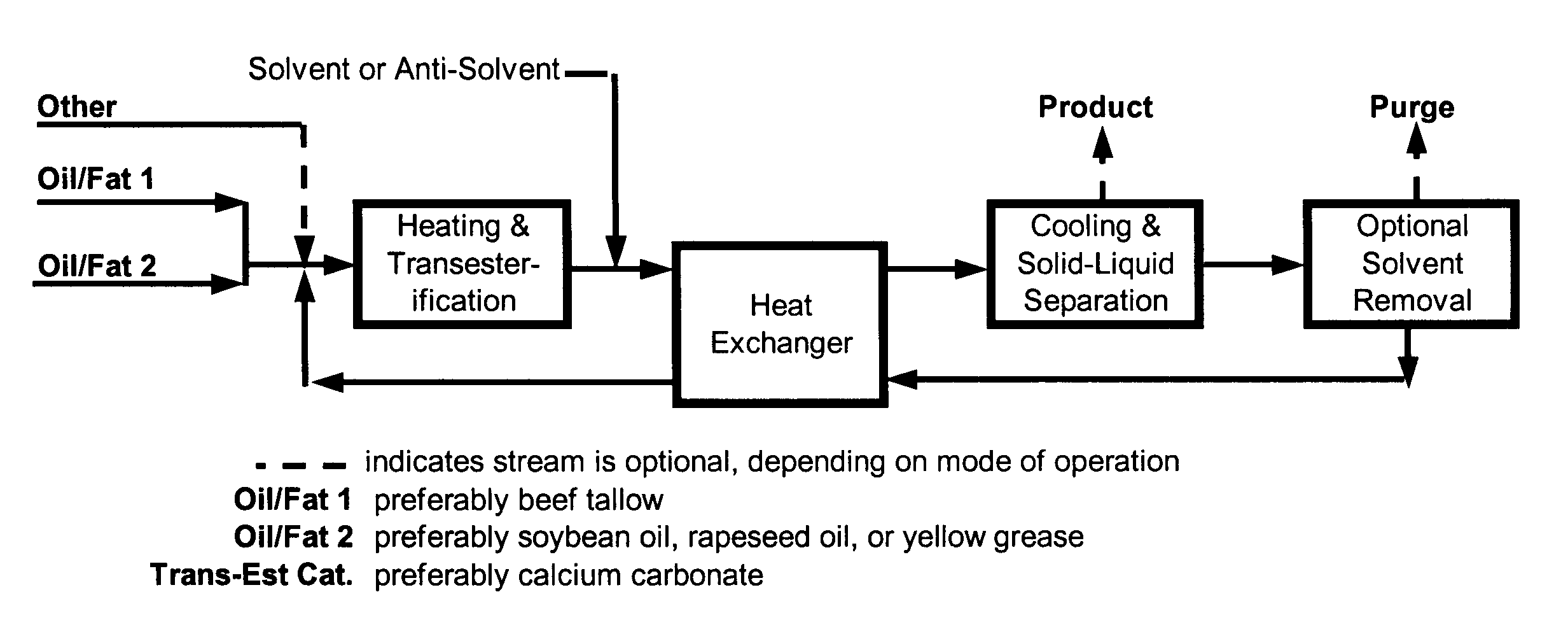
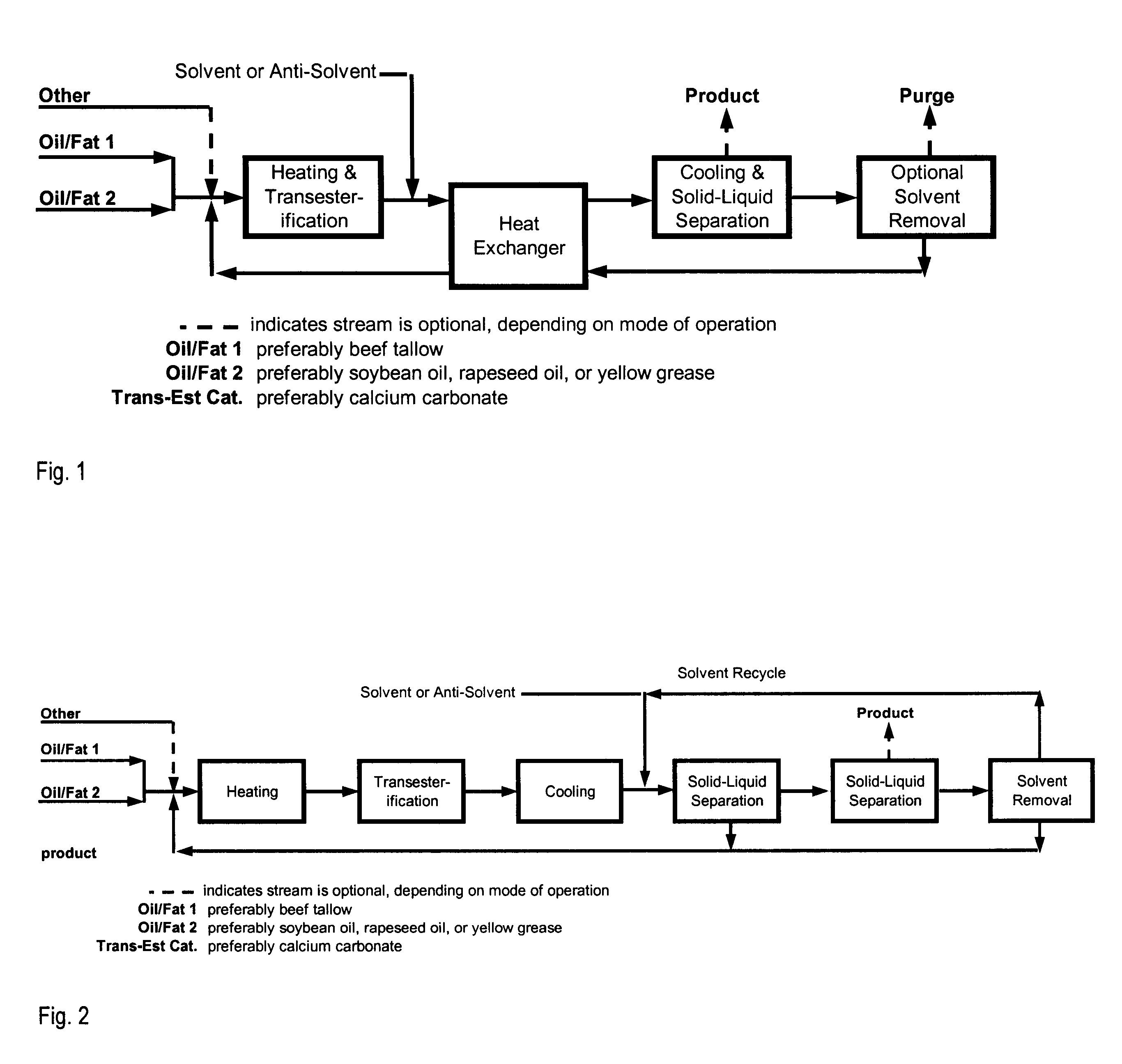
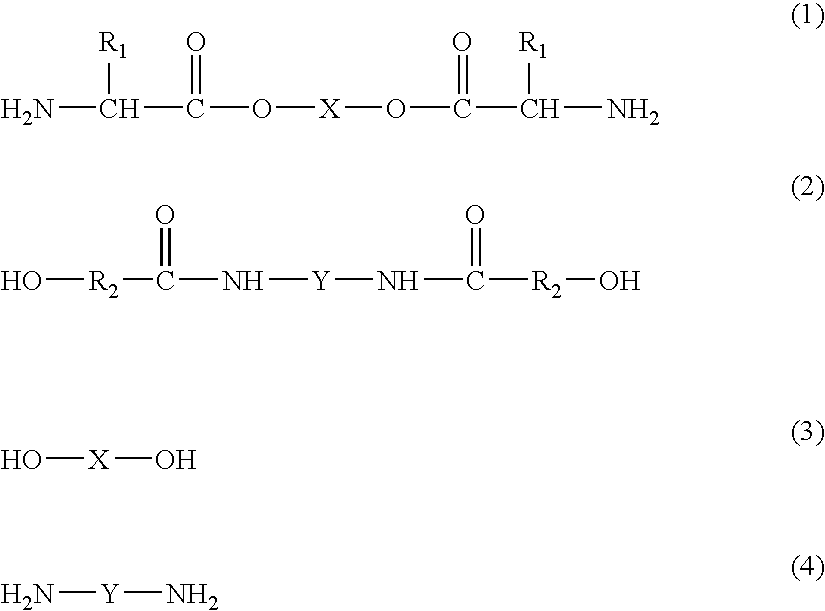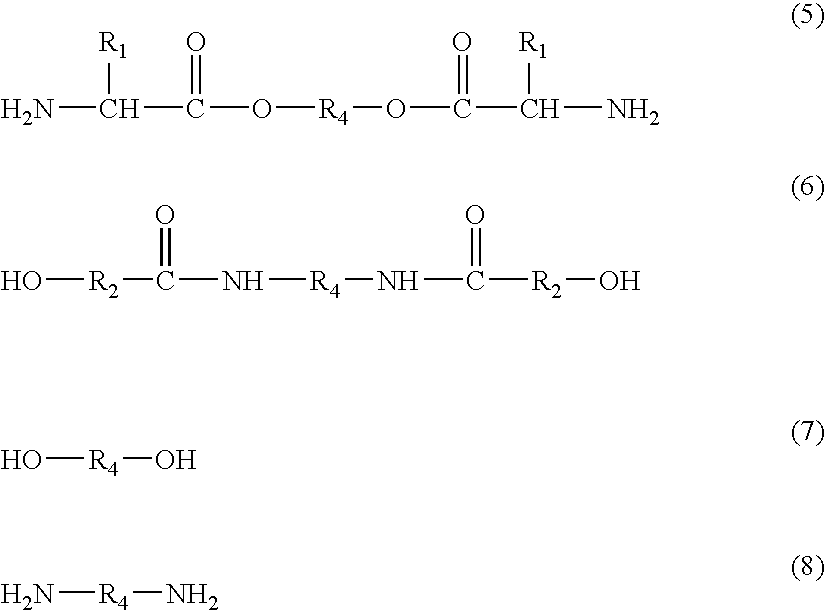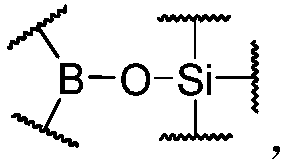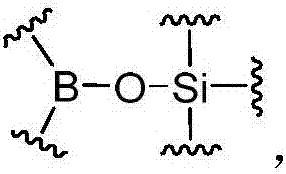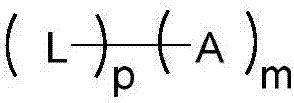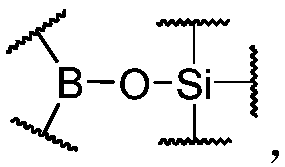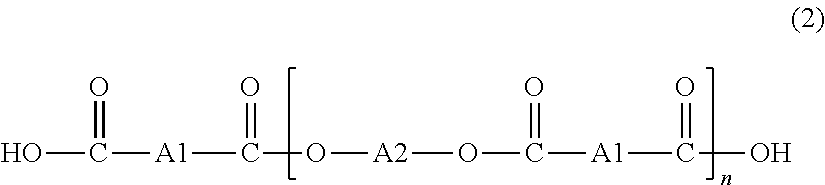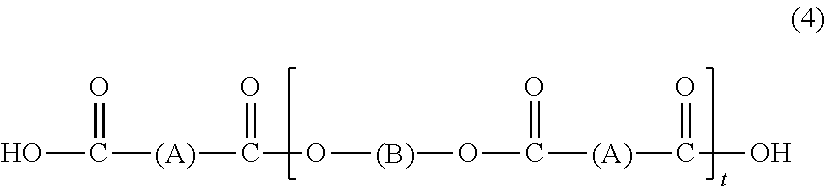Patents
Literature
1690 results about "Ester bond" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An ester bond is the bond between an alcohol group (-OH) and a carboxylic acid group (-COOH), formed by the elimination of a molecule of water (H 2O). Previous definition.
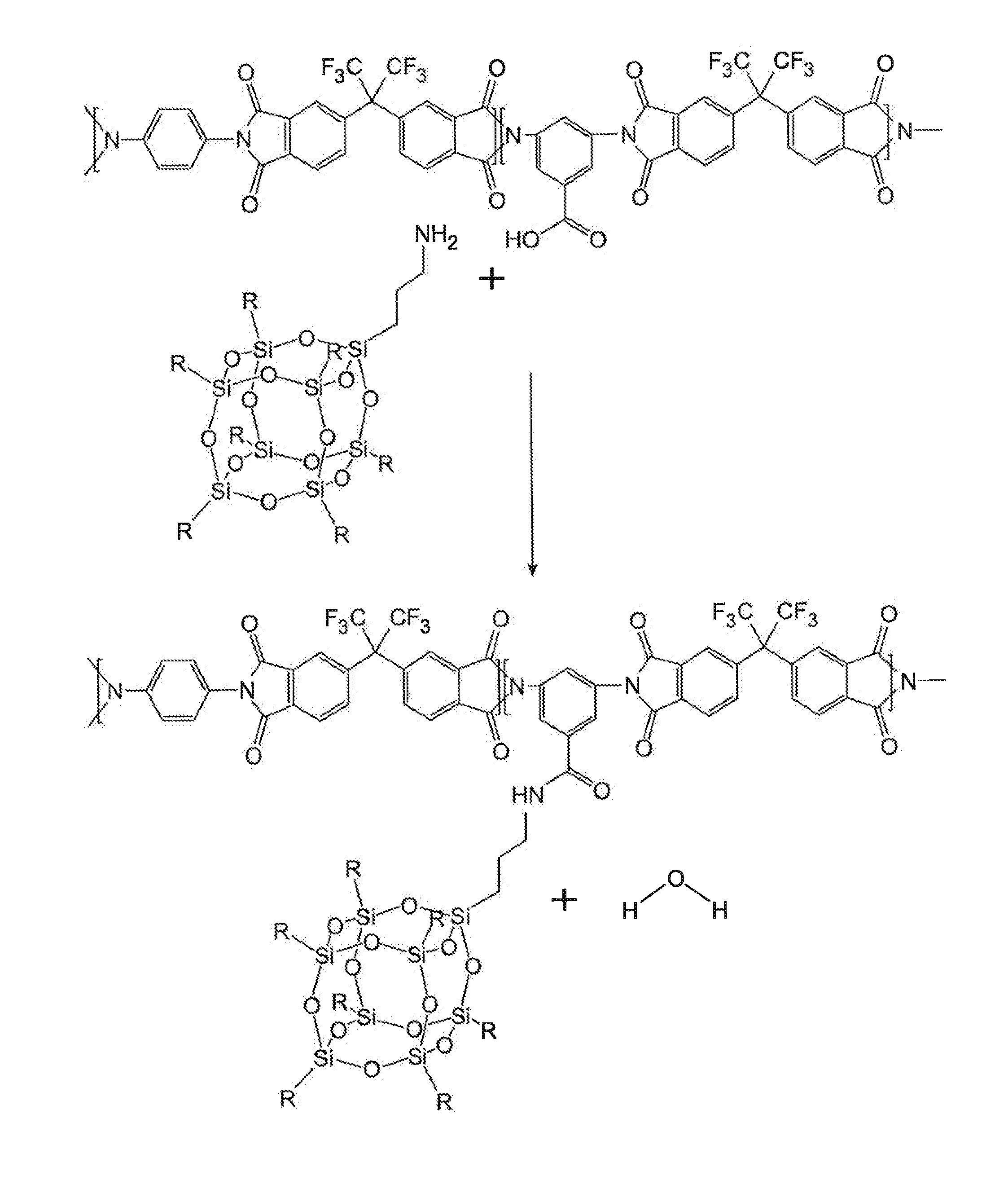
Polyimide polymer with oligomeric silsesquioxane
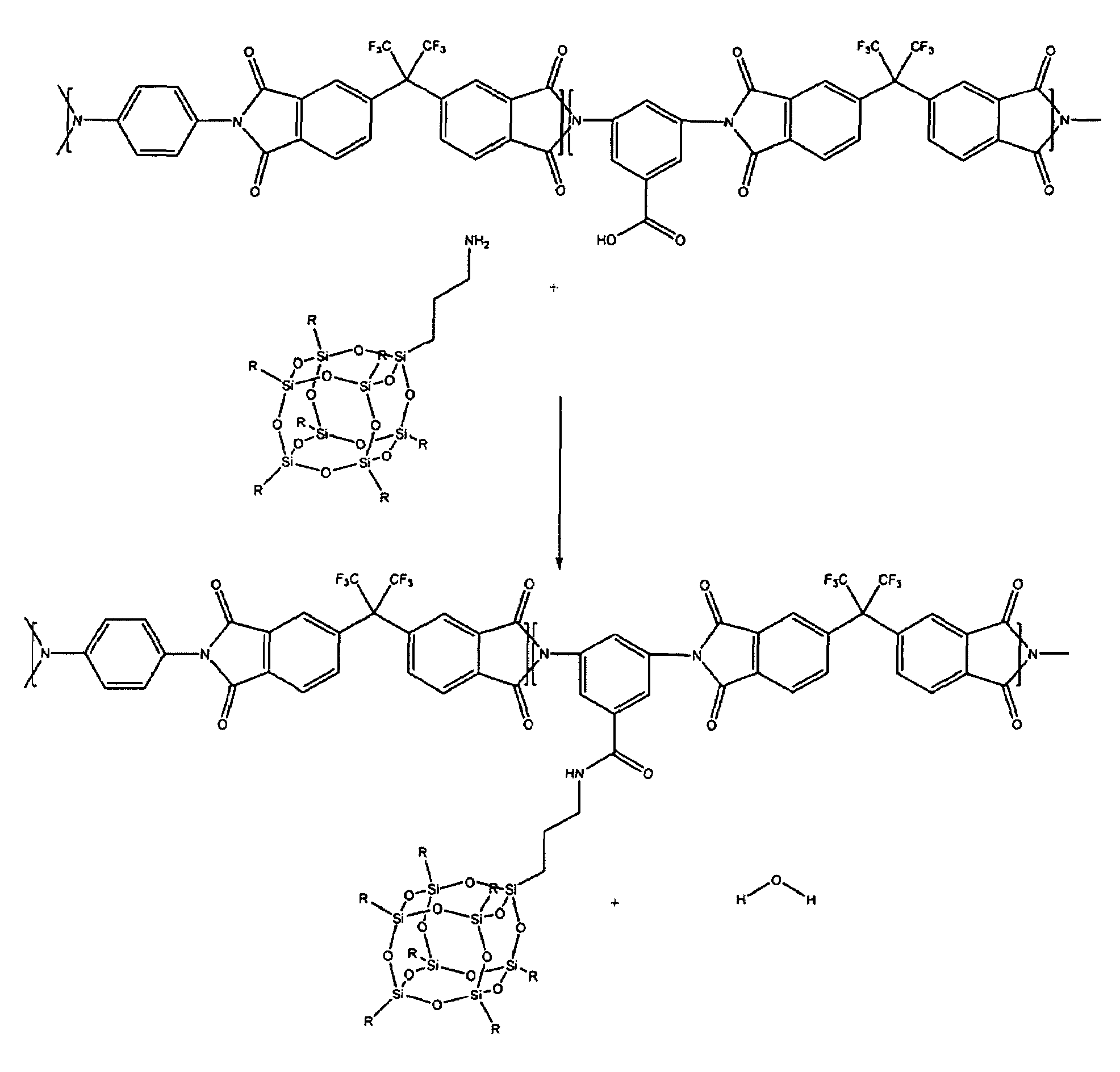
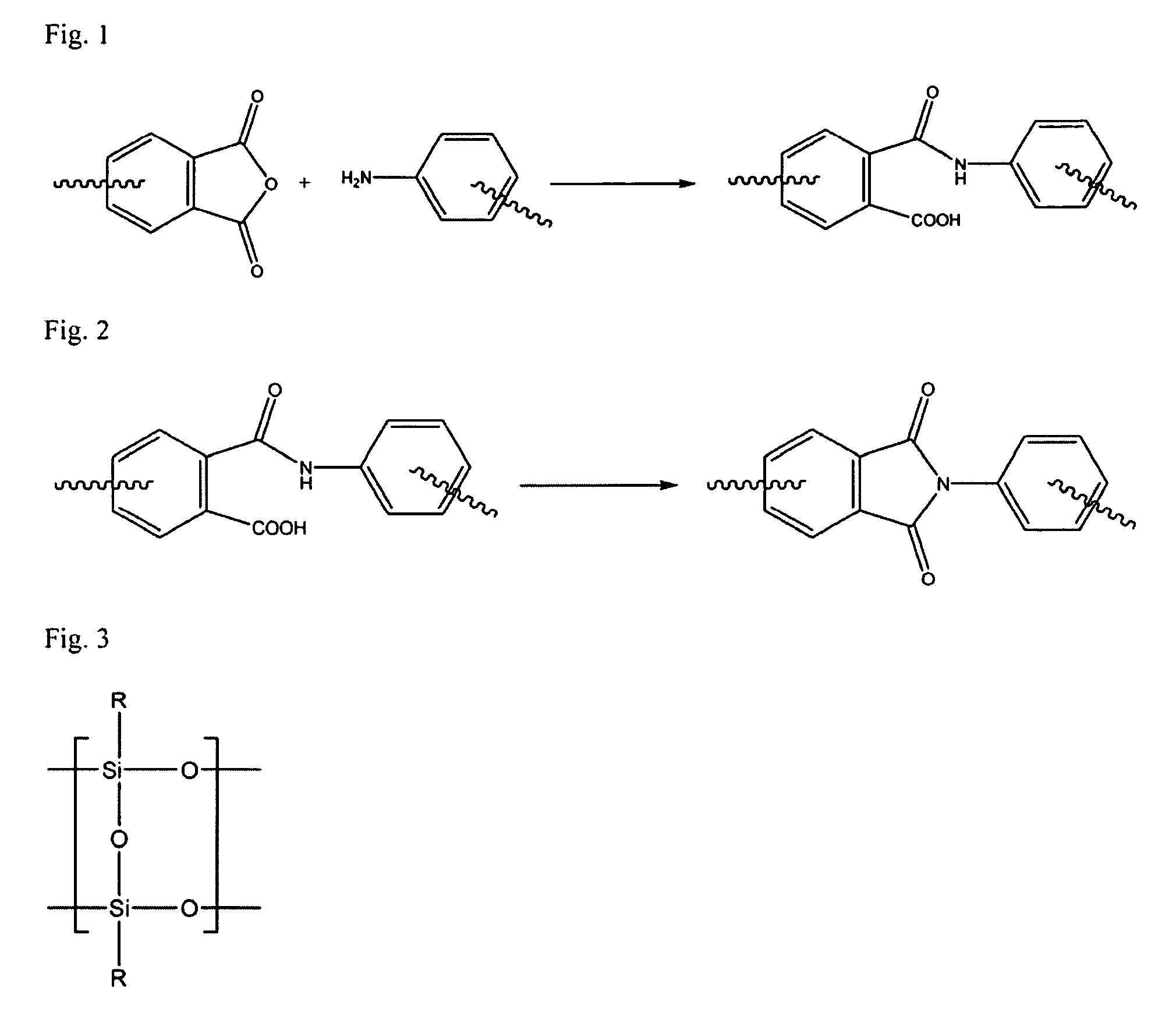
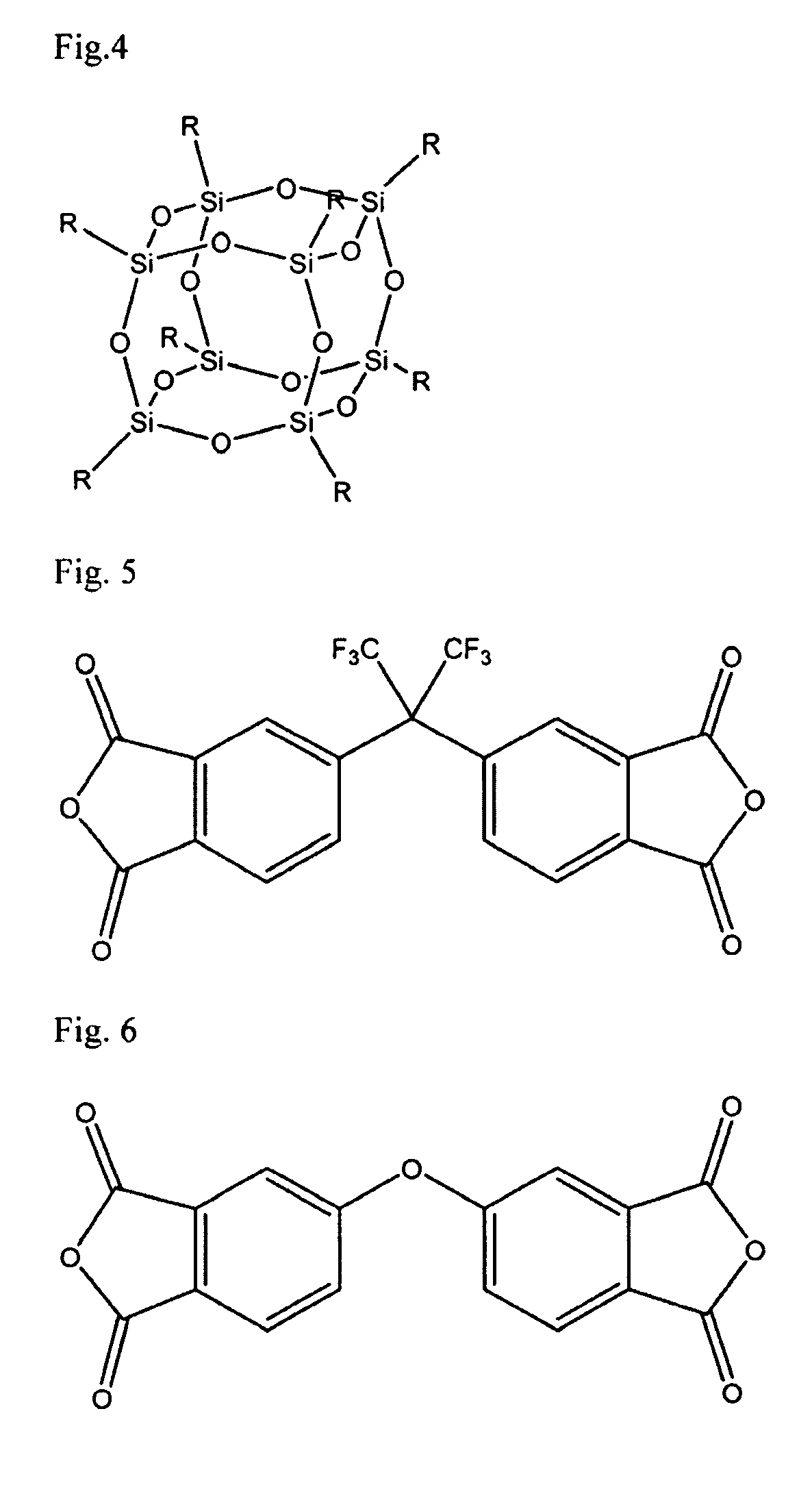
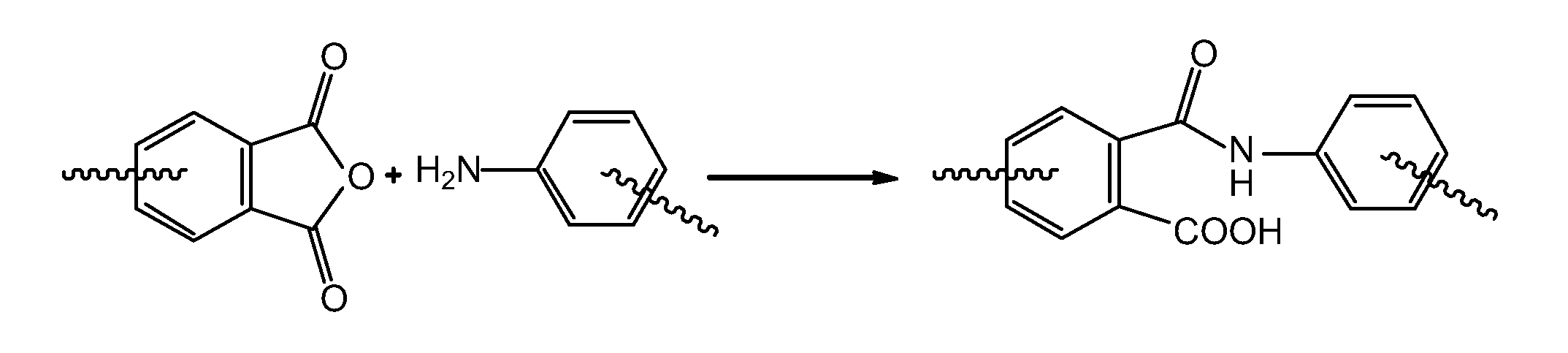
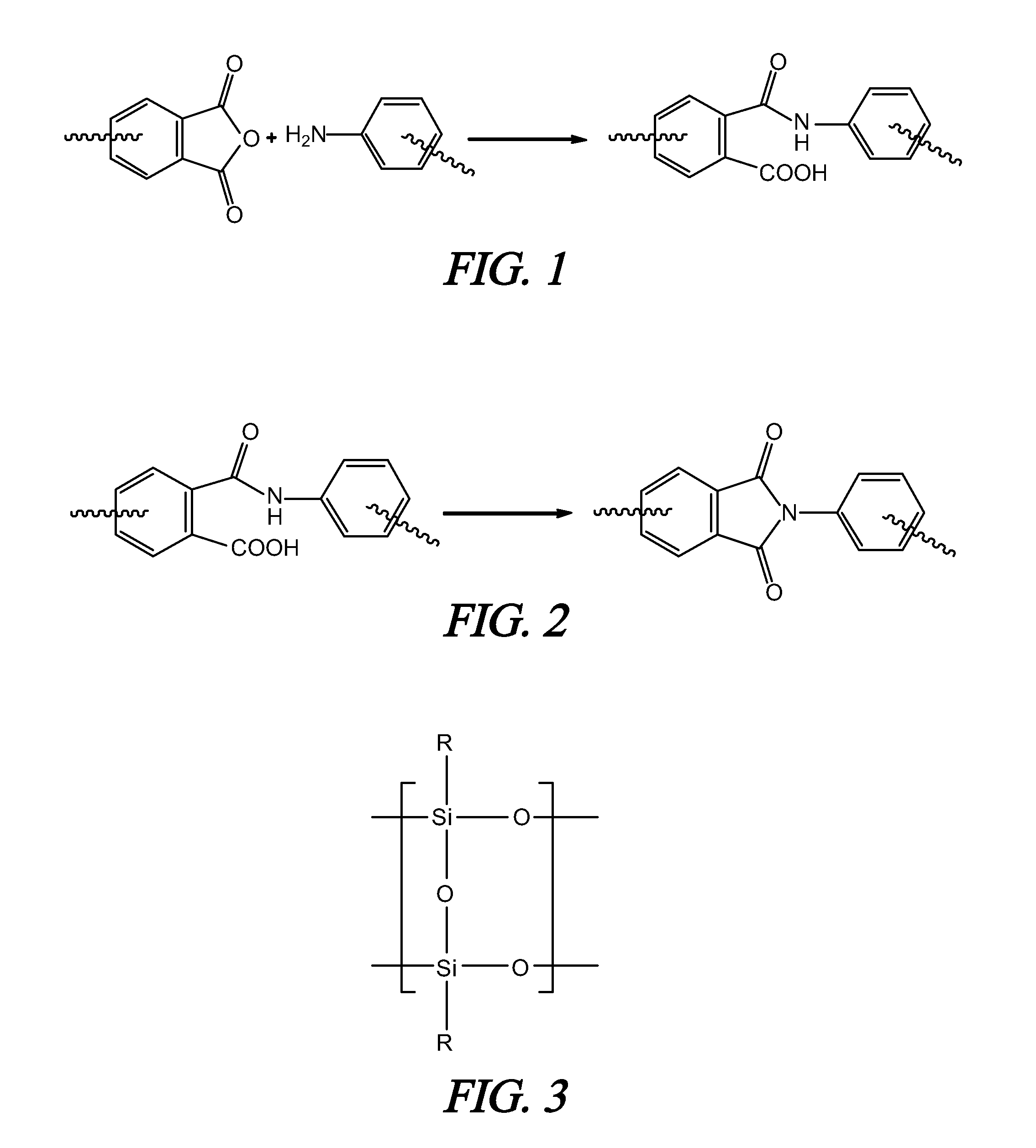
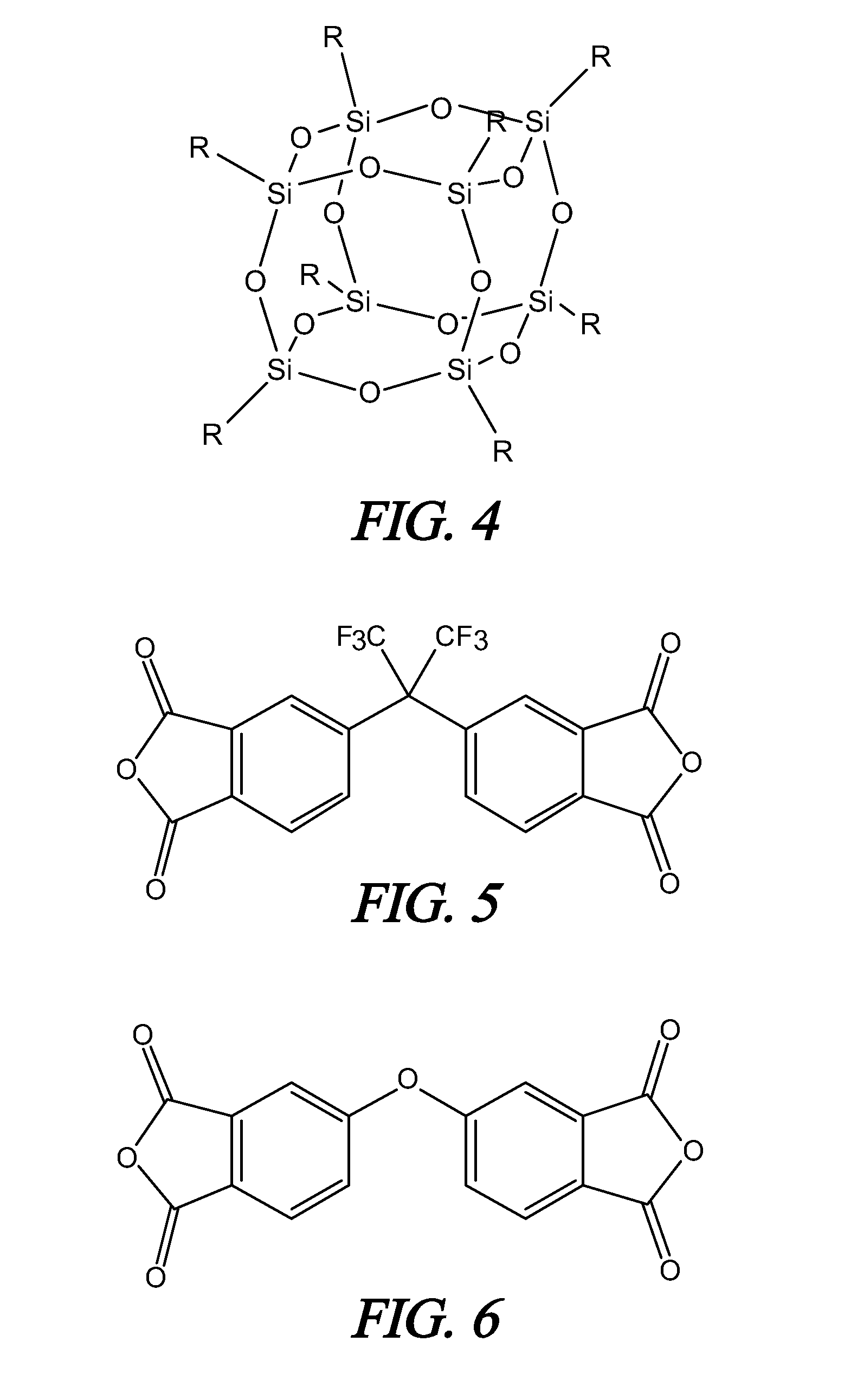
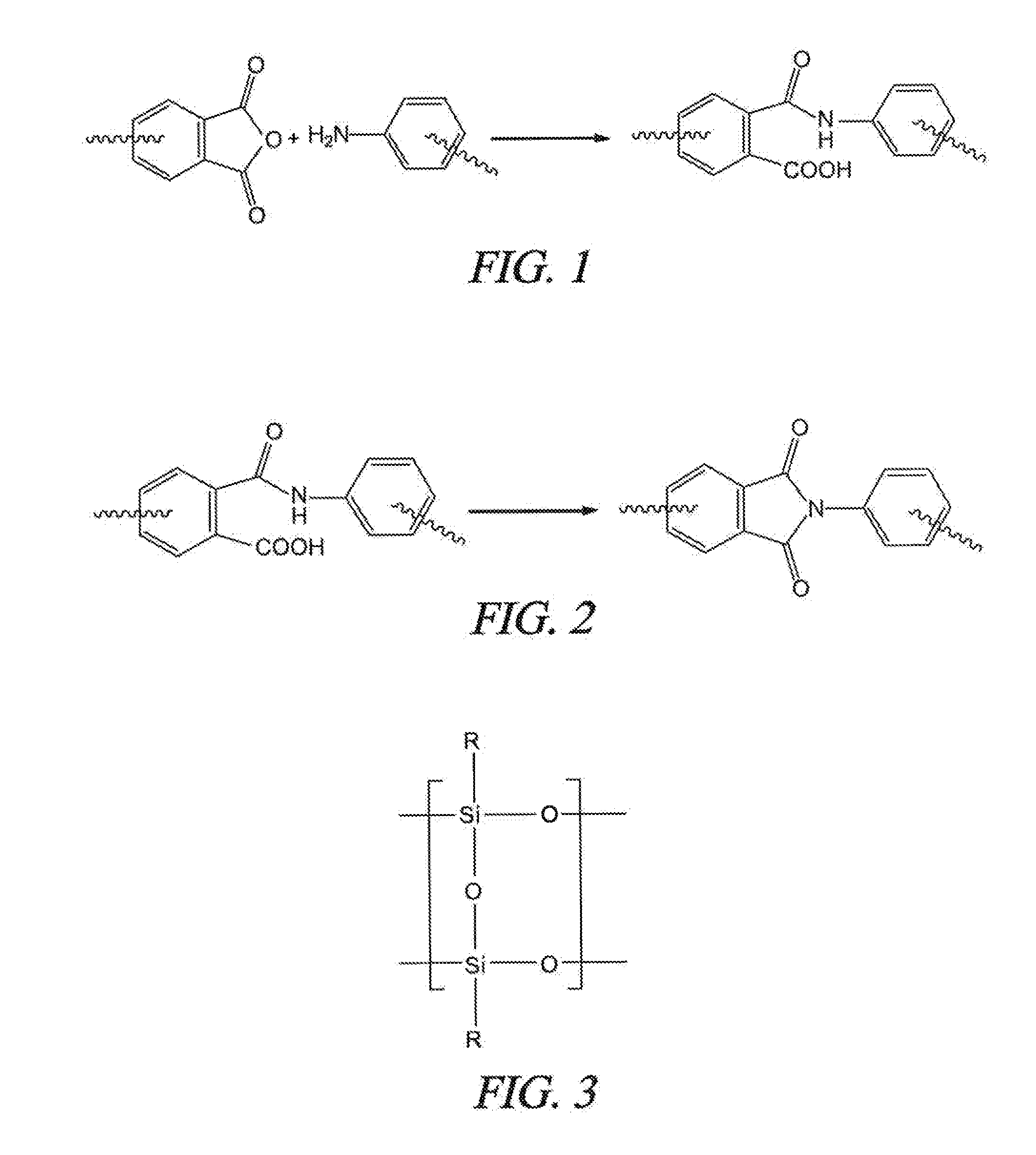
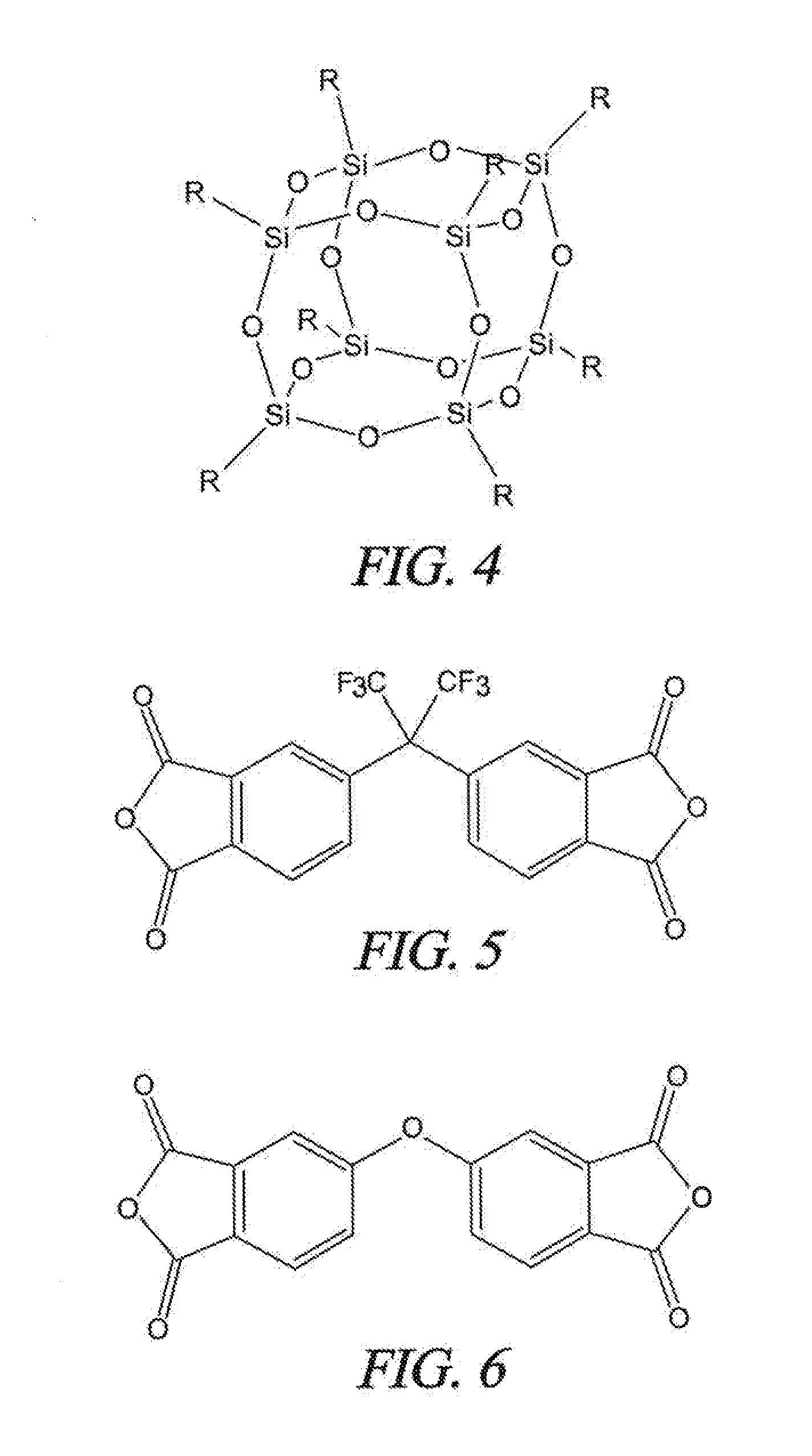
A soluble polyimide polymer with tethered oligomeric silsesquioxane compounds is produced using efficient, gentle reactions. A carboxylic acid attachment point on the polymer backbone is used to connect the oligomeric silsesquioxane. The oligomeric silsesquioxane compound includes an amine or an alcohol on an organic tether, which reacts with the carboxylic acid attachment point to produce either an amide or an ester bond. The amide or ester bond includes a carbonyl carbon directly connected to a phenyl group in the polymer backbone. The resultant polyimide polymer has many beneficial properties.
Owner:NEXOLVE HLDG CO LLC
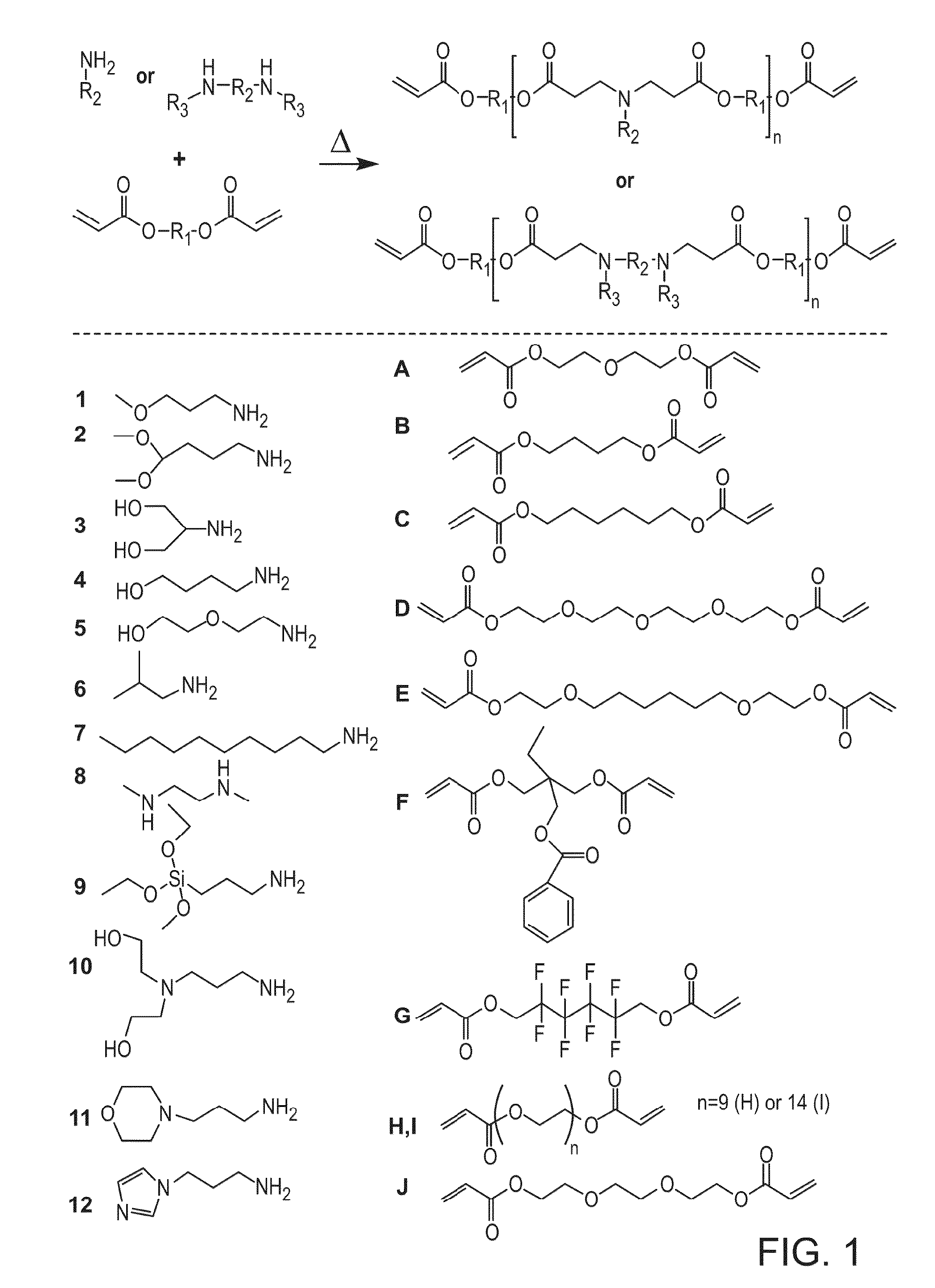
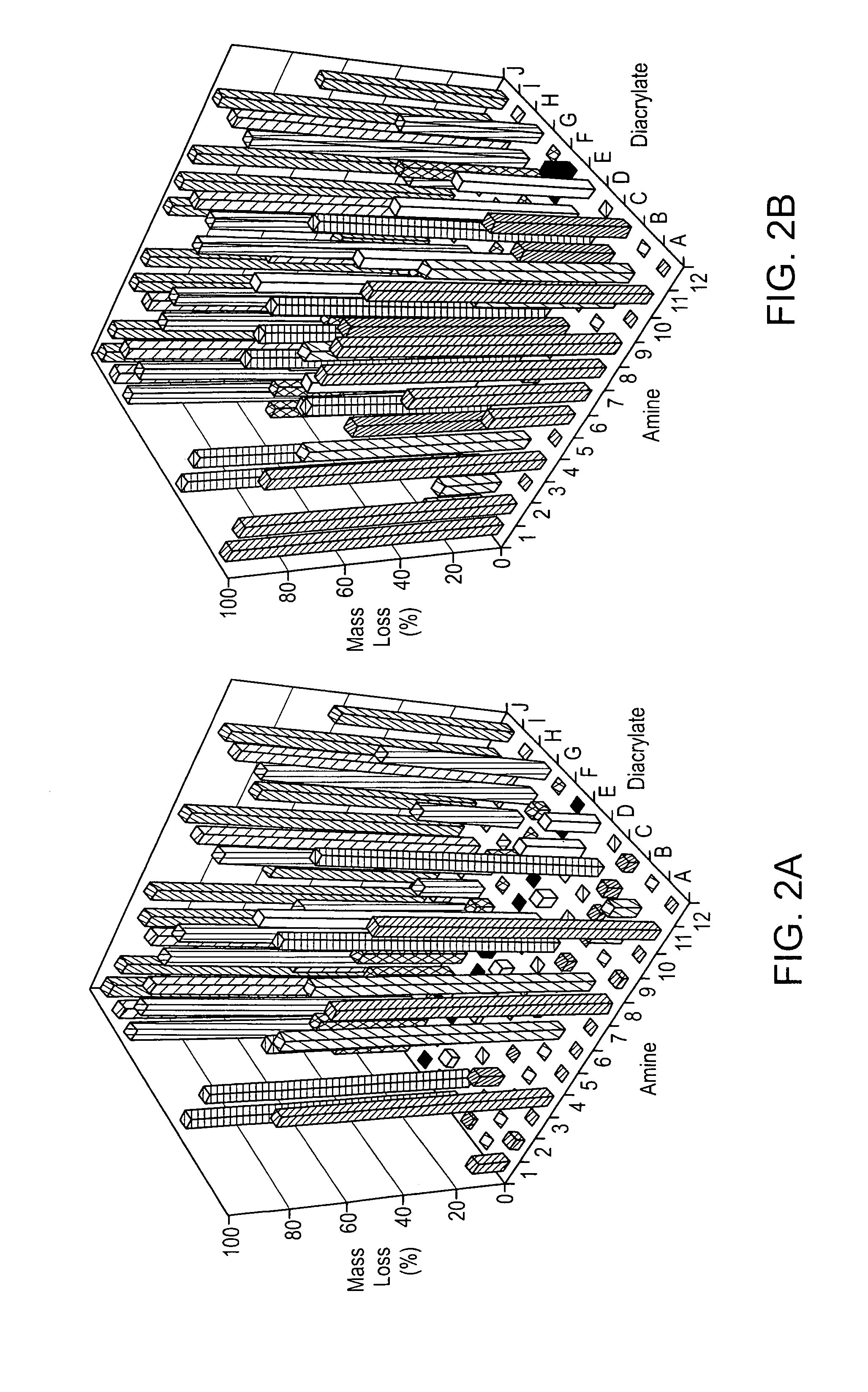
Crosslinked, degradable polymers and uses thereof
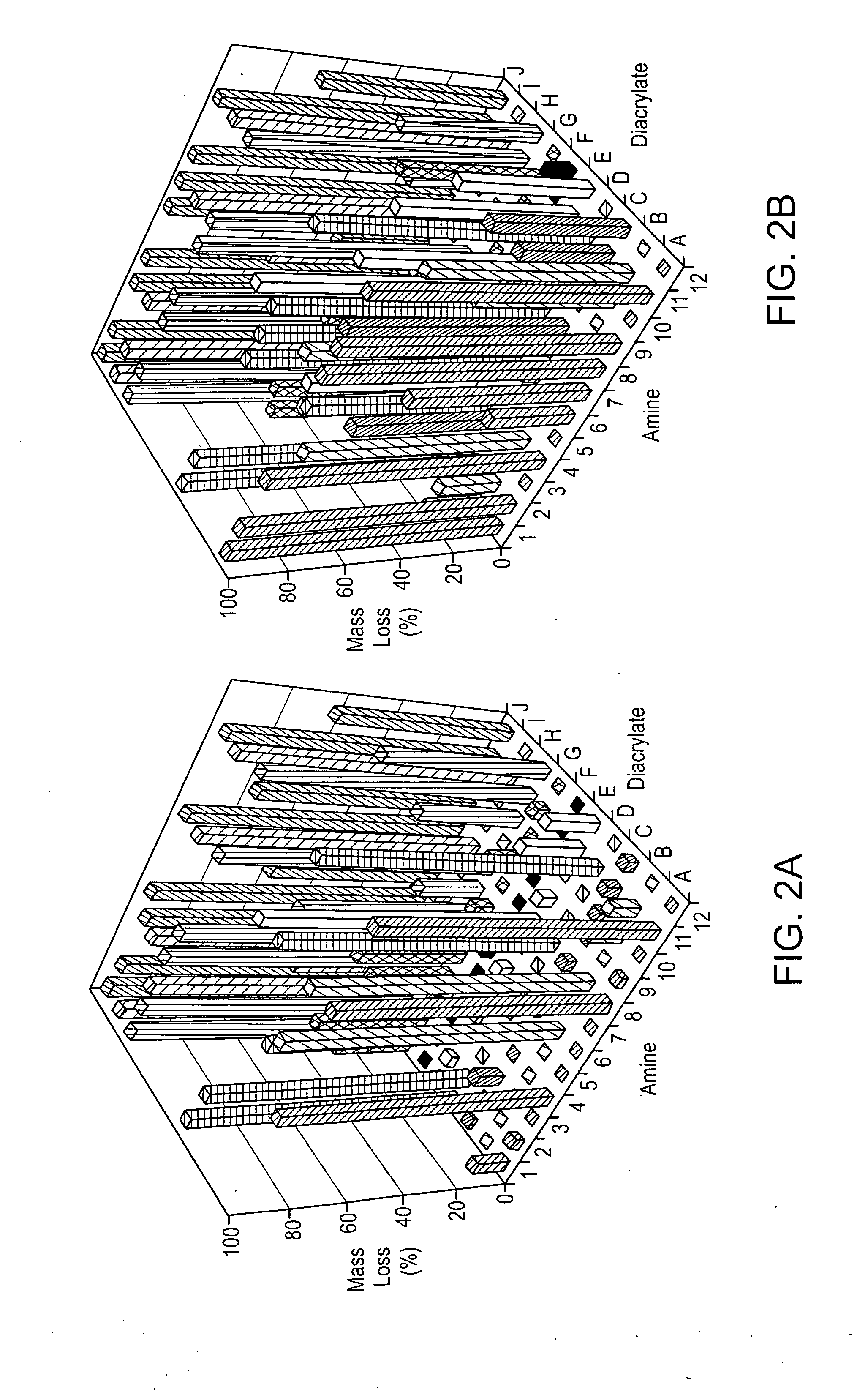
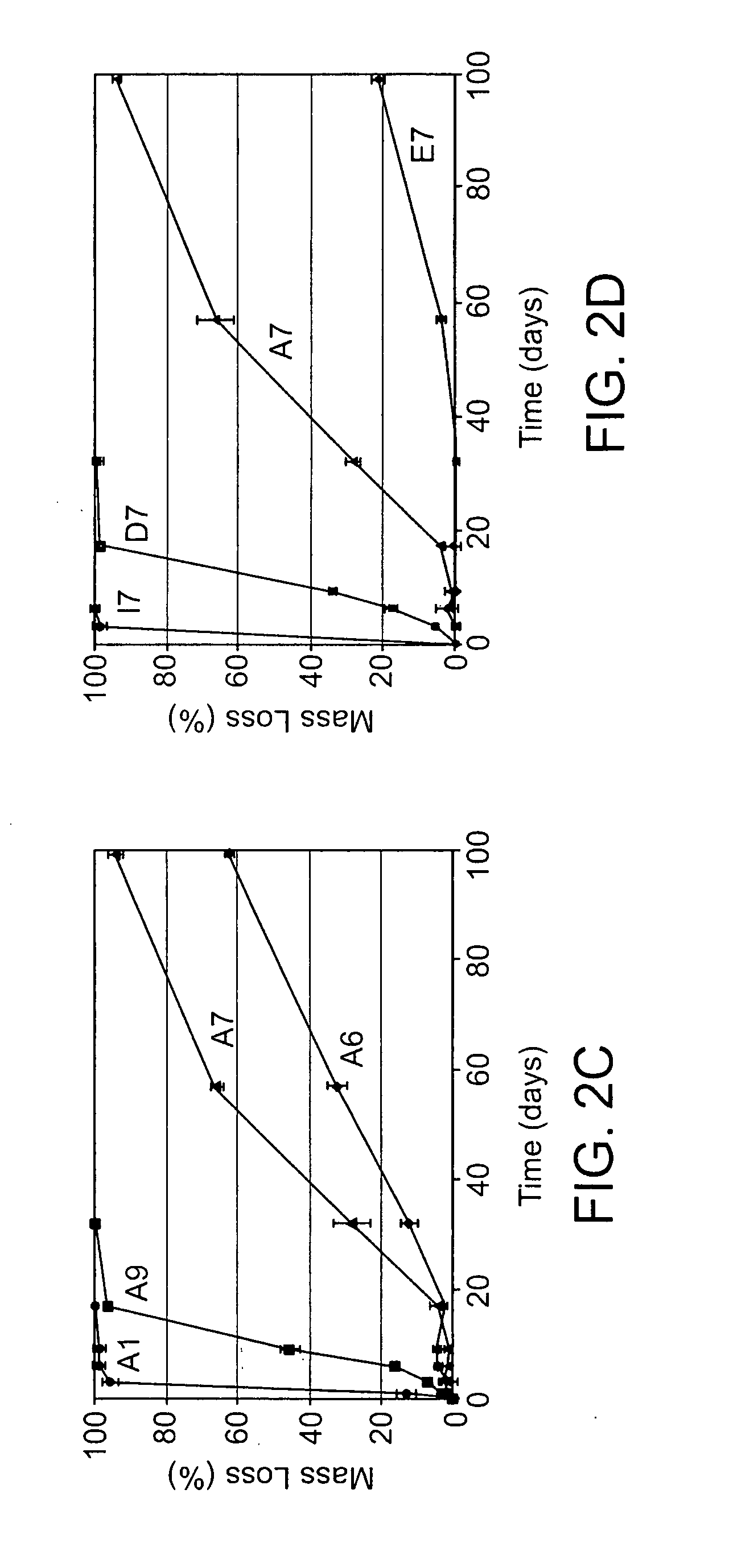
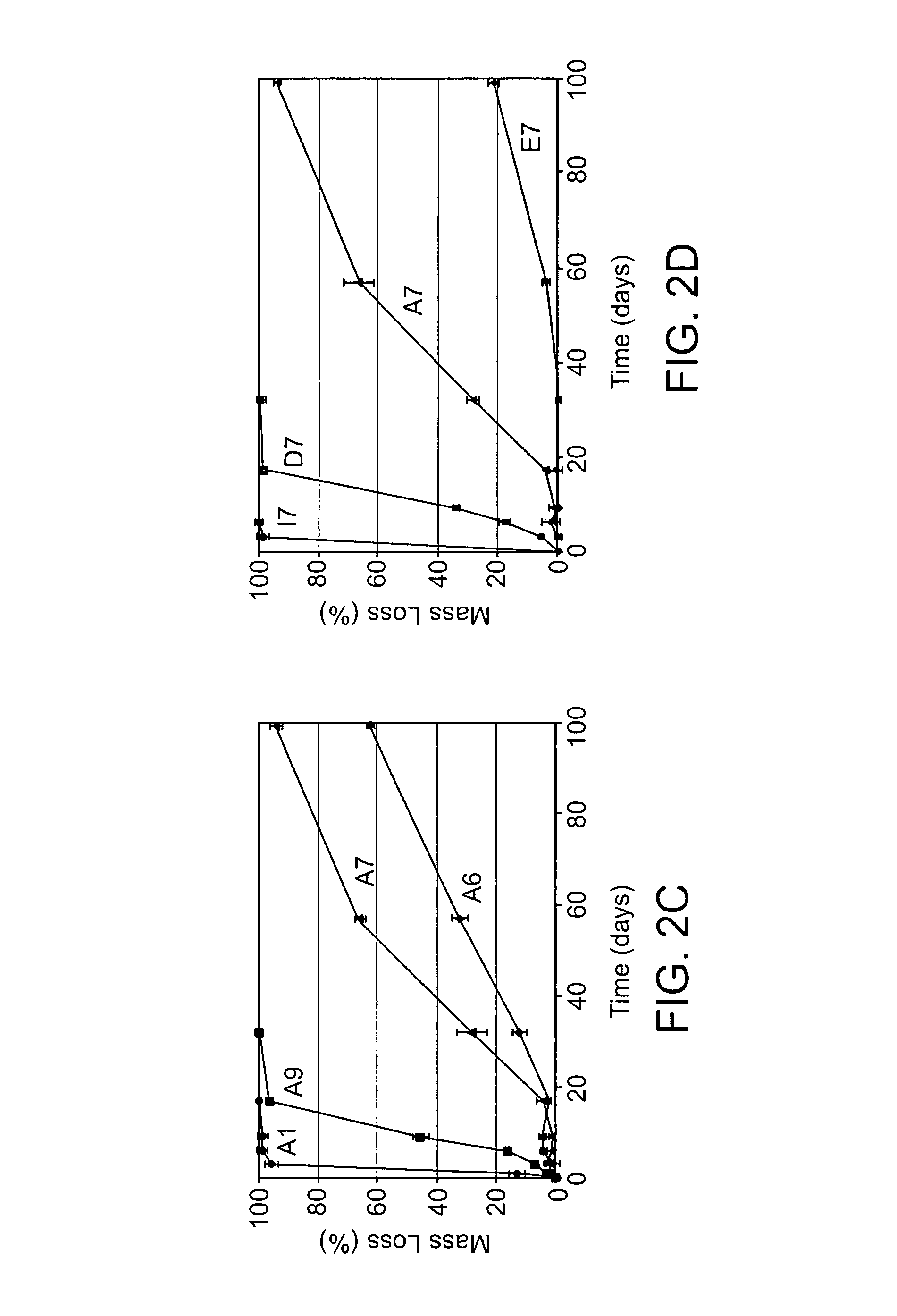
Acrylate-terminated poly(beta-amino esters) are cross-linked to form materials useful in the medical as well as non-medical field. The polymeric starting material is combined with a free radical initiator, either a thermal initiator or a photoinitiator, and the mixture for cross-linking is heated or exposed to light depending on the initiator used. The resulting materials due to the hydrolysable ester bond in the polymer backbone are biodegradable under physiological conditions. These cross-linked materials are particular useful as drug delivery vehicles, tissue engineering scaffolds, and in fabricating microdevices. The materials may also be used as plastics, coating, adhesives, inks, etc. The cross-linked materials prepared exhibit a wide range of degradation times, mass loss profiles, and mechanical properties. Therefore, the properties of the material may be tuned for the desired use. The high-throughput approach to preparing a library of cross-linked poly(beta-amino esters) allows for the rapid screening and design of degradable polymers for a variety of applications.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Use of cocoa solids having high cocoa polyphenol content in tabletting compositions and capsule filling compositions
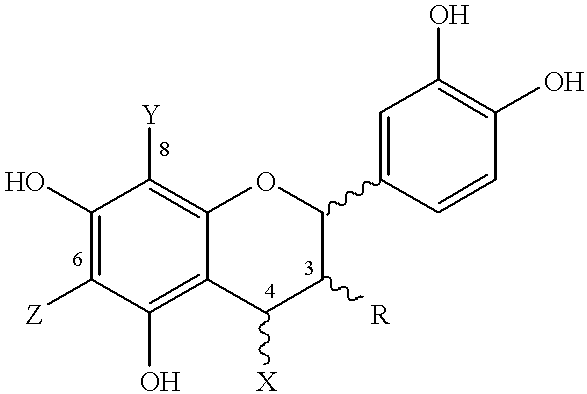
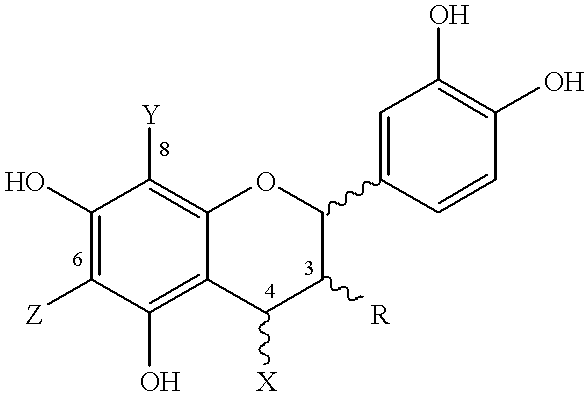
Disclosed and claimed are cocoa extracts, compounds, combinations thereof and compositions containing the same, such as polyphenols or procyanidins, methods for preparing such extracts, compounds and compositions, as well as uses for them, especially a polymeric compound of the formula An, wherein A is a monomer of the formula:wherein n is an integer from 2 to 18, such that there is at least one terminal monomeric unit A, and one or a plurality of additional monomeric units;R is 3-(alpha)-OH, 3-(beta)-OH, 3-(alpha)-O-sugar, or 3-(beta)-O-sugar;bonding between adjacent monomers takes place at positions 4, 6 or 8;a bond of an additional monomeric unit in position 4 has alpha or beta stereochemistry;X, Y and Z are selected from the group consisting of monomeric unit A, hydrogen, and a sugar, with the provisos that as to the at least one terminal monomeric unit, bonding of the additional monomeric unit thereto (the bonding of the additional monomeric unit adjacent to the terminal monomeric unit) is at position 4 and optionally Y=Z=hydrogen;the sugar is optionally substituted with a phenolic moiety, at any position on the sugar, for instance via an ester bond, andpharmaceutically acceptable salts or derivatives thereof (including oxidation products).
Owner:MARS INC
Method for producing fluorine-containing ploymer, aqueous dispersion of fluorine-containing polymer,2-acyloxycarboxylic acid derivative , and surface active agent
ActiveUS20060223924A1Low residual surfactant contentGood physical propertiesOrganic chemistrySynthetic resin layered productsAcid derivativeCarboxylic salt
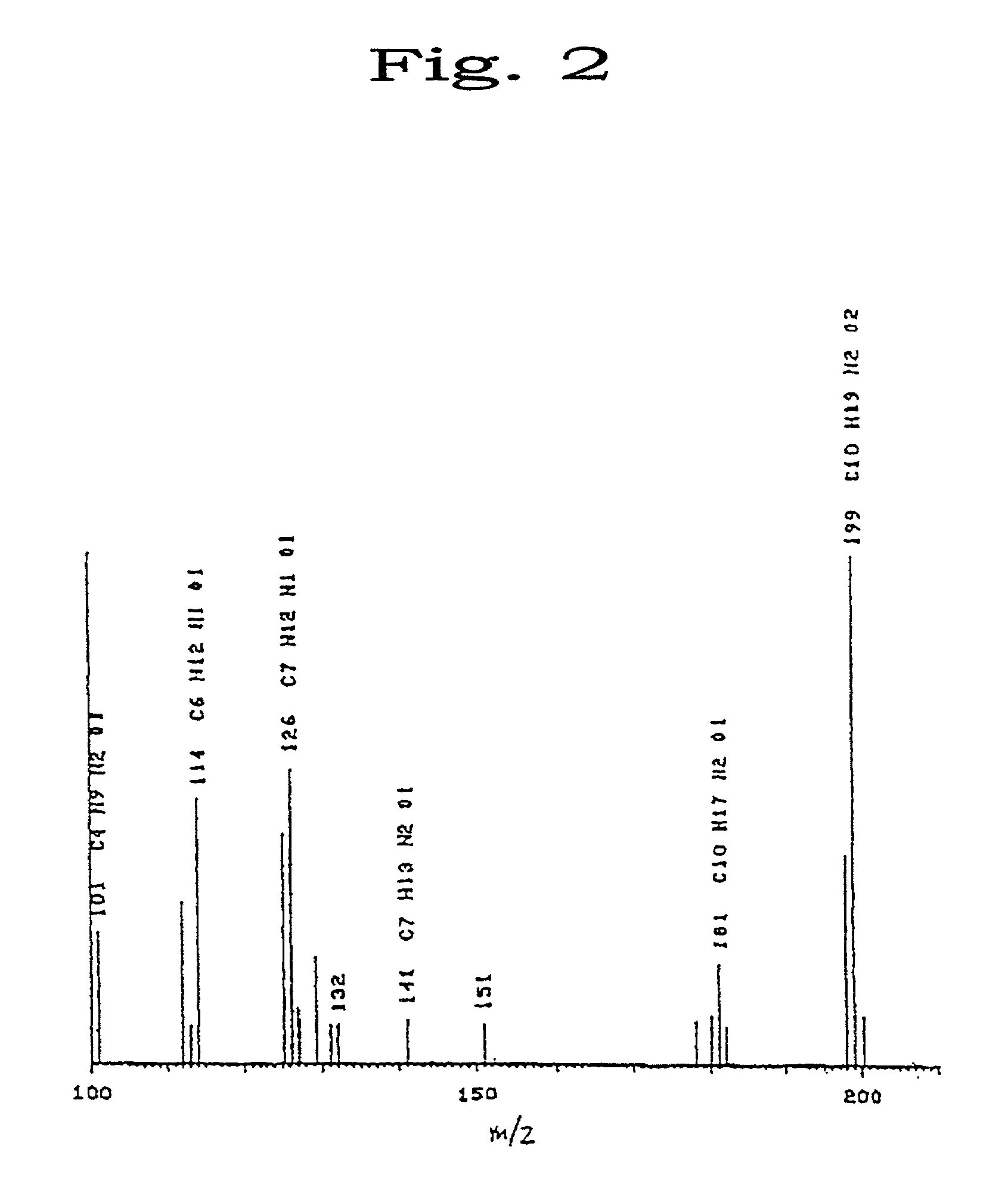
The present invention provides a method of producing a fluoropolymer, wherein polymerization using a carboxylate ester bond-containing carboxylic acid derivative as a surfactant in an aqueous medium to give the fluoropolymer is conducted, the above carboxylate ester bond-containing carboxylic acid derivative has a carboxylate ester bond and —COOM (M representing H, NH4, Li, Na or K), the above carboxylate ester bond may optionally be substituted by fluorine atom.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Biologically absorbable coatings for implantable devices based on copolymers having ester bonds and methods for fabricating the same
Coatings for an implantable medical device and a method of fabricating thereof are disclosed, and the coatings comprise biologically absorbable poly(ester amides).
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Dual phase drug release system
The present invention relates to conjugate comprising a carrier substituted with one or more occurrences of a moiety having the structure (I): wherein each occurrence of M is independently a modifier having a molecular weight ≦10 kDa; denotes direct of indirect attachment of M to linker LM; and each occurrence of LM is independently an optionally substituted succinamide-containing linker, whereby the modifier M is directly or indirectly attached to the succinamide linker through an amide bond, and the carrier is linked directly or indirectly to each occurrence of the succinamide linker through an ester bond. In another aspect, the invention provides compositions comprising the conjugates, methods for their preparation, and methods of use thereof in the treatment of various disorder, including, but not limited to cancer.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Degradable coronary stent and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102228721AImprove hydrogen evolution corrosion rateIncreased corrosion/degradation rateStentsSurgeryMedicineBiocompatibility
The invention provides a degradable coronary stent, which is characterized in that an iron-based material is taken as a matrix, and the surface of the matrix is covered with a degradable macromolecule coating; and components in the degradable macromolecule coating contain ester bonds (-COO-). The manufacturing method comprises the following concrete steps: a macromolecule material containing the ester bonds is dissolved in an organic solvent; and a dip-coating or spray-coating method is utilized to coat the mixture on the surface of an iron-based alloyed matrix, wherein the coating thickness is 1-40mu m. The degradable coronary stent is used for enhancing the degradation / corrosion speed of the iron-based coronary stent and improving the biocompatibility of the iron-based alloy, and is beneficial to rapid endothelialisation of endothelial cells on the surface of the stent. The method is simple and is convention to operate.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Crosslinked, degradable polymers and uses thereof
Acrylate-terminated poly(beta-amino esters) are cross-linked to form materials useful in the medical as well as non-medical field. The polymeric starting material is combined with a free radical initiator, either a thermal initiator or a photoinitiator, and the mixture for cross-linking is heated or exposed to light depending on the initiator used. The resulting materials due to the hydrolysable ester bond in the polymer backbone are biodegradable under physiological conditions. These cross-linked materials are particular useful as drug delivery vehicles, tissue engineering scaffolds, and in fabricating microdevices. The materials may also be used as plastics, coating, adhesives, inks, etc. The cross-linked materials prepared exhibit a wide range of degradation times, mass loss profiles, and mechanical properties. Therefore, the properties of the material may be tuned for the desired use. The high-throughput approach to preparing a library of cross-linked poly(beta-amino esters) allows for the rapid screening and design of degradable polymers for a variety of applications.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Temperature-responsive polymer compound and process for producing the same
InactiveUS6956077B1Improve hydrophobicityComponent separationOther chemical processesChemical compoundSide chain
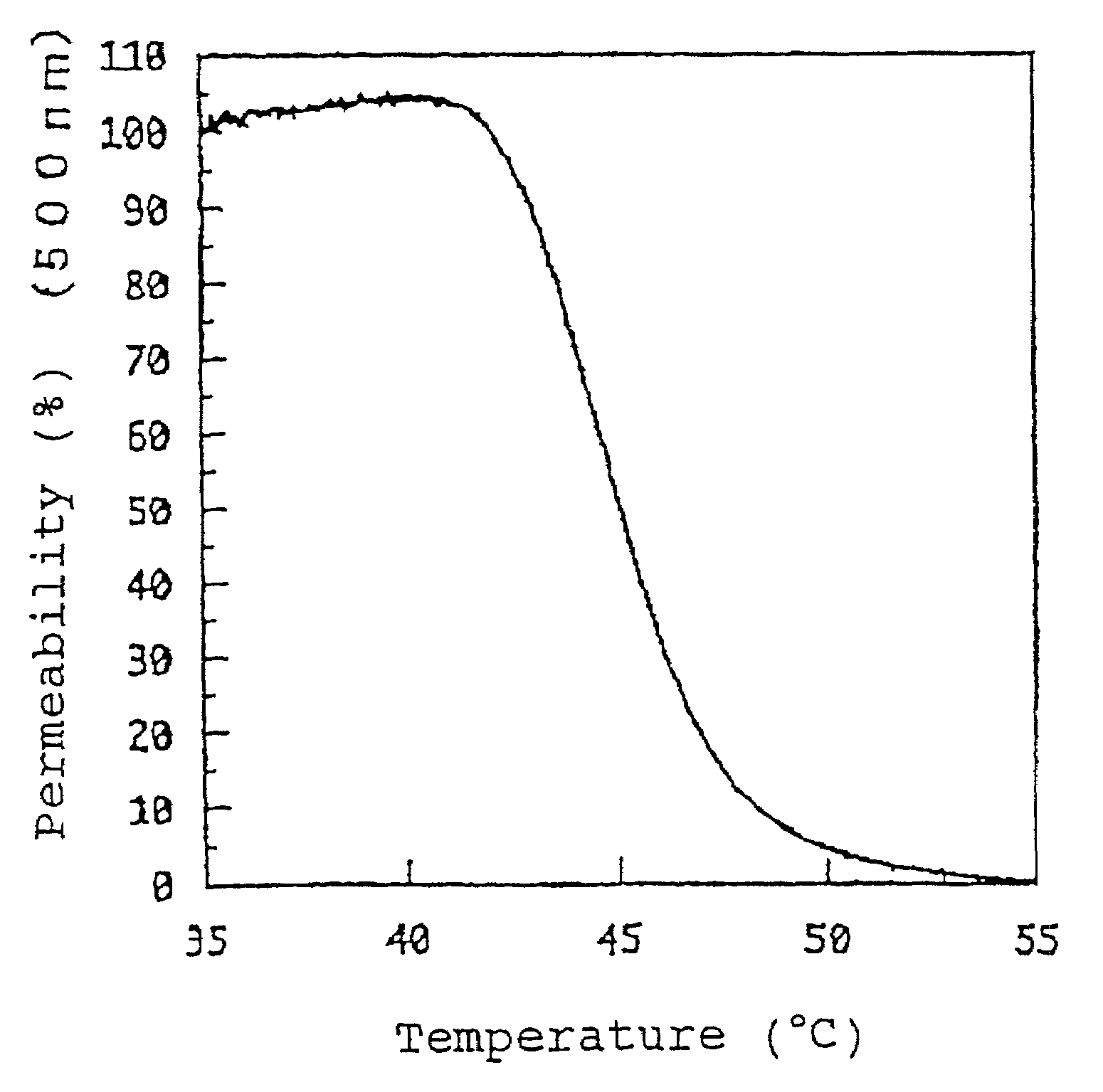
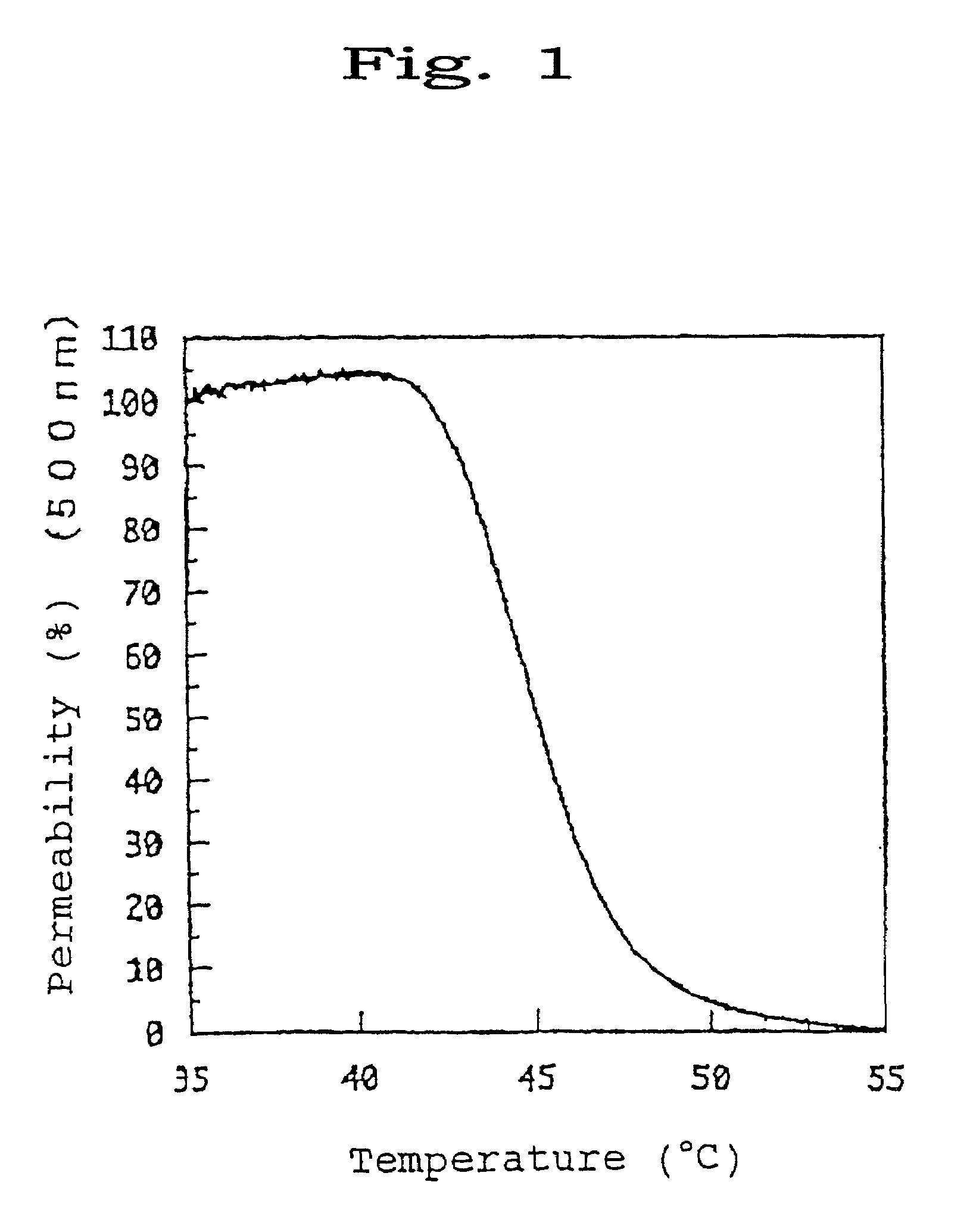
A temperature-responsive polymer and polymer material which has ester bond(s) and / or acid amide bond(s) respectively at one or more sites in the side chain and can be arbitrarily controlled by varying the side chain is provided.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Fluorine-containing polyurethane and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102115524AImprove waterproof performanceGood oil resistanceFibre treatmentPaper coatingPolymer scienceWater resistant
The invention discloses fluorine-containing polyurethane which is water-resistant, oil-resistant and conglutination-resistant and a preparation method thereof. The simple and effective method prepares the fluorine-containing polymer diol chain extender, so that the fluorine alkyl base chain is vertical to the main chain of polyurethane by ammonia ester bond, therefore, the three-protection capability and the hydrolysis resistance of the fluorine-containing polyurethane are reinforcing. The fluorine-containing polyurethane can be used as textile finishing agent, paper and leather finishing agent, self-cleaning coating additive, releasing agent and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI HEDA POLYMERIC TECH
Dynamic polymer having hybrid cross-linked network and application thereof
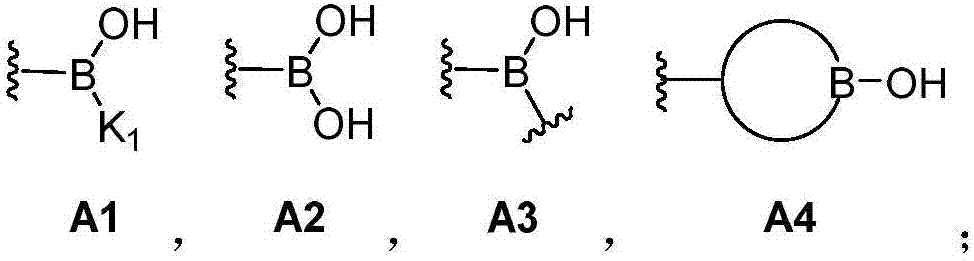
The invention discloses a dynamic polymer having a hybrid cross-linked network, and contains common covalent crosslinking and dynamic covalent crosslinking; and the dynamic covalent crosslinking is realized by organic boric acid silicon ester bonds. The dynamic polymer combines the advantages of dynamic covalent organic boric acid silicon ester bonds and a common covalent bond, and by regulation and control of a reactant structure, a dynamic polymer having abundant structure and various properties can be prepared. The dynamic covalent crosslinking in the dynamic polymer has strong dynamic reversibility, the polymer can present function characteristics of stimulation responsiveness and self-repair performance, and the common covalent crosslinking endows certain intensity and stability to the polymer; in addition, the dynamic nature of the organic organic boric acid silicon ester bonds can generate good energy dissipation and energy-absorbing effect, and is capable of toughening, dampingand resisting impact on a material in a specific structure. The dynamic polymer can be used for preparing a shock-absorption material, a shock-resistant protection material, a self-repair material, and a toughness material.
Owner:厦门天策材料科技有限公司
Polymeric coating for protecting objects
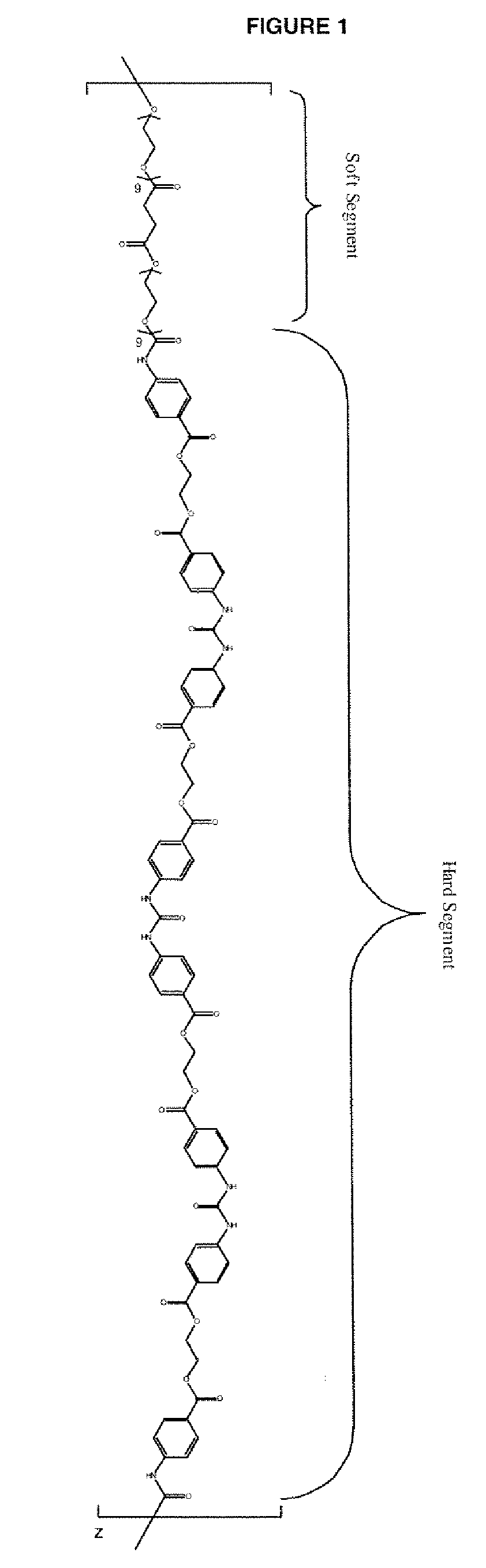
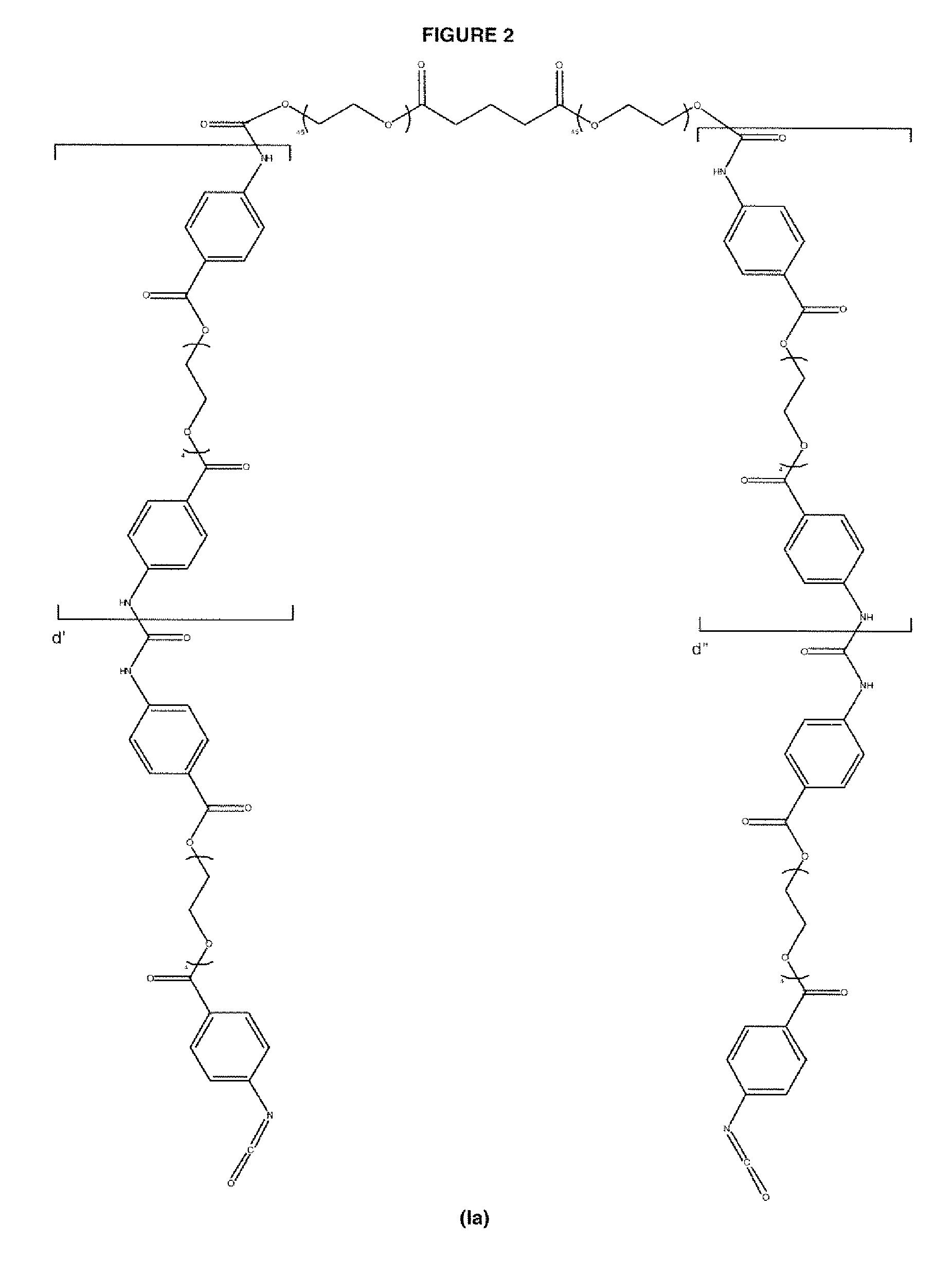
ActiveUS20100063244A1Provide protectionCosmonautic power supply systemsCosmonautic thermal protectionPhenyl groupPolyimide
A protective polymeric coating is applied to the surface of various objects which are to be exposed to a harsh environment. The protective polymeric coating covers the exposed surface, where the polymeric coating includes a polyimide polymer. The polyimide polymer in the polymeric coating has a backbone with at least one non-terminal phenyl group. A linkage is connected to the non-terminal phenyl group, where the linkage can be an amide linkage or an ester linkage. An oligomeric silsesquioxane compound is connected to the linkage through an organic substituent, where the oligomeric silsesquioxane is not incorporated into the polymer backbone. The polymeric coating provides protection to the underlying object.
Owner:NEXOLVE HLDG CO LLC
Backsheet for solar cell module and solar cell module
To provide a lightweight and highly productive backsheet for a solar cell module, wherein a cured coating film layer of a fluoropolymer coating material formed on one or each side of a substrate sheet is free from problems such as cracking, fracturing, whitening and separation.A back sheet for a solar cell, comprising a substrate sheet and a cured coating film layer of a coating material formed on one side or each side of the substrate sheet, said coating material comprising a fluoropolymer (A) having repeating units based on a fluoroolefin (a), repeating units based on a crosslinkable group-containing monomer (b) and repeating units based on an alkyl group-containing monomer (c) wherein a C2-20 linear or branched alkyl group having no quaternary carbon atom, and a polymerizable unsaturated group are linked to each other by an ether bond or ester bond; and a solar cell module using such a backsheet.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Ruthenium metathesis catalyst and method for producing olefin reaction product by metathesis reaction using the same
InactiveUS6175047B1Easy to prepareHigh catalytic activityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalystsCarbon–carbon bondReducing agent
The invention has an object of safely and simply preparing a large amount of a ruthenium metathesis catalyst, which is used as a catalyst for a carbon-carbon bond formation using, particularly, a metathesis reaction. The metathesis catalyst has the following complex composition (A) or (B). The composition (A) includes RuX12(arene)(PR1R2R3) and R4CHX22, R5C=CH or R4CHX2 and a reducing agent, wherein X1 and X2 respectively are a halogen atom; arene is a hydrocarbon having a benzene ring; R1, R2 and R3, which may be the same or different, respectively are an alkyl group having 1-8 carbon atoms, a cycloalkyl group having 3-8 carbon atoms or an optionally substituted aryl group, wherein the substituent group is an alkyl group having 1-8 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1-8 carbon atoms, an alkylamino group having 1-8 carbon atoms or a halogen atom; R4 is an alkyl group which has 1-8 carbon atoms and may have an ether bond or an ester bond, an optionally subsituted aryl group, wherein the substituent group is a halogen atom or a hydroxyl group; or cycloalkyl group having 3-8 carbon atoms; and R5 is an optionally substituted alkyl group which has 1-8 carbon atoms and may have an ether bond or an ester bond, wherein the substituent group is a halogen atom or a hydroxyl group, an aryl group or a cycloalkyl group having 3-8 carbon atoms. The composition B includes [RuX12(arene)]2, PR1R2R3, R5C=CH or R4CHX2 and a reducing agent, wherein X1, arene, R1, R2, R3, R4 and R5 are the same as defined above.
Owner:TAKASAGO INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Diisocyanate terminated macromer and formulation thereof for use as an internal adhesive or sealant
A novel macromer or mixture thereof is described herein, comprising benzoyl isocyanate terminal moieties and at least two residues of a water-soluble polymer having a molecular weight ranging from 80 to 10,000 adjacent to the carbonyl group of the benzoyl isocyanate moieties, thereby forming at least two ester linkages in the macromer or mixture thereof. A method for making a polyisocyanate macromer is also described herein.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Process for producing conductive polymer
A process for producing conductive polymers with excellent electrochemical strain per redox cycle is provided. A process for producing conductive polymers by an electrochemical polymerization method, wherein said conductive polymers have deformation property by electrochemical redox, said electrochemical polymerization method is a polymerization method using electrolyte including organic compounds as solvents, and wherein said organic compounds include (1) chemical bond species selected at least one from a group composed of the chemical bond consisting of ether bond, ester bond, carbon-halogen bond, and carbonate bond and / or (2) functional groups selected at least one from a group composed of functional groups consisting of hydroxyl group, nitro group, sulfone group, and nitryl group in a molecule, and said electrolyte includes anions which include trifluoromethanesulfonate ion and / or plural of fluorine atoms which bond to central atom is used.
Owner:EAMEX
Cationic lipid having improved intracellular kinetics
ActiveUS9708628B2Stable structureFacilitated releaseOrganic chemistryMicroencapsulation basedLipid formationCarbamate
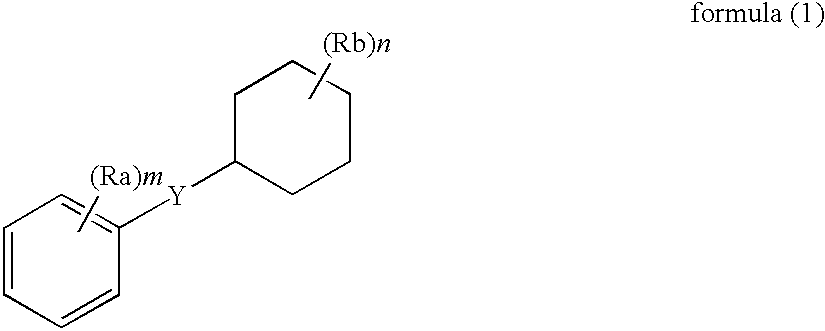
The present invention relates to a compound represented by the formula (1)wherein Xa and Xb are each independently X1 or X2;s is 1 or 2,R4 is an alkyl group having 1-6 carbon atoms,na and nb are each independently 0 or 1,R1a and R1b are each independently an alkylene group having 1-6 carbon atoms,R2a and R2b are each independently an alkylene group having 1-6 carbon atoms,Ya and Yb are each independently an ester bond, an amide bond, a carbamate bond, an ether bond or a urea bond, andR3a and R3b are each independently a sterol residue, a liposoluble vitamin residue or an aliphatic hydrocarbon group having 12-22 carbon atoms,and use thereof.
Owner:NOF CORP +1
Fatty-acid thermal storage devices, cycle, and chemicals
InactiveUS6574971B2Low costIncrease productionOther chemical processesLighting and heating apparatusChemical synthesisChemical reaction
Owner:RENEWABLE ALTERNATIVES LLC
Dynamic polymer with dynamic cross-linked structure
The invention discloses a dynamic polymer with a dynamic cross-linked structure. Organic boric acid silicon ester bonds are contained on polymer chain skeletons of a cross-linked network and / or on cross-linked link skeletons between polymer chains, wherein the organic boric acid silicon ester bonds are necessary for forming / maintaining a dynamic polymer structure. The dynamic polymer is rich in structure and diverse in properties. By regulating and controlling the structure of a reactant, the dynamic polymers with different properties can be prepared. In addition, due to strong dynamic reversibility of the organic boric acid silicon ester bonds in the polymer, the polymer can exhibit functional characteristics of stimulus responsiveness, self-healing property, recoverability and the like; and besides, due to the presence of the organic boric acid silicon ester bonds, the polymer can also have the energy absorbing effects, and polymer materials can be toughened in a given structure. The dynamic polymer can be used for making shock-absorption cushioning materials, impact-resistance protection materials, self-healing materials, ductile materials and the like.
Owner:厦门天策材料科技有限公司
Cellulose ester film, its manufacturing method, polarizing plate, and liquid crystal display
InactiveUS6844033B2Good moisture vapor transmittanceGood dimensional stabilityLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic non-macromolecular adhesiveCelluloseLiquid-crystal display
A cellulose ester film and its manufacturing method are disclosed, the cellulose ester film comprising a compound represented by the following formula (1) in an amount of from 1 to 30% by weight, wherein Y represents an ester bond or a divalent organic group containing an ester bond, RTA and Rd independently represent a substituent, and m and n independently represent an integer of 0 to 5, provided that when m or n is not less than 2, plural Ras or Rbs may be the same or different.
Owner:KONICA CORP
Surface-modified titanium dioxide fine particles and dispersion comprising the same, and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20060264520A1Good dispersionGood dispersibilityAntibacterial agentsHeavy metal active ingredientsWater solubleMicroparticle
Surface-modified titanium dioxide particles which have a surface chemically modified with a hydrophilic polymer, wherein a carboxyl group of the hydrophilic polymer and titanium dioxide are bound through an ester bonding; and a method for producing the surface-modified titanium dioxide fine particles, which comprises mixing a dispersion comprising titanium dioxide fine particles having a particle size of 2 to 200 nm and a solution of a water-soluble polymer, heating the resultant mixture to a temperature of 80 to 220° C., to thereby bind both the components through an ester bonding, and removing an unbound water-soluble polymer, to purify the resuultant particles. The surface-modified titanium dioxide fine particles exhibit excellent dispersibility and stability in an aqueous solvent over a wide pH region including a neutral range.
Owner:STARBOARD TECH +1
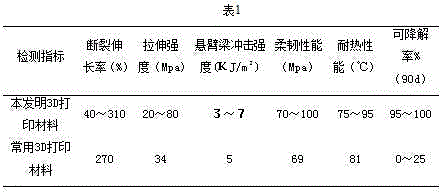
Bio-based 3D printing material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104448738AIncrease added valueLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationPolymer scienceCross linker
The invention relates to a bio-based 3D printing material and a preparation method thereof, and aims to solve the problems that a conventional 3D printing material of polylactic acid is relatively small in crystallization degree, small in bond energy of ester bonds in molecule chains and has high probability of cracking. The bio-based 3D printing material is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 20-40% of polyactic acid, 35-60% of thermoplastic starch, 3-10% of a toughening agent, 5-10% of a cross-linking agent, 5-13.4% of a filling agent, 0.5-2% of a thermal stabilizing agent, 1-3% of a lubricating agent and 0.1-5% of a preservative. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing polyactic acid with the thermoplastic starch, the toughening agent, the cross-linking agent, the filling agent, the thermal stabilizing agent, the lubricating agent and the preservative, pelleting and performing injection molding to obtain a modified polylactic acid. Due to adoption of the polyactic acid and the thermoplastic starch, the bio-based 3D printing material is good in compatibility, the elongation at break, the strength, the flexibility and the thermal resistance of the modified polyactic acid are all improved, and the additional value of a starch material is also increased.
Owner:甘肃圣大方舟马铃薯变性淀粉有限公司
Polymeric coating for the protection of objects
ActiveUS20120052293A1Provide protectionCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic radiation protectionPhenyl groupPolyimide
A protective polymeric coating is applied to the surface of various objects which are to be exposed to a harsh environment. The protective polymeric coating covers the exposed surface, where the polymeric coating includes a polyimide polymer. The polyimide polymer in the polymeric coating has a backbone with at least one non-terminal phenyl group. A linkage is connected to the non-terminal phenyl group, where the linkage can be an amide linkage or an ester linkage. An oligomeric silsesquioxane compound is connected to the linkage through an organic substituent, where the oligomeric silsesquioxane is not incorporated into the polymer backbone. The polymeric coating provides protection to the underlying object.
Owner:NEXOLVE HLDG CO LLC
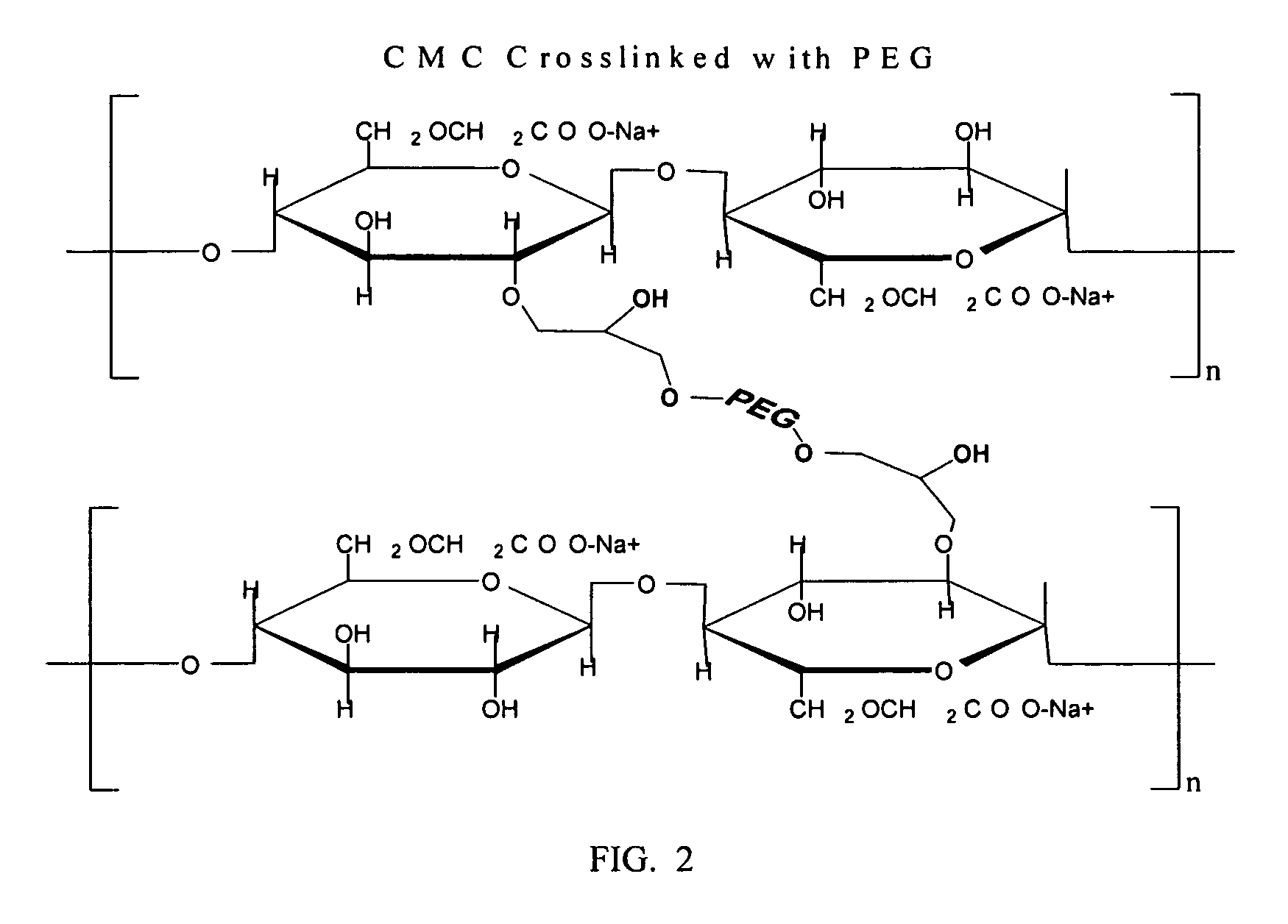
Carboxymethylcellulose polyethylene glycol compositions for medical uses
ActiveUS20080103228A1High inherent elasticityGood biocompatibilityCosmetic preparationsImpression capsCross-linkPolyethylene glycol
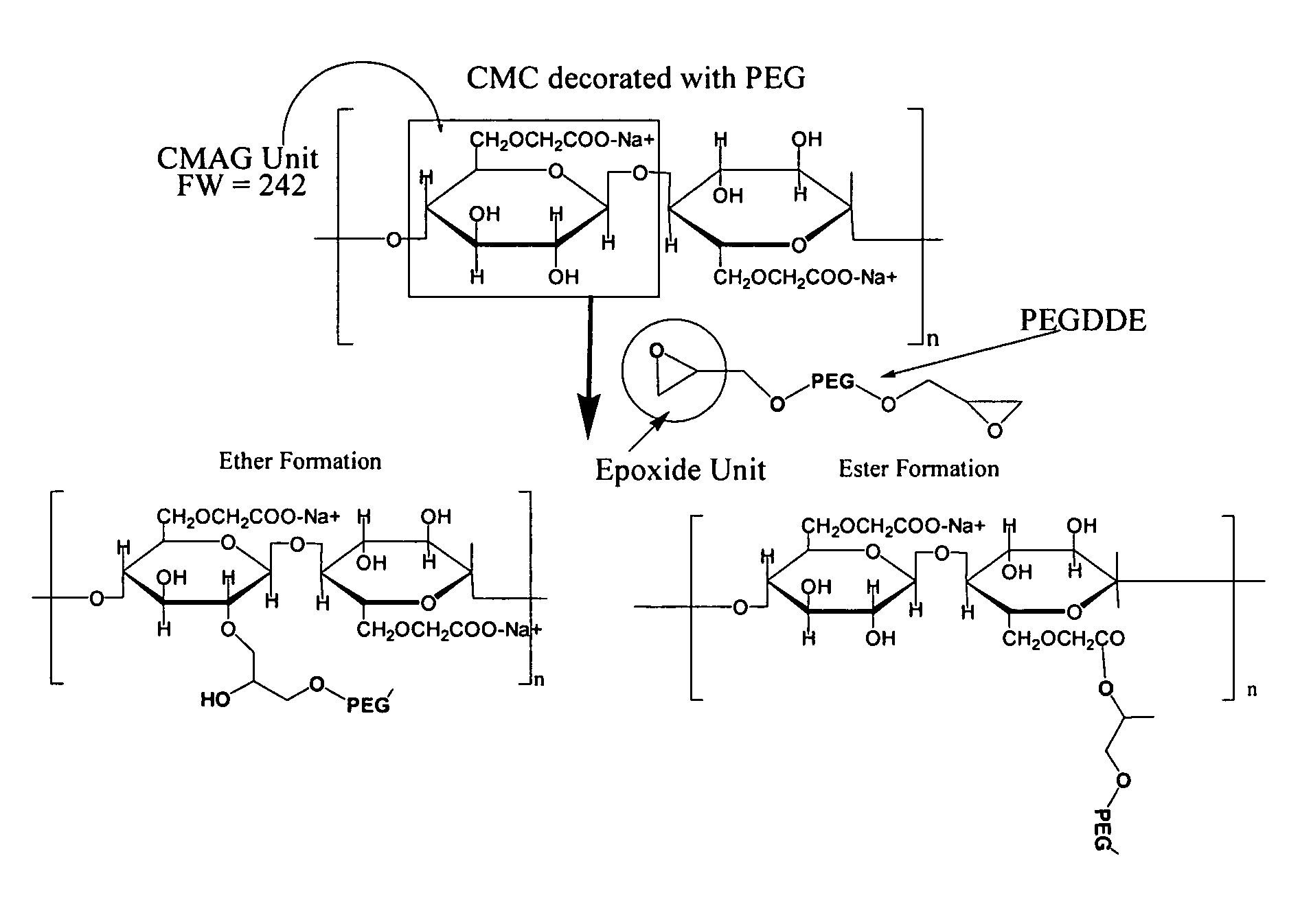
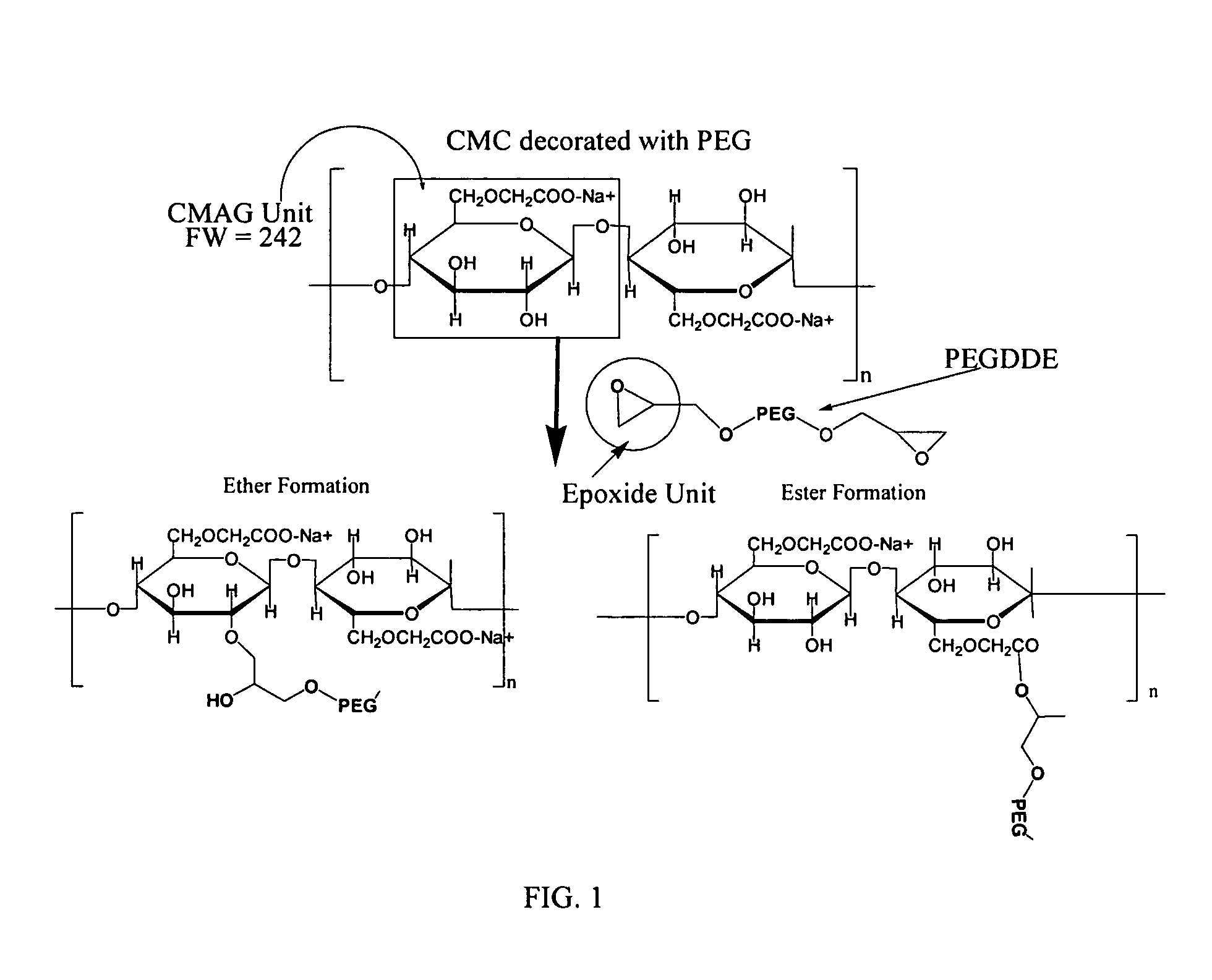
Compositions comprising carboxypolysaccharides (CPS) including carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and polyethylene glycols (PEGs) are provided where the PEG is a PEG-epoxide covalently linked to the CPS via an addition reaction. In certain embodiments, the PEG attaches to only one CPS, forming a decorated CPS. In other embodiments, bi-functional PEG molecules are attached to adjacent CPSs, thereby forming a covalently cross-linked composition. In certain of these embodiments, a PEG is linked to the CPS by way of an ether linkage, and in other embodiments, a PEG is linked to the CPS by way of an ester linkage, and in still further embodiments, PEG molecule(s) can be attached to CPS molecule(s) by way of both ether and ester linkages. Additional embodiments include PEG / CMC compositions where the PEG is a multi-branch PEG and / or a multi-arm PEG. PEG / CMC compositions can be made with desired viscoelastic properties, and such compositions can be used as space-filling materials, load-bearing materials, anti-adhesion compositions, for drug delivery vehicles or for lubrication of tissues and medical instruments.
Owner:FZIOMED
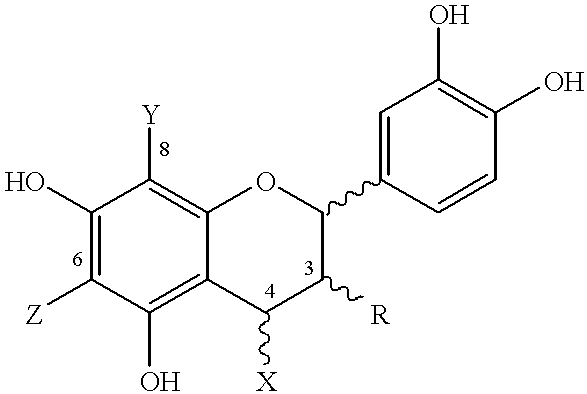
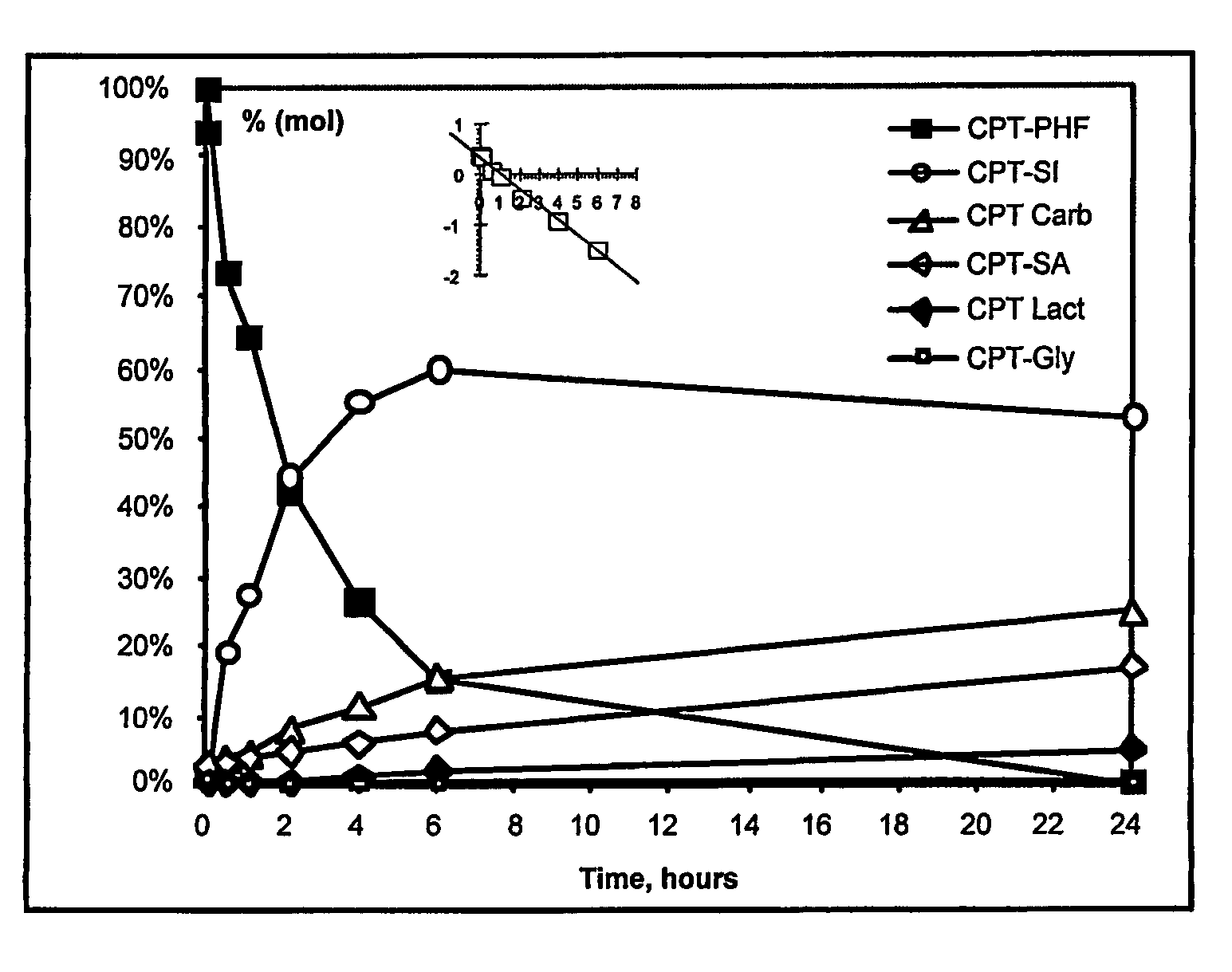
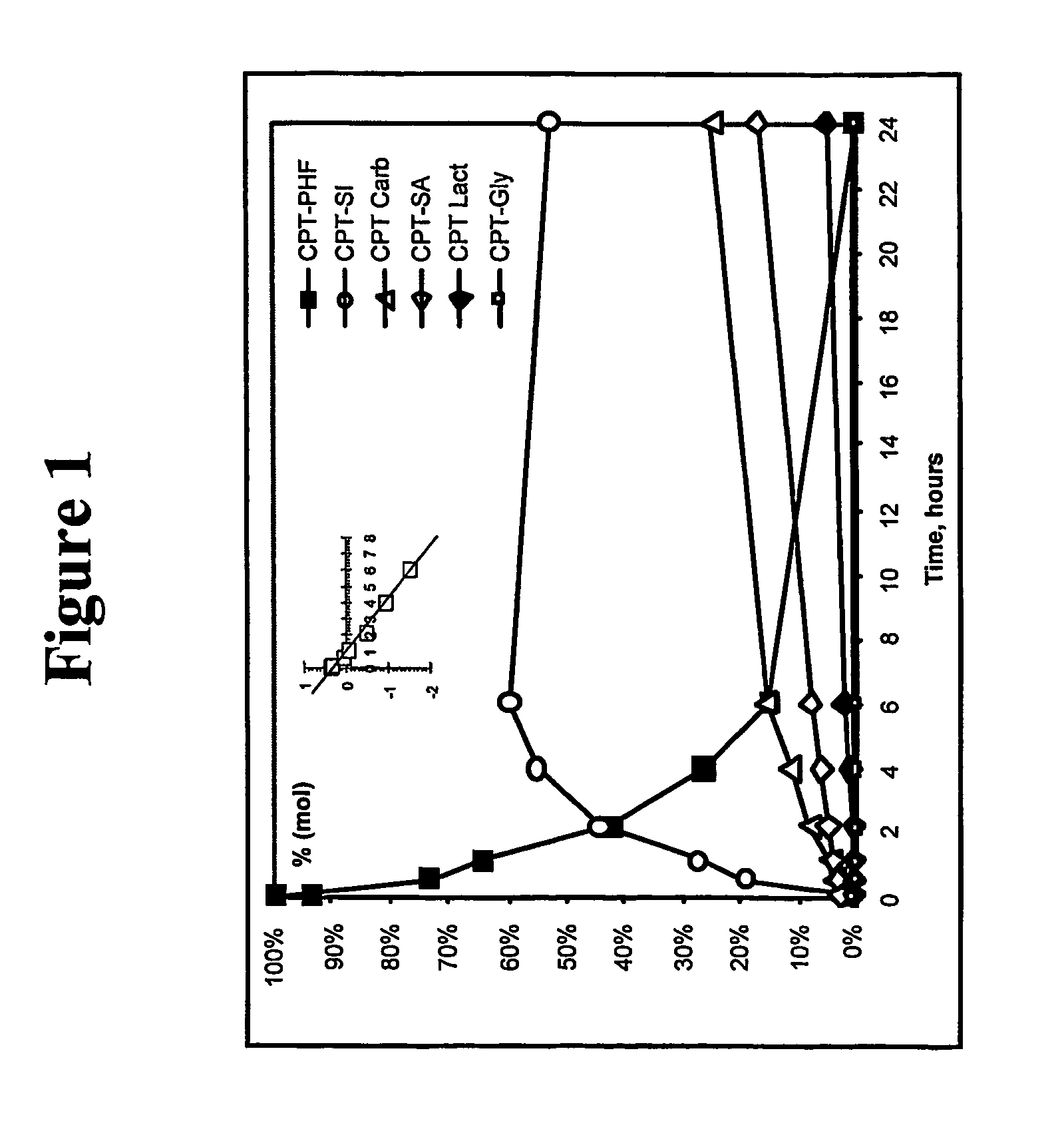
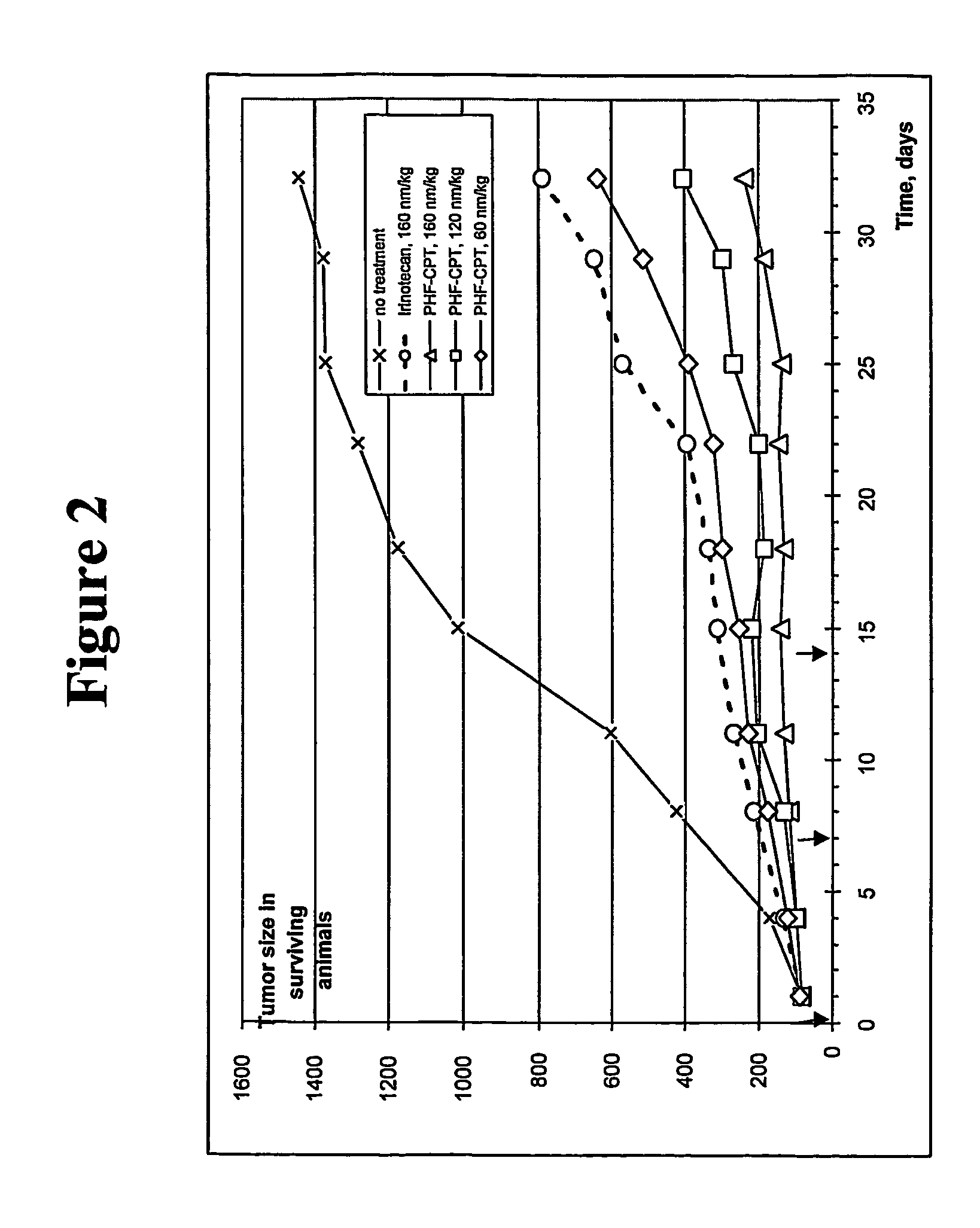
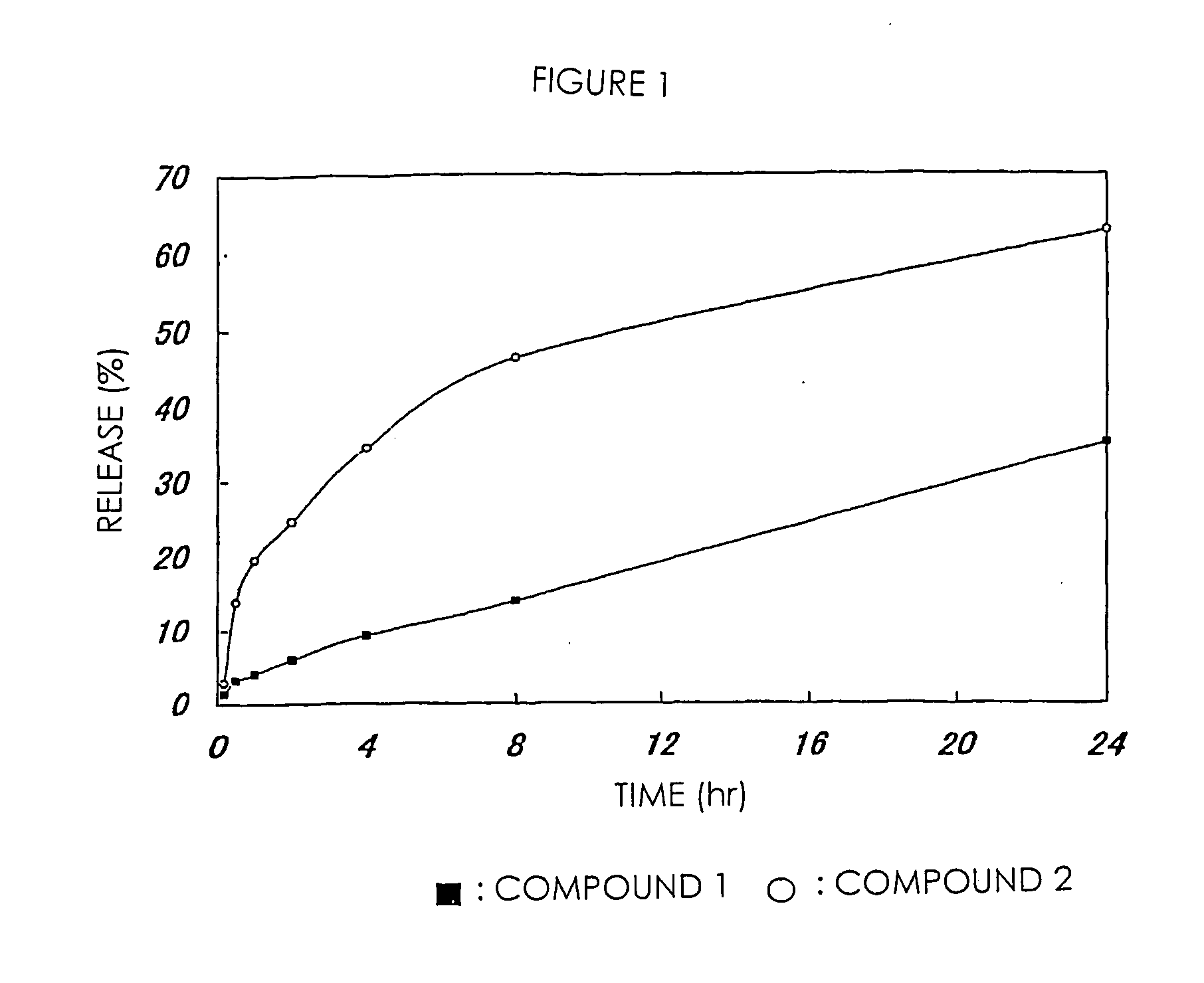
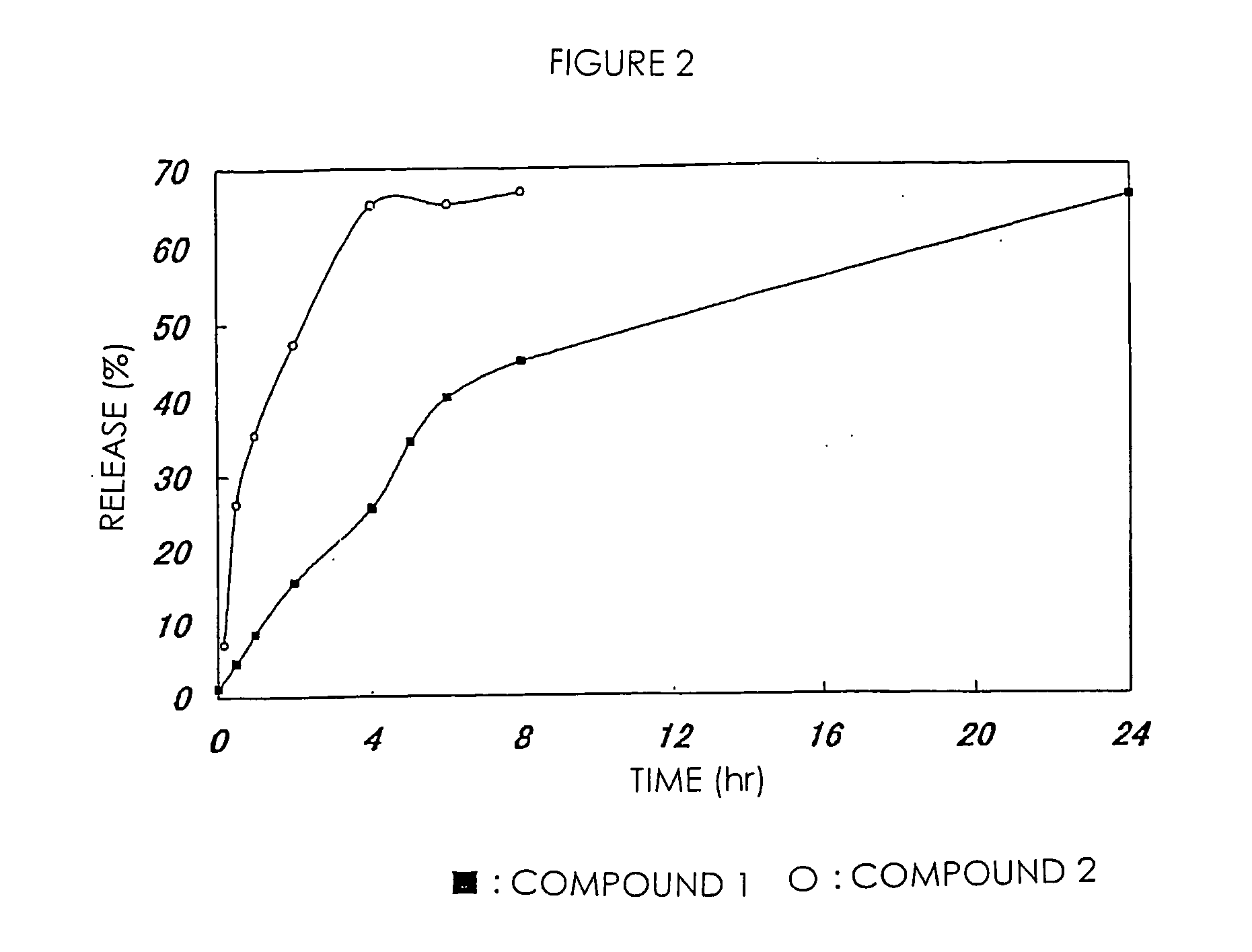
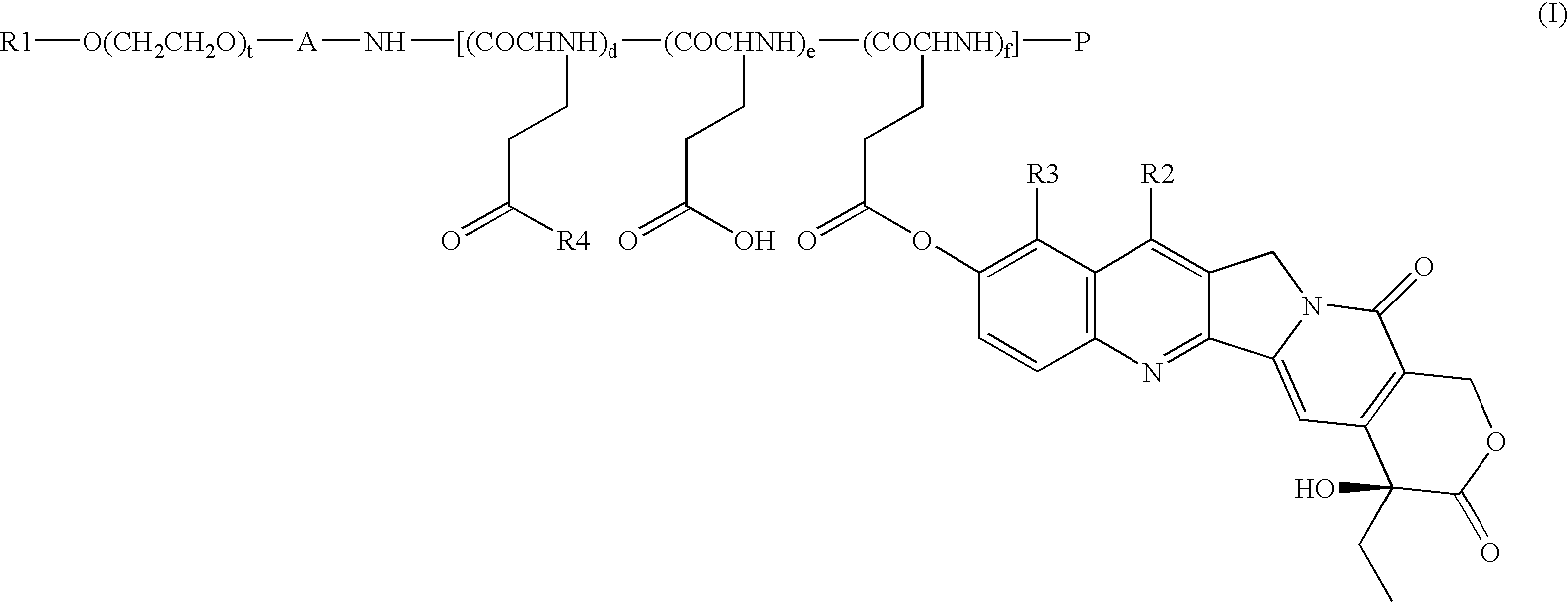
High-molecular weight derivatives of camptothecins
ActiveUS20060067910A1Sustained releaseGood treatment effectOrganic active ingredientsSilicon organic compoundsPolyethylene glycolWater soluble
It is intended to provide water-soluble derivative of camptothecins which are excellent in therapeutic effect and suitable for chemotherapy for cancer. Namely, a water-soluble high-molecular weight derivative of camptothencins being excellent in sustained-release which is obtained by ester-bonding a carboxylic acid group of a polyethylene glycol-polycarboxylic acid polymer to a phenolic hydroxyl group of phenolic camptothencins.
Owner:NIPPON KAYAKU CO LTD
Dynamic polymer having non-covalent crosslinking structure and application thereof
ActiveCN107805309AFast self-healingAchieve synthesisPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesFibre treatmentBoric acidBiomimetic materials
The invention discloses a dynamic polymer having a non-covalent crosslinking structure. The dynamic polymer contains organic boric acid silicon ester bonds on polymer chain backbone; wherein the organic boric acid silicon ester bonds are existed as polymeric chain contacts of the dynamic polymer, and are the necessary condition for forming or maintaining a dynamic polymer structure. The dynamic polymer has energy dissipation performance by means of the organic boric acid silicon ester bonds having strong dynamic reversibility, embodies functional characteristics of stimulation responsiveness and self-repairability, and has a wide application prospect in the fields of sport protection, a functional coating, and a bionic material.
Owner:厦门天策材料科技有限公司
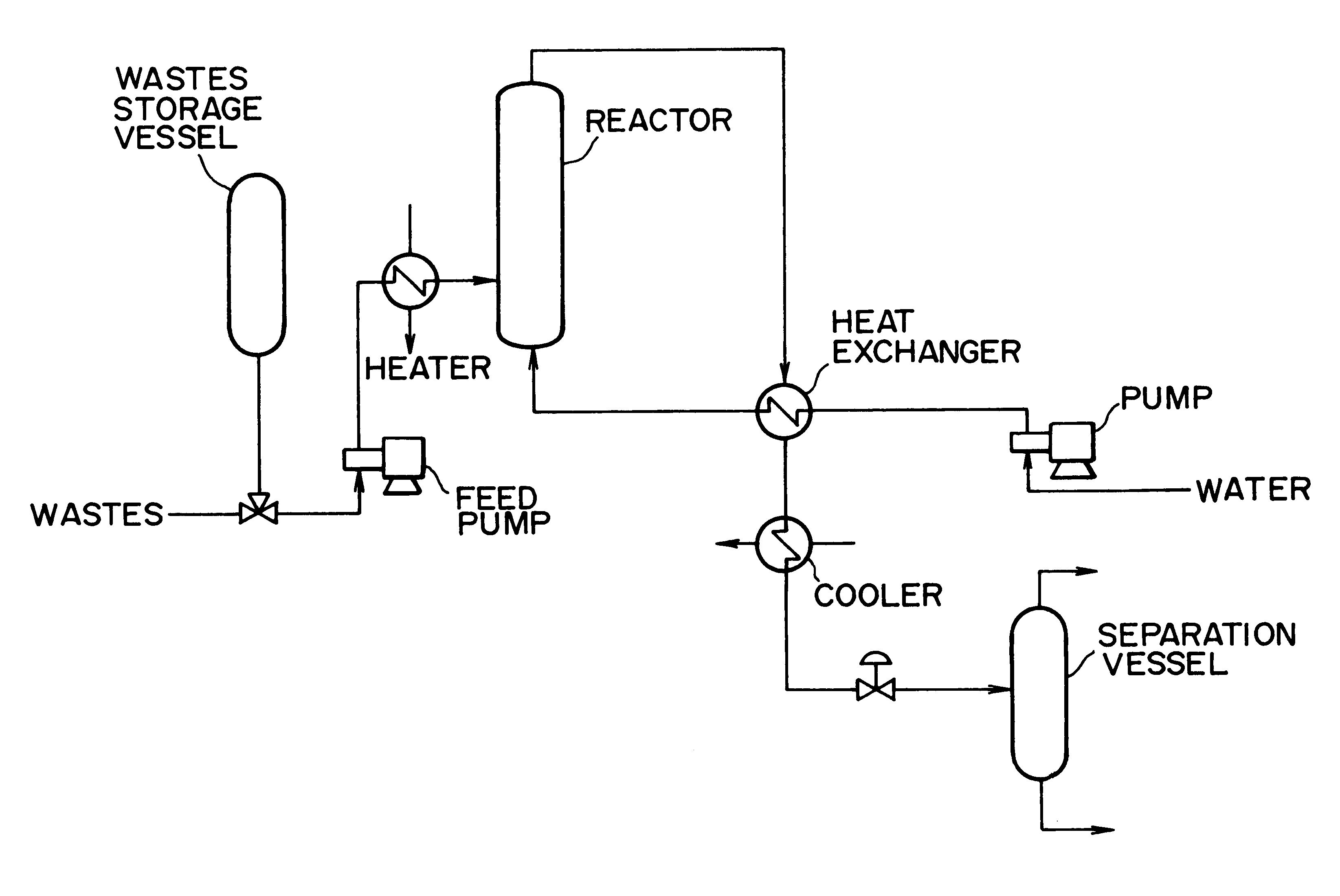
Method of and apparatus for decomposing wastes
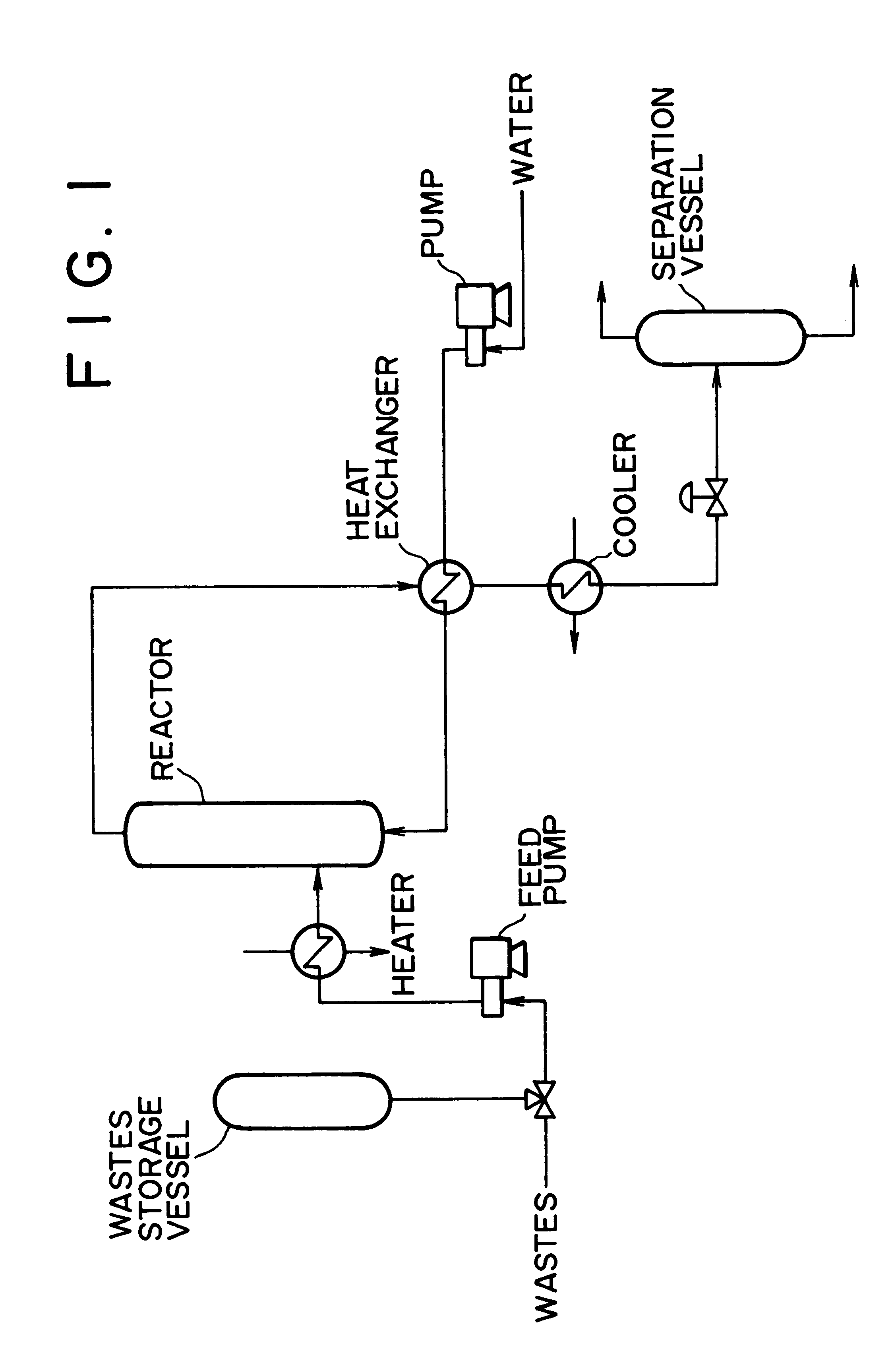
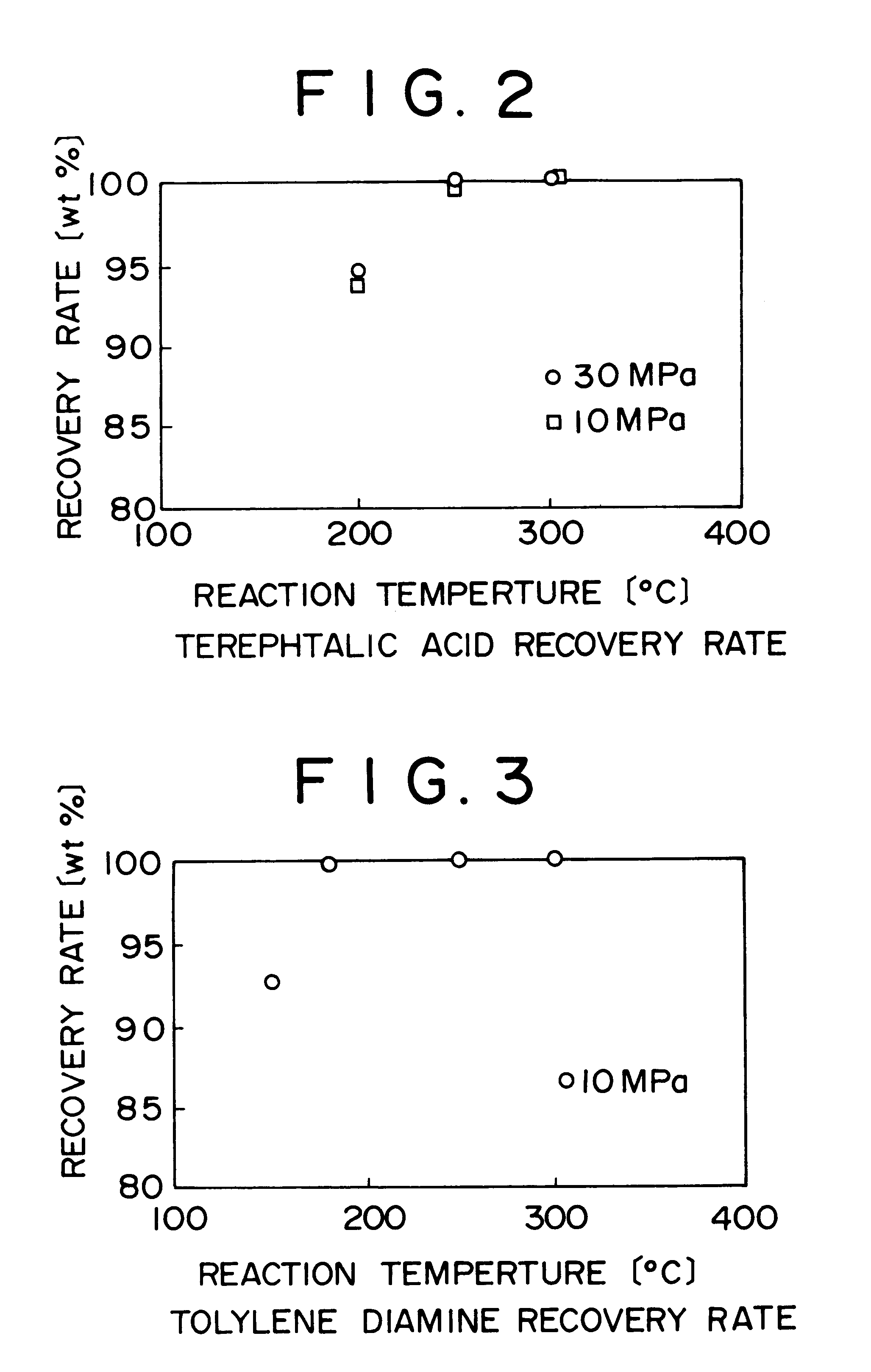
InactiveUS6255529B1Useful operationResultant decomposition products can be utilized effectivelySolid waste disposalIndirect heat exchangersMolten stateLiquid state
A method of decomposing wastes containing target compounds having one or more of hydrolyzable bonds of ether bond, ester bond, amide bond and isocyanate bond wherein the method comprises continuously supplying the wastes in a molten state or liquid state to a reactor, continuously supplying super-critical water or high pressure / high temperature water to the reactor, bringing the water into contact with the wastes, thereby decomposing the target compounds and then recovering them as raw material compounds or derivatives thereof for the target compounds. Target compounds contained in wastes in chemical plants which could not be utilized but merely incinerated or discarded so far are continuously decomposed into raw material compounds or derivatives thereof for the aimed compound and can be reutilized effectively.
Owner:TAKEDA CHEM IND LTD 50
Toner, method of supplying the same and process cartridge
InactiveUS20080102393A1Good low temperature fixabilityGood preservabilityDevelopersElectrographic process apparatusPolyester resinEster bond
A toner including a colorant, a binder resin, and a releasing agent, wherein the toner has a number average particle diameter measured by a Coulter Counter method of from 3.5 to 6.5 μm and a peak top molecular weight (MPT) of from 2,500 to 4,800, the binder resin contains a crystalline polyester resin and a hybrid resin component containing a styrene-acryl resin and a polyester resin, a content A of the crystalline polyester resin and a content B of the hybrid resin component satisfy the following relationship (1): ½ A≦B≦3 A, and the crystalline polyester resin has a structure represented by a following chemical formula (A) having at least 60 mol % of whole ester bonds in the binder resin: —OOC—R—COO—(CH2)n—, (A); a method for supplying the toner and a process cartridge useful in the method.
Owner:RICOH KK
Polymer conjugate of taxane
ActiveUS20100234537A1Significant effectPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSolubilityPolymer science
[Problems] To provide a novel taxane derivative which can release the medicinal substance in a bioenzyme-independent manner, is expected to have an effective therapeutic efficacy, and has a water-solubility.[Means for Solving Problems] Disclosed is a polymer conjugate of a taxane, which comprises a polymer having a polyethylene glycol moiety and two or more succinic acid monoamide moieties and a taxane, wherein a carboxylate group in the polymer and an alcoholic hydroxyl group in the taxane are bound to each other via an ester bonding.
Owner:NIPPON KAYAKU CO LTD
Antistatic agent, antistatic agent composition, antistatic resin composition, and molded body
ActiveUS20150353796A1Improve antistatic performanceSufficient persistenceOther chemical processesConductive materialEpoxyPolyester
Provided are: an antistatic agent which is capable of imparting excellent antistatic effect in a small amount and has sufficient persistence and wiping resistance; an antistatic agent composition; an antistatic resin composition; and a molded article. The antistatic agent comprises a polymer compound (E) having a structure in which a block polymer (C) and an epoxy compound (D) are bound via an ester bond formed by a carboxyl group of the block polymer (C) and an epoxy group of the epoxy compound (D), the block polymer (C) having a structure comprising carboxyl groups at both ends, in which structure a block constituted by a polyester (A) having carboxyl groups at both ends and a block constituted by a compound (B) having hydroxyl groups at both ends are repeatedly and alternately bound via ester bonds formed by the carboxyl groups and the hydroxyl groups, and the epoxy compound (D) comprising two or more epoxy groups.
Owner:ADEKA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com