Body fluid circulation DNA quantitative determination method and kit
A quantitative detection method and real-time fluorescence quantitative technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problems affecting the precision and stability of quantitative results, low detection sensitivity, and large differences between tubes.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
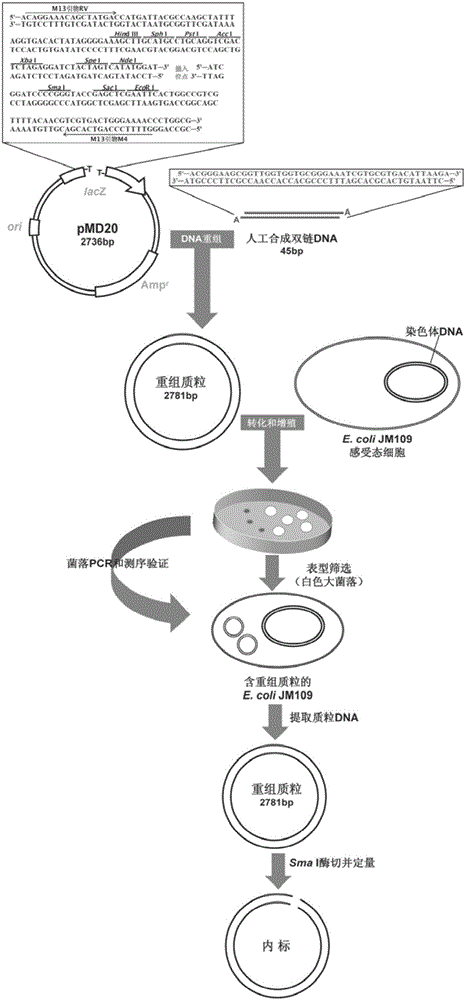
[0036] (1) Synthesis of internal standard
[0037] Artificially synthesized linear double-stranded DNA fragments with "A" cohesive ends, the sequence is as follows:
[0038] 5'-ACGGGAAGCGGTTGGTGGTGCGGGAAATCGTGCGTGACATTAAGA-3'
[0039] 3’-ATGCCCTT CGCCAACCACCACGCCC TTT AGCACGCACTGTAATTC-5’
[0040] Dilute the two artificially designed complementary oligonucleotides to 20 μmol / L with Tris-EDTA buffer, mix them with equal volumes, put them in a boiling water bath at 100°C for 10 minutes, and then let them cool naturally at room temperature to obtain linear double-stranded DNA fragments; Recombine the linear double-stranded DNA fragment into the plasmid vector T-Vector pMD20 (for the insertion site, see figure 2 ), transfected into E.coli JM109 competent cells, cultured in vitro and inoculated on L-agar plate medium containing X-Gal, IPTG, Amp, directly screened large white colonies containing recombinant clones, and then sequenced by M13 Universal primers RV and M4 were used ...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Example 3 Detection of Plasma Samples from Healthy Examiners
[0078] 400 healthy subjects, aged 25-60 years, with an average age of 43 years, 200 males and 200 females. Collect EDTA-K 2 Anticoagulated peripheral venous blood was separated by two-step centrifugation to obtain cell-free plasma samples. The plasma DNA was extracted using the magnetic bead method kit, and quantitatively determined by the method of the present invention, the internal standard method in the early stage, the traditional external standard method and the fluorescence method. The results Such as Figure 6 . The detection result of the method of the present invention is significantly higher than that of the previous internal standard method, traditional external standard method and fluorescence method, and the difference is statistically significant (P<0.001). The present invention eliminates the measurement error caused by the loss of nucleic acid extraction through the internal reference fun...
Embodiment 4
[0079] Example 4 Detection of healthy person's urine sample
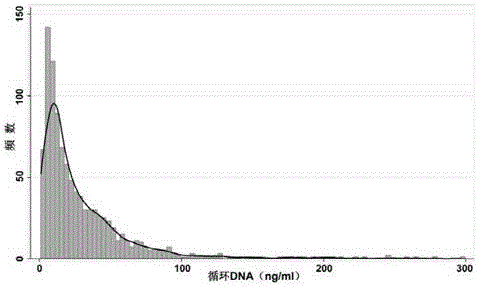
[0080] 1000 healthy persons, aged 25-60 years, with an average age of 42 years, 500 males and 500 females. Collect morning urine specimens, two-step centrifugal separation to obtain cell-free urine specimens, use the magnetic bead method kit to extract urine DNA, and use the method of the present invention for quantitative determination. The results are as follows: Figure 7 . The quantitative range of urine DNA in healthy individuals ranged from 1.0 to 296.4 ng / ml (median: 18.1 ng / ml; interquartile range: 30.5 ng / ml), of which 84% had urine DNA below 50 ng / ml, and 12 % was between 50-100ng / ml, 4% exceeded 100ng / ml, and the urine DNA level was positively skewed in the 1000 cases of healthy people ( Figure 7 ). There was no statistically significant difference in urine DNA content between different sex or age groups.
[0081] Nanjing Meclelin Biomedical Technology Co., Ltd.
[0082] Method and Kit for Quantit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com