Patents
Literature
472 results about "Light Cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A cell located in the collecting tube of the nephron..
Thin film solar concentrator/collector
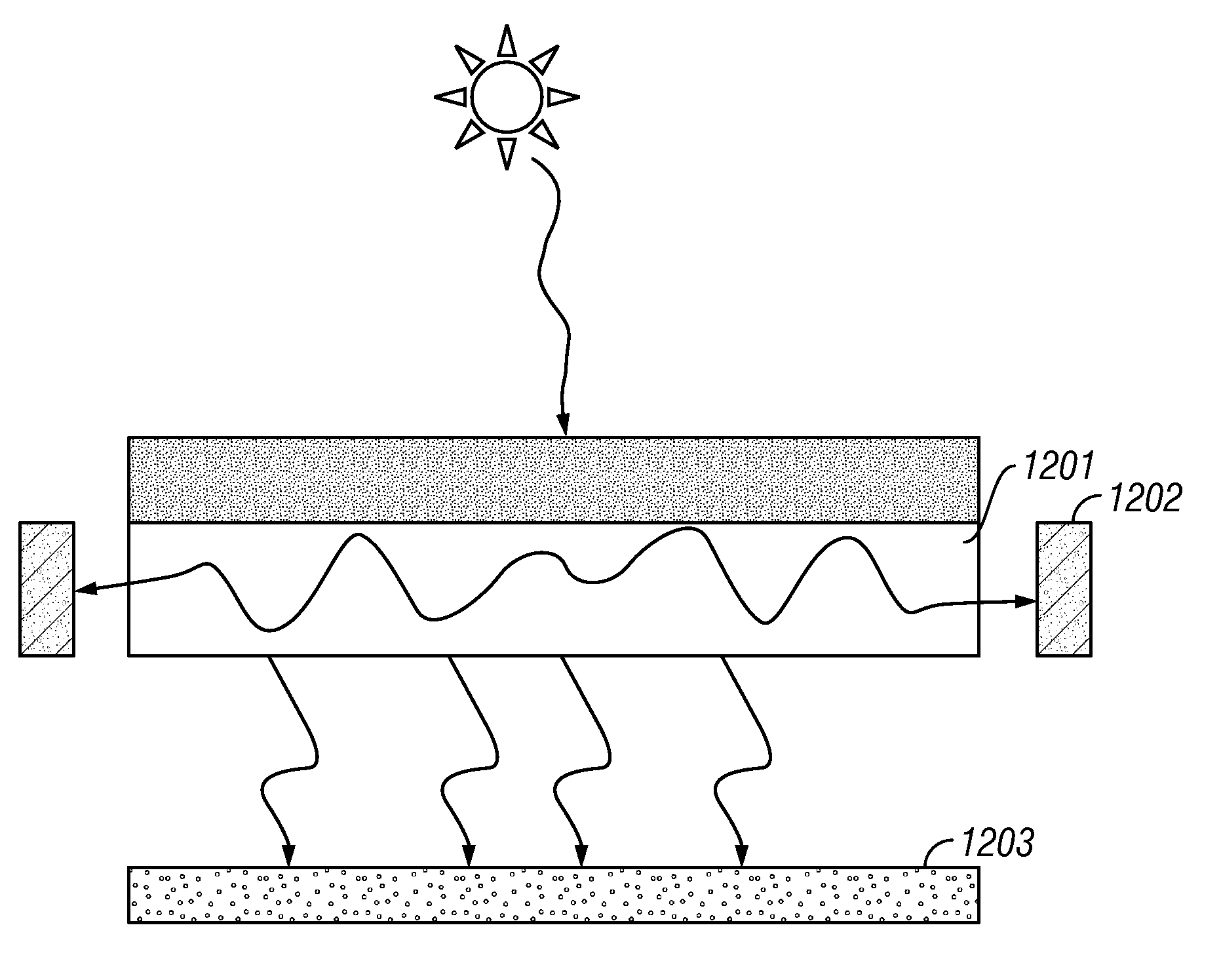
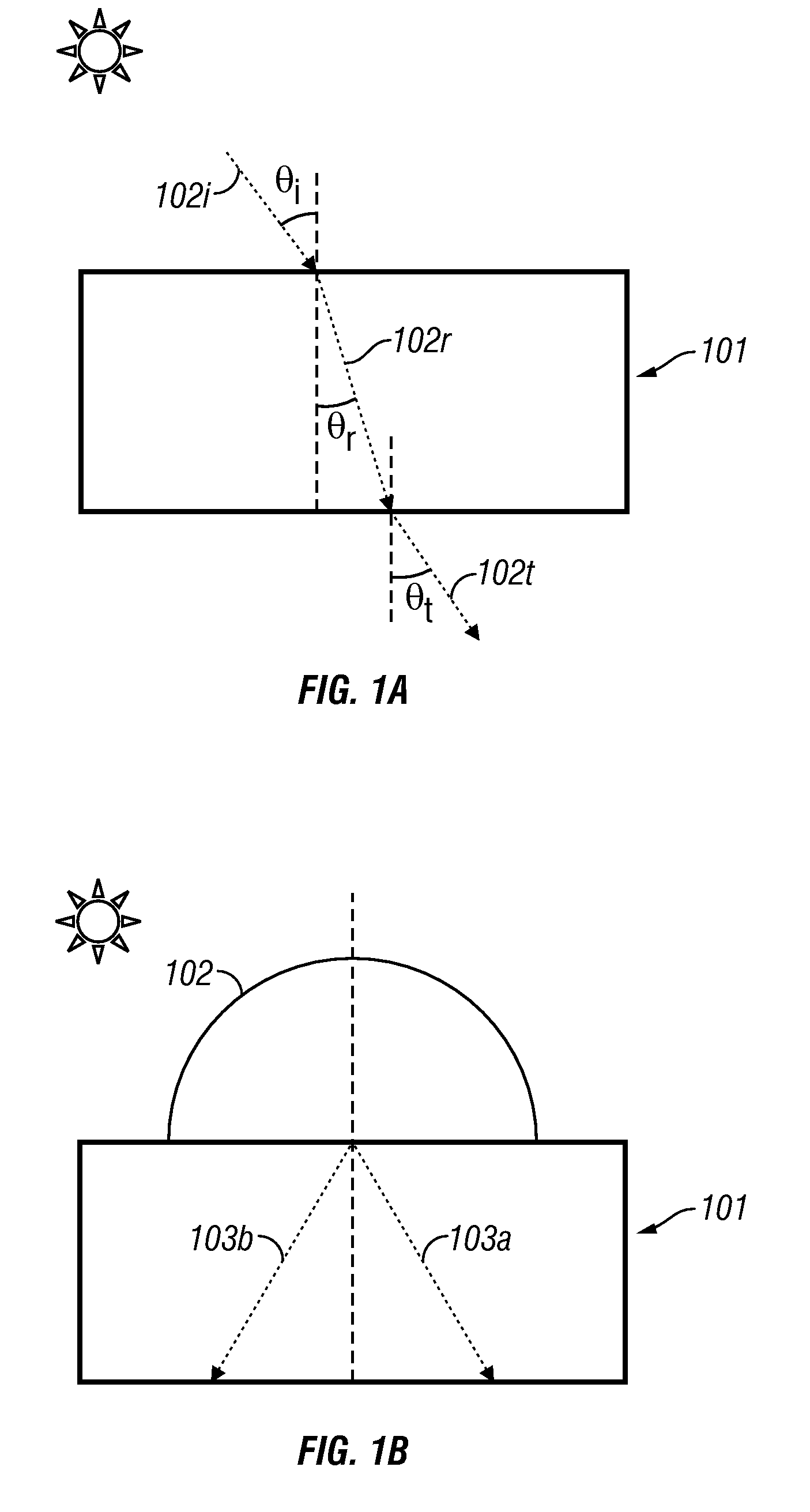
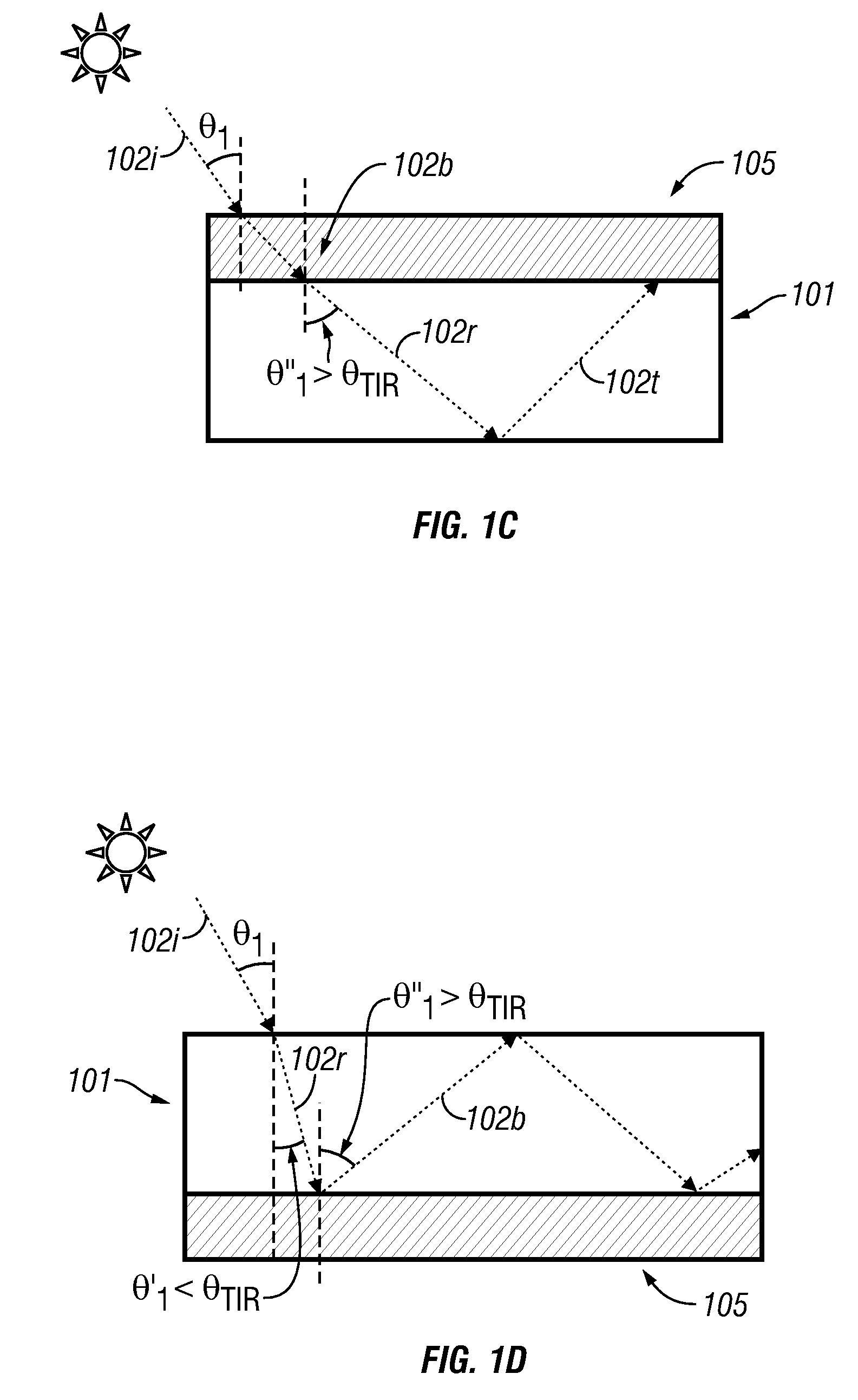
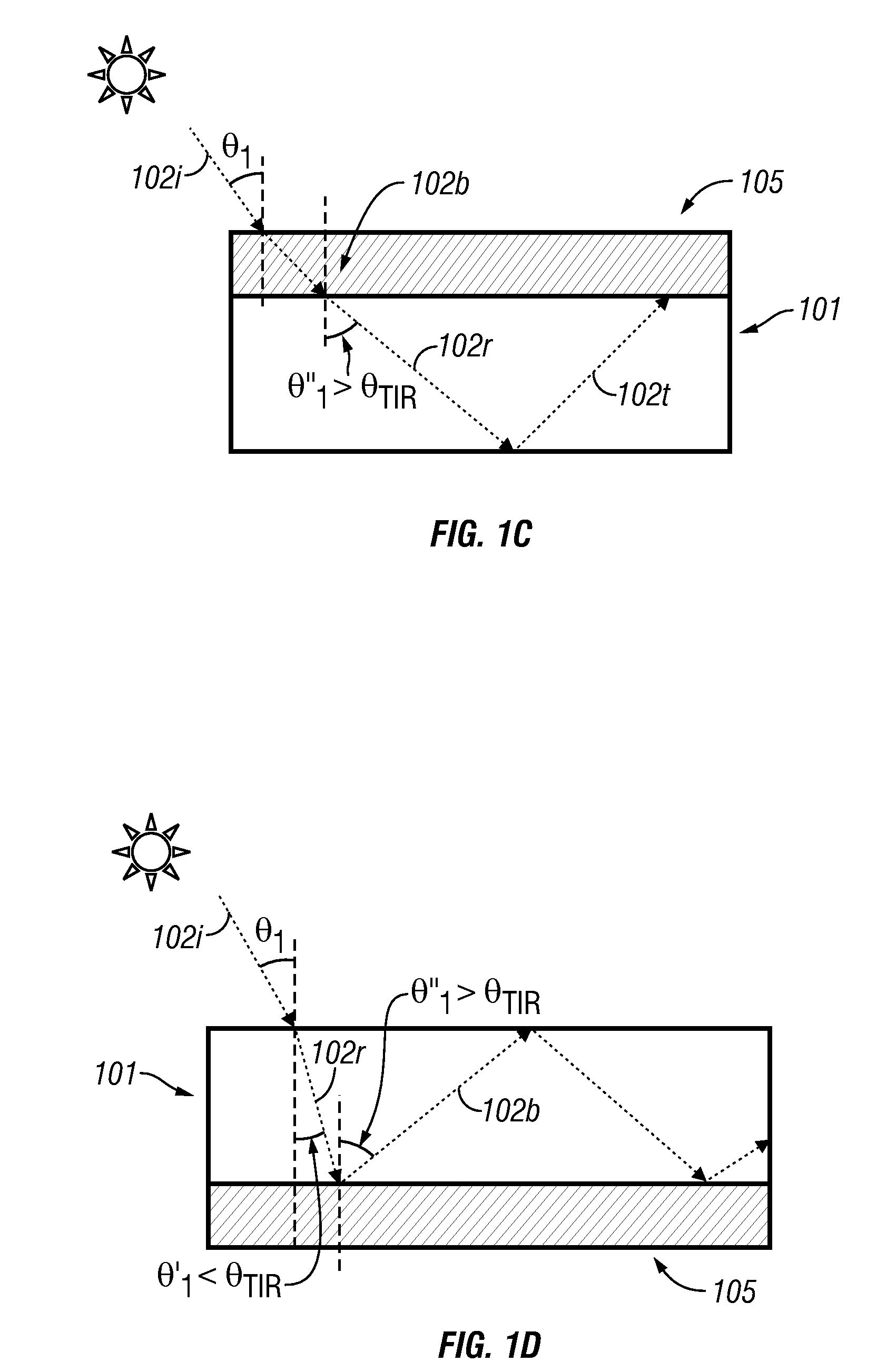
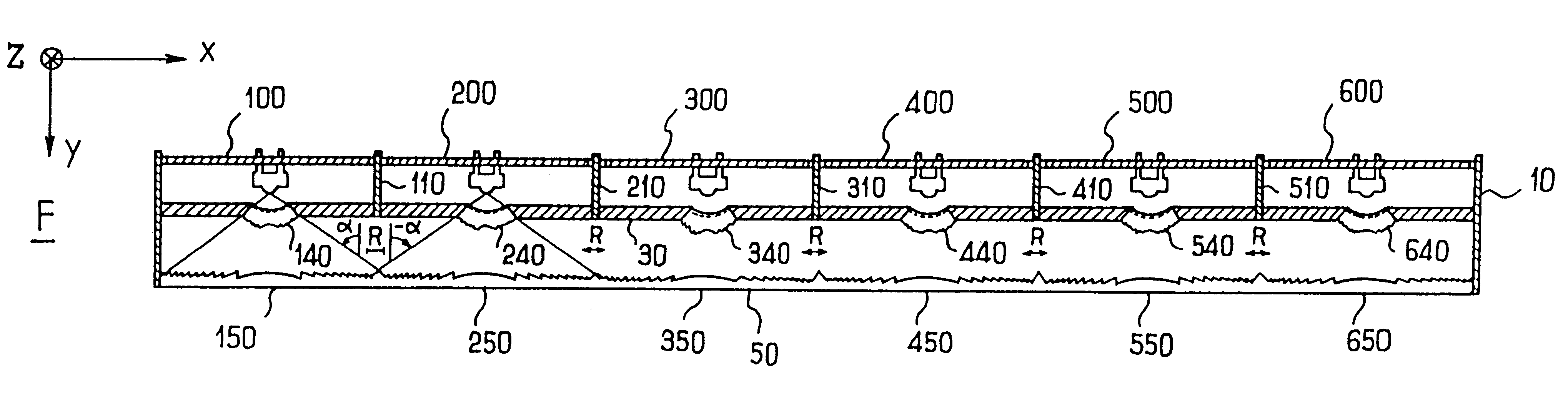
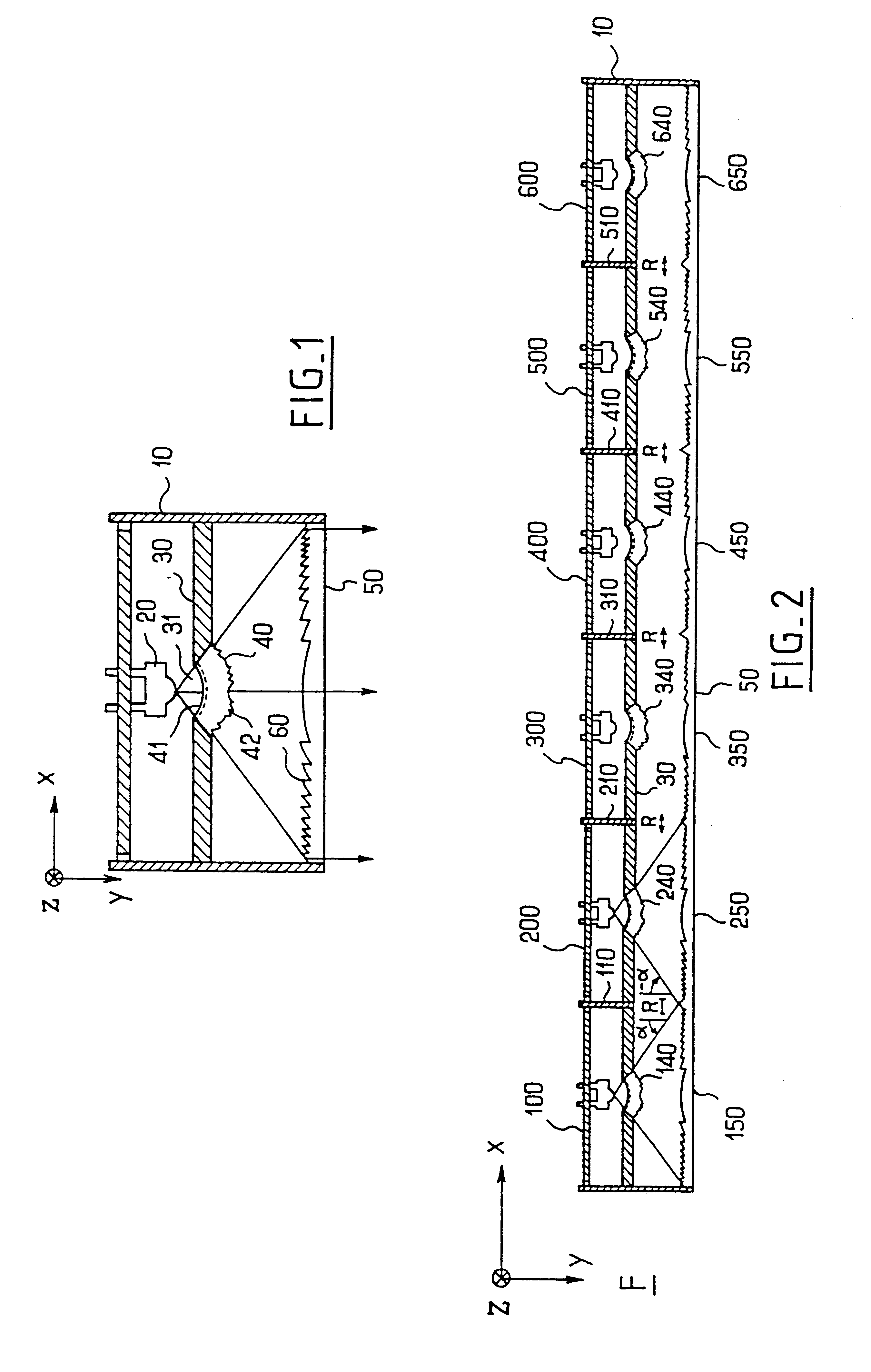
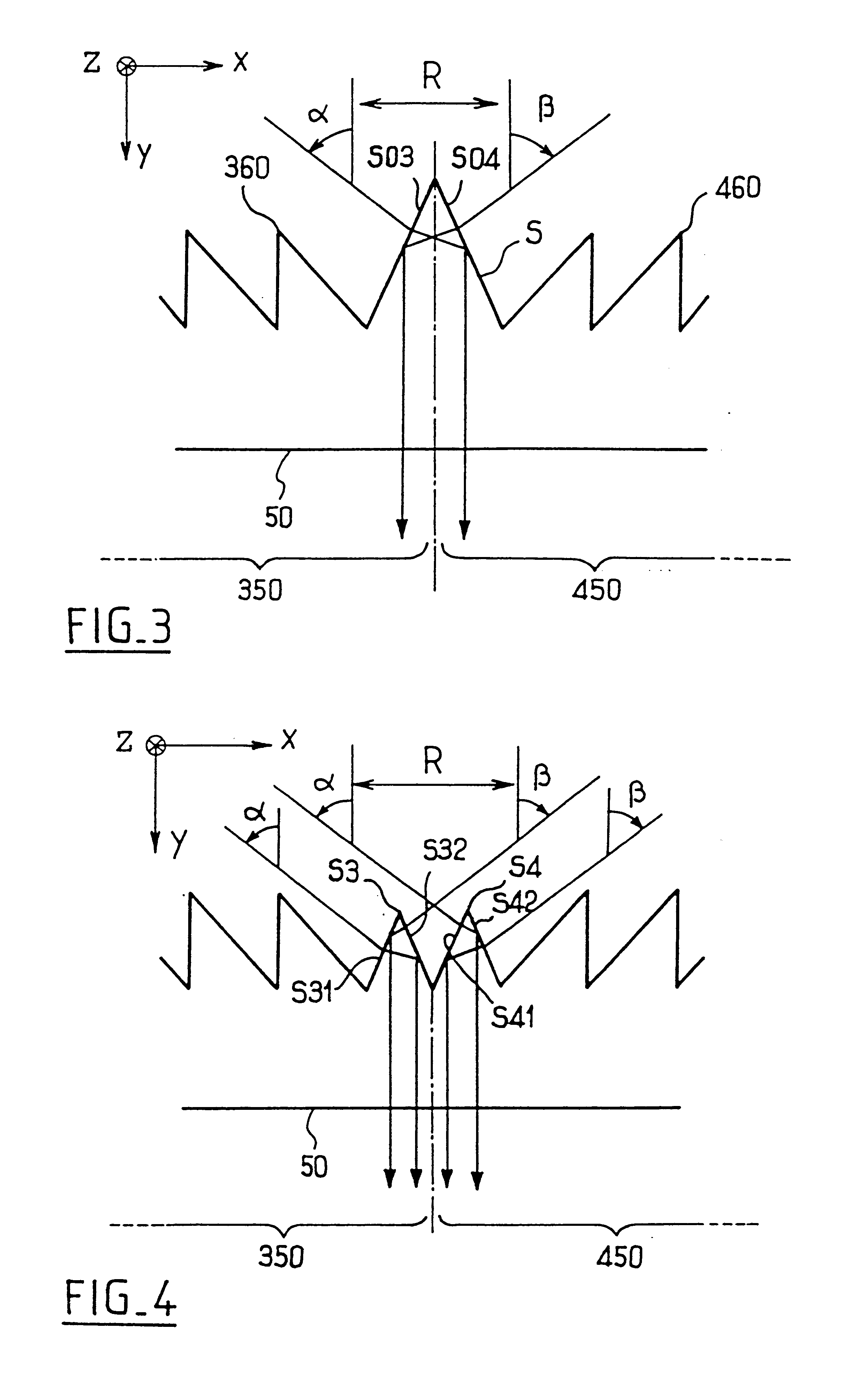
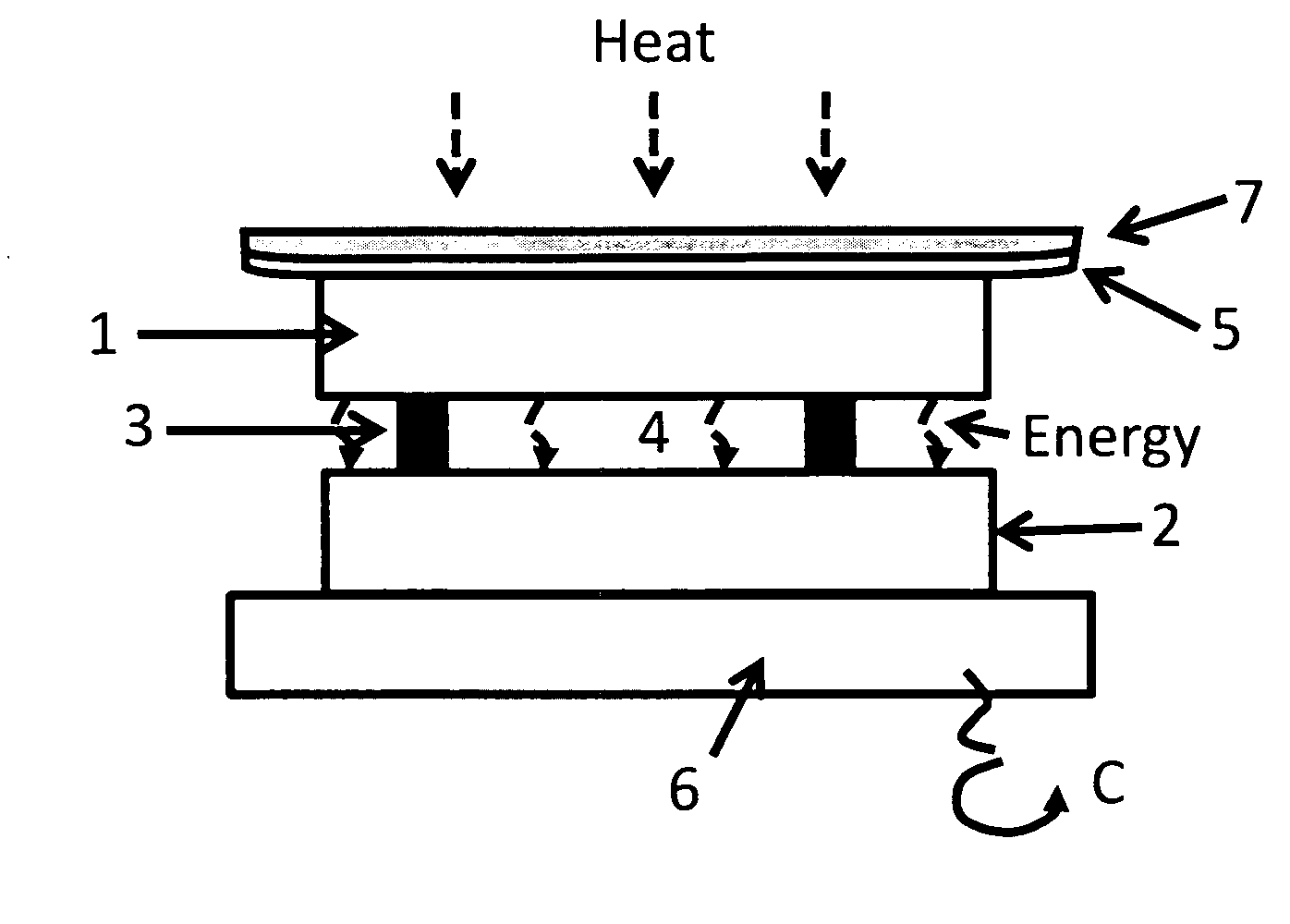
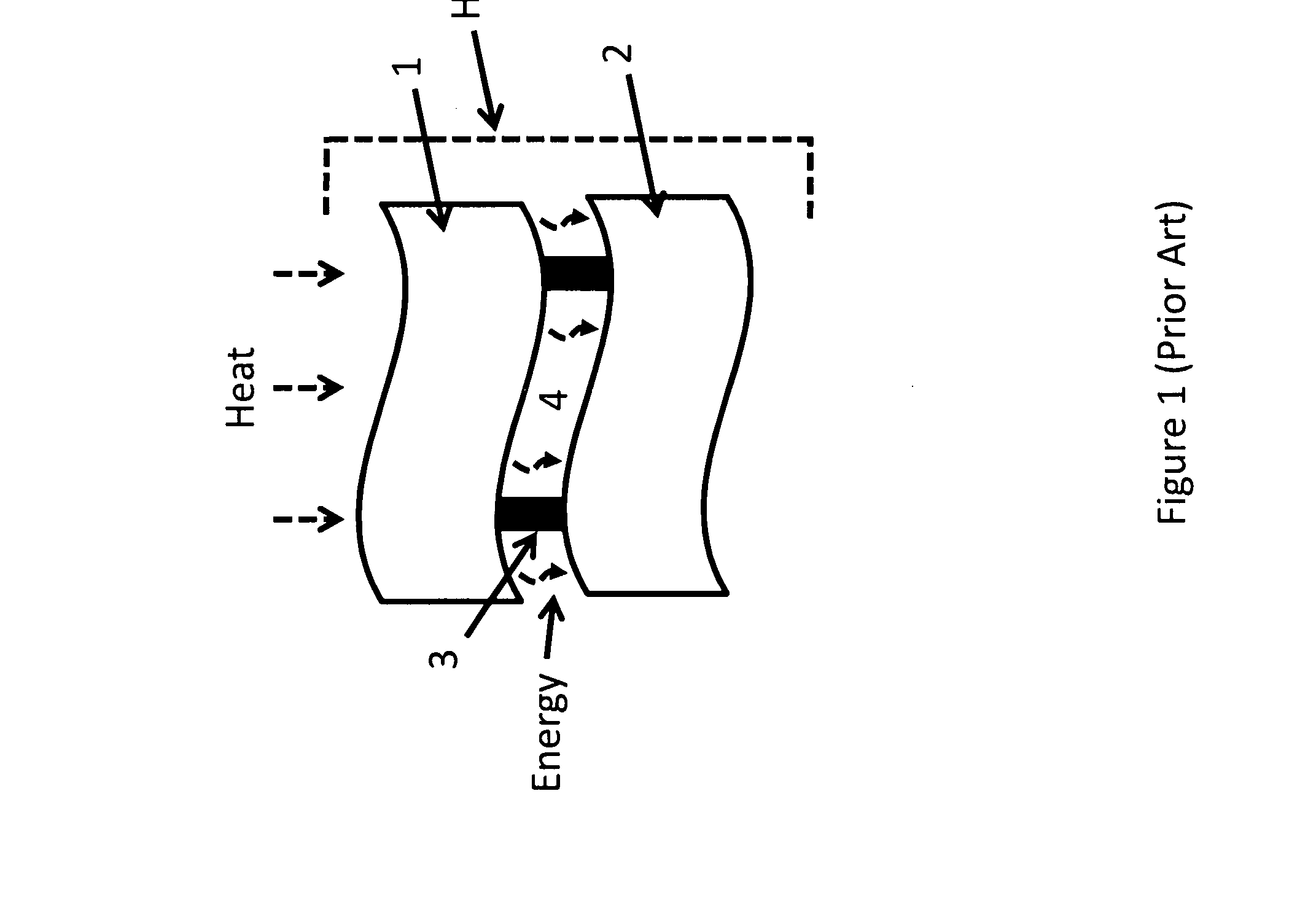
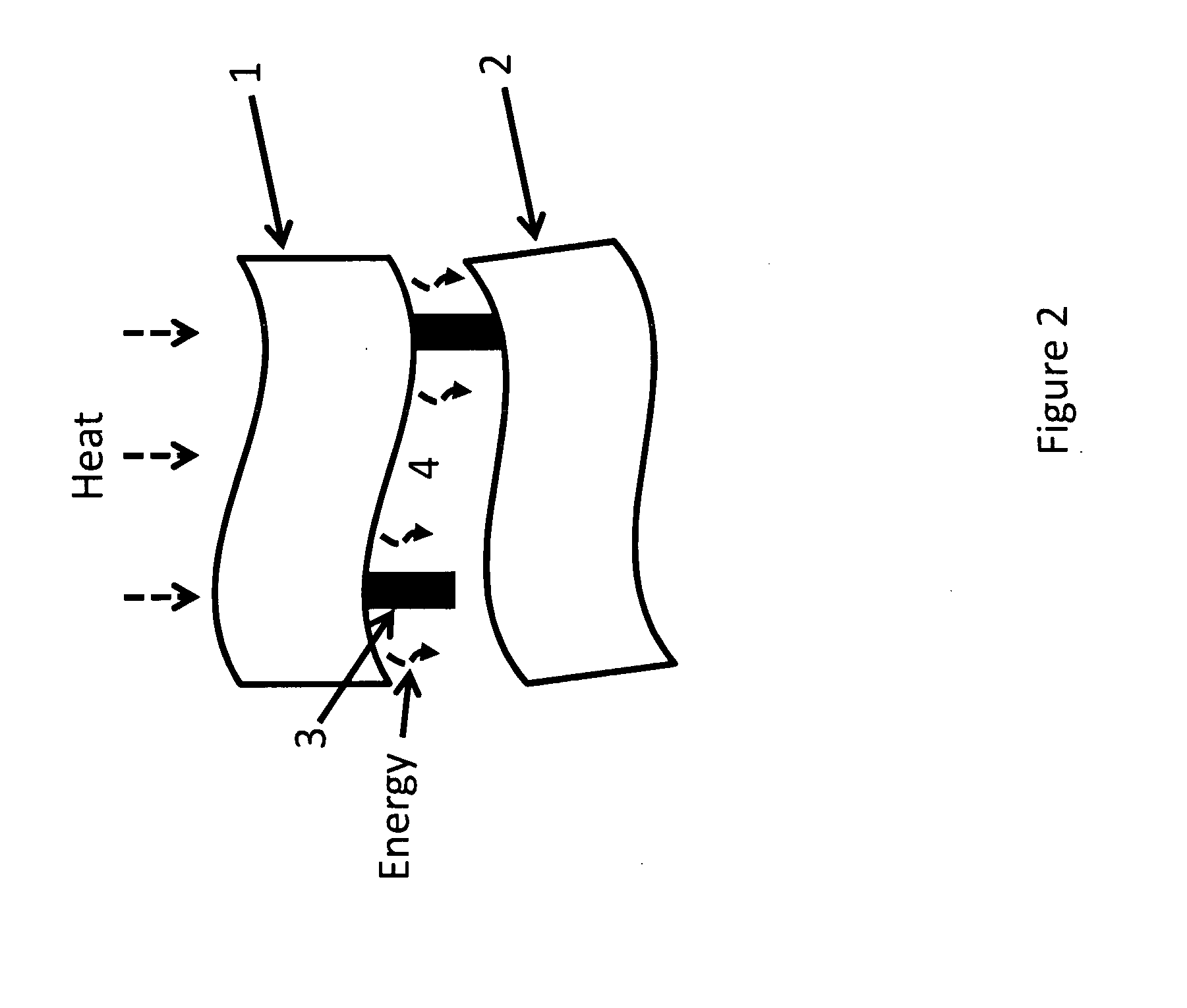
InactiveUS20090126792A1Solar heating energyWave amplification devicesTotal internal reflectionLight guide
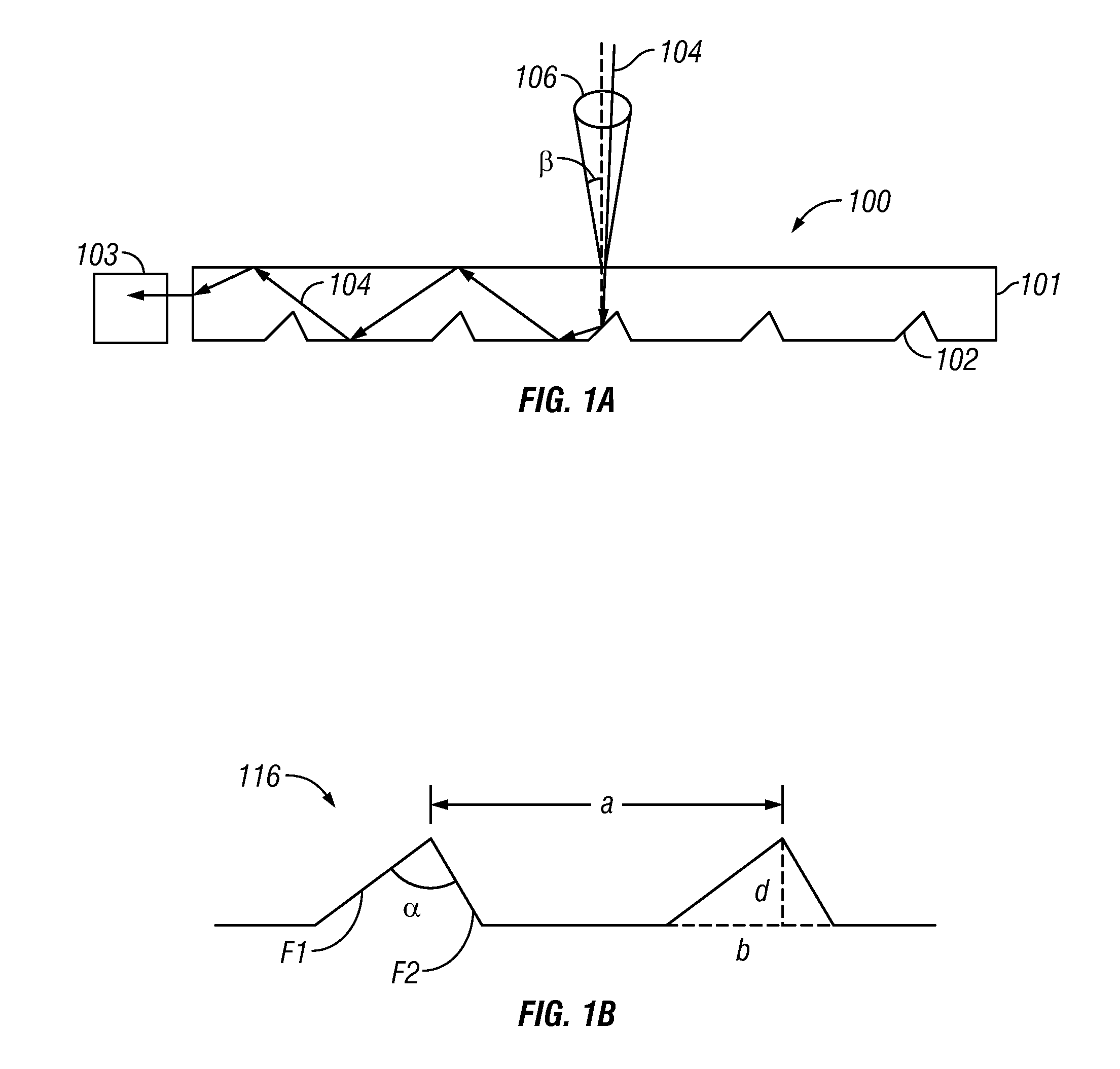
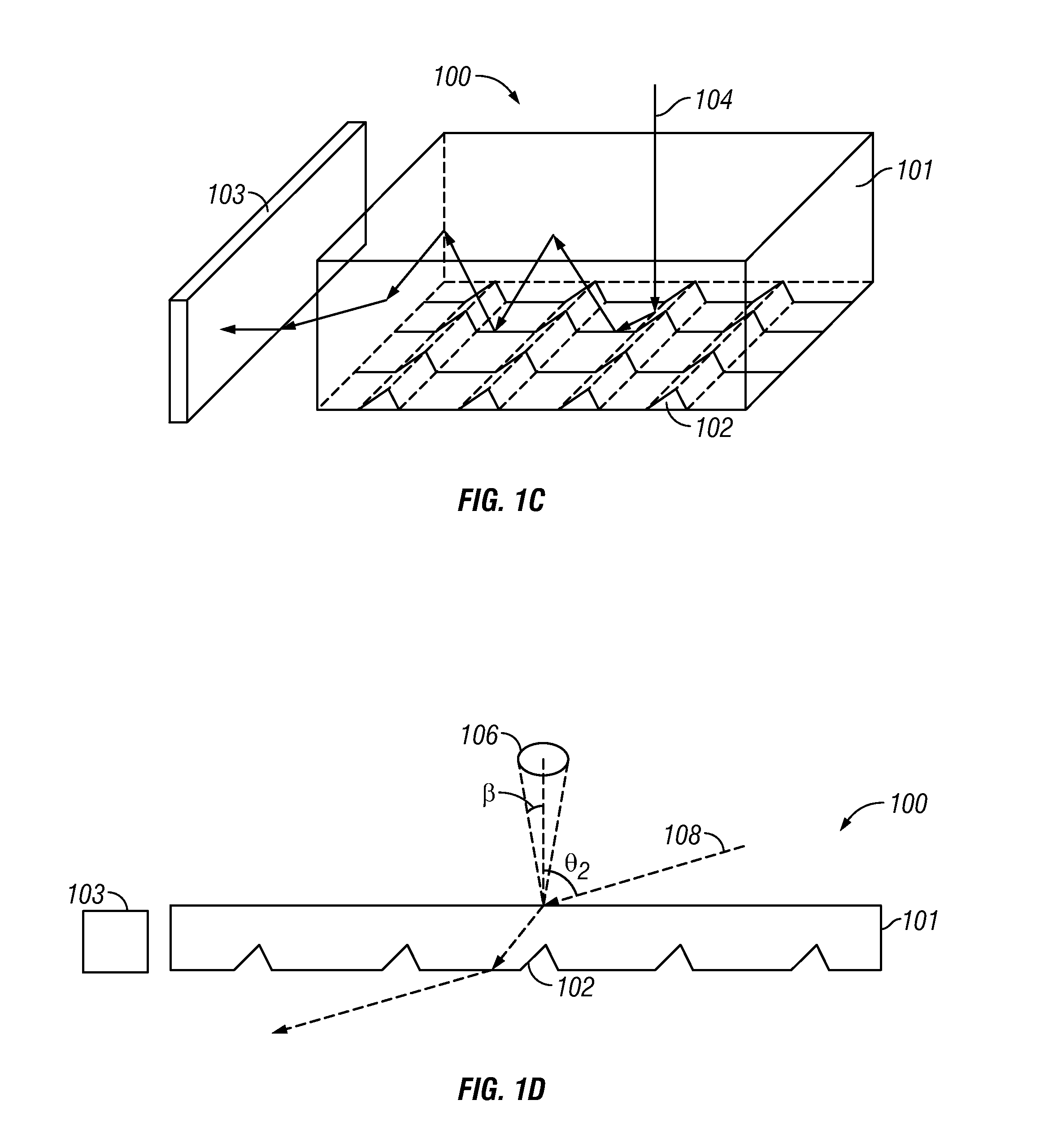
In various embodiments described herein, a device comprising a light guiding layer optically coupled to a photocell is described. A plurality of surface features are formed on one the surface of the light guiding layer. The surface features can comprise facets that are angled with respect to each other. Light incident on the surface of the light guide is redirected by the surface features and guided through the light guide by multiple total internal reflections. The guided light is directed towards a photocell.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
High efficiency multi-active layer tunnel regenerated white light emitting diode
InactiveUS20050067627A1Improved current spreadingEasy to spreadSemiconductor devicesGreen cellSemiconductor materials
A high efficiency and high brightness multi-active layer tunneling regenerated white color semiconductor light emitting diode having a p type electrode 1, a monolithic red light cell 14, a tunnel junction 9, a monolithic green light 15 and blue light cell 16 (or a monolithic cyan light cell 19), wherein each of said cells are electrically connected by tunnel junctions 9, and the red cell physically connected with blue and green cell (or cyan cell) by wafer bonding layer 8. The lights from each cell synthesize white color light. The white light emitting diode only has one time optical-electrical conversion, so the quantum efficiency is high. Moreover, the white LED totally made from semiconductor materials, the lifetime of the white LED lamp is not limited by the relatively short lifetime of fluorescent material.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Tandem cell for water cleavage by visible light
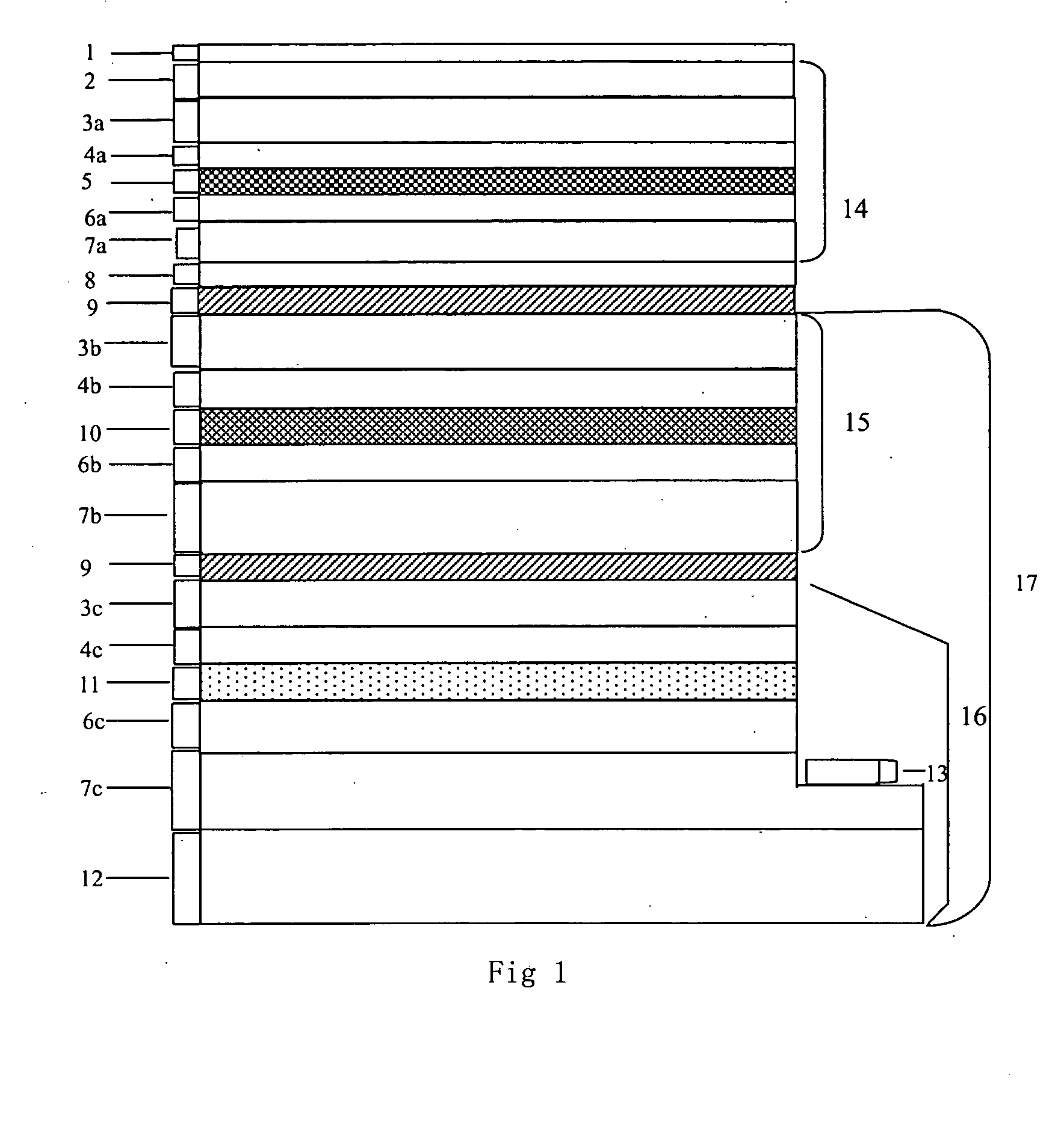
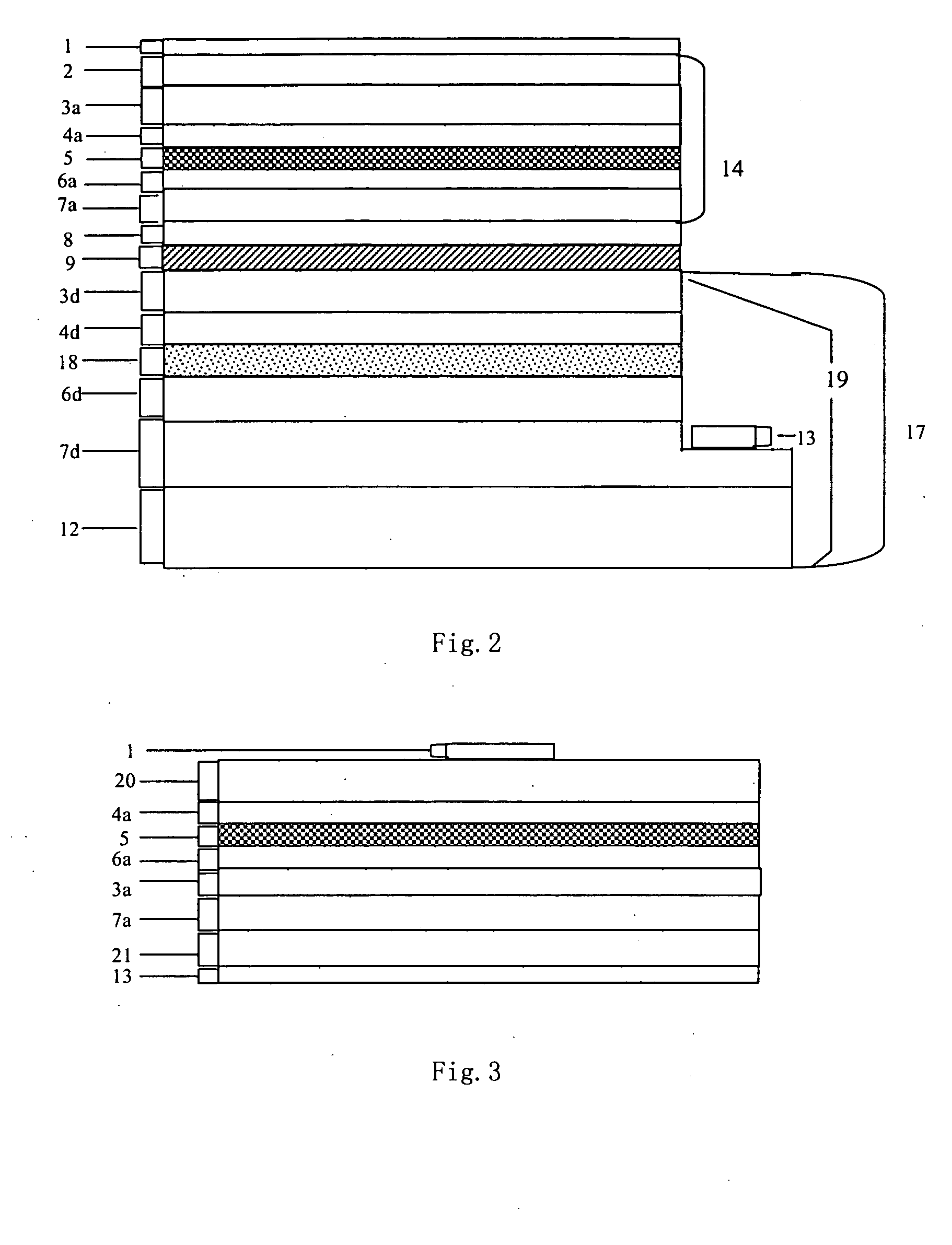
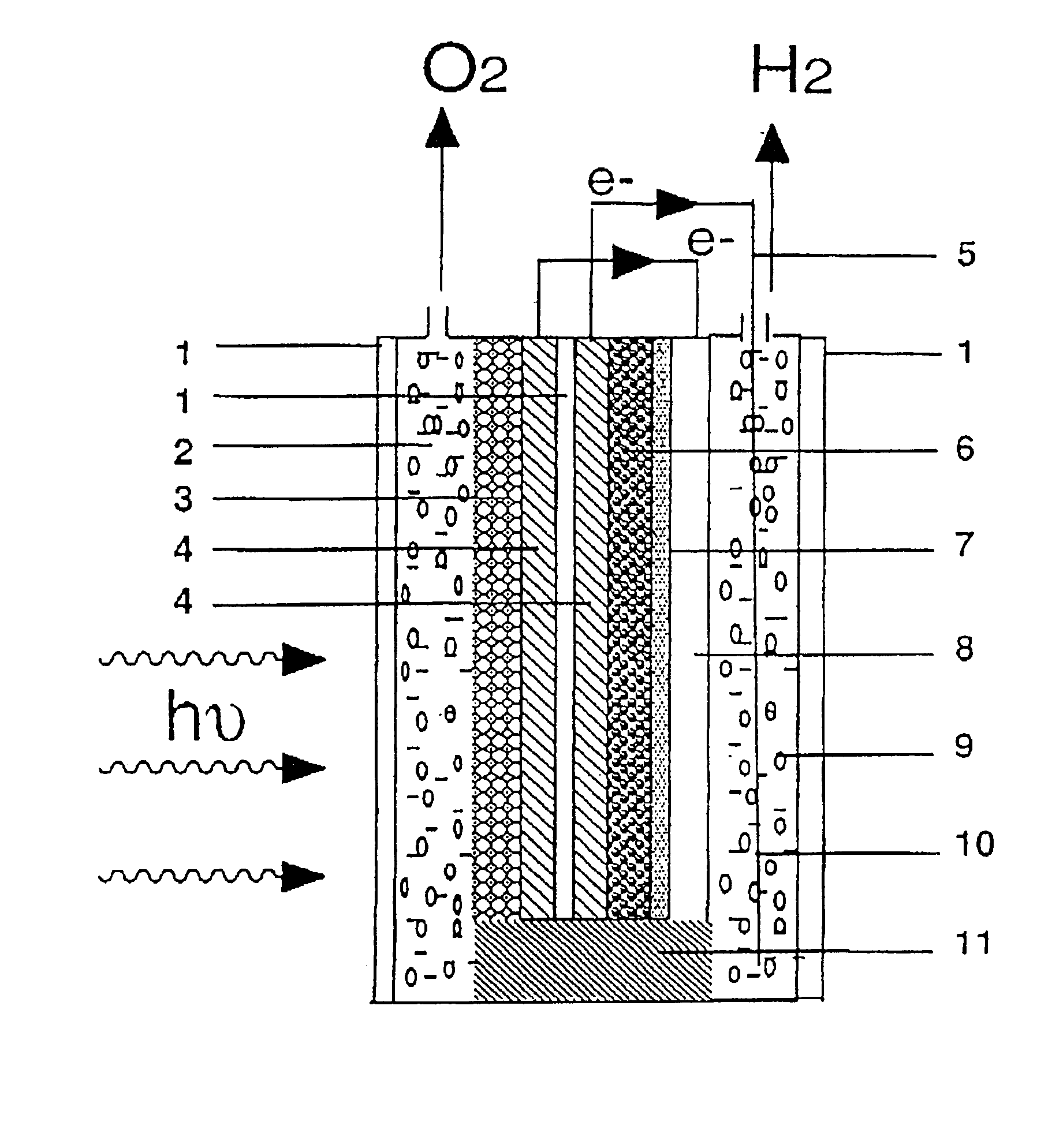
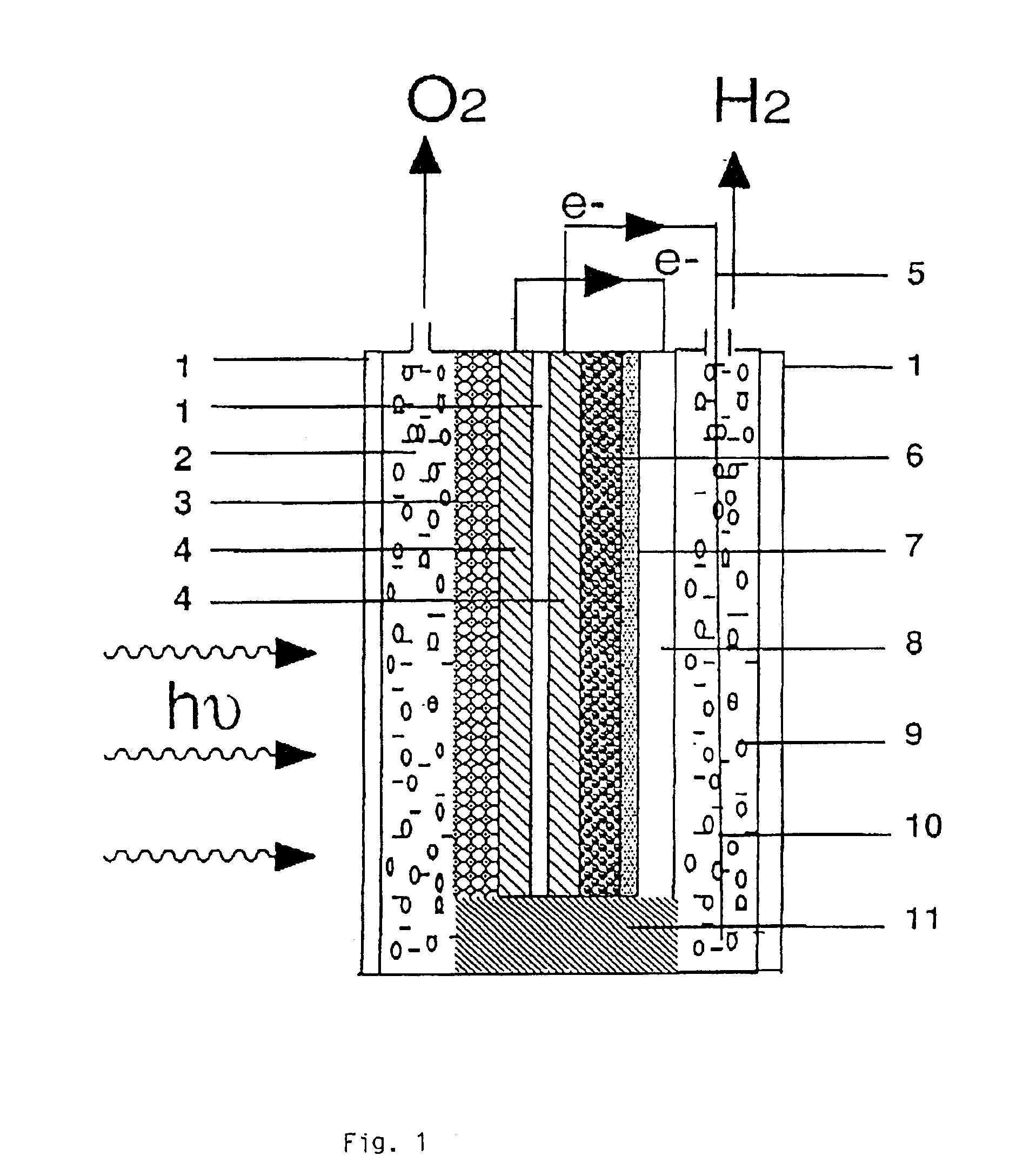
A tandem cell or photoelectrochemical system for the cleavage of water to hydrogen and oxygen by visible light has two superimposed photocells, both cells being connected electrically. The photoactive material in the top cell is a semiconducting oxide placed in contact with an aqueous solution. This semiconducting oxide absorbs the blue and green part of the solar emission spectrum of a light source or light sources and generates with the energy collected oxygen and protons from water. The not absorbed yellow and red light transmits the top cell and enters a second photocell, the bottom cell, which is mounted, in the direction of the light behind, preferably directly behind the top cell. The bottom cell includes a dye-sensitized mesoporous photovoltaic film. The bottom cell converts the yellow, red and near infrared portion of the sunlight to drive the reduction of the protons, which are produced in the top cell during the photo catalytic water oxidation process, to hydrogen.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Color-tuned volumetric light using high quantum yield nanocrystals
ActiveUS7235792B2Good colorAffects colorOptical radiation measurementElectric circuit arrangementsQuantum yieldDisplay device
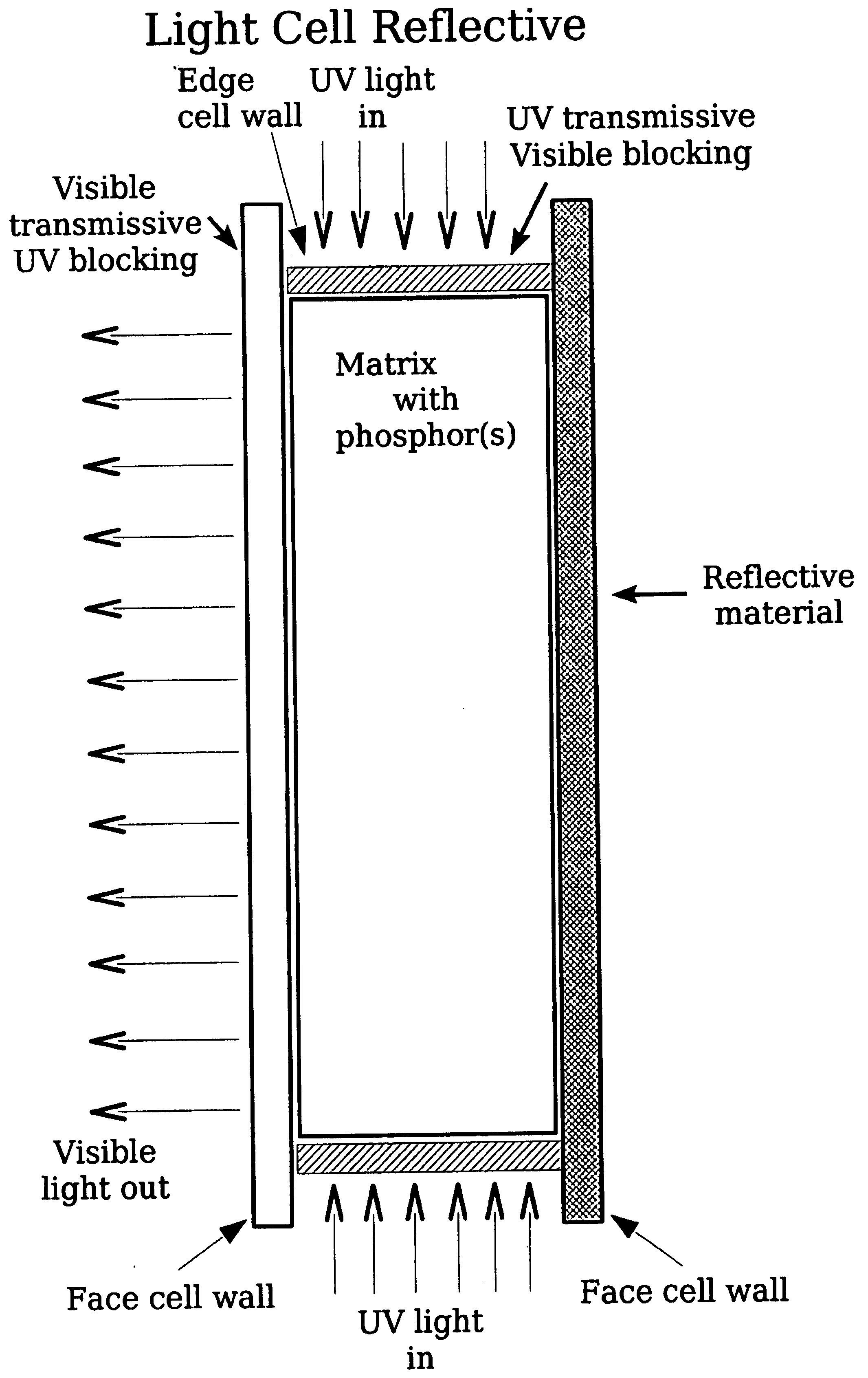
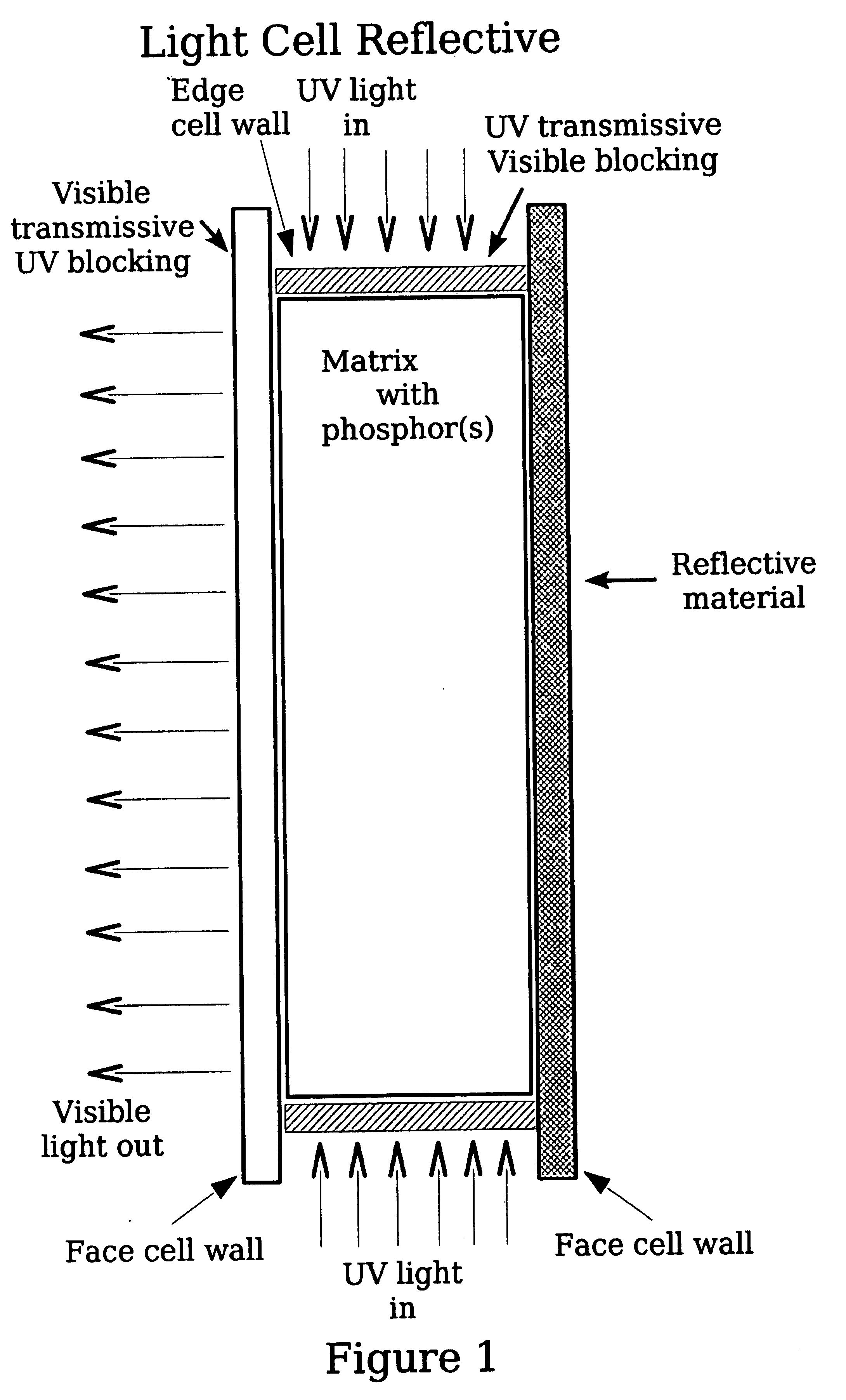
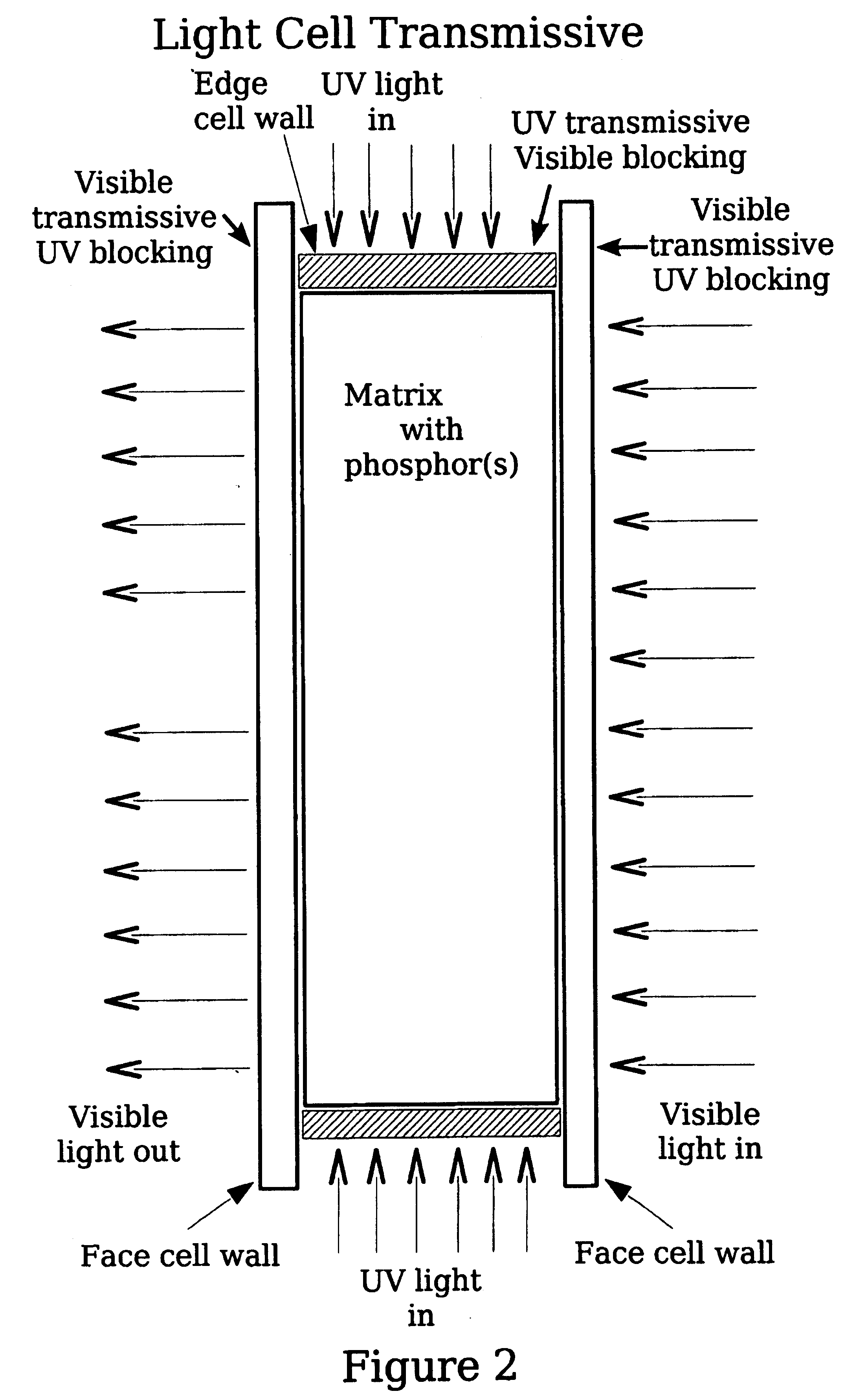
A light source of coaxially stacked volumetric light cells that can be used either in a lamp or a display. Each light cell is composed of high quantum yield nanocrystals in a silica aerogel matrix that is excited by a controlled ultraviolet light source. From these stacked cell assemblies visible light is emitted of a desired color or color temperature and brightness.
Owner:ELOFSON CARL SCOTT
Thin film holographic solar concentrator/collector
InactiveUS20090199893A1High diffraction efficiencyImprove efficiencySolar heating energyPV power plantsTotal internal reflectionLight Cell
In various embodiments described herein, a device comprising a light collector optically coupled to a photocell is described. The device further comprises a light turning film or layer comprising volume or surface diffractive features or holograms. Light incident on the light collector is turned by volume or surface diffractive features or holograms that are reflective or transmissive and guided through the light collector by multiple total internal reflections. The guided light is directed towards a photocell. In various embodiments, the light collector is thin (e.g., less than 1 millimeter) and comprises, for example, a thin film. The light collector may be formed of a flexible material.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Method for signalling the presence of prey in traps for vermin and device for carrying out this method
A method and a device for automatically detecting and signaling the presence of prey caught in a trap. The trap has inlet ports equipped with a one-way inlet mechanism such that once a rodent has passed a central point the rodent is contained within the trap. After the rodent has passed the central point, the trap is reset to the start position in order to attract additional prey. The trap is provided with a device for signaling the presence of vermin in the trap. The mechanism may be operable via a push button operated by movement of the vermin. Alternatively, means for detecting the rodent may include the use of vertical or horizontally elongated elements that are actuated by the movement of the vermin. A further embodiment includes a photocell, or a sensor, to indicate the presence of rodents. The mechanism for signaling may include lights or sound devices that can be secured to the trap or remotely activated via wired or wireless means. The signaling device can be time delayed such that additional vermin can enter the trap before intervention by the operator and is also capable of monitoring several traps concurrently.
Owner:CRISTOFORI GILBERTO +1
Thin film holographic solar concentrator/collector
InactiveUS20090199900A1Improve efficiencySolar heating energySolar heat devicesElectricityTotal internal reflection
In various embodiments described herein, a device comprising one or more light guides that is optically coupled to one or more photocells is described. The device further comprises one or more light turning films or layers comprising volume or surface diffractive features or holograms. Light incident on the light guides is turned by volume or surface diffractive features or holograms that are reflective or transmissive and guided through the light guides by multiple total internal reflections. The guided light is directed towards the photocells. In certain embodiments, solar energy is also used to power or heat a thermal generator to heat water or produce electricity from steam. Various embodiments may comprise an air gap or an optical isolation layer disposed between the multiple light guides.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Methods and apparatuses for manufacturing geometric multicrystalline cast silicon and geometric multicrystalline cast silicon bodies for photovoltaics
InactiveCN101370969AFinal product manufactureFrom frozen solutionsPolycrystalline siliconCrystalline silicon
Methods and apparatuses are provided for casting silicon for photovoltaic cells and other applications. With such methods and apparatuses, a cast body of geometrically ordered multi-crystalline silicon may be formed that is free or substantially free of radially-distributed impurities and defects and having at least two dimensions that are each at least about 10 cm is provided.
Owner:AMG IDEAL CAST SOLAR
Scent dispenser and method
InactiveUS6050016APrecise positioningReduce usageAnimal huntingInsect catchers and killersToggle switchEngineering
A scent dispenser including a housing and a hook for suspending the dispenser attached to the housing is provided. The housing includes a pair of aligned openings to draw air through the housing and across a scent receptacle. Battery powered circuitry connects a fan to timer circuitry and to a photo cell for control of the fan during scent dispersion. An LED is provided to indicate the operating status of the device while a toggle switch provides manual on / off control.
Owner:COX LARRY R
System and method of light spot position and color detection
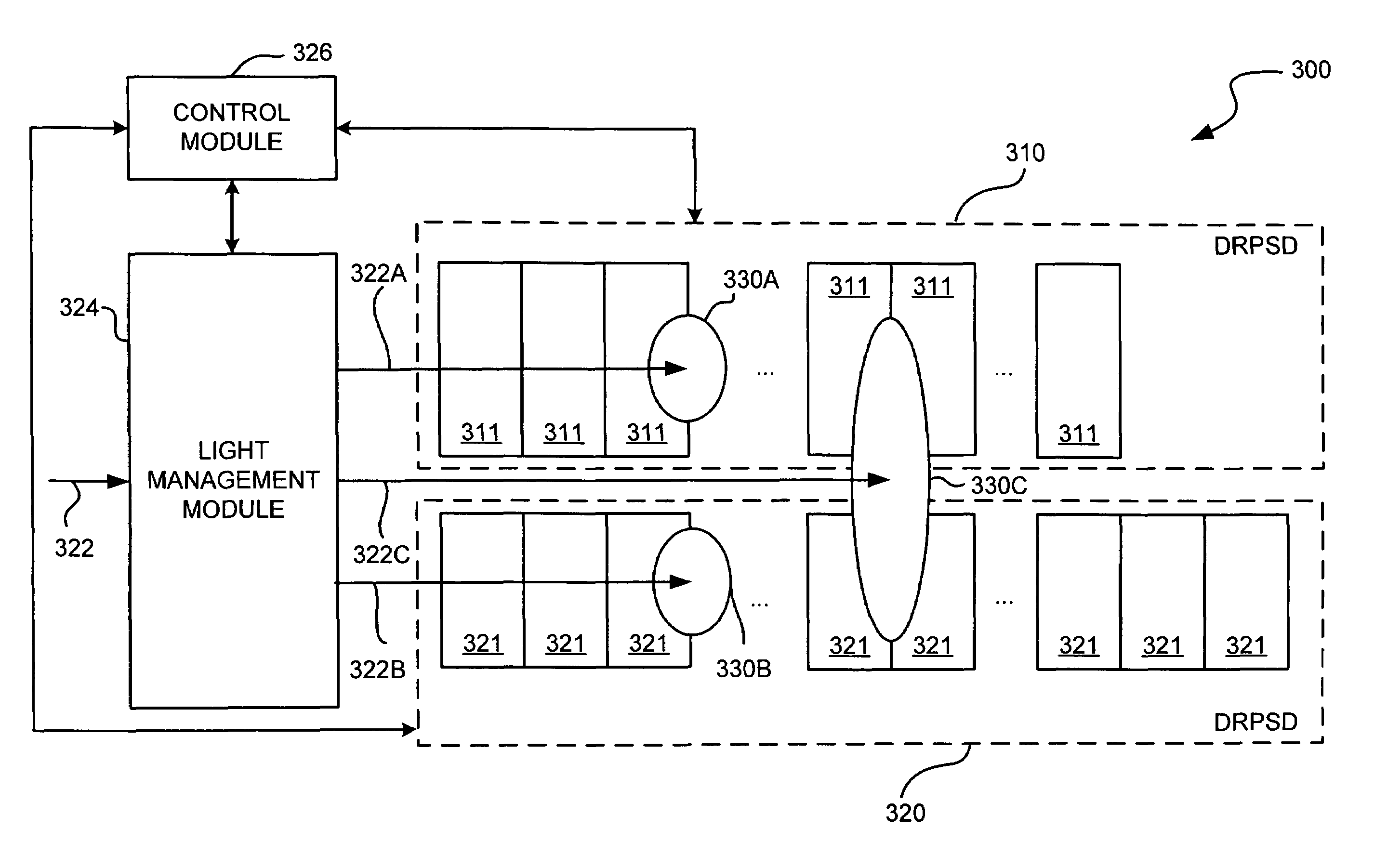
A position and color detection sensor (for detecting a position of a light spot in a light distribution that can include stray light components, e.g. from other lasers, ambient lighting etc.) includes two discrete response position sensitive detectors (DRPSDs). The first DRPSD is used to calculate a raw estimate of the spot position and the second DRPSD is used to calculate the actual spot position based on information from the first DRPSD. Color is supported by further dividing each pixel of the first DRPSD into elementary photocells, each one covered with an appropriate optical filter. The use of two DRPSDs differing in pixel geometries makes them suitable for integration on the same chip using the same process. This reduces production and alignment costs. Further, analogue microelectronic processes can be used for color filter deposition and simple optics can be used for beam splitting and shaping.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA +1
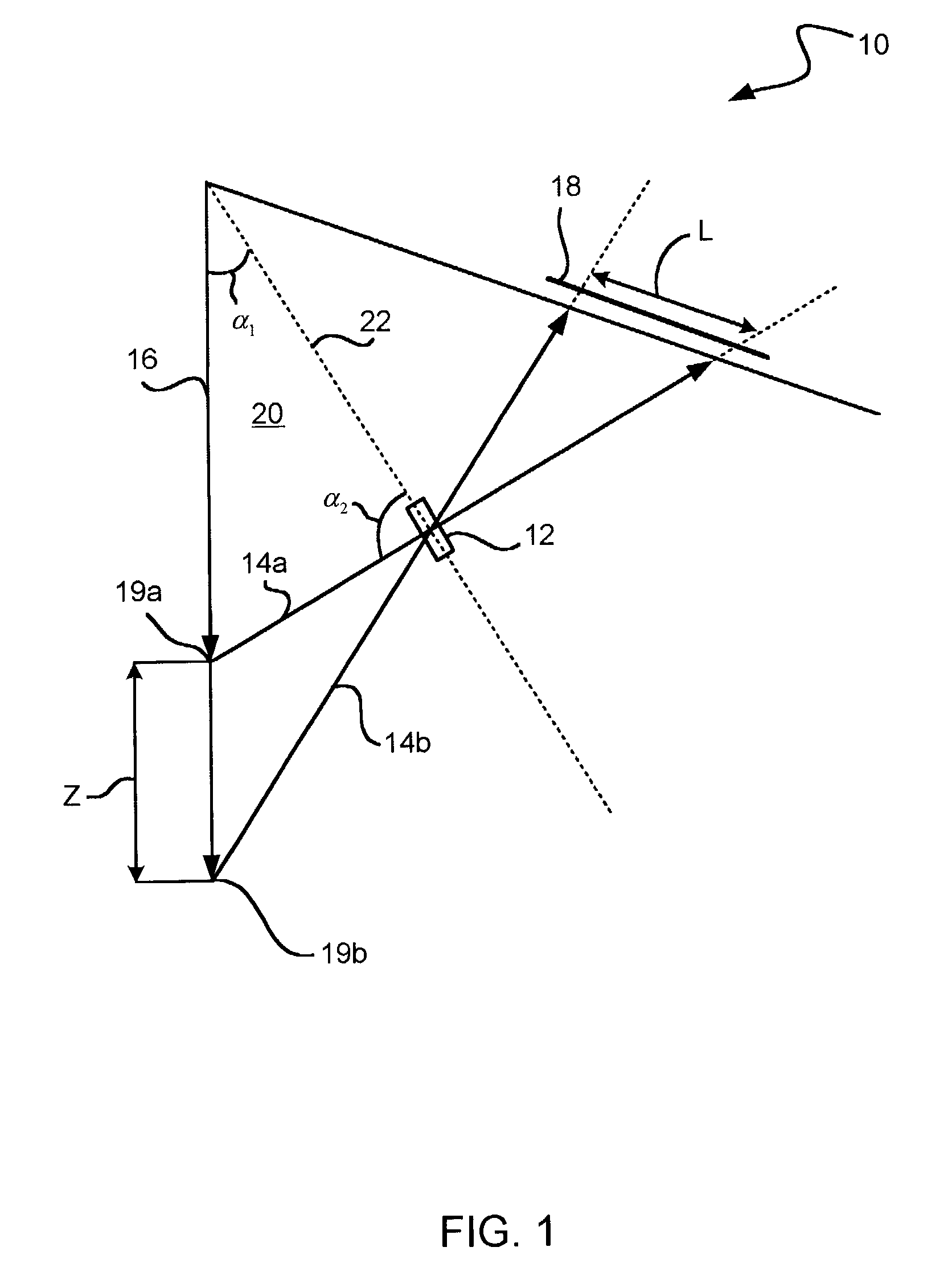
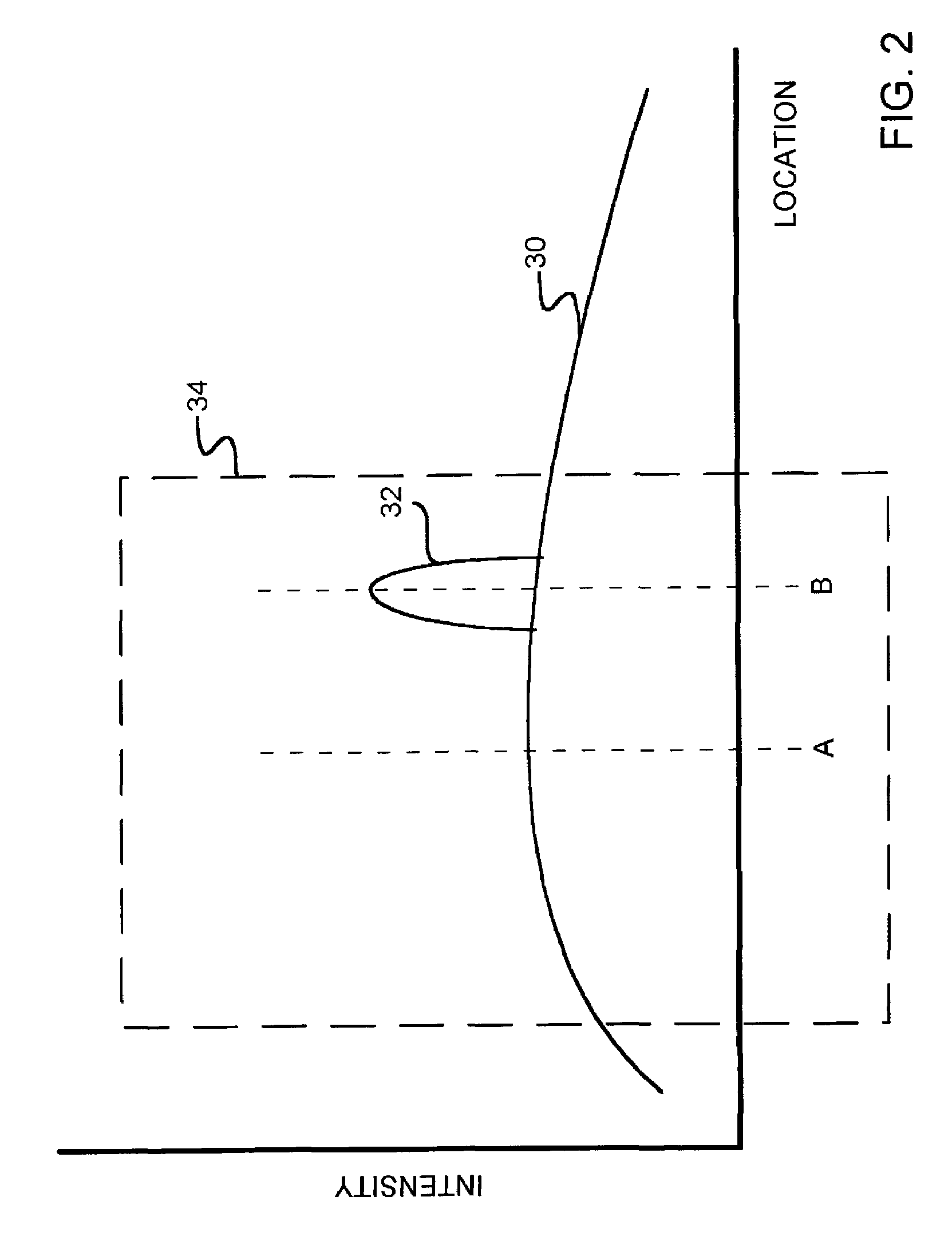
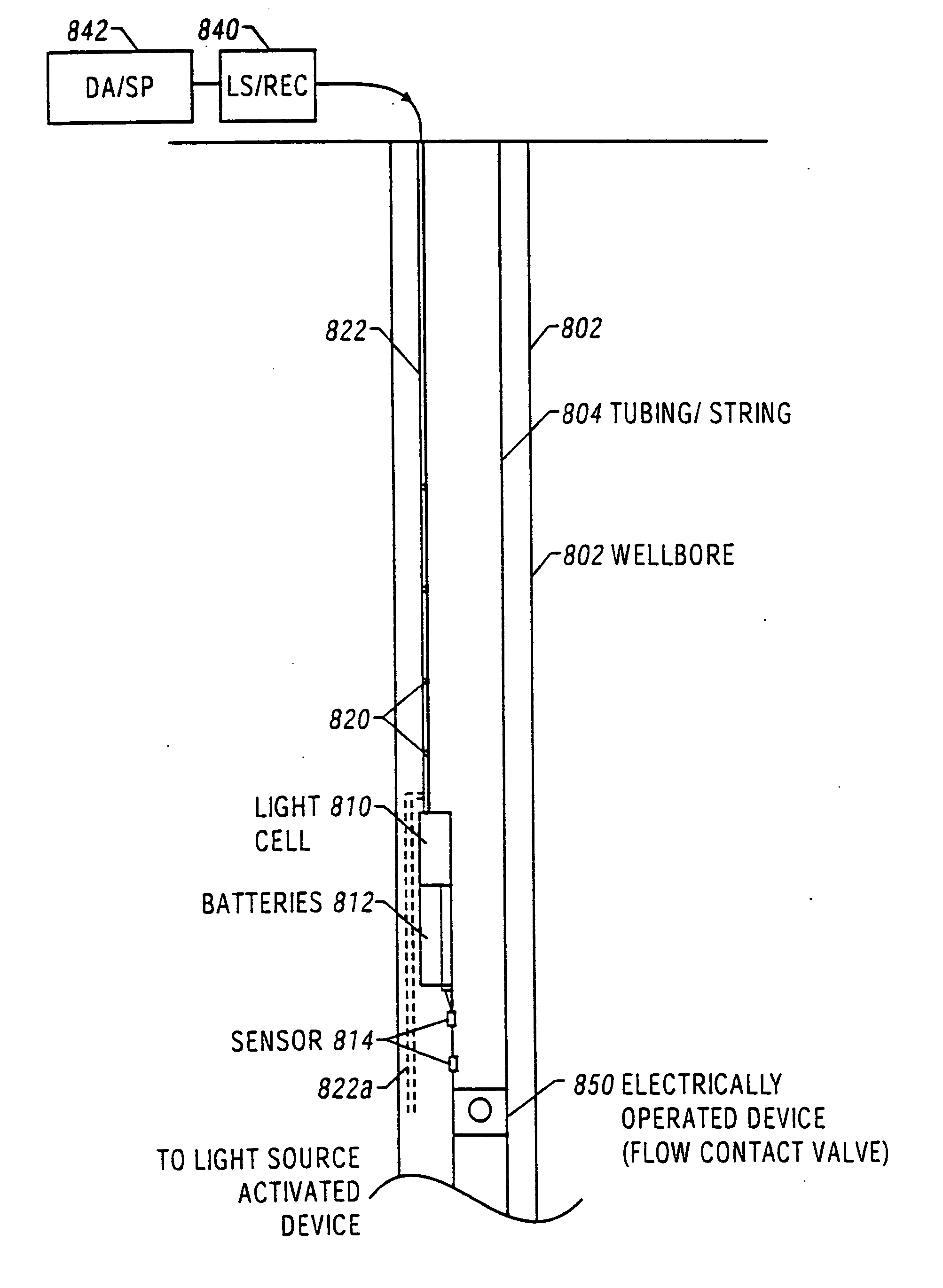
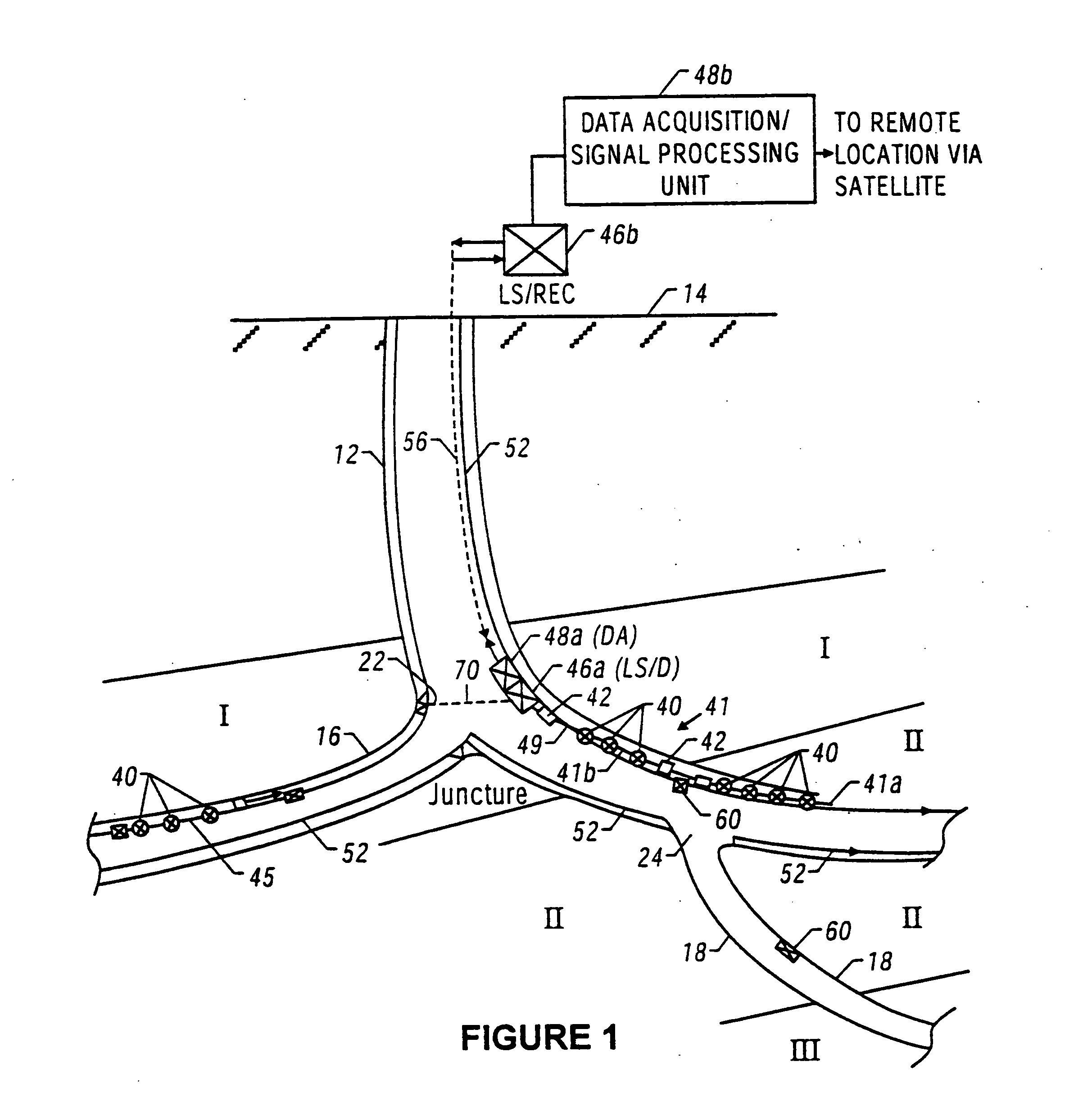
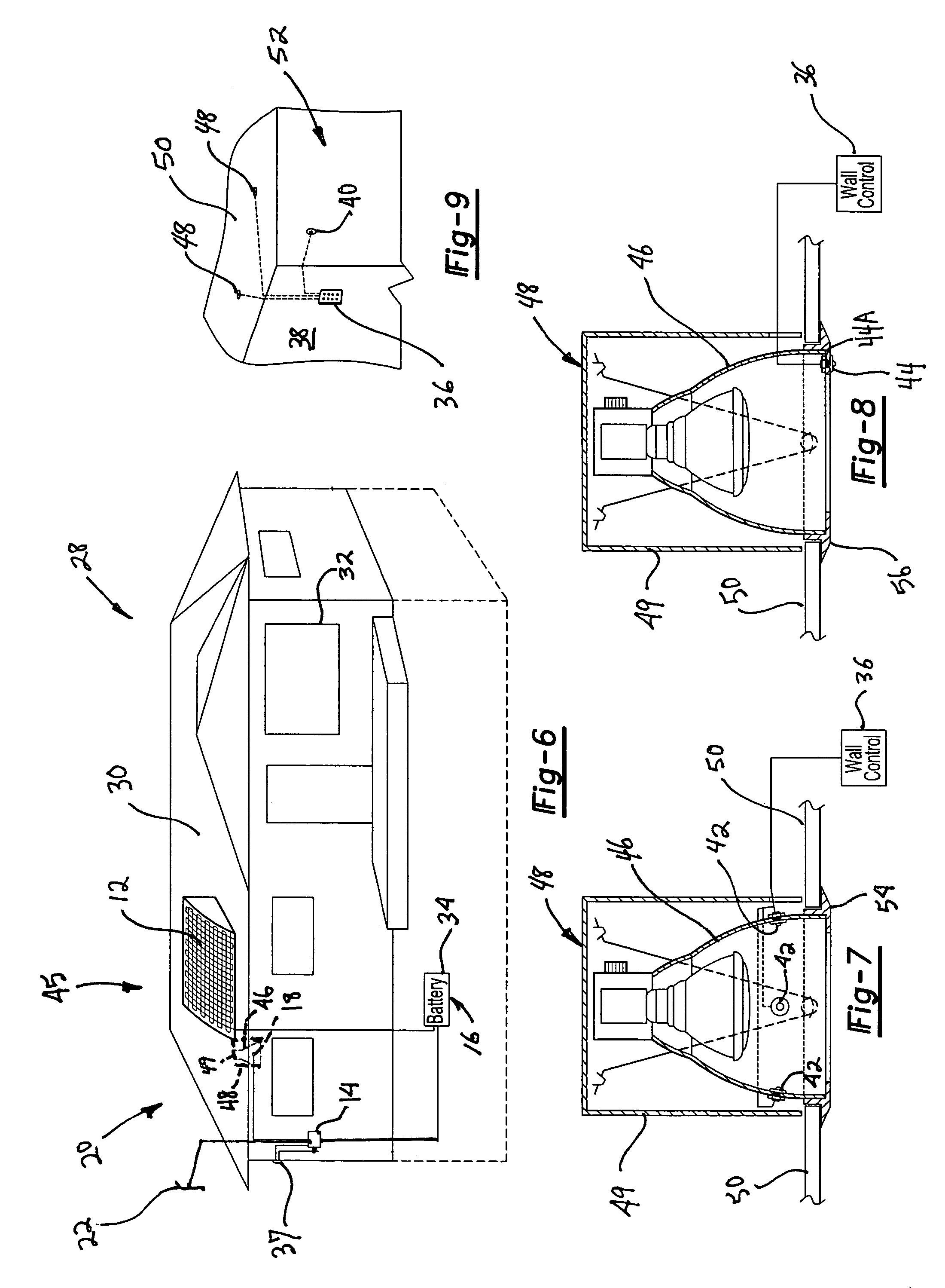
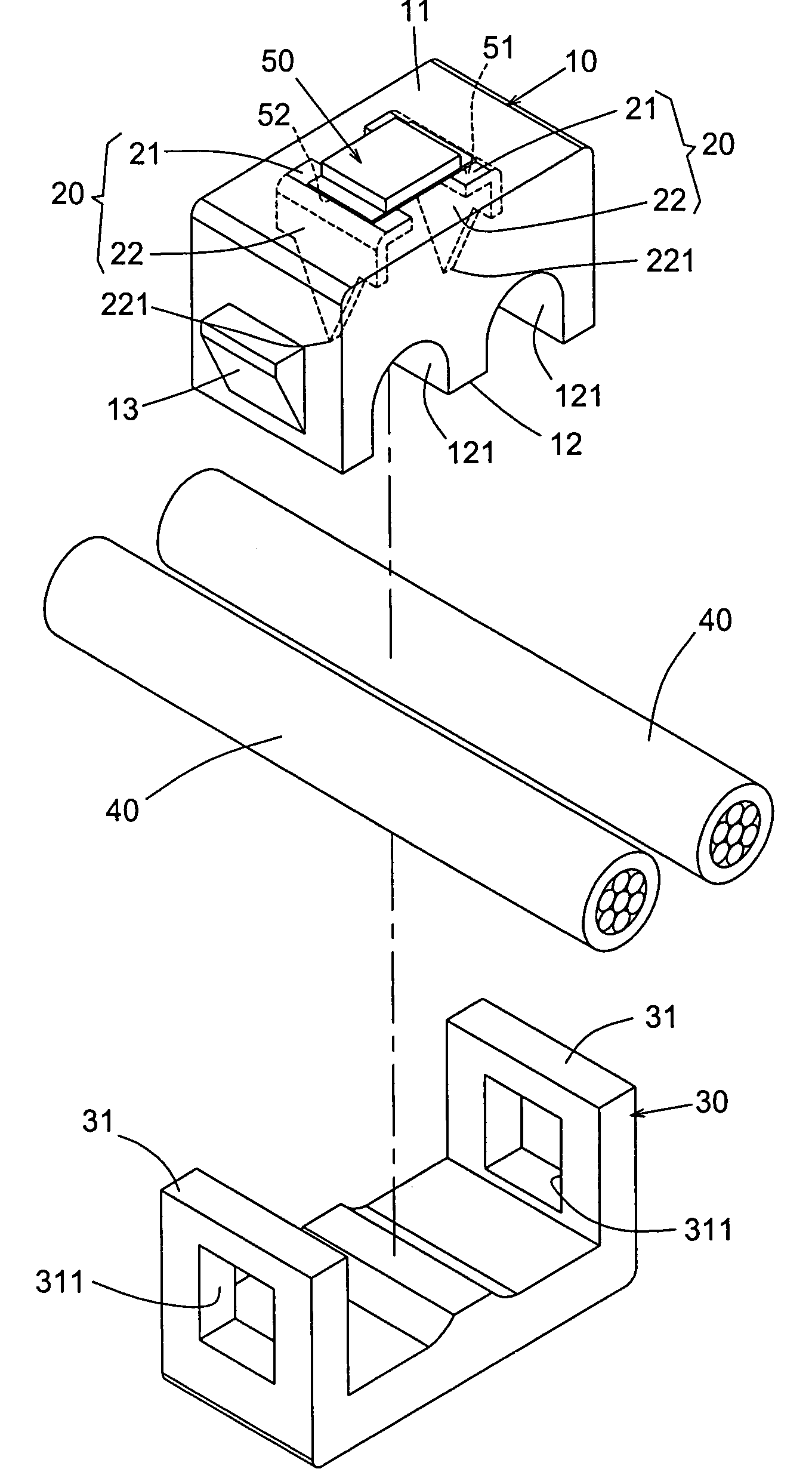
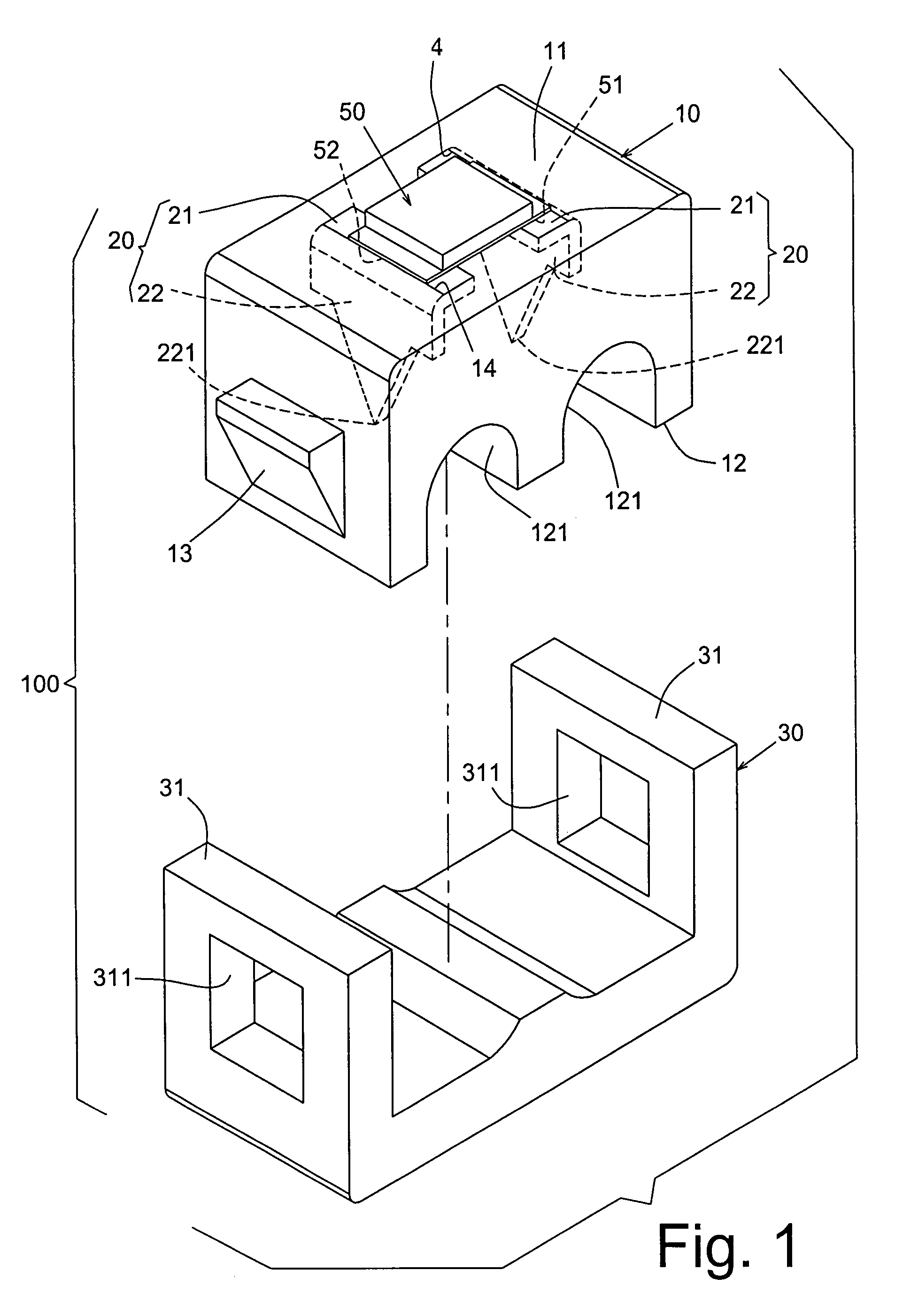
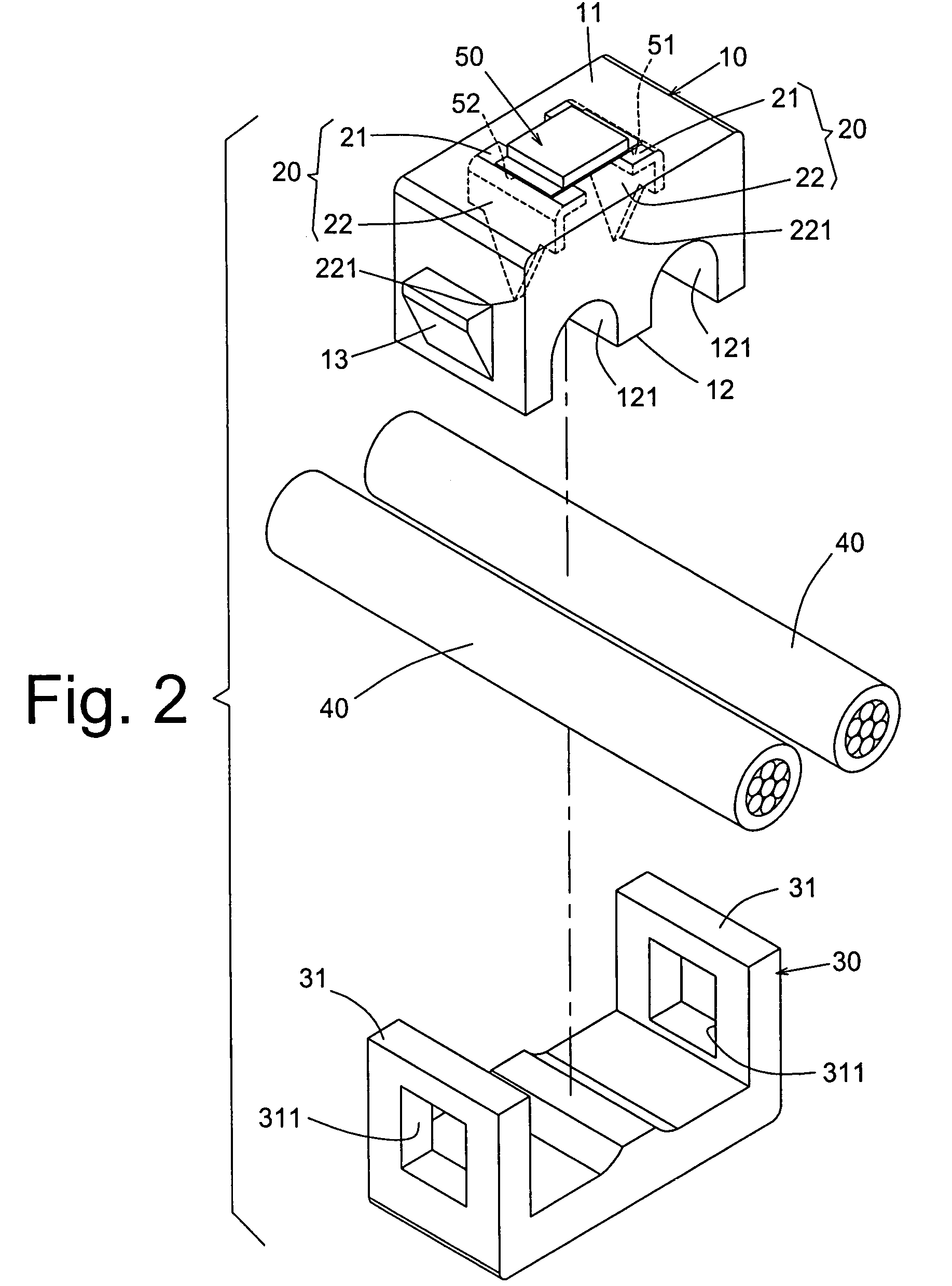
Providing a light cell in a wellbore
InactiveUS20050012036A1Enhanced overall recoveryEasy to operateConstructionsOptical prospectingForms of energyCompound (substance)
This invention provides a method for controlling production operations using fiber optic devices. An optical fiber carrying fiber-optic sensors is deployed downhole to provide information about downhole conditions. Parameters related to the chemicals being used for surface treatments are measured in real time and on-line, and these measured parameters are used to control the dosage of chemicals into the surface treatment system. The information is also used to control downhole devices that may be a packer, choke, sliding sleeve, perforating device, flow control valve, completion device, an anchor or any other device. Provision is also made for control of secondary recovery operations online using the downhole sensors to monitor the reservoir conditions. The present invention also provides a method of generating motive power in a wellbore utilizing optical energy. This can be done directly or indirectly, e.g., by first producing electrical energy that is then converted to another form of energy.
Owner:SENSOR HIGHWAY LTD
Increasing the angular range of light collection in solar collectors/concentrators
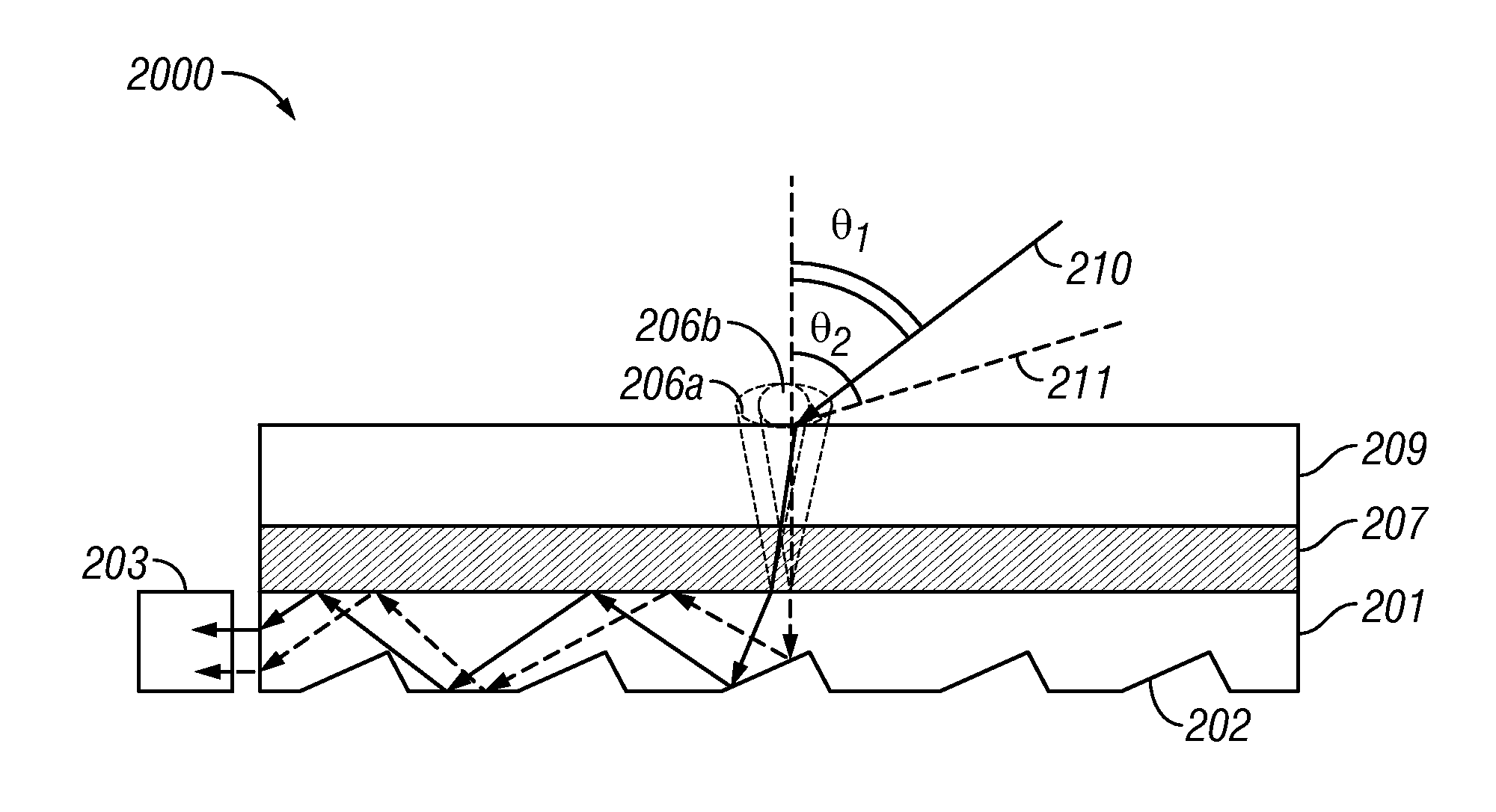
In various embodiments described herein, a device comprises an angle turning layer disposed over a light guiding layer that is optically coupled to a photocell. A plurality of surface features is formed on one of the surfaces of the light guiding layer. The surface features can comprise facets that are angled with respect to each other. The angle turning layer can comprise diffractive features that are volume features or surface-relief features. Light incident on the angle turning layer at a first angle is turned towards the light guiding layer at a second angle and subsequently redirected at a third angle by the surface features of the light guiding layer and guided through the light guide by multiple total internal reflections. The guided light is directed towards a photocell.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Indicating light display having several light sources
InactiveUS6170971B1Small sizeReduce in quantityNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceOptical processingDisplay device
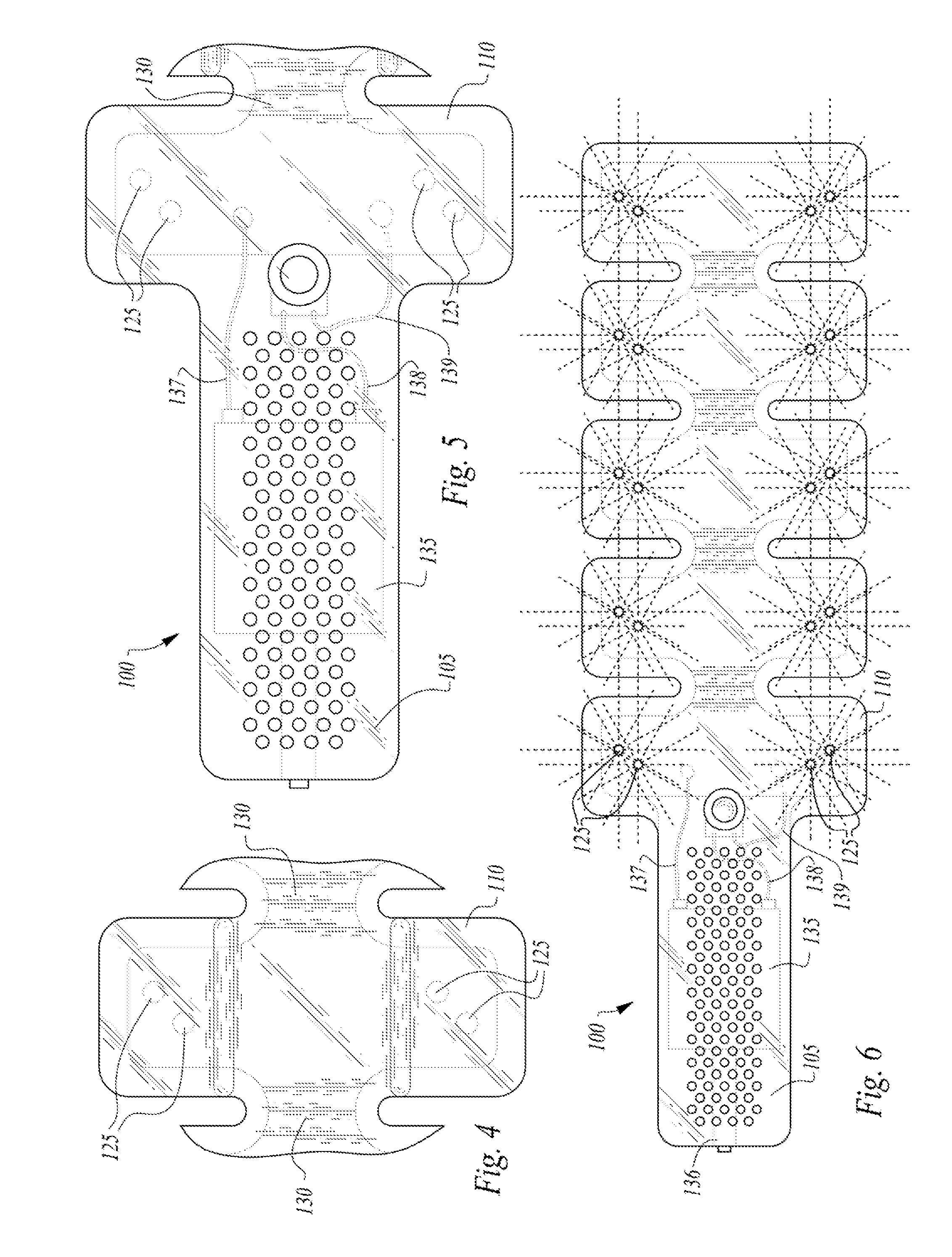
An indicating light display for a motor vehicle, and in particular a raised stop light in the form of a strip which contains a plurality of light sources, also includes optical processing means for redirecting the light received from the light sources so that it will be propagated in the general emission direction. The display thus consists of a series of light cells, each defining a transition zone between each cell and the next. The optical processing means include, in association with each light source, a first element for distributing the light, in a plane at right angles to the general emission direction, on a second element in the form of an optical plate. This optical plate is divided into zones each associated with one of the cells and formed with projecting striations. Each transition between a zone and the next zone is formed with a transition striation which receive light from both of the two adjacent light sources and redirects this towards the general emission direction.
Owner:VALEO VISION SA
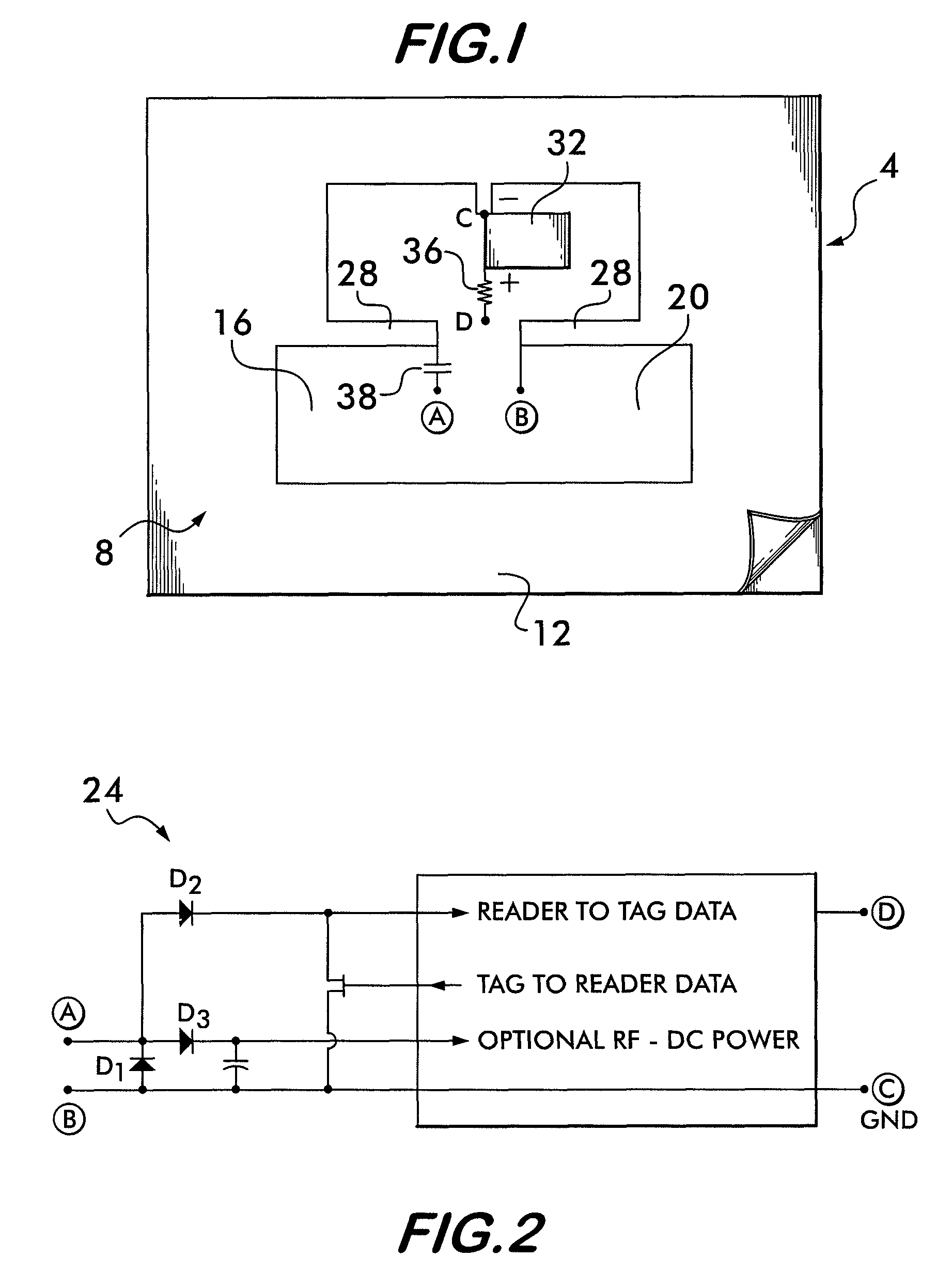
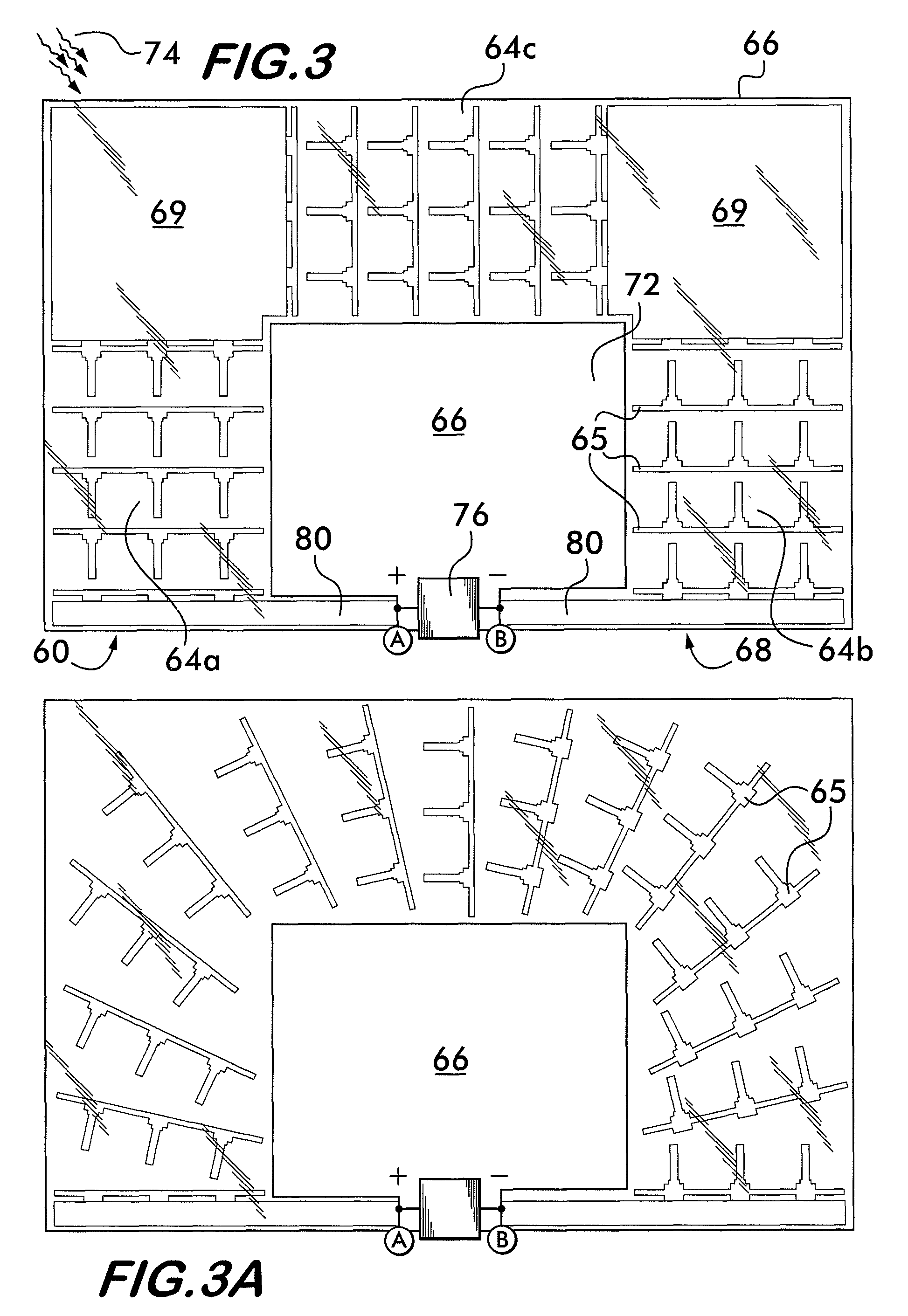
Light activated RFID tag
ActiveUS7791481B2Increase rangeSevere restrictionRecord carriers used with machinesBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalElectricityEngineering
A radio frequency identification (RFID) device is arranged for use with a remote interrogator unit. The RFID device comprises an integrated circuit configured to send, in response to a signal received from the remote interrogator unit or automatically, a responsive signal which includes identification information. A communication antenna is electrically coupled to the integrated circuit and is provided for wireless communication with the remote interrogator unit. At least one photovoltaic cell is provided for converting radiation into electrical energy and providing power to the integrated circuit. The photocell may be designed to form all or part of the RF antenna of the RFID device.
Owner:AMTECH SYST
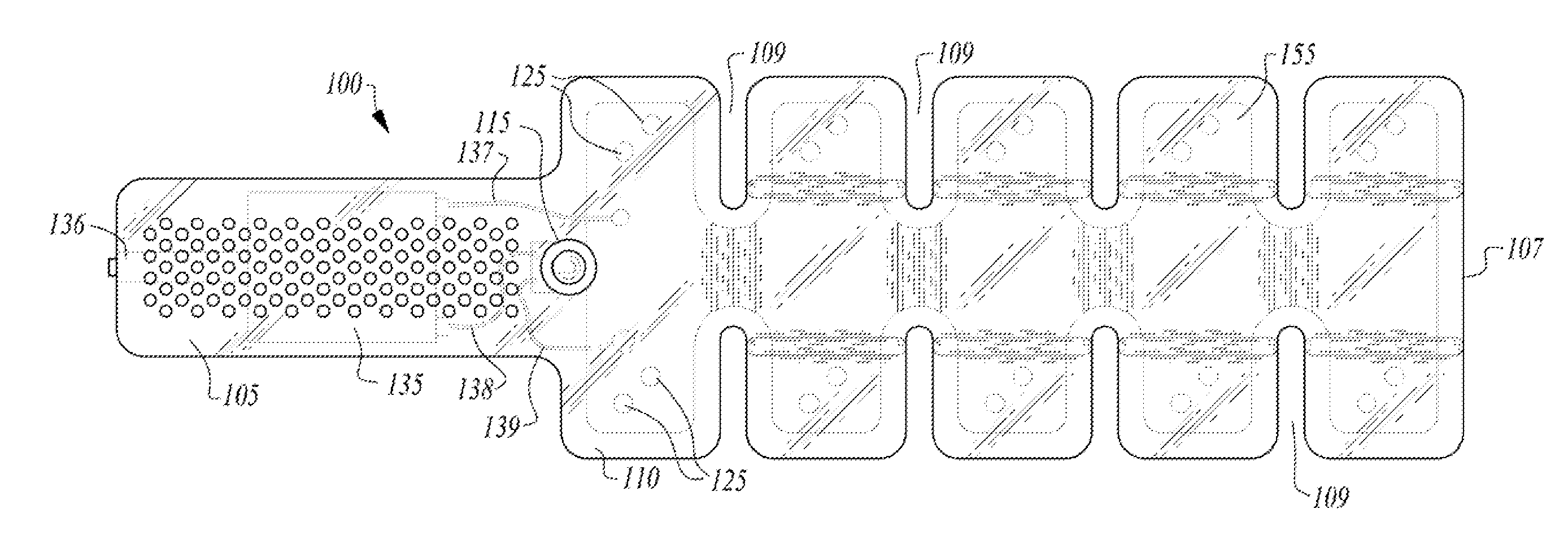
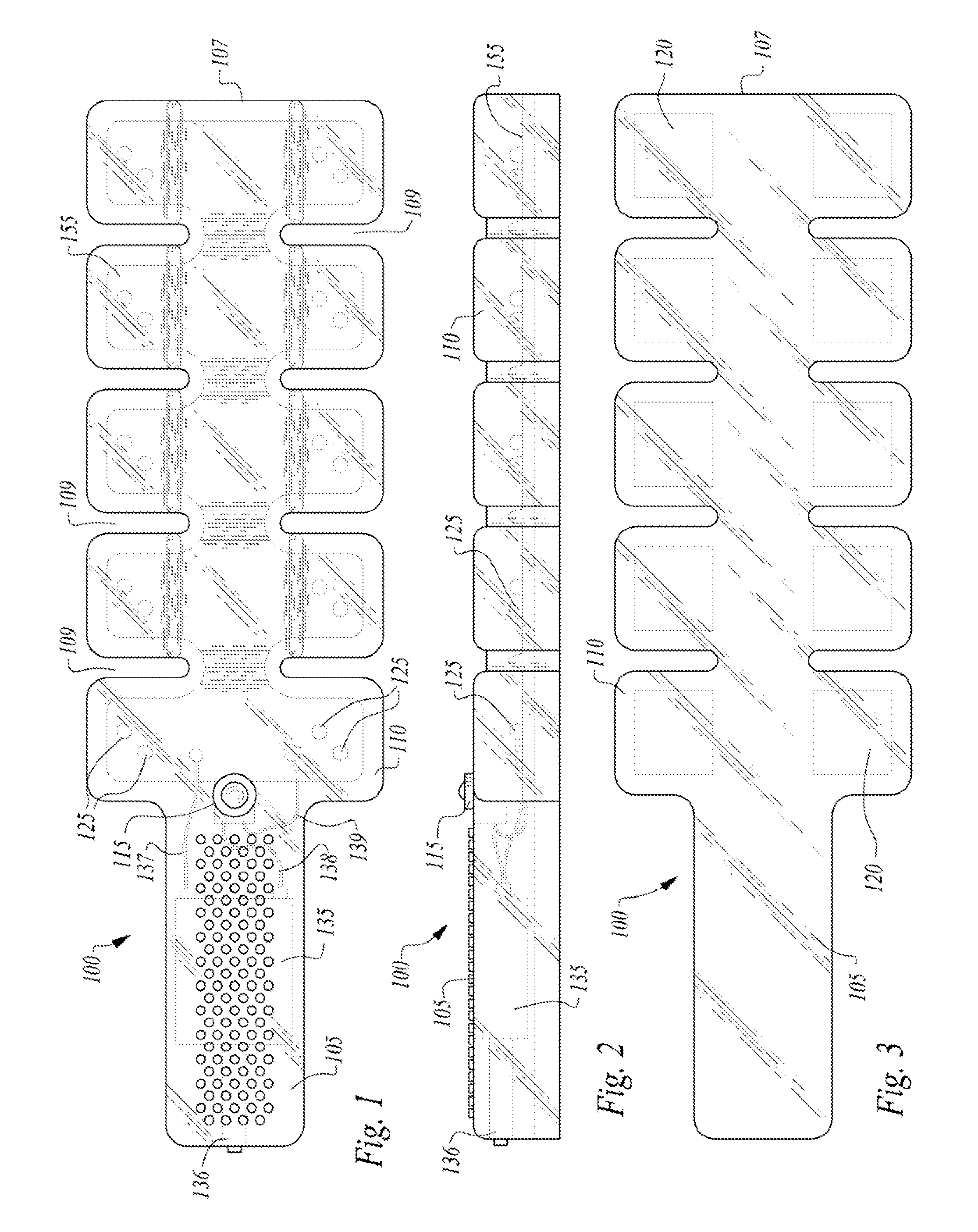
Portable and bendable utility light
InactiveUS20120243212A1Printed circuit assemblingPoint-like light sourceElectrical connectionMetallic materials
A portable and bendable utility light is disclosed. Example embodiments include a body fabricated from a flexible non-metallic material, the body including a spine and a handle, the spine including a plurality of articulated light cells and corresponding radiused gaps between each light cell to facilitate bending of the spine in a plurality of directions; and an electrical assembly enveloped within the body, the electrical assembly including a conducting plane, a plurality of light emitting diodes (LEDs) in electrical connection with the conducting plane and positioned within each of the plurality of articulated light cells, as power source in electrical connection with the conducting plane, and a switch in electrical connection with the power source and the conducting plane.
Owner:SMITH DAVID +2
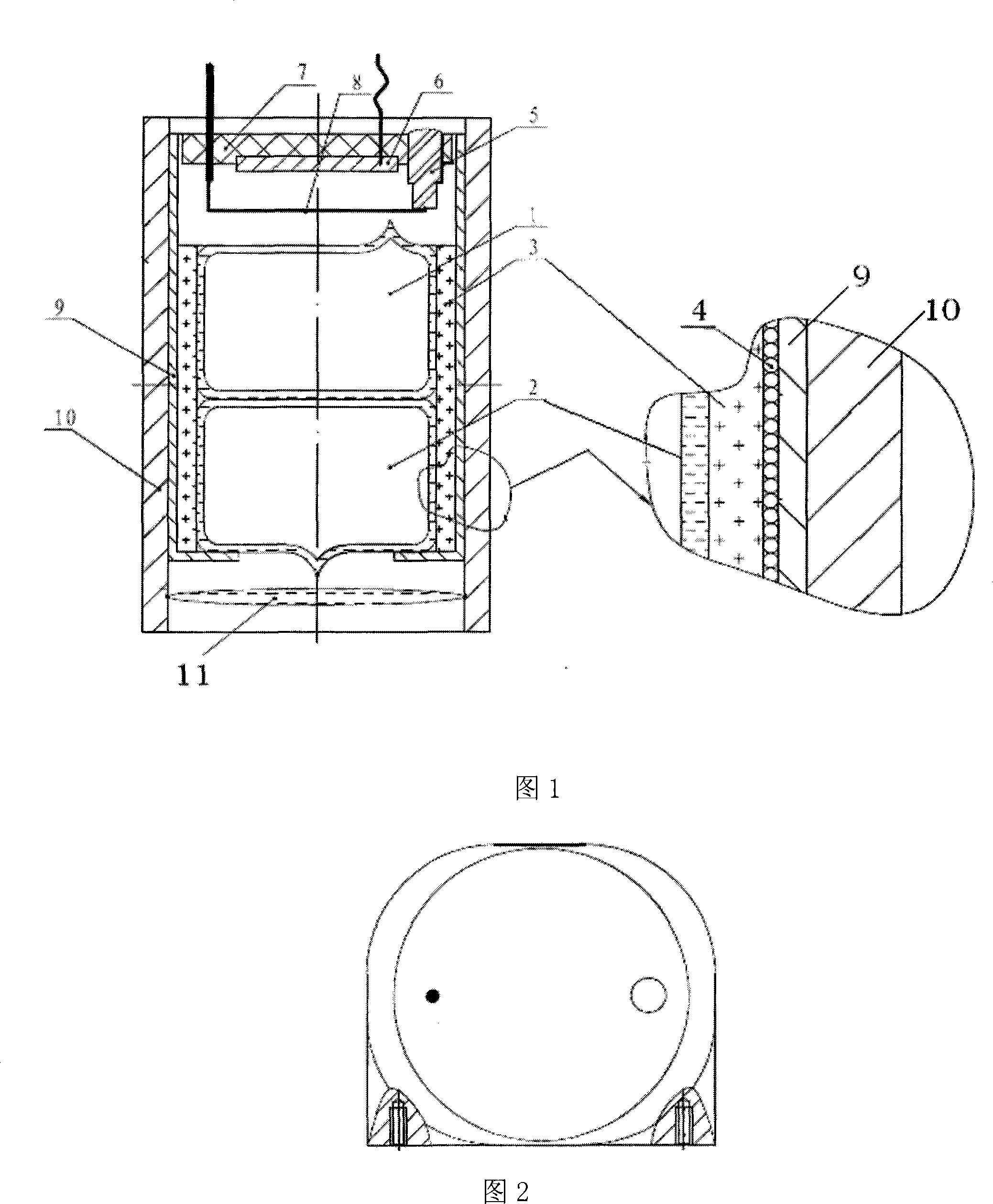
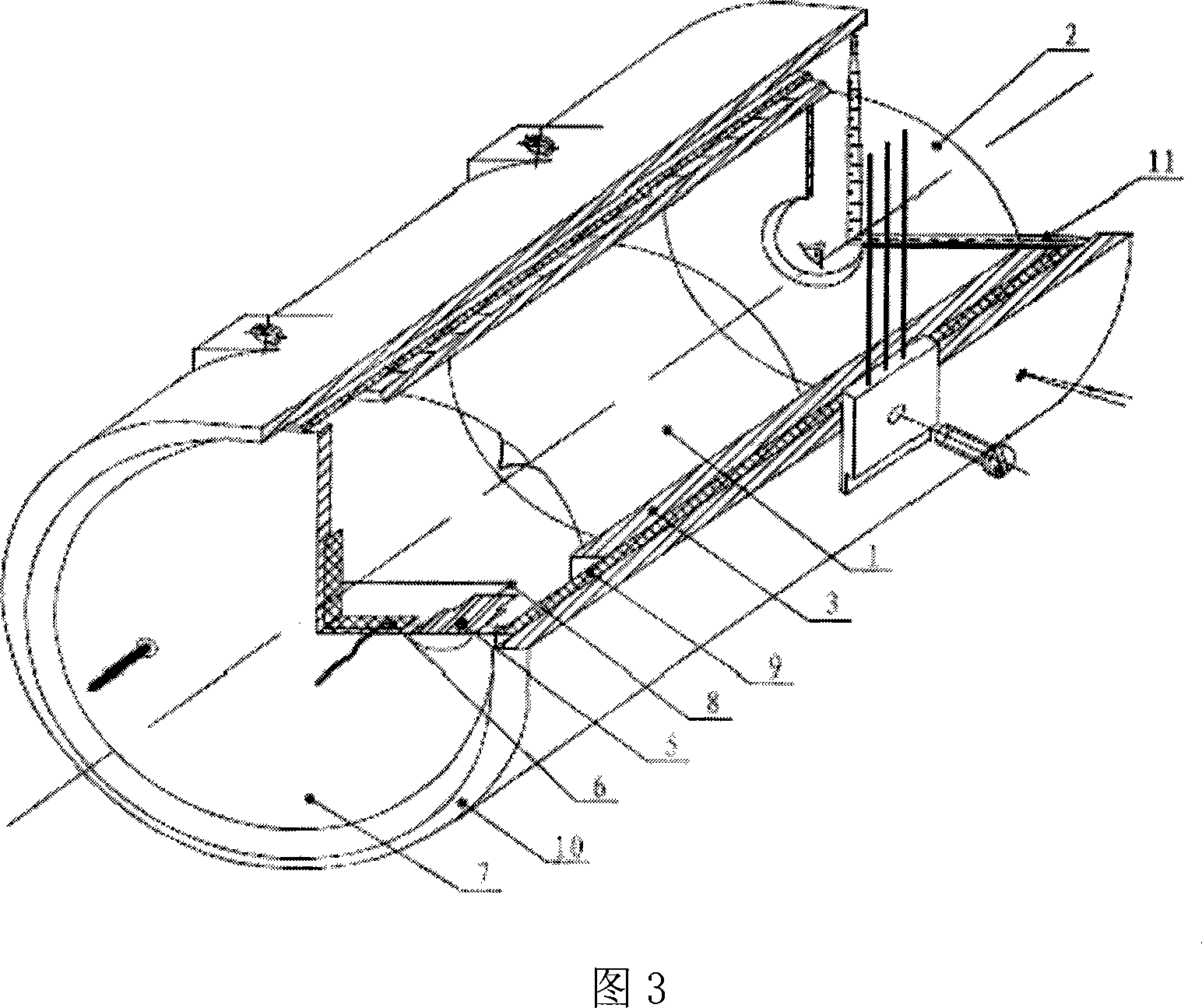
Small Rb atom frequency marking cavity bubble system
InactiveCN101237077AReduce volumeReduce design difficultyPulse automatic controlGaseous masersDielectric cylinderCell system
The present invention discloses a miniaturized rubidium atomic frequency standard cavity-cell system, wherein, a microwave cavity cylinder is made from high magnetic permeability material; the microwave cavity cylinder is sleeved with a heating cylinder; a pump light incident port of the heating cylinder is also provided with a convex lens which gathers and transmits rays emitted by a rubidium spectral lamp into a microwave cavity; a C field coil is directly wound on a dielectric cylinder arranged between the microwave cavity cylinder and an absorption cell; a cusp on the tail part of a light-filtering cell is concentrated at the center of a circular plane at the end of the cell; a cusp on the tail part of the absorption cell is concentrated at the edge of a circular plane at the end of the cell; a photocell and a snap-off diode are fixed on the end face of the inner wall of a cavity end cover which can be movably fixed. The present invention has no machinery regulating rod inside the cavity, uses an intracavity frequency doubling mode, adopts a cylindrical TE111 mode and a dielectric filling method to get rid of the complex structure of a magnetic shield cylinder in the prior art, and reduces the volume of the cavity-cell system. As the pump light incident port of the heating cylinder is provided with the convex lens to increase the light intensity of pump light, the performance of the cavity-cell system is guaranteed. A mobile photoelectric component is adopted for cavity frequency fine adjustment, which is convenient for debugging and cannot cause field form distortion.
Owner:SICHUAN TIANAO XINGHUA TIME & FREQUENCY
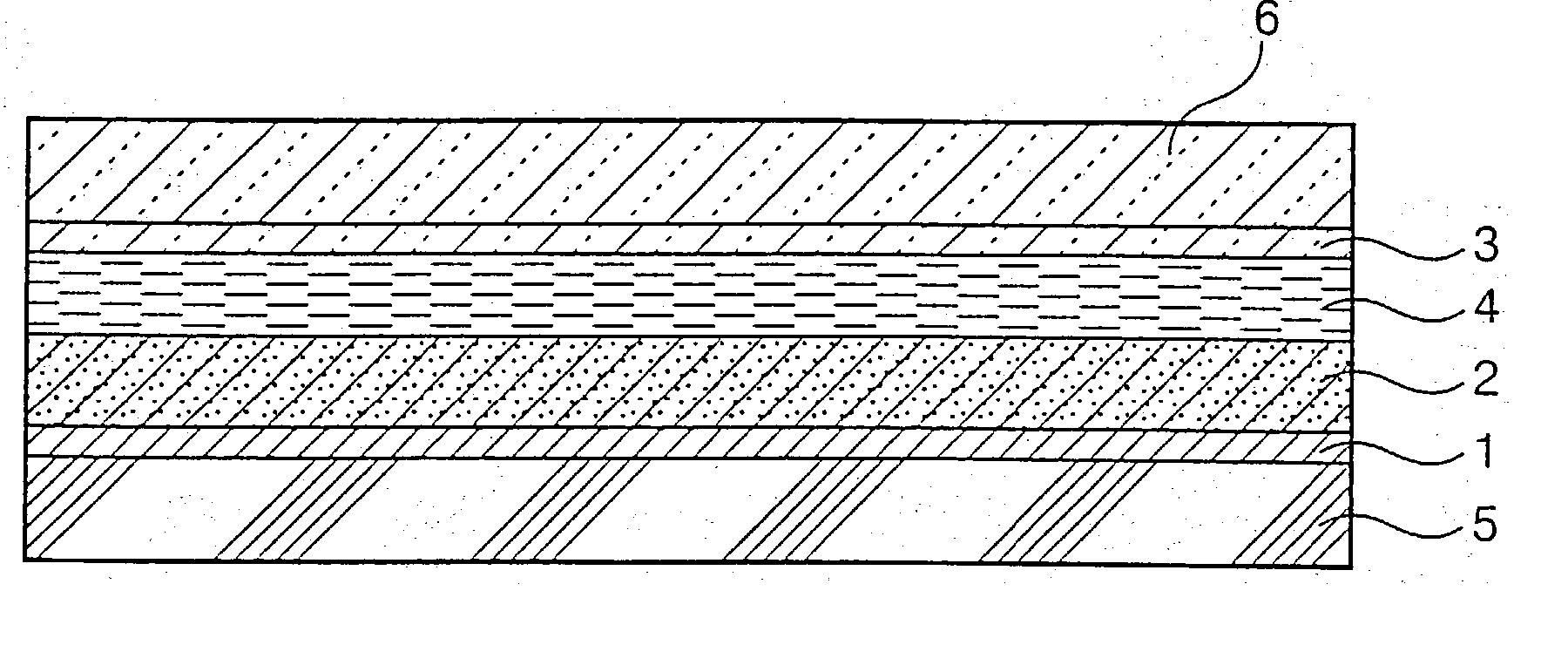
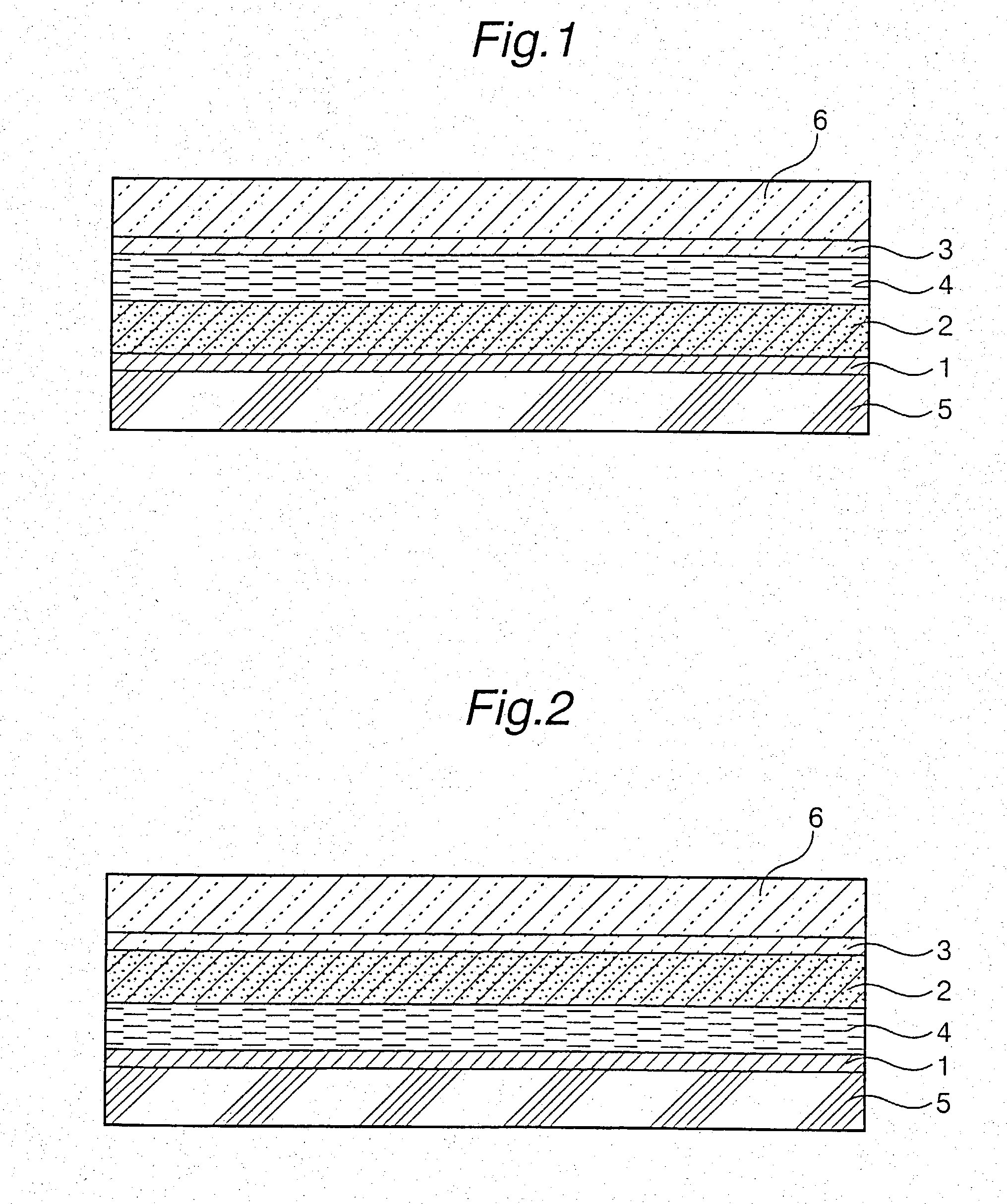
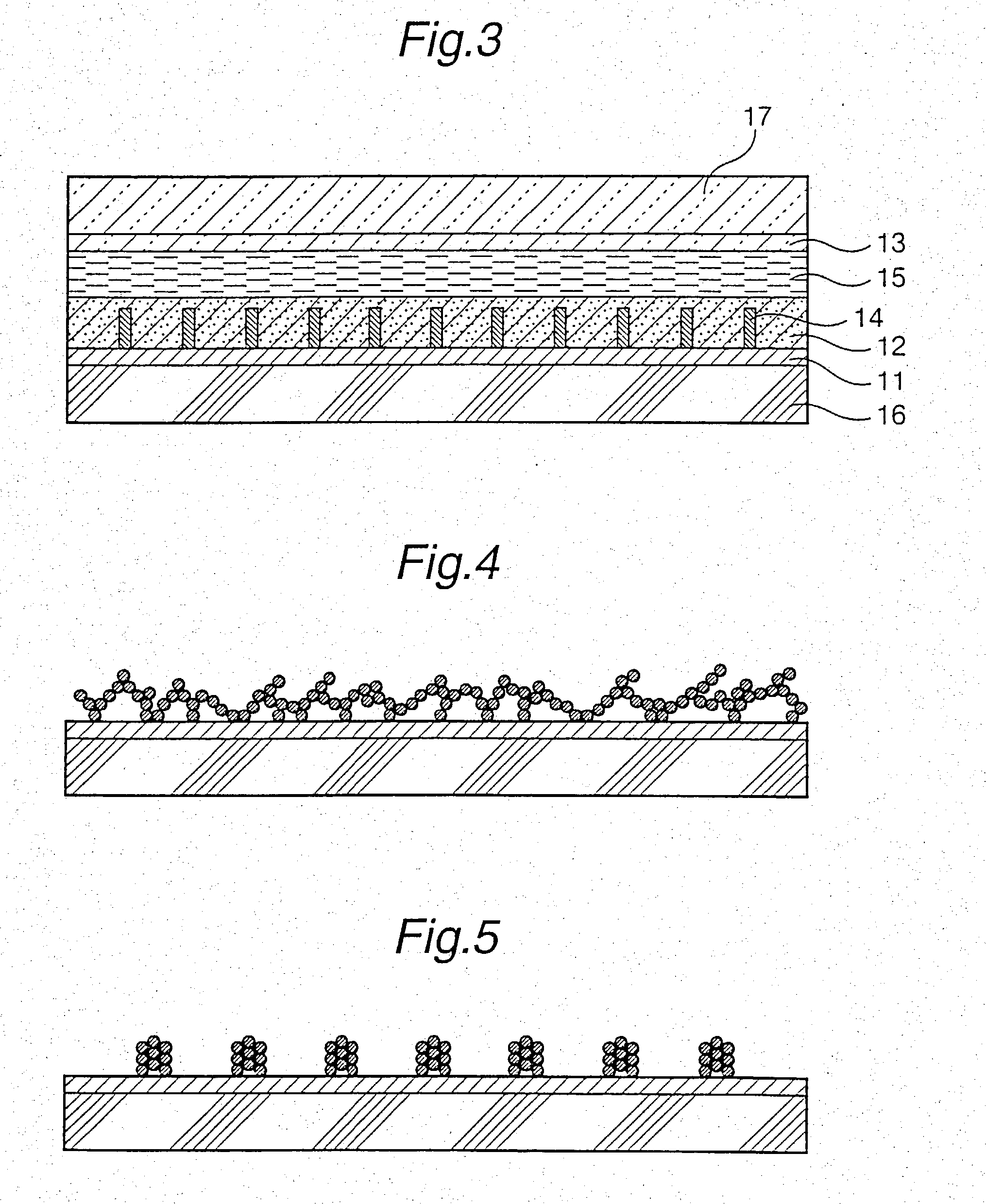
Photoelectric cell and process for producing metal oxide semiconductor film for use in photoelectric cell
InactiveUS20030150485A1High photoelectric transfer efficiencyExcellent in photoelectric transfer efficiencyPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyTitanium oxideElectron
The first photoelectric cell of the present invention comprises: an insulating base having on its surface an electrode layer (1), the electrode layer (1) having on its surface a metal oxide semiconductor film (2) on which a photosensitizer is adsorbed; an insulating base having on its surface an electrode layer (3), the electrode layer (1) and the electrode layer (3) arranged opposite to each other; and an electrolyte sealed between the metal oxide semiconductor film (2) and the electrode layer (3), wherein at least one of the electrode-having insulating bases is transparent; and the metal oxide semiconductor film (2) comprises anatase titanium oxide particles. This first photoelectric cell includes a semiconductor film comprising anatase titanium oxide particles, having a high proportion of photosensitizer adsorbed, so that the electron mobility in the semiconductor film is high to thereby realize excellent photoelectric transfer efficiency. The second photoelectric cell of the present invention comprises: an insulating base having on its surface an electrode layer (1), the electrode layer (1) having on its surface a metal oxide semiconductor layer (2) on which a photosensitizer is adsorbed; an insulating base having on its surface an electrode layer (3), the electrode layer (1) and the electrode layer (3) arranged opposite to each other; and an electrolyte sealed between the metal oxide semiconductor layer (2) and the electrode layer (3), wherein conductive protrusions (4) jutting from the surface of the electrode layer (1) exist, the metal oxide semiconductor layer (2) formed so as to cover the conductive protrusions (4) and the electrode layer (1), and at least one of the electrode-layer-having insulating bases is transparent. In this second photoelectric cell, conductive protrusions are provided on the electrode surface, so that generated electrons not only can rapidly move toward the electrode but also are free from recombining with the photosensitizer. Moreover, in this photoelectric cell, not only is the adsorption proportion of photosensitizer high but also the moving of generated electrons is smooth. Therefore, the second photoelectric cell exhibits excellent photoelectric transfer efficiency.
Owner:CATALYSTS & CHEM
System for providing pathway indications through unlit areas
Owner:HARWOOD RONALD P
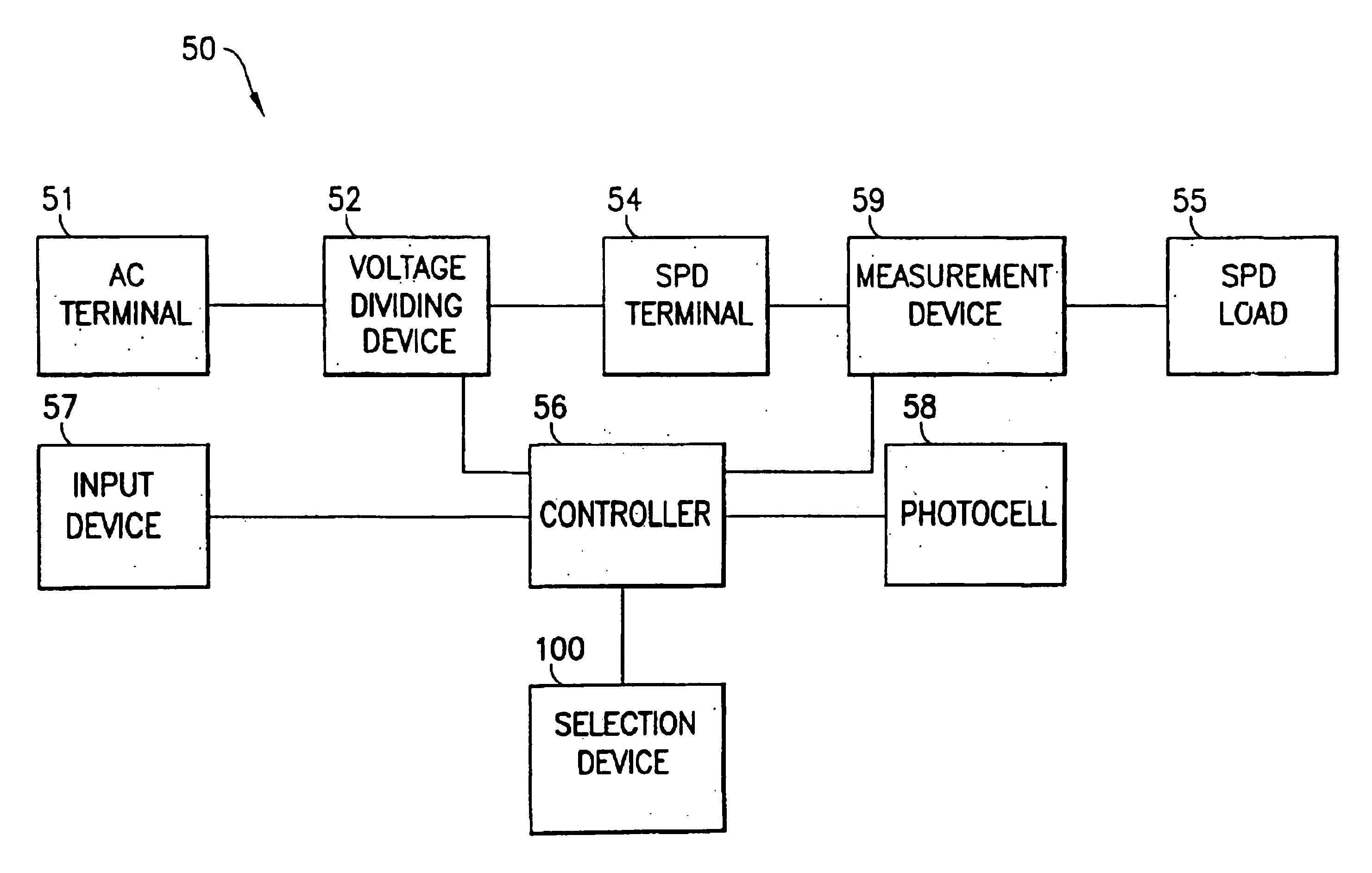
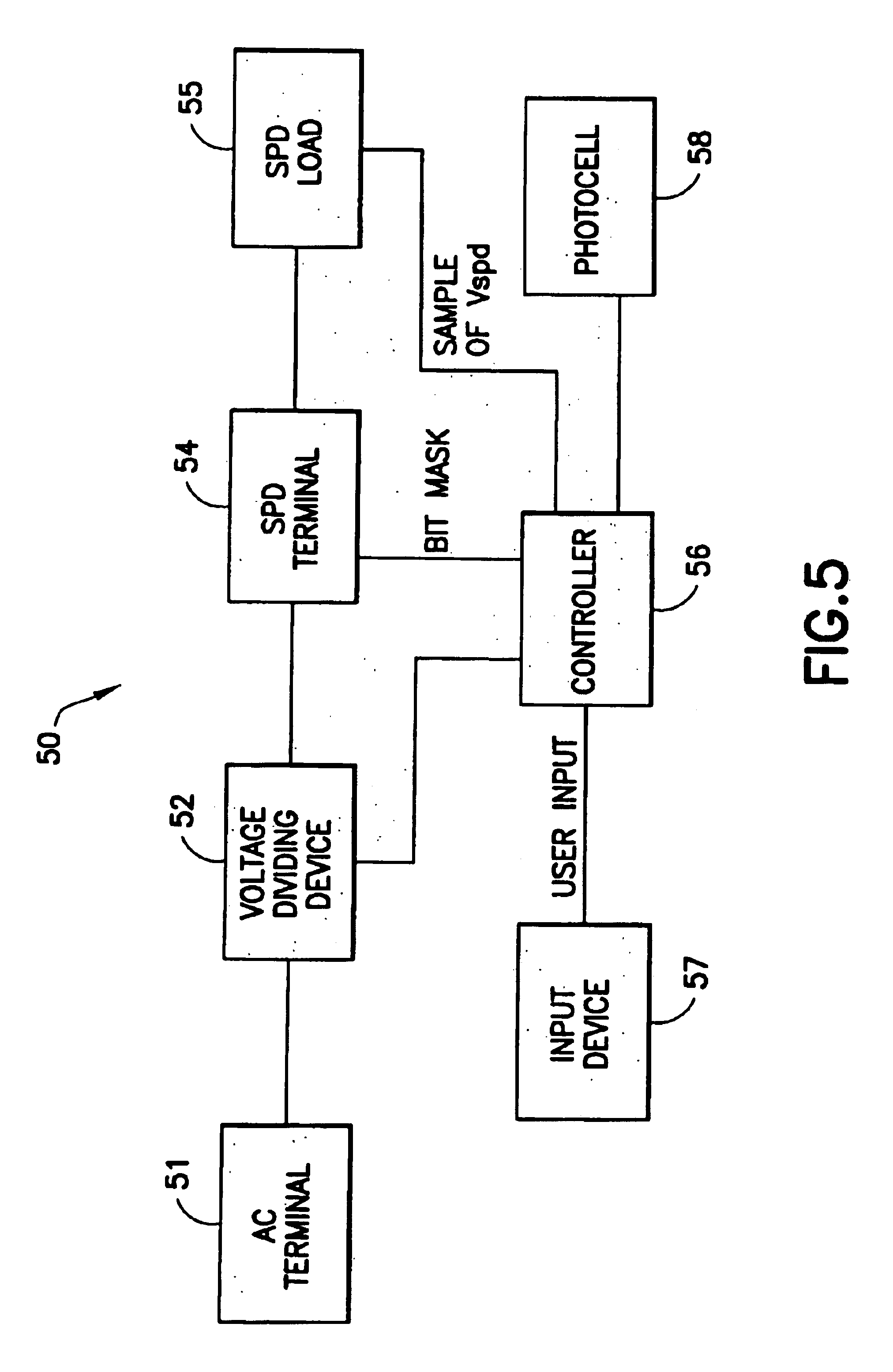
Method and device for controlling voltage provided to a suspended particle device
InactiveUS6897997B2Conversion without intermediate conversion to dcNon-linear opticsSuspended particlesLight Cell
A voltage controlling device includes an AC terminal receiving an AC voltage signal, a voltage dividing device adapted to divide the AC voltage signal into a plurality of distinct voltage signals within a predetermined range, a controller adapted to control the voltage dividing device to provide a selected voltage level based on voltage level information and an SPD terminal for providing the selected voltage level to a suspended particle device. Voltage level information may be provided via an input device and / or from a photocell that monitors a light level at the suspended particle device. A separate AC power supply may also be provided. The controller may also monitor an SPD load voltage to control the voltage level provided to the SPD terminal in order to prevent shocking of a user.
Owner:RES FRONTIERS
Light-emitting cell module
A light-emitting cell module includes a base seat and multiple terminals respectively inlaid in the base seat. A first end of each terminal being exposed to outer side of a first end of the base seat. A second end of each terminal having a sharp thrust section protruding from a second end of the base seat. A connecting seat latched with the second end of the base seat, the connecting seat and the second end of the base seat together tightly clamping and holding multiple leads of positive electrode and negative electrode, the second ends of the terminals being aligned with the corresponding leads, whereby the thrust sections of the second ends thrust into the leads to electrically connect the terminals with the leads. A light-emitting cell having two pins which are soldered with the first ends of the terminals of the positive electrode and the negative electrode.
Owner:SUPER LINK ELECTRONICS
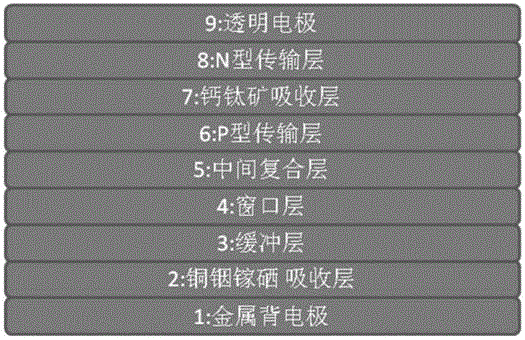
High-efficiency low-cost copper indium gallium selenium / perovskite double-junction solar photocell prepared through all-solution method
ActiveCN104022225AReduce manufacturing costPromote absorptionFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesIndiumHole transport layer
The invention discloses a high-efficiency low-cost copper indium gallium selenium / perovskite double-junction solar photocell prepared through an all-solution method. The double-junction solar photocell comprises a metal back electrode, a copper indium gallium selenium absorbing layer, a P-type buffer layer, a window layer, a carrier composite layer, a hole transporting layer, a perovskite absorbing layer, an electron transporting layer and a transparent oxide electrode. The high-efficiency double-junction solar photocell can be prepared through the all-solution method and has the advantages of being low in cost and capable of being produced on a large scale. Copper indium gallium selenium and perovskite serve as the absorbing layers of sunlight; on one hand, the copper indium gallium selenium with the adjustable bandwidth and the high-conversion-efficiency perovskite made of broadband gap materials can effectively cover solar spectra and be utilized efficiently; on the other hand, both the copper indium gallium selenium and the perovskite can be prepared through the all-solution method, so a whole laminating device can have higher conversion efficiency and maintain low production cost at the same time.
Owner:苏州柯利达集团有限公司
Method and structure, using flexible membrane surfaces, for setting and/or maintaining a uniform micron/sub-micron gap separation between juxtaposed photosensitive and heat-supplying surfaces of photovoltaic chips and the like for the generation of electrical power
ActiveUS20090277488A1Thermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentPV power plantsLight CellField energy
A near-field energy conversion structure and method of assembling the same, utilizing a sub-micrometer “near field” gap between juxtaposed photocell infrared radiation receiver and heat emitter surfaces, wherein compliant membrane structures, preferably fluid-filled, are interposed in the structure.
Owner:MTPV POWER CORP
Method for testing film residual stress and its layered deep distribution
InactiveCN1793842AEliminate the effects ofInnovative designMaterial analysis by optical meansComplex mathematical operationsTest sampleLight beam
A method for testing film residual stress and its distribution along layer depth includes calculating test sample curvity radius by utilizing relation slope obtained from linear relation of test sample movement distance to distance moved by silicon light cell in following with light beam deflection; applying chemical manner to peel off film layer by layer for solving out equivalent variable R1 of test sample curvity radius before and after each pooling ¿C off; substituting said variable, base plate elastic constant E and v, base plate thickness h and thickness of each pooling ¿C off in a formula to obtain residual stress on each layer of film.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Color-tuned volumetric light using high quantum yield nanocrystals
ActiveUS20050279915A1Good colorAffects colorOptical radiation measurementBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsQuantum yieldDisplay device
A light source of coaxially stacked volumetric light cells that can be used either in a lamp or a display. Each light cell is composed of high quantum yield nanocrystals in a silica aerogel matrix that is excited by a controlled ultraviolet light source. From these stacked cell assemblies visible light is emitted of a desired color or color temperature and brightness.
Owner:ELOFSON CARL SCOTT
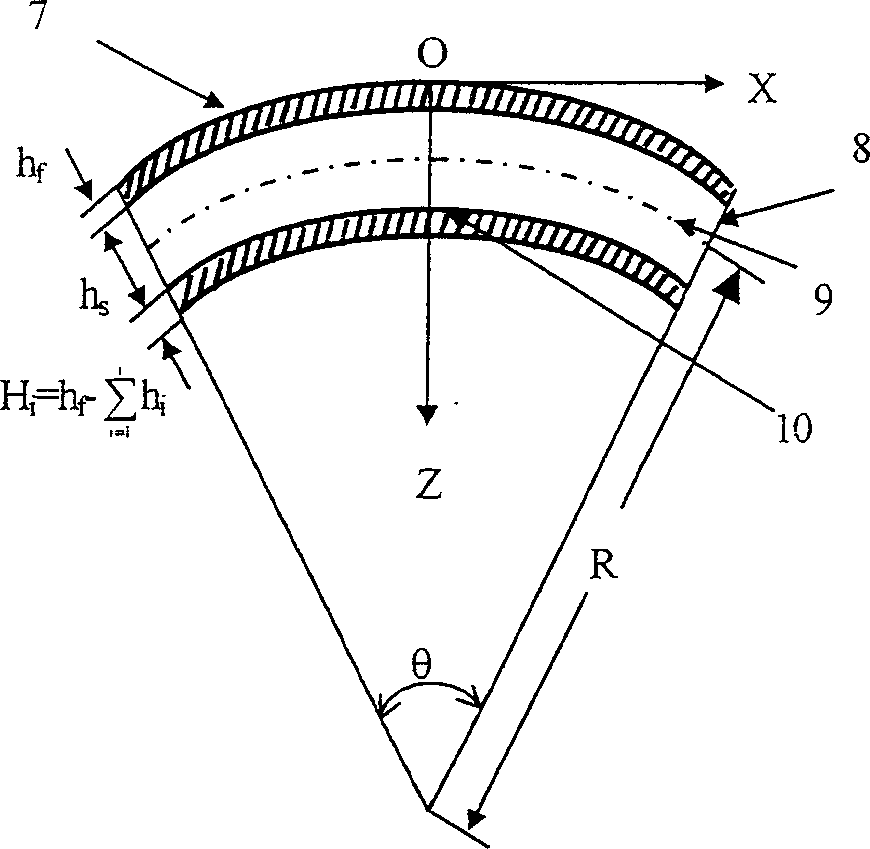
Thin film planar solar concentrator/collector
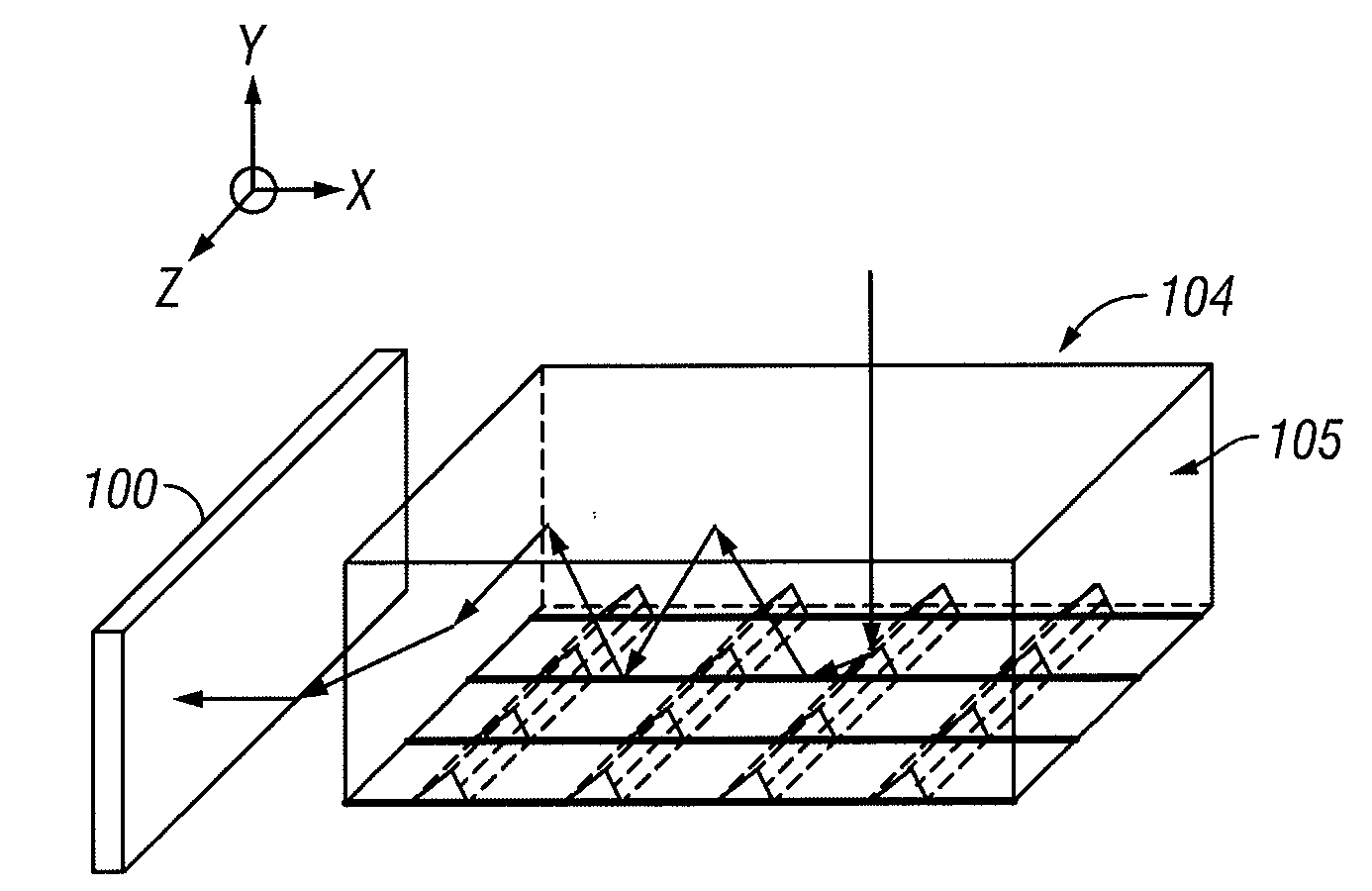
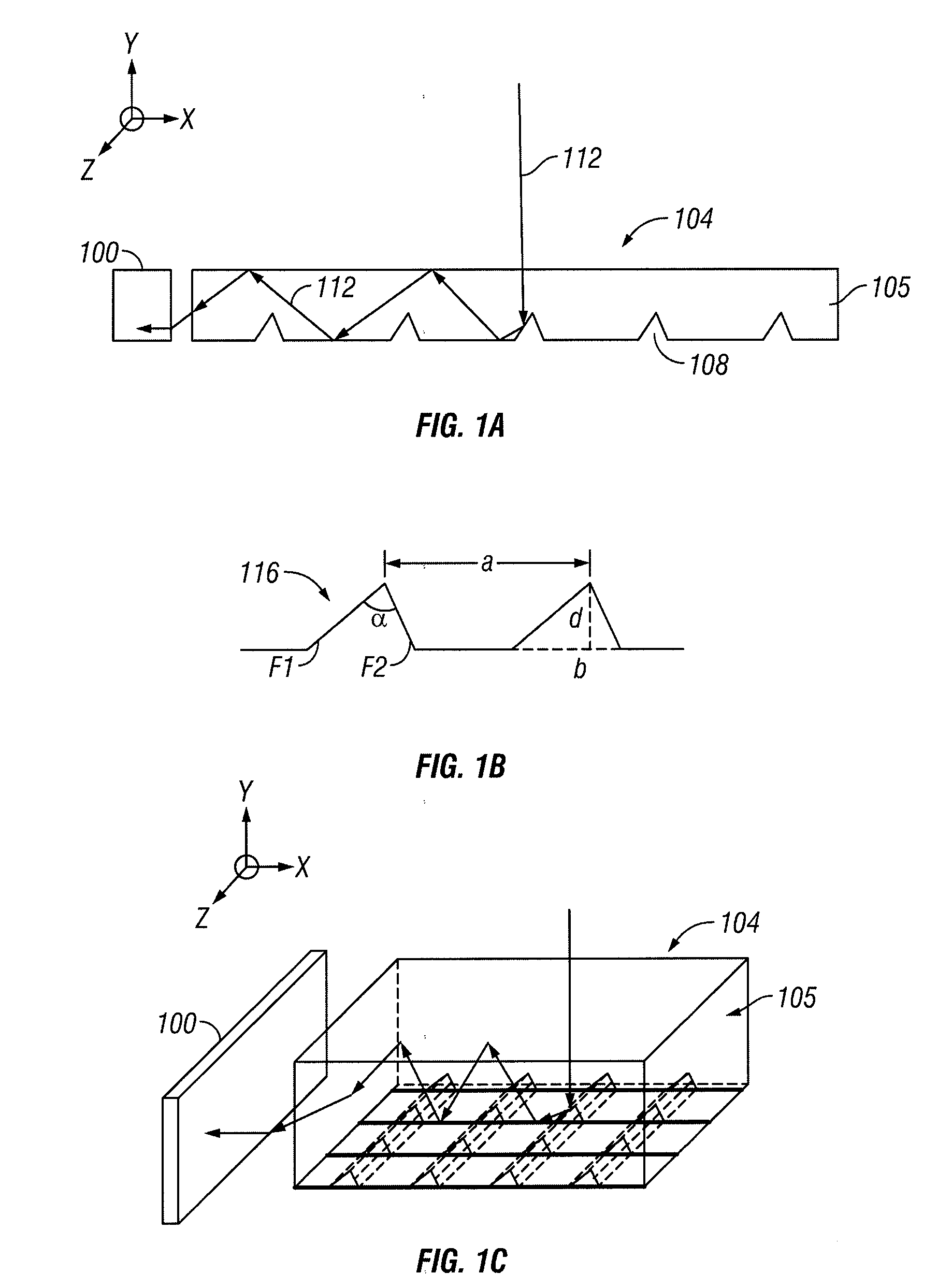
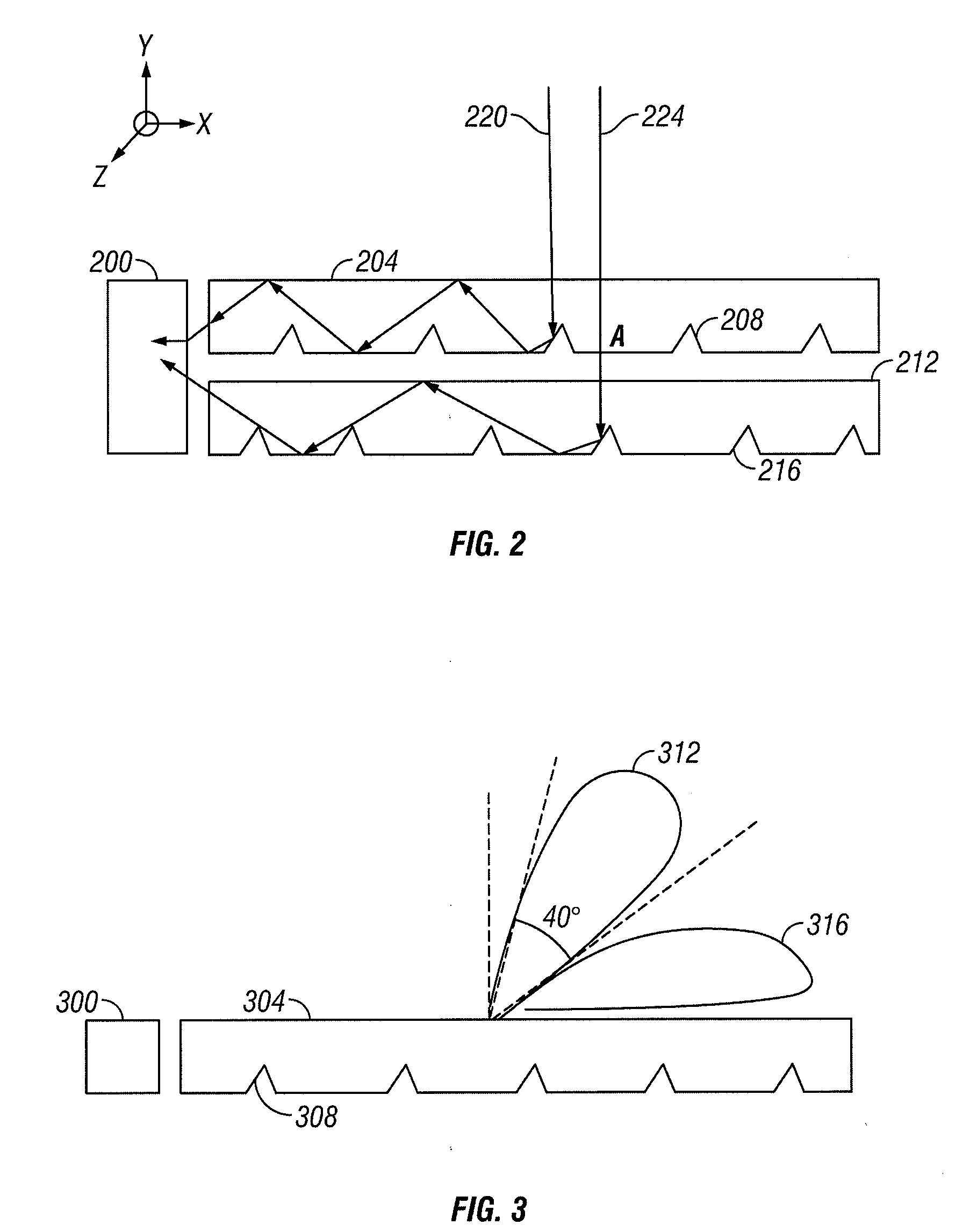
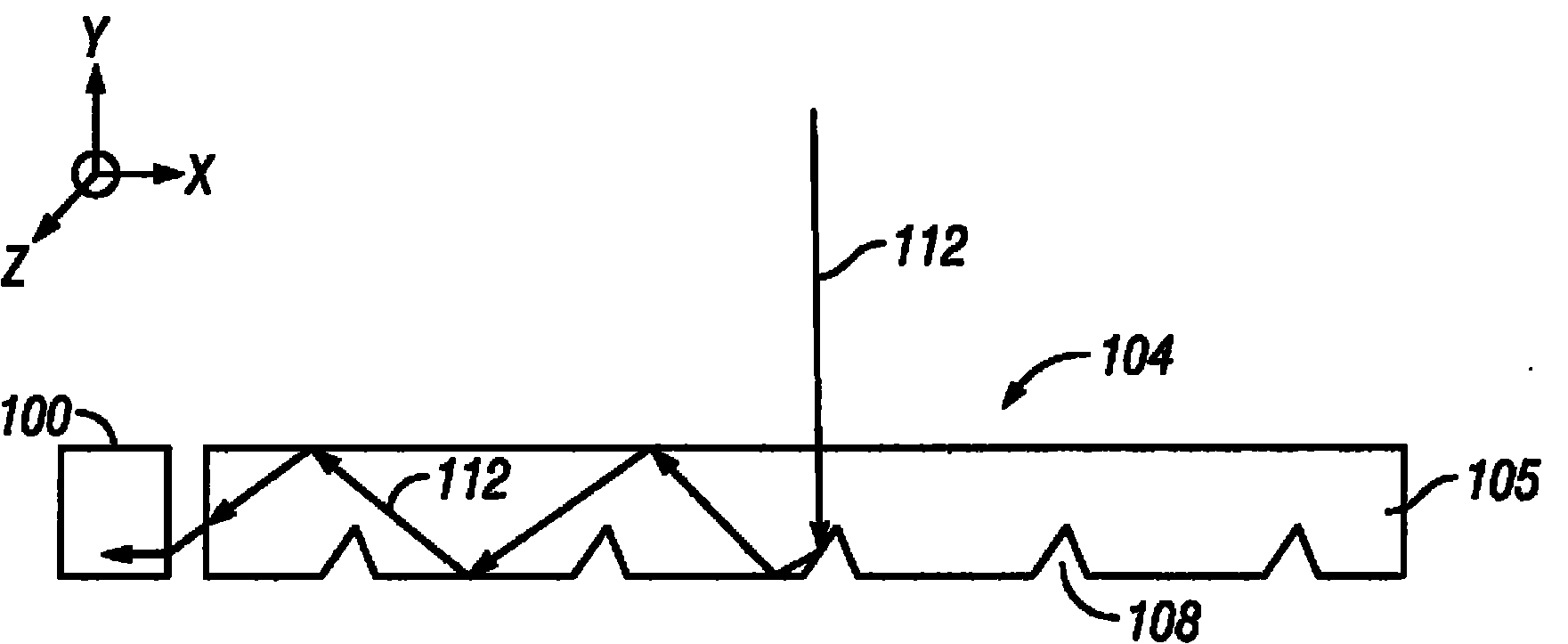
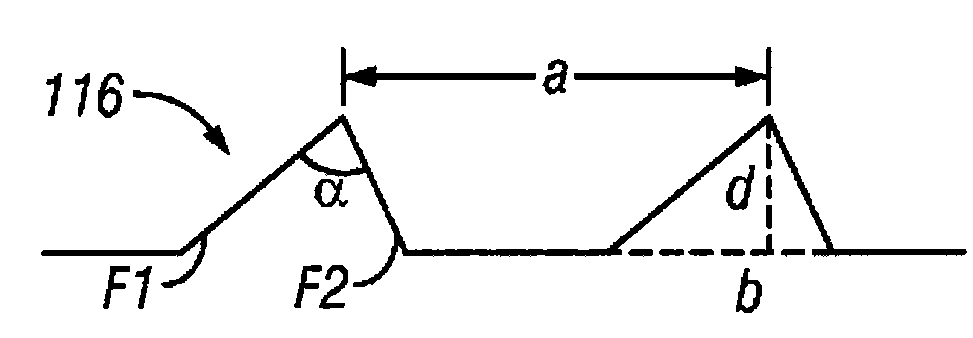
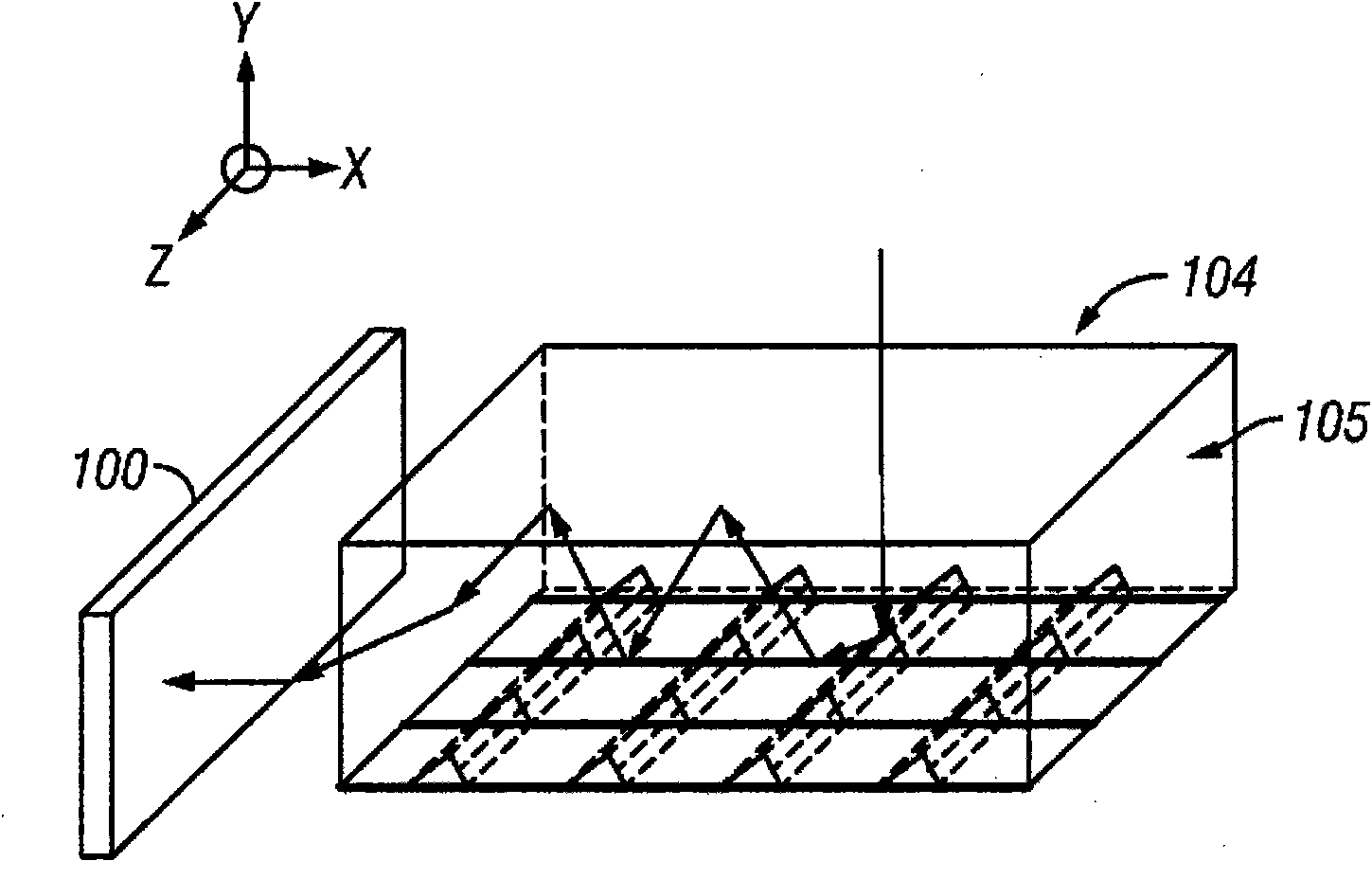
In various embodiments described herein, a device comprising a light guiding layer (204, 212) optically coupled to a photocell (200) is described. A plurality of surface features (208, 216) are formed on one of the surfaces of the light guiding layer (204, 212). The surface features (208, 216) can comprise facets that are angled with respect to each other. Light (220, 224) incident on the surface of the light guide is redirected by the surface features and guided through the light guide (204, 212) by multiple total internal reflections. The guided light is directed towards a photocell (200).
Owner:IDC LLC
Lighting fixture
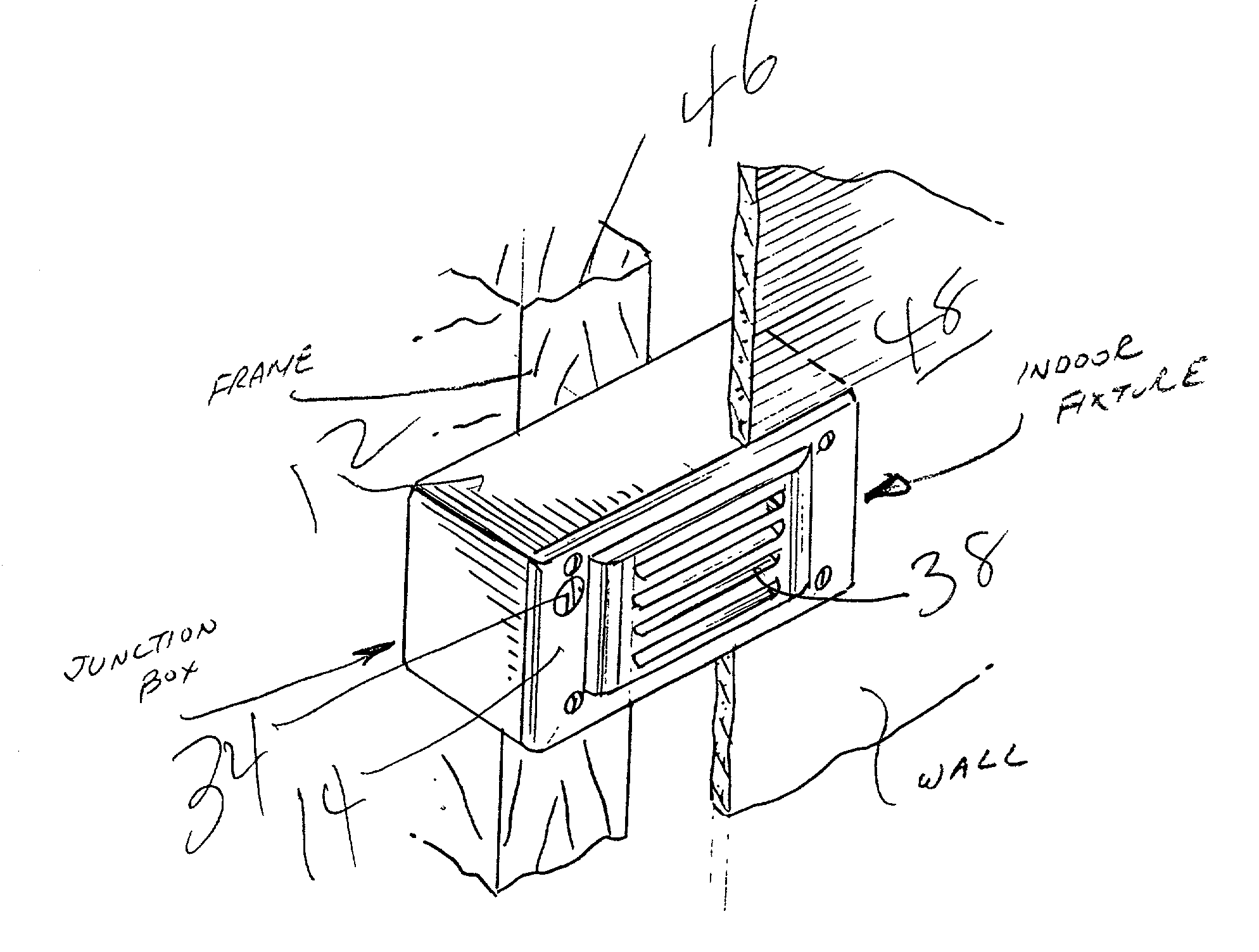
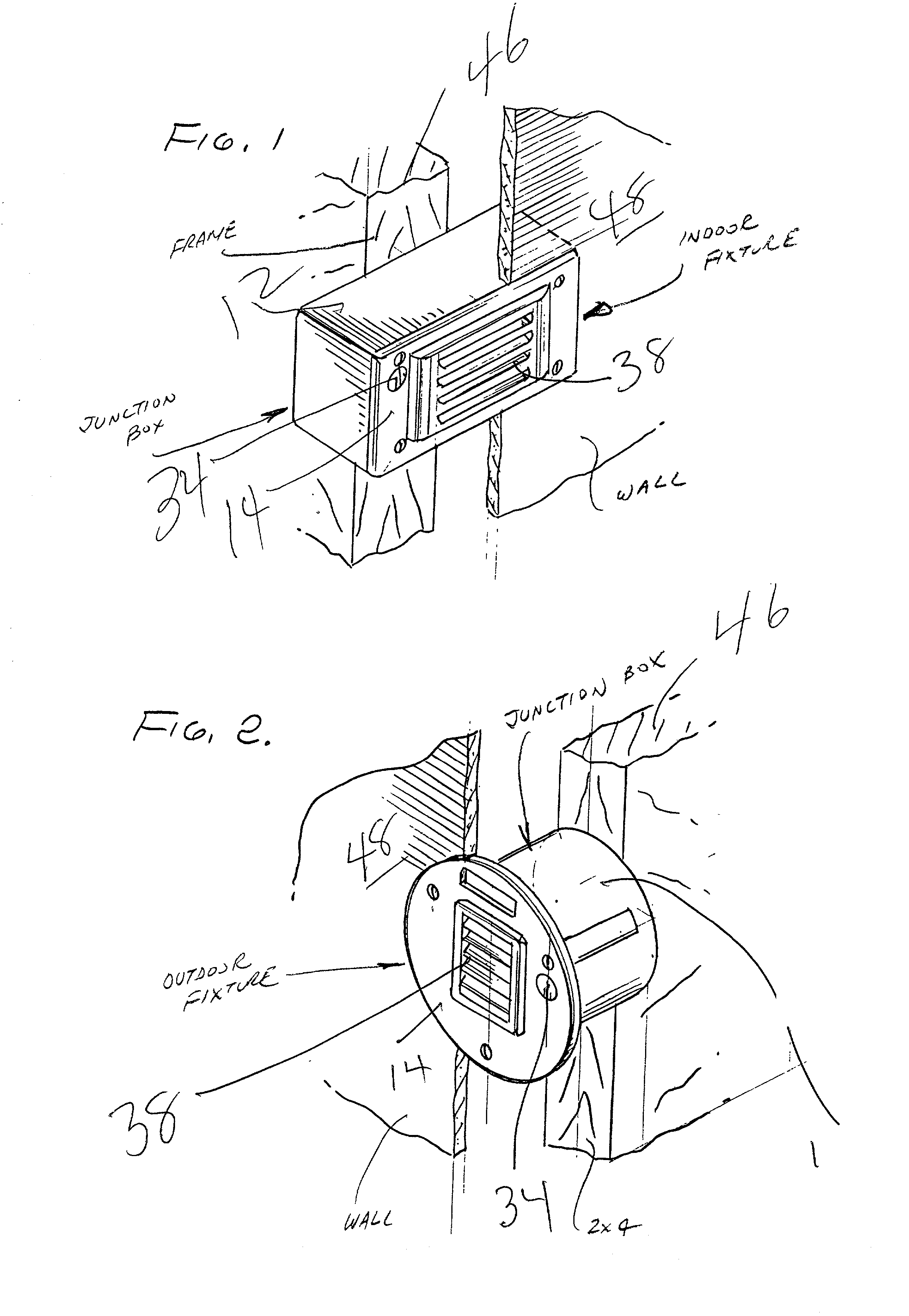
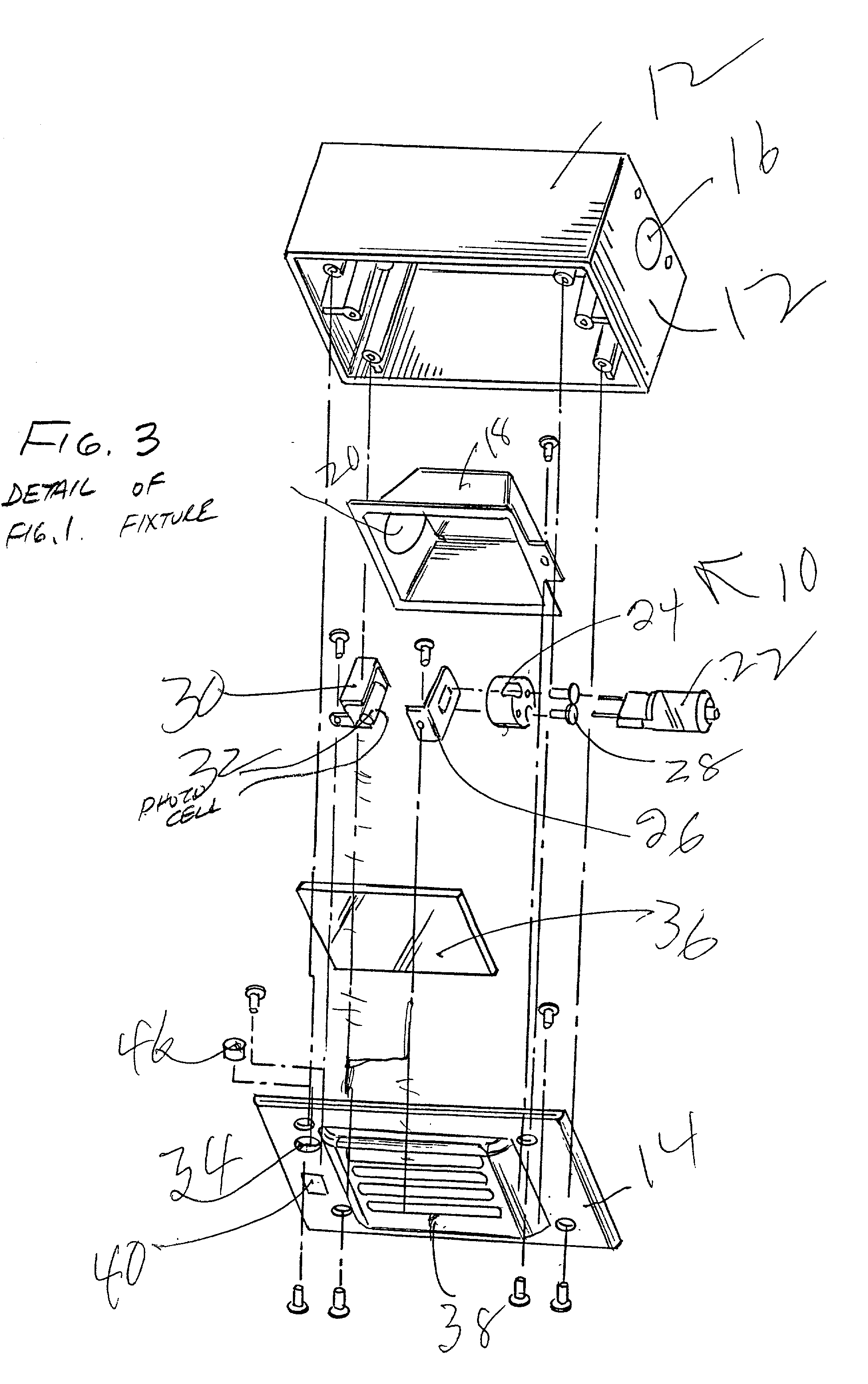
A night lighting fixture comprising a junction box including at least one front plate, within said junction box an electrical light source and light reflector, said fixture including a visible light detecting photocell, a first opening in said front plate for allowing external ambient light to reach said photocell, said photocell and light source being in electrical communication whereby said photocell is adapted to turn said light source off when the photocell detects ambient light and on when the photocell does not detect ambient light and another opening in said front plate to allow for the passage of light from said electrical light source to provide illumination in the external space. A structural wall having a night lighting fixture comprising a junction box recessed within said wall, at least one front plate which is exposed on the surface of said wall, within said junction box an electrical light source and light reflector, said fixture including a visible light detecting photocell, a first opening in a front surface for allowing external ambient light to reach said photocell, said photocell and light source being in electrical communication whereby said photocell is adapted to turn said light source off when the photocell detects ambient light and on when the photocell does not detect ambient light and another opening in a said front surface to allow for the passage of light from said electrical light source to provide illumination in the external space.
Owner:WEN CHUNG FRANK TSAO
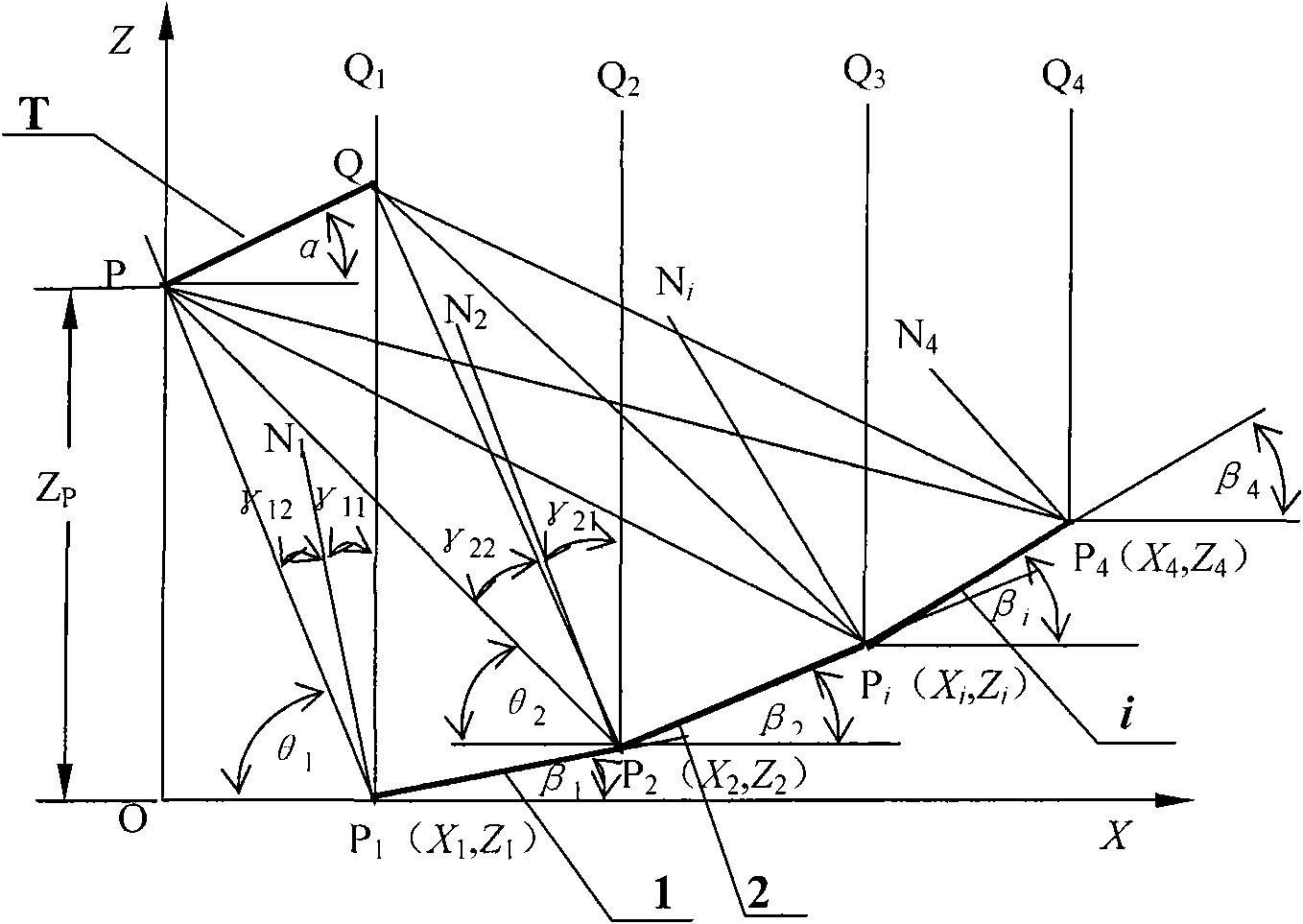
Design method of solar energy uniform light superposition reflective condenser
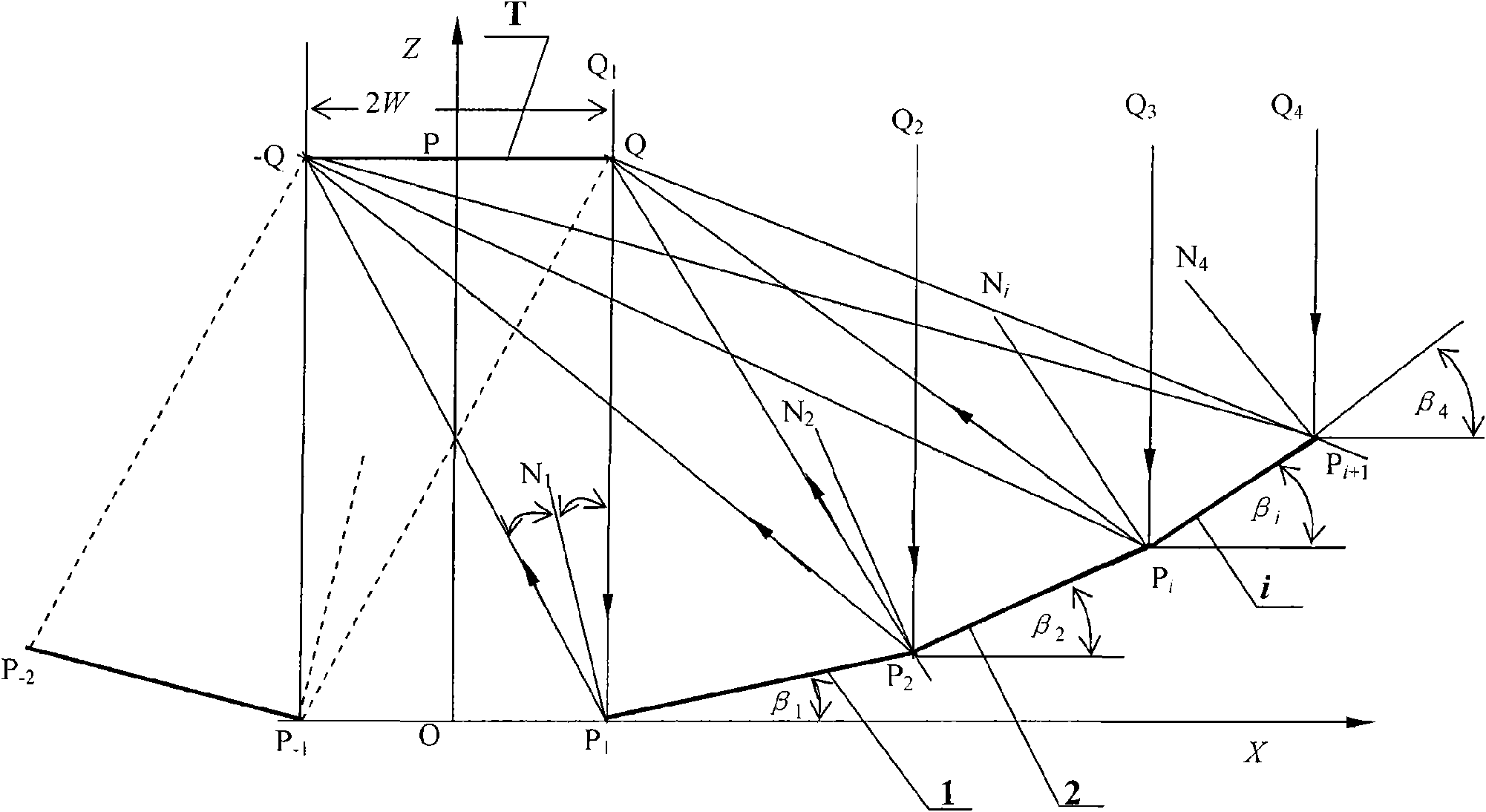
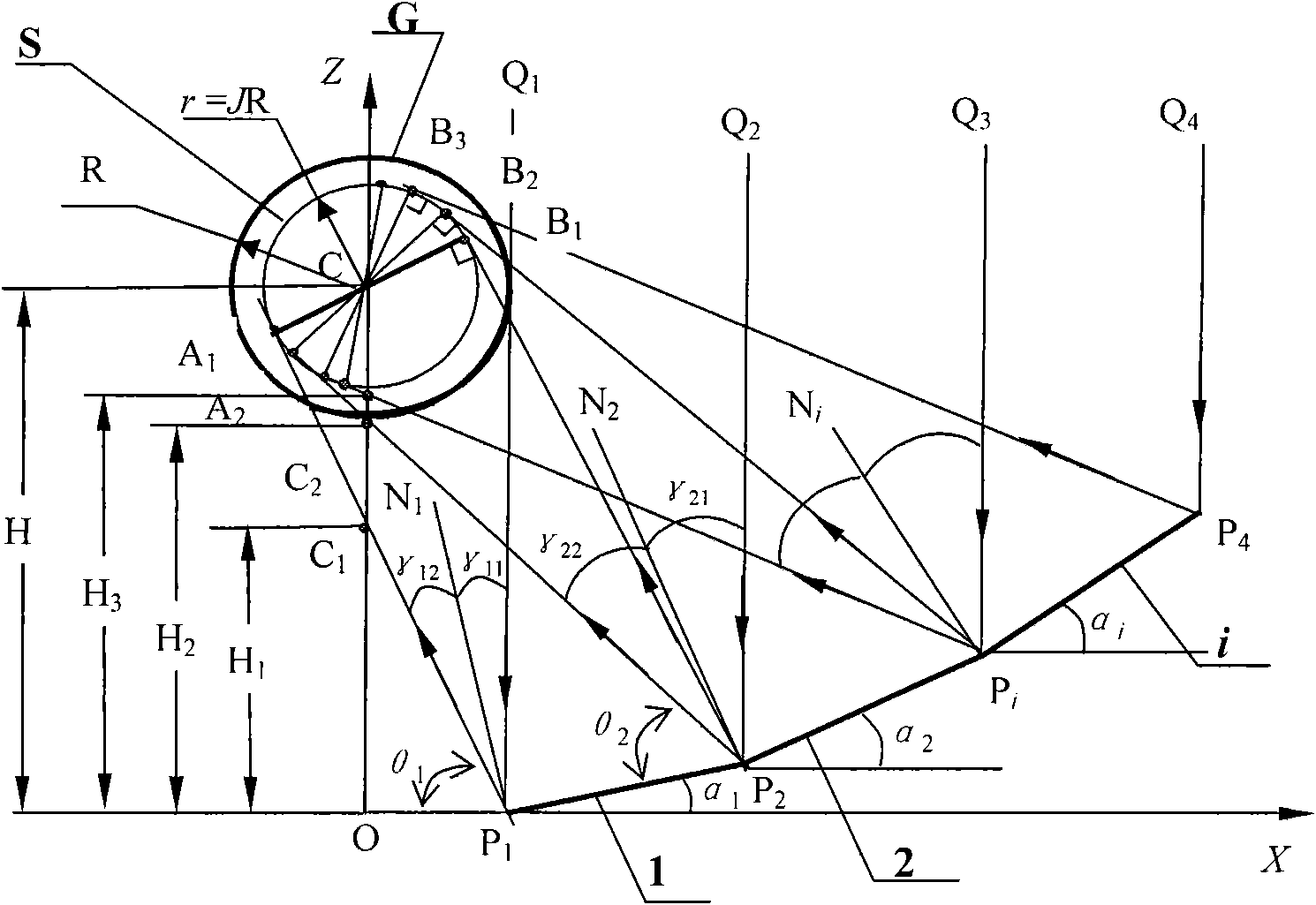
InactiveCN101667604AUniform light receivingImprove optical efficiencySolar heat devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationOptoelectronicsLight Cell
The invention discloses a design method of a solar energy uniform light superposition reflective condenser, wherein a light receiving surface is a photocell plate or a circular heat collection pipe. The design method is characterized in that a condensing lens consists of a limited number of flat plate reflection mirrors and broken line-shaped reflection mirror slot frames and is placed on a solartracking frame, a precise calculation formula of the width and the position of a space coordinate of each reflection mirror and the detailed steps of the geometric mapping method are deduced accordingto the constraint condition that two parallel light rays reflected by two end points of a line segment of a cross section of each reflection mirror respectively fall on two end points of a line segment of the cross section of the photocell plate or are respectively tangent with the circumference of the cross section of the circular heat collection pipe and the normal line of a mirror surface of the reflection mirror is an angle bisector of an included angle between incident light and reflected light, thereby ensuring that the reflected light of each flat plate reflection mirror is uniformly superposed on the light receiving surface, leading the single-chip output features of the photocell to be consistent, improving the light-emitting efficiency of components, leading the processing of the condenser to be easy and reducing the cost. The calculation formula can be used for optimizing the tilt angle and the nominal focal length of the photocell plate.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Apparatus for the processing of photovoltaic cells
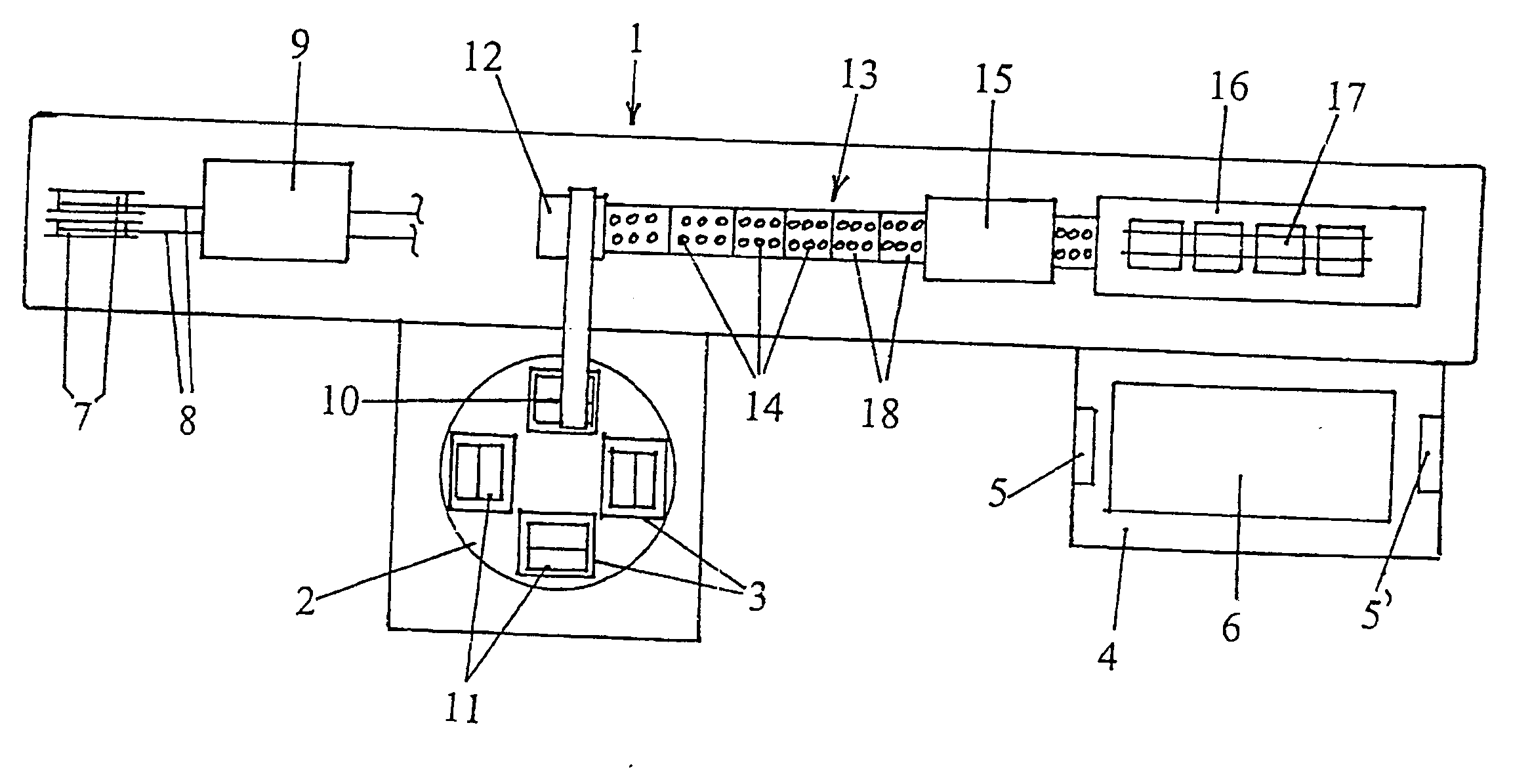
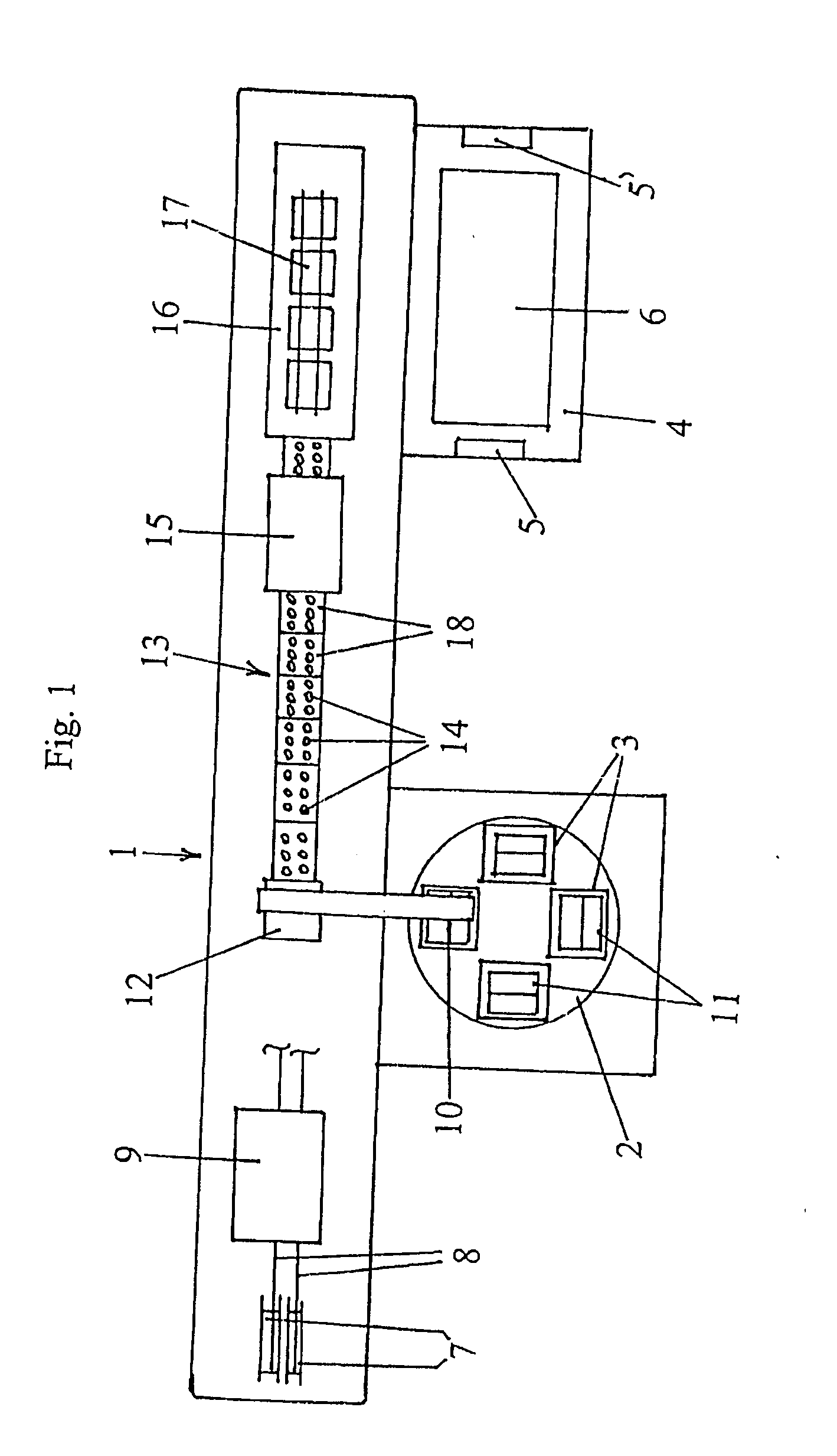
InactiveUS20070294883A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationProduction lineLight Cell
The apparatus according to the invention concerns a production line (1) for the automated processing of individual photocells (11) for the production of strings (17) where the individual photocells (11) are taken up by means of a suction pad gripper (10) from a supply magazine (3) and moved to a centering unit, subsequently pass through a soldering station (15) where they are connected with crimped, electrically conductive metallic connectors (8) in series to one another, and the completed strings (17) being removed from the production line (1) by a string lifter (16). It is distinguished by the fact that it can process photocells (11) of varying dimensions and thicknesses and that transportation through the production line is accomplished exclusively by means of vacuum.
Owner:KIOTO CLEAR ENERGY
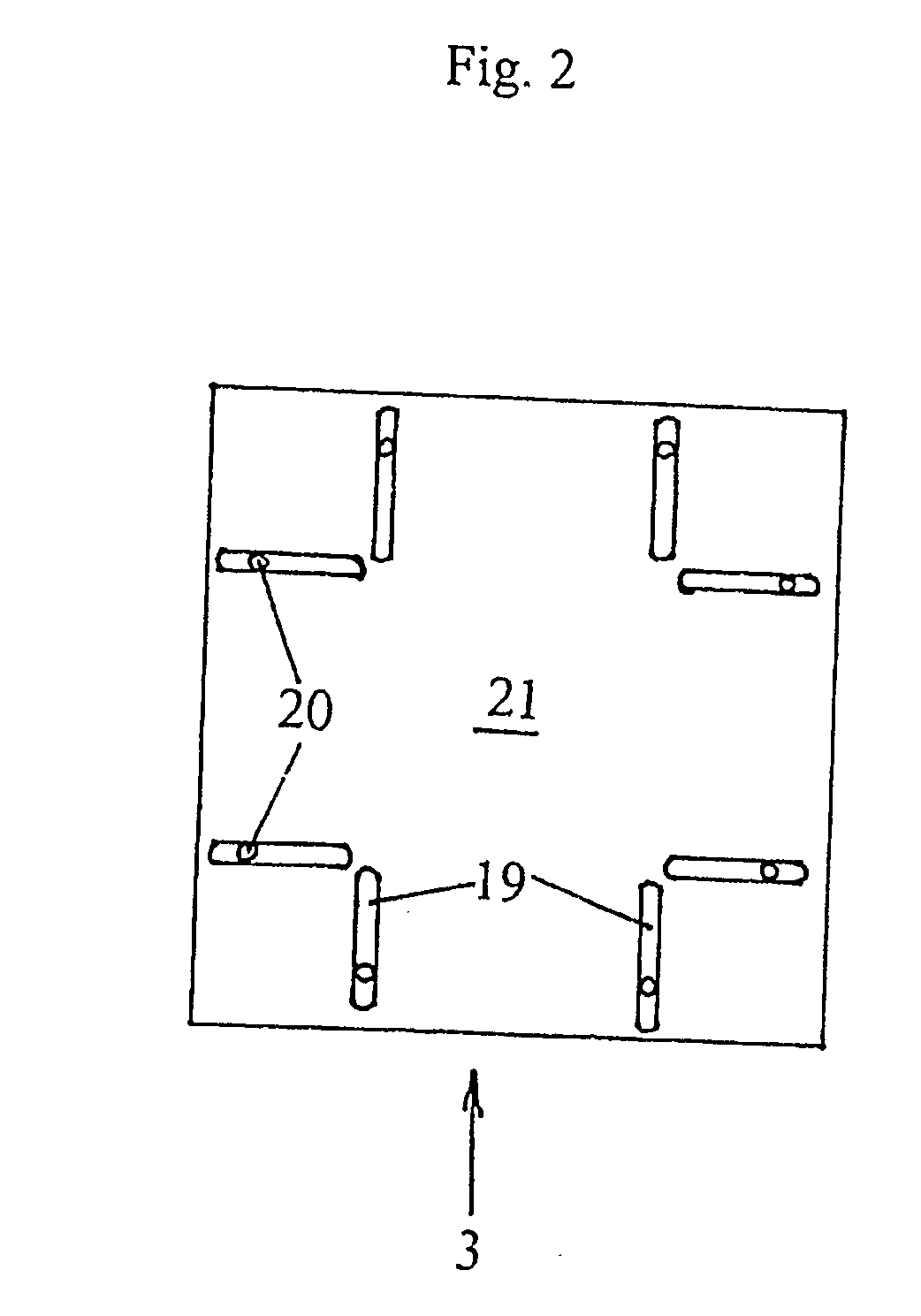
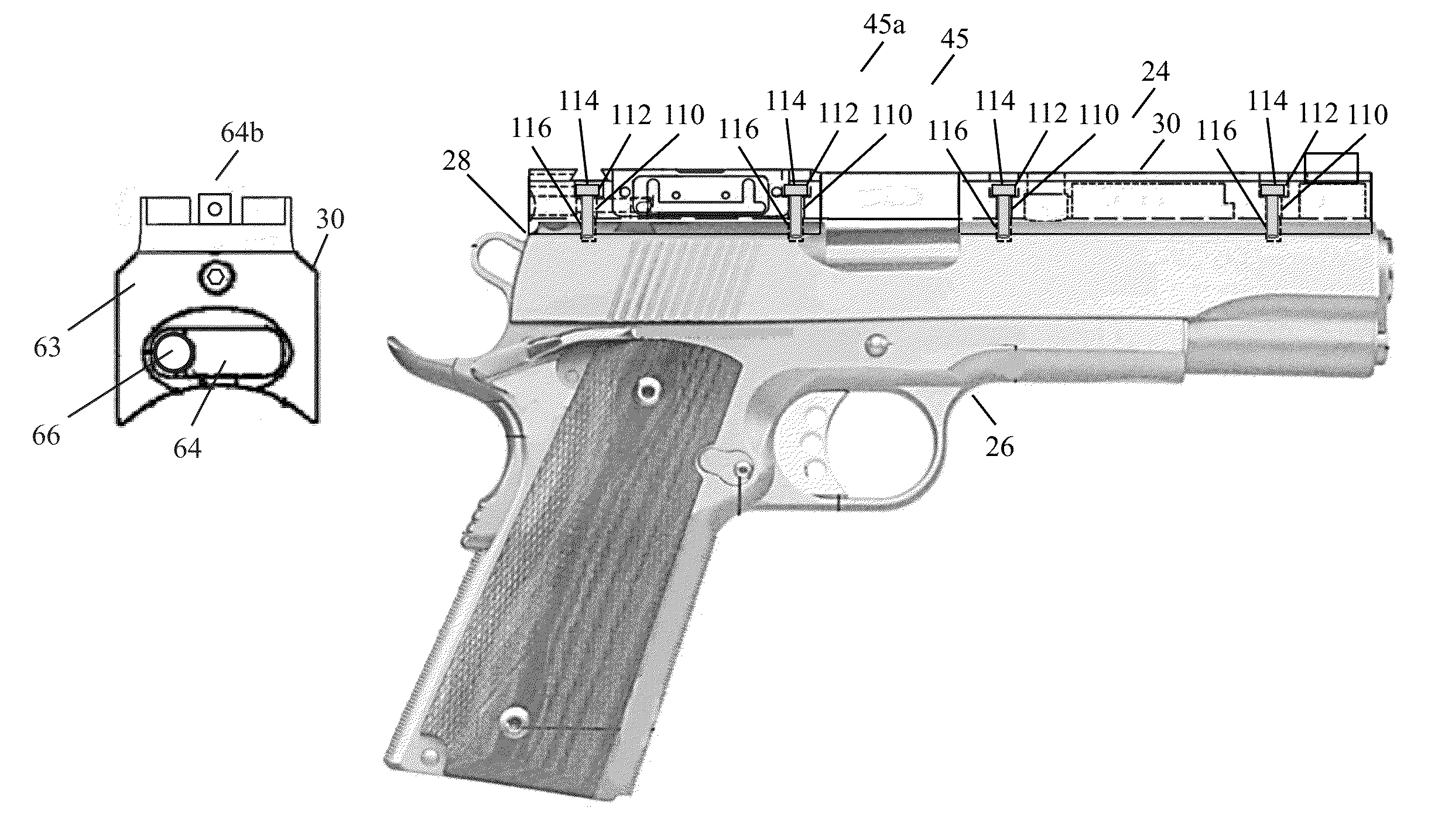
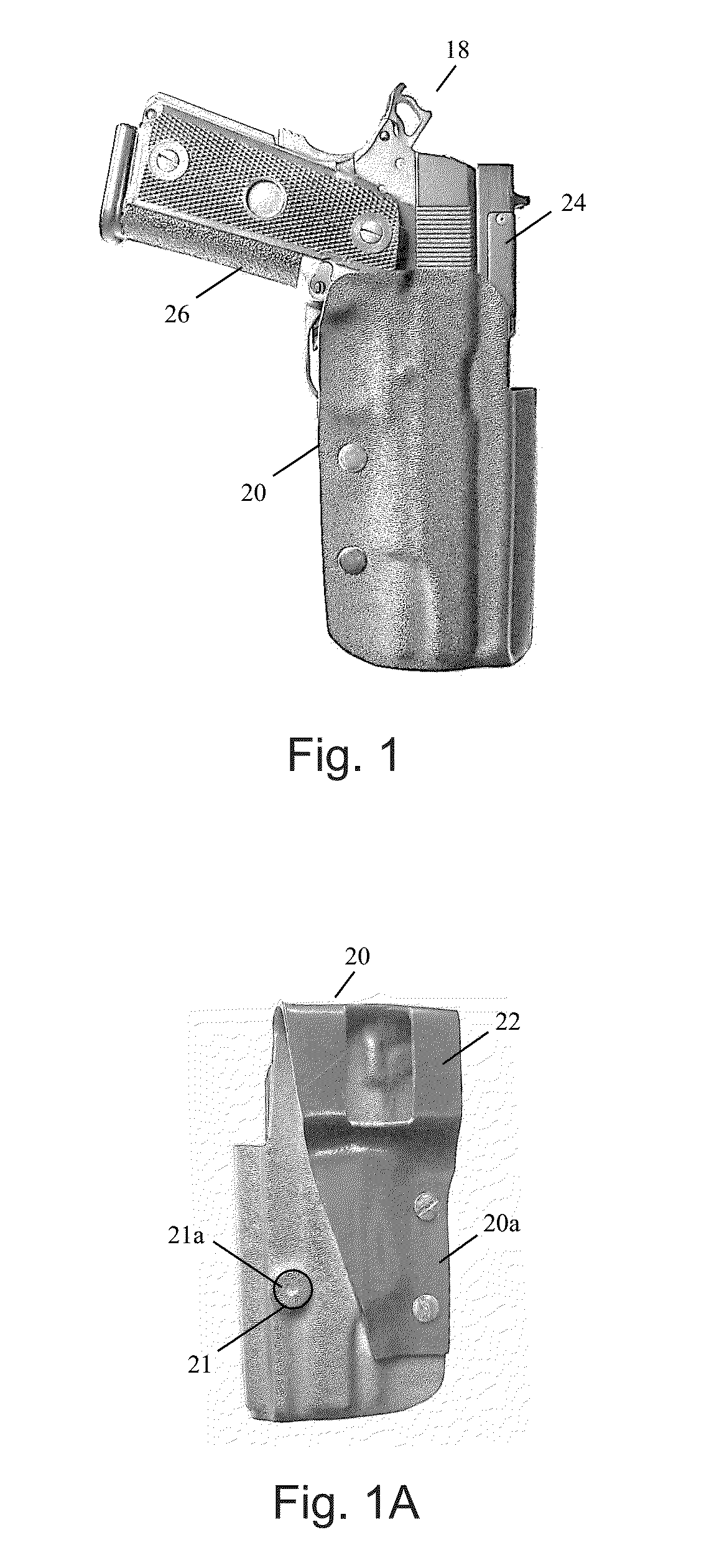
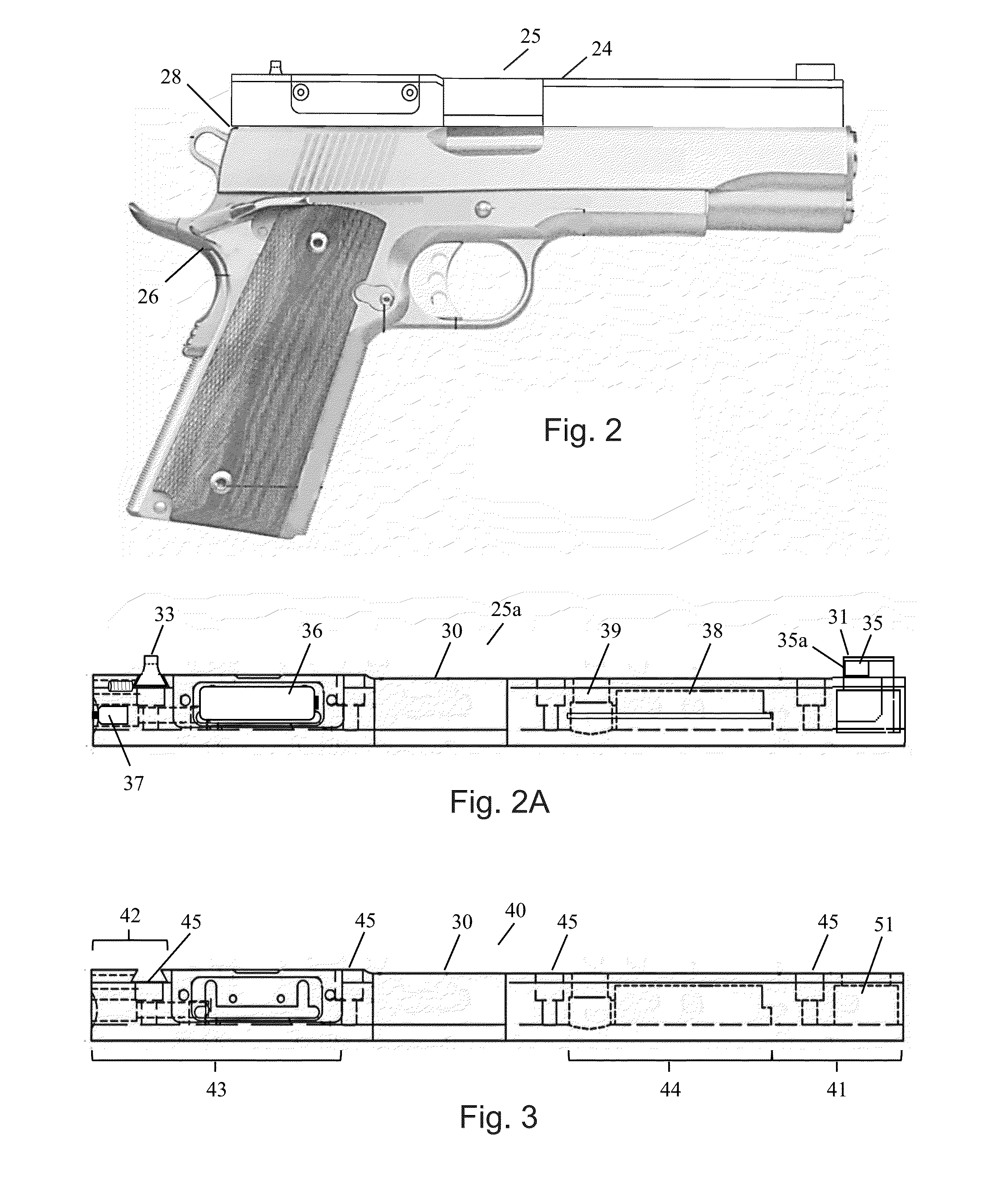
Handgun automatic sighting system
A handgun sighting system that adjusts the intensity of a lighted front sight based on the ambient light conditions. A sighting rib on the handgun includes an electronic circuit having a power supply, a light emitting diode (LED), a photocell, and a reed switch. A holster for use with the sighting system includes a magnet therein. Return of the handgun to the holster brings the reed switch of the weapon in close proximity to the magnet and deactivates the LED and the electronic circuit. Withdrawal of the handgun from the holster activates the LED and the electronic circuit. The handgun sighting system automatically adjusts the intensity of the LED in accordance with changes in the ambient light conditions, as measured by the photocell, to provide an optimal sighting presentation for the shooter.
Owner:PATTERSON WILLIAM Q +1
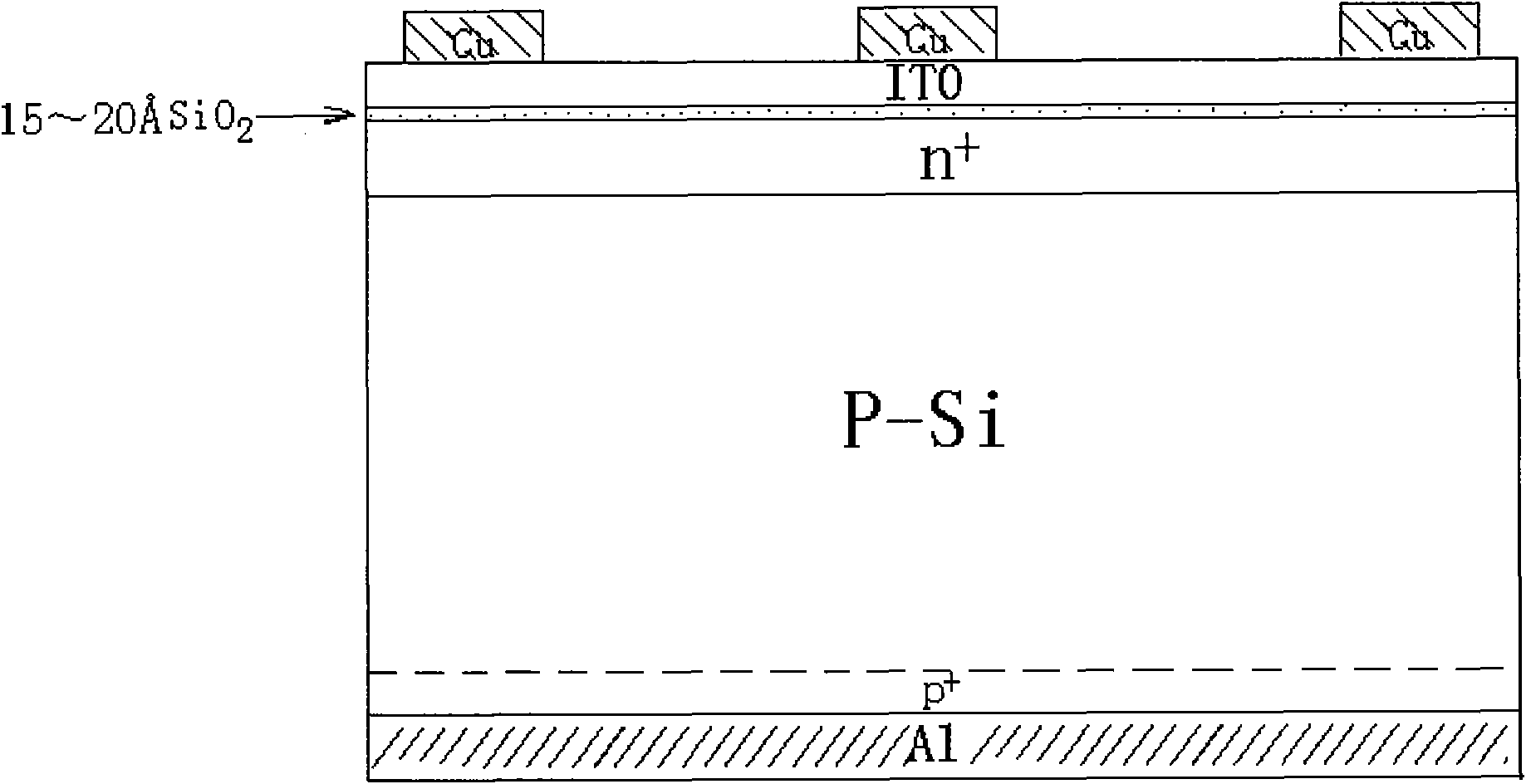
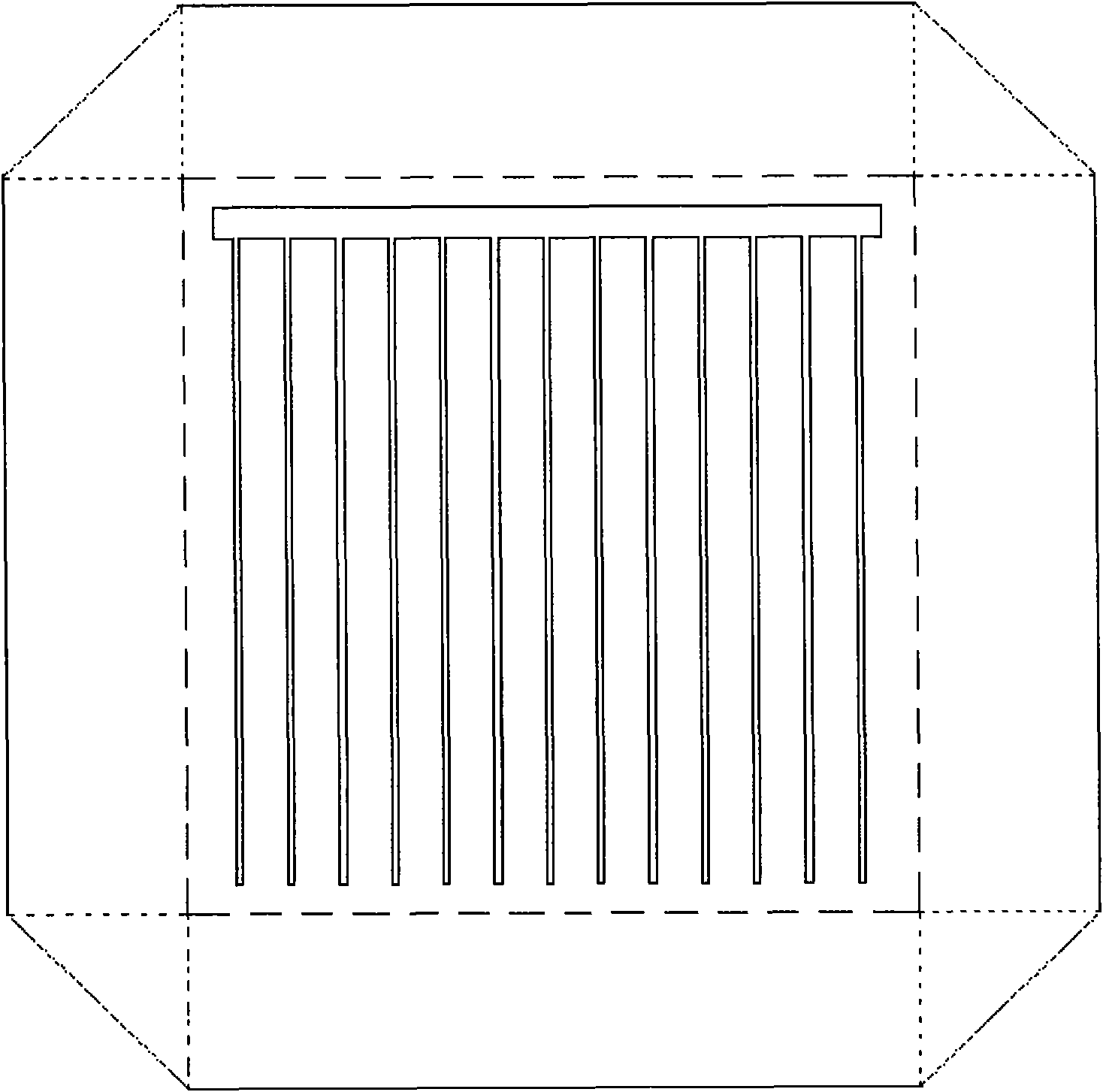
Novel SINP silicone blue-violet battery and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101587913AImprove quantum efficiencyReduce the impactFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationRadio frequency magnetron sputteringSingle crystal
he invention relates to a novel SINP silicone blue-violet battery and a preparation method thereof. The invention uses shallow junctions formed from thermally diffused phosphorus, an ultra-thin SiO2 layer formed by low-temperature thermal oxidization and an ITO dereflection / collection electrode film formed by RF magnetron sputtering to prepares a novel ITO / SiO2 / np blue-violet reinforced SINP silicone photo-battery. Preparation method of the invention is to take a silicon single crystal flake which is P type, and has crystallographic orientation of 100, electric resistivity of 2 2omega.cm and thickness of 220mu m, as a substrate. The substrate is cleaned and is etched by routine chemistry, and then is thermally diffused by POC3 liquid source to form n regions (the invention prepares two pieces of novel SINP photo-batteries, one being routine SINP photo-battery having emitting region square resistance of 10 Omega / square and junction depth of 1 Mu m, and the other one being SINP silicone blue-violet battery having emitting region square resistance of 37 Omega / square and junction depth of 0.4 Mu m). Removing the phosphorosilicate glass (HF:H2O=1:10) at front face; steaming Al at back of the silicon chip; thermally oxidizing the silicon chip at 400 to 500 DEG C and condition of V2:O2=4:1 for 15 to 30min to generate a layer of 15 to 20 ultra-thin SiO2 layer, and at the same time alloying the Al at the back. Then RF magnetron sputtering the ITO dereflection / collection electrode film (ITO film is also deposited on the glass to study electrooptical characteristic thereof) having high transmittance and high conductivity, and sputtering a Cu gate electrode by metal mask direct-current magnetron. Finally, cutting the outer edge part of the battery by a diamond excircle downward cutting / a dicing saw so as to prevent short circuit of the edge of the photo-battery.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com