Patents
Literature
3322 results about "Solar module" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
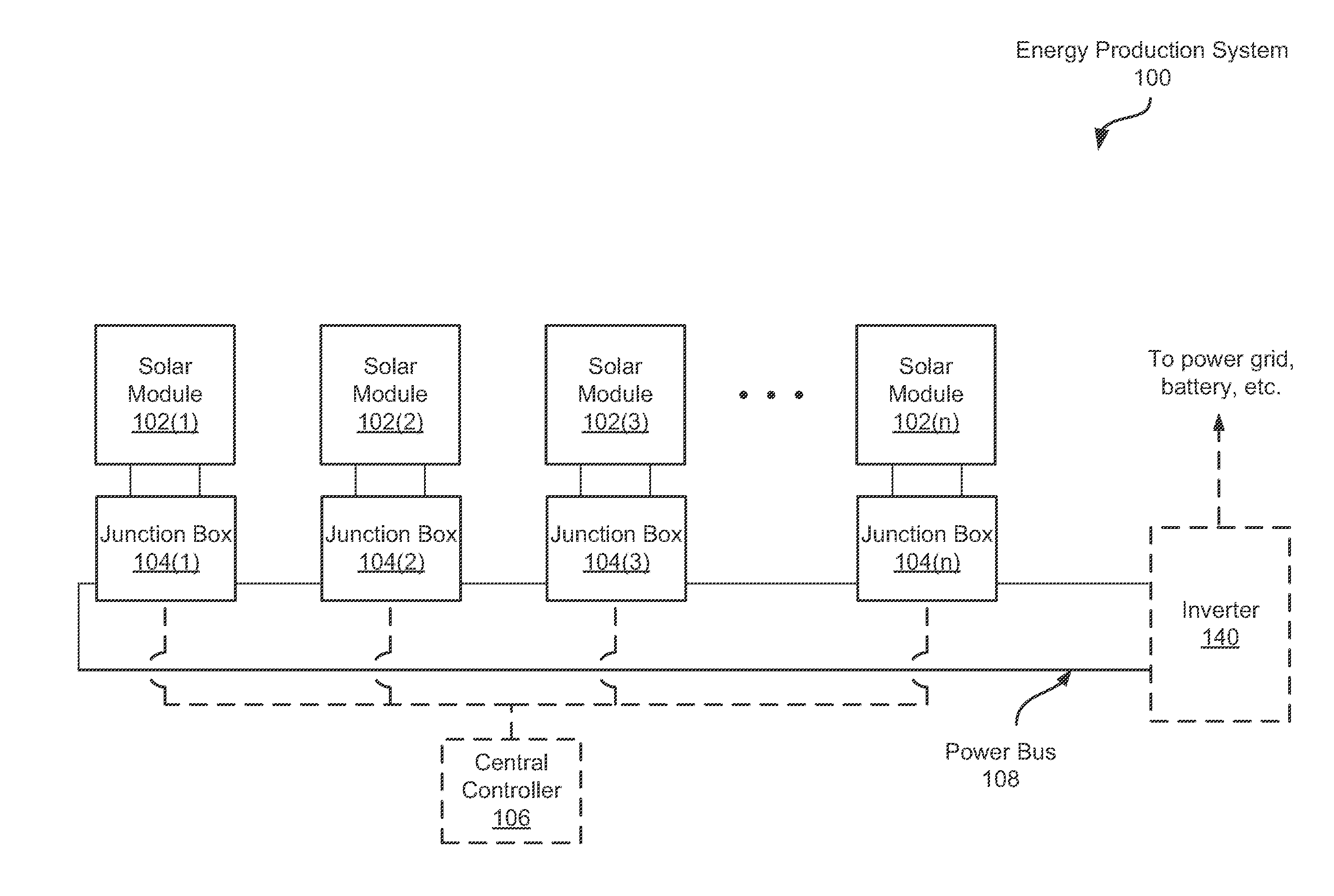
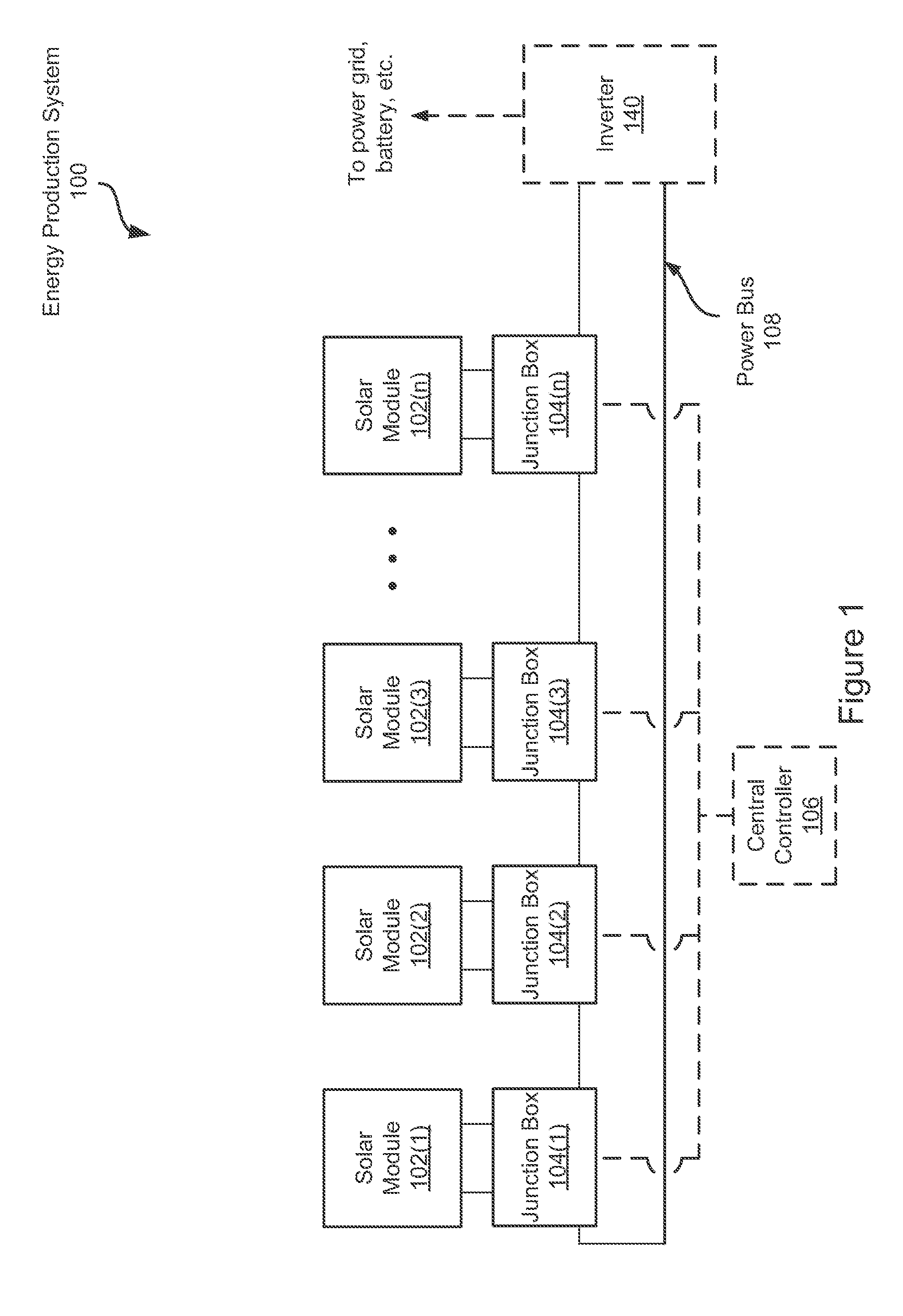
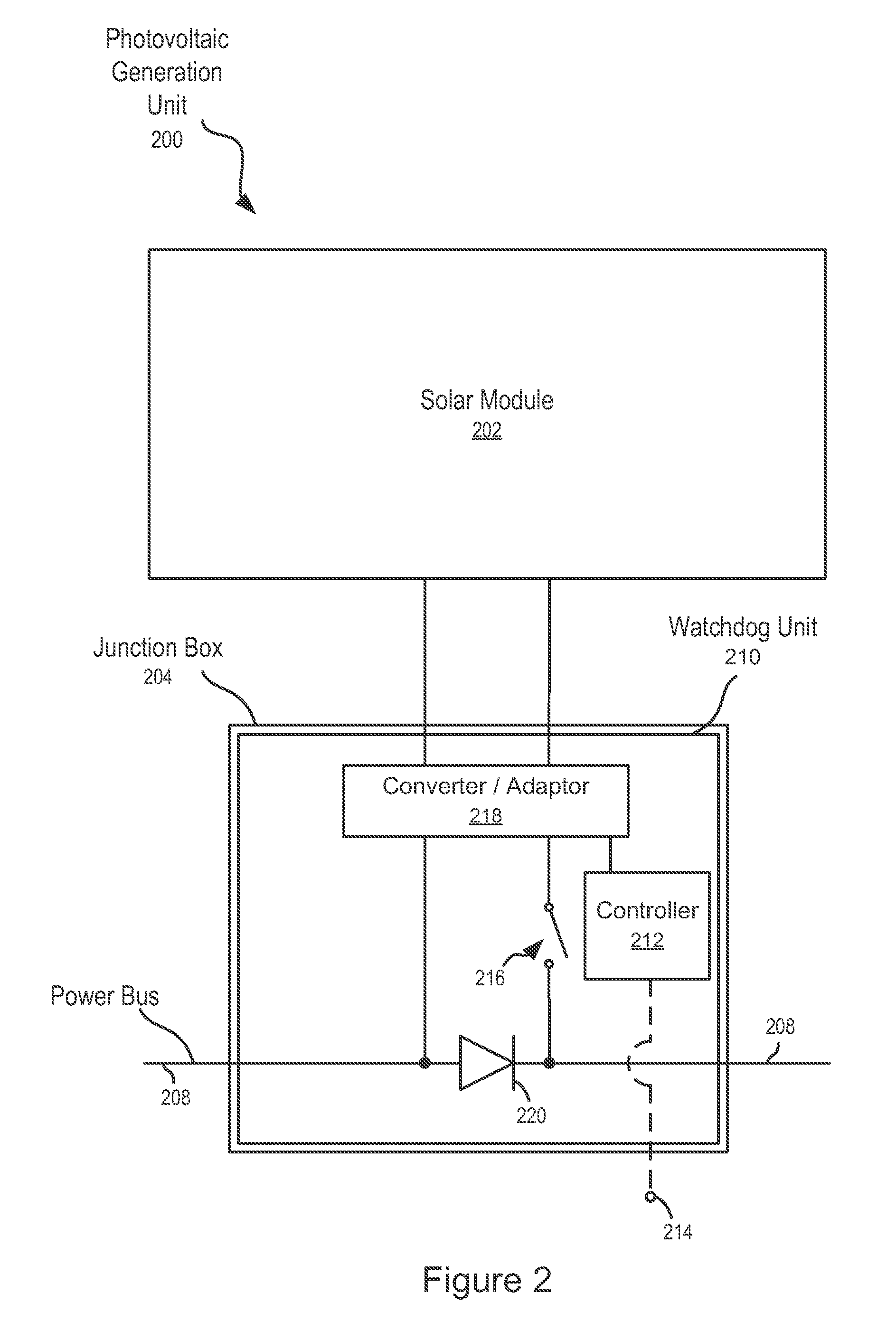
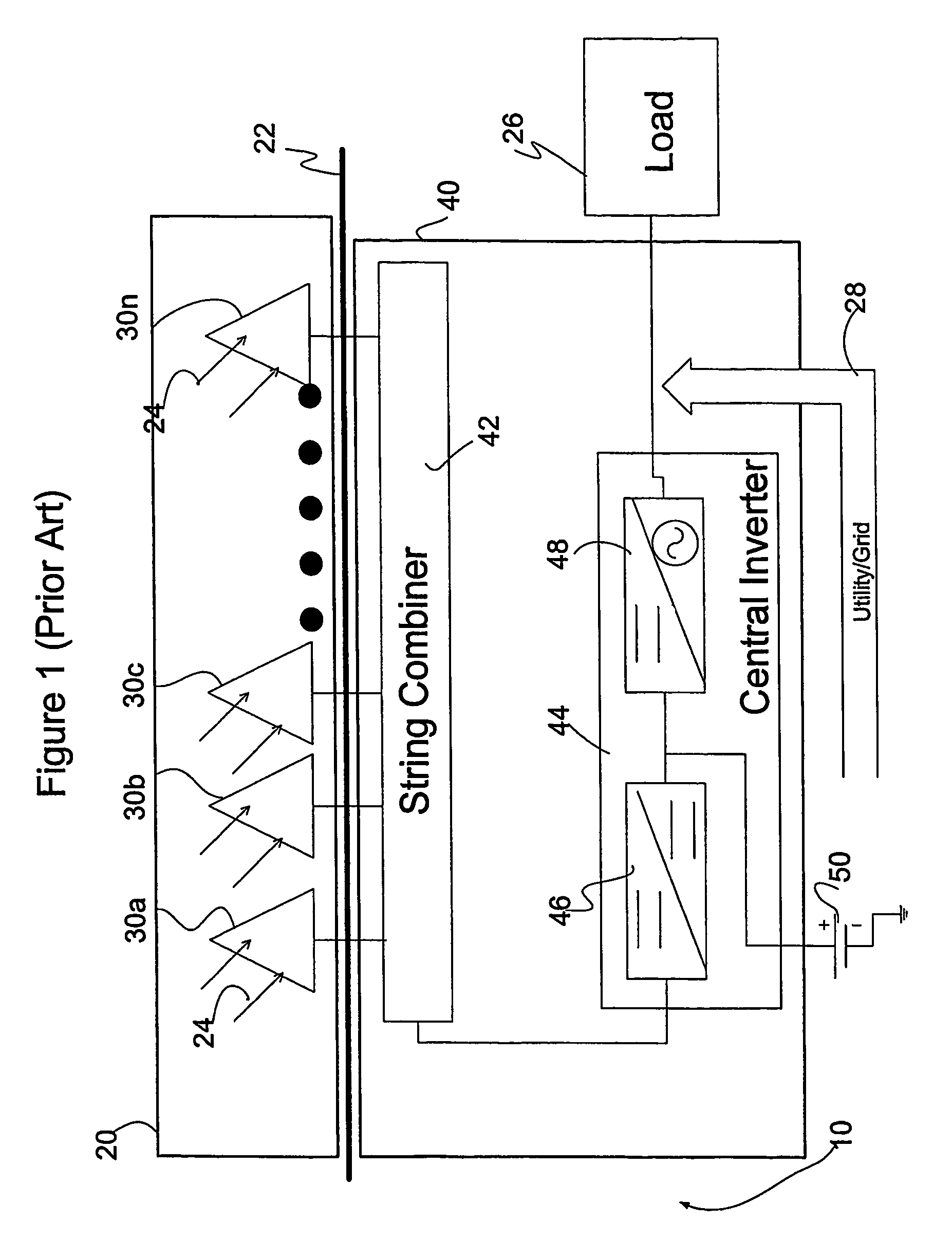
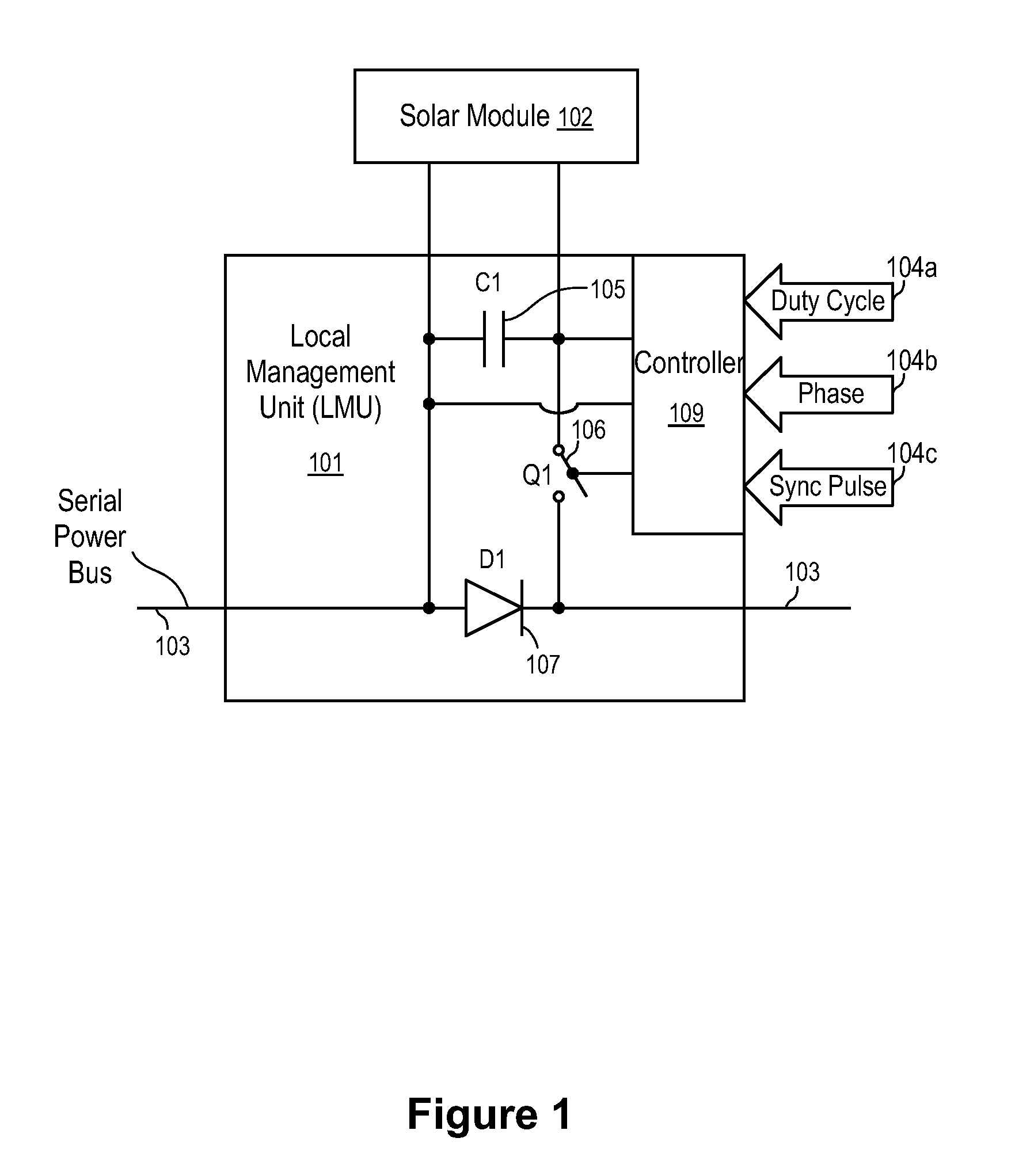
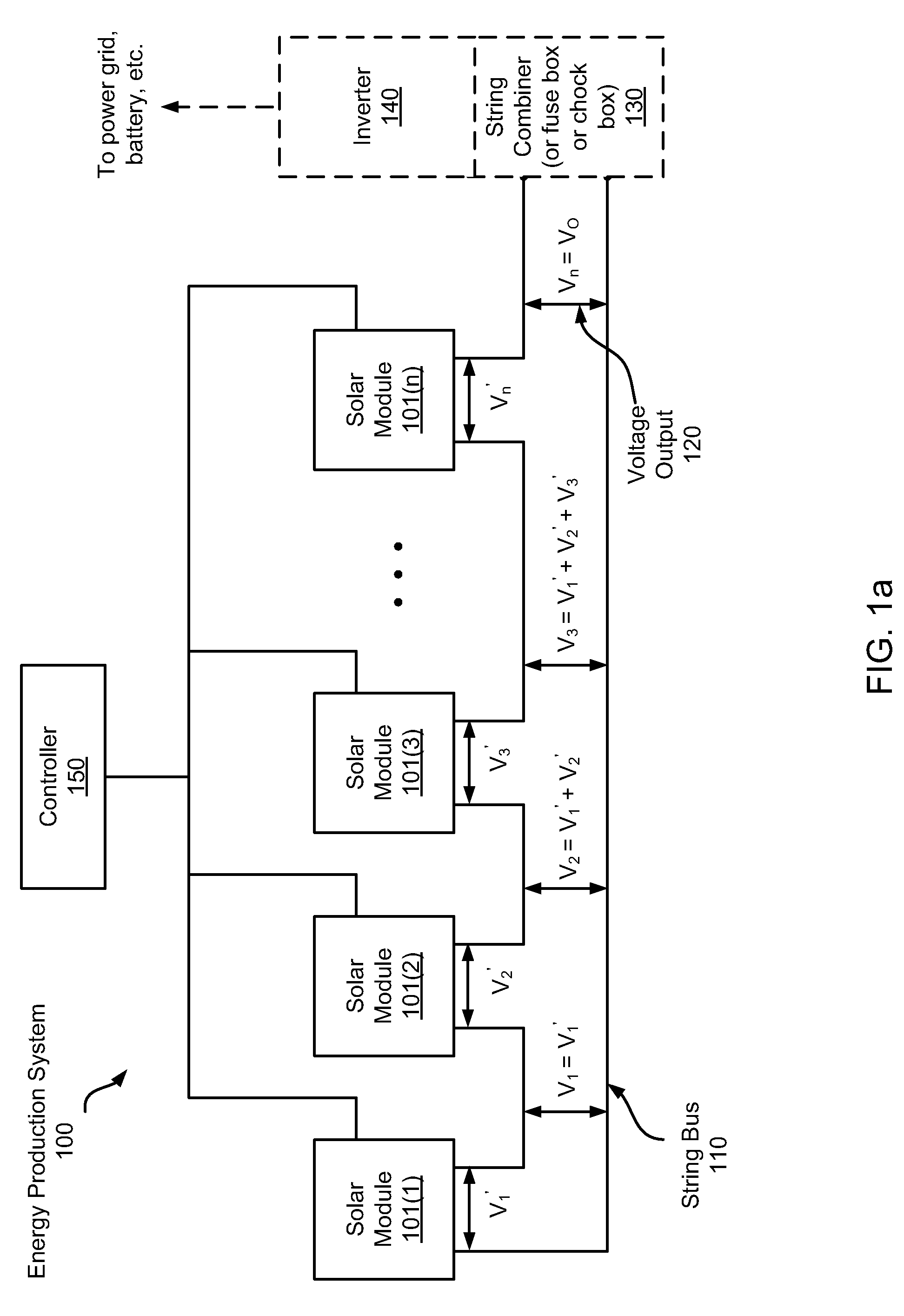
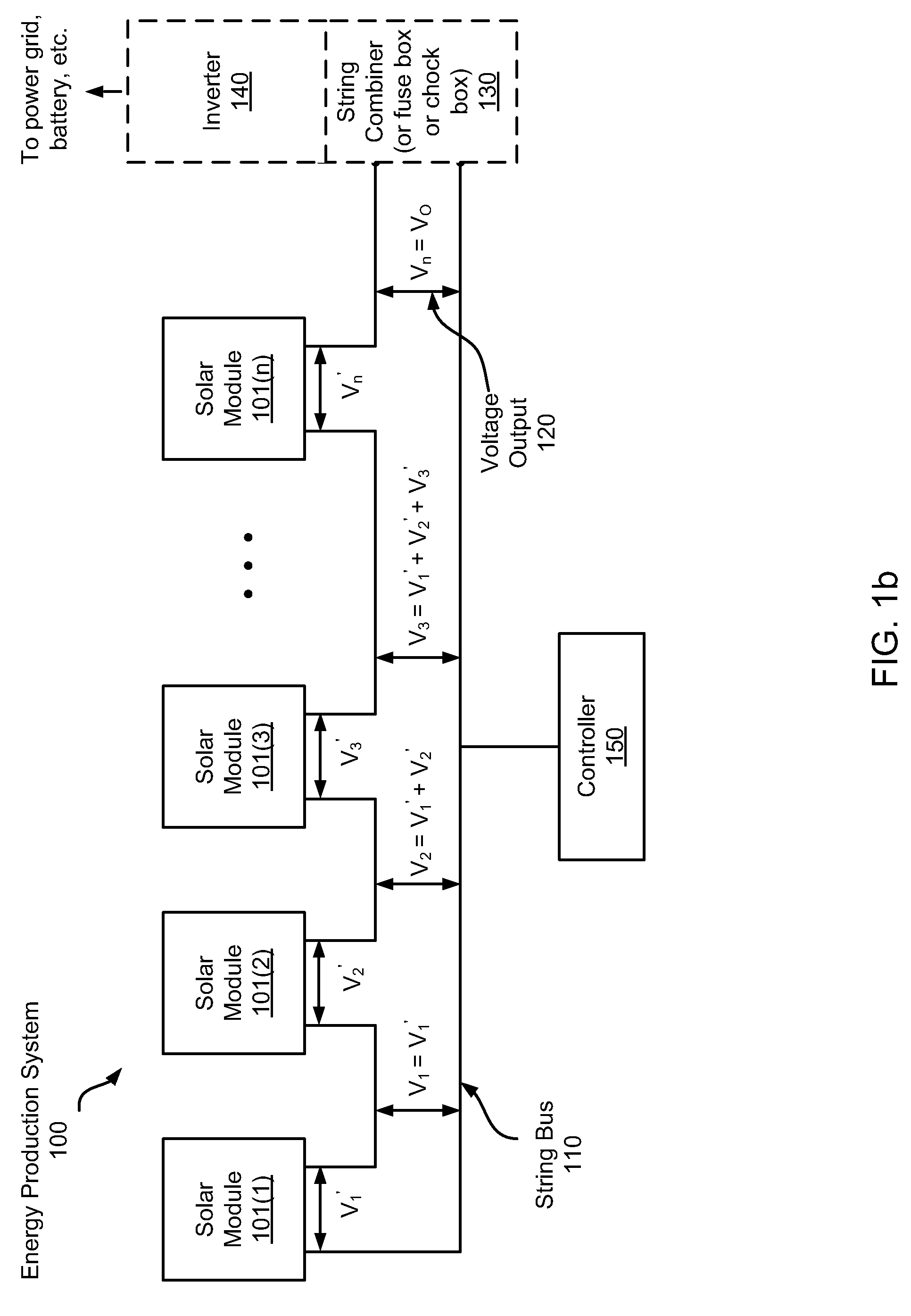
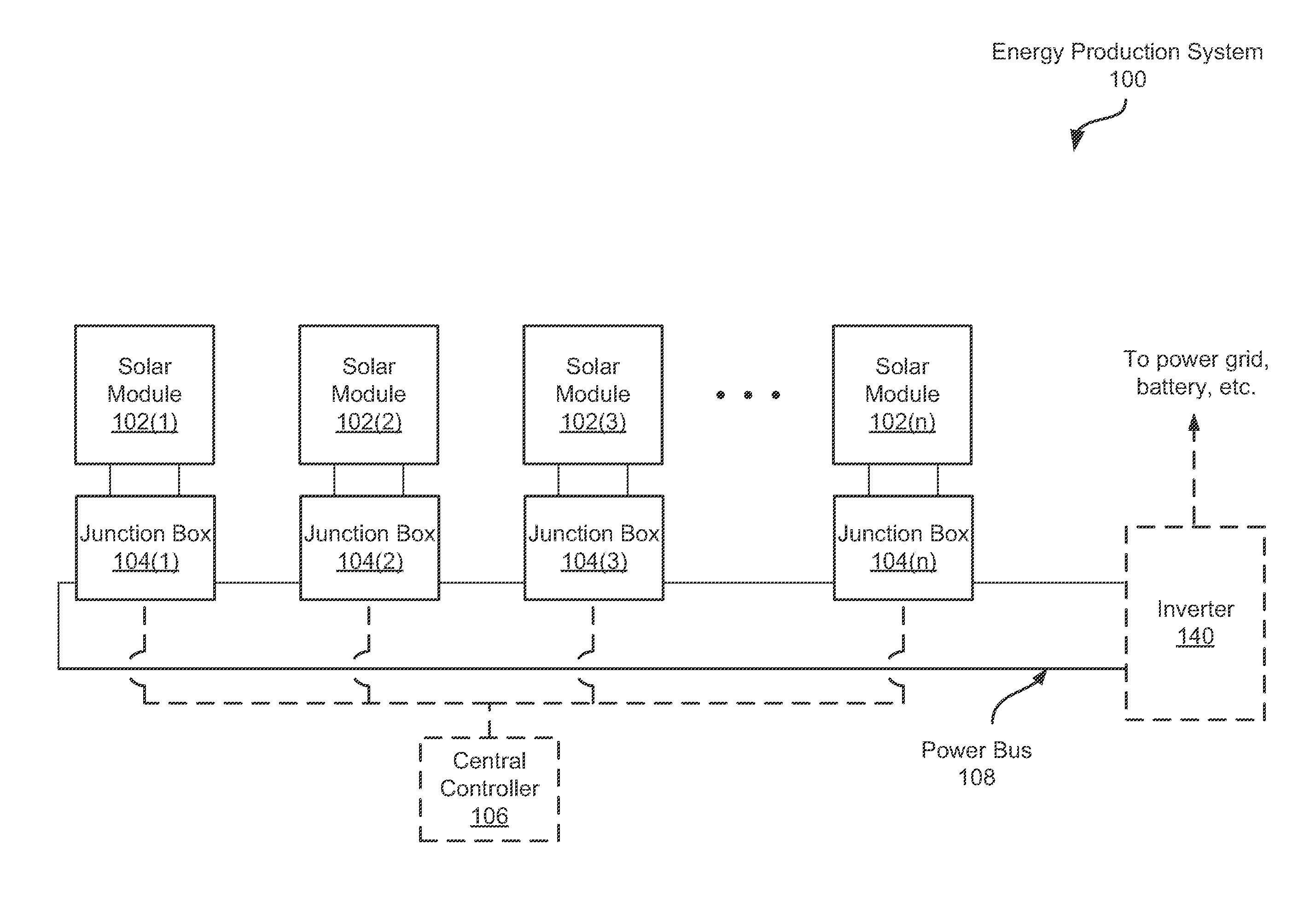
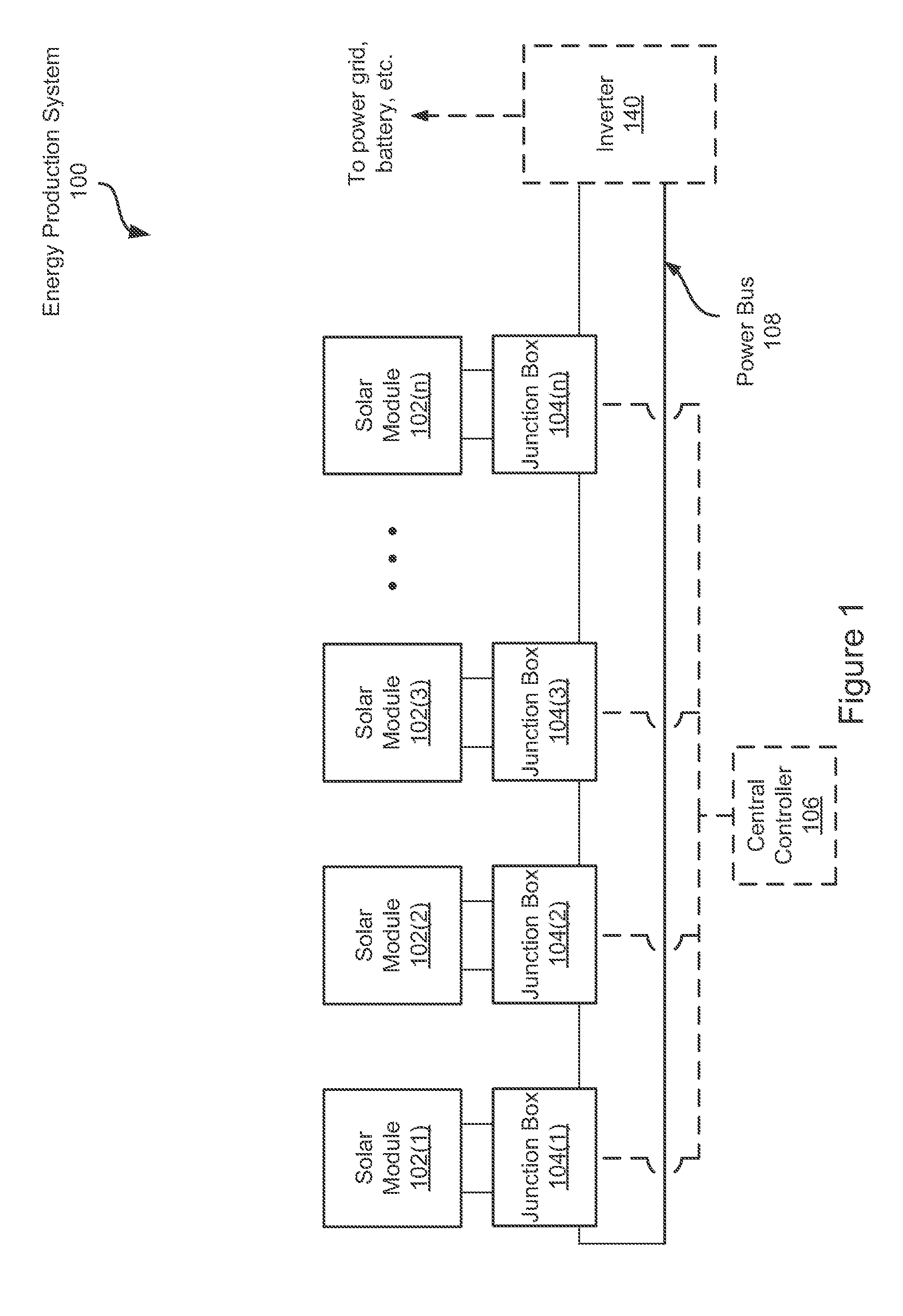
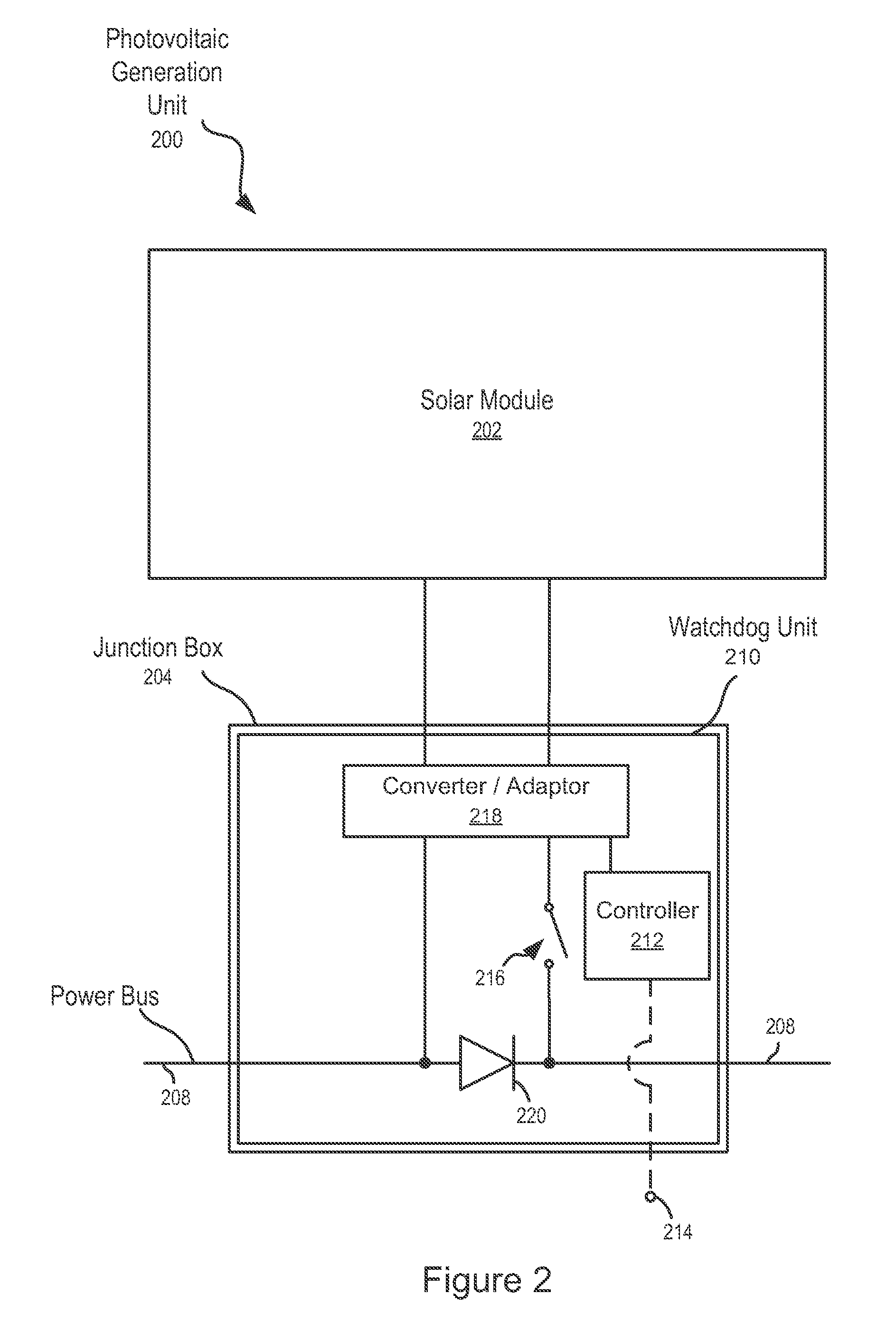
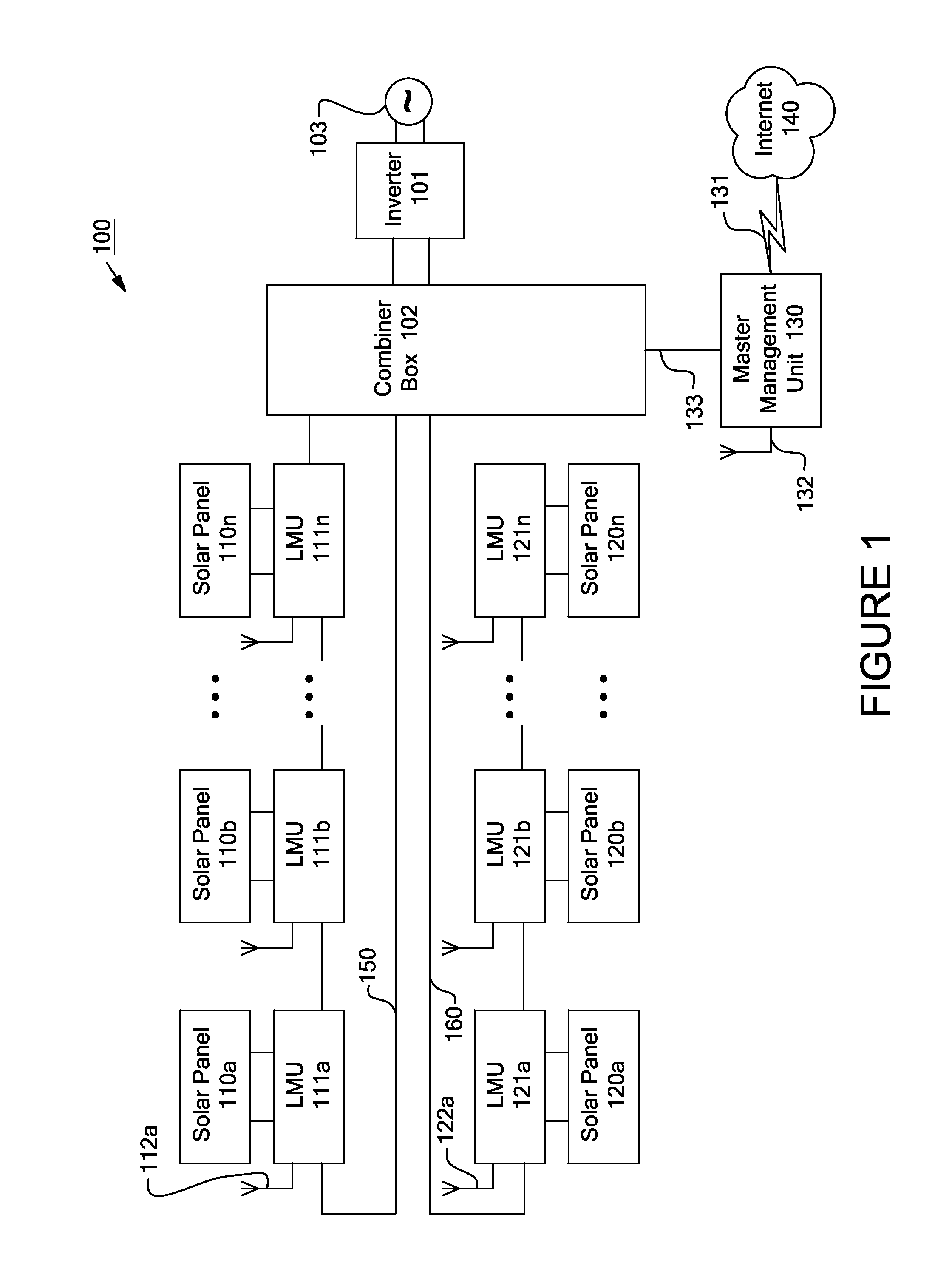
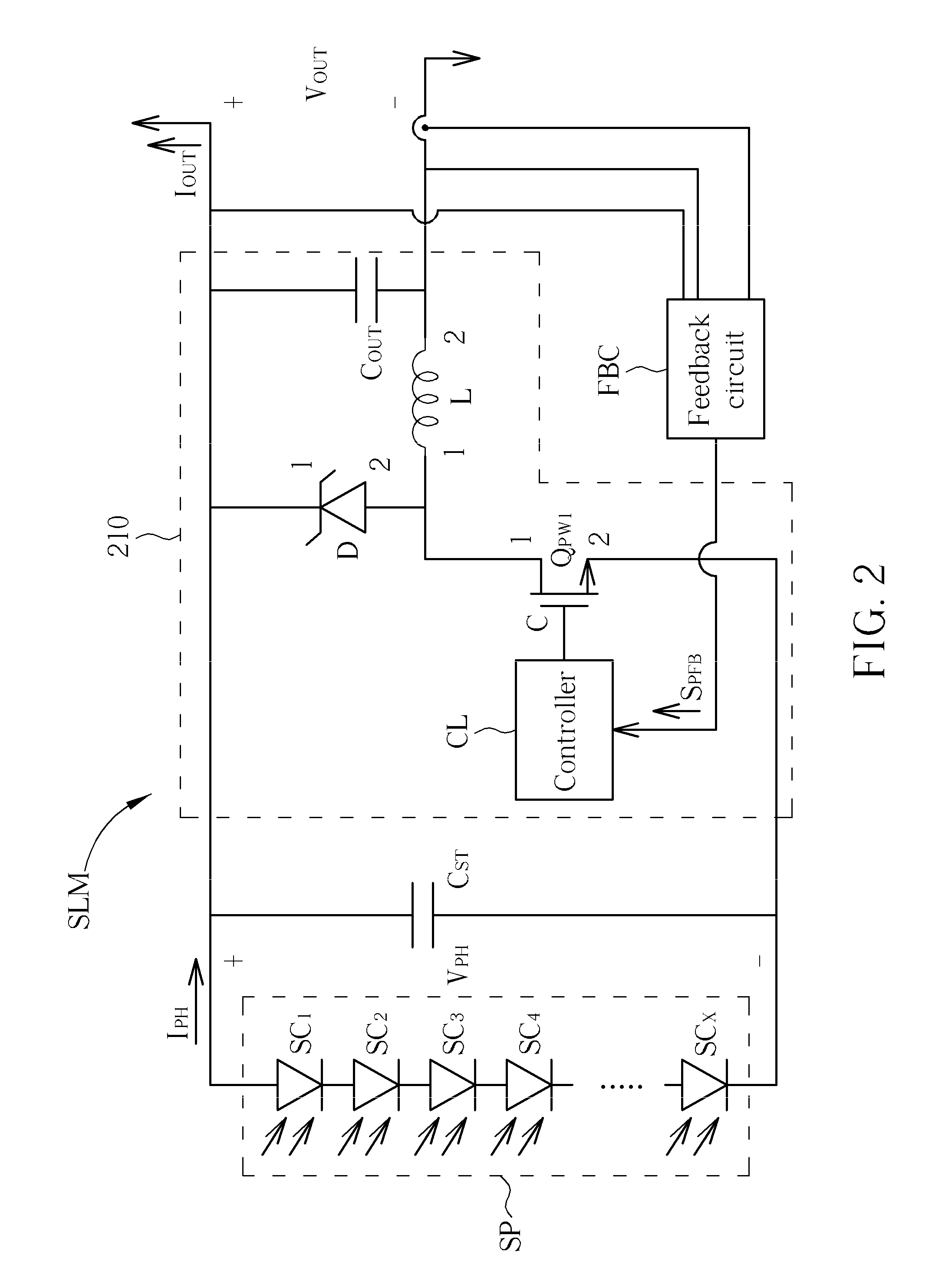
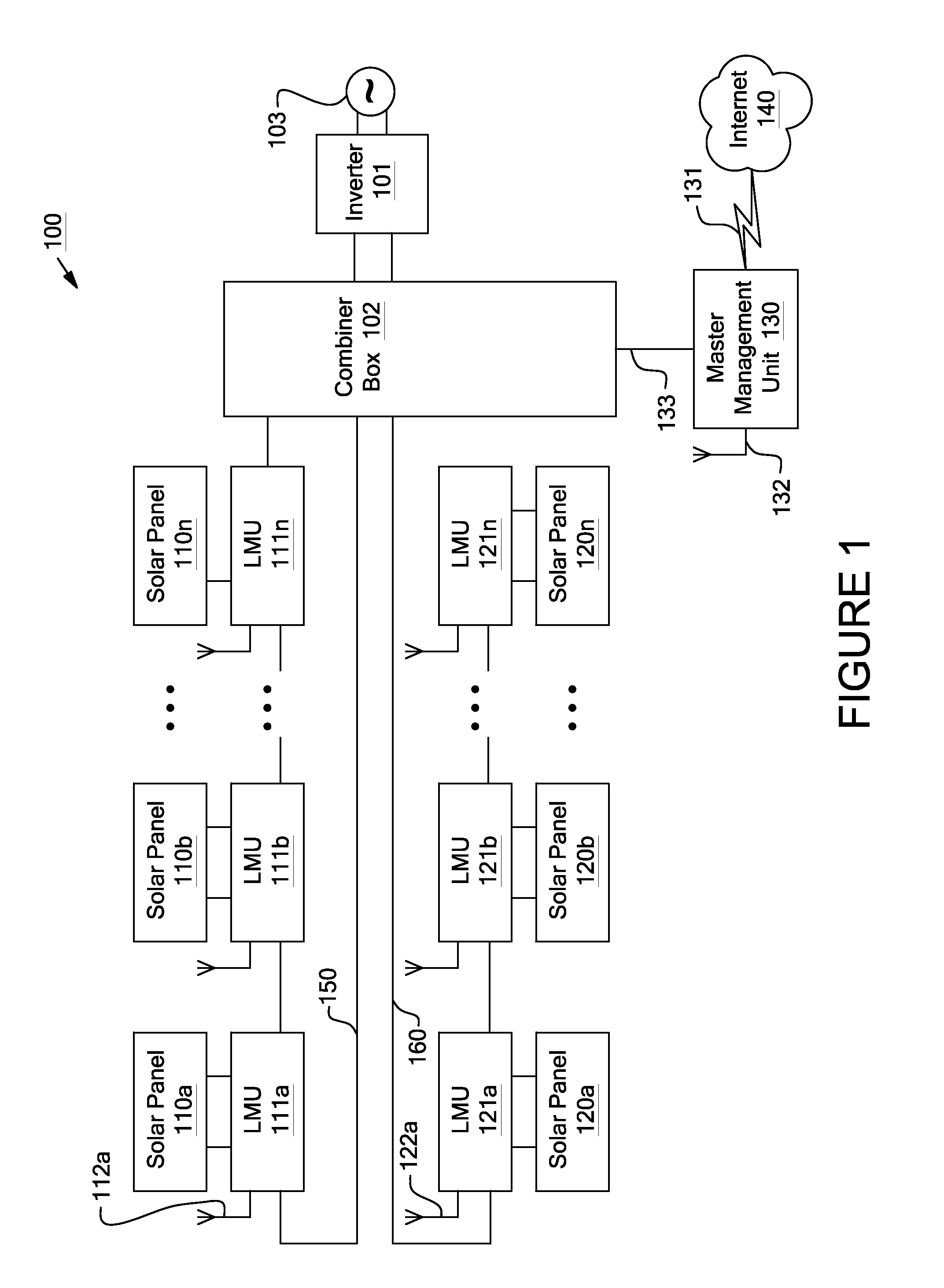
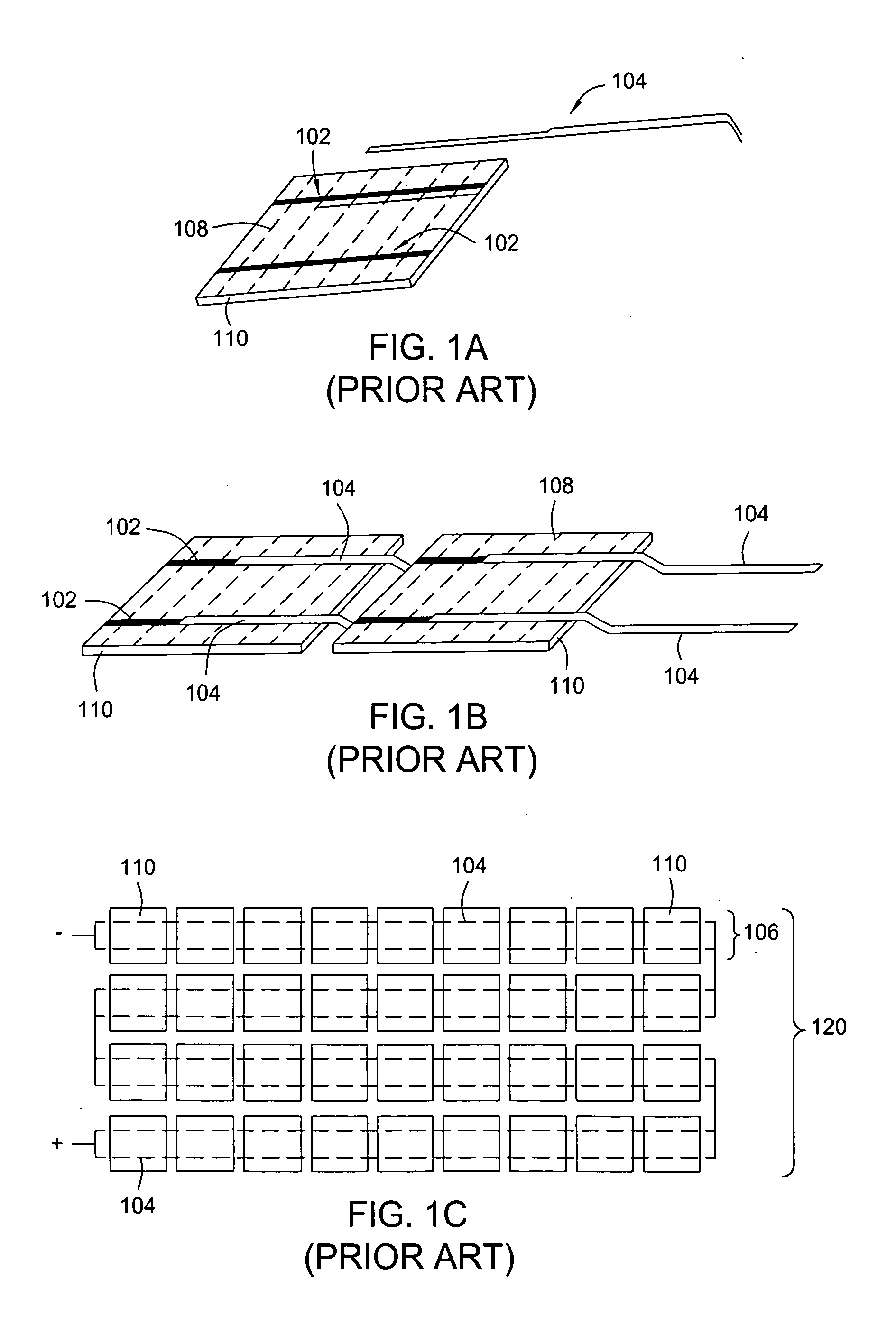
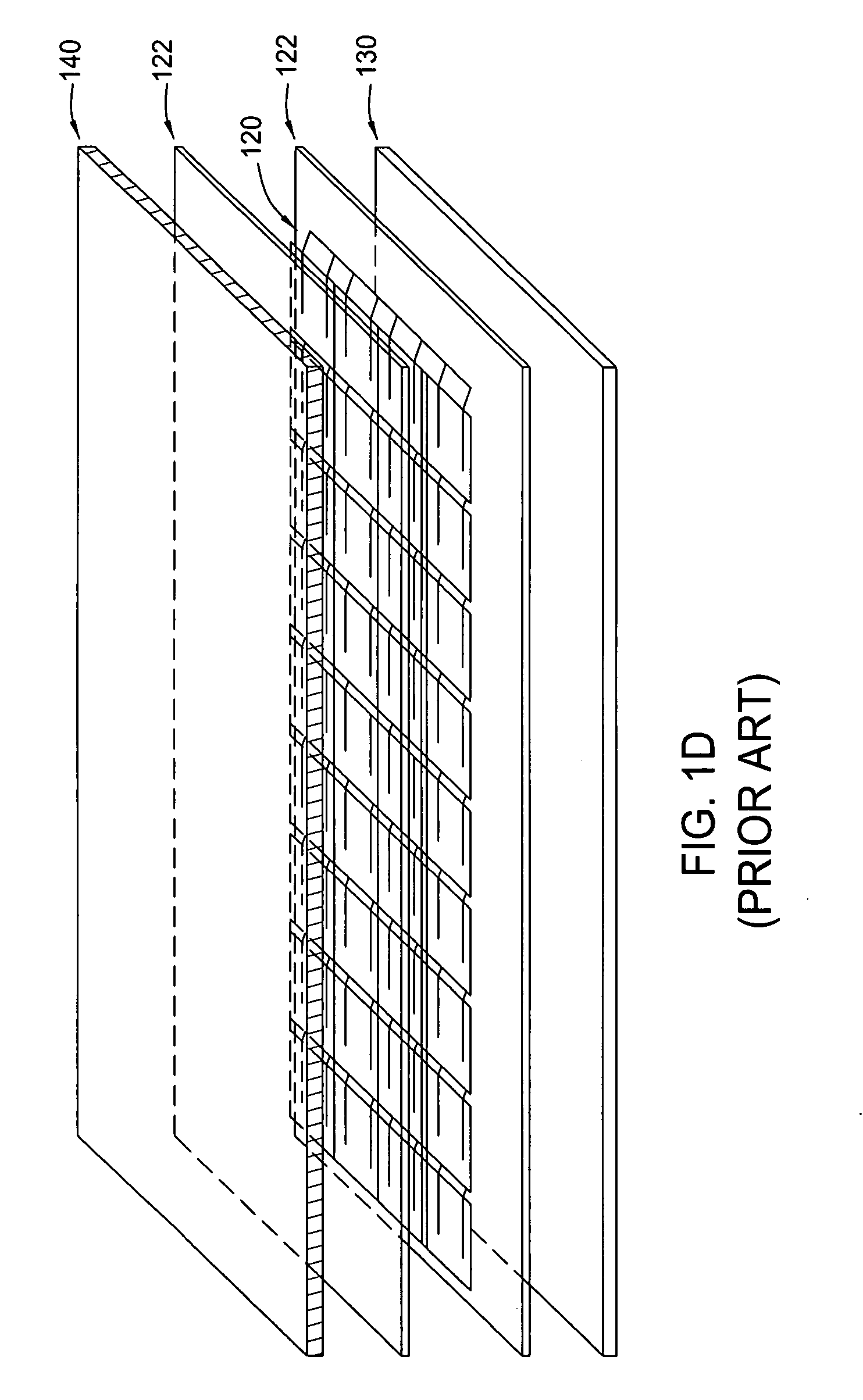
Systems and Methods for an Enhanced Watchdog in Solar Module Installations
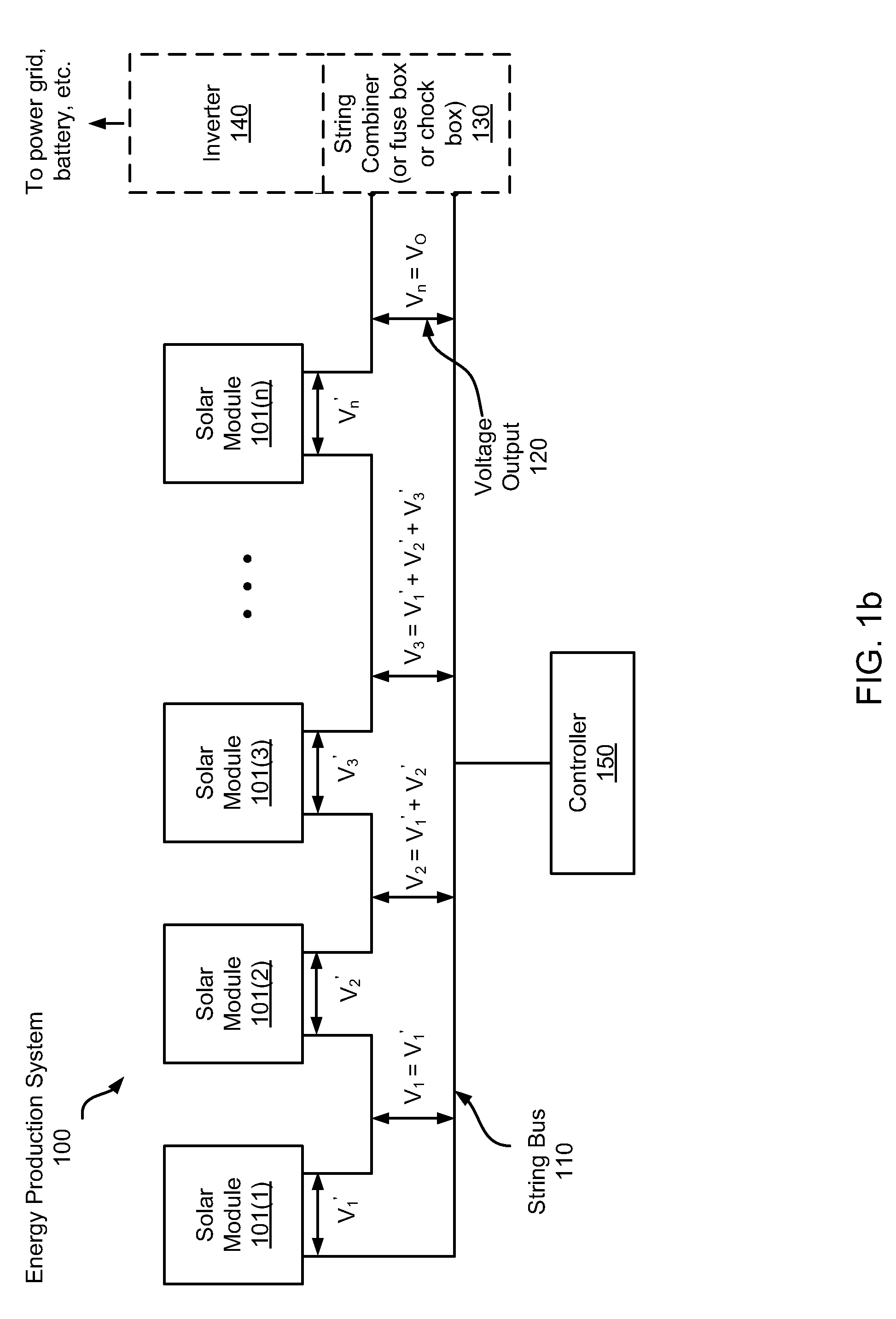
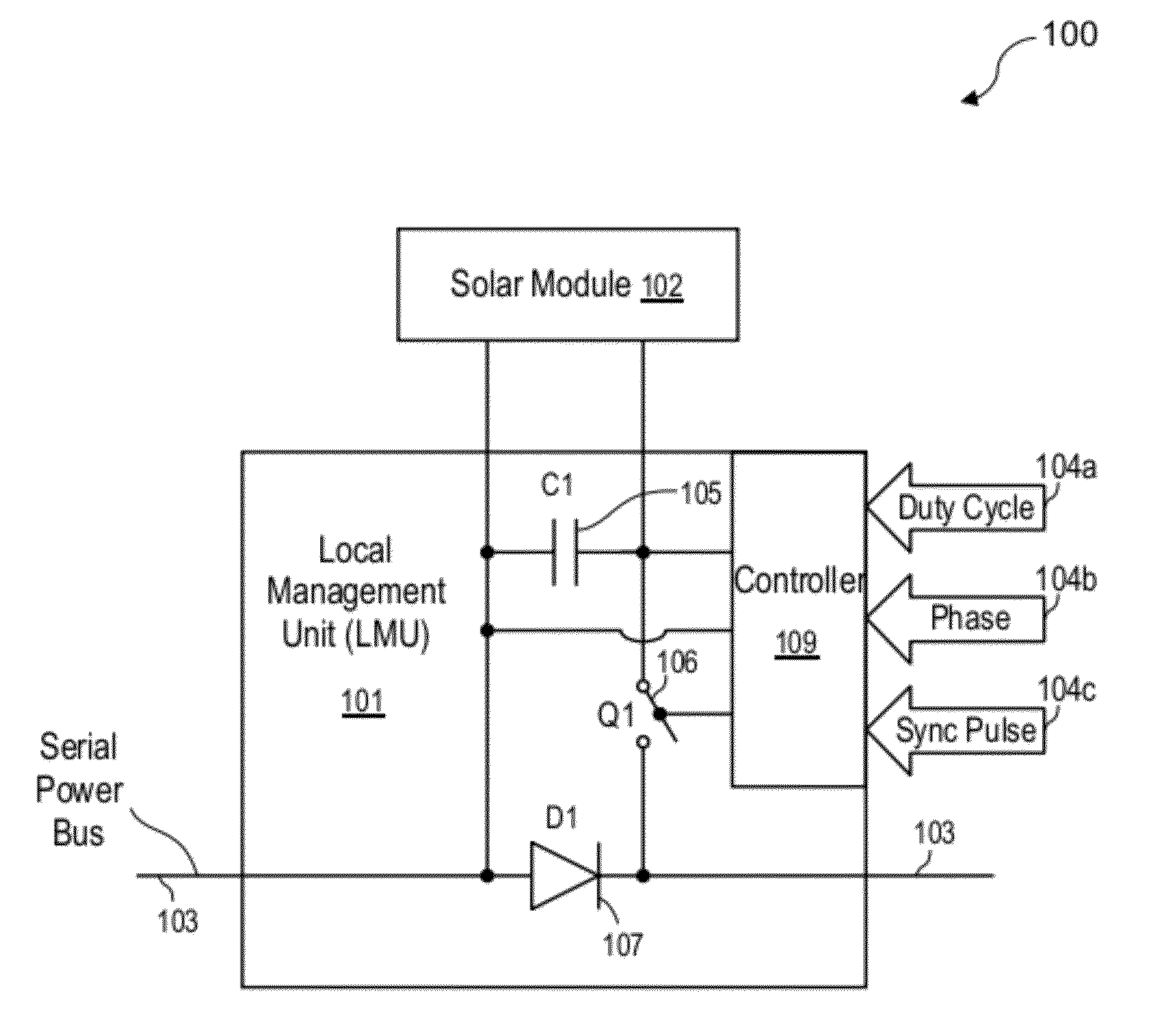
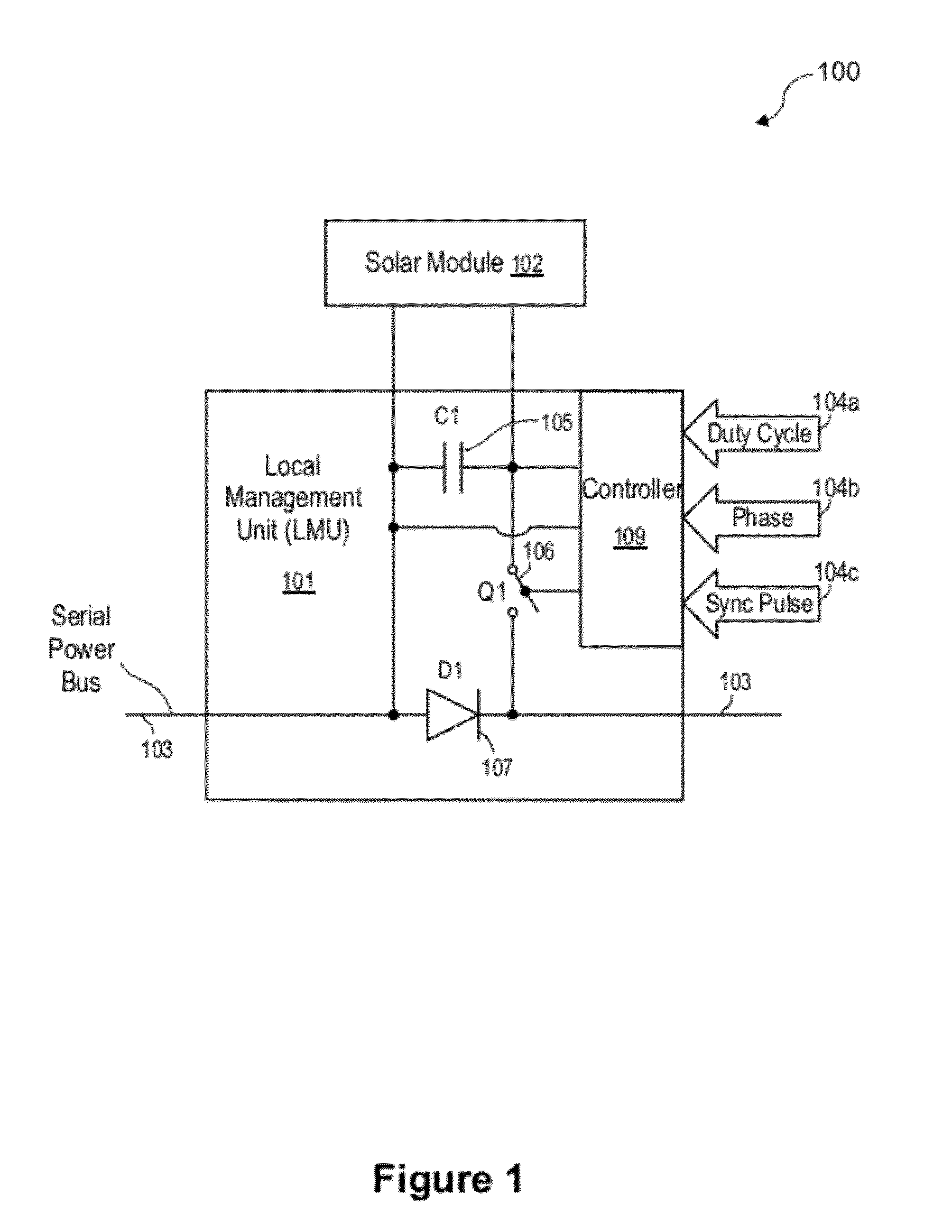
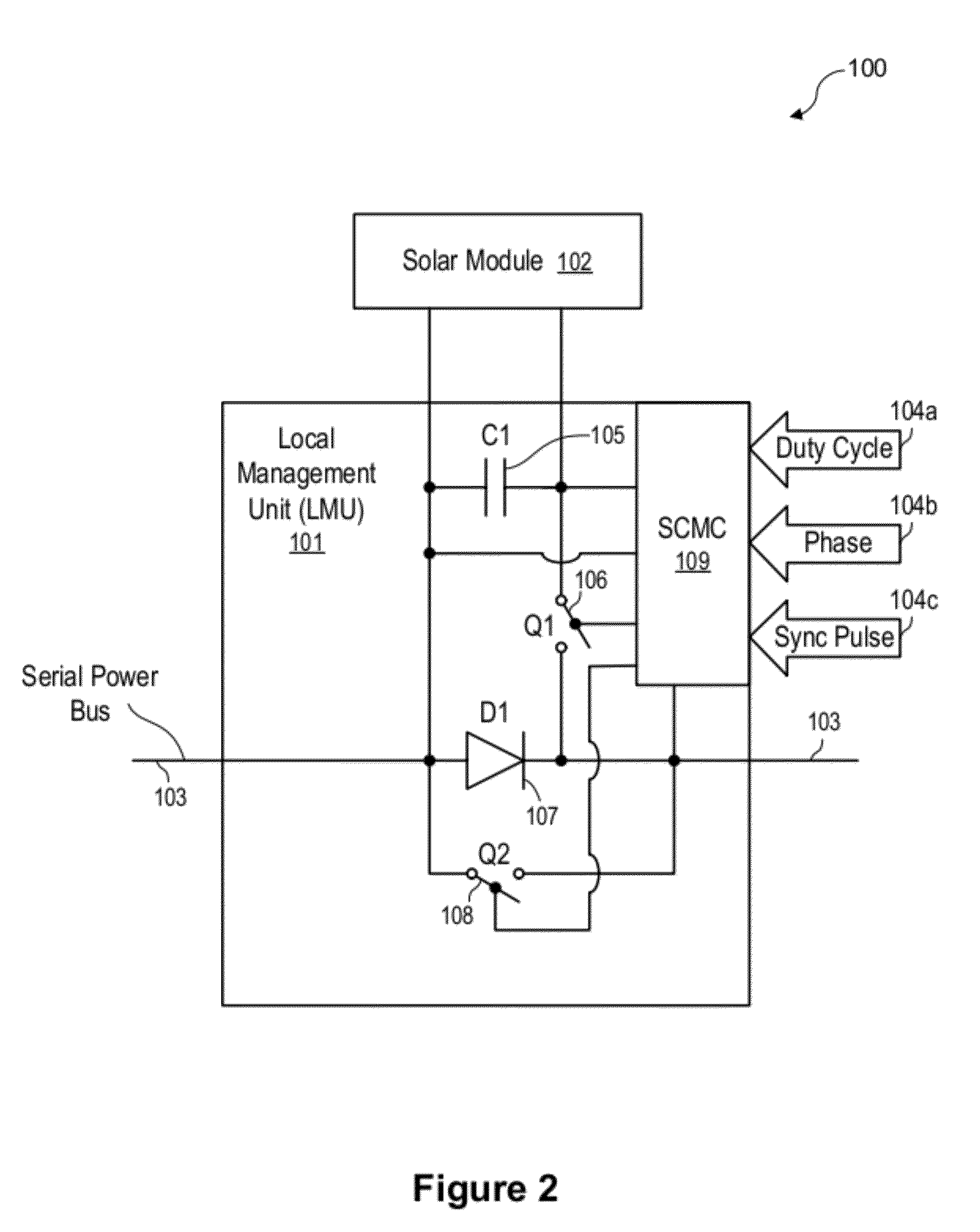
Systems and methods are disclosed for automatically or remotely rendering a solar array safe during an emergency or maintenance. A watchdog unit is disclosed for monitoring a signal from a central controller. If the signal is lost, interrupted, or becomes irregular, or if a shutdown signal is received, then the watchdog unit can shutdown one or more solar modules. Shutting down a solar module can mean disconnecting it from a power bus of the solar array or lowering the solar module voltage to a safe level.
Owner:NEWLIGHT CAPITAL LLC
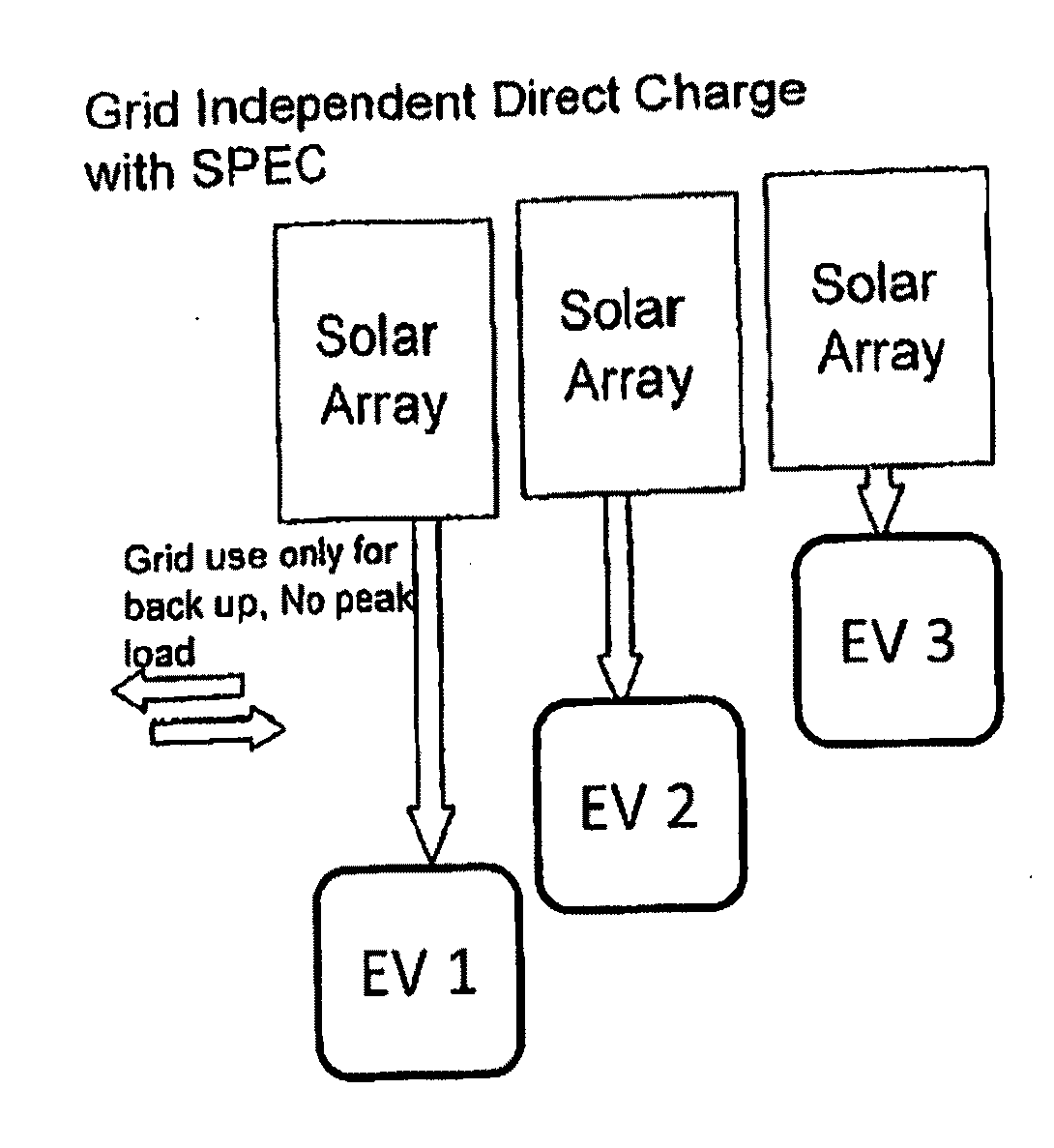
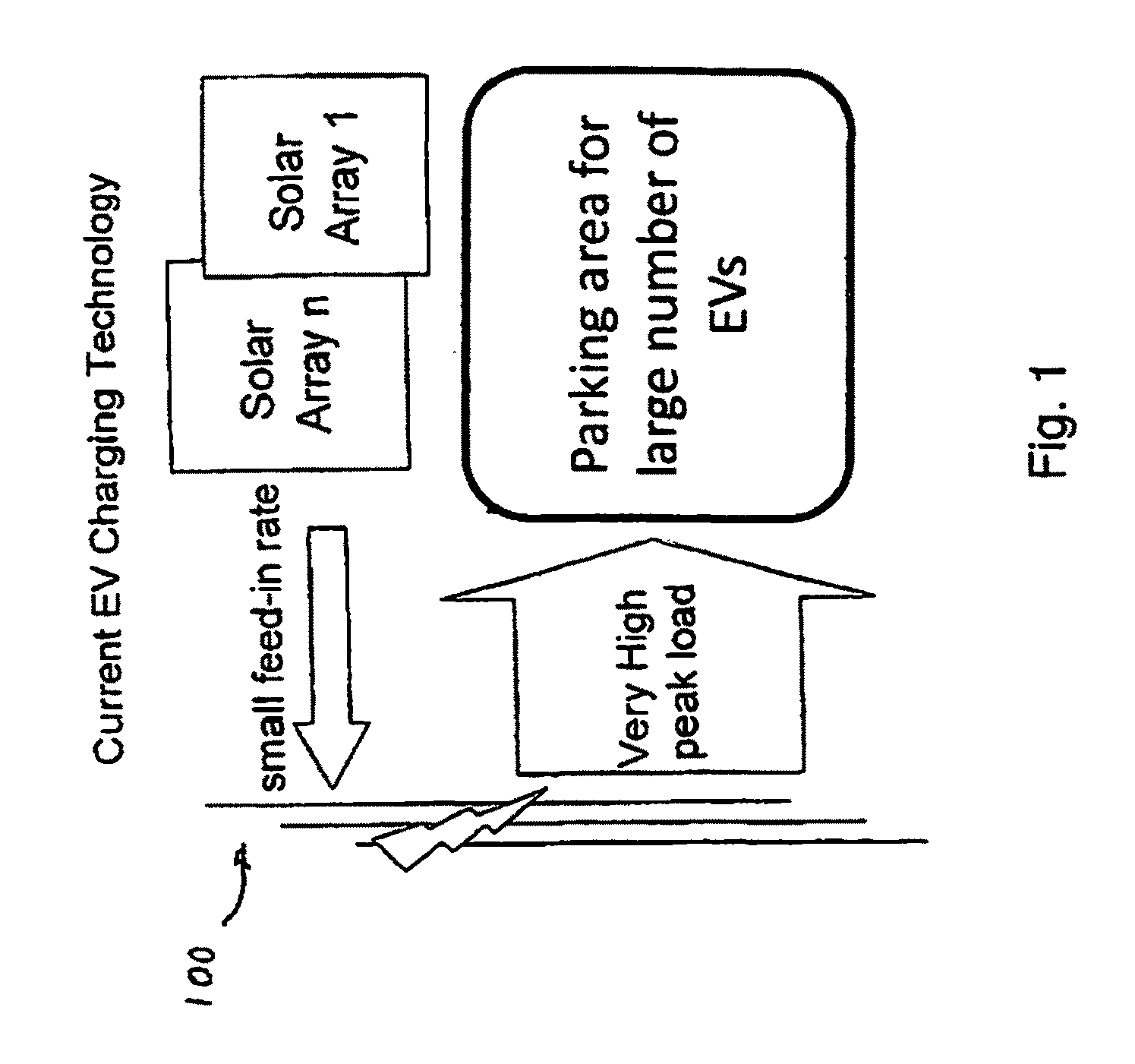
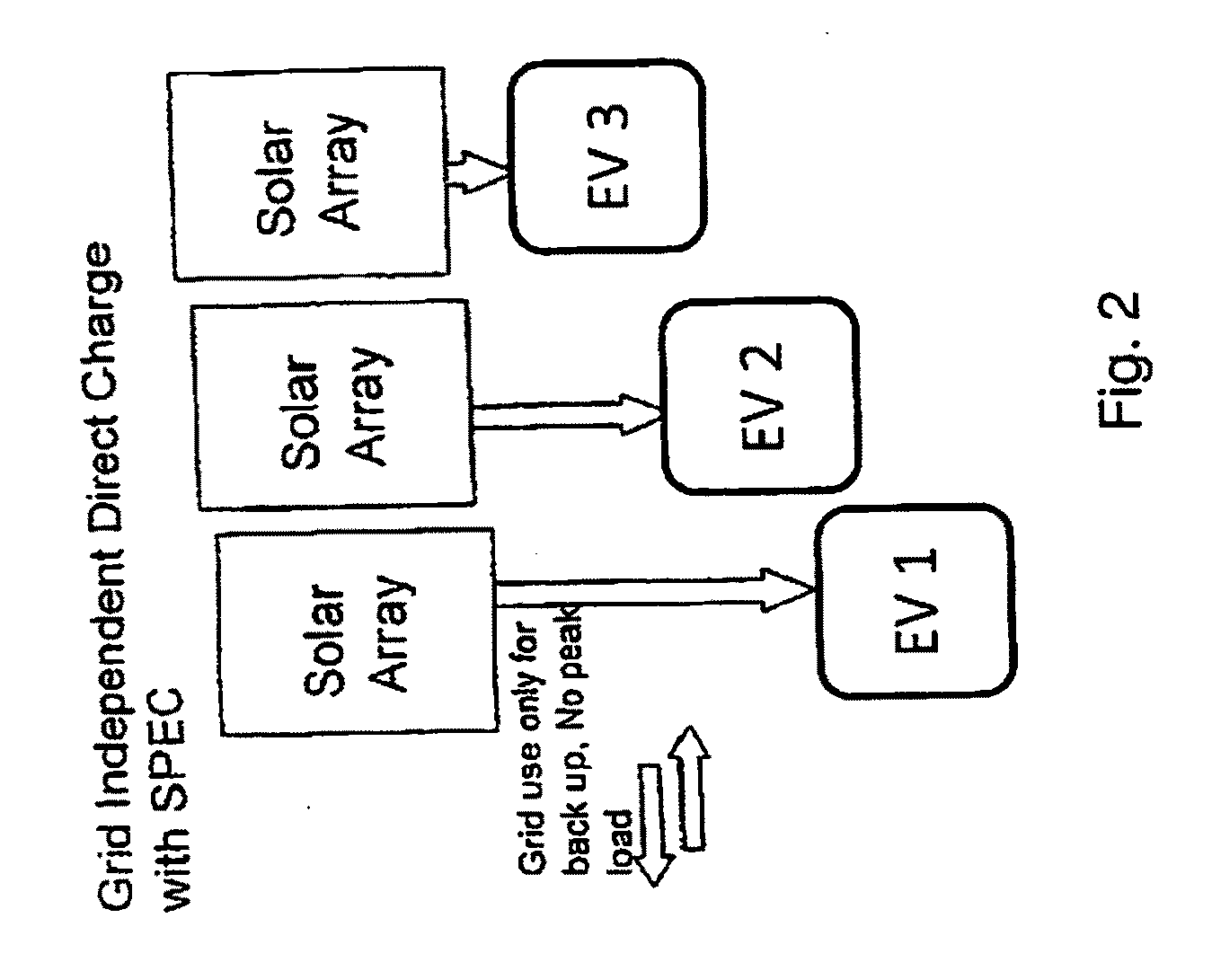
Solar powered, grid independent EV charging system
InactiveUS20100181957A1Facilitating full environmental benefitNeed can be addressedHybrid vehiclesCharge equalisation circuitLow demandCharge rate
A system for charging a multiplicity of commuter EVs without dependence on the power grid is provided, using the EV batteries themselves as distributed off grid storage for all EVs connected to the system. The EV charging system comprises low cost solar modules and an intelligent charge management system capable of a providing flexible charge rate to EVs based on user demand, that is decoupled from the grid and thus does not add to peak power demands. Only a low capacity grid connection is provided for backup, and buffer solar panels may be provided for load balancing. Excessive solar energy is fed into the grid during times of low demand at the charging stations, such as on weekends.
Owner:SURYA POWER
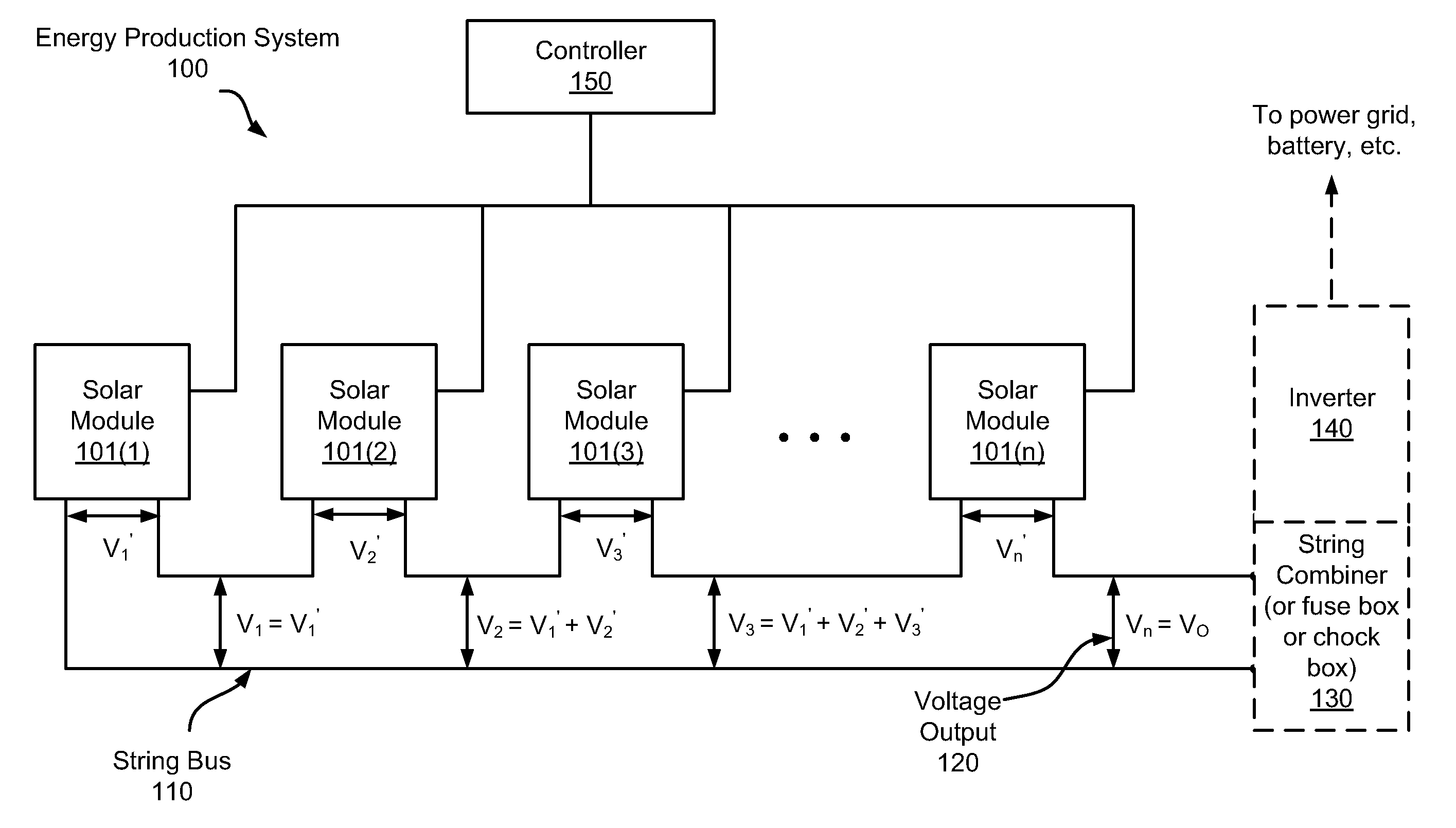
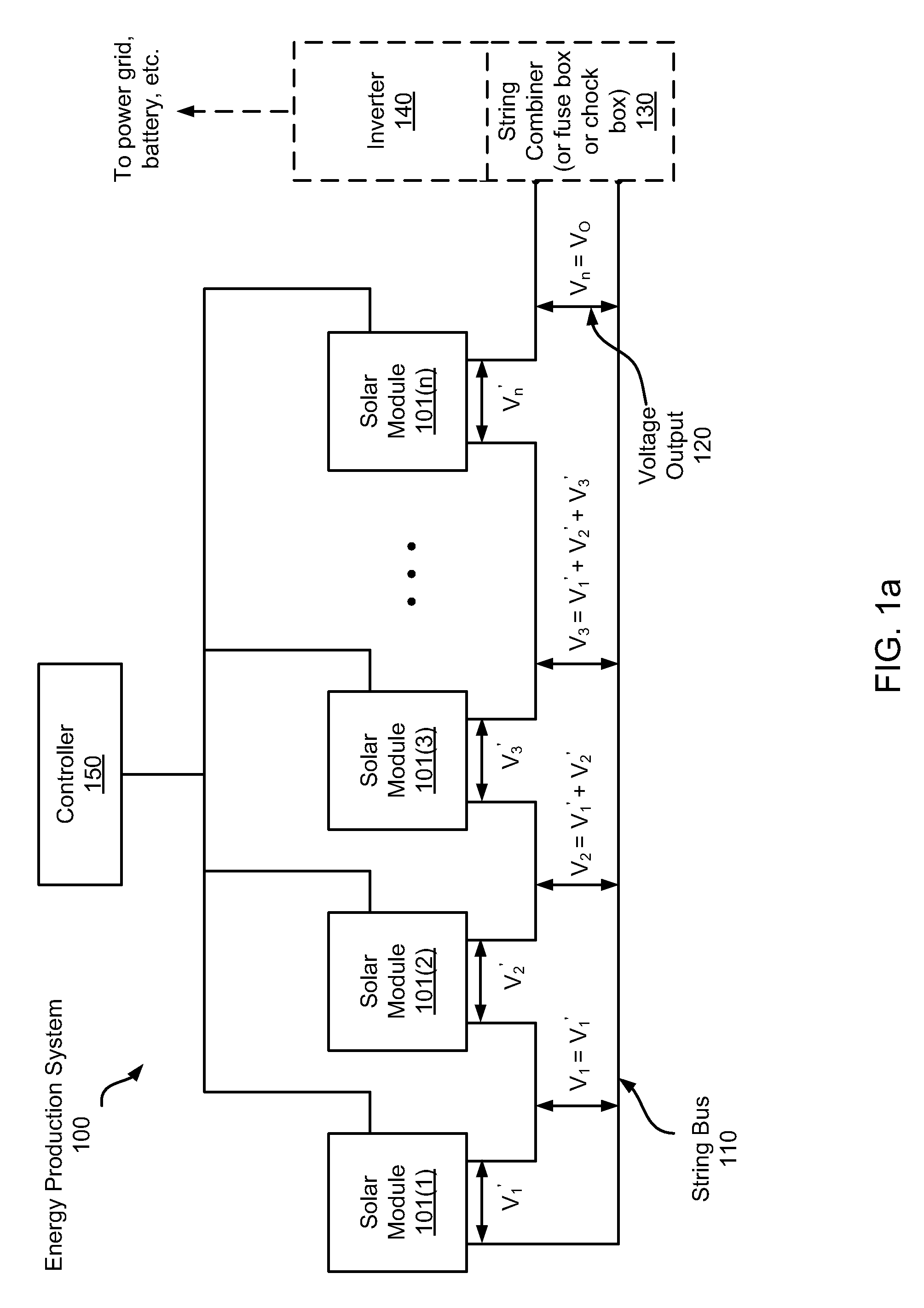
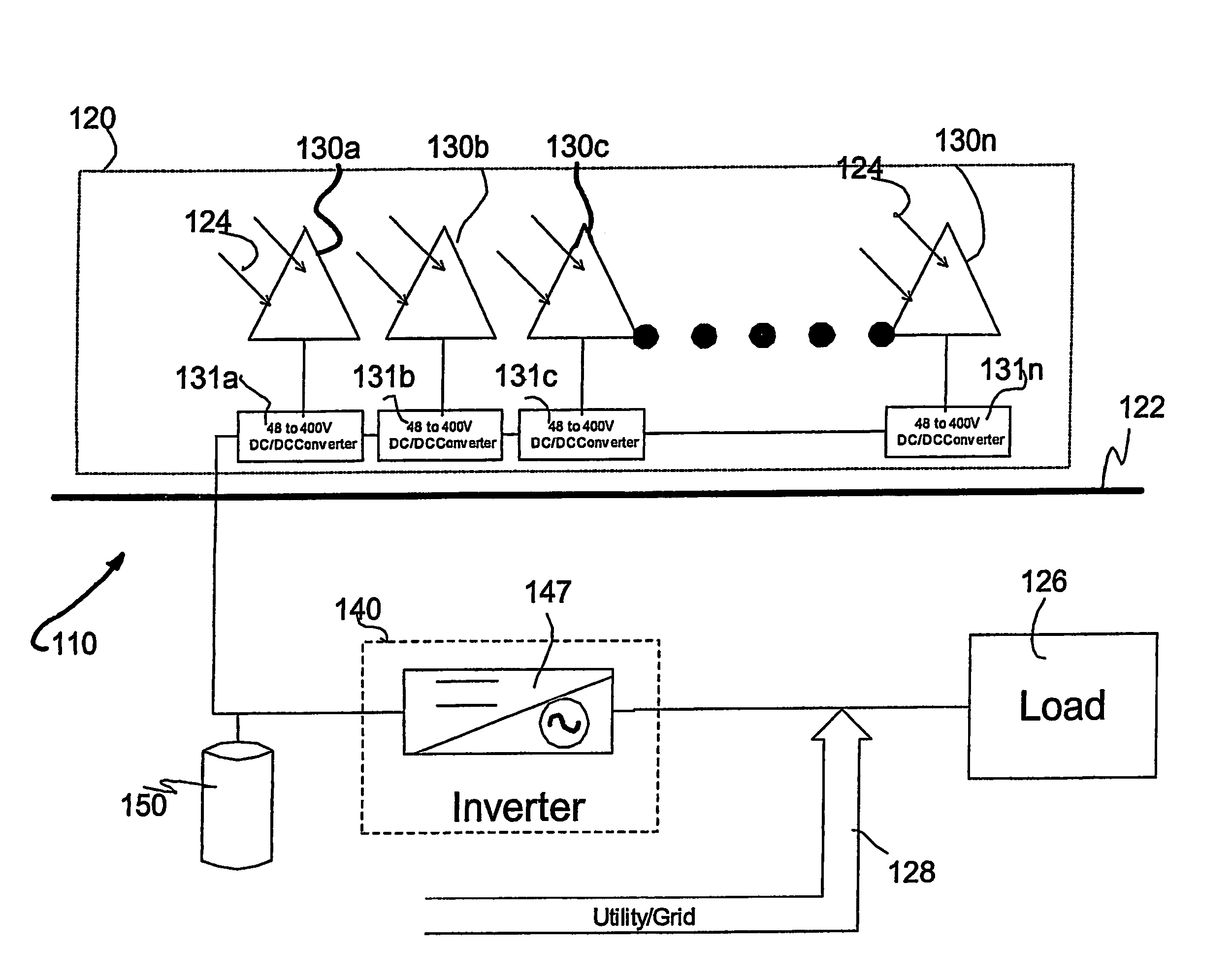
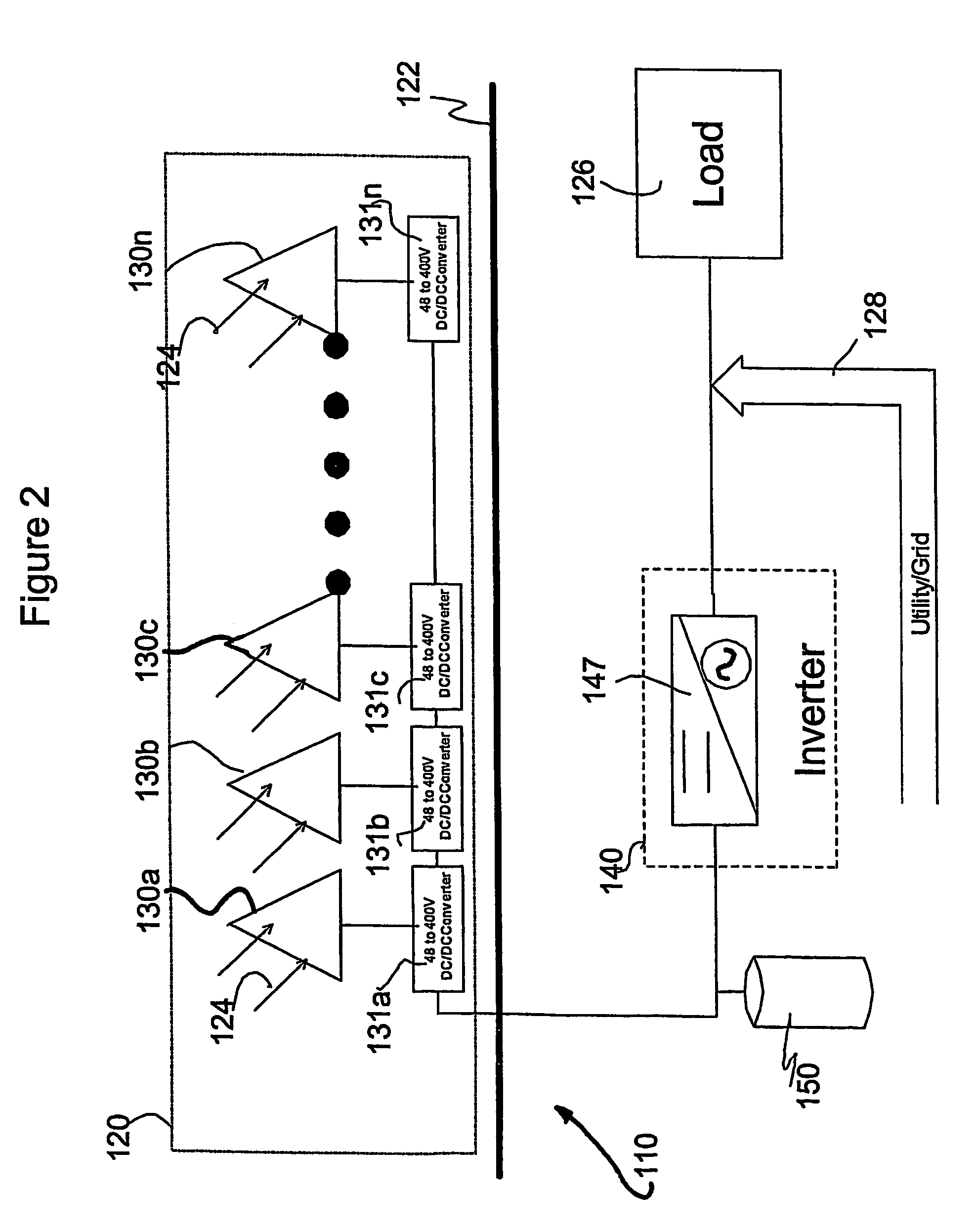
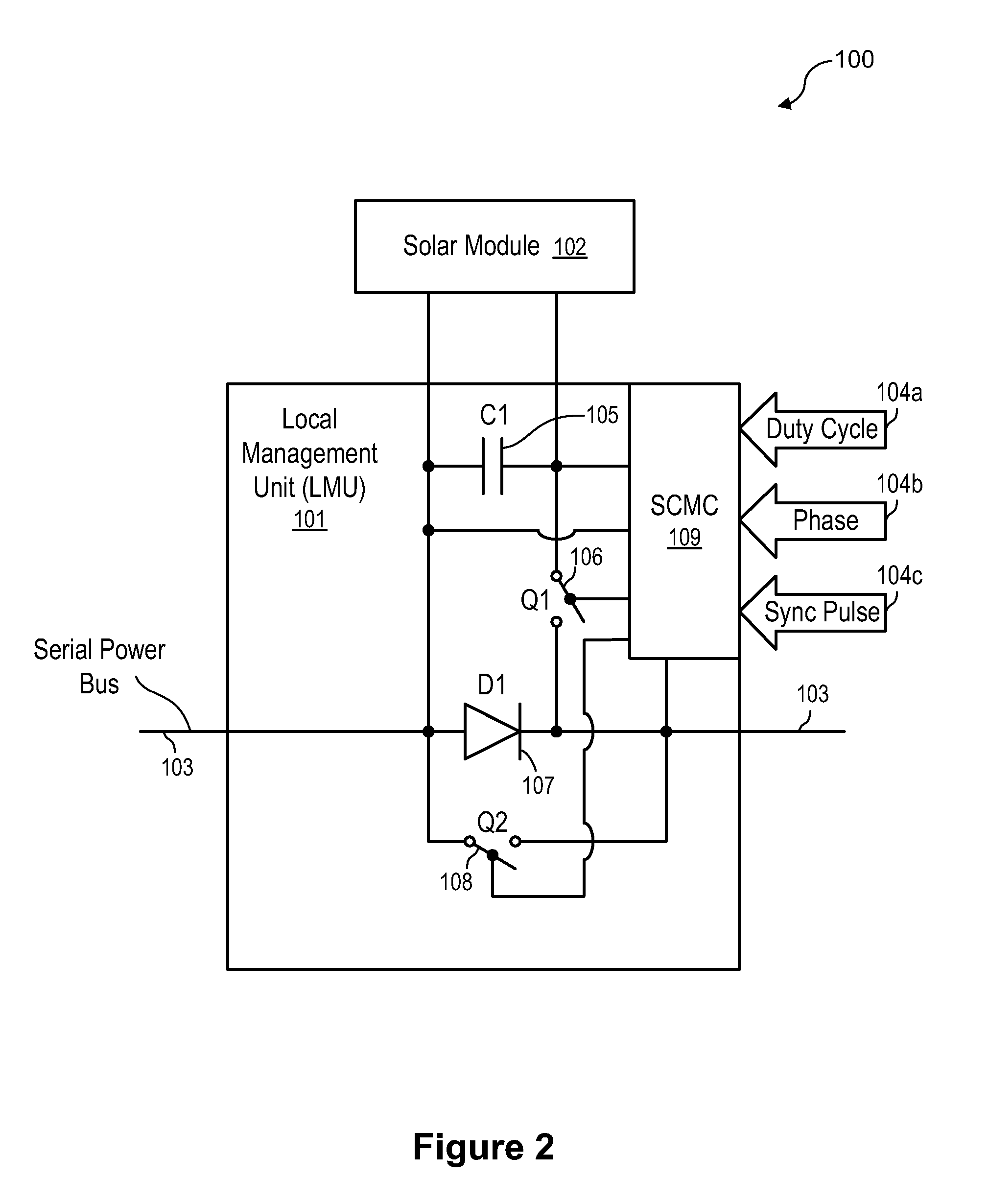
Systems and method for limiting maximum voltage in solar photovoltaic power generation systems
ActiveUS20110025130A1Dc network circuit arrangementsPower distribution line transmissionManagement unitComputer module
Apparatuses and methods are disclosed for regulating or limiting the voltage output from solar modules connected in series such that the voltage on a string bus connecting those solar modules does not exceed regulatory or safety limitations. This can be accomplished via a controller, local management units (for downconverting solar module voltage output), or a combination of the two.
Owner:NEWLIGHT CAPITAL LLC
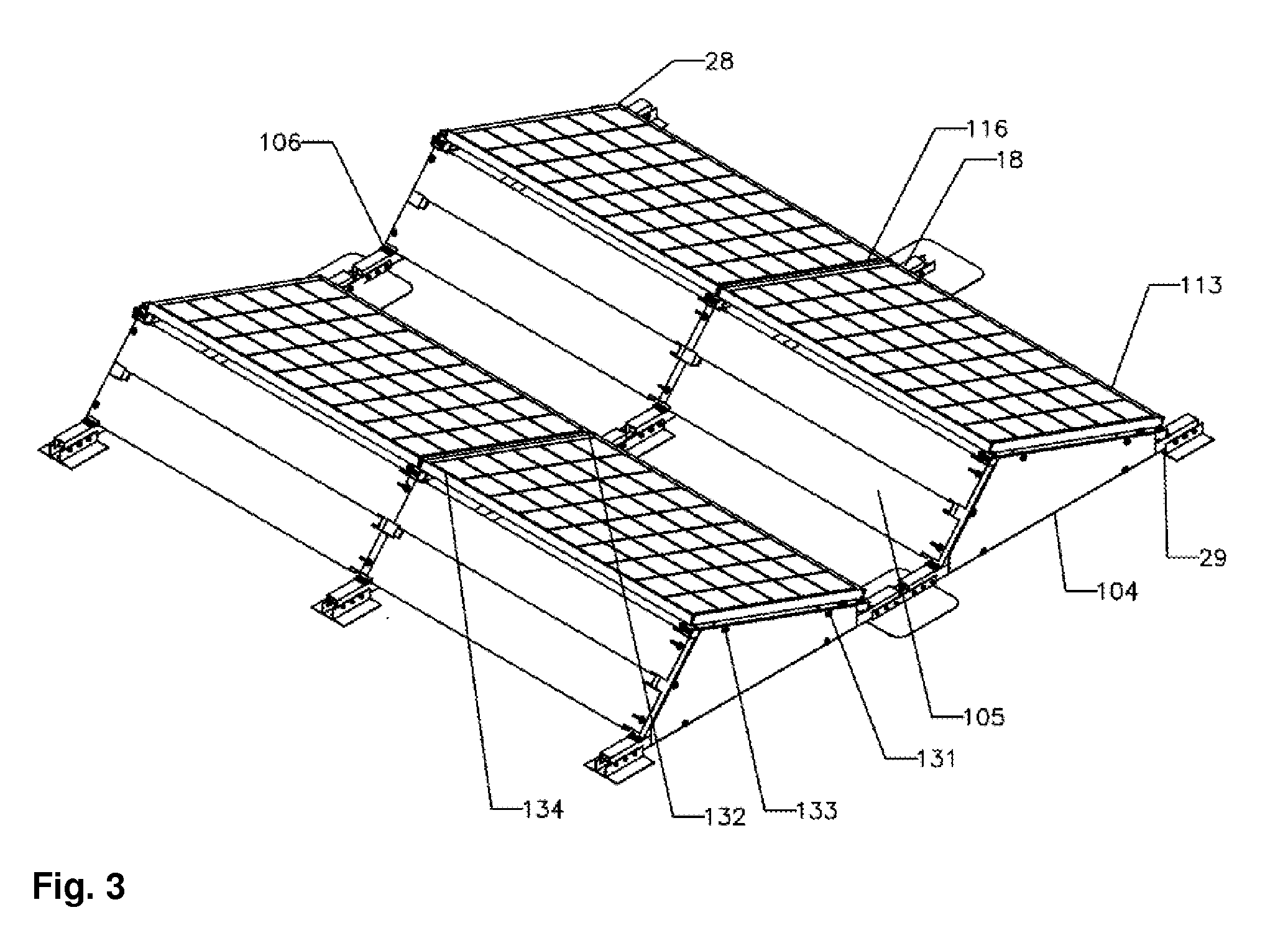
Mounting system for solar panels
InactiveUS20090078299A1Simplify assembly of moduleChange defectsPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyComputer moduleEngineering
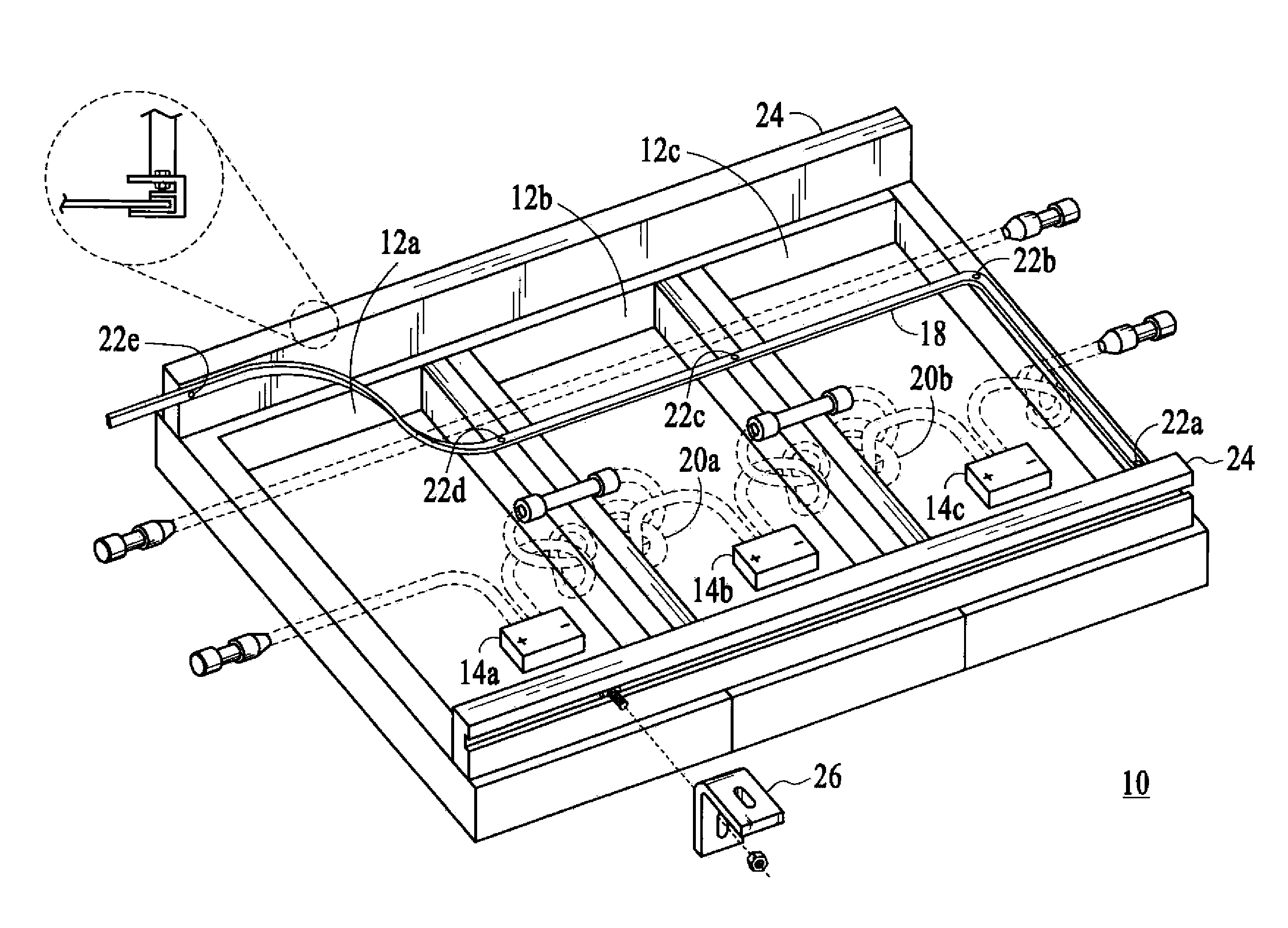
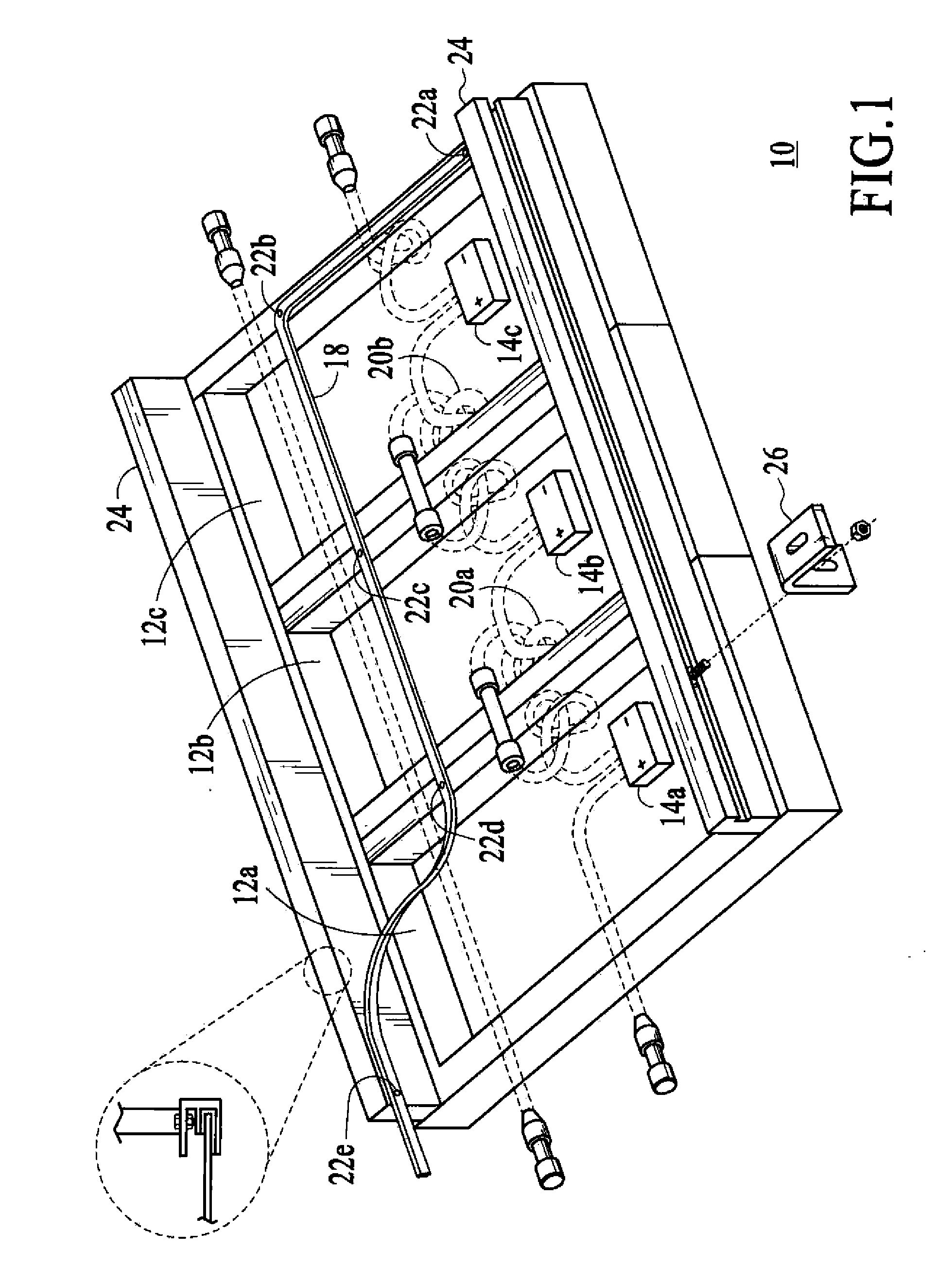
An integrated module frame and racking system for a solar panel is disclosed. The solar panel comprises a plurality of solar modules and a plurality of splices for coupling the plurality of solar modules together. The plurality of splices provide a way to make the connected modules mechanically rigid both during transport to the roof and after mounting for the lifetime of the system, provide wiring connections between modules, provide an electrical grounding path for the modules, provide a way to add modules to the panel, and provide a way to remove or change a defective module. Connector mount assemblies are provided on the sides of the modules to simplify the electrical assembly of modules when the modules are connected together with splices and to simplify the final connection of external wiring to the module.
Owner:ANDALAY SOLAR
Technique for electrically bonding solar modules and mounting assemblies
ActiveUS20080053517A1Photovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyElectric current flowMechanical engineering
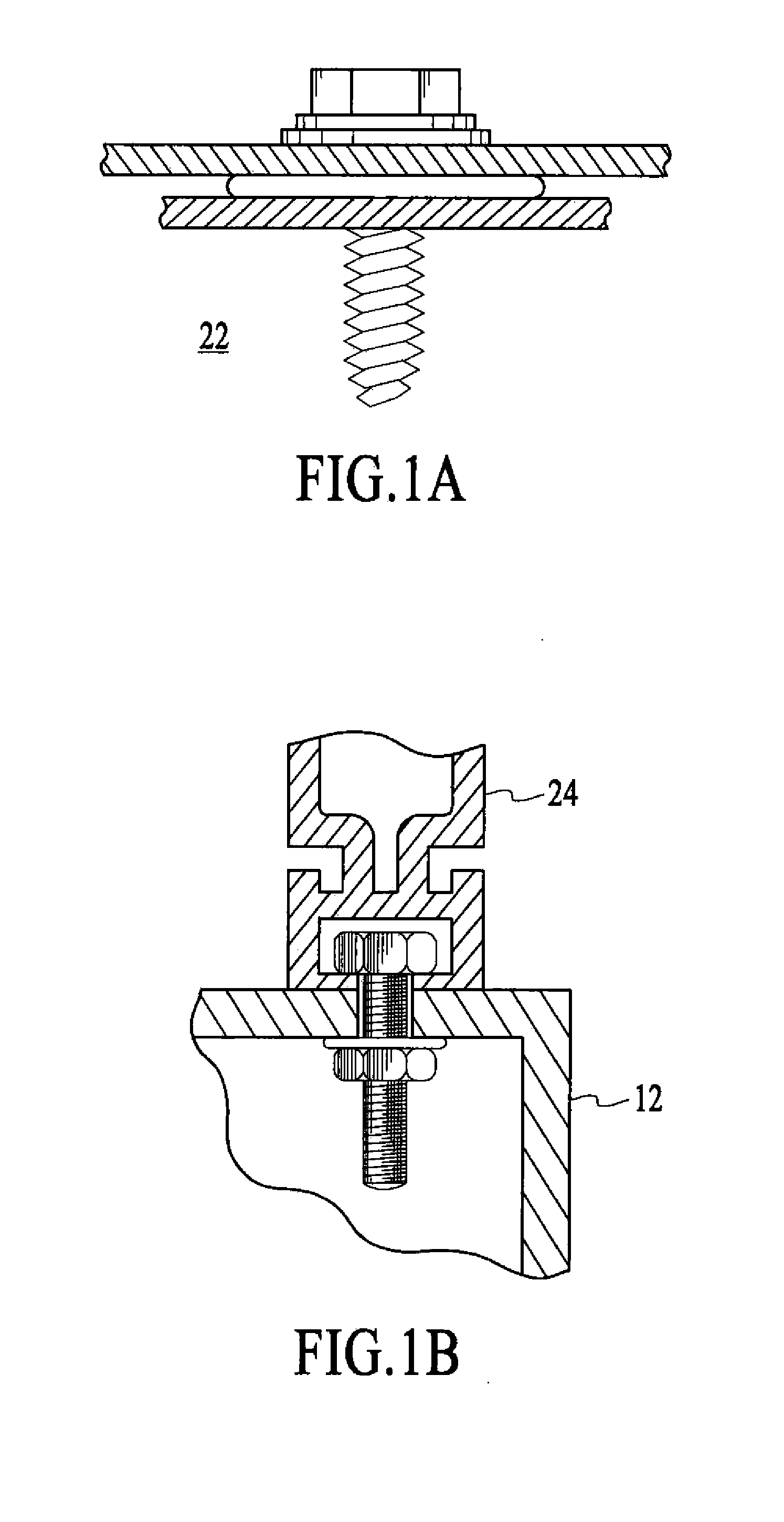
A mounting system is provided for an array of solar modules. The mounting system includes one or more rail assemblies that extend lengthwise in a first direction to support a plurality of solar modules that comprise the array. Each of the one or more rail assemblies may be configured to compress in order to retain an edge section of one or more of the plurality of solar modules in an operable position. A conductive element may be positioned to bond the edge section of at least one of the plurality of solar modules with at least a section of the rail assembly that retains that edge section in the operable position, so as to form a conductive path for electrical current.
Owner:FTC SOLAR INC
Power converter for a solar panel
ActiveUS20070103108A1Output maximizationMaximize power outputDc network circuit arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsElectricityControl system
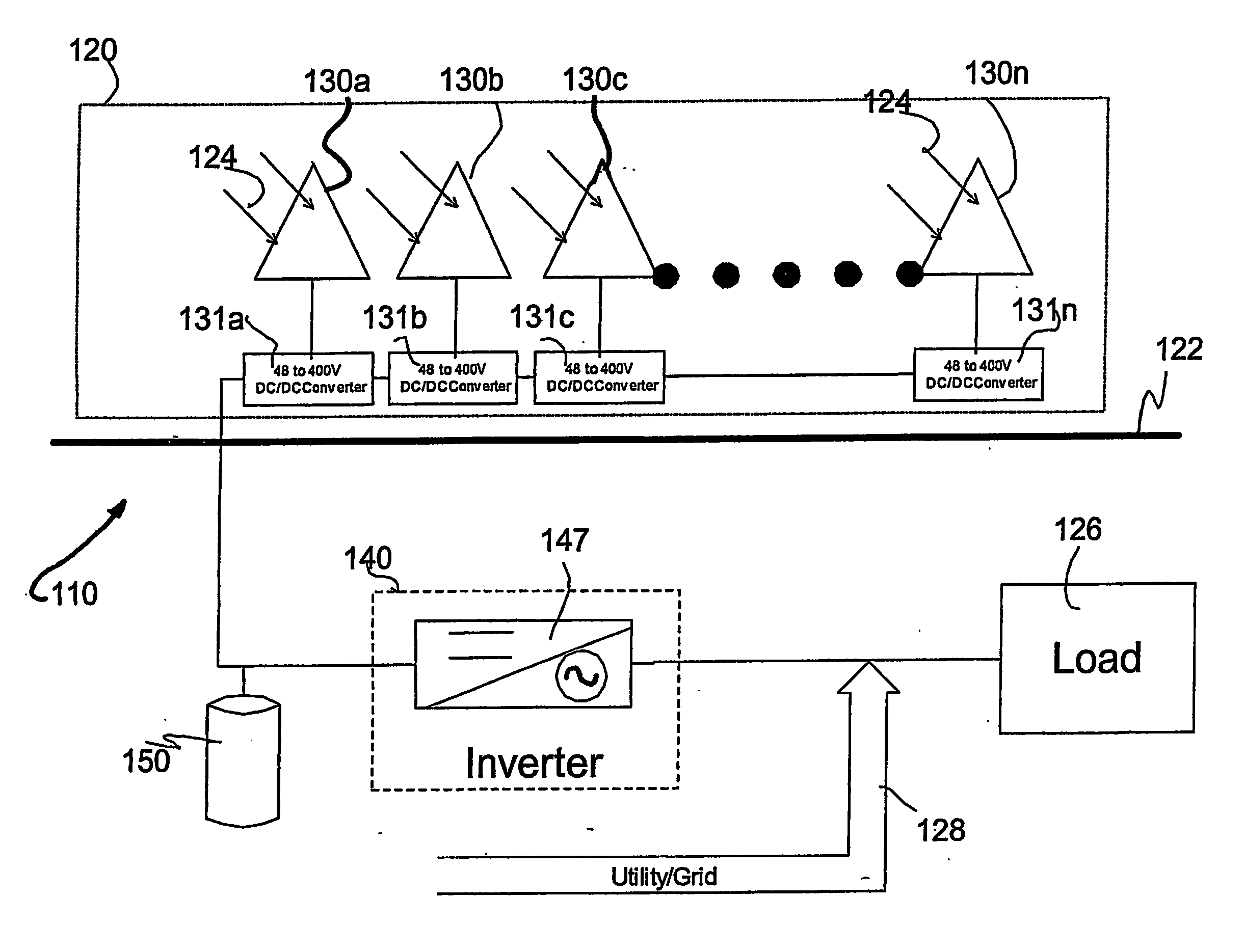
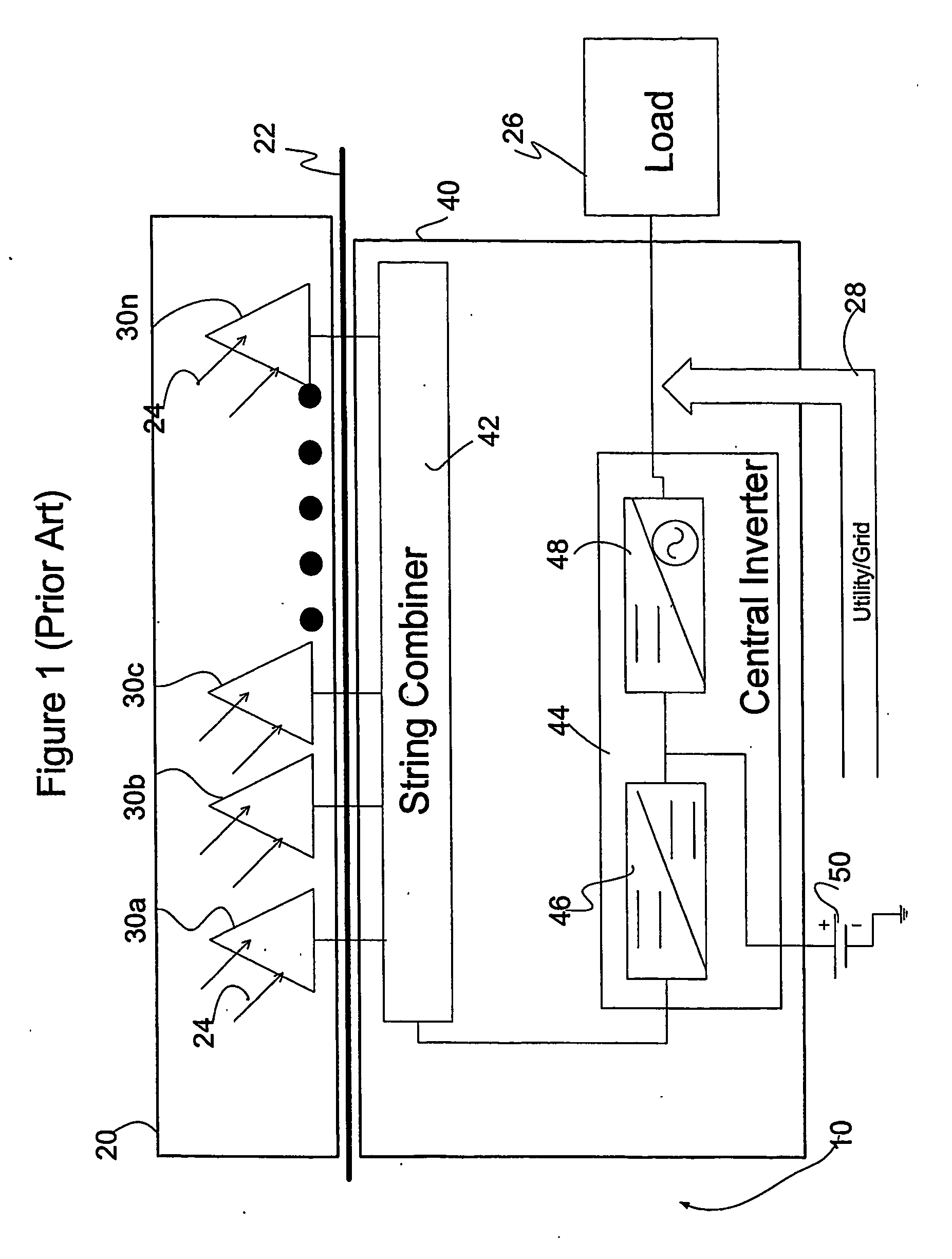
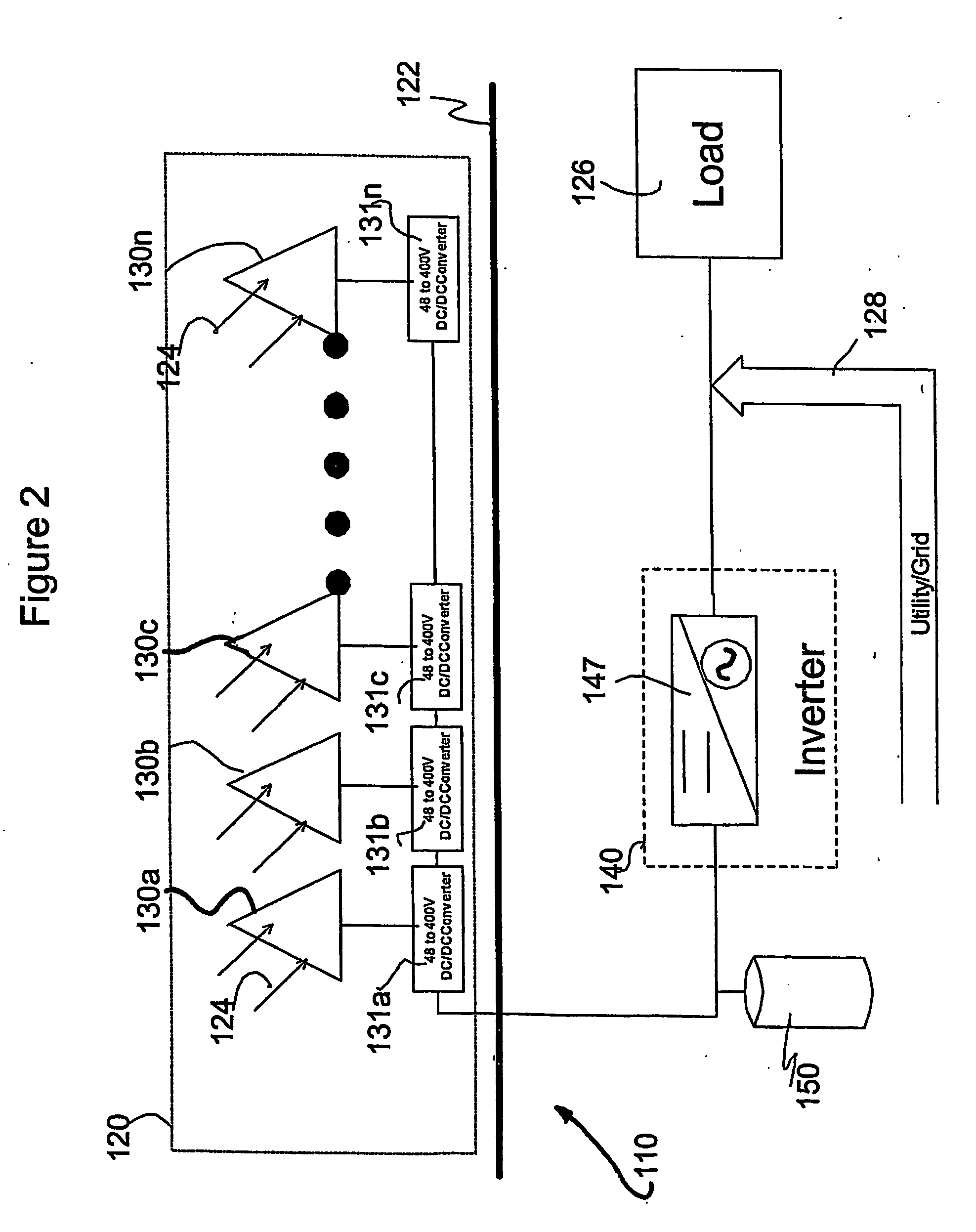
A solar array power generation system includes a solar array electrically connected to a control system. The solar array has a plurality of solar modules, each module having at least one DC / DC converter for converting the raw panel output to an optimized high voltage, low current output. In a further embodiment, each DC / DC converter requires a signal to enable power output of the solar modules.
Owner:SOLAREDGE TECH LTD
Solar modules with tracking and concentrating features
InactiveUS20070251569A1Reduce in quantityImprove photovoltaic efficiencyPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyElectricityRotational freedom
Disclosed are fixed solar-electric modules having arrays of solar concentrator assemblies capable of separately tracking movements through one or two degrees of rotational freedom to follow the movement of the sun daily and / or seasonally. The concentrators can include optical elements to direct and concentrate light onto photovoltaic and / or thermoelectric receivers for generation of electric current.
Owner:INTEMATIX
Photovoltaic unit comprising a matrix of frameless solar modules
InactiveUS20100282290A1Improve fit accuracyAvoid large displacementPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyEngineeringEdge region
A photovoltaic unit includes a matrix having a plurality of frameless rectangular solar modules, and at least one module rail disposed on an underside of each solar module. Each of the at least one module rail is coupled to a substrate rail, which is releasably connected to a substrate. Each of the at least one module rail and the at least one substrate rail has a guide rail running parallel to an edge of the respective solar module on at least a longitudinal side of the respective rail facing towards an edge region of the solar module. The guide rails on the module and substrate rails are releasably connected to each other by at least one connecting element. A spacer gap of sufficient width for operating the connecting element is provided between adjacent solar modules of the plurality of frameless rectangular solar modules.
Owner:SOLON SE
Power converter for a solar panel
ActiveUS8102144B2Increase capacityReduce complexityBatteries circuit arrangementsPV power plantsElectricityControl system
Owner:SOLAREDGE TECH LTD
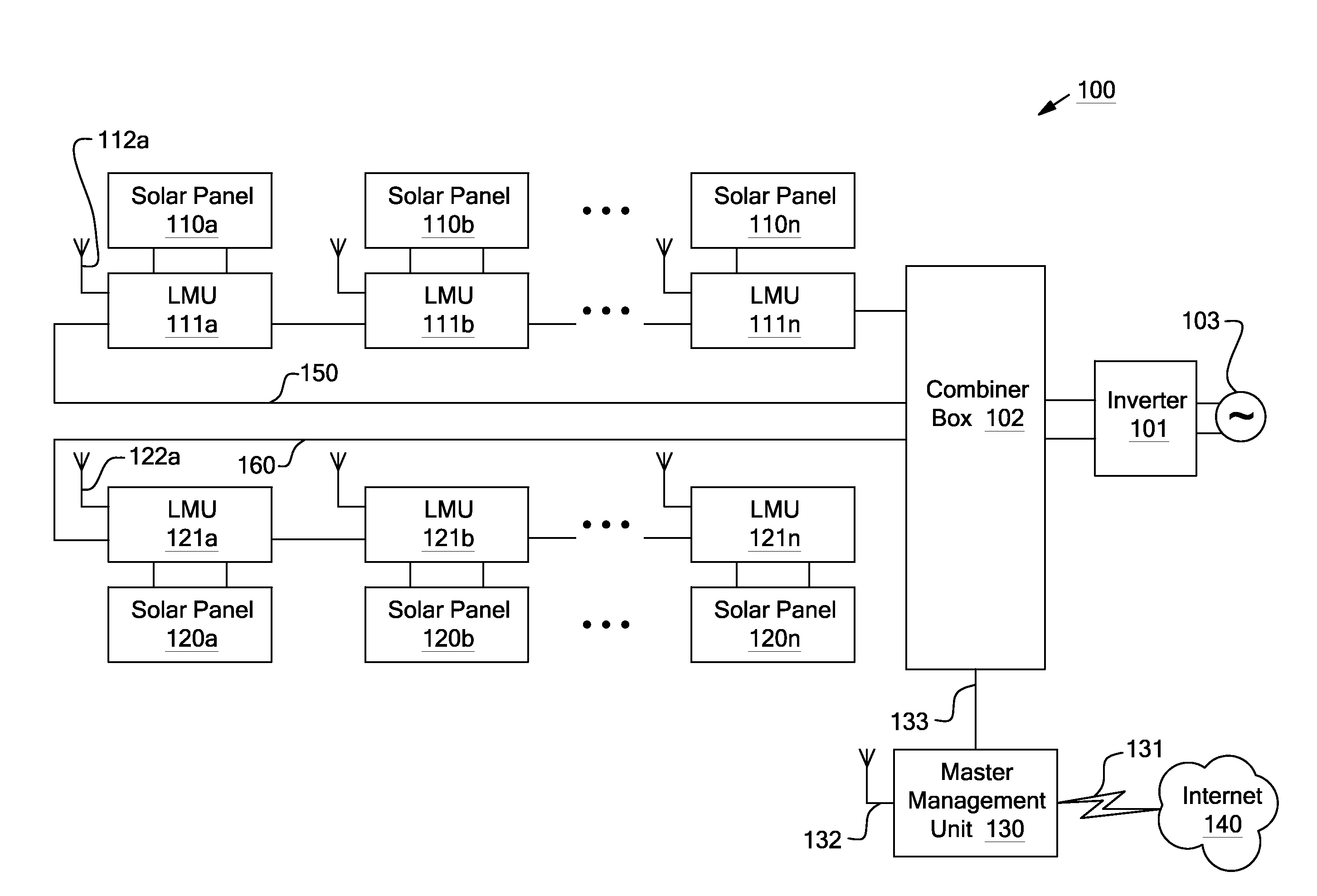
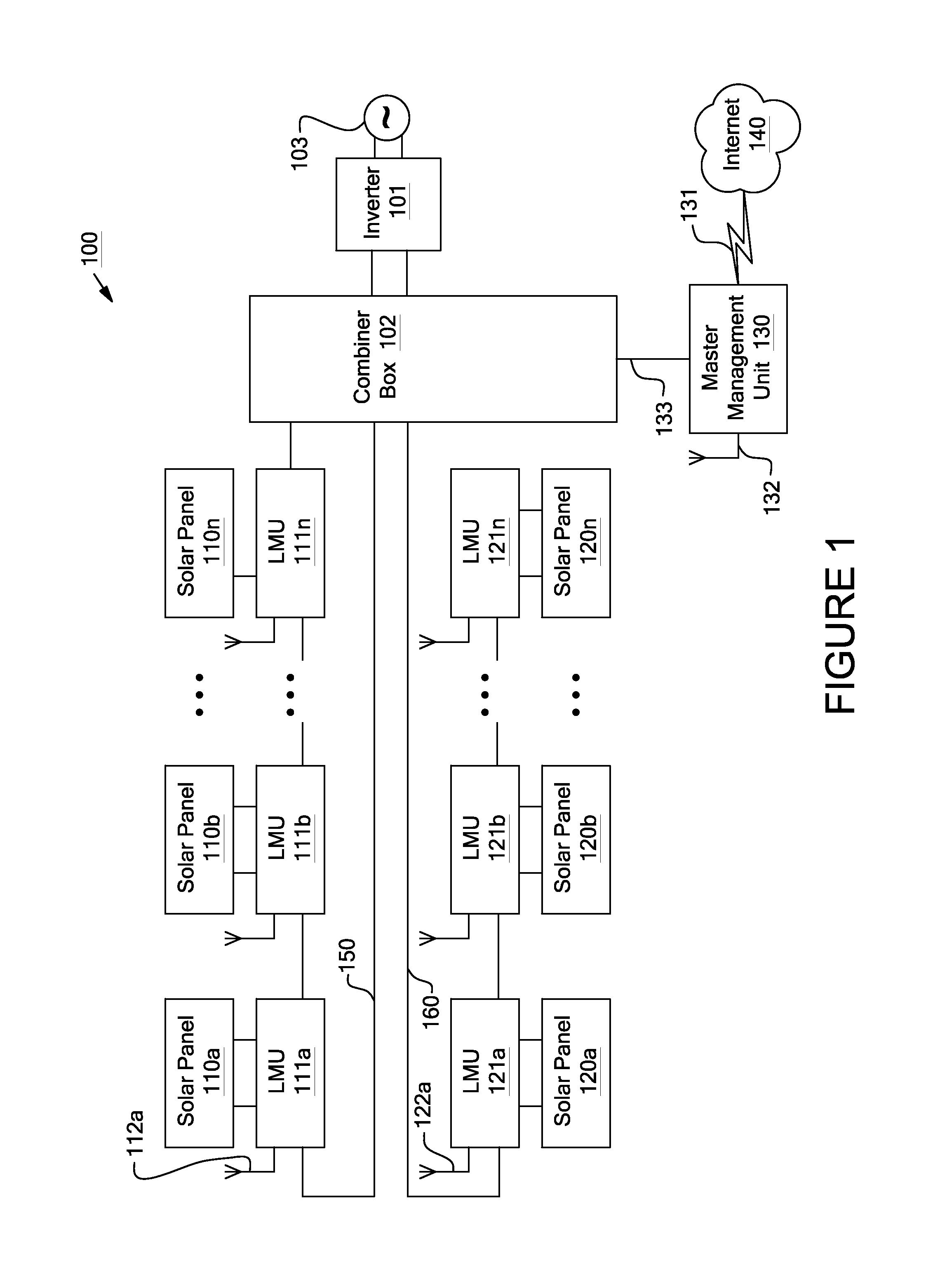
Systems and methods for remote or local shut-off of a photovoltaic system
ActiveUS8854193B2Dc network circuit arrangementsElectric signal transmission systemsUser deviceManagement unit
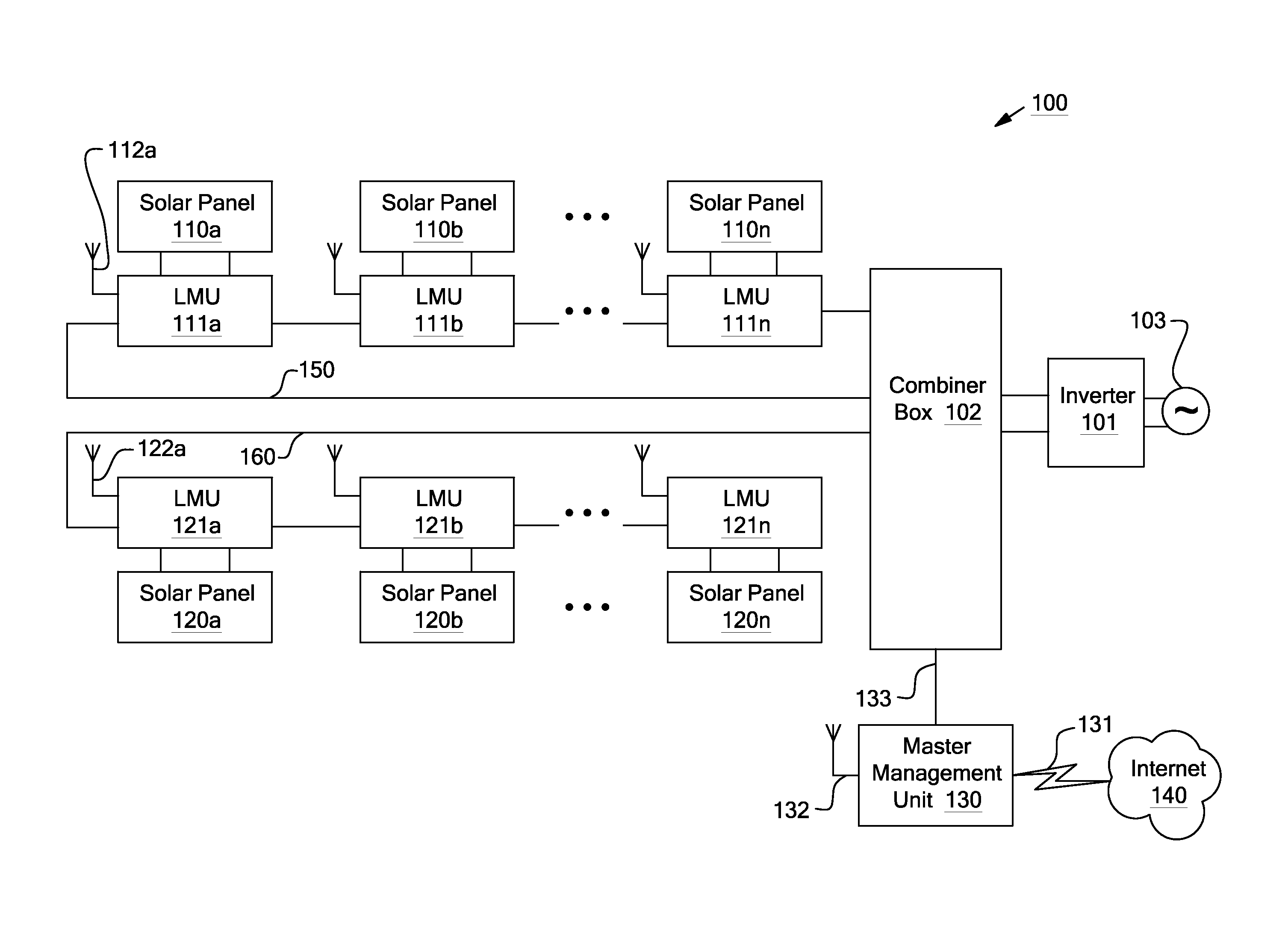
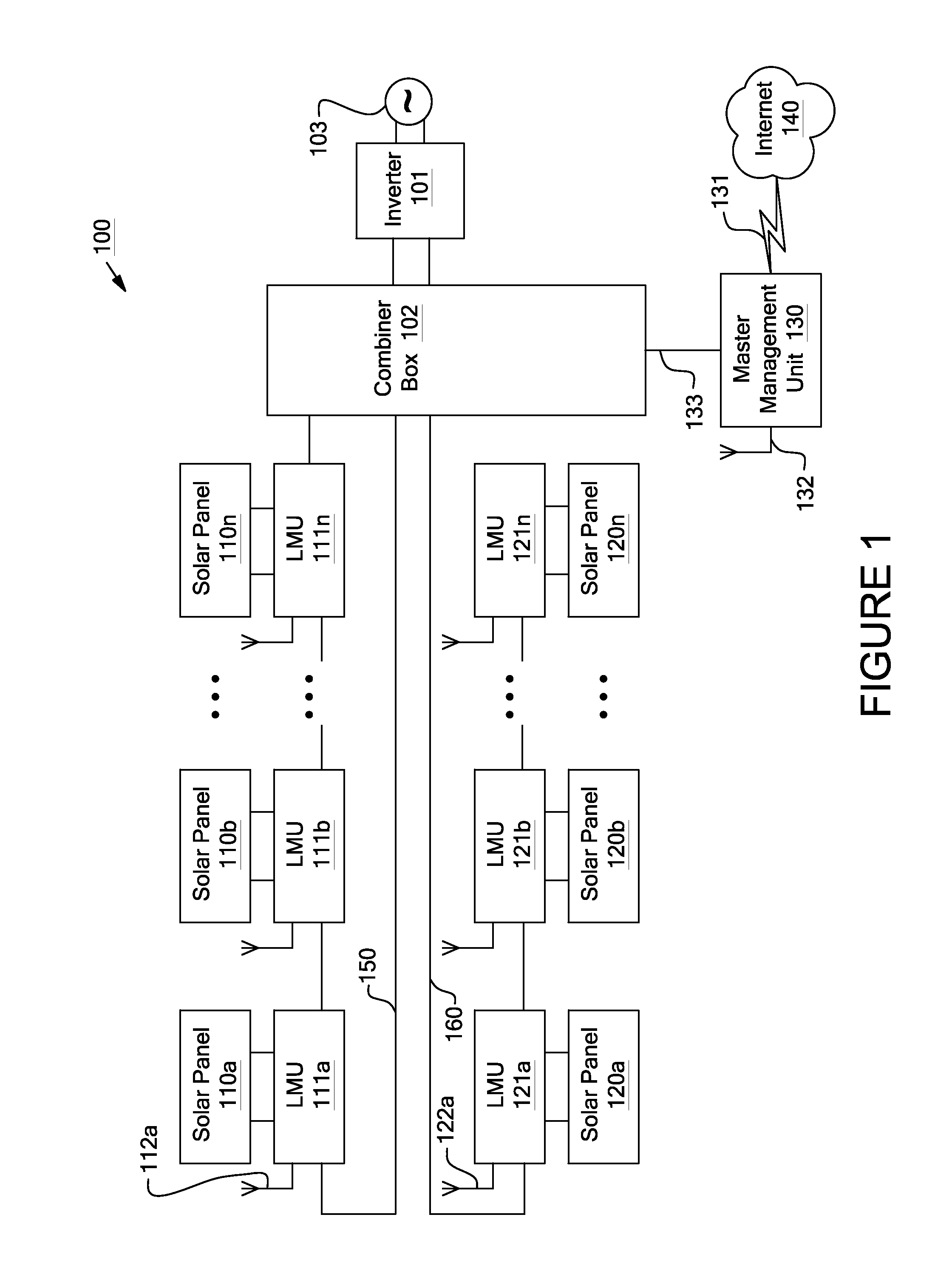
Systems and methods for shut-down of a photovoltaic system. In one embodiment, a method implemented in a computer system includes: communicating, via a central controller, with a plurality of local management units (LMUs), each of the LMUs coupled to control a respective solar module; receiving, via the central controller, a shut-down signal from a user device (e.g., a hand-held device, a computer, or a wireless switch unit); and in response to receiving the shut-down signal, shutting down operation of the respective solar module for each of the LMUs.
Owner:NEWLIGHT CAPITAL LLC
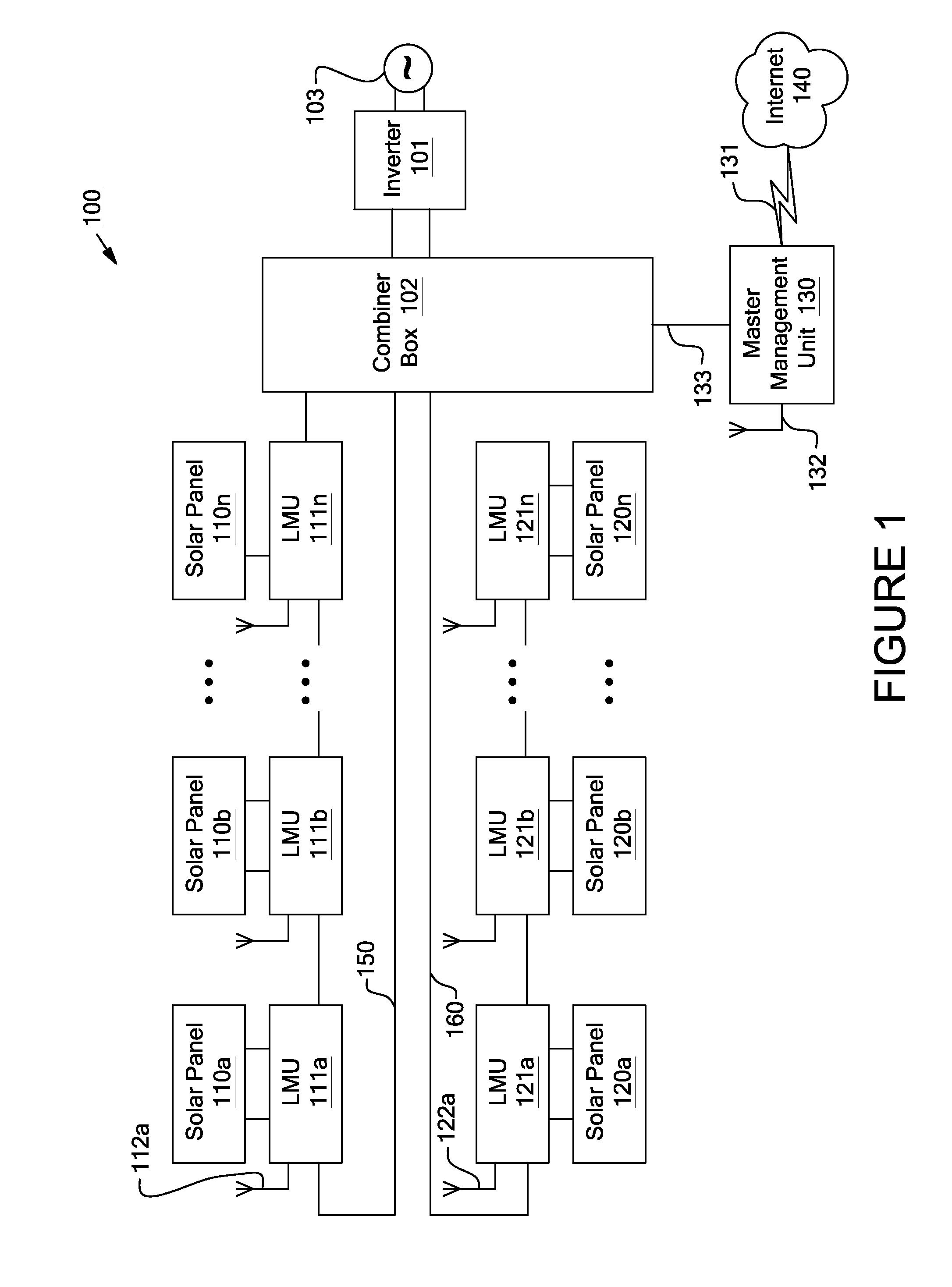
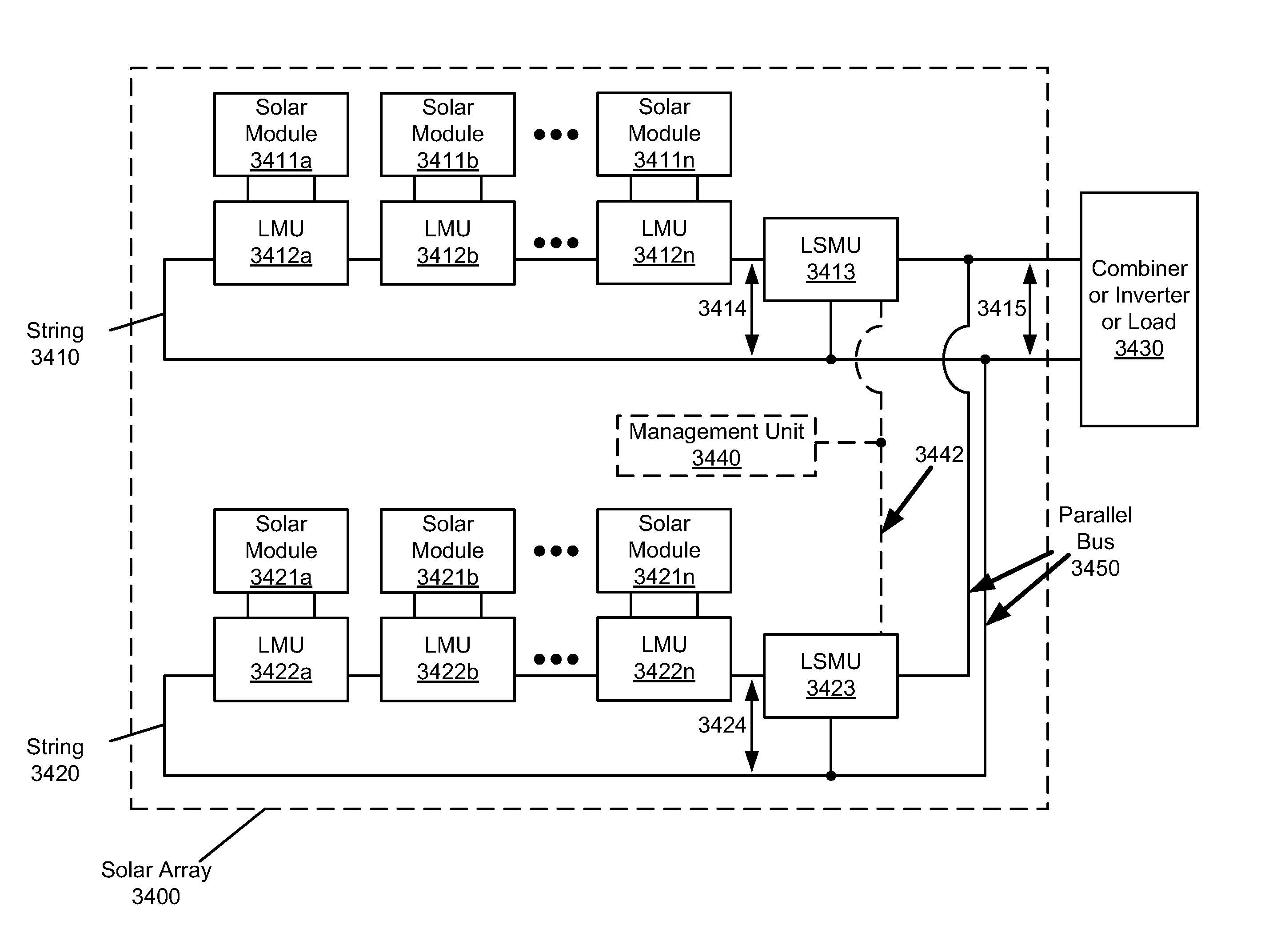
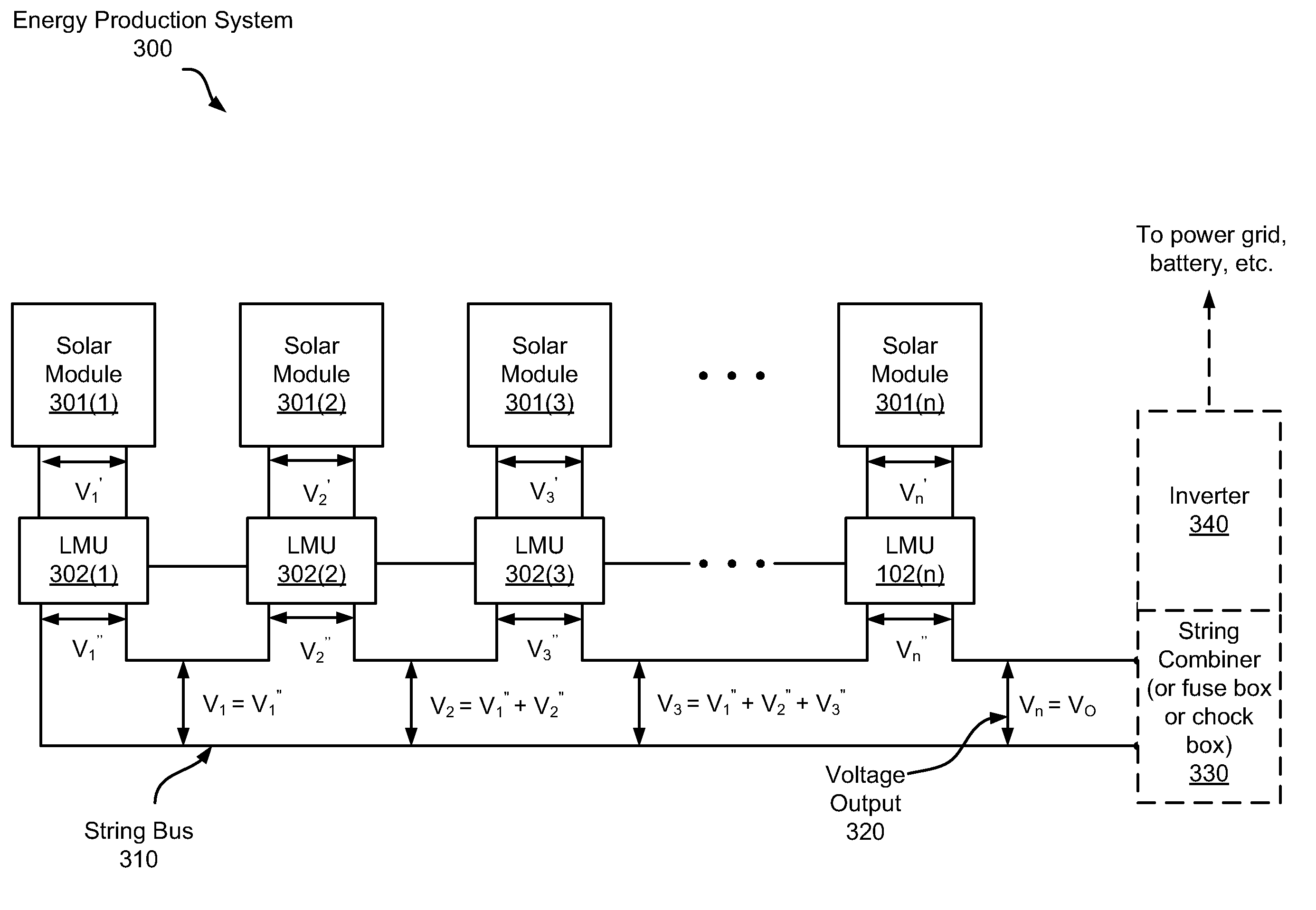
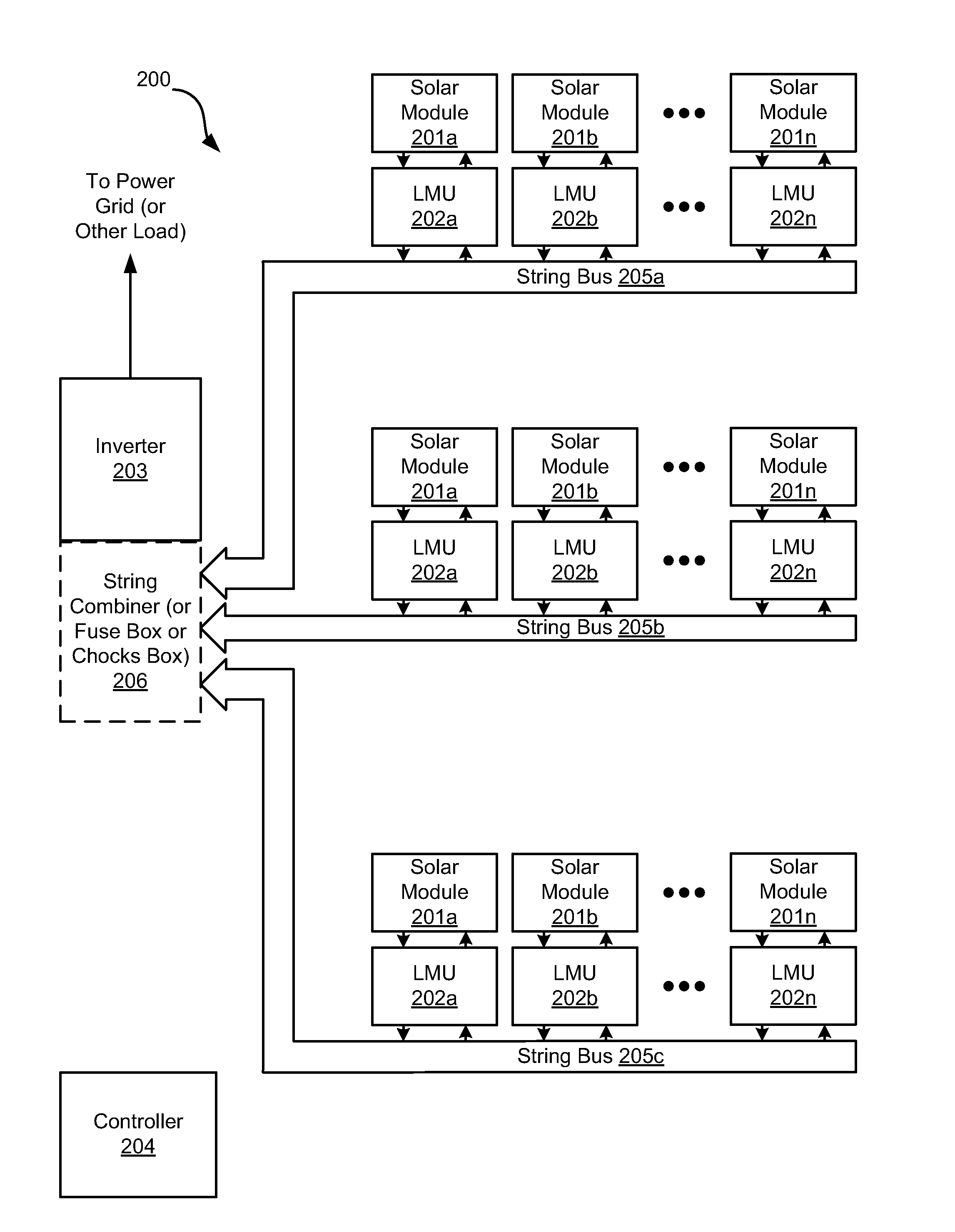
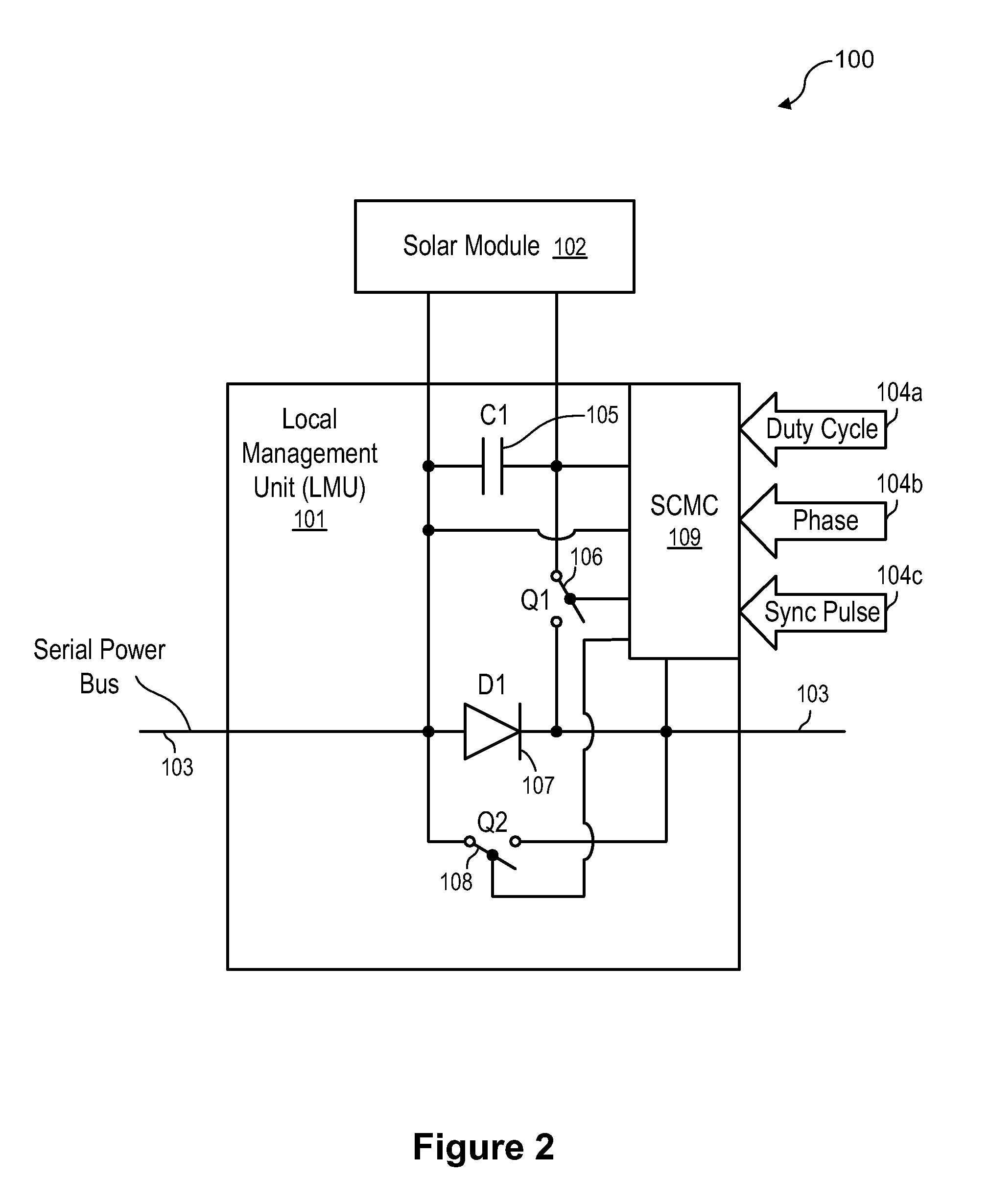
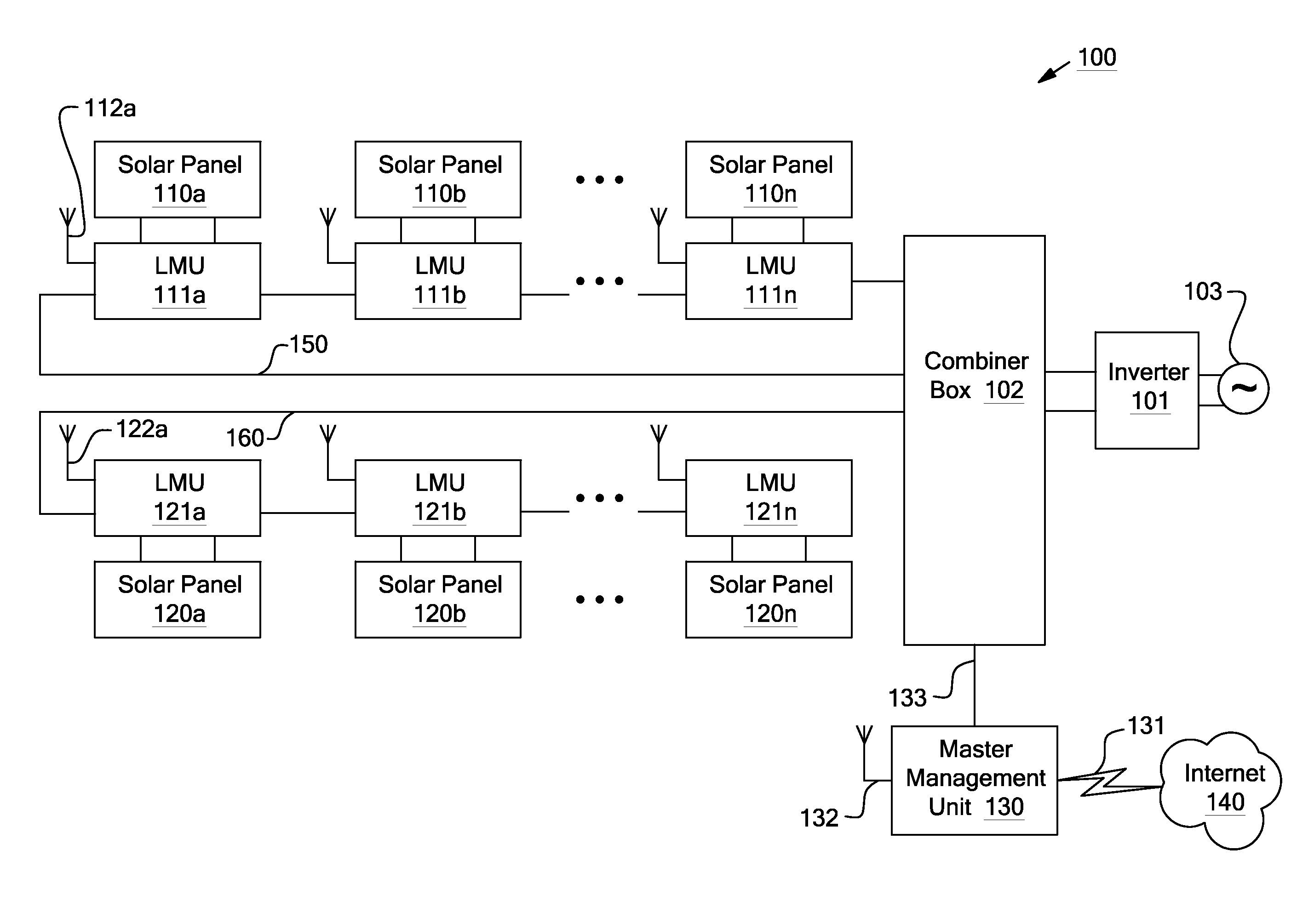
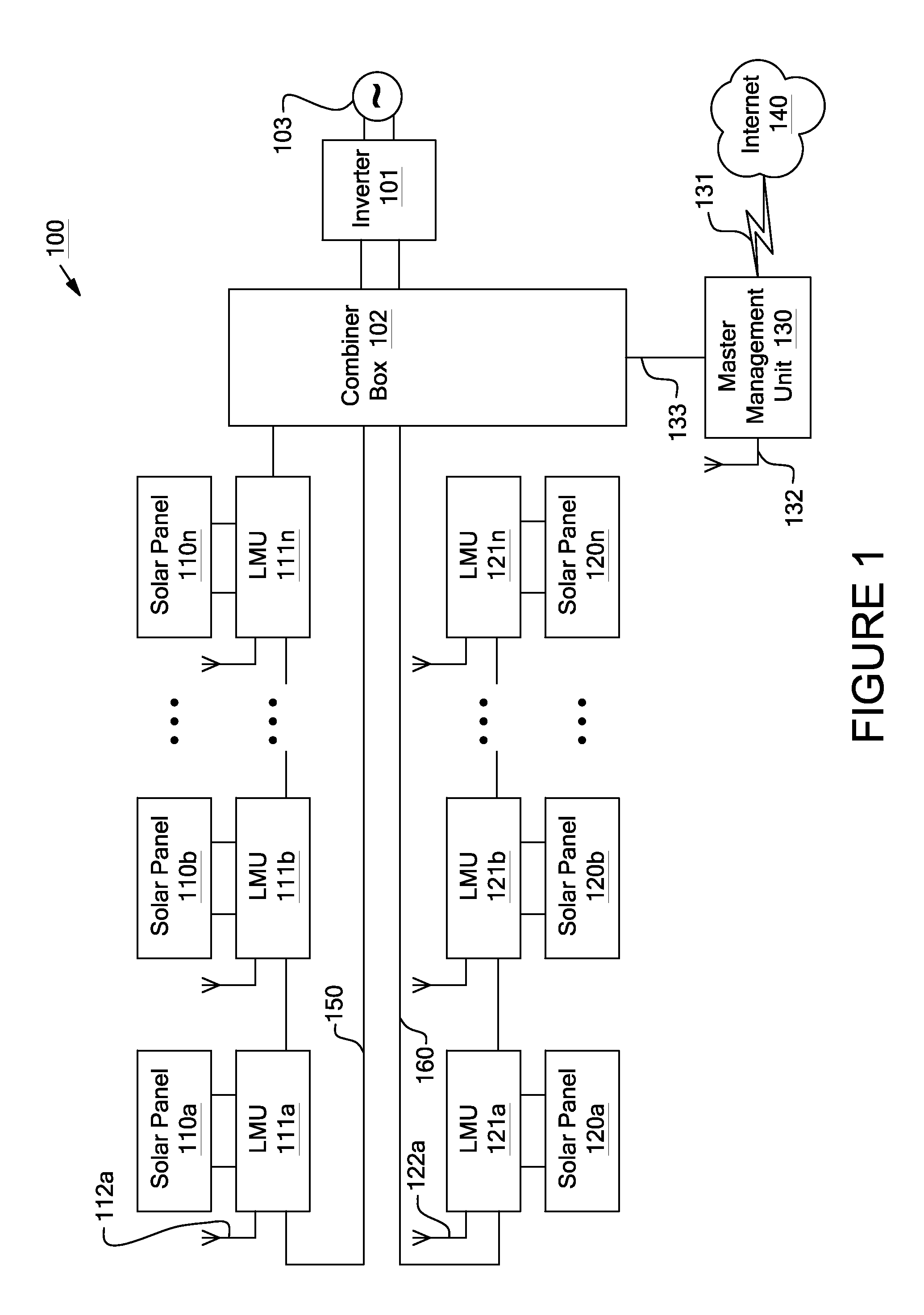
System and method for local string management unit
Apparatuses and methods include a solar array having one or more strings of series-connected local management units (LMUs). Each LMU is parallel-connected to one of a plurality of solar modules. The strings are connected in parallel via a parallel bus. Local string management units (LSMUs) can increase or decrease an output voltage of the solar array by upconverting or downconverting string output voltages from each string. LSMUs can also operate in a bypass mode to increase overall power output.
Owner:NEWLIGHT CAPITAL LLC
Systems and method for limiting maximum voltage in solar photovoltaic power generation systems
Owner:NEWLIGHT CAPITAL LLC
Systems and methods for an enhanced watchdog in solar module installations
ActiveUS8933321B2Engagement/disengagement of coupling partsPhotovoltaic monitoringEngineeringEmergency situations
Systems and methods are disclosed for automatically or remotely rendering a solar array safe during an emergency or maintenance. A watchdog unit is disclosed for monitoring a signal from a central controller. If the signal is lost, interrupted, or becomes irregular, or if a shutdown signal is received, then the watchdog unit can shutdown one or more solar modules. Shutting down a solar module can mean disconnecting it from a power bus of the solar array or lowering the solar module voltage to a safe level.
Owner:NEWLIGHT CAPITAL LLC
Systems and methods for an identification protocol between a local controller and a master controller in a photovoltaic power generation system
Owner:NEWLIGHT CAPITAL LLC
System and Method for Local String Management Unit
Apparatuses and methods include a solar array having one or more strings of series-connected local management units (LMUs). Each LMU is parallel-connected to one of a plurality of solar modules. The strings are connected in parallel via a parallel bus. Local string management units (LSMUs) can increase or decrease an output voltage of the solar array by upconverting or downconverting string output voltages from each string. LSMUs can also operate in a bypass mode to increase overall power output.
Owner:NEWLIGHT CAPITAL LLC
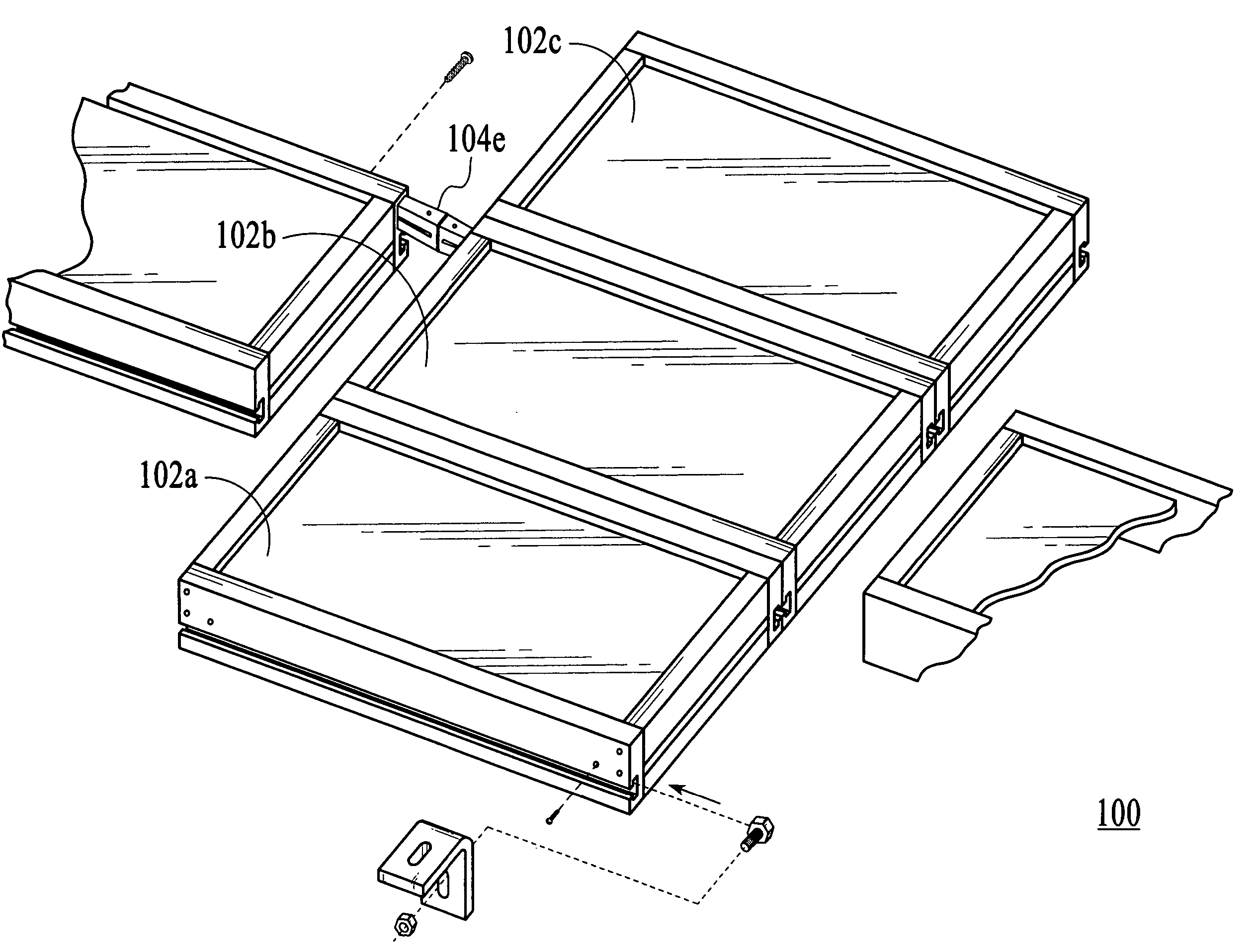
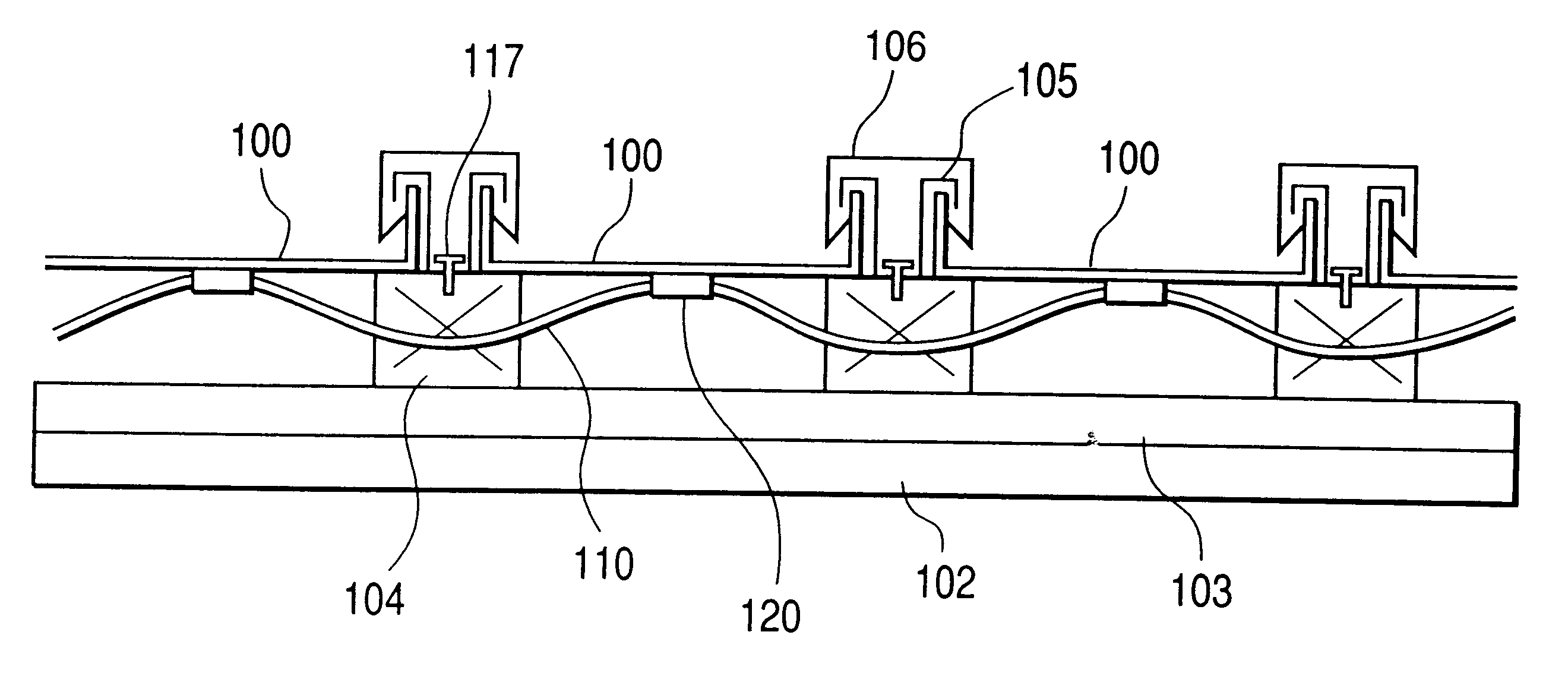
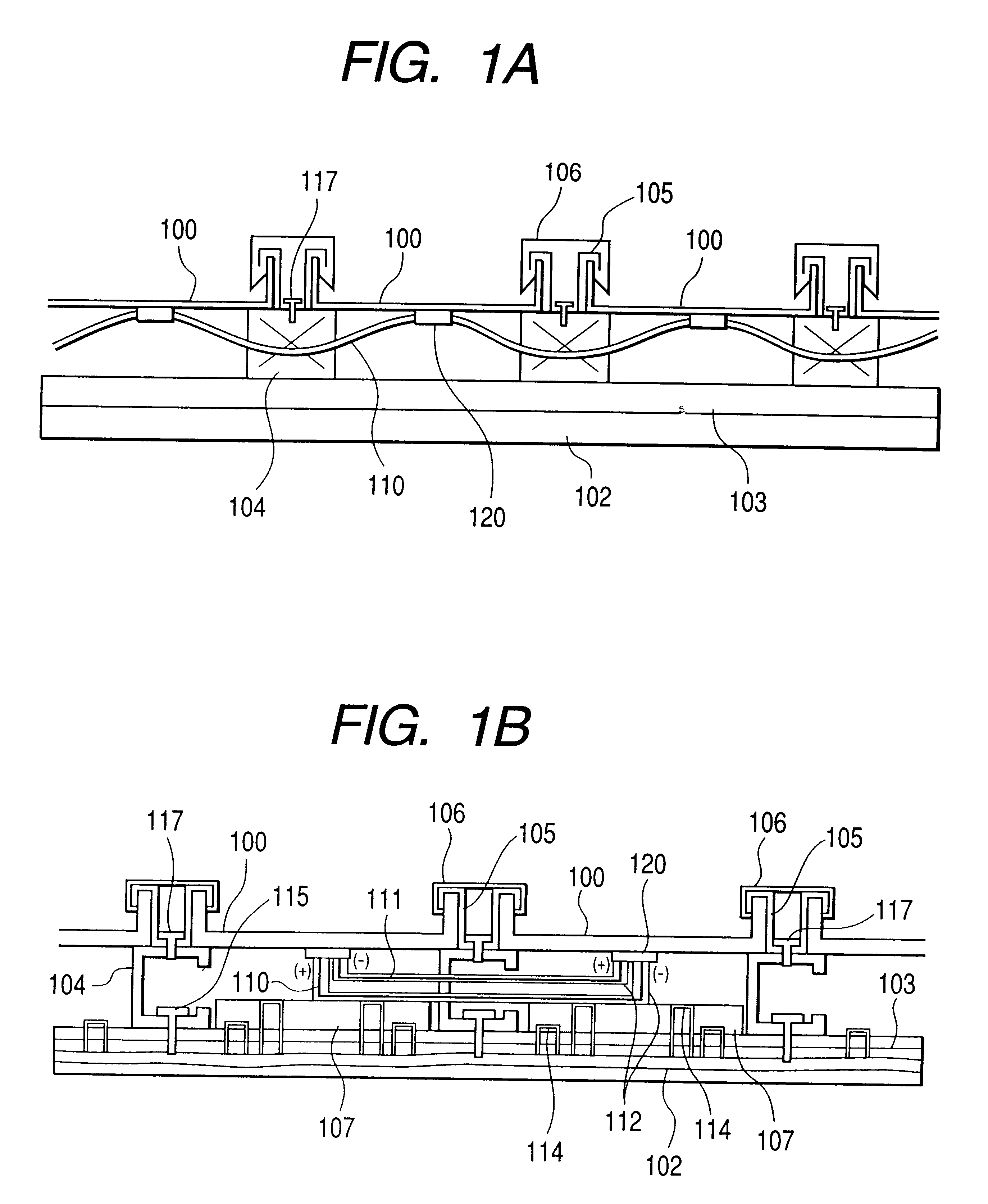
Mounting system for a solar panel
InactiveUS20050257453A1Simplify electrical assembly of moduleChange defectsPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyEngineeringSolar module
An integrated module frame and racking system for a solar panel is disclosed. The solar panel comprises a plurality of solar modules and a plurality of splices for coupling the plurality of solar modules together. The plurality of splices provide a way to make the connected modules mechanically rigid both during transport to the roof and after mounting for the lifetime of the system, provide wiring connections between modules, provide an electrical grounding path for the modules, provide a way to add modules to the panel, and provide a way to remove or change a defective module. Connector sockets are provided on the sides of the modules to simplify the electrical assembly of modules when the modules are connected together with splices.
Owner:ANDALAY SOLAR
Enhanced Systems and Methods for Using a Power Converter for Balancing Modules in Single-String and Multi-String Configurations
ActiveUS20120255591A1Mechanical power/torque controlDc network circuit arrangementsManagement unitEngineering
Apparatuses and methods include a solar array having one or more string buses of series-connected solar modules. The current outputs from the solar modules on each string bus can be balanced along with the voltage output from the string buses. Local management units coupled between the solar modules and the string buses are configured to control the voltage output from each solar module. When the solar modules on each string are balanced, and when the string buses are balanced (or before the solar modules and string buses are balanced), an inverter or other device connected to the solar array can find the array's maximum power point via a maximum power point tracking algorithm.
Owner:NEWLIGHT CAPITAL LLC
Series solar system with current-matching function
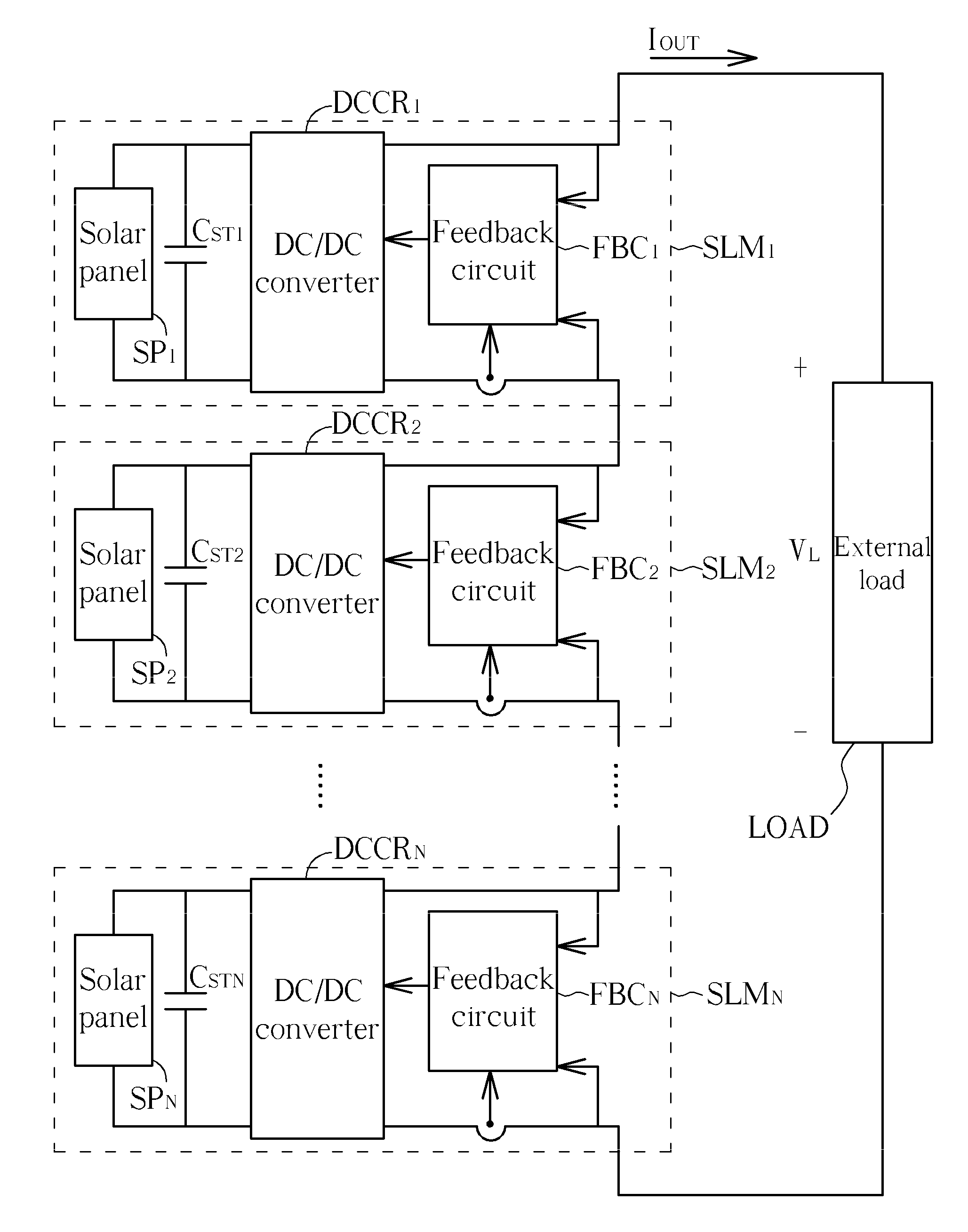
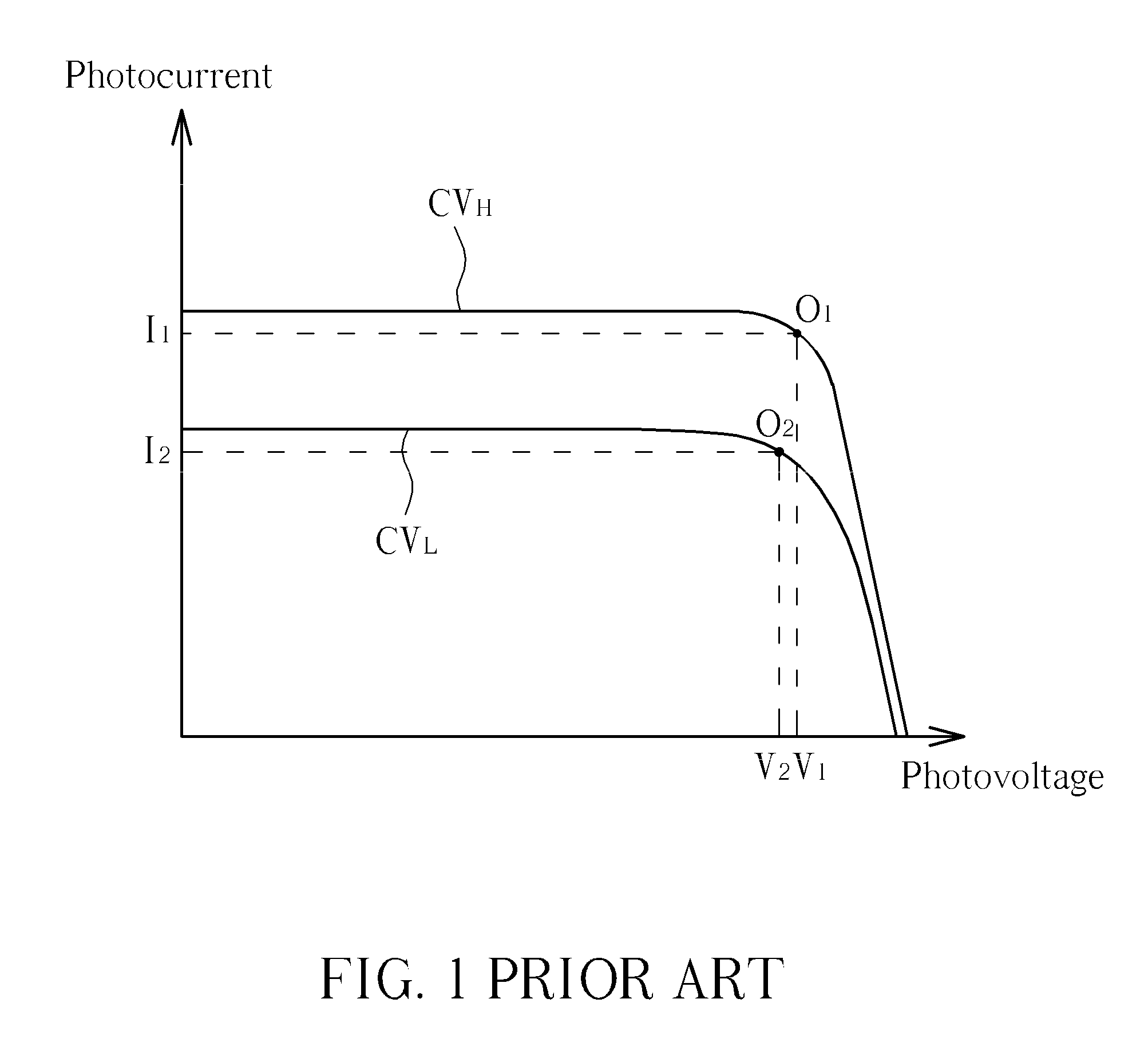
InactiveUS20110056533A1Increase powerDc network circuit arrangementsPV power plantsElectricityOperating point
A series solar system with current-matching function includes a plurality of solar modules. The plurality of the solar modules is electrically connected in series. Each solar module includes a DC / DC converter and a solar panel electrically connected in parallel. The photocurrent generated by the solar panel is matched with the current generated by the solar panel operating at the optimum operating point by means of adjusting the duty cycle of the DC / DC converter, so that the solar panel can generate maximum output power. Therefore, in the series solar system, even a solar module is covered, causing the received light intensity of the solar module is reduced, and the series solar system still can generate maximum output power.
Owner:INERGY TECH
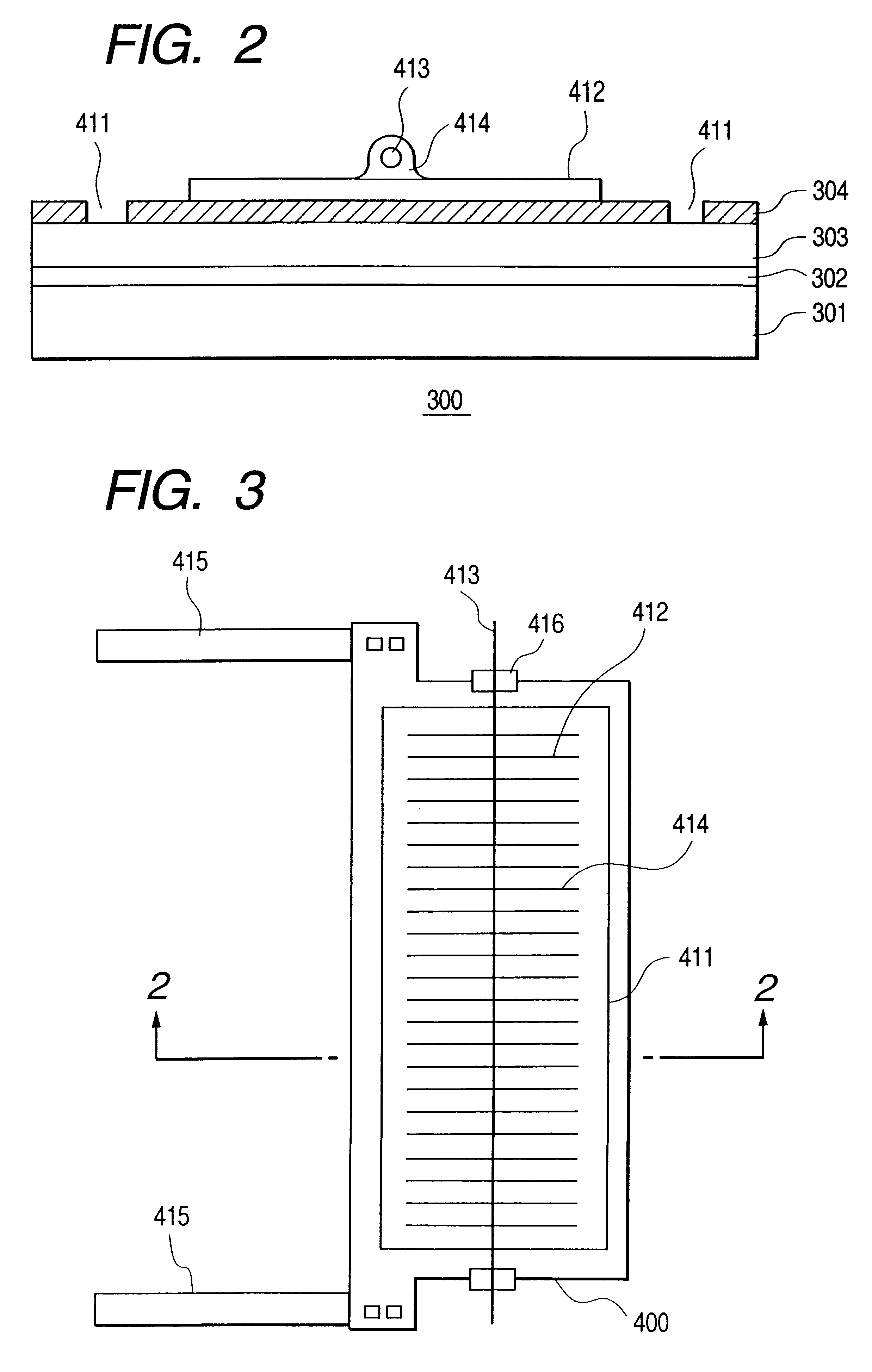
Solar cell module, enclosure with solar cells, enclosure installation method, and solar cell system
InactiveUS6245987B1Improve reliabilityAvoid crackingPhotovoltaic supportsRoof covering using slabs/sheetsElectrical batteryComputer module
By providing a non-contact means and / or a non-contact space between electric connecting members and an underlaying material and / or a substrate material and / or a rear material, the temporal degradation of a solar cell module can be prevented which is caused by a contact between the electric connecting members for the module and the underlaying material and / or the substrate material and / or the rear material.
Owner:CANON KK
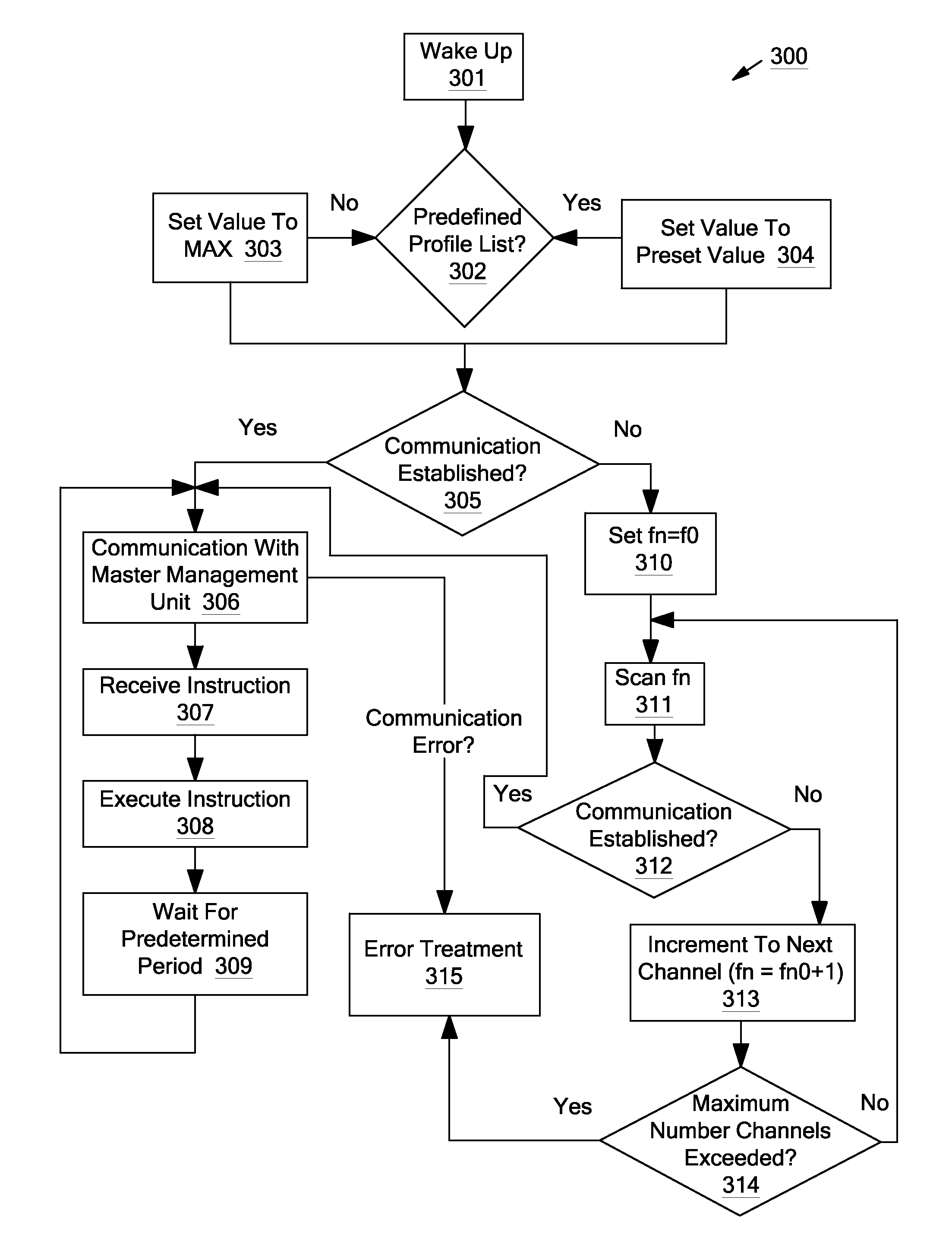
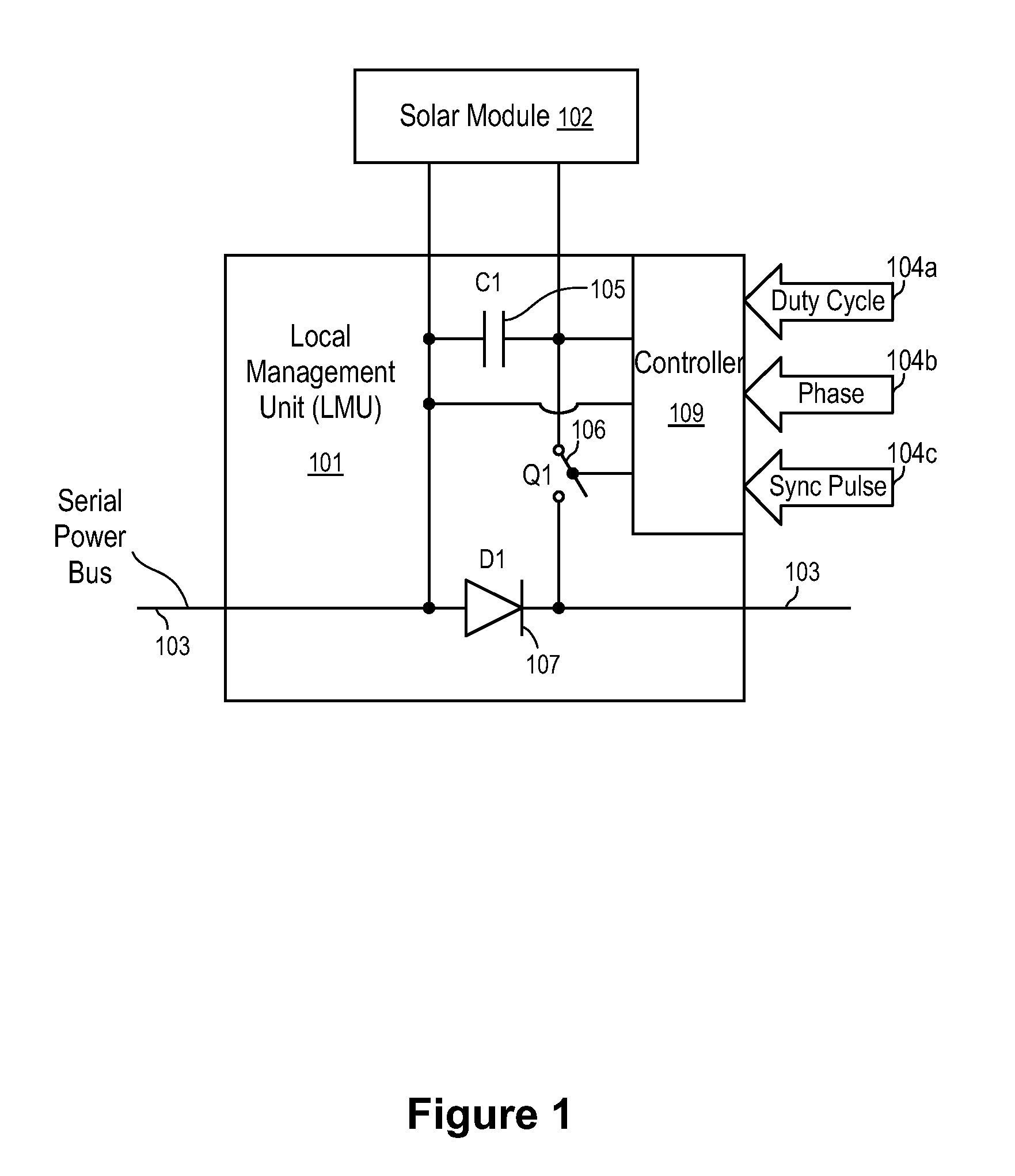
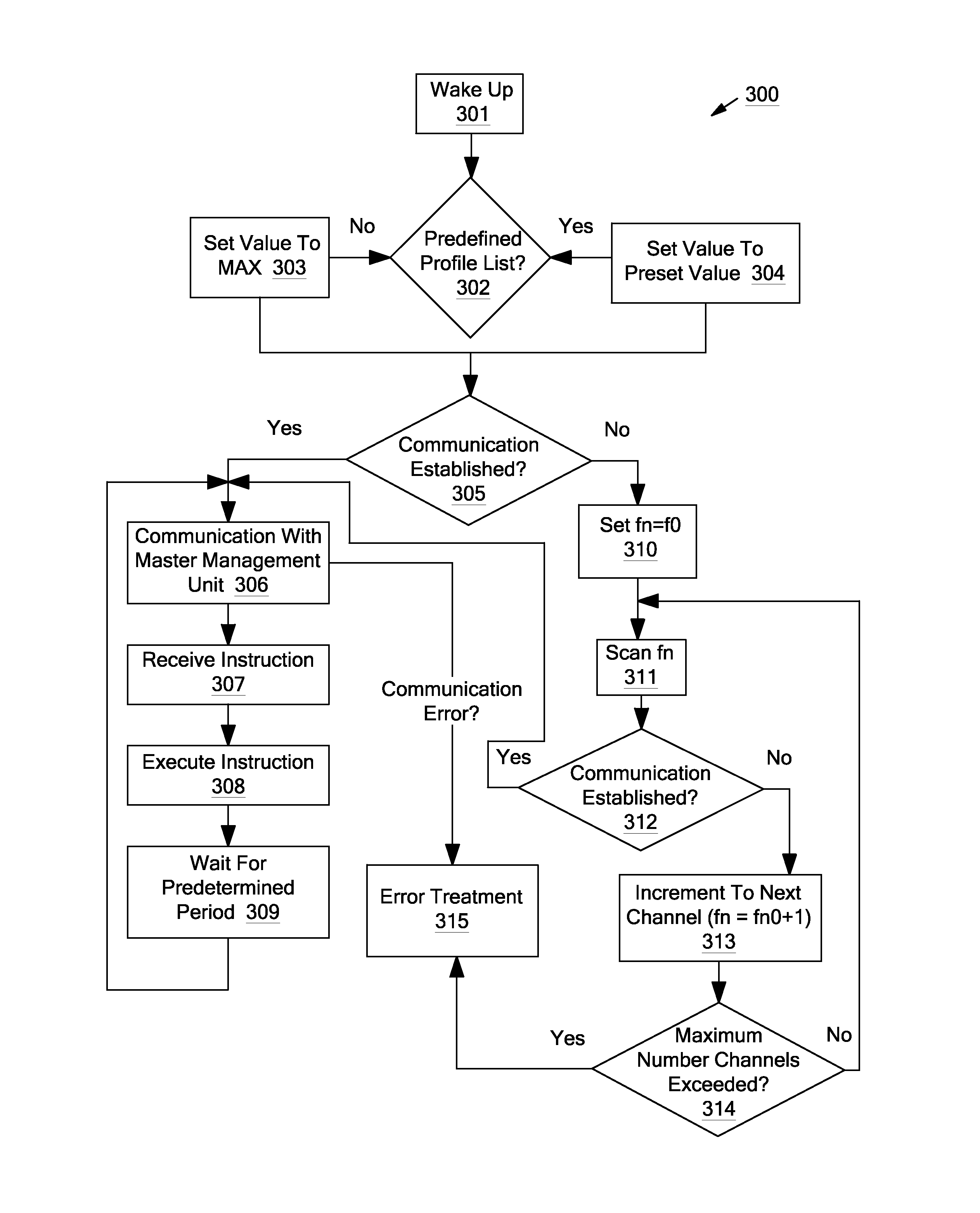
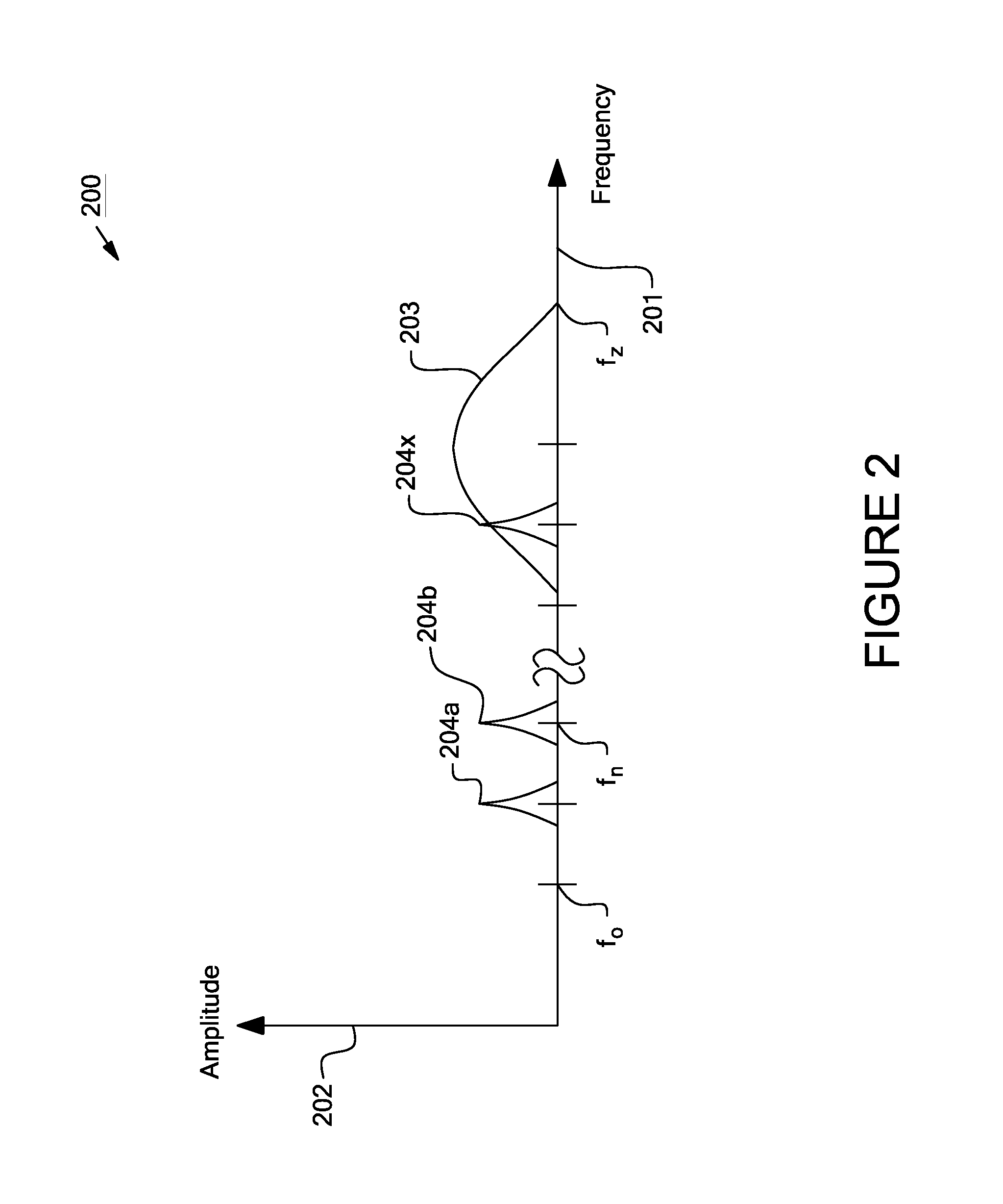
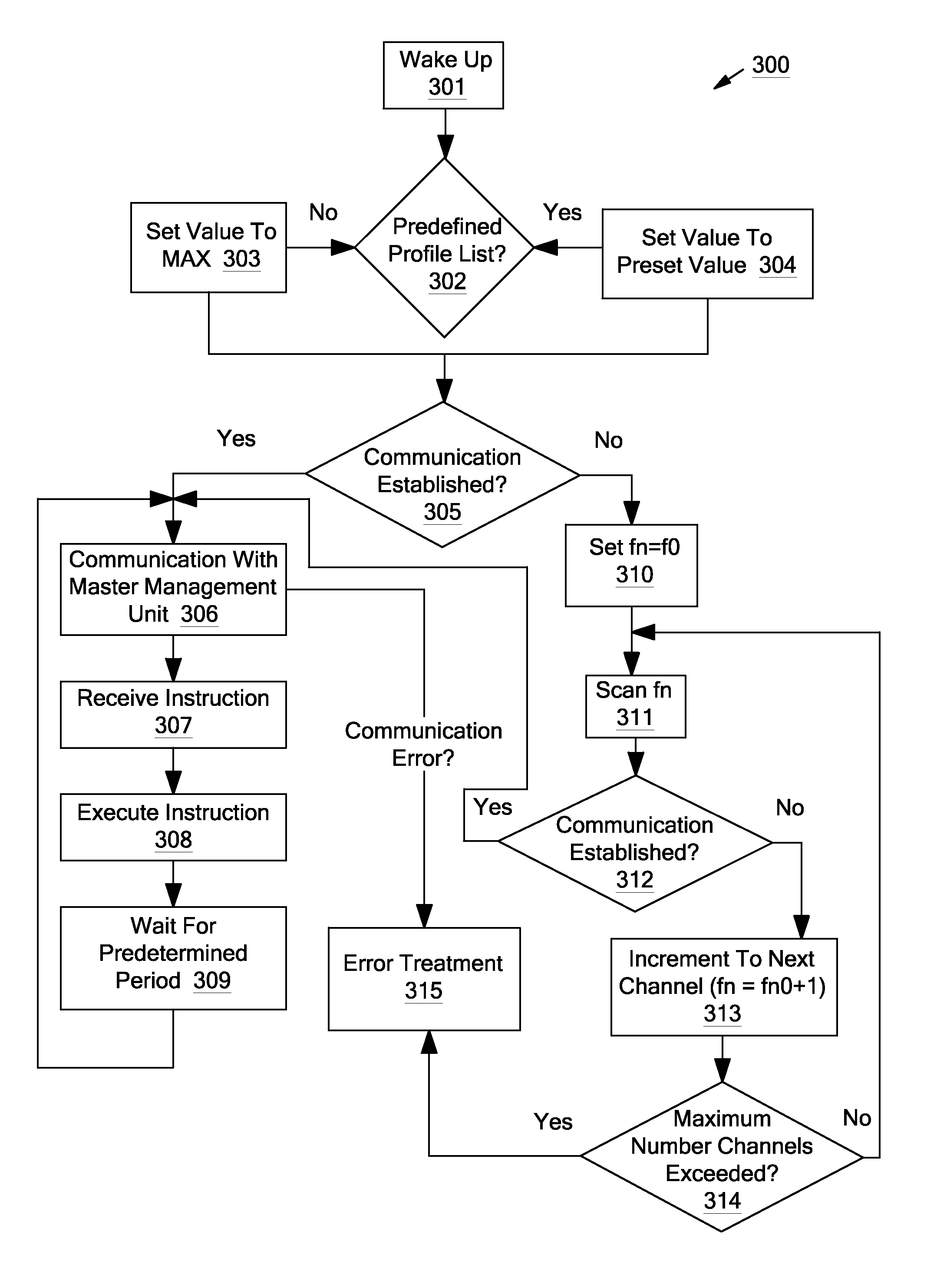
Systems and methods for a communication protocol between a local controller and a master controller
Systems and methods for local management units in a photovoltaic energy system. In one embodiment, a method implemented in a computer system includes: attempting to communicate on a first active channel with a master management unit from a local management unit that controls a solar module; if communication with the master management unit on the first active channel has not been established, attempting to communicate on a second active channel with the master management unit.
Owner:NEWLIGHT CAPITAL LLC
Systems and Methods for an Identification Protocol Between a Local Controller and a Master Controller
ActiveUS20110173276A1Generation forecast in ac networkLevel controlManagement unitComputerized system
Systems and methods for local and master management units in a photovoltaic energy system. In one embodiment, a method implemented in a computer system includes sending a first identification code from a local management unit to a master management unit. The first identification code is associated with the first local management unit, and the local management unit controls a solar module. An authentication of the first identification code is received from the master management unit. In response to receiving the authentication, active operation of the local management unit is continued (e.g., for a set time period).
Owner:NEWLIGHT CAPITAL LLC
Photovoltaic units, methods of operating photovoltaic units and controllers therefor
InactiveUS20120098344A1Low costUnnecessary to performBatteries circuit arrangementsPhotovoltaicsElectrical batteryComputer module
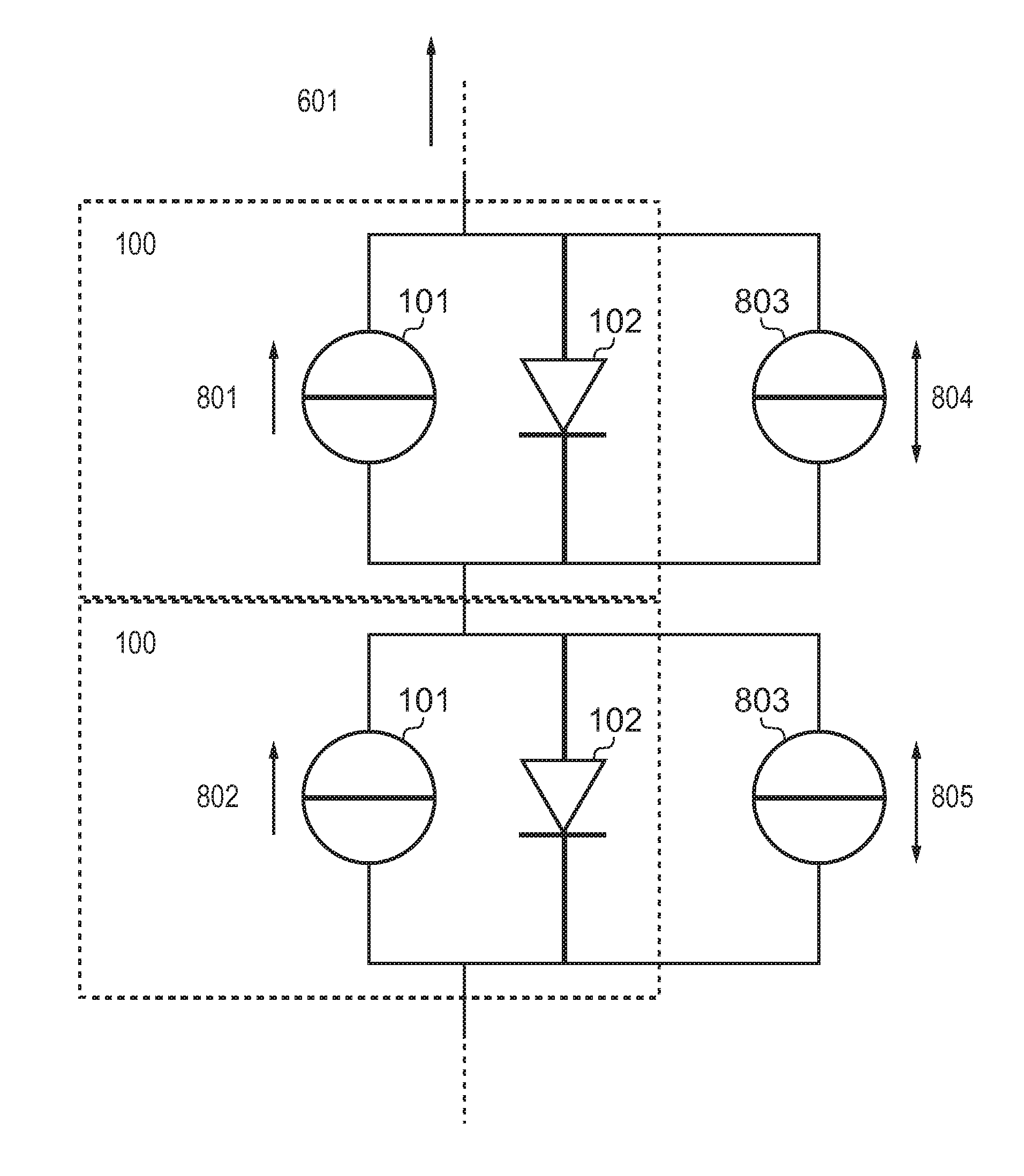
The present invention relates to the field of photovoltaic systems with solar cell (s) or modules having insolation differences or mismatch. Each solar module is formed by placing a large number of solar cells in series. The PV system is then formed by placing a number of solar modules in series in a string and sometimes by placing multiple strings of series-connected solar modules in parallel, depending on the desired output voltage and power range of the PV system. In practical cases, differences will exist between output powers of the solar cells in the various modules, e.g. due to (part of) the modules being temporarily shaded, pollution on one or more solar cells, or even spread in solar-cell behaviour that may become worse during aging. Due to the current-source-type behaviour of solar cells and their series connection these differences will lead to a relatively large drop in output power coming from the PV system. This invention addresses this problem by adding DC-DC converters (803) on a single or multiple solar-cell level that source or sink difference currents thereby increasing the output power of the complete PV system. In embodiments, the efficiency of photovoltaic systems with solar cell (s) or modules is improved by compensating for output-power loss caused by insolation difference and mismatch.
Owner:NXP BV
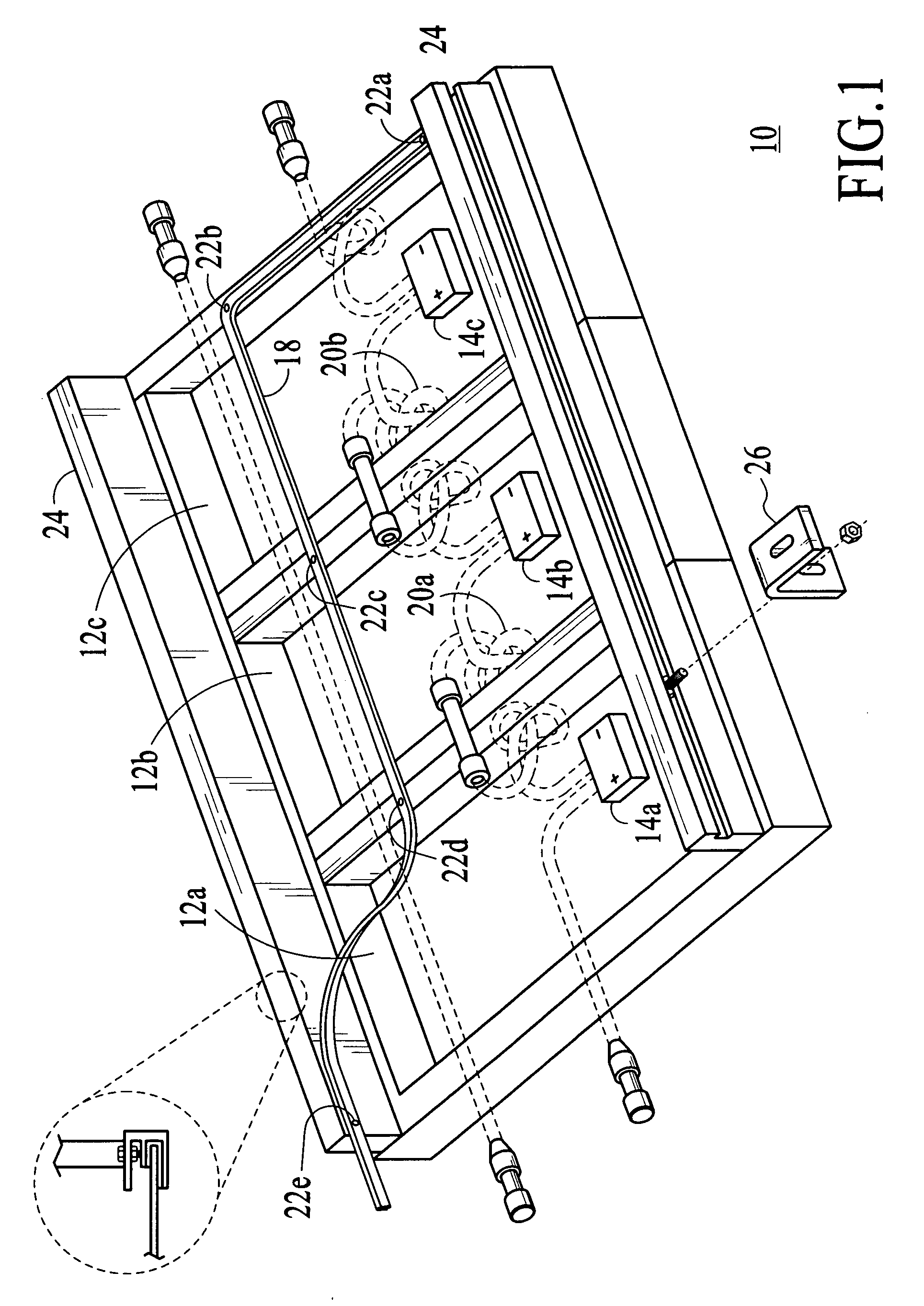
Flat Roof Mounted Solar Panel Support System
InactiveUS20100243023A1Easy to installPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energySupporting systemSolar power
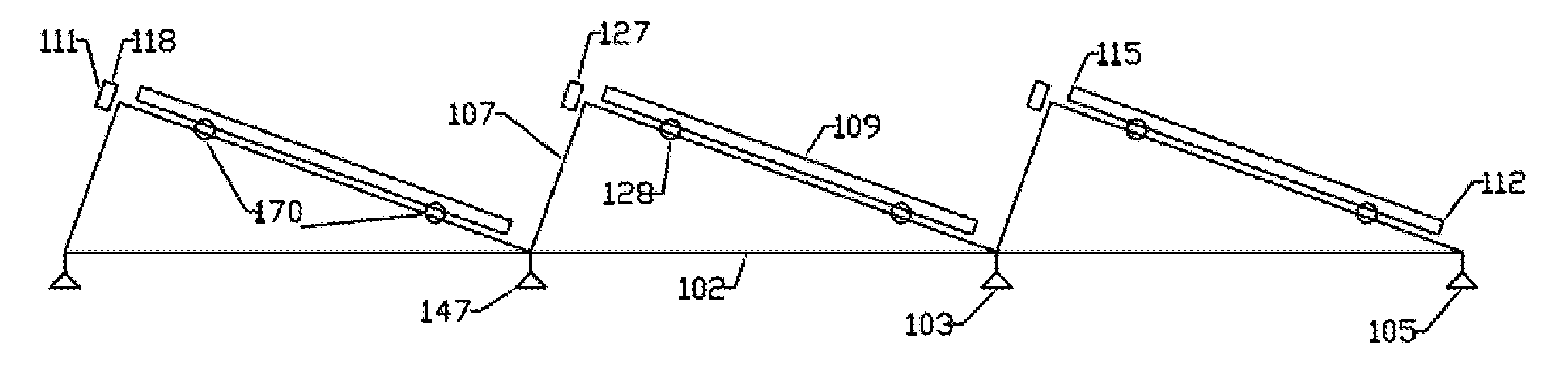
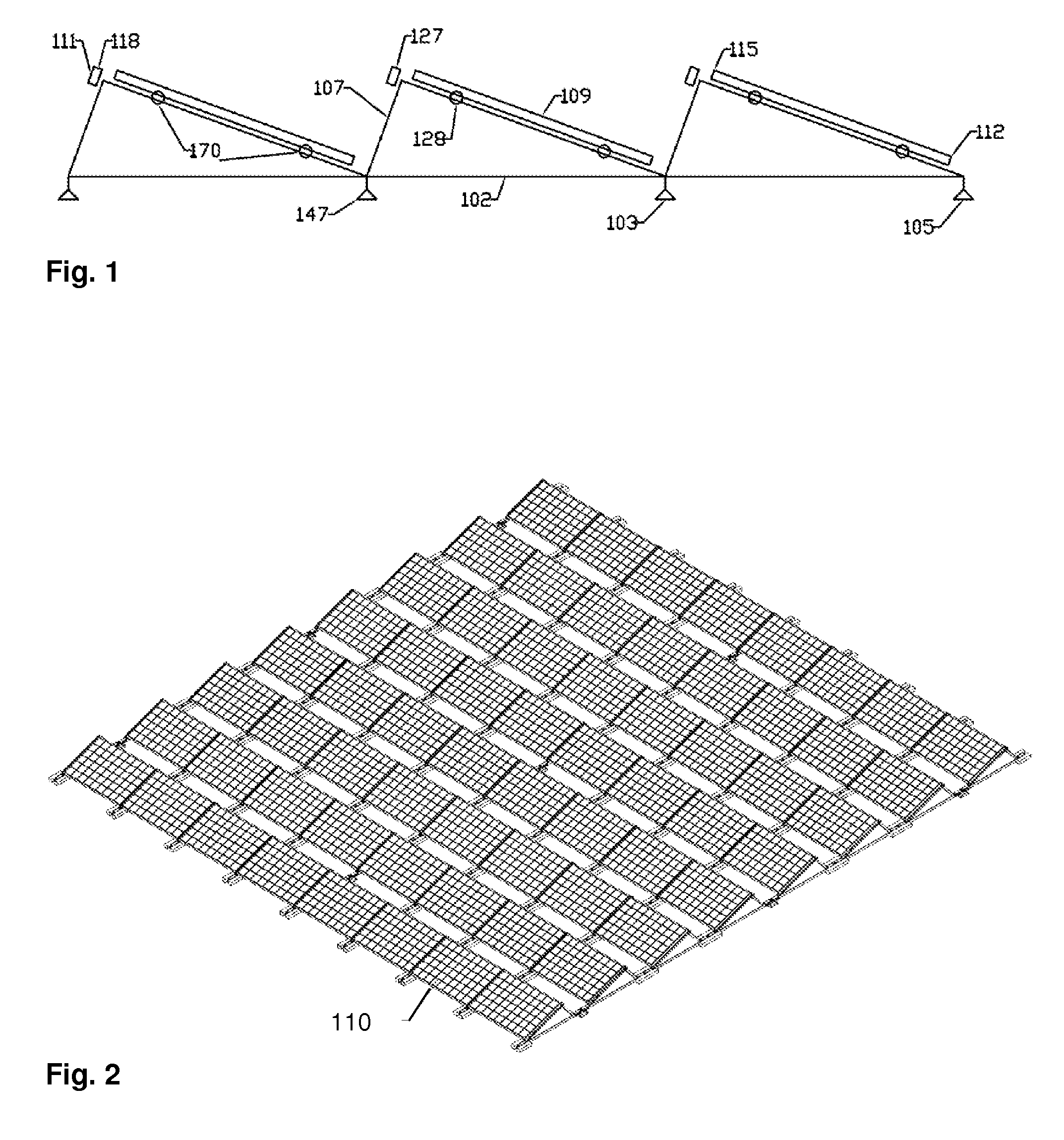
A solar power system is mounted to a solar power componentry support structure (104) suspended above a pre-existing surface (101) by a collective of solar collector suspension base supports (103) Suspended solar power system row support structure members (105) and suspended solar power system column support structure members (106) may for a solar component position lattice (107) to which a matrix of individual solar power components such as solar panels (18) can be attached Solar module quick-fasten assemblages (111) may serve also as solar componentry emergency releases (118) and may include loose axis retainers (128) and firm axis fasteners (127) such as dual component, single point operative emergency releases (121) and fasteners Slide-in retainers and corner slot tabs (136) can be included as well as frame alignment notches (138) Fulcrum pivot fasteners (139) and slide wedge releases (142) can aid in installation and release
Owner:SOLARPOWER
Systems and Methods for an Identification Protocol Between a Local Controller and a Master Controller
Systems and methods for local and master management units in a photovoltaic energy system. In one embodiment, a method implemented in a computer system includes sending a first identification code from a local management unit to a master management unit. The first identification code is associated with the first local management unit, and the local management unit controls a solar module. An authentication of the first identification code is received from the master management unit. In response to receiving the authentication, active operation of the local management unit is continued (e.g., for a set time period).
Owner:NEWLIGHT CAPITAL LLC
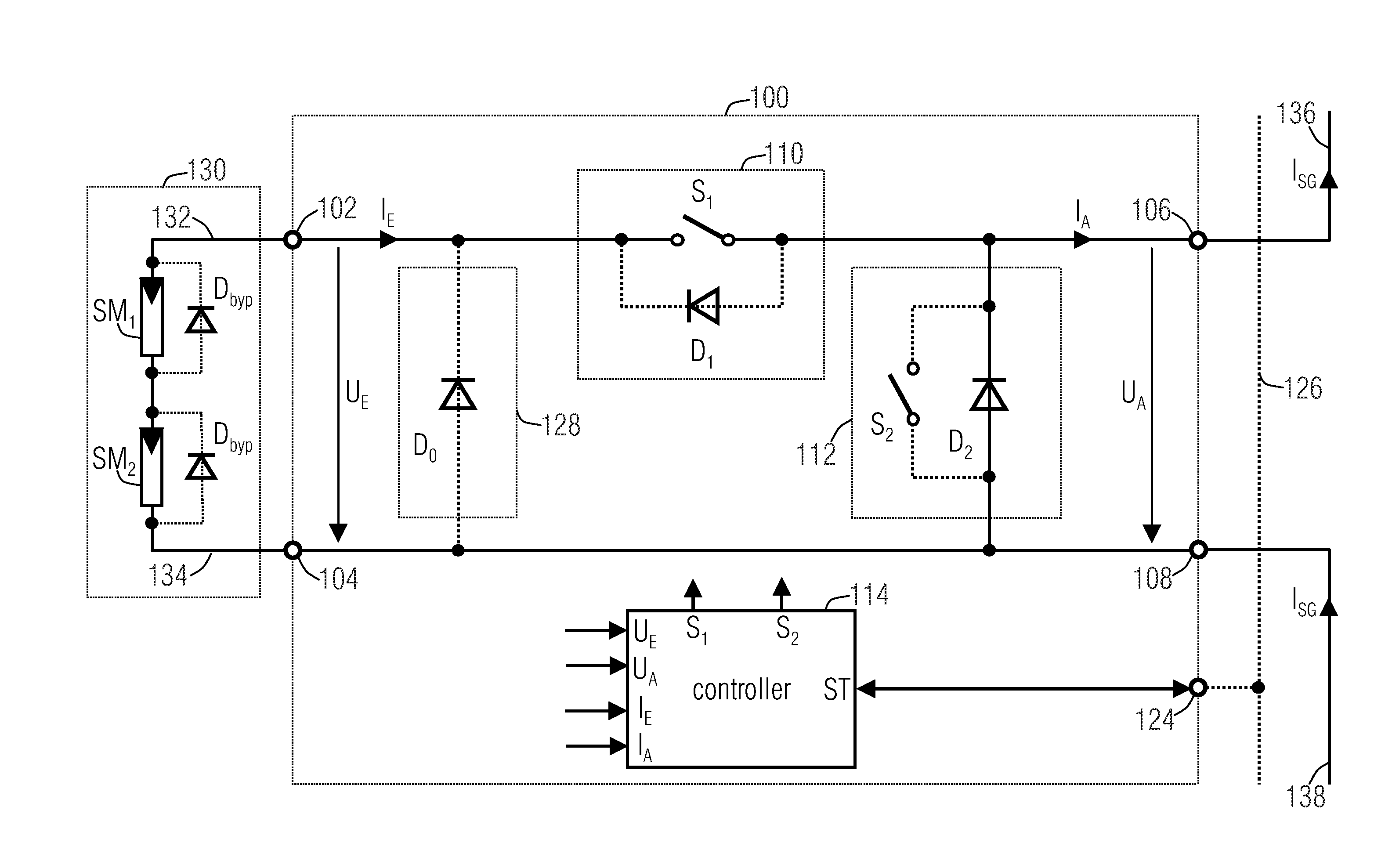
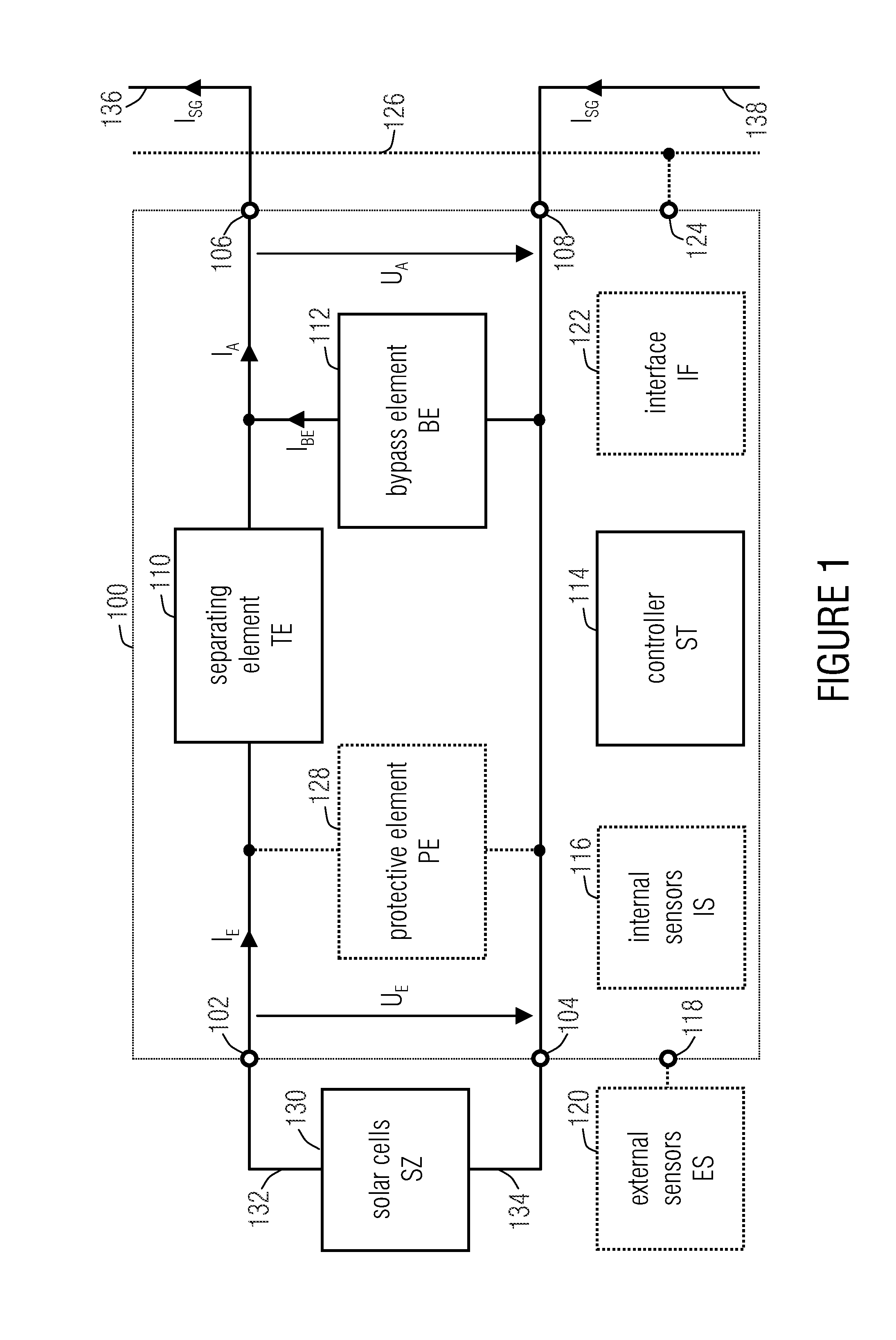
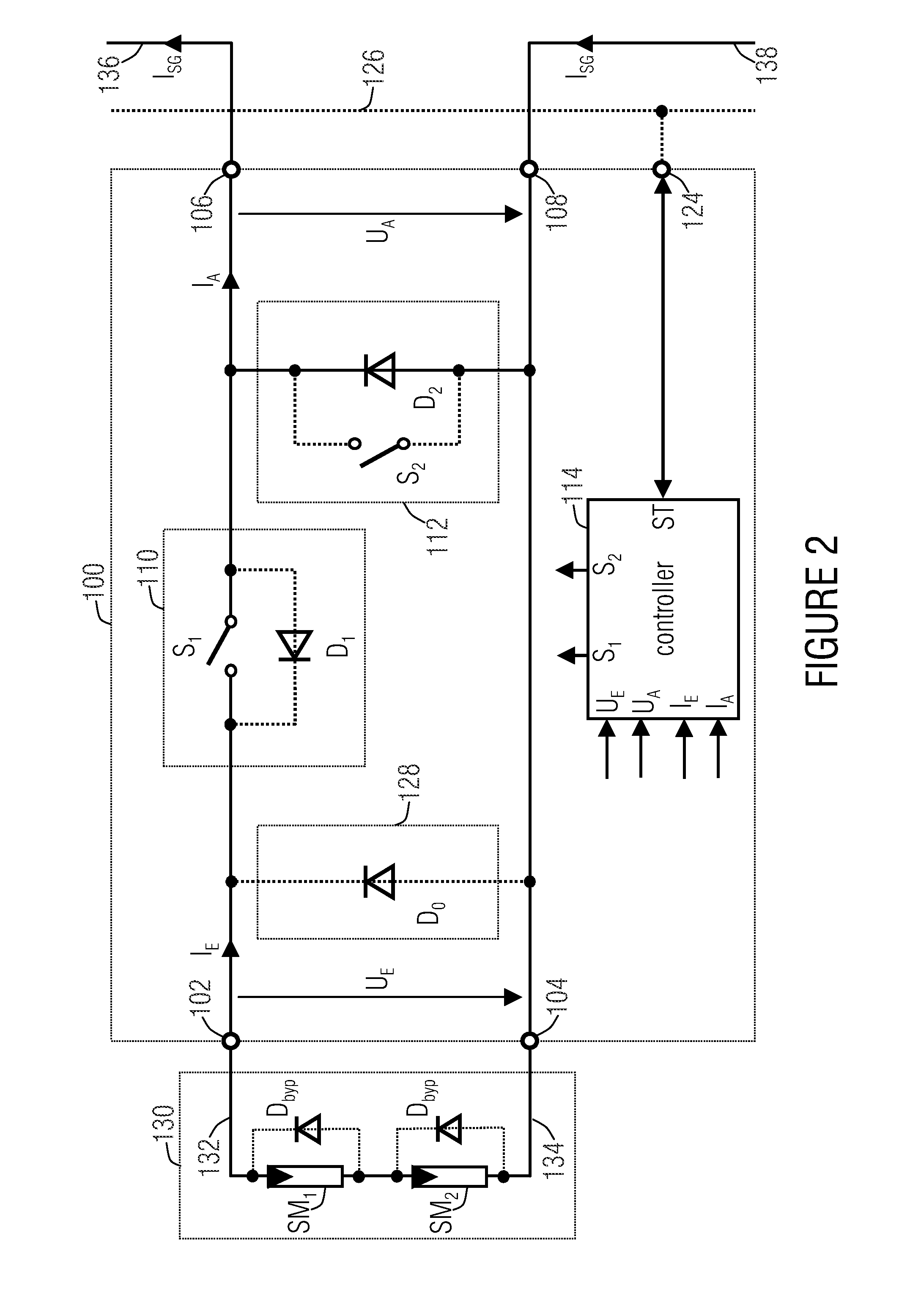
Bypass and protection circuit for a solar module and method of controlling a solar module
InactiveUS20120194003A1Boards/switchyards circuit arrangementsProtective switchesComputer moduleSolar module
A bypass and protection circuit for a solar module includes an input for connecting the solar module, an output, a bypass element connected in parallel to the output, and a separating element connected between the input and the output and configured to control the connection between the input and the output. The separating element is configured to control a connection between the input and the output in dependence on whether the solar module associated with the circuit is completely or partially shaded, or whether the solar module associated with the circuit is to be switched on or off.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Weather-resistant and high thermal conductive coating, radiating solar rear panel and efficient solar cell panel
InactiveCN102516852AImprove thermal conductivityMeet service life requirementsPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesPhotovoltaicsWeather resistanceConductive coating
The invention discloses a weather-resistant and high thermal conductive coating, a radiating solar rear panel and an efficient solar cell panel. The weather-resistant and high thermal conductive coating consists of 10 to 50 parts of weather-resistant resin, 5 to 30 parts of curing agent, 0.1 to 5 parts of organic filler, 30 to 80 parts of inorganic filler, and 30 to 100 parts of solvent. The radiating solar rear panel comprises a base layer, and the weather-resistant and high thermal conductive coating is arranged on at least one surface of the base layer or arranged between the base layers. The efficient solar cell panel comprises a solar front panel and the radiating solar rear panel, a solar cell circuit is arranged between the solar front panel and the radiating solar rear panel, and an encapsulation material is arranged on one side or two sides of the solar cell circuit. The weather-resistant and high thermal conductive coating can be directly coated on a base material and has high binding power and an excellent thermal conductive effect, and the weather resistance of the coating meets the requirement of a solar module for the service life of over 25 years.
Owner:ALLSTAE TECH ZHONGSHAN
Systems and Methods for a Communication Protocol Between a Local Controller and a Master Controller
ActiveUS20110161722A1Error preventionPhotovoltaic energy generationManagement unitComputerized system
Systems and methods for local management units in a photovoltaic energy system. In one embodiment, a method implemented in a computer system includes: attempting to communicate on a first active channel with a master management unit from a local management unit that controls a solar module; if communication with the master management unit on the first active channel has not been established, attempting to communicate on a second active channel with the master management unit.
Owner:NEWLIGHT CAPITAL LLC
Solar module structures and assembly methods for pyramidal three-dimensional thin-film solar cells
InactiveUS20080210294A1Eliminate and reduce disadvantageEliminate and reduce and problemFinal product manufacturePV power plantsEngineeringSolar power
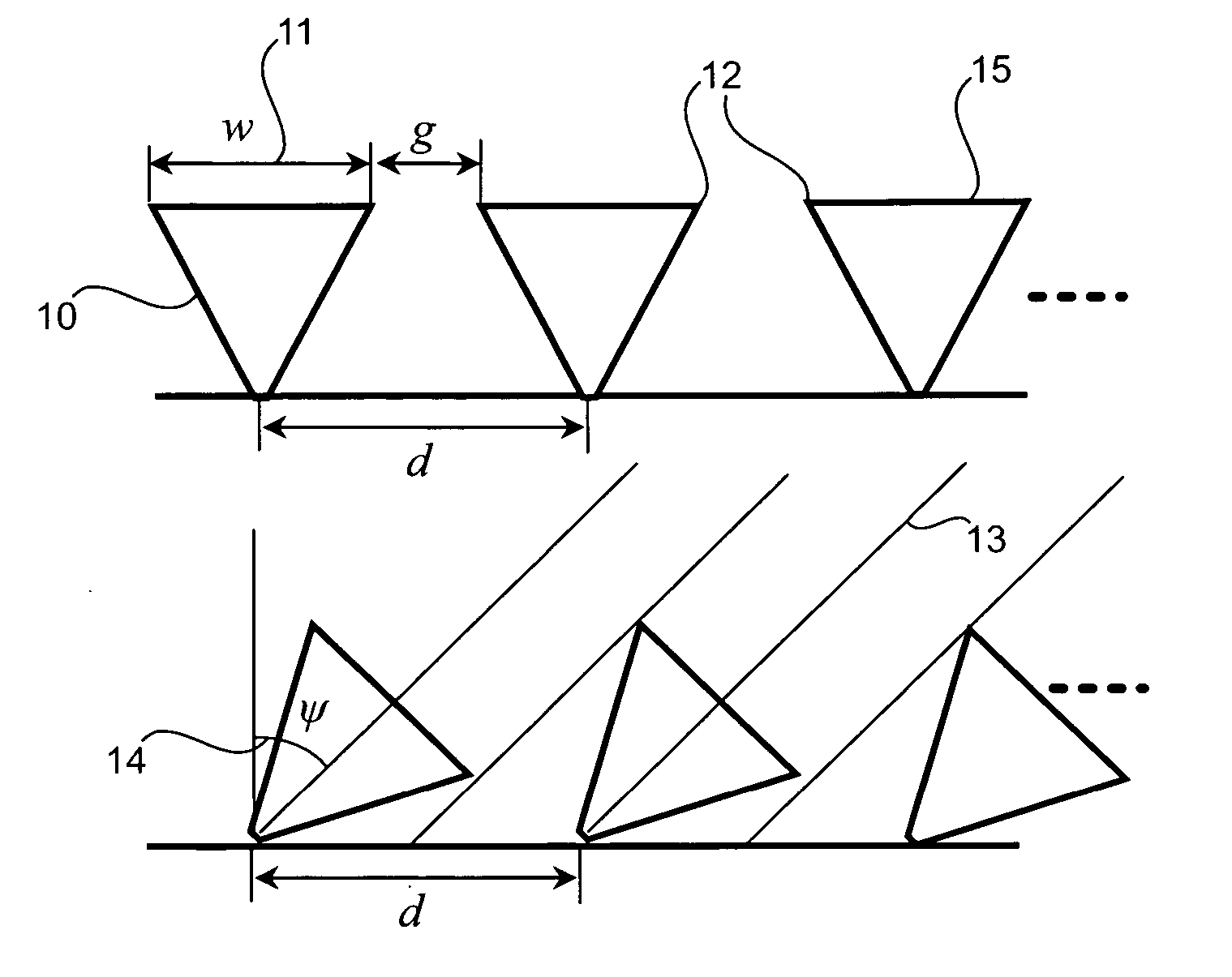
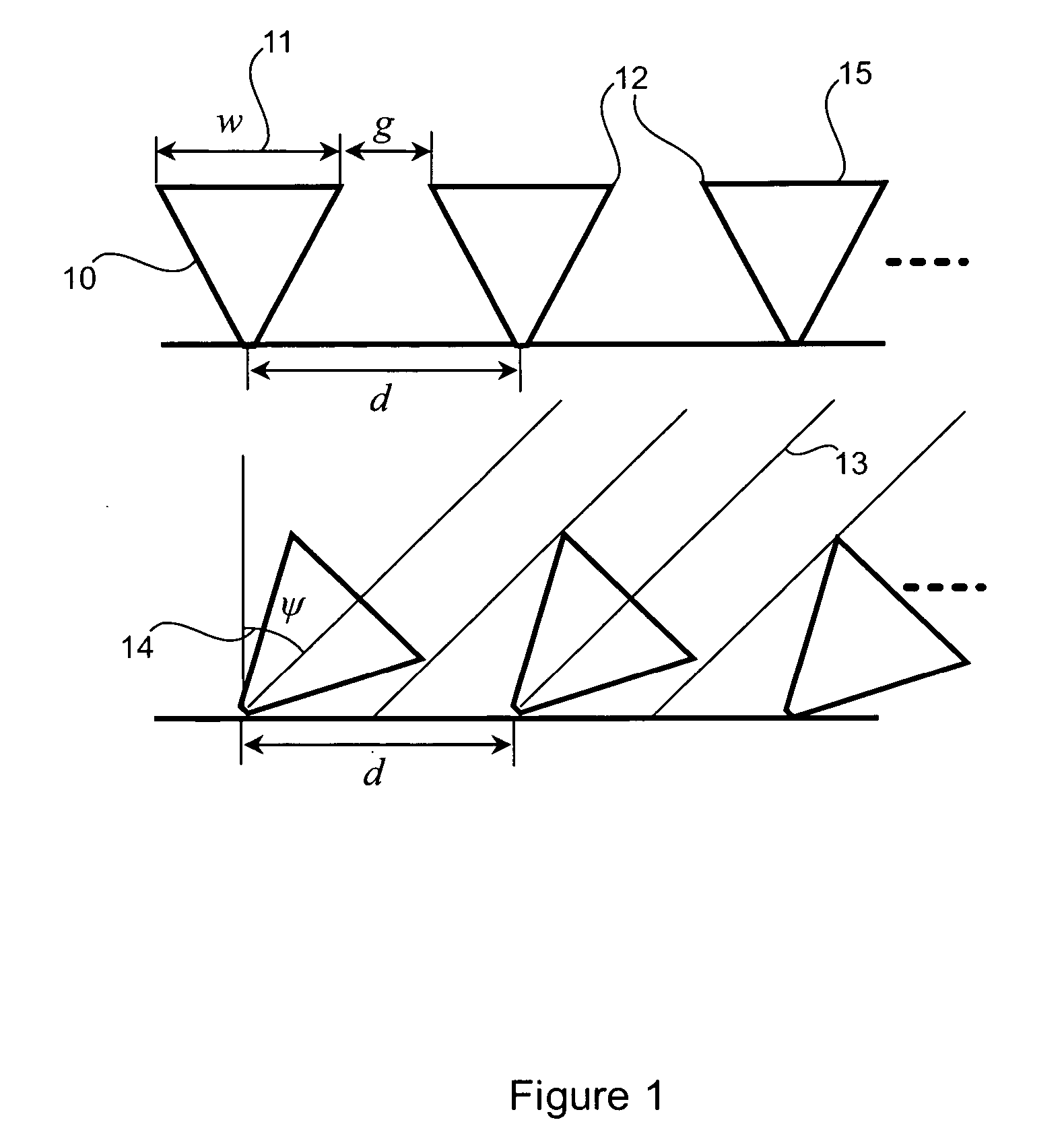
Solar module structures and methods for assembling solar module structures. The solar module structures comprise pyramidal three-dimensional thin-film solar cells arranged in solar module structures. The pyramidal three-dimensional thin-film solar cell comprises a pyramidal three-dimensional thin-film solar cell substrate with emitter junction regions and doped base regions. The three-dimensional thin-film solar cell further includes emitter metallization regions and base metallization regions. The three-dimensional thin-film solar cell substrate comprises a plurality of pyramid-shaped unit cells. The solar module structures may be used in solar glass applications, building façade applications, rooftop installation applications as well as for centralized solar electricity generation.
Owner:BEAMREACH SOLAR INC
Rigging system for supporting and pointing solar concentrator arrays
InactiveUS20080168981A1Reduce bending forceConvenient and reliable cable-tension adjustmentPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyTerrainRotational axis
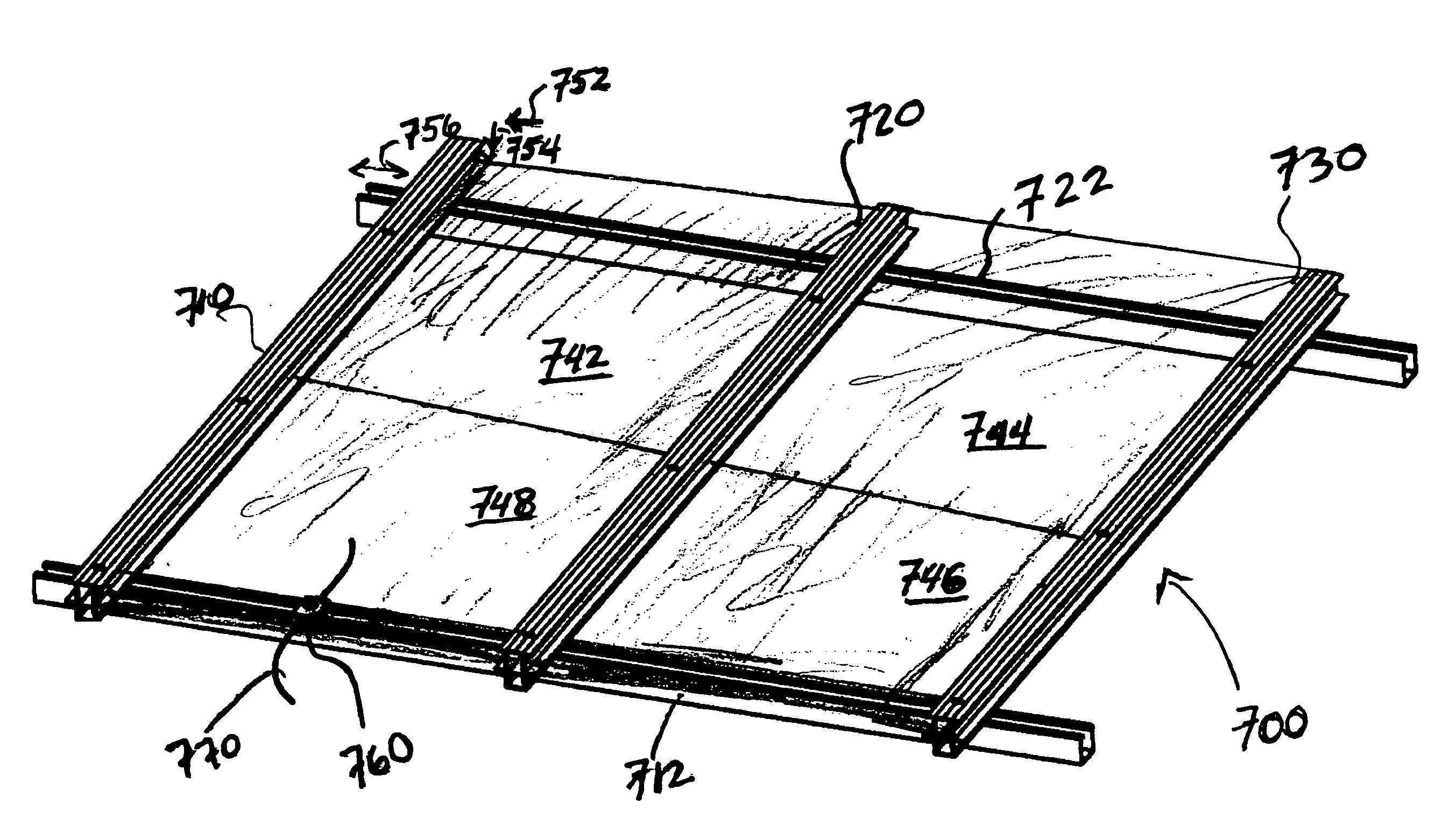
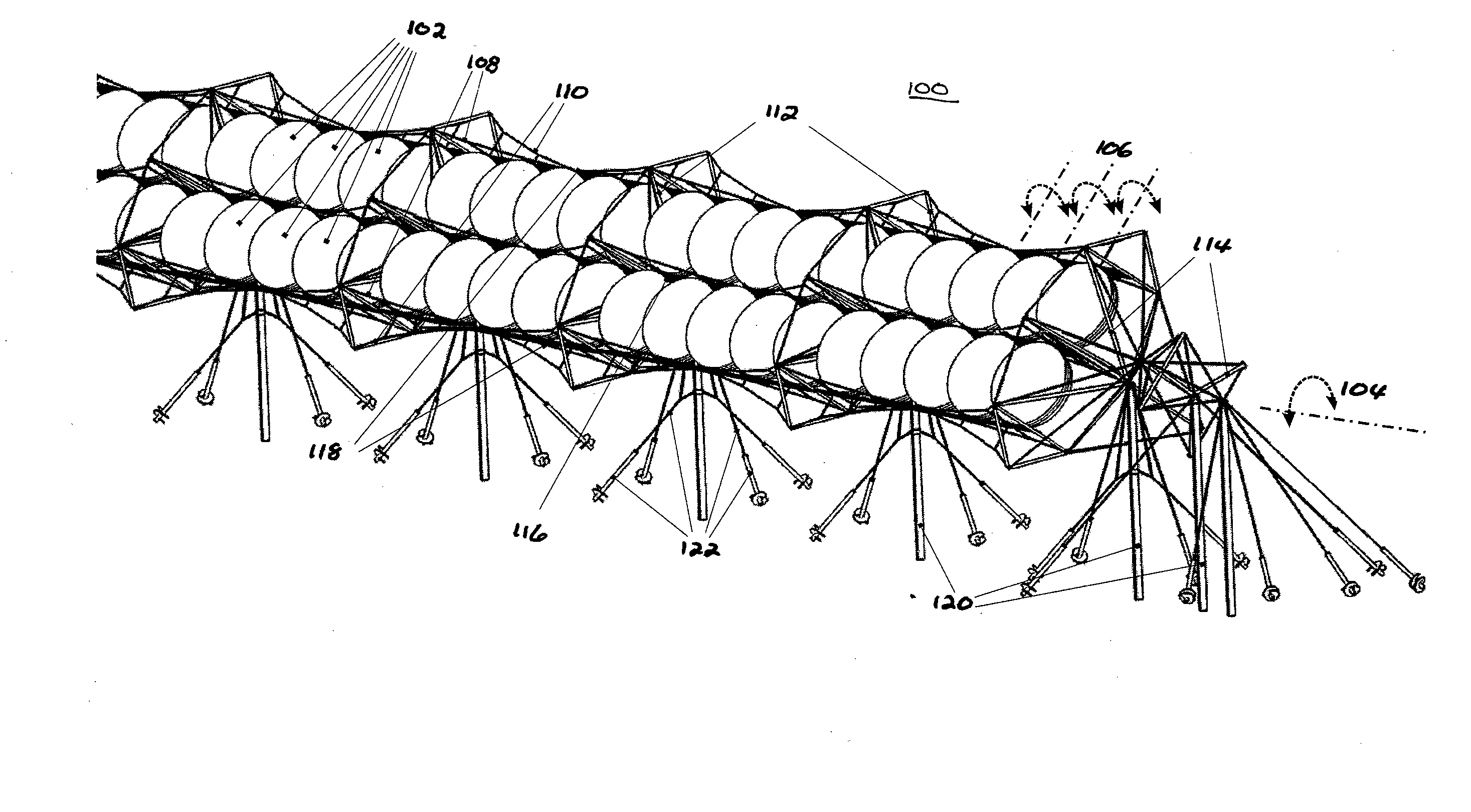
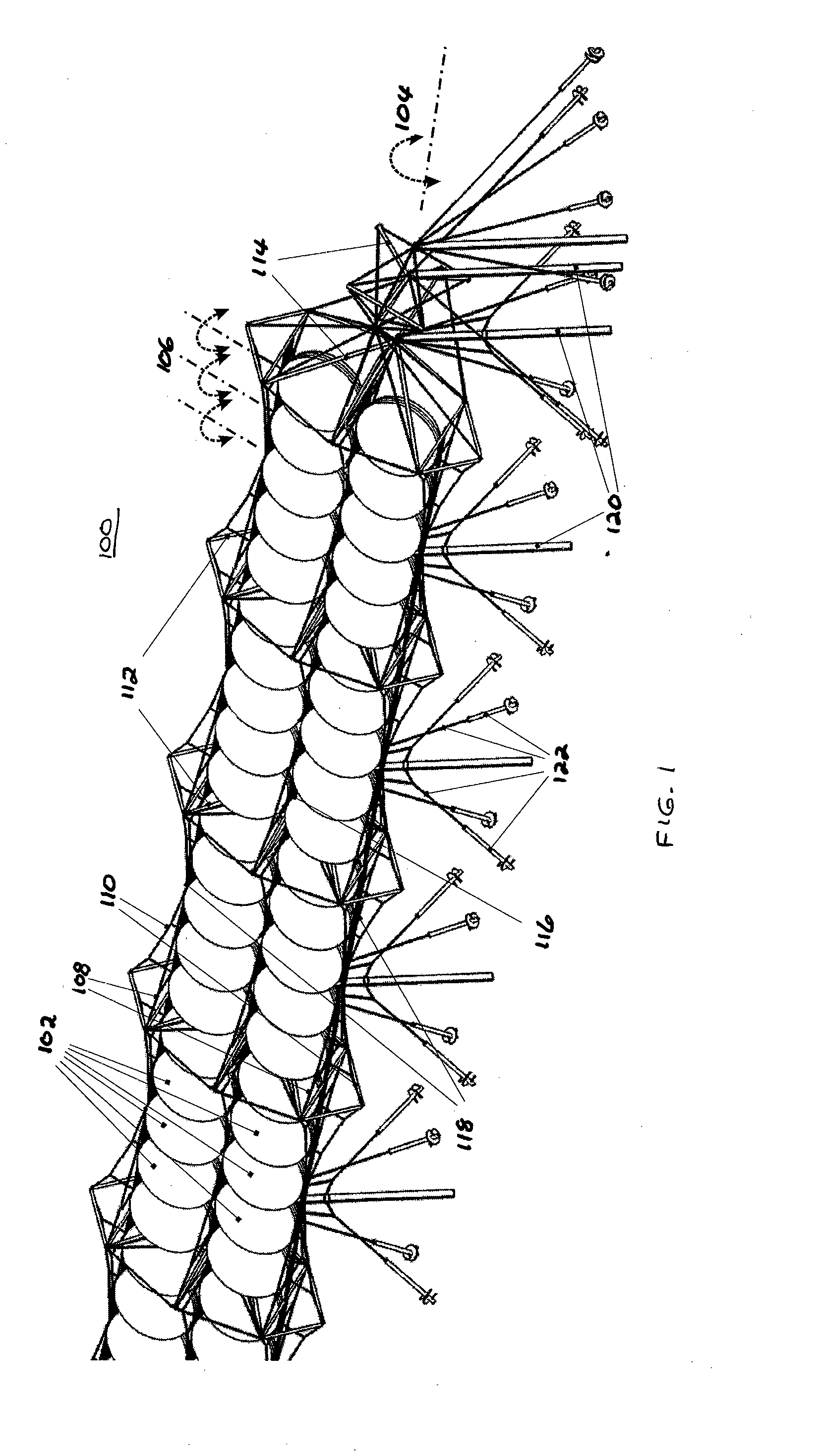
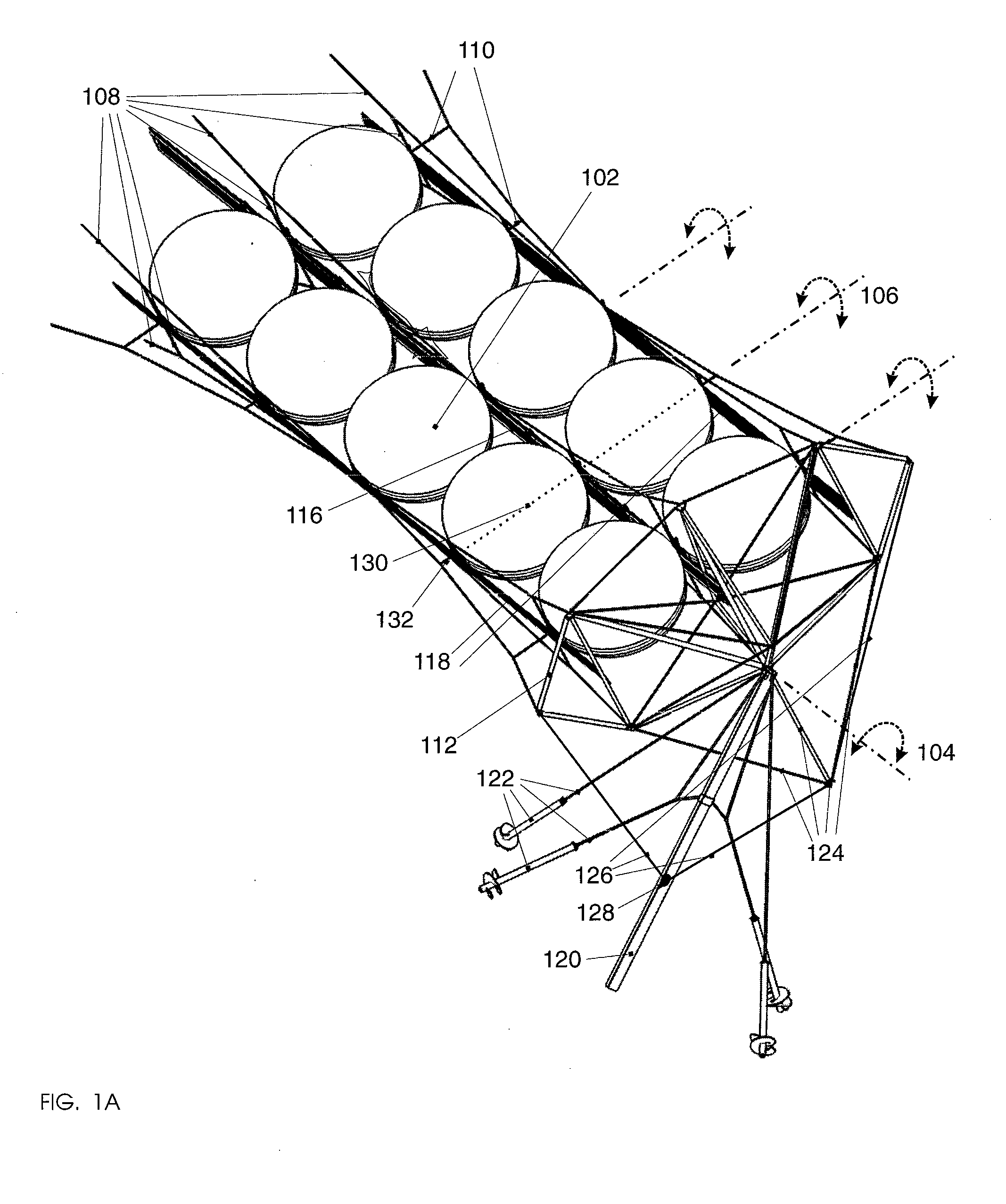
Embodiments in accordance with the present invention relate to the design of inexpensive mounting and pointing apparatuses for linear arrays of solar energy collectors and converters. Particular embodiments in accordance with the present invention disclose a rigging system comprising at least one, and preferably a plurality of, tensile cables onto which a plurality of solar modules are fastened. Such an arrangement provides a way of suspending solar modules over land, vegetation, bodies of water, and other geographic features without substantial perturbation of the underlying terrain. Certain embodiments comprise additional tensile cables fastened to the solar modules, such that differential axial motion of the cables produces a rotational motion component of the individual solar modules of the array. This rotational motion component effects an orientation control along one rotational axis.
Owner:COOLEARTH SOLAR
Scalable photovoltaic cell and solar panel manufacturing with improved wiring
InactiveUS20060213548A1Improve wiringPV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringCell assembly
A method and apparatus for fabricating large scale PV cell and solar module / panel is disclosed. The method includes designing a PV cell wiring scheme for a number of PV cells and patterning a plurality of features on a large size silicon sheet. A number of large scale silicon sheets, having a number of PV cells on each silicon sheet, can be bonded to a wiring plane to directly manufacture into a solar module / panel. Each PV cell on the solar module is then isolated. Methods of the invention greatly cut down the cost of solar module / panel manufacturing and PV cell assembly.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com