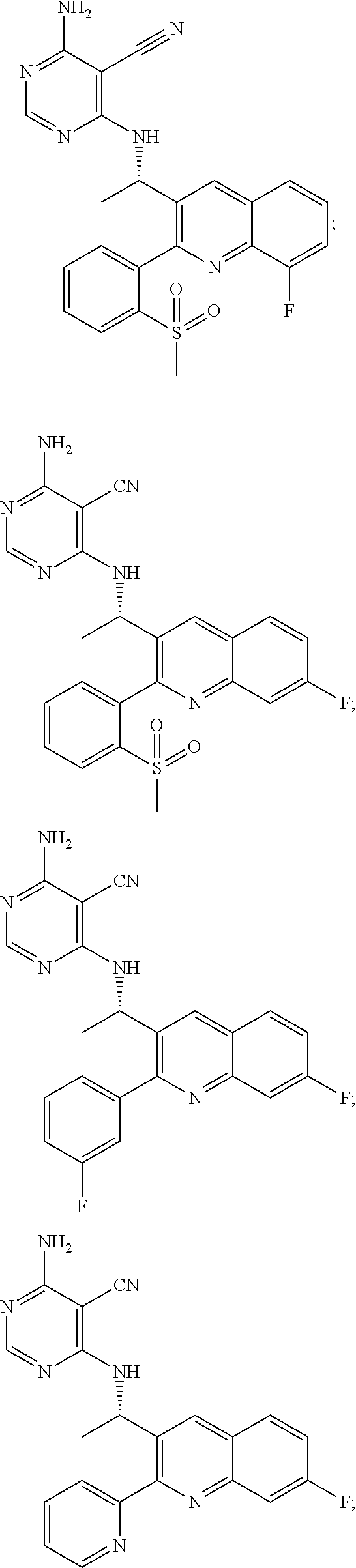
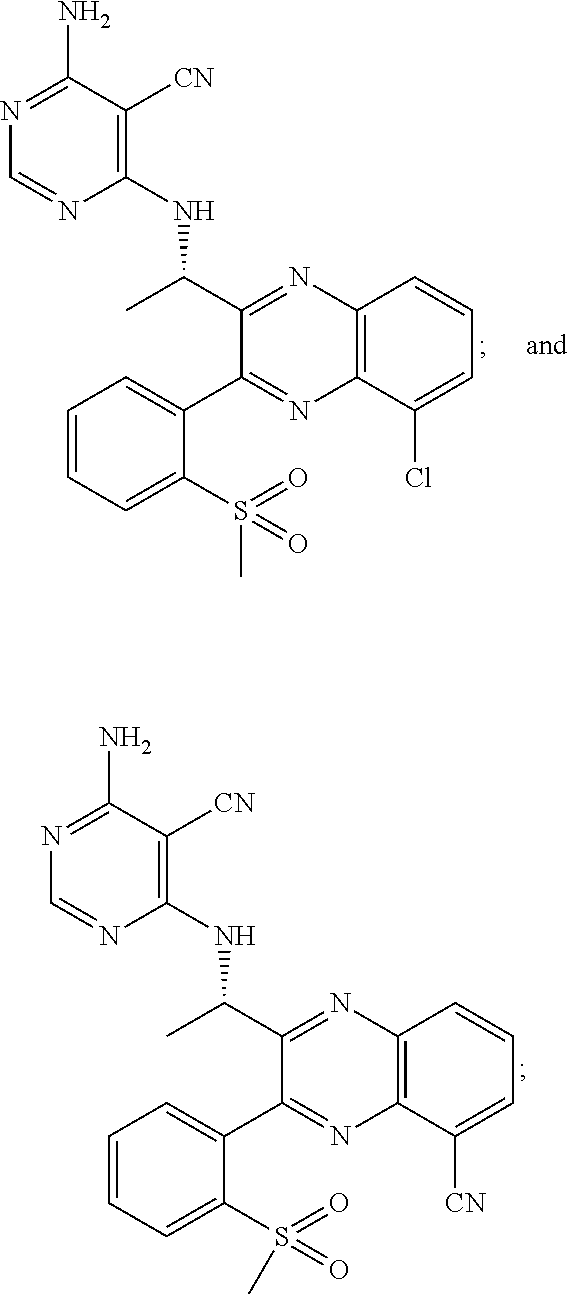
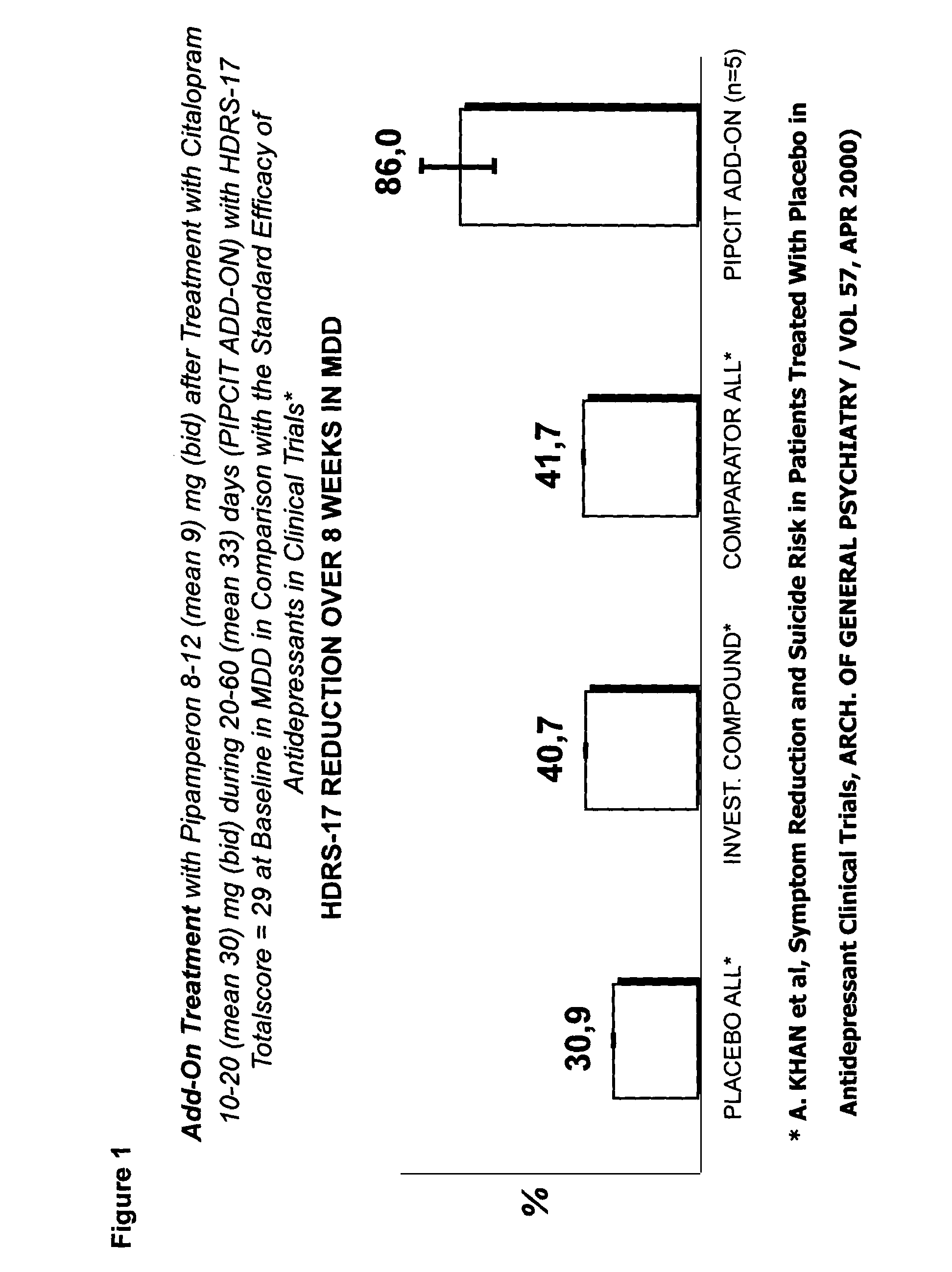
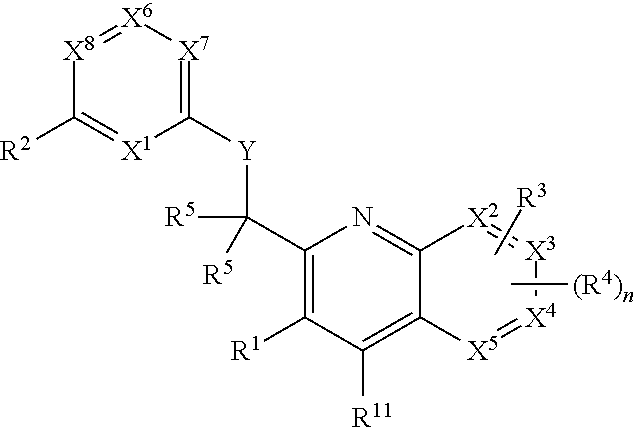
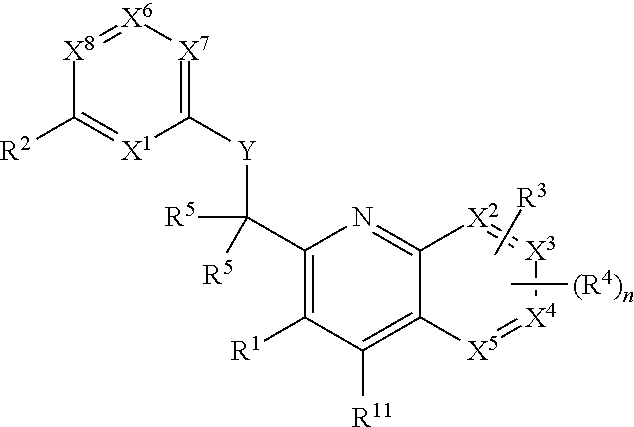
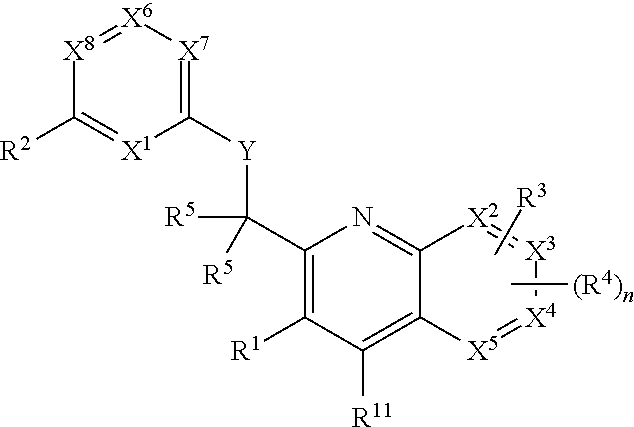
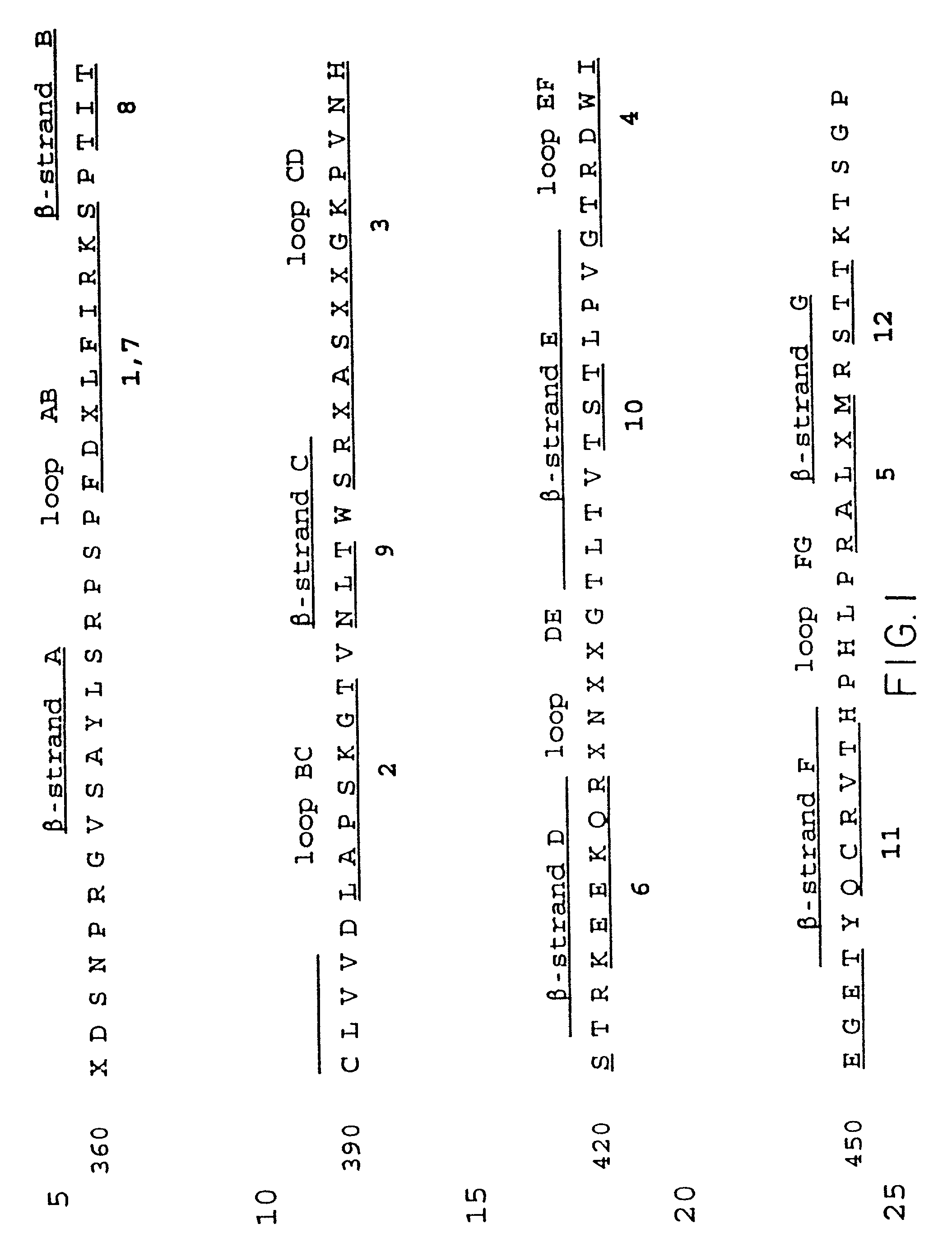Patents
Literature
192 results about "Hypersensitivity reaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hypersensitivity (also called hypersensitivity reaction or intolerance) refers to undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. They are usually referred to as an over-reaction of the immune system and these reactions may be damaging, uncomfortable, or occasionally fatal.
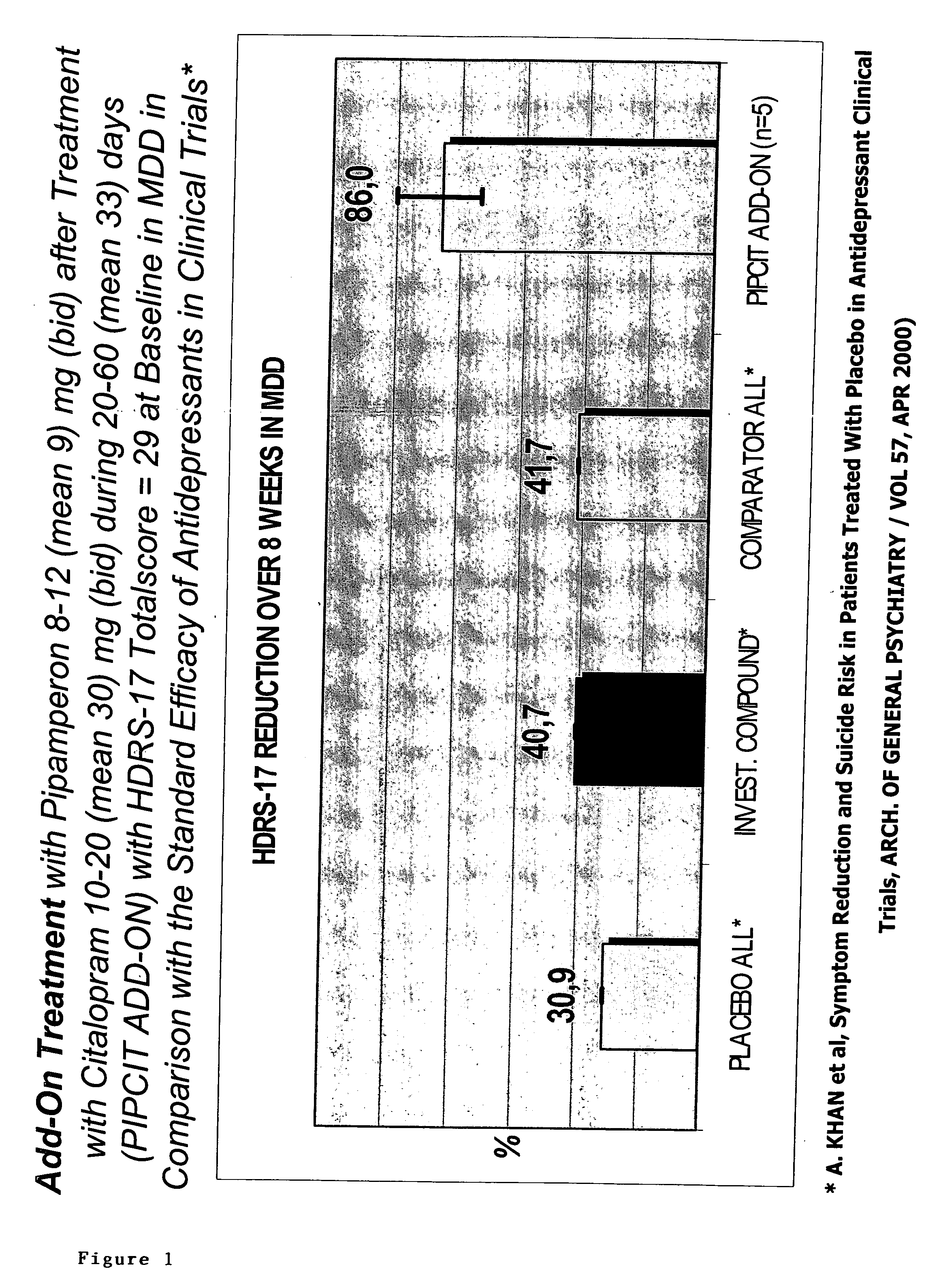
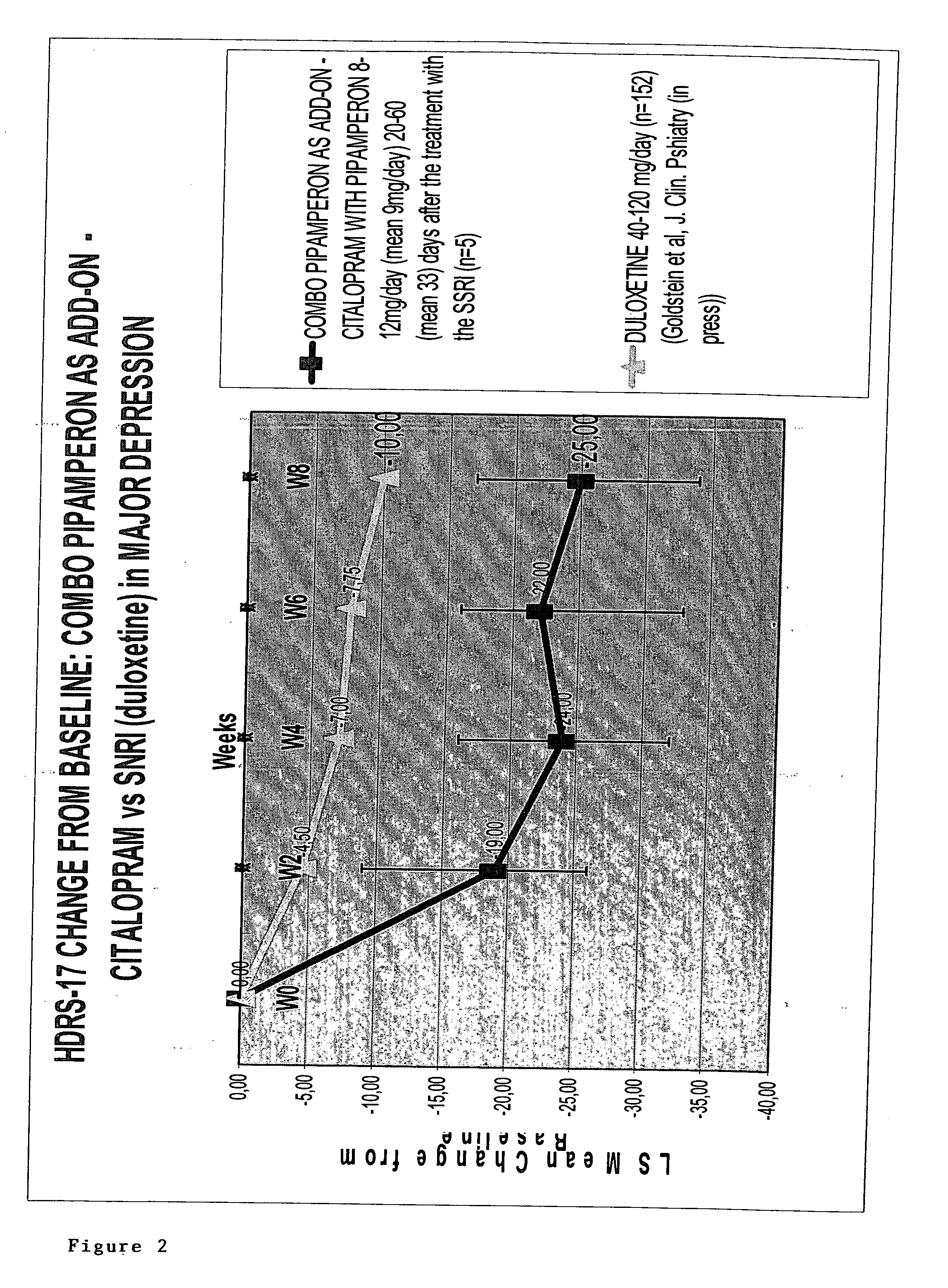
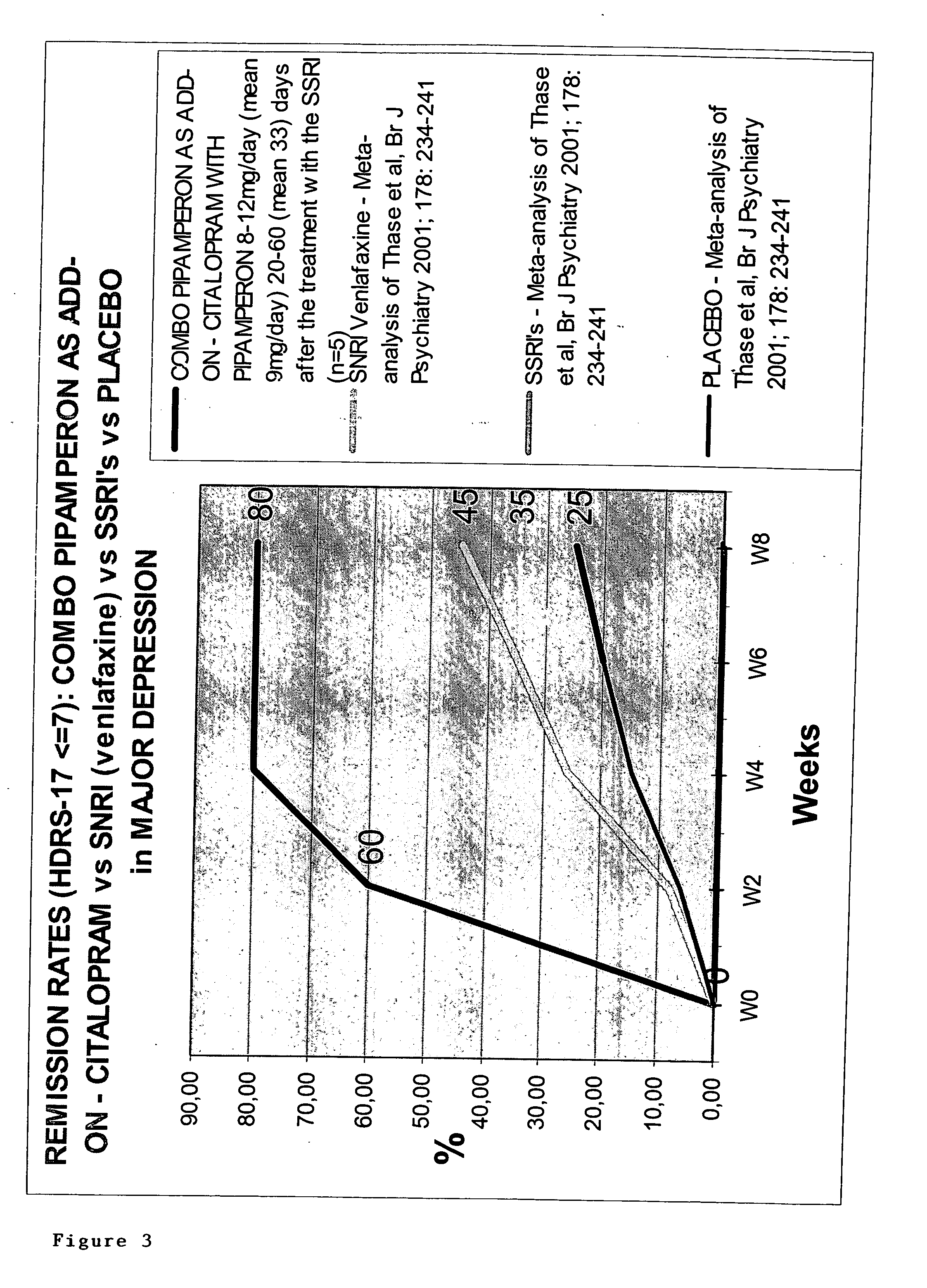
Use of D4 and 5-HT2A antagonists, inverse agonists or partial agonists
InactiveUS20050203130A1Augment effectEffect be very fastBiocideAnimal repellantsCompound (substance)Partial agonist
The present invention relates to the use of compounds and compositions of compounds having D4 and 5-HT2A antagonistic, partial agonistic or inverse agonistic activity for the treatment of the underlying dysregulation of the emotional functionality of mental disorders (i.e. affect instability-hypersensitivity-hyperaesthesia-dissociative phenomena-etc). The invention also relates to methods comprising administering to a patient diagnosed as having a neuropsychiatric disorder a pharmaceutical composition containing (i) compounds having D4 antagonistic, partial agonistic or inverse agonistic activity and (ii) compounds having 5-HT2A antagonistic, partial agonistic or inverse agonistic, and (iii) any known medicinal compound and compositions of said compounds. The combined D4 and 5-HT2A antagonistic, partial agonistic or inverse agonistic effects may reside within the same chemical or biological compound or in two different chemical and / or biological compounds.
Owner:PHARMANEUROBOOST
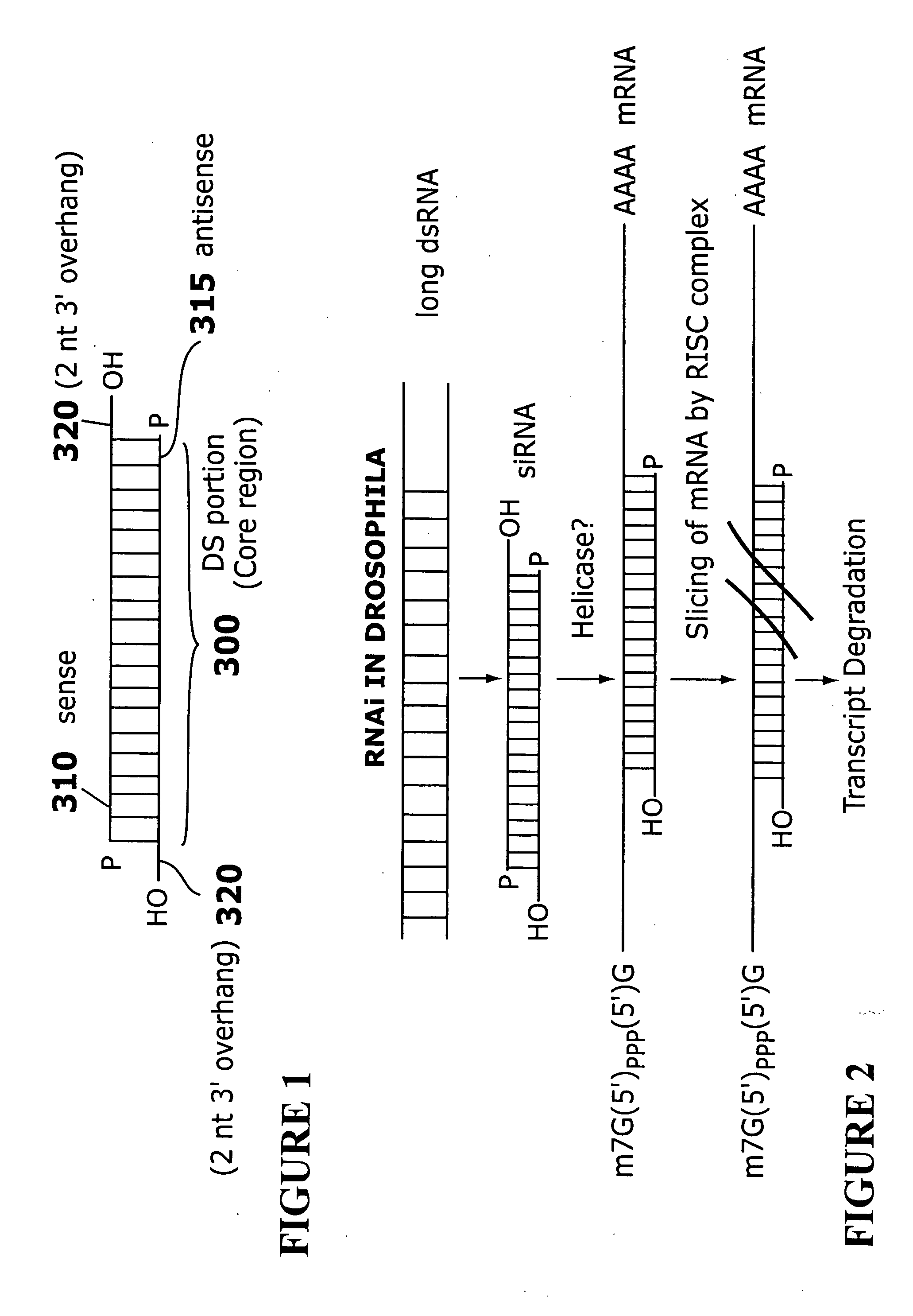
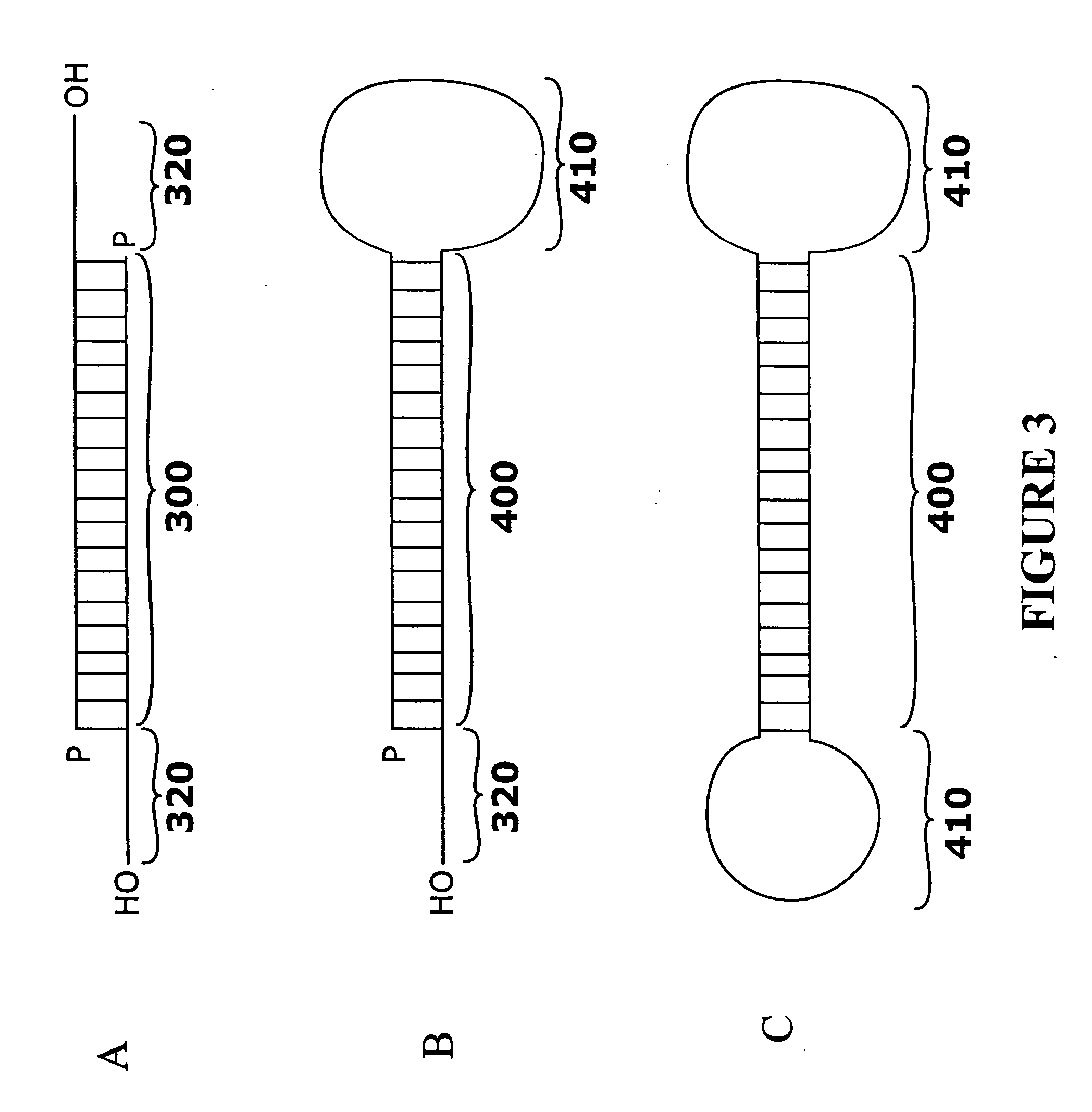
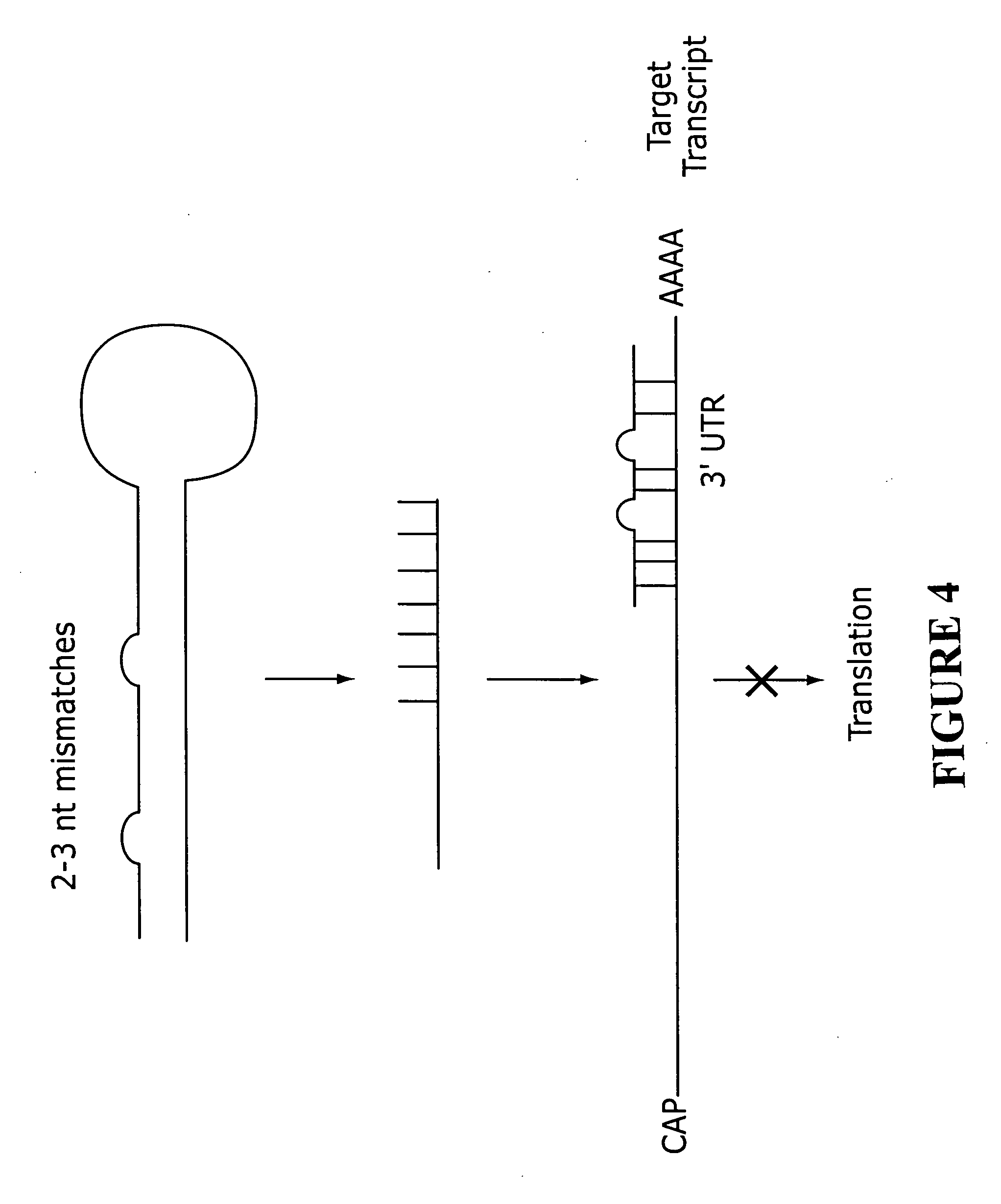
RNAi-based therapeutics for allergic rhinitis and asthma
InactiveUS20060058255A1Suppress gene expressionGood curative effectAntibacterial agentsSpecial deliveryTLR8Disease
The present invention provides compositions comprising one or more RNAi agents (e.g., siRNAs, shRNAs, or RNAi vectors) for the treatment of conditions and diseases mediated by (e.g., featuring IgE-mediated hypersensitivity), as well as systems for identifying RNAi agents effective for this purpose. The compositions are suitable for the treatment of allergic rhinitis and / or asthma. In certain embodiments of the invention the RNAi agent is targeted to a transcript that encodes a protein selected from the group consisisting of the FCεRIα chain, the FCεRIβ chain, c-Kit, Lyn, Syk, ICOS, OX40L, CD40, CD80, CD86, Re1A, Re1B, 4-1BB ligand, TLR1, TLR2, TLR3, TLR4, TLR5, TLR6, TLR7, TLR8, TLR9, CD83, SLAM, common γ chain, and COX-2. In addition, the invention provides RNAi agent / delivery agent compositions and methods of use. In certain embodiments of the invention compositions comprising an RNAi agent are delivered by the respiratory route.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
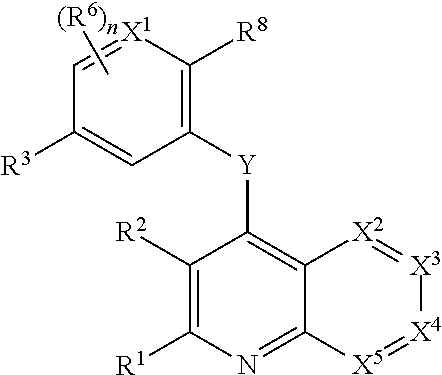
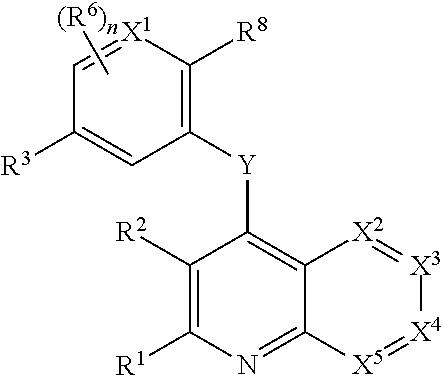
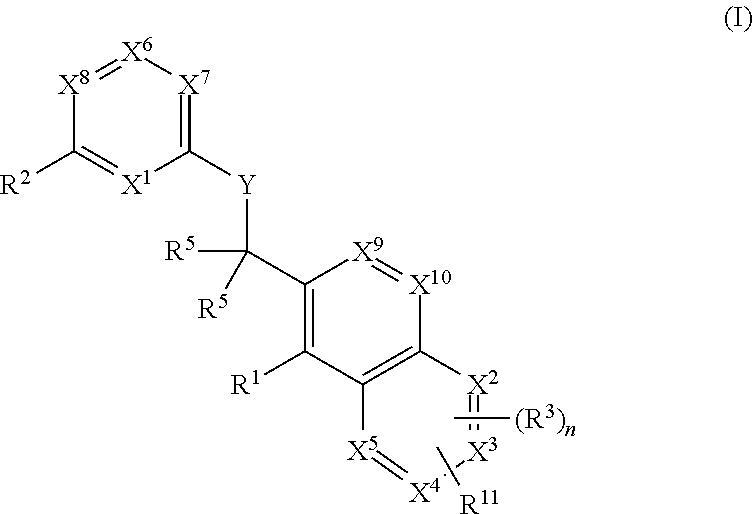
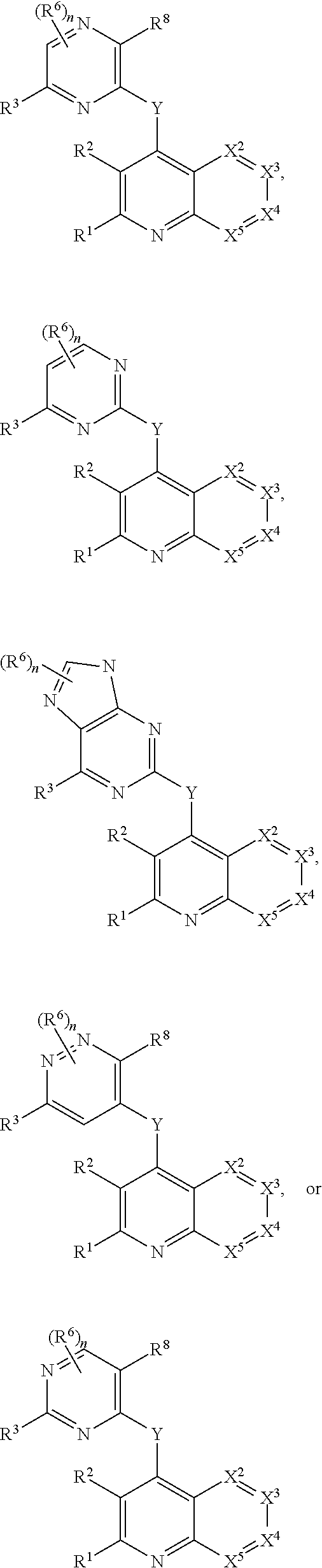
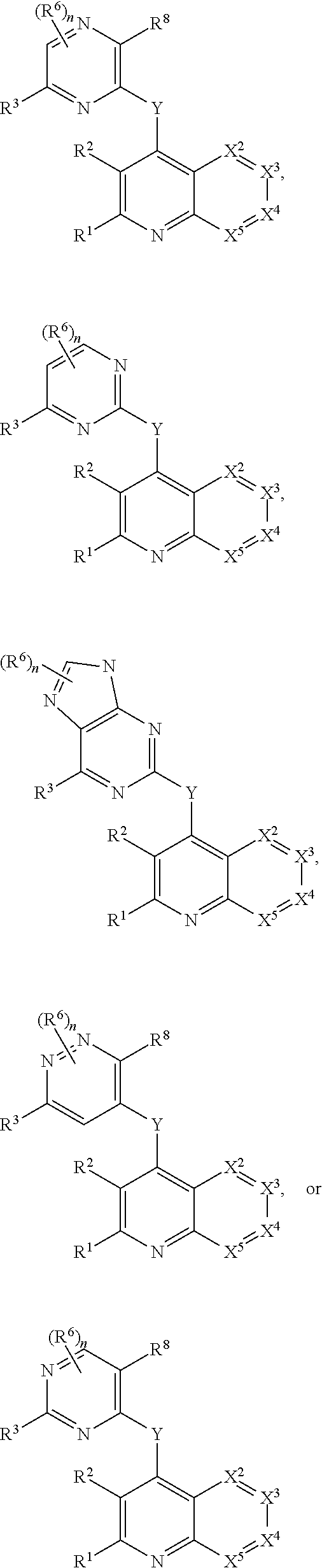
Heterocyclic compounds and their uses
Substituted bicyclic heteroaryls and compositions containing them, for the treatment of general inflammation, arthritis, rheumatic diseases, osteoarthritis, inflammatory bowel disorders, inflammatory eye disorders, inflammatory or unstable bladder disorders, psoriasis, skin complaints with inflammatory components, chronic inflammatory conditions, including but not restricted to autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosis (SLE), myestenia gravis, rheumatoid arthritis, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, multiples sclerosis, Sjogren's syndrome and autoimmune hemolytic anemia, allergic conditions including all forms of hypersensitivity, The present invention also enables methods for treating cancers that are mediated, dependent on or associated with p110δ activity, including but not restricted to leukemias, such as Acute Myeloid leukaemia (AML) Myelo-dysplastic syndrome (MDS) myelo-proliferative diseases (MPD) Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic leukaemia (T-ALL) B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic leukaemia (B-ALL) Non Hodgkins Lymphoma (NHL) B-cell lymphoma and solid tumors, such as breast cancer.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Reduced side-effect hemoglobin compositions
The invention relates to novel hemoglobin compositions, particularly novel recombinant mutant hemoglobin compositions, which eliminate or substantially reduce 1) the creation of heart lesions, 2) gastrointestinal discomfort, 3) pressor effects, and 4) endotoxin hypersensitivity associated with the administration of extracellular hemoglobin compositions in various therapeutic applications. Applications described include treatments for anemia, head injury, hemorrhage or hypovolemia, ischemia, cachexia, sickle cell crisis and stroke; enhancing cancer treatments; stimulating hematopoiesis; improving repair of physically damaged tissues; alleviating cardiogenic shock; and shock resuscitation.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
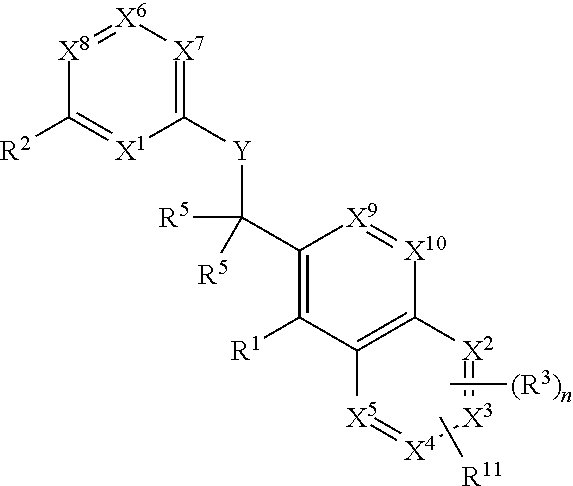
Heterocyclic compounds and their uses
Substituted bicyclic heteroaryls and compositions containing them, for the treatment of general inflammation, arthritis, rheumatic diseases, osteoarthritis, inflammatory bowel disorders, inflammatory eye disorders, inflammatory or unstable bladder disorders, psoriasis, skin complaints with inflammatory components, chronic inflammatory conditions, including but not restricted to autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosis (SLE), myestenia gravis, rheumatoid arthritis, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, multiples sclerosis, Sjoegren's syndrome and autoimmune hemolytic anemia, allergic conditions including all forms of hypersensitivity. The present invention also enables methods for treating cancers that are mediated, dependent on or associated with pi 105 activity, including but not restricted to leukemias, such as Acute Myeloid leukaemia (AML) Myelo-dysplastic syndrome (MDS) myelo-proliferative diseases (MPD) Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic leukaemia (T-ALL) B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic leukaemia (B-ALL) Non Hodgkins Lymphoma (NHL) B-cell lymphoma and solid tumors, such as breast cancer.
Owner:AMGEN INC
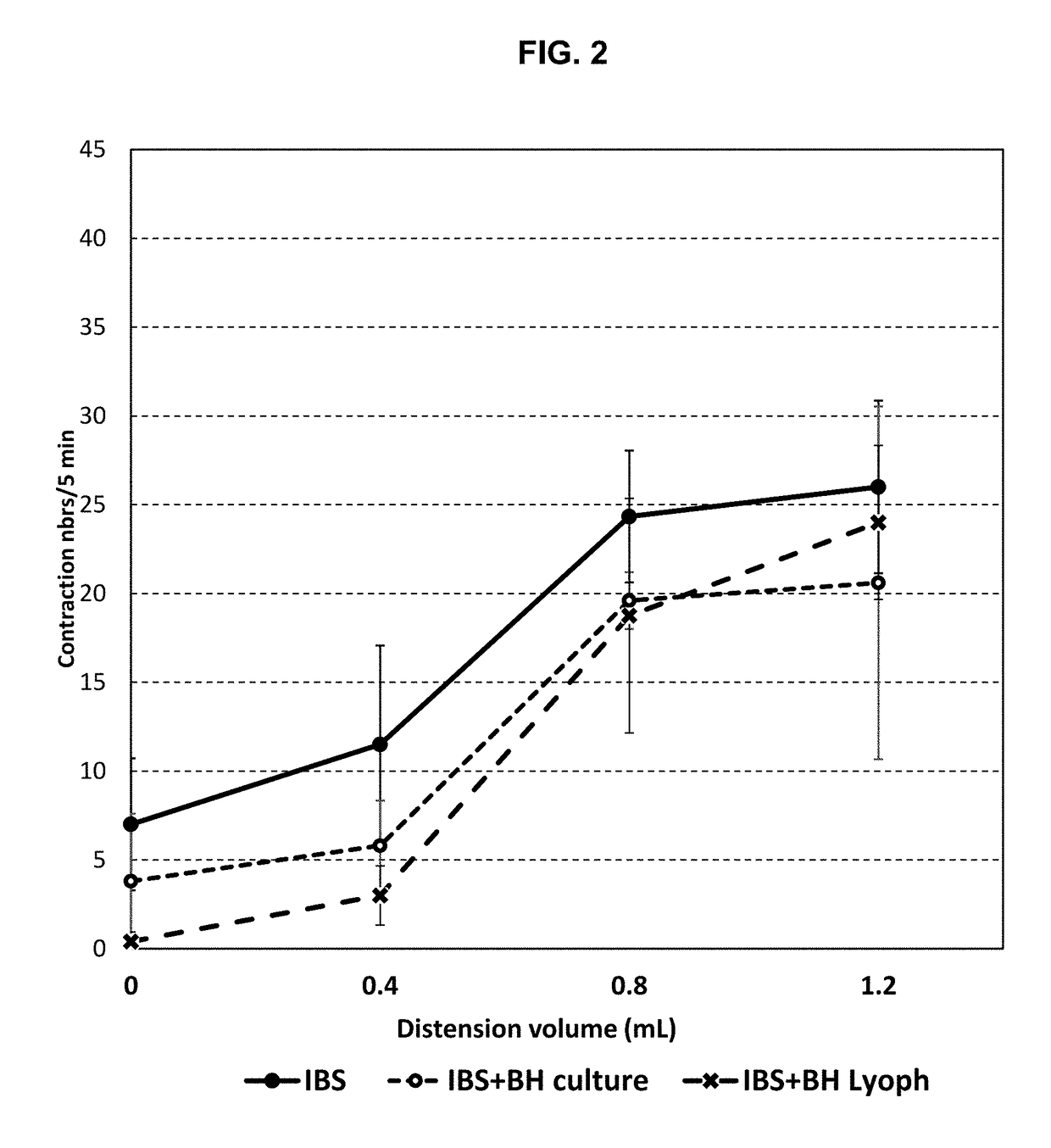
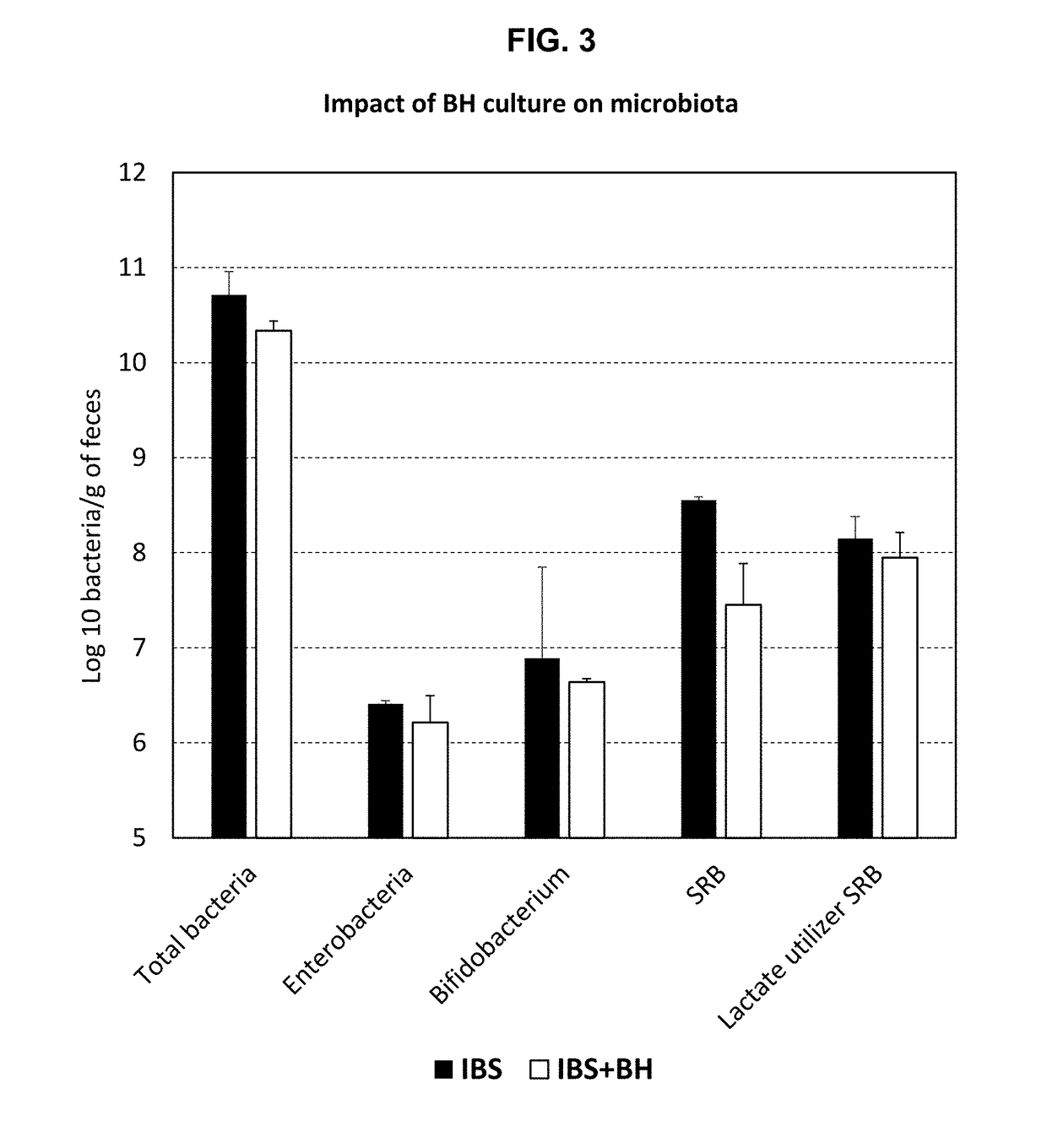
Compositions comprising bacterial strains
Owner:ARMISTICE CAPITAL MASTER FUND LTD +1
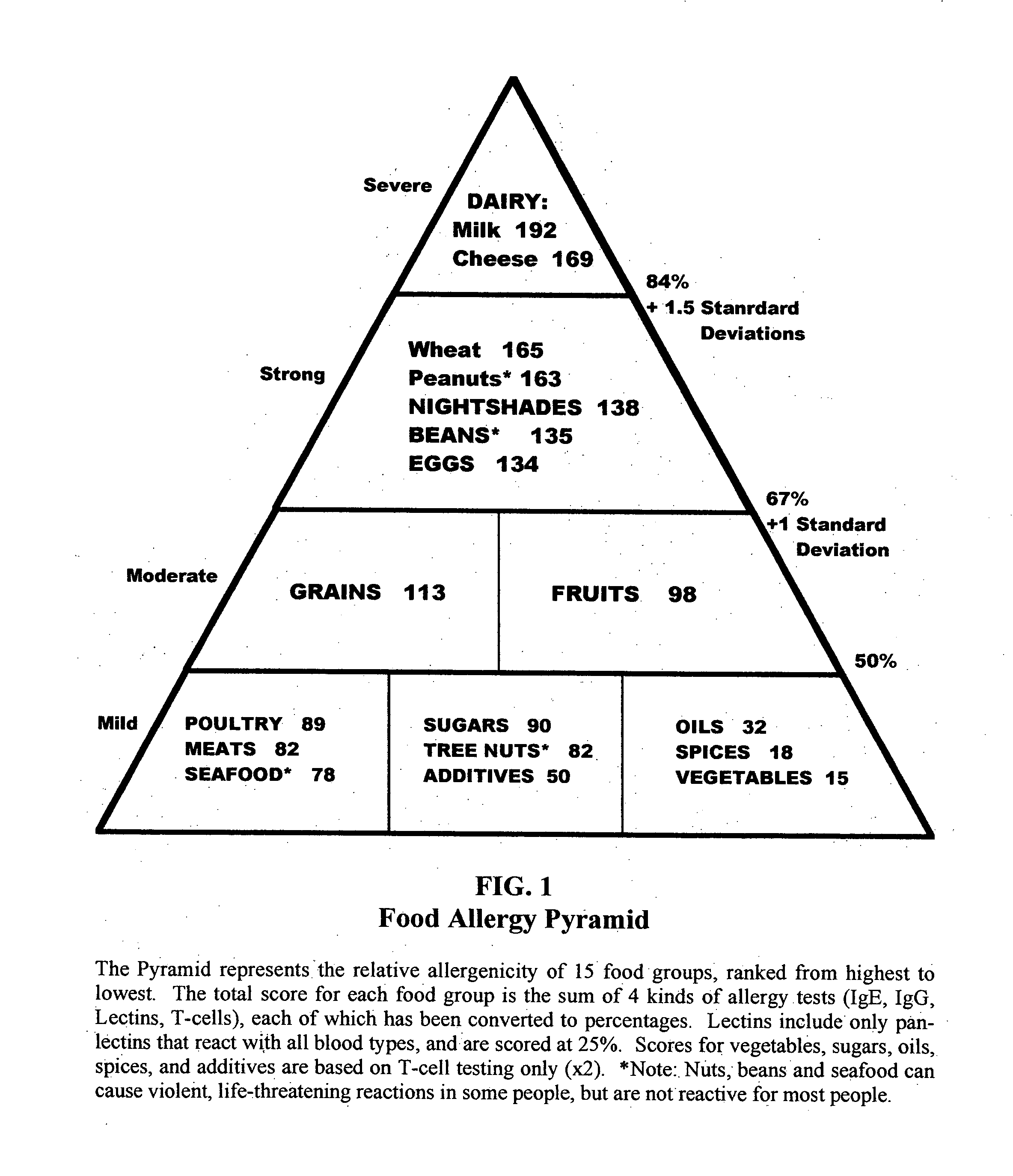
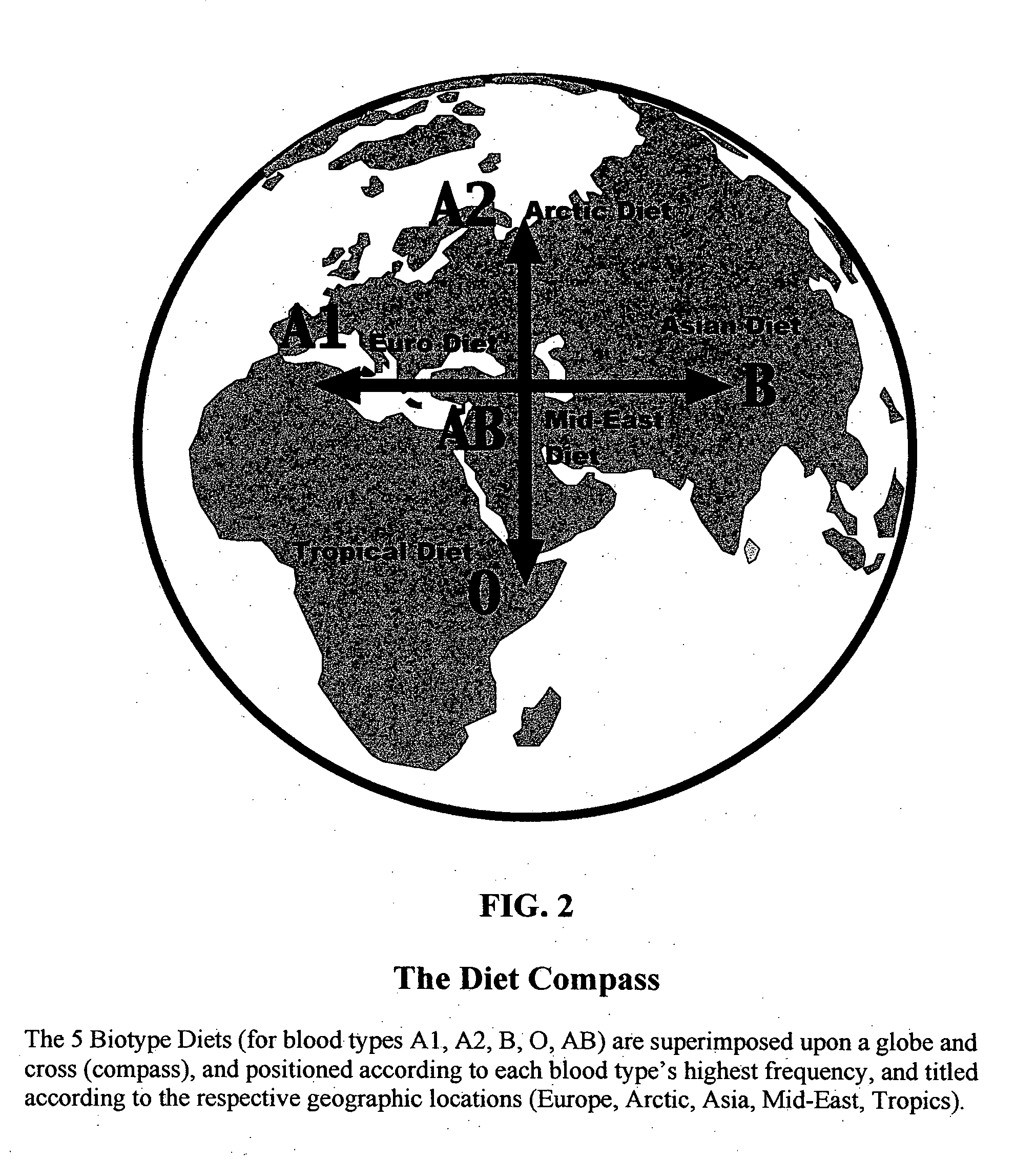
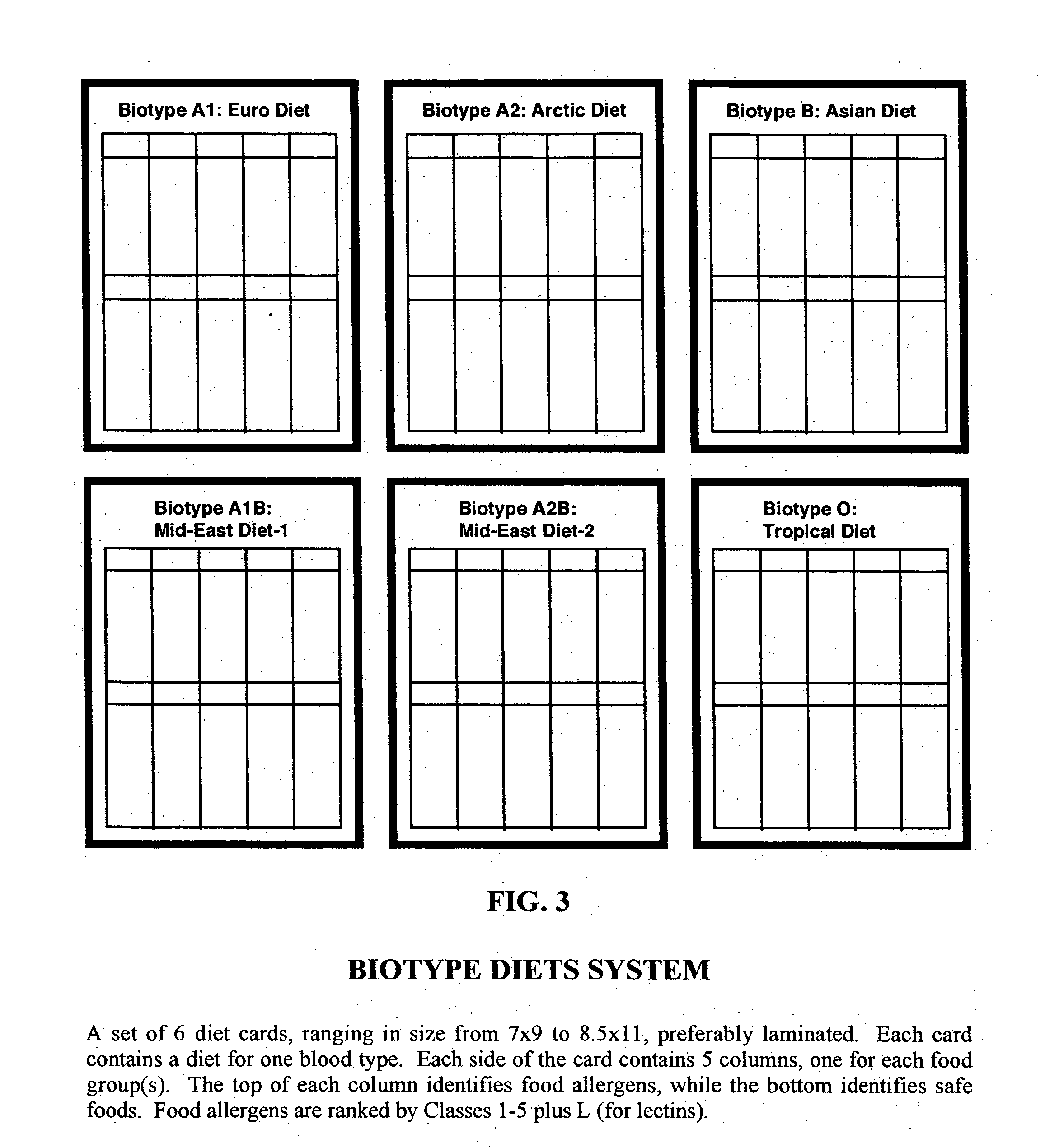
Biotype diets system: predicting food allergies by blood type
InactiveUS20060013773A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsGroup A - bloodAntigen
The invention is a diet-typing system for humans, including novel methods for diagnosis and treatment of food allergies and hypersensitivities. The diagnostic method correlates blood types (immunologically reactive antigens on RBC, skin and membranes) to four kinds of food allergies / hypersensitivities (IgE antibodies, IgG antibodies, T-cells, and Lectins). The results are used to identify and predict food allergies and hypersensitivities for six biological types (blood types A1, A2, B, O, A1B, and A2B), plus diet modifications for three subtypes (blood type Rh-negative, males and females). The treatment method uses the results to make food recommendations (to eat, limit, or avoid), based on the strength or classification of allergy scores, to mitigate the risk of food allergies and hypersensitivities in future persons. The diet-typing system presents the results on six diet cards, one for each blood type. The methods and resulting diets are unique, and differ substantially from prior inventions.
Owner:POWER LAURA W
Compositions comprising bacterial strains
Owner:CJ BIOSCIENCE INC +1
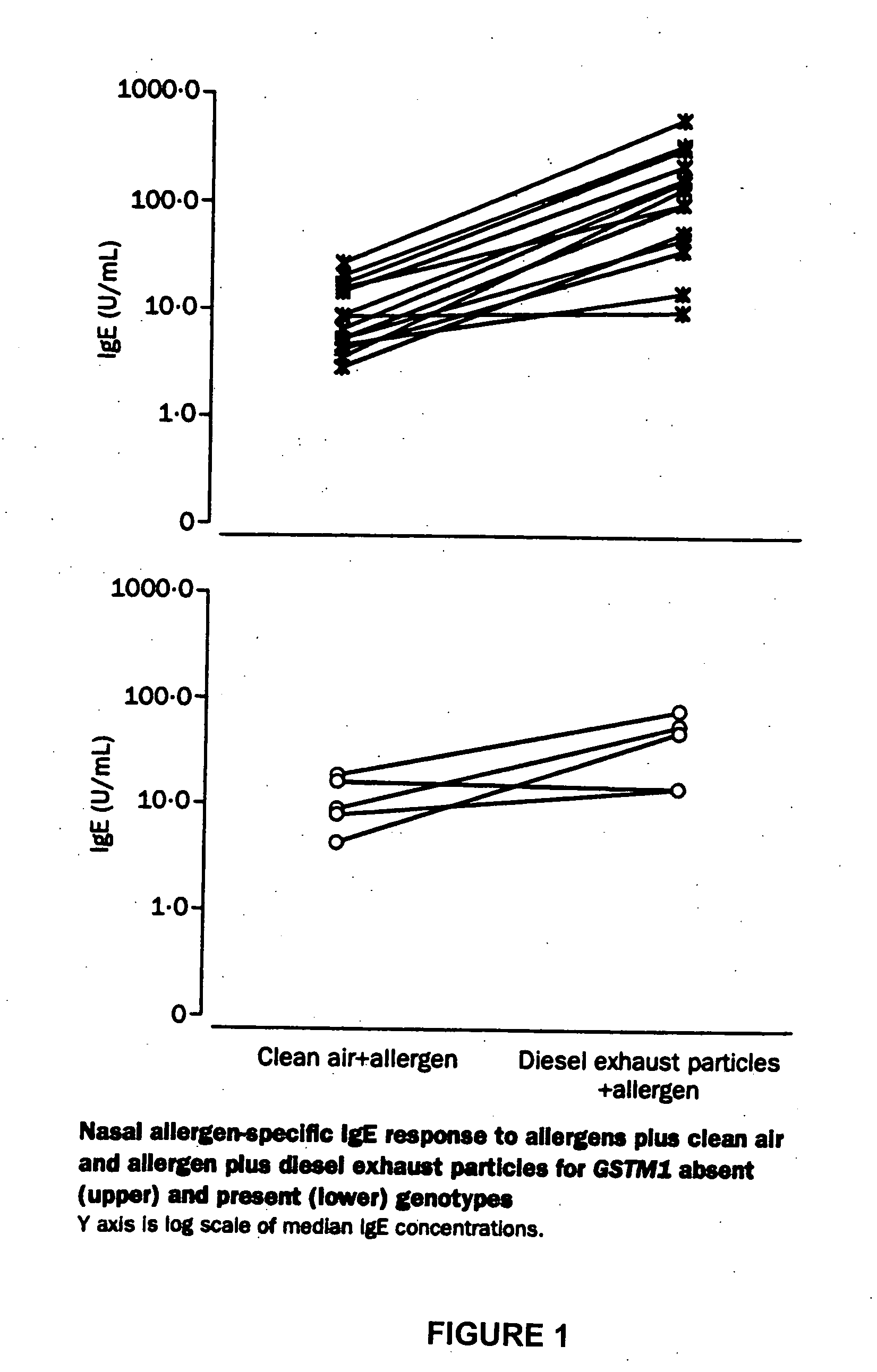
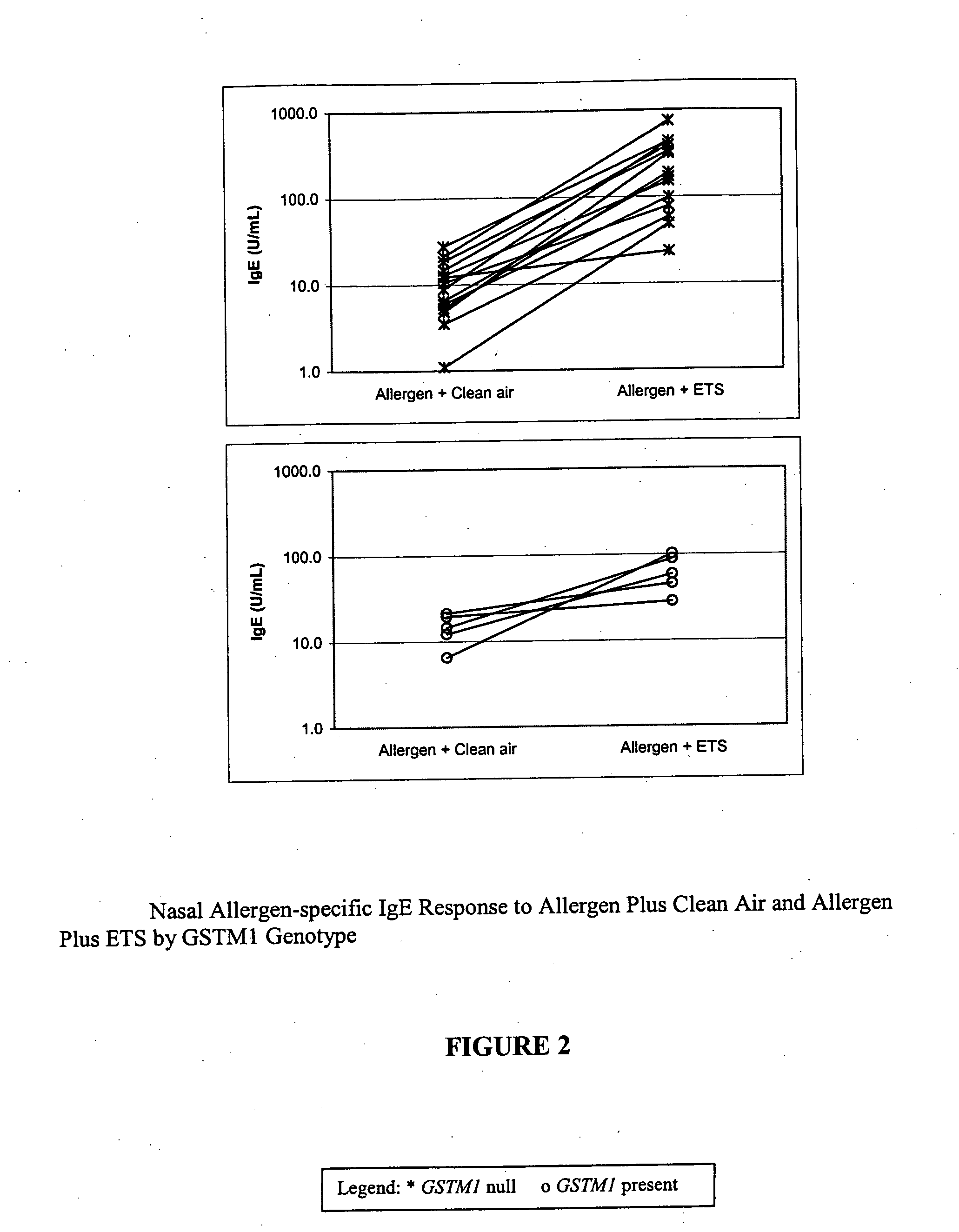
Method for determining susceptibility of an individual to allergen induced hypersensitivity
The present invention is related generally to a method for screening subjects to determine those subjects more likely to exhibit a hypersensitivity to allergen in the presence of airborne pollutants, such subject having a GSTM1 null genotype and / or a GSTP1 Ile / Ile genotype. This invention also provides novel or improved pharmaceutical compositions and therapeutic strategies for the treatment of immune diseases resulting from inappropriate or unwanted immune response such as allergic reactions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +2
Methods and compositions for treating inflammatory disorders
ActiveUS20150196590A1Prevents “ flare-up ”Inhibits and reduces symptomBiocidePowder deliveryMedicinePolymicrobial Infections
The present invention provides methods for treating conditions that involve infection and / or inflammation, including acute and chronic inflammation, as well as delayed-type and immediate-type hypersensitivity. The invention in various embodiments provides methods for treating microbial infection and the associated inflammatory response, as well methods for treating inflammatory conditions that spawn or are susceptible to secondary microbial infection. Further, the invention provides methods for treating inflammation, such as chronic inflammation, without any associated microbial infection
Owner:URGO US INC
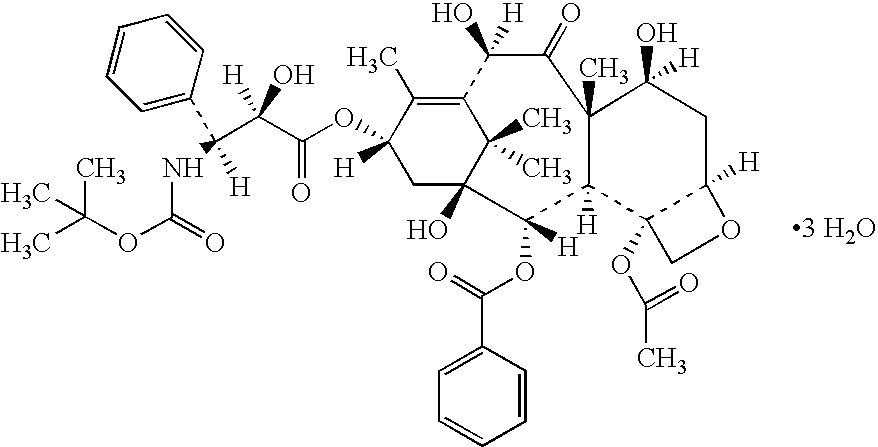
Solubilized formulation of docetaxel without tween 80
InactiveUS20080319048A1Avoid side effectsAvoid hypersensitivityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDocetaxel-PNPDocetaxel
Lyophilizates containing docetaxel and the use thereof in preparing concentrated liquid formulations, and ready to use formulations for injection, as well as such concentrates and ready to use formulations themselves are disclosed in which Tween surfactants are avoided so that hypersensitivity reactions to Tween surfactants can be avoided and docetaxel can be administered at higher doses and / or for longer periods of time and / or for additional treatment cycles.
Owner:SCIDOSE
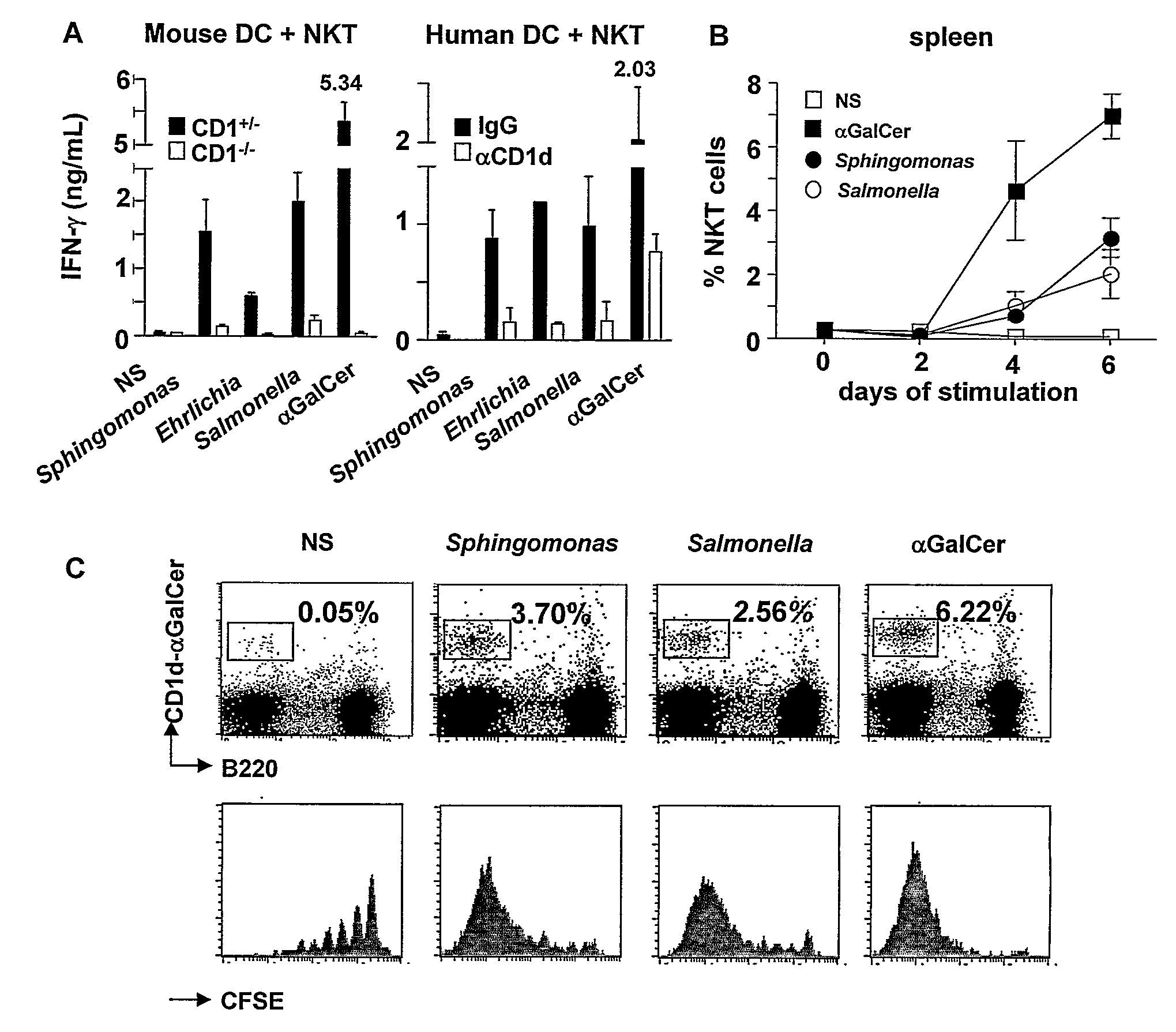
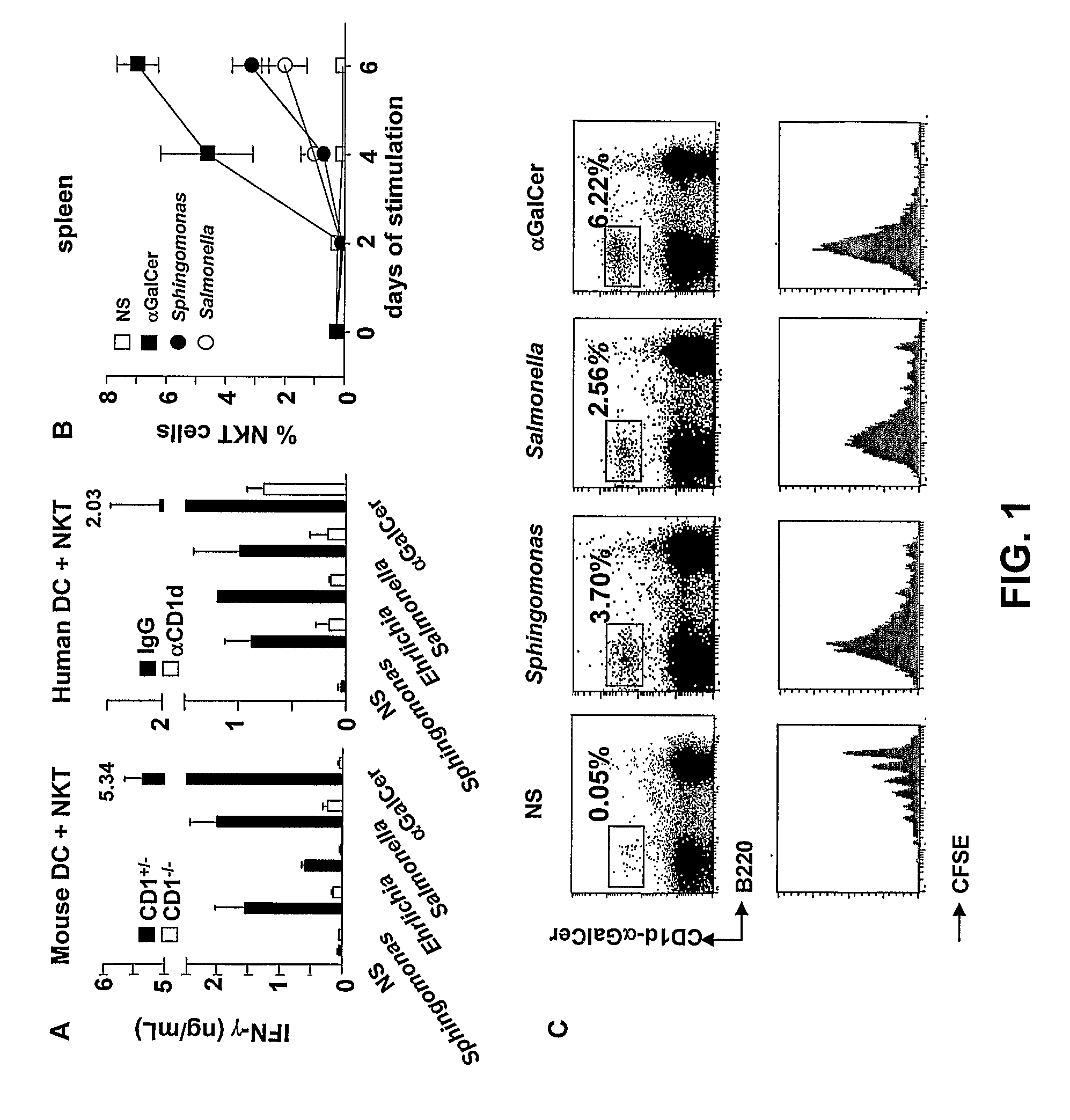
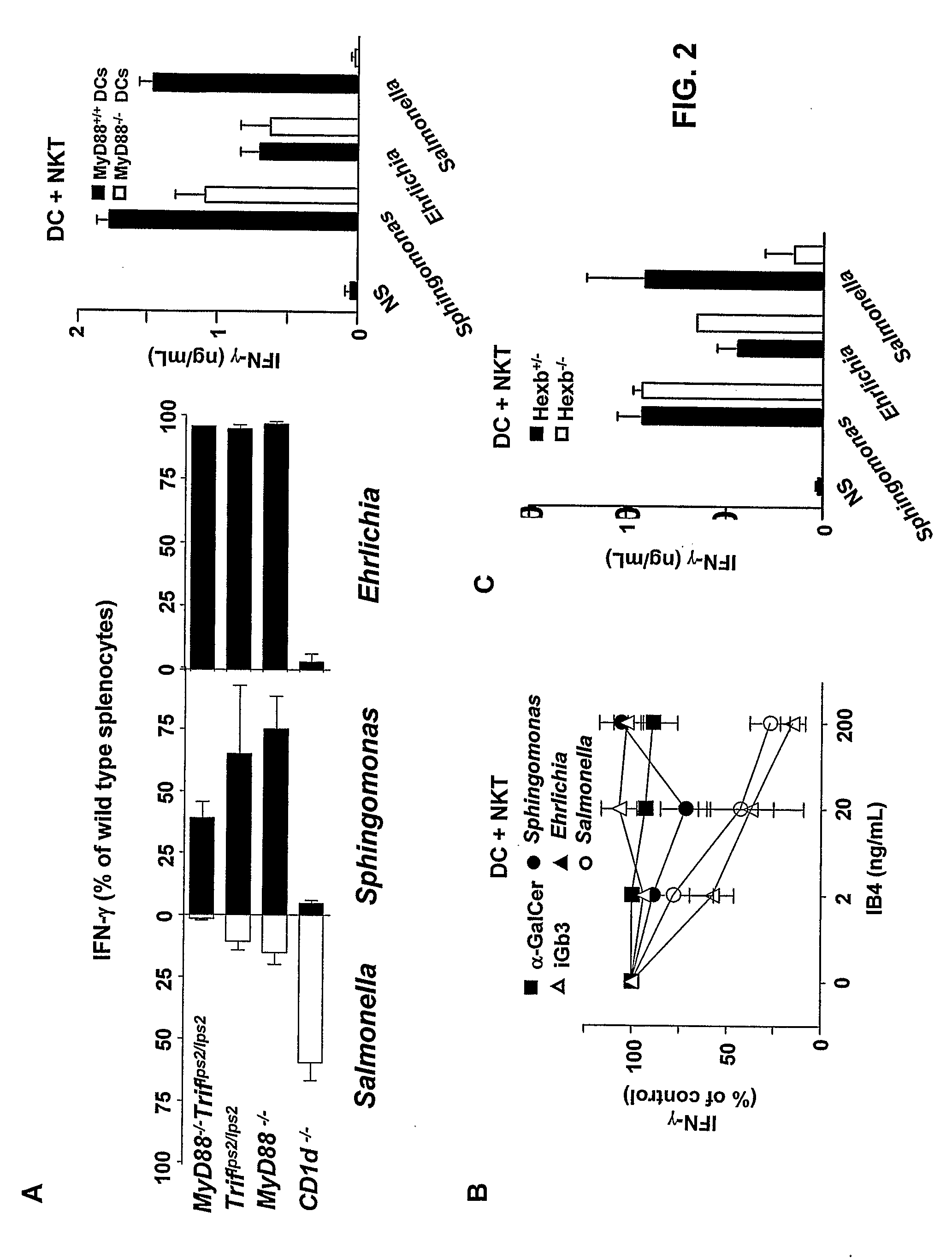
Bacterial Glycolipid Activation of Cd1d-Restricted Nkt Cells
InactiveUS20080279894A1Improving vaccine efficacyPromoting tumor rejectionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBacilliWilms' tumor
Disclosed are methods for activating an NKT cell, methods of stimulating an immune response in a subject, methods of improving vaccine efficacy, and methods of treating an infection. Also disclosed are methods of promoting tumor rejection, treating cancer, modulating autoimmunity and inhibiting allergen-induced hypersensitivity in subjects. The methods include contacting an NKT cell with a bacterial glycolipid complexed with a CD1 molecule to activate the NKT cell. The bacterial glycolipid may be derived from a member of the Class Alphaproteobacteria.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +2
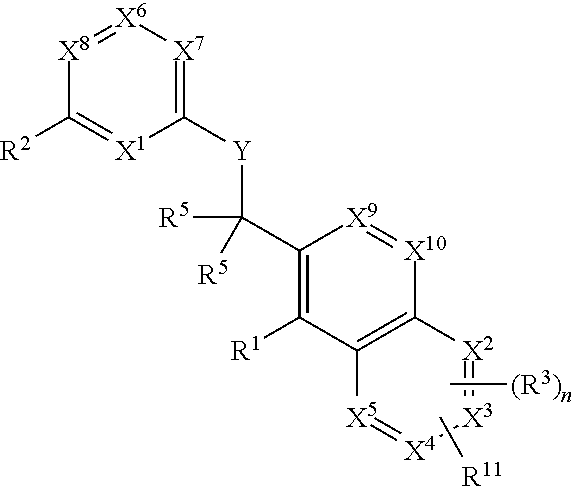
Heterocyclic compounds and their uses
InactiveUS20130079342A1Organic active ingredientsSenses disorderB-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemiaAutoimmune disease
Substituted bicyclic heteroaryls of the following formulae and compositions containing them, for the treatment of general inflammation, arthritis, rheumatic diseases, osteoarthritis, inflammatory bowel disorders, inflammatory eye disorders, inflammatory or unstable bladder disorders, psoriasis, skin complaints with inflammatory components, chronic inflammatory conditions, including but not restricted to autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosis (SLE), myestenia gravis, rheumatoid arthritis, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, multiples sclerosis, Sjoegren's syndrome and autoimmune hemolytic anemia, allergic conditions including all forms of hypersensitivity, The present invention also enables methods for treating cancers that are mediated, dependent on or associated with p110 activity, including but not restricted to leukemias, such as Acute Myeloid leukaemia (AML) Myelo-dysplastic syndrome (MDS) myelo-proliferative diseases (MPD) Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic leukaemia (T-ALL) B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic leukaemia ALL) Non Hodgkins Lymphoma (NHL) B-cell lymphoma and solid tumors, such as breast cancer.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Chitosan oligosaccharides and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070167400A1Reduce inflammationMinimization reductionBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsDietary supplementMedicine
The present invention is directed towards compositions and methods for reducing or controlling inflammation and for treating inflammatory disease processes and other pathological conditions. The present invention relates to mixtures comprising at least one oligosaccharide of chitosan or a component thereof as novel pharmaceuticals, dietary supplements or cosmetic compositions containing such mixtures, and to the use of such mixtures for preparing a medicament or a dietary supplement for the suppression of hypersensitivity reaction and / or inflammation in human and animals.
Owner:DNP CANADA
Heterocyclic compounds and their uses
Substituted bicyclic heteroaryls and compositions containing them, for the treatment of general inflammation, arthritis, rheumatic diseases, osteoarthritis, inflammatory bowel disorders, inflammatory eye disorders, inflammatory or unstable bladder disorders, psoriasis, skin complaints with inflammatory components, chronic inflammatory conditions, including but not restricted to autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosis (SLE), myestenia gravis, rheumatoid arthritis, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, multiples sclerosis, Sjoegren's syndrome and autoimmune hemolytic anemia, allergic conditions including all forms of hypersensitivity, The present invention also enables methods for treating cancers that are mediated, dependent on or associated with p110δ activity, including but not restricted to leukemias, such as Acute Myeloid leukaemia (AML) Myelo-dysplastic syndrome (MDS) myelo-proliferative diseases (MPD) Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic leukaemia (T-ALL) B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic leukaemia (B-ALL) Non Hodgkins Lymphoma (NHL) B-cell lymphoma and solid tumors, such as breast cancer.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Use of D4 and 5-HT2A antagonists, inverse agonists or partial agonists
InactiveUS8304431B2Good treatment effectRapid onsetBiocideNervous disorderPharmaceutical drugMedicinal chemistry
The present invention relates to the use of compounds and compositions of compounds having D4 and 5-HT2A antagonistic, partial agonistic or inverse agonistic activity for the treatment of the underlying dysregulation of the emotional functionality of mental disorders (i.e. affect instability-hypersensitivity-hyperaesthesia-dissociative phenomena-etc). The invention also relates to methods comprising administering to a patient diagnosed as having a neuropsychiatric disorder a pharmaceutical composition containing (i) compounds having D4 antagonistic, partial agonistic or inverse agonistic activity and (ii) compounds having 5-HT2A antagonistic, partial agonistic or inverse agonistic, and (iii) any known medicinal compound and compositions of said compounds. The combined D4 and 5-HT2A antagonistic, partial agonistic or inverse agonistic effects may reside within the same chemical or biological compound or in two different chemical and / or biological compounds.
Owner:PHARMANEUROBOOST
Elicitor peptides having disrupted hypersensitive response box and use thereof
ActiveUS20160095315A1Extend your lifeImparting resistanceBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDNA constructHypersensitive response
Disclosed are peptides that induce an active plant response, but not a hypersensitive response, when applied to plant tissue. These peptides also preferably exhibit improved solubility, stability, resistance to chemical degradation, or a combination of these properties. Use of these peptides or fusion polypeptides, or DNA constructs encoding the same, for modulating plant biochemical signaling, imparting disease resistance to plants, enhancing plant growth, imparting tolerance to biotic stress, imparting tolerance and resistance to abiotic stress, imparting desiccation resistance to cuttings removed from ornamental plants, imparting post-harvest disease or post-harvest desiccation resistance to a fruit or vegetable, or enhancing the longevity of fruit or vegetable ripeness are also disclosed.
Owner:PLANT HEALTH CARE INC
Externally applied formulation of cetirizine hydrochloride
InactiveCN1634063APharmacologically activeIncreased free drug concentrationOrganic active ingredientsAerosol deliverySkin sensitizationWhole body
Pharmacological test shows that the externally-used preparation of Cetirizine has ideal allergy resistant and anti-inflammatory action to the rat passive cutaneous anaphylaxis (Rat PCA) model and dimethylbenzene caused mouse otitis model, and also prevents the adverse effect to the central system caused by whole body administration. It is also found in the test, that the externally used preparation of Cetirizine also has very fine inhibitory action to dinitrofluorobenzene caused mouse porphyria hypersensitivity (PTH), the novel pharmacological action of the Cetirizine shows that the Cetirizine external preparation has good therapeutic action to skin inflammations which mainly include porphyria hypersensitivity.
Owner:LUNAN PHARMA GROUP CORPORATION
Anaphylatoxins for detecting clinical conditions
InactiveUS20090226374A1Compounds screening/testingMicrobiological testing/measurementVasculitisBasophilia
Non-allergic hypersensitivity reactions can be observed in a sample of cells from a subject in response to anaphylatoxins. Accordingly, methods are provided for detecting clinical conditions such as cellular hyper-reactivity, non-allergic hypersensitivity, asthma, inflammation, chronic or acute infection, bacterial infection, viral infection, parasite infection, adverse drug reaction, organ rejection, vasculitis, mastocytosis, eosinophilia, basophilia, leukemia, and / or C3a or C5a receptor defects in a subject. Also provided are kits for detecting such clinical conditions in a subject.
Owner:HEALTH AIRE
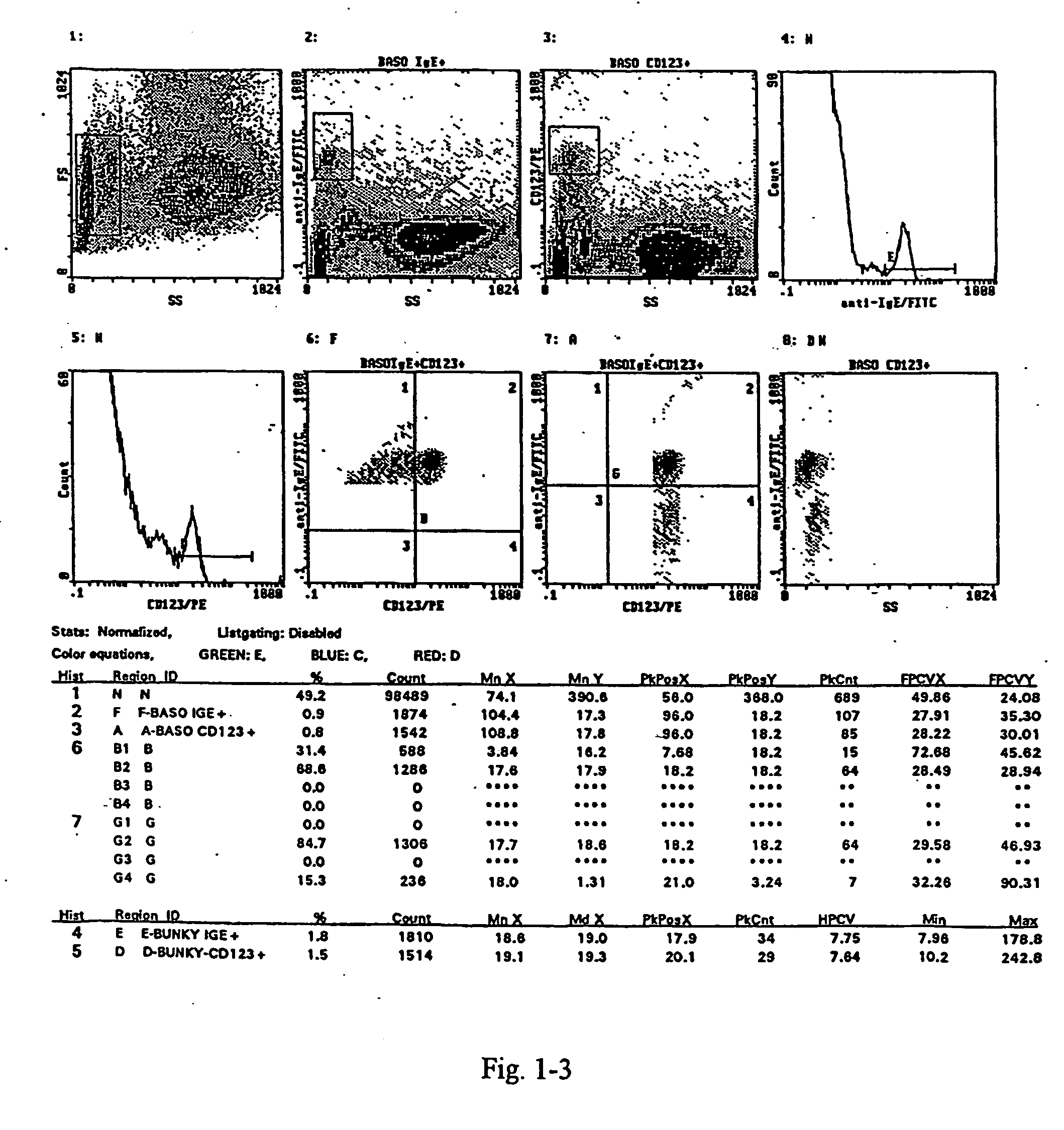
Method and kit for the measurement of the activation of basophils induced by allergen to determine hypersensitivity to some substances
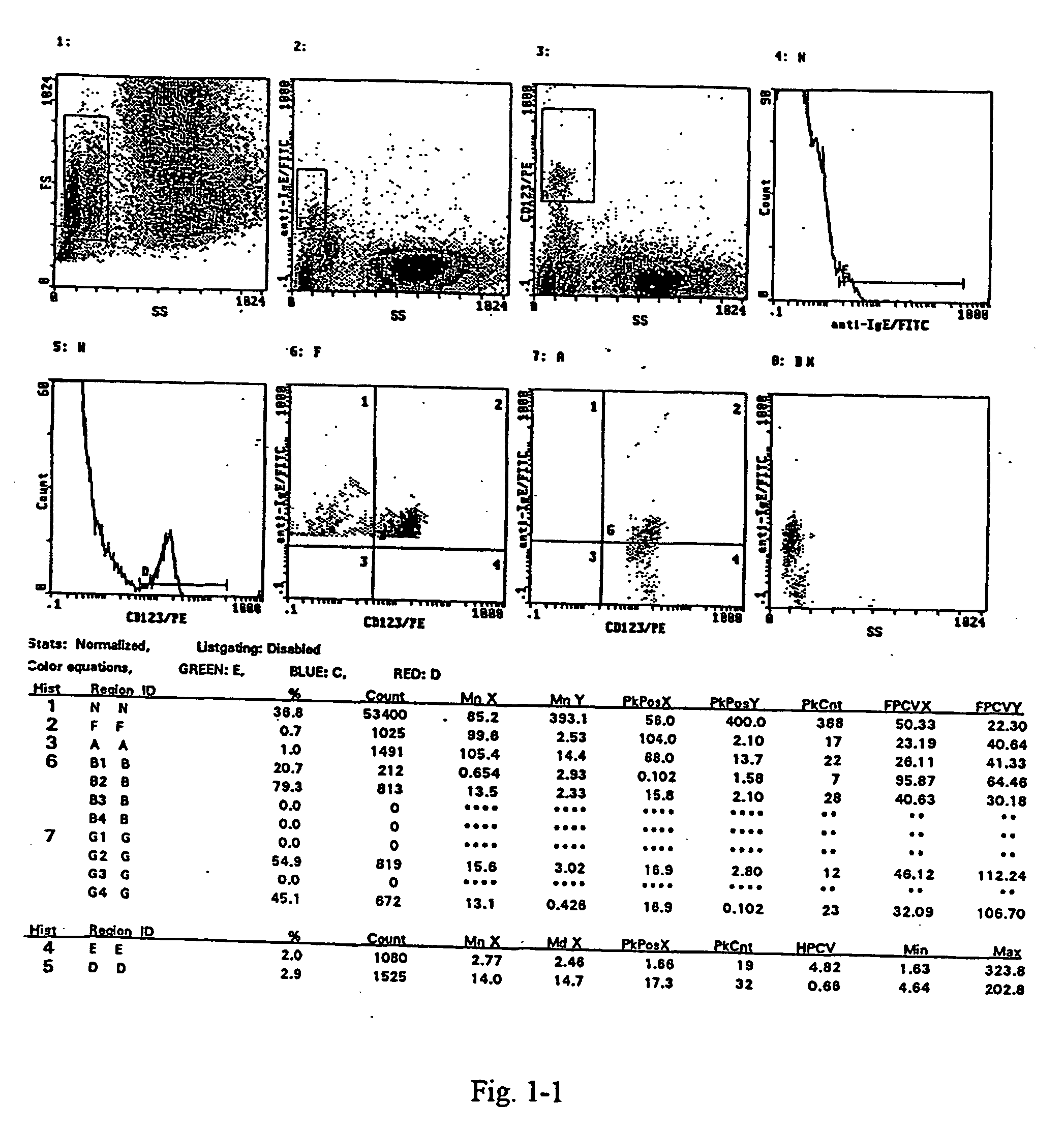
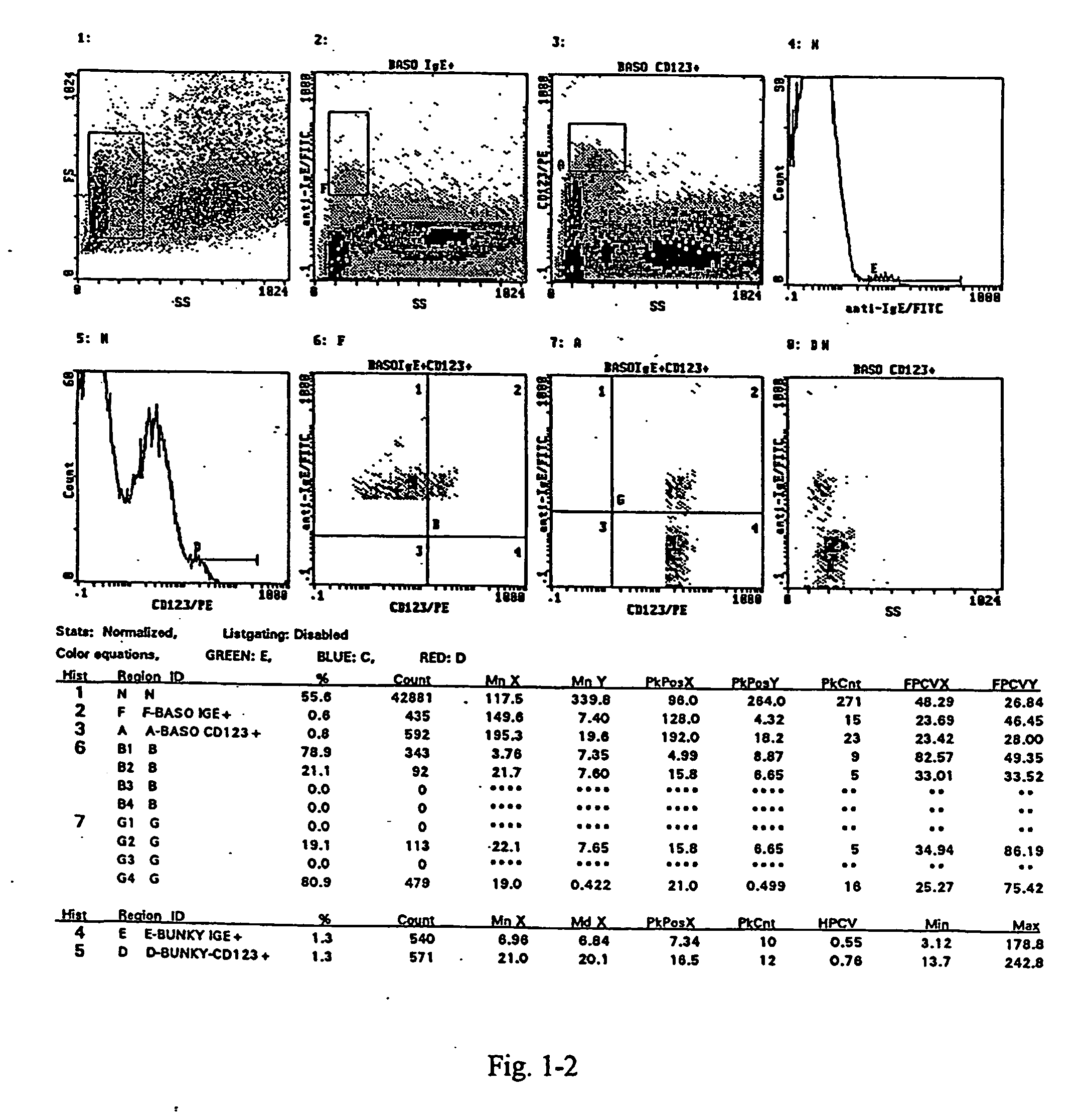
InactiveUS20040265925A1Lower IgE levelsOvercome disadvantagesBiological material analysisAllergen ingredientsStainingCD63
A method for the measurement of the activation of the basophils following stimulation with an allergen to determine hypersensitivity to some substances, in which a blood sample with an addition of interleukin-3 in a quantity of 0.05 to 50 ng / ml based on the volume of the sample, and of appropriately diluted allergen in a quantity of 0.5 to 100 units / ml is incubated at the temperature corresponding to the physiological environment for 15 to 45 minutes, whereafter a staining with anti-CD63.antibody in an amount of 3 to 30 .mu.l / 100 .mu.l of blood and with the antibody against a receptor of the basophil in an amount of 3 to 30 .mu.l / 100 .mu.l of blood are added at a temperature of 0 to +10.degree. C. and the sample, after vortexing, is then incubated in an ice bath for 15 to 30 minutes, and then is lysed and subjected to flow cytometry.
Owner:HAVRANOVA MARIE
Synergistic compositions containing aromatic compounds and terpenoids present in Alpinia galanga
InactiveUS7252845B2Suppress hypersensitivity reactionCosmetic preparationsBiocideImmunologic disordersUlcerative colitis
Novel compositions of matter containing aromatic compounds and terpenoids which are present in and may preferably be derived from the plant Alpinia galanga (Zingiberaceae) show synergistic effects with respect to immunomodulation, and they significantly suppress hypersensitivity reactions. Thus they are used for preparing medicaments for these purposes and, more specifically, for the treatment or prevention of IgE mediated allergic reactions and conditions, such as asthma, allergic rhinitis, atopic eczema or anaphylaxis, and autoimmune disorders, such as Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis or psoriasis, as well as for the alleviation of pain. They can for example be formulated into pharmaceuticals, cosmetics or dietary supplements. A method of preparing such compositions from Alpinia galanga is also described.
Owner:AS FERROSAN
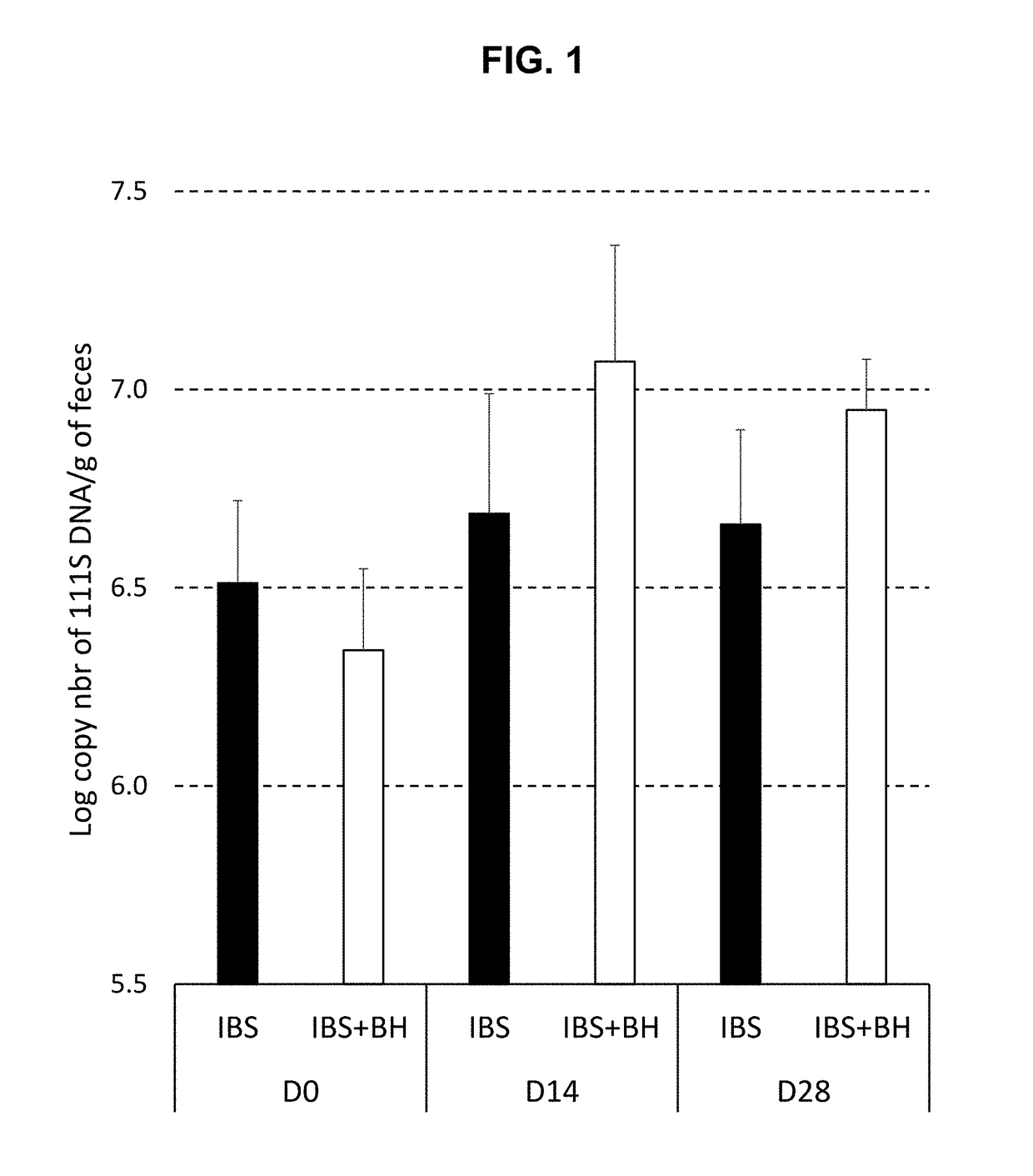
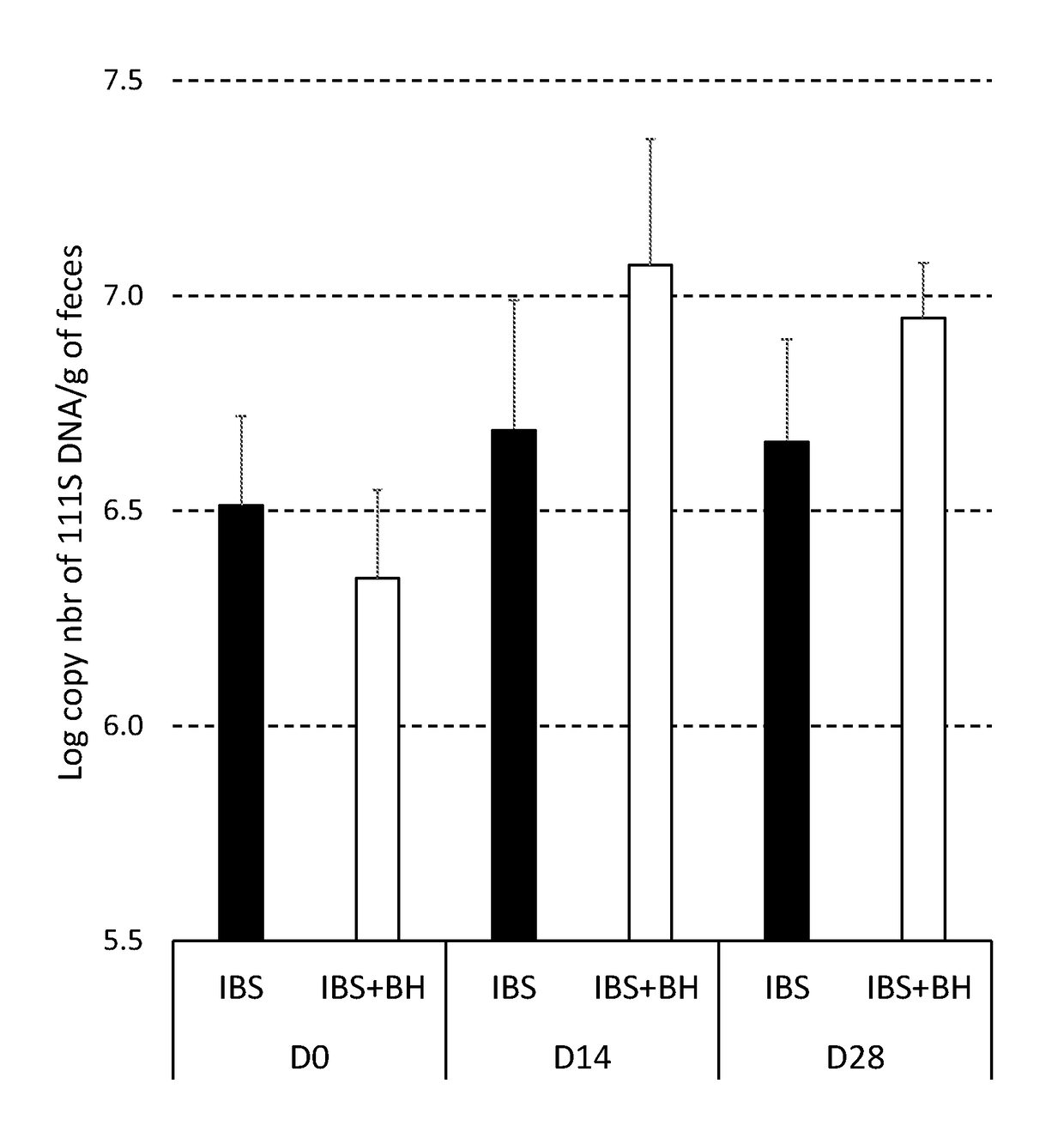
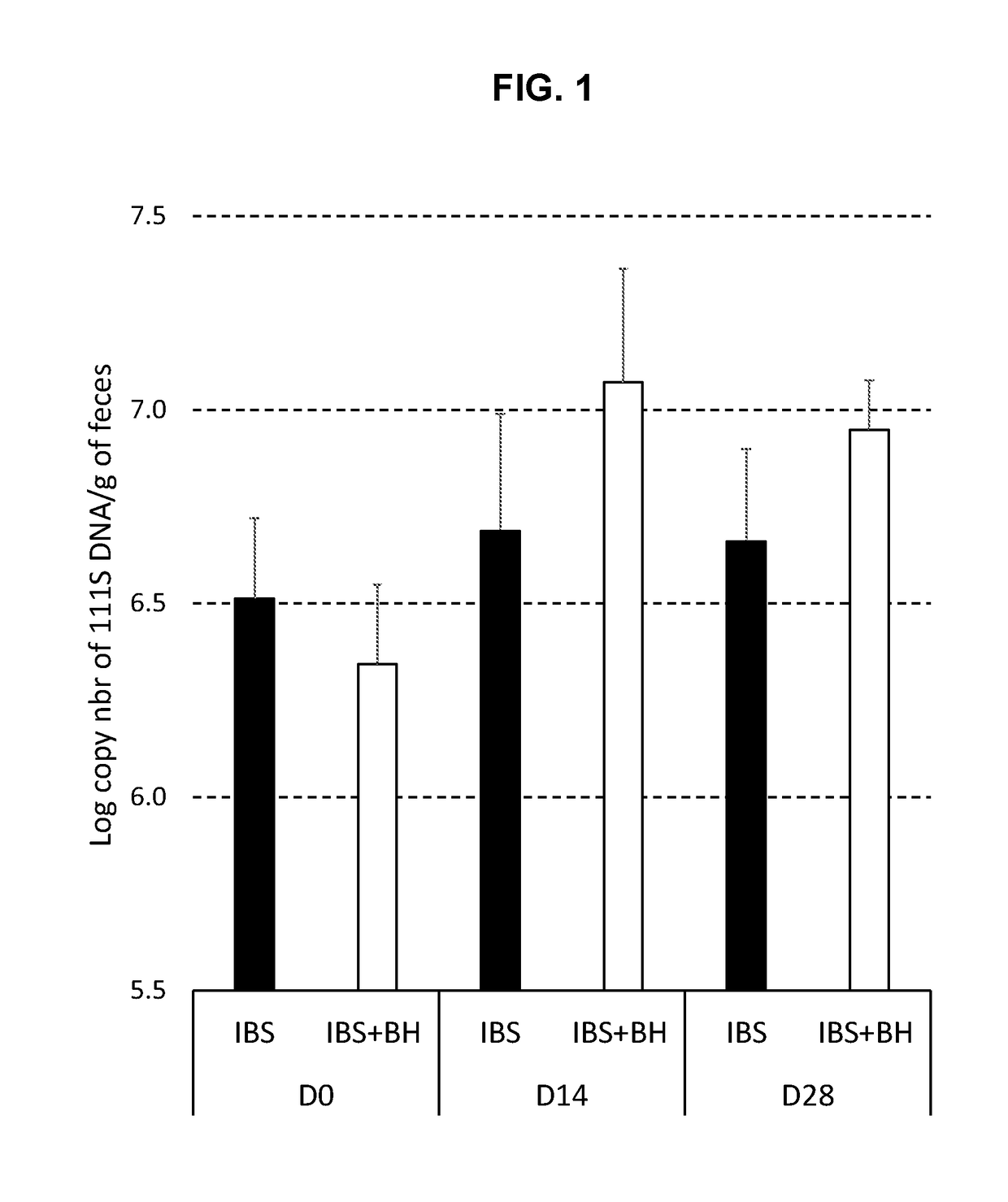
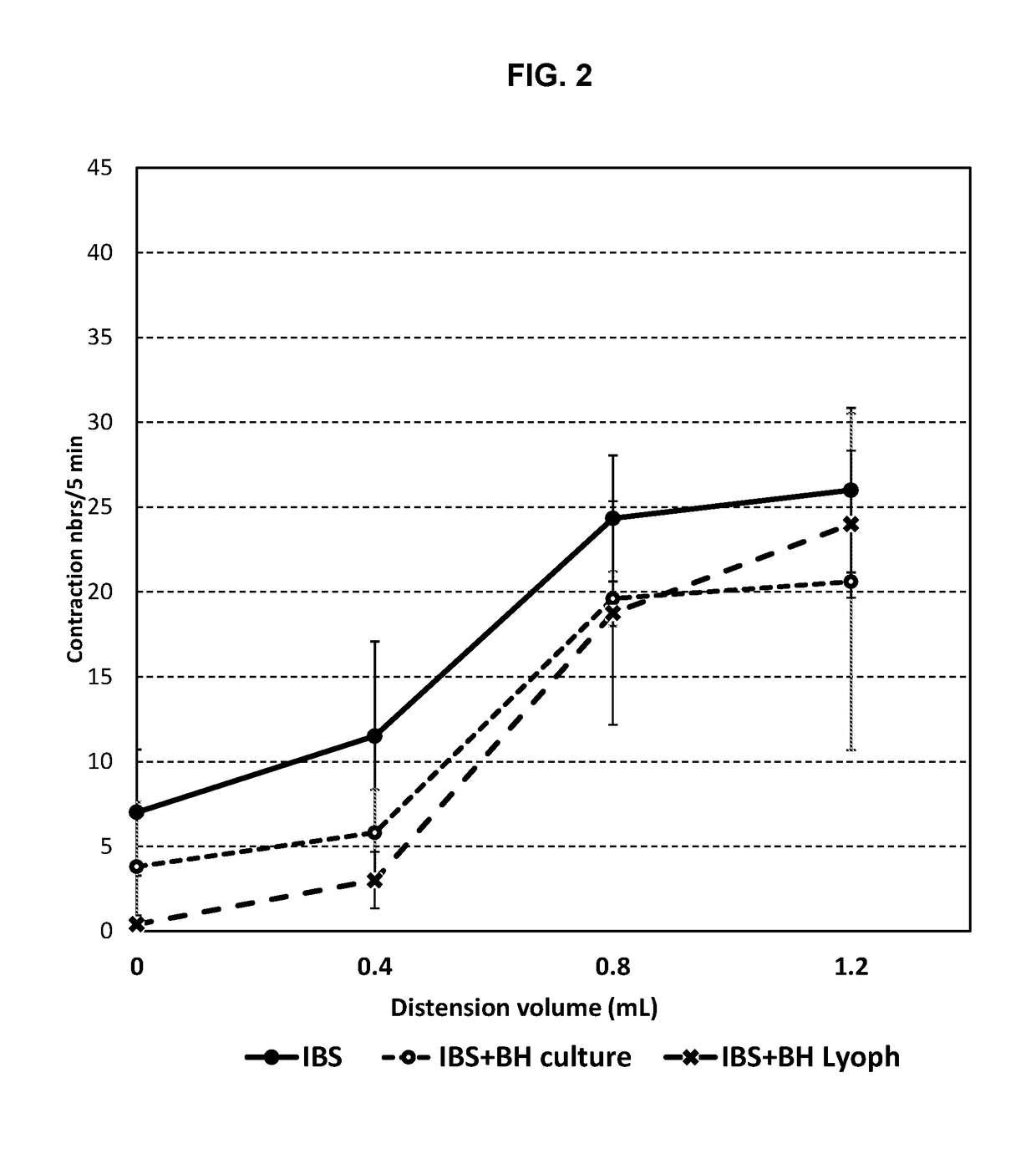
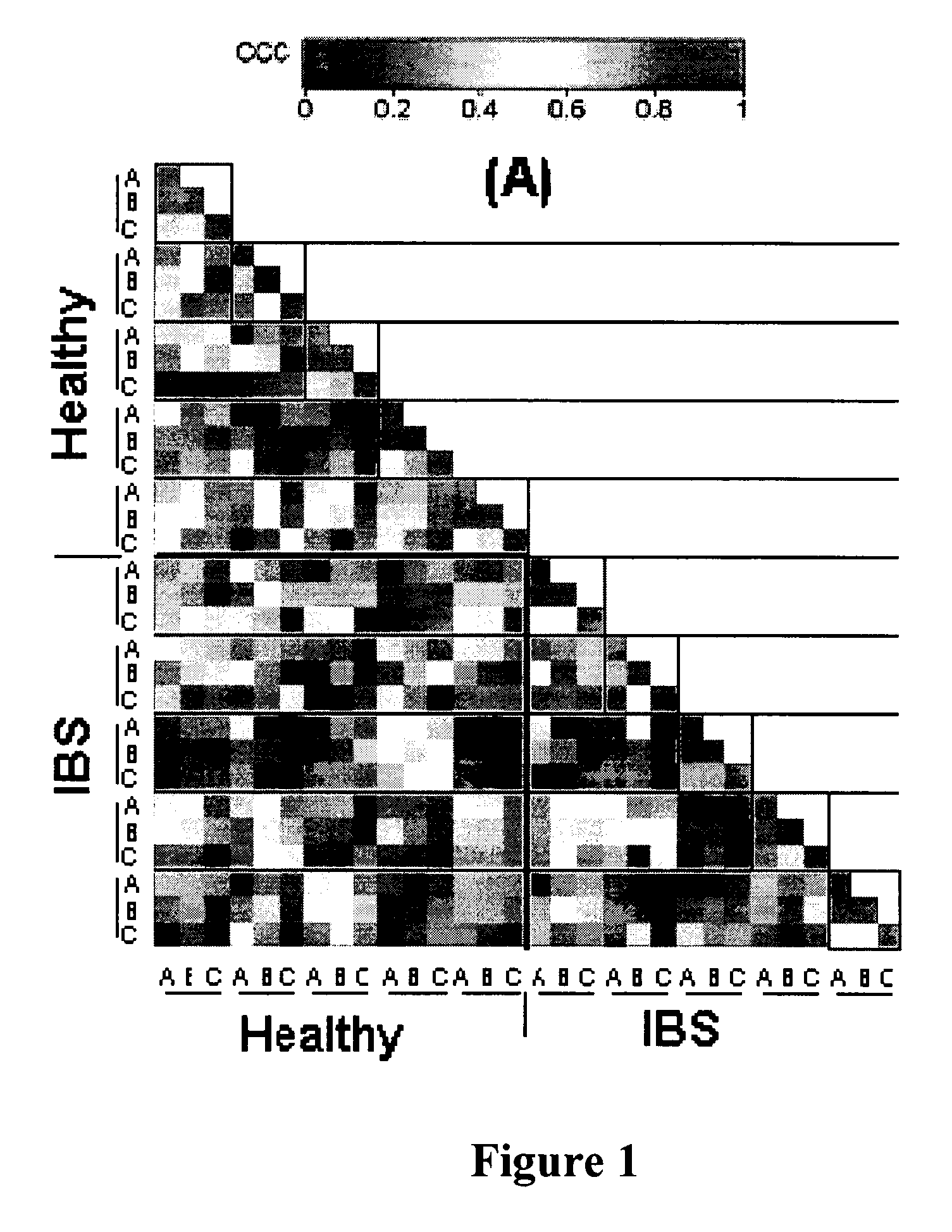
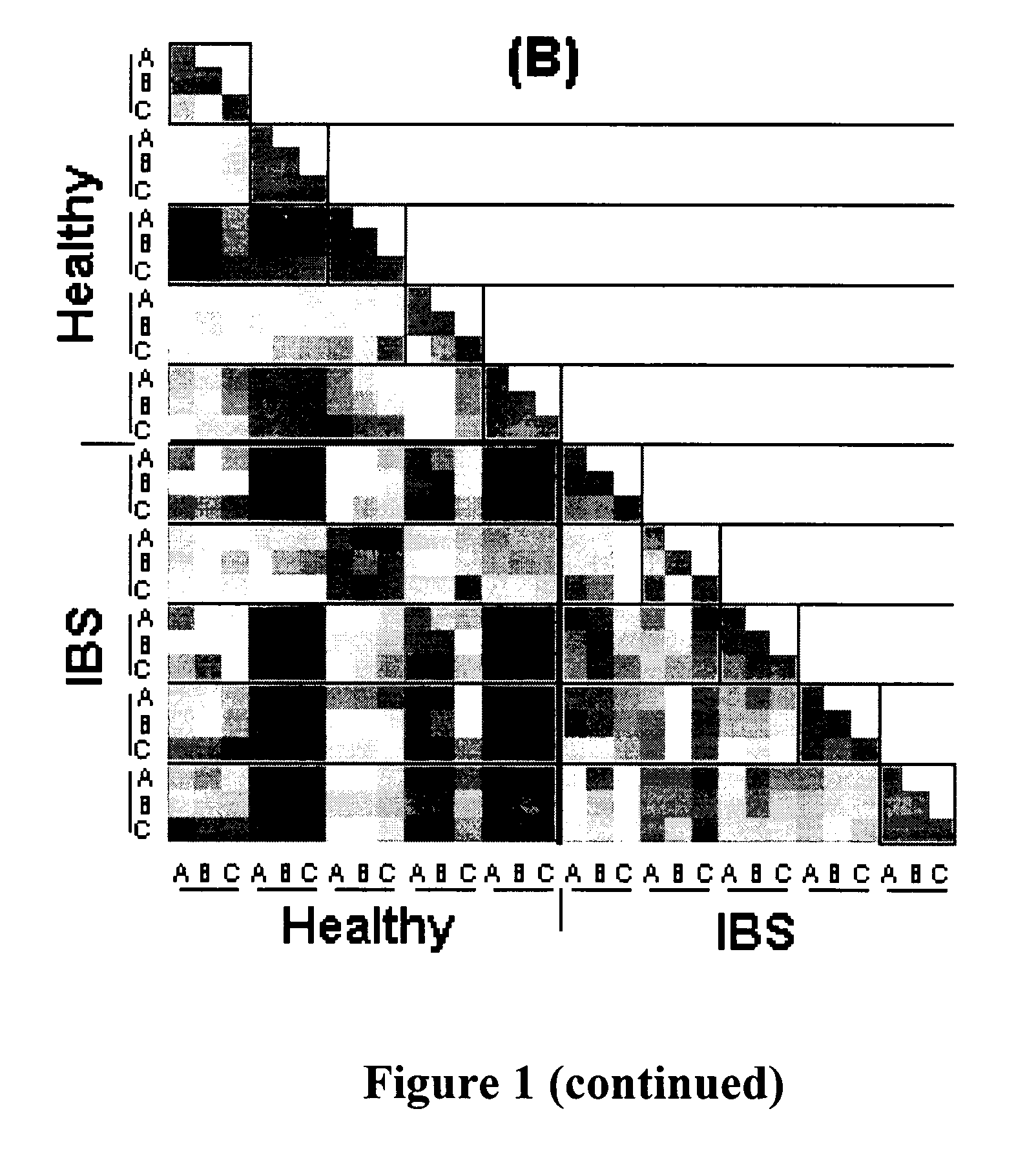
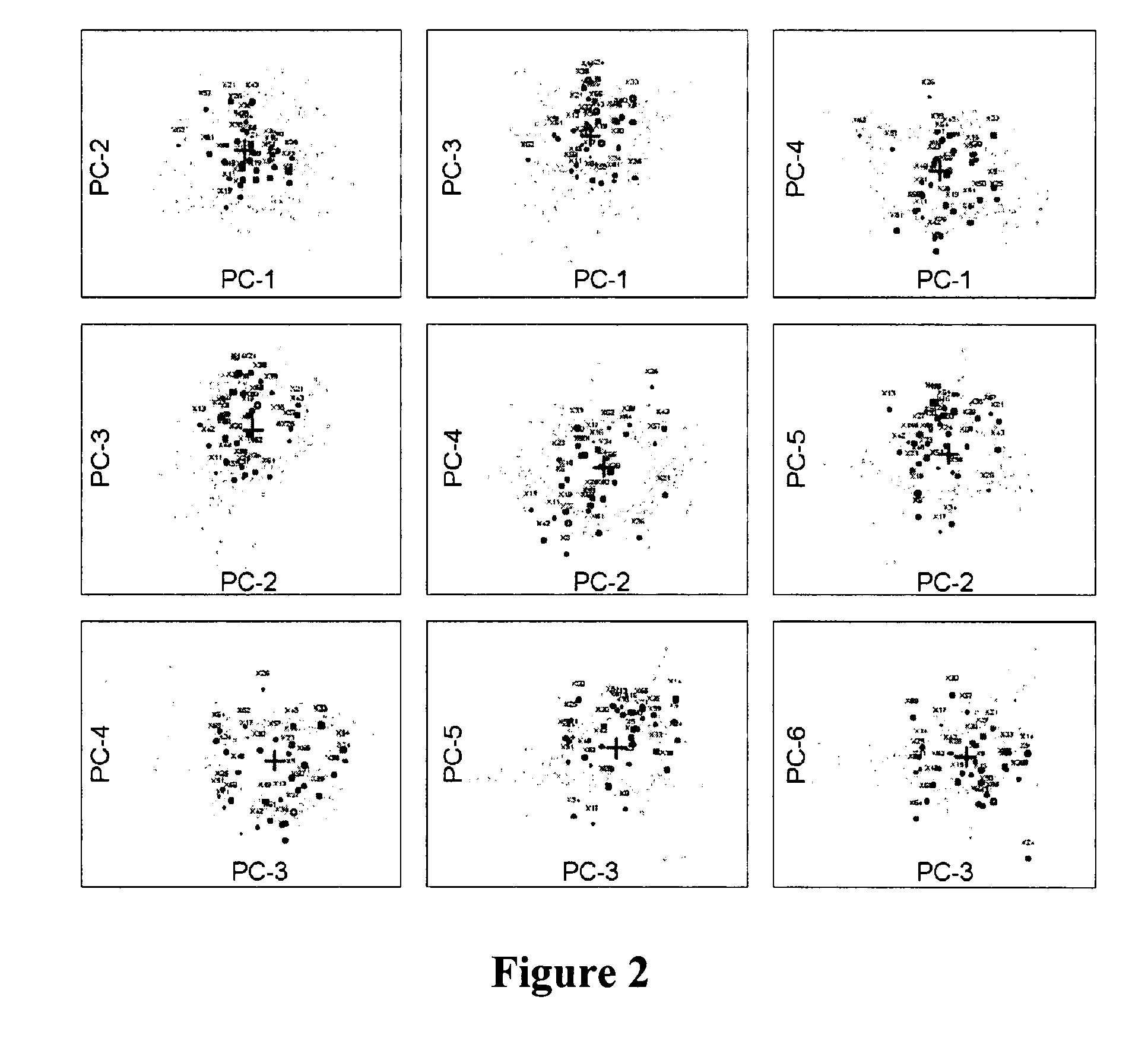
Compositions and methods for treating and diagnosing irritable bowel syndrome
The present invention relates generally to therapy and diagnosis of disorders associated with chronic visceral hypersensitivity (CVH), and in particular irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). In particular, this invention relates to the polypeptides as well as to the polynucleotides encoding these polypeptides, wherein said polypeptides are shown to be associated with CVH. These polypeptides and polynucleotides are useful in the diagnosis, treatment and / or prevention of disorders associated with CVH, in particular in the diagnosis, treatment and / or prevention of disorders associated with IBS.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES +1
Heterocyclic compounds and their uses
Substituted bicyclic heteroaryls and compositions containing them, for the treatment of general inflammation, arthritis, rheumatic diseases, osteoarthritis, inflammatory bowel disorders, inflammatory eye disorders, inflammatory or unstable bladder disorders, psoriasis, skin complaints with inflammatory components, chronic inflammatory conditions, including but not restricted to autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosis (SLE), myestenia gravis, rheumatoid arthritis, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, multiples sclerosis, Sjoegren's syndrome and autoimmune hemolytic anemia, allergic conditions including all forms of hypersensitivity, The present invention also enables methods for treating cancers that are mediated, dependent on or associated with p110δ activity, including but not restricted to leukemias, such as Acute Myeloid leukaemia (AML) Myelo-dysplastic syndrome (MDS) myelo-proliferative diseases (MPD) Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic leukaemia (T-ALL) B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic leukaemia (B-ALL) Non Hodgkins Lymphoma (NHL) B-cell lymphoma and solid tumors, such as breast cancer.
Owner:AMGEN INC
In-vitro tissue preserving fluid and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101999344ANo apparent cytotoxicityStable in natureDead animal preservationPotassiumChemistry
The invention discloses in-vitro tissue preserving fluid and a preparation method thereof. Each 1,000 milliliters of preserving fluid comprises the following components by weight: 5 to 200 grams of osmotic pressure regulator, 0.2 to 40 grams of a pH value buffer pair, 3 to 15 grams of potassium chloride, 1 to 5 grams of sodium chloride, 10 to 300 milligrams of antibiotic, 5 to 100 grams of glucose and the balance of deionized water. In the invention, a non-CO2 dependent buffer pair is used to reduce the dependence on CO2 in transport and an air exposure process and reduce the fluctuations of the pH value; a hypertonic and high-potassium environment is used to reduce the swelling of cells and tissues and improve the activities of the cells and tissues; and the antibiotic used is free from causing hypersensitivity reaction. The preparation method is simple and in-vitro tissue preserving fluid has a remarkable in-vitro tissue preserving effect. The in-vitro tissue preserving fluid is low in cost, has low transport requirements, and can be stored at room temperature and conveniently.
Owner:UNION STEMCELL & GENE ENG
Method of treating allergic disorders
InactiveUS20010033842A1Hybrid immunoglobulinsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAnaphylactic reaction
The present invention describes IgE antagonists (including variant anti-IgE antibodies) and their use in diagnosis, therapy or prophylaxis of allergic and other IgE-mediated disorders, including asthma, food allergies, hypersensitivity and anaphylactic reactions.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Elicitor peptides having disrupted hypersensitive response box and use thereof
ActiveUS20160353735A1Extend your lifePromote plant growthBiocidePeptide-nucleic acidsBiotechnologyDNA construct
Disclosed are peptides that induce an active plant response, but not a hypersensitive response, when applied to plant tissue. These peptides also preferably exhibit improved solubility, stability, resistance to chemical degradation, or a combination of these properties. Use of these peptides or fusion polypeptides, or DNA constructs encoding the same, for modulating plant biochemical signaling, imparting disease resistance to plants, enhancing plant growth, imparting tolerance to biotic stress, imparting tolerance and resistance to abiotic stress, imparting desiccation resistance to cuttings removed from ornamental plants, imparting post-harvest disease or post-harvest desiccation resistance to a fruit or vegetable, or enhancing the longevity of fruit or vegetable ripeness are also disclosed.
Owner:PLANT HEALTH CARE INC
Heterocyclic compounds and their uses
Substituted bicyclic heteroaryls and compositions containing them, for the treatment of general inflammation, arthritis, rheumatic diseases, osteoarthritis, inflammatory bowel disorders, inflammatory eye disorders, inflammatory or unstable bladder disorders, psoriasis, skin complaints with inflammatory components, chronic inflammatory conditions, including but not restricted to autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosis (SLE), myestenia gravis, rheumatoid arthritis, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, multiples sclerosis, Sjoegren's syndrome and autoimmune hemolytic anemia, allergic conditions including all forms of hypersensitivity, The present invention also enables methods for treating cancers that are mediated, dependent on or associated with pi 110δ activity, including but not restricted to leukemias, such as Acute Myeloid leukaemia (AML) Myelo-dysplastic syndrome (MDS) myelo-proliferative diseases (MPD) Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic leukaemia (T-ALL) B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic leukaemia (B-ALL) Non Hodgkins Lymphoma (NHL) B-cell lymphoma and solid tumors, such as breast cancer.
Owner:AMGEN INC
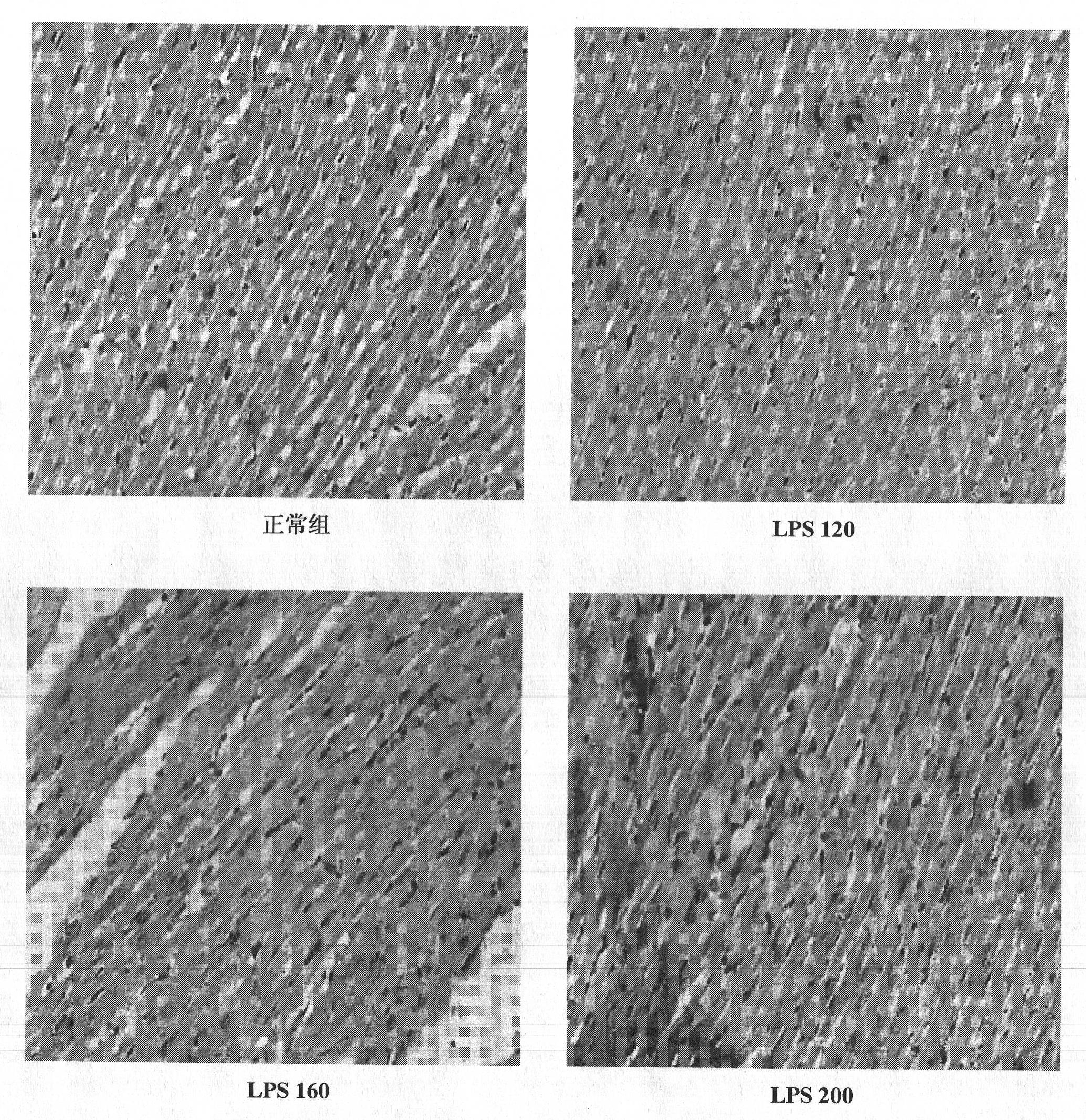
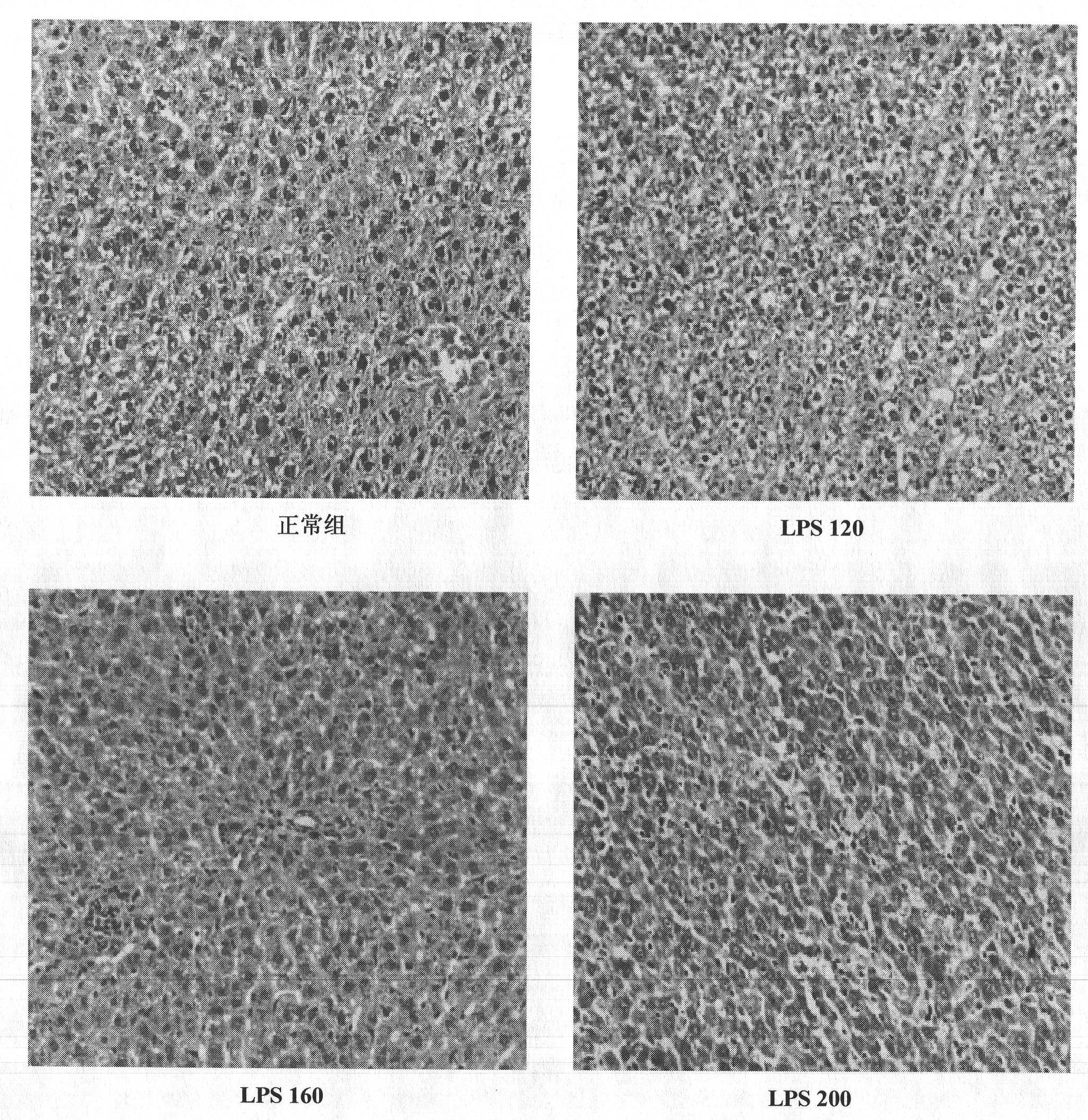
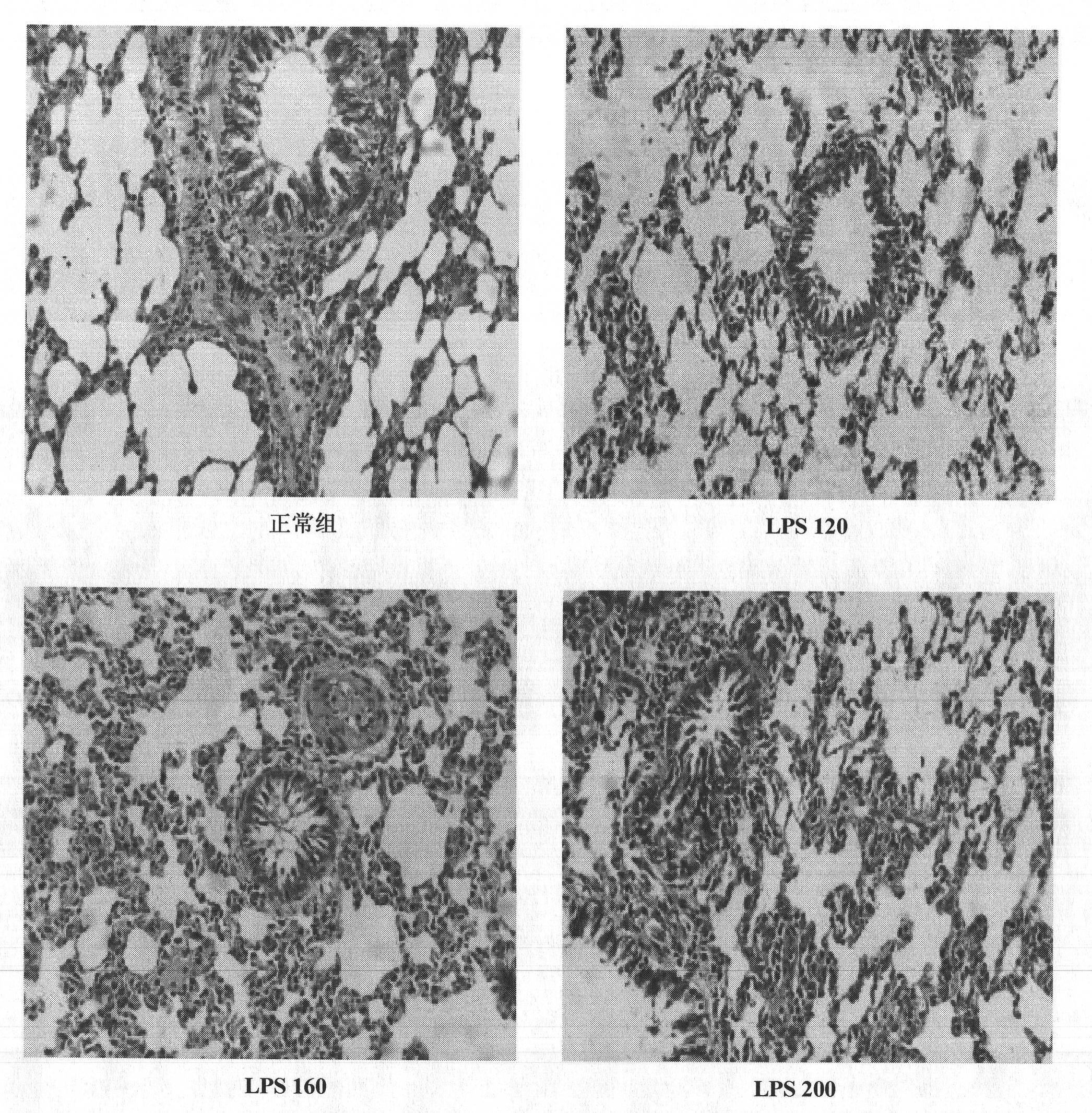
Construction method of animal model of chronic inflammation
InactiveCN102188442AOrganic active ingredientsIn-vivo testing preparationsClinico pathologicalWhite blood cell number
The invention belongs to the fields of medical evaluation, detection technology and experimental zoology, and specifically relates to a construction method of animal model of rat which is used for screening medicaments for treating chronic inflammation, and evaluating methods for treating systematic chronic inflammation. The method comprises the following step that healthy male SD rats are administered with lipopolysaccharide by tail intravenous injection, on an every first day of a week for 4-8 weeks persistently, at a dosage of 120-300 [mu]g per kg of body weight, so that pathologic changes, which meet pathological characteristics of chronic inflammation, mainly of an increased ratio of peripheral blood leucocyte count to neutrophile granulocyte, an increased serum hypersensitive C-creative protein level, infiltration of heart, liver, lung, kidney in inflammatory cells, and haemostasis and oedema of tissues are generated. The method has a good repeatability, and operation of the method is simple, easily controllable and mechanism-clear, besides indexes can be analyzed quantitatively and are convenient for statistics treatments. In addition, the constructed animal model is more ideal and more conform to clinic pathological and physiological changes of the type of disease.
Owner:广西中医学院
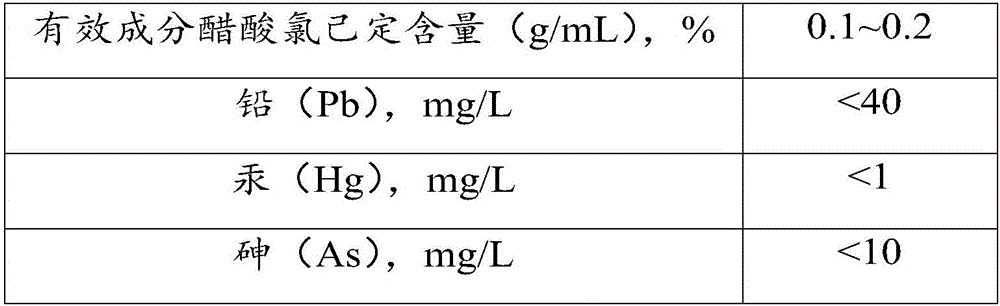
Antibacterial preparation and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106109451AGood biocompatibilityPromote absorptionAntimycoticsHydroxy compound active ingredientsEscherichia coliChlorhexidine Acetate
The embodiment of the invention discloses an antibacterial preparation and a preparation method thereof. The antibacterial preparation adopts compatibility of chlorhexidine acetate, borneol, menthol and glycerol, can effectively kill pathogenic bacteria and has good killing effect on pathogenic bacteria resulting in gynecological inflammation, namely pathogens such as staphylococcus aureus, candida albicans and escherichia coli, antibacterial rate is more than or equal to 90%, and the lowest content of heavy metals is less than 1ppm. The antibacterial preparation disclosed by the embodiment of the invention also has good biocompatibility, low cytotoxicity and no delayed type hypersensitivity; and each index meets relevant national standards or regulations. Meanwhile, the antibacterial preparation has good anti-inflammation, sterilization and itching relieving effects, is wide in application range and can also be applied to antibacteria and anti-inflammation of human skin and mucosae.
Owner:武汉德仁科技开发有限公司
Method for treating diseases associated with changes of qualitative and/quantitative composition of blood extracellular dna
The invention relates to medicine and veterinary science and can be used for treating diseases associated with changes of the qualitative and / quantitative composition of blood extracellular DNA, namely generalised infection diseases provoked by bacteria, diseases provoked by fungi and protozoa, atherosclerosis, pancreatic diabetes, allergic diseases associated with delayed response hypersensitivity and diseases due to somatic cell gene mutations. The inventive method for treating diseases associated with modifications of the qualitative and / or quantitative composition of blood extracellular DNA, namely generalised infection diseases provoked by bacteria, diseases provoked by fungi and protozoa, atherosclerosis, pancreatic diabetes, allergic diseases associated with delayed response hypersensitivity and diseases due to somatic cell gene mutations consists in injecting an agent destroying blood extracellular DNA. DNAse enzyme injected into a systemic blood circulation in doses which modify the electrophoretic profile of the blood extracellular DNA definable by pulse-electrophoresis can be used in the form of an agent destroying said blood extracellular DNA. Said DNAse enzyme can be injected in doses and at regimes ensuring the level of a blood plasma DNA-hydrolytic activity which is measured in the blood plasma and is higher than 150 Kunz units per litre of plasma during a total time higher than 12 hours a day. The inventive method makes it possible to develop a high-efficient and low-toxic method for treating diseases associated with modifications of qualitative and / or quantitative composition of blood extracellular DNA individually or in combination thereof.
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com