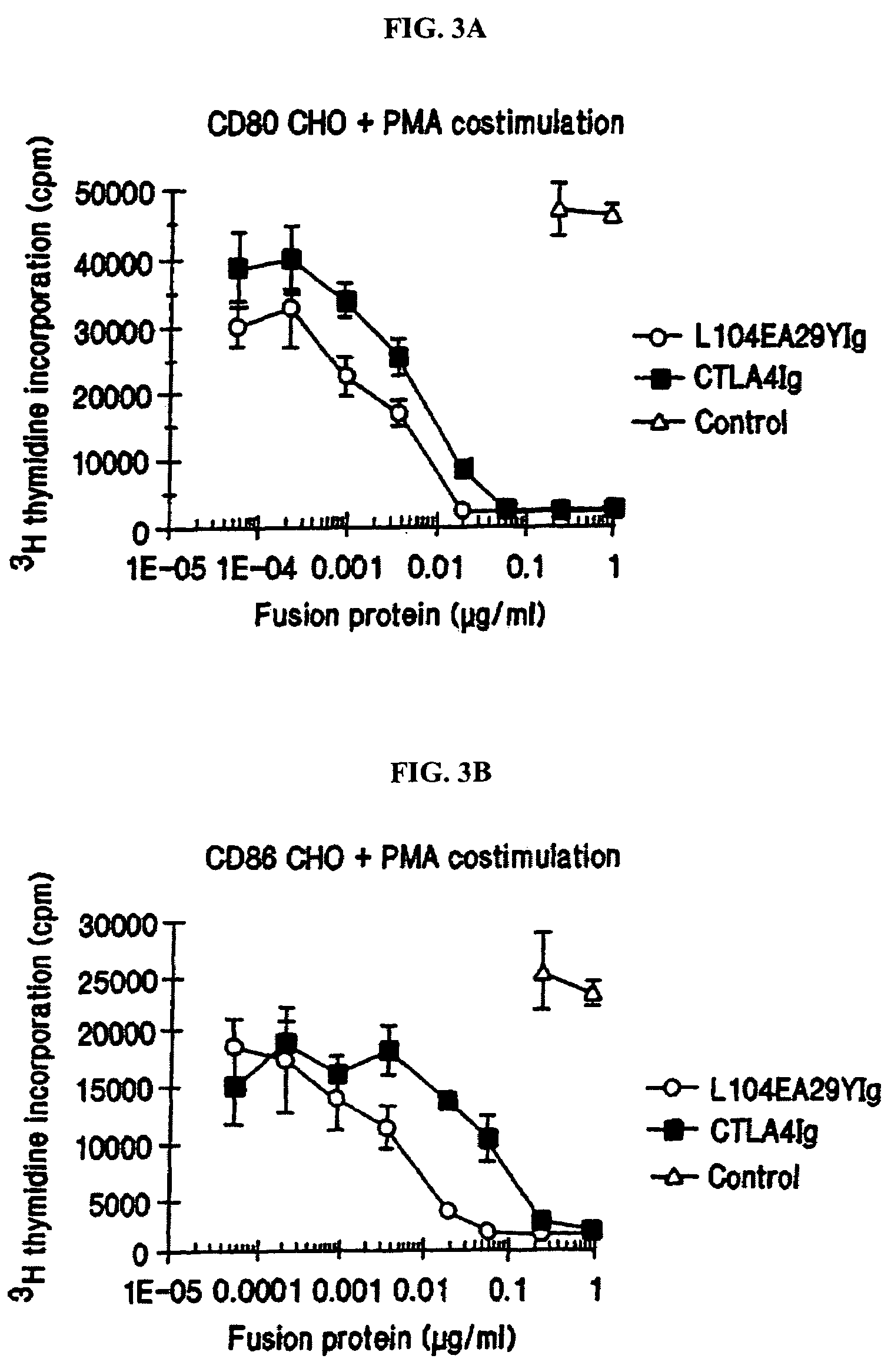
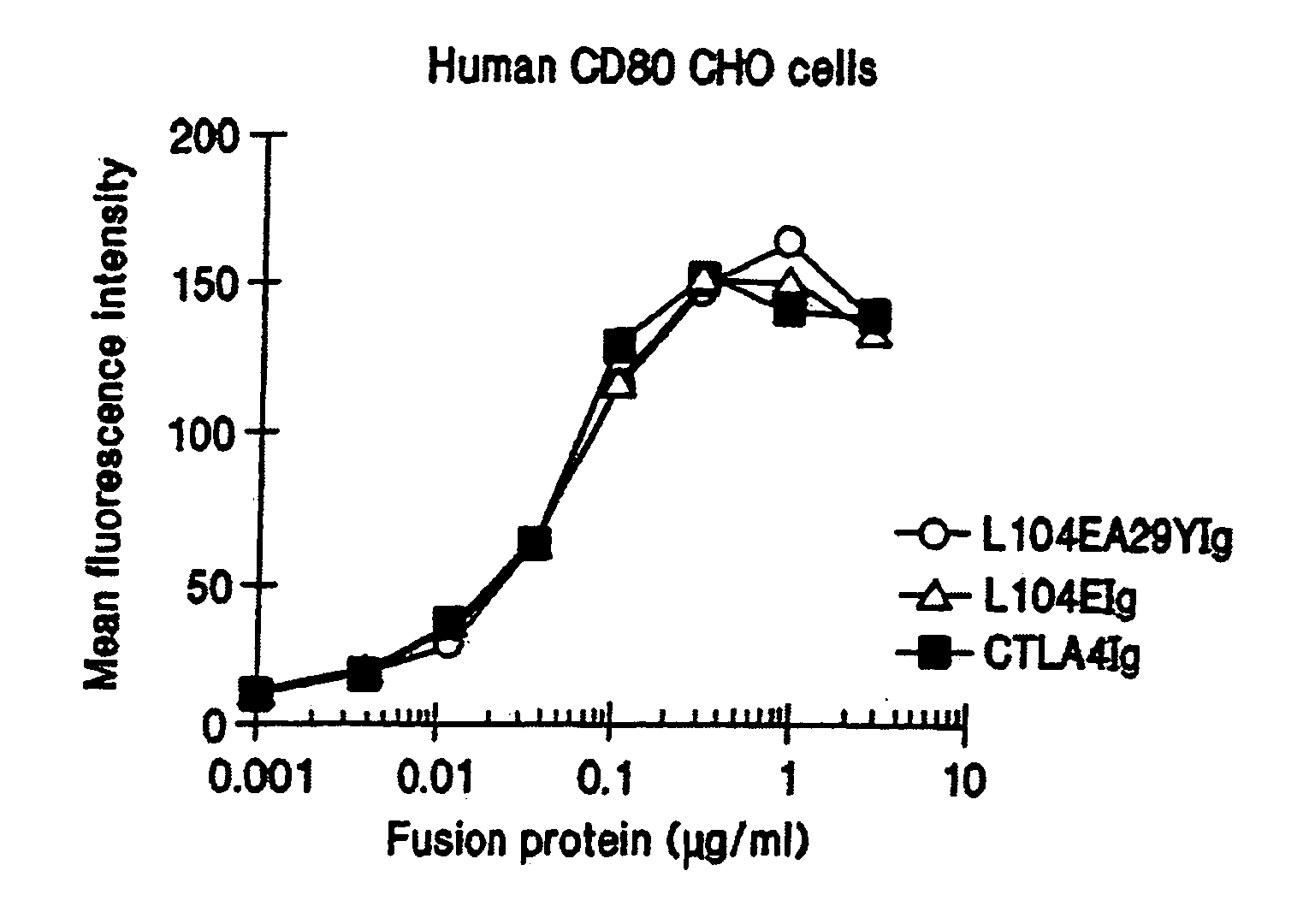
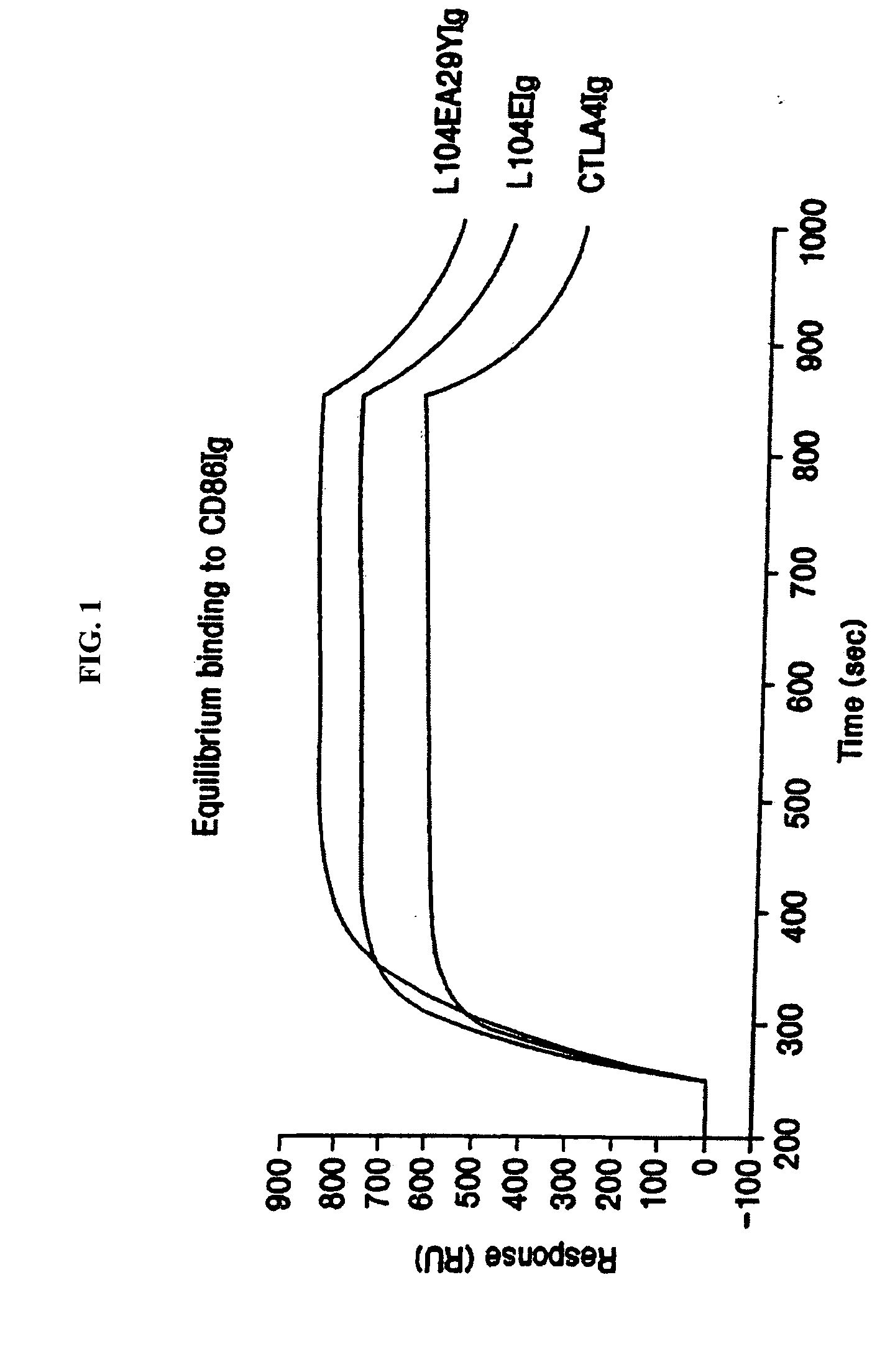
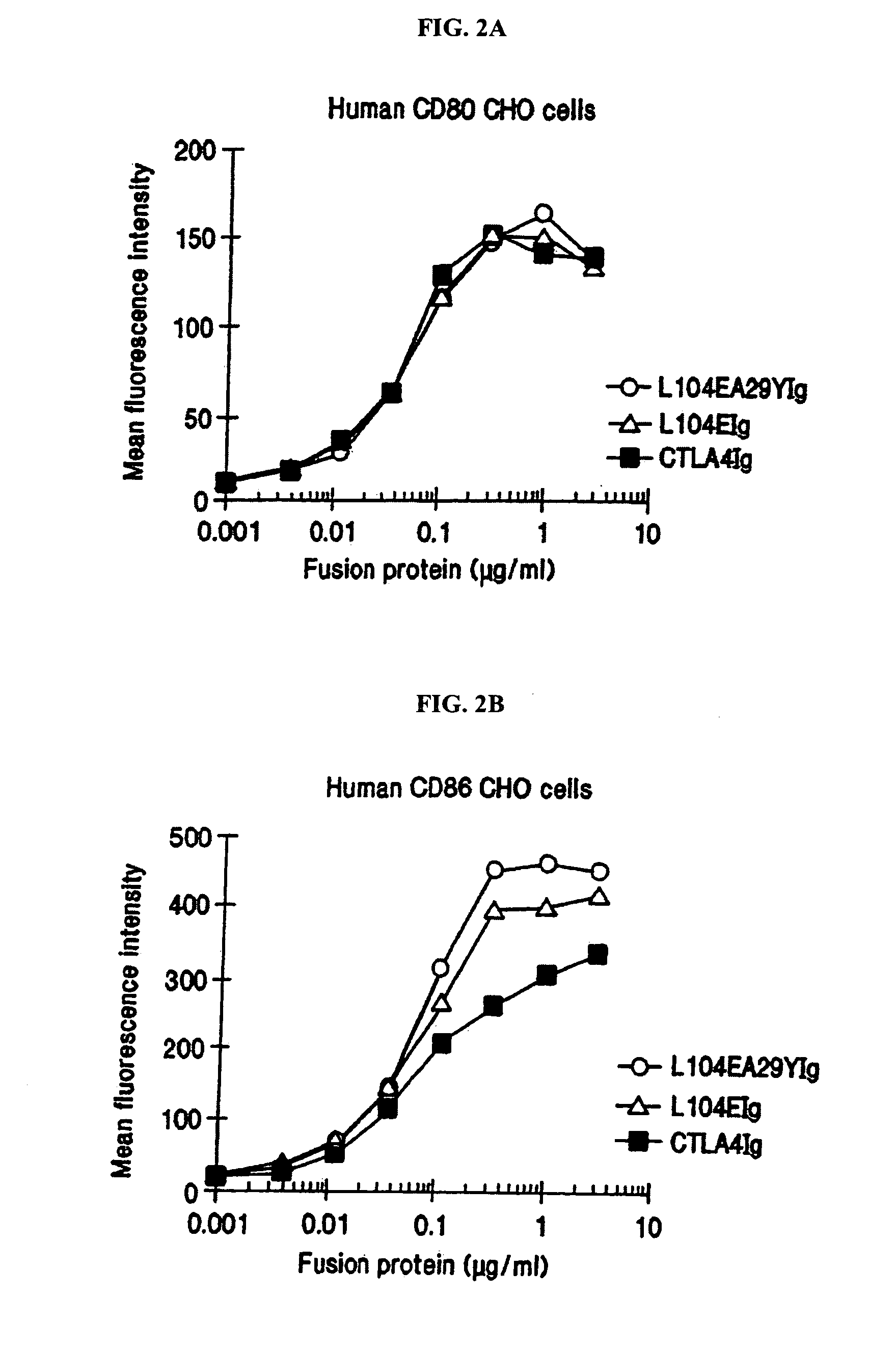
The present invention provides soluble CTLA4 mutant molecules which bind with greater avidity to the CD80 and / or CD86 antigen than wild type CTLA4 or non-mutated CTLA4Ig. The soluble CTLA4 molecules have a first amino acid sequence comprising the extracellular domain of CTLA4, where certain amino acid residues within the S25-R33 region and M97-G107 region are mutated. The mutant molecules of the invention may also include a second amino acid sequence which increases the solubility of the mutant molecule.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Delivery of as-oligonucleotide microspheres to induce dendritic cell tolerance for the treatment of autoimmune type 1 diabetes
AS-oligonucleotides are delivered in microsphere form in order to induce dendritic cell tolerance, particularly in the non-obese-diabetic (NOD) mouse model. The microspheres incorporate antisense (AS) oligonucleotides. A process includes using an antisense approach to prevent an autoimmune diabetes condition in NOD mice in vivo and in situ. The oligonucleotides are targeted to bind to primary transcripts CD40, CD80, CD86 and their combinations.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +2
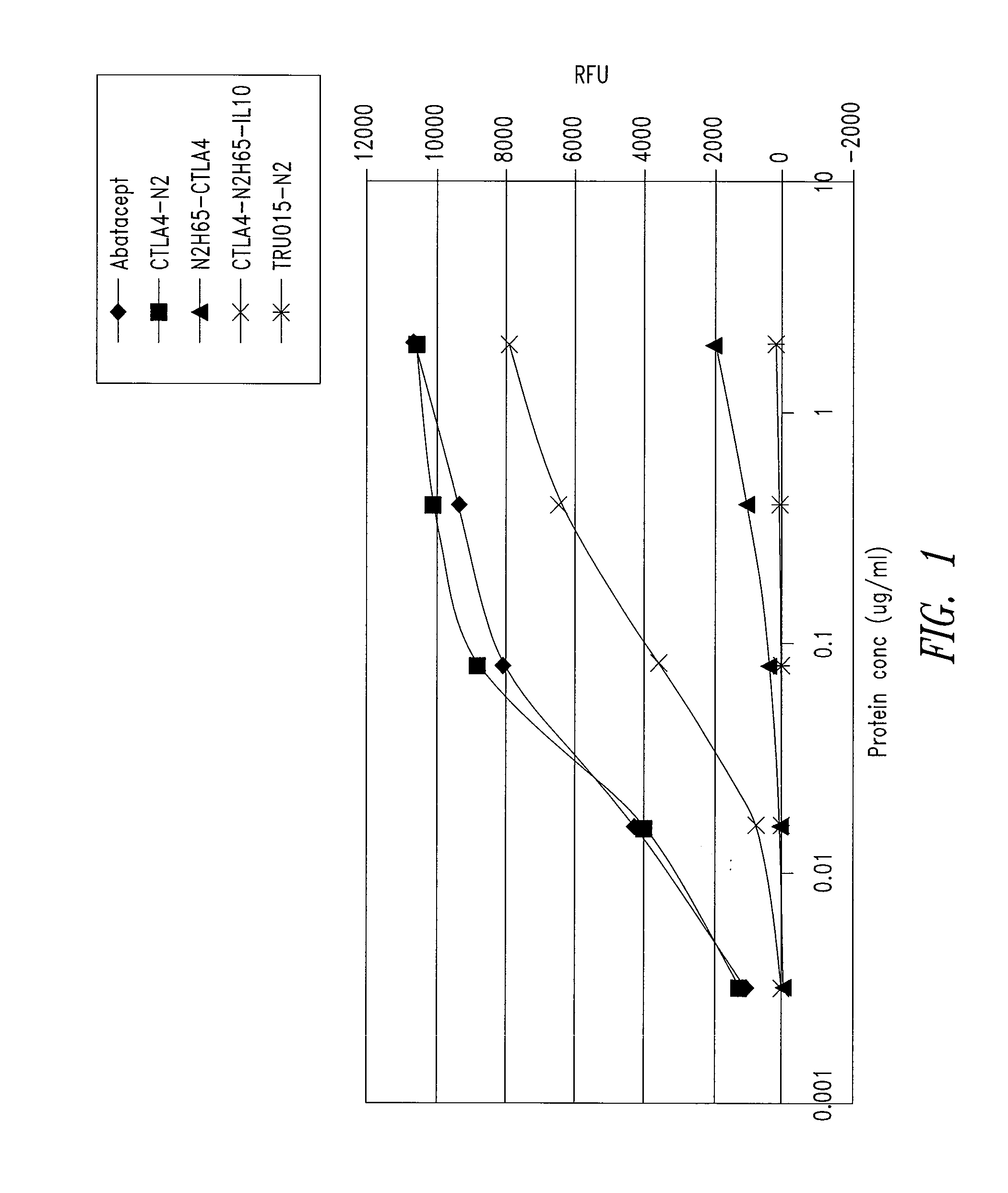
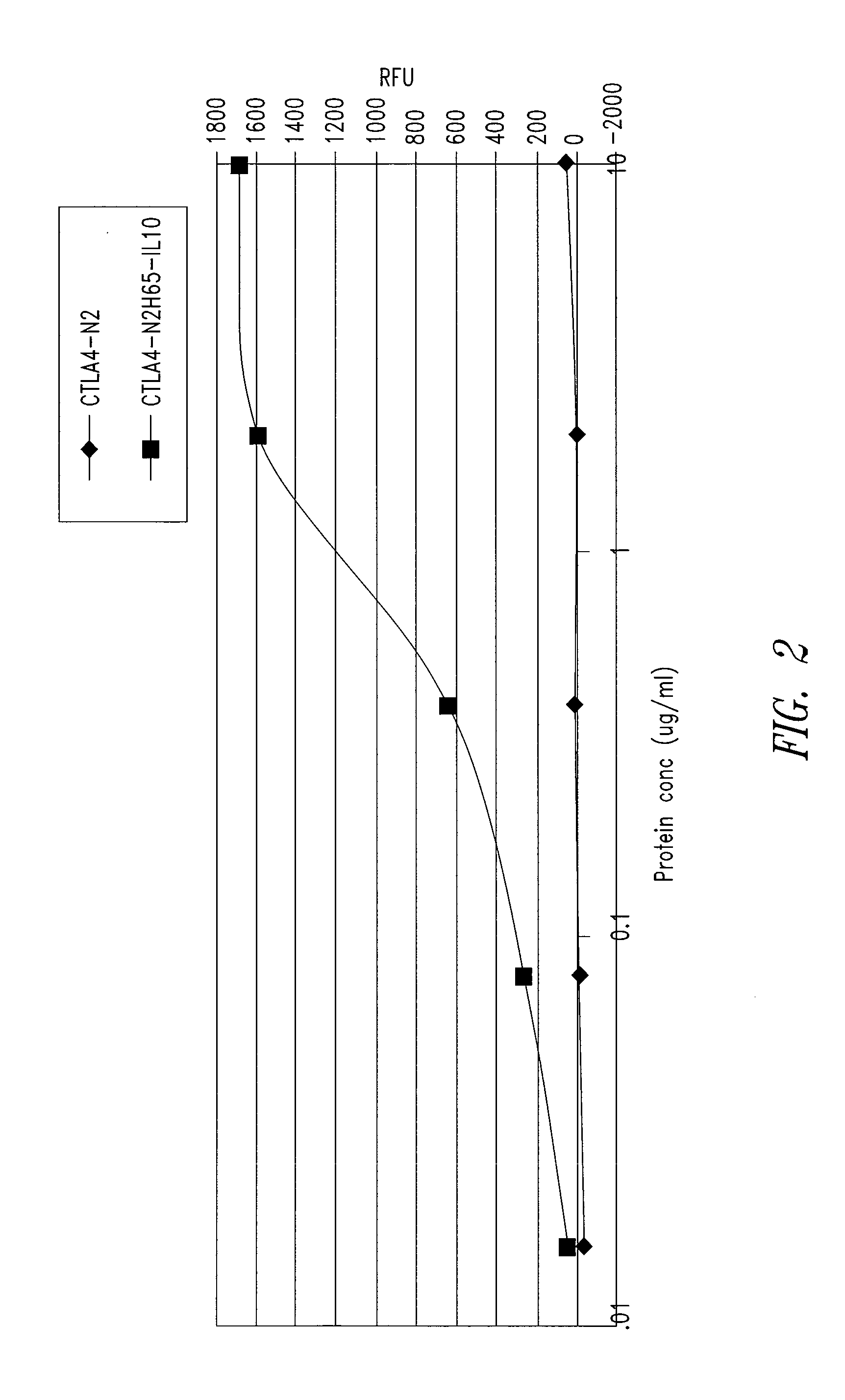
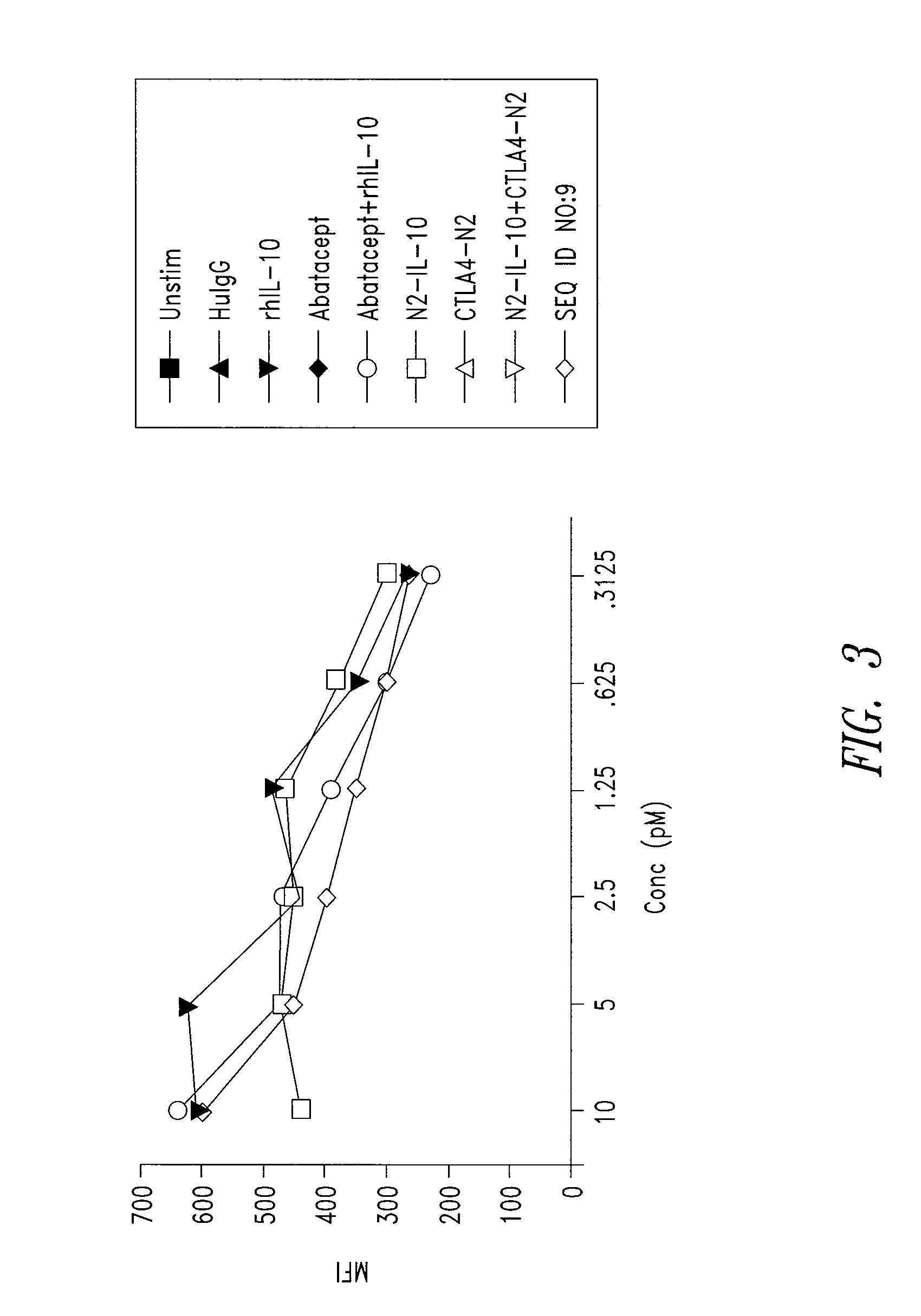
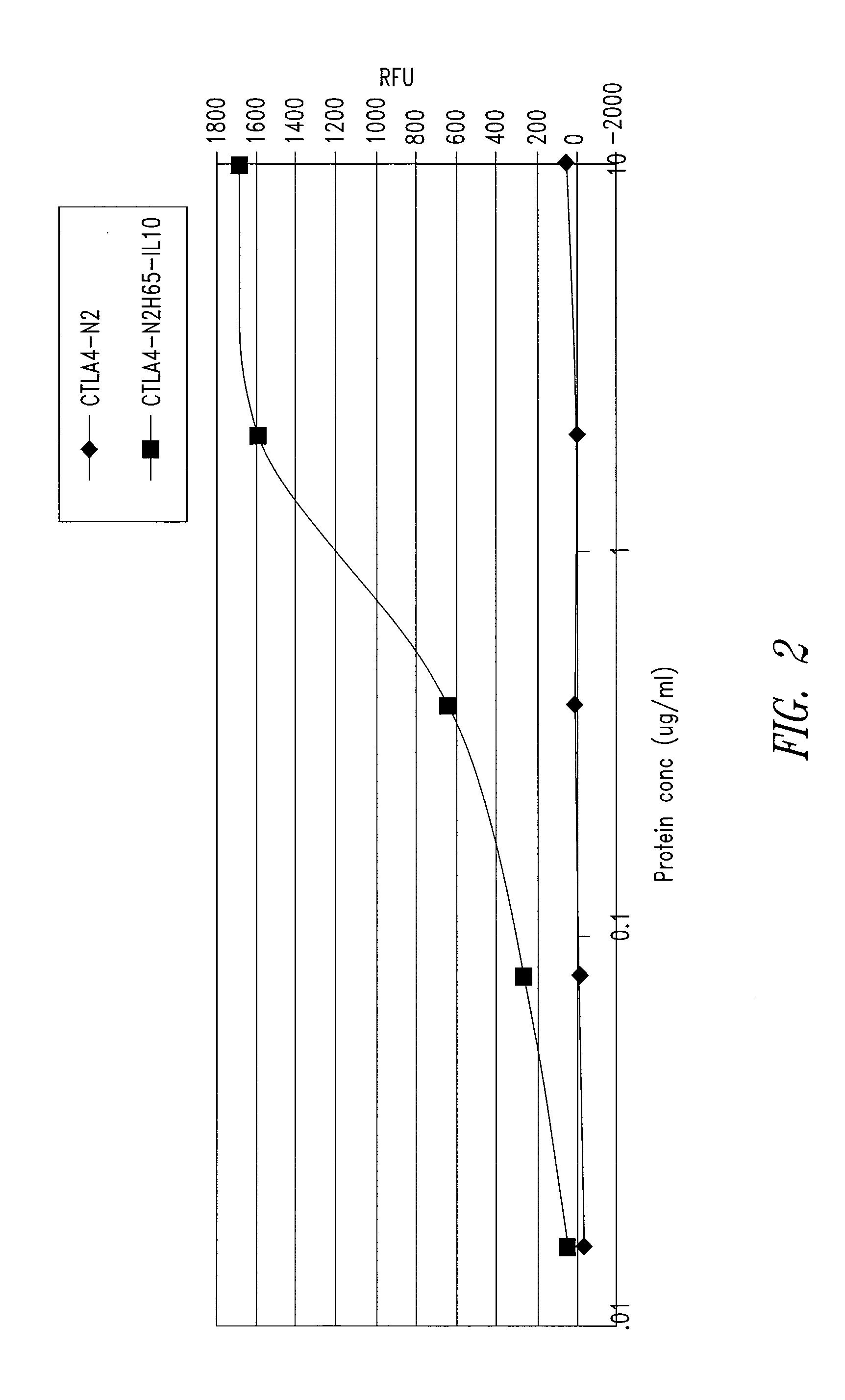
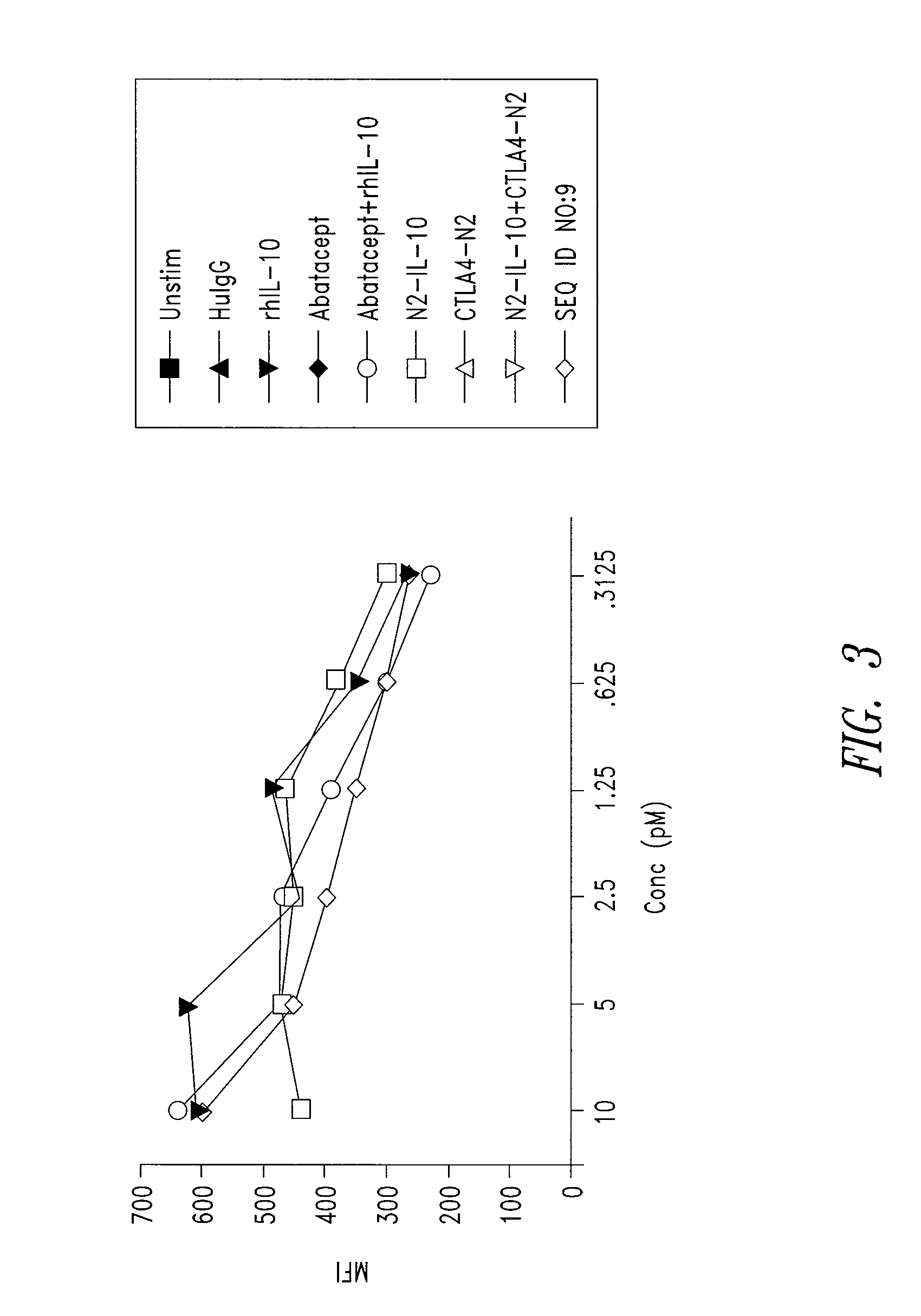
CD86 Antagonist Multi-Target Binding Proteins
This disclosure provides a multi-specific fusion protein composed of a CD86 antagonist binding domain and another binding domain that is an IL-10 agonist, an HLA-G agonist, an HGF agonist, an IL-35 agonist, a PD-1 agonist, a BTLA agonist, a LIGHT antagonist, a GITRL antagonist or a CD40 antagonist. The multi-specific fusion protein may also include an intervening domain that separates the other domains. This disclosure also provides polynucleotides encoding the multi-specific fusion proteins, compositions of the fusion proteins, and methods of using the multi-specific fusion proteins and compositions.
Owner:APTEVO RES & DEV LLC
Suppression of transplant rejection
InactiveUS20070166307A1Vertebrate cellsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAutoimmune conditionRegulatory T cell
The present invention relates to a transplant rejection in an animal suppressed by administration of an antibody directed at a cell surface antigen selected from the group consisting of CD4, CD8, CD154, LFA-1, CD80, CD86 and ICAM-1, preferably an anti-CD4 antibody, together with a non-cellular protein antigen to generate in the animal a population of regulatory T-lymphocytes; reactivating said population of regulatory T-lymphocytes by further administration to the animal of the non-cellular protein antigen; and transplanting said organ or tissue whilst said population of regulatory T-lymphocytes is activated. Regulatory T cells can be generated ex vivo by culturing T cells with an antibody directed at a cell surface antigen selected from the group consisting of CD4, CD8, CD154, LFA-1, CD80, CD86 and ICAM-1, in the presence of cells that present either alloantigen or a non-cellular protein antigen. Ex vivo generated T-lymphocytes can be used as an alternative method of overcoming transplant rejection or in combination with the in vivo method. A similar approach can be adopted for the treatment of autoimmune conditions.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
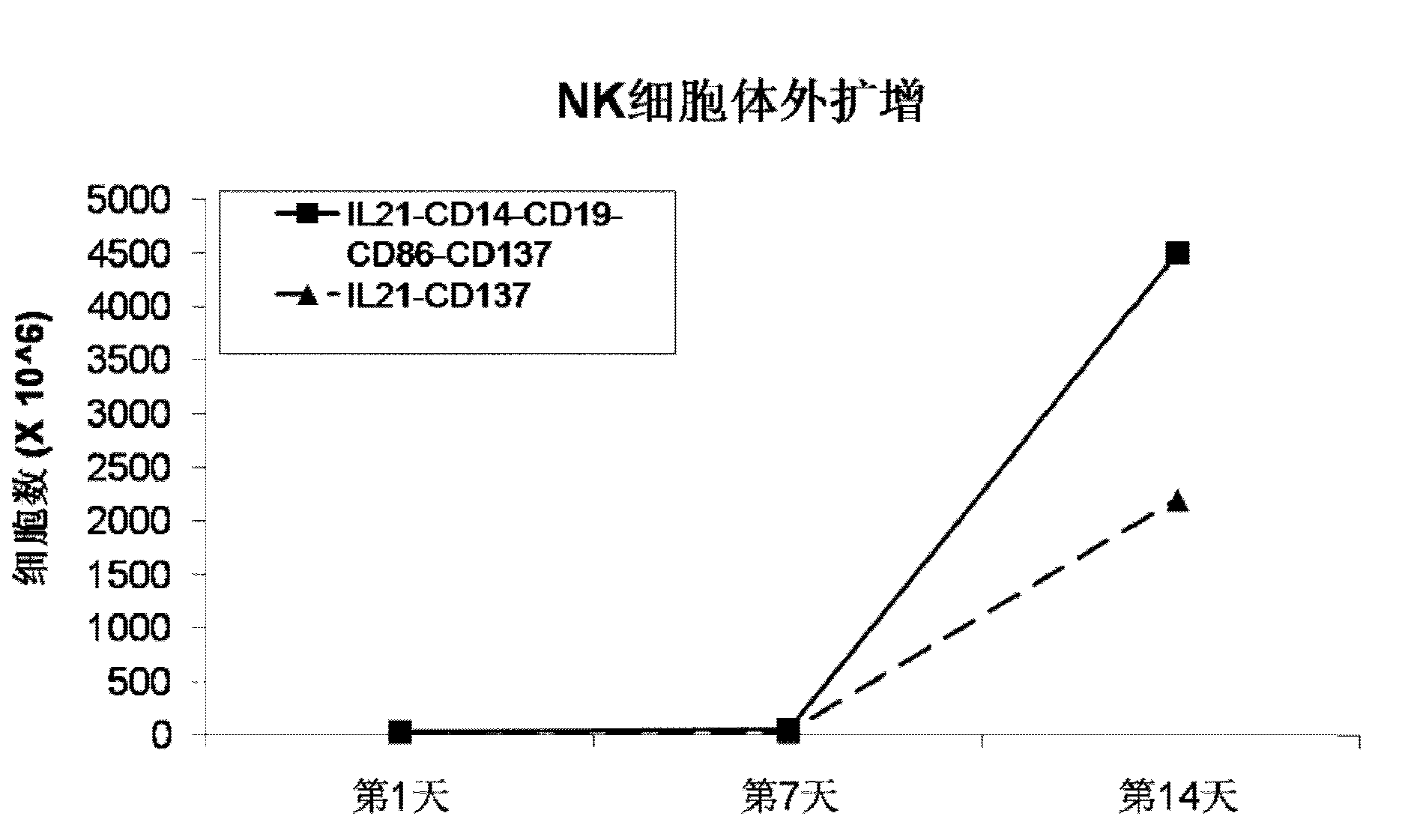
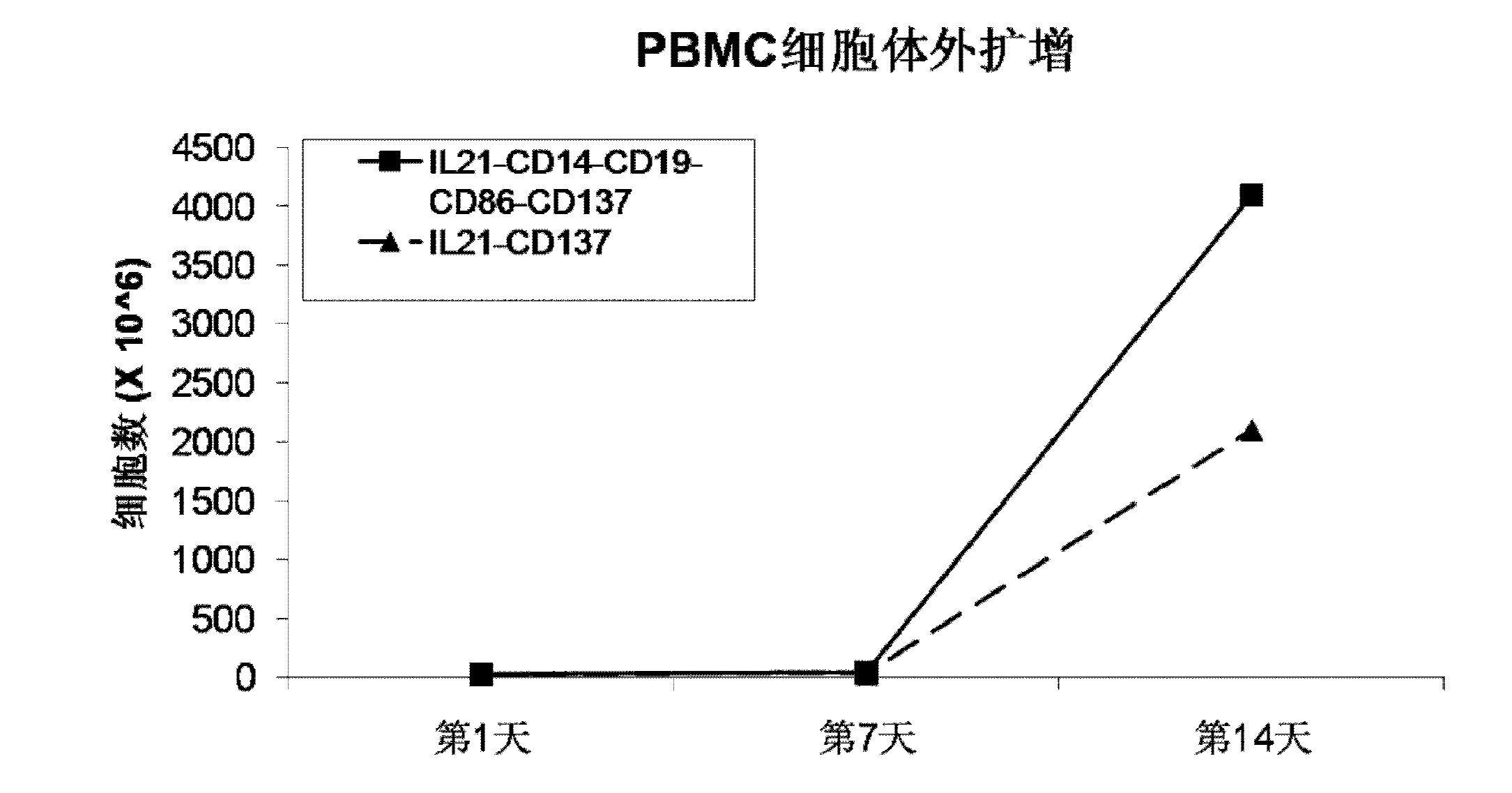
Method for amplification and activation of NK cells by K562 cells
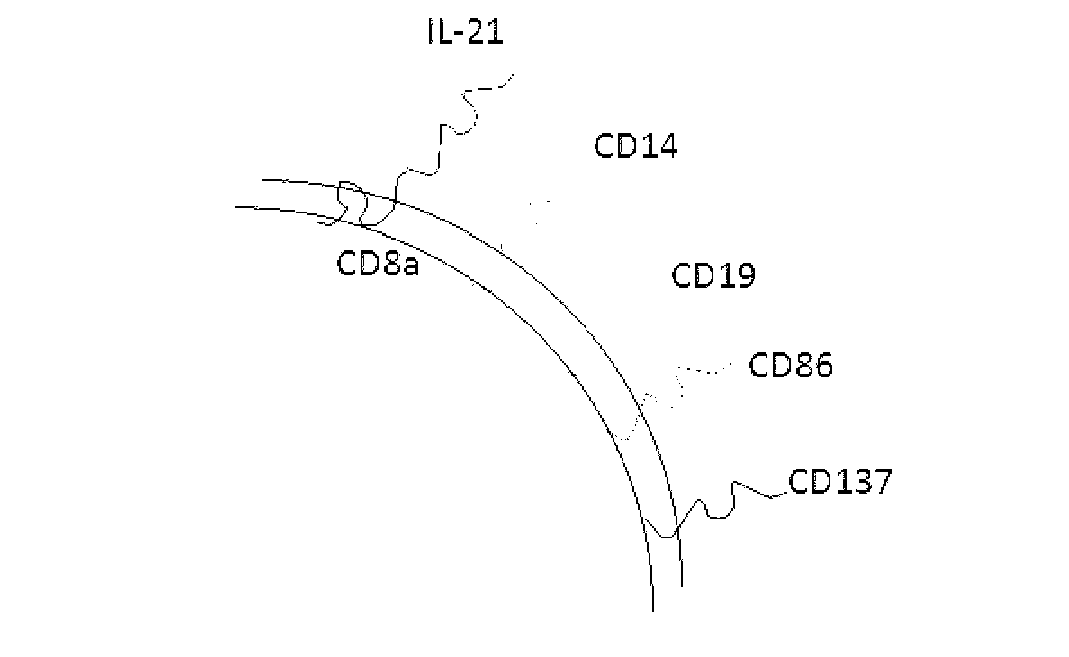
ActiveCN103232973AHelp identify and killHelp activate recognition and killMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory ReceptorsCD86
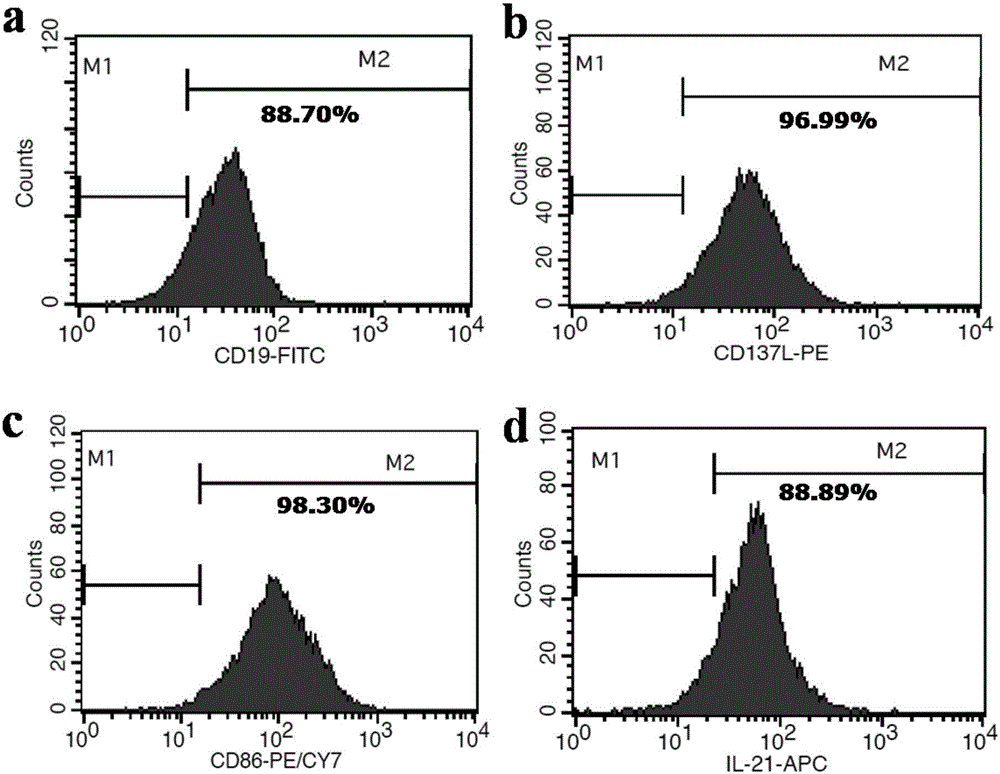
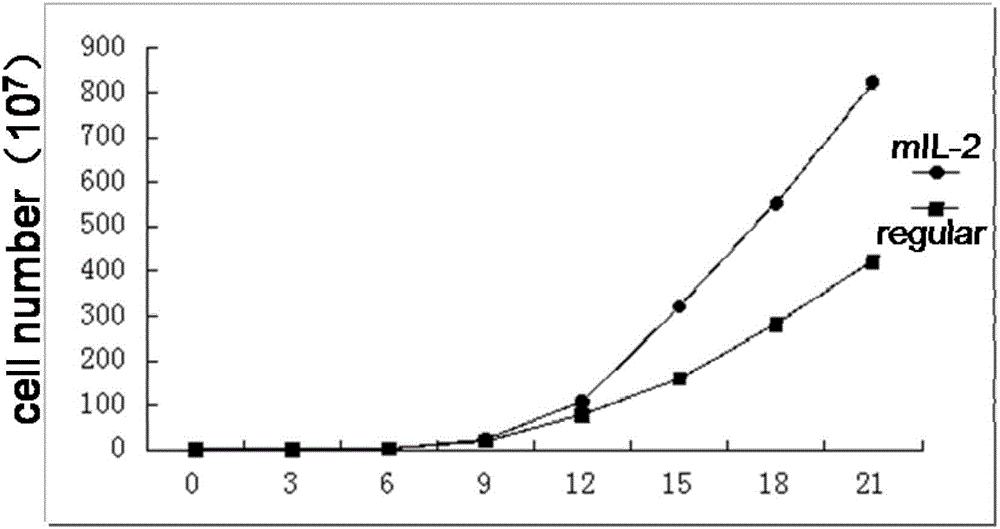
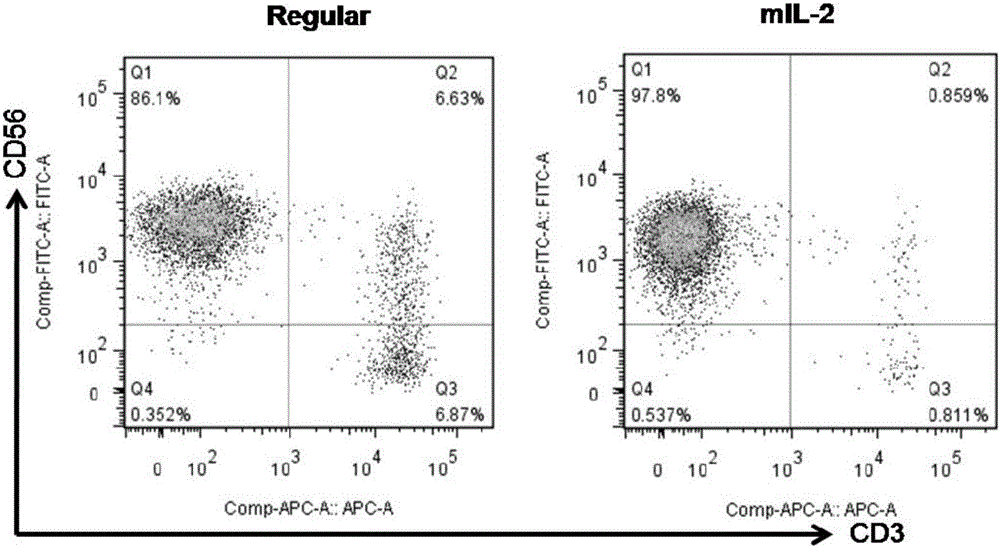
The invention discloses a method for amplification and activation of NK cells by K562 cells. The method comprises that through synergism of K562 cells transfected by transmembrane interleukin 21, CD14, CD19, CD86 and CD137, and low-concentration interleukin 2, NK cells are subjected to directed amplification and activation. Compared with the existing similar compounds, the compound provided by the invention has a stronger lymphocyte amplification and activation capability and higher efficiency. The method has wide prospects in immunological therapy.
Owner:杭州中赢生物医疗科技有限公司
Markers associated with the therapeutic efficacy of glatiramer acetate
InactiveUS20100285600A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingImmunologic disordersCD86
The present invention is directed to methods and kits based, at least in part, on the identification of allele-specific responsiveness or non-responsiveness to glatiramer acetate for the treatment of autoimmune disorders, such as relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. The allele-specific responsiveness or non-responsiveness is based on polymorphisms in the following genes, CTSS, MBP, TCRB, CD95, CD86, IL-1R1, CD80, SCYA5, MMP9, MOG, SPP1 and IL-12RB2.
Owner:TEVA PHARMA IND LTD
Naturally occuring IgM antibodies that bind to lymphocytes
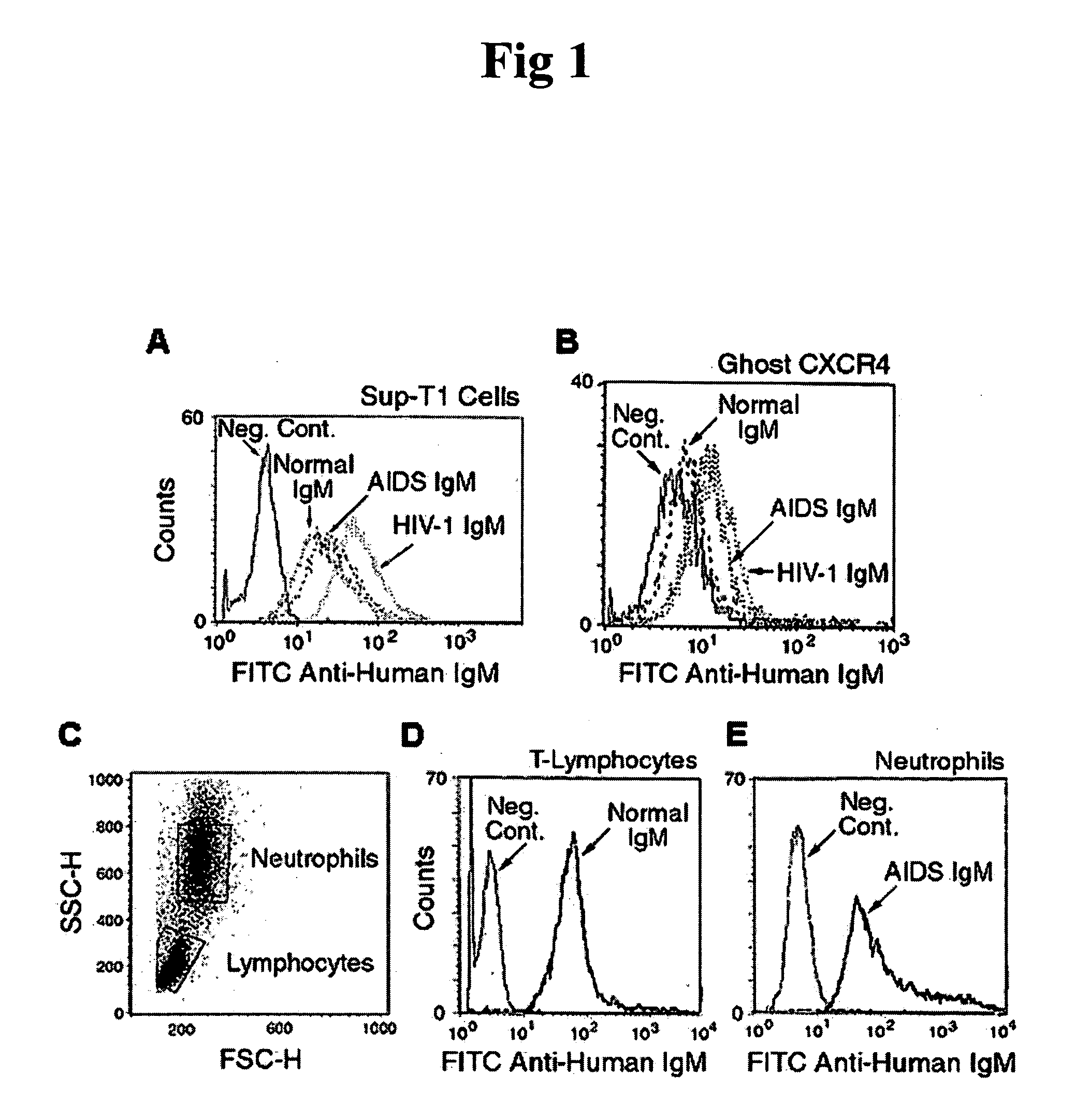
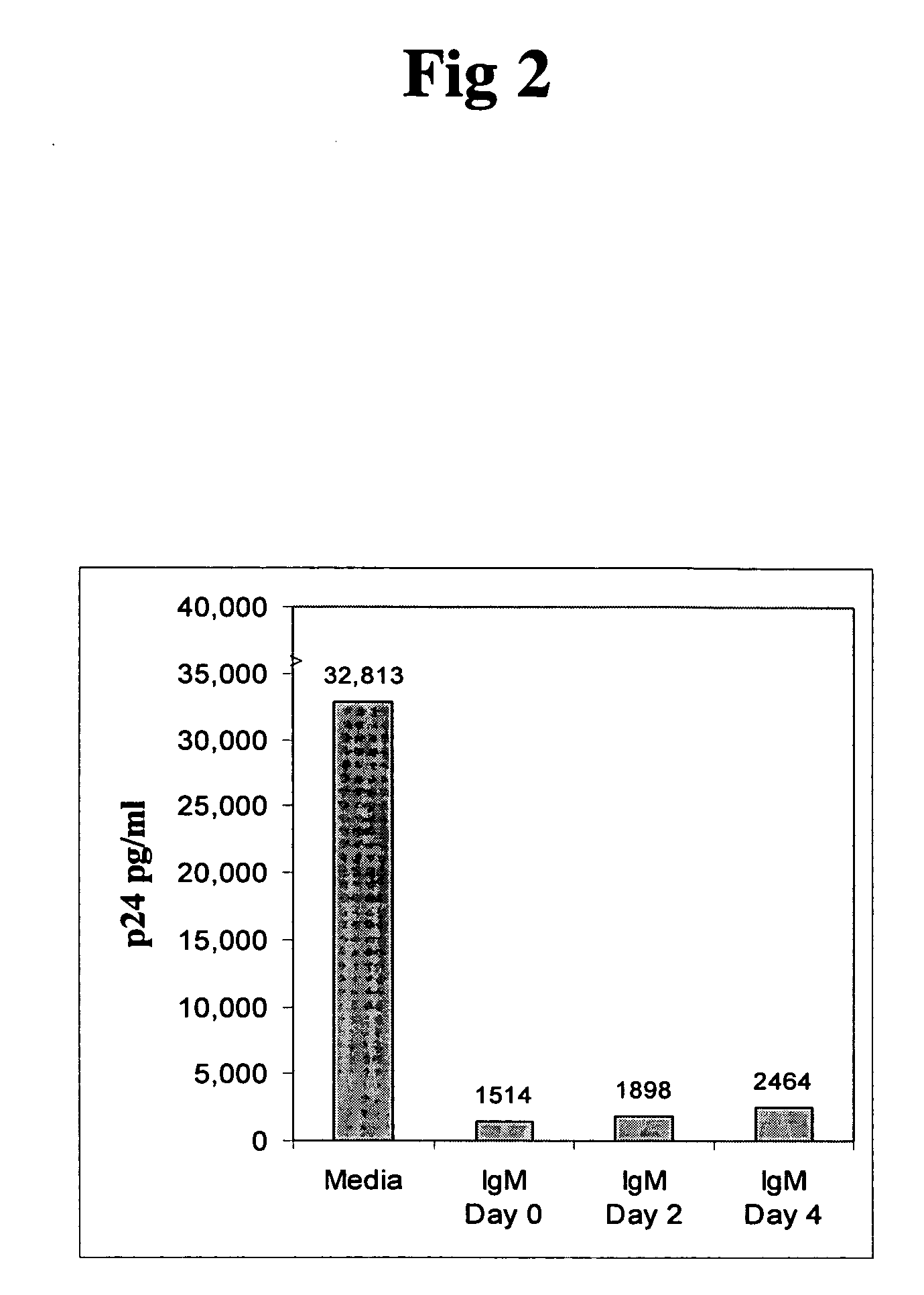
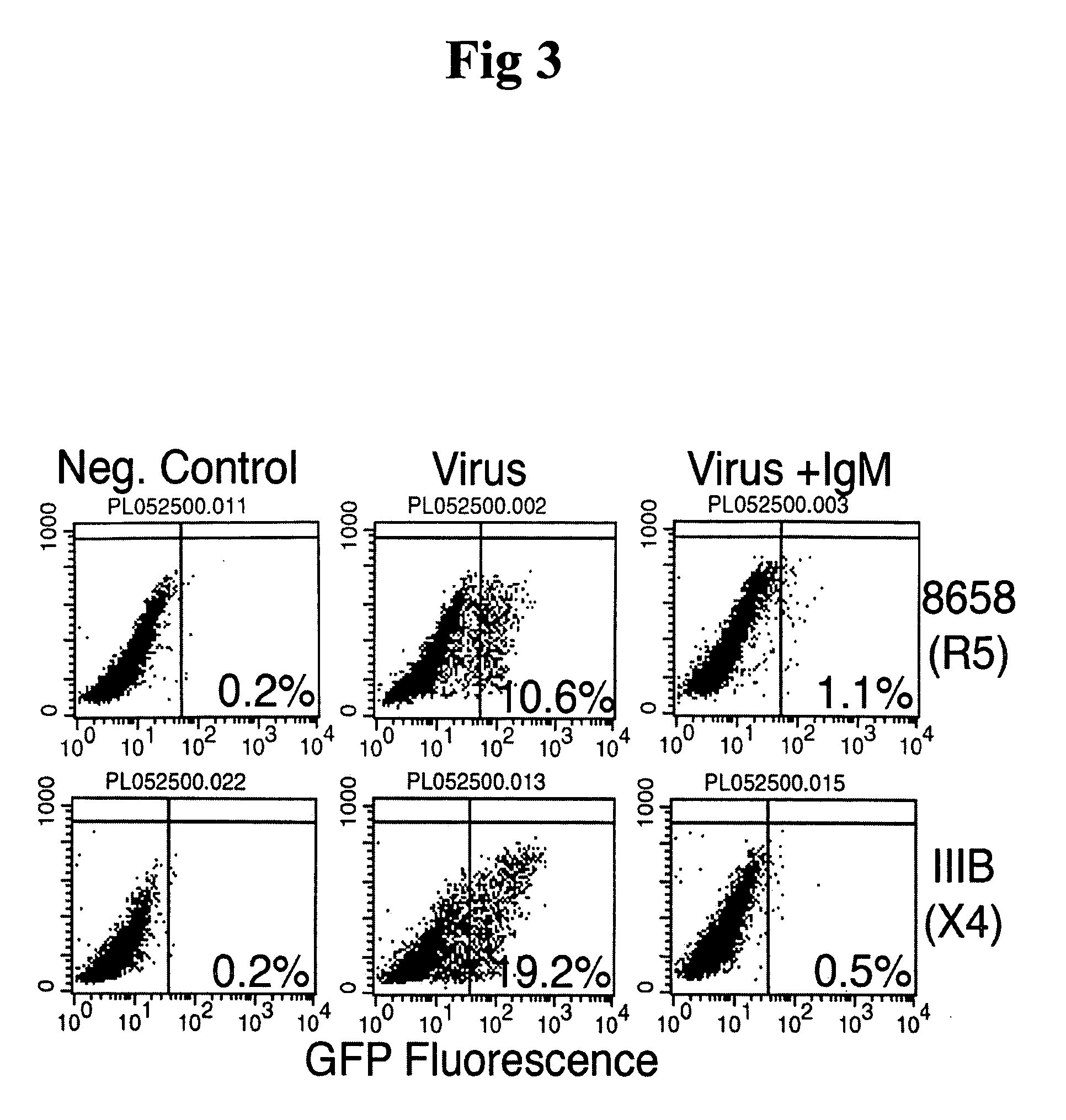
InactiveUS20050220787A1Inhibits HIV- infectivityImprove the level ofImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsLymphocyte AntibodyDisease
In this invention, the inventor discloses that naturally occurring IgM anti-lymphocyte antibodies bind to chemokine and non-chemokine receptors on lymphocytes and other cells, and downmodulate certain receptors including CD4 and CD2 on T cells and CD80 and CD86 on macrophages. The inventor also discloses that such antibodies (i) inhibit HIV-1 and other viruses from infecting cells (ii) inhibits activation and proliferation of T lymphocytes (iii) inhibits cytokine and chemokine production (iv) inhibits inflammatory processes, and (v) enhances death of malignant cells. This art or invention is novel in that the antibodies described herein are “naturally occurring” i.e. develop in absence of deliberate immunization and secondly these antibodies are distinct from disease causing autoantibodies in that these naturally occurring antibodies are polyreactive with low binding affinity.
Owner:LOBO PETER ISAAC
Methods for treating immune disorders associated with graft transplantation with soluble CTLA4 mutant molecules
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Antisense oligomers and methods for inducing immune tolerance and immunosuppression
InactiveUS20050234002A1Reduce capacityIncrease productionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideExtracellularDendritic cell
A method and composition for inducing human dendritic cells to a condition of reduced capacity for antigen-specific activation of T cells, and, in mature dendritic cells, increased production of extracellular IL-10 is disclosed. A population of dendritic cells is exposed to a substantially uncharged antisense compound containing 12-40 subunits and a base sequence effective to hybridize to an expression-sensitive region of a preprocessed or processed human CD86 transcript identified, in its processed form, by SEQ ID NO:33, to form a duplex structure between said compound and transcript having a Tm of at least 45° C. Formation of the duplex blocks expression of full-length CD86 in said cells, which in turn leads to reduced capacity for antigen-specific activation of T cells, and, in mature dendritic cells, increased production of extracellular IL-10.
Owner:AVI BIOPHARMA
Methods for treating immune disorders associated with graft transplantation with soluble CTLA4 mutant molecules
ActiveUS20070009511A1Great avidityImprove solubilityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderGraft transplantCD80
The present invention provides use of soluble CTLA4 mutant molecules which bind with greater avidity to the CD80 and / or CD86 antigen than wild type CTLA4 or non-mutated CTLA4Ig in the treatment of immune disorders associated with graft transplantation.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Treatment of B cell lymphoma using anti-CD80 antibodies that do not inhibit the binding of CD80 to CTLA-4
InactiveUS7153508B2Prevent rejectionAvoid immune responseCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAntigen
Owner:BIOGEN INC
Methods of treatment using CTLA4 mutant molecules
The present invention provides soluble CTLA4 mutant molecules which bind with greater avidity to the CD80 and / or CD86 antigen than wild type CTLA4 or non-mutated CTLA4Ig. The soluble CTLA4 molecules have a first amino acid sequence comprising the extracellular domain of CTLA4, where certain amino acid residues within the S25-R33 region and M97-G107 region are mutated. The mutant molecules of the invention may also include a second amino acid sequence which increases the solubility of the mutant molecule.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
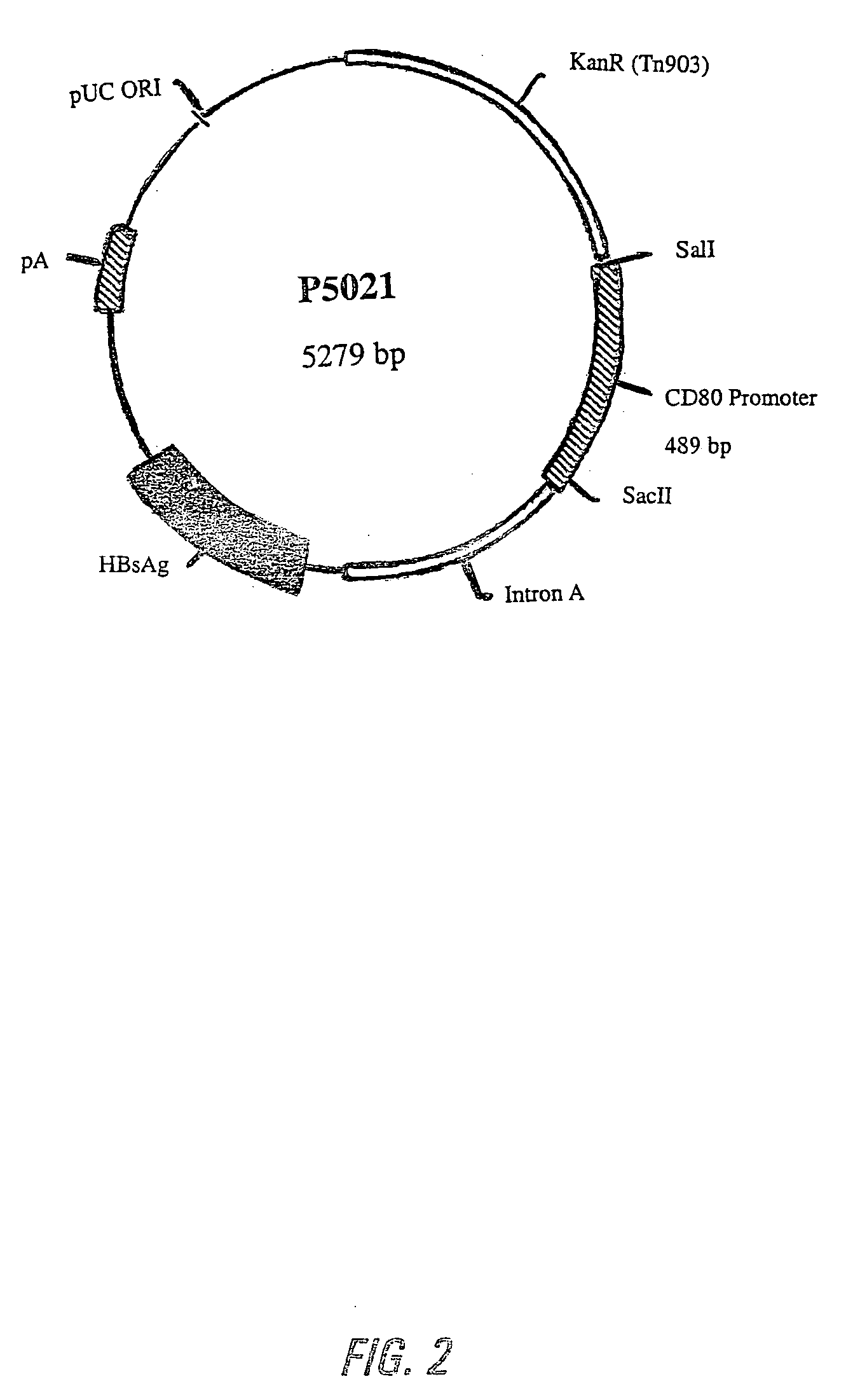
Nucleic acid vaccine compositions having a mammalian CD80/CD86 gene promoter driving antigen expression
Polynucleotides encoding at least one immunizing antigen whose expression is controlled by a promoter derived from a gene encoding a co-stimulatory molecule are provided. The polynucleotides may also encode adjuvants. Compositions comprising at least one immunizing agent and at least one cytokine that enhance dendritic cell stimulation and / or survival are also provided. Methods for eliciting an immune response against the immunizing agent are also provided. The method includes the steps of administering the polynucleotides and, optionally, co-administering an adjuvant.
Owner:POWDERJECT RES LTD OXFORD (GB)
Method for efficiently amplifying NK cells
InactiveCN106754730AEnhanced lethalityEnhanced ADCC effectBlood/immune system cellsCell culture active agentsNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory ReceptorsCD86
The invention discloses a method for efficiently amplifying NK cells, in particular to a method for efficiently amplifying NK cells using K562 engineered cells of high expression membrane proteins CD19, CD137L, CD86, CD64 and transmembrane protein IL- 21 and combining with human IL-2 mutants. The method has the advantages of simple operation, low cost, large number of obtained NK cells, high purity and good killing effect; the method is suitable for large-scale preparation of the NK cells and lays a good foundation for the application of NK cell adoptive immunotherapy in clinical practice.
Owner:SHANGHAI BIOMED UNION BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Engineered artificial antigen presenting cells for tumor infiltrating lymphocyte expansion
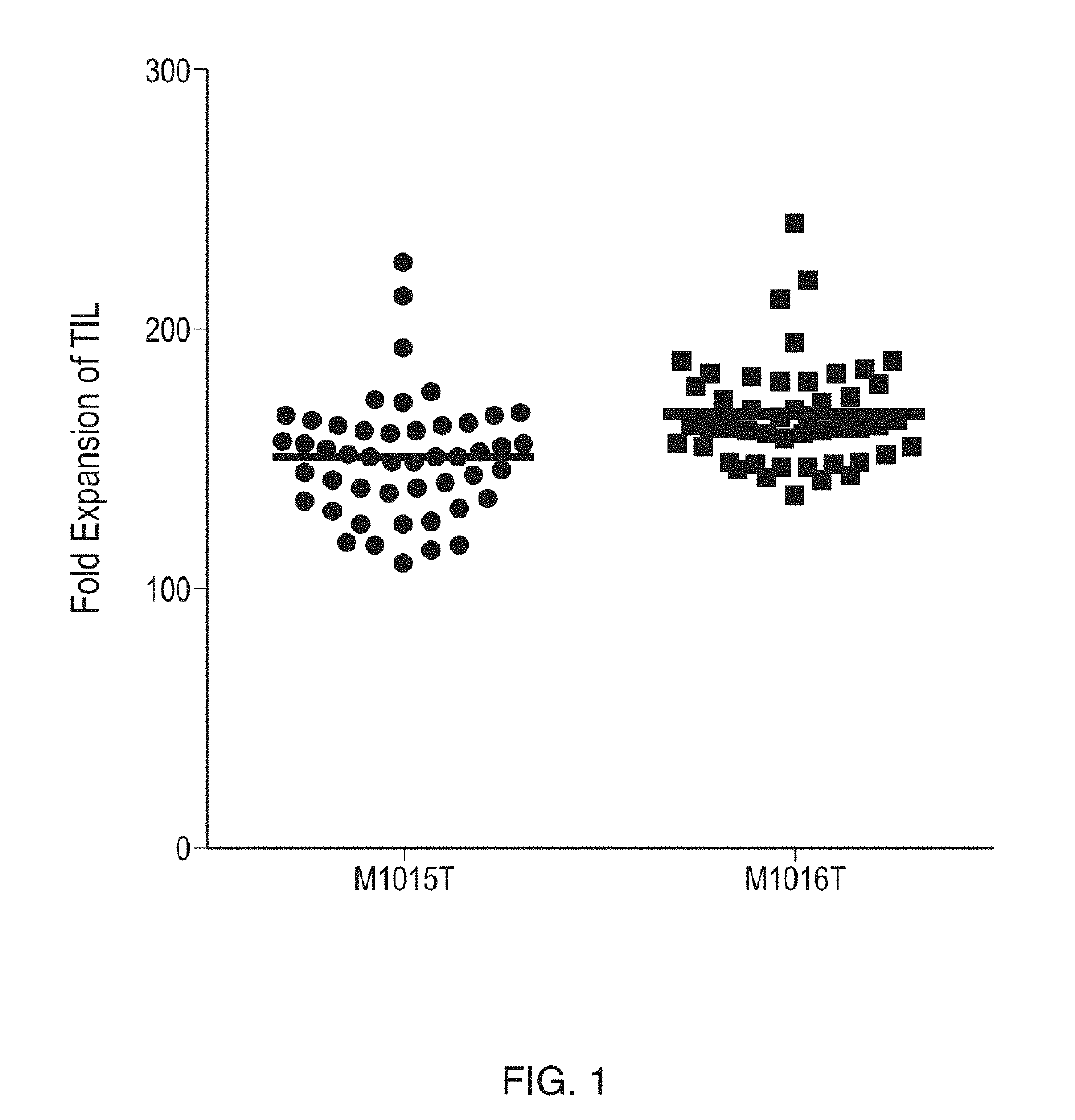
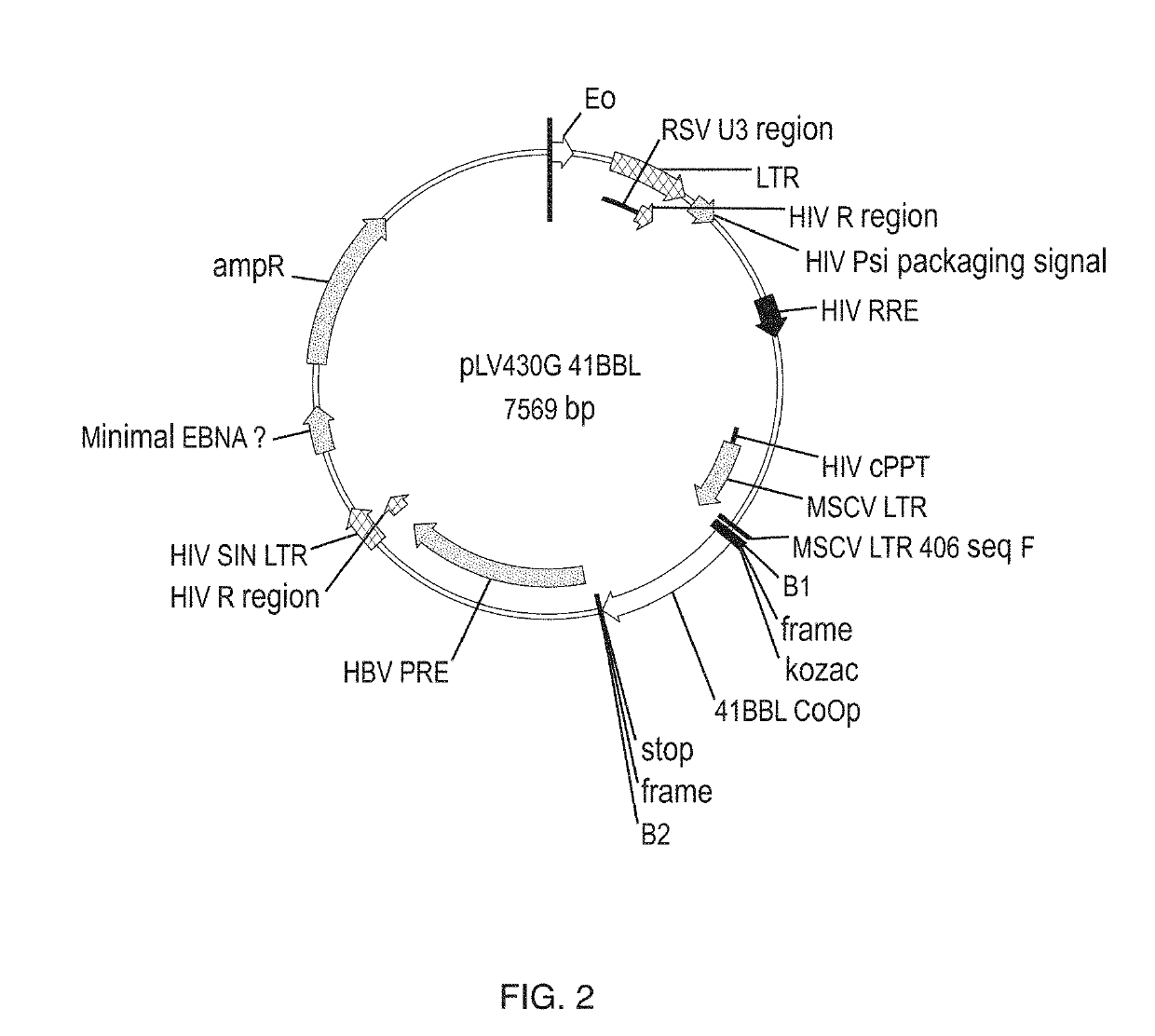
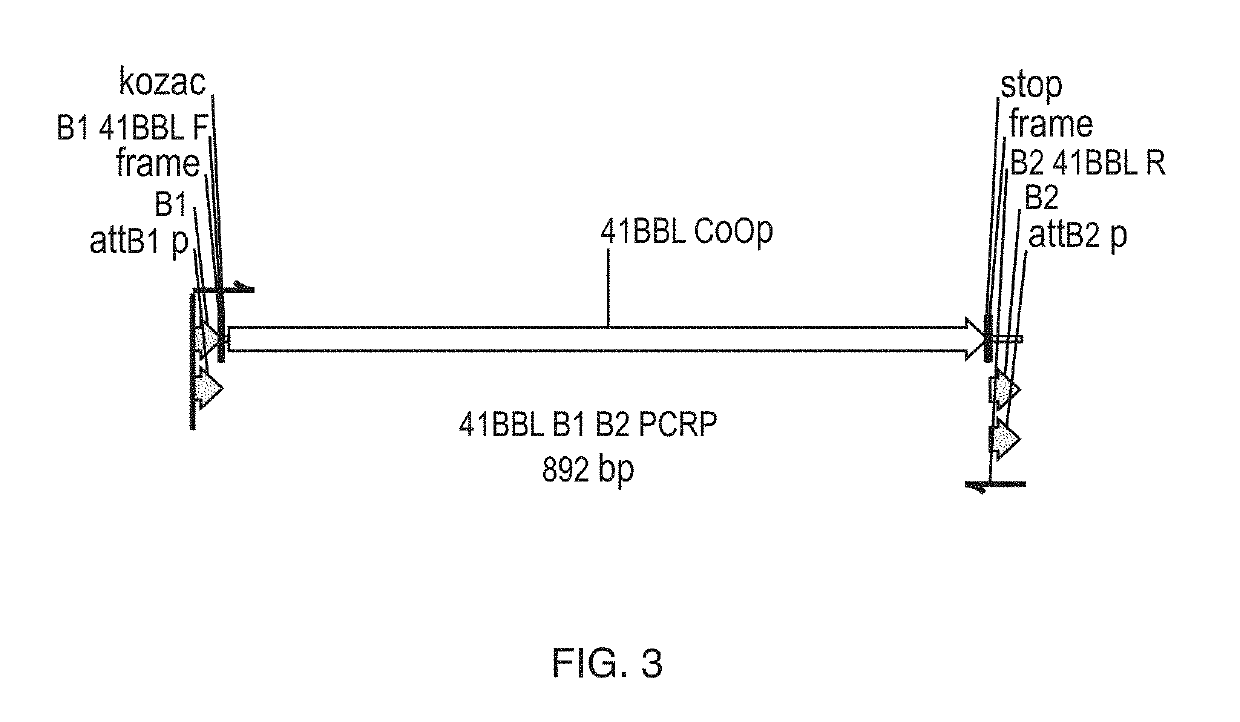
In some embodiments, compositions and methods relating to isolated artificial antigen presenting cells (aAPCs) are disclosed, including aAPCs comprising a myeloid cell transduced with one or more viral vectors, such as a MOLM-14 or a EM-3 myeloid cell, wherein the myeloid cell endogenously expresses HLA-AB / C, ICOS-L, and CD58, and wherein the one or more viral vectors comprise a nucleic acid encoding CD86 and a nucleic acid encoding 4-1BBL and / or OX40L and transduce the myeloid cell to express CD86 and 4-1BBL and / or OX40L proteins. In some embodiments, methods of expanding tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) with aAPCs and methods of treating cancers using TILs after expansion with aAPCs are also disclosed.
Owner:IOVANCE BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Treating intestinal inflammation with anti-CD80 antibodies that do not inhibit CD80 binding to CTLA-4
InactiveUS7175847B1Prevent rejectionAvoid immune responseImmunoglobulins against bacteriaImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsAntigenCD80
Owner:BIOGEN INC
Artificial antigen submit cell and preparation method thereof
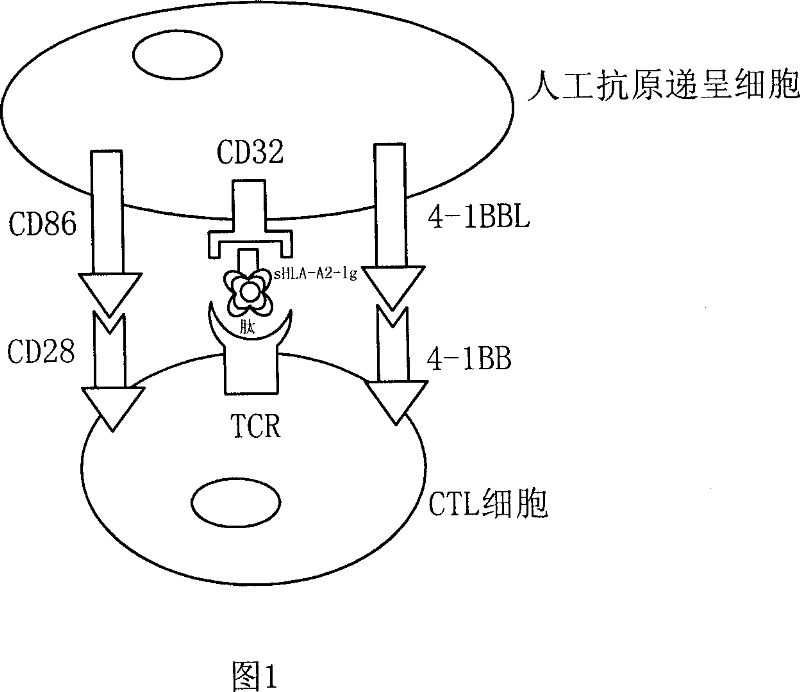
InactiveCN101041816AEfficient activationInhibit apoptosisVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsAntigenCD86
The invention discloses an artificial antigen submitting cell and preparing method, which comprises the following steps: choosing human chronic granular leukocyte leukemia bacterial strain K562 cell as carrier; transfer-dying and expressing eucaryon expressing carrier of CD32a; expressing CD32 molecular on the surface of K562 cell stably through G418 screening and flowed cell sorting device sorting; forming K32 cell; producing eucaryon expressing carrier of double expressing CD86 and 4-1BBL co-simulating signal; proceeding homomycin screen and sort with flowed cell device for the K32 cell; getting stable expression K32 cell of CD86 and 4-1BBL molecule; getting the end product. This invention possesses low cost and good repeatability, which can inhibit die effectively.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Chimeric protein and method of controlling tumor growth using the protein
A chimeric protein expressed from a transgene tranduced into a mammalian tumor cell and method of using the chimeric protein for cancer treatment. The chimeric protein comprises an effector and an anchor, which are linked by a spacer. The chimeric protein, when expressed and exposed on the tumor cell surface in vivo can activate T cells, which further lead to lysis of the tumor cells. The anti-tumor effects can be enhanced by co-expression of certain co-stimulators, such as CD80 or CD86.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Generation and use of new types of dendritic cells
InactiveUS20050042751A1Eliminate effectiveEffective preventionArtificial cell constructsCancer antigen ingredientsCD86Human leukocyte antigen DR
Owner:INNATE PHARMA SA
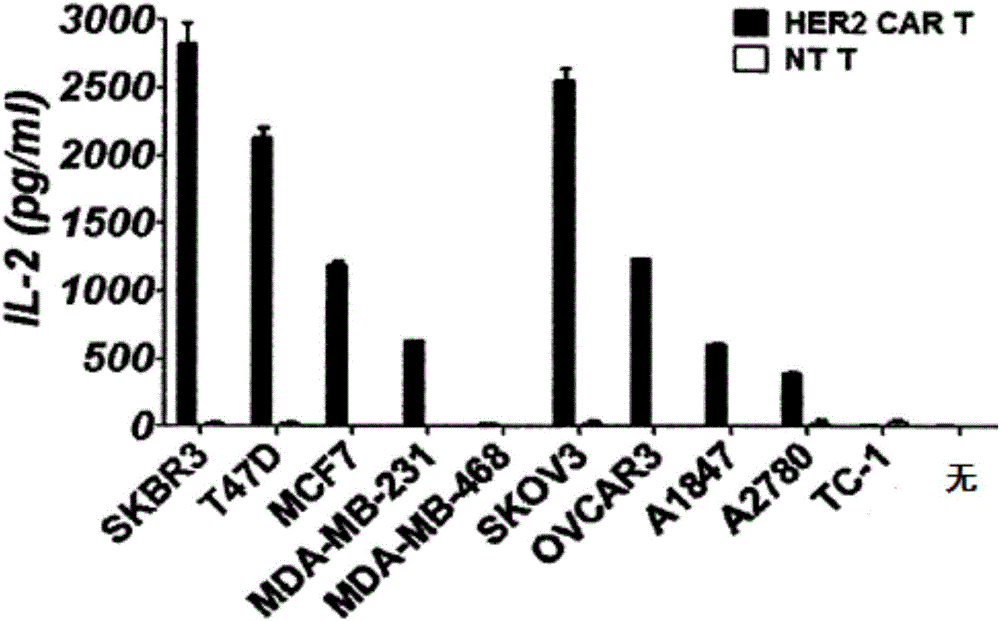
CAR-T cell as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106047817APromote secretionEnhance the effect of killing tumor cellsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNGF/TNF-superfamilyAntigenCell membrane
Owner:SHEN ZHEN ISTEM REGENERATIVE MEDICINE SCI TECH CO LTD
Soluble CTLA4 mutant molecules and uses thereof
InactiveCN101255192AReduce dissociationHigh affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSolubilityDiamino acid
The present invention provides soluble CTLA4 mutant molecules which bind with greater avidity to the CD80 and / or CD86 antigen than wild type CTLA4 or non-mutated CTLA4Ig. The soluble CTLA4 molecules have a first amino acid sequence comprising the extracellular domain of CTLA4, where certain amino acid residues within the S25-R33 region and M97-G107 region are mutated. The mutant molecules of the invention may also include a second amino acid sequence which increases the solubility of the mutant molecule.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
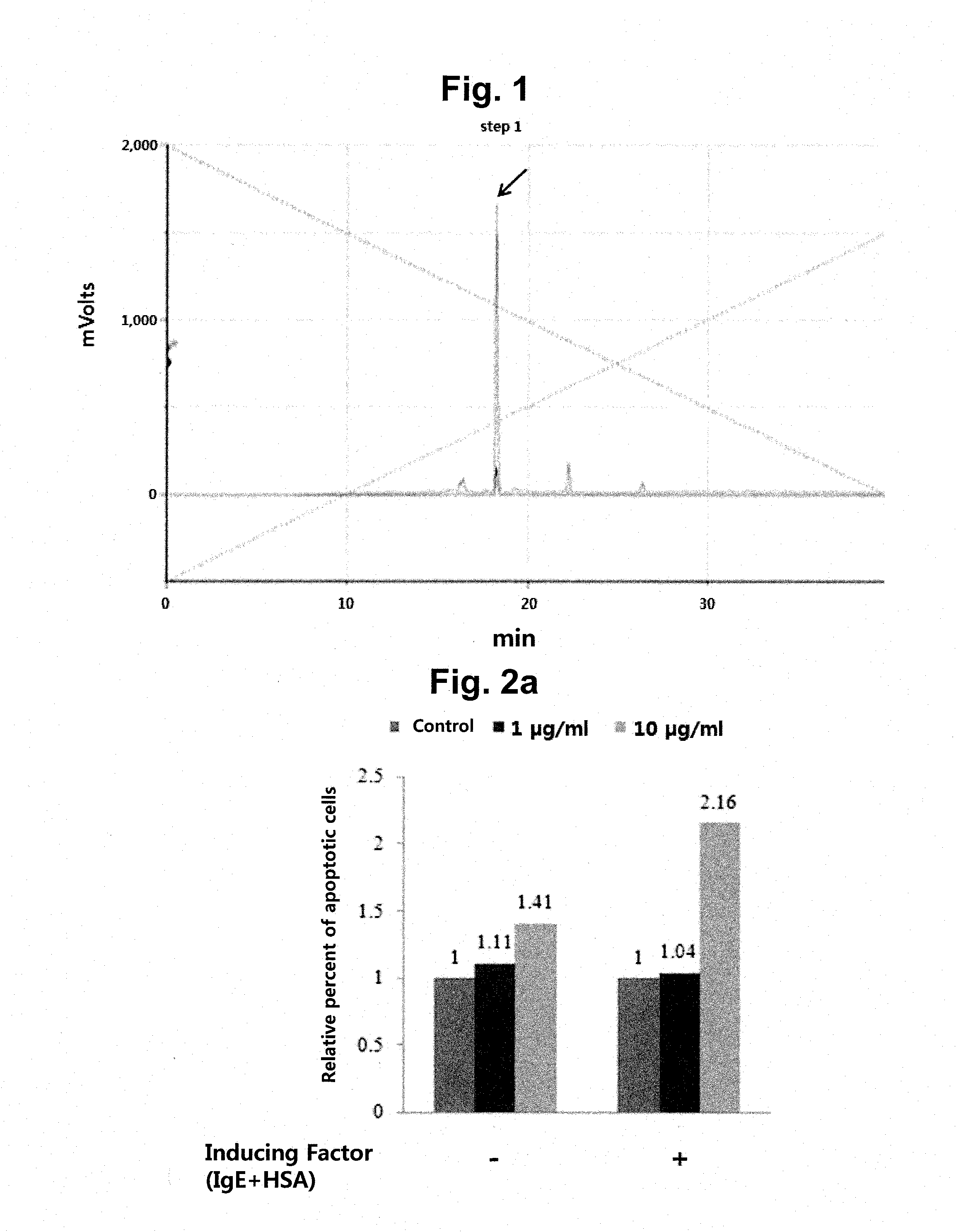
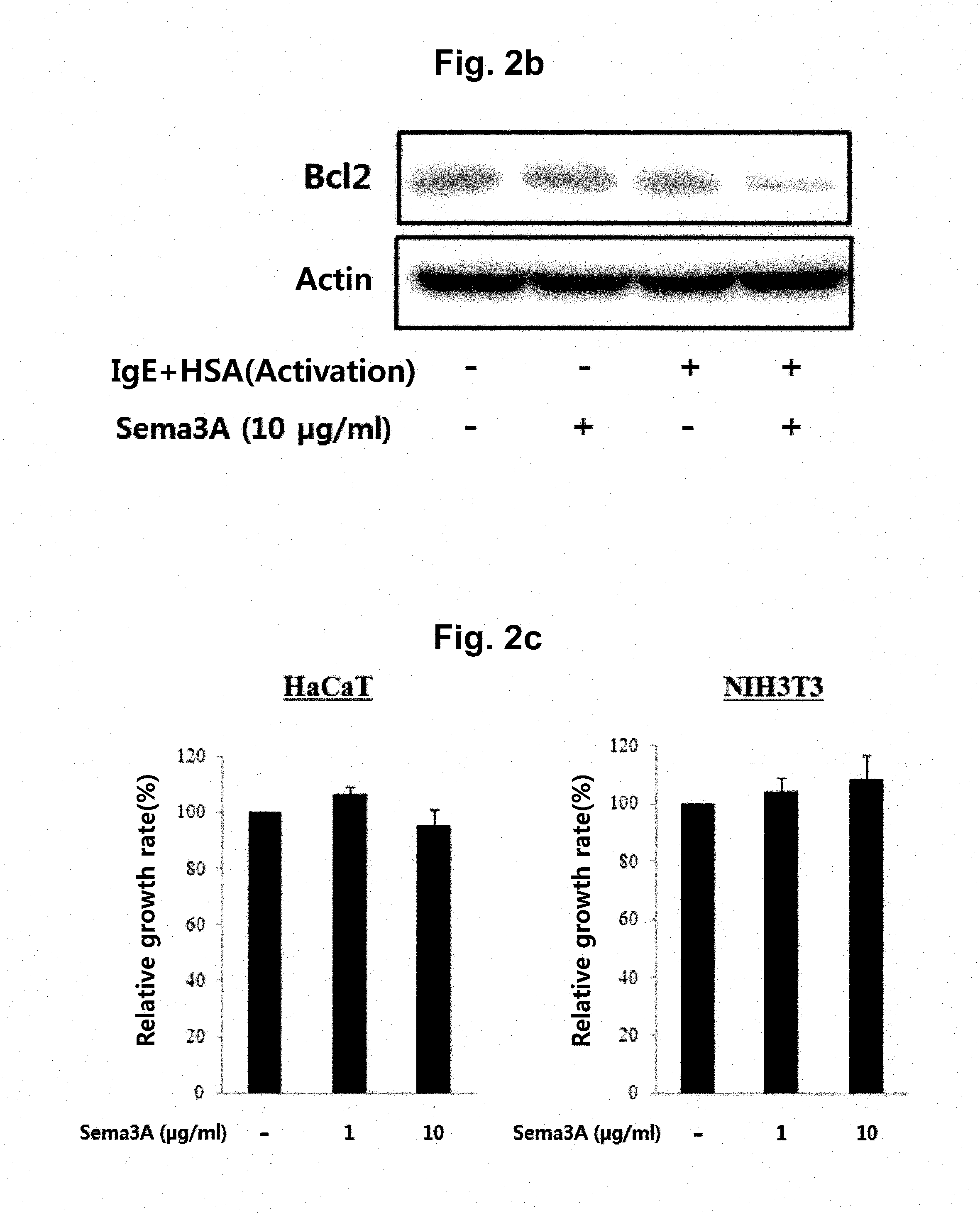
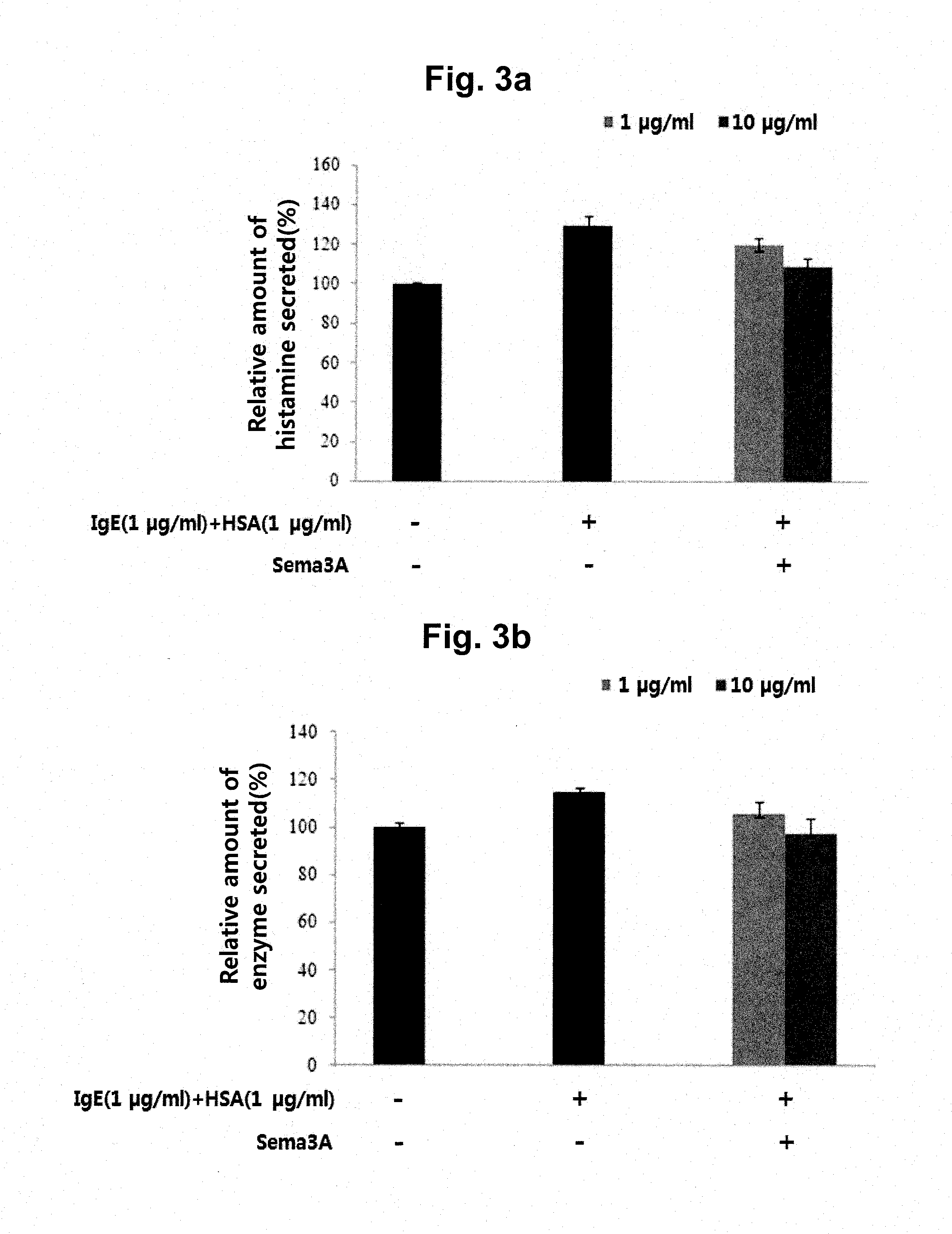
Peptide for inducing mast cell-specific apoptosis and use thereof
ActiveUS20160075739A1Good skin permeabilityInhibitory activityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionDiseaseAntigen
A peptide according to the present invention can perform a function identical or similar to the function of natural CTLA-4 and has an excellent degree of skin penetration due to a small size. The peptide according to the present invention effectively binds to antigen presenting cell surface proteins (CD80 and CD86) to inhibit activity of T cells and thus is capable of inhibiting the expression of inflammatory cytokines (for example, IL-2 and IFN-γ). As a result, a composition comprising the peptide according to the present invention exhibits excellent effects in terms of preventing, treating, or improving Th1-mediated immune diseases. Therefore, the superior activity and stability of the peptide according to the present invention can be useful when applied to medicine, quasi-drugs, and cosmetics.
Owner:CAREGEN
CD86 antagonist multi-target binding proteins
This disclosure provides a multi-specific fusion protein composed of a CD86 antagonist binding domain and another binding domain that is an IL-10 agonist, an HLA-G agonist, an HGF agonist, an IL-35 agonist, a PD-1 agonist, a BTLA agonist, a LIGHT antagonist, a GITRL antagonist or a CD40 antagonist. The multi-specific fusion protein may also include an intervening domain that separates the other domains. This disclosure also provides polynucleotides encoding the multi-specific fusion proteins, compositions of the fusion proteins, and methods of using the multi-specific fusion proteins and compositions.
Owner:APTEVO RES & DEV LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com