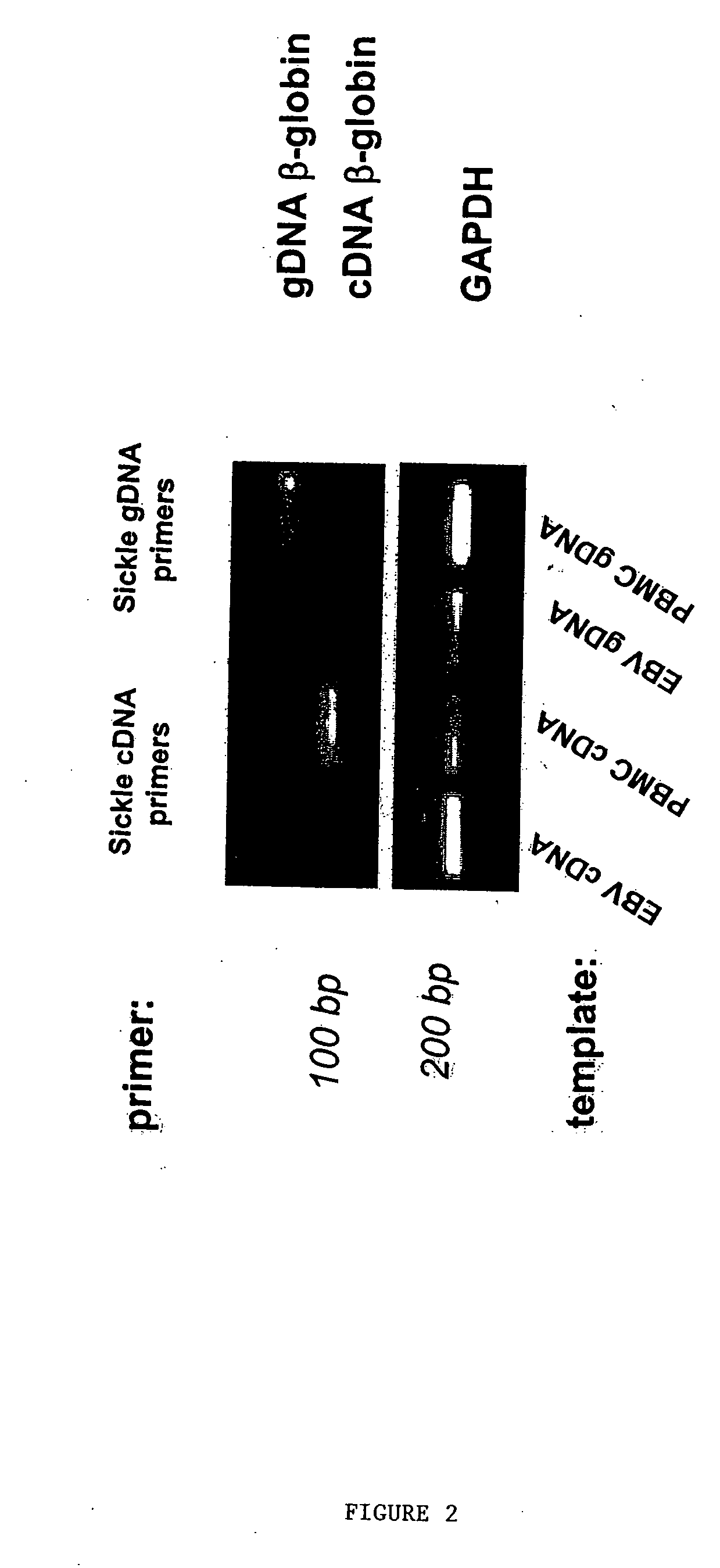
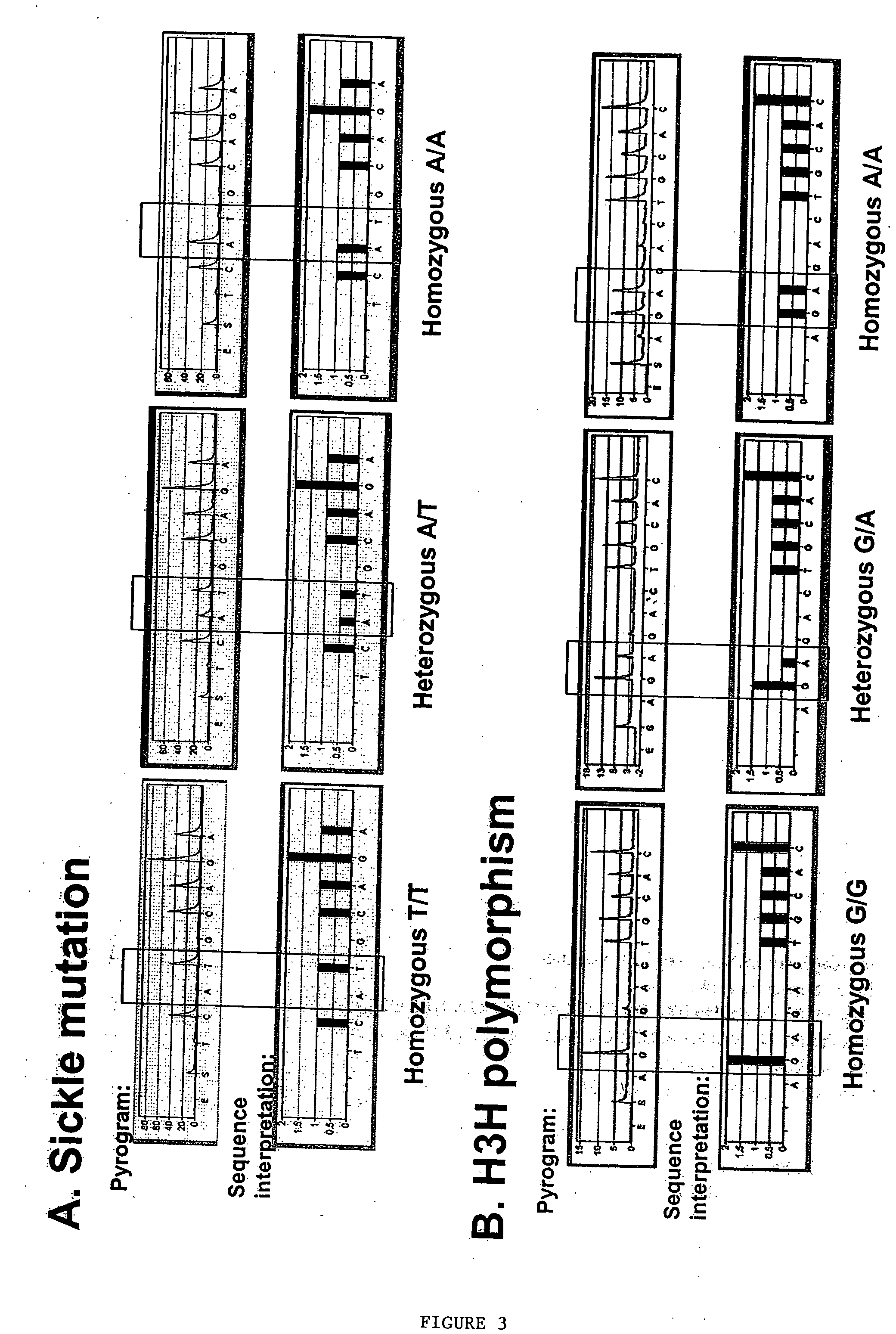
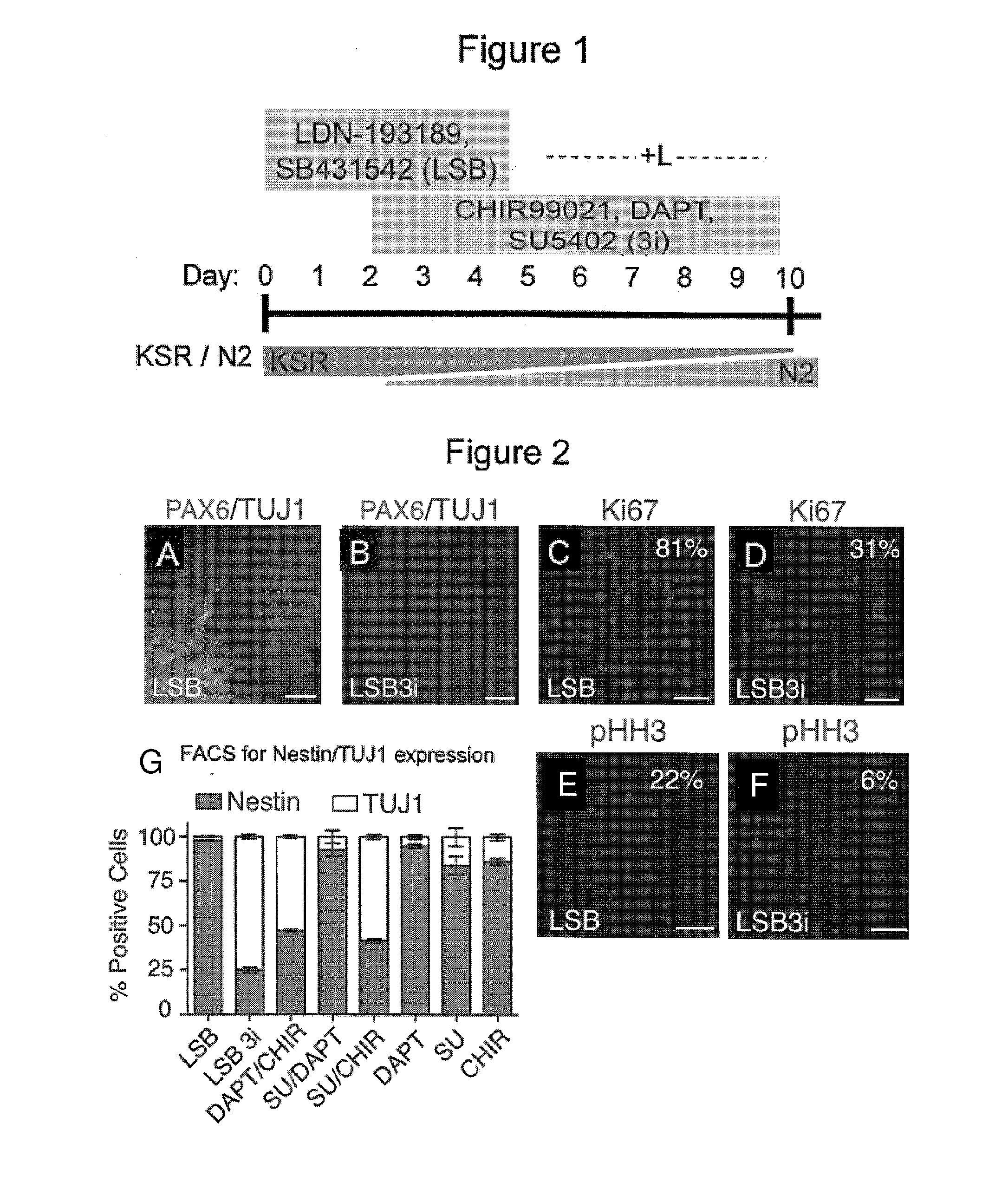
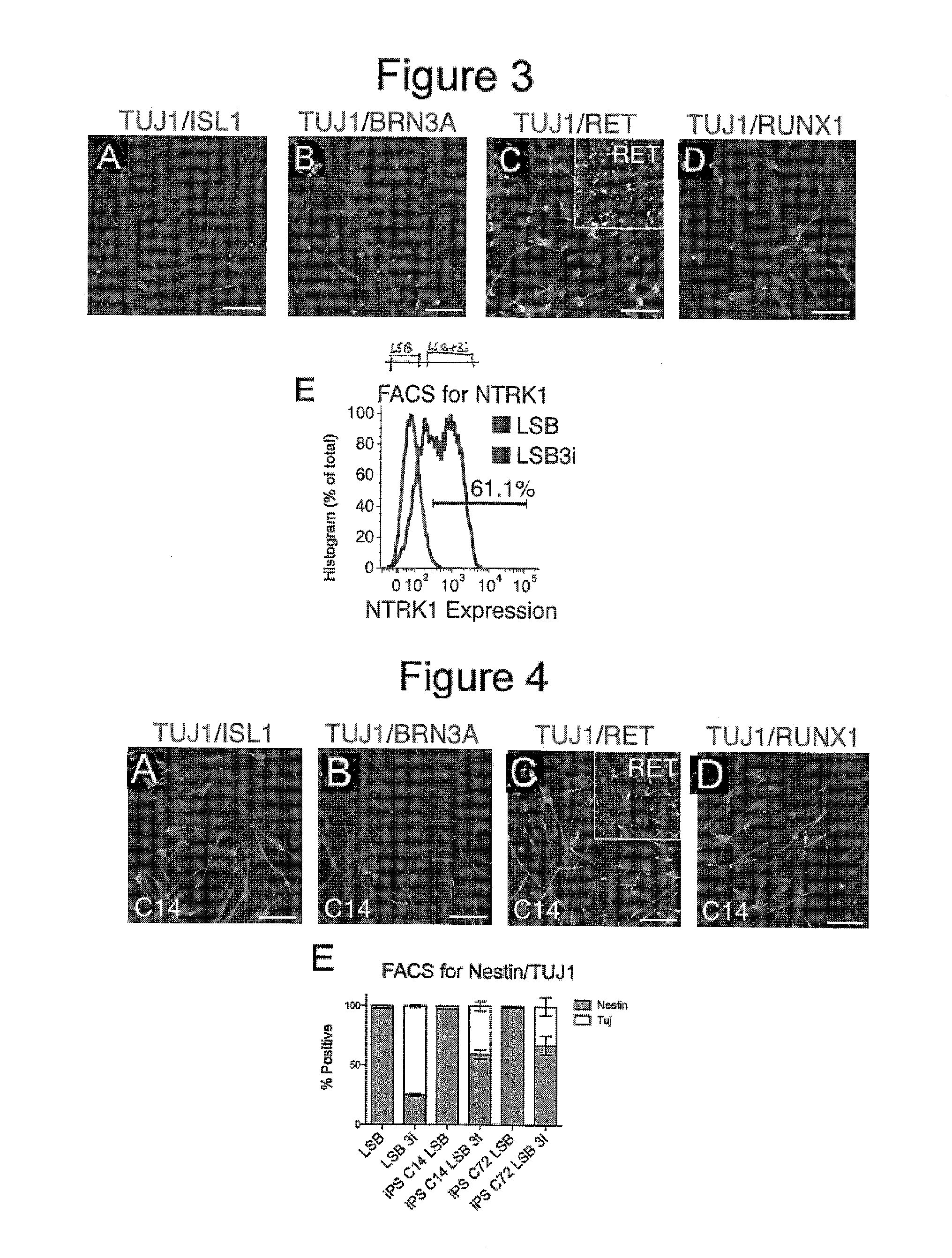
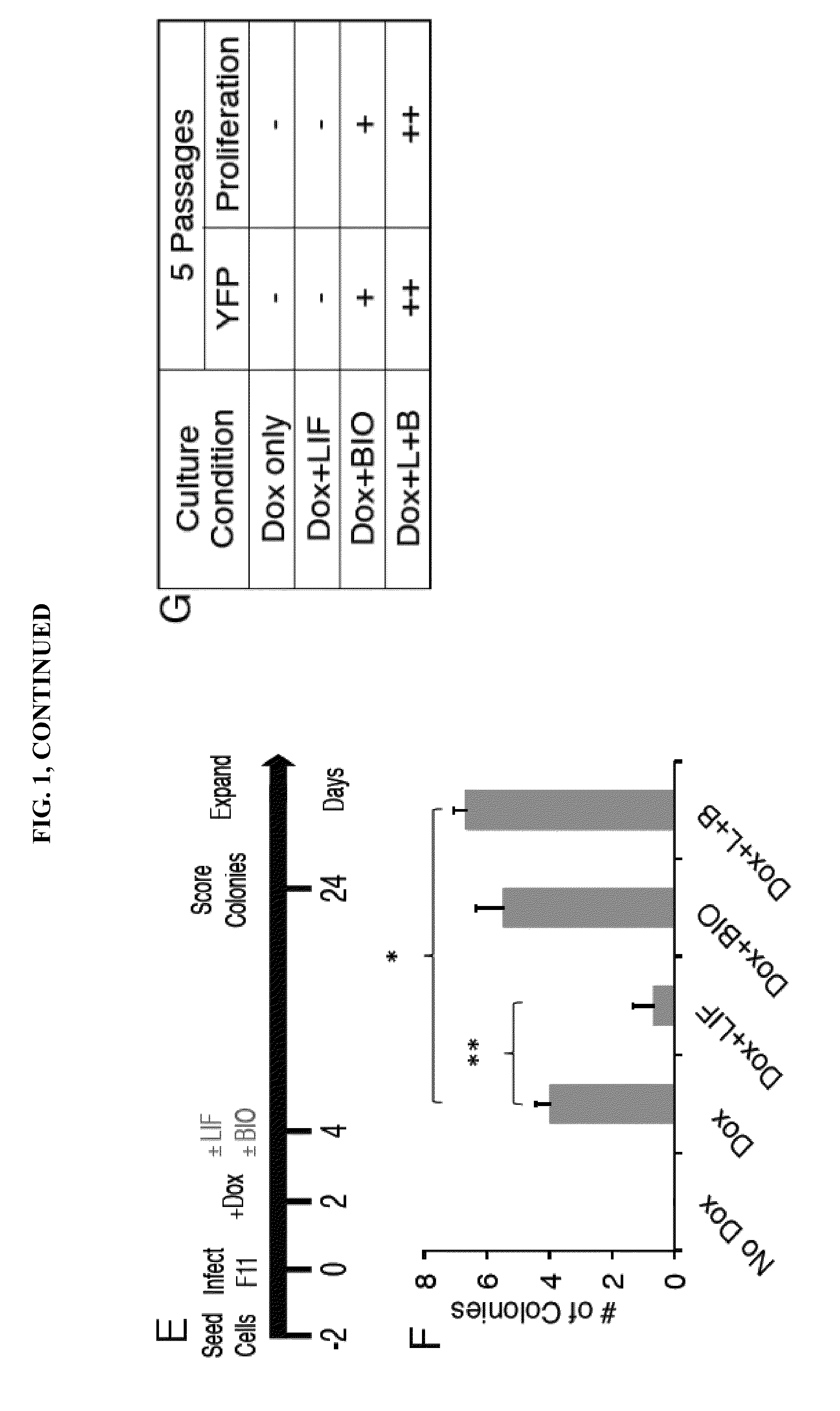
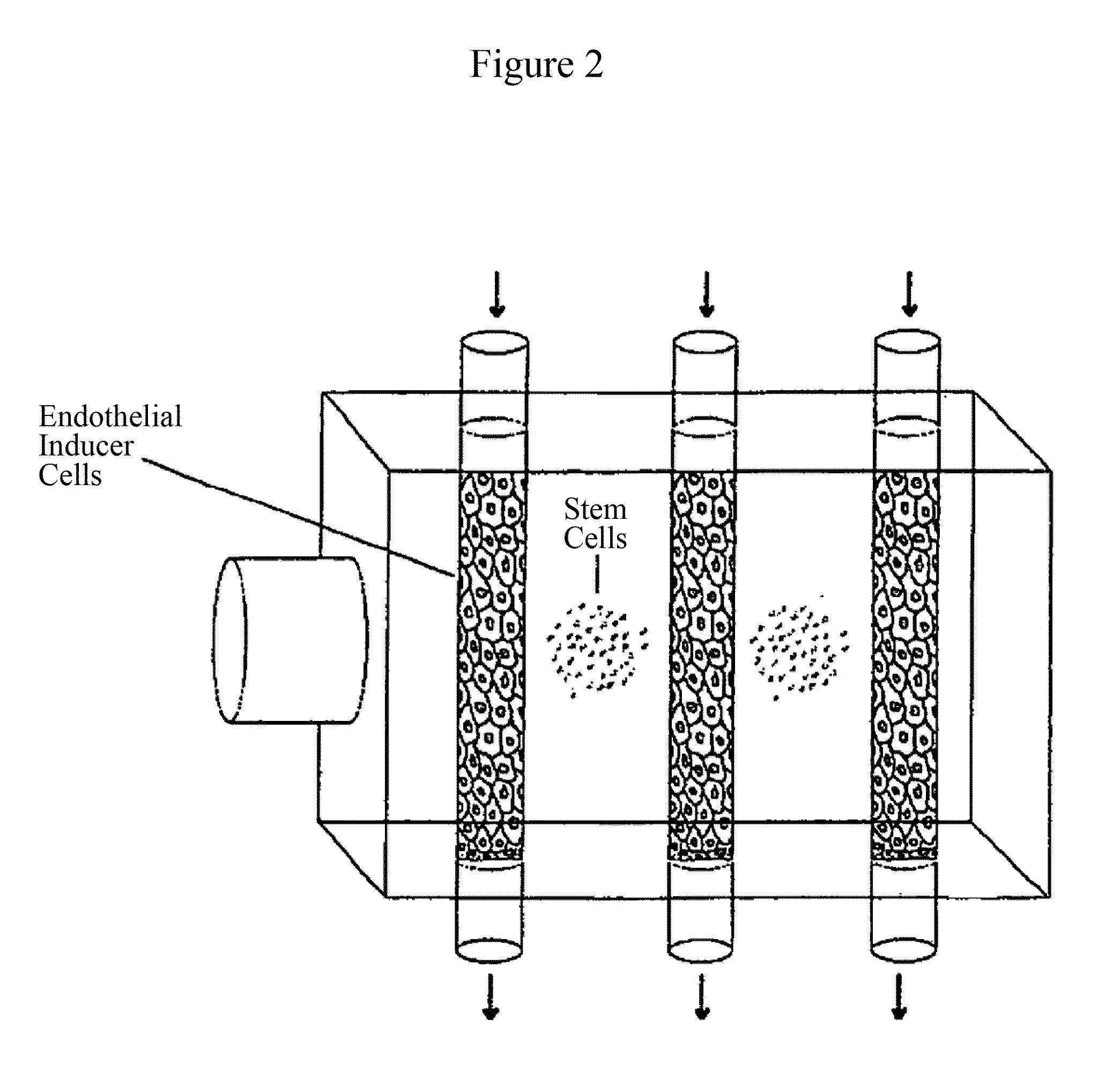
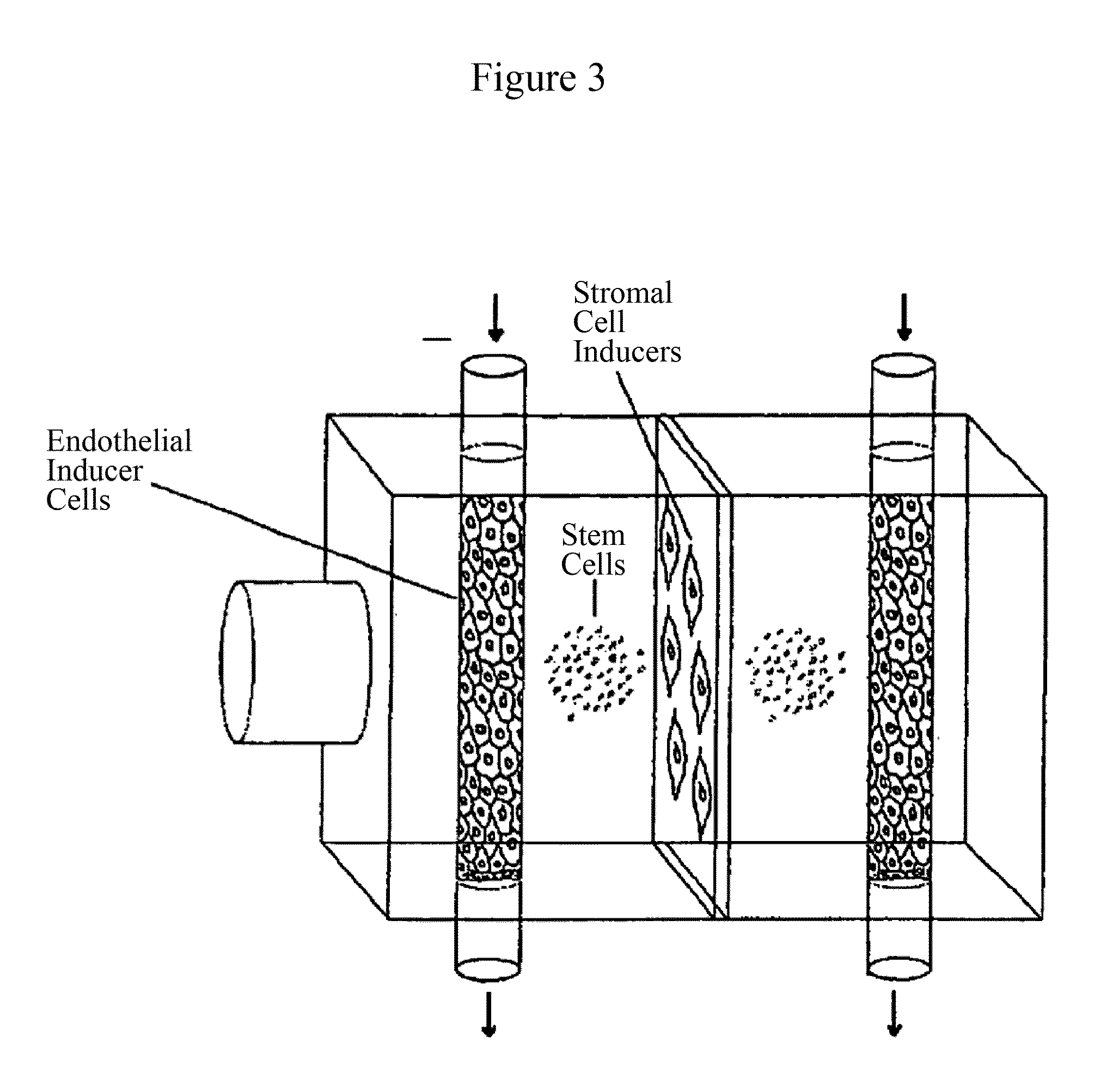
Patents
Literature
47 results about "Lineage specific" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Defined media for stem cell culture
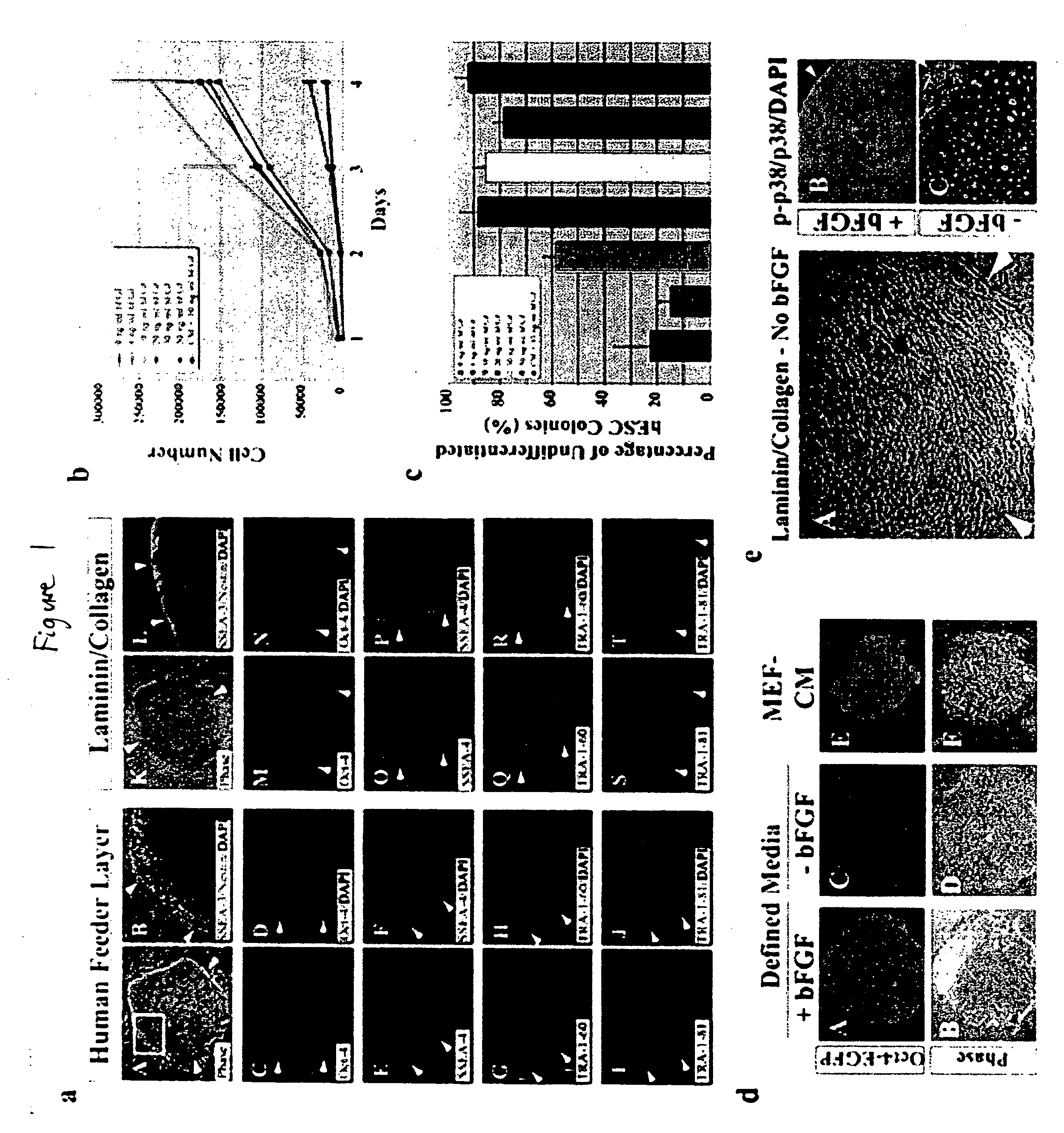
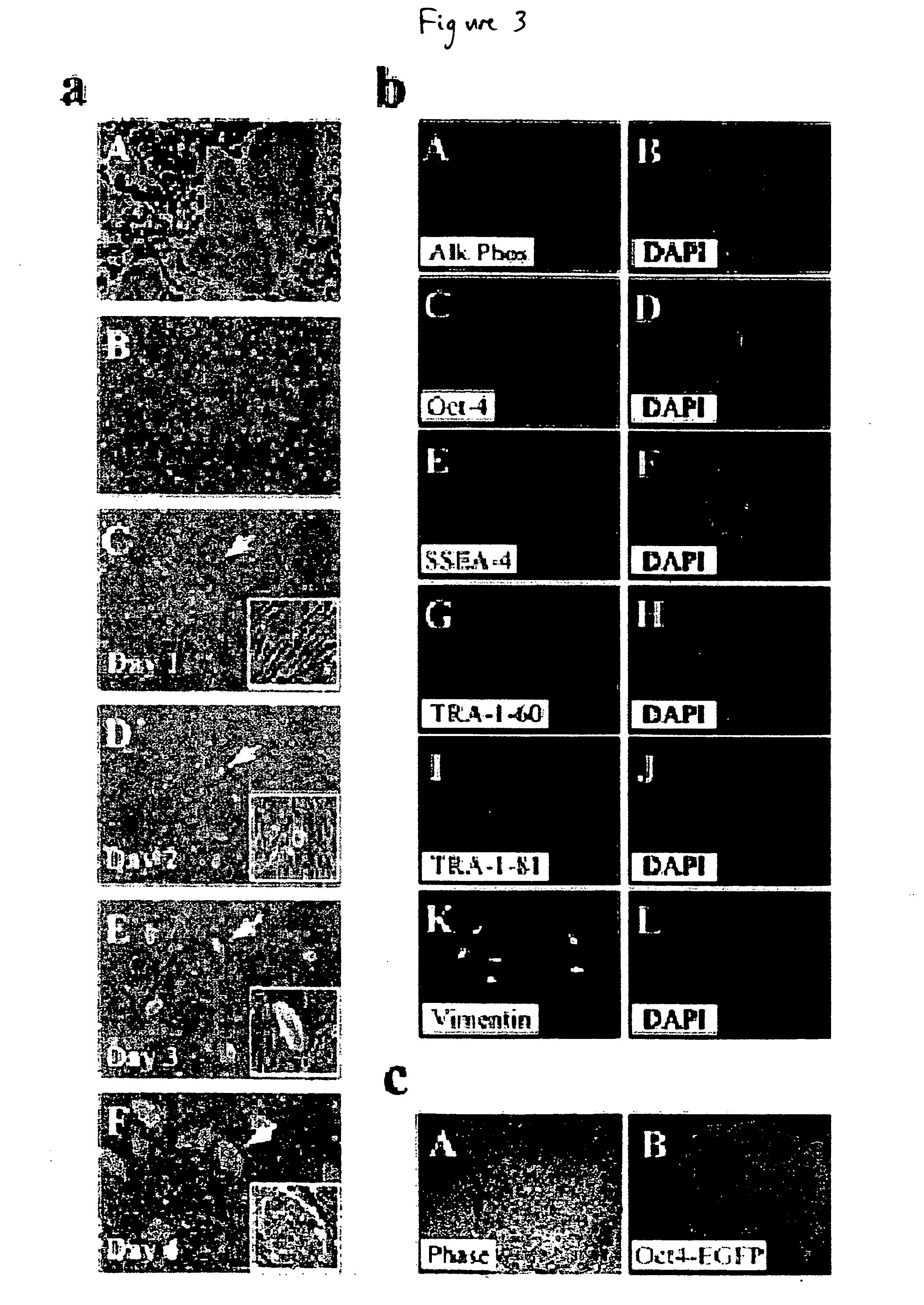
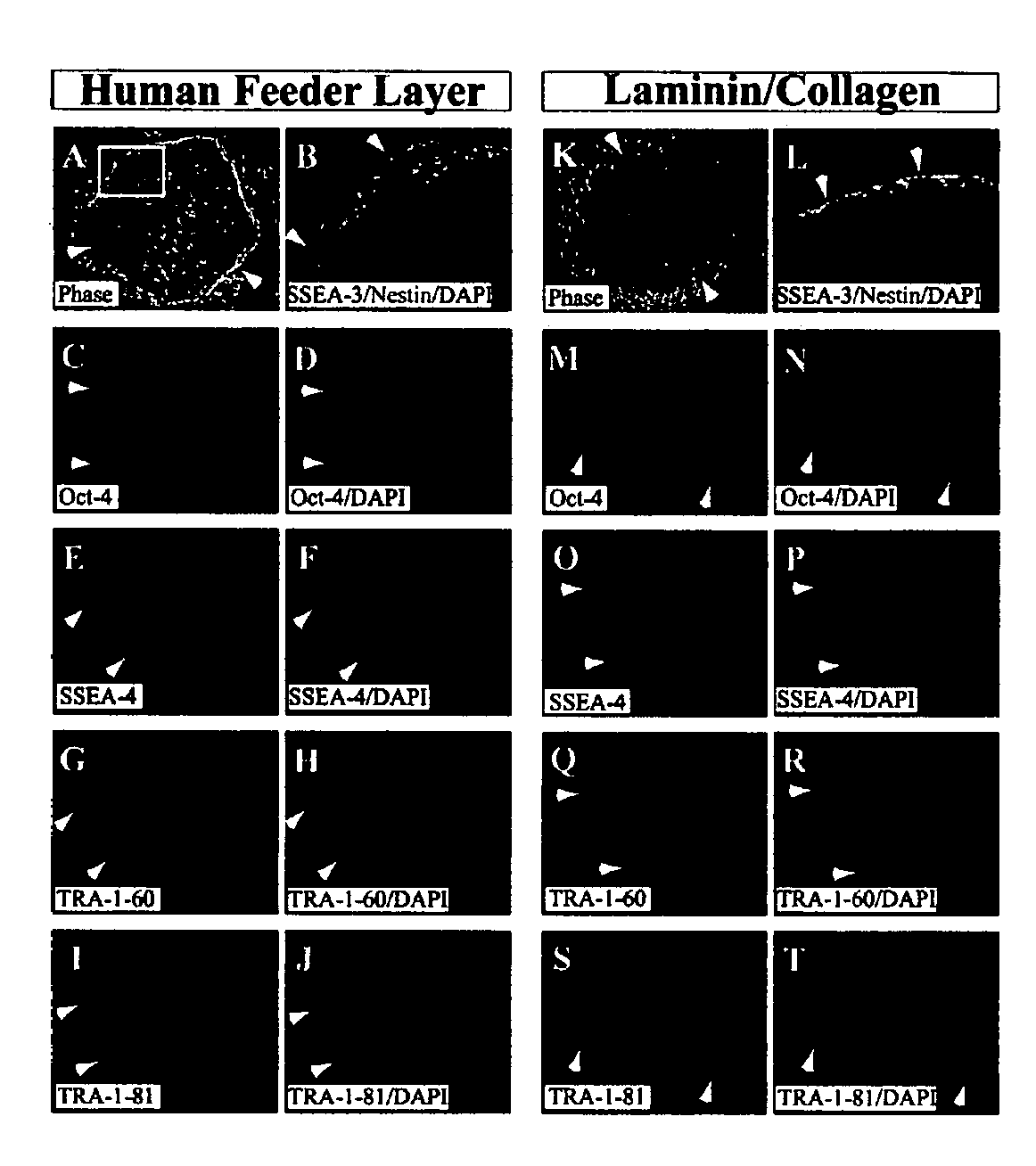
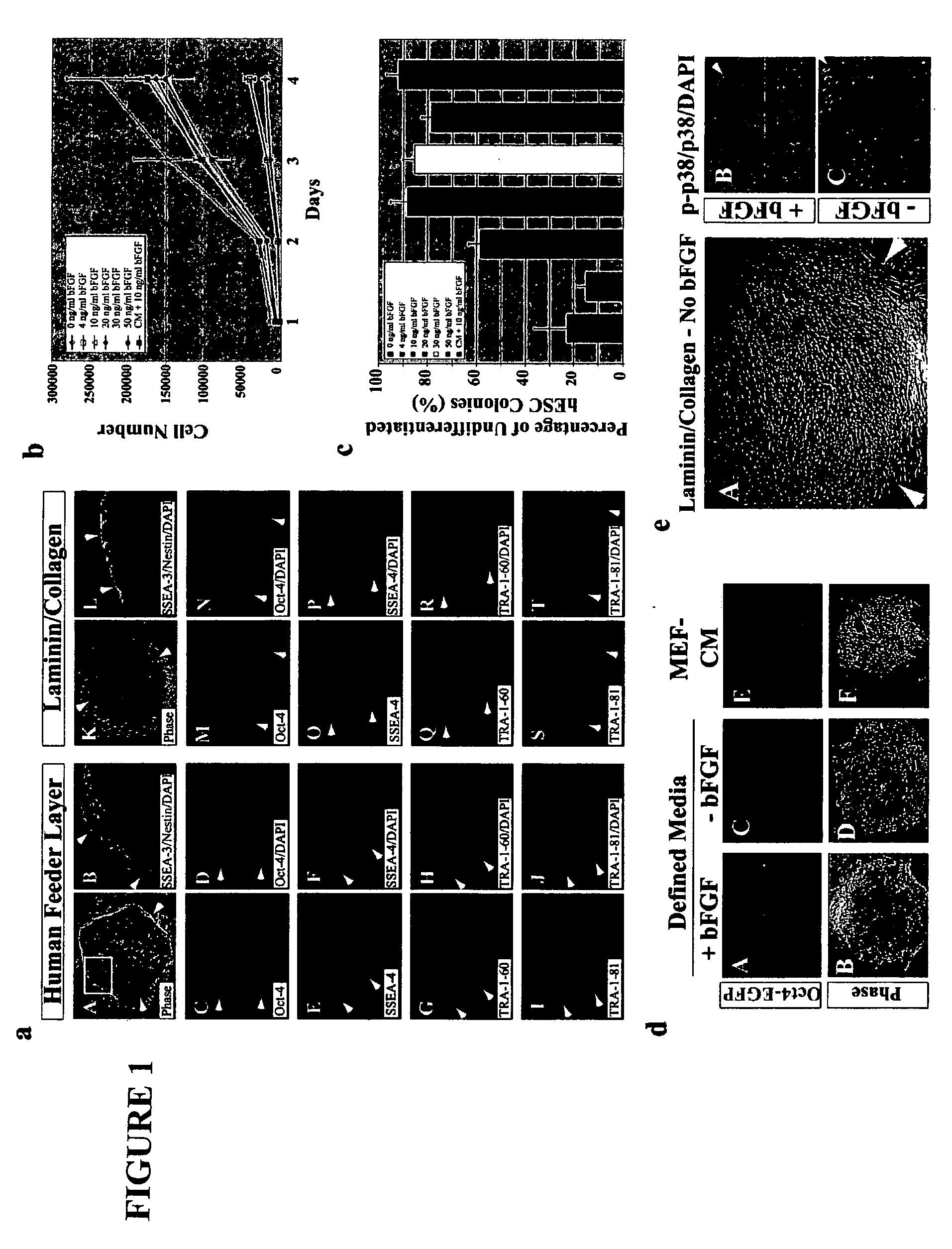
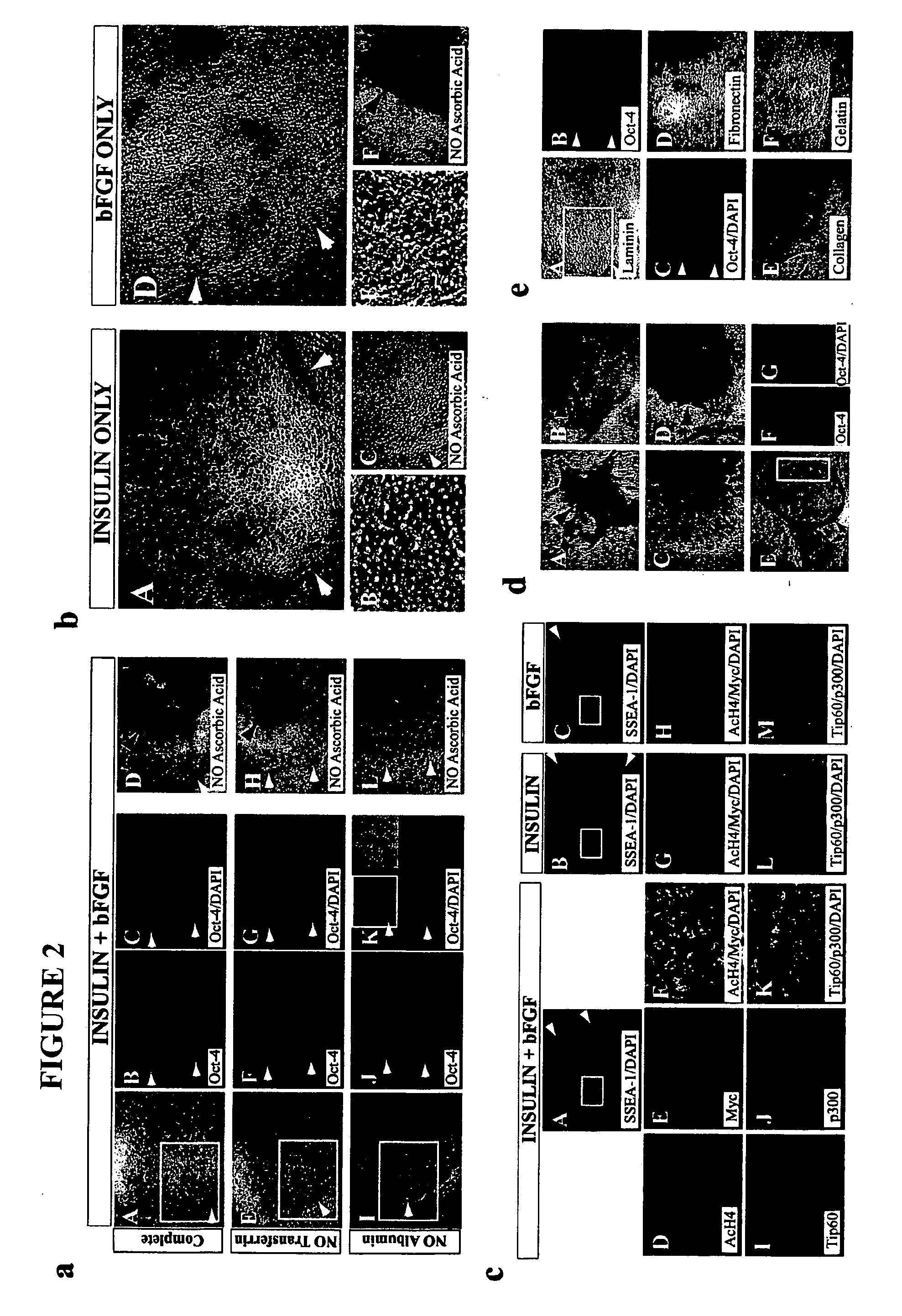
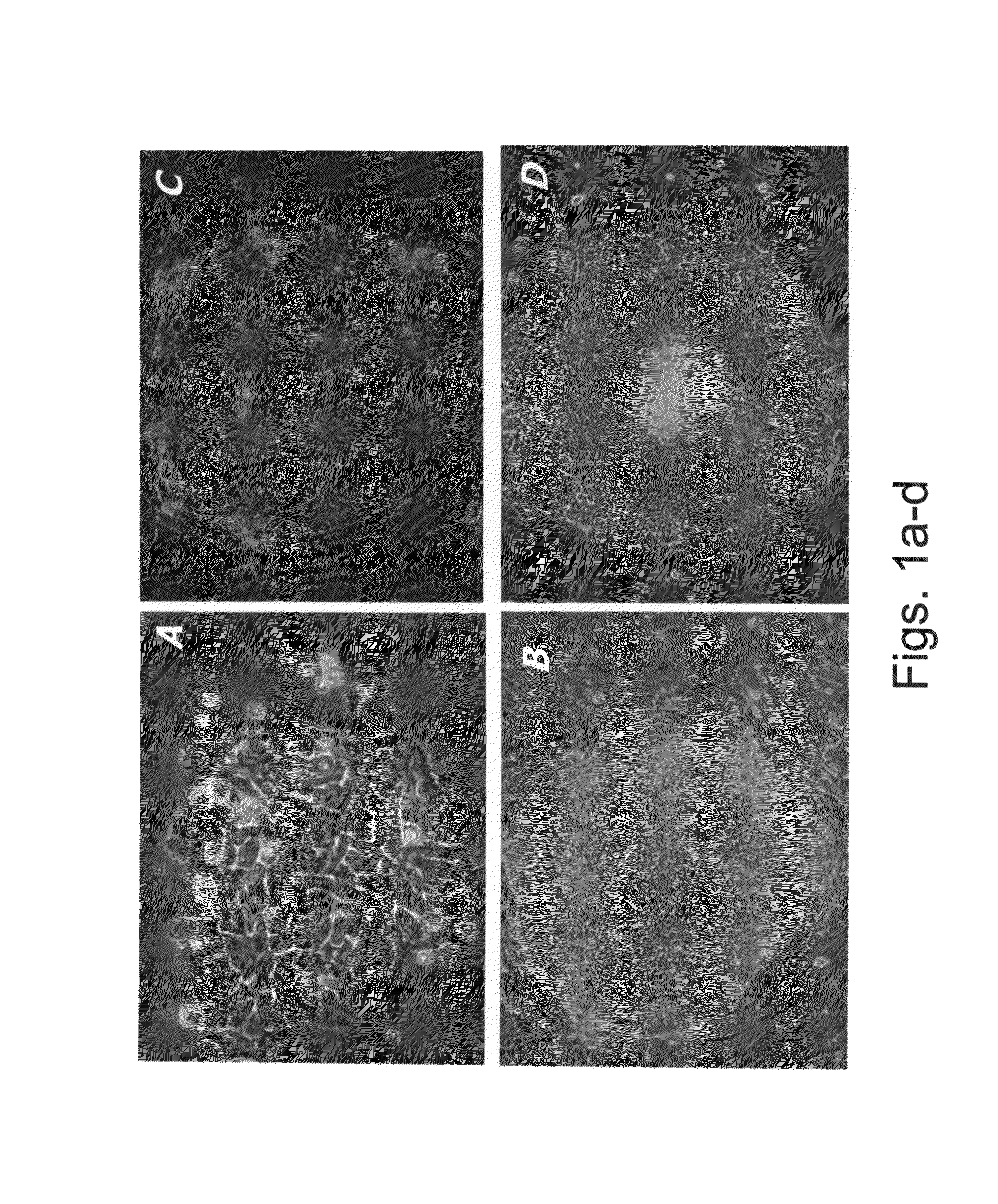
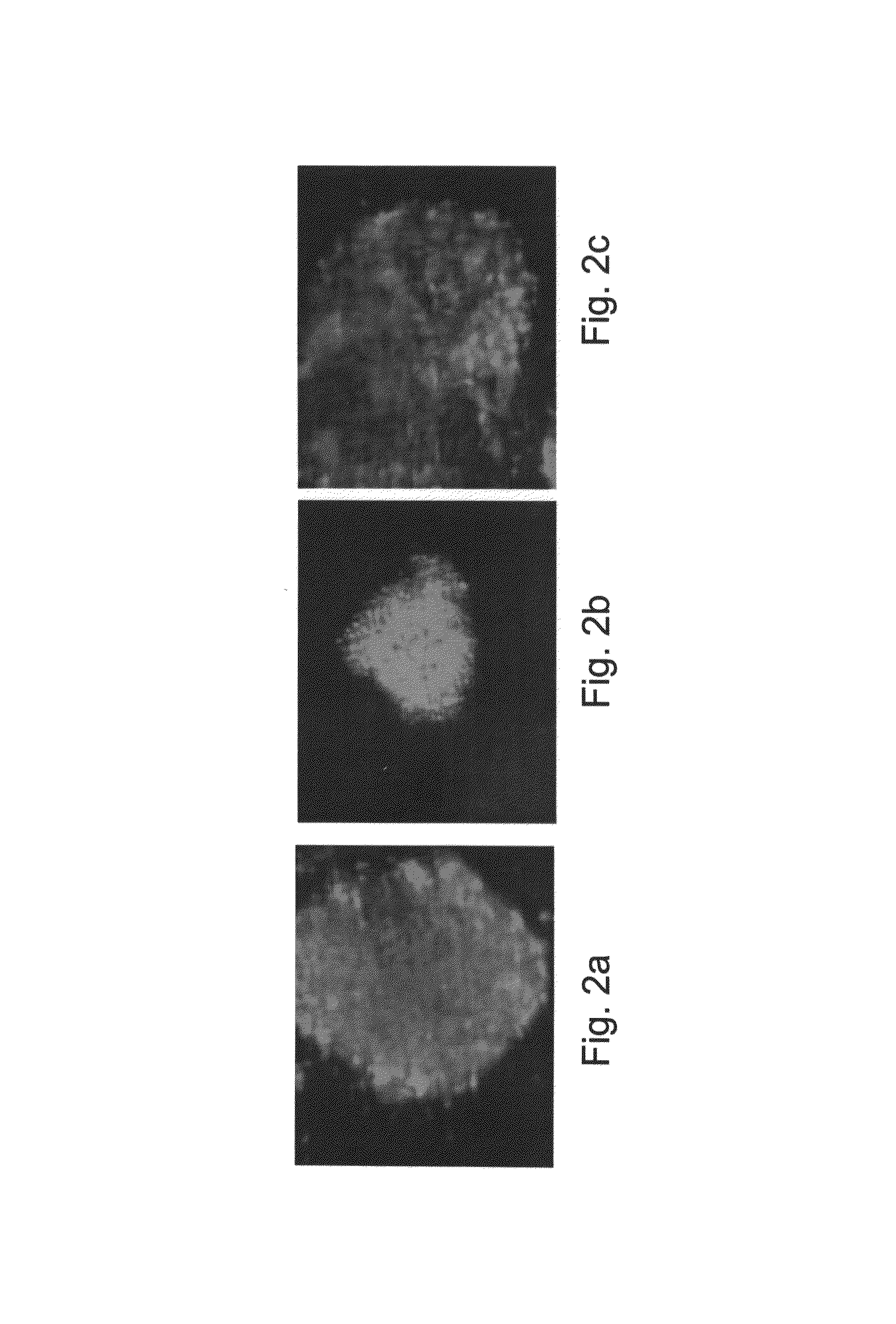
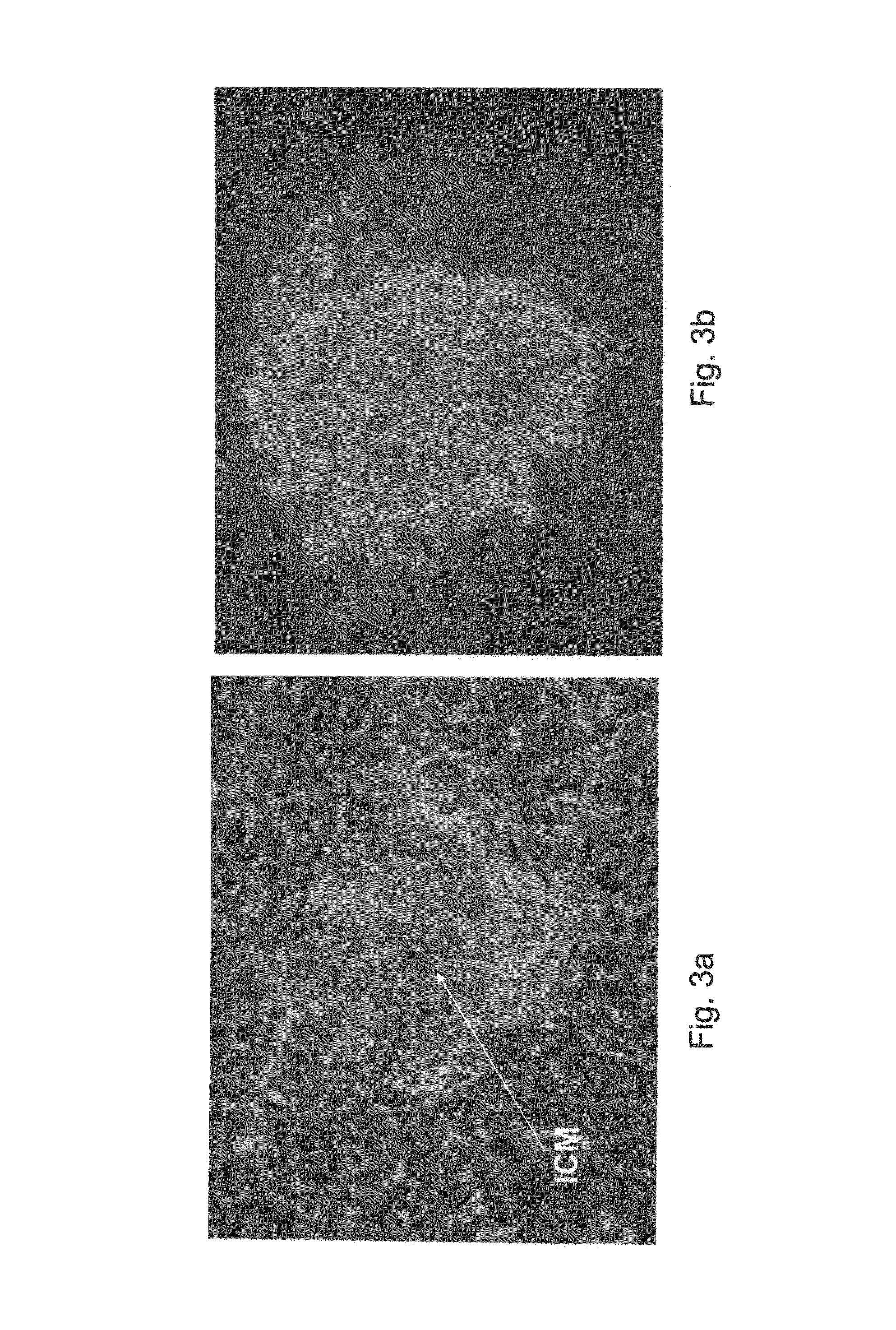
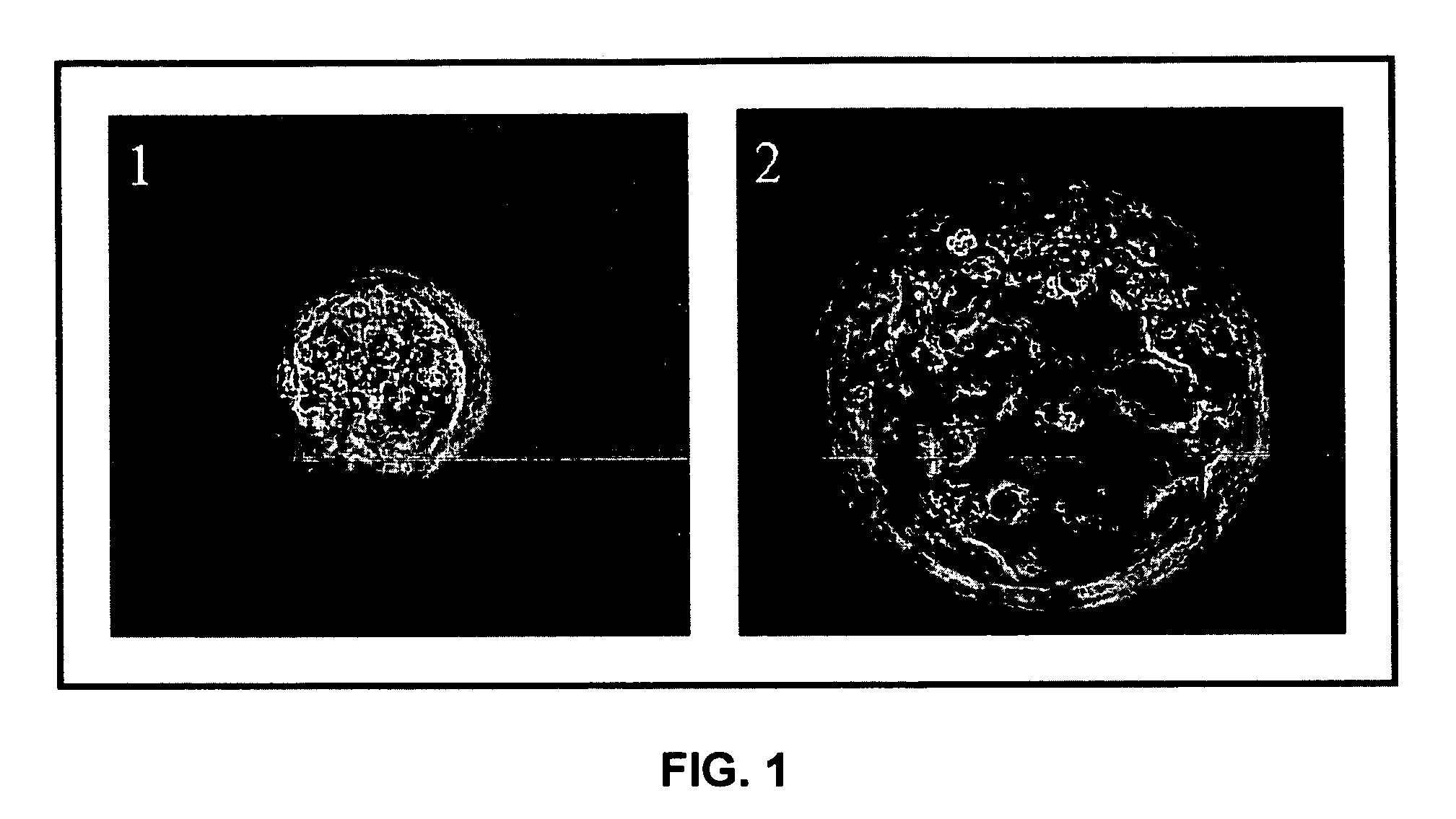
Stem cells, including mammalian, and particularly primate primordial stem cells (pPSCs) such as human embryonic stem cells (hESCs), hold great promise for restoring cell, tissue, and organ function. However, cultivation of stem cells, particularly undifferentiated hESCs, in serum-free, feeder-free, and conditioned-medium-free conditions remains crucial for large-scale, uniform production of pluripotent cells for cell-based therapies, as well as for controlling conditions for efficiently directing their lineage-specific differentiation. This instant invention is based on the discovery of the formulation of minimal essential components necessary for maintaining the long-term growth of pPSCs, particularly undifferentiated hESCs. Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), insulin, ascorbic acid, and laminin were identified to be both sufficient and necessary for maintaining hESCs in a healthy self-renewing undifferentiated state capable of both prolonged propagation and then directed differentiation. Having discerned these minimal molecular requirements, conditions that would permit the substitution of poorly-characterized and unspecified biological additives and substrates were derived and optimized with entirely defined constituents, providing a “biologics”-free (i.e., animal-, feeder-, serum-, and conditioned-medium-free) system for the efficient long-term cultivation of pPSCs, particularly pluripotent hESCs. Such culture systems allow the derivation and large-scale production of stem cells such as pPSCs, particularly pluripotent hESCs, in optimal yet well-defined biologics-free culture conditions from which they can be efficiently directed towards a lineage-specific differentiated fate in vitro, and thus are important, for instance, in connection with clinical applications based on stem cell therapy and in drug discovery processes.
Owner:THE BURNHAM INST
Defined media for pluripotent stem cell culture
Stem cells, including mammalian, and particularly primate primordial stem cells (pPSCs) such as human embryonic stem cells (hESCs), hold great promise for restoring cell, tissue, and organ function. However, cultivation of stem cells, particularly undifferentiated hESCs, in serum-free, feeder-free, and conditioned-medium-free conditions remains crucial for large-scale, uniform production of pluripotent cells for cell-based therapies, as well as for controlling conditions for efficiently directing their lineage-specific differentiation. This instant invention is based on the discovery of the formulation of minimal essential components necessary for maintaining the long-term growth of pPSCs, particularly undifferentiated hESCs. Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), insulin, ascorbic acid, and laminin were identified to be both sufficient and necessary for maintaining hESCs in a healthy self-renewing undifferentiated state capable of both prolonged propagation and then directed differentiation. Having discerned these minimal molecular requirements, conditions that would permit the substitution of poorly-characterized and unspecified biological additives and substrates were derived and optimized with entirely defined constituents, providing a “biologics”-free (i.e., animal-, feeder-, serum-, and conditioned-medium-free) system for the efficient long-term cultivation of pPSCs, particularly pluripotent hESCs. Such culture systems allow the derivation and large-scale production of stem cells such as pPSCs, particularly pluripotent hESCs, in optimal yet well-defined biologics-free culture conditions from which they can be efficiently directed towards a lineage-specific differentiated fate in vitro, and thus are important, for instance, in connection with clinical applications based on stem cell therapy and in drug discovery processes.
Owner:THE BURNHAM INST
Media for culturing stem cells
Well-defined, xeno-free culture media which comprise a TGF-beta isoform or the chimera formed between IL6 and the soluble IL6 receptor (IL6RIL6), which are capable of maintaining stem cells, and particularly, human embryonic stem cells, in an undifferentiated state are provided. Also provided are cell cultures comprising the culture media and the stem cells and methods of expanding and deriving embryonic stem cells in such well-defined, xeno-free culture media. In addition, the present invention provides methods of differentiating ESCs or EBs formed therefrom for the generation of lineage specific cells.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Methods to detect lineage-specific cells
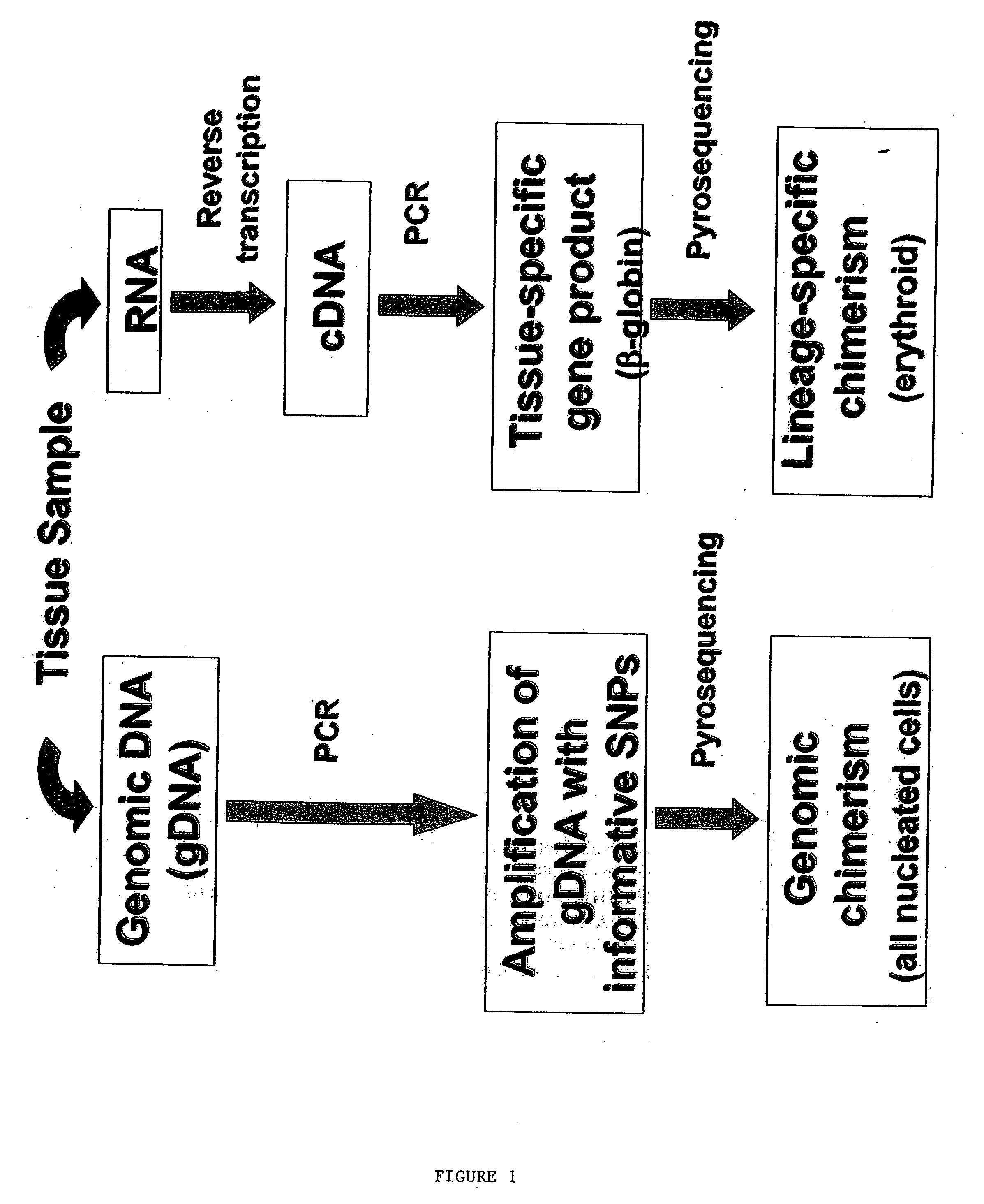
The present invention is based, at least in part, on methods to identify and quantify lineage-specific cells. The present invention provides methods of detecting lineage-specific cells in a biological sample, and monitoring the effectiveness of progenitor cell transfer in a subject. The invention further provides methods of determining an effective dose of progenitor cell transfer in a subject and methods of quantifying progenitor cell transfer in a subject. Additionally, methods are provided to identify allelic variants in lineage-specific cells.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
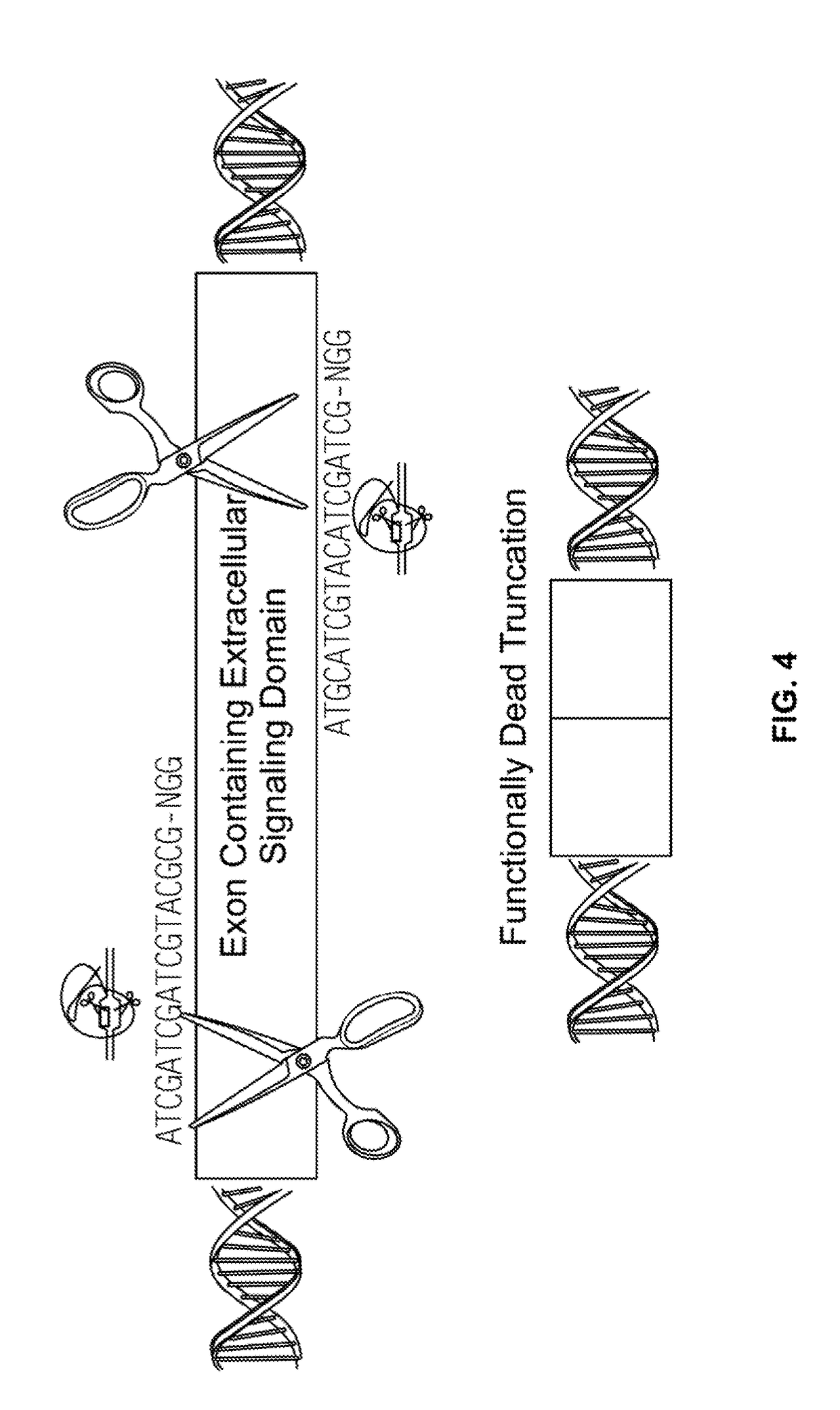
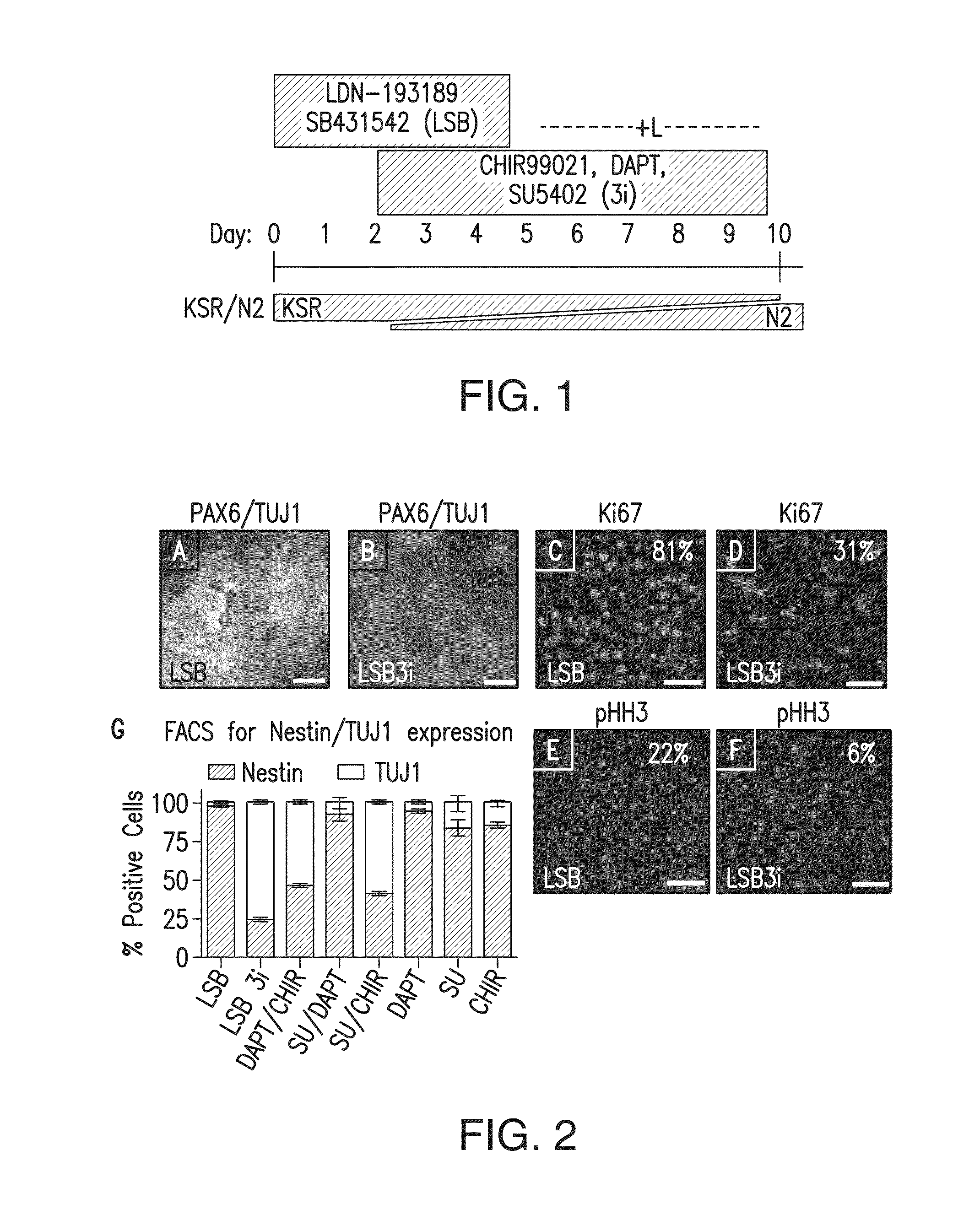
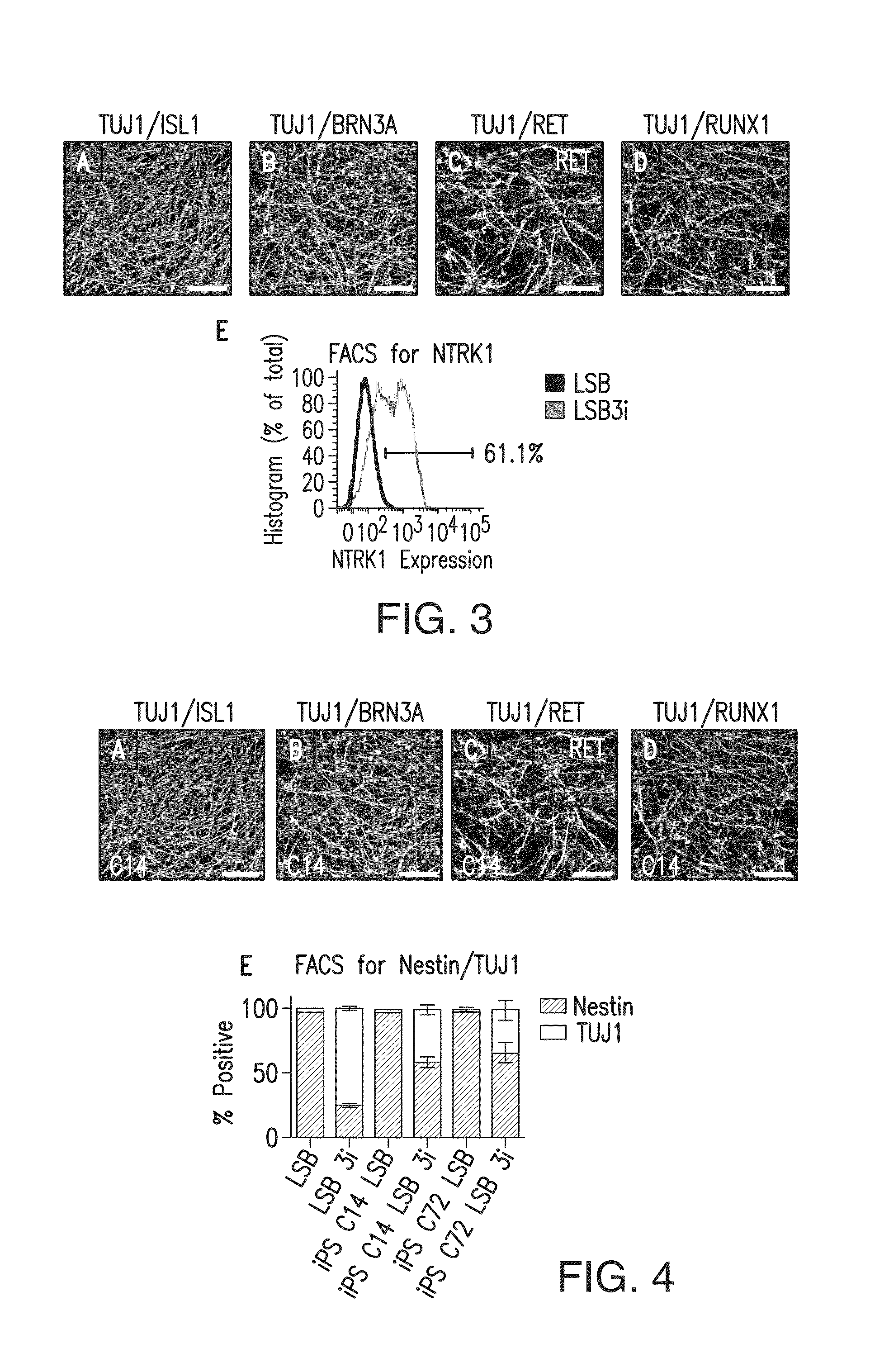
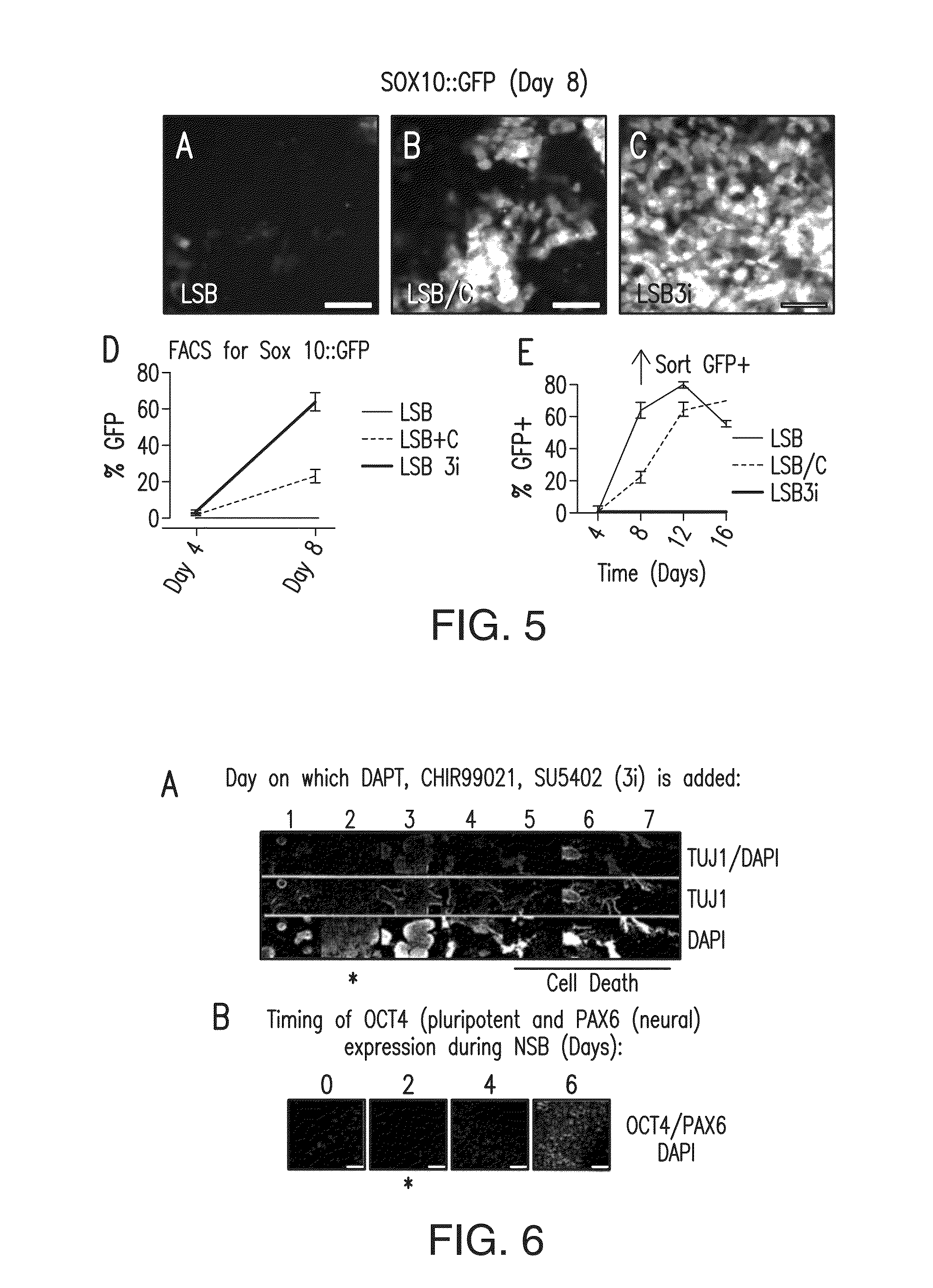
Method of nociceptor differentiation of human embryonic stem cells and uses thereof
ActiveUS20130183674A1Nervous disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementNervous systemLineage specific
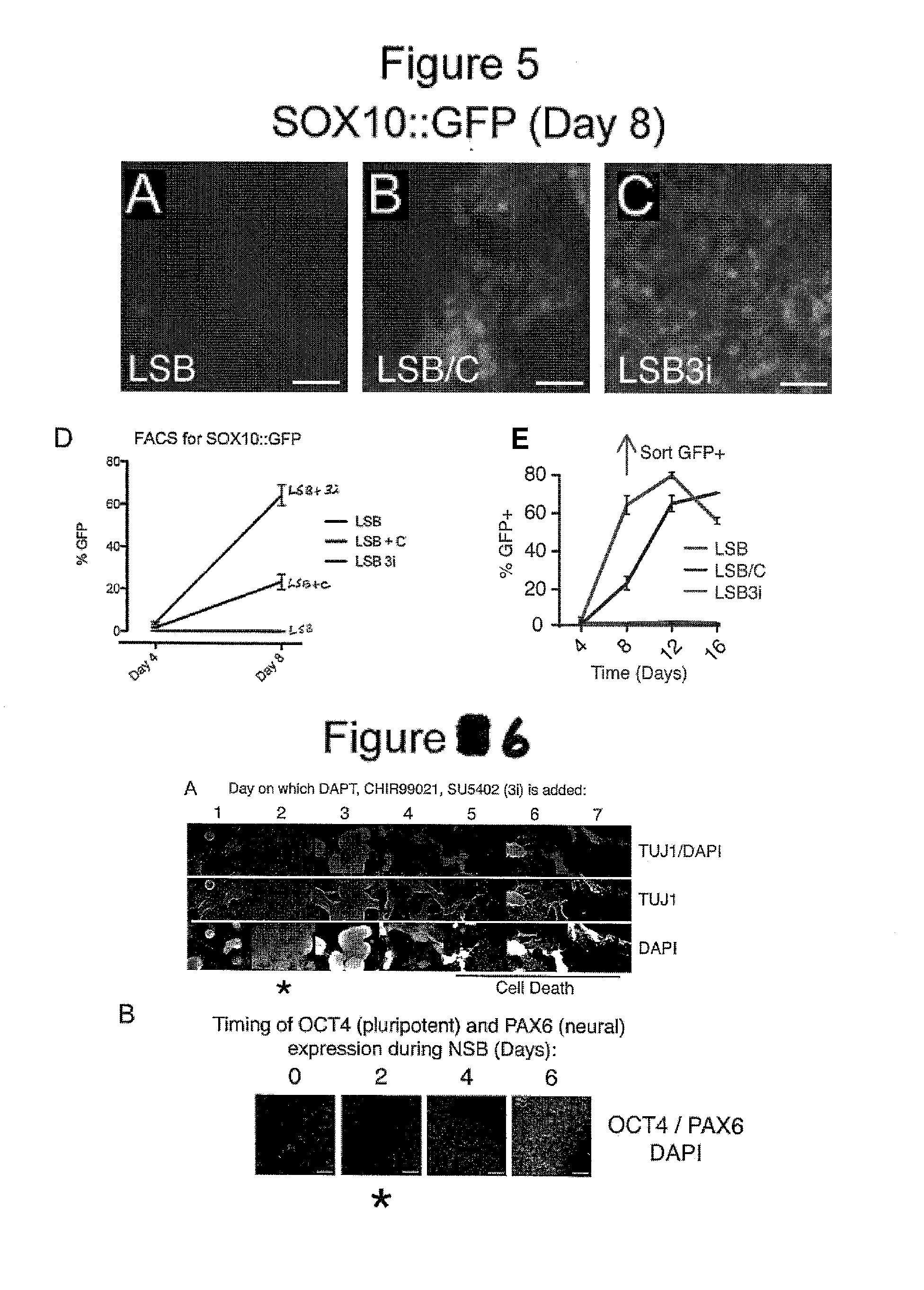
The present invention relates to the field of stem cell biology, in particular the linage specific differentiation of pluripotent or multipotent stem cells, which can include, but is not limited to, human embryonic stem cells (hESC), human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC), somatic stem cells, cancer stem cells, or any other cell capable of lineage specific differentiation. Specifically described are methods to direct the lineage specific differentiation of hESC and / or hiPSC to nociceptors (i.e. nociceptor cells) using novel culture conditions. The nociceptors made using the methods of the present invention are further contemplated for various uses including, but limited to, use in in vitro drug discovery assays, pain research, and as a therapeutic to reverse disease of, or damage to, the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Further, compositions and methods are provided for producing melanocytes from human pluripotent stem cells for use in disease modeling.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
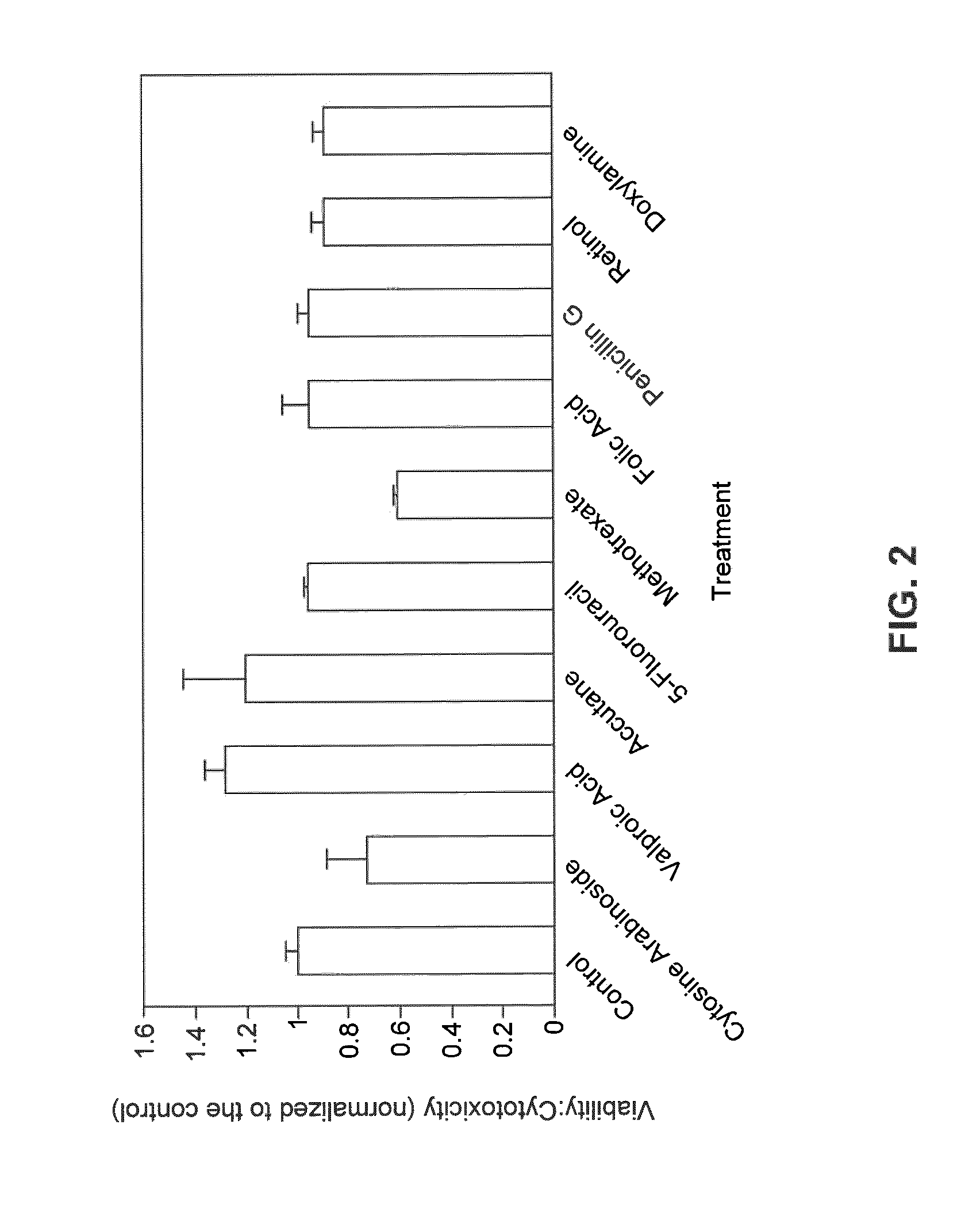
Reagents and Methods for Using Human Embryonic Stem Cells to Evaluate Toxicity of Pharmaceutical Compounds and Other Chemicals
ActiveUS20070248947A1Reliably determinedPotential for false negatives is reducedCompound screeningApoptosis detectionTesting toxicityChemical compound
The invention provides biomarker profiles of cellular metabolites and methods for screening chemical compounds including pharmaceutical agents, lead and candidate drug compounds and other chemicals using human embryonic stem cells (hESC) or lineage-specific cells produced therefrom. The inventive methods are useful for testing toxicity, particularly developmental toxicity and detecting teratogenic effects of such chemical compounds.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for promoting hematopoietic and mesenchymal cell proliferation and differentiation
InactiveUS7118748B1Increasing hematopoietic cell survivalReducing and preventing side effectPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCell culture mediaAngiogenesis growth factor
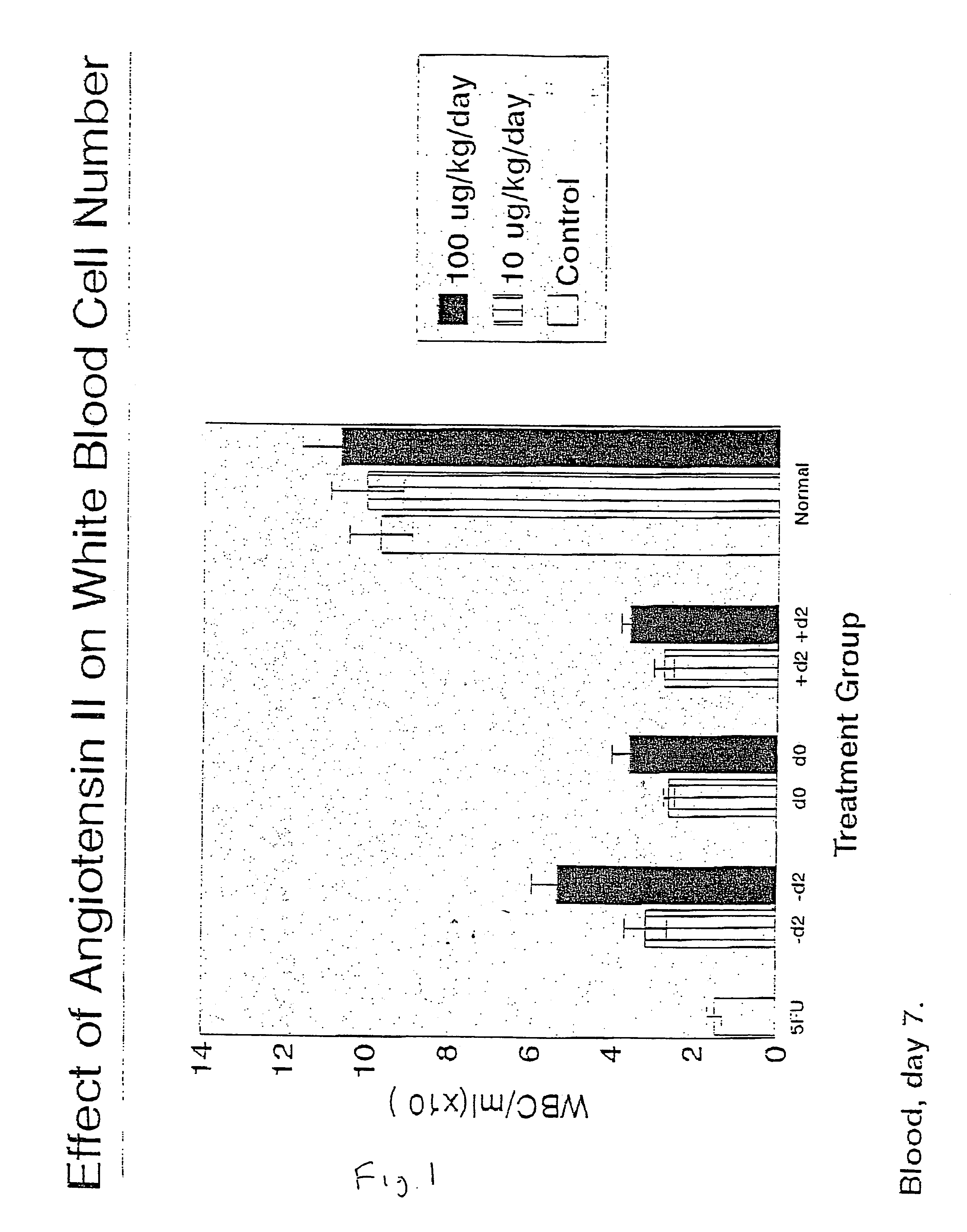
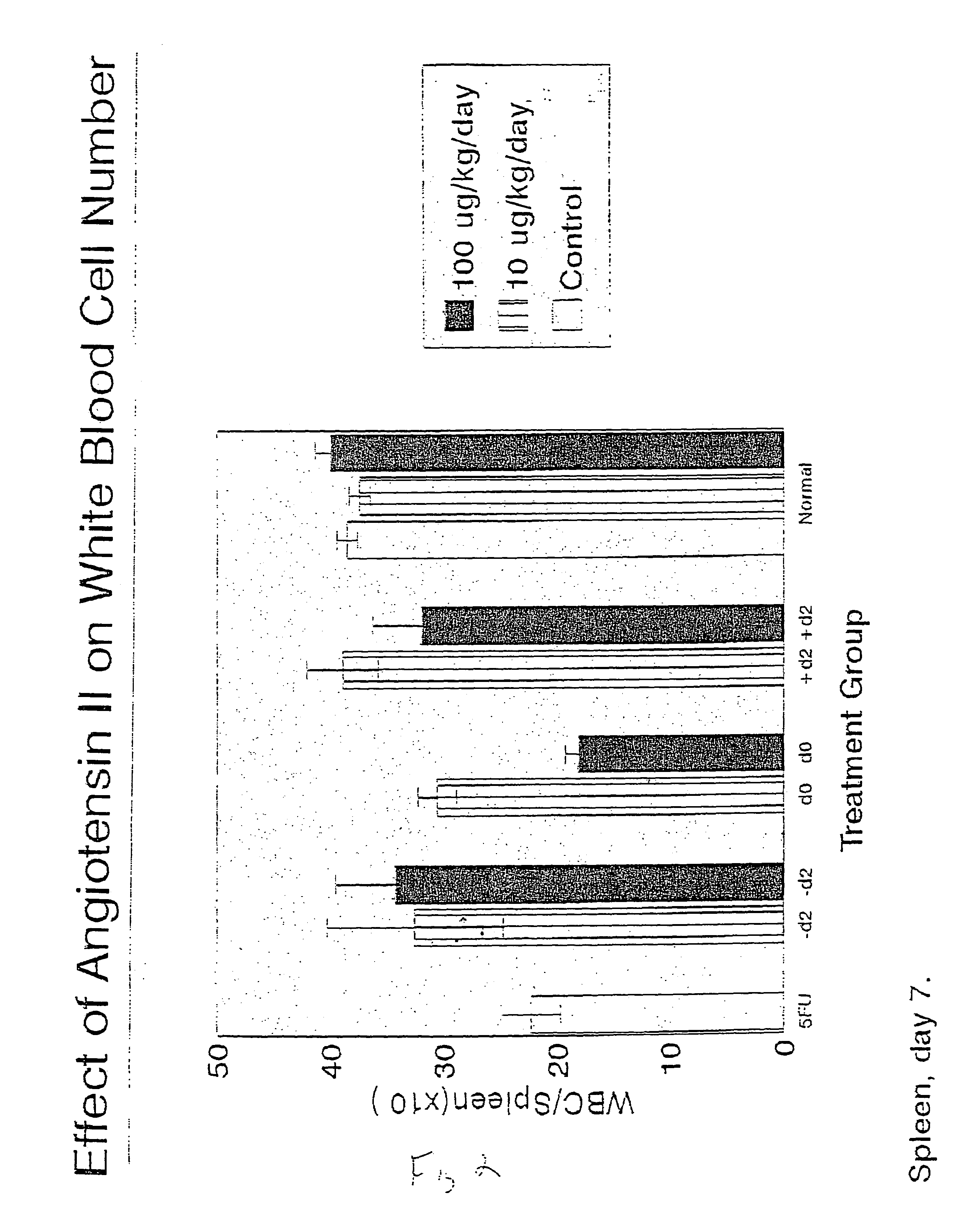
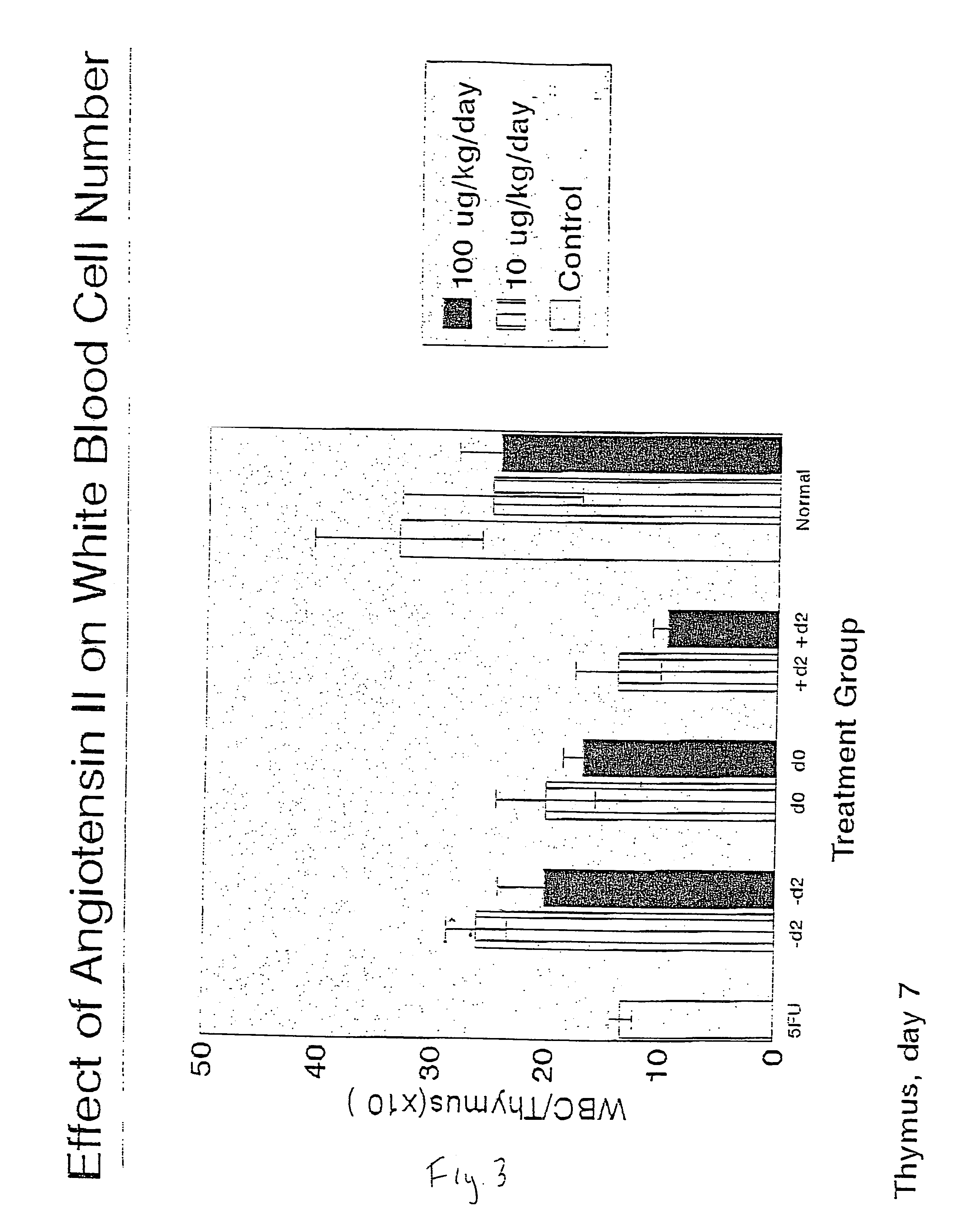
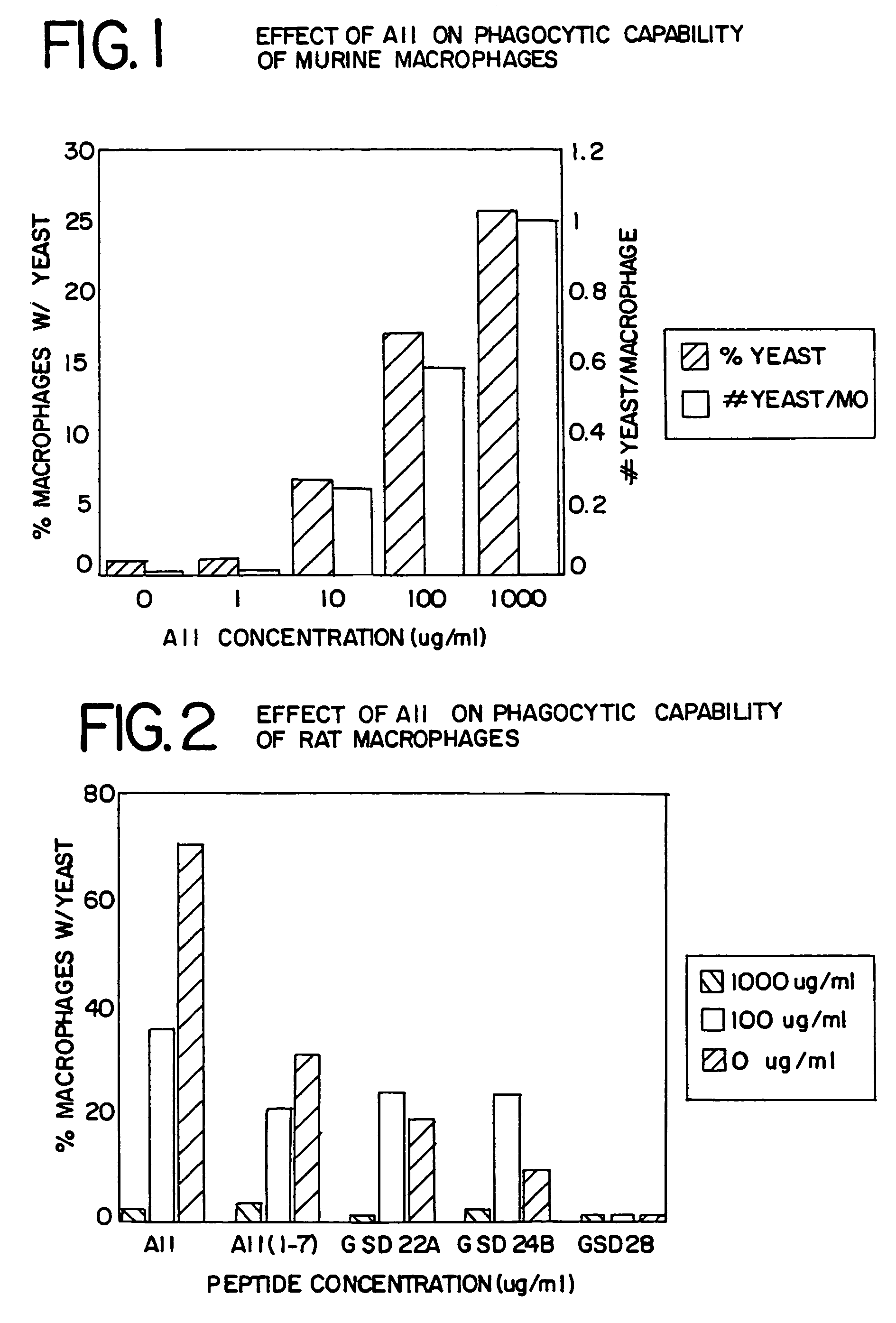
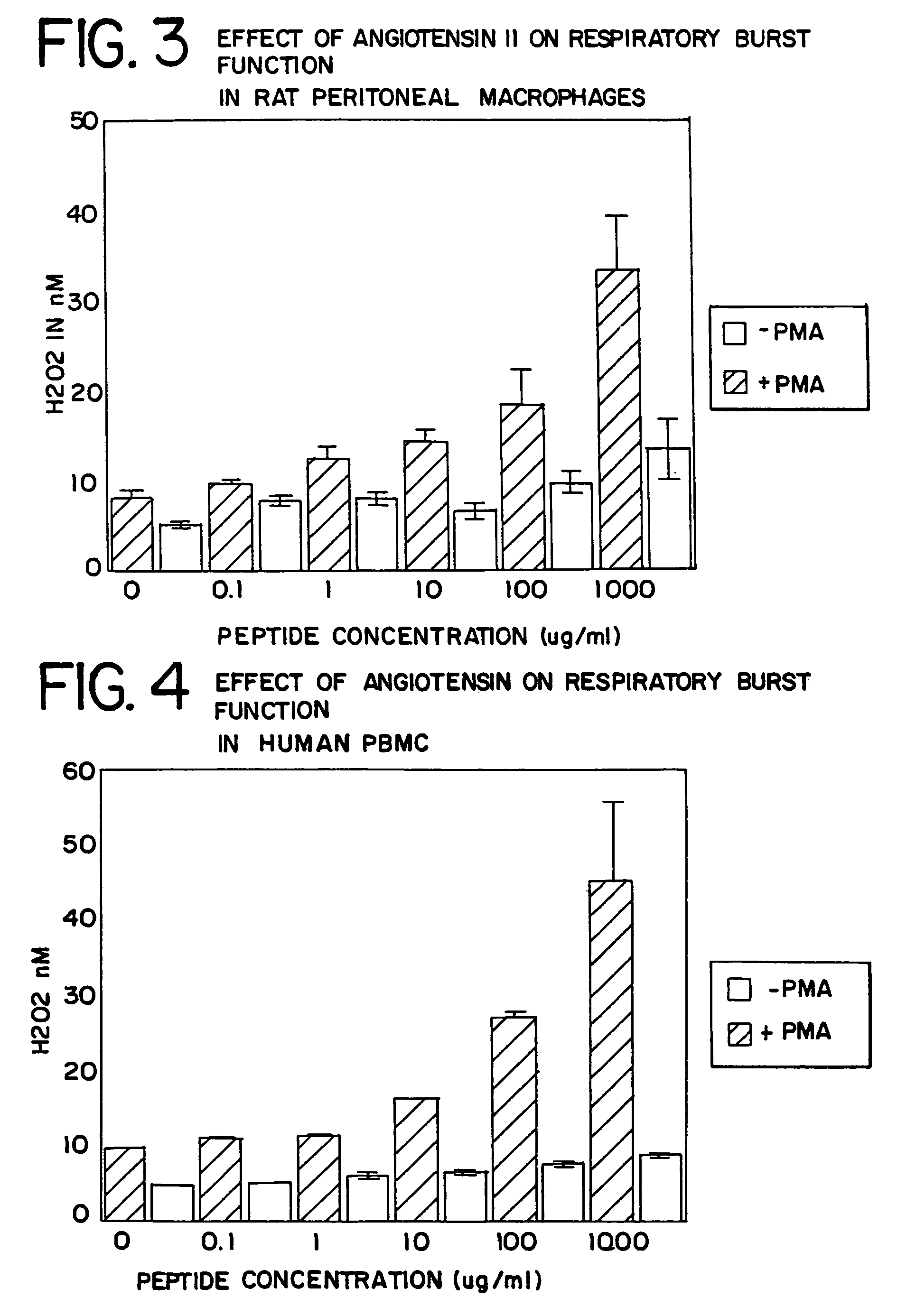
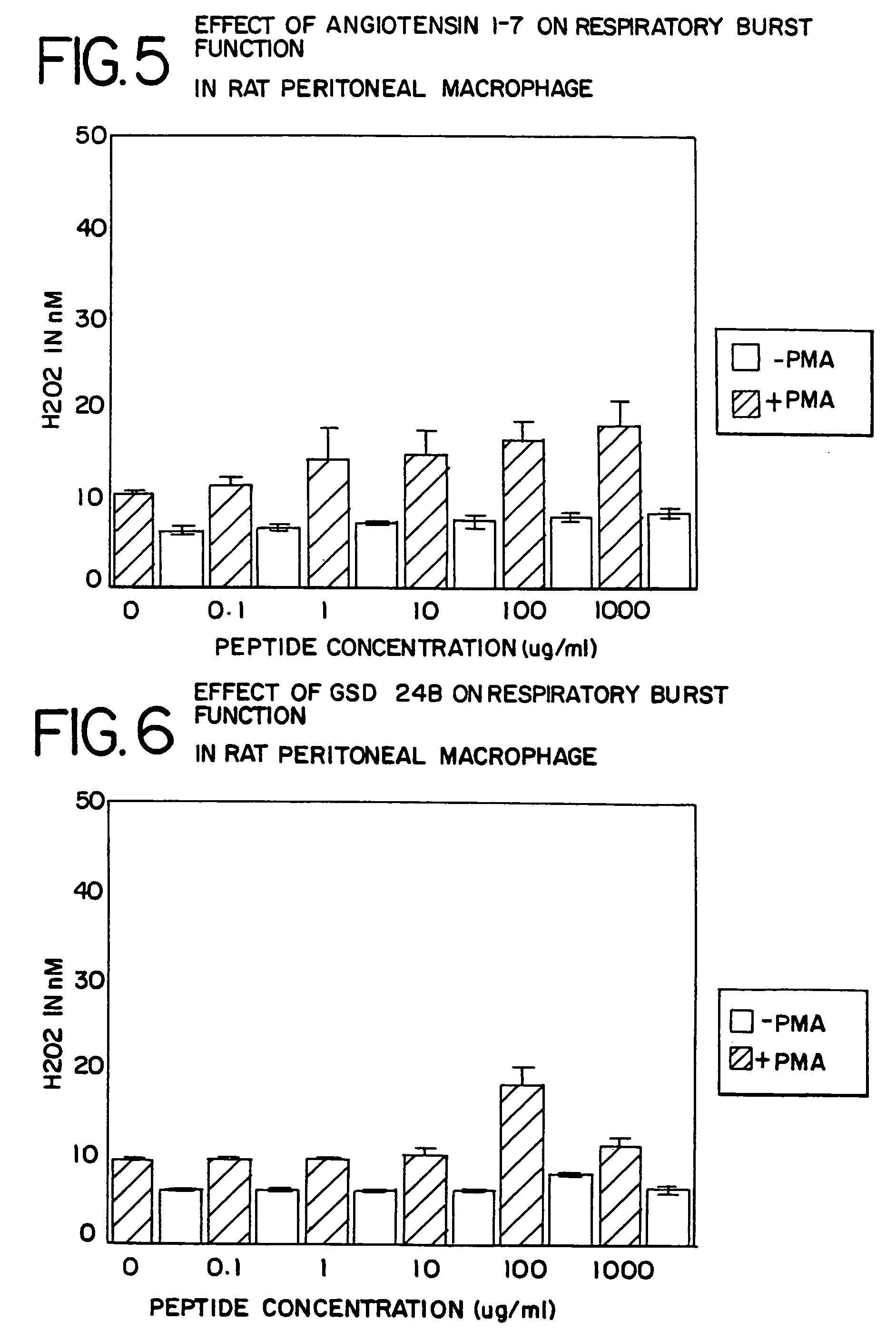
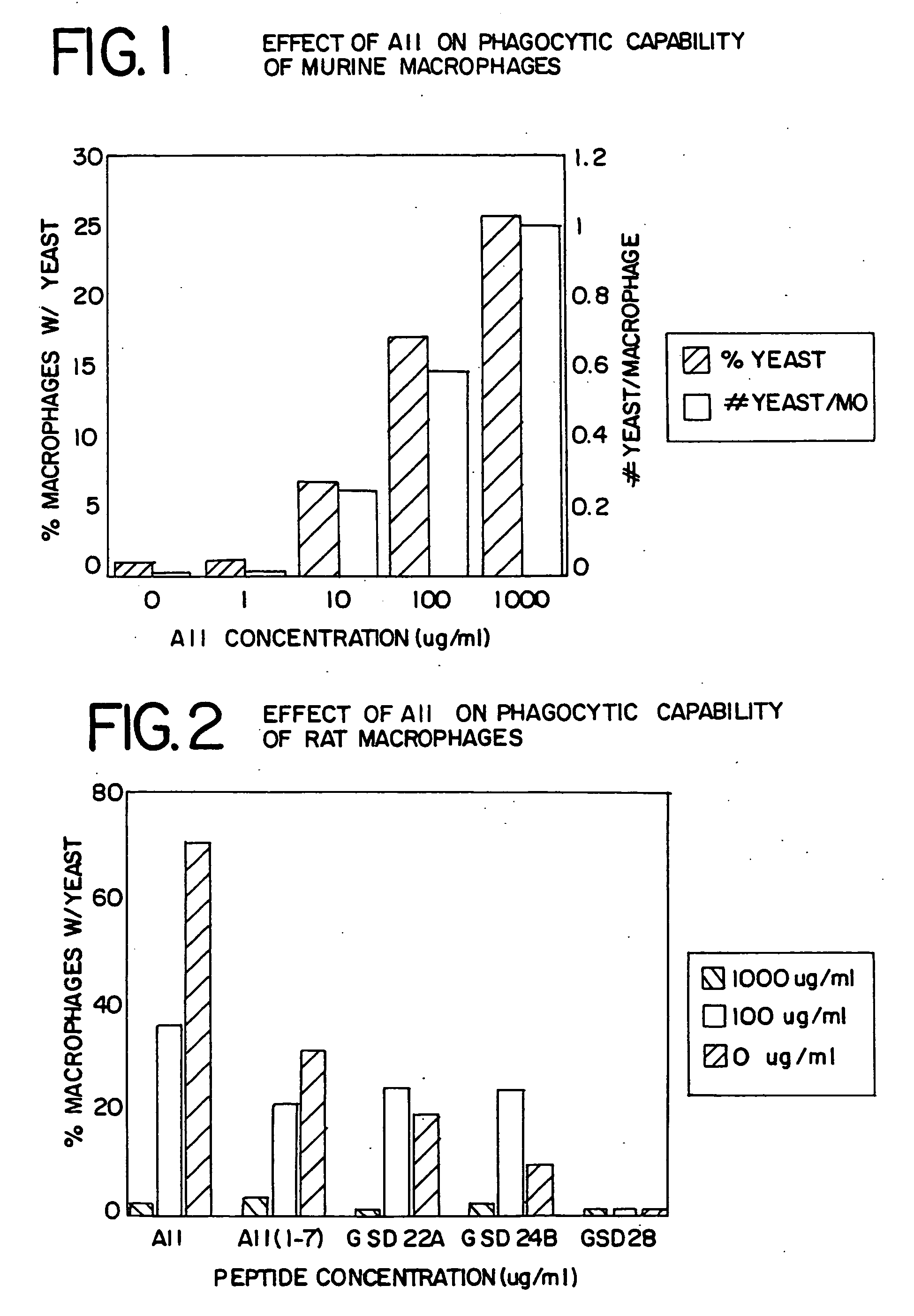
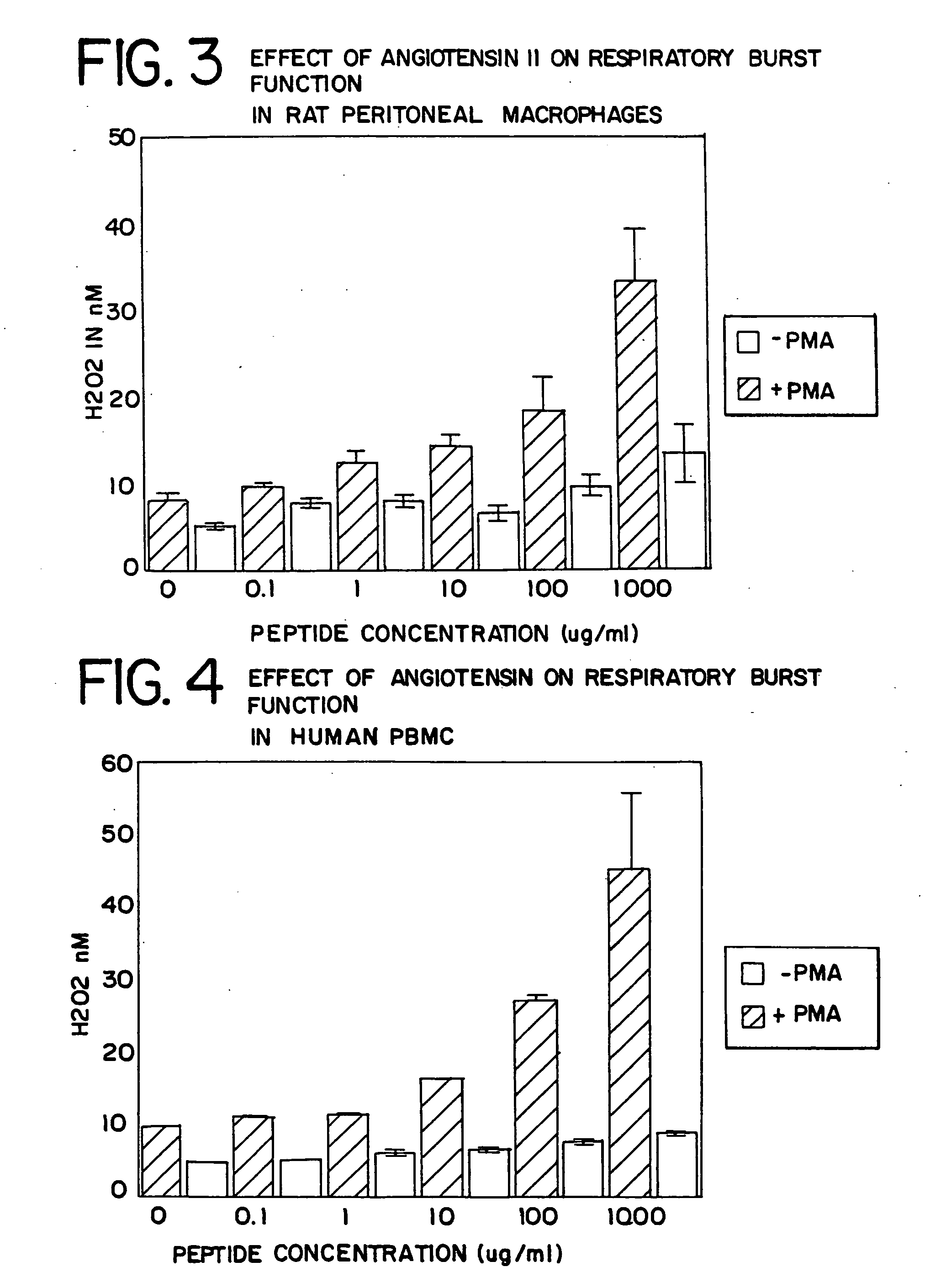
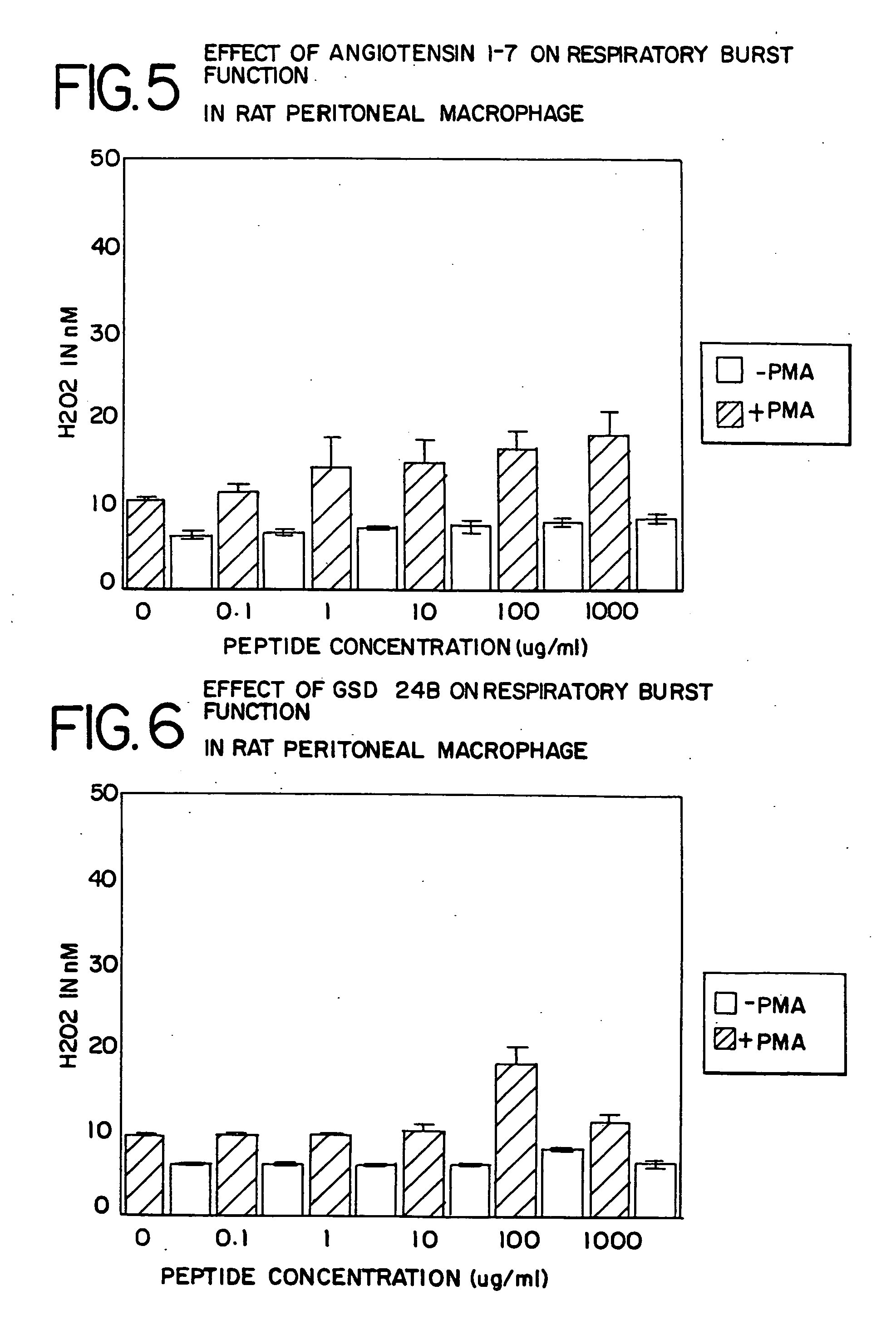
The present invention provides methods, improved cell culture medium and kits for promoting hematopoietic and mesenchymal stem and lineage-specific cell proliferation and differentiation by growth in the presence of angiotensinogen, angiotensin I (Al), AI analogues, AI fragments and analogues thereof, angiotensin II (AII), AII analogues, AII fragments or analogues thereof or AII AT2 type 2 receptor agonists, either alone or in combination with other growth factors and cytokines.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
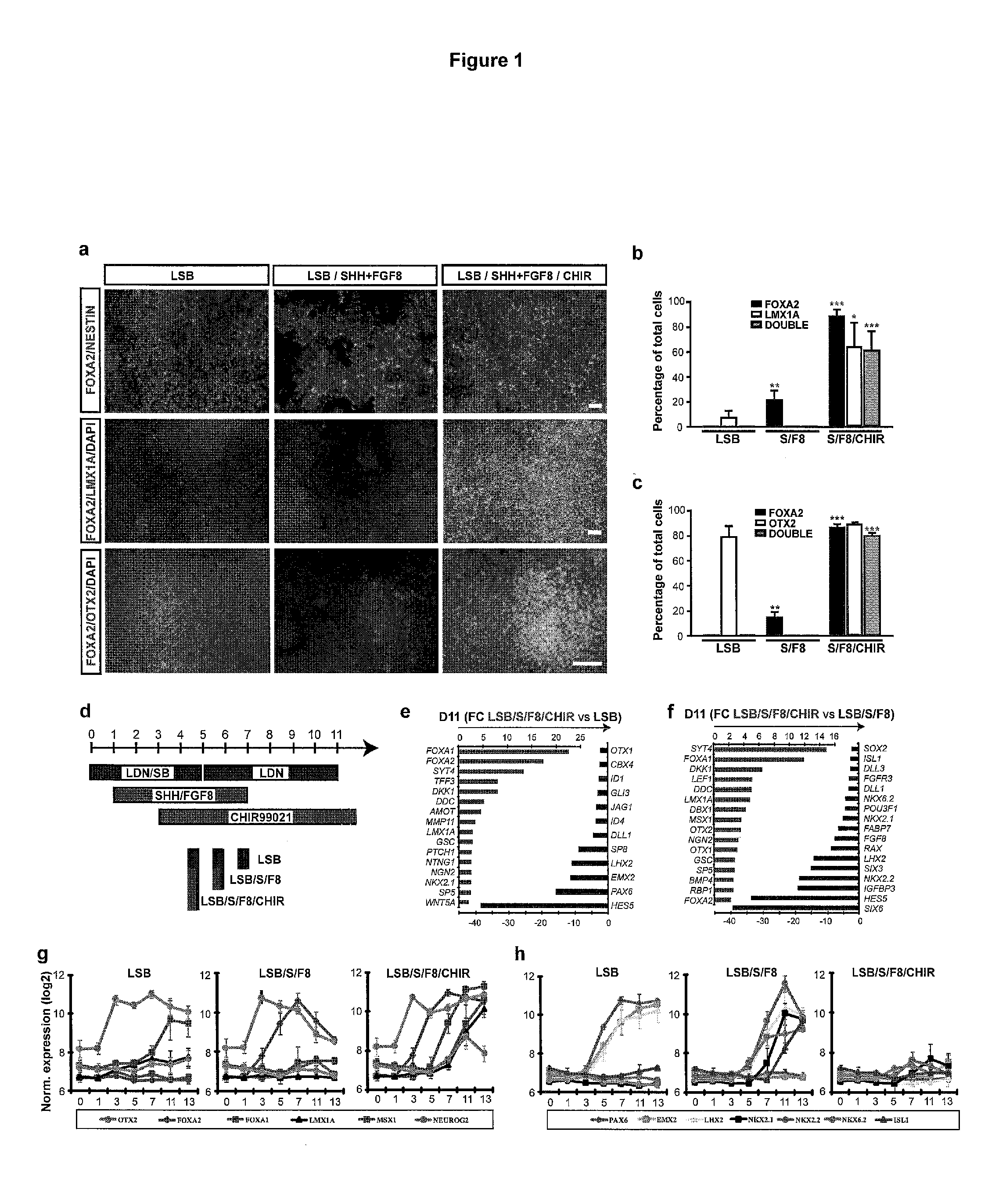
Midbrain dopamine (DA) neurons for engraftment
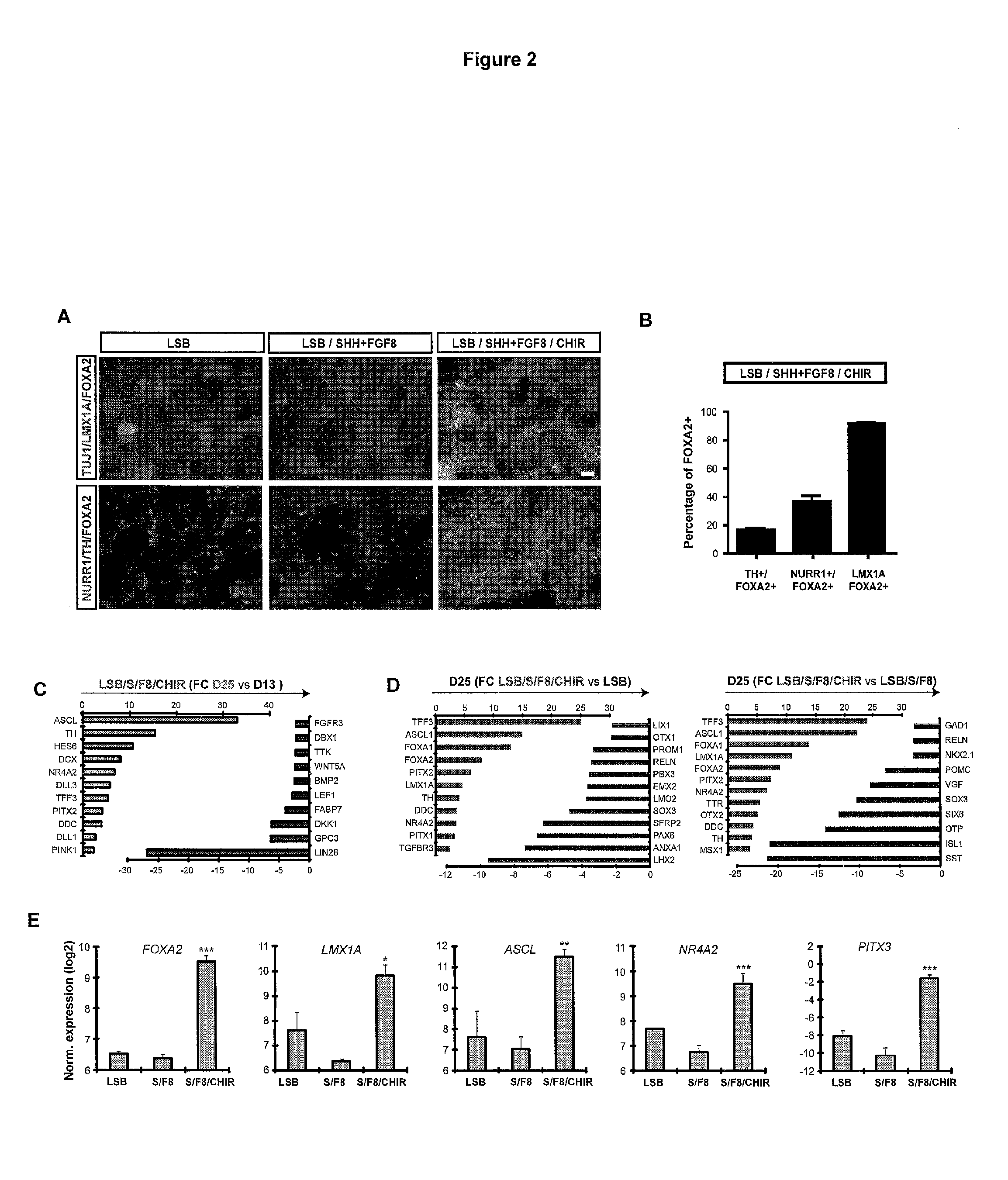
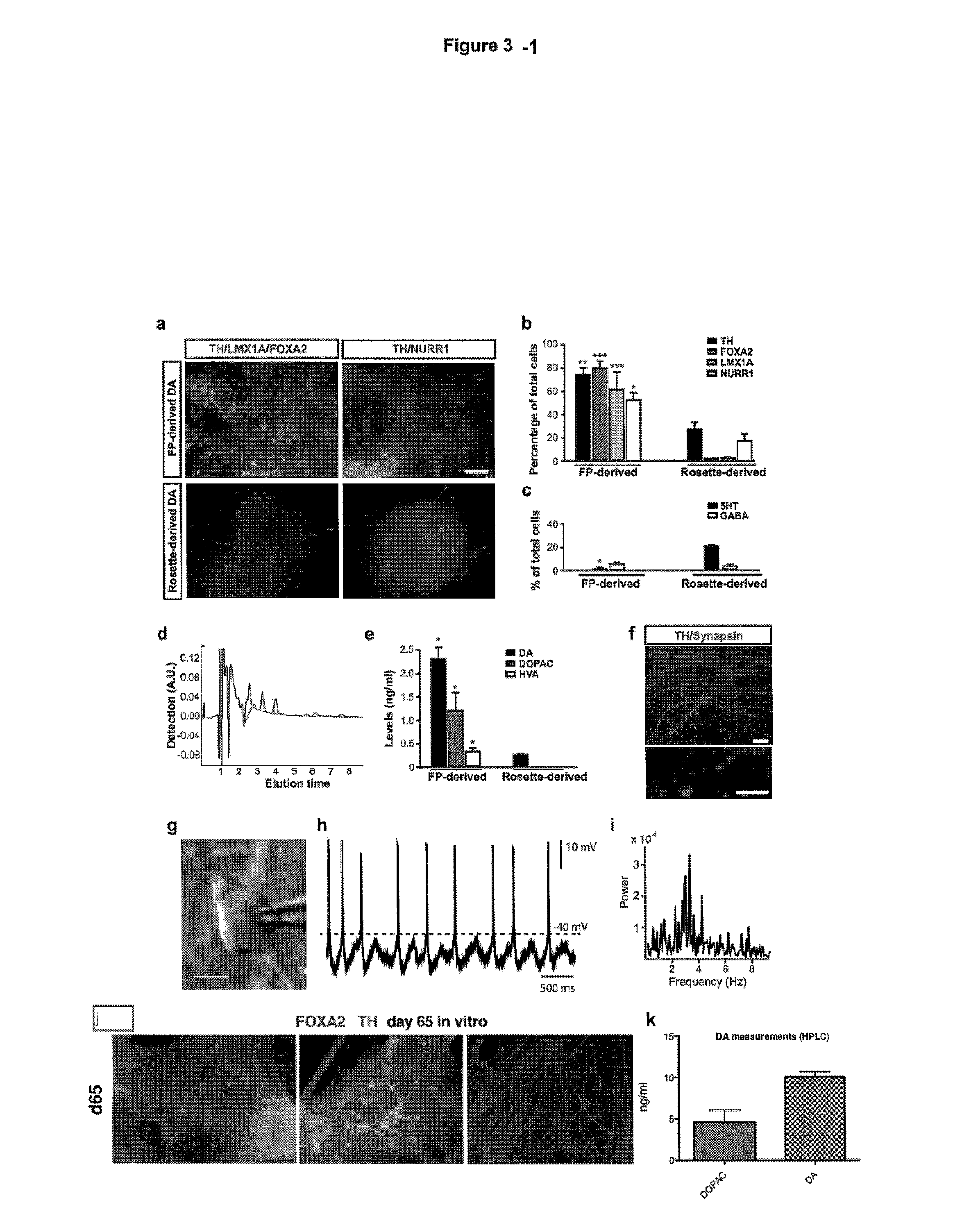
The present invention relates to the field of stem cell biology, in particular the lineage specific differentiation of pluripotent or multipotent stem cells, which can include, but is not limited to, human embryonic stem cells (hESC) in addition to nonembryonic human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC), somatic stem cells, stem cells from patients with a disease, or any other cell capable of lineage specific differentiation. Specifically described are methods to direct the lineage specific differentiation of hESC and / or hiPSC into floor plate midbrain progenitor cells and then further into large populations of midbrain fate FOXA2+LMX1A+TH+ dopamine (DA) neurons using novel culture conditions. The midbrain fate FOXA2+LMX1A+TH+ dopamine (DA) neurons made using the methods of the present invention are further contemplated for various uses including, but not limited to, use in in vitro drug discovery assays, neurology research, and as a therapeutic to reverse disease of, or damage to, a lack of dopamine neurons in a patient. Further, compositions and methods are provided for differentiating midbrain fate FOXA2+LMX1A+TH+ dopamine (DA) neurons from human pluripotent stem cells for use in disease modeling, in particular Parkinson's disease. Additionally, authentic DA neurons are enriched for markers, such as CD142, and A9 type neuronal cells.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Methods of promoting hematopoietic and mesenchymal cell proliferation and differentiation
InactiveUS7744927B2Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCell culture mediaAngiotensinogen mrna
The present invention provides methods, improved cell culture medium and kits for promoting hematopoietic and mesenchymal stem and lineage-specific cell proliferation and differentiation by growth in the presence of angiotensinogen, angiotensin I (AI), AI analogues, AI fragments and analogues thereof, angiotensin II (AII), AII analogues, AII fragments or analogues thereof or AII AT2 type 2 receptor agonists, either alone or in combination with other growth factors and cytokines.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Use of RNA interference for the creation of lineage specific ES and other undifferentiated cells and production of differentiated cells in vitro by co-culture
InactiveUS20060240556A1Facilitate vivo enrichmentNew breed animal cellsMammal material medical ingredientsEmbryonic StageReprogramming
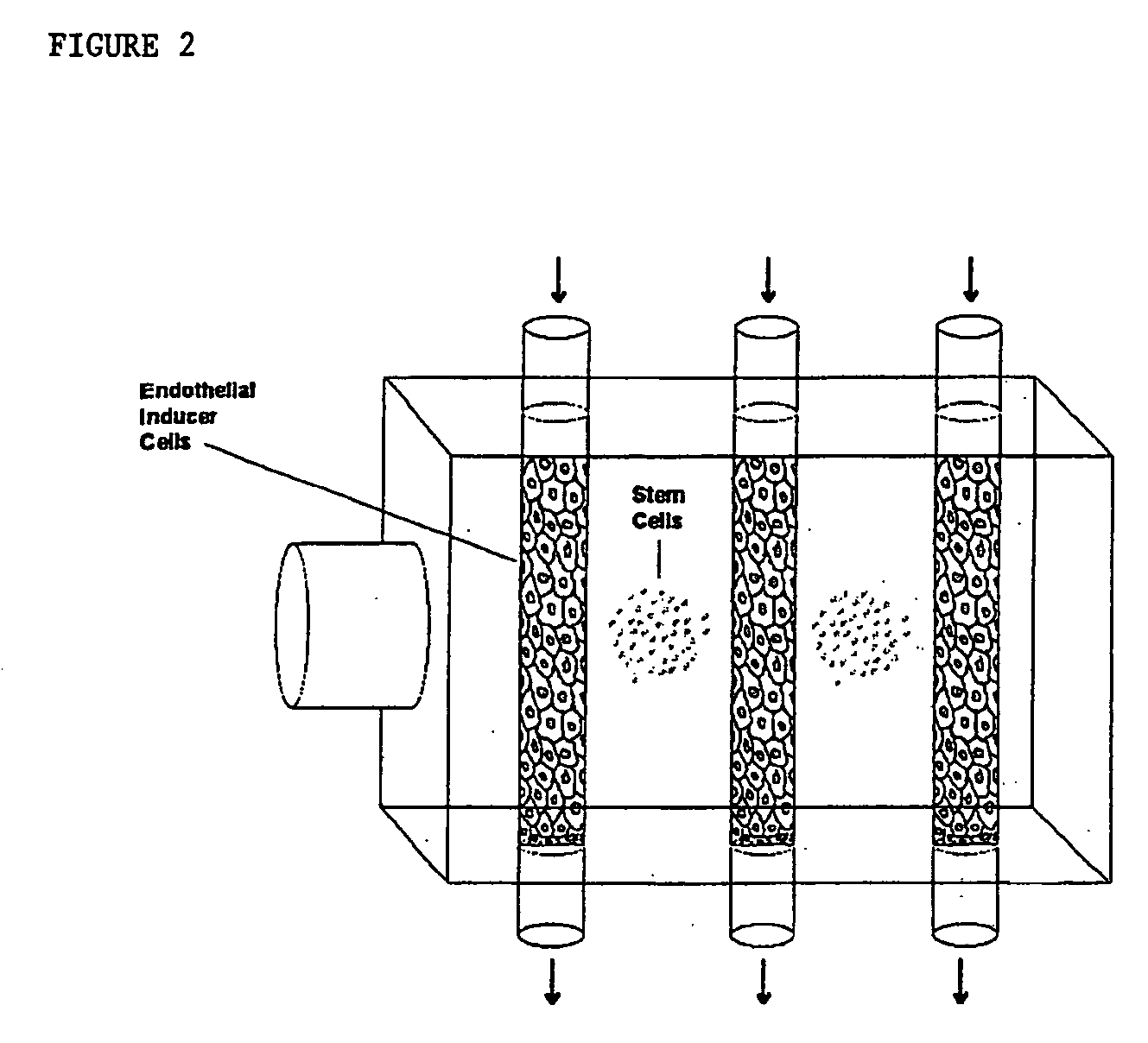
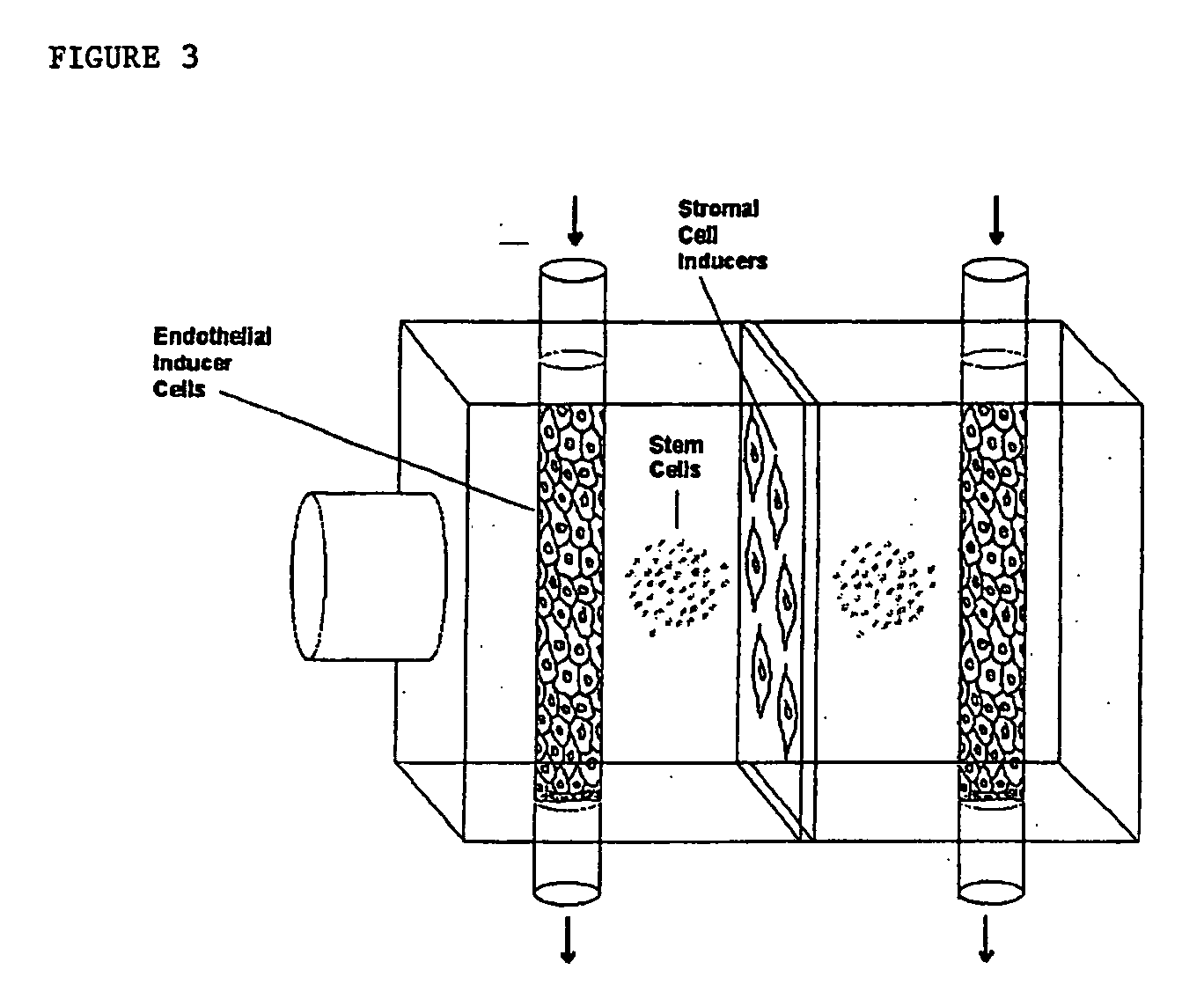
Methods for making human ES cells and human differentiated cells and tissues for transplantation are described, whereby the cells and tissues are created following somatic cell nuclear transfer. The nuclear transfer donor is genetically modified prior to nuclear transfer such that cells of at least one developmental lineage are de-differentiated, i.e., unable to develop, thereby resolving the ethical dilemmas involved in reprogramming somatic cells back to the embryonic stage. The method concomitantly directs differentiation such that the desired cells and tissues may be more readily isolated.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Predicting Human Developmental Toxicity of Pharmaceuticals Using Human Stem-Like Cells and Metabolomics
ActiveUS20110312019A1Increased toxicityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisTesting toxicityMetabolite
The invention provides biomarker profiles of metabolites and methods for screening chemical compounds including pharmaceutical agents, lead and candidate drug compounds and other chemicals using human stem-like cells (hSLCs) or lineage-specific cells produced therefrom. The inventive methods are useful for testing toxicity, particularly developmental toxicity and detecting teratogenic effects of such chemical compounds. Specifically, a more predictive developmental toxicity model, based on an in vitro method that utilizes both hSLCs and metabolomics to discover biomarkers of developmental toxicity is disclosed.
Owner:STEMINA BIOMARKER DISCOVERY
LINEAGE REPROGRAMMING TO INDUCED CARDIAC PROGENITOR CELLS (iCPC) BY DEFINED FACTORS
ActiveUS20150140658A1Facilitated DiffusionSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell culture active agentsLineage specificCells heart
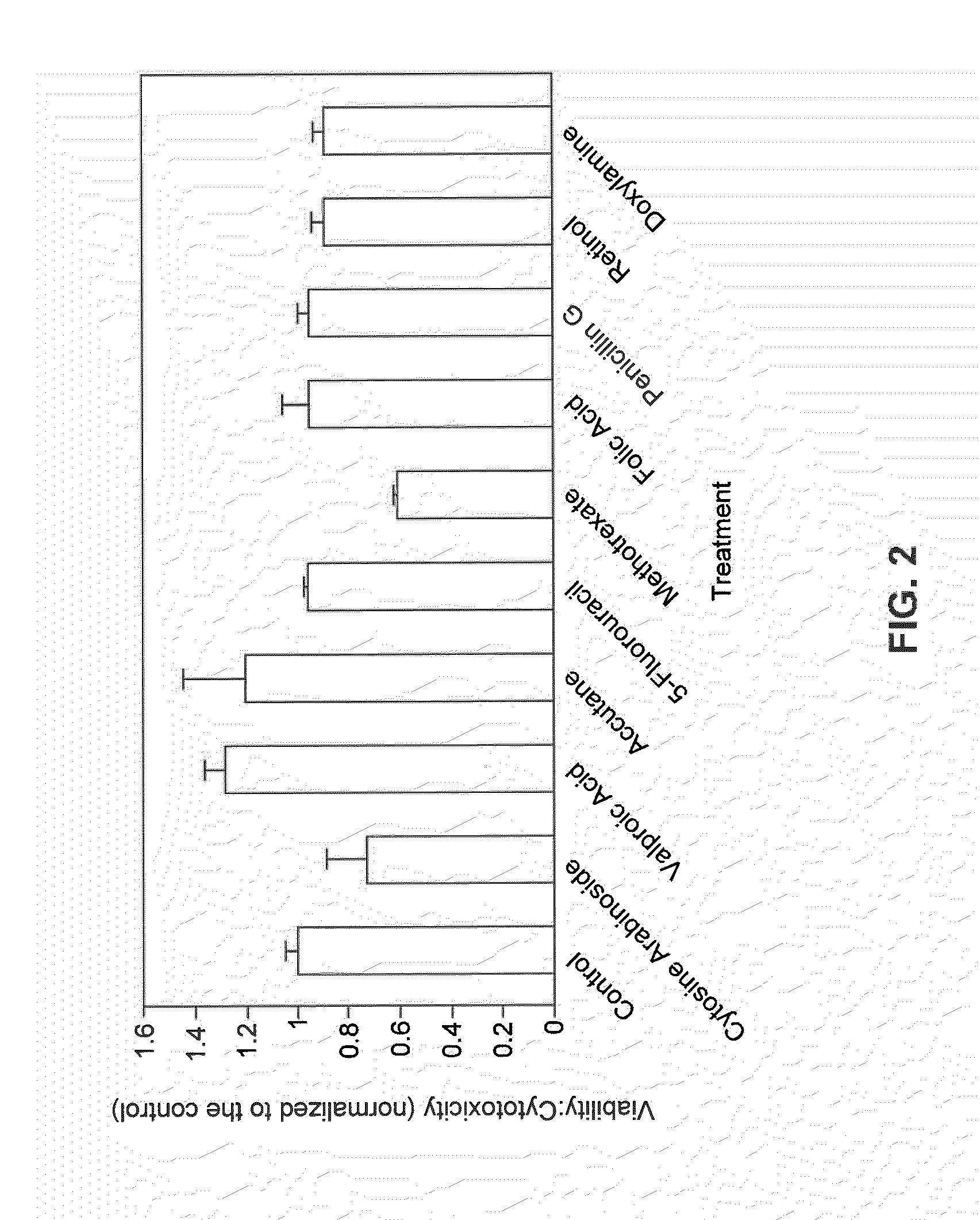
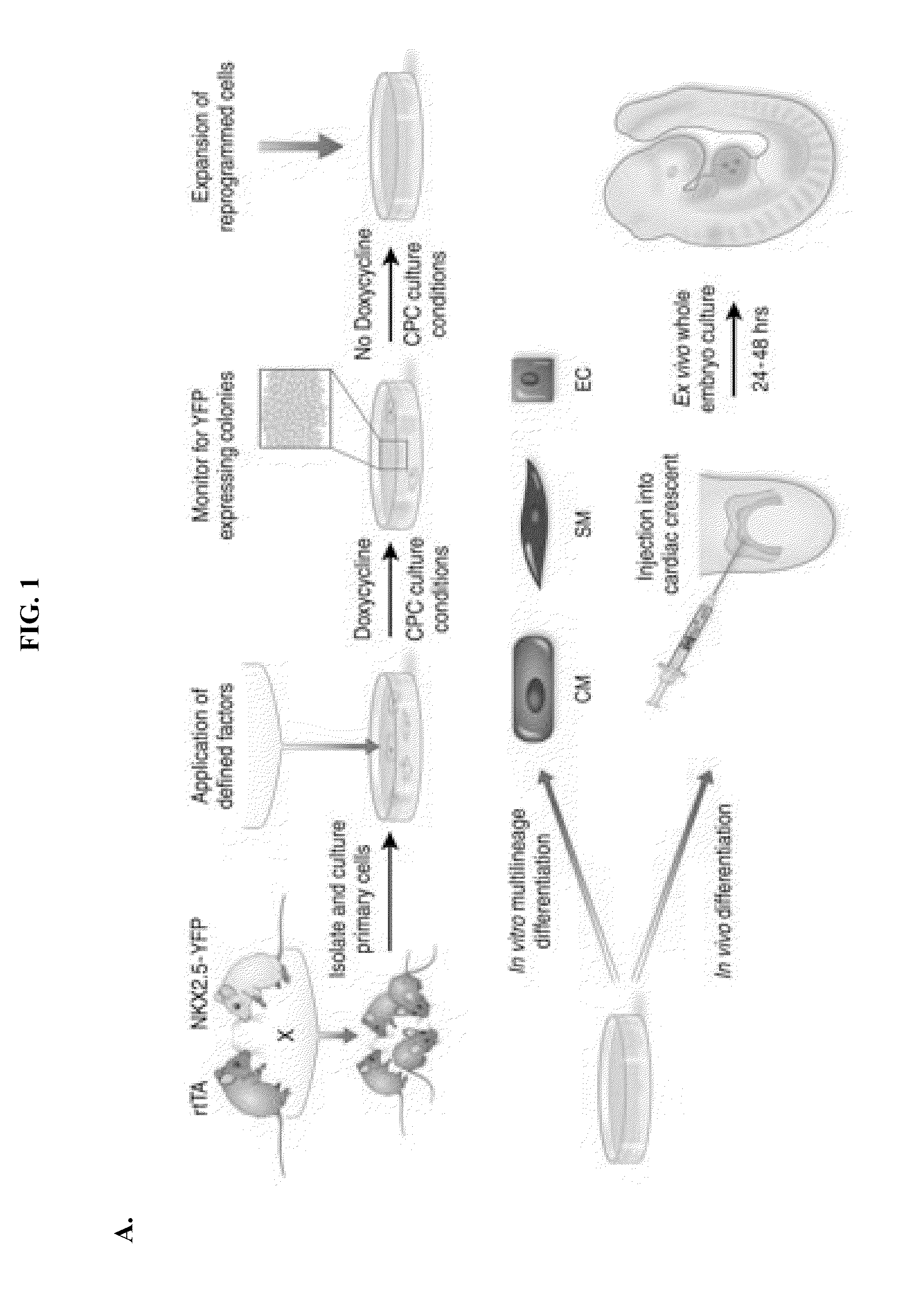
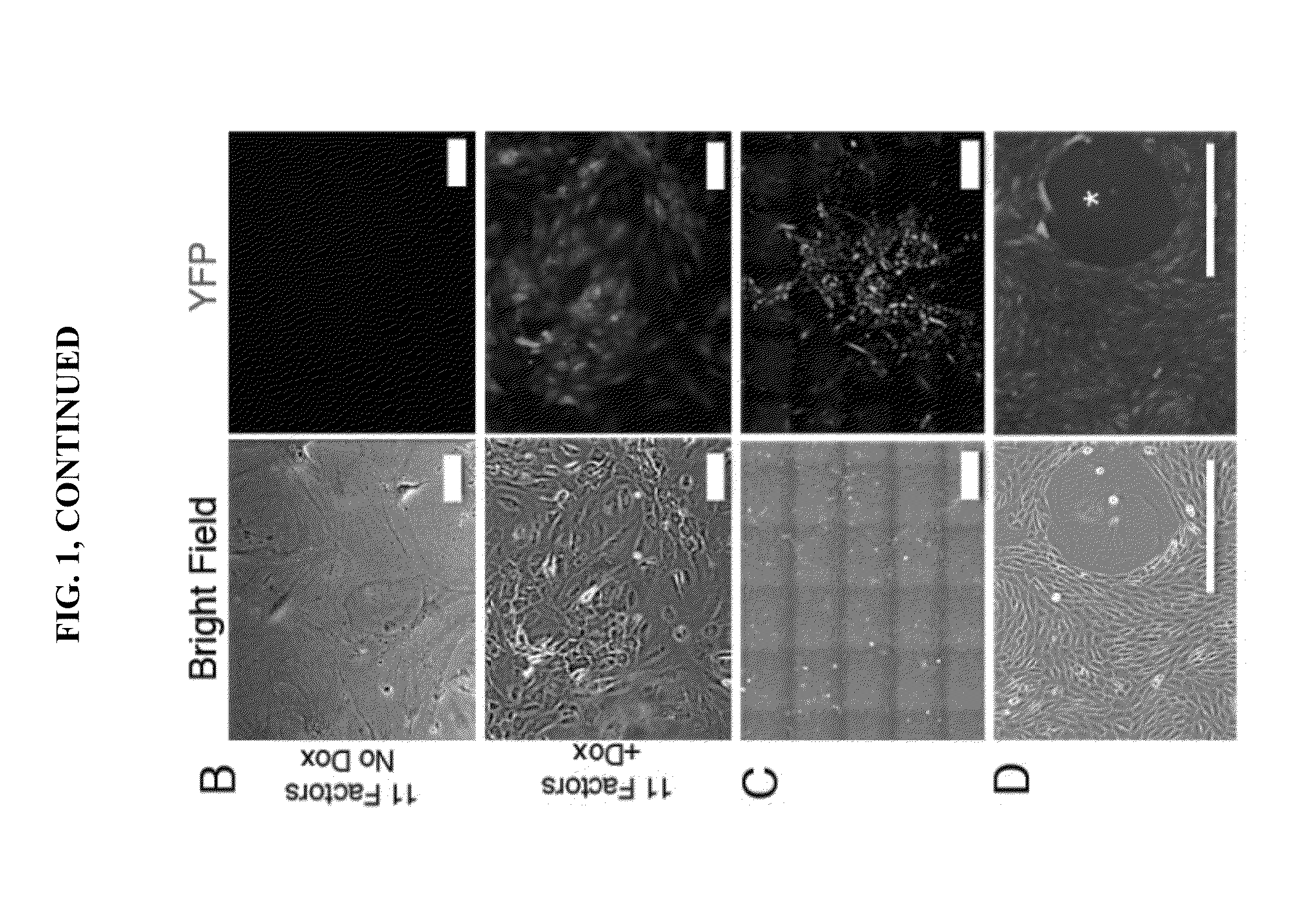
Animal cells, notably adult fibroblasts, are advantageously reprogrammed in direct lineage reprogramming methods using defined factors to produce proliferative and multipotent induced cardiac progenitor cells (iCPC). The iCPC thus produced can be differentiated under suitable differentiation conditions to cardiac lineage cells including cardiomyocytes, smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells, as evidenced by expression of lineage specific markers. Sets of factors effective in combination to reprogram the fibroblasts can include a set that includes some or all of 5 factors (Mesp1, Baf60c, Nkx2.5, Gata4, Tbx5), a set that includes some or all of 11 factors (Mesp1, Mesp2, Gata4, Gata6, Baf60c, SRF, Isl1, Nkx2.5, Irx4, Tbx5, Tbx20), a set that includes some or all of 18 factors (T, Mesp1, Mesp2, Tbx5, Tbx20, Isl1, Gata4, Gata6, Irx4, Nkx2.5, Hand1, Hand2, Tbx20, Tbx18, Tip60, Baf60c, SRF, Hey2), and a set that includes some or all of 22 factors (T, Mesp1, Mesp2, Tbx5, Tbx20, Isl1, Gata4, Gata6, Irx4, Nkx2.5, Hand1, Hand2, Tbx20, Tbx18, Tip60, Baf60c, SRF, Hey2, Oct4, Klf4, Sox2, L-myc).
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Mesenchymal stem cells for in vitro modeling and cell-based therapy of human diseases and banks thereof
A method of qualifying a mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) population is disclosed. The method comprises:(a) ex vivo differentiating a population of mesenchymal stem cells originating from the subject towards a first lineage-specific cell, the first lineage-specific cell being associated with a brain disease;(b) ex vivo differentiating a population of mesenchymal stem cells originating from a healthy subject towards the first lineage-specific cell;(c) comparing an effect of the first lineage specific cell derived from the subject with an effect of the first lineage specific cell derived from the healthy subject on a second lineage specific cell associated with the brain disease, wherein a difference in the effect above or below a predetermined level is indicative of a qualification of a mesenchymal stem cell population for cell therapy of said brain disease.
Owner:BRAINSTEM BIOTEC +1
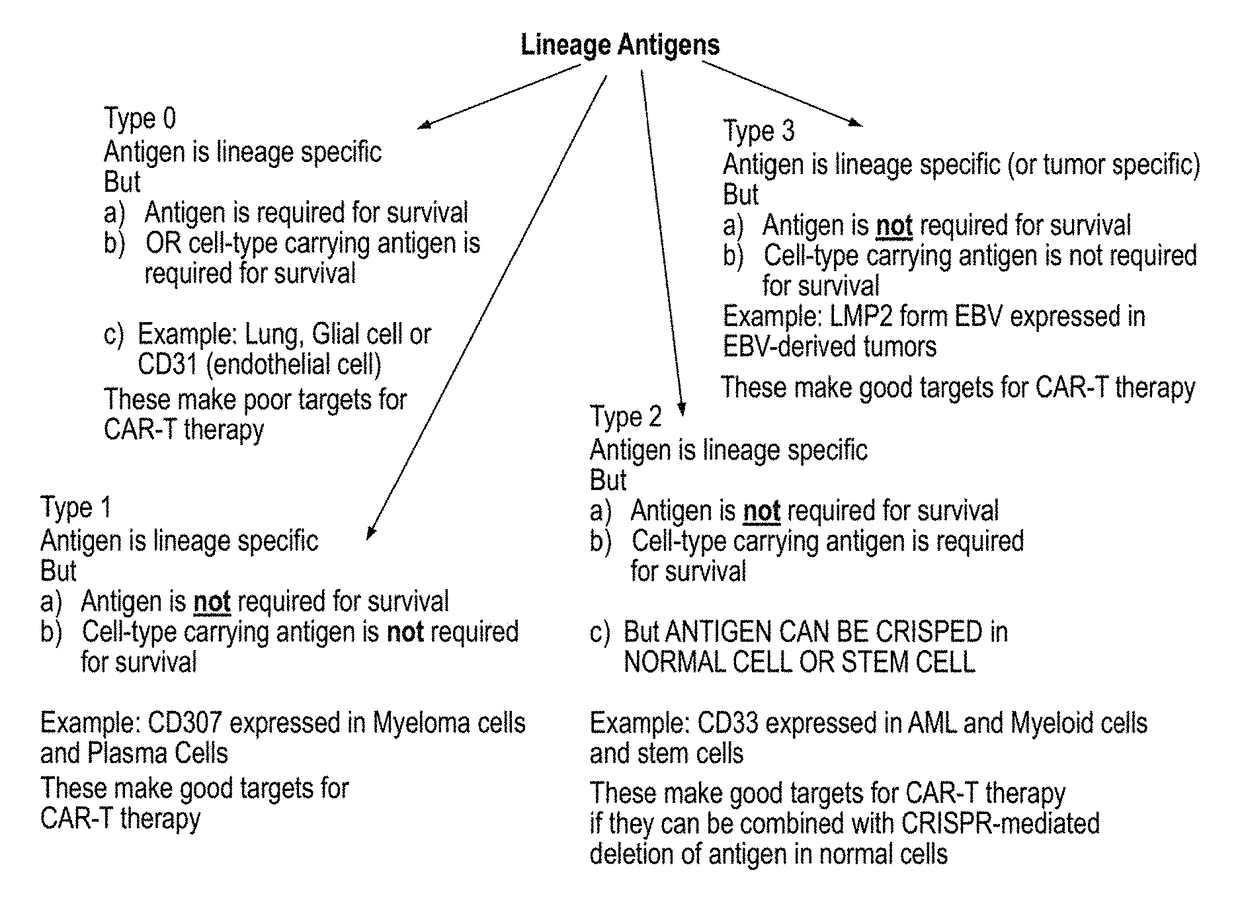
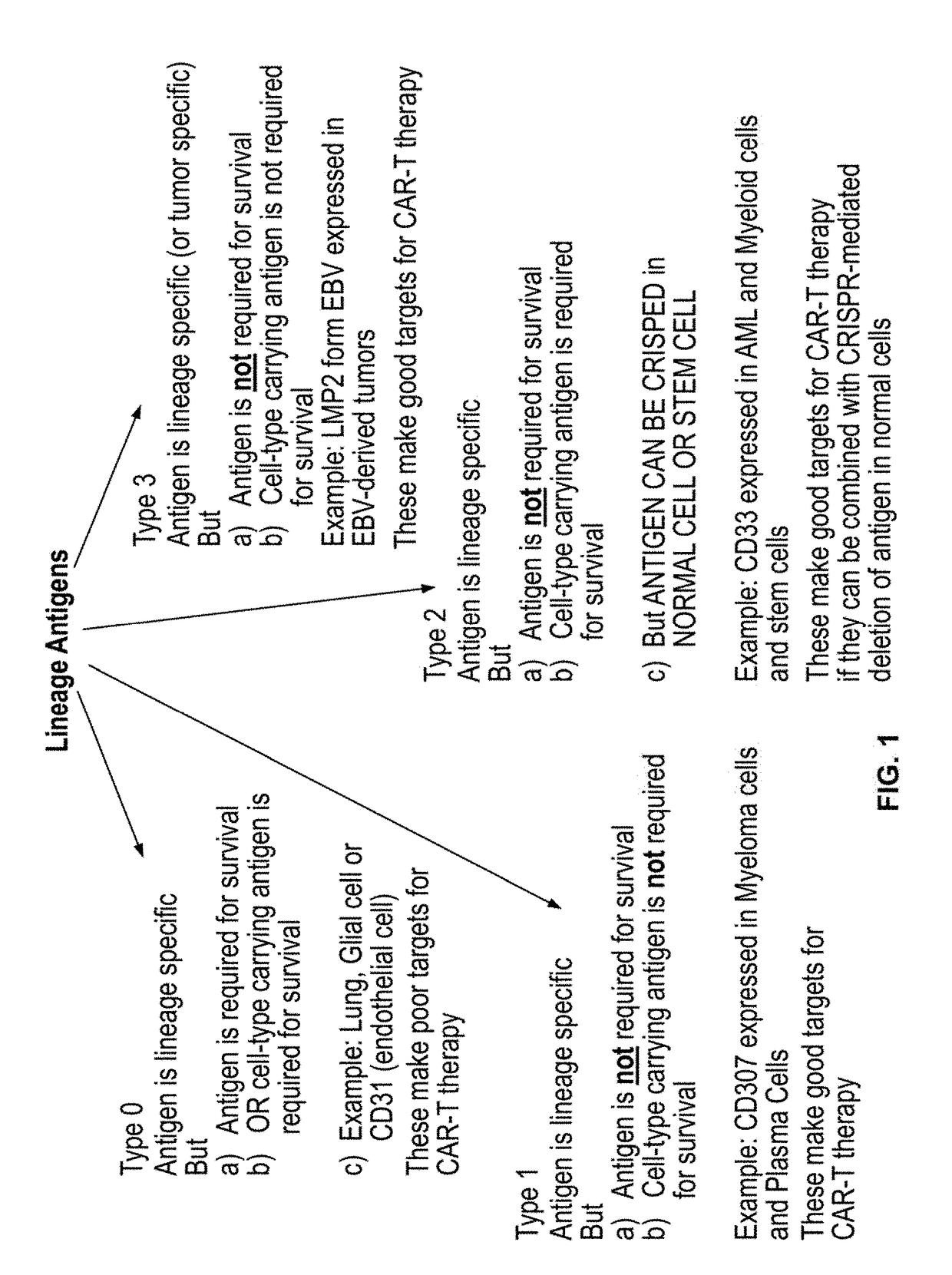
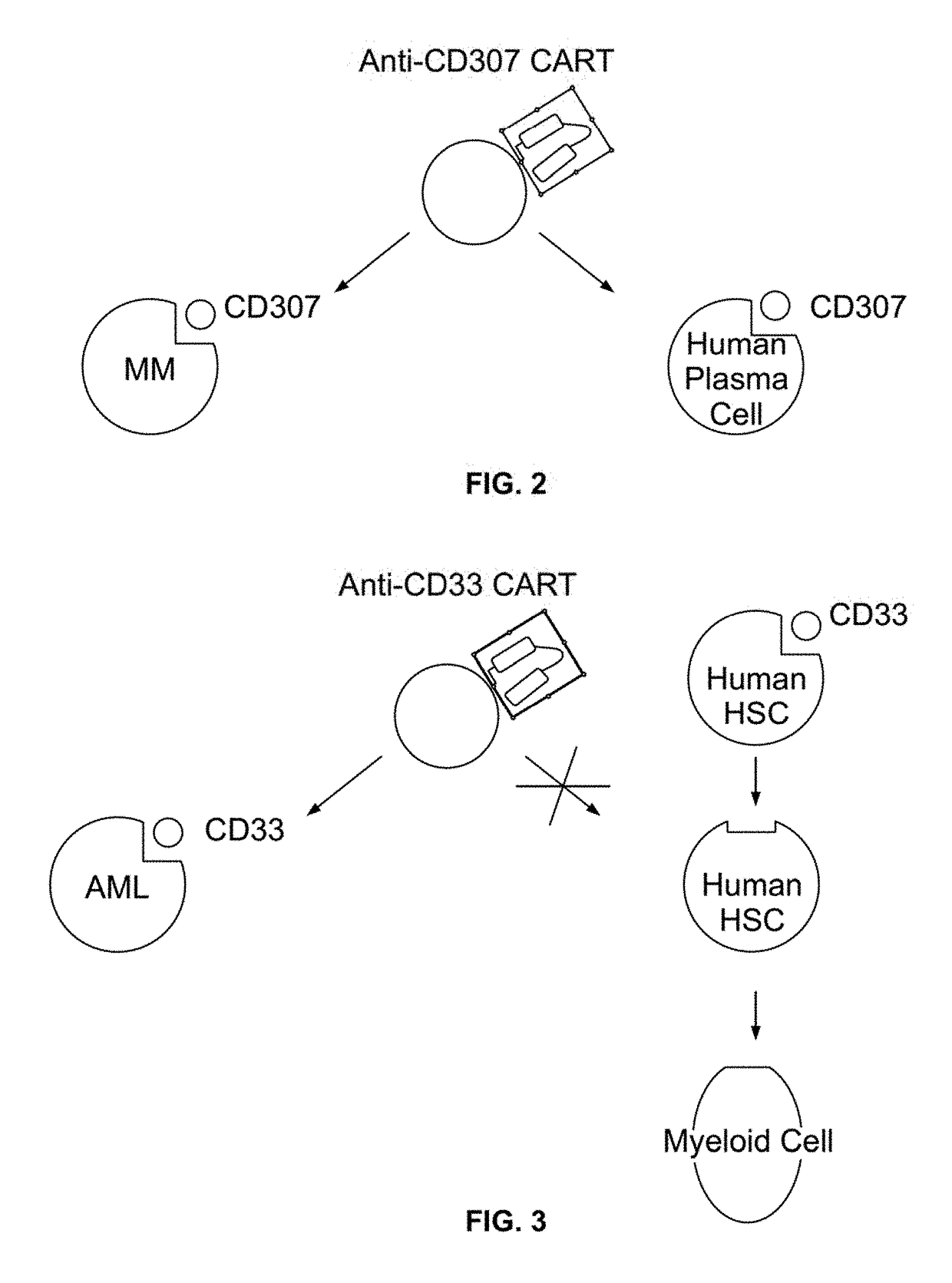
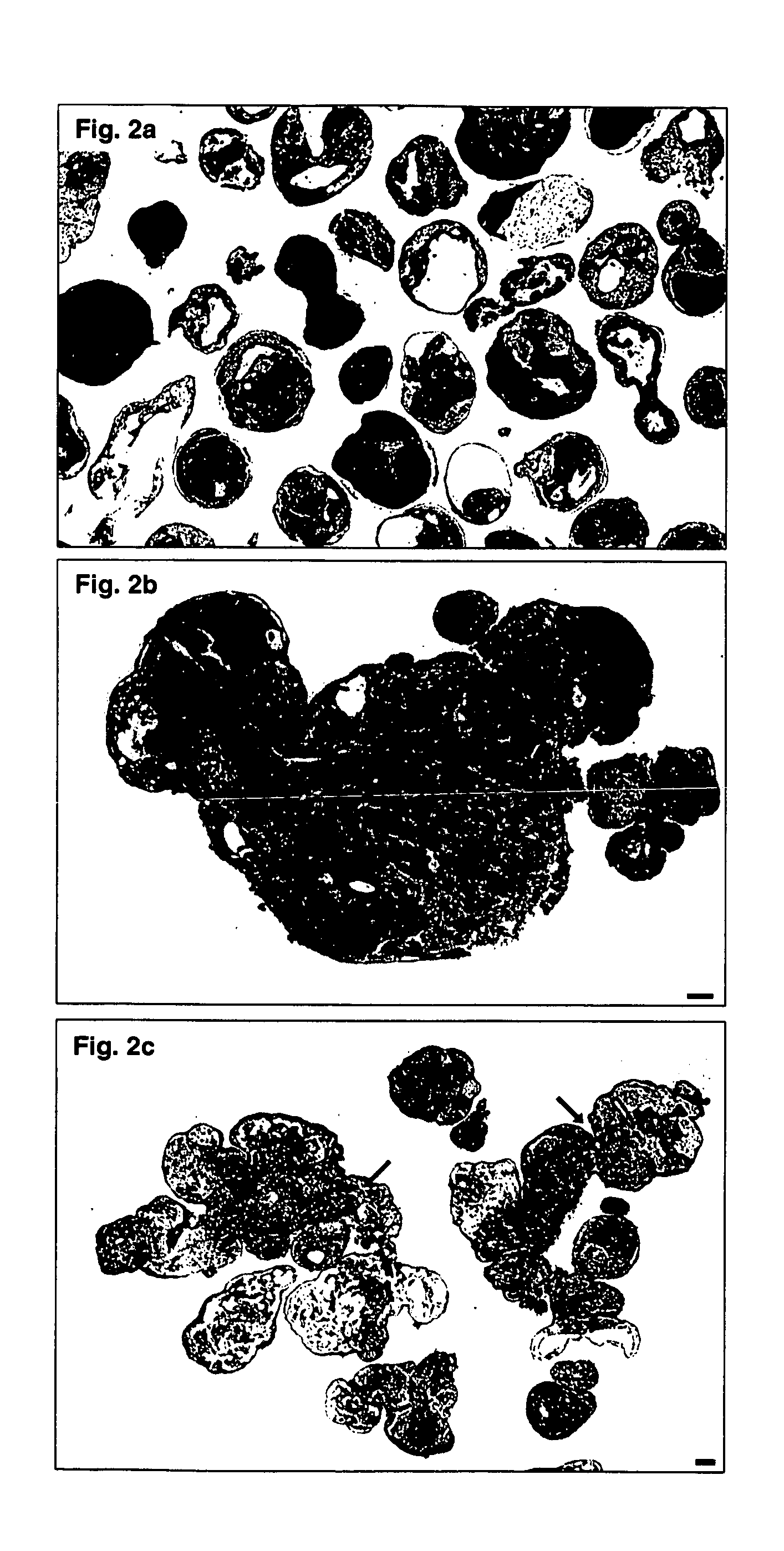
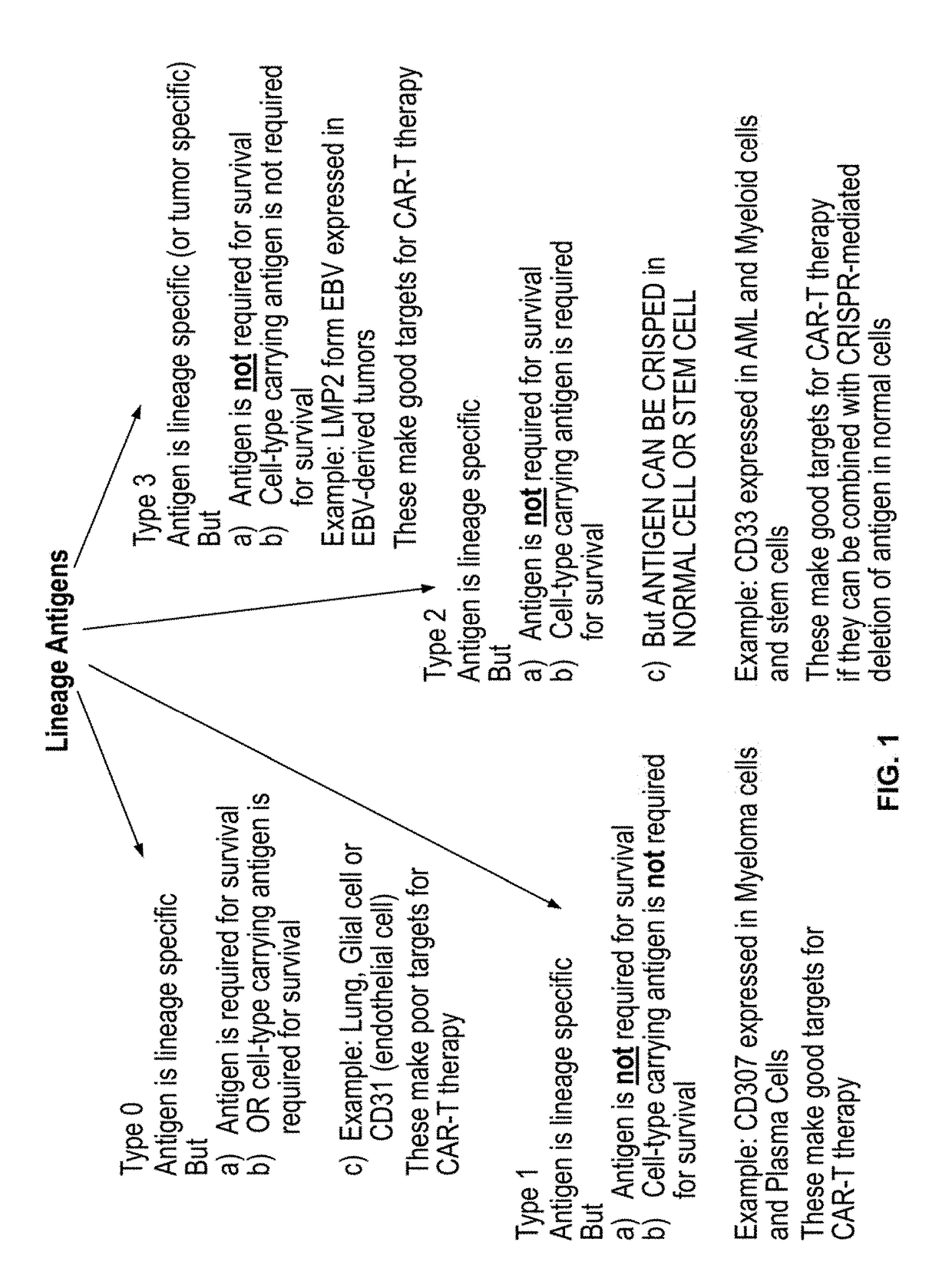
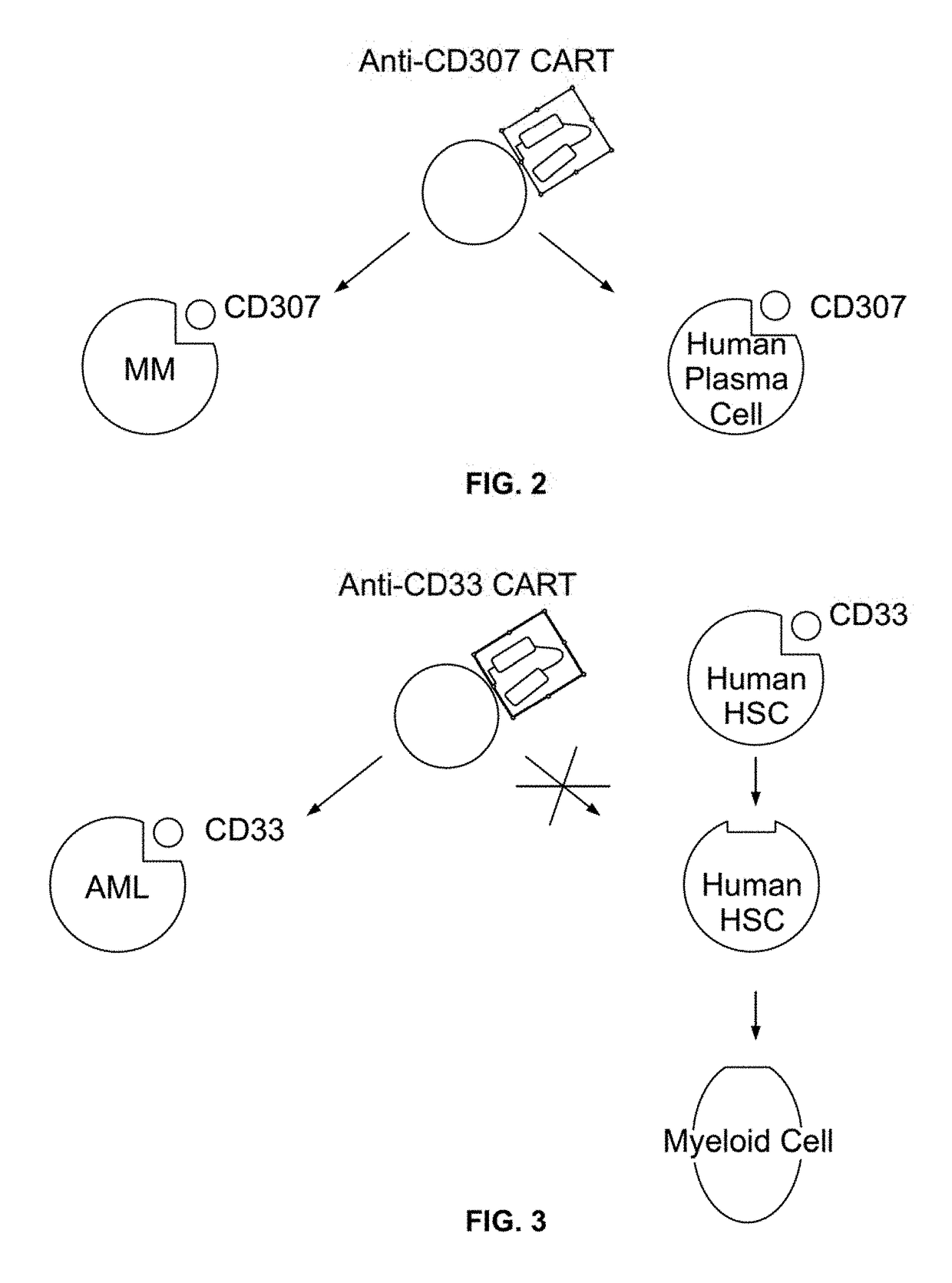
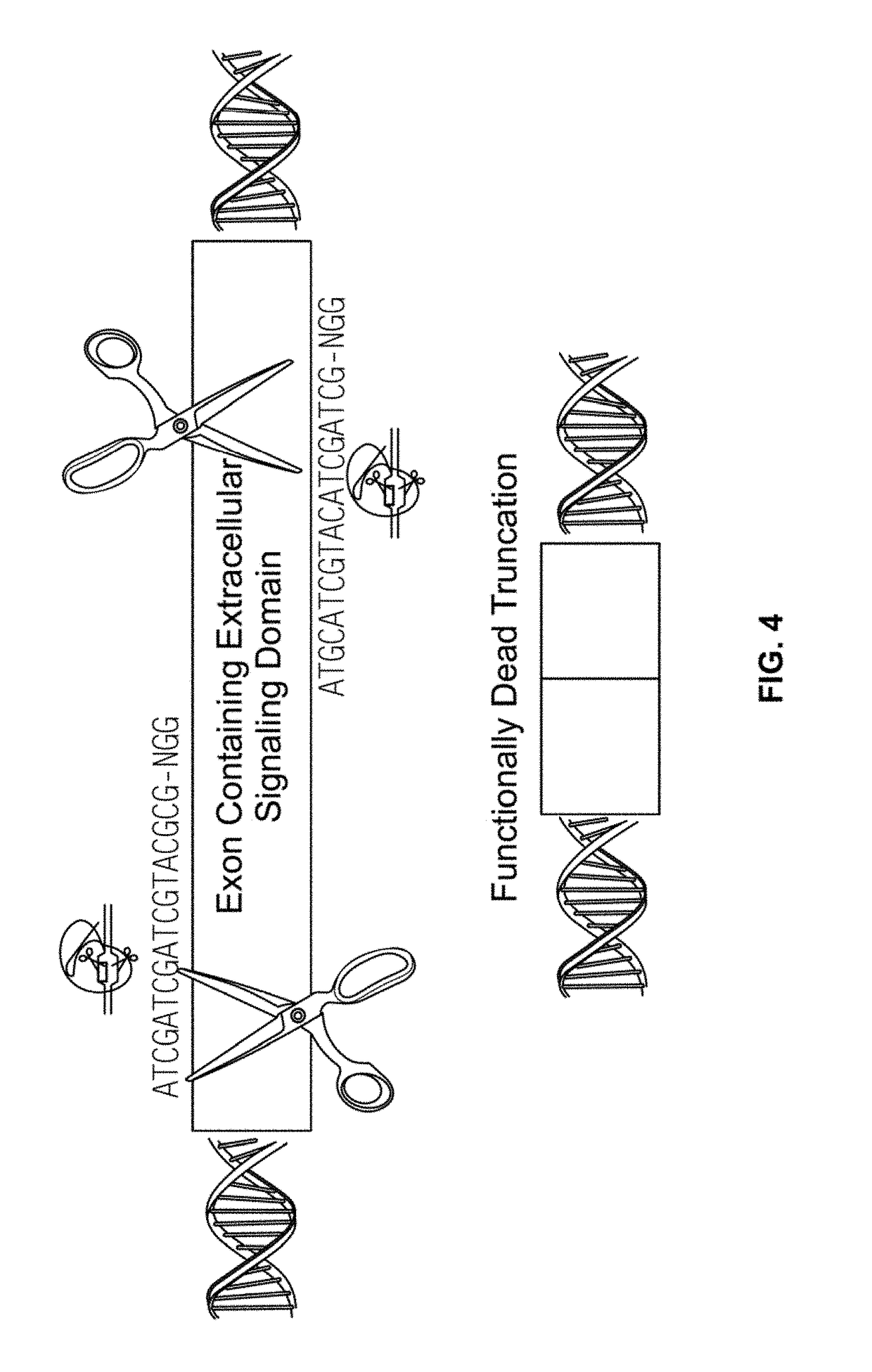
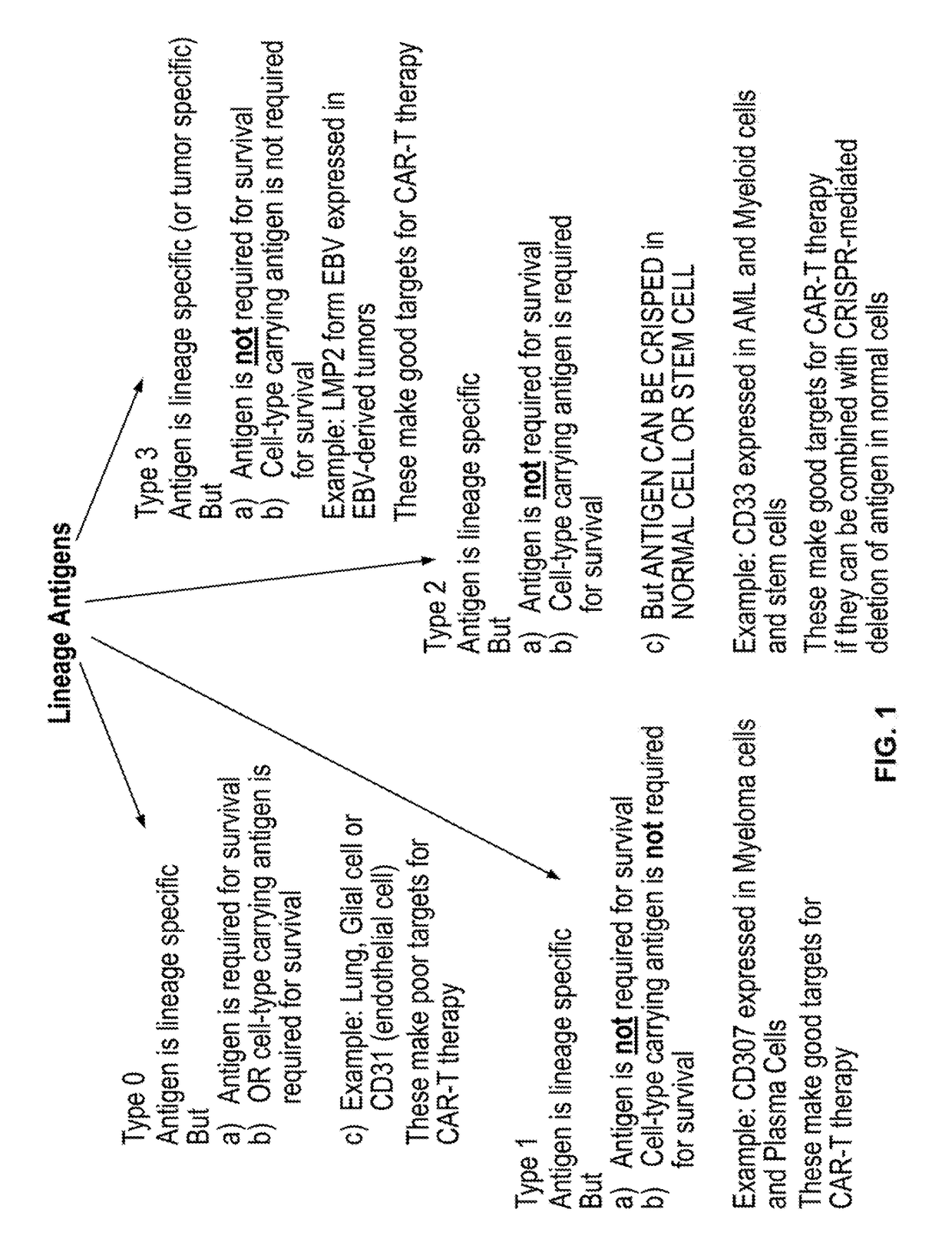
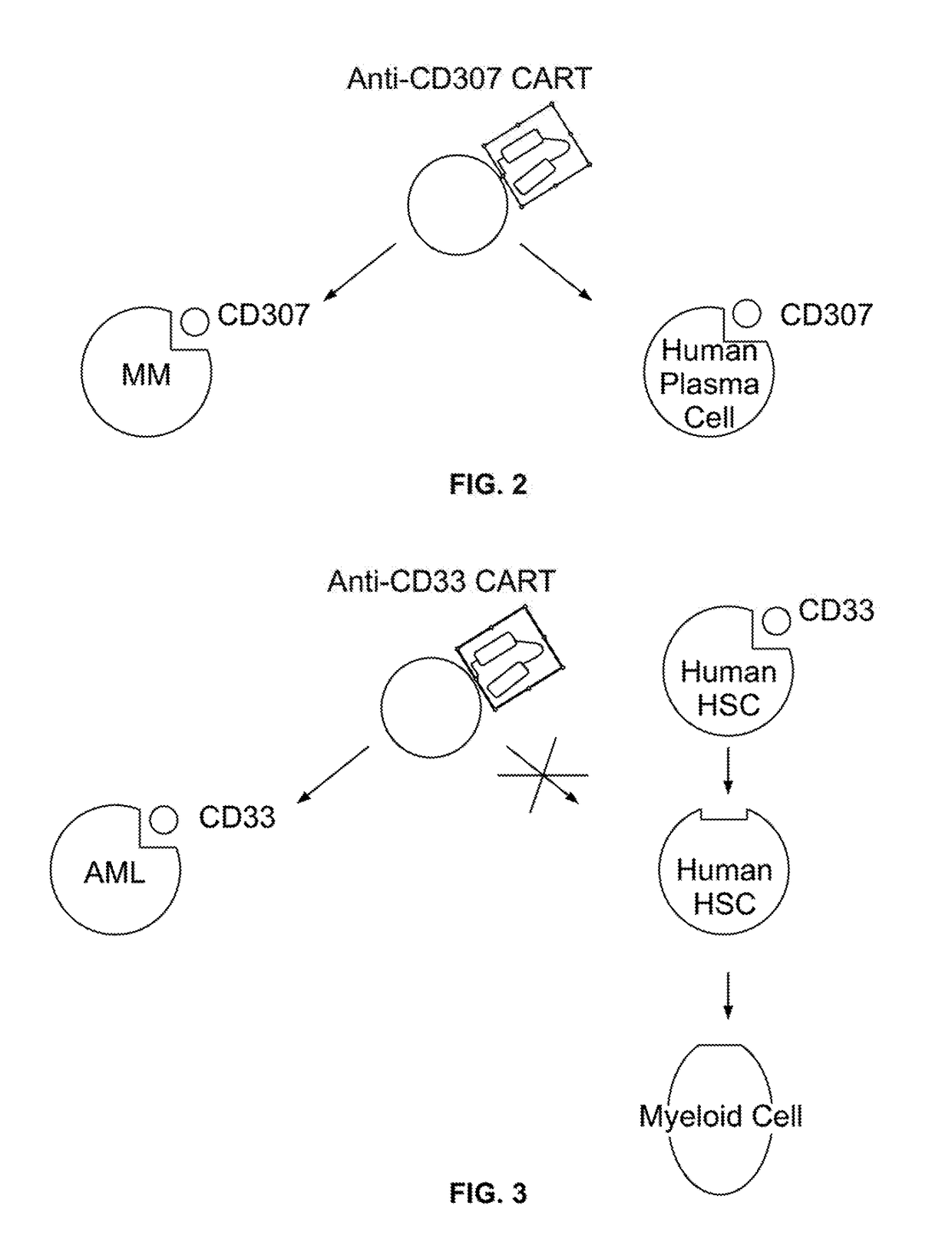
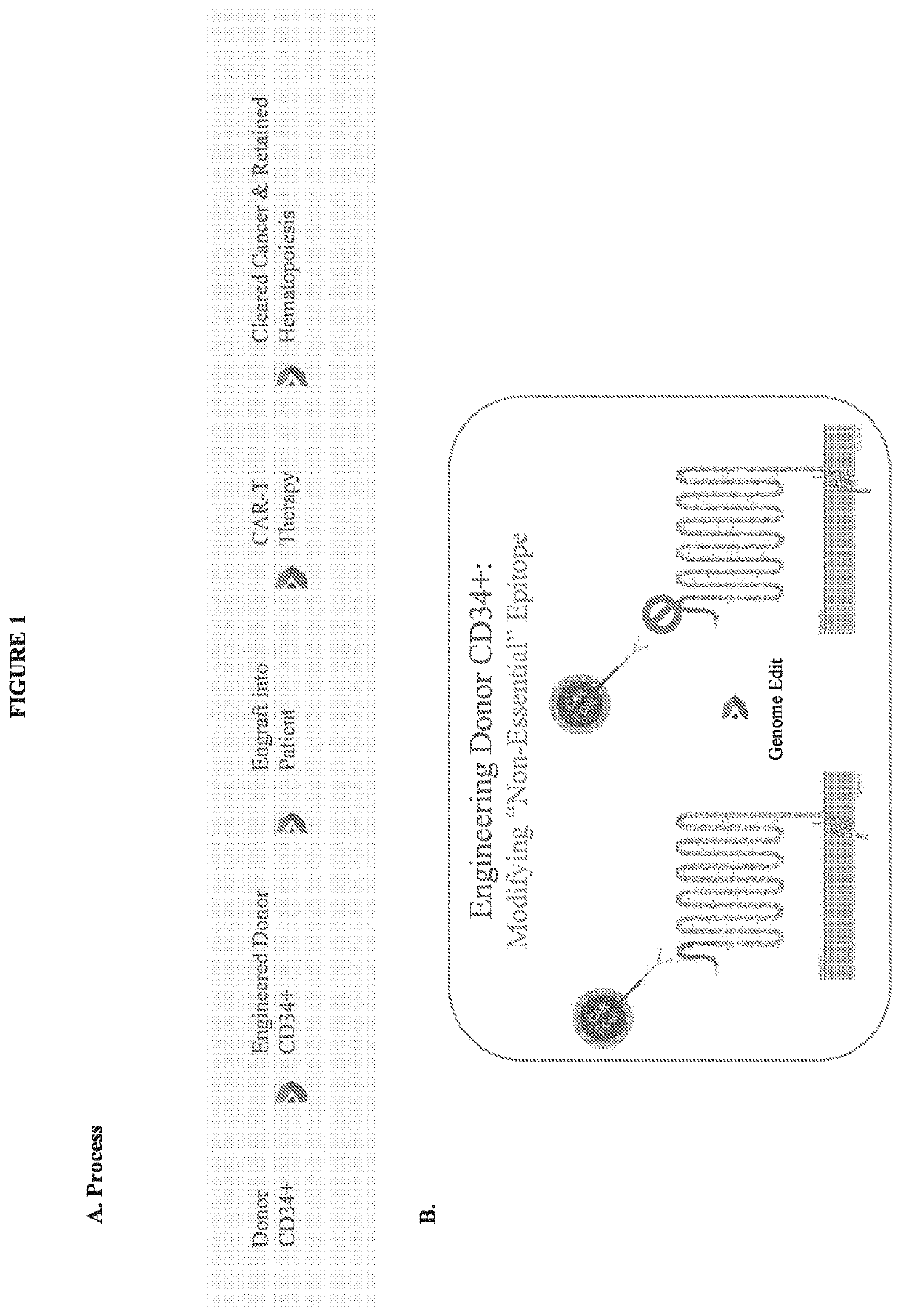
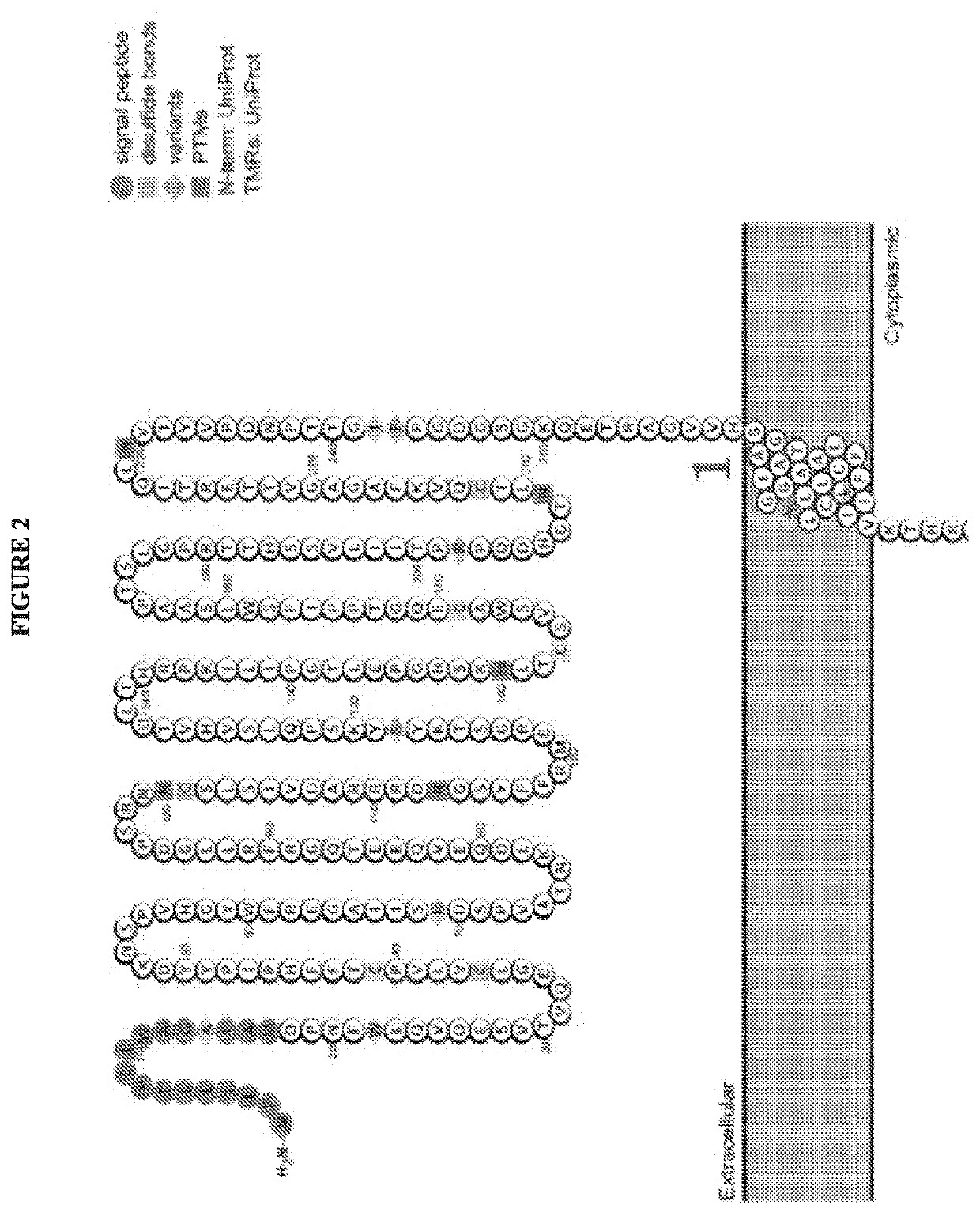
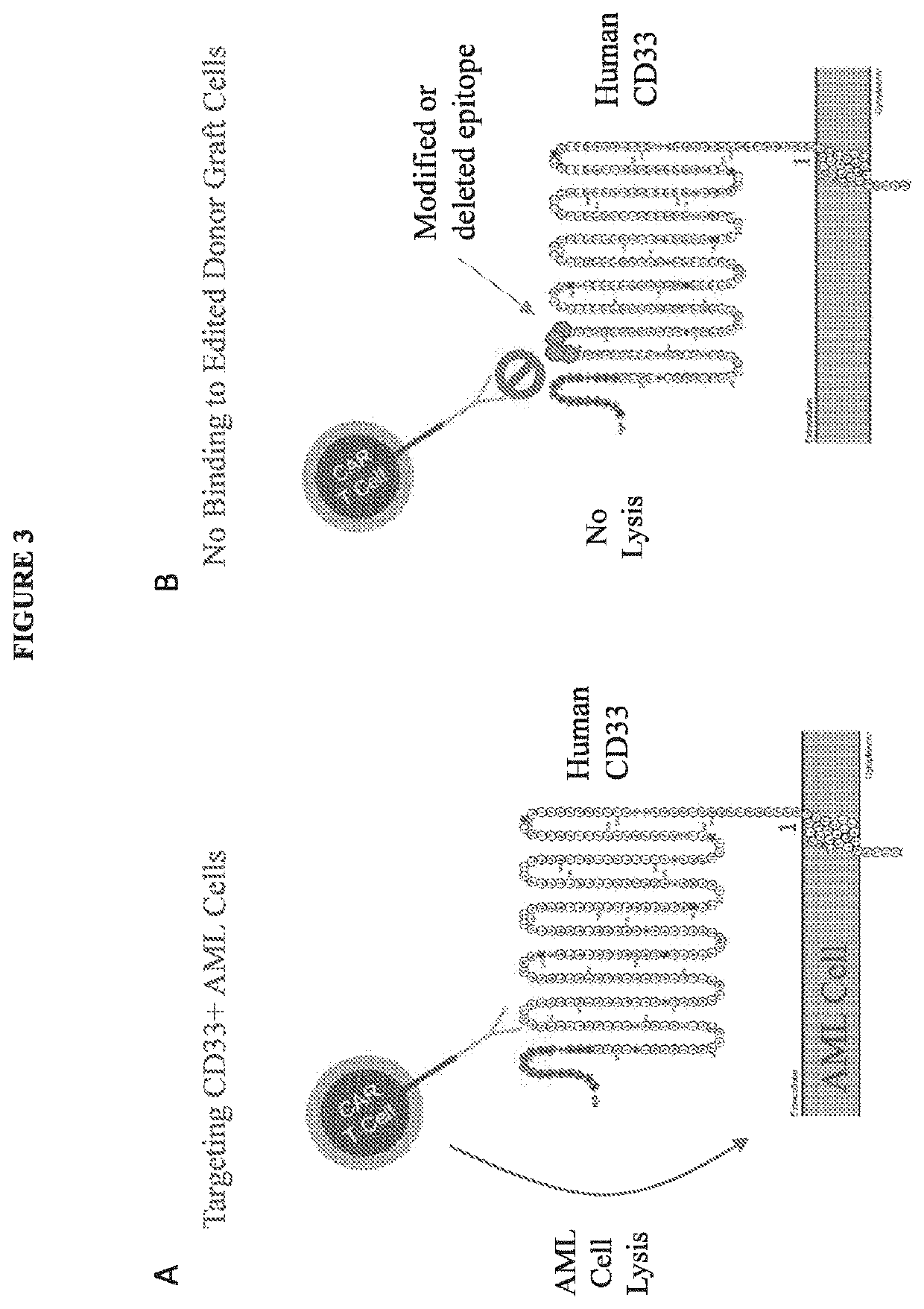
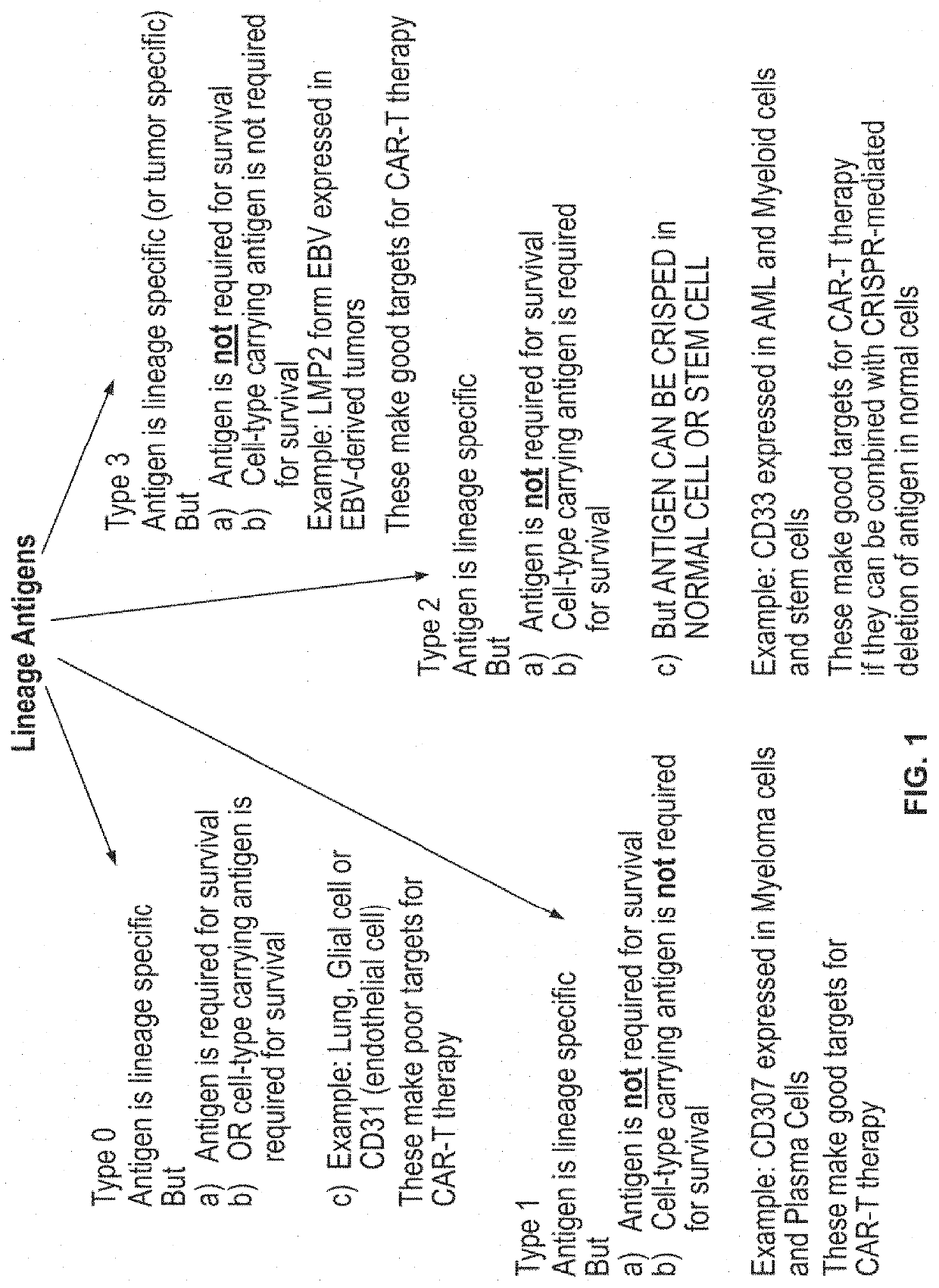
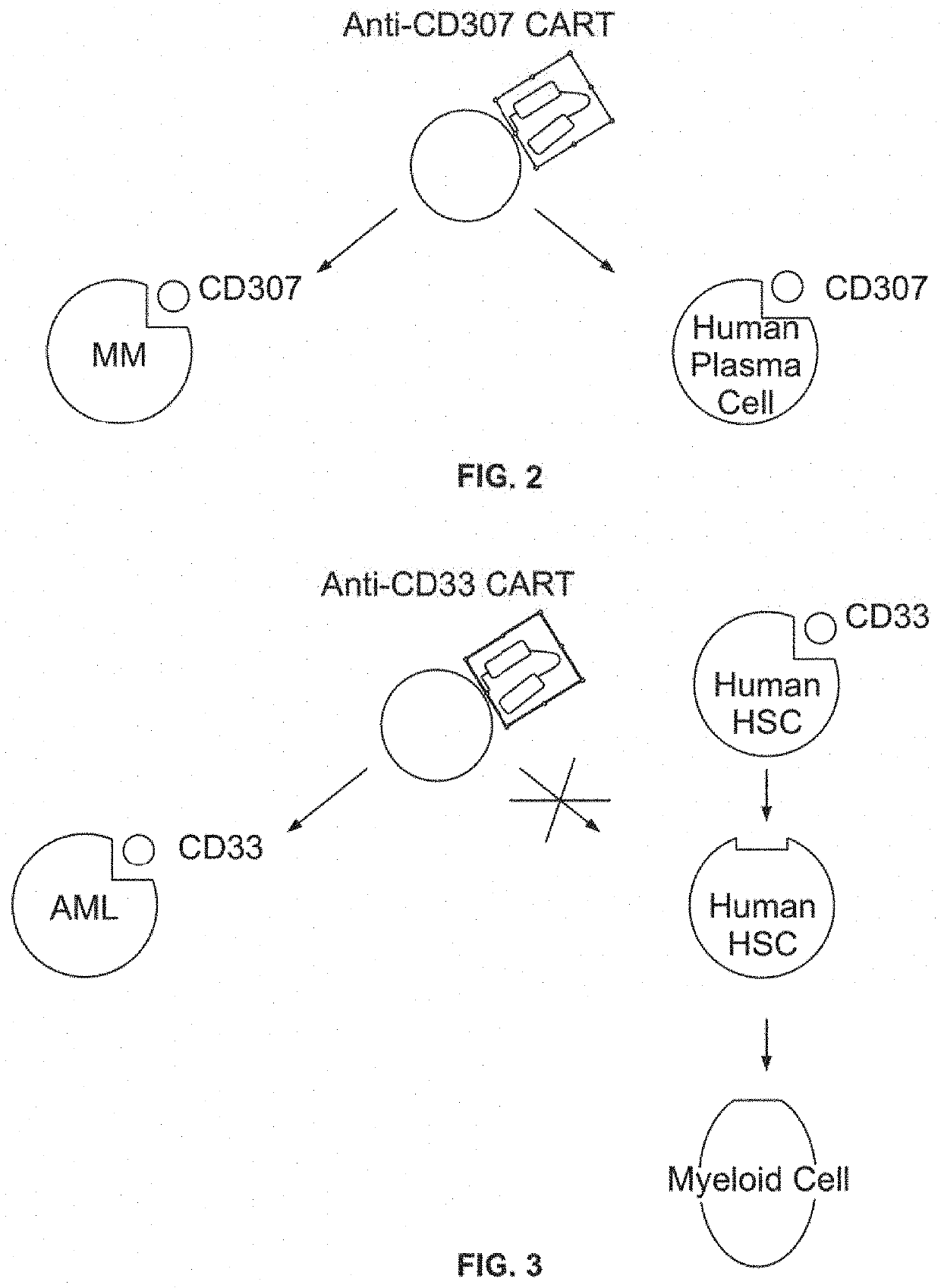
Compositions and methods for inhibition of lineage specific antigens
ActiveUS20170326179A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigenHematopoietic cell
Disclosed herein are methods of administering an agent targeting a lineage-specific cell-surface antigen and a population of hematopoietic cells that are deficient in the lineage-specific cell-surface antigen for immunotherapy of hematological malignancies.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Method of dynamically culturing embryonic stem cells
he present invention is of a method of dynamically generating human embryoid bodies which can be used for generating lineage specific cells and cell lines. Specifically, the present invention can be used to generate ESC-differentiated cells for cell-replacement therapy.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Compositions and methods for inhibition of lineage specific antigens
ActiveUS10137155B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigenHematopoietic cell
Disclosed herein are methods of administering an agent targeting a lineage-specific cell-surface antigen and a population of hematopoietic cells that are deficient in the lineage-specific cell-surface antigen for immunotherapy of hematological malignancies.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Compositions and methods for inhibition of lineage specific antigens
ActiveUS20190046580A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigenHematopoietic cell
Disclosed herein are methods of administering an agent targeting a lineage-specific cell-surface antigen and a population of hematopoietic cells that are deficient in the lineage-specific cell-surface antigen for immunotherapy of hematological malignancies.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Methods of expanding embryonic stem cells in a suspension culture
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Establishment of a human embryonic stem cell line using mammalian cells
InactiveUS7811817B2Improve matchIncrease valueBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementGerm layerFGF4
Purified preparations of human embryonic stem cells with certain population-specific characteristics are disclosed. This preparation is characterized by the positive expression of the following pluripotent cell surface markers: SSEA-1 (−); SSEA-4 (+); TRA-1-60 (+); TRA-1-81 (+); alkaline phosphatase (+), as well as a set of ES cell markers including Oct-4, Nanog, Rex1, Sox2, Thy1, FGF4, ABCG2, Dppa5, UTF1, Cripto1, hTERT, Connexin-43 and Connexin-45. The cells of the preparation are negative for lineage specific markers like Keratin 8, Sox-1, NFH (ectoderm), MyoD, brachyury, cardiac-actin (mesoderm), HNF-3 beta, albumin, and PDX1 (endoderm). The cells of the preparation are human embryonic stem cells, have normal karyotypes, exhibit high telomerase activity and continue to proliferate in an undifferentiated state after continuous culture for over 40 passages. The embryonic stem cell line Relicell™ hES1 also retains the ability, throughout the culture, to differentiate into cell and tissue types derived from all three embryonic germ layers (endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm). Methods for isolating a human embryonic stem cell line are also disclosed.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
Compositions and methods for inhibition of lineage specific antigens
ActiveUS20190046581A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigenHematopoietic cell
Disclosed herein are methods of administering an agent targeting a lineage-specific cell-surface antigen and a population of hematopoietic cells that are deficient in the lineage-specific cell-surface antigen for immunotherapy of hematological malignancies.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Method of nociceptor differentiation of human embryonic stem cells and uses thereof
The present invention relates to the field of stem cell biology, in particular the linage specific differentiation of pluripotent or multipotent stem cells, which can include, but is not limited to, human embryonic stem cells (hESC), human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC), somatic stem cells, cancer stem cells, or any other cell capable of lineage specific differentiation. Specifically described are methods to direct the lineage specific differentiation of hESC and / or hiPSC to nociceptors (i.e. nociceptor cells) using novel culture conditions. The nociceptors made using the methods of the present invention are further contemplated for various uses including, but limited to, use in in vitro drug discovery assays, pain research, and as a therapeutic to reverse disease of, or damage to, the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Further, compositions and methods are provided for producing melanocytes from human pluripotent stem cells for use in disease modeling.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Compositions and methods for inhibition of lineage specific proteins
PendingUS20200030381A1Reduce the binding forceTreatment safetyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyHematopoietic cellCell Surface Proteins
Disclosed herein are compositions, methods, and kits for use in treating hematopoietic malignancies, the compositions, methods, and kits comprise a cytotoxic agent targeting cells expressing a lineage-specific cell-surface protein and a population of hematopoietic cells that express the lineage-specific cell-surface protein, the hematopoietic cells being manipulated such that they do not bind the cytotoxic agent.
Owner:VOR BIOPHARMA INC
Generation of functional cells from stem cells
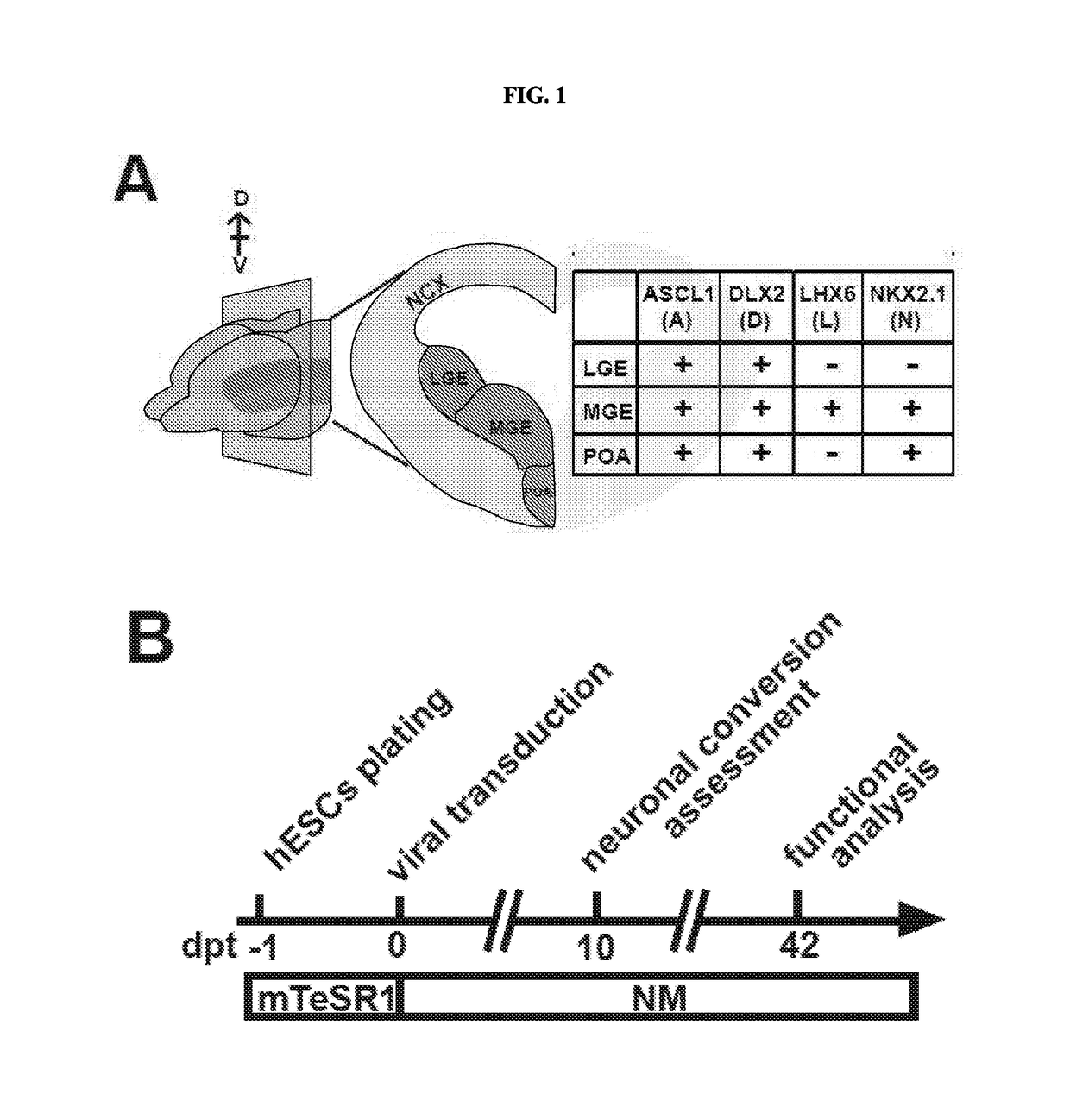
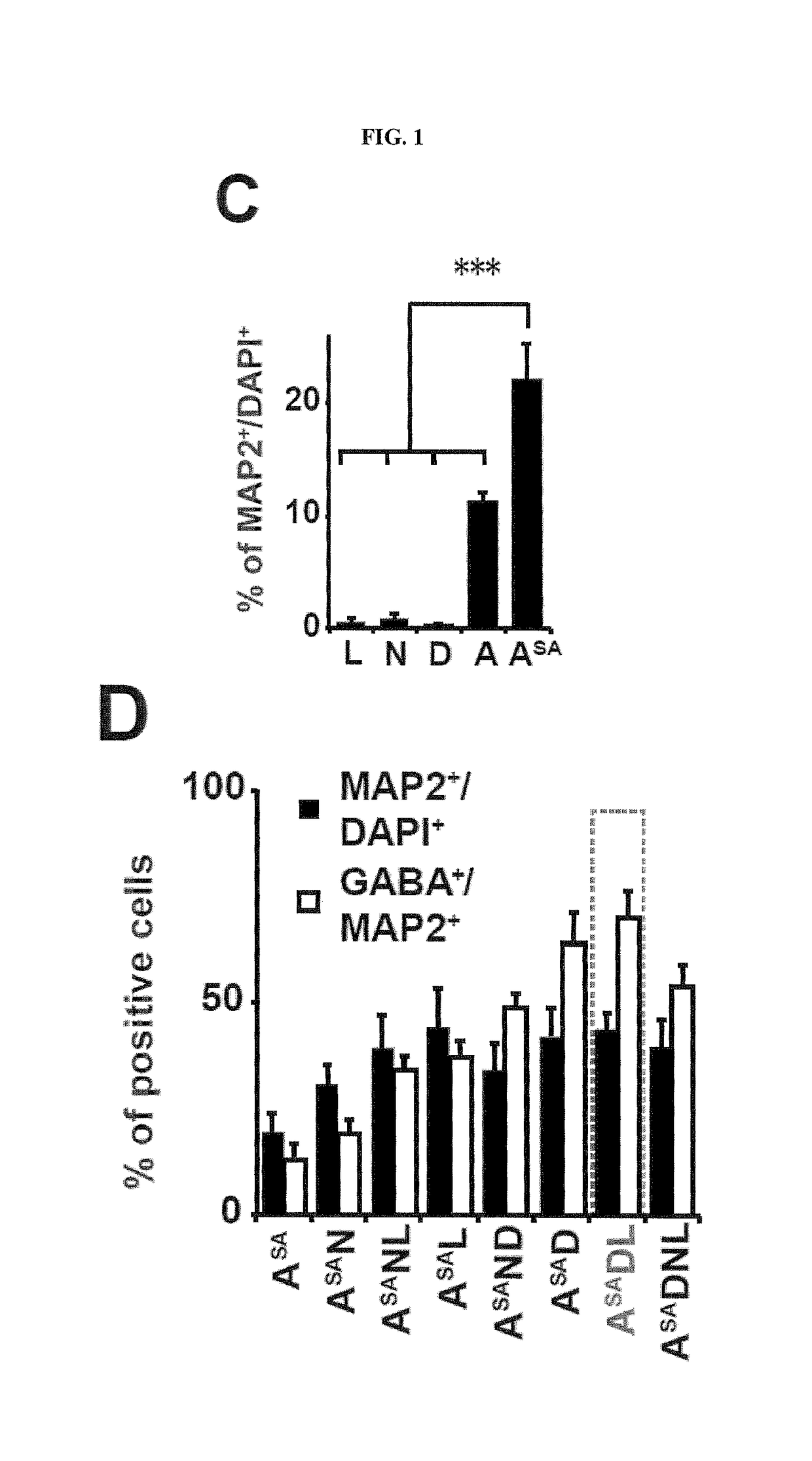
The present disclosure provides a method of directly converting a stem cell into a lineage specific cell, comprising the steps of a) transfecting a stem cell with at least one expression vector comprising i) one or more cell lineage reprogramming factors operably linked to an inducible promoter and ii) a selection marker; and b) inducing the transfected stem cell from stem a) with an inducing agent to directly convert said stem cell into a lineage-specific cell. Particularly exemplified are methods of transfecting a stem cell with SA-ASCL1 (phospho-mutant), DLX2, LHX6 and miR-9 / 9*-124 linked to a doxycycline inducible promoter to convert the stem cell into an inhibitory neuron and transfecting with NeuroD2 linked to a doxycycline inducible promoter to convert a stem cell into an excitatory neuron. Methods of screening one or more factors and / or one or more genetic mutations that modulate a pre-selected activity of the lineage specific cell, kits and directly convertible stem cells obtained using method of the invention are also provided.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Predicting human developmental toxicity of pharmaceuticals using human stem-like cells and metabolomics
ActiveUS8703424B2Increased toxicityMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue cultureTesting toxicityMetabolite
The invention provides biomarker profiles of metabolites and methods for screening chemical compounds including pharmaceutical agents, lead and candidate drug compounds and other chemicals using human stem-like cells (hSLCs) or lineage-specific cells produced therefrom. The inventive methods are useful for testing toxicity, particularly developmental toxicity and detecting teratogenic effects of such chemical compounds. Specifically, a more predictive developmental toxicity model, based on an in vitro method that utilizes both hSLCs and metabolomics to discover biomarkers of developmental toxicity is disclosed.
Owner:STEMINA BIOMARKER DISCOVERY
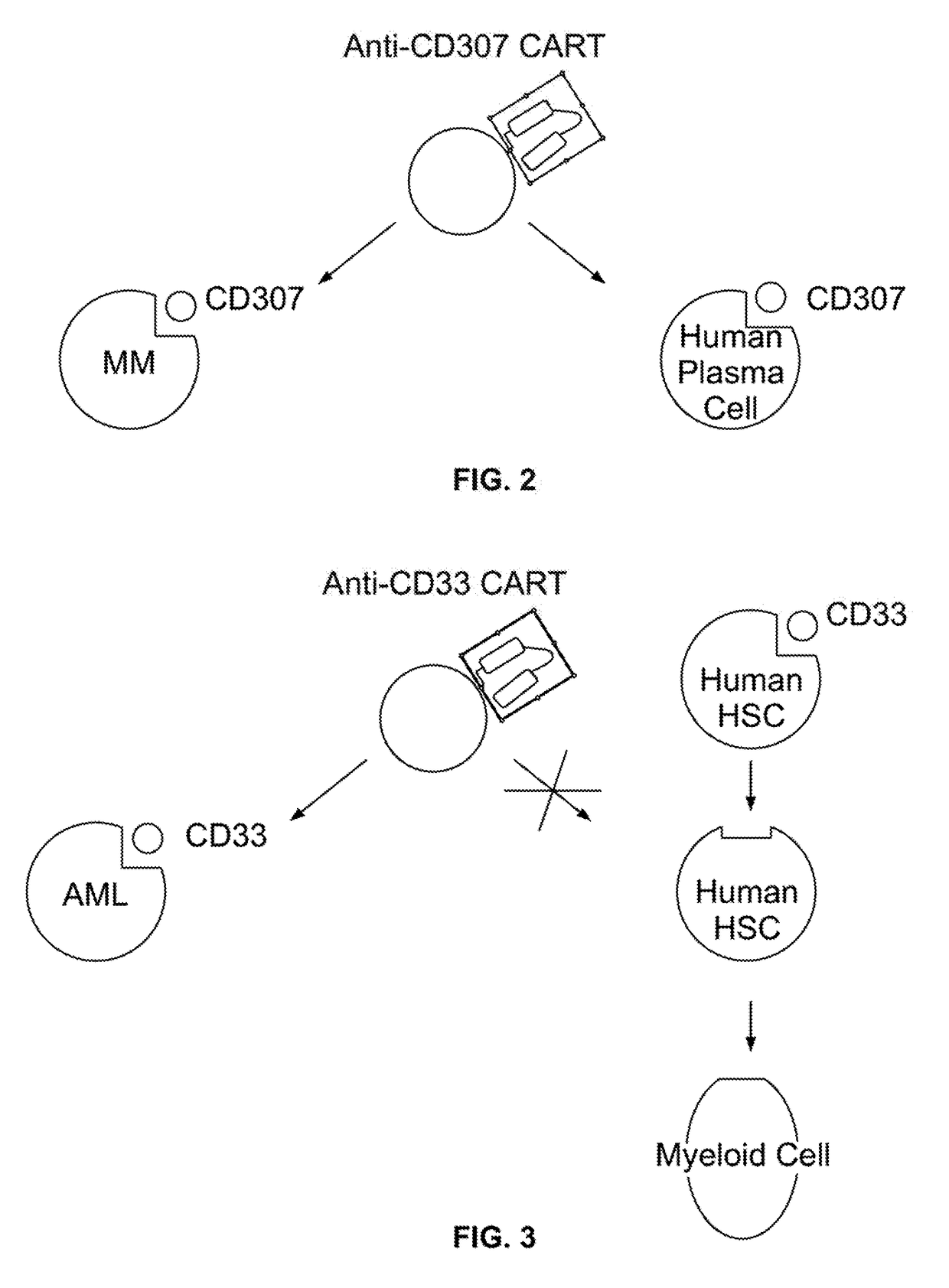
Compositions and methods for inhibition of lineage specific antigens
PendingUS20210260130A1Reduce expressionLow cytotoxicityCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsHydrolasesAntigenHematopoietic cell
Disclosed herein are methods of administering an agent targeting a lineage-specific cell-surface antigen, e.g., CD33, and a population of hematopoietic cells that are deficient in the lineage-specific cell-surface antigen, e.g., CD33 for immunotherapy of hematological malignancies. Cells comprising mutations in CD33 are also provided, as are gRNAs targeting CD33.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Methods for promoting hematopoietic and mesenchymal cell proliferation and differentiation
InactiveUS20090069246A1Genetic material ingredientsTetrapeptide ingredientsCell culture mediaAngiotensinogen mrna
The present invention provides methods, improved cell culture medium and kits for promoting hematopoietic and mesenchymal stem and lineage-specific cell proliferation and differentiation by growth in the presence of angiotensinogen, angiotensin I (AI), AI analogues, AI fragments and analogues thereof, angiotensin II (AII), AII analogues, AII fragments or analogues thereof or AII AT2 type 2 receptor agonists, either alone or in combination with other growth factors and cytokines.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Reagents and methods for using human embryonic stem cells to evaluate toxicity of pharmaceutical compounds and other chemicals
ActiveUS8703483B2Reliably determinedPotential for false negatives is reducedCompound screeningApoptosis detectionTesting toxicityDrug compound
The invention provides biomarker profiles of cellular metabolites and methods for screening chemical compounds including pharmaceutical agents, lead and candidate drug compounds and other chemicals using human embryonic stem cells (hESC) or lineage-specific cells produced therefrom. The inventive methods are useful for testing toxicity, particularly developmental toxicity and detecting teratogenic effects of such chemical compounds.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
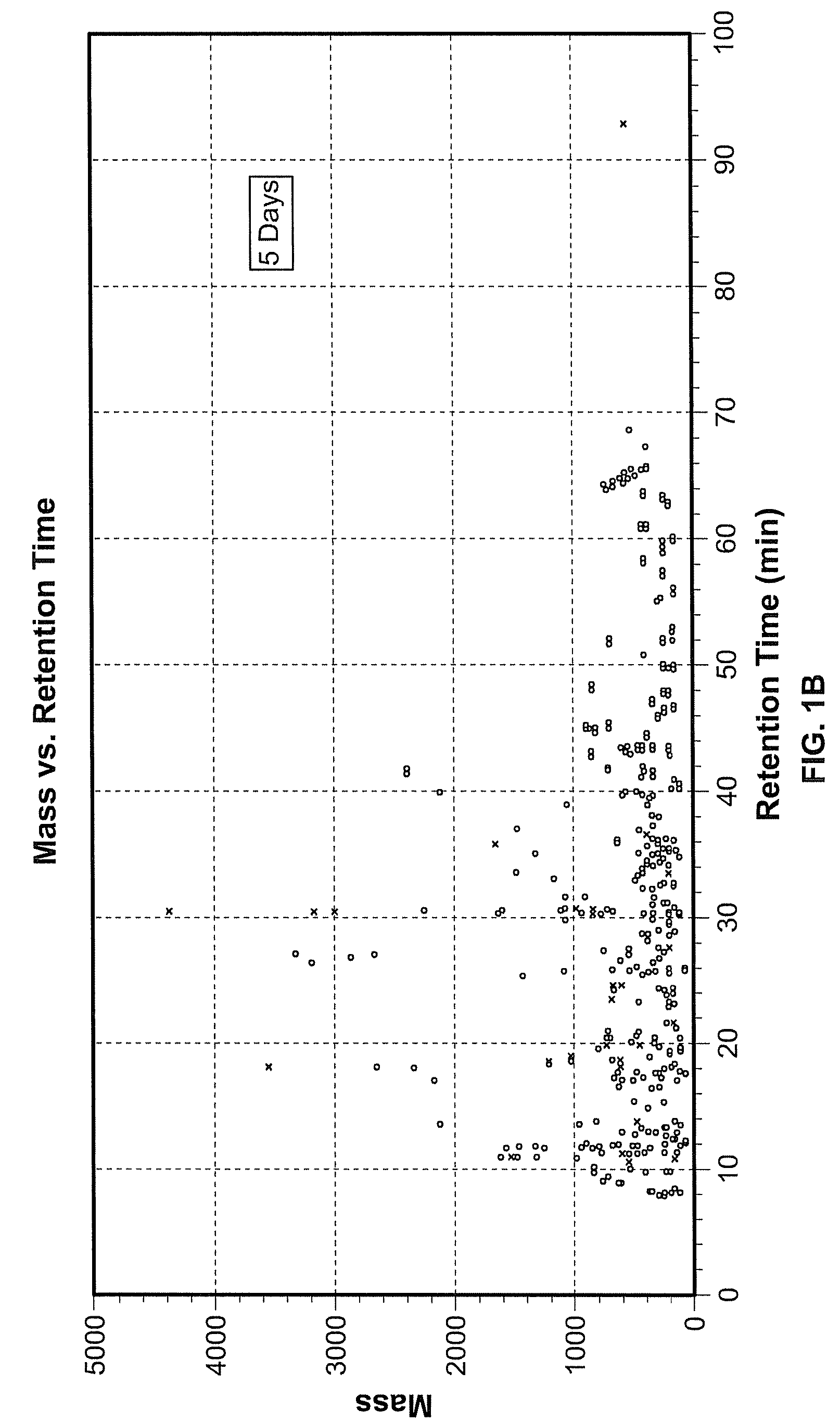
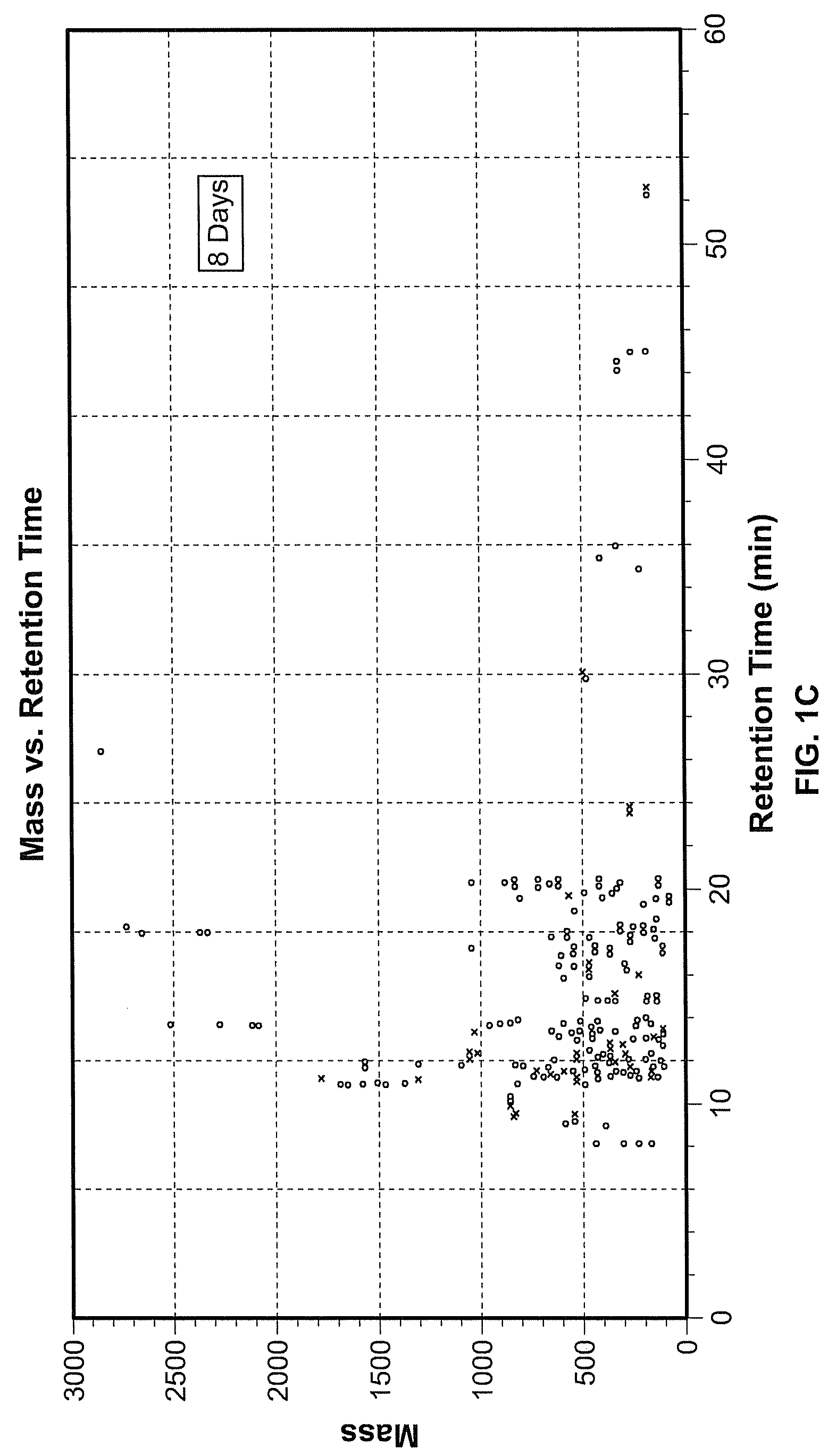
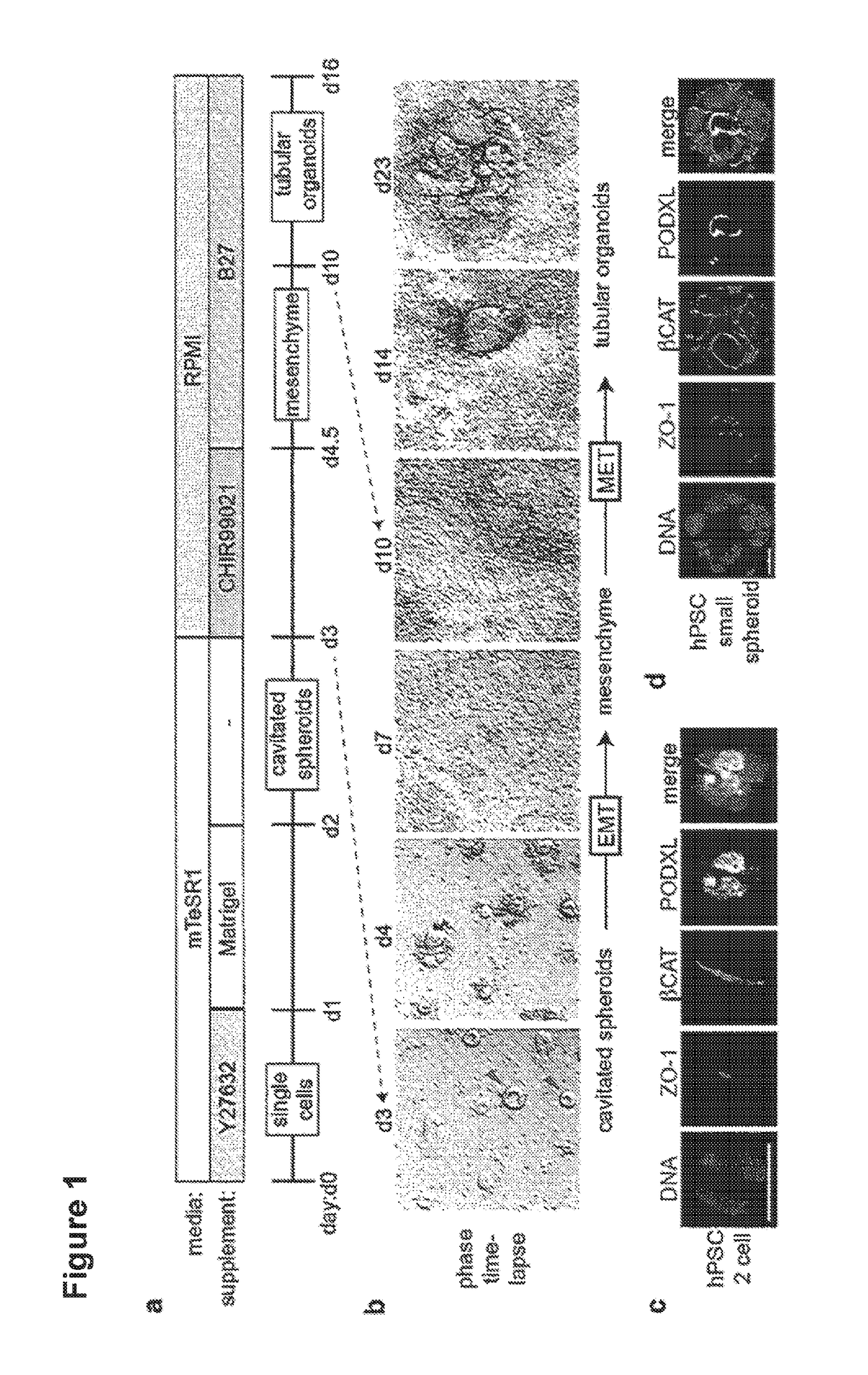
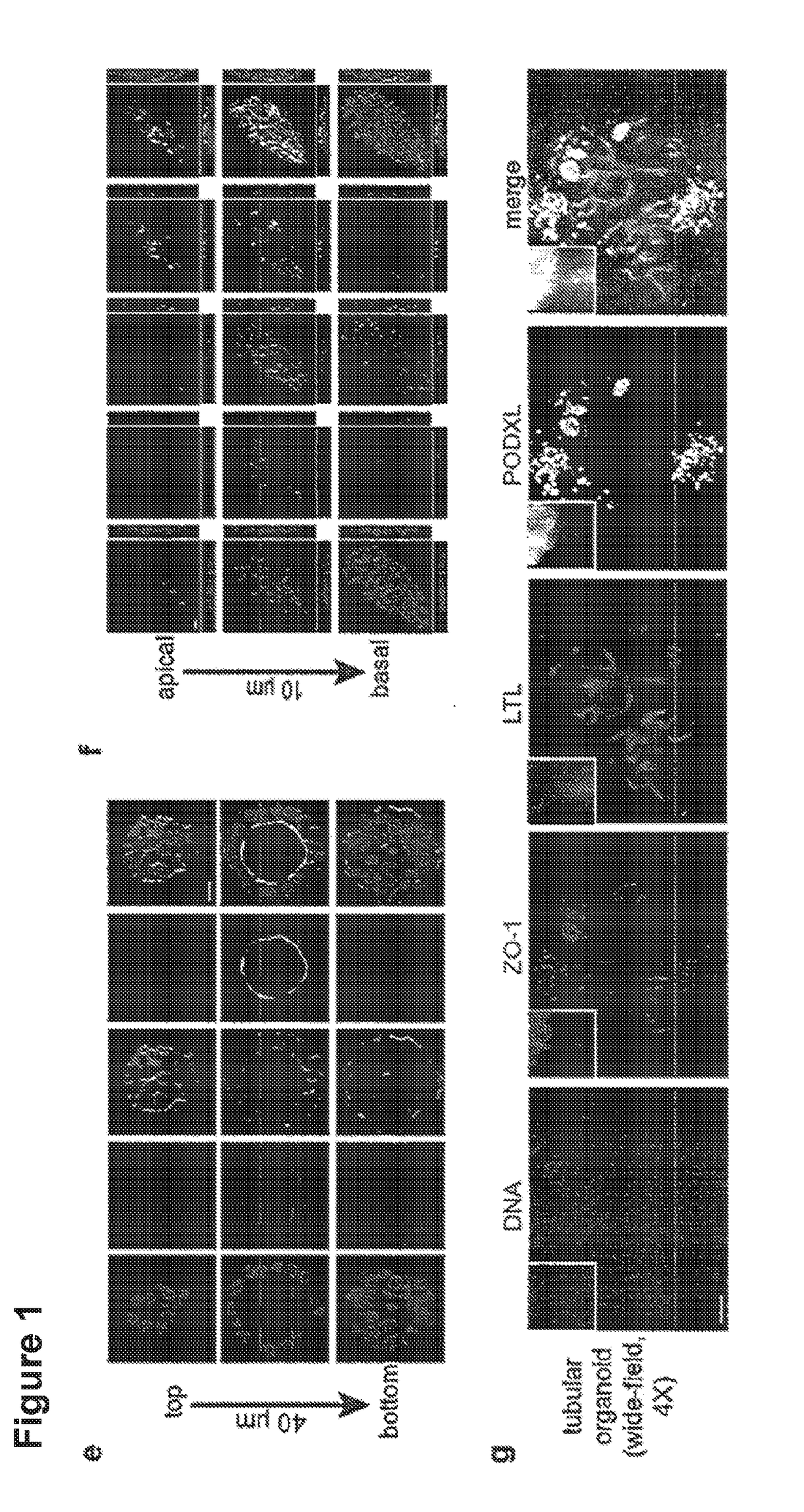
Three-dimensional differentiation of epiblast spheroids to kidney organoids models stage-specific epithelial physiology, morphogenesis, and disease
ActiveUS20180245050A1High expressionReduced feature requirementsCulture processArtificial cell constructsGerm layerStage specific
Human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) have dual value as microphysiological laboratory models and regenerative therapeutics. hPSCs are epithelial cells, but the extent to which hPSCs and descendant epithelia can reconstitute lineage-specific functions remains poorly understood. Here the Inventors show that hPSCs in three-dimensional cultures and their differentiated descendants can functionally recapitulate tissue-specific epithelial morphogenesis, physiology, and disease.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
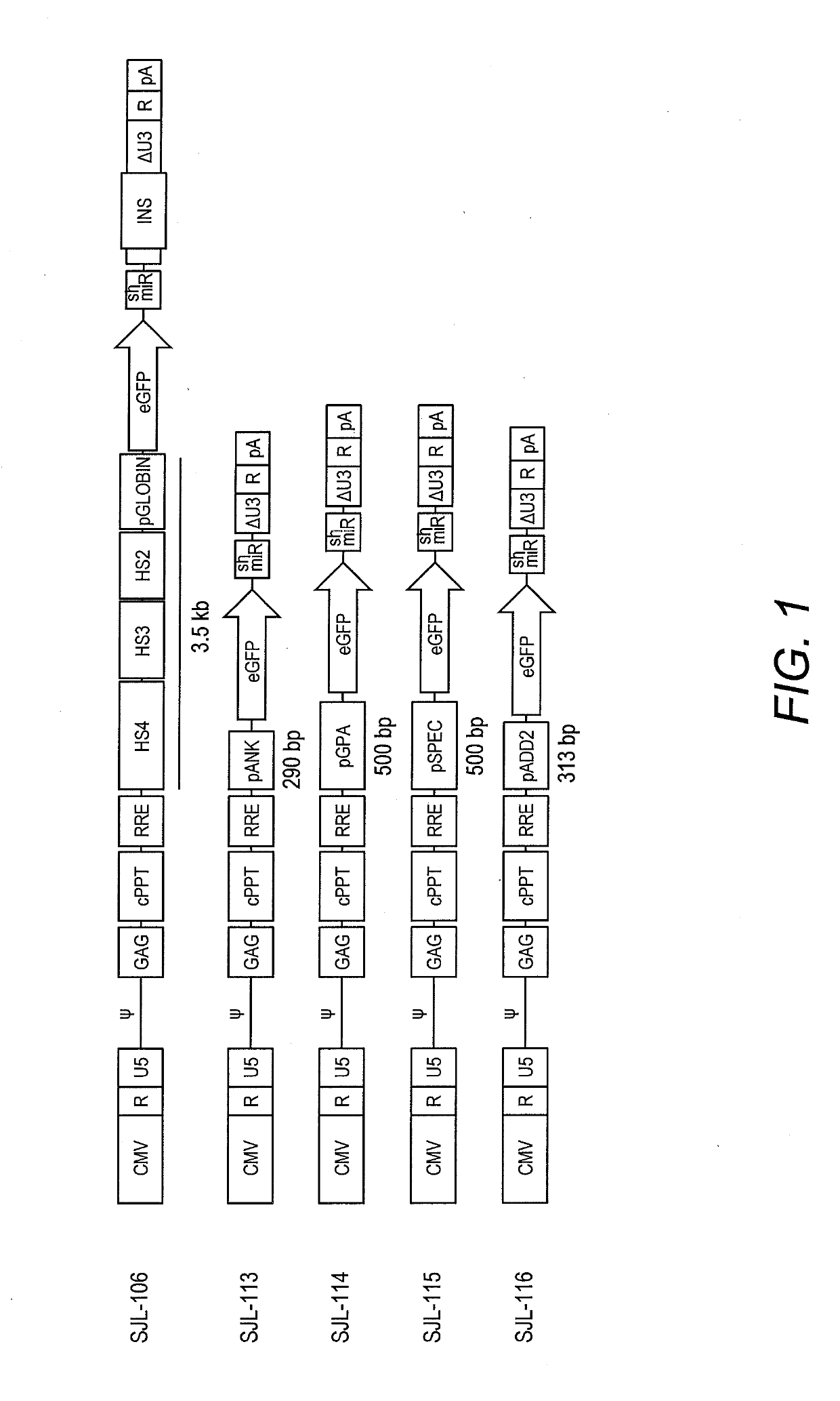
Erythroid-specific promoter and method of use thereof
A DNA construct containing an erythroid lineage-specific promoter operably linked to a nucleotide coding sequence of interest and a method of using the same in the prevention or treatment of a hematopoietic disorder such as a hemoglobinopathy are described. Further disclosed are erythroid-specific promoters and erythroid-specific enhancers that can be used in the DNA construct.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
Use of RNA interference for the creation of lineage specific ES and other undifferentiated cells and production of differentiated cells in vitro by co-culture
InactiveUS20130065307A1Facilitate vivo enrichmentNew breed animal cellsHybrid cell preparationEmbryonic StageReprogramming
Owner:CIBELLI JOSE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com