Patents
Literature
2136results about "Material thermal conductivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
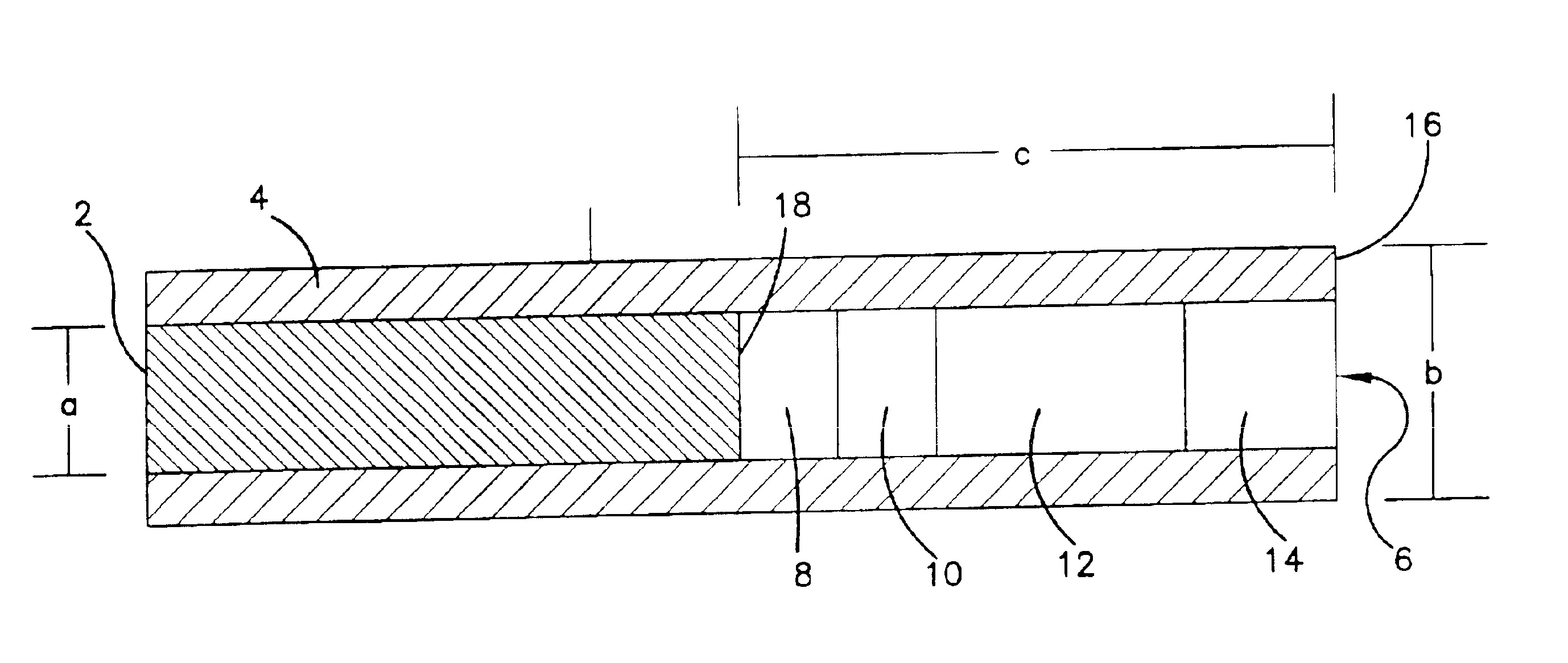
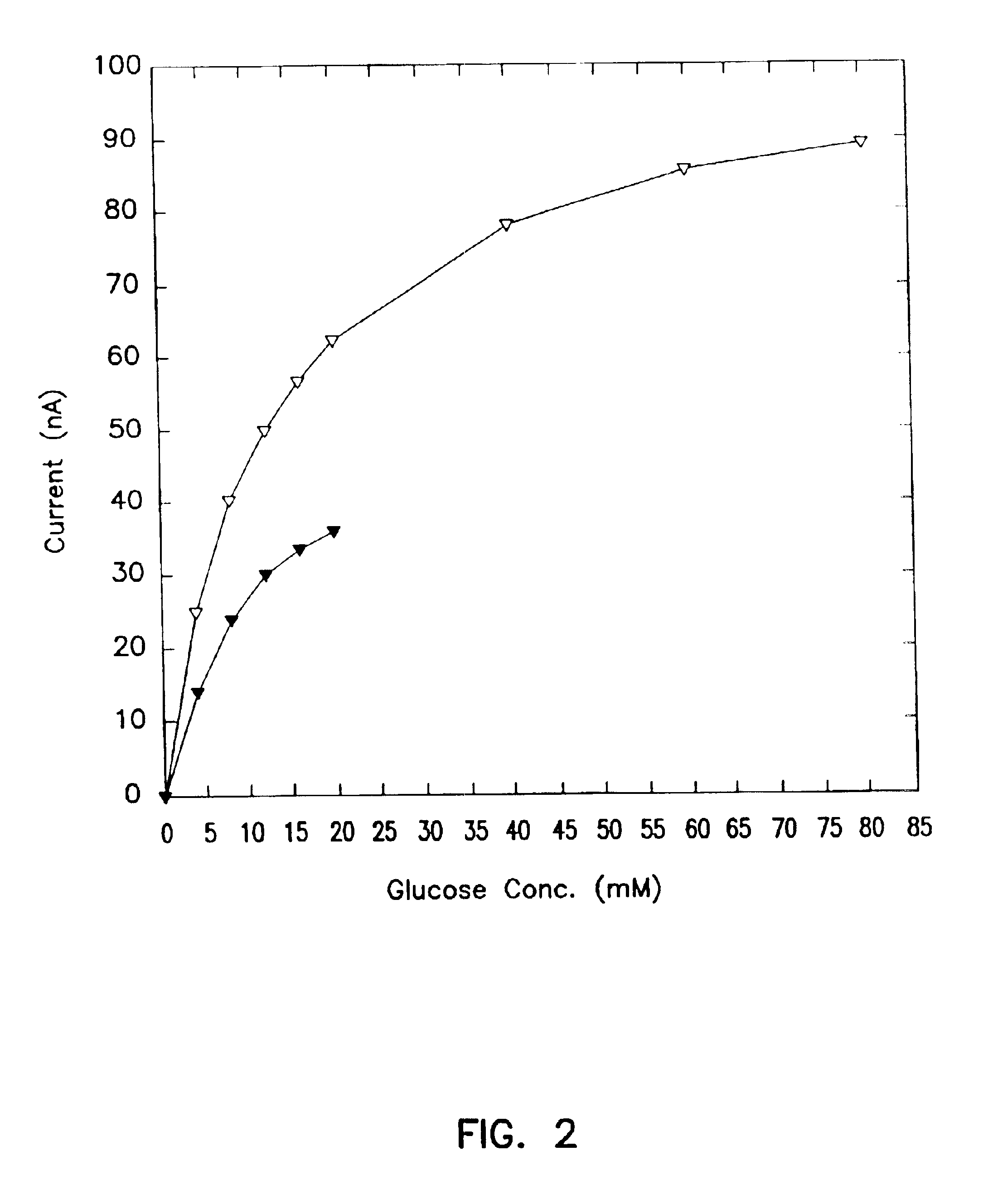
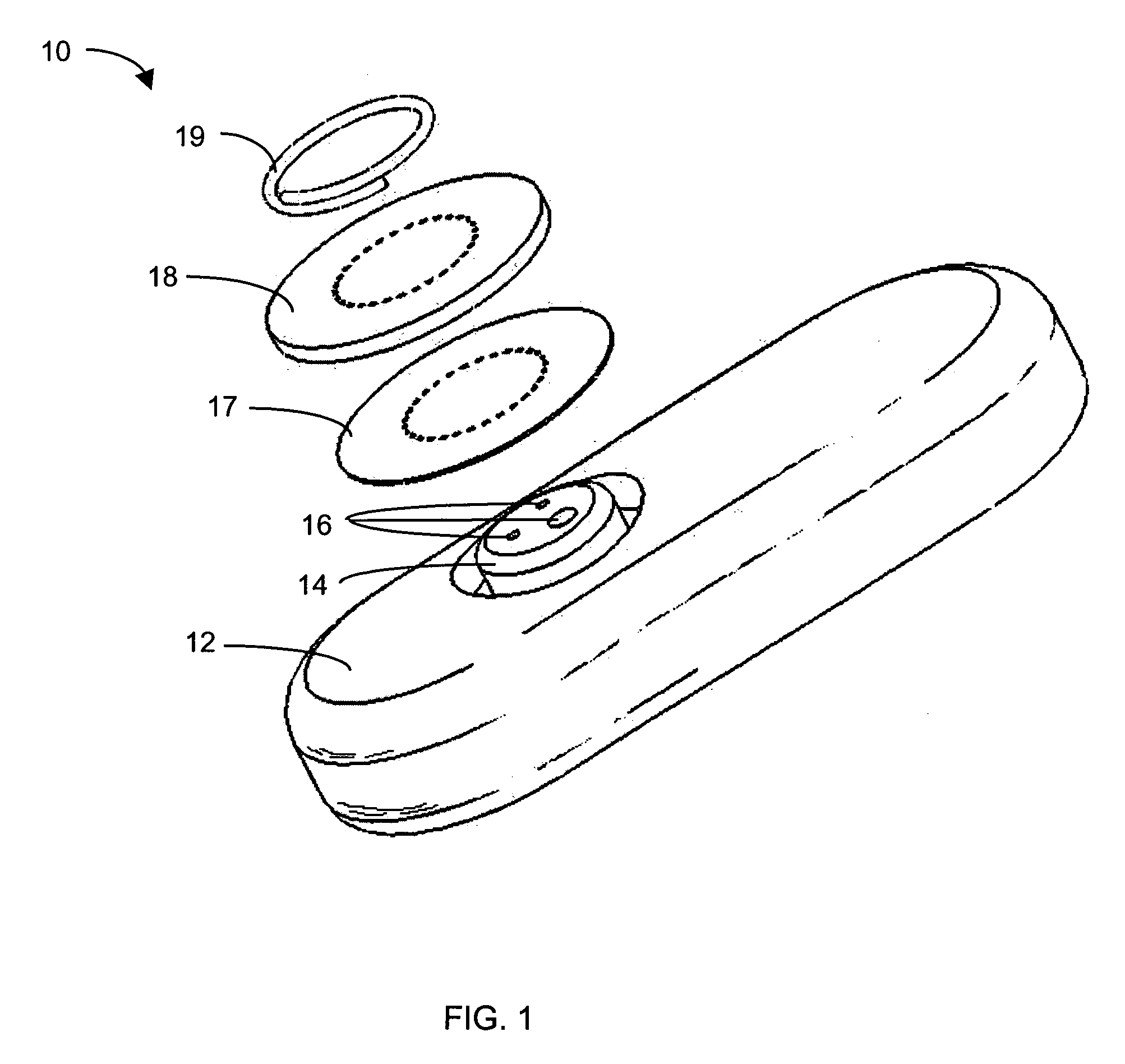
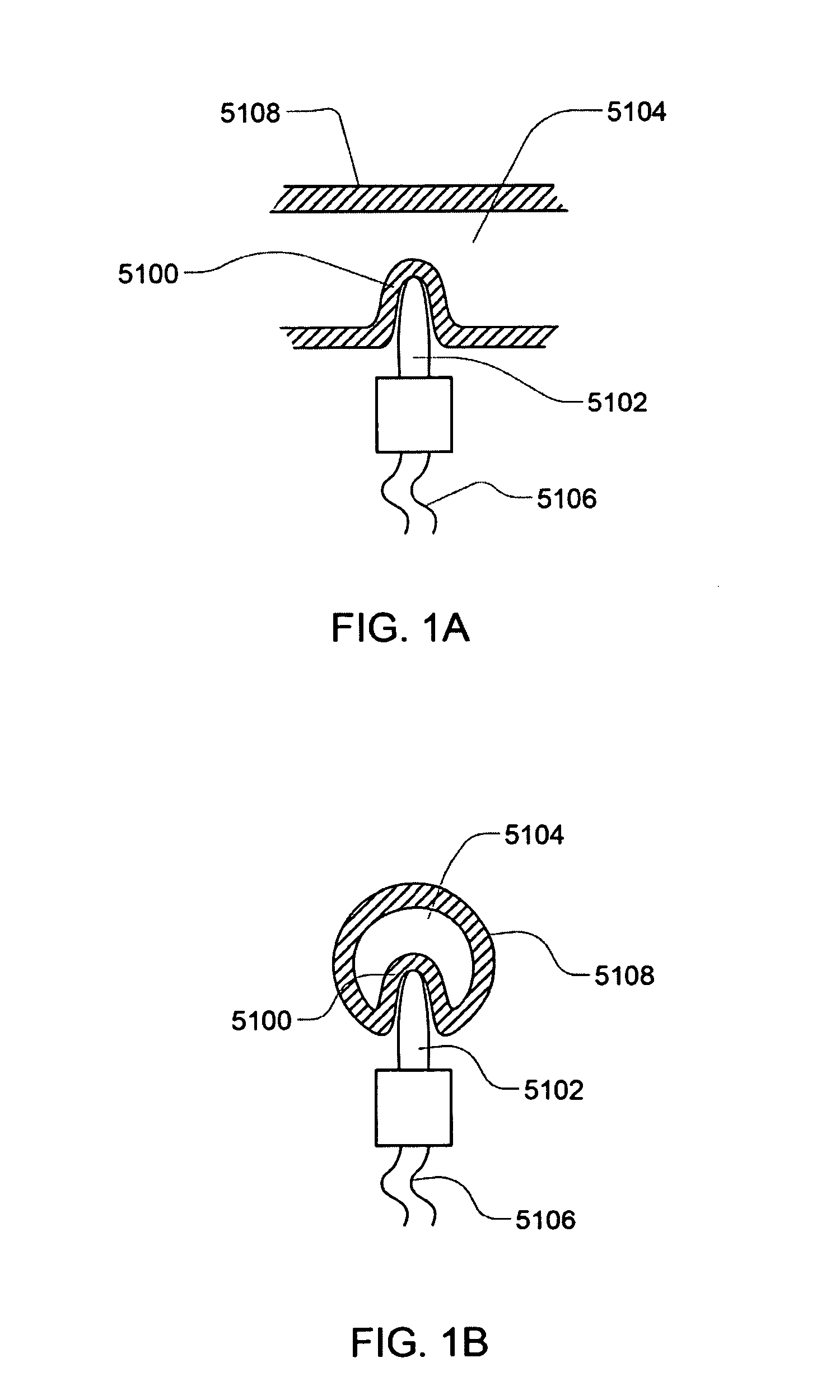
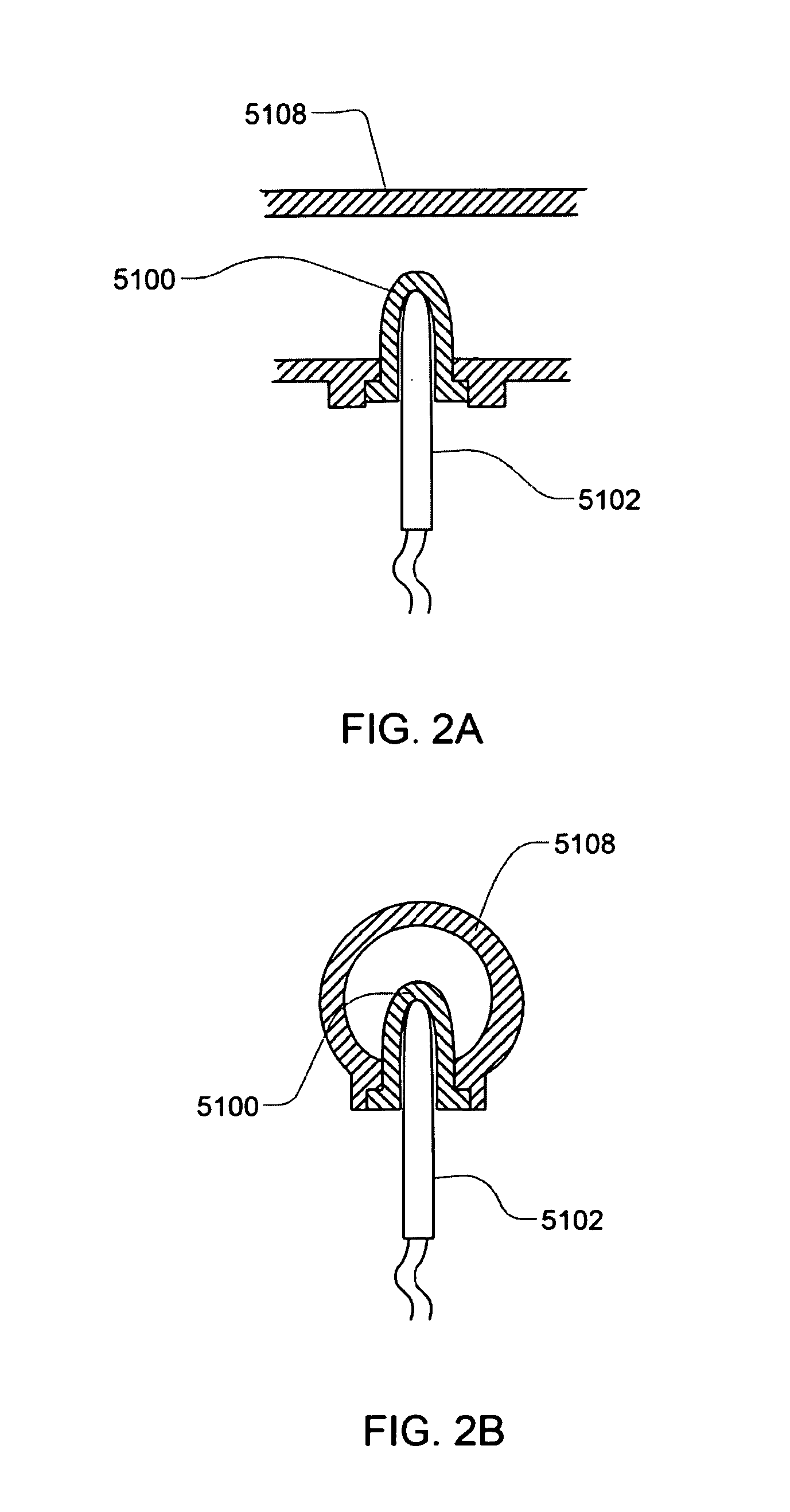
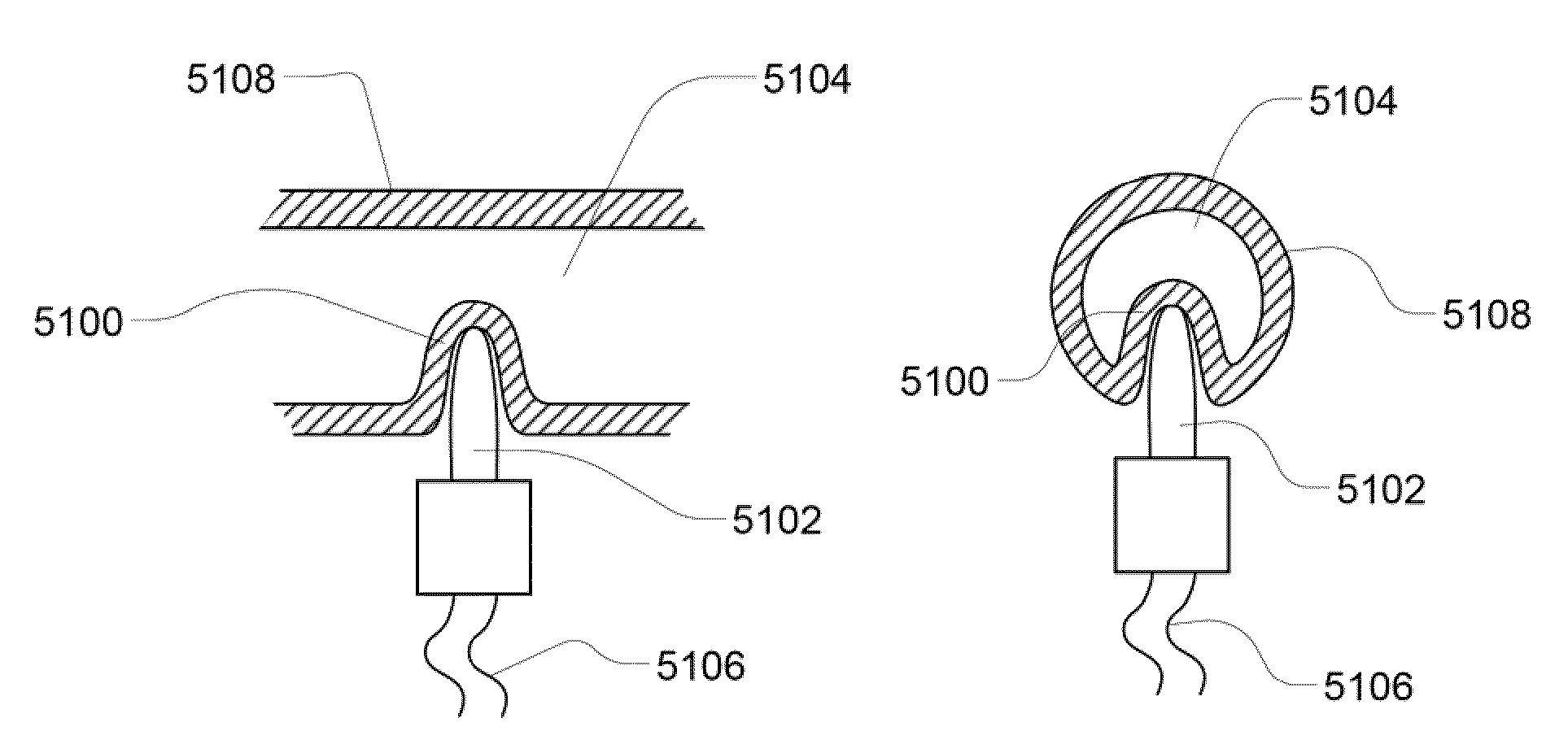
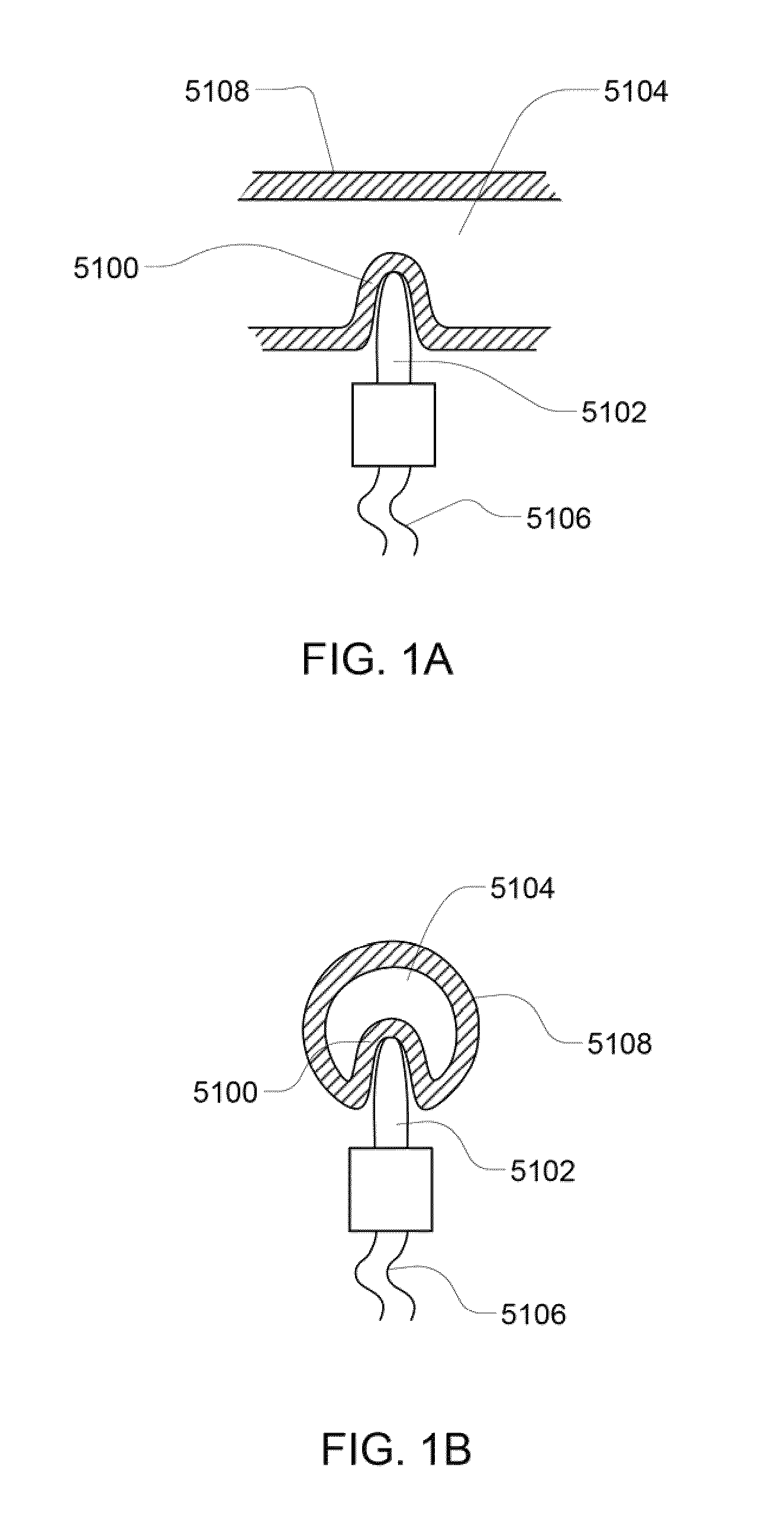
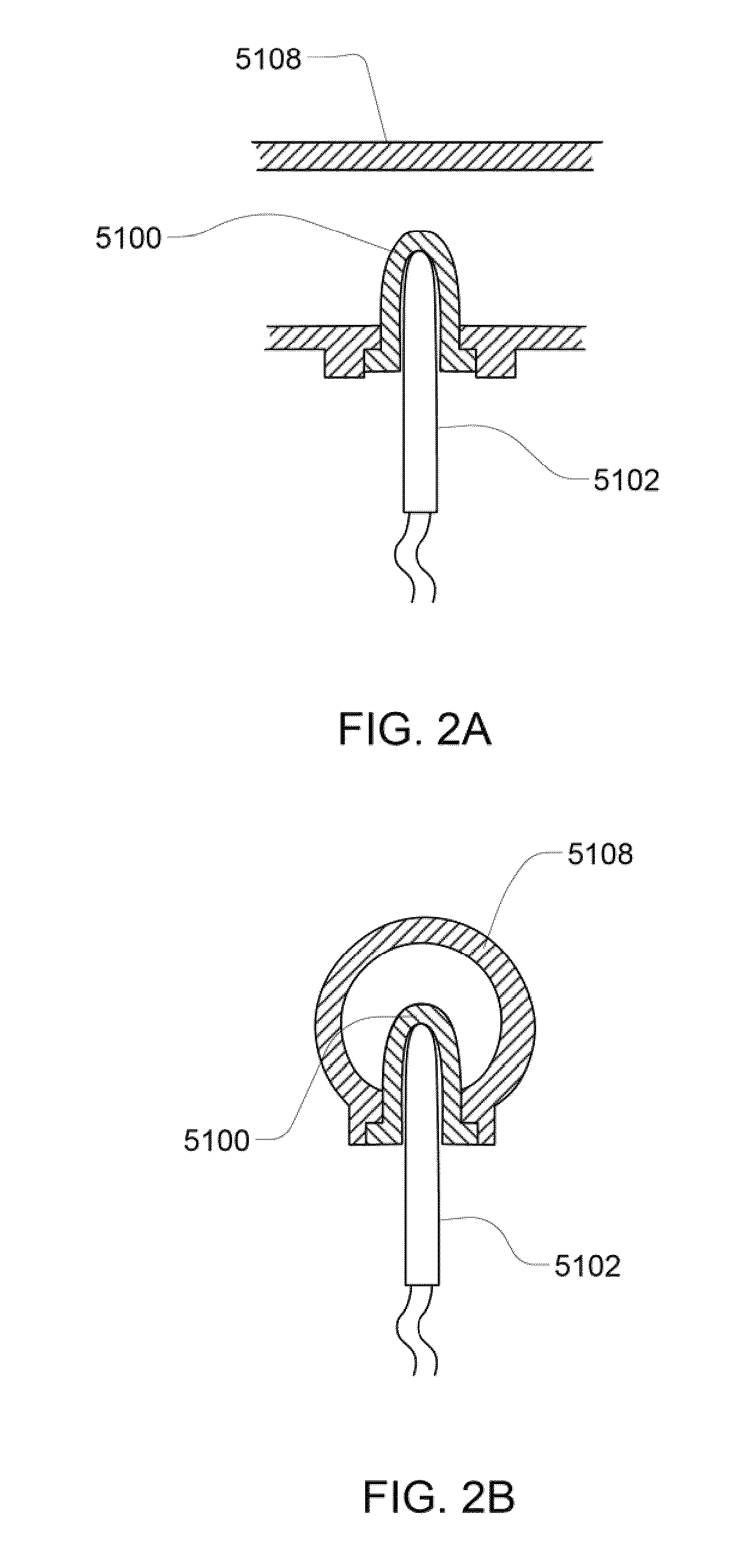
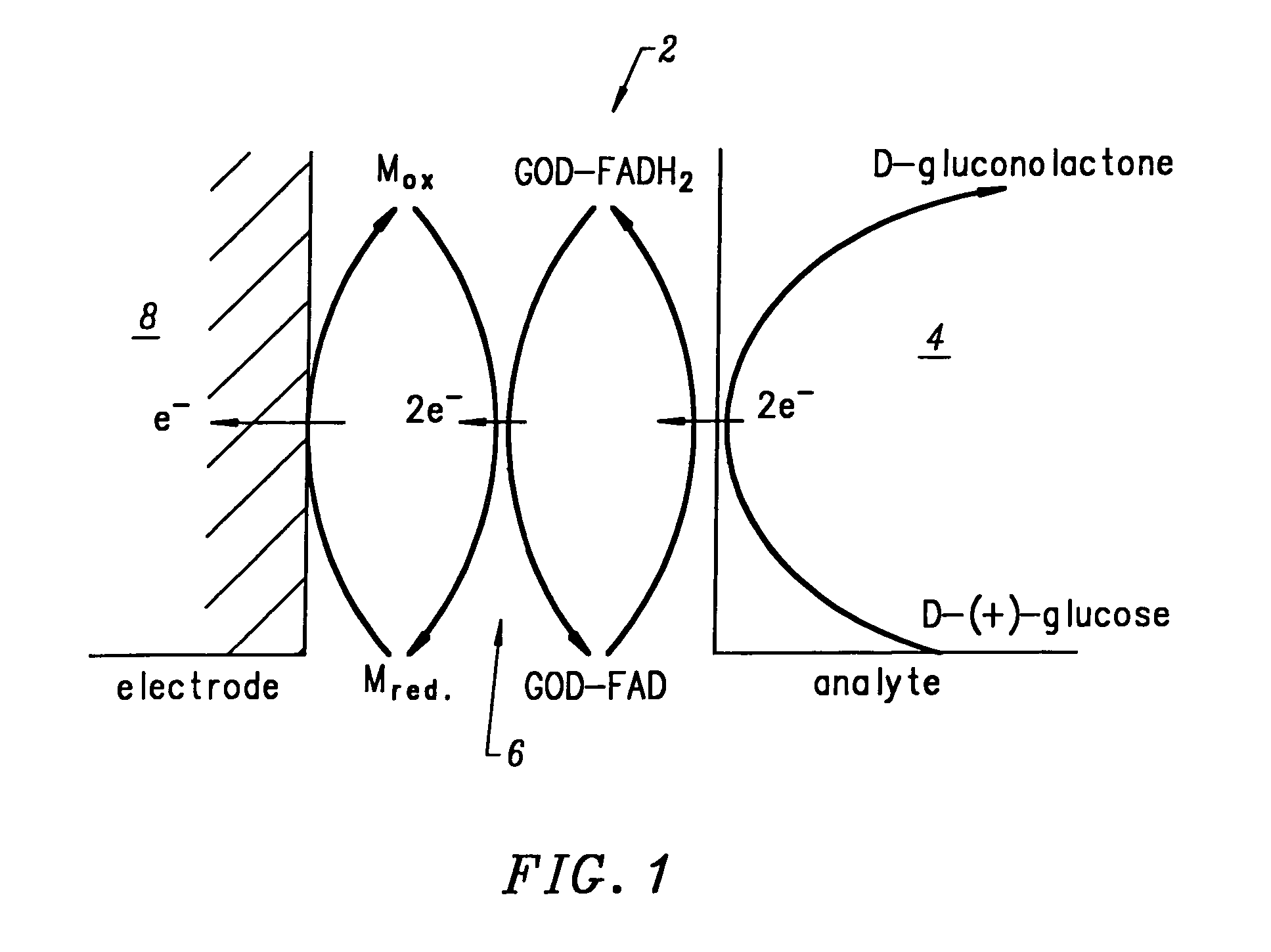
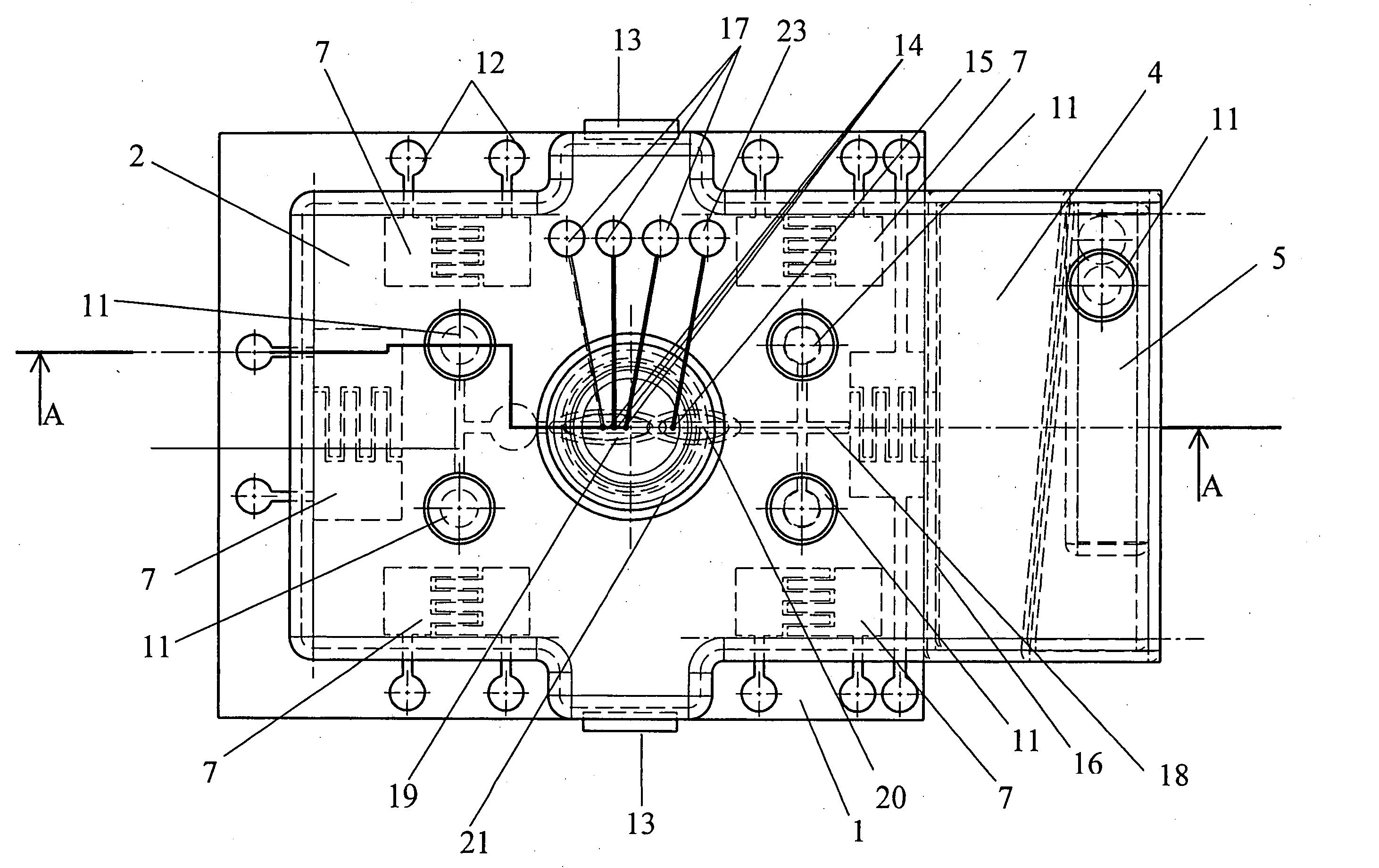
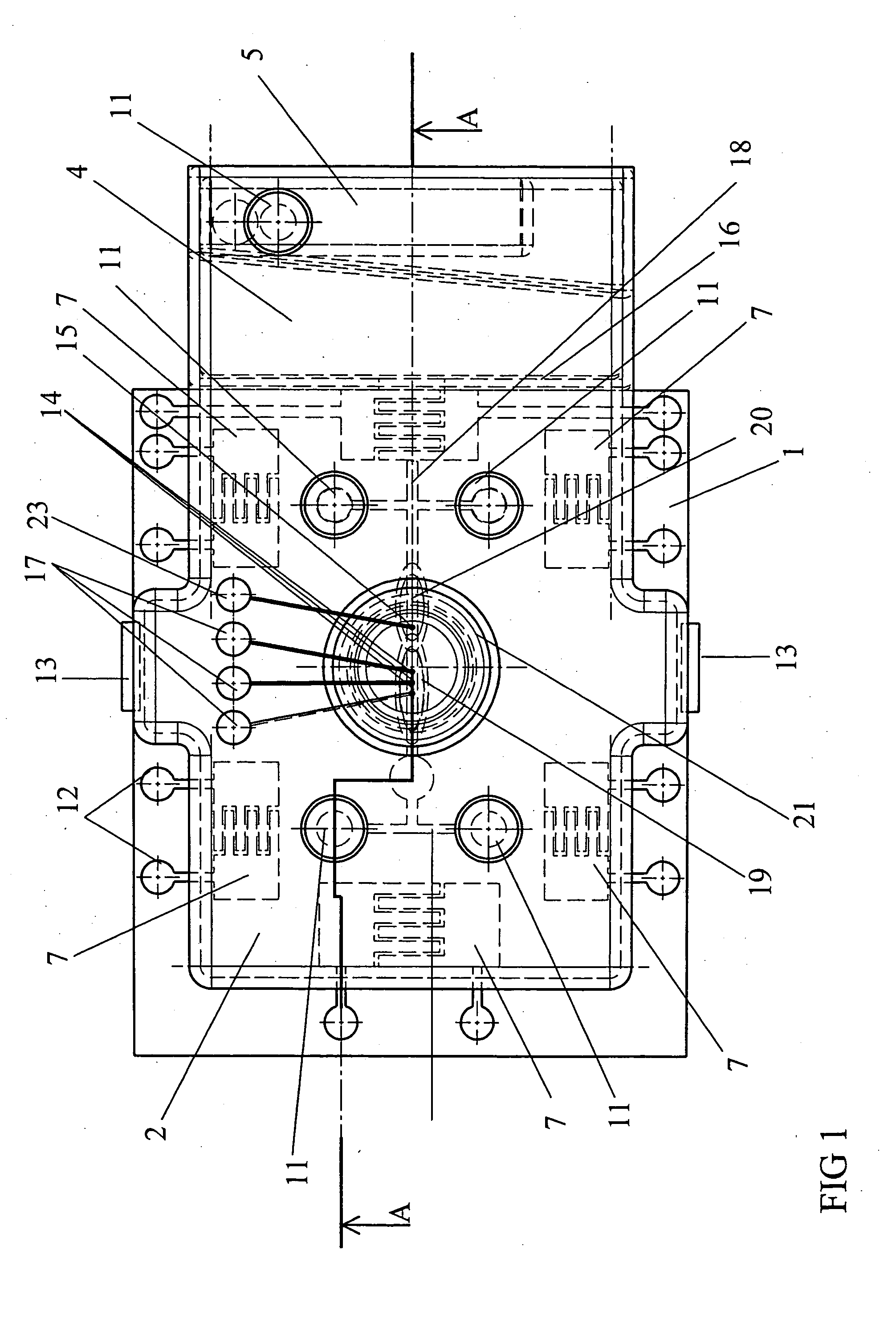
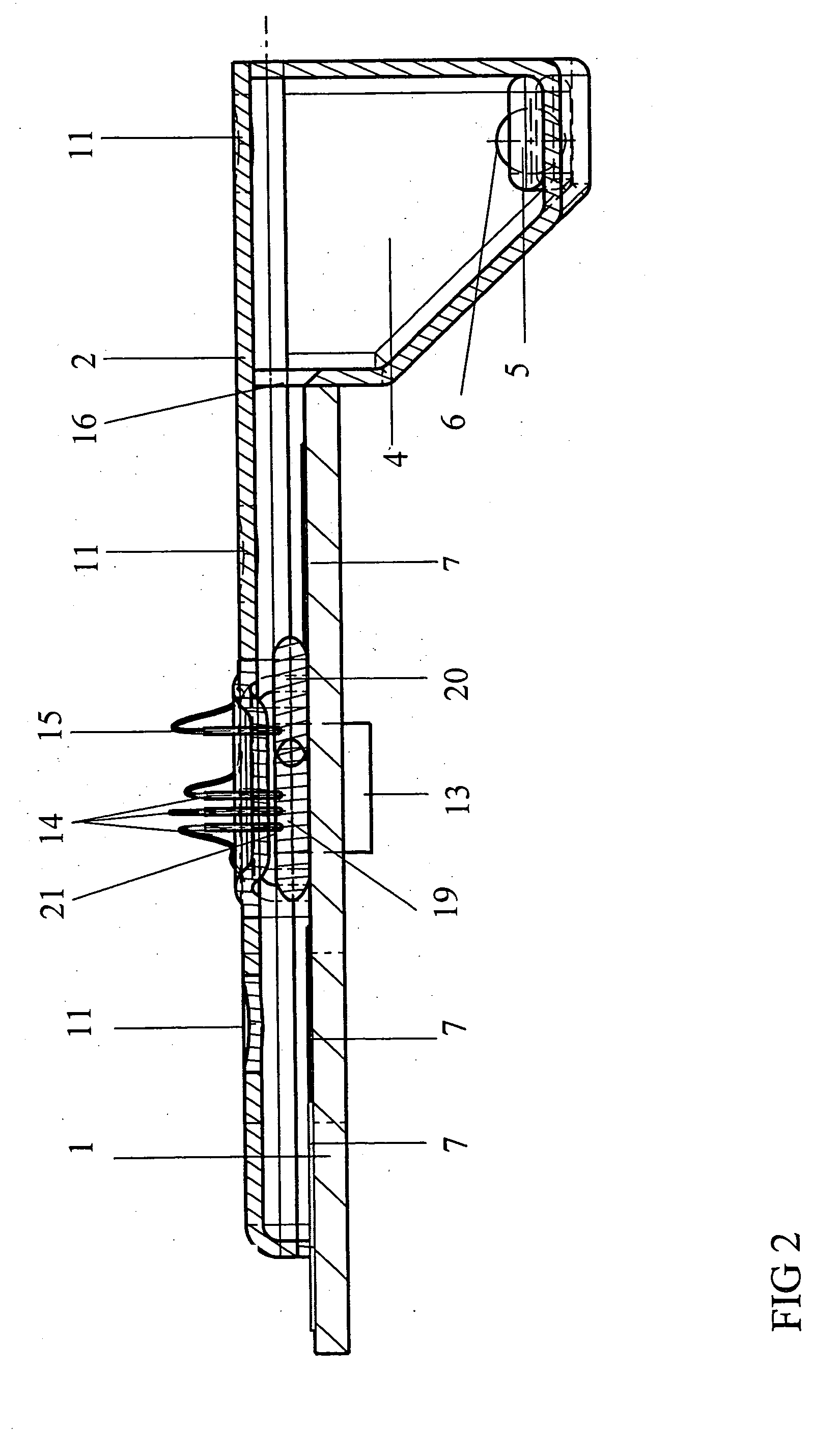
Subcutaneous glucose electrode
InactiveUS6881551B2Reduce transportationAccurate measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsConcentrations glucosePolyamide
A small diameter flexible electrode designed for subcutaneous in vivo amperometric monitoring of glucose is described. The electrode is designed to allow “one-point” in vivo calibration, i.e., to have zero output current at zero glucose concentration, even in the presence of other electroreactive species of serum or blood. The electrode is preferably three or four-layered, with the layers serially deposited within a recess upon the tip of a polyamide insulated gold wire. A first glucose concentration-to-current transducing layer is overcoated with an electrically insulating and glucose flux limiting layer (second layer) on which, optionally, an immobilized interference-eliminating horseradish peroxidase based film is deposited (third layer). An outer (fourth) layer is biocompatible.
Owner:THERASENSE
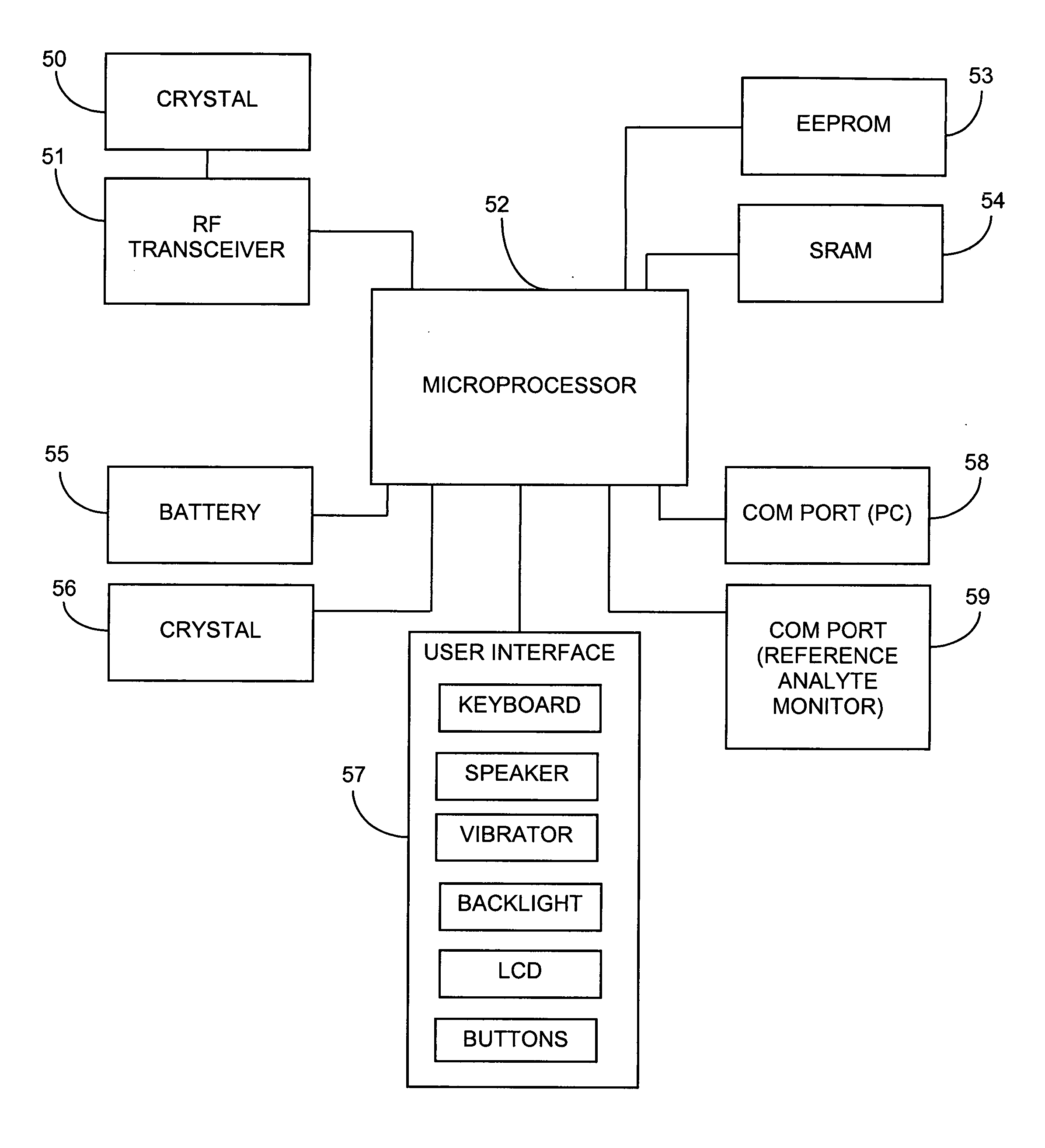
System and methods for processing analyte sensor data
ActiveUS20050027463A1Material thermal conductivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalyteData system
Systems and methods for processing sensor analyte data, including initiating calibration, updating calibration, evaluating clinical acceptability of reference and sensor analyte data, and evaluating the quality of sensor calibration. During initial calibration, the analyte sensor data is evaluated over a period of time to determine stability of the sensor. The sensor may be calibrated using a calibration set of one or more matched sensor and reference analyte data pairs. The calibration may be updated after evaluating the calibration set for best calibration based on inclusion criteria with newly received reference analyte data. Fail-safe mechanisms are provided based on clinical acceptability of reference and analyte data and quality of sensor calibration. Algorithms provide for optimized prospective and retrospective analysis of estimated blood analyte data from an analyte sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM
System and method for analyte measurement
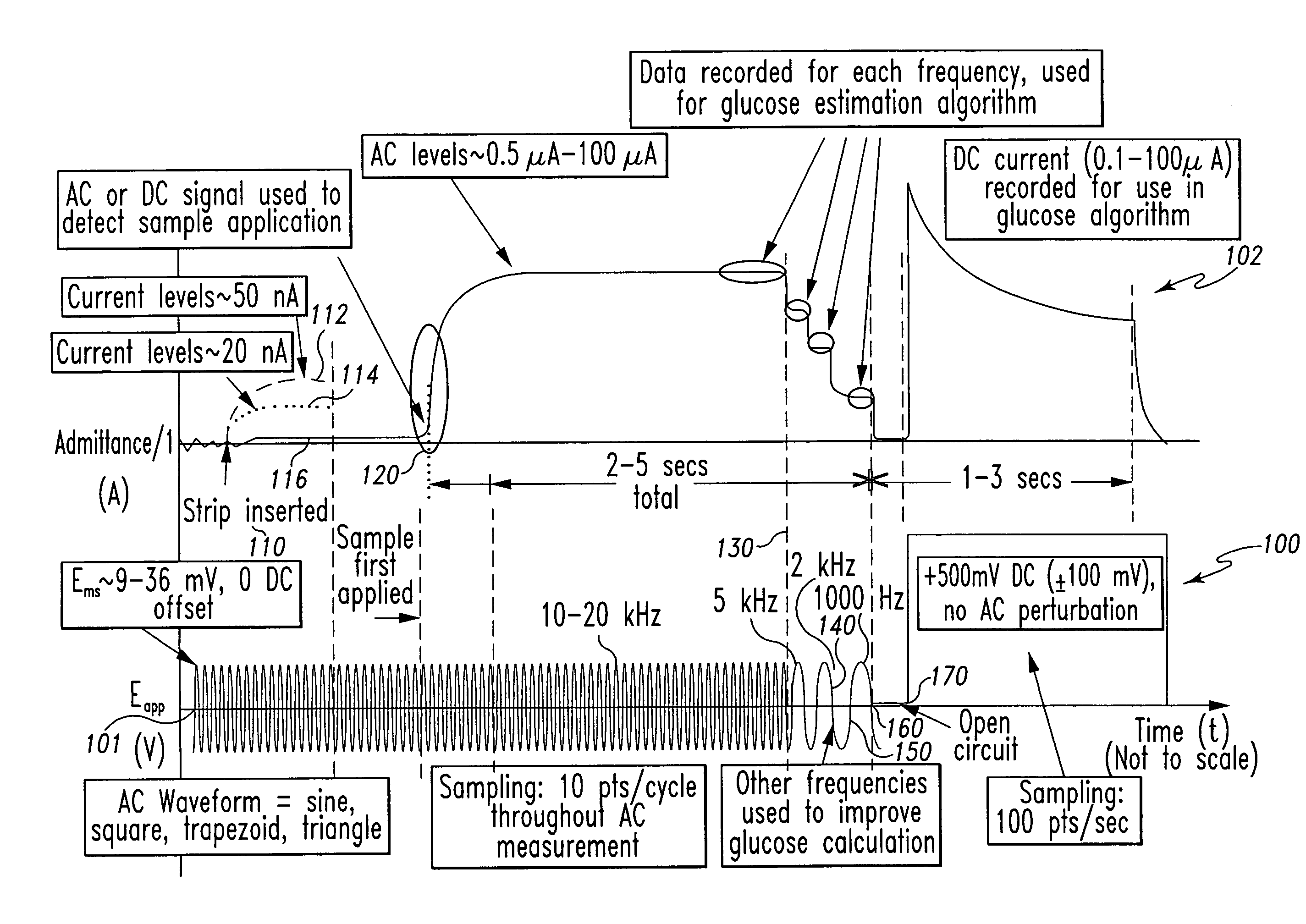
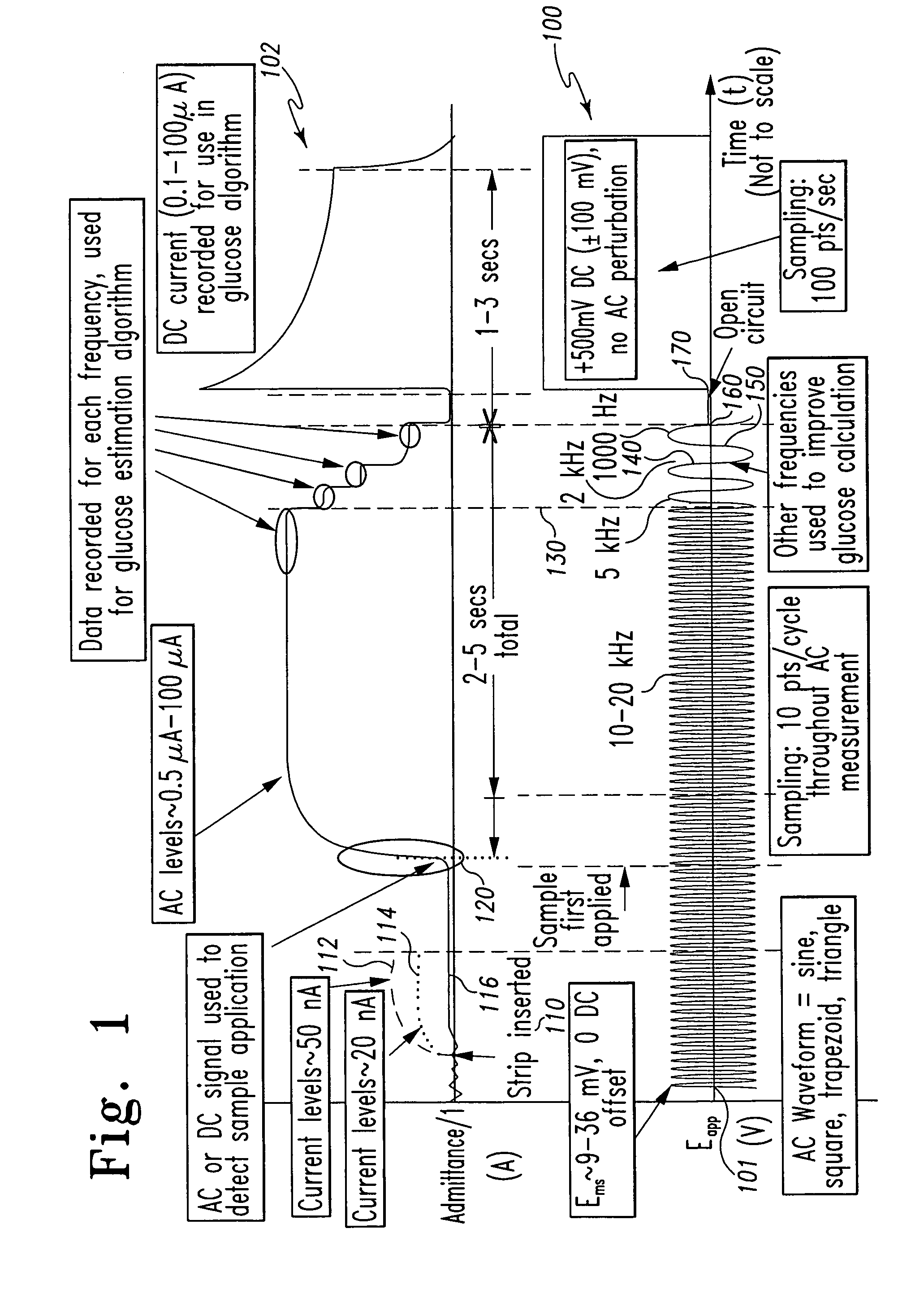
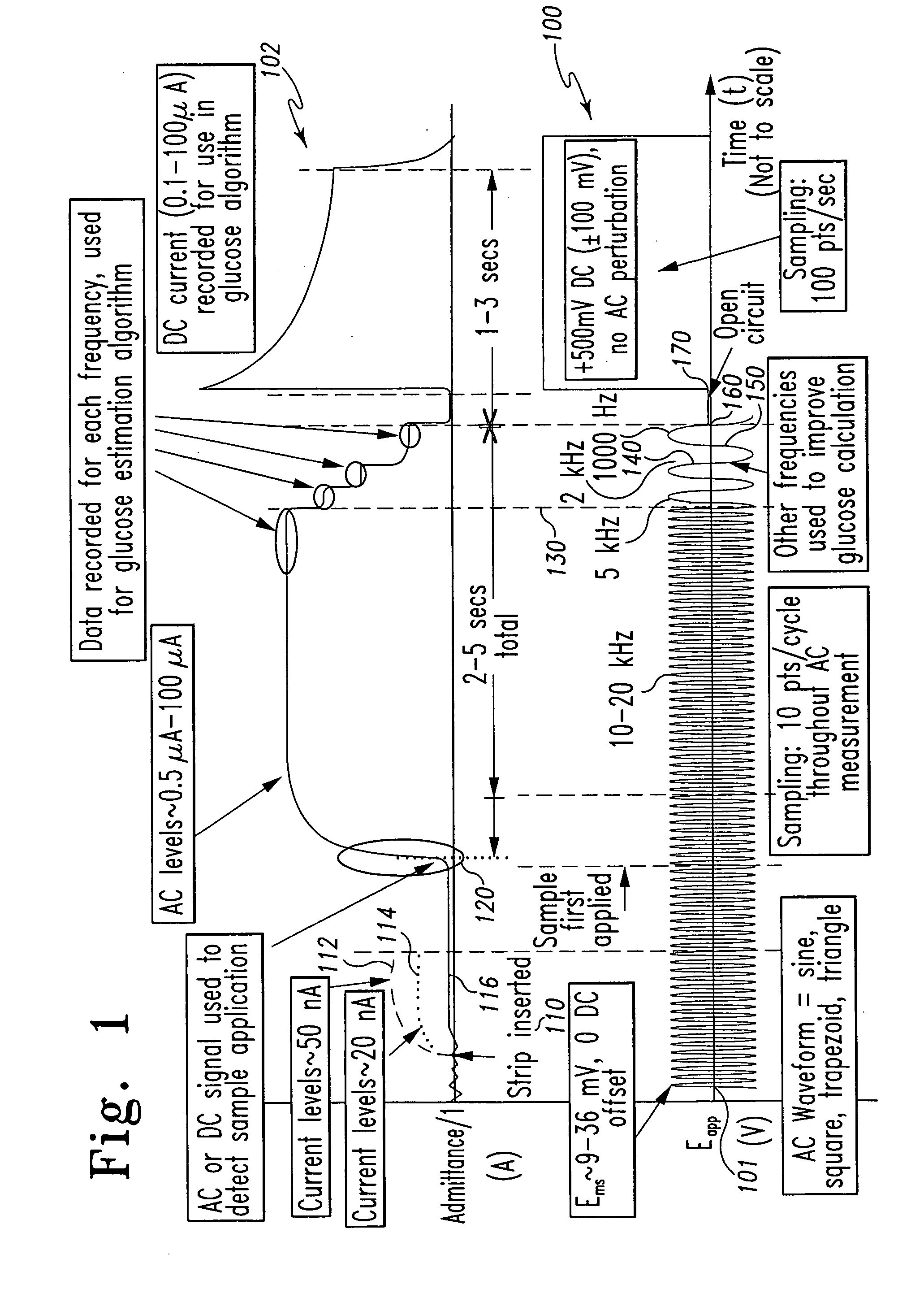
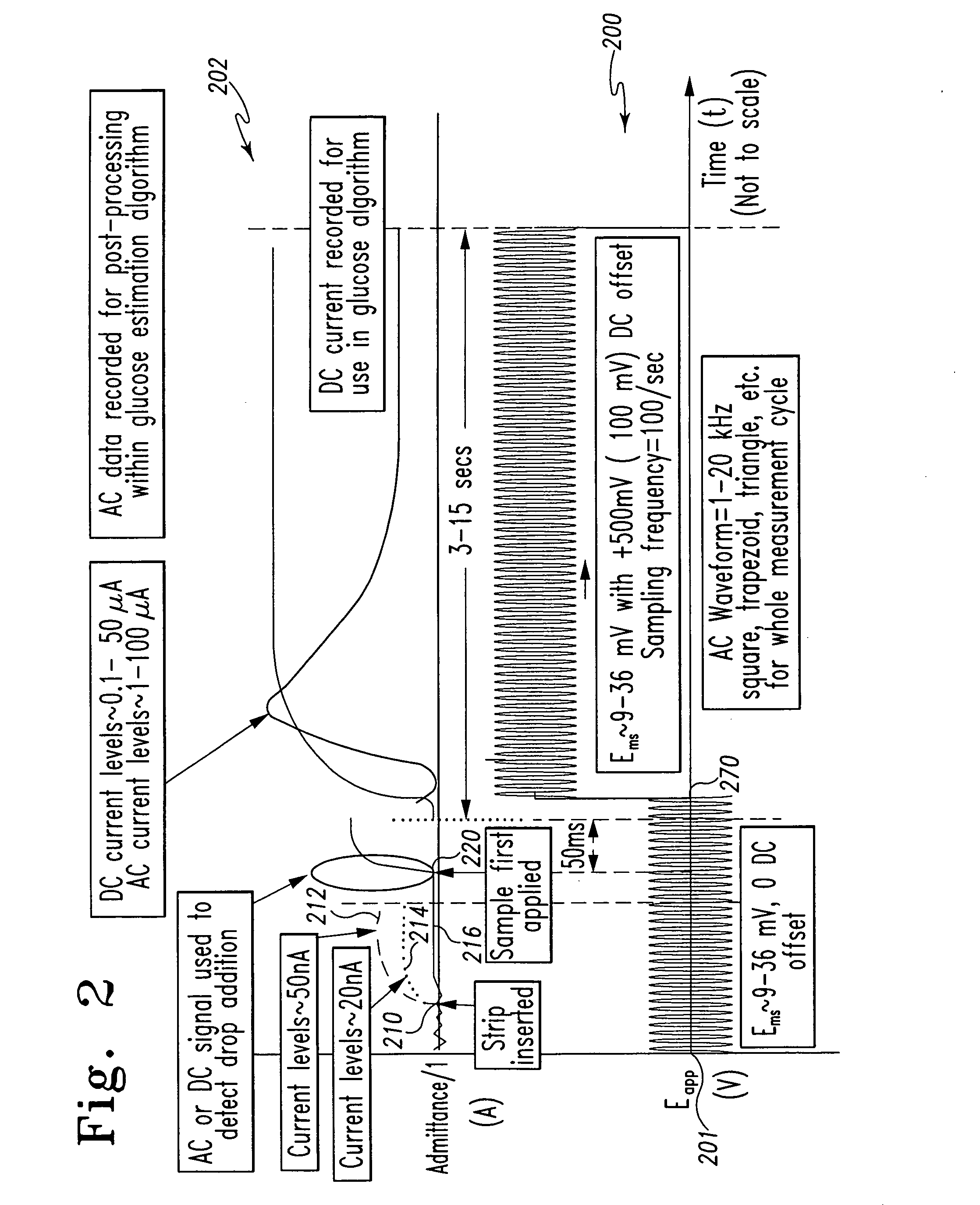
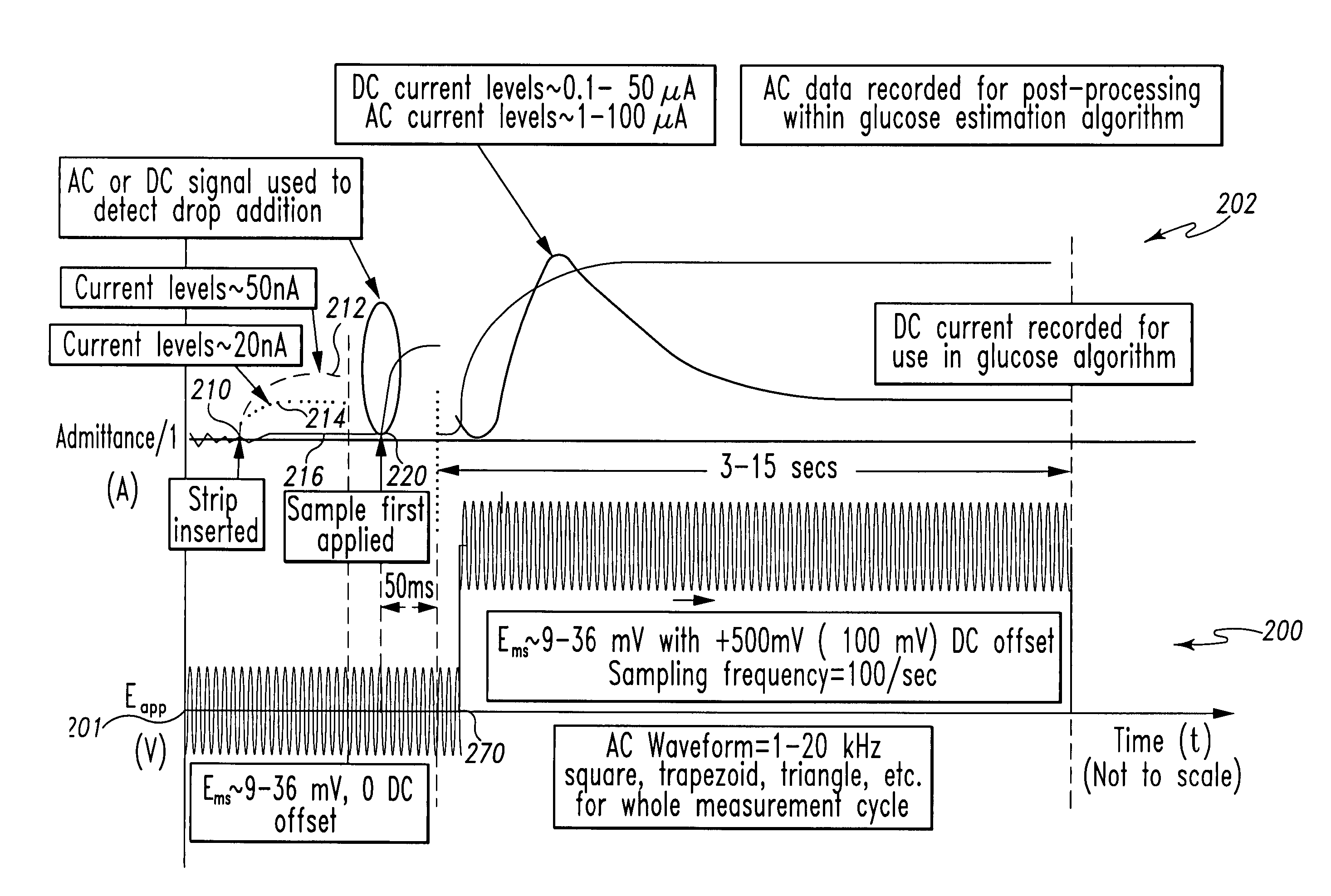
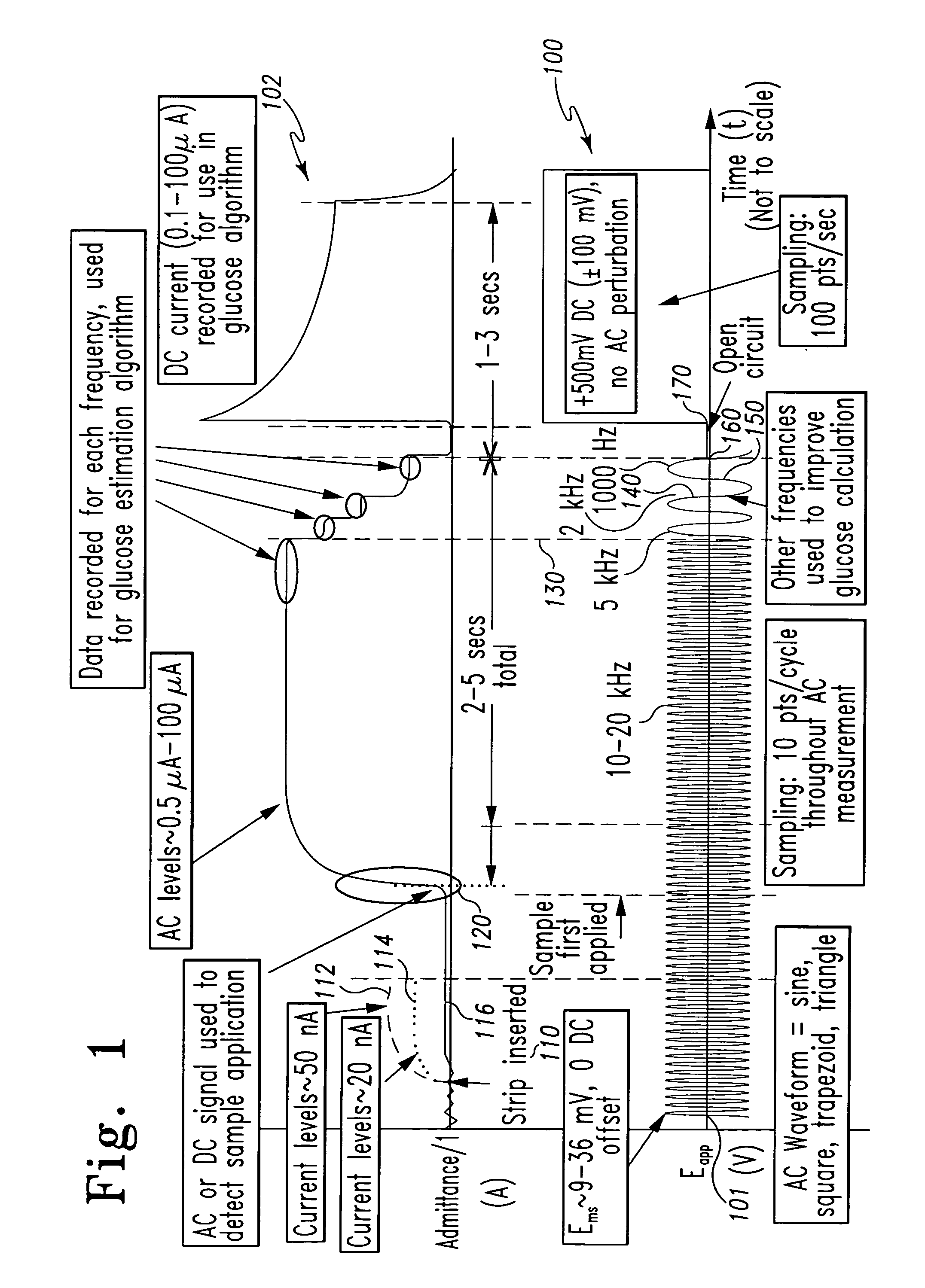
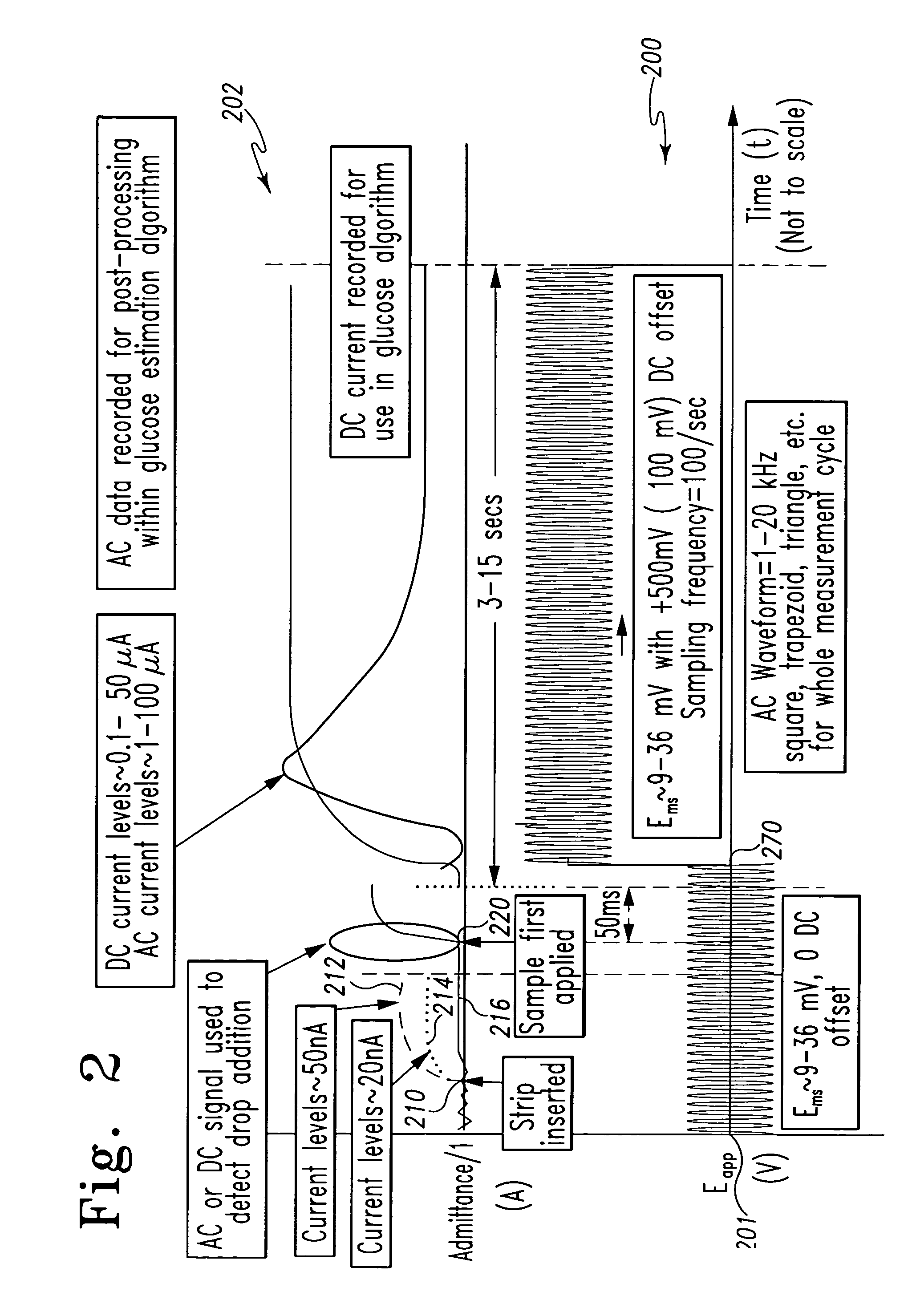
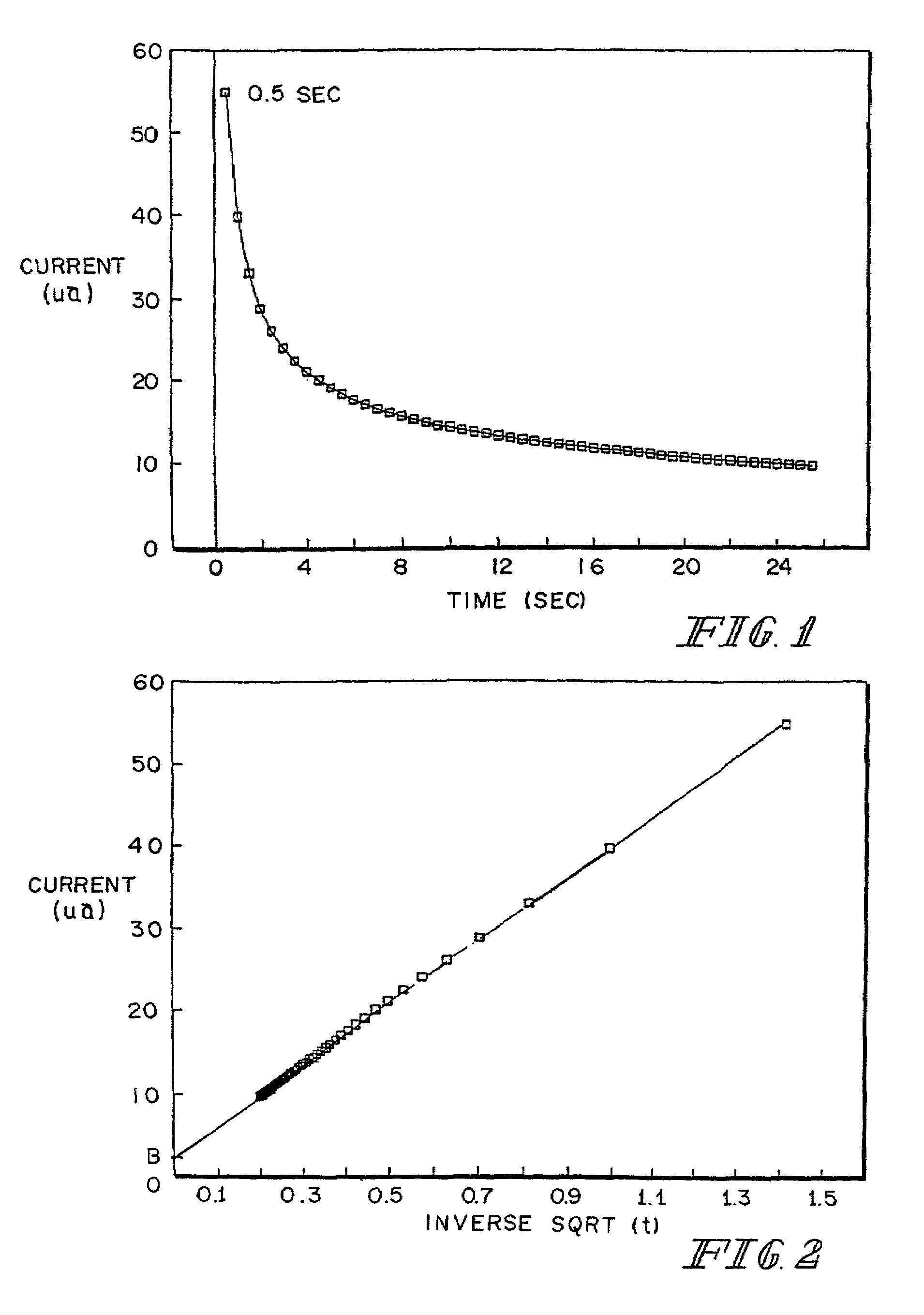
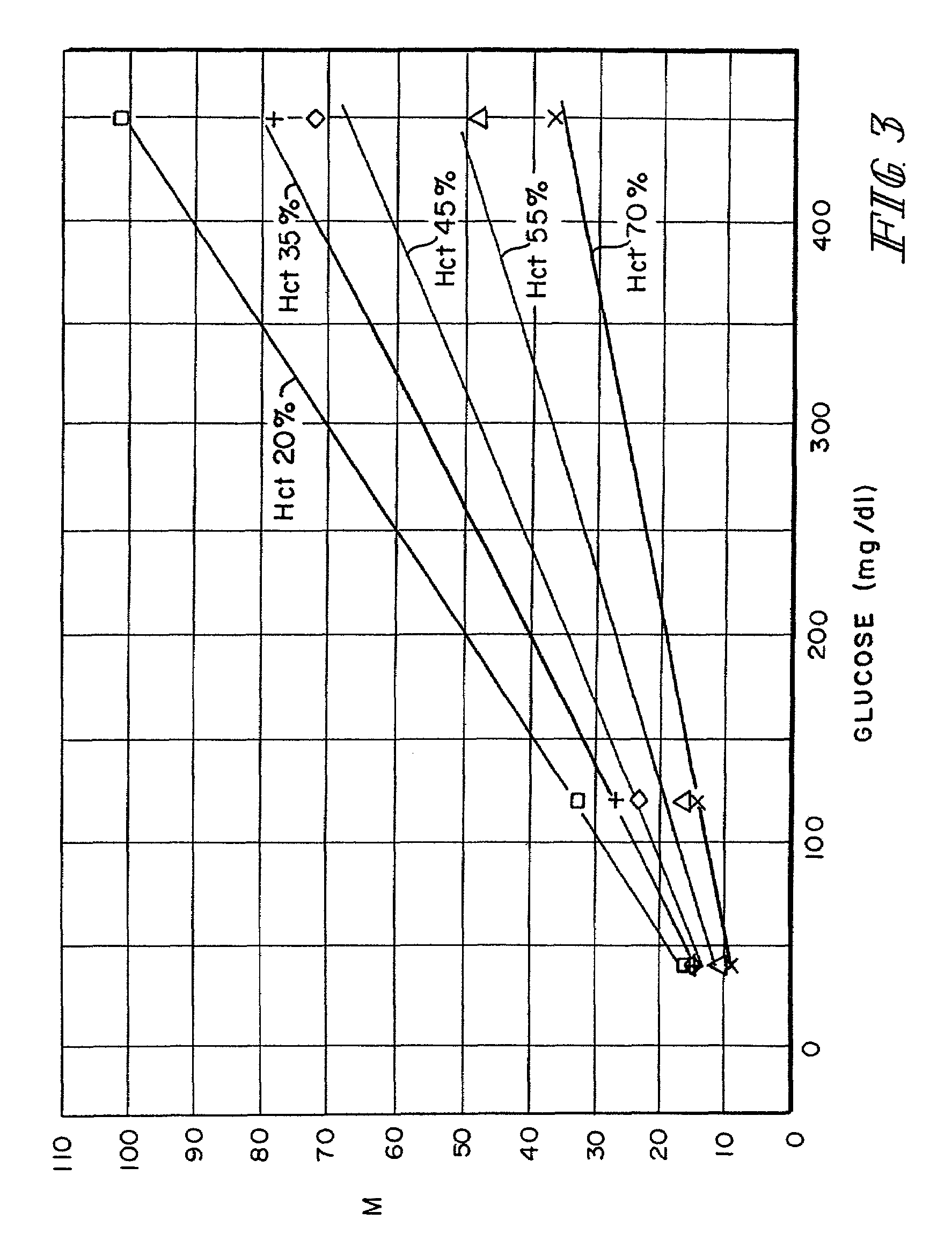
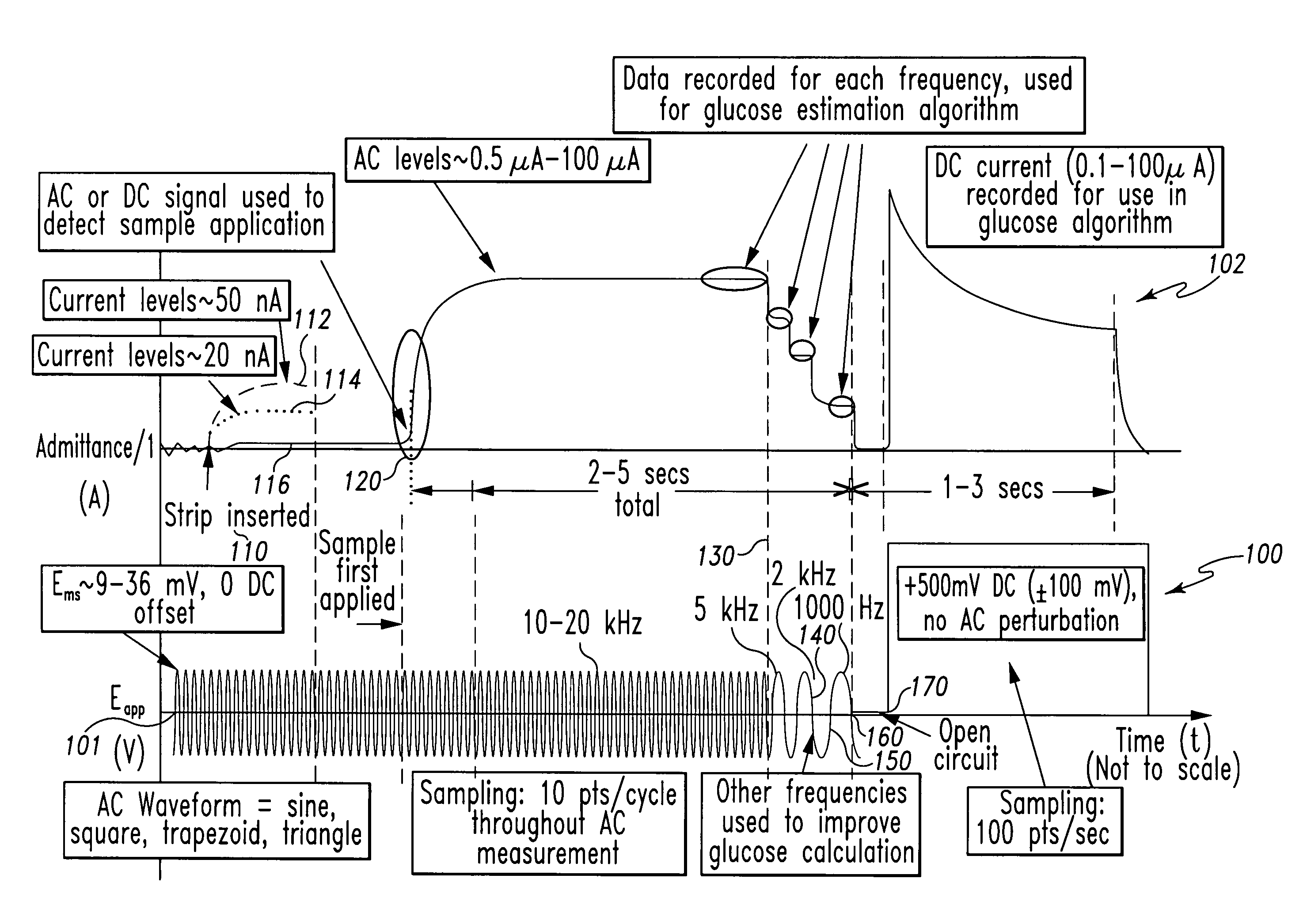
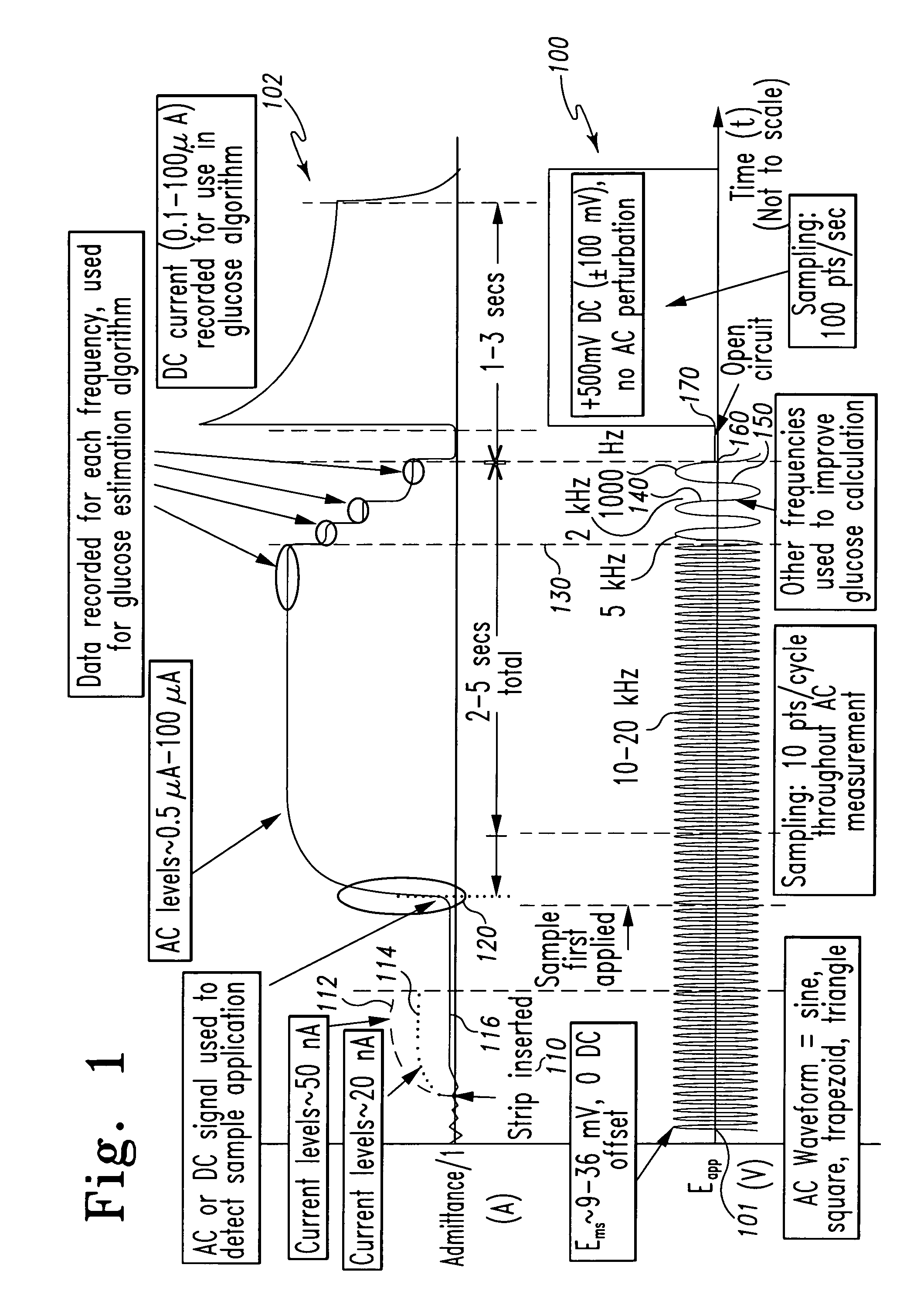
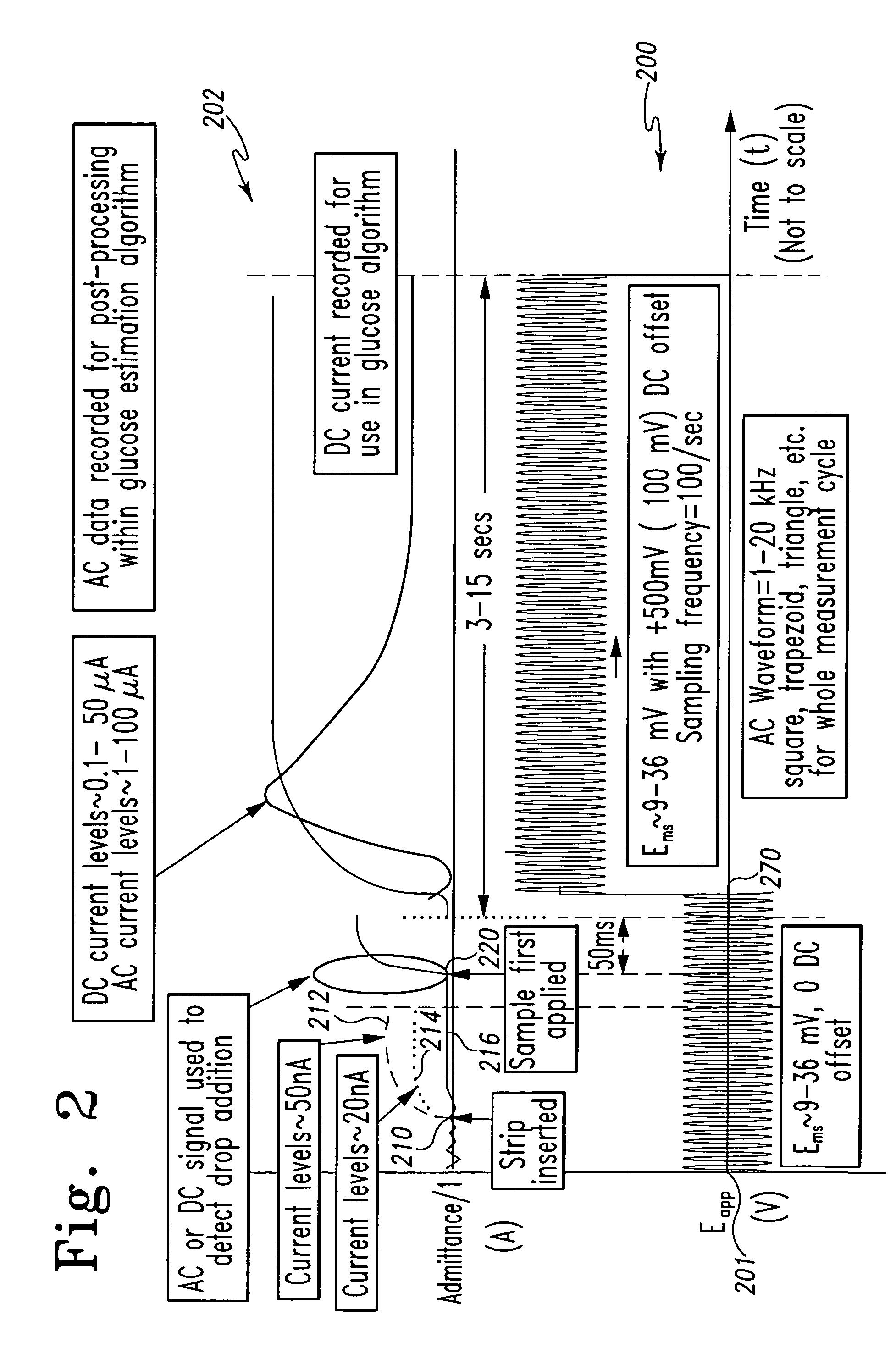
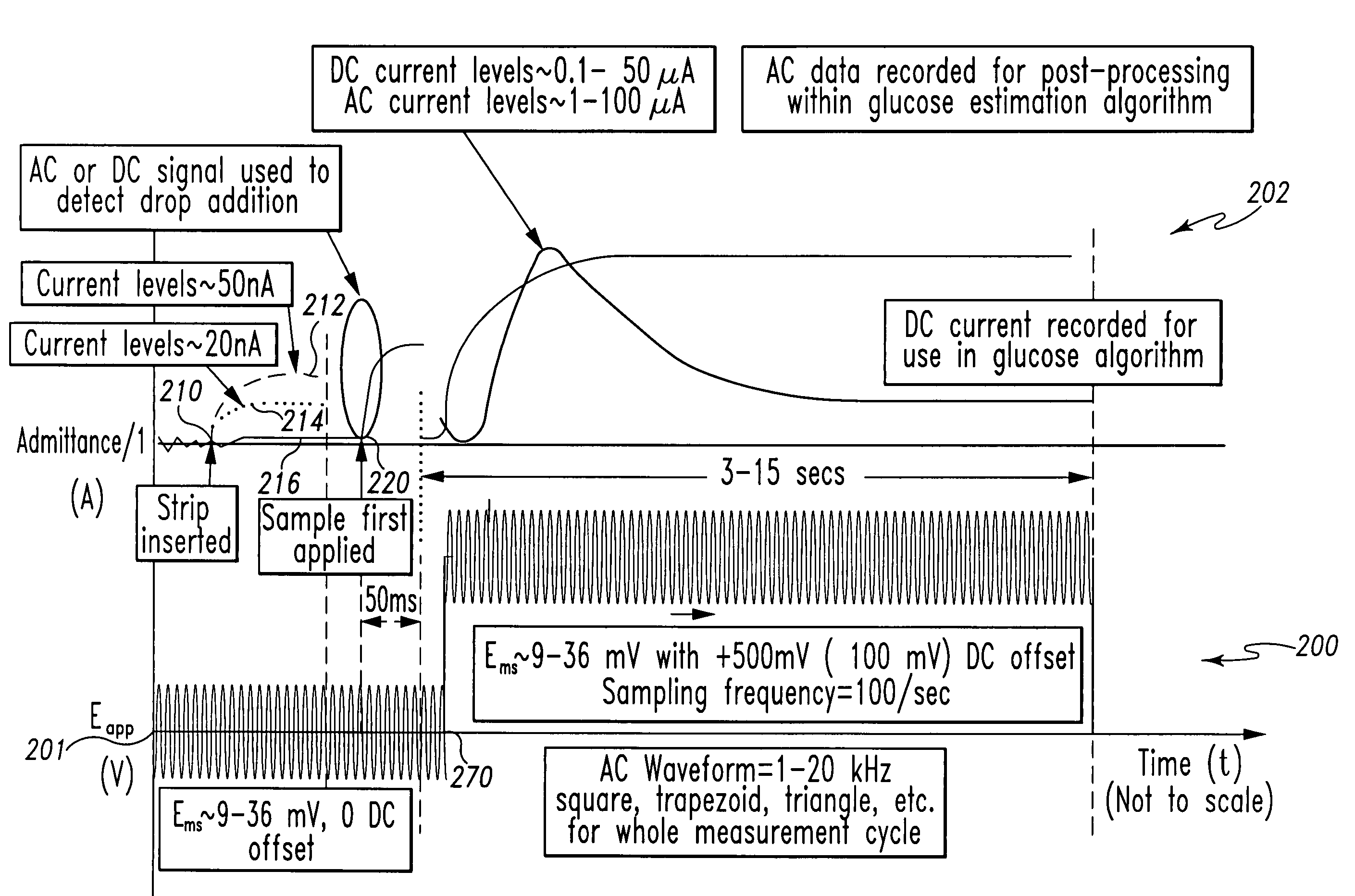
InactiveUS7338639B2Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial thermal conductivityAnalyteExcitation signal
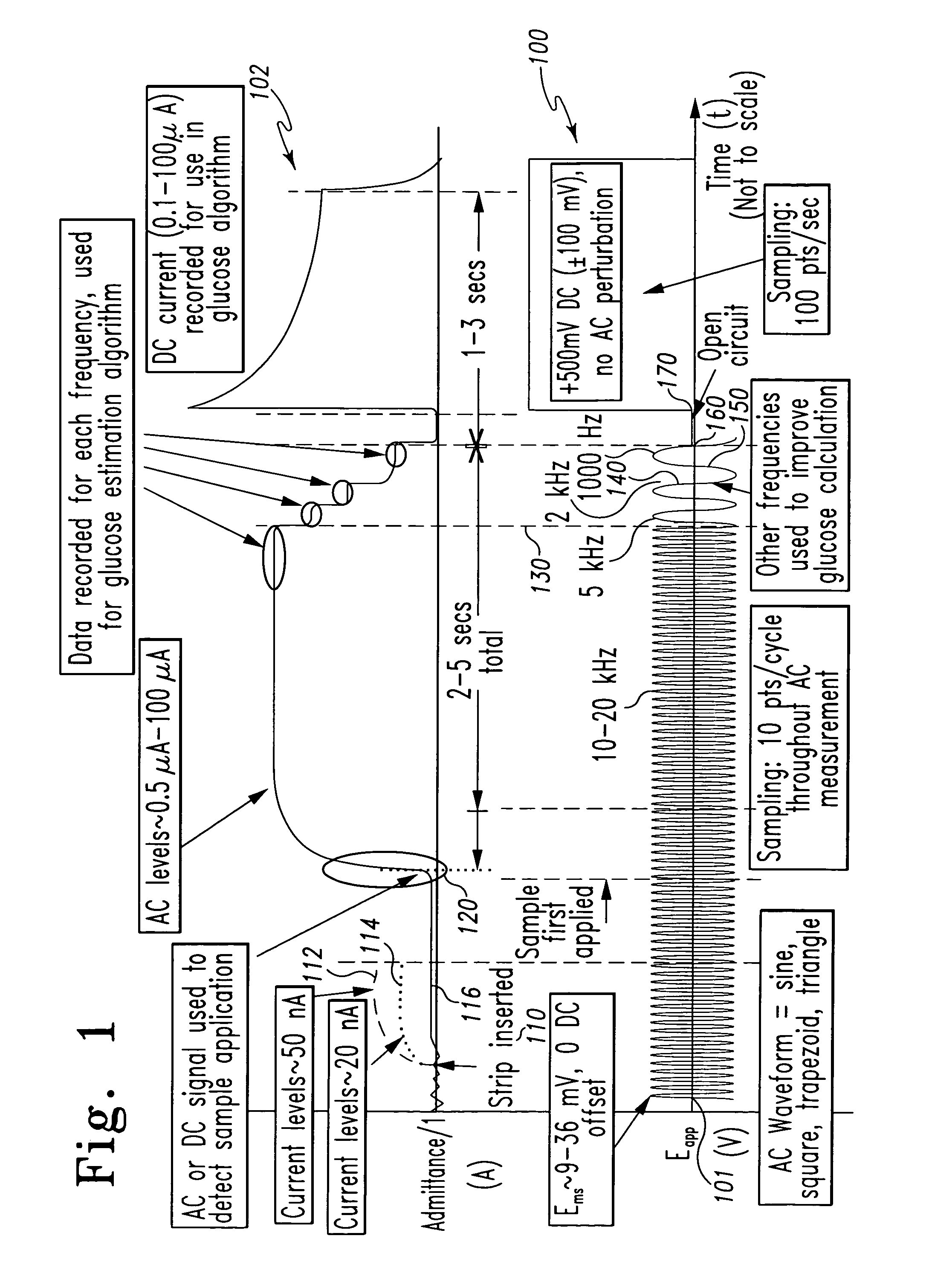
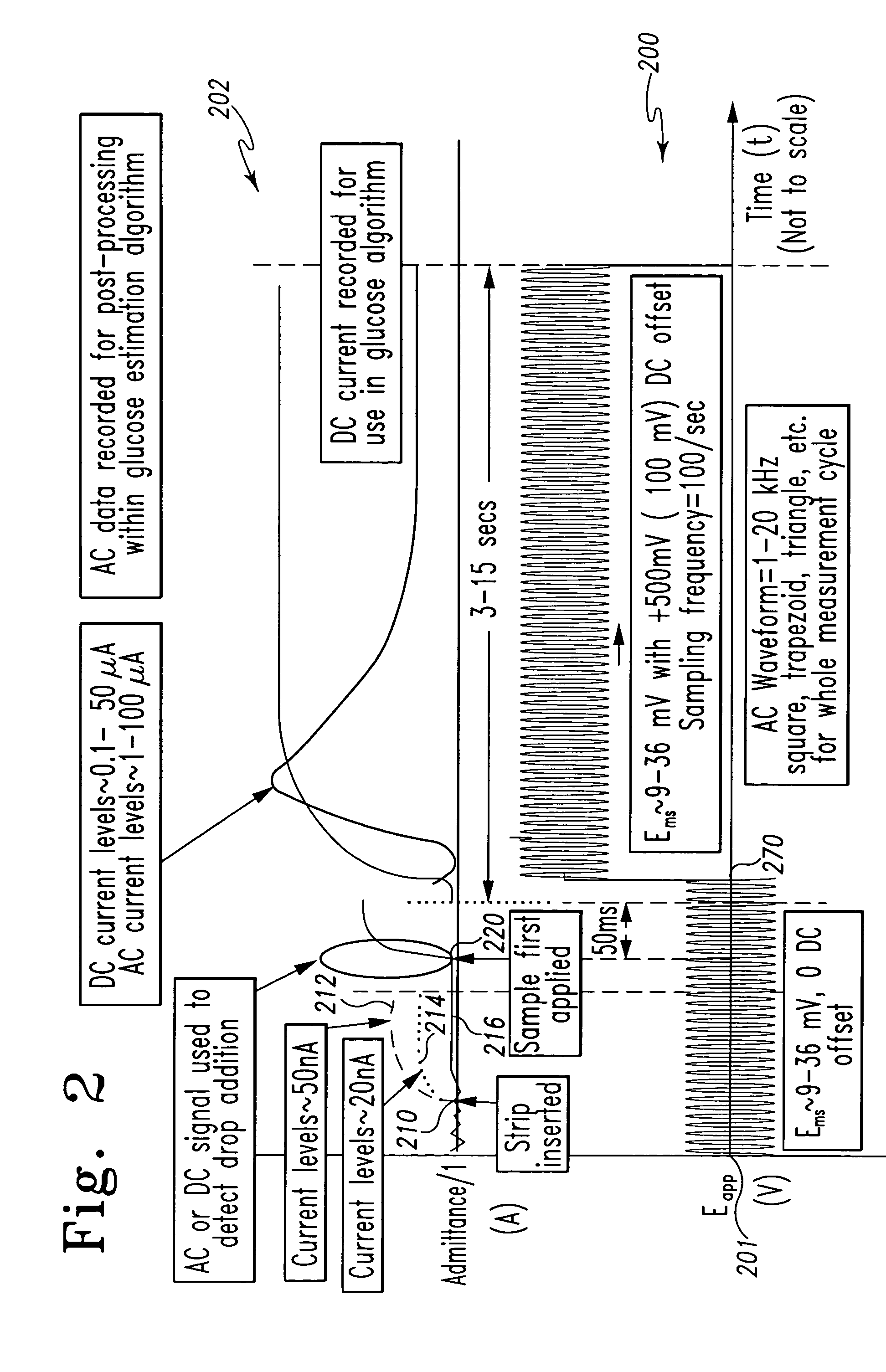
A method of measuring an analyte in a biological fluid comprises applying an excitation signal having a DC component and an AC component. The AC and DC responses are measured; a corrected DC response is determined using the AC response; and a concentration of the analyte is determined based upon the corrected DC response. Other methods and devices are disclosed.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC +1
Systems and methods for optical actuation of microfluidics based on opto-electrowetting
InactiveUS6958132B2Improve performanceSludge treatmentMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectricityMicrofluidics
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Droplet-based washing
ActiveUS20070241068A1Reduces and eliminates build-upImprove efficiencyHeating or cooling apparatusShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersLiquid dropChemistry
The present invention relates to droplet-based washing. According to one embodiment, a method of providing a droplet in contact with a surface with a reduced concentration of a substance is provided, wherein the method includes: (a) providing a surface in contact with a droplet comprising a starting concentration and starting quantity of the substance and having a starting volume; (b) conducting one or more droplet operations to merge a wash droplet with the droplet provided in step (a) to yield a combined droplet; and (c) conducting one or more droplet operations to divide the combined droplet to yield a set of droplets comprising: (i) a droplet in contact with the surface having a decreased concentration of the substance relative to the starting concentration; and (ii) a droplet which is separated from the surface.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC +1
System and method for determining a temperature during analyte measurement
InactiveUS20060156796A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial thermal conductivityAnalyteExcitation signal
A method of measuring an analyte in a biological fluid comprises applying an excitation signal having a DC component and an AC component. The AC and DC responses are measured; a corrected DC response is determined using the AC response; and a concentration of the analyte is determined based upon the corrected DC response. Other methods and devices are disclosed.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC +1
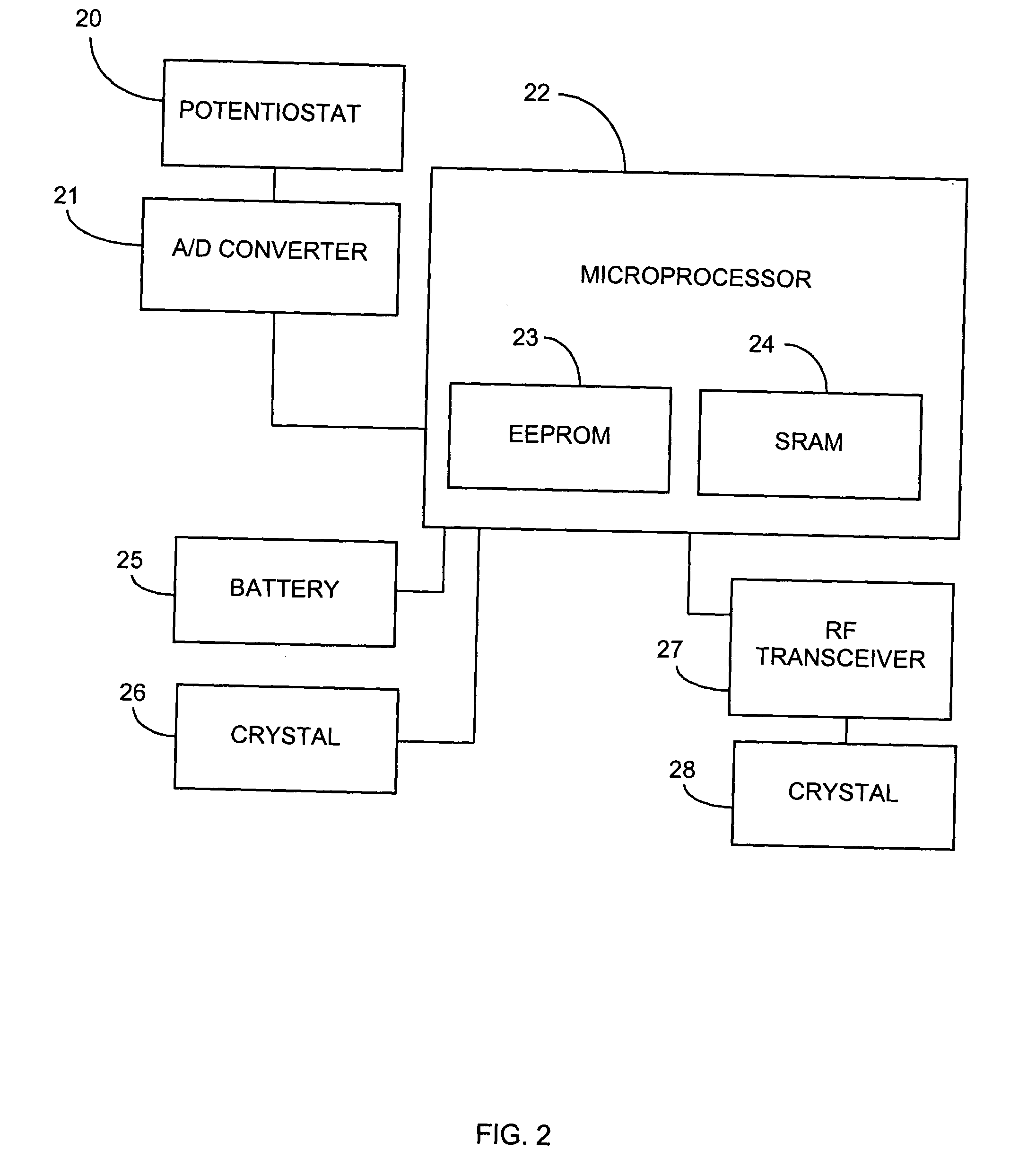
Systems and methods for blood glucose sensing
InactiveUS6964871B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrical conductorEngineering
A system for measuring a glucose level in a blood sample includes a test strip and a meter. The test strip includes a sample chamber or other testing zone, a working electrode, a counter electrode, fill-detect electrodes, and an auto-on conductor. A reagent layer is disposed in the testing zone. The auto-on conductor causes the meter to wake up and perform a test strip sequence when the test strip is inserted in the meter. The meter uses the working and counter electrodes to initially detect the blood sample in the sample chamber and uses the fill-detect electrodes to check that the blood sample has mixed with the reagent layer. The meter applies an assay voltage between the working and counter electrodes and measures the resulting current. The meter calculates the glucose level based on the measured current and calibration data saved in memory from a removable data storage device associated with the test strip.
Owner:TRIVIDIA HEALTH
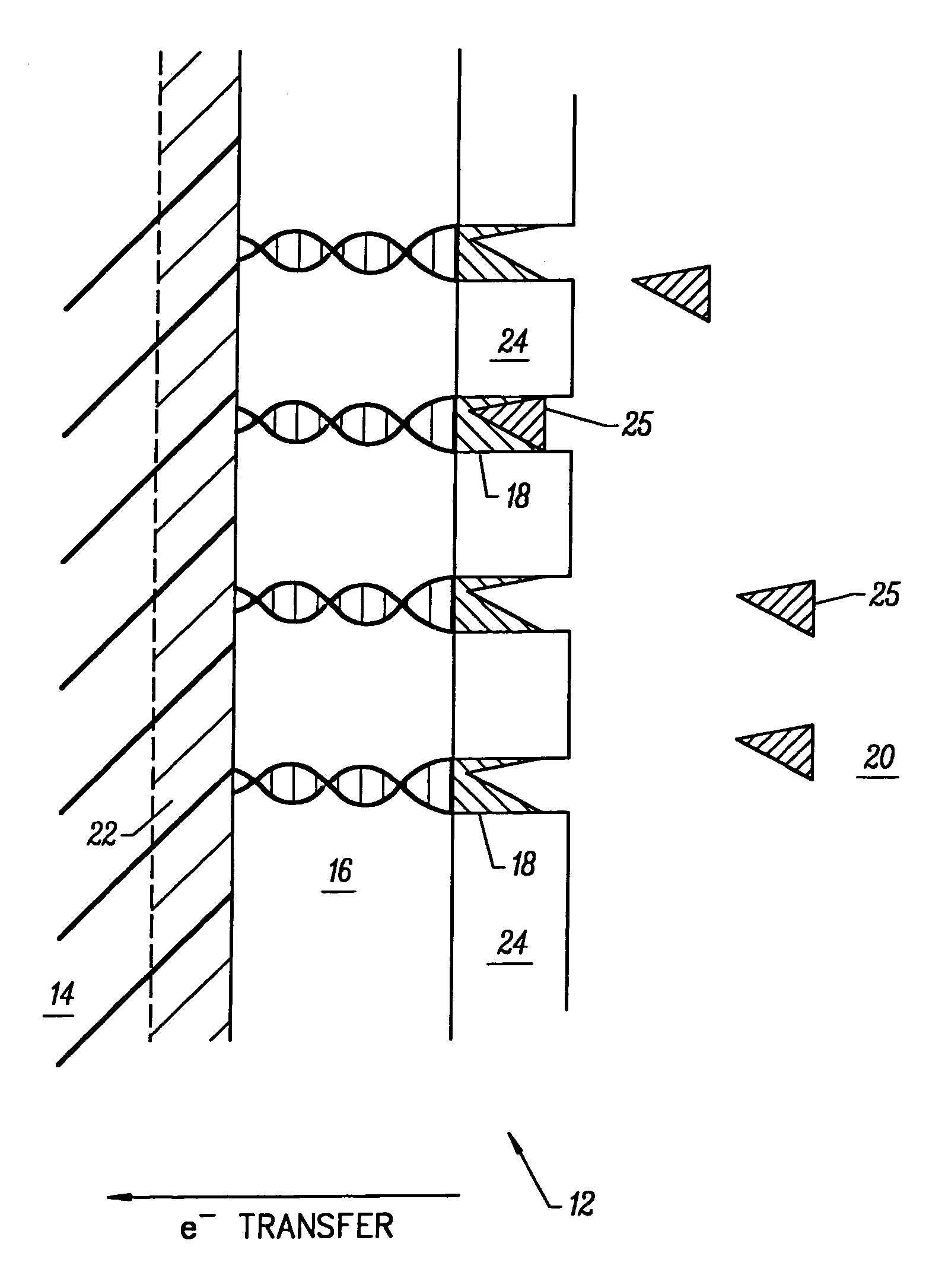
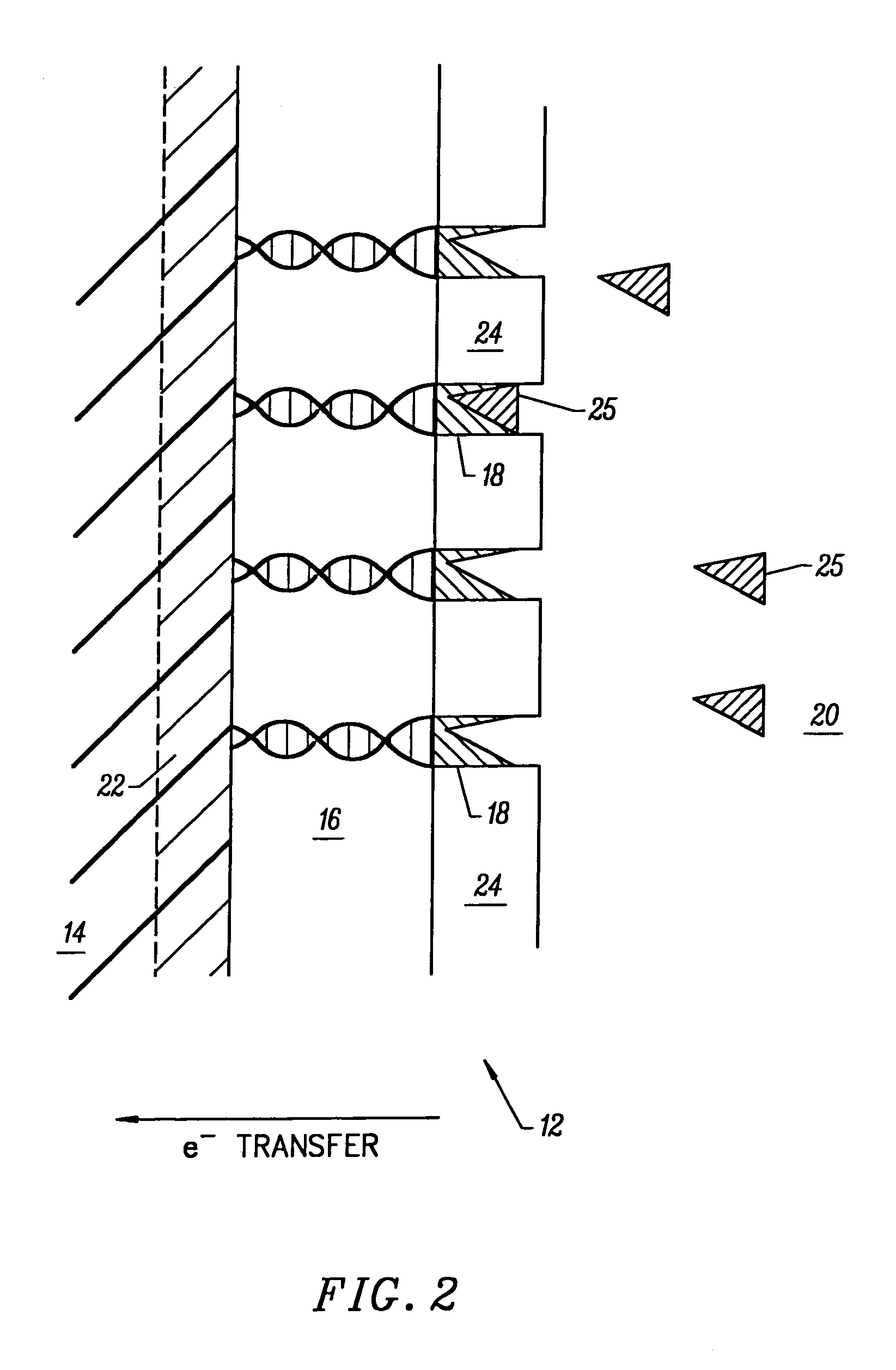
Molecular wire injection sensors
InactiveUS20060115857A1Rapid responseHigh sensitivityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsConductive polymerMolecular wire
Disclosed is a sensor for sensing the presence of an analyte component without relying on redox mediators. This sensor includes (a) a plurality of conductive polymer strands each having at least a first end and a second end and each aligned in a substantially common orientation; (b) a plurality of molecular recognition headgroups having an affinity for the analyte component and being attached to the first ends of the conductive polymer strands; and (c) an electrode substrate attached to the conductive polymer strands at the second ends. The electrode substrate is capable of reporting to an electronic circuit reception of mobile charge carriers (electrons or holes) from the conductive polymer strands. The electrode substrate may be a photovoltaic diode.
Owner:KEENSENSE
System and method for analyte measurement using AC excitation
A method of measuring an analyte in a biological fluid comprises applying an excitation signal having a DC component and an AC component. The AC and DC responses are measured; a corrected DC response is determined using the AC response; and a concentration of the analyte is determined based upon the corrected DC response. Other methods and devices are disclosed.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Sensor Apparatus Systems, Devices and Methods
ActiveUS20080253427A1Provide flexibilitySolvent extractionFlexible member pumpsCombined useConductive materials
A sensor apparatus and sensor apparatus system for use in conjunction with a cassette, including a disposable or replaceable cassette. In some embodiments, the cassette includes a thermal well for permitting the sensing of various properties of a subject media. The thermal well includes a hollow housing of a thermally conductive material. In other embodiments, the cassette includes sensor leads for sensing of various properties of a subject media. The thermal well has an inner surface shaped so as to form a mating relationship with a sensing probe. The mating thermally couples the inner surface with a sensing probe. In some embodiments, the thermal well is located on a disposable portion and the sensing probe on a reusable portion.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
Analyte concentration determination meters and methods of using the same
InactiveUS6881578B2The process is simple and convenientEase and low cost manufactureImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteEngineering
Devices and methods for determining the concentration of an analyte in a physiological sample are provided. The subject devices are meters characterized by having an internal structure that includes a test strip selecting element having a continuously reduced cross-sectional area configured to select a single test strip at a time and means for determining the concentration of an analyte in a physiological sample applied to the selected test strip. In the subject methods for containing at least one test strip and dispensing a single test strip at a time, a meter having at least one test strip contained therein is provided. The meter is positioned with respect to the ground to cause the single test strip to move from a contained position to a dispensed position. The subject invention also includes kits for use in practicing the subject methods.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Blood sugar level measuring apparatus
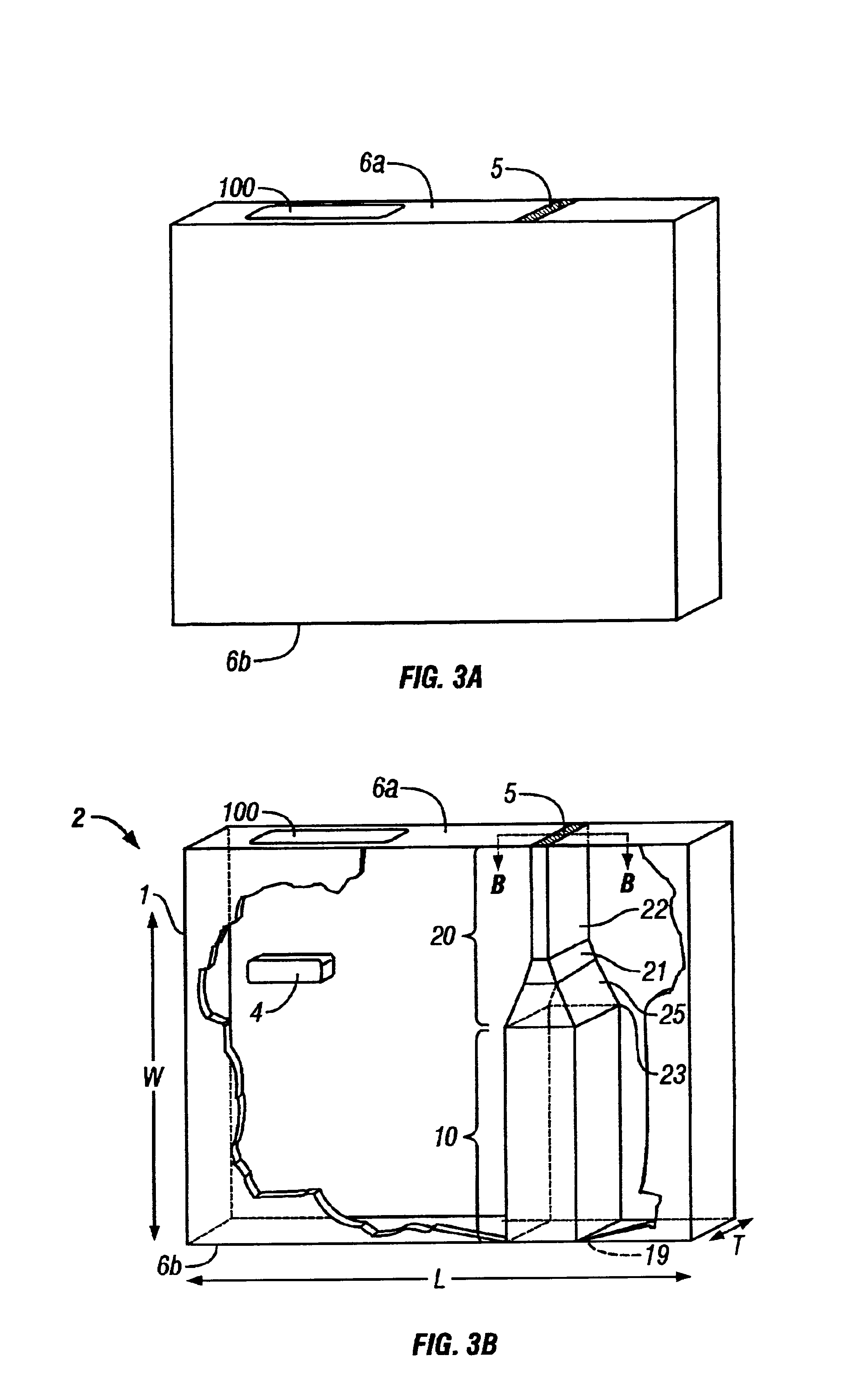
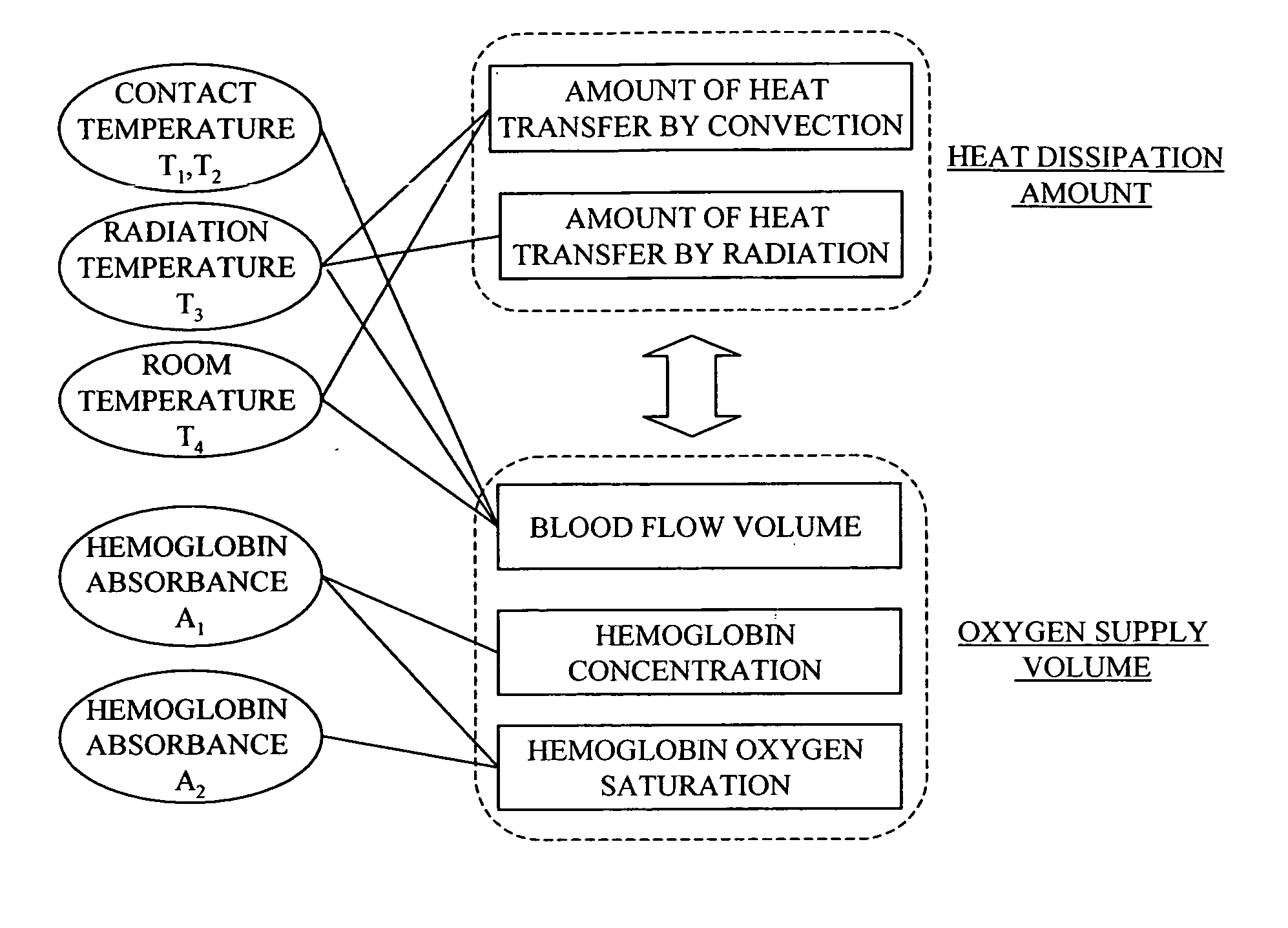
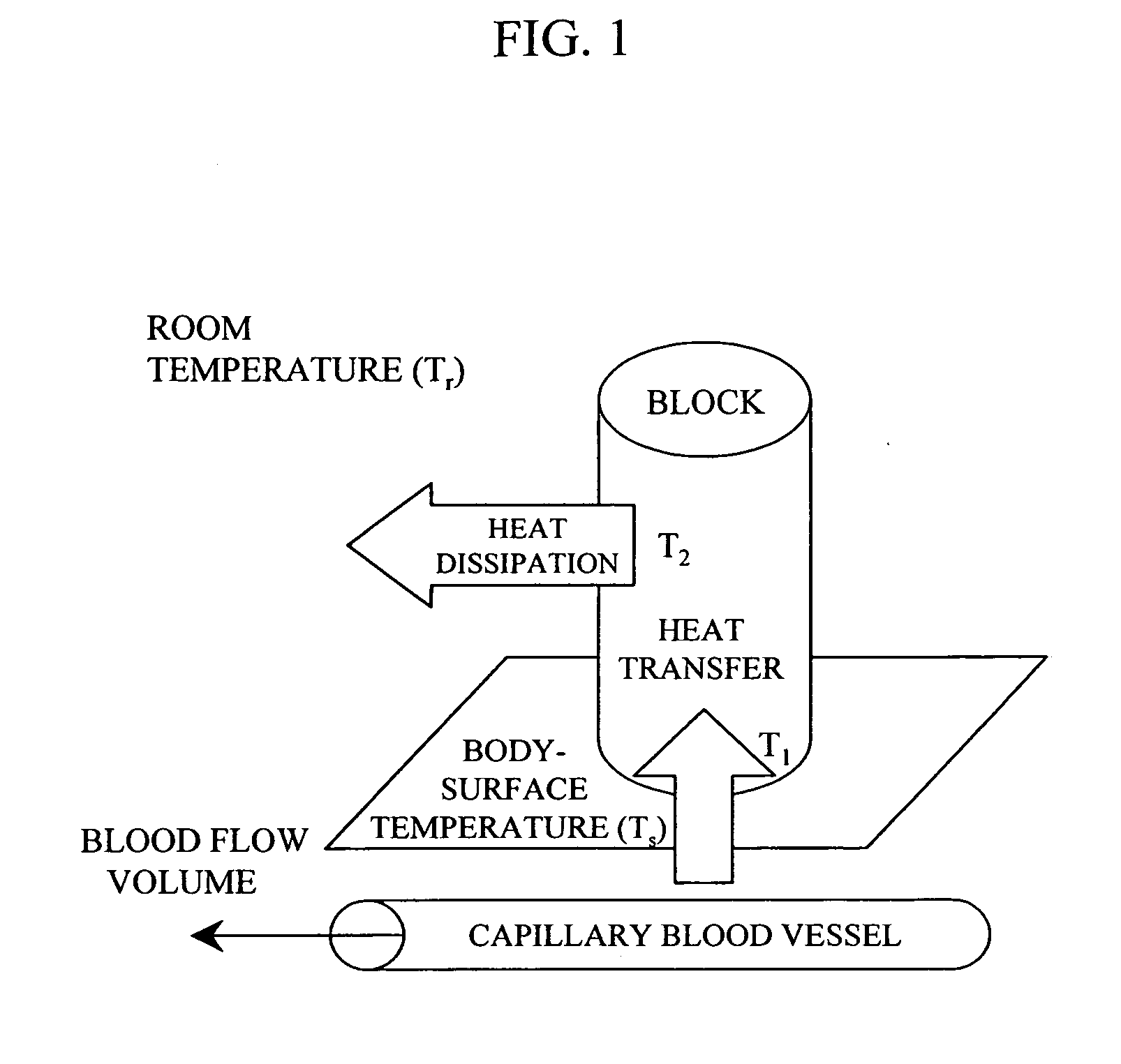
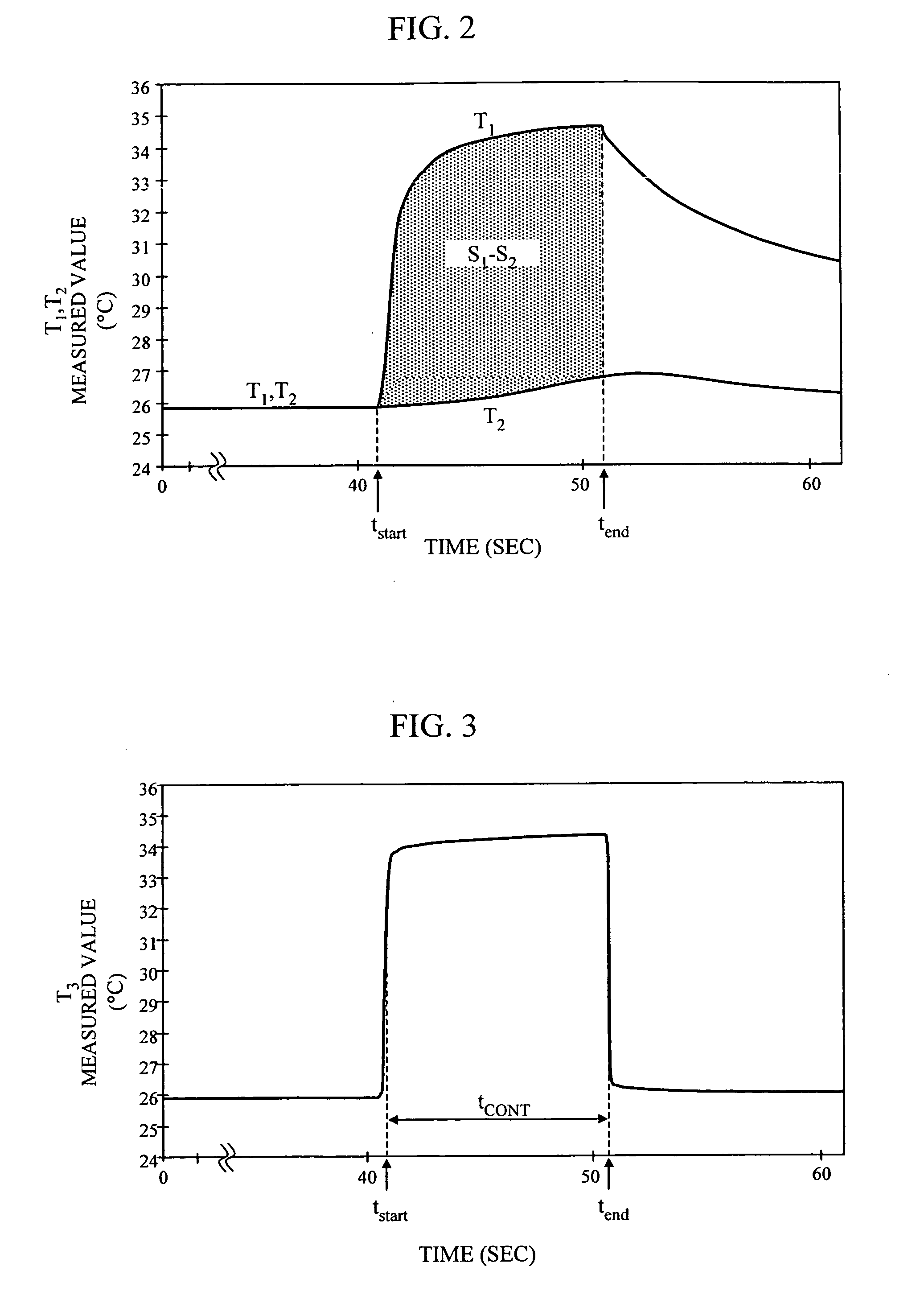
InactiveUS20050187442A1Improve accuracyMaterial thermal conductivityBody temperature measurementBlood sugarOxygen saturation
Blood sugar levels are measured non-invasively based on temperature measurement. Non-invasively measured blood sugar level values obtained by a temperature measurement scheme are corrected by blood oxygen saturation and blood flow volume, thereby stabilizing the measurement data.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Impedance spectroscopy based systems and methods
InactiveUS7315767B2Reduce supplyImpede tissue fluxSampled-variable control systemsMaterial thermal conductivitySpectroscopyData treatment
One aspect of the invention provides a device that non-invasively determines the concentration of a substance in a target. The device includes a first electrode, a measuring circuit, and a data processor. In one embodiment of the device, the first electrode can be electrically insulated from the target, e.g., a cover layer of insulating material covers the first electrode.
Owner:SOLIANIS HLDG
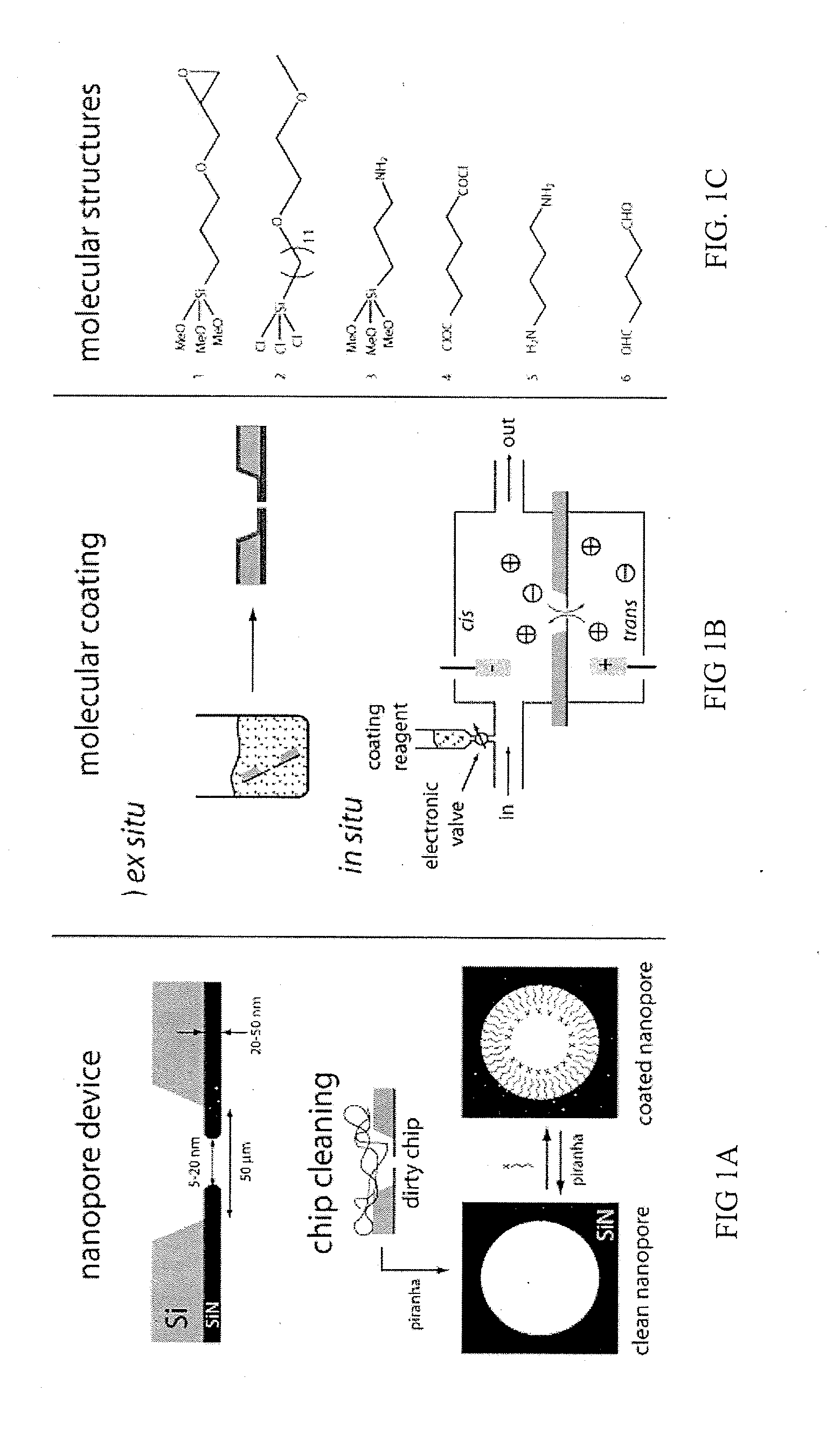
Chemical functionalization of solid-state nanopores and nanopore arrays and applications thereof
ActiveUS20110053284A1Avoid stickingChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiopolymerElectron
Chemical functionalization of solid-state nanopores and nanopore arrays and applications thereof. Nanopores are extremely sensitive single-molecule sensors. Recently, electron beams have been used to fabricate synthetic nanopores in thin solid-state membranes with sub-nanometer resolution. A new class of chemically modified nanopore sensors are provided with two approaches for monolayer coating of nanopores by: (1) self-assembly from solution, in which nanopores −10 nm diameter can be reproducibly coated, and (2) self-assembly under voltage-driven electrolyte flow, in which 5 nm nanopores may be coated. Applications of chemically modified nanopore are provided including: the detection of biopolymers such as DNA and RNA; immobilizing enzymes or other proteins for detection or for generating chemical gradients; and localized pH sensing.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Instrument
InactiveUS7018843B2Material thermal conductivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological fluidsAnalytical chemistry
A method and apparatus for performing a first measurement on a biological fluid or control, which first measurement varies with both the concentration of a first component and at least one of the presence and concentration of a second component. The method and apparatus perform a second measurement on the biological fluid or control, which second measurement varies primarily only with the at least one of the presence and concentration of the second component to develop an indication of the at least one of the presence and concentration of the second component. The first and second measurements may be made sequentially or simultaneously. The method and apparatus then remove an amount representative of the indicated presence or concentration of the second component from the concentration of the first component indicated by the first measurement.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Chemical detection sensor system
InactiveUS7022288B1Material nanotechnologyAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionChemical reactionPhysical chemistry
A chemical detection sensor system comprises a support structure; multiple SERS chemical detection sensors supported by the support structure; multiple chemical reaction sensors, wherein each of the chemical reaction sensors is disposed for undergoing a state change in response to an occurrence of a chemical reaction at one of the SERS chemical detection sensors; a processor supported by the support structure for recording data representing occurrence of a chemical reaction at any of the chemical detection sensors in response to sensing the state change; and a power source for energizing the processor.
Owner:NAVY SEC OF THE UNITED STATES
Sensing Apparatus and Method
ActiveUS20100255595A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical reactionReaction intermediate
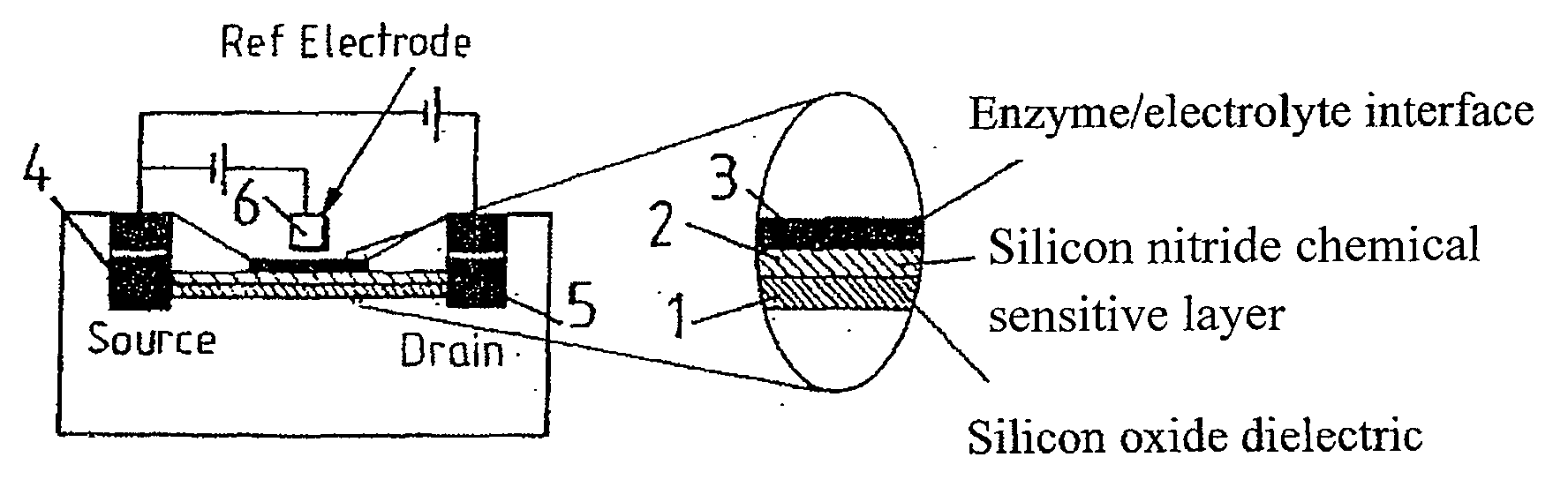
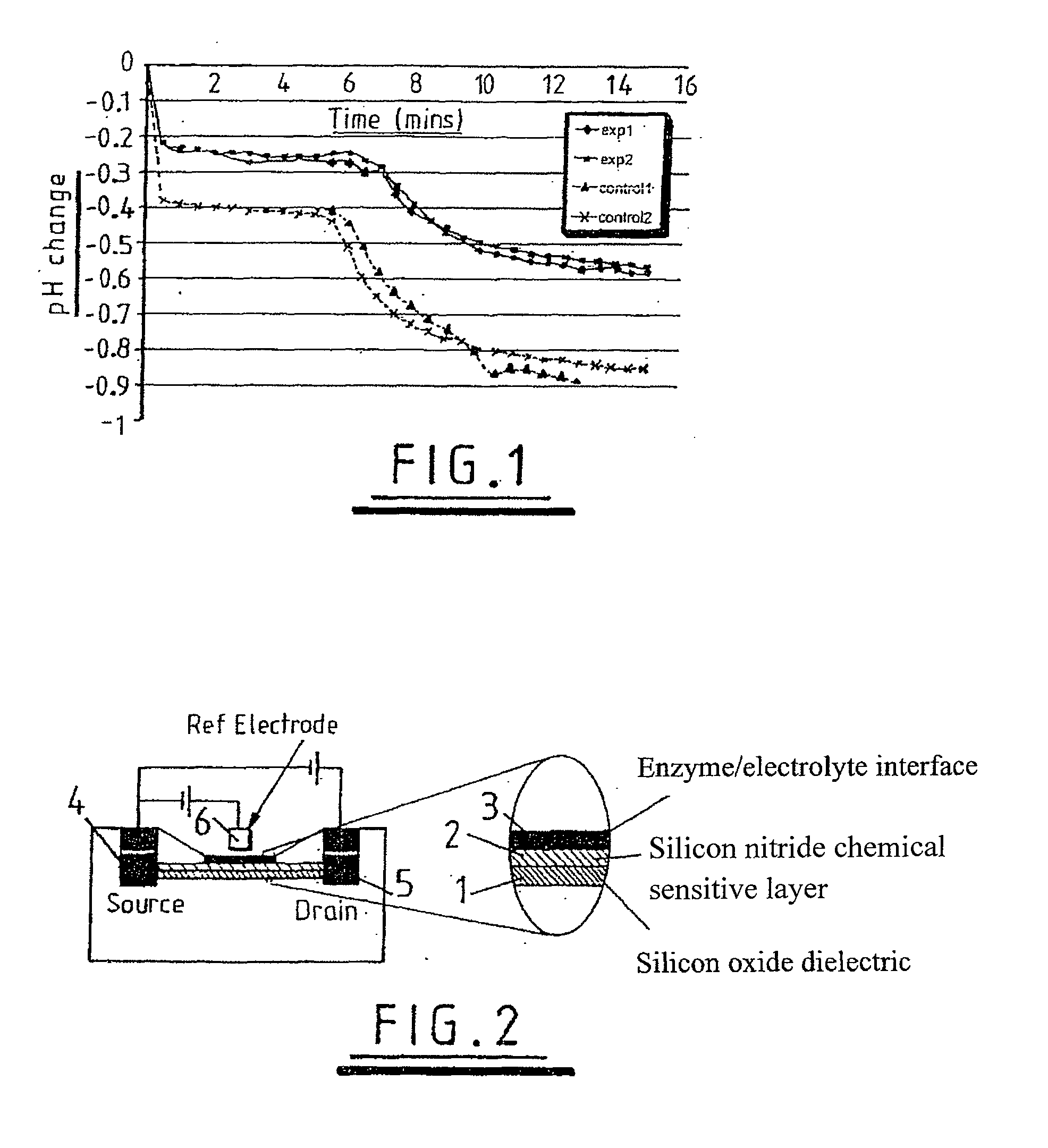
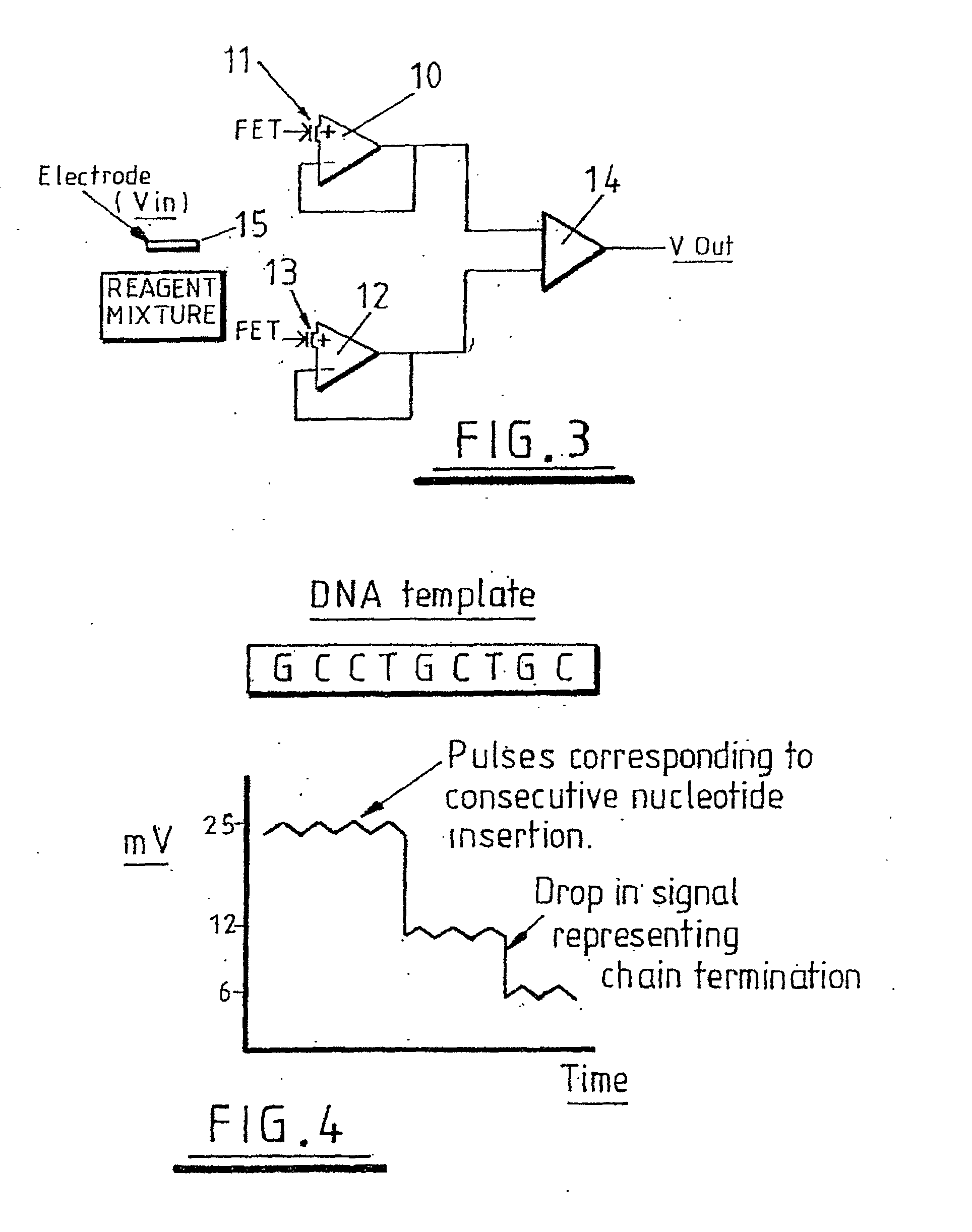
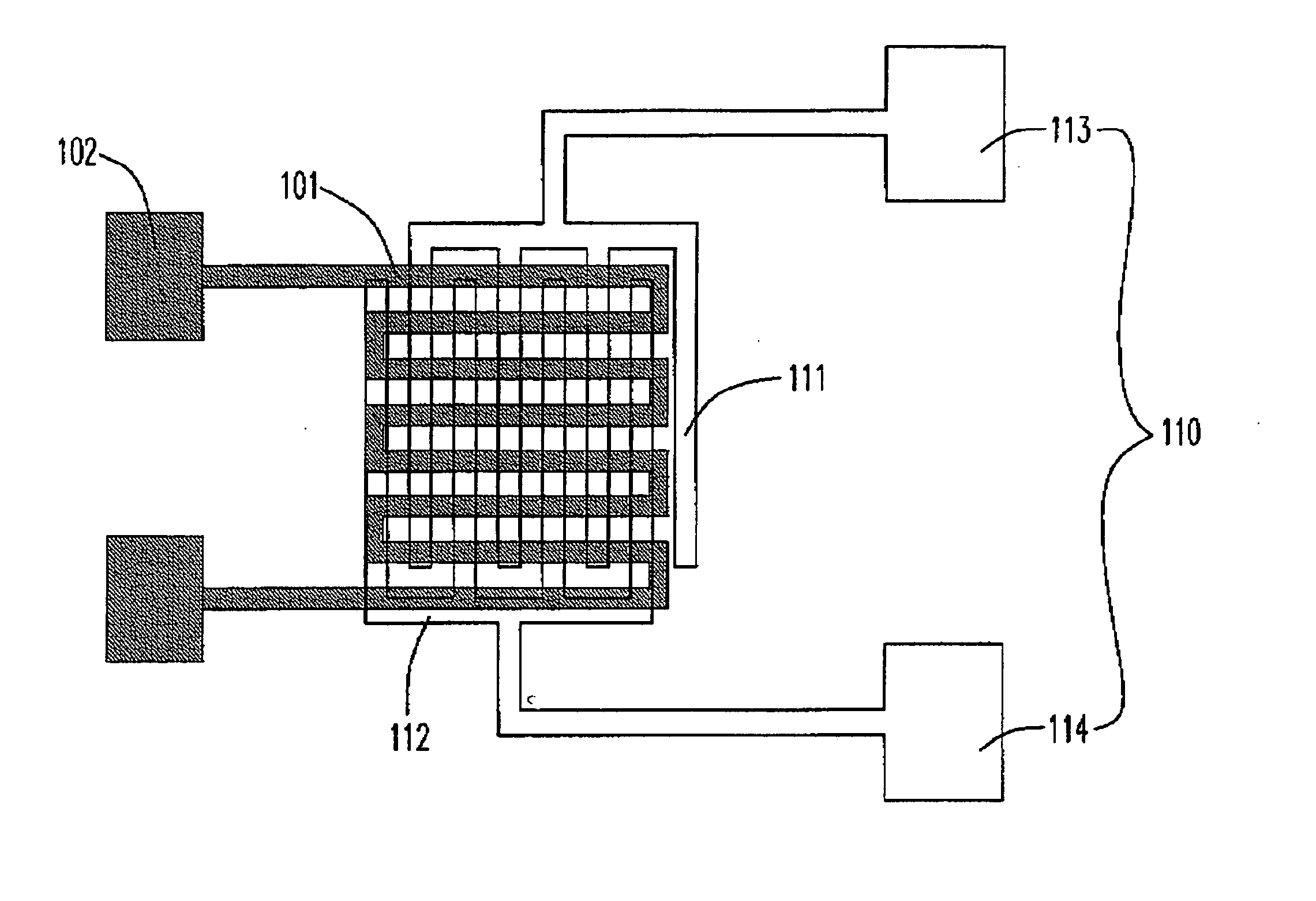
A method of observing reaction intermediaries during a chemical reaction and comprising detecting an electrical signal output from an ion sensitive field effect transistor exposed to said reaction, and monitoring the detected electrical signal to discriminate discrete fluctuations in the electrical signal, the discrete fluctuations indicating reaction intermediaries occurring during a chemical reaction.
Owner:DNAE GRP HLDG
Electrowetting electrode device with electromagnetic field for actuation of magnetic-bead biochemical detection system
InactiveUS20050056569A1Reduce dissipationEnhanced magnetic forceMaterial thermal conductivityMicrobiological testing/measurementElectricityMagnetic bead
A detecting device for biochemical detections is provided. The detecting device includes a first substrate, a magnetic layer located on the first substrate, an isolation layer located on the magnetic layer, at least a first electrode located on the isolation layer, a first dielectric layer located on the first electrode, a first hydrophobic layer located on the first dielectric layer, a second substrate, at least a second electrode located on the second substrate and having a cathode and an anode, a second dielectric layer located on the second electrode and a second hydrophobic layer located on the second dielectric layer. The first electrode is zigzag-shaped, and the cathode and the anode of the second electrode are comb-shaped and interlaced with each other.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY +1
Microfluidic channel network device
ActiveUS7223371B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringMicrofluidic channel
Described herein is microfluidic device for joining fluids and a related method for doing the same. The device according to the present invention includes a microfluidic junction, an outlet channel, and a plurality of circuit units. A microfluidic junction is an area for converging multiple fluids. An outlet channel is capable of receiving fluid from the microfluidic junction. An outlet channel includes a first end connected with the microfluidic junction, a second end connected with a waste reservoir, and an analysis region positioned between the first end and the second end of the outlet channel. The device also includes a plurality of circuit units. Each circuit unit includes a source channel with a first end capable of receiving sample fluid and a second end connected with the microfluidic junction; a branch channel connected with the source channel at an intersection; and a flow diversion system capable of differentially directing fluid flowing through a source channel either into the microfluidic junction or into a branch channel.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Biological fluid constituent sampling and measurement devices and methods
A device for accessing biological fluid, sampling biological fluid constituents and determining the concentration of at least one target constituent within the accessed biological fluid is provided. The device has at least one micro-piercing member used to penetrate the skin to a selected depth and to access biological fluid, a constituent sampling means and a constituent measuring means. The constituent sampling means comprises a constituent transfer medium, such as a hydrophilic gel material, by which sampled constituents are transferred from the micro-piercing member to the measuring means. The measuring means includes an electrochemical cell having at least one porous electrode through which at least one sampled constituent is caused to enter into the electrochemical cell. Methods of sampling constituents within the skin and measuring the sampled constituents, as well as kits for practicing the invention are provided.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Apparatus for regulating the temperature of a biological and/or chemical sample and method of using the same
InactiveUS20070196237A1Temperature regulationHeating or cooling apparatusMaterial thermal conductivityTemperature controlElectrical conductor
The invention provides an apparatus for regulating the temperature of a chemical and / or biological sample and a method of using the same. The apparatus includes at least one temperature control module. The temperature control module includes a heater, a conductor of caloric, and a temperature sensor. The heater of the temperature control module is adapted to thermally communicate with a removable substrate, on which said chemical and / or biological sample is placed, via the conductor of caloric. The temperature sensor of the temperature control module is adapted to detect and control the temperature of the substrate via the conductor of caloric. The apparatus is designed such that the substrate is situated above said temperature control module to entirely cover said temperature control module.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
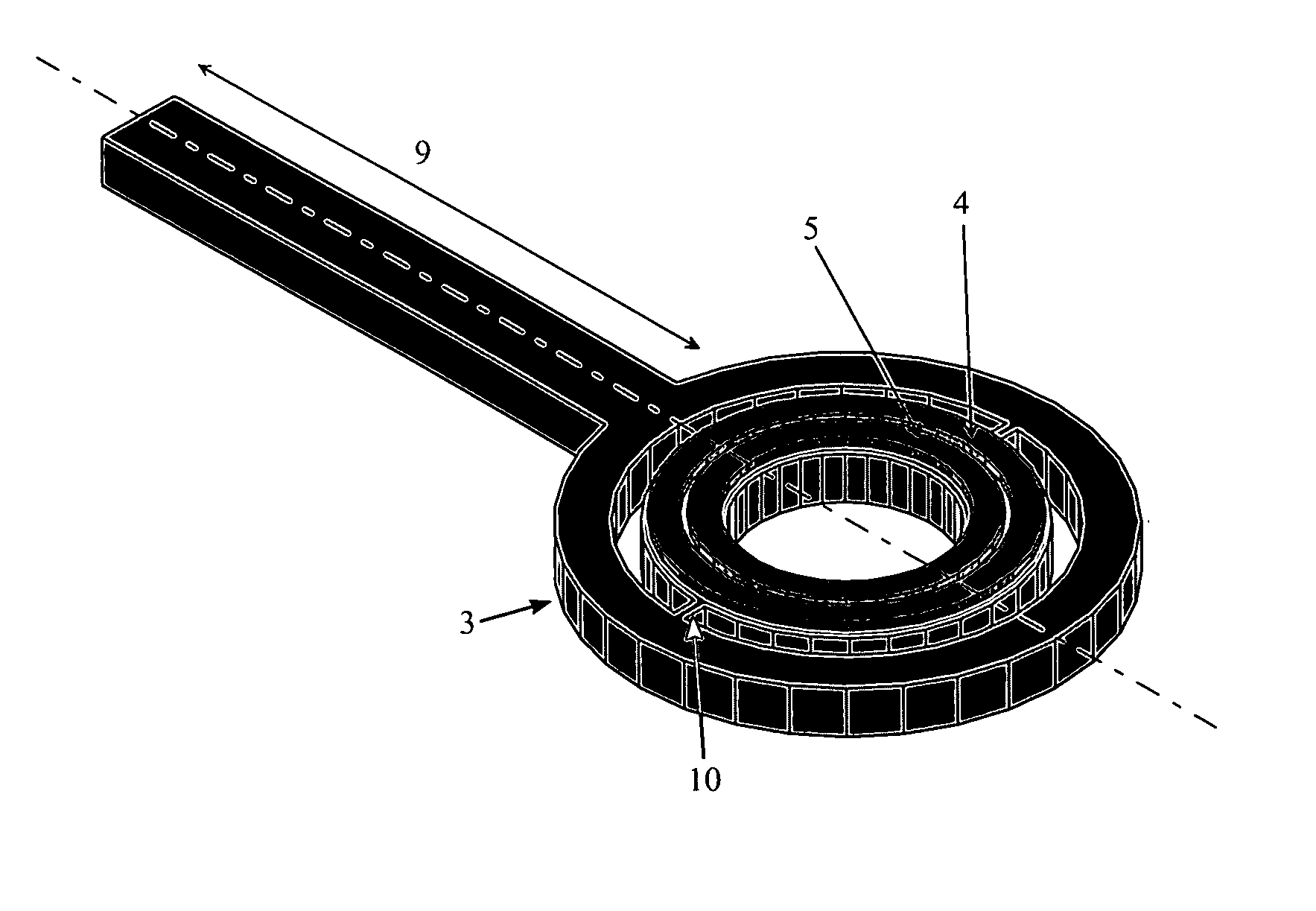
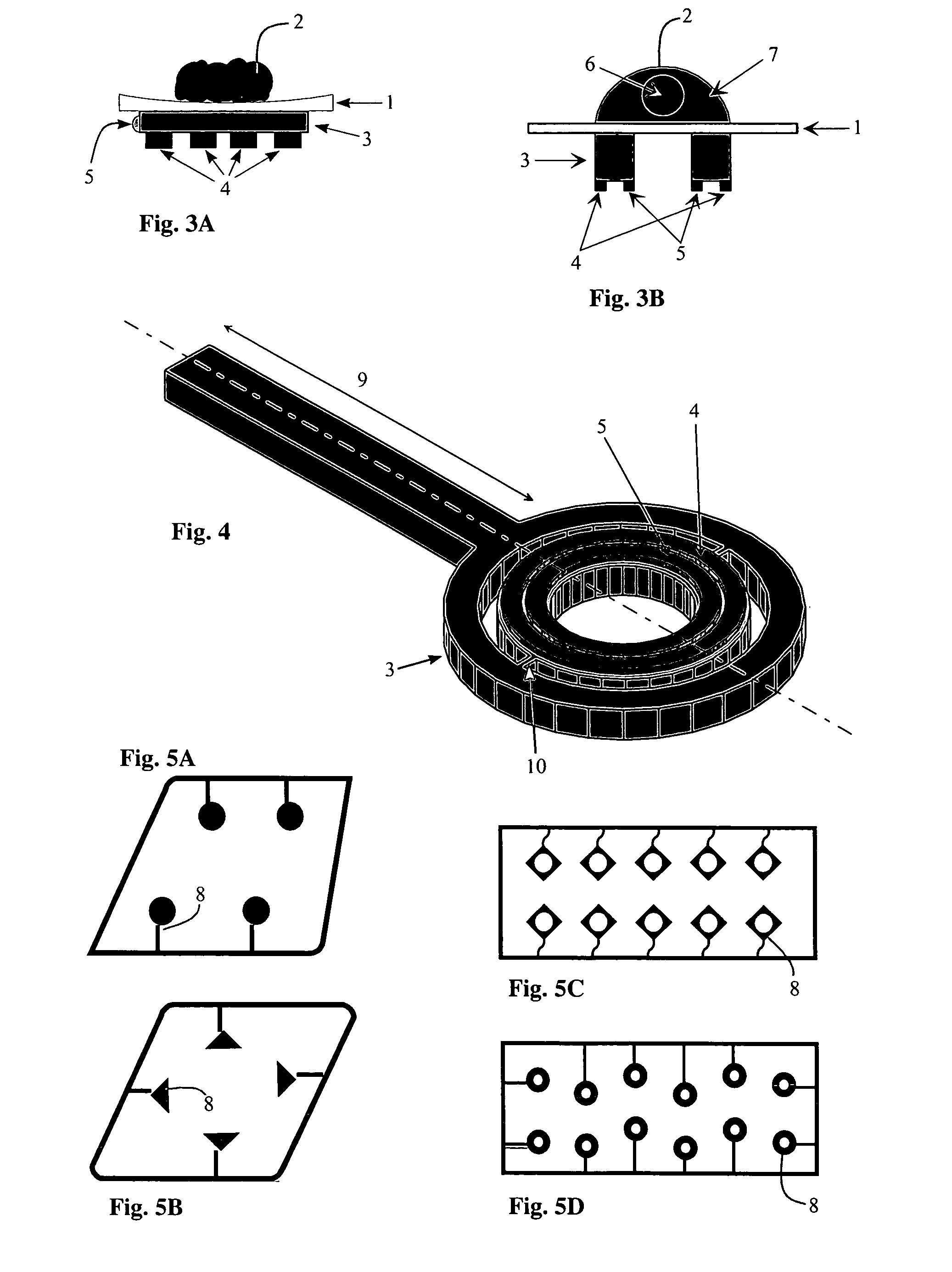
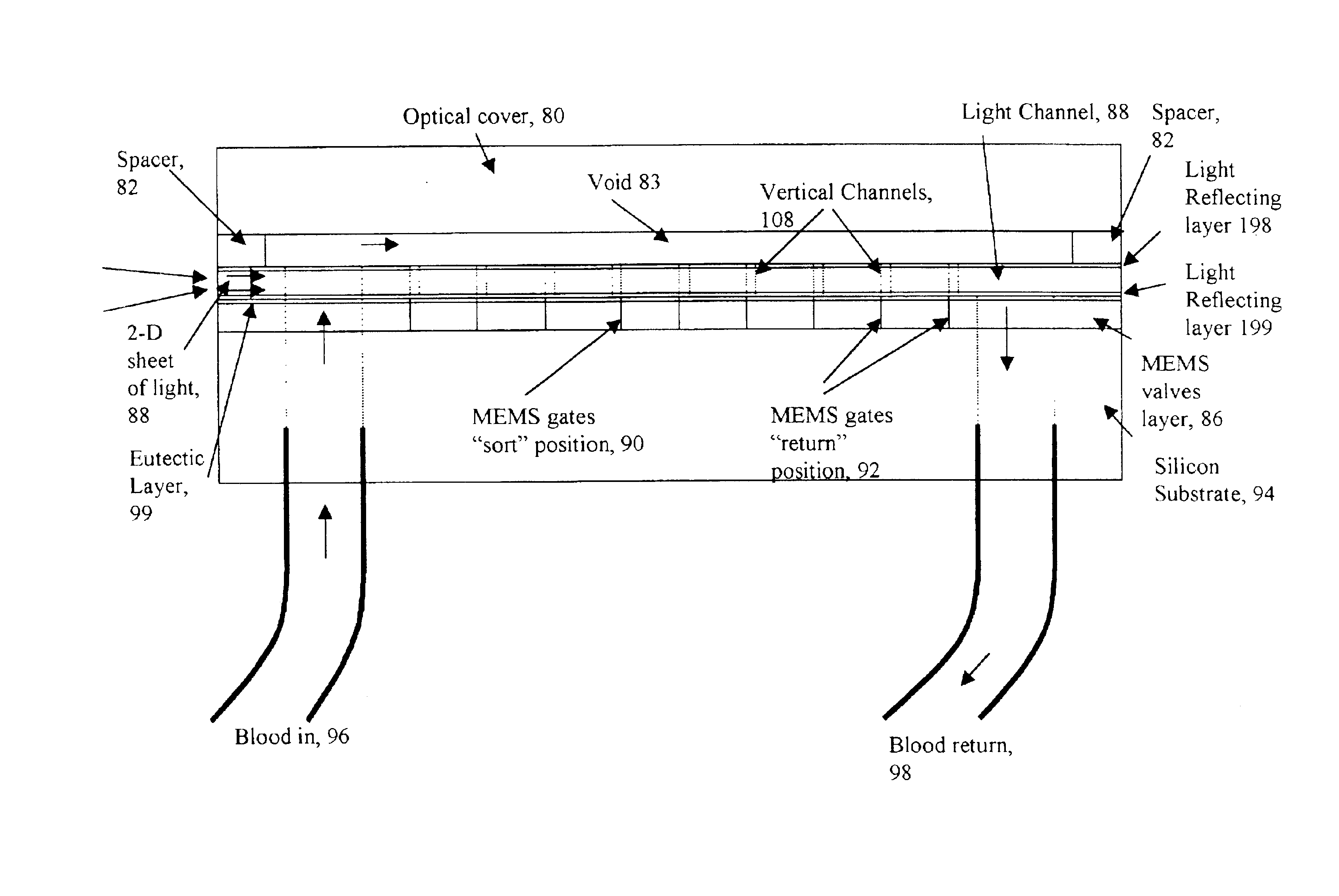
Method and apparatus for sorting biological cells with a MEMS device
InactiveUS6838056B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological cellLaser light
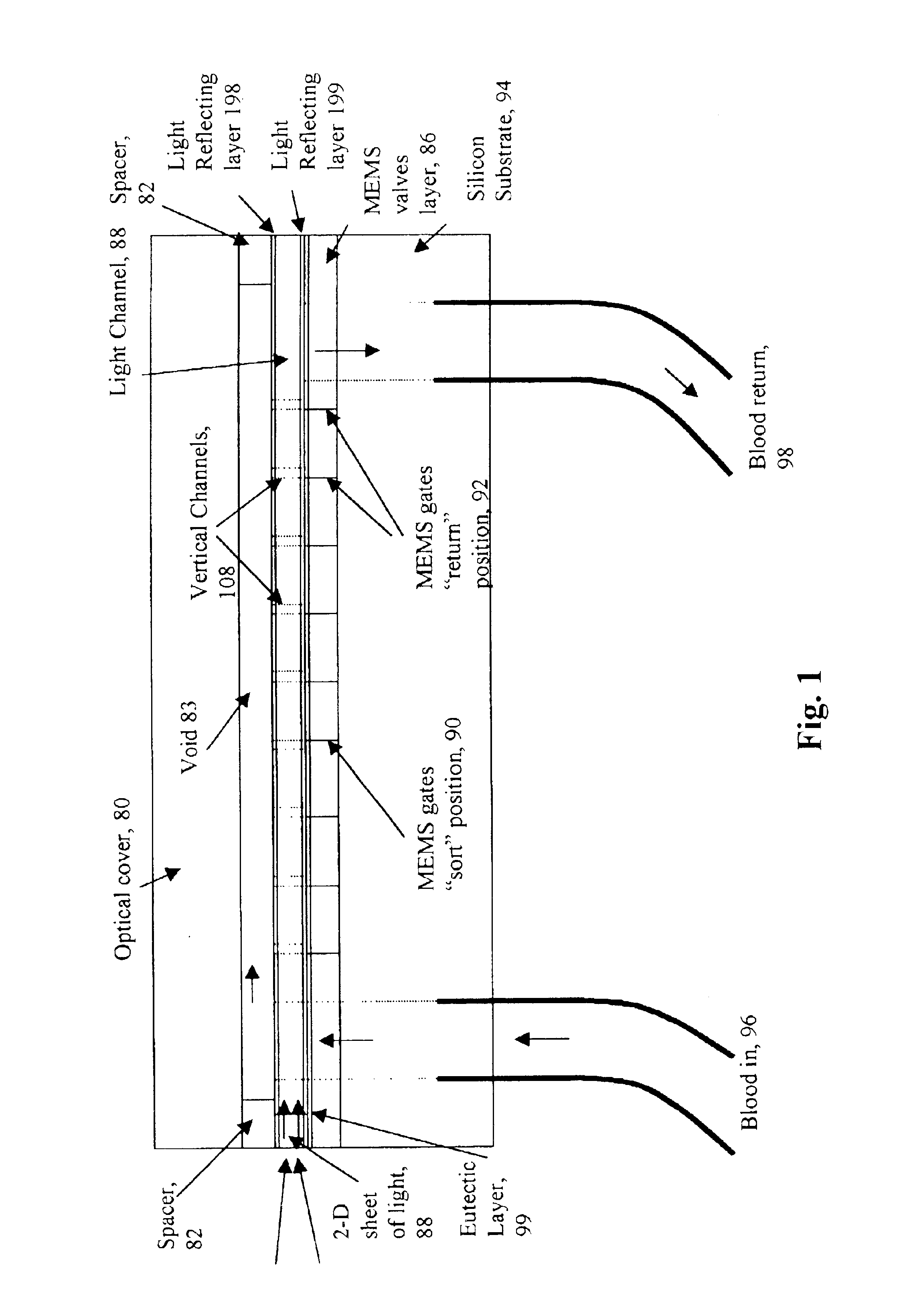
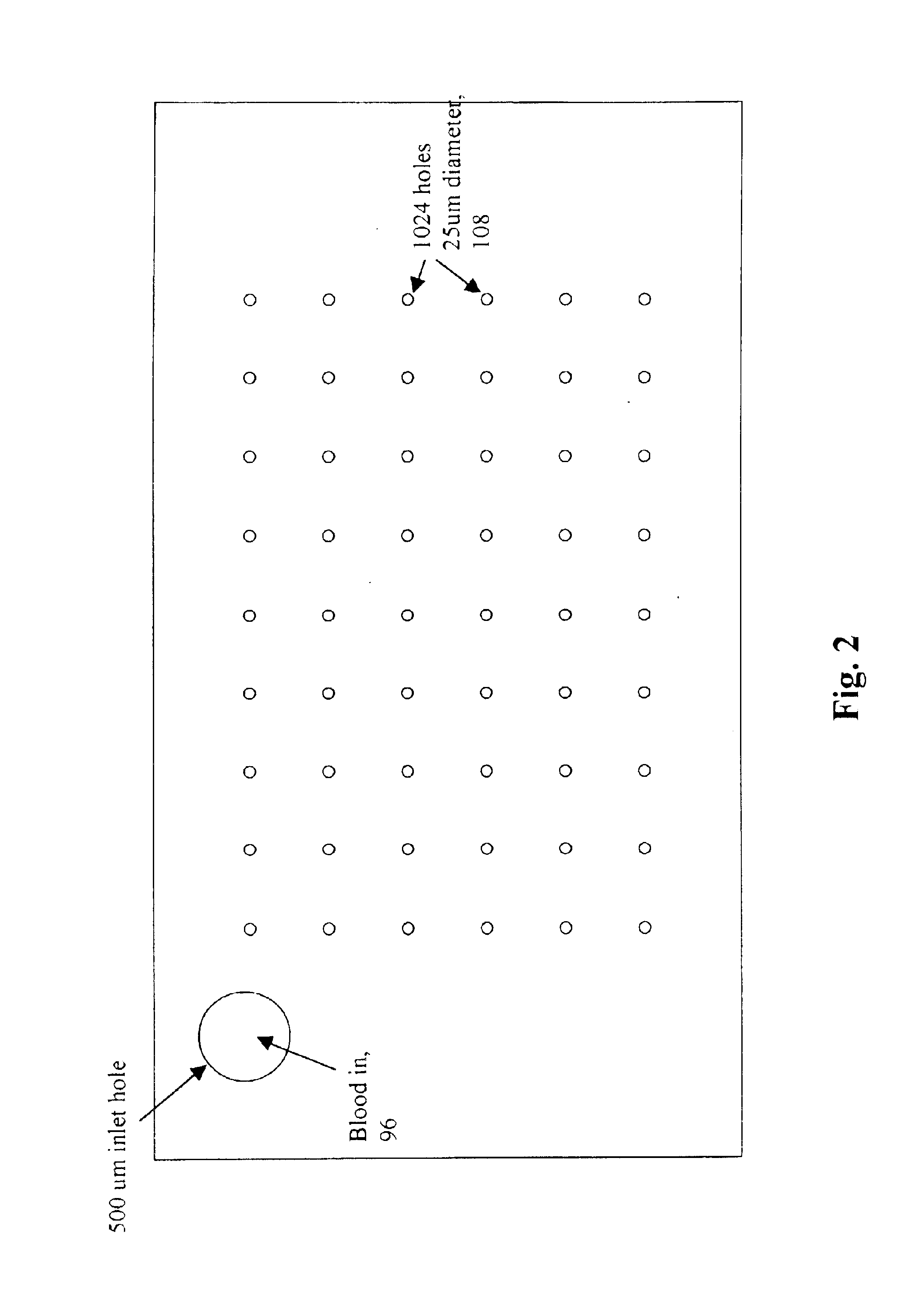
A micromechanical actuator for sorting hematopoietic stem cells for use in cancer therapies. The actuator operates by diverting cells into one of a number of possible pathways fabricated in the fabrication substrate of the micromechanical actuator, when fluorescence is detected emanating from the cells. The fluorescence results from irradiating the cells with laser light, which excites a fluorescent tag attached to the cell. The micromechanical actuator thereby sorts the cells individually, with an operation rate of 3.3 kHz, however with the massively parallel 1024-fold device described herein, a throughput of 3.3 million events / second is achievable.
Owner:OWL BIOMEDICAL
System and method for analyte measurement using AC phase angle measurements
A method of measuring an analyte in a biological fluid comprises applying an excitation signal having a DC component and an AC component. The AC and DC responses are measured; a corrected DC response is determined using the AC response; and a concentration of the analyte is determined based upon the corrected DC response. Other methods and devices are disclosed.
Owner:ROCHE OPERATIONS +1
Auto-calibration label and apparatus comprising same
ActiveUS7316929B2Reduce in quantityReduce harmMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansComputer scienceInstrumentation
An auto-calibration label for use with one or more sensing instruments. The label includes first and second encoded calibration information. The second encoded calibration information may correspond to a different instrument than the first encoded calibration information. The second encoded information may also be used to provide additional calibration information for use with the first instrument. The label may be removably attached to a sensor package including a plurality of sensors. A first conductive ink pattern is disposed on the label to define the first encoded calibration information. The first conductive ink pattern is disposed contemporaneously with or without a portion of a second conductive ink pattern defining the second encoded calibration information. An insulating layer is disposed on the first pattern. The second ink pattern is disposed on the insulating layer. The first pattern is operable with the first instrument, not the second instrument. The second pattern is operable with the second instrument, not the first instrument.
Owner:ASCENSIA DIABETES CARE HLDG AG
Sensor apparatus systems, devices and methods
A sensor apparatus and sensor apparatus system for use in conjunction with a cassette, including a disposable or replaceable cassette. In some embodiments, the cassette includes a thermal well for permitting the sensing of various properties of a subject media. The thermal well includes a hollow housing of a thermally conductive material. In other embodiments, the cassette includes sensor leads for sensing of various properties of a subject media. The thermal well has an inner surface shaped so as to form a mating relationship with a sensing probe. The mating thermally couples the inner surface with a sensing probe. In some embodiments, the thermal well is located on a disposable portion and the sensing probe on a reusable portion.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
Molecular wire injection sensors
InactiveUS6979544B2Accurate readingRapid responseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsConductive polymerMolecular wire
Disclosed is a sensor for sensing the presence of an analyte component without relying on redox mediators. This sensor includes (a) a plurality of conductive polymer strands each having at least a first end and a second end and each aligned in a substantially common orientation; (b) a plurality of molecular recognition headgroups having an affinity for the analyte component and being attached to the first ends of the conductive polymer strands; and (c) an electrode substrate attached to the conductive polymer strands at the second ends. The electrode substrate is capable of reporting to an electronic circuit reception of mobile charge carriers (electrons or holes) from the conductive polymer strands. The electrode substrate may be a photovoltaic diode.
Owner:KEENSENSE
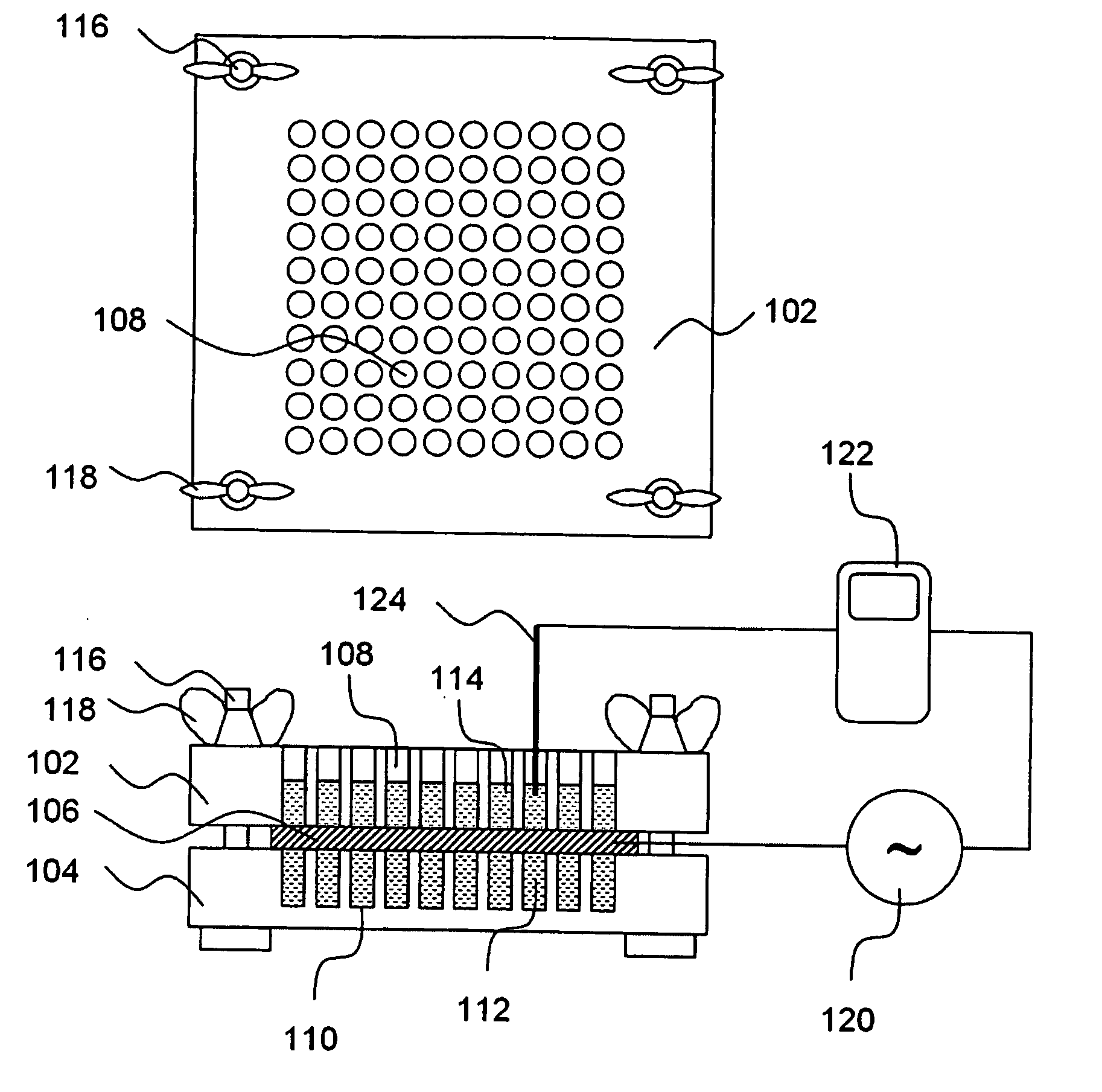
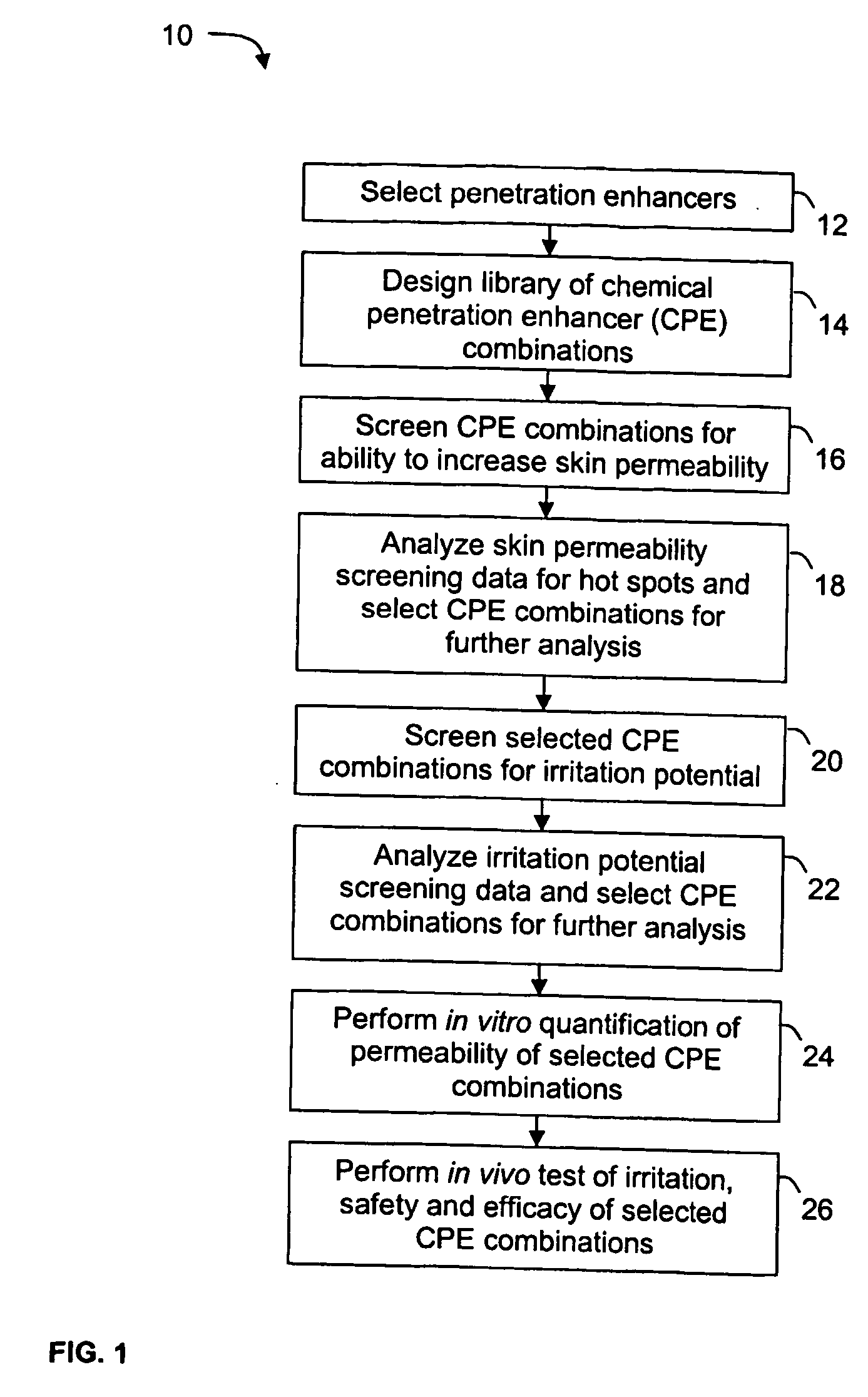
Penetration Enhancer Combinations for Transdermal Delivery
InactiveUS20070269379A1Easy to transportLess irritatingOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsIrritation
A high throughput screening and isolation system identifies rare enhancer mixtures from a candidate pool of penetration enhancer combinations. The combinations are screened for high penetration but low irritation potential using a unique data mining method to find new potent and safe chemical penetration enhancer combinations. The members of a library of chemical penetration enhancer combinations are screened with a high throughput device to identify “hot spots”, particular combinations that show higher chemical penetration enhancement compared to neighboring compositions. The irritation potentials of the hot spot combinations are measured to identify combinations that also show low irritation potential. A active component, such as a drug, is then combined with the combination in a formulation which is tested for the ability of the drug to penetrate into or through skin. It is then assessed whether the formulation can deliver the quantity of drug required, and animal tests are conducted to confirm in vivo the ability of the chemical penetration enhancer combinations to facilitate transport of sufficient active molecules across the skin to achieve therapeutic levels of the active molecule in the animal's blood. The invention provides specific unique and rare mixtures of chemical penetration enhancers that enhance skin permeability to hydrophilic macromolecules by more than 50-fold without inducing skin irritation, such as combinations of sodium laurel ether sulfate and 1-phenyl piperazine, and combinations of N-lauryl sarcosine and Span 20 / sorbitan monolaurate.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Electrowetting electrode device with electromagnetic field for actuation of magnetic-bead biochemical detection system
InactiveUS7189359B2Reduce dissipationEnhanced magnetic forceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaboratory glasswaresElectricityMagnetic bead
A detecting device for biochemical detections is provided. The detecting device includes a first substrate, a magnetic layer located on the first substrate, an isolation layer located on the magnetic layer, at least a first electrode located on the isolation layer, a first dielectric layer located on the first electrode, a first hydrophobic layer located on the first dielectric layer, a second substrate, at least a second electrode located on the second substrate and having a cathode and an anode, a second dielectric layer located on the second electrode' and a second hydrophobic layer located on the second dielectric layer. The first electrode is zigzag-shaped, and the cathode and the anode of the second electrode are comb-shaped and interlaced with each other.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY +1
Method and device for determining analytes in a liquid
InactiveUS20050106742A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteChemistry
A method for determining analytes in a liquid is provided comprising applying a liquid volume to be examined to a substrate of a transport plane; moving the liquid volume to be examined on the substrate of the transport plane to a site of examination; contacting the liquid volume to be examined with at least one sensory element, wherein the sensory element is located in a detection plane opposite to the substrate of the transport plane; and determining an analyte in the liquid volume to be examined by the sensory element, wherein the liquid volume is only in contact with the substrate of the transport plane during the step of moving the liquid volume to be examined on the substrate of the transport plane to a site of examination. The application also concerns a device for determining analytes in a liquid corresponding to the method according to the invention.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
System and method for determining an abused sensor during analyte measurement
ActiveUS7488601B2Measurement arrangements for variableCounting objects with random distributionAnalyteExcitation signal
A method of measuring an analyte in a biological fluid comprises applying an excitation signal having a DC component and an AC component. The AC and DC responses are measured; a corrected DC response is determined using the AC response; and a concentration of the analyte is determined based upon the corrected DC response. Other methods and devices are disclosed.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com