Patents
Literature
664 results about "Cell assembly" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
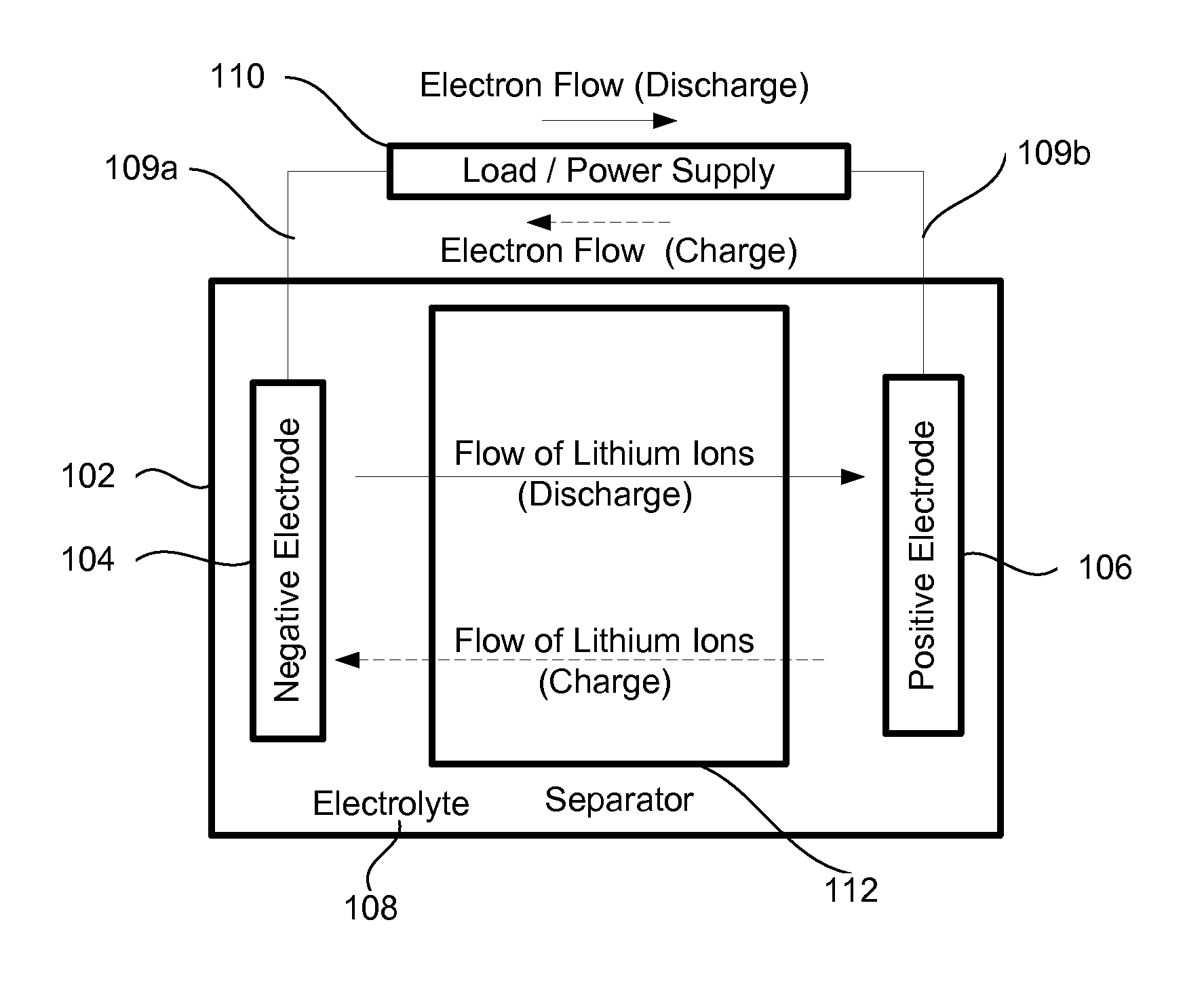
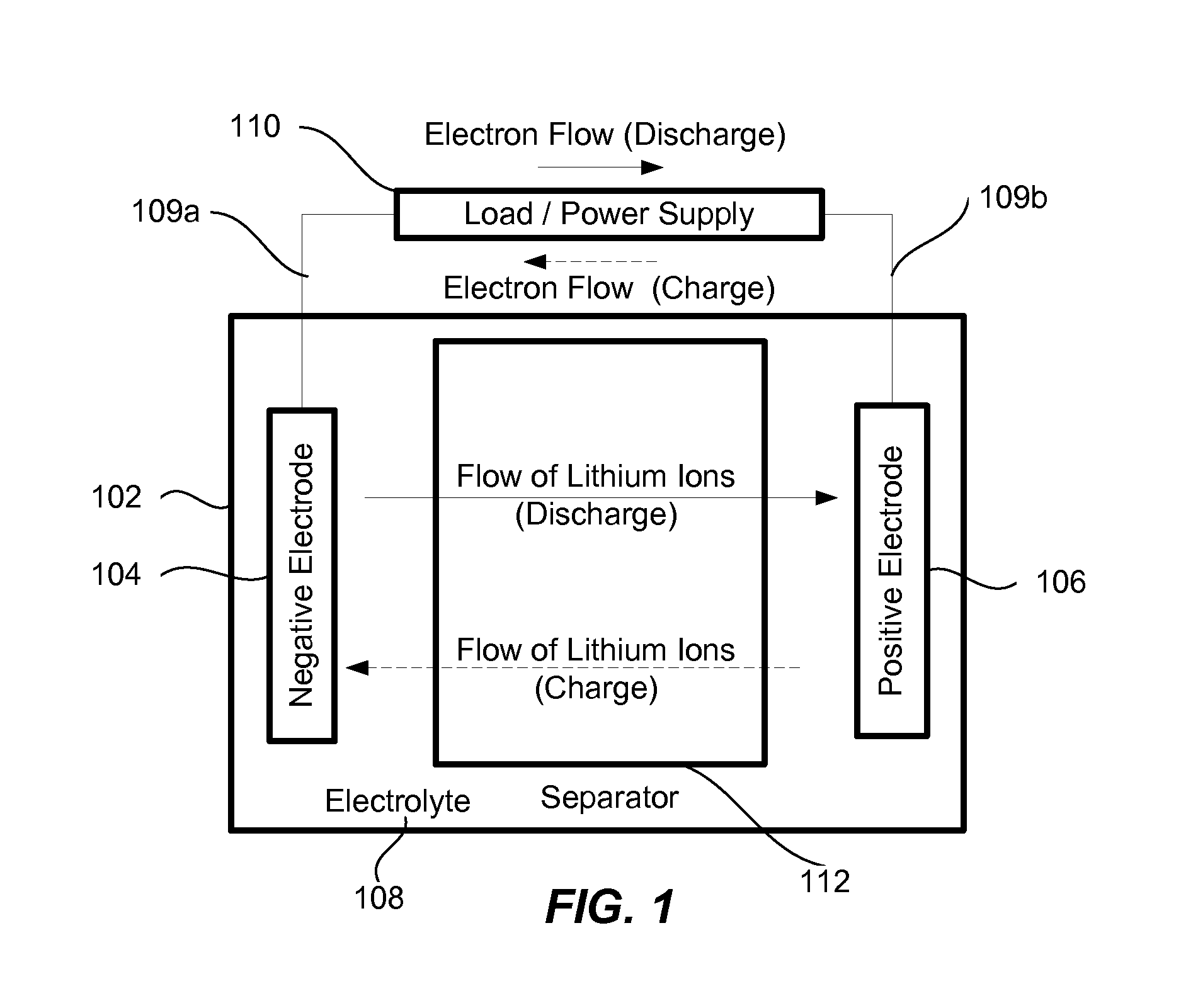
Nowadays the concept of cell assembly is used loosely to describe a group of neurons that perform a given action or represent a given percept or concept in the brain. Typically, one thinks of the group as having strong internal synaptic interactions which set them apart from other groups of neurons.
Self-cleaning protective coatings for use with photovoltaic cells
InactiveUS20070017567A1Maintain efficiencyTime-consuming effortPV power plantsSynthetic resin layered productsCells panelAlbedo
Systems and materials to improve photovoltaic cell efficiency by implementing a self-cleaning function on photovoltaic cells and on albedo surfaces associated with photovoltaic cell assemblies are provided. Materials for protecting albedo surfaces that surround photovoltaic cell assemblies, thereby maximizing energy input into the photovoltaic cell assemblies, are provided. Materials for self-cleaning photovoltaic cell panels, thereby maintaining their efficiency, are provided. Portable albedo collecting devices associated with photovoltaic cell assemblies are provided.
Owner:BARNES CHRISTOPHER
Scalable photovoltaic cell and solar panel manufacturing with improved wiring
InactiveUS20060213548A1Improve wiringPV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringCell assembly
A method and apparatus for fabricating large scale PV cell and solar module / panel is disclosed. The method includes designing a PV cell wiring scheme for a number of PV cells and patterning a plurality of features on a large size silicon sheet. A number of large scale silicon sheets, having a number of PV cells on each silicon sheet, can be bonded to a wiring plane to directly manufacture into a solar module / panel. Each PV cell on the solar module is then isolated. Methods of the invention greatly cut down the cost of solar module / panel manufacturing and PV cell assembly.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Photovoltaic cell assembly and the method of producing one such assembly
InactiveUS20050000561A1Reduce manufacturing costAccounting/billing servicesPV power plantsElectrical conductorEngineering
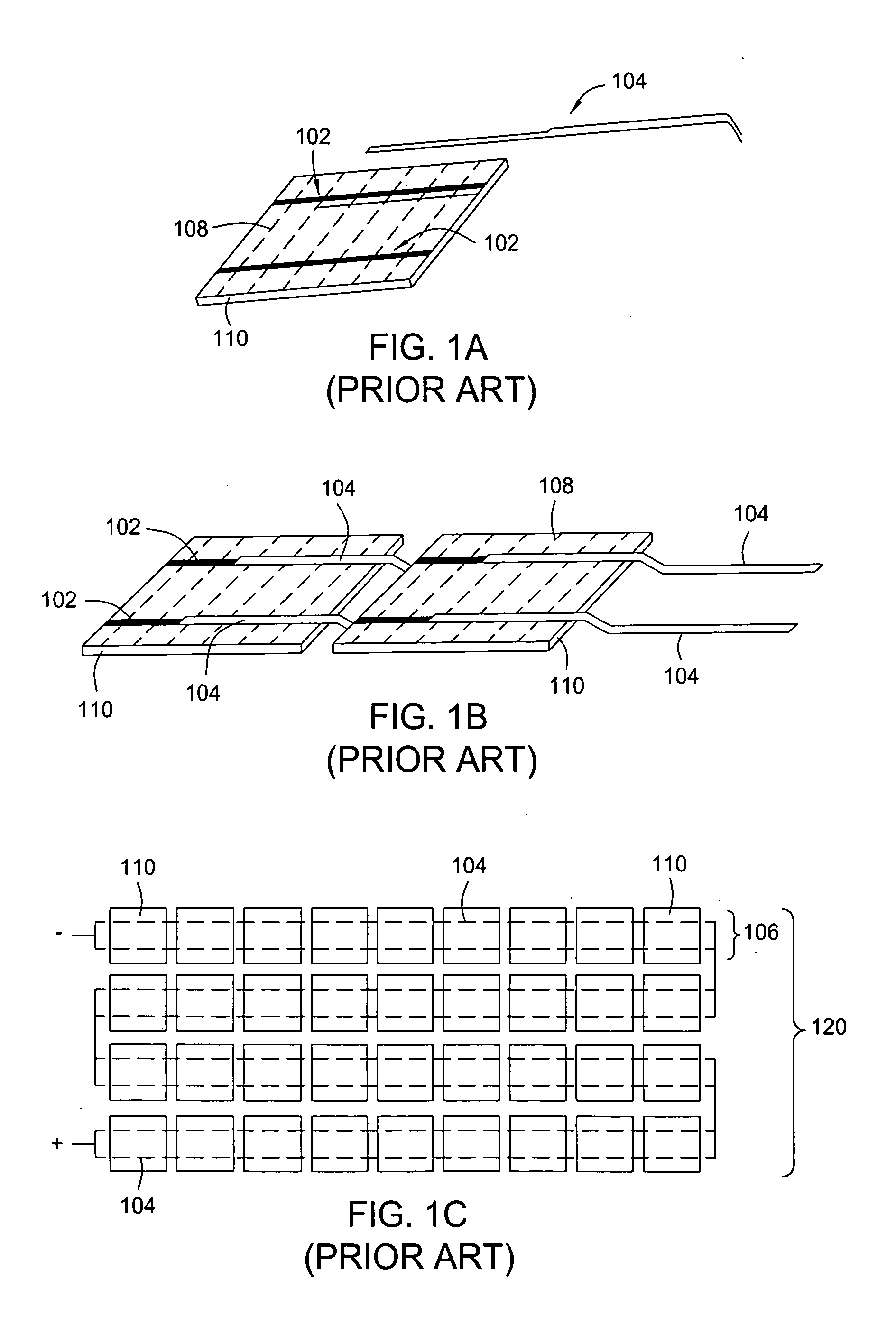
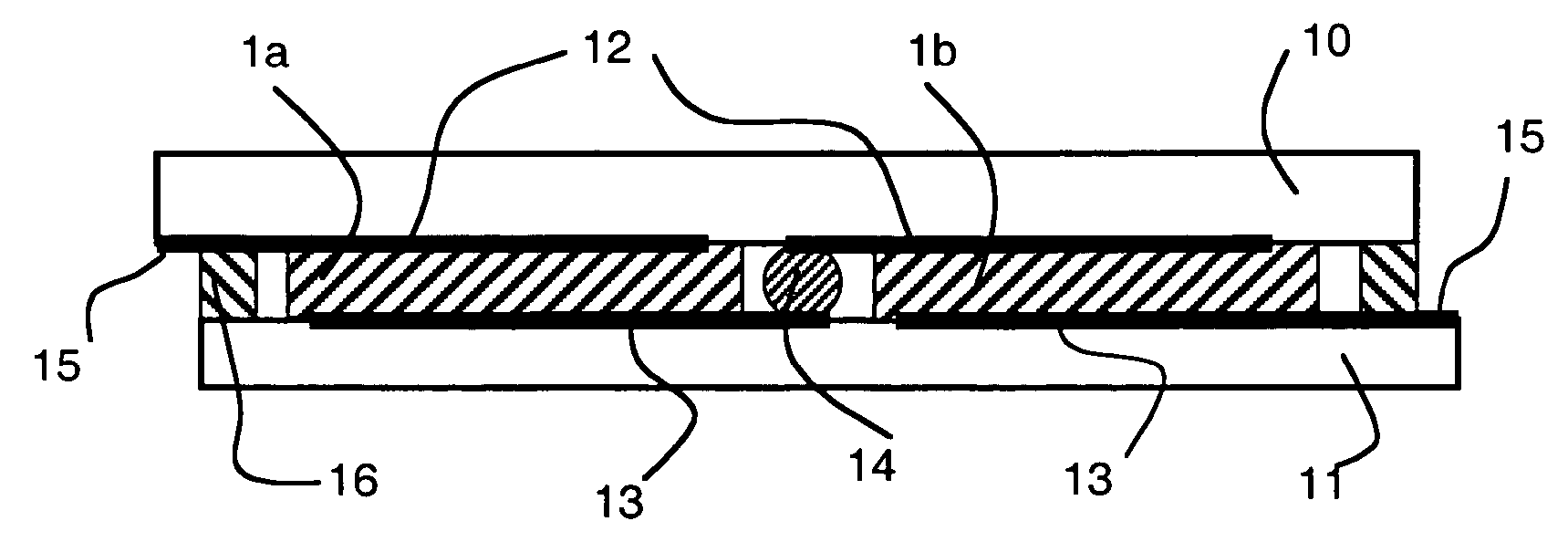
The photovoltaic cells (1a, 1b) of the assembly are disposed side by side between a front (10) and rear (11) glass substrates and are connected in series by means of front (12) and (13) rear connecting conductors and of interconnection elements (14). The connecting conductors can be formed on the internal face of each glass substrate facing the location of each of the cells or obtained by laser cutting, through the glass substrates, of conducting strips tightened beforehand between the cells and the glass substrates. The electrical interconnection elements (14) are disposed between two adjacent cells (1) to connect the opposite connecting conductors associated to two adjacent cells. A sealing joint (16), made of inorganic material, arranged between the two glass substrates (10, 11), defines a sealed internal volume which contains all the cells (1). Sealing is performed between 380° C. and 480° C. for a period of less than 30 minutes.
Owner:APOLLON SOLAR SAS
Innovative bottom-up cell assembly approach to three-dimensional tissue formation using nano-or micro-fibers
The present invention provides a synthetic tissue scaffold, the scaffold comprising alternating layers of electrospun polymers and mammalian cells sandwiched within. A novel method is also provided for generating a three-dimensional tissue by electrospinning polymers and seeding cells in alternating layers on an aqueous solution in a desired shape. This invention is suitable for generating animal tissue as well as for delivery of drugs or other substances to a recipient.
Owner:WANG HONGJUN
Color-tuned volumetric light using high quantum yield nanocrystals
ActiveUS7235792B2Good colorAffects colorOptical radiation measurementElectric circuit arrangementsQuantum yieldDisplay device
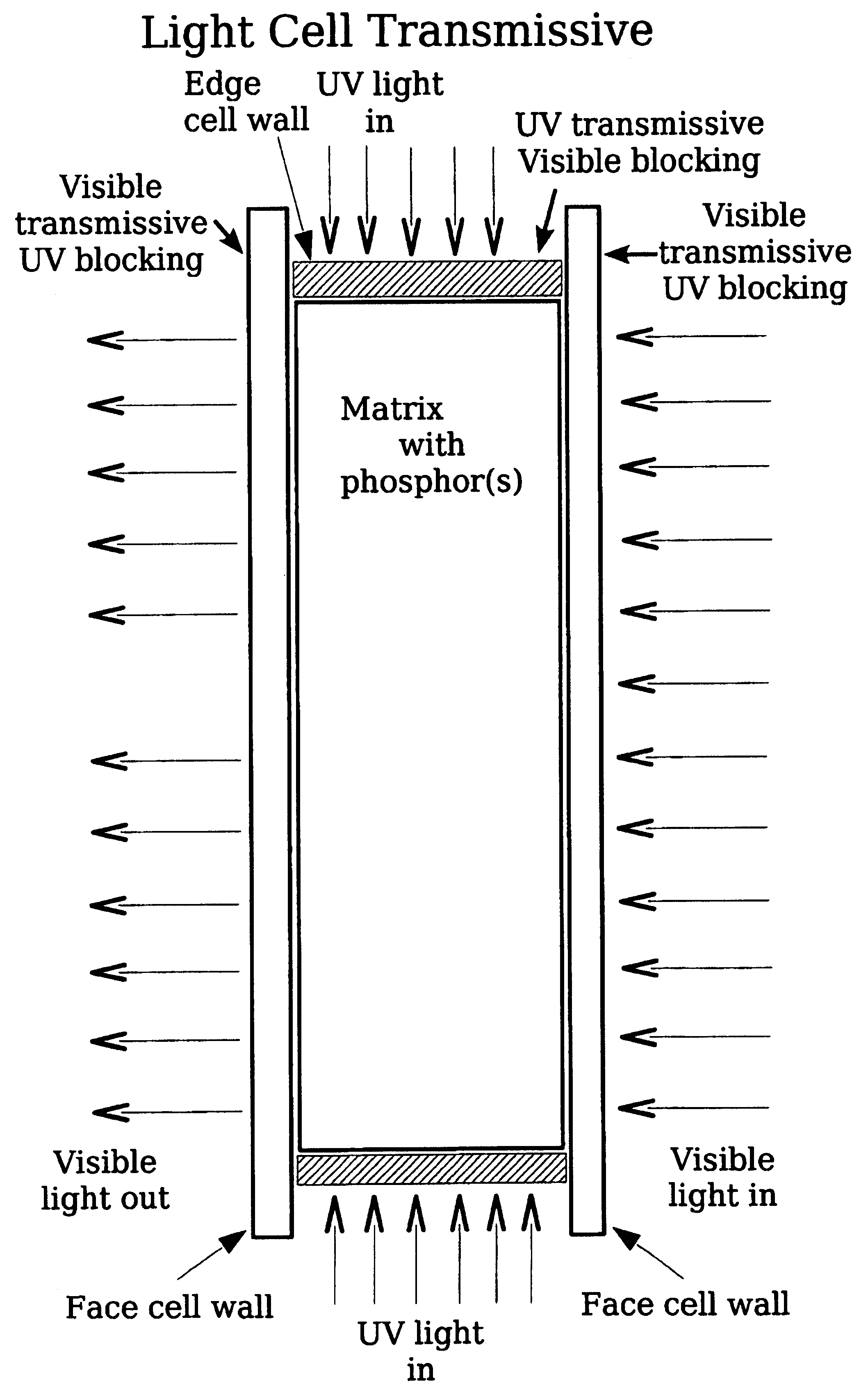
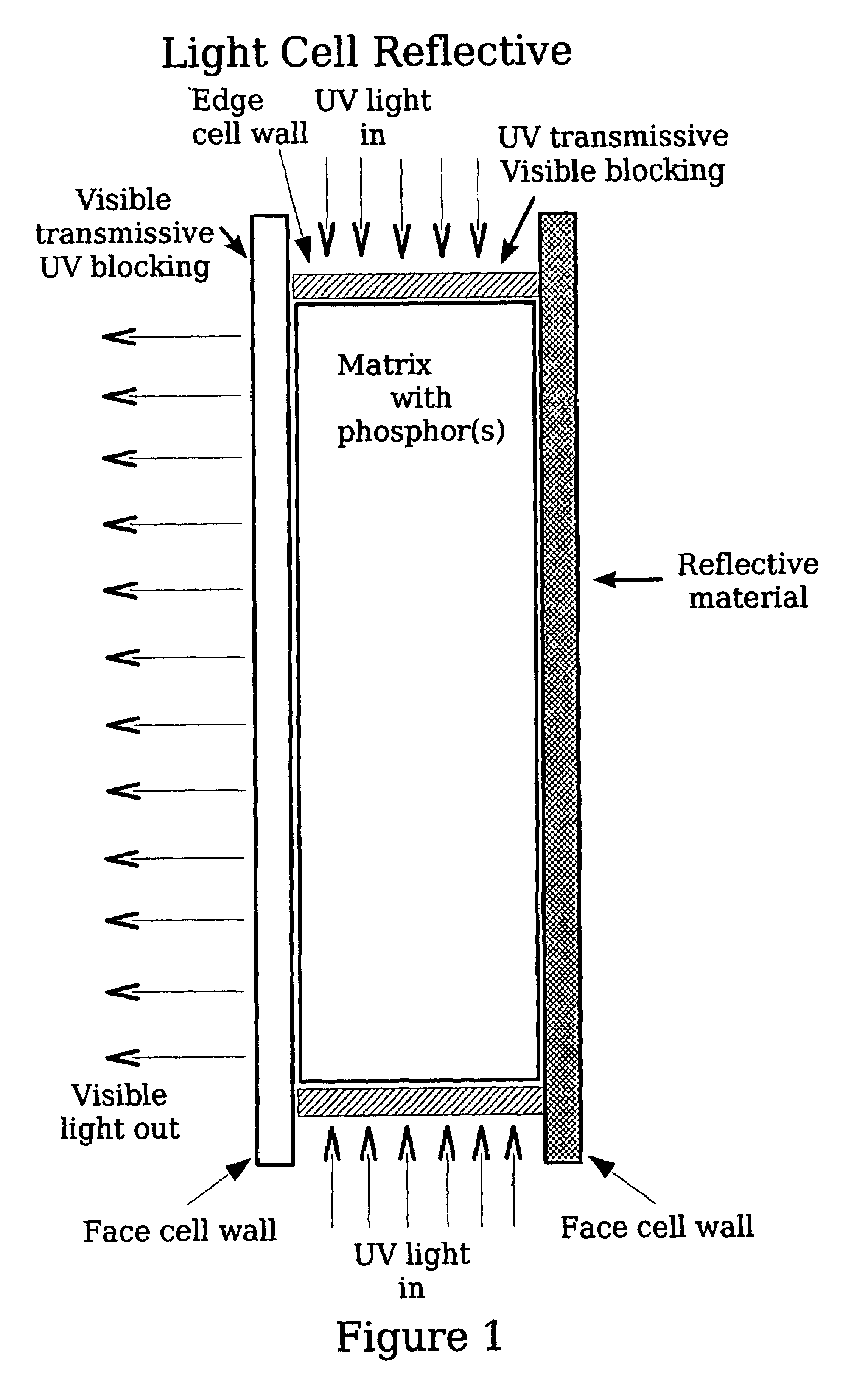
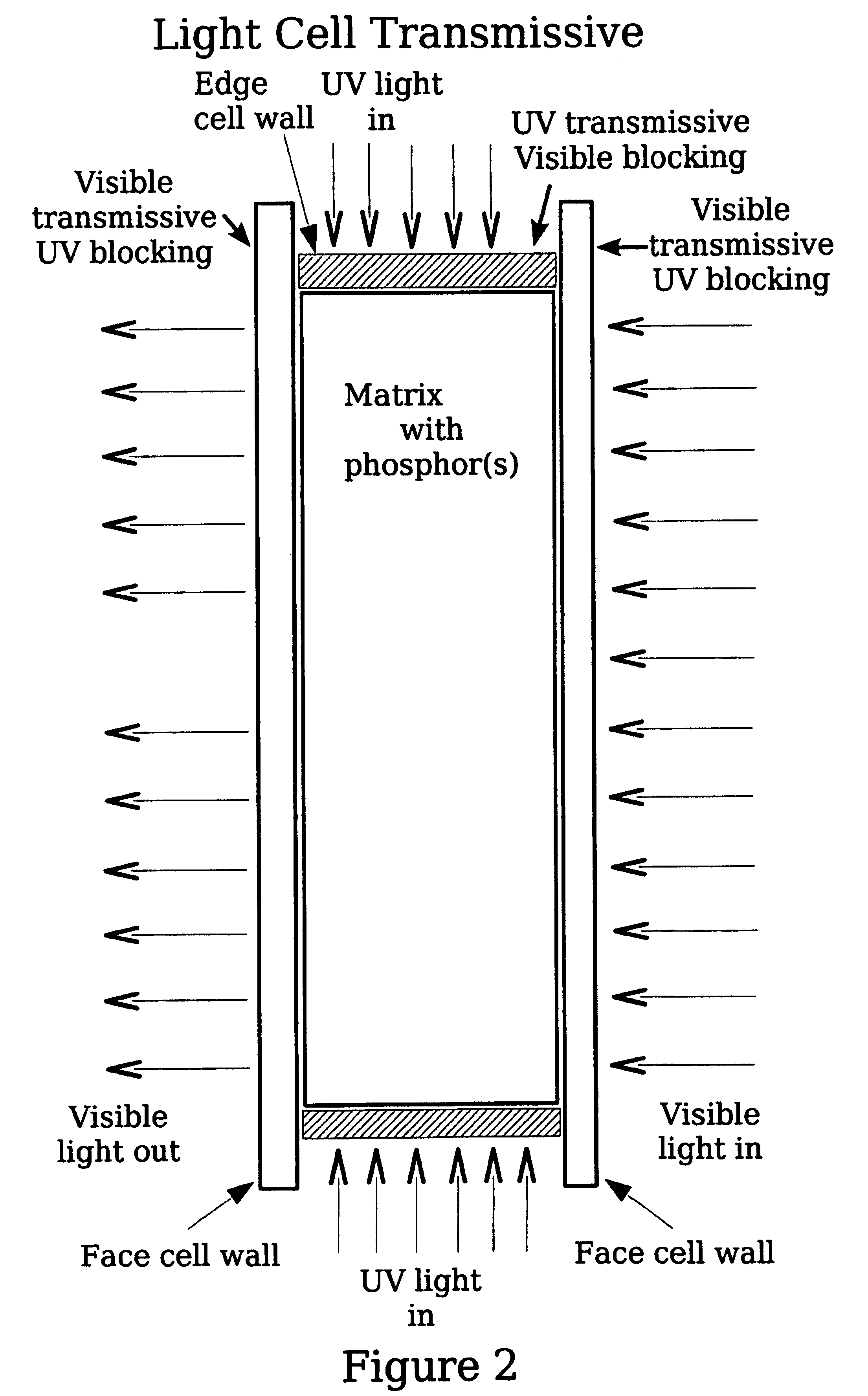
A light source of coaxially stacked volumetric light cells that can be used either in a lamp or a display. Each light cell is composed of high quantum yield nanocrystals in a silica aerogel matrix that is excited by a controlled ultraviolet light source. From these stacked cell assemblies visible light is emitted of a desired color or color temperature and brightness.
Owner:ELOFSON CARL SCOTT
Combined illuminated reticle and focus knob
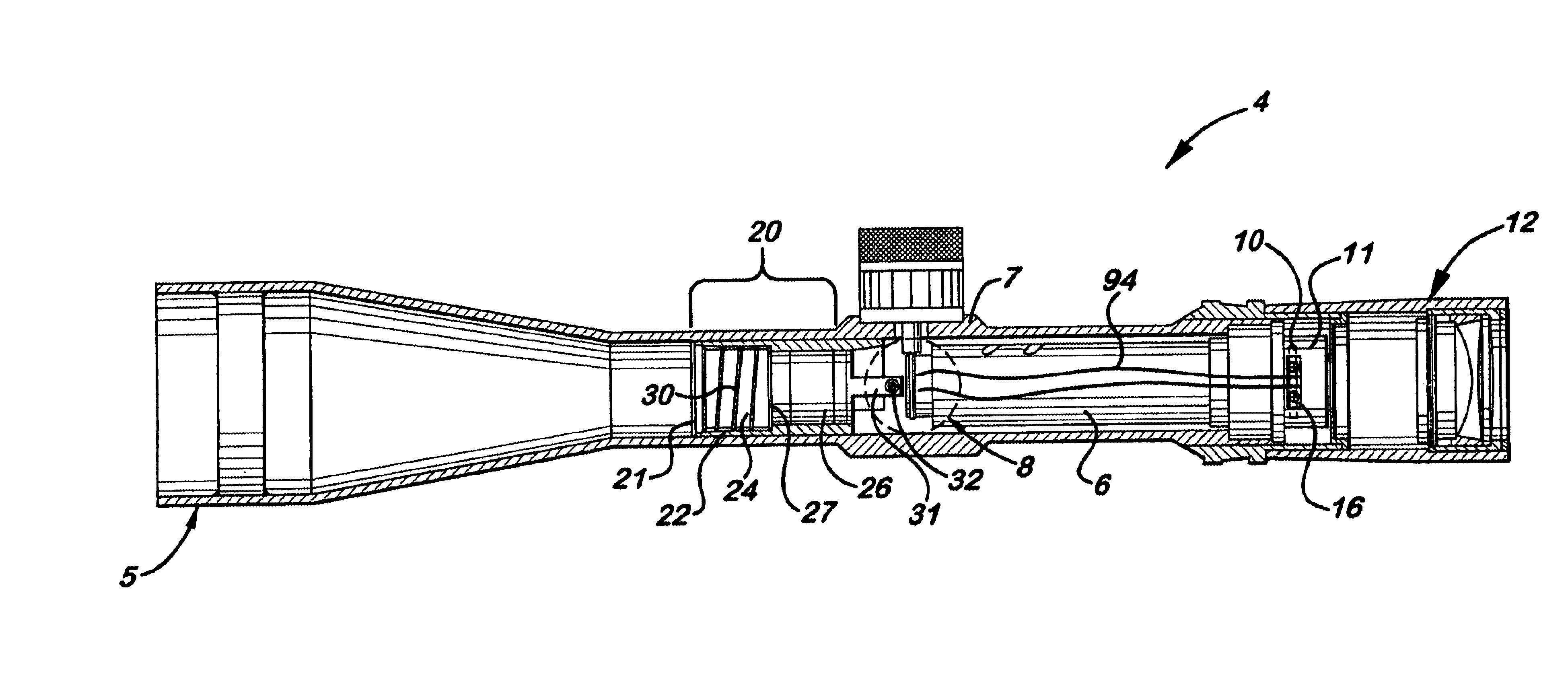
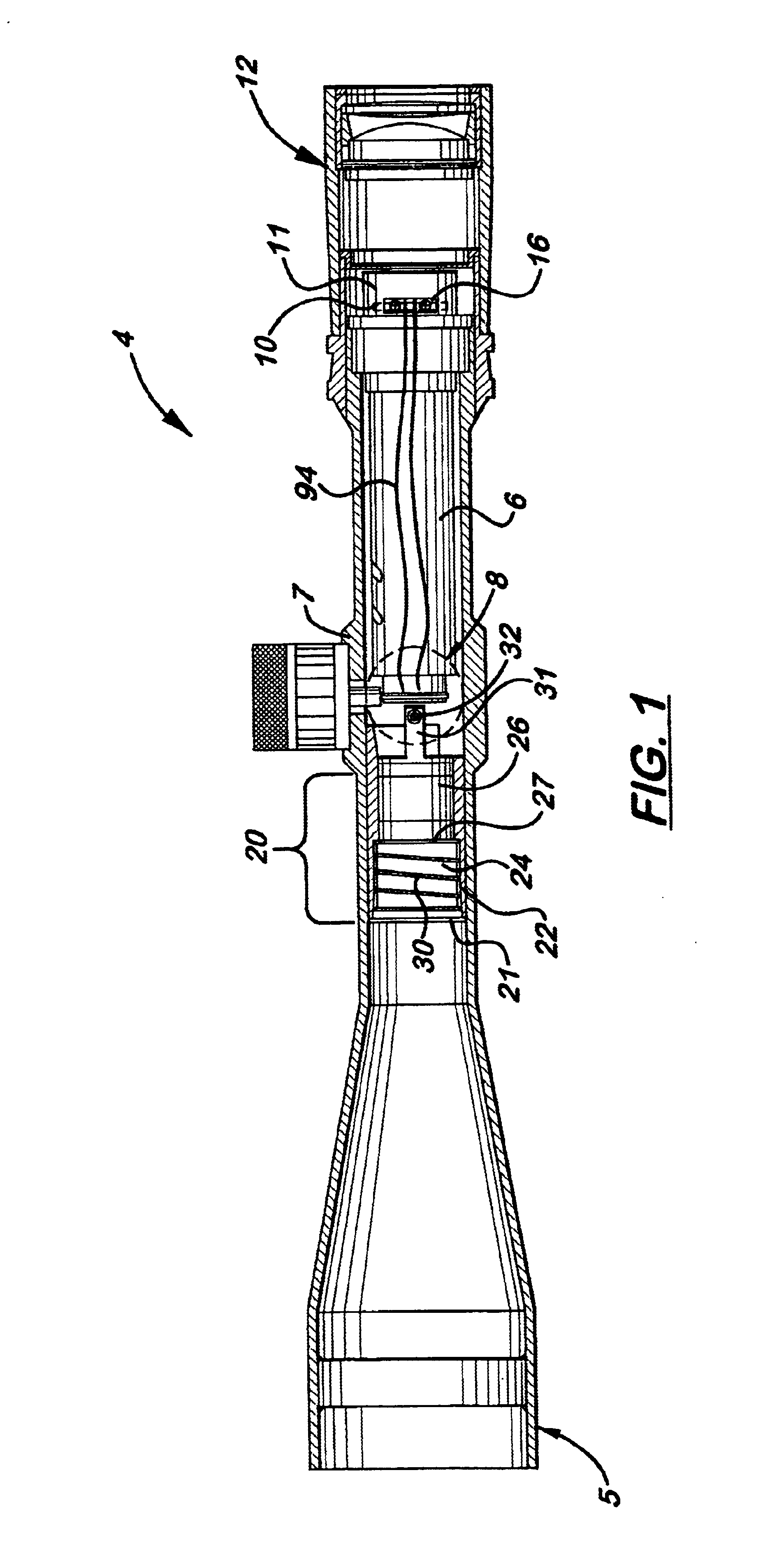
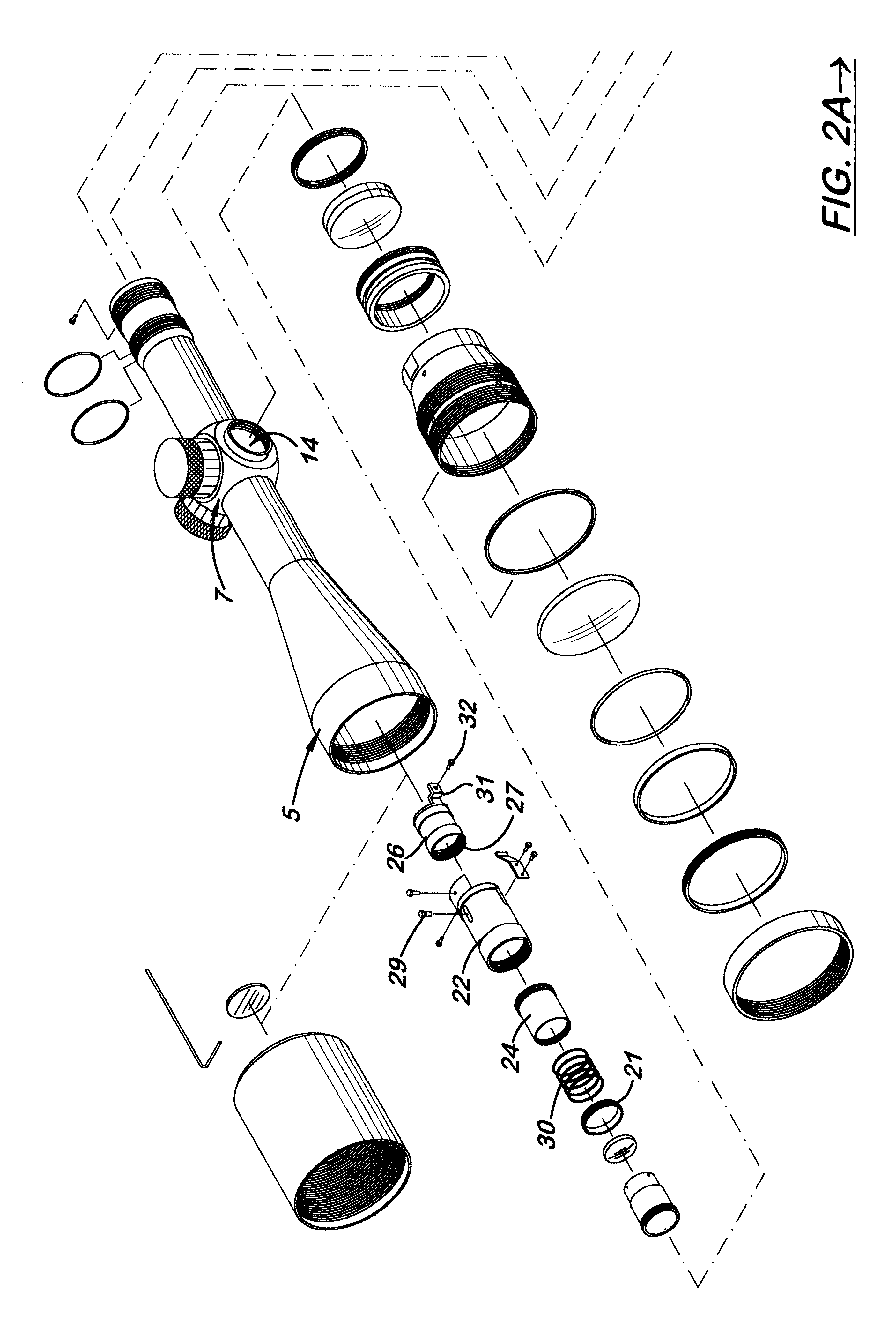
A combined focus and reticle illumination system for a riflescope which uses a single, dual functioning turn knob mounted on the scope turret for focusing and activating and deactivating the illuminated reticle. During use, the turn knob is rotated to adjust the relative position of a sliding focusing cell assembly located inside the scope body in front of the erector tube. The reticle, attached to the proximal end of the erector tube, includes a side mounted LED. The turn knob has a push-pull movement and a battery located therein that disconnects and connects, respectively, the electric circuit. The sliding focusing cell includes a rigid outer housing that is resistant to bending and a rear sliding lens cell that is biased in a rearward direction to be self-centering during recoil. Wires extend from the turn knob to the LED along the scope sidewalls and are designed to preclude twisting.
Owner:LIGHTFORCE USA
Solid high polymer type cell assembly
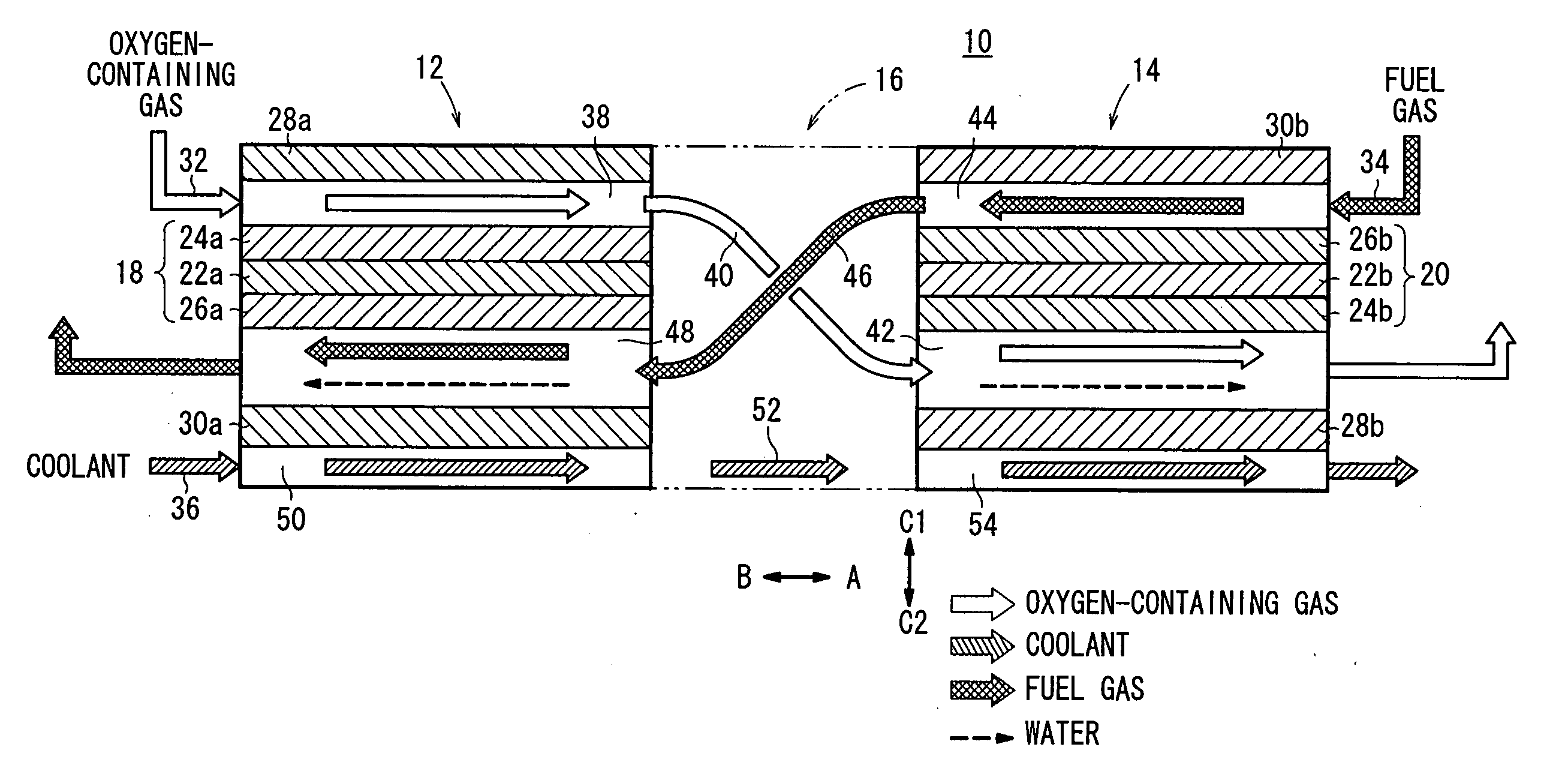
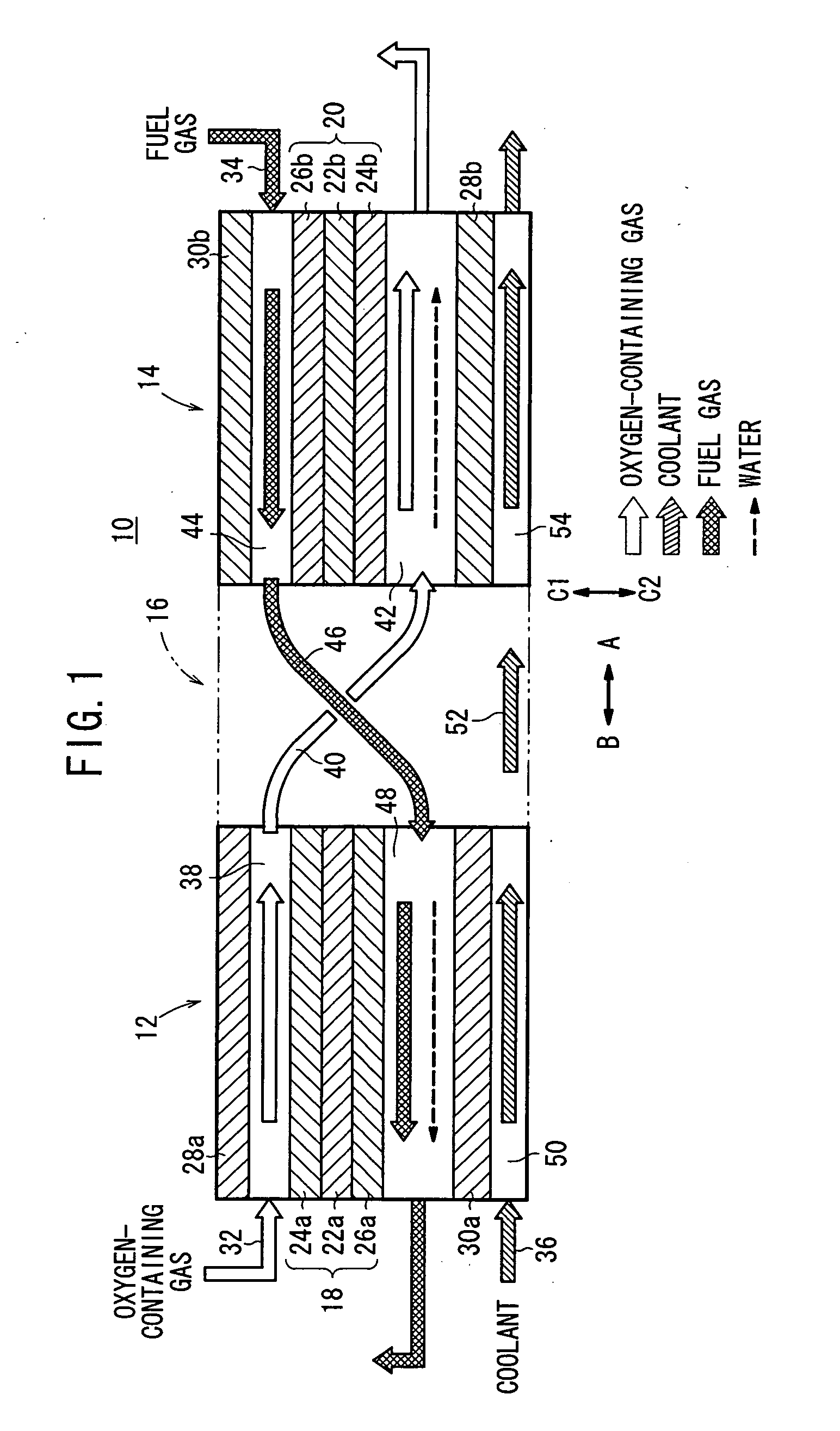
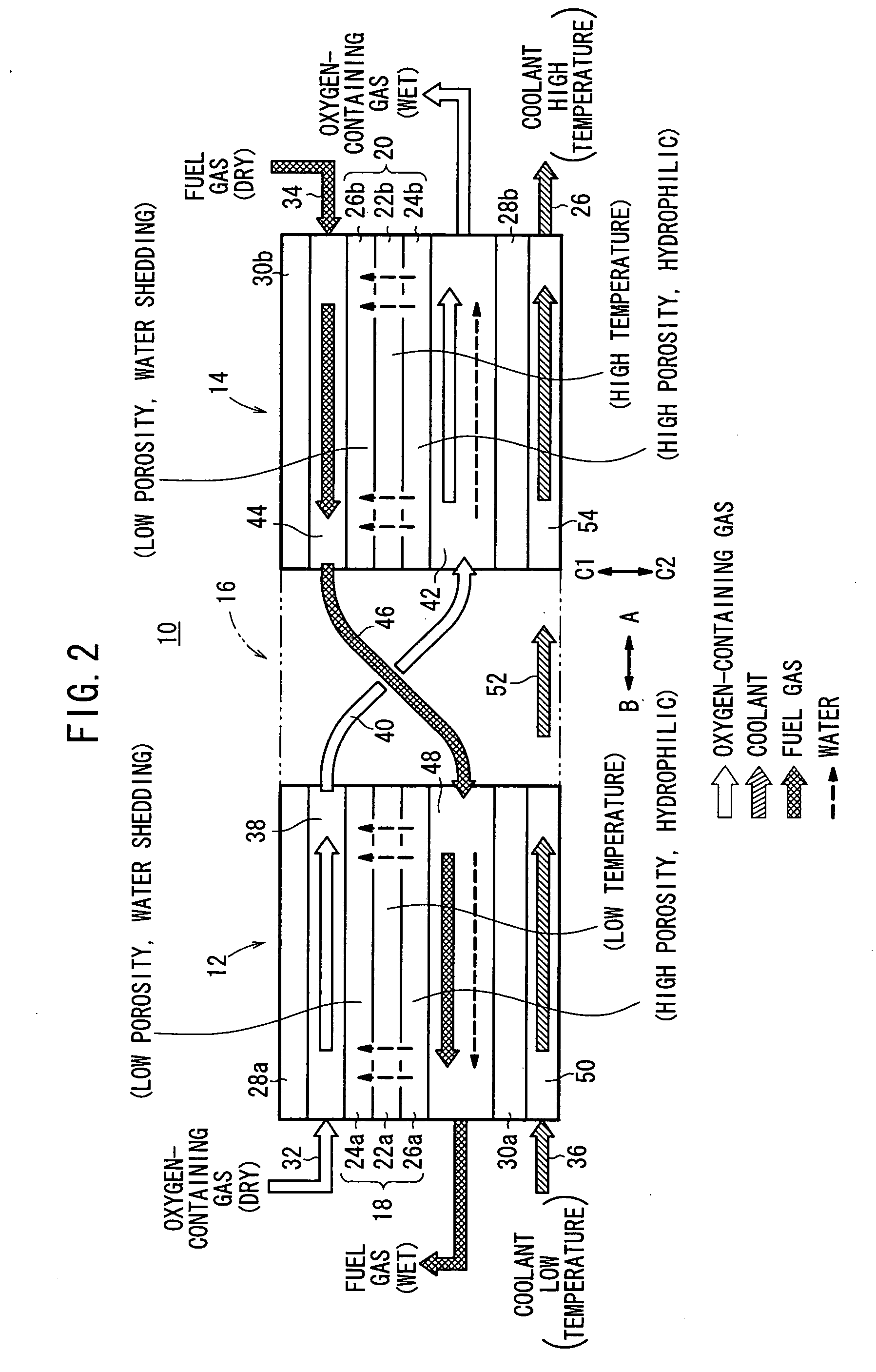
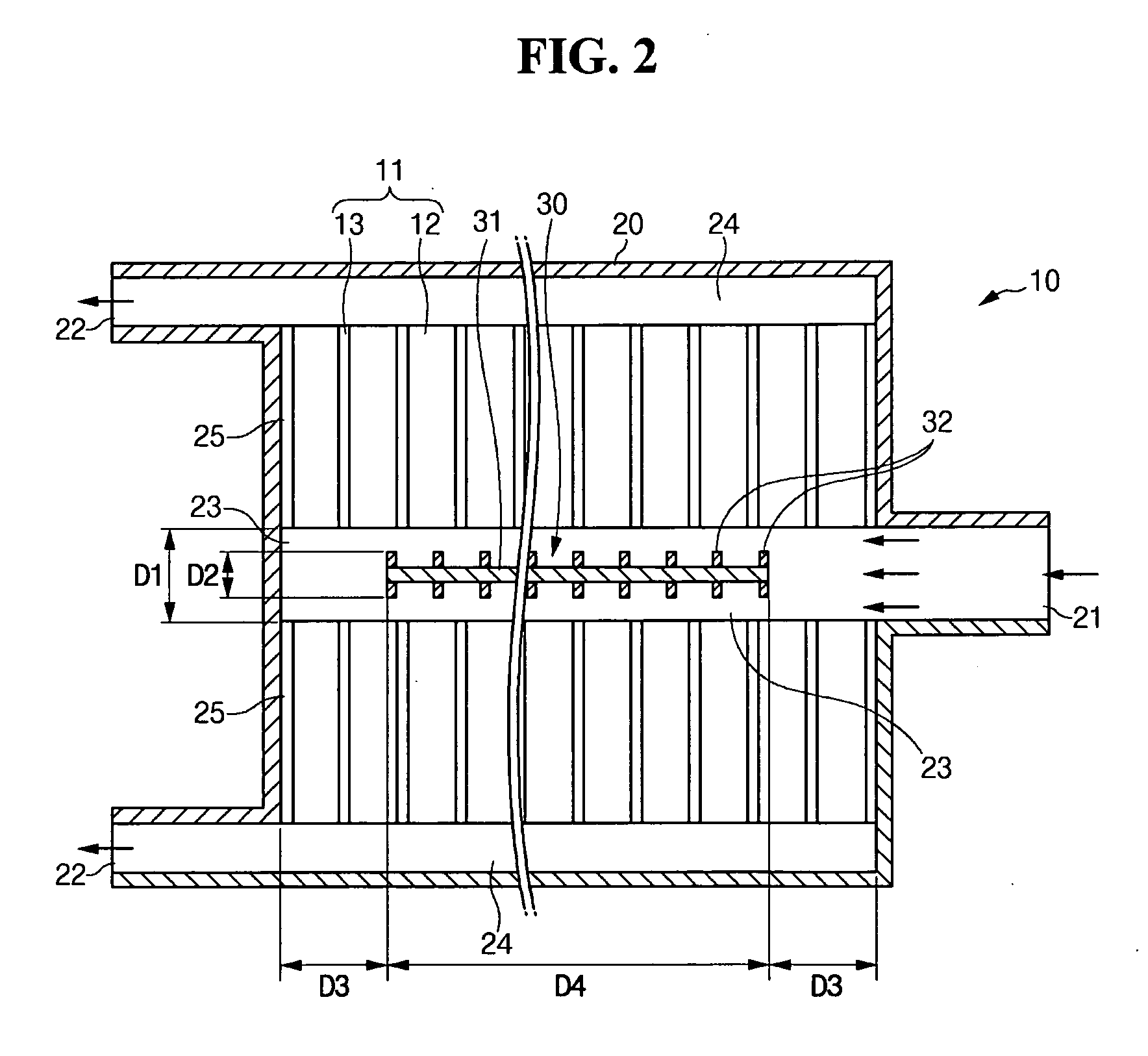
InactiveUS20050233181A1Increase flow rateReduce concentrationFuel cells groupingWater management in fuel cellsCell assemblyOxygen
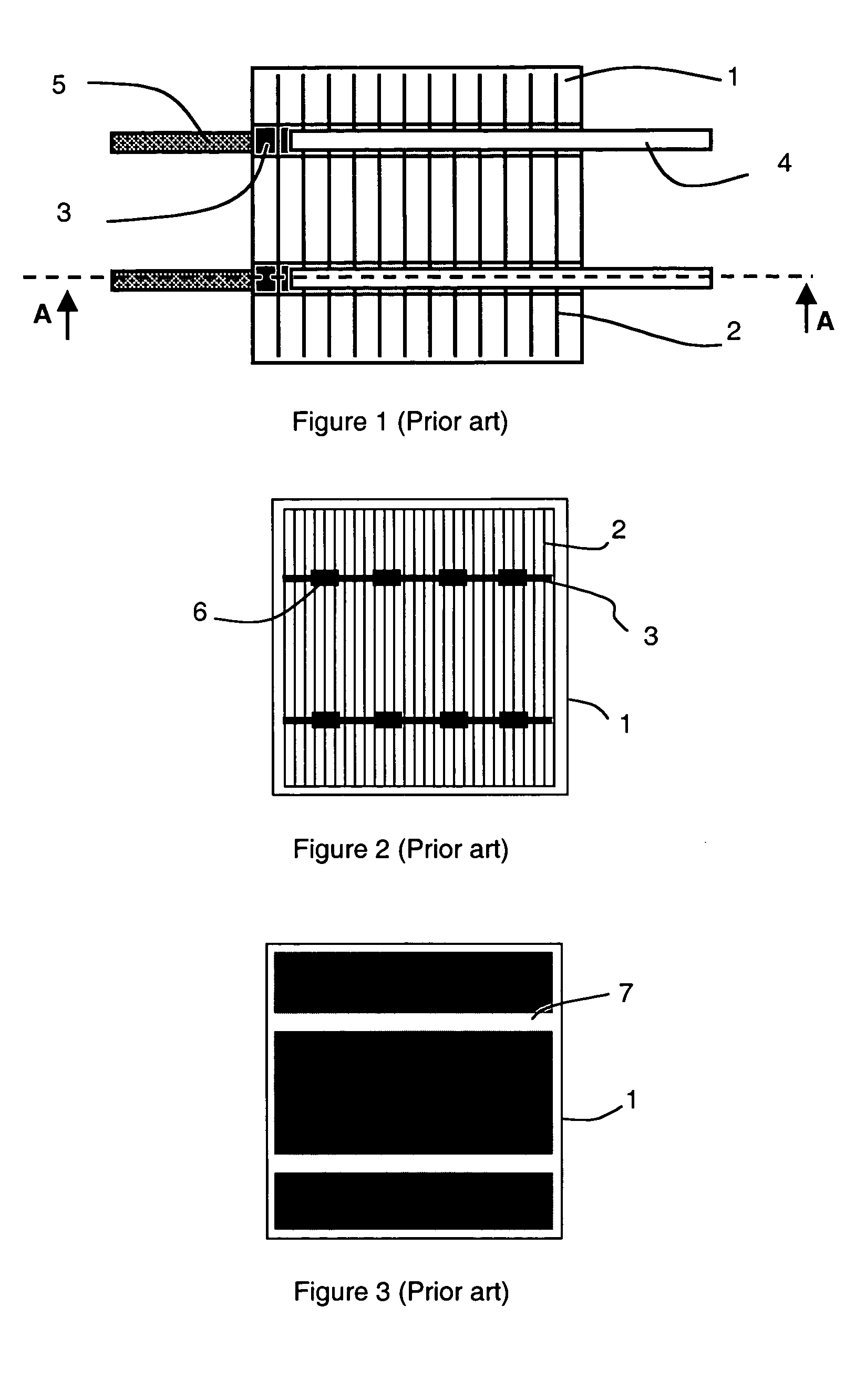
A cell assembly (10) includes a first unit cell (12) and a second unit cell (14). The first unit cell (12) and the second unit cell (14) are juxtaposed such that electrode surfaces of the first unit cell (12) and electrode surfaces of the second unit cell (14) are aligned in parallel with each other. An oxygen-containing gas flow passage (32) includes a first oxygen-containing gas passage (38) in the first unit cell (12), an oxygen-containing gas connection passage (40) in a connection passage member (16), and a second oxygen-containing gas passage (42) in the second unit cell (14). The first oxygen-containing gas passage (38), the oxygen-containing gas connection passage (40), and the second oxygen-containing gas passage (42) are connected serially from the first unit cell (12) to the second unit cell (14).
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Single-component silicone fluid sealant for solar energy cell assembly and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101353563AImprove adhesionImprove waterproof performanceAdhesivesPhotovoltaic energy generationWater vaporStructural formula
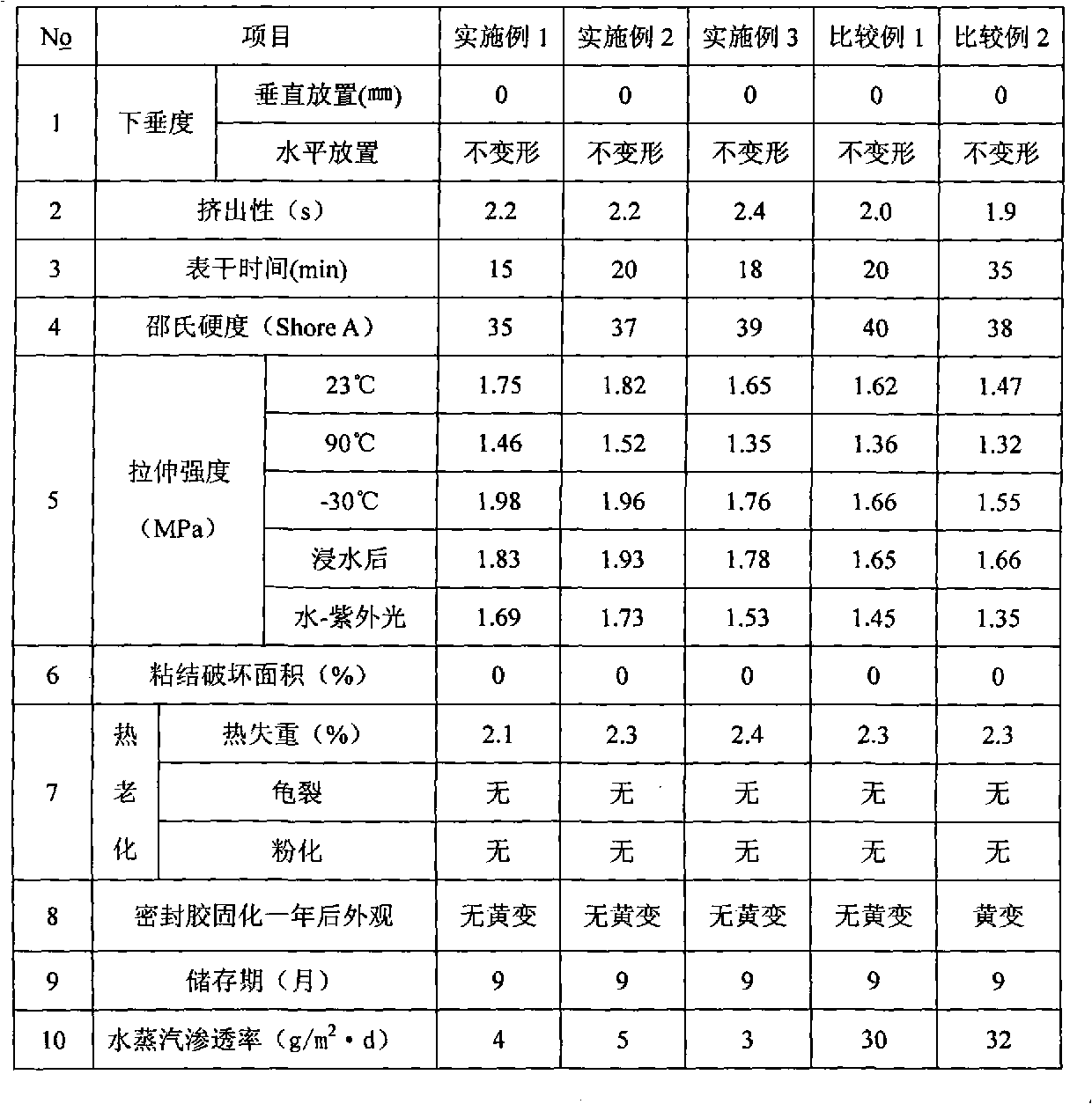
A single component silicone sealant used for a solar module and a manufacturing method thereof are characterized in that the structural formula is as the right formula, n is equal to Alpha between 100 and 2000, according to part by weight, Omega-dihydroxyl dimethicone is 100 parts, petroresins is 1-5 parts, activated chalk is 10-40 parts, and silica micropowder is 30-70 parts, all the materials are added into a vacuum kneader and dehydrated and blended for 30-200 minutes under the conditions of the temperature of 100-150 DEG C and the vacuum degree of 0.06-0.099MPa, and the base stock is obtained after cooling; at room temperature, 1-5 parts of pyrogenic silica, 10-17 parts of crosslinkers, 1-3.5 parts of silane coupling agent, 0.5-1.5 parts of catalysts and 1-10 parts of silicone oil plasticizers, according to parts by weight, are further added into a high-speed dispersator or a planetary stirrer filled with the base stock and stirred for 30-150 minutes under the conditions of the vacuum degree of 0.06-0.099MPa and the rotating speed of 200-600rpm, thus preparing the single component silicone sealant. The single component silicone sealant has excellent weathering resistance and yellowing resistance, low moisture-vapor transmission and good storage stability.
Owner:CHENGDU GUIBAO SCI & TECH
Battery module having improved cooling efficiency
ActiveUS20070031728A1Easy to optimizeEasy temperature controlPrimary cell to battery groupingCell temperature controlTemperature controlCell assembly
A battery module includes one or more cell assemblies with a plurality of unit cells, and a housing for mounting the cell assemblies therein and circulating a temperature control cooling medium through the cell assemblies. The cell assemblies are arranged in the longitudinal direction of the housing. A guidance unit is installed in a cooling medium passage formed in the longitudinal direction of the housing, and proceeds along the passage to guide cooling medium flow along the passage toward the cell assemblies.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Clustered solar-energy conversion array and method therefor
InactiveUS20060243319A1Increase percentageDead zone area can be reducedSolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersEngineeringCell assembly
Owner:ARIZONA PUBLIC SERVICE
Variable capacity cell assembly
InactiveUS20110171502A1Increase electrode capacityLarge capacityBatteries circuit arrangementsAlkaline accumulatorsCapacity lossActive component
Electrochemical cells containing nanostructured negative active materials and composite positive active materials and methods of fabricating such electrochemical cells are provided. Positive active materials may have inactive components and active components. Inactive components may be activated and release additional lithium ions, which may offset some irreversible capacity losses in the electrochemical cells. In certain embodiments, the activation releases lithium ion having a columbic content of at least about 400 mAh / g based on the weight of the activated material.
Owner:AMPRIUS INC
Building integrated photovoltaic having injection molded component
InactiveUS20110100438A1Photovoltaic supportsMixingCell assemblyElectrical and Electronics engineering
The invention is a photovoltaic device comprising a photovoltaic cell assembly with an injection molded portion connected to at least one edge of the photovoltaic cell assembly where the body portion has properties and a composition enabling robust function over a period of years when the photovoltaic device is mounted on the exterior of a building.
Owner:GASTON RYAN S +7
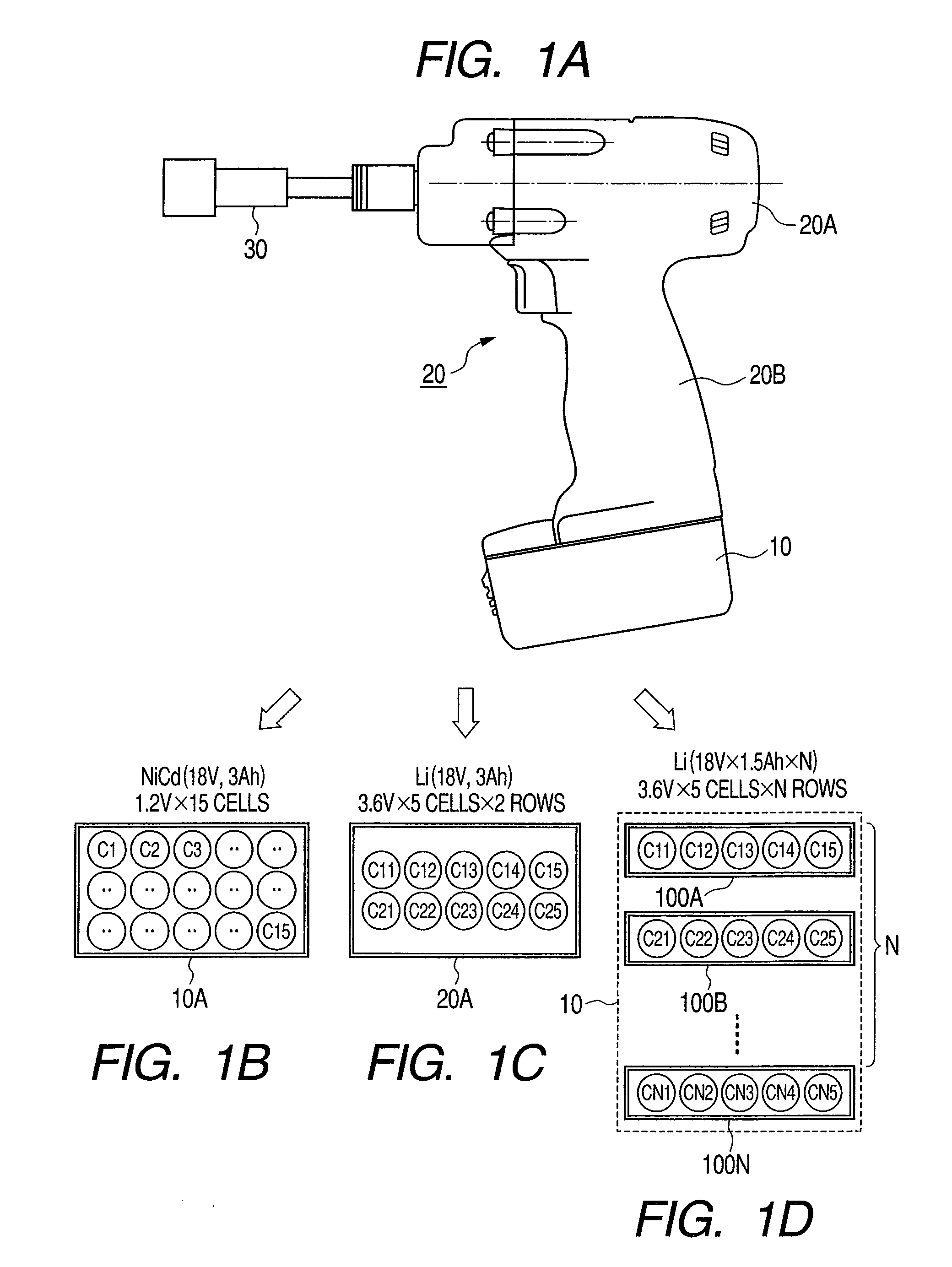
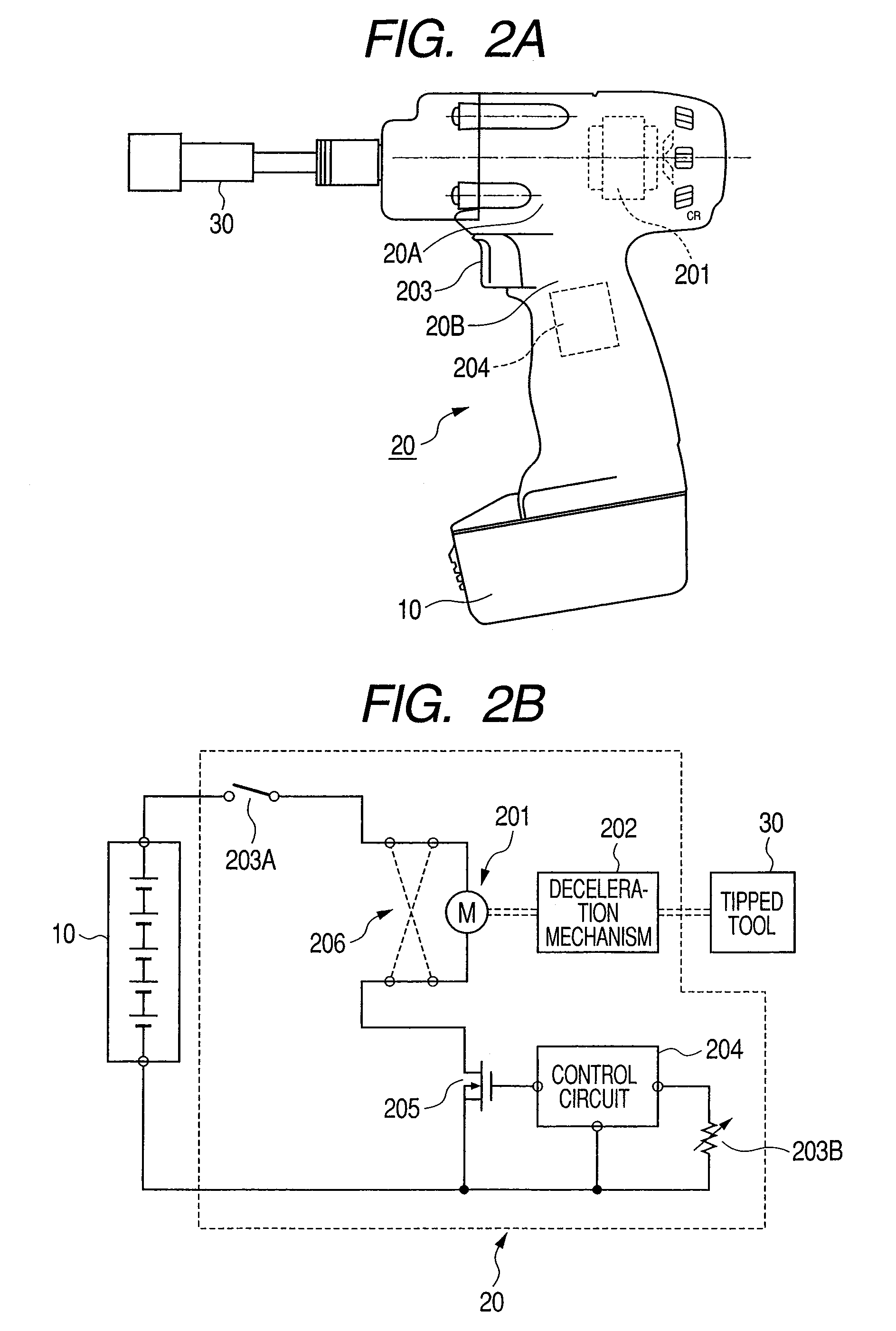
Cordless power tool and battery device used for same
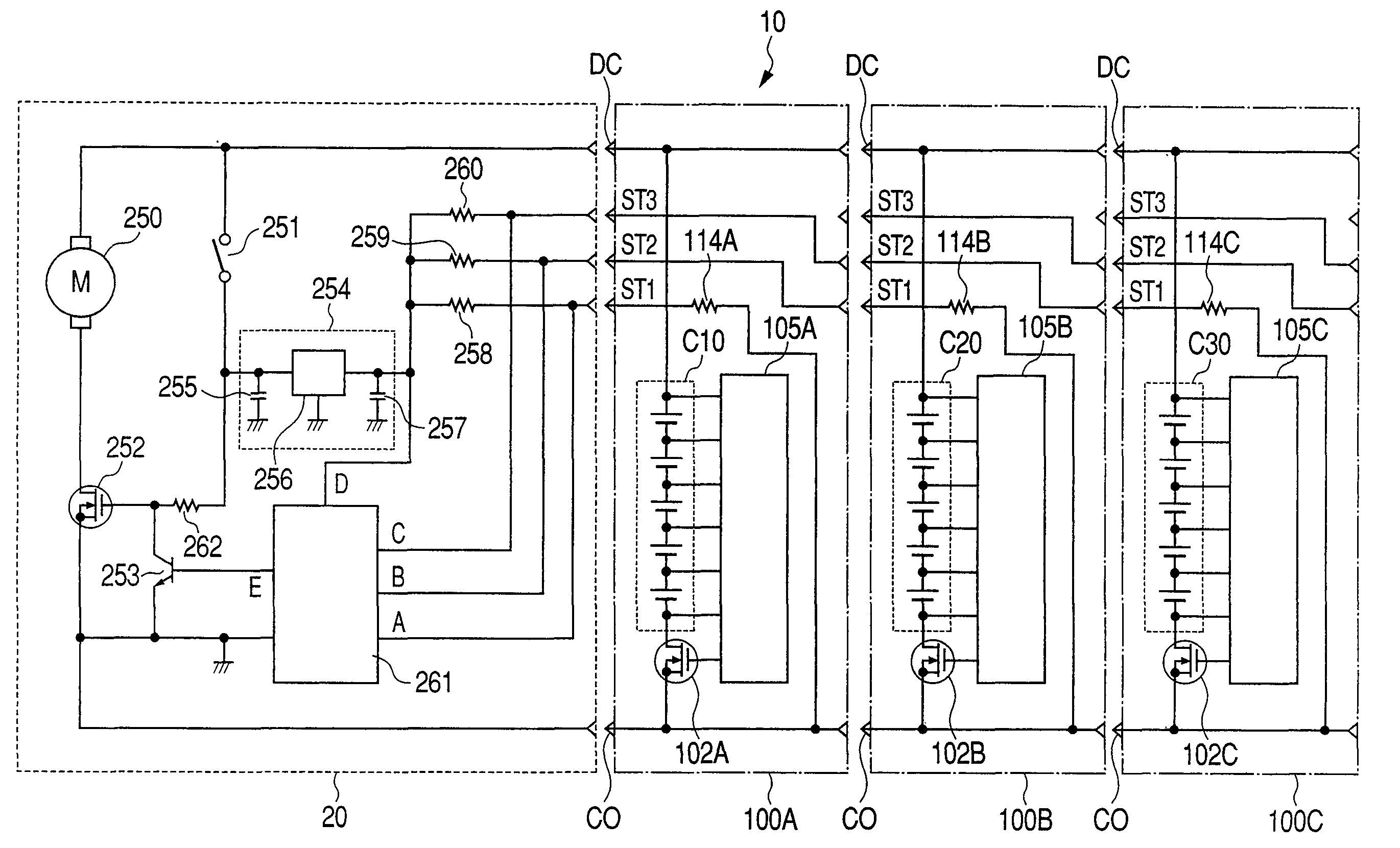
ActiveUS8198835B2Avoid damageCells structural combinationDynamo-electric converter controlDc currentCell assembly
Owner:KOKI HLDG CO LTD
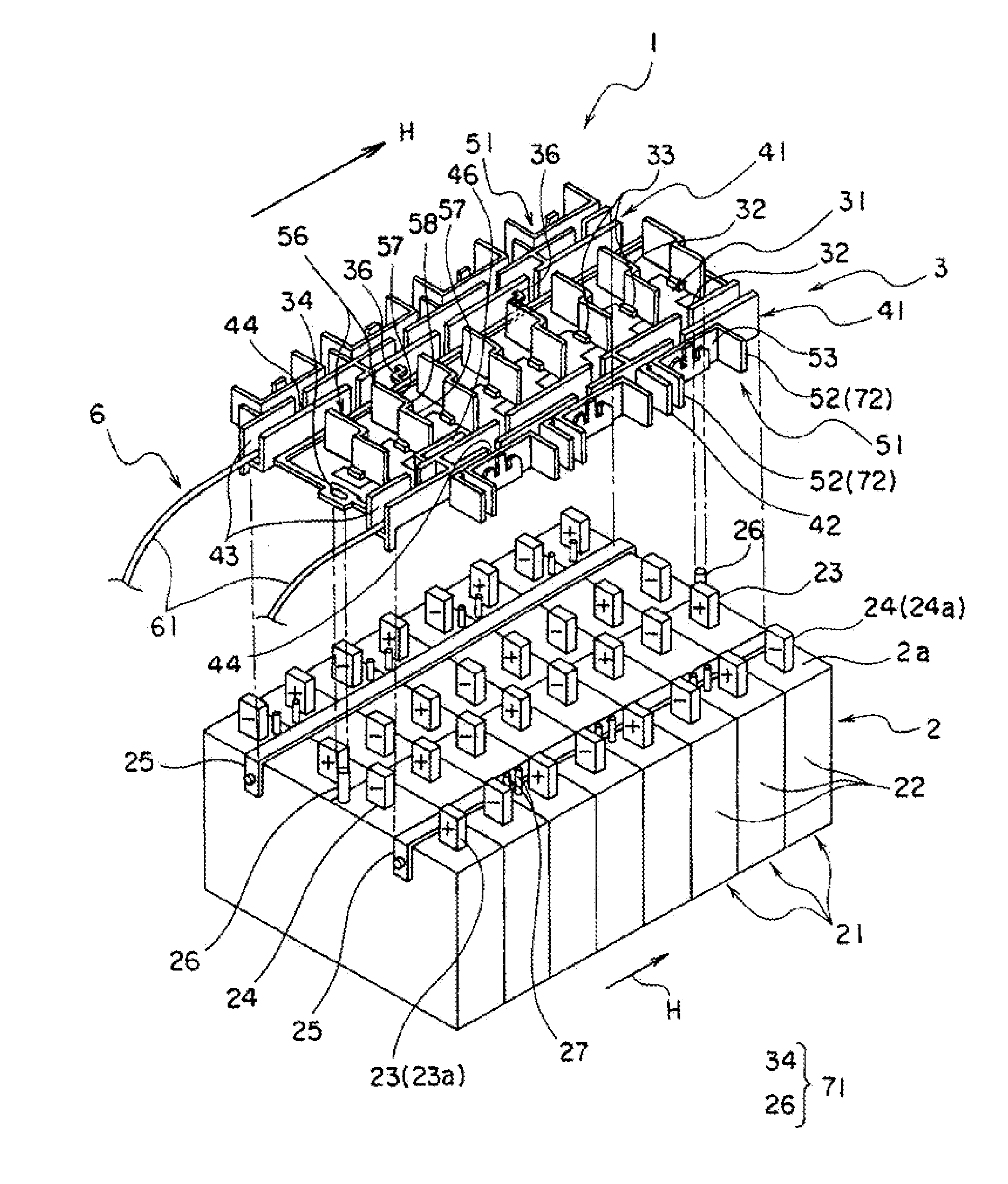
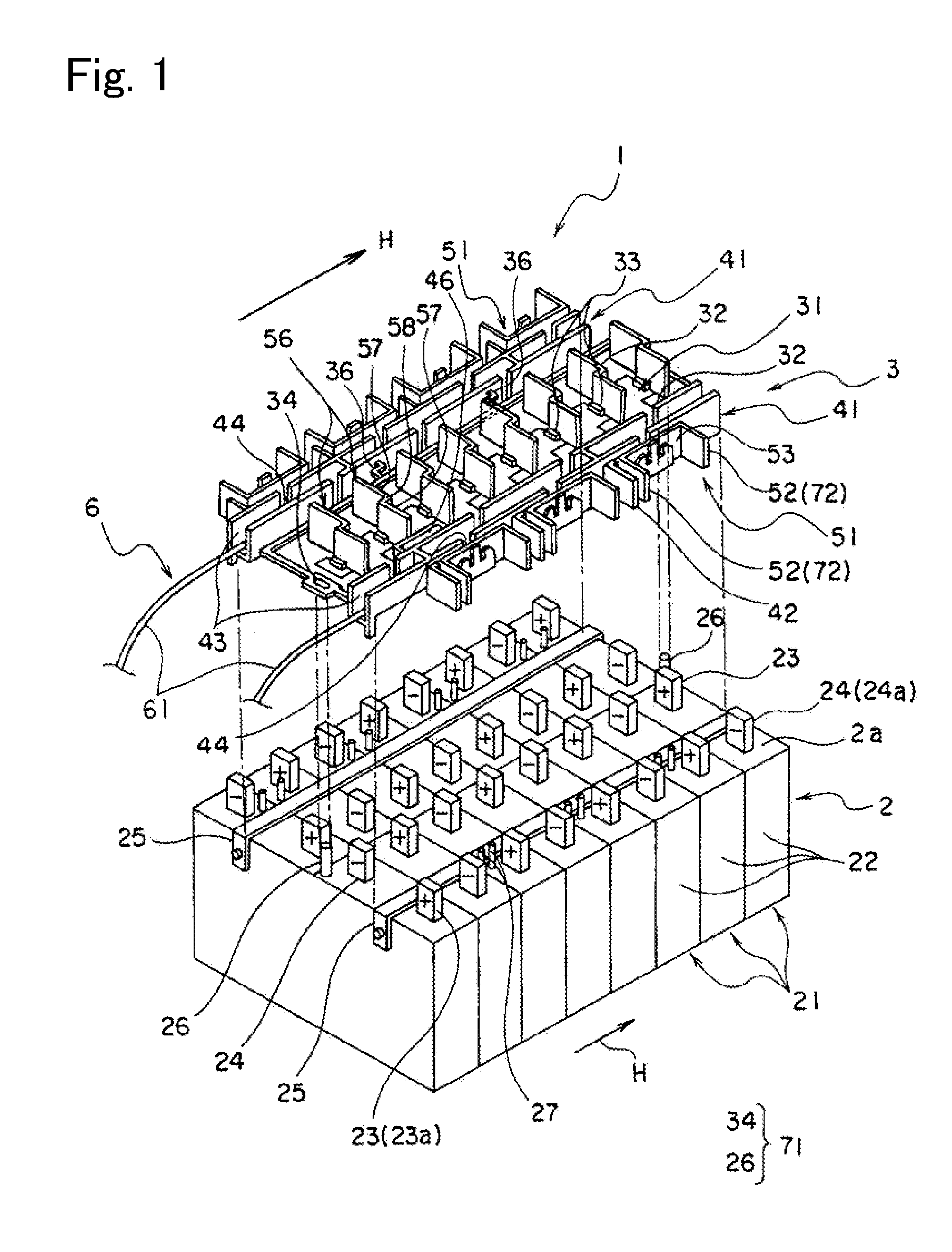
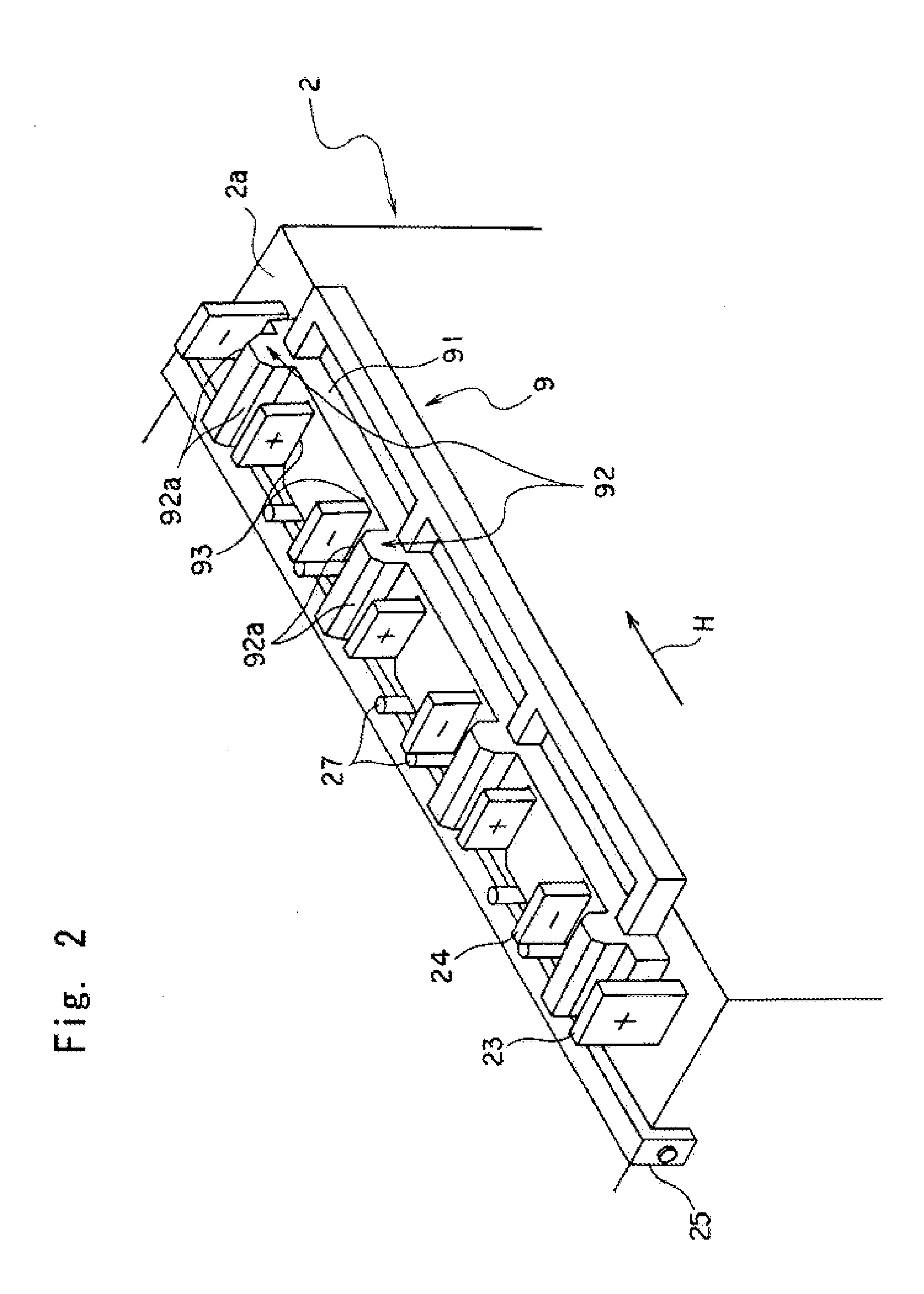
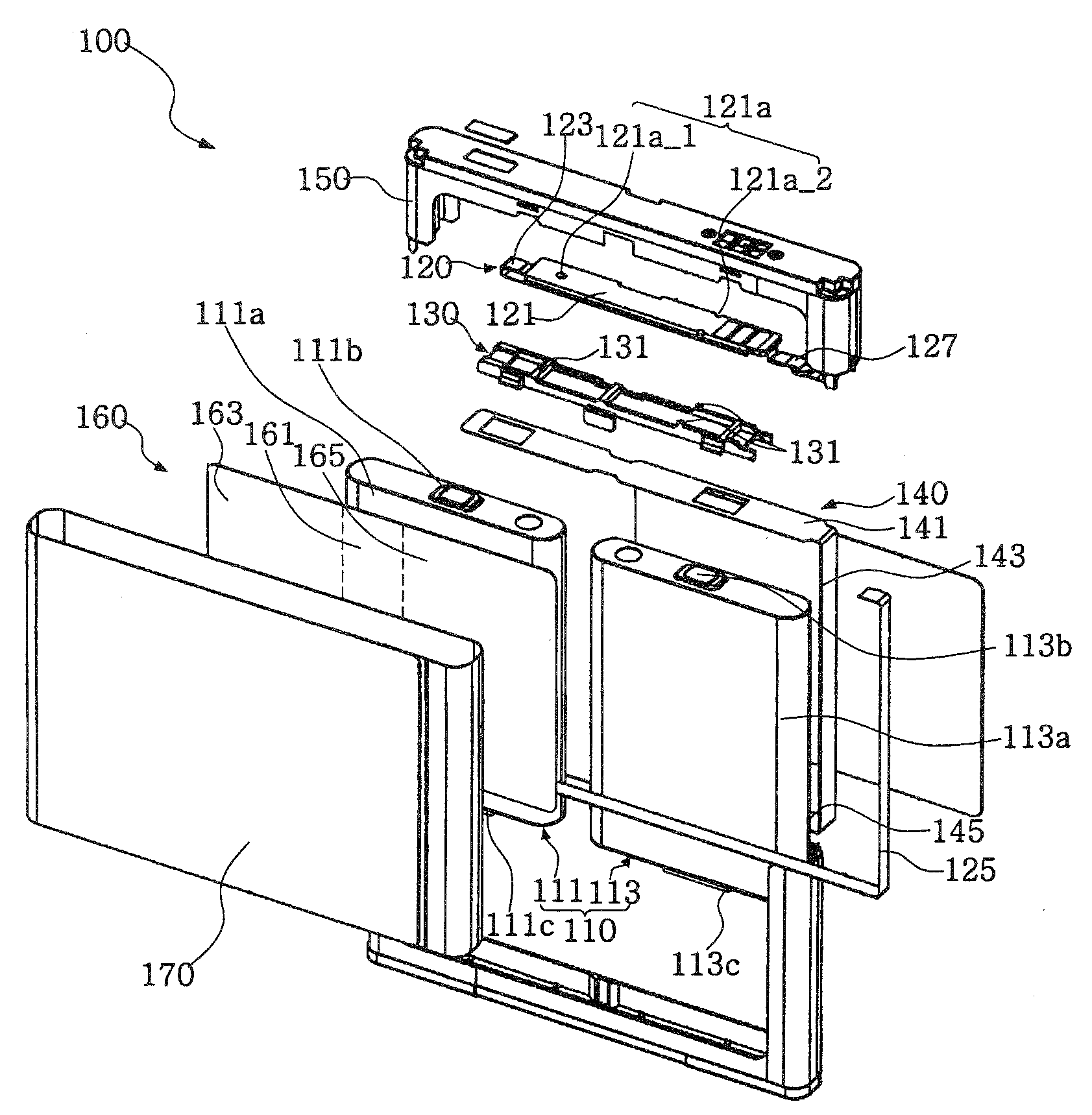
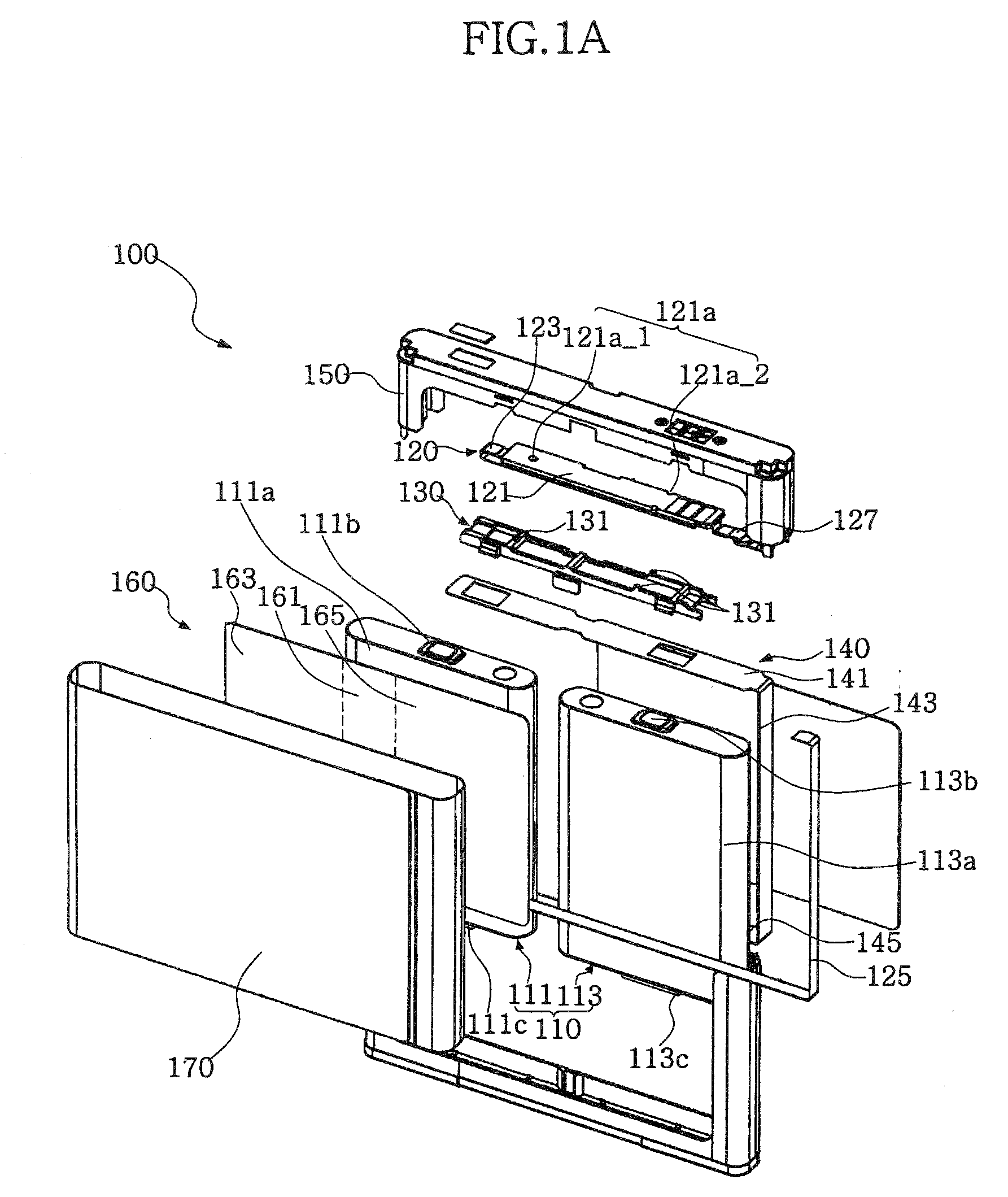
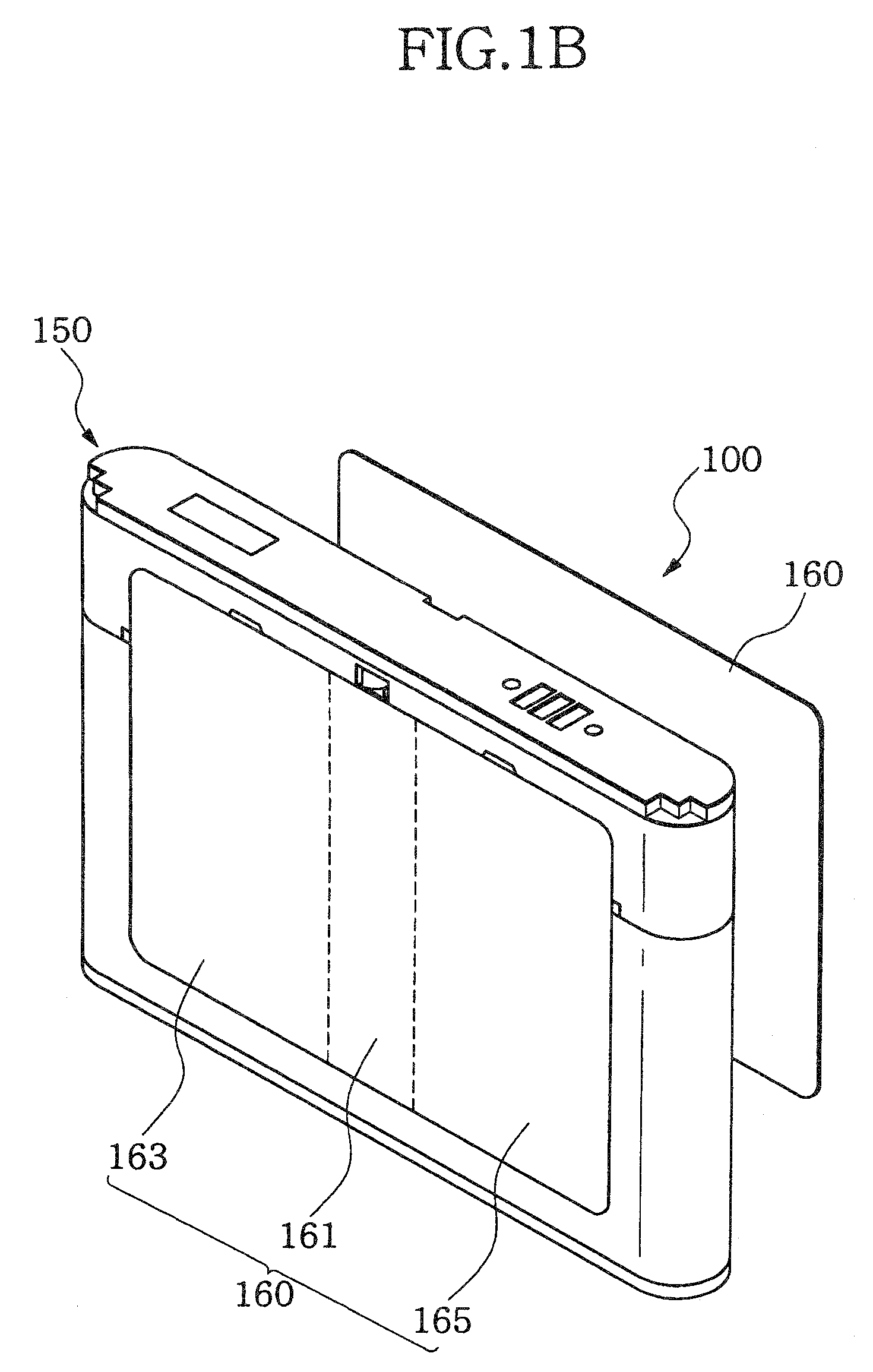
Power supply device
ActiveUS20120009447A1Simplify workEasy to assemblePrimary cell to battery groupingSecondary cellsElectrical and Electronics engineeringCell assembly
A power supply device, which is simply assembled and in which a cell assembly and a measuring section are freely inserted and detached, is provided. A power supply device 1 includes a cell assembly 2, a plurality of first bus bars 51, a plate 3 to which the plurality of bus bars 51 are attached. The plate is overlapped on the cell assembly 2. The cell assembly 2 has a plurality of cells 21 respectively including positive electrodes 23 at one ends and negative electrodes 24 at the other ends. The first bus bars 51 connect the positive electrodes 23 of the one cells 21 to the negative electrodes 24 of the other cells 21 of the cell assembly 2 which are mutually adjacent when the plate 3 is overlapped or overlaid on the cell assembly 2. The power supply device 1 includes a positioning unit 71 that relatively positions the cell assembly 2 to the plate 3 and a guide unit 72 that guides the plurality of first bus bars 51 to positions where the first bus bars 51 connect the respectively corresponding positive electrodes 23 to the negative electrodes 24 when the plate 3 is attached to the cell assembly 2.
Owner:YAZAKI CORP +1
Battery Pack
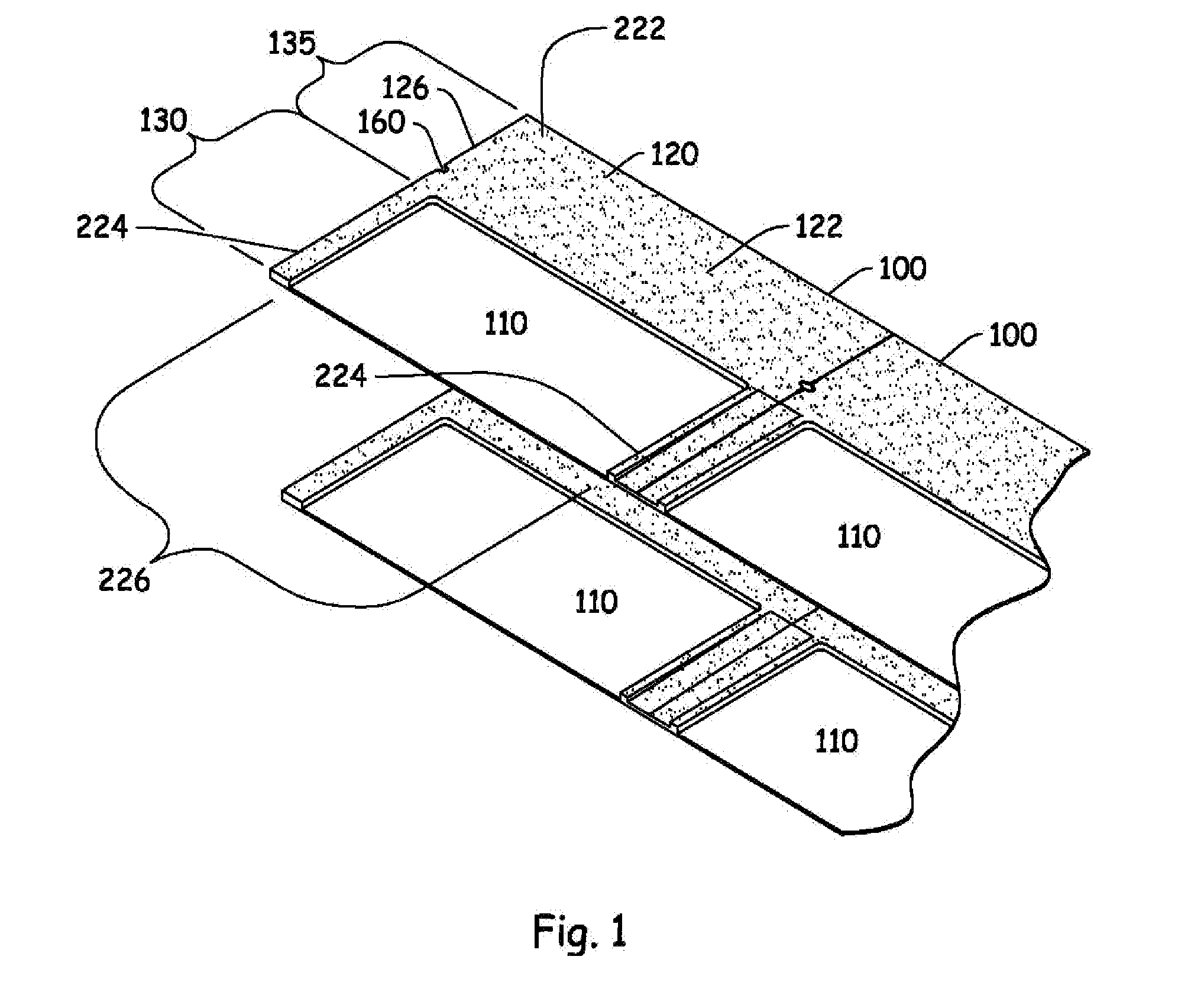
InactiveUS20090053585A1Avoid deformationPrimary cell to battery groupingLarge-sized flat cells/batteriesCell assemblyBattery cell
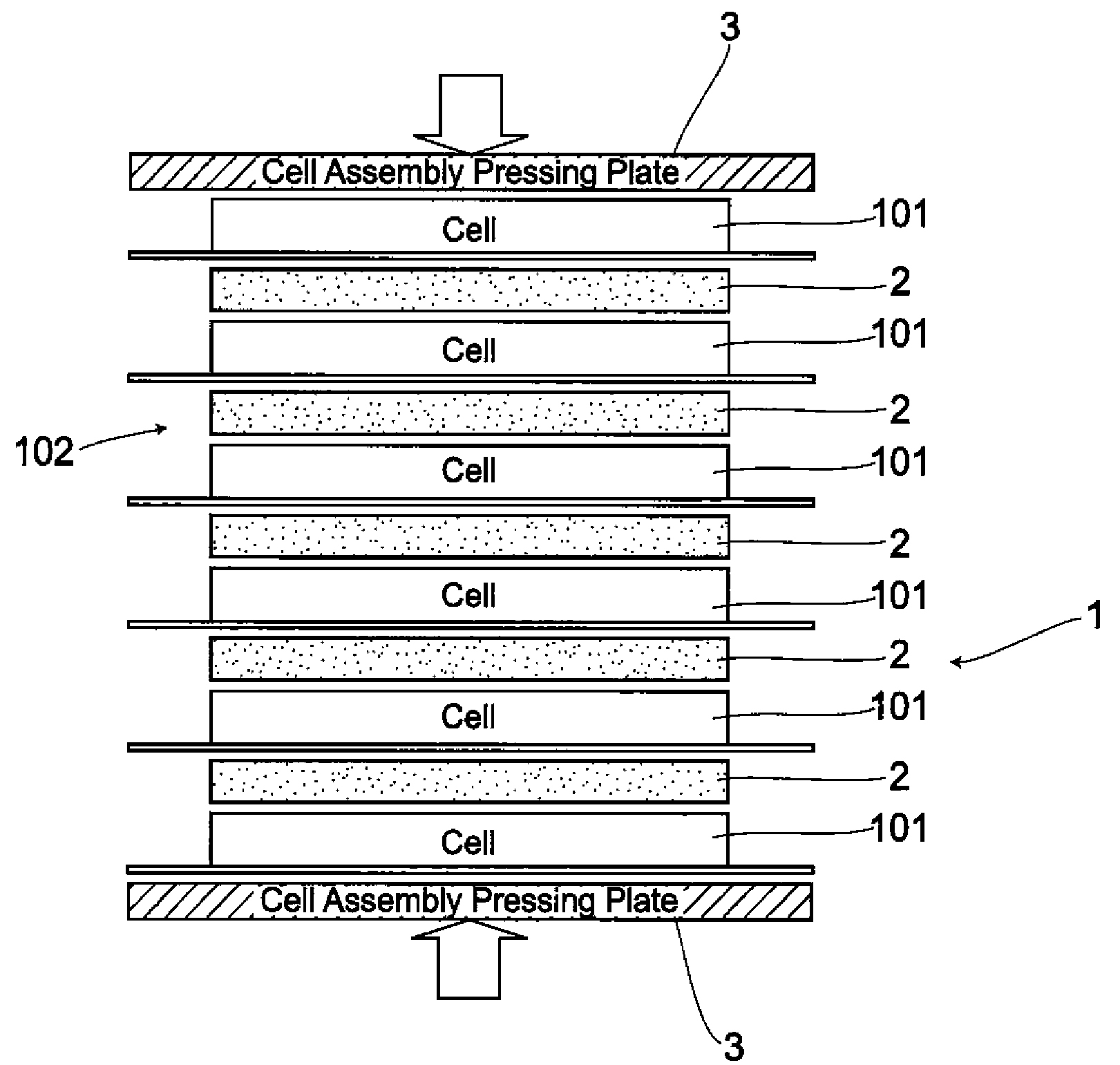
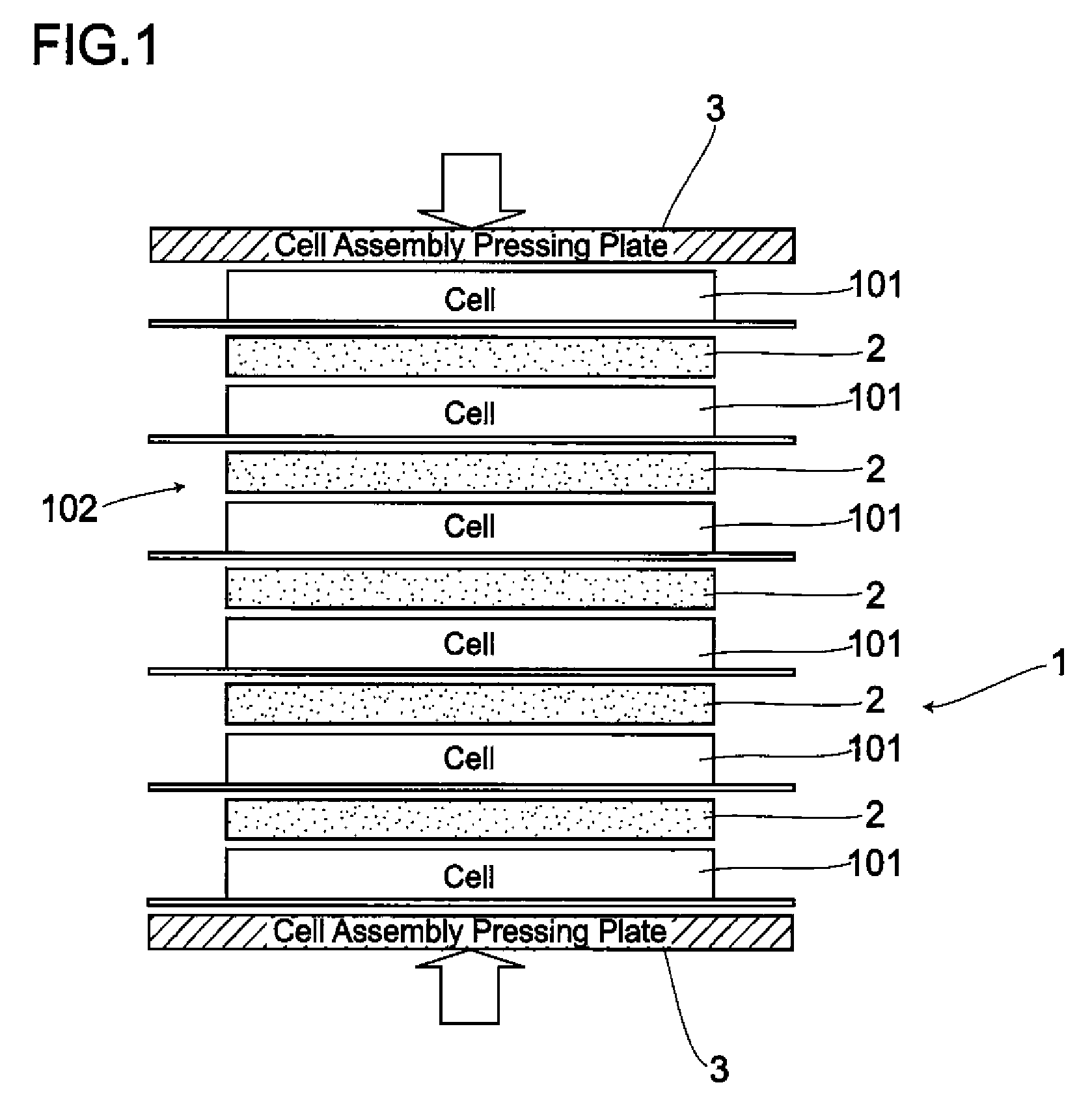
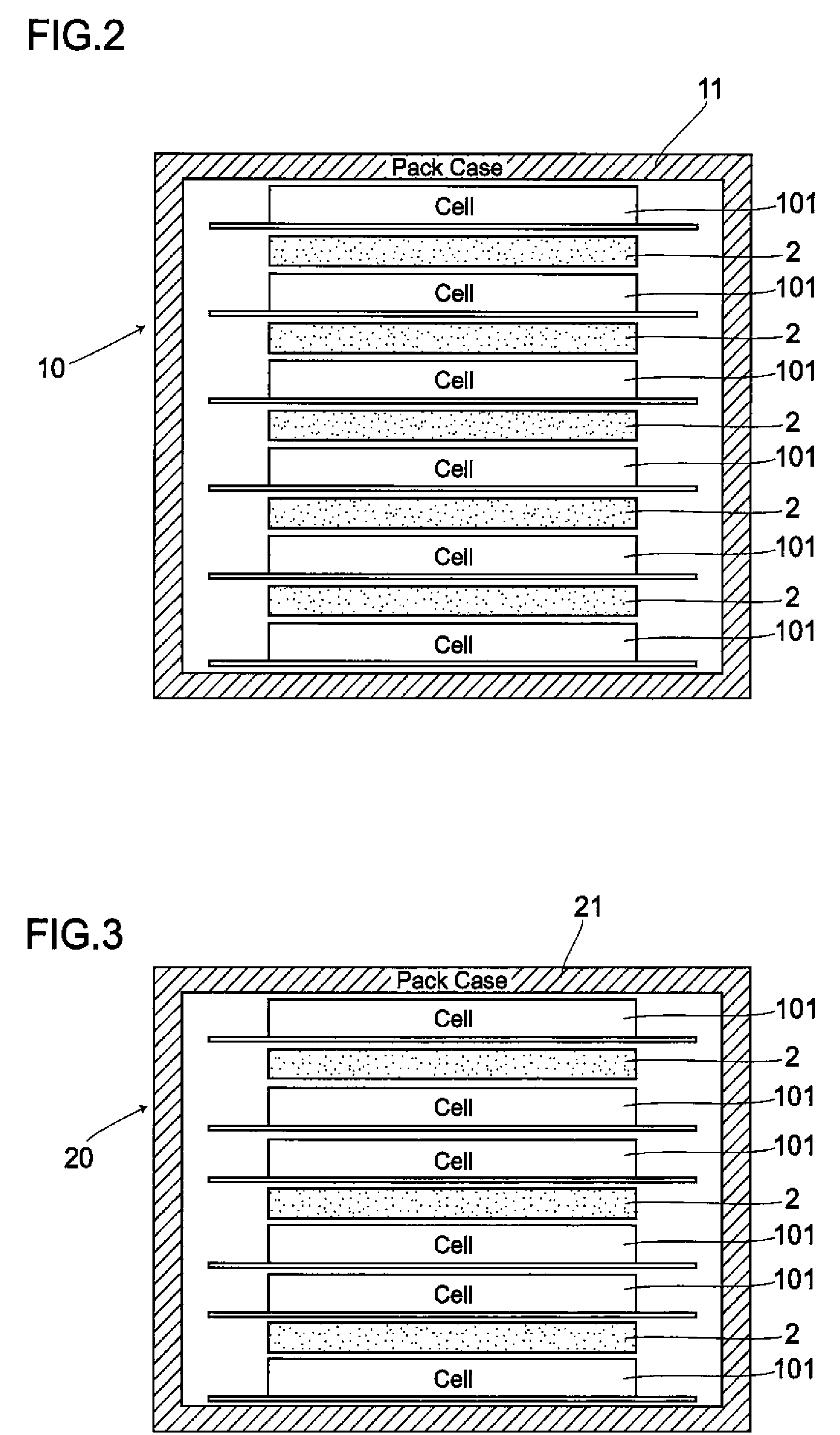
A battery cell 101 has an internal structure where after building up an assembled unit by stacking positive-and negative-electrode materials 110, 111 and a separator 112 in some layers, the assembled units, together with an electrolyte, are sealed with aluminum laminates 114, 114. The battery pack 1 comprises cell assemblies 102 formed by stacking one on top of another in a plurality of the battery cells 101. A deformation-preventive plate 2 is inserted into a portion between each of the battery cells 101 stacked. The cell assemblies 102 inserted by the deformation-preventive plates 2 between each of the battery cells are pressed by cell assembly pressing plates 3, 3 from the upper and lower sides of the battery assemblies. The cell assemblies 102 are pressed by the cell assembly pressing plates 3, 3 to be subjected to some degree of pressure. Hence, the cell assemblies 102 expand not largely to be maintained as an approximately the same form as that at a normal time.
Owner:TDK LAMBDA CORP
Biosensor electromagnetic noise cancellation
InactiveUS6858433B1Material thermal conductivityWeather/light/corrosion resistanceAnalyteCell assembly
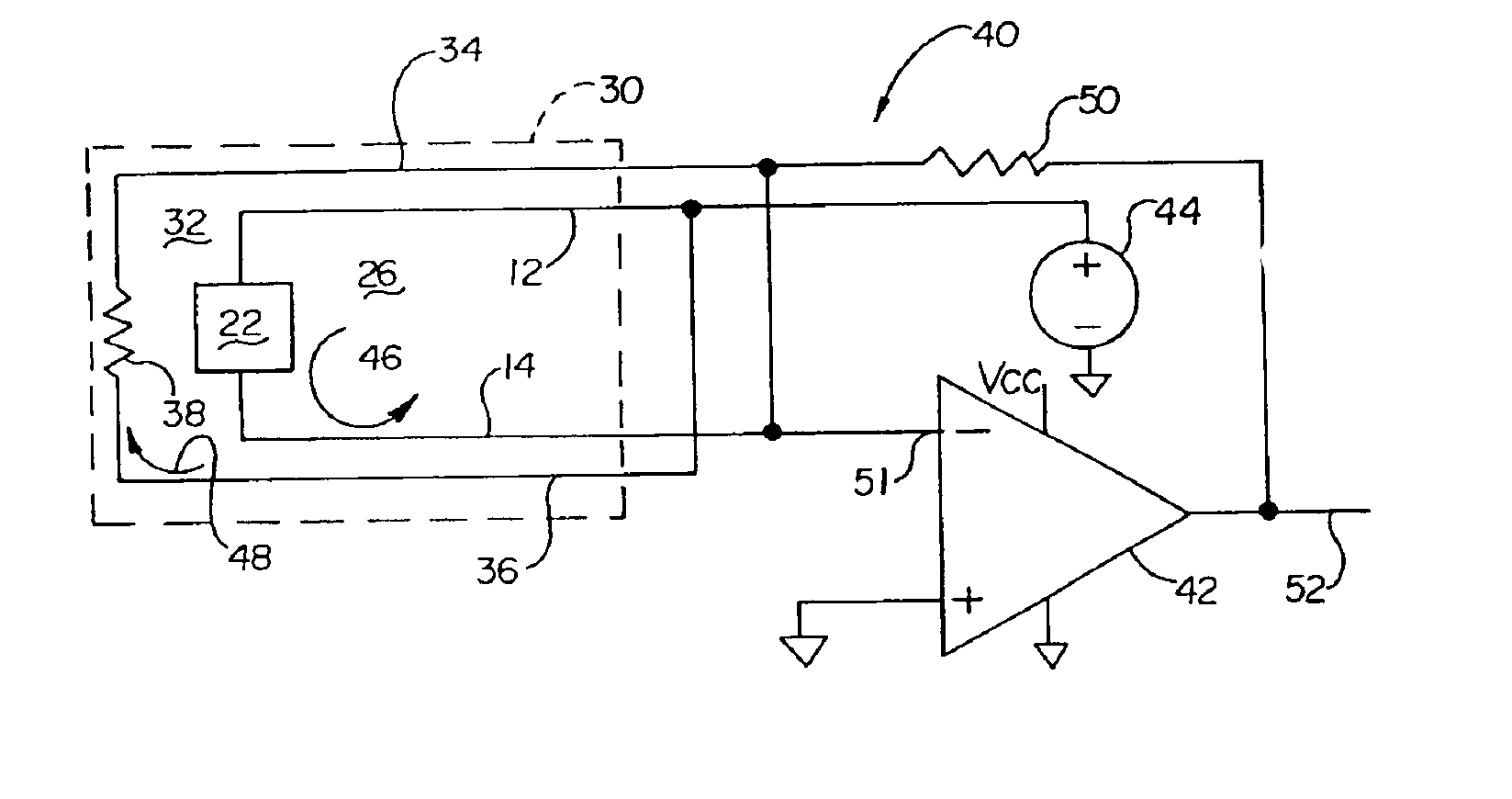
A biosensing cell assembly having a measurement loop with a test cell having an analyte reaction zone for amperometric measurement of a response current to determine analyte concentration and a noise cancellation loop arranged to be physically exposed to the same electromagnetic environment as the measurement loop. The noise cancellation loop has a predetermined impedance within a range of the impedance of the test cell analyte reaction zone and provides a current to cancel or reduce the effects of the electromagnetic environment on the measurement loop.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Electrolysis cell assembly
A compression sealable electrolysis cell that is easily and reliably manufactured, maintained and repaired comprises two insulating end pieces which can position and seal two electrode tubes with electrical contacts separated by a ceramic membrane tube where fluid can be introduced at one end piece and removed at the other end piece in the spaces between the electrode tubes and the ceramic membrane tube. The design permits the compression of the entire assembly via the fixing of nuts on one or more threaded rods extending through both end pieces without the use of an adhesive or cement and without the imposition of torque or compressive stress on the ceramic membrane tube. The water or other fluid to be electrolyzed can be introduced tangentially to spaces between the electrode tubes and the ceramic membrane tube at a angle of 0 to 15 degrees to optimize flow and contact with the electrode tubes.
Owner:CLARTECH HLDG
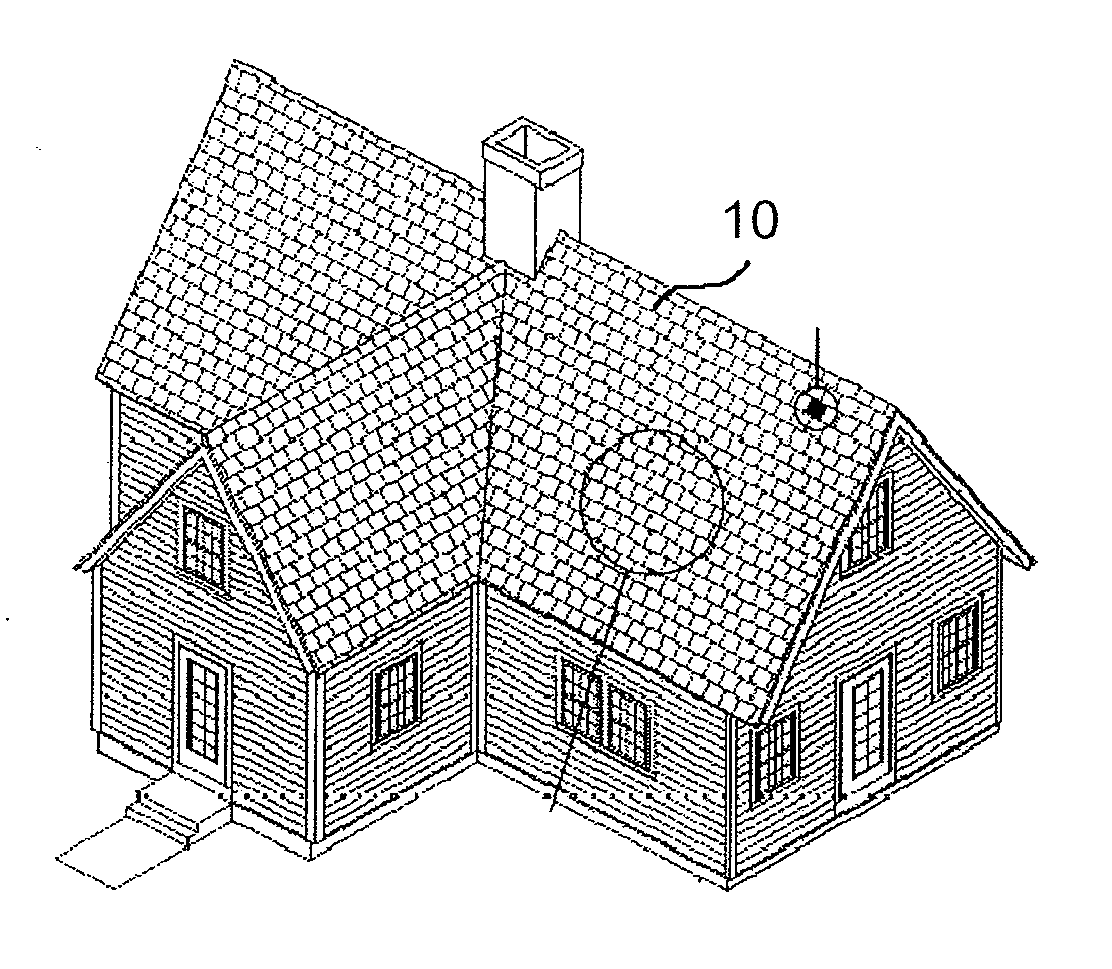
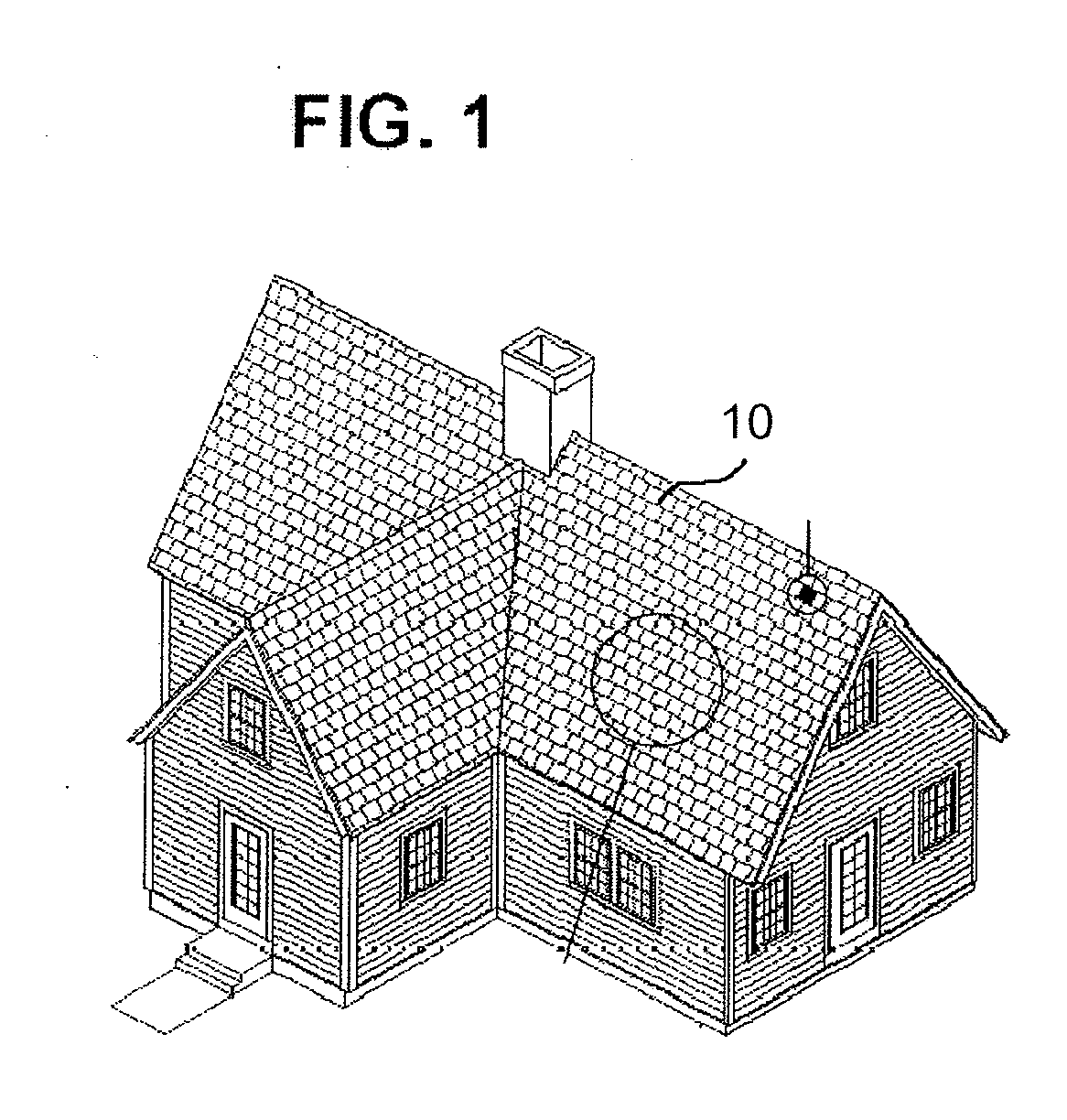
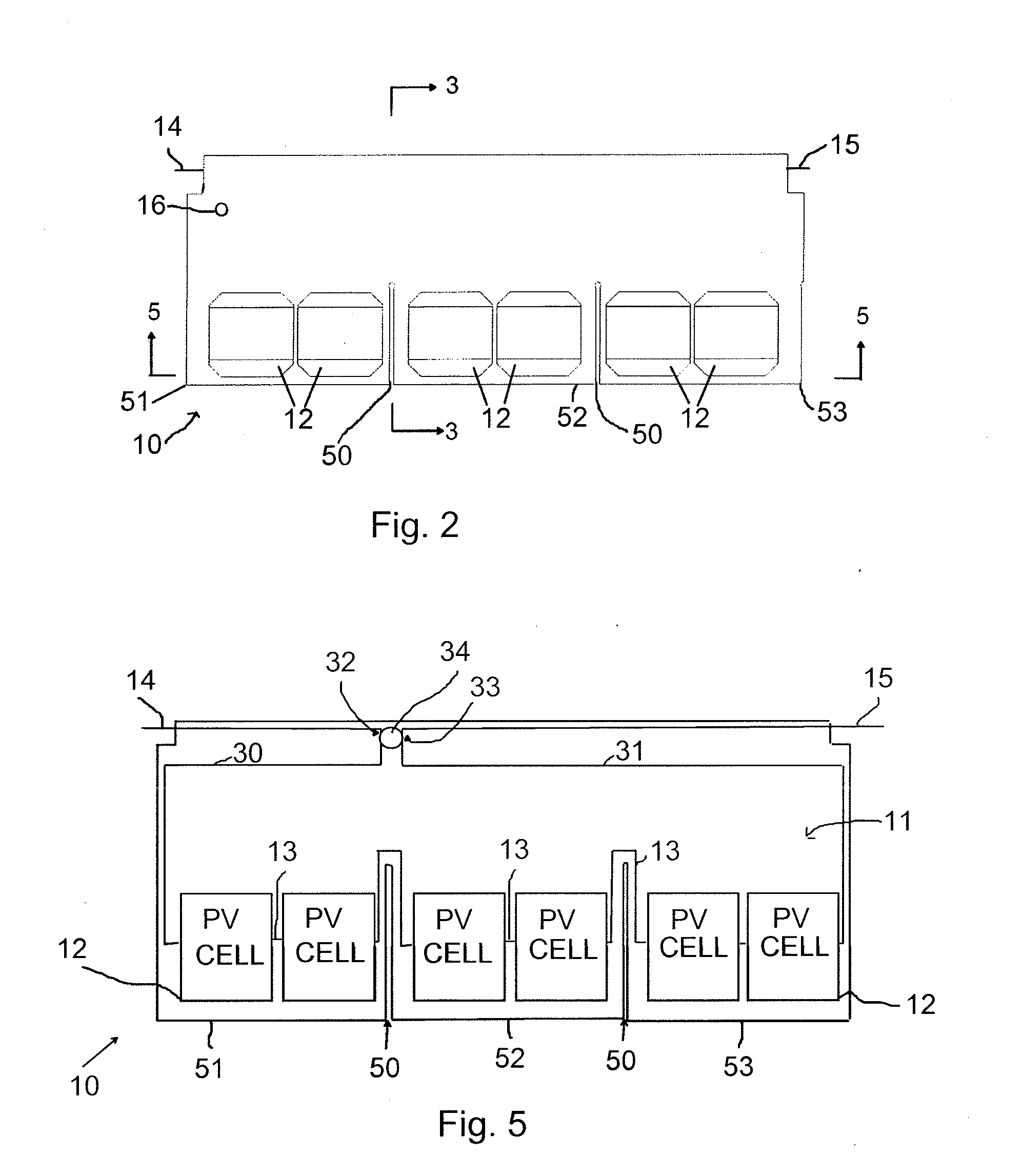
Photovoltaic Shingle
InactiveUS20120204927A1Minimal instructionComplete coveragePhotovoltaic supportsPV power plantsCell assemblyPolymer
A photovoltaic shingle integrates a photovoltaic assembly within a roofing shingle. The shingle includes a first encapsulating material layer disposed on a substrate followed by the photovoltaic cell assembly and a second encapsulating material layer disposed on the photovoltaic assembly. A transparent superstrate such as a resin with polymer film is formed on the second encapsulating material layer. In one advantageous form, the photovoltaic shingle has at least two channels formed completely through the shingle in a stacking direction of the respective layers but only partially through in a direction perpendicular to the stacking direction thereby defining at least two tabs. In alternative forms, there may be additional channels such as but not limited to, two channels defining three tabs or five channels defining six tabs. The photovoltaic shingles may be arranged in an array to form a primary waterproof layer of a suitably pitched roof structure.
Owner:PETERSON GEORGE D +1
Method of automated prismatic electrochemical cells production and method of the cell assembly and construction
InactiveUS20060159999A1Increase energy densityImprove power densityHybrid capacitor separatorsElectrolytic capacitorsHigh energyEngineering
The present invention pertains to electrochemical devices having a thin micro porous polytetrafluoroethylene separator bonded to their porous electrodes without special treatment of the separator and without additional adhesive layers. Structures of superior high energy density and power density are disclosed herein, as well as the methods of their assembly and automated production.
Owner:KEJHA JOSEPH B +2
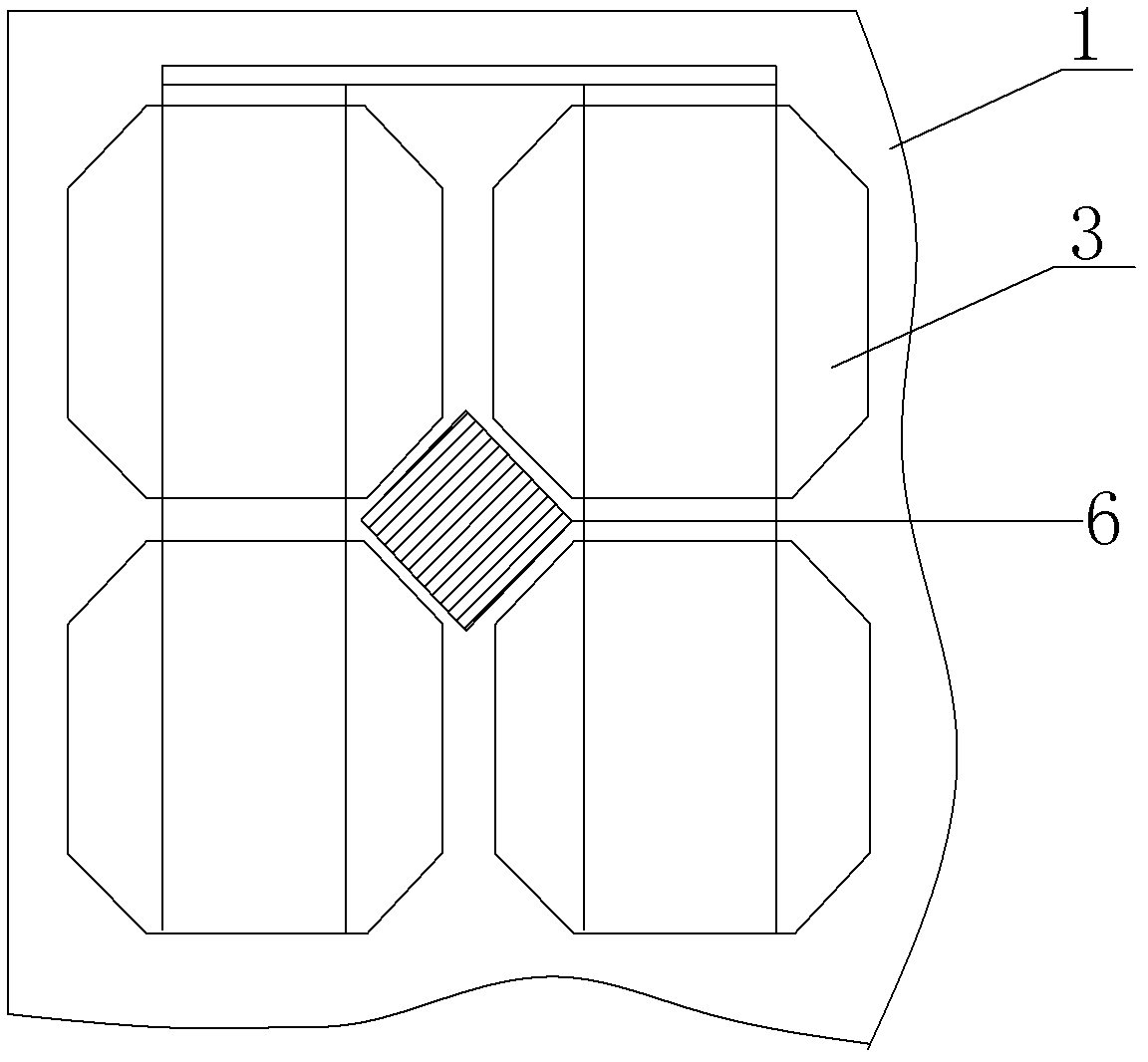
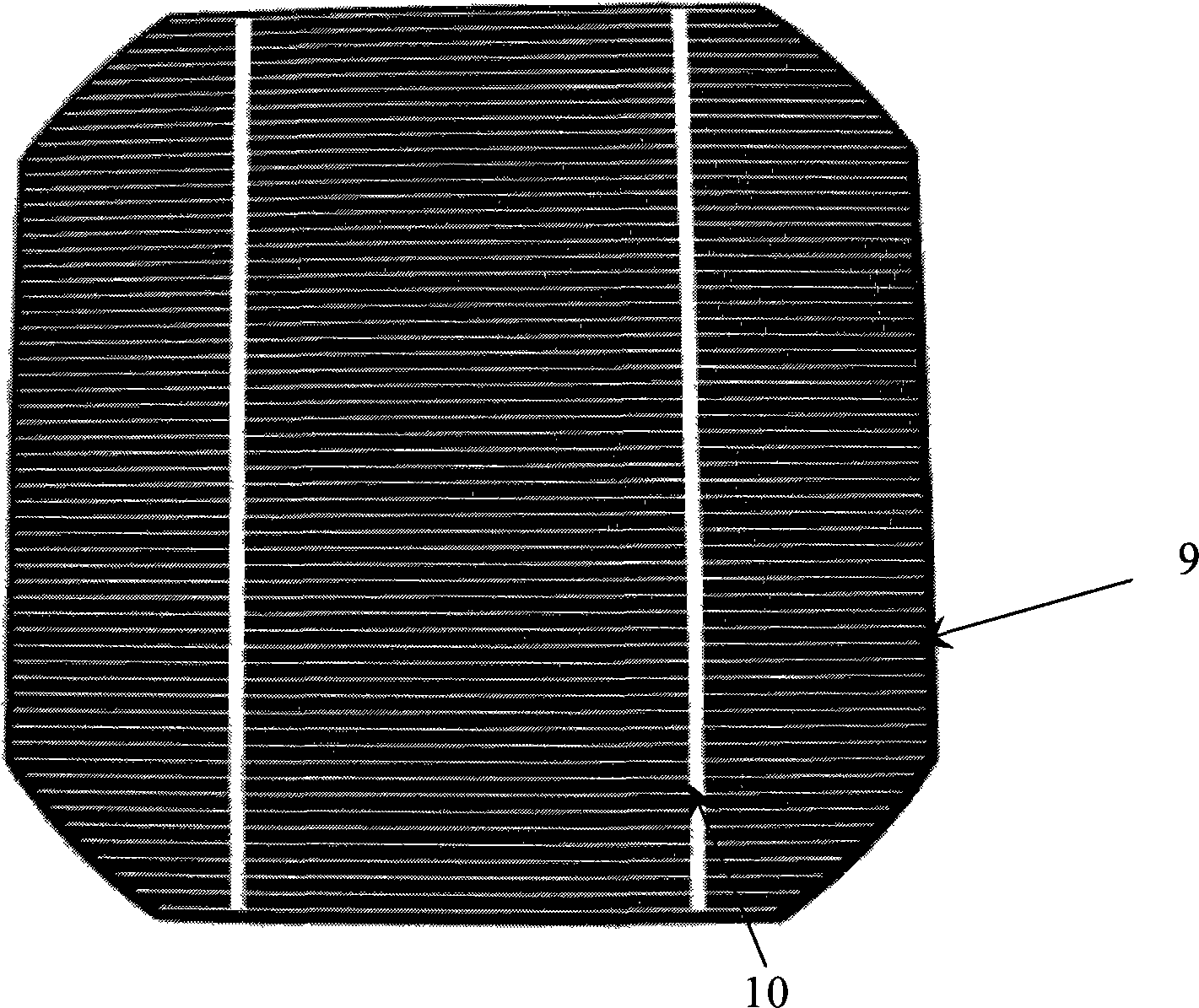
Solar cell assembly for increasing light energy utilization ratio
ActiveCN102544174AImprove power efficiencyImprove conversion efficiencyPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesLight energyCell assembly
The invention discloses a solar cell assembly for increasing the light energy utilization ratio. The solar cell assembly comprises ultra-white low-iron toughened glass (1), a first EVA (Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate) layer (21), interconnected solar cells (3), a second EVA layer (22) and a back plate (4) arranged in sequence from top to bottom and encapsulated integrally, and is characterized in that: texturing treatment is performed on the surface of a welding band (5) for connecting the solar cells (3); gaps among the solar cells (3) are provided with cell gap reflecting layers (6); and texturing treatment is performed on the surfaces of the cell gap reflecting layers (6). Compared with the prior art, the solar cell assembly has the advantages that: the light utilization ratio of the assembly can be increased greatly, light rays which cannot be utilized by the assembly originally are reflected onto the solar cells and absorbed by the solar cells, photo-generated current is indirectly increased, and the output power and conversion efficiency of the assembly are increased.
Owner:WORLDWIDE ENERGY & MFG NANTONG
Battery pack
ActiveUS20090258285A1High strengthCells structural combinationJackets/cases materialsCell assemblyEngineering
A battery pack includes a multi cell assembly having a plurality of bare cells, the multi cell assembly defining opposing planar surfaces. The battery pack also includes a protection circuit at one side of the multi cell assembly, a case surrounding a periphery of the multi cell assembly and the protection circuit and exposing the opposing planar surfaces of the multi cell assembly to an exterior of the multi cell assembly and reinforcing tape attached to the opposing planar surfaces.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Lead acid battery with gelled electrolyte contained within compressed absorbent separator mat and method of making the same
A method for producing a valve-regulated lead acid battery includes the steps of (i) providing a battery comprising a preformed positive electrode plate, a preformed negative electrode plate and a porous separator mat having pores and being compressibly disposed between the electrodes to define a cell assembly, and a container for securably and sealingly holding the cell assembly; (ii) forming a electrolyte mixture comprising an aqueous colloidal dispersion of silica and sulfuric acid that is a precursor to a flowable thixotropic gel; (iii) applying a vacuum to the container; and (iv) introducing a quantity of the gel-precursor electrolyte into the container under a vacuum so that the flowable electrolyte mixture penetrates into the pores of the compressed mat, whereby as the acid absorbs onto the plates, the flowable electrolyte solidifies and forms a thixotropic gel within the pores and around peripheral edges of the mat to surround and seal the cell assembly. A battery produced by these steps include (i) a positive electrode plate; (ii) a negative electrode plate; (iii) an absorbent glass mat compressibly disposed between the electrodes, wherein the glass mat is in substantial contact with both electrodes; and (iv) gelled electrolyte disposed within the pores of the compressed glass mat and around peripheral edges of the glass mat, wherein the gelled electrolyte comprises of an intimate mixture of colloidal alkali metal polysilica having a particle size from about 4 nanometers to about 20 nanometers and sulfuric acid.
Owner:C&D CHARTER HLDG
Zinc/air cell
ActiveUS7001689B2Optimized diameterBe consistentFuel and primary cellsFilling tube/pocket electrodesInterference fitButton battery
A zinc / air cell having thin walled cup shaped anode casing and cathode casing. The cell may be a button cell having an anode comprising zinc and a cathode, which may be catalytic, comprising manganese dioxide. The anode and cathode casings have small wall thicknesses, preferably between 2 and 5 mil (0.0508 and 0.127 mm), desirably between about 2 and 3 mil (0.0508 and 0.0762 mm). There is an insulating seal ring covering at least a portion of the anode casing side walls. During cell assembly the cathode casing side wall is pushed over at least a portion of the anode casing side wall with insulating sealing disk therebetween. A tight interference fit is achieved with the outside diameter of the anode casing plus insulating seal thereon being preferably between about 2 and 4.5 mil (0.0508 and 0.114 mm) greater than the inside diameter of the cathode casing. This reduces the tendency of the casing side walls to spring back after crimping.
Owner:DURACELL U S OPERATIONS
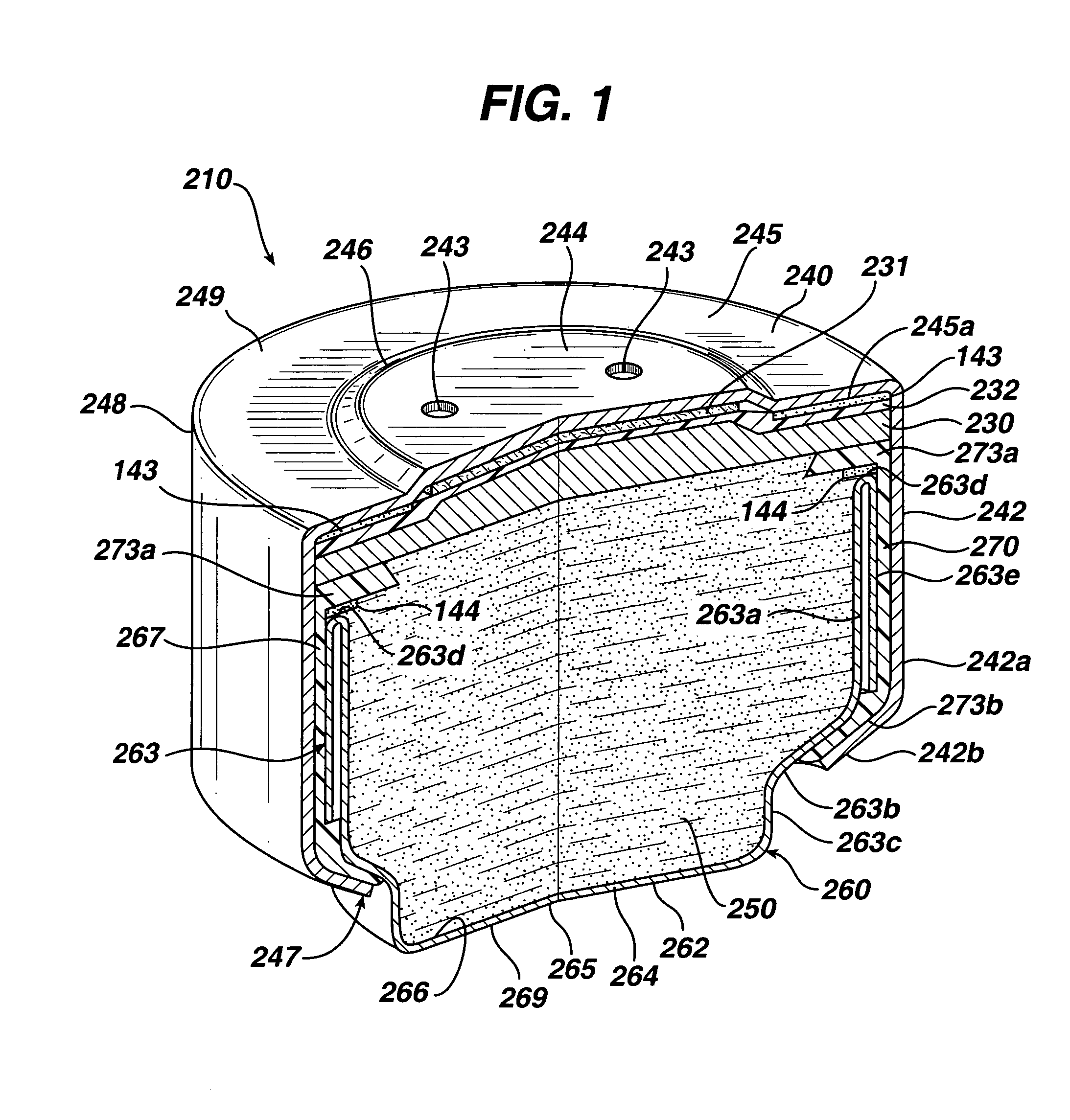
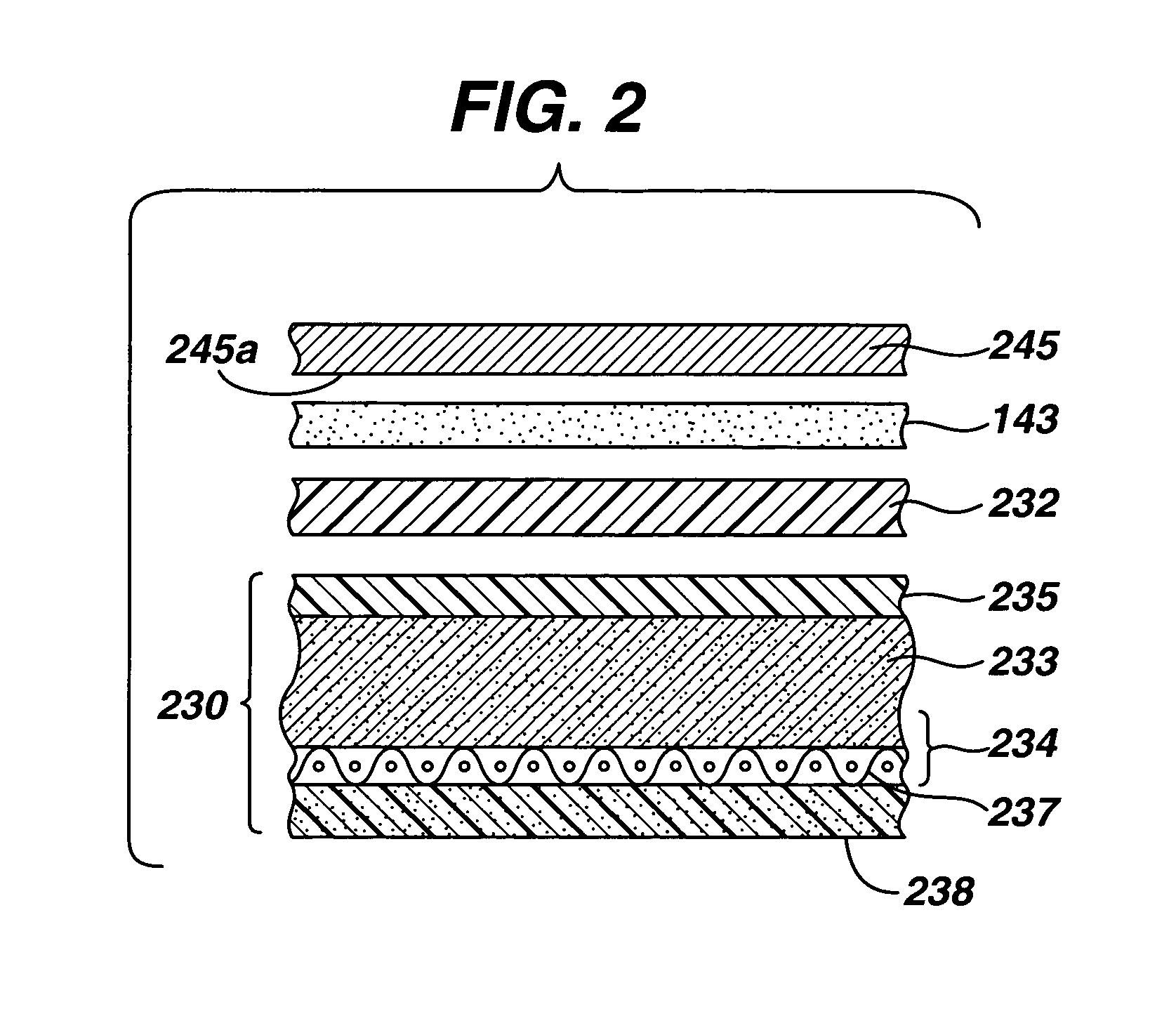
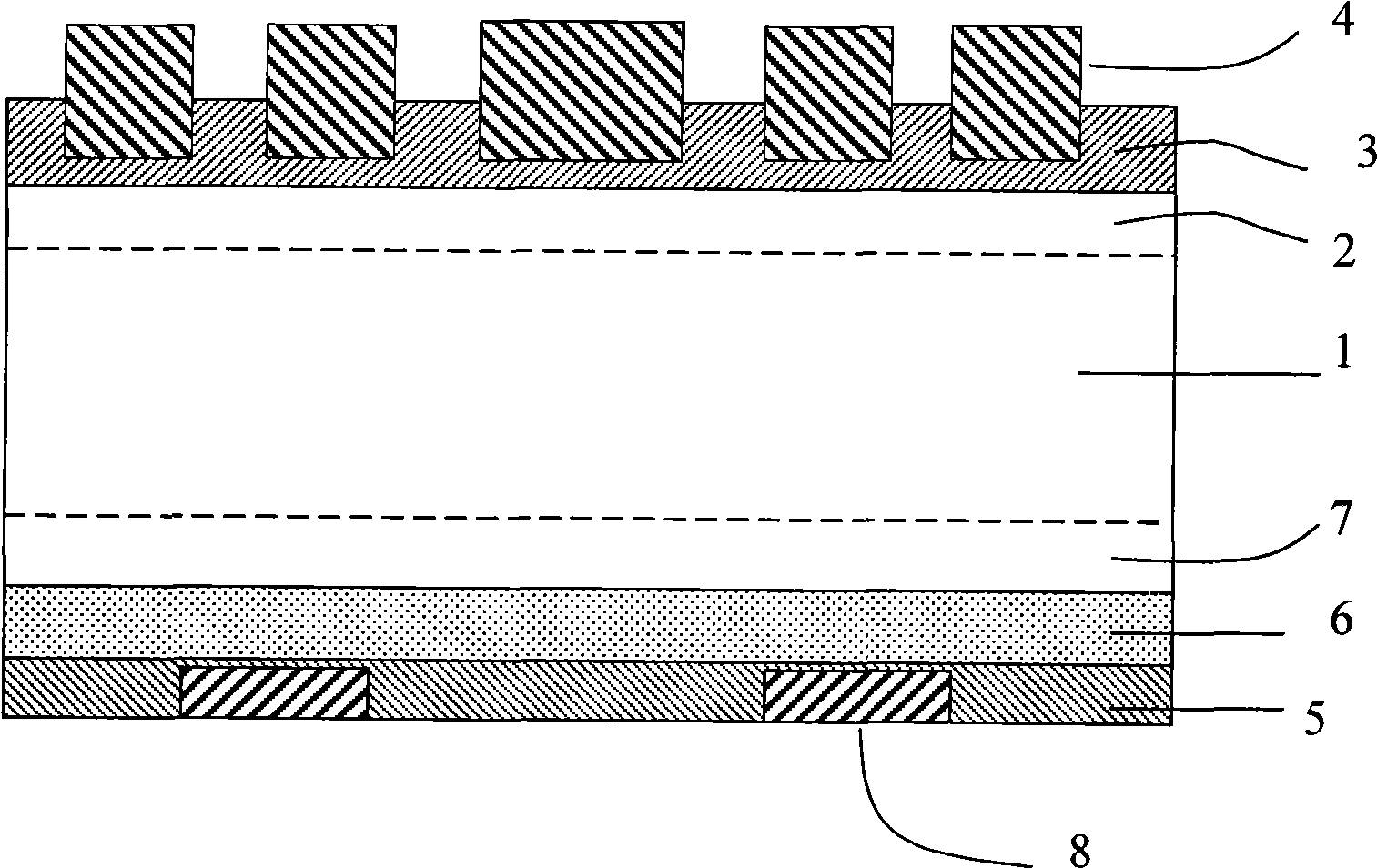
Photovoltaic cell assembly
InactiveUS9147788B2Reduce the amount requiredImprove the immunityPhotovoltaic supportsPV power plantsAdhesiveCell assembly
The present invention is premised upon an improved photovoltaic cell assembly that include at least plurality of photovoltaic cells with a photoactive portion with a top surface, a top collection structure on the top surface and an opposing conductive substrate layer on a side of the photoactive portion opposite the top surface. Also including a first conductive element with a first surface and wherein the first conductive element is bent at least once and wherein the first surface is in contact with the top collection structure and / or the top surface of a first photovoltaic cell and the opposing conductive substrate layer of an adjacent second photovoltaic cell; further wherein at least a portion of the first surface is held in contact to the cells by an adhesive.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Battery pack and cordless tool using the same
ActiveUS8381829B2Not to damageAdjustable weightDrilling rodsConstructionsPower flowElectrical battery
A battery device is constituted by connecting such cell assemblies in parallel as each includes: a first cell group having a plurality of cells connected in series; a housing container for housing the first cell group; current detector housed in the container for detecting a current to flow through the first cell group; a switching element connected with the first cell group for turning ON / OFF the current to flow through the first cell group; and a controller for controlling the ON / OFF of the switching element in response to the output signal of the current detector.
Owner:KOKI HLDG CO LTD
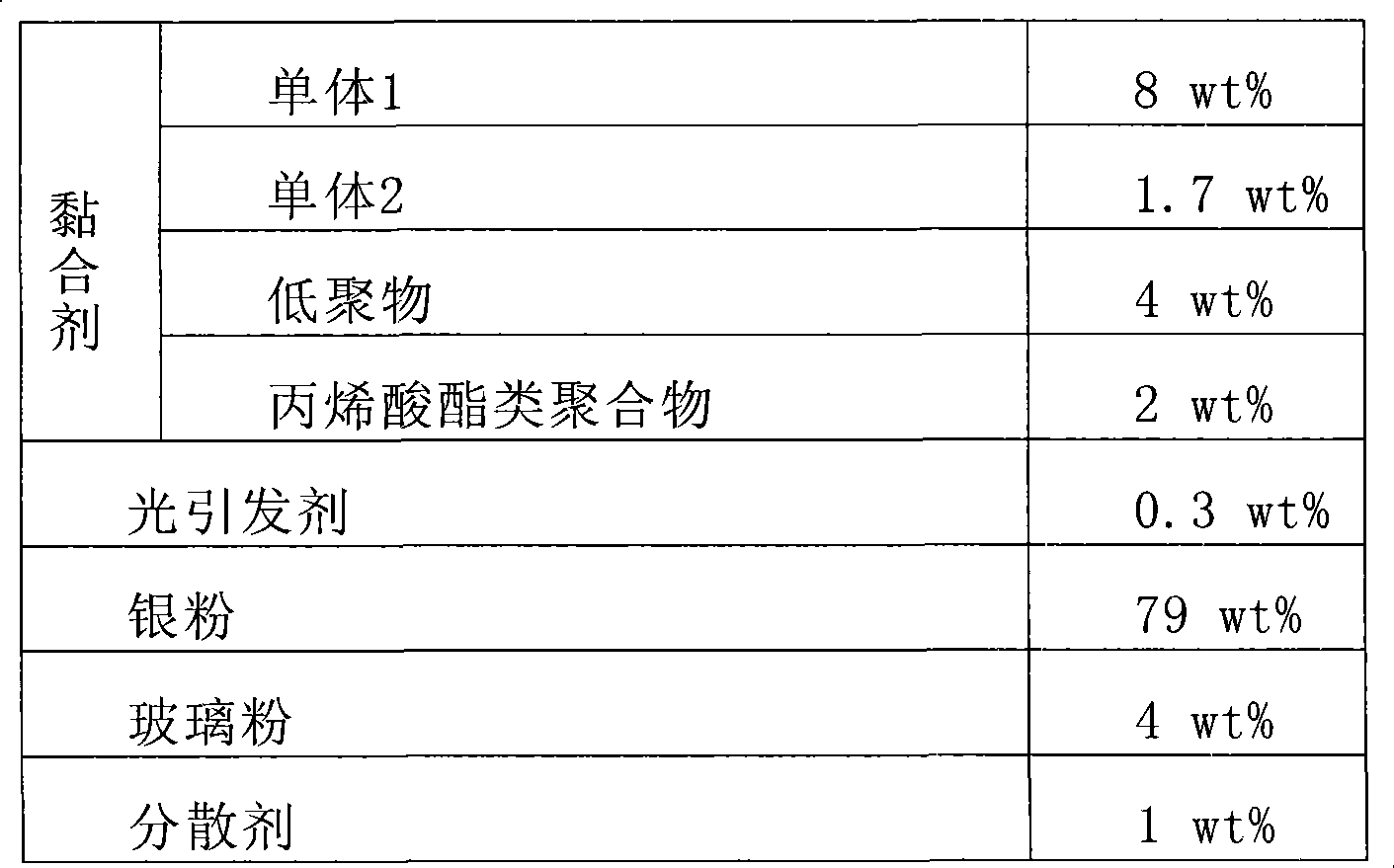
Solvent-free conductive adhesive constituent and solar energy cell assembly with the same
InactiveCN101475780AGood coating propertiesFinal product manufactureOrganic non-macromolecular adhesiveSolvent freeCell assembly
The invention provides a nonsolvent conductive adhesive composition. The nonsolvent conductive adhesive composition comprises (a) an adhesive; (b) an evocating agent, (c) glass powder, and (d) conductive powder. The invention also provides a solar cell component; and the solar cell component comprises an electrode or a conducting wire which is formed through the coating of the conductive adhesive composition on a silicon semiconductor substrate and sintering of the silicon semiconductor substrate. As the conductive adhesive comprises no solvent, the conductive adhesive has no problem of environmental pollution caused by solvent volatilization, is not easy to diffuse, is favorable for the design of thinning and high depth-to-width ratio, and can effectively increase photoelectric conversion efficiency of the solar cell component.
Owner:ETERNAL MATERIALS CO LTD
Preparation method and application of three-dimensional graphene aerogel load molybdenum disulfide nano-sheet hybridization material
The invention belongs to the technical field of a new energy nano function material, and specifically relates to a preparation method and application of a three-dimensional graphene load molybdenum disulfide nano-sheet hybridization material. A three-dimensional graphene aerogel macroscopic body is prepared through a hydrothermal reduction self-assembly method, and nano-sheet layer crystal-phase molybdenum disulfide grows on a three-dimensional graphene aerogel skeleton through adoption of a H<2> reduction method. According to the three-dimensional graphene load molybdenum disulfide nano-sheet hybridization material prepared in the invention, a large specific surface of three-dimensional graphene provides more active sites for growth of molybdenum disulfide nano sheets, the nano-sheet layer crystal-phase molybdenum disulfide as an active catalyst disperse on a surface of a three-dimensional graphene aerogel, heterojunction structure is formed between the molybdenum disulfide nano sheet and the three-dimensional graphene aerogel through intermolecular forces, and edge activity of the molybdenum disulfide nano sheet is fully exposed. The high catalytic property of molybdenum disulfide is combined with the high specific surface area and excellent eectrical conductivity of the three-dimensional graphene. The hybridization material is applied to fuel cell counter electrode preparation to perform cell assembly so that photoelectric conversion efficiency is improved.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
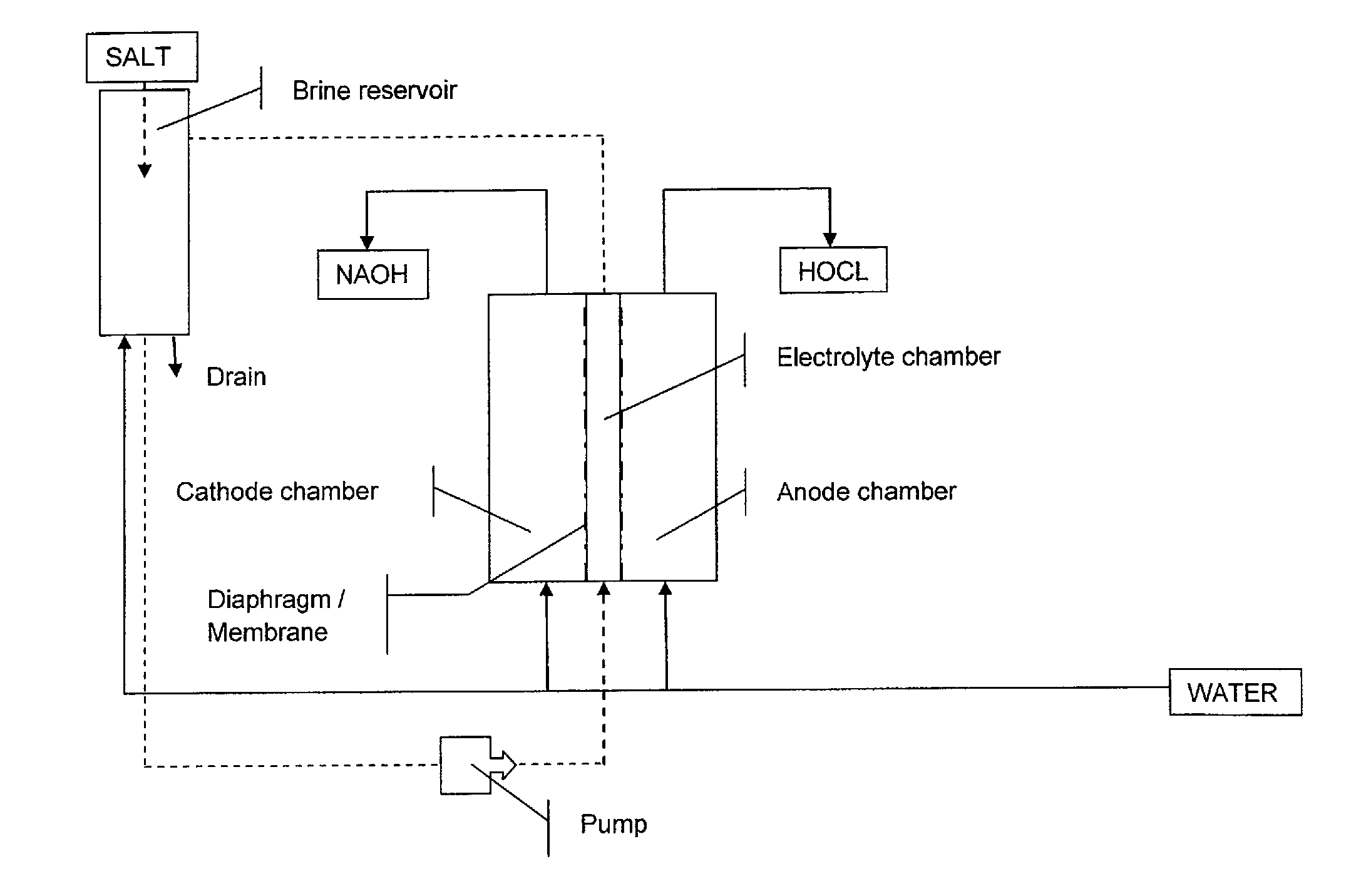
Dual diaphragm electrolysis cell assembly and method for generating a cleaning solution without any salt residues and simultaneously generating a sanitizing solution having a predetermined level of available free chlorine and pH
InactiveUS20130146473A1Improve cleanlinessSanitizing all hard surfacesCellsPhotography auxillary processesPotassiumCell assembly
An Electrolysis cell assembly to produce diluted Sodium Hydroxide solutions (NAOH) and diluted Hypochlorous Acid (HOCL) solutions having cleaning and sanitizing properties. The electrolysis cell consists of two insulating end pieces for a cylindrical electrolysis cell comprising at least two cylindrical electrodes with two cylindrical diaphragms arranged co-axially between them. The method of producing different volumes and concentrations of diluted NAOH solutions and diluted HOCL solutions comprises recirculating an aqueous sodium chloride or potassium chloride solution into the middle chamber of the cylindrical electrolytic cell and feeding softened filtered water into the cathode chamber and into the anode chamber of the cylindrical electrolysis cell.
Owner:AQUAOX
Single-cell assembly and test tool of fuel cell
ActiveCN101969131AQuick assemblyQuick testFinal product manufactureElectrical testingFuel cellsElectrical battery
The invention relates to a single-cell assembly and test tool of a fuel cell, which comprises a base plate, a pressure applying device, a pressure measuring device and a single-cell test part, wherein the pressure applying device comprises a screw rod for adjusting pressure, a fixed nut, a pressure adjusting nut, a screw rod fixing device and a pressure distributing device; the screw rod fixing device is a clamp fixed on the base plate; the screw rod is fixed at a U-shaped handle of the clamp of the screw rod fixing device by the fixed nut; the lower end of the screw rod is in contact with the pressure distributing device; the lower surface of the pressure distributing device is in contact with an electrode test part; the pressure measuring device comprises a pressure sensor and a digital pressure gauge which are connected by a signal line; and the single-cell test part is positioned between the pressure distributing device and the pressure sensor. The invention has the characteristics of simple structure, complete function, convenient mass use, simple and convenient assembly and disassembly, high efficiency, no supply of compressed gas or hydraulic device, easy manufacture and low cost and facilitates mass use.
Owner:江苏新源动力有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com