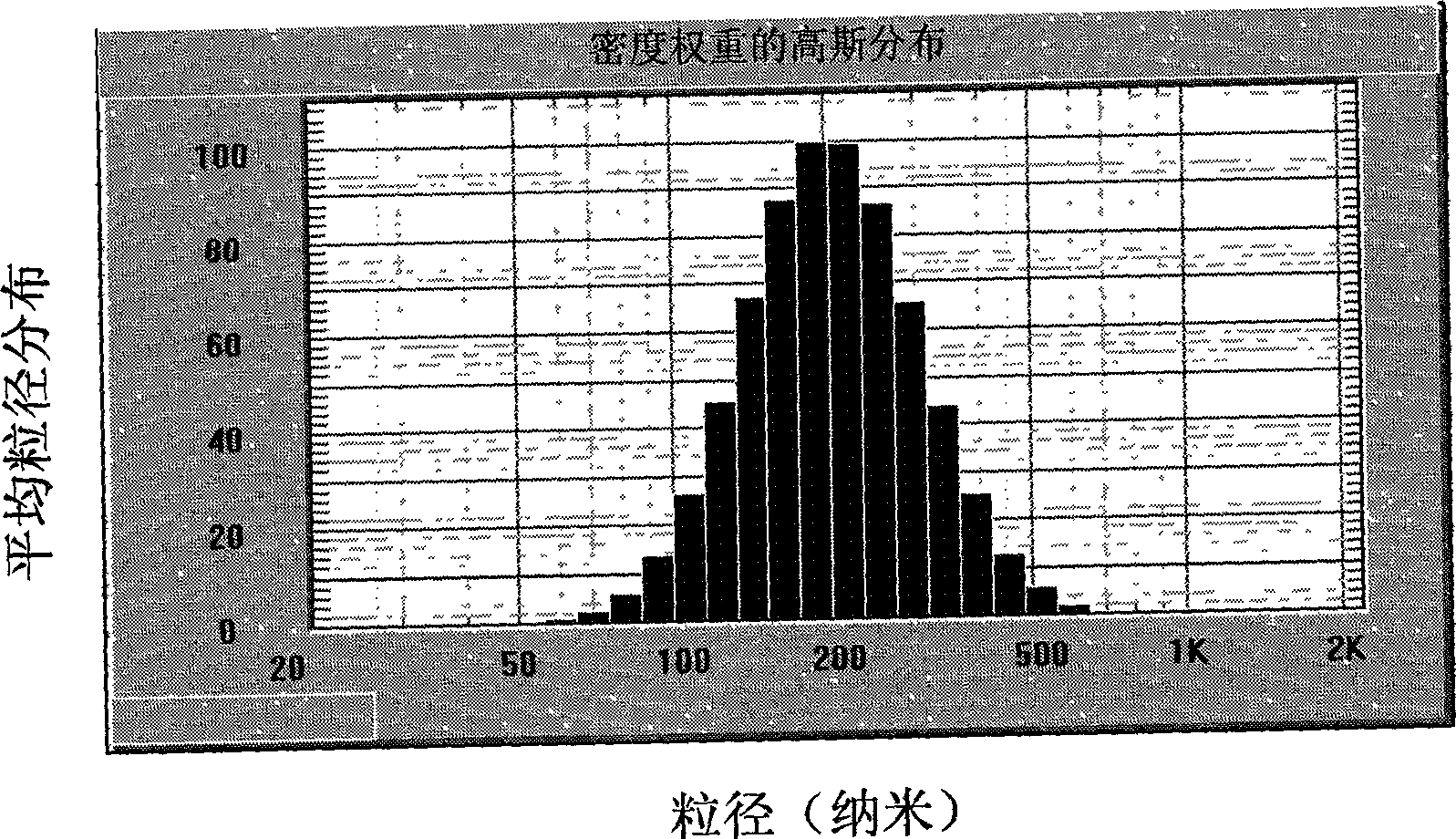
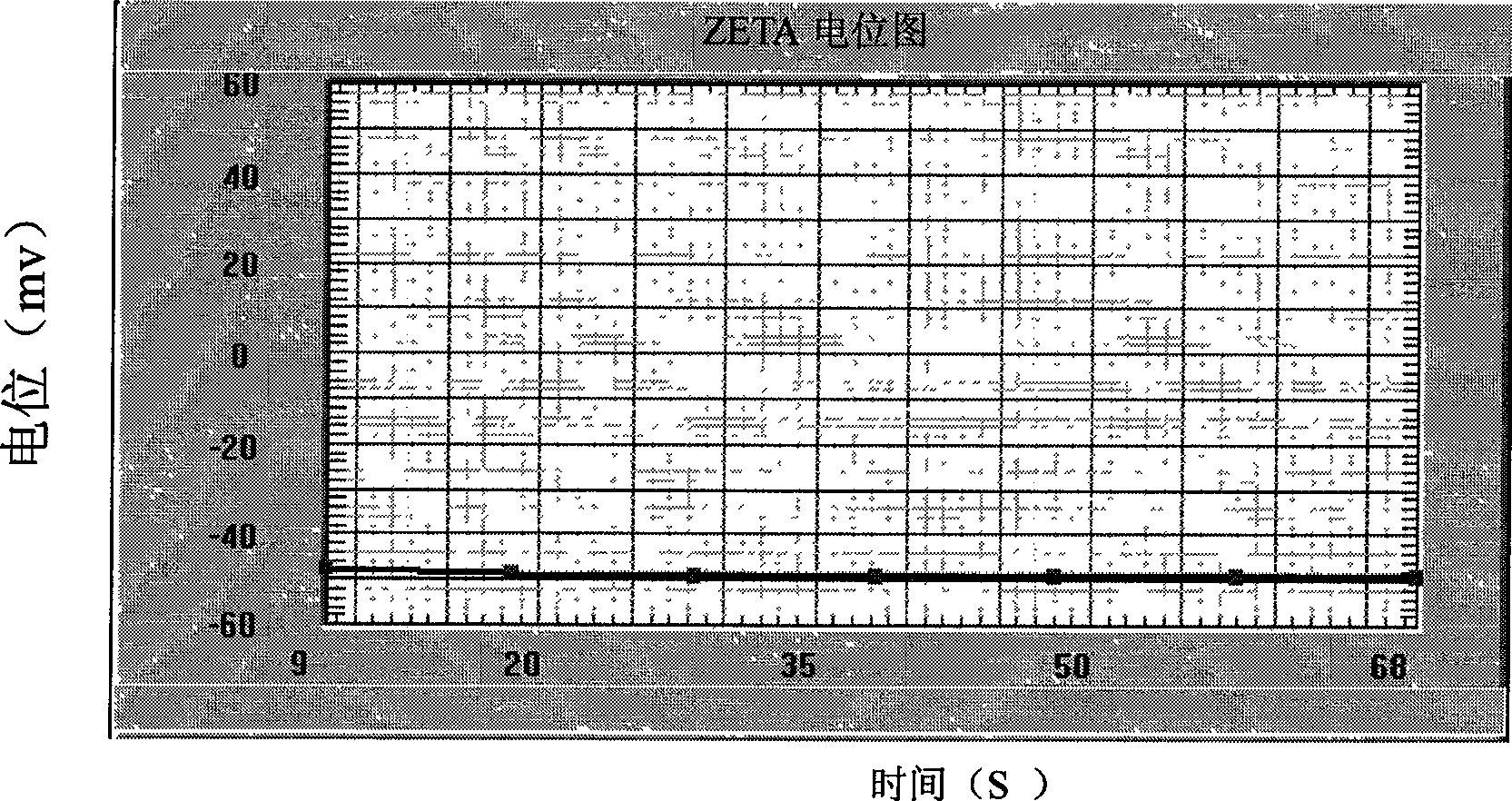
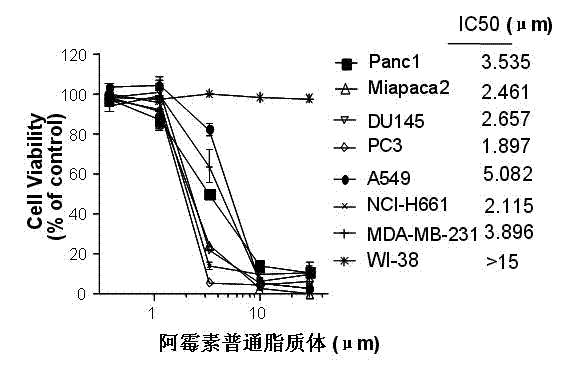
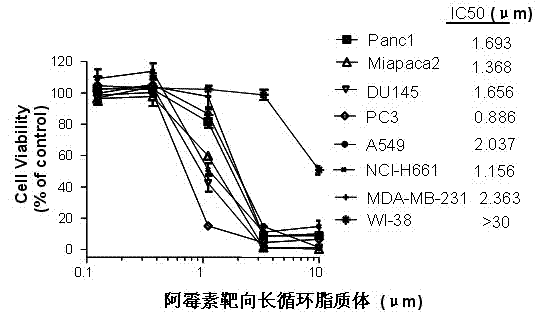
Patents
Literature
251 results about "Phosphatidylethanolamine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
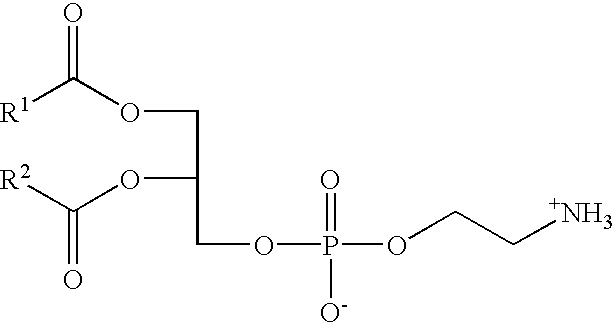
Phosphatidylethanolamines are a class of phospholipids found in biological membranes. They are synthesized by the addition of cytidine diphosphate-ethanolamine to diglycerides, releasing cytidine monophosphate. S-Adenosyl methionine can subsequently methylate the amine of phosphatidylethanolamines to yield phosphatidylcholines. It can mainly be found in the inner (cytoplasmic) leaflet of the lipid bilayer.
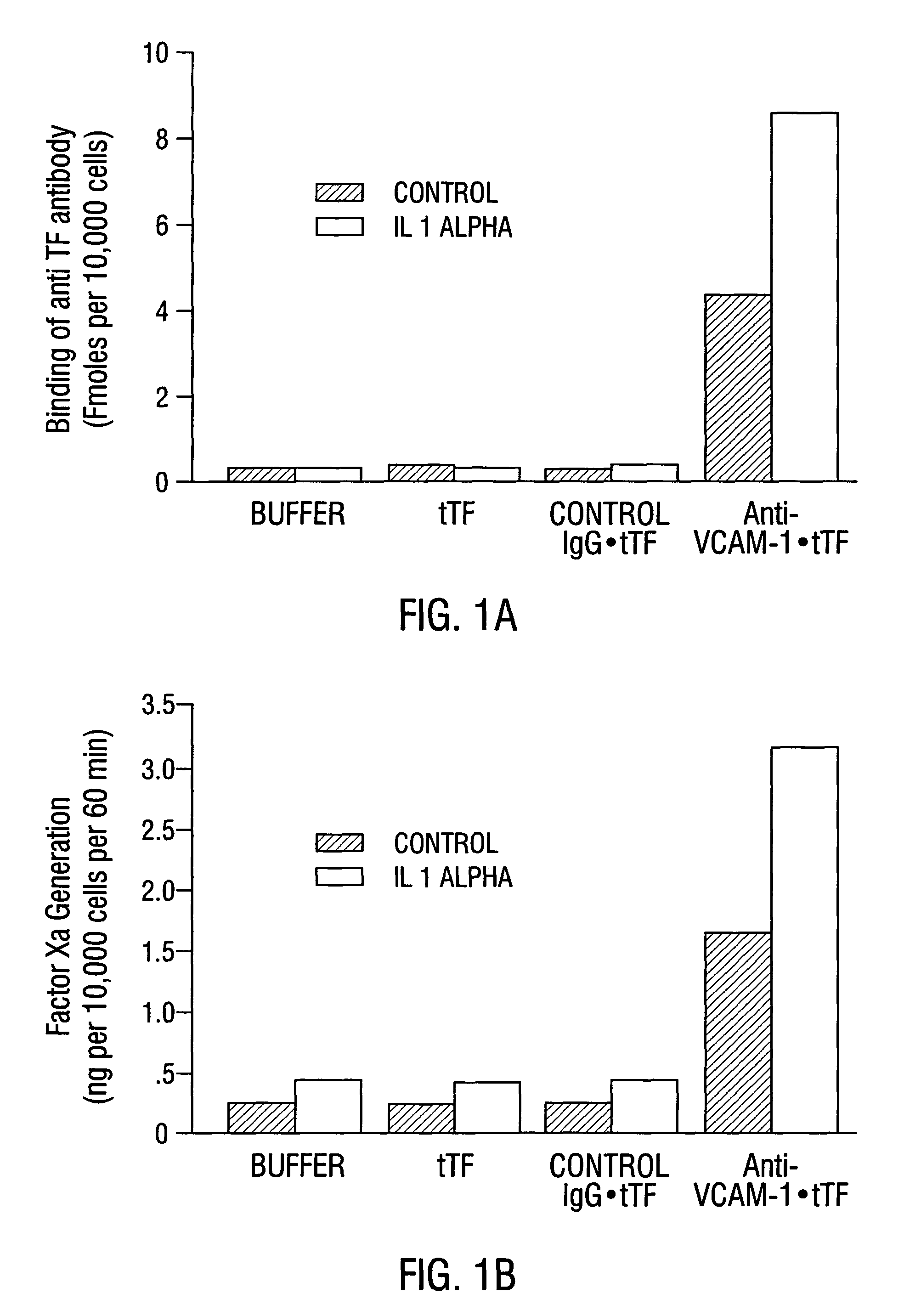
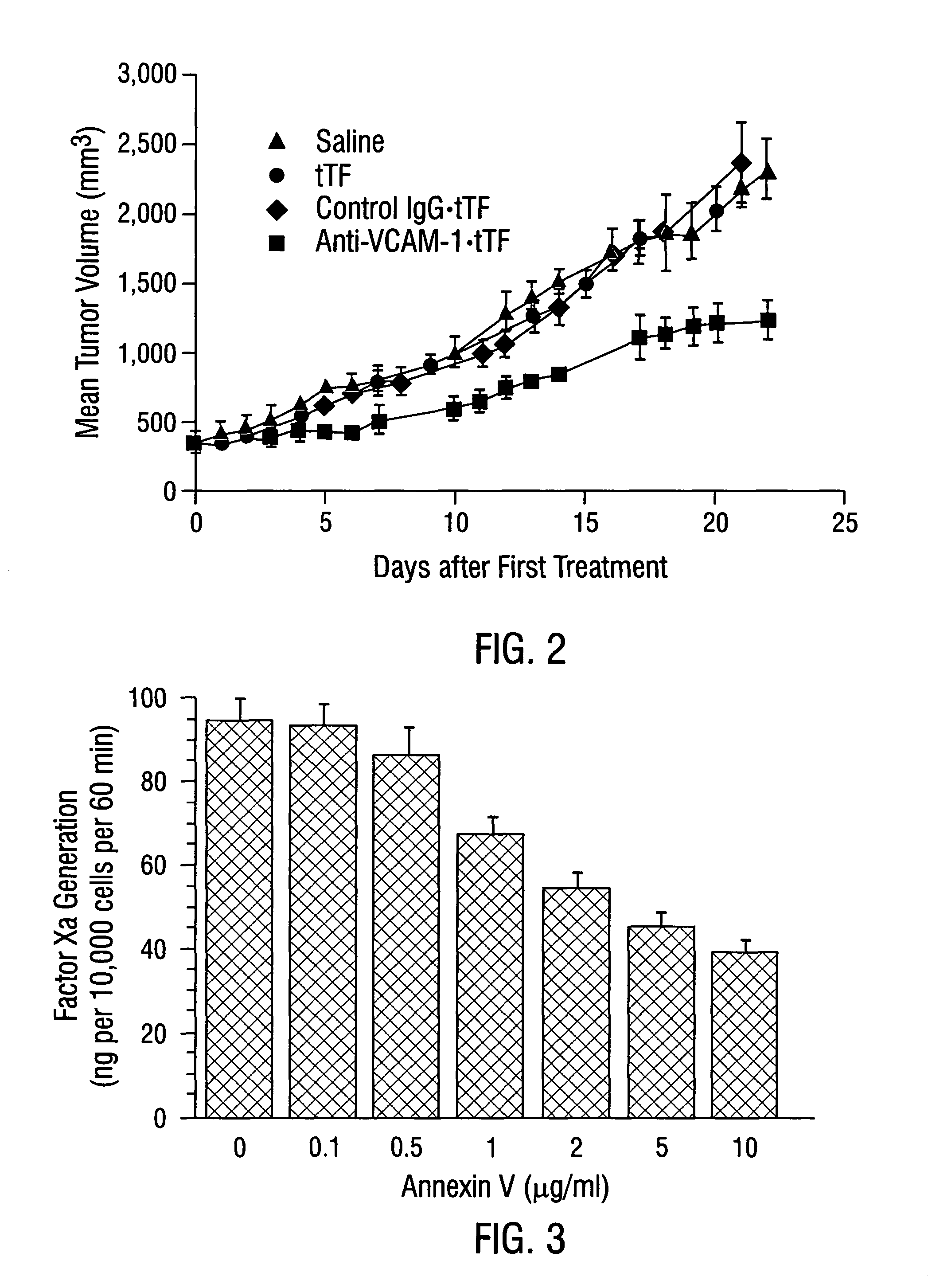
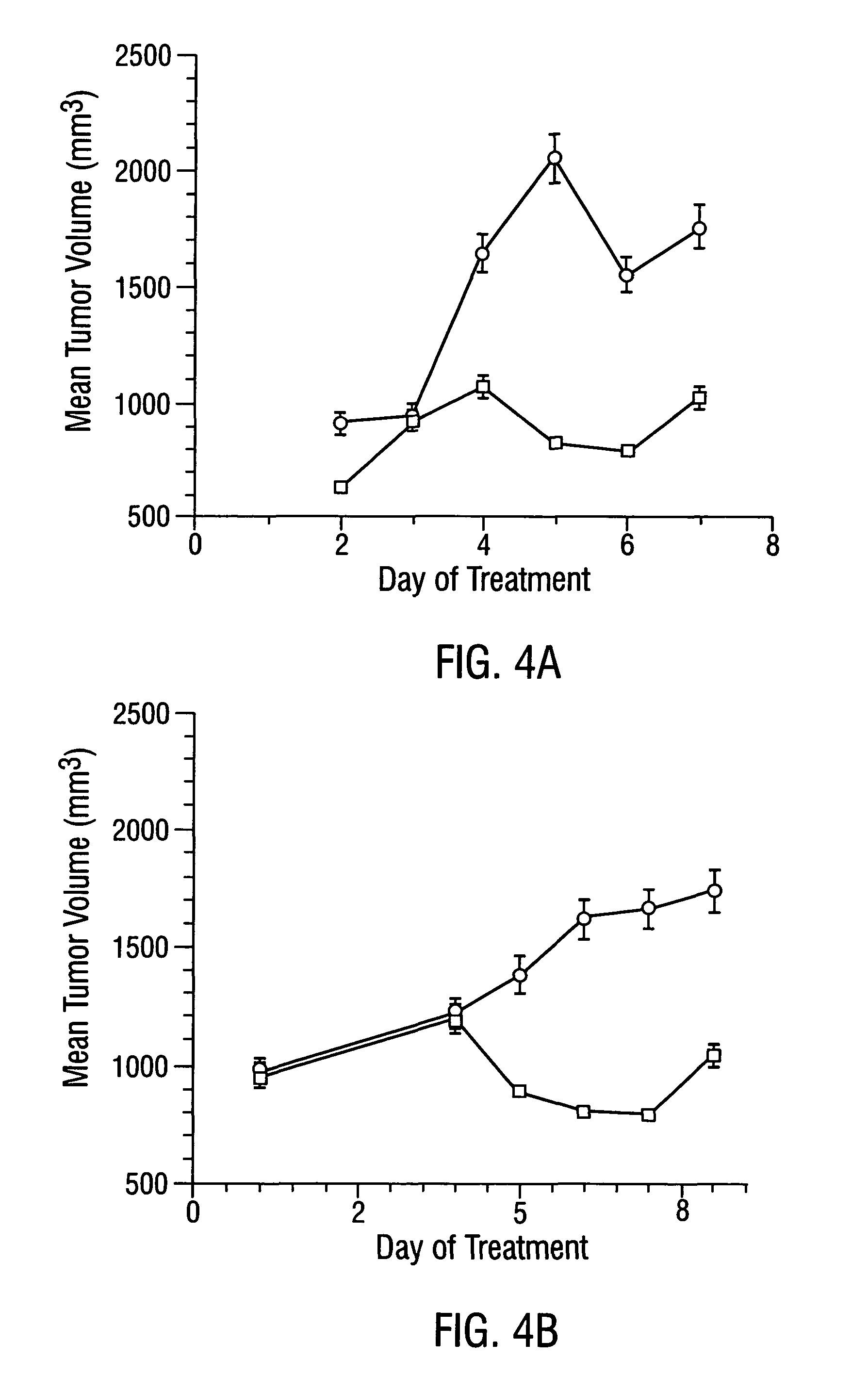
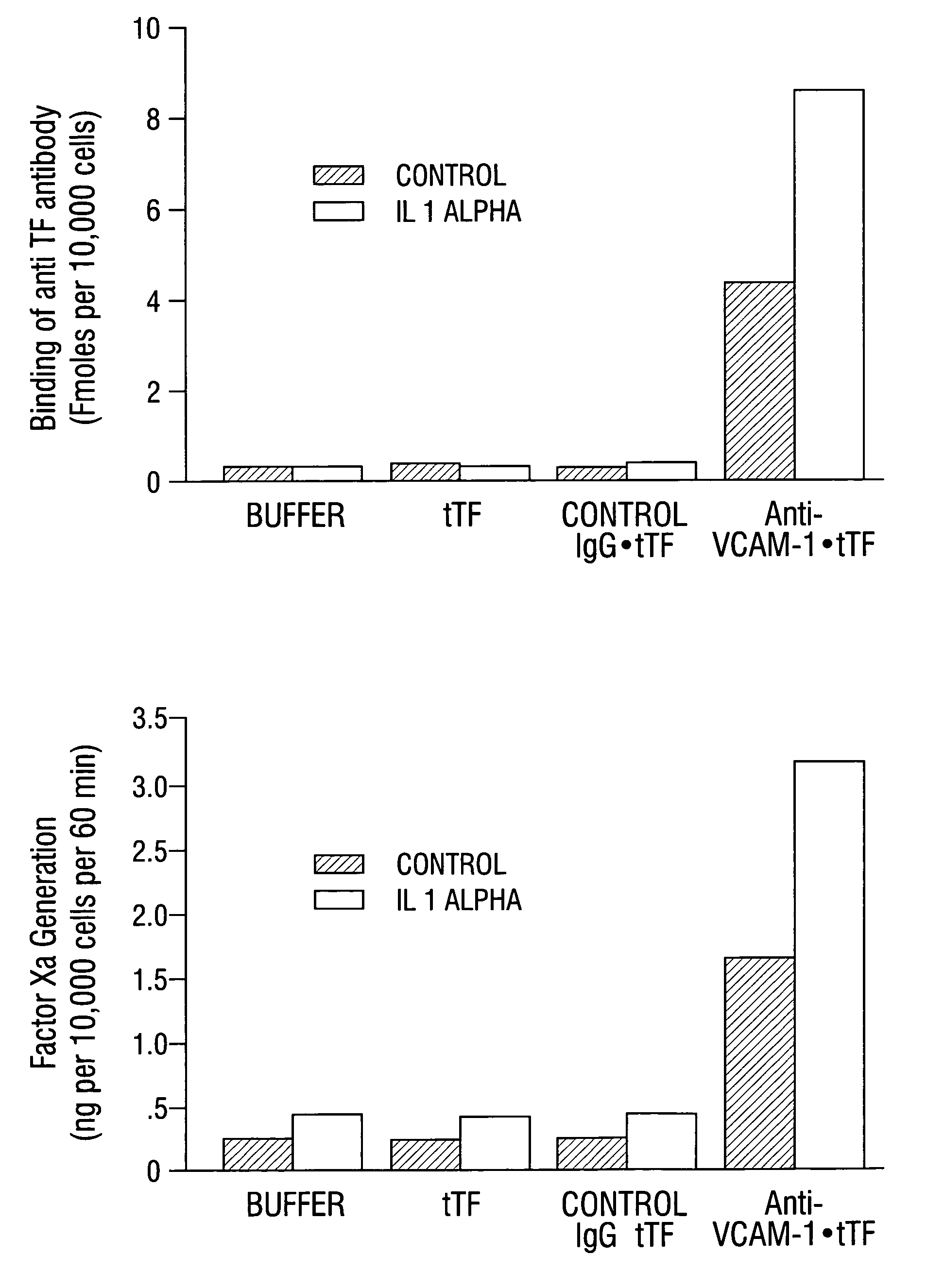
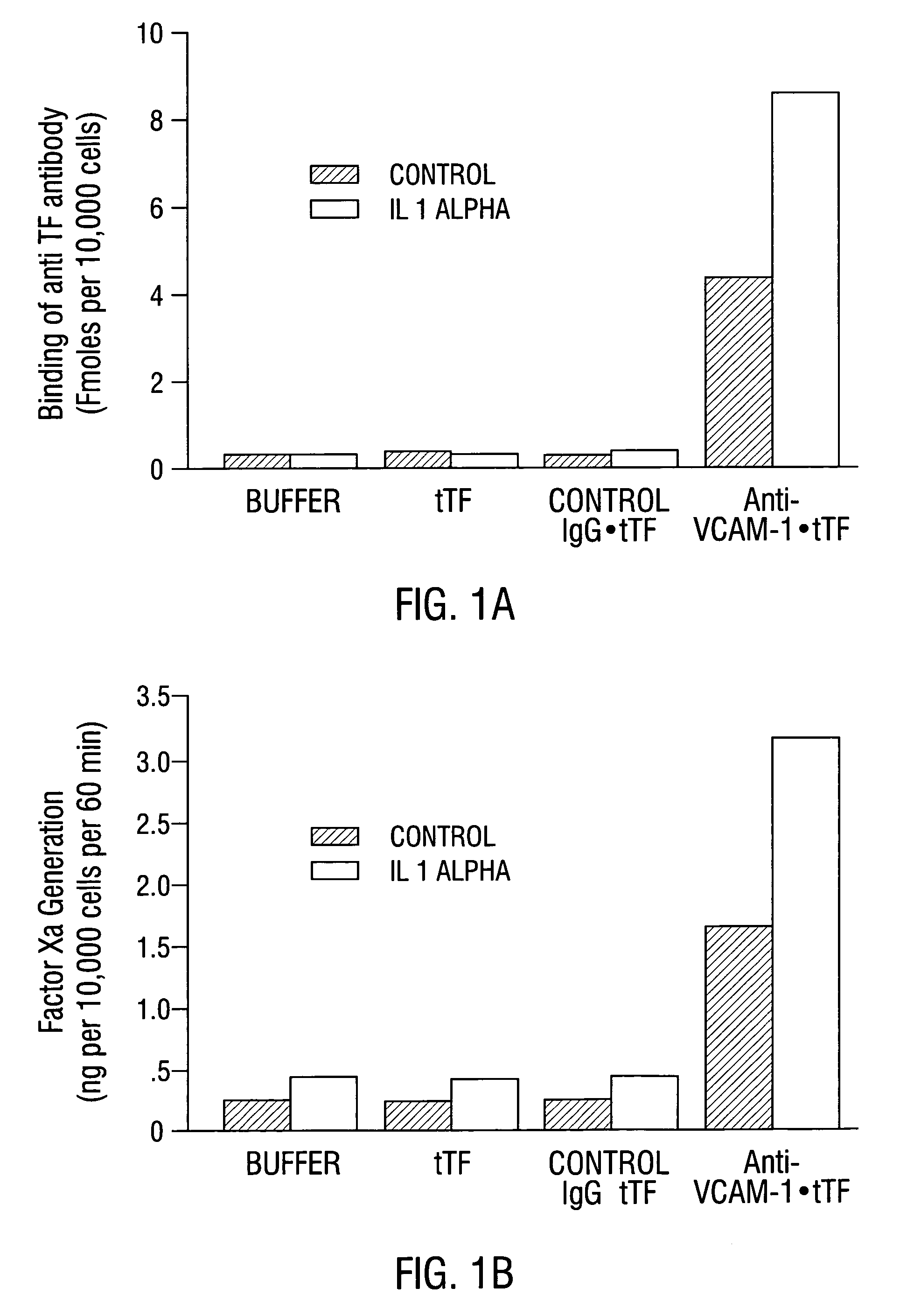
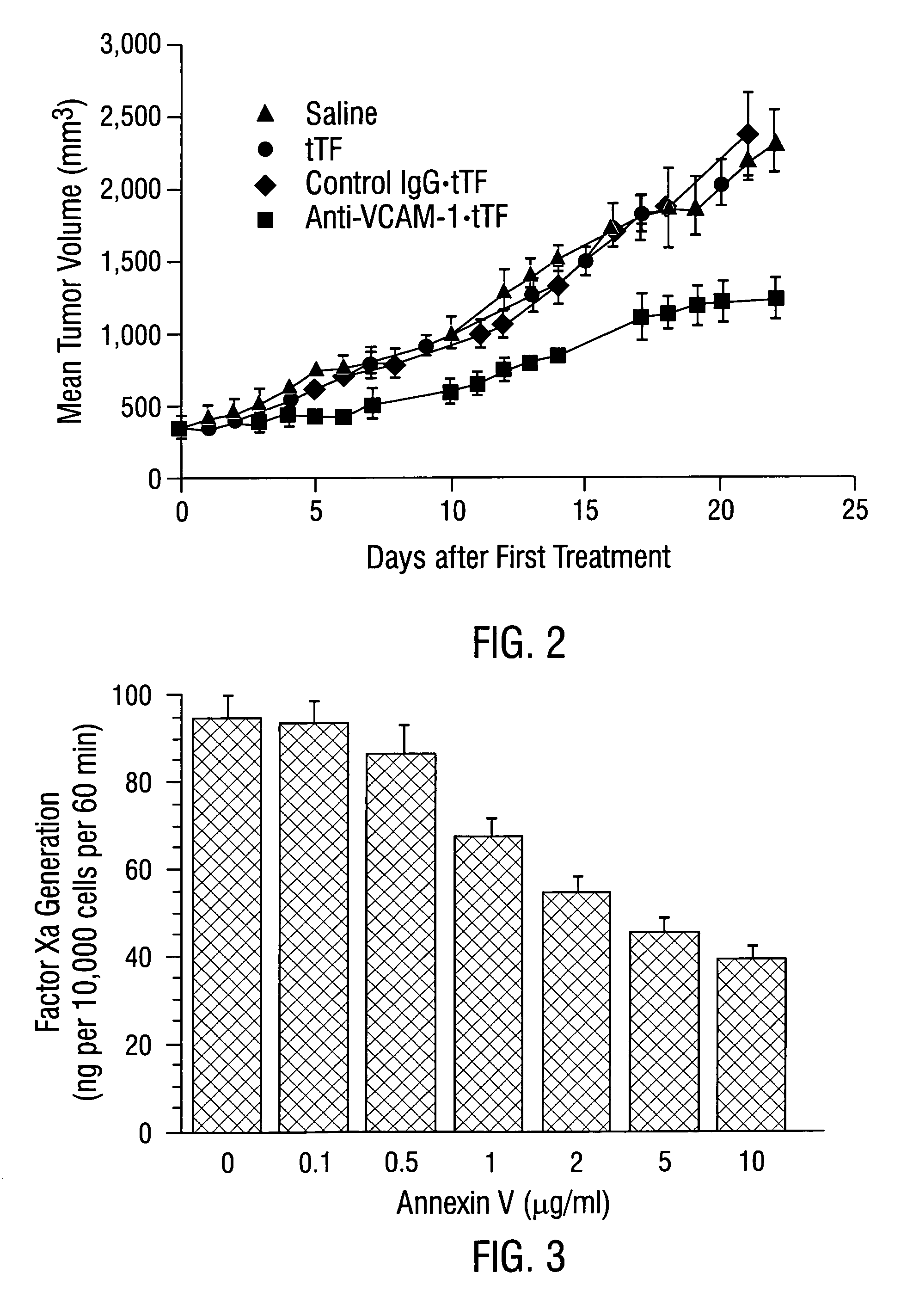
Cancer treatment kits comprising therapeutic conjugates that bind to aminophospholipids
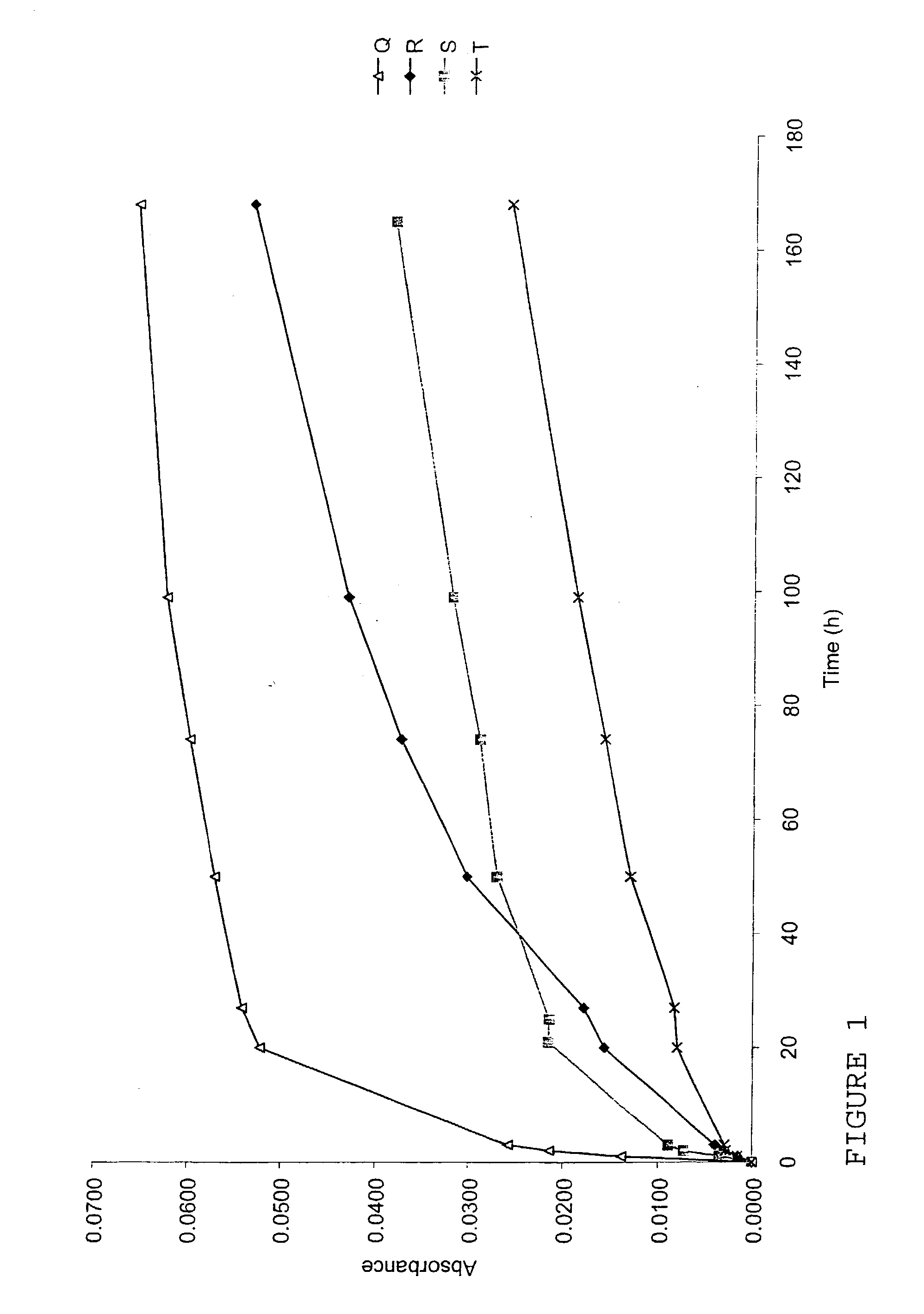
InactiveUS7067109B1Stable expressionAmple targeting opportunitiesPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsThrombusTumor regression
Disclosed is the surprising discovery that aminophospholipids, such as phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine, are specific, accessible and stable markers of the luminal surface of tumor blood vessels. The present invention thus provides aminophospholipid-targeted diagnostic and therapeutic constructs for use in tumor intervention. Antibody-therapeutic agent conjugates and constructs that bind to aminophospholipids are particularly provided, as are methods of specifically delivering therapeutic agents, including toxins and coagulants, to the stably-expressed aminophospholipids of tumor blood vessels, thereby inducing thrombosis, necrosis and tumor regression.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
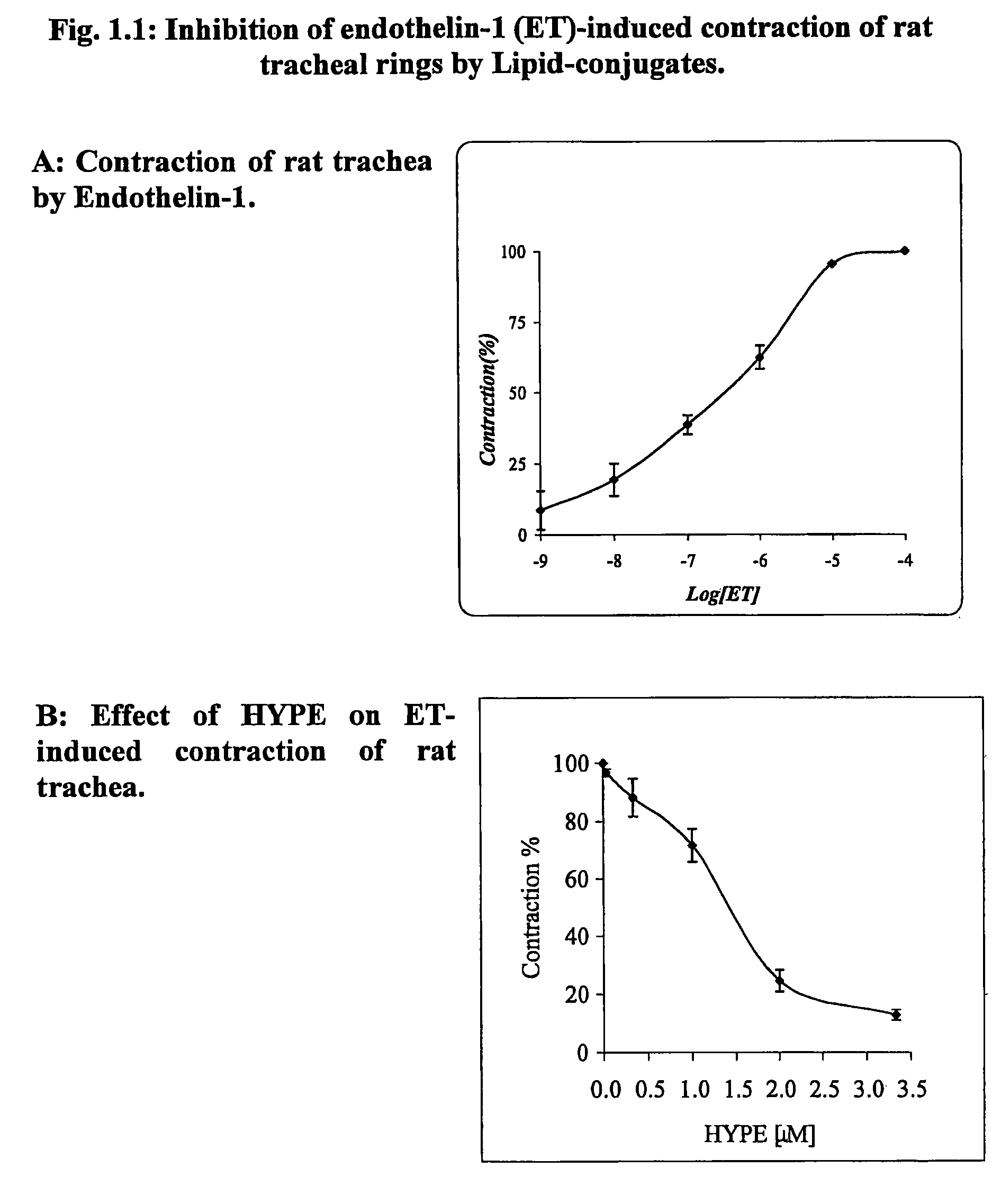
Use of lipid conjugates in the treatment of diseases
InactiveUS7101859B2Reduce molecular weightIncrease rangeAntibacterial agentsBiocideLymphatic SpreadContact dermatitis
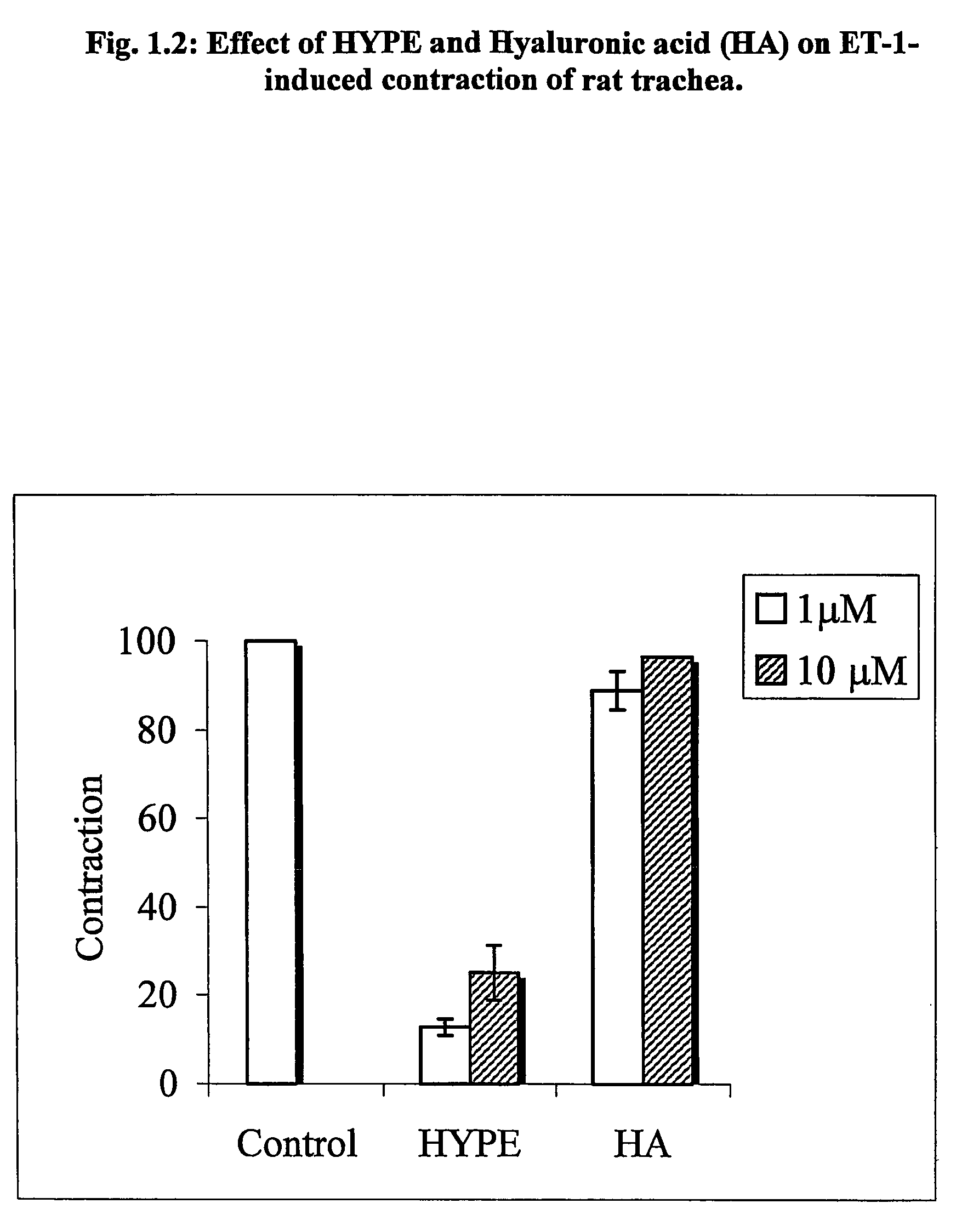
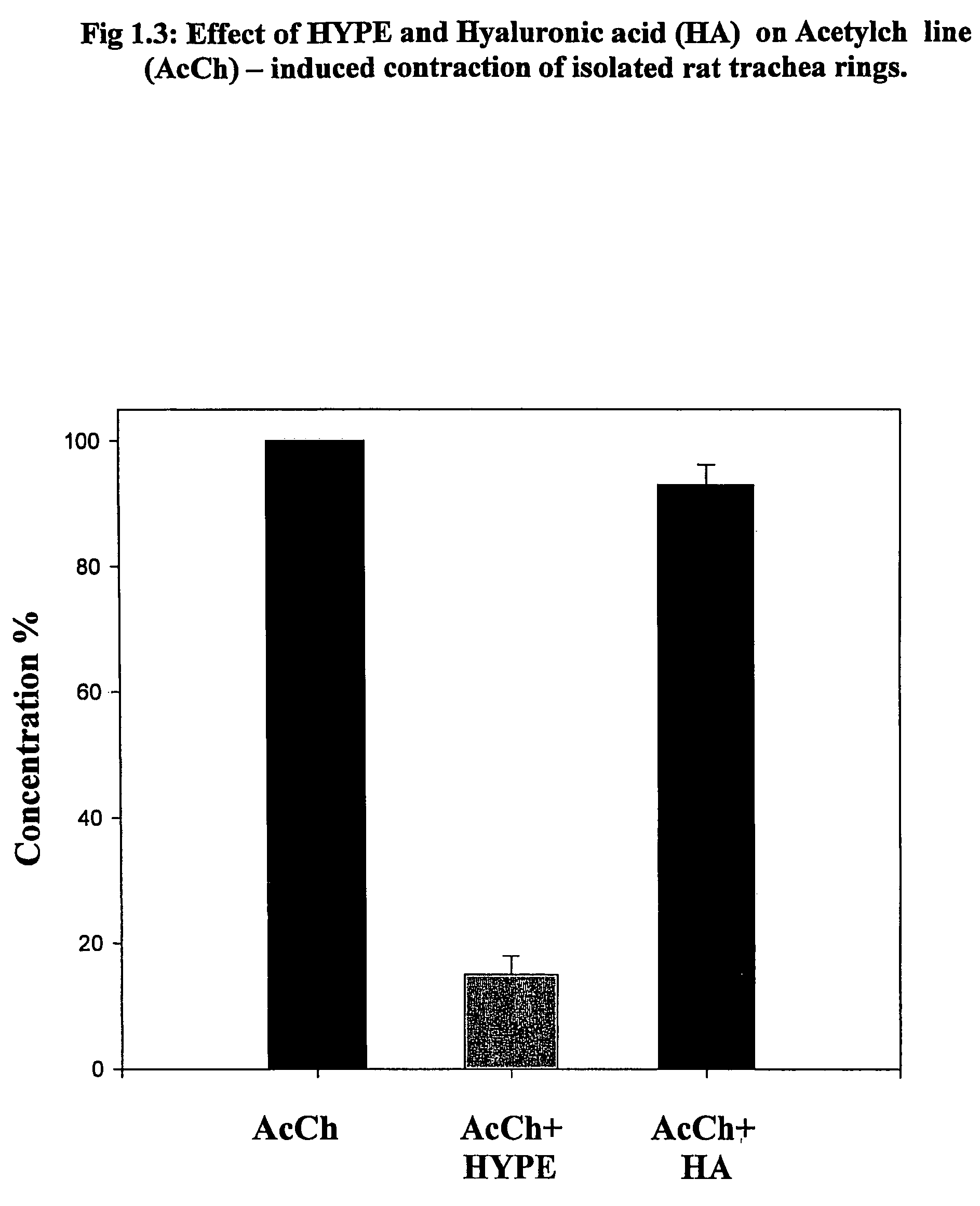
The invention provides novel methods for treating disease based upon the medicinal use of lipids and phospholipids covalently bound to physiologically acceptable monomers or polymers. Phosphatidylethanolamine moieties conjugated to physiologically acceptable monomers and polymers (PE conjugates) manifest an unexpectedly wide range of pharmacological effects, including stabilizing cell membranes; limiting oxidative damage to cell and blood components; limiting cell proliferation, cell extravasation and (tumor) cell migratory behavior; suppressing immune responses; and attenuating physiological reactions to stress, as expressed in elevated chemokine levels. The surprisingly manifold pharmacological properties of the PL-conjugates allow for the invention, disclosed herein, of novel methods for the treatment of a diverse range of disease states, including obstructive respiratory disease, including asthma; colitis and Crohn's disease; central nervous system insult, including blood brain barrier compromise, ischemic stroke, and multiple sclerosis; contact dermatitis; psoriasis; cardiovascular disease, including ischemic conditions and prophylaxis for invasive vascular procedures; cellular proliferative disorders, including anti-tumor vasculogenesis, invasiveness, and metastases; anti-oxidant therapy; hemolytic syndromes; sepsis; acute respiratory distress syndrome; tissue transplant rejection syndromes; autoimmune disease; viral infection; and hypersensitivity conjunctivitis. The therapeutic methods of the invention include administration of phosphatidylethanolamine bound to carboxymethylcellulose, heparin, hyaluronic acid, polyethylene glycol, and Polygeline (haemaccel). Disclosed herein are also new compounds comprised of phospholipid moieties bound to low molecular weight monomers and dimers, including mono- and disaccharides, carboxylated disaccharides, mono- and dicarboxylic acids, salicylates, bile acids, and fatty acids.
Owner:YEDGAR SAUL
Formulation for spray-drying large porous particles
InactiveUS7279182B2Reduce and eliminate needEasy to preparePowder deliveryBiocidePrillVolumetric Mass Density
Particles having a tap density less than about 0.4 g / cm3 are formed by spray drying from a colloidal solution including a carboxylic acid or salt thereof, a phospholipid, a divalent salt and a solvent such as an aqueous-organic solvent. The colloidal solution can also include a therapeutic, prophylactic or diagnostic agent. Preferred carboxylic acids include at least two carboxyl groups. Preferred phospholipids include phosphatidylcholines, phosphatidylethanolamines, phosphatidylglycerols, phophstidylserines, phosphatidylinositols and combinations thereof. The particles are suitable for pulmonary delivery.
Owner:CIVITAS THERAPEUTICS
Nutritional compositions containing a neurologic component and uses thereof
InactiveUS20140199265A1Promoting neurologicalPromote brainBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsDeveloping nervous systemCytidine diphosphate
The present disclosure relates to nutritional compositions comprising a neurologic component, wherein, the neurologic component may promote brain and nervous system development and further provide neurological protection and repair. The neurologic component may include phosphatidylethanolamine, sphingomyelin, cytidine diphosphate-choline, ceramide, uridine, at least one ganglioside, and mixtures thereof. The disclosure further relates to methods of promoting brain and nervous system health by providing said nutritional compositions to target subjects, which includes pediatric subjects.
Owner:MEAD JOHNSON NUTRITION
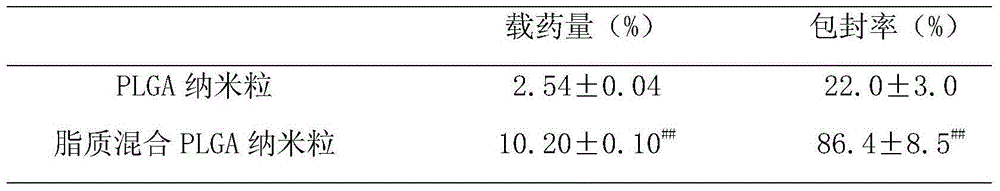
Nanoparticle and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101708162AGood biocompatibilityDimensional stabilityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsGranular deliveryLactideHalf-life
The invention relates to a nanoparticle and a preparation method thereof. Poly(lactide-glycolide acid) (PLGA) is in the center to serve as a core, phospholipid surrounds the surface of the PLGA core in monolayer and distearoyl phosphatidylethanolamine-polyethyleneglycol-carboxyl (DSPE-PEG-COOH) penetrates the monolayer phospholipid to serve as the shell. The phospholipid, the DSPE-PEG-COOH and the PLGA have good biocompatibility, can entrap hydrophobic drugs and control the drugs to release slowly in the human bodies. The phospholipid surrounds the surface of the PLGA, thus ensuring that the particle can avoid immune system recognition so that the circulating half life of the particle is lengthened. The PEG shell ensures the particle to have spatial stability, static stability, long circulation and other characteristics and to be not easily agglomerated. Meanwhile, carboxyl is easily crosslinked with such ligands as antibodies, peptide, probes and the like, thus ensuring the particle to have targeting characteristic. The preparation method of the nanoparticle is simple, convenient practical and is easy to operate and popularize.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Therapeutic vaccine targeted against p-glycoprotein 170 for inhibiting multidrug resistance in the treatment of cancers
InactiveUS20080026995A1High expressionSaccharide peptide ingredientsImmunoglobulinsPolyethylene glycolPhospholipid
The invention relates to conjugates comprising all or part of the amino acid sequences of at least one peptide derived from an extracellular loop of the P-170 protein. The peptide may be covalently attached to spacers which may be polyethyleneglycol (PEG), polyglycine, polylysine or any polymer chain suitable for human use and is coupled at its free end to a phospholipids, e.g., phosphatidylethanolamine or any other chemically suitable phospholipid.
Owner:AC IMMUNE SA
Mixtures of and methods of use for polyunsaturated fatty acid-containing phospholipids and alkyl ether phospholipids species
Mixtures of natural phosphatidylcholine species, natural lysophosphatidylcholine species, phosphatidylserine species, phosphatidylethanolamine species, 1-hydroxy-2-acyl-phosphatidylcholine species, 1-hydroxy-2-acyl-phosphatidylserine molecular species, 1-hydroxy-2-acyl-phosphatidylethanolamine molecular species, 1-O-alkyl-2-hydroxy phosphatidylcholine species, 1-O-alkyl-2-docosaheaxnoyl phosphatidylcholine species 1-O-alkyl-2-docosahexaenoyl phosphatidylserine species, and 1-O-alkyl-2-docosahexaenoyl phosphatidylethanolamine species, Methods using the above disclosed mixtures in mammals to treat various conditions.
Owner:CHEN SU +1
Reductively-responsive paclitaxel prodrug and preparation method for nano-micelle carrier
InactiveCN106083769AEasy to prepareHigh drug loadingOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryHigh concentrationDspe peg
The invention discloses a reductively-responsive paclitaxel prodrug. The reductively-responsive paclitaxel prodrug is synthesized from paclitaxel (PTX) and dithiodicarboxylic acid in a mol ratio of 2: 1 through covalent combination via an ester bond, and the molecular structure of the synthesized paclitaxel prodrug is PTX-SS-PTX. A PTX prodrug nano-micelle carrier is mainly composed of PTX-SS-PTX and distearoyl-phosphatidylethanolamine-polyethylene glycol (DSPE-PEG). According to the PTX-SS-PTX prodrug in the invention, a disulfide bond can rotate freely; and on the condition that the paclitaxel prodrug and a paclitaxel prodrug nano-micelle drug delivery system provided by the invent are stimulated by a high-concentration glutathione reductive environment in tumor cells, the disulfide bond breaks, and a parent drug is released. The reductively-responsive paclitaxel prodrug can obviously improve the drug loading capacity and encapsulation efficiency of PTX and improves stability of a PTX nanometer drug delivery system.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Polar lipid mixtures, their preparation and uses
InactiveUS20110294757A1Milk preparationOrganic active ingredientsPhosphatidyl inositolPhosphatidylethanolamine
Disclosed herein are polar lipid mixtures, comprising glycerophospholipids such as phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidylserine (PS) and phosphatidyl-inositol (PI), and sphingolipids such as sphyngomyelin (SM). Most importantly, the ratio of phospholipids in said mixture is comparable to that of HMF, and is represented by SM>PC>PE>PS>PI or SM=PC>PE>PS>PI. Processes for the preparation of said mixtures and uses thereof are also described herein.
Owner:ENZYMOTEC
Lipids containing omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids
InactiveUS20080085319A1Enhance memoryReduce stressBiocideEdible oils/fats ingredientsLipid formationAcyl group
A lipid preparation including a glycerophospholipid or salt, conjugate and derivatives thereof, particularly phosphatidylserine (PS), phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidyl-inositol (PI), phosphatidylglycerol (PG) and phosphatidic acid (PA), and poly-unsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) acyl groups, particularly long-chain poly-unsaturated fatty acid (LC-PUFA) acyl groups such as omega-3 and / or omega-6 acyl groups, wherein said PUFA is covalently bound to said glycerophospholipid. The preparation possesses an improved bioactivity, and is useful in the treatment of various cognitive and mental conditions and disorders and for maintenance of normal functions of brain-related systems and processes.
Owner:ENZYMOTEC
Pharmaceutical formulations employing short-chain sphingolipids and their use
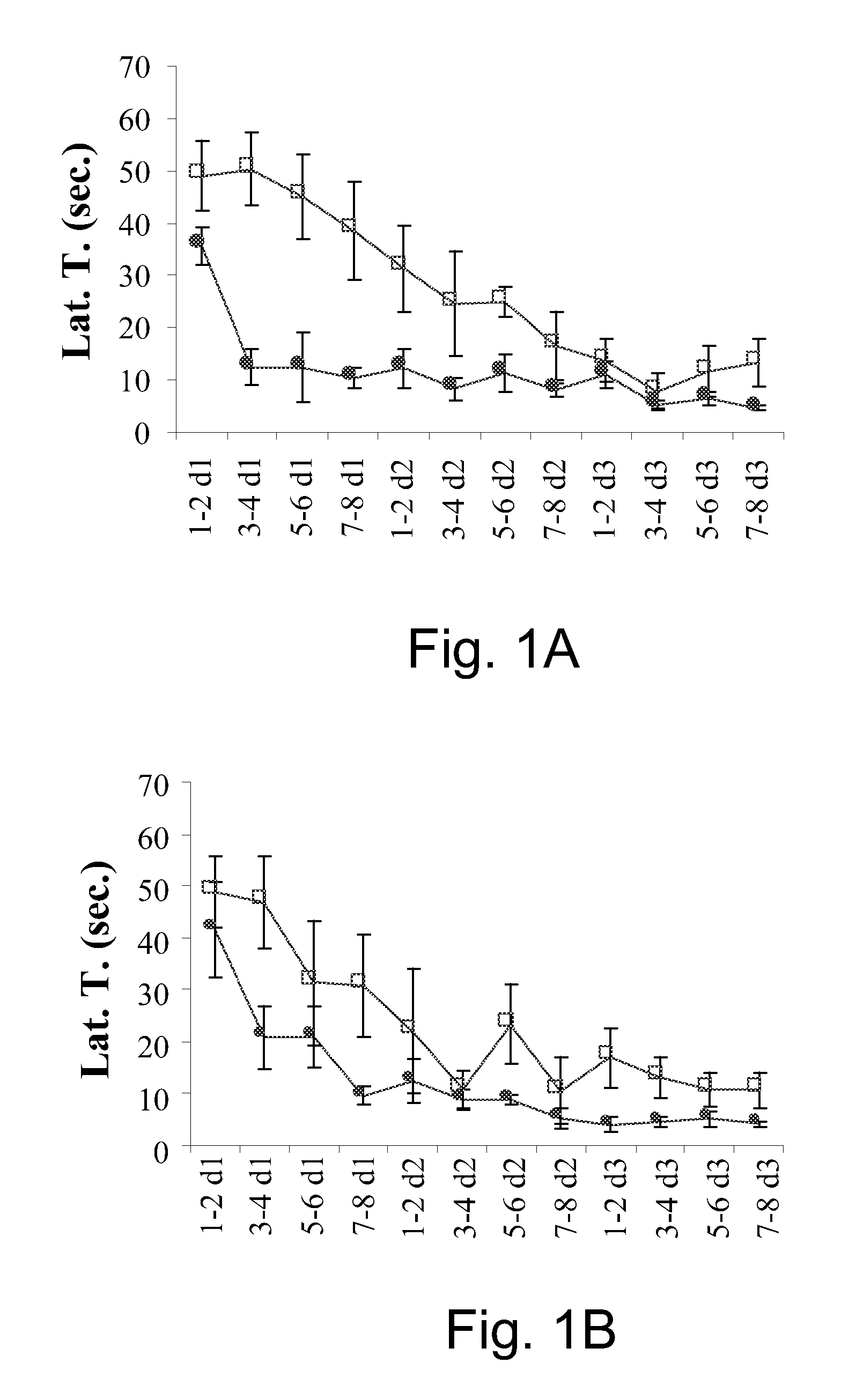
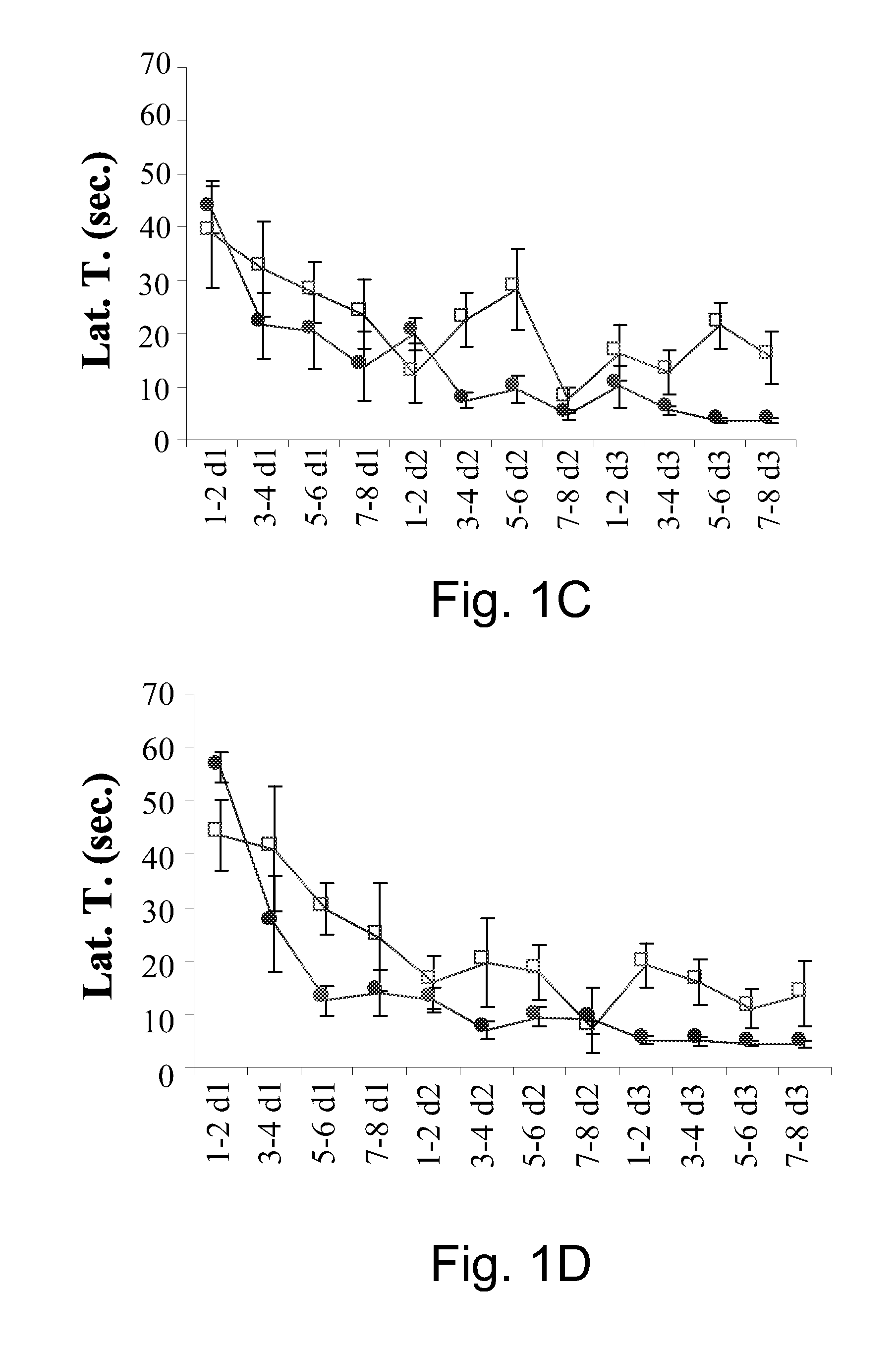
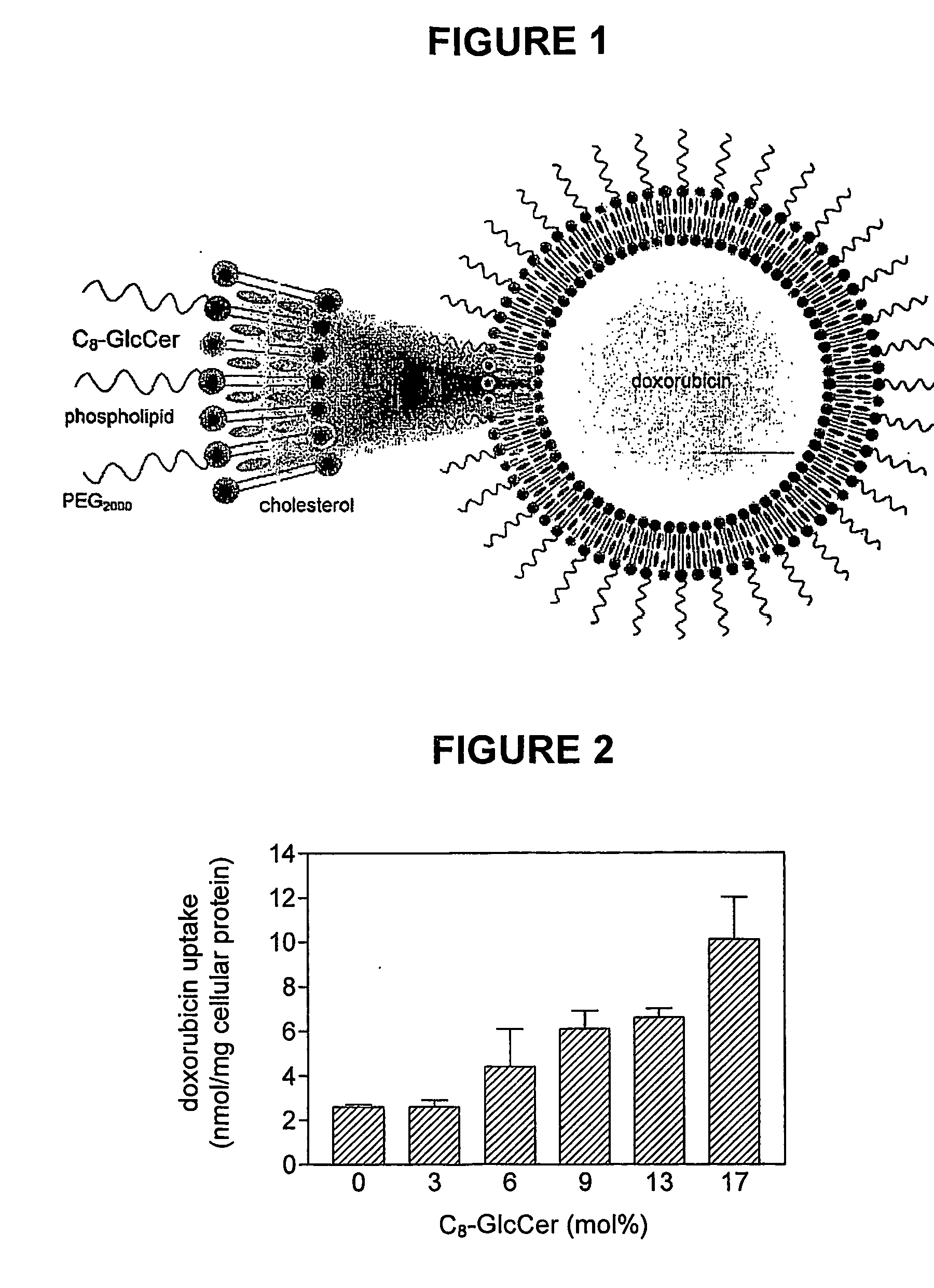
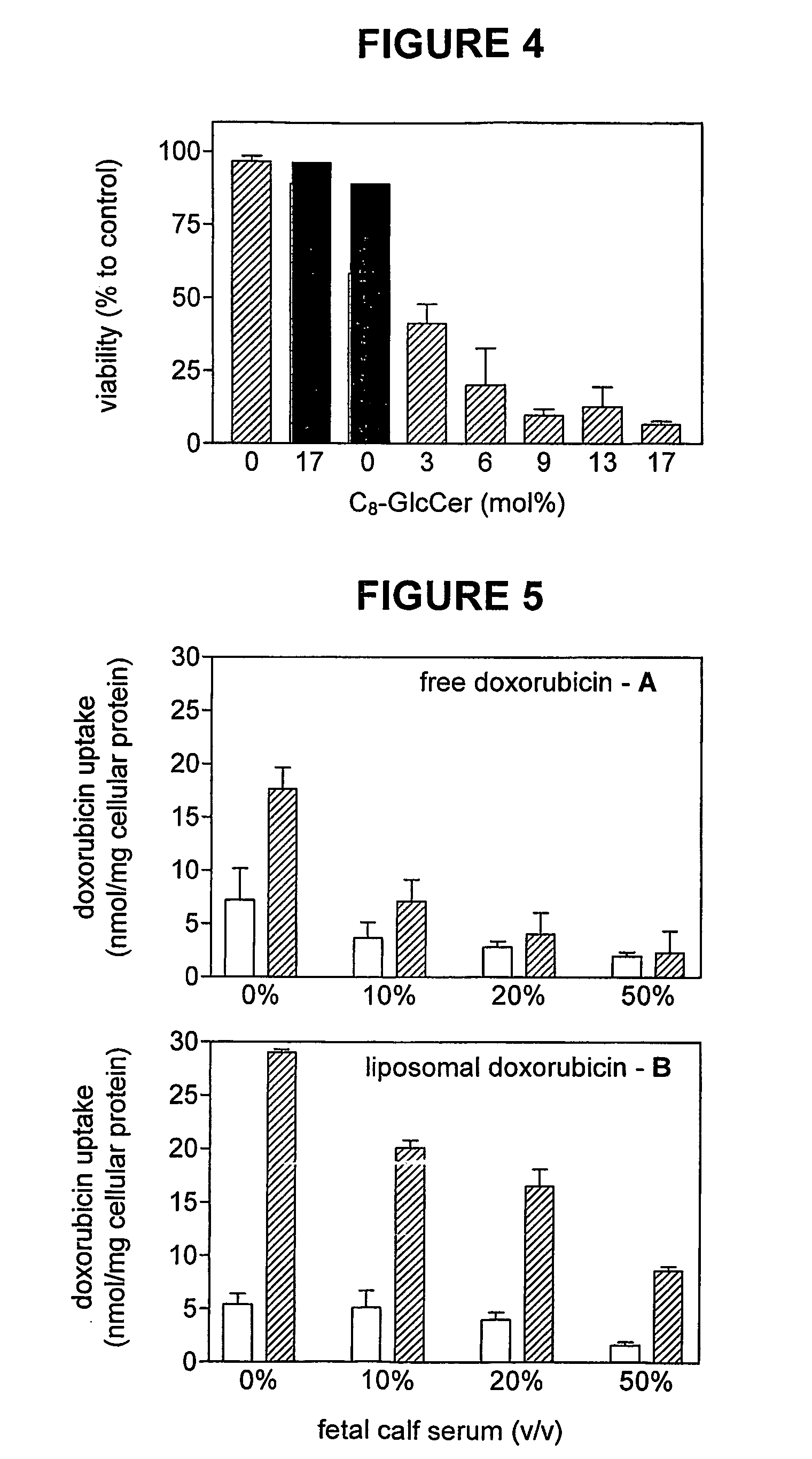
This invention pertains to pharmaceutical formulations which comprise (i) a drug (e.g., an amphiphilic drug) (e.g., an anthracycline) (e.g., doxorubicin) and (ii) a short-chain sphingolipid (e.g., a short-chain glycosphingolipid or a short-chain sphingomyelin) (e.g., N-octanoyl-glucosylceramide, referred to as C8-GlcCer) (e.g., N-hexanoyl-sphingomyelin, referred to herein as C6-SM), and which provide improved drug delivery and efficacy. The short-chain sphingolipidis selected from compounds of the following formula: wherein: R1 is independently: an O-linked saccharide group; or an O-linked polyhydric alcohol group; or: R1 is independently: an O-linked (optionally N-(C1-4alkyl)-substituted amino)-C1-6alkyl-phosphate group; or an O-linked (polyhydric alcohol-substituted)-C1-6alkyl-phosphate group; R2 is independently C3-9alkyl, and is independently unsubstituted or substituted; R3 is independently C7-19alkyl, and is independently unsubstituted or substituted; R4 is independently —H, —OH, or —O—C1-4alkyl; RN is independently —H or C1-4alkyl; the bond marked with an alpha (α) is independently a single bond or a double bond; if the bond marked with an alpha (α) is a double bond, then R5 is —H; if the bond marked with an alpha (α) is a single bond, then R5 is —H or —OH; the carbon atom marked (*) is independently in an R-configuration or an S-configuration; the carbon atom marked (**) is independently in an R-configuration or an S-configuration; and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, solvates, esters, ethers, chemically protected forms thereof. In one embodiment, the pharmaceutical formulation is a liposomal pharmaceutical formulation prepared using a mixture of lipids comprising, at least, vesicle-forming lipids (e.g., phospholipids) (e.g., phosphatidylcholines) (e.g., fully hydrogenated soy phosphatidylcholine (HSPC)) (e.g., dipalmitoyl-phosphatidylcholine (DPPC)) and said short-chain sphingolipid, and optionally cholesterol and optionally a vesicle-forming lipid which is derivatized with a polymer chain (e.g., a phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) which is derivatized with polyethyleneglycol (PEG)) (e.g., N-(carbonyl-methoxypolyethylene glycol 2000)-1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine sodium salt (MPEG2000-DSPE). The present invention also pertains to methods for the preparation and use of such formulations.
Owner:NETHERLANDS CANCER INST
Preparation for the prevention and/or treatment of vascular disorders
The present invention relates to a preparation suitable for the prevention and / or treatment of vascular disorders, comprising the following fractions:fraction a) consisting of long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids;fraction b) consisting of phospholipids, which fraction contains at least two different phospholipids selected from the group consisting of phosphatidylserine, phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine.fraction c) consisting of compounds which are a factor in methionine metabolism, which fraction contains at least one member selected from the group consisting of folic acid, vitamin B12, vitamin B6, magnesium and zinc.
Owner:NV NUTRICIA
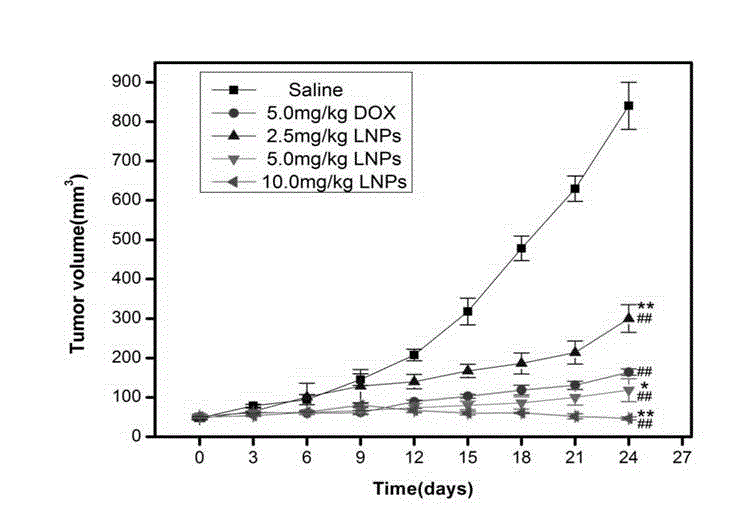
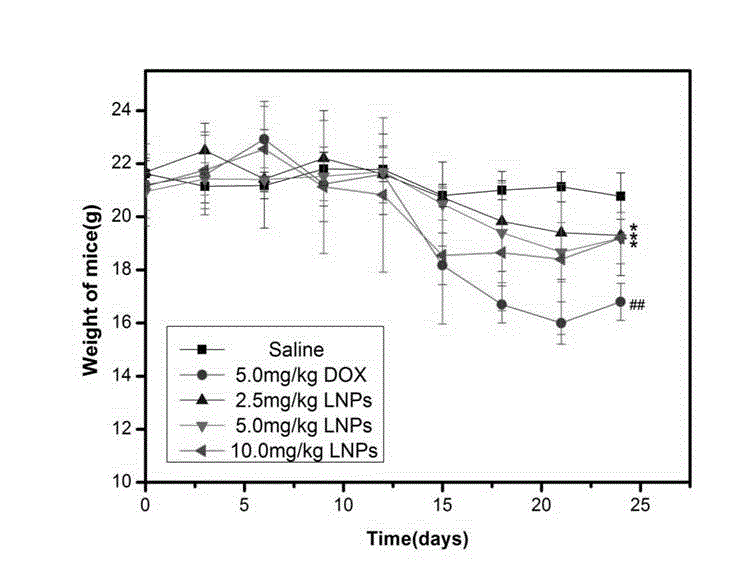
Lipid-mixed poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanoparticle having high drug loading amount and active targeting effect
InactiveCN104434806AHigh drug loadingHigh encapsulation efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryLipid formationSide effect
The invention provides a lipid-mixed poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanoparticle having a high drug loading amount and an active targeting effect. The nanoparticle is of a core-shell structure, wherein the core is a poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA), and distearoyl-phosphatidylethanolamine-polyethylene glycol-folic acid and cholesterol-arginine-histidine methyl ester are embedded in the surface of the core. The nanoparticle disclosed by the invention can be used for remarkably improving the drug loading amount and the encapsulation efficiency of adriamycin, enhancing the cytotoxicity of the adriamycin to tumor cells and presenting a certain anti-multidrug resistance activity; the nanoparticles loaded with the adriamycin are mainly concentrated in tumor tissues after entering a body, so that the anti-tumor effect of the adriamycin is improved, and toxic and side effects are remarkably reduced; and a new strategy for the development of antitumor pharmaceutical preparations is provided.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Synthetic membrane vesicles containing functionally active fusion peptides as drug delivery systems
PCT No. PCT / EP92 / 00089 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 2, 1992 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 2, 1992 PCT Filed Jan. 17, 1992 PCT Pub. No. WO92 / 13525 PCT Pub. Date Aug. 20, 1992The phospholipid bilayer contains at least one pharmaceutically active drug and comprises cell-specific markers on the membrane which have at least 90% biological activity when measured according to Luescher & Glueck, Antiviral Research 14, 39-50. In the membrane, the cholesterol content is preferably less than 2% by weight, the detergent content preferably less than 1 ppb. The vesicle diameter preferably is about 80 nm. the phospholipid in the membrane may comprise 70 to 95% by weight of phosphatidylcholine and preferably 10 to 20% by weight of phosphatidylethanolamine; preferably 6-8% by weight of a crosslinker, preferably of a sulfosuccinimidyl derivate, and at least one cell-specific fusion peptide are linked to the membrane. The vesicles are used for the preparation of pharmaceuticals against AIDS and carcinomas.
Owner:NIKA HEALTH PRODUCT LTD
Ginkgolide B nanometric liposomes medicine and the preparing method thereof
InactiveCN101036642AImprove solubilityPhysiological activity unchangedPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsCholesterolPolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to a ginkgolide B nanoliposomes drug and a method for preparing the same. The invention provides the ginkgolide B nanoliposomes drug including the following materials and the following radios: 8-12 mol compositions of cephalin and distearoyl choline with mole ratio of 1:3-6; 6-8 mol compositions of sojasterol and cholesterin with mole ratio of 1:2-4; 4-6 mol compositions of gamma-cyclodextrin / 2-hychoxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin and alpha-cyclodextrin with mole ratio of 3:1; 0.2-0.4 mol methoxy polyethylene glycol 2000-hydrogenated soybean phosphatidylethanolamine; 2 mol ginkgolide B; and 0.1-0.5 mol vitamine E. A method for preparing the ginkgolide B nanoliposomes drug is also provided in the invention to produce the ginkgolide B nanoliposomes for target treating blocking of vessel or endothelial cell thereof, with a better healing effect than ordinary preparations of ginkgolide B.
Owner:江苏仲德医药科技有限公司
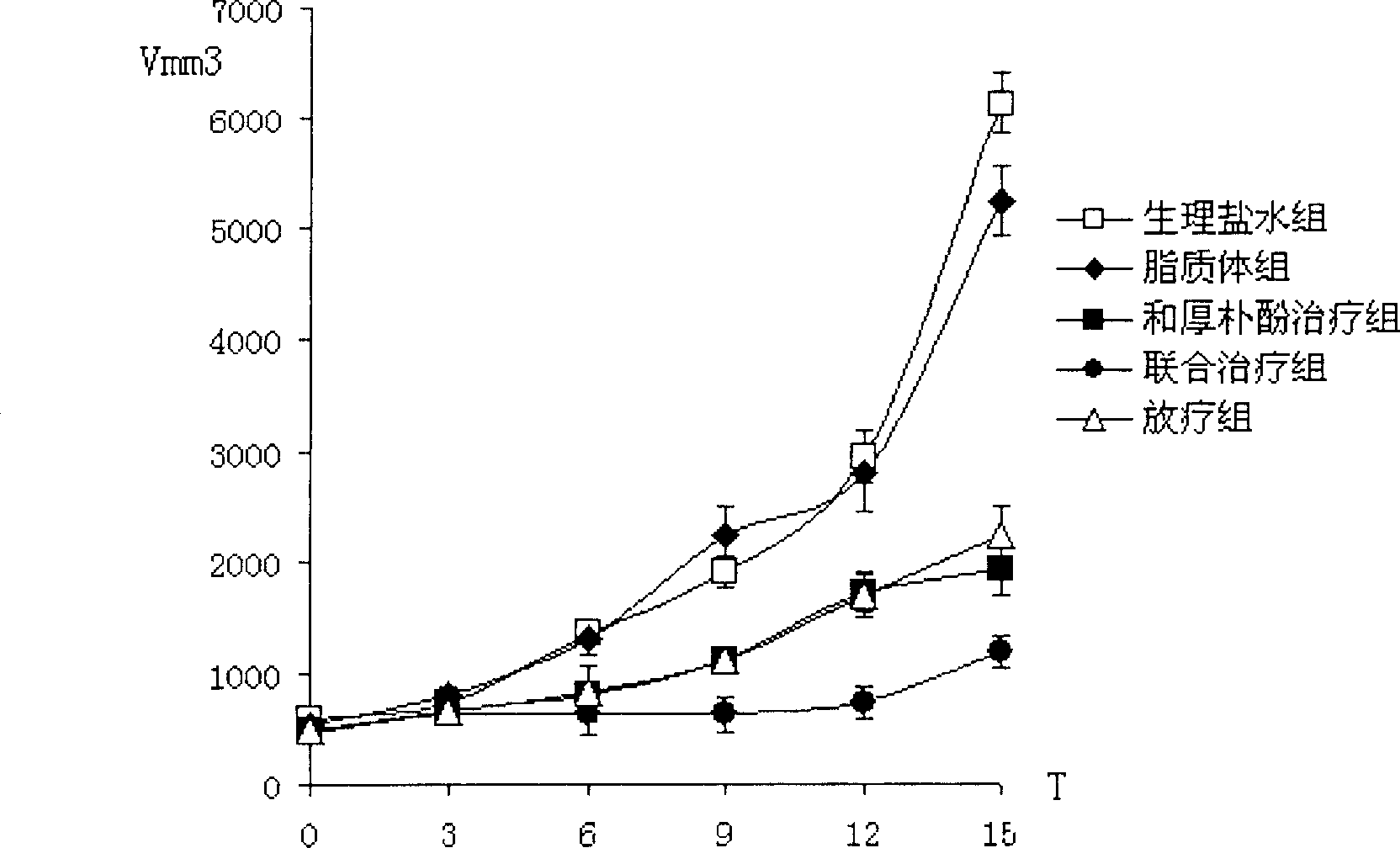
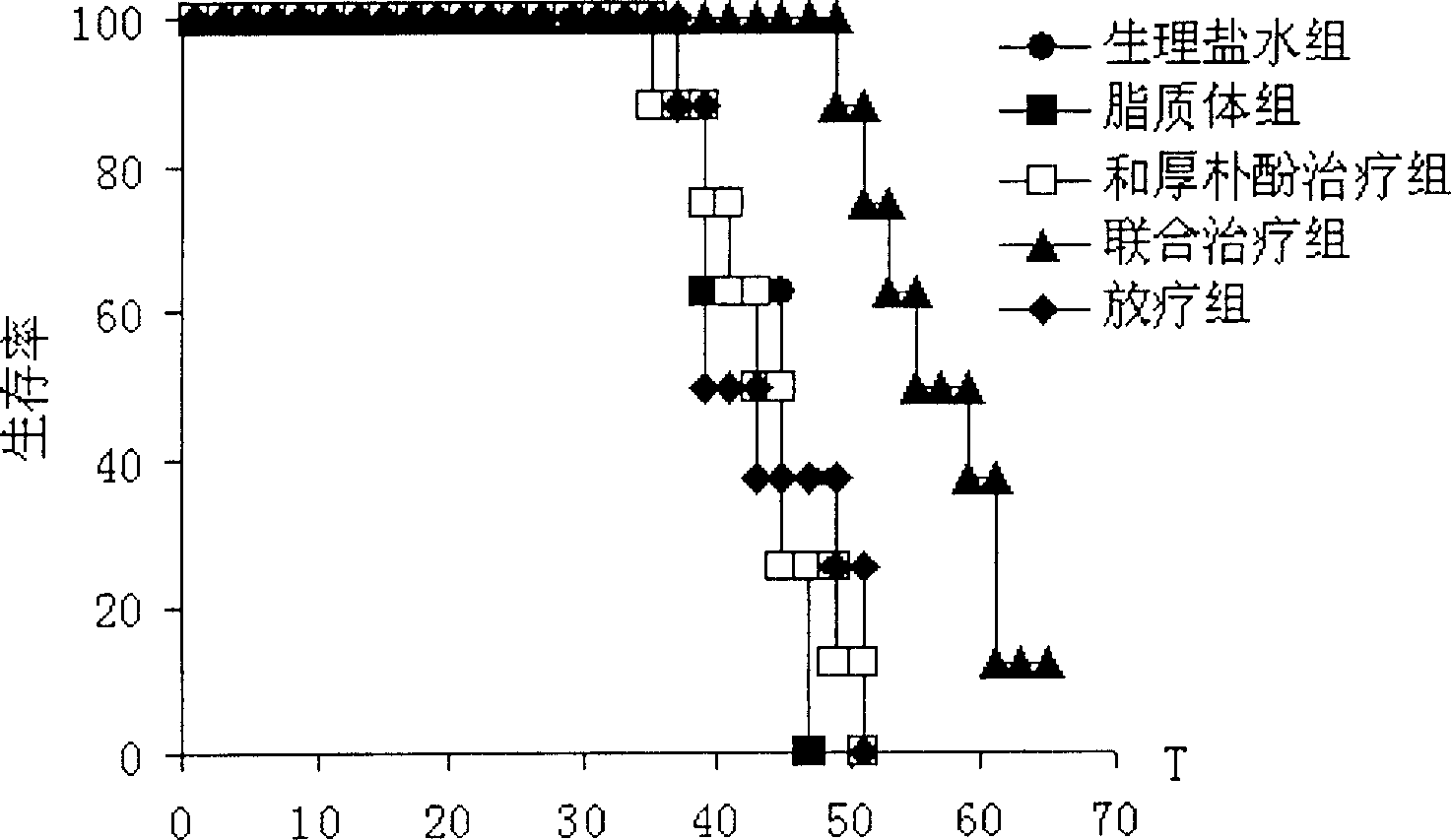
Officinal magnolia phenol lipid frozen dried powder preparation and its use in preparing drug for cancers
ActiveCN1895237AImprove the efficiency of tumor suppressionBoost and/or modulate immunityPowder deliveryHydroxy compound active ingredientsOfficinalCholesterol
A freeze-dried powder of honokiol liposome for preparing the medicines to treat lung cancer and mammary cancer is proportionally prepared from honokiol, polyethanediol-phosphatidylethanolamine, lecithin and cholesterol. It has high synergistic and sensitizing action when it is applied in conjunction with chemicotherapeutic medicine.
Owner:CHENGDU JINRUI FOUND BIOTECH CO LTD
Lipids containing omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids
InactiveUS20080085320A1Enhance memoryReduce stressOrganic active ingredientsBiocideLipid formationAcyl group
Owner:ENZYMOTEC
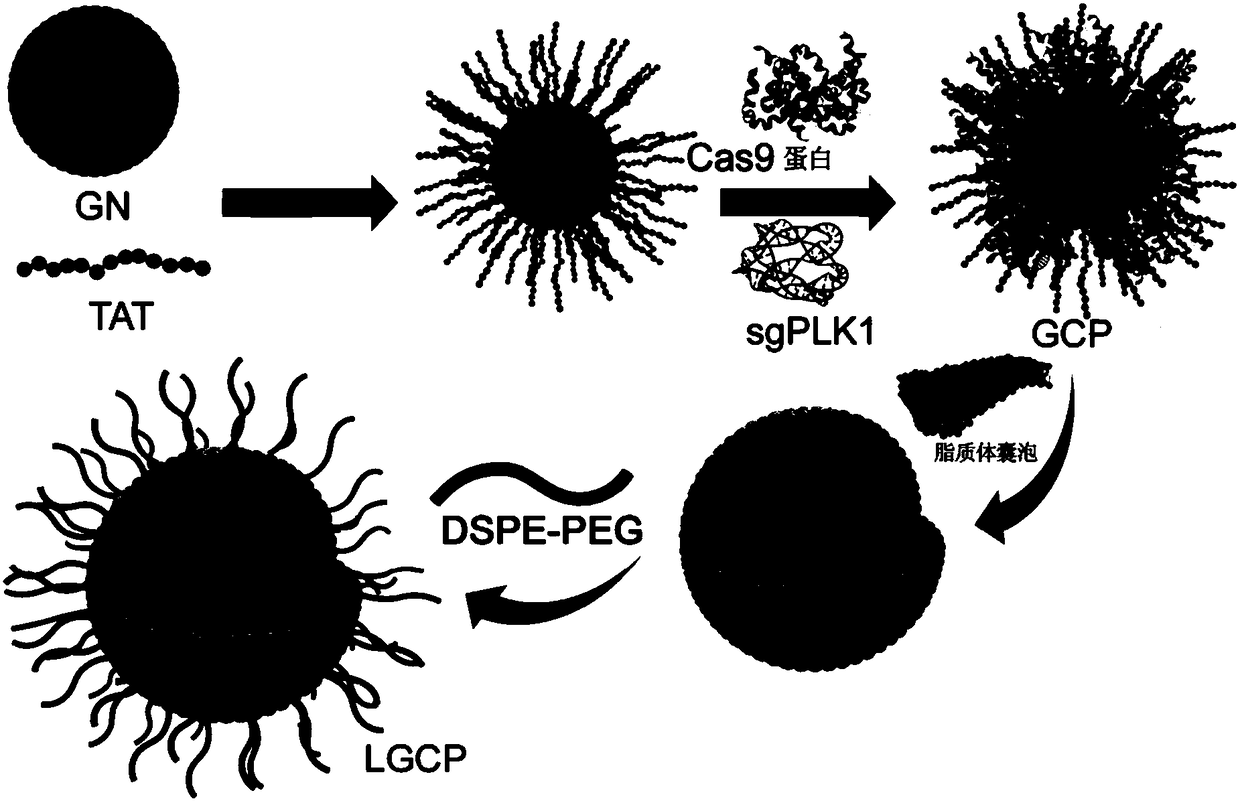
Gold nanocluster-liposome composite nanoparticles, preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN108498460AImprove transfection efficiencyEfficient deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsTreatment effectLiposome Vesicle
The present invention provides gold nanocluster-liposome composite nanoparticles, which are a gold nanocluster encapsulated with a liposome vesicle, wherein the surface of the liposome vesicle is modified with distearoyl phosphatidylethanolamine-polyethylene glycol, the surface of the gold particle in the gold nanocluster is modified with a penetrating peptide and is bound to Cas9 protein and guiding ribonucleic acid, and the liposome vesicle comprises dioleoyl phosphoethanolamine, 2,3-dioleyloxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride and cholesterol. The invention further provides a preparation method and applications of the gold nanocluster-liposome composite nanoparticles. According to the present invention, by using the gold nanocluster-liposome composite nanoparticles, the CRISPR / Cas9 system can be efficiently delivered into cells without any other transfection reagents so as to improve the cell intake rate and the transfection efficiency, such that the gene treatment effects on a variety of tumors can be achieved, and the tracing effect can be achieved.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Lipid carrier
The invention refers to a lipid carrier composition for controlled release of a bioactive substance, which comprises at least one triglyceride oil, and at least one polar lipid selected from the group consisting of phosphatidylethanolamine and monohexosylceramide, and ethanol, which is characterised in that the carrier composition has the ability to form a cohesive structure, which structure is retained in an aqueous environment. The invention also refers to a pharmaceutical composition consisting of said lipid carrier and a bioactive substance dissolved or dispersed in the carrier, preferably an injectable composition.
Owner:LIPOCORE HLDG AB
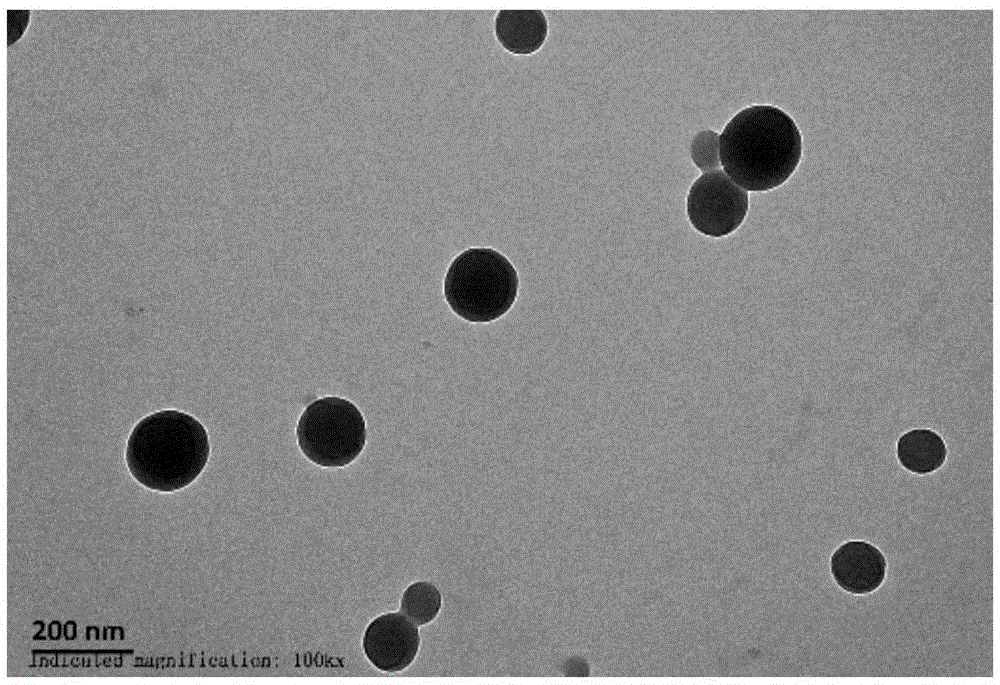
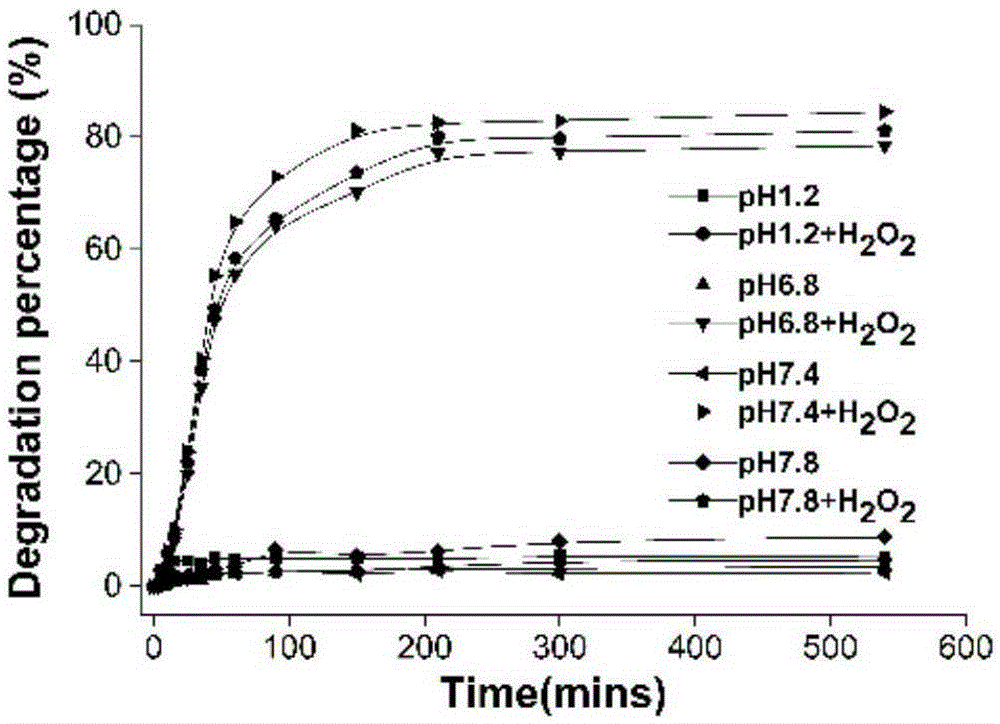
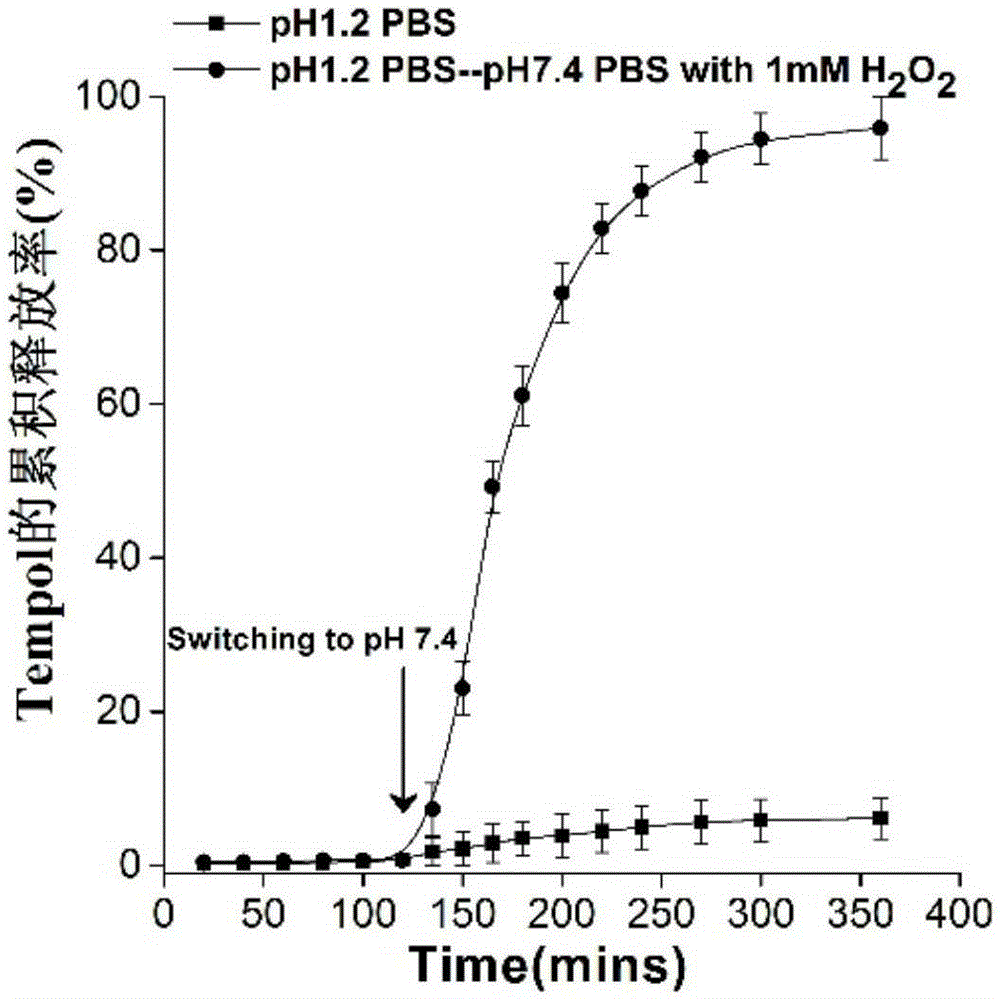
Nano-drug simulating superoxide dismutase or catalase and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a nano-drug simulating superoxide dismutase or catalase and a preparation method and application thereof. A nano-carrier is prepared from cyclodextrin derivatives with the hydrogen peroxide removing capacity, free radical scavenger drugs, lecithin and polyethylene glycol-distearoyl-phosphatidylethanolamine, wherein the mass ratio of the polyethylene glycol-distearoyl-phosphatidylethanolamine to the cyclodextrin derivatives is 2:100-1:1. The nano-drug prepared through the method is in a spherical shape, the particle size range is about 20-800 nm, and the free radical scavenger drugs are evenly distributed in the nano-drug. The preparation method comprises the steps that firstly, the lecithin and the polyethylene glycol-distearoyl-phosphatidylethanolamine are dissolved in water to obtain a water phase, and the cyclodextrin derivatives and the free radical scavenger drugs are dissolved in organic solvent to obtain an organic phase; secondly, the organic phase is slowly and dropwise added in the preheated water phase, centrifugal washing is performed, freeze drying is performed, and then the nano-drug is obtained. The nano-drug has the obvious preventing and treating effects on oxidative stress injury correlation diseases such as inflammatory bowel diseases, myocardial infarction and congestive heart failure.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Method for extracting lipid mixture containing phospholipids comprising polyunsaturated fatty acids from viscera of fish, method for preserving viscera prior to extraction, and lipid mixture extracted thereby
InactiveUS7189418B2Simple and low-cost methodReduce lossesFatty substance recovery/refiningGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsLipid formationHigh concentration
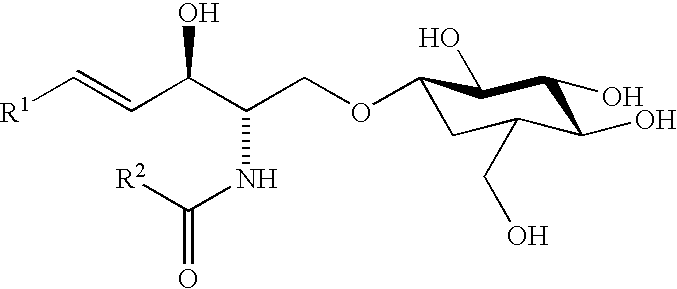
The present invention provides a method for extracting a lipid mixture having a high percentage of phospholipids comprising polyunsaturated fatty acids. The method comprises the steps of (a) heating the viscera of fish with hot water or steam; and (b) extracting from the heated viscera of fish, using a solvent, the lipid mixture containing phospholipids comprising polyunsaturated fatty acids. The lipid mixture obtained by the present method contains phosphatidylserine comprising docosahexaenoic acid and phosphatidylethanolamine comprising docosahexaenoic acid in high concentration.
Owner:MARUHACHI MURAMATSU +1
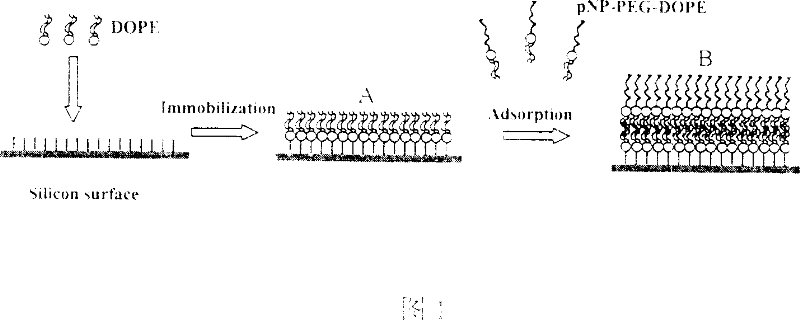
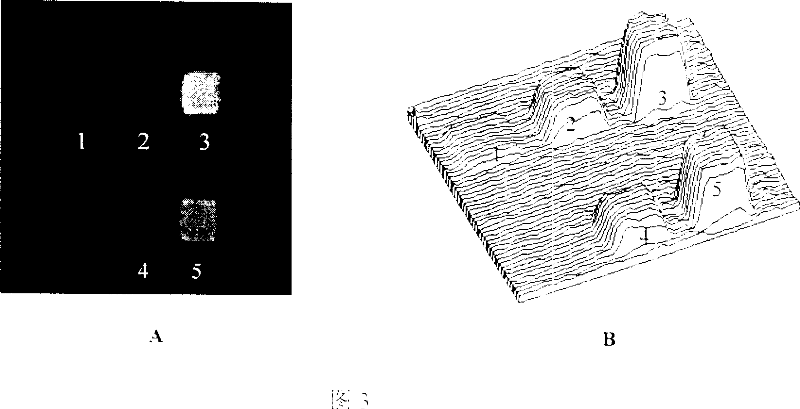
Bilayer lipid membrane surface modified protein chip and its manufacturing method and use
ActiveCN101038290AHigh selectivityPrevent non-specific adsorptionBiological testingLipid formationProtein insertion
The present invention relates to a bilayer lipids membrane surface modified protein chip, a silicon substrate being a solid substrate on which being, in turn, a L-alpha-phosphatidylethanolamine monomolecular layer linked to the silicon substrate through covalent bonds and a p-nitrophenyl ester-polyethylene glycol-(1,2-dioleoyl-3-glycerophosphatide ethanolamine) layer associated with the phosphatidylethanolamine monomolecular layer by a hydrophobic effect. The protein chip is obtained by fixing the L-alpha-phosphatidylethanolamine monomolecular layer at the surface of the silicon substrate through covalent bonds in a micro- runner system and then adsorbing the p-nitrophenyl ester-polyethylene glycol-(1,2-dioleoyl-3-glycerophosphatide ethanolamine) layer. Said protein chip is capable of applied in an imaging ellipsometry biosensor to explore target molecules capable of associating specifically therewith by covalently fixing ligands molecules at terminal tetrafunctional radicals of the protein chip surface PEG, wherein the surface morphology changes of the protein chip are capable of being observed in said imaging ellipsometry system, after both are associated. The bilayer lipids membrane surface modified protein chip in accordance with the present invention is capable of avoiding effectively a nonspecific adsorption, with its ligands molecules having excellent stability and being kept high biological activities.
Owner:INST OF MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Macrocyclic polyamine [12]aneN3 compound based on TPA-BI, and preparation method and application thereof
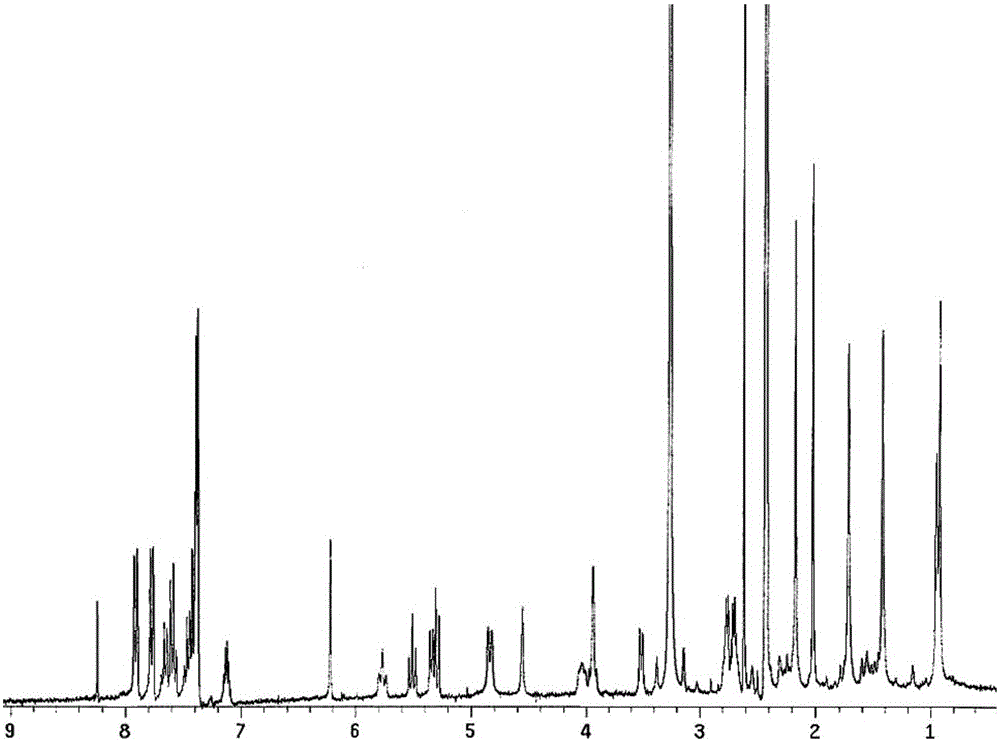
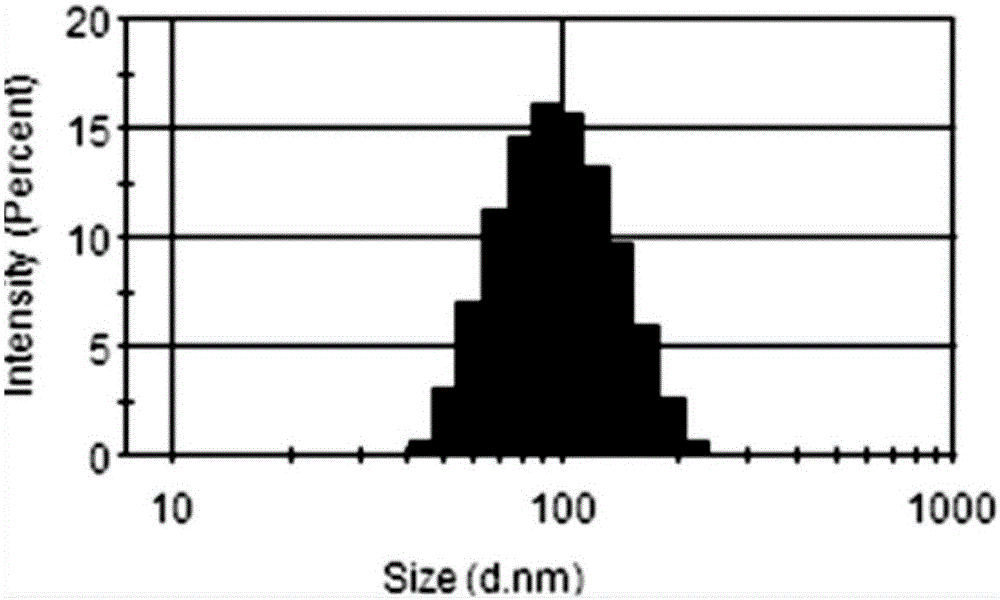
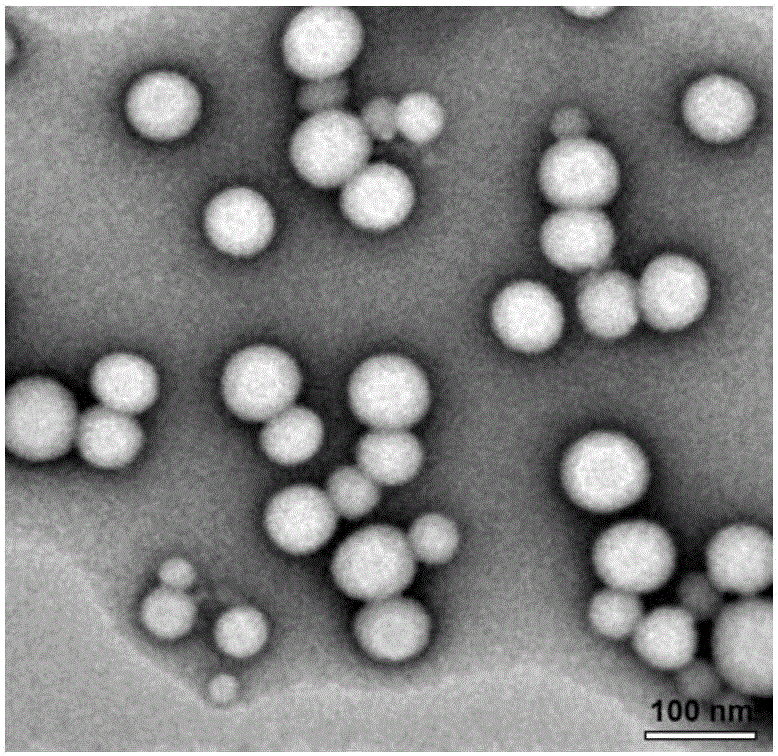
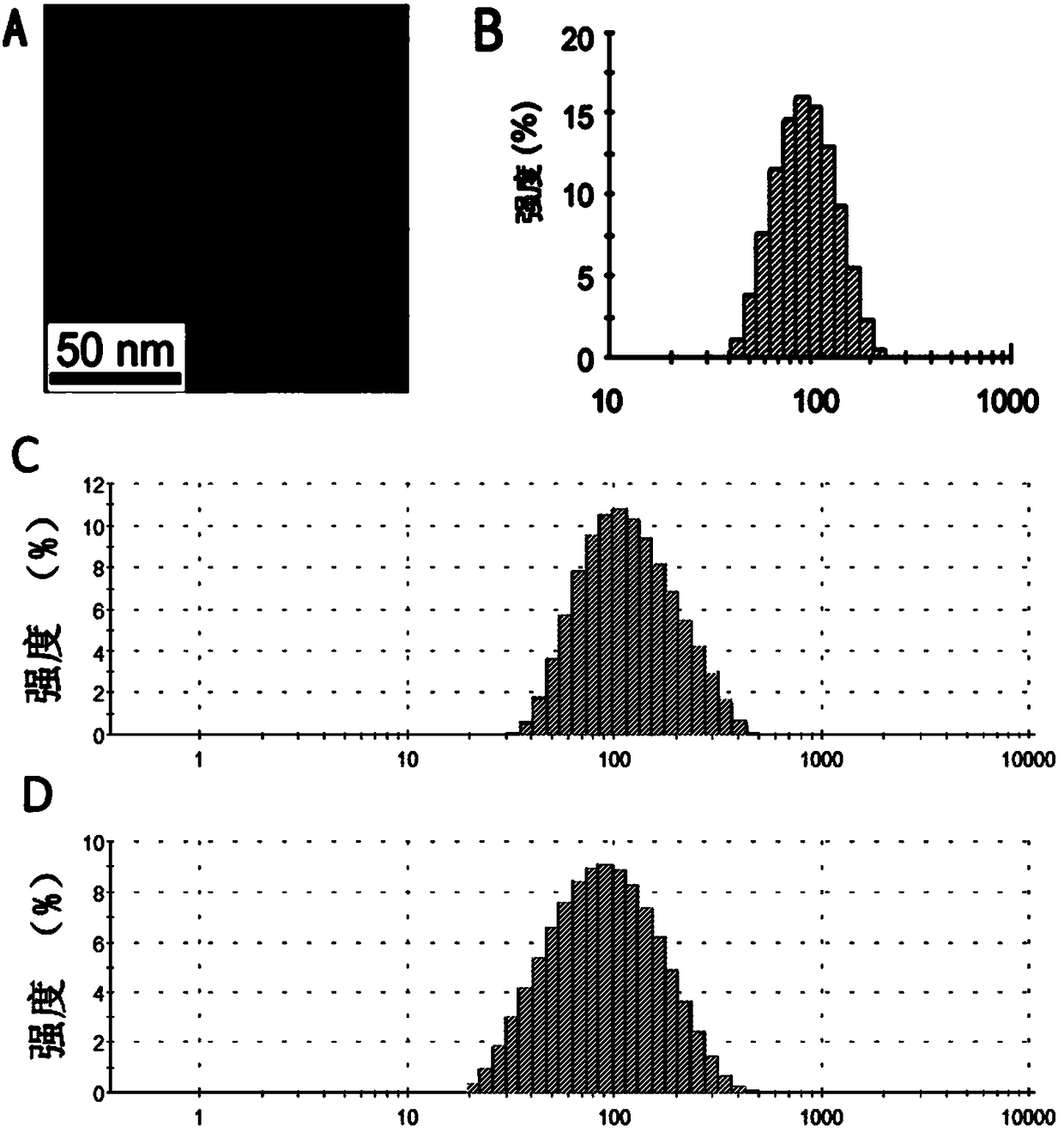
ActiveCN109369621AAggregation inducing effectWith large Stoke displacementOrganic chemistryOther foreign material introduction processesFluorescencePolyamine
The invention relates to a macrocyclic polyamine [12]aneN3 compound based on TPA-BI, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The compound disclosed by the invention is mainly prepared andsynthesized by means of Suzuki coupling, esterification reaction and Click reaction. The compound provided by the invention has the advantages of great Stock displacement and two-photon fluorescenceproperty as well as long wave excitation, low self-Illumination and high 3D resolution. The compound has an aggregation-inductive effect (AIE). The compound provided by the invention can form a pH stimulation responding cationic liposome with dioleoyl phosphatidylethanolamine (DOPE) to promote release of DNA in cells. The cationic liposome can enter cell nucleus efficiently so as to improve the transfection efficiency of the cells.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Cancer treatment kits using antibodies to aminophospholipids
InactiveUS8486391B2Method securityEasy to getPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntibody conjugateThrombus
Disclosed are the surprising discoveries that aminophospholipids, such as phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine, are stable and specific markers accessible on the luminal surface of tumor blood vessels, and that the administration of an anti-aminophospholipid antibody alone is sufficient to induce thrombosis, tumor necrosis and tumor regression in vivo. This invention therefore provides anti-aminophospholipid antibody-based methods and compositions for use in the specific destruction of tumor blood vessels and in the treatment of solid tumors. Although various antibody conjugates and combinations are thus provided, the use of naked, or unconjugated, anti-phosphatidylserine antibodies is a particularly important aspect of the invention, due to simplicity and effectiveness of the approach.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Taste-improving agent and food or drink containing same
ActiveUS20150125589A1Improving and reducing unpleasant bitternessImproving and reducing and astringent taste and taste and tasteFood ingredient as taste affecting agentPhosphatide foodstuff compositionsArgininePotassium
Provided is a taste improver that improves or decreases unpleasant bitterness, astringent taste, harsh taste, bitter taste, or the like that results from potassium salts, magnesium salts, calcium salts, and ammonium salts without adversely affecting savoriness of a food or drink. The taste improver includes a vegetable extract and / or a phospholipid. In the taste improver, the aforementioned vegetable extract includes a vegetable-derived glycoside and / or glycoside aglycone. In the taste improver, the aforementioned phospholipid is phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylserine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylinositol, and / or a lyso form thereof. Arginine is further added to the aforementioned taste improver. Trehalose and / or hydrogenated starch syrup are further added to the taste improver. A manufacturing method of such and an improvement method for the unpleasant bitterness, astringent taste, harsh taste, bitter taste, or the like caused by potassium salts, magnesium salts, calcium salts, and ammonium salts using these taste improvers. A food or drink including these taste improvers.
Owner:NIPPON SUISAN KAISHA LTD
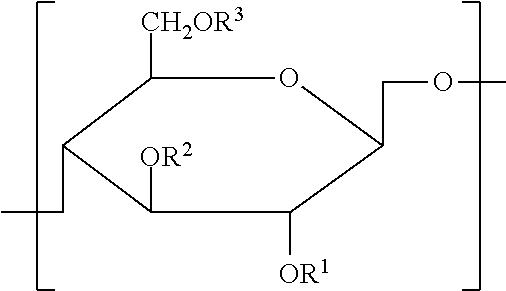
Cellulose derivative and method for production thereof
InactiveUS8455001B2Improve viscoelasticity and therefore retentionImprove barrier propertiesPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsPolymer scienceAlkaline earth metal
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
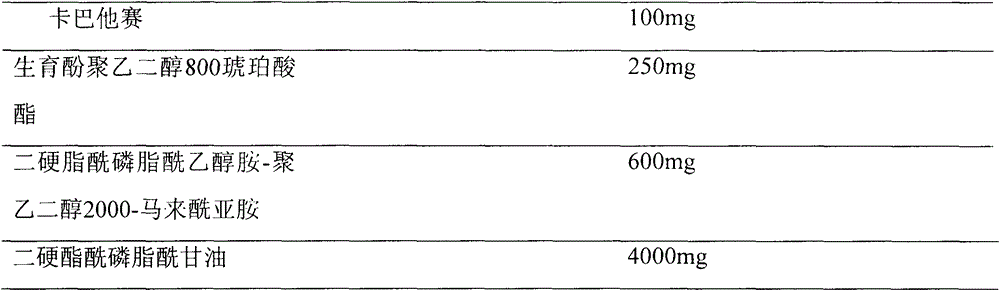
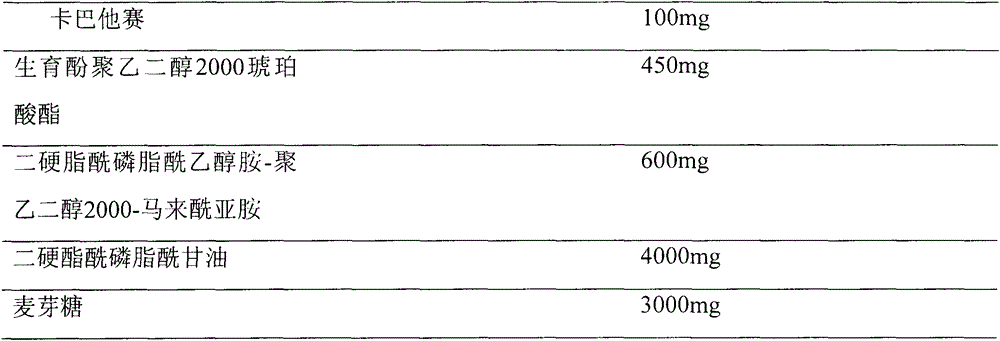
Cabazitaxel long-circulation liposome injection and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104473873AHigh encapsulation efficiencyImprove bioavailabilityOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMedicinePhospholipid
The invention provides cabazitaxel long-circulation liposome injection and a preparation method thereof. The cabazitaxel long-circulation liposome injection comprises cabazitaxel or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, tocopherol polyethylene glycol succinate, distearoyl-phosphatidylethanolamine-polyethylene glycol-maleimide and phospholipid. The cabazitaxel long-circulation liposome injection is prepared by a film method. The liposome not only has the advantages of reduced toxicity, simple and convenient clinical use and improved bioavailability, but also has good stability of storage and use.
Owner:南京西默思博检测技术有限公司
Fluorocarbon nano medicine-carrying system and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a fluorocarbon nanodrug delivery system, which comprises a superparamagnetic full fluorocarbon core and a drug delivery lipid layer, wherein the lipid layer is coated with a glucocorticoid anti-inflammatory agent, a magnetic resonance contrast agent and phosphatidylethanolamine which is connected with biotins; full fluorocarbon accounts for 26 to 32 weight percent of the nanodrug delivery system; the lipid layer accounts for 6.8 to 7.2 weight percent of the nanodrug delivery system; the balance is water; the glucocorticoid anti-inflammatory agent in the lipid layer accounts for 1.5 to 3 weight percent; the magnetic resonance contrast agent in the lipid layer accounts for 62 to 68 weight percent; the phosphatidylethanolamine which is connected with the biotins accounts for 0.5 to 1 weight percent in the lipid layer; and the balance is lipid material. Nano particles are connected with special antibodies through a biotin-avidin system and combined with antibody epi positions of target cells; the nano surface lipid layer and cell surfaces are subjected to lipid exchange to achieve the aim of slow release of medicines; the full fluorocarbon core can strengthen the strength of magnetic resonance detection signals of a paramagnetic contrast agent on the vector surface; and the fluorocarbon nanodrug delivery system can perform early diagnosis on diseases through a pathological mechanism of the diseases positioned and displayed by target molecules.
Owner:RENJI HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Polyethylene glycol-modified phospholipid derivative taking anilino-quinazoline as targeting ligand and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102649841APharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsSulfonyl chlorideTumor therapy
The invention provides a polyethylene glycol-modified phospholipid derivative taking a 4-substituted anilino-quinazoline group as a targeting ligand and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: performing condensation with para-methylbenzene sulfonyl chloride, substitution with phthalimide potassium salt and hydrolysis with a hydrazine hydrate by taking polyethylene glycol (PEG) as a starting raw material to obtain diamine PEG; and reacting with targeting ligands, i.e., N-(3-chlorin-4-fluorin)-6-(3-chloropropyl)-7-methoxylquinazoline-4-amine and distearoylphosphatidylethanolamine (DSPE) to respectively obtain 4-anilino-quinazoline group-PEG-DSPE. A liposome preparation of the 4-anilino-quinazoline group-PEG-DSPE can be used for realizing target administration of tumor cells and reducing the toxic and side effects of a tumor medicament; and the pharmacodynamic structure of gefitinib can give play to dual medicament effects together with other liposome-coated antitumor medicaments, so that the tumor treatment effect is enhanced greatly.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Glycerophospholipids containing omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids
InactiveCN1897955AGuaranteed functionImprove and treat ADHDOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderGlycerolOmega-6 fatty acid
Disclosed is a lipid preparation comprising a glycerophospholipid or salt, conjugate and derivatives thereof, particularly phosphatidylserine (PS), phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidyl-inositol (PI), phosphatidylglycerol (PG) and phosphatidic acid (PA), and poly-unsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) acyl groups, particularly long-chain poly-unsaturated fatty acid (LC-PUFA) acyl groups such as omega-3 and / or omega-6 acyl groups, wherein said PUFA is covalently bound to said glycerophospholipid. The disclosed preparations possess an improved bioactivity, and are useful in the treatment of various cognitive and mental conditions and disorders and for maintenance of normal functions of brain-related systems and processes, for example ADHD.
Owner:ENZYMOTEC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com






![Macrocyclic polyamine [12]aneN3 compound based on TPA-BI, and preparation method and application thereof Macrocyclic polyamine [12]aneN3 compound based on TPA-BI, and preparation method and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/3137547f-a8a4-4294-b07d-a483a2f35ffd/HDA0001835140750000011.png)
![Macrocyclic polyamine [12]aneN3 compound based on TPA-BI, and preparation method and application thereof Macrocyclic polyamine [12]aneN3 compound based on TPA-BI, and preparation method and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/3137547f-a8a4-4294-b07d-a483a2f35ffd/HDA0001835140750000021.png)
![Macrocyclic polyamine [12]aneN3 compound based on TPA-BI, and preparation method and application thereof Macrocyclic polyamine [12]aneN3 compound based on TPA-BI, and preparation method and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/3137547f-a8a4-4294-b07d-a483a2f35ffd/HDA0001835140750000031.png)