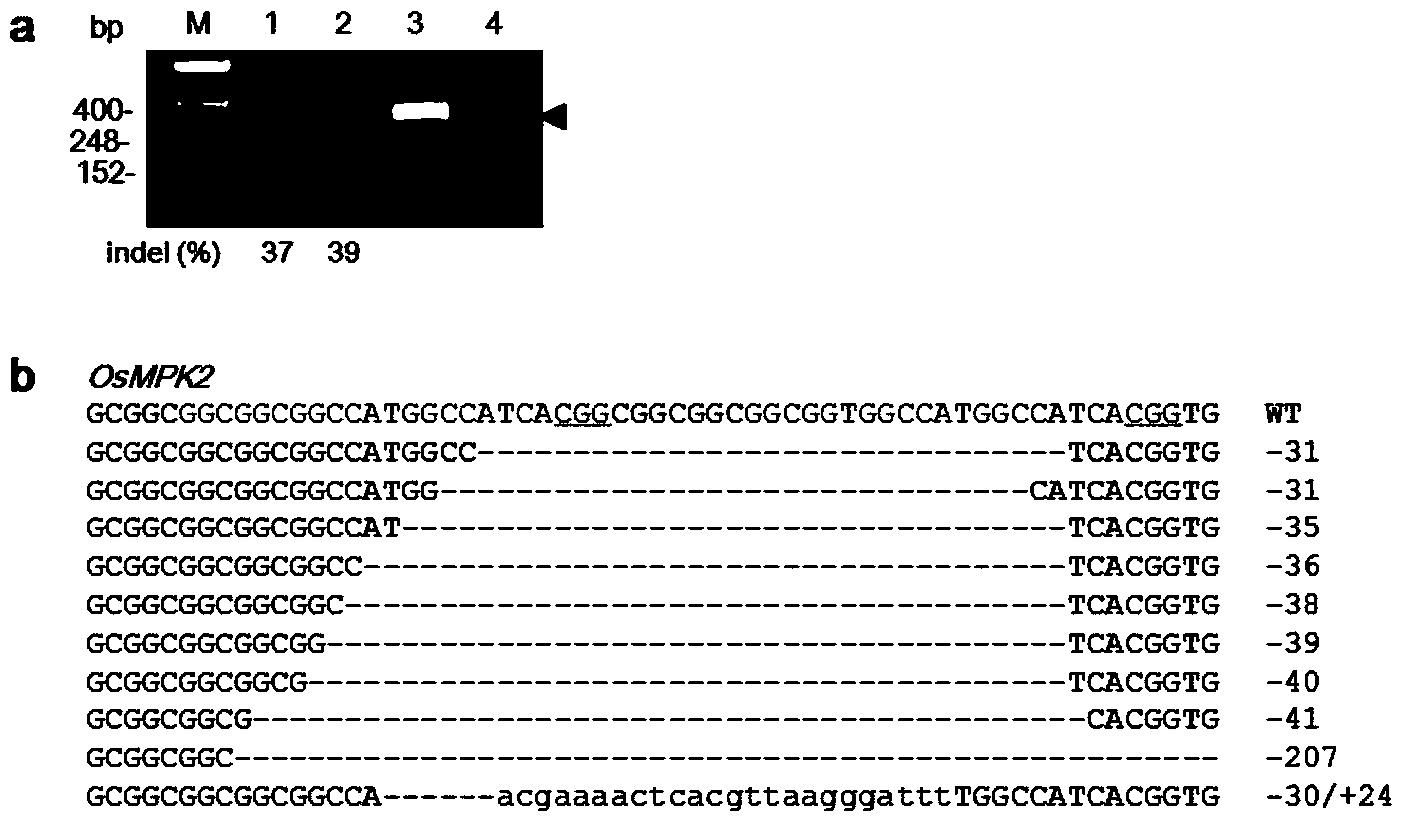
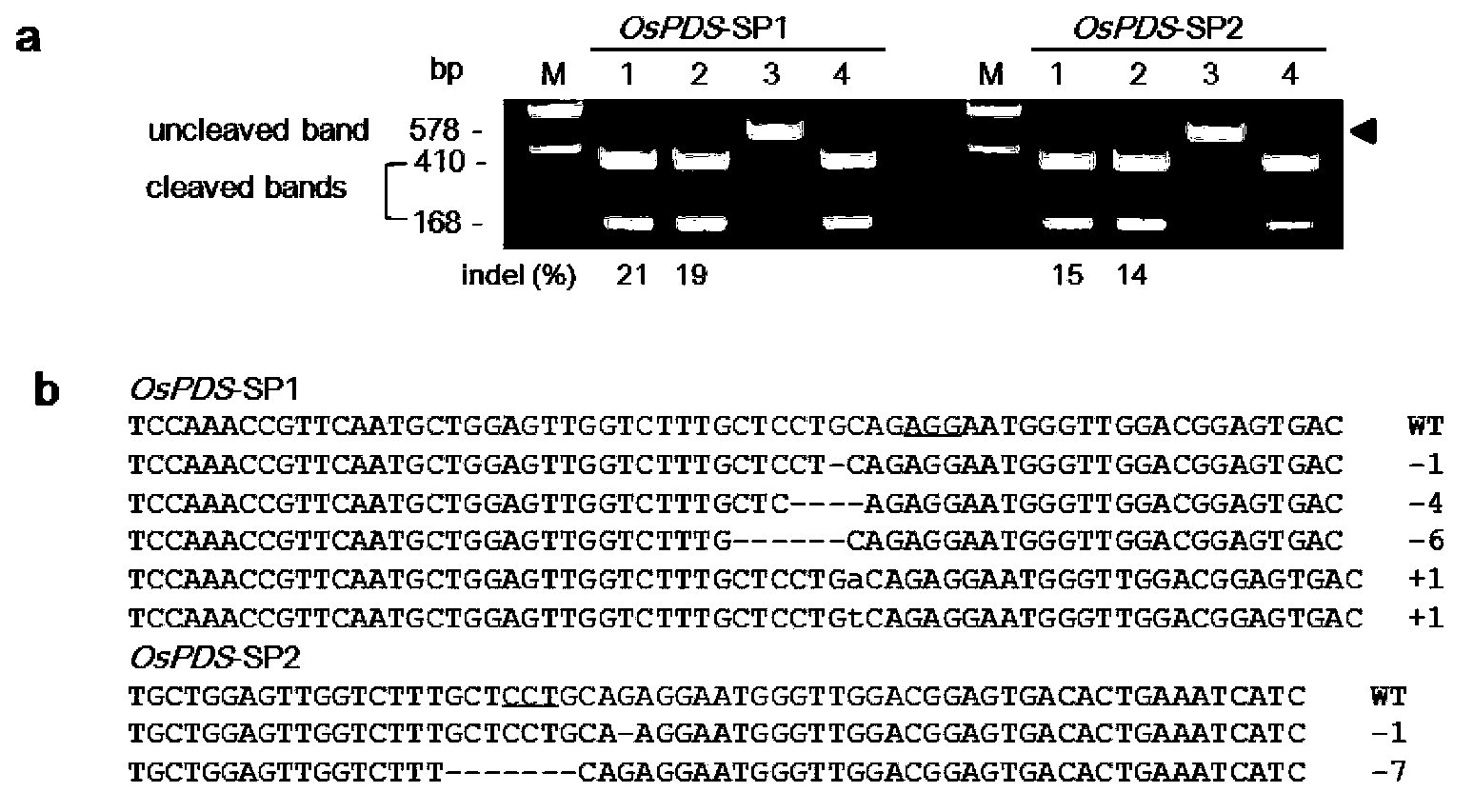
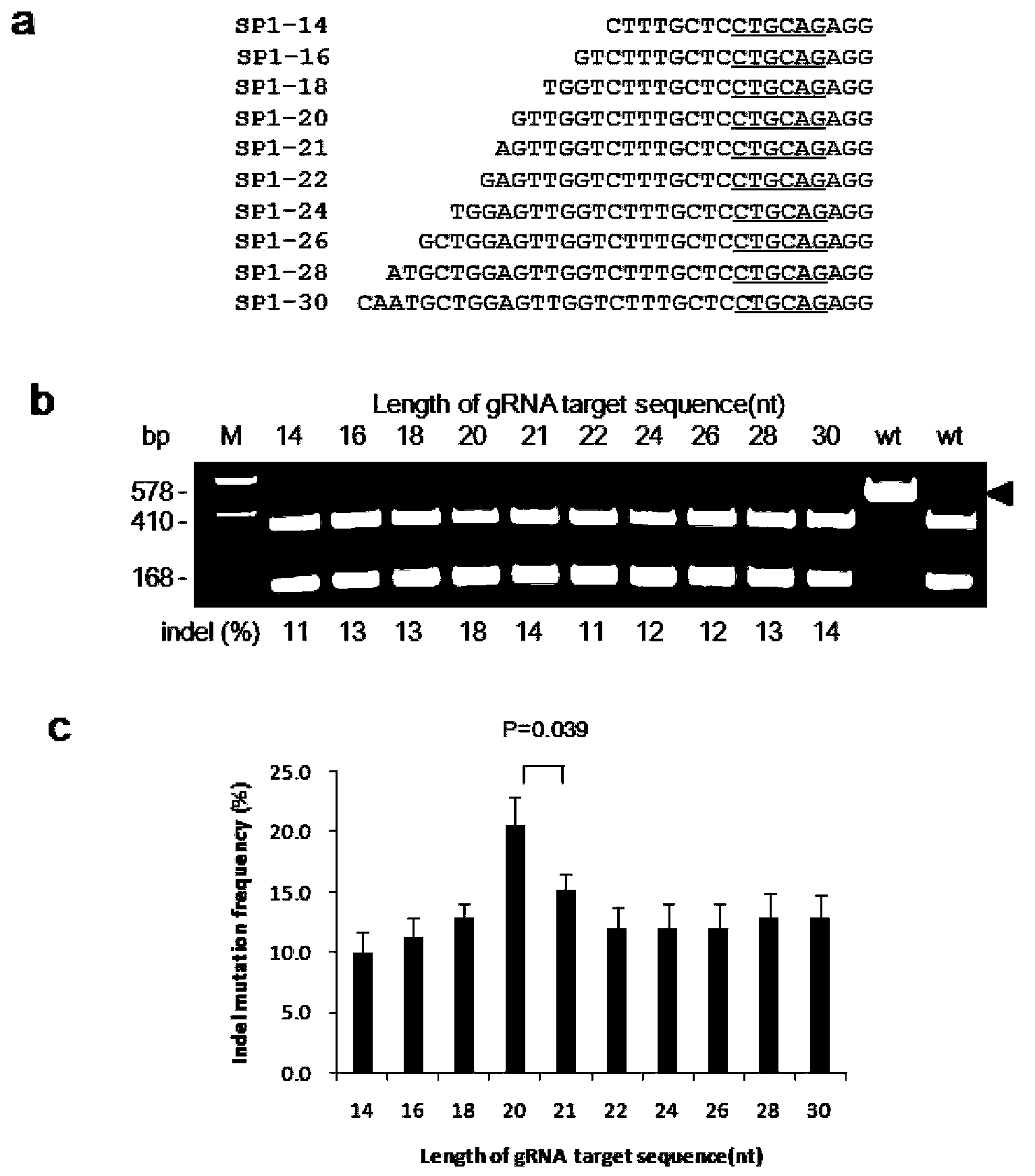
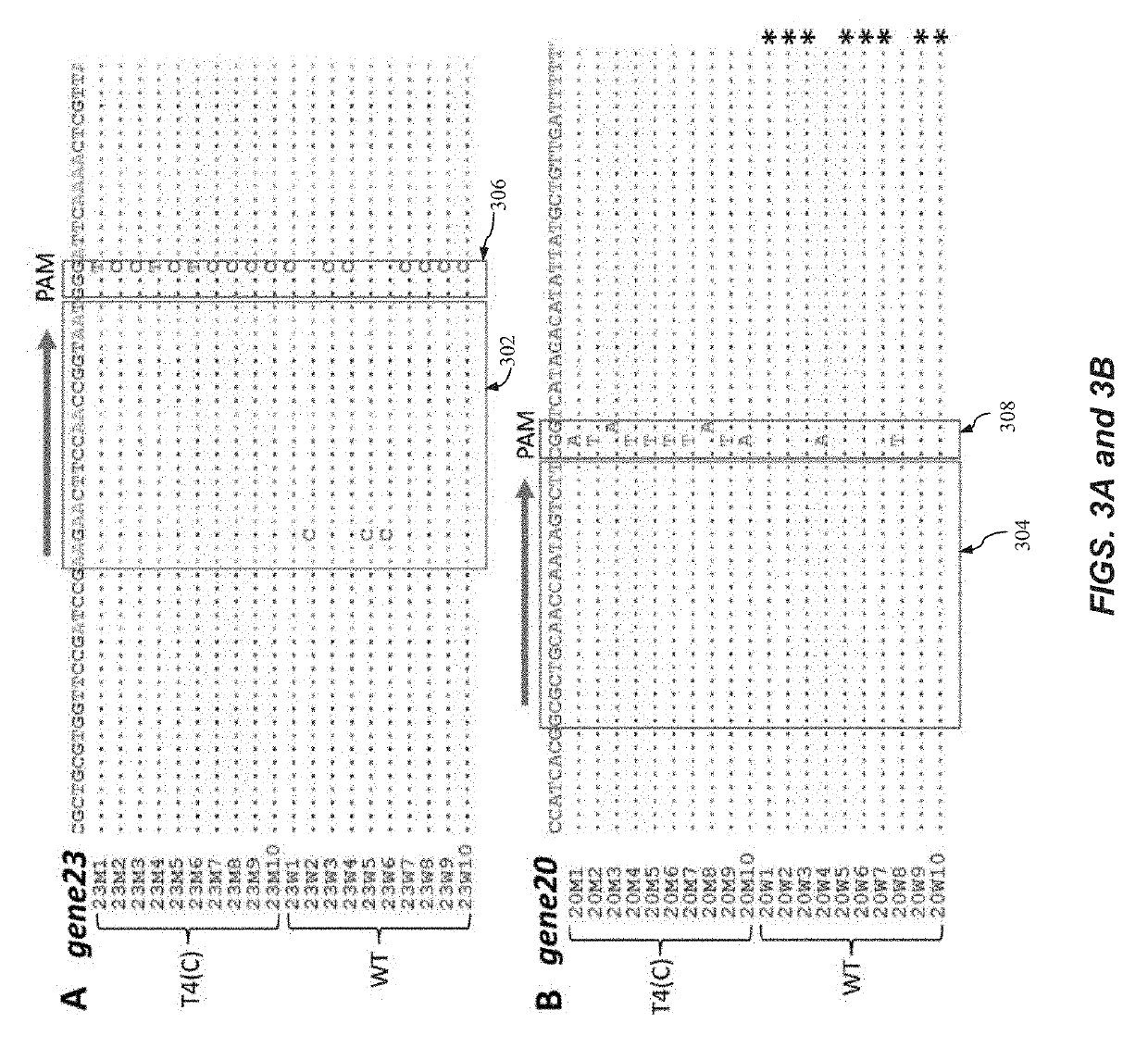
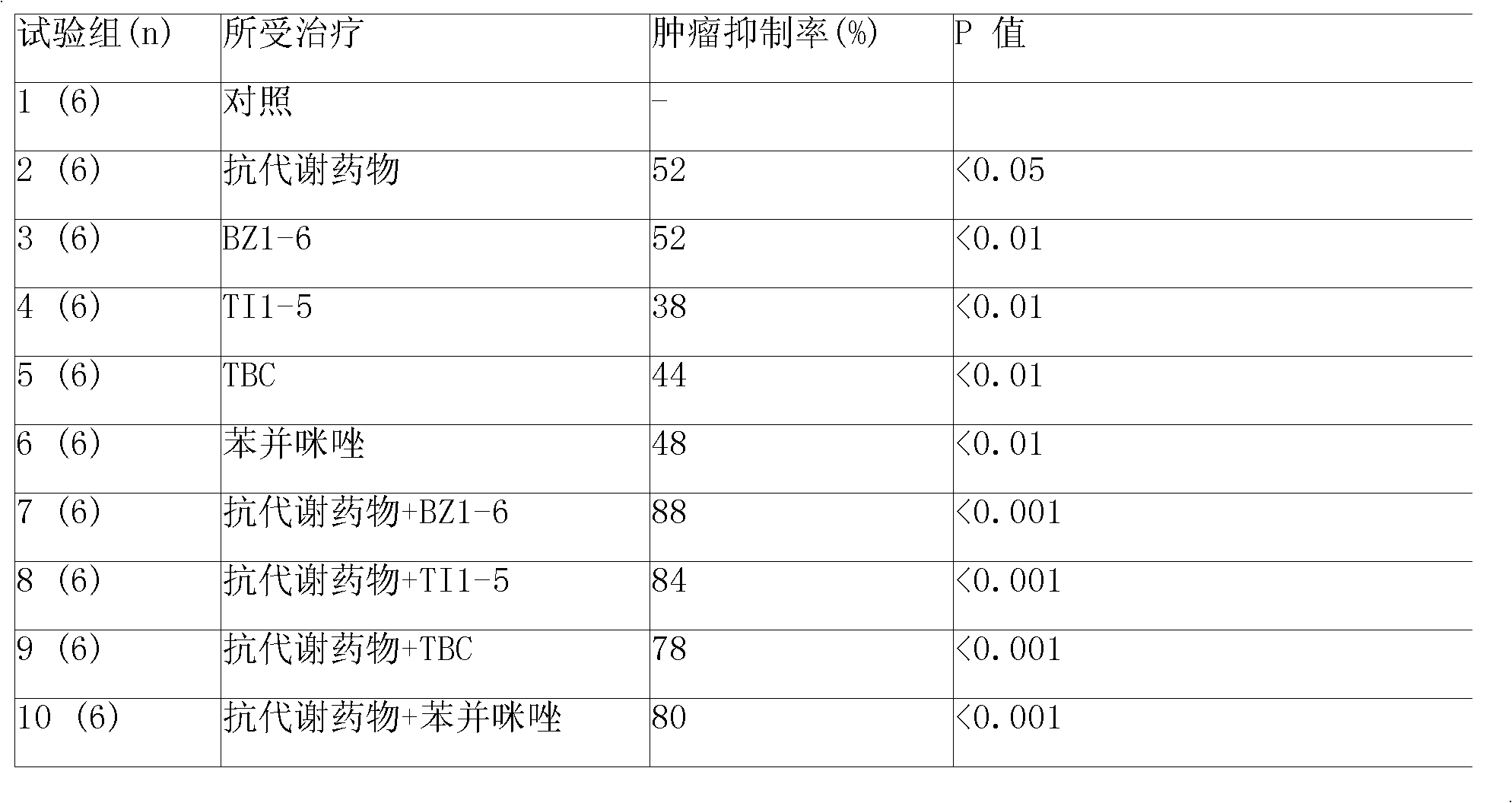
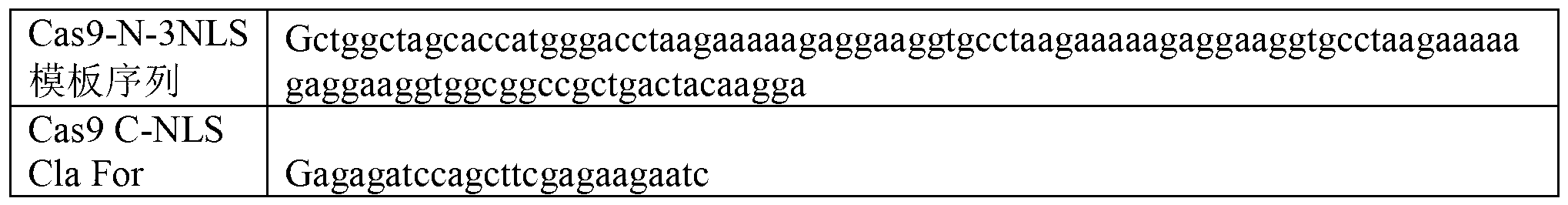Patents
Literature
100 results about "DNA repair" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in as many as 1 million individual molecular lesions per cell per day. Many of these lesions cause structural damage to the DNA molecule and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability to transcribe the gene that the affected DNA encodes. Other lesions induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells after it undergoes mitosis. As a consequence, the DNA repair process is constantly active as it responds to damage in the DNA structure. When normal repair processes fail, and when cellular apoptosis does not occur, irreparable DNA damage may occur, including double-strand breaks and DNA crosslinkages (interstrand crosslinks or ICLs). This can eventually lead to malignant tumors, or cancer as per the two hit hypothesis.
Specie limitation-free eucaryote gene targeting method having no bio-safety influence and helical-structure DNA sequence
ActiveCN103233028AUnable to cutImprove accuracyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionDNA repairEucoenogenes
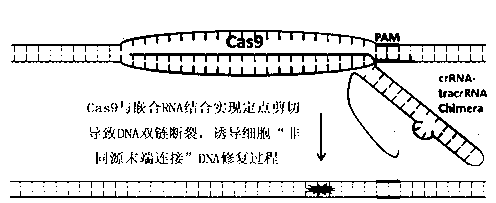
The invention discloses a specie limitation-free eucaryote gene targeting method having no bio-safety influence and a helical-structure DNA sequence, and belongs to the field of gene engineering. The specie limitation-free eucaryote gene targeting method comprises the following steps of 1, designing and constructing CRISPR / Cas9 and chimeric RNA, and 2, carrying out Cas9mRNA internal translation so that Cas9 nuclease and the chimeric RNA are bonded, carrying out fixed point clipping so that DNA double-chain cleavage is realized after the clipping, and introducing an exogenous DNA by induction of a natural DNA restoration process which is a non-homologous end bonding process of cells so that cell endogenous gene modification is realized. The specie limitation-free eucaryote gene targeting method has simple processes, realizes flexible site recognition and has low energy consumption.
Owner:NANJING SYNC BIOTECH
Wheat genome site-specific modification method
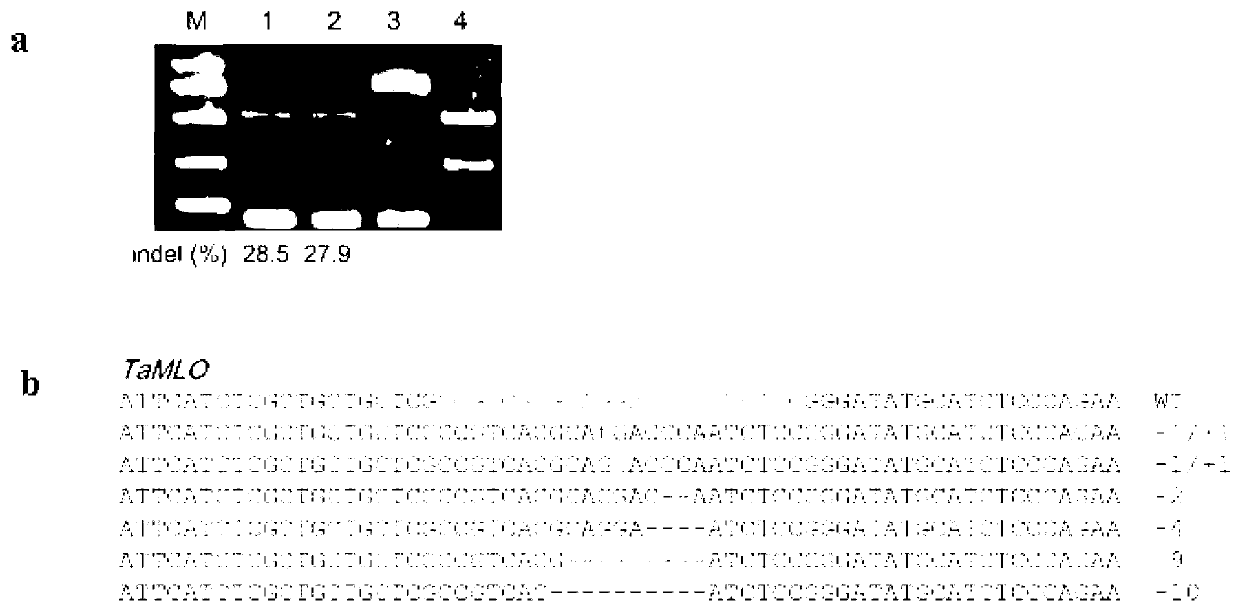
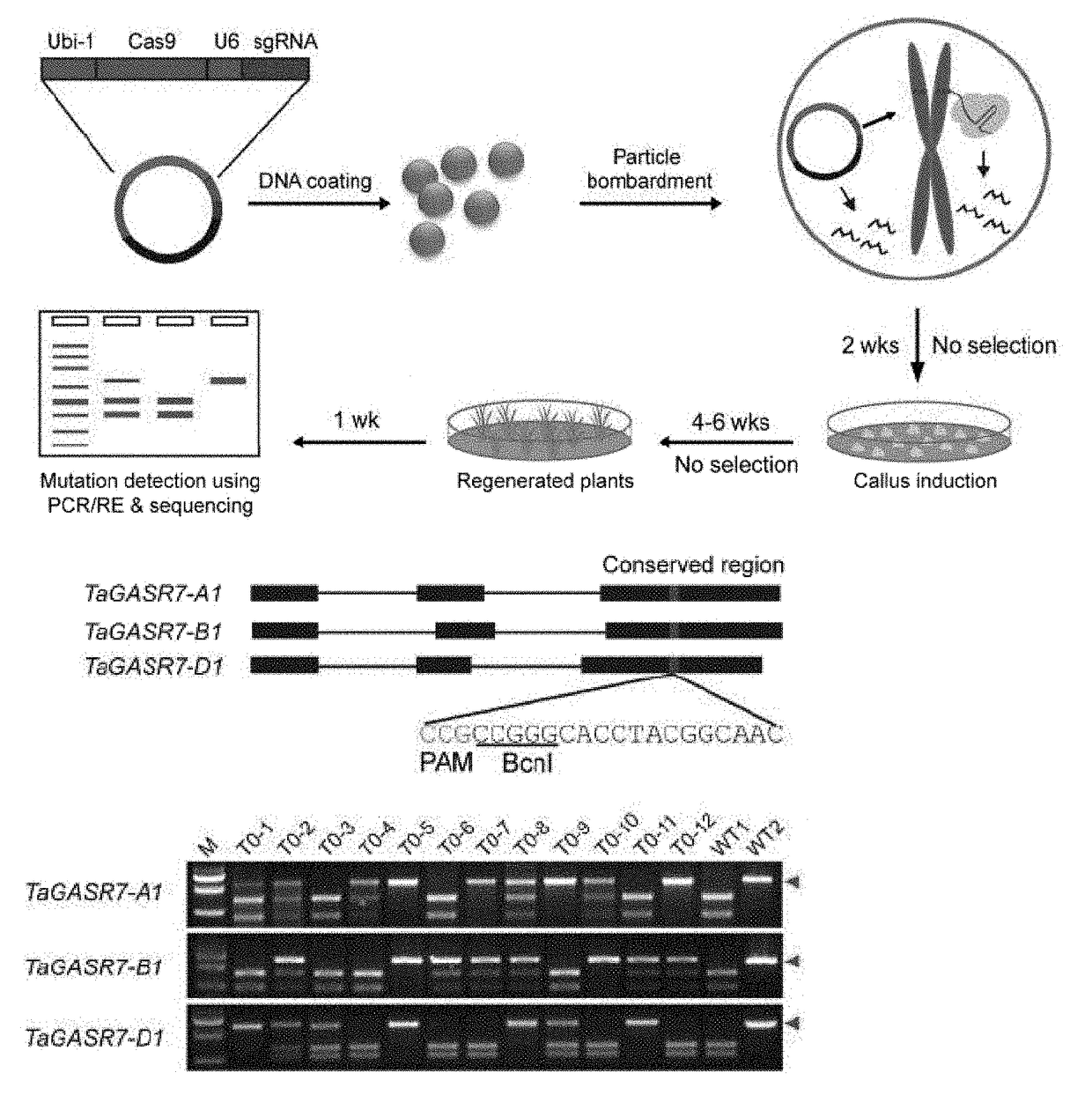
The invention discloses a wheat genome site-specific modification method which comprises the following steps: enabling wheat tissues to contain guide RNA (ribonucleic acid) and Cas9 nuclease; under the coaction of the guide RNA and Cas9 nuclease, cutting a double-chain target segment on the target gene; and by utilizing the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) restoration function of the wheat cells, finally implementing random insertion and / or random deletion on the target segment in the wheat target gene. The experiment proves that the method disclosed by the invention can successfully perform gene mutation on wheat.
Owner:SUZHOU QI BIODESIGN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Method for acquiring aromatic rice strain by targeting Badh2 gene via CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing technology
InactiveCN105505979AScalableEasy to operateVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsAromatic riceGenomic DNA
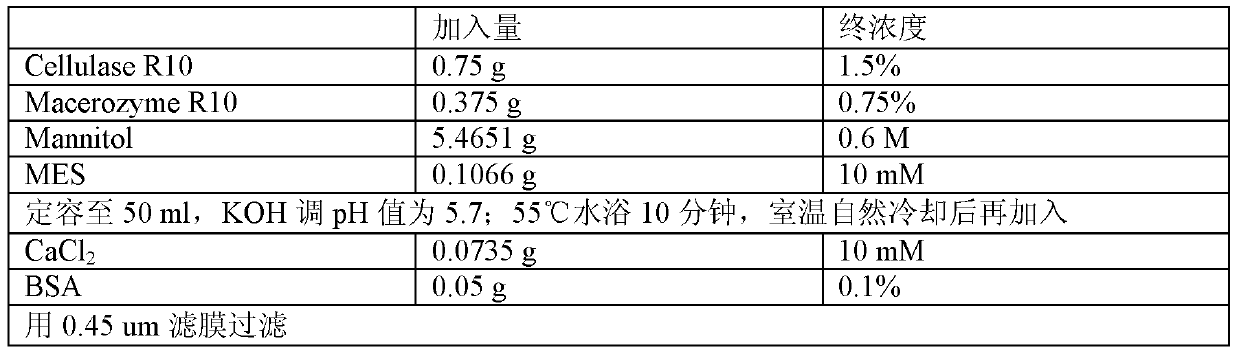
The invention discloses a method for acquiring an aromatic rice strain by targeting a Badh2 gene via CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing technology. The method comprises the following steps: separately targeting sequences, recognizable by Cas9, of every exon and intron of an aromatic gene by using the CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing technology and then cutting a genomic DNA sequence to initiate DNA restoration so as to obtain an afunctional Badh2 gene; with the callus of Indica rice, japonica rice or glutinous rice as a receptor material of genetic transformation and an mature embryo, young ear, ovary or the like as explant, carrying out induction so as to obtain a diploid callus, introducing a targeting vector into cells of the callus by using an Agrobacterium mediated transformation method, screening and identifying positive plants and separating the plants from a T1 colony so as to obtain an aromatic rice strain; and with anther, pollen, unfertilized ovary or the like as explant, carrying out induction so as to obtain a haploid callus, introducing the targeting vector into cells of the callus by using the Agrobacterium mediated transformation method, screening a positive callus, reduplicating the positive callus by using colchicine, carrying out differentiation to form seedlings and identifying genetic transformation positive plants so as to eventually obtain the aromatic rice strain.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Site-directed modification method of rice genome
The invention discloses a gene modification method which is capable of realizing random insertion and / or random deletion on a target segment of a rice target gene. The gene modification method comprises following steps: a guide RNA and Cas9 nuclease are induced in rice tissues; the double-chain target segment of the target gene is sliced because of the combined effect of the guide RNA and Cas9 nuclease; and then the random insertion and / or random deletion on the target segment of the rice target gene are / is realized because of DNA self-repairing function of rice cells. The gene modification method is capable of inducing gene mutation of rice.
Owner:SUZHOU QI BIODESIGN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
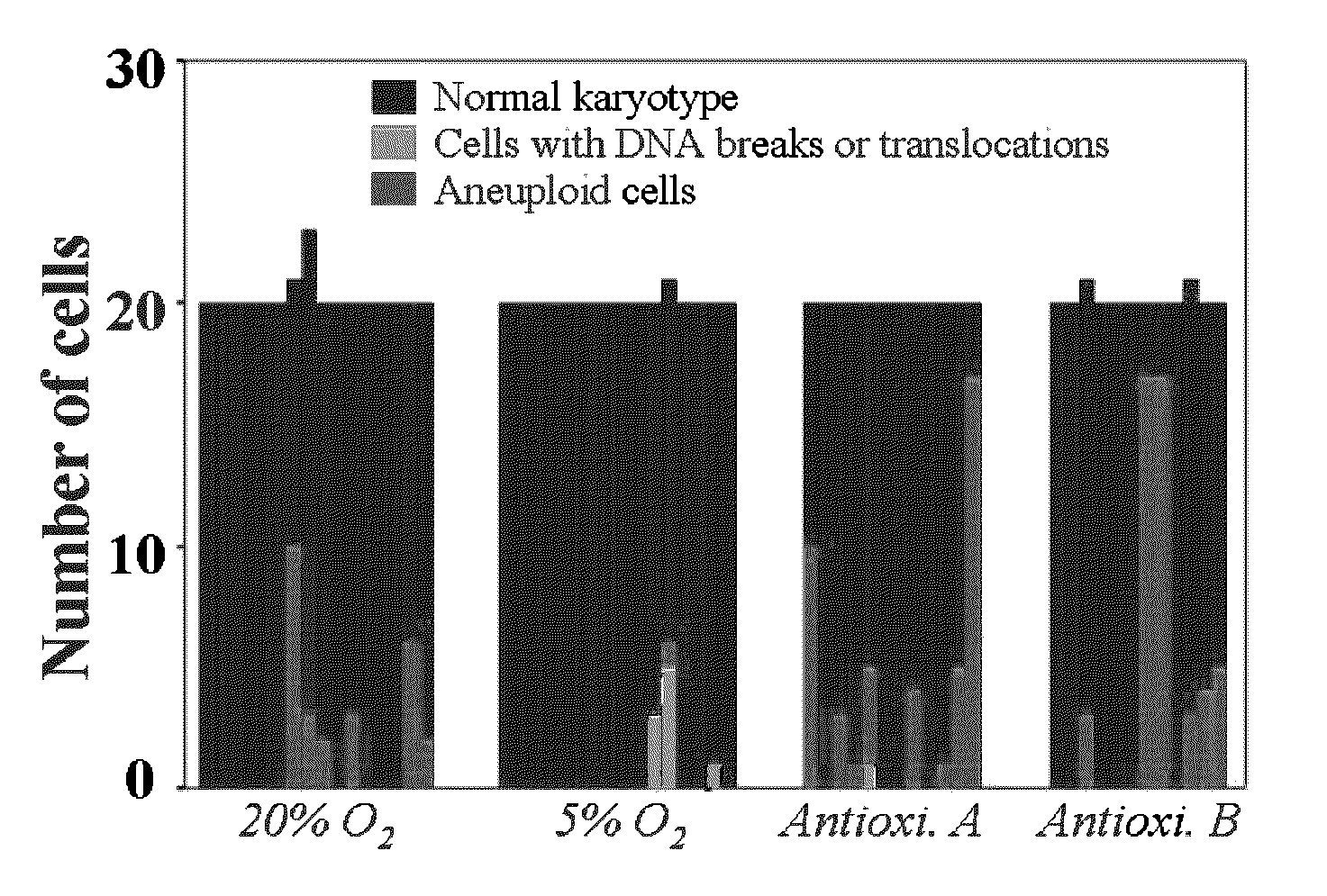
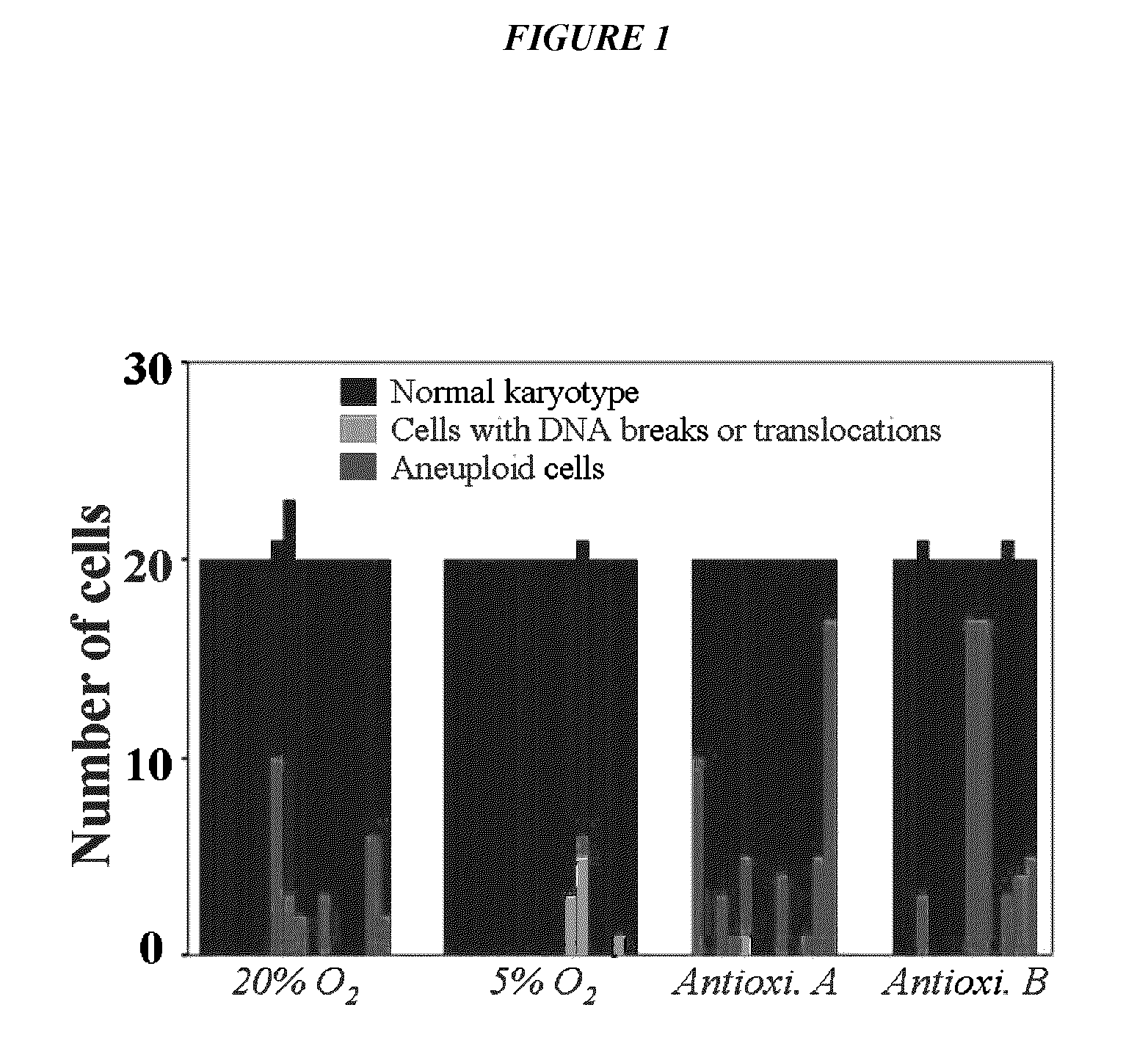
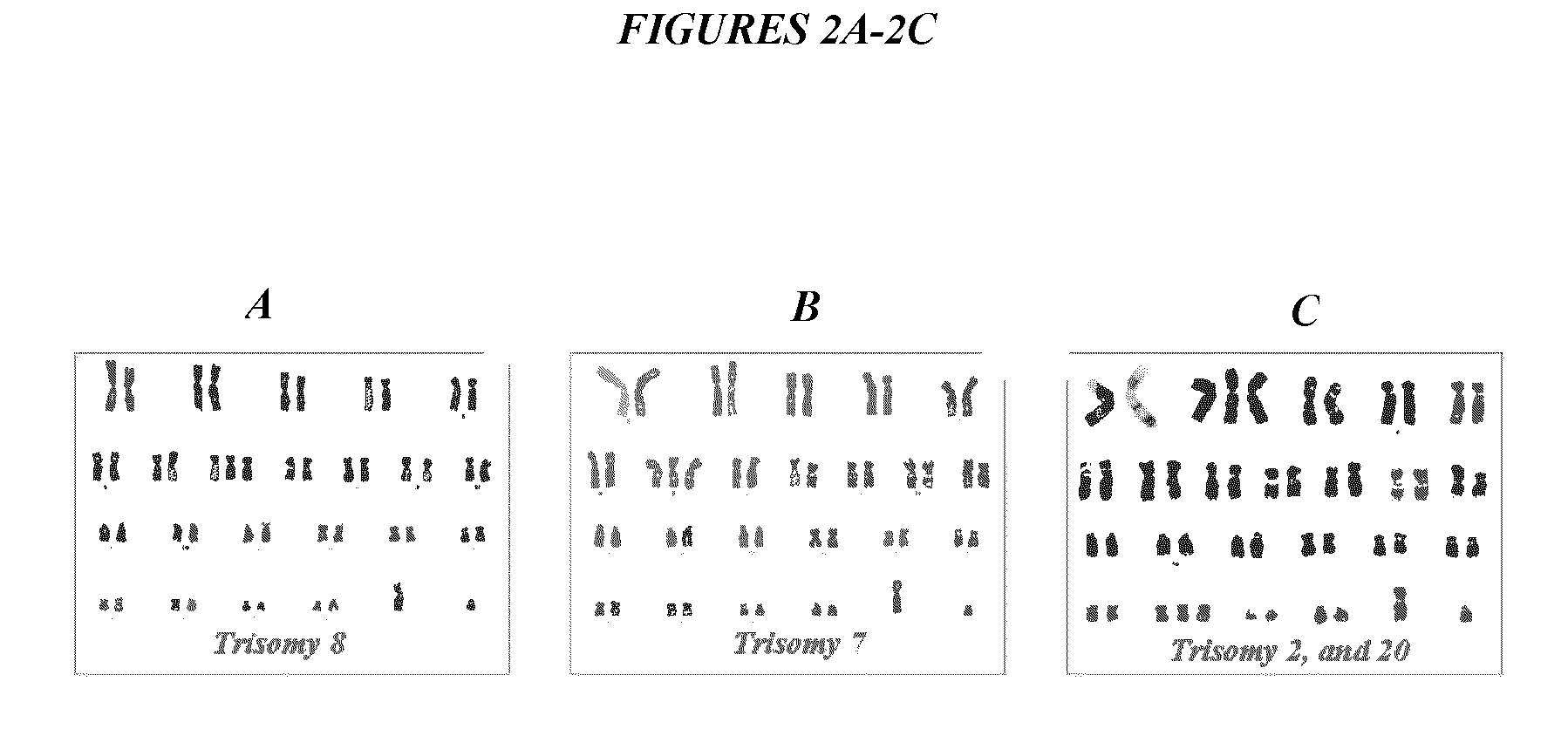
Methods for enhancing yield of stem cell cultures and enhancing stem cell therapy
InactiveUS20110300112A1Low efficacyImprove stabilityBiocideCulture processDNA repairKaryotypic abnormality
The present application relates to methods and compositions for the generation of therapeutic cells having reduced incidence of karyotypic abnormalities. In several embodiments cardiac stem cells are cultured in an antioxidant-supplemented media that reduces levels of reactive oxygen species, but does not down regulate DNA repair mechanisms. In several embodiments, physiological oxygen concentrations are used during culture in order to increase the proliferation of stem cells, decrease the senescence of the cells, decrease genomic instability, and / or augment the functionality of such cells for cellular therapies.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Anti solid tumor medicine composition
InactiveCN1628850AImprove anti-cancer effectInhibitory activityAntineoplastic agentsPharmaceutical active ingredientsHydroxylamineAdjuvant
Disclosed is an anti solid tumor medicine composition, which comprises medicinal adjuvant and DNA restoring enzyme inhibitor and / or Nitrosoureas anti-cancer drugs, wherein the DAN restoring enzyme inhibitor is selected from methoxamine, hydroxylamine and their analogues, which can effectively destroy the DNA restoring function in the tumor cells, and lower the survivability of tumor cell to Semustine anti-cancer drugs and their analogues, the medicinal adjuvant is biological compactable, degradable and absorbing macromolecular polymer, which can slowly release the DNA restoring enzyme inhibitor onto tumor partially during the degradation and absorption process, thus the whole body toxicity reaction is reduced appreciably , and the effective medicinal concentration can be sustained to the tumor partially. By dispensing the composition to the tumor partially, the whole body toxicity reaction of Nitrosoureas anti-cancer drugs and / or DNA restoring enzyme inhibitor can be lowered, selectively increase the tumor local medicinal concentration, and the treatment effect of the non-operative treatment methods such as chemotherapy, medicament and radiation can be improved.
Owner:南京天一药业有限公司
Anticarcinogenic internal implant agent
InactiveCN1679950APharmaceutical delivery mechanismAmide active ingredientsTreatment effectWhole body
An anticancer in vivo implant applied locally is prepared from the anticancer nitrosourea-type medicine, the anticancer synergist chosen from nitrogen mustard compound, mitotic inhibitor and antimetabolic anticancer medicine, and the biocompatible and biodegradable high-molecular polymer as medicinal additive.
Owner:DASEN BIOLOGICAL PHARMA CO LTD
Anti-cancer medicine composition
The invention provides an anti-cancer medicine composition, with comprises medicinal adjuvant and DNA restoring enzyme inhibitor containing effective anticancer constituents, wherein the DNA restoring enzyme inhibitor is selected from poly (ADP-ribose) poly enzyme inhibitor and / or DNA-dependent protein kinase inhibitor, which can effectively destroy the DNA restoring function in the tumor cells, and lower the survivability of tumor cell to Nitrosoureas anti-cancer drugs and their analogues, and the medicinal adjuvant mainly comprises biological compactable, degradable and absorbing macromolecular polymers, which can slowly release the DNA restoring enzyme inhibitor onto tumor partially during the degradation and absorption process, thus the whole body toxicity reaction is reduced appreciably , and the effective medicinal concentration can be sustained to the tumor partially. The anti-cancer medicinal composition also contain Nitrosoureas anti-cancer drugs and their analogues, by dispensing the composition to the tumor partially, the whole body toxicity reaction of Nitrosoureas anti-cancer drugs and / or DNA restoring enzyme inhibitor can be lowered, and the treatment effect of the non-operative treatment methods such as chemotherapy, medicament and radiation can be improved.
Owner:南京天一药业有限公司
Method for efficiently and rapidly separating T-DNA insertion site flanking sequence, and uses thereof
InactiveCN107190003AQuick analysisEasy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMagnetic beadSeparation technology
The invention provides a method for efficiently and rapidly separating a T-DNA insertion site flanking sequence. The method comprises: extracting the genomic DNA of an Agrobacterium-mediated transgenic plant; fragmenting the genomic DNA, carrying out DNA repairing, adding A, linking, carrying out fragment selection by using magnetic beads, carrying out library construction, carrying out hybridization capture on the constructed library and a T-DNA boundary sequence, and carrying out PCR enrichment; and carrying out high-throughput sequencing on the library, and carrying out bioinformatics analysis on the sequenced data so as to obtain the T-DNA insertion site. According to the present invention, the capture is performed with the target DNA, and the low-throughput sequencing is specially performed on the T-DNA boundary sequence; the disadvantages of low throughput, low efficiency and low success rate of the existing flanking sequence separation technology are overcome with the method of the present invention; and with the method of the present invention, the DNA capture and the second-generation sequencing technology are combined, the T-DNA boundary sequence is specially sequenced and the simple analysis is performed to obtain the T-DNA insertion site flanking sequence, and the method has characteristics of high efficiency, economy, and simple analysis.
Owner:武汉天问生物科技有限公司
Anticancer sustained release agent containing epothilone
InactiveCN1969816AEasy injectionIncrease drug concentrationOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPolyethylene glycolDepressant
Disclosed is an anti-cancer drugs slow release agent containing Epothilone which comprises slow release microspheres and dissolvent, wherein the slow release microballoons comprise anti-cancer active constituents and slow release auxiliary materials, the dissolvent being specific dissolvent containing suspension adjuvant. The anticancer active constituents include Epothilone, Epothilone derivatives, Epothilone B, Epothilone D and combination of anti-cancer drugs selected from phosphoinositide-3-kinase inhibitor, of pyrimidine analogues and / or DNA restoring enzyme inhibitor, the slow release auxiliary materials include polylactic acid and its copolymer, polyethylene glycol, PLA-COOH copolymer, di-aliphatic acid and sebacylic acid copolymer, poly(erucic aciddipolymer-sebacylic acid), poly(fumaric acid-sebacylic acid), Polifeprosan, polylactic acid and other biocompatible high polymers, the viscosity of the suspension adjuvant is 100-3000cp (at 20-30 deg C), and is selected from sodium carboxymethylcellulose. The anticancer active constituents and the slow release microspheres can also be prepared into slow release implanting agent for intra-tumor or around-tumor injection or placement for the effective suppression of tumor growth and for the appreciable enhancement for curative effects of non-operative treatments such as chemotherapy.
Owner:JINAN SHUAIHUA PHARMA TECH
Methods and compositions for heat activated gene therapy using cytolethal distending toxin
The invention provides compositions and methods for gene therapy using cytolethal distending toxins (CDTs). In a preferred embodiment, a gene therapy vector according to the invention includes a gene encoding a B subunit of a CDT and an antisense oligonucleotide that inhibits a DNA repair mechanism. An inducible promoter is operably linked to the gene and oligonucleotide. Preferably, the promoter is strictly inducible by heat shock.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
Slow-released injection containing methotrexate and its synergist
The slow released anticancer injection containing methotrexate and its synergist consists of slow released microballoon and solvent. The slow released microballoon includes effective anticancer component and slow releasing supplementary material, and the solvent is common solvent or special solvent containing suspending agent. The effective anticancer component is methotrexate synergist or the composition of methotrexate and its synergist; the methotrexate synergist is selected from phosphorinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor, pyrimidine analogue and DNA repair enzyme inhibitor; the slow releasing supplementary material is PLA, PLGA, EVAc, etc or their composition; and the suspending agent is sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, etc. The slow released microballoon may be also prepared into slow released implantation preparation. Implanting or injecting the slow released preparation to local tumor part can lower the systematic toxic reaction of the medicine and raise the medicine concentration of local tumor part selectively to raise the treating effect.
Owner:JINAN SHUAIHUA PHARMA TECH
Anti-cancer medicine composition
The present invention relates to an anticancer medicine composition and belongs to the field of medicine technology. The anticancer medicine composition contains tetrazine medicine and medicinal supplementary material. The tetrazine medicinecan inhibit intracellular DNA repair function and reduce the tolerance one tumor cell on anticancer nitrosourea medicine; and the medicine supplementary material is mainly degradable biocompatible polymer. During the degrading and absorption process of the supplementary material, the anticancer medicine is released slowly to the tumor part, and this can lower the systemic toxic reaction while maintaining local effective medicine concentration. The anticancer medicine composition contains also anticancer nitrosourea medicine, and is set to the tumor part locally to enhance the treatment effect.
Owner:广州多福医药科技有限公司
Method for fixed-point transformation of plants by virtue of gene transient expression
ActiveCN105802991AImprove regenerative abilityHigh biosecurityHydrolasesNucleic acid vectorDNA repairNuclease
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
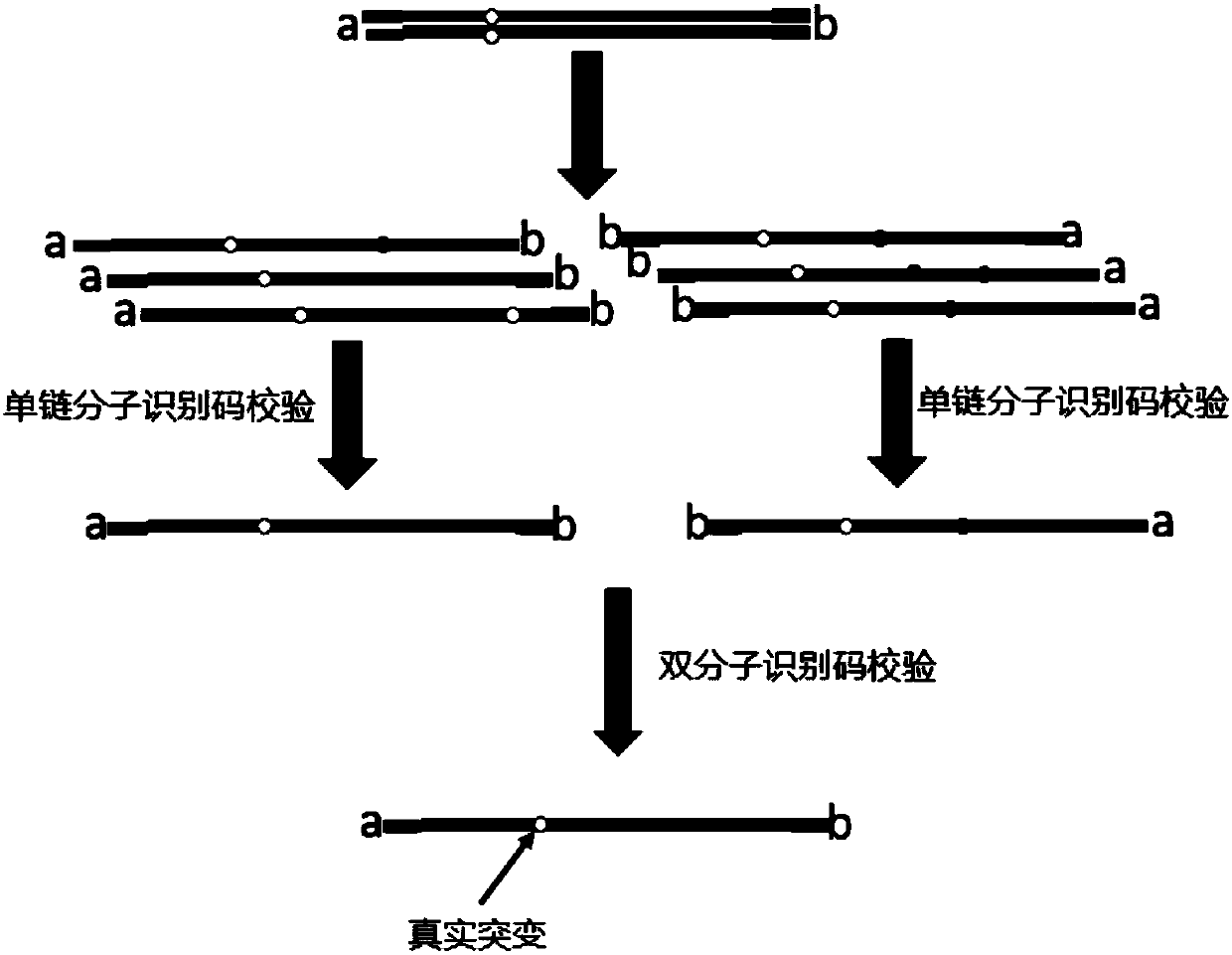
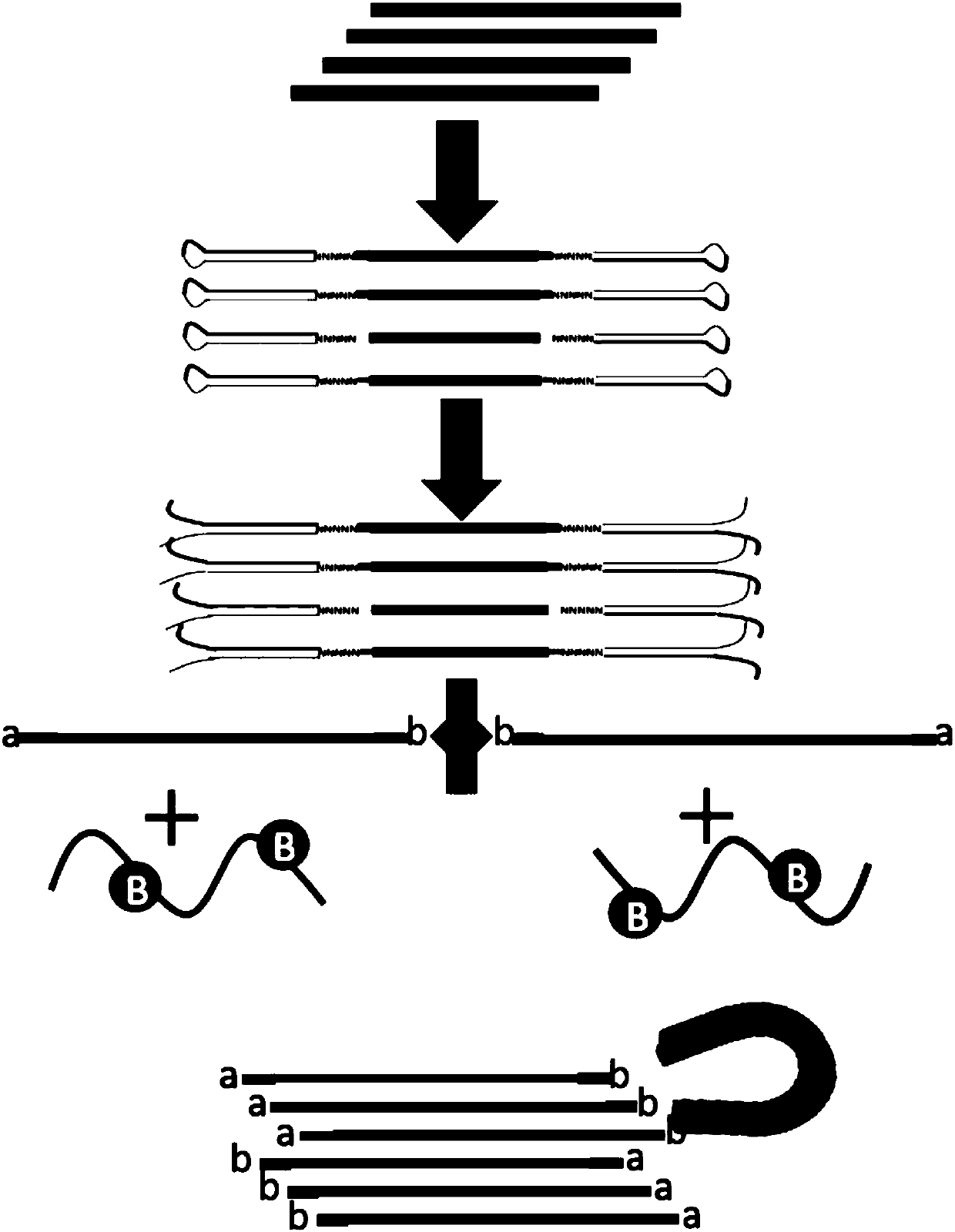
Second-generation sequencing method for dimolecular self-checking library preparation and hybrid capture used for trace DNA ultralow frequency mutation detection
ActiveCN107604046AIncrease profitHigh yieldNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary preparationData error
The invention discloses a second-generation sequencing method for dimolecular self-checking library preparation and hybrid capture used for trace DNA ultralow frequency mutation detection. The methodcomprises the following steps: extracting plasma free DNA, performing DNA chemical error repair, preparing a self-checking dimolecular identification code hairpin type joint, repairing plasma free DNA, connecting DNA with the joint, and performing Pre-PCR amplification, excessive hybrid capture, Post-PCR amplification, computer sequencing, data error correction, and mutation analysis and annotation. The method disclosed by the invention can efficiently realize low frequency mutation detection of plasma free DNA. DNA error repair and dual redundancy checking technology can enable the method tohave ultralow false positive rate and high sensitity while detecting trace samples, thus avoiding defects of existing plasma circulating free DNA detection methods, not only realizing cancer mutationdetection and targeted medication guidance, but also realizing early screening of genetic and birth defects of fetus.
Owner:SHANGHAI DYNASTYGENE CO
Methods and compositions for heat activated gene therapy using cytolethal distending toxin
The invention provides compositions and methods for gene therapy using cytolethal distending toxins (CDTs). In a preferred embodiment, a gene therapy vector according to the invention includes a gene encoding a B subunit of a CDT and an antisense oligonucleotide that inhibits a DNA repair mechanism. An inducible promoter is operably linked to the gene and oligonucleotide. Preferably, the promoter is strictly inducible by heat shock.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
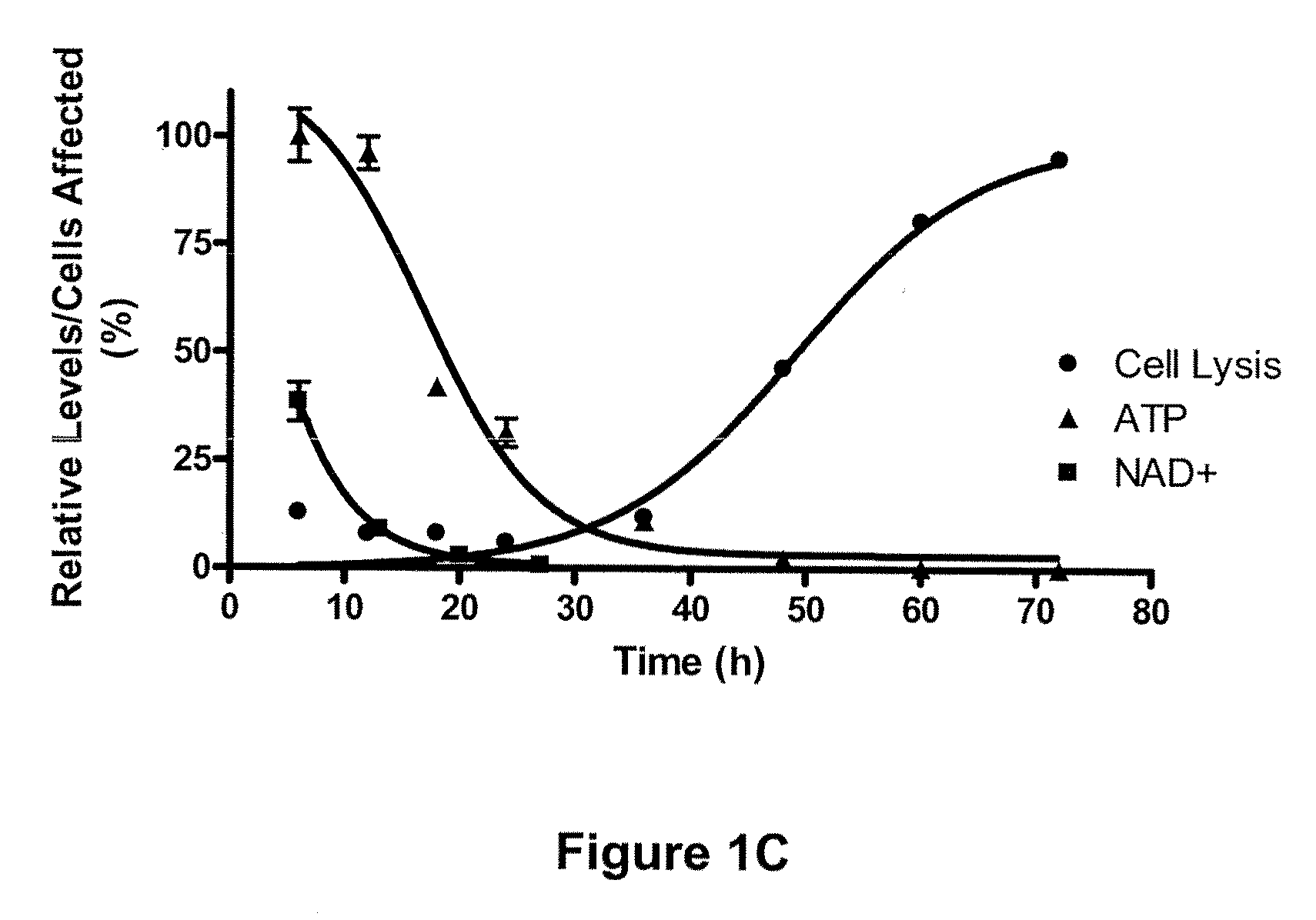
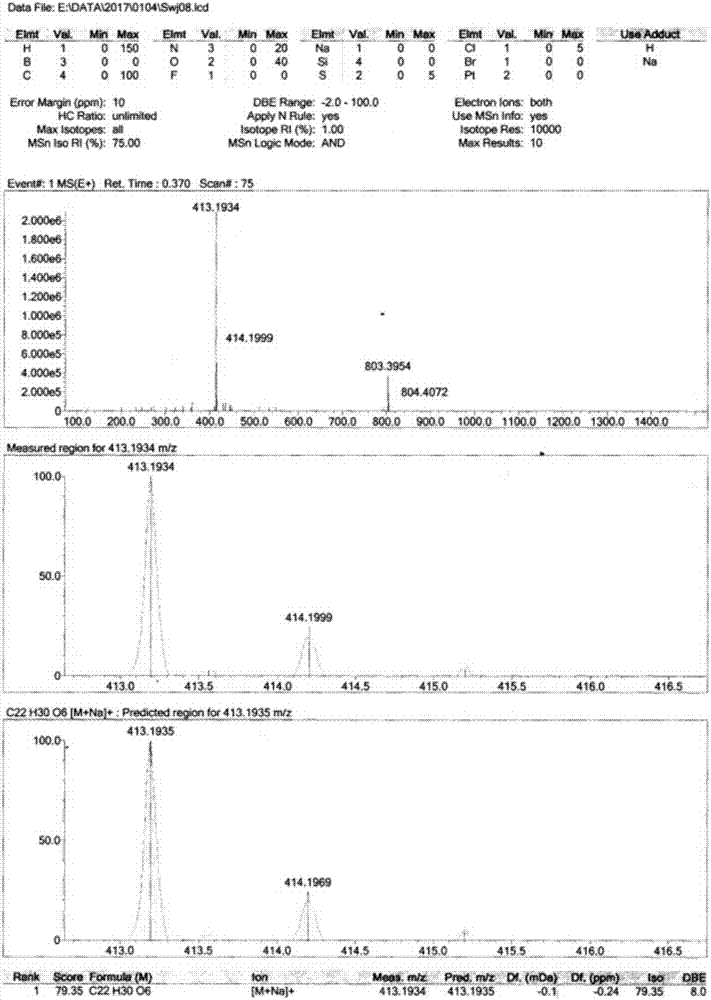
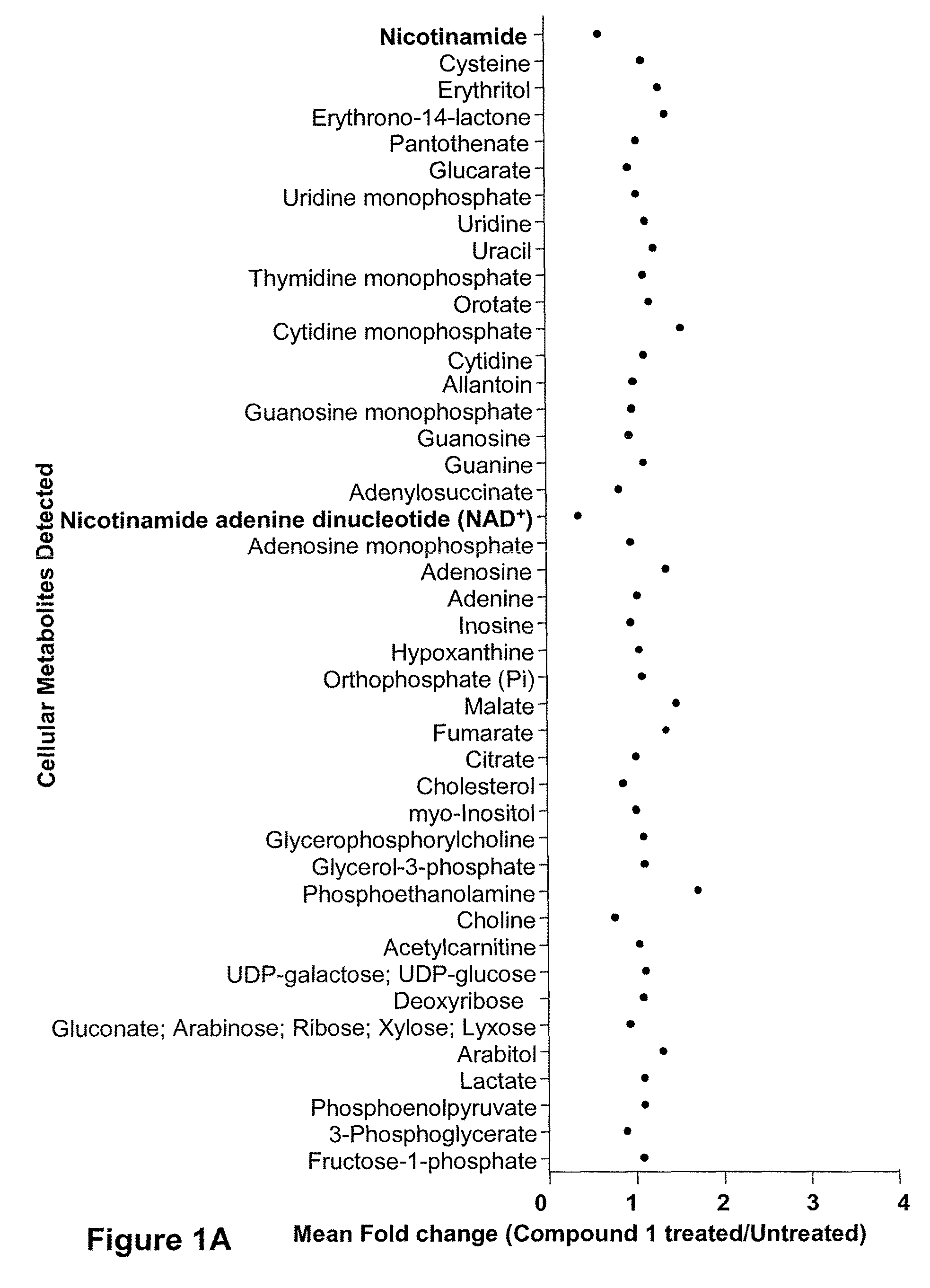
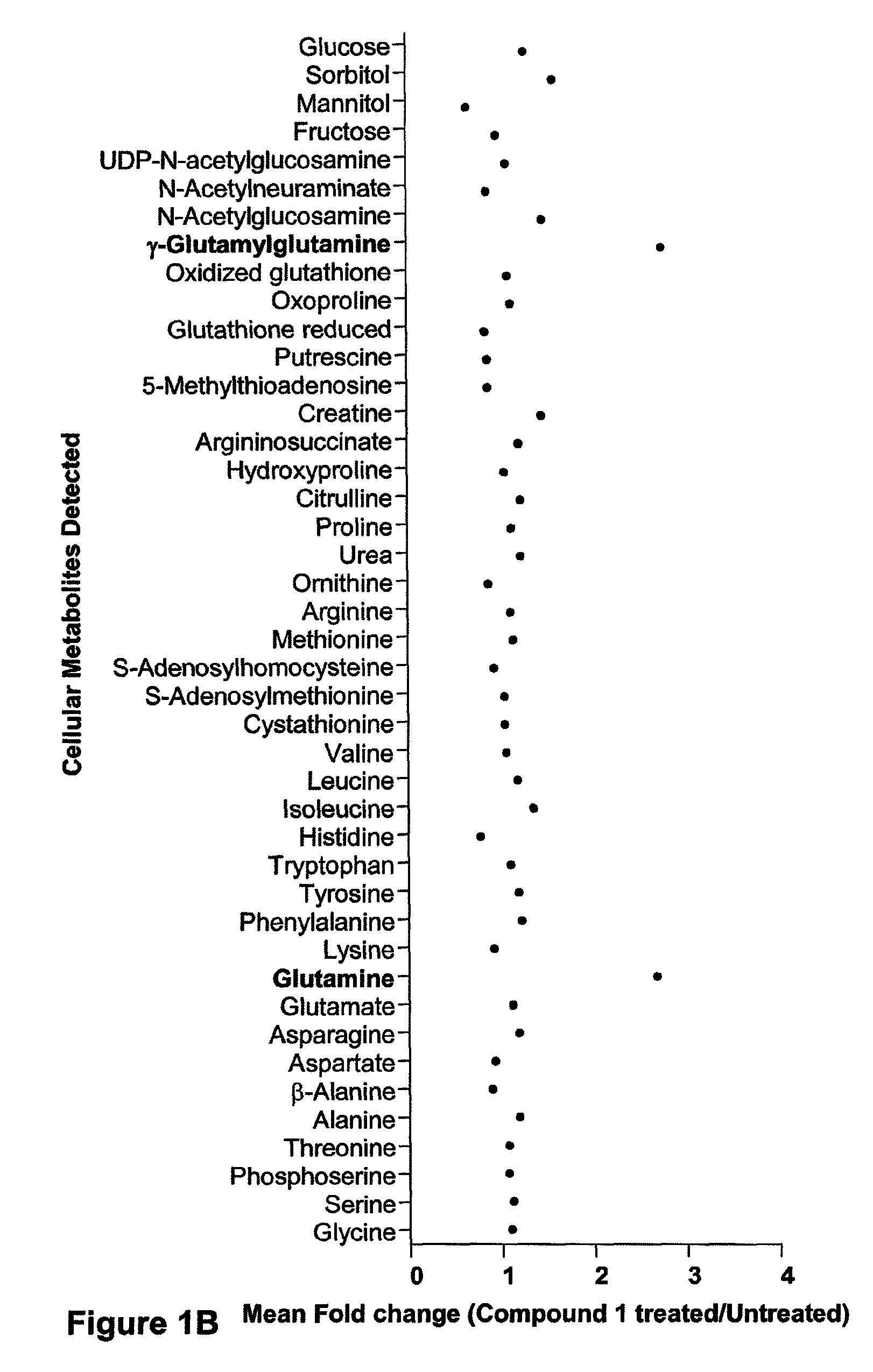
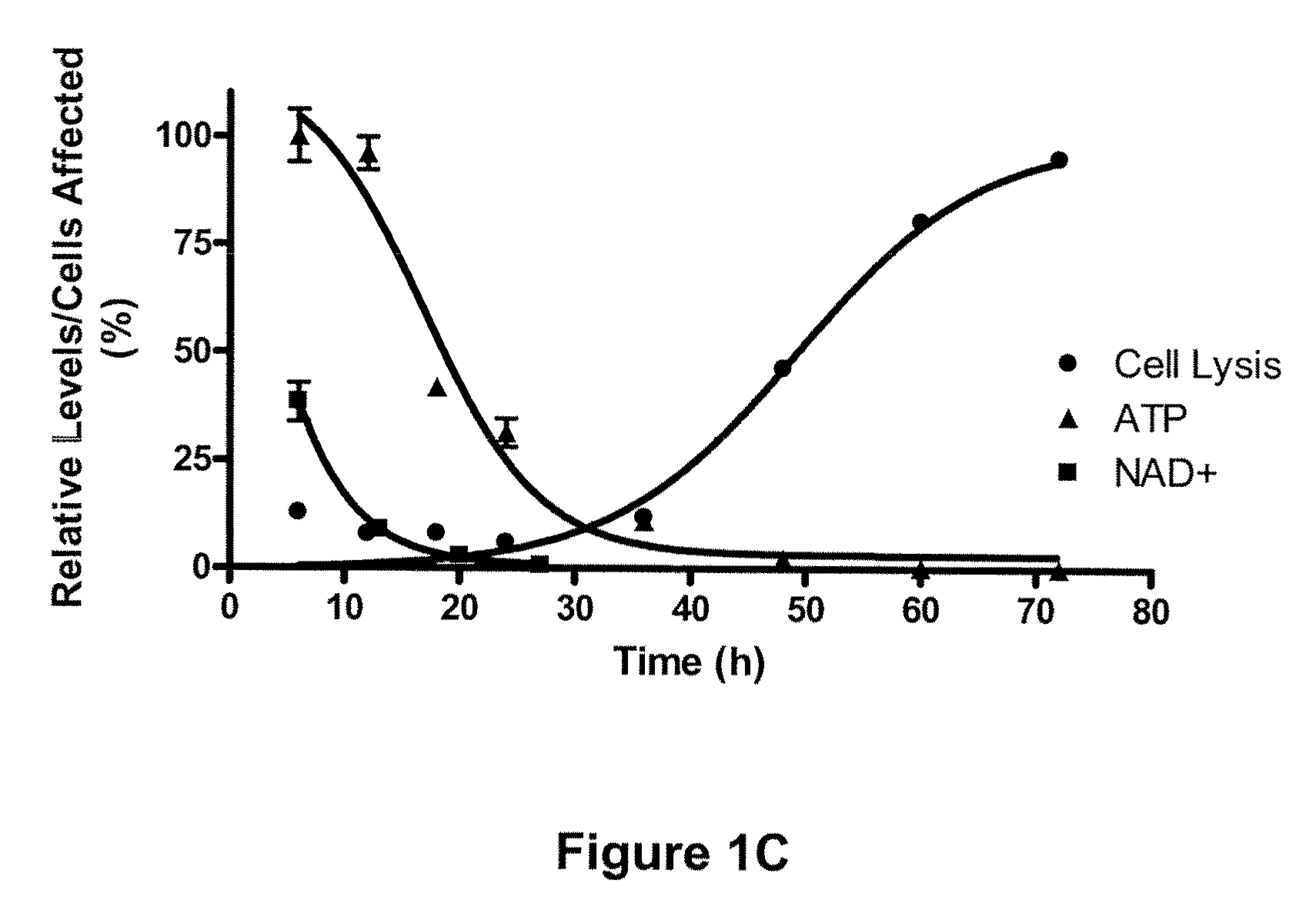
Compositions and methods for effecting nad+ levels using a nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase inhibitor
The present invention relates to methods for decreasing cellular DNA repair in a patient diagnosed with or suspected to have chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL); decreasing cellular NAD+ biosynthesis in a patient diagnosed with or suspected to have CLL; or sensitizing a patient diagnosed with or suspected to have CLL to a DNA damaging therapy. The invention relates to methods for treating a patient diagnosed with or suspected to have CLL.
Owner:GEMIN X PHARMA CANADA INC (CA)
Cosmetic composition and methods
ActiveUS7959953B2Improve aestheticsImprove abilitiesAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsDNA repairMedicine
Owner:ACCESS BUSINESS GRP INT LLC
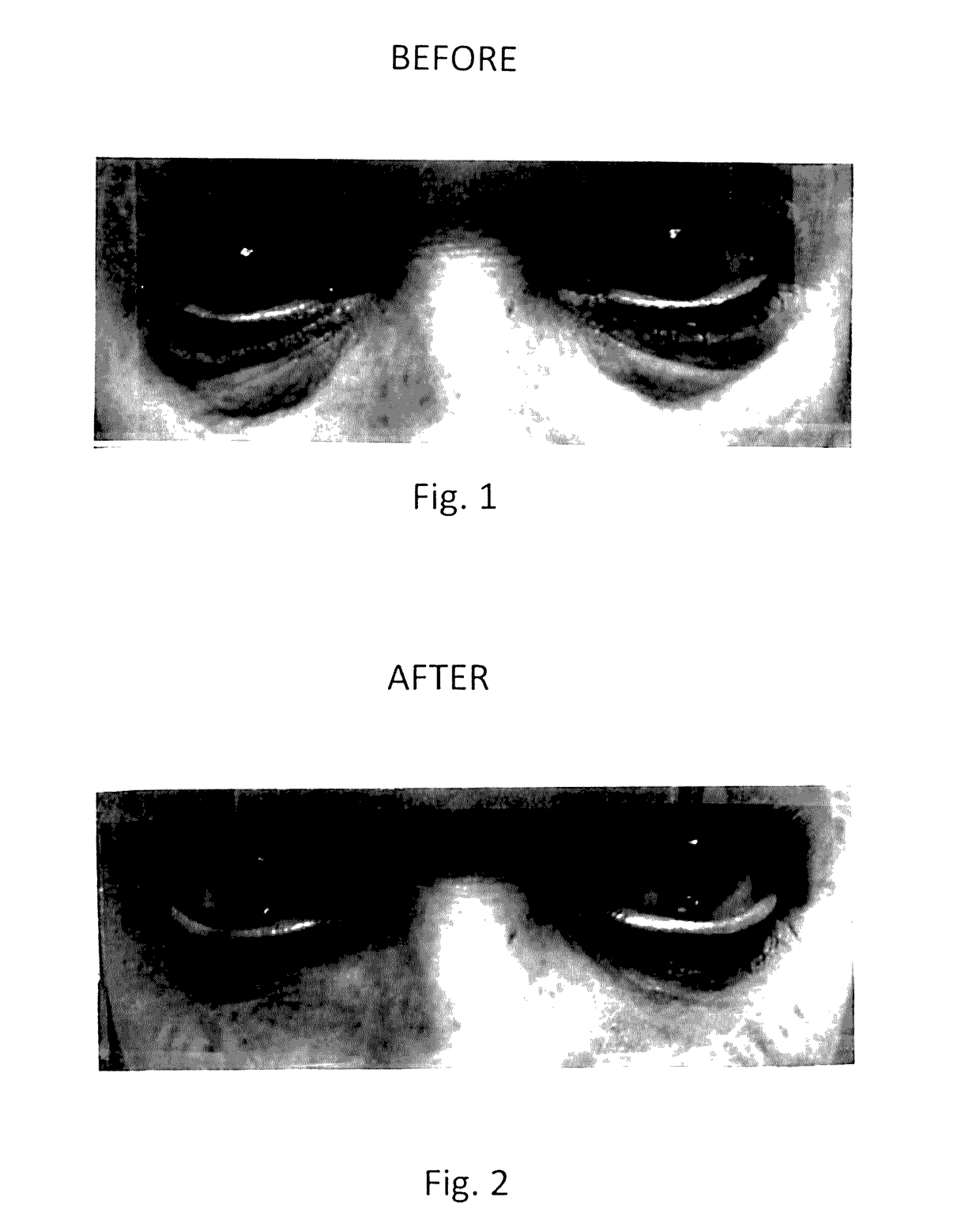
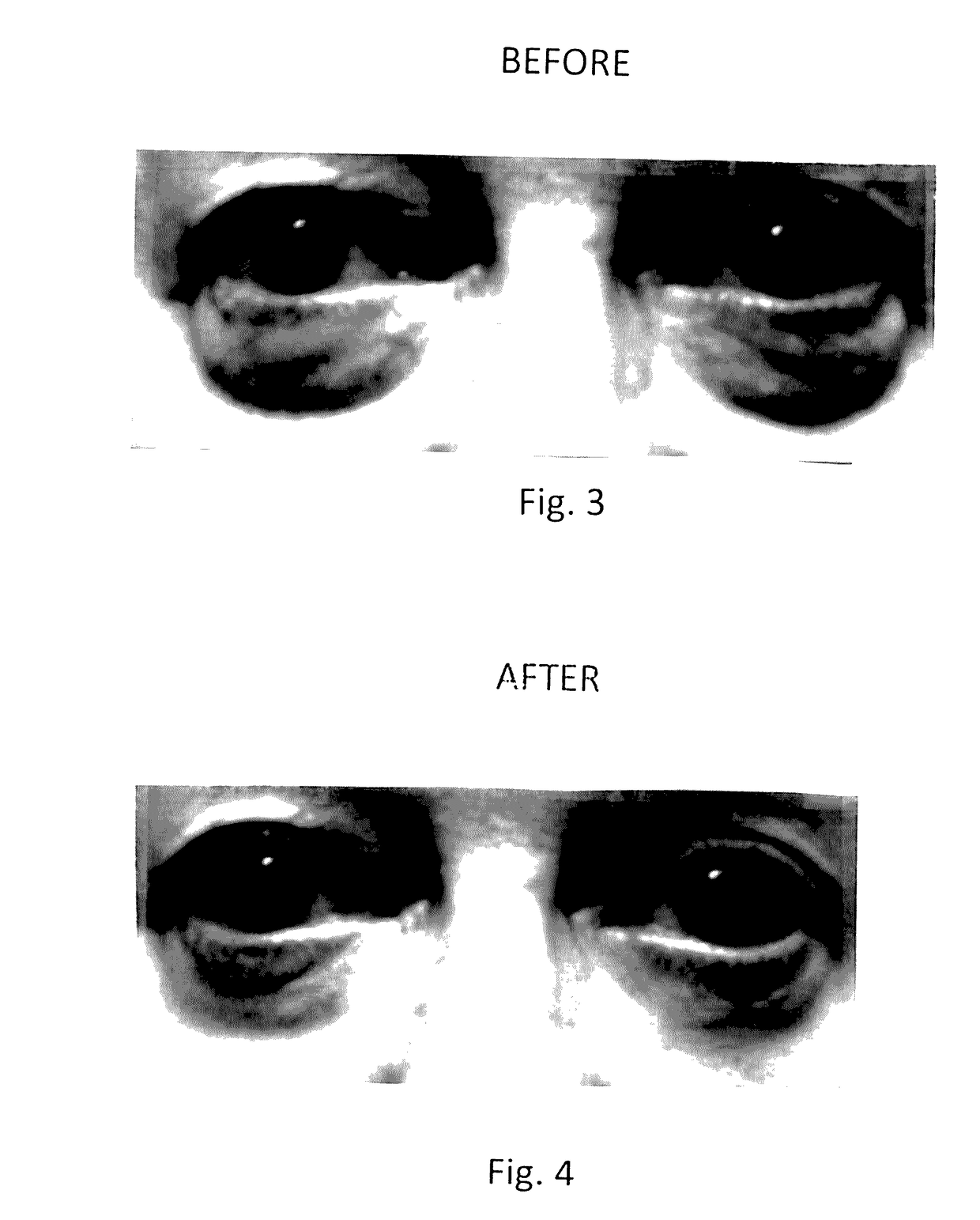
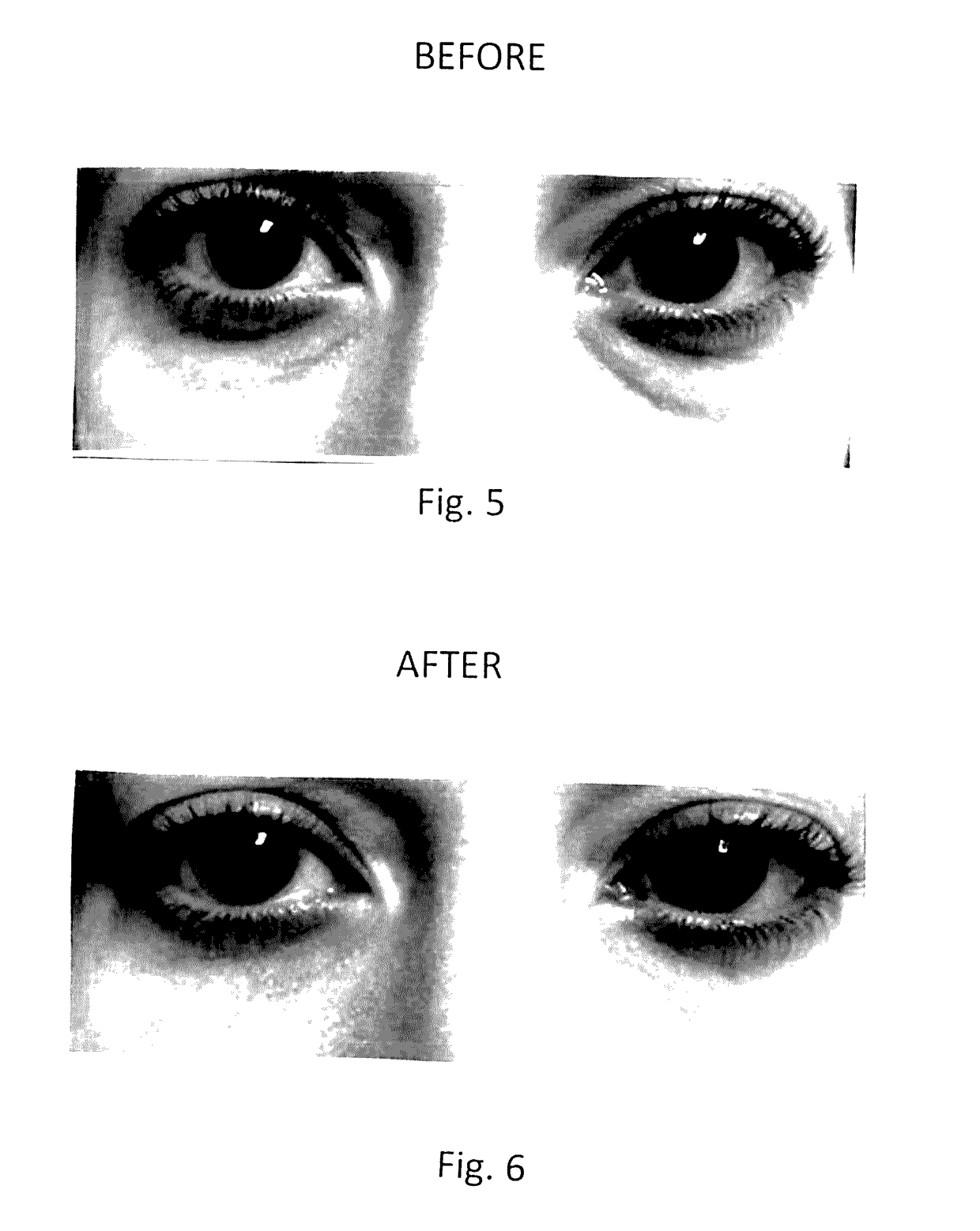
Topical composition for skin treatment to reduce lines and wrinkles of the face and body using a dual DNA repair mechanism to address damage caused by aging and ultra-voilet induced damage to the skin with combination of skin turgor enhancement compounds
InactiveUS20170128355A1Reduction of pigmentation spotImprove skin toneCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsWrinkle skinSkin color
A topical composition for anti-aging and anti-UV damage treatment of the skin includes water soluble extract of Uncaria species, Arabidopsis thaliana extract, alpha lipoic acid, dimethylethanolamine, tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate, dimethyl sulfoxide, Glycyrrhiza Glabra (licorice) root extract, methylsulfonylmethane, phytosterols, D-ribose, tocotrienol, tocopherol, glucosamine hydrochloride, Pisum sativum extract; silicates of sodium, magnesium and aluminum, and a dermatologically acceptable liposomal delivery medium. The composition is useful in a method using it for anti-aging skin treatment effecting DNA repair in both the nucleus and the mitochondria. The topical composition can be applied on the skin of a person daily, and can also be applied in a dermal infusion treatment, with or without micro-dermal abrasion or skin suction. Topical application of the composition achieves effective reduction of pigmentation spots, degree of winkles, and improvement of skin color, tone and turgidity, particularly of the eyelid and facial areas.
Owner:GIAMPAPA VINCENT C +2
Slow released anticancer combination of medication embedded the interior of the body
InactiveCN1660438AAddress sensitivityOvercoming toxicityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAntineoplastic agentsDNA repairTreatment effect
A slowly-releasing anticanser composite medicine implanted in human body is composed of the anticancer medicine prepared from implantation agent, slowly releasing agent and dichloroethane-kind medicine for suppressing the growth of tumor cells and the medicinal additive chosen from biocompatible and biodegradable polymer for slowly releasing said anticancer medicine toward tumor.
Owner:DASEN BIOLOGICAL PHARMA CO LTD
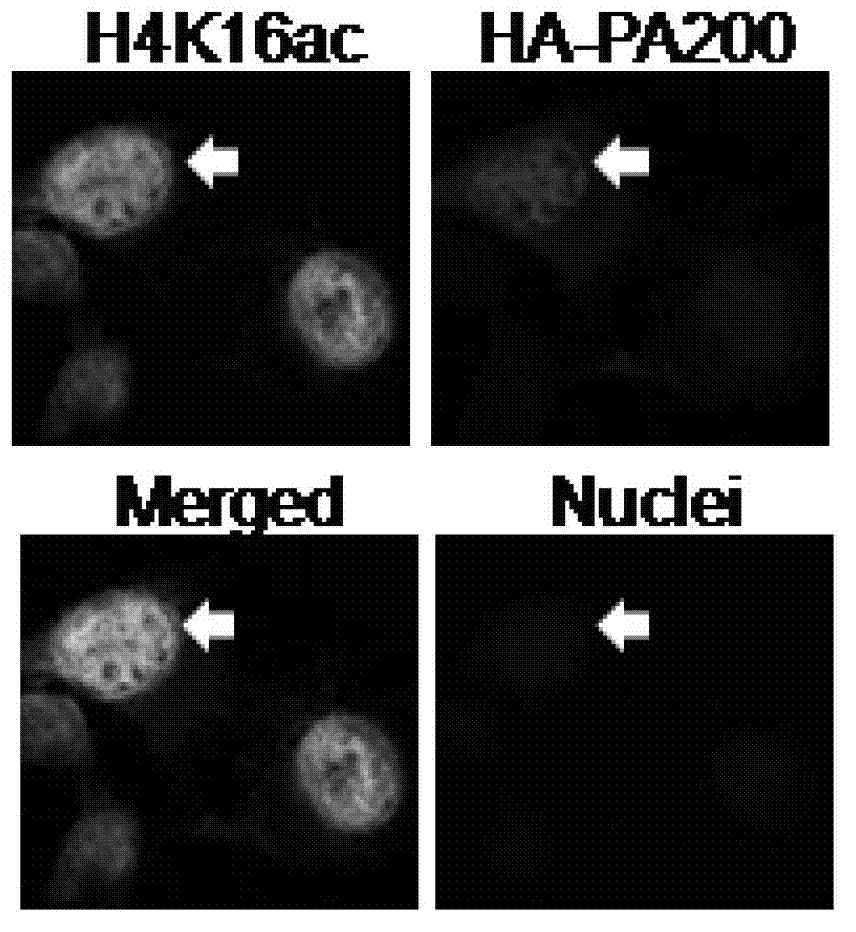
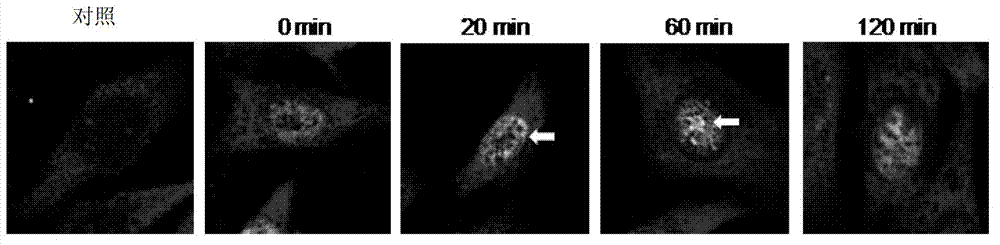
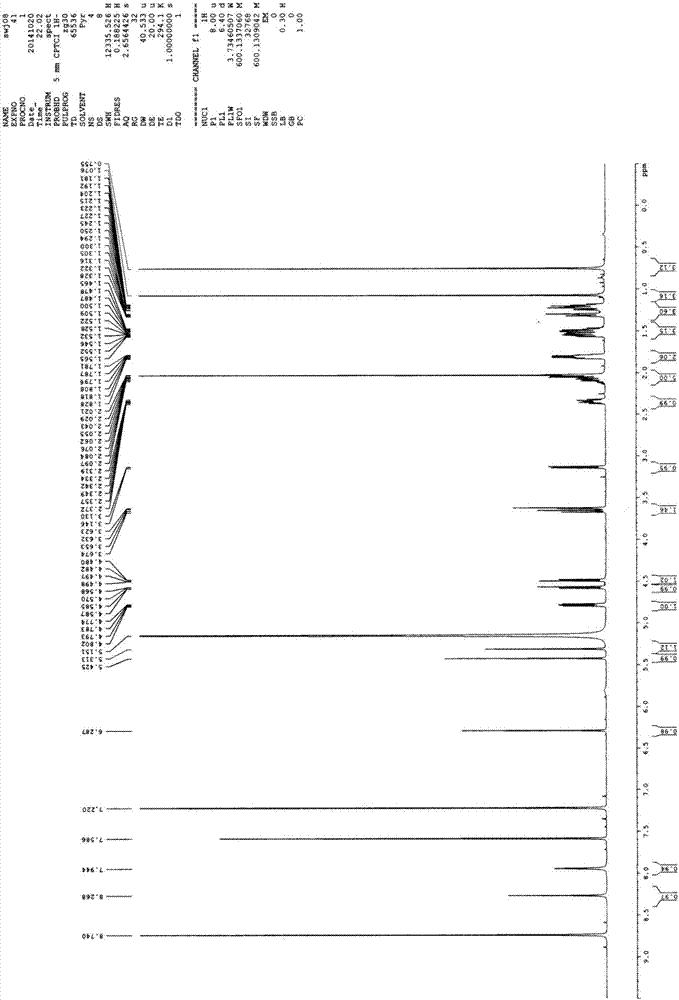
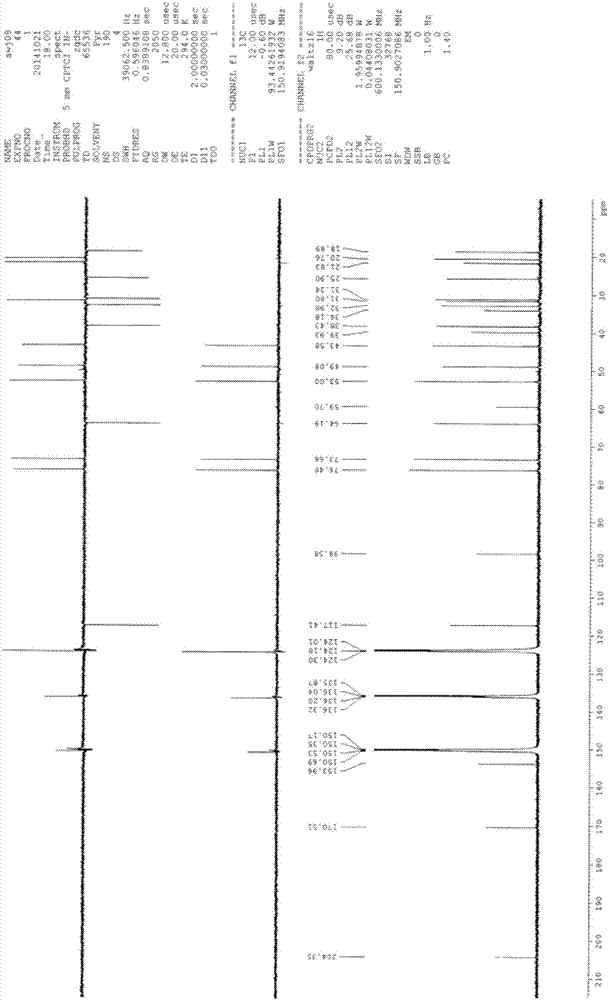
Degradation of PA200 and acetylation-mediated core histones through proteasome
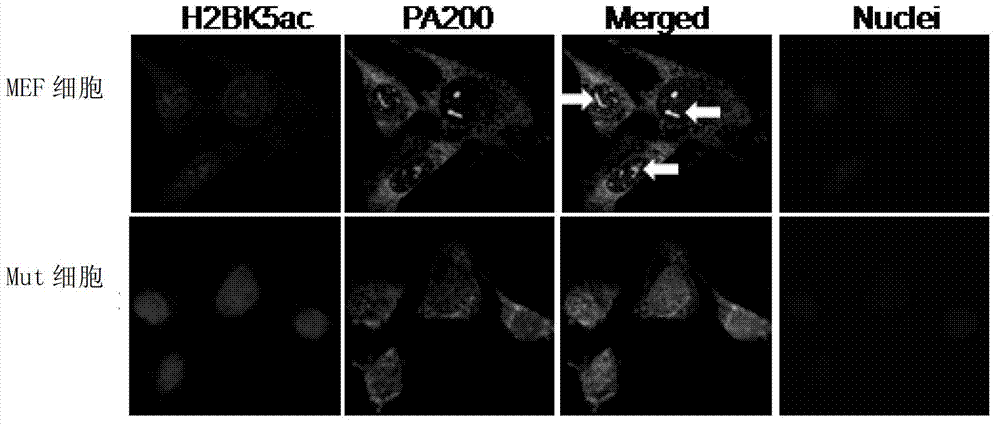
ActiveCN103191412APromote degradationIncreased sensitivityPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesDNA repairTestis specific
The invention discloses an application of PA200 proteins in preparation of products. The products have at least one of the following functions from (1) to (4): (1) combining with acetylated proteins; (2) promoting the degradation of the acetylated proteins; (3) participating in repair of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) damages of somatic cells; and (4) participating in the formation of sperms. The invention has breakthroughs in four following aspects: (1) finding a mechanism of regulation and control of degradation of the histones, the sperm formation and the DNA repair by acetylation; (2) revealing the degradation of the histones medicated by acetylation rather than ubiquitination through PA200 / Blm10 proteasome; (3) finding novel testis-specific proteasome containing PA200 and alpha 4s, and revealing the core histones as a first type biological substrate for the proteasome; and (4) revealing that a histone deacetylase inhibitor can promote the degradation of the histones which are induced by DNA double-strand breaks and medicated by acetylation, enhance the sensitivity of cells to DNA damages and easily lead to the death of the cells.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Application of rabdocetsin in preparing product for inhibiting proliferation of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells
ActiveCN107213145APrevent proliferationInhibition of clonogenicityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDNA repairAbnormal tissue growth
The invention discloses application of rabdocetsin in preparing a product for inhibiting proliferation of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells. Proofed by experiment, the application has the advantages that the rabdocetsin can effectively inhibit the proliferation of the esophageal squamous carcinoma cells, the cloning formation of the esophageal squamous carcinoma cells, affecting the cycle progress of the esophageal squamous carcinoma cells, inducing the retardation of the cycle of the esophageal squamous carcinoma cells, inhibiting the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) restoration of the esophageal squamous carcinoma cells, inducing the withering of the esophageal squamous carcinoma cells, regulating up the expression amount of cleaved-caspase-9, regulating up the expression amount of cleaved-caspase-3, regulating up the expression amount of cleaved-PARP, inhibiting Akt signal pathways, inhibiting NF-kappa B signal pathways, and inhibiting the growth of tumors caused by the esophageal squamous carcinoma cells; the important application value is realized.
Owner:CANCER INST & HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI +1
Compositions and methods for effecting NAD+ levels using a nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase inhibitor
The present invention relates to methods for decreasing cellular DNA repair in a patient diagnosed with or suspected to have chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL); decreasing cellular NAD+ biosynthesis in a patient diagnosed with or suspected to have CLL; or sensitizing a patient diagnosed with or suspected to have CLL to a DNA damaging therapy. The invention relates to methods for treating a patient diagnosed with or suspected to have CLL.
Owner:GEMIN X PHARMA CANADA INC (CA)
Dietary supplement and related method
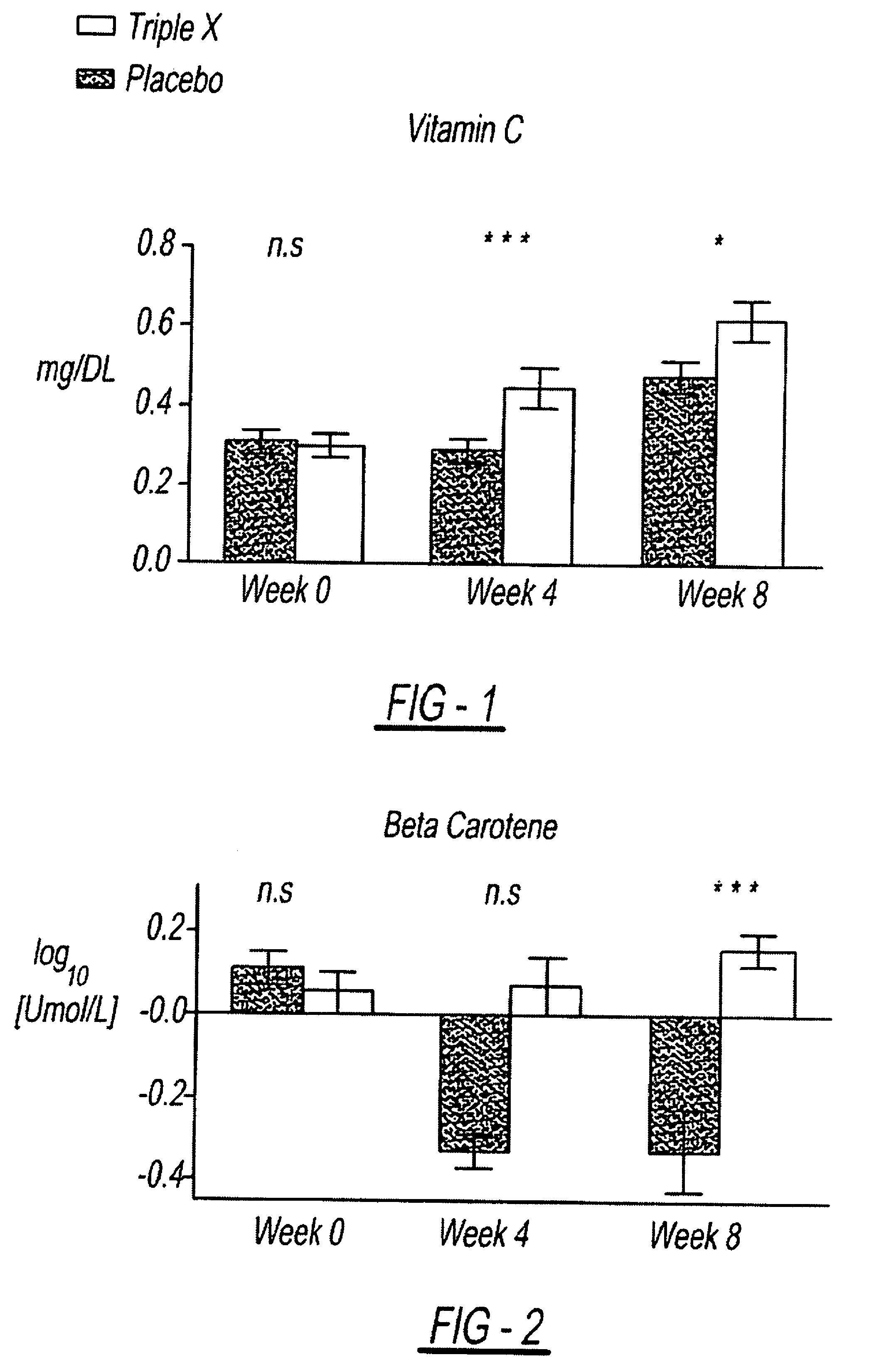
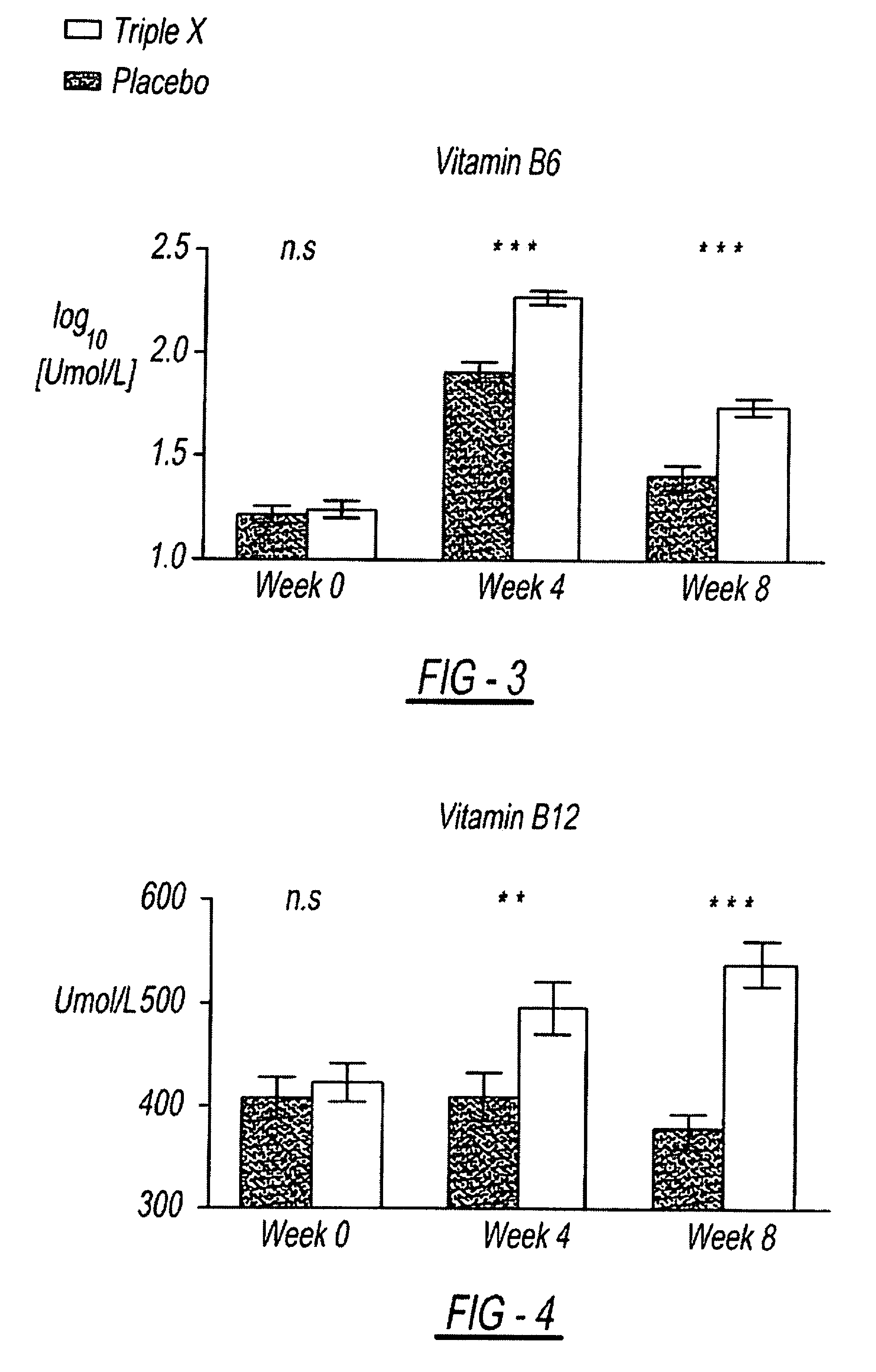
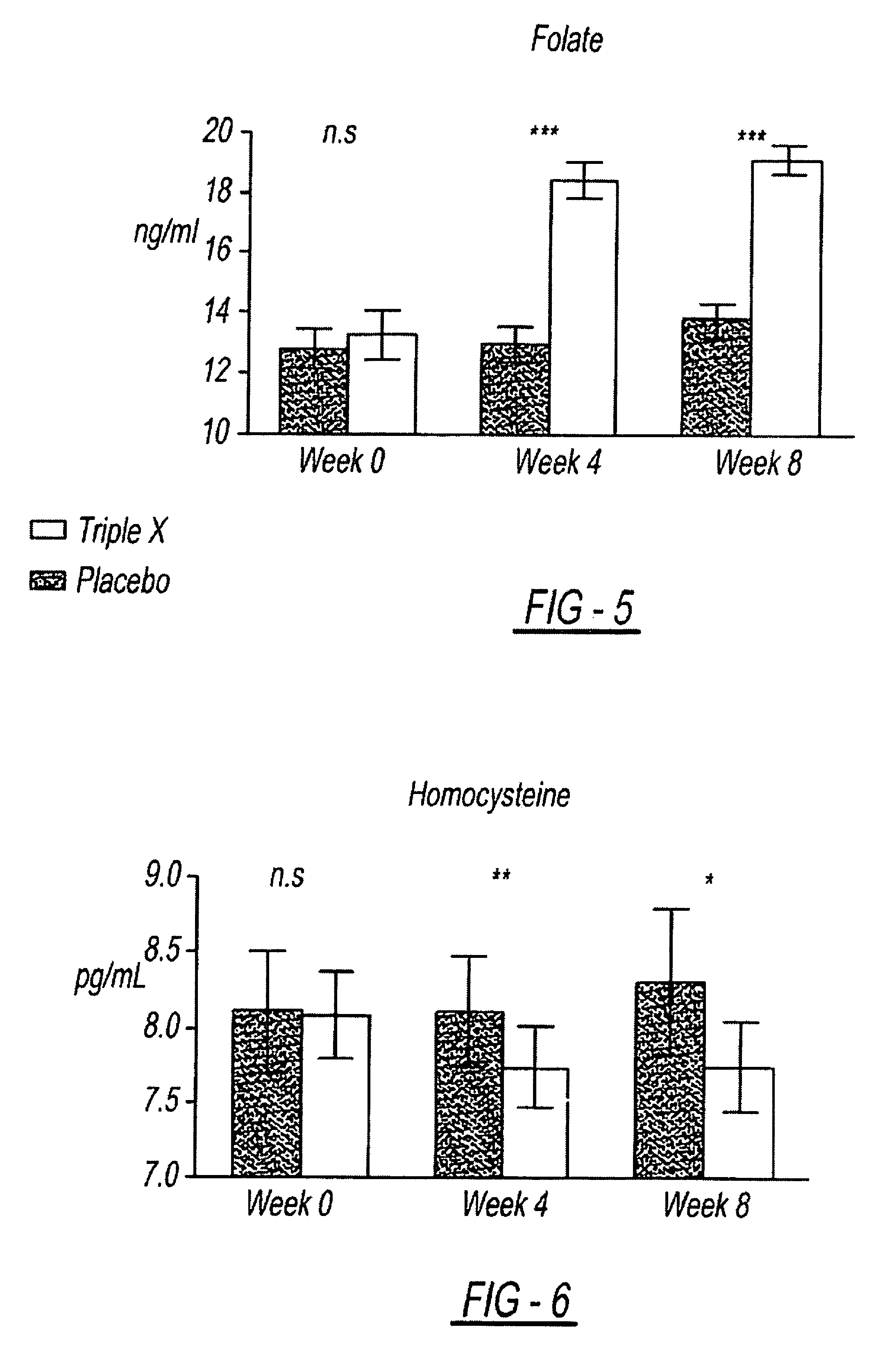
InactiveUS7939115B2Improve antioxidant and nutrient statusImprove the status of specific biomarkersHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocidePhytochemicalDietary supplement
A composition including a unique combination of fruits, vegetables, herbs, and optionally vitamins, minerals and specialty ingredients. The composition can include a fruit ingredient, a vegetable ingredient and an herbal ingredient, wherein the fruit ingredient is at least one of pomegranate and citrus bioflavonoids, wherein the vegetable ingredient, is at least one of asparagus, lutein, lycopene and watercress, and wherein the herbal ingredient is at least one of basil, oregano and rosemary. The composition can be administered to subjects to correct a dietary deficiency of phytochemicals and other nutrients, improve plasma concentrations of antioxidant nutrients, and increase the activity of genetic mechanisms for DNA repair and stability.
Owner:ACCESS BUSINESS GRP INT LLC
A method for precise modification of plant via transient gene expression
PendingUS20180073035A1Improve regenerative abilitySmooth transmissionHydrolasesNucleic acid vectorDNA repairNuclease
Provided is a method for conducting site-specific modification in a plant through gene transient expression, comprising the following steps: transiently expressing a sequence-specific nuclease specific to the target fragment in the cell or tissue of the plant of interest, wherein the sequence-specific nuclease is specific to the target site and the target site is cleaved by the nuclease, thereby the site-specific modification of the target site is achieved through DNA repairing of the plant.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
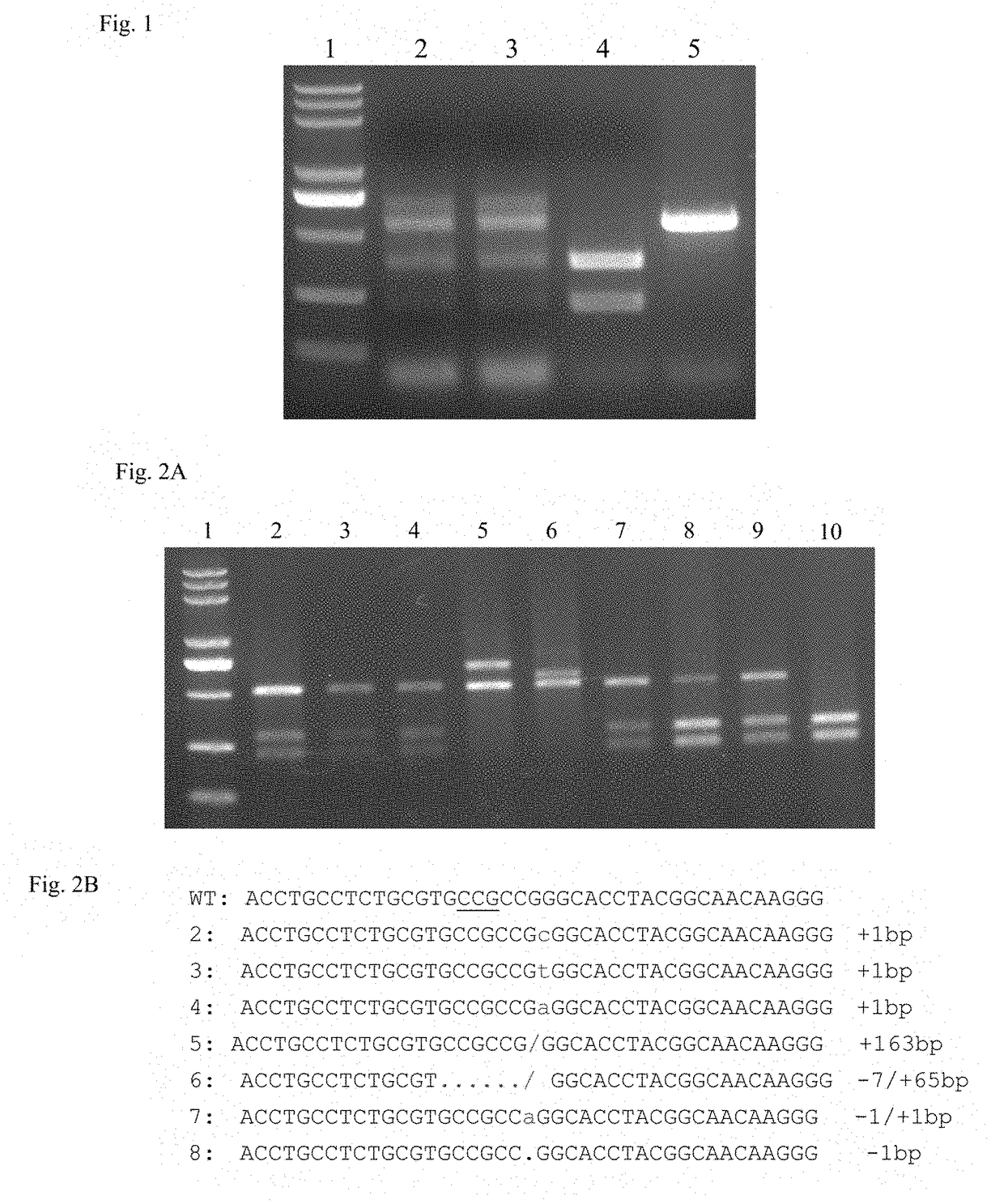
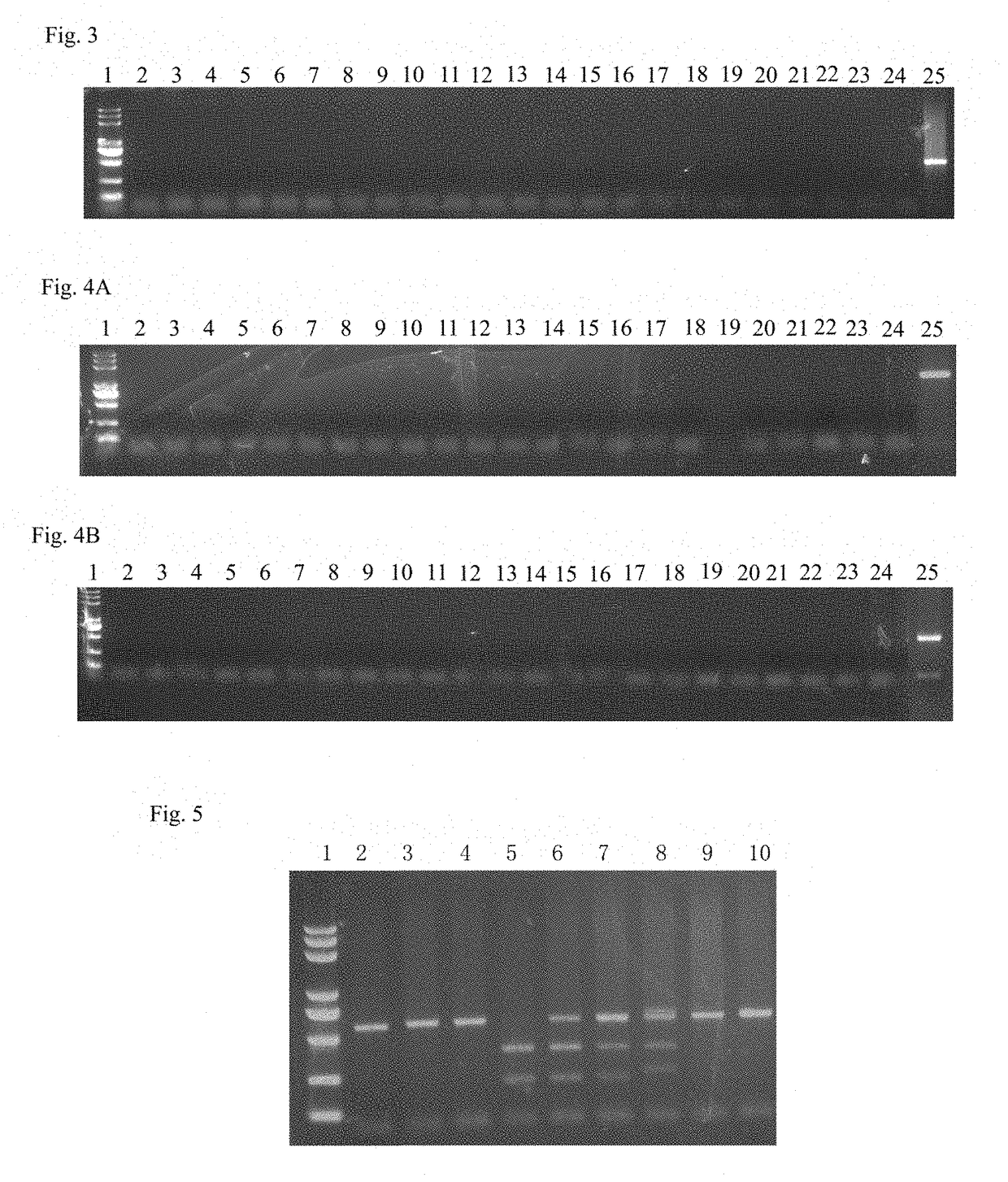
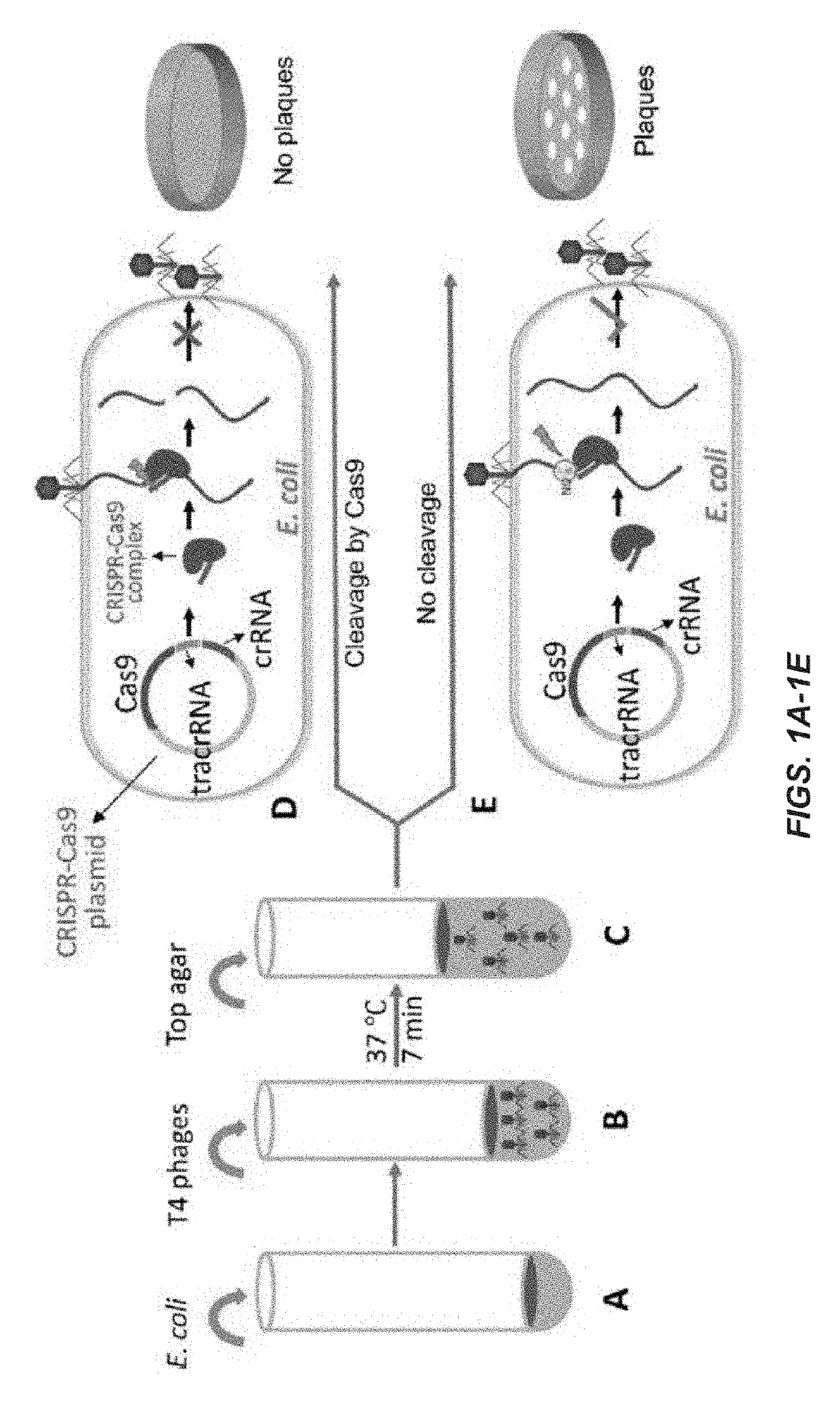
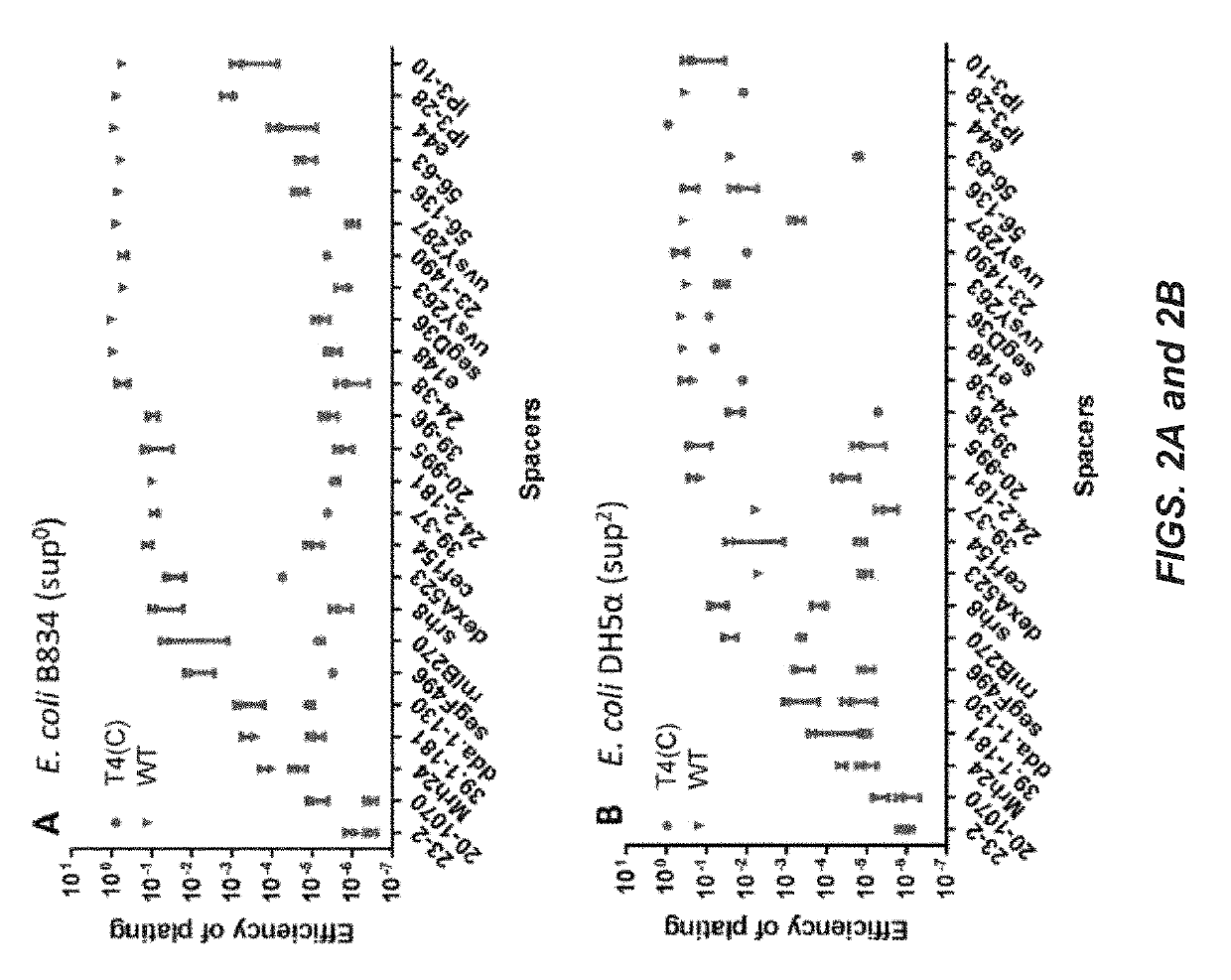
Engineering of bacteriophages by genome editing using the crispr-cas9 system
Embodiments of the invention provide systems, methods, and kits for CRISPR-based editing of DNA targets by a CRISPR-associated (Cas) enzyme. The systems include a bacterial host cell adapted to produce an engineered bacteriophage comprising a Cas protein and guide RNA that do not naturally occur together, i.e. they are engineered to occur together, as well as a DNA repair template comprising a donor DNA having a desired mutation. The guide RNA comprises a trans-activating crRNA and a guide sequence complementary to a target protospacer in a bacteriophage genome. A wild-type bacteriophage or a glucosylhydroxymethyl cytosine (ghmC)-unmodified mutant bacteriophage may be delivered into a disclosed bacterial host cell to create recombinants of bacteriophage having the desired mutation provided by the donor DNA.
Owner:CATHOLIC UNIV OF AMERICA
Anti-cancer drug slow release injection containing gemcitabine
The invention relates to an anti-cancer drug slow release injection containing gemcitabine, which comprises slow release microspheres and a menstruum, wherein the microsphere comprises anti-cancer active ingredients and slow release auxiliary materials, and the menstruum is a special menstruum containing a suspending agent; the anti-cancer active ingredients are gemcitabine, or antimetabolites selected from zalcitabine, emtricitabine, galocitabine, ibacitabine, ancitabine, decitabine, flurocitabine, enocitabine, imidazole gemcitabine, capecitabine, gemcitabine, fludarabine or cladribine, and / or antimetabolite potentiating agents selected from phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor, pyrimidine analogue and / or DNA repair enzyme inhibitor; the slow release auxiliary materials are polifeprosan, dienoic fatty acid, decanedioic acid copolymer, polylactic acid copolymer, EVAc and the like; the suspending agent has a viscosity of 100cp-3000cp (20-30 DEG C), and is selected from sodium carboxymethylcellulose and the like. The slow release microspheres can be prepared into slow release implants. When injected or placed into tumors or at peripheries of tumors, the slow release microspheres can enhance the treatment effect of non-operative treatment methods, such as radiotherapy, chemotherapy, etc.
Owner:SHANDONG LANJIN PHARMA +1
Slow-releasing injection contg. platinum compounds and its potentiator type anticarcinogen
InactiveCN1861050AEasy to operateGood repeatabilitySolution deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAnticarcinogenMicrosphere
A slow-release anticancer injection contains the slow-release microspheres and solvent. Said slow-release microsphere contains the active anticancer component chosen from 6 Pt compounds including bicycloplatinum, etc and 3 cytotoxins including phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor, pyrimidine analog or DNA repairase inhibitor, and the slow-release auxiliary.
Owner:SHANDONG LANJIN PHARMA +1
Slow-releasing injection contg anticarcinogen of Jixitabin
A slow-release anticancer injection contains the slow-release microspheres and solvent. Said slow-release microsphere contains the active anticancer component chosen from 13 antimetabolic medicines including gemcitabine, zalcitabine, etc and 3 cytotoxins including phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor, pyrimidine analog or DNA repairase inhibitor, and the slow-release auxiliary.
Owner:SHANDONG LANJIN PHARMA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com