Patents
Literature
214 results about "Healthy subjects" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
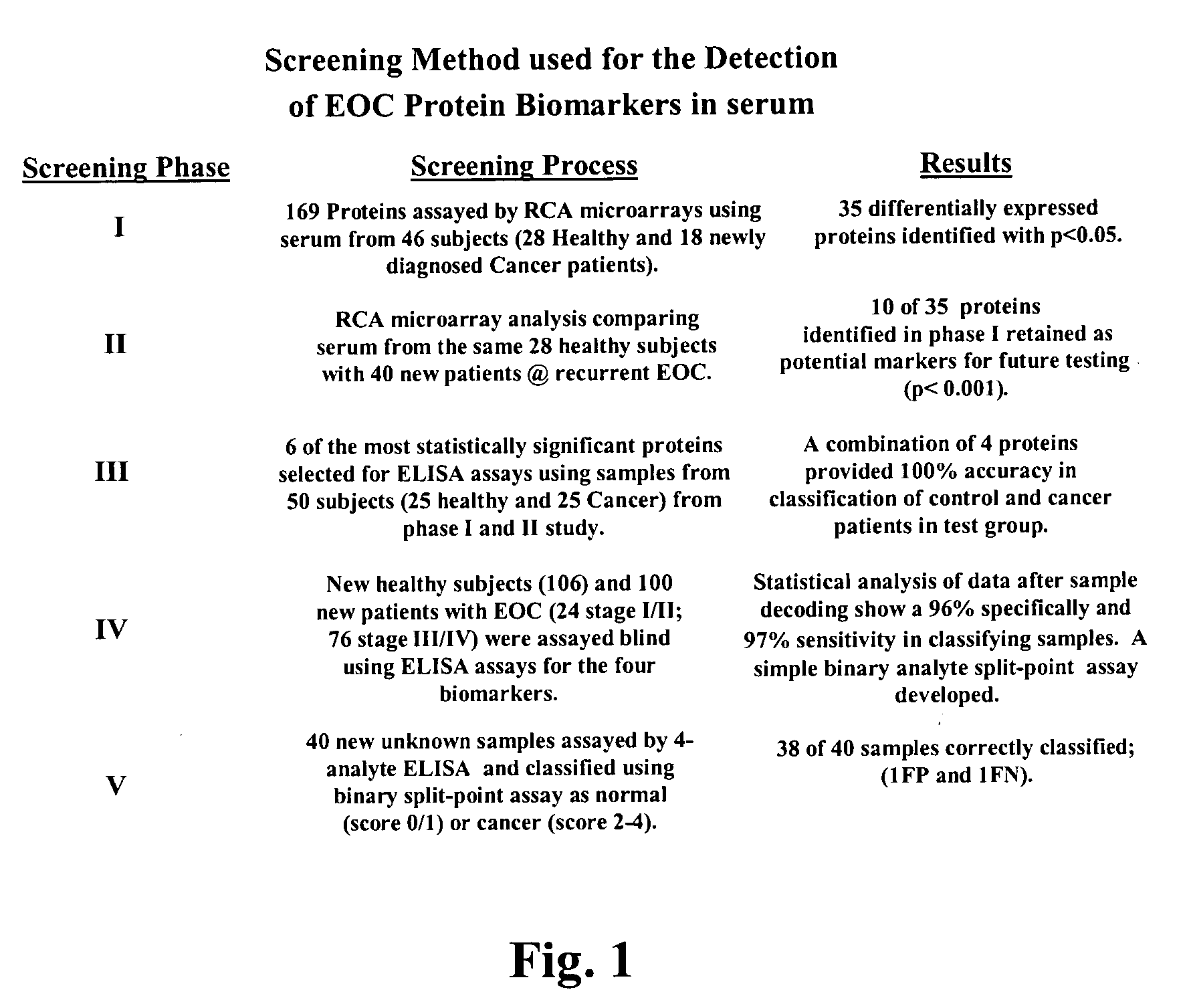
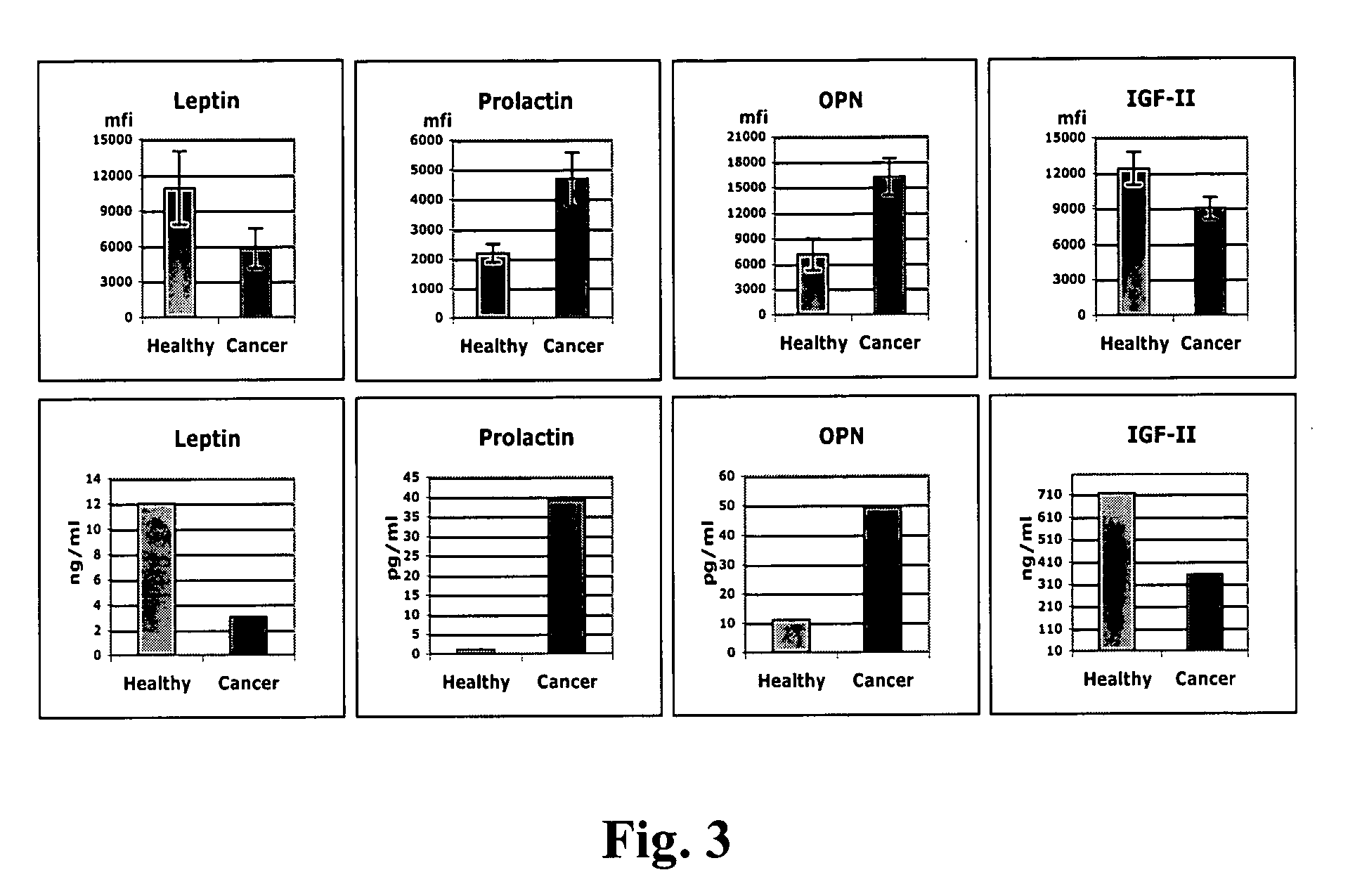
Identification of cancer protein biomarkers using proteomic techniques
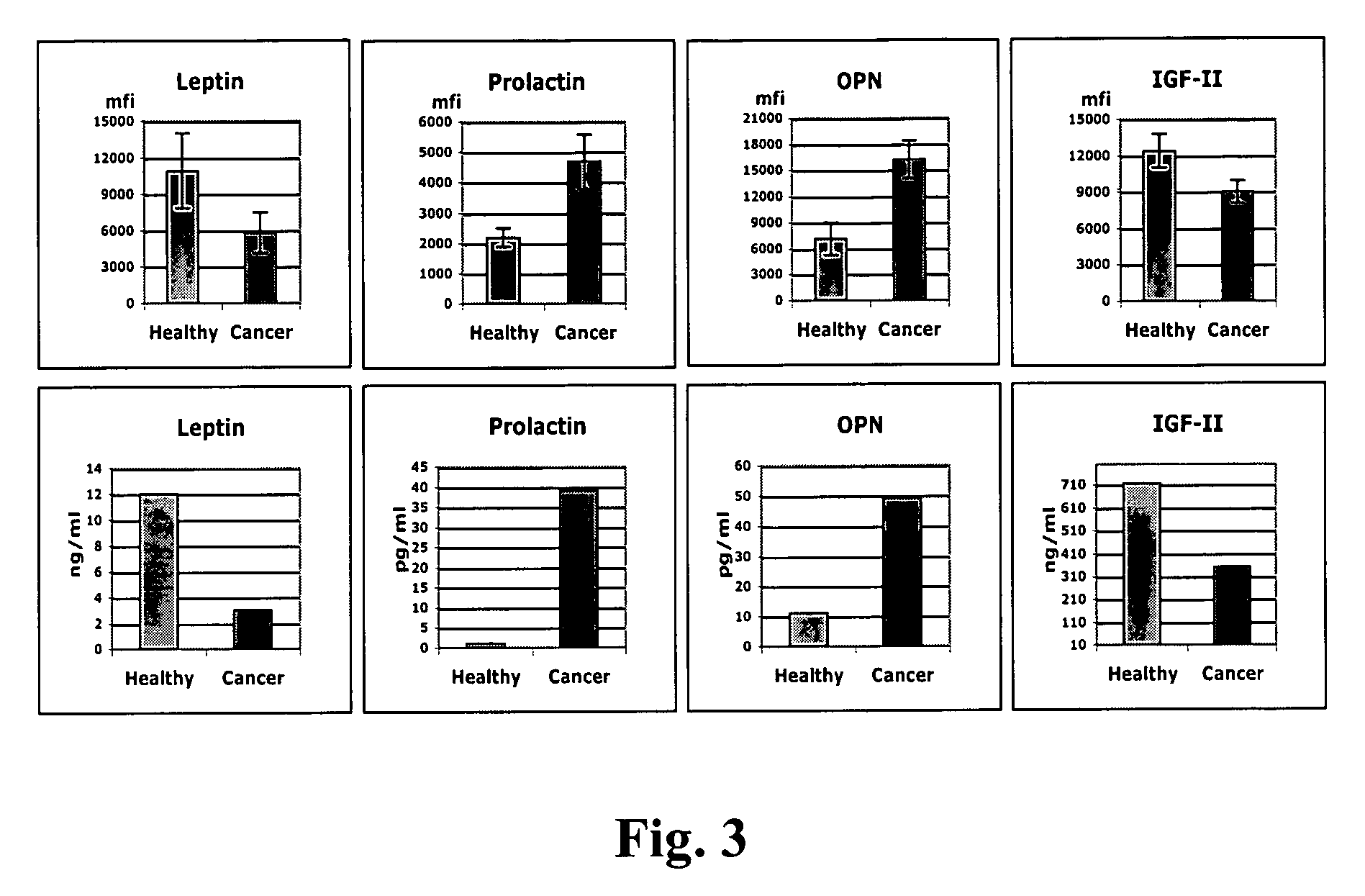
The claimed invention describes methods to diagnose or aid in the diagnosis of cancer. The claimed methods are based on the identification of biomarkers which are particularly well suited to discriminate between cancer subjects and healthy subjects. These biomarkers were identified using a unique and novel screening method described herein. The biomarkers identified herein can also be used in the prognosis and monitoring of cancer. The invention comprises the use of leptin, prolactin, OPN and IGF-II for diagnosing, prognosis and monitoring of ovarian cancer.
Owner:YALE UNIV
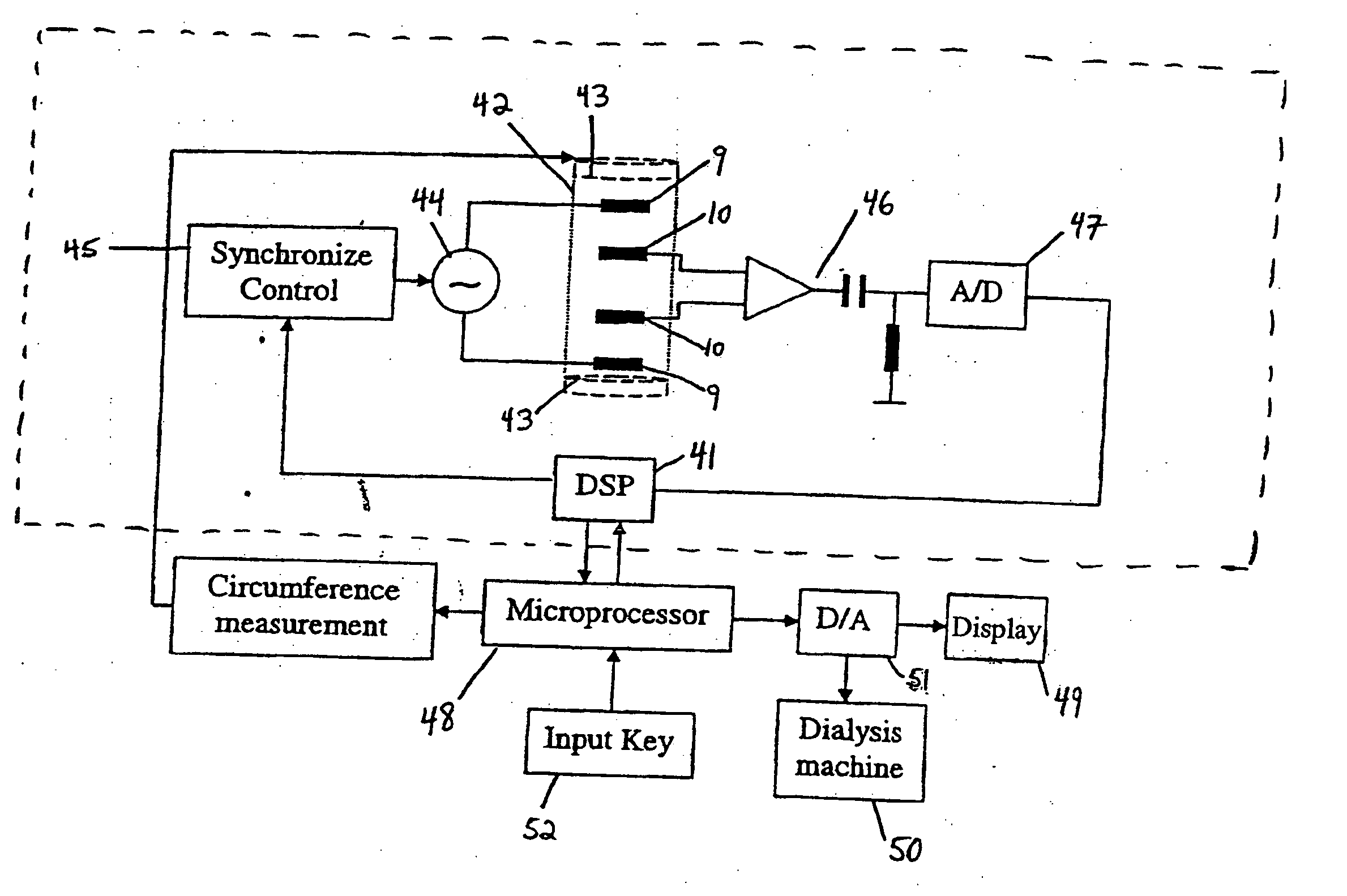
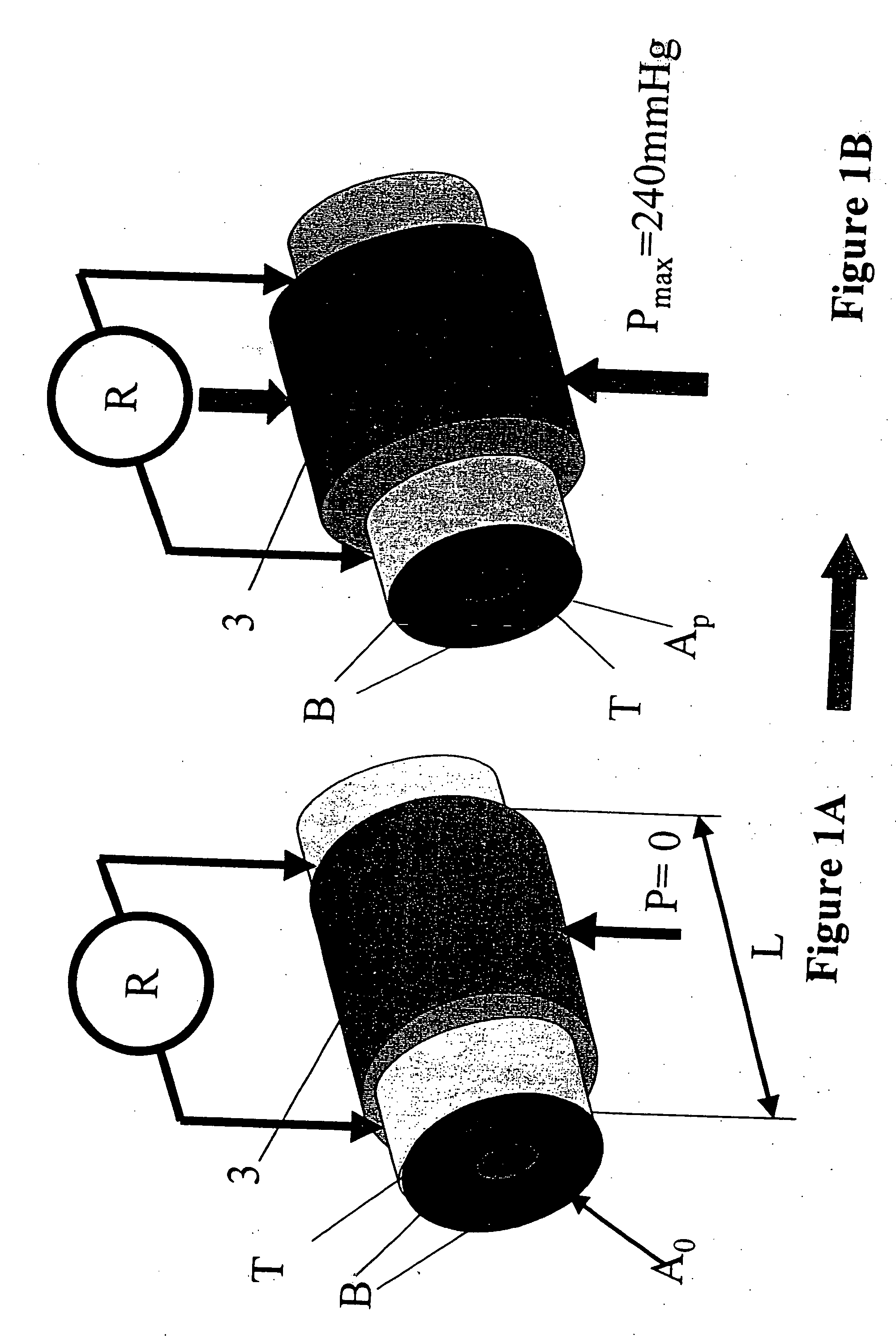
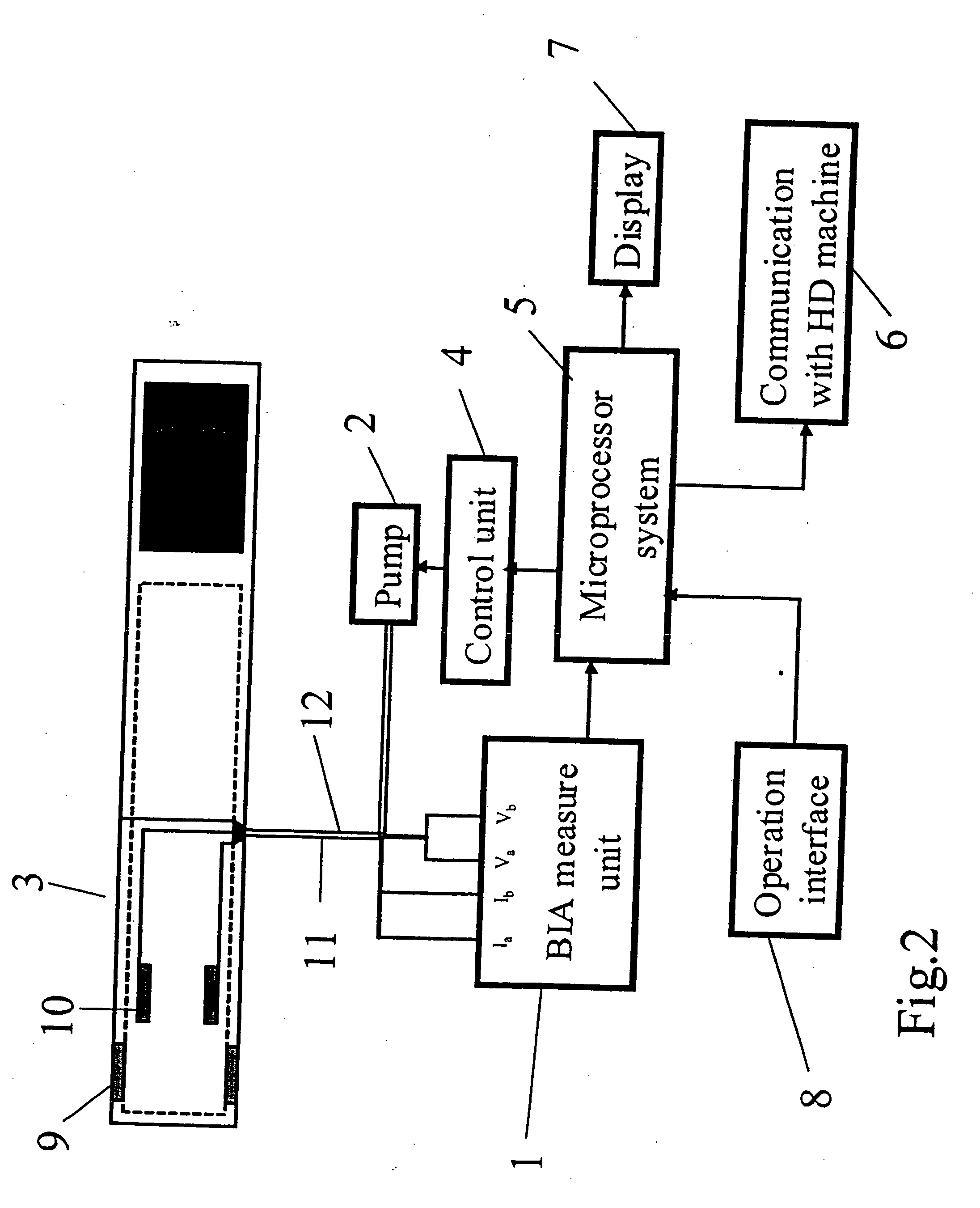
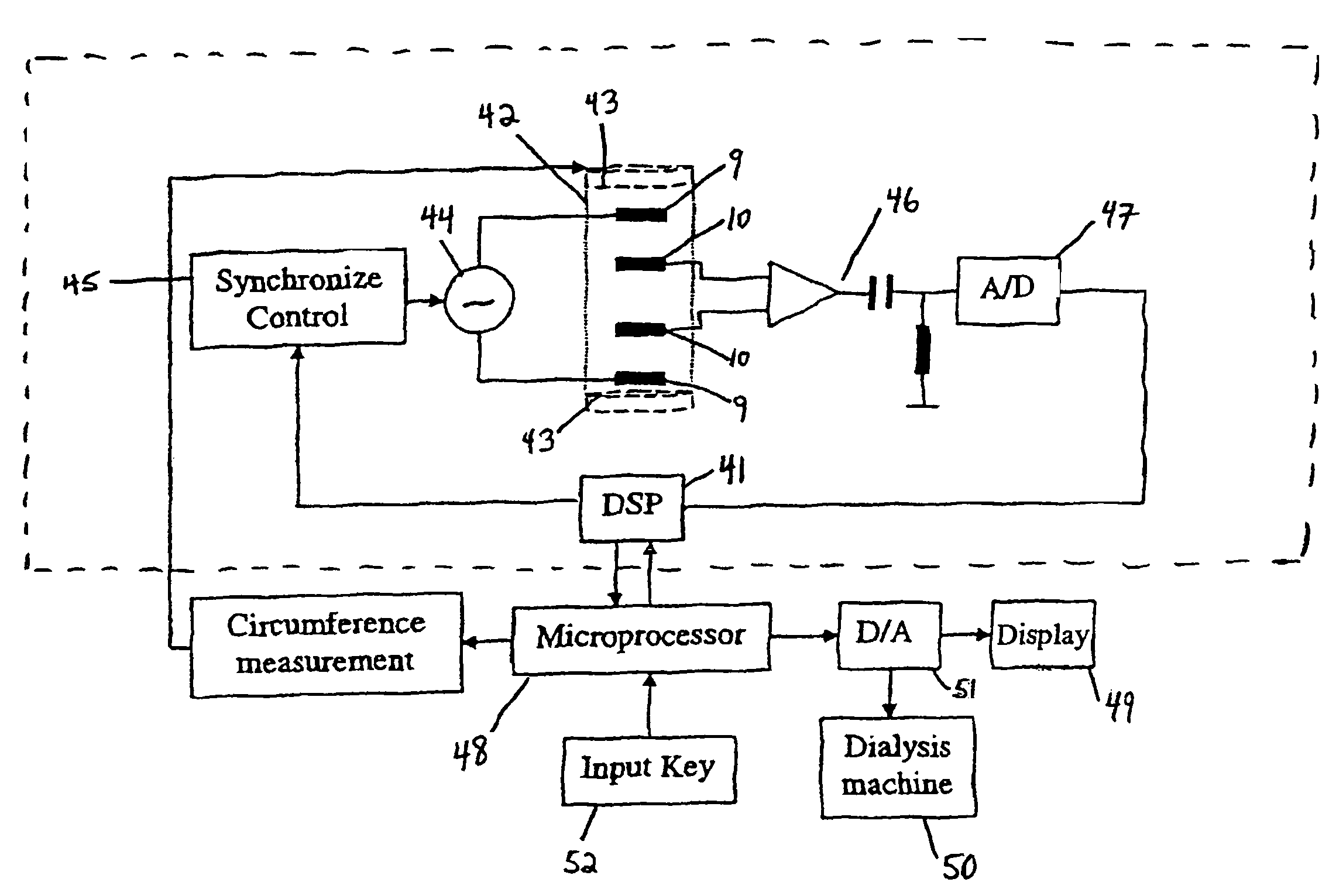
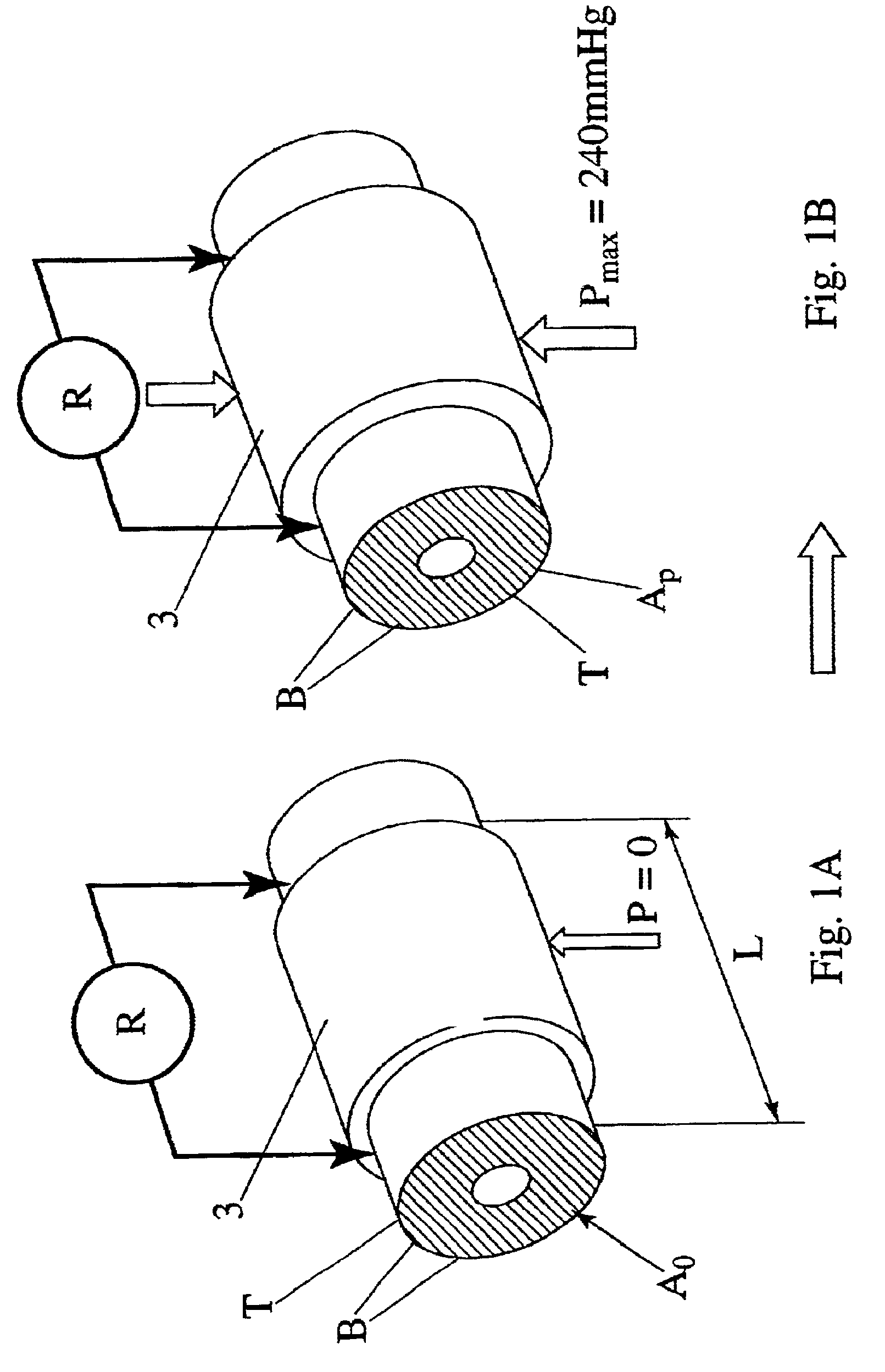
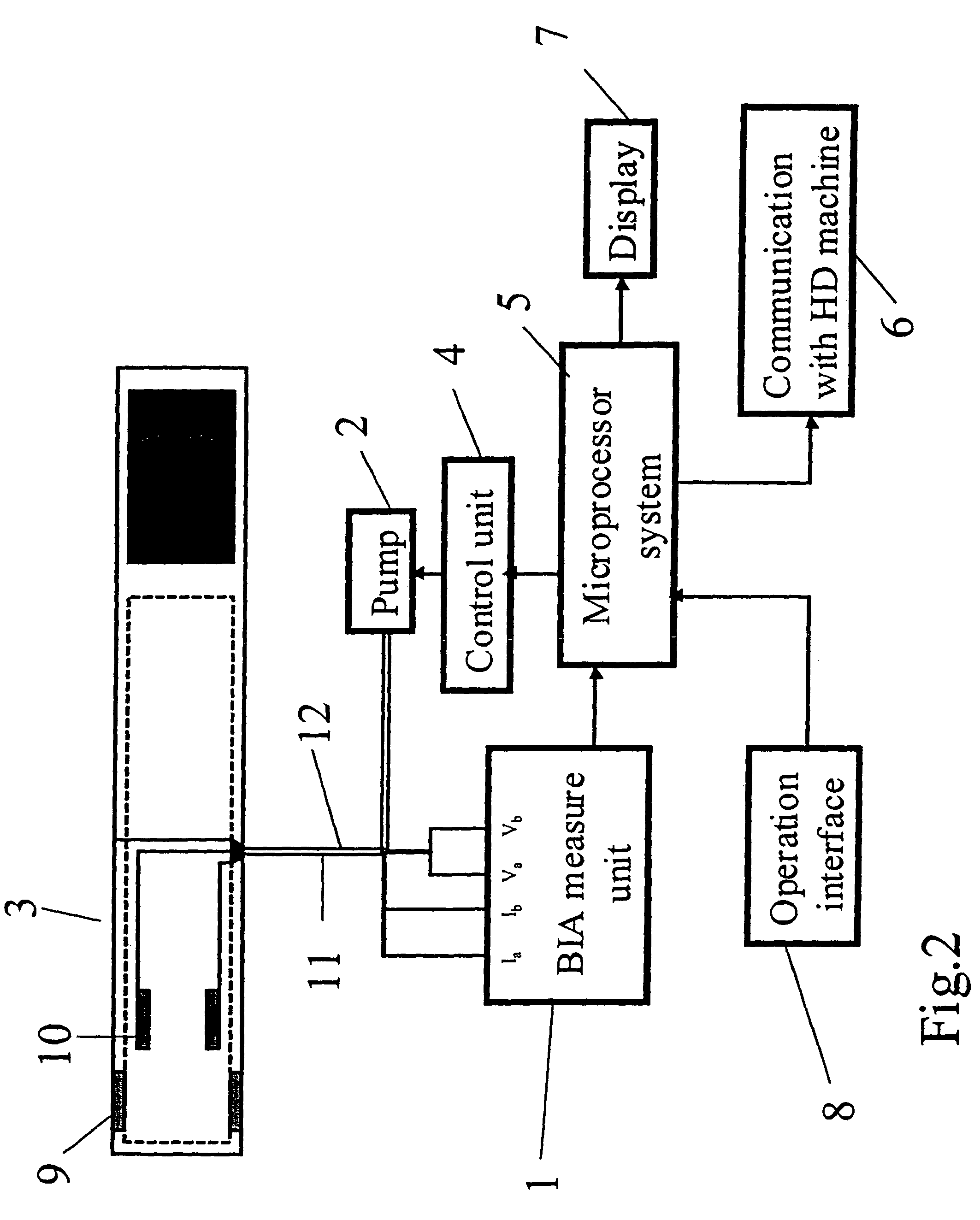
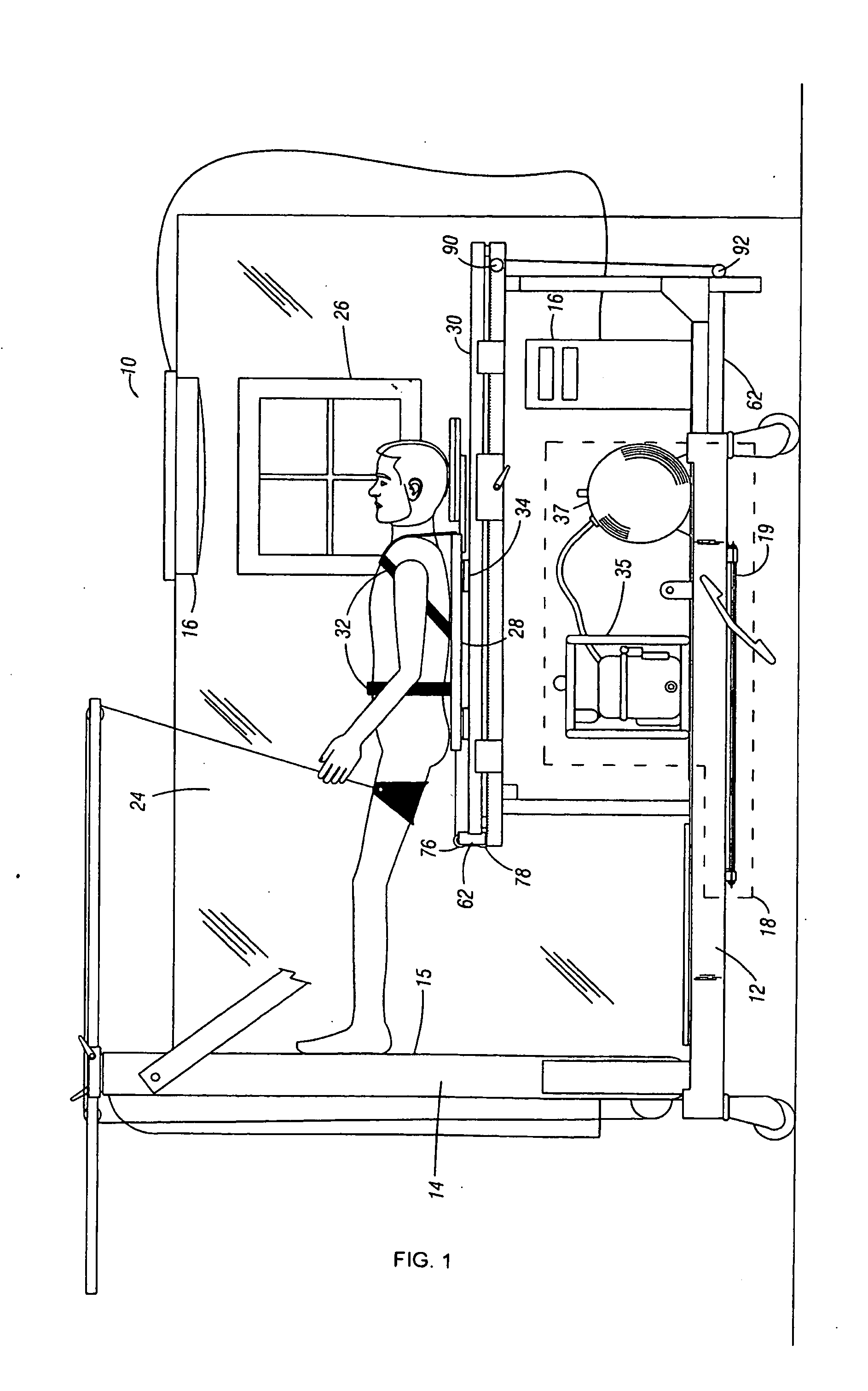
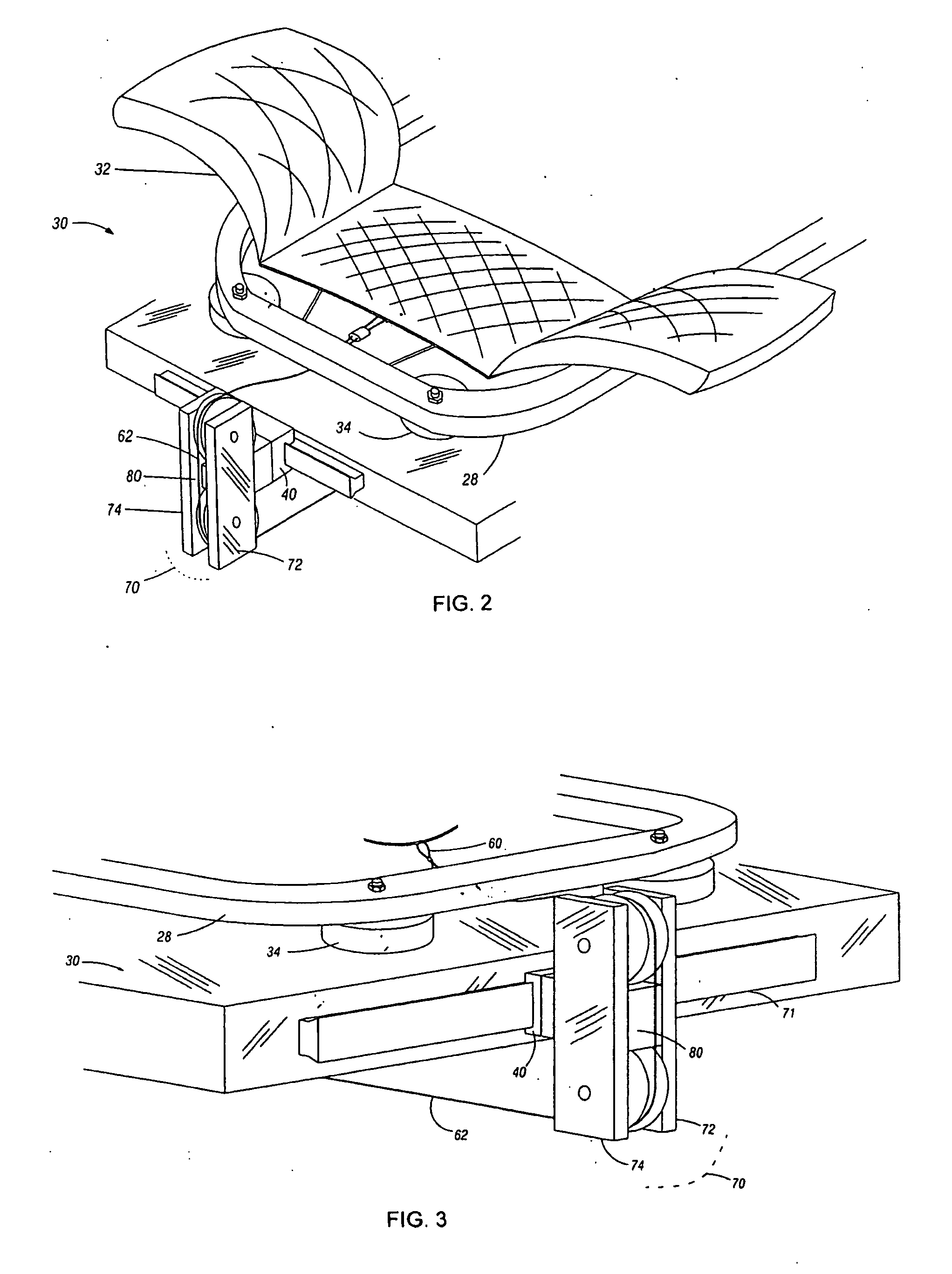
Device and method for the determination of dry weight by continuous measurement of resistance and calculation of circumference in a body segment using segmental bioimpedance analysis
InactiveUS20060122540A1Person identificationEvaluation of blood vesselsElectrical resistance and conductanceContinuous measurement
A method and device for continuously calculating the circumference of a body segment is based on the continuous measurement of the extracellular resistance of the body segment. Also disclosed is a method and device for determining the dry weight of a dialysis patient wherein the time at which the dry weight of the patient has been achieved is identified as the time at which the patient's normalized resistivity as a function of time (ρN(t)) is greater than or equal to a minimum level of normalized resistivity in healthy subjects (ρN,H).
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
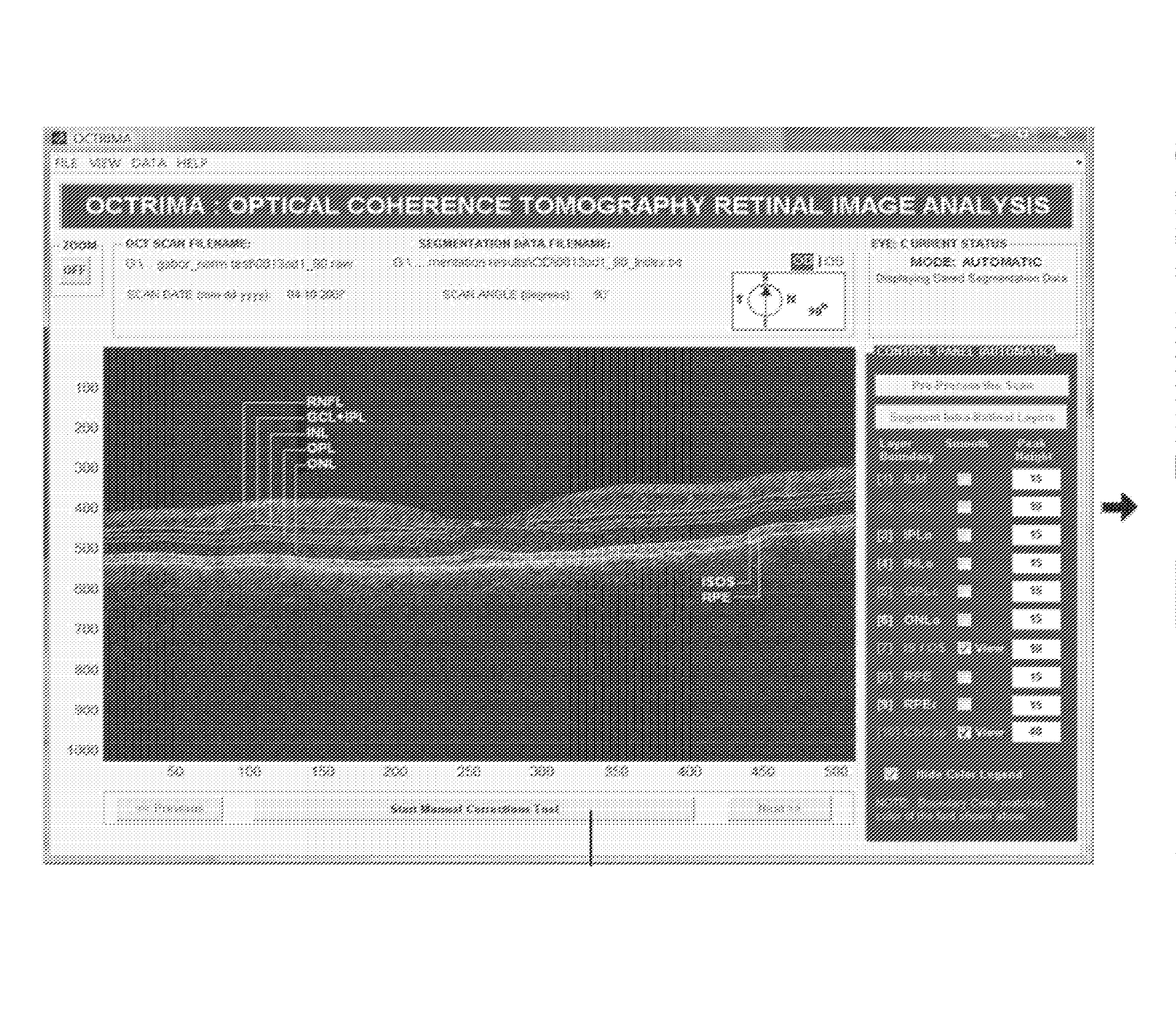
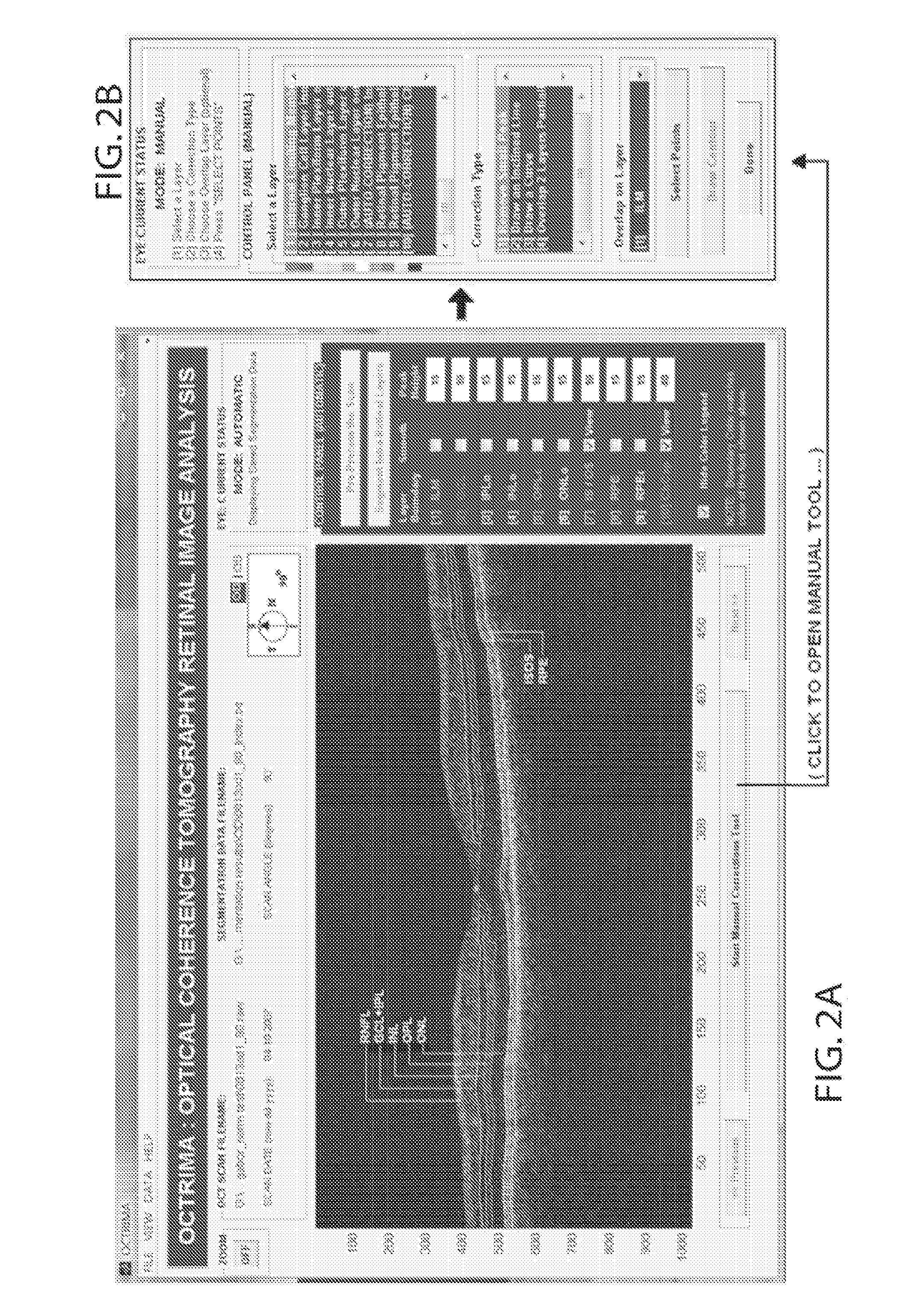
System and Method for Early Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy Using Optical Coherence Tomography
A system for the imaging, processing and evaluation of tissues provides prognostic and diagnostic details regarding diseased tissue. A set of quantitative measures were developed and integrated in an image-base analysis software tool designed for OCT images. The system and methods in this invention is significant because it allows assessing the optical properties and structure morphology differences between normal healthy subjects and diabetic patients with retinopathy up to ETDRS level 35 and without retinopathy.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
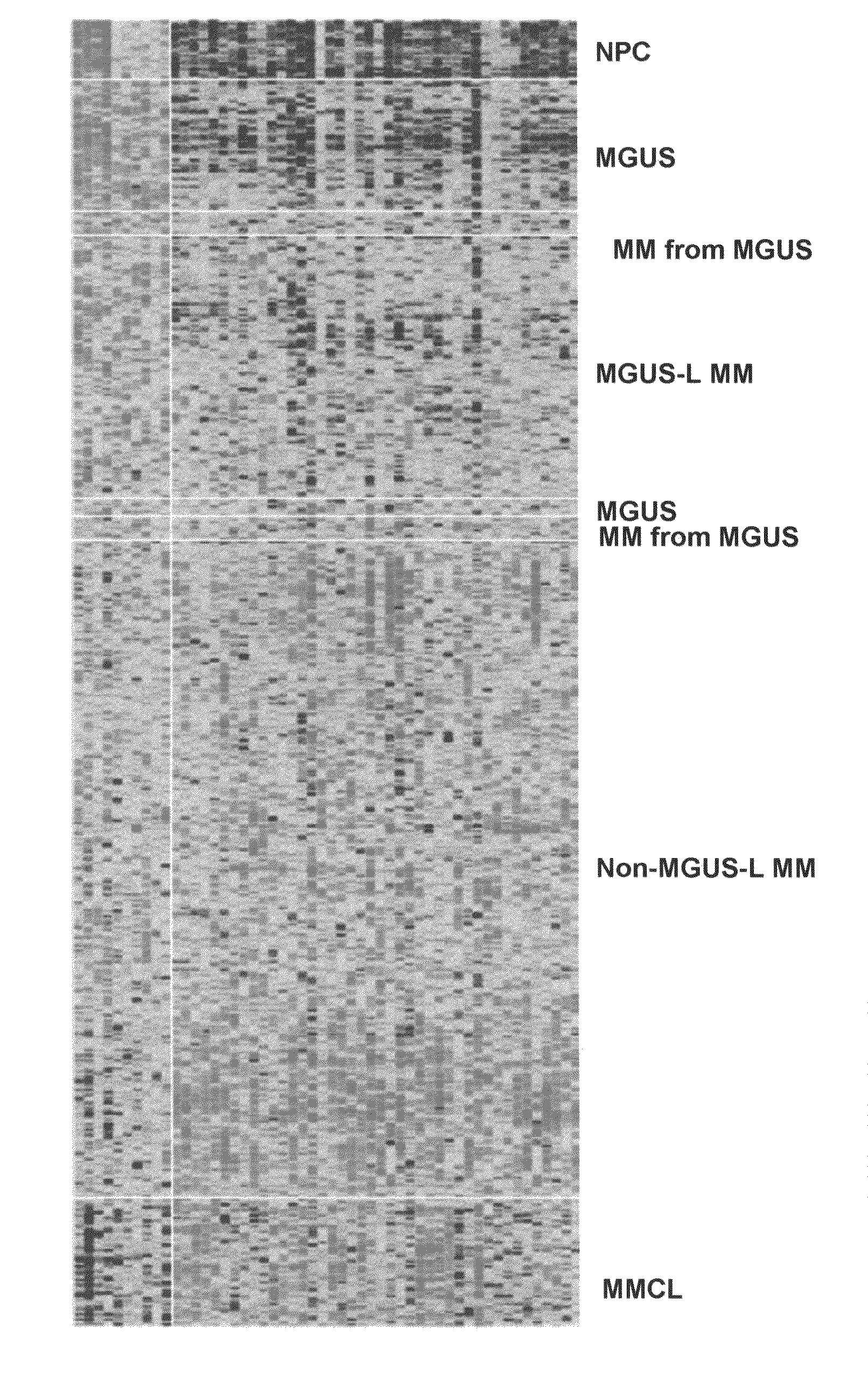
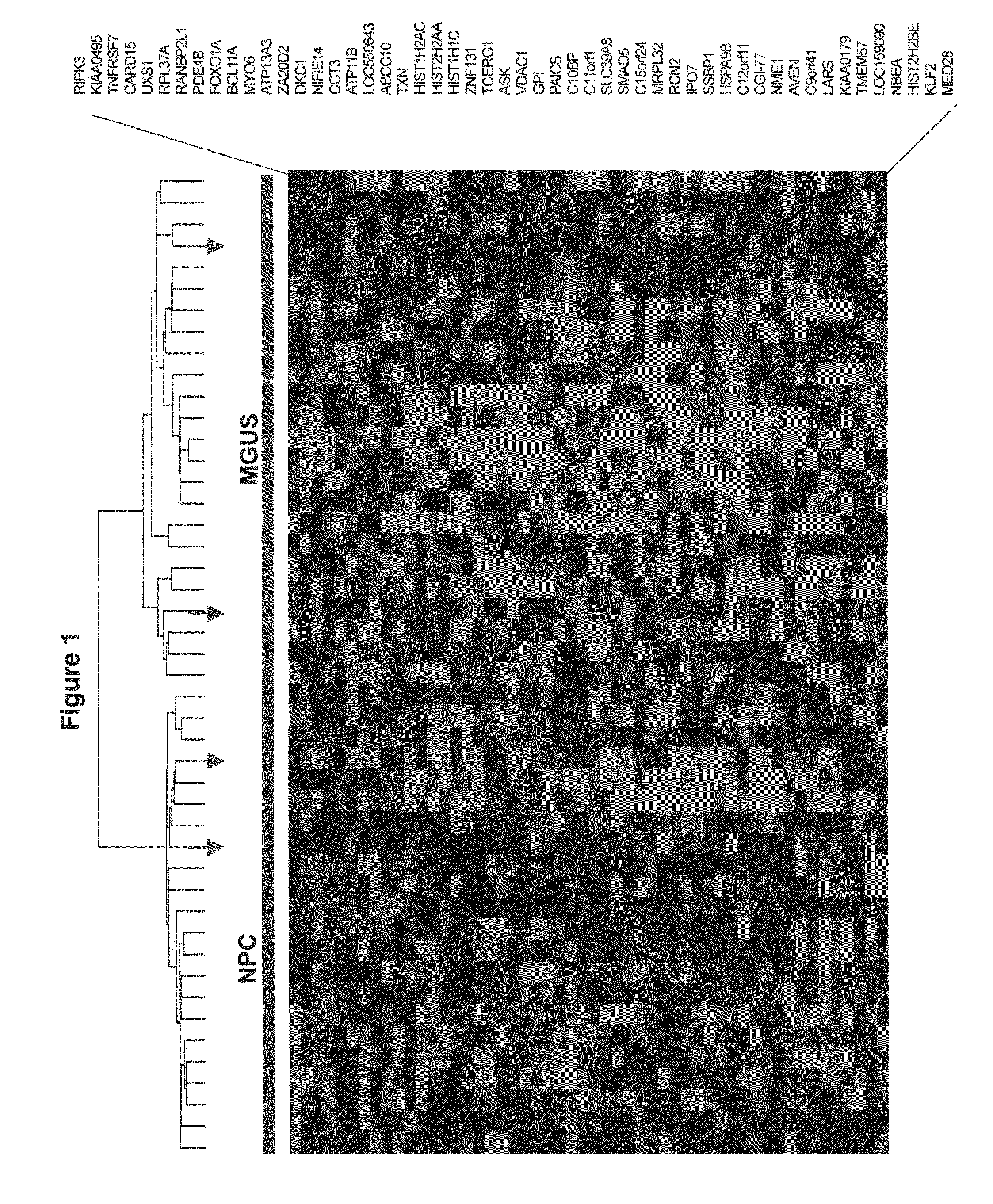
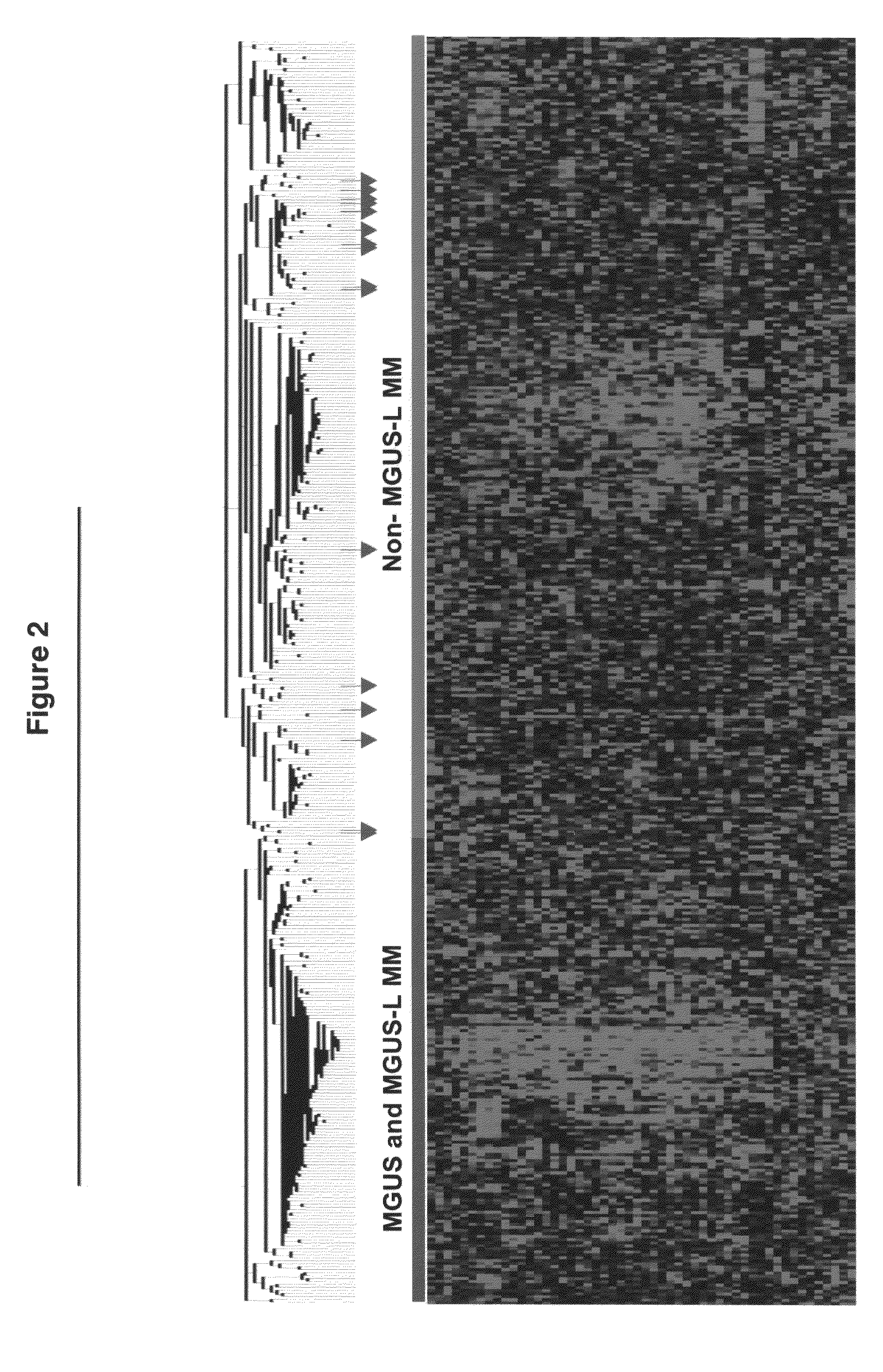
Gene expression profiling based identification of genomic signatures of multiple myeloma and uses thereof
InactiveUS20080280779A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningComplete remissionLower risk
Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance can progress to multiple myeloma. Applying significance analysis of microarrays, 52 genes, involved in important pathways related to cancer, were differentially expressed between plasma cells from healthy subjects and patients with stringently defined monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance / smoldering multiple myeloma and symptomatic multiple myeloma. Unsupervised hierarchical clustering of 351 multiple myeloma and 44 cases of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance and 16 cases of multiple myeloma with a monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance history, created two major cluster branches, one containing 82% of the monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance cases and 28% of the multiple myeloma, termed monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance-like multiple myeloma. Using the same clustering approach on an independent cohort of 213 cases of multiple myeloma revealed 27% with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance-like multiple myeloma which, despite a lower incidence of complete remission, was associated with low-risk clinical and molecular features and superior survival. The monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance-like multiple myeloma signature was also seen in patients surviving more than 10 years after autotransplant.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
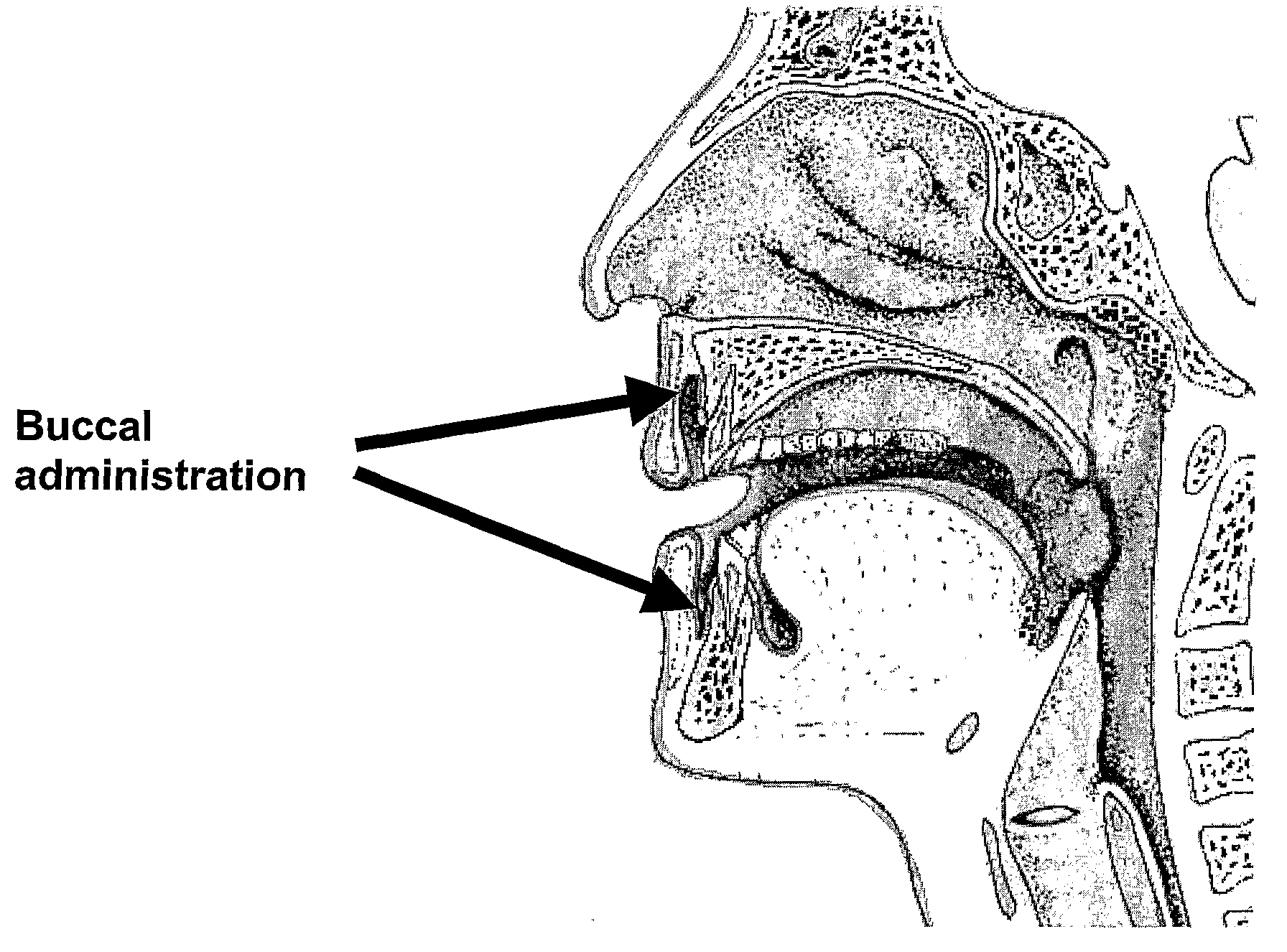
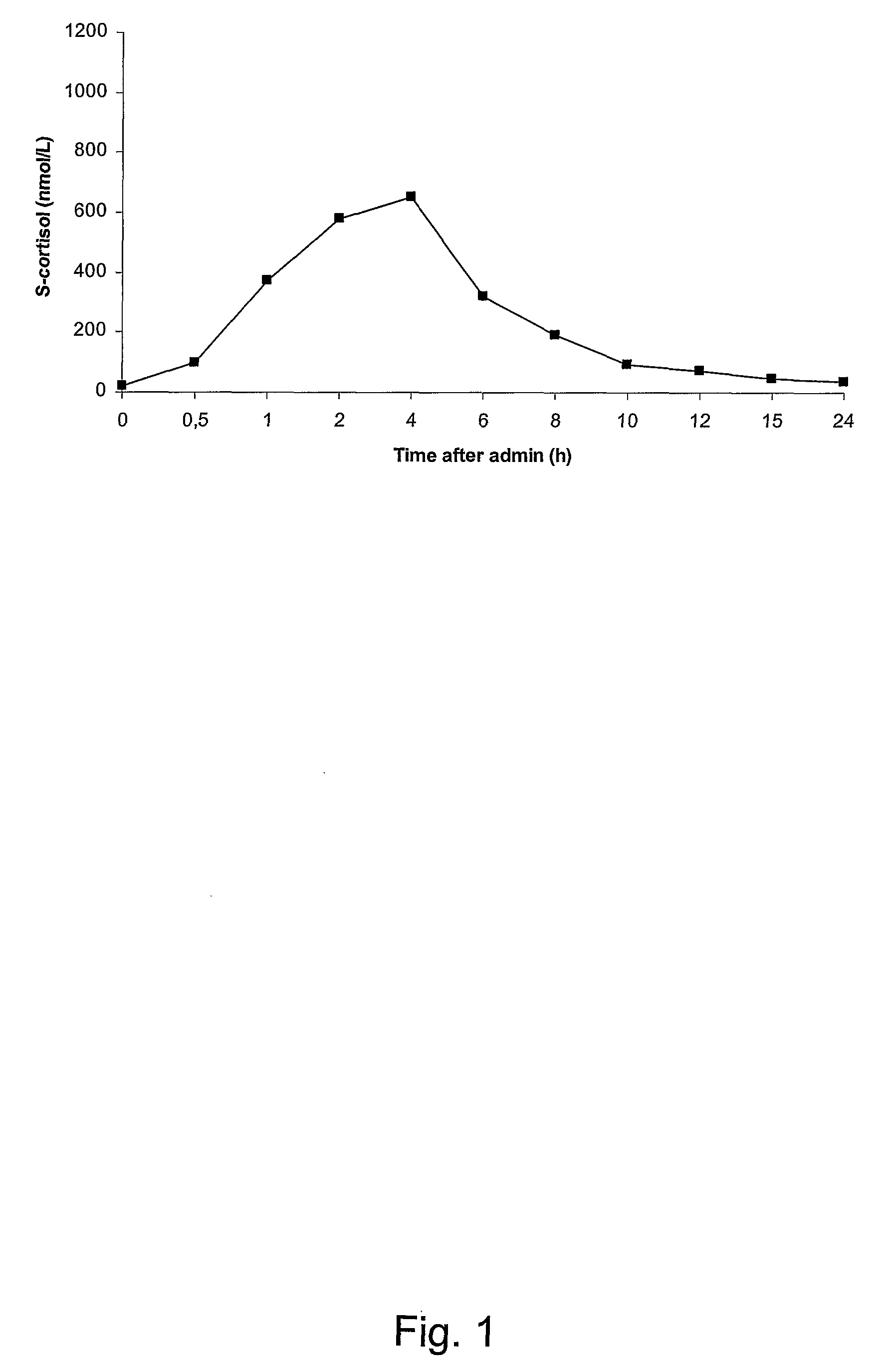
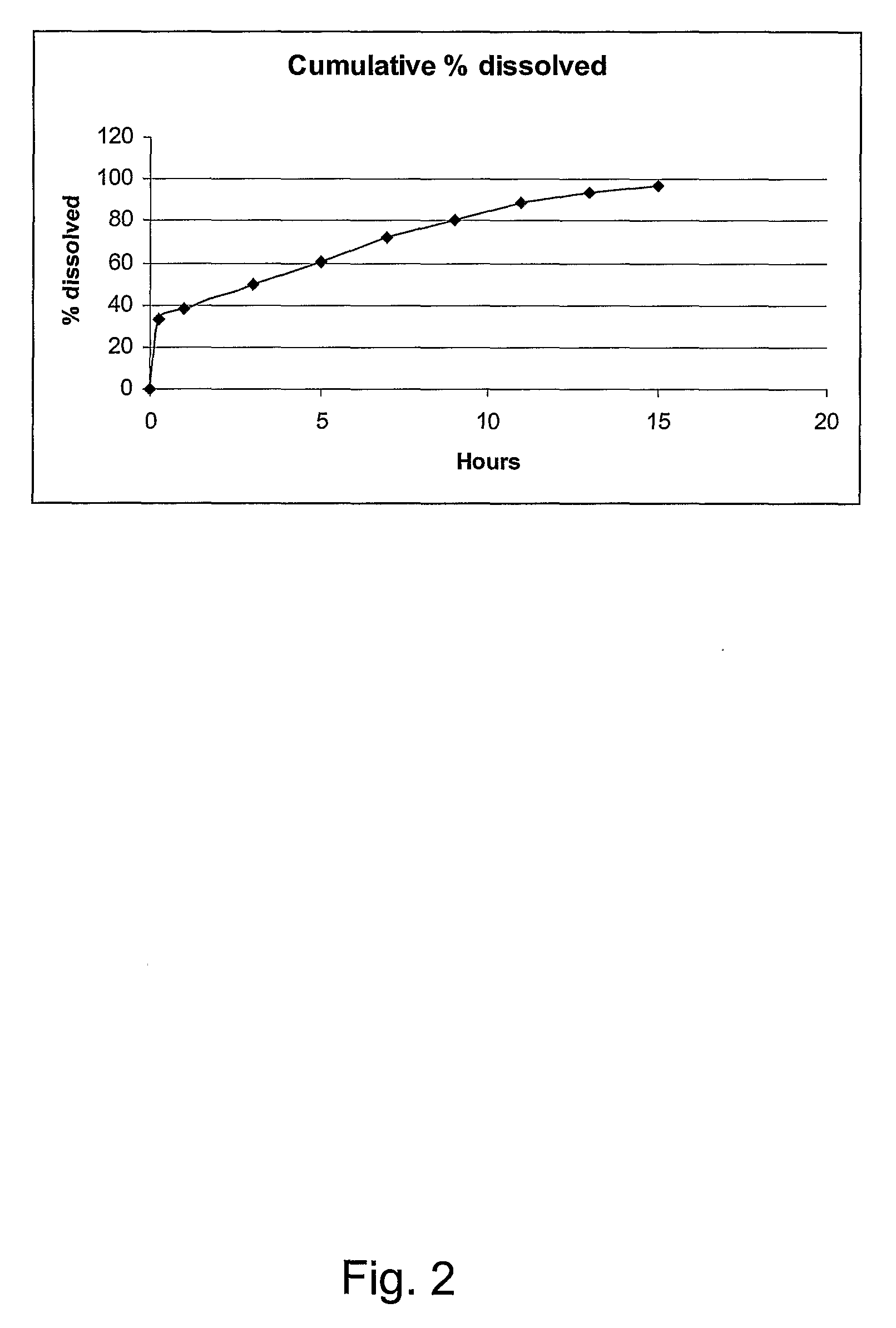
Pharmaceutical Compositions for Glucocorticoid Replacement Therapy
ActiveUS20080187586A1Solve the lack of precisionSignificant changeOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseImmediate release
The invention relates to glucocorticoid replacement therapy and provides pharmaceutical compositions and kits designed to deliver one or more glucocorticoids to a subject in need thereof in a manner that results in serum levels of the glucocorticoid that essentially mimic that of a healthy subject for a clinically relevant period of time. The pharmaceutical composition comprises one or more glucocorticoids, wherein a first part of one or more glucocorticoids is substantially immediately released and a second part of one or more glucocorticoids is released over an extended period of time of at least about 8 hours, and the amount of the one or more glucocorticoids of the first part, expressed as hydrocortisone equivalents, is in a range of from about 15 to about 50% of the total hydrocortisone equivalents. The invention also relates to a kit comprising a first and a second component, the first component designed to release one or more glucocorticoids substantially immediately and the second component is designed to release one or more glucocorticoids over an extended period of time of at least 8 hours. The invention also relates to a method for treating diseases requiring glucocorticoid treatment such as in subjects having a glucocorticoid deficiency disorder. In another aspect the invention relates to the use of a first and a second amount of one or more glucocorticoids for the preparation of a pharmaceutical composition or kit for the treatment of a glucocorticoid deficiency disorder.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Diagnostic assay
The present invention relates generally to a diagnostic device including a prognostic assay for parameters which are indicative of a condition or event associated with the systemic vasculature. More particularly, the present invention provides an assay to detect parameters associated with a vascular disease including cardiovascular, stroke, pulmonary, renovascular, cerebrovascular, thrombotic or generalized arterial or venous condition or event including acute coronary syndrome such as but not limited to acute myocardial infarction, heart failure, atheromoma or a thrombotic condition. The identification of these parameters or more particularly a pattern of parameters enables the diagnosis of a condition or event or the determination of the risk of development of a condition or event associated to the systemic vasculature. Still more particularly, the present invention is directed to a diagnostic device comprising a set of members wherein one or more of said members has or have specific or generic binding partners in a biological sample from an animal including human subject wherein the pattern of binding of the members to the binding partners is indicative, predictive or otherwise associated with a likelihood of a condition or event within the systemic vasculature. The absence of detection of specific or generic binding partners is also of indicative or predictive value. This is particularly important in cases where patients are unable to communicate advice to a physician on their own condition, such as during surgery or for patients in a coma. It is also useful in determining the risk of a vascular disease including cardiovascular, stroke, pulmonary, renovascular, cerebrovascular, thrombotic or generalized arterial or venous conditions or events in a healthy subject or a subject entering into an exposure to risk such as surgery or chemotherapy. The present invention is useful inter alia for the identification and / or quantitation of biochemical markers of conditions or events in the systemic vasculature such as heart disease, heart disorders, infections of the heart, stroke and thrombosis as well as the determination of a risk of development of these conditions including the absence of disorders or absence of risk of the development of a disorder. The assessment of such conditions may be made in a clinical setting, as part of triage, as part of a routine testing protocol and / or as a laboratory procedure.
Owner:SYDNEY UNIV OF
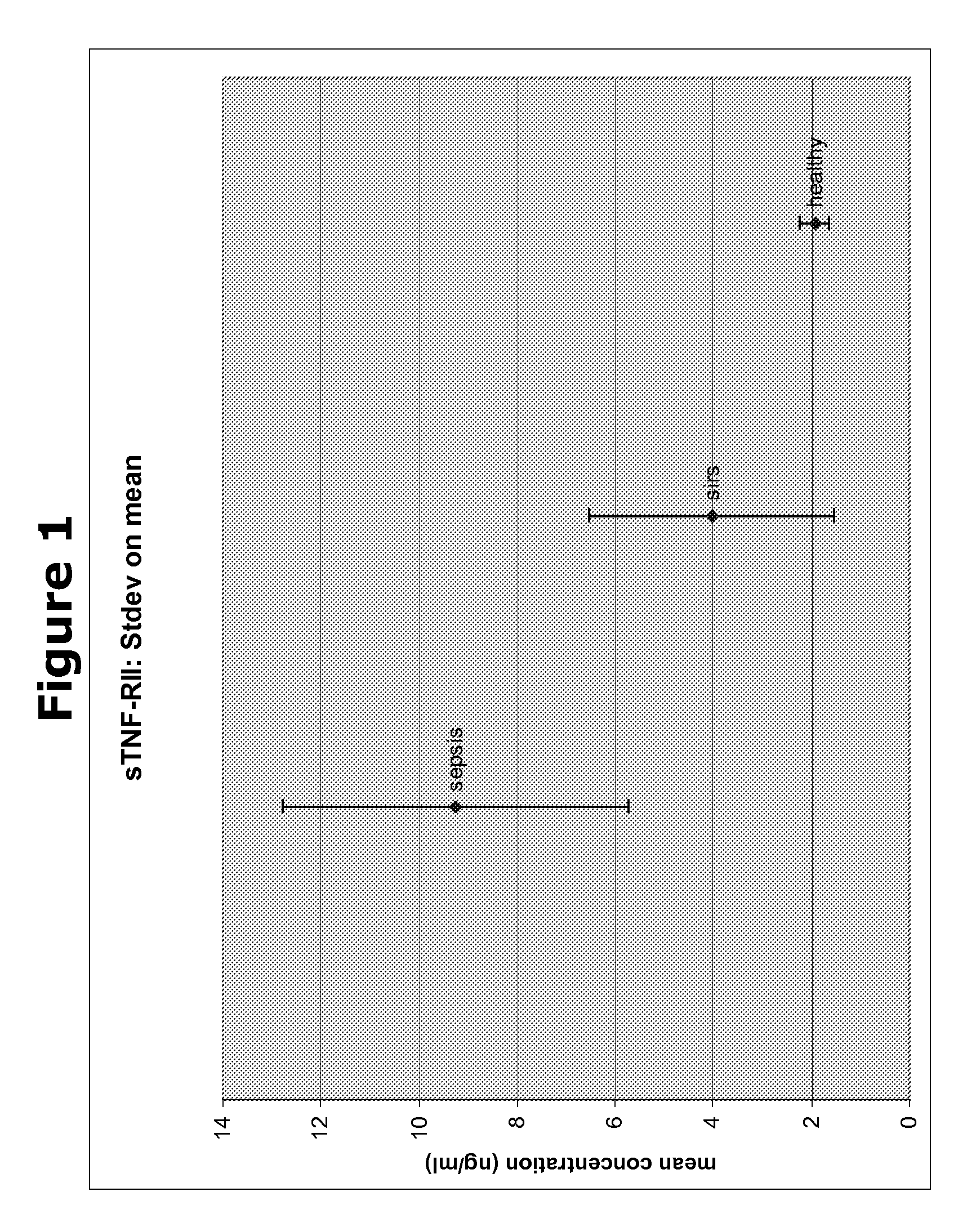
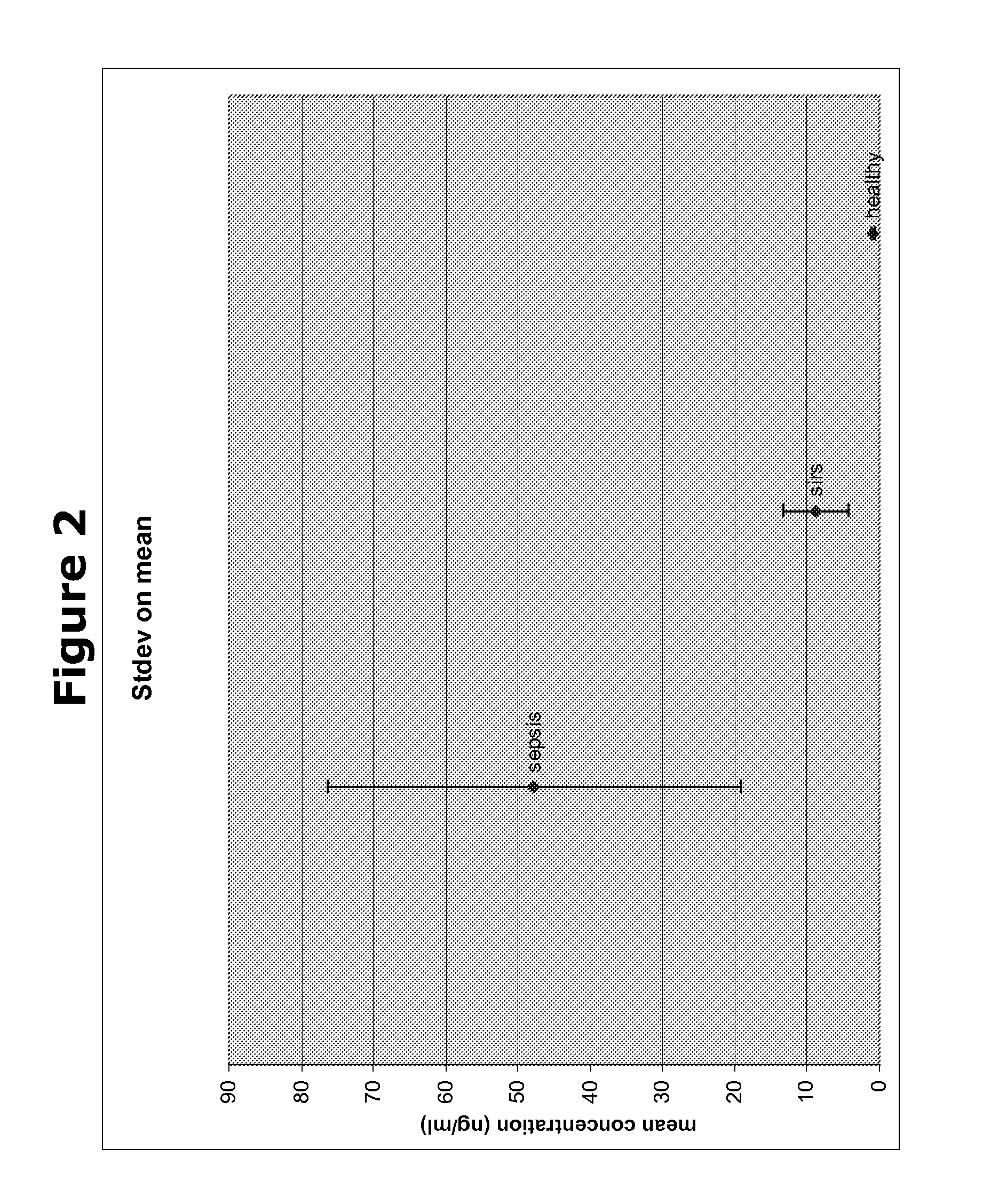
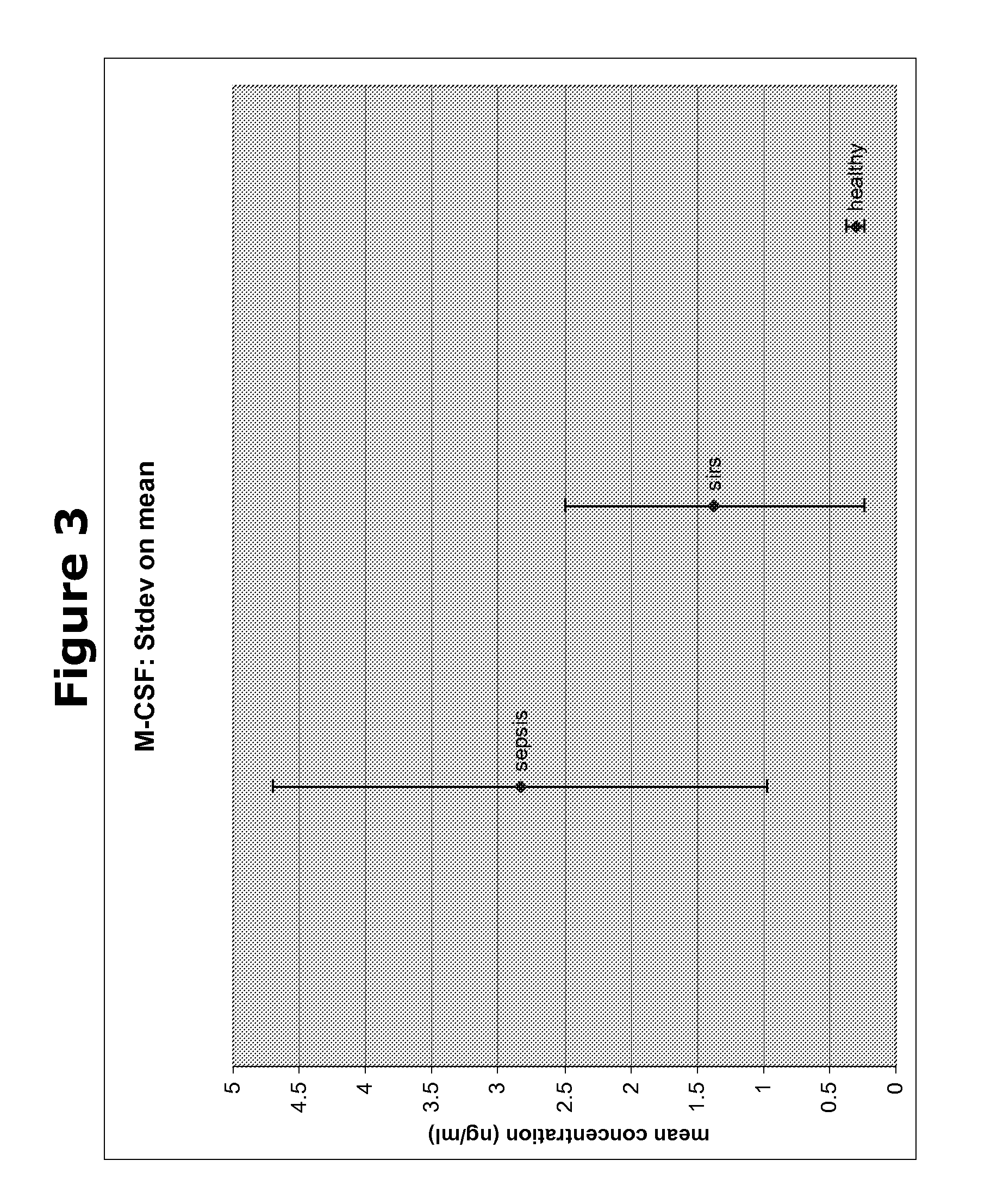
Biomarkers and methods for diagnosing, predicting and/or prognosing sepsis and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100292131A1Peptide librariesPeptide/protein ingredientsHealthy subjectsBiomarker (petroleum)
The present invention provides kits and methods for the diagnosis, prognosis and prediction of sepsis in a subject or for the differentiation between sepsis and SIRS in a subject, the method comprising(a) measuring the level of pro-hepcidin (pro-HEPC) in a biological sample taken from said subject, (b) measuring the level of at least one further biomarker selected from the group consisting of soluble TNF-receptor 2 (sTNFR2), Pentraxin-3 (PTX-3), Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor (MCSF), pro-Brain Natriuretic Protein (pro-BNP), one or more members of the Histone protein family, Procalcitonin (PCT) and c-Reactive Protein (CRP) in a biological sample from said subject, (c) using said measurements obtained in steps (a) and (b) to create a profile for said biomarkers and (d) comparing said profile with a reference biomarker profile obtained form a patient having SIRS or from a healthy subject.
Owner:BIOCARTIS NV
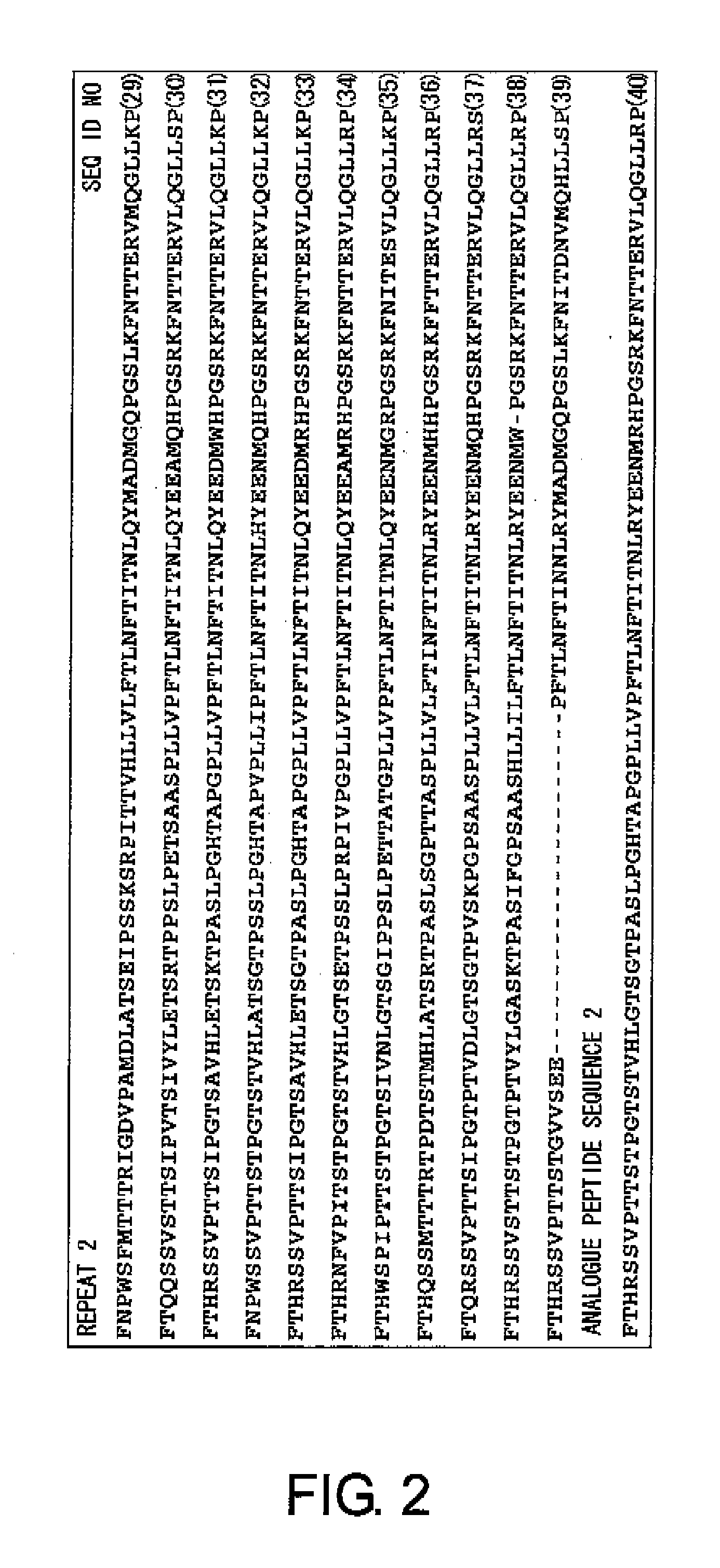
Cancer-associated antigen analogue peptides and uses thereof
InactiveUS20110229481A1Improve long-term prognosisPrevent recurrenceFungiBacteriaEpitopeActivation cells
First, to solve the problems of the present invention, the present inventors confirmed the presence of ovarian cancer antigen-specific T cells in the peripheral blood of ovarian cancer patients by using an experimental system that detects combinations of CD4 and IL-4 or IFNγ. Next, using analogue peptides of the core protein MUC16 of the ovarian cancer-associated antibody C125, the present inventors revealed that antigen-specific CD4-positive T cells are present at an average frequency of about 4% in the peripheral mononuclear cells of patients and healthy subjects. Then, the present inventors analyzed the epitope for T cells in the core protein MUC16 of the ovarian cancer-associated antigen CA125, and determined the amino acid sequence FTLNFTITN (SEQ ID NO: 1) to be a shorter epitope. The present inventors further discovered that the analogue peptide OVCA11: GHTAPOPLLVPFTLNFTITN (SEQ ID NO: 11) is suitable for T cell activation.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Device and method for the determination of dry weight by continuous measurement of resistance and calculation of circumference in a body segment using segmental bioimpedance analysis
InactiveUS7801598B2Person identificationEvaluation of blood vesselsContinuous measurementElectrical resistance and conductance
A method and device for continuously calculating the circumference of a body segment is based on the continuous measurement of the extracellular resistance of the body segment. Also disclosed is a method and device for determining the dry weight of a dialysis patient wherein the time at which the dry weight of the patient has been achieved is identified as the time at which the patient's normalized resistivity as a function of time (ρN(t)) is greater than or equal to a minimum level of normalized resistivity in healthy subjects (ρN,H).
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
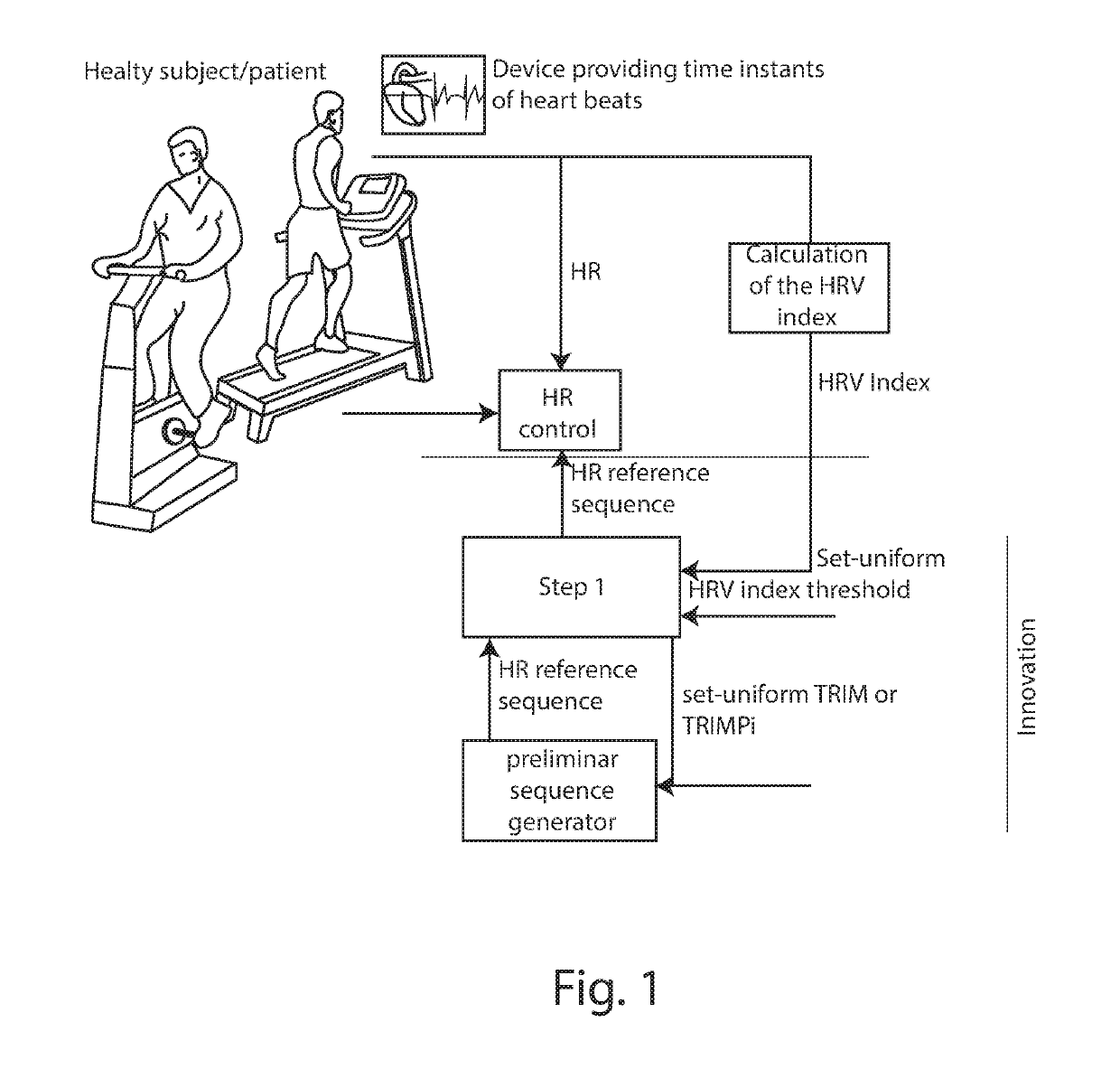
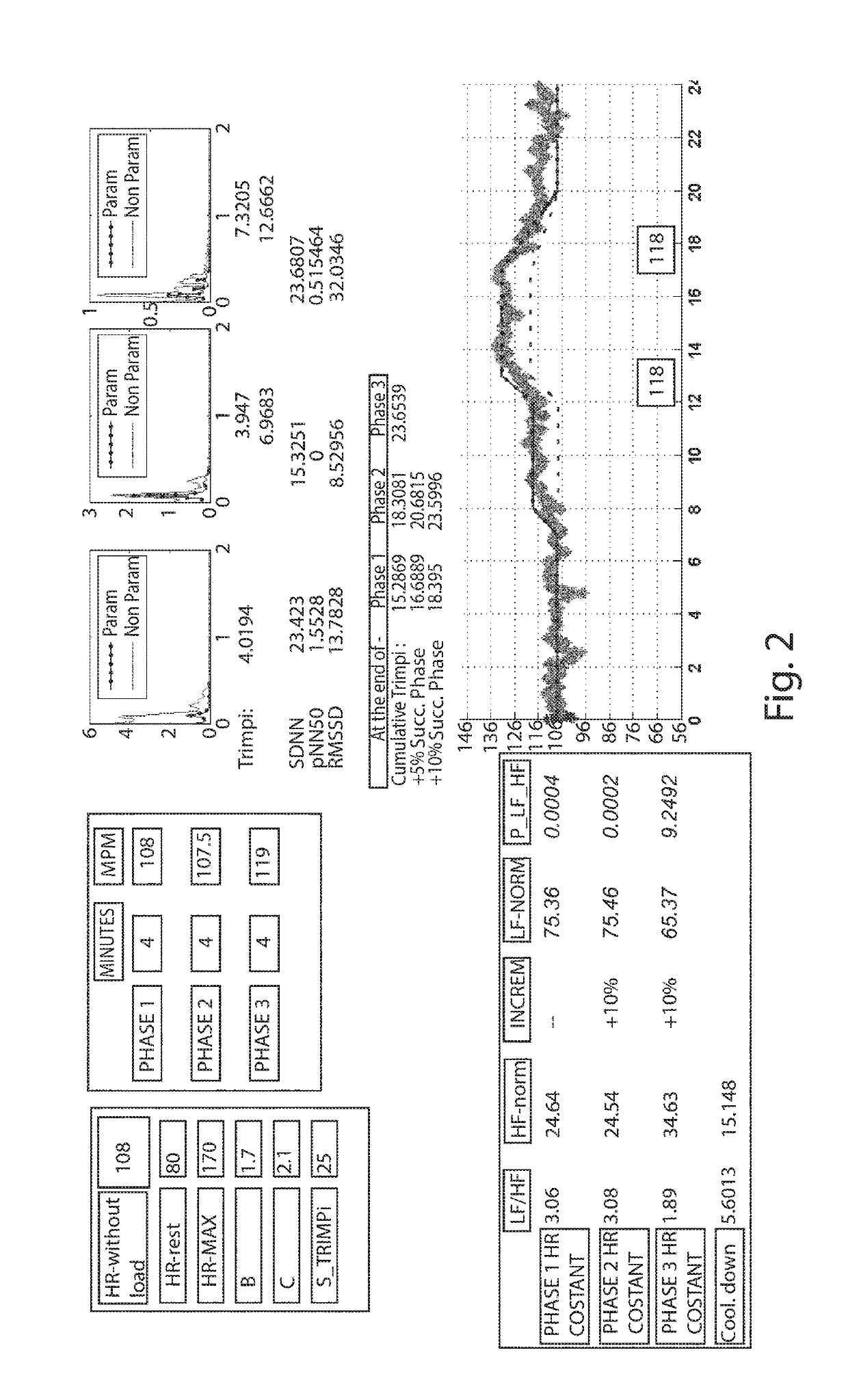
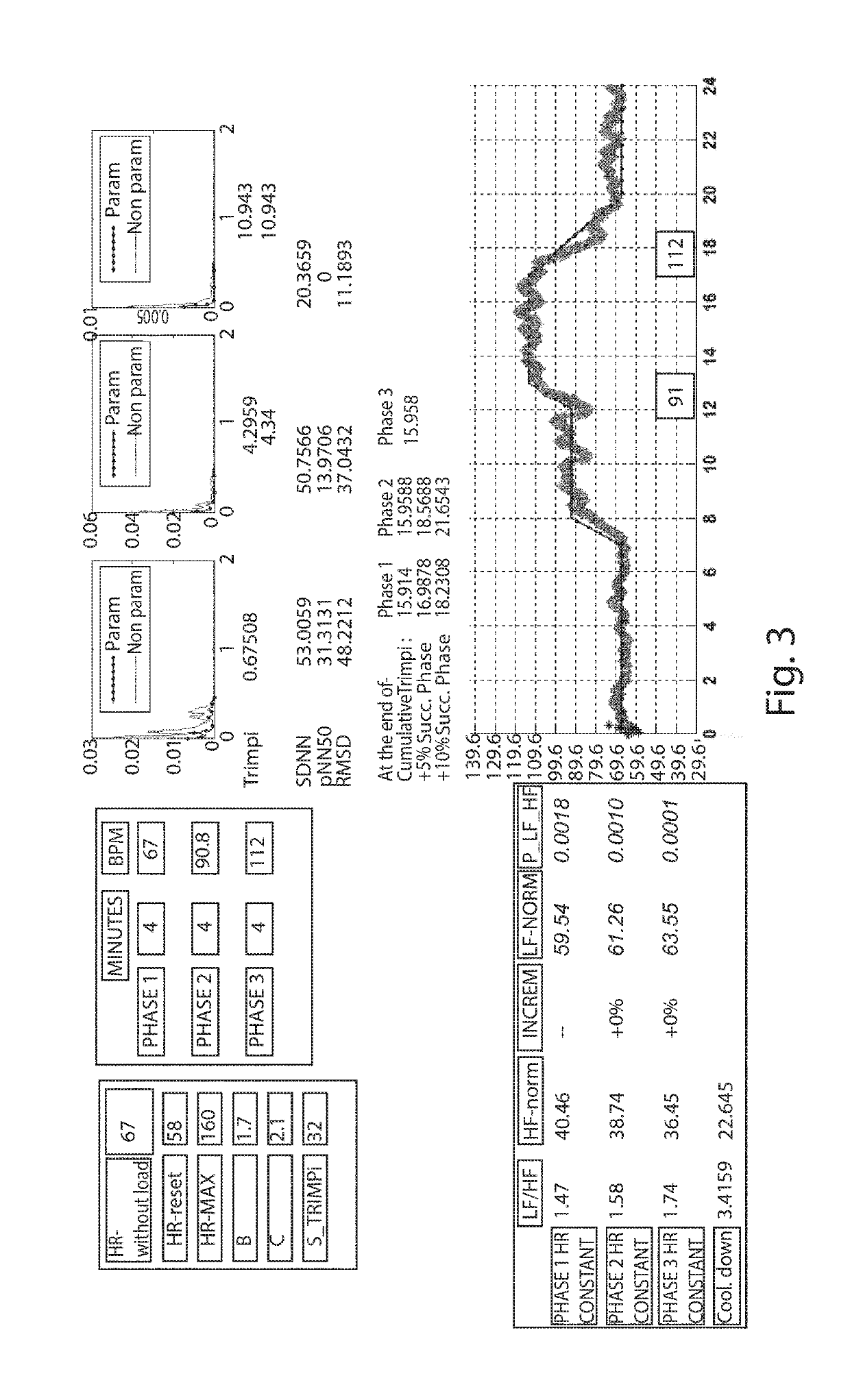
Individually tailored exercise training and rehabilitation technique: medical personal trainer
The present invention concerns a new individually tailored exercise training and rehabilitation technique, referred to as “MPT: Medical Personal Trainer”. More precisely, the invention concerns an innovative method to be used in the field of physical activity and exercise training / rehabilitation programs for healthy individuals and for patients with chronic diseases. It merges together, in an interactive way, advanced notions from medicine, engineering, mathematics, artificial intelligence, in order to provide new clinical perspectives for automatic personalized health care as well as novel insights on individually-tailored management and advanced treatment, in a user-familiar setting, of healthy subjects (including elderly) and patients with chronic diseases.
Owner:SAN RAFFAELE ROMA SRL
Methods and assays for detecting and quantifying pure subpopulations of white blood cells in immune system disorders
ActiveUS20100112628A1Determining susceptibility to an allergic reactionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDiseaseWhite blood cell
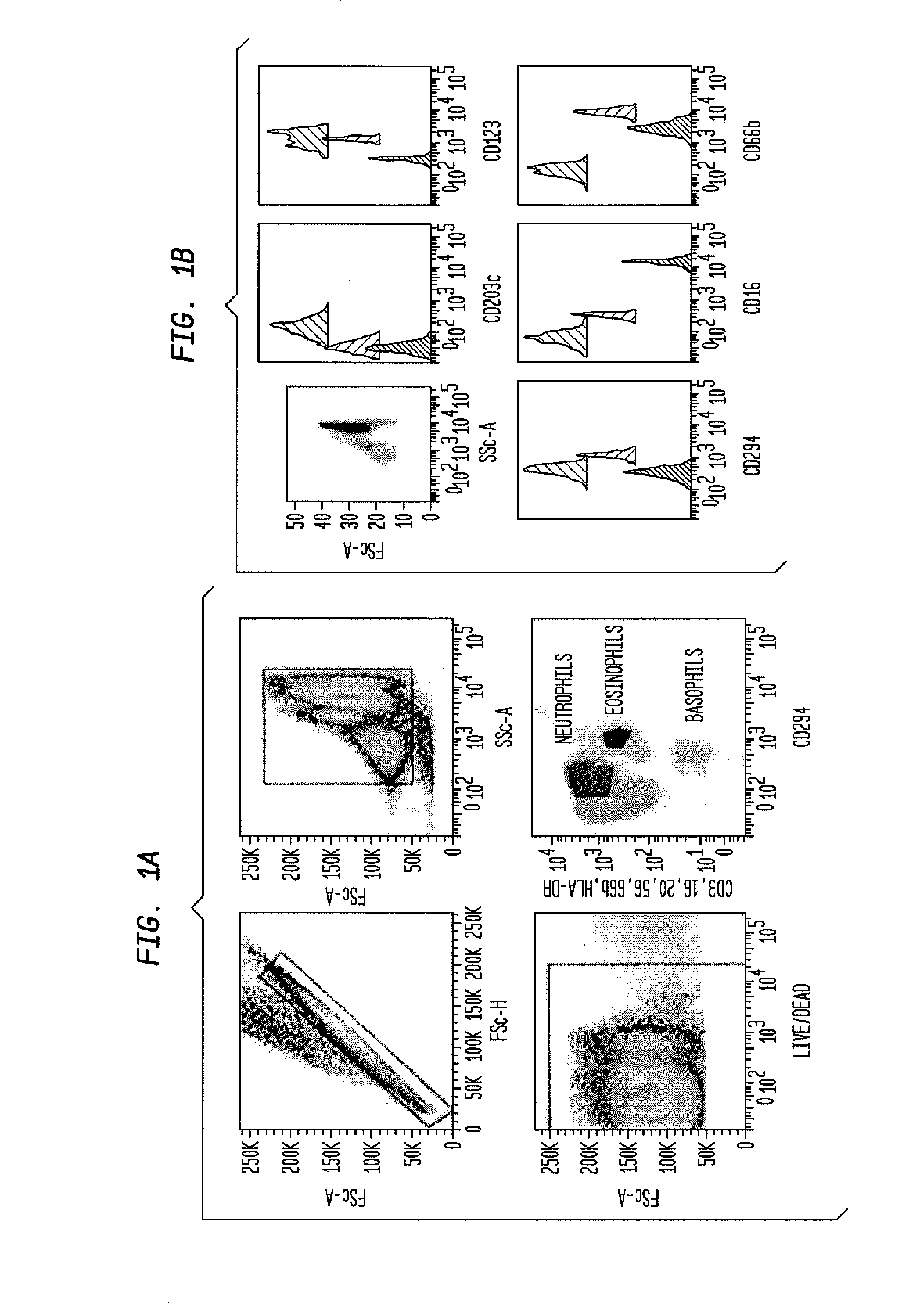
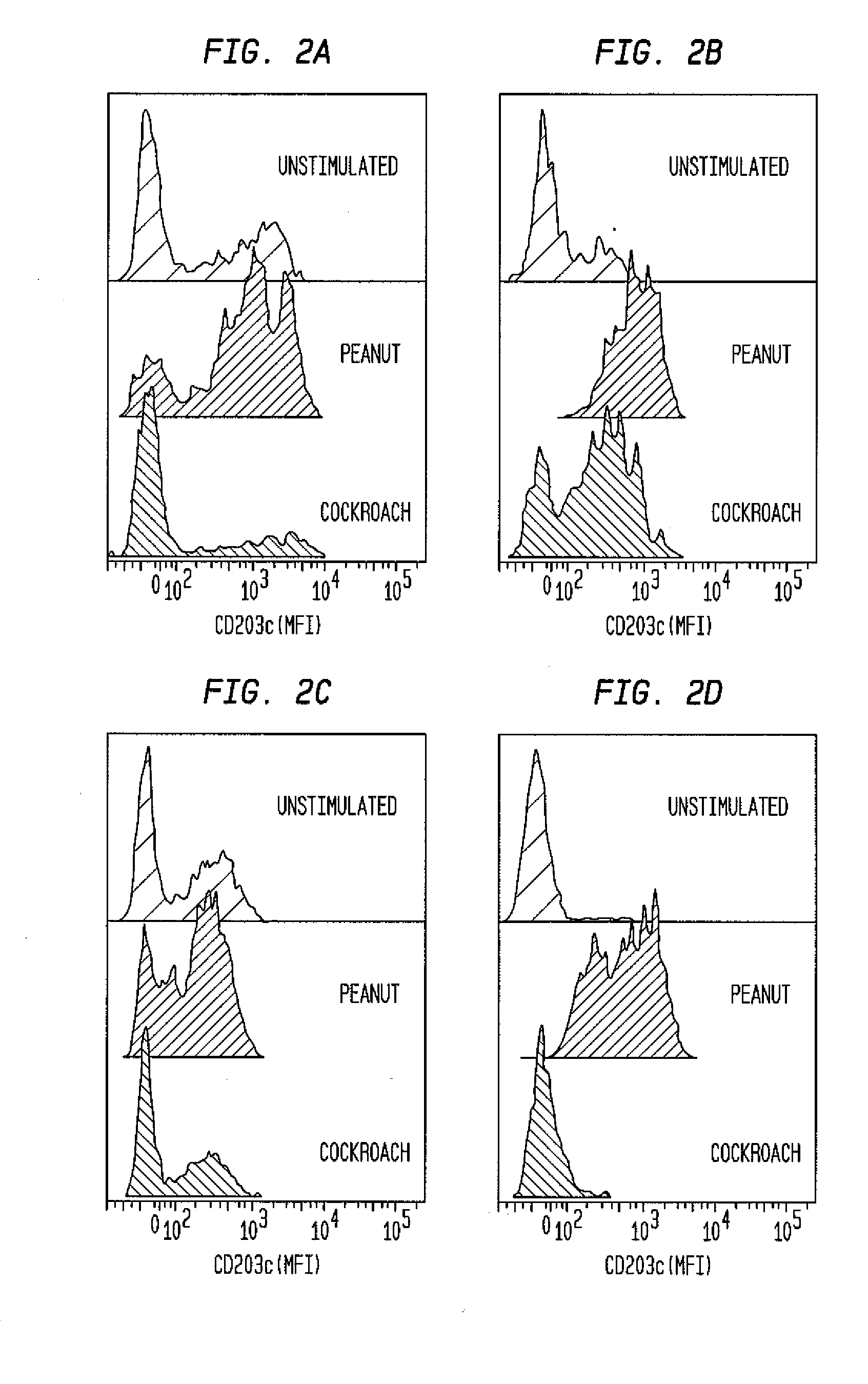
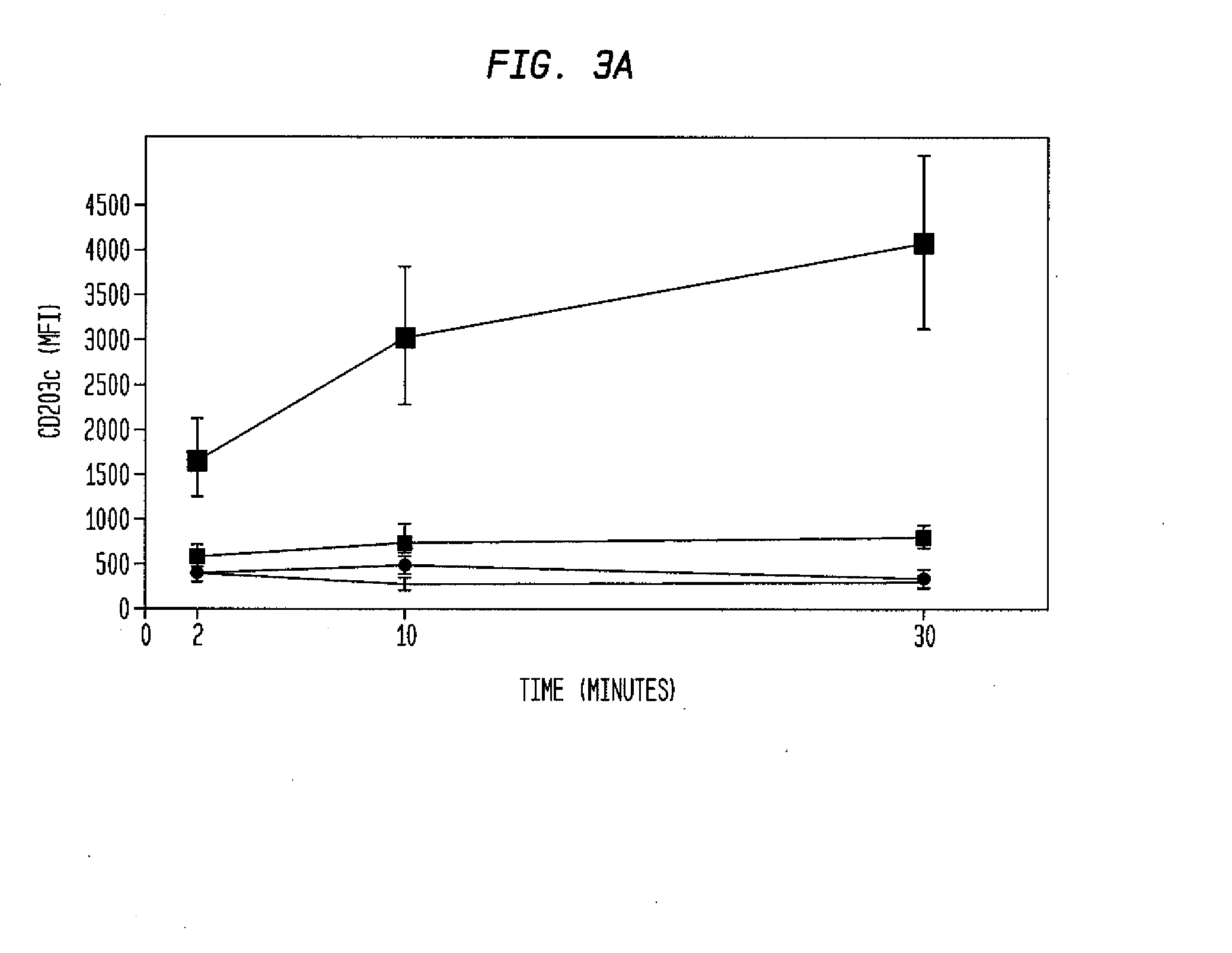
Methods for detecting nonactivated basophils in a whole blood sample obtained from a normal healthy subject, methods for determining a subject's susceptibility to an allergic reaction to an allergen, where the subject has no known allergy to the allergen, methods for measuring a response to challenge with a potential allergen in a whole blood sample obtained from a subject with known allergic reactivity to allergens other than the potential allergen; and an in vitro system for reliable detection or quantification of a specific white blood cell population in a whole blood sample are described.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method for blood infrared spectroscopy diagnosing of inner organs pathology
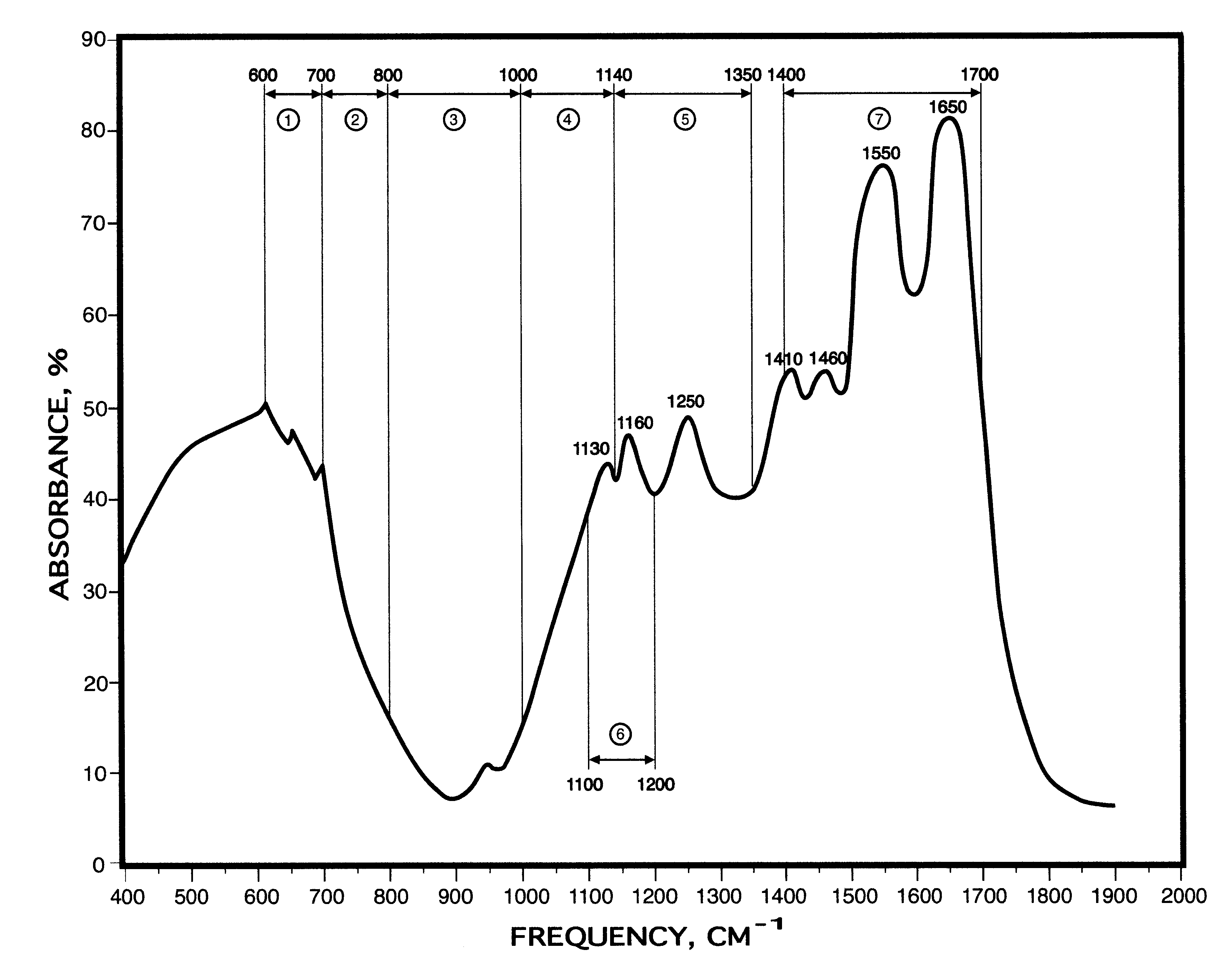
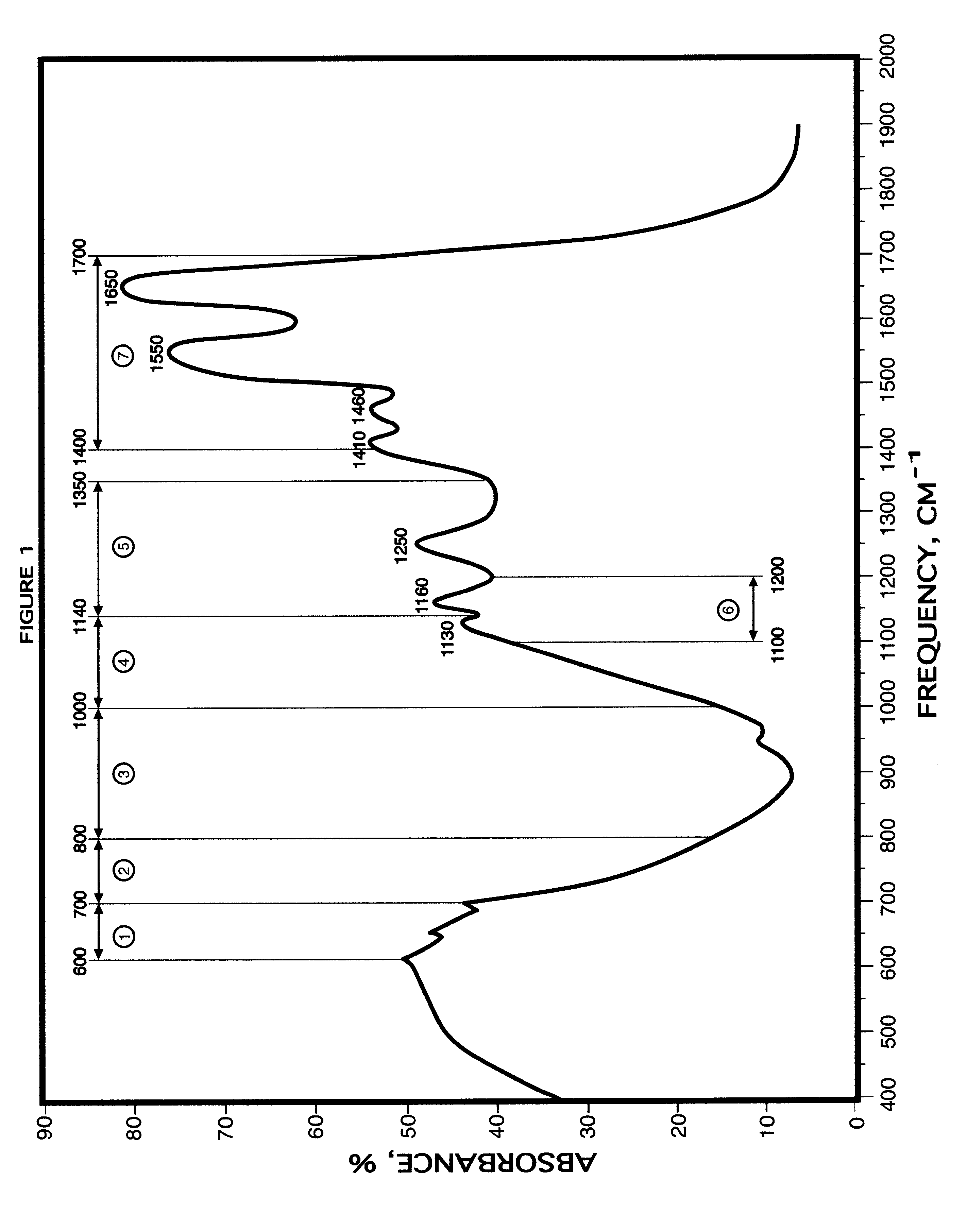
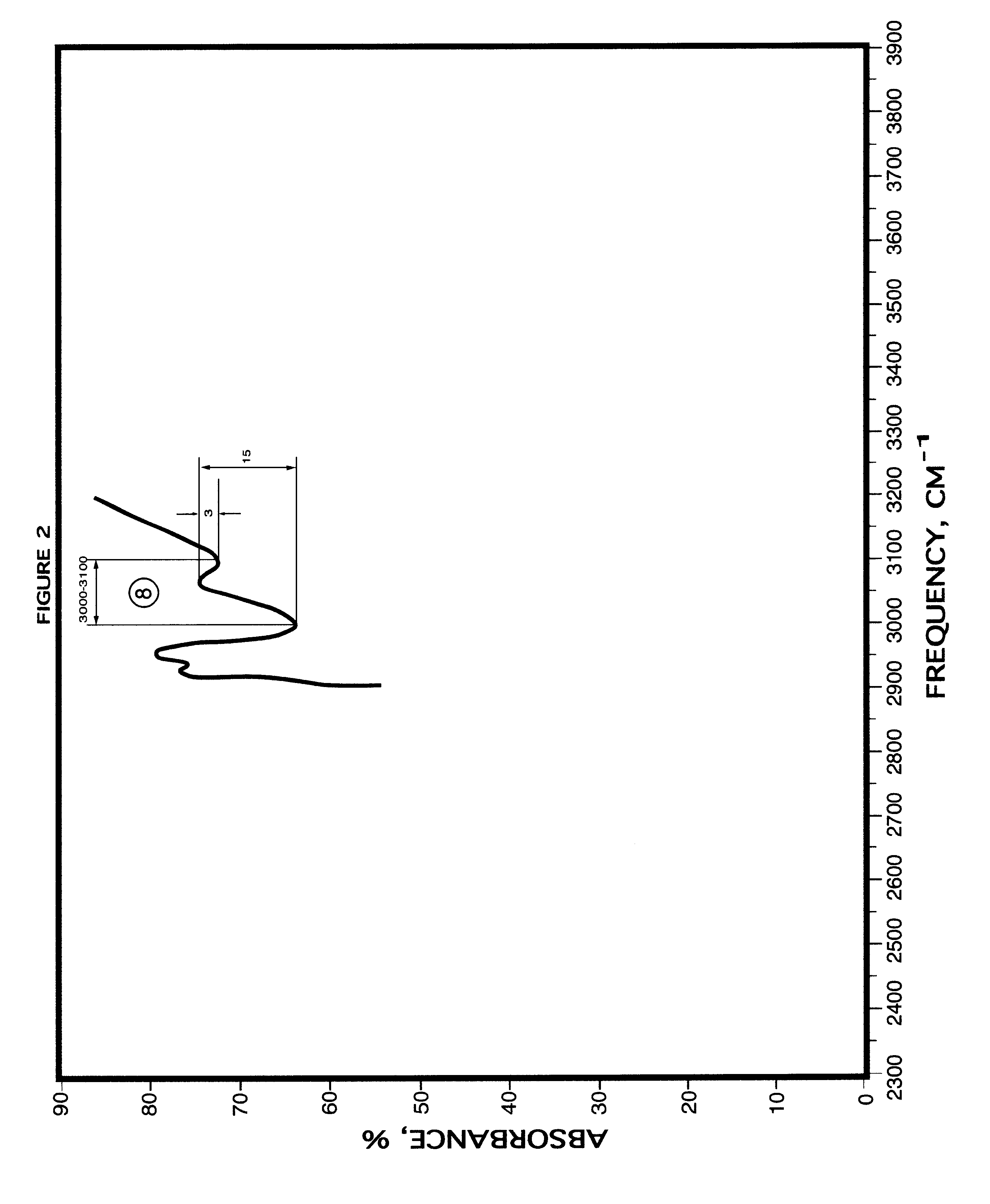
InactiveUS6749565B2Rapid and accurate early diagnosisQuick distinctionRadiation pyrometryDiagnostic recording/measuringDiseaseSpectroscopy
A rapid diagnosis method for organ specific disease state is based on obtaining an infrared absorbance spectra of a patient's blood at a frequency range from about 400 cm<-1 >to about 2000 cm<-1 >and further from about 3000 cm<-1 >to about 3100 cm<-1>. Comparing it with the predetermined normal infrared absorbance spectra of known healthy subjects for the presence or absence of predetermined features such as increase or decrease of infrared absorbance, peaks at particular frequencies allows for accurate diagnosis of a disease of an organ, including most major organs such as a heart, lungs, stomach, liver, kidneys, brain, etc.
Owner:CHUDNER VICTOR
Identification of cancer protein biomarkers using proteomic techniques
The claimed invention describes methods to diagnose or aid in the diagnosis of cancer. The claimed methods are based on the identification of biomarkers which are particularly well suited to discriminate between cancer subjects and healthy subjects. These biomarkers were identified using a unique and novel screening method described herein. The biomarkers identified herein can also be used in the prognosis and monitoring of cancer. The invention comprises the use of leptin, prolactin, OPN and IGF-II for diagnosing, prognosis and monitoring of ovarian cancer.
Owner:YALE UNIV
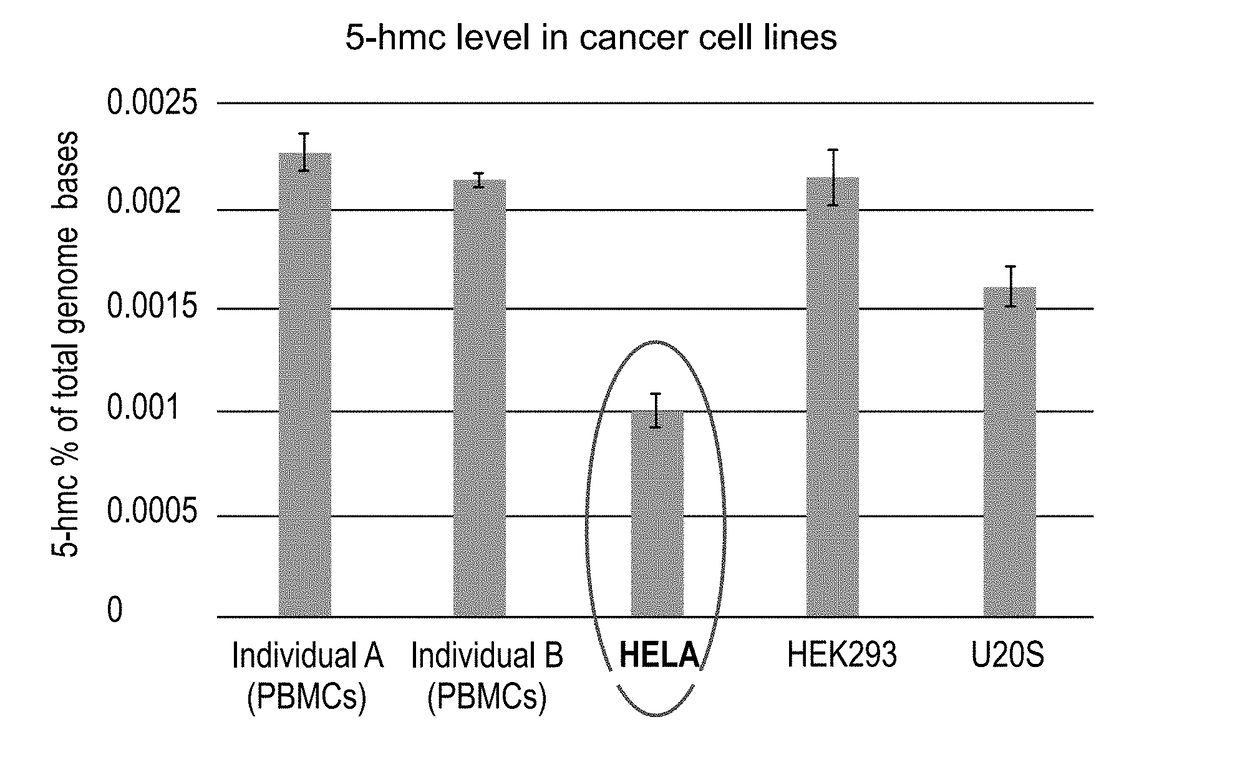
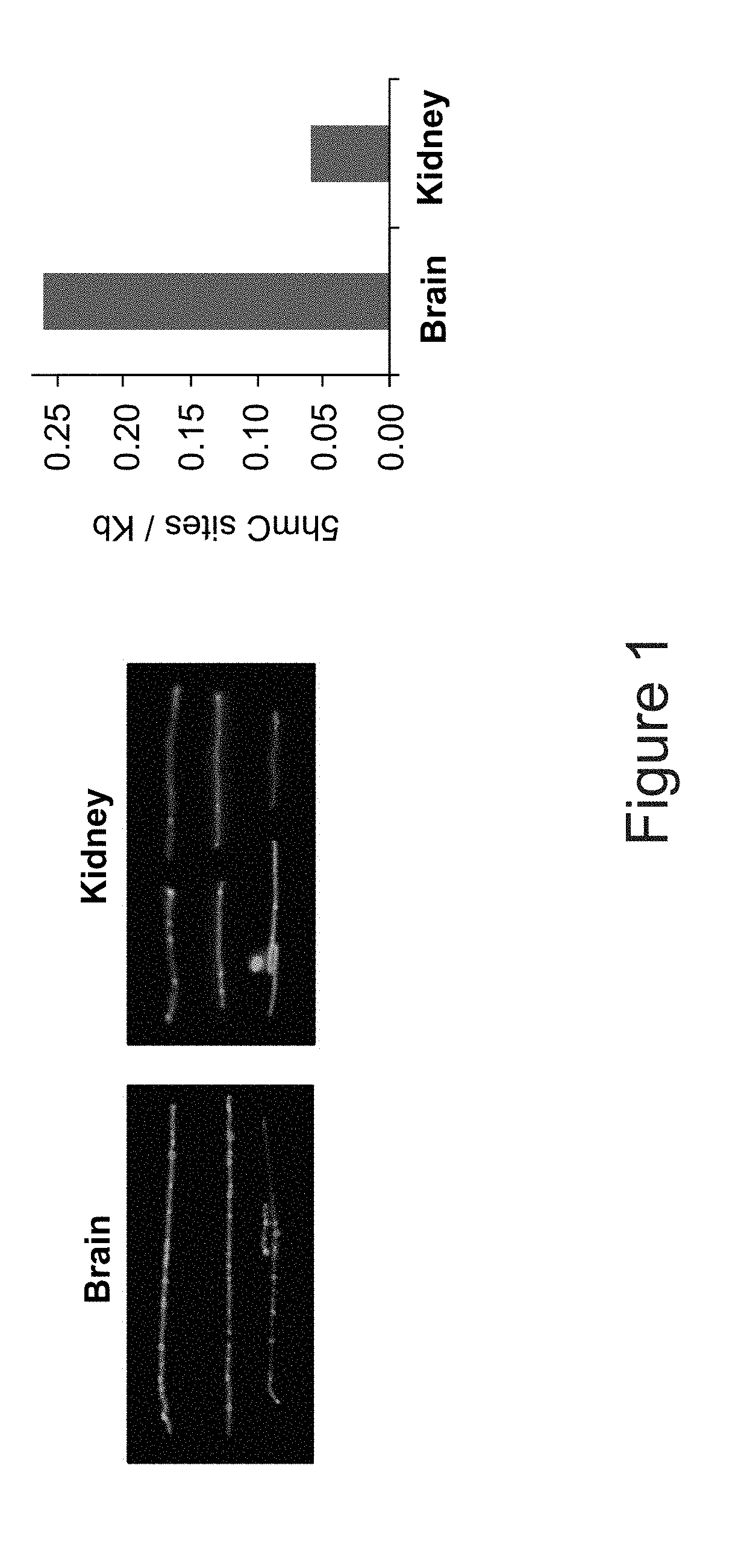
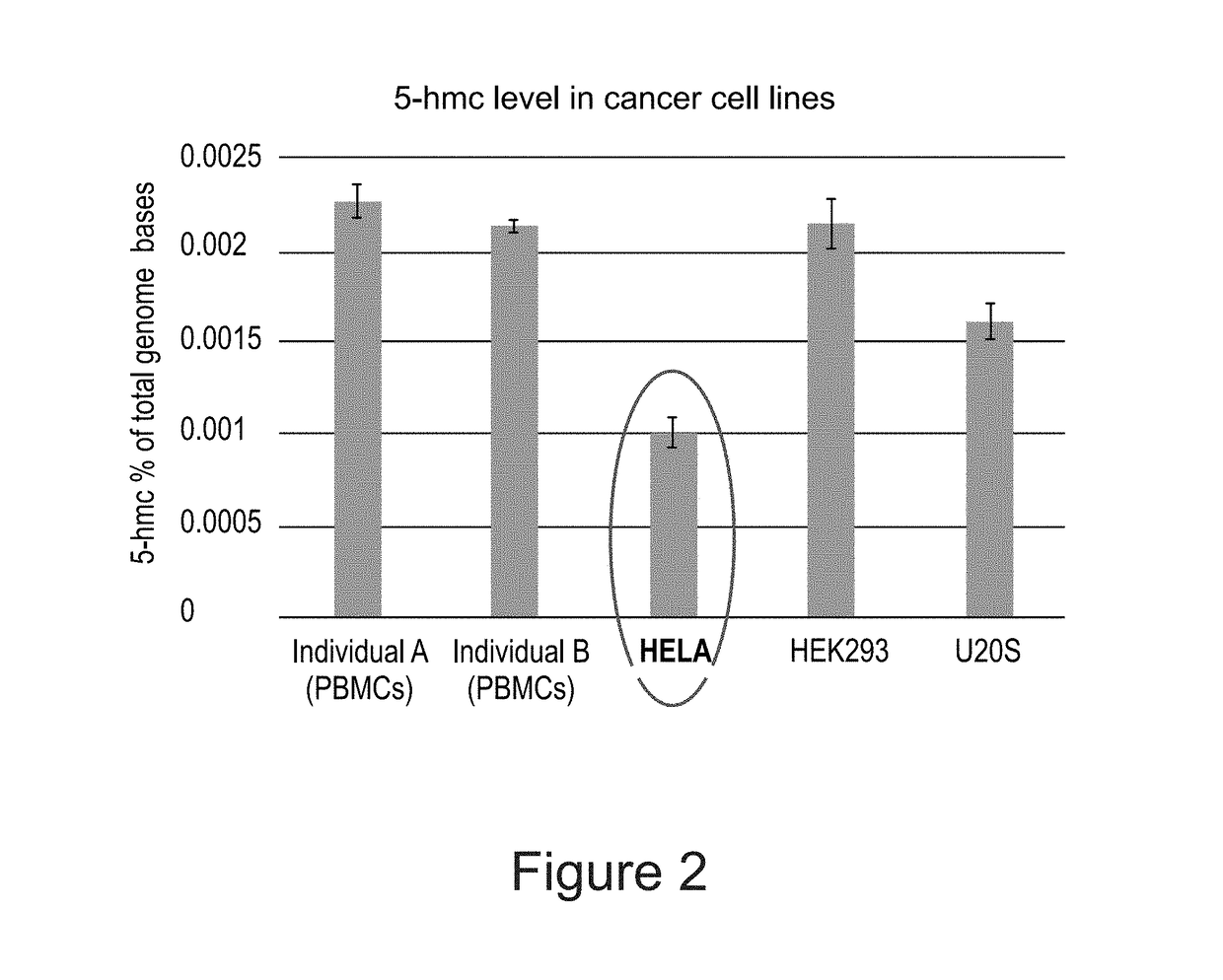
Methods of detecting 5-hydroxymethylcytosine and diagnosing of cancer
A method of detecting the level of 5-hydroxymethylcytosines (5-hmc) in a DNA molecule of a cell having a 5-hmc prevalence lower than 0.002% of total DNA bases is provided. The method comprising:(a) attaching a 5-hmc labeling agent to the DNA molecule; and(b) subjecting the DNA molecule to an imaging method suitable for detecting the labeling agent, thereby detecting the level of 5-hmc in the DNA molecule. Also provided is a method of diagnosing cancer in a subject in need thereof, the method comprising:(a) providing a DNA sample of a cell of the subject;(b) detecting the level of 5-hmc in the DNA sample as described herein;wherein a significant decrease in the level of 5-hmc in the DNA sample, as compared to a control DNA sample from a healthy subject is indicative that the subject has cancer.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
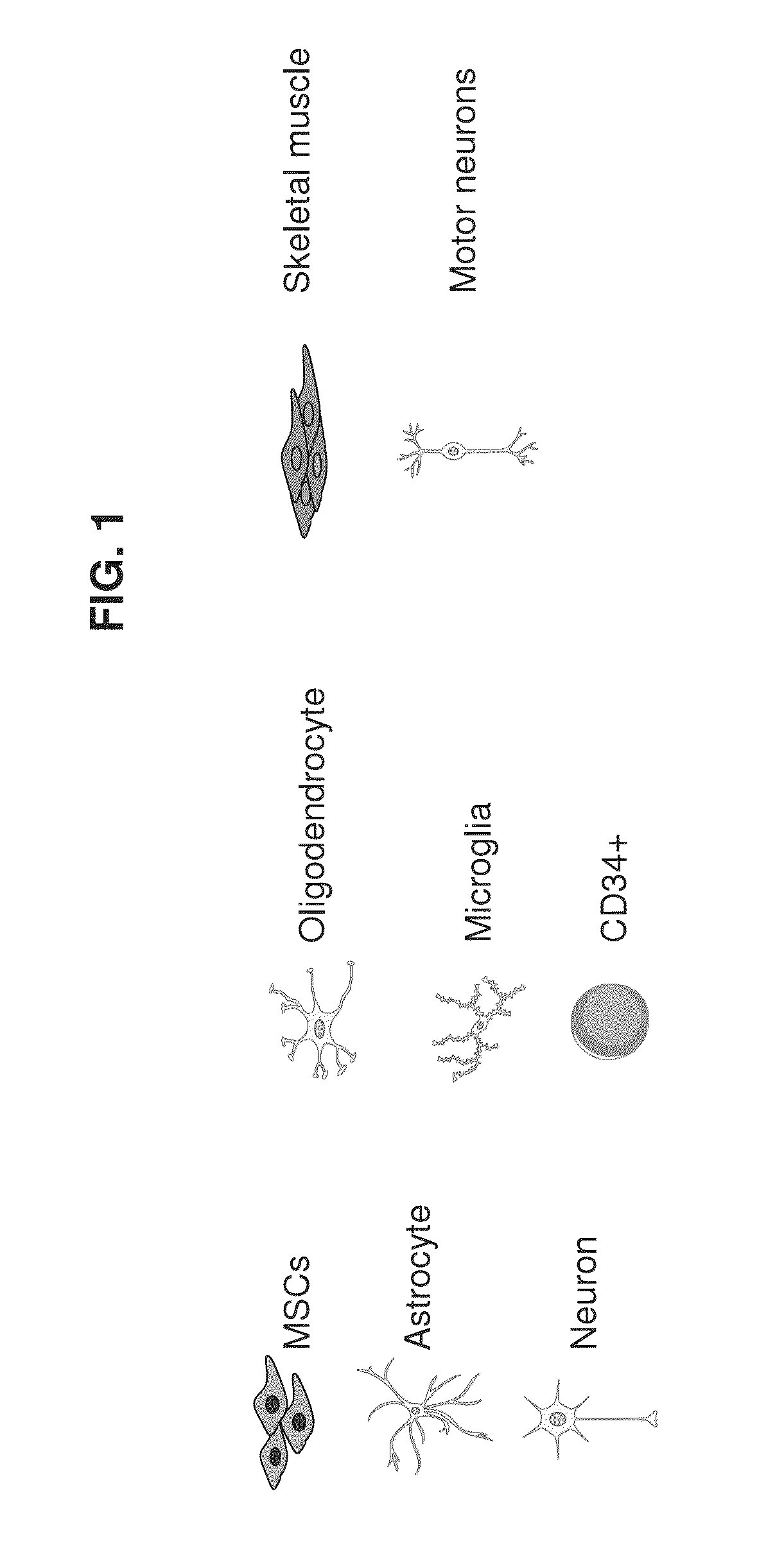
Mesenchymal stem cells for in vitro modeling and cell-based therapy of human diseases and banks thereof
A method of qualifying a mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) population is disclosed. The method comprises:(a) ex vivo differentiating a population of mesenchymal stem cells originating from the subject towards a first lineage-specific cell, the first lineage-specific cell being associated with a brain disease;(b) ex vivo differentiating a population of mesenchymal stem cells originating from a healthy subject towards the first lineage-specific cell;(c) comparing an effect of the first lineage specific cell derived from the subject with an effect of the first lineage specific cell derived from the healthy subject on a second lineage specific cell associated with the brain disease, wherein a difference in the effect above or below a predetermined level is indicative of a qualification of a mesenchymal stem cell population for cell therapy of said brain disease.
Owner:BRAINSTEM BIOTEC +1
Method of diagnosing integration dysfunction syndrome using blood
InactiveUS20060099593A1Reliable methodForcing riskBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsClinical psychologyHealthy subjects
An object of the present invention is. to provide an objective method for diagnosis of schizophrenia using gene expression in mononuclear cells of peripheral blood as an index, and this invention provide a method for diagnosing whether a test subject suffers from schizophrenia or not. The method according to this invention is a method for diagnosing whether a test subject suffers from schizophrenia or not, the method comprising the steps of; obtaining mononuclear cells in blood containing nucleic acid from said subject, measuring the content of at least one nucleic acid selected from the group consisting of nucleic acid(s) (containing its fragment and a nucleic acid complementary to the nucleic acid) defining gene(s) exhibiting altered expression by occurrence of schizophrenia or nucleic acid(s) (containing its fragment and a nucleic acid complementary to the nucleic acid) defining gene(s) exhibiting altered expression by progression of schizophrenia in said mononuclear cells, and determining alteration of the quantified level(s) of the gene(s) in said test subject is statistically significant in comparison with the quantified level(s) of said nucleic acid(s) defining gene(s) exhibiting altered expression by occurrence of schizophrenia or said nucleic acid(s) defining gene(s) exhibiting altered expression by progression of schizophrenia in healthy subjects or schizophrenic patients, thereby diagnosing whether said subject is suffering from schizophrenia or not.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
Use of drugs that activate P2Y receptors to enhance synaptogenesis
The present invention encompasses compositions and methods that activate P2Y receptors for the increased production of new synapses in the central nervous system. The formulations of the invention may be administered to a healthy subject or to a subject in need thereof to restore synapses.
Owner:BACK BAY SCI
Biomarkers in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells for Diagnosing or Detecting Lung Cancers
ActiveUS20110251098A1Sugar derivativesNucleotide librariesReference samplePeripheral blood mononuclear cell
Methods and compositions are provided for diagnosing or detecting a condition, e.g., lung disease in a mammalian subject by use of a micro-RNA expression level or an expression level profile of multiple miRNA in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) of the subject which is characteristic of COPD or NSCLC. Detection of changes in expression in specific miRNA biomarkers from that of a reference sample or miRNA expression profile are correlated with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and / or COPD and permit differentiation among healthy subjects, subjects with COPD and subjects with adenocarcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma.
Owner:THE WISTAR INST OF ANATOMY & BIOLOGY
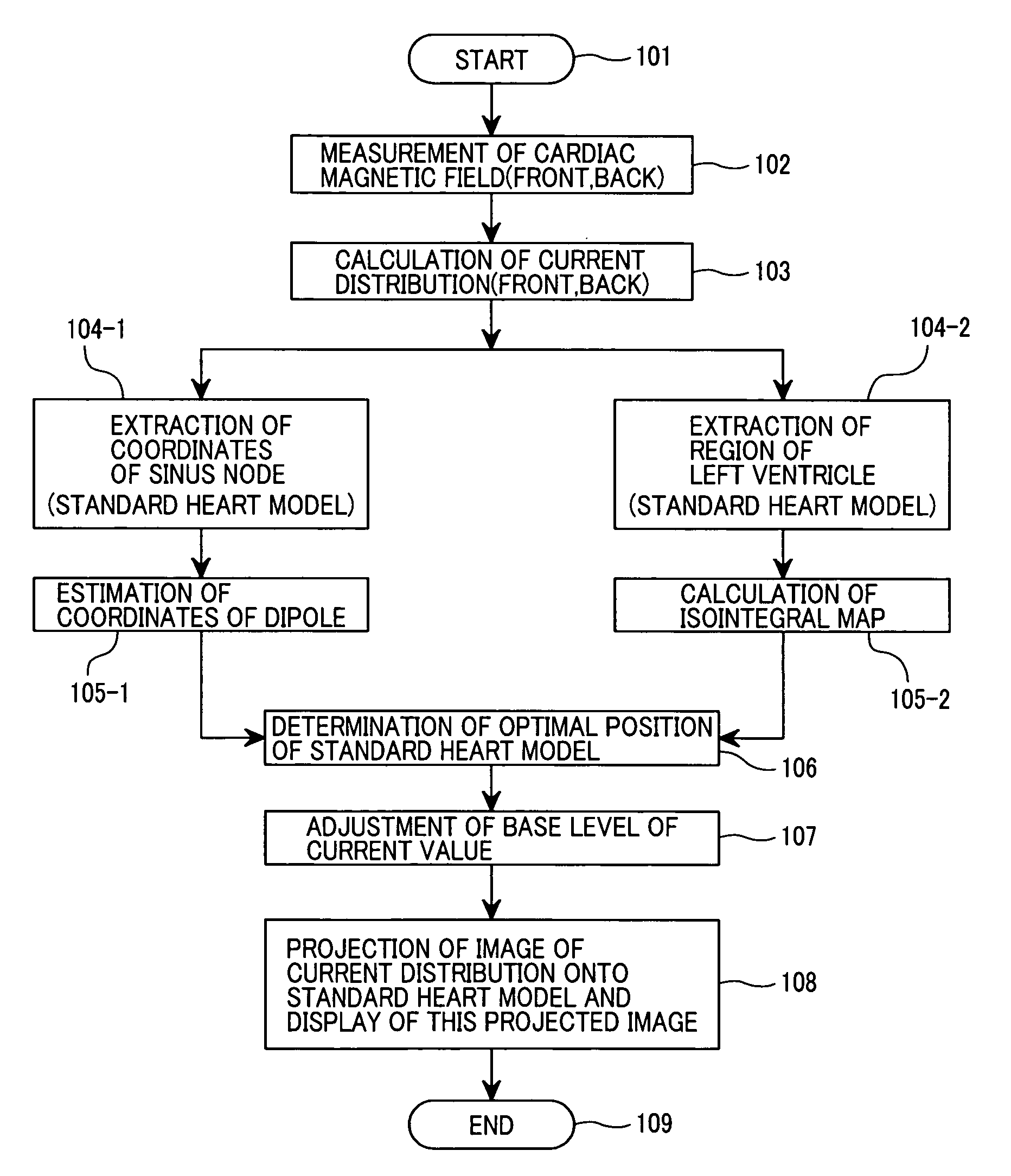
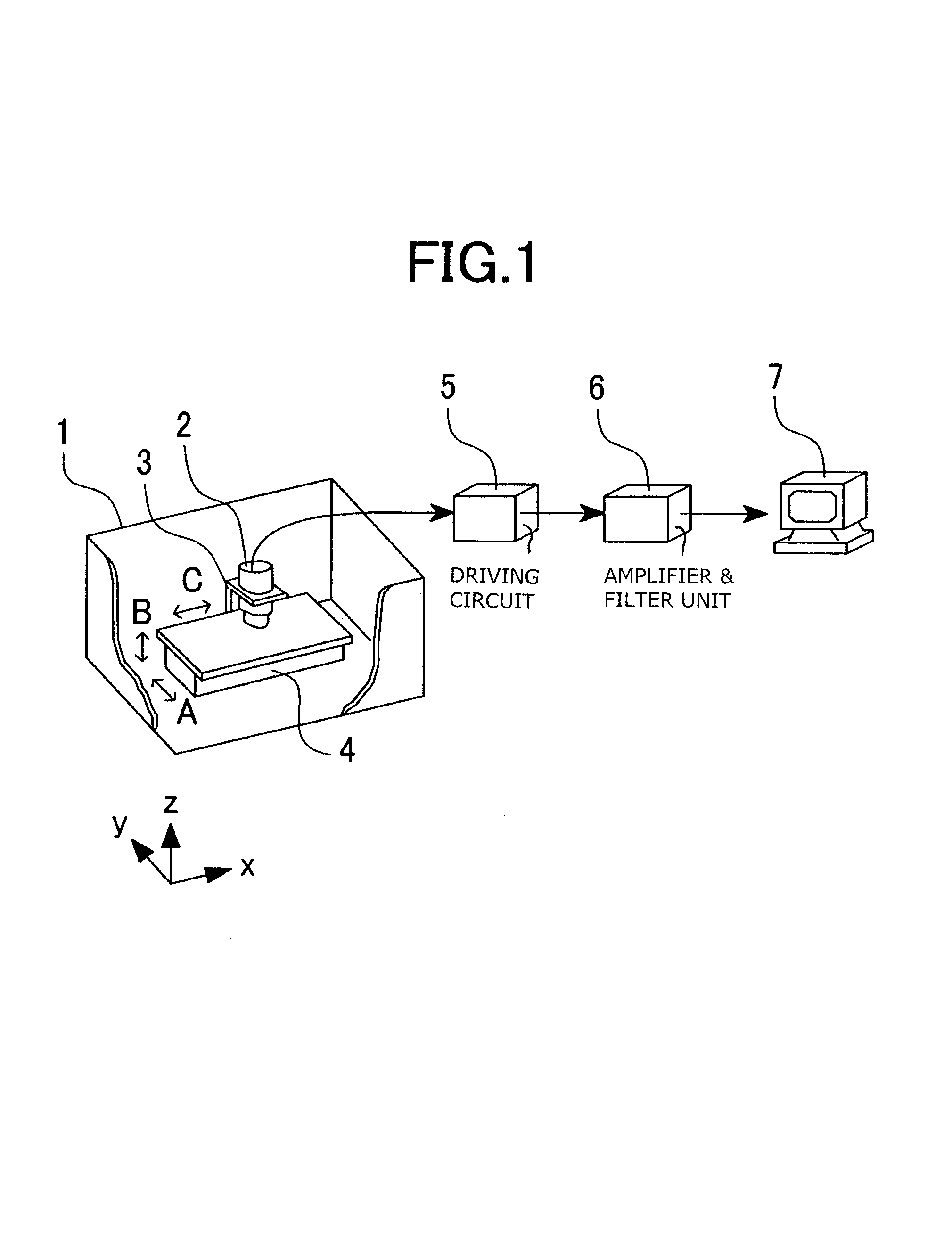
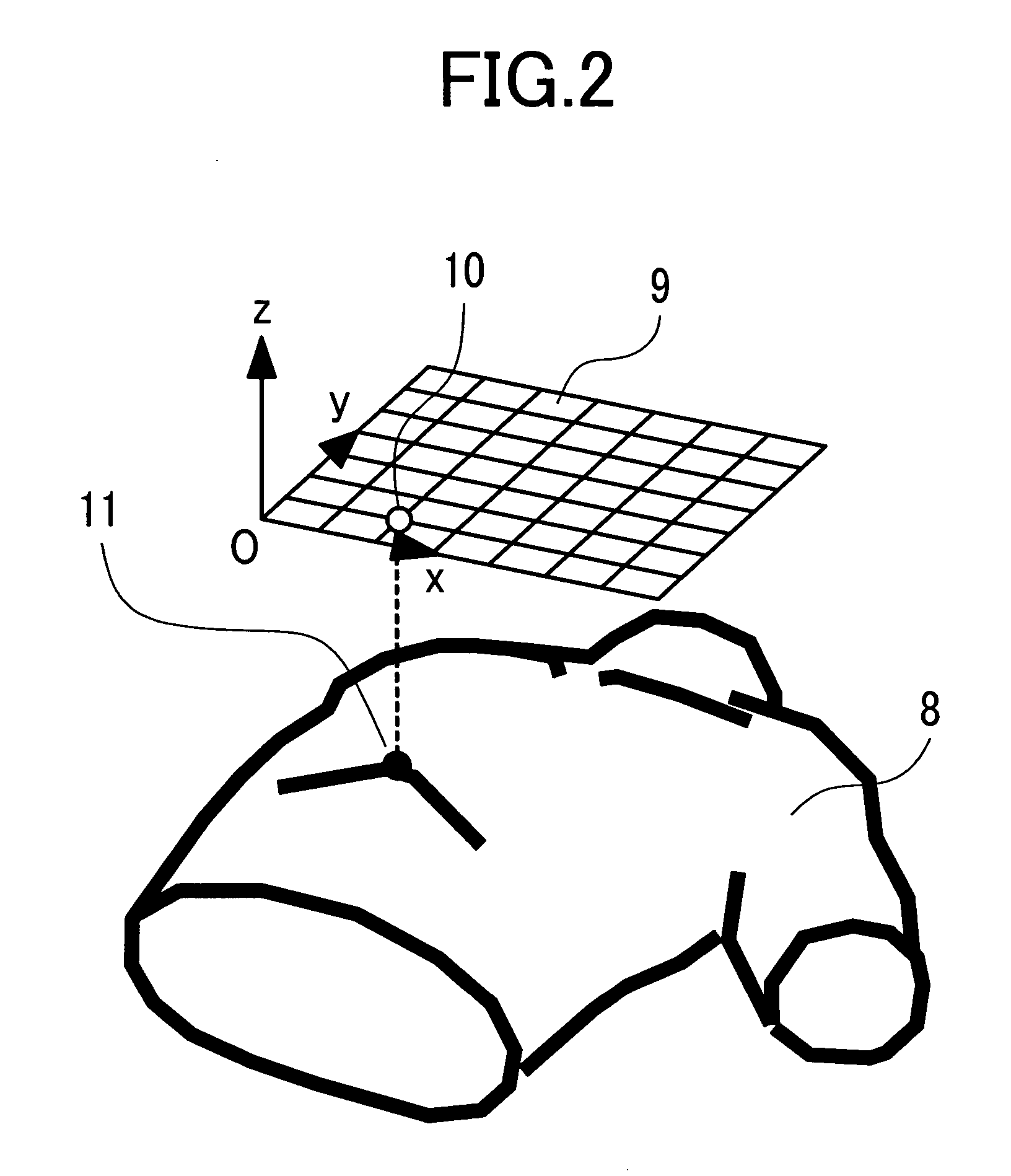
Biomagnetic measurement apparatus
ActiveUS7363070B2Minimize the differenceCharacter and pattern recognitionComputerised tomographsSinoatrial nodePower flow
Disclosed herein is a biomagnetic measurement apparatus capable of visualizing cardiac electrical current distributions with information on the cardiac morphology of a subject. A magnetic field component in the z direction, vertical to the chest surface of a subject, is measured from two directions, front and back of the chest, and then to calculate the current distributions in the two directions and the distributions of the amplitudes of those current distributions. A three-dimensional standard heart model is created from average data on the cardiac morphology obtained from plural healthy subjects. An optimal position of the model is determined using the coordinates of the sinus node and the coordinates of the left ventricle. Then, a weight coefficient is obtained by front and back current distributions and front and back the distributions of the amplitudes of those current distributions on a set boundary of the model.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
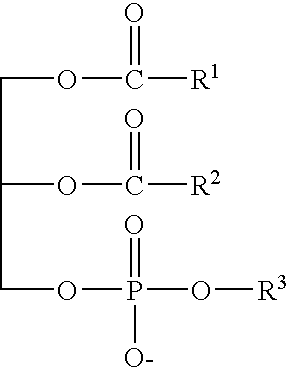
Novel applications of omega-3 rich phospholipids
InactiveUS20080058286A1Avoid weightAvoid inductionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSustained ventricular tachycardiaPhospholipid
This invention disclose novel uses of omega-3 rich phospholipids for treating diabetes type II, metabolic syndrome, sustained ventricular tachycardia and inflammatory disease. In addition to improving fertility in asthenozoospermic males. The invention also discloses the use of omega-3 rich phospholipids in healthy subject for improving physical endurances, reducing delayed onset muscle soreness as well as preventing obesity.
Owner:AKER BIOMARINE ASA
Diagnostic assay
The present invention relates generally to a diagnostic device including a prognostic assay for parameters which are indicative of a condition or event associated with the systemic vasculature. More particularly, the present invention provides an assay to detect parameters associated with a vascular disease including cardiovascular, stroke, pulmonary, renovascular, cerebrovascular, thrombotic or generalized arterial or venous condition or event including acute coronary syndrome such as but not limited to acute myocardial infarction, heart failure, atheromoma or a thrombotic condition. The identification of these parameters or more particularly a pattern of parameters enables the diagnosis of a condition or event or the determination of the risk of development of a condition or event associated to the systemic vasculature. Still more particularly, the present invention is directed to a diagnostic device comprising a set of members wherein one or more of said members has o r have specific or generic binding partners in a biological sample from an animal including human subject wherein the pattern of binding of the members to the binding partners is indicative, predictive or otherwise associated with a likelihood of a condition or event within the systemic vasculature. The absence of detection of specific or generic binding partners is also of indicative o r predictive value.
Owner:THE UNIV OF SYDNEY
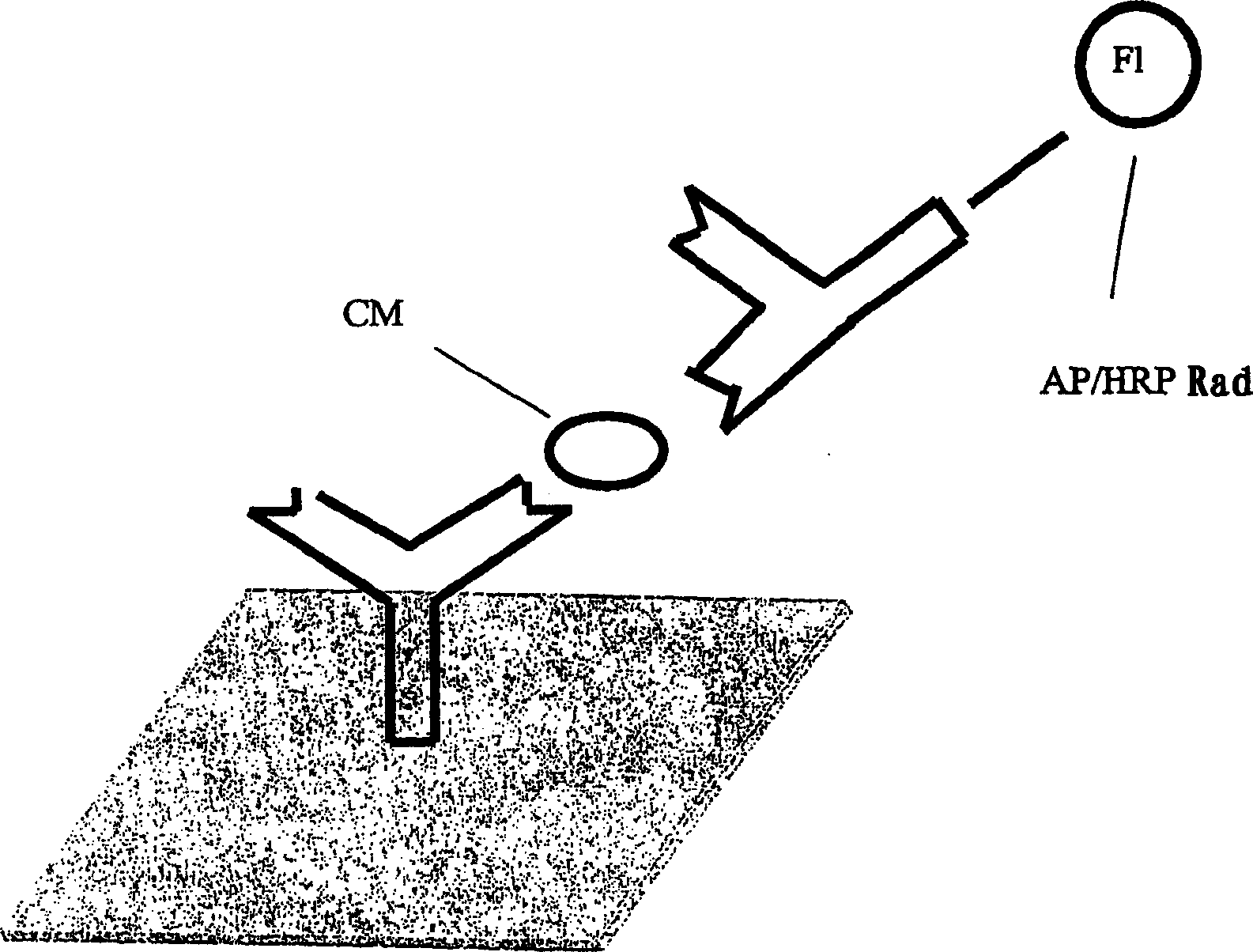
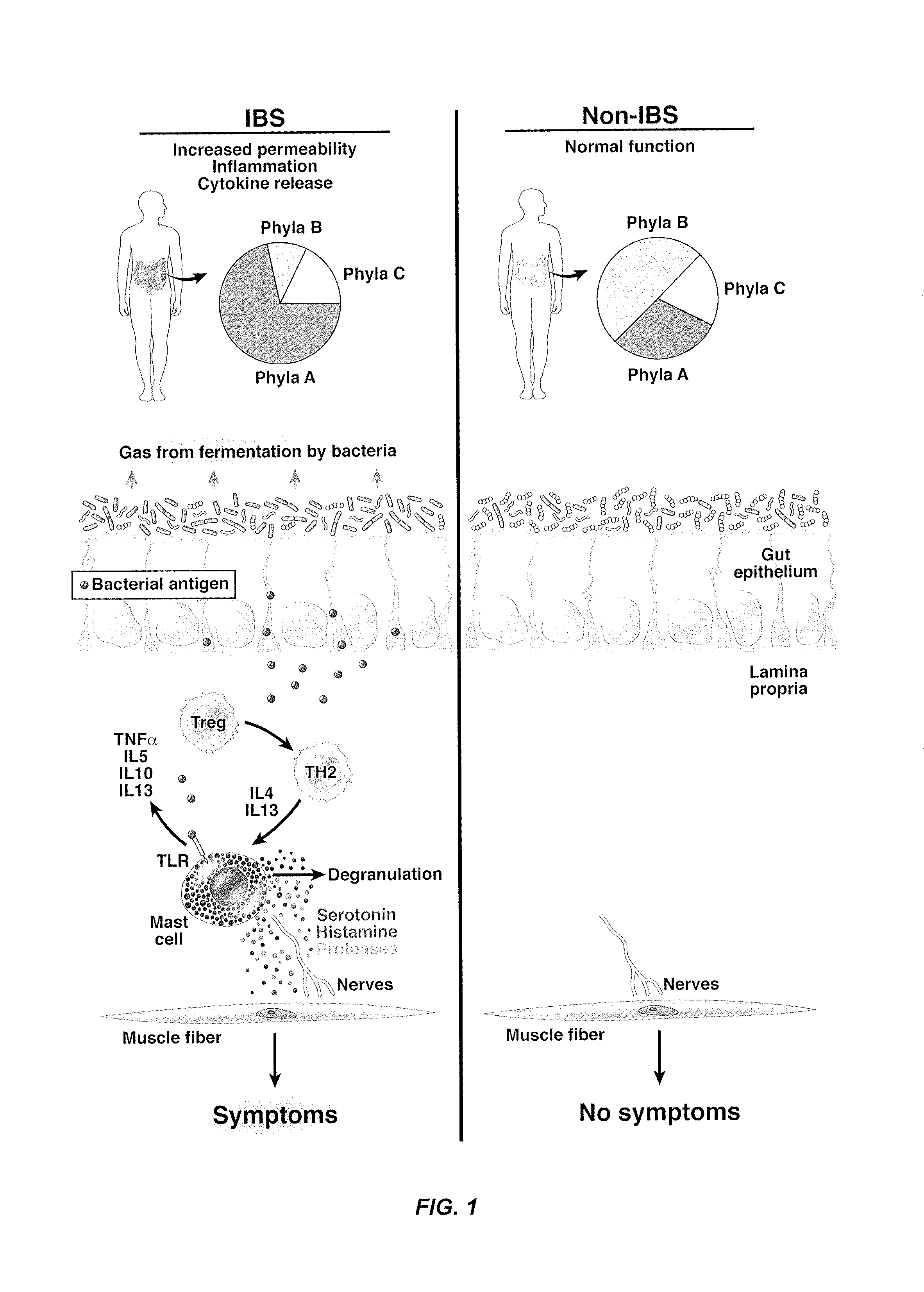
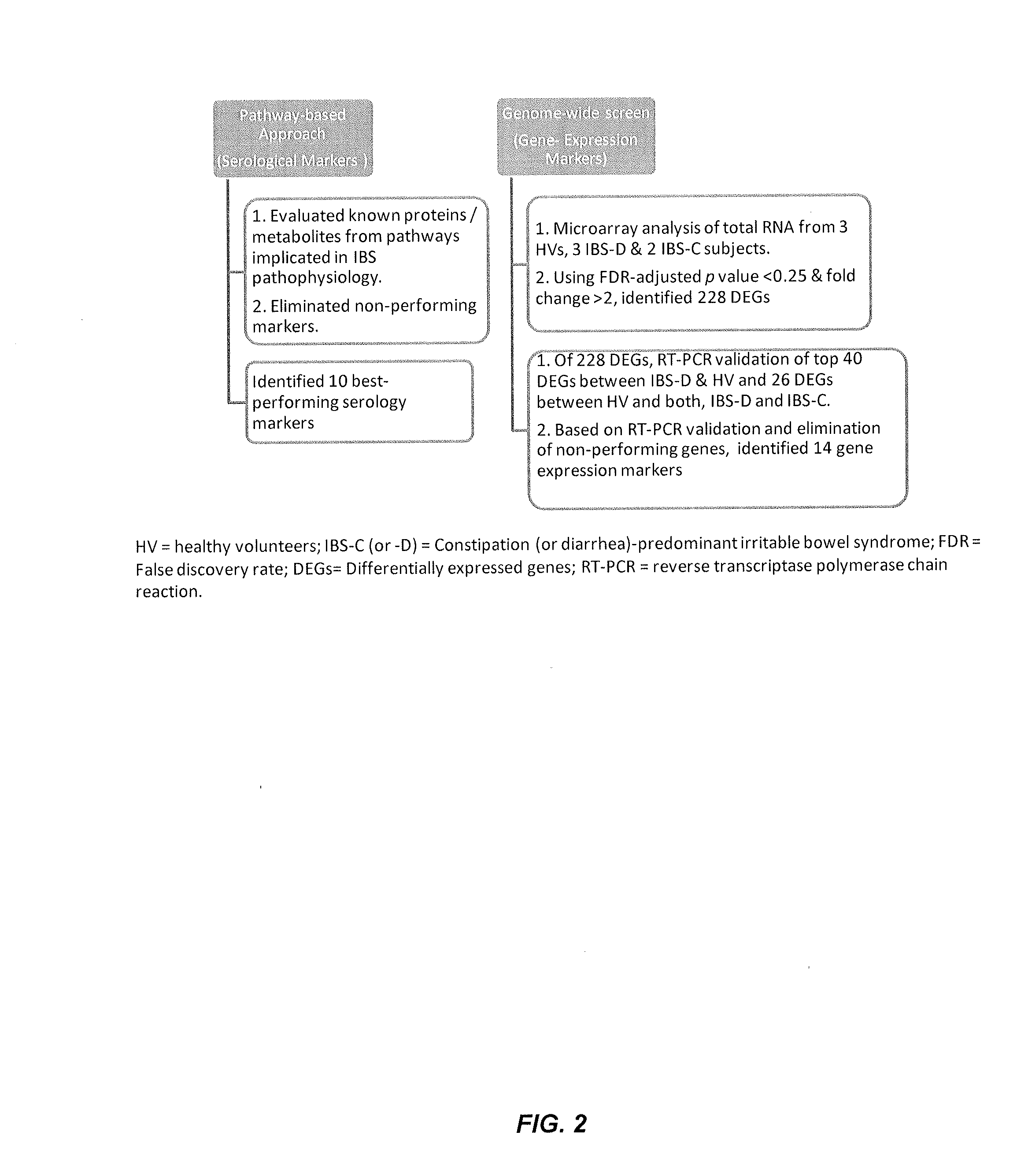
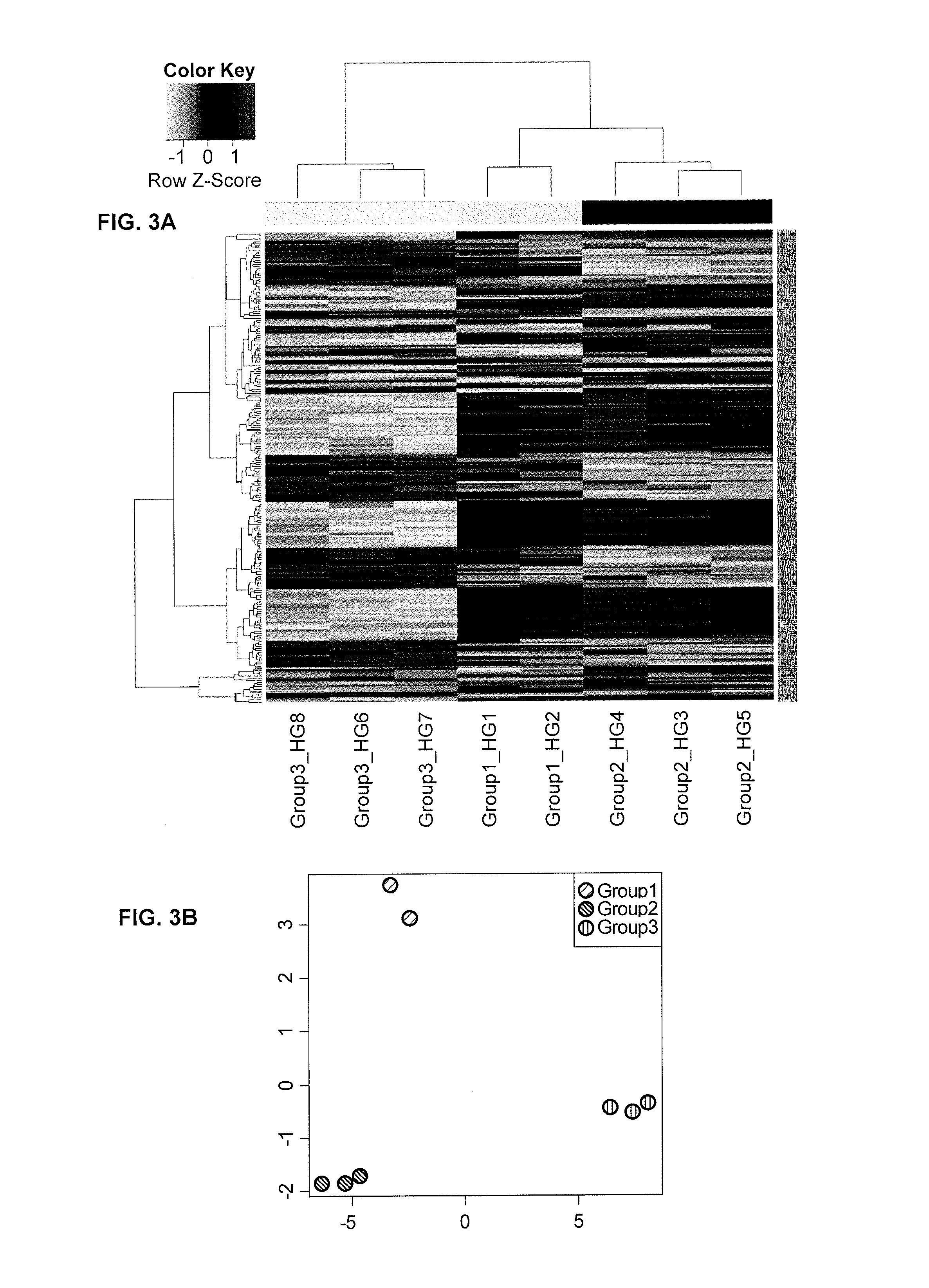
Performance of a biomarker panel for irritable bowel syndrome
InactiveUS20140141990A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningBiomarker panelHealthy subjects
The present invention provides a method of using a panel of serological and genetic biomarkers to distinguish IBS subjects from healthy subjects and / or to differentiate IBS subtypes from each other. The present invention also provides a method of using one or more psychological measures of a subject in conjunction with a panel of serological and / or genetic biomarkers to further aid in diagnosing IBS or discriminating IBS subtypes from each other.
Owner:NESTEC SA
Brain activity training device and brain activity training system
Provided is a brain activity training device for performing a training modifying correlation of connectivity between brain areas, using correlation of measured connectivity between brain areas in feedback information. A correlation matrix is derived for the activity degree between predetermined brain regions for each subject, from data of functional connectivity MRI at rest measured in a group of healthy subjects and in a group of patients (S102). Feature extraction is performed (S104) by regularized canonical correlation analysis on the correlation matrix and on subjects characteristics containing subjects patients / healthy labels. Based on the results of the regularized canonical correlation analysis, a discriminatory analysis (S106) is performed by sparse logistic regression and discriminants are generated (S108). The brain activity training device gives a score in feedback to subjects, based on the results of discriminants for data of functional connectivity MRI relative to the subjects.
Owner:ATR ADVANCED TELECOMM RES INST INT
Biomarkers for lymphoma
A biomarker, method, test kit, and diagnostic system for detecting the presence of lymphoma in a person are disclosed. The lymphoma may be Hodgkin's lymphoma or non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. The person may be a high-risk subject. In one embodiment, a plasma sample from a person is obtained. The level of at least one protein listed in Table S3 in the plasma sample is measured. The level of at least one protein in the plasma sample is compared with the level in a normal or healthy subject. The lymphoma is diagnosed based upon the level of the at least one protein in the plasma sample in comparison to the normal or healthy level.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Method and device for gravity like simulation of natural balance movements
We present a tool that can enhance the concept of BWS training by allowing natural APAs to occur mediolaterally. While in a supine position in a 90 degree tilted environment built around a modified hospital bed, subjects wear a backpack frame that is freely moving on air-hearings, as a puck on an air hockey table, and attached through a cable to a pneumatic cylinder that provides a load that can be set to emulate various G-like loads. Veridical visual input is provided through two 3-D automultiscopic displays that allow glasses free 3-D vision representing a virtual surrounding environment that may be acquired from sites chosen by the patient. Two groups of 12 healthy subjects were exposed to either strength training alone or a combination of strength and balance training in such a tilted environment over a period of four weeks.
Owner:ODDSSON LARS
Nutrients solutions for enhancement of cognitive function
The present invention relates to dietary supplements, medical foods, or pharmaceutical compositions for use in the method of enhancement of cognitive function in healthy subjects and / or subjects person suffering from a cognitive deficit, comprising aqueous solution of a nutrient, wherein solution comprises a water having content of deuterium from 90 to about 135 ppm and 1H216O isotopologue up to 99.759%. In one embodiment of the invention relates to a succinate salt of choline as the nutrient.
Owner:MITOCHONDRIAL SUBSTRATE INVENTION
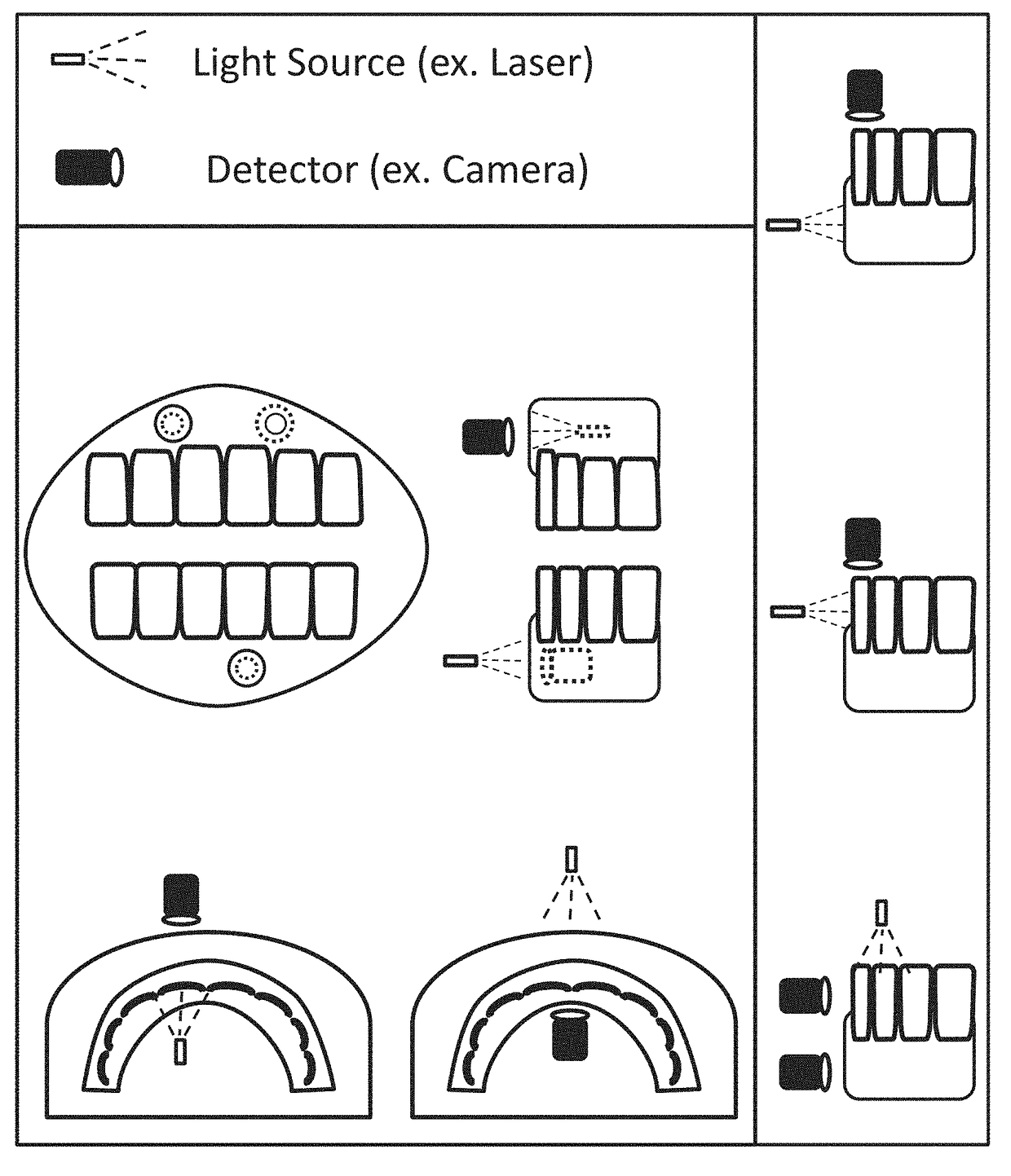
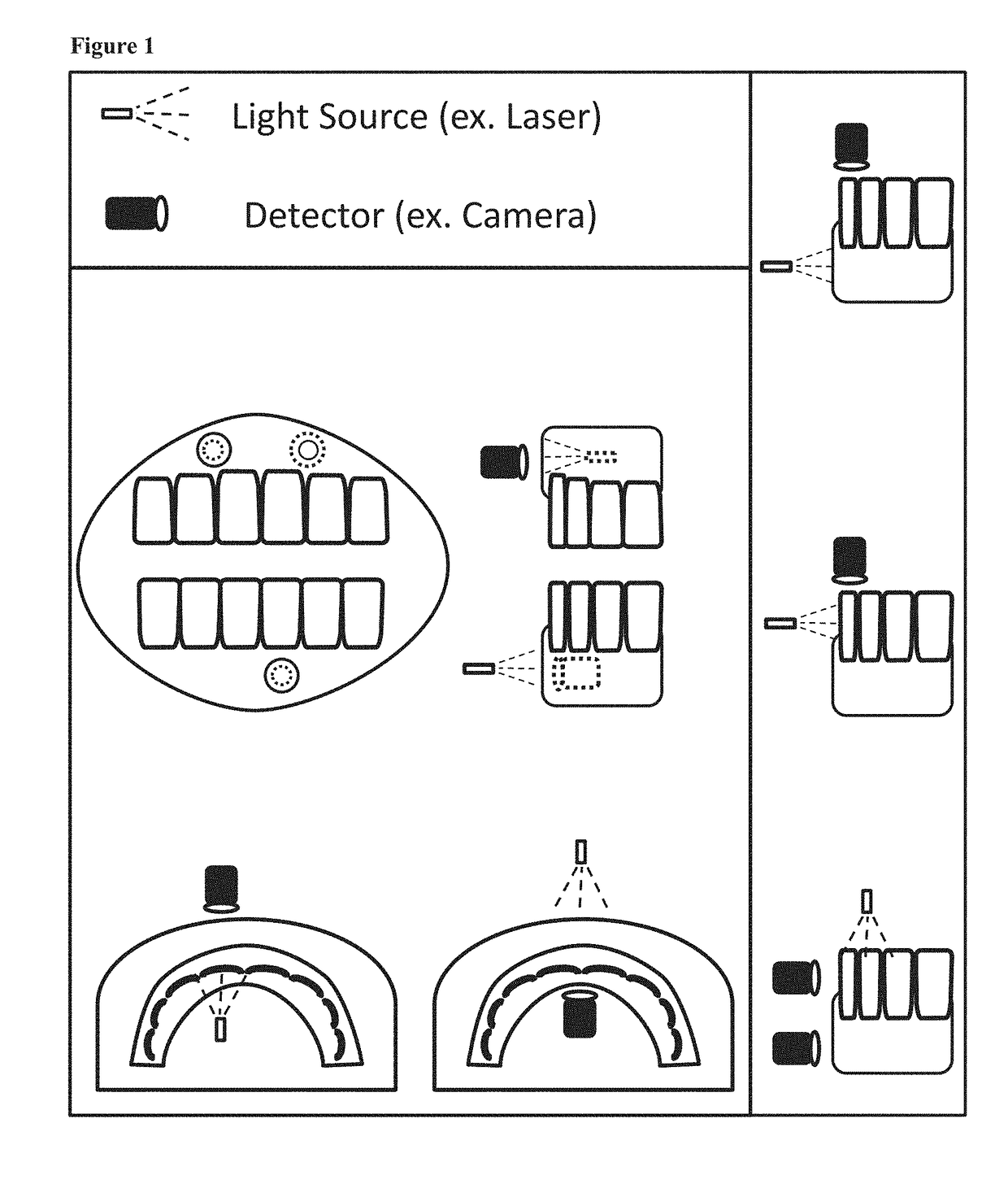
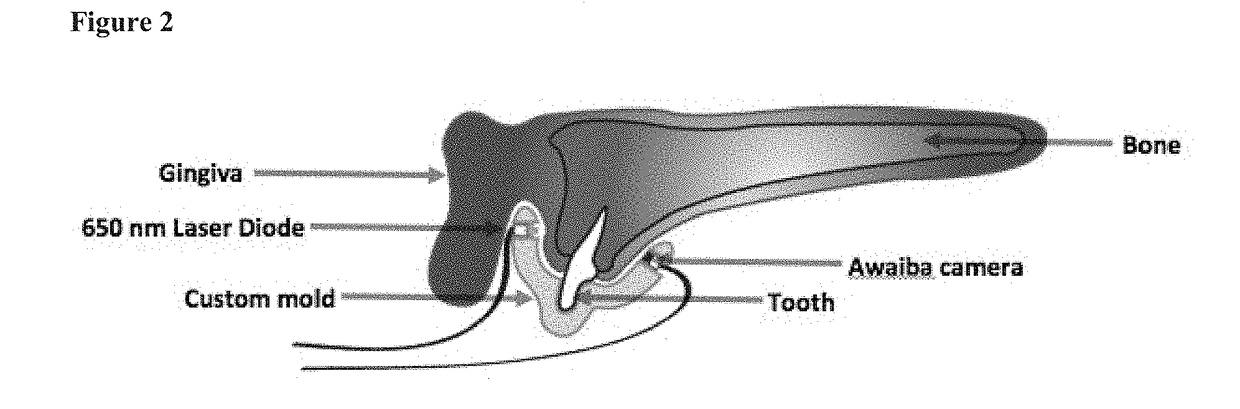
Methods and apparatus for the assessment of gingival blood flow
Disclosed herein are methods and apparatus for diagnosing a disease in the gingival region of an individual, comprising: quantitatively measuring blood flow or changes in blood flow in the gingival region of the individual, potentially comparing these data to that of a healthy subject, and diagnosing the disease based one of more of these quantities.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
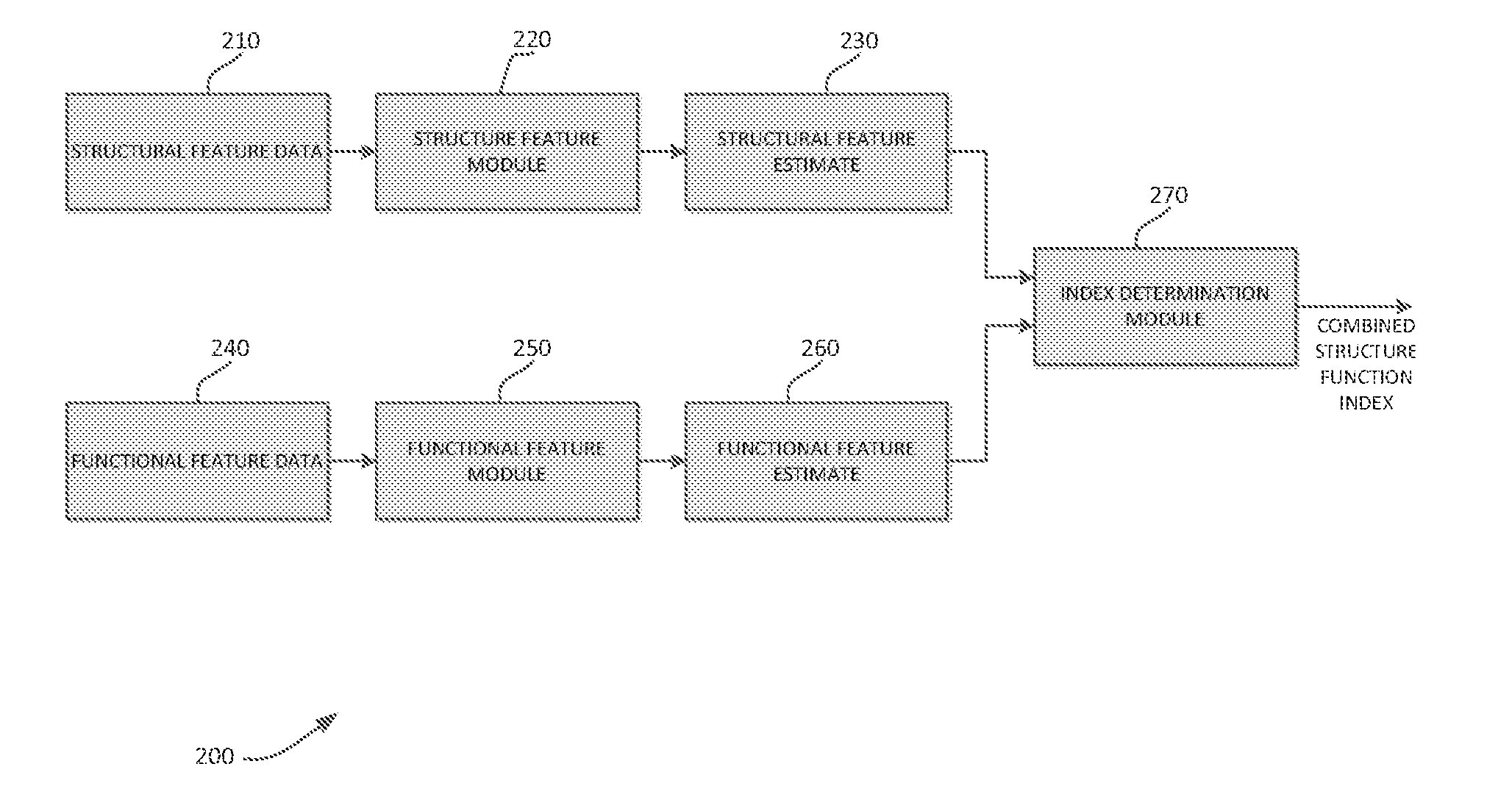
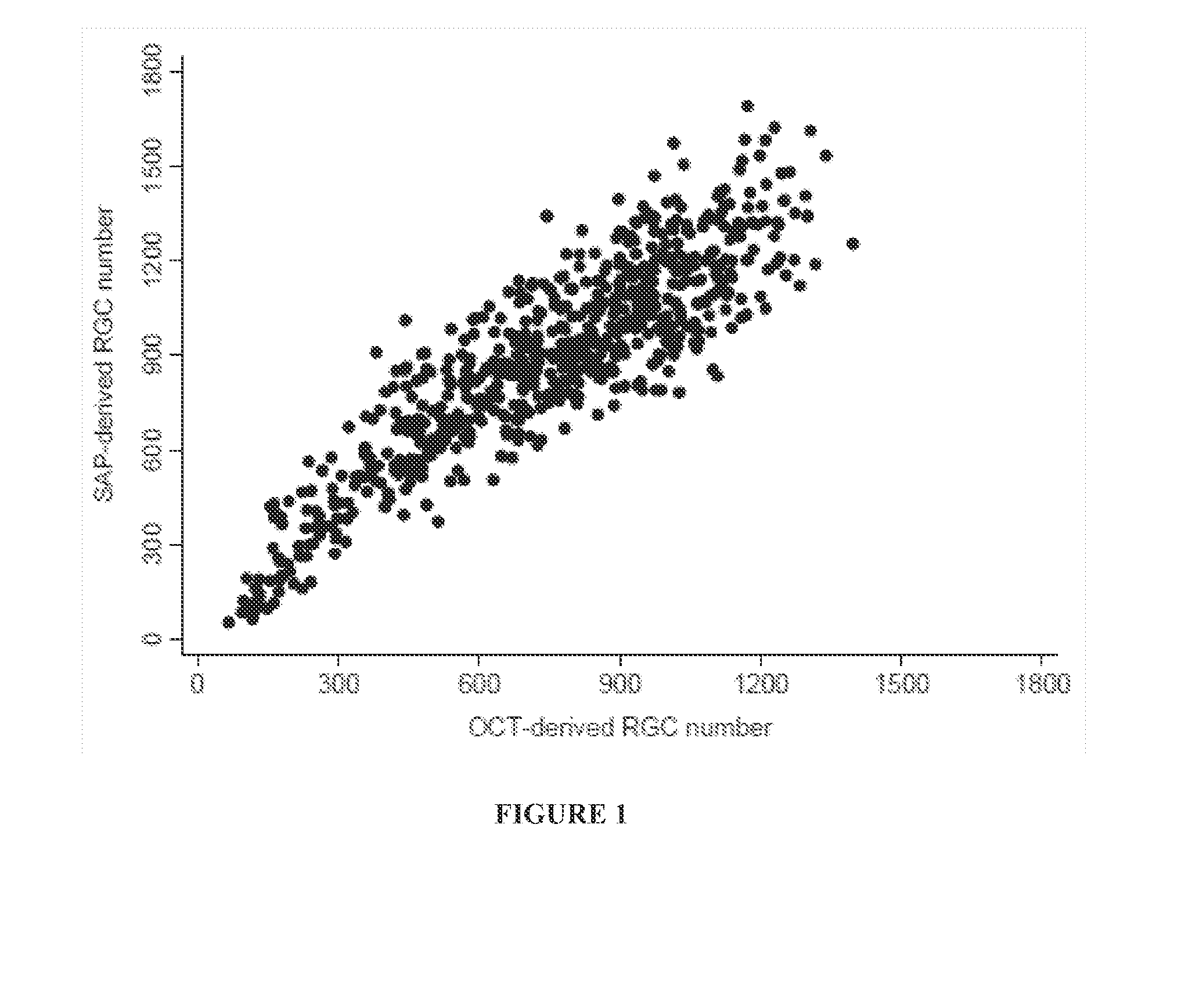
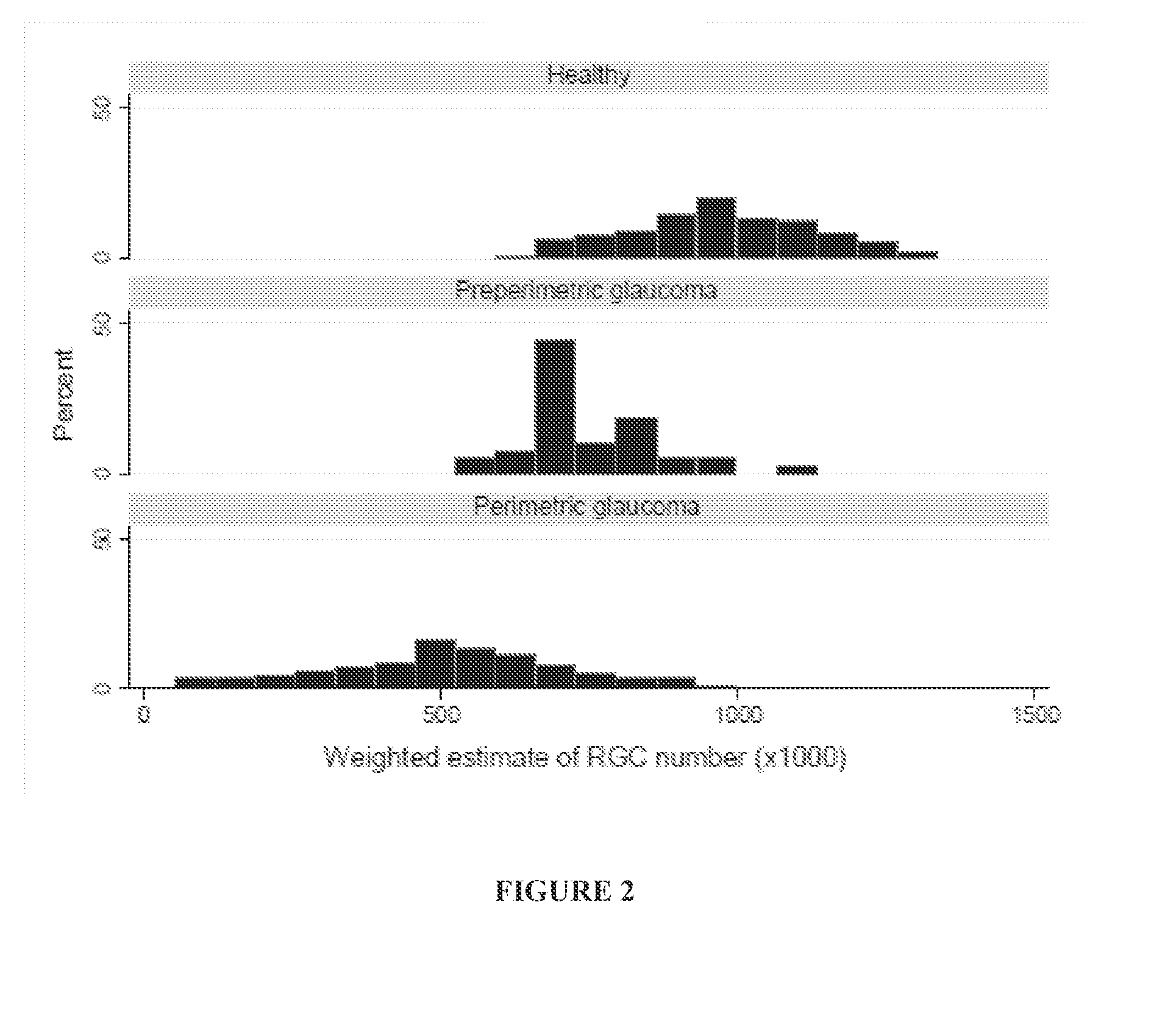
Systems and methods for determining retinal ganglion cell populations and associated treatments
A new combined index of structure and function (CSFI) for staging and detecting glaucomatous damage is provided. An observational study including 333 glaucomatous eyes (295 with perimetric glaucoma and 38 with preperimetric glaucoma) and 330 eyes of healthy subjects is described. All eyes were tested with standard automated perimetry (SAP) and spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SDOCT) within 6 months. Estimates of the number of retinal ganglion cells (RGC) were obtained from SAP and SDOCT and a weighted averaging scheme was used to obtain a final estimate of the number of RGCs for each eye. The CSFI was calculated as the percent loss of RGCs obtained by subtracting estimated from expected RGC numbers. The performance of the CSFI for discriminating glaucoma from normal eyes and the different stages of disease was evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. The mean CSFI, representing the mean estimated percent loss of RGCs, was 41% and 17% in the perimetric and pre-perimetric groups, respectively (P<0.001). They were both significantly higher than the mean CSFI in the normal group (P<Q.0( )1). The CSFI had larger ROC curve areas than isolated indexes of structure and function for detecting perimetric and preperimetric glaucoma and differentiating among early, moderate and advanced stages of visual field loss. An index combining structure and function performed better than isolated structural and functional measures for detection of perimetric and preperimetric glaucoma as well as for discriminating different stages of the disease.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
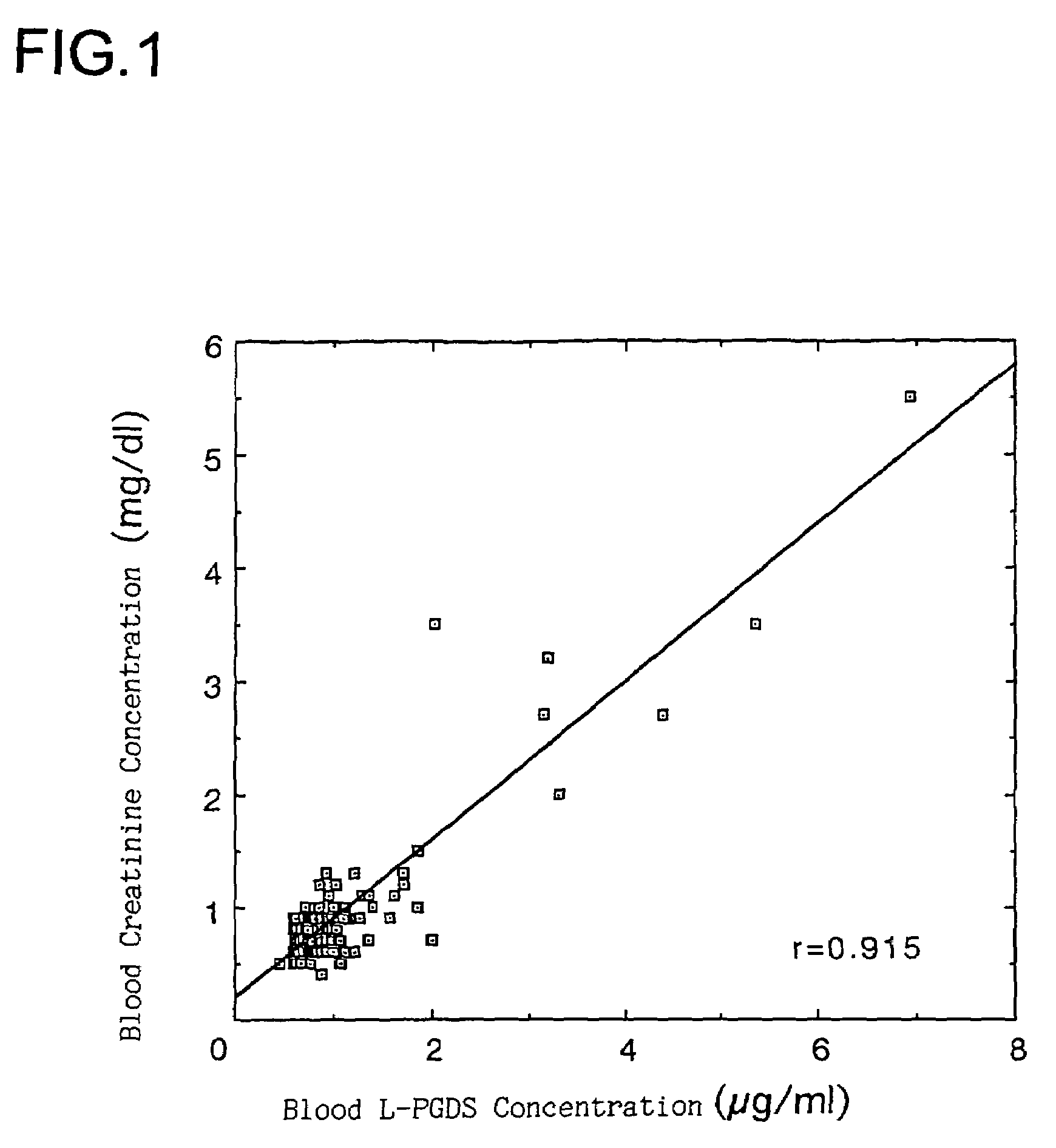
Method of detection and disease state management for renal diseases
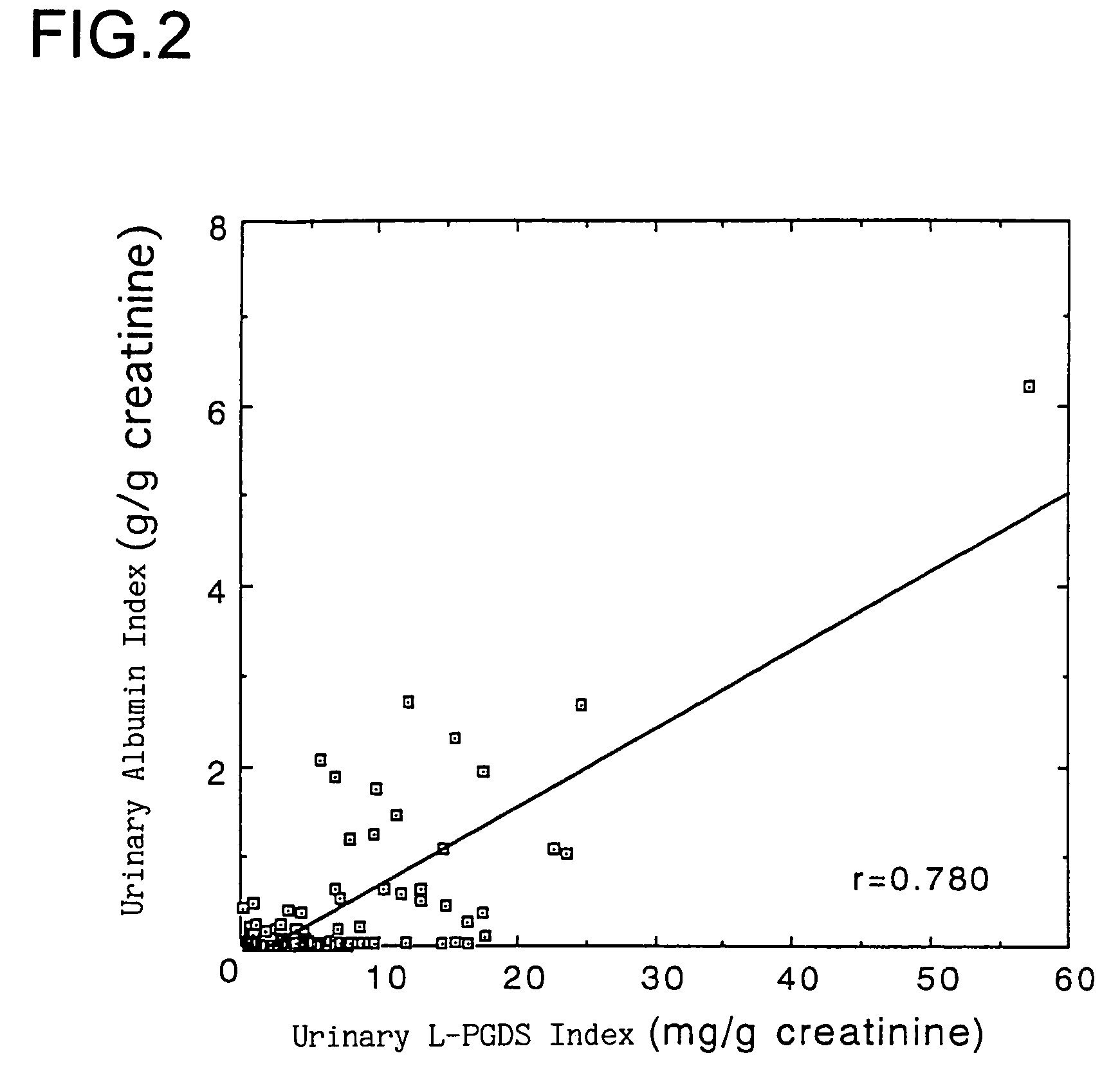
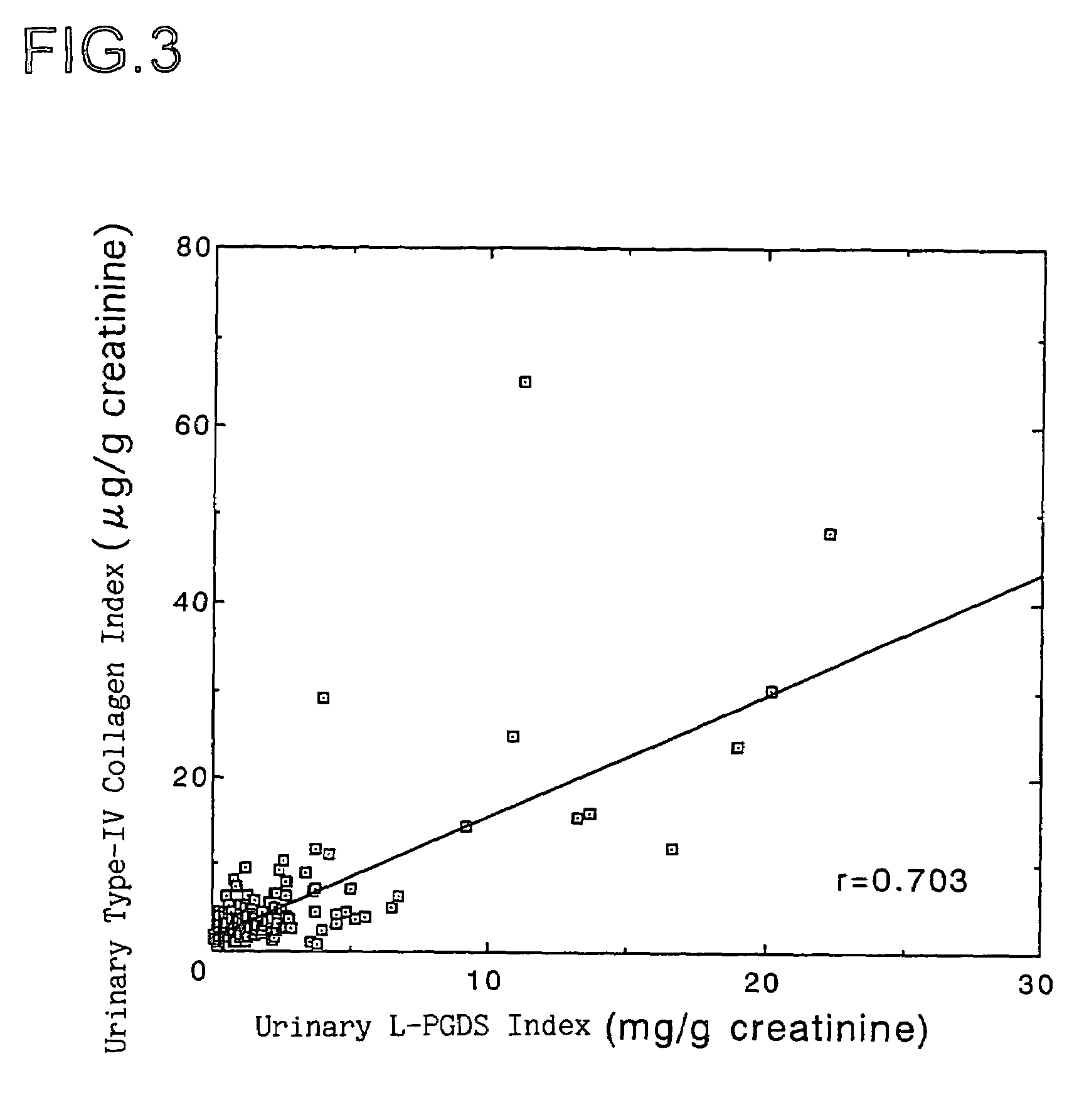
InactiveUS7109044B1Big burden to solveEvaluate simply and in a short time glomerular filtration abilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisNephrosisValue set
The present invention relates to a method of detection of an early-stage renal disease, comprising determining the concentration of human lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase in a body fluid sample taken from a subject and comparing the determined concentration with a reference value set by determining the concentrations of human lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase in body fluid samples taken from healthy subjects; and a method of disease state management for a renal disease, comprising determining the concentration of human lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase in a body fluid sample taken from a subject and evaluating the glomerular filtration ability of the subject from the determined concentration.
Owner:MARUHA NICHIRO
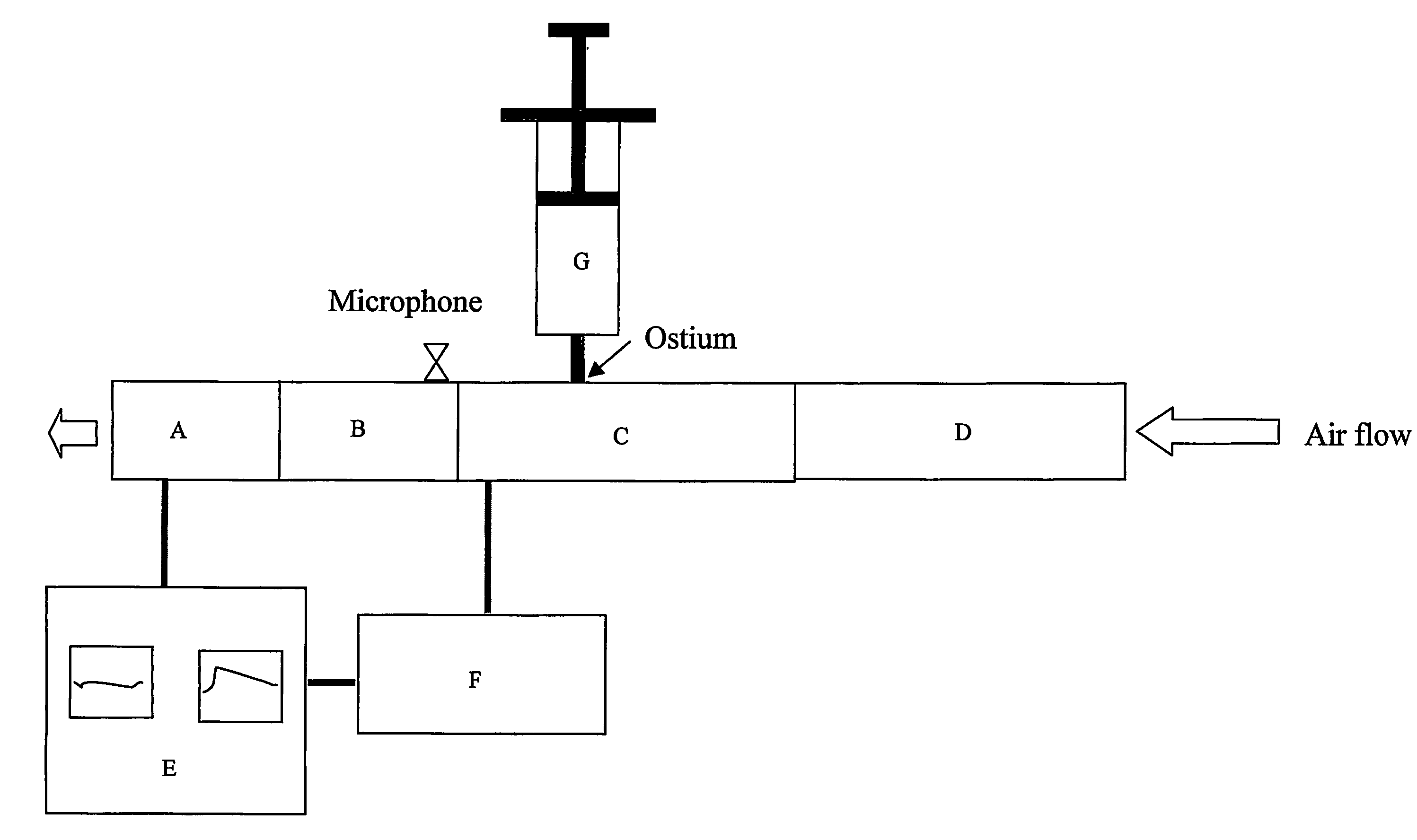
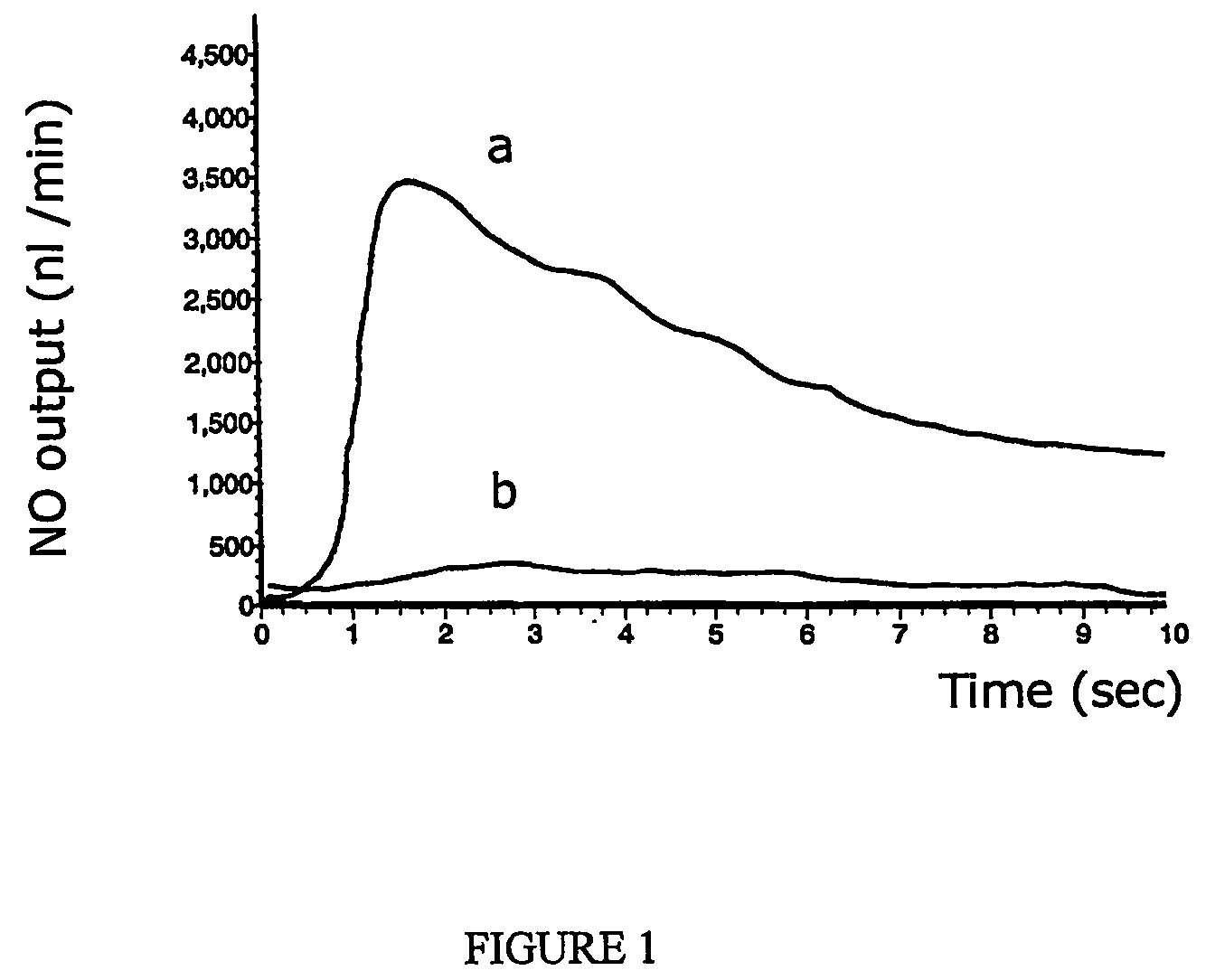
Method and device for diagnosis using an oscillating airflow
Owner:CIRCASSIA AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com