Patents
Literature
3555 results about "Magnetic bead" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Reagents, methods, and libraries for bead-based sequencing
InactiveUS20080003571A1Efficient methodEfficient implementationMaterial nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotideNucleic acid sequencing
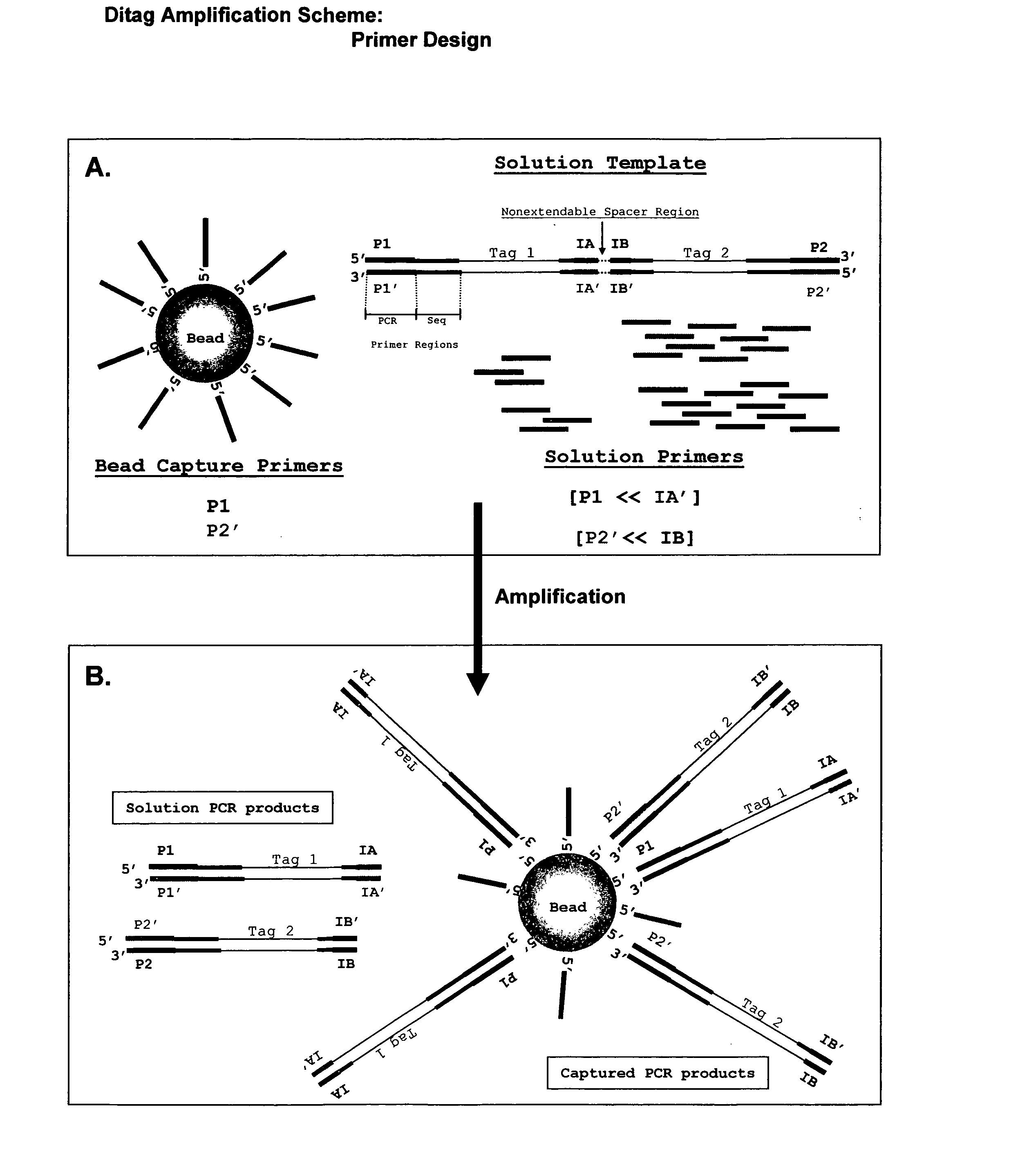
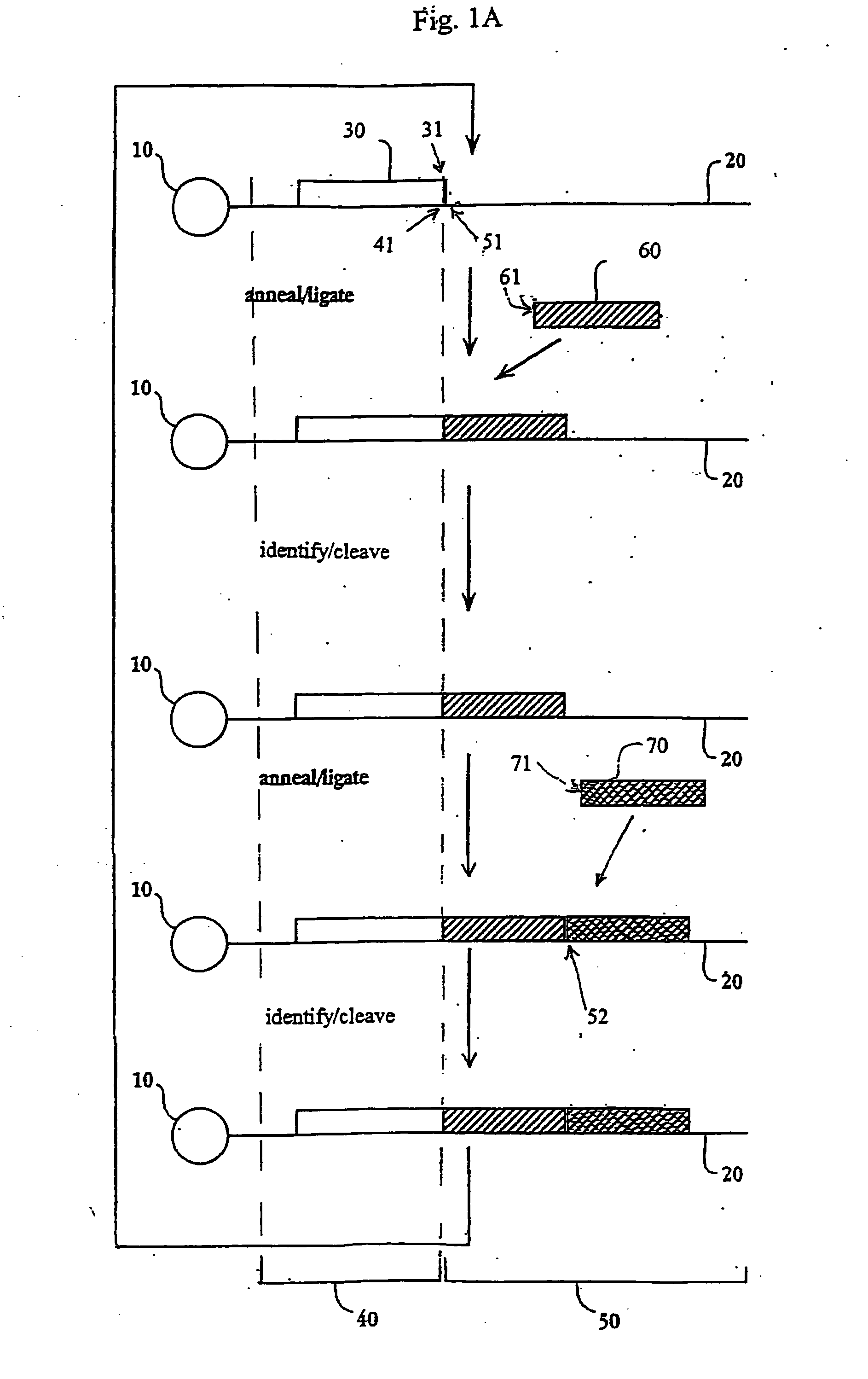
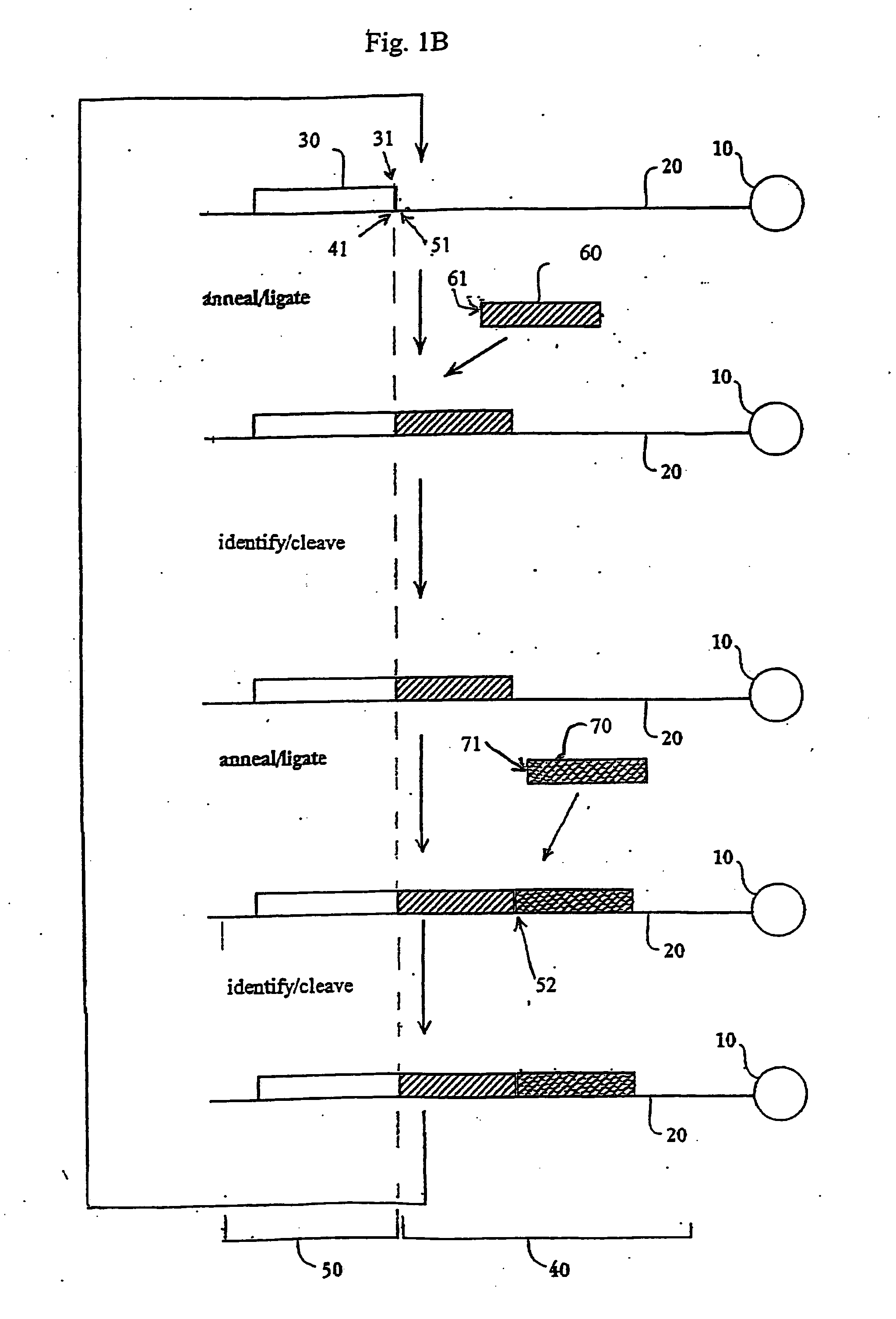
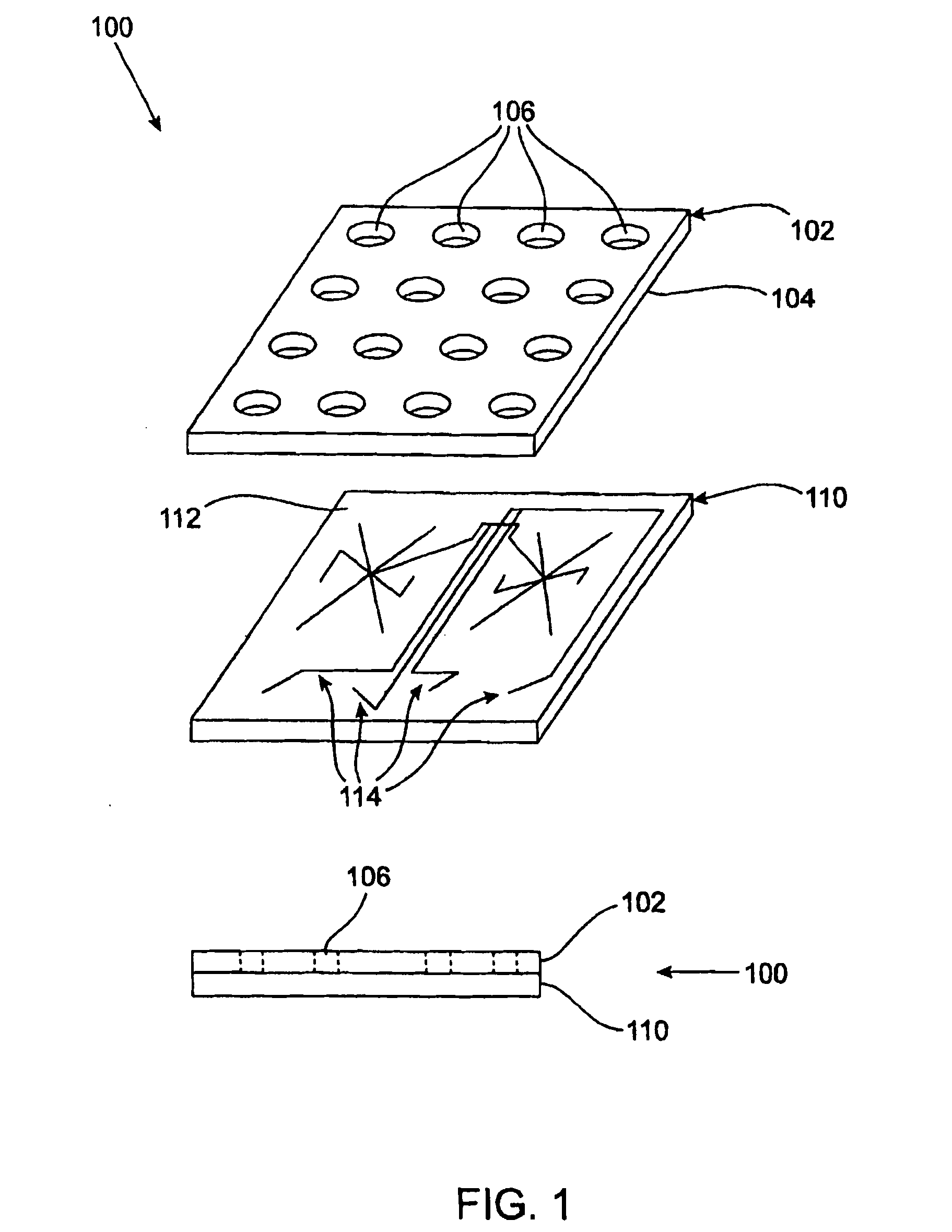
The present invention provides methods for determining a nucleic acid sequence by performing successive cycles of duplex extension along a single stranded template. The cycles comprise steps of extension, ligation, and, preferably, cleavage. In certain embodiments the methods make use of extension probes containing phosphorothiolate linkages and employ agents appropriate to cleave such linkages. In certain embodiments the methods make use of extension probes containing an abasic residue or a damaged base and employ agents appropriate to cleave linkages between a nucleoside and an abasic residue and / or agents appropriate to remove a damaged base from a nucleic acid. The invention provides methods of determining information about a sequence using at least two distinguishably labeled probe families. In certain embodiments the methods acquire less than 2 bits of information from each of a plurality of nucleotides in the template in each cycle. In certain embodiments the sequencing reactions are performed on templates attached to beads, which are immobilized in or on a semi-solid support. The invention further provides sets of labeled extension probes containing phosphorothiolate linkages or trigger residues that are suitable for use in the method. In addition, the invention includes performing multiple sequencing reactions on a single template by removing initializing oligonucleotides and extended strands and performing subsequent reactions using different initializing oligonucleotides. The invention further provides efficient methods for preparing templates, particularly for performing sequencing multiple different templates in parallel. The invention also provides methods for performing ligation and cleavage. The invention also provides new libraries of nucleic acid fragments containing paired tags, and methods of preparing microparticles having multiple different templates (e.g., containing paired tags) attached thereto and of sequencing the templates individually. The invention also provides automated sequencing systems, flow cells, image processing methods, and computer-readable media that store computer-executable instructions (e.g., to perform the image-processing methods) and / or sequence information. In certain embodiments the sequence information is stored in a database.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Microfluidic device for purifying a biological component using magnetic beads
InactiveUS20070184463A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMagnetic beadElution
A method of purifying a biological component found in a biological sample by extracting the biological component from the biological sample. The method is performed using a microfluidic device having at least one well for receiving the biological sample and at least one channel for introducing and removing fluids. A plurality of magnetic beads having a factor with an affinity for the biological component is introduced to the well together with a suitable biological sample. The biological sample is manipulated to release the biological component in proximity to the magnetic beads which are then segregated within the well while removing the biological sample. An elution solution for the biological component is introduced to the well and the elution solution together with the biological component are withdrawn therefrom.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC +1
Methods and compositions for separating rare cells from fluid samples
InactiveUS20070202536A1Aid in diagnosis and prognosisPromote recoveryMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationCancer cellRare cell
The present invention includes methods of enriching rare cells, such as cancer cells, from biological samples, such as blood samples. The methods include performing at least one debulking step on a blood sample and selectively removing at least one type undesirable component from the blood sample to obtain a blood sample that is enriched in a rare cell of interest. In some embodiments magnetic beads coupled to specific binding members are used to selectively removed components.
Owner:AVIVA BIOSCI
Microfluidic mixing and analytical apparatus
ActiveUS20070183935A1Efficient mixingPromote turbulent mixingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMagnetic beadEngineering
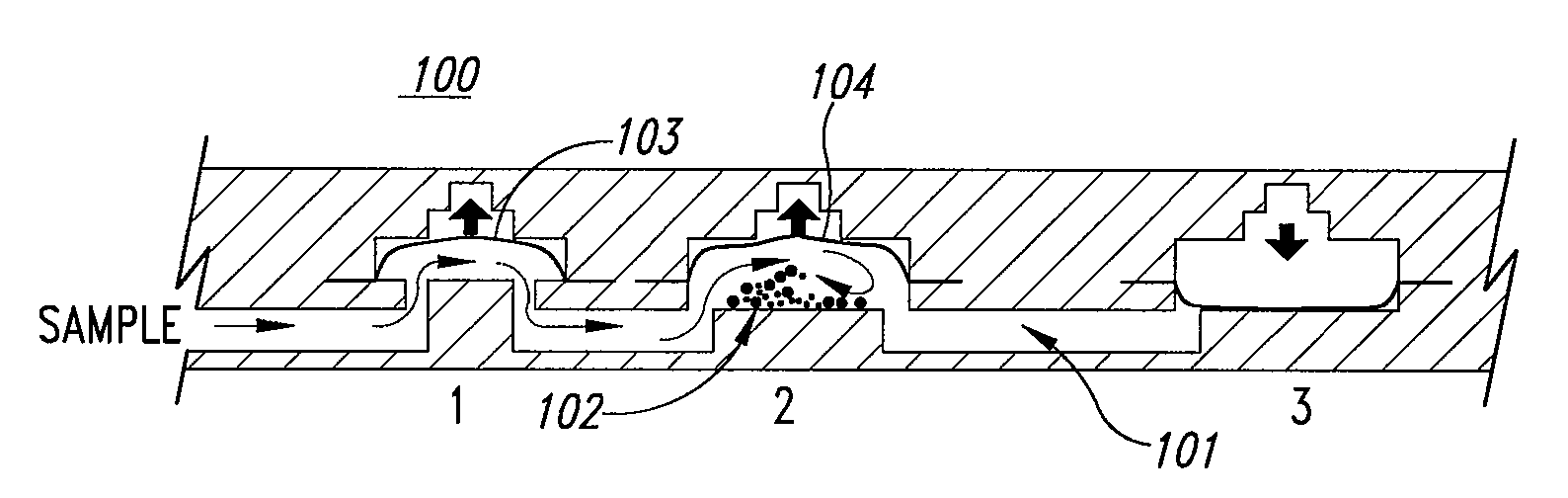
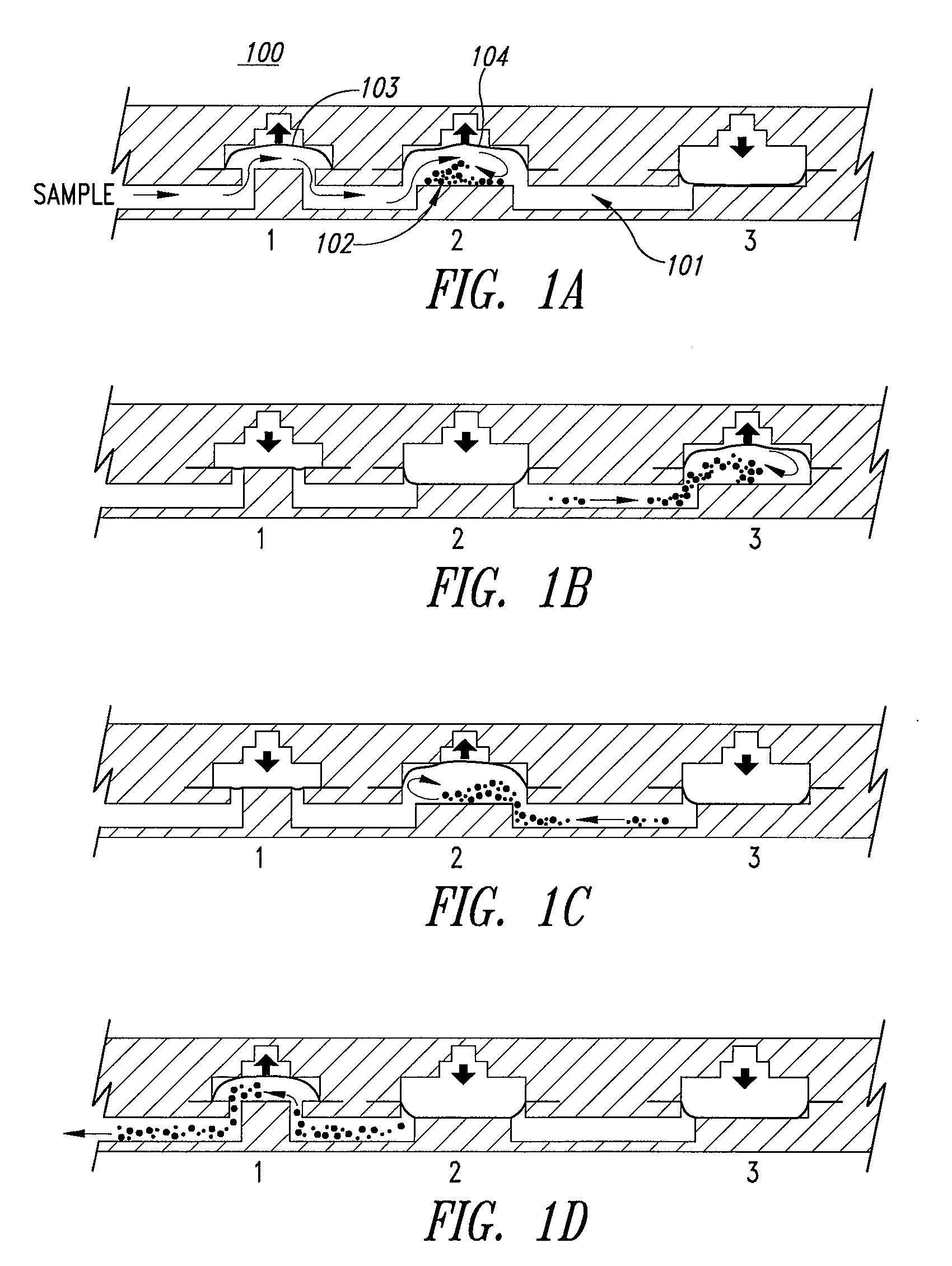
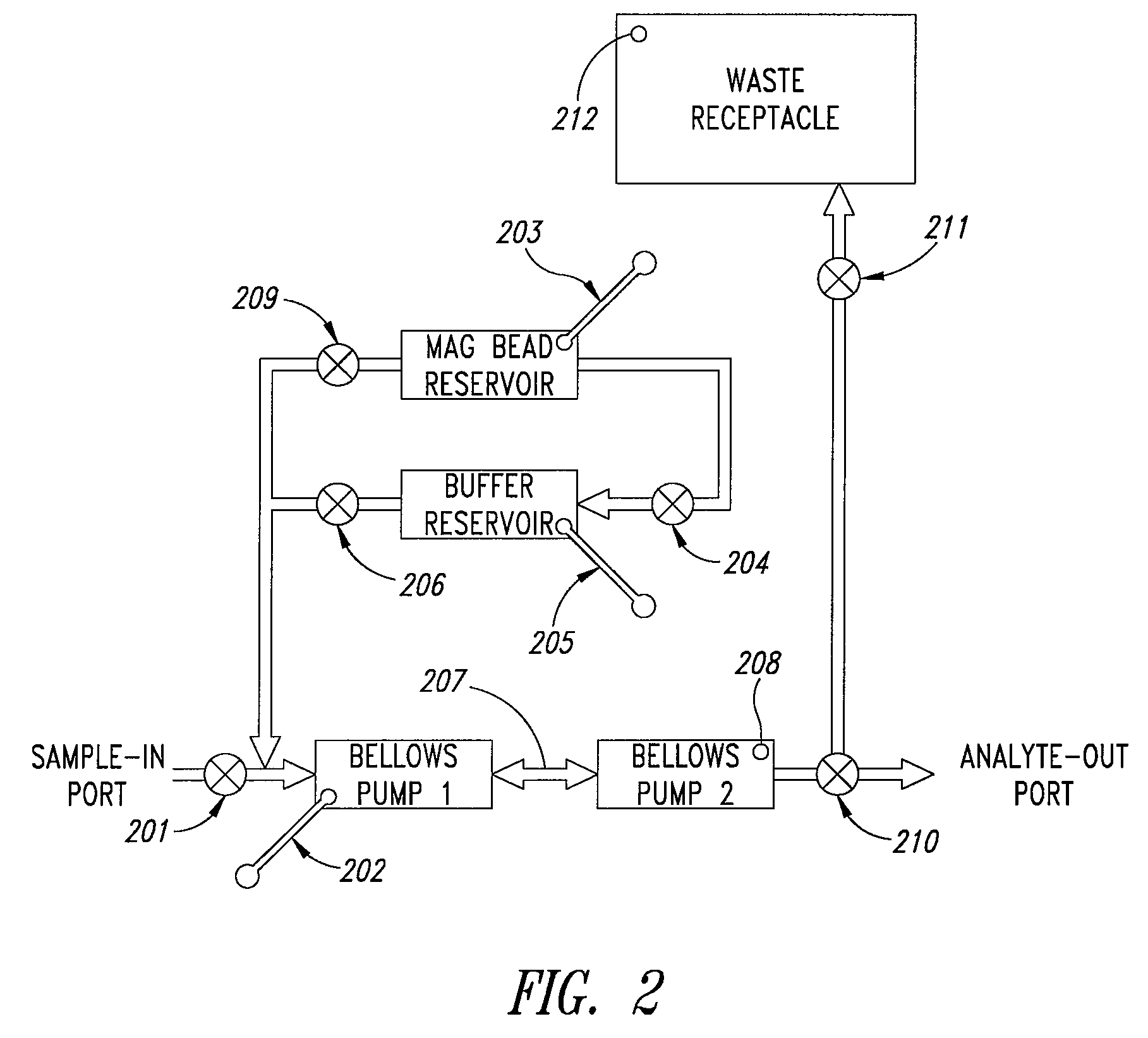
Disclosed herein is a device comprising a pair of bellows pumps configured for efficient mixing at a microfluidic scale. By moving a fluid sample and particles in suspension through an aperture between the paired bellows pump mixing chambers, molecular collisions leading to binding between the particles and ligands in the sample are enhanced. Such devices provide an alternative for mixing that does not use a vent and can be used with a variety of particles in suspension such as magnetic beads to capture or purify useful cells and molecules.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Electrowetting electrode device with electromagnetic field for actuation of magnetic-bead biochemical detection system
InactiveUS20050056569A1Reduce dissipationEnhanced magnetic forceMaterial thermal conductivityMicrobiological testing/measurementElectricityMagnetic bead
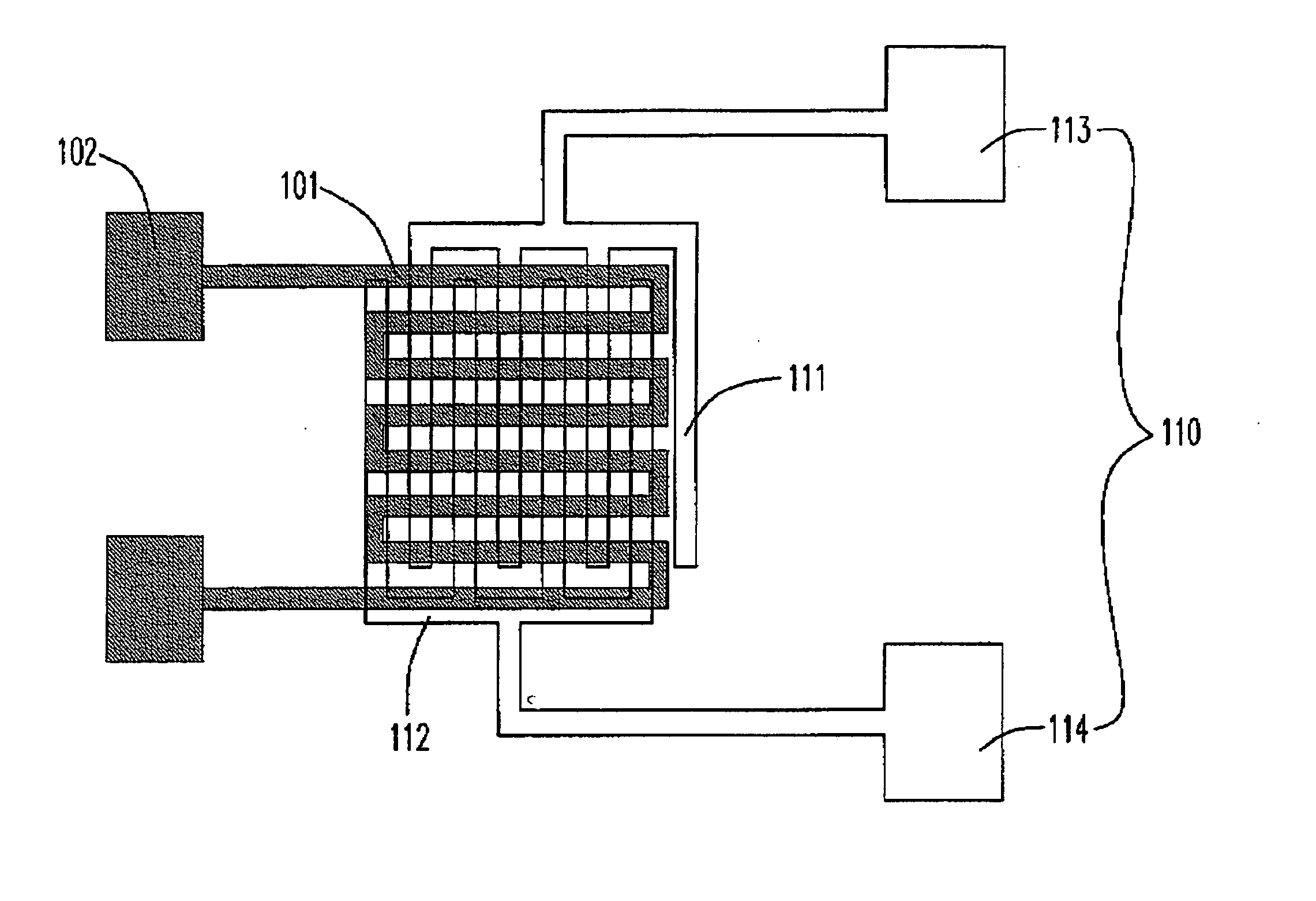
A detecting device for biochemical detections is provided. The detecting device includes a first substrate, a magnetic layer located on the first substrate, an isolation layer located on the magnetic layer, at least a first electrode located on the isolation layer, a first dielectric layer located on the first electrode, a first hydrophobic layer located on the first dielectric layer, a second substrate, at least a second electrode located on the second substrate and having a cathode and an anode, a second dielectric layer located on the second electrode and a second hydrophobic layer located on the second dielectric layer. The first electrode is zigzag-shaped, and the cathode and the anode of the second electrode are comb-shaped and interlaced with each other.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY +1
Electrowetting electrode device with electromagnetic field for actuation of magnetic-bead biochemical detection system
InactiveUS7189359B2Reduce dissipationEnhanced magnetic forceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaboratory glasswaresElectricityMagnetic bead
A detecting device for biochemical detections is provided. The detecting device includes a first substrate, a magnetic layer located on the first substrate, an isolation layer located on the magnetic layer, at least a first electrode located on the isolation layer, a first dielectric layer located on the first electrode, a first hydrophobic layer located on the first dielectric layer, a second substrate, at least a second electrode located on the second substrate and having a cathode and an anode, a second dielectric layer located on the second electrode' and a second hydrophobic layer located on the second dielectric layer. The first electrode is zigzag-shaped, and the cathode and the anode of the second electrode are comb-shaped and interlaced with each other.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY +1
Multichannel micro-fluidic chip specially used for AIDS diagnosis and comprising quasi-one-dimensional sensitive electrodes
InactiveCN101581725AFast diagnosisReduce diagnostic costsMaterial electrochemical variablesMagnetic beadCapillary channel
The invention relates to a multichannel micro-fluidic chip specially used for AIDS diagnosis and comprising quasi-one-dimensional sensitive electrodes, belonging to the field of test. One of the hopes in the progress of medical techniques is to quickly diagnose AIDS at low cost. The invention provides a micro-fluidic chip that uses a plurality of AIDS characteristic antibodies to simultaneously detect and quickly diagnose AIDS. The chip is provided with three micro liquid storage tanks. The key points of the proposal lie in that the inner of the chip contains capillary channels of parallel structure, the parallel structure contains four micro-channels mutually connected in parallel, four working electrodes of bead string structure in total are respectively arranged in the four micro-channels, the substances on the superficial coats of the four working electrodes of bead string structure are respectively four antibody substances, namely, AIDS antibodies p24, gp41, gp120 and gp36. The application of the chip is conducive to increasing the diagnosis efficiency of AIDS as shown by the structural characteristics.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Special micro-fluidic chip for cholera diagnosis with one-dimensional self-assembly magnetic bead chain electrodes
InactiveCN101587123AImprove diagnostic efficiencyReduce dosageMaterial electrochemical variablesAgainst vector-borne diseasesMycoproteinMagnetic bead
The invention relates to a special micro-fluidic chip for cholera diagnosis with one-dimensional self-assembly magnetic bead chain electrodes, belonging to the field of testing. Rapid diagnosis of fulminating infectious disease cholera with low cost is one of many expectations in the development of medical technology, and the invention provides a micro-fluidic chip for simultaneously detecting and rapidly diagnosing cholera by using multiple characteristic antibodies of cholera. The chip is provided with three micro liquid storage tanks, and the invention is characterized in that capillary passages in parallel configuration contain in the chip, the parallel configuration contains four micro-passages that are mutually in parallel, four magnetic bead chain working electrodes are respectively installed inside the four micro-passages, the surface substances of the four magnetic bead chain working electrodes are respectively four antibody substances that are cholera TP0821 antibody, cholera TP0319 antibody, cholera TP0624 antibody and cholera O139 mycoprotein antibody. The integrated structure and the appearances of specific magnetic bead chain working electrodes facilitate to improve the diagnosis efficiency of cholera diseases.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Device and method for combined microfluidic-micromagnetic separation of material in continuous flow
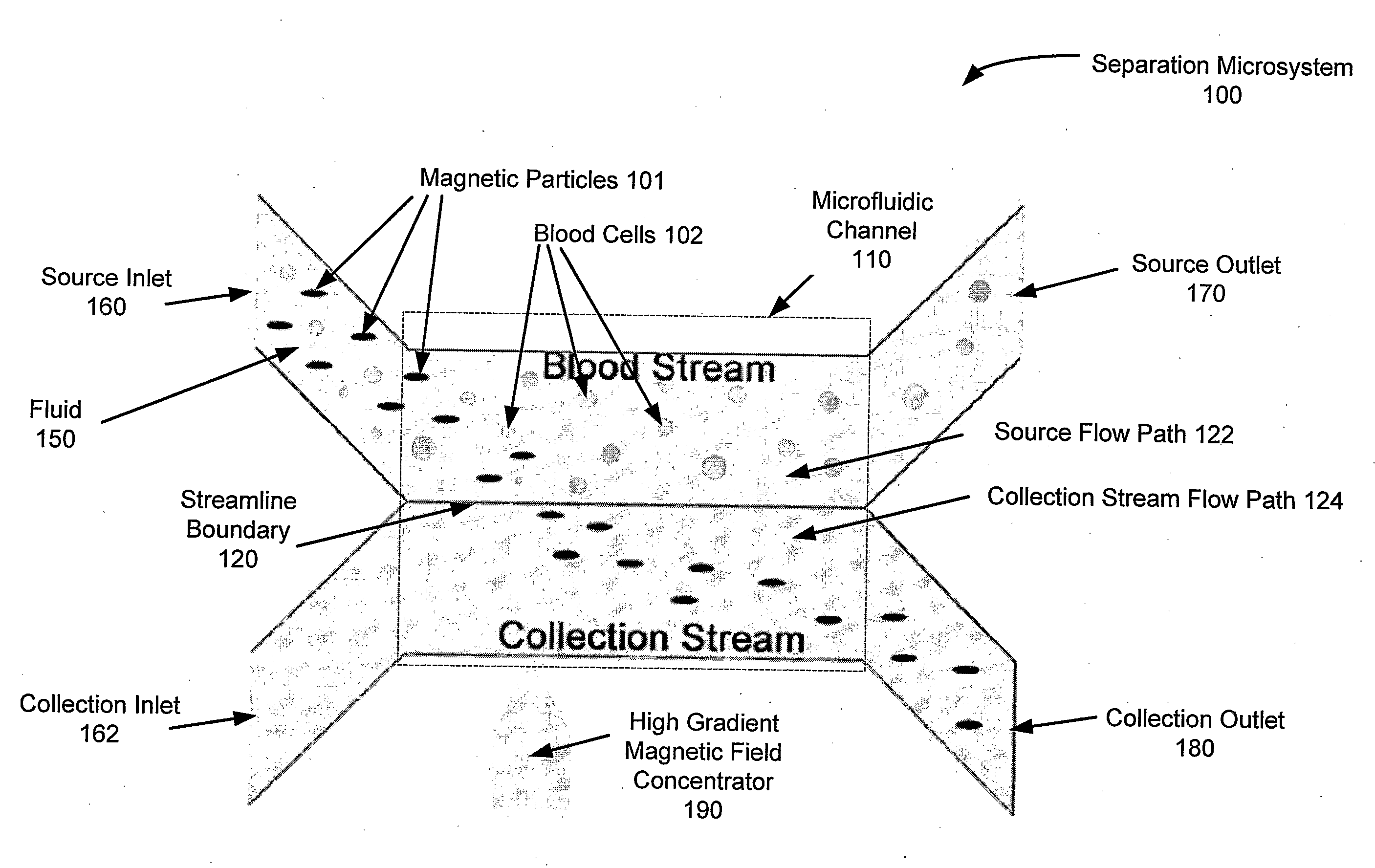
ActiveUS20090220932A1Minimize disturbanceEfficient separationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMagnetic field gradientChemical physics
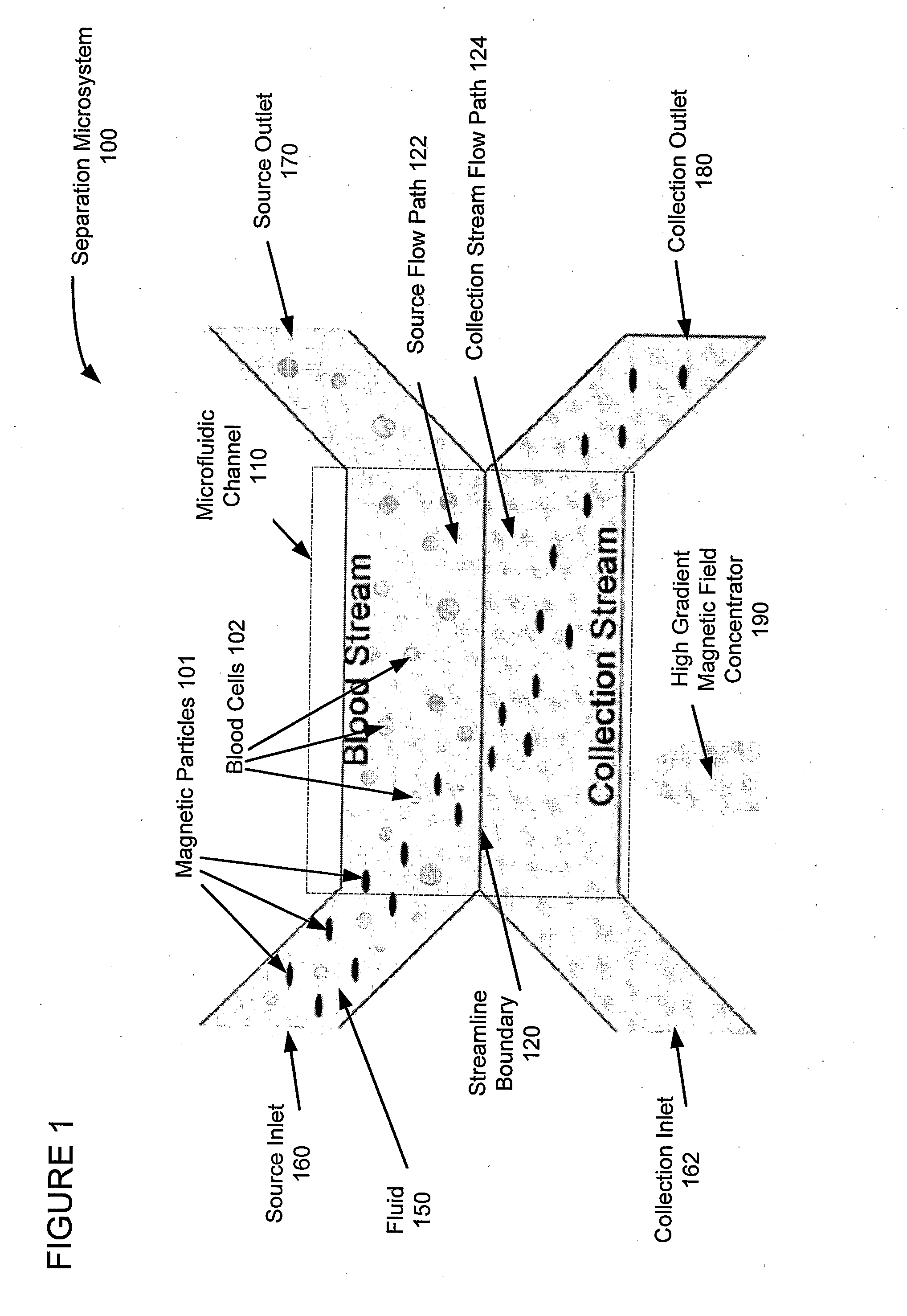
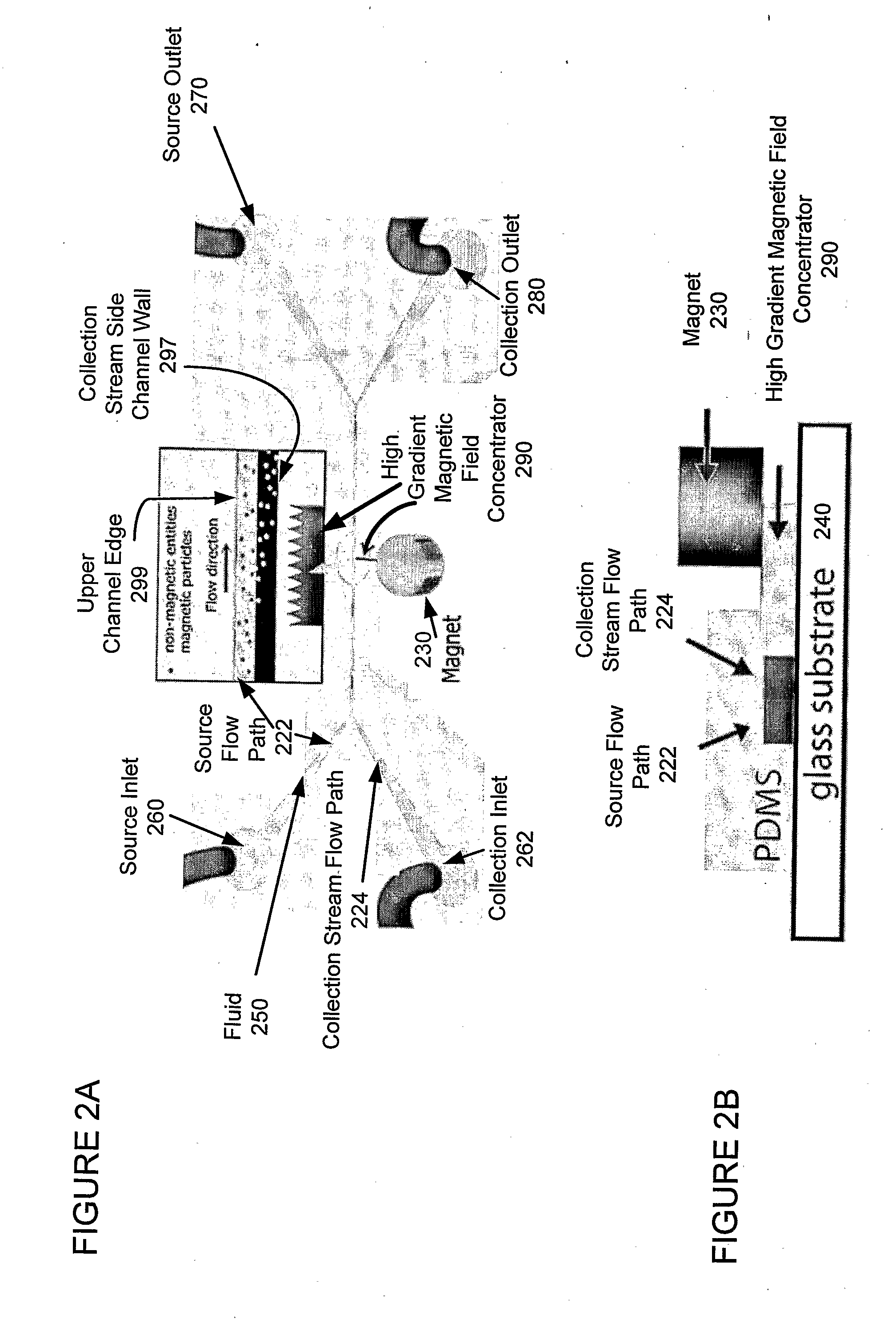
A miniaturized, integrated, microfluidic device pulls materials bound to magnetic particles from one laminar flow path to another by applying a local magnetic field gradient. The device removes microbial and mammalian cells from flowing biological fluids without any wash steps. A microfabricated high-gradient magnetic field concentrator (HGMC) is integrated at one side of a microfluidic channel. When magnetic particles are introduced into one flow path, they remain limited to that flow path. When the HGMC is magnetized, the magnetic beads are pulled from the initial flow path into the collection stream, thereby cleansing the fluid. The microdevice allows large numbers of beads and materials to be sorted simultaneously, has no capacity limit, does not lose separation efficiency as particles are removed, and is useful for cell separations from blood and other biological fluids. This on-chip separator allows cell separations to be performed in the field outside of hospitals and laboratories.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Close shaped magnetic multi-layer film comprising or not comprising a metal core and the manufacture method and the application of the same
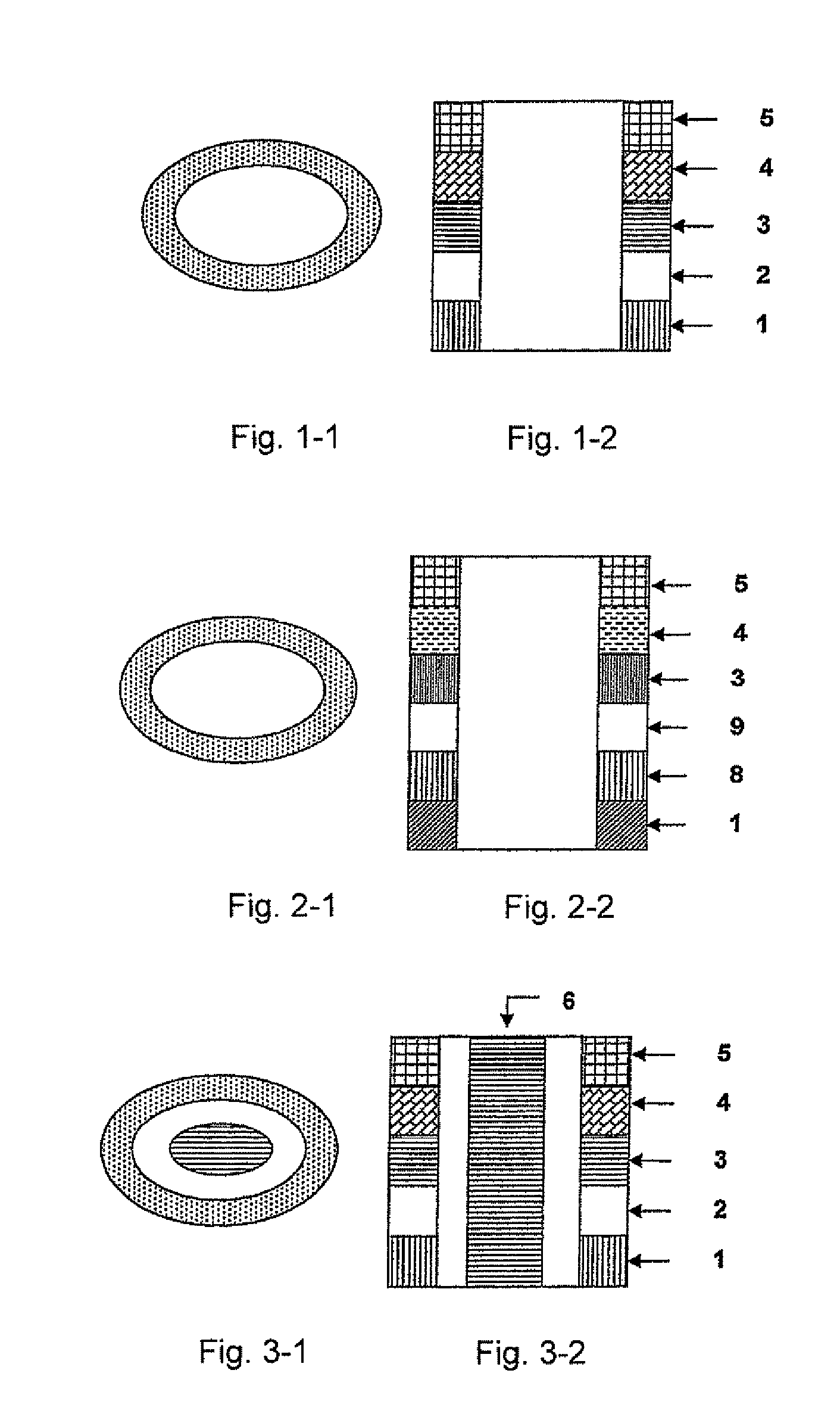
InactiveUS7936595B2High densitySmall scaleNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic beadMagnetic logic
Each layer in the magnetic multilayer film is a closed ring or oval ring and the magnetic moment or flux of the ferromagnetic film in the magnetic unit is in close state either clockwise or counterclockwise. A metal core is put in the geometry center position in the close-shaped magnetic multilayer film. The cross section of the metal core is a corresponding circular or oval. A MRAM is made of the closed magnetic multilayer film with or without a metal core. The close-shaped magnetic multilayer film is formed by micro process method. The close-shaped magnetic multilayer film can be used broadly in a great variety of device that uses a magnetic multilayer film as the core, such as MRAM, magnetic bead in computer, magnetic sensitive sensor, magnetic logic device and spin transistor.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Centrifugal force-based microfluidic device for nucleic acid extraction and microfluidic system including the microfluidic device
ActiveUS20080108120A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsValve arrangementsExternal energyMicrofluidics
A centrifugal force-based microfluidic device for nucleic acid extraction and a microfluidic system are provided. The microfluidic device includes a body of revolution; a microfluidic structure disposed in the body of revolution, the microfluidic structure including a plurality of chambers, channels connecting the chambers, and valves disposed in the channels to control fluid flow, the microfluidic structure transmitting the fluid using centrifugal force due to rotation of the body of revolution; and magnetic beads contained in one of the chambers which collect a target material from a biomaterial sample flowing into the chamber, wherein the microfluidic structure washes the magnetic beads which collect the target material, and separates nucleic acid by electromagnetic wave irradiation from an external energy source to the magnetic beads. The microfluidic system includes the microfluidic device; a rotation operating unit which rotates the body of revolution; and an external energy source which irradiates electromagnetic waves.
Owner:PRECISIONBIOSENSOR INC
Microfluidic devices and uses thereof
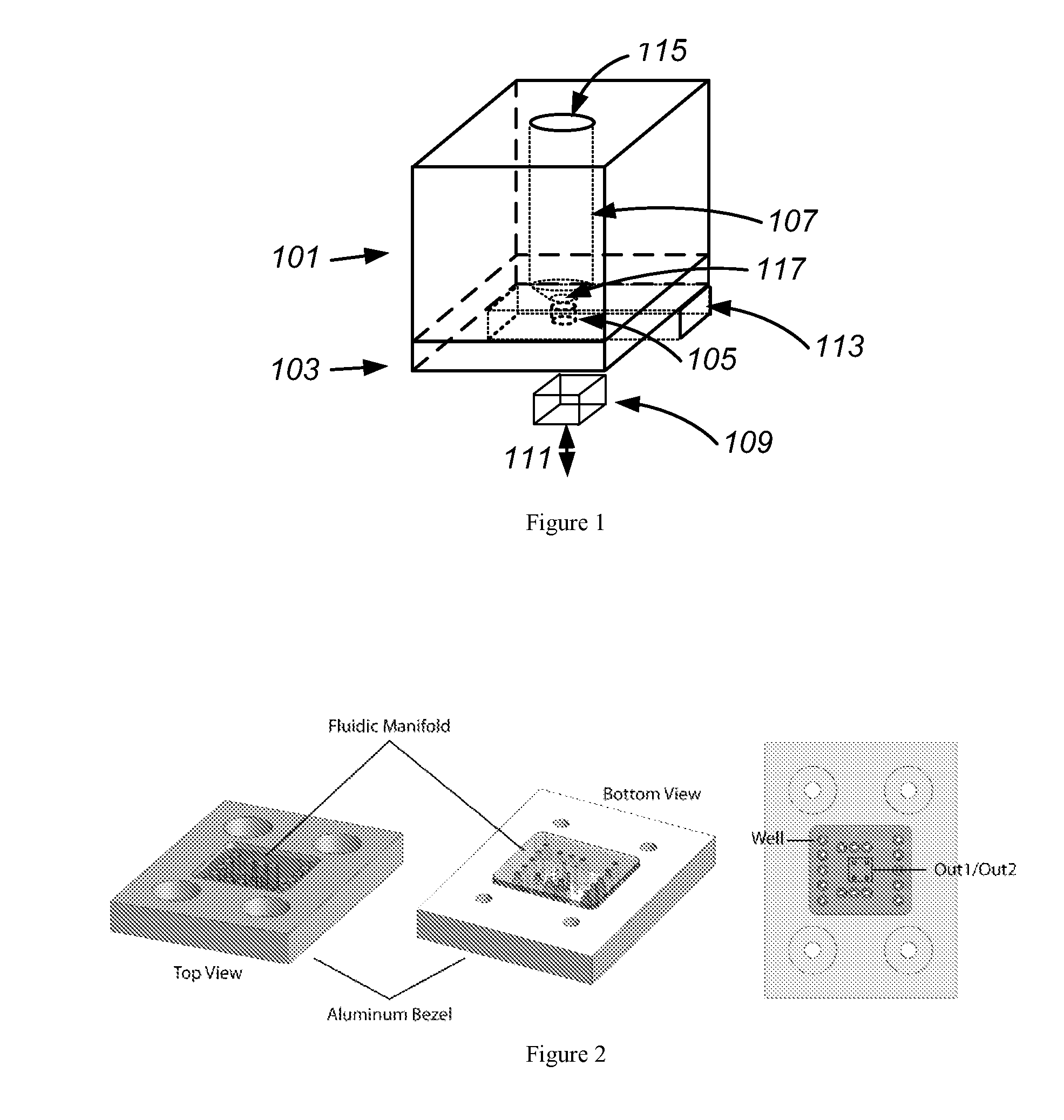
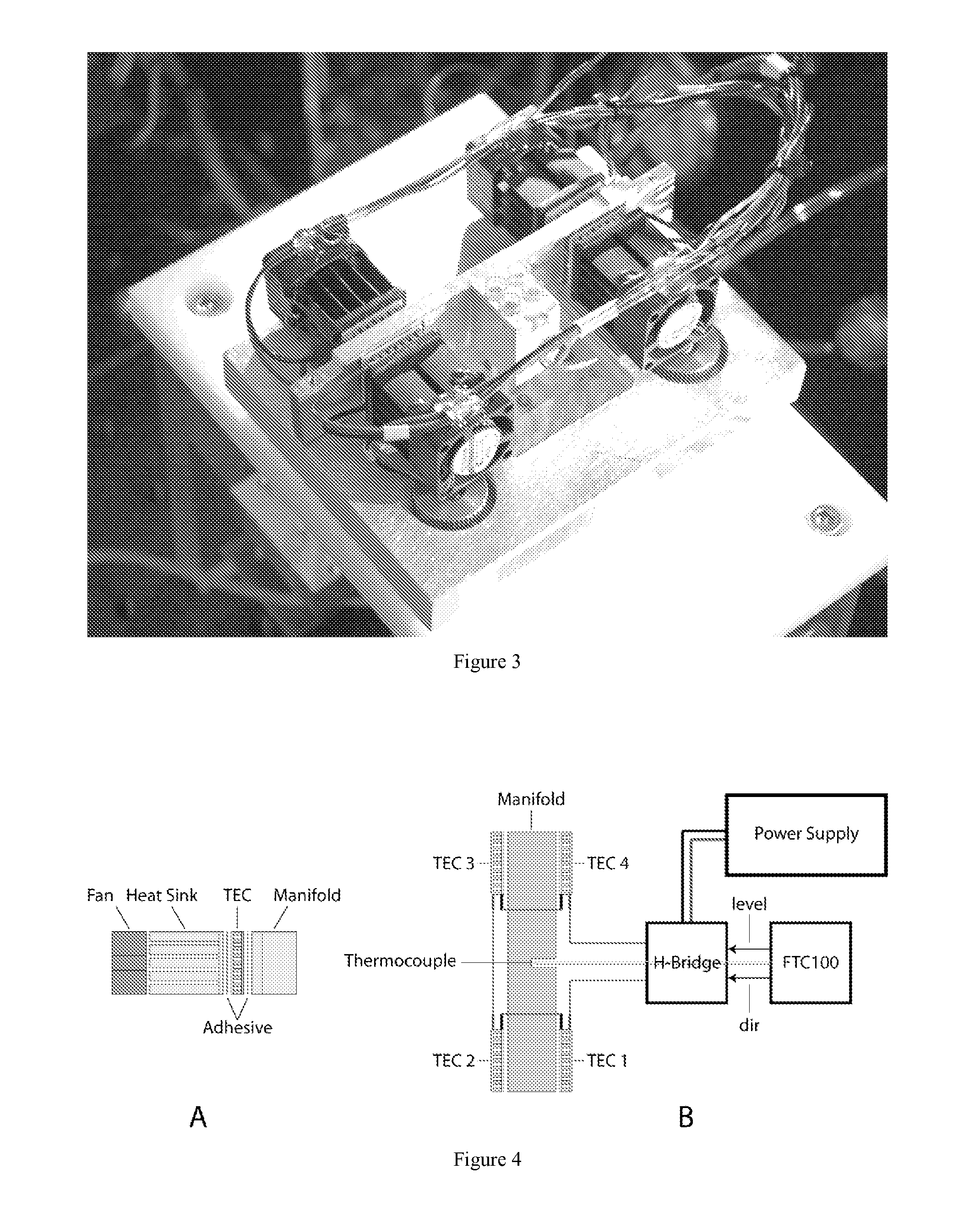
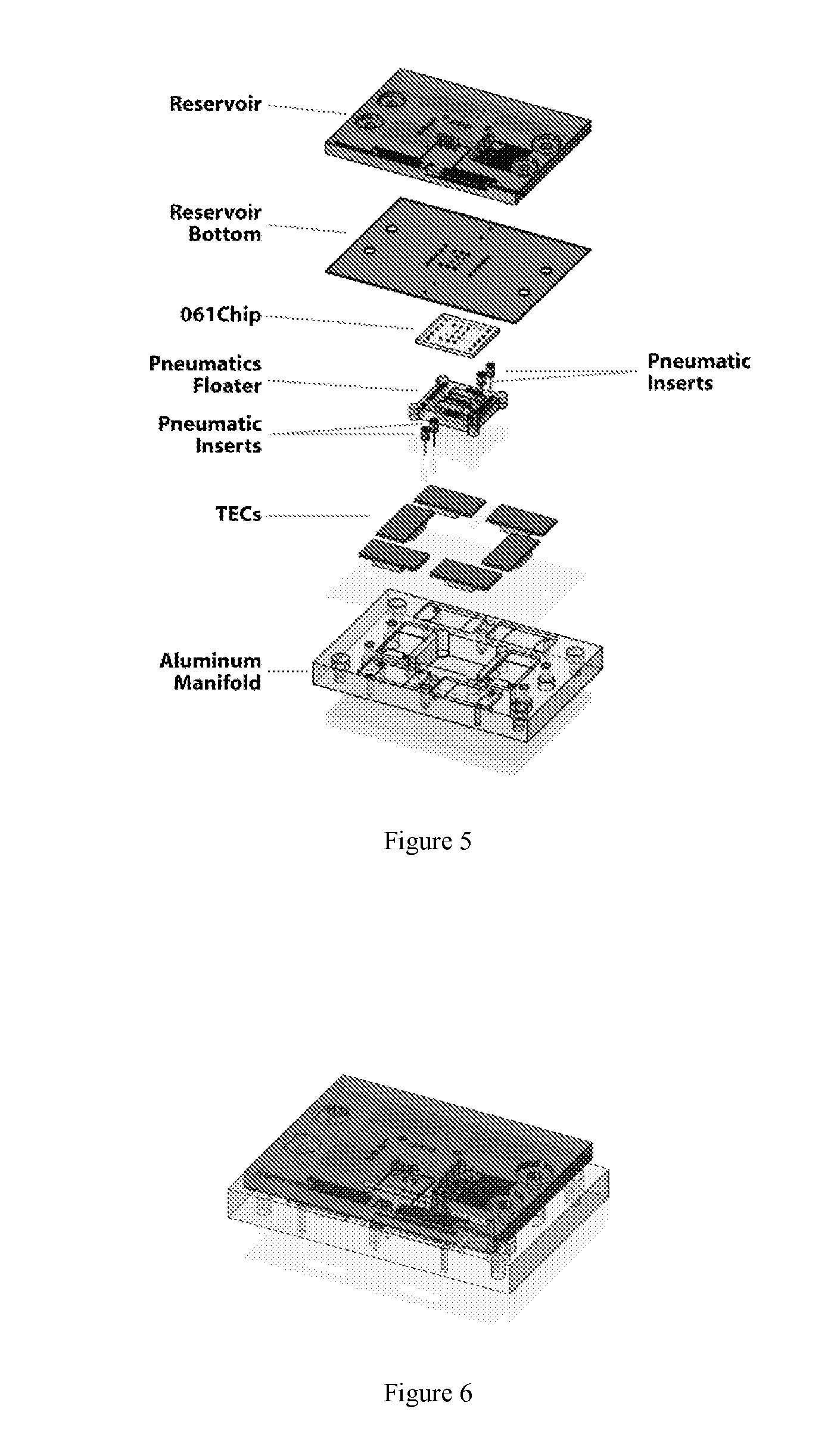
InactiveUS20120164036A1Heating or cooling apparatusLaboratory glasswaresMagnetic beadBiomedical engineering
The invention provides for devices and methods for interfacing microchips to cartridges and pneumatic manifolds. The design of the cartridges, microchips, and pneumatic manifolds can allow for the use of magnetic forces to capture magnetic beads in a chamber formed between the microchip and the cartridge or a chamber within the microchip. The devices of the invention can be used for mRNA amplification and purification.
Owner:INTEGENX
Close shaped magnetic multi-layer film comprising or not comprising a metal core and the manufacture method and the application of the same
InactiveUS20090168506A1High densitySmall scaleNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic beadMagnetic logic
Each layer in the magnetic multilayer film is a closed ring or oval ring and the magnetic moment or flux of the ferromagnetic film in the magnetic unit is in close state either clockwise or counterclockwise. A metal core is put in the geometry center position in the close-shaped magnetic multilayer film. The cross section of the metal core is a corresponding circular or oval. A MRAM is made of the closed magnetic multilayer film with or without a metal core. The close-shaped magnetic multilayer film is formed by micro process method. The close-shaped magnetic multilayer film can be used broadly in a great variety of device that uses a magnetic multilayer film as the core, such as MRAM, magnetic bead in computer, magnetic sensitive sensor, magnetic logic device and spin transistor.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for establishing hematopoietic stem cells bank by extracting hematopoietic cells from placenta tissues
InactiveCN1407088AIncrease the number ofSave livesMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsHigh concentrationHematopoietic cell
A process for extracting hemopoietic stem cells from the placenta of healthy puerperant to create hemopoistic stem cell bank features that the mechanical, enzyme digestive and monoclonal antibody-magnetic bead method is used to extract blood stem cells from placenta, and concentrate and purify them. Its advantages are high activity and high concentration.
Owner:上海厚东生物科技有限公司
Method for sex determination of mammalian offspring
InactiveUS6489092B1Increase probabilityImprove integrityMicrobiological testing/measurementDead animal preservationSemen sampleMagnetic bead
A method for increasing the percentage of mammalian offspring of either sex which comprises contacting a semen sample with an antibody specific for the spermatozoa determinative of one sex and separating said spermatozoa from spermatozoa determinative of the other sex, said antibody being bound to a non-porous magnetic bead support having a diameter of 0.1 to 2 microns.
Owner:VICAM
Timed pulsatile drug delivery systems
A pharmaceutical dosage form such as a capsule capable of delivering therapeutic agents into the body in a time-controlled or position-controlled pulsatile release fashion, is composed of a multitude of multicoated particulates (beads, pellets, granules, etc.) made of one or more populations of beads. Each of these beads except an immediate release bead has at least two coated membrane barriers. One of the membrane barriers is composed of an enteric polymer while the second membrane barrier is composed of a mixture of water insoluble polymer and an enteric polymer. The composition and the thickness of the polymeric membrane barriers determine the lag time and duration of drug release from each of the bead populations. Optionally, an organic acid containing intermediate membrane may be applied for further modifying the lag time and / or the duration of drug release. The pulsatile delivery may comprise one or more pulses to provide a plasma concentration-time profile for a therapeutic agent, predicted based on both its pharmaco-kinetic and pharmaco-dynamic considerations and in vitro / in vivo correlations.
Owner:ADARE PHARM INC
Apparatus for and method of purifying nucleic acids by different laser absorption of beads
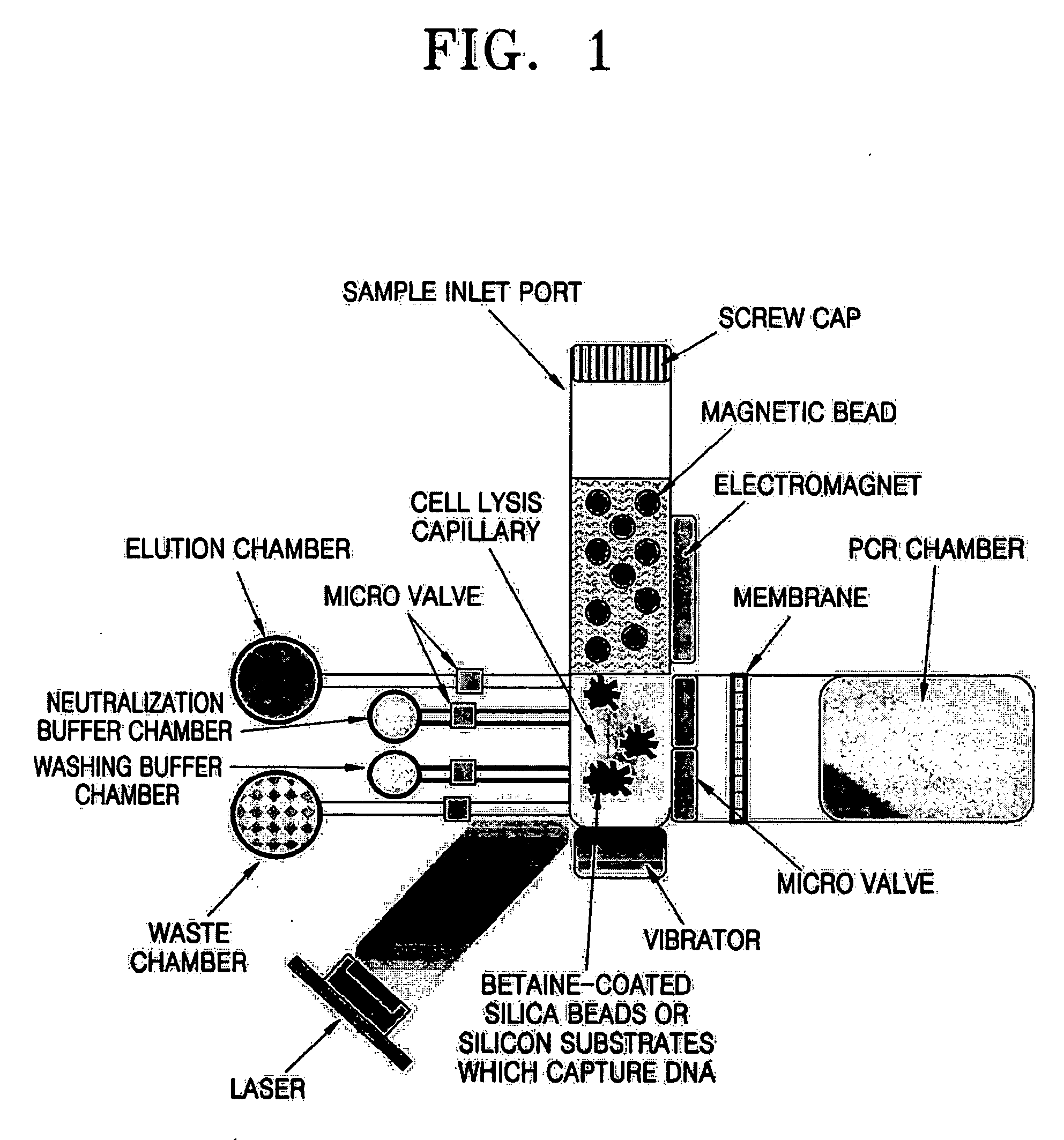
InactiveUS20060110725A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLysisMagnetic bead
An apparatus for and method of purifying nucleic acids of cells or viruses are provided. The nucleic acid purification apparatus includes: a cell lysis capillary having a sample inlet through which samples, magnetic beads, and a solid support are introduced; a vibrator attached to the capillary and mixing the samples, magnetic beads, and solid support in the capillary; a laser generator attached to the capillary and irradiating a laser beam onto the capillary; a magnetic force generator attached to the capillary and fixing the magnetic beads to a capillary wall; a waste chamber attached to the capillary and discharging a lysate; an elution buffer chamber attached to the capillary and eluting nucleic acids from the solid support having nucleic acids bound thereto; and a neutralization buffer chamber attached to the capillary and supplying a neutralization buffer for neutralizing the eluted nucleic acid solution. According to the apparatus and method, PCR inhibitors can be removed to increase PCR yield and nucleic acids can be purified using a silicon substrate or silica beads. Thus, the apparatus and method can be applied to LOC fabrication.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Automatic extraction device and method of nucleic acid based on nano magnetic beads
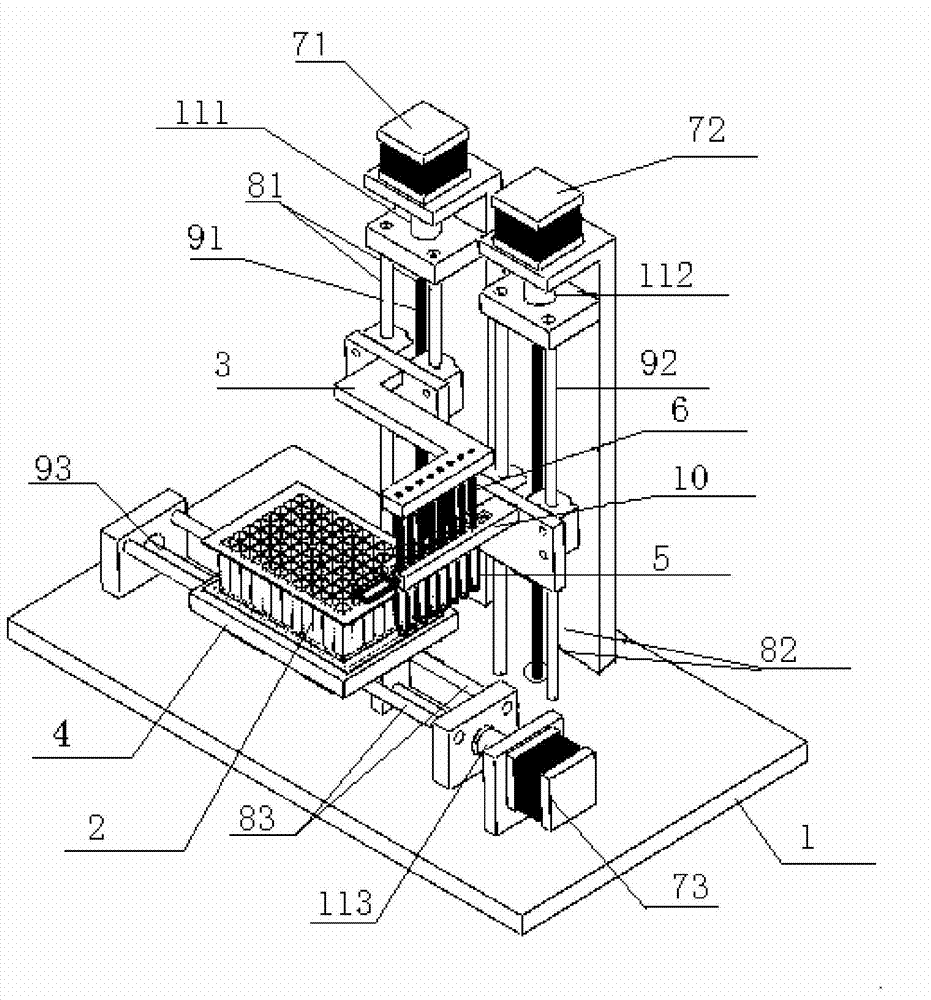
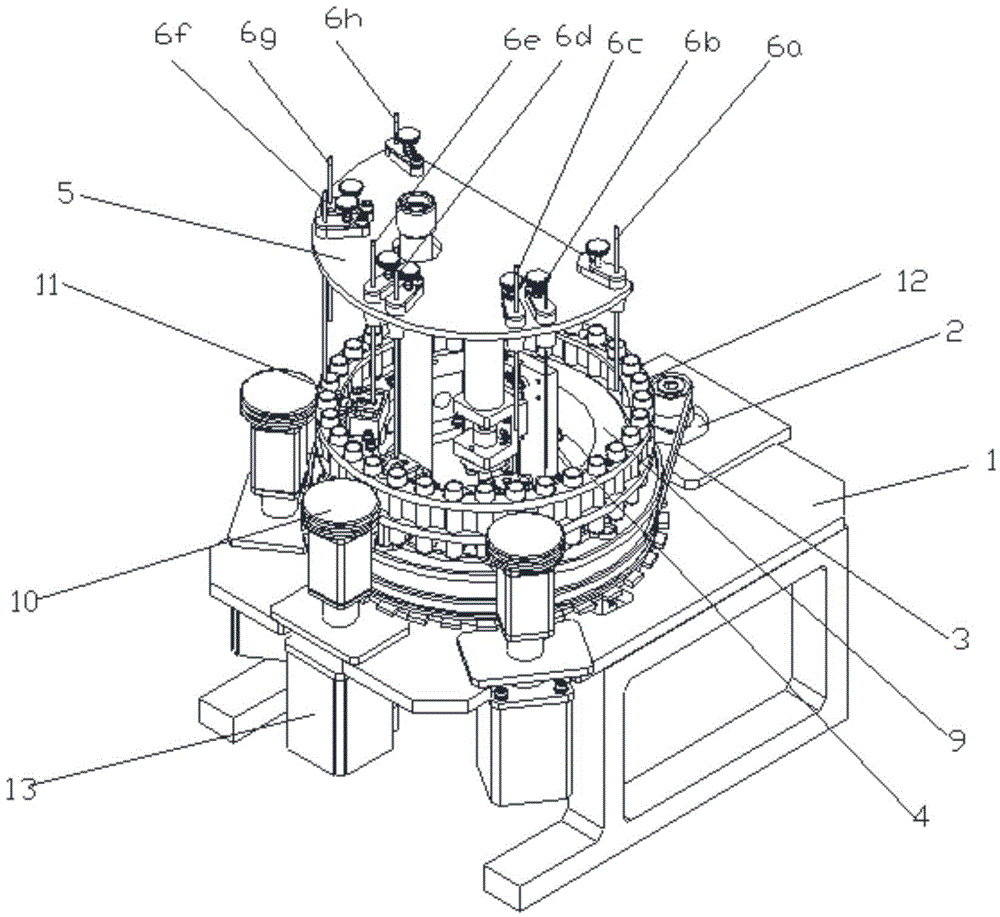
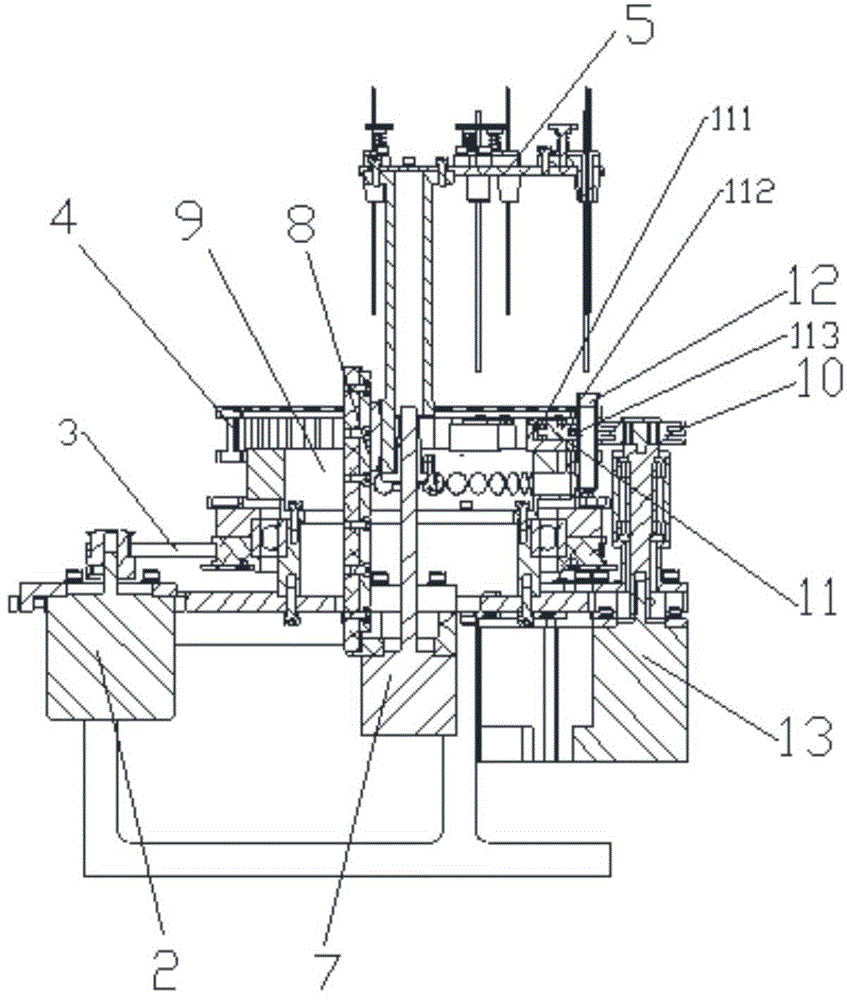
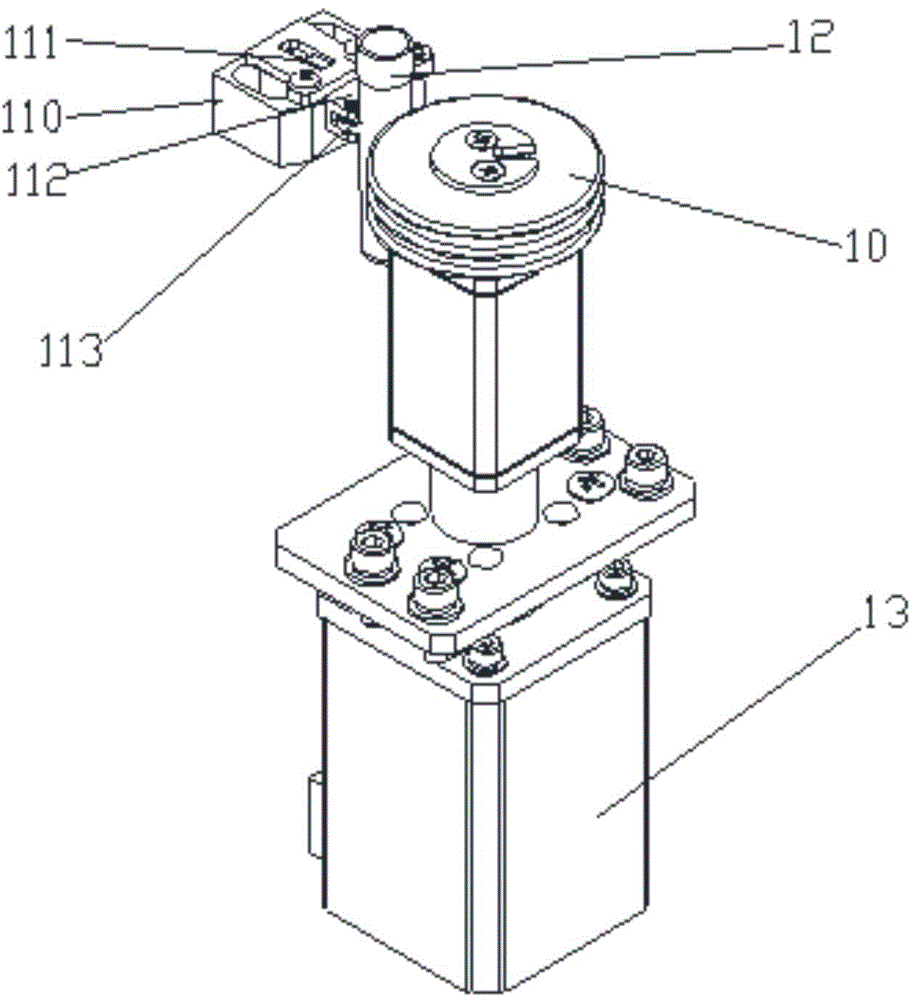
InactiveCN103897987AEnsure consistencyReduce human interferenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMagnetic beadEngineering
The invention provides an automatic extraction device and an automatic extraction method of a nucleic acid based on nano magnetic beads. The device comprises a base (1), as well as a motor, a magnetic bar (6), a magnetic bar clamping mechanism (3), a stirring sleeve (5), a stirring sleeve clamping mechanism (10), a deep hole plate (2), a control circuit and an upper computer which are arranged on the base (1). According to the device and the method which are provided by the invention, the nucleic acid is combined with the nano magnetic beads; and then, the nucleic acid is extracted from a nucleic acid cracking liquid under the attraction of the magnetic bar (6). Thus, the consistency of sample treatment is guaranteed to a great extent; the human interference is reduced; and the cross interference risk is decreased. The device and the method provided by the invention are suitable for the pretreatment of sample inspection in the medicinal field, the biological field, the agricultural field and the like.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Purification of antigen-specific T cells
InactiveUS20060134125A1Snake antigen ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsMHC class IAbnormal tissue growth
A new method to capture, purify and expand antigen-specific T lymphocytes has been developed using magnetic beads coated with recombinant MHC class I molecules. This method was optimized using homogenous populations of naive T cells purified from mice transgenic for the 2C T cell receptor (TCR). These T cells were captured on beads coated with MHC class I molecules and the relevant antigenic peptides. MHC and peptide specificity was confirmed by the usage of irrelevant MHC peptide combinations. An enrichment of 800 to 1600 fold was measured, using 2C T cells mixed with irrelevant T cells, starting from a 2C T cell frequency of 1 / 3000. The same approach was used to purify antigen-specific CD8+ T cells from total CD8+ T cells from naive mice. The recovered cells could be expanded and specifically kill target cells in vitro; they had a significant effect in vivo as well. We expect this procedure to be suitable to purify and expand in vitro tumor- and virus-specific killer T cells for use in cell therapy.
Owner:ORTHO PHARMA
Method for sex determination of mammalian offspring
InactiveUS6153373AIncrease probabilityImprove integrityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsArtificial cell constructsSemen sampleMagnetic bead
A method for increasing the percentage of mammalian offspring of either sex which comprises contacting a semen sample with an antibody specific for the spermatozoa determinative of one sex and separating said spermatozoa from spermatozoa determinative of the other sex, said antibody being bound to a non-porous magnetic bead support having a diameter of 0.1 to 2 microns.
Owner:VICAM
Detection of analytes using electrochemistry
InactiveUS6100045ALow costReduce lossesImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemical responseMatrix solution
The present invention relates to diagnostic assays whereby the detection means is based on electrochemical reactions. This means that the label to be detected provides an electric signal. Preferred labels are enzymes giving such a signal. Provided is a flow cell whereby a solid phase is provided in a flow stream of the sample, in close proximity to a working electrode to detect any electrical signal. In a typical embodiment, a sample is mixed with molecule having specific binding affinity for an analyte of which the presence in the sample is to be detected, whereby said specific binding molecule is provided with a label. The conjugate of labelled specific binding molecule and analyte is then immobilized on the solid phase in the vicinity of the working electrode, the flow cell is rinsed with a solution and afterwards a substrate solution for the label (an enzyme) is provided upon which an electrical signal is generated and can be detected by the working electrode. The methods and devices of the present invention are particular useful for liquids which comprise many substances that may disturb measurement in conventional assays. The design of the flow cell allows for removal of said interfering substances before measurement. In a preferred embodiment at least part of the solid phase is provided in the form of magnetic beads. In this embodiment the solid phase can be mixed with the sample thereby creating a longer reaction time, a better sensitivity and a higher speed of the assay.
Owner:DSM NV
Rapid magnetic flow assays
InactiveUS20090148847A1Full antigenicityFull binding integrityHeating or cooling apparatusShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersAssayMagnetic bead
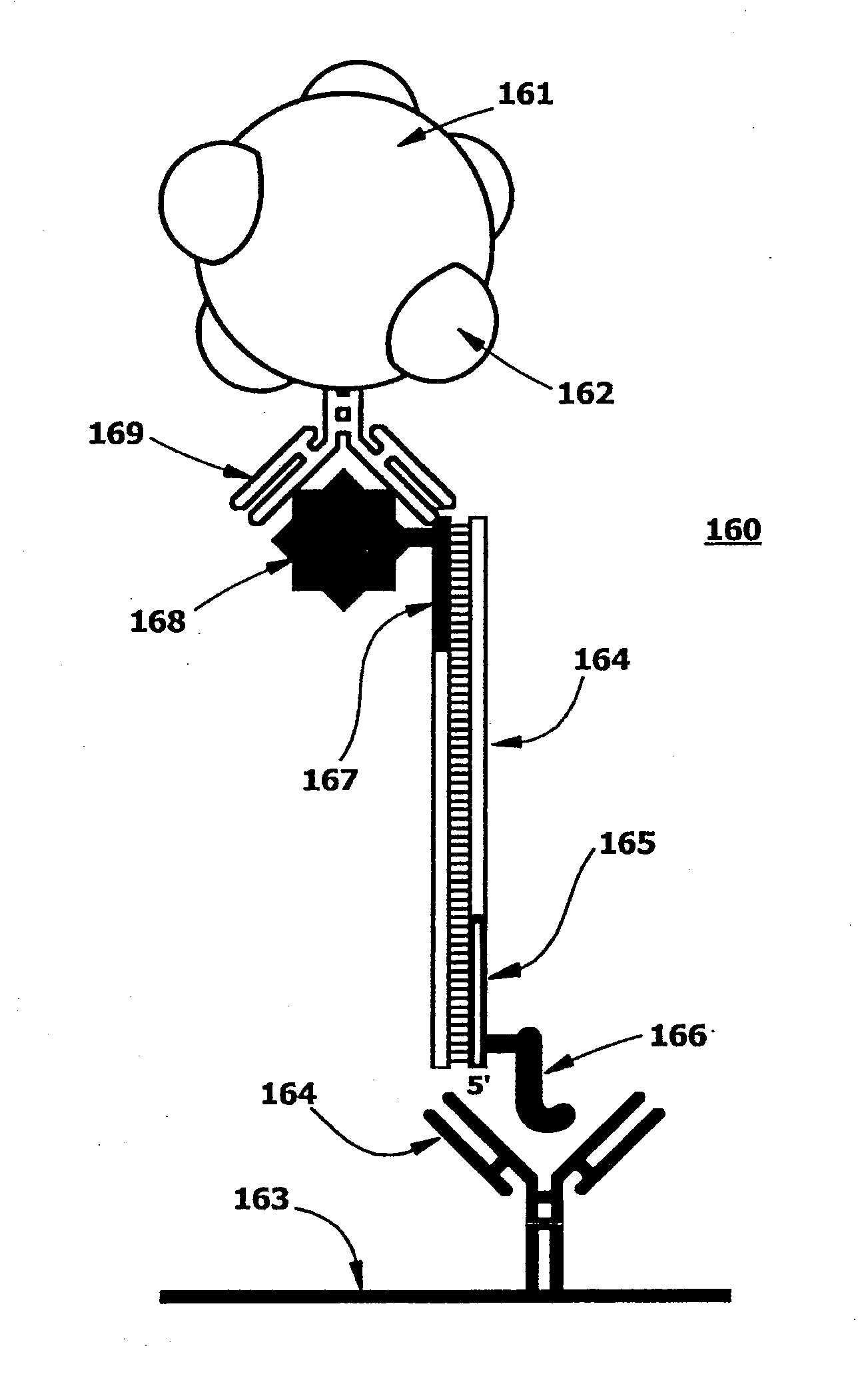
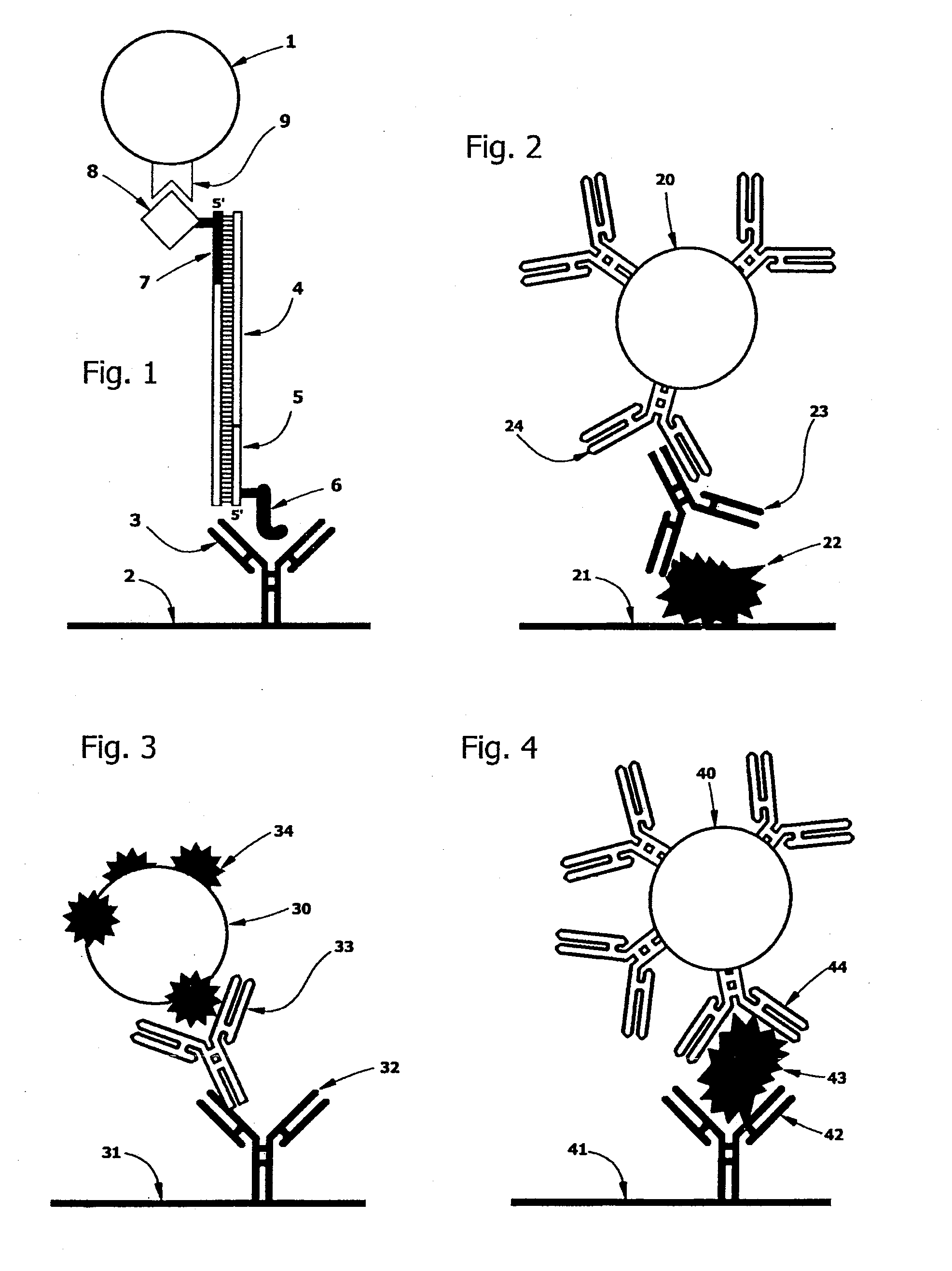
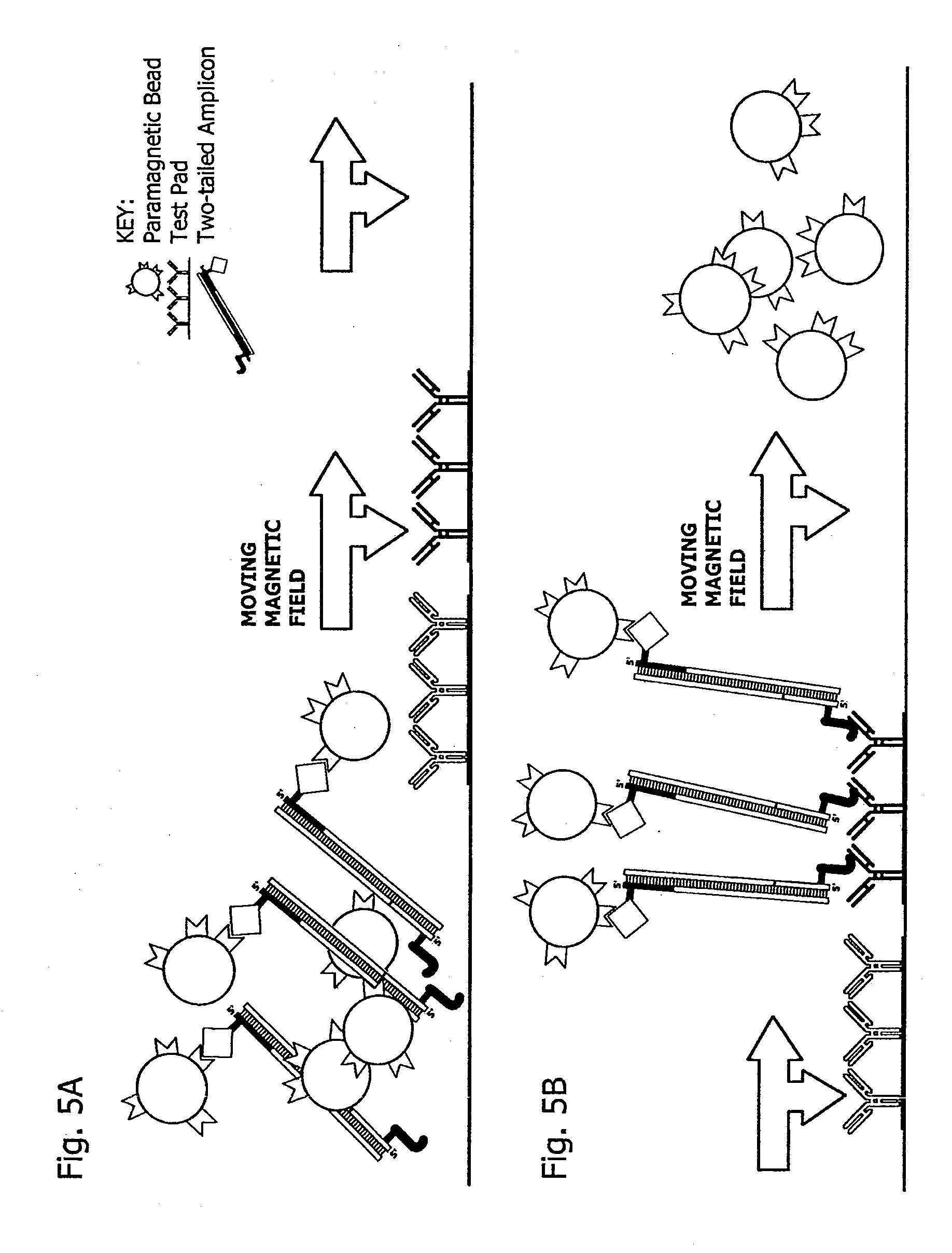
Disclosed is an improvement in methods for nucleic acid and immunological bioassays. The methods comprise a step for “sweeping” paramagnetic bead: target molecule complexes so as to capture them with an affinity capture agent on a test pad by moving a magnetic force field from outside to inside the test pad area so as to bring into contact the paramagnetic complexes with the capture agent, while sweeping any unbound paramagnetic material off the test pad by moving the magnetic field from inside to outside the test pad area. Surprisingly, the paramagnetic complexes are rapidly affinity-extracted from the moving magnetic field.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
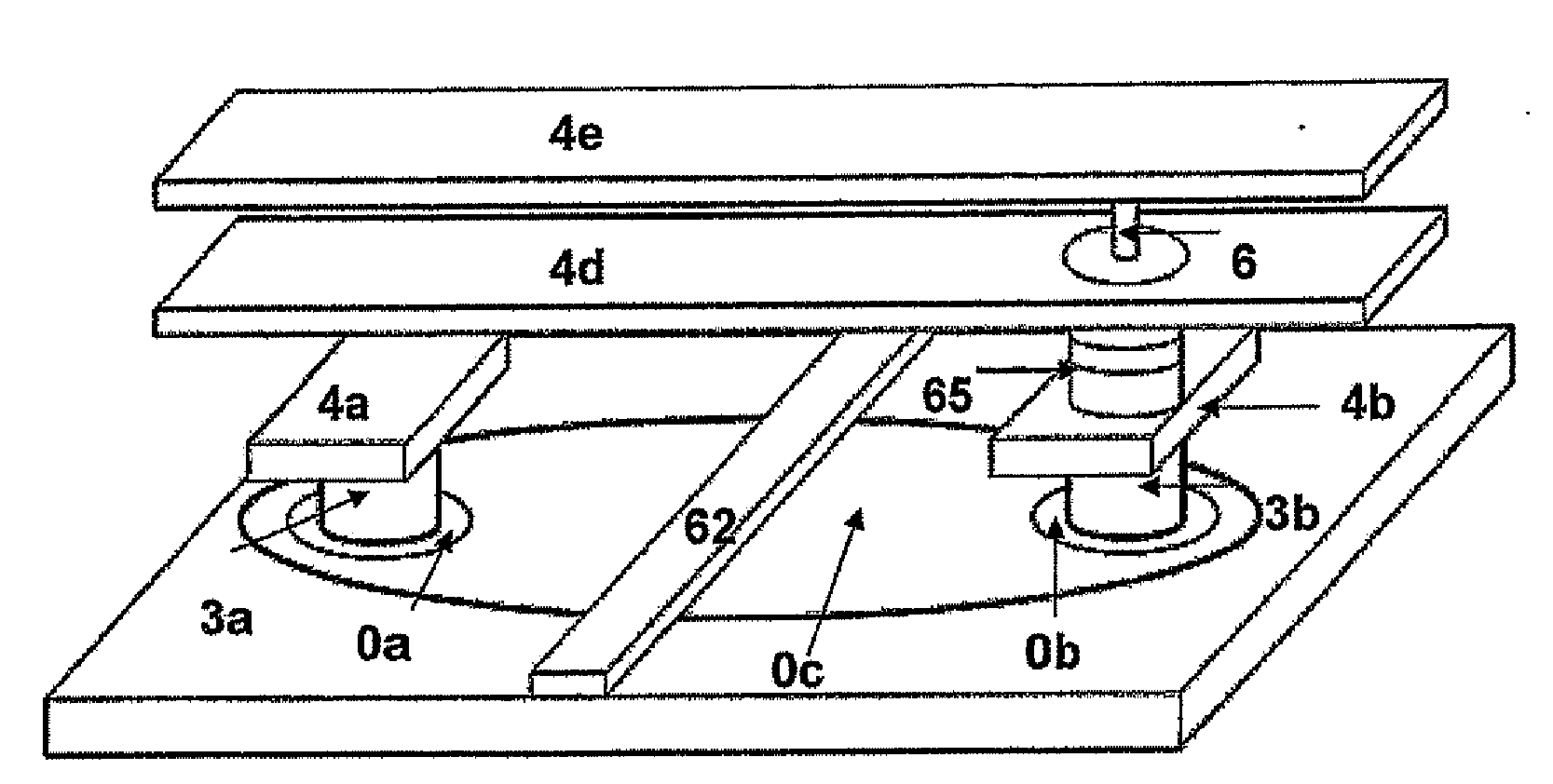
Magnetic bead manipulation and transport device
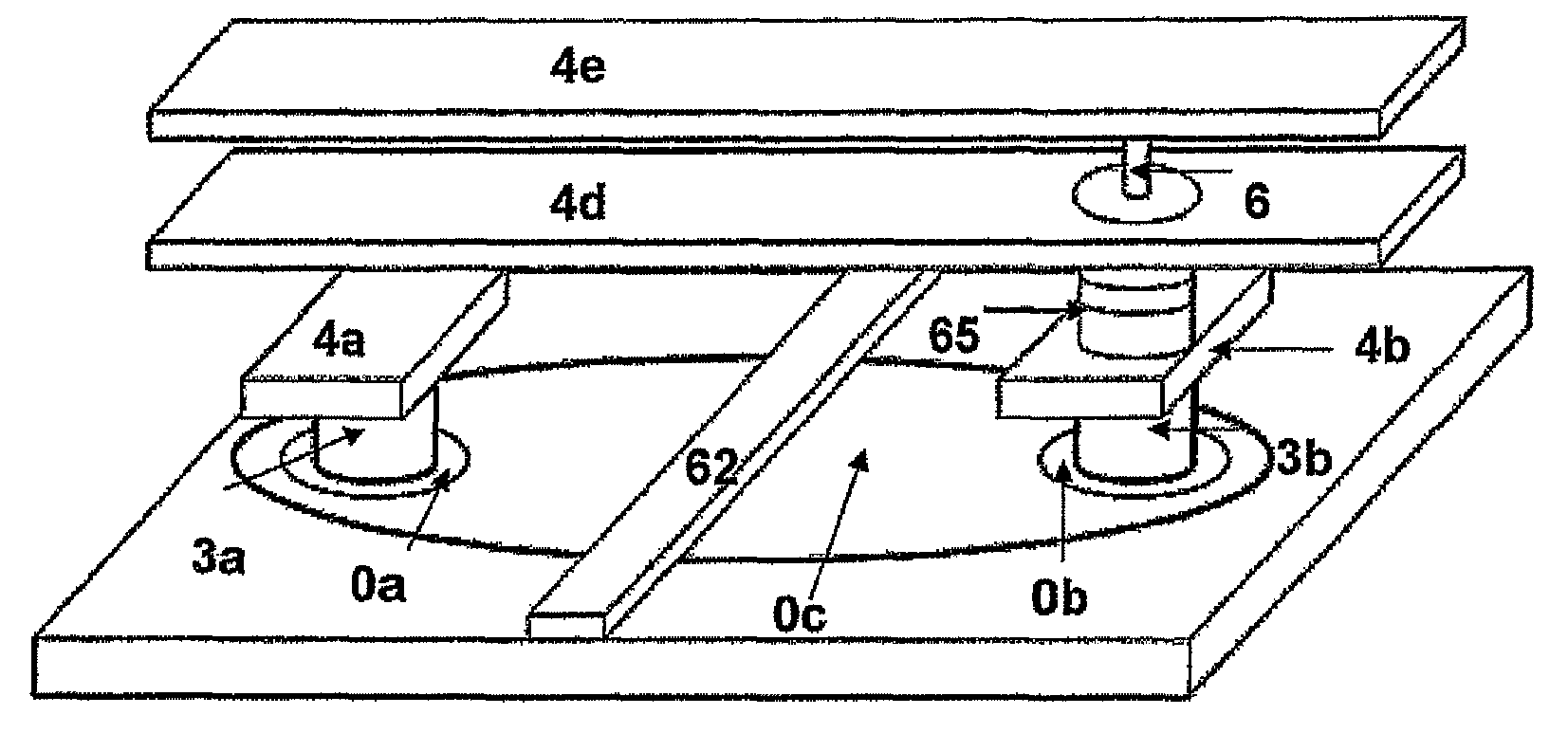
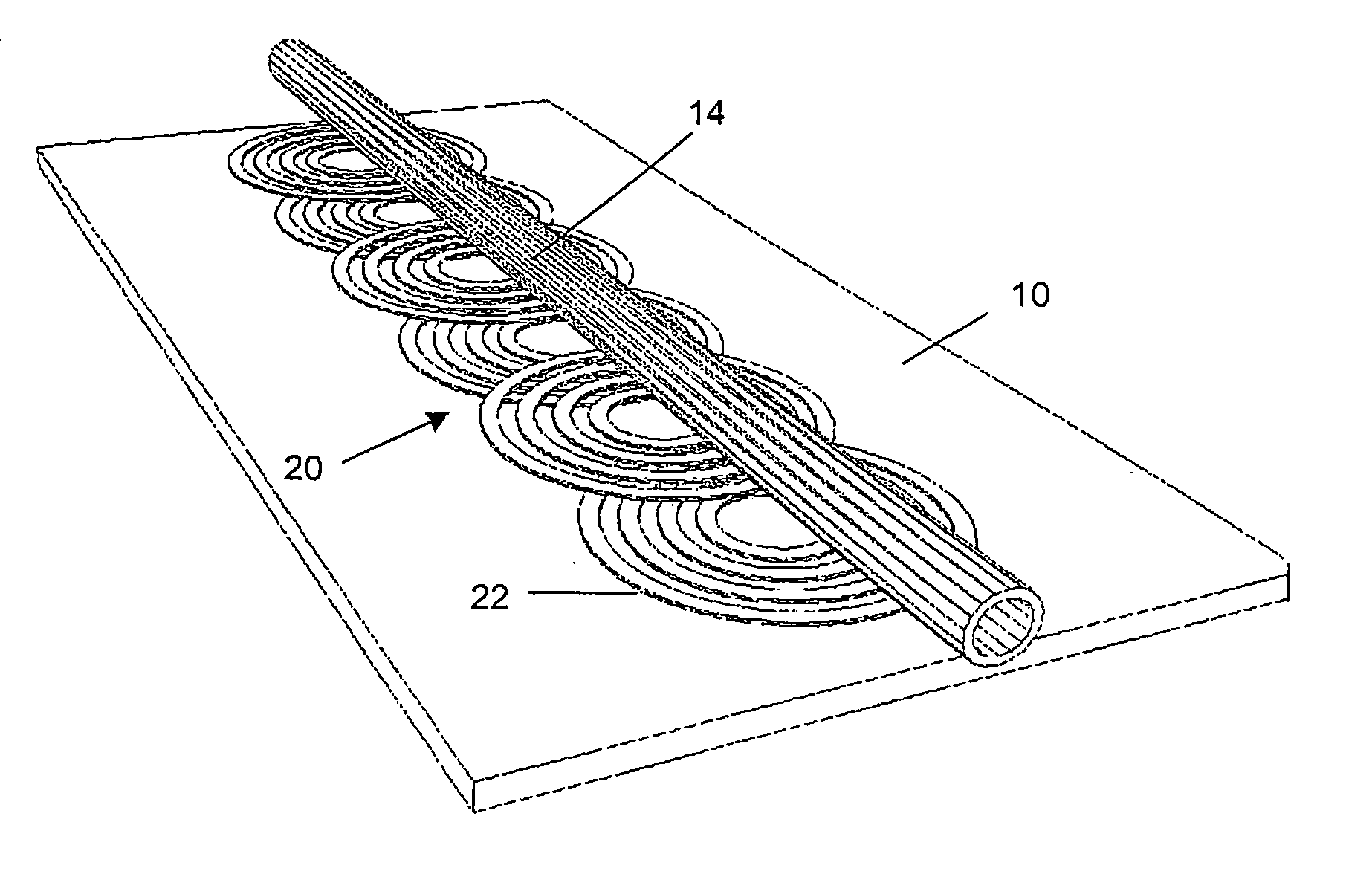
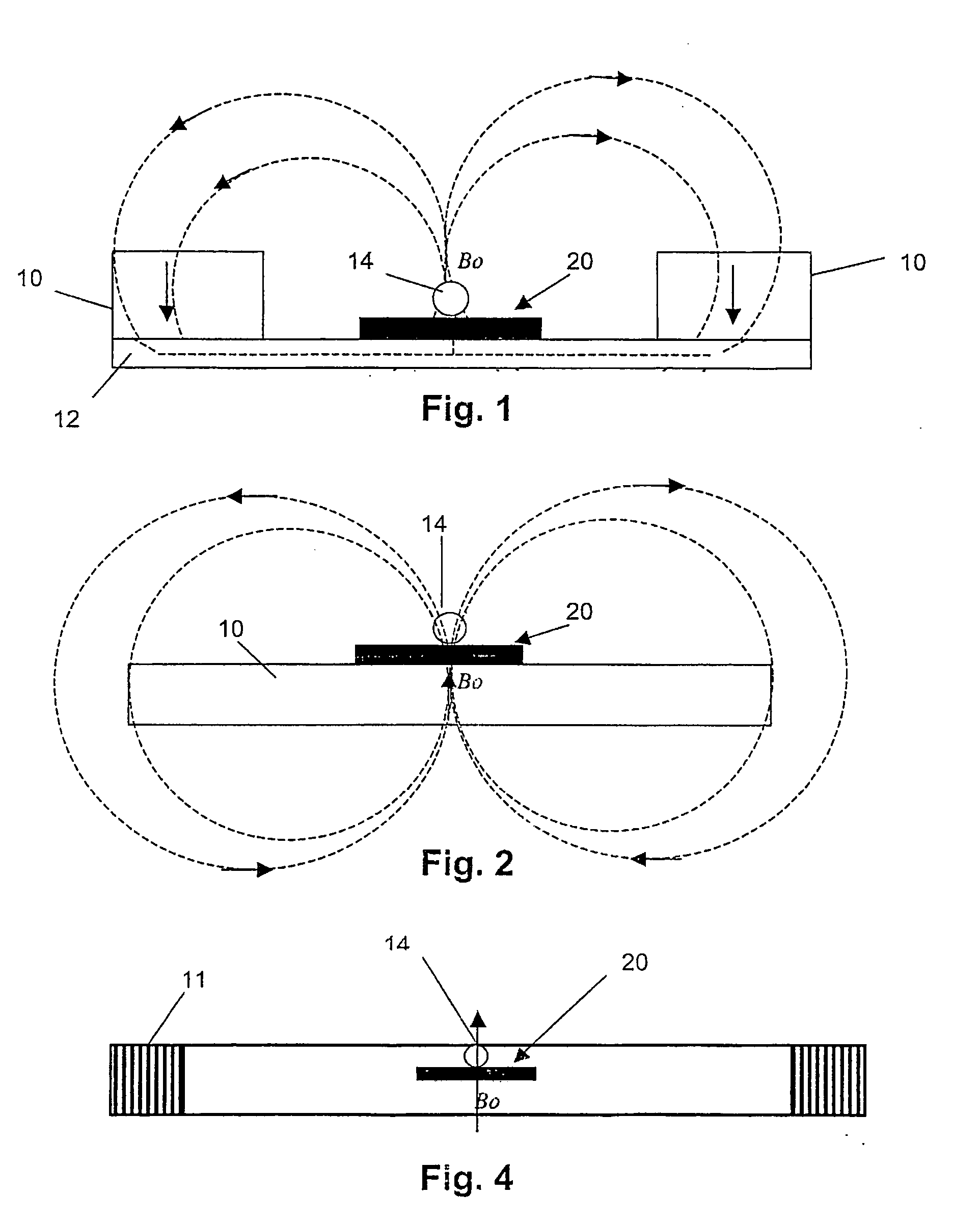
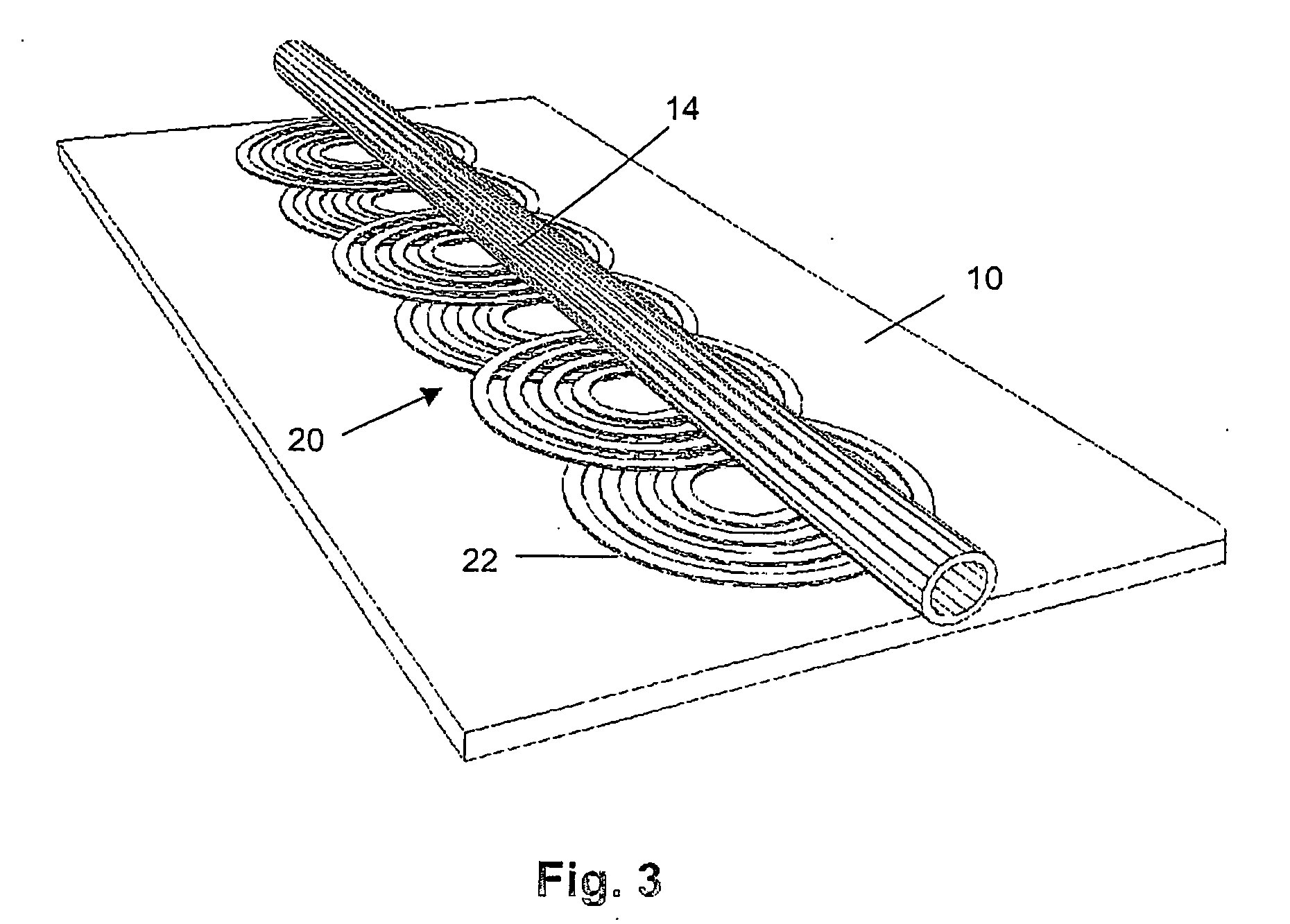
InactiveUS20050284817A1Increase speedLow magnetic fieldsElectrostatic separationTransportation and packagingClinical chemistryMagnetic bead
A device for transporting magnetic or magnetisable microbeads (25) in a capillary chamber (14) comprises a permanent magnet (10) or an electromagnet (11) for subjecting the capillary chamber to a substantially uniform magnetic field, to apply a permanent magnetic moment to the microbeads (25). At least one planar coil (22) and preferably an array of overlapping coils are located adjacent to the capillary chamber (14) for applying a complementary magnetic field on the microbeads parallel or antiparallel to said substantially uniform magnetic field, to drive the microbeads. An arrangement is provided for switching the current applied to the coil(s) (22) to invert the field produced thereby, to selectively apply an attractive or repulsive driving force on the microbeads (25). The device is usable to transport microbeads for performing chemical and biochemical reactions or assay, as is done for instance in clinical chemistry assays for medical diagnostic purposes.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Force discrimination assay
InactiveUS6180418B1Eliminate the effects ofMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansTarget analysisAnalyte
A sensor for a selected target species has (a) a substrate which has been chemically modified by attachment of substrate modifiers; (b) one or more magnetically active beads which have been chemically modified by attachment of bead modifiers, where these bead modifiers will have a binding affinity for the substrate modifiers in the presence of the target species, and a measurably different binding affinity for the substrate modifiers in the absence of the target species; (c) an adjustable source of a magnetic field for exerting a force on the beads; and (d) an imaging system, for observing and counting beads bound to the substrate. In a preferred embodiment, the invention further has a system for identifying clusters of beads, and for removing the effect of such clusters from measurements of the target analyte. As with other assays, the sensor relies on the ability of certain molecules to bind with specific target (analyte) molecules. By coating the beads and the substrate with appropriate molecules, the beads will (or will not) bind specifically to the substrate in the presence (or absence) of the target molecule. When a magnetic field is applied to the substrate, the magnetic beads will be pulled away from the substrate. If the beads are specifically bound to the substrate, however, the beads will be retained on the substrate, indicating the presence (or absence) of the target species.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
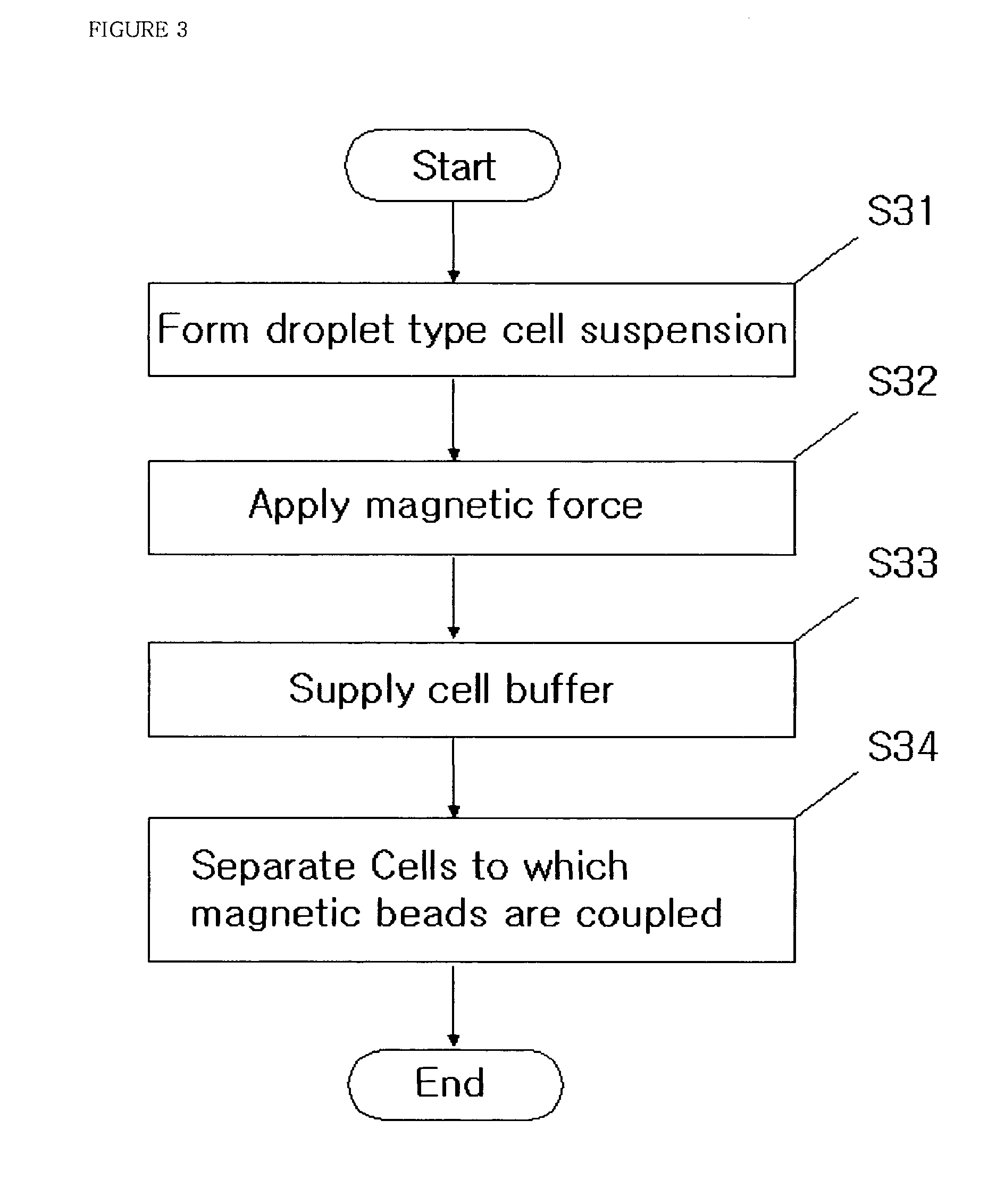
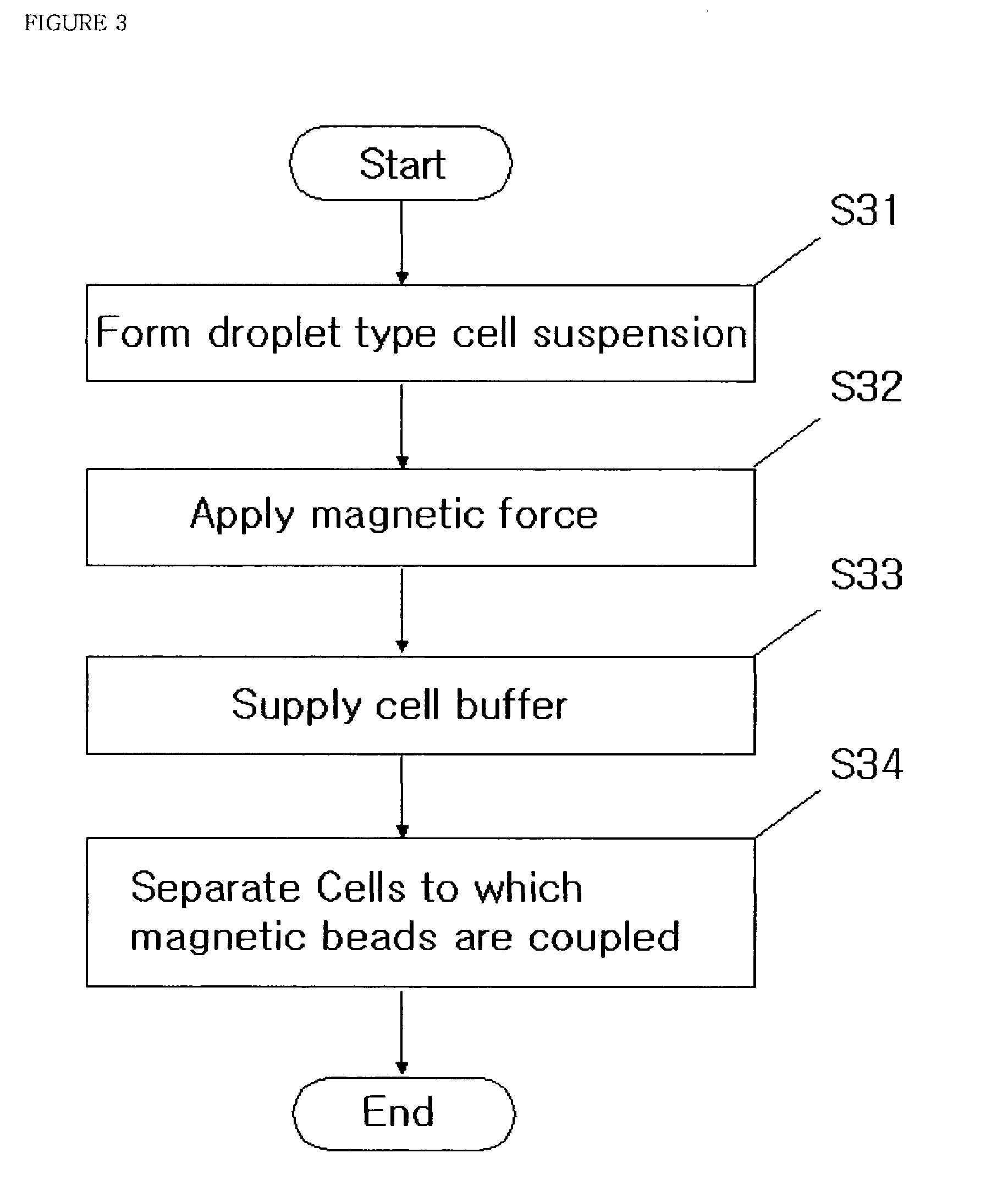
Methods and apparatuses of separating cells using magnets and droplet type cell suspension
InactiveUS7189560B2Efficient separationEasy to separateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMagnetic beadEngineering
Disclosed are methods and apparatuses for separating cells using magnets and droplet type cell suspension according to the present invention, which may effectively separate cells by forming droplet type cell suspension with cell suspension sample containing cells to which magnetic beads are coupled and applying magnetic force to the droplet type cell suspension.The apparatus of separating cells according to the present invention includes: a droplet type cell suspension forming part for forming a droplet type cell suspension under a lower part of the droplet type cell suspension forming part with cell suspension sample containing cells to which magnetic beads are coupled; a cell suspension inlet for supplying the droplet type cell suspension forming part with the cell suspension sample; a magnet for applying magnetic force to the droplet type cell suspension; a cell buffer inlet for supplying the droplet type cell suspension with cell buffer; and a temperature maintaining part for maintaining a temperature of the droplet type cell suspension.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
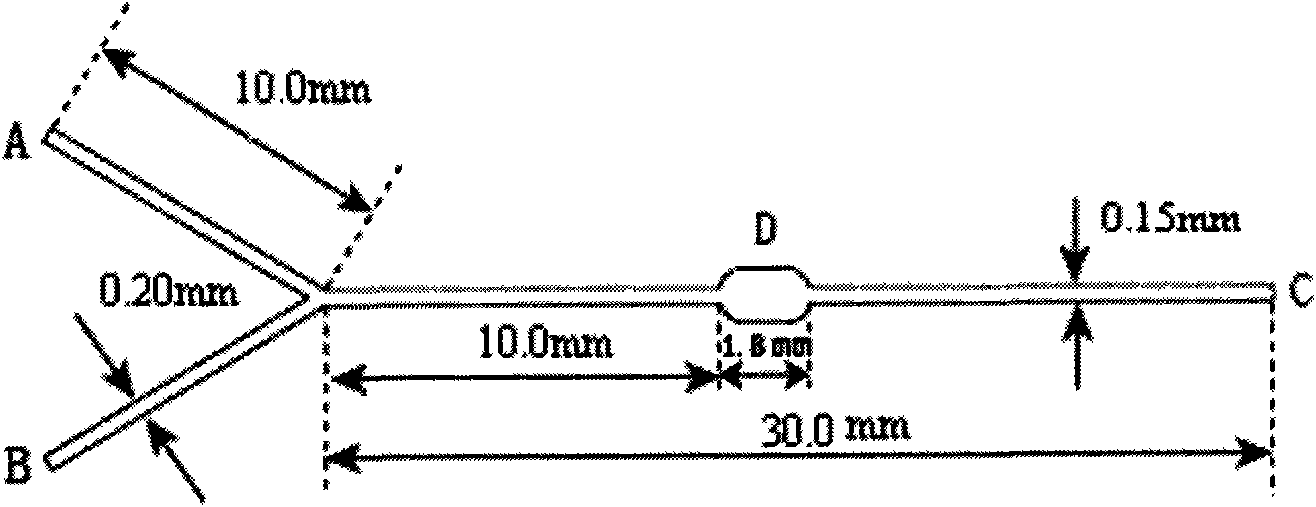
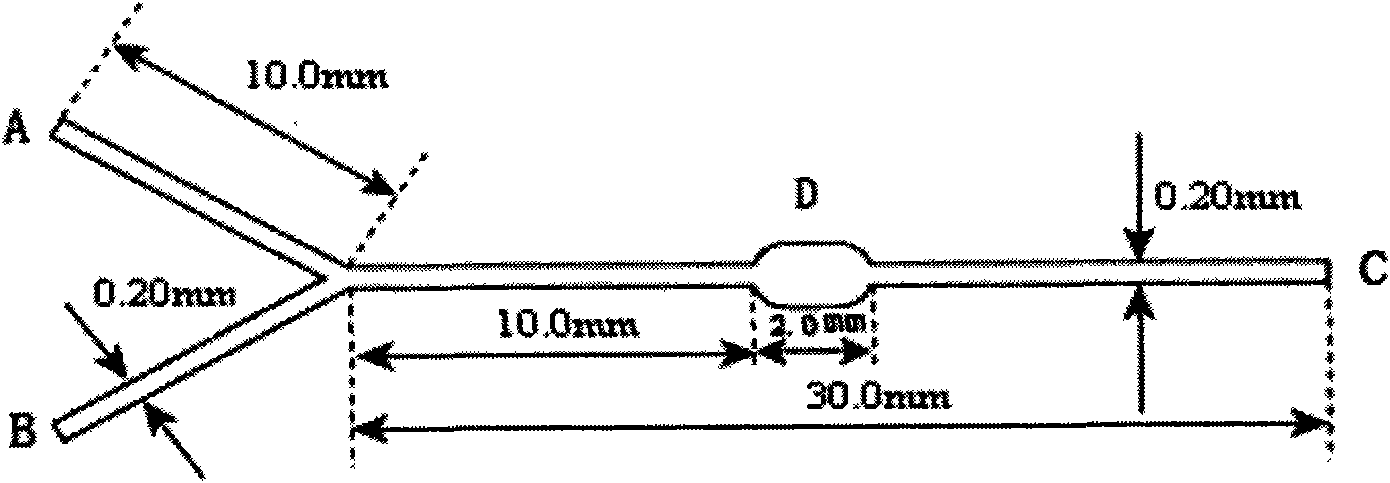
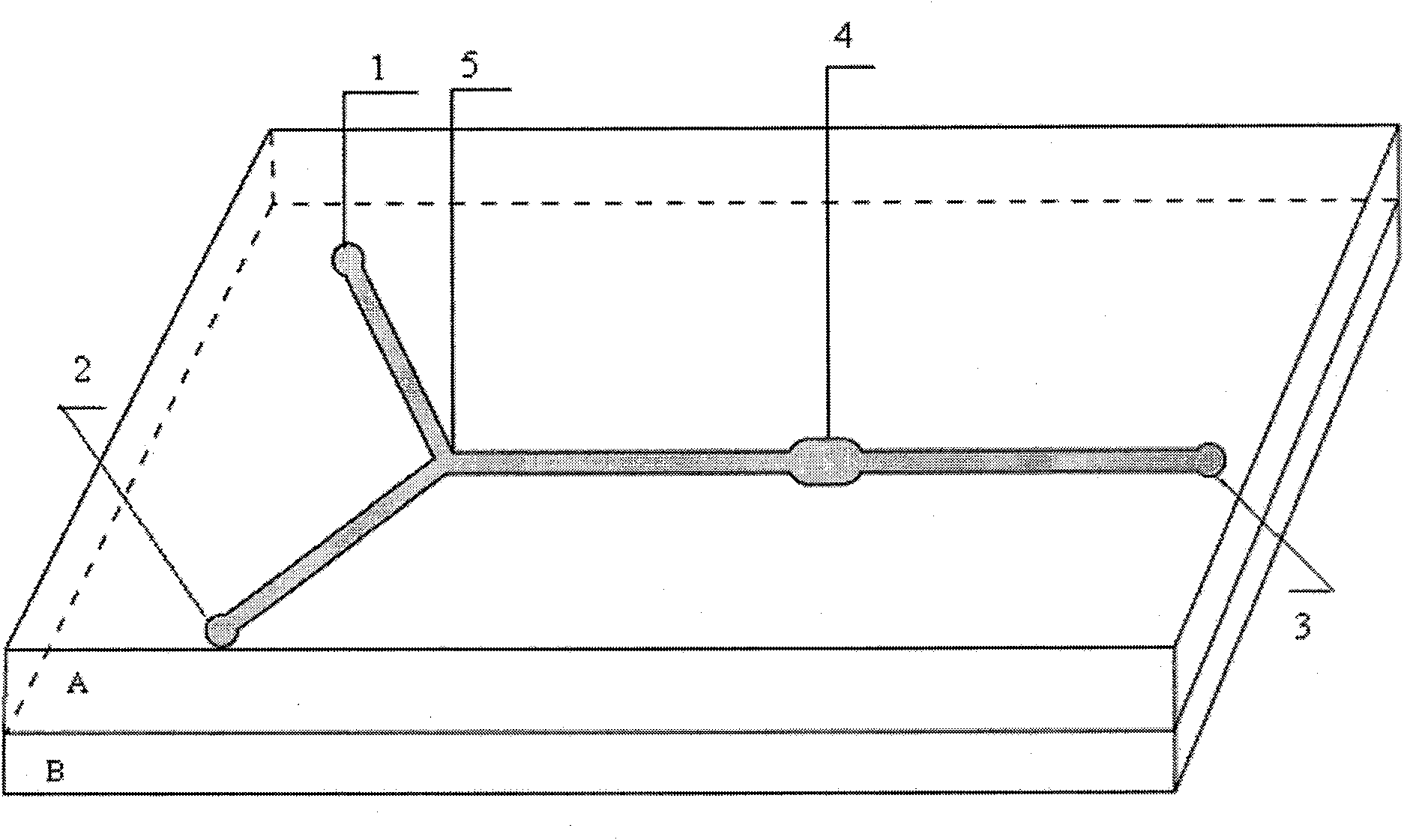
Cell sorter micro-fluidic chip based on immunomagnetic separation technology and application thereof in aspect of enrichment of rare cells
InactiveCN101643701AReduce manufacturing costEase of mass productionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiomass after-treatmentAntigenCell sorter
The invention discloses a cell sorter micro-fluidic chip based on the immunomagnetic separation technology and application thereof in the aspect of enrichment of rare cells, belonging to the technicalfield of micro-fluidic chips. The micro-fluidic chip, improved on the basis of the existing Y-type micro-fluidic chip, comprises a substrate and a cover-slip, wherein a Y-shaped micro-channel, a sample cell (1) and a buffer cell (2) respectively located at two end points of the upper part of the Y-shaped micro-channel, and an effluent cell (3) located at the end point of the lower part of the Y-shaped micro-channel are arranged on the substrate; and an antigen / antibody immunological reaction chamber (4) located on the micro-channel between the cross point (5) of the Y-shaped micro-channel andthe effluent cell (3) is further arranged on the substrate, wherein the width of the antigen / antibody immunological reaction chamber (4) is 2 to 5 times that of the micro-channel. The chip of the invention can effectively and rapidly fix the magnetic beads, increase the sample size of cells, improve the analysis flux, reduce the dead volume of sample introduction and reduce the retention and cross infection.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Full-automatic chemiluminescence immune analyzer magnetic bead washing device
ActiveCN103599898ARealize pipeline cleaningReduce lossesCleaning using liquidsLiquid wasteIndependent function
A full-automatic chemiluminescence immune analyzer magnetic bead washing device comprises a reaction cup rotation disc, a lifting needle support, a magnetic bead absorbing device and mixing devices. The lifting needle support is driven by a lead screw motor to move vertically along a linear sliding track. An eight-washing-needle assembly is arranged on the lifting needle support, four needles are liquid injecting needles and used for injecting washing liquid into a reaction cup, and other four needles are liquid sucking needles and used for sucking waste liquid in the reaction cup. The eight washing needles conduct washing liquid injection movement and waste liquid sucking movement on the reaction cup sequentially, and once diluting and three-time washing are conducted on magnetic beads in the reaction cup. An annular magnetic bead absorbing device is arranged below the inner side of the reaction cup rotation disc, and the plurality of mixing devices are arranged above two sides of the reaction cup rotation disc respectively. By means of the device, assembly line type washing of the magnetic beads is achieved, washing is thorough, magnetic bead loss is smaller, structure is optimized, control is simple, relatively independent functions are achieved, and the device is suitable for a whole automatic system.
Owner:BEIJING LEADMAN BIOCHEM
Cell enriching, separating and extracting method and instrument and single cell analysis method
ActiveCN102690786AEnrichment reachedEfficient collectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiomass after-treatmentImmunofluorescence stainingMagnetic bead
The invention discloses a method and an automatic instrument device for enriching and extracting target cells and separating single cells by using a positive magnetic bead method and performing immunity and molecular biology identification and analysis on single cells. By the method and the instrument device, the on / off of a capture magnet and a release magnet is controlled by various methods to complete target cell searching, capturing, cleaning and releasing operation once or for multiple times, so that the target cell detection sensitivity and stability are improved. When the capture magnet searches and captures the target cells, the search line is circular, square, comb-shaped, S-shaped or U-shaped. In addition, the captured substances are filtered, most free micro magnetic beads are removed, the purity of the product is further improved and the product can be used as a good experimental material. By combining a special filter and the adsorption of the capture magnet, more than 95 percent of free micro magnetic beads can be effectively removed. Meanwhile, the types of the single cells are identified and biological characteristics of the single cells are analyzed by an immunofluorescence staining method and a method in molecular biology, and effective biological indexes are provided for clinical diagnosis and treatment of cancers.
Owner:GD TECH INC
Methods and apparatuses of separating cells using magnets and droplet type cell suspension
InactiveUS20050227349A1Efficient separationEasy to separateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMagnetic beadEngineering
Disclosed are methods and apparatuses for separating cells using magnets and droplet type cell suspension according to the present invention, which may effectively separate cells by forming droplet type cell suspension with cell suspension sample containing cells to which magnetic beads are coupled and applying magnetic force to the droplet type cell suspension. The apparatus of separating cells according to the present invention includes: a droplet type cell suspension forming part for forming a droplet type cell suspension under a lower part of the droplet type cell suspension forming part with cell suspension sample containing cells to which magnetic beads are coupled; a cell suspension inlet for supplying the droplet type cell suspension forming part with the cell suspension sample; a magnet for applying magnetic force to the droplet type cell suspension; a cell buffer inlet for supplying the droplet type cell suspension with cell buffer; and a temperature maintaining part for maintaining a temperature of the droplet type cell suspension.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Method for extracting and purifying DNA
InactiveCN101613697AEasy to operateImplement extractionSugar derivativesDNA preparationBiological cellLysis
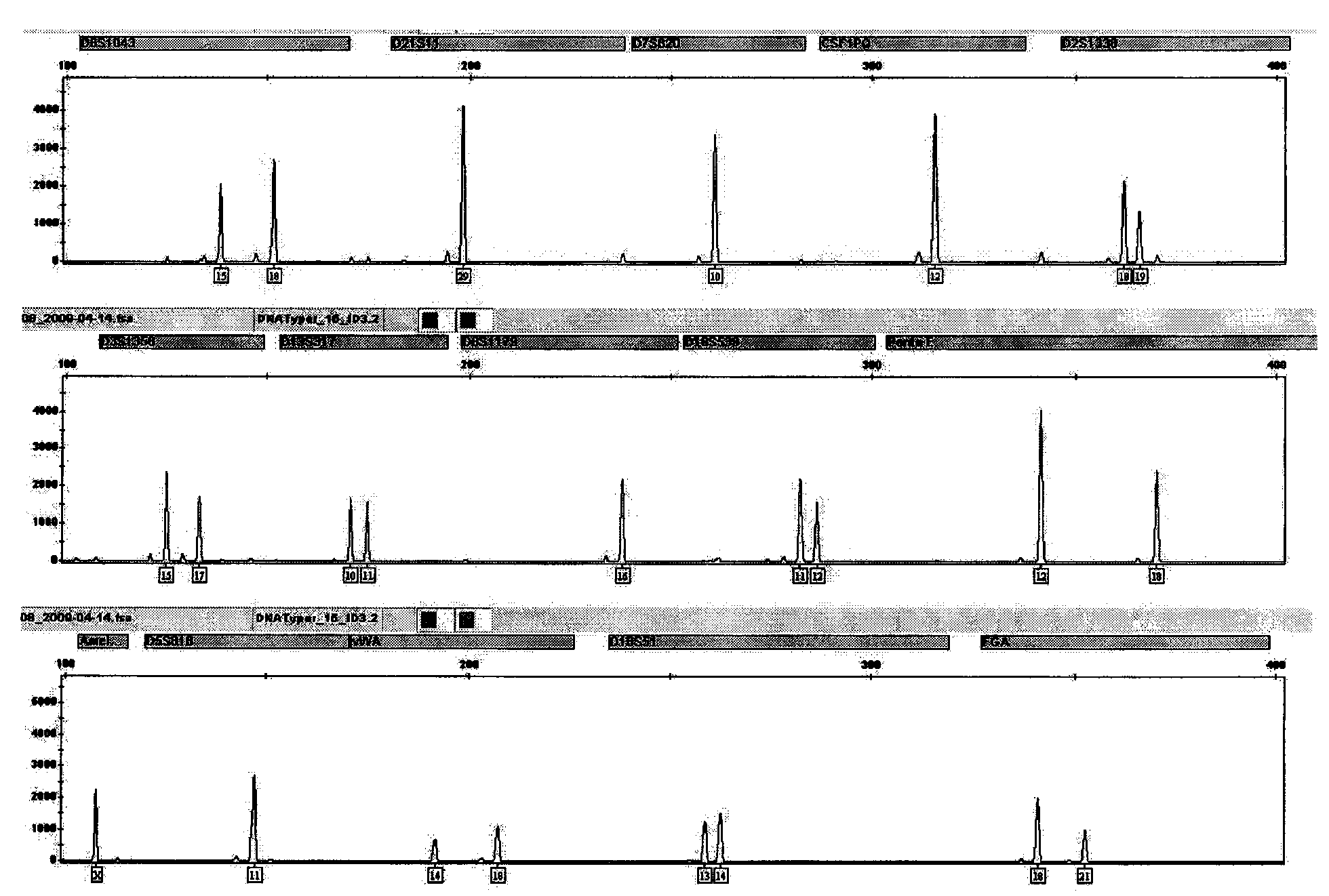
The invention discloses a method for extracting and purifying DNA, comprising the following steps: 1) pre-treatment: a biological sample is in contact with pre-treated lysis solution, and solid substance adhering to biological cells is removed to obtain rude lysis solution; 2) nucleic acid adsorption: the rude lysis solution obtained in step 1 is mixed with lyse combined liquid and magnetic bead suspension to form a solution system containing magnetic nanosphere-DNA composite body, and the magnetic nanosphere-DNA composite body in the solution system is collected; 3) washing: the magnetic nanosphere-DNA composite body obtained in step 2 is successively washed with a cleaning solution I and a cleaning solution II, and then DNA is dissolved out by spent regenerant. The method provided by the invention has 90% of the DNA extracting efficiency, the extracted DNA can be used in down stream analysis operation, such as STR multiplex amplification, DNA sequencing, DNA quantitation and the like.
Owner:INST OF FORENSIC SCI OF MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com