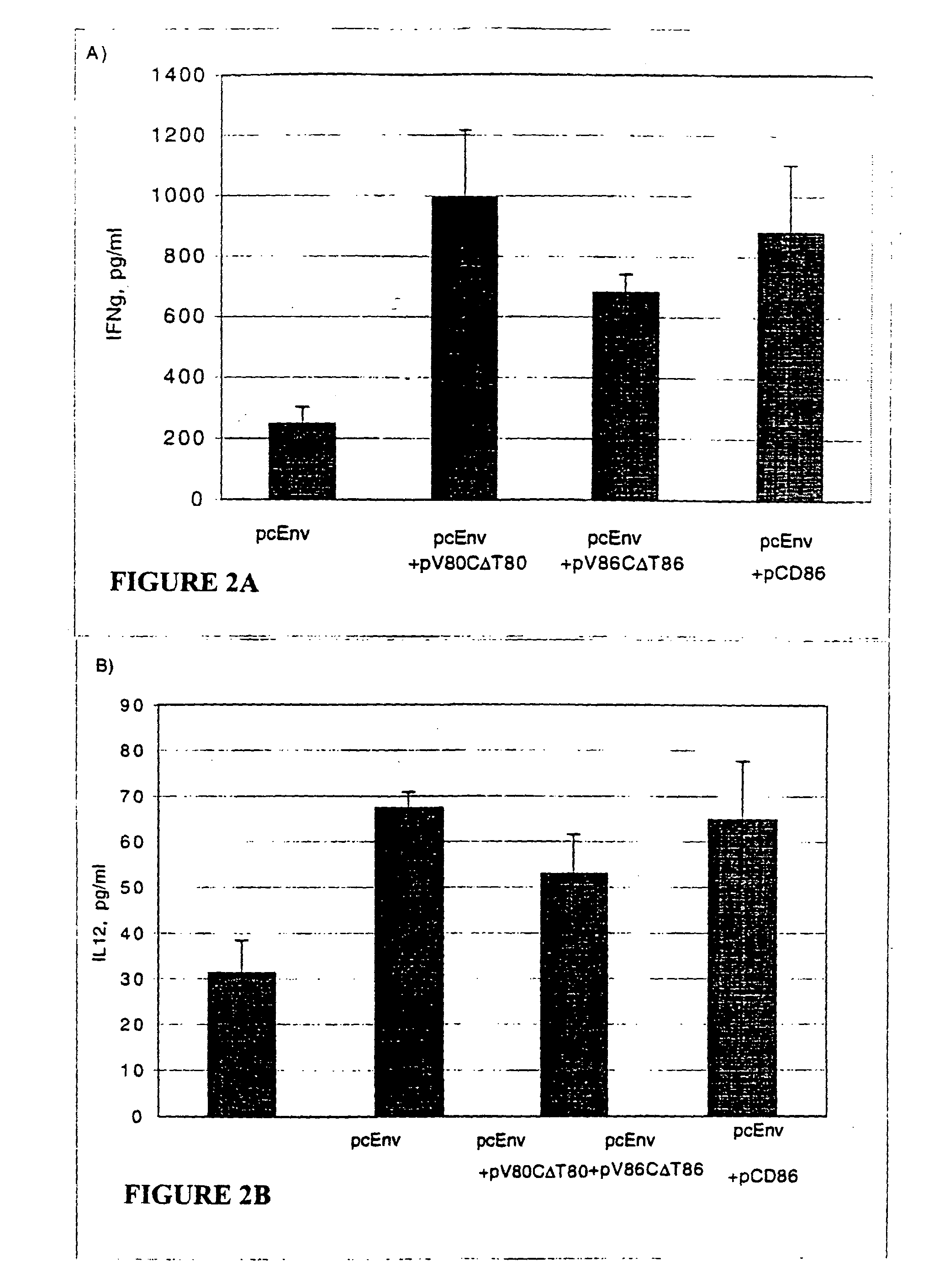
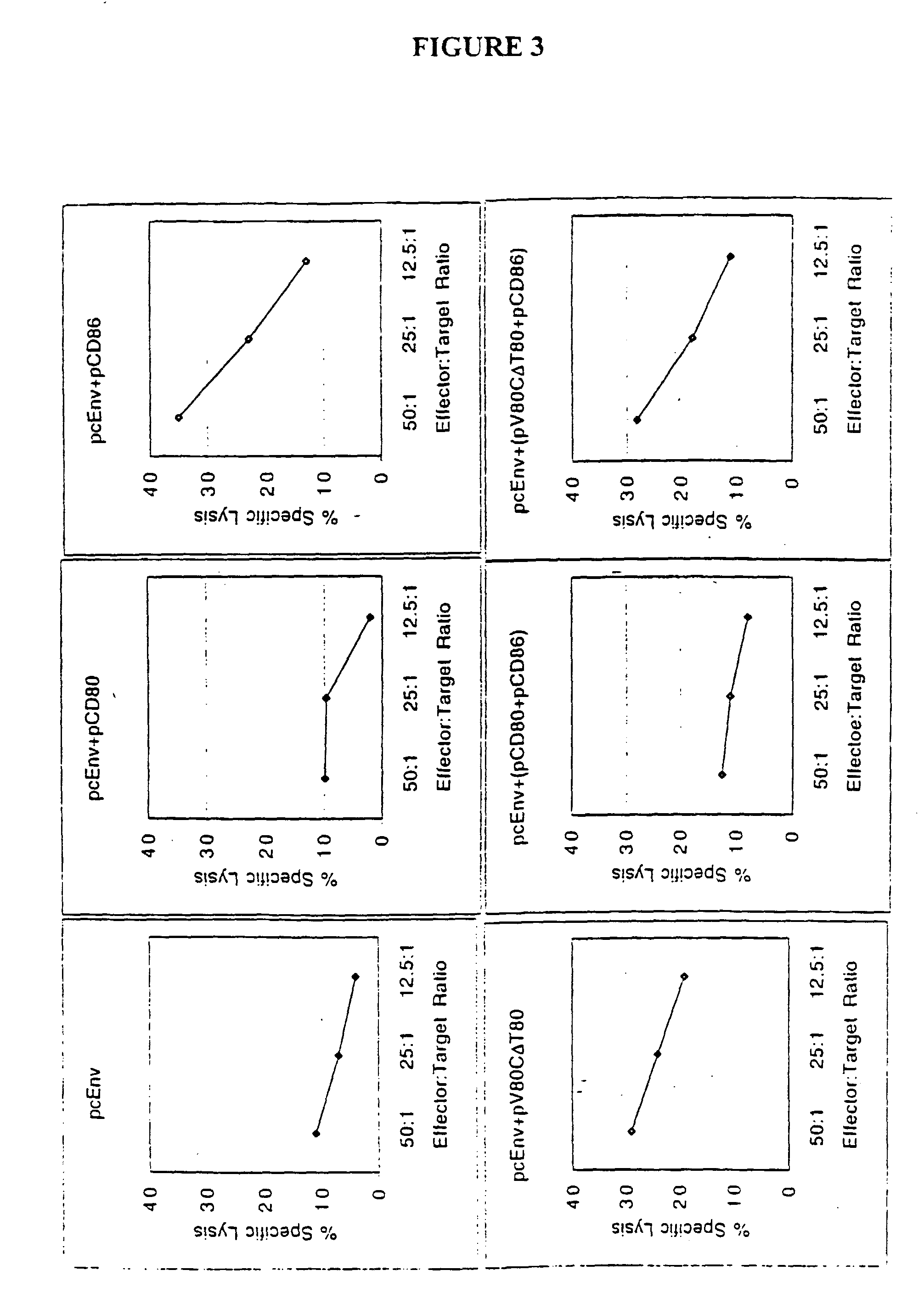
Patents
Literature
169 results about "CD80" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cluster of differentiation 80 (also CD80 and B7-1) is a B7, type I membrane proteinthat is in the immunoglobulin superfamily, with an extracellular immunoglobulin constant-like domain and a variable-like domain required for receptor binding. It is closely related to CD86, another B7 protein (B7-2), and often works in tandem, binding to the same receptors to prime T cells.
Soluble CTLA4 mutant molecules
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
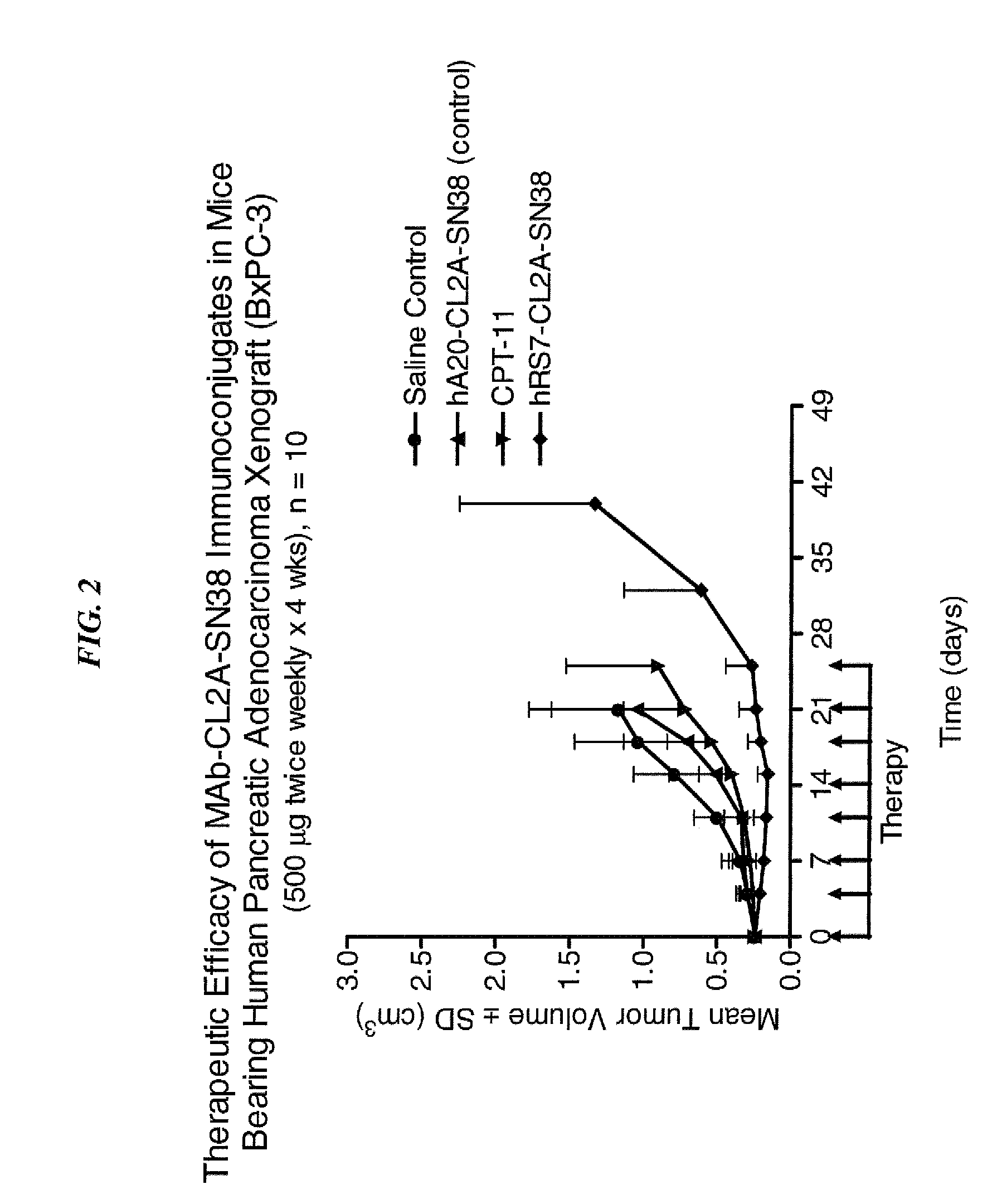
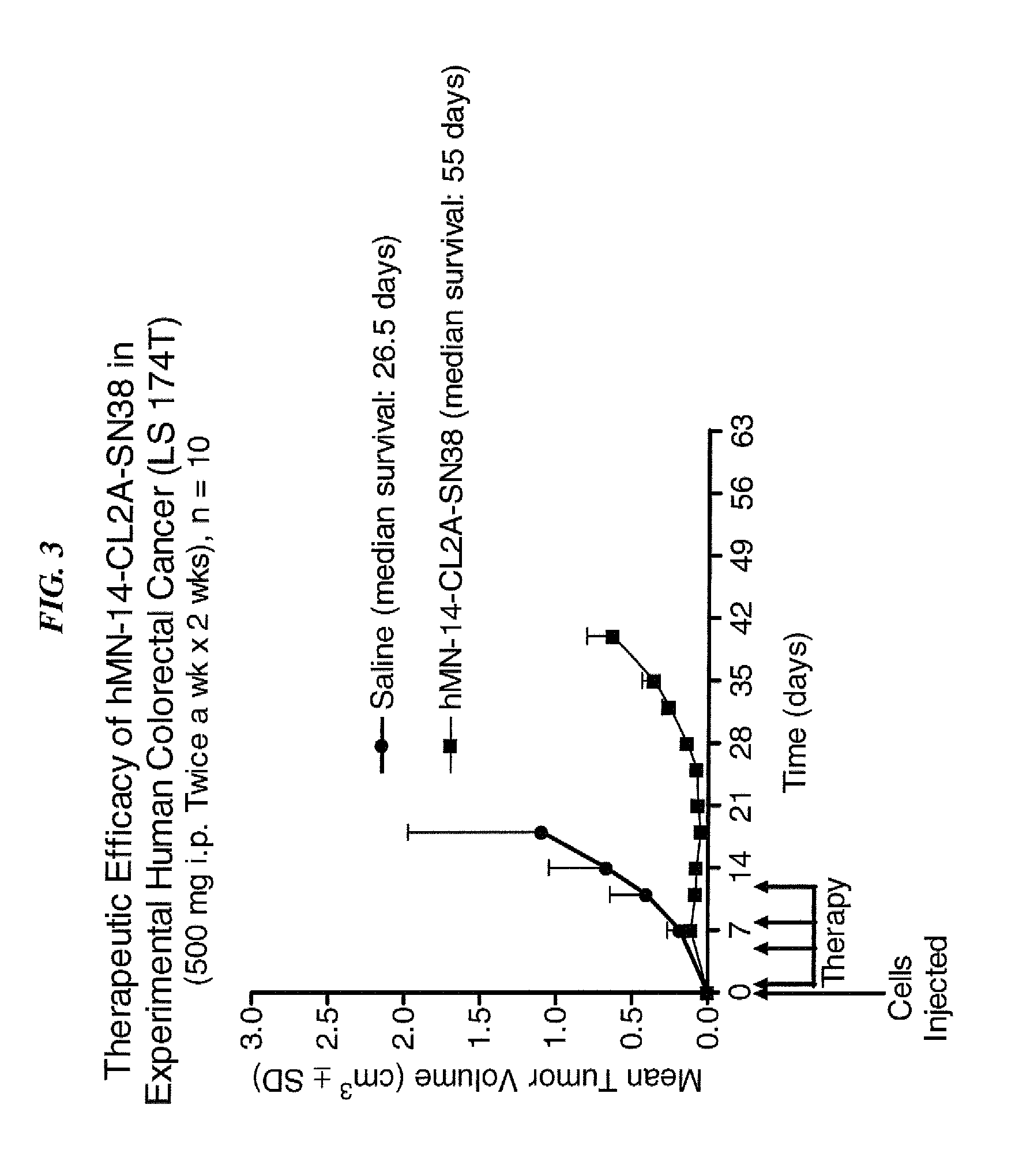
Camptothecin Conjugates of Anti-CD22 Antibodies for Treatment of B Cell Diseases
ActiveUS20110305631A1Increase the number ofNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsCD20Autoimmune condition
Disclosed herein are compositions and methods of use comprising combinations of anti-CD22 antibodies with a therapeutic agent. The therapeutic agent may be attached to the anti-CD22 antibody or may be separately administered, either before, simultaneously with or after the anti-CD22 antibody. In preferred embodiments, the therapeutic agent is an antibody or fragment thereof that binds to an antigen different from CD22, such as CD19, CD20, CD21, CD22, CD23, CD37, CD40, CD40L, CD52, CD80 and HLA-DR. However, the therapeutic agent may an immunomodulator, a cytokine, a toxin or other therapeutic agent known in the art. More preferably, the anti-CD22 antibody is part of a DNL complex, such as a hexavalent DNL complex. Most preferably, combination therapy with the anti-CD22 antibody or fragment and the therapeutic agent is more effective than the antibody alone, the therapeutic agent alone, or the combination of anti-CD22 antibody and therapeutic agent that are not conjugated to each other. Administration of the anti-CD22 antibody and therapeutic agent induces apoptosis and cell death of target cells in diseases such as B-cell lymphomas or leukemias, autoimmune disease or immune dysfunction disease.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
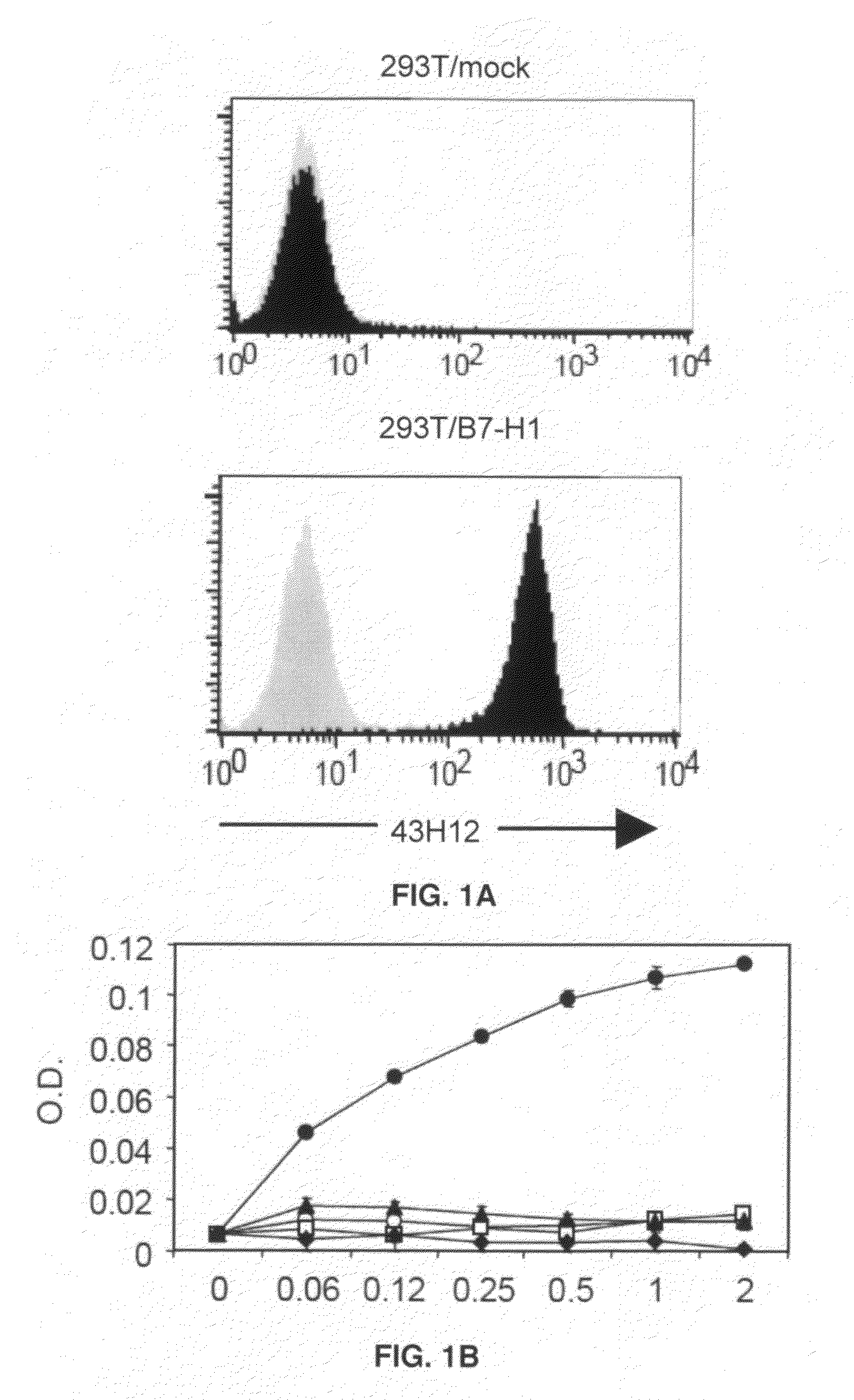
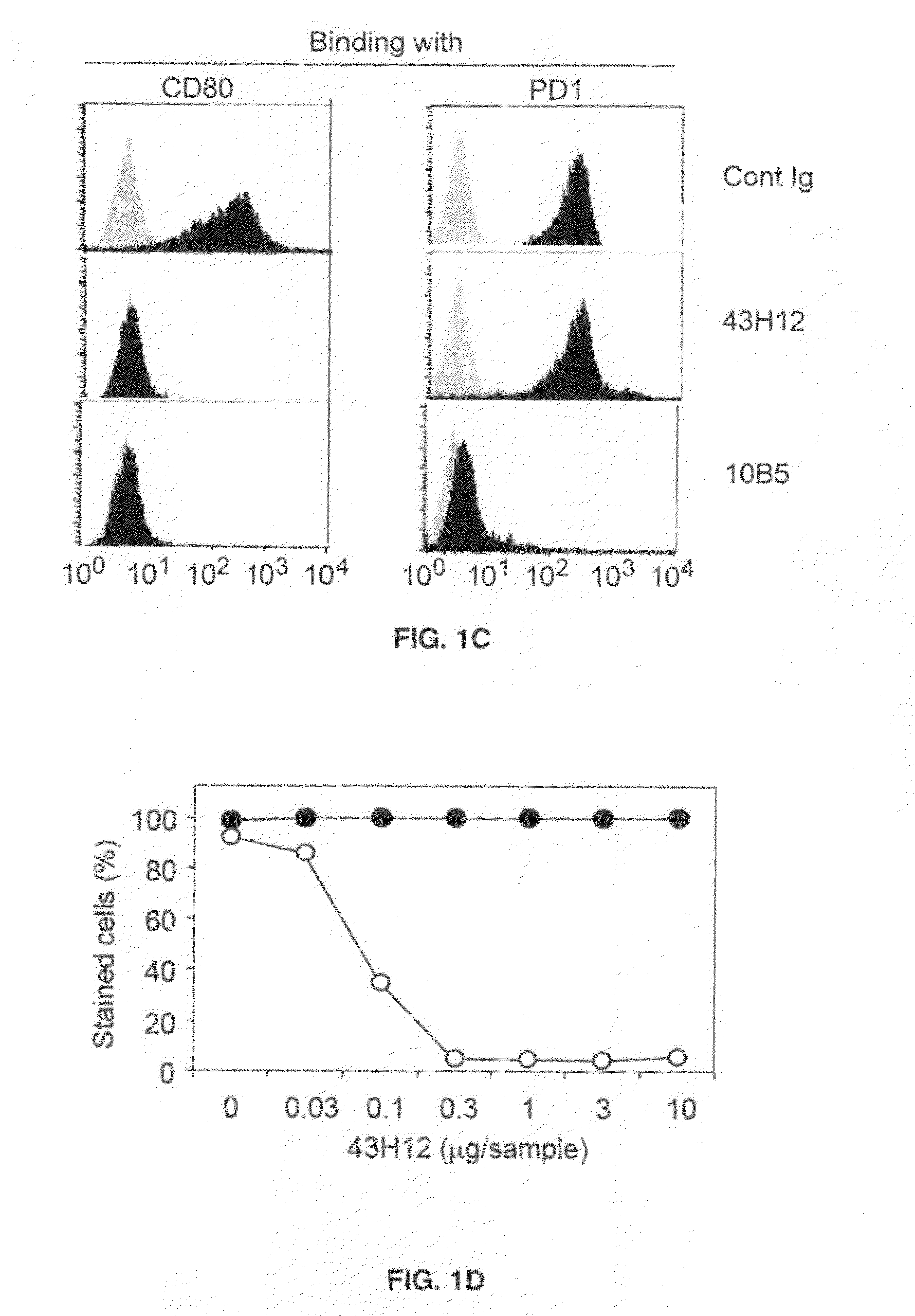
Inhibition of B7-H1/CD80 interaction and uses thereof
InactiveUS20110280877A1Restored Ag responsivenessIncrease heightImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntiviralsMedicineCD80
The present invention provides a composition comprising an agent which specifically blocks interaction between B7-H1 and CD80 but not interaction between B7-H1 and PD-1 and a vaccine, optionally in a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. Further provided is a method of treating or inhibiting abnormal cell proliferation or a viral infection in a host comprising the step of administering an agent which specifically blocks interaction between B7-H1 and CD80 but does not block interaction between B7-H1 and PD-1 in combination with a vaccine against the cancer to a host in need thereof.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
RNAi-based therapeutics for allergic rhinitis and asthma
InactiveUS20060058255A1Suppress gene expressionGood curative effectAntibacterial agentsSpecial deliveryTLR8Disease
The present invention provides compositions comprising one or more RNAi agents (e.g., siRNAs, shRNAs, or RNAi vectors) for the treatment of conditions and diseases mediated by (e.g., featuring IgE-mediated hypersensitivity), as well as systems for identifying RNAi agents effective for this purpose. The compositions are suitable for the treatment of allergic rhinitis and / or asthma. In certain embodiments of the invention the RNAi agent is targeted to a transcript that encodes a protein selected from the group consisisting of the FCεRIα chain, the FCεRIβ chain, c-Kit, Lyn, Syk, ICOS, OX40L, CD40, CD80, CD86, Re1A, Re1B, 4-1BB ligand, TLR1, TLR2, TLR3, TLR4, TLR5, TLR6, TLR7, TLR8, TLR9, CD83, SLAM, common γ chain, and COX-2. In addition, the invention provides RNAi agent / delivery agent compositions and methods of use. In certain embodiments of the invention compositions comprising an RNAi agent are delivered by the respiratory route.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Novel ctla4-ig immunoadhesins
Owner:XENCOR
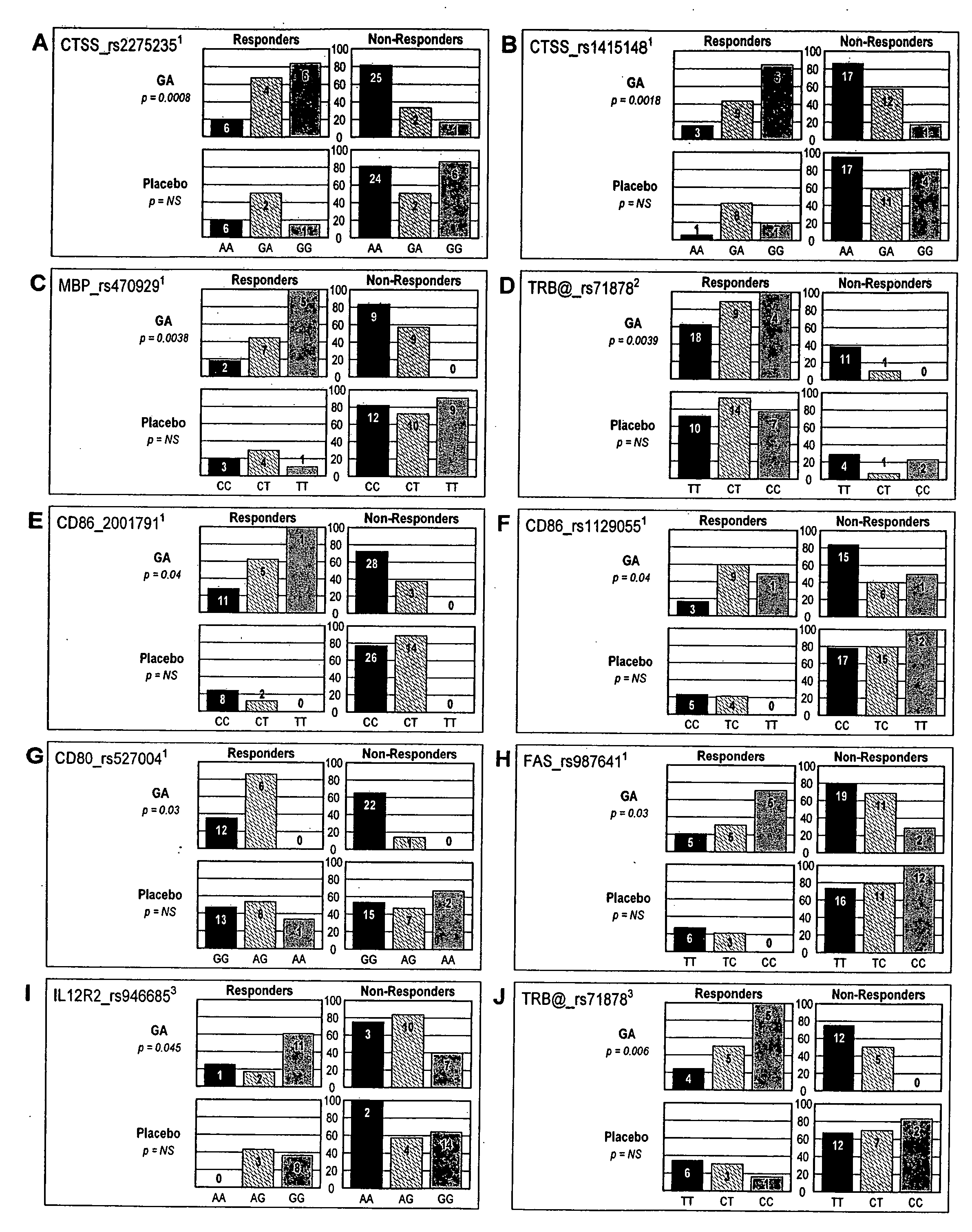
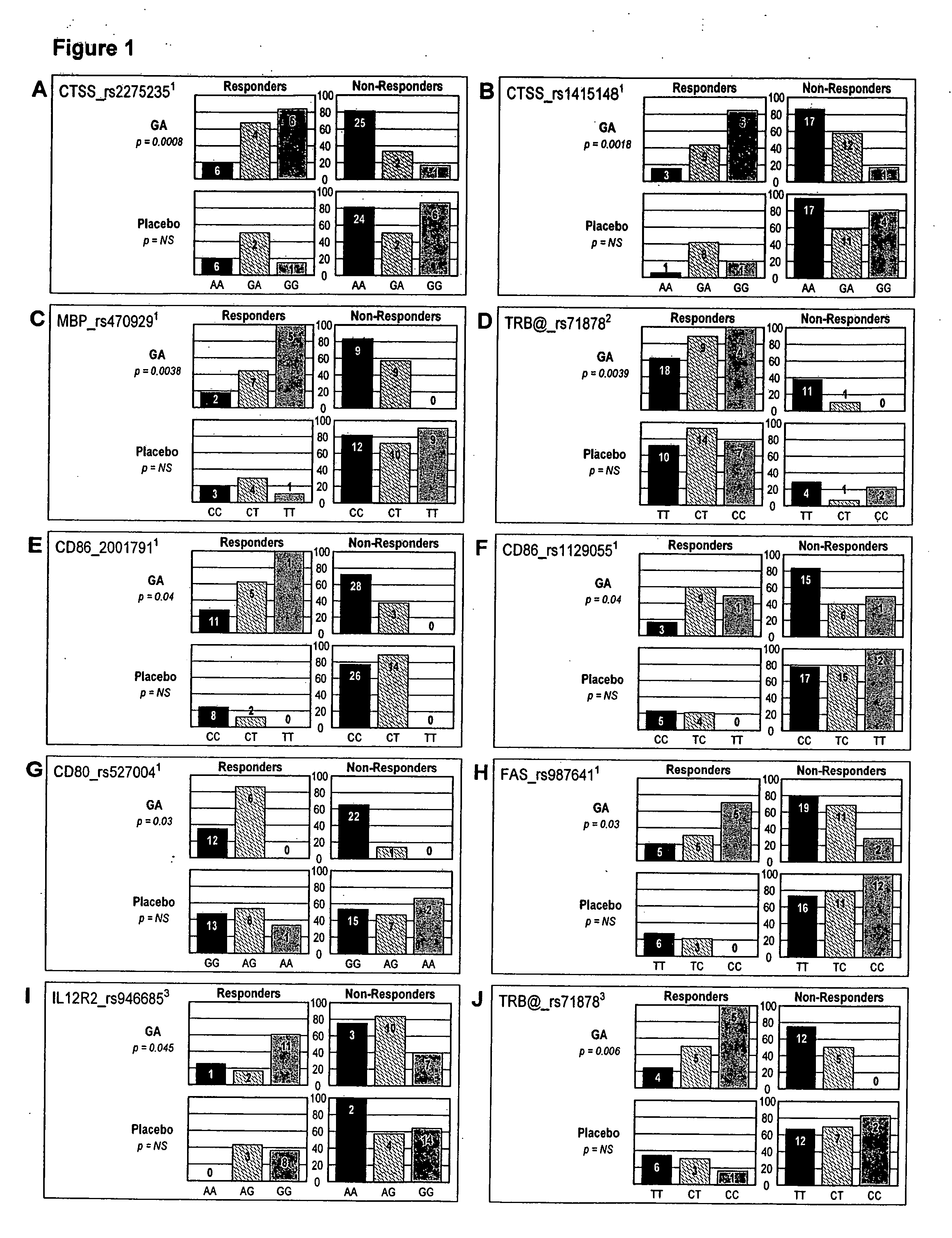
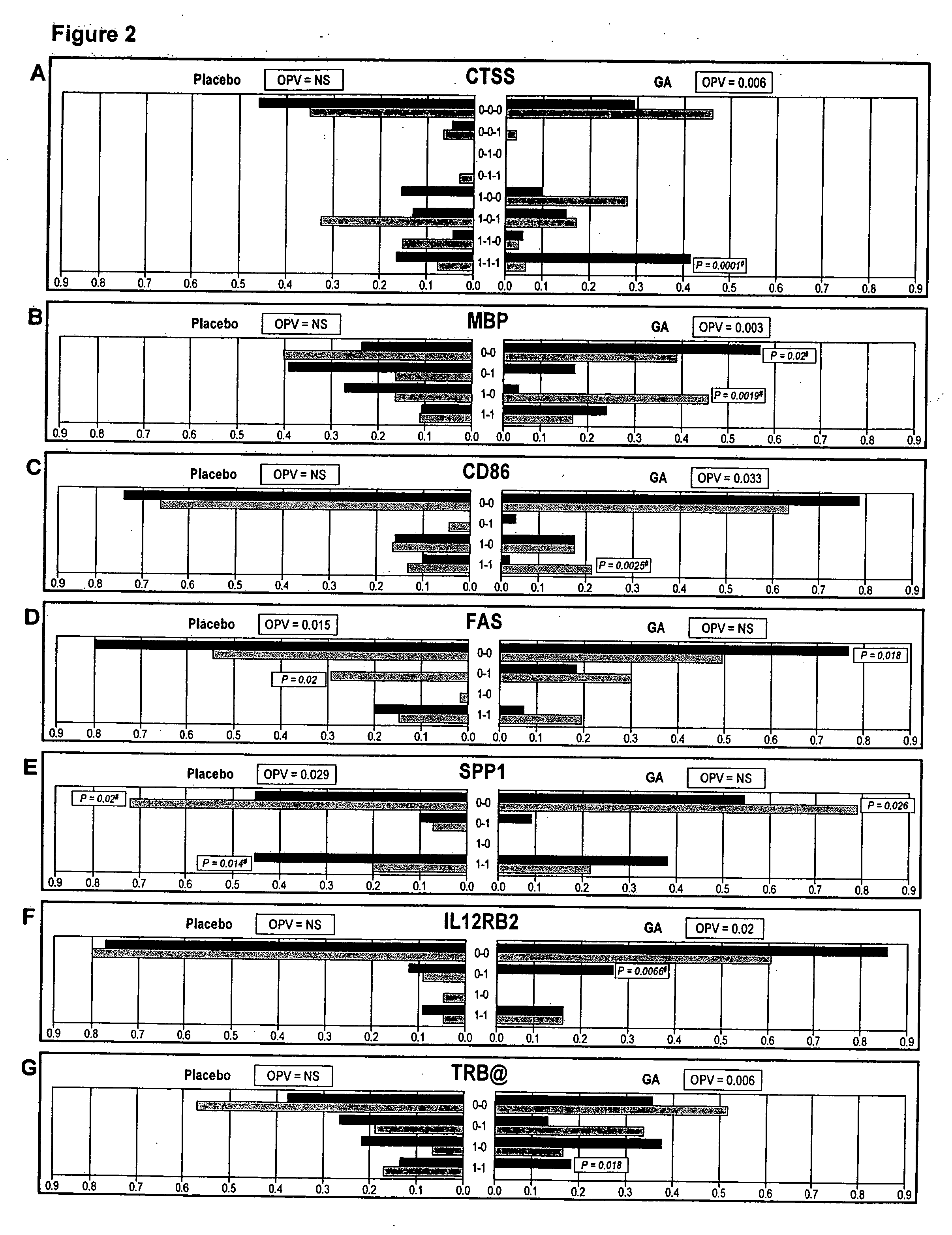
Markers associated with the therapeutic efficacy of glatiramer acetate
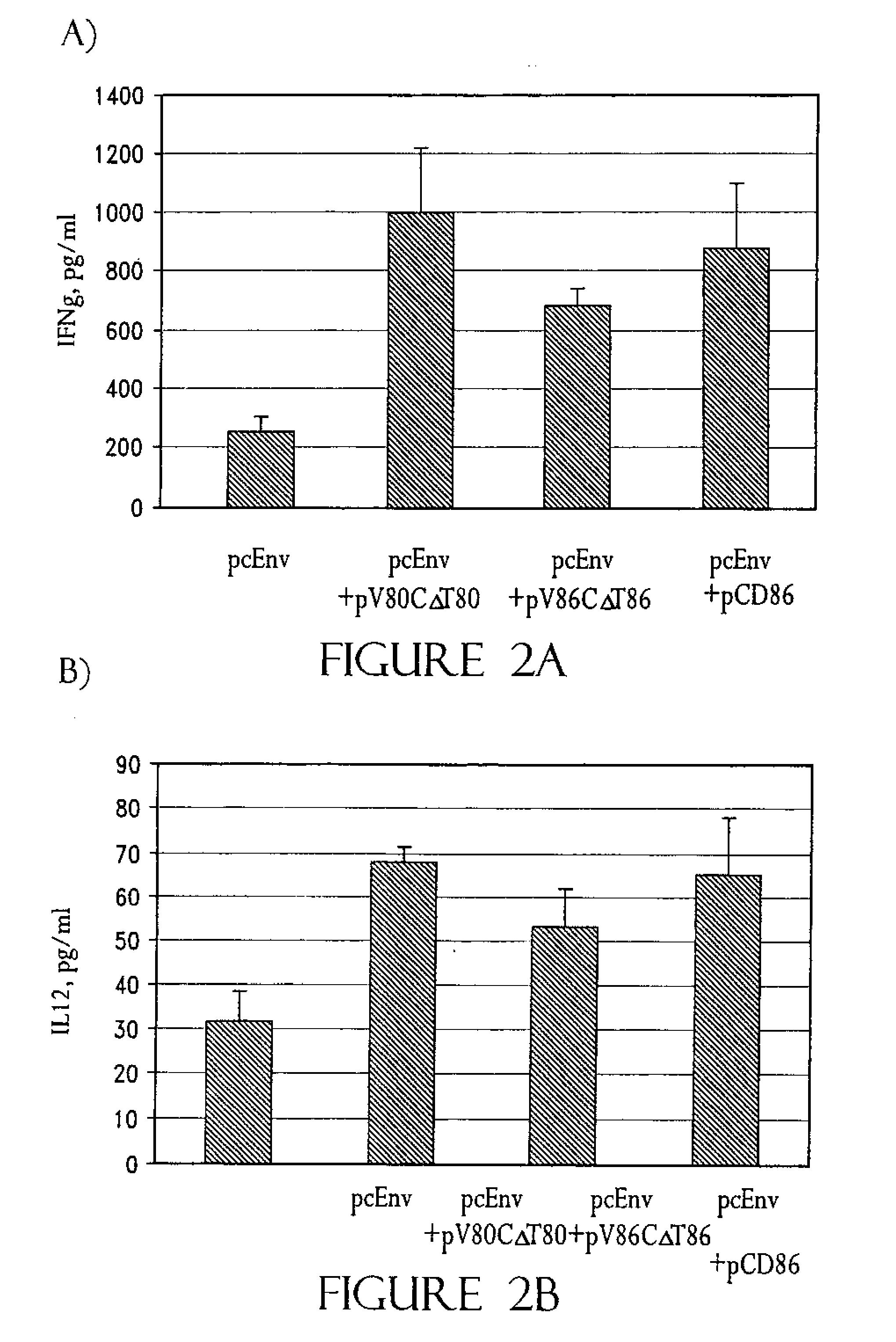
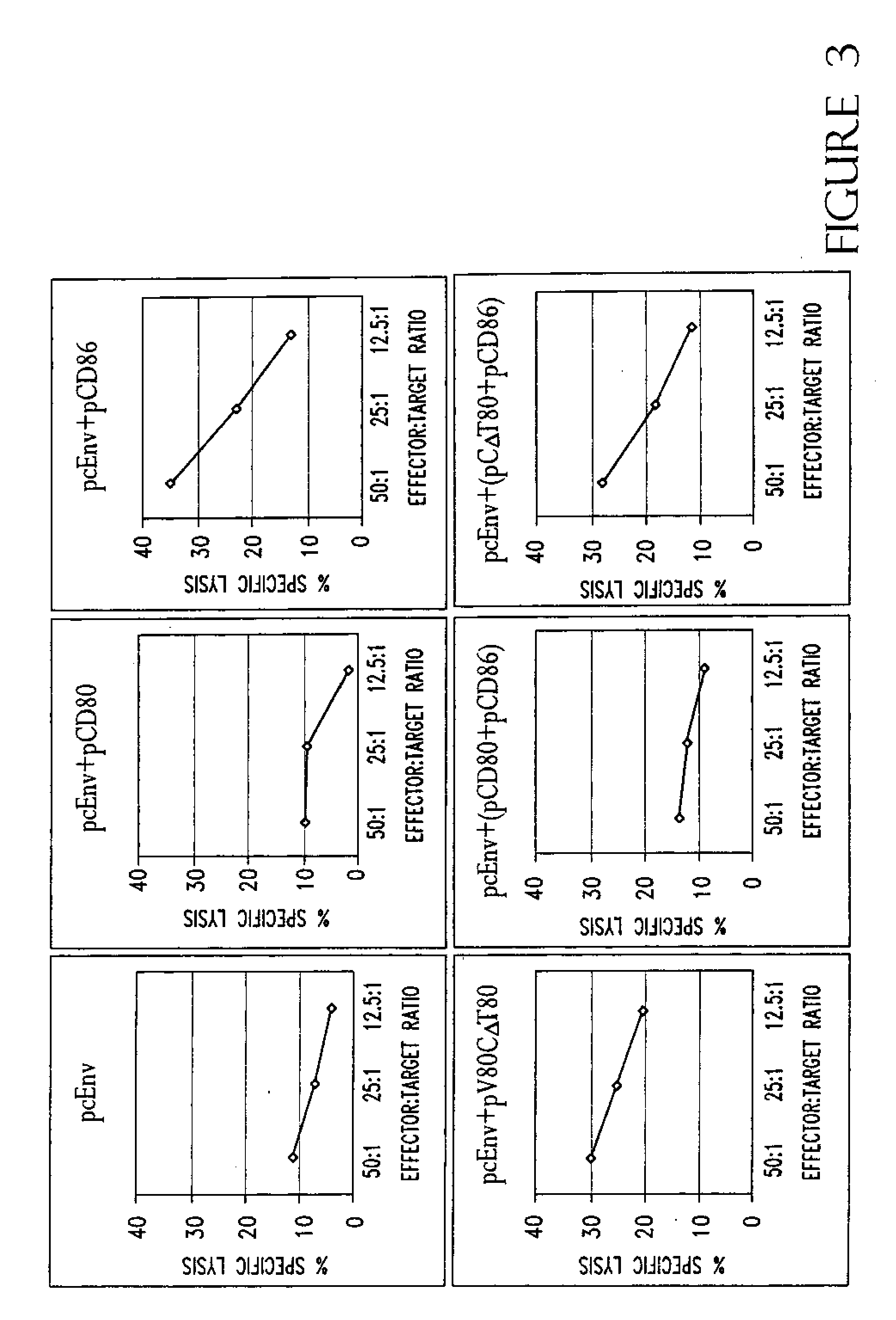
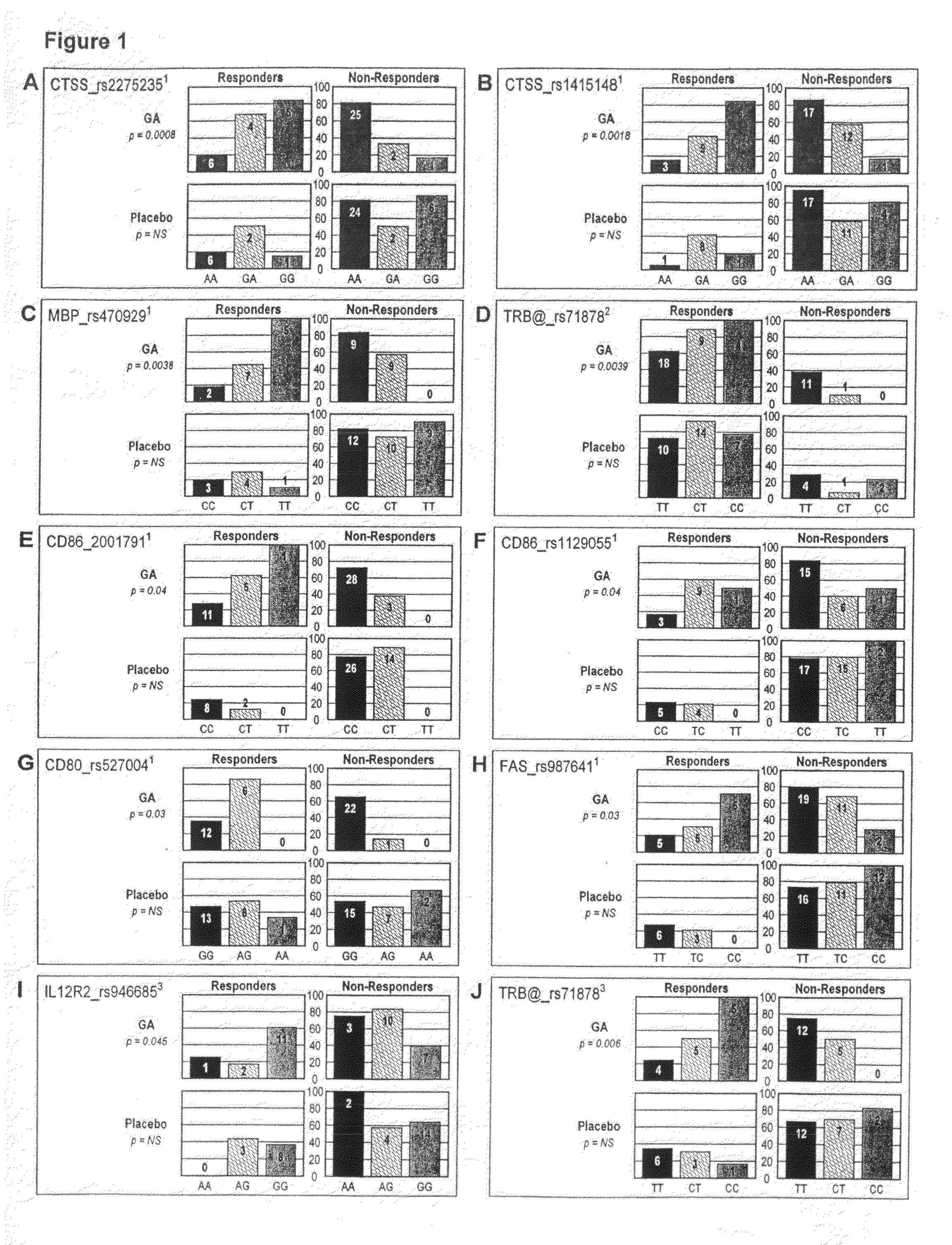
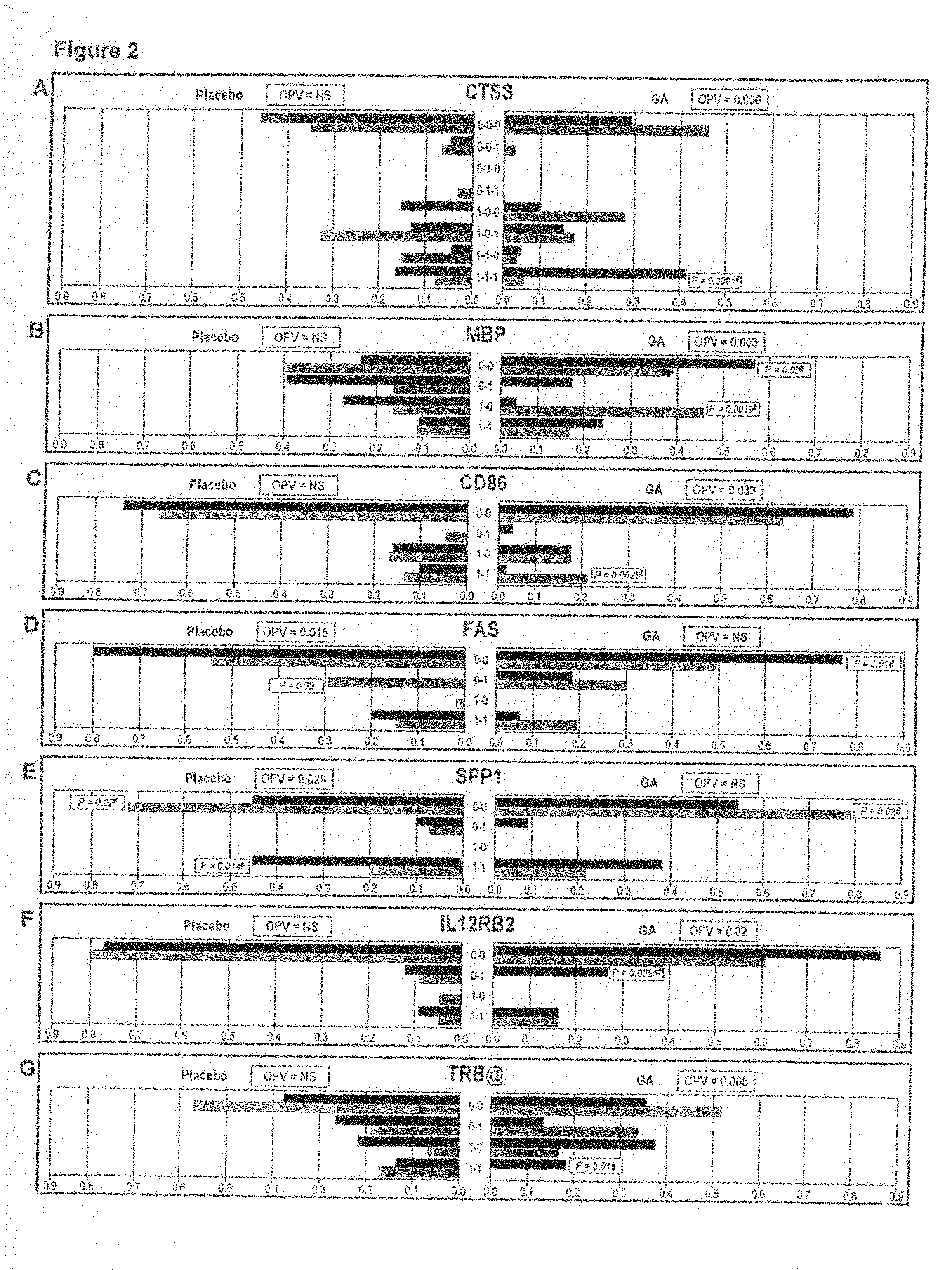
The present invention is directed to methods and kits based, at least in part, on the identification of allele-specific responsiveness or non-responsiveness to glatiramer acetate for the treatment of immune disorders, such as relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. The allele-specific responsiveness or non-responsiveness is based on polymorphisms in the following genes, CTSS, MBP, TCRB, CD95, CD86, IL-1R1, CD80, SCYA5, MMP9, MOG, SPP1 and IL-12RB2.
Owner:RAPPAPORT FAMILY INSTITUTE FOR RESEACH IN THE MEDICAL SCIENCES +2
Tolerogenic antigen-presenting cells
InactiveUS20060147432A1Conveniently achievedFavorable antigen presentationBiocideGenetic material ingredientsDendritic cellCD80
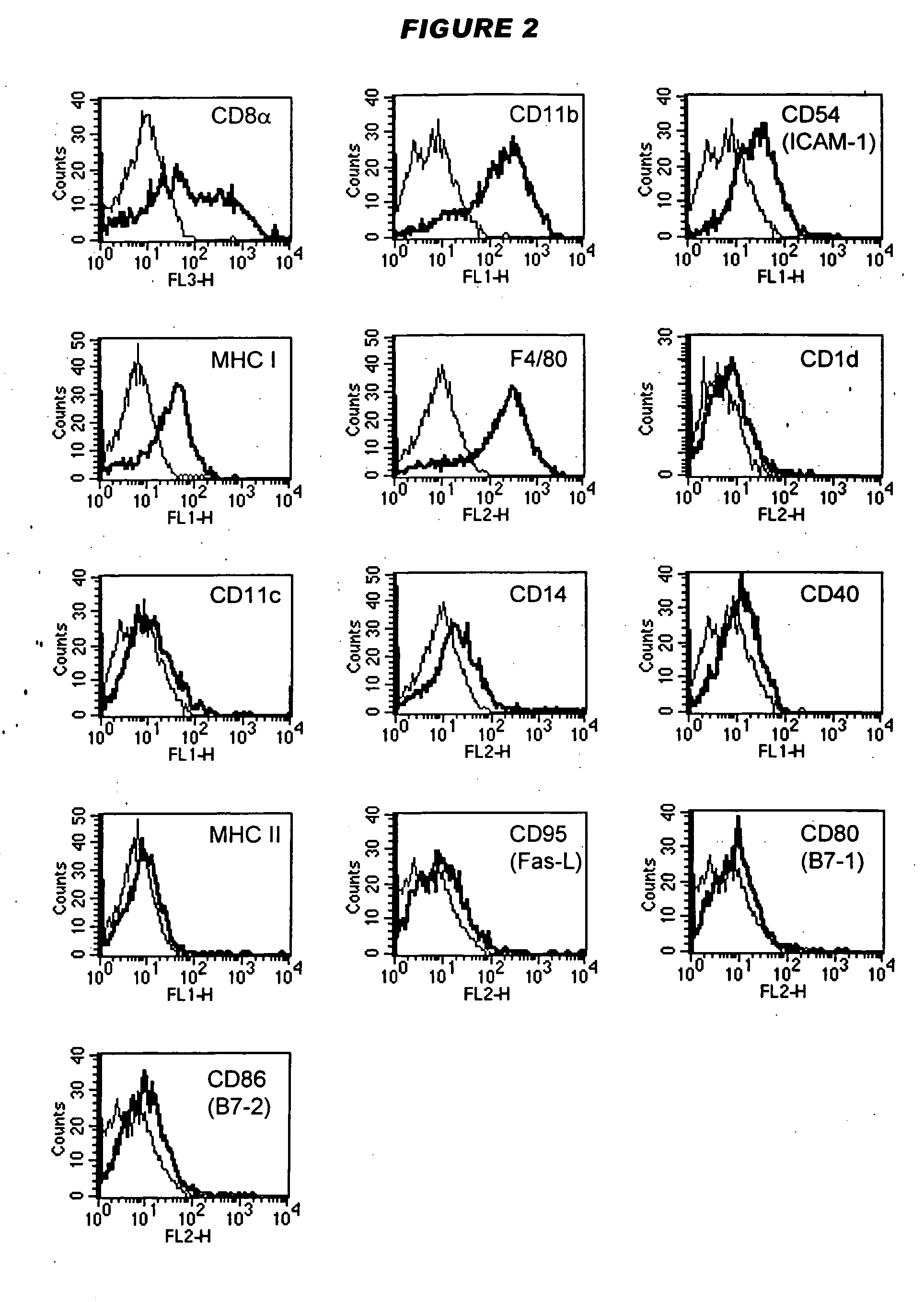
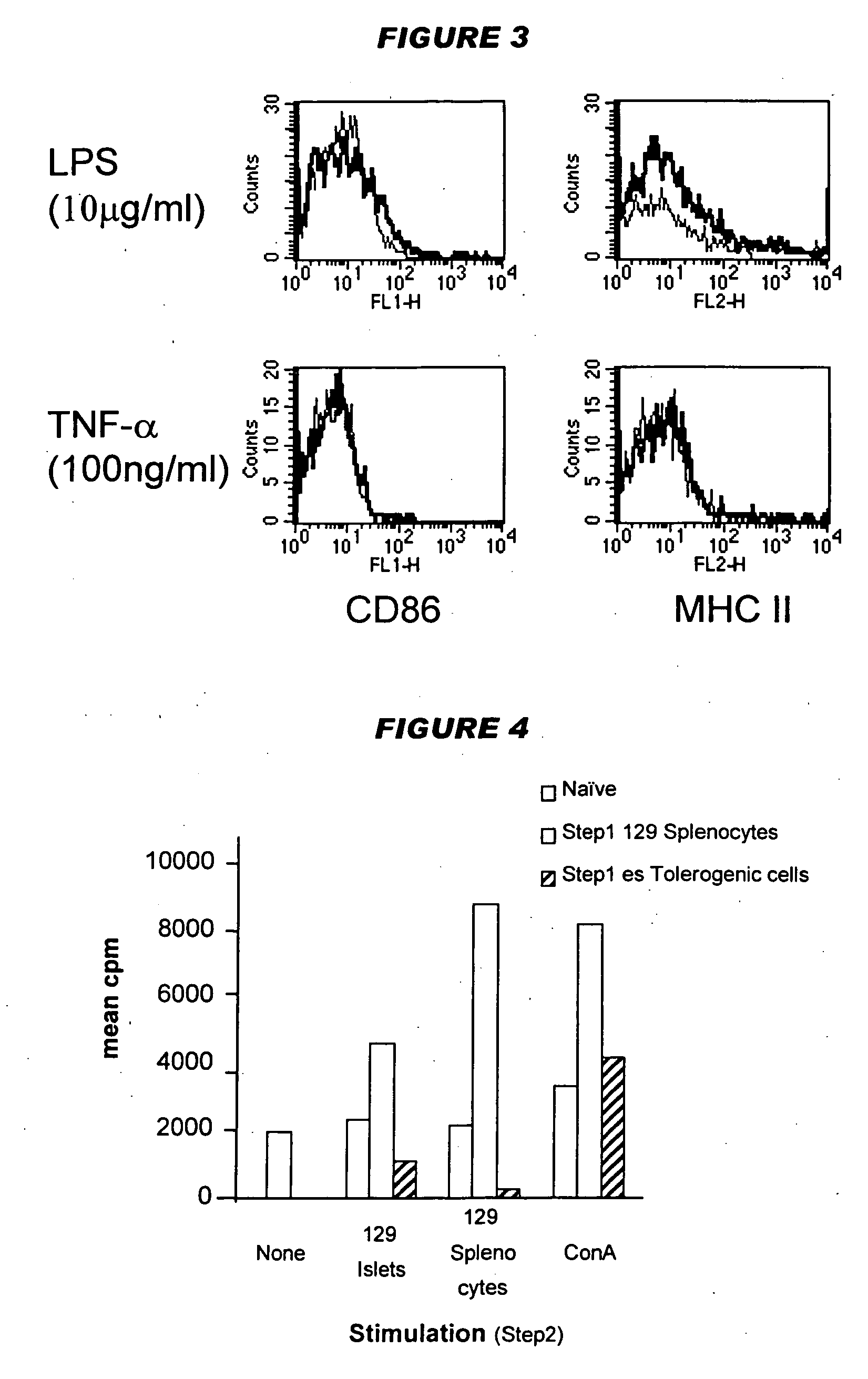
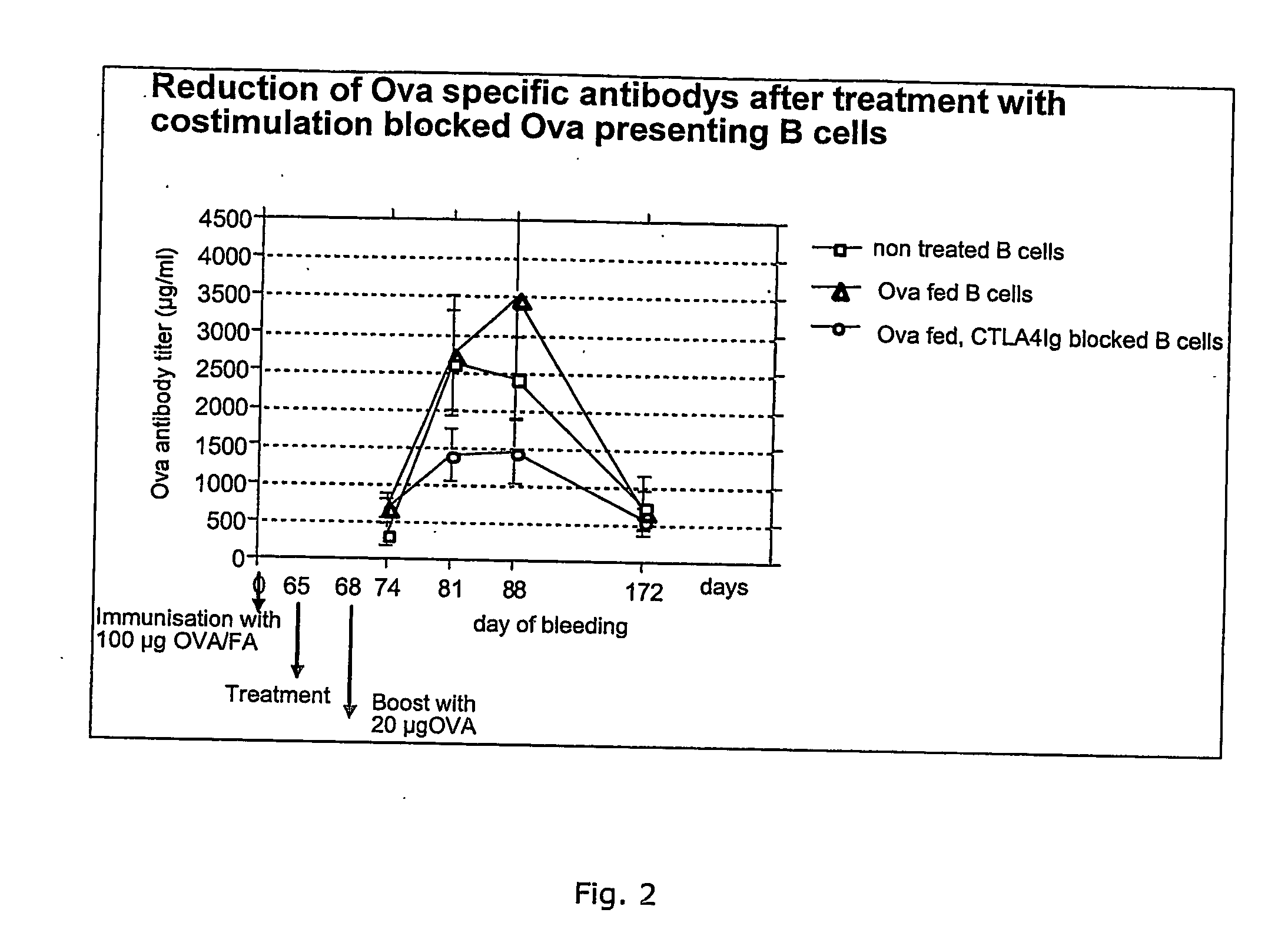
It has been found that dendritic cells can be prepared which cannot mature. These cells can provide signal 1 to T cells but cannot provide co-stimulatory signal 2. T cells which are stimulated by the permanently immature dendritic cells therefore anergise, so the dendritic cells are tolerogenic rather than immunogenic. The cells are generally CD40−ve, CD80−ve and CD86−ve, and remain so when stimulated by inflammatory mediators such as lipopolysaccharide. The cells can be prepared conveniently by the culturing adherent embryonic stem cells in the presence of GM-CSF.
Owner:REVIVICOR INC
Molecule which binds cd80 and cd86
InactiveUS20070148162A1Prevent rejectionAvoid immune responseAnimal cellsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenT cell mediated immunity
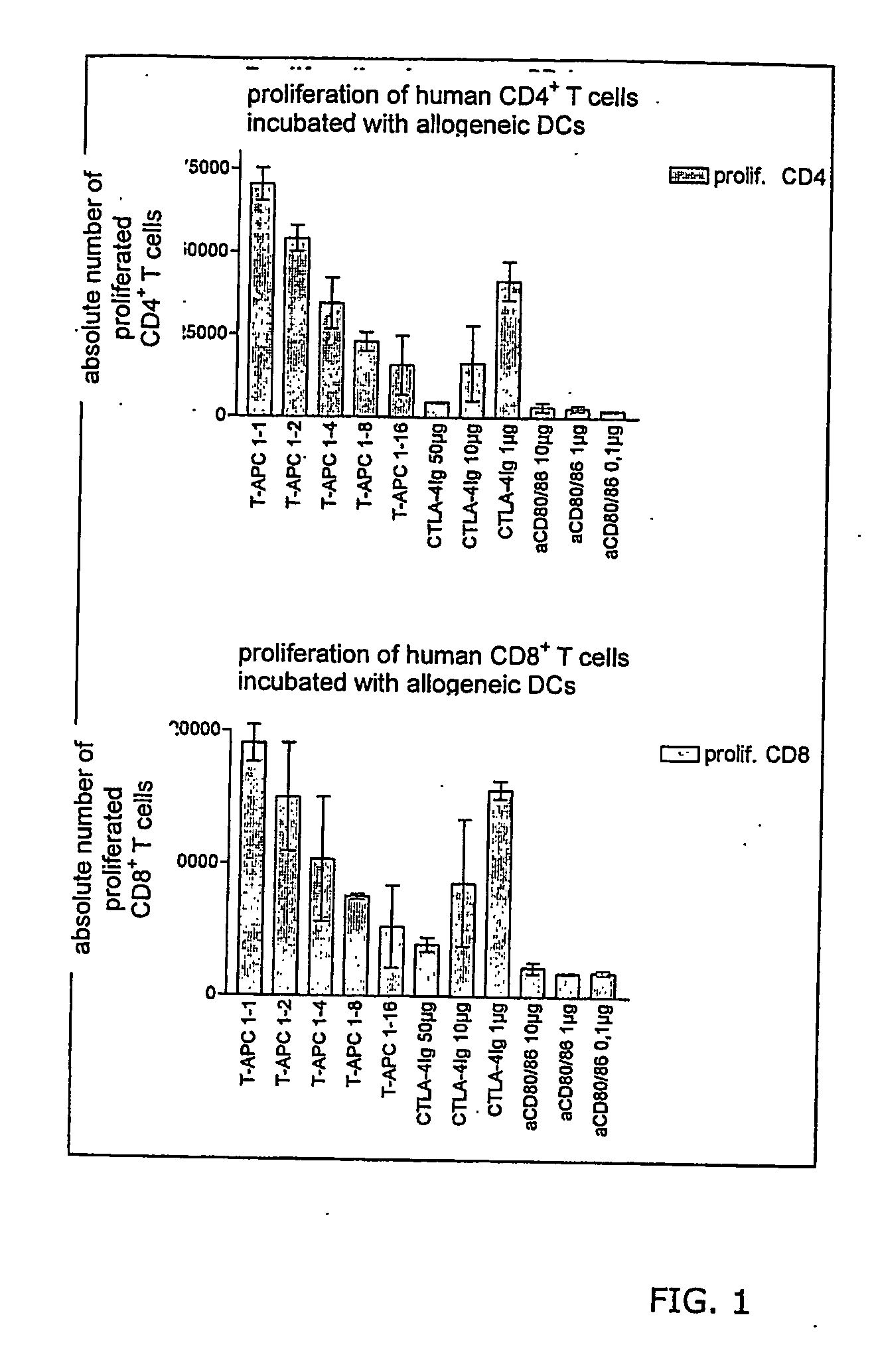
The present invention relates to the identification of molecules, which are specific to CD80 and CD86 antigens. Also preferably, such antibodies are capable of inhibiting the binding of CD28 and CTLA4 to those receptors. Those molecules are able to inhibit T cell mediated immune reactions.
Owner:THERAVISION
Soluble CTLA4 mutant molecules and uses thereof
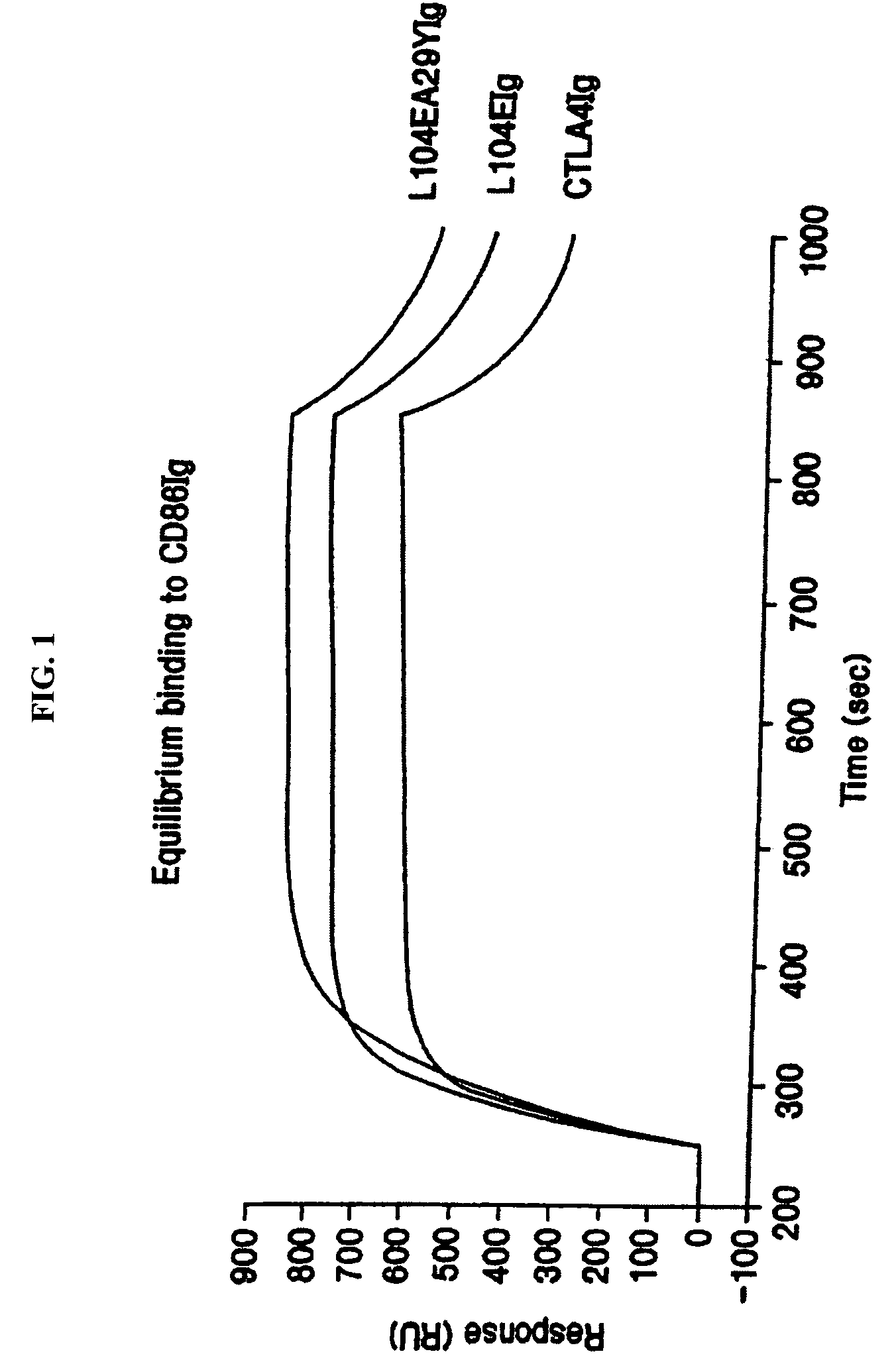
InactiveUS20050214313A1Faster rateHigh affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSolubilityCD80
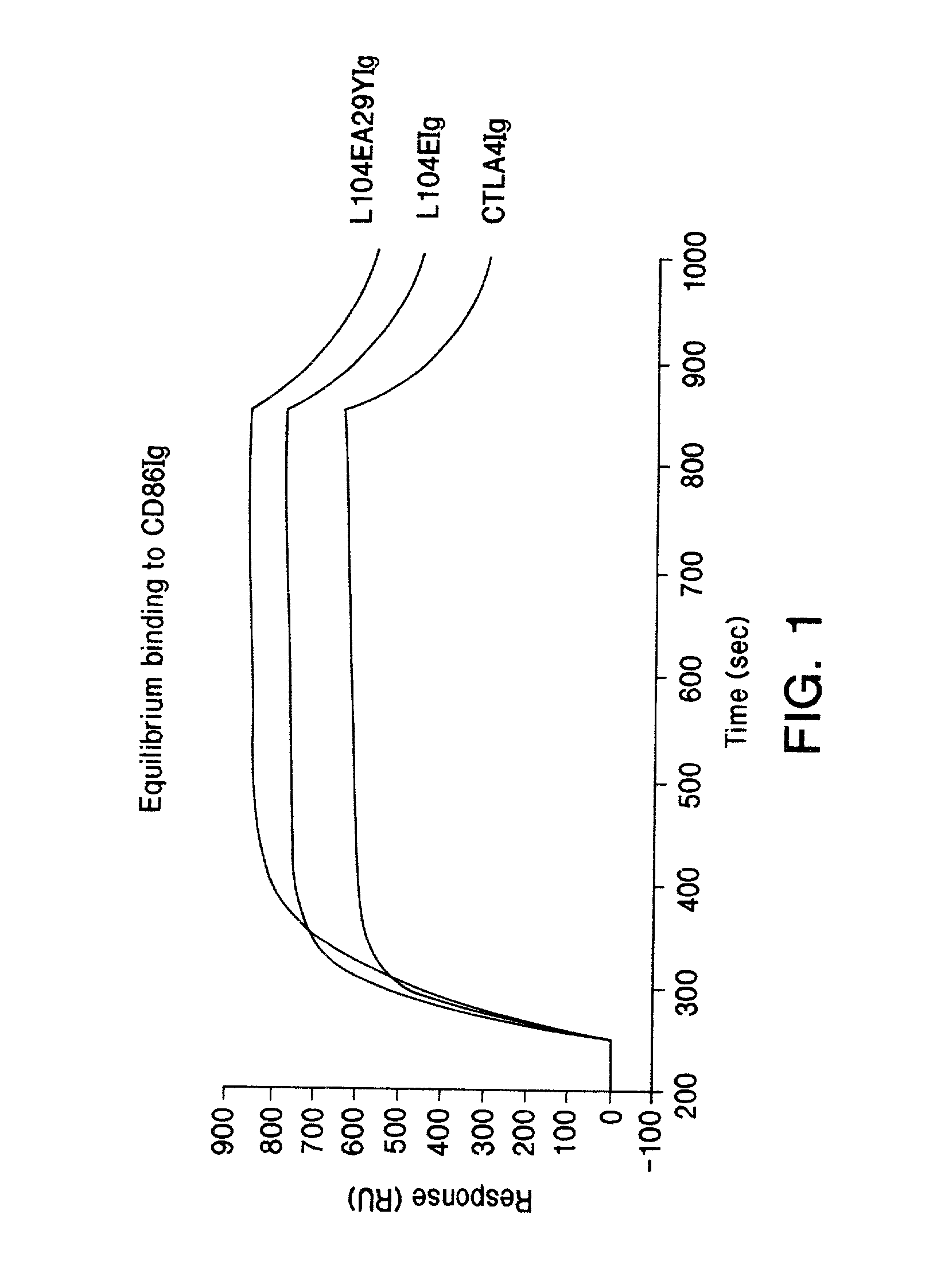
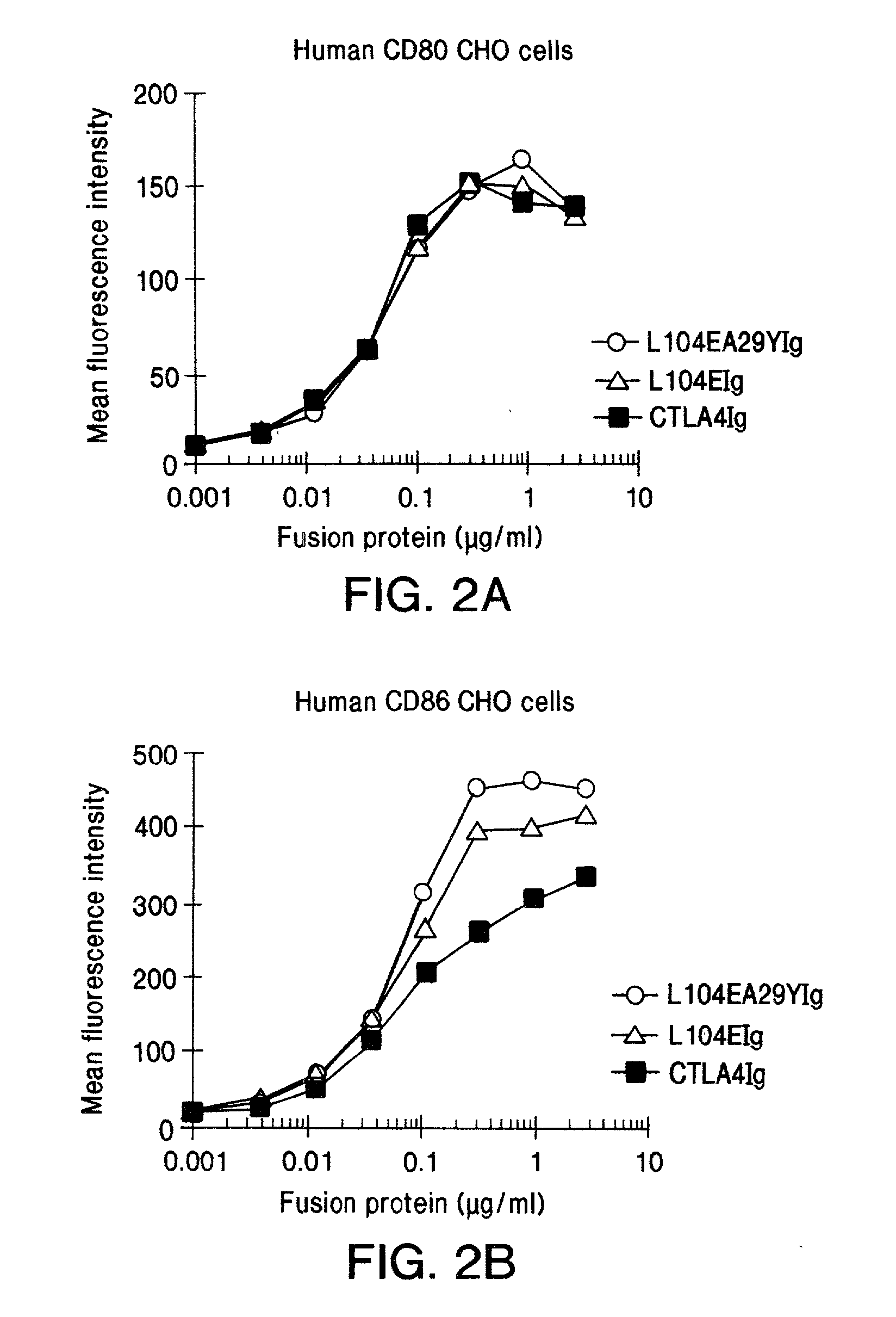
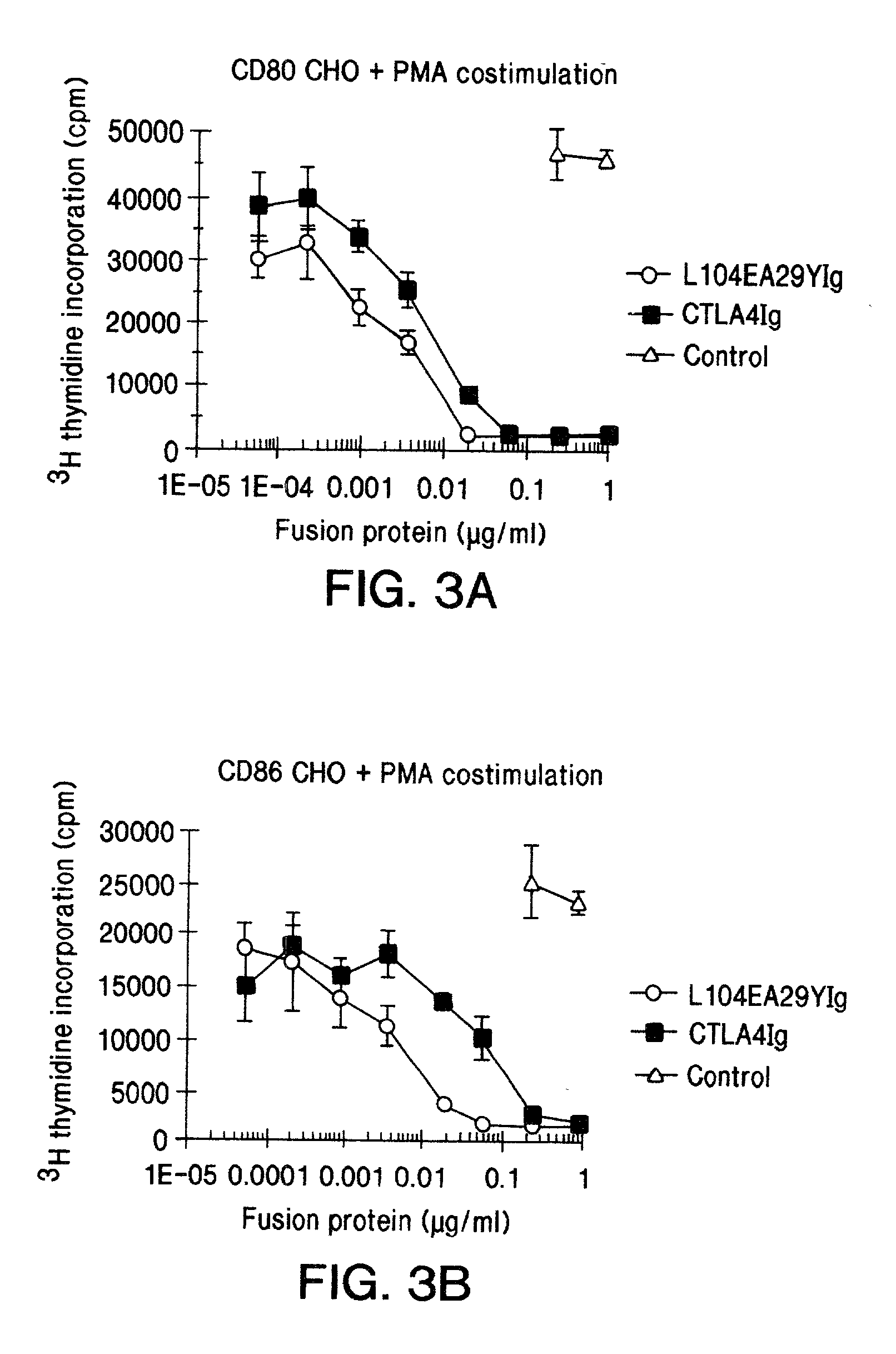
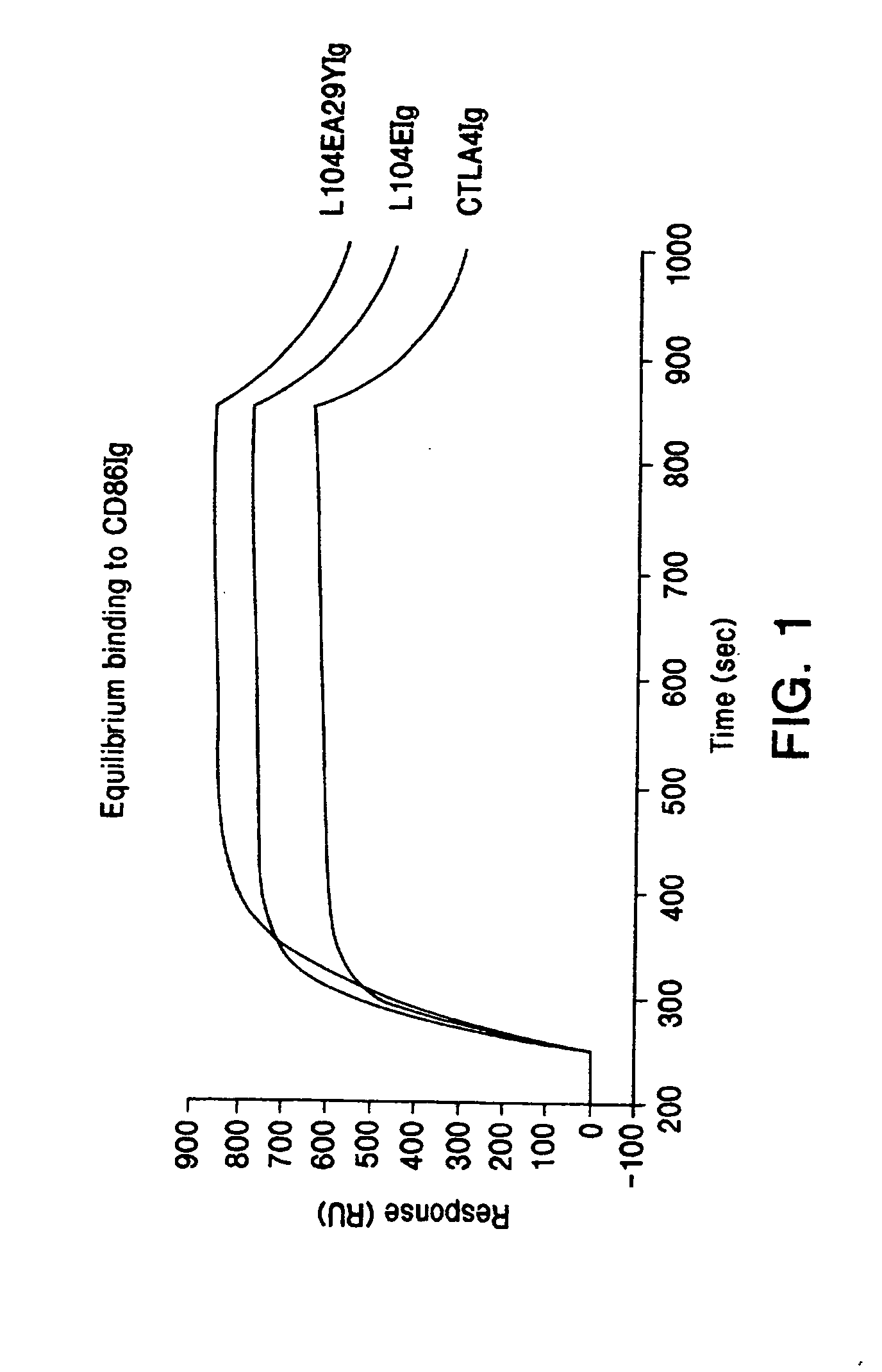
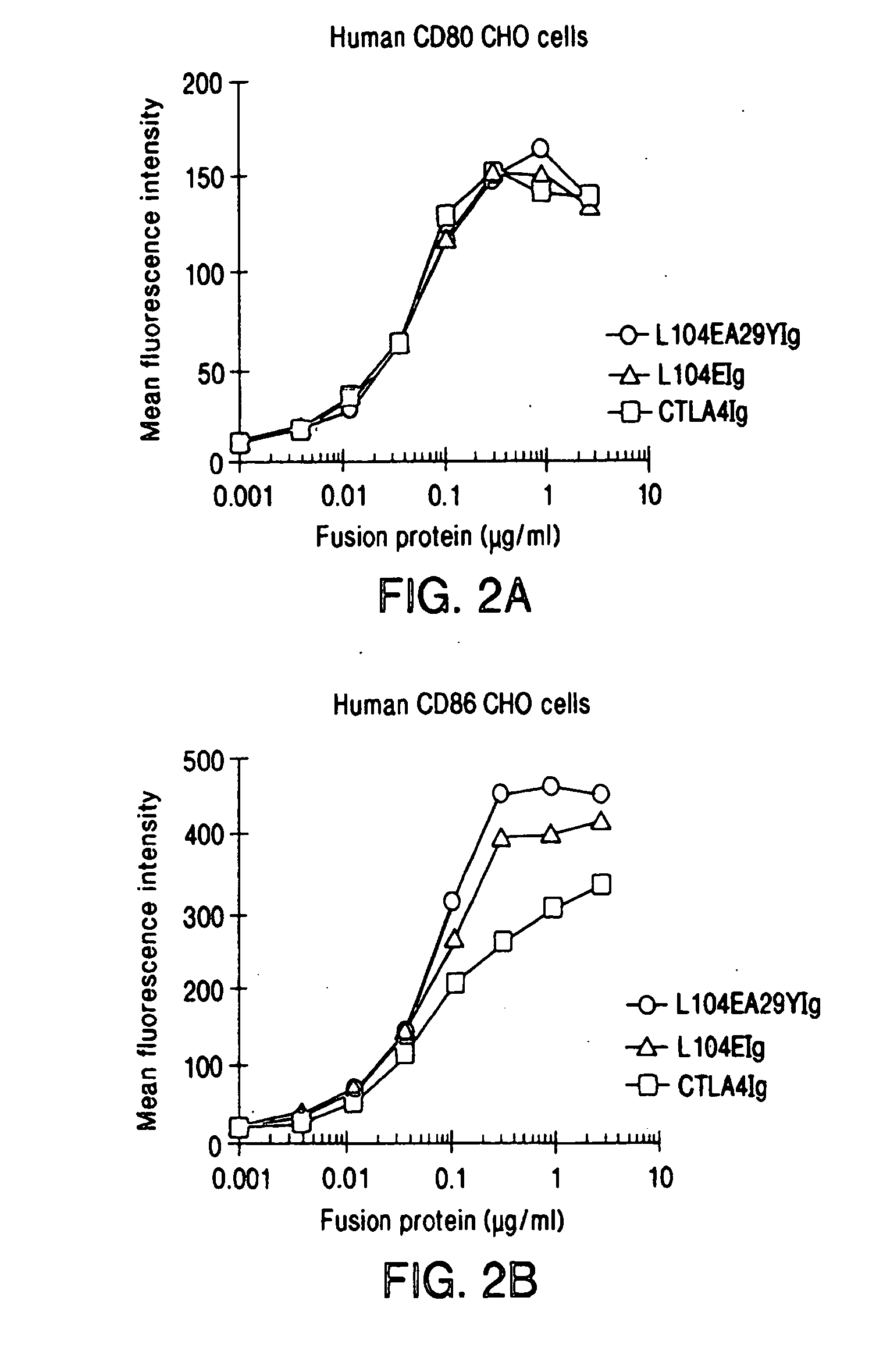
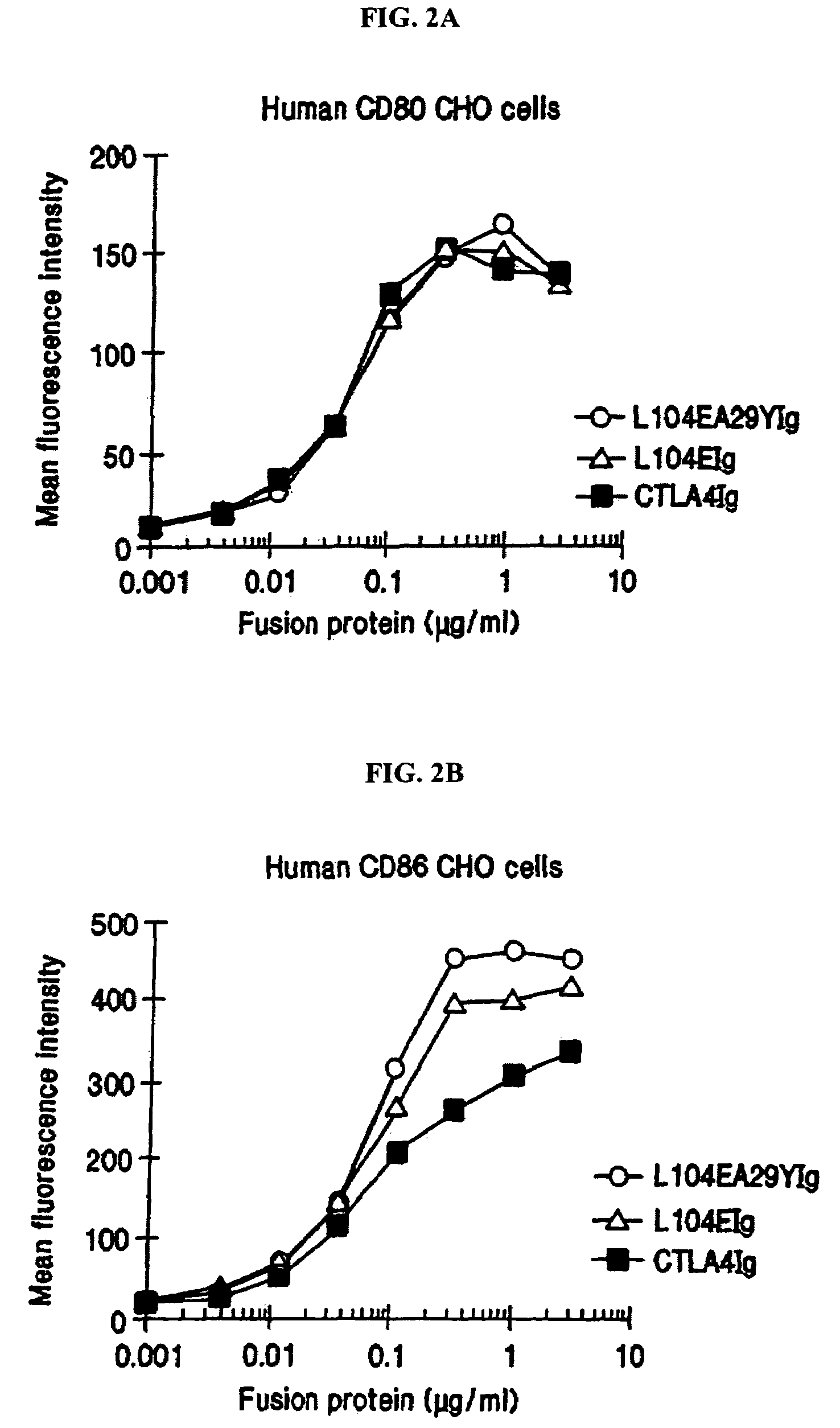
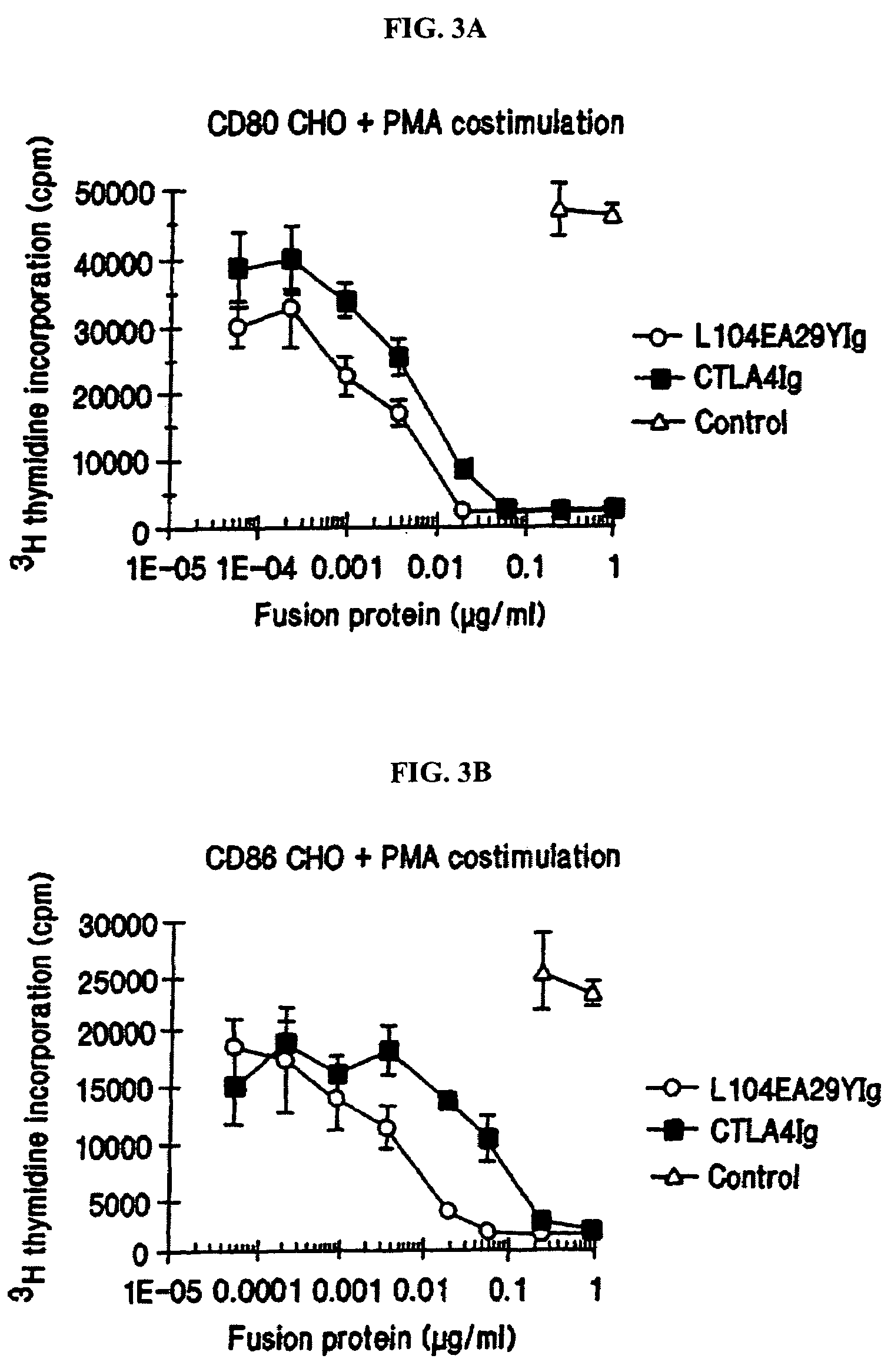
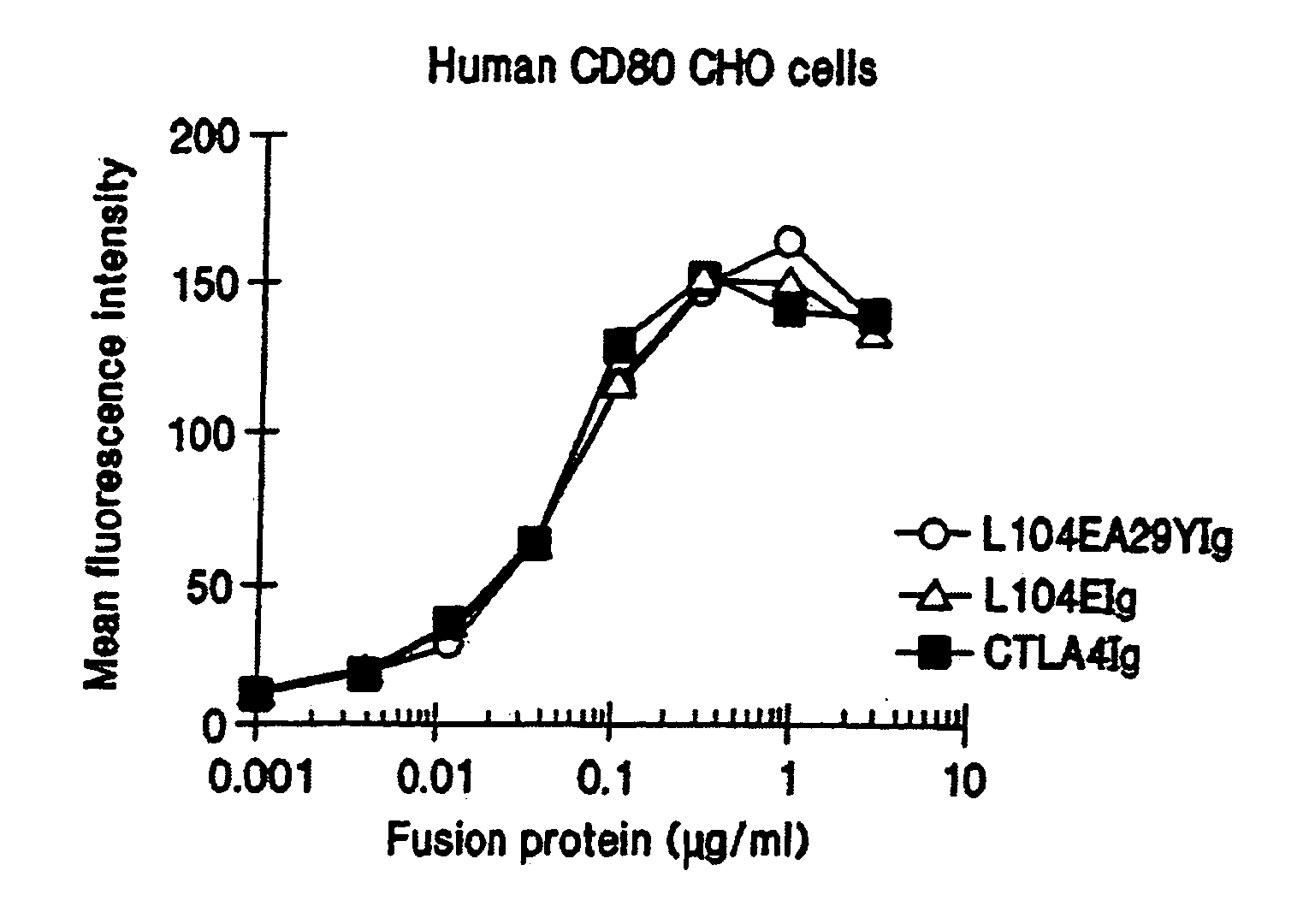
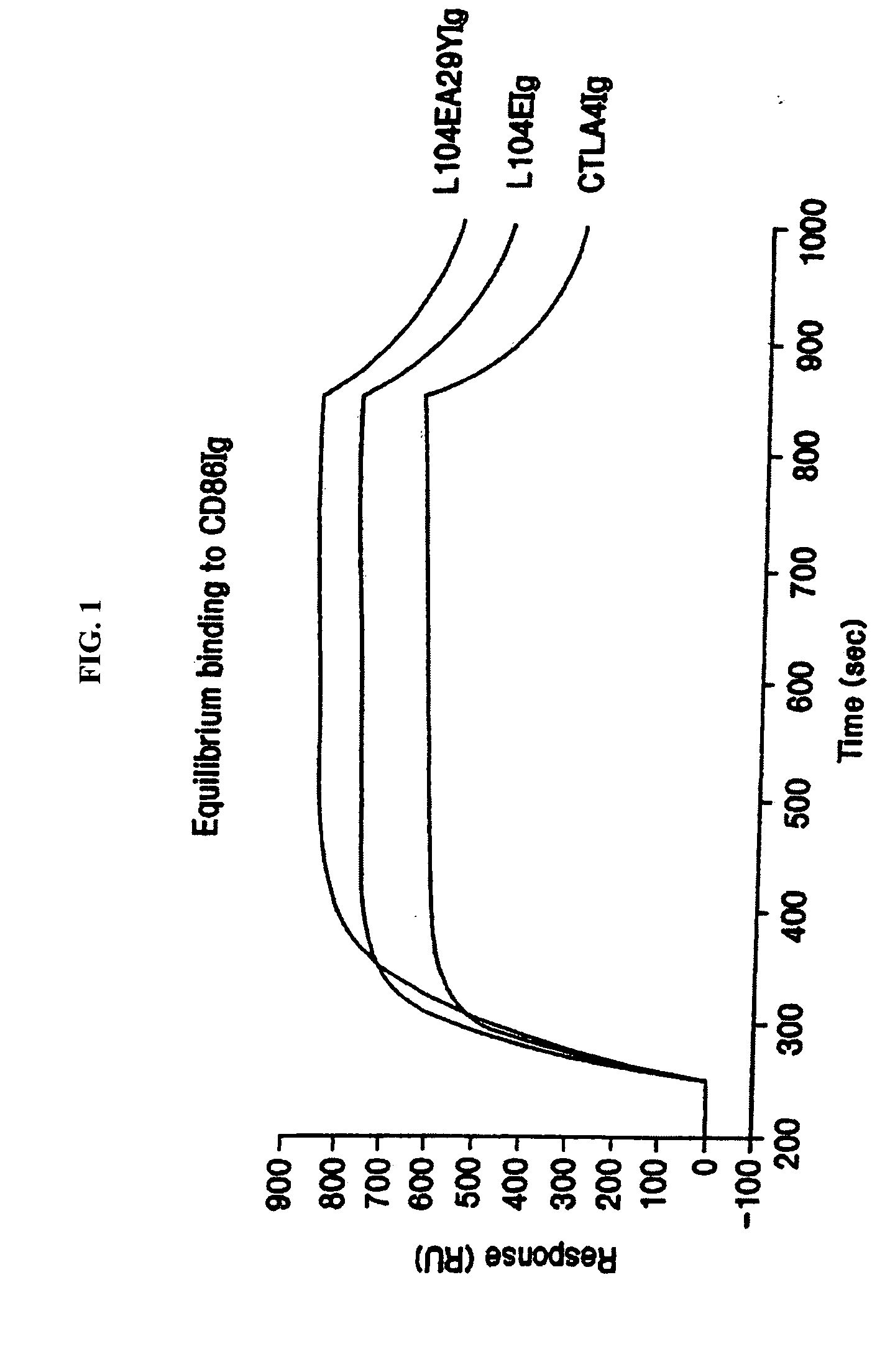
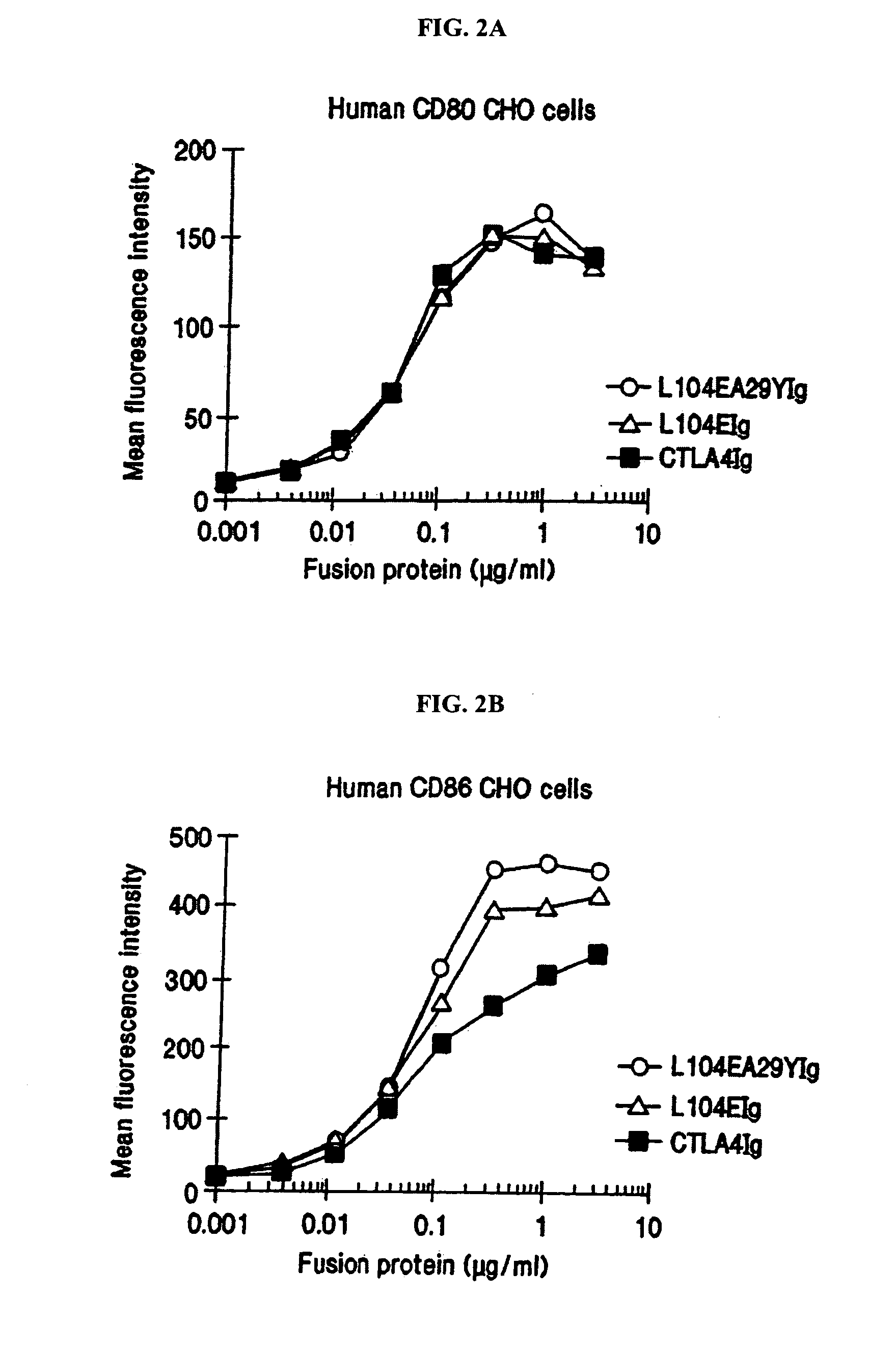
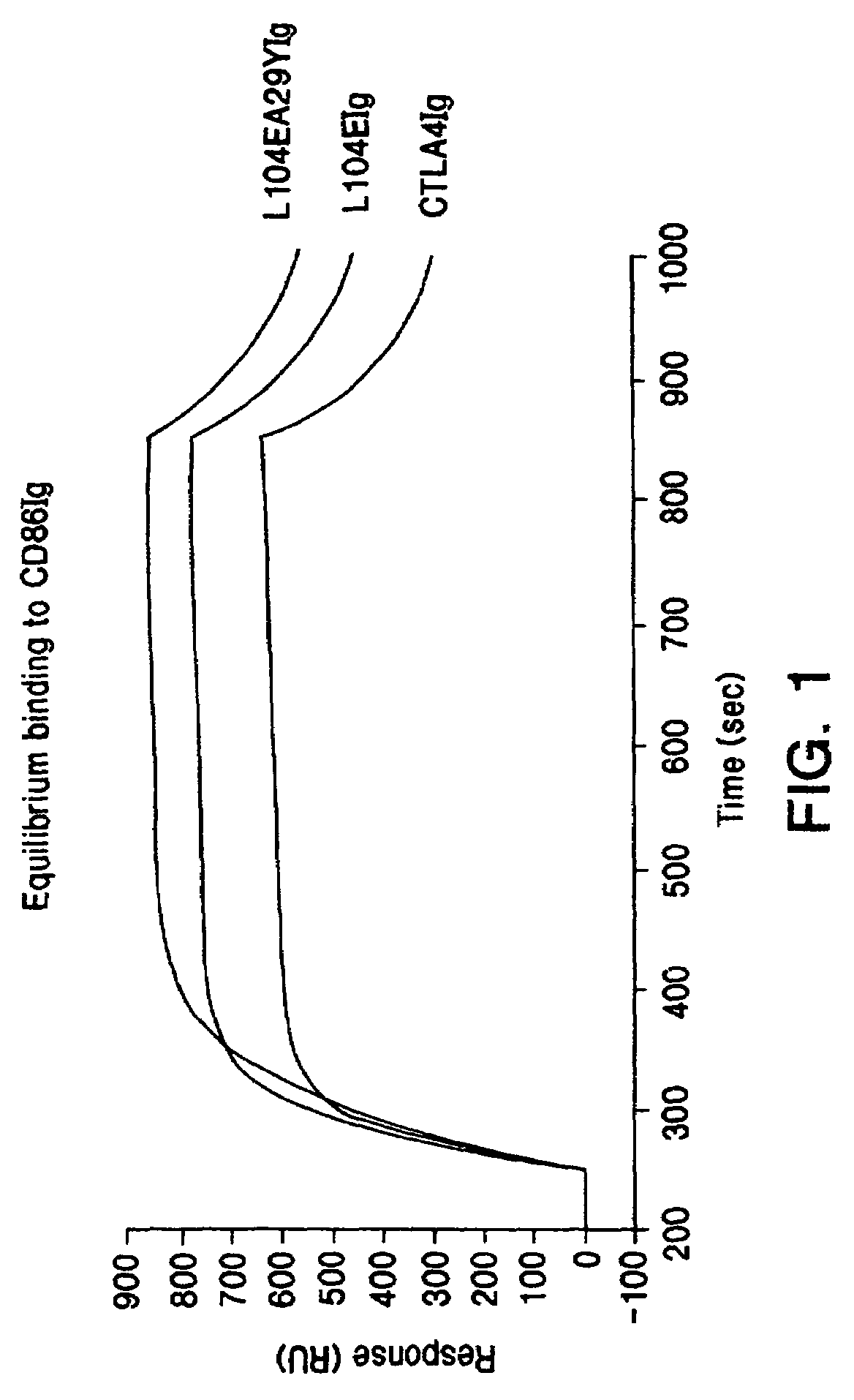
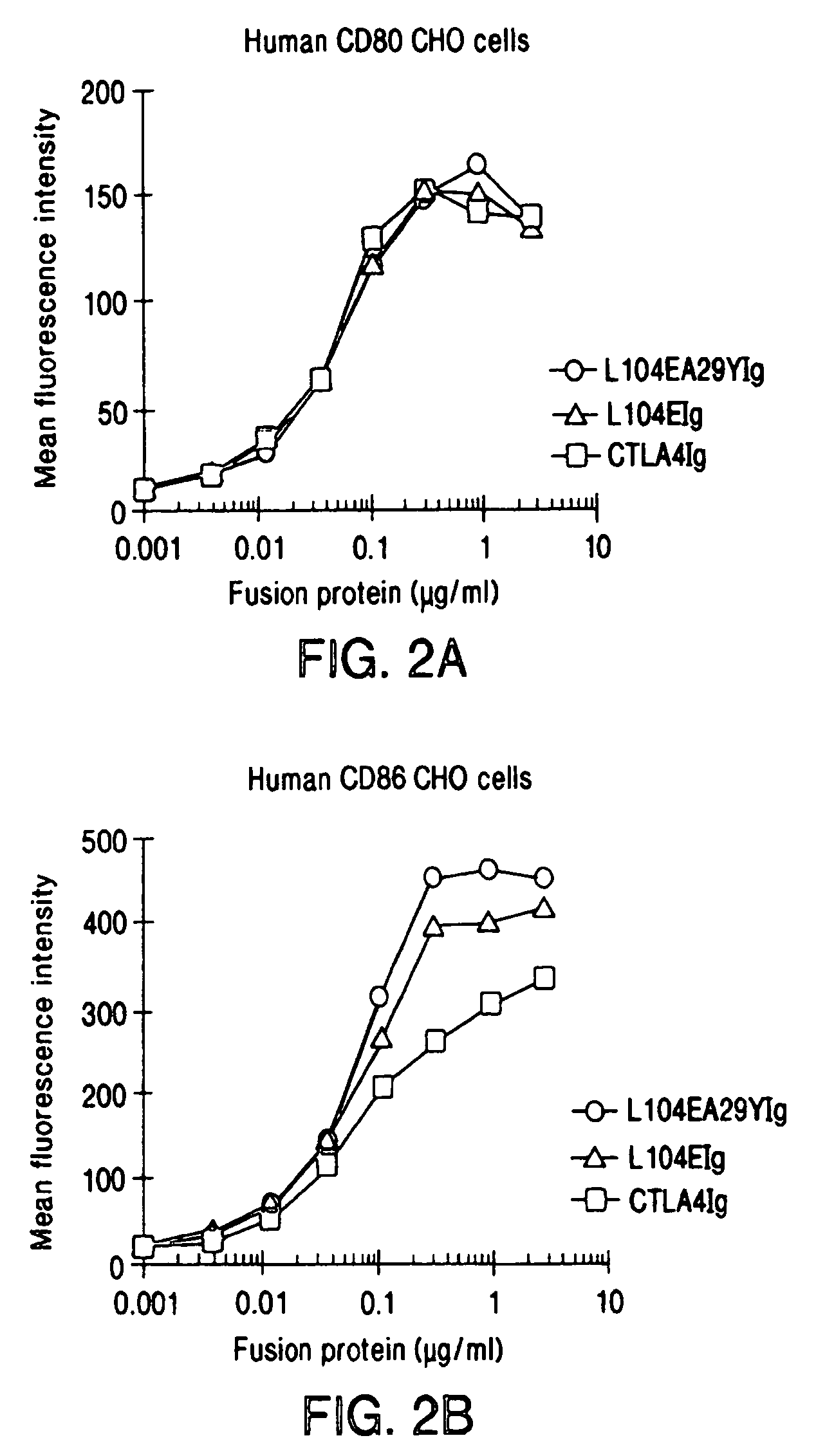
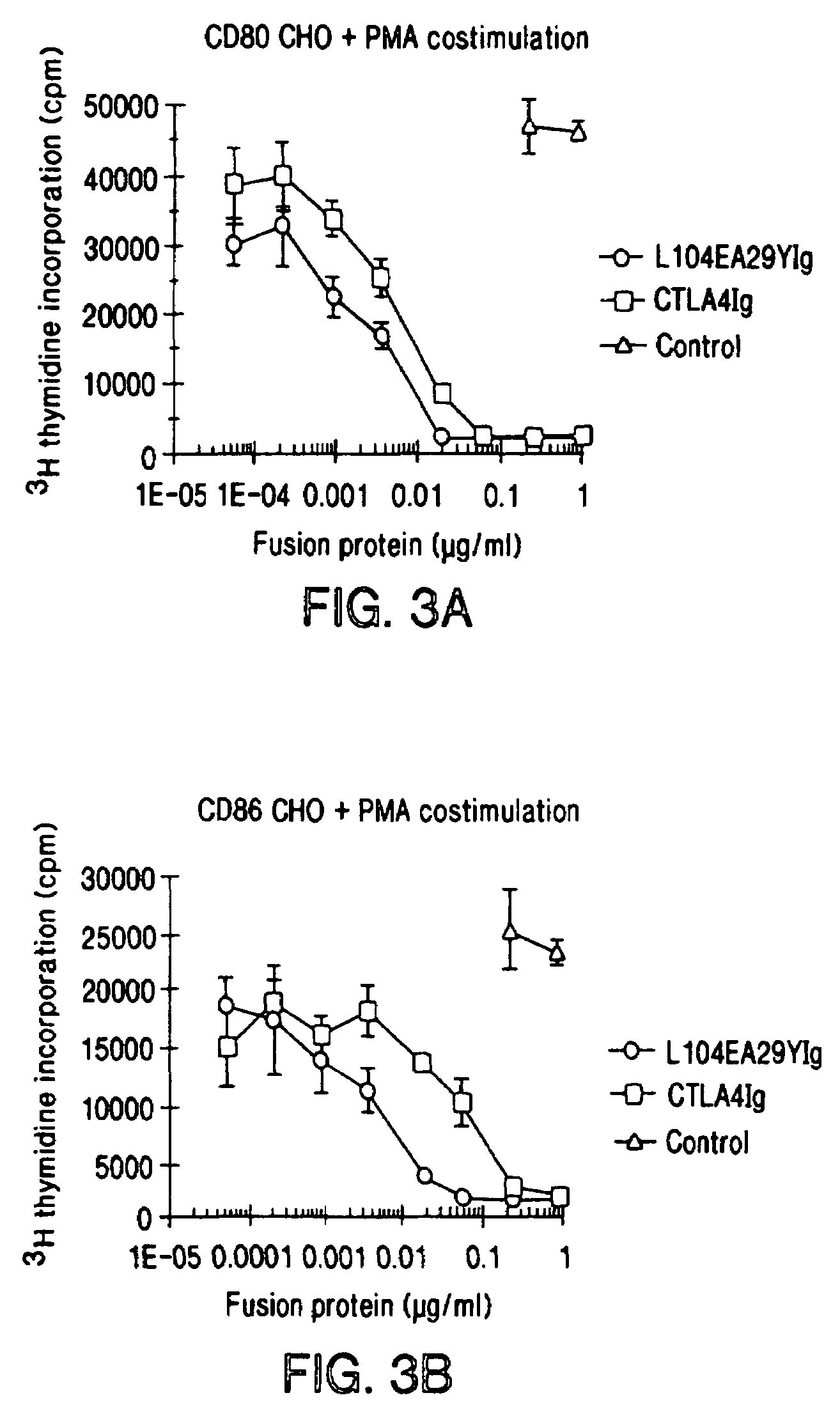
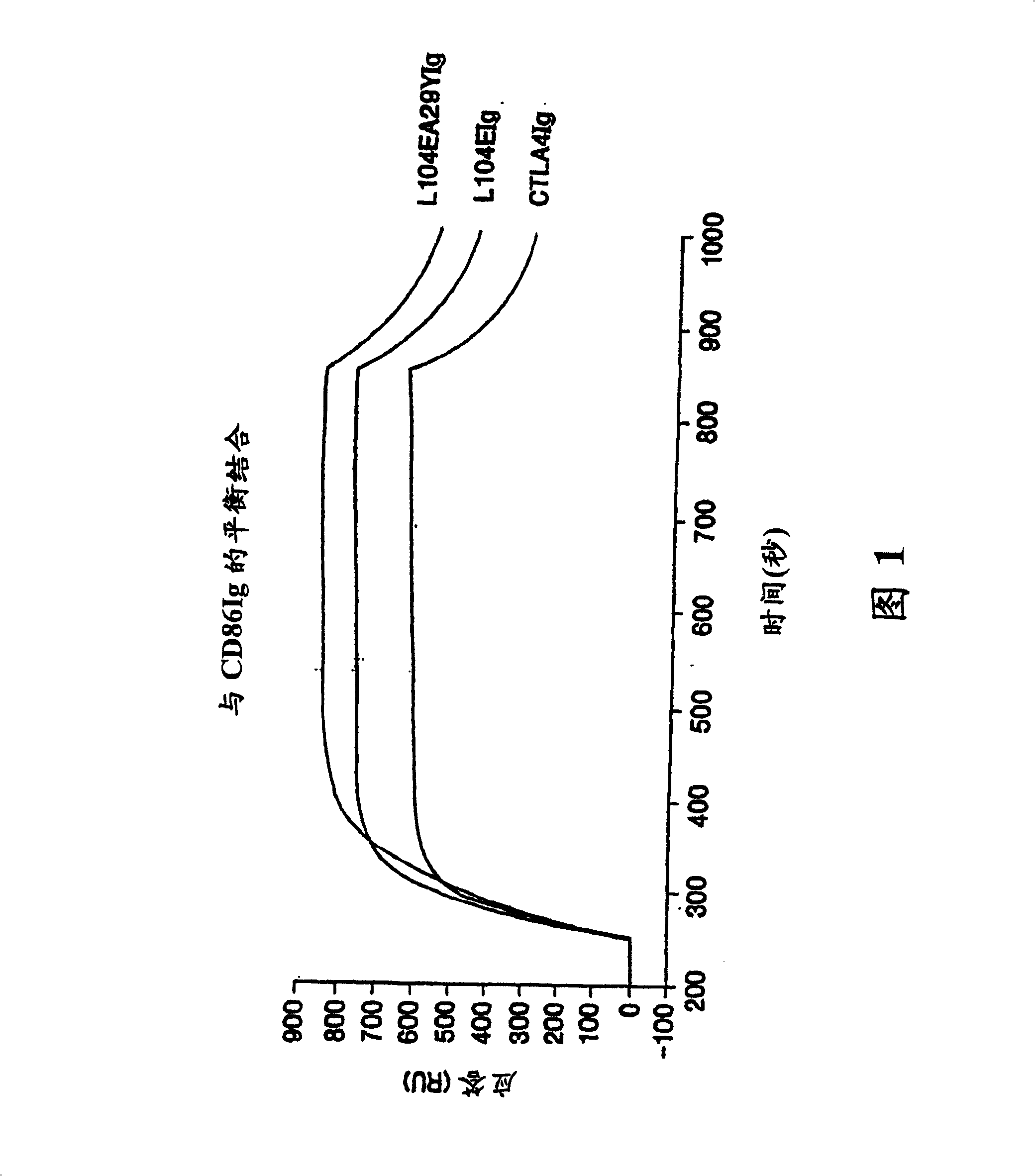
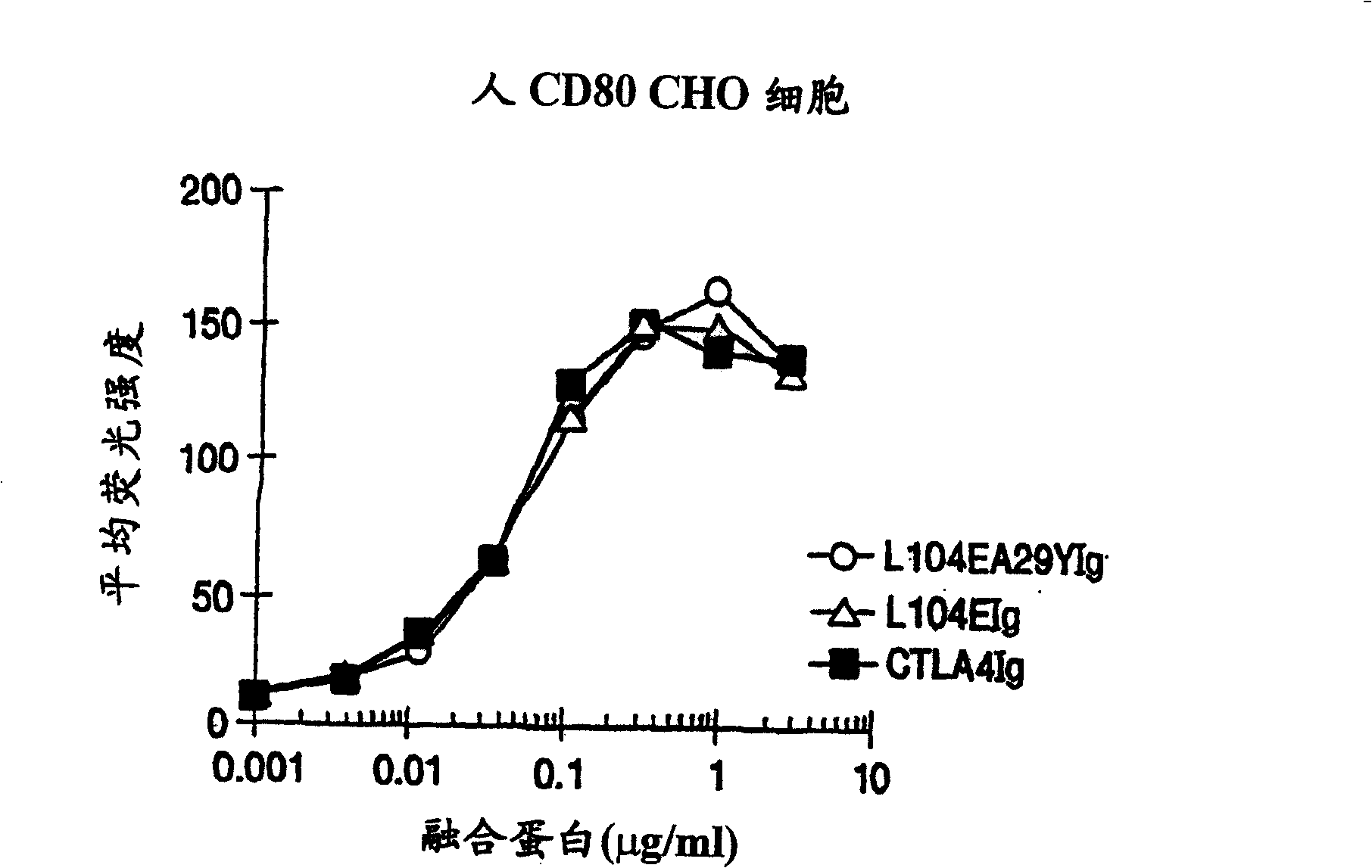
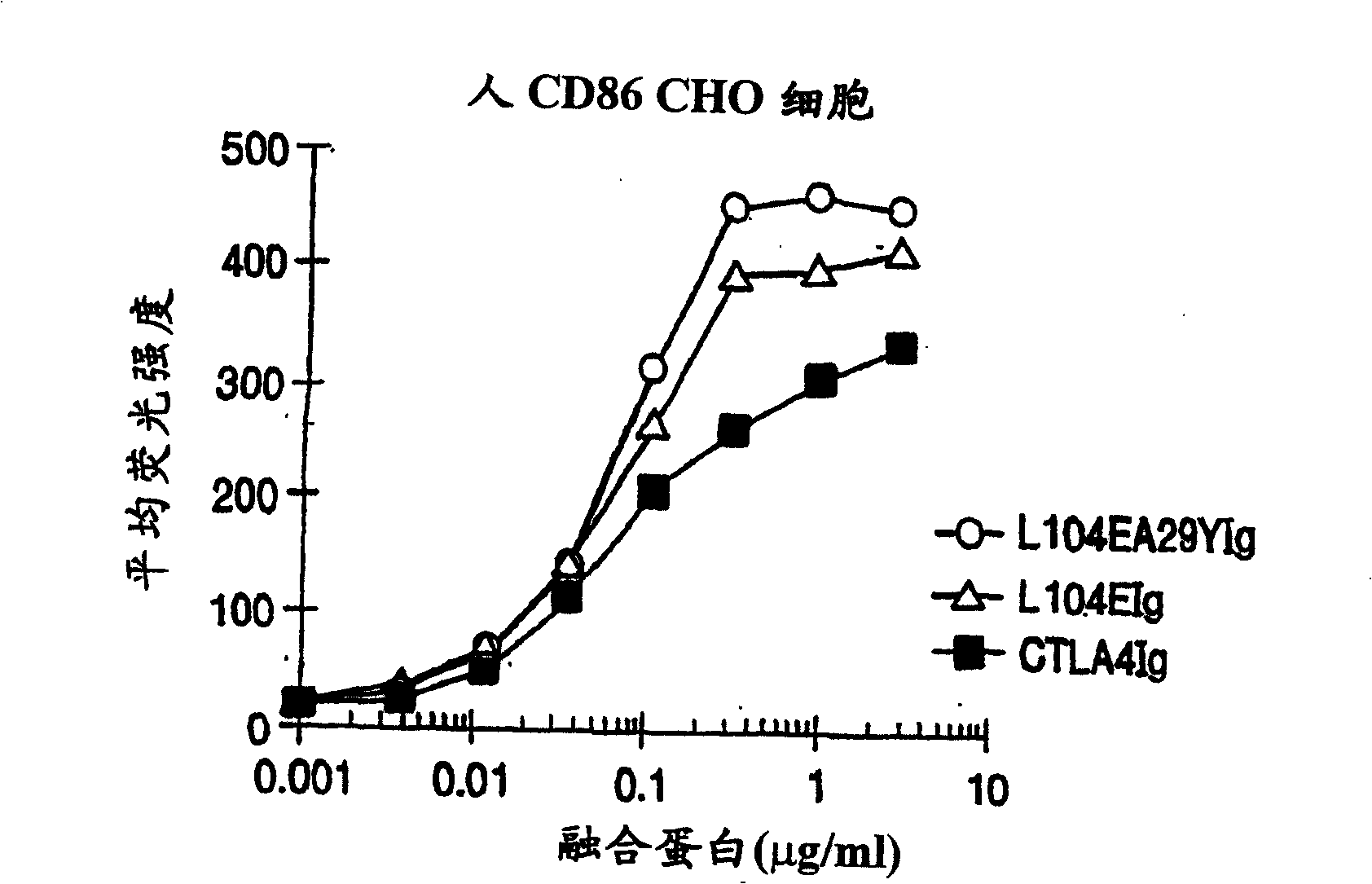
The present invention provides soluble CTLA4 mutant molecules which bind with greater avidity to the CD80 and / or CD86 antigen than wild type CTLA4 or non-mutated CTLA4Ig. The soluble CTLA4 molecules have a first amino acid sequence comprising the extracellular domain of CTLA4, where certain amino acid residues within the S25-R33 region and M97-G107 region are mutated. The mutant molecules of the invention may also include a second amino acid sequence which increases the solubility of the mutant molecule.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
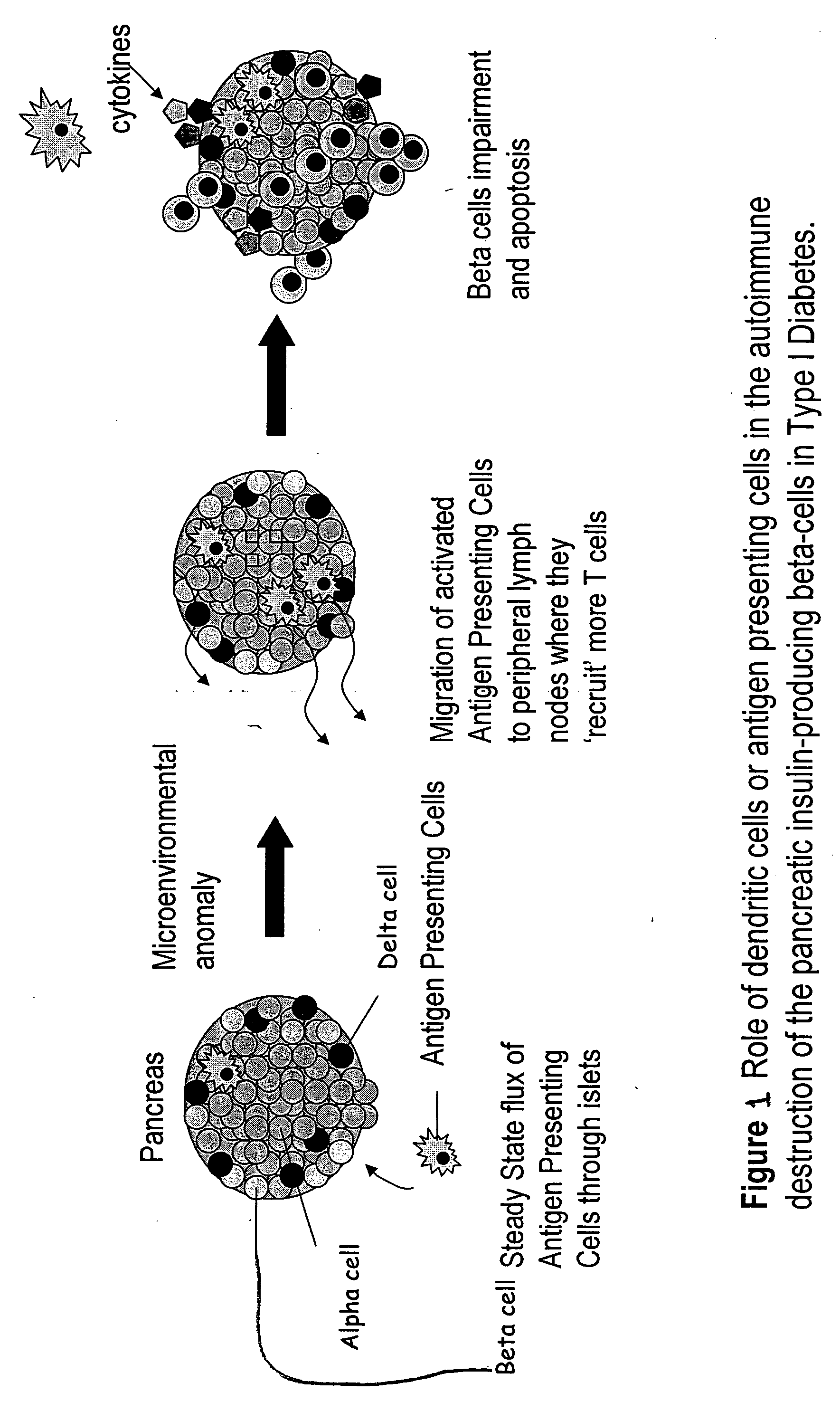
Delivery of as-oligonucleotide microspheres to induce dendritic cell tolerance for the treatment of autoimmune type 1 diabetes
AS-oligonucleotides are delivered in microsphere form in order to induce dendritic cell tolerance, particularly in the non-obese-diabetic (NOD) mouse model. The microspheres incorporate antisense (AS) oligonucleotides. A process includes using an antisense approach to prevent an autoimmune diabetes condition in NOD mice in vivo and in situ. The oligonucleotides are targeted to bind to primary transcripts CD40, CD80, CD86 and their combinations.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +2
Suppression of transplant rejection
InactiveUS20070166307A1Vertebrate cellsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAutoimmune conditionRegulatory T cell
The present invention relates to a transplant rejection in an animal suppressed by administration of an antibody directed at a cell surface antigen selected from the group consisting of CD4, CD8, CD154, LFA-1, CD80, CD86 and ICAM-1, preferably an anti-CD4 antibody, together with a non-cellular protein antigen to generate in the animal a population of regulatory T-lymphocytes; reactivating said population of regulatory T-lymphocytes by further administration to the animal of the non-cellular protein antigen; and transplanting said organ or tissue whilst said population of regulatory T-lymphocytes is activated. Regulatory T cells can be generated ex vivo by culturing T cells with an antibody directed at a cell surface antigen selected from the group consisting of CD4, CD8, CD154, LFA-1, CD80, CD86 and ICAM-1, in the presence of cells that present either alloantigen or a non-cellular protein antigen. Ex vivo generated T-lymphocytes can be used as an alternative method of overcoming transplant rejection or in combination with the in vivo method. A similar approach can be adopted for the treatment of autoimmune conditions.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
Mutant human cd80 and compositions for and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS20110002956A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAutoimmune conditionCD80
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +2
Markers associated with the therapeutic efficacy of glatiramer acetate
InactiveUS20100285600A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingImmunologic disordersCD86
The present invention is directed to methods and kits based, at least in part, on the identification of allele-specific responsiveness or non-responsiveness to glatiramer acetate for the treatment of autoimmune disorders, such as relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. The allele-specific responsiveness or non-responsiveness is based on polymorphisms in the following genes, CTSS, MBP, TCRB, CD95, CD86, IL-1R1, CD80, SCYA5, MMP9, MOG, SPP1 and IL-12RB2.
Owner:TEVA PHARMA IND LTD
Naturally occuring IgM antibodies that bind to lymphocytes
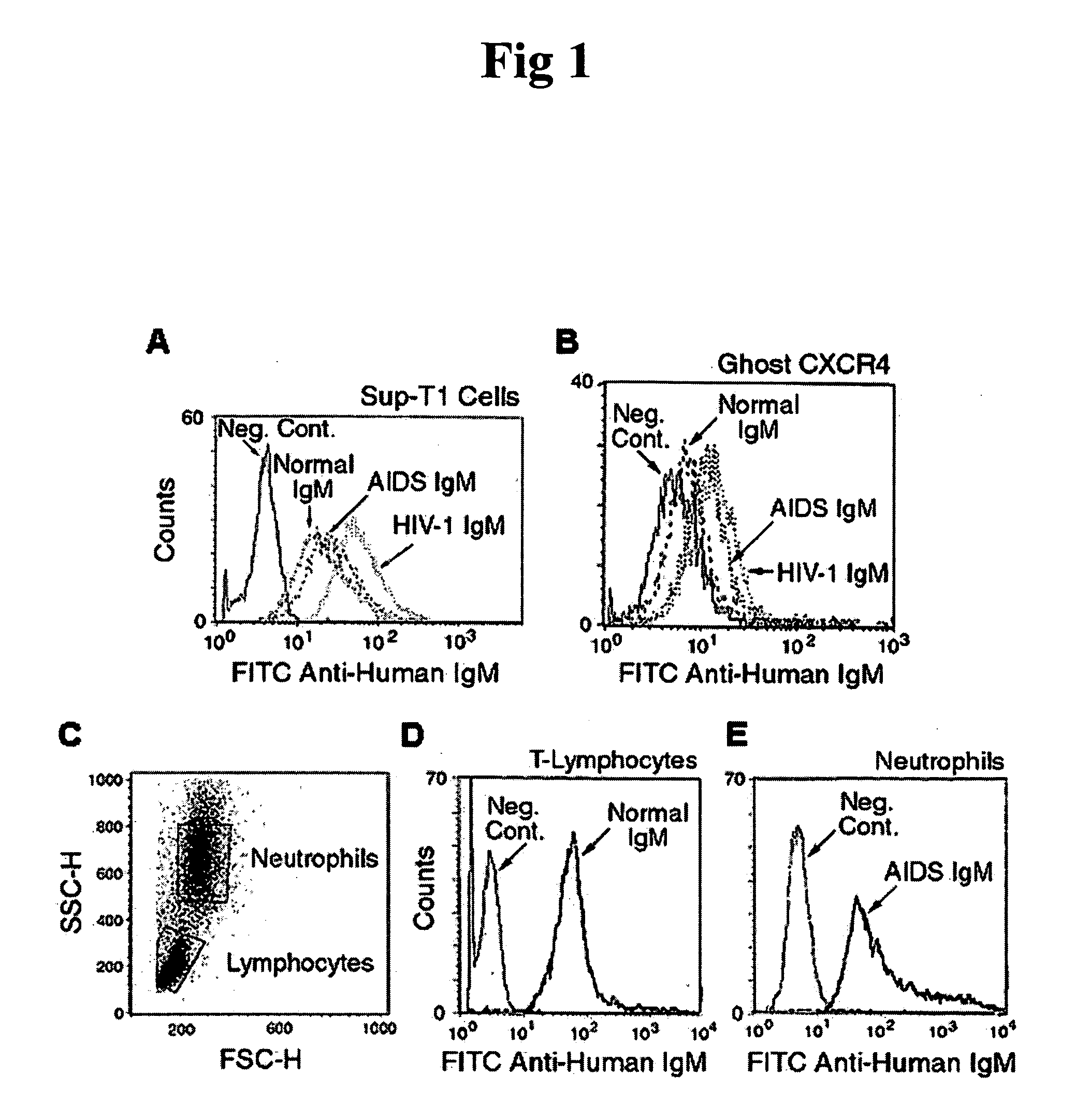
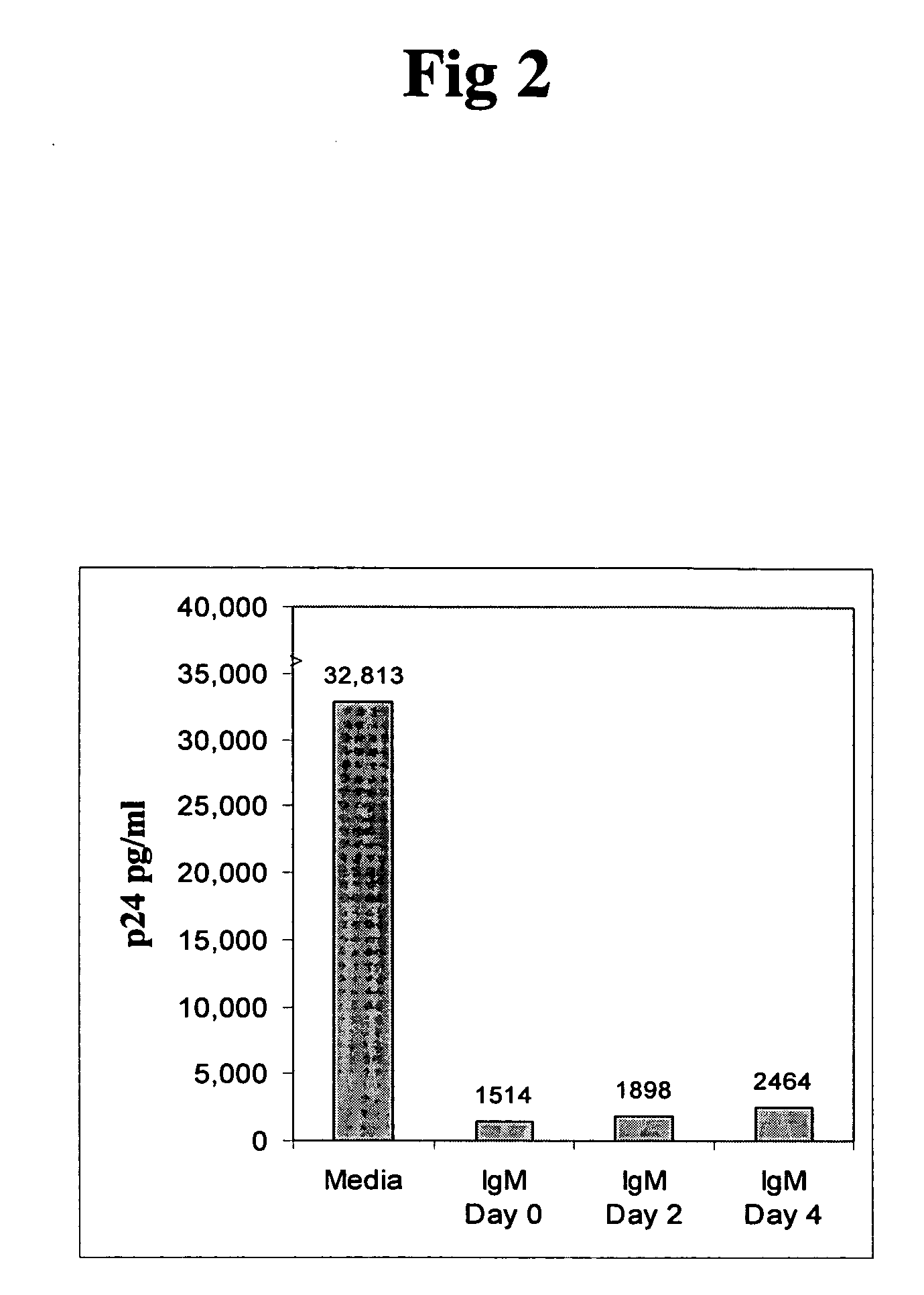
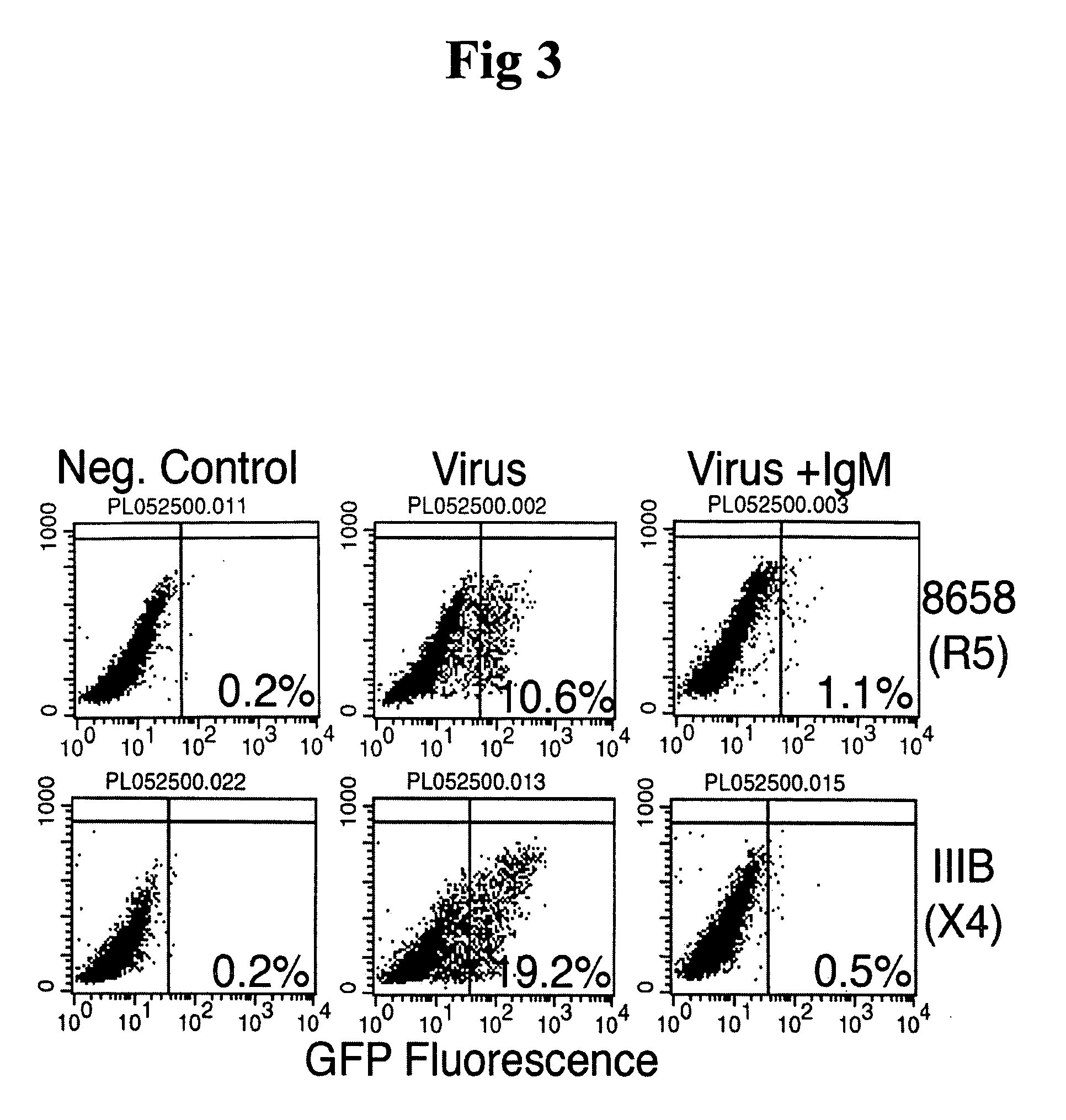
InactiveUS20050220787A1Inhibits HIV- infectivityImprove the level ofImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsLymphocyte AntibodyDisease
In this invention, the inventor discloses that naturally occurring IgM anti-lymphocyte antibodies bind to chemokine and non-chemokine receptors on lymphocytes and other cells, and downmodulate certain receptors including CD4 and CD2 on T cells and CD80 and CD86 on macrophages. The inventor also discloses that such antibodies (i) inhibit HIV-1 and other viruses from infecting cells (ii) inhibits activation and proliferation of T lymphocytes (iii) inhibits cytokine and chemokine production (iv) inhibits inflammatory processes, and (v) enhances death of malignant cells. This art or invention is novel in that the antibodies described herein are “naturally occurring” i.e. develop in absence of deliberate immunization and secondly these antibodies are distinct from disease causing autoantibodies in that these naturally occurring antibodies are polyreactive with low binding affinity.
Owner:LOBO PETER ISAAC
Methods for treating immune disorders associated with graft transplantation with soluble CTLA4 mutant molecules
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Methods for treating immune disorders associated with graft transplantation with soluble CTLA4 mutant molecules
ActiveUS20070009511A1Great avidityImprove solubilityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderGraft transplantCD80
The present invention provides use of soluble CTLA4 mutant molecules which bind with greater avidity to the CD80 and / or CD86 antigen than wild type CTLA4 or non-mutated CTLA4Ig in the treatment of immune disorders associated with graft transplantation.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Treatment of B cell lymphoma using anti-CD80 antibodies that do not inhibit the binding of CD80 to CTLA-4
InactiveUS7153508B2Prevent rejectionAvoid immune responseCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAntigen
Owner:BIOGEN INC
Methods of treatment using CTLA4 mutant molecules
The present invention provides soluble CTLA4 mutant molecules which bind with greater avidity to the CD80 and / or CD86 antigen than wild type CTLA4 or non-mutated CTLA4Ig. The soluble CTLA4 molecules have a first amino acid sequence comprising the extracellular domain of CTLA4, where certain amino acid residues within the S25-R33 region and M97-G107 region are mutated. The mutant molecules of the invention may also include a second amino acid sequence which increases the solubility of the mutant molecule.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Artificial antigen presenting cell as well as preparation method and application thereof
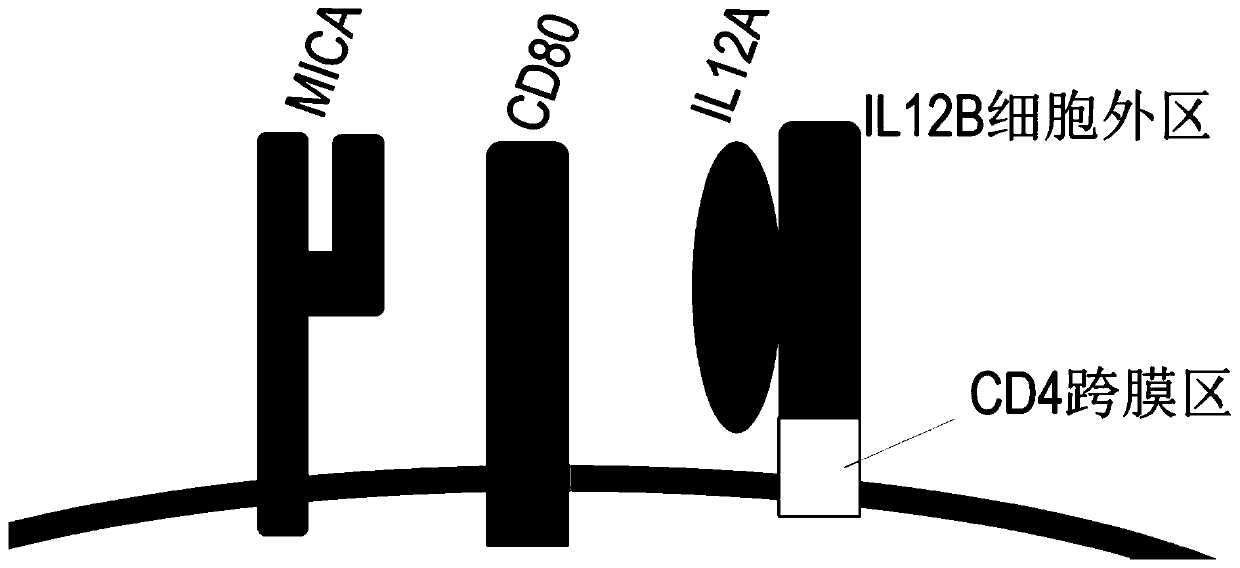
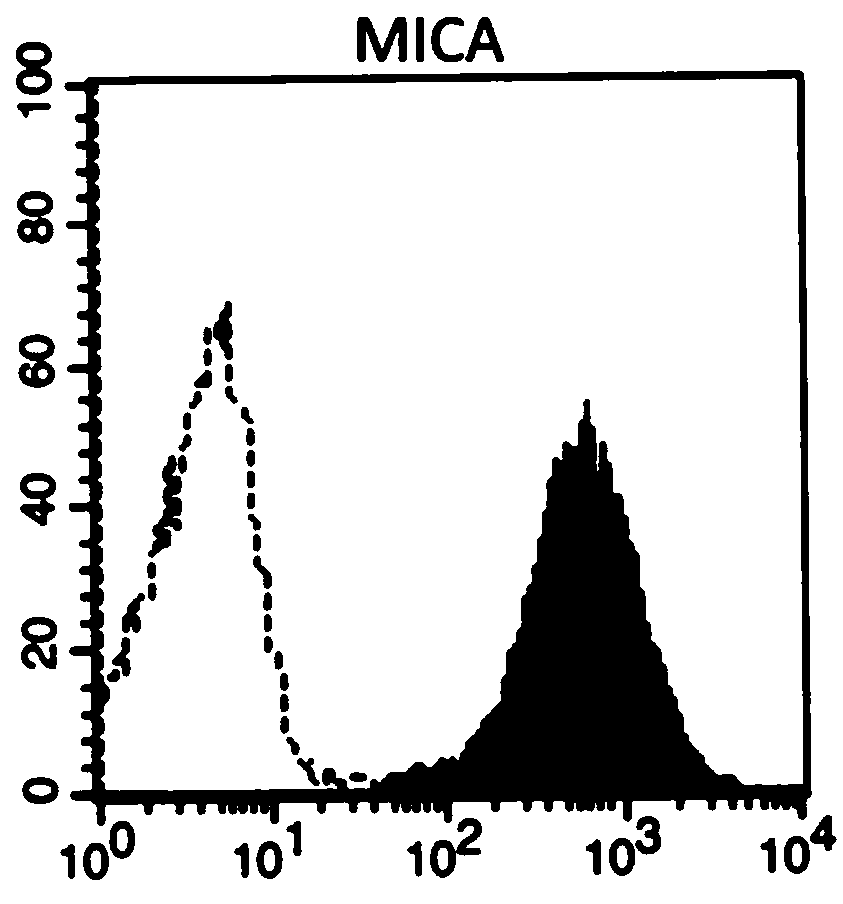
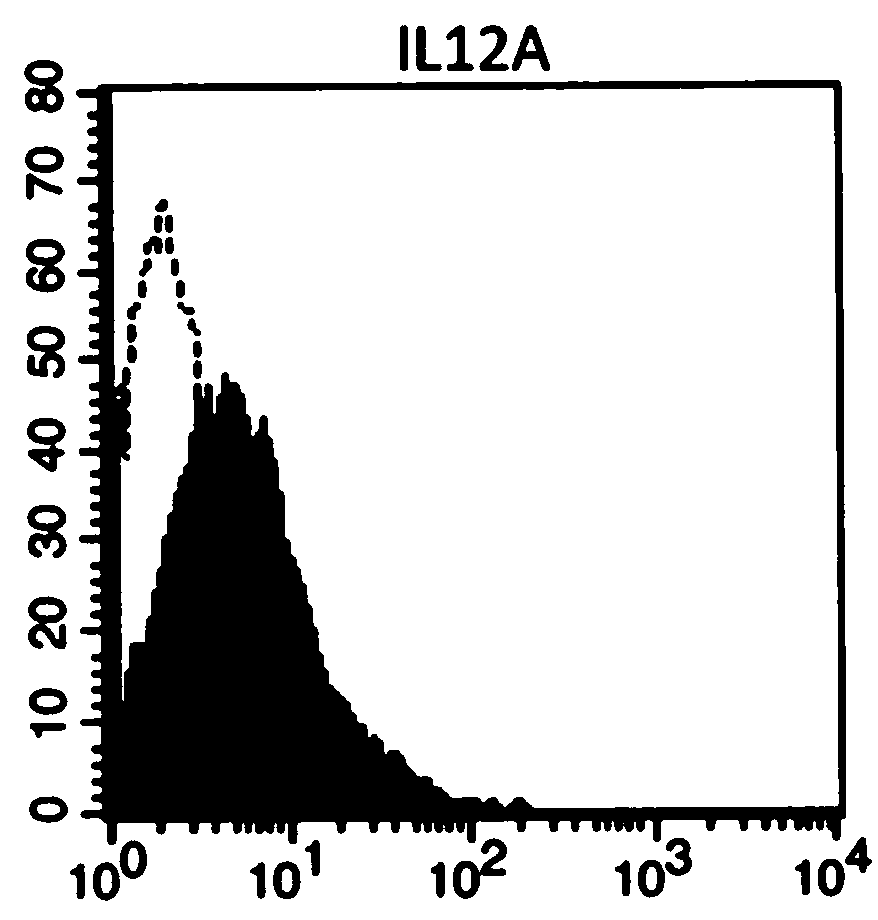
ActiveCN110964698AIncrease the number ofIncreased toxicityMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsAntigenPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The invention provides an artificial antigen presenting cell as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. Wherein the artificial antigen presenting cell expresses membrane proteins MICA, IL-12 and CD80, the artificial antigen presenting cell is used for culturing NK cells or peripheral blood mononuclear cells containing the NK cells, the number of the NK cells can be remarkably increased, the service life of the NK cells is prolonged, the activity of the NK cells is improved, and compared with an existing artificial antigen presenting cell for expressing MICA, the artificial antigen presenting cell has a stronger effect of amplifying and activating the NK cells.
Owner:杭州中赢生物医疗科技有限公司
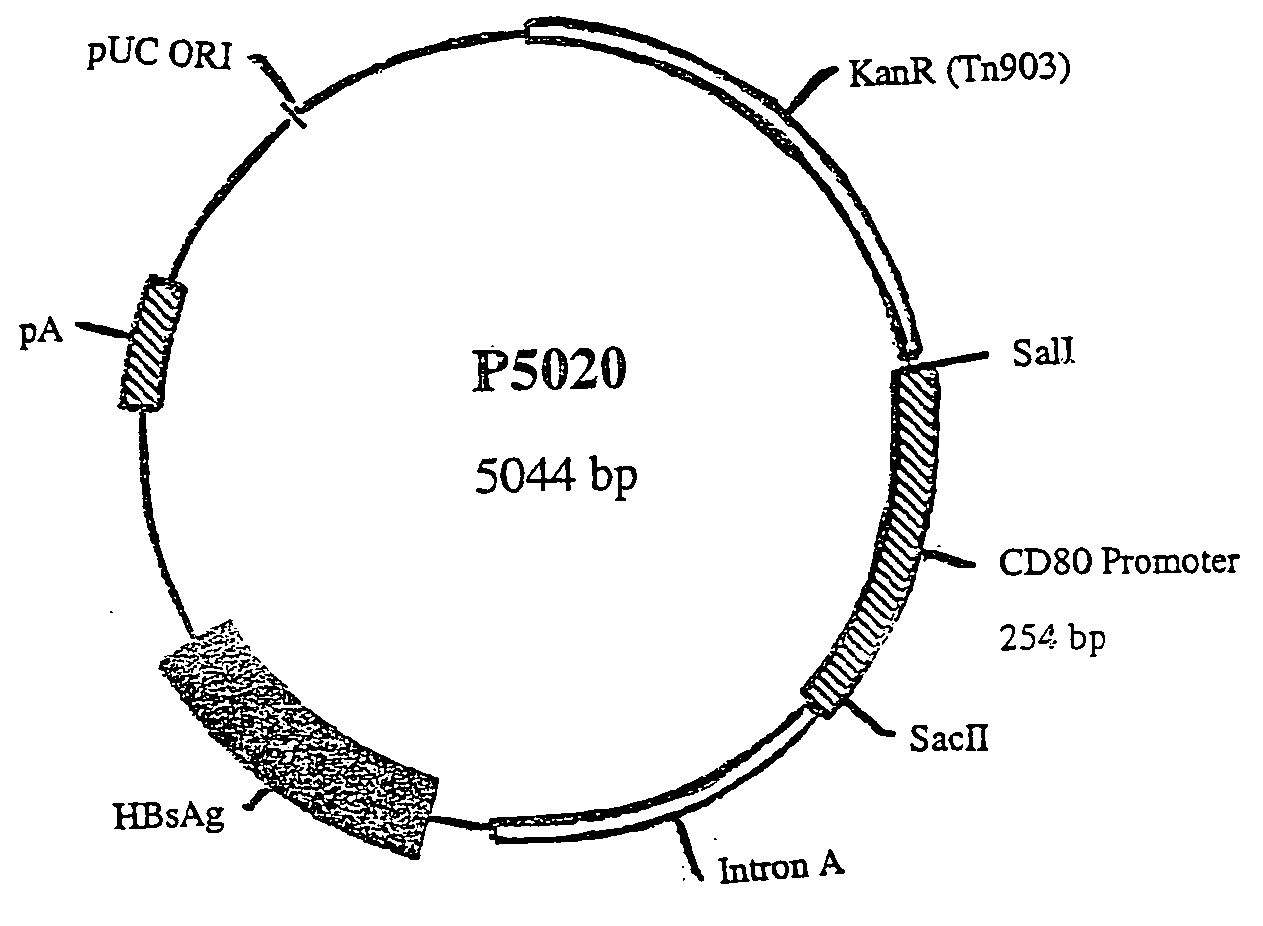
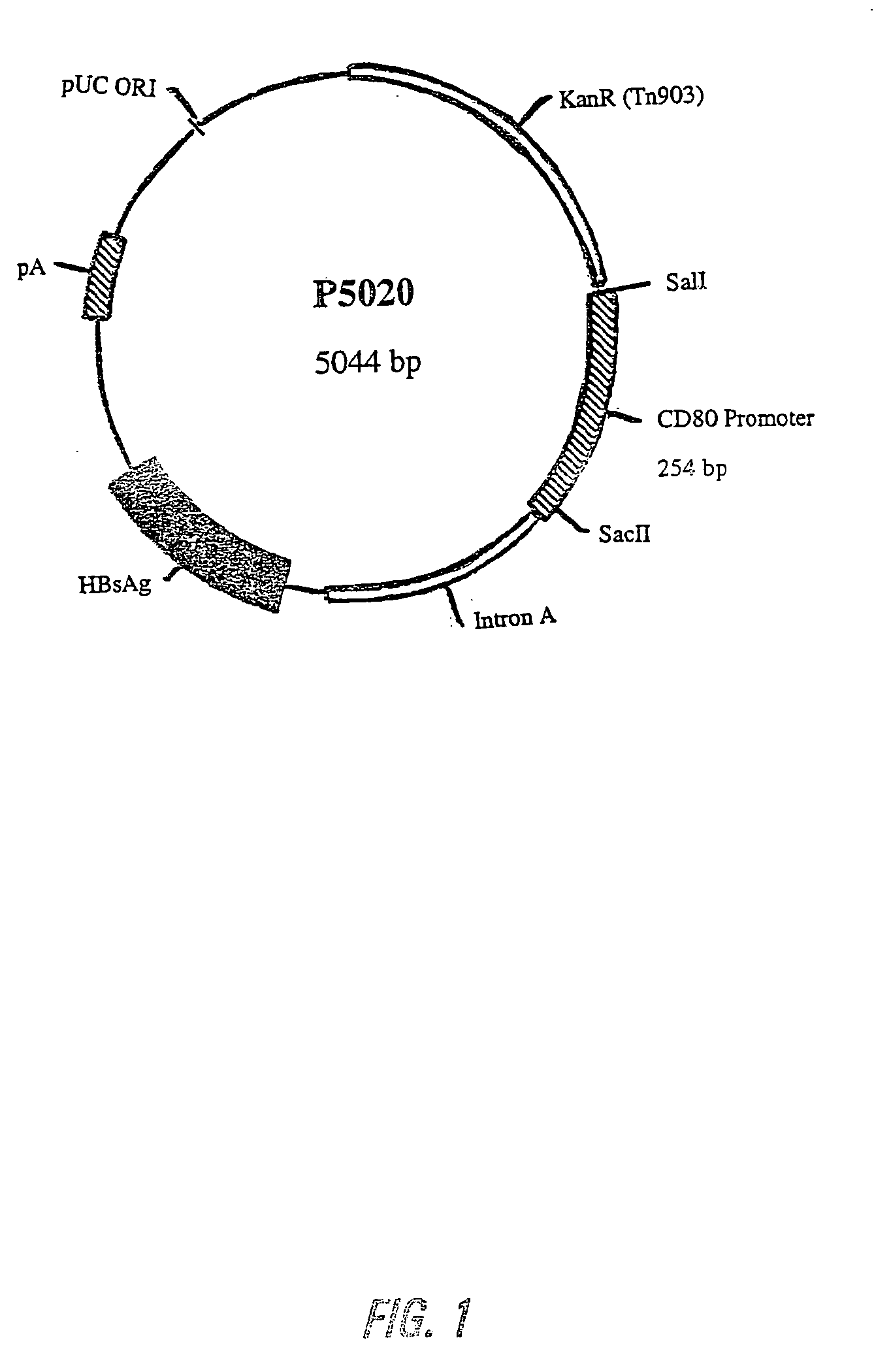
Nucleic acid vaccine compositions having a mammalian CD80/CD86 gene promoter driving antigen expression
Polynucleotides encoding at least one immunizing antigen whose expression is controlled by a promoter derived from a gene encoding a co-stimulatory molecule are provided. The polynucleotides may also encode adjuvants. Compositions comprising at least one immunizing agent and at least one cytokine that enhance dendritic cell stimulation and / or survival are also provided. Methods for eliciting an immune response against the immunizing agent are also provided. The method includes the steps of administering the polynucleotides and, optionally, co-administering an adjuvant.
Owner:POWDERJECT RES LTD OXFORD (GB)
Treating intestinal inflammation with anti-CD80 antibodies that do not inhibit CD80 binding to CTLA-4
InactiveUS7175847B1Prevent rejectionAvoid immune responseImmunoglobulins against bacteriaImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsAntigenCD80
Owner:BIOGEN INC
Modulation of tumor microenvironment
InactiveUS20100203010A1Inhibiting tumor progressionSuppress production of one or more inflammatory cytokinesPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody ingredientsDiseaseRegulatory T cell
Compositions comprising CD80-targeted therapeutics and methods of using these compositions are provided for the treatment of a disease or disorder in which CD80-expressing cells or regulatory T cell function contribute to or exacerbate the associated pathology.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
Nucleic acids encoding mutant human CD80 and compositions comprising the same
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +2
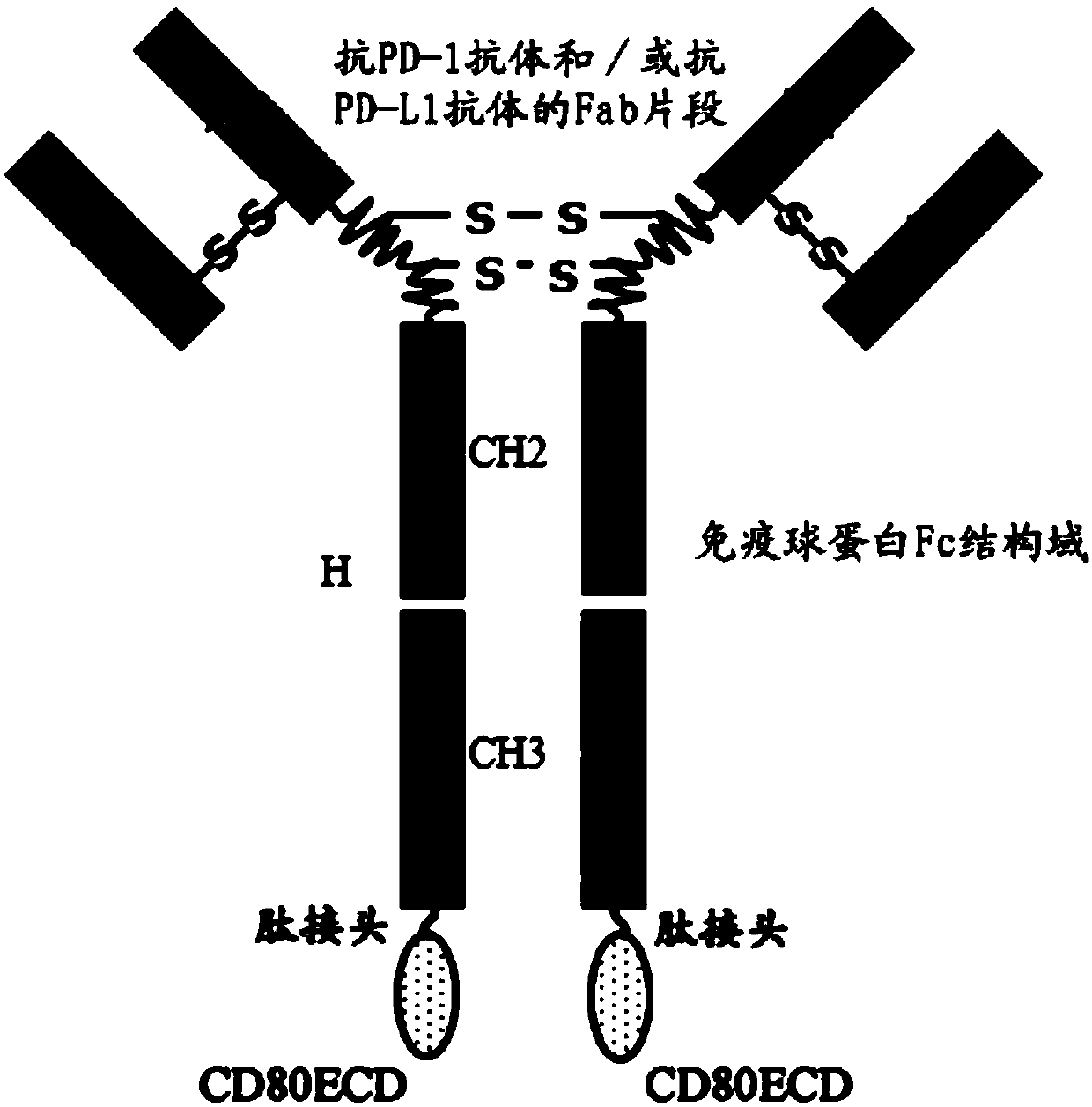
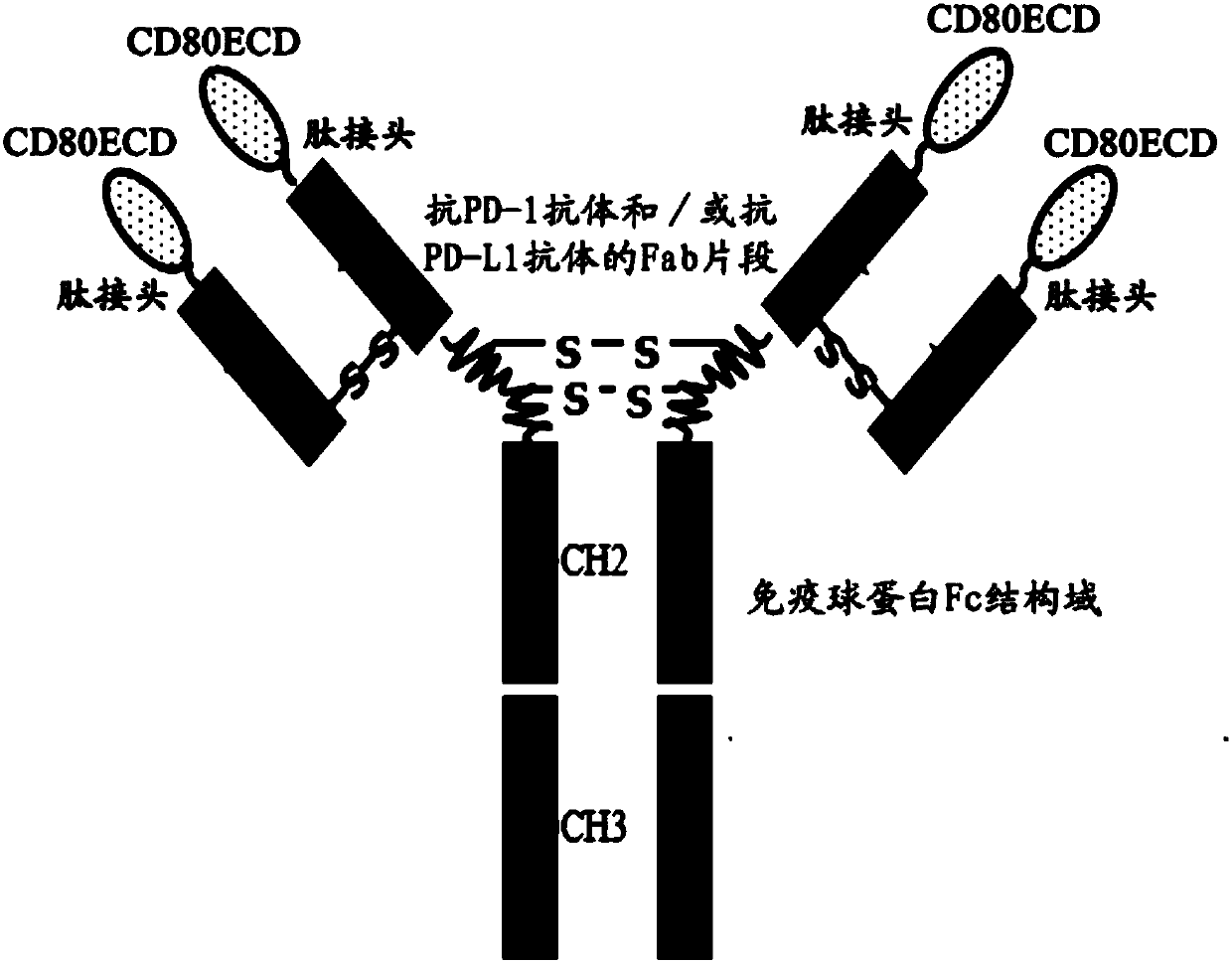
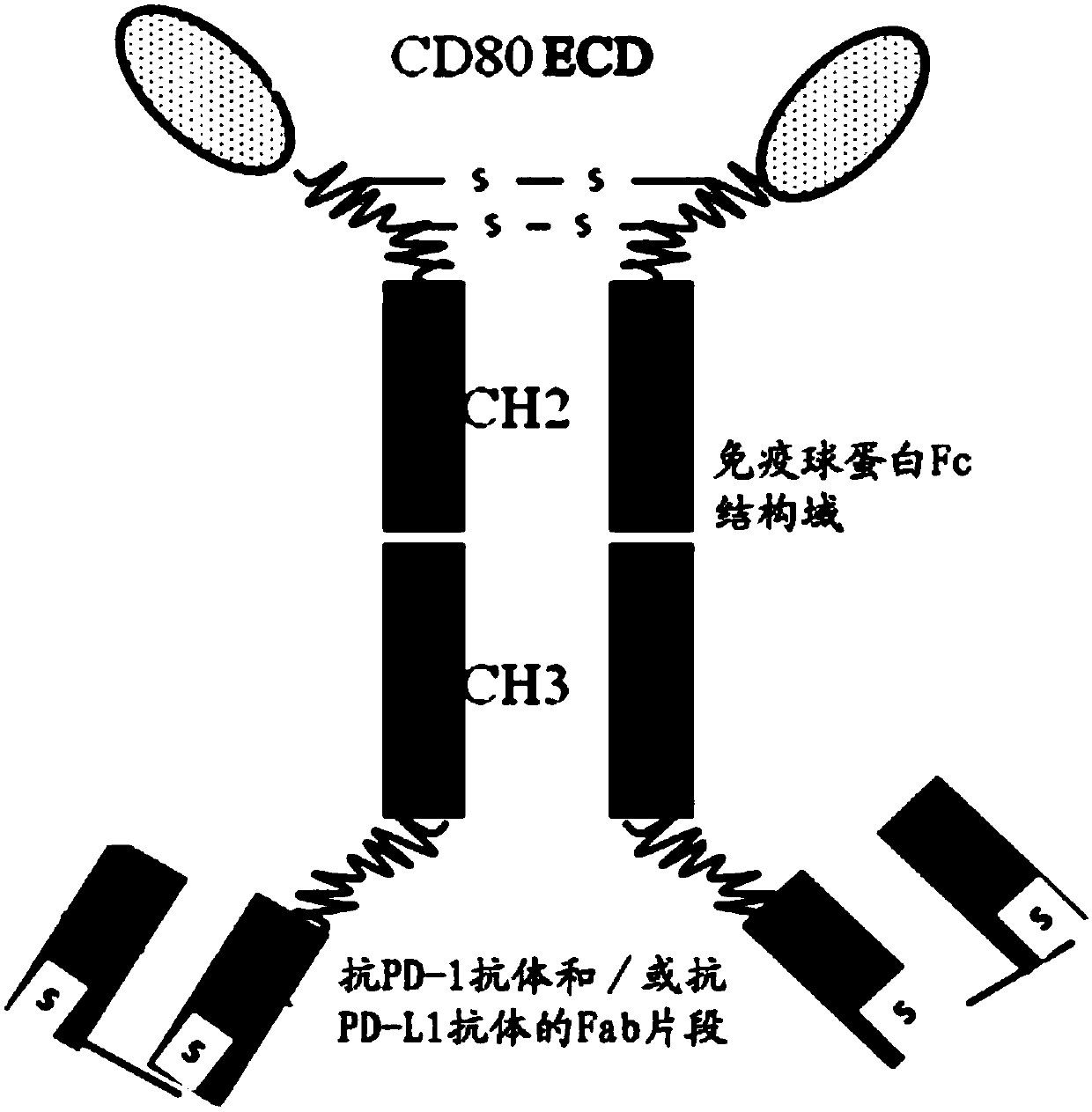
Fusion protein capable of blocking PD-1/PD-L1 signaling conduction pathway and activating T cells and use thereof
The present invention provides a fusion protein capable of blocking a PD-1 / PD-L1 signaling conduction pathway and activating T cells. The fusion protein comprises (i) an antigen-binding fragment derived from an anti-PD-1 antibody and / or an anti-PD-L1 antibody; (ii) an immunoglobulin Fc domain; and (iii) a CD80 extracellular domain (ECD). The present invention also provides a polynucleotide encoding the fusion protein, a vector comprising the polynucleotide, a host cell comprising the polynucleotide or vector, and a use of the fusion protein in individual treating, preventing and / or diagnosingdiseases related with PD-1 / PD-L1 signaling pathway activation and T cell function inhibition.
Owner:BEIJING BIYANG BIOTECH
Use of cyclic dinucleotide cGAMP and its derivatives as potential immunologic adjuvants
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine and relates to a use of cyclic dinucleotide cGAMP and its derivatives as immunologic adjuvants. The study result shows that cGAMP and its derivatives can stimulate the innate immunity of the human body, are effective immunomodulators, can significantly improve the immune response and antibody titer, can stimulate expression of immature dendritic cell surface histocompatible complex MHCII antigens and an enhancement molecule CD80 / CD86, can increase secretion of cytokines and chemokines (such as interleukin and interferon), and can activate and enhance dendritic cells and T cells. Therefore, cGAMP and its derivatives can be used as potential immunologic adjuvants and play an important role in preparation of vaccines.
Owner:LIAOCHENG CITY ORIENT BIOMEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Chimeric protein and method of controlling tumor growth using the protein
A chimeric protein expressed from a transgene tranduced into a mammalian tumor cell and method of using the chimeric protein for cancer treatment. The chimeric protein comprises an effector and an anchor, which are linked by a spacer. The chimeric protein, when expressed and exposed on the tumor cell surface in vivo can activate T cells, which further lead to lysis of the tumor cells. The anti-tumor effects can be enhanced by co-expression of certain co-stimulators, such as CD80 or CD86.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
CAR-T cell as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106047817APromote secretionEnhance the effect of killing tumor cellsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNGF/TNF-superfamilyAntigenCell membrane
Owner:SHEN ZHEN ISTEM REGENERATIVE MEDICINE SCI TECH CO LTD
Soluble CTLA4 mutant molecules and uses thereof
InactiveCN101255192AReduce dissociationHigh affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSolubilityDiamino acid
The present invention provides soluble CTLA4 mutant molecules which bind with greater avidity to the CD80 and / or CD86 antigen than wild type CTLA4 or non-mutated CTLA4Ig. The soluble CTLA4 molecules have a first amino acid sequence comprising the extracellular domain of CTLA4, where certain amino acid residues within the S25-R33 region and M97-G107 region are mutated. The mutant molecules of the invention may also include a second amino acid sequence which increases the solubility of the mutant molecule.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
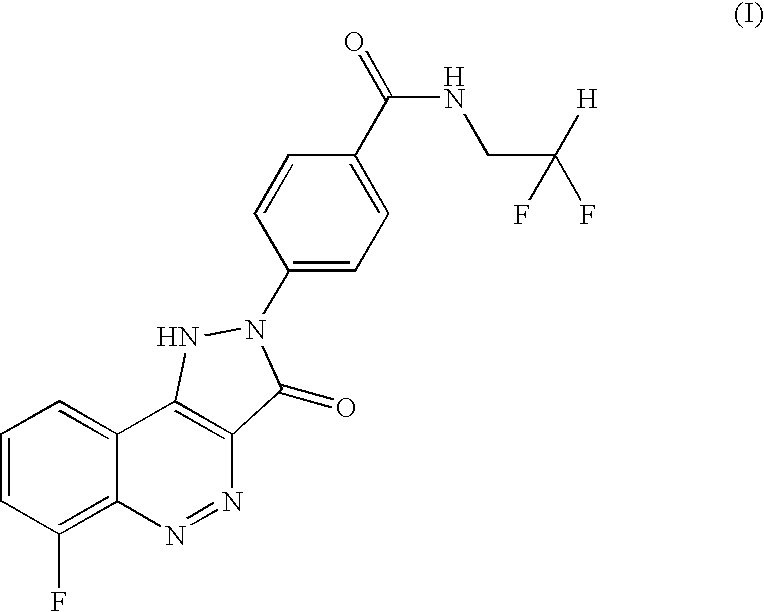
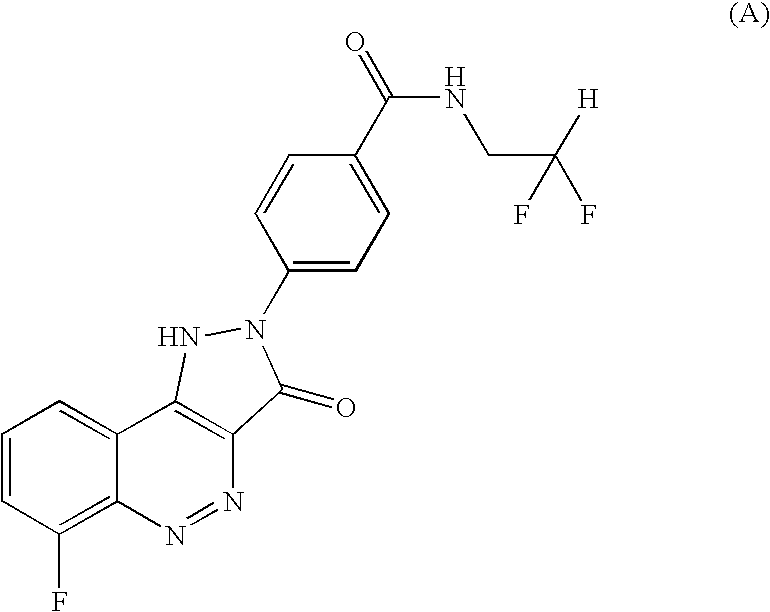
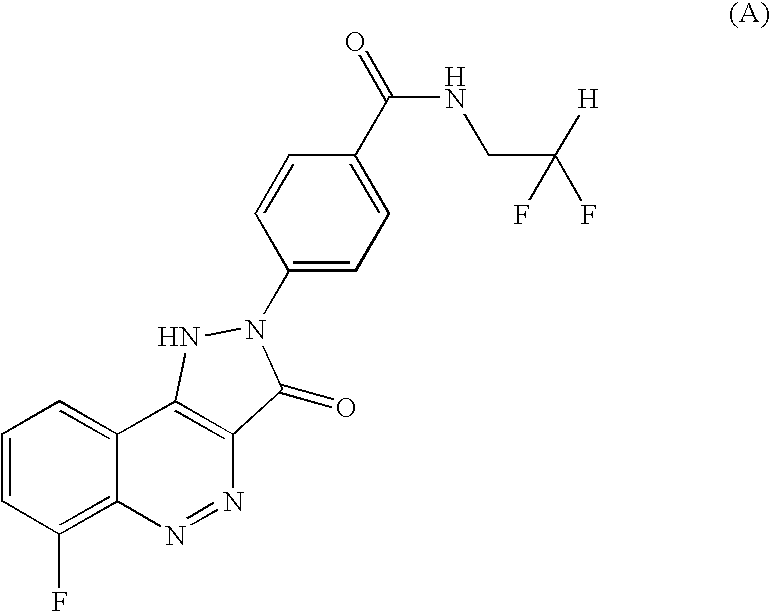
Salt of CD 80 antagonist
The choline salt of the CD80 antagonist compound 4-(6-fluoro-3-oxo-1,3-dihydro-pyrazolo[4,3-c]cinnolin-2-yl)-N-(2,2-difluoro-ethyl)-benzamide (I) has good aqueous solubility and is therefore convenient for pharmaceutical use.
Owner:MEDIGENE
Peptide for inducing mast cell-specific apoptosis and use thereof
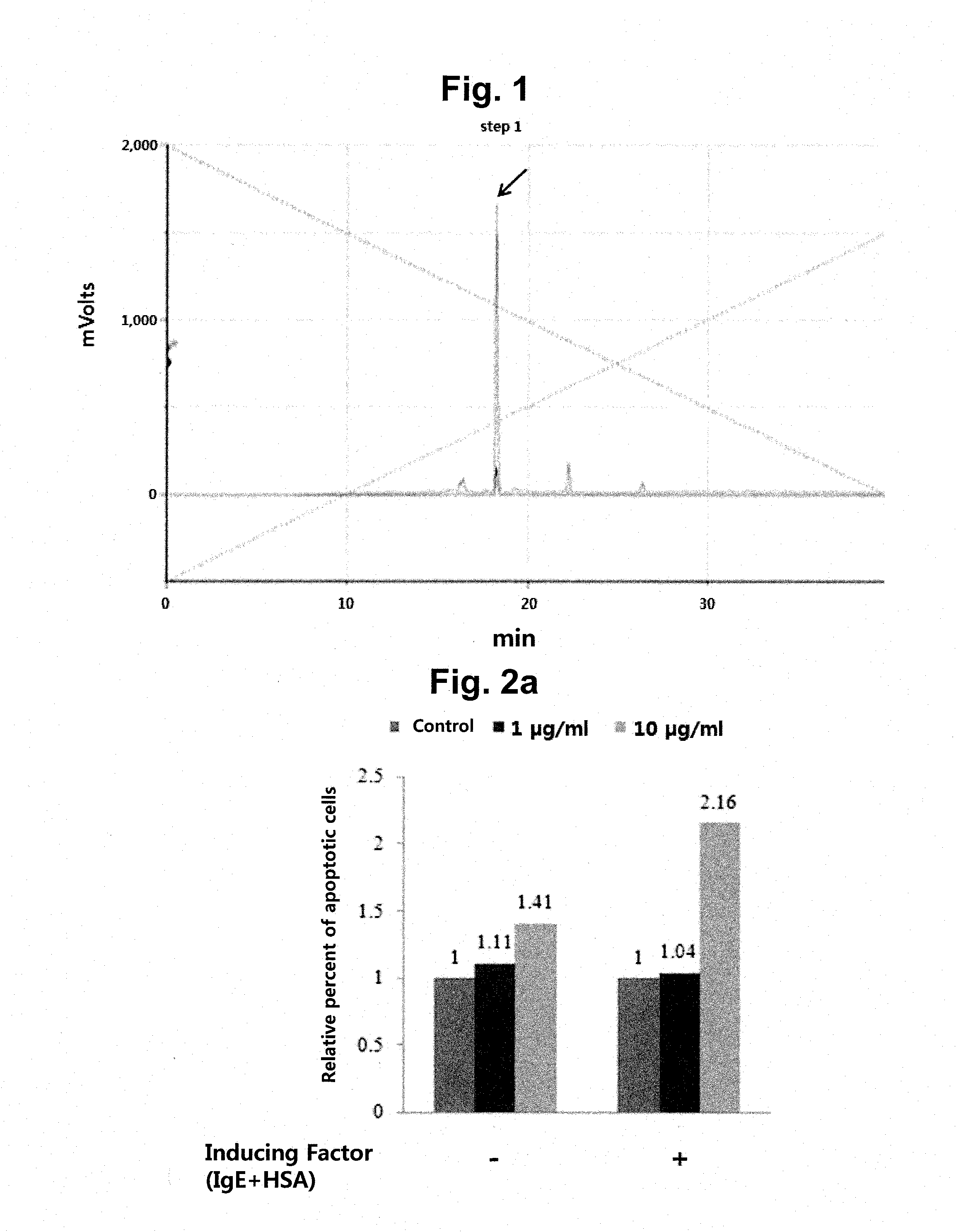
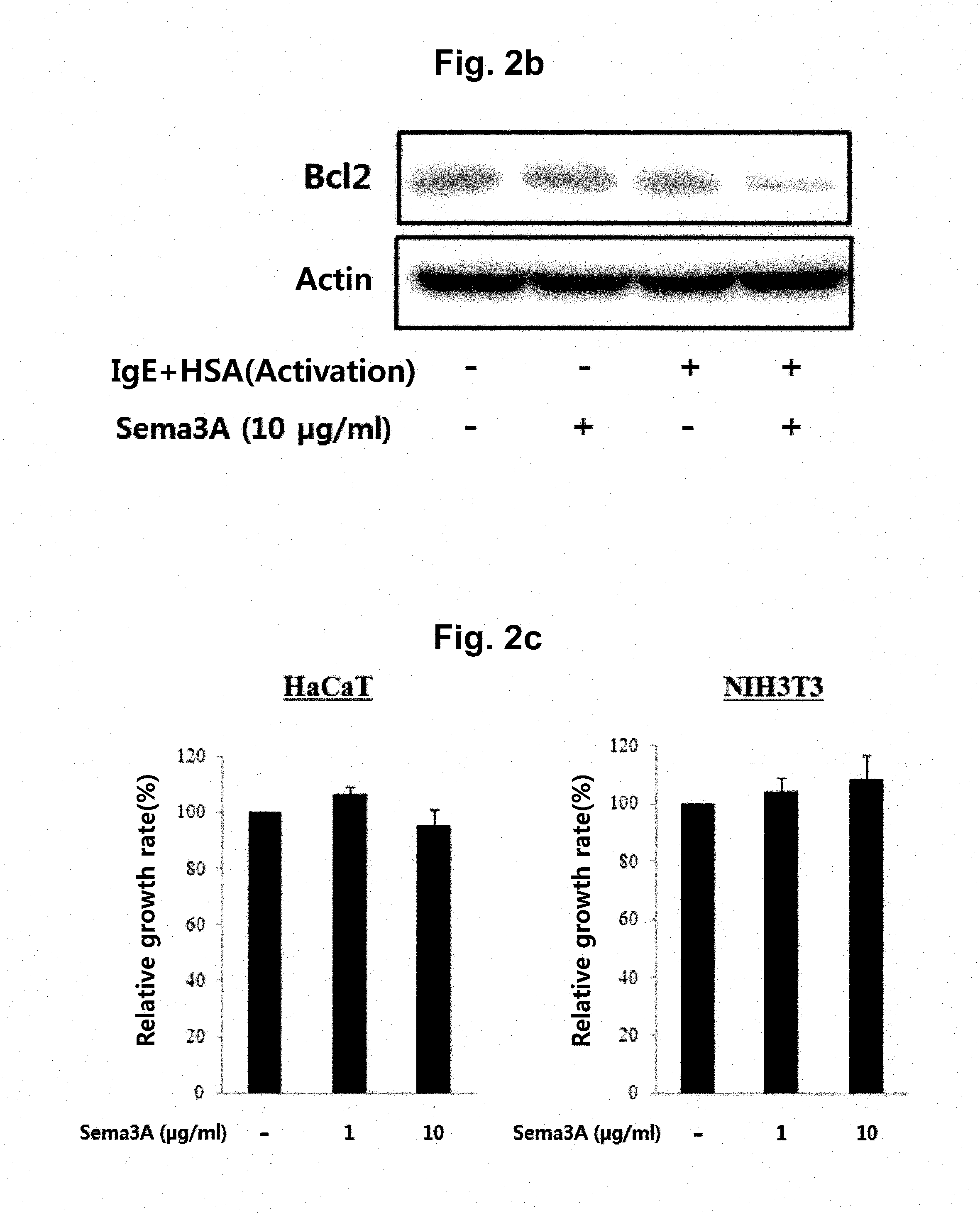
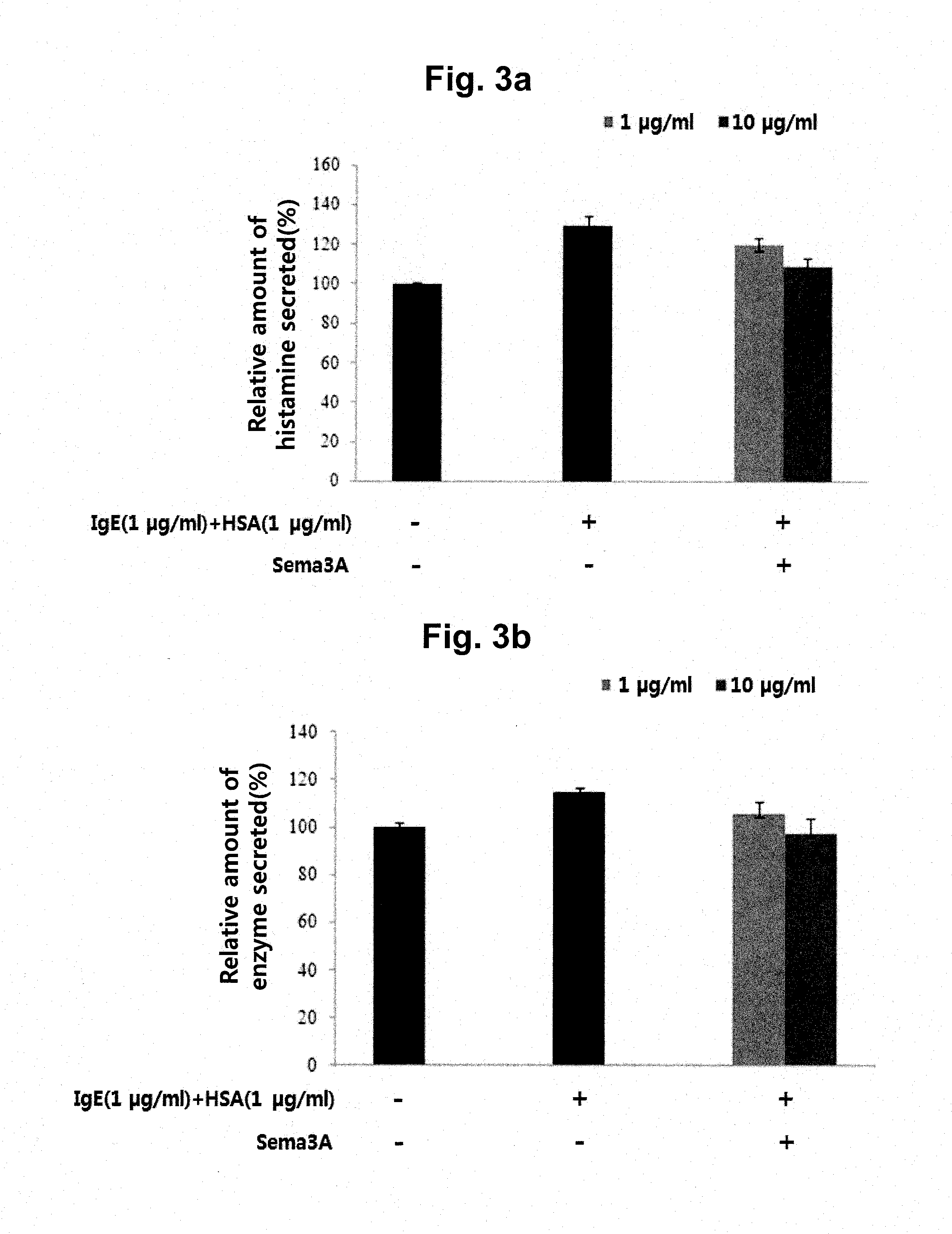
ActiveUS20160075739A1Good skin permeabilityInhibitory activityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionDiseaseAntigen
A peptide according to the present invention can perform a function identical or similar to the function of natural CTLA-4 and has an excellent degree of skin penetration due to a small size. The peptide according to the present invention effectively binds to antigen presenting cell surface proteins (CD80 and CD86) to inhibit activity of T cells and thus is capable of inhibiting the expression of inflammatory cytokines (for example, IL-2 and IFN-γ). As a result, a composition comprising the peptide according to the present invention exhibits excellent effects in terms of preventing, treating, or improving Th1-mediated immune diseases. Therefore, the superior activity and stability of the peptide according to the present invention can be useful when applied to medicine, quasi-drugs, and cosmetics.
Owner:CAREGEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com