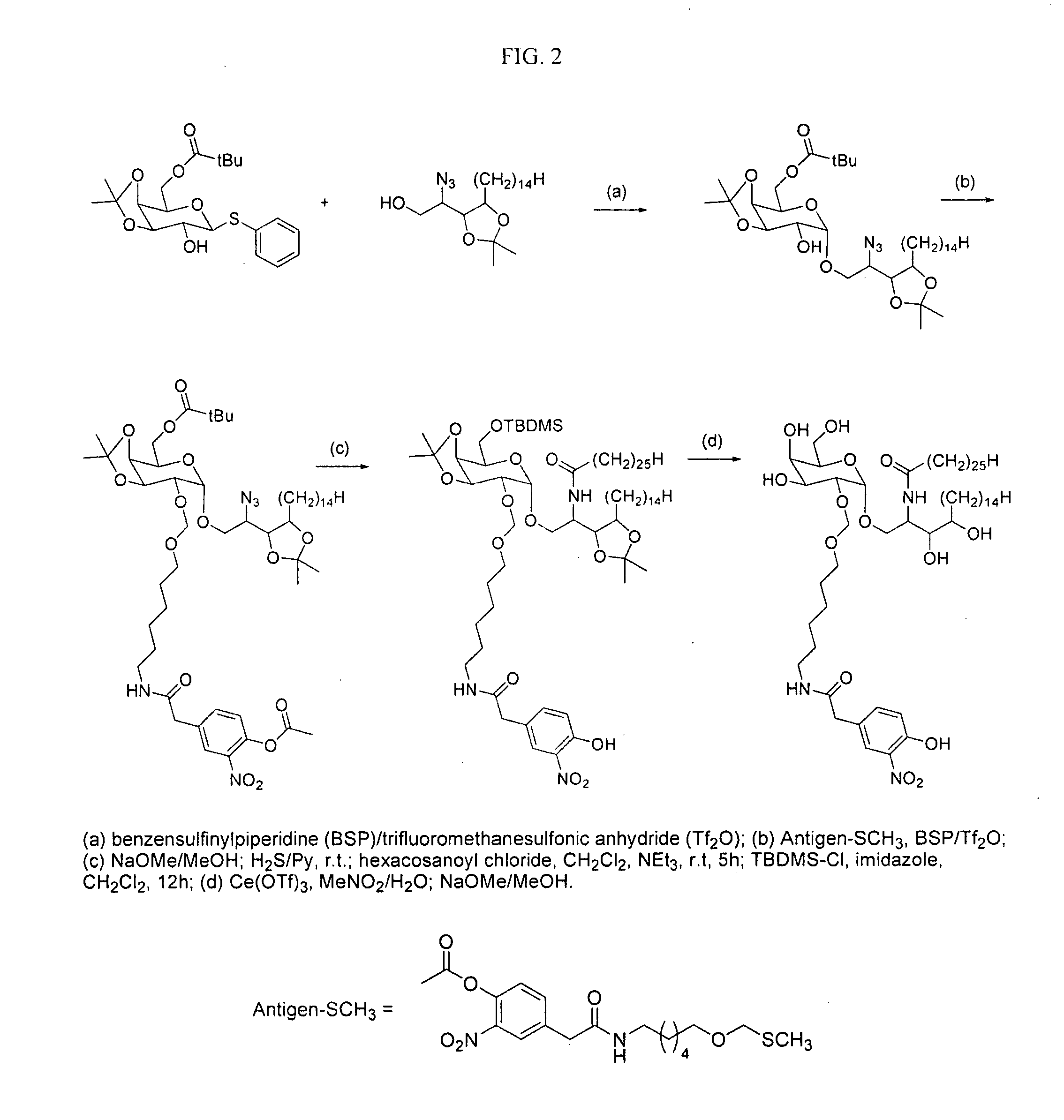
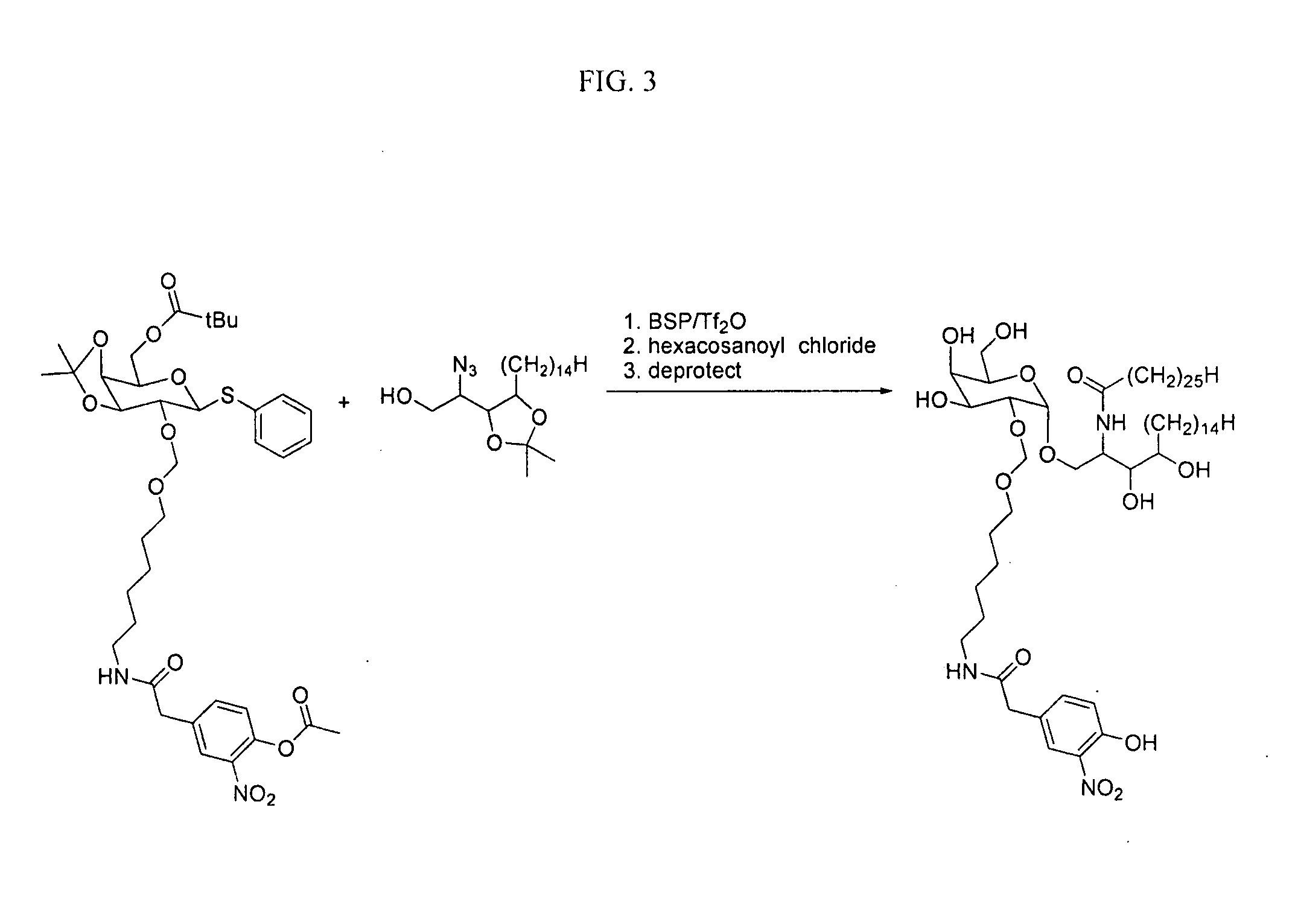
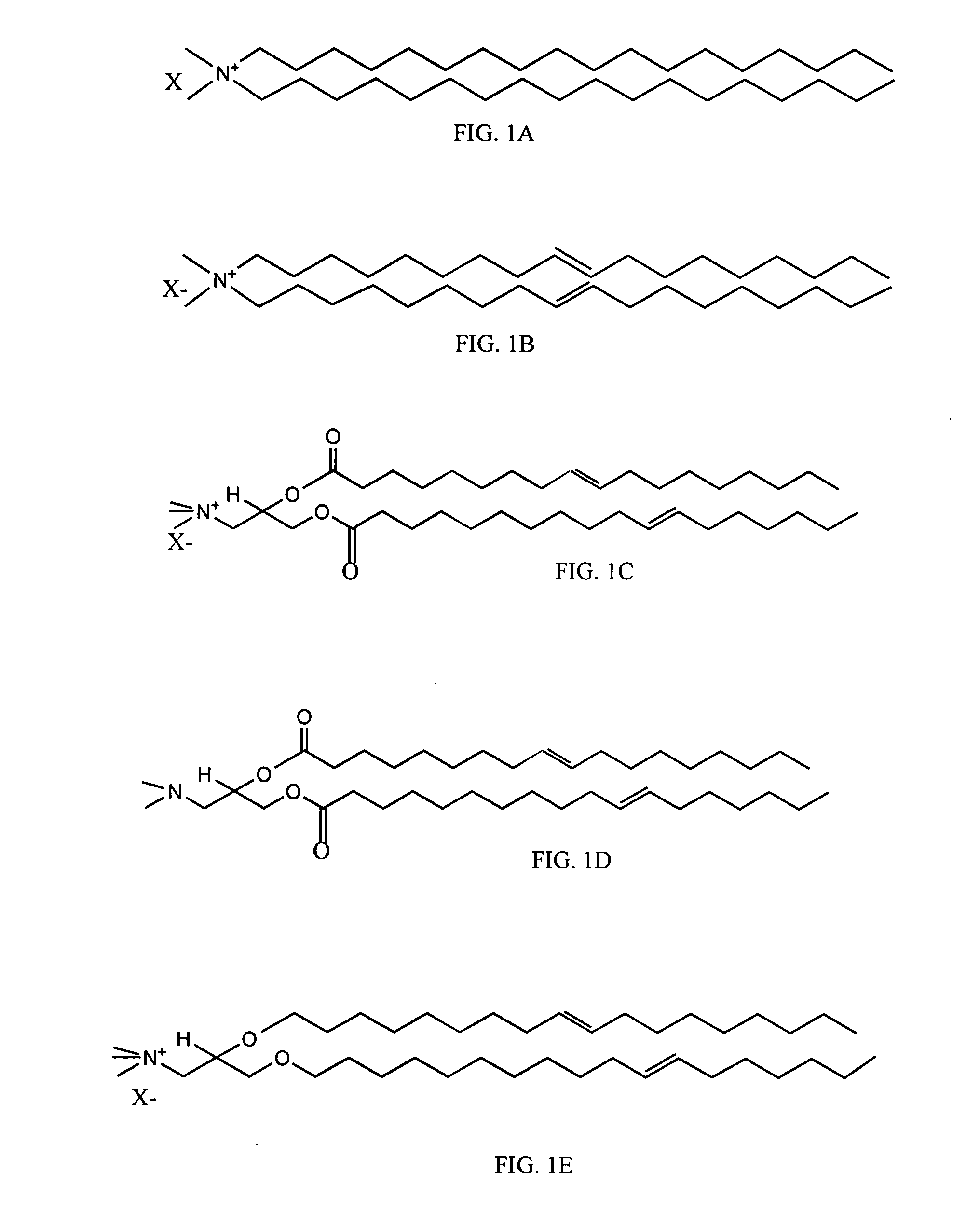
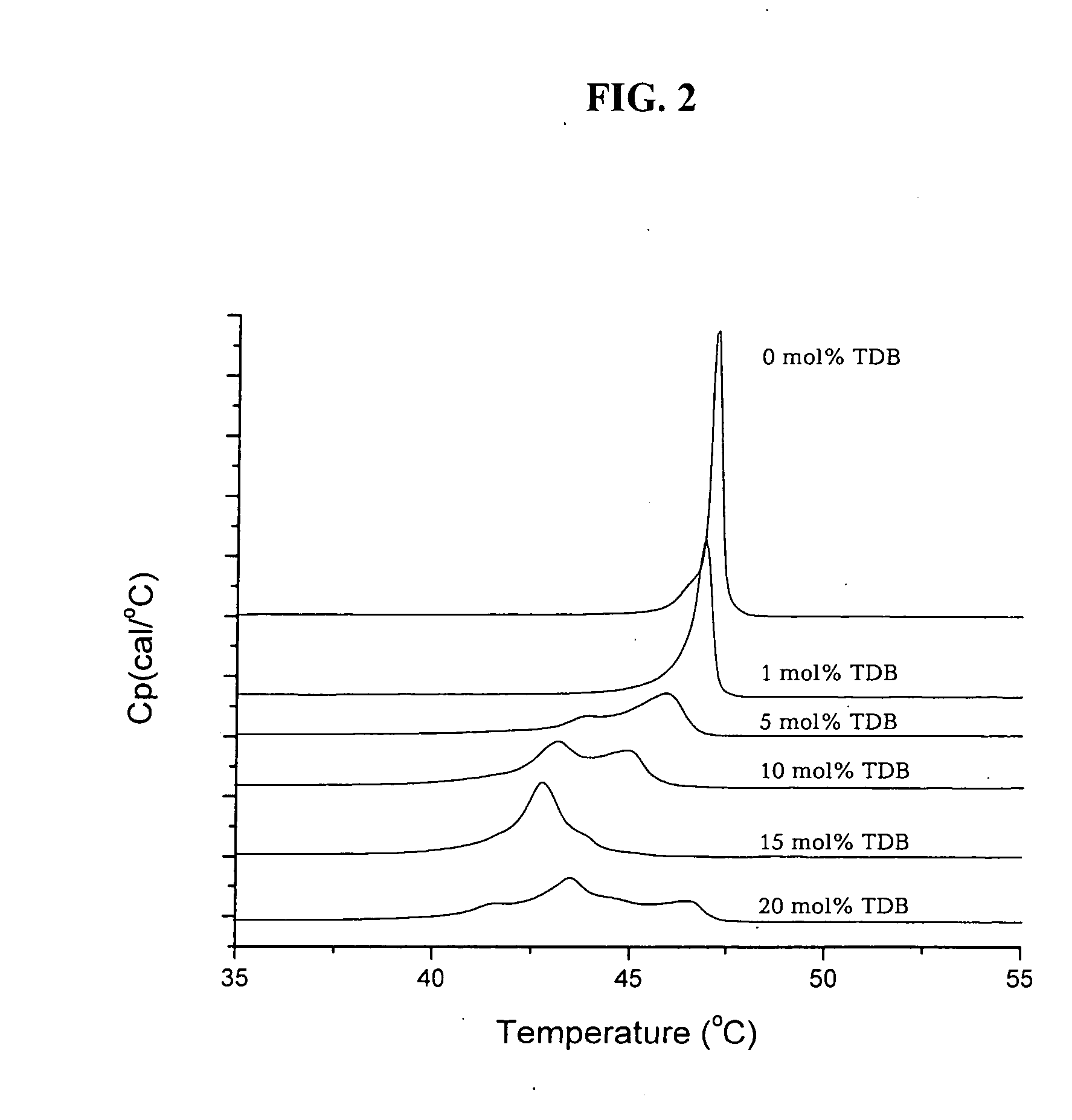
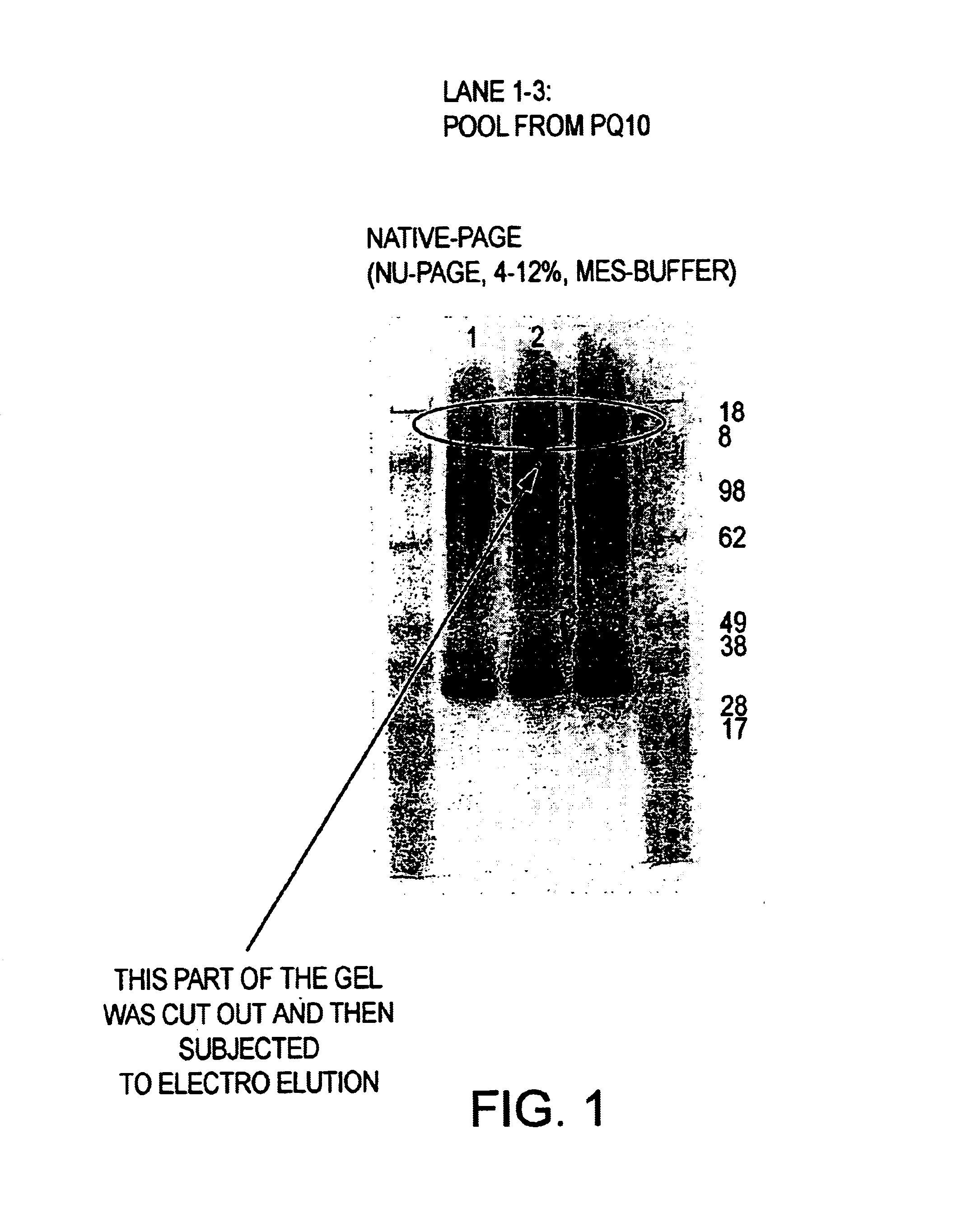
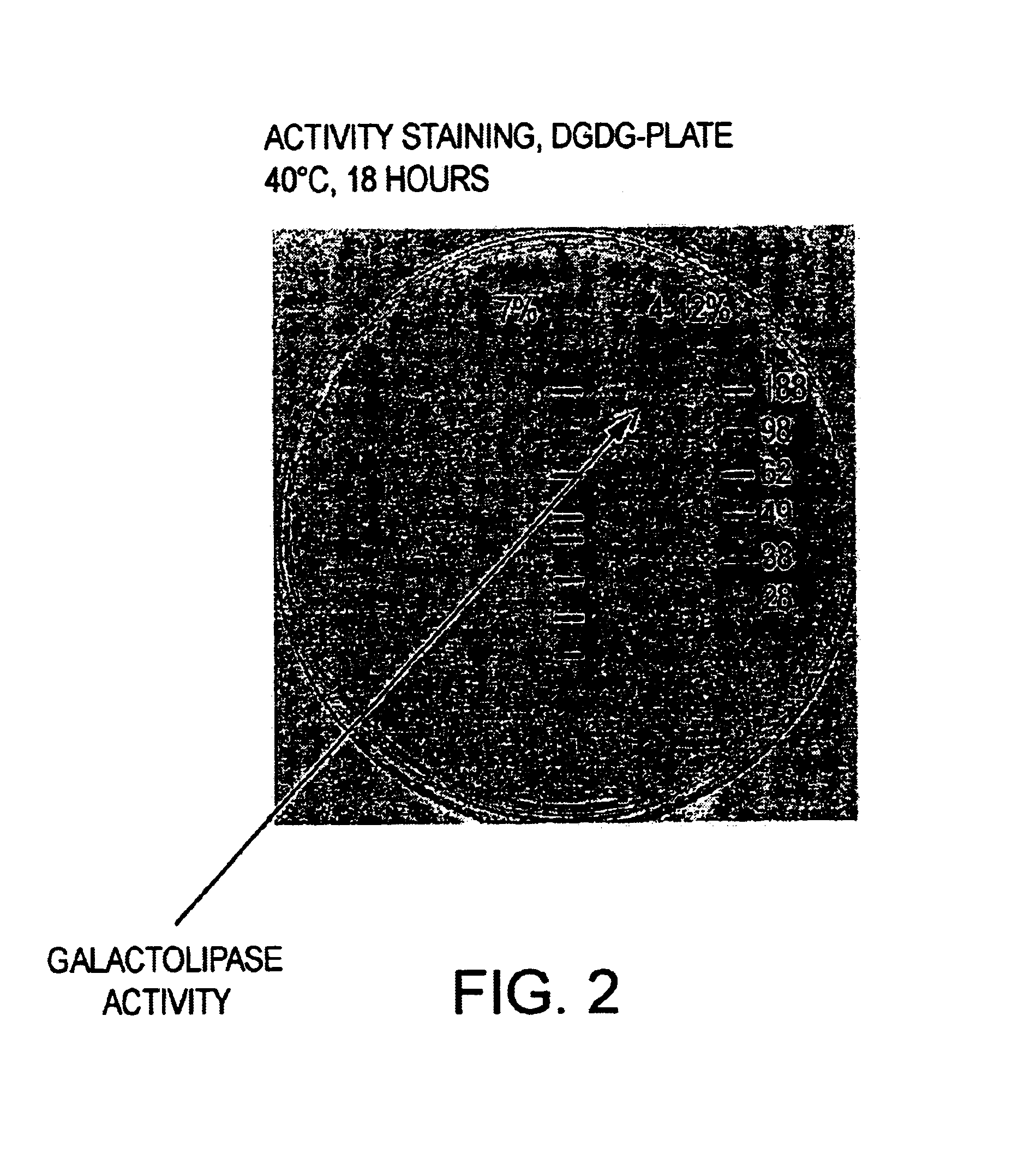
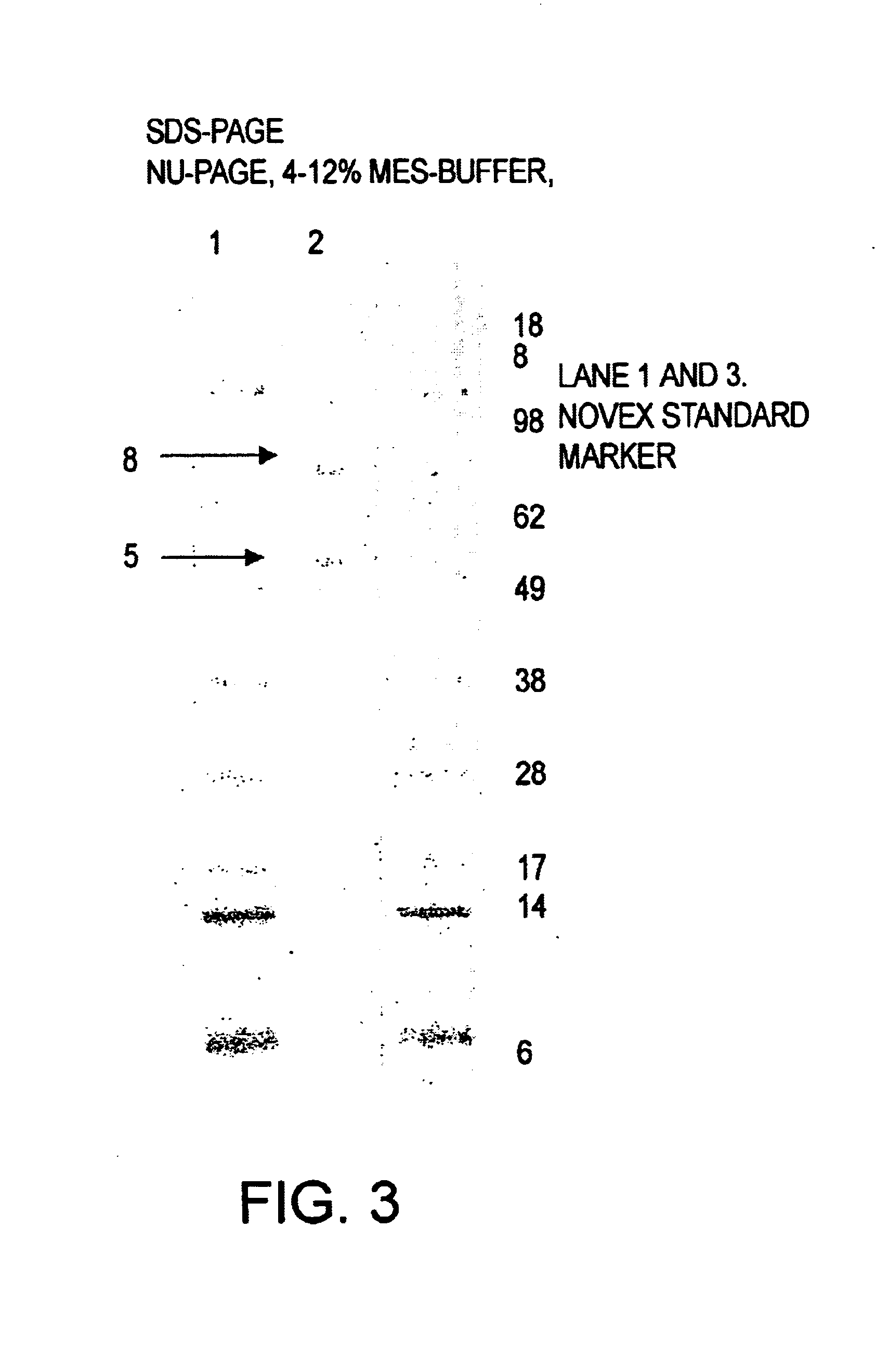
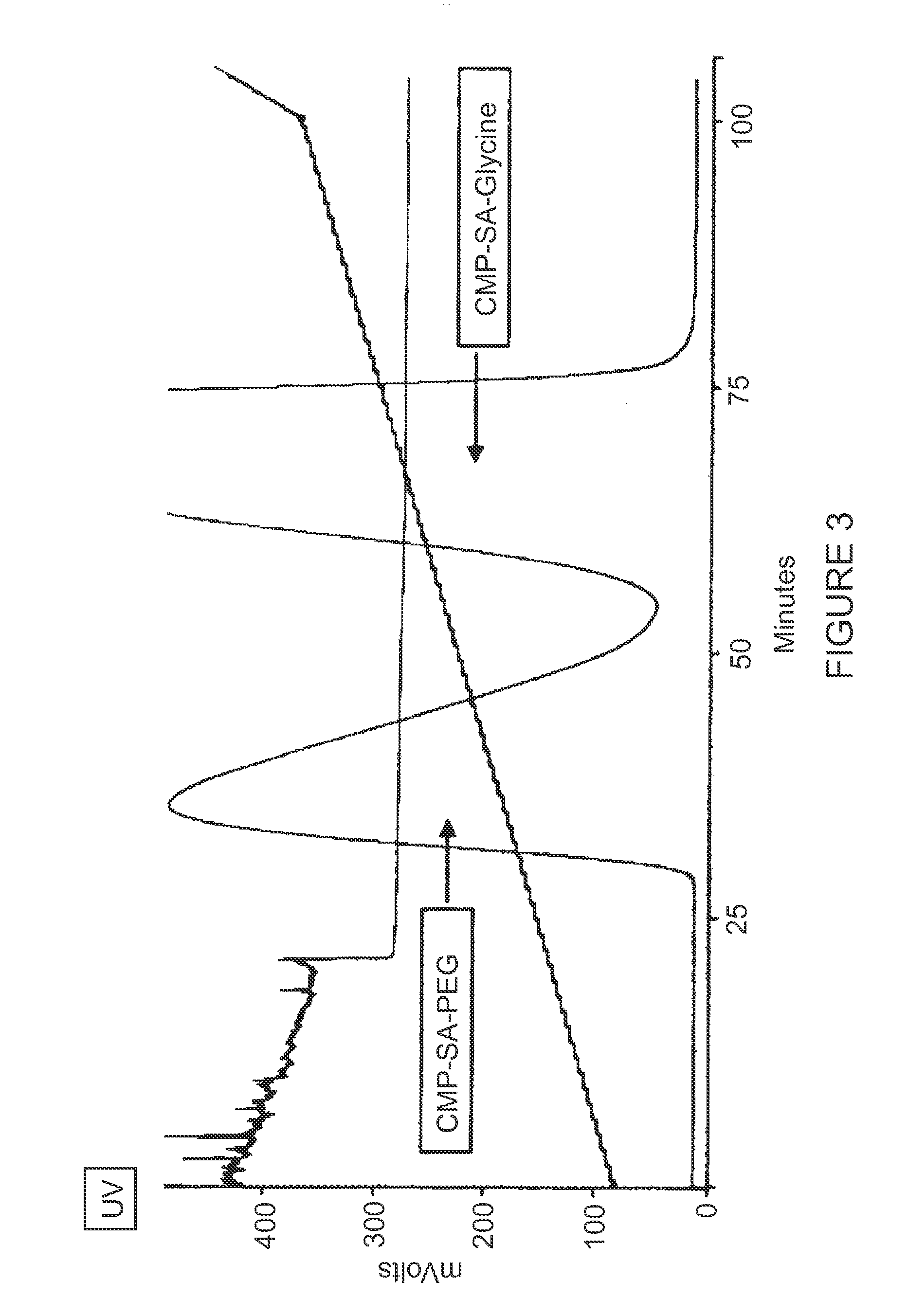
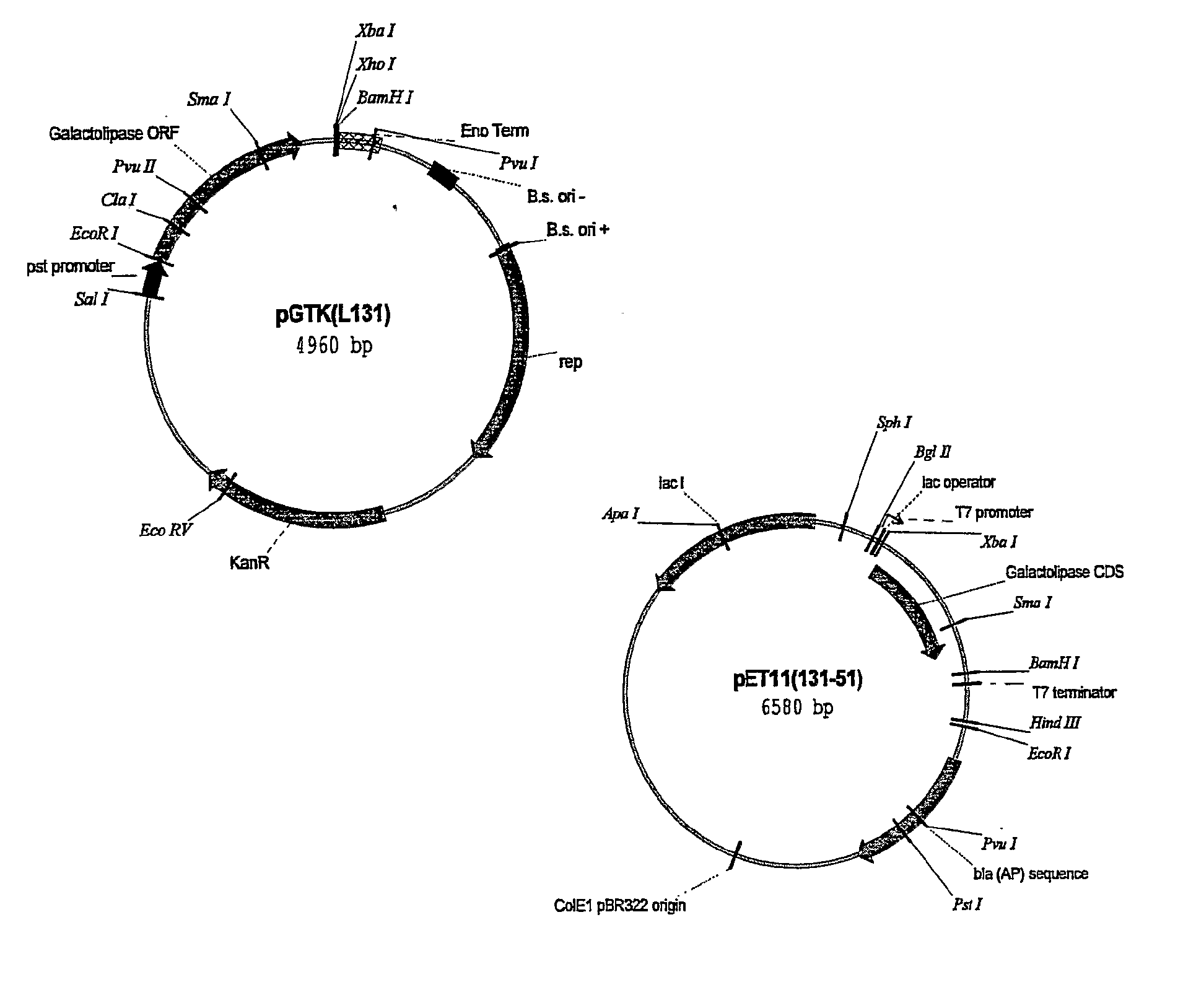
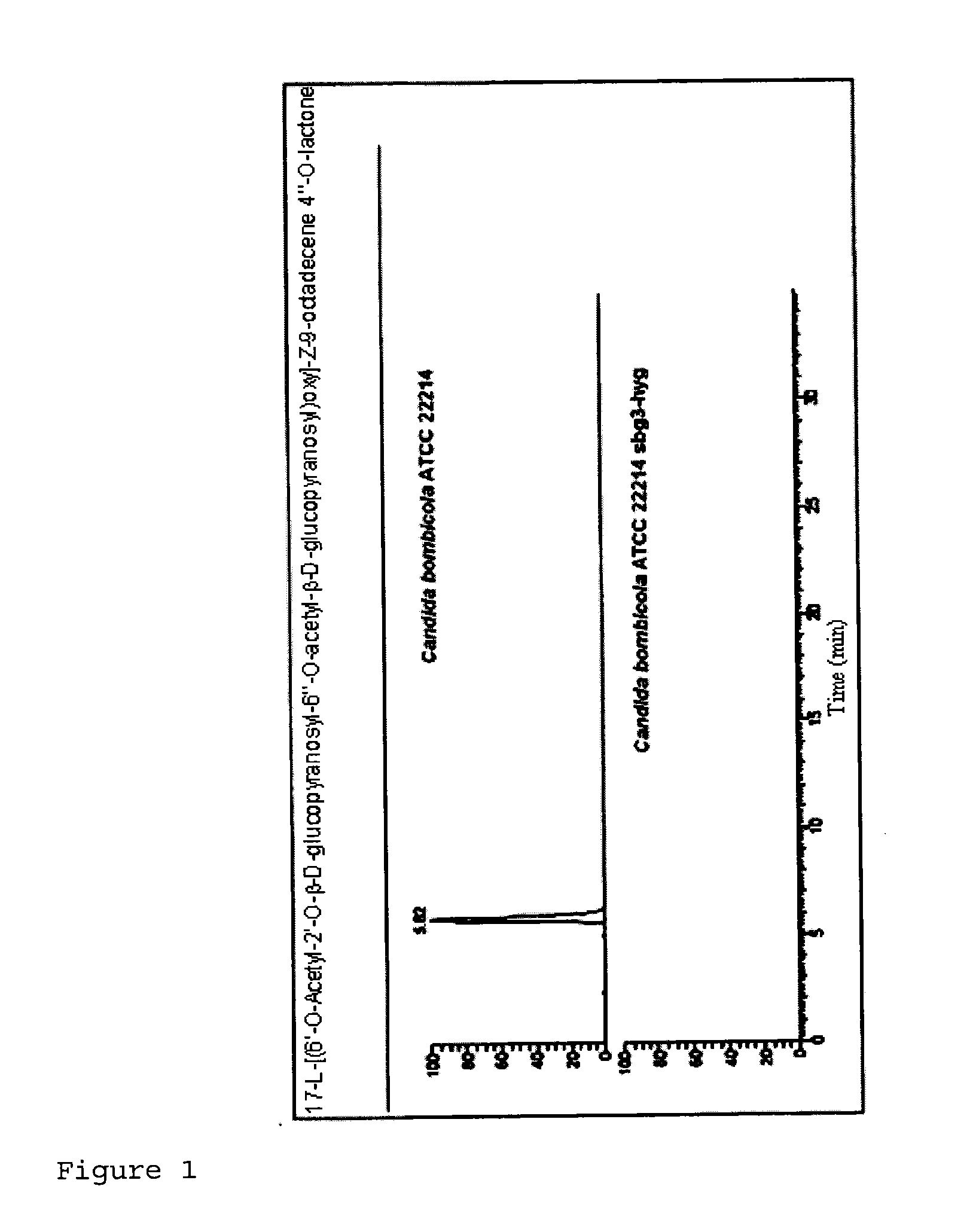
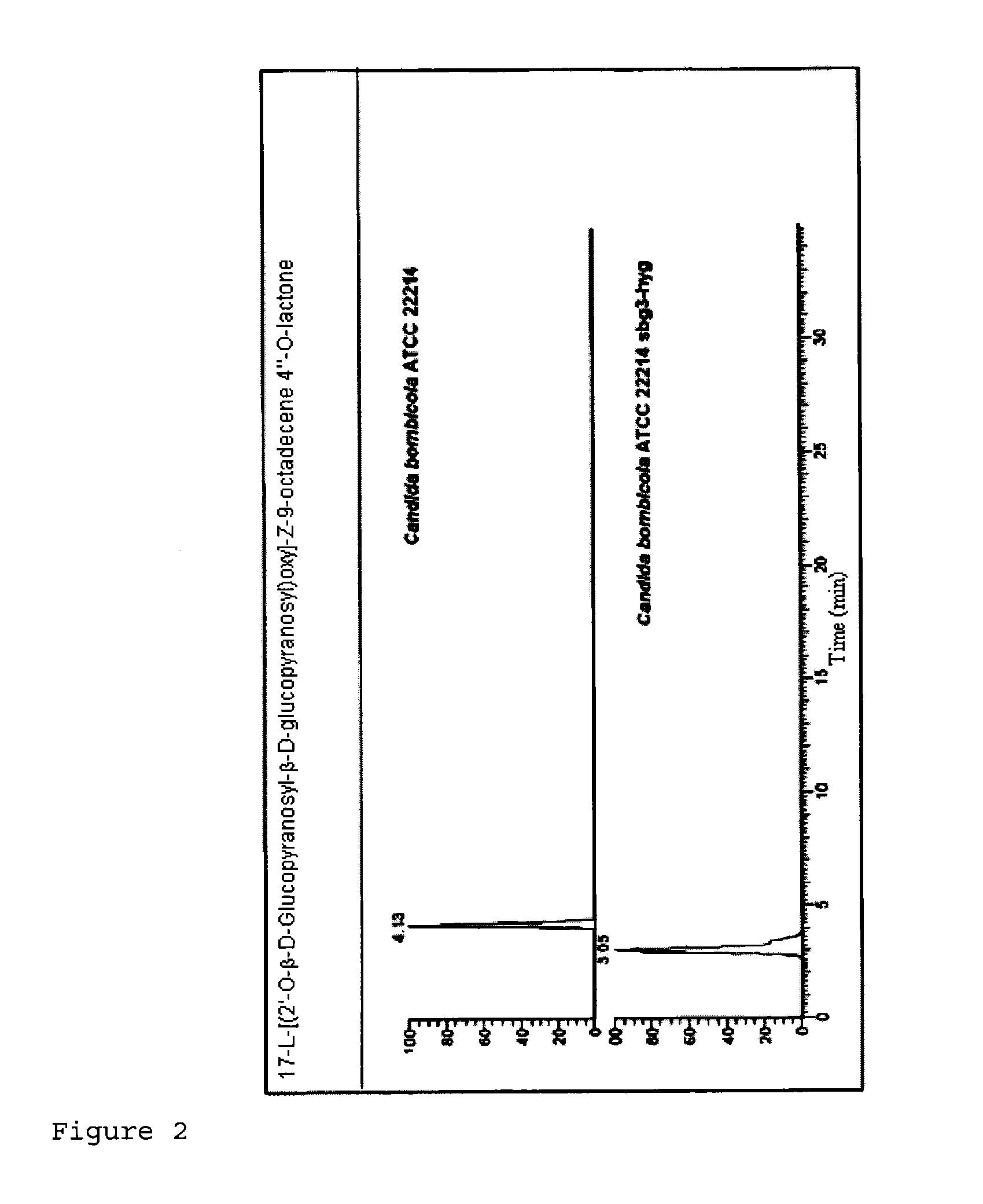
Patents
Literature
790 results about "Glycolipid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
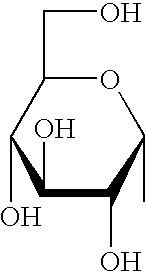
Glycolipids are lipids with a carbohydrate attached by a glycosidic (covalent) bond. Their role is to maintain the stability of the cell membrane and to facilitate cellular recognition, which is crucial to the immune response and in the connections that allow cells to connect to one another to form tissues. Glycolipids are found on the surface of all eukaryotic cell membranes, where they extend from the phospholipid bilayer into the extracellular environment.
Compositions and methods for treatment of neoplastic disease
InactiveUS20050112141A1High productFacilitates their targetingFusions for specific cell targetingReceptors for cytokines/lymphoines/interferonsAbnormal tissue growthDisease
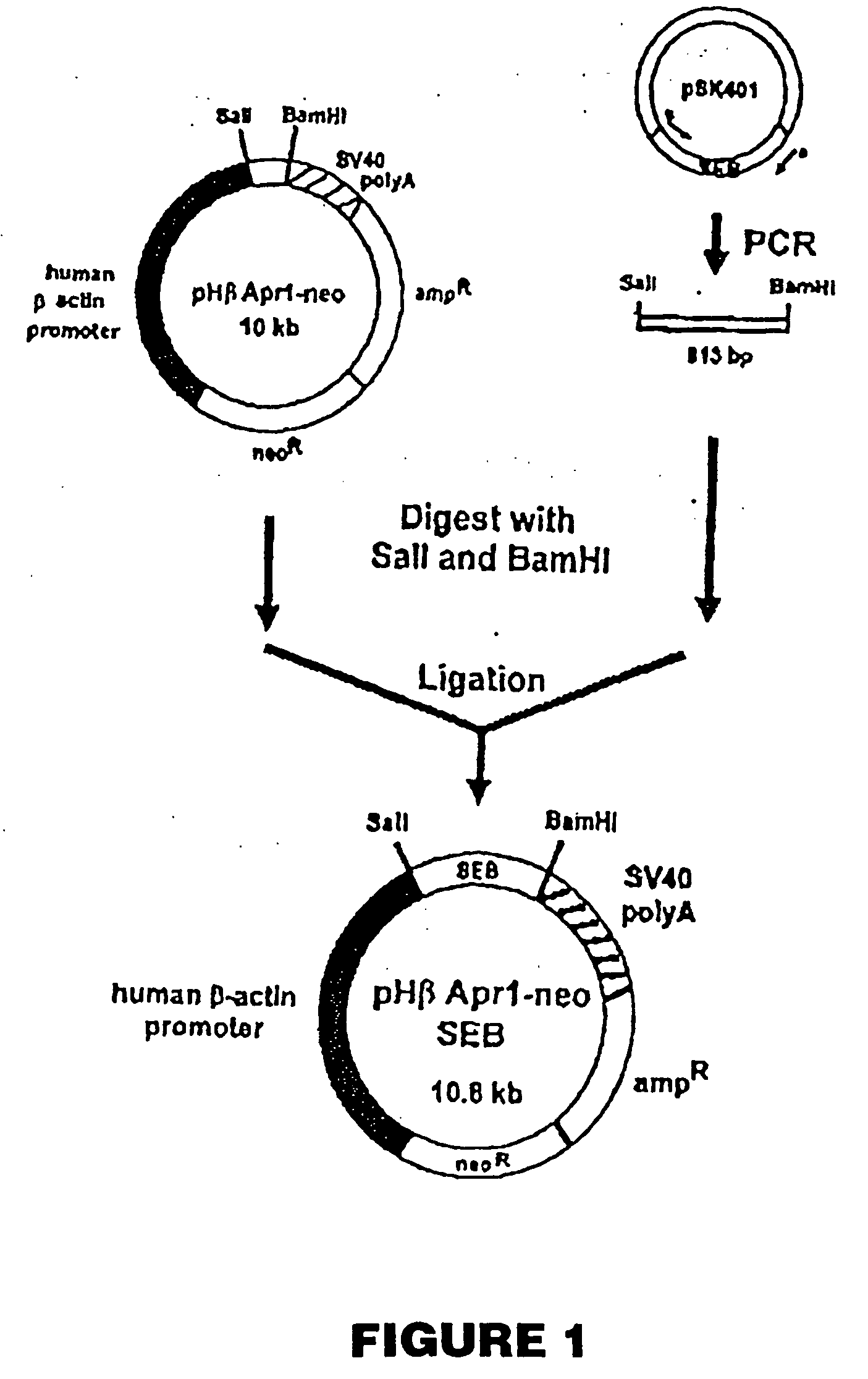
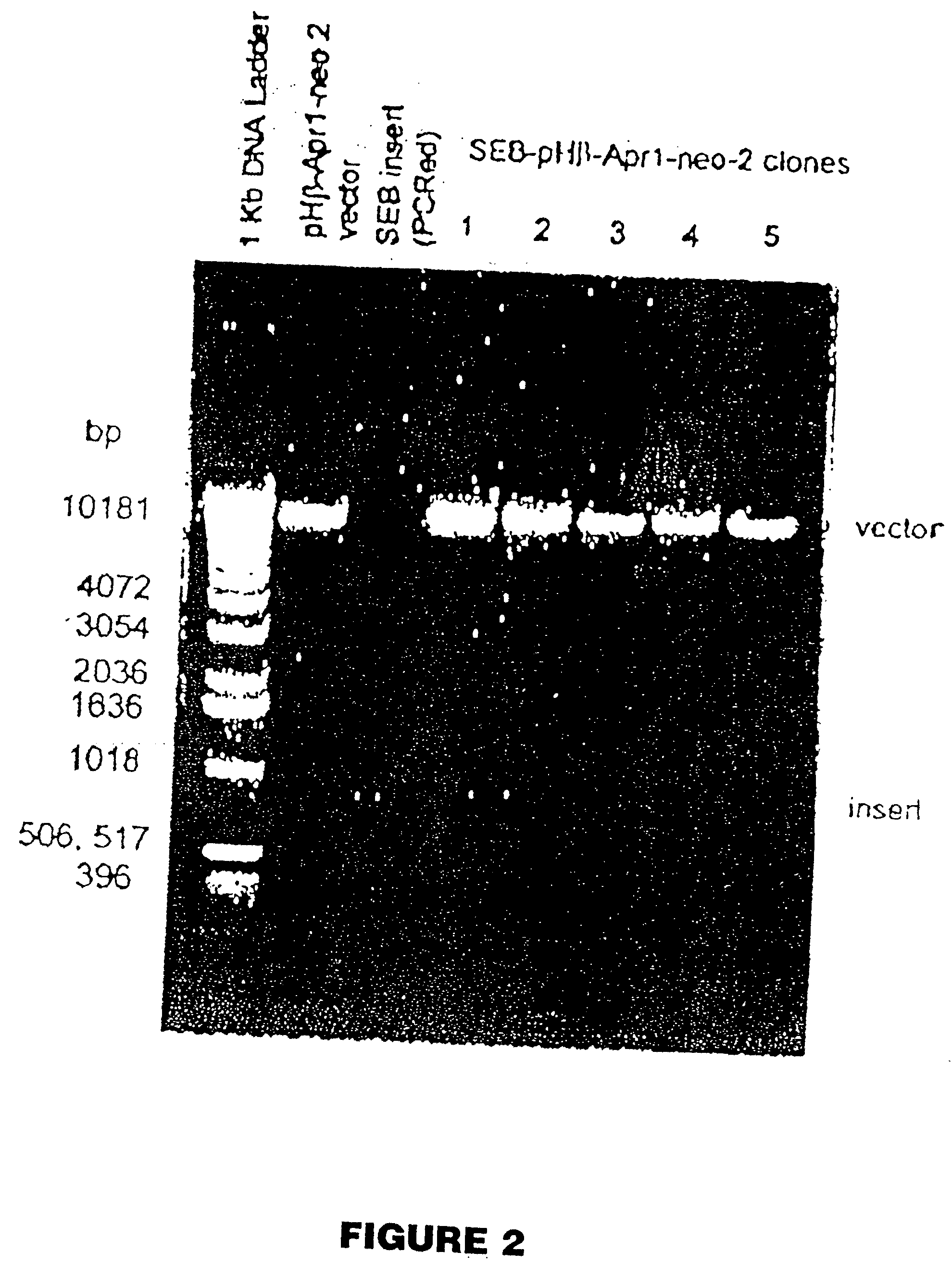
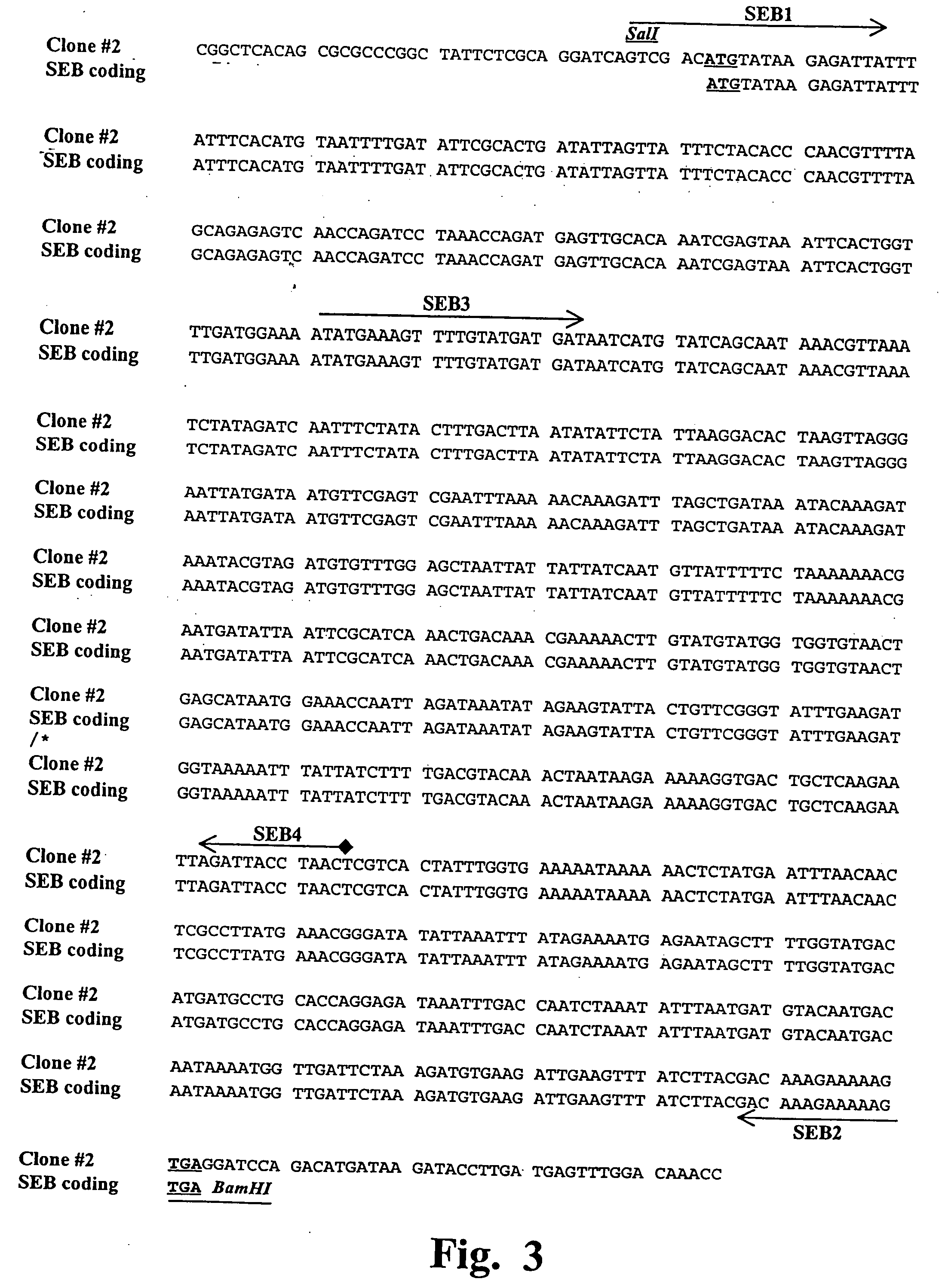
The present invention comprises compositions and methods for treating a tumor or neoplastic disease in a host, The methods employ conjugates comprising superantigen polypeptides or nucleic acids with other structures that preferentially bind to tumor cells and are capable of inducing apoptosis. Also provided are superantigen-glycolipid conjugates and vesicles that are loaded onto antigen presenting cells to activate both T cells and NKT cells. Cell-based vaccines comprise tumor cells engineered to express a superantigen along with glycolipids products which, when expressed, render the cells capable of eliciting an effective anti-tumor immune response in a mammal into which these cells are introduced. Included among these compositions are tumor cells, hybrid cells of tumor cells and accessory cells, preferably dendritic cells. Also provided are T cells and NKT cells activated by the above compositions that can be administered for adoptive immunotherapy.
Owner:TERMAN DAVID
Use of synthetic glycolipids as universal adjuvants for vaccines against cancer and infectious diseases
InactiveUS20050192248A1Enhancement and extension of durationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseAdjuvant
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for augmenting an immunogenicity of an antigen in a mammal, comprising administering said antigen together with an adjuvant composition that includes a synthetic glycolipid compound of Formula I, as described herein. According to the present invention, the use of a compound of Formula I as an adjuvant is attributed at least in part to the enhancement and / or extension of antigen-specific Th1-type responses, in particular, CD8+ T cell responses. The methods and compositions of the present invention can be useful for prophylaxis and treatment of various infectious and neoplastic diseases.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV +1
Embryo modification and implantation
InactiveUS7819796B2Low specificityNanomedicinePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsIvf treatmentEmbryo
The present invention relates to constructs and methods used to enhance the attachment and implantation of an embryo. It is shown that modified glycolipids and glycolipid-attachment molecule constructs can be used to modify embryos, or localised to target tissues, to enhance interaction between the embryo and the target tissue, (typically the endometrium). The invention may advantageously be used to enhance implantation of embryos in the uterus, for example, in IVF treatments.
Owner:KODE BIOTECH
Synthetic C-glycolipid and its use for treating cancer, infectious diseases and autoimmune diseases
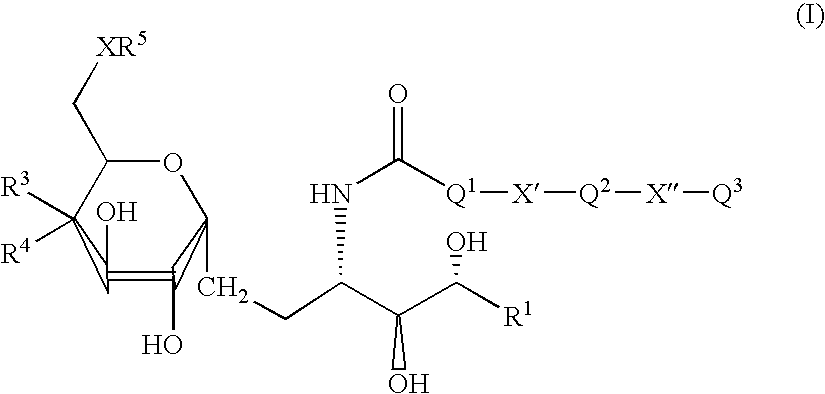
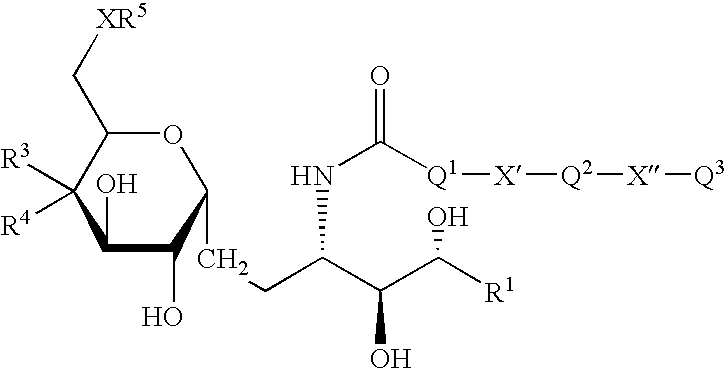
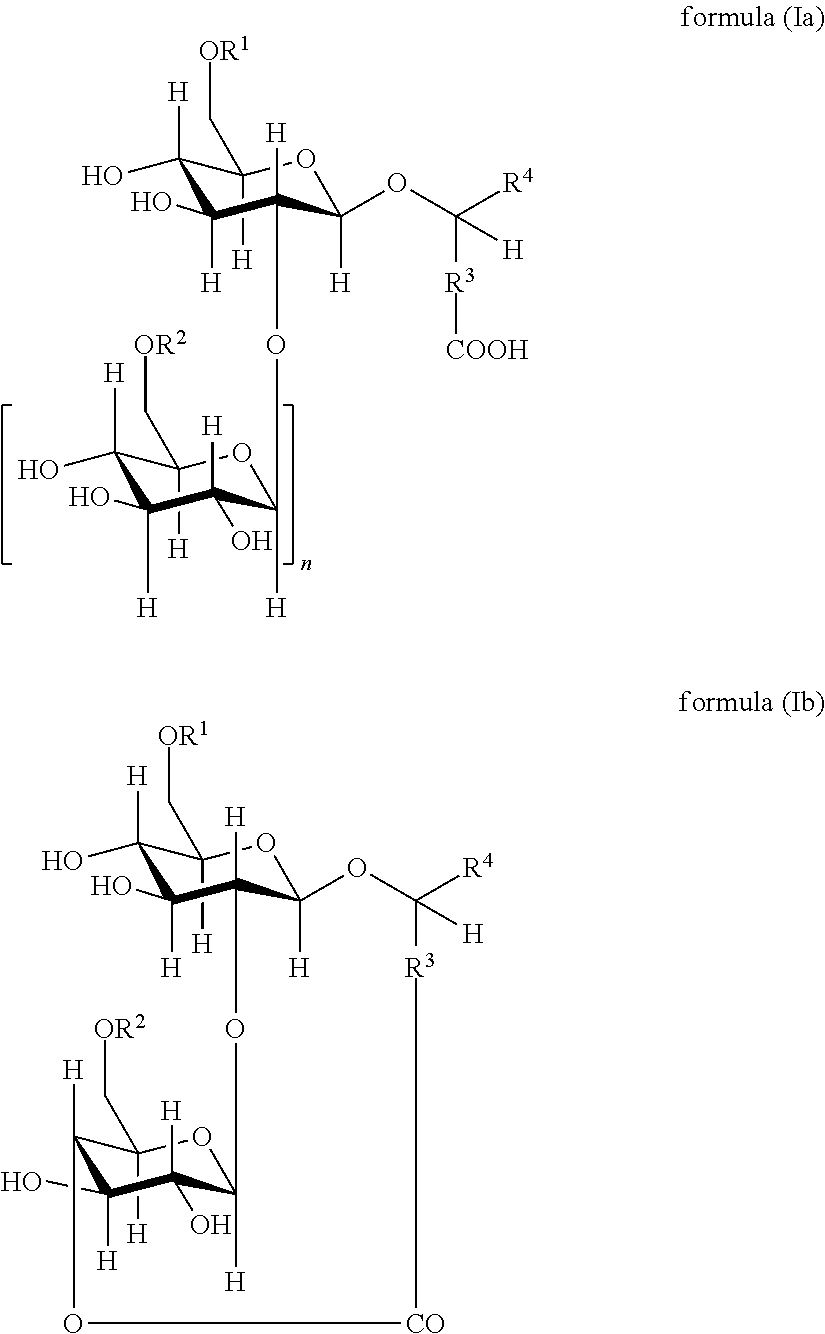
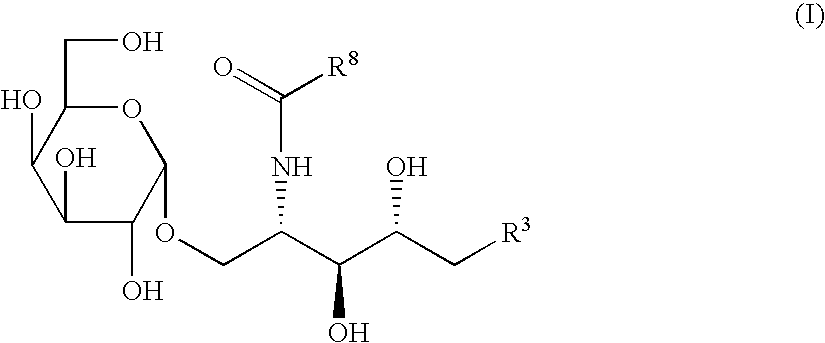
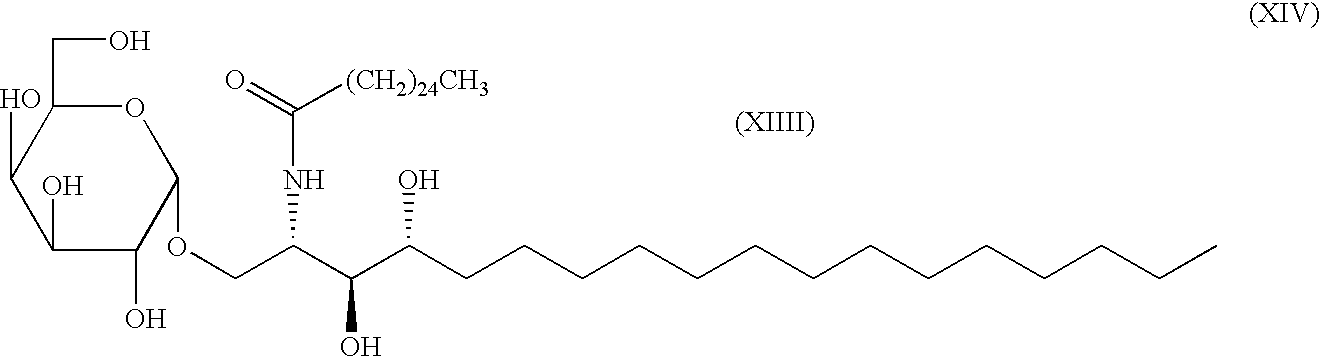
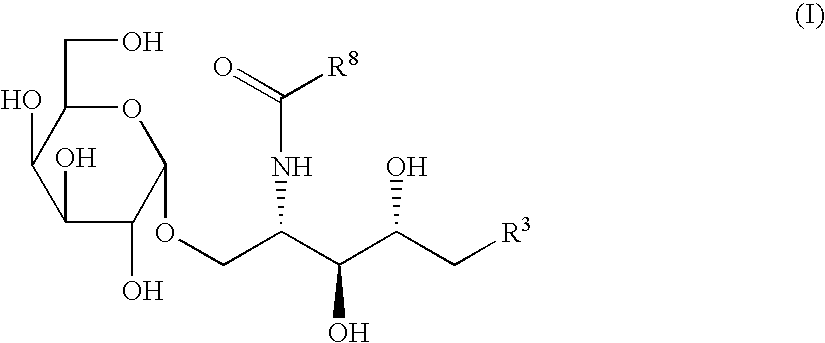
The invention is directed to compounds of formula (I) wherein X is O or NH; R' is a hydrocarbon chain; R<3 >and R<4 >are hydrogen, OH or a monosaccharide; R<5 >is hydrogen or a monosaccharide; Q' is optionally present and may be a C1-10 hydrocarbon; X' is optionally present and may be O, S or NR<8>; and Q<3 >may be a hydrocarbon or hydrogen. The invention is also directed to the use of the compounds for treating cancer, infectious diseases and autoimmune diseases. The invention is also directed to syntheses of the compounds of formula (I).
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
Ophthalmic devices for delivery of hydrophobic comfort agents
ActiveUS20100140114A1Easy to understandPackage sterilisationPharmaceutical delivery mechanismLipid formationMonoglyceride
The invention relates to a soft hydrogel contact lens, especially a silicone hydrogel contact lens, which has a capability of delivering a hydrophobic comfort agent into the eye of a wearer. The hydrophobic comfort agent includes without limitation a monoglyceride, a diglyceride, a triglyceride, a glycolipid, a glyceroglycolipid, a sphingolipid, a sphingo-glycolipid, a phospholipid, a fatty acid, a fatty alcohol, a hydrocarbon having a C12-C28 chain in length, a mineral oil, a silicone oil, or a mixture thereof. It can be released from the soft hydrogel contact lens into the eye of a wearer when being worn so as to strengthen and stabilize the tear film lipid layer and alleviate the dryness of the eye.
Owner:ALCON INC
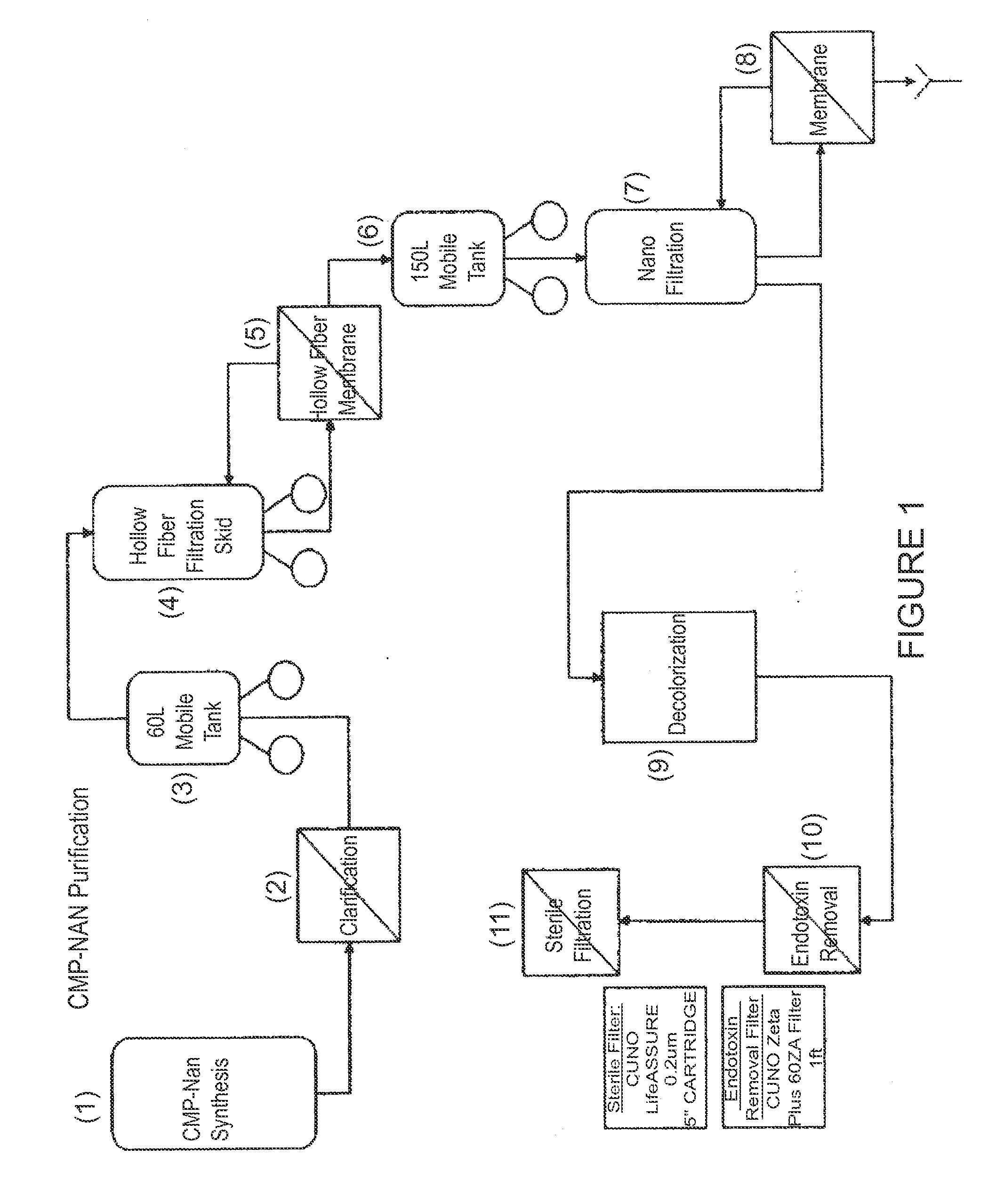
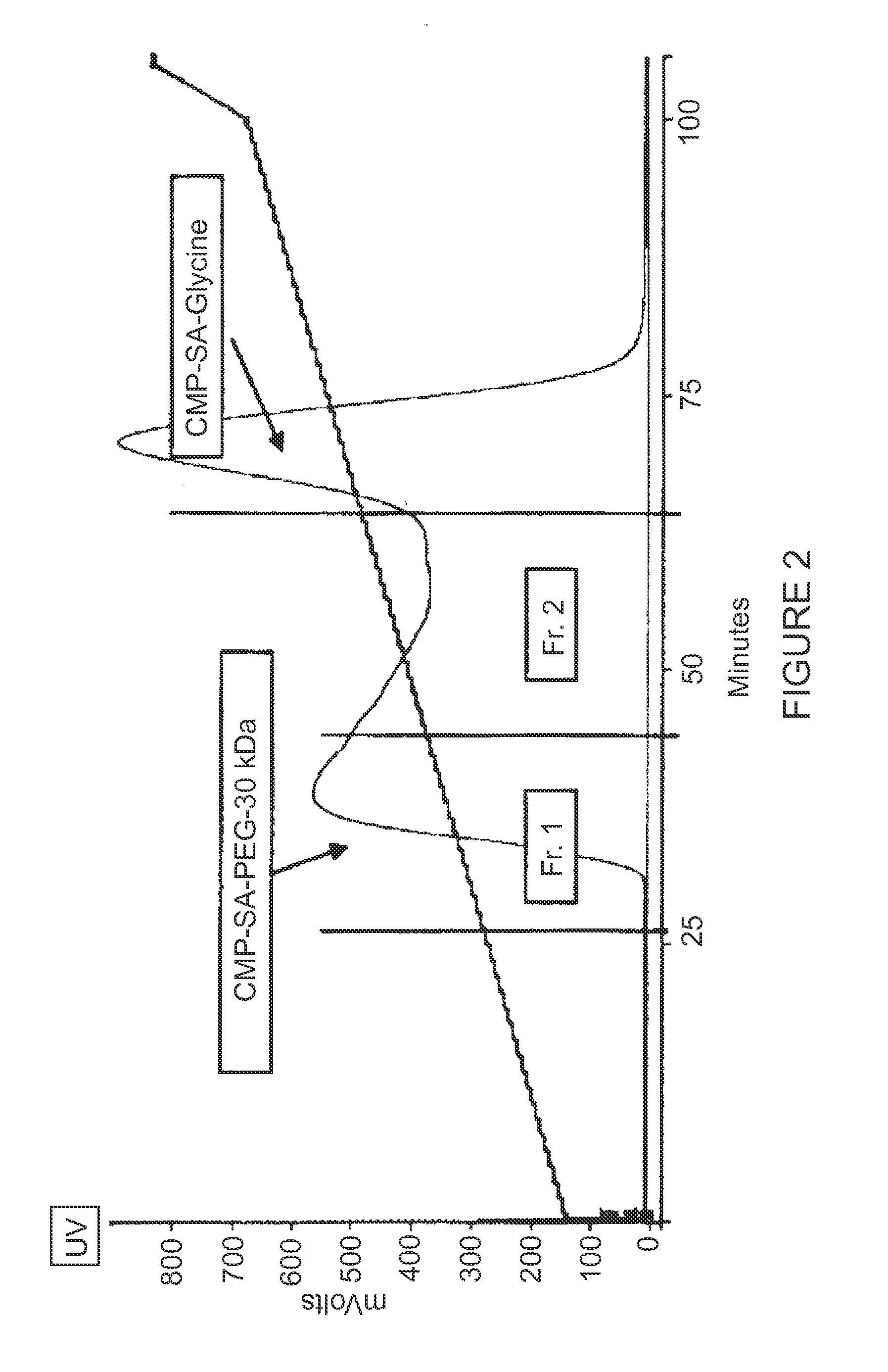
Nucleotide Sugar Purification Using Membranes
InactiveUS20090048440A1Raise the ratioReduce concentrationSugar derivativesChemical recyclingNucleotidePhosphate
The invention provides methods of removing contaminants from a mixture of a desired product and contaminants by pH adjustments and molecular weight cut-offs. The contaminants include phosphate groups, magnesium sulfate, sodium pyruvate and tetrasodium pyrophosphate groups. The desired product includes nucleotide sugars, glycolipids, LnNT, sialyl lactose, and salts.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
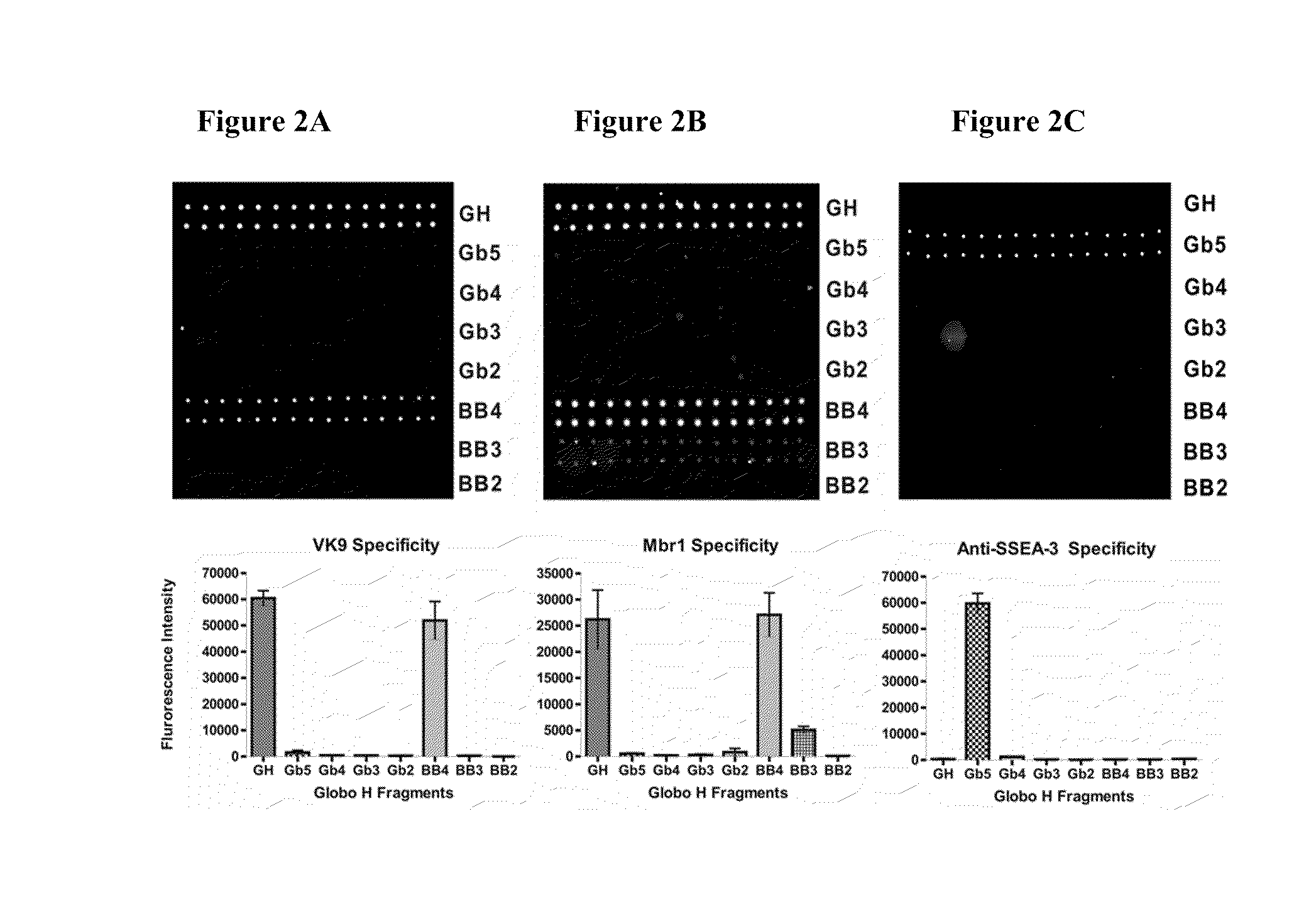
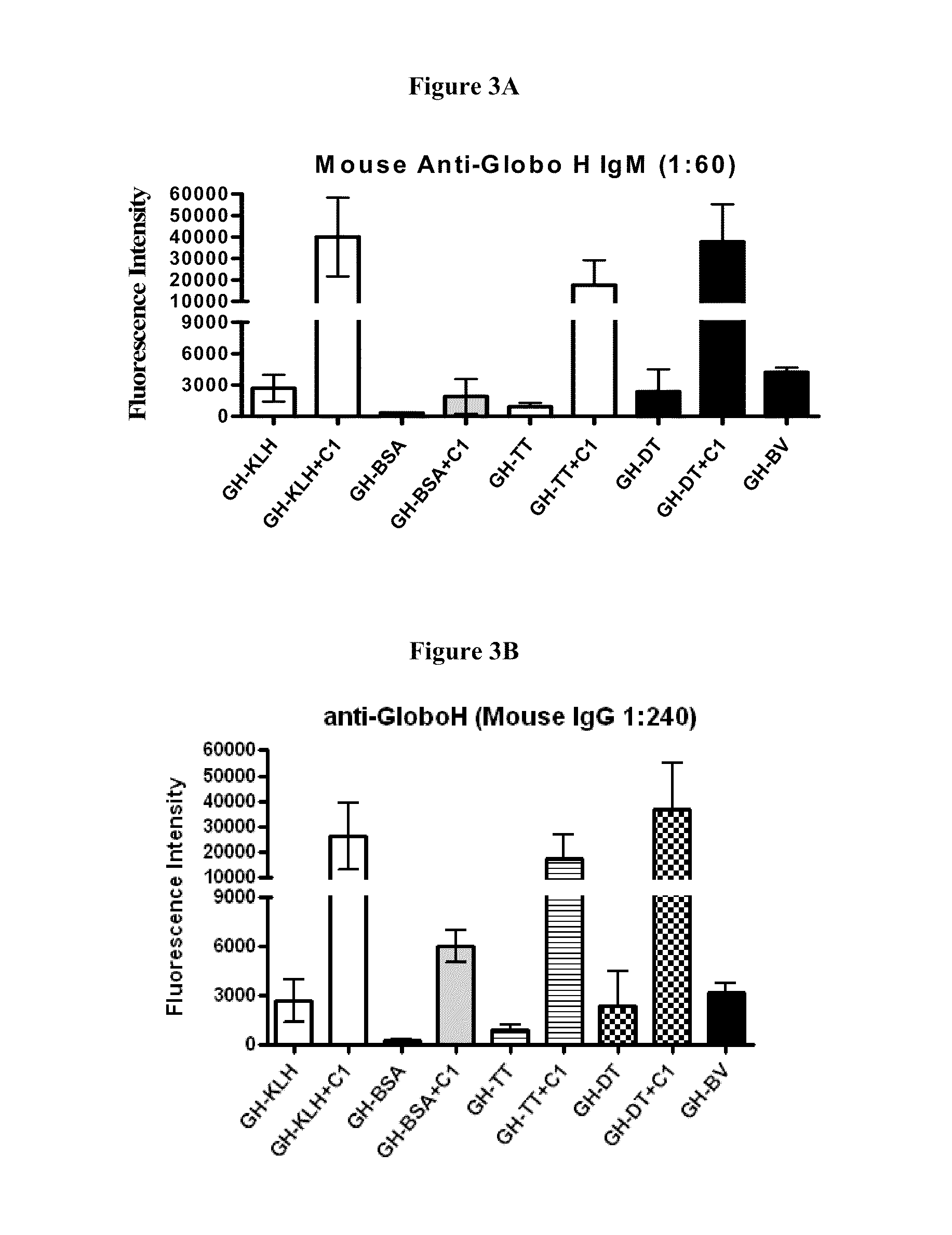
Globo h and related Anti-cancer vaccines with novel glycolipid adjuvants
ActiveUS20100136042A1Shrink tumorInhibit tumor growthOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDendritic cellAdjuvant
Owner:ACAD SINIC
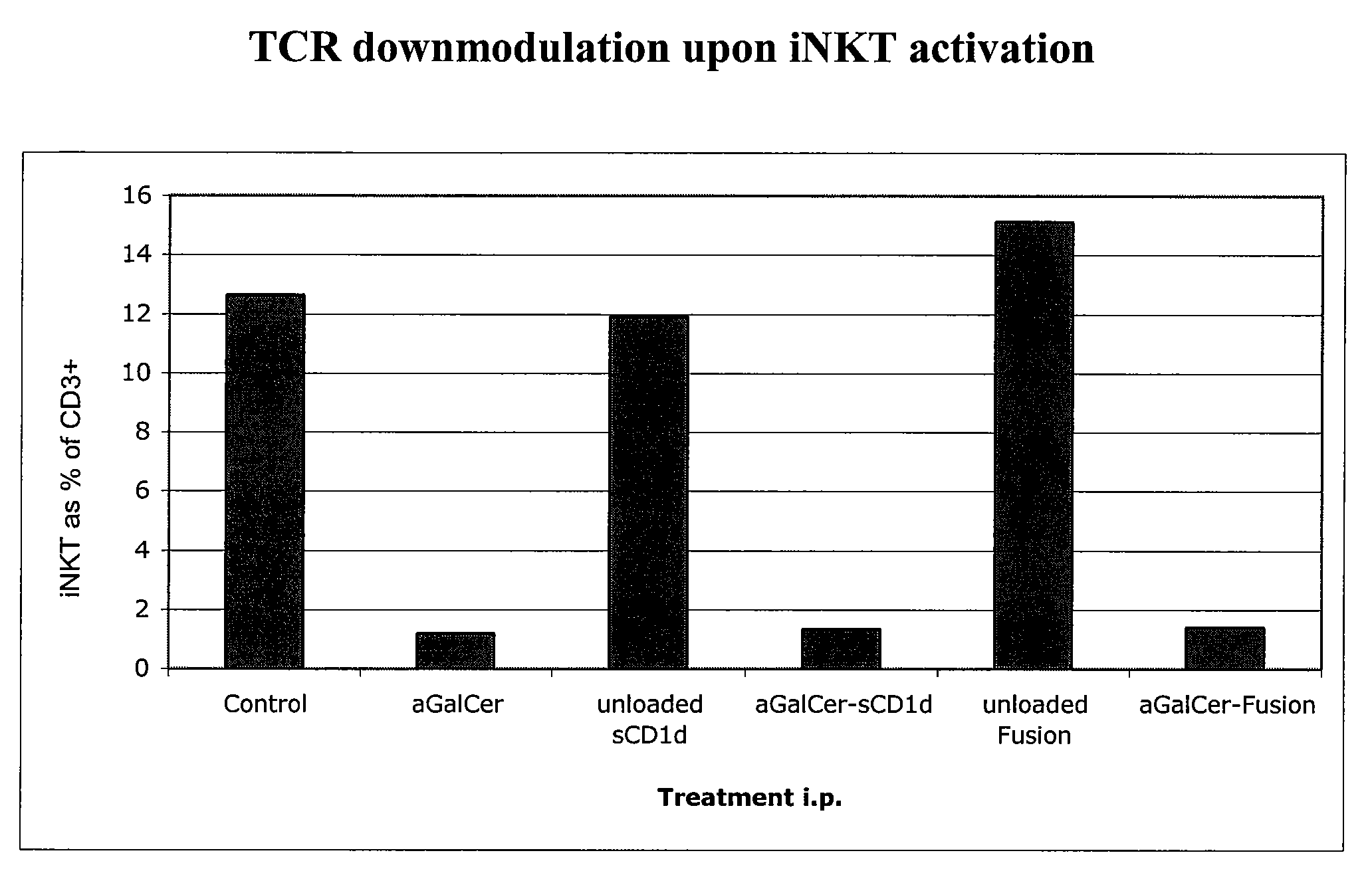
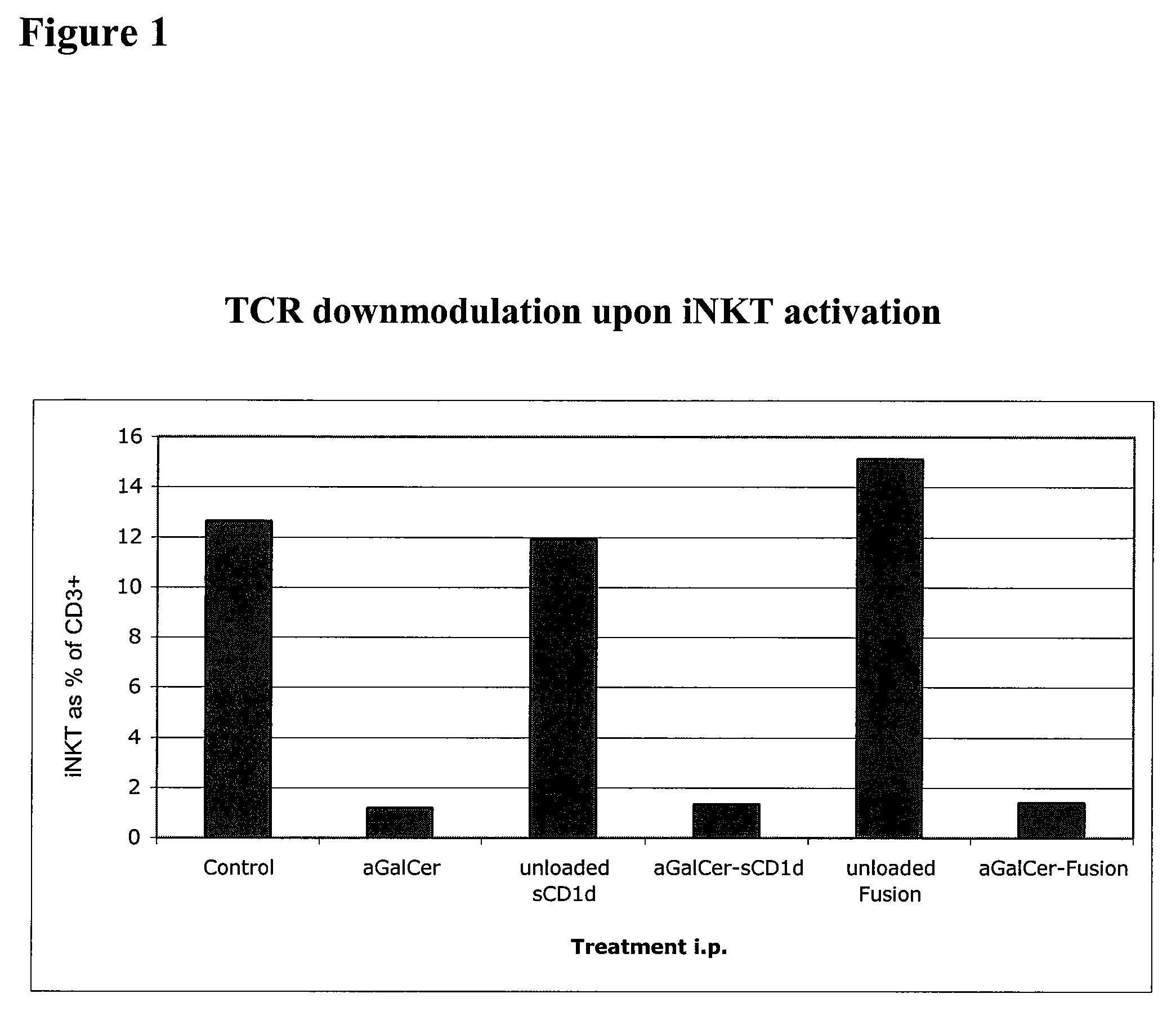
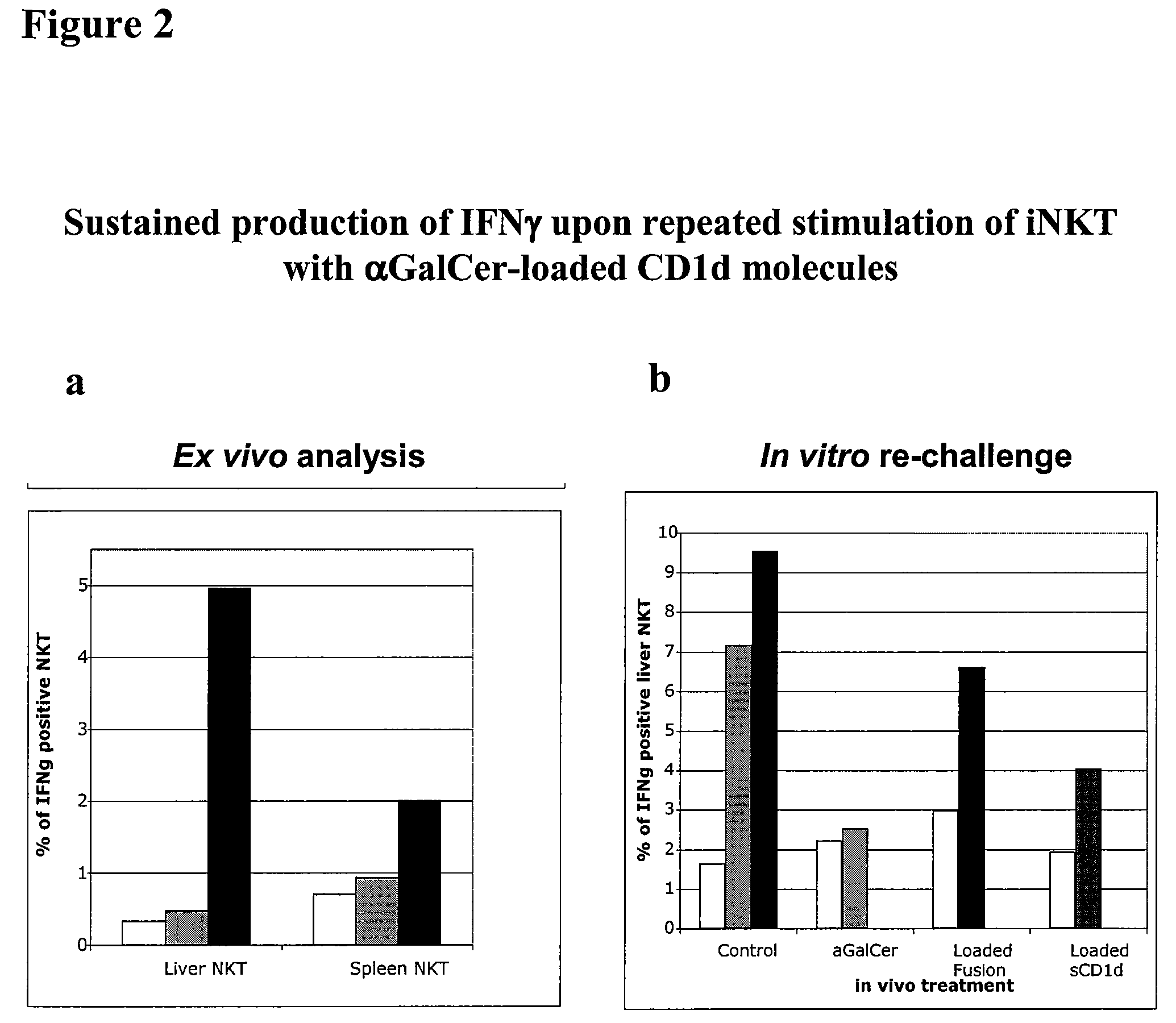
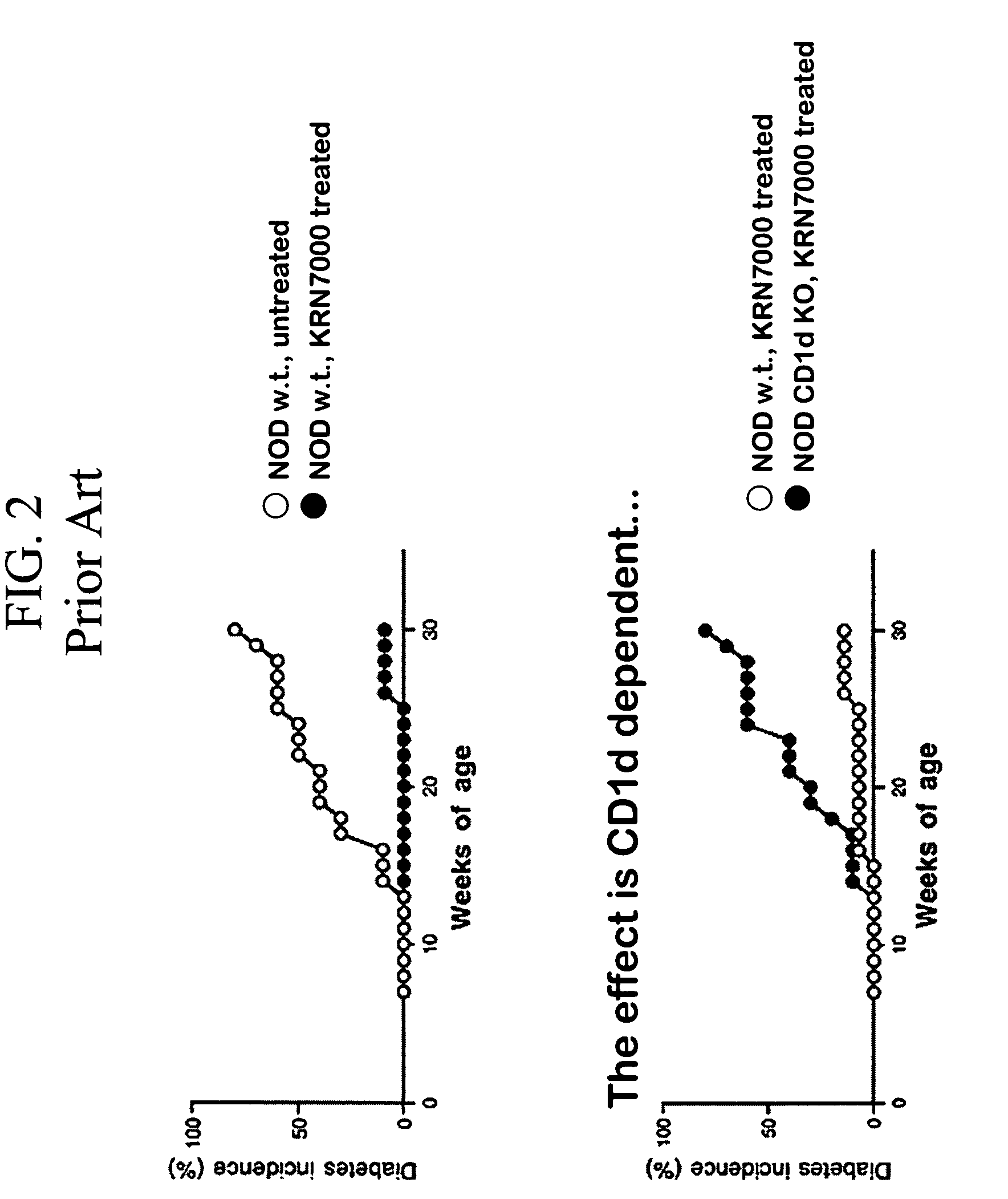
Modulation of NKT Cell Activity with Antigen-Loaded CD1d Molecules
The invention is directed to methods of modulating an immune response in an animal, comprising administering a composition comprising one or more soluble CD1d complexes, in particular non-specific soluble CD1d complexes. Soluble CD1d complexes comprise a soluble CD1d polypeptide, a β2-microglobulin polypeptide, and a ceramide-like glycolipid antigen bound to the CD1d antigen binding groove, and in certain embodiments, an immunogen. The administration of compositions of the present invention affects the activity of CD1d-restricted NKT cells, and in particular, allows for multiple administrations without causing CD1d-restricted NKT cell anergy.
Owner:VACCINEX
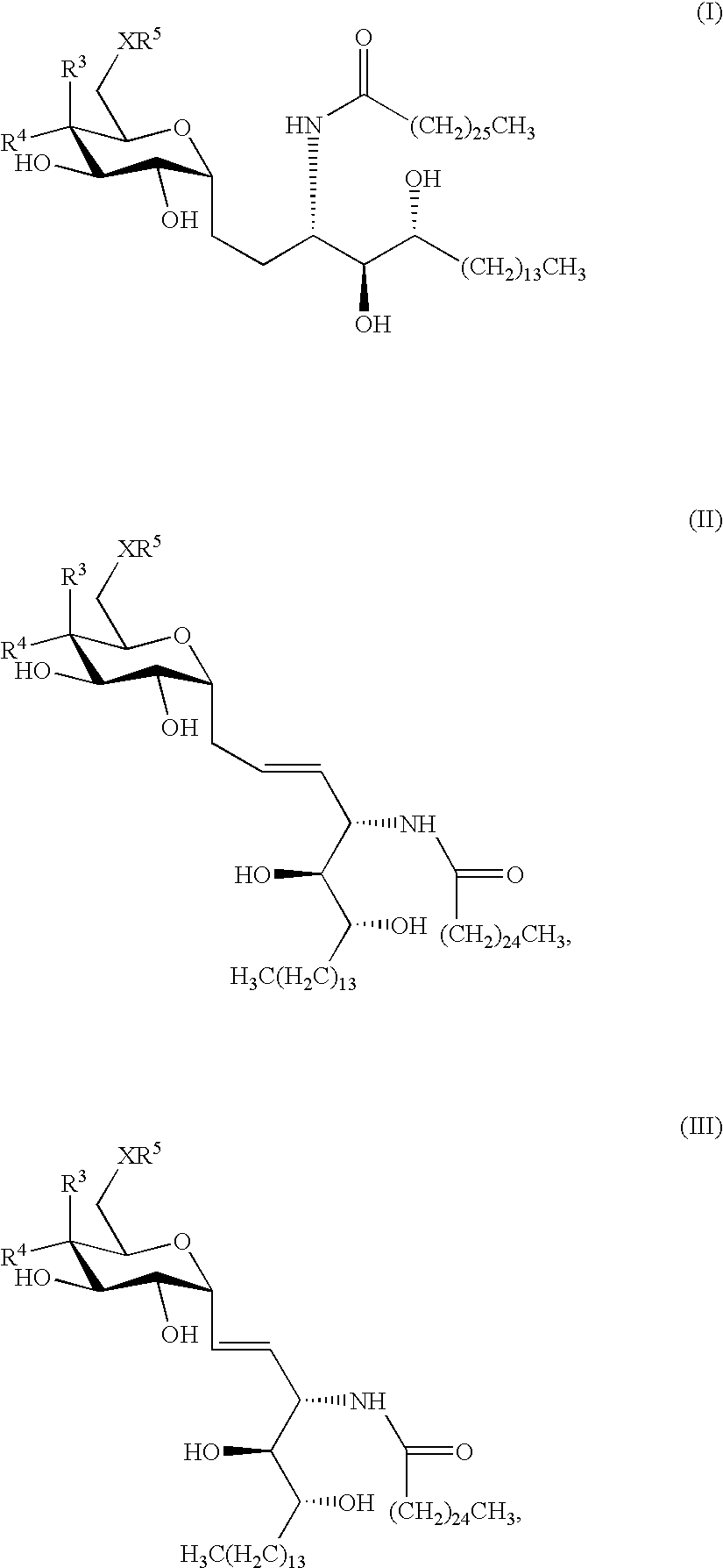
Novel synthetic C-glycolipids, their synthesis and use to treat infections, cancer and autoimmune diseases
InactiveUS20050222048A1Esterified saccharide compoundsAntibacterial agentsAutoimmune diseaseGlycolipid
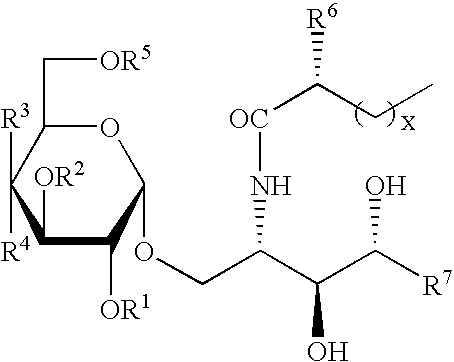
The invention is directed to novel compounds of formulae (I), (II) and (III): wherein X is O or NH; R3 is OH or a monosaccharide and R4 is hydrogen, or R3 is hydrogen and R4 is OH or a monosaccharide; R5 is hydrogen or a monosaccharide; and pharmaceutically acceptable salts or esters thereof. The invention is also directed to the use of the compounds both directly and as immune adjuvants for treating cancer, infectious diseases and autoimmune diseases. The invention is also directed to syntheses of the intermediates which can be used to make these novel compounds.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
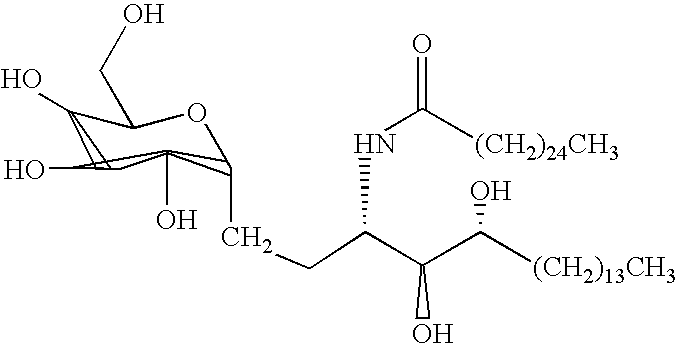
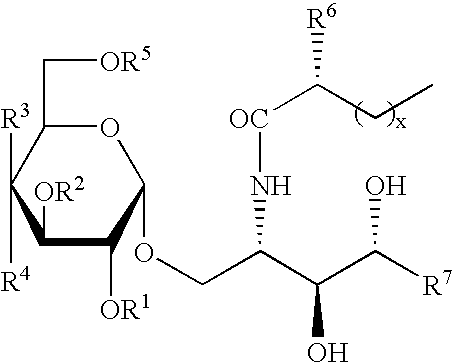
Glycolipid derivative
InactiveUS6635622B2Antitumor activitySave at room temperatureEsterified saccharide compoundsBiocideDouble bondCarbon chain
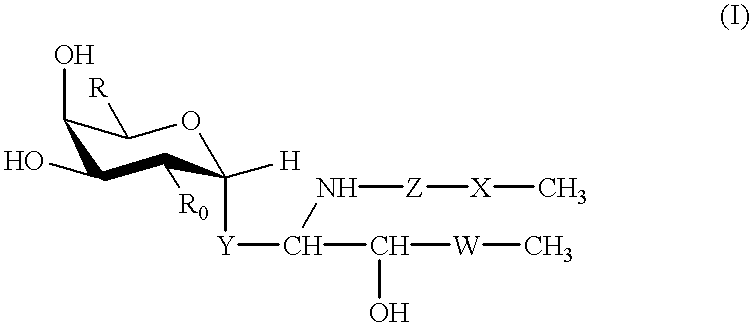
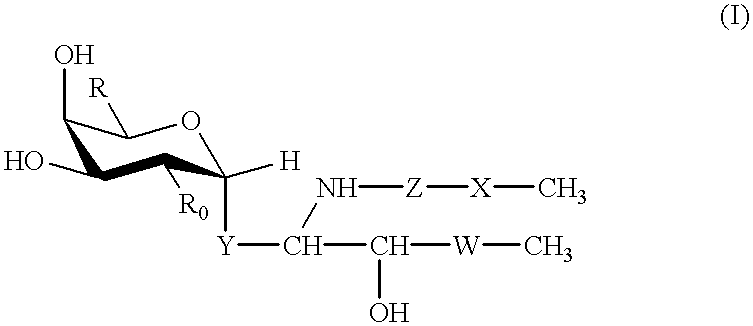
The present invention is a compound of general formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of,wherein W represents carbon chain from 9 to 17 which containing double bond or hydroxy group occasionally; X represents carbon chain from 11 to 25 which containing double bond or hydroxy group occasionally; Y represents -(CH2)a-CH=CH-(CH2)a'-, -(CH2)a- (a, a' denotes an integer of 0-5 and a+a' is 5 and under.), -S(O)0-2CH2-, -NHCH2-; Z represents -CO-, -SO2-; R represents -CH2OH, CO2H, CH2OCH2CO2SO3H; R0 represents -OH, -NH2, -NHAc.
Owner:KOTOBUKI PHARMA CO LTD
Conjugate vaccines for non-proteinaceous antigens
InactiveUS20070231344A1Strong and rapid effectStrong and rapid immune responseBacterial antigen ingredientsLipid/lipoprotein ingredientsAntigenConjugate vaccine
The present invention is directed to pharmaceutical compositions that can be used to immunize subjects using, for example, lipid, glycan, or nucleic acid antigens. These antigens are conjugated to a glycosphingolipid.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Compositions and methods for stabilizing lipid based adjuvant formulations using glycolipids
ActiveUS20060008519A1Increase moisturePrevent dehydrationBacterial antigen ingredientsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsLipid formationAntigen
The present invention relates to liposome formulations that are physically stable. In particular the present invention relates to steric stabilization of cationic liposomes by incorporating glycolipids into the liposomes. The stabilized liposomes can be used either as an adjuvant for antigenic components or as a drug delivery system. In particular the invention relates to vaccines with adjuvants in aqueous media for immunization, where the final product is stable.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST
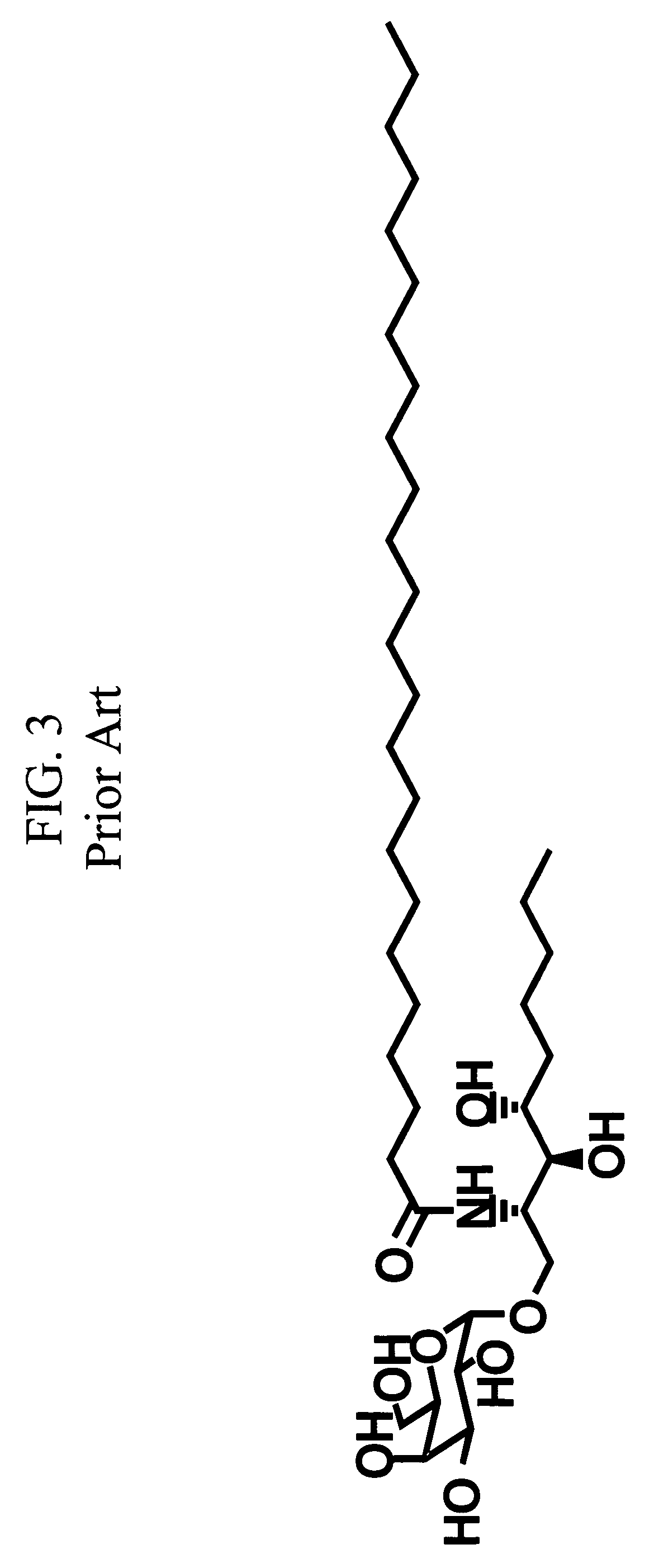
Ceramide derivatives as modulators of immunity and autoimmunity
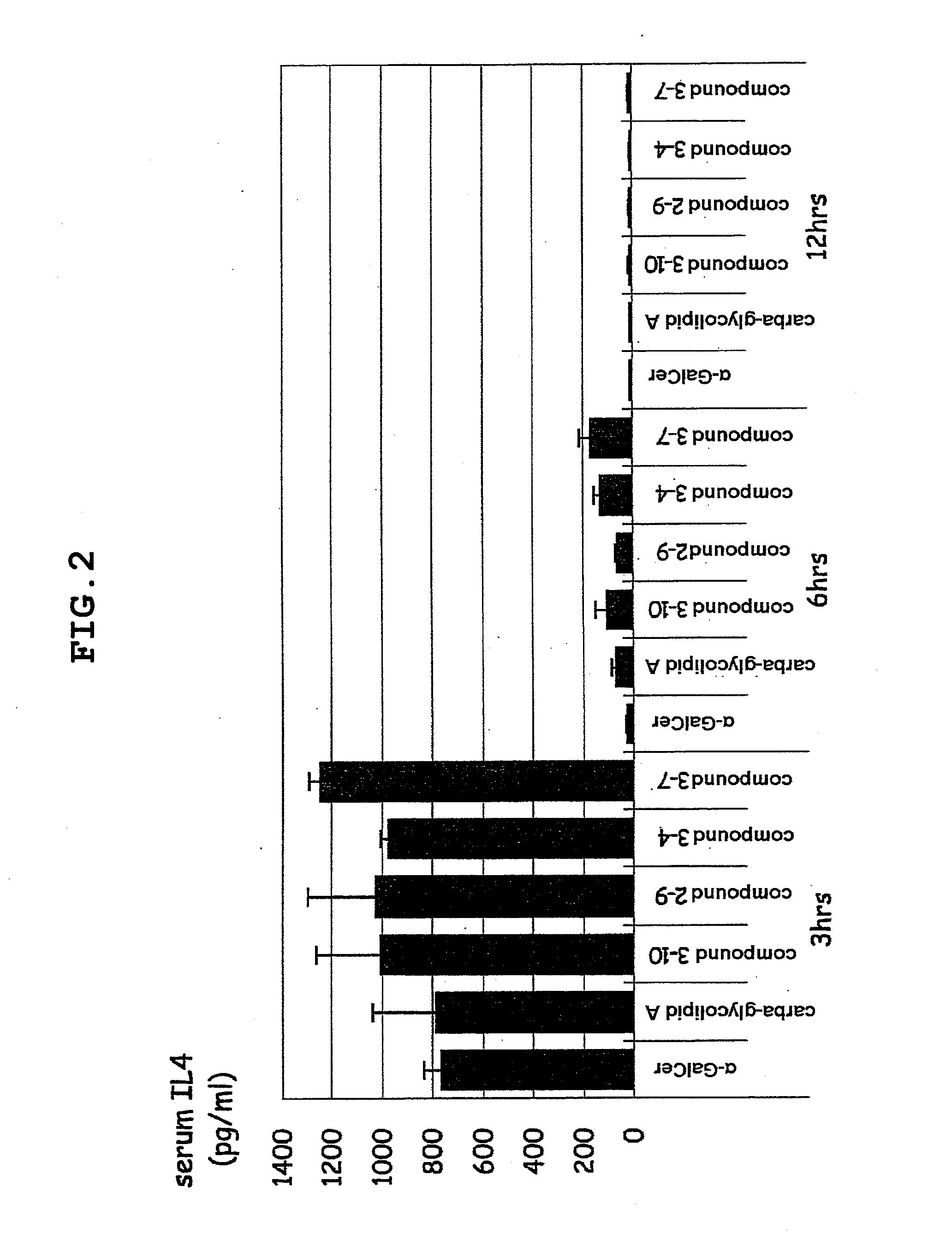
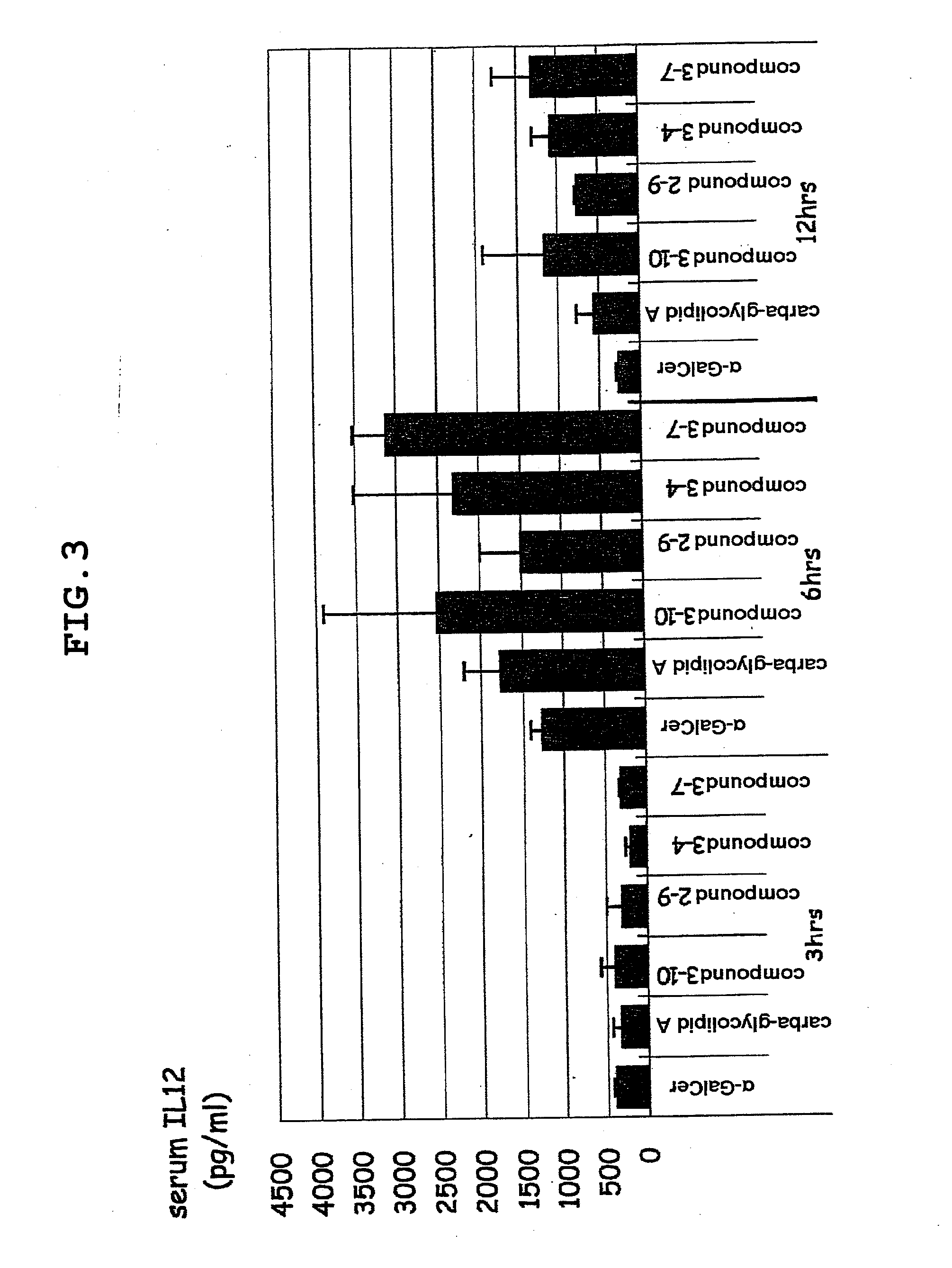
α-Galactosylceramides and glycosylceramides (“ceramide-like glycolipids”) that modulate NK T cells. The ceramide-like glycolipids vary in the cytokines induced in NK T cells and vary in the antigen-presenting cells that are capable of efficiently presenting the compounds to NK T cells. Pharmaceutical compositions of the ceramide-like glycolipids are provided, as are pharmaceutical compositions of the ceramide-like glycolipids combined with dendritic cells. Methods utilizing the ceramide-like glycolipids in vaccines, to activate NK T cells, to stimulate the immune system, and to treat mammals are also provided. The invention also provides methods of evaluating a compound for its ability to activate an NK T cell in the presence of a cell expressing a CD1d protein.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
Compositions having glycolipid to lighten skin and alter post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation
InactiveUS20040126344A1Decreasing rate of uptake and processing and retentionAlter recognitionCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsGlycolipidDermatology
There is provided a composition for lightening skin having an effective amount of a glycolipid. There is also provided a composition for lightening skin having an effective amount of a glycolipid and a second lightening material. There is also provided methods for lightening skin including applying the compositions of the present invention to the skin.
Owner:AVON PROD INC
Method of improving dough and bread quality
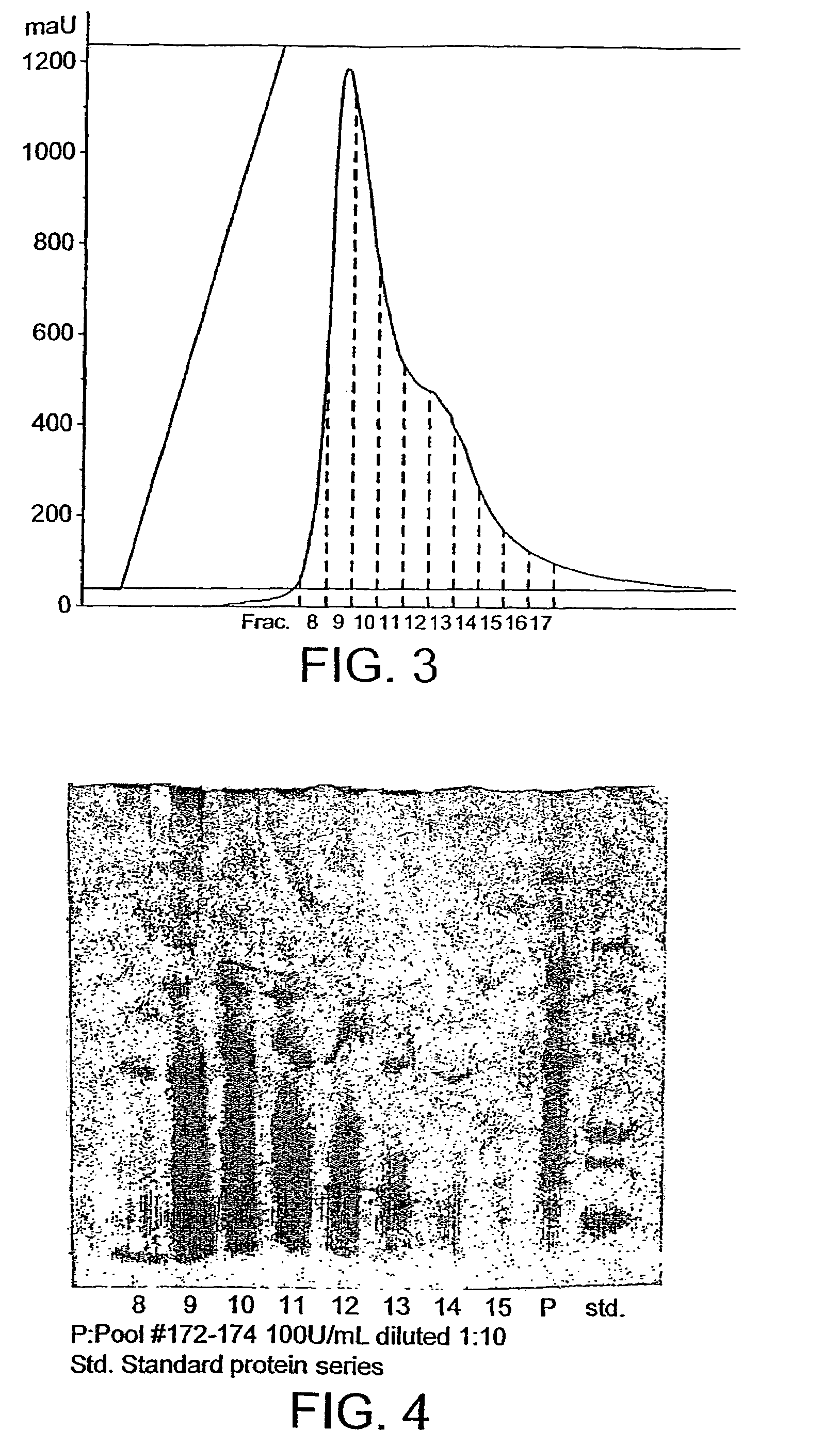
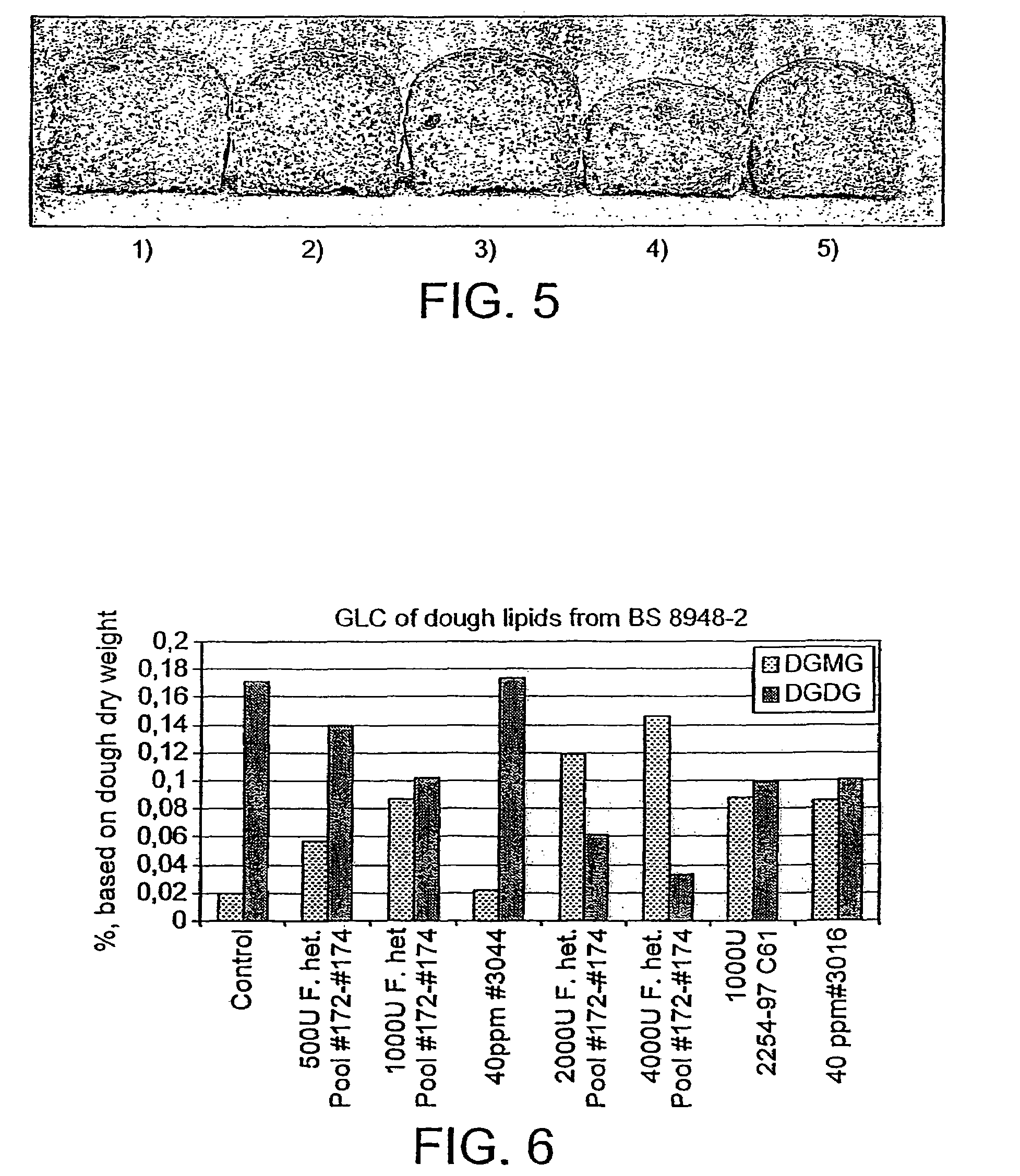
InactiveUS6967035B2Increase gluten strengthDough is prevented from becoming too stiffDough treatmentHydrolasesMonoglycerideTriglyceride
A method of preparing a flour dough, said method comprising adding to the dough components an enzyme that under dough conditions is capable of hydrolysing a glycolipid and a phospholipid, wherein said enzyme is incapable, or substantially incapable, of hydrolysing a triglyceride and / or a 1-monoglyceride, or a composition comprising said enzyme, and mixing the dough components to obtain the dough.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Ceramide derivatives as modulators of immunity and autoimmunity
α-Galactosylceramides and glycosylceramides (“ceramide-like glycolipids”) that modulate NK T cells. The ceramide-like glycolipids vary in the cytokines induced in NK T cells and vary in the antigen-presenting cells that are capable of efficiently presenting the compounds to NK T cells. Pharmaceutical compositions of the ceramide-like glycolipids are provided, as are pharmaceutical compositions of the ceramide-like glycolipids combined with dendritic cells. Methods utilizing the ceramide-like glycolipids in vaccines, to activate NK T cells, to stimulate the immune system, and to treat mammals are also provided. The invention also provides methods of evaluating a compound for its ability to activate an NK T cell in the presence of a cell expressing a CD1d protein.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
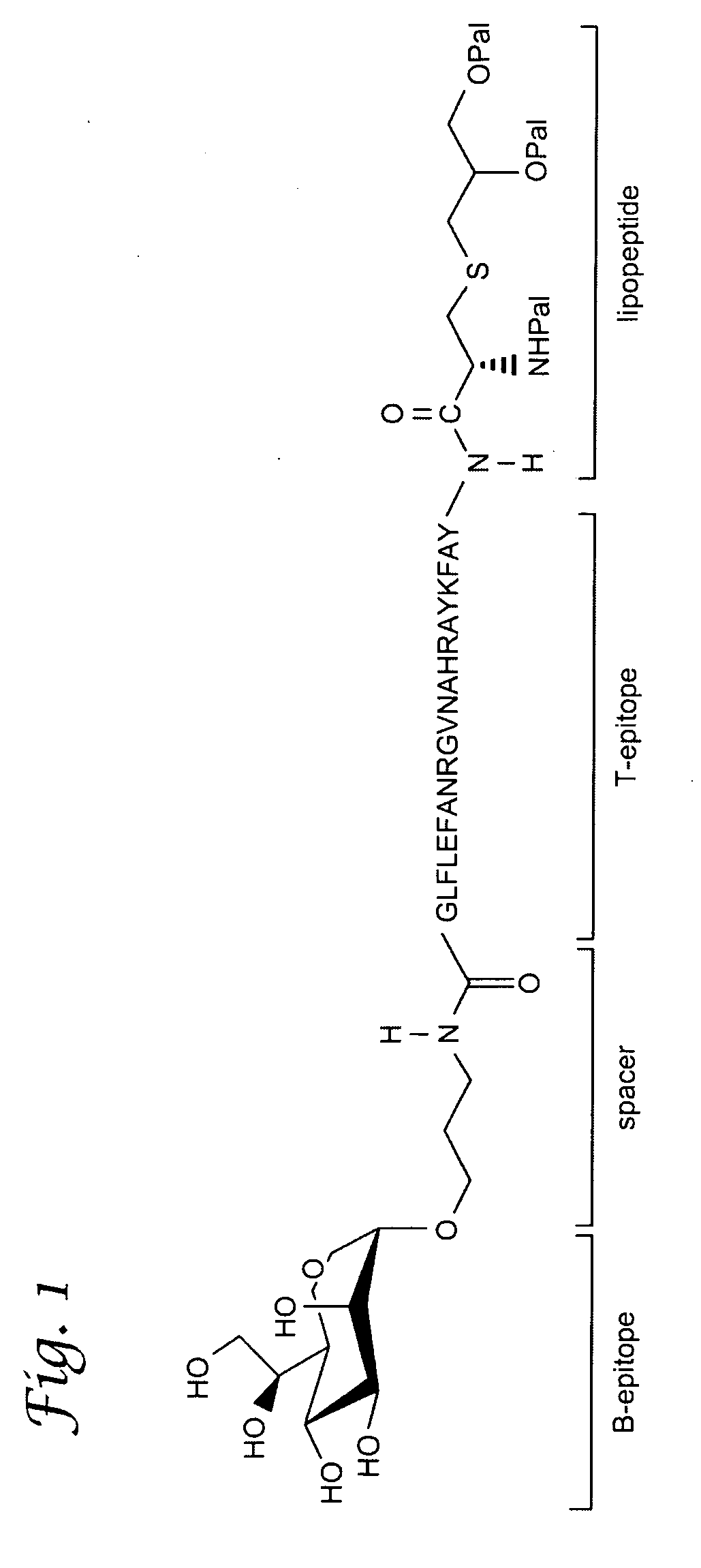
Glycolipopeptide and uses thereof
ActiveUS20090041836A1Reduce deliveryConvenience to mergeAntibacterial agentsVirusesPolyclonal antibodiesGlycolipid
A glycolipopeptide comprising a carbohydrate component, a peptide component and a lipid component, for use as a therapeutic or prophylactic vaccine. Also provided are monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies that recognize the glycolipopeptide of the invention, as well as uses thereof.
Owner:GEORGIA RESERACH FOUND INC UNIV OF
Synthetic C-glycolipid and its use for treating cancer, infectious diseases, and autoimmune diseases
InactiveUS20060019246A1Improve in vivo stabilityBiocideAntiviralsAutoimmune conditionInfectious Disorder
The invention is directed to compounds of formula (I) wherein X is O or NH; R′ is a hydrocarbon chain; R3 and R4 are hydrogen, OH or a monosaccharide; R5 is hydrogen or a monosaccharide; Q′ is optionally present and may be a C1-10 hydrocarbon; X′ is optionally present and may be O, S or NR8; and Q3 may be a hydrocarbon or hydrogen. The invention is also directed to the use of the compounds for treating cancer, infectious diseases and autoimmune diseases. The invention is also directed to syntheses of the compounds of formula (I).
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV +1
Long chain glycolipids useful to avoid perishing or microbial contamination of materials
InactiveUS20140178444A1Cost-effective processReduce the overall heightAntibacterial agentsBiocideMicroorganismCompound (substance)
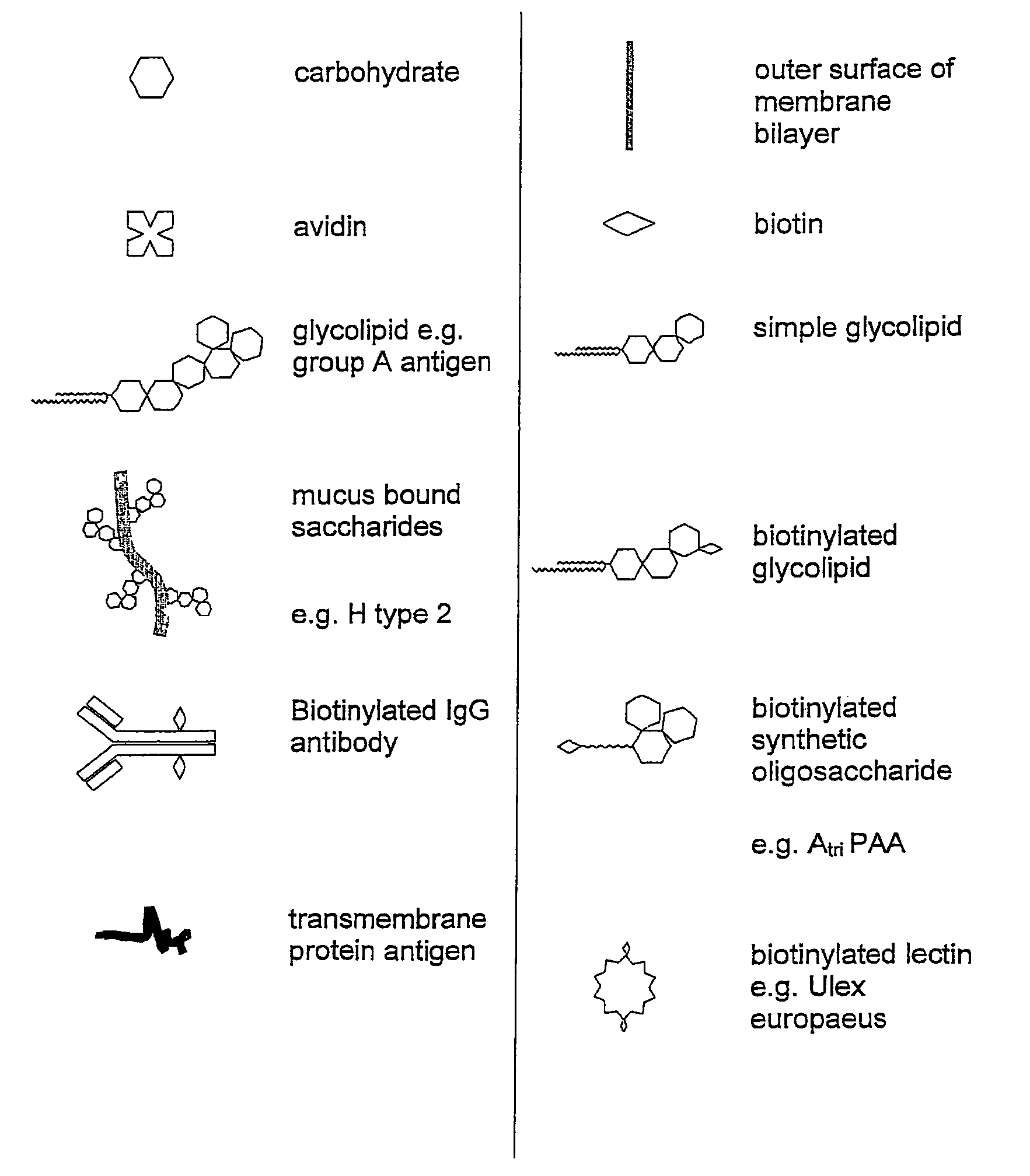
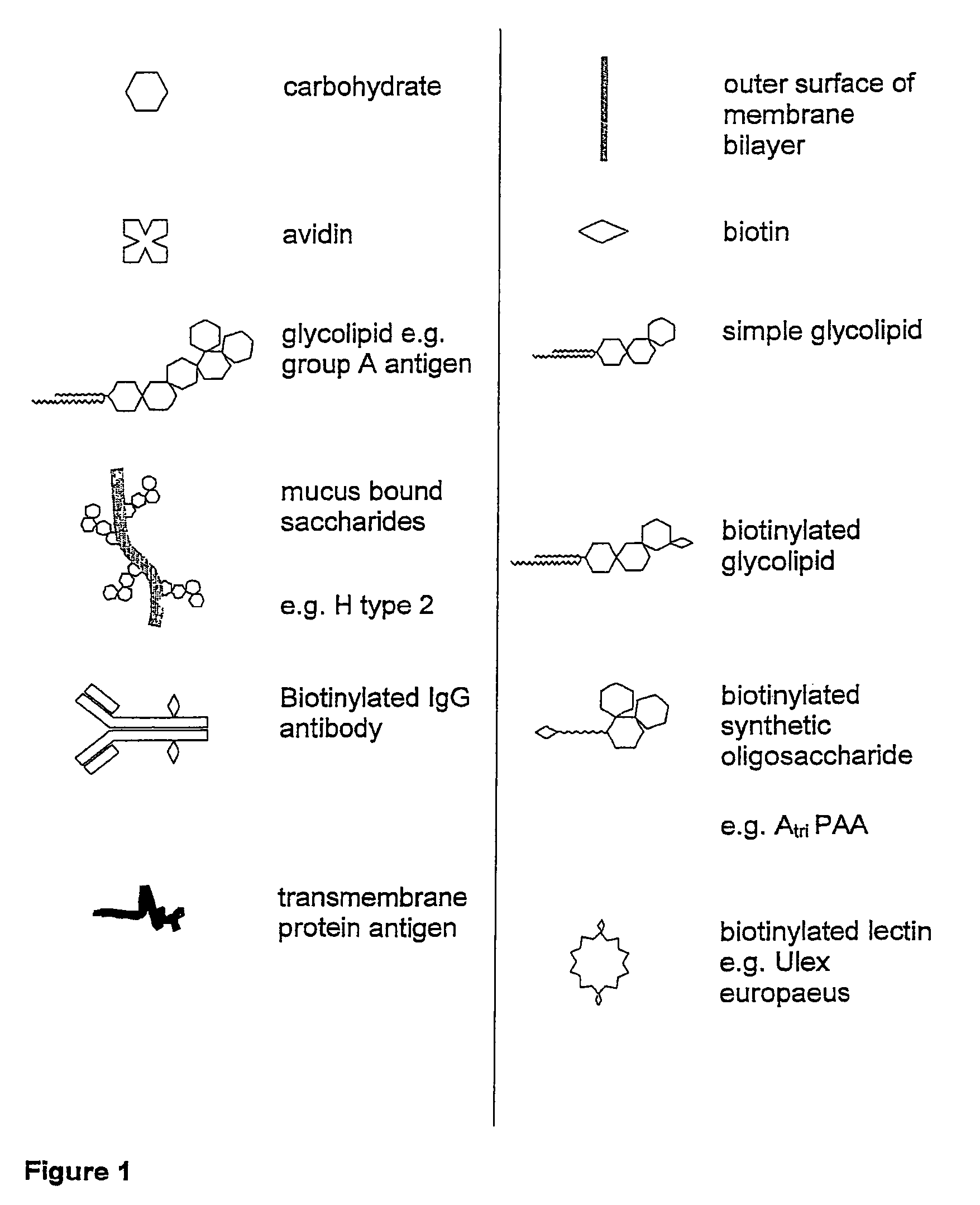
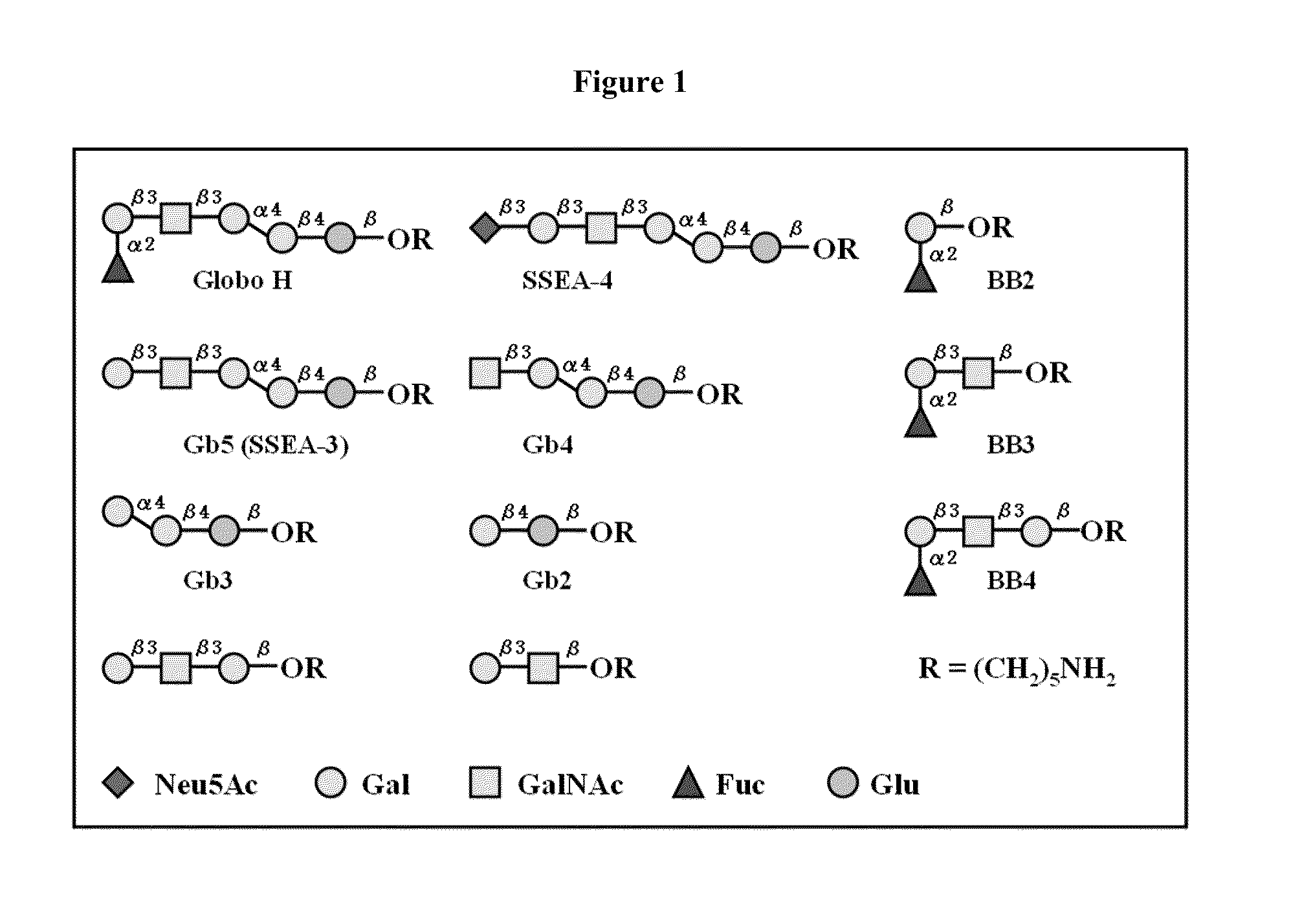
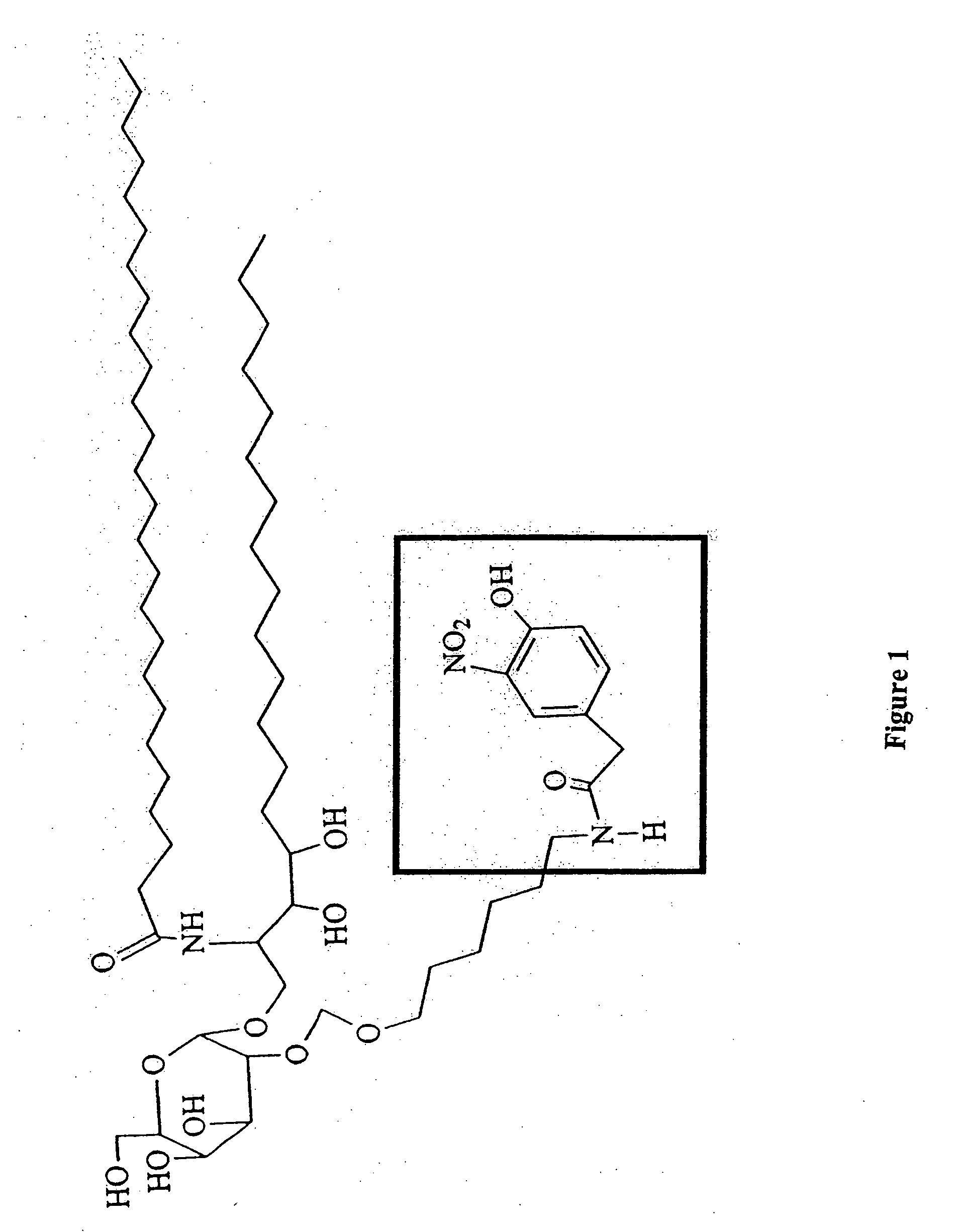
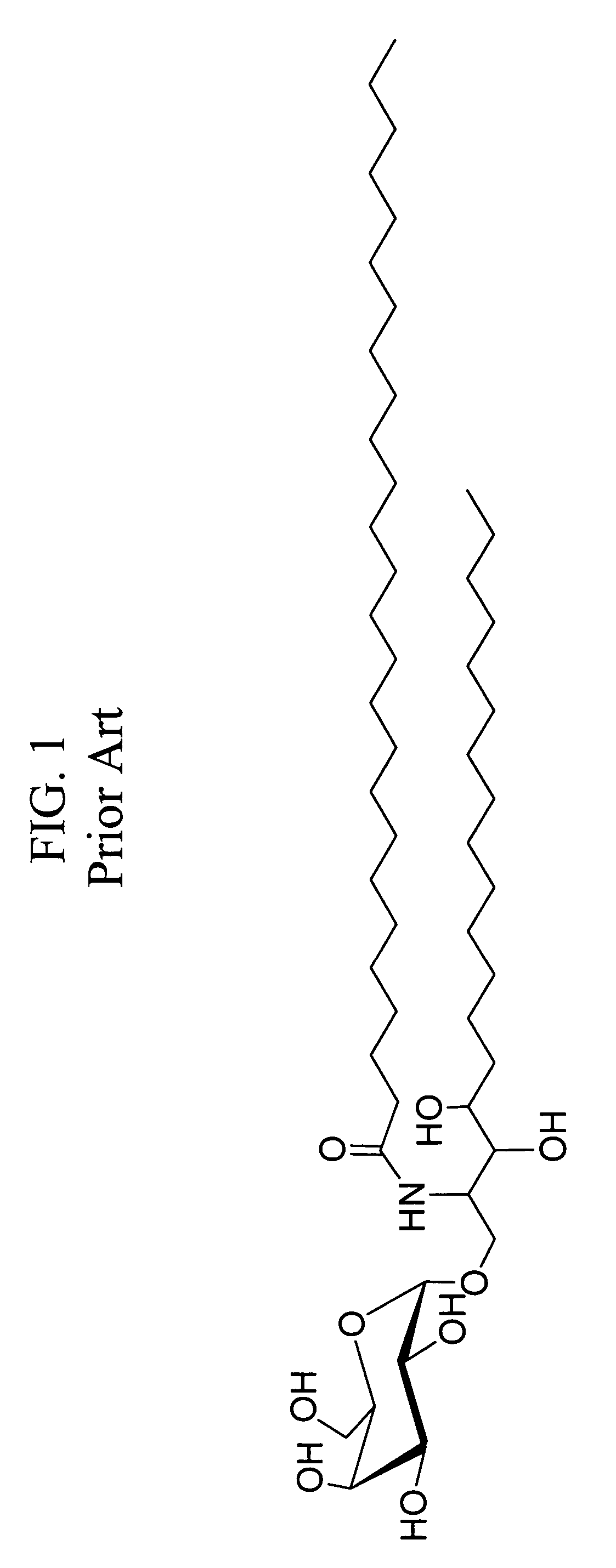
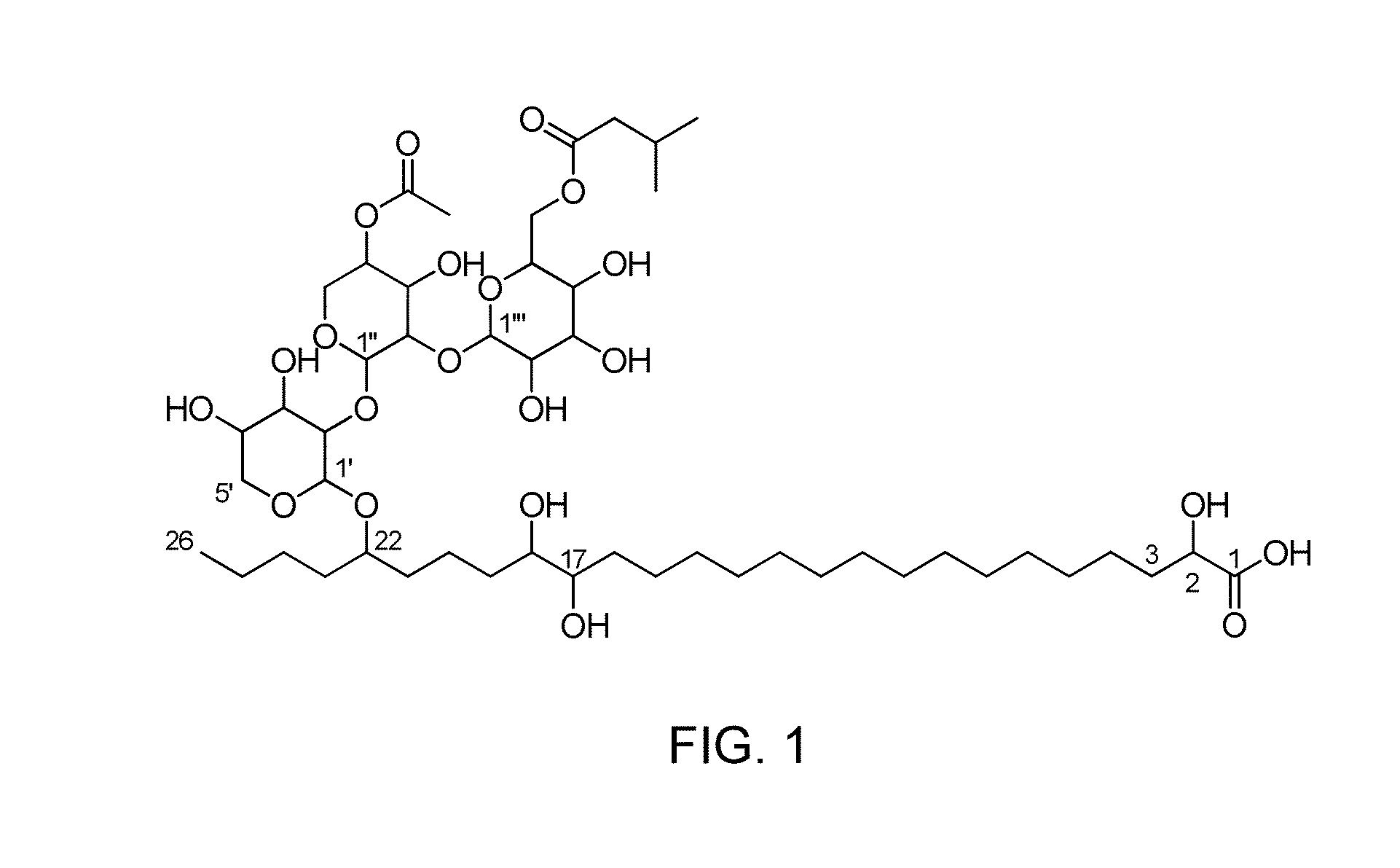
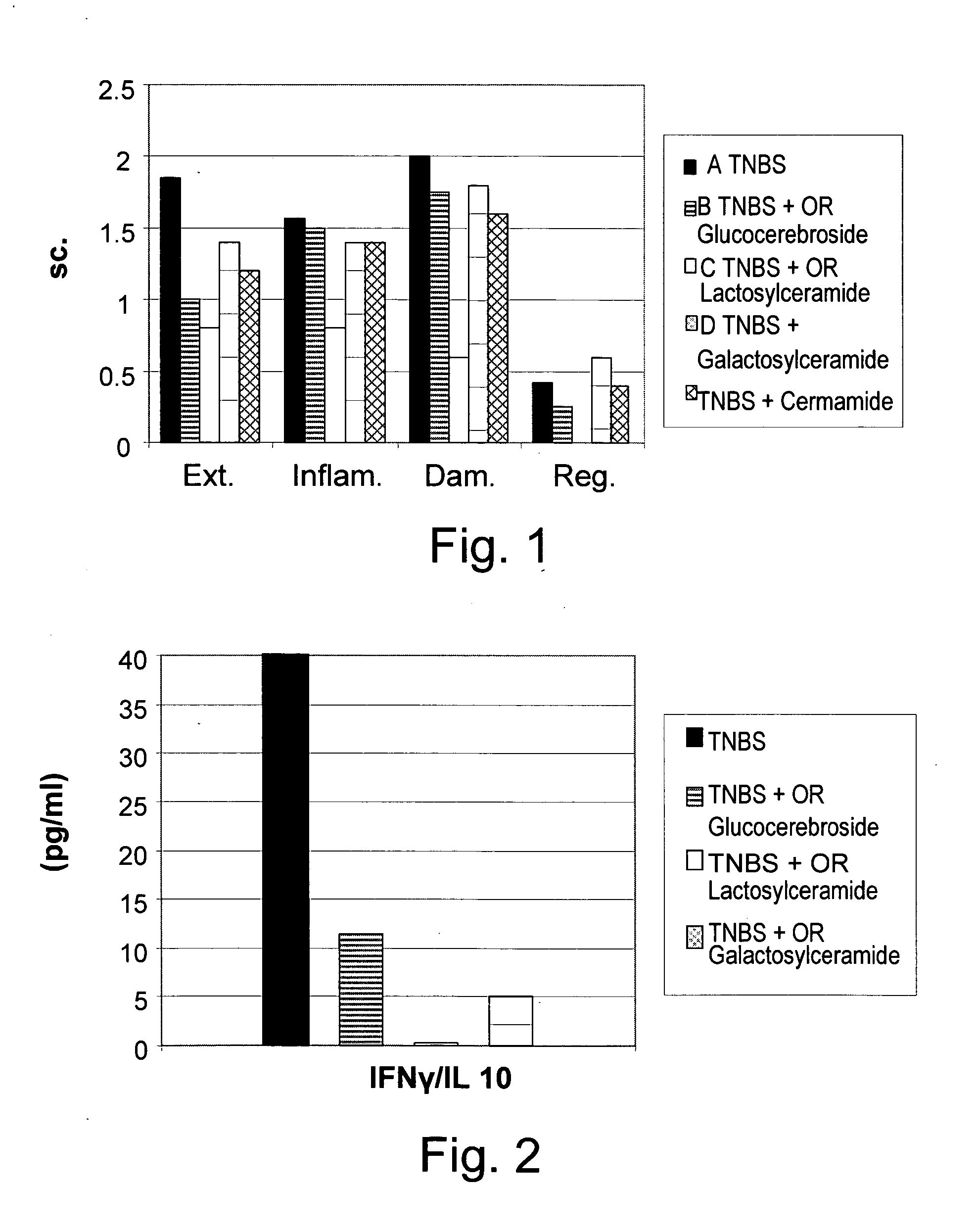
The invention relates to the use of, and methods of use employing, certain glycolipid compounds as defined in detail below and having preservative or antimicrobial properties, novel compounds of the glycolipid class, and related invention embodiments.The compounds have the formula Iwherein m is 3 to 5, n is 2 to 5, o is 0 or 1 and p is 3 to 17, with the proviso that the sum m+n+o+p is not less than 14; andR is a carbohydrate moiety bound via one of its carbon atoms to the binding oxygen,and / or a physiologically, especially pharmaceutically or nutraceutically or cosmetically, acceptable salt thereof, or an ester thereof,as such or in the form of a composition,where the compound may be present in open chain form and / or in the form of a lactone (FIG. 1).
Owner:IMD NATURAL SOLUTIONS GMBH
Novel glycolipid and use thereof
ActiveUS20110104188A1Guaranteed specific capacityEffective treatmentBiocideSkeletal disorderCancer treatmentGlycolipid
The invention provides a glycolipid effective for cancer treatment and the like and a synthetic intermediate therefor, as well as a medicament containing the glycolipid and the like. The glycolipid is represented by the formula (1) or a salt thereof
Owner:RIKEN
Nucleotide sugar purification using membranes
The invention provides methods of removing contaminants from a mixture of a desired product and contaminants by pH adjustments and molecular weight cut-offs. The contaminants include phosphate groups, magnesium sulfate, sodium pyruvate and tetrasodium pyrophosphate groups. The desired product includes nucleotide sugars, glycolipids, LnNT, sialyl lactose, and salts.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Lipolytic enzyme: uses thereof in the food industry
The invention encompasses the use of a lipolytic enzyme obtainable from one of the following genera: Streptomyces, Corynebacterium and Thermobifida in various methods and uses, wherein said lipolytic enzyme is capable of hydrolysing a glycolipid or a phospholipid or transferring an acyl group from a glycolipid or phospholipids to an acyl acceptor. Preferably, the lipolytic enzyme for use in these methods and uses comprises an amino acid sequence as shown in any one of SEQ ID NOs: 4, 5, 7, 8, 12, 14 or 16 or an amino acid sequence having at least 70% identity therewith or comprises a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 3, 6, 9, 13, 15 or 17 or a nucleotide sequence which has at least 70% identity therewith. The present invention also relates to a lipolytic enzyme capable of hydrolysing at least a galactolipid or capable of transferring an acyl group from a galactolipid to one or more acyl acceptor substrates, wherein the enzyme is obtainable from Streptomyces species and includes a lipolytic enzyme comprising an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 4 or an amino acid sequence which has at least 60% identity thereto. The enzyme may be encoded by a nucleic acid selected from the group consisting of: a) a nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence show in SEQ ID NO: 3; b) a nucleic acid which is related to the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO: 3 by the degeneration of the genetic code; and c) a nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence which has at least 70% identity with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 3.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Freezer to retarder to oven dough
A frozen dough comprising flour, a high yeast level comprising one or more yeast with activity covering temperature range of 33-140° F., emulsifiers, dough conditioners, stabilizers, sugar, lipid source and optionally supplemental gluten such that the frozen dough does not require a conventional proofing (proofer) step prior to freezing or prior to baking. When the frozen dough is thawed in a retarder at 33-42° F. for at least 12 hours, or at an elevated temperature of between 43-85° F. for at least 1 hour, and then baked, the baked products have good appearance, taste and texture, and a specific volume of at least 4 cc / gram.
Owner:RICH PRODUCTS
Process for the preparation of rice bran oil low in phosphorous content
InactiveUS6706299B2Simple and economical and fast processReduce processing stepsFatty-oils/fats refiningCheese manufacturePhosphoric acidPulp and paper industry
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Cells, nucleic acids, enzymes and use thereof, and methods for the production of sophorolipids
InactiveUS20130035403A1Performance parameters of sophorolipid formation, suchHigh yieldOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsEnzymeNucleic acid
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Methods for therapeutic use of glucosylceramide synthesis inhibitors and composition thereof
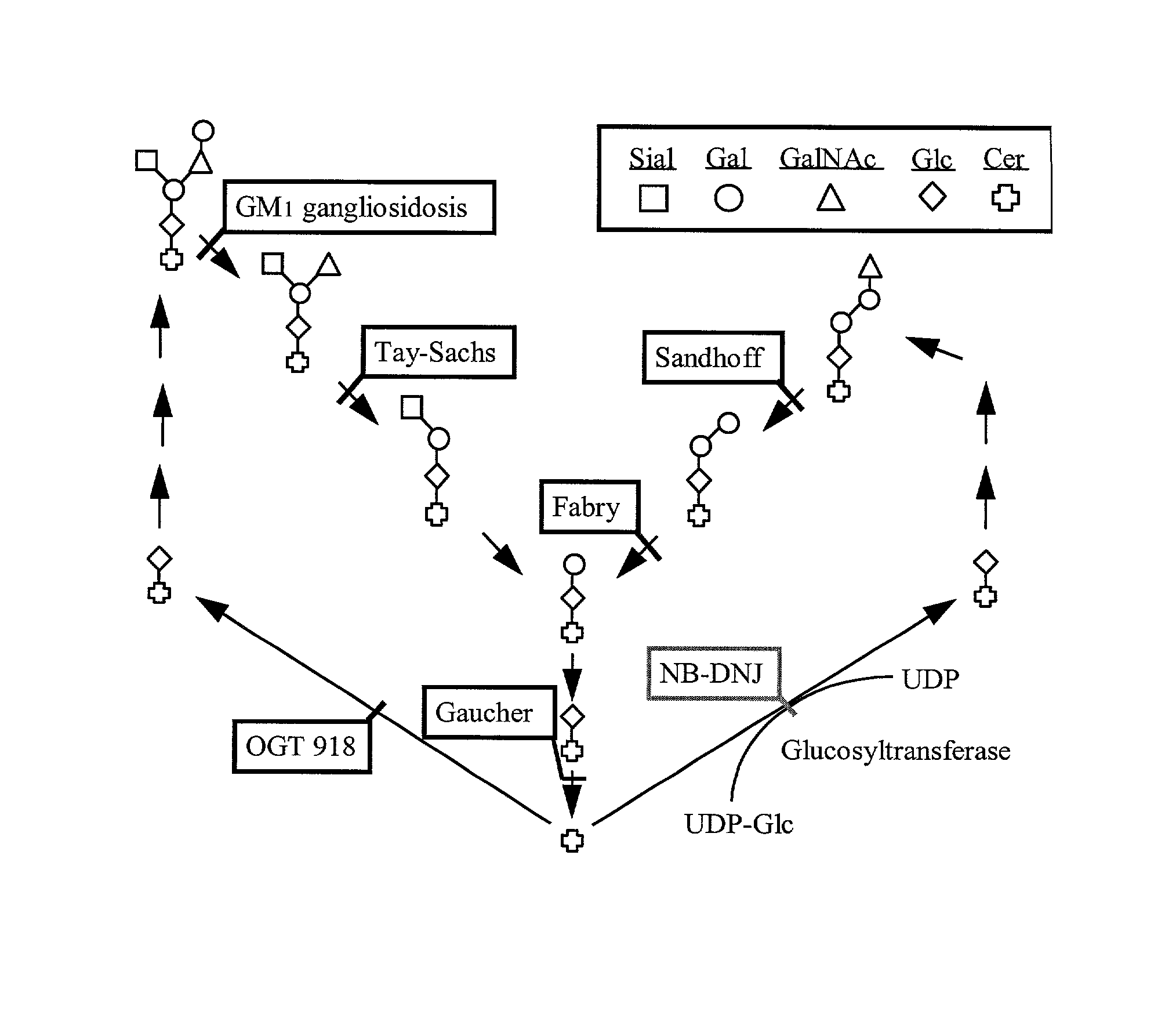
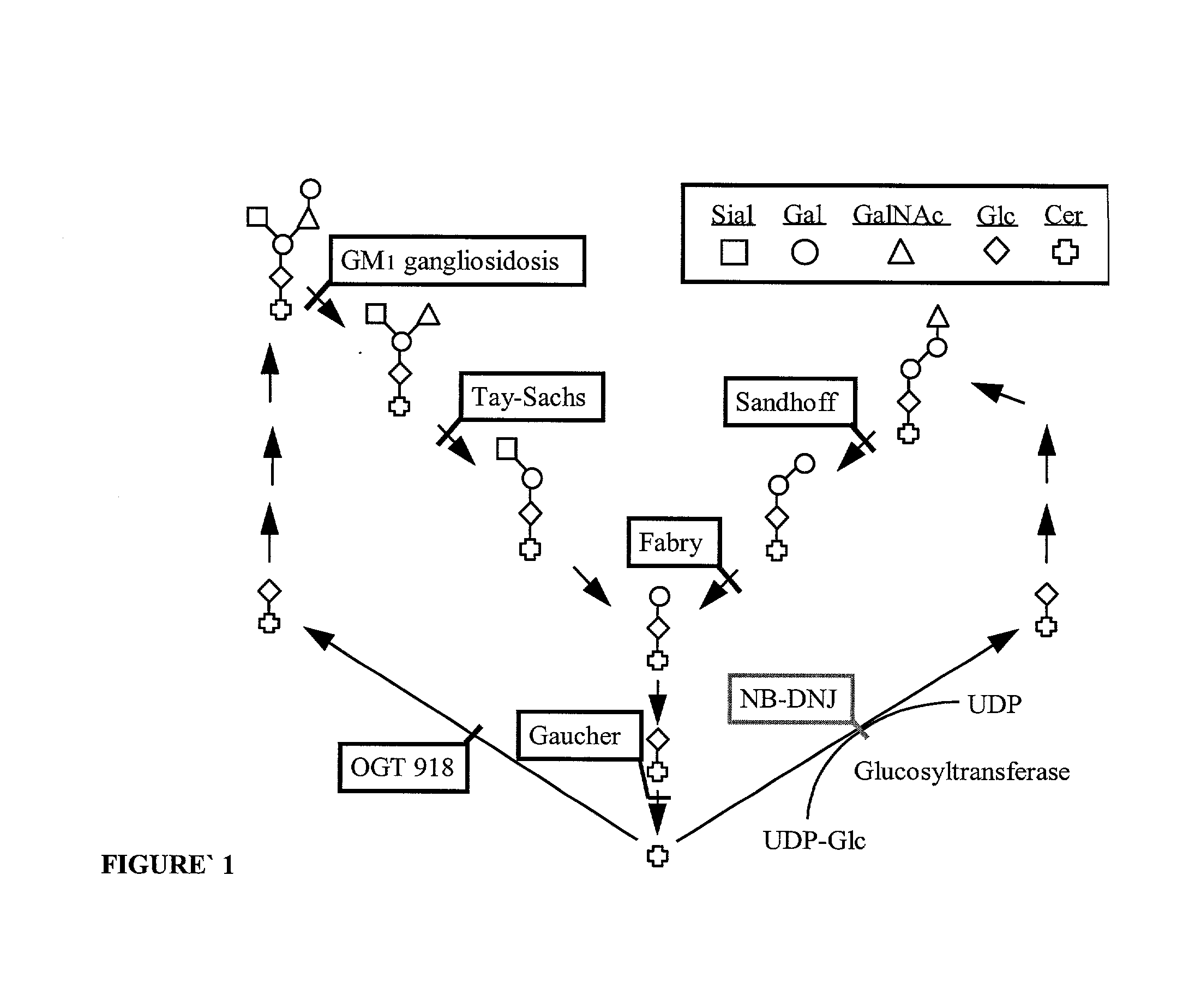
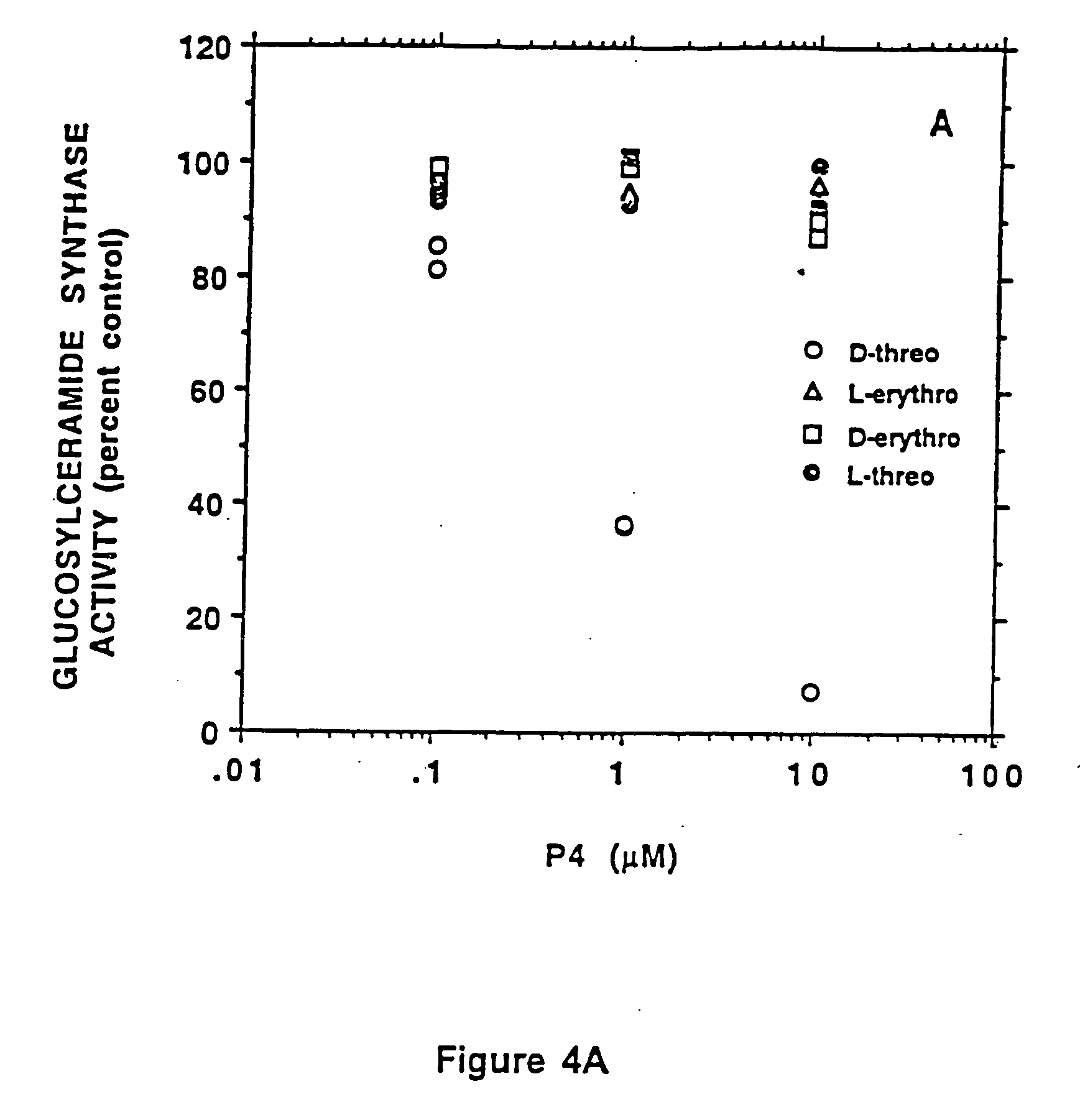
Methods for treatment of disorders associated with glycolipid accumulation, such as Niemann-Pick Type C (NPC) disease, comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of an inhibitor of glucosylceramide synthesis. Inhibitors of glucosylceramide synthesis include N-butyldeoxynojirimycin, N-butyldeoxygalactonojirimycin, and N-nonyldeoxynojirimycin; 1-phenyl-2-decanoylamino-3-morpholino-1-propanol (PDMP), D-threo-1-phenyl-2-decanoylamino-3-morpholino-1-propanol and structurally related analogues thereof; and agents capable of increasing the rate of neuronal glycolipid degradation.
Owner:ACTELION PHARM LTD
Fungal lipolytic enzymes, nucleic acids encoding, and uses thereof
A fungal wild-type lipolytic enzyme having a higher ratio of activity on polar lipids compared with triglycerides, wherein the enzyme preferably has a phospholipid:triglyceride activity ratio of at least 4. Preferably, the lipolytic enzyme according to the present invention has a glycolipid:triglyceride hydrolyzing activity ratio of at least 1.5. In one embodiment, the fungal lipolytic enzyme according to the present invention comprises an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 or SEQ ID No. 2 or SEQ ID No. 4 or SEQ ID No. 6 or an amino acid sequence which has at least 90% identity thereto. The present invention further encompasses a nucleic acid encoding a fungal lipolytic enzyme, which nucleic acid is selected from the group consisting of: (a) a nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide shown in SEQ ID No. 3, SEQ ID No. 5 or SEQ ID No. 7; (b) a nucleic acid which is related to the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID No. 3, SEQ ID No. 5 or SEQ ID No. 7 by the degeneration of the genetic code; and (c) nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence which has at least 90% identity with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 3, SEQ ID No. 5 or SEQ ID No. 7.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Amino ceramide-like compounds and therapeutic methods of use
InactiveUS20050049235A1Lower Level RequirementsSolve low usageAntibacterial agentsBiocideGlycosphingolipidGlcCer synthase
The present invention provides amino ceramide-like compounds which inhibit glucosyl ceramide (GlyCer) formation by inhibiting the enzyme GlyCer synthase, thereby lowering the level of glycosphingolipids. The compounds of the present invention have improved GlcCer synthase inhibition activity and are therefore useful in therapeutic methods for treating various conditions and diseases associated with altered glycosphingolipid levels.
Owner:GENZYME CORP +1
Beta glycolipids as immuno-modulators
The present invention relates to a process for the modulation of the Th1 / Th2 cell balance toward anti-inflammatory cytokine producing cells, in a subject suffering from an immune related disorder. The process of the invention comprises the step of increasing the intracellular, extra-cellular or serum level of a naturally occurring β-glycolipid in a subject in need thereof. The invention further relates to methods for the treatment of a subject suffering from an immune-related disease. Therapeutic compositions and method for the preparation of these compositions are also provided.
Owner:ENZO THERAPEUTICS ENZO BIOCHEM
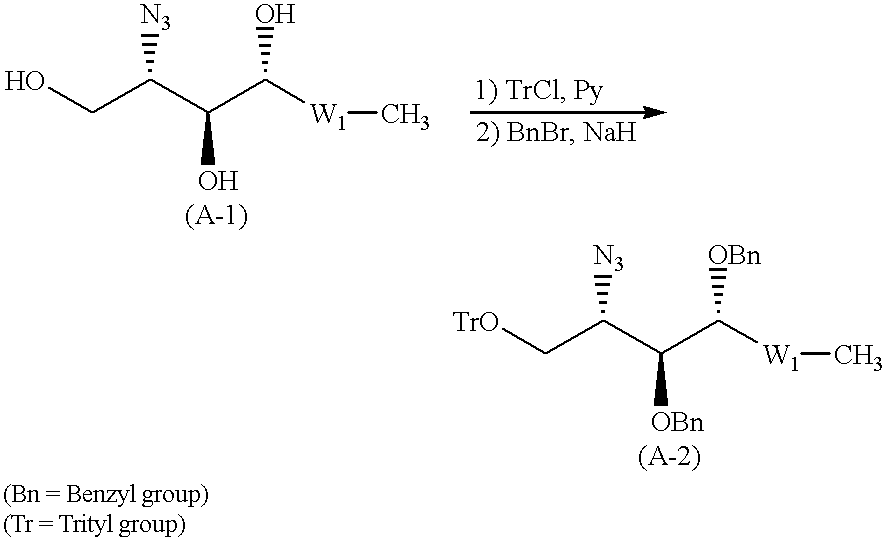
Glycolipids and synthetic method thereof as well as their synthetic intermediates, and synthetic intermediates, and synthetic method thereof
ActiveUS7732583B2Good quality improved in physical propertyUseful in preparationBiocideNervous disorderChemical synthesisAryl
Owner:JAPAN REPRESENTED BY PRESIDENT OF NAT CENT OF NEUROLOGY & PSYCHIATRY KODAIRA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com