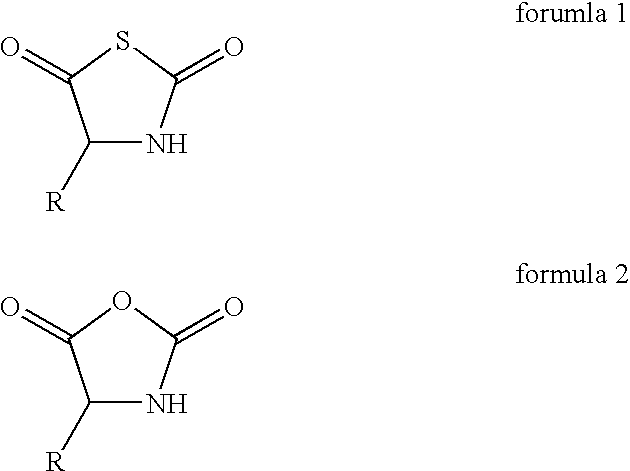
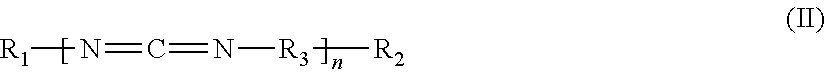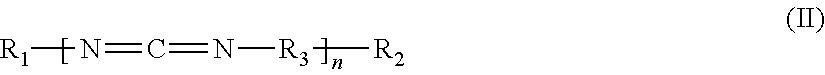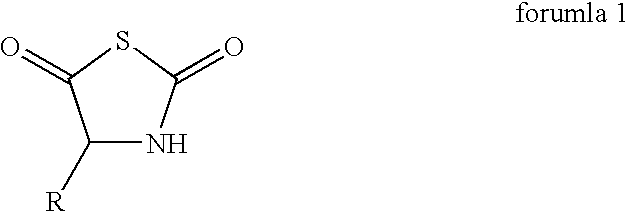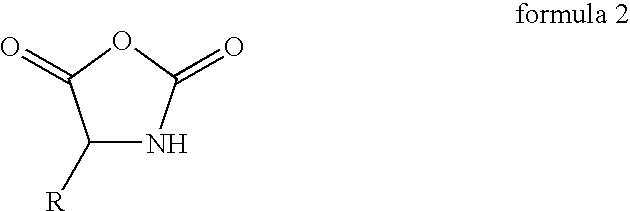Patents
Literature
108results about How to "Cost-effective process" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
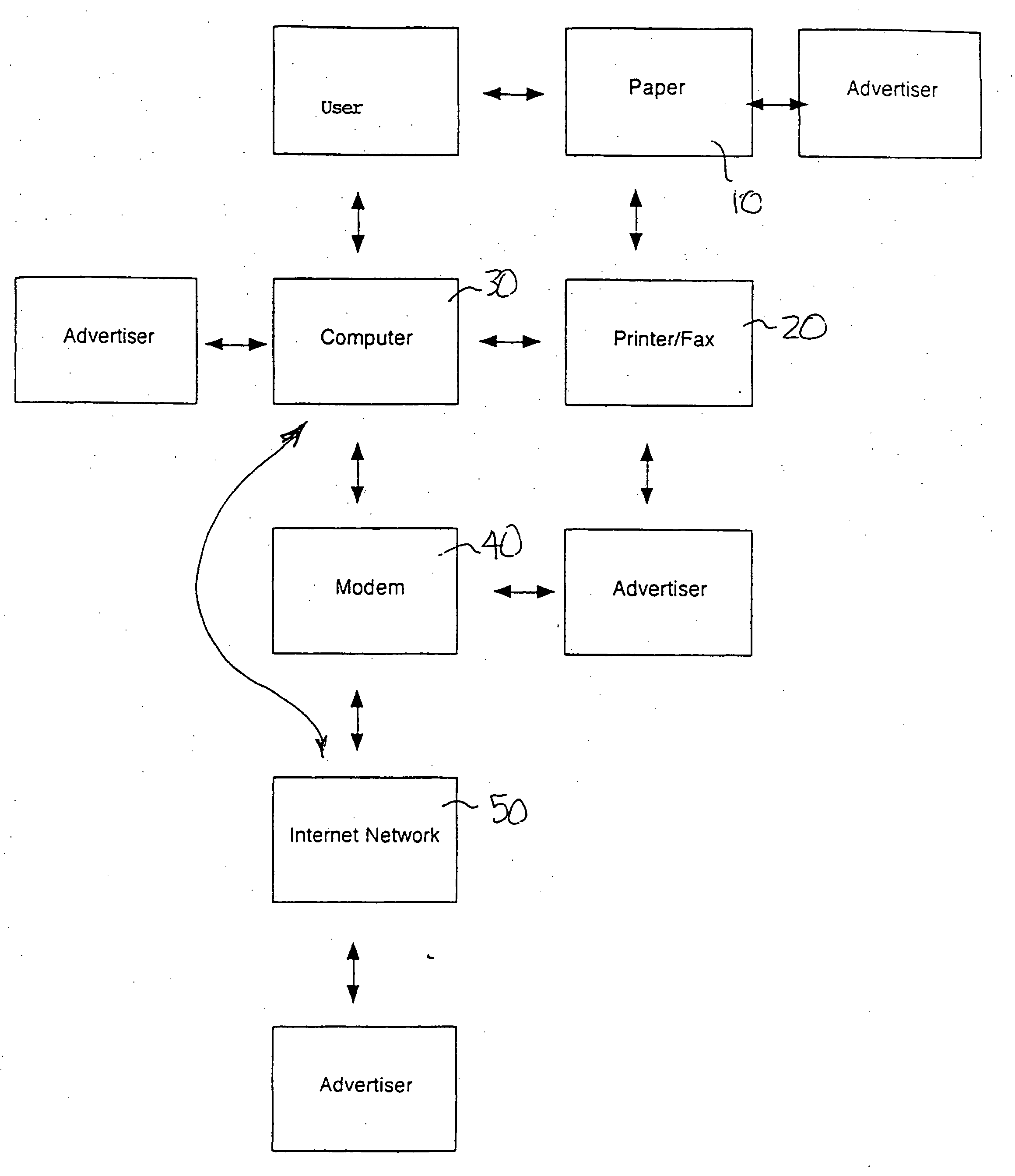
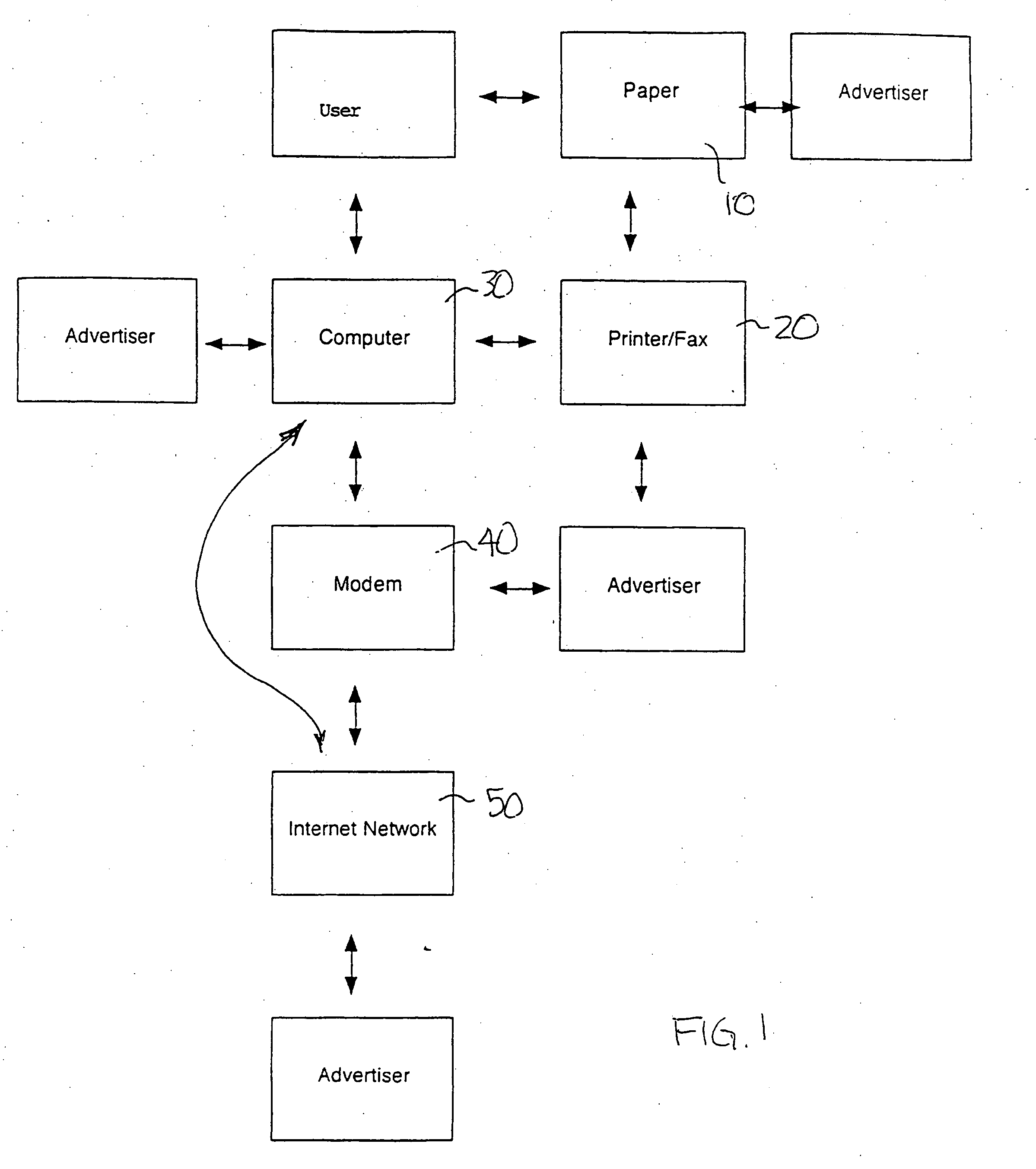
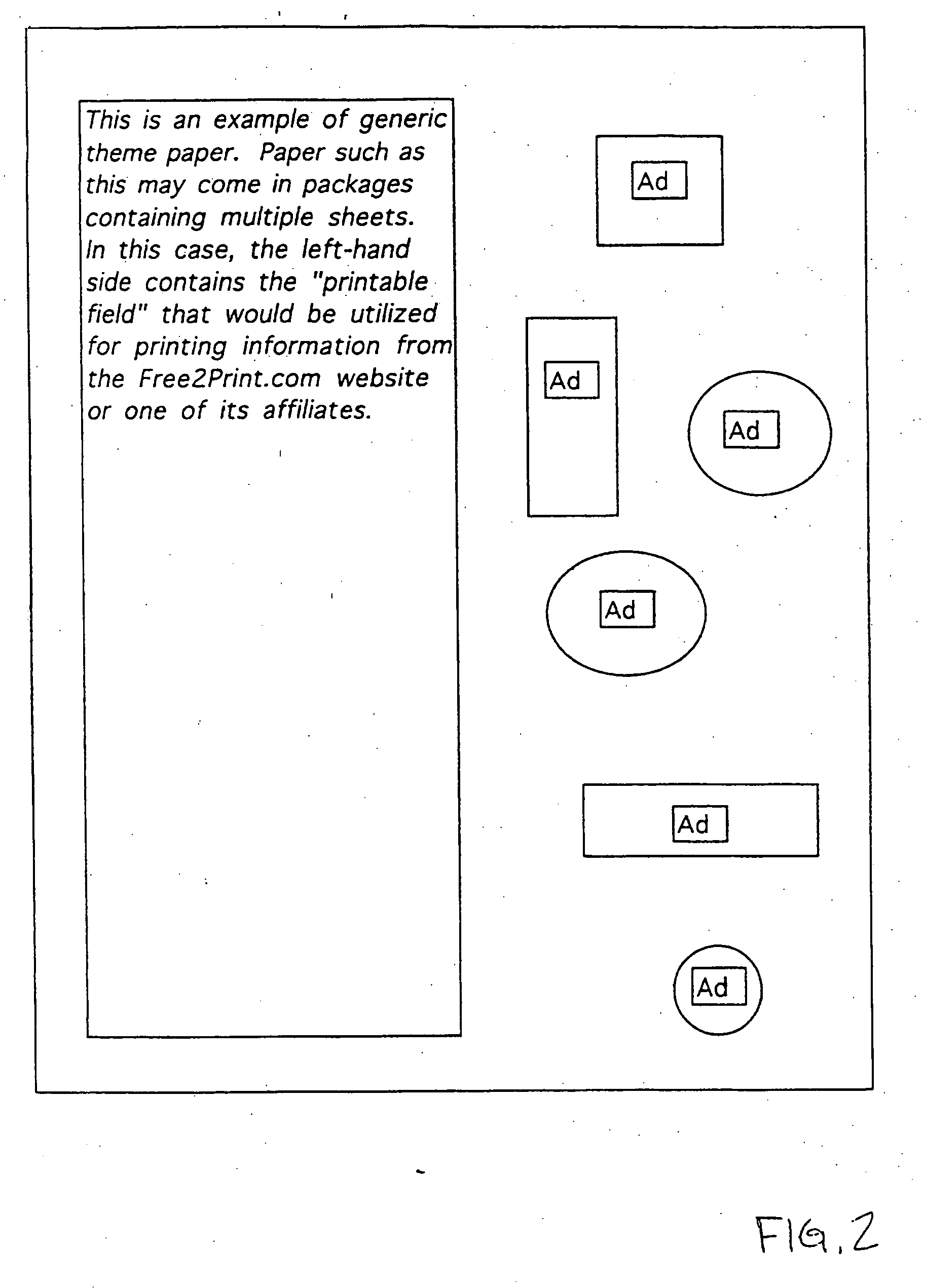
Method of distributing printed advertising
InactiveUS20060229940A1Cost-effectiveCost-effective processLogisticsMarketingWeb siteComputer printing
A method and system for distributing printed advertising. Printed advertising may be pre-printed on printable paper sheets and leaving a printable field free of printed advertising on each of the plurality of sheets. The partially-printed paper is distributed to a plurality of users. Users access a website to confirm acquisition of the partially-printed paper. The website records usage of the partially-printed paper and increases a credit account associated with the user based on usage of the partially-printed paper. In an alternate method, the printed advertisement is formatted for marginal printing on printable paper sheets by a user's printer when a registered user downloads printed information via the Internet. A website records printing of the advertising information formatted for marginal printing and increases a credit account associated with the user based on printing of the advertising information formatted for marginal printing.
Owner:GROSSMAN JAMES
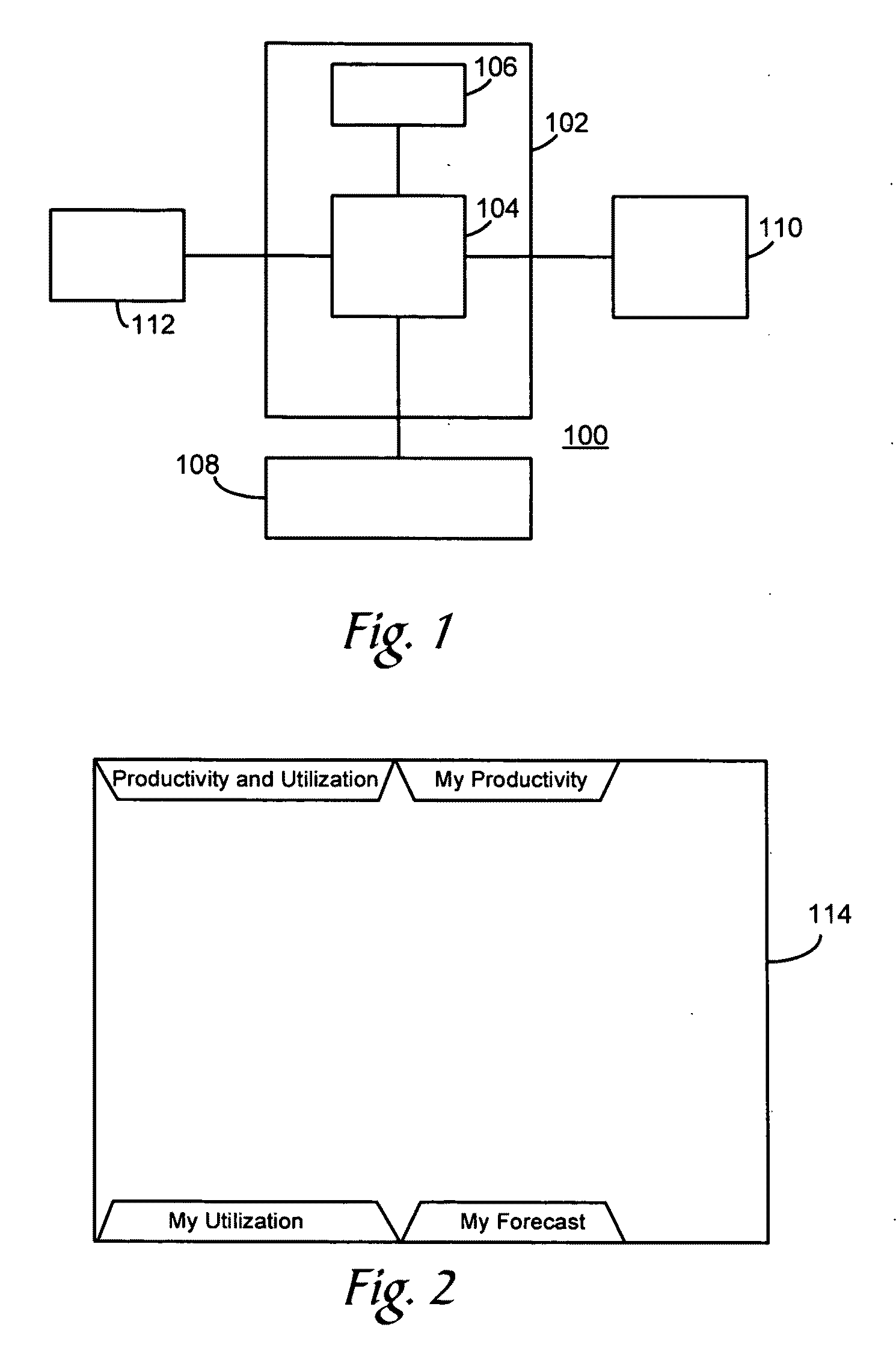
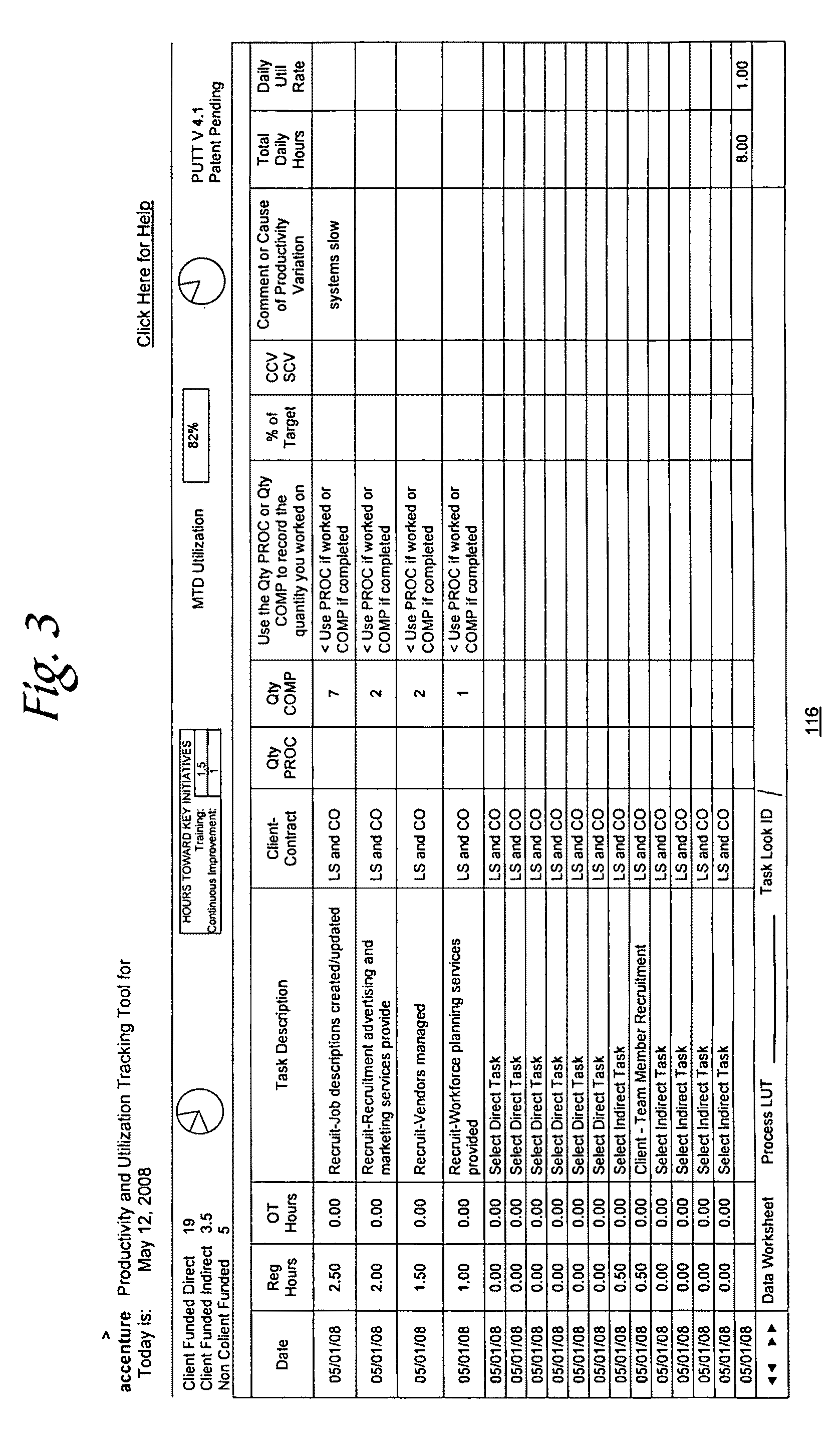
Individual productivity and utilization tracking tool
ActiveUS20100023385A1Efficient analysisProvide feedbackHardware monitoringResourcesDisplay deviceData science
A method of tracking productivity and utilization information regarding an individual of an organization. The method including entering via an input device information regarding the individual into a database that: 1) identifies each direct task worked on by the individual during a session of work, 2) direct time applied to each of the identified direct tasks during the session of work, and 3) a number of units processed or completed for each of the identified direct tasks corresponding to each of the applied direct times. The method further including displaying on a display information regarding productivity and utilization for the individual based on the direct tasks, the direct times and the number of units that are present in the database.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
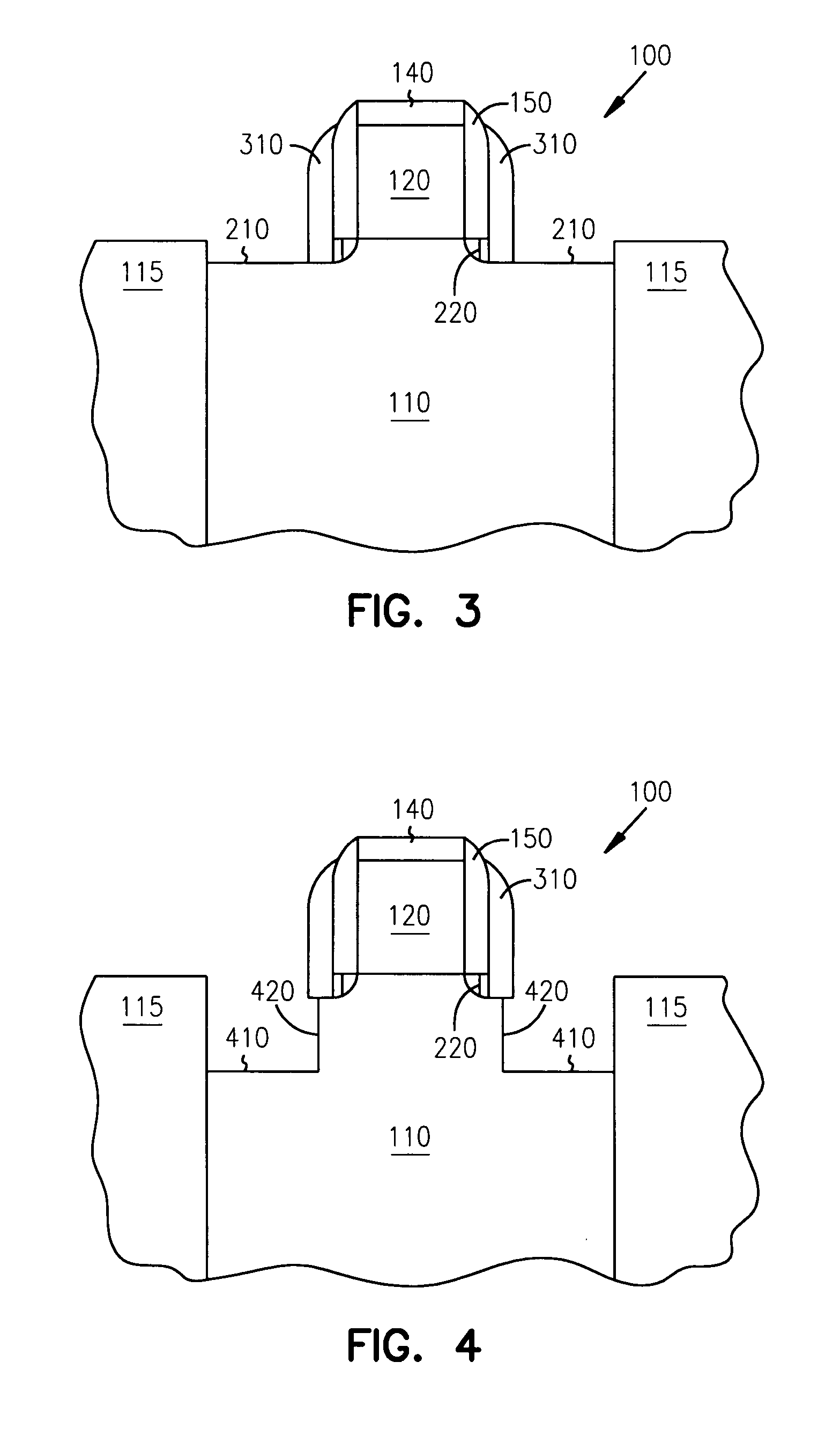
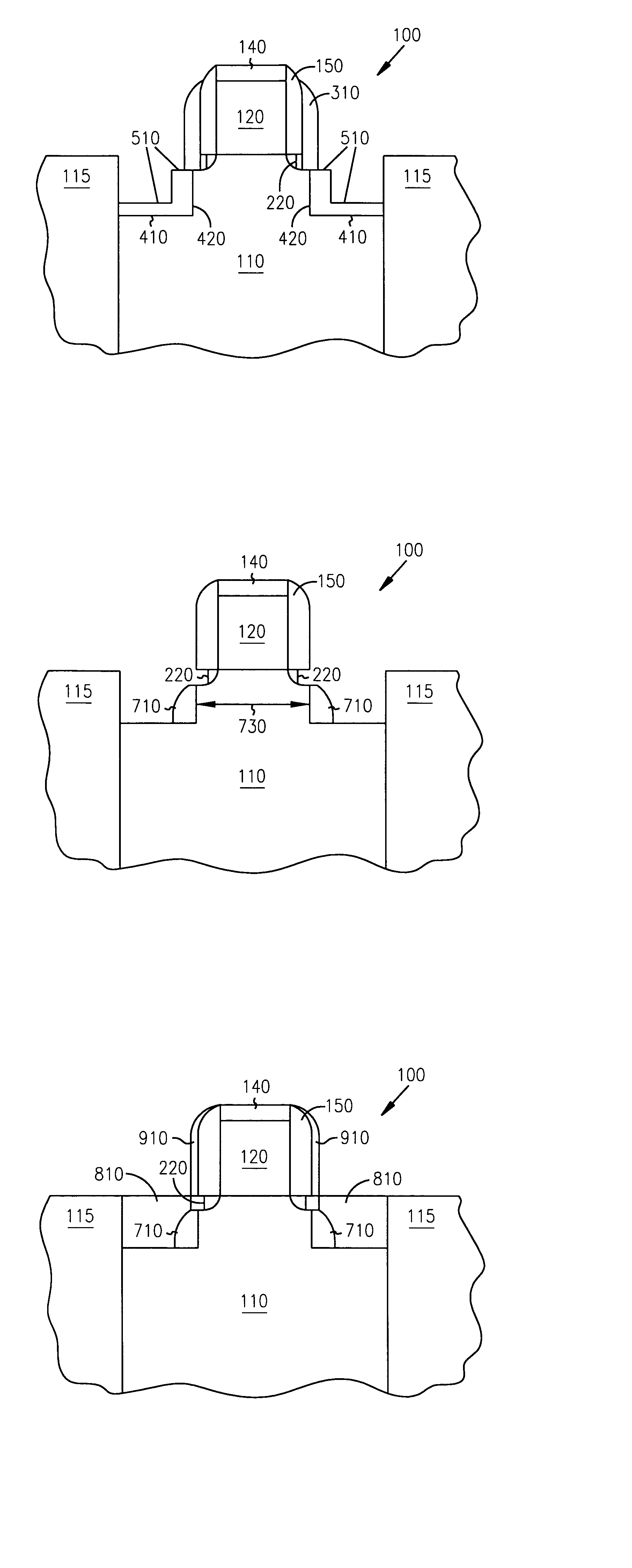
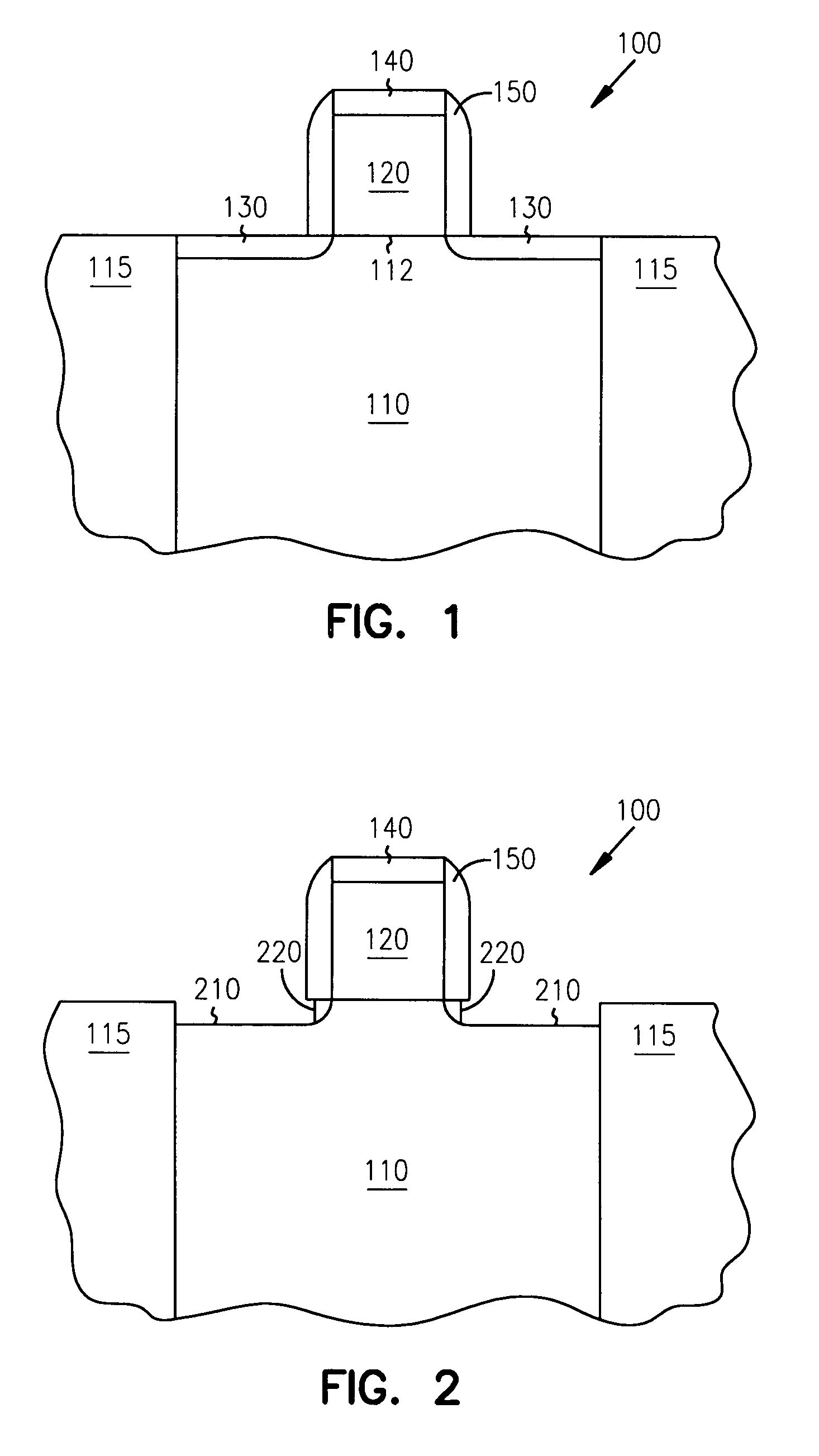
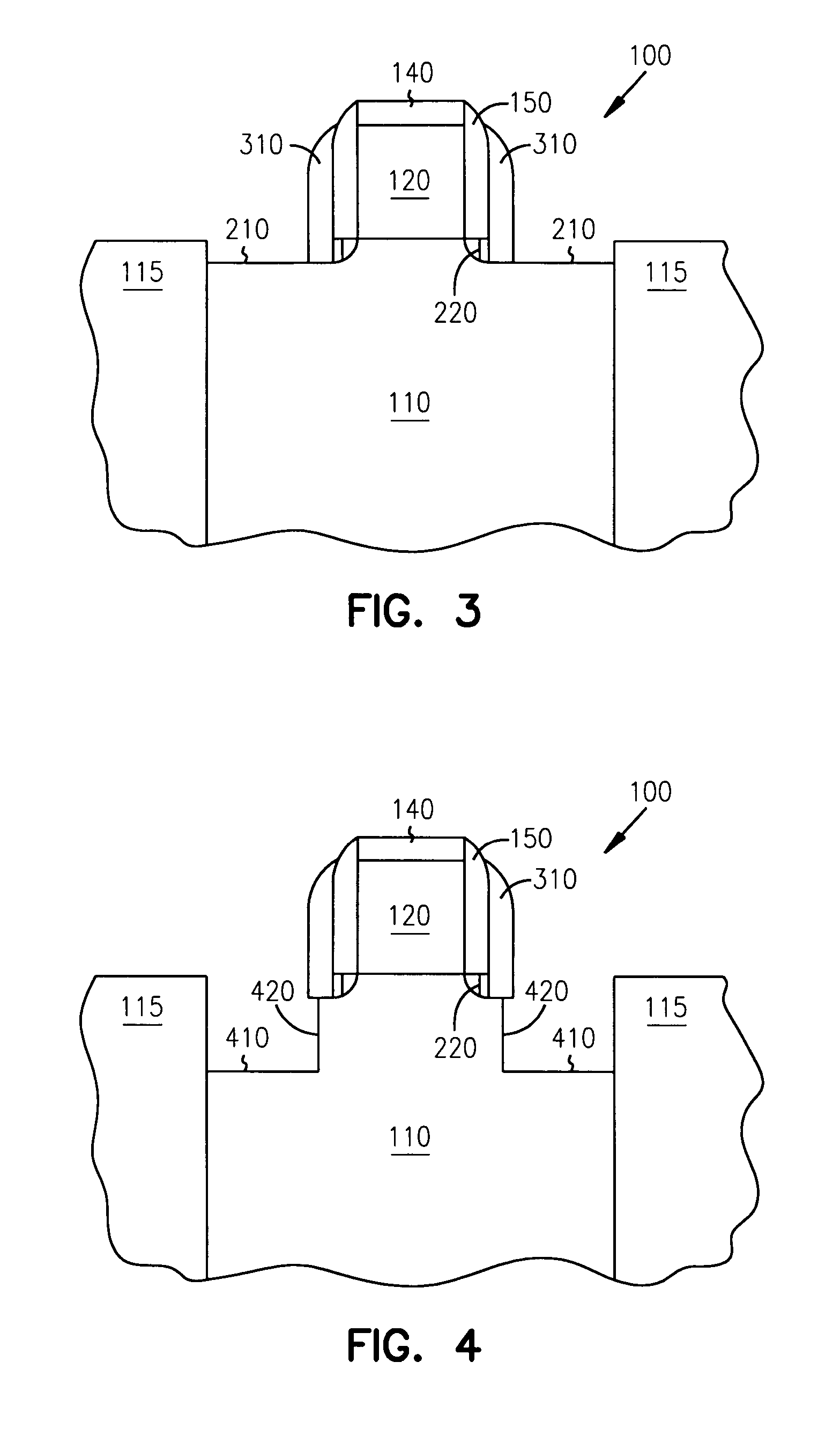
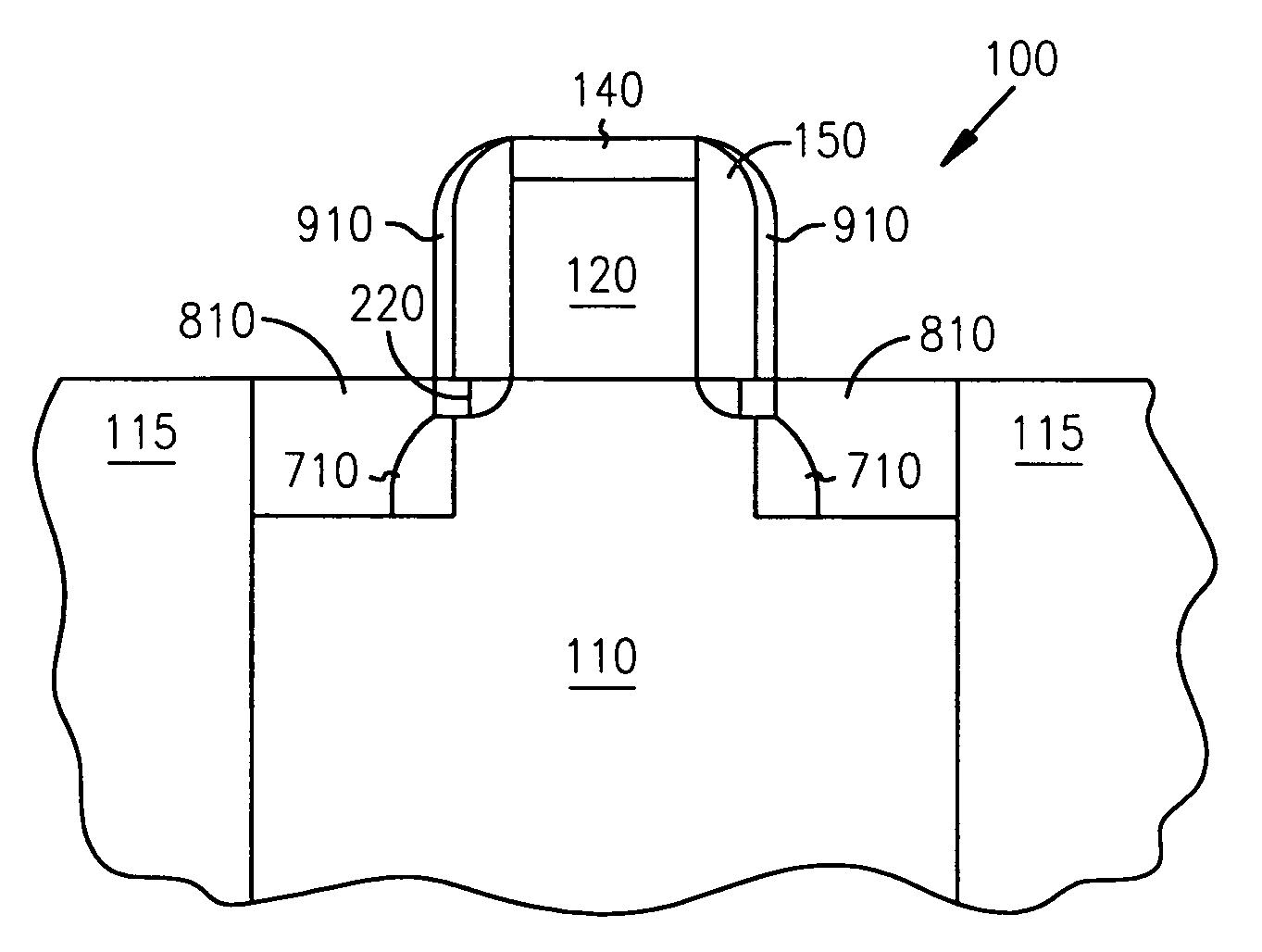
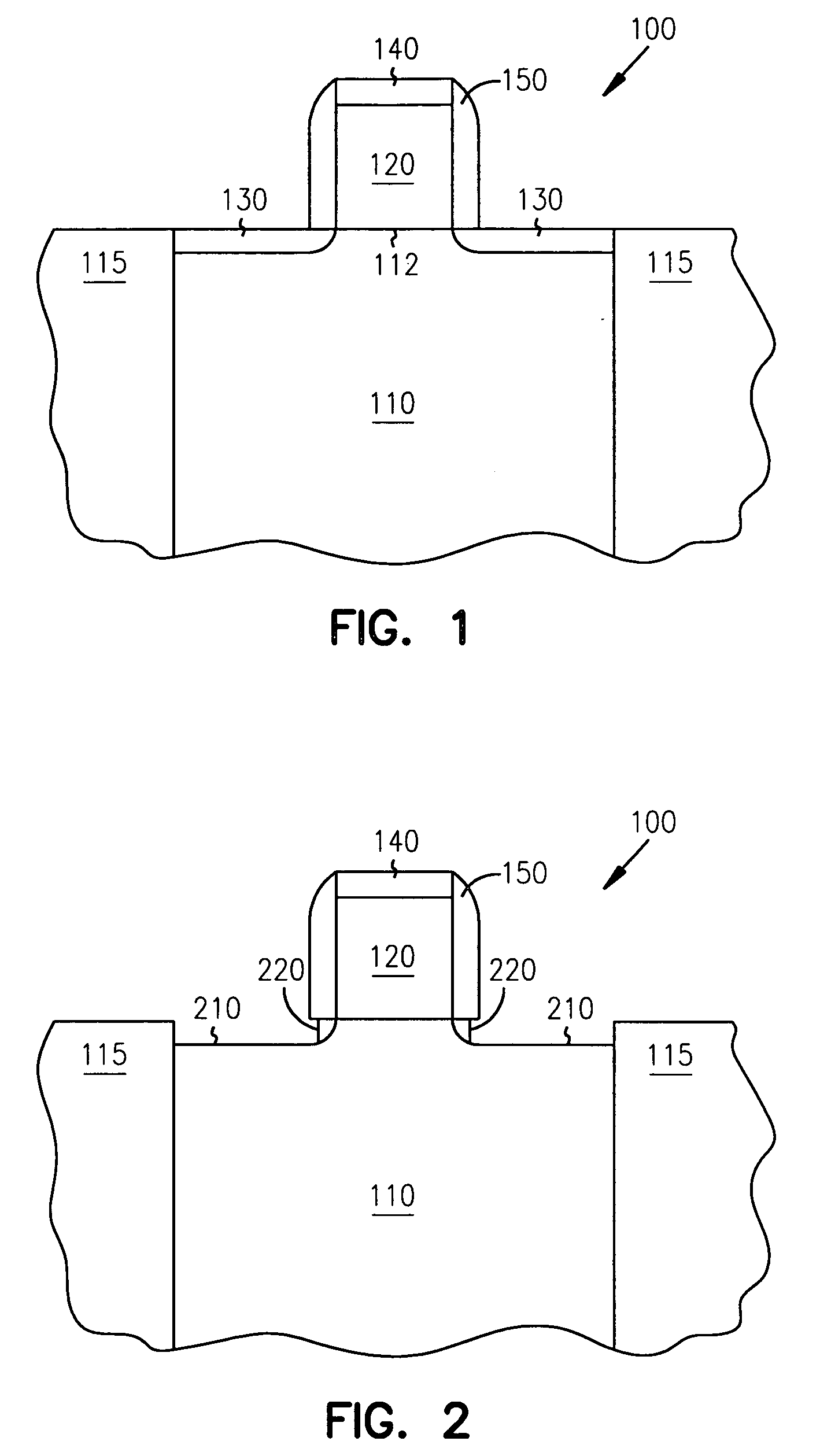
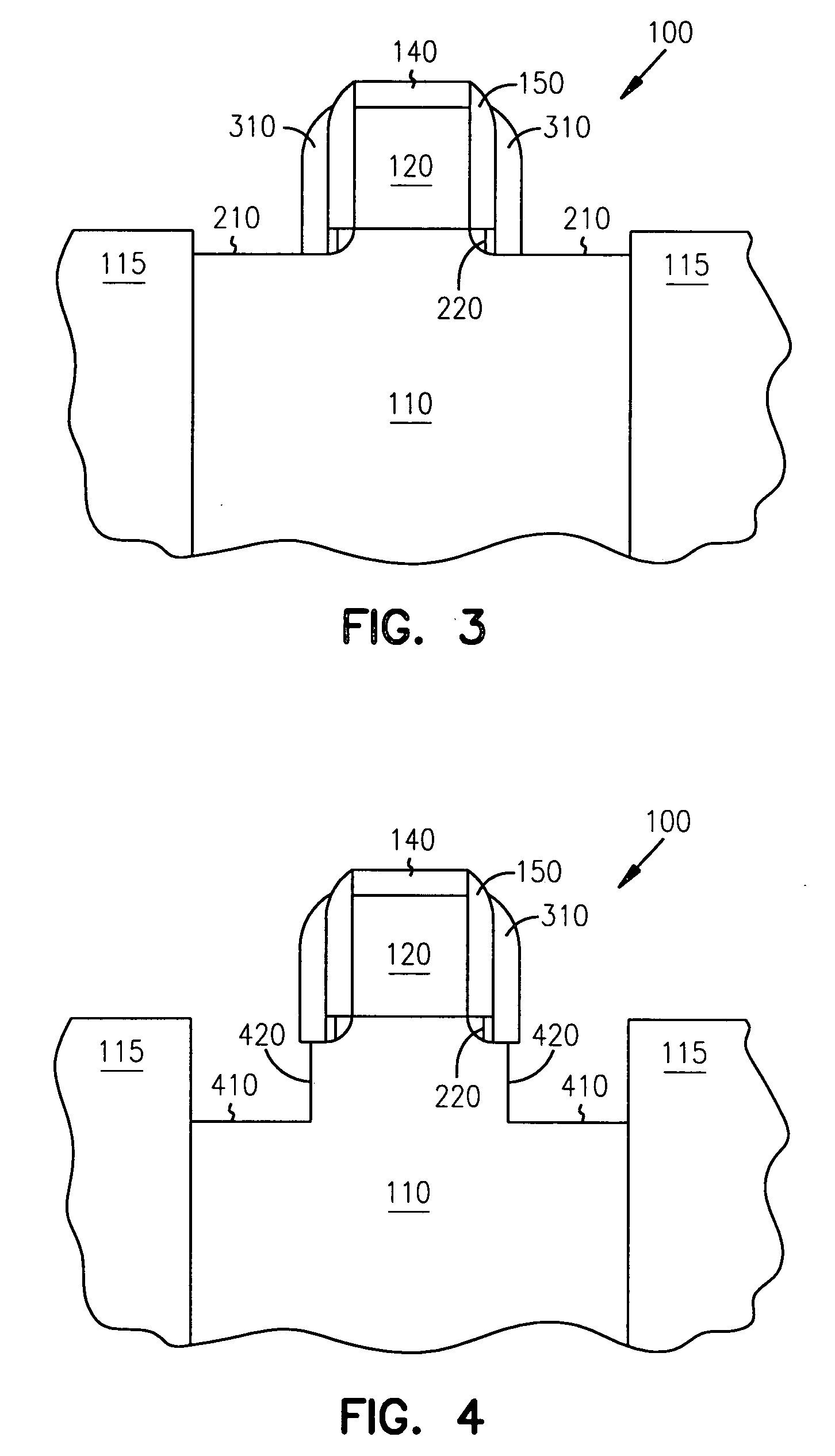
Methods of fabricating a dielectric plug in MOSFETs to suppress short-channel effects
InactiveUS20050035408A1Increasing source-drain junction capacitanceEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBulk negative resistance effect devicesDielectricShort-channel effect
The invention provides a technique to fabricate a dielectric plug in a MOSFET. The dielectric plug is fabricated by forming an oxide layer over exposed source and drain regions in the substrate including a gate electrode stack. The formed oxide layer in the source and drain regions are then substantially removed to expose the substrate in the source and drain regions and to leave a portion of the oxide layer under the gate electrode stack to form the dielectric plug and a channel region between the source and drain regions.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
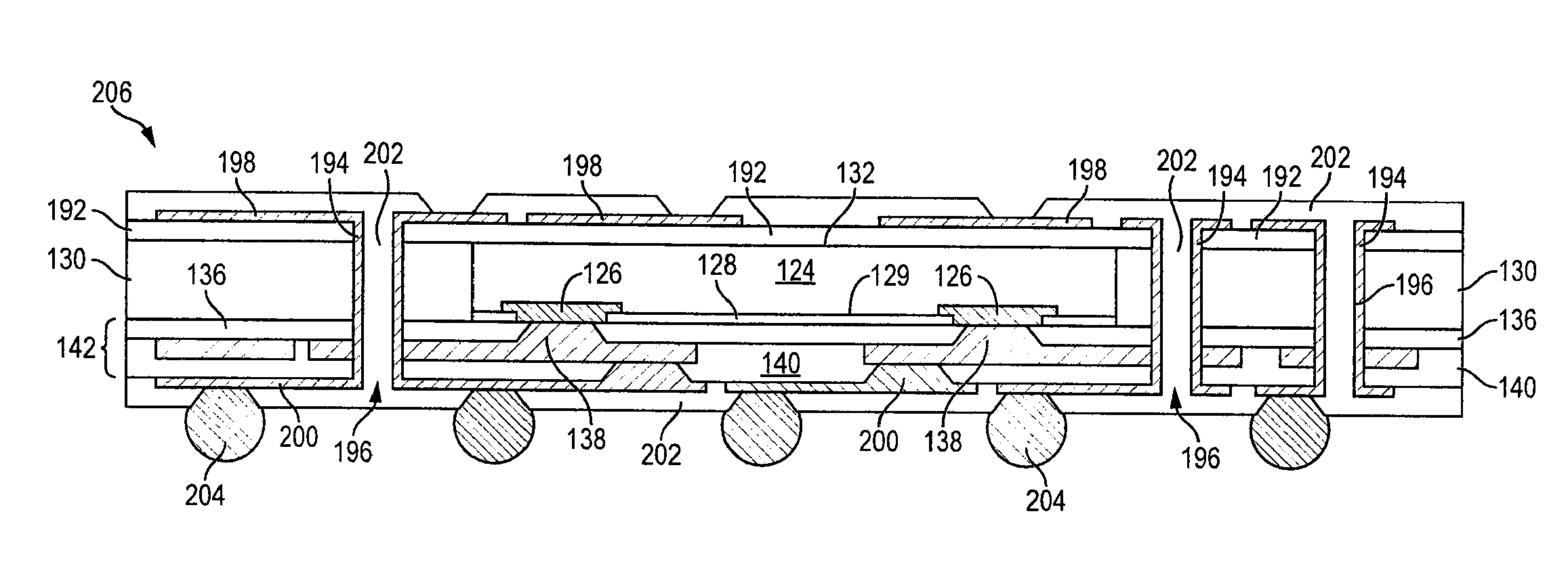
Semiconductor Device and Method of Forming Conductive Vias Through Interconnect Structures and Encapsulant of WLCSP
ActiveUS20110221054A1Simple and cost-effectiveCost-effective processSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsEngineeringSemiconductor components
Owner:JCET SEMICON (SHAOXING) CO LTD
Electrochemical system with fluid passage integrated within a sealing bead
ActiveUS7718293B2Maintain good propertiesCost-effective processCellsFuel cells groupingElectrolysisEngineering
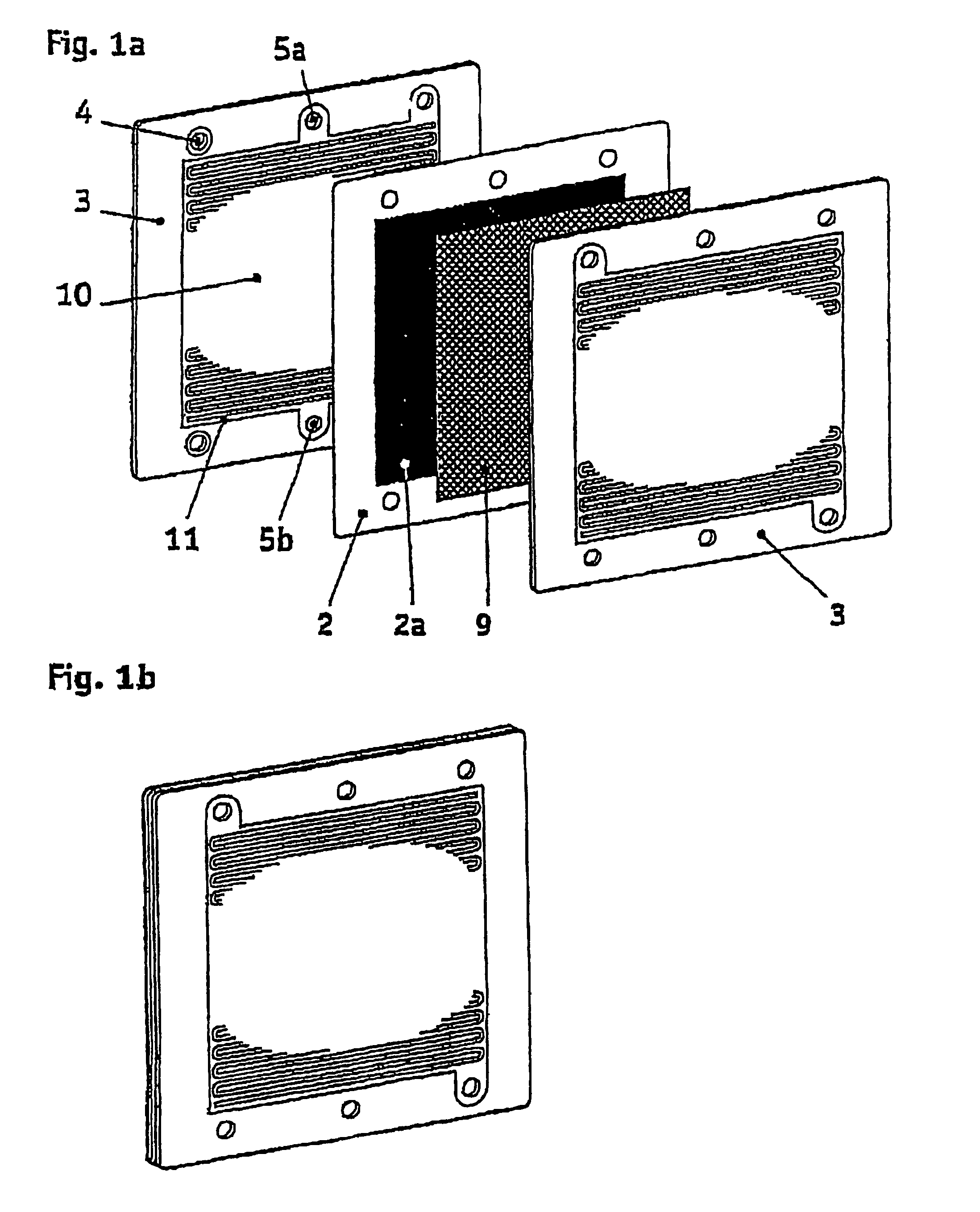
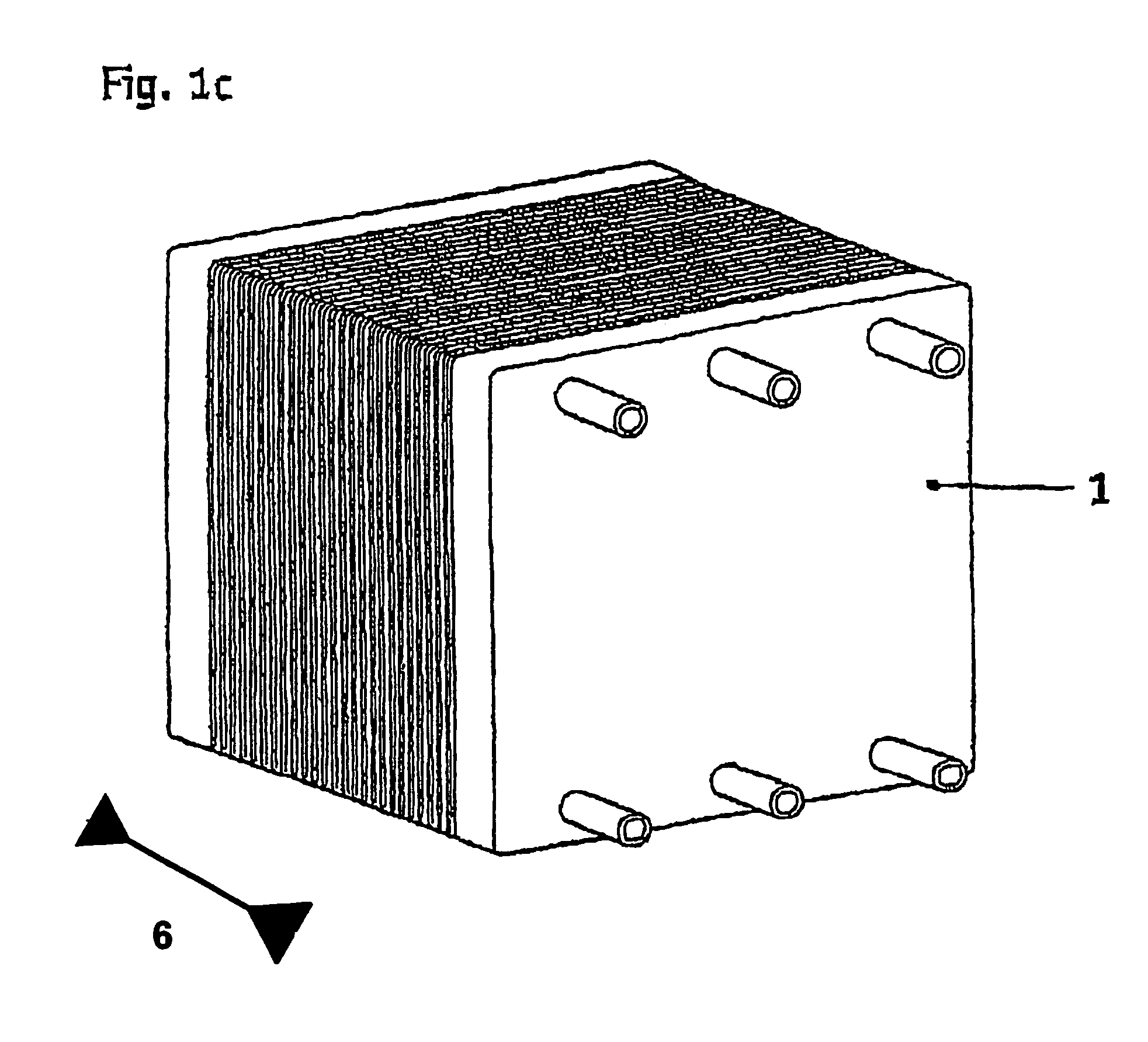
The invention deals with an electrochemical system for compressing gases and / or for producing gases by electrolysis, consisting of an electrochemical compressor stack (1) having layering of several electrochemical cells, which are separated from one another in each case by bipolar plates (3; 3′), wherein the bipolar plates have openings for media supply and media discharge (5a, 5b) for the electrochemical cells and the electrochemical cell stack can be placed under mechanical compressive strain in direction (6) of the layering. The bead arrangements (7; 7′) are resilient and are provided at least in some regions to seal the openings (4, 5a, 5b) and / or an electrochemically active region (10) of the electrochemical cells.
Owner:REINZ DICHTUNGS
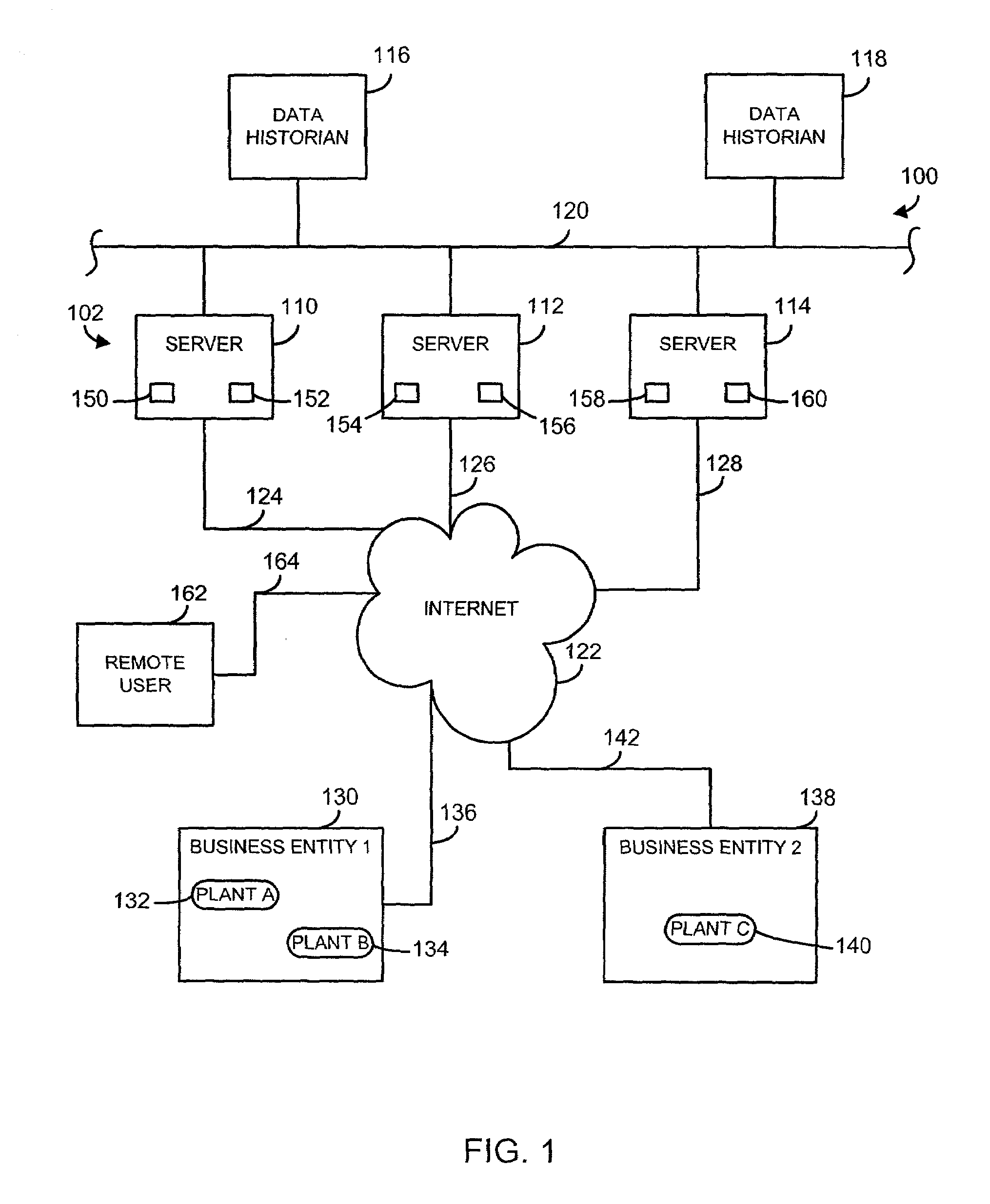
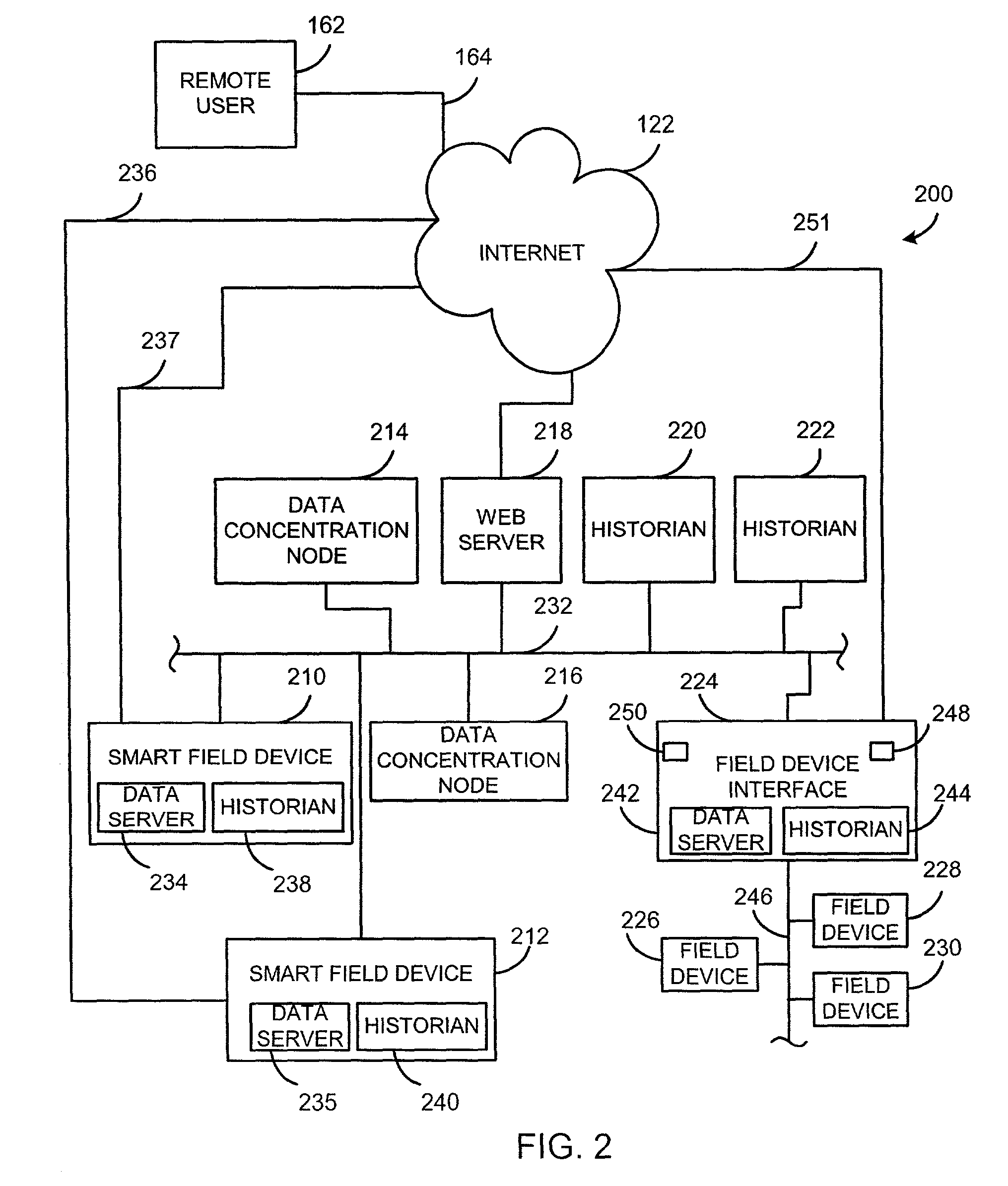
Shared-use data processing for process control systems
InactiveUS7568000B2Low costCost-effective processSafety arrangmentsComputer controlData processing systemControl system
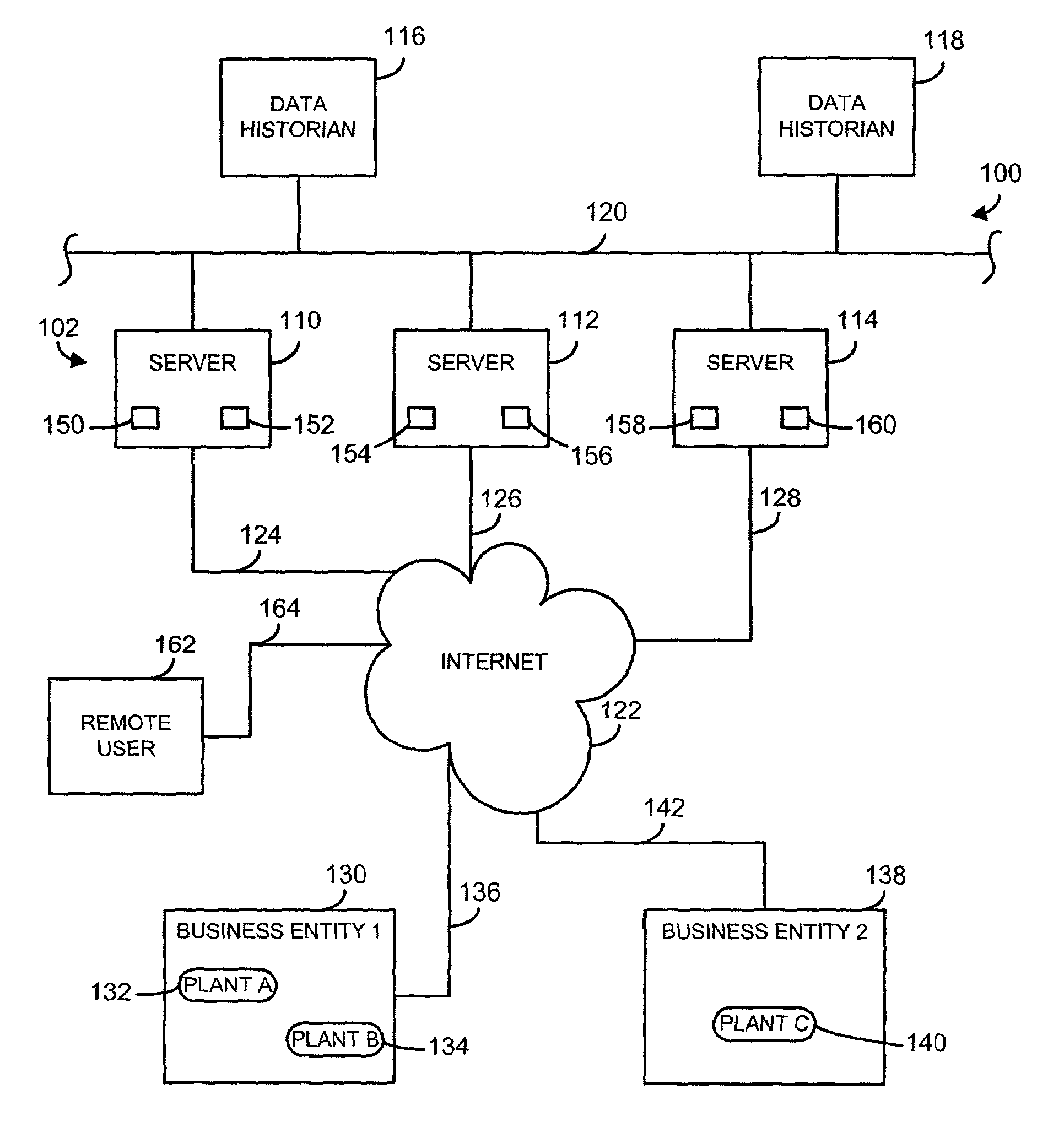
A data processing system and method for use with a process control system enables a plurality of process plants associated with different business entities to share a remotely situated data processing facility. The data processing facility includes a cluster of redundant servers that are communicatively coupled via a local network. Each of the redundant servers is adapted to acquire and process data received from the plurality of process plants. The data processing facility also includes a plurality of redundant data historians that are communicatively coupled to each other and to the cluster of redundant servers for storage of process data and analysis results. Each of the plurality of process plants includes internet-enabled field devices, internet-enabled field device interfaces, and / or internet-enabled data concentration nodes that send information to and receive information from the data processing facility via the Internet.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT ANALYTICAL
Microwave induced functionalization of single wall carbon nanotubes and composites prepared therefrom
InactiveUS7754054B2High purityRapid funtionalizationMaterial nanotechnologyGroup 1/11 element organic compoundsMicrowaveCarbon nanotube
The invention is directed to a method of forming, producing or manufacturing functionalized nanomaterials, and, specifically, soluble functionalized nanomaterials. The presently described invention also relates to nanomaterial-based composites consisting of a target material, which can include ceramic, polymer, or metallic matrices incorporated into or grown on nanomaterials, as well as a method or synthesis technique for the formation, production, or manufacture of nanomaterial-based composites through microwave-induced reaction.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
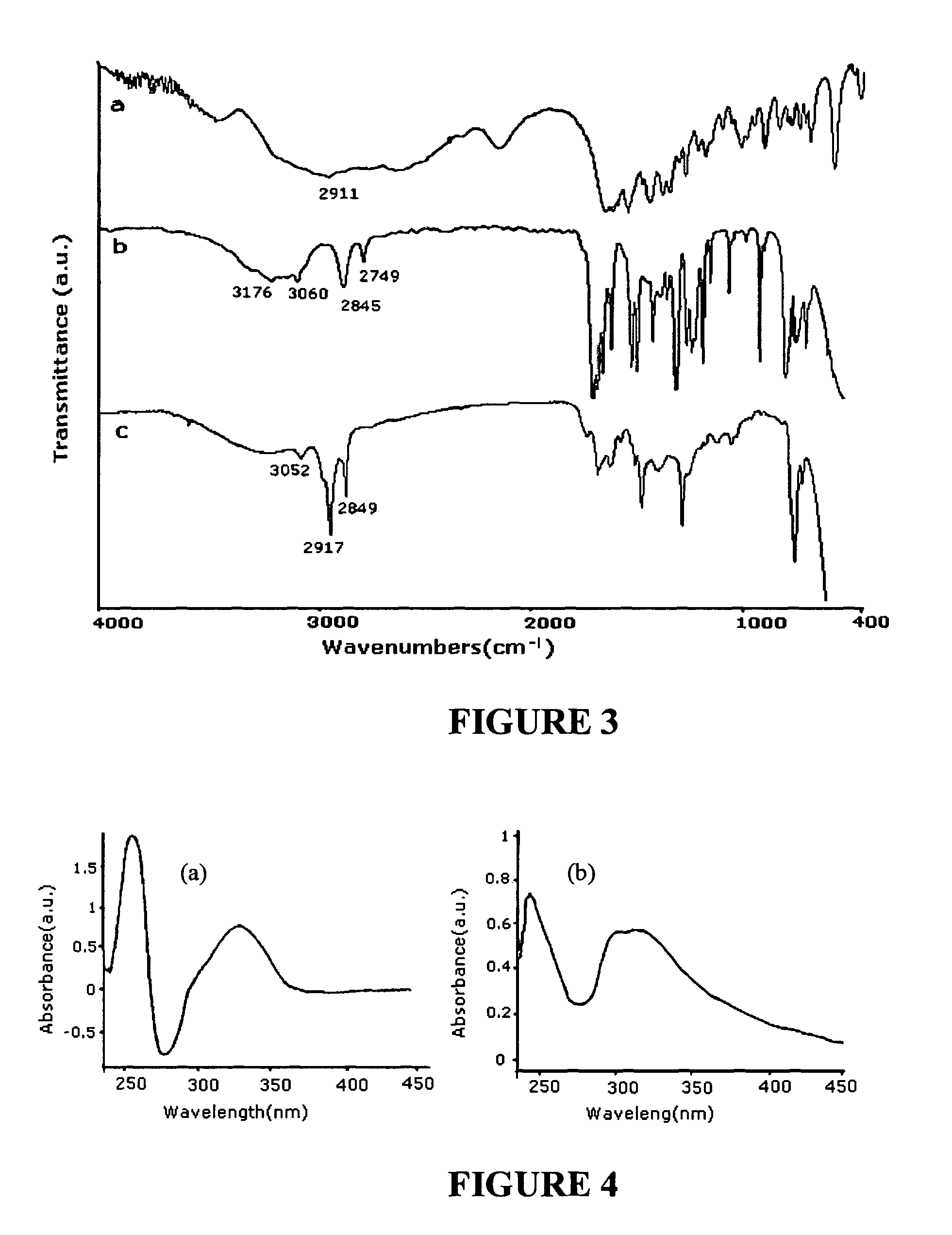
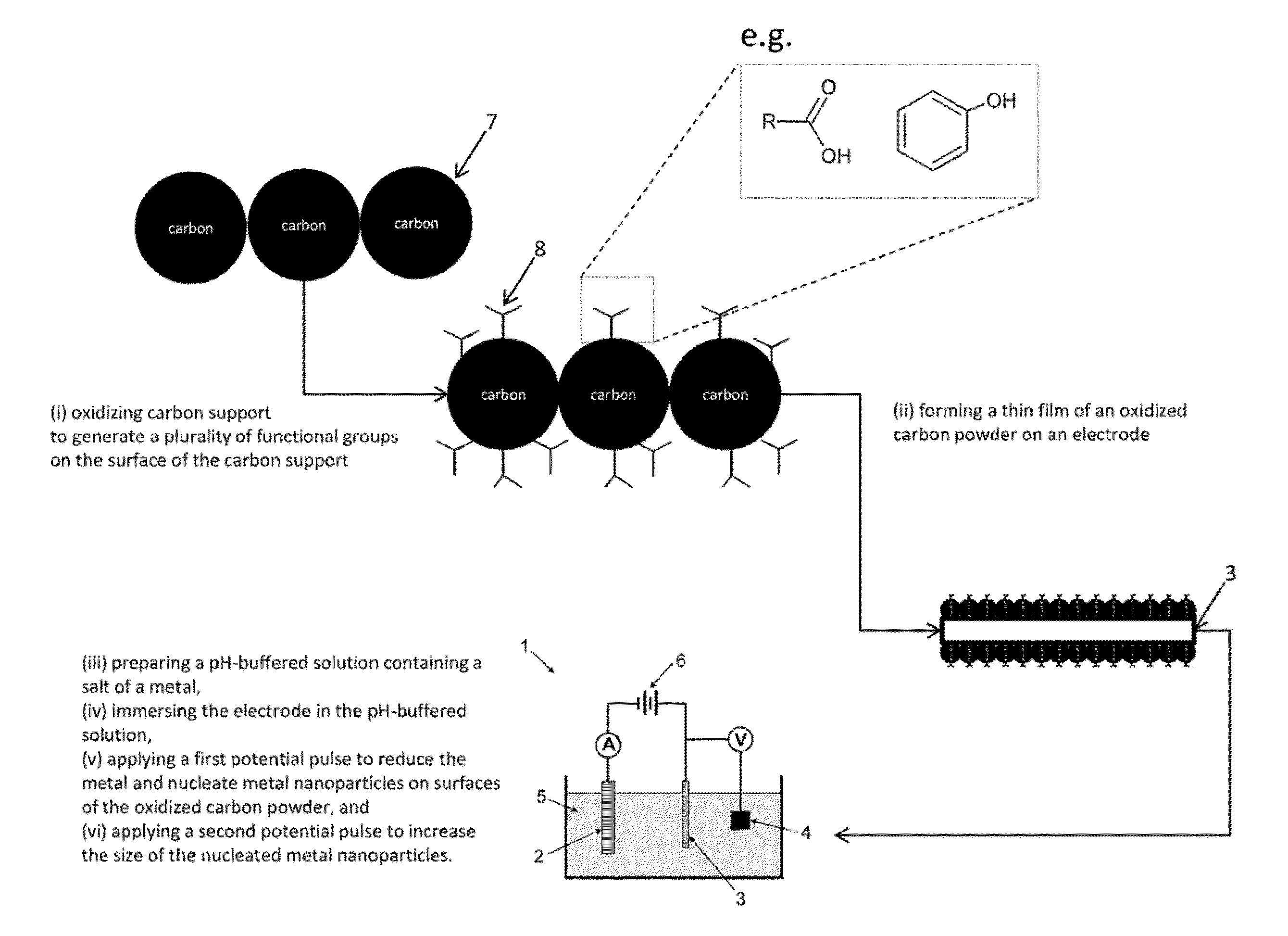
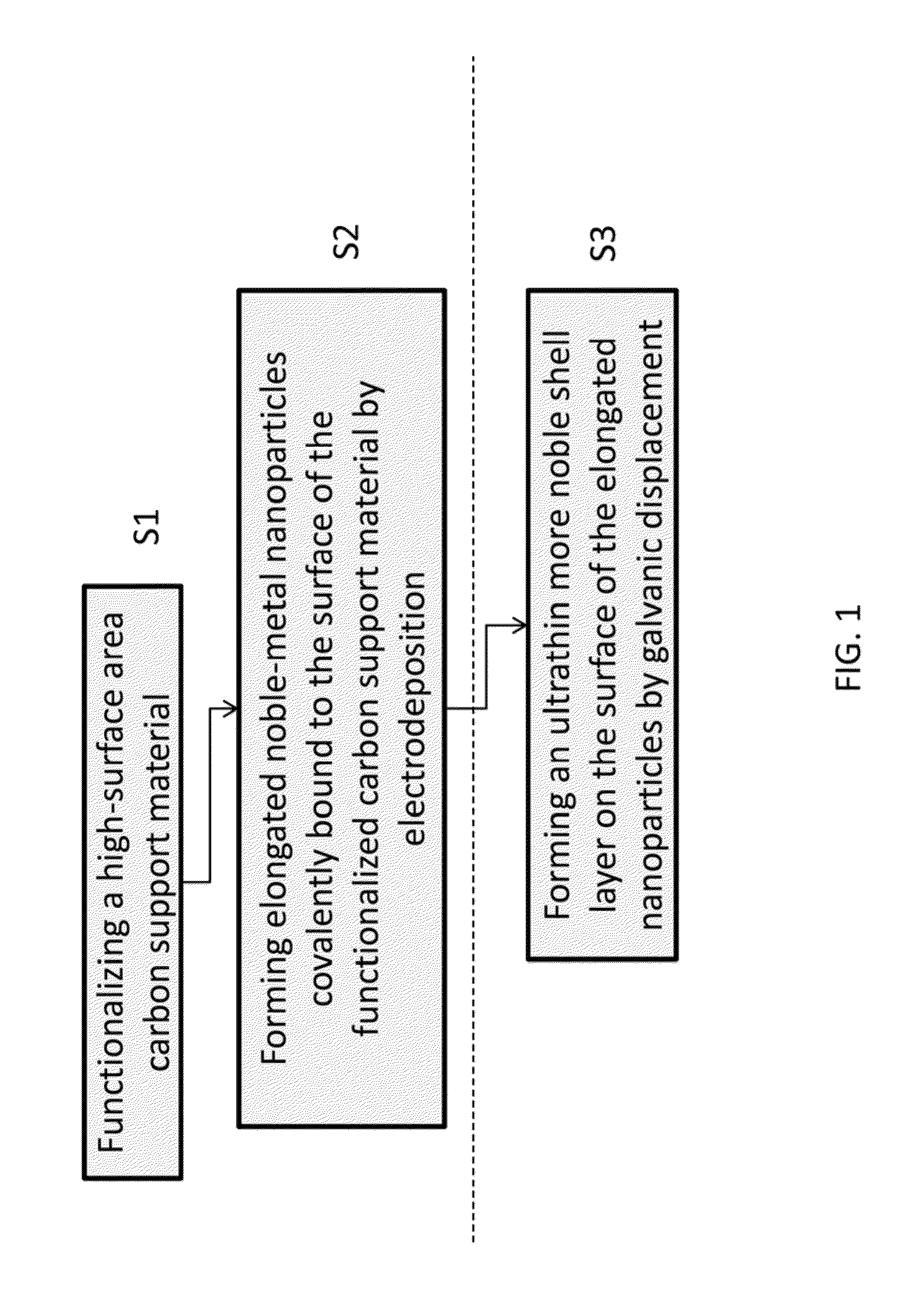
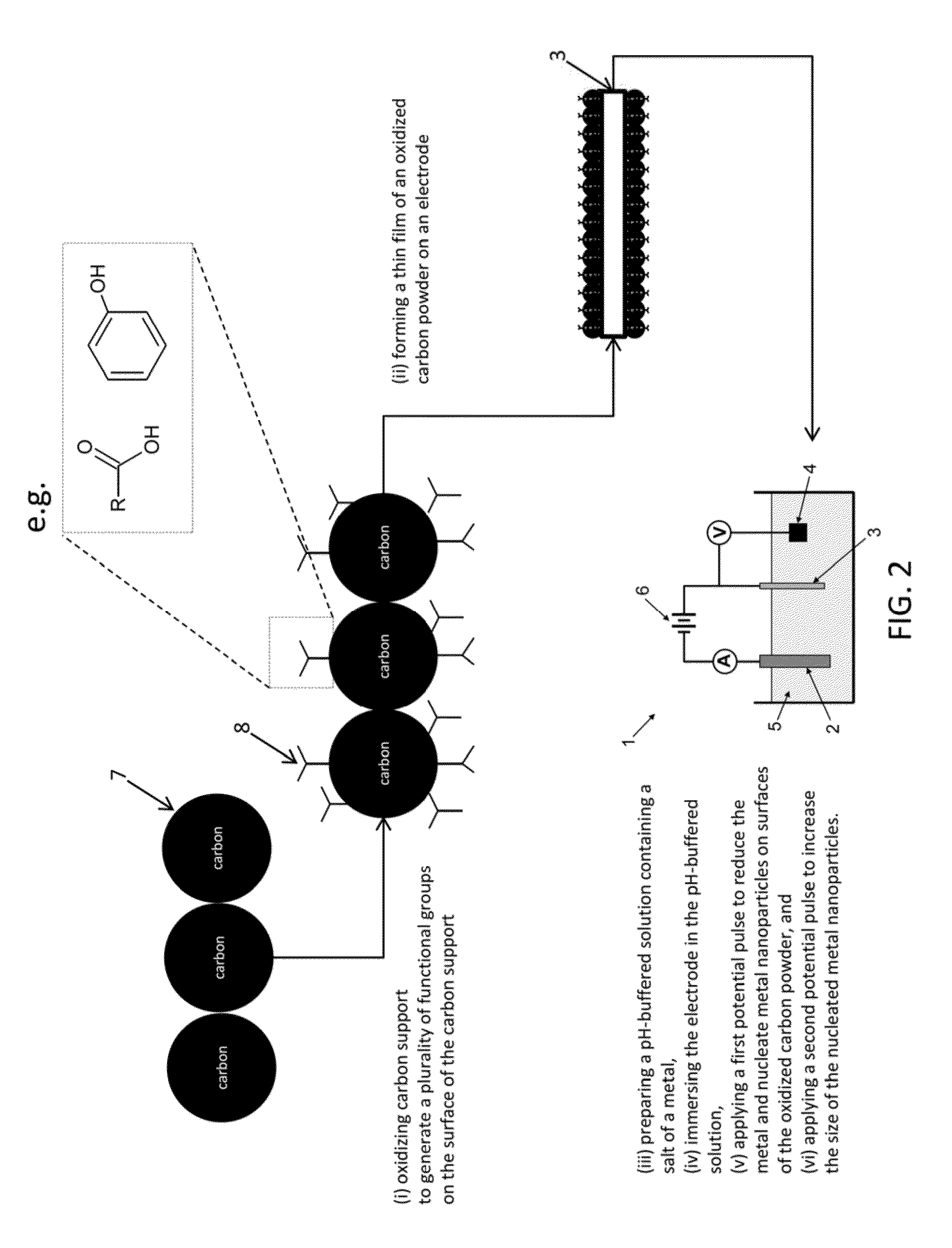
Electrochemical Synthesis of Elongated Noble Metal Nanoparticles, such as Nanowires and Nanorods, on High-Surface Area Carbon Supports
InactiveUS20130034803A1High catalytic activitySimple and cost-effective processMaterial nanotechnologyNon-insulated conductorsNanowireCarbon Nanoparticles
Elongated noble-metal nanoparticles and methods for their manufacture are disclosed. The method involves the formation of a plurality of elongated noble-metal nanoparticles by electrochemical deposition of the noble metal on a high surface area carbon support, such as carbon nanoparticles. Prior to electrochemical deposition, the carbon support may be functionalized by oxidation, thus making the manufacturing process simple and cost-effective. The generated elongated nanoparticles are covalently bound to the carbon support and can be used directly in electrocatalysis. The process provides elongated noble-metal nanoparticles with high catalytic activities and improved durability in combination with high catalyst utilization since the nanoparticles are deposited and covalently bound to the carbon support in their final position and will not change in forming an electrode assembly.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Semiconductor wafer regenerating system and method
InactiveUS7261617B1Less planarityLess purityAbrasive feedersAbrasive blasting machinesSand blastingSemiconductor
A semiconductor wafer regenerating system is capable of easily and efficiently removing fabricating patterns formed on a semiconductor wafer to enable reuse of the semiconductor wafer. The system, which removes patterns of the semiconductor wafer in a dry manner by using blasting grit, includes a mesh conveyor, a grit blaster, a swinging element, a collecting element, a separating element, and a dust collector. The mesh conveyor transports the semiconductor wafer so that the patterns face upward. The grit blaster is installed above the mesh conveyor and has at least one blasting nozzle for blasting grits toward the semiconductor wafer to remove the patterns from the semiconductor wafer. The swinging element swings the blasting nozzle in a plane perpendicular to a transporting path of the semiconductor wafer along the mesh conveyor. The collecting element underneath the mesh conveyor collects pulverulent bodies including grits, chips, and dusts falling from the mesh conveyor. The separating element is connected to the collecting element to separate the grits and chips from the dusts. The dust collector is connected to the separating element to collect the dusts separated by the separating element.
Owner:SILFINE
Photovoltaic thin-film solar modules and method for manufacturing such thin-film solar modules
InactiveUS20150068580A1Avoid consumptionMultiple method stepFinal product manufacturePV power plantsOhmic contactContact layer
A photovoltaic thin-film solar module includes in the following sequence: a substrate layer; a back electrode layer directly adjoining the substrate layer; a conductive barrier layer directly adjoining at least one of the back electrode layer and the substrate layer; an ohmic contact layer directly adjoining the barrier layer; one of a chalcopyrite or kesterite semiconductor absorber layer directly adjoining the contact layer; a first buffer layer directly adjoining the semiconductor absorber layer and containing one of Zn(S,OH) or In2S3; a second buffer layer directly adjoining one of the semiconductor absorber layer or the first buffer layer; and a transparent front electrode layer directly adjoining at least one of the semiconductor absorber layer, the first buffer layer, and the second buffer layer, the transparent front electrode layer containing n-doped zinc oxide.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
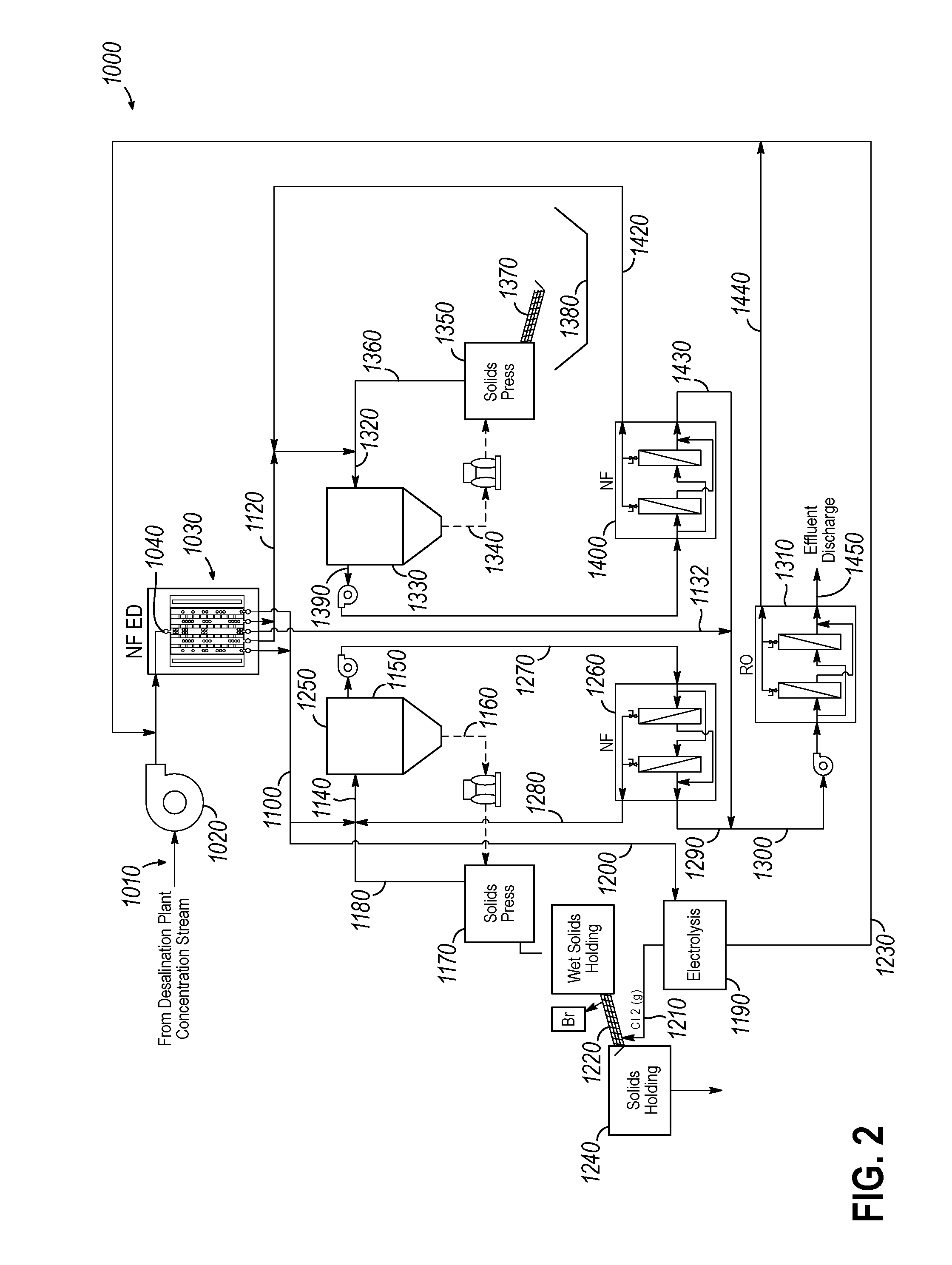
Systems, Apparatus, and Methods for Separating Salts from Water
InactiveUS20140299529A1Offsetting costsCost-effectiveSludge treatmentElectrostatic separatorsIonSolvent
A system, method, and apparatus for desalinating water, such as seawater. The system, method, and / or apparatus includes an electrodialysis cell that can separate monovalent ionic species from multivalent ionic species, so they may be separately treated. Each separate treatment may include precipitation of salt via the use of an organic solvent, followed by processing of precipitated salts and membrane treatment of water to remove solvent and remaining salts.
Owner:ADVANCED WATER RECOVERY
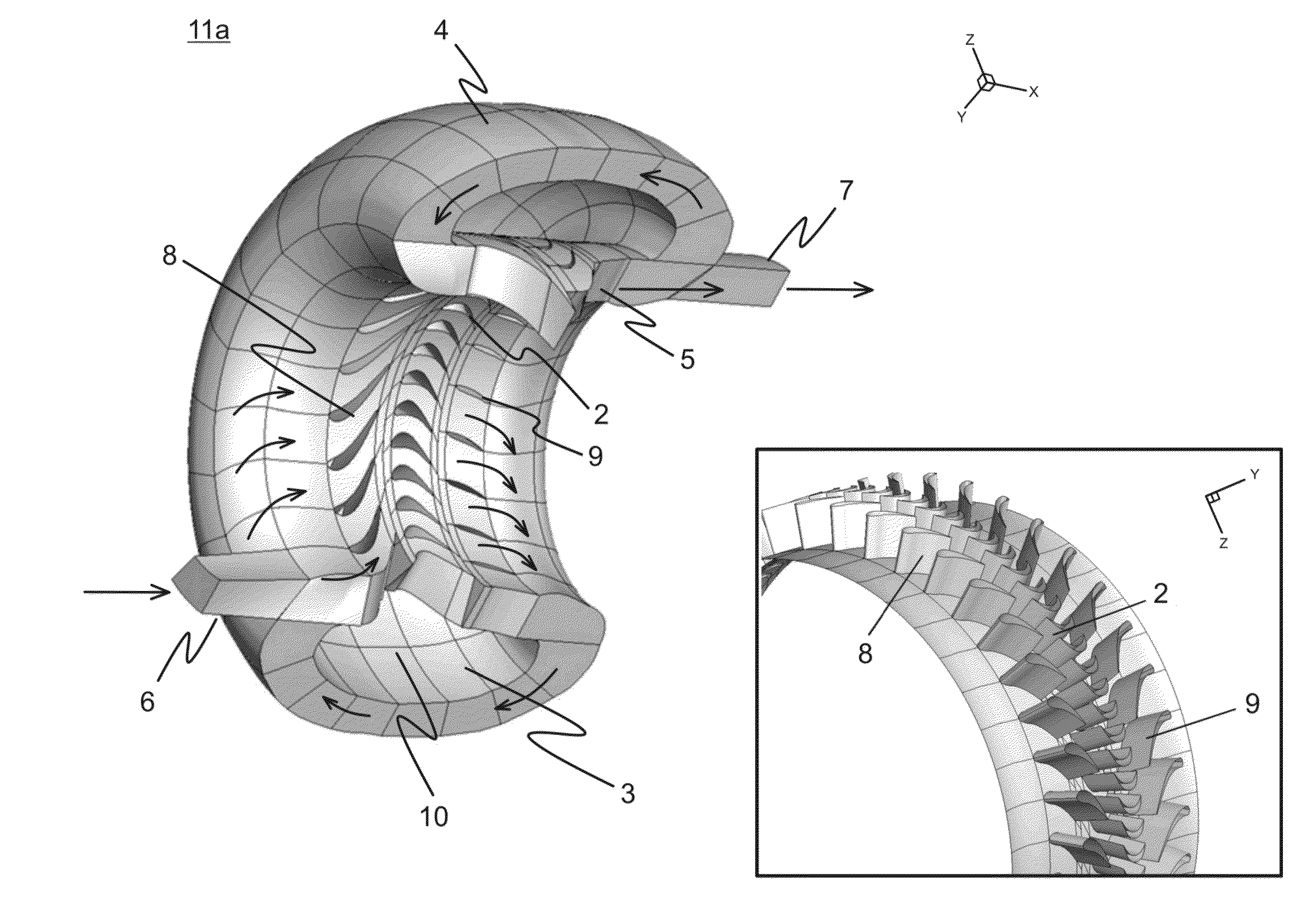
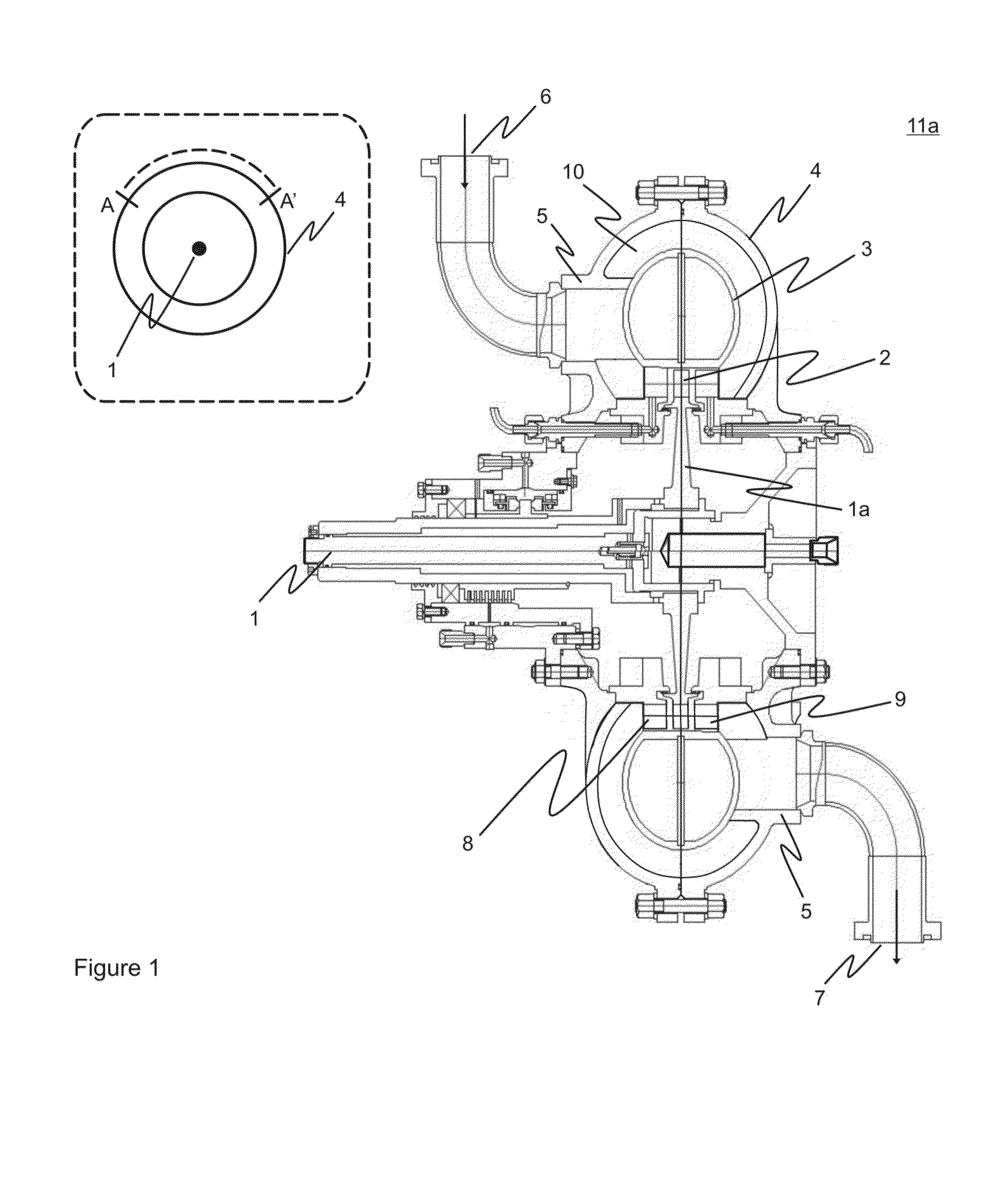
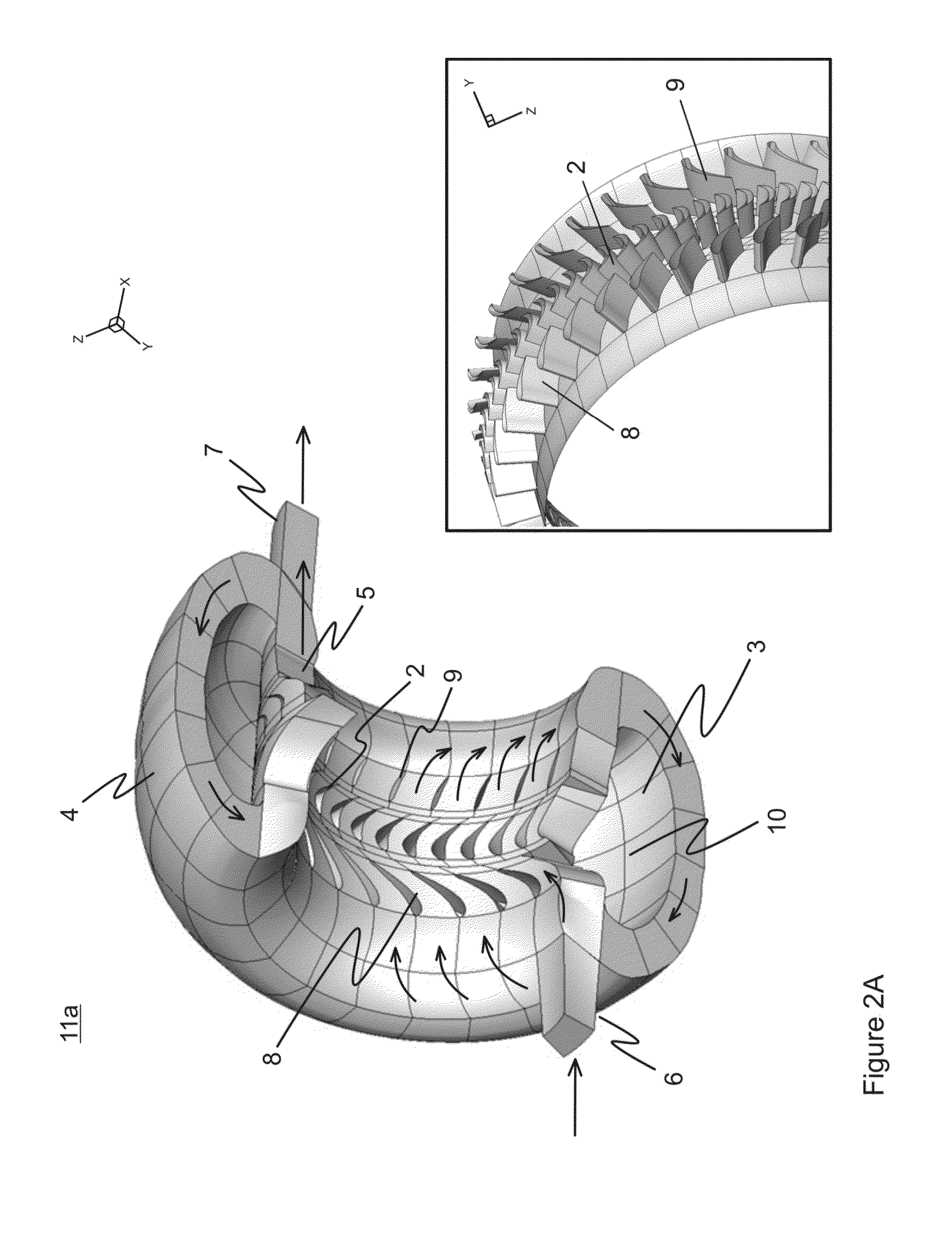
Process and rotary machine type reactor
ActiveUS20140243569A1Overcome limitationsReduce time of residenceThermal non-catalytic crackingUltra-high pressure processesShock waveProcess engineering
A rotary machine type shock wave reactor suitable for thermal cracking of hydrocarbon-containing materials includes a casing, a rotor whose periphery contains an axial-flow blade cascade, and a directing rim, provided with at least two stationary vane cascades, adjoining an axial-flow rotor cascade, wherein the casing substantially encloses the periphery of the rotor and the directing rim. The cascades are configured to direct feedstock containing process stream to repeatedly pass the cascades in a helical trajectory while propagating within the duct between the inlet and exit and to generate stationary shock-waves to heat the feedstock. The axial-flow rotor cascade is configured to provide kinetic energy and add velocity to feedstock containing process stream, and the stationary vanes located downstream the rotor cascade are configured to reduce the velocity of the stream and convert kinetic energy into heat. The reactor may also process carbohydrate- and glyceride-based feedstock, and gaseous biomass matter.
Owner:COOLBROOK
Commercially viable process for in vitro mass culture of jatropha curcas
InactiveUS20080196121A1Reduced phytohormone levelCost-effective processOther foreign material introduction processesTissue cultureJatrophaDisease free
The present invention relates to a commercially viable process for in vitro mass culture of Jatropha curcas. The process for in vitro mass culture of Jatropha curcas is simple, faster, and suitable for production of disease-free root tubers of uniform quality and employs media with a reduced concentration of phytohormones.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
MOSFETs including a dielectric plug to suppress short-channel effects
InactiveUS6977419B2Increasing source-drain junction capacitanceEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricShort-channel effect
The invention provides a technique to fabricate a dielectric plug in a MOSFET. The dielectric plug is fabricated by forming an oxide layer over exposed source and drain regions in the substrate including a gate electrode stack. The formed oxide layer in the source and drain regions are then substantially removed to expose the substrate in the source and drain regions and to leave a portion of the oxide layer under the gate electrode stack to form the dielectric plug and a channel region between the source and drain regions.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
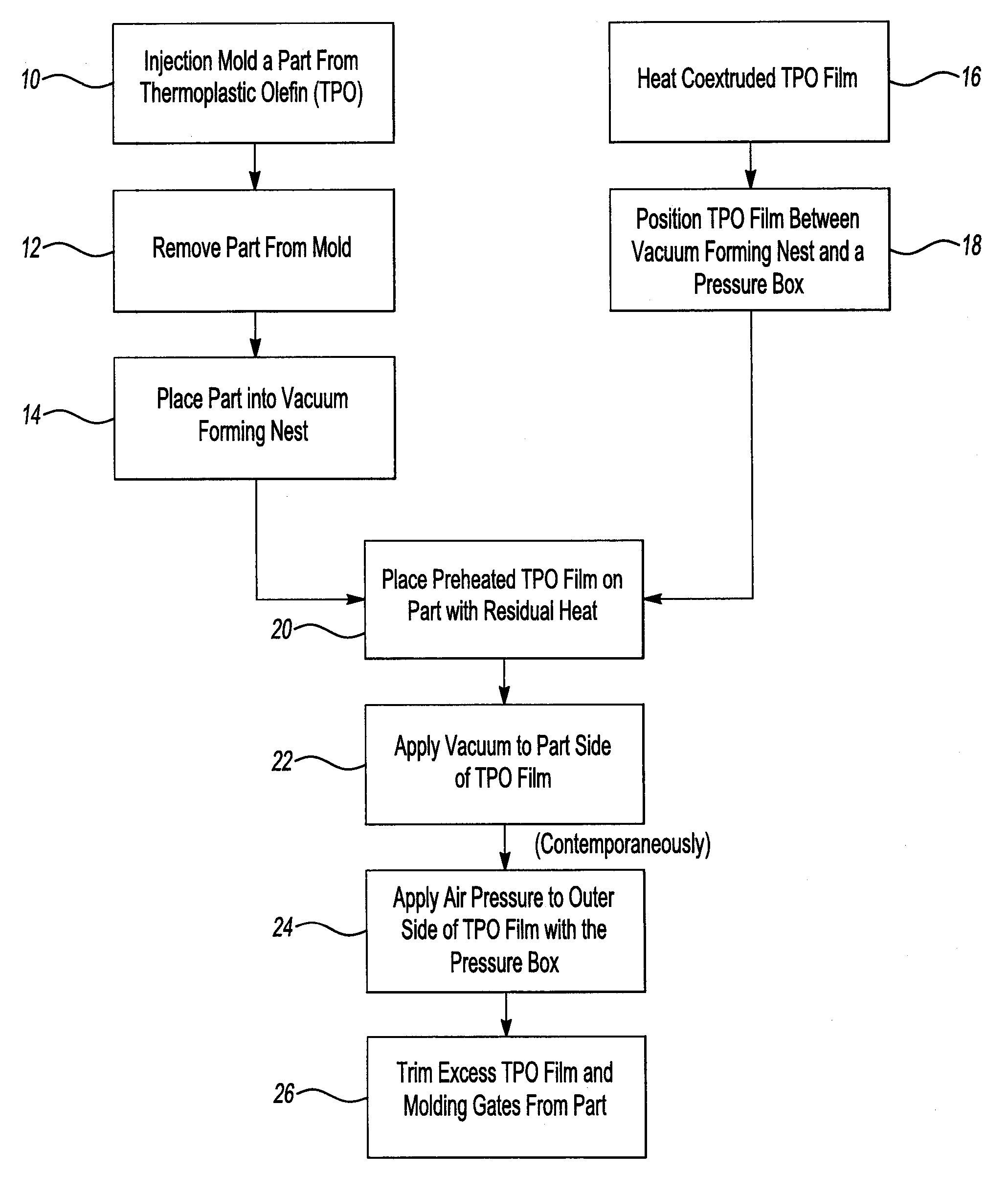
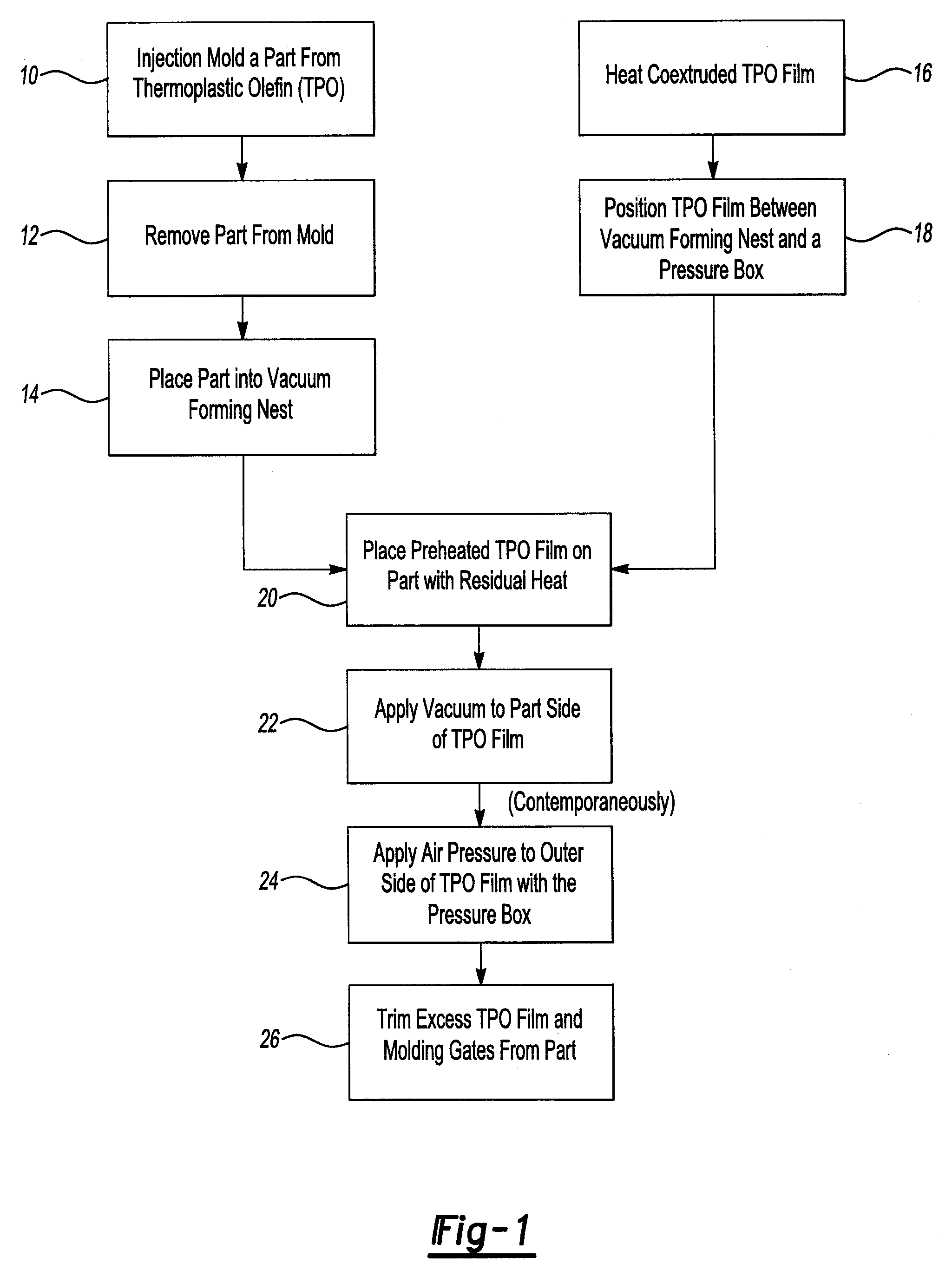
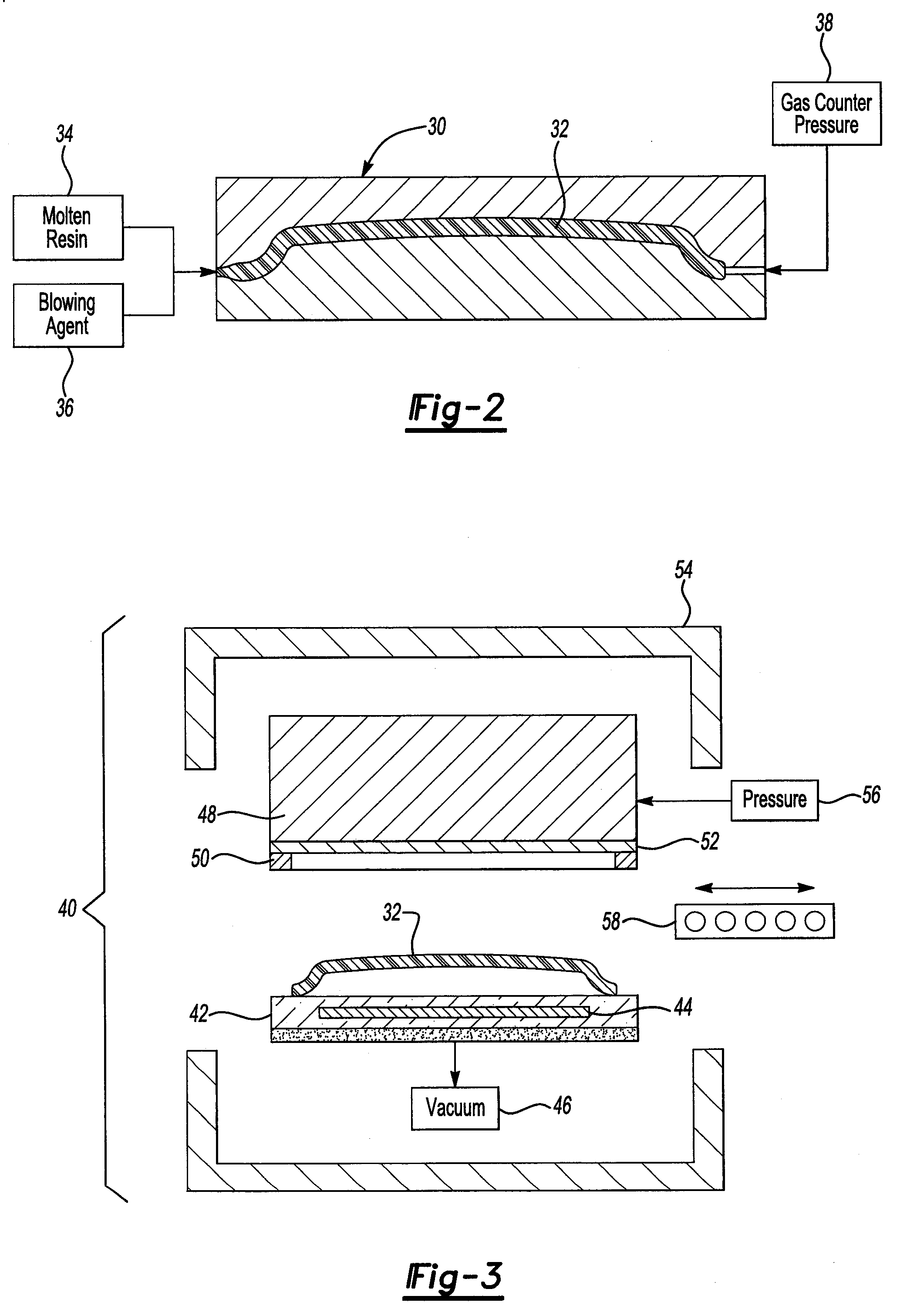
Post molding application of an extruded film to an injection molded part
InactiveUS8062451B2Cost-effectiveCost-effective processVehicle componentsBaby linensShell moldingAdhesive
A method of laminating a decorative layer to a molded part comprises molding a part formed of an amorphous or semi-crystalline thermoplastic resin and applying a segment of co-extruded an amorphous or semi-crystalline thermoplastic resin film to the part. The part is loaded into a vacuum forming nest and maintained in a heated state. The film is heated and then positioned over the part in a pressure box. A vacuum is applied through the vacuum forming nest to a first side of the film facing the part at the same time air pressure is applied through the pressure box to a second side of the film. The film is bonded directly to the part without the need for an adhesive.
Owner:DELTA ENGINEERED PLASTICS
Milk chocolate containing water
InactiveUS7186435B2Improve sensory propertiesEasy to demouldFrozen sweetsConfectioneryButter cocoaMilk Chocolate
A process for manufacturing milk chocolate products containing a higher than normal water content by preparing a dark chocolate containing up to 30% by weight of water, adding a milk powder suspension optionally together with seed crystals of cocoa butter or cocoa butter equivalent, and mixing under low shear. The invention also relates to high water content milk chocolate products, methods of preparing a chocolate coated ice cream article with such products and to the resulting chocolate coated ice cream articles.
Owner:NESTEC SA
Organic solvent pretreatment of biomass to enhance enzymatic saccharification
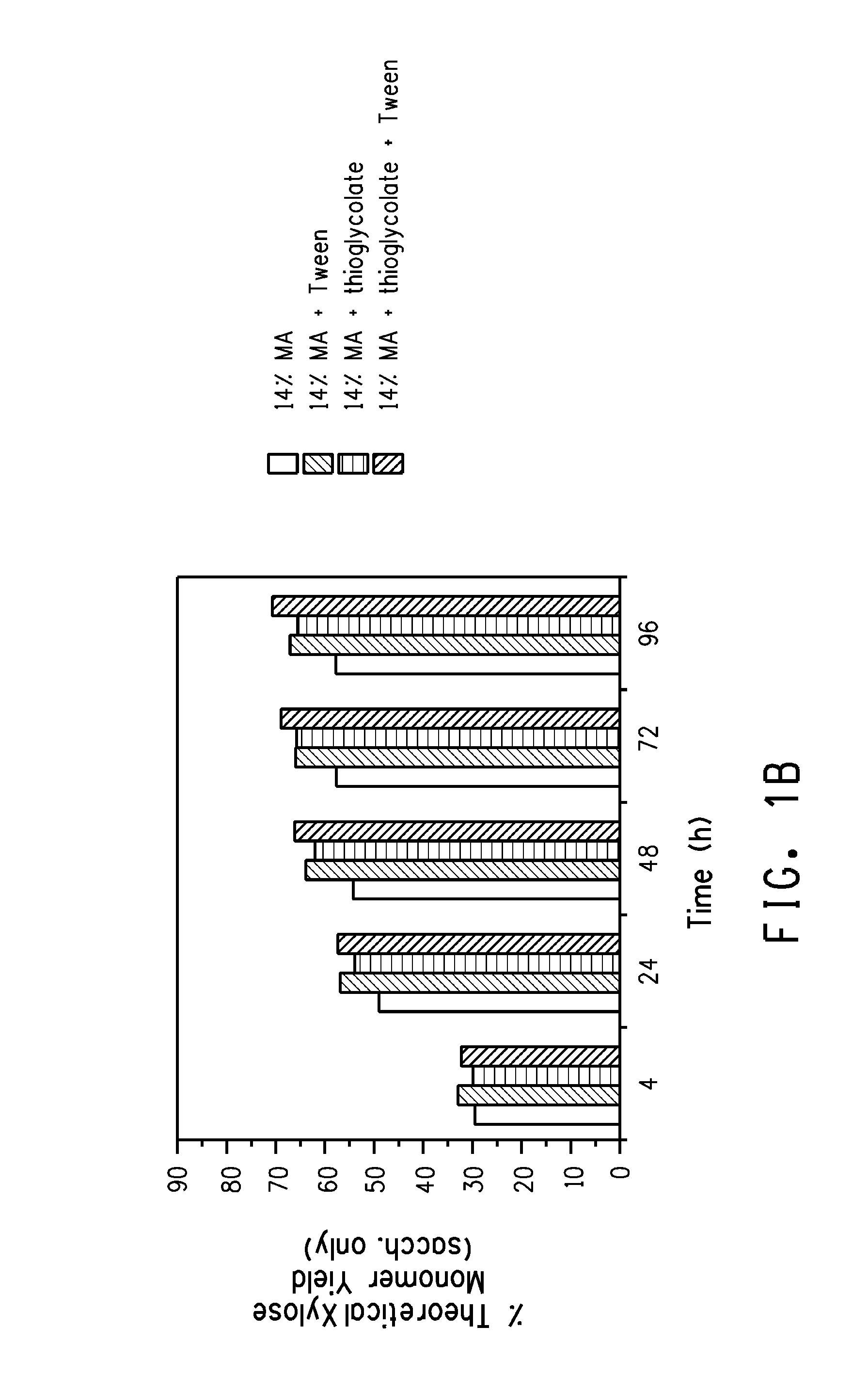
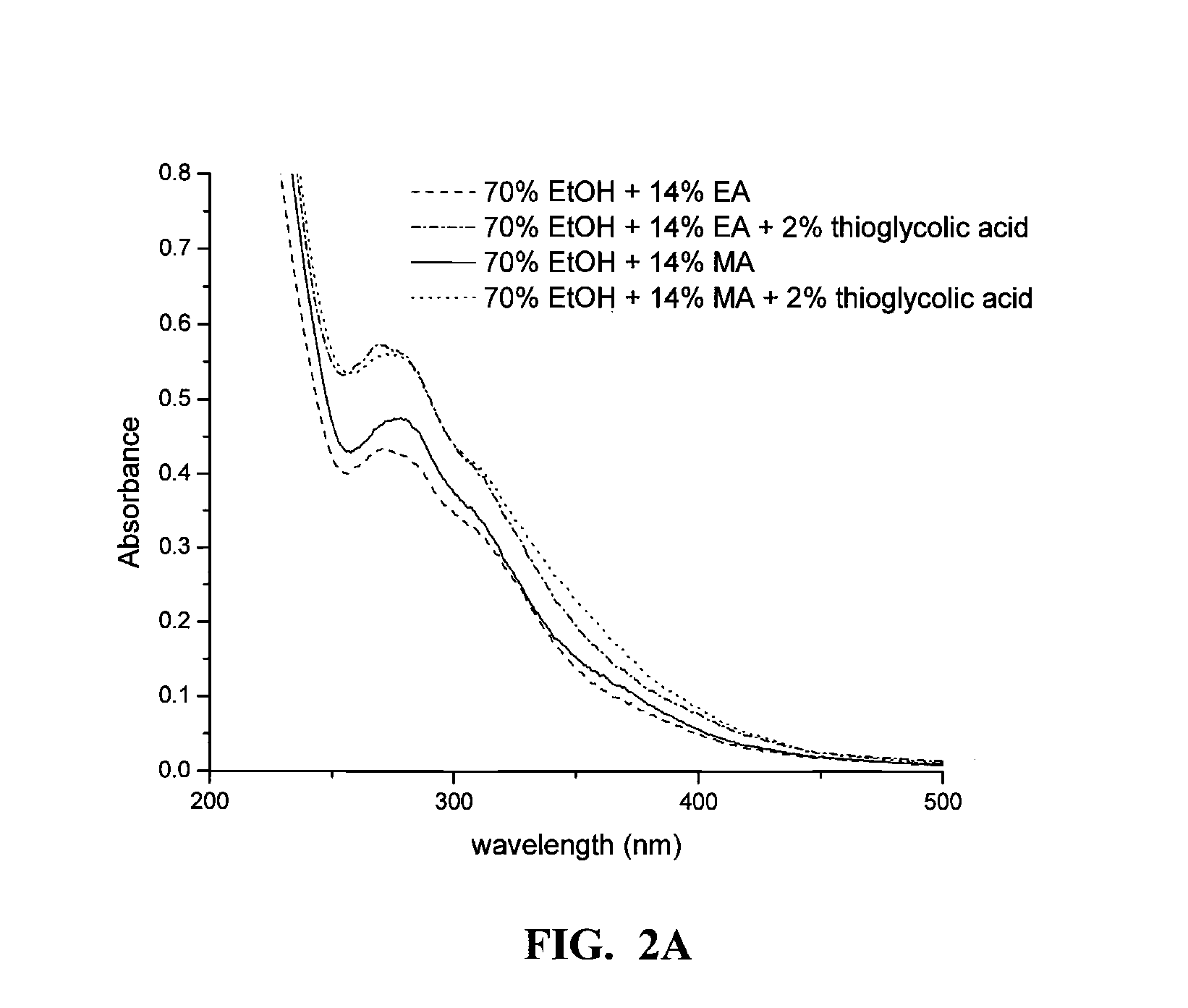
ActiveUS20100159516A1Cost-effectiveHigh yieldSugar derivativesPulping with organic compoundsOrganic solventFermentable sugar
Biomass is pretreated using an organic solvent solution under alkaline conditions in the presence of one or more alkylamine and optionally one or more additional nucleophile to fragment and extract lignin. Pretreated biomass is further hydrolyzed with a saccharification enzyme consortium. Fermentable sugars released by saccharification may be utilized for the production of target chemicals by fermentation.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE TECH CORP
Amber-colored Polyester Film with Particular Suitability for Metallization and Steel-lamination
ActiveUS20080318073A1Cost-effective processGood appearanceLiquid surface applicatorsCovering/liningsPolyesterNanometre
The present invention relates to a biaxially oriented polyester film, whicha) has a base layer B, which includes a yellow dye and a red dye,b) has, on each side of the base layer B, at least one layer (A or C) which includes, based on the weight of layer A or C, less than 0.01% by weight of the yellow dye and less than 0.01% by weight of the red dye, andc) the film has one absorption maximum lying at from 400 to 500 nm in the UV / visible spectrum from 400 to 800 nm.Preferred dyes are anthraquinone dyes and perinone dyes; the polyester is preferably PET. After metallization or lamination, the film has a gold appearance, and is a suitable packaging material.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POLYESTER FILM
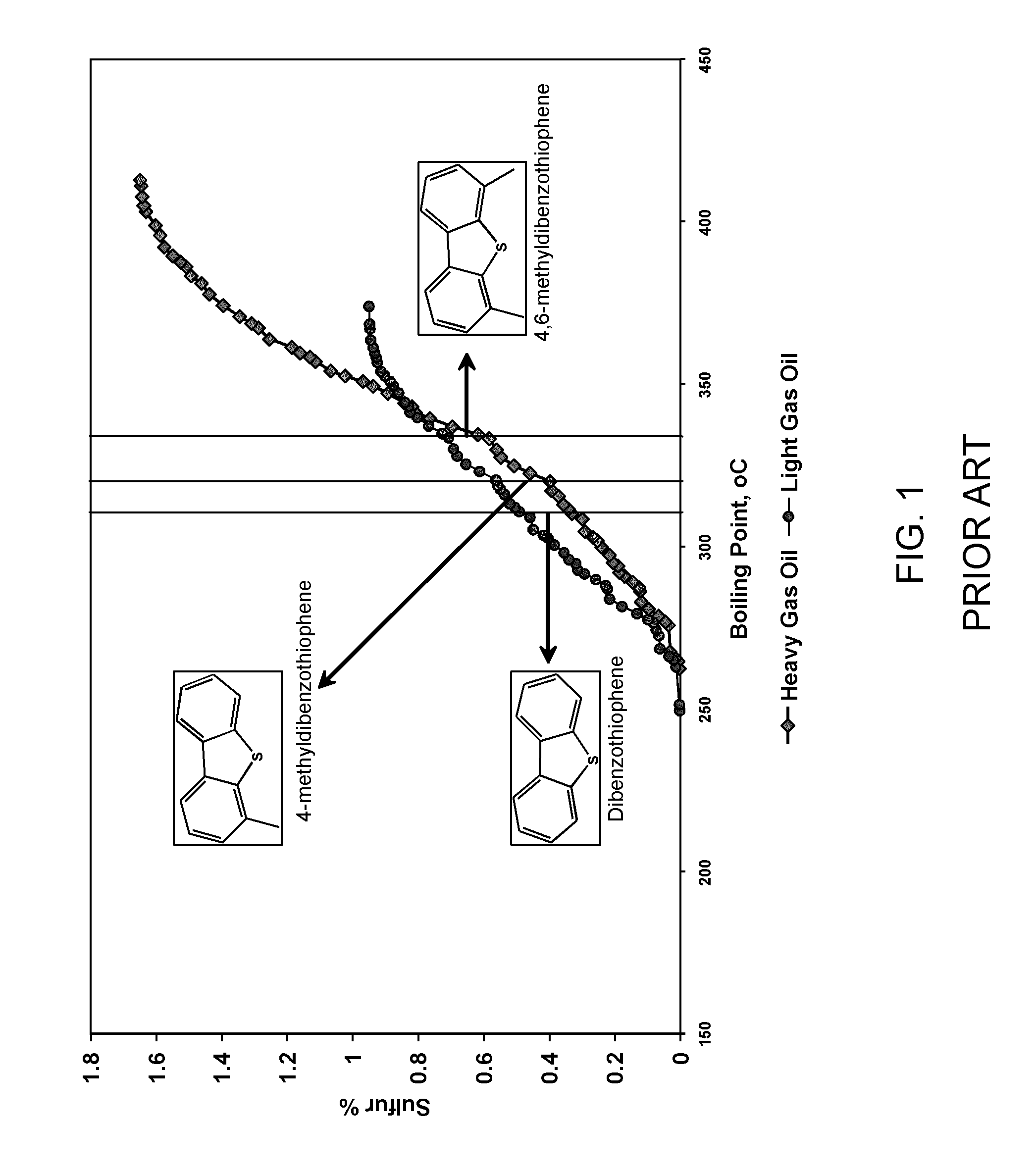
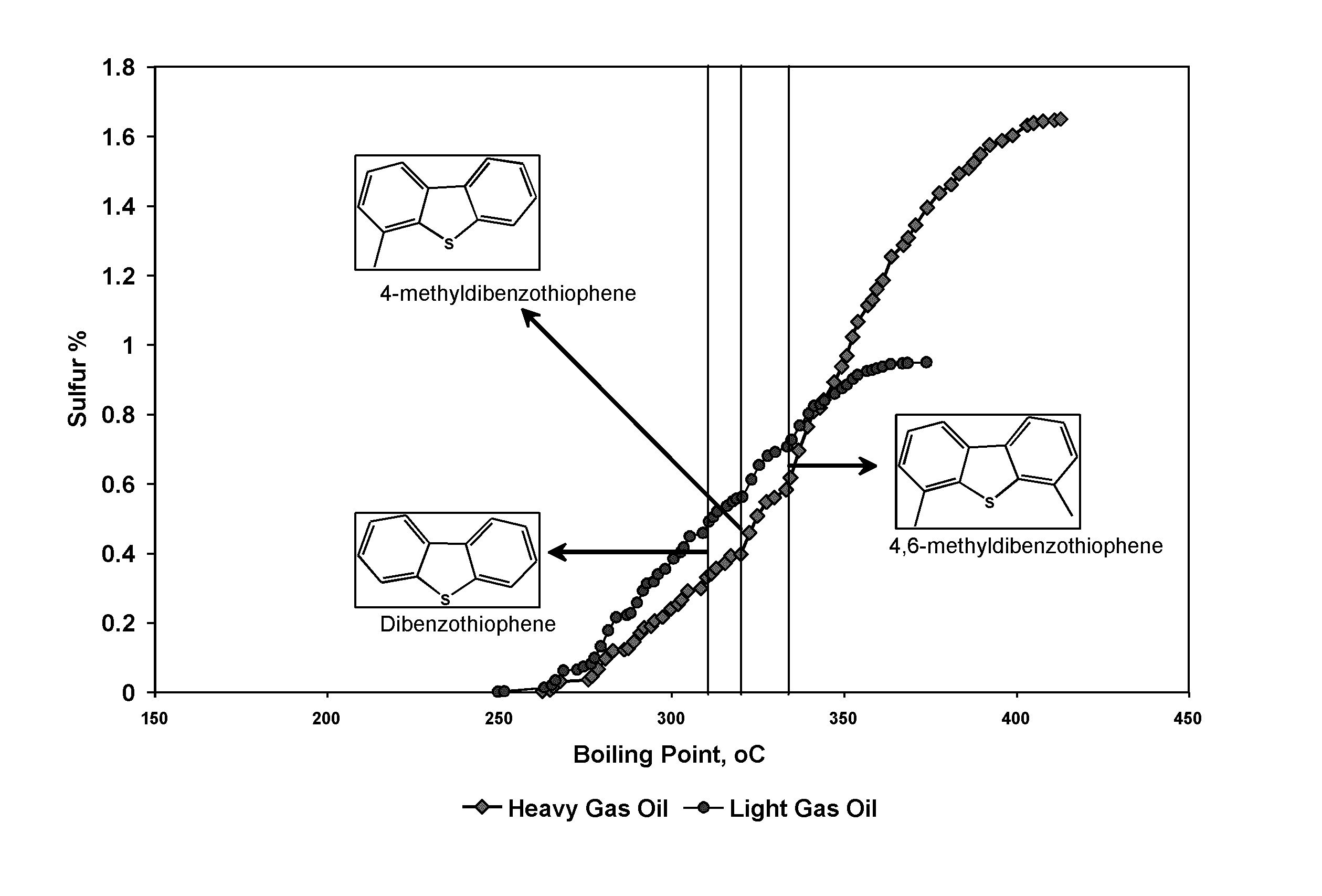
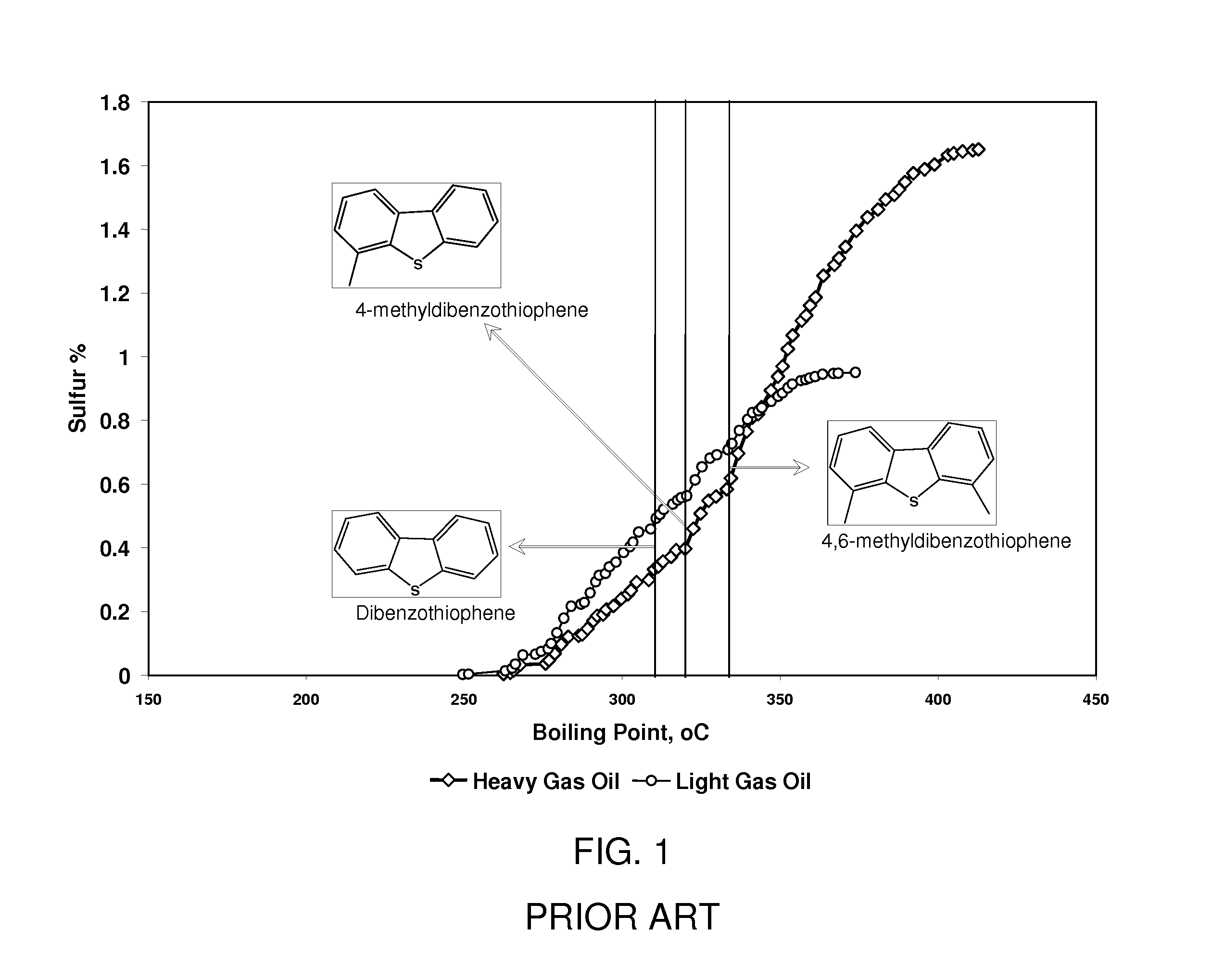
Mild hydrodesulfurization integrating gas phase catalytic oxidation to produce fuels having an ultra-low level of organosulfur compounds
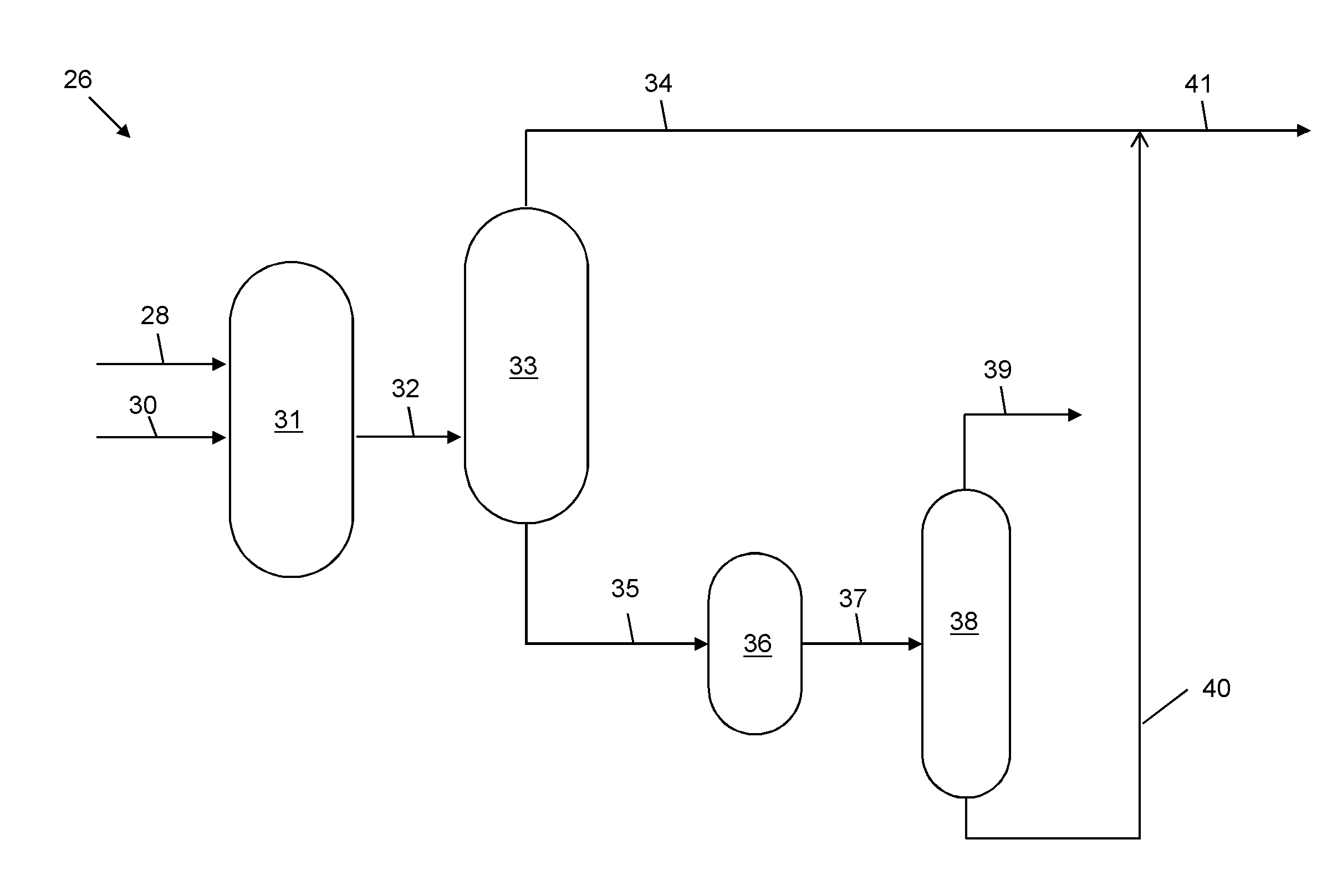
InactiveUS8906227B2Easy to useLow costRefining with metalsRefining with oxygen compoundsGas phaseHydrodesulfurization
Desulfurization of hydrocarbon feeds is achieved by first contacting the entire feed with a hydrodesulfurization catalyst in a hydrodesulfurization reaction zone operating under mild conditions; a flashing column downstream of the hydrodesulfurization reaction zone fractionates the effluent to obtain a first fraction which contains refractory organosulfur compounds and a second fraction that is substantially free of organosulfur compounds, since the organosulfur compounds boiling in the range of this fraction were the labile organosulfur compounds which were initially removed by mild hydrodesulfurization. The first fraction is contacted with a gaseous oxidizing agent over an oxidation catalyst having a formula CuxZn1-xAl2O4 in a gas phase catalytic oxidation reaction zone to convert the refractory organosulfur compounds to SOx and low sulfur hydrocarbons. The by-product SOx is subsequently removed, producing a stream containing a reduced level of organosulfur compounds.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO +1
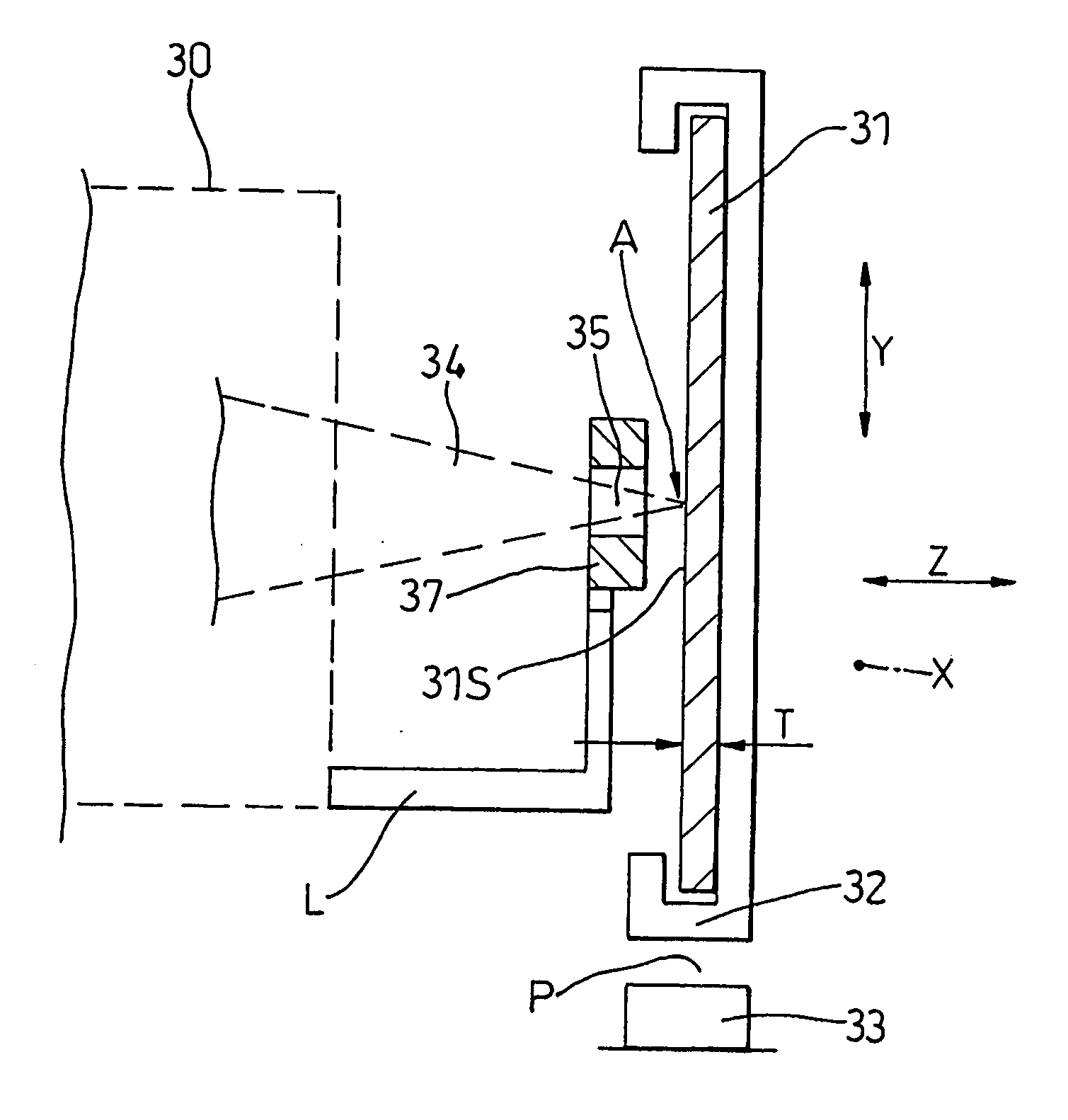
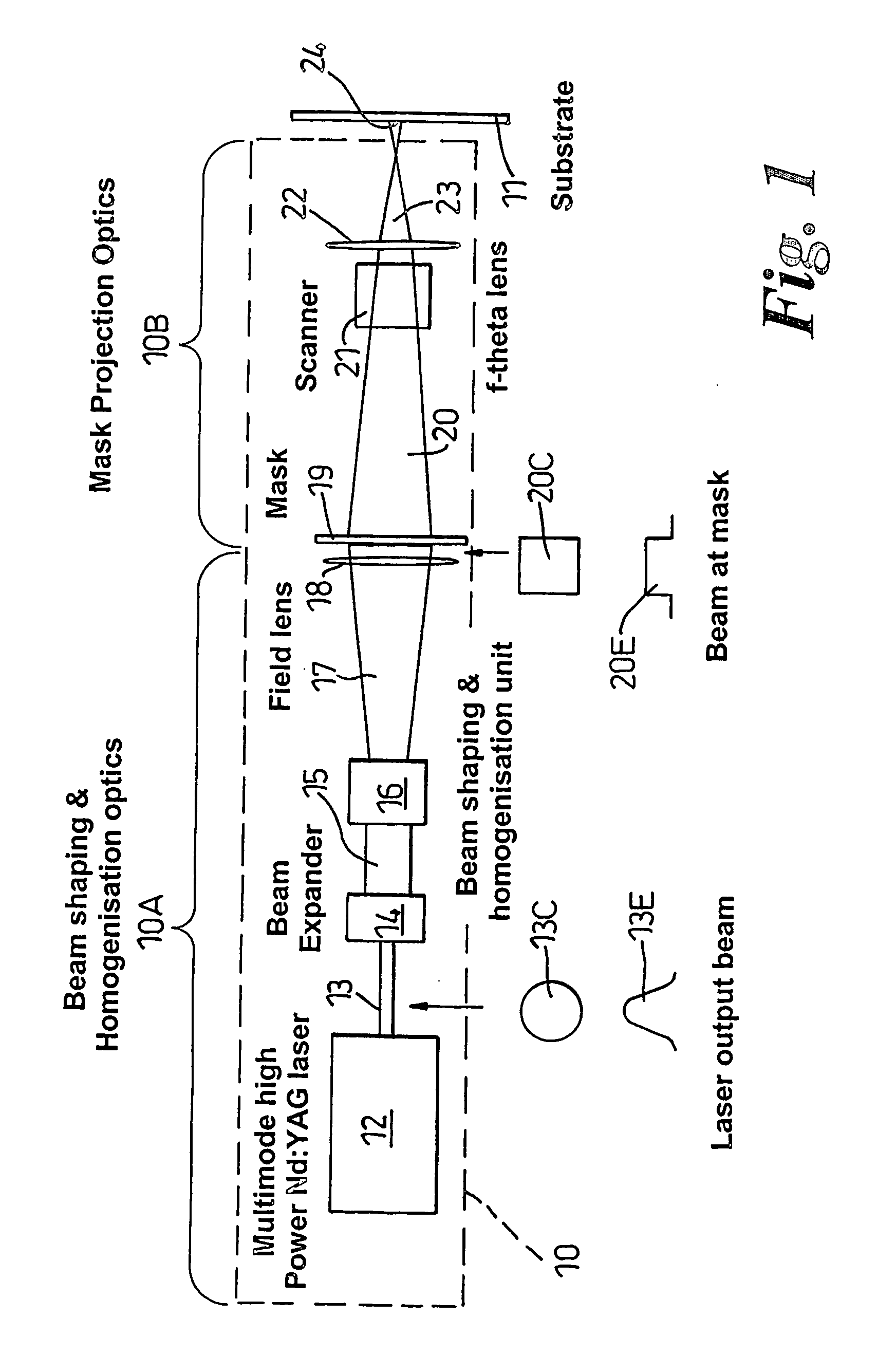
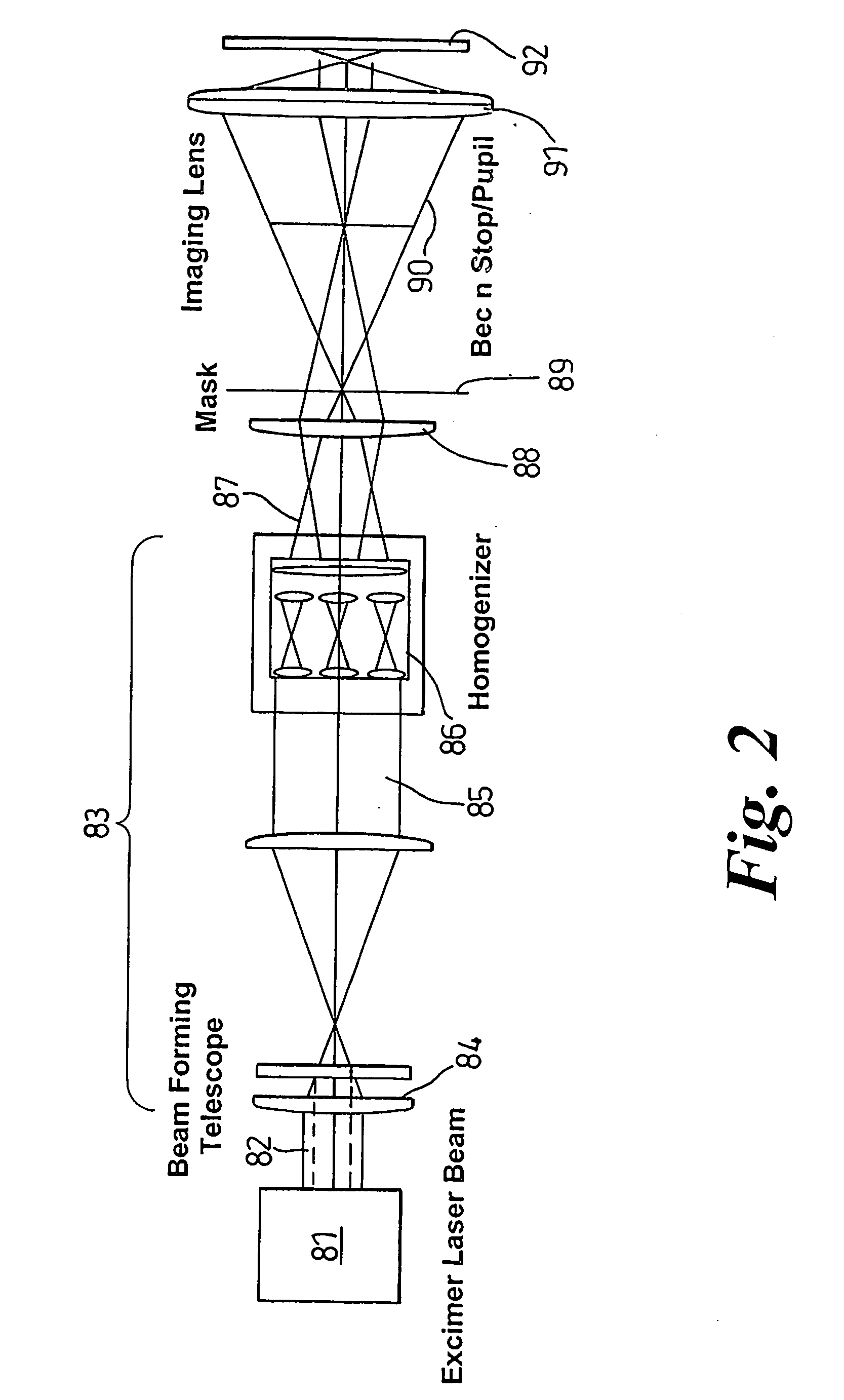
Positioning method, apparatus and a product thereof
InactiveUS20060196852A1Cost-effective processMetal working apparatusLaser beam welding apparatusTransport systemLight beam
A method of laser micro-machining a work piece, with a laser, including the steps of: locating the workpiece on a carrier forming a part of a transport system, the carrier can be displaced along a path parallel to an X-axis of the workpiece, a Y-axis lying transverse the path, and a Z-axis lying transverse the path; focusing an image generated by an output beam from the laser at a working datum position defined relative to the path which path is established by the transport system to traverse the first datum position; a plane defined by the X- and Y-axis lying substantially perpendicular to the output beam; and displacing the workpiece along the path by way of the transport system so as to enable the work-piece to be subject to micro-machining by way of the laser.
Owner:OERLIKON SOLAR AG (TRUEBBACH)
Dielectric plug in mosfets to suppress short-channel effects
InactiveUS20060076619A1Increasing source-drain junction capacitanceEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricShort-channel effect
The invention provides a technique to fabricate a dielectric plug in a MOSFET. The invention includes apparatus and systems that include one or more devices including a MOSFET having a dielectric plug. The dielectric plug is fabricated by forming an oxide layer over exposed source and drain regions in the substrate including a gate electrode stack. The formed oxide layer in the source and drain regions are then substantially removed to expose the substrate in the source and drain regions and to leave a portion of the oxide layer under the gate electrode stack to form the dielectric plug and a channel region between the source and drain regions.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Targeted desulfurization process and apparatus integrating gas phase oxidative desulfurization and hydrodesulfurization to produce diesel fuel having an ultra-low level of organosulfur compounds
InactiveUS8920635B2Easy to useLow costRefining with metalsRefining with oxygen compoundsGas phaseHydrodesulfurization
Desulfurization of hydrocarbon feeds is achieved by flashing the feed at a target cut point temperature to obtain two fractions. A first fraction contains refractory organosulfur compounds, which boils at or above the target cut point temperature. A second fraction boiling below the target cut point temperature is substantially free of refractory sulfur-containing compounds. The second fraction is contacted with a hydrodesulfurization catalyst in a hydrodesulfurization reaction zone operating under mild conditions to reduce the quantity of organosulfur compounds to an ultra-low level. The first fraction is contacted with gaseous oxidizing agent over an oxidation catalyst having a formula CuxZn1-xAl2O4 in a gas phase catalytic oxidation reaction zone to convert the refractory organosulfur compounds to SOx and low sulfur hydrocarbons. The by-product SOx is subsequently removed, producing a stream containing a reduced level of organo sulfur compounds.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO +1
Mild hydrodesulfurization integrating targeted oxidative desulfurization to produce diesel fuel having an ultra-low level of organosulfur compounds
InactiveUS20110220550A1Efficiently and cost-effectively reducingEasy to useRefining with oxygen compoundsTreatment with hydrotreatment processesOrganosulfur compoundsHydrodesulfurization
Deep desulfurization of hydrocarbon feeds containing undesired organosulfur compounds to produce a hydrocarbon product having low levels of sulfur, i.e., 15 ppmw or less of sulfur, is achieved by first contacting the entire feed with a hydrodesulfurization catalyst in a hydrodesulfurization reaction zone operating under mild conditions to remove the labile organosulfur compounds. A flashing column downstream of the hydrodesulfurization reaction zone fractionates the effluent at a target cut point temperature to obtain two hydrocarbon fuel fractions. A first fraction boiling at or above the target cut point temperature contains the remaining refractory organosulfur compounds. A second fraction boiling below the target cut point temperature is substantially free of organosulfur compounds, since the organosulfur compounds boiling in the range of this fraction were the labile organosulfur compounds which were initially removed by mild hydrodesulfurization. The first fraction is contacted with an oxidizing agent and an active metal catalyst in an oxidation reaction zone to convert the refractory organosulfur compounds to oxidized organosulfur compounds. These oxidized organosulfur compounds are subsequently removed, producing a stream containing an ultra-low level of organosulfur compounds. The two streams can be combined to obtain a full range hydrocarbon product having an ultra-low level of organosulfur compounds.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
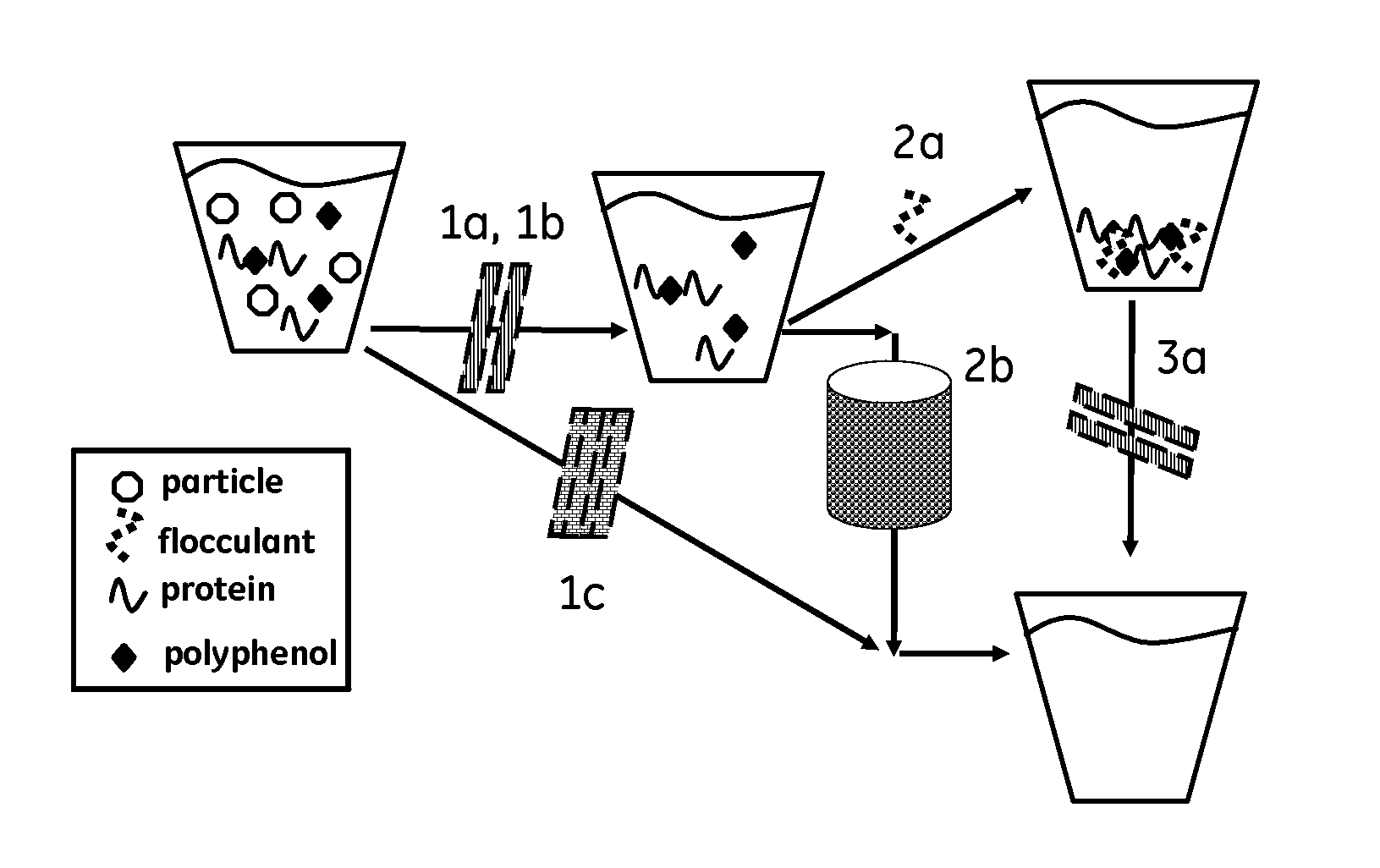
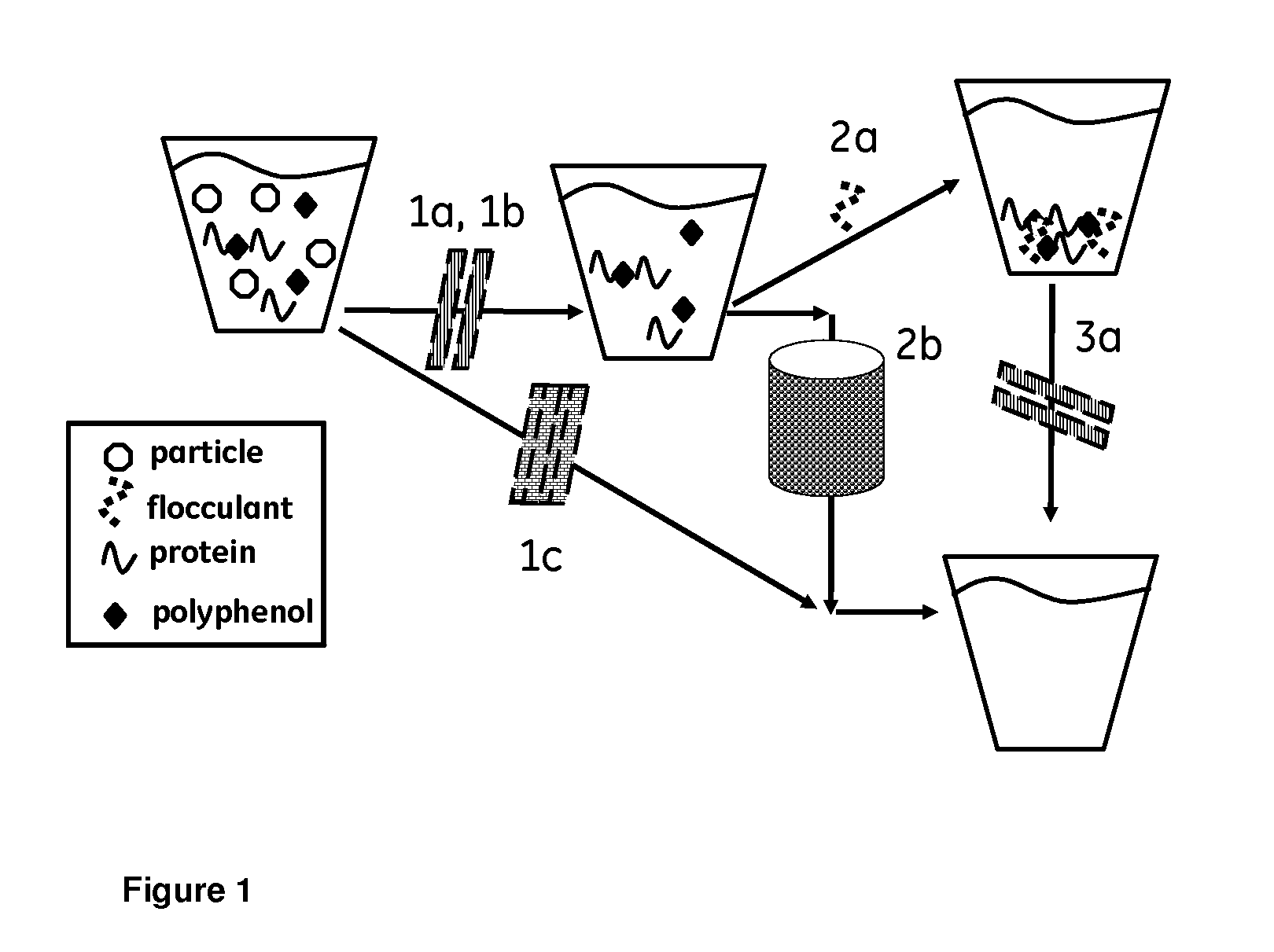
Method for liquid processing
InactiveUS20110097464A1More cost-effectivelyCost-effective processWort preparationWine preparationSuspended particlesWAS PROTEIN
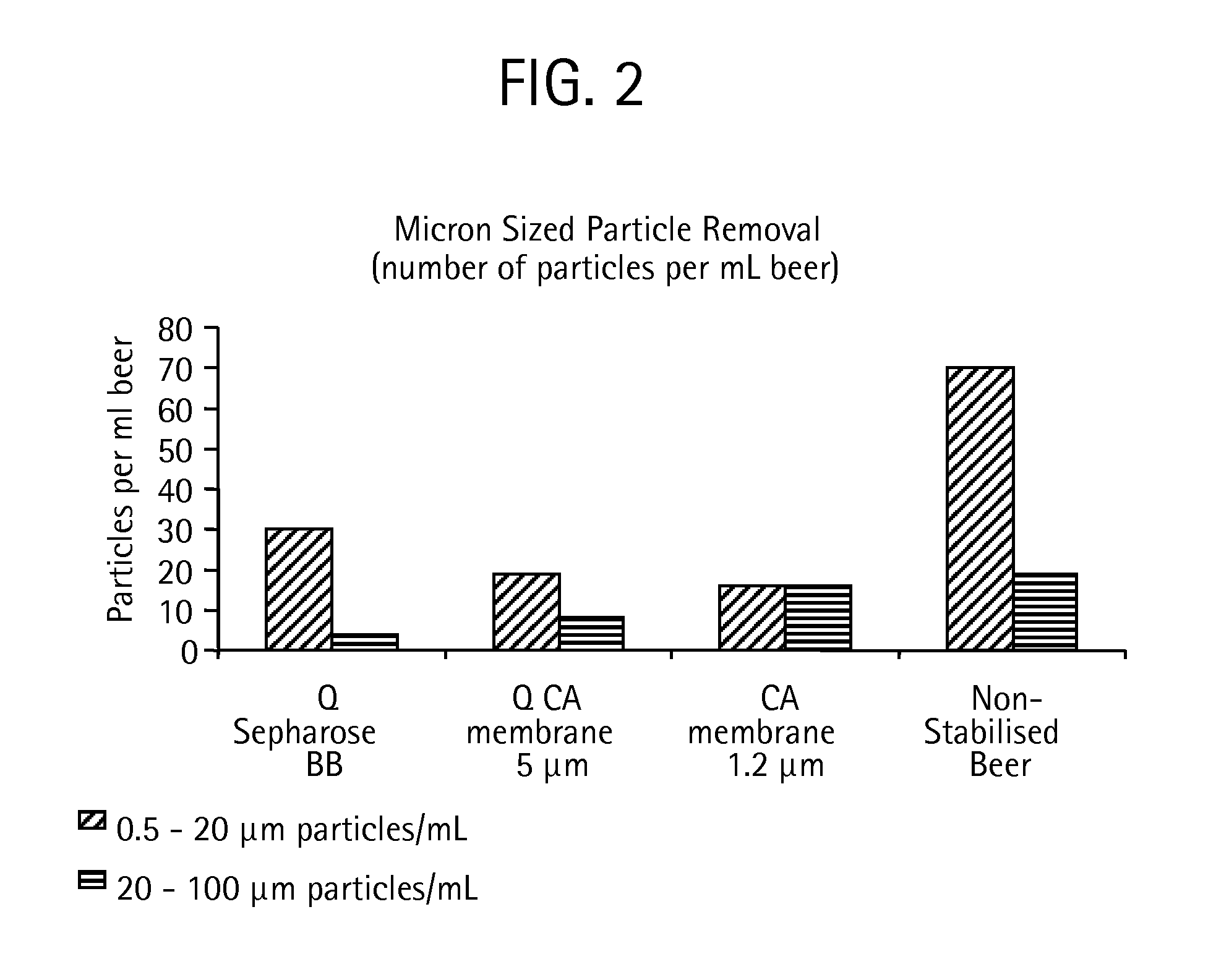
The present invention relates to liquid clarification and stabilization. More closely, the invention relates to both clarification by removal of suspended particles, as well as stabilization against formation of non-microbial haze via reduction of haze forming substances in various liquids. The haze forming substances are proteins and polyphenol tannins which occur in various plant related fluids such as beer wine, juices, flavorings, plant extracts, and even bioprocess streams. The method of the invention accomplishes both size based removal of colloidal non-haze related particles as well as adsorption based removal of haze forming substances without a need for added flocculants. The to method of the invention utilizes hydrophilic surfaces for adsorption of haze forming substances with such surfaces presented by materials arranged in manner so that size based exclusion of suspended particles is also achieved.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Thermoplastic moulding compositions with increased hydrolysis resistance
This invention relates to thermoplastic moulding compositions comprising A) polyamide and / or copolyamide, B) at least one copolymer of at least one olefin and of at least one acrylate of an aliphatic alcohol, C) at least one filler and / or reinforcing material, D) at least one oligomeric and / or polymeric carbodiimide, and optionally also at least one other additive E) and optionally at least one impact modifier F). The invention further relates to mouldings or semifinished products which are produced from the moulding compositions according to the invention, preferably by means of injection moulding. However, the present invention also relates to the use of a substance combination made of at least one component B) and of at least one component D) for improving the hydrolysis resistance of polyamide-based products.
Owner:LANXESS DEUTDCHLAND GMBH
Process for the preparation of a polypeptide
InactiveUS20090035816A1Improve stabilityEase of storage and transportationPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsTyrosineL-alanosine
A process for the preparation of a polypeptide made from amino acids L-alanine, L-glutamic acid, L-lysine, and L-tyrosine comprising using N-thiocarboxyanhydride of at least one amino acid as a starting material.
Owner:SCINOPHARM TAIWAN LTD
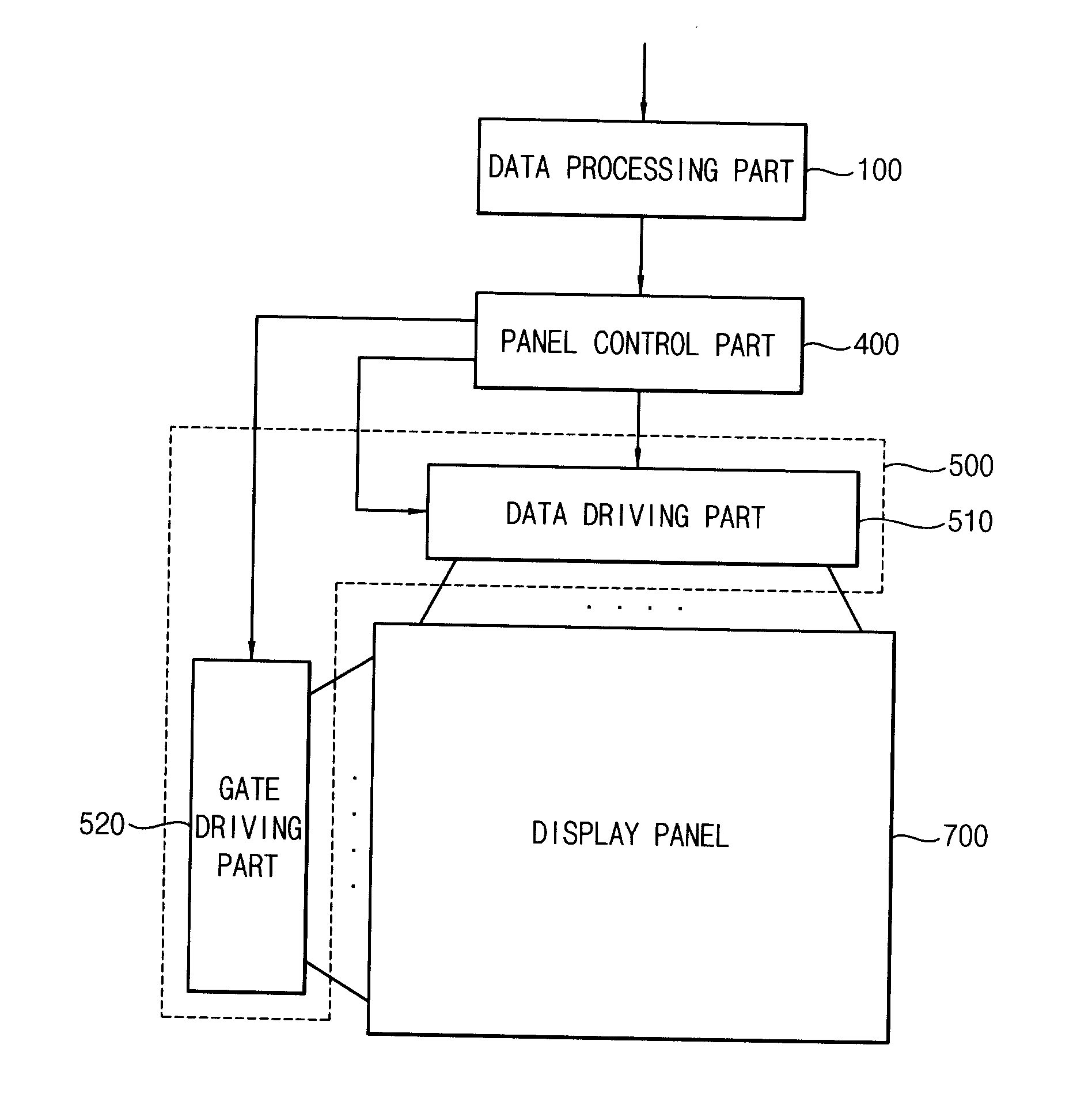
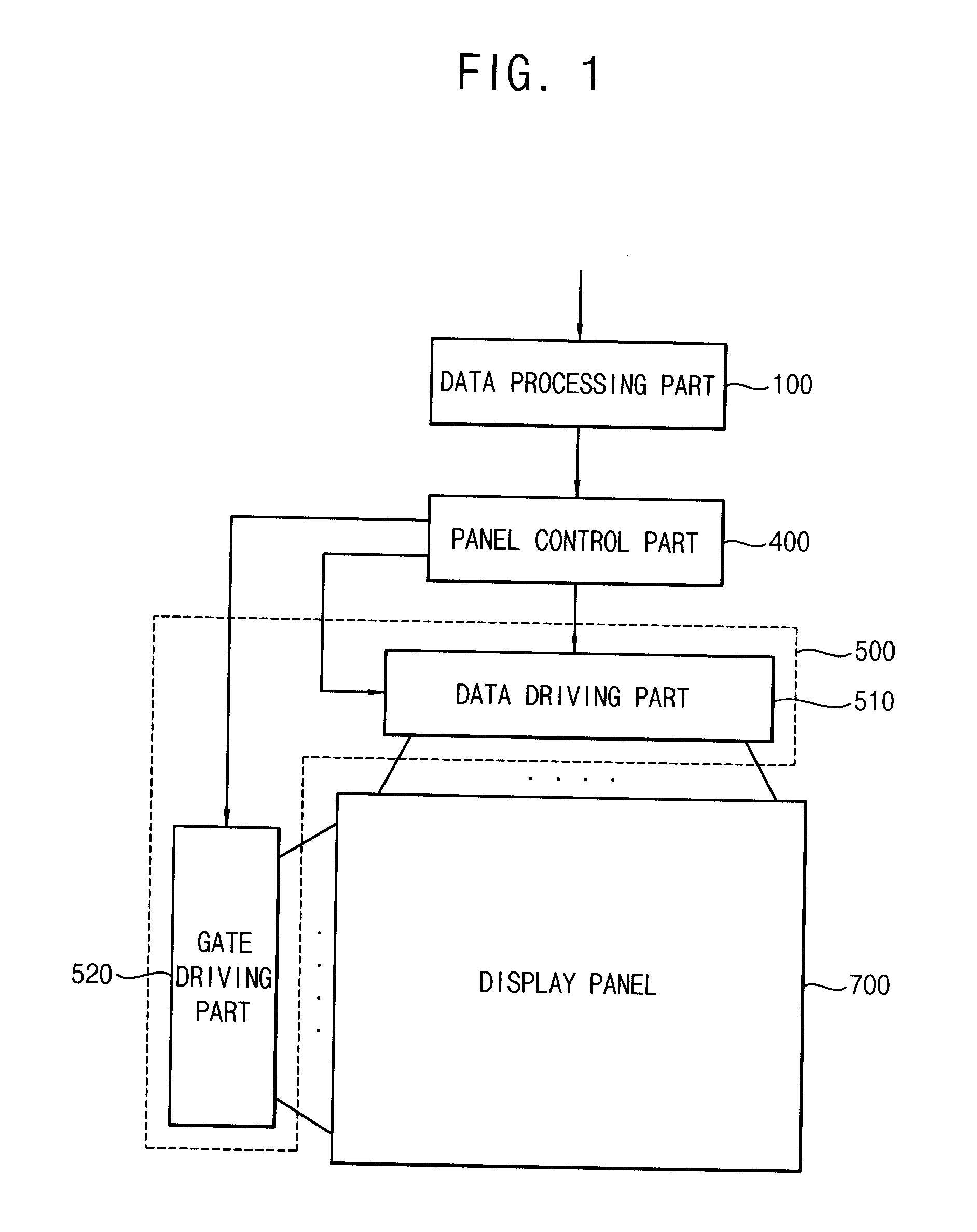
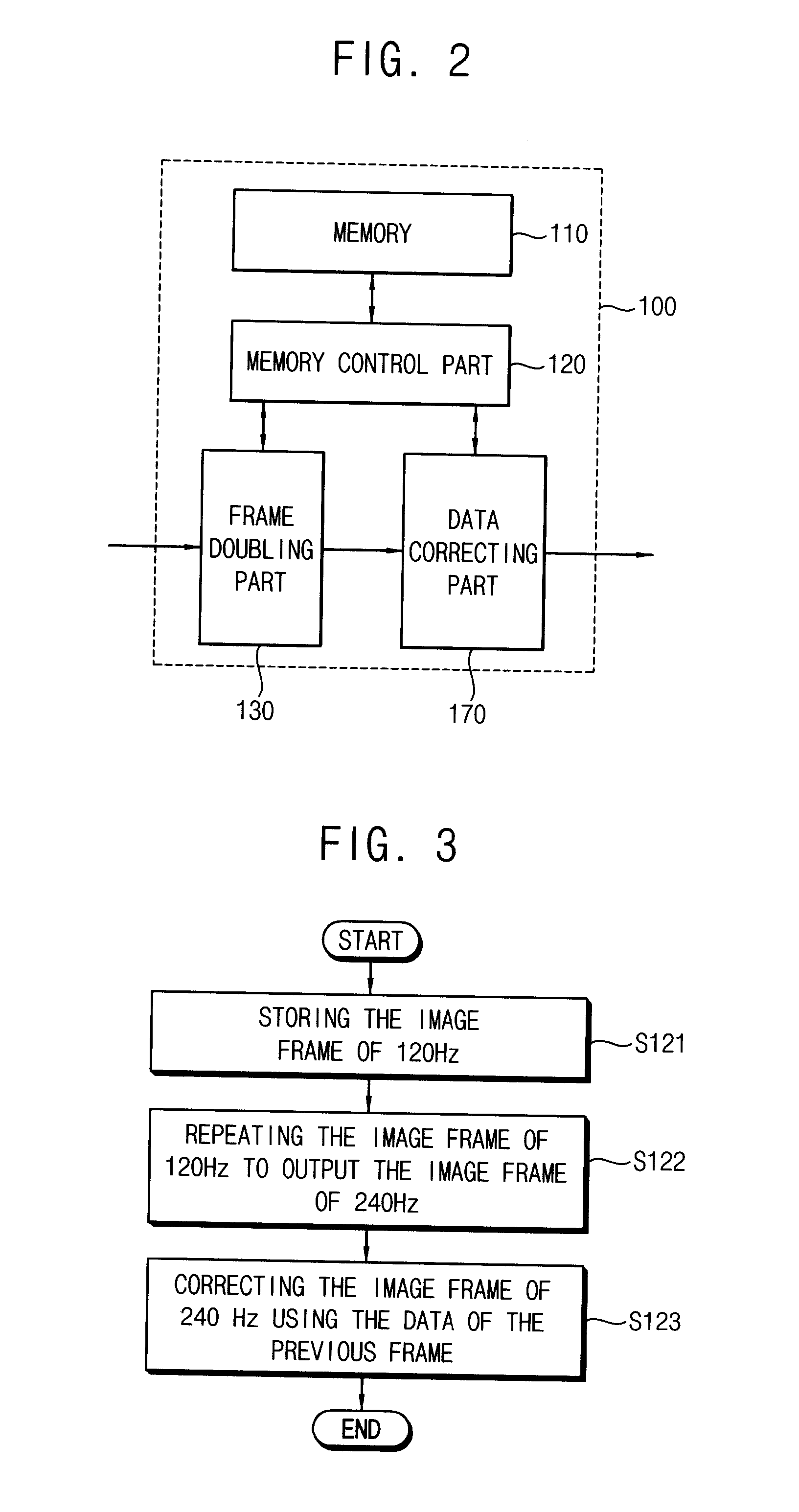
Method of processing image data, method of displaying image using the same and display apparatus performing the method of displaying image
ActiveUS20120068999A1Cost-effective processCost-effectiveCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsData storingData store
A method of processing image data comprises storing image frame data in a first memory, repetitively reading the image frame data stored in the first memory to output high frequency image frame data and correcting the high frequency image frame data based on previous frame data.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Process for preparing alkylene oxide
InactiveUS6365761B1Extended service lifeLong catalyst lifeMolecular sieve catalystsOther chemical processesSufficient timeFixed bed
Process for the preparation of alkylene oxide, which process comprises passing a feed comprising an organic hydroperoxide and alkene through a bank of at least two serially connected reactors all containing a bed of heterogeneous epoxidation catalyst particles and operated in a cyclic mode, in which process:(a) the first reactor of the cyclically operated bank is put in a position further down this bank, when the activity of the epoxidation catalyst contained therein has decreased to an undesirably low level;(b) in this position the catalyst with decreased activity is contacted with the effluent from the reactor in the preceding position at a temperature which is at least 5° C. higher than the final temperature at which the catalyst was in use in the first position of the bank and for sufficient time to restore its activity to the desired level. The bank of cyclically operated epoxidation reactors may be followed by one or more additional fixed bed epoxidation reactors which are not operated cyclically.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Commercially viable process for in vitro mass culture of jatropha curcas
InactiveUS20080194026A1Reduced phytohormone levelCost-effective processTissue culturePlant tissue cultureJatropha platyphyllaDisease free
The present invention relates to a commercially viable process for in vitro mass culture of Jatropha curcas. The process for in vitro mass culture of Jatropha curcas is simple, faster, and suitable for production of disease-free root tubers of uniform quality and employs media with a reduced concentration of phytohormones.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
Apparatus, method and use for screening the magnetic field of an RFID transponder
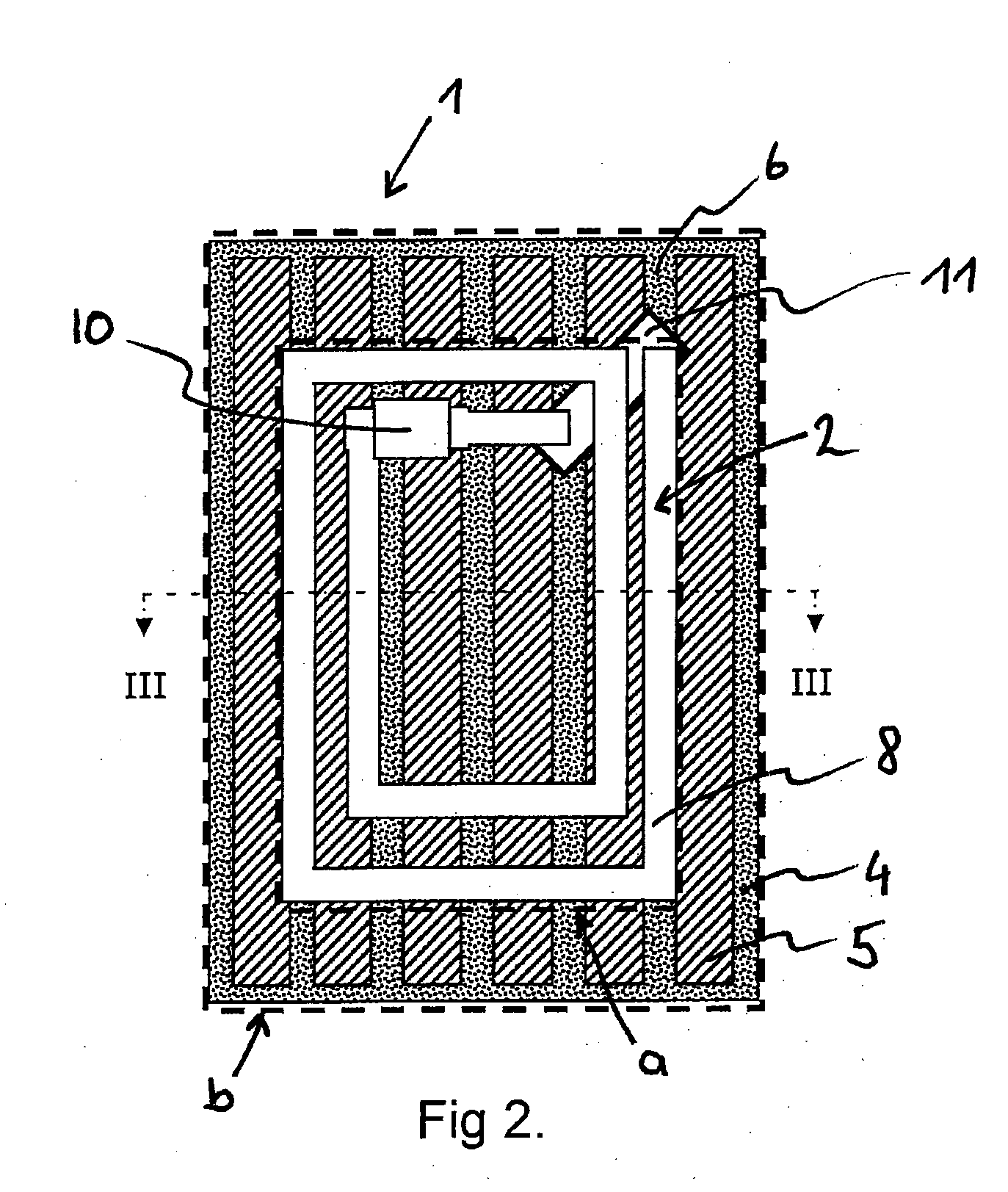
ActiveUS20100201596A1Reduced loss of functionalityCost-effective processNear-field transmissionAntenna couplingsElectrical conductorEddy current
An apparatus for screening the magnetic field of a transponder is described, which apparatus comprises, in a first area section, at least one flat antenna structure which comprises conductor tracks for conducting current in a direction of current flow and has an application-specific extent, wherein the apparatus comprises a second area section or carrier to which strips of a highly permeable screening material are applied such that they are oriented with respect to one another in a predetermined manner, wherein the second area section is arranged parallel to the first area section. In order to effectively screen the magnetic field which is beamed in from the outside, for instance by a reader, and in order to effectively screen the magnetic field which is generated by the antenna structure of the transponder itself following excitation, and in order to reduce eddy current losses in a metal area arranged underneath, the highly permeable screening material has either anisotropic permeability, wherein increased permeability is provided in the direction of current flow, in particular in the direction of the conductor tracks of important sections of the antenna structure, or else provides for the strips to be oriented parallel to one another in important sections, wherein the longitudinal edges of the strips are provided in the direction of current flow, in particular in the direction of the conductor tracks of important sections of the antenna structure.
Owner:IDENTIV GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com