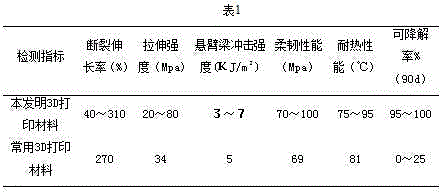
Bio-based 3D printing material and preparation method thereof
A 3D printing, bio-based technology, applied in the field of biodegradable polymer materials, can solve the problems of low ester bond energy, easy to break, low polylactic acid crystallinity, etc., to increase added value, flexibility and heat resistance , Improve the effect of low heat distortion temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] A bio-based 3D printing material and a preparation method thereof, comprising preparation of lactic acid, synthesis of polylactic acid, modification of polylactic acid, the specific steps are as follows:
[0042] (1) Preparation of lactic acid
[0043] Preparation of lactic acid by fermentation method: saccharification of corn by amylase, followed by microbial fermentation and conversion, to generate lactic acid; in this example, Bacillus was used as the starting strain, and lactic acid was prepared with abundant and cheap potato starch as the carbon source.
[0044] a. Strain preparation
[0045] Introduce Bacillus licheniformis (Baclicus lincheniformis) into the medium, keep the temperature in the incubator at 45°C, and ferment for 4 hours, then add calcium carbonate neutralizer to keep the pH of the culture solution at 7, and ferment for 15 hours.
[0046] The components of the culture medium are: hydrolyzed sugar 5%, bran 1%, neutralizer (calcium carbonate) 10g / L, ...
Embodiment 2
[0066] A bio-based 3D printing material and a preparation method thereof, comprising preparation of lactic acid, synthesis of polylactic acid, modification of polylactic acid, the specific steps are as follows:
[0067] (1) Preparation of lactic acid
[0068] Preparation of lactic acid by fermentation: use glucoamylase to saccharify wheat, and then carry out microbial fermentation transformation to generate lactic acid. In this example, Bacillus was used as the starting strain, and the abundant and cheap potato starch was used as the carbon source to prepare lactic acid.
[0069] a. Strain preparation
[0070] Insert Bacillus coagulans into the medium, keep the temperature in the incubator at 55°C, and after 6 hours of fermentation, add calcium carbonate neutralizer to keep the pH of the culture solution at 7.8, and ferment for 25 hours.
[0071] The above-mentioned culture medium components are: hydrolyzed sugar 25%, barley root 5%, neutralizer (calcium carbonate) 30g / L, am...
Embodiment 3
[0091] A bio-based 3D printing material and a preparation method thereof, comprising preparation of lactic acid, synthesis of polylactic acid, modification of polylactic acid, the specific steps are as follows:
[0092] (1) Preparation of lactic acid
[0093] Preparation of lactic acid by fermentation: use amylase to saccharify corn, and then carry out microbial fermentation transformation to generate lactic acid. In this example, the bacillus
[0094] Bacteria was used as the starting strain, and the abundant and cheap potato starch was used as the carbon source for the preparation of lactic acid.
[0095] a. Strain preparation
[0096] Insert Bacillus stearothermophilus into the culture medium, keep the temperature in the incubator at 50°C, and after 6 hours of fermentation, add calcium carbonate neutralizer to keep the pH of the culture medium at 7.4, and ferment for 20 hours.
[0097] The above-mentioned culture medium components are: hydrolyzed sugar 15%, bran 3%, neut...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com