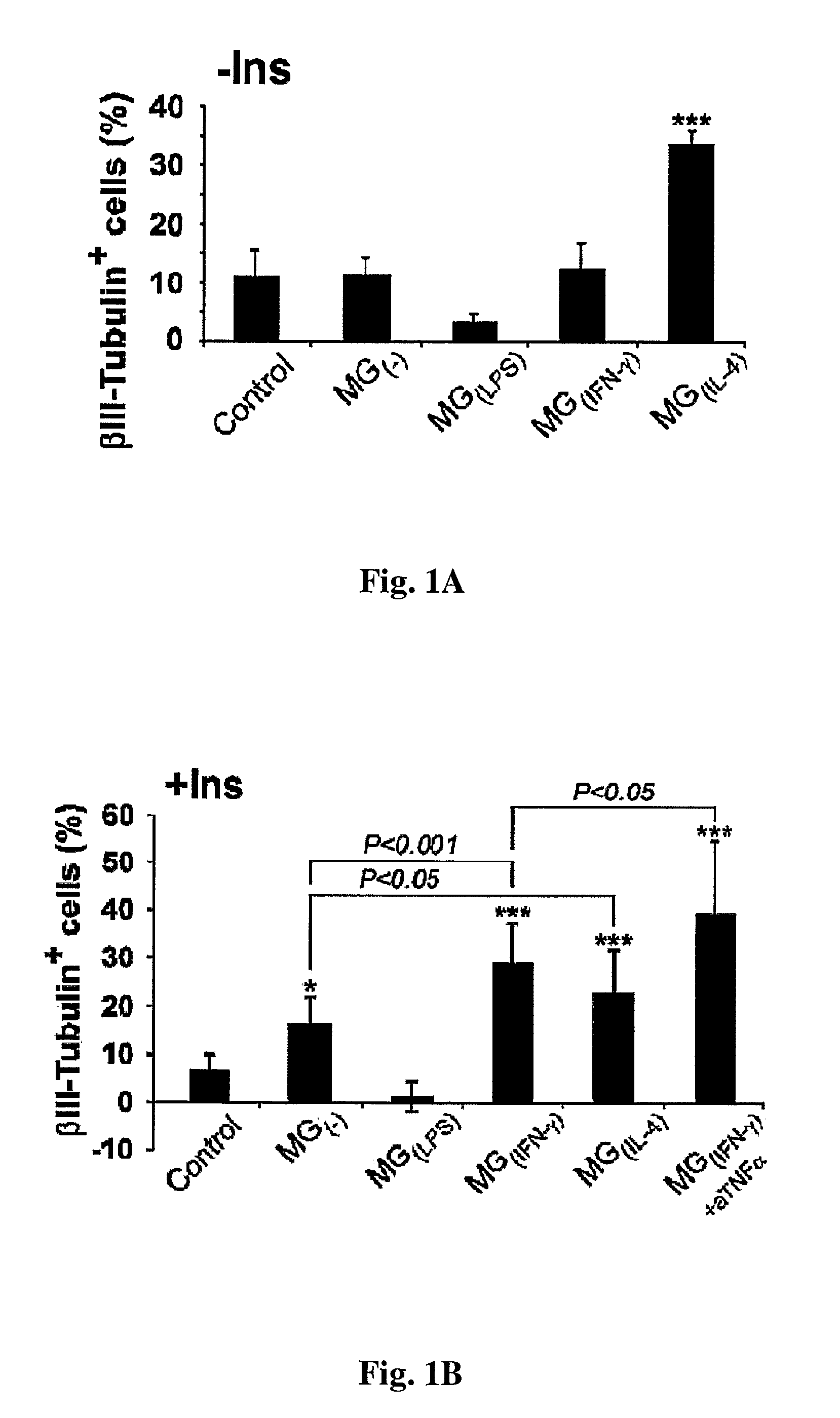
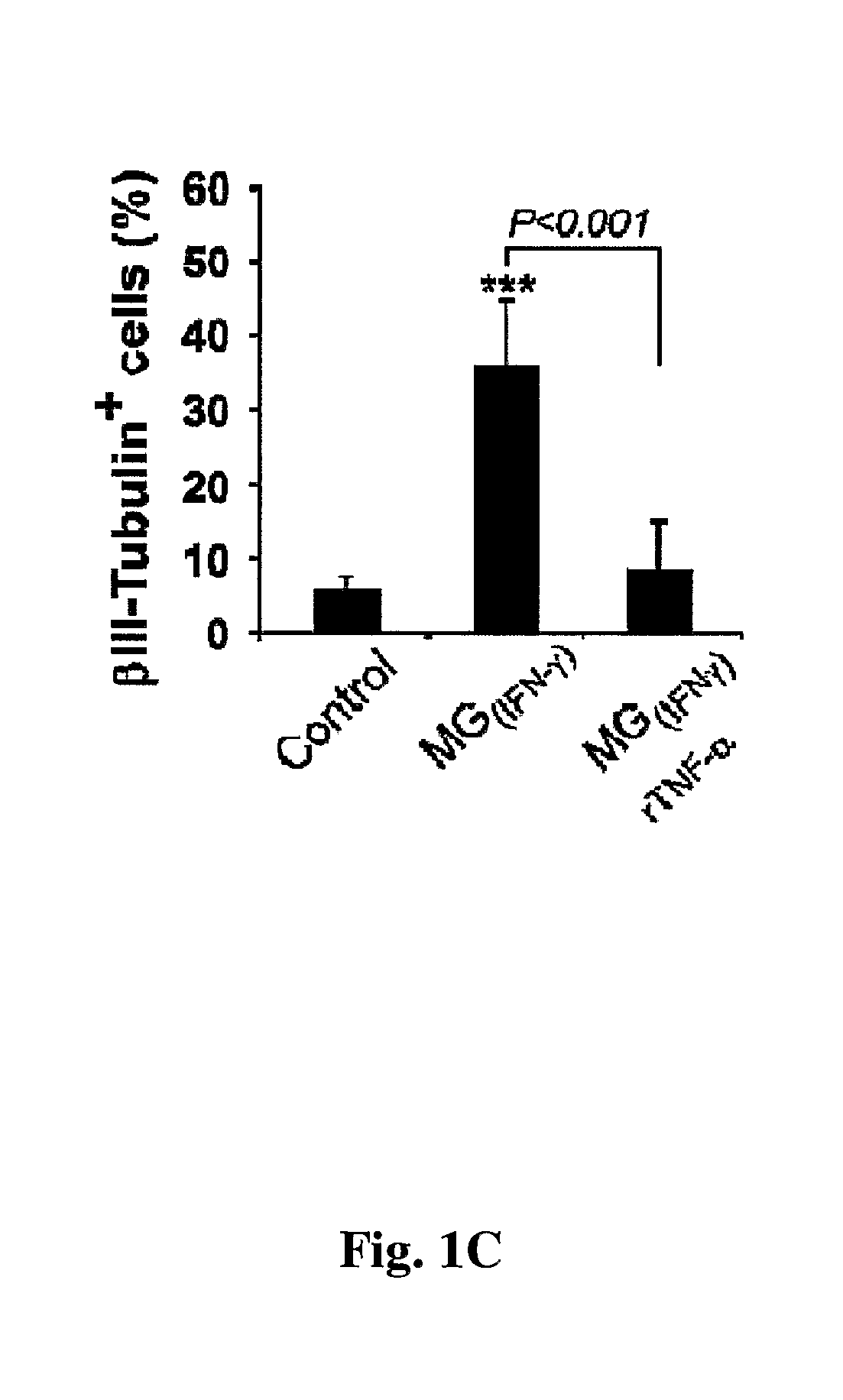
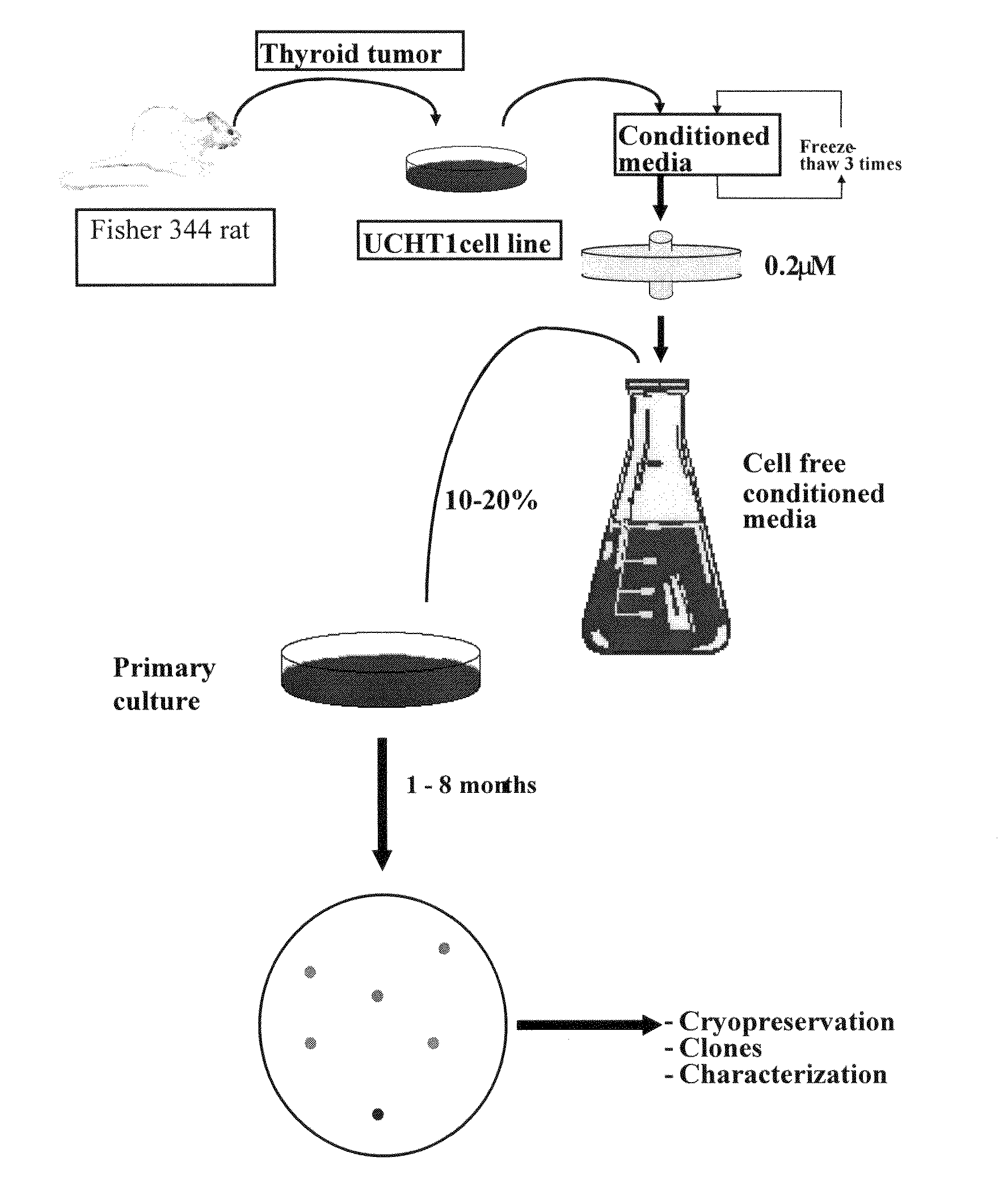
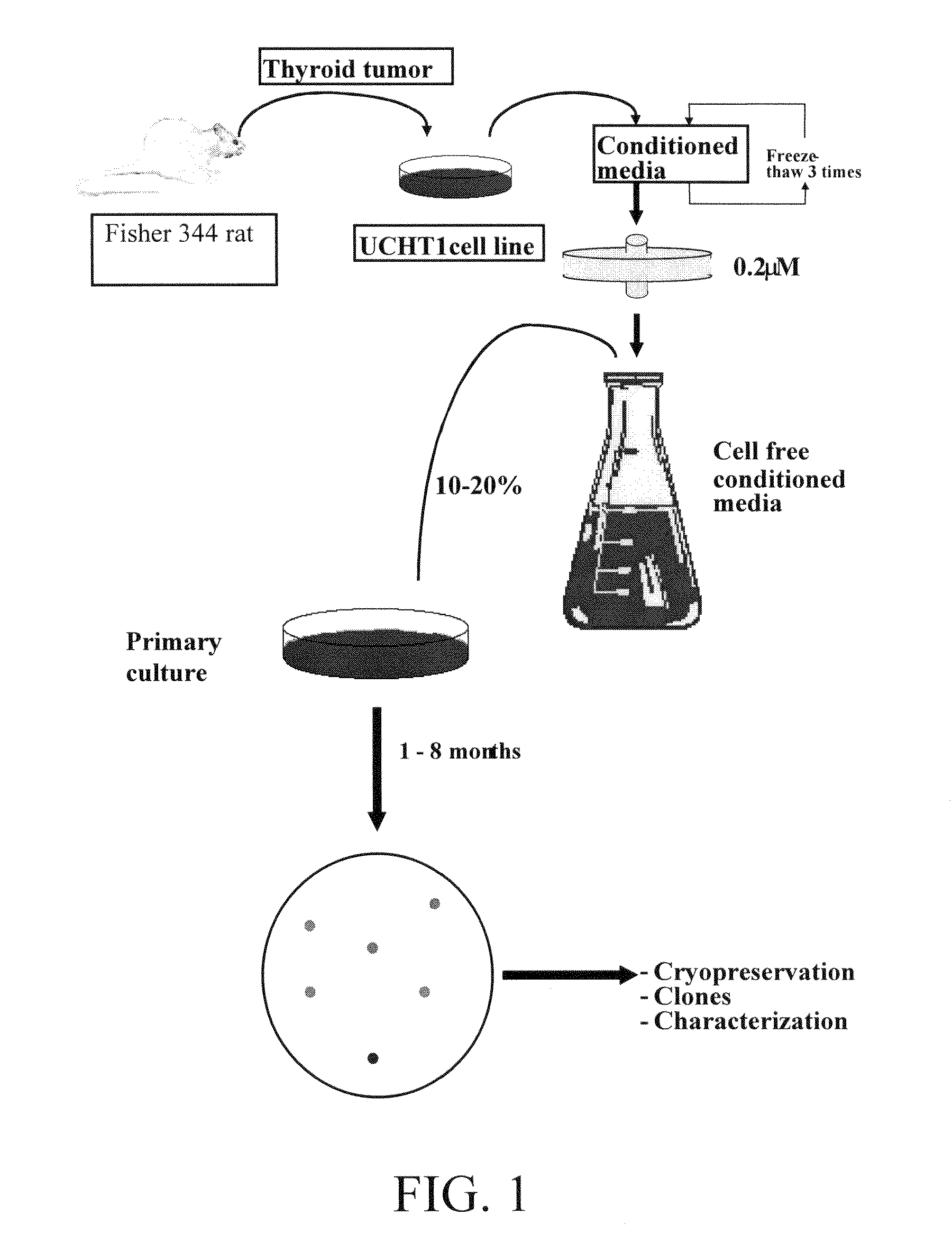
Patents
Literature
240 results about "Stem-cell therapy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Stem-cell therapy is the use of stem cells to treat or prevent a disease or condition. Bone marrow transplant is the most widely used stem-cell therapy, but some therapies derived from umbilical cord blood are also in use. Research is underway to develop various sources for stem cells, as well as to apply stem-cell treatments for neurodegenerative diseases and conditions such as diabetes and heart disease, among others.
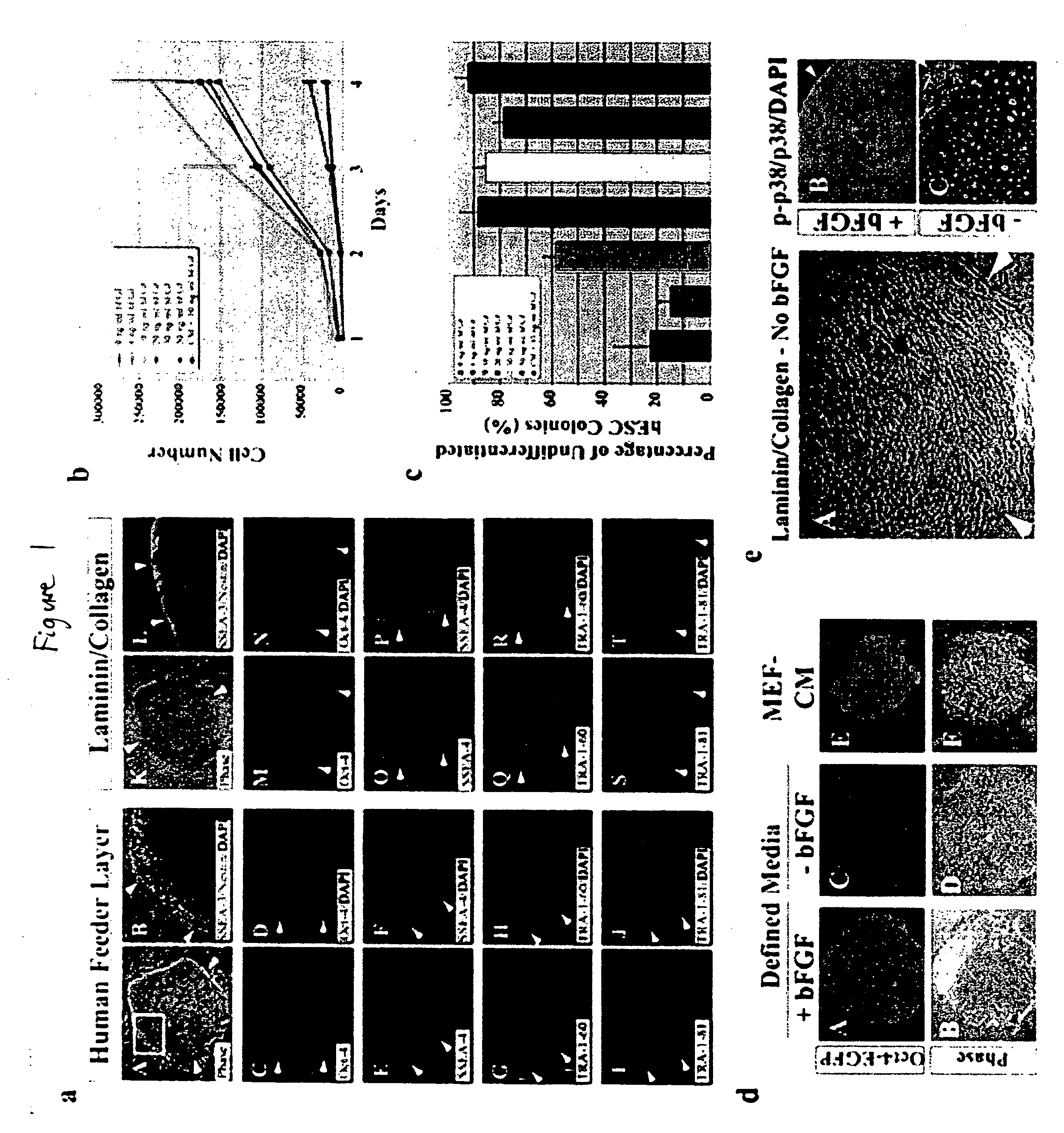
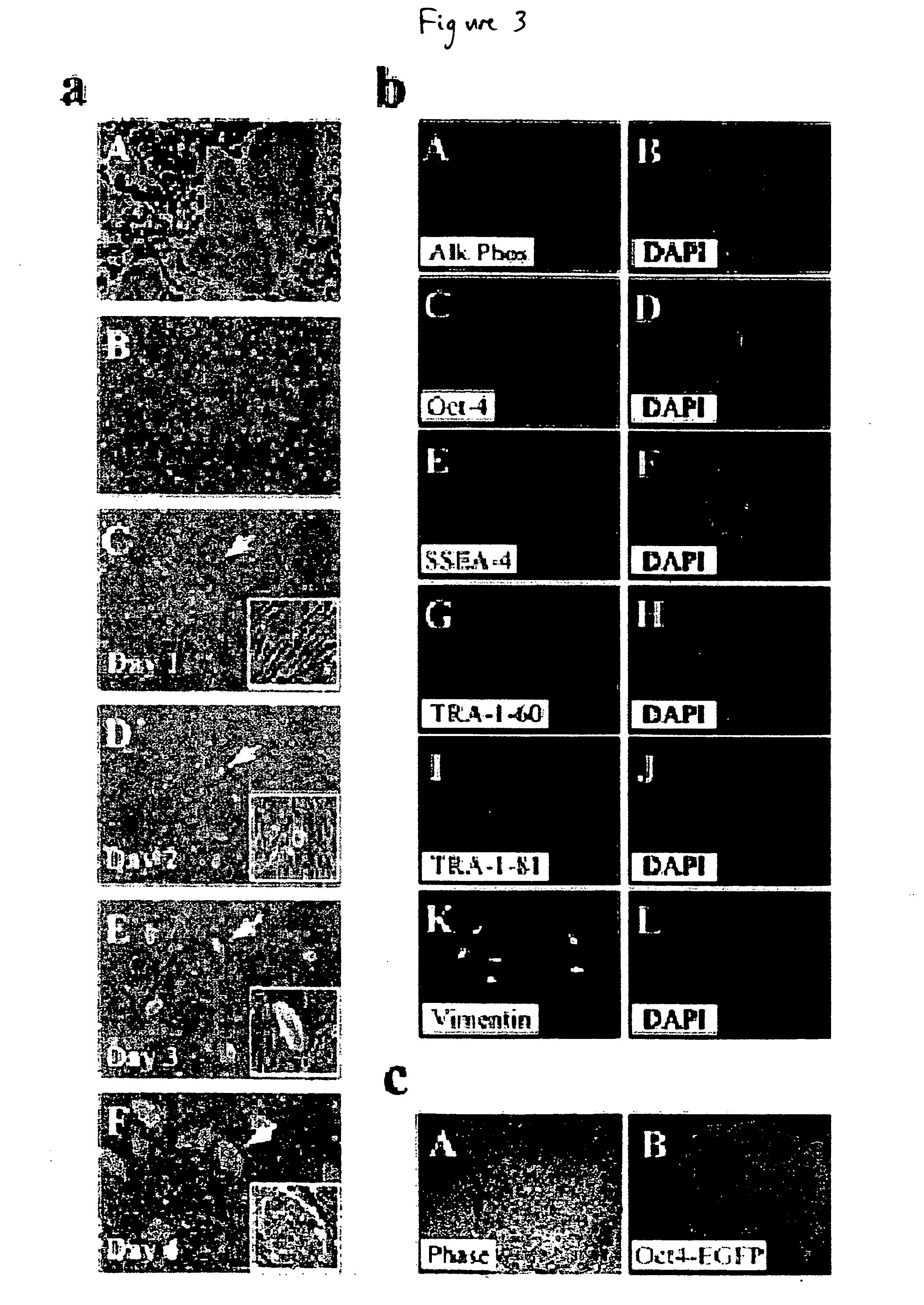
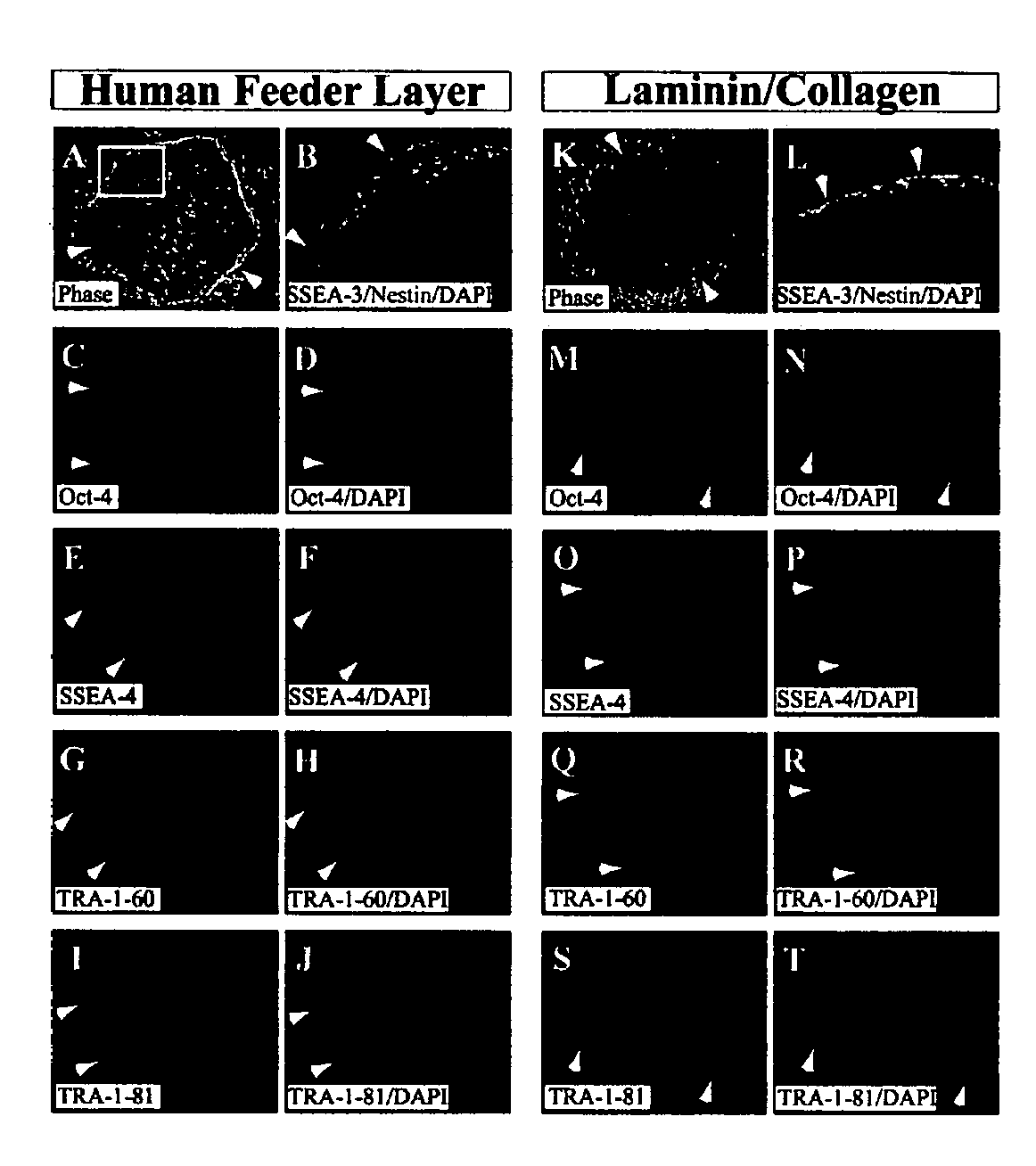
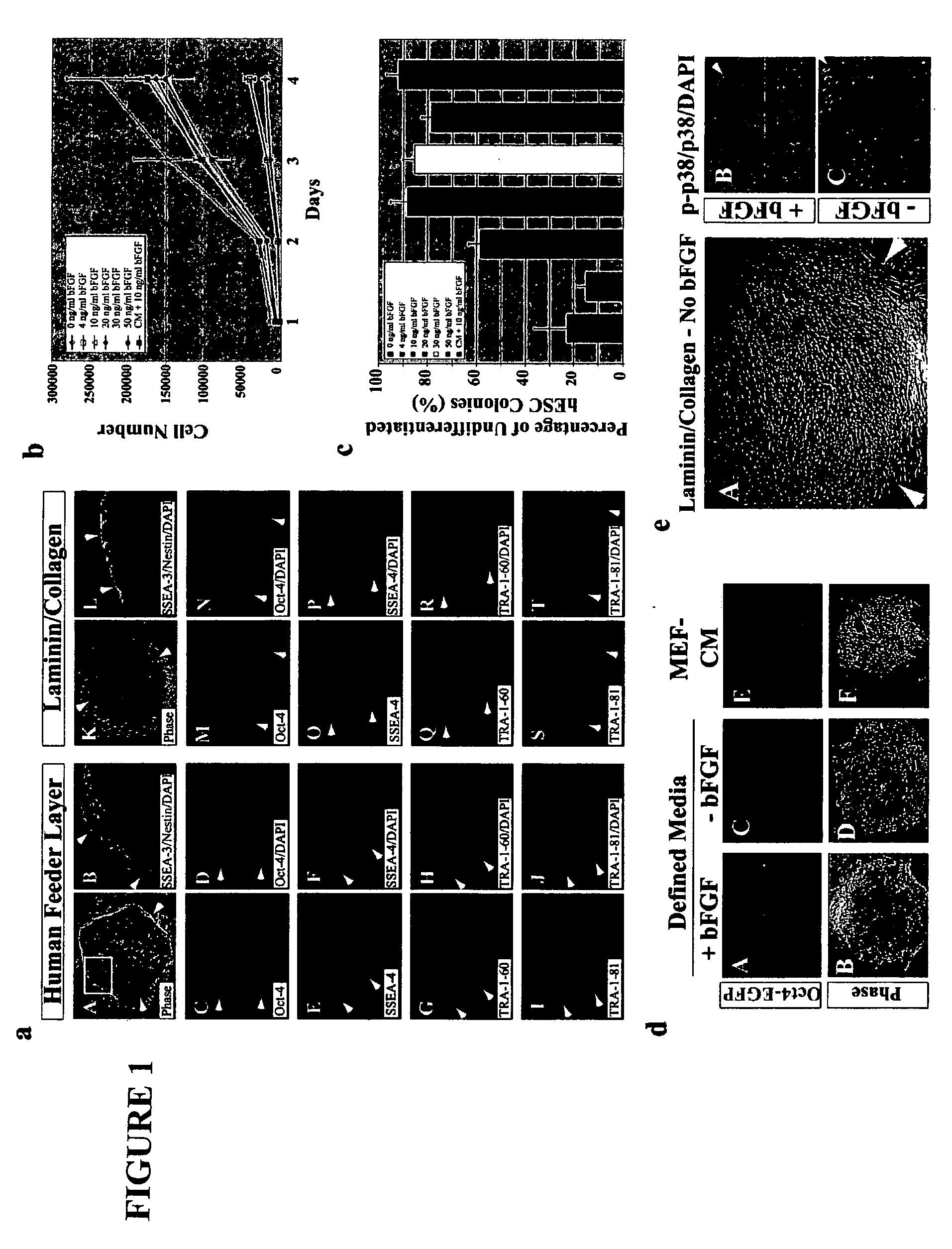
Defined media for stem cell culture
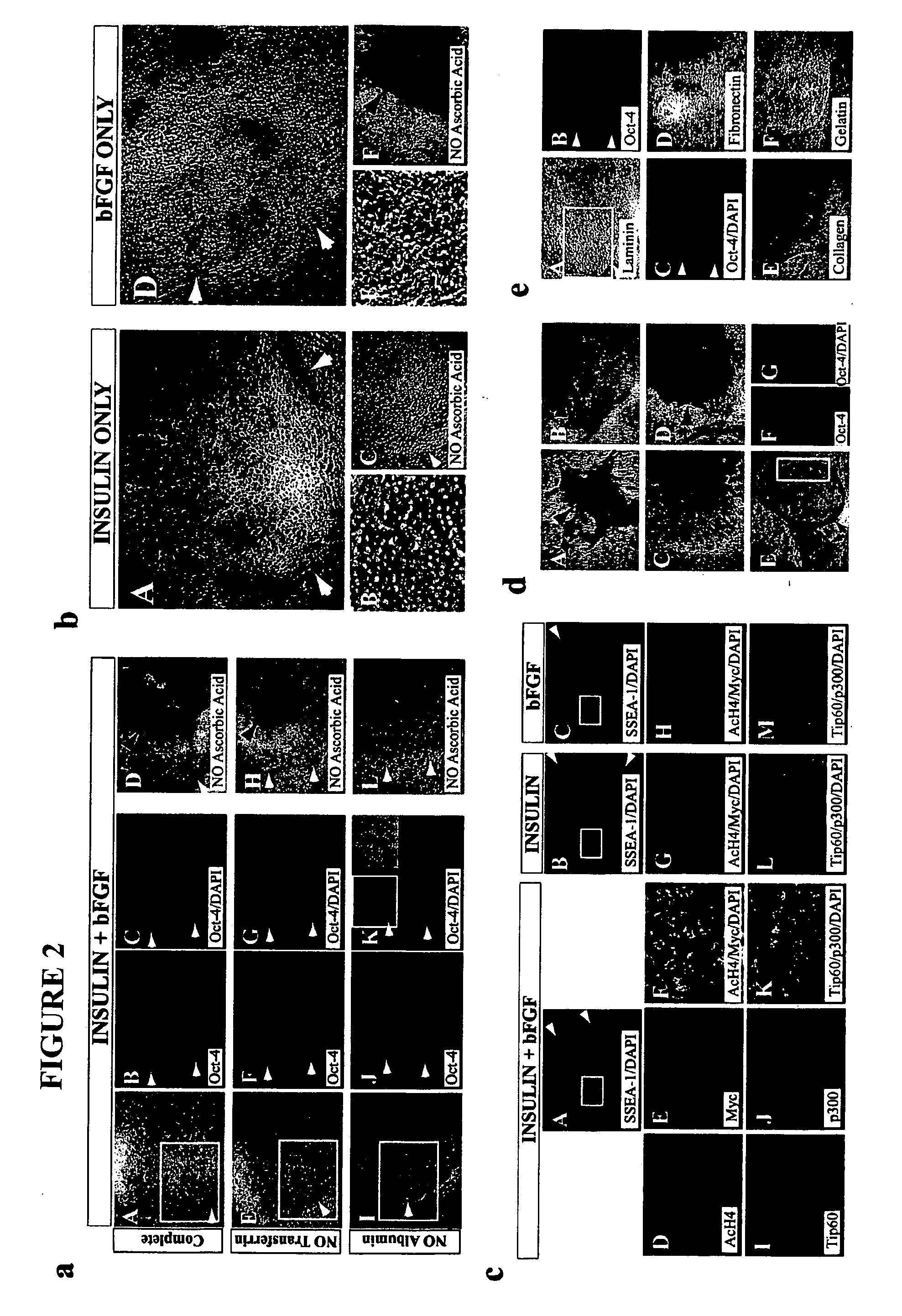
Stem cells, including mammalian, and particularly primate primordial stem cells (pPSCs) such as human embryonic stem cells (hESCs), hold great promise for restoring cell, tissue, and organ function. However, cultivation of stem cells, particularly undifferentiated hESCs, in serum-free, feeder-free, and conditioned-medium-free conditions remains crucial for large-scale, uniform production of pluripotent cells for cell-based therapies, as well as for controlling conditions for efficiently directing their lineage-specific differentiation. This instant invention is based on the discovery of the formulation of minimal essential components necessary for maintaining the long-term growth of pPSCs, particularly undifferentiated hESCs. Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), insulin, ascorbic acid, and laminin were identified to be both sufficient and necessary for maintaining hESCs in a healthy self-renewing undifferentiated state capable of both prolonged propagation and then directed differentiation. Having discerned these minimal molecular requirements, conditions that would permit the substitution of poorly-characterized and unspecified biological additives and substrates were derived and optimized with entirely defined constituents, providing a “biologics”-free (i.e., animal-, feeder-, serum-, and conditioned-medium-free) system for the efficient long-term cultivation of pPSCs, particularly pluripotent hESCs. Such culture systems allow the derivation and large-scale production of stem cells such as pPSCs, particularly pluripotent hESCs, in optimal yet well-defined biologics-free culture conditions from which they can be efficiently directed towards a lineage-specific differentiated fate in vitro, and thus are important, for instance, in connection with clinical applications based on stem cell therapy and in drug discovery processes.
Owner:THE BURNHAM INST
Defined media for pluripotent stem cell culture
Stem cells, including mammalian, and particularly primate primordial stem cells (pPSCs) such as human embryonic stem cells (hESCs), hold great promise for restoring cell, tissue, and organ function. However, cultivation of stem cells, particularly undifferentiated hESCs, in serum-free, feeder-free, and conditioned-medium-free conditions remains crucial for large-scale, uniform production of pluripotent cells for cell-based therapies, as well as for controlling conditions for efficiently directing their lineage-specific differentiation. This instant invention is based on the discovery of the formulation of minimal essential components necessary for maintaining the long-term growth of pPSCs, particularly undifferentiated hESCs. Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), insulin, ascorbic acid, and laminin were identified to be both sufficient and necessary for maintaining hESCs in a healthy self-renewing undifferentiated state capable of both prolonged propagation and then directed differentiation. Having discerned these minimal molecular requirements, conditions that would permit the substitution of poorly-characterized and unspecified biological additives and substrates were derived and optimized with entirely defined constituents, providing a “biologics”-free (i.e., animal-, feeder-, serum-, and conditioned-medium-free) system for the efficient long-term cultivation of pPSCs, particularly pluripotent hESCs. Such culture systems allow the derivation and large-scale production of stem cells such as pPSCs, particularly pluripotent hESCs, in optimal yet well-defined biologics-free culture conditions from which they can be efficiently directed towards a lineage-specific differentiated fate in vitro, and thus are important, for instance, in connection with clinical applications based on stem cell therapy and in drug discovery processes.
Owner:THE BURNHAM INST
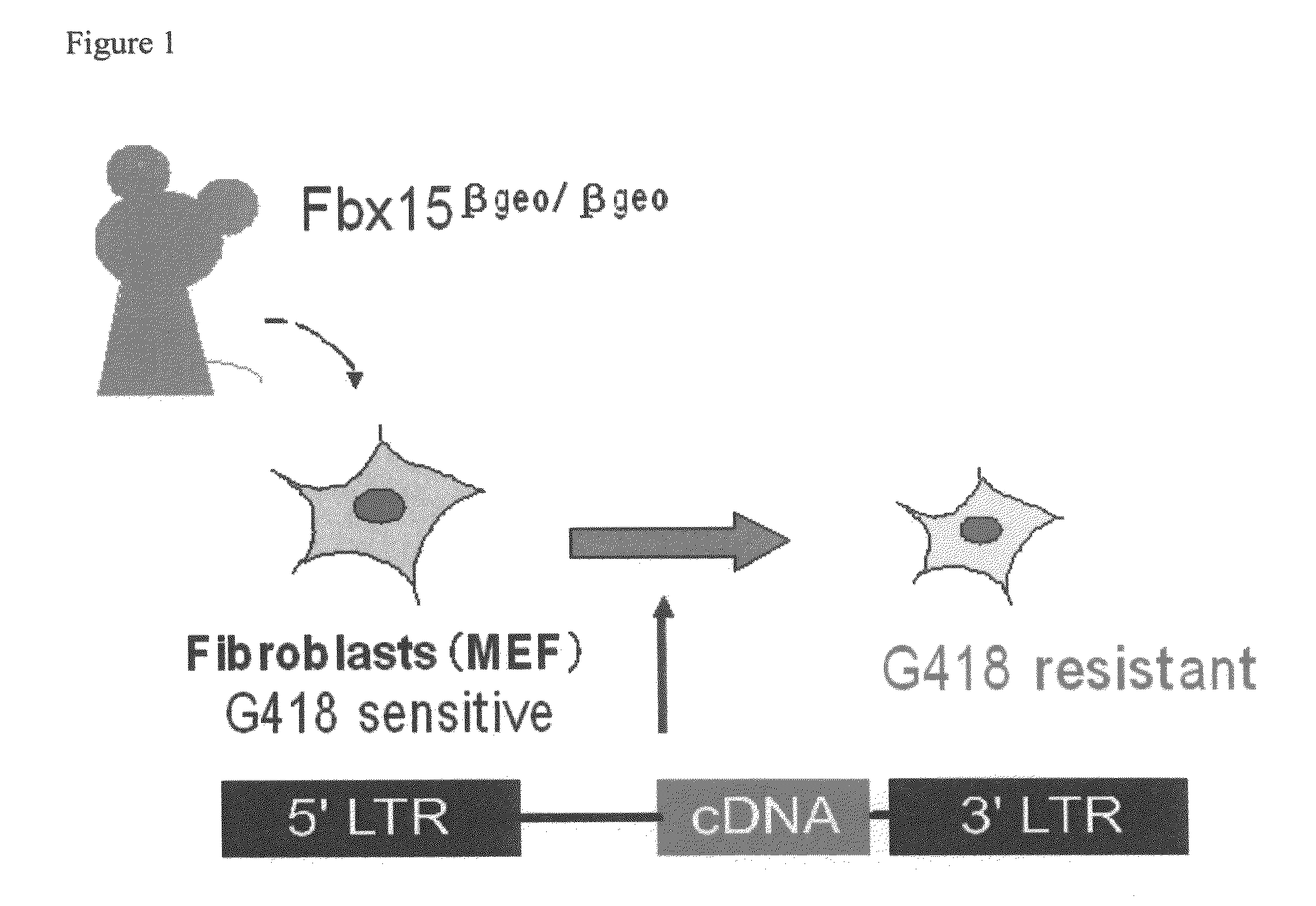
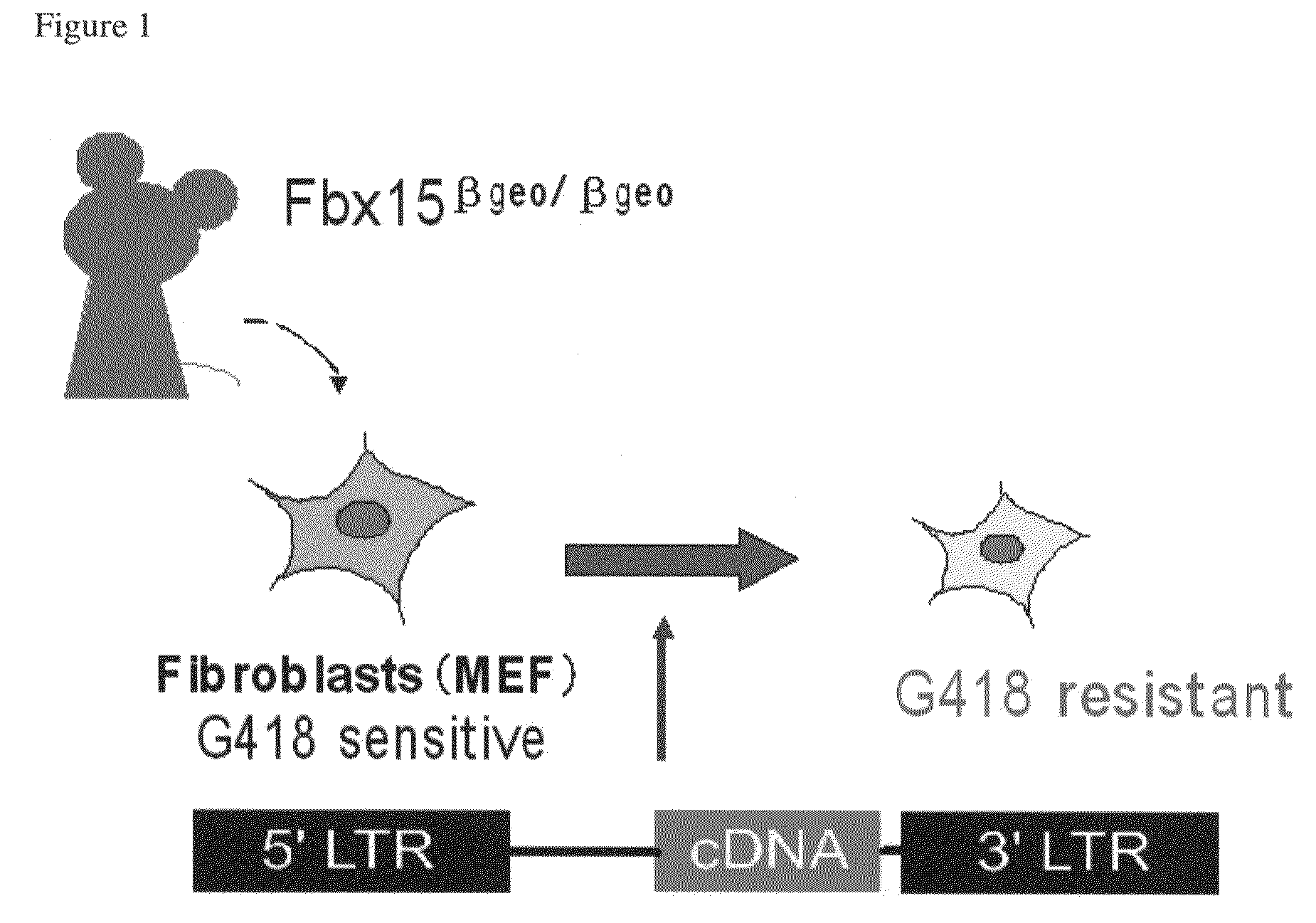
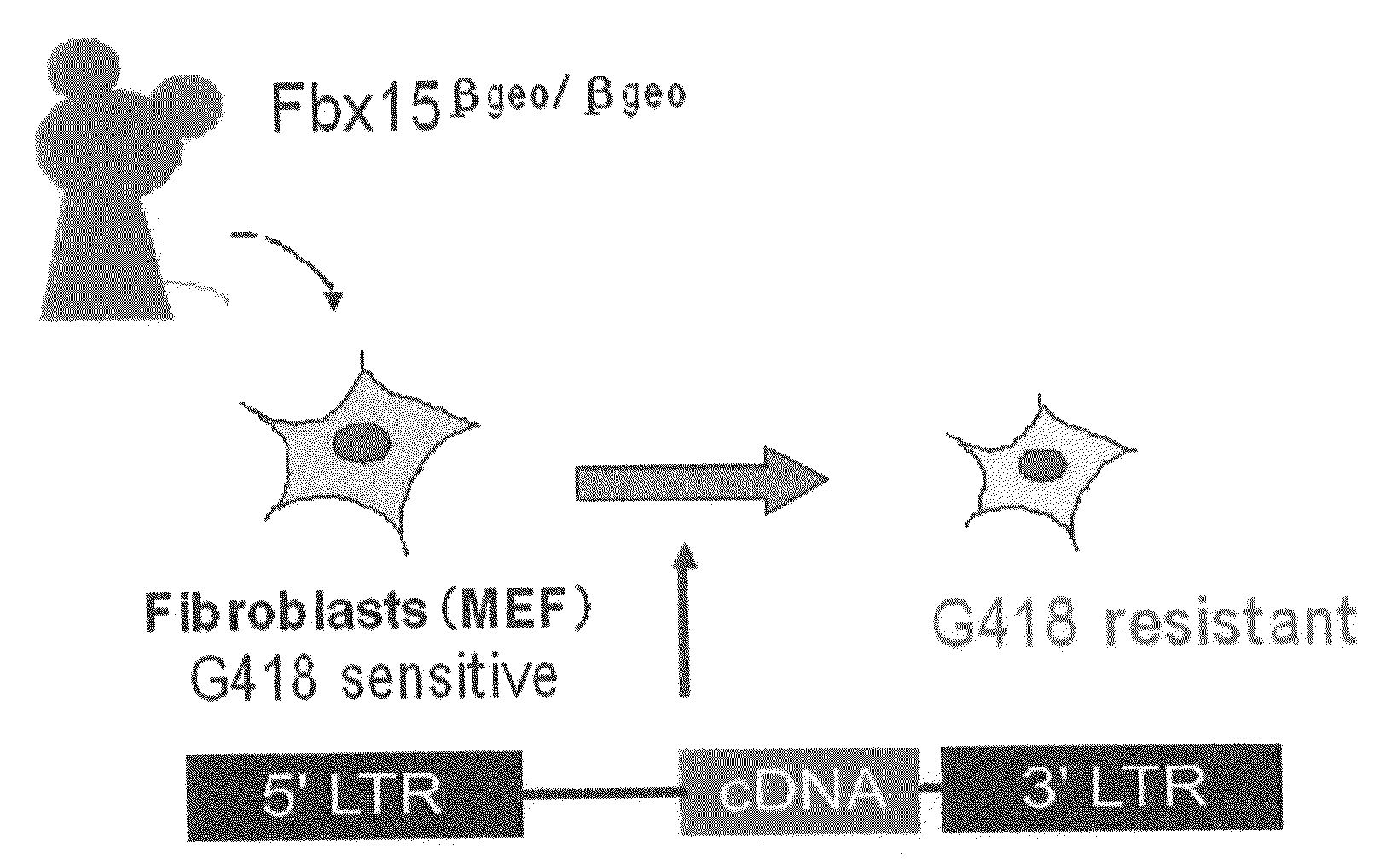
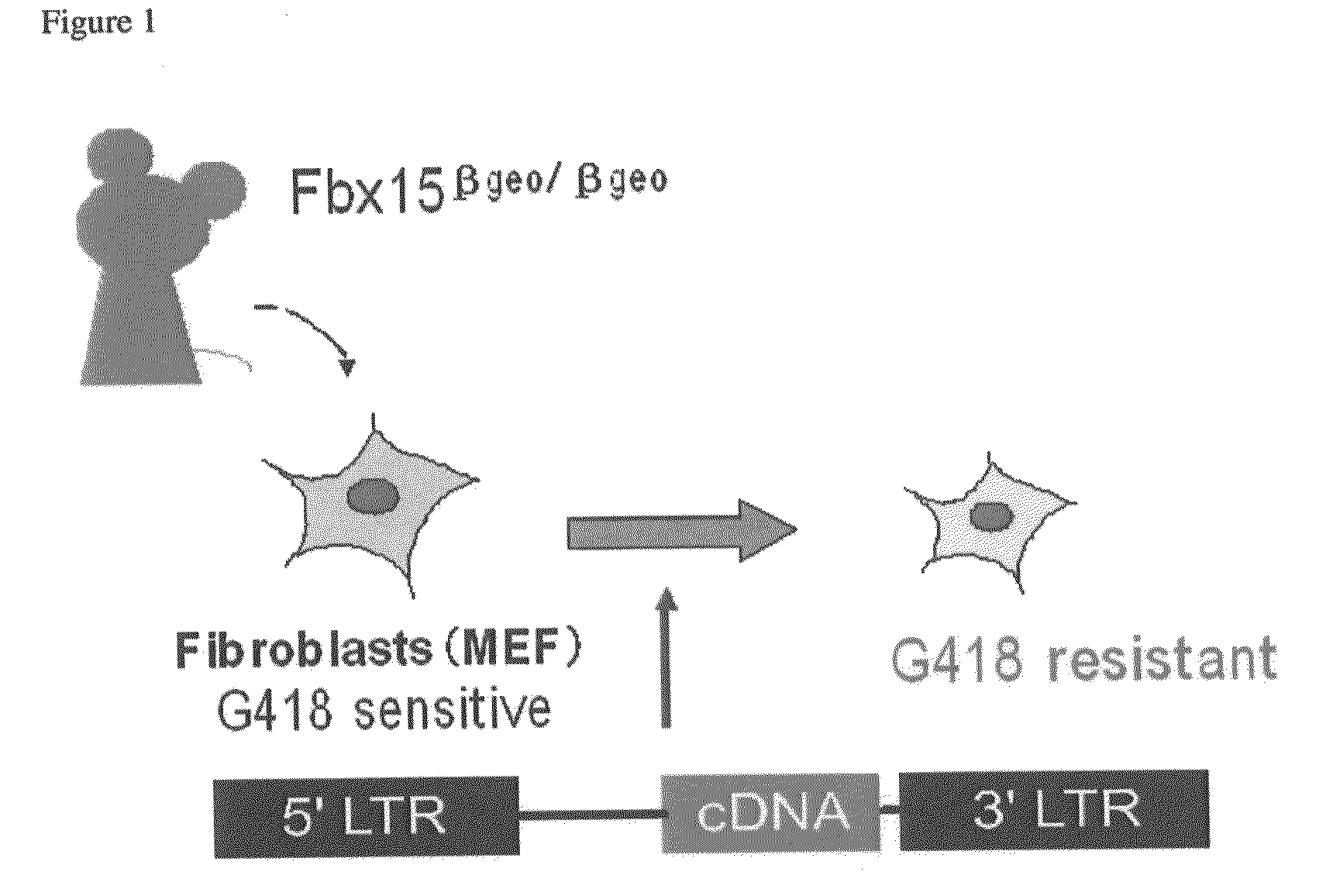
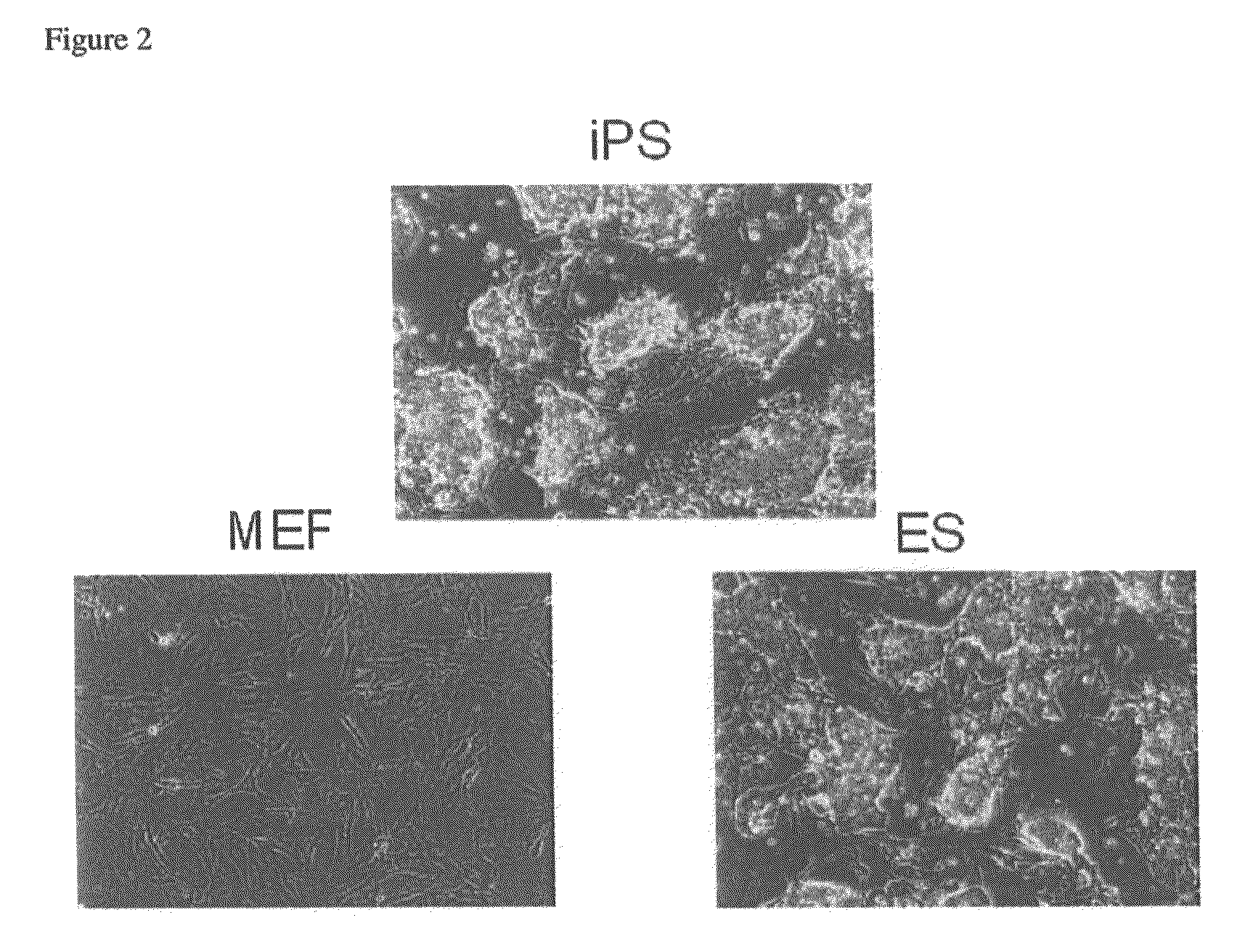
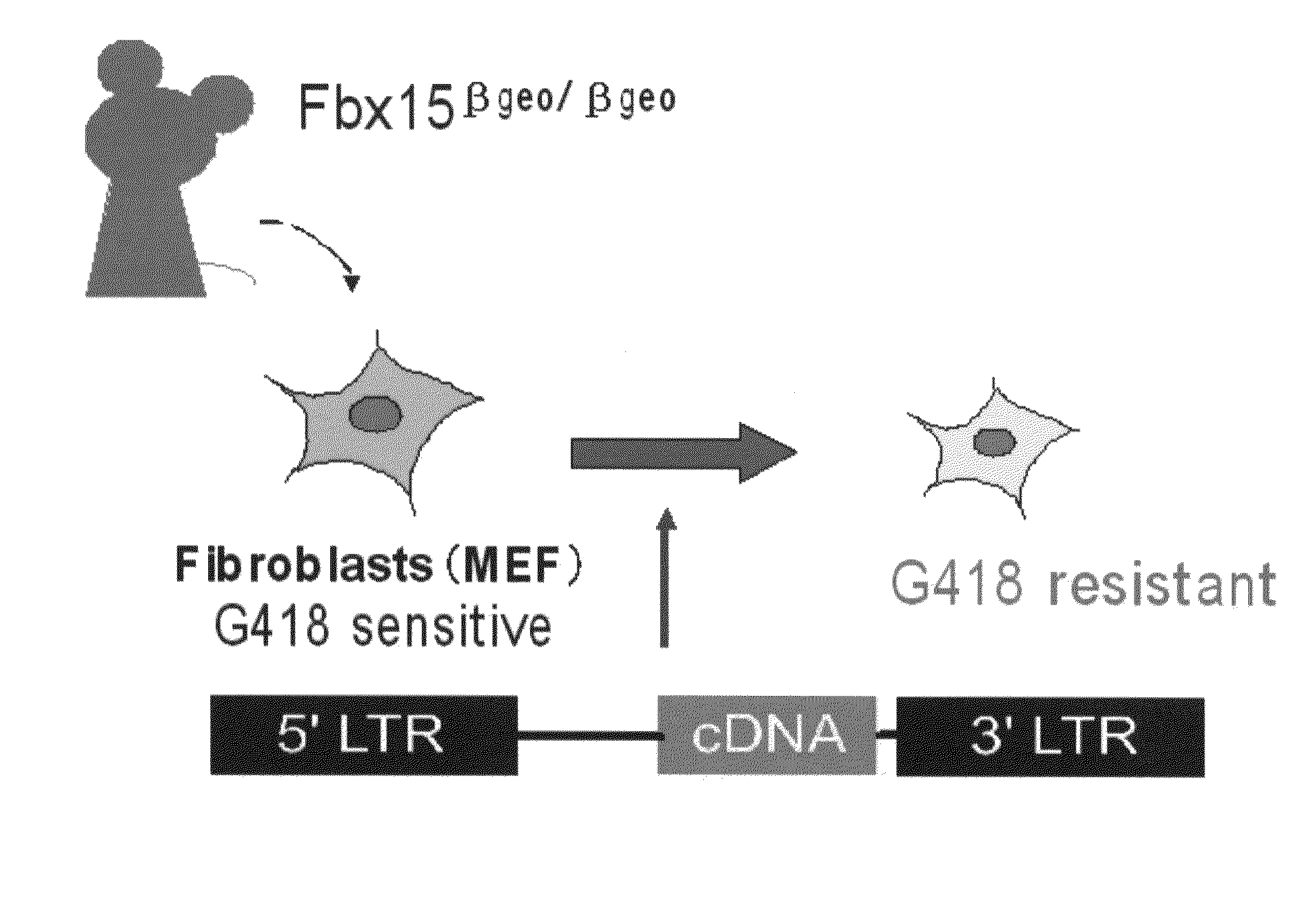
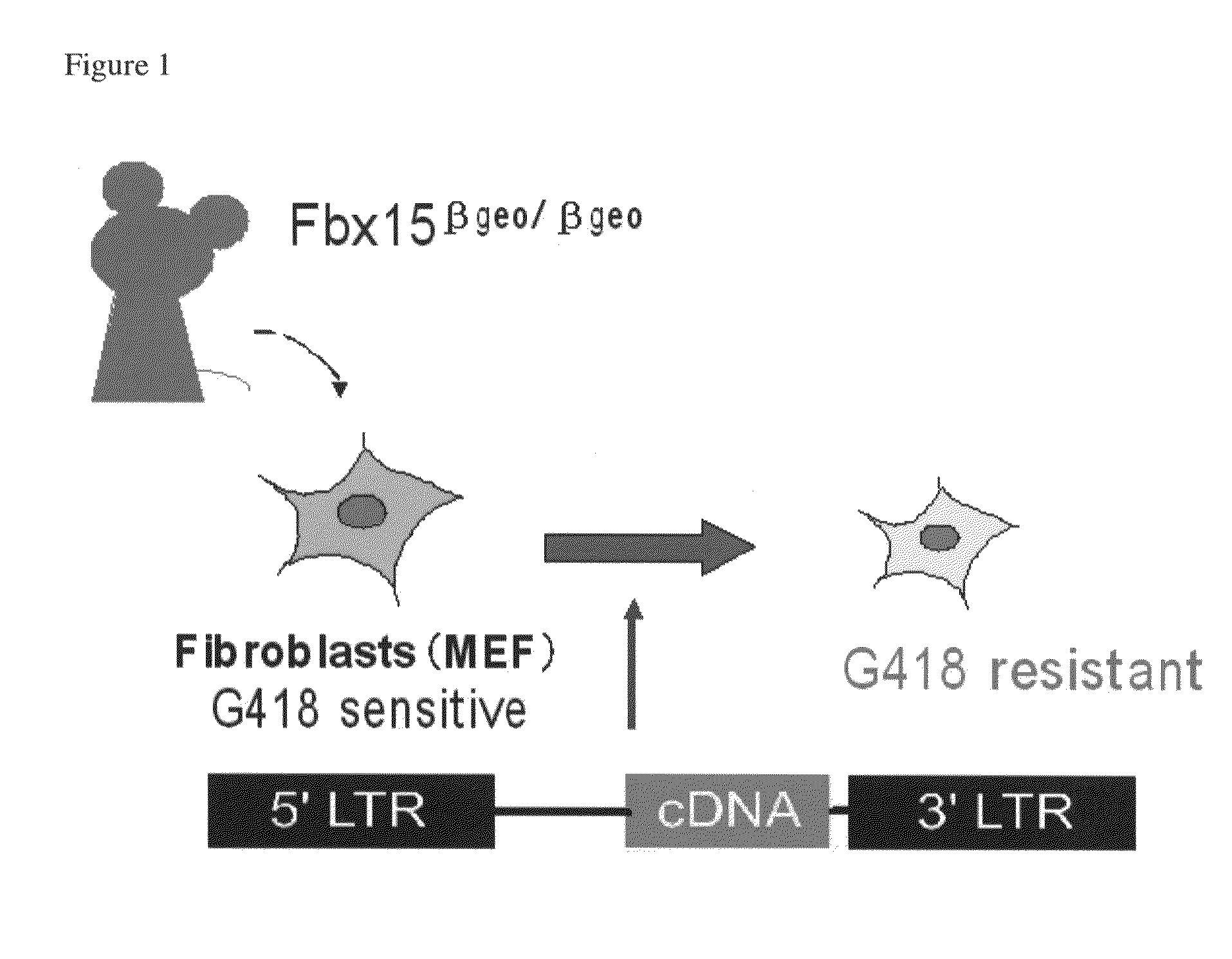
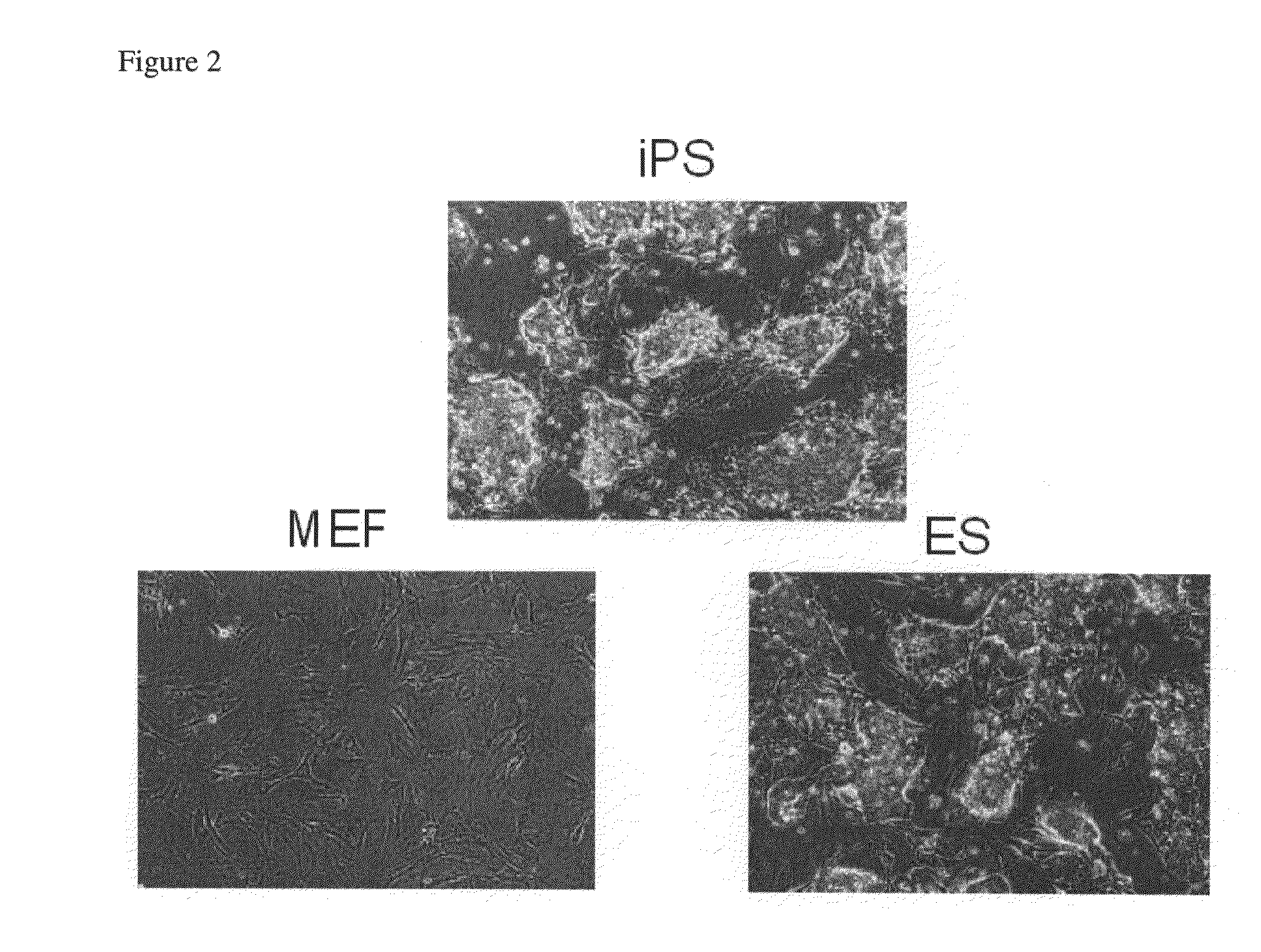
Nuclear reprogramming factor and induced pluripotent stem cells
InactiveUS20090227032A1Easy to prepareEffective isolationGenetically modified cellsPeptidesNuclear reprogrammingCell therapy
The present invention relates to a nuclear reprogramming factor having an action of reprogramming a differentiated somatic cell to derive an induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell. The present invention also relates to the aforementioned iPS cells, methods of generating and maintaining iPS cells, and methods of using iPS cells, including screening and testing methods as well as methods of stem cell therapy. The present invention also relates to somatic cells derived by inducing differentiation of the aforementioned iPS cells.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Somatic cell reprogramming by retroviral vectors encoding Oct3/4. Klf4, c-Myc and Sox2
ActiveUS8129187B2Easy to prepareEffective isolationGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsNuclear reprogrammingCell therapy
The present invention relates to a nuclear reprogramming factor having an action of reprogramming a differentiated somatic cell to derive an induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell. The present invention also relates to the aforementioned iPS cells, methods of generating and maintaining iPS cells, and methods of using iPS cells, including screening and testing methods as well as methods of stem cell therapy. The present invention also relates to somatic cells derived by inducing differentiation of the aforementioned iPS cells.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Stem cell therapy for cardiac valvular dysfunction
InactiveUS20080050347A1Raise transfer toReduce needBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsSexual dysfunctionTricuspid valve function
Disclosed are methods, compounds and compositions useful for treatment of a patient with valvular dysfunction. The invention relates to using stem cells, modified stem cells, derivatives thereof, and agents stimulatory to stem cells in order to substantially ameliorate, and in some cases induce a therapeutic benefit, to a patient suffering from a dysfunction of the mitral, aortic, tricuspid, or pulmonary valve. In some embodiments the invention treats the valve dysfunction itself, whereas in other embodiments treatment of associated cardiac structures is performed. Furthermore, in other embodiments the invention permits physiological compensation for the valve dysfunction, prolonging the time until surgical intervention is needed.
Owner:MEDISTEM LAB
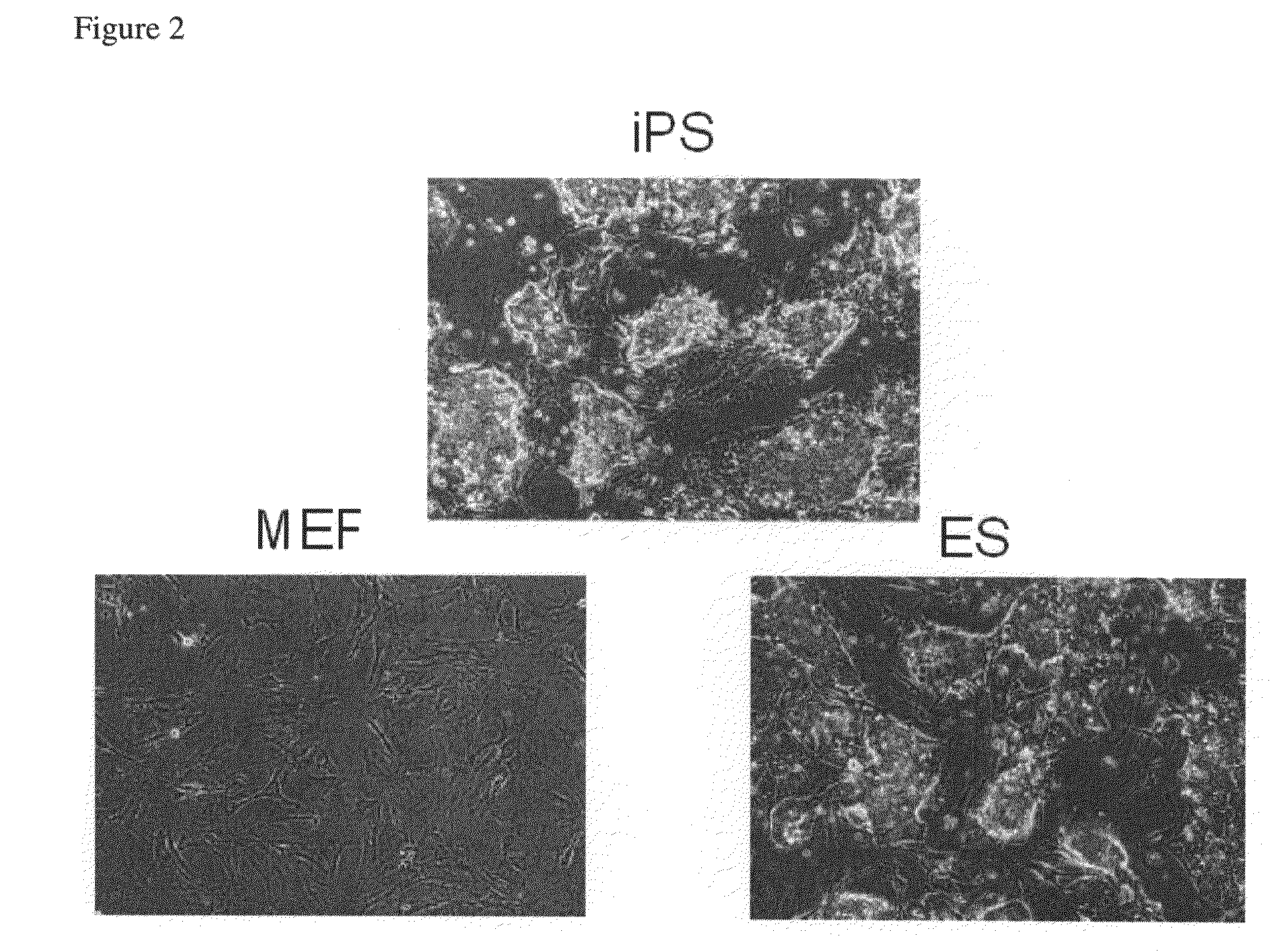
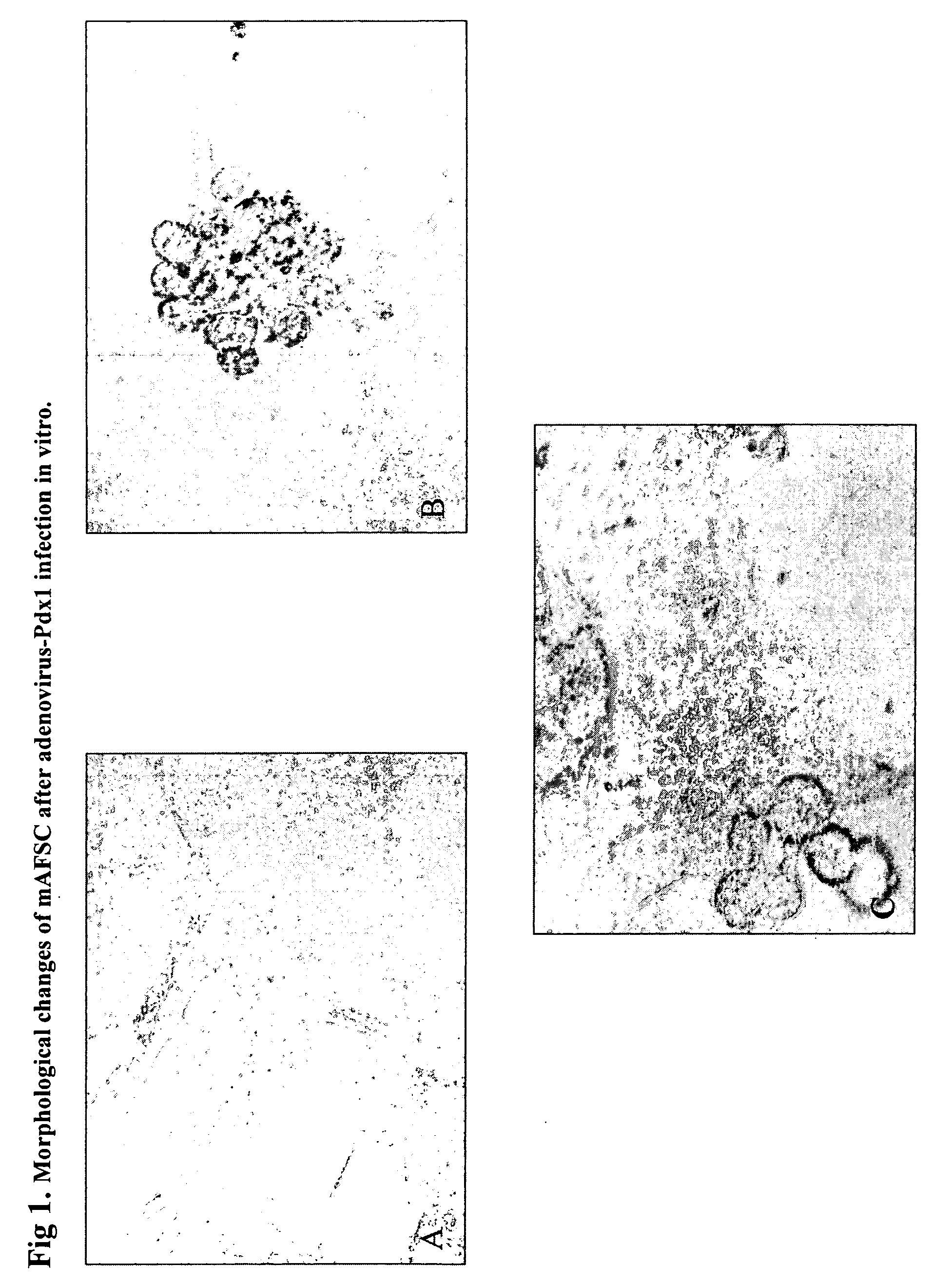
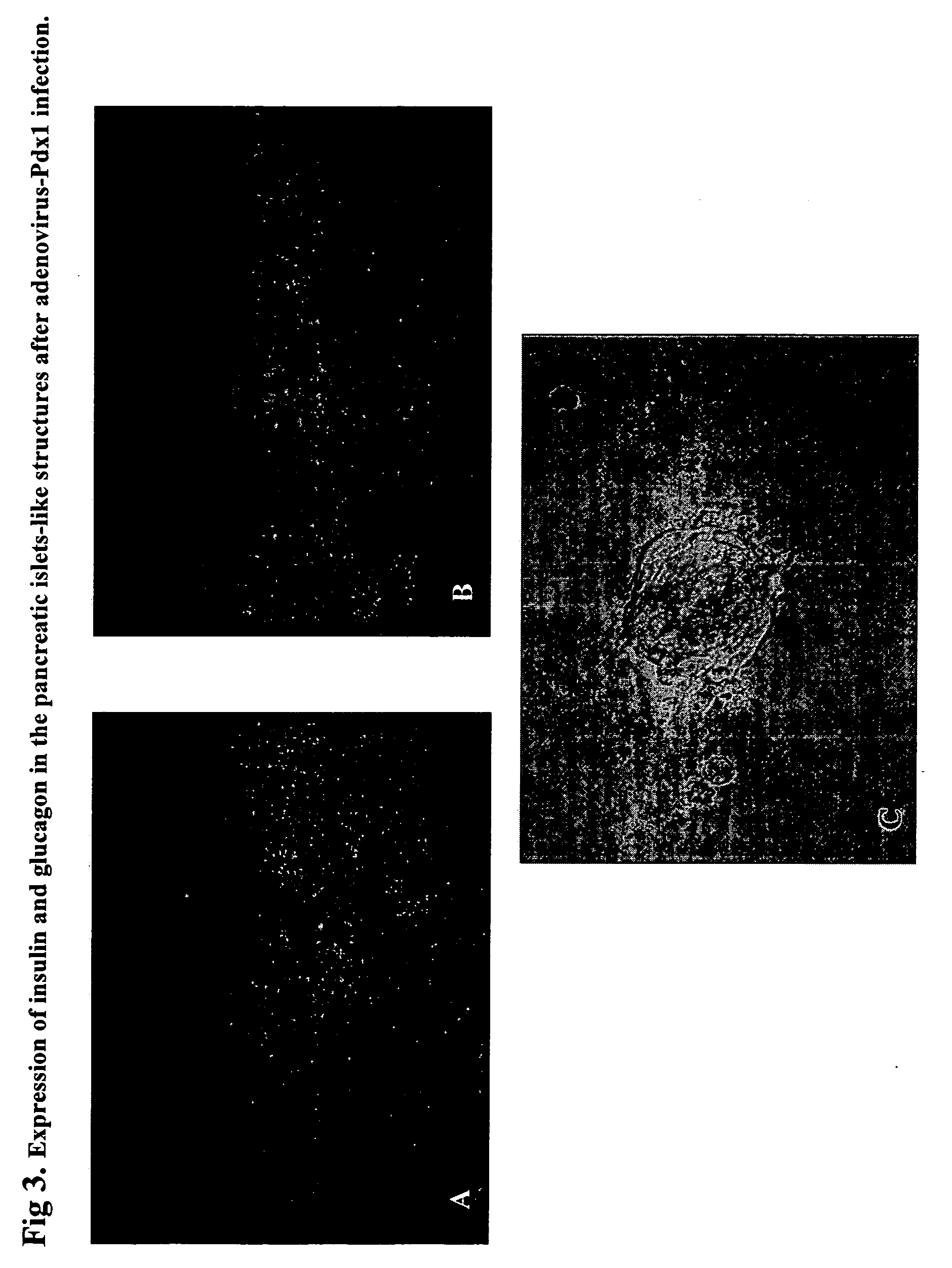
Regeneration of pancreatic islets by amniotic fluid stem cell therapy
A method of treating diabetes in a mammalian subject is carried out by: (a) providing mammalian amniotic fluid stem cells, and then (b) administering the cells to the subject in an amount effective to treat diabetes. Optionally, the cells may be differentiated into pancreatic-like cells or at least treated to initiate subsequent differentiation into-pancreatic-like cells, prior to administration.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIVERSITY
Enhanced stem cell therapy and stem cell production through the administration of low level light energy
ActiveUS20110060266A1Efficient productionGood effectElectrotherapyElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentDiseaseTreatment effect
Methods of enhancing stem cell therapy through the administration of low level light energy are provided in several embodiments. Some embodiments comprise irradiating stem cells before or after implantation at a target tissue having loss of function due to damage or disease, with a resultant increase in the efficacy of the cell therapy. In some embodiments, light energy enhances one or more of the viability, proliferation, migration or engraftment of the stem cells, thereby enhancing the therapeutic effects of the irradiated cells during cell therapy.
Owner:PHOTOTHERA IP HLDG
Nuclear reprogramming factor and induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20100062533A1Easy to prepareEffective isolationGenetically modified cellsPeptidesNuclear reprogrammingCell therapy
The present invention relates to a nuclear reprogramming factor having an action of reprogramming a differentiated somatic cell to derive an induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell. The present invention also relates to the aforementioned iPS cells, methods of generating and maintaining iPS cells, and methods of using iPS cells, including screening and testing methods as well as methods of stem cell therapy. The present invention also relates to somatic cells derived by inducing differentiation of the aforementioned iPS cells.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Cell therapy for chronic stroke
A method of treating stroke in a patient who has undergone a stroke comprising administering at least 2 million suitable neuronal cells to at least one brain area involved in the stroke. The method comprises the step of using a twist drill or a burr to form a hole in the skull through which the cells could be administered. Exemplary cells are hNT neuronal cells, HCN-1 cells, fetal pig cells, neural crest cells, neural stem cells, or a combination thereof. Also disclosed herein is a pharmaceutical composition of 95% pure hNT neuronal cells, which composition further includes a vial containing PBS and human neuronal cells. This vial is provided in a container with liquid nitrogen, whereby the composition is frozen and maintained at -170° C. before use. Also disclosed are methods of improving speech, cognitive, sensory, and motor function in a person who has experienced brain damage which interferes with function by administering a sterile composition of a sufficient number of neuronal cells or neural stem cells to the damaged area. Also disclosed is a method of replacing central nervous cells lost to neurodegenerative disease, trauma, ischemia or poisoning.
Owner:LAYTON BIOSCI +1
Stem cell therapy for the treatment of central nervous system disorders
The invention provides a method for treating CNS disorders by administering a neural stem cell composition and a mesenchymal stem cell composition on opposing sides of the blood brain barrier. The neural stem cell composition is administered to the central nervous system, while the mesenchymal stem cell composition is administered to the circulatory system, such as by intravenous injection. The method finds use in the treatment of degenerative GNS disorders, as well as traumatic CNS disorders such as stroke and spinal cord injury.
Owner:MIRONOV NIKOLAY
Nuclear reprogramming factor and induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20100216236A1Effective isolationEasy to prepareGenetically modified cellsPeptidesNuclear reprogrammingCell therapy
The present invention relates to a nuclear reprogramming factor having an action of reprogramming a differentiated somatic cell to derive an induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell. The present invention also relates to the aforementioned iPS cells, methods of generating and maintaining iPS cells, and methods of using iPS cells, including screening and testing methods as well as methods of stem cell therapy. The present invention also relates to somatic cells derived by inducing differentiation of the aforementioned iPS cells.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Treatment of erectile dysfunction by stem cell therapy
ActiveUS20090311223A1Enhance the beneficial effectSufficient durationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSmooth muscleCell therapy
Methods, cells and compositions of matter are provided for treatment of erectile dysfunction using stem cell therapy. In particular, various stem cells are modified or administered freshly isolated in order to induce smooth muscle regeneration, neural regeneration, and restoration of endothelial function. In some embodiments endogenous stem cells are mobilized or activated to achieve therapeutic benefit. In other embodiments compositions derived from stem cells are utilized for treatment of erectile dysfunction.
Owner:CREATIVE MEDICAL TECH INC
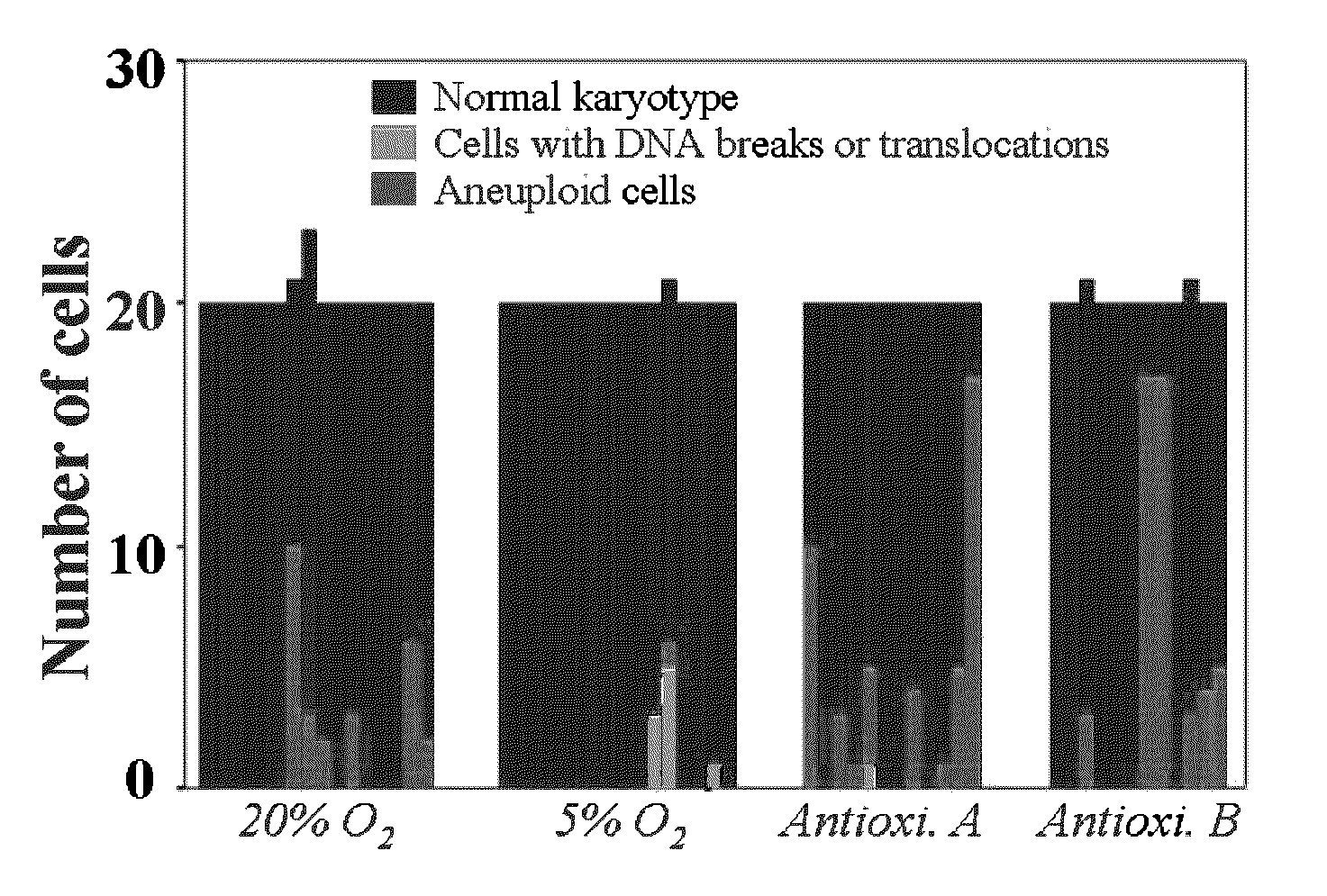
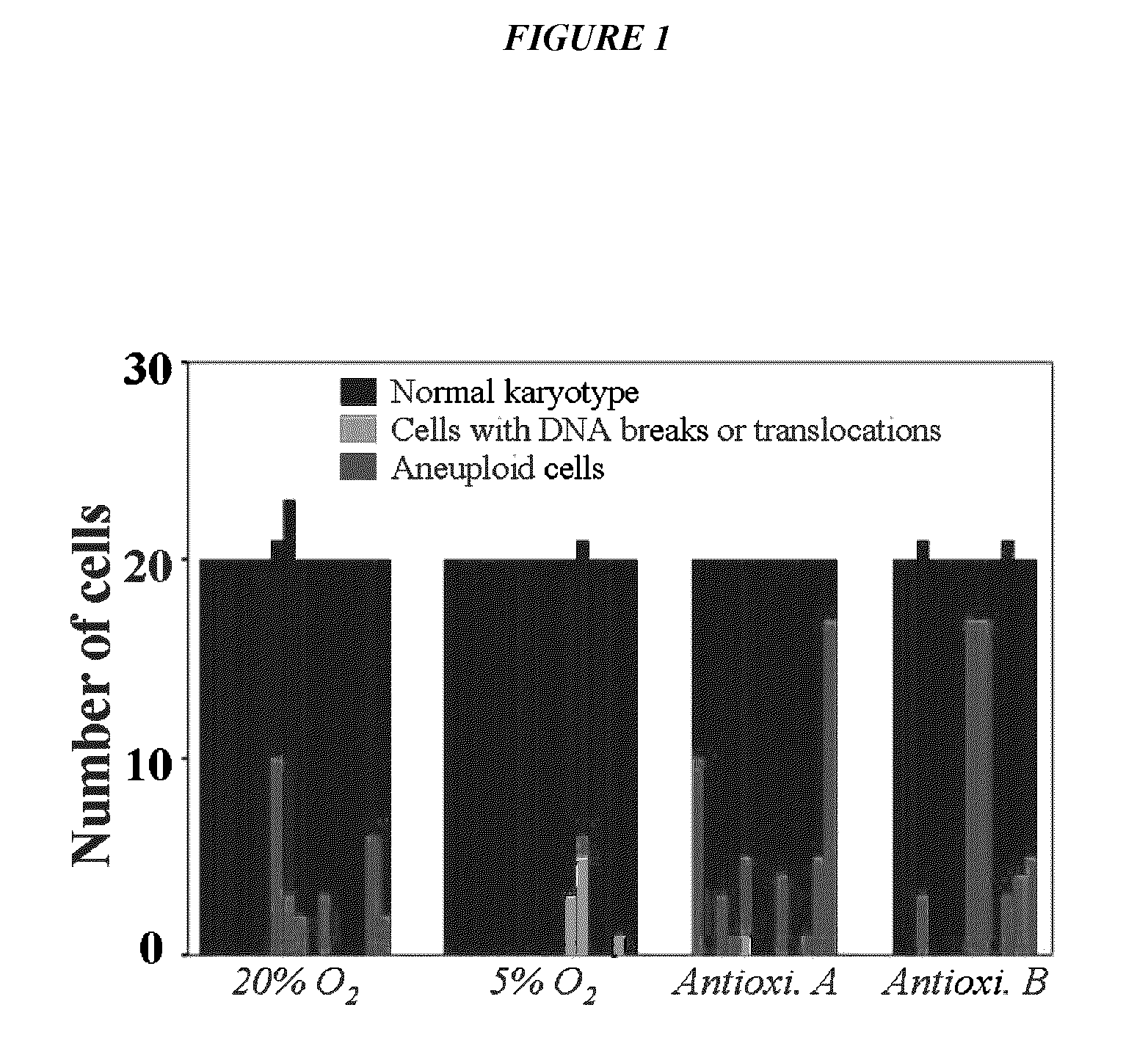
Methods for enhancing yield of stem cell cultures and enhancing stem cell therapy
InactiveUS20110300112A1Low efficacyImprove stabilityBiocideCulture processDNA repairKaryotypic abnormality
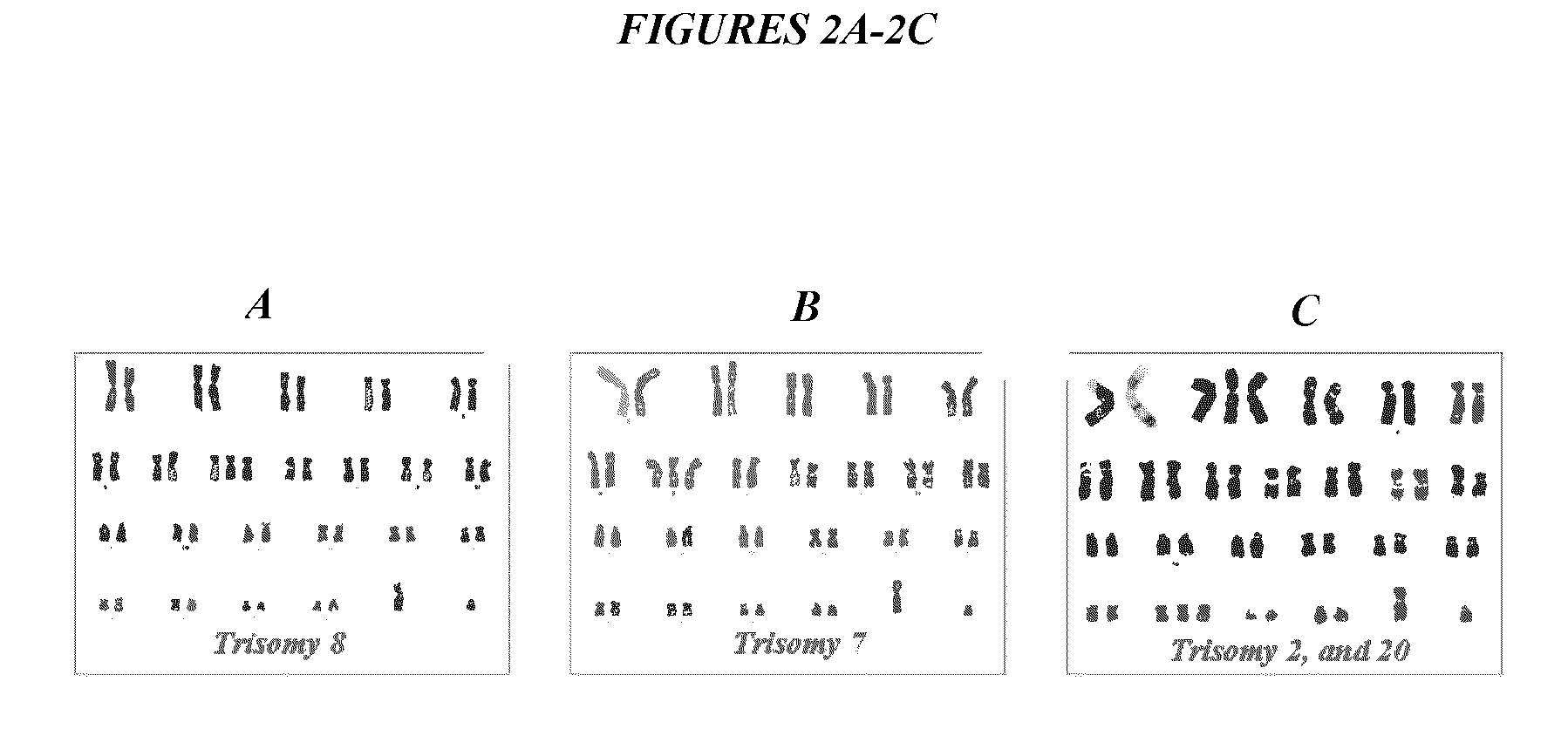
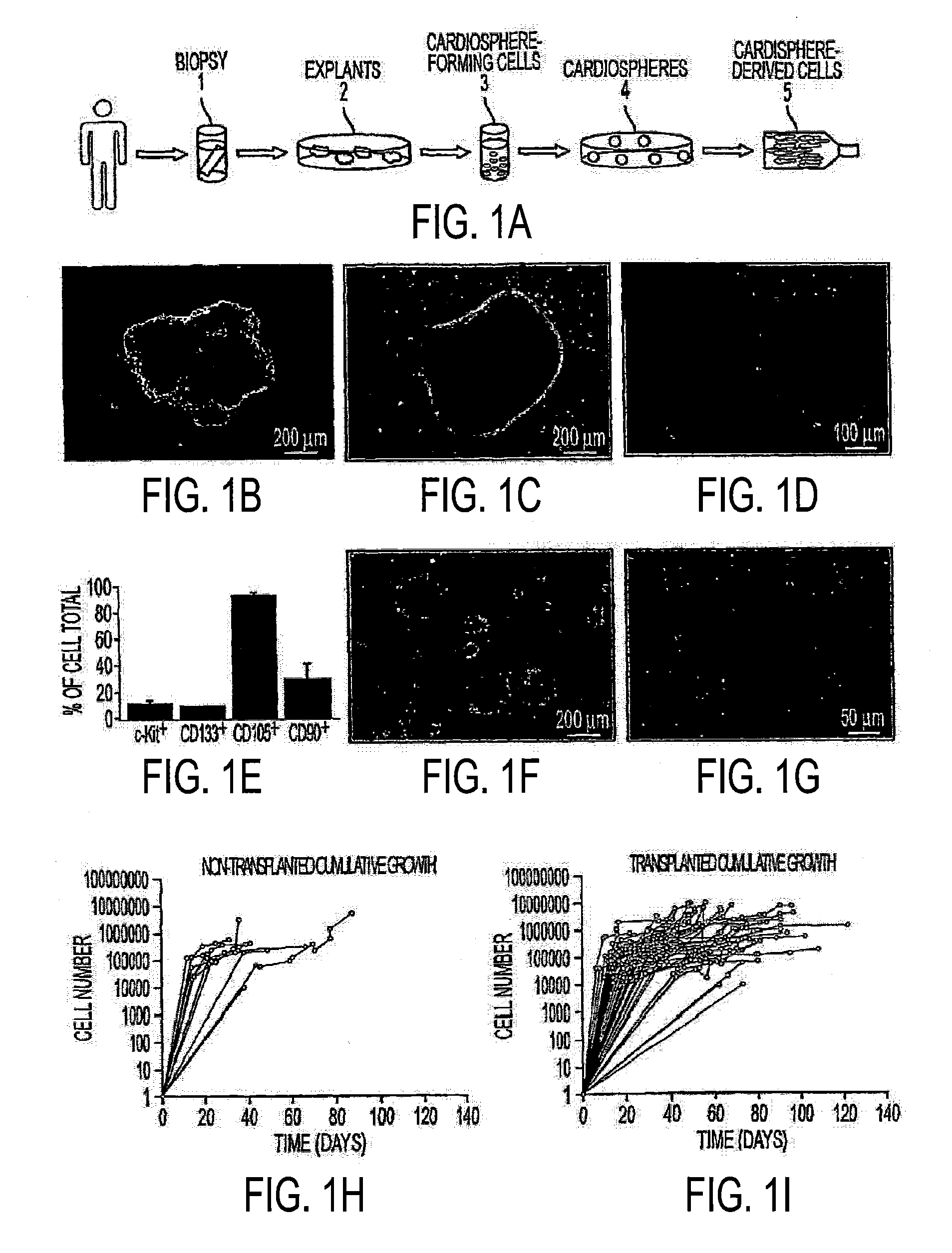
The present application relates to methods and compositions for the generation of therapeutic cells having reduced incidence of karyotypic abnormalities. In several embodiments cardiac stem cells are cultured in an antioxidant-supplemented media that reduces levels of reactive oxygen species, but does not down regulate DNA repair mechanisms. In several embodiments, physiological oxygen concentrations are used during culture in order to increase the proliferation of stem cells, decrease the senescence of the cells, decrease genomic instability, and / or augment the functionality of such cells for cellular therapies.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Compositions and Methods for Stem Cell Expansion and Differentiation
InactiveUS20070280989A1Free from damagePositively chargedBiocideGenetic material ingredientsCross-linkProgenitor
The present invention relates to compositions comprising stem cells and partially committed progenitor cells and to methods of controlling cell proliferation and differentiation, which can be used for expansion of stem cells and their subsequent differentiation. The present invention provides expanded population of essentially undifferentiated stem cells, which are useful in clinical procedures involving stem cell therapy, and a population derived thereof of which at least part of the cells are differentiated. The cells can be used per se, as a part of a cell-bearing composition comprising cross-linked hyaluronic acid-laminin gels or as a part of a composite implant for tissue regeneration.
Owner:NVR LABS
Methods of Reducing Teratoma Formation During Allogeneic Stem Cell Therapy
ActiveUS20120315252A1Reduce infarct sizeImprovement in ventricular functionBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsCell therapyCell harvest
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
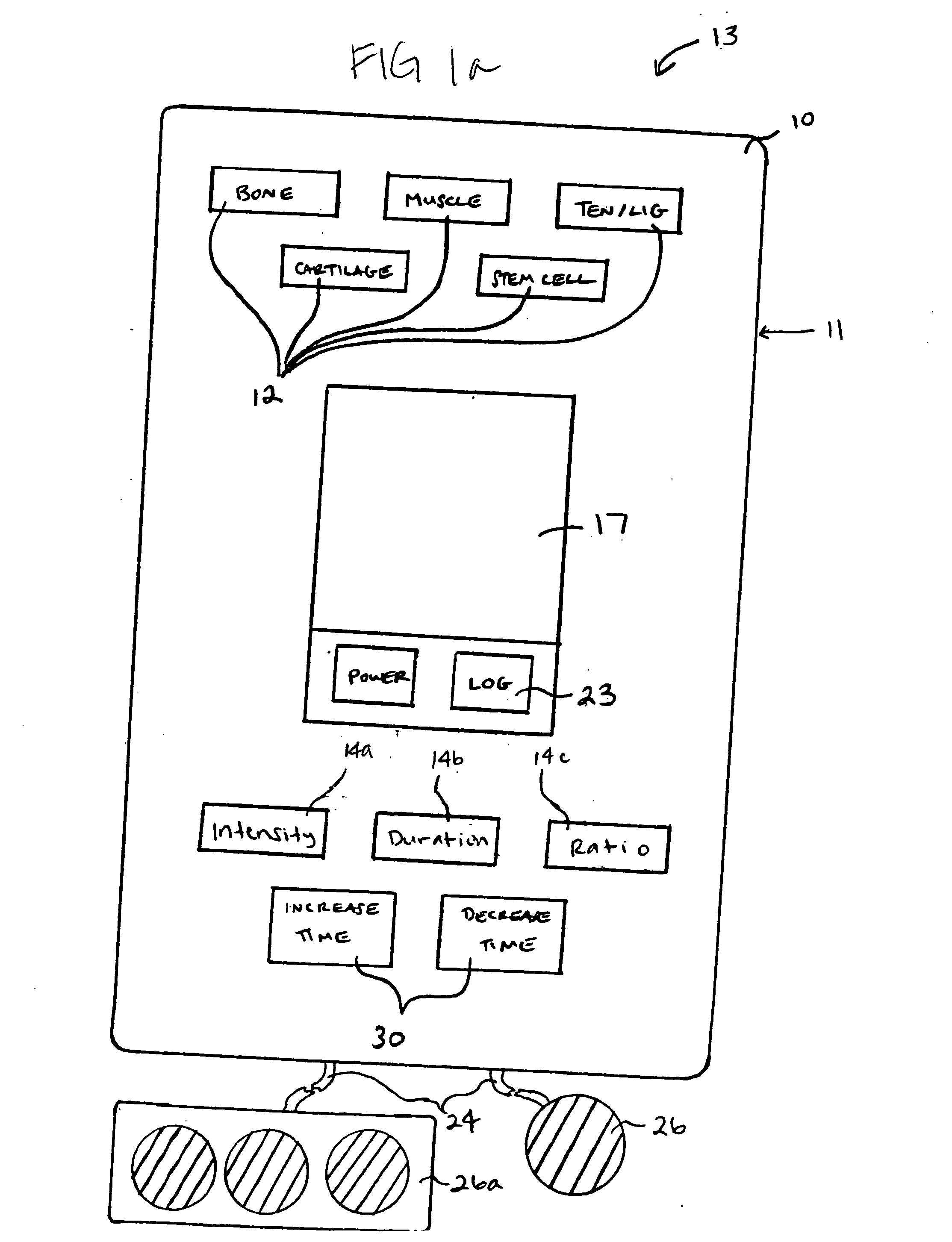
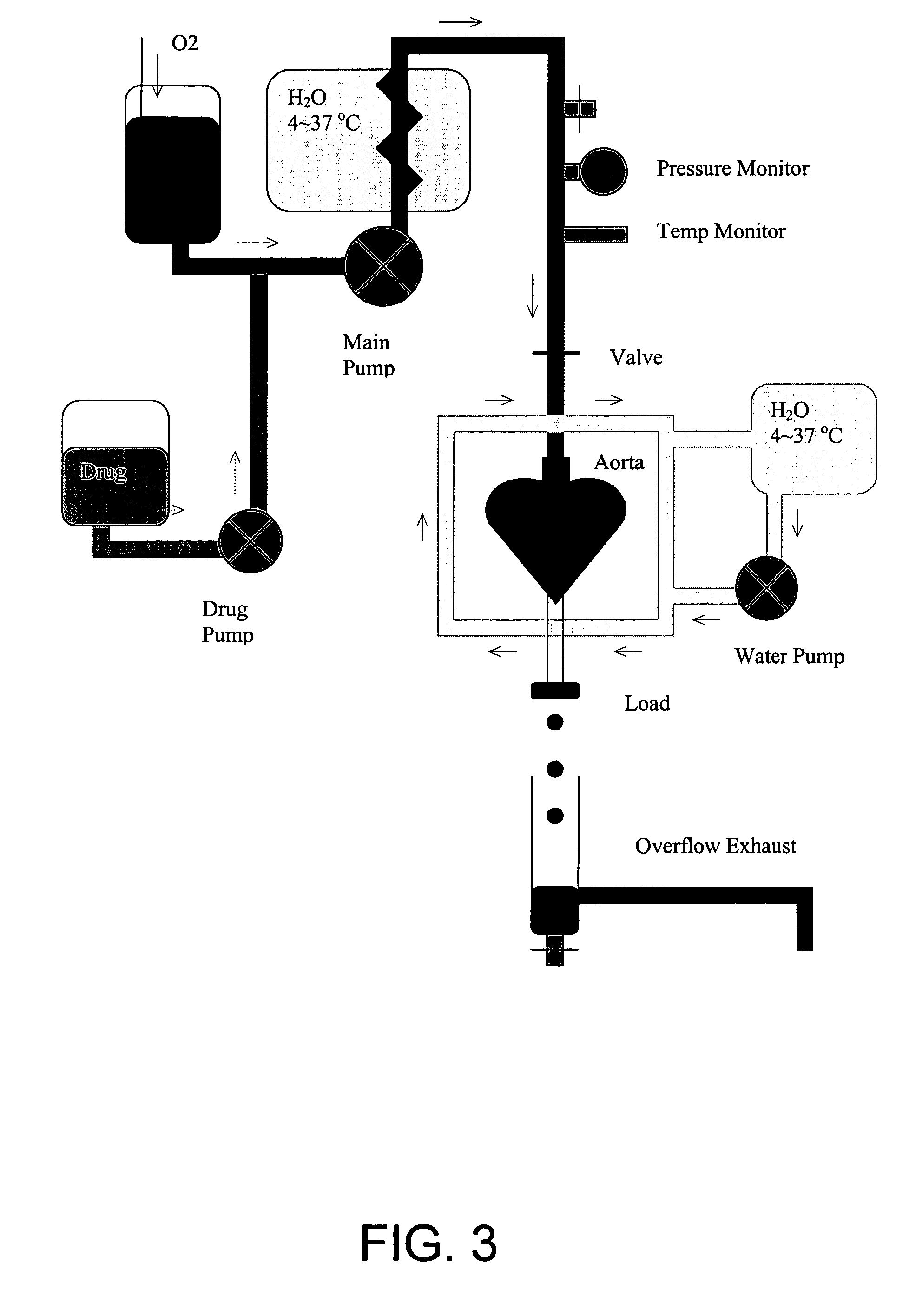
Apparatus and method for the static application of therapeutic ultrasound and stem cell therapy of living tissues
InactiveUS20070249046A1Controlled and safe increaseIncrease temperatureGenetic material ingredientsDiagnosticsVariable intensityTherapeutic ultrasound
Devices and methods for treating tissue injuries and augmenting the maturation and differentiation of stem cell populations are provided. The devices comprises ultrasonic oscillators capable of variable frequency output, user-selectable based on the tissue being treated. The devices produce therapeutic ultrasound that is pulsed and has a modulated amplitude and varying waveform of variable intensity.
Owner:SHIELDS DONALD J JR
Preparation for treating heart disease used in cell therapy
ActiveUS20100303909A1Improve survivalSufficient degreeBiocidePowder deliveryInduced pluripotent stem cellCardiac muscle
An object of the present invention is to establish a cell transplantation method which can markedly improve the survival of grafted pluripotent stem cells and the efficiency of cardiomyocyte regeneration in cell therapy using pluripotent stem cells derived from heart tissue and can treat heart disease further effectively. Specifically, according to the present invention, enhancement in the survival of grafted pluripotent stem cells and significant improvement in the efficiency of cardiomyocyte regeneration are achieved by using, in combination, pluripotent stem cells derived from heart tissue and a hydrogel containing a basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) in cell therapy for heart disease.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
B and T lymphocyte attenuator marker for use in adoptive T-cell therapy
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
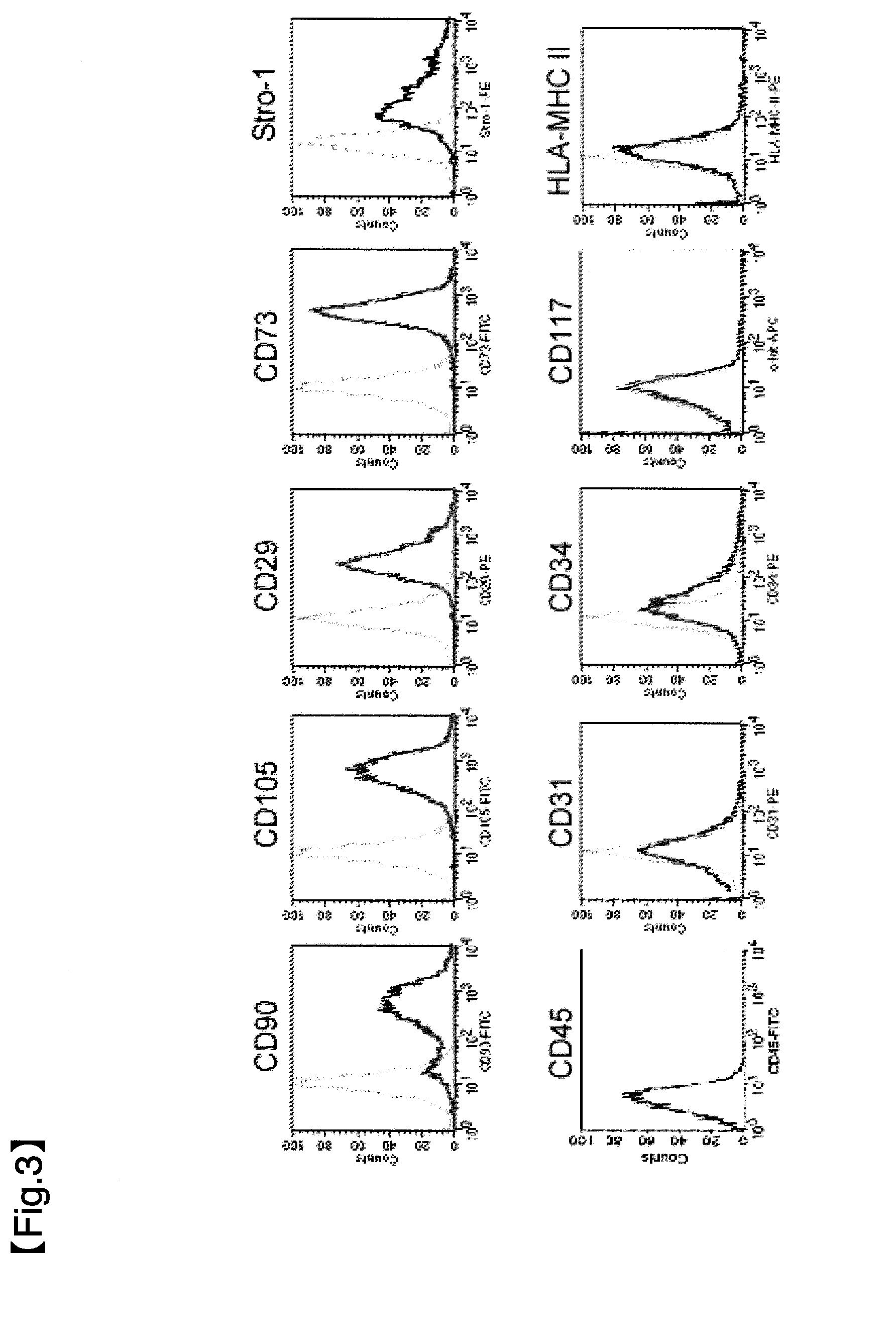
Embryonic-like stem cells derived from adult human peripheral blood and methods of use
ActiveUS8835163B2High expressionPrevent proliferationBiocidePancreatic cellsHematopoietic cellAutoimmune disease
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
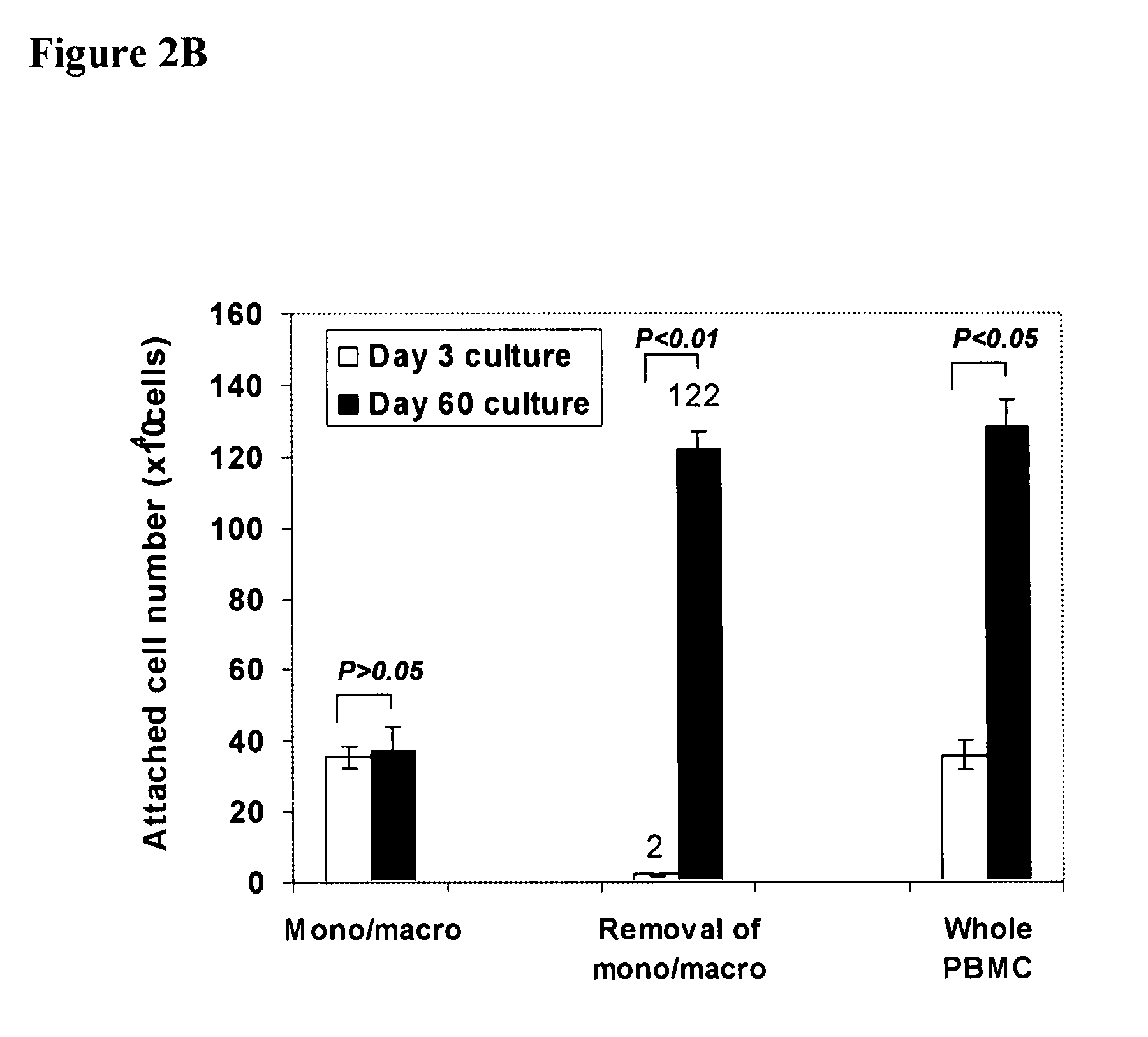
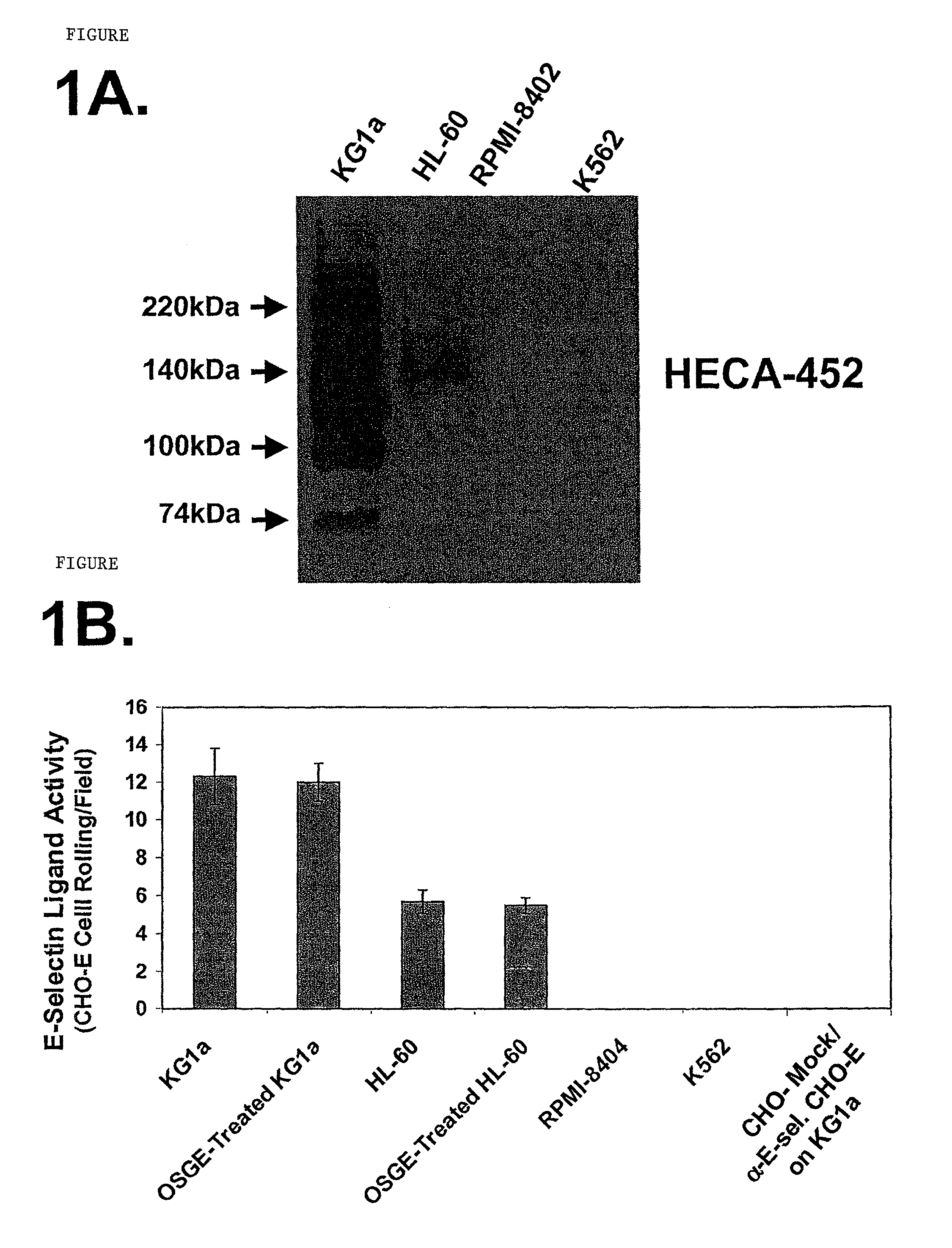
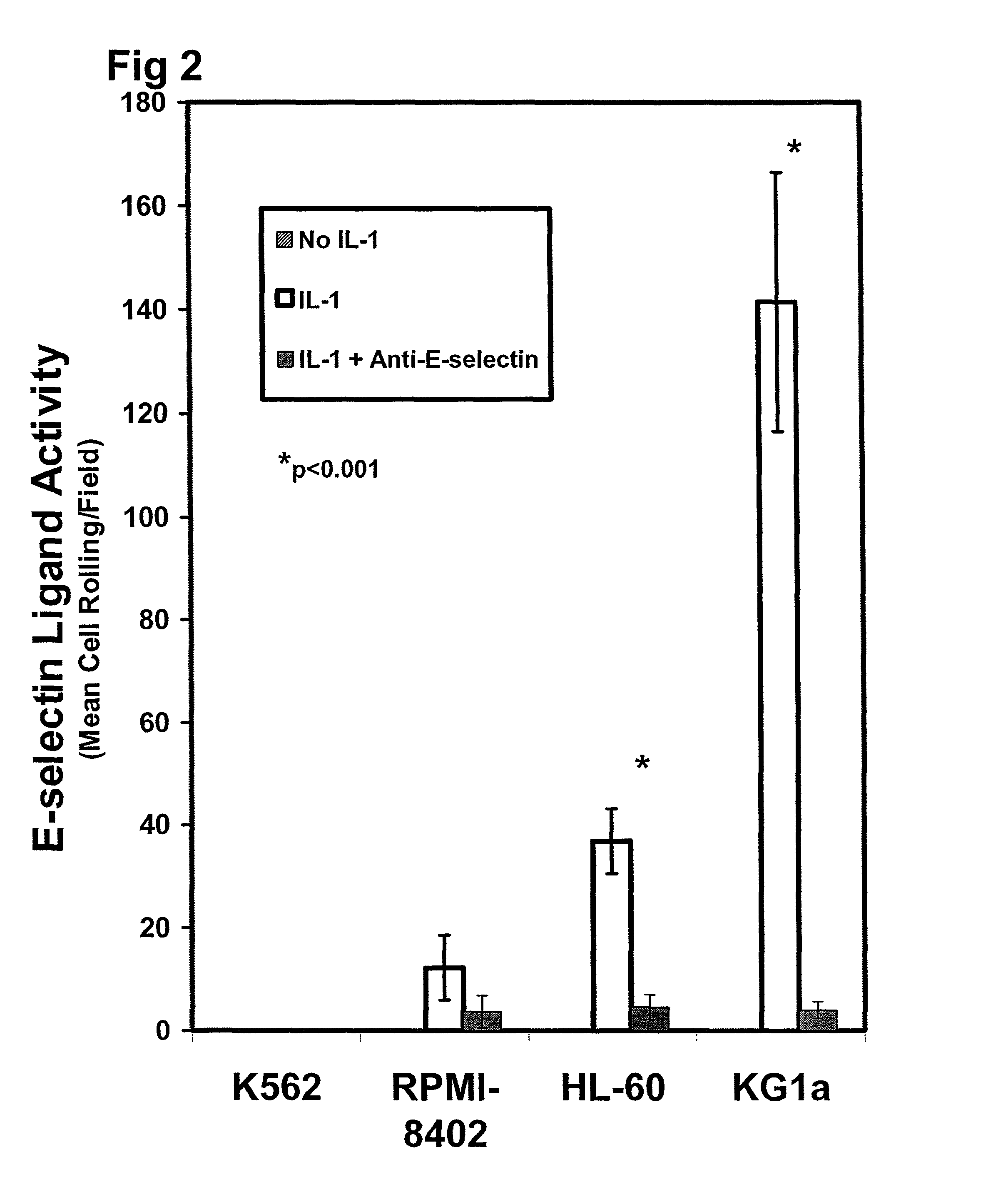
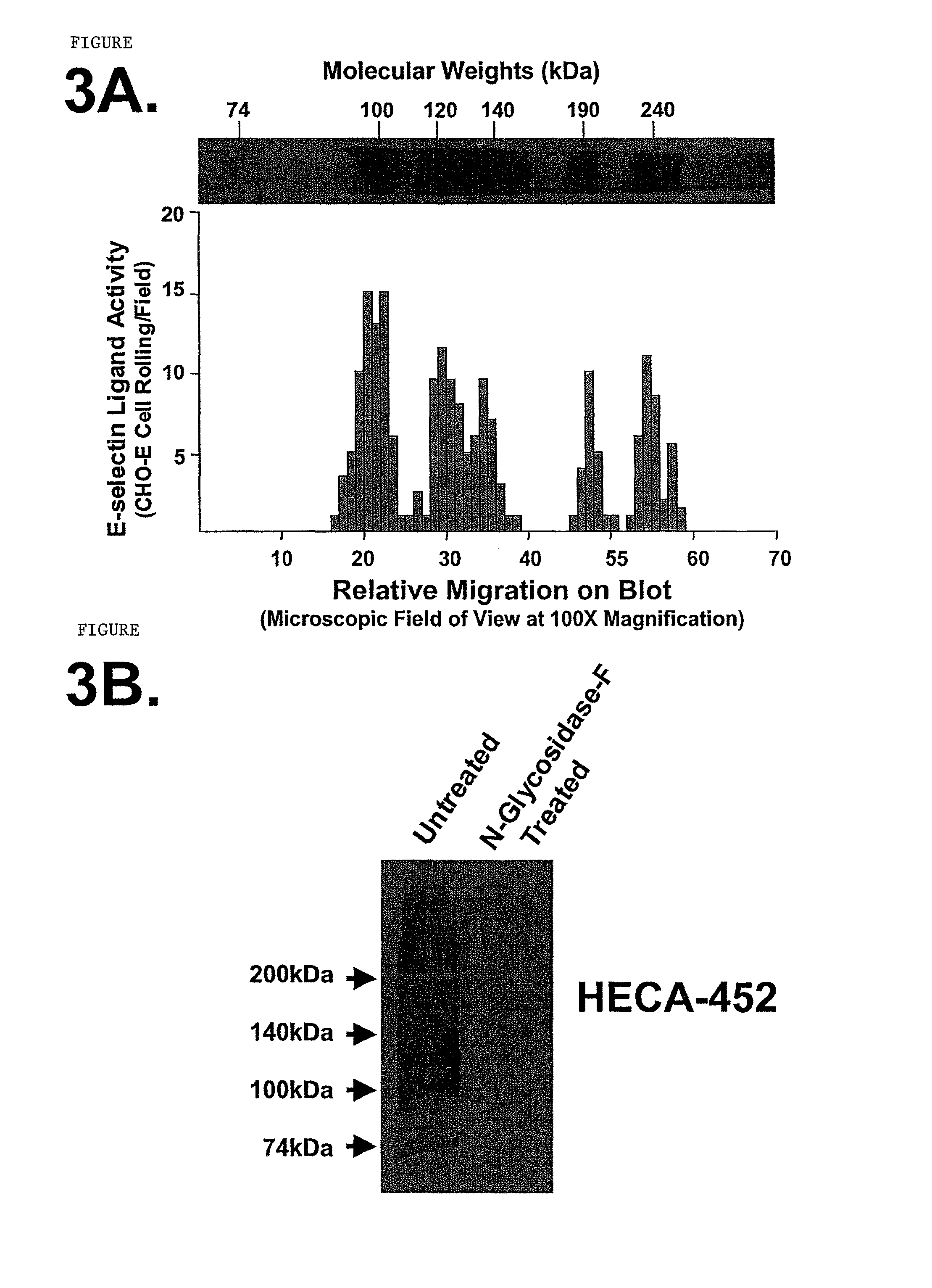
Hematopoietic cell E-selectin / L-selectin ligand glycosylated CD44 polypeptide
InactiveUS7875585B2High affinityHigh activityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticE-selectinHematopoietic cell
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
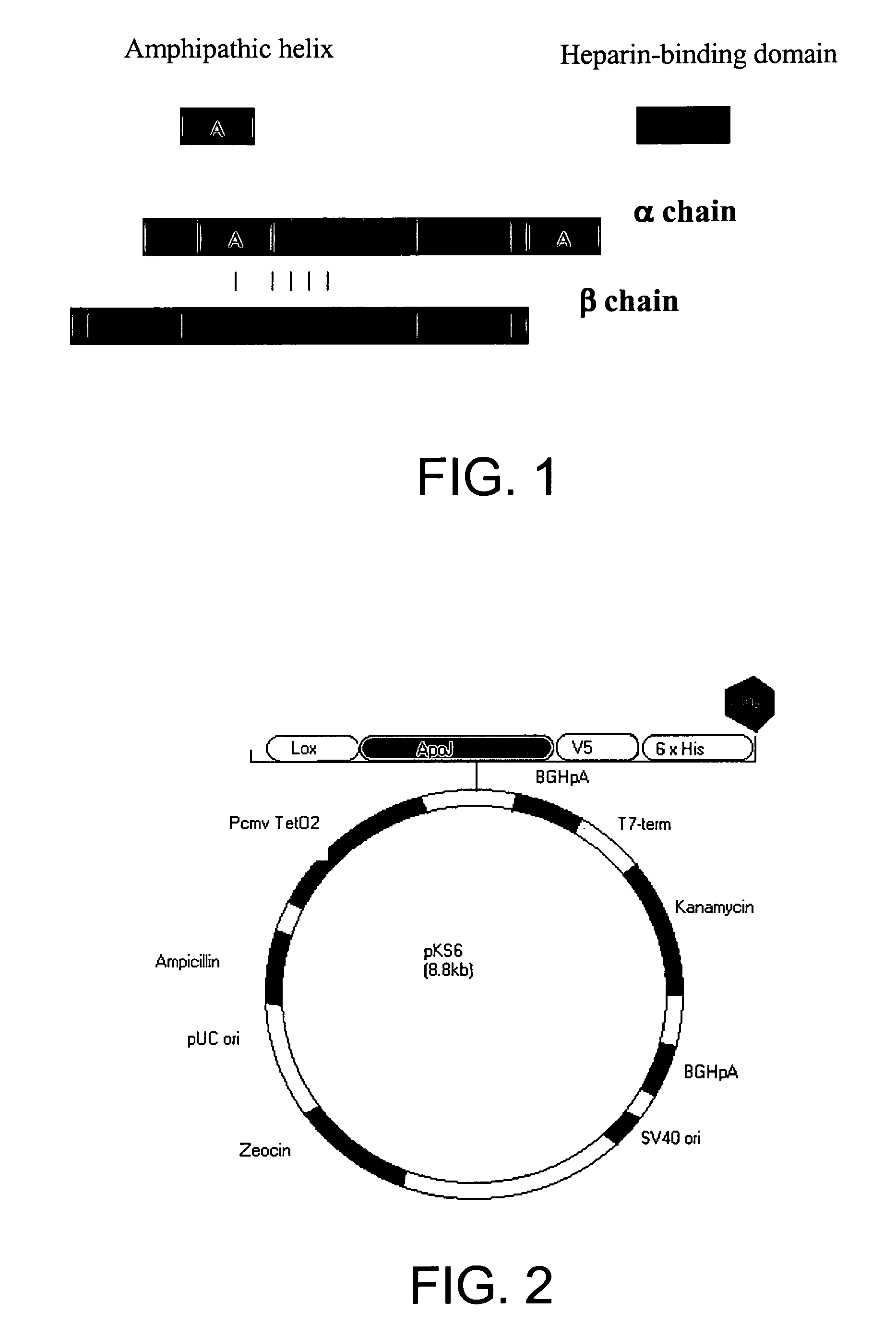
Composition and method for clusterin-mediated stem cell therapy for treatment of atherosclerosis and heart failure
ActiveUS20060099194A1Reduce riskAvoid cell deathBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsOxysterolCytotoxicity
Methods and compositions are disclosed for inhibiting, deterring or preventing apoptosis of cardiac myocytes, transplanted stem cells, vascular stem cells, and vascular smooth muscle cells by means of expressing or synthesizing clusterin. Also disclosed are methods and compositions for producing recombinant clusterin, or its biologically active peptides, and for induction of clusterin-associated lipoproteins or enzymes for deterring or preventing inflammatory injury and apoptosis induced by oxLDL, oxysterols, cytokines, and Fas Ligand. Also disclosed is an induction method and composition for enhancing expression of ALDH and ALDH-associated enzymes or co-factors to prevent cytotoxicity or detoxification. Therapeutic methods providing new expression or overexpression of clusterin in vascular or cardiac tissue are expected to inhibit the formation of atherosclerotic lesions, stabilize existing atherosclerotic plaques, and repair failing or damaged cardiac tissue.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
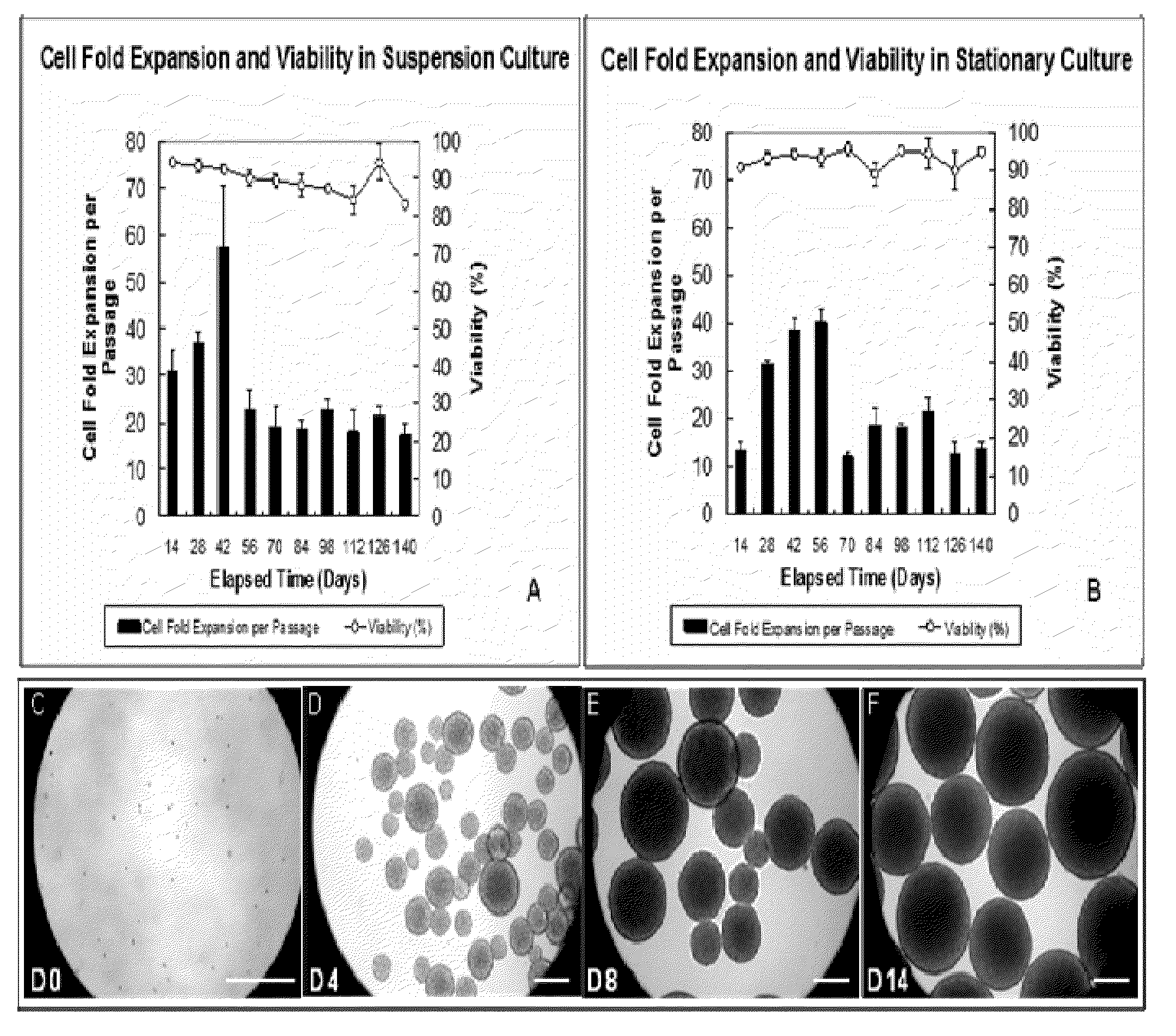
Methods and Compositions for Culturing of neural Precursor Cells
ActiveUS20090233360A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHuntingtons choreaNeuropathic pain
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the propagation and expansion of neural precursor cells (NPCs). NPCs may be used in the clinical implementation of stem cell therapy to treat disorders such as Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, neuropathic pain and other diseases of the central nervous system. The large-scale production of NPCs in bioreactors allows for the generation of clinical quantities of these cells.
Owner:UTI LLP
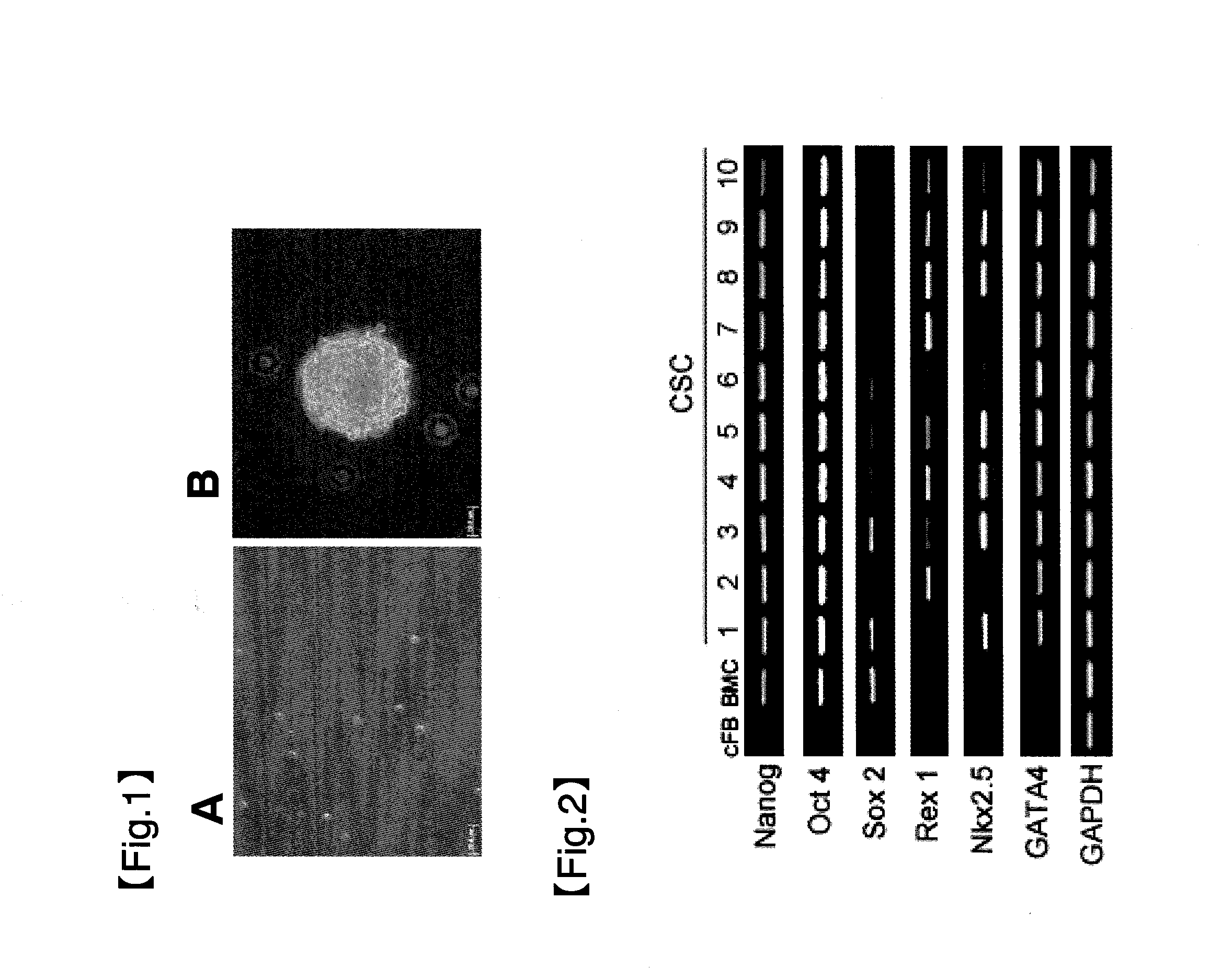
Metabolite for improving production, maintenance and proliferation of pluripotent stem cells, composition comprising the same, and method of culturing pluripotent stem cell using the same
InactiveUS20150072416A1Improve efficiencyInhibits induction of senescenceOrganic chemistryCulture processMetaboliteReprogramming
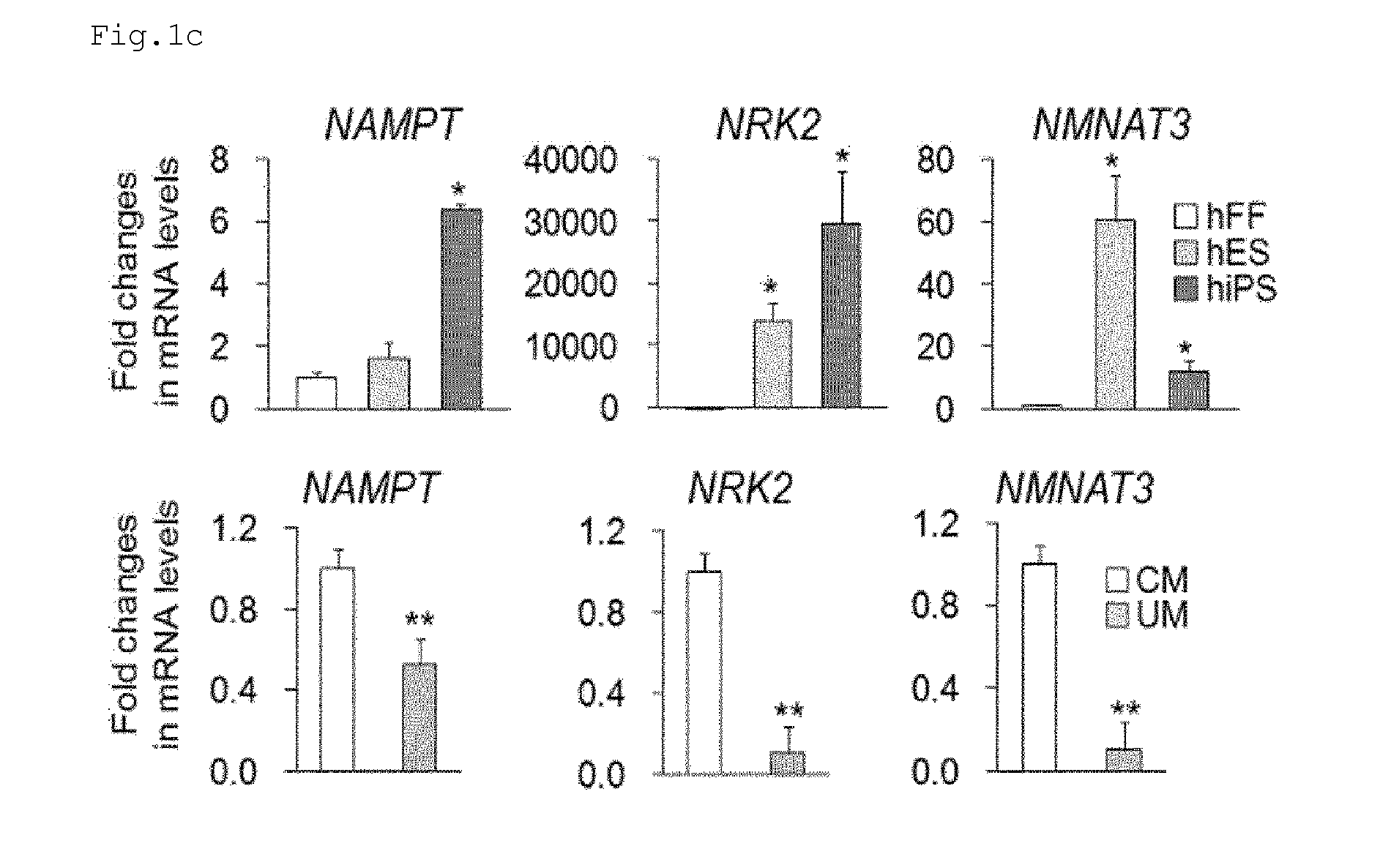
According to the present invention, when nicotinamide is added in a culture process for producing pluripotent stem cells from human differentiated cells, it can increase the efficiency of reprogramming and can significantly reduce the time required for induction of reprogramming. It was verified that nicotinamide inhibits the induction of senescence and oxidative stress in the reprogramming process and increases cell proliferation and mitochondrial activity to effectively improve culture conditions for induction of reprogramming. Particularly, the present invention will contribute to optimizing a process of producing induced pluripotent stem cells from a small amount of patient-specific somatic cells obtained from various sources, and thus it will significantly improve a process of developing clinically applicable personalized stem cell therapy agents and new drugs and will facilitate the practical application of these agents and drugs. In another aspect, according to the present invention, in defined culture conditions in which feeder cells and serum were not used, it was found that nicotinamide can provide a culture medium composition effective for maintaining the undifferentiated state of human embryonic stem cells and human induced pluripotent stem cells, which are typical pluripotent stem cells. The invention can be effectively used for the development of a high-efficiency system for culturing large amounts of human pluripotent stem cells, which is required for the industrialization of human pluripotent stem cells.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
Probe and non-invasive kit for detecting pseudo-hypertrophic muscular dystrophy
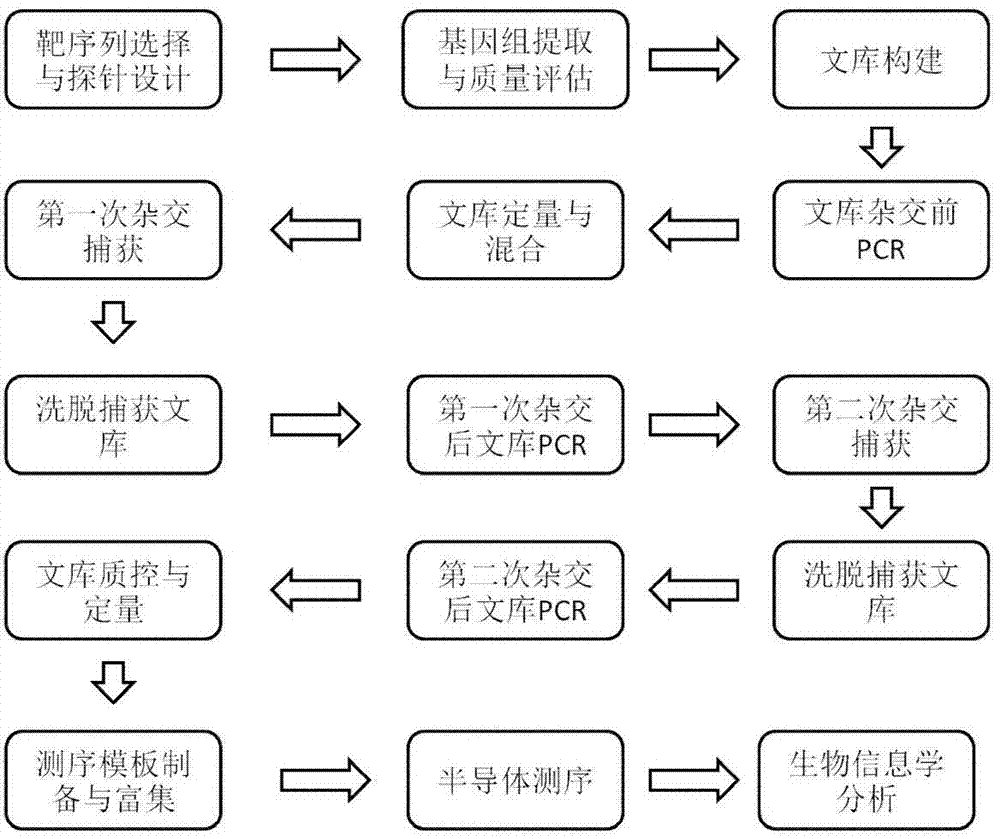
ActiveCN104498614ASolve bottlenecksFair priceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDmd geneAmniotic fluid
The invention discloses a probe and a kit for detecting pseudo-hypertrophic muscular dystrophy. The probe for detecting pseudo-hypertrophic muscular dystrophy comprises nucleic acid sequences shown by SEQ NO:1-SEQ ID NO:546, and the kit for detecting pseudo-hypertrophic muscular dystrophy comprises nucleic acid sequences shown by SEQ ID NO:1-SEQ ID NO:546. The probe and the kit for detecting pseudo-hypertrophic muscular dystrophy can be used for detecting complete mutation information of DMD genes, including exon deletion / repetition and point mutation, have the advantages of completeness, rapidness, accuracy and appropriate price, and can be used for solving the problems of DMD molecular diagnosis; the kit disclosed by the invention is suitable for detection of various tissue samples of muscle, blood, amniotic fluid and the like, can detect pathogenic mutation of exons and introns as well as known mutations and unreported pathogenic mutations, and is also used for detecting whether patient genotypes are corrected or not after stem cell therapy.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HETAI TECH CO LTD
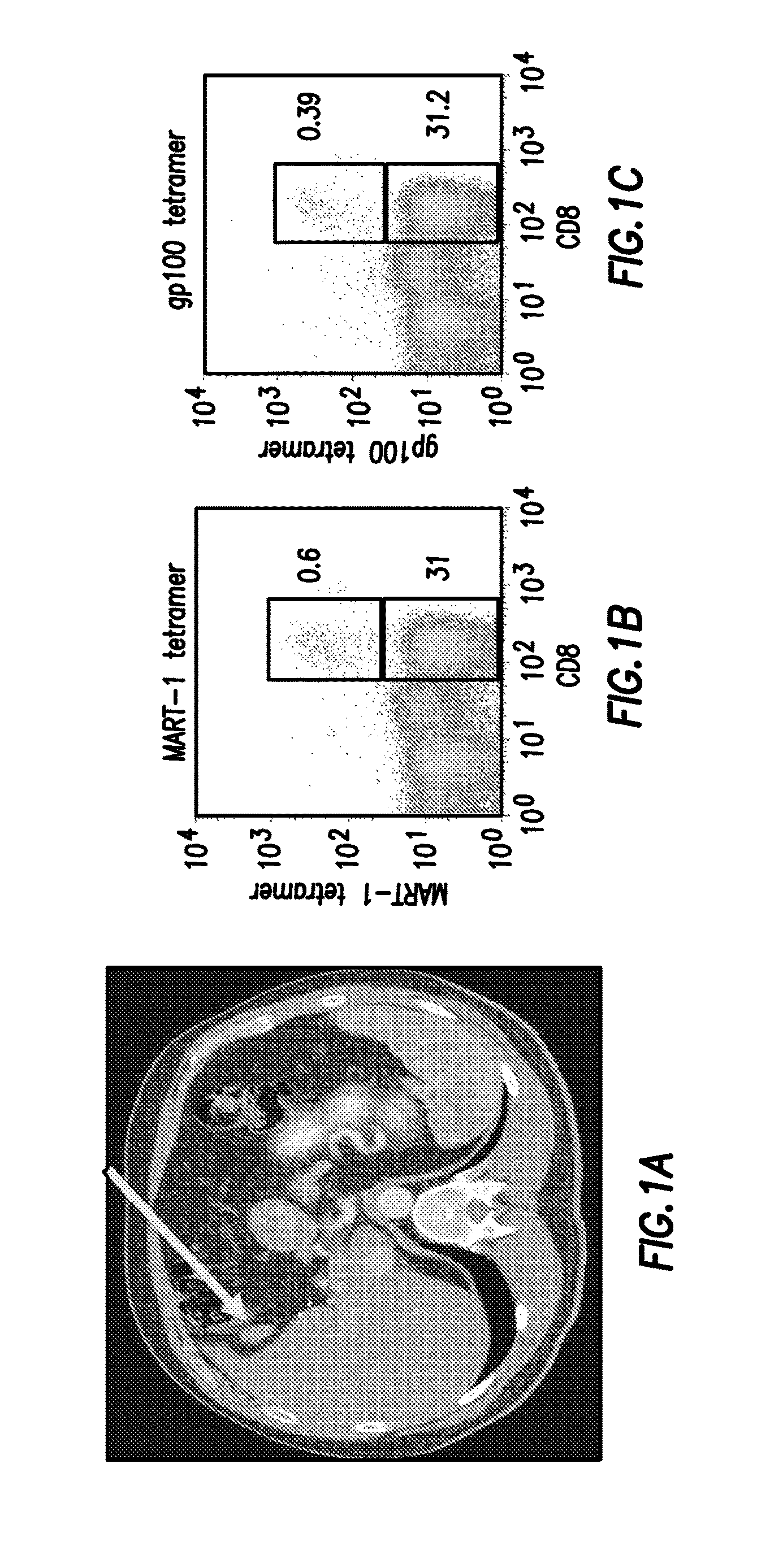
Methods of Cell Therapy, Neurogenesis and Oligodendrogenesis
InactiveUS20090010873A1Enhancing neurogenesisEnhancing oligodendrogenesisBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAntigenNervous system
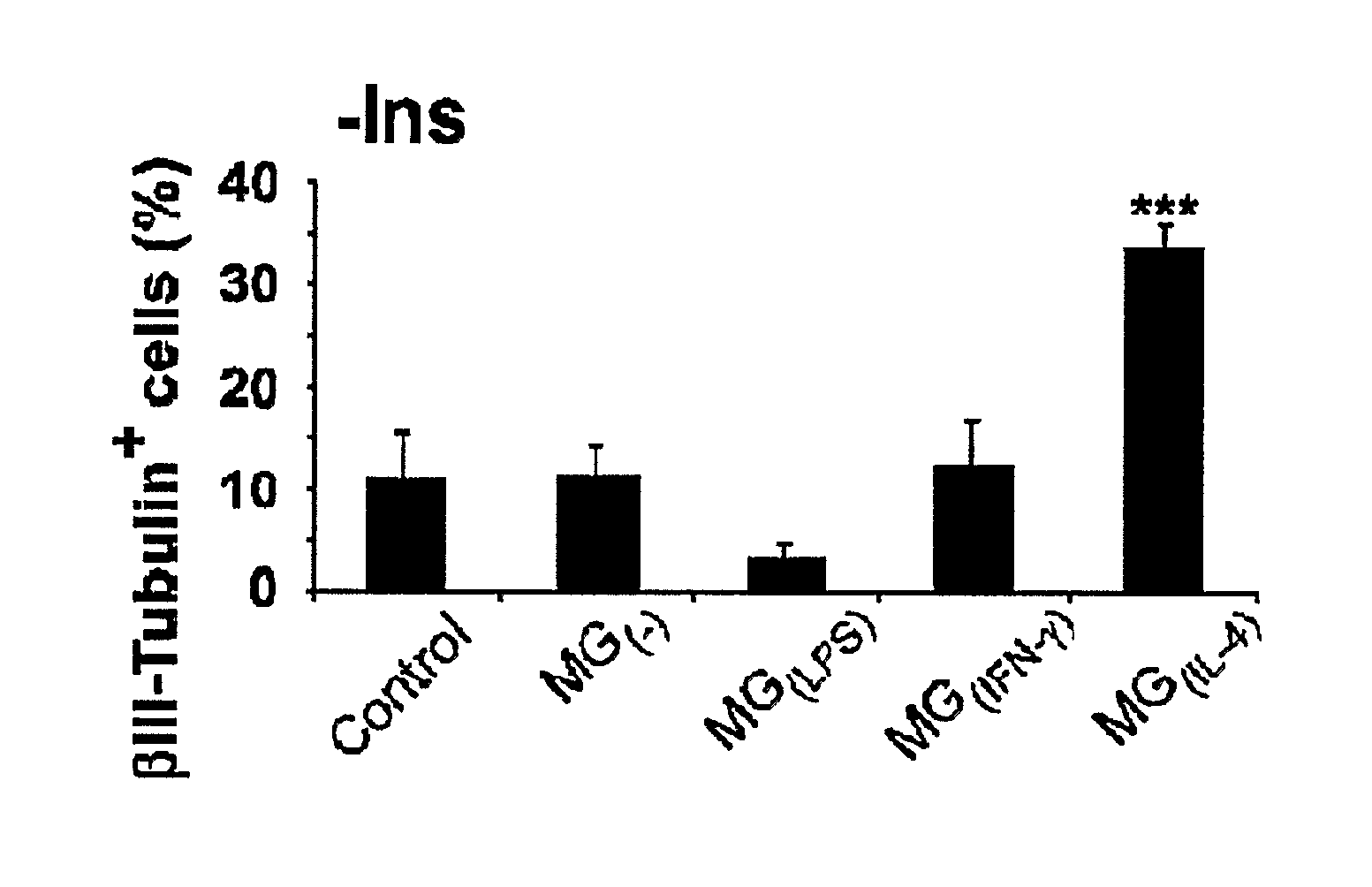
A method is provided for inducing and enhancing neurogenesis and / or oligodendrogenesis from endogenous as well as from exogenously administered stem cells, which comprises administering to an individual in need a neuroprotective agent such as a nervous system (NS)-specific antigen, a peptide derived therefrom, T cells activated therewith, poly-YE, microglia activated by IFN-γ and / or IL-4 and combinations thereof. The method includes stem cell therapy in combination with the neuroprotective agent.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Proliferated cell lines and uses thereof
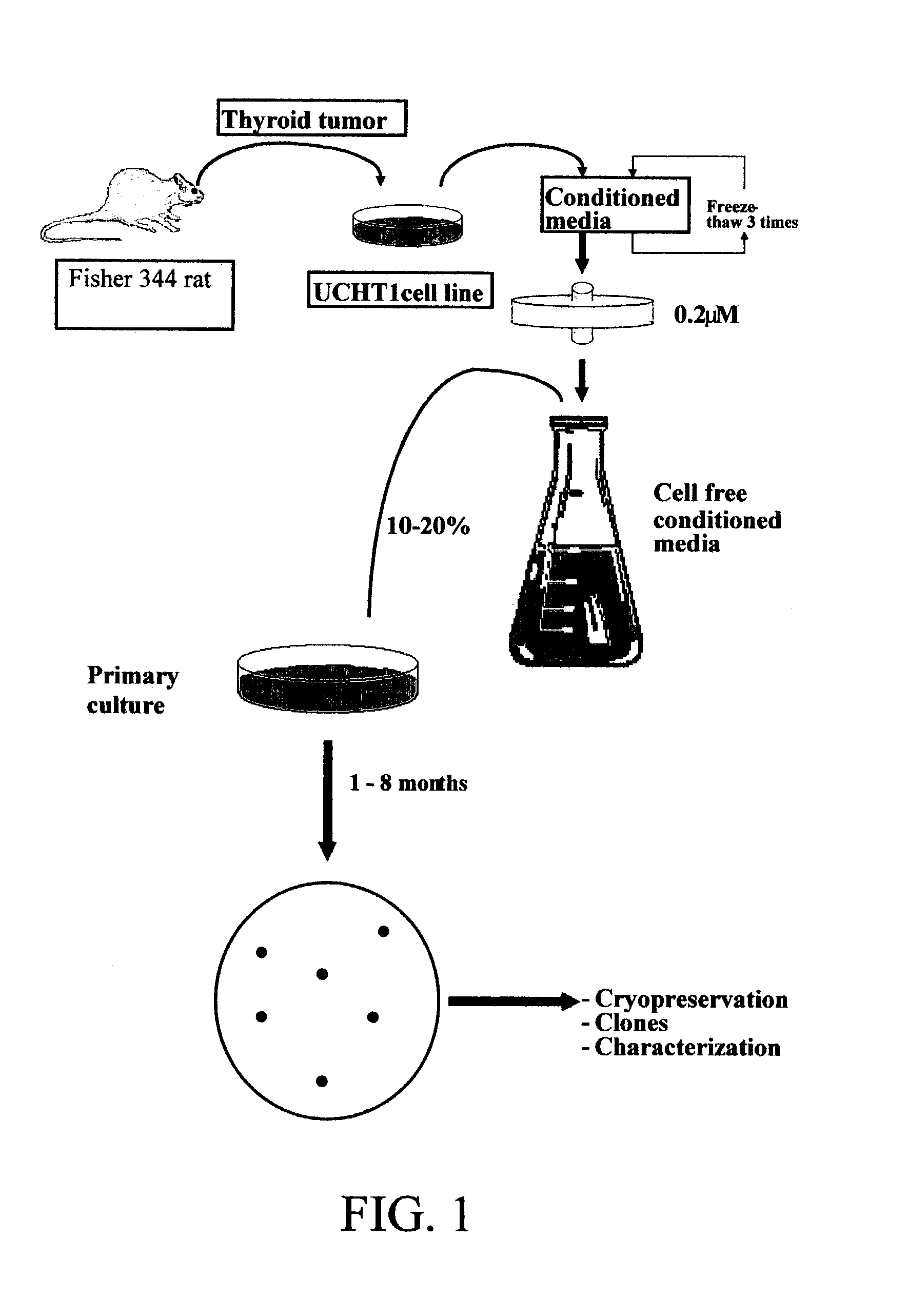
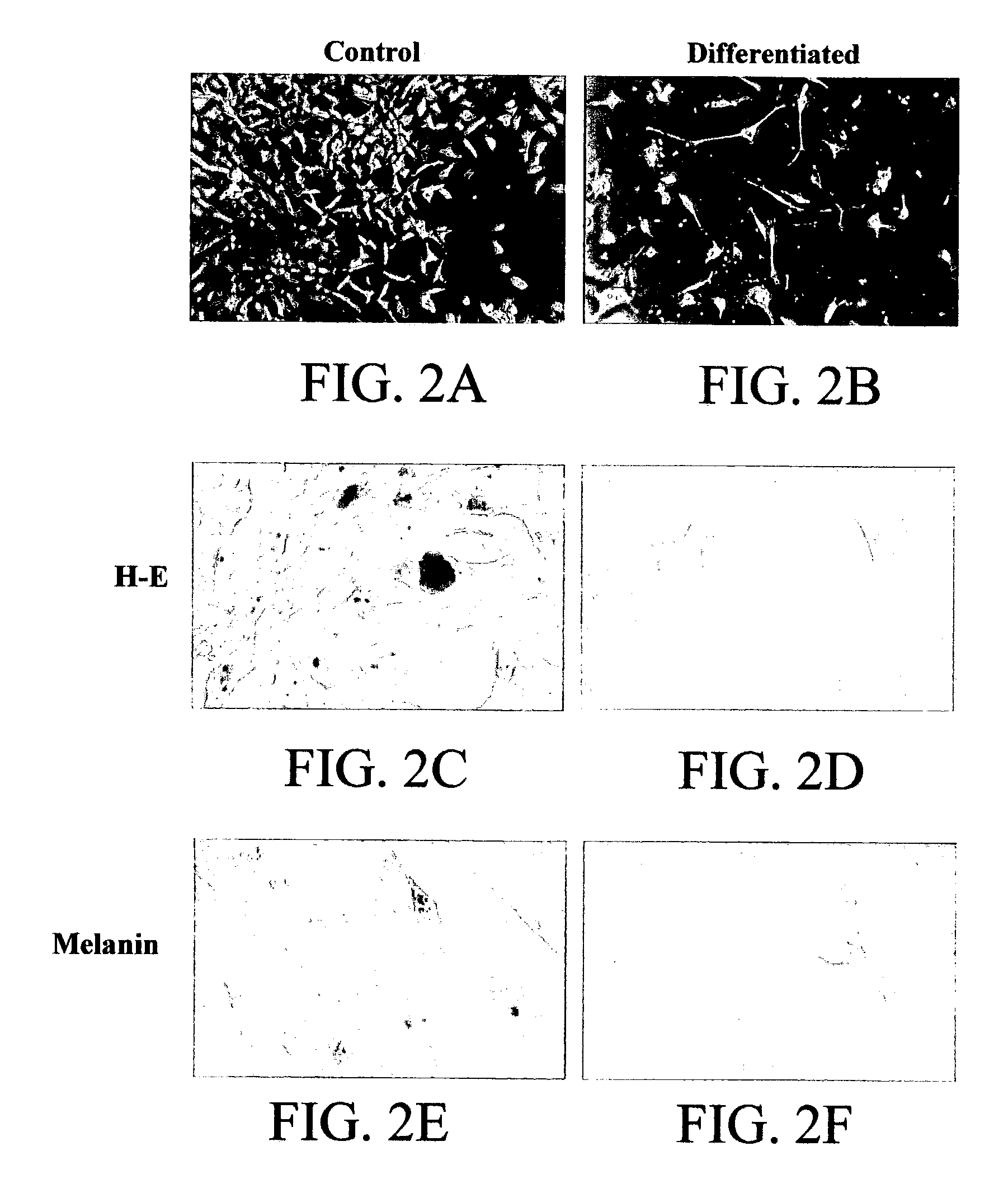
ActiveUS20080175828A1Increase proliferation potentialEnhance proliferation potentialSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsProgenitorCell therapy
The subject invention pertains to tumor cell lines useful for increasing the proliferation potential of any human or animal cell in culture, thereby providing immortalized or continuous cell lines and cultures. The invention also concerns proliferation factors, and compositions containing the factors, which are capable of increasing the proliferation potential of any human or other animal cell in culture. The subject invention further pertains to a method for proliferating cells in culture by containing cells with the proliferation factors. The proliferated cells can range in plasticity and can include, for example, blast cells, fertilized ova, non-fertilized gametes, embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells, precursor or progenitor cells, and highly specialized cells. Optionally, the cells can be induced to cease proliferation. The proliferated cells of the subject invention are useful for cell therapy, cell / gene therapy, biological production of molecules, and as in vitro models for research, toxicity testing, and drug development.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA +1
Somatic cells for use in cell therapy
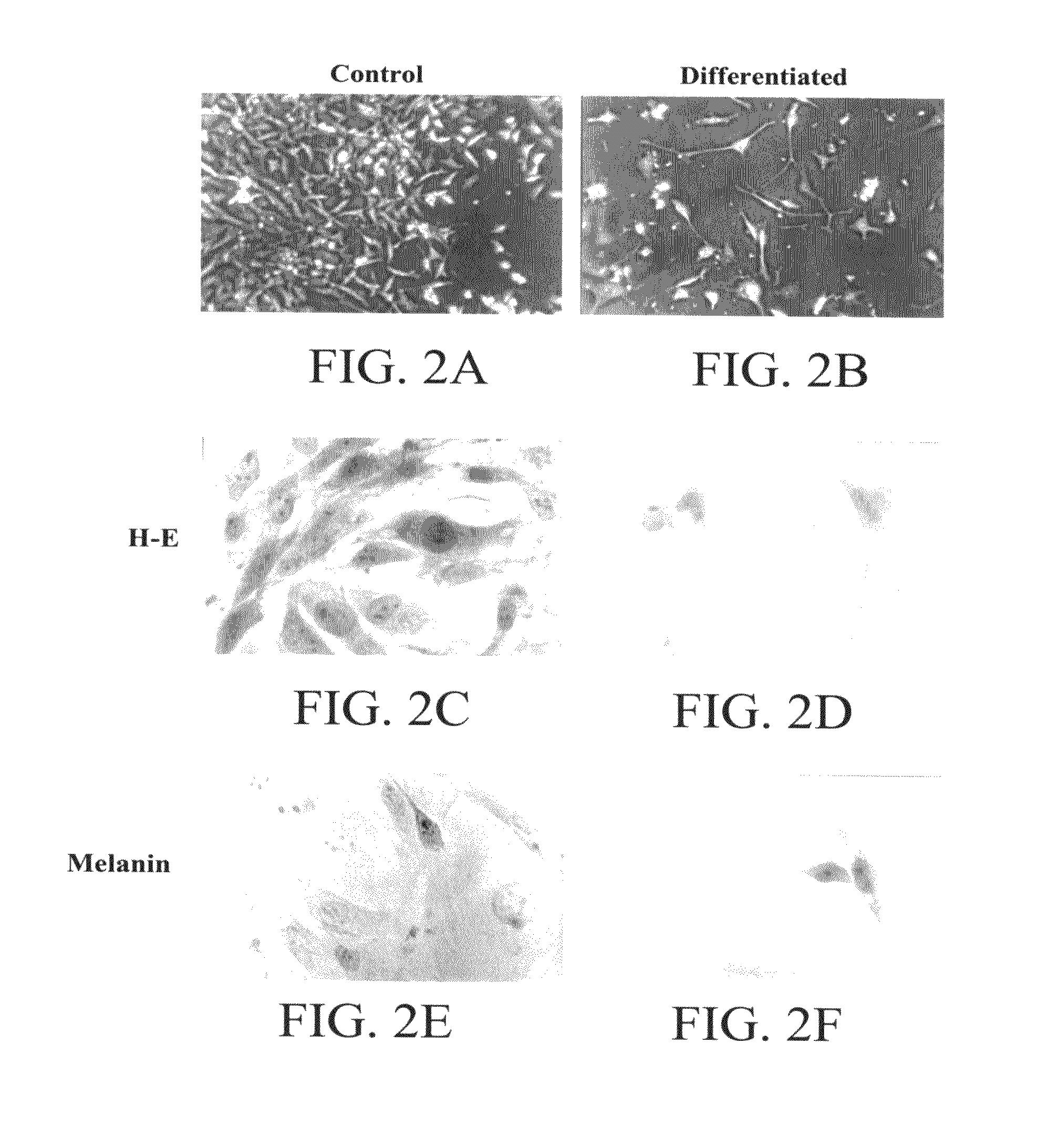
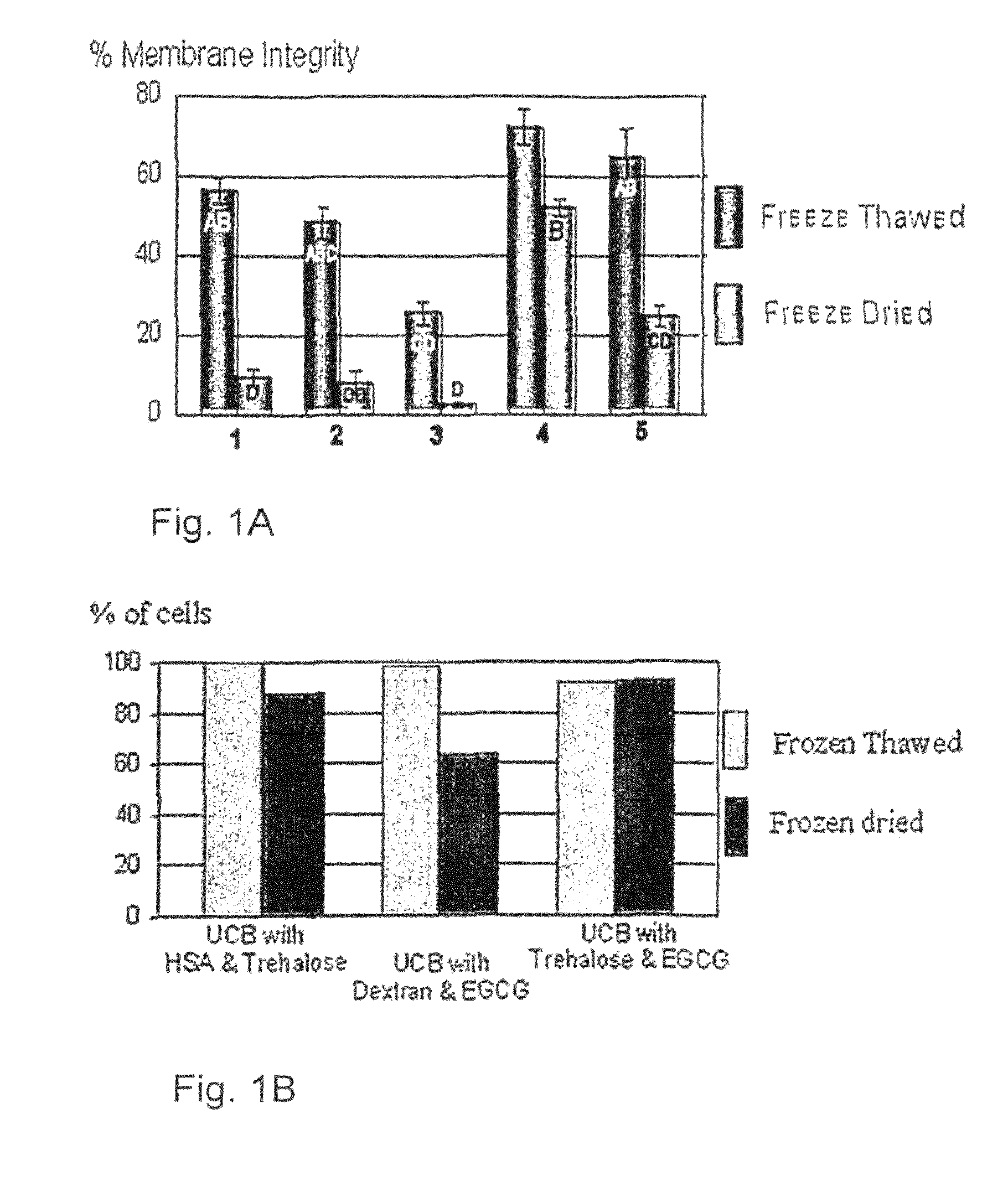
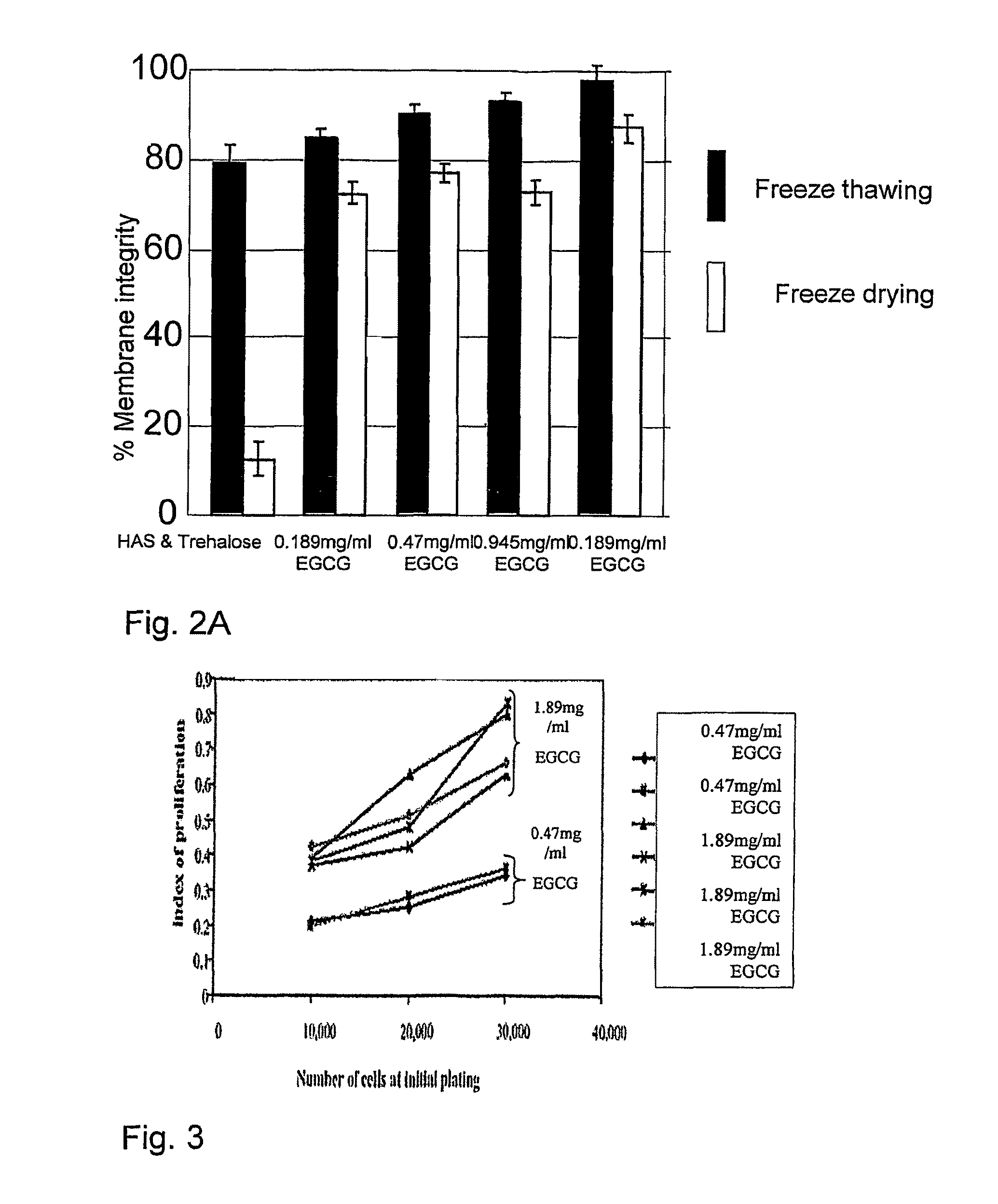
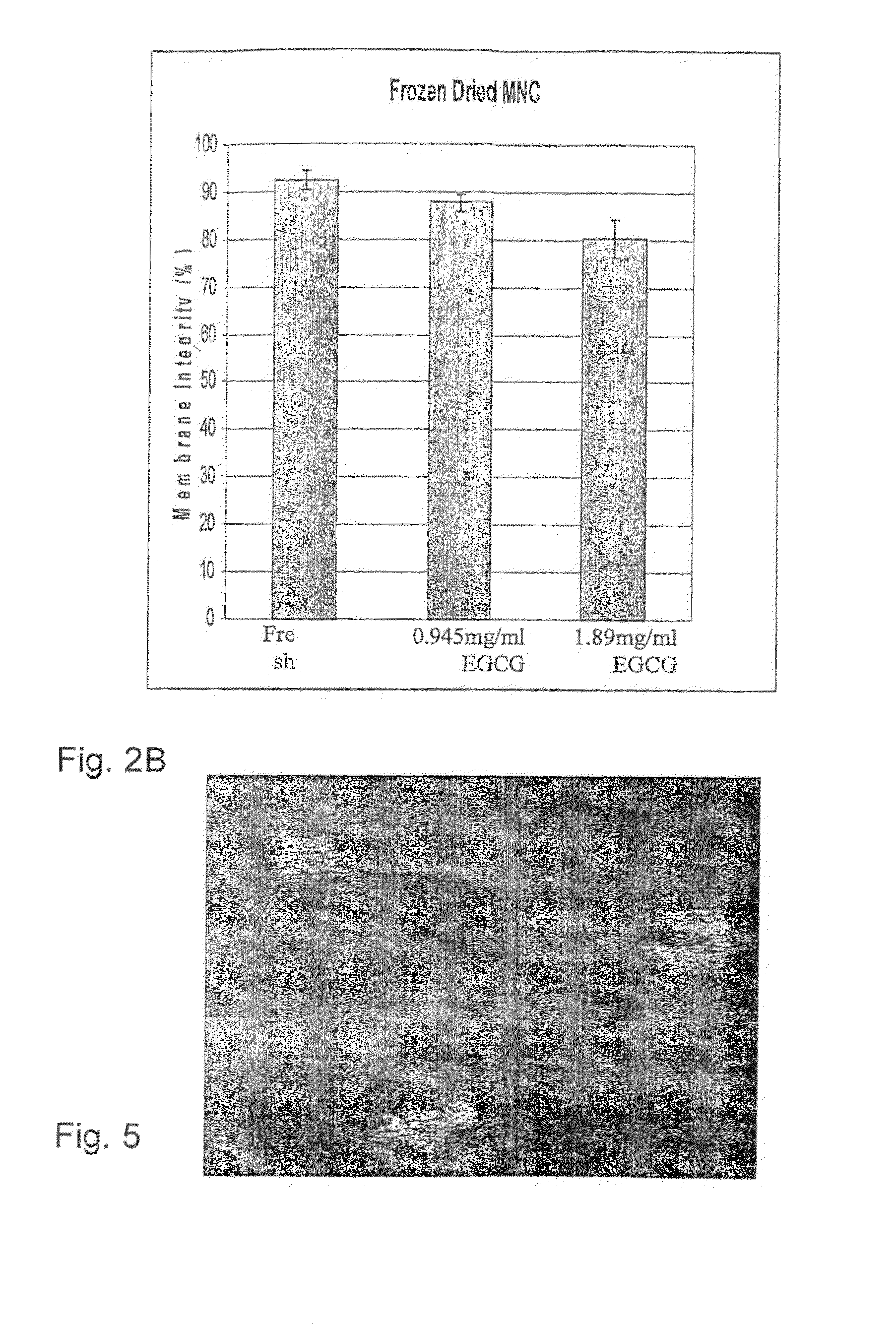
InactiveUS8198085B2Maintaining functionalityMaintaining viabilityVertebrate cellsDead animal preservationPolyphenolSomatic cell
The present invention generally concerns cell therapy and products for use in such therapy. Particularly, the invention provides a preserved cell preparation essentially free of one or more members of a group of cryoprotecting agents consisting of polyalcohols, DMSO and cryoprotecting proteins, the preserved cell preparation comprising somatic cells and at least one polyphenol, wherein upon reconstitution of cells in the cell preparation, at least a portion of said stem cells are viable, said portion being sufficient for use of the cell preparation in stem cell therapy. The invention also provides cells reconstituted from preserved somatic cells, and the use of the reconstituted cells in cell therapy. A preferred cell preparation in accordance with the invention comprises stem cells, preferably human stem cells.
Owner:CORE DYNAMICS
Preparation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived exosomes and application of the same in acute lung injury
InactiveCN104694466AImprove securityIncrease concentrationSkeletal/connective tissue cellsUnknown materialsFicollPurification methods
The invention relates to preparation and a purification production process of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived exosomes, and application of the exosomes as a non-cell therapy in the treatment of acute lung injury. The MSCs deriving the exosomes belong to the wall adhesion type of stem cells, and the preparation and purification process have the characteristics that (1) parathyroid hormone is added specially for the preparation of MSCs condition medium, and (2) discontinuous Ficoll density gradient method and immunomagnetic beads separation and purification method are combined for separation and purification so as to obtain the exosomes. Rat acute lung injury (ALI) model experiments confirm that the exosomes can be used for treatment of ALI, so as to lay the foundation for the realization of non-stem cell therapies to substitute stem cells therapies.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
Treatment of erectile dysfunction by stem cell therapy
Methods, cells and compositions of matter are provided for treatment of erectile dysfunction using stem cell therapy. In particular, various stem cells are modified or administered freshly isolated in order to induce smooth muscle regeneration, neural regeneration, and restoration of endothelial function. In some embodiments endogenous stem cells are mobilized or activated to achieve therapeutic benefit. In other embodiments compositions derived from stem cells are utilized for treatment of erectile dysfunction.
Owner:CREATIVE MEDICAL TECH INC
Proliferated cell lines and uses thereof
ActiveUS7416885B2Increase proliferation potentialEnhance proliferation potentialSenses disorderAntipyreticProgenitorDrug development
The subject invention pertains to tumor cell lines useful for increasing the proliferation potential of any human or animal cell in culture, thereby providing immortalized or continuous cell lines and cultures. The invention also concerns proliferation factors, and compositions containing the factors, which are capable of increasing the proliferation potential of any human or other animal cell in culture. The subject invention further pertains to a method for proliferation cells in culture by contacting cells with the proliferation factors. The proliferated cells can range in plasticity and can include, for example, blast cells, fertilized ova, non-fertilized gametes, embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells, precursor or progenitor cells, and highly specialized cells. Optionally, the cells can be induced to cease proliferation. The proliferation cells of the subject invention are useful for cell therapy, cell / gene therapy, biological production of molecules, and as in vitro models for research, toxicity testing, and drug development.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com