Patents
Literature
130 results about "Polar lipids" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polar lipids are naturally occurring molecules derived from cell membranes (such as those found in oats) that provide various benefits to the health of the equine gastrointestinal tract.
Pharmaceutical compositions for lipophilic drugs
InactiveUS7070802B1Good self-emulsifying performanceShelf-stableCyclic peptide ingredientsCapsule deliveryMonoglycerideCyclosporins
Stable solutions of lipophilic drugs, such as cyclosporin, forming a polar lipid self-emulsifying drug delivery system. The solutions can include lipophilic drugs, such as cyclosporin, dissolved in a polar lipid, such as having a C6-C12 fatty acid monoglyceride content of at least about 50%, surfactants and triglycerides. The composition forms a fine emulsion on exposure to water. The encapsulated dosage form of this composition needs neither a hydrophilic component nor air-tight blister packaging, and is particularly suitable for oral administration.
Owner:WATSON LAB INC
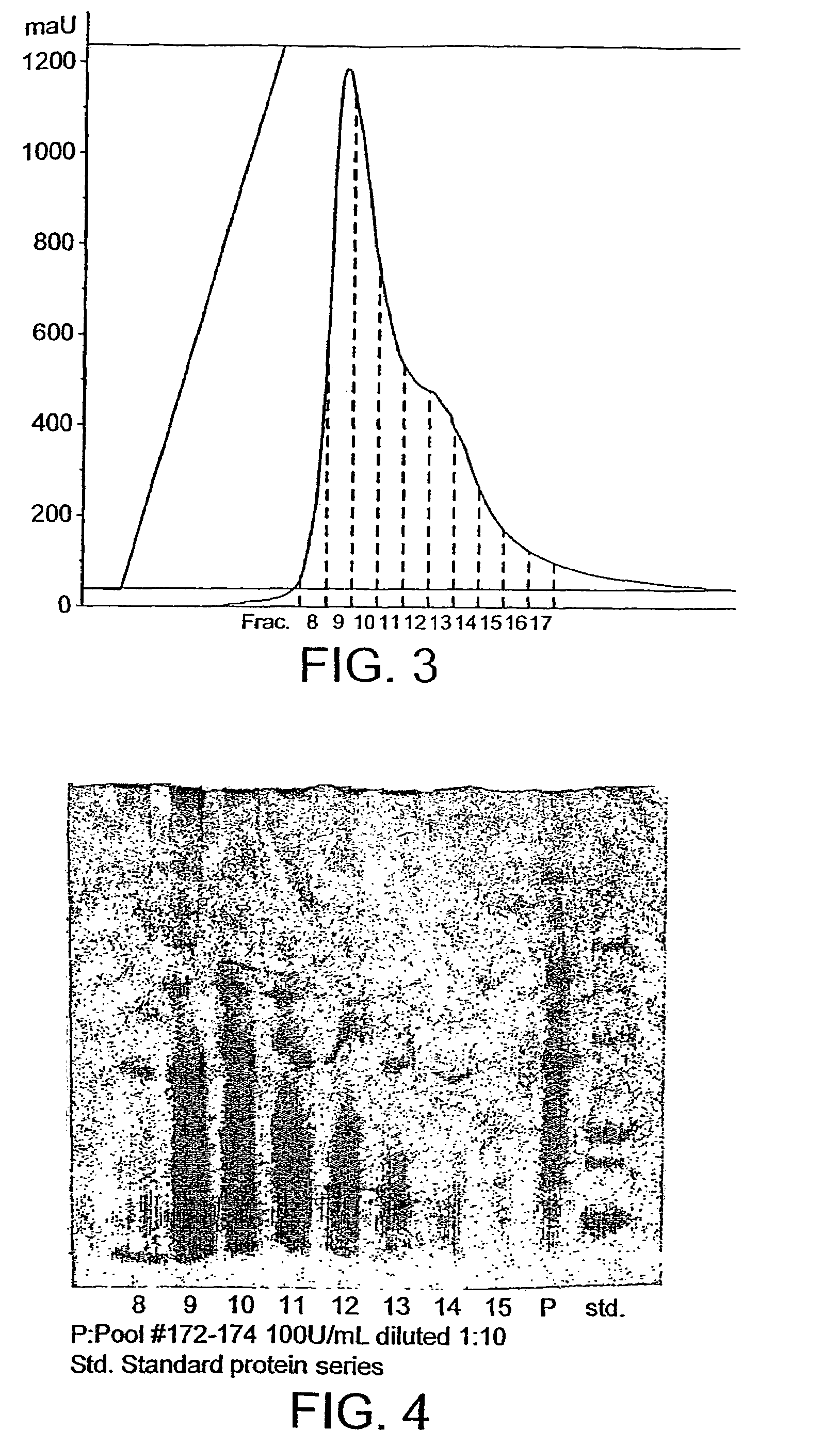
Production of ultrapure epa and polar lipids from largely heterotrophic culture
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) compositions and EPA-rich polar lipids for prophylactic or therapeutic applications are described. Production from certain cultured micro-organisms (like Nitzschia laevis) promotes synthesis of EPA, including polar lipids including EPA. The EPA-rich polar lipids themselves may be used as polar compounds. EPA can be selectively hydrolysed from particular positions in isolated polar lipids by lipase activity, then optionally further purified. The process bypasses reliance on diminishing fish stocks and on physico-chemical processes that may not adequately separate desirable n-3 HUFAs from unwanted products like DHA also found in fish oil and cultured organisms.
Owner:FERMENTALG
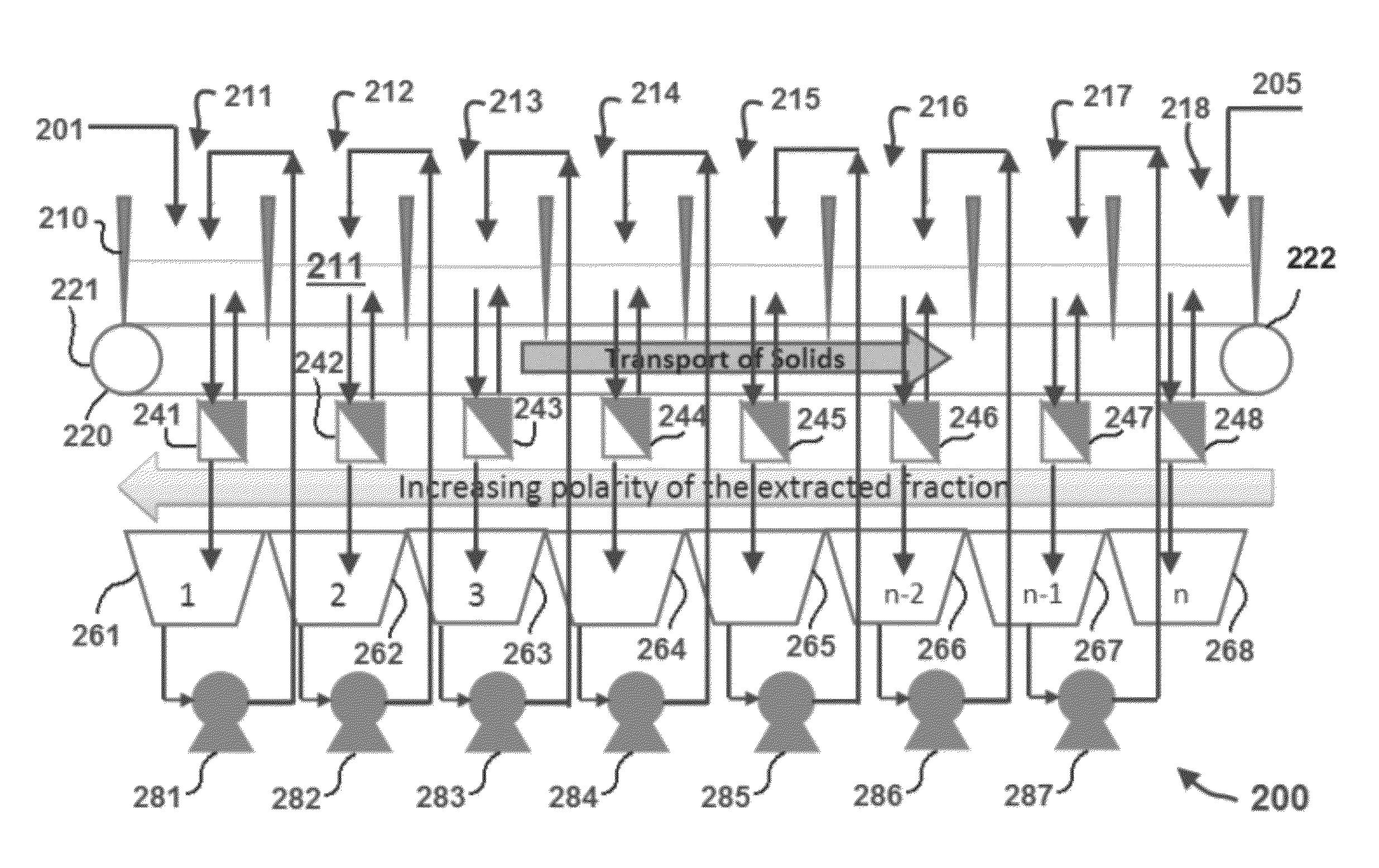
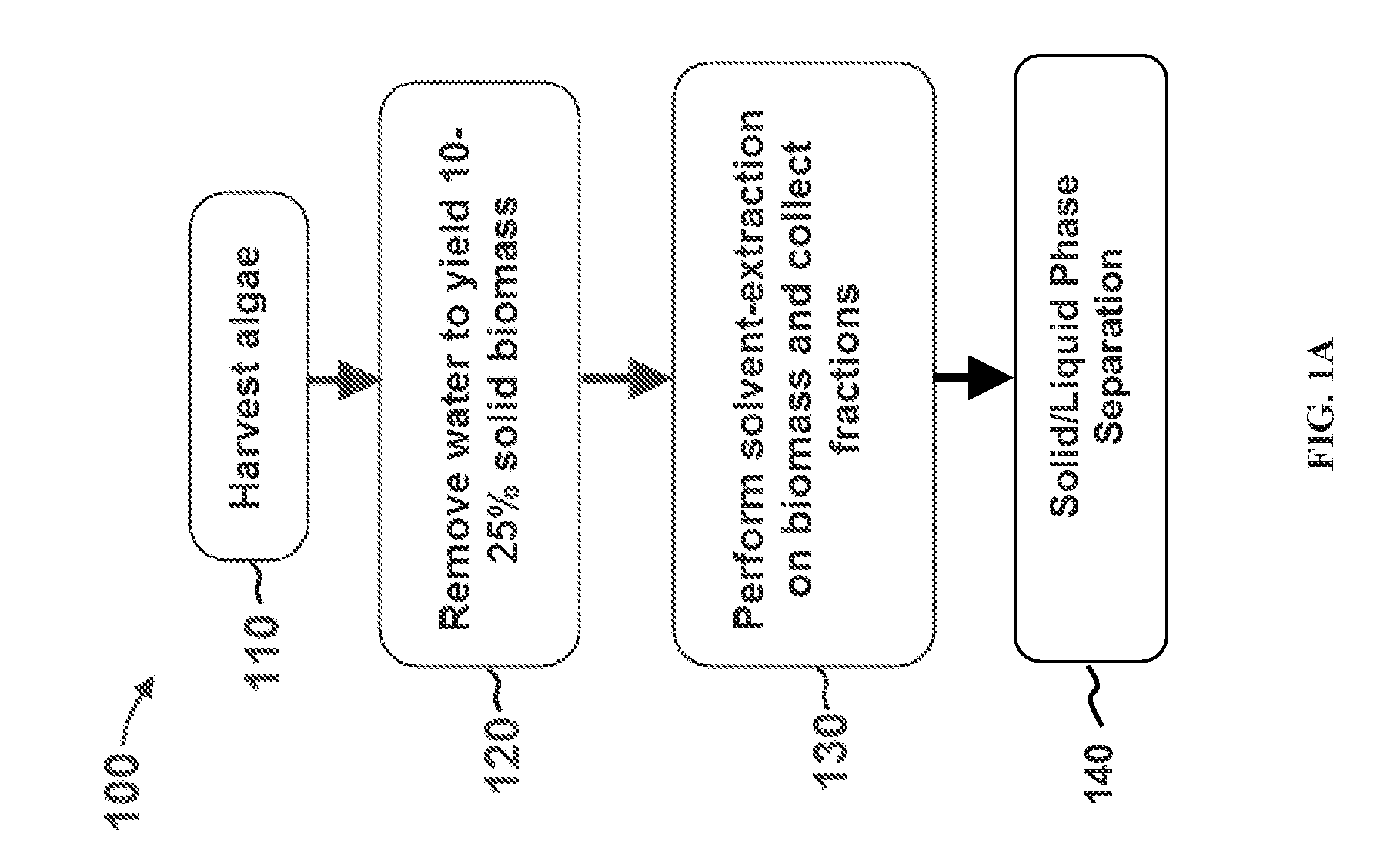
Systems, apparatuses, and methods for extracting non-polar lipids from an aqueous algae slurry and lipids produced therefrom
InactiveUS20110095225A1Increase volume flowEasy extractionLiquid separation by electricityMicroorganism lysisLipid formationPhospholipid
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for extracting non-polar lipids from microalgae are achieved using a lipid extraction device having an anode and a cathode that forms a channel and defines a fluid flow path through which an aqueous slurry is passed. An electromotive force is applied across the channel at a gap distance in a range from 0.5 mm to 200 mm to cause the non-polar lipids to be released from the algae cells. The non-polar lipids can be extracted at a high throughput rate and with low concentrations of polar lipids such as phospholipids and chlorophyll.
Owner:ORGINOIL INC
Production and use of a polar lipid-rich fraction containing omega-3 and/or omega-6 highly unsaturated fatty acids from microbes, genetically modified plant seeds and marine organisms
InactiveUS20050129739A1Speed up the processAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsPlanting seedAdemetionine
The production and use, and in particular, the extraction, separation, synthesis and recovery of polar lipid-rich fractions containing eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), docosapentaenoic acid (DPA(n-3) or DPA(n-6)), arachidonic acid (ARA), and eicosatetraneonoic acid (C20:4n-3) from microorganisms, genetically modified seeds and marine organisms (including fish and squid) and their use in human food applications, animal feed, pharmaceutical applications and cosmetic applications.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
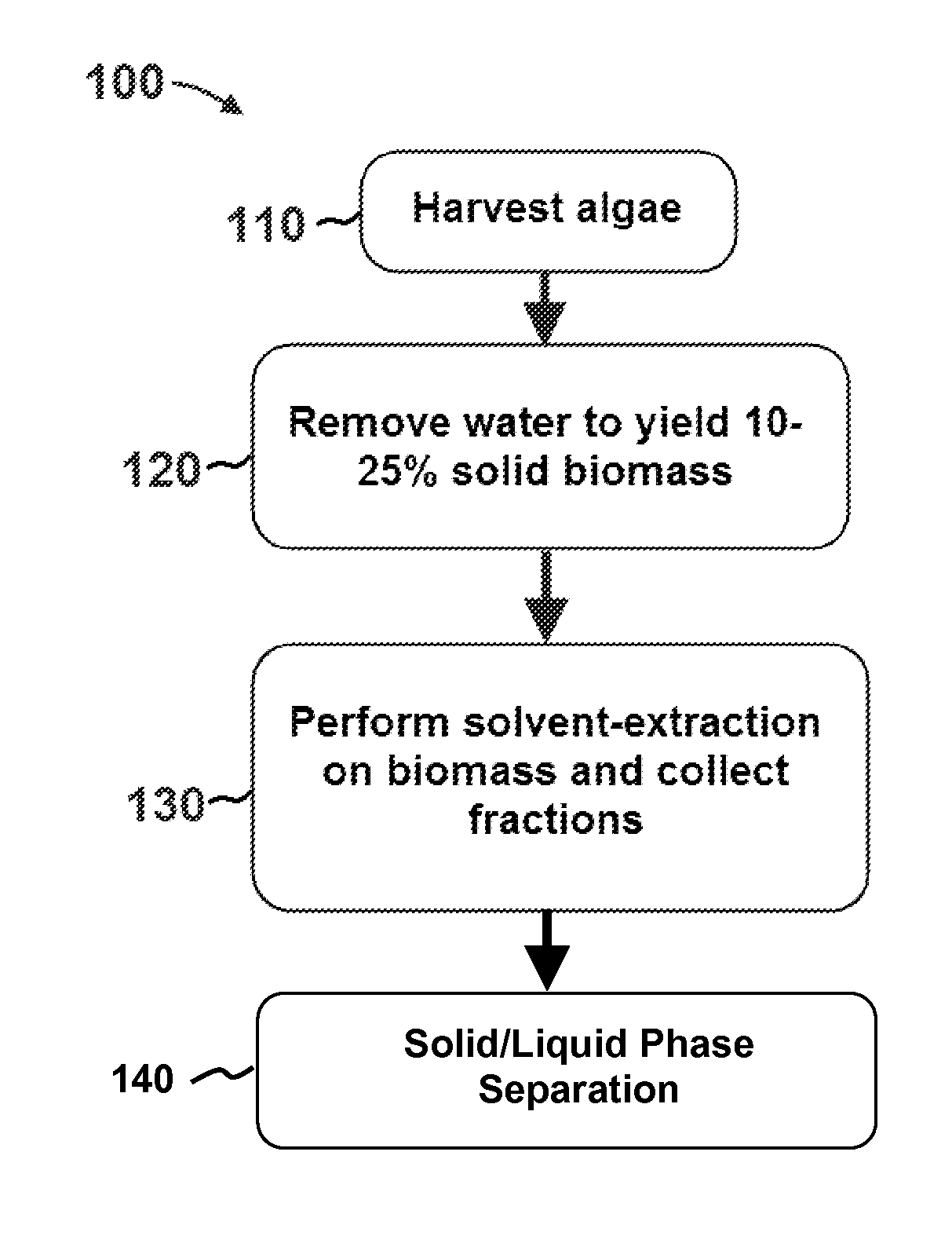
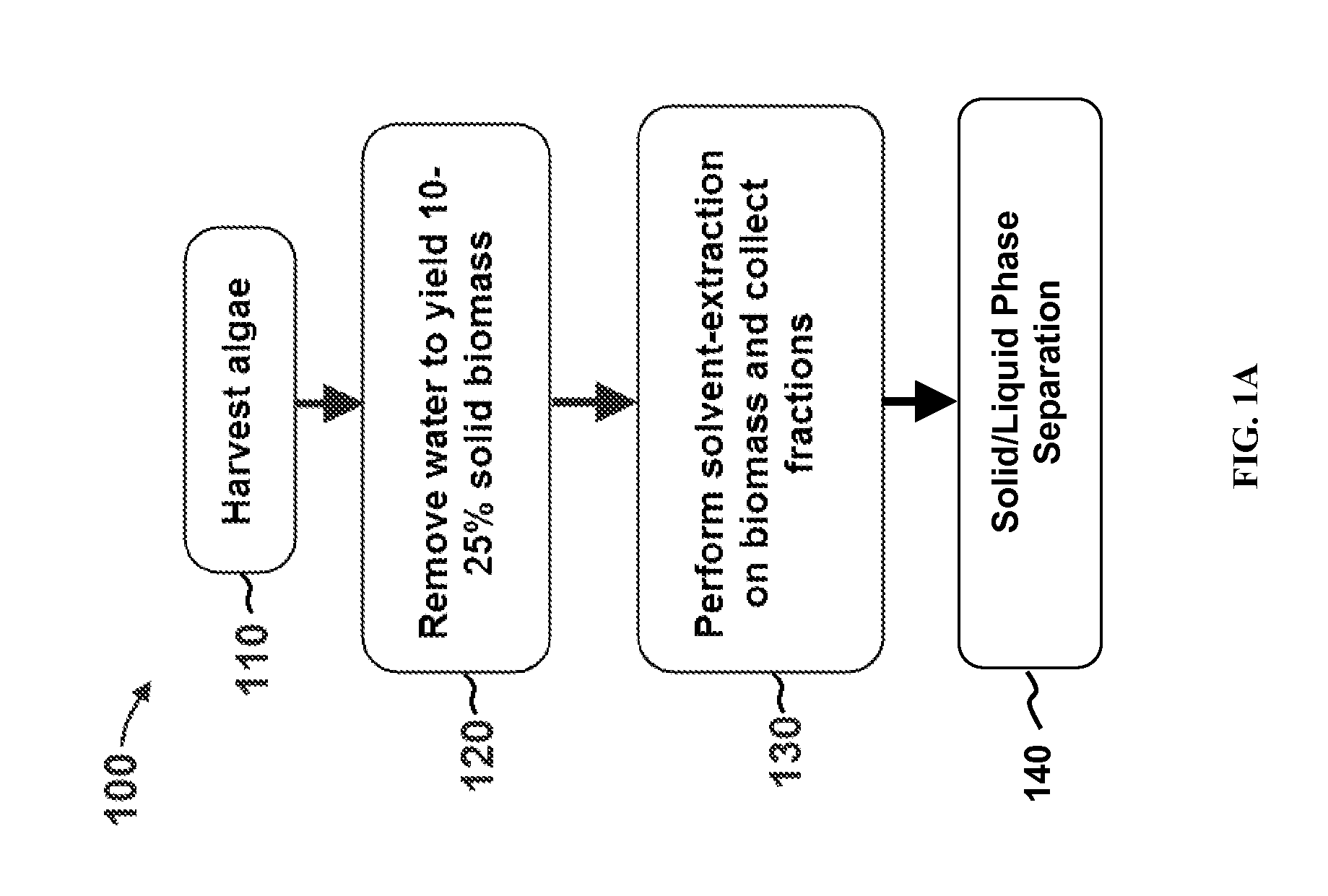
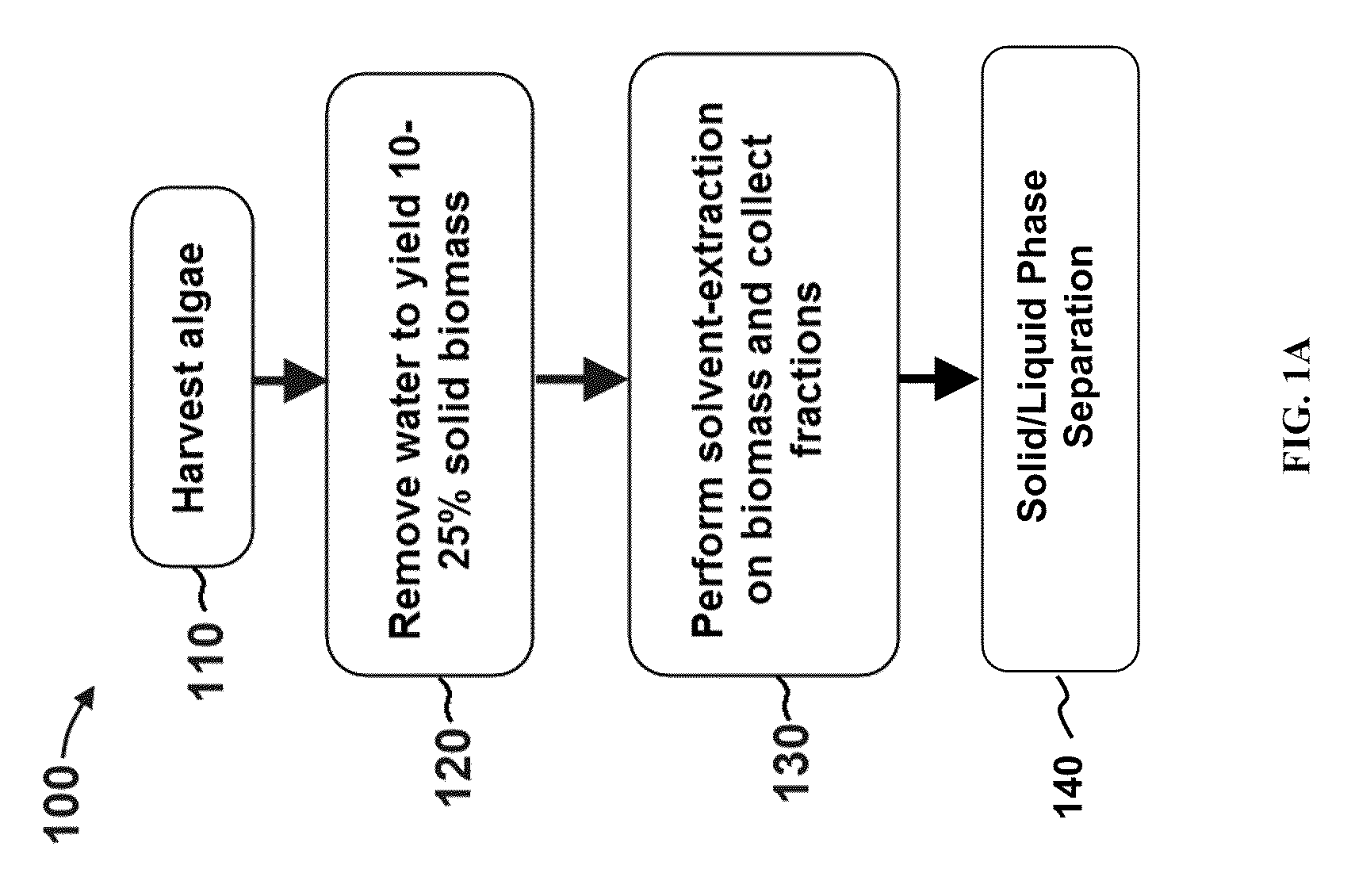
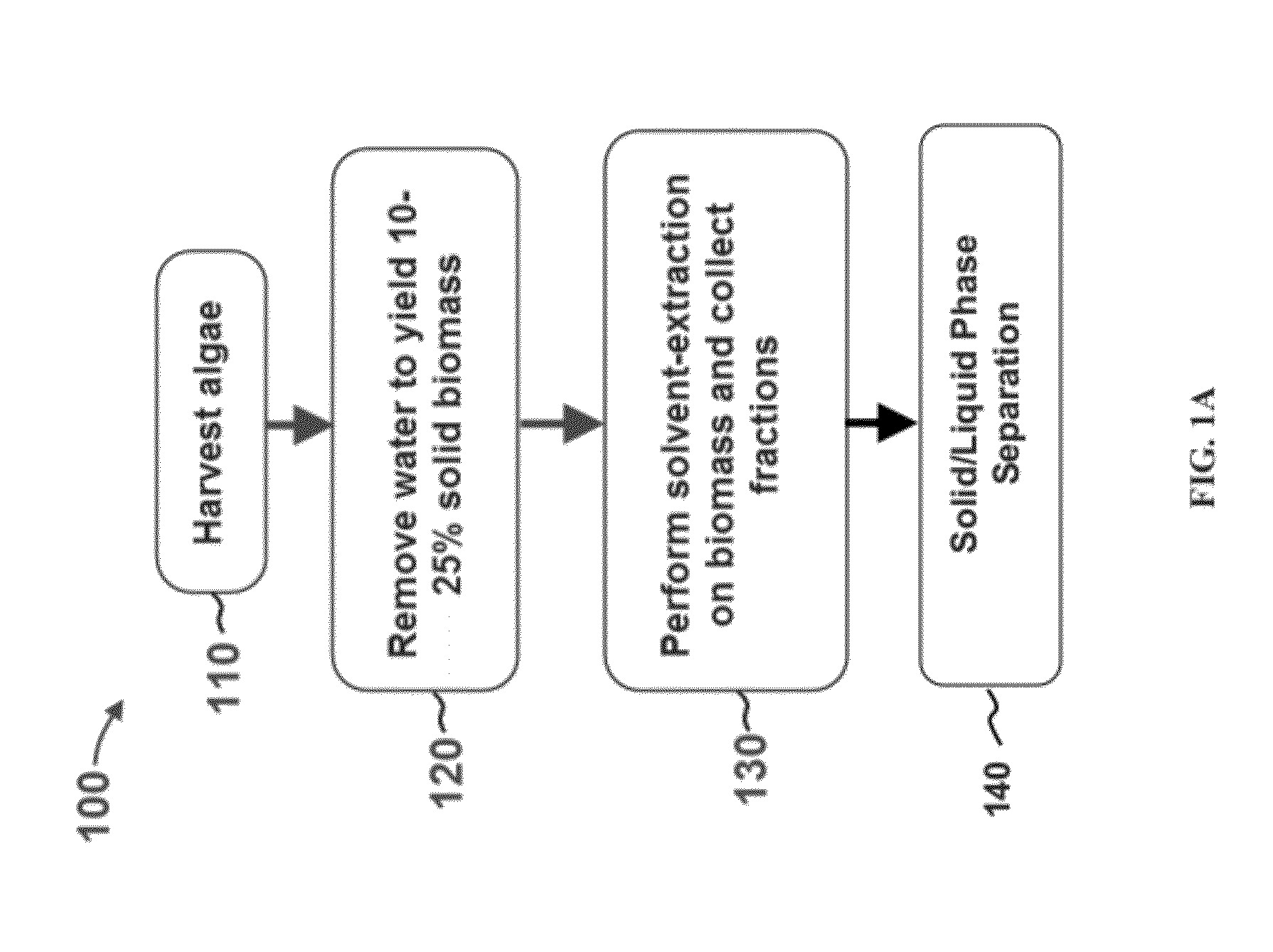
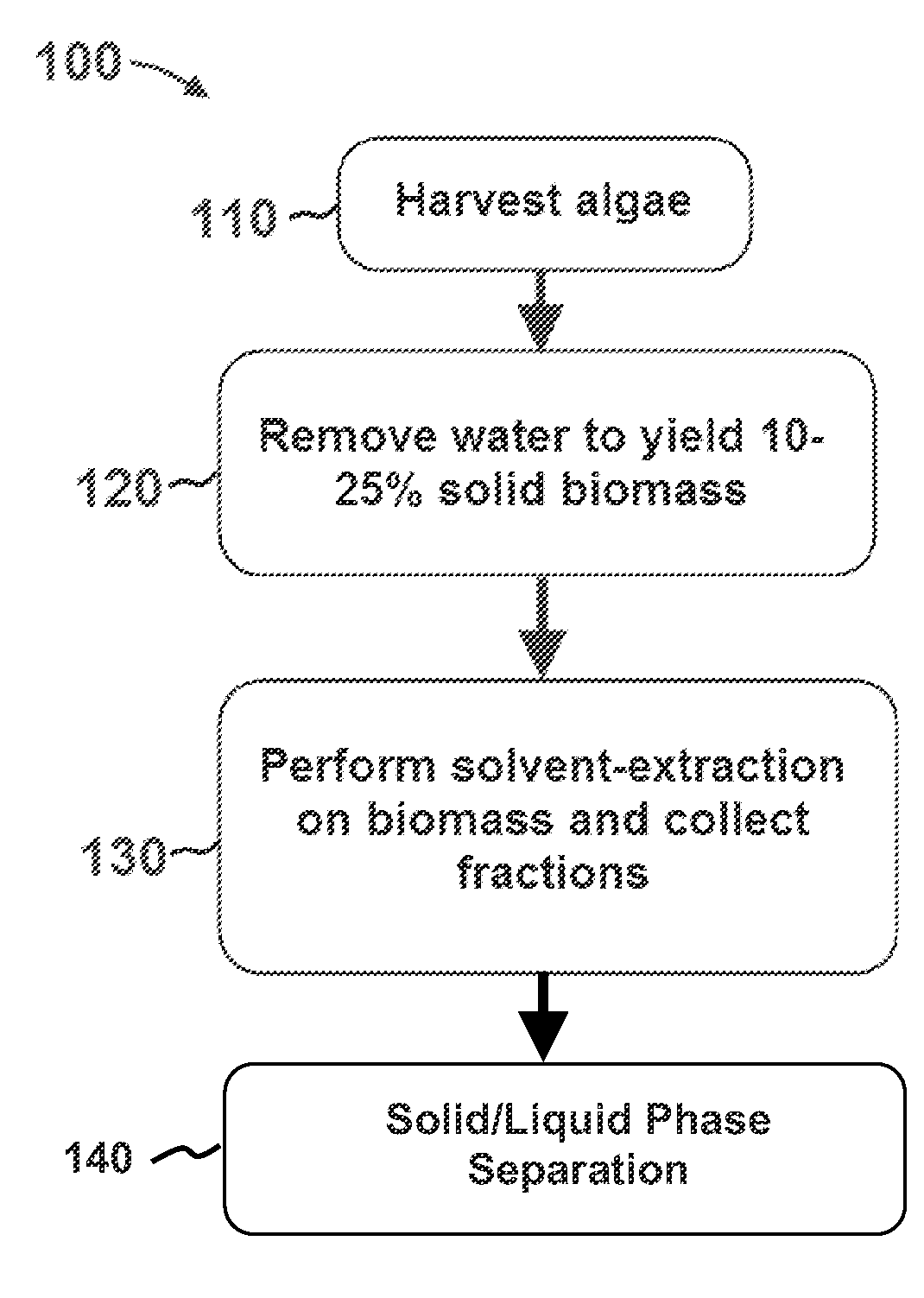
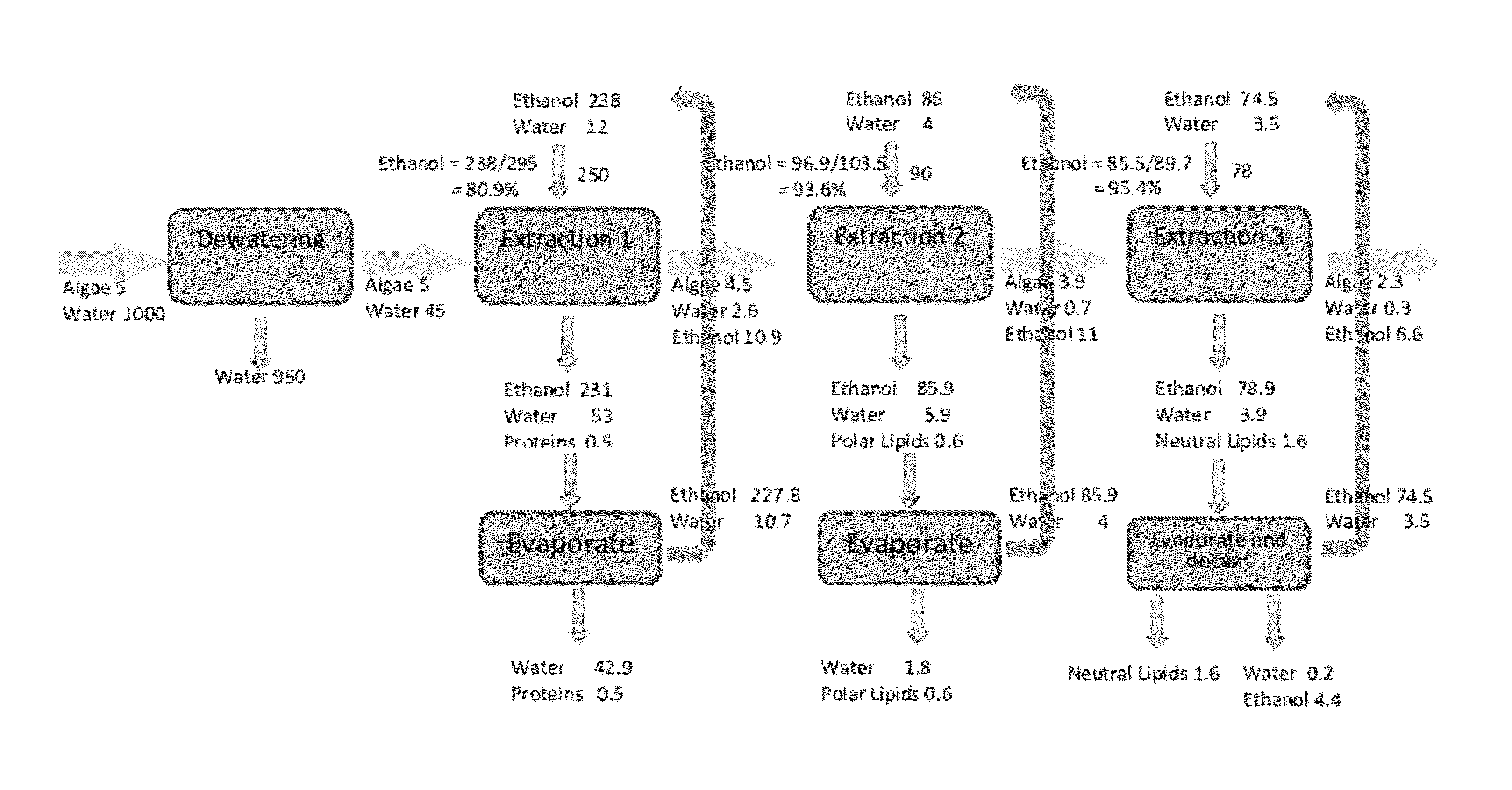
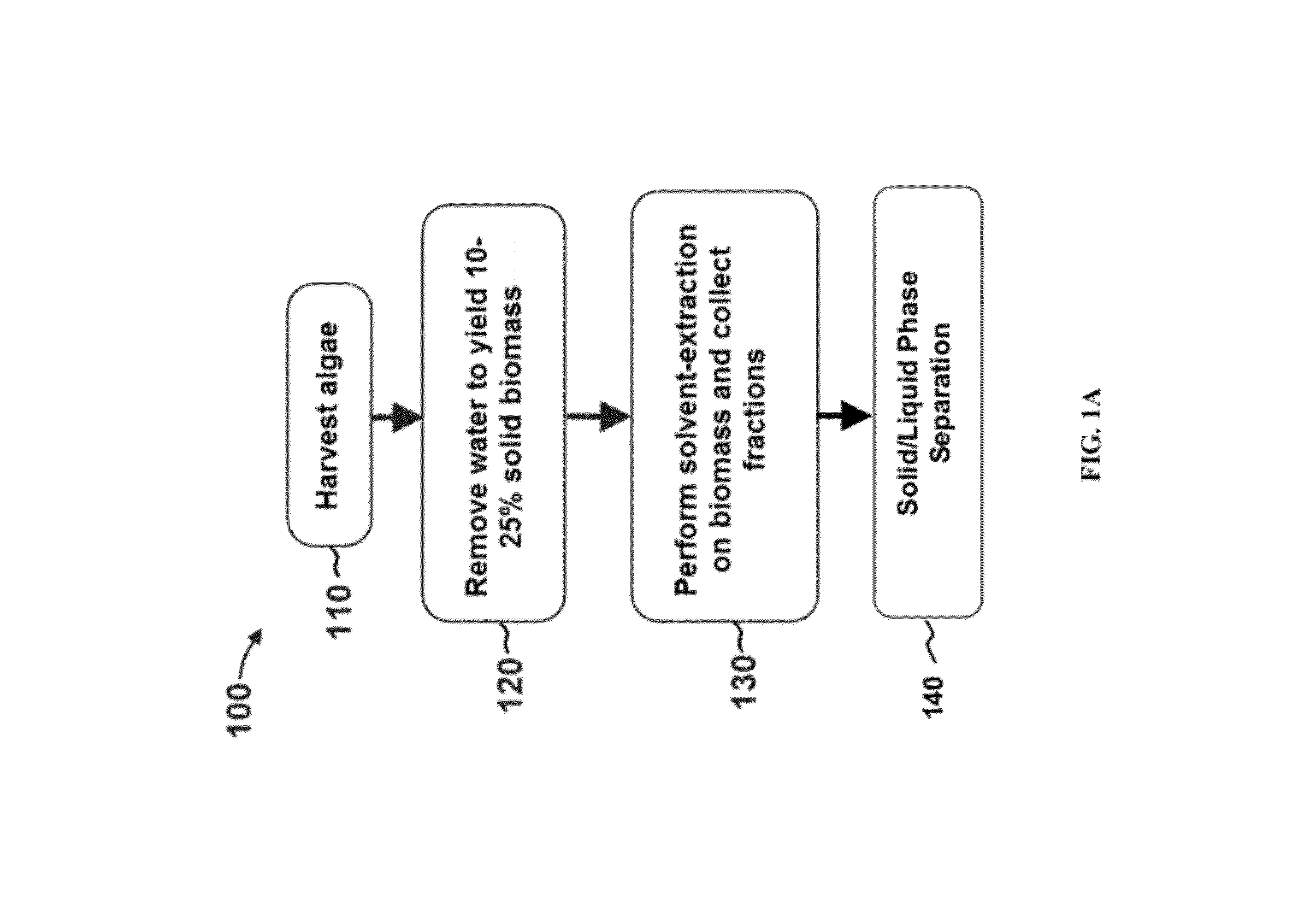
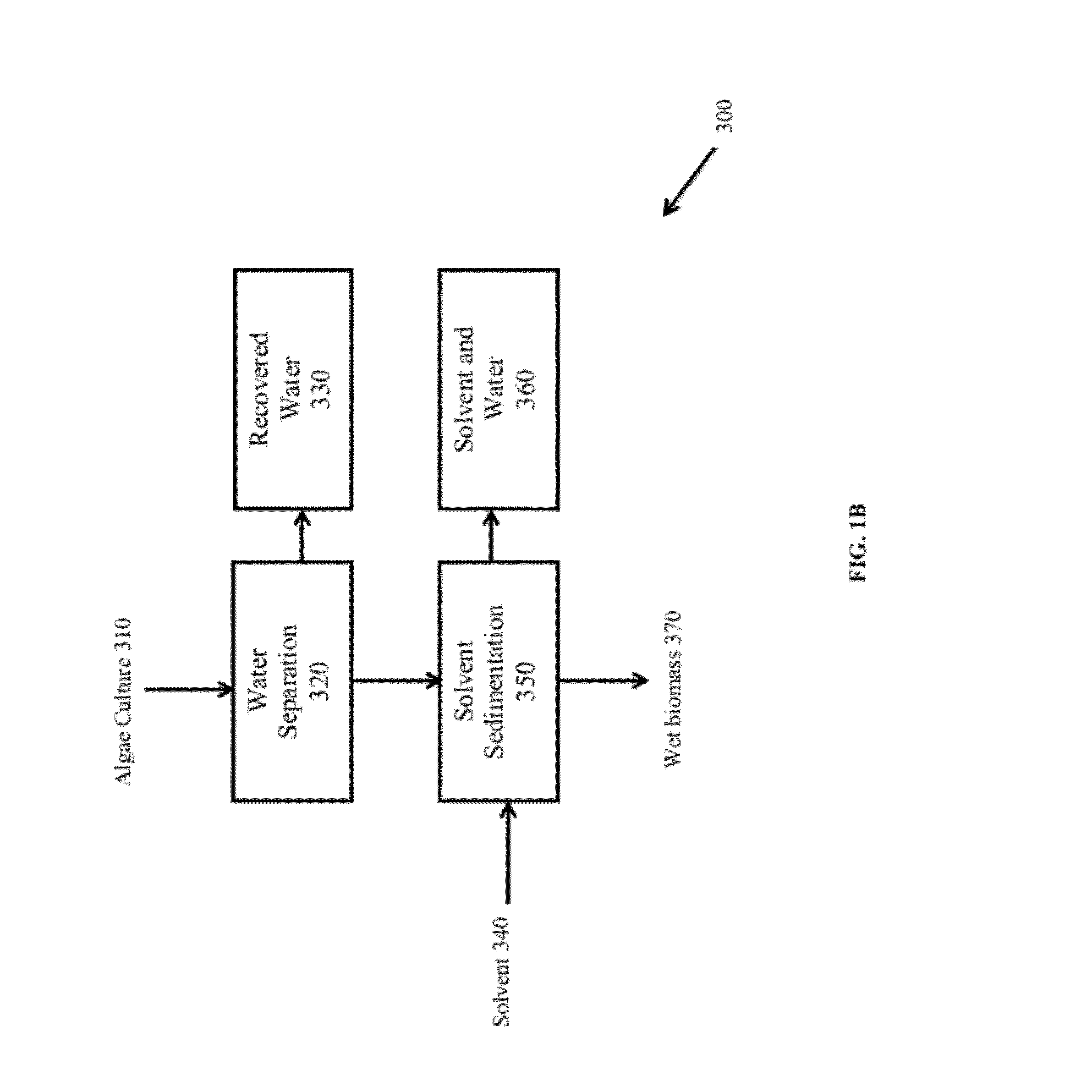
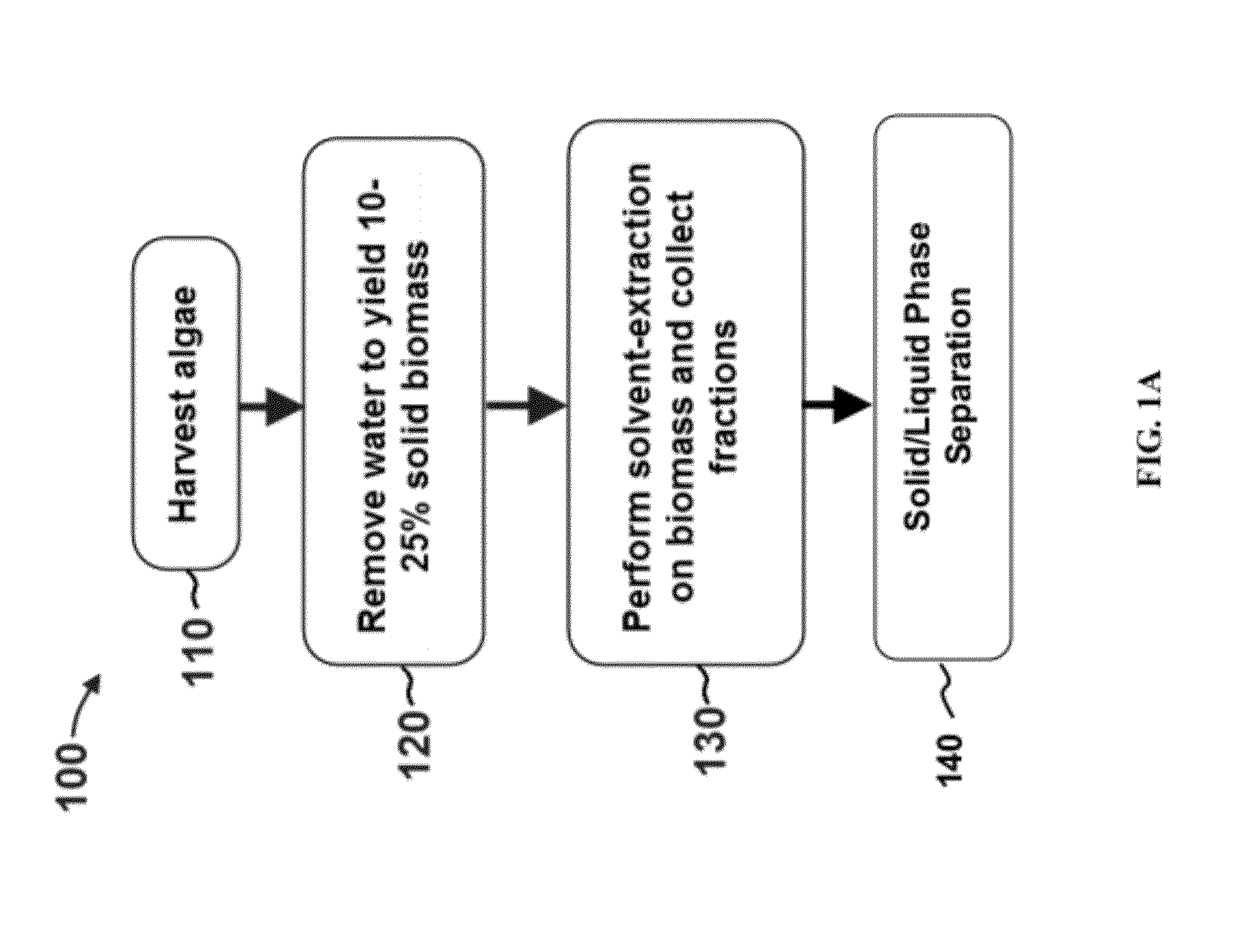
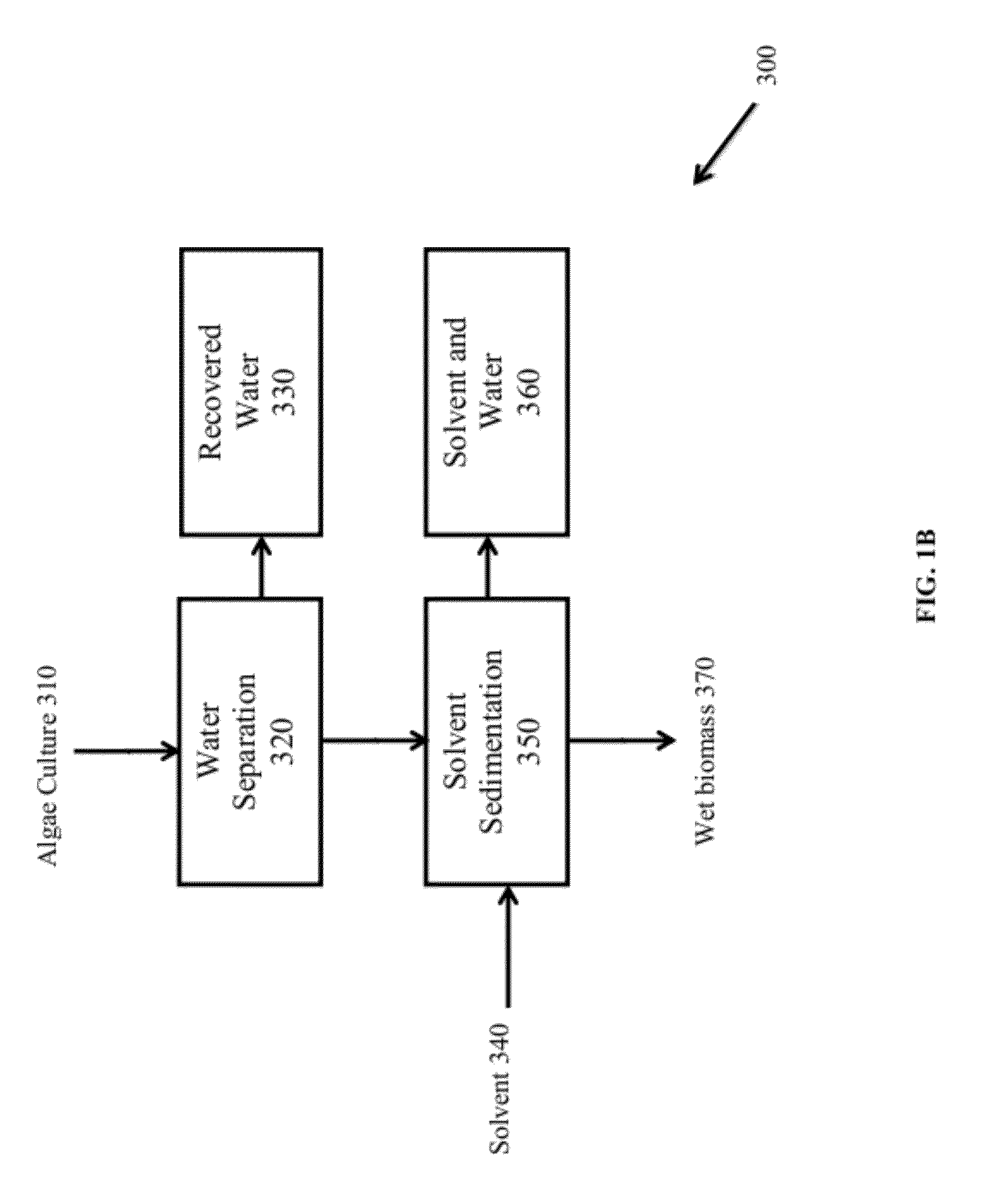
Methods of and Systems for Isolating Nutraceutical Products from Algae
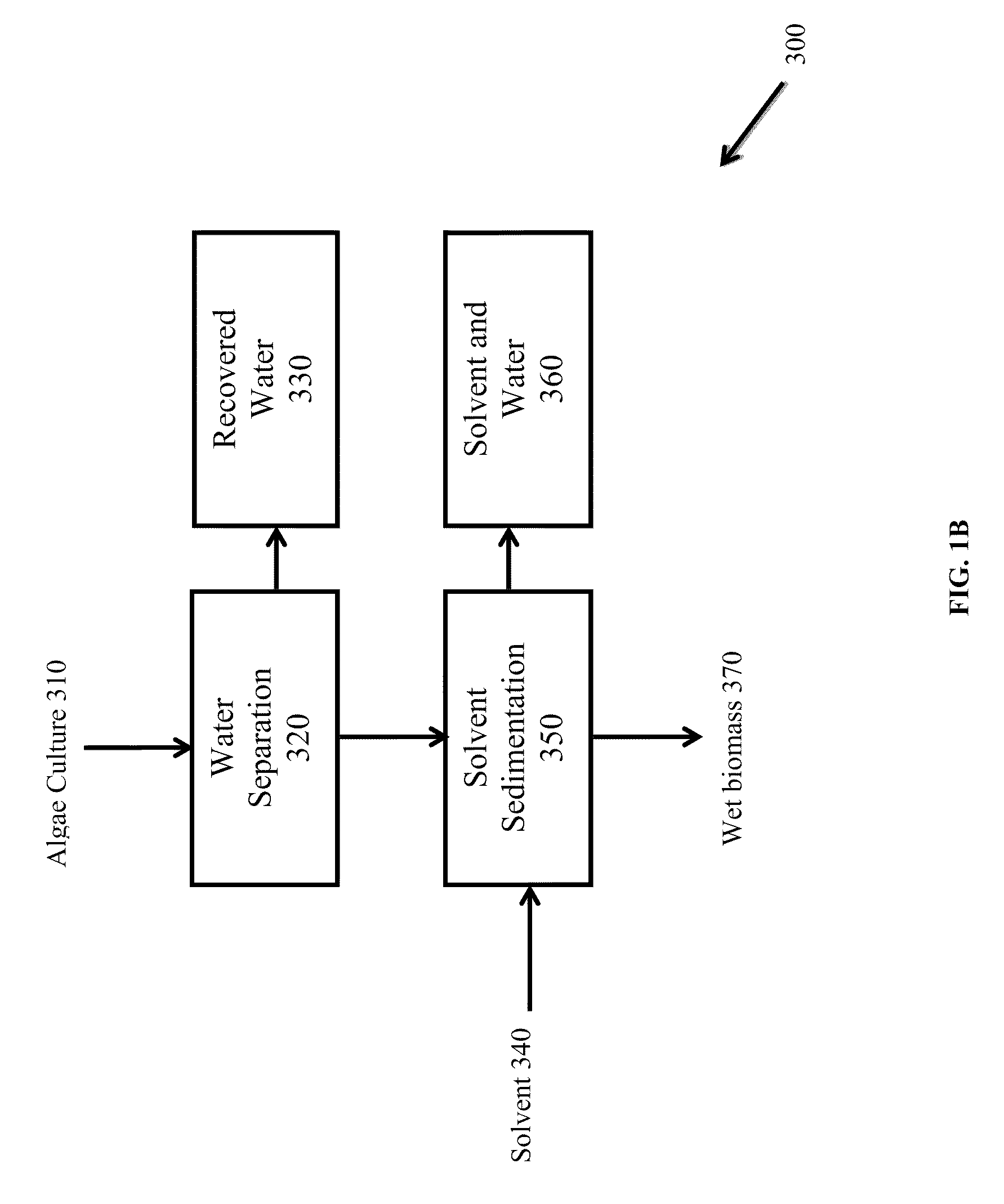
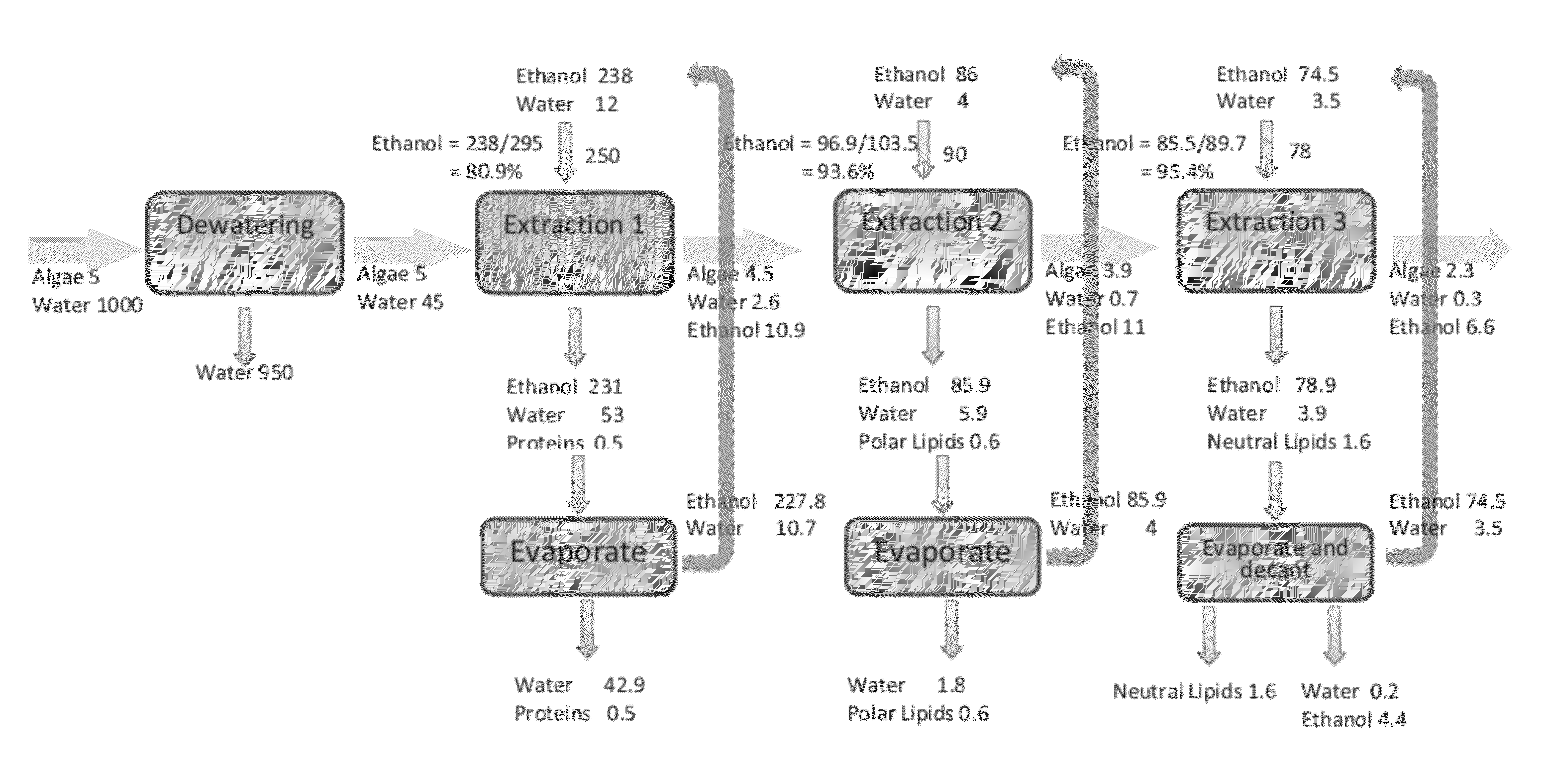
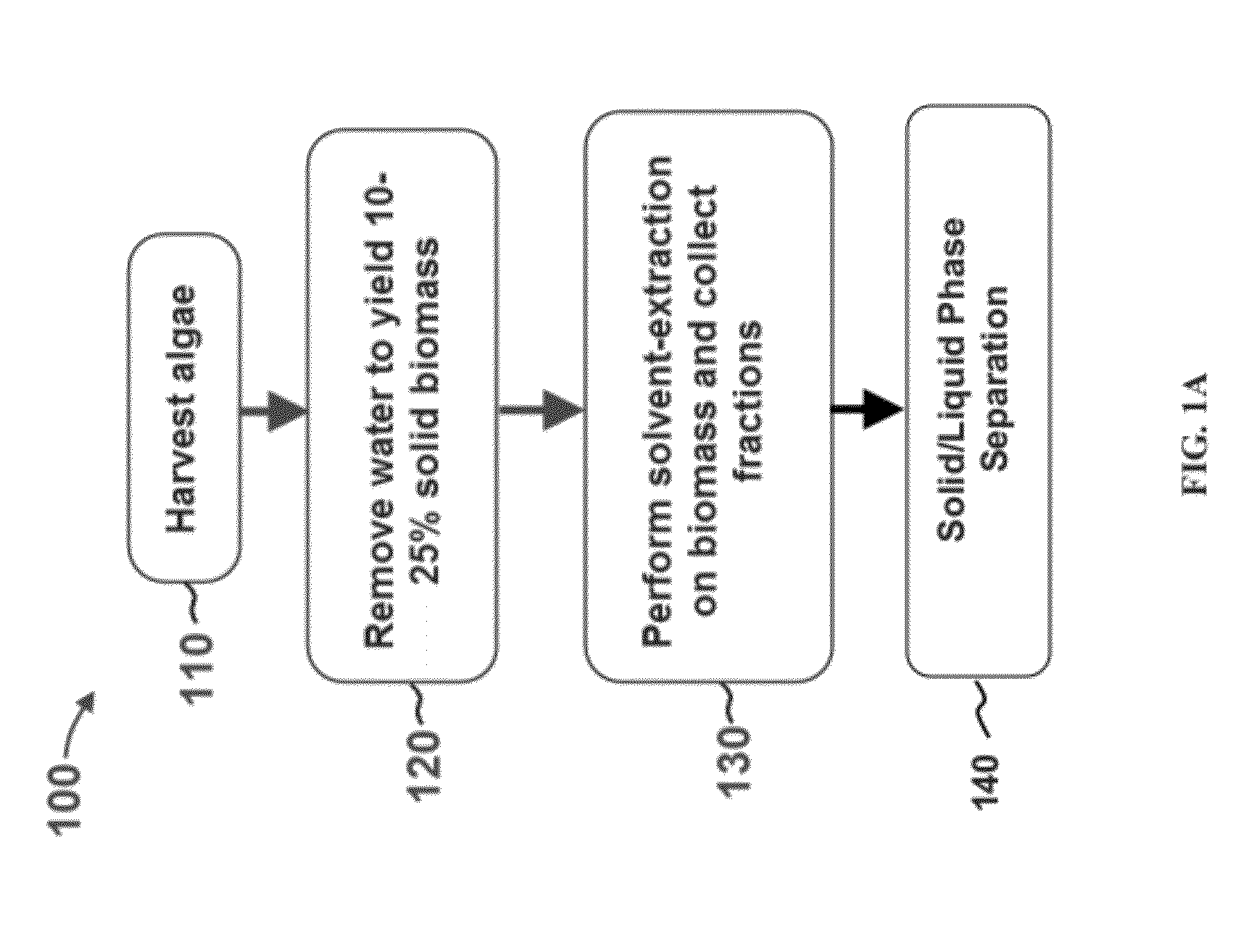
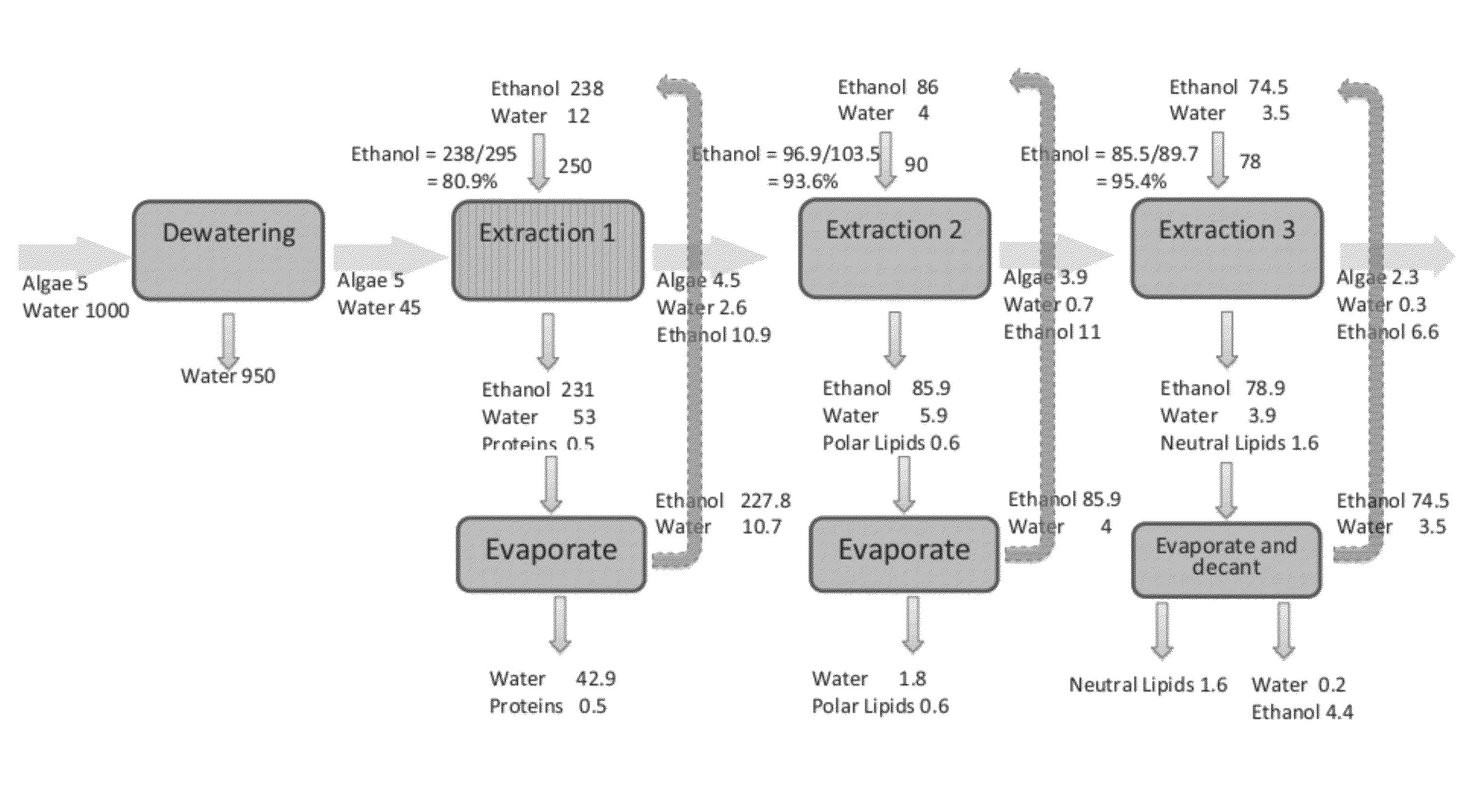
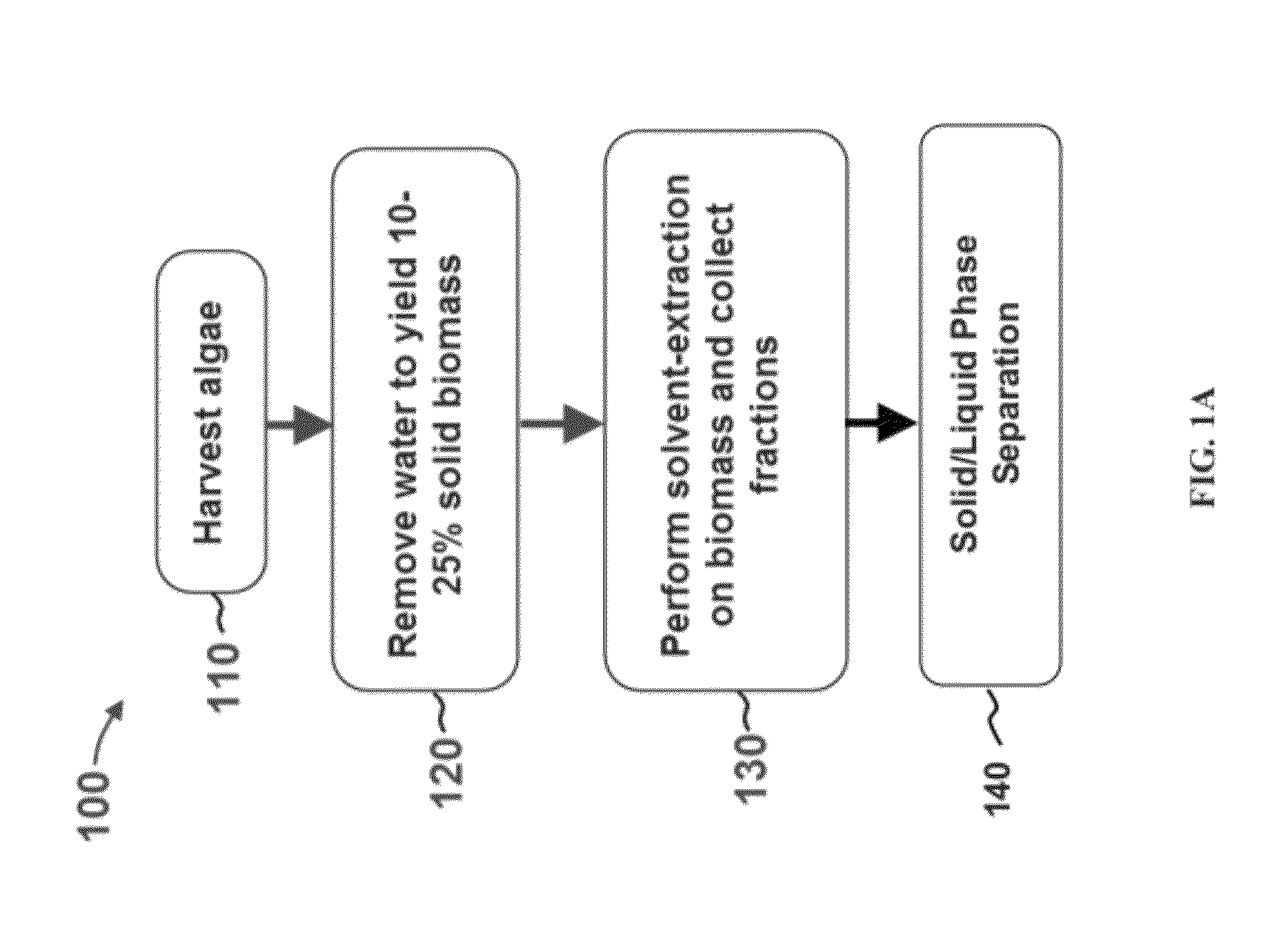
A method of isolating nutraceuticals products from algae is provided. A method of isolating carotenoids and omega-3 rich oil from algae includes dewatering substantially intact algal cells to make an algal biomass and adding a first ethanol fraction to the algal biomass. The method also includes separating a first substantially solid biomass fraction from a first substantially liquid fraction comprising proteins and combining the first substantially solid biomass fraction with a second ethanol fraction. The method further includes separating a second substantially solid biomass fraction from a second substantially liquid fraction comprising polar lipids and combining the second substantially solid biomass fraction with a third ethanol solvent fraction. The method also includes separating a third substantially solid biomass fraction from a third substantially liquid fraction comprising neutral lipids, wherein the third substantially solid biomass fraction comprises carbohydrates and separating the neutral lipids into carotenoids and omega-3 rich oil.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Methods of and systems for isolating nutraceutical products from algae
A method of isolating nutraceuticals products from algae is provided. A method of isolating carotenoids and omega-3 rich oil from algae includes dewatering substantially intact algal cells to make an algal biomass and adding a first ethanol fraction to the algal biomass. The method also includes separating a first substantially solid biomass fraction from a first substantially liquid fraction comprising proteins and combining the first substantially solid biomass fraction with a second ethanol fraction. The method further includes separating a second substantially solid biomass fraction from a second substantially liquid fraction comprising polar lipids and combining the second substantially solid biomass fraction with a third ethanol solvent fraction. The method also includes separating a third substantially solid biomass fraction from a third substantially liquid fraction comprising neutral lipids, wherein the third substantially solid biomass fraction comprises carbohydrates and separating the neutral lipids into carotenoids and omega-3 rich oil.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
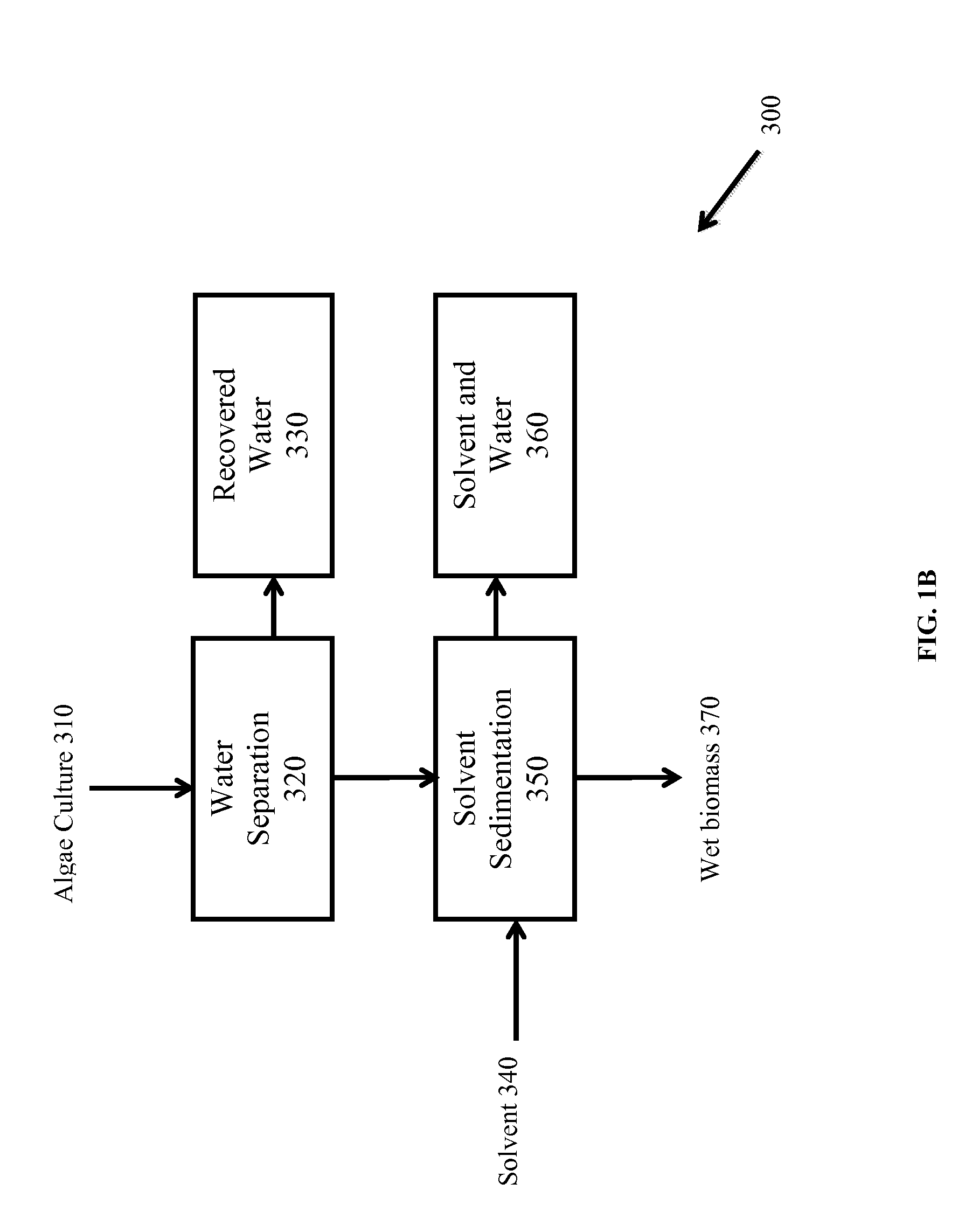
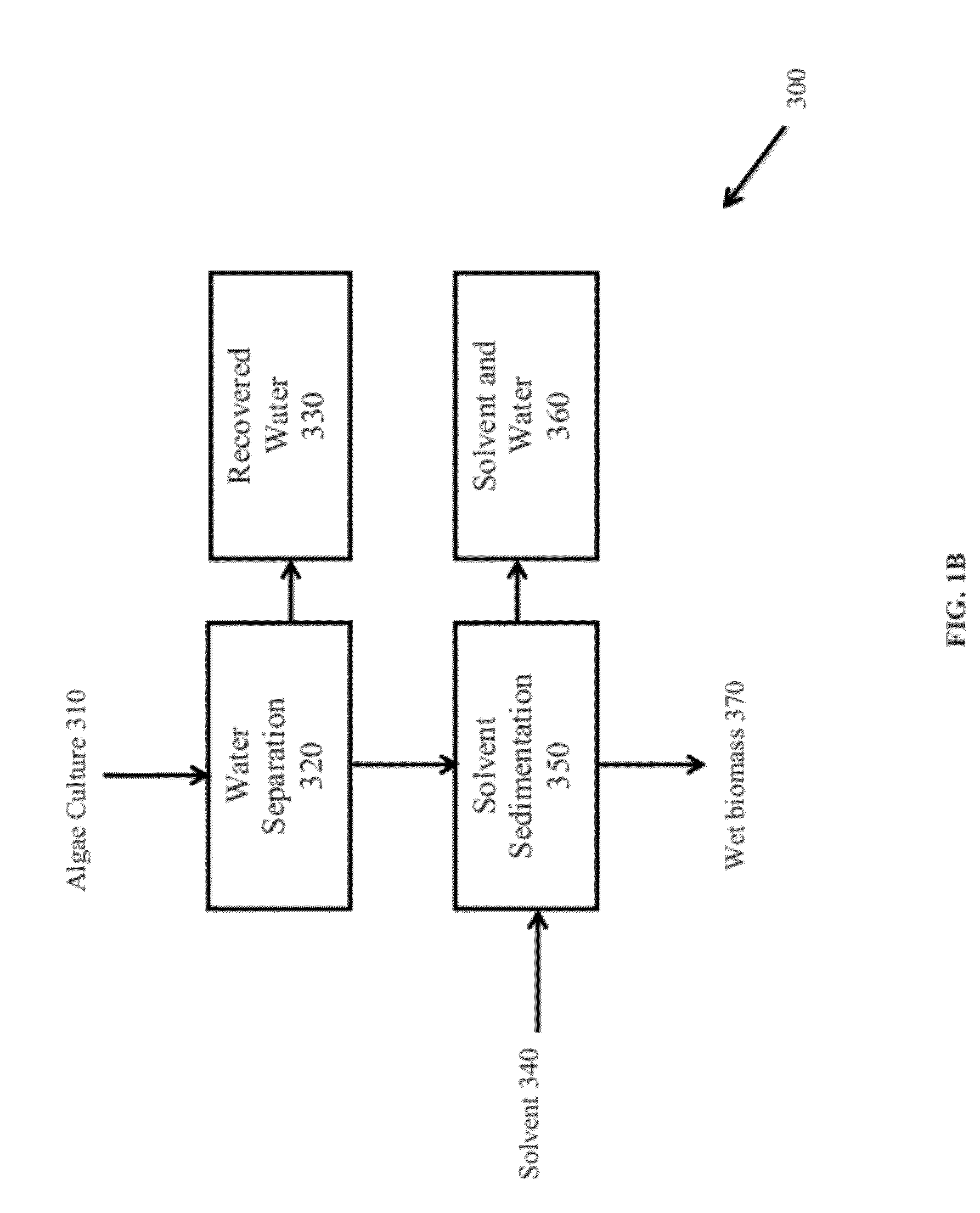
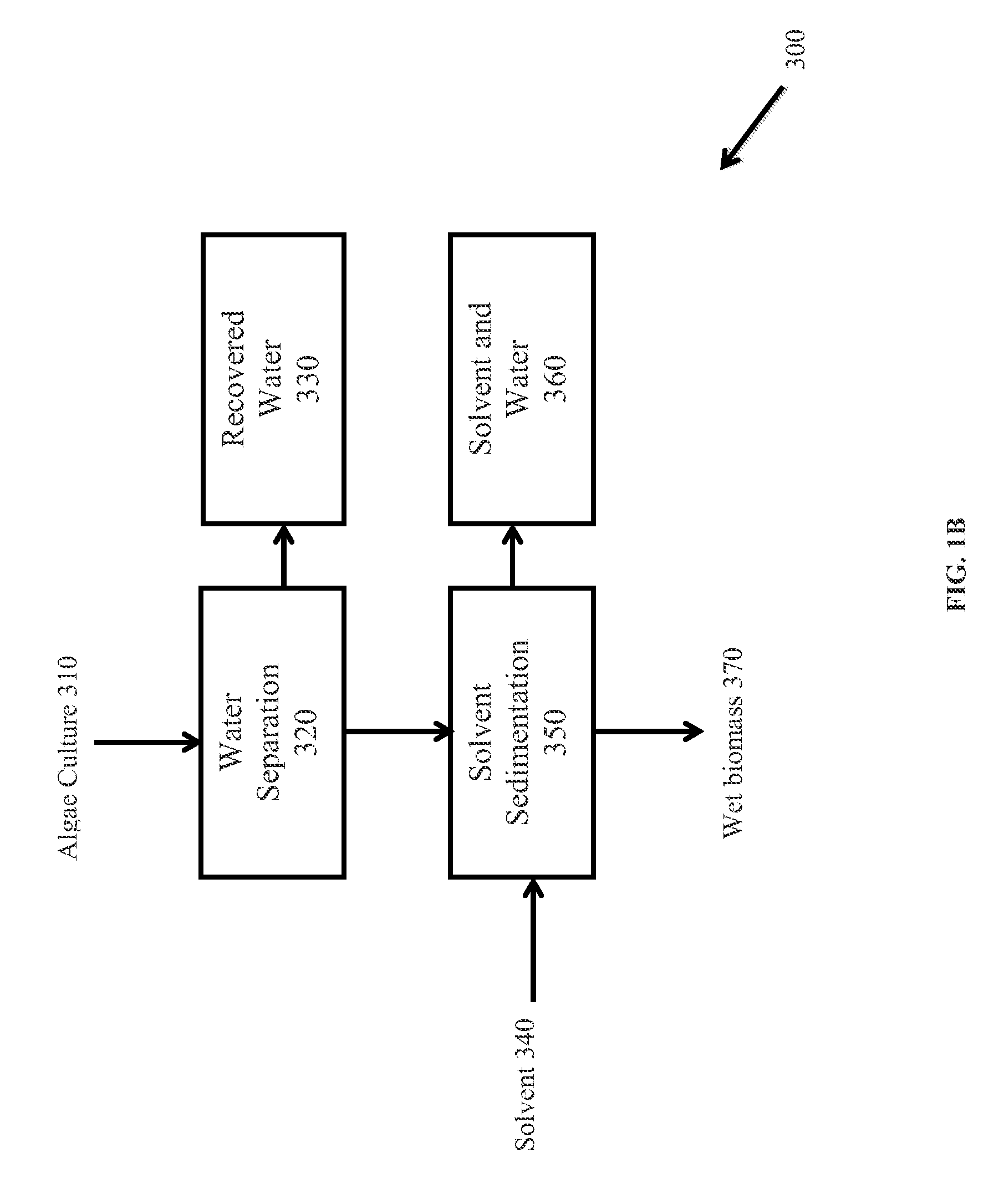
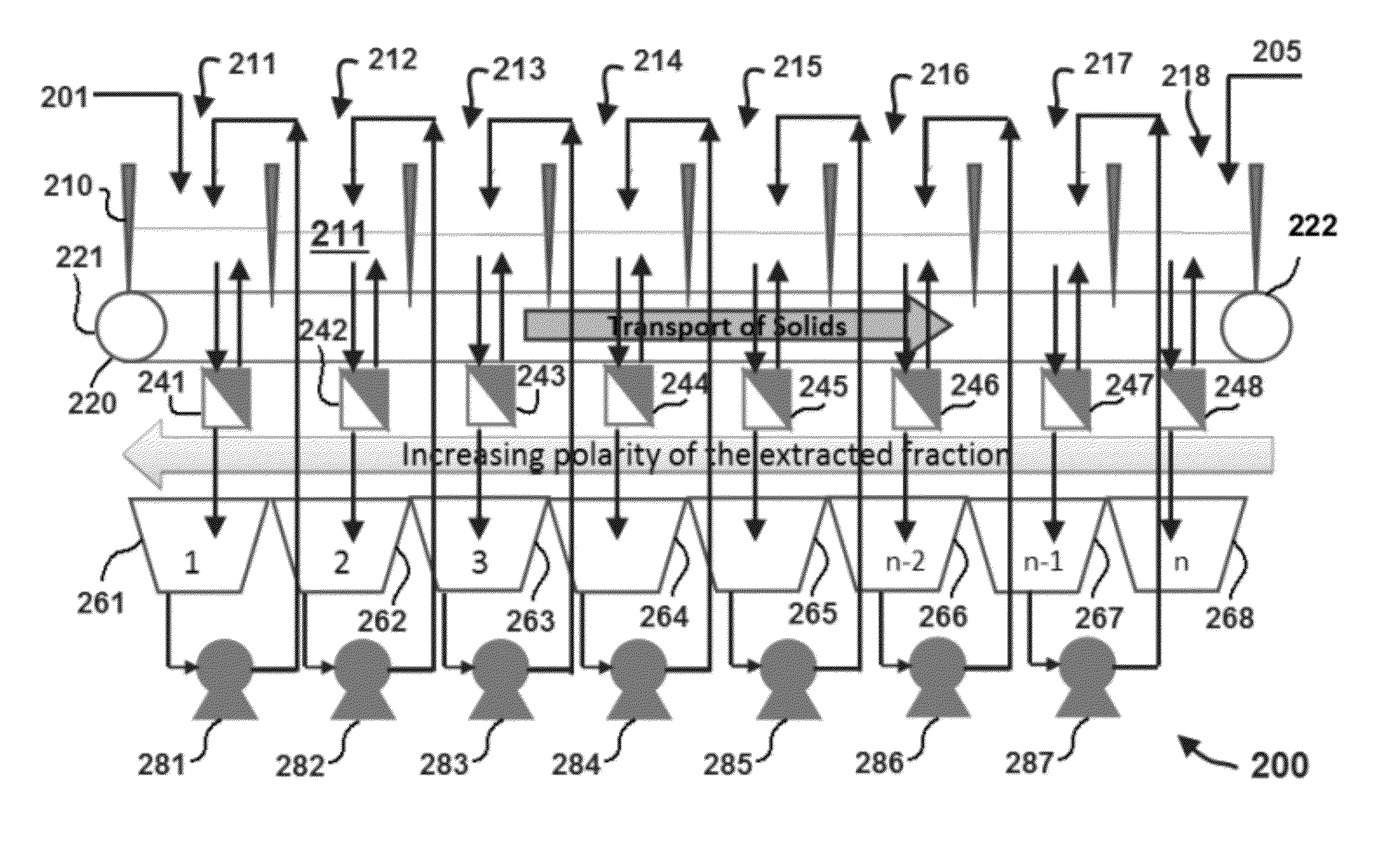
Extraction of neutral lipids by a two solvent method
InactiveUS8202425B2Quantity minimizationReduce processing latencyWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationSemi-permeable membranesSolventPolar lipids
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Nicotine compositions
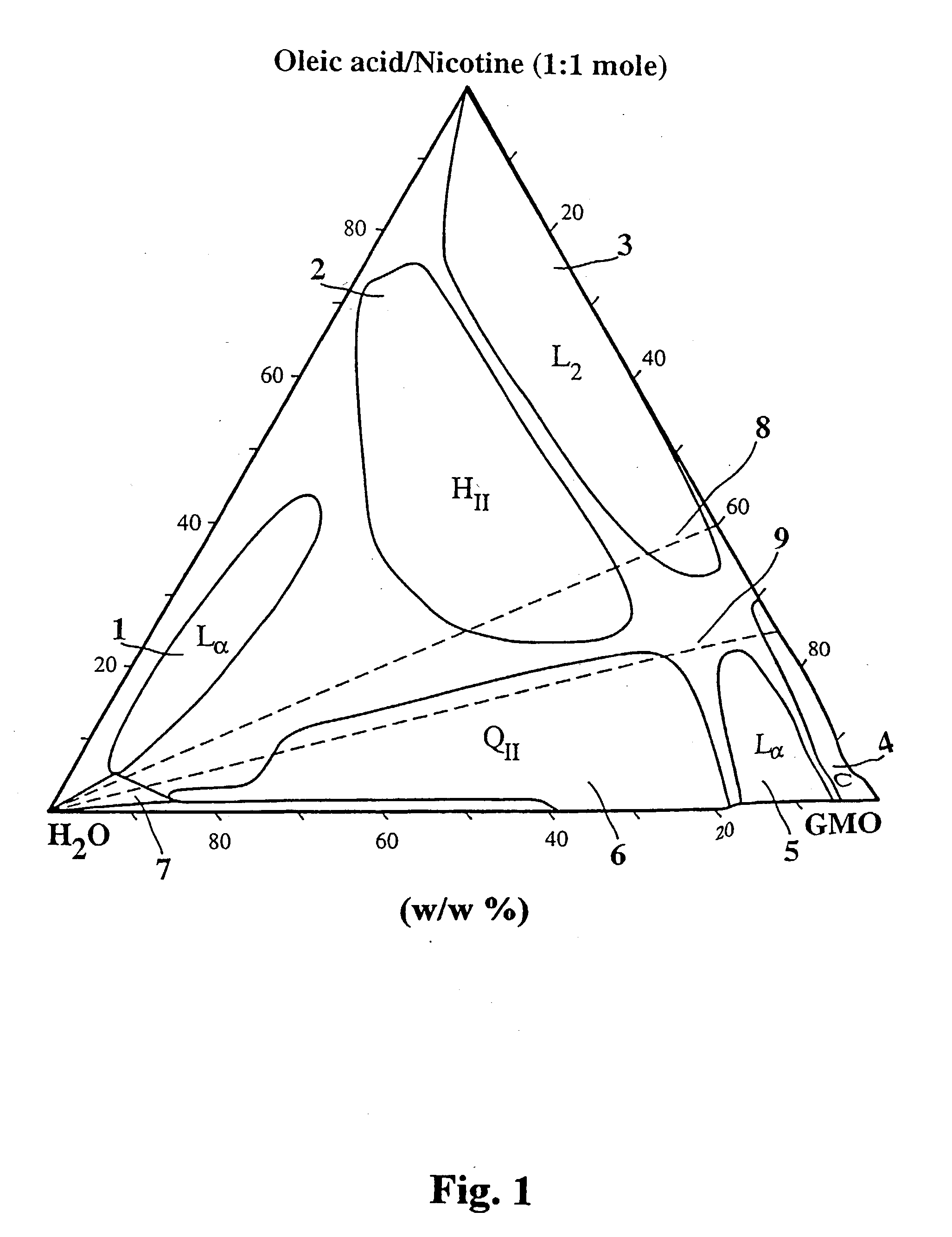
The present invention relates to compositions of nicotine comprising polar lipids and one or more fatty acids. The compositions may further comprise one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients selected from the group consisting of flavoring agents, sweeteners, buffering agents, chewing gum base and preservatives. In specific aspects, the invention is directed to compositions comprising nicotine and one or more polar lipids which are capable of forming a liquid crystalline phase or a precursor or offspring thereof when placed in a polar solvent. The composition can be administered via a buccal, pulmonary, nasal or topical route.
Owner:ANDERSSON SVEN +2
Extraction of polar lipids by a two solvent method
InactiveUS20120053357A1Reduce processing latencyQuantity minimizationWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationSemi-permeable membranesFood additiveSolvent
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Production and use of a polar lipid-rich fraction containing stearidonic acid and gamma linolenic acid from plant seeds and microbes
The production and use, and in particular, the extraction, separation, synthesis and recovery of polar lipid-rich fractions containing gamma linolenic acid (GLA) and / or stearidonic acid (SDA) from seeds and microorganisms and their use in human food applications, animal feed, pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Extraction of neutral lipids by a two solvent method
InactiveUS20120046477A1Quantity minimizationReduce processing latencyWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationSemi-permeable membranesSolventPolar lipids
A method for separating neutral lipids from plant material, in particular, intact algal cells, using an amphipathic solvent set and a hydrophobic solvent set. Some embodiments include dewatering intact algal cells and then extracting neutral lipids from the algal cells. The methods provide for single and multistep extraction processes which allow for efficient separation of algal neutral lipids from a wet algal biomass while avoiding emulsification of extraction mixtures. The neutral lipids are removed after first removing a polar lipid fraction and a protein fraction. These neutral lipids can be used to generate renewable fuels as well as food products and supplements.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
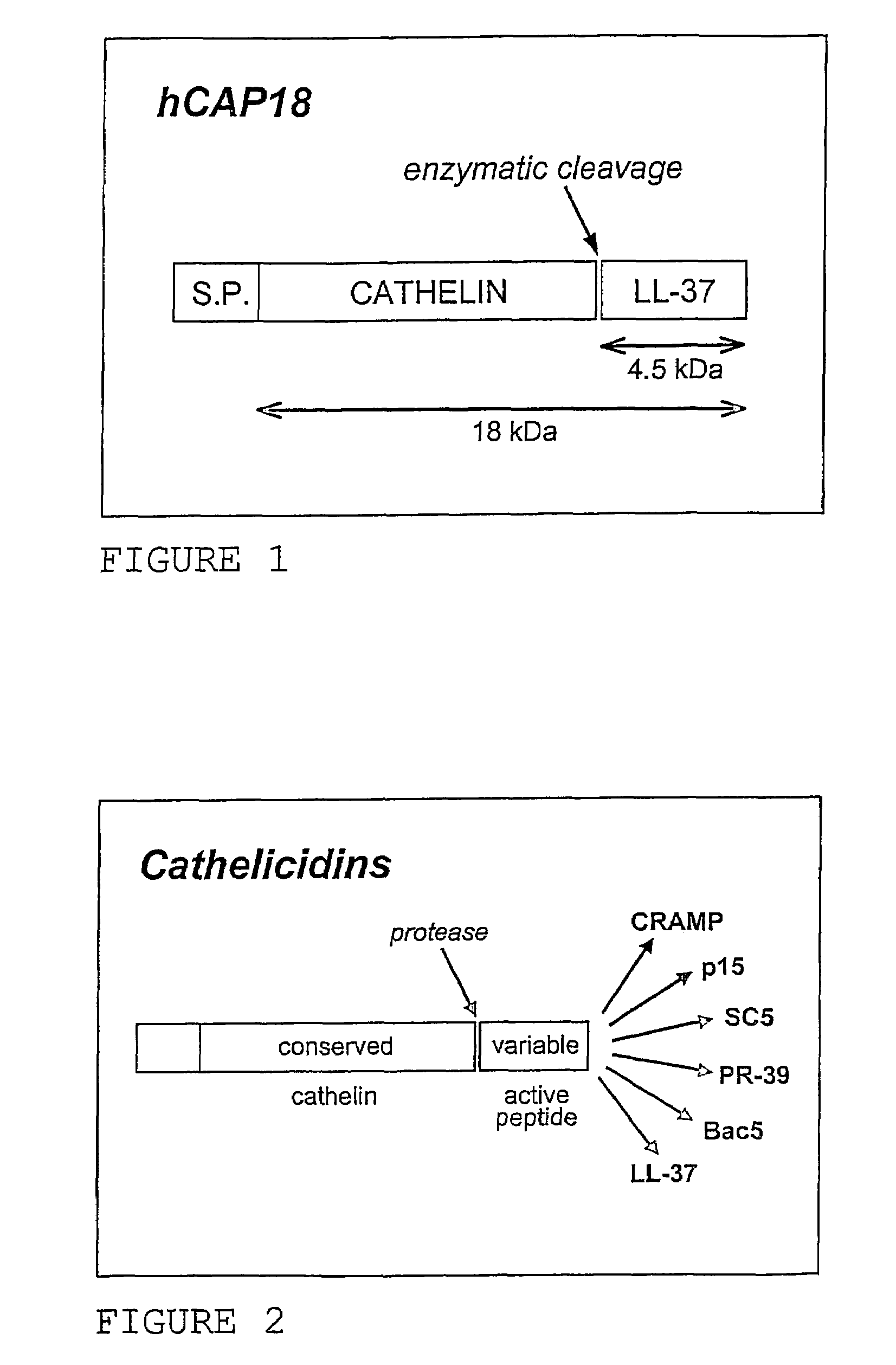
Use of the cathelicidin LL-37 and derivatives thereof for wound healing
ActiveUS7452864B2Promote regenerationWound be enhancedAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsCytotoxicityCell culture media
Use of the antimicrobial cathelicidin peptide ll-37, N-terminal fragments of LL-37 or extended sequences of LL-37 having 1-3 amino acids in the C-terminal end, for stimulating proliferation of epithalial and stromal cells and thereby healing of wounds, such as chronic ulcers. The cytotoxic effect of LL-37 may be reduced by including a bilayer-forming polar lipid, especially a digalactosyldiacylglycerol, in pharmaceutical compositions and growth media comprising LL-37.
Owner:PROMORE PHARMA AB
Adjuvant combinations of liposomes and mycobacterial lipids for immunization compositions and vaccines
ActiveUS8241610B2Good auxiliary effectEnhance immune responseAntibacterial agentsBiocideLiposomeMycobacterium
The present invention provides a vaccine adjuvant consisting of a combination of a surfactant i.e. dimethyldeoctadecylammonium-bromide / chloride (DDA) and a lipid extract from Mycobacterium bovis BCG. The total lipid extract contains both apolar lipids, polar lipids, and lipids of intermediate polarity of which the apolar lipids were found to induce the most powerful immune responses. The total lipids may be extracted with chloroform / methanol and re-dissolved in water before the addition of surfactant. This preparation may be used to induce prominent cell-mediated immune responses in a mammal in order to combat pathogens, or as a treatment for cancer.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST
Extraction of polar lipids by a two solvent method
InactiveUS8211308B2Quantity minimizationReduce processing latencyWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationSemi-permeable membranesFood additiveSolvent
A method for separating polar lipids from plant material, in particular, intact algal cells, using an amphipathic solvent set and a hydrophobic solvent set. Some embodiments include dewatering intact algal cells and then extracting polar lipids from the algal cells. The methods provide for single and multistep extraction processes which allow for efficient separation of algal polar lipids from a wet algal biomass while avoiding emulsification of extraction mixtures. These polar lipids are high value products which can be used as surfactants, detergents, and food additives. Neutral lipids remaining in the algal biomass after extraction of polar lipids can be used to generate renewable fuels.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
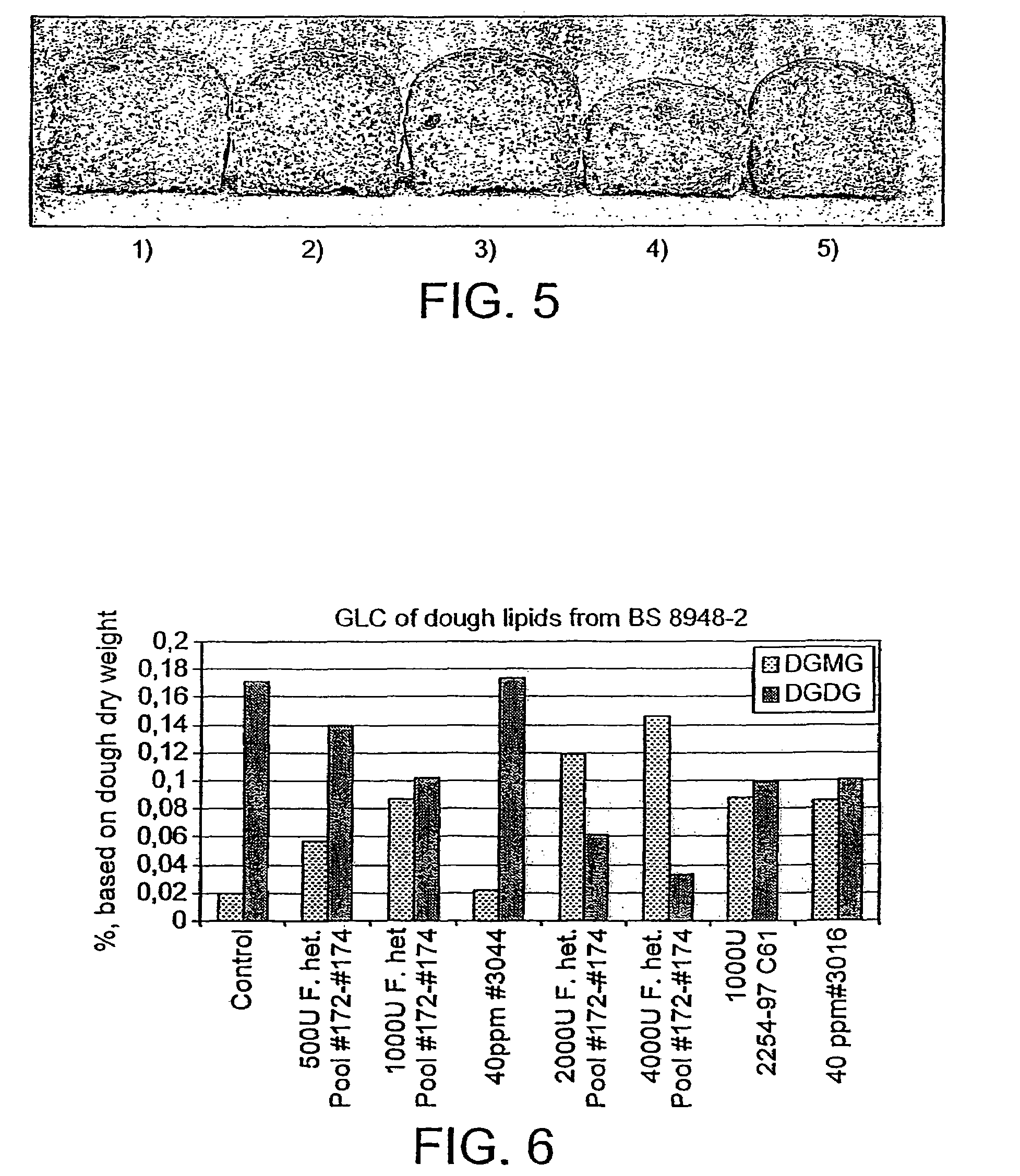
Fungal lipolytic enzymes, nucleic acids encoding, and uses thereof
A fungal wild-type lipolytic enzyme having a higher ratio of activity on polar lipids compared with triglycerides, wherein the enzyme preferably has a phospholipid:triglyceride activity ratio of at least 4. Preferably, the lipolytic enzyme according to the present invention has a glycolipid:triglyceride hydrolyzing activity ratio of at least 1.5. In one embodiment, the fungal lipolytic enzyme according to the present invention comprises an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 or SEQ ID No. 2 or SEQ ID No. 4 or SEQ ID No. 6 or an amino acid sequence which has at least 90% identity thereto. The present invention further encompasses a nucleic acid encoding a fungal lipolytic enzyme, which nucleic acid is selected from the group consisting of: (a) a nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide shown in SEQ ID No. 3, SEQ ID No. 5 or SEQ ID No. 7; (b) a nucleic acid which is related to the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID No. 3, SEQ ID No. 5 or SEQ ID No. 7 by the degeneration of the genetic code; and (c) nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence which has at least 90% identity with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 3, SEQ ID No. 5 or SEQ ID No. 7.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Extraction of neutral lipids by a two solvent method
InactiveUS8273248B1Reduce processing latencyQuantity minimizationTreatment involving filtrationSolid sorbent liquid separationSolventPolar lipids
A method for separating neutral lipids from plant material, in particular, intact algal cells, using an amphipathic solvent set and a hydrophobic solvent set. Some embodiments include dewatering intact algal cells and then extracting neutral lipids from the algal cells. The methods provide for single and multistep extraction processes which allow for efficient separation of algal neutral lipids from a wet algal biomass while avoiding emulsification of extraction mixtures. The neutral lipids are removed after first removing a polar lipid fraction and a protein fraction. These neutral lipids can be used to generate renewable fuels as well as food products and supplements.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Extraction of polar lipids by a two solvent method
InactiveUS20120277450A1Reduce processing latencyQuantity minimizationFatty-oils/fats productionFood additiveSolvent
A method for separating polar lipids from plant material, in particular, intact algal cells, using an amphipathic solvent set and a hydrophobic solvent set. Some embodiments include dewatering intact algal cells and then extracting polar lipids from the algal cells. The methods provide for single and multistep extraction processes which allow for efficient separation of algal polar lipids from a wet algal biomass while avoiding emulsification of extraction mixtures. These polar lipids are high value products which can be used as surfactants, detergents, and food additives. Neutral lipids remaining in the algal biomass after extraction of polar lipids can be used to generate renewable fuels.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Prolamine-plant polar lipid composition, its method of preparation and applications thereof
Prolamine-plant polar lipid compositions are provided, said compositions including a mixture of a prolamine, a plant polar lipid, at least one polyalcohol in a hydro-alcoholic solution, and an active agent, wherein the composition forms a substantially homogeneous dispersion with skin adhesive properties; wherein the dispersion forms a film and wherein the film contains a gradient of concentrations of the active agent.
Owner:THALLIUM HLDG CO LLC
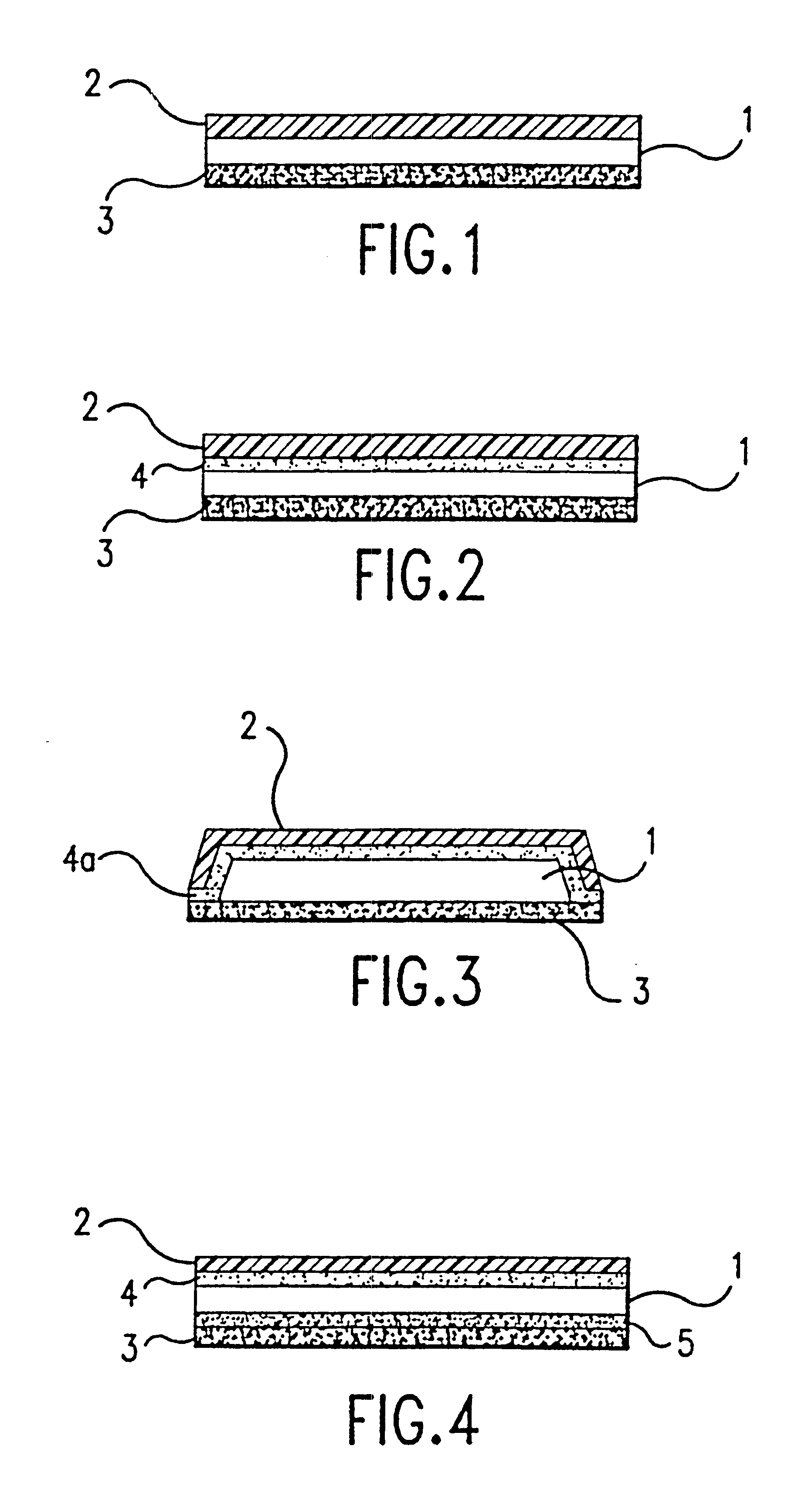
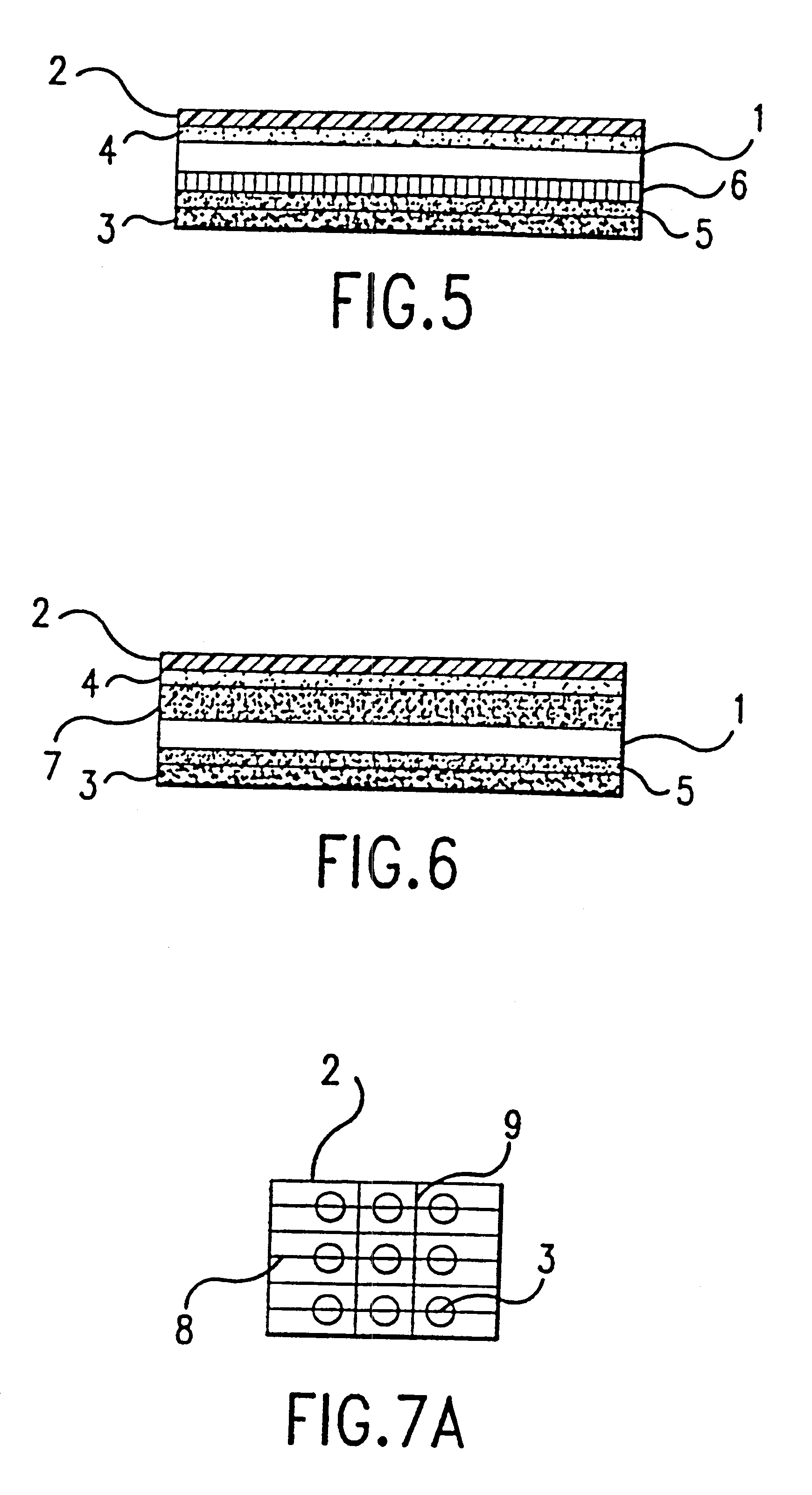
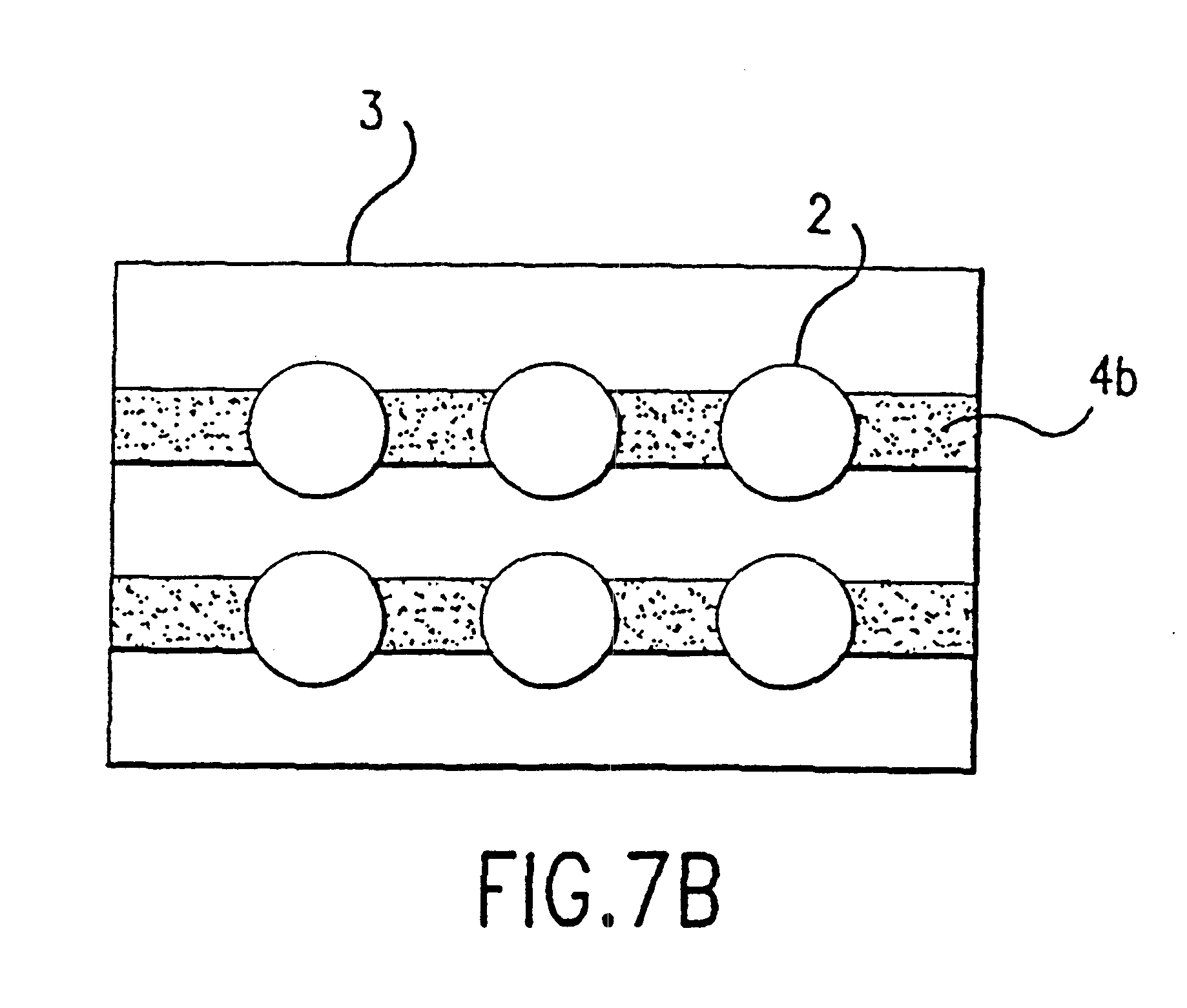
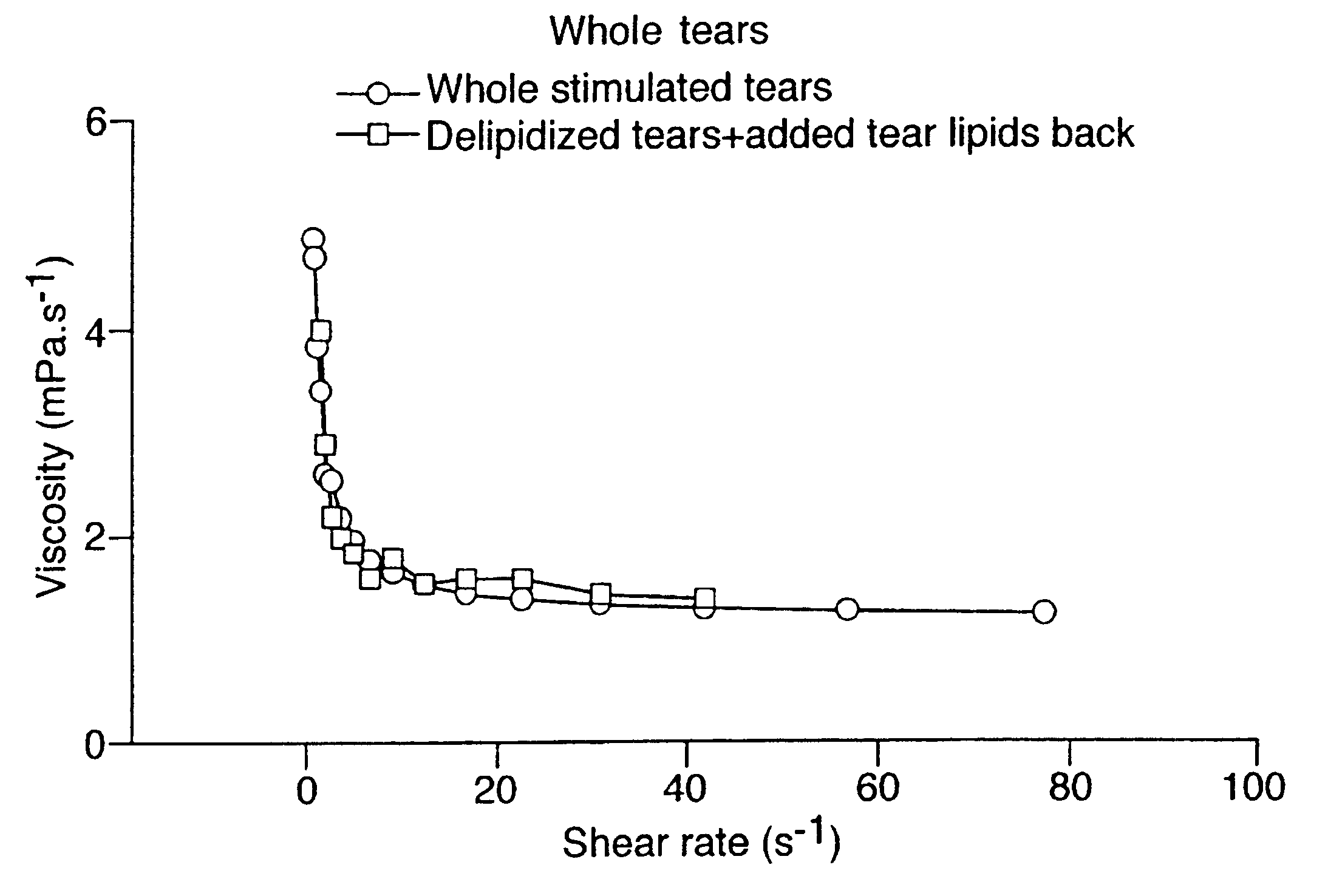
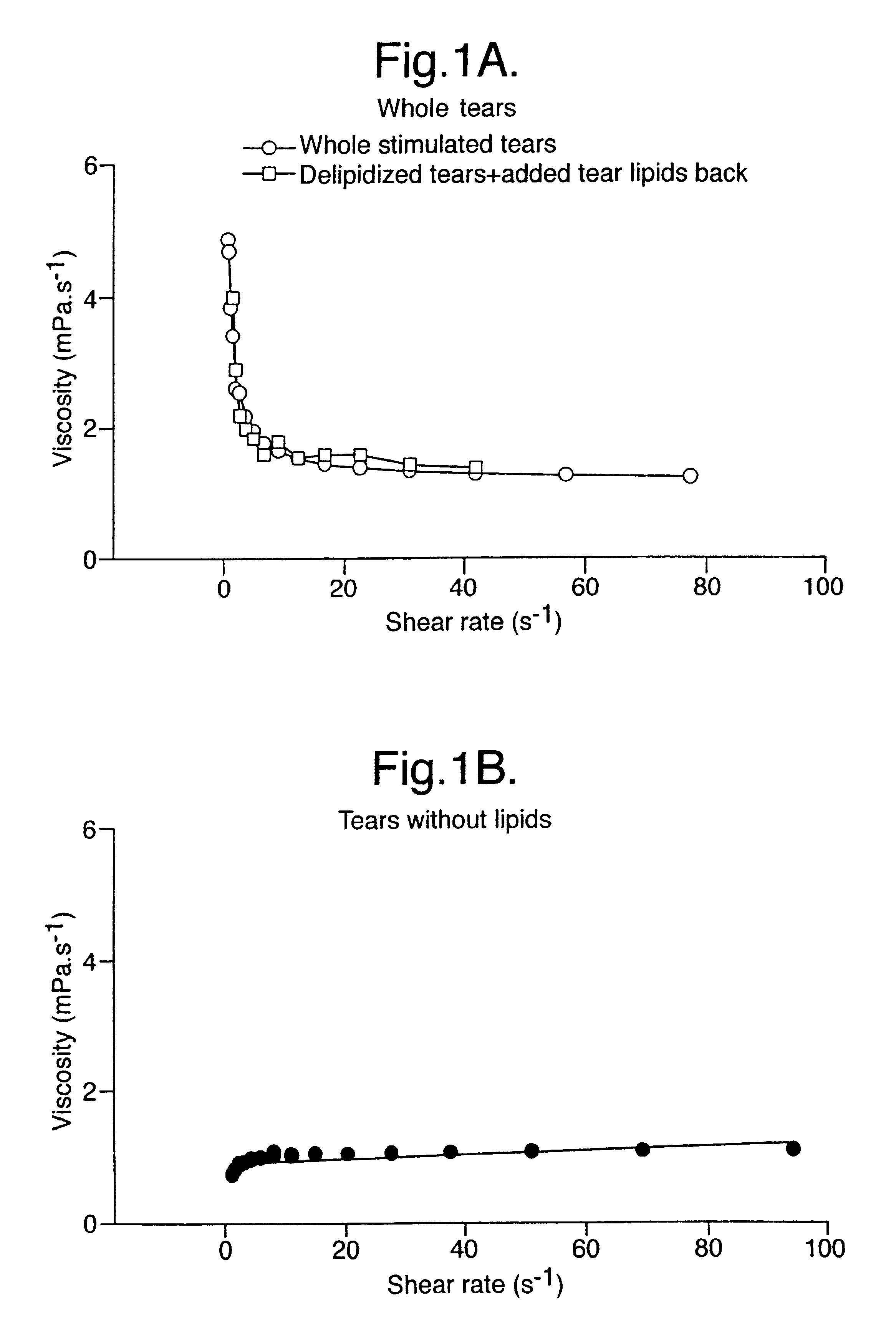
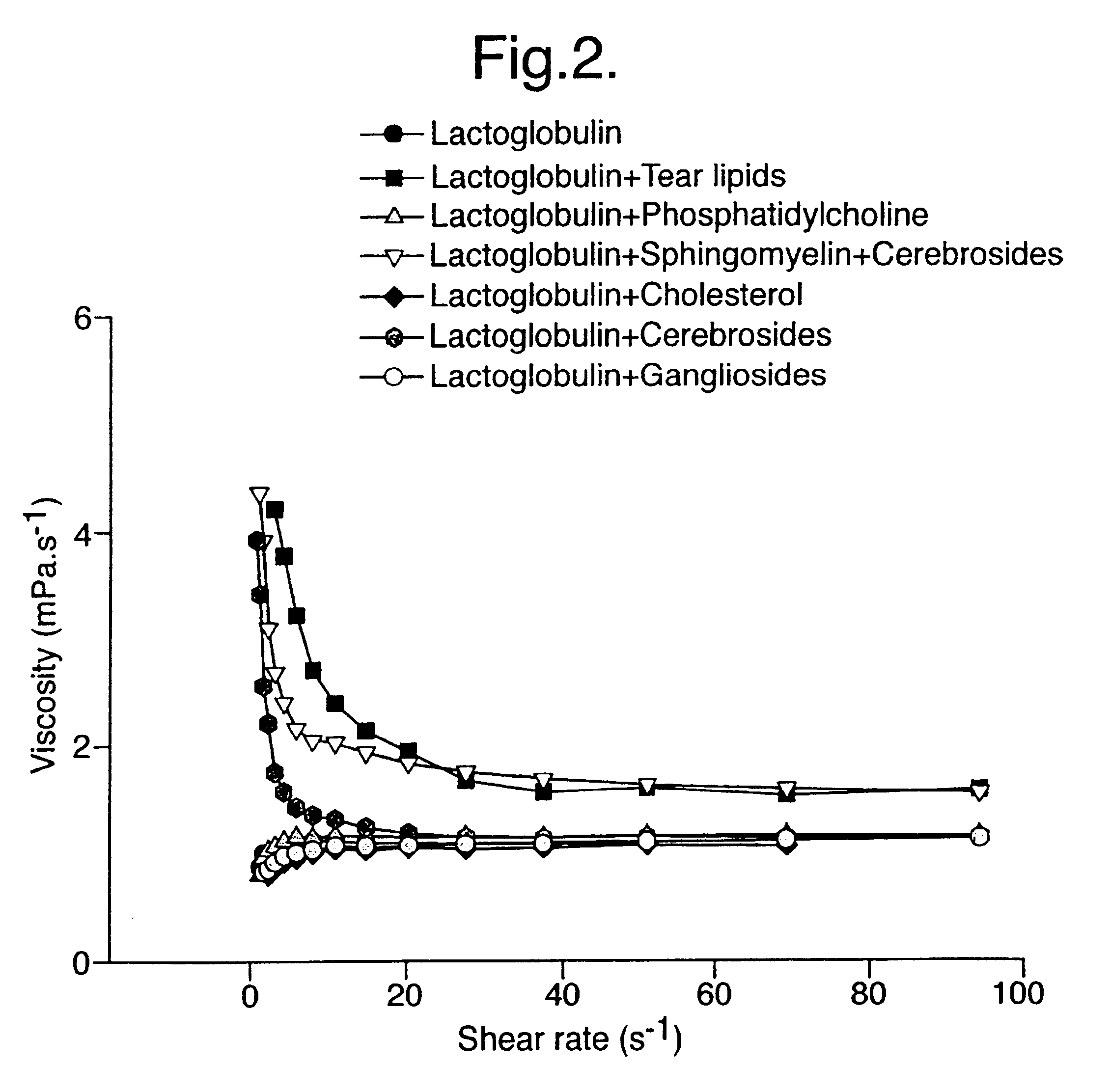
Artificial tear formulation
Provided by the present invention are formulations suitable for application to mammalian eyes which contain a lipid binding protein and a polar lipid, present as a soluble complex in an aqueous electrolyte. The formulations described have shear-thinning (non-Newtonian viscosity) and surface tension properties to natural tears and are therefore useful as artificial tear substitutes for the treatment of dry eyes (e.g. keratoconjunctivitis sicca) and useful in ophthalmic applications in general.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
Nutritional compositions containing synergistic combination and uses thereof
A composition and method for enhancing brain development in a pediatric subject, the method including administering to the pediatric subject a nutritional composition having up to about 7 g / 100 kcal of a fat or lipid source, wherein the fat or lipid source includes at least about 0.5 mg / 100 kcal of milk or non-milk polar lipids; up to about 5 g / 100 kcal of a protein source; at least about 15 mg / 100 kcal of lactoferrin from a non-human source; about 0.015 g / 100 kcal to about 0.15 g / 100 kcal of a prebiotic composition including polydextrose and / or galactooligosaccharide; and at least about 5 mg / 100 kcal of a source of long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Owner:MEAD JOHNSON NUTRITION
Method for quickly and simply analyzing microbial community structure of yeast for traditional brewage
InactiveCN102033114AAvoid Analytical ErrorsAvoid time consumingComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementGas phaseVapor phase chromatography
The invention relates to a culture-free biochemical method for analyzing the microbial community structure of yeast for traditional brewage, in particular to a method for analyzing the microbial community structure of yeast for traditional brewage by using the phospholipid fatty acid spectrogram analysis technique. The method comprises the following steps: (1) weighting a certain amount of yeast sample which is pulverized and evenly mixed; (2) adding a buffer solution and an organic reagent to obtain an organic phase containing lipids; (3) separating the organic phase by small silica gel columns, eluting and collecting organic components containing polar lipids; (4) carrying out methyl esterification under mild condition, and adding an extracting reagent to obtain corresponding fatty acid methyl ester; (5) carrying out quantitative analysis on the fatty acid methyl ester by using a gas chromatogram-mass spectrogram combined instrument; and (6) determining the characteristics of the microbial community structure in the sample according to characteristics of different phospholipid fatty acid compositions. The invention provides an accurate and quick culture-free detection means for researching the composition of the microbial community structure of yeast for brewage and knowing the law of growth and decline of different microbial communities in the yeast preparation process.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Composition containing porous microparticle impregnated with biologically-active compound for treatment of infection
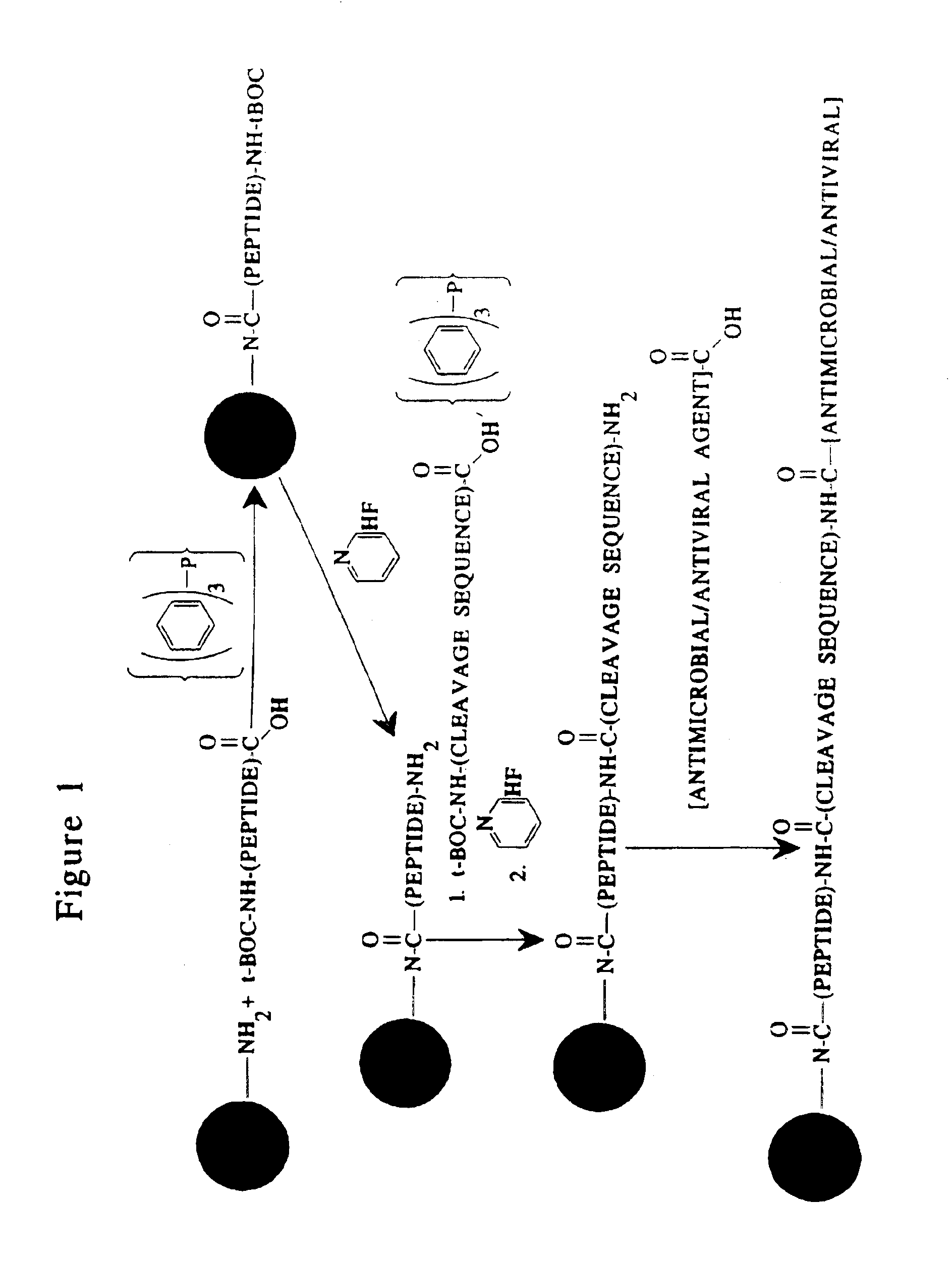
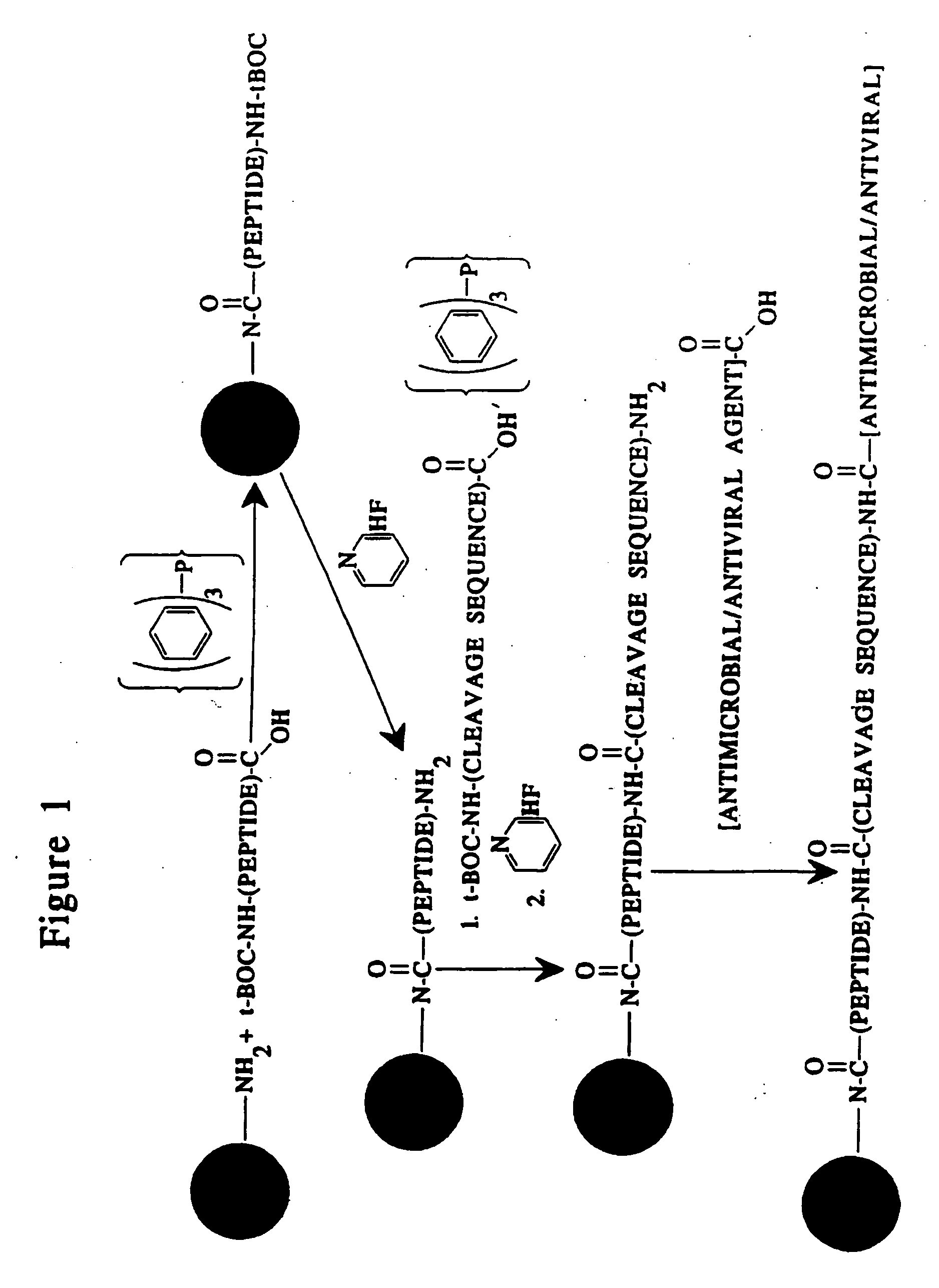
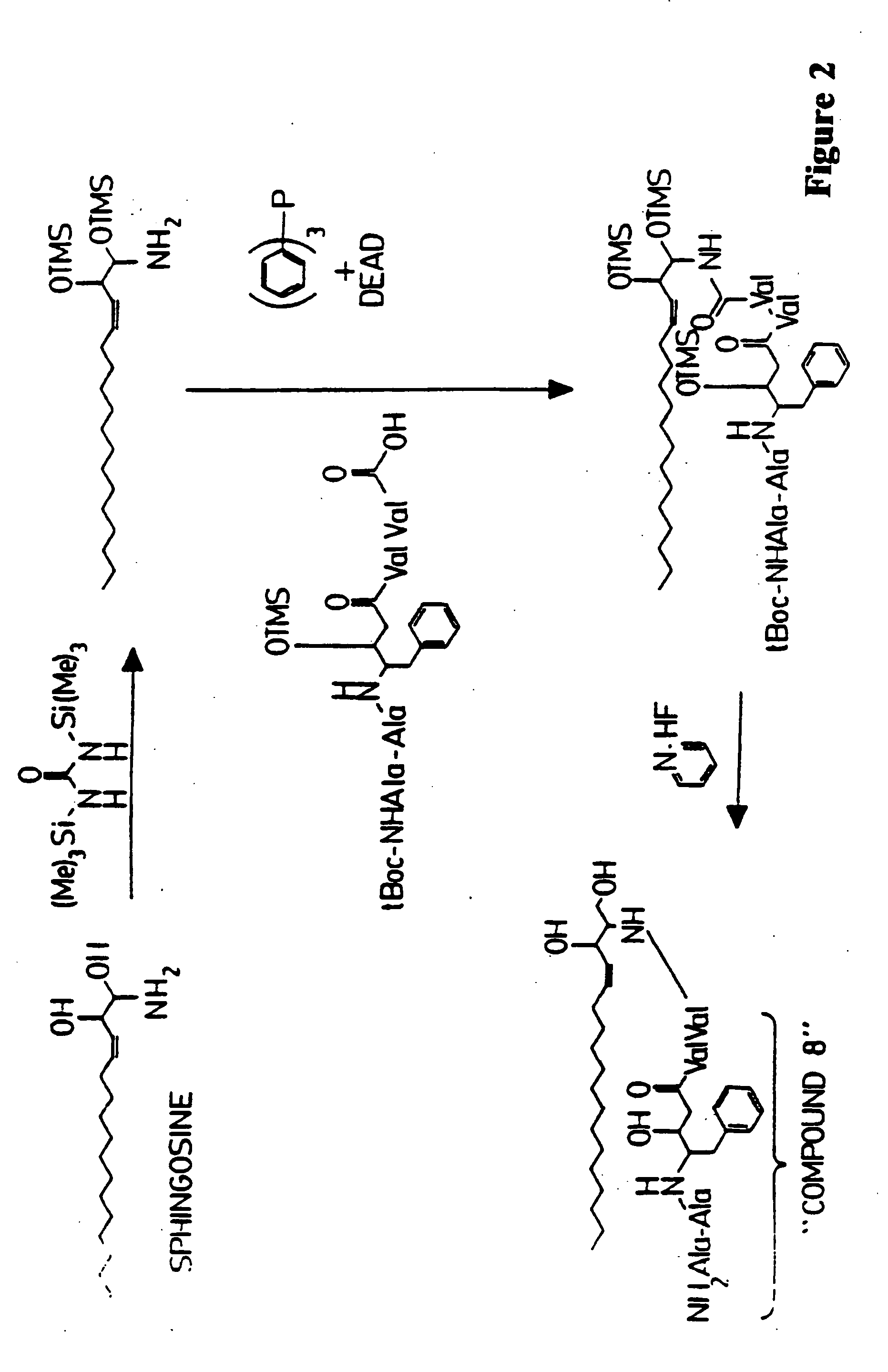
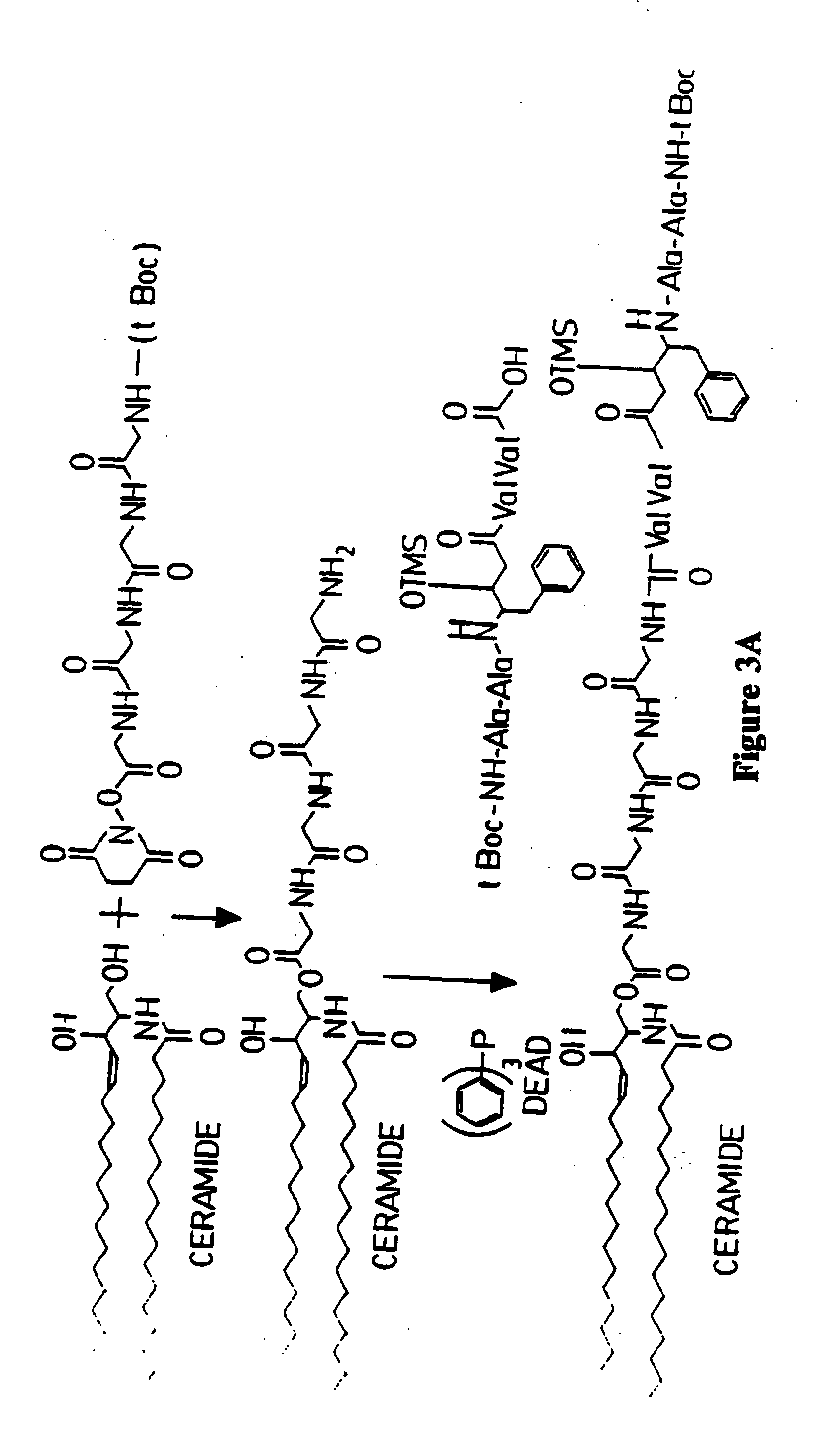
Methods and reagents are provided for specifically targeting biologically active compounds such as antiviral and antimicrobial drugs, or prodrugs containing the biologically active compound to specific sites such as specific organelles in phagocytic mammalian cells. The biologically active compound or prodrug is linked to a microparticle with a linker that is non-specifically or specifically cleaved inside a phagocytic mammalian cell. Alternatively, the biologically active compound or prodrug is impregnated into a porous microparticle or coated on a nonporous microparticle, and then coated with a coating material that is non-specifically or specifically degraded inside a phagocytic mammalian cell. The prodrug contains the biologically active compound linked to a polar lipid such as ceramide with a specific linker such as a peptide that is specifically cleaved to activate the prodrug in a phagocytic mammalian cell infected with a microorganism. A microparticle linked antimicrobial drug or prodrug may be used for killing a microorganism infecting a phagocytic mammalian cell in vivo or in vitro.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
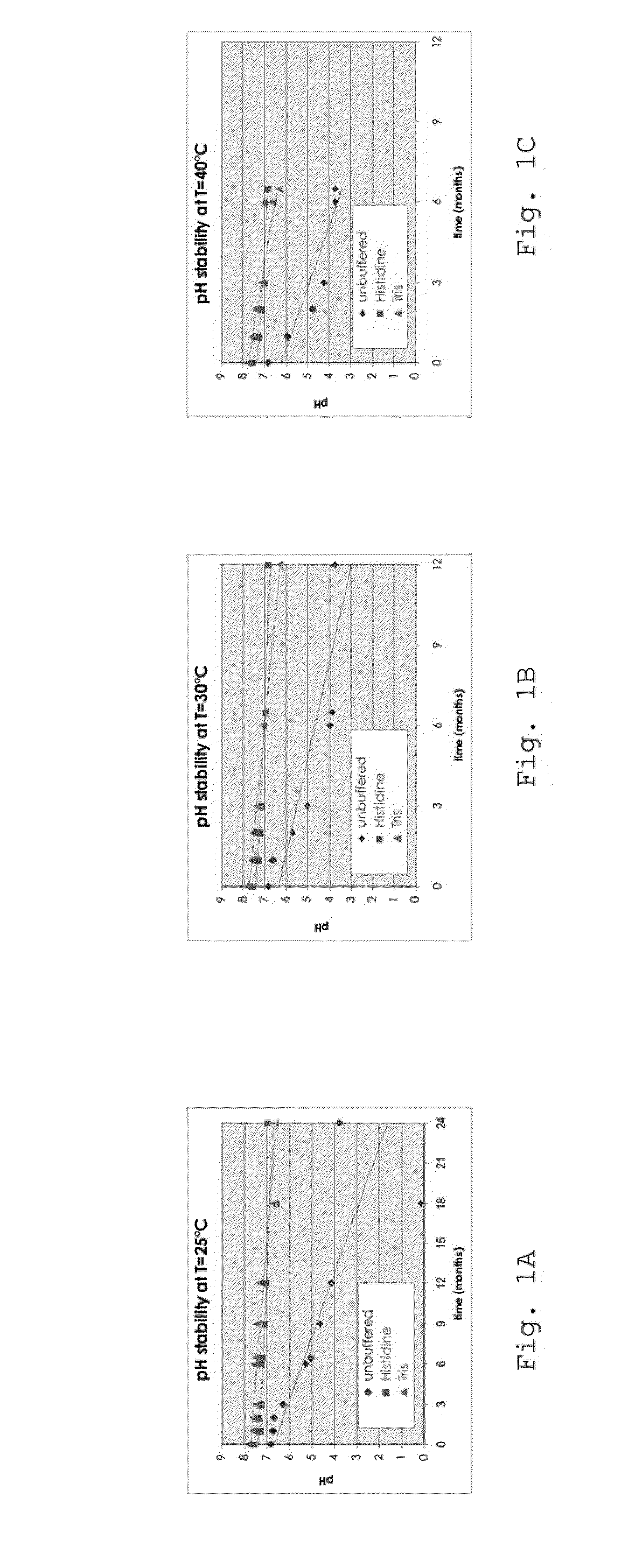
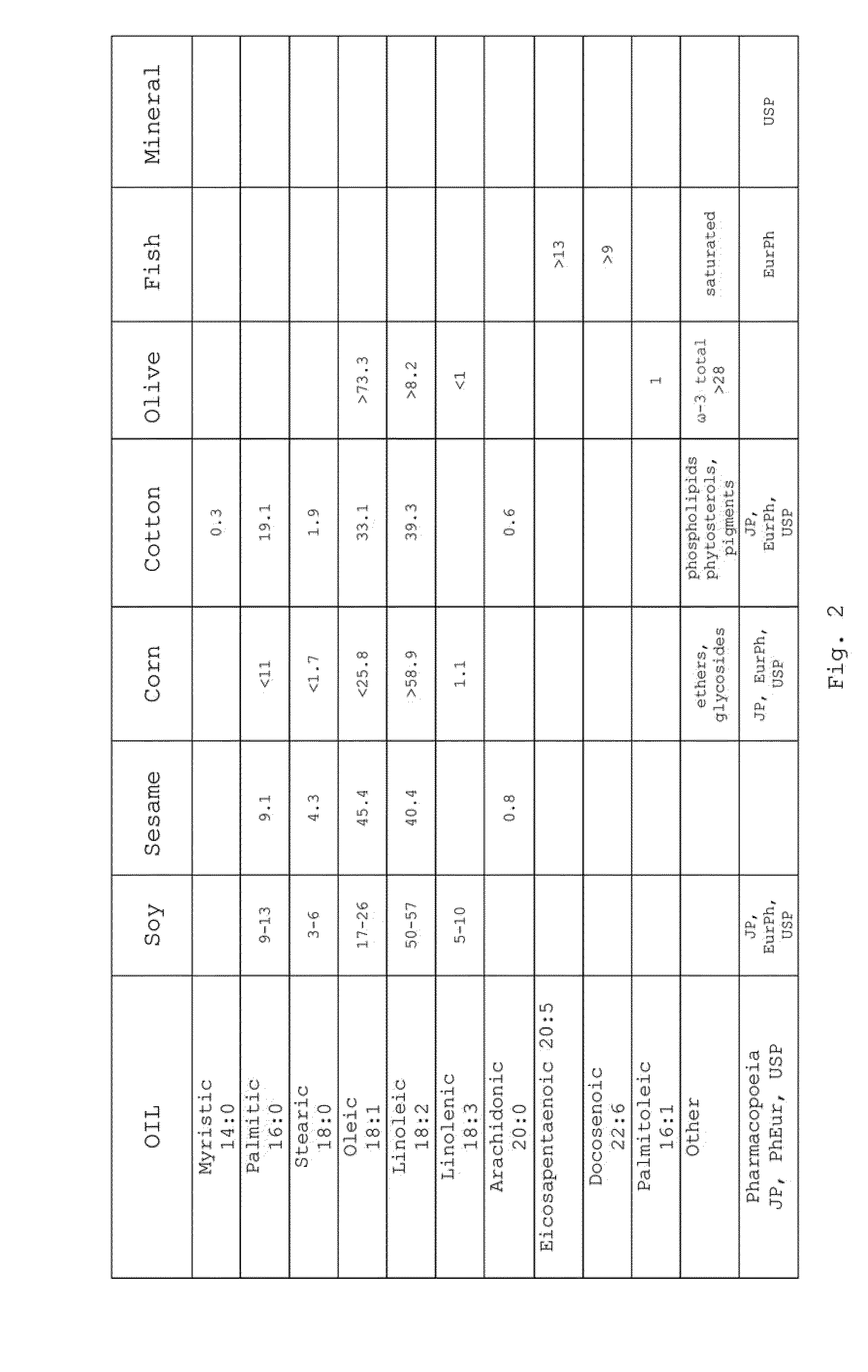
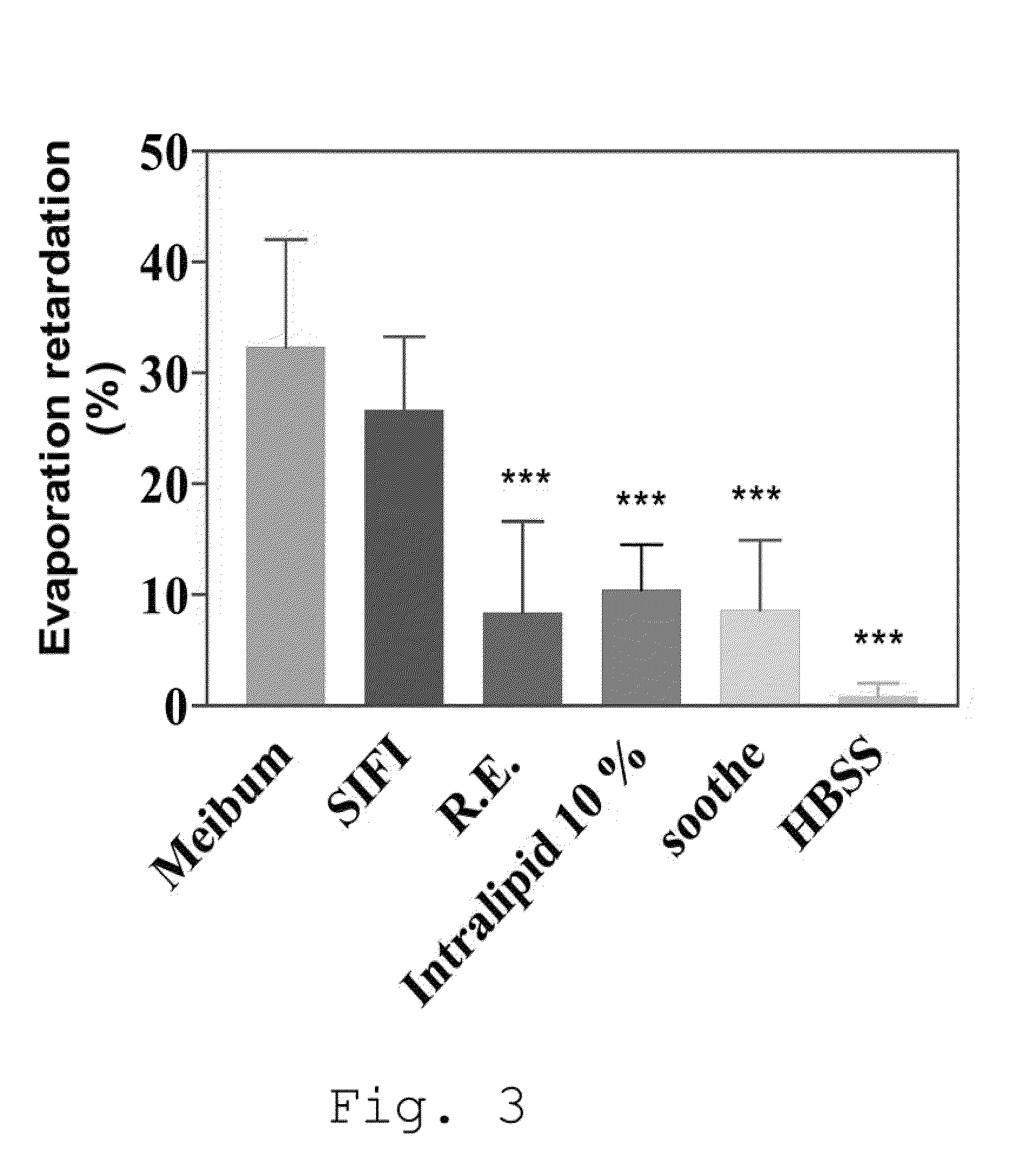
Pharmaceutical Formulations Based on Apolar and Polar Lipids for Ophthalmic Use
ActiveUS20100291226A1Reduce evaporationEffective conditioningBiocideSenses disorderNatural sourceLipid formation
The present invention refers to pharmaceutical formulations based on lipids for ophthalmic use comprising a phospholipid component composed of zwitterionic phospholipids of natural origin and an oily component composed of oils of natural origin emulsified in water. In particular, the invention refers to ophthalmic formulations useful, for example, for transporting drugs to the eye and in the treatment of ocular dryness, capable of restoring the lipid layer of the tear film. In particular, in a non-transitory but pathological situation such as the dry eye syndrome, such formulations also succeed in reducing the often-present inflammatory component.
Owner:S I F I SPA
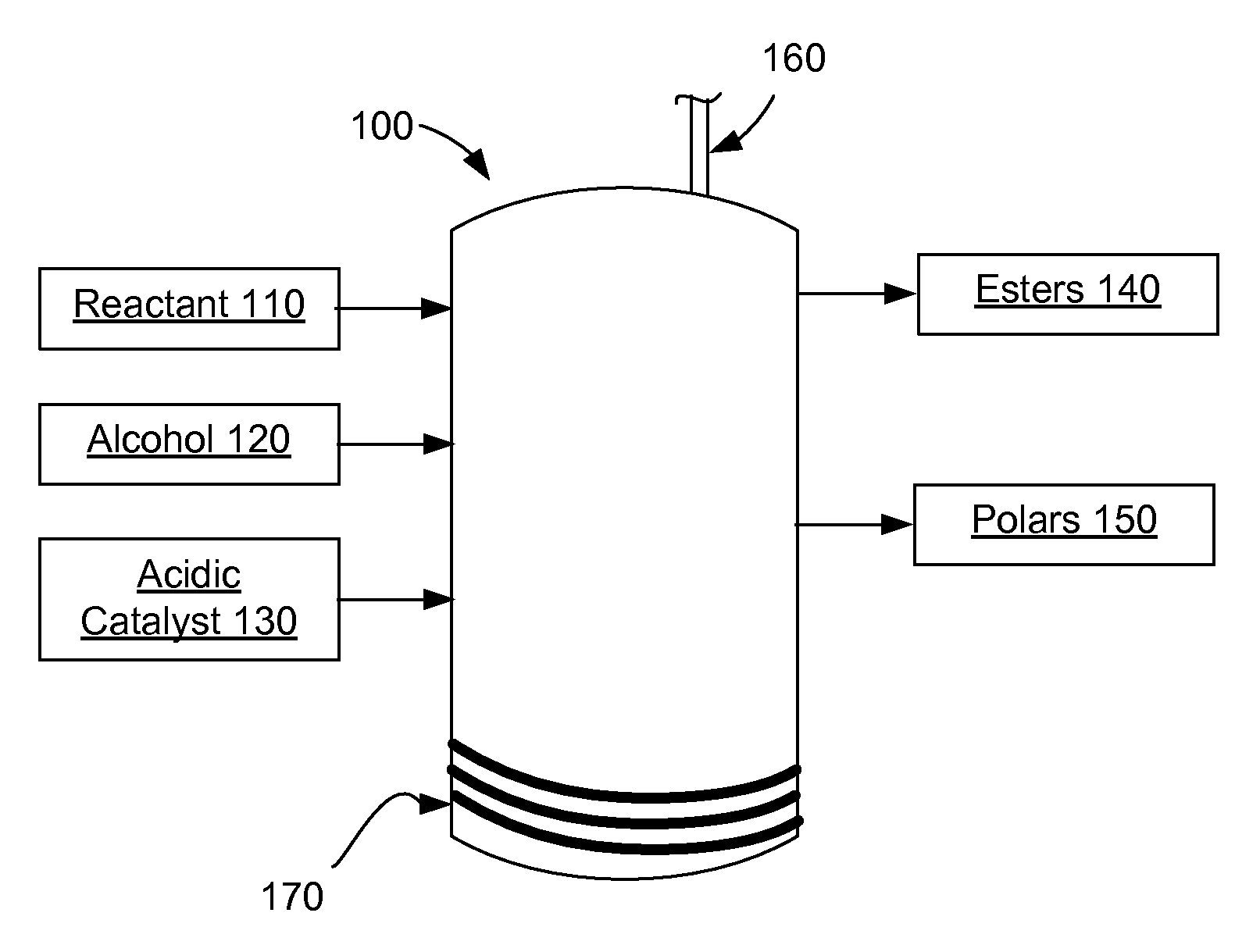
Processing Lipids
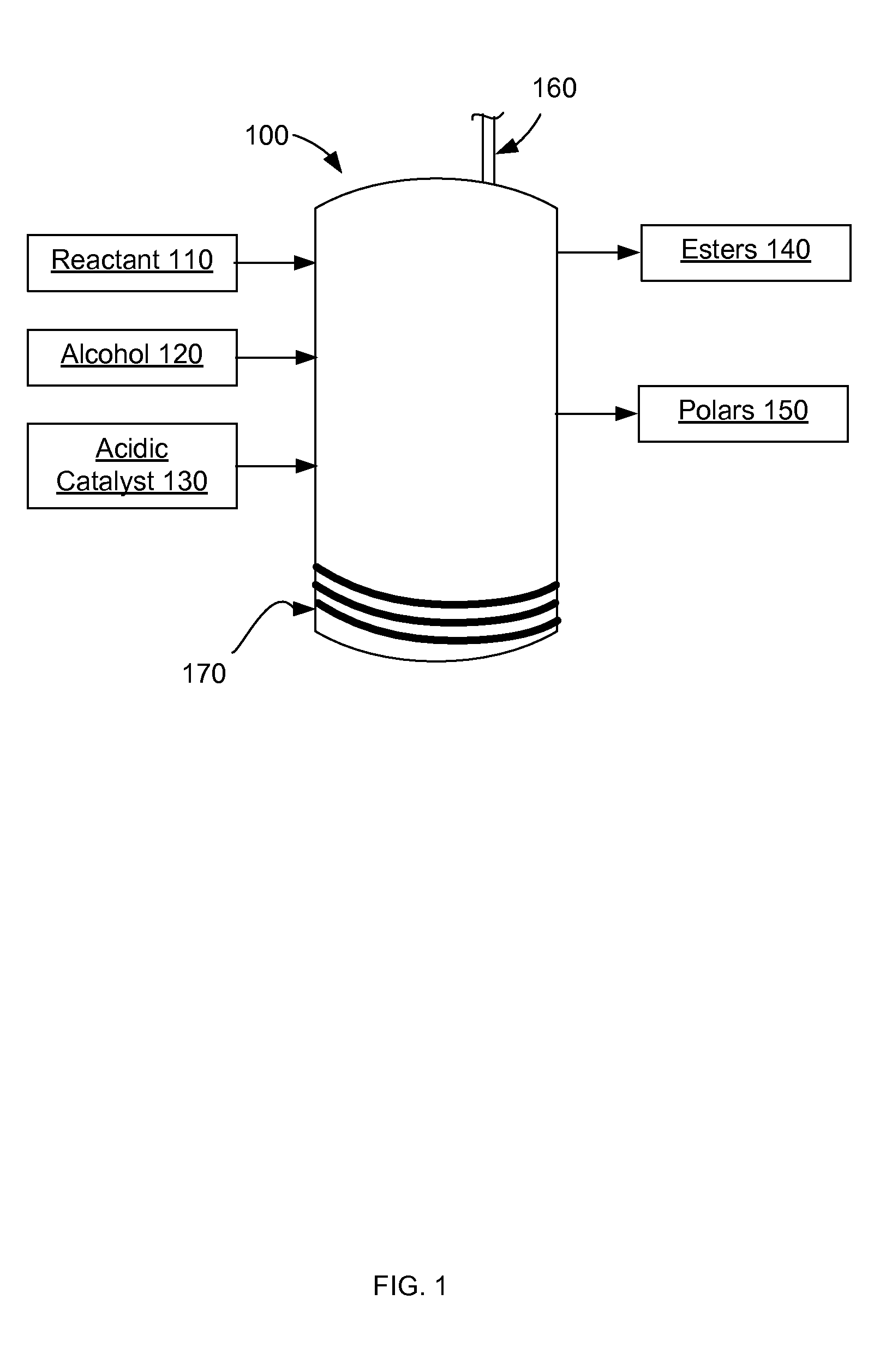
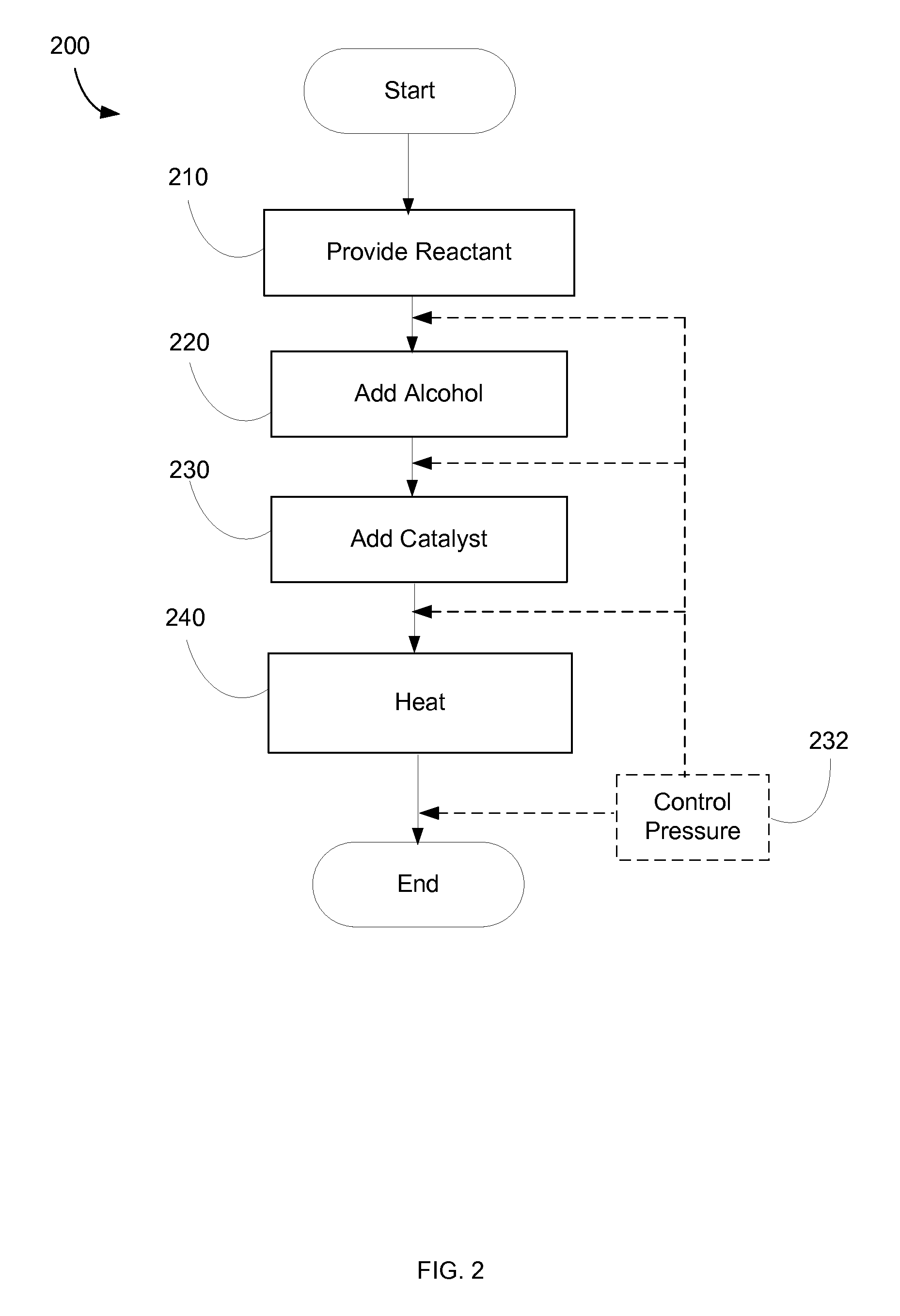
InactiveUS20110072713A1Fatty acid esterificationPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionAlcoholCelsius Degree
A method for converting lipids to alkyl esters may include receiving a reactant comprising one or more lipids. In some cases, the reactant may include substantial amounts of polar lipids and / or free fatty acids. Some reactants may be derived from photosynthetic organisms, such as algae and / or diatoms. The reactant may be mixed with an alcohol and a catalyst to form a mixture. The mixture may be heated, for example, to a temperature between 50 and 350 degrees Celsius, including between 80 and 220 degrees Celsius. Pressure may be controlled to be between 1 and 200 bar, including between 10 and 100 bar. At least a portion of the reactant may be converted to one or more alkyl esters. A biofuel may include alkyl esters made from lipids according to various methods.
Owner:AURORA ALGAE
Method and composition for treating inflammatory disorders
There is provided homogeneous pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of inflammatory disorders comprising an antiinflammatory and / or antihistaminic active ingredient, a polar lipid liposome and a pharmaceutically-acceptable aqueous carrier.
Owner:MEDA AB
Microparticle-drug conjugates for biological targeting
InactiveUS20060008461A1Control releasePowder deliveryTripeptide ingredientsAntimicrobial drugMicroparticle
This invention provides novel methods and reagents for specifically delivering biologically active compounds to phagocytic mammalian cells. The invention also relates to specific uptake of such biologically active compounds by phagocytic cells and delivery of such compounds to specific sites intracellularly. The invention specifically relates to methods of facilitating the entry of antiviral and antimicrobial drugs and other agents into phagocytic cells and for targeting such compounds to specific organelles within the cell. The invention specifically provides compositions of matter and pharmaceutical embodiments of such compositions comprising conjugates of such antimicrobial drugs and agents covalently linked to particulate carriers generally termed microparticles. In particular embodiments, the antimicrobial drug is covalently linked to a microparticle via a cleavable linker moiety that is non-specifically cleaved in a phagocytic cell. In additional embodiments, the biologically-active compound is provided in an inactive, prodrug form that is activated by a chemical or enzymatic activity specific for cells infected by a microorganism, particularly a pathological or disease-causing microorganism. Thus, the invention provides cell targeting of drugs wherein the targeted drug is only activated in cells infected with a particular microorganism. Alternative embodiments of such specific drug delivery compositions also contain polar lipid carrier molecules effective in achieving intracellular organelle targeting in infected phagocytic mammalian cells. Particular embodiments of such conjugates comprise antimicrobial drugs covalently linked both to a microparticle via a cleavable linker molecule and to a polar lipid compound, to facilitate targeting of such drugs to particular subcellular organelles within the cell. Also provided are porous microparticles impregnated with antiviral and antimicrobial drugs and agents wherein the surface or outside extent of the microparticle is covered with a degradable coating that is degraded within a phagocytic mammalian cell. Also provided are nonporous microparticles coated with an antiviral or antimicrobial drug and further coated wherein the surface or outside extent of the microparticle is covered with a degradable coating that is degraded within a phagocytic mammalian cell. Methods of inhibiting, attenuating, arresting, combating and overcoming microbial infection of phagocytic mammalian cells in vivo and in vitro are also provided.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
Nutritional compositions with lipid globules with a core comprising vegetable lipids and a coating comprising phospholipids or polar lipids
ActiveUS20110206743A1Fat massImproved body compositionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyLipid formation
The present invention relates to a nutritional composition for infants and / or toddlers comprising a lipid component which has a large lipid globule size. The composition can be used to prevent obesity and / or improve body composition later in life. Said lipid component comprises 10-50 wt % vegetable lipids, and the lipid globules have a volume-weighted diameter above 1.0 m and / or a diameter of 2-12 m in an amount of at least 45 vol %.
Owner:NV NUTRICIA
Processes for obtaining sterols and polar lipids from vegetable oil lecithin fractions
InactiveUS20050130281A1Reduce contentHigh purityLactams separation/purificationUltrafiltrationVegetable oilUltrafiltration
Processes for the simultaneous production of sterols and polar lipids, in which preparations of vegetable oil lecithin fractions are subjected to ultrafiltration and, on the one hand, the sterols in the permeate and, on the other hand, the polar lipids in the retentate are enriched. The permeate and retentate can subsequently be worked up by methods known per se.
Owner:COGNIS IP MANAGEMENT GMBH
Polar lipid mixtures, their preparation and uses
InactiveUS20110294757A1Milk preparationOrganic active ingredientsPhosphatidyl inositolPhosphatidylethanolamine
Disclosed herein are polar lipid mixtures, comprising glycerophospholipids such as phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidylserine (PS) and phosphatidyl-inositol (PI), and sphingolipids such as sphyngomyelin (SM). Most importantly, the ratio of phospholipids in said mixture is comparable to that of HMF, and is represented by SM>PC>PE>PS>PI or SM=PC>PE>PS>PI. Processes for the preparation of said mixtures and uses thereof are also described herein.
Owner:ENZYMOTEC
Nutritional compositions with coated lipid globules
ActiveUS20110217411A1No significant effect on body weightReduce the total massOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderLipid formationDry weight
The present invention relates to a nutritional composition for infants and / or toddlers comprising a lipid component which has a lipid globules coated with polar lipids. The composition can be used to prevent obesity and / or improve body composition later in life. Said liquid comprises 10-50 wt % vegetable liquids based on the dry weight of the composition, and (i) 0.5-20 wt % phospholipids based on total weight or (ii) 0.6-25 wt % of polar lipids based on total lipids, wherein polar lipids are the sum of phospholipids, glycosphingolipids and cholesterol, and said composition comprises lipid globules with a core comprising said vegetable lipids and a coating comprising said phospholipids or polar lipids.
Owner:NV NUTRICIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com