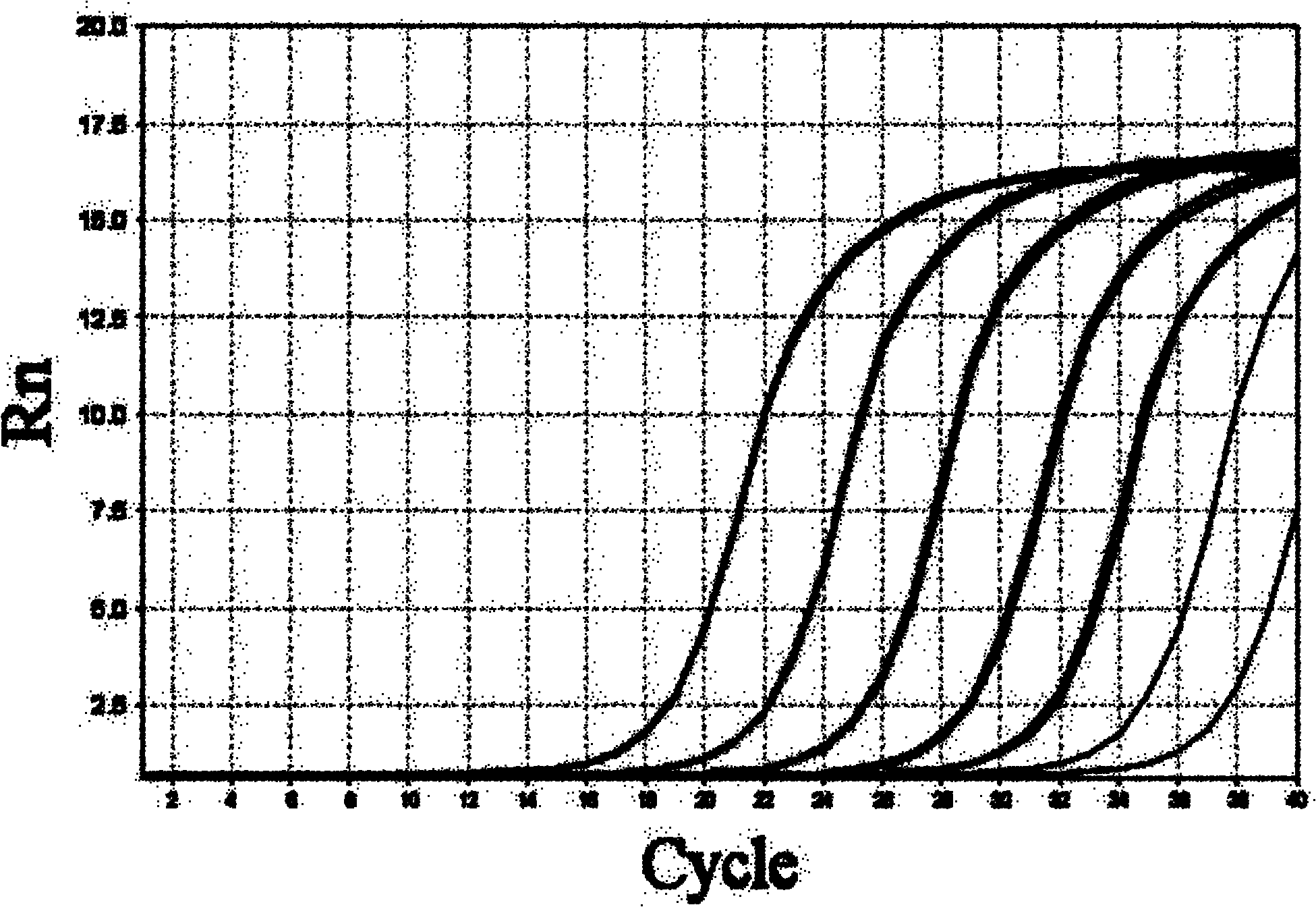
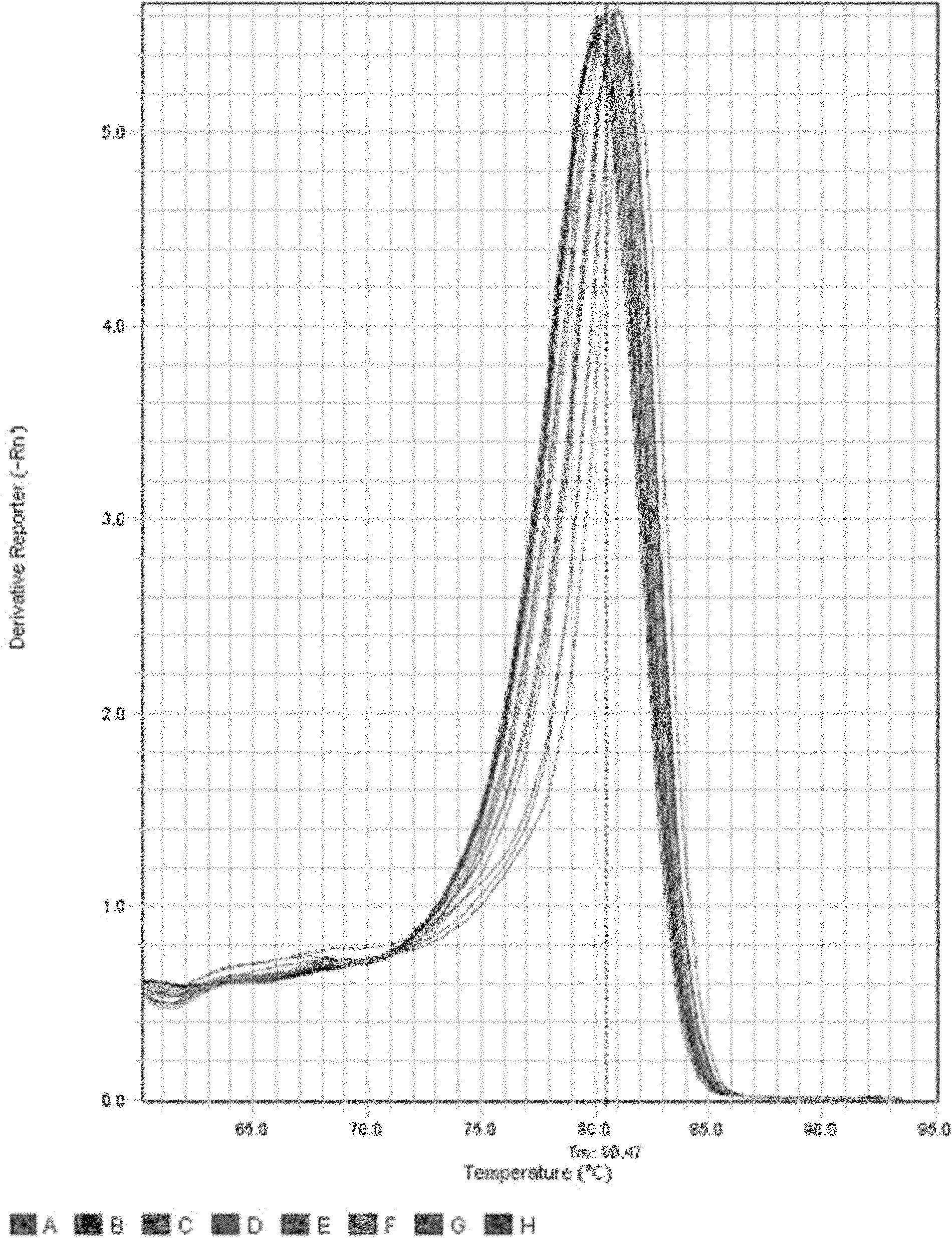
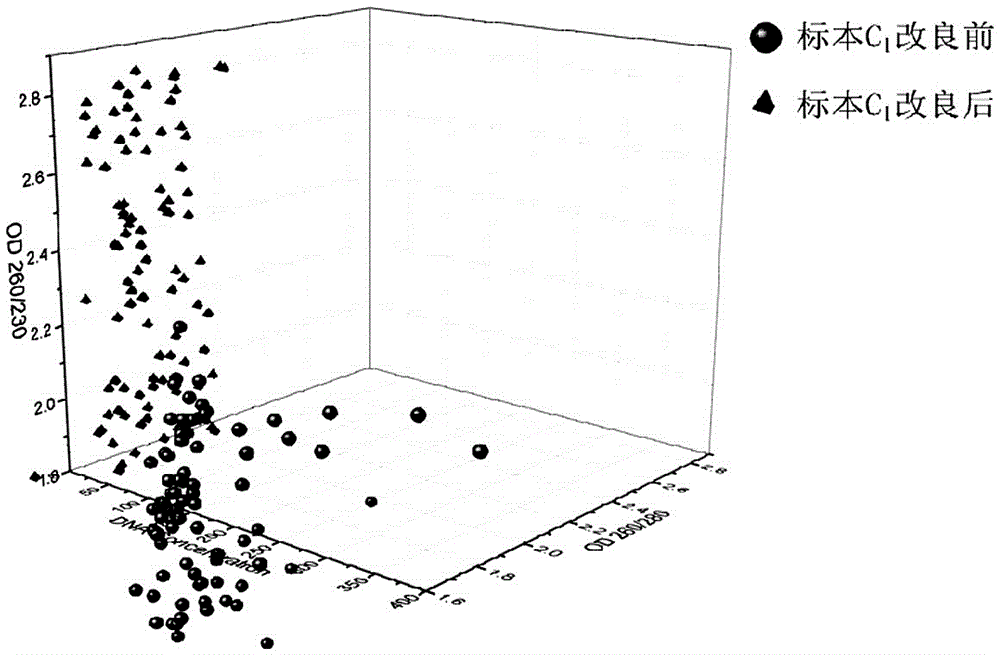
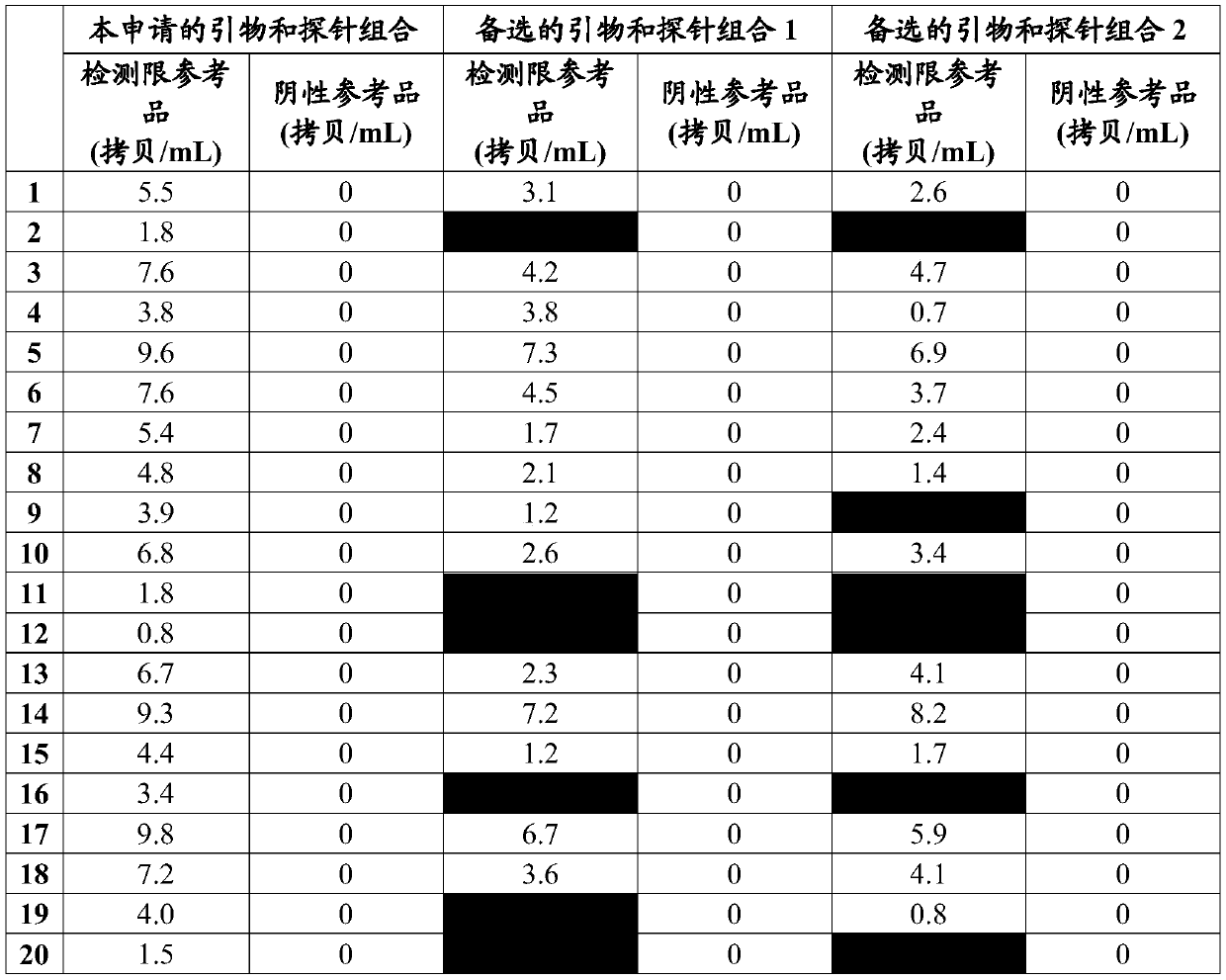
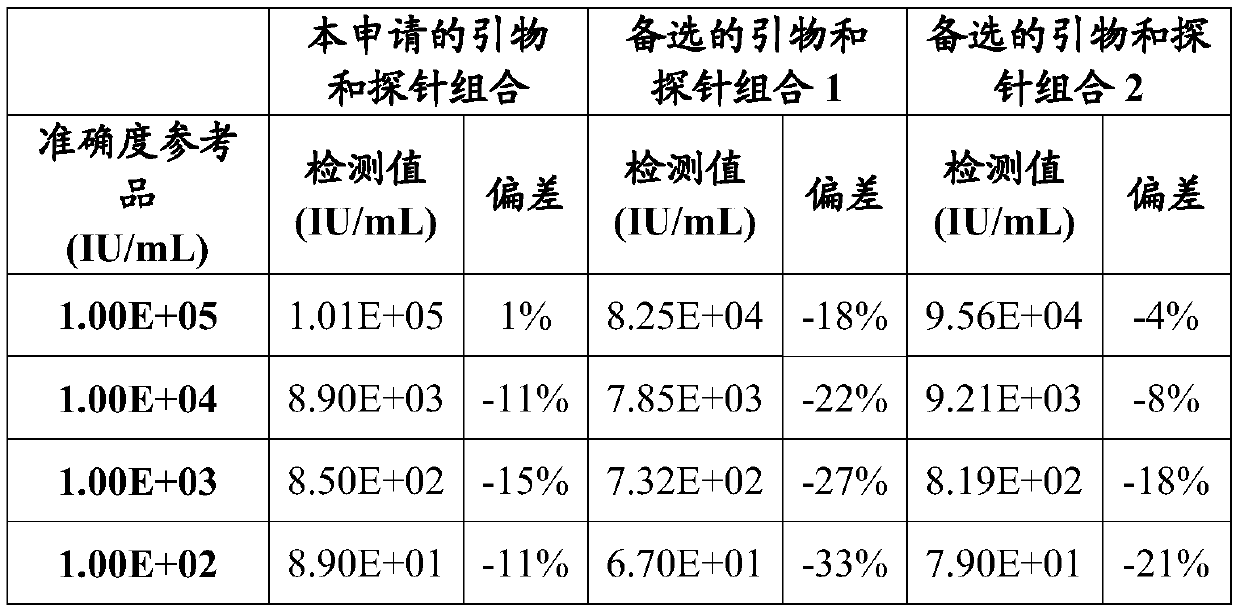
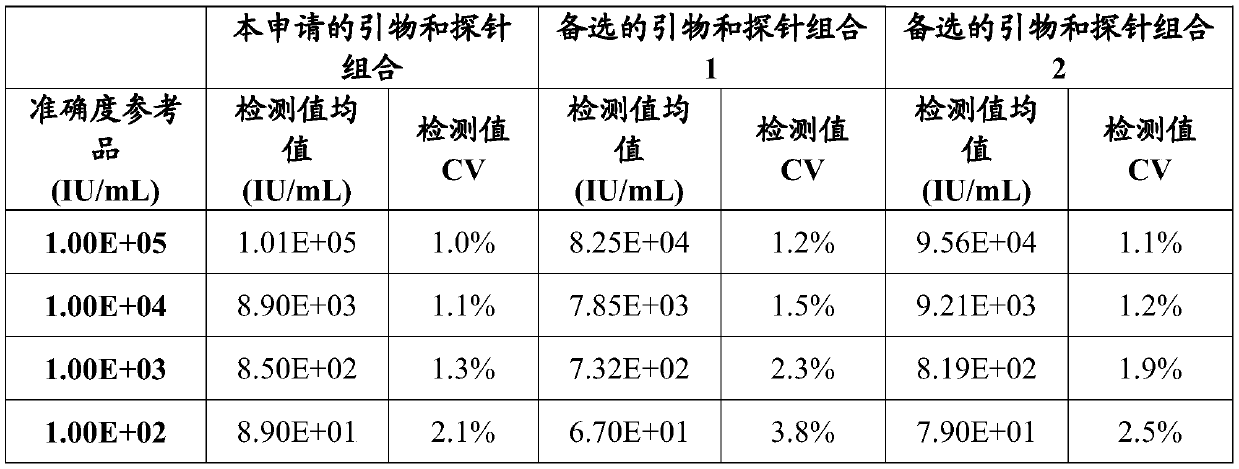
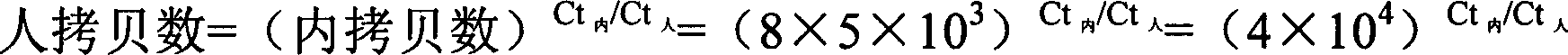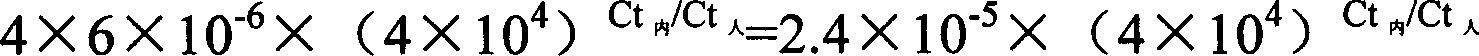Patents
Literature
61 results about "Dna quantitation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
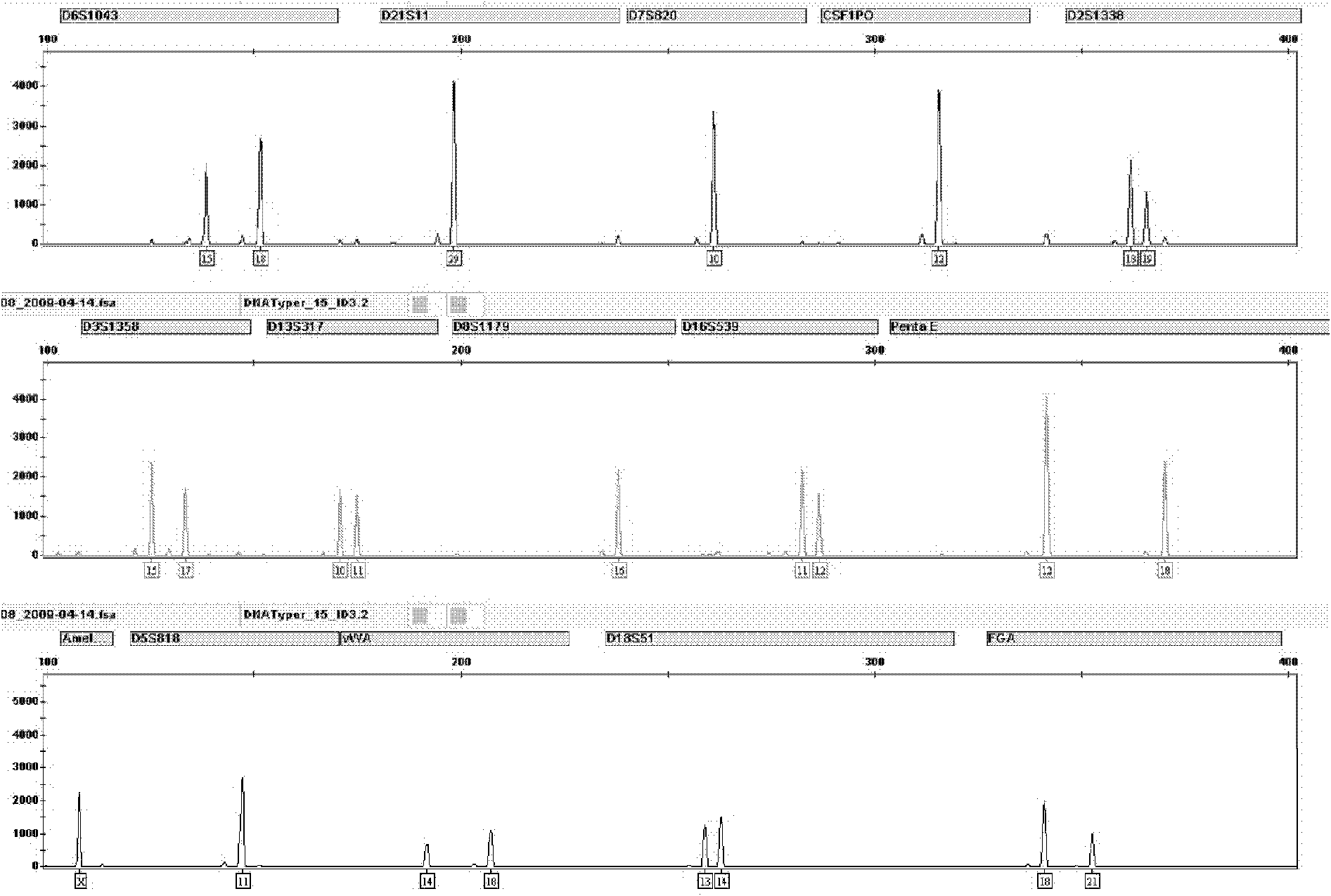
Method for extracting and purifying DNA
InactiveCN101613697AEasy to operateImplement extractionSugar derivativesDNA preparationBiological cellLysis
The invention discloses a method for extracting and purifying DNA, comprising the following steps: 1) pre-treatment: a biological sample is in contact with pre-treated lysis solution, and solid substance adhering to biological cells is removed to obtain rude lysis solution; 2) nucleic acid adsorption: the rude lysis solution obtained in step 1 is mixed with lyse combined liquid and magnetic bead suspension to form a solution system containing magnetic nanosphere-DNA composite body, and the magnetic nanosphere-DNA composite body in the solution system is collected; 3) washing: the magnetic nanosphere-DNA composite body obtained in step 2 is successively washed with a cleaning solution I and a cleaning solution II, and then DNA is dissolved out by spent regenerant. The method provided by the invention has 90% of the DNA extracting efficiency, the extracted DNA can be used in down stream analysis operation, such as STR multiplex amplification, DNA sequencing, DNA quantitation and the like.
Owner:INST OF FORENSIC SCI OF MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY
Method for treating systemic bacterial, fungal and protozoan infection
ActiveUS8431123B2Low-toxicLower Level RequirementsHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsBacteroidesProtozoa
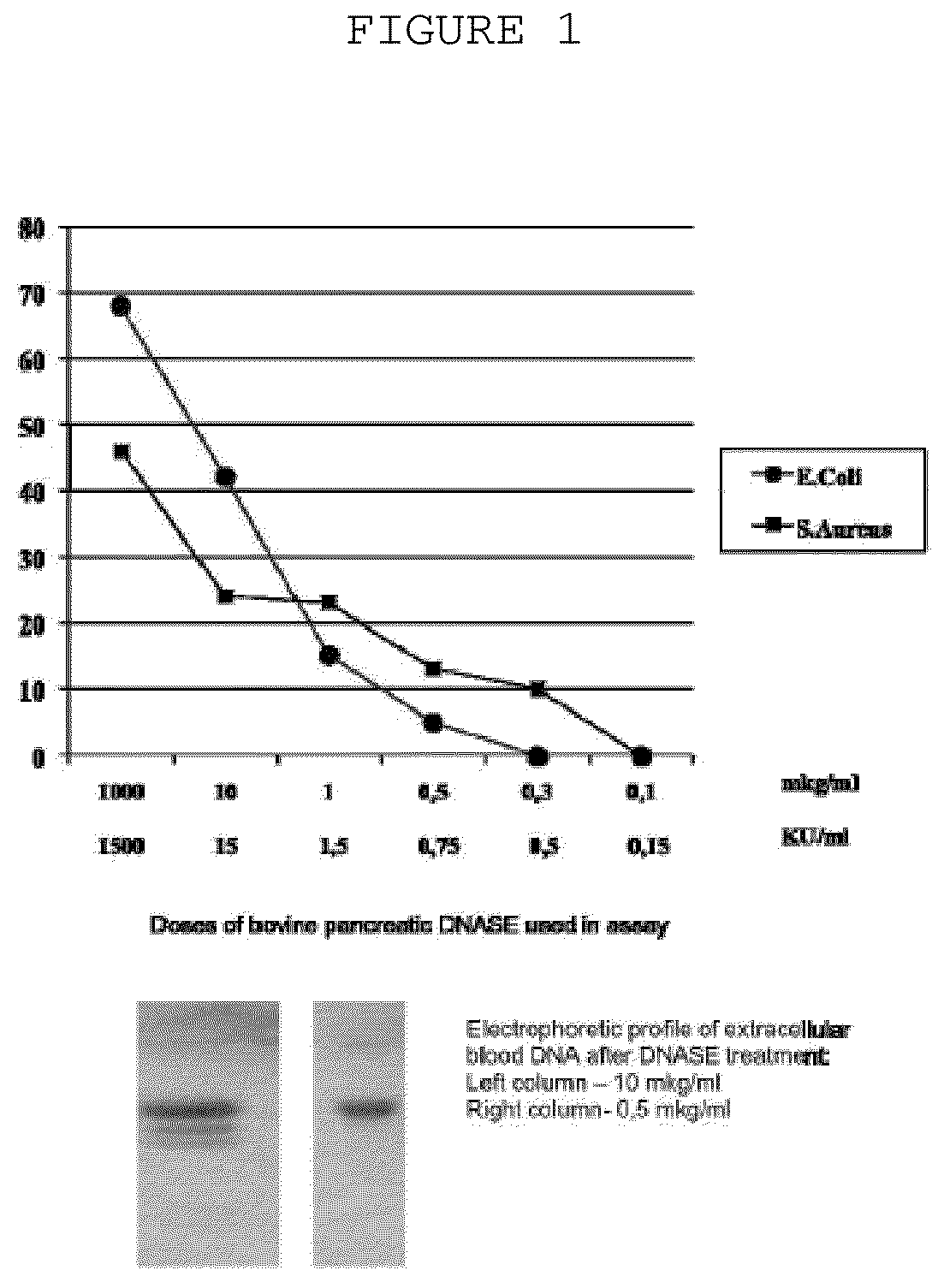
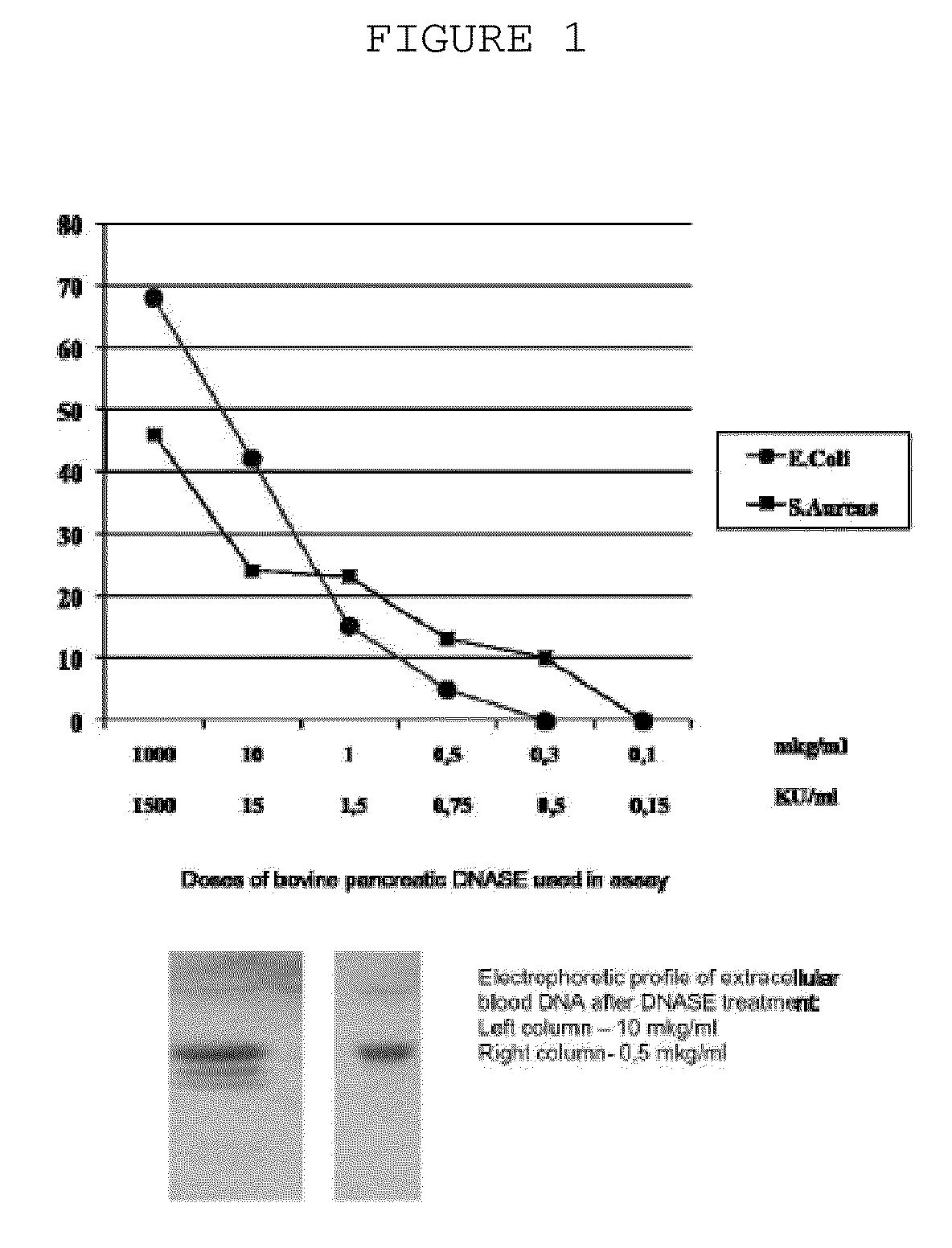
The invention is directed to a treatment of diseases that are accompanied by quantitative and / or qualitative changes of blood extracellular DNA and, more particularly, to a treatment of systemic bacterial, fungal and protozoan infections. The inventive method comprises introducing a treatment agent into a circulating blood system of a patient diagnosed with systemic infection caused by bacteria, fungi or protozoa, wherein said treatment agent destroys extracellular DNA in said blood of said patient and wherein said treatment agent used to destroy said extracellular DNA is a DNase enzyme: said agent being administered in doses and regimens which are sufficient to decrease the average molecular weight of circulating extracellular blood DNA in the blood of said patient; such decrease in the average molecular weight can be measured by gel electrophoresis of extracellular blood DNA fraction from the blood of said patient. A DNase enzyme may be applied in a dose and regimen that provide a DNase DNA hydrolytic activity measured in blood plasma that exceeds 1.5 Kunitz units per 1 ml of blood plasma for more than 12 hours within a period of 24 hours.
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
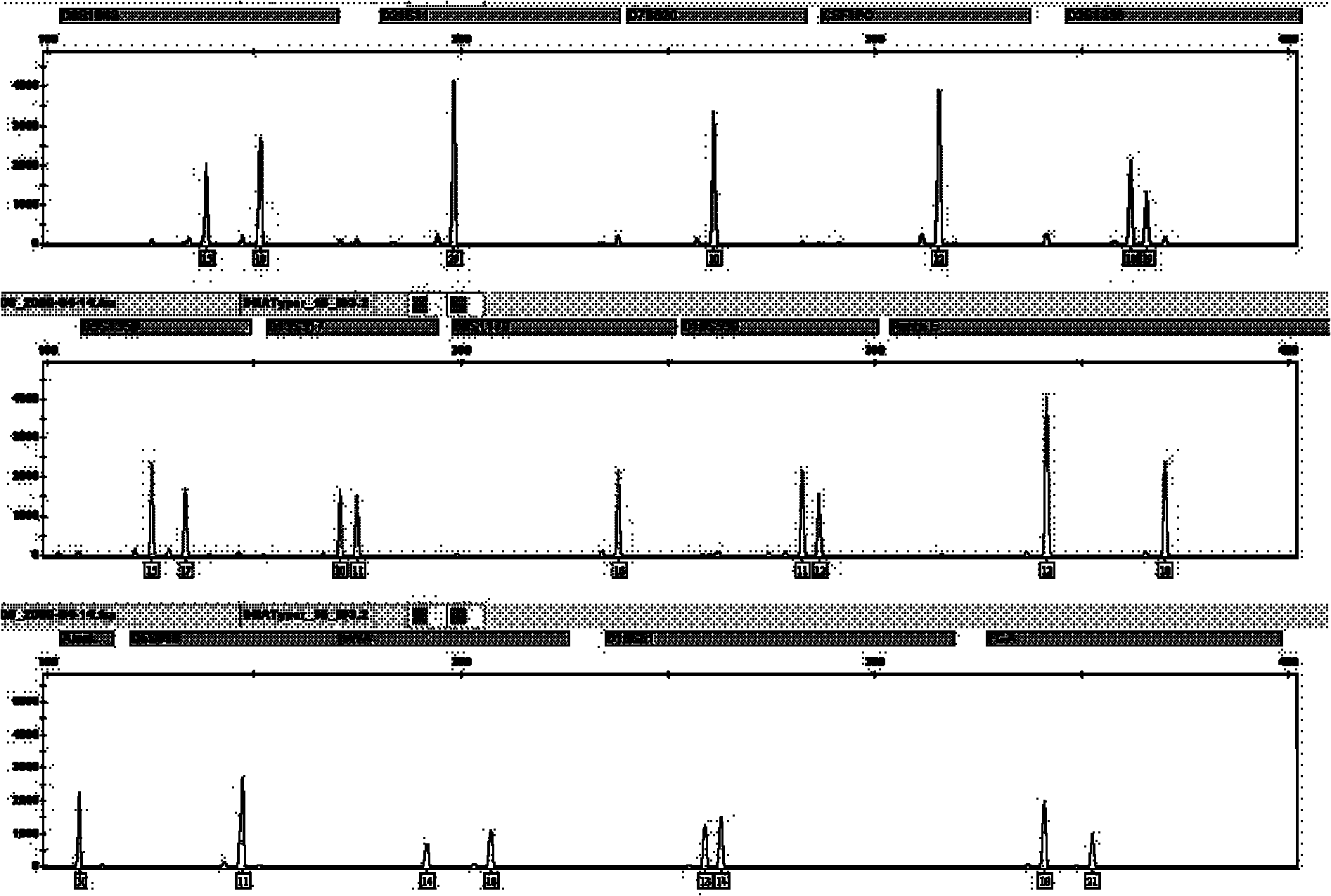
Method for extracting and purifying spittle DNA
InactiveCN102220310AMeet the extraction requirementsEasy to operateDNA preparationBiological cellLysis
The invention discloses a method for extracting and purifying spittle DNA, which comprises the following: 1) a step of pre-treatment, which is to contact the spittle with pretreatment lysis solution, remove solid matters adhered onto cells and obtain coarse lysis solution; 2) a step of nucleic acid absorption, which is to mix the coarse lysis solution obtained by the step 1) with lysis binding solution and magnetic bead suspension to form a solution system containing magnetic nano microsphere and DNA composite and is to collect the magnetic nano microsphere and DNA composite from the solutionsystem; and 3) a step of washing, which is to wash the magnetic nano microsphere and DNA composite obtained by the step 2) with washing liquid I and washing liquid II in turn, and dissolve out DNA byusing eluent. When the method provided by the invention is used, the DNA extraction efficiency may reach 90 percent, the extracted DNA can be used in short tandem repeat (STR) composite amplification, DNA sequencing, DNA quantification and other downstream analysis and operation.
Owner:INST OF FORENSIC SCI OF MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY
Method for extracting purified DNA from human exfoliative cells
InactiveCN102181434AMeet the extraction requirementsEasy to operateDNA preparationBiological cellLysis
The invention discloses a method for extracting purified DNA from human exfoliative cells. The method comprises the following steps: 1) pretreating: contacting the human exfoliative cells with pretreating lysate to remove the solid matters adhering to the biological cells to obtain coarse lysate; 2) nucleic acid adsorbing: mixing the coarse lysate obtained in the step 1) with lysis integrated liquid and magnetic bead suspension to form a solution system containing a magnetic nano microsphere-DNA compound and collecting the magnetic nano microsphere-DNA compound in the solution system; and 3) washing: washing the magnetic nano microsphere-DNA compound obtained in the step 2) with washing liquid I and washing liquid II respectively and then dissolving out the DNA with eluent. The efficiency of extracting DNA by the method can reach 90% and the extracted DNA can be applied to such downstream analysis operations as STR (short tandem repeat) multiplex amplification, DNA sequencing, DNA quantifying and the like.
Owner:INST OF FORENSIC SCI OF MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY
Preparation of DNA-containing extract for PCR amplification
Environmental samples typically include impurities that interfere with PCR amplification and DNA quantitation. Samples of soil, river water, and aerosol were taken from the environment and added to an aqueous buffer (with or without detergent). Cells from the sample are lysed, releasing their DNA into the buffer. After removing insoluble cell components, the remaining soluble DNA-containing extract is treated with N-phenacylthiazolium bromide, which causes rapid precipitation of impurities. Centrifugation provides a supernatant that can be used or diluted for PCR amplification of DNA, or further purified. The method may provide a DNA-containing extract sufficiently pure for PCR amplification within 5–10 minutes.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Method for Treating Systemic Bacterial, Fungal and Protozoan Infection
ActiveUS20110189156A1Low-toxicLower Level RequirementsAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsDiseaseBacteroides
A treatment for the diseases that are accompanied by quantitative and qualitative changes of blood extracellular DNA and, more particularly, to a treatment of systemic bacterial, fungal and protozoan infections. The inventive method consist from introducing a treatment agent into a circulating blood system of a patient diagnosed with systemic infection caused by bacteria, fungi or protozoa when said treatment agent destroys extracellular DNA in said blood of said patient and wherein said treatment agent used to destroy said extracellular DNA is a DNASE enzyme: said agent must be administered in doses and regimens which sufficient to decrease number average molecular weight of circulating extracellular blood DNA in the blood of said patient; such decrease of number average molecular weight might be measured by gel electrophoresis of extracellular blood DNA fraction from the blood of said patient. A DNASE enzyme may be further applied in a dose and regime that provide a DNA hydrolytic activity measured in blood plasma exceeding 1.5 Kunitz units per 1 ml of blood plasma for more than 12 hours within a period of 24 hours.
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
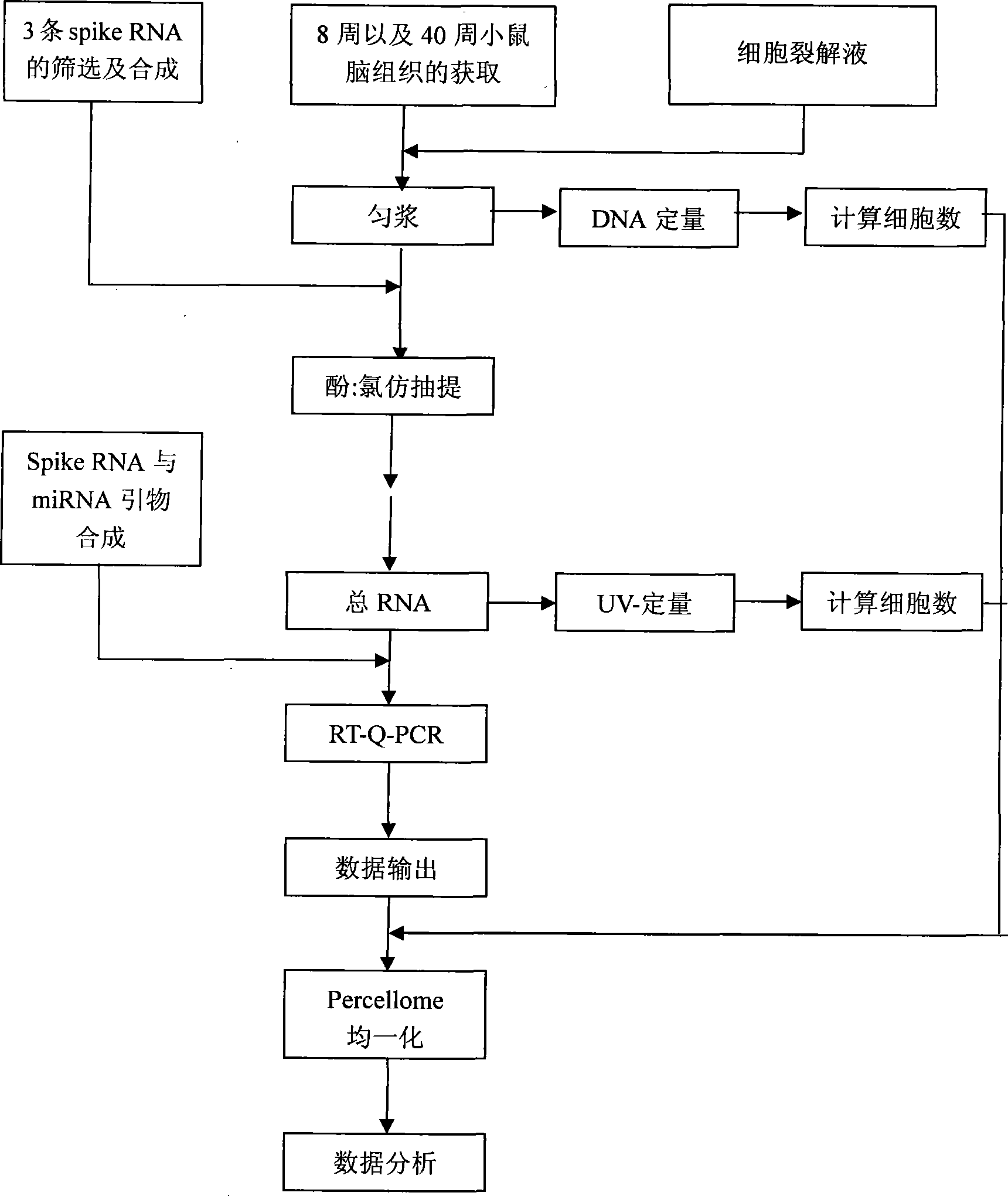
Detection method of miRNA absolute expression level in biological sample
InactiveCN101363057AMake up for the shortcomings that can only reflect relative differencesReliable analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansLoss rateRNA extraction
The invention relates a method for measuring miRNA absolute expression quantity in biological samples, which comprises the following steps: 1) material selection: 8 weeks and 40 weeks of mouse brain tissues are selected; 2) total RNA extract; 3) RT(reverse transcription)-Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR); 4) quantifying DNA; 5) drawing specification curve; 6) data processing: loss rate and average loss rate of little RNA is figured out in the process of extracting RNA according to the copy number of spike RNA in the extracted total RNA which is detected by the PCR; the expression quantity of every initial cell of the little RNA at the levels of DNA and RNA is figured out according to the cell number of original sample that is respectively expressed from the levels of DNA and RNA. The method has the advantages of miRNA expression quantity is faithfully transformed into the absolute expression quantity in the original sample through the cell number in the sample homogenate which is worked out from the two levels of DNA and RNA; the disadvantage that relative differentiation can only be reflected by taking housekeeping genes as an internal reference, and the analysis is truer and more reliable from the two levels of DNA and RNA.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV +1
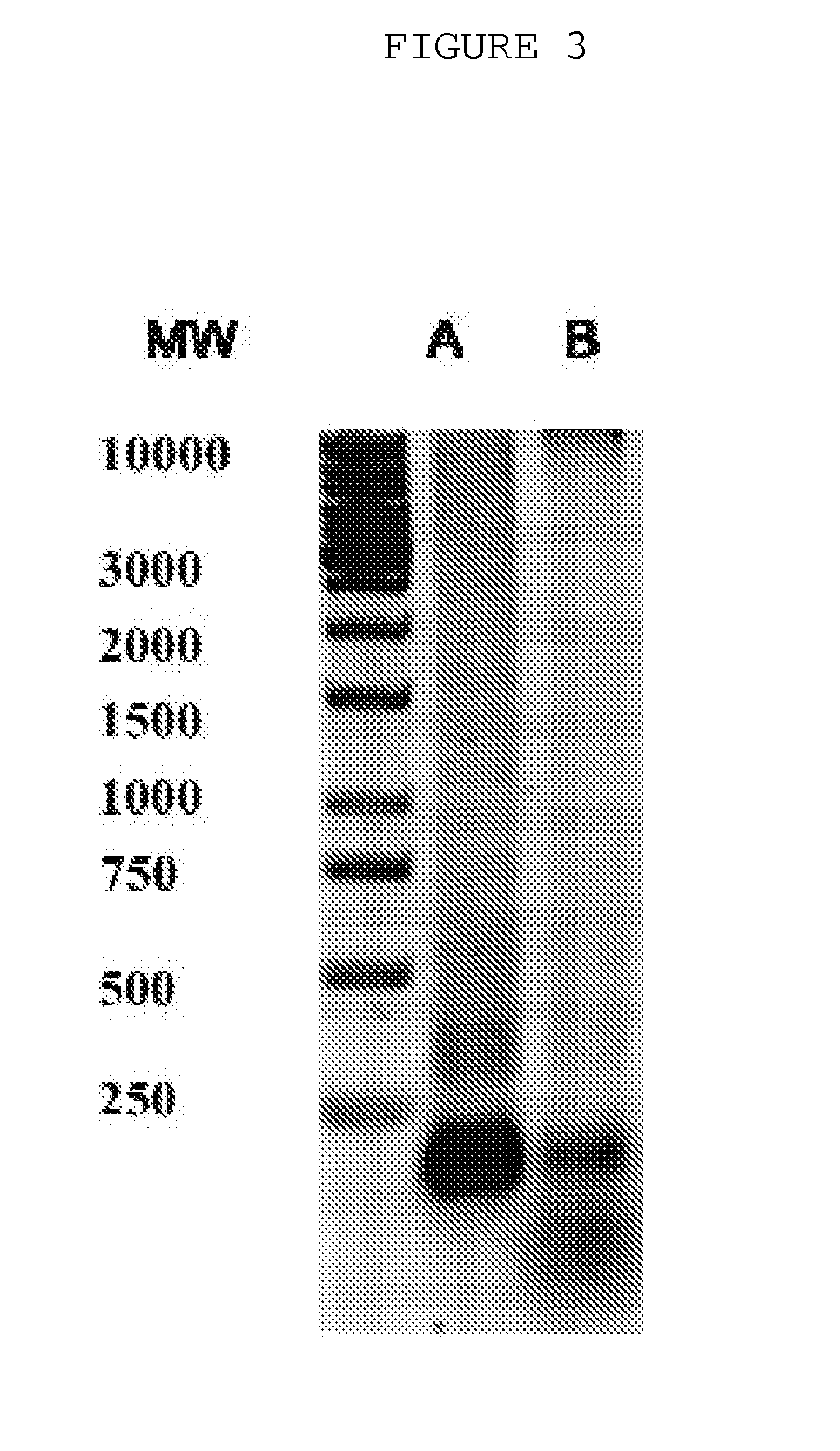
Huaman plasma DNA quantitative analyser
InactiveCN1811387AAccurate quantitative detectionOvercoming Extraction EfficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceTherapeutic effect
The present invention relates to a quantitative detection analysis method of human plasma DNA level. Said method includes the following steps: selecting artificially-synthetic exogenous DNA series whose extraction efficiency is identical to or similar to that of human plasma DNA, but they are non-homologous, selecting housekeeping gene beta actin as determination gene, inserting artificially-synthetic exogenous DNA into carrier pMD18T and placing it in the bacteria to make culture, making blue and white spot screening, colony PCR identification, enzyme-cutting into linearity, placing the above-mentioned material into plasma, adopting double fluorescent quantitative gene amplification, fluorescent groups are respectively FAM and HEX, extracting known exogenous positive plasmid recovery efficiency, using computation formula to make computation so as to obtain the quantity of plasma DNA.
Owner:潘世扬
Kit for detecting DNA residues of CHO cell and using method thereof
ActiveCN102181530AHigh sensitivityReliable Quality Control EvidenceMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceReference product
The invention relates to a kit for detecting deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) residues of a Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell and a using method thereof. The kit comprises DNA extracting solution, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification reaction liquid, a DNA quantitative reference product of a CHO cell genome, a negative quality control product, a positive quality control product and DNA diluent. In the kit, EvaGreen is used as a fluorescent dye, and the DNA of the CHO cell genome is detected by a real-time quantitative PCR technology; and products such as a treatment protein medicament, a recombinant vaccine, a monoclonal antibody and the like from the CHO cell can be accurately and quantitatively detected.
Owner:SHANGHAI HENLIUS BIOTECH INC
DNA quantitative analysis method based on cell microscope image
ActiveCN106340016AQuick identificationAccurate identificationImage enhancementImage analysisNODALPositive sample
The invention discloses a DNA quantitative analysis method based on a cell microscope image. The method comprises the following steps that 1) pretreatment is carried out; 2) an MSER algorithm is used to extract candidate areas, and single-tine trees or single nodes are obtained; 3) a simple feature training classifier C1 is extracted from the area on the basis of a training set, the possibility that the classifier belongs to a cell of interest is calculated, and the single-tine trees obtained in the step 2) are further simplified based on the classifier; 4) a statistical, shape and texture feature training classifier C2 are extracted on the basis of simple features of the extraction area of the training set, and the classifier C2 is used to further classify all the candidate areas of positive samples output by the classifier C1; and 5) a DI value of a nucleus is calculated. According to the invention, a maximum stable area algorithm is used to extract a lot of candidate areas from the image, and a cascaded classifier composed of the classifier C1 and the classifier C2 is trained to identify the candidate areas rapidly and accurately.
Owner:湖南品信生物工程有限公司
DNA or RNA detection and/or quantification using spectroscopic shifts or two or more optical cavities
InactiveUS20090093375A1Possible to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningResonance wavelengthSemiconductor chip
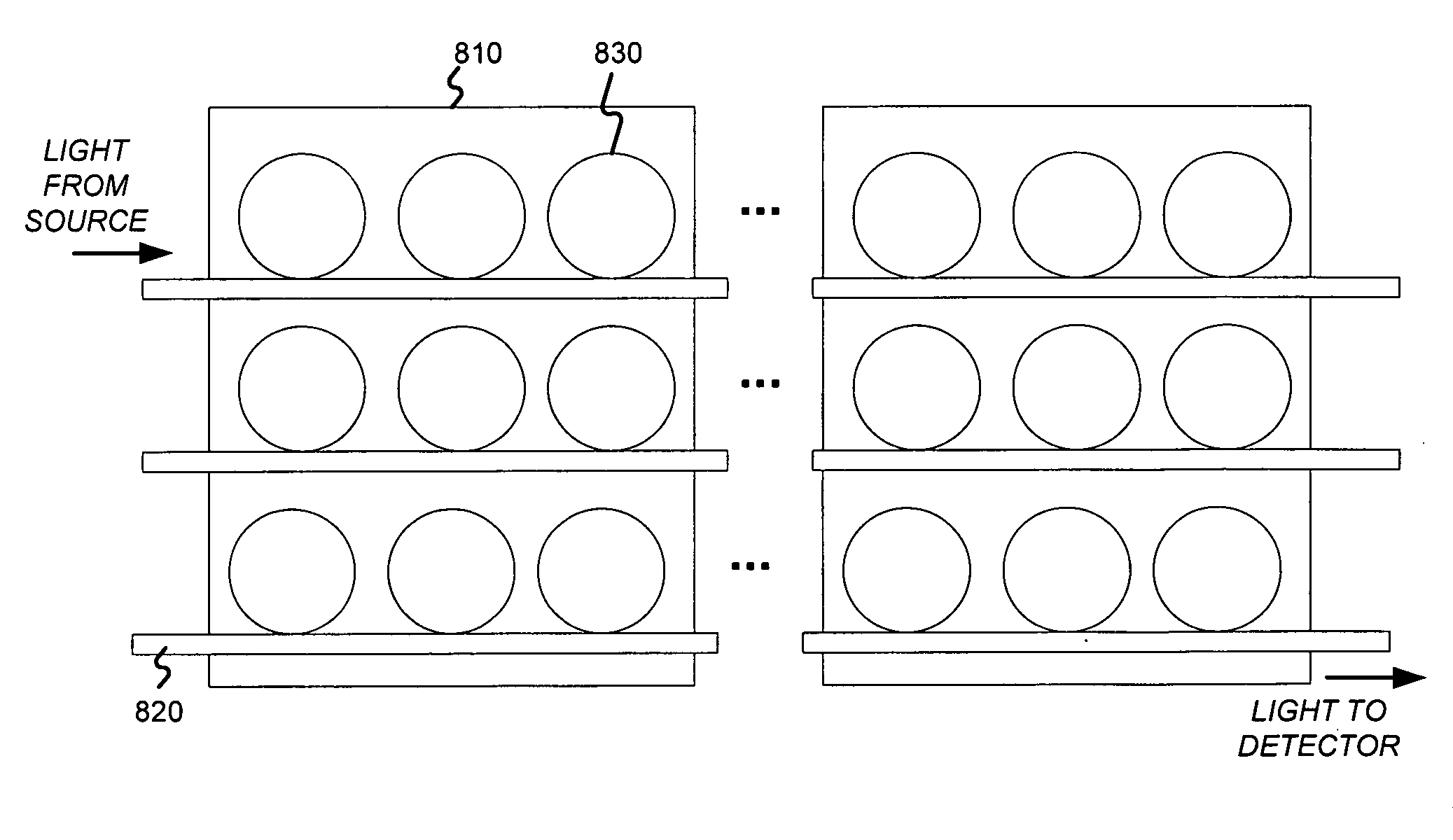
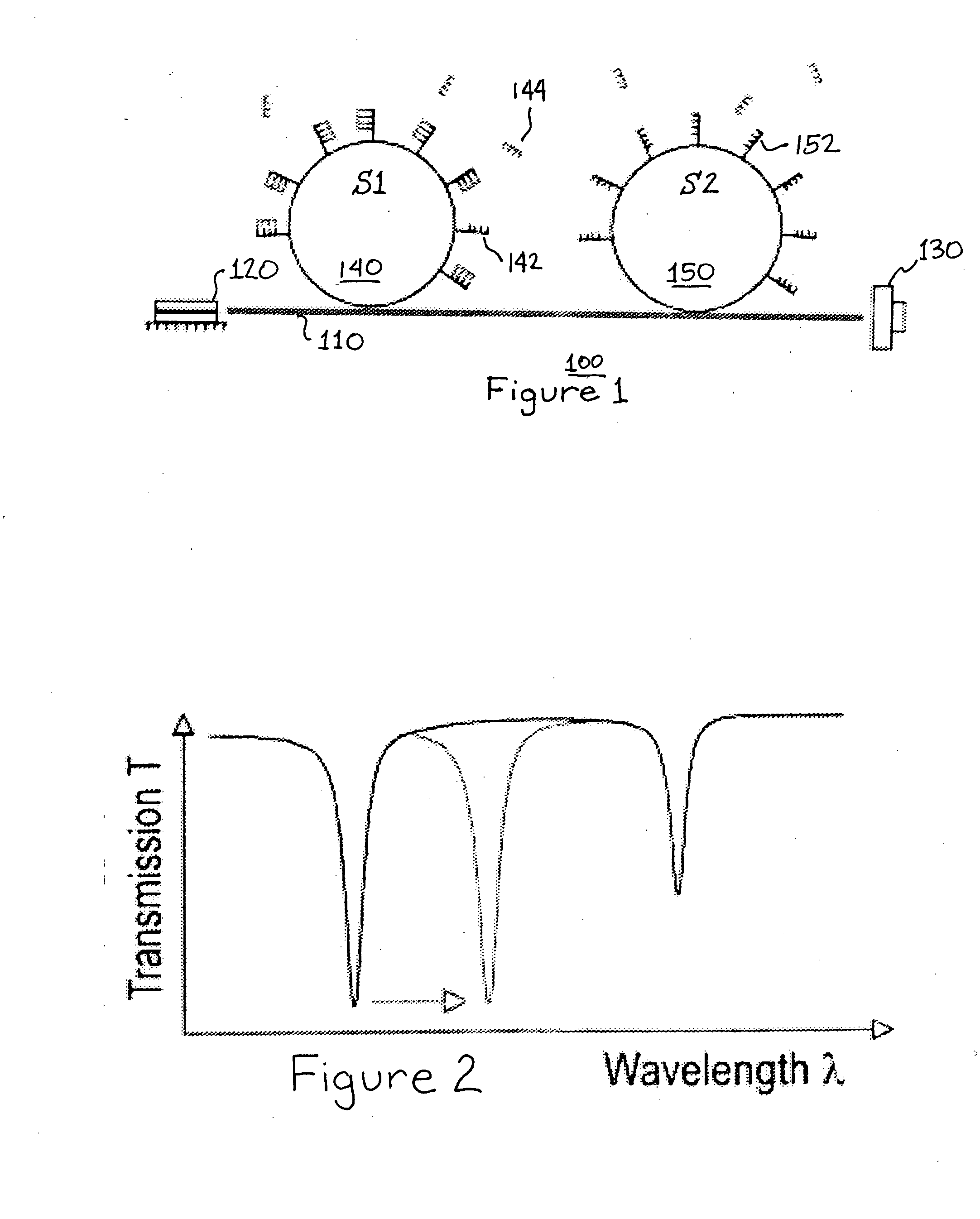
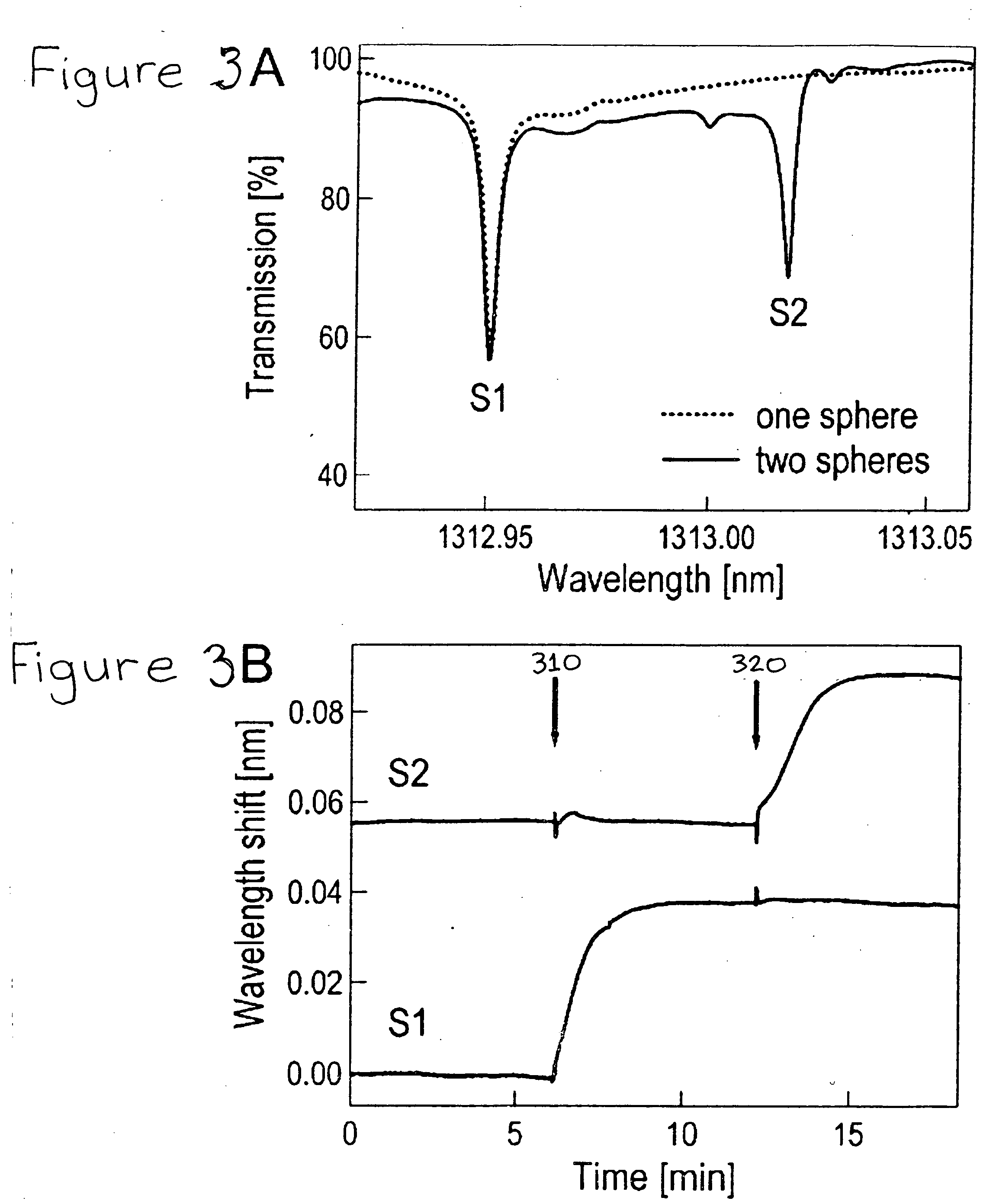
A spectroscopic technique for high-sensitivity, label free DNA quantification uses a shift in an optical resonance (whispering gallery mode, WGM) excited in a micron-sized optical cavity (e.g., a silica sphere) to detect and measure nucleic acids. The surface of the silica sphere is chemically modified with oligonucleotides. Hybridization to the target DNA leads to a red-shift of the optical resonance wavelength. The sensitivity of this resonance technique is higher than most optical single-pass devices such as surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Each microsphere can be identified by its unique resonance wavelength. Specific, multiplexed DNA detection may be provided by using two or more microspheres. The multiplexed signal from two or more microspheres illustrates that a single nucleotide mismatch in an 11-mer oligonucleotide can be discriminated with a high signal-to-noise of 54. This all-photonic WGM biosensor can be integrated on a chip, such as a semiconductor chip, which makes it an easy to manufacture, analytic component for a portable, robust lab-on-a-chip device.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
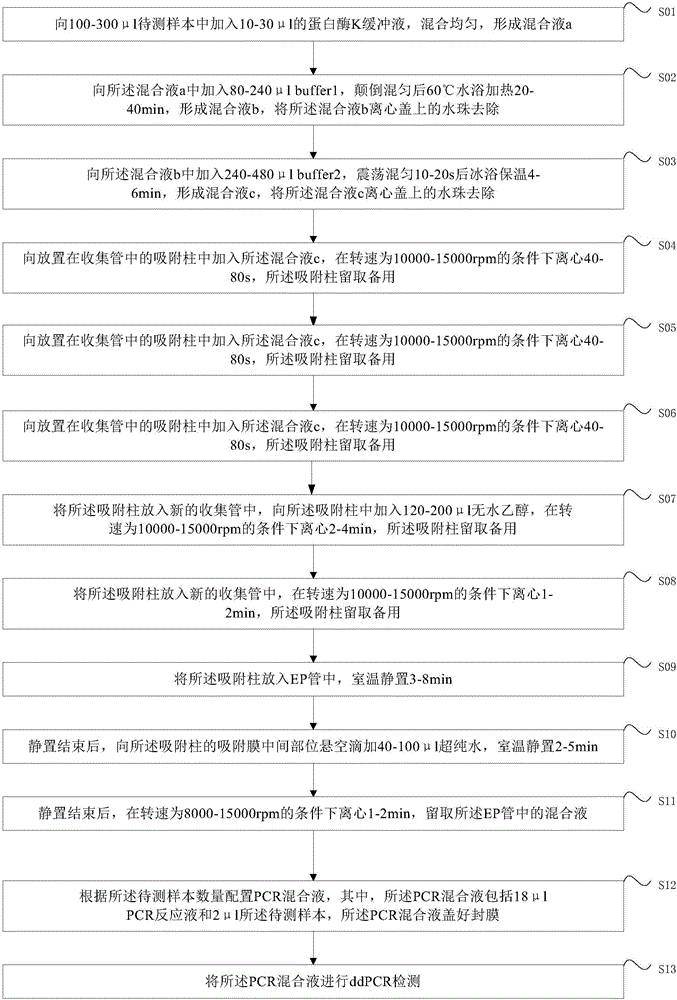
High-sensitivity EBV DNA quantitative detection kit based on ddPCR and using method thereof
PendingCN106381344AHigh purityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDiseaseEBV Positive
The invention provides a high-sensitivity EBV DNA quantitative detection kit based on ddPCR and a using method thereof. The kit comprises DNA extraction buffer solution, PCR primers and probes, a PCR reaction solution and EBV positive and negative control. When the kit provided by the invention is used for detecting ddPCR, the influences of PCR equipment, standard substances and the like can be effectively eliminated, and further high-sensitivity absolute quantification is further realized. The EBV DNA quantitative detection kit provided by the invention is capable of performing high-sensitivity accurate quantification on EBV in serum and plasma through a ddPCR technology, and providing a reference basis for diagnosis and curative effect monitoring of EBV related diseases. According to the kit, a function relationship between the international unit and common unit of EBV DNA international standard substances is determined to be 1IU / ml=2.5Copy / ml, the international traceability of EBV DNA is realized, and the international comparability between the detection results and quantification unit is realized.
Owner:林勤 +2
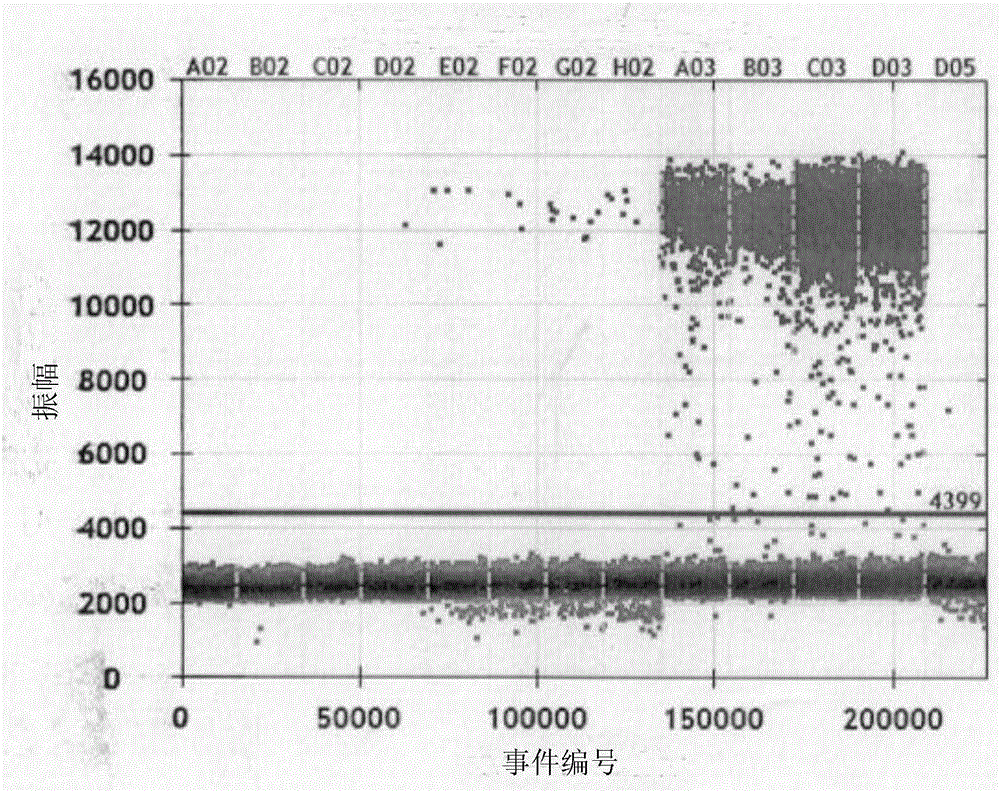
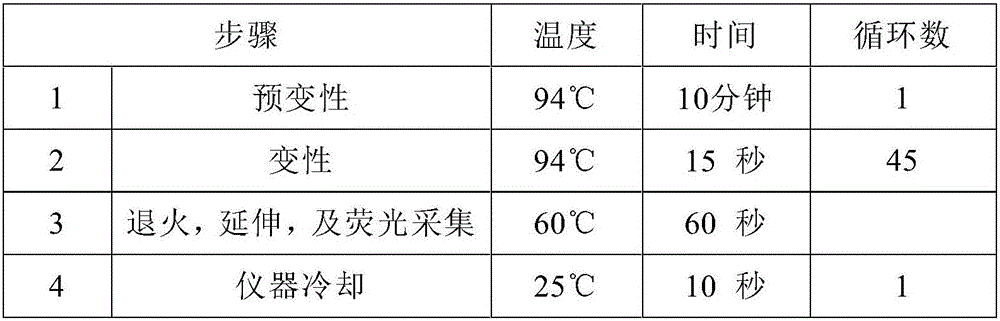
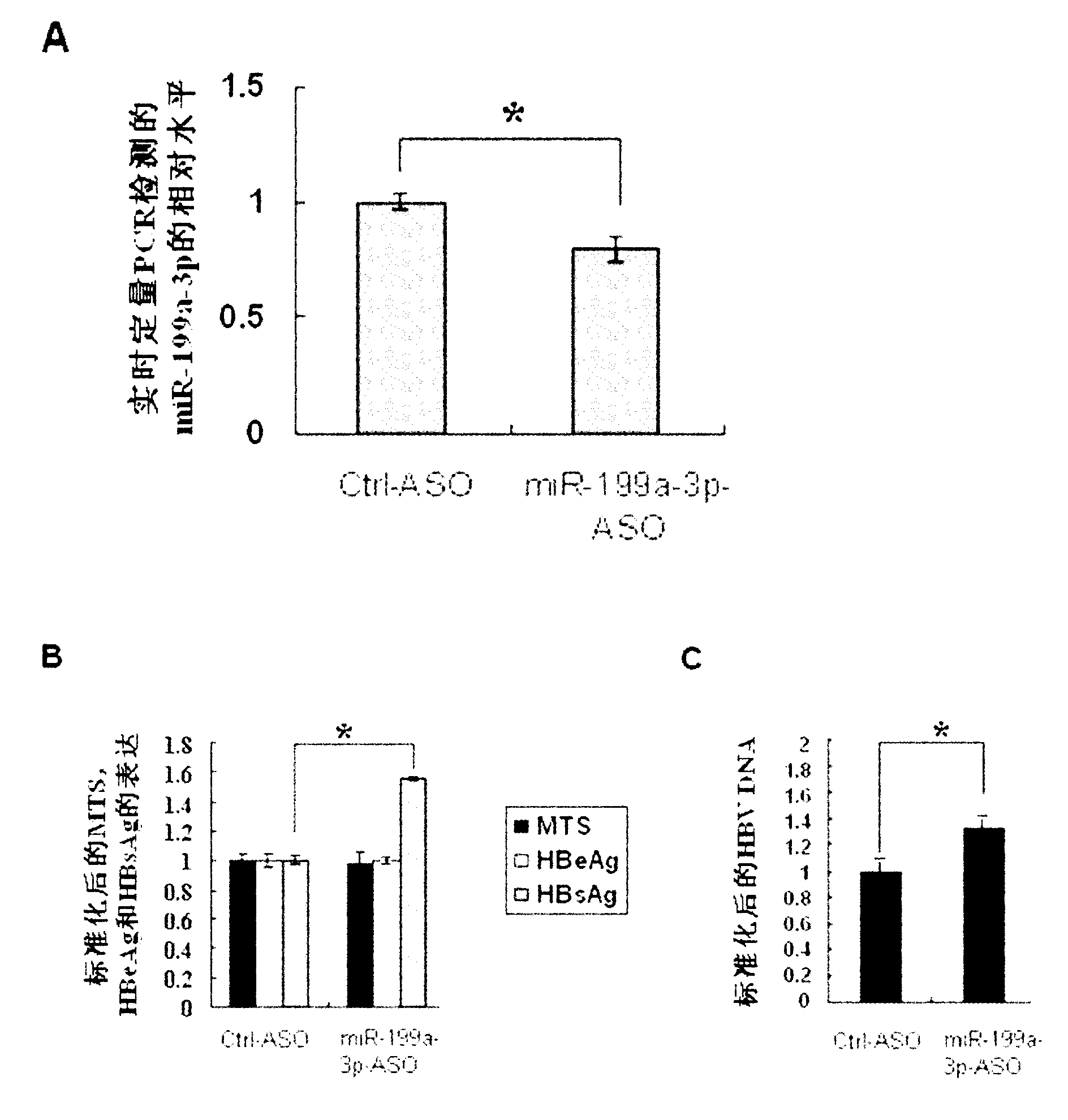
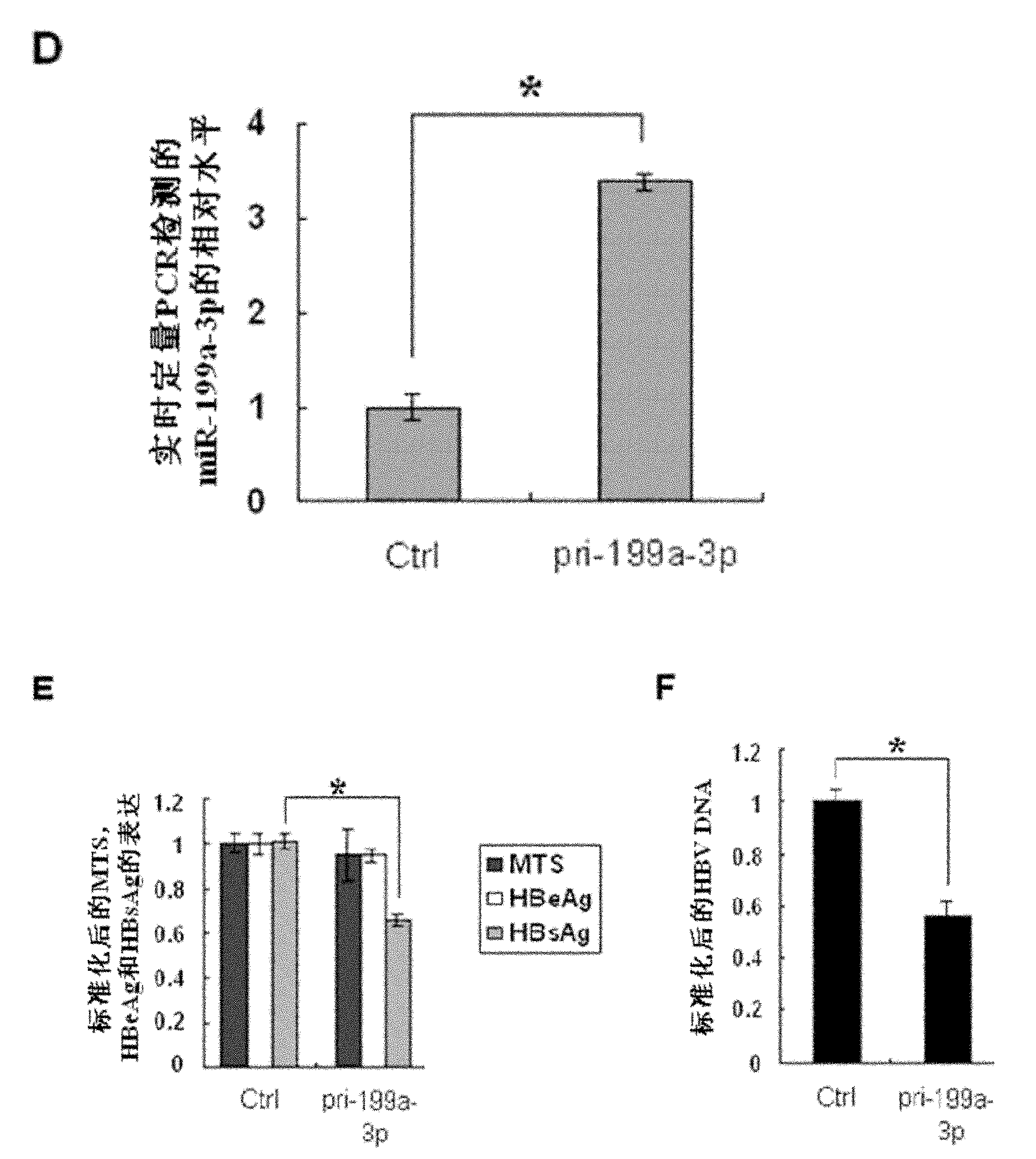
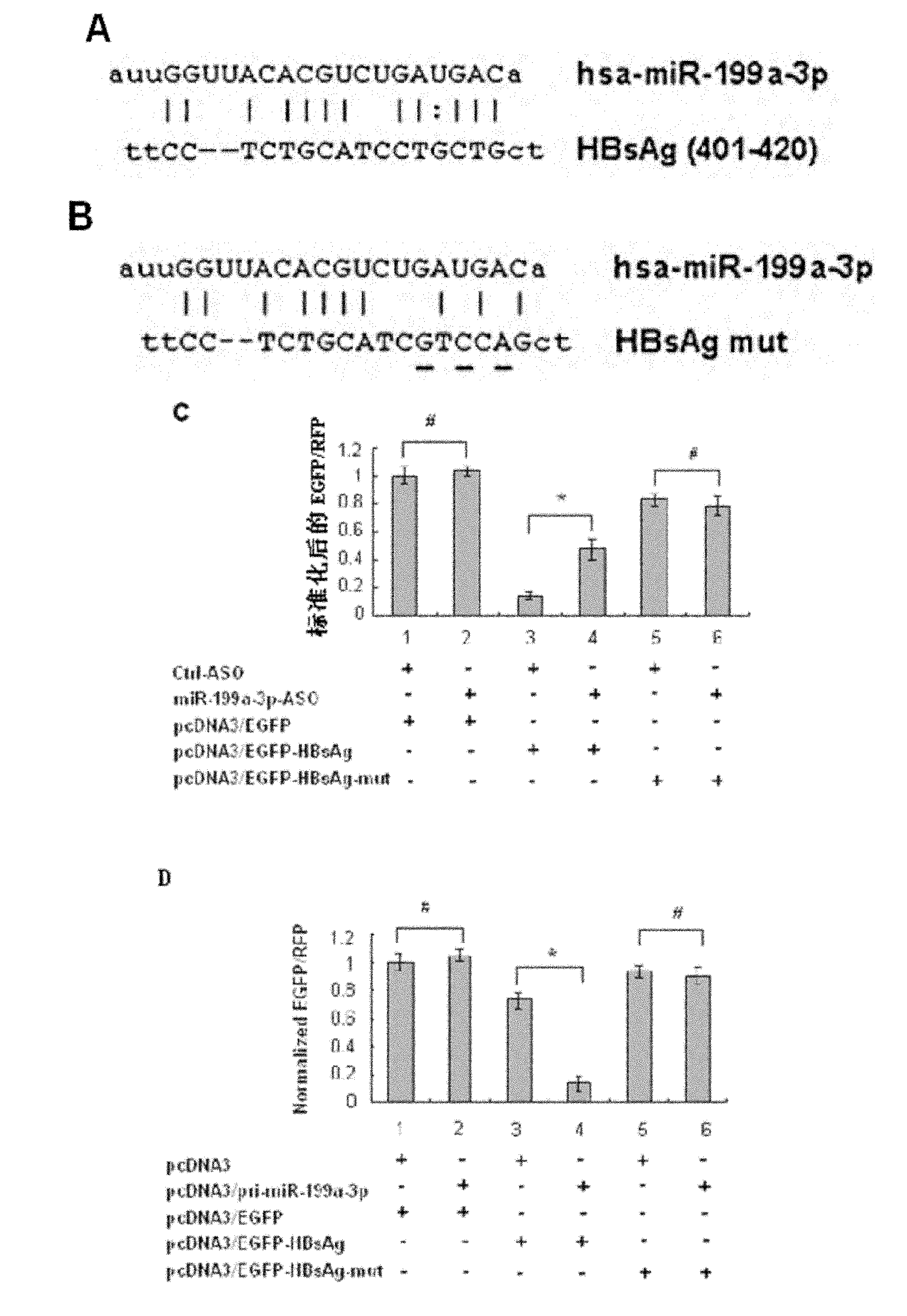
Application of miR-199a-3p in preparation of medicine for resisting hepatitis B virus
InactiveCN101954094AReduce expressionDoes not affect proliferationOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsHBsAgFluorescence
The invention discloses application of miR-199a-3p in the preparation of a medicine for resisting hepatitis B virus (HBV). MiR-199a-3p is a nucleotide sequence described in the sequence table SEQ ID NO:1. Experimental results show that miR-199a-3p can effectively reduce the expression of HBsAg, but can not influence the proliferation of HepG2 2.2.15 cells. Real time PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) to HBV DNA quantitatively displays that miR-199a-3p inhibits the replication of the virus. Bioinformatic analysis shows that the HBsAg coding area has a binding site of miR-199a-3p; fluorescence report carrier experiments verify the influence of miR-199a-3p on HBV transcription products; and meanwhile, real time PCR and western blot are used for further verifying that miR-199a-3p has inhibition action on the expression of HBsAg. The results imply that miR-199a-3p plays an important role in regulating and controlling the replication of HBC and can be prepared into a medicine for resisting HBV.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
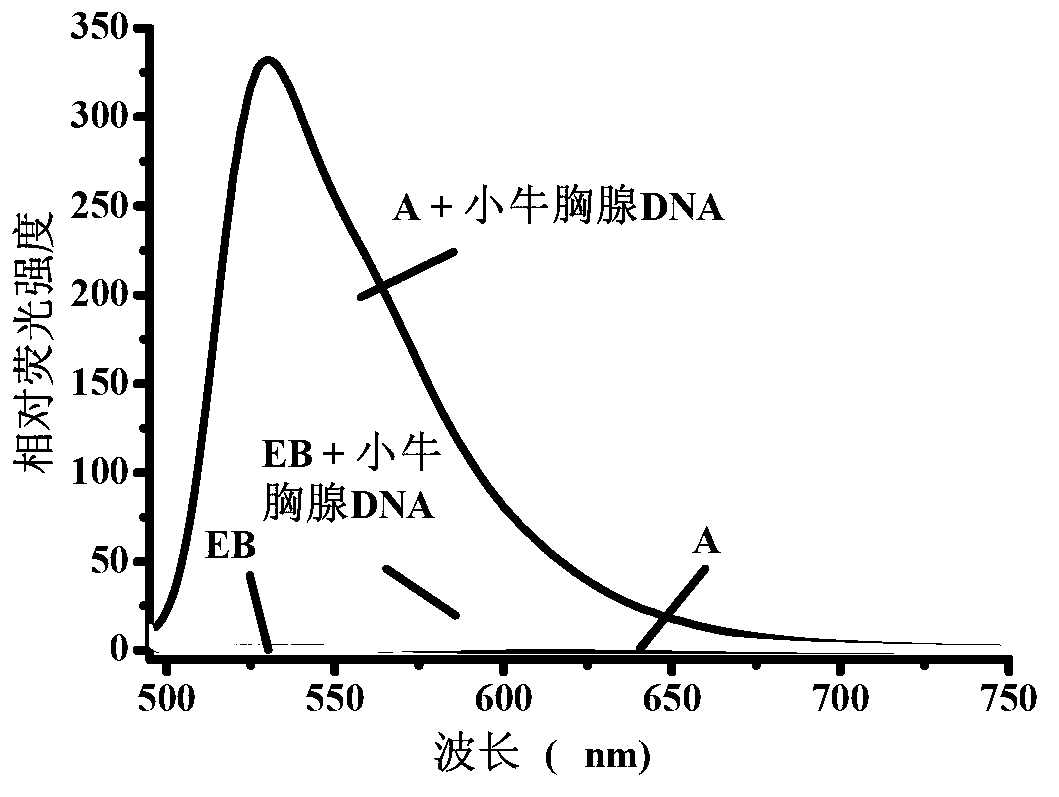
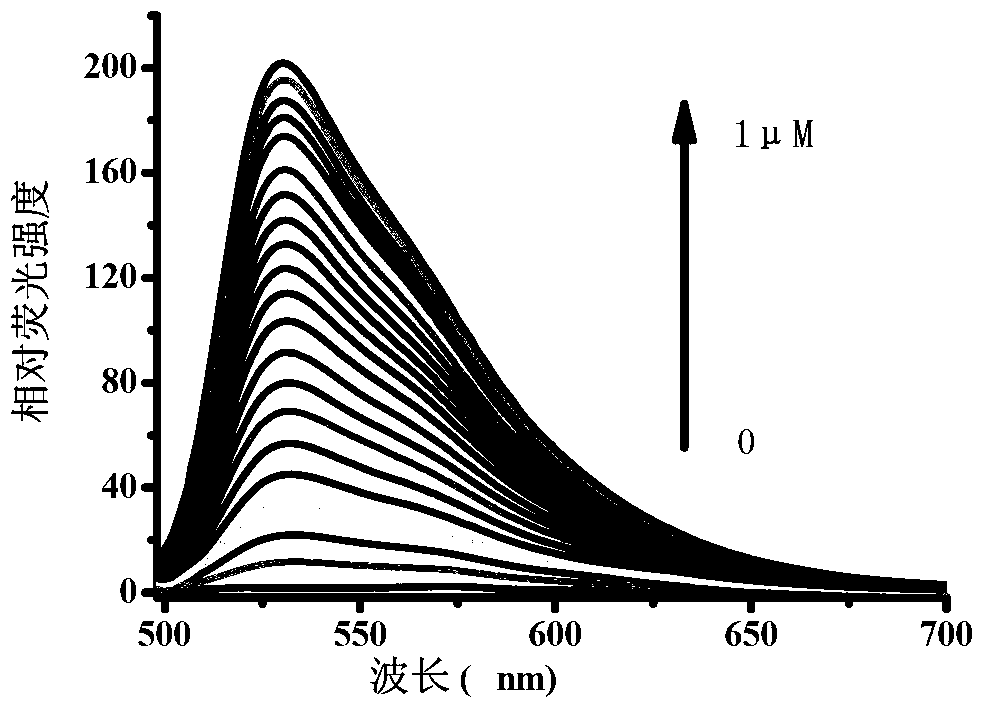
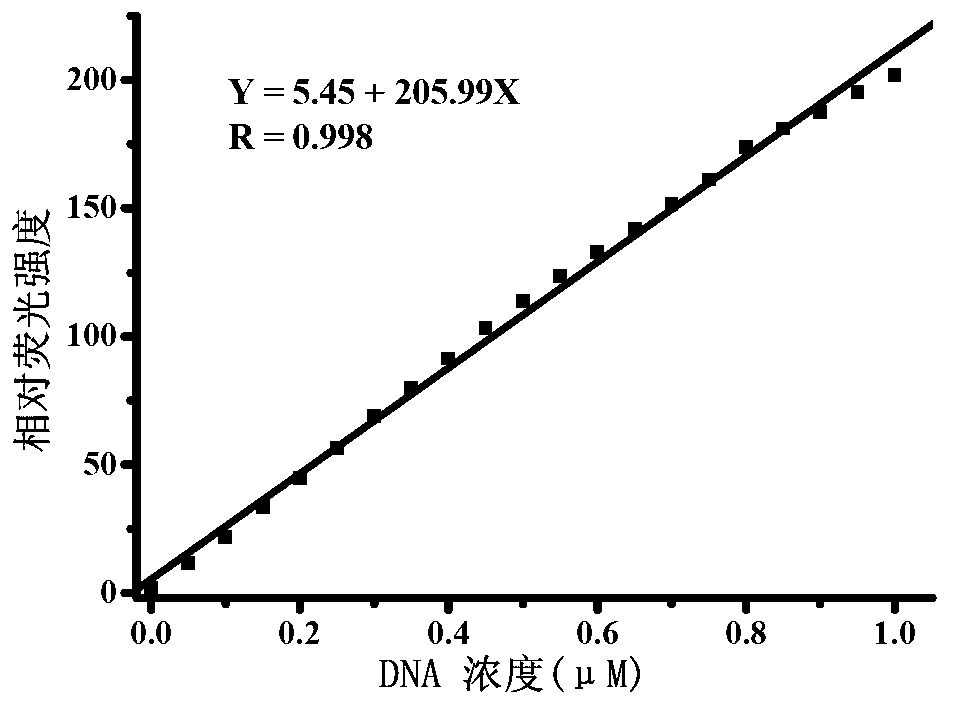
Green fluorescence cyanine dye and preparation method as well as application thereof
InactiveCN102702769ALow fluorescent backgroundHigh fluorescence quantum yieldMethine/polymethine dyesMicrobiological testing/measurementCyanineBlood cell analysis
The invention provides a green fluorescence cyanine dye, which has a structural general formula I shown in the specification, wherein in the formula, X is C(CH3)2, O, S or Se; R1 and R2 are independently selected form H, C1-18 alkyl groups, OR6, C1-6 alkyl group OR6 or halogen respectively; R3 is N(R5)(R7); R4 is selected from C1-18 alkyl groups, benzyl groups and substituted benzyl groups; the substituted benzyl groups are arbitrarily substituted by the following groups: C1-18 alkyl groups, CN, COOH, NH2, NO2, OH, SH, C1-6 alkoxy groups, C1-6 alkyl amino groups, C1-6 acylamino groups, halogen or C1-6 halogenated alkyl groups; R5 and R7 are independently selected from H or C1-18 alkyl groups respectively; R6 is H or C1-18 alkyl groups; and Y is negative ions. The fluorescence dye can be used for DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) quantitative detection and biological dyeing, and is applied to the fields of nucleic acid marking, blood cell analysis, clinic medical diagnosis, immune analysis detection and the like.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Quantitative plasmid DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) detection kit
InactiveCN102980878AMake up for the shortcomings of not being able to quantify quality DNAHigh sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescencePlasmid dna
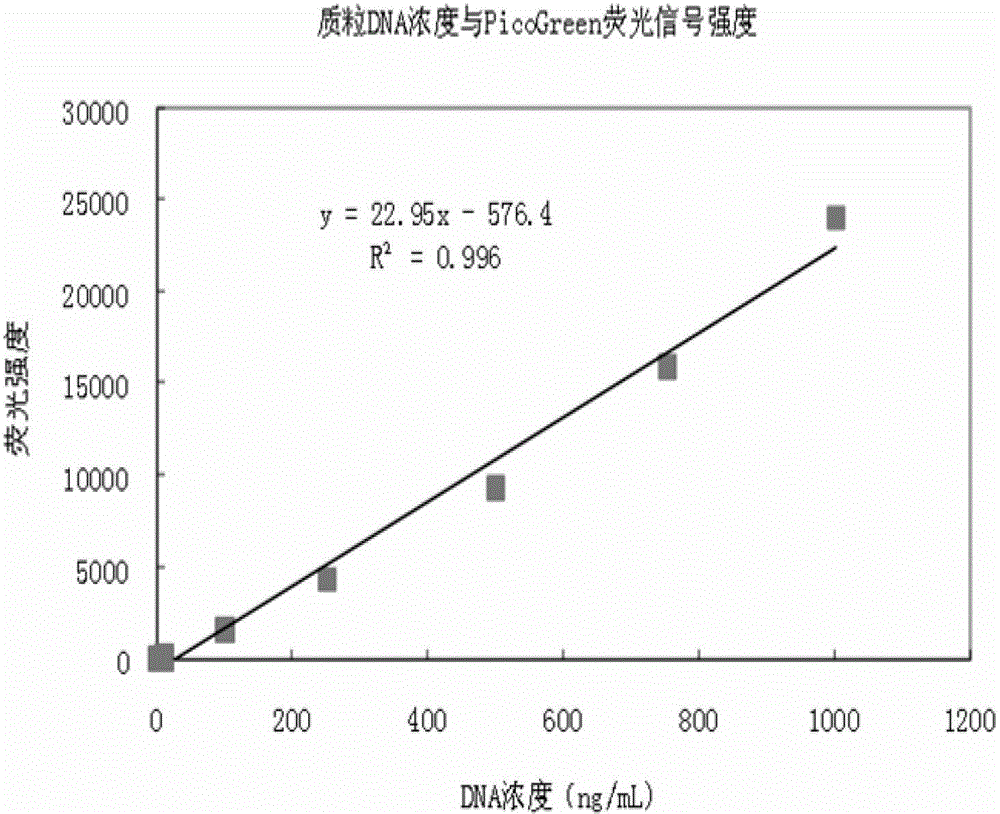
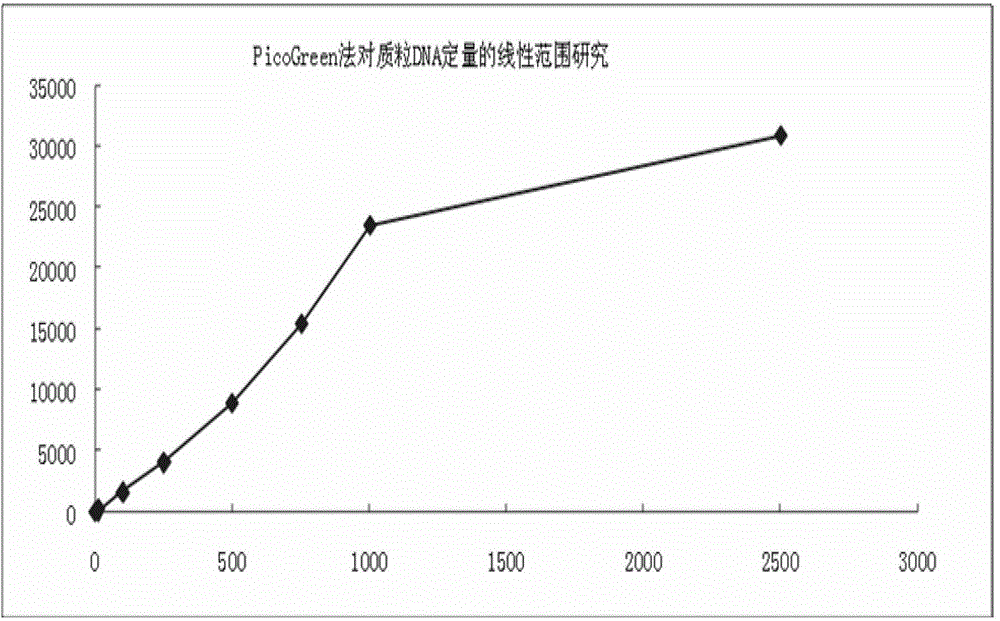
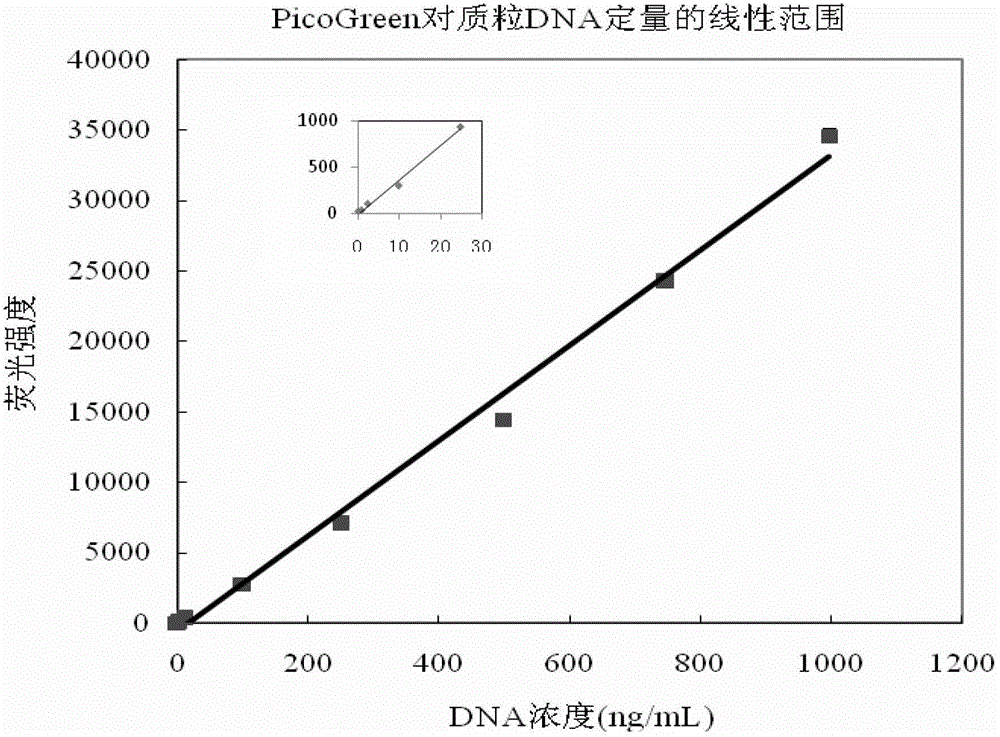
The invention provides a quantitative plasmid DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) detection kit which has the characteristics of adopting a plasmid DNA standard substance to accurately quantify by using an ultrasonic-isotope dilution mass-spectrography with high accuracy, and making up the defect that a conventional kit cannot quantify the plasmid DNA. The invention further provides a plasmid DNA quantitative detection method which comprises the following steps of: respectively measuring fluorescence signal strengths of the plasmid DNA standard substances of different concentrations; drawing a concentration-fluorescence signal strength standard curve; subsequently measuring the fluorescence signal strength of a plasmid DNA sample to be measured; and accurately calculating the DNA concentration of the sample to be measured according to the drawn standard curve. According to the method and the kit, standard plasmids are adopted to be used as the DNA standard to quantify in a fluorescent dye method for the first time with high sensitivity, and DNA as low as 1pg can be detected; the linear range is wide, and plasmid DNA of 0.25-1000ng / Ml can be detected; and the standard plasmids are quantified by using the ultrasonic-isotope dilution mass-spectrography, and the quantitative value obtained is low in uncertainty and high in accuracy.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
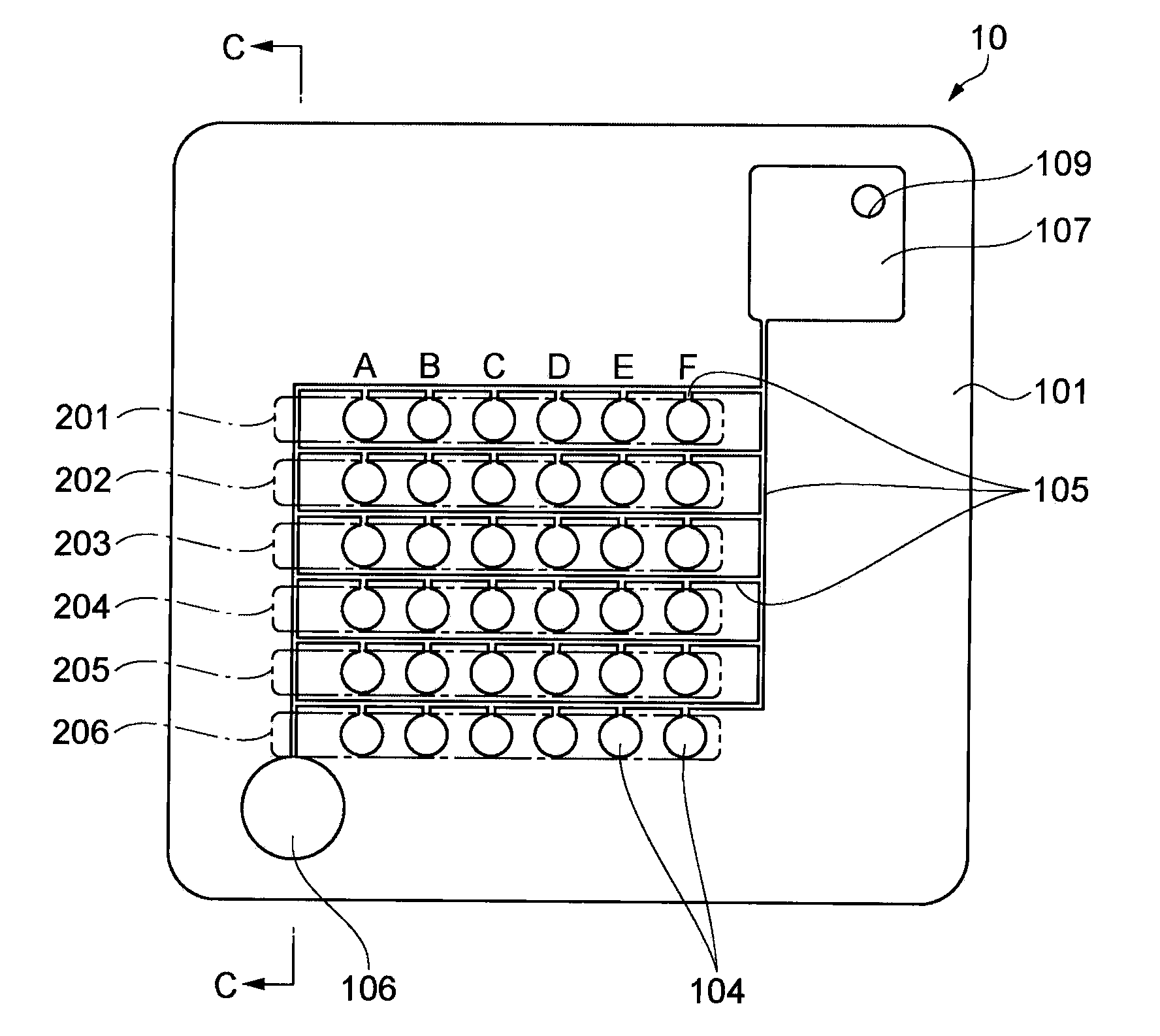
Biochip and target DNA quantitative method
InactiveUS20110065591A1Easy to quantifyEasy to implementHeating or cooling apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementInternal standardFluorescence
A biochip used for quantitative analysis of a target DNA contained in a sample, includes a type I chamber that includes: a primer that is designed to bind to the target DNA; a internal standard DNA of a first amount that has a sequence different from a sequence of the target DNA, and is amplifiable with the primer; and a fluorescent probe that is designed to bind to a part of an PCR product of the target DNA and to a part of an PCR product of the internal standard DNA, and fluoresces differently for the PCR product of the target DNA and the PCR product of the internal standard DNA, and a type II chamber including: the internal standard DNA of a second amount different from the first amount; and the primer and the fluorescent probe.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Cell nucleus DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) staining method
InactiveCN102967499AEasy to fixReduce acidolysisPreparing sample for investigation3-deoxyriboseFeulgen stain
The invention discloses a cell nucleus DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) staining method. The cell nucleus DNA staining method is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1, fixation: sequentially placing sample slices into a BS fixing solution at the temperature of 30-40 DEG C to fix for 20-30 minutes, and rinsing; 2, hydrolyzation: completely fixing the sample slices, hydrolyzing in 5N hydrochloric acid at the temperature of 30-40 DEG C for 20-30 minutes, and rinsing; 3, staining: after the hydrolyzation is completed, staining in a Thionin staining solution at the temperature of 30-40 DEG C for 30-40 minutes, and rinsing; 4, after the staining is completed, dewatering by adopting fast gradient ethanol, and mounting. In conclusion, compared with other Feulgen staining methods, the cell nucleus DNA cell nucleus DNA has the obvious advantages of practicability, stability, efficiency, cost saving, repeatability, compatibility of automated equipment and the like and can meet the requirement of clinical DNA quantitative cytology on fast diagnosis.
Owner:MOTIC XIAMEN MEDICAL DIAGNOSTICS SYST
Blood plasma specific fragment free DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) quantitative detection kit
ActiveCN104073554AEliminate errorsEliminate distractionsMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerBlood plasma
The invention discloses a blood plasma specific fragment free DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) quantitative detection kit comprising the following components: two primer pairs for amplifying TP53 gene fragments of which the lengths are respectively 400bp and 150bp, a primer pair for amplifying a reference gene Beta-actin, and fetal genome DNA, wherein the two primer pairs are consistent in backward primer sites, and the lengths of the amplified TP53 gene fragments are determined by virtue of a forward primer. According to the kit disclosed by the invention, a calibration system is introduced based on a fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology, the fetal genome DNA is used as background DNA, a house-keeping gene Beta-actin is used as the reference gene, a cancer suppressor gene TP53 is used as a target gene, an amplification primer is designed aiming at different lengths of fragments of the cancer suppressor gene TP53, different lengths of the fragments of the Beta-actin gene and the TP53 gene are synchronously amplified by adopting a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR process, and the content of free DNA with specific fragment sizes in blood plasma can be quantitatively detected.
Owner:JIANGSU MICRODIAG BIOMEDICINE TECH CO LTD
Preparation method of next-generation sequencing library
ActiveCN108866155ADistribution influenceReduce workloadMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationCDNA libraryDNA fragmentation
The invention discloses a preparation method of a next-generation sequencing library. The preparation method is carried out according to the following steps: quantifying DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid); adding a needed DNA linker sequence in a sequencing process at two ends of a DNA fragment to be detected; detecting the concentration of a DNA library and a DNA fragment length distribution mode; calculating a mixing ratio of the DNA library and mixing; selecting a fragment of a mixed library; detecting and quantifying the selected DNA library; sequencing the selected DNA library. According to themethod disclosed by the invention, a plurality of libraries are mixed together after being subjected to PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) and are subjected to primary fragment sorting and Q-PCR (Quantitative-Polymerase Chain Reaction) quantifying, so that the working amount is greatly reduced; the distribution of a final sequencing data quantity in different samples is not remarkably influenced.
Owner:AGRI GENOME INST OF SHENZHEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
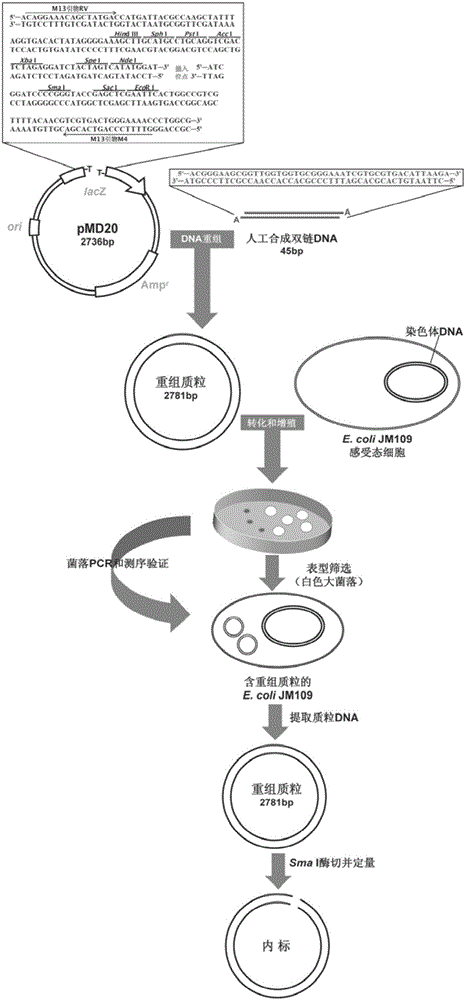
Body fluid circulation DNA quantitative determination method and kit
ActiveCN106399536AAvoid mutual interferenceMutual interference will not causeMicrobiological testing/measurementDetection biasPlasmid dna
The invention discloses a body fluid circulation DNA quantitative determination method and kit. The method includes steps of selecting artificial single copy house-keeping gene Beta-action as the detection target gene, and artificially compounding a dual-chain DNA segment with length of 45 bp, wherein it includes sequences with the same 25 bp and Beta-action genes, and recombining to a plasma carrier T-Vector pMD 20 and obtaining the recombined plasmid DNA as an interior label, and feeding a certain quantity of interior label to a body fluid sample to be tested; synchronously storing with the body fluid circular DNA, and performing nucleic acid extraction and purification, and fluorogenic quantitative PCR amplification, so as to perform the body fluid circulation DNA quantitative analysis. Through setting up a special internal label, the method eliminates the detection bias caused by nucleic acid degradation, extraction loss and PCR amplification efficiency before and in body fluid sample analysis, and can perform more stable and exact quantitative determination on the body fluid circulation DNA.
Owner:JIANGSU CODE BIOMEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Preparation method of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) quantitative detection standard
ActiveCN103063783AGood precisionImprove accuracyComponent separationChromatographic separationNucleotide
The invention discloses a preparation method of a plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) quantitative detection standard for the first time. Plasmid DNA is ultrasonically treated into fragments with the lengths of less than 200bp, and is subjected to enzymolysis, a nucleotide marked by a nucleotide standard and an isotope is taken as an internal standard, and mononucleotides are separated and accurately quantified by using high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. An optimal condition for the ultrasonic treatment of the plasmid DNA and a condition for the high-performance liquid chromatographic separation of four nucleotides are created. The method is high in precision and accuracy, namely the nucleotide standard is adopted, and dependence on a DNA standard is eliminated, so that a measurement result can be traced back to a nucleotide certified standard material, and the reliability and a traceable source of the measurement result are ensured. The method can be used for absolutely quantifying the plasmid DNA and preparing the plasmid DNA quantitative detection standard.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
Semi-automatic smearing method of hydrothorax and ascite liquid-base cytology
InactiveCN105675374AReduce in quantityMuch overlapPreparing sample for investigationLiquid base cytologyStaining
The invention discloses a semi-automatic method for producing pleural and ascites liquid-based cytology. After the sample is collected, it is placed in a preservation solution bottle, and the preservation solution bottle is placed on a vibrator, and then passed through a centrifuge tube with a sharp bottom in a centrifuge. Add the cell dispersion liquid into the sampler, absorb and discard the supernatant in the test tube, remove the remaining liquid, and place the centrifuged sample on the sample delivery device of the film maker, and each sample passes through the spectrometer in turn, and the sample is aspirated The sample is placed on the corresponding slide in the transfer module, and the dried slide can be used for Papanicolaou staining or HE staining for cytological diagnosis, and Feulgen special staining for DNA quantitative analysis. The present invention is mainly used to improve and solve the problems existing in the non-cervical cell extraction, including the small number of cells, the overlapping of cells, the long production time, the background impurities of the produced films, and the low degree of automation. The quality of slides is improved, the number and distribution of cells on slides are more uniform, easy to use, and has the value of popularization and application.
Owner:刘崇梅
Method for extracting genomic DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) from whole blood on basis of improved immunomagnetic bead method
The invention relates to a method for extracting genomic DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) from whole blood on basis of an improved immunomagnetic bead method.The method includes steps: erythrocyte splitting, leukocyte splitting, DNA adsorption, DNA purification and DNA elution.DNA concentration and purity are measured by a DNA quantometer, sequencing of PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification products is realized by a sequencer, and HLA (human leukocyte antigen) classification result analysis is performed through relevant analysis software.The method has the advantages of high DNA concentration uniformity, high purity, substantial increase of HLA classification result success rate, and high acceptability of a signal-to-noise ratio, thereby being widely applicable to extraction of the genomic DNA from whole blood samples.
Owner:武汉血液中心
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA quantitative detection kit
ActiveCN110241264ASimple designImprove the detection rateMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesTherapeutic effectHepatitis B virus
The invention provides a hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA quantitative detection kit. The kit utilizes a digital polymerase chain reaction (dPCR) technology to quantitatively detect HBV DNA in biological samples and can be used for monitoring baseline level and change conditions of HBV DNA in patients suffering from hepatitis B and evaluating the response and therapeutic effect of antiviral therapy.
Owner:BEIJING DAWEI BIOTECH LTD
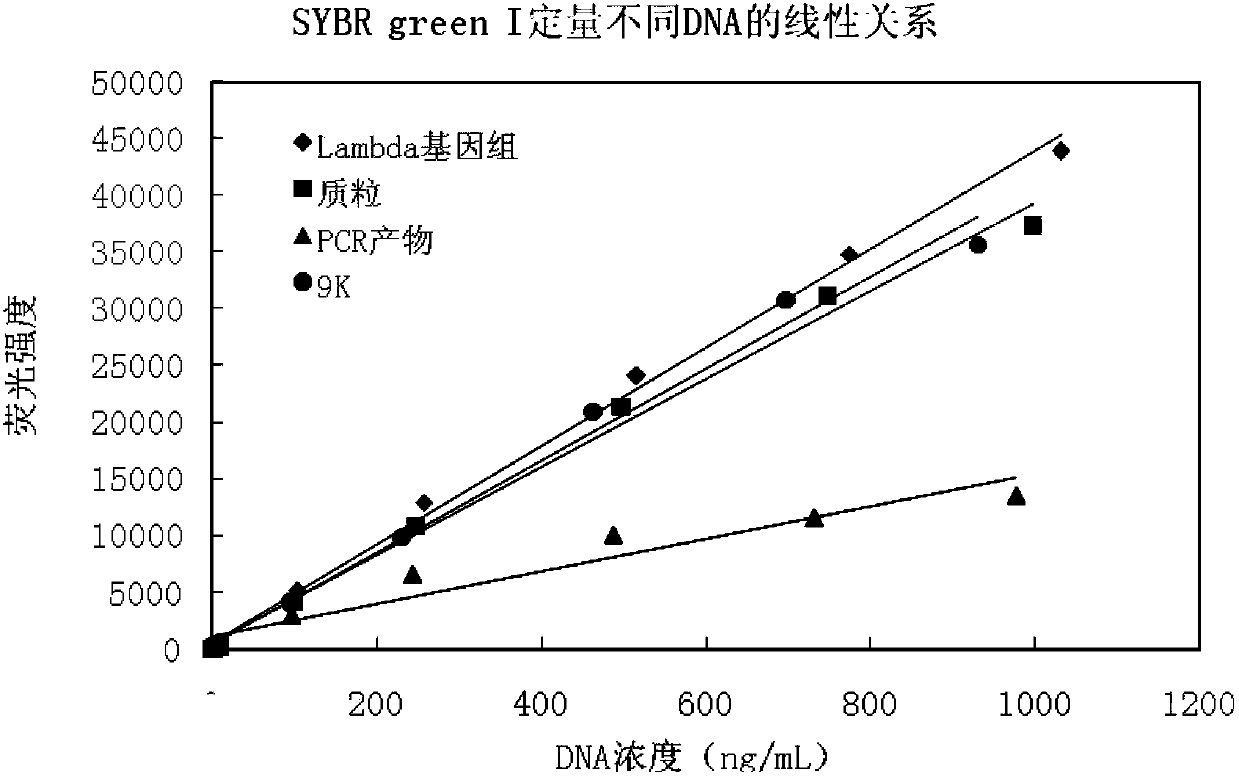
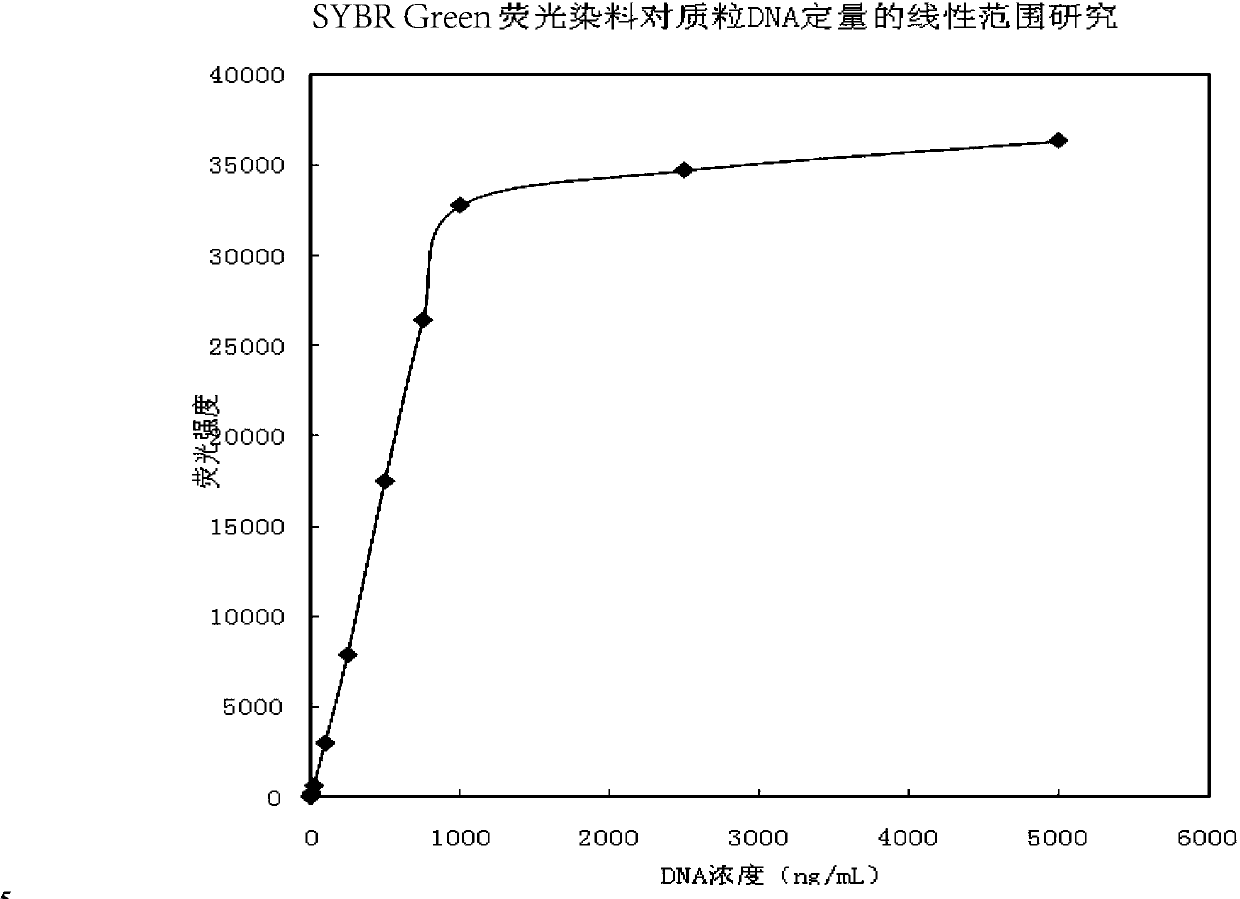
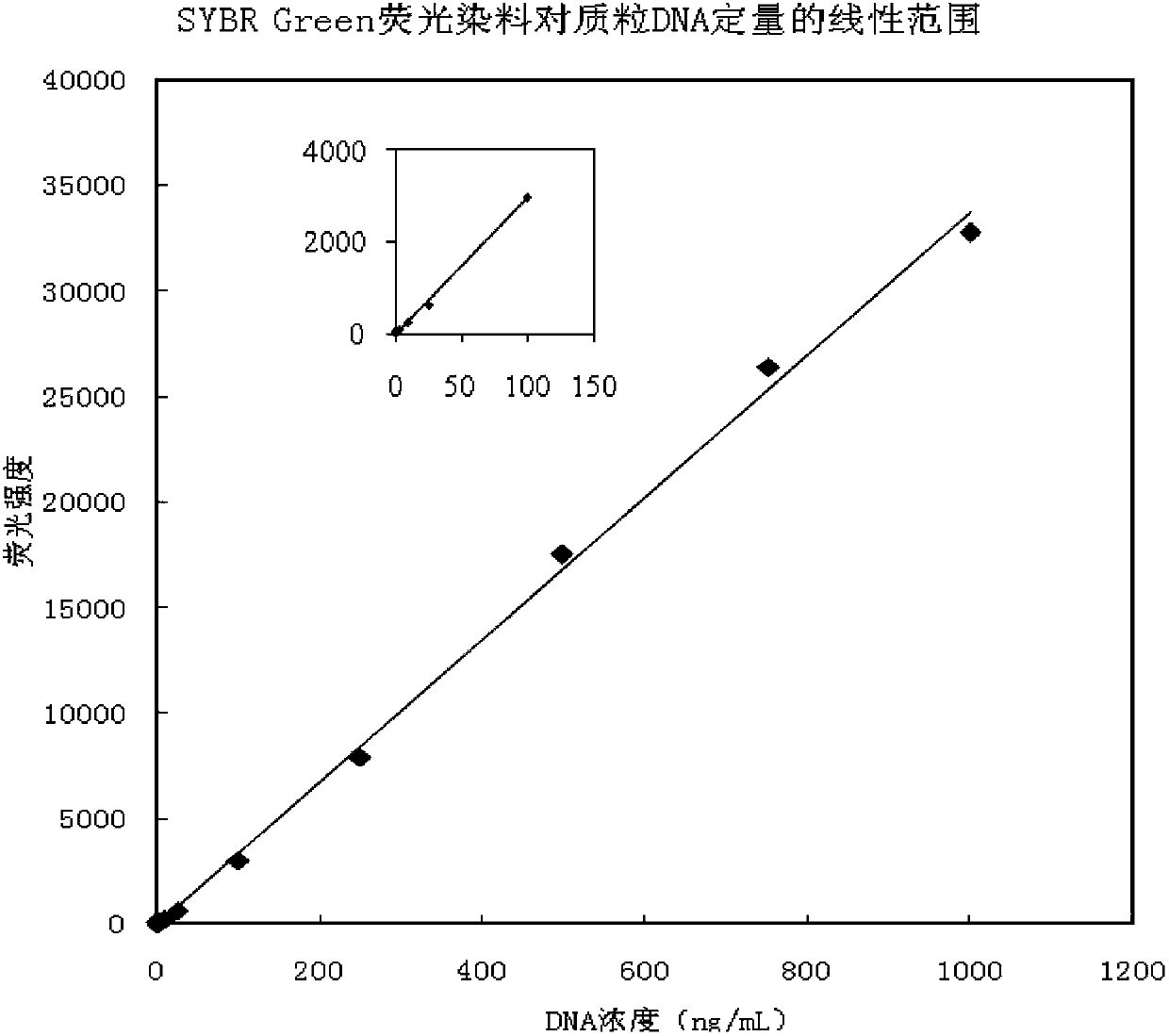
DNA quantitative detection method and kit using SYBR Green fluorescent dye
InactiveCN103865984AMake up for the disadvantage of not being able to quantify plasmid DNAHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansFluorescenceGenomic DNA
The invention relates to a DNA quantitative detection method and a detection kit. The DNA quantitative detection method establishes the conditions of SYBR Green I fluorescent dye method for DNA quantification to obtain the linear range and sensitivity of the method, and the accurate content of a DNA sample can be fast and accurately obtained. According to the DNA quantitative detection method, plasmid molecules and genomic DNA standard substances are also constructed and prepared, two DNA standard substances are accurately quantified by use of a digital PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method, the standard plasmid and genomic DNA can be used for gradient dilution to obtain a standard curve of the SYBR Green I fluorescent dye method for the DNA quantification, and the accurate content of a to-be-tested DNA sample can be obtained according to the standard curve.
Owner:王泽广
Methods for quantitating DNA using digital multiple displacement amplification
ActiveUS10487354B2Improve throughput and reliabilityReduce impactMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDNADye molecule
The present invention relates to methods of quantifying nucleic acids involving (a) contacting a sample to be tested with whole-genome amplification (WGA) reaction components and a dye molecule to form a reaction sample, wherein the dye molecule detects the nucleic acid; (b) partitioning the reaction sample wherein each partitioned reaction sample corresponds to a single reaction; (c) allowing the reaction to occur in the partitioned reaction sample and (d) determining the number of partitioned reaction samples having the dye molecule, wherein the dye molecule indicates the presence of the nucleic acid; thereby quantifying the nucleic acid in the sample to be tested.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +1
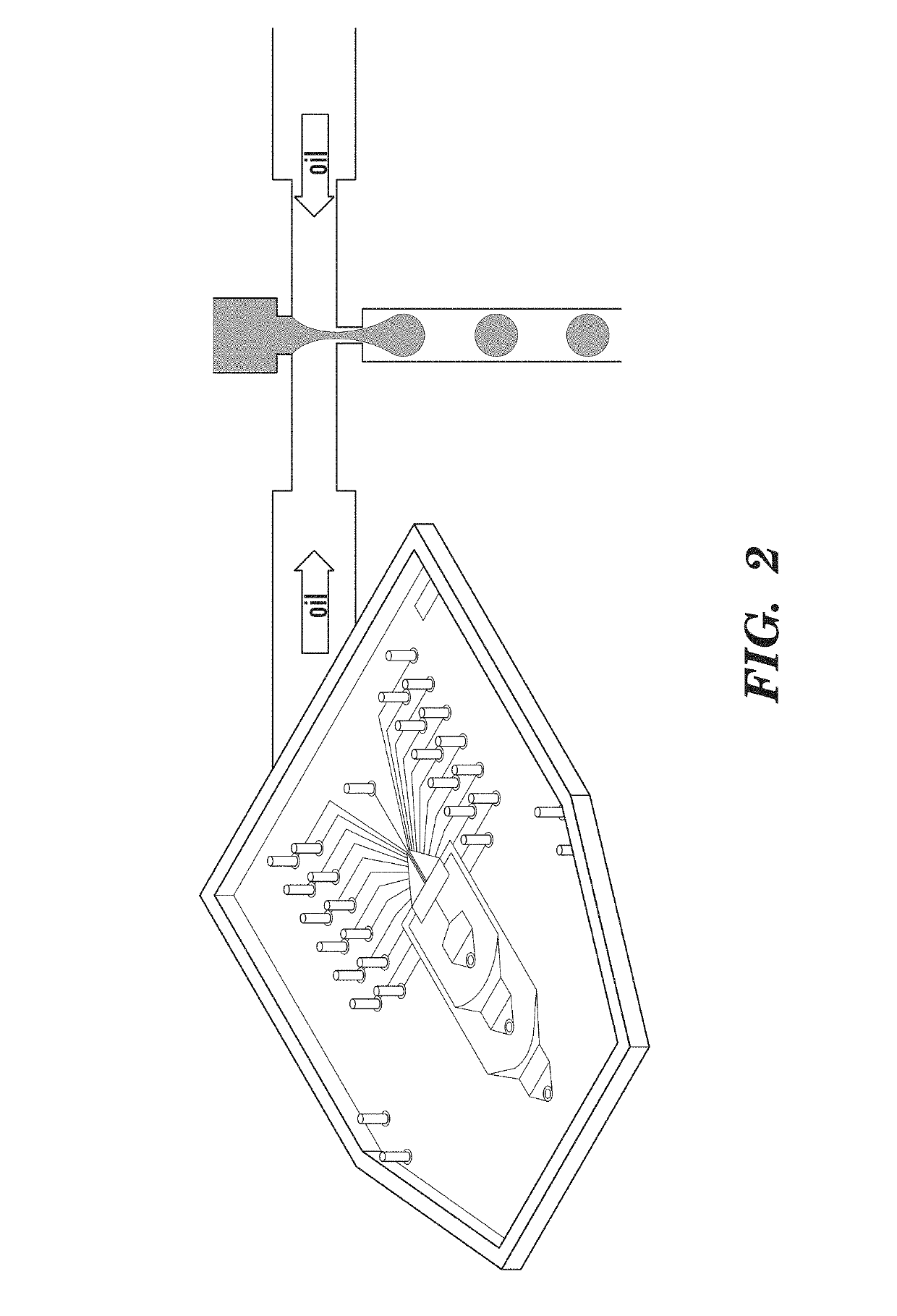
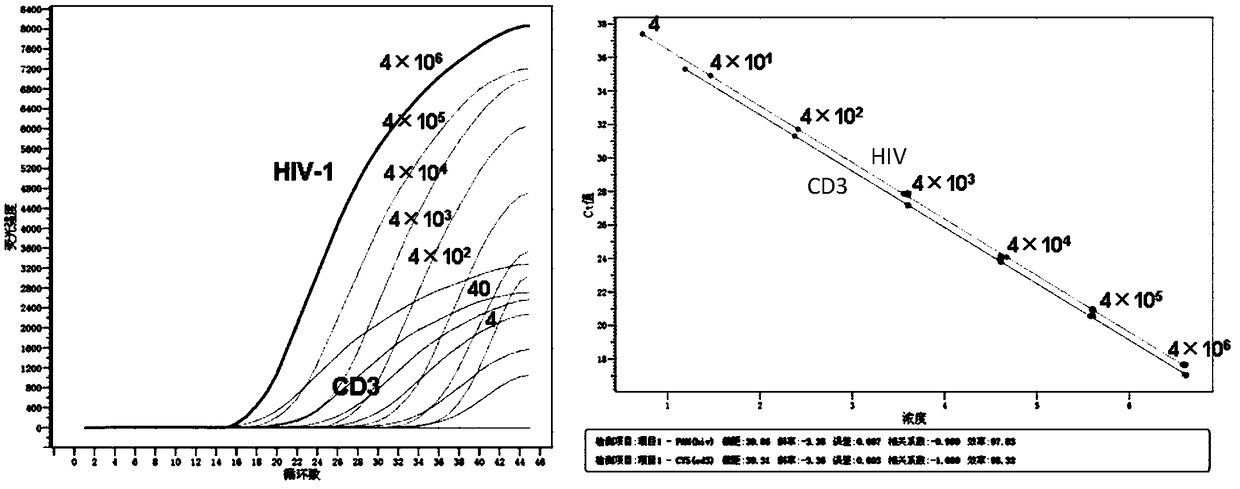
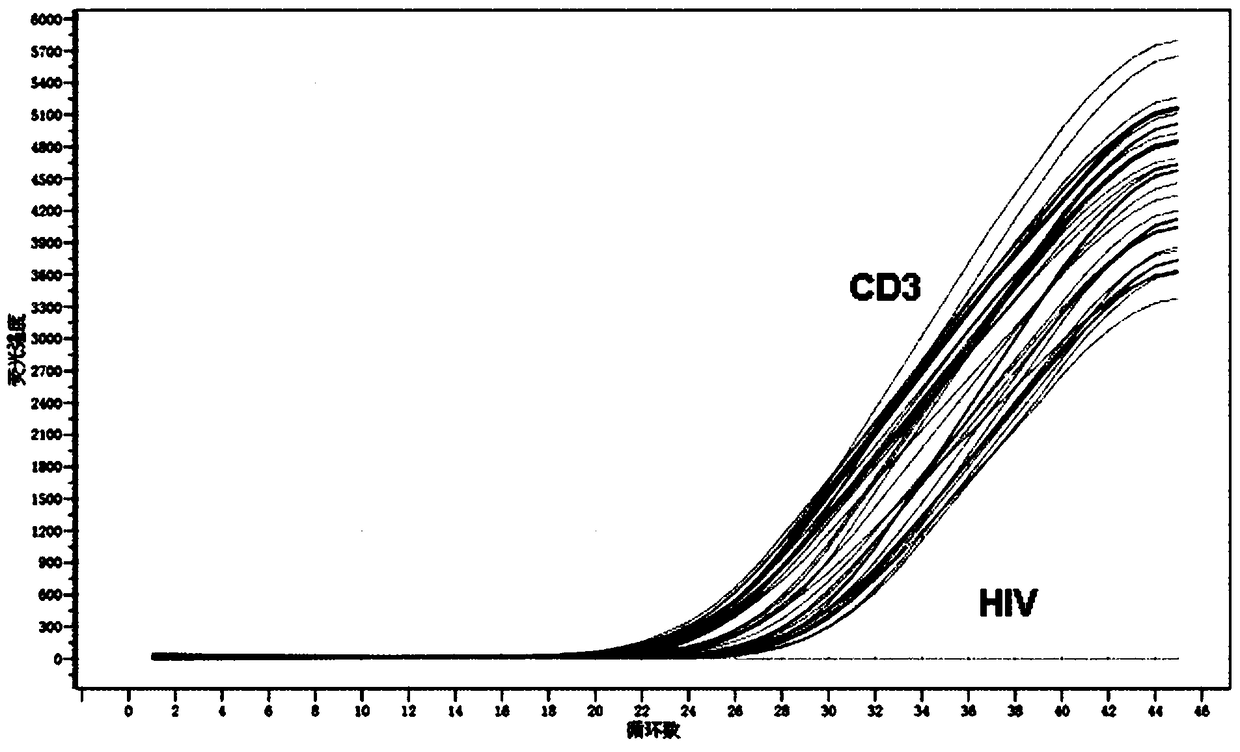
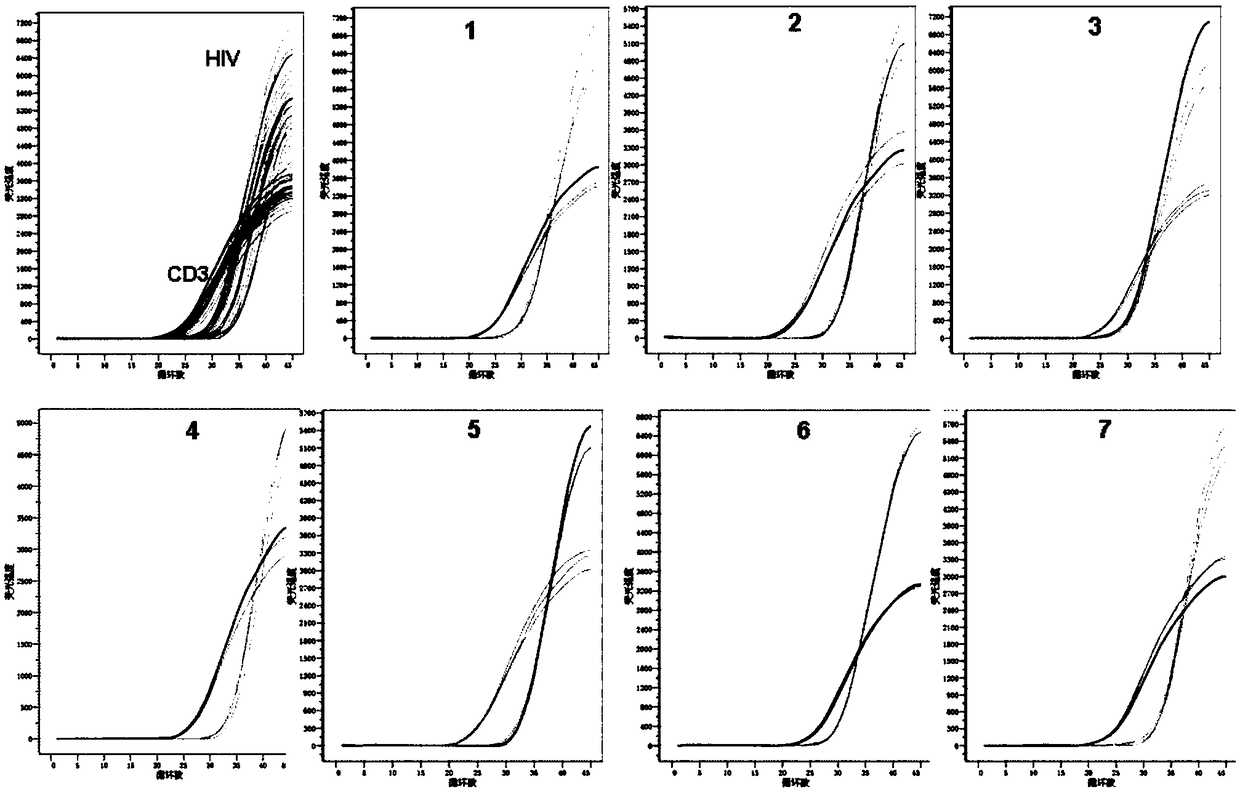
Primer pair, probe and kit used for quantitative detection total DNAs of HIV-1 and capable of covering multiple subtypes of HIV-1
ActiveCN108998570ABroad Subtype Detection CoverageOvercome operabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceHIV positives
The invention discloses a primer pair, probe and kit used for quantitative detection total DNAs of HIV-1 and capable of covering multiple subtypes of HIV-1. The sequence of the upstream primer HIV-U1of the primer pair is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1; the sequence of the downstream primer HIV-R1 of the primer pair is as shown in SEQ ID No. 2; the sequence of the probe Probe-HIV is as shown in SEQ ID No. 3. According to the invention, degenerate primers are utilized for high-sensitivity high-specificity detection of HIV DNA, and 12 common subtypes of HIV and rare HIV subtypes can be successfully detected, so the detection kit of the invention has wider subtype detection coverage compared with other conventional commercial detection kits. The primer pair, probe and kit provided by the inventioncan be used for quantification of total HIV DNAs of current prevalent HIV strains in China. A method provided by the invention is simple to operate, can complete procedures from sample DNA extractionto real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR amplification in one day, has low price, can be used for monitoring the persistent infection status of HIV-infected individuals in large cohorts, evaluating the effect of cART treatment, and is also applicable to auxiliary diagnosis of early HIV infection and diagnosis of neonatal infection in HIV-positive mothers.
Owner:BEIJING YOUAN HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Method for quickly and quantitatively detecting mammalian cell deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA)
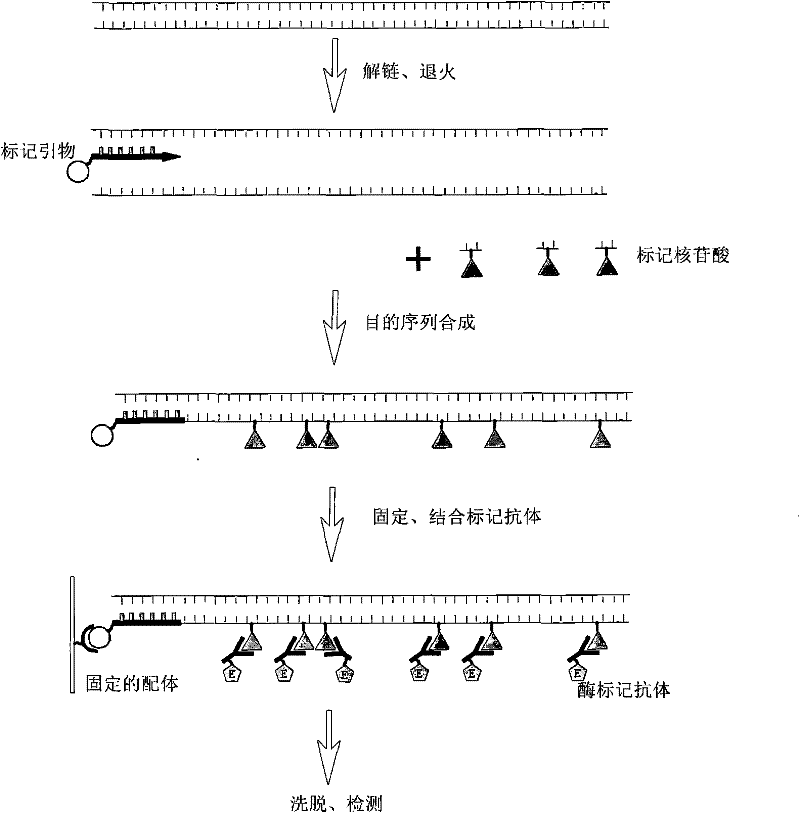
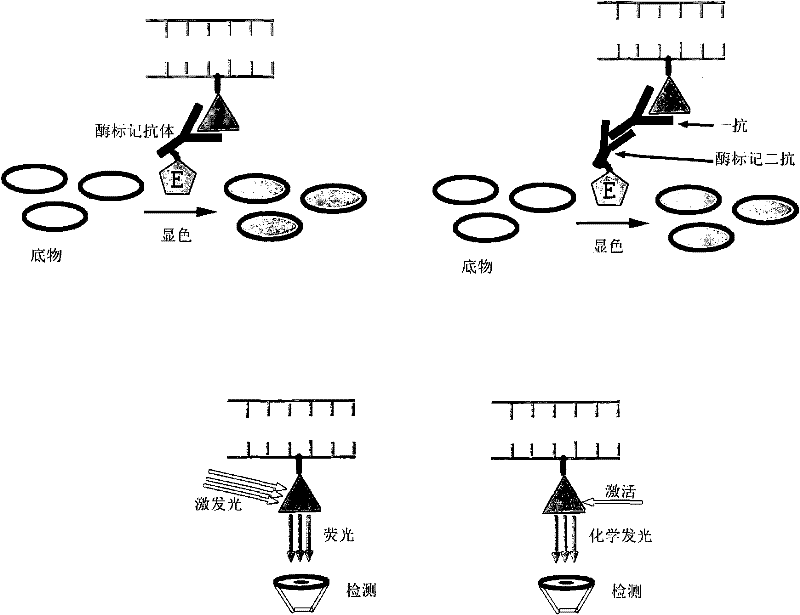
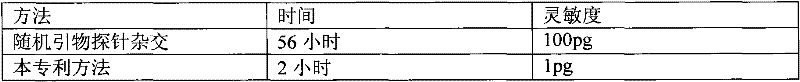
The invention relates to a method for quantitatively detecting mammalian cell deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA), which is used for detecting host cell DNA remained in a biological product which takes mammalian cells as matrixes. Multicopy genes in a mammalian cell genome are used as detection tag sequence templates, DNA polymerase, a molecular marker primer and molecular marker DNA are synthesized into a detection purpose sequence, and the detection purpose sequence is quantitatively analyzed. Compared with a molecular hybrid method, the method has the characteristics of short detection time (a detection process can be finished within two hours), stable detection results and high sensitivity.
Owner:BEIJING XINYI YUANCHENG BIOLOGICAL TECH
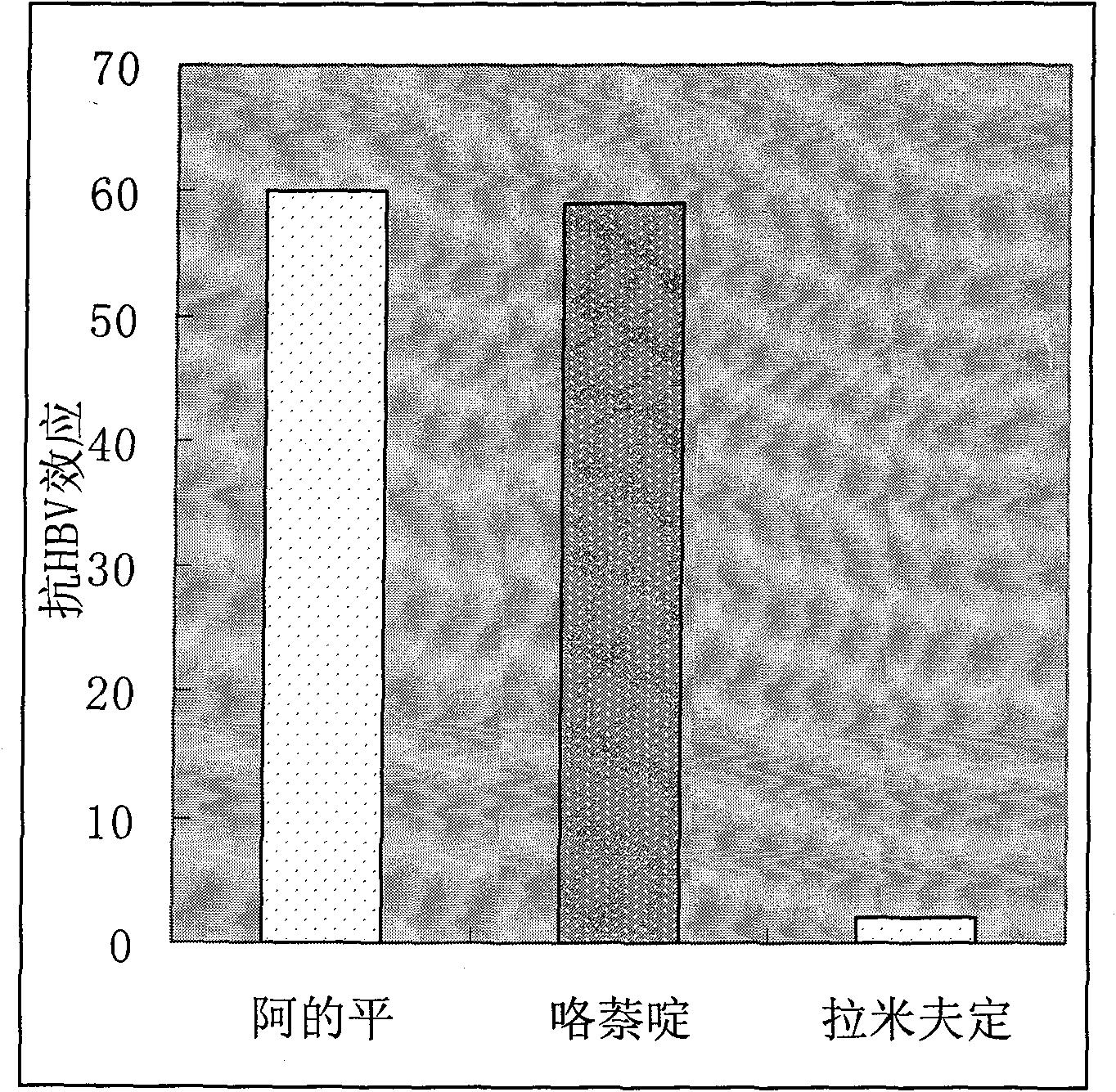
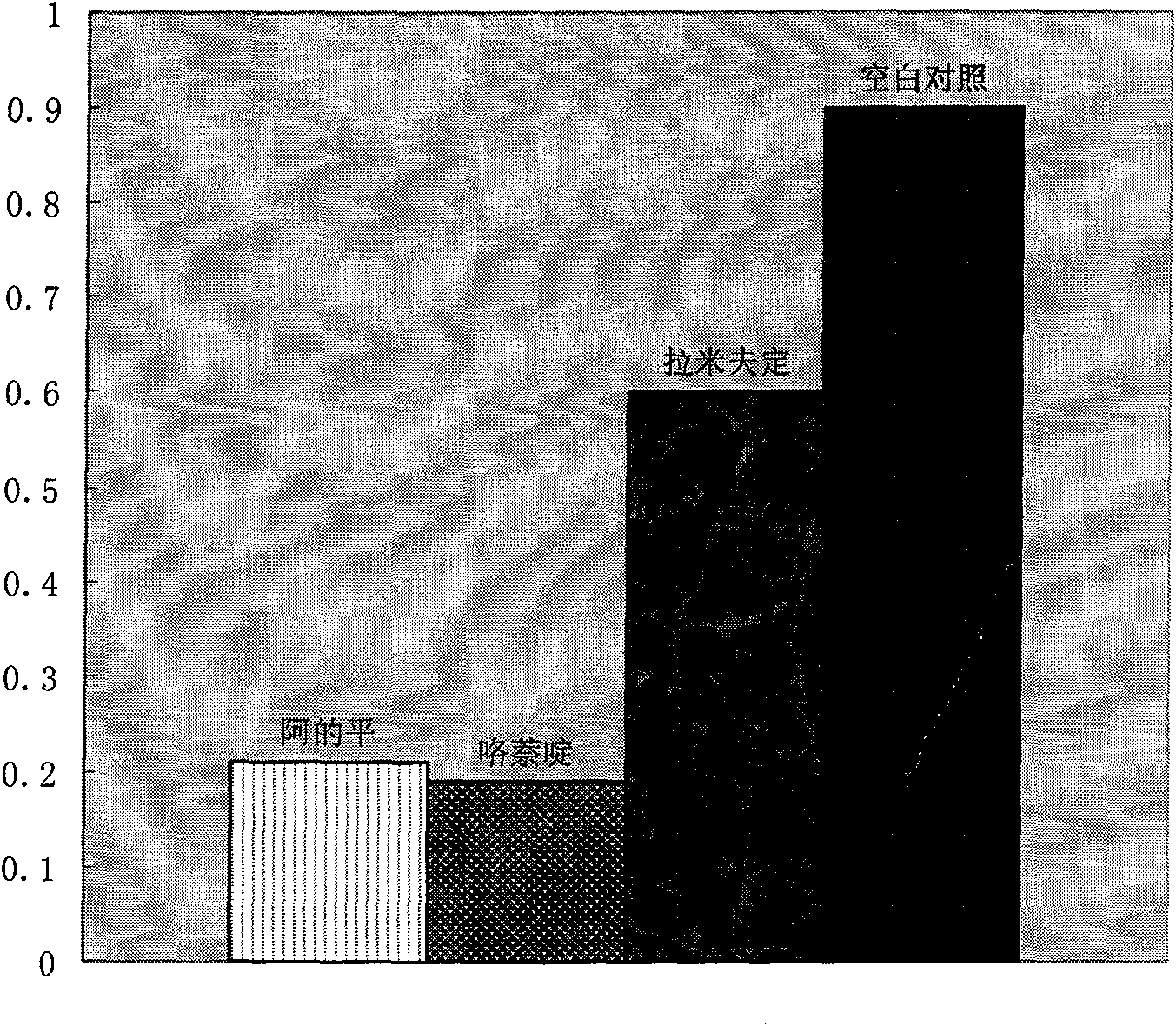
Therapeutical effect of atabrine and substitutes thereof on hepatitis B
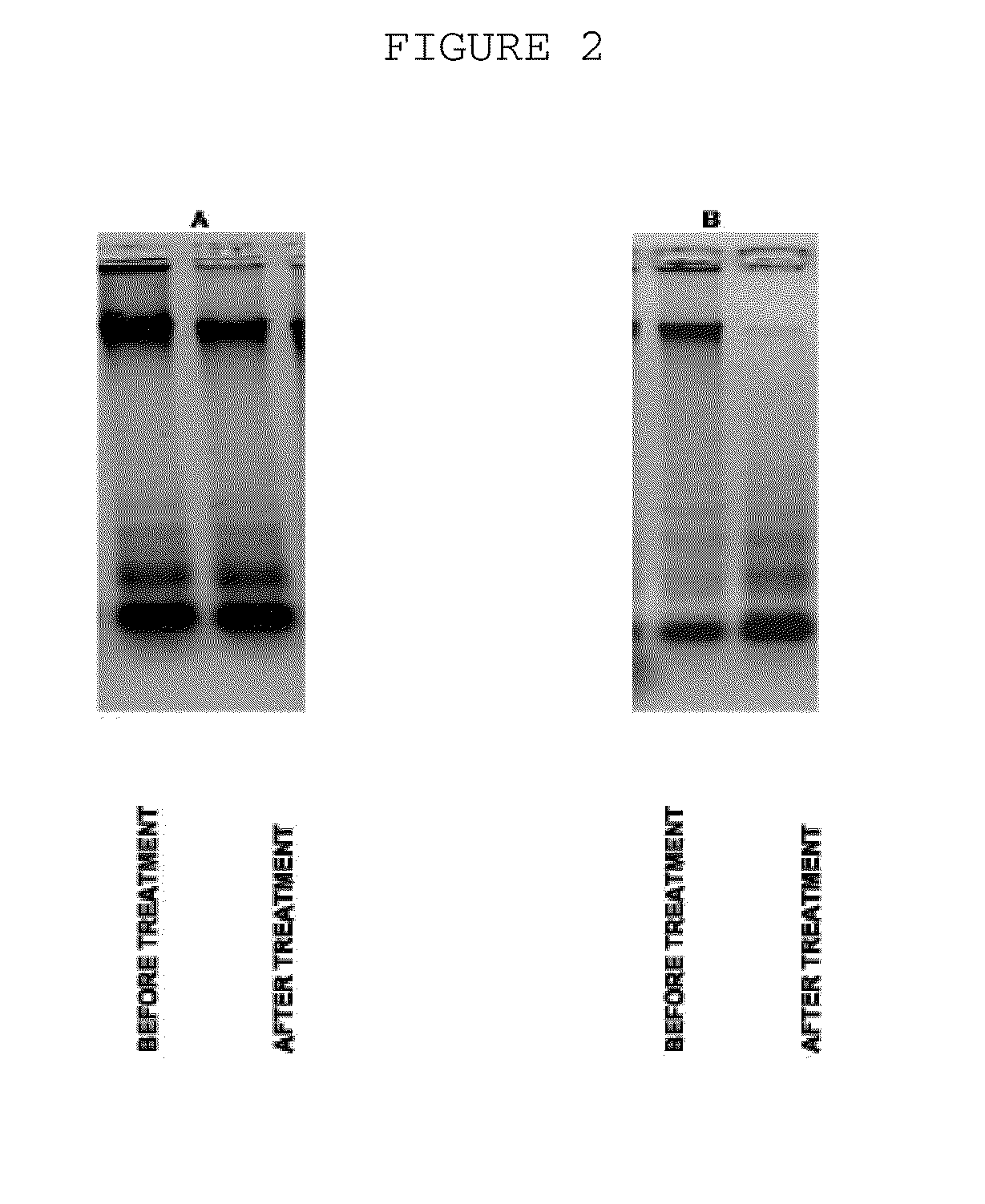
InactiveCN101856355ALower titerInhibition killOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsAntigenNorthern blot
Owner:蔡荣 +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com