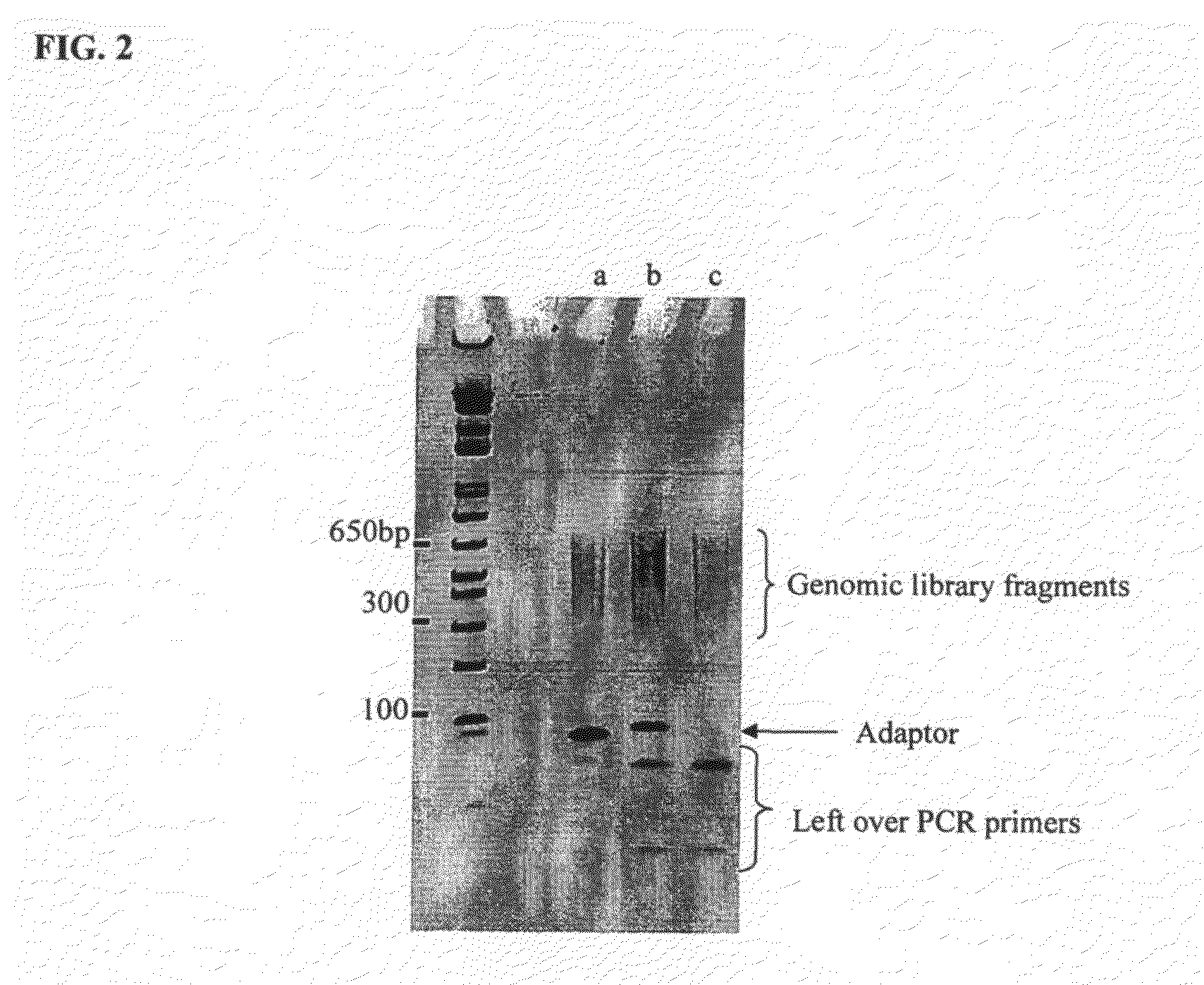
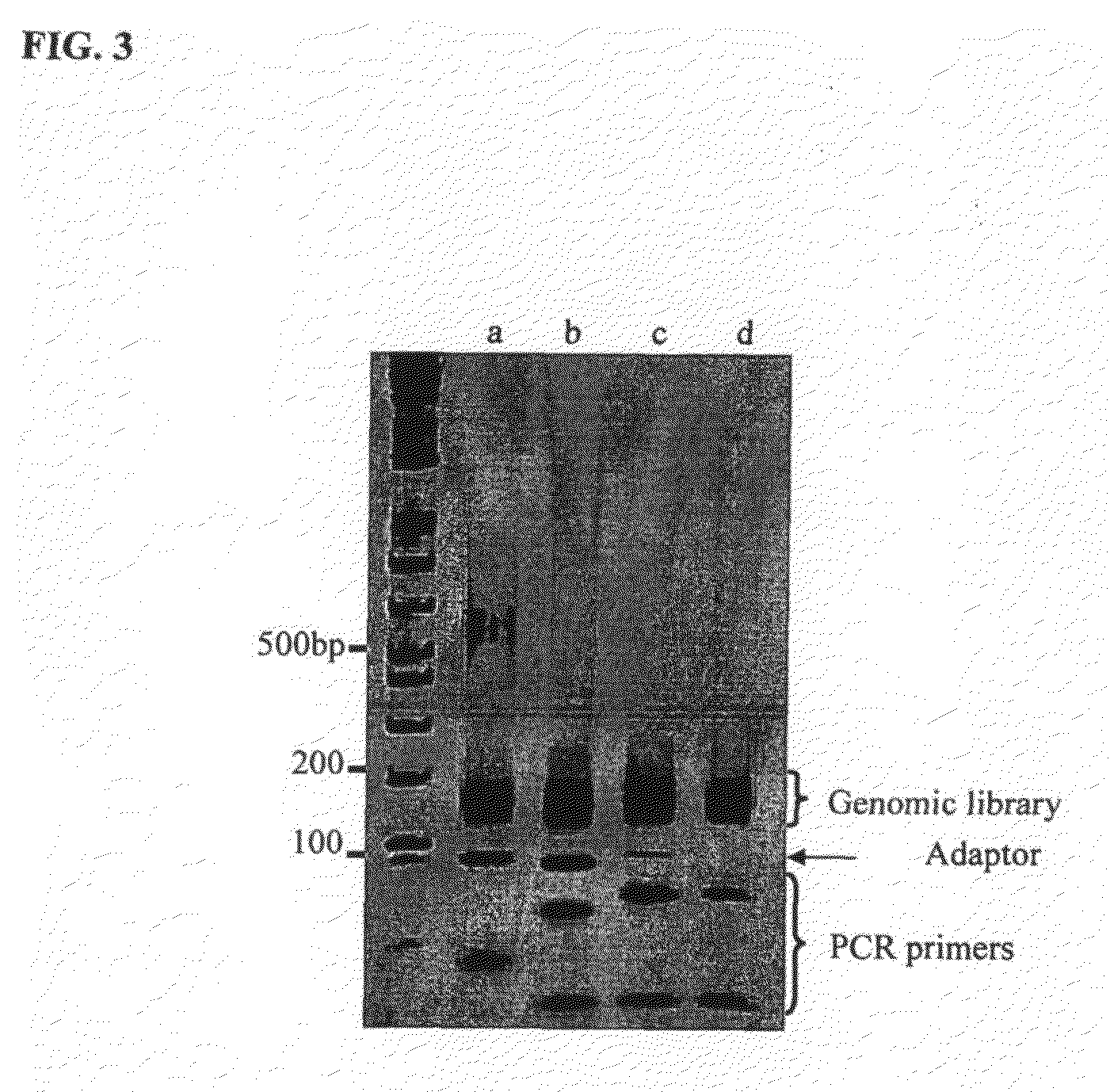
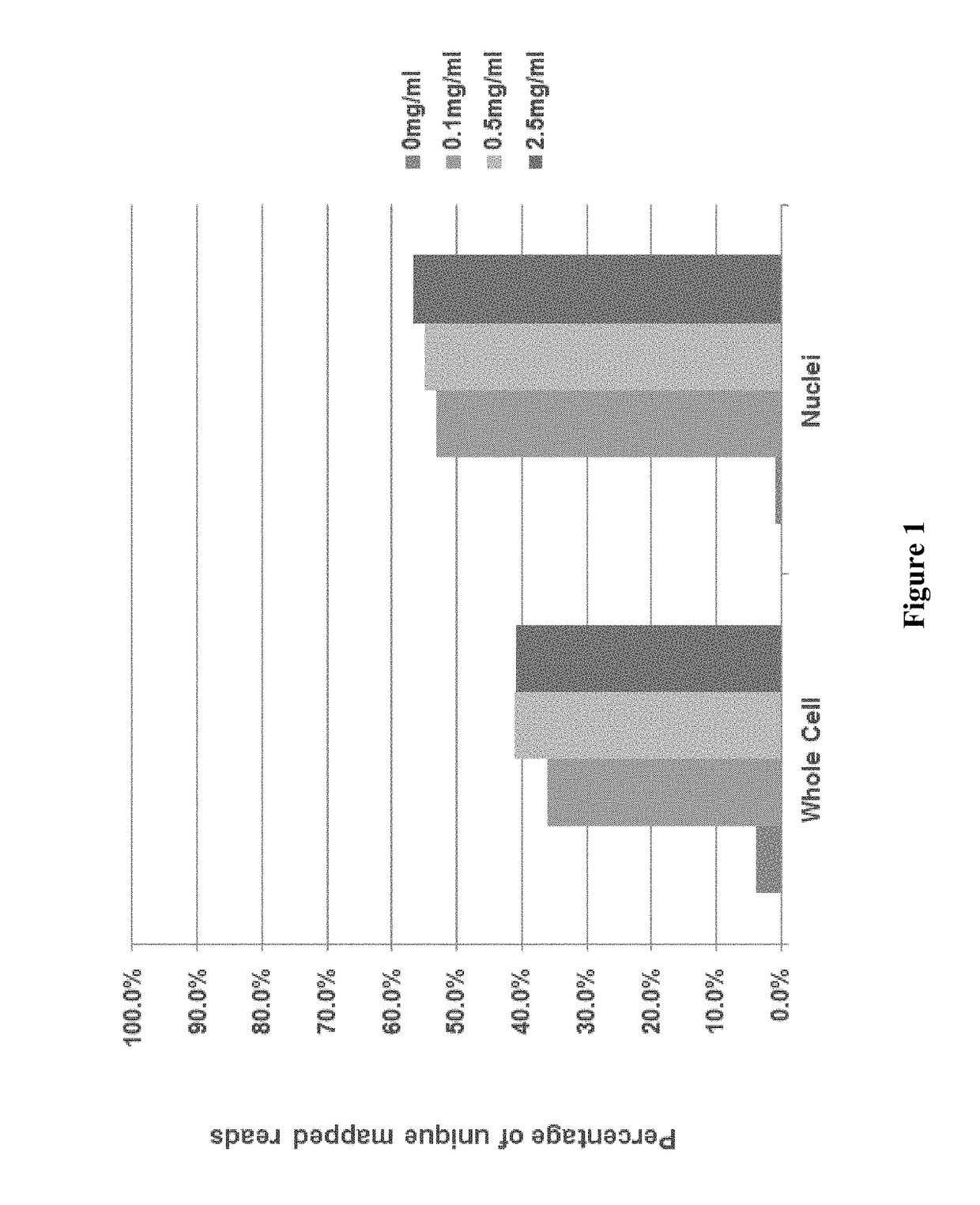
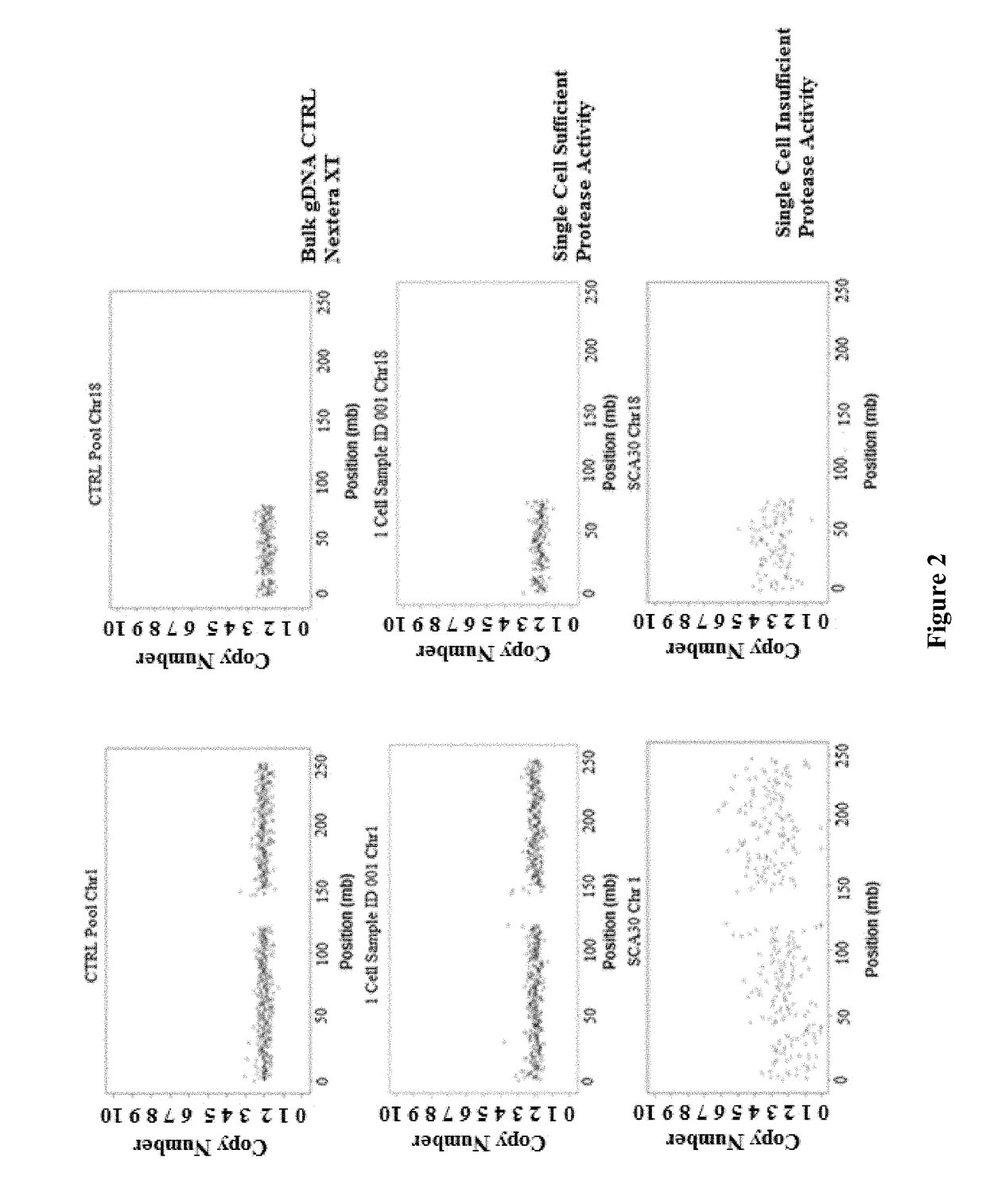
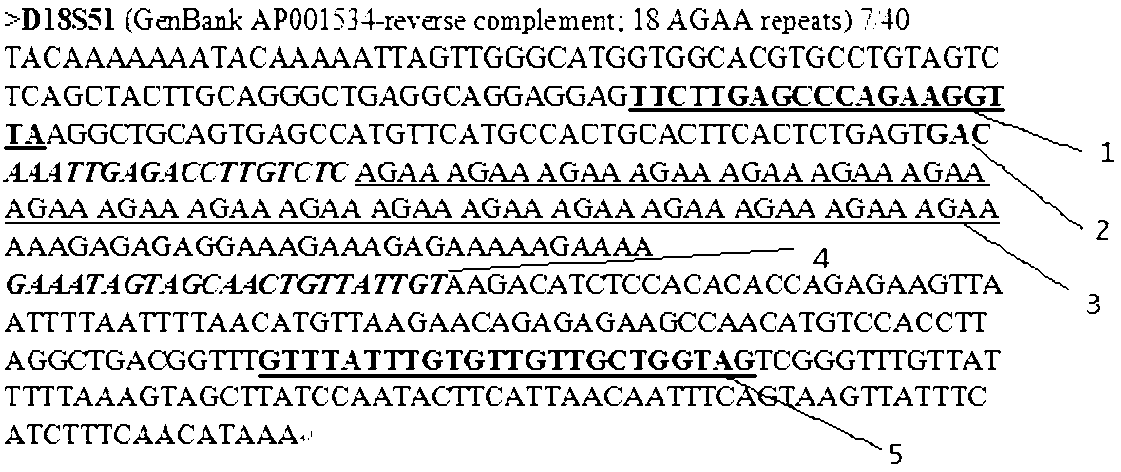Patents
Literature
134 results about "Library preparation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
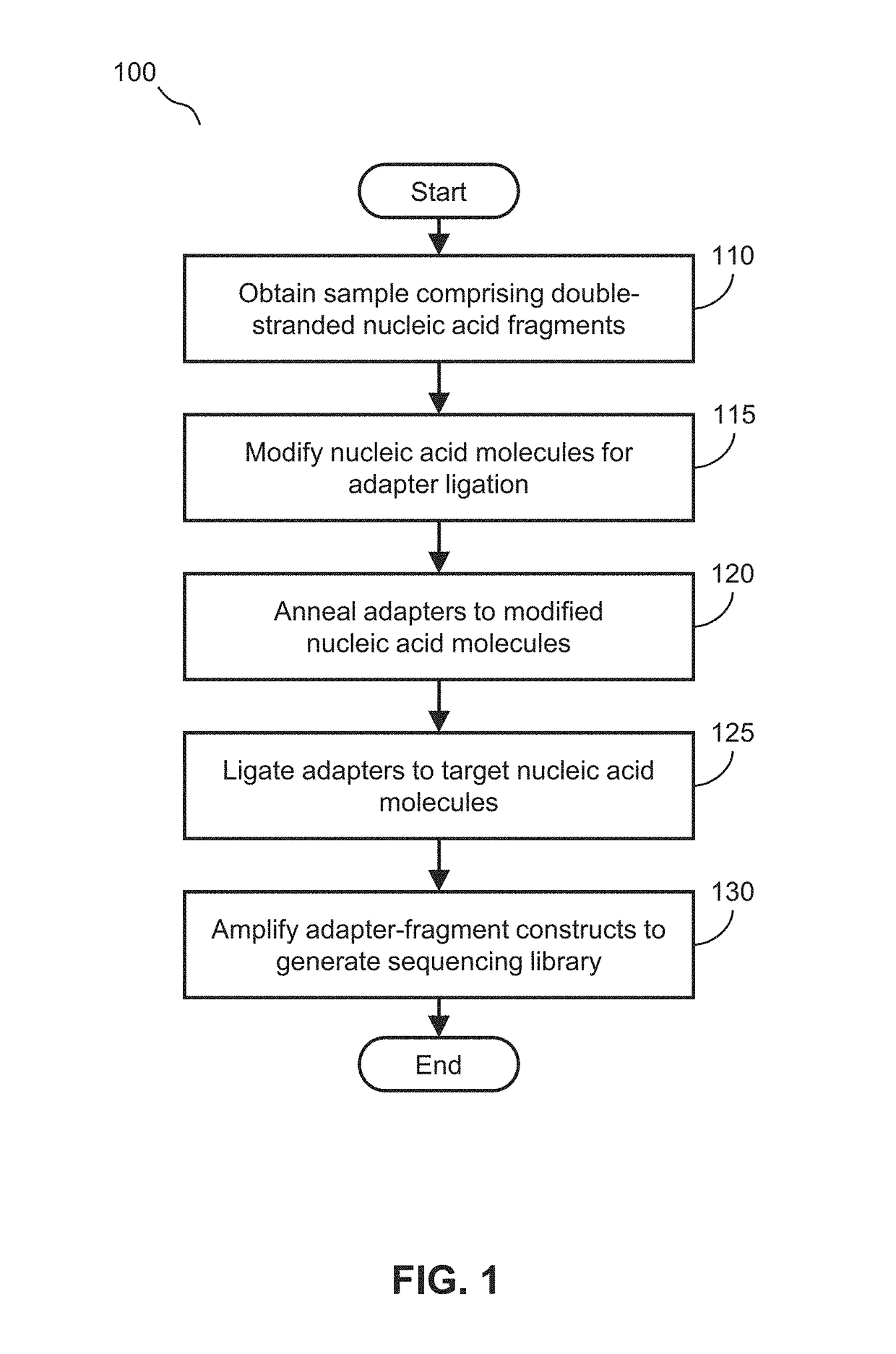
Library preparation involves generating a collection of DNA fragments for sequencing. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) libraries are typically prepared by fragmenting a genomic DNA sample and ligating specialized adapters to both fragment ends.
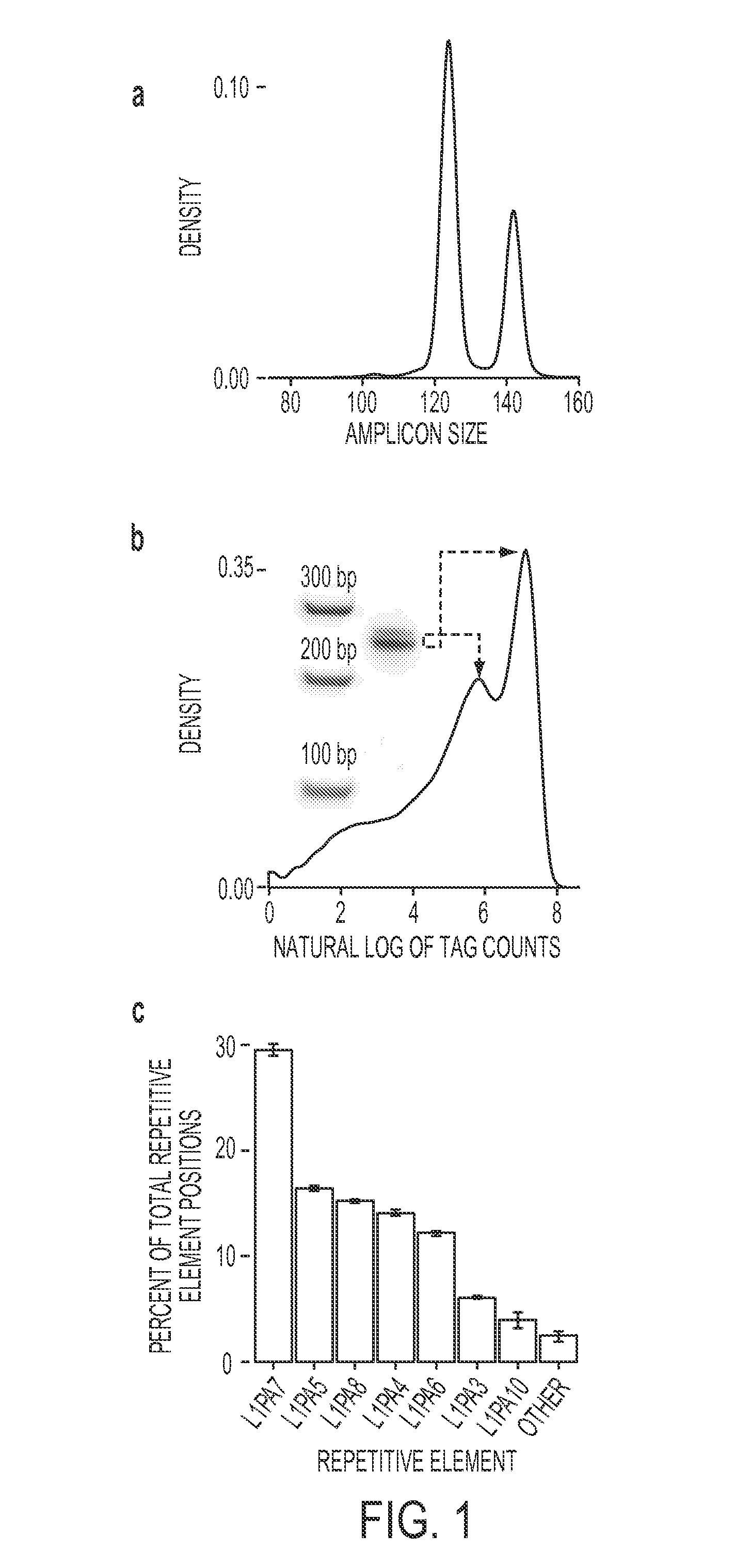
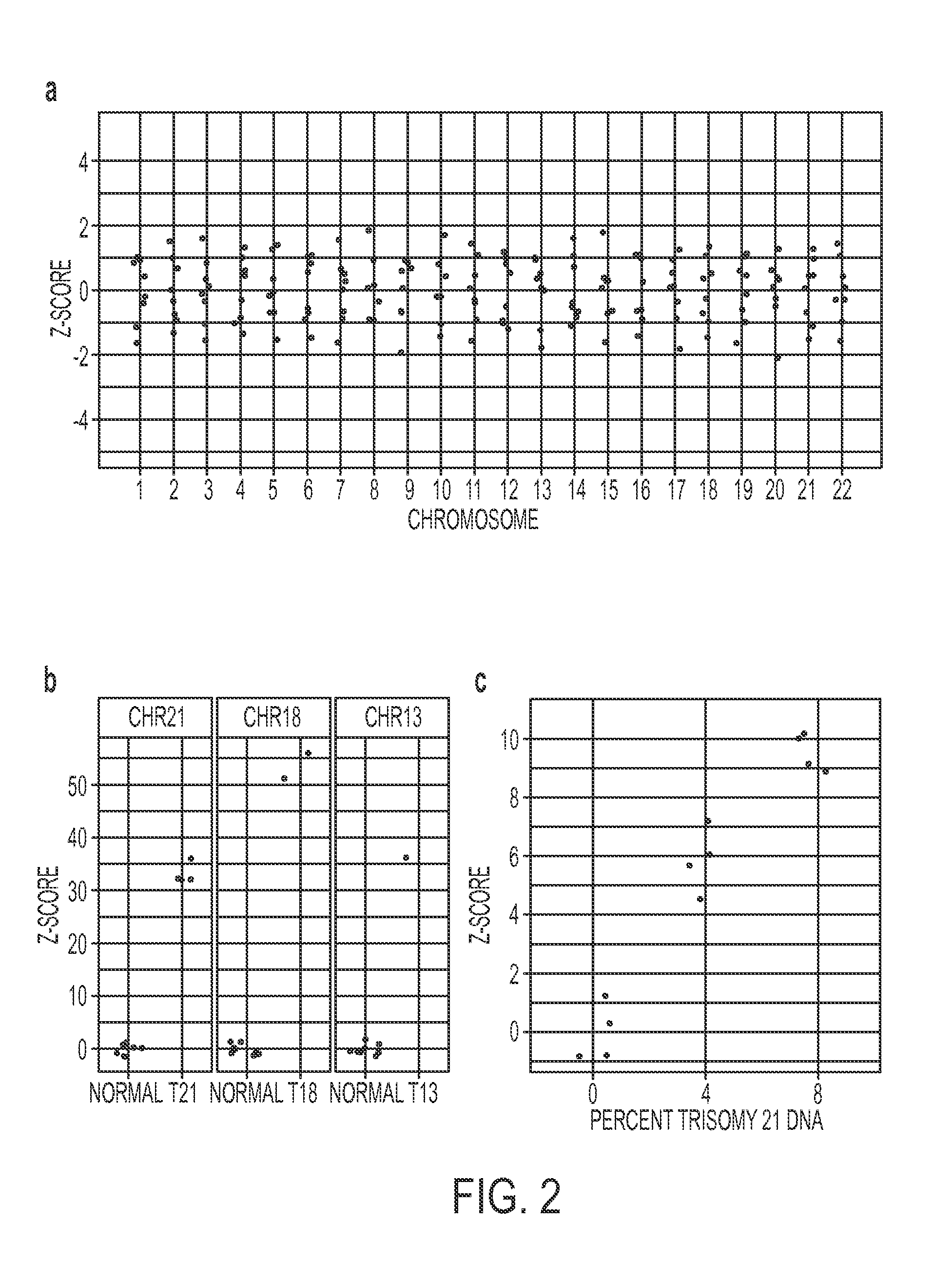
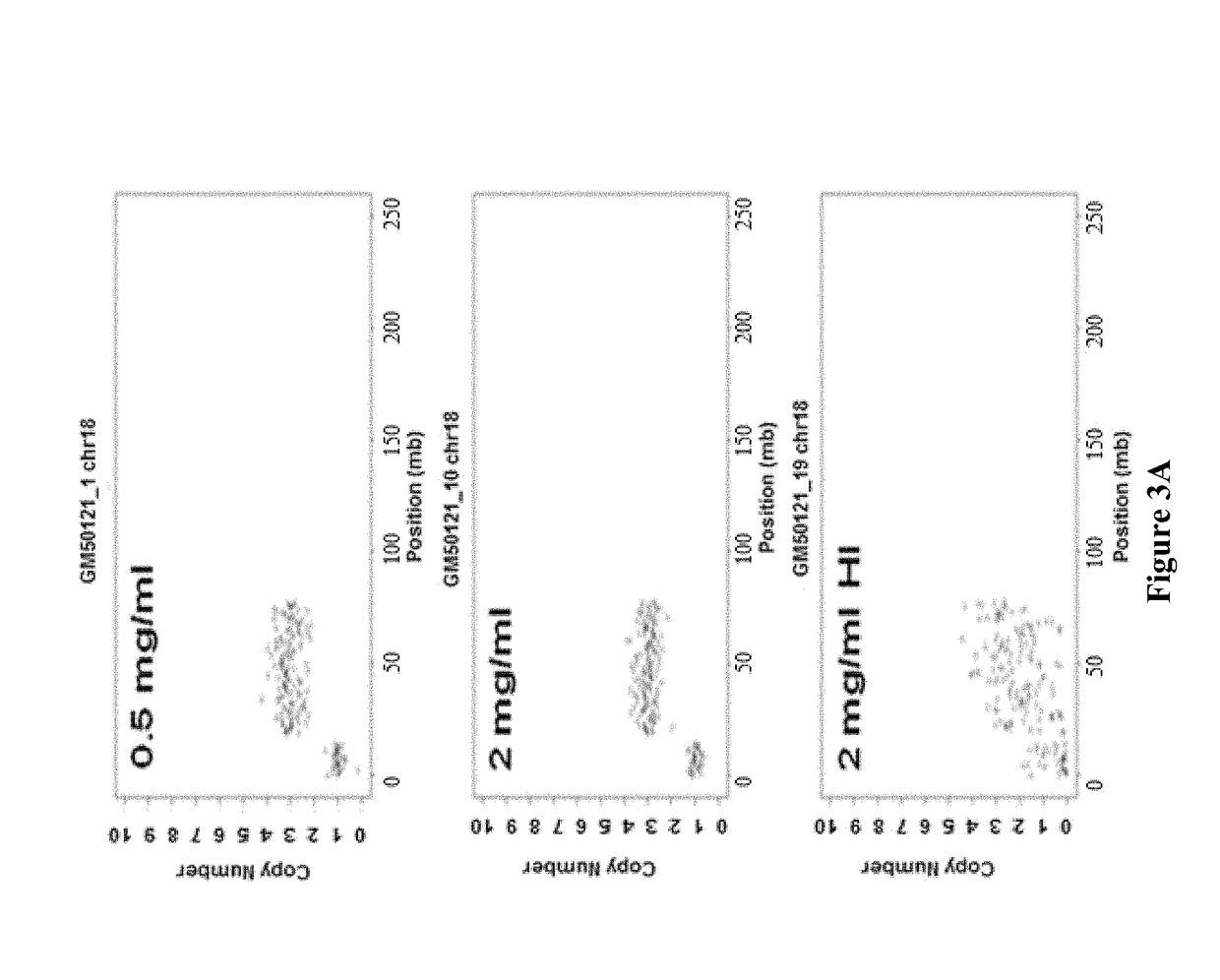
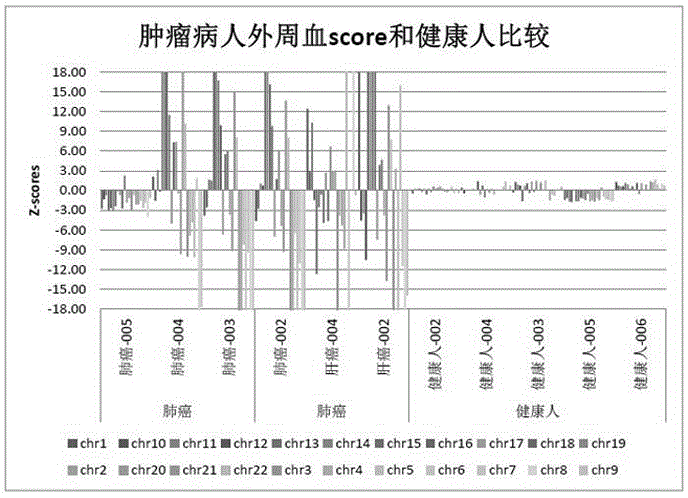
Rapid aneuploidy detection
ActiveUS20150051085A1Assessing genomic copy number sensitively and rapidlyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementCell freeTrisomy
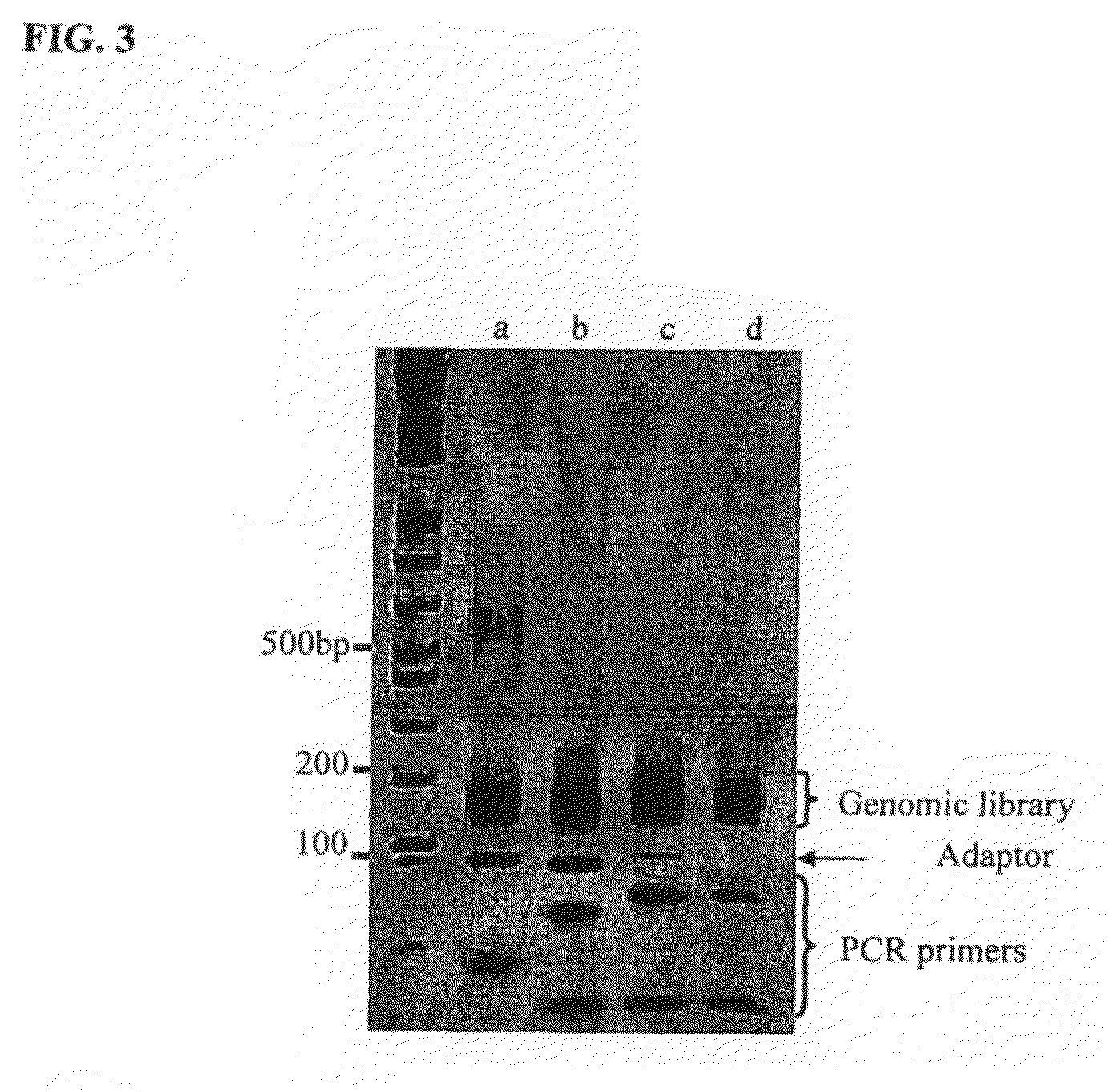
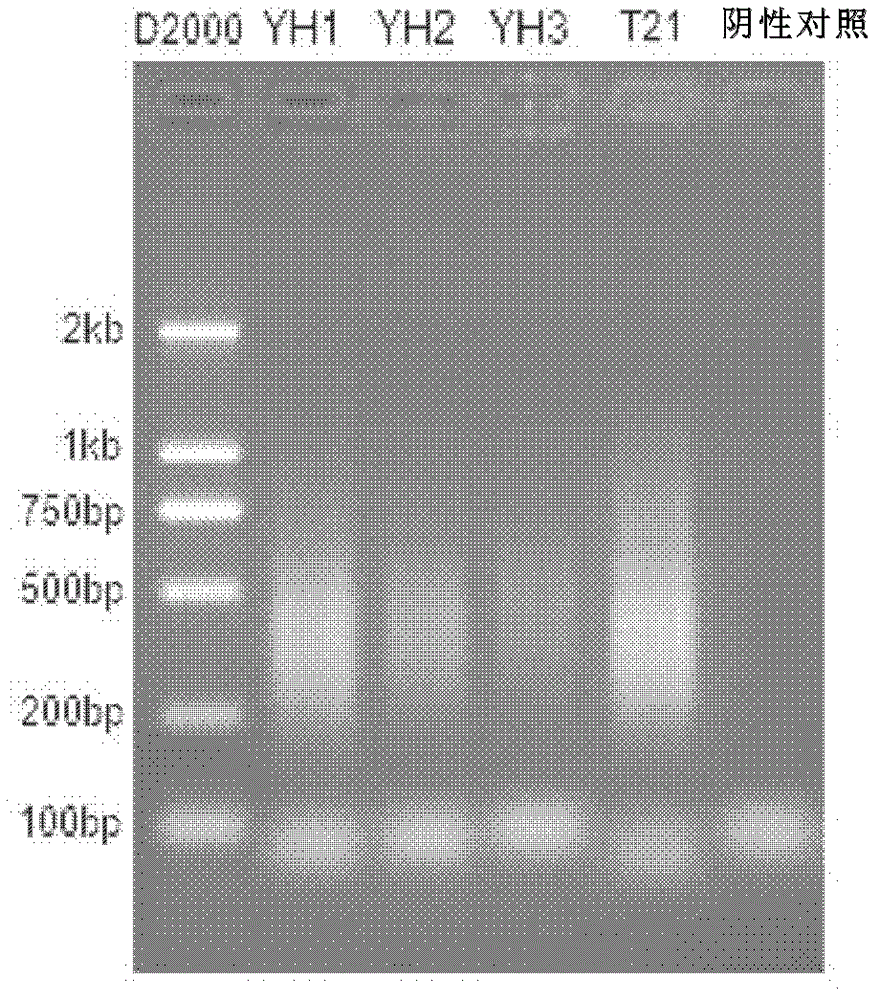
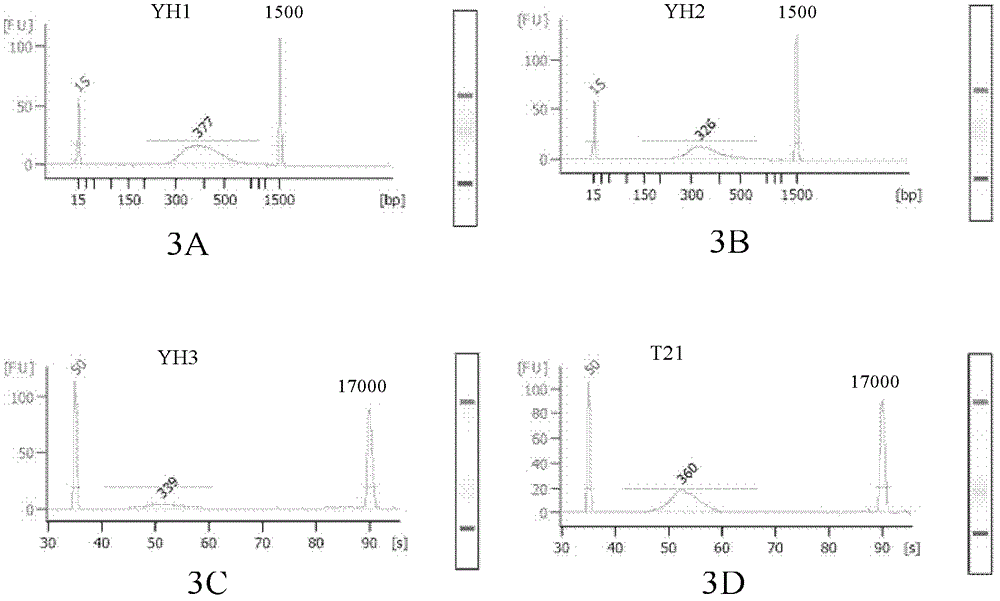
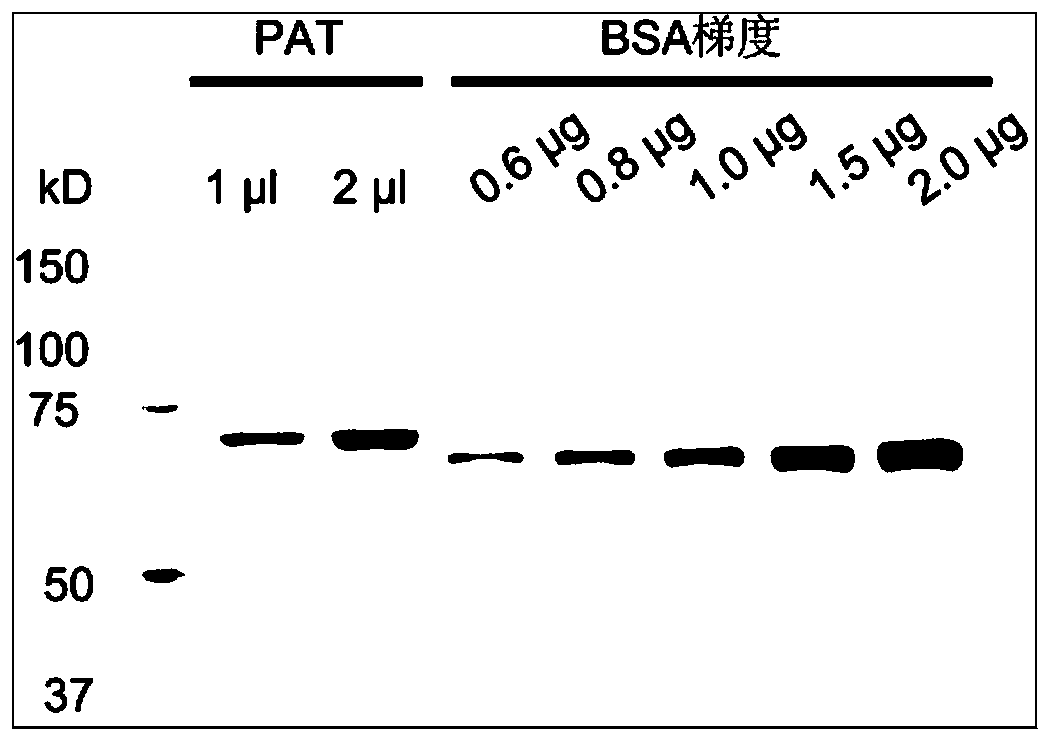
Massively parallel sequencing of cell-free, maternal plasma DNA was recently demonstrated to be a safe and effective screening method for fetal chromosomal aneuploidies. Here, we report an improved sequencing method achieving significantly increased throughput and decreased cost by replacing laborious sequencing library preparation steps with PCR employing a single primer pair. Using this approach, samples containing as little as 4% trisomy 21 DNA could be readily distinguished from euploid samples.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
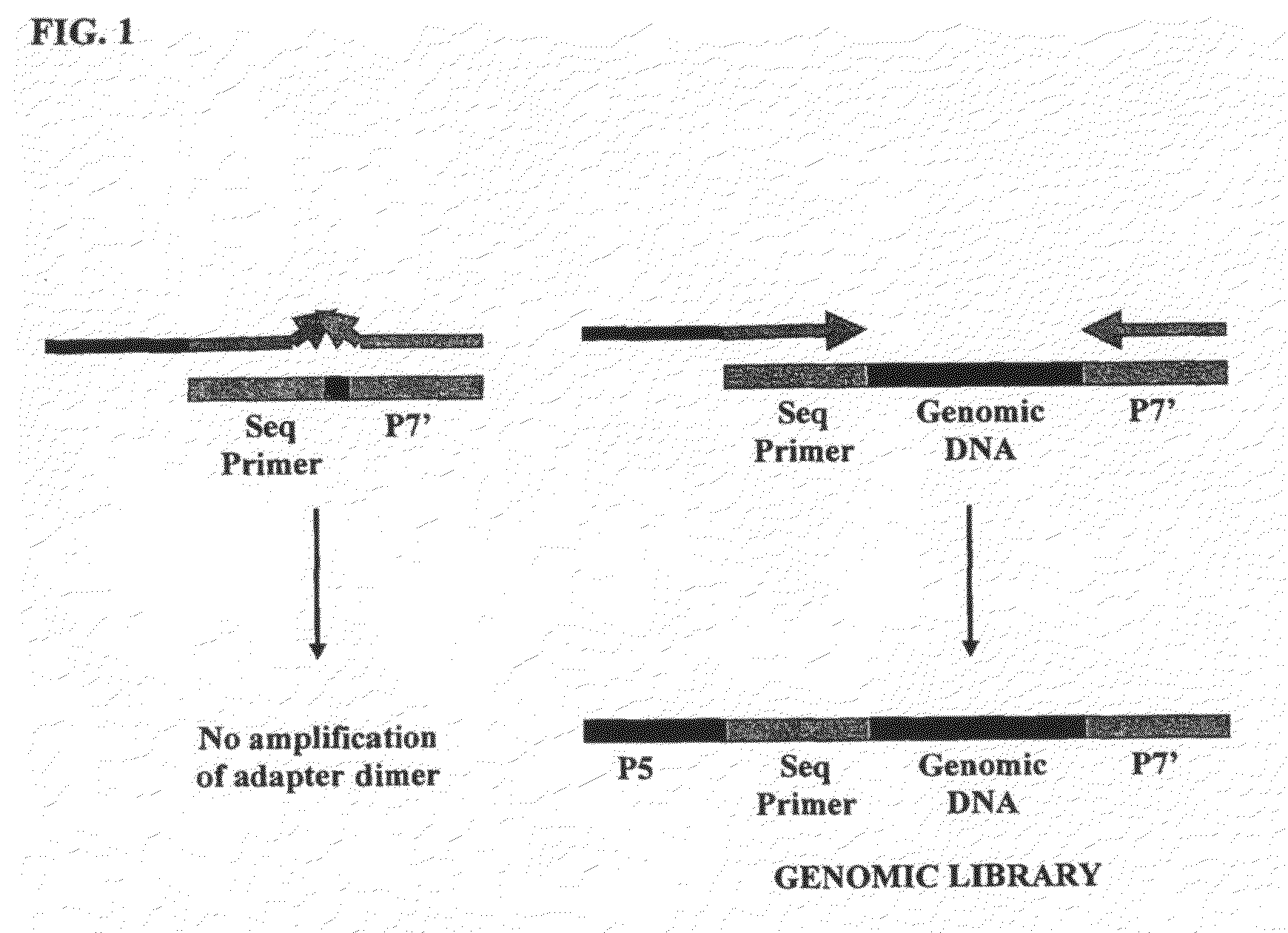
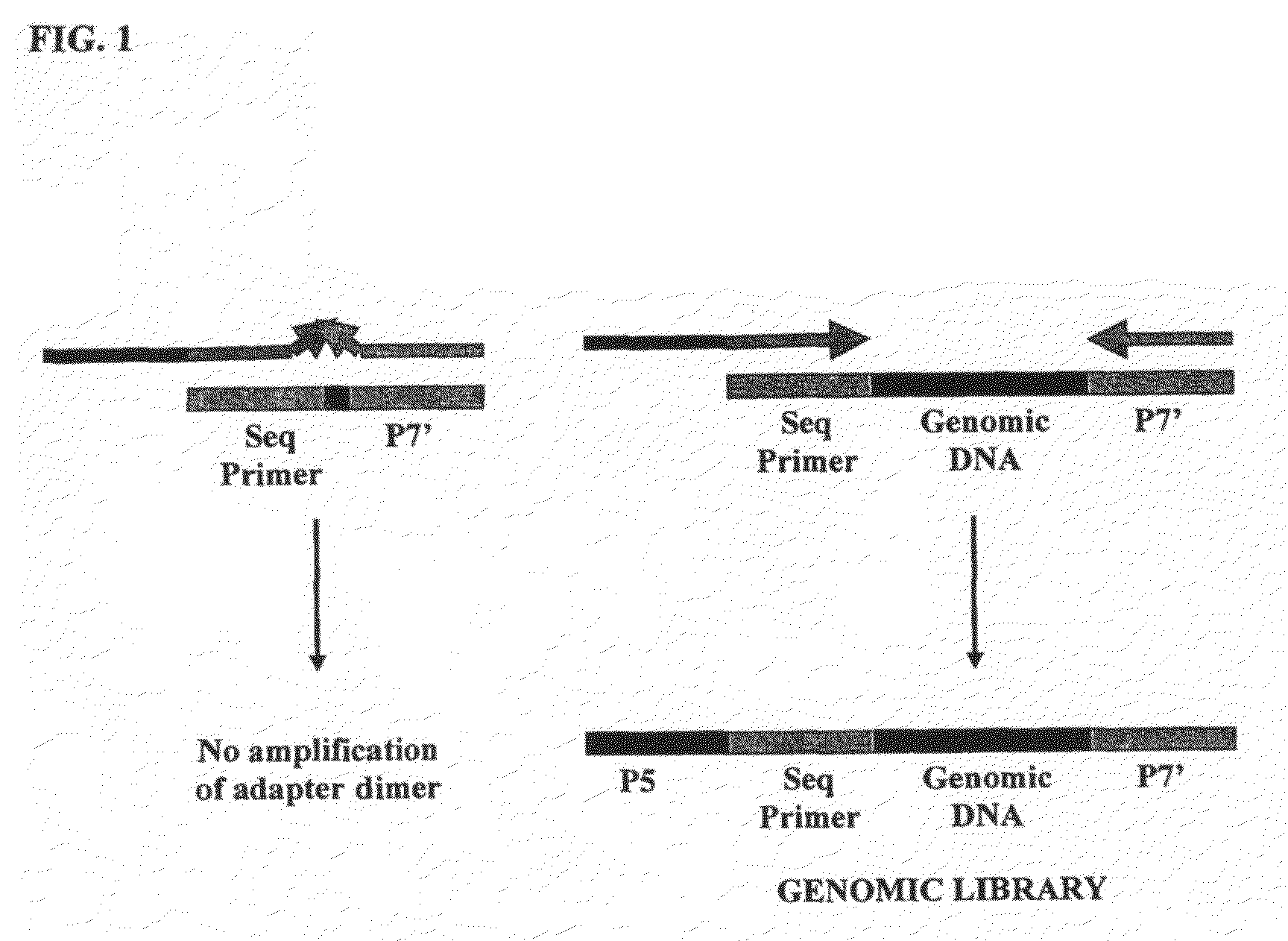
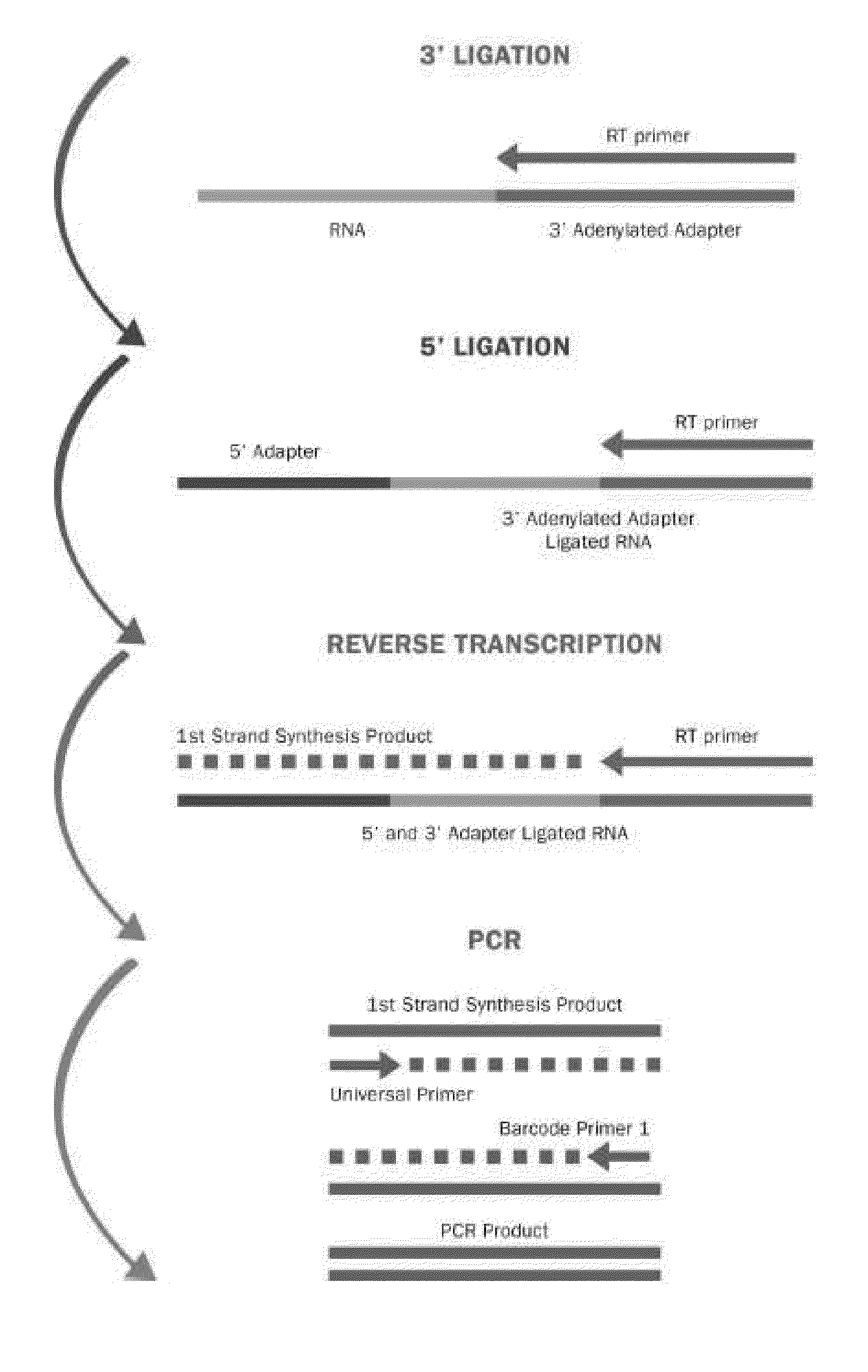
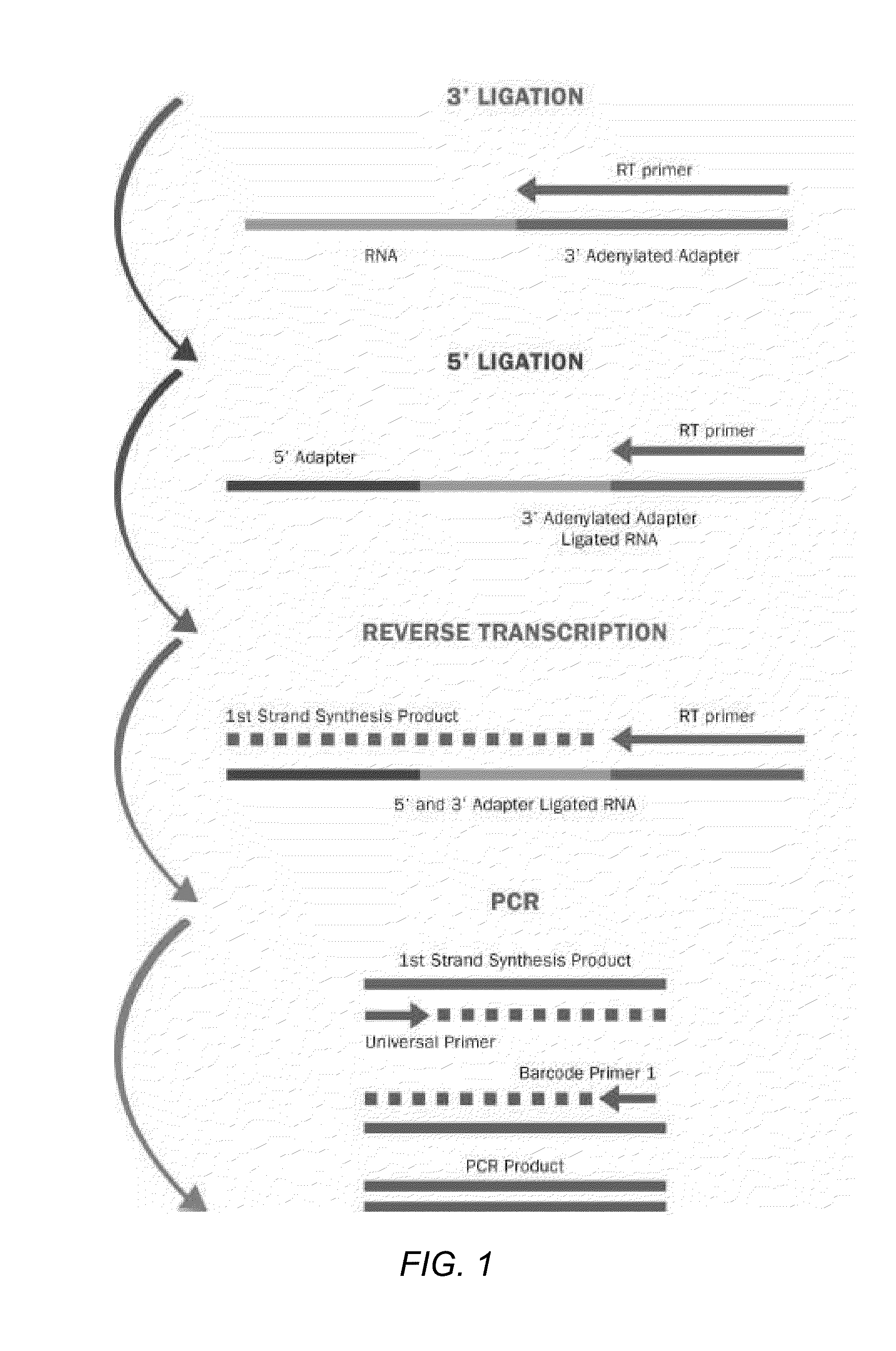
Method of library preparation avoiding the formation of adaptor dimers
ActiveUS20100167954A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary creationLibrary preparationPolynucleotide
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Library preparation of tagged nucleic acid
A method of preparing a library of tagged nucleic acid fragments including contacting a population of cells directly with a lysis reagent having one or more protease to generate a cell lysate; inactivating the protease to generate an inactivated cell lysate, and applying a transposase and a transposon end composition containing a transferred strand to the inactivated cell lysate under conditions wherein the target nucleic acid and the transposon end composition undergo a transposition reaction.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
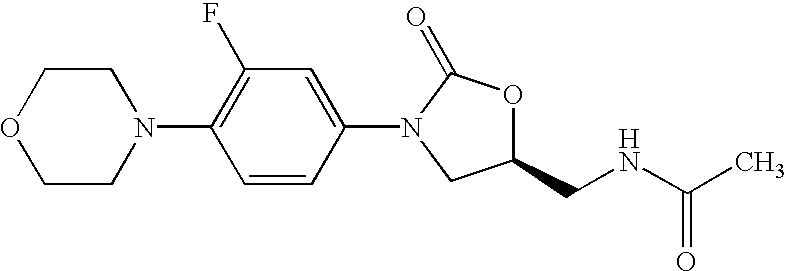
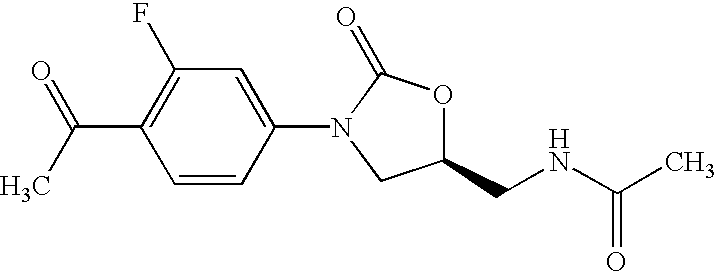
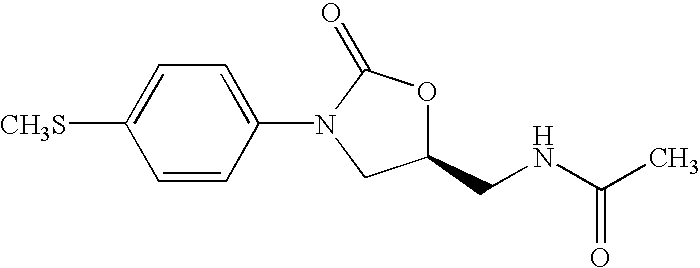
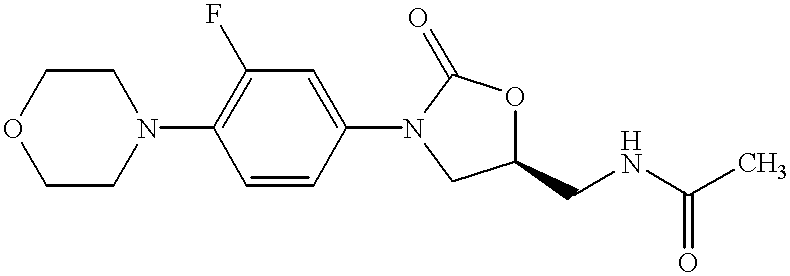
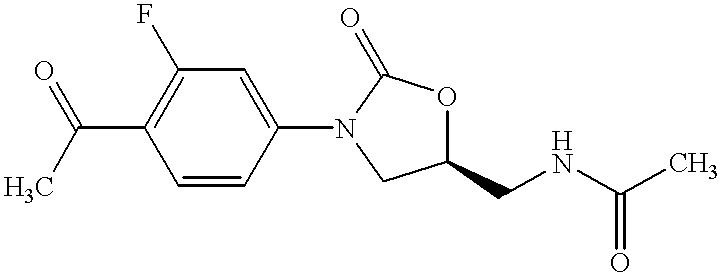
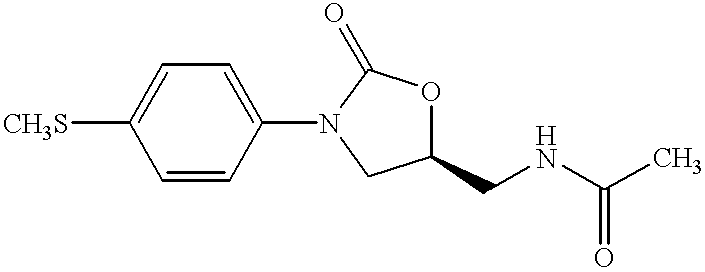
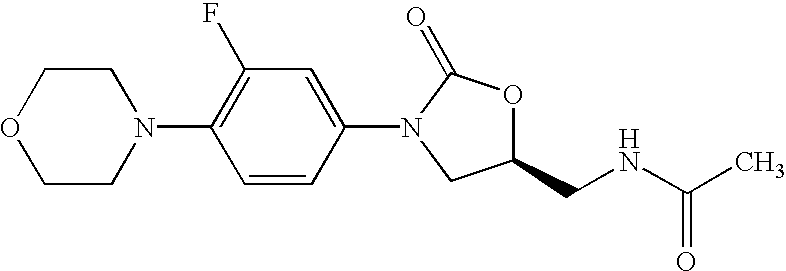
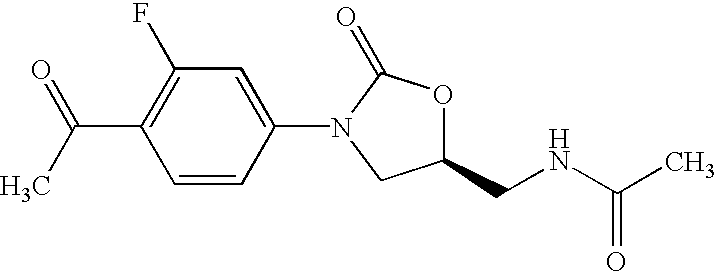
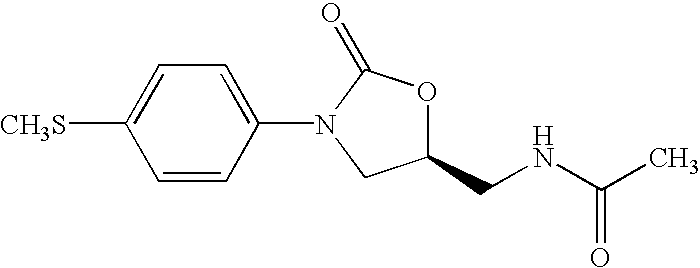
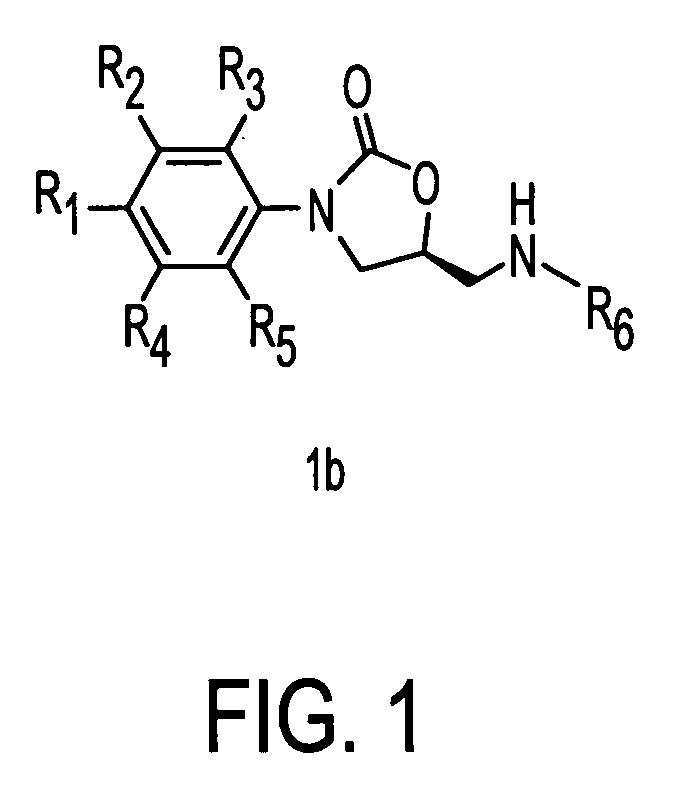
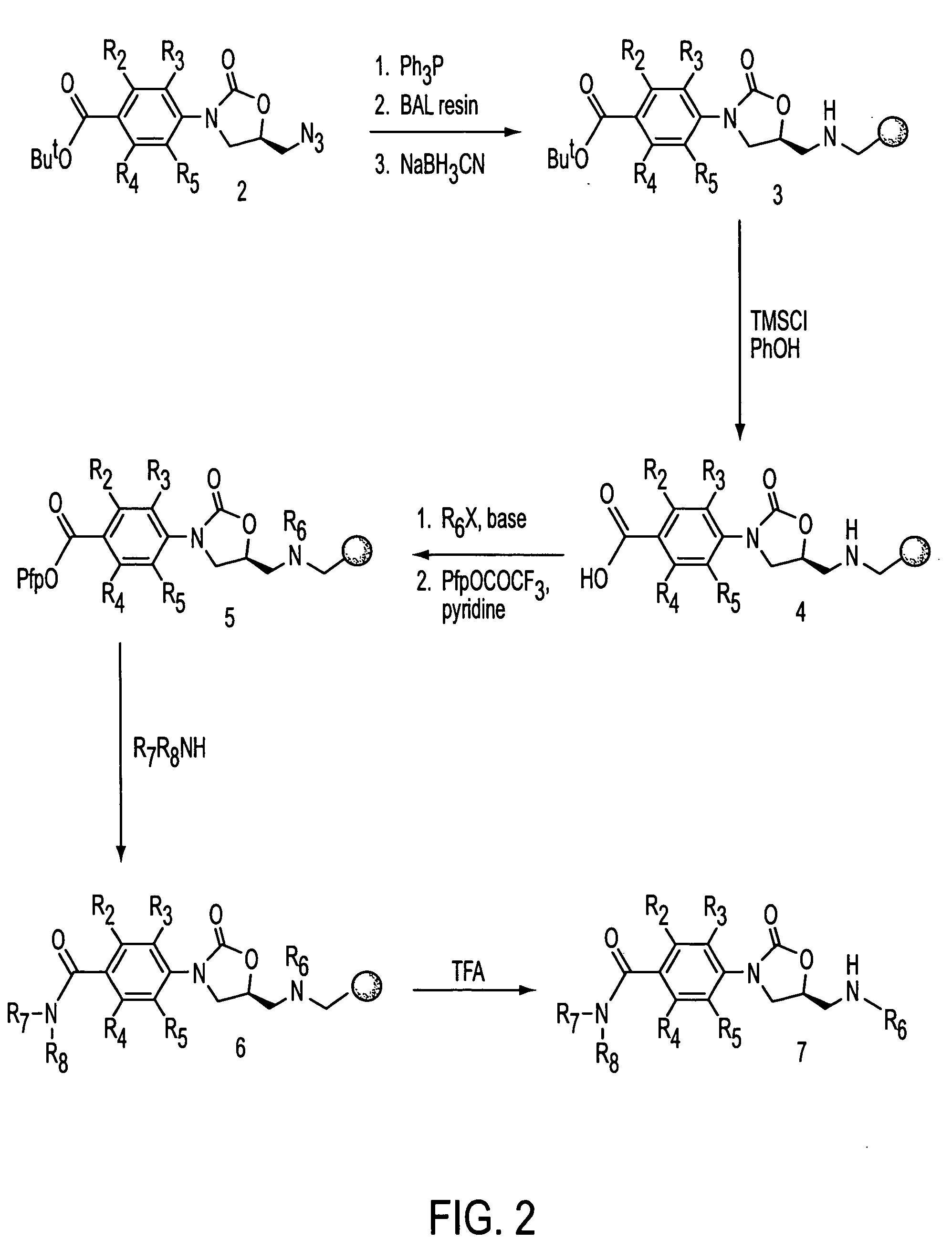
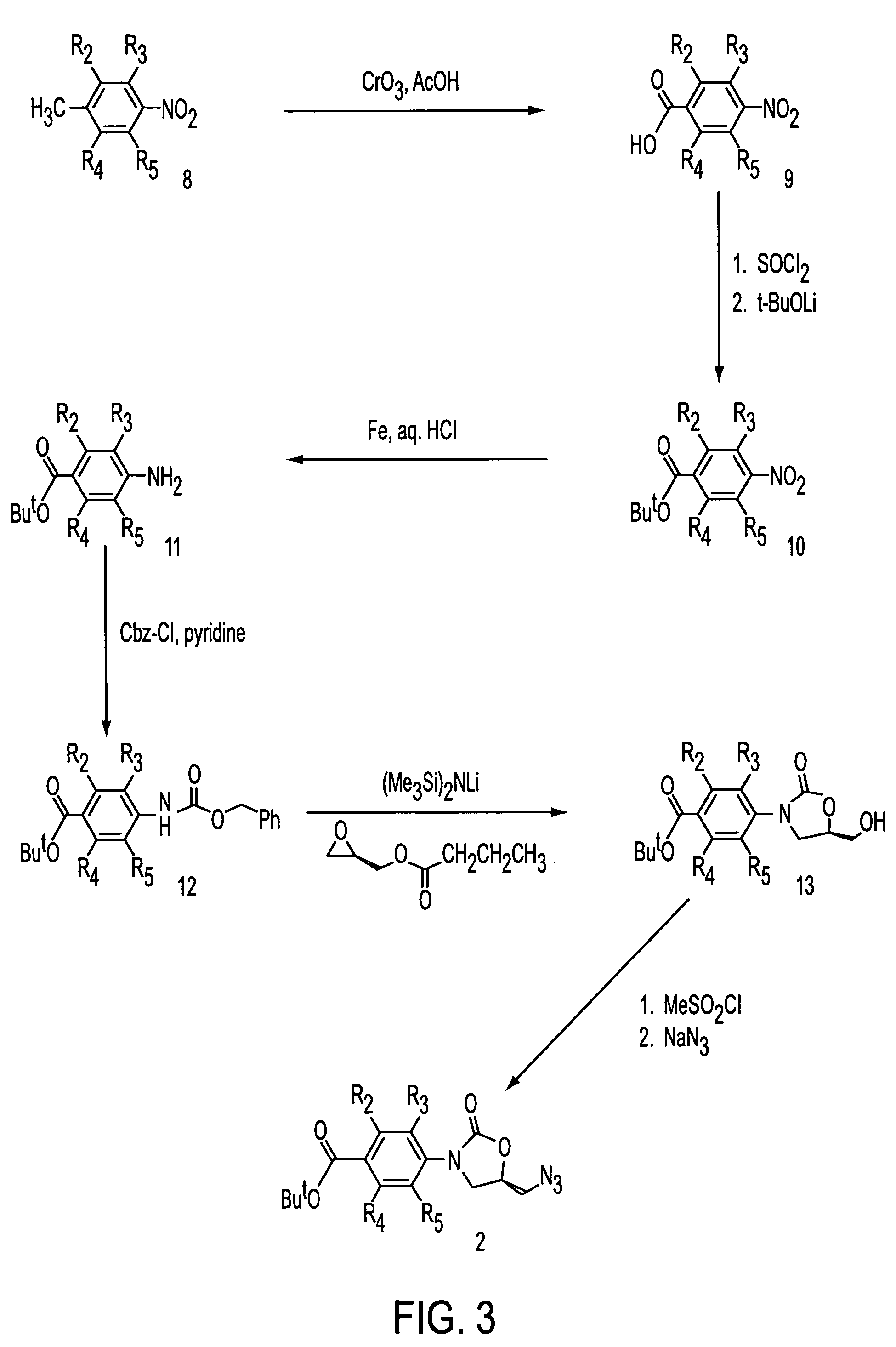
Oxazolidinone combinatorial libraries, compositions and methods of preparation
InactiveUS20020183371A1Rapid productionEasy to synthesizeBiocideGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsLibrary preparationCombinatorial chemistry
Oxazolidinones and methods for their synthesis are provided. Also provided are combinatorial libraries comprising oxazolidinones, and methods to prepare the libraries. Further provided are methods of making biologically active oxazolidinones as well as pharmaceutically acceptable compositions comprising the oxazolidinones. The methods of library preparation include the attachment of oxazolidinones to a solid support. The methods of compound preparation in one embodiment involve the reaction of an iminophosphorane with a carbonyl containing polymeric support.
Owner:PHARMACIA & UPJOHN CO
Oxazolidinone combinatorial libraries, compositions and methods of preparation
InactiveUS6531470B1Rapid productionEasy to synthesizeAntibacterial agentsBiocideSynthesis methodsLibrary preparation
Oxazolidinones and methods for their synthesis are provided. Also provided are combinatorial libraries comprising oxazolidinones, and methods to prepare the libraries. Further provided are methods of making biologically active oxazolidinones as well as pharmaceutically acceptable compositions comprising the oxazolidinones. The methods of library preparation include the attachment of oxazolidinones to a solid support. The methods of compound preparation in one embodiment involve the reaction of an iminophosphorane with a carbonyl containing polymeric support.
Owner:PHARMACIA & UPJOHN CO
Method of library preparation avoiding the formation of adaptor dimers
ActiveUS9328378B2Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary creationLibrary preparationPolynucleotide
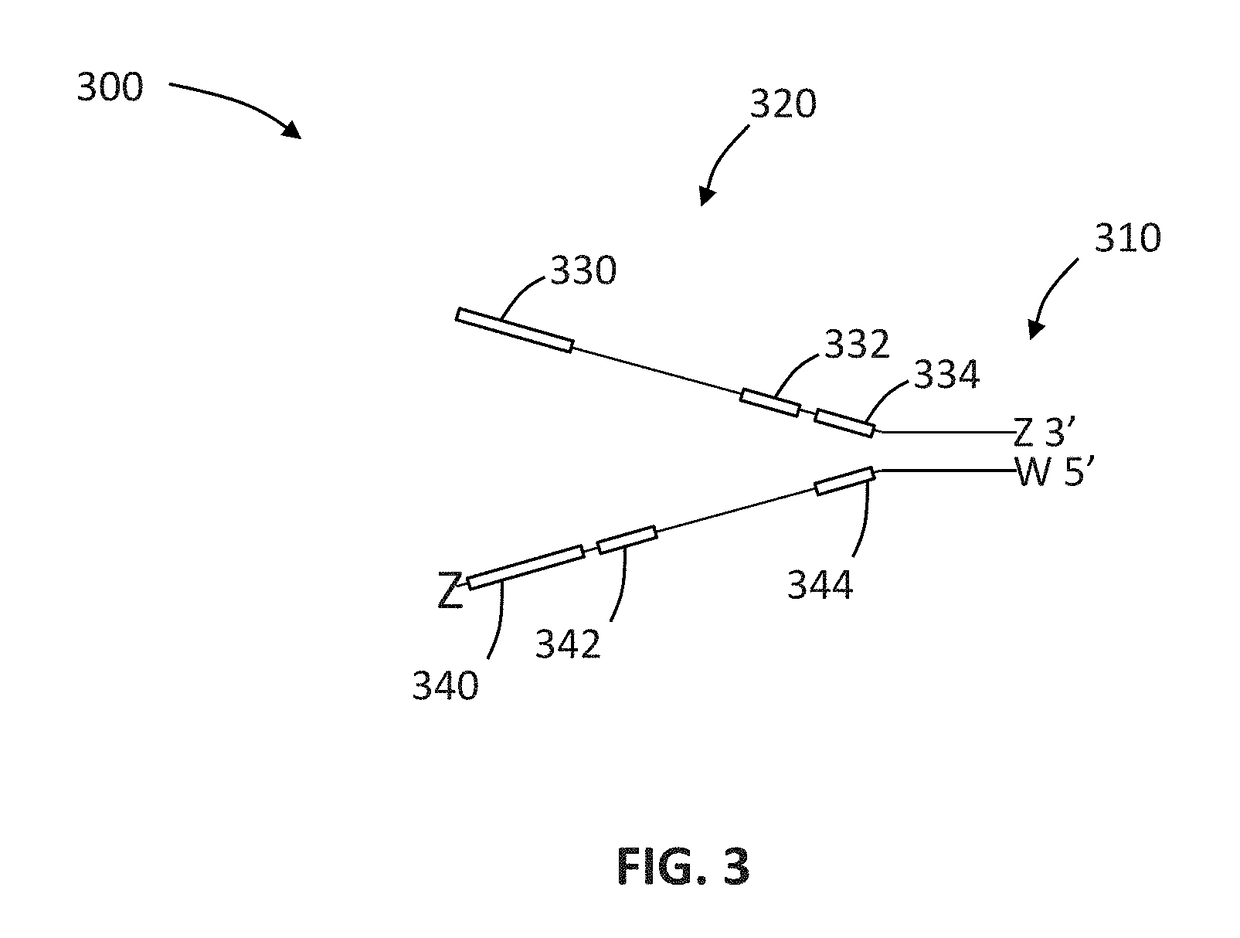
The invention relates to a method of preparing a library of template polynucleotides which reduces and / or prevents the formation of adaptor-dimers. The invention also relates to the use of a library of templates prepared using the method of the invention for solid-phase nucleic acid amplification. In particular, the invention relates to a method of preparing a library of template polynucleotides which have common sequences at their 5′ ends and at their 3′ ends which is substantially free of adaptor-dimers.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Method for differentiation of polynucleotide strands
ActiveUS20120237943A1Easy to implementImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisLibrary preparationPolynucleotide
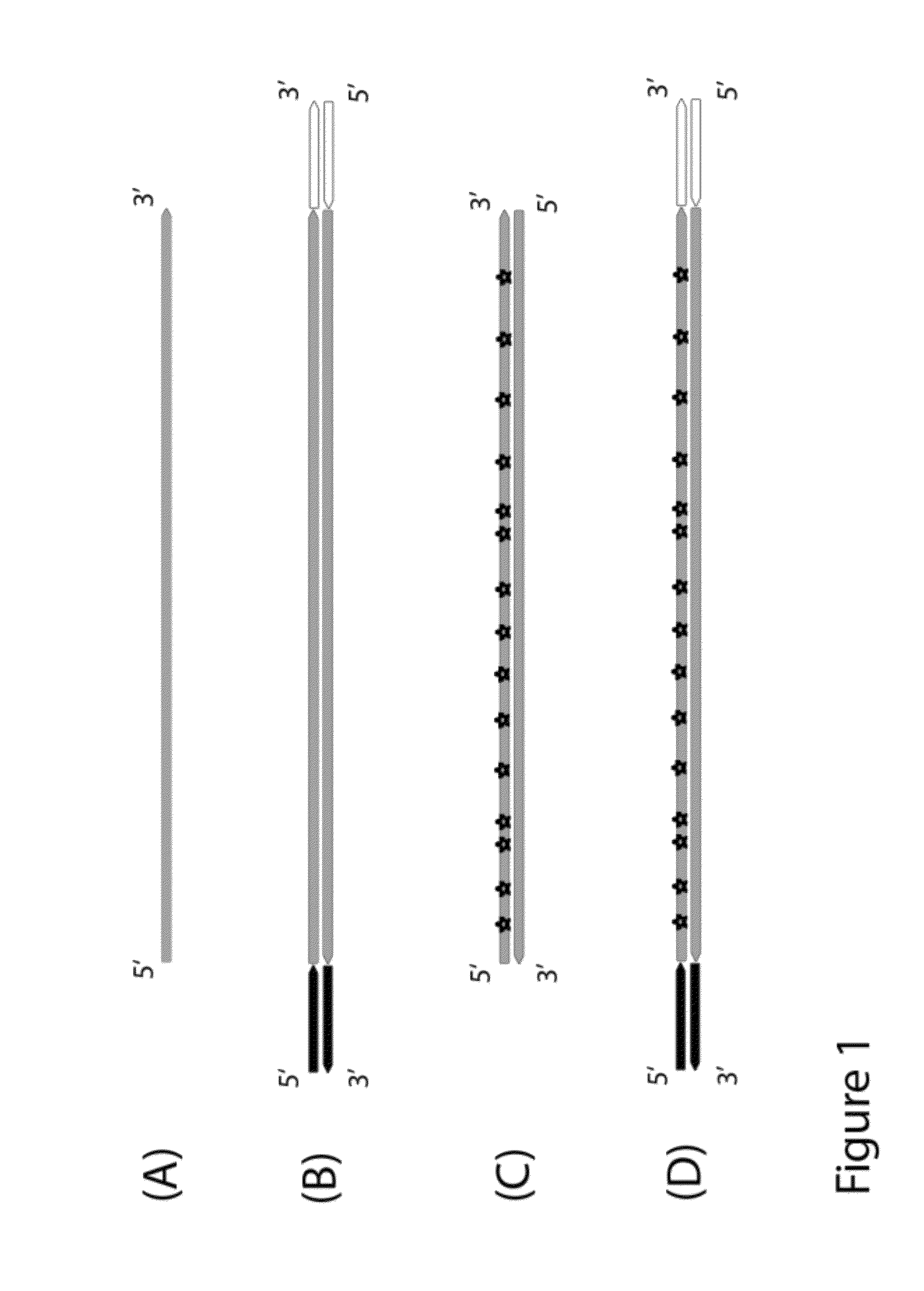
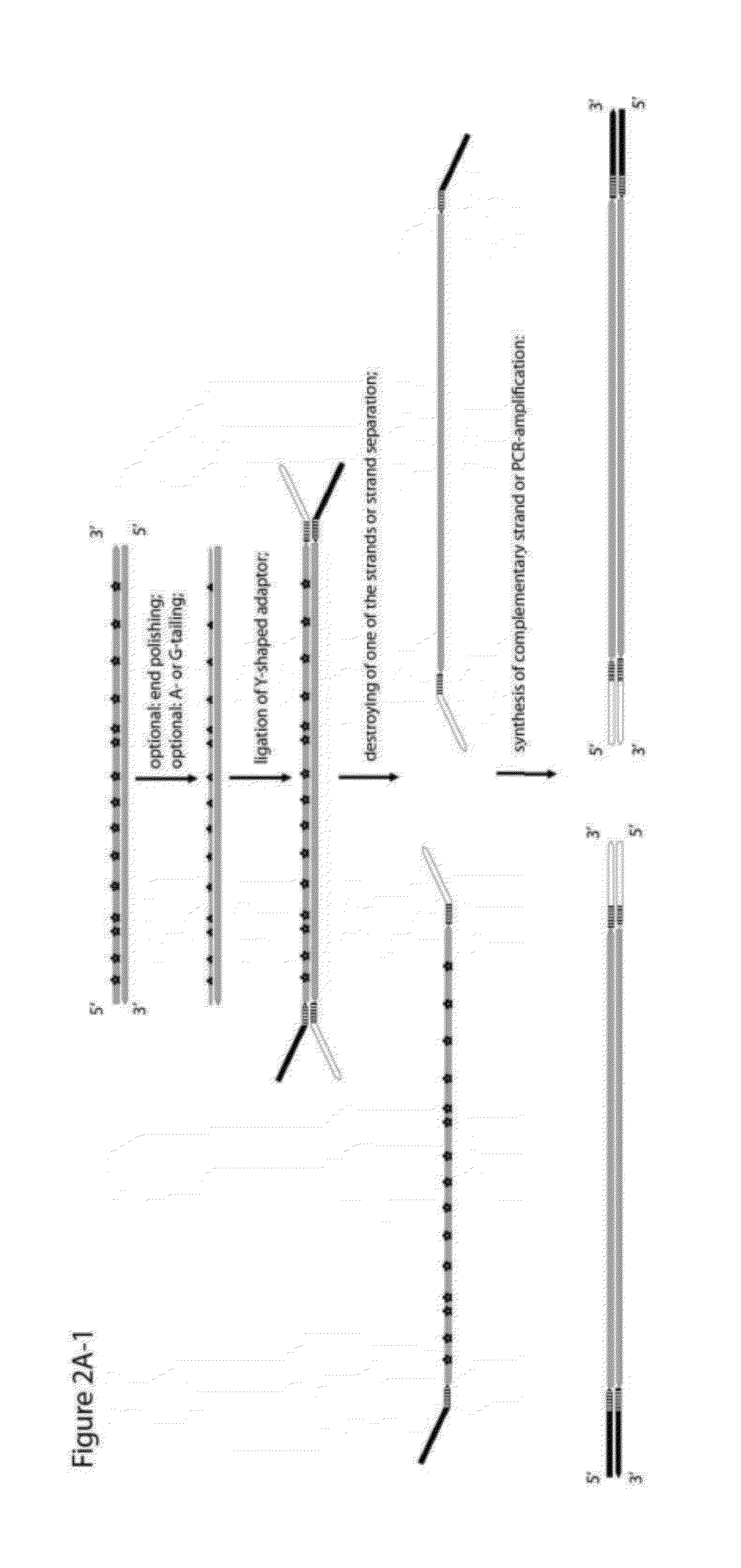
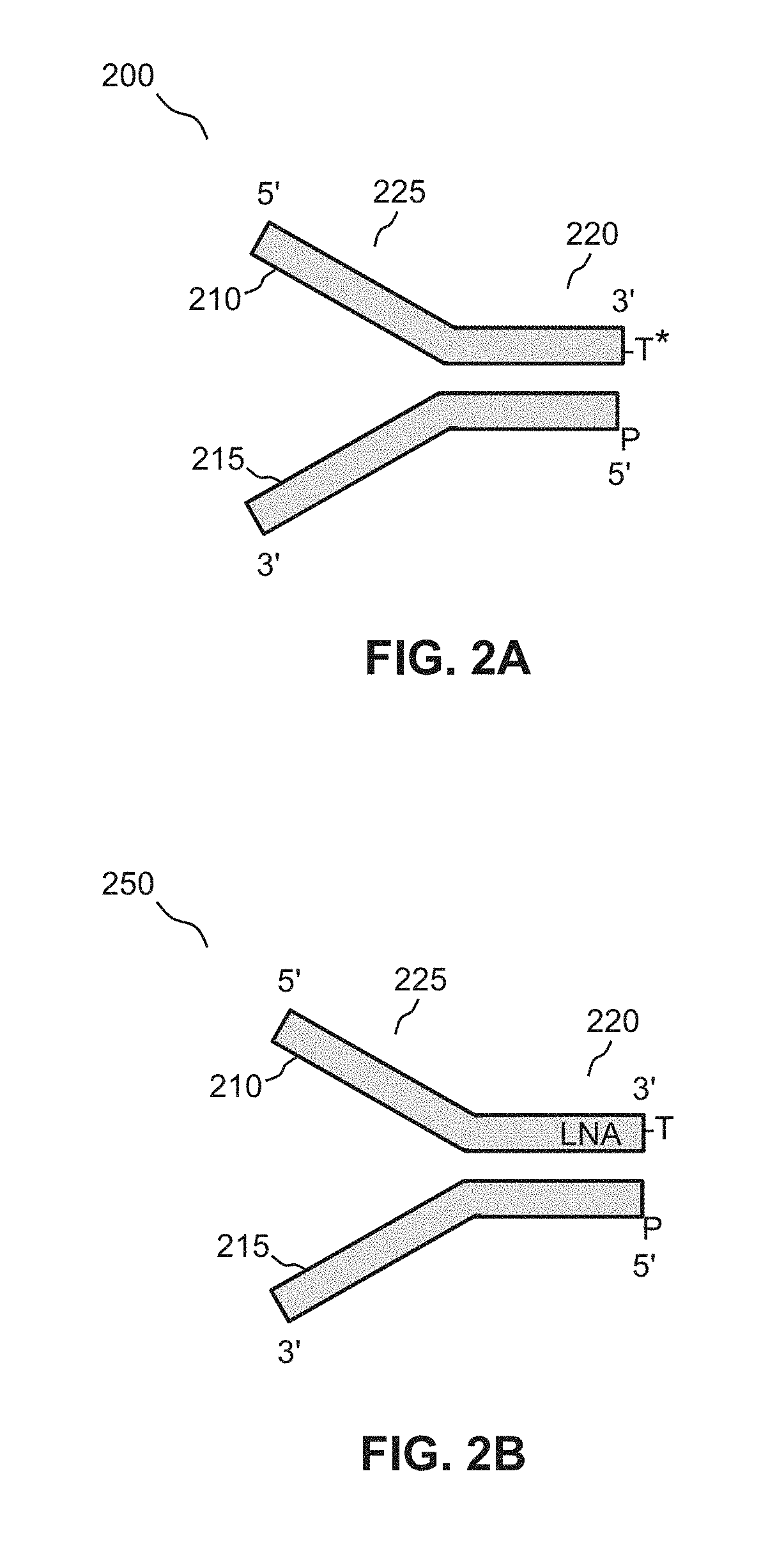
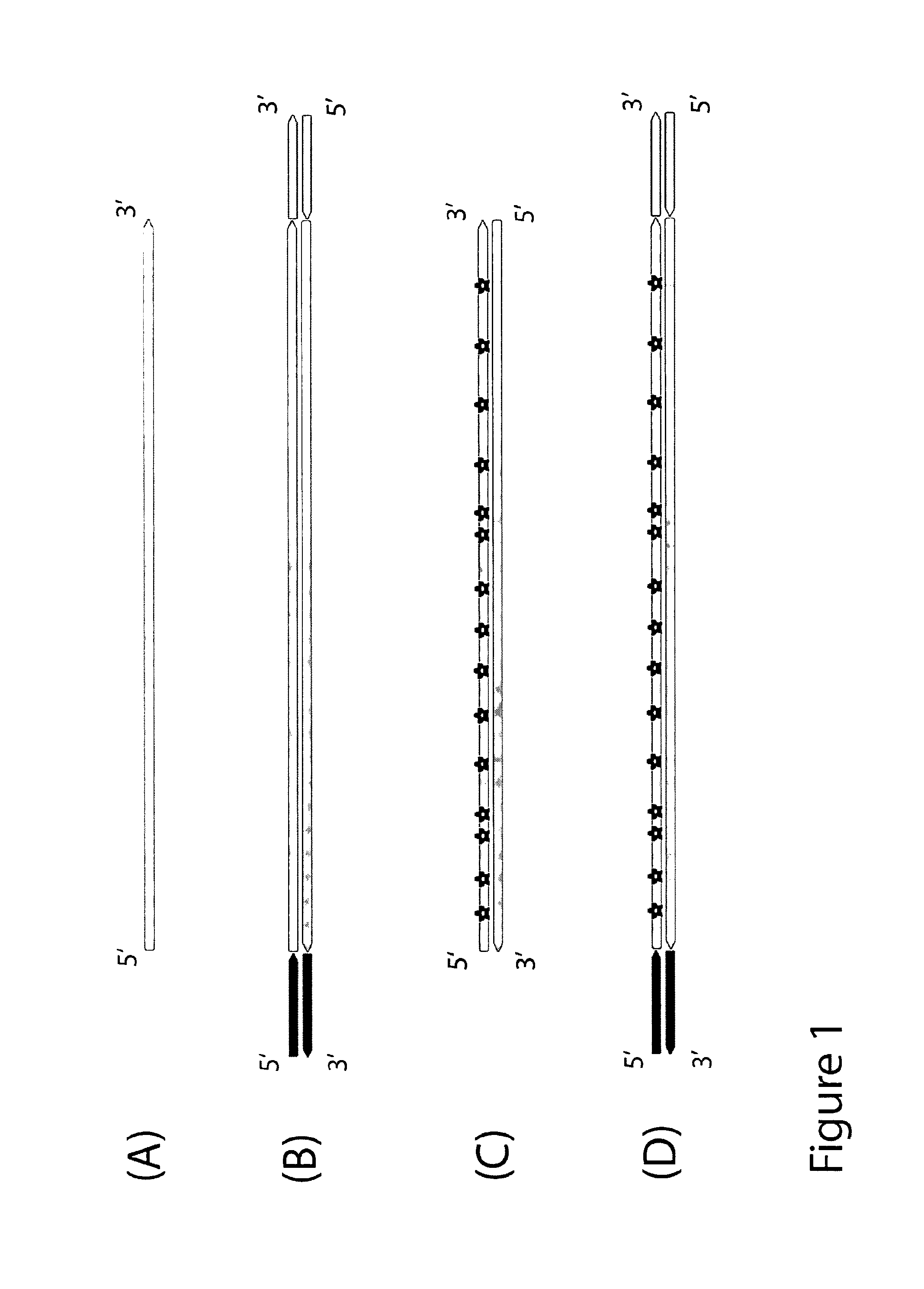
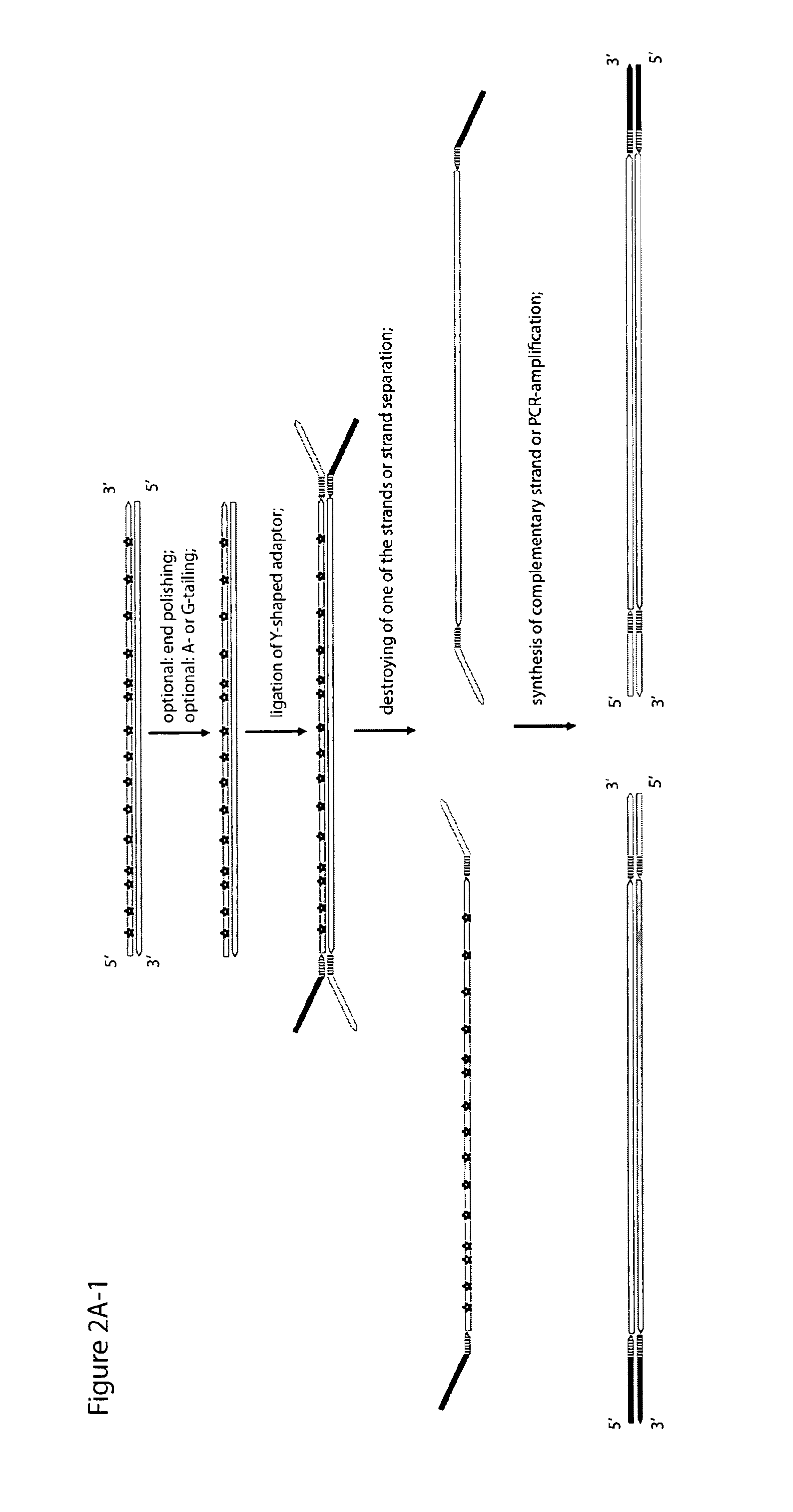
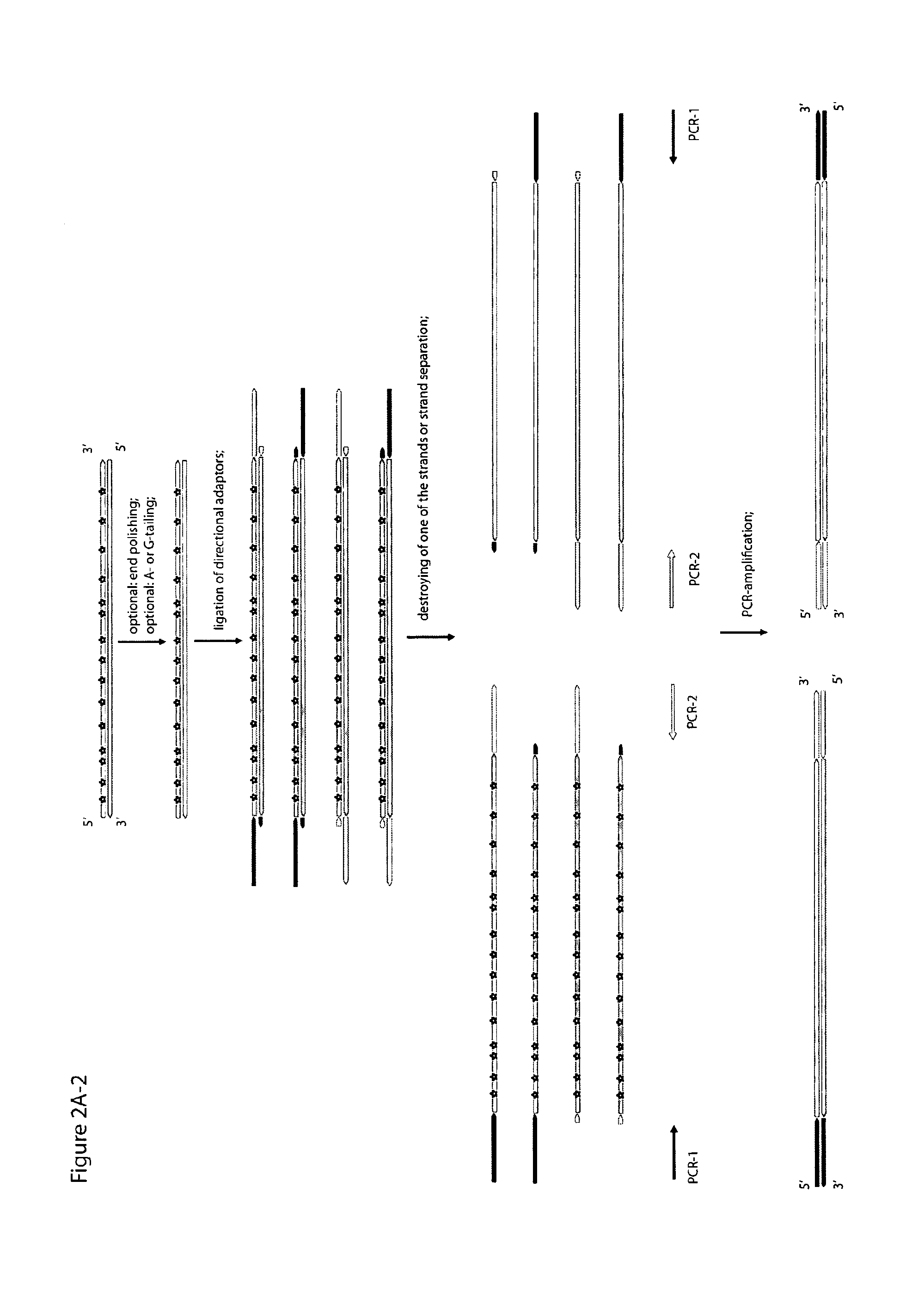
Objective of the present invention is to provide a method for keeping of directional information in double-stranded DNA. We suggest to convert polynucleotide into a hybrid double-stranded DNA. One particular strand of this hybrid double-stranded DNA should be synthesised using at least one modified nucleotide. Thus, this particular strand would contain modified nucleotides along the whole length. Density of directional markers would not depend on the length of polynucleotides. Any internal fragments of the hybrid double-stranded DNA would have directional information. When it is necessary the modified strand may be easily degraded or separated from the other strand. It was found that such hybrid double-stranded DNA may be easily generated in a number of molecular biology tasks and may be used for molecular cloning, library preparation and strand separation.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
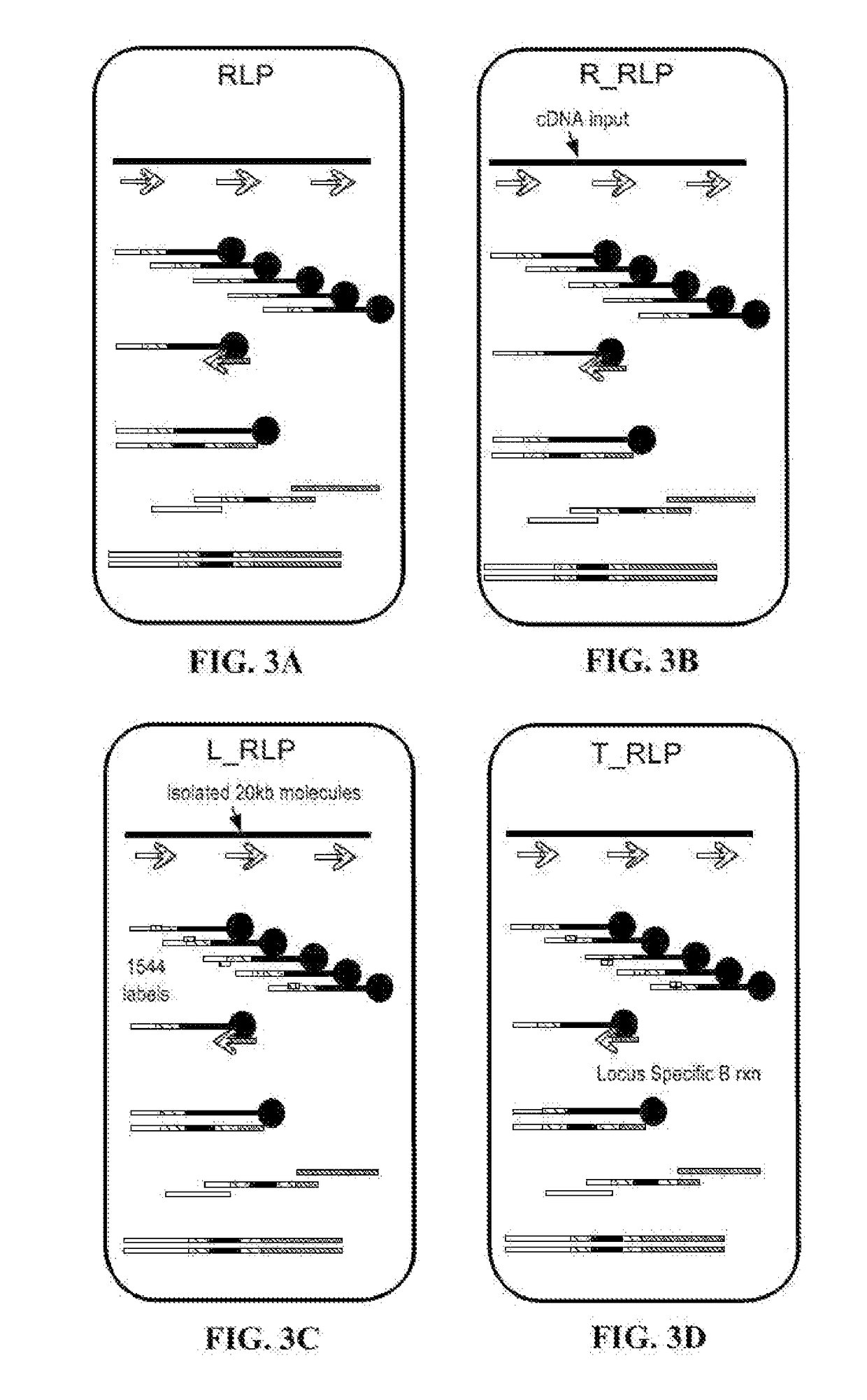
Library preparation method of trace nucleic acid sample and application thereof
ActiveCN103060924ANucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideLibrary preparation
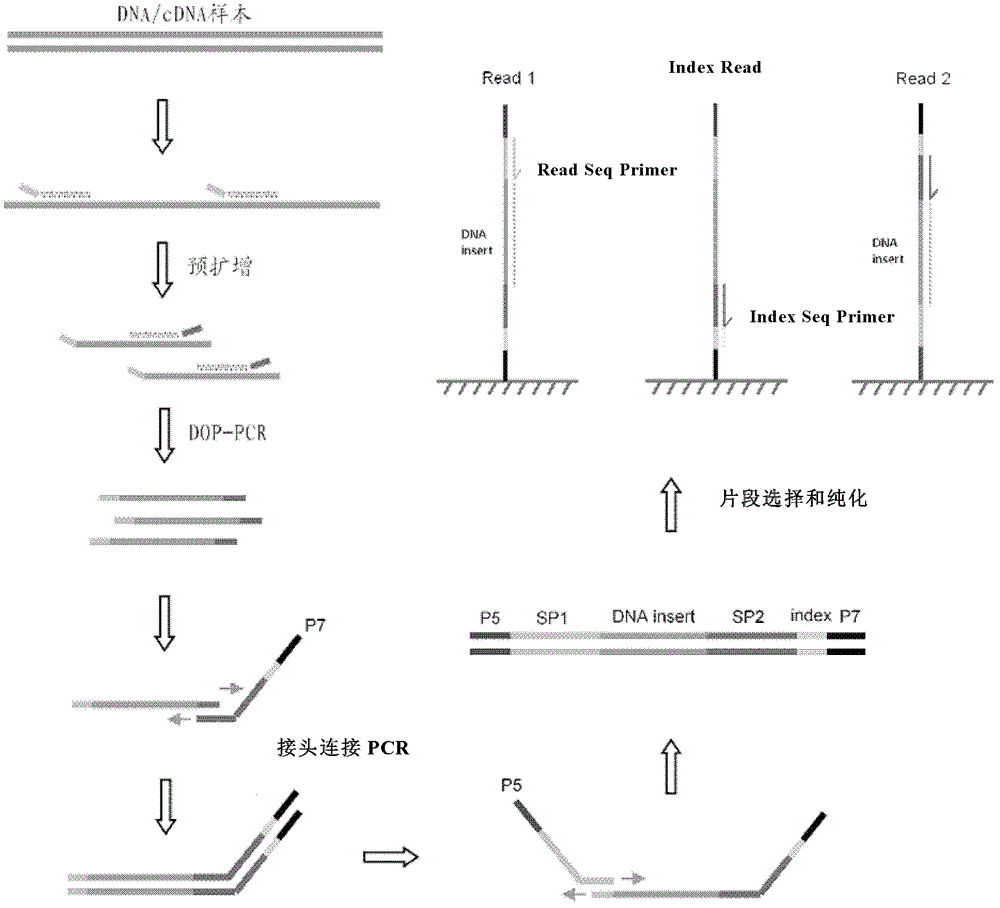
The invention relates to a library preparation method of a trace nucleic acid sample and application thereof. The method comprises: using a DOP (Degenerate Oligonucleotide Primed) primer to perform first amplification on DNA in the sample, with a DOP primer sequence having at least a 5' terminal nondegenerate nucleotide zone and a 3' terminal degenerate nucleotide zone; employing a DOP-Amp primer to conduct second amplification on a first PCR product so as to obtain a second PCR amplification product; and carrying out adaptor-ligation PCR on the second PCR amplification product to obtain a third PCR product, and taking the third PCR product with sequencing adaptors on both ends as the nucleic acid library. The library can be used for fragment size selection and high-throughput sequencing to obtain gene information related to diseases in the sample. The invention also provides a kit and its application in preparation of the trace nucleic acid sample library.
Owner:BGI BIOTECH WUHAN CO LTD
Oxazolidinone combinatorial libraries, compositions and methods of preparation
InactiveUS6562844B2Rapid productionEasy to synthesizeBiocideGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsLibrary preparationCombinatorial chemistry
Oxazolidinones and methods for their synthesis are provided. Also provided are combinatorial libraries comprising oxazolidinones, and methods to prepare the libraries. Further provided are methods of making biologically active oxazolidinones as well as pharmaceutically acceptable compositions comprising the oxazolidinones. The methods of library preparation include the attachment of oxazolidinones to a solid support. The methods of compound preparation in one embodiment involve the reaction of an iminophosphorane with a carbonyl containing polymeric support.
Owner:PHARMACIA & UPJOHN CO
STR (short tandem repeat) sequence high-throughput detection method with base selective controllable extension and detection reagent thereof
InactiveCN102703595AHigh detection throughputLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary preparationHigh throughput sequence
The invention relates to an STR (short tandem repeat) sequence high-throughput detection method with base selective controllable extension and a detection reagent thereof. The basic principle of an STR sequence detection method and a high-throughput DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequencing technology are combined, and the method which runs on a high-throughput sequencing platform for detecting massive STR sequence samples and the corresponding detection reagent are provided. The method comprises the following steps of: directly or indirectly fixing STR sequences of the samples to be detected on a detection chip according to a library preparation method corresponding to a sequencing system, adding the appropriate detection reagent according to the detection flow process, controlling reaction conditions, adopting the base selective controllable extension technical scheme to detect fluorescence intensity signals emitted by all reaction sites where the samples are located, and finally getting the detection results of the massive samples by analyzing fluorescence signal photos of all the detection sites during the whole detection process. The greatest advantage of the method disclosed by the invention is that the number of the samples which can be detected every time is greatly increased, and detection cost and time consumption can be further greatly reduced.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Compositions and methods for improving sample identification in indexed nucleic acid libraries
ActiveUS20180305751A1Lowering indexNucleotide librariesLibrary tagsLibrary preparationPolynucleotide
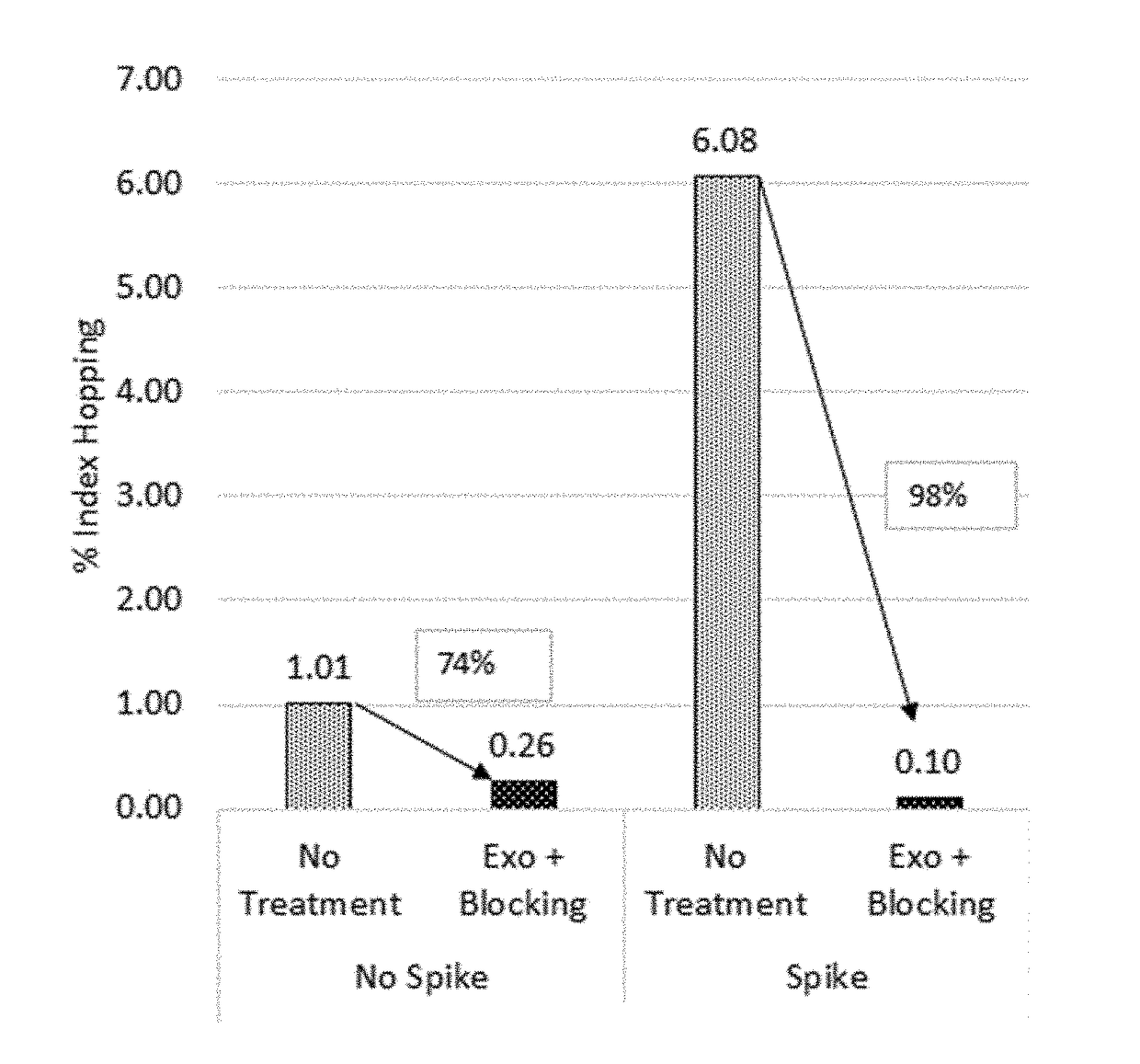
The present invention is concerned with compositions and methods for improving the rate of correct sample identification in indexed nucleic acid library preparations for multiplex next generation sequencing by exonuclease treatment after protective adapters are ligated to target polynucleotides to degrade unincorporated adapters prior to amplification and sequencing.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC +1
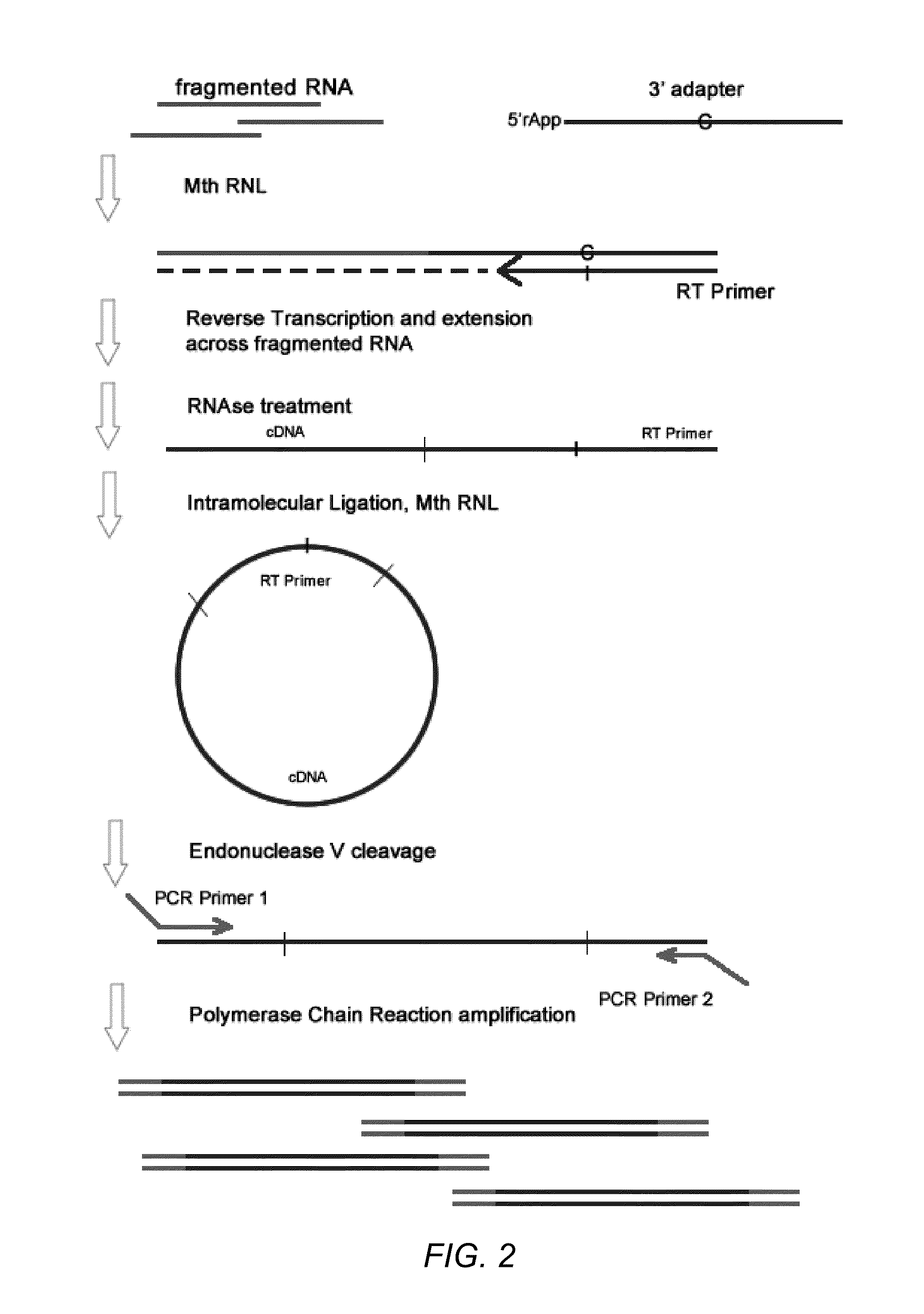
Methods and compositions for rapid nucleic acid library preparation
ActiveUS20170247689A1Easy to analyzeEliminate risk of amplification biasNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementRapid identificationLibrary preparation
Rapid nucleic acid libraries, methods of generation, kits, and compositions relating to library synthesis, including reagents, intermediaries and final products are disclosed herein. The disclosure enables rapid synthesis of libraries that allow independent verification of sequence information and rapid identification of sequence information with template of origin.
Owner:IGENOMX INT GENOMICS
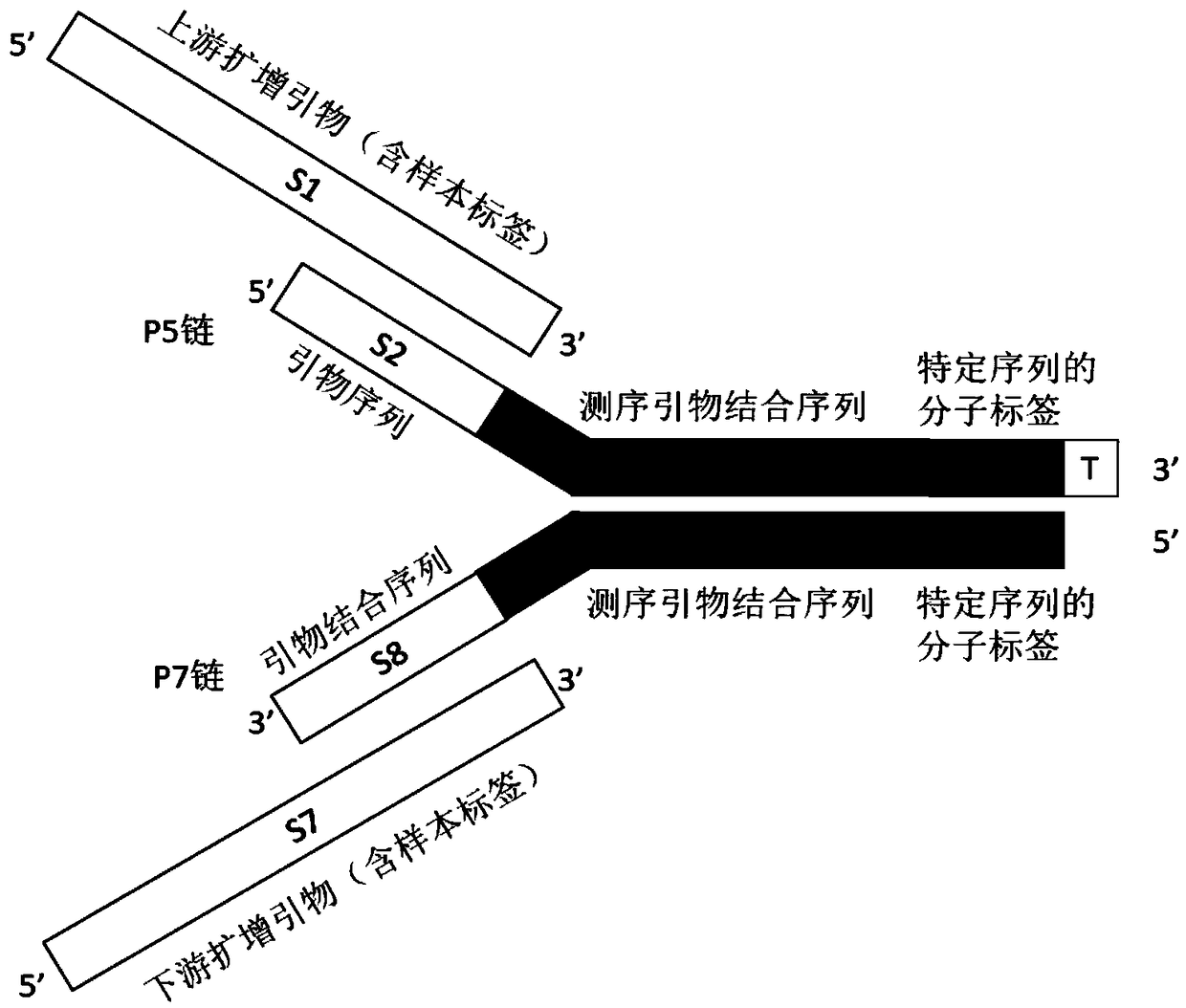
Linker for detecting low-frequency variation, linker mixture and corresponding method
InactiveCN109439729AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationInformation analysisLibrary preparation
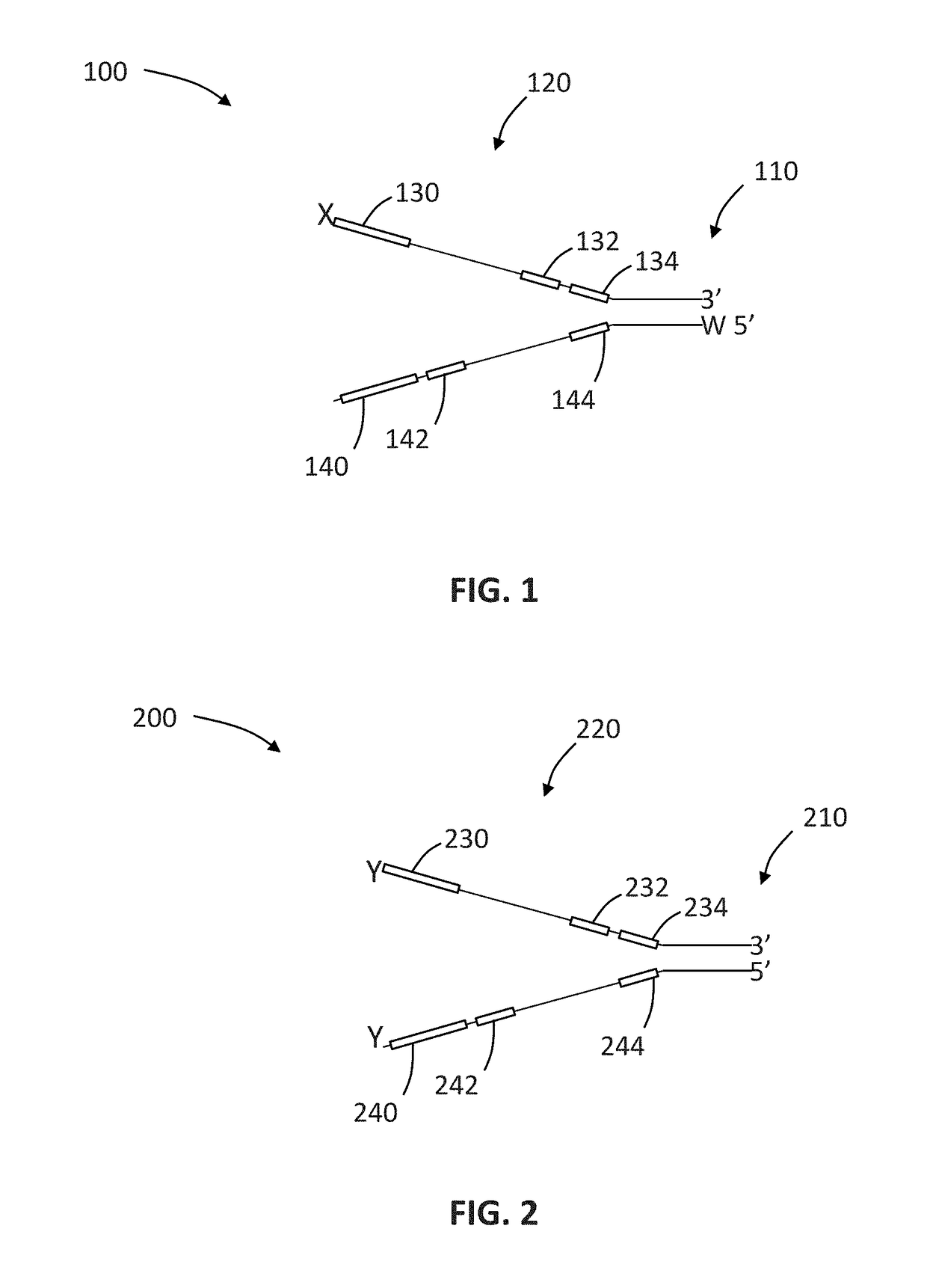
The invention relates to a linker for detecting low-frequency variation. The linker comprises two complementary DNA single chains, wherein one chain P5 comprises a sequence locally coincided with an upstream amplification primer, a sequence combined with an upstream sequencing primer, a molecular label of a specific nucleotide sequence combination and a bulged base T in turn from 5' end to 3' end;and the other chain P7 comprises the following three parts in turn from 5' end to 3' end: a molecular label reversely complementing to the molecular label in the chain P5, a sequence combined with adownstream sequencing primer and a sequence combined with a downstream amplification primer. The invention also relates to a linker mixture for detecting low-frequency variation and a corresponding method. The linker mixture provided by the invention is used for performing library preparation and high-throughput sequencing on the samples containing low-frequency variation and with damaged single chains, and the biological information analysis process and algorithm disclosed by the invention are adopted for effectively increasing the accuracy of variation detection.
Owner:XUKANG MEDICAL SCI & TECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD
Cancer detection kit based on large-scale data mining and detection method
InactiveCN105653898AGroundbreaking improvementSecurity Enhancements and ImprovementsBiostatisticsSequence analysisCancer cellLibrary preparation
The invention discloses a cancer detection kit based on large-scale mining and a detection method, and belongs to the technical field of biomedical detection. The kit comprises a DNA extraction reagent, a high-throughput sequencing library preparation reagent, gene sequence alignment software and chromosome cover degree calculation software. The method comprises the steps that firstly, peripheral blood is collected from a subject and plasma is separated out; DNA polymerase is used for amplification and a sequencing library is prepared; large-scale sequencing is performed on the prepared library; sequence alignment is performed on a sequencing result, statistic is performed on the distribution situation on a genome, and whether a cancer cell genomic sequence from tumor tissue exists or not is judged, so that whether a detection object carries a cancer or not is judged. According to the cancer detection kit and the detection method, the defect that existing cancer screening specificity and sensitivity are poor is overcome, the method causes no irradiation or wounds, and cancer detection can be achieved only through 4-10 mL of peripheral blood.
Owner:江苏格致生命科技有限公司
Methods for improving ligation steps to minimize bias during production of libraries for massively parallel sequencing
Owner:BICO SCI CORP
Enhanced ligation in sequencing library preparation
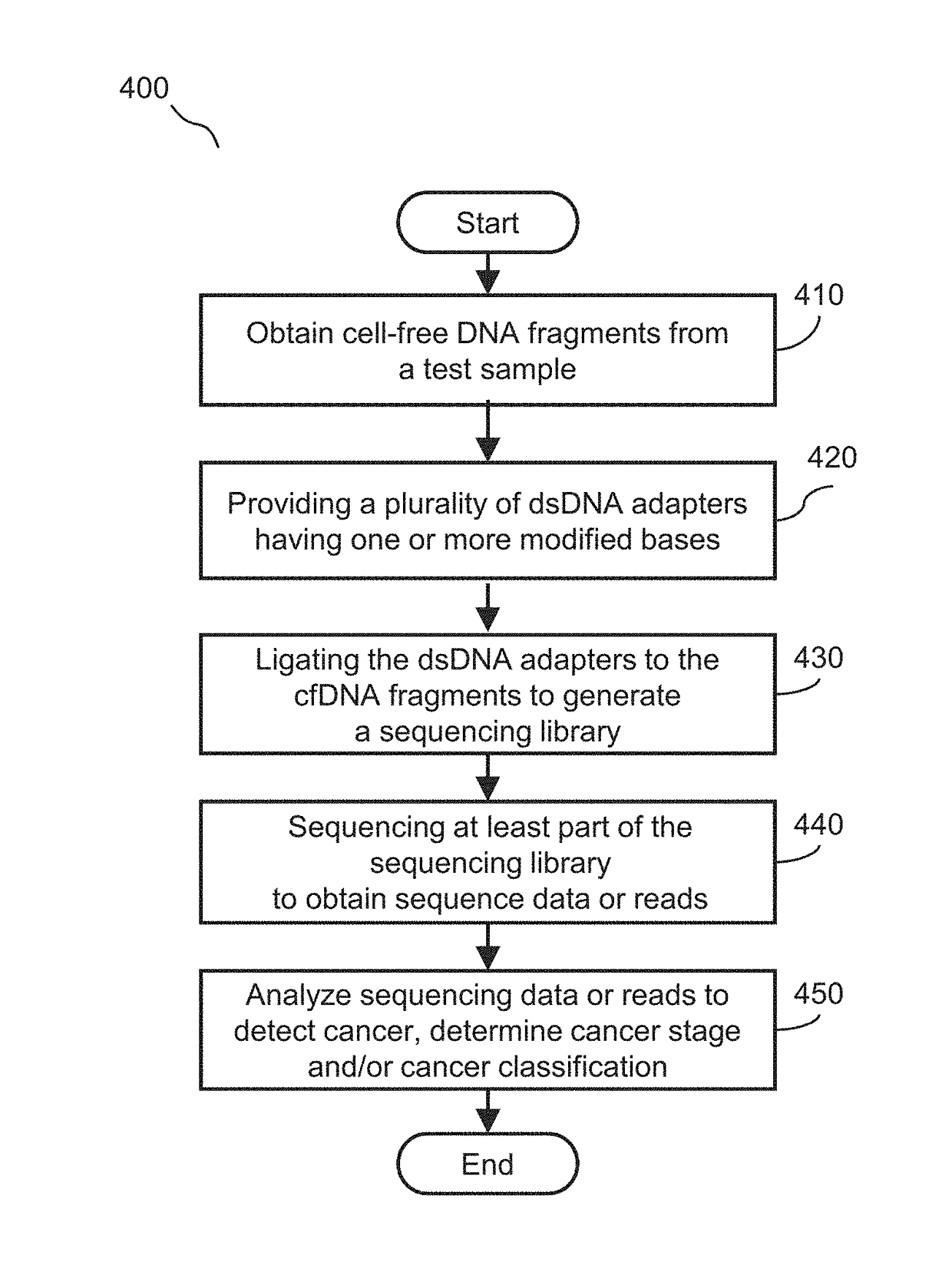
ActiveUS20180291445A1Enhance library preparation conversion efficiencyPromote recoveryMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionTest sampleTransformation efficiency
Methods for preparing a sequencing library from a DNA-containing test sample are provided. In some embodiments, the methods involve rescuing a partially ligated DNA fragment to enhance library preparation conversion efficiencies. In some embodiments, the methods involve improving recovery of duplex sequence information from double-stranded DNA.
Owner:GRAIL LLC
PCR-free sequencing library preparation method for genome DNA
InactiveCN105734048AWide applicabilityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationLibrary preparationGenome
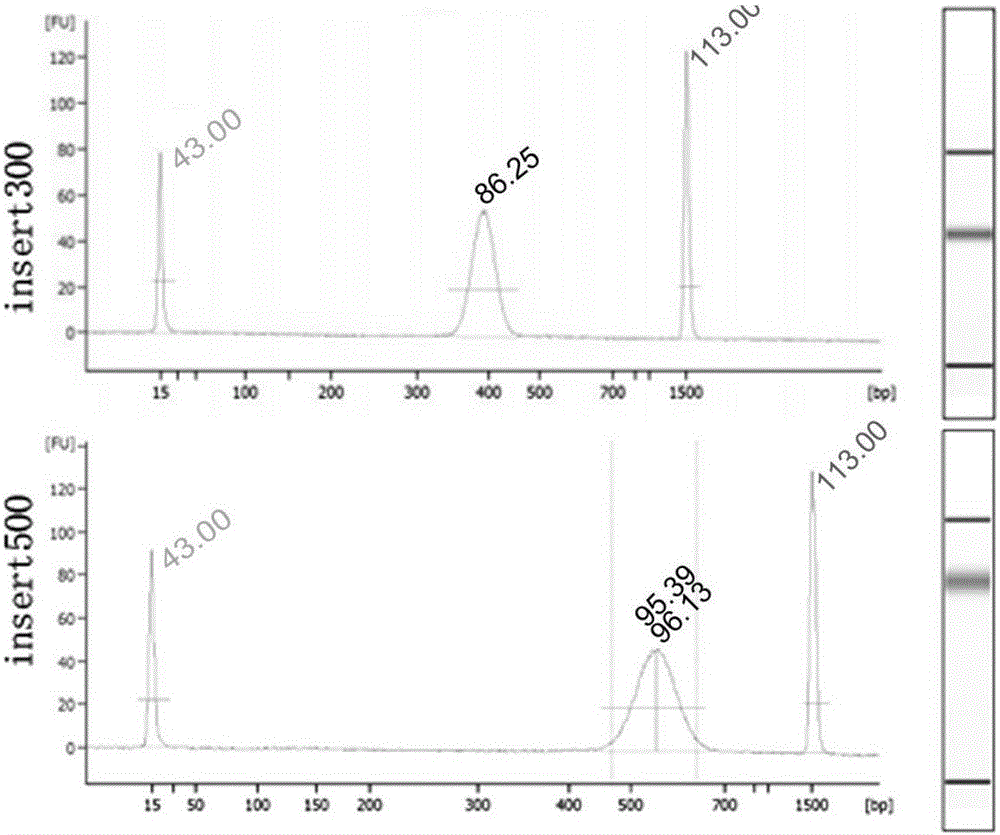
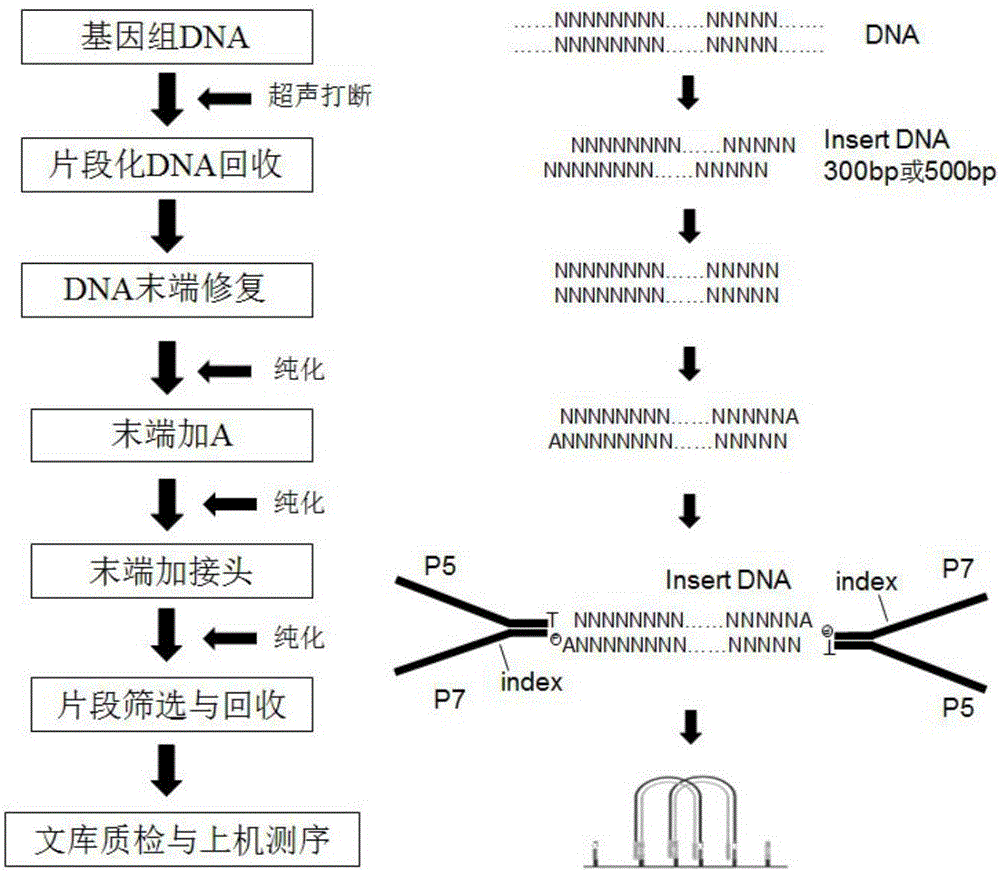
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular biologics, and discloses a PCR-free sequencing library preparation method for genome DNA. The PCR-free sequencing library preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) breaking genome DNA with ultrasonic waves; (2) purifying and recycling DNA fragments; (3) repairing tail ends of the fragmented DNA; (4) purifying and recycling tail end repairing products; (5) adding A to the tail ends of DNA; (6) purifying and recycling the tail end A-added product; (7) adding sequencing connectors on two sides of DNA so as to implement connection reaction; (8) performing fragment screening on connection products, and recycling products, so as to obtain a sequencing library; (9) performing quality inspection and loading sequencing on the library. The invention provides a genome DNA ultrasonic breaking method used in the step (1), methods for purifying the products in the steps (2, 4 and 6), reaction systems and conditions in the steps (3, 5 and 7), and design and use methods of the sequencing connectors which are compatible with an Illumina secondary sequencing instrument in the step (7), so that the PCR-free sequencing library preparation method disclosed by the invention can be rapidly and smoothly implemented, and the loading sequencing library can be directly prepared without PCR reaction (PCR-free) according to the preparation method.
Owner:WUHAN BINGGANG BIOTECH CO LTD
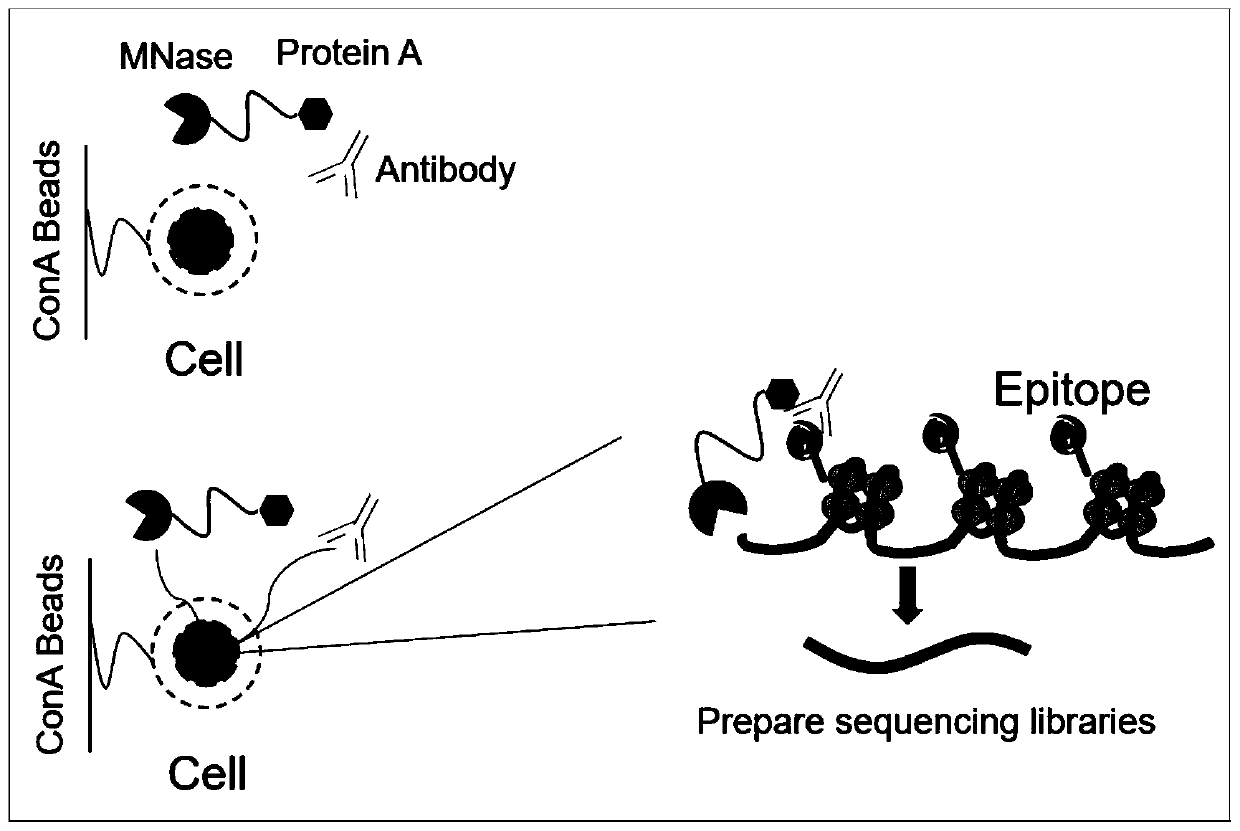
Fusion protein used for single-cell ChIP-seq library preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN110372799AImprove accuracySimplify the experimental processPolypeptide with affinity tagMicrobiological testing/measurementTn5 transposaseFc binding
The invention relates to a fusion protein used for single-cell ChIP-seq library preparation and application thereof. The fusion protein comprises Tn5 transposase and an Fc binding protein; a kit comprises the fusion protein and other auxiliary detection reagents; a method uses the fusion protein or the kit for ChIP-seq detection. The fusion protein, the kit and the method can improve the library building efficiency and lower the library background in the ChIP-seq detection process, so that the accuracy of the ChIP-seq detection method can be improved, and the experimental flow of ChIP-seq canbe simplified.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for differentiation of polynucleotide strands
ActiveUS8999677B1Easy to implementImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideLibrary preparation
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
DNA barcode compositions and methods of in situ identification in a microfluidic device
PendingUS20190345488A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsCell specificSequence analysis
Apparatuses, compositions and processes for DNA barcode deconvolution are described herein. A DNA barcode may be used to provide a bead specific identifier, which may be detected in situ using hybridization strategies. The DNA barcode provides identification by sequencing analysis. The dual mode of detection may be used in a wide variety of applications to link positional information with assay information including but not limited to genetic analysis. Methods are described for generation of barcoded single cell sequencing libraries. Isolation of nucleic acids from a single cell within a microfluidic environment can provide the foundation for cell specific sequencing library preparation.
Owner:BERKELEY LIGHTS
Methods for single-stranded nucleic acid library preparation
ActiveUS20180119216A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationLibrary preparationDiagnostic information
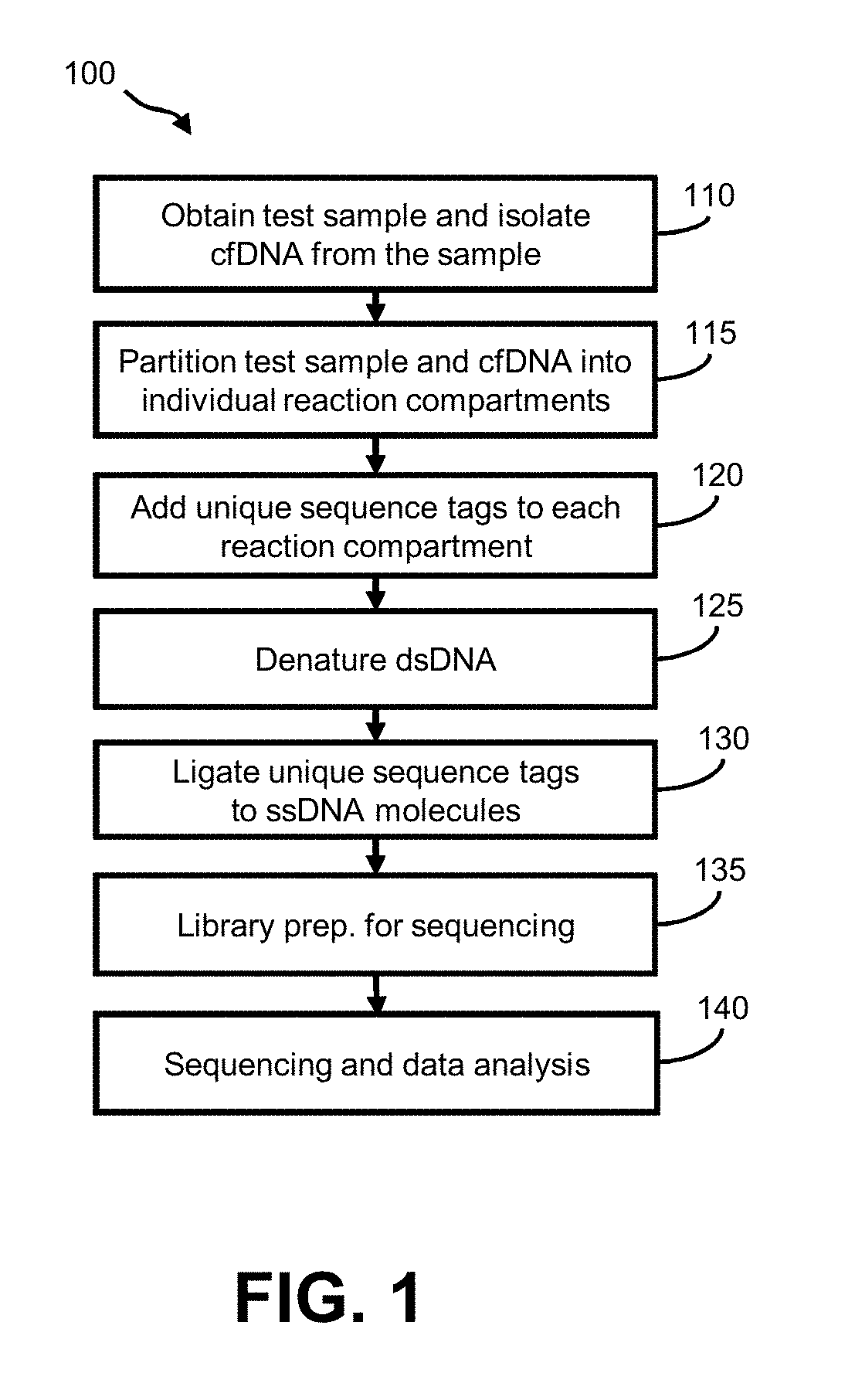
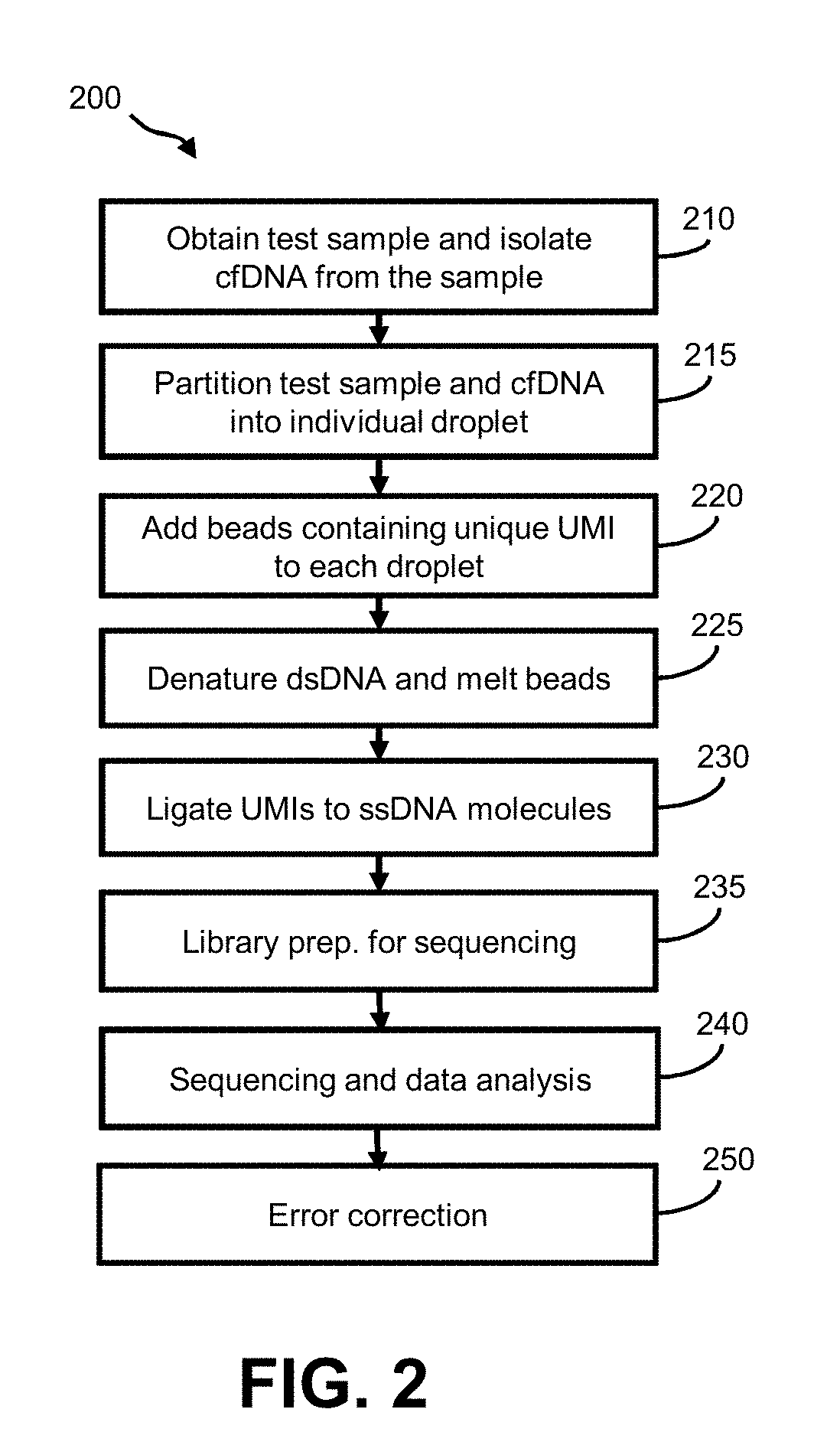
Aspects of the invention relate to methods and compositions for preparing and analyzing a single-stranded sequencing library from a double-stranded DNA (e.g., double-stranded cfDNA) sample. In some embodiments, the sample includes double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) molecules, and damaged dsDNA (e.g., nicked dsDNA) molecules. In some embodiments, the sample includes single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) molecules. The subject methods facilitate the collection of information, including strand-pairing and connectivity information, from dsDNA, ssDNA and damaged DNA (e.g., nicked DNA) molecules in a sample, thereby providing enhanced diagnostic information as compared to sequencing libraries that are prepared using conventional methods.
Owner:GRAIL LLC
Compositions and methods for improving sample identification in indexed nucleic acid libraries
ActiveUS20180305753A1Narrowing activity of exonucleaseIndex can be reduced and eliminatedNucleotide librariesLibrary tagsNucleotideLibrary preparation
The present invention is concerned with compositions and methods for improving the rate of correct sample identification in indexed nucleic acid library preparations for multiplex next generation sequencing by exonuclease treatment and optionally blocking the 3′ ends of pooled indexed polynucleotides from multiple samples prior to amplification and sequencing.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Gene sequencing chip and gene sequencing method
ActiveCN107118955AHighly integratedPrecise handlingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsMicrofluidicsLibrary preparation
The invention provides a gene sequencing chip. The gene sequencing chip comprises an upper substrate and a lower substrate, wherein the upper substrate comprises a plurality of liquid inlets used for liquid drops to enter; the lower substrate is opposite to the upper substrate and separated from the upper substrate by a gap; the gap is used for storing the liquid drop; the lower substrate comprises a liquid drop operation area; the liquid drop operation area comprises a plurality of first line arrays used for preparing a gene library, and a plurality of second line arrays used for gene sequencing; each of the plurality of first line arrays is adjacent to each of the plurality of first line arrays. The gene sequencing chip and the gene sequencing method can accurately control minute drop to perform liquid drop movement, fusion and separation operation through a digital microfluidic technology, and programmatically accomplish all steps of the entire gene sequencing from library preparation up to gene detection on one chip. The chip is high in integration level, can accurately control the liquid drop, reduces the consumption of reagents, and is simple and mature in preparation technology.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Oxazolidinone combinatorial libraries, compositions and methods of preparation
InactiveUS20050004174A1Rapid productionBiocideGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsLibrary preparationCombinatorial chemistry
Oxazolidinones and methods for their synthesis are provided. Also provided are combinatorial libraries comprising oxazolidinones, and methods to prepare the libraries. Further provided are methods of making biologically active oxazolidinones as well as pharmaceutically acceptable compositions comprising the oxazolidinones. The methods of library preparation include the attachment of oxazolidinones to a solid support. The methods of compound preparation in one embodiment involve the reaction of an iminophosphorane with a carbonyl containing polymeric support.
Owner:GORDEEV MIKHAIL F +4
Isothermal Amplification of Nucleic Acid, and Library Preparation and Clone Generation in Sequencing
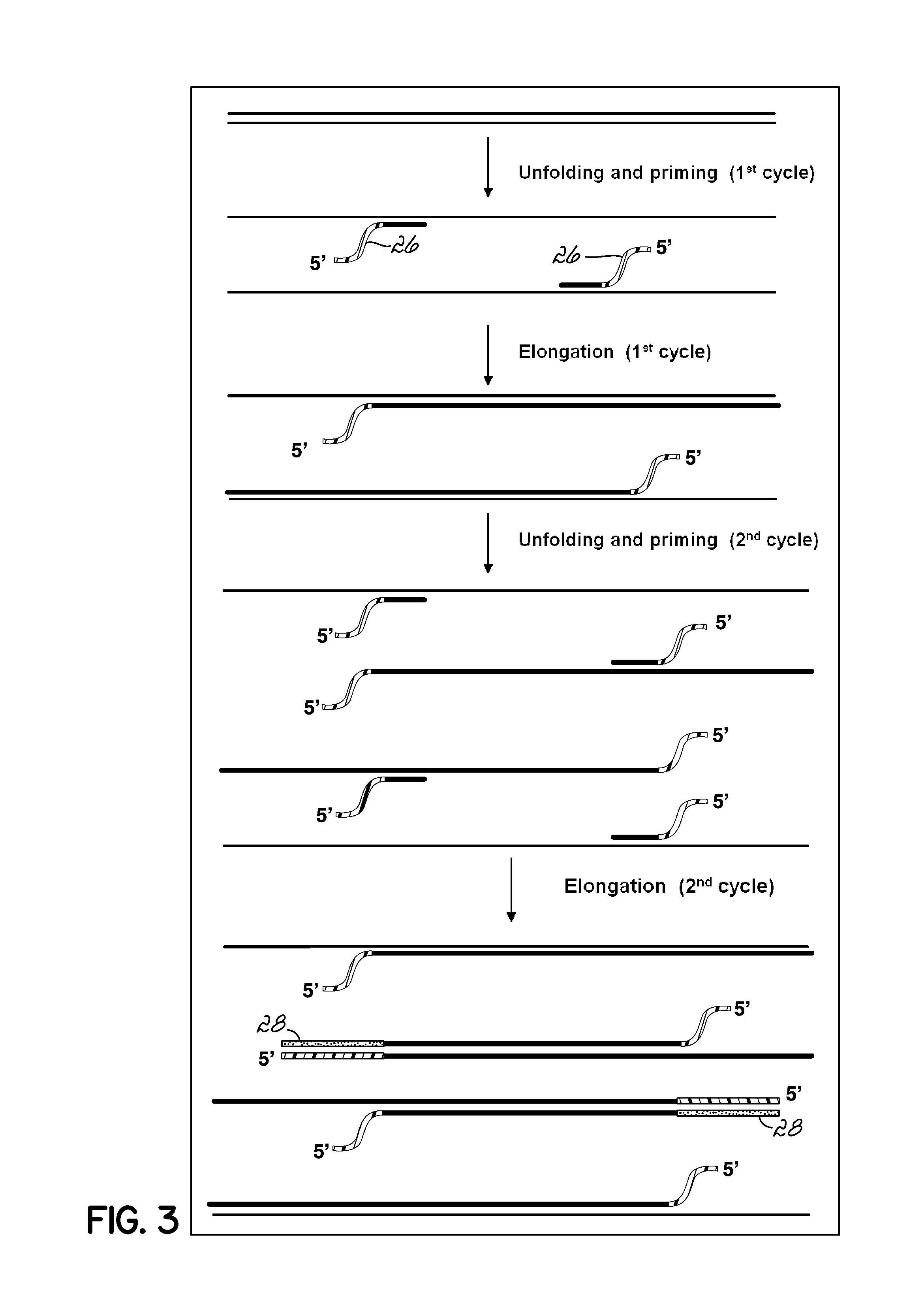
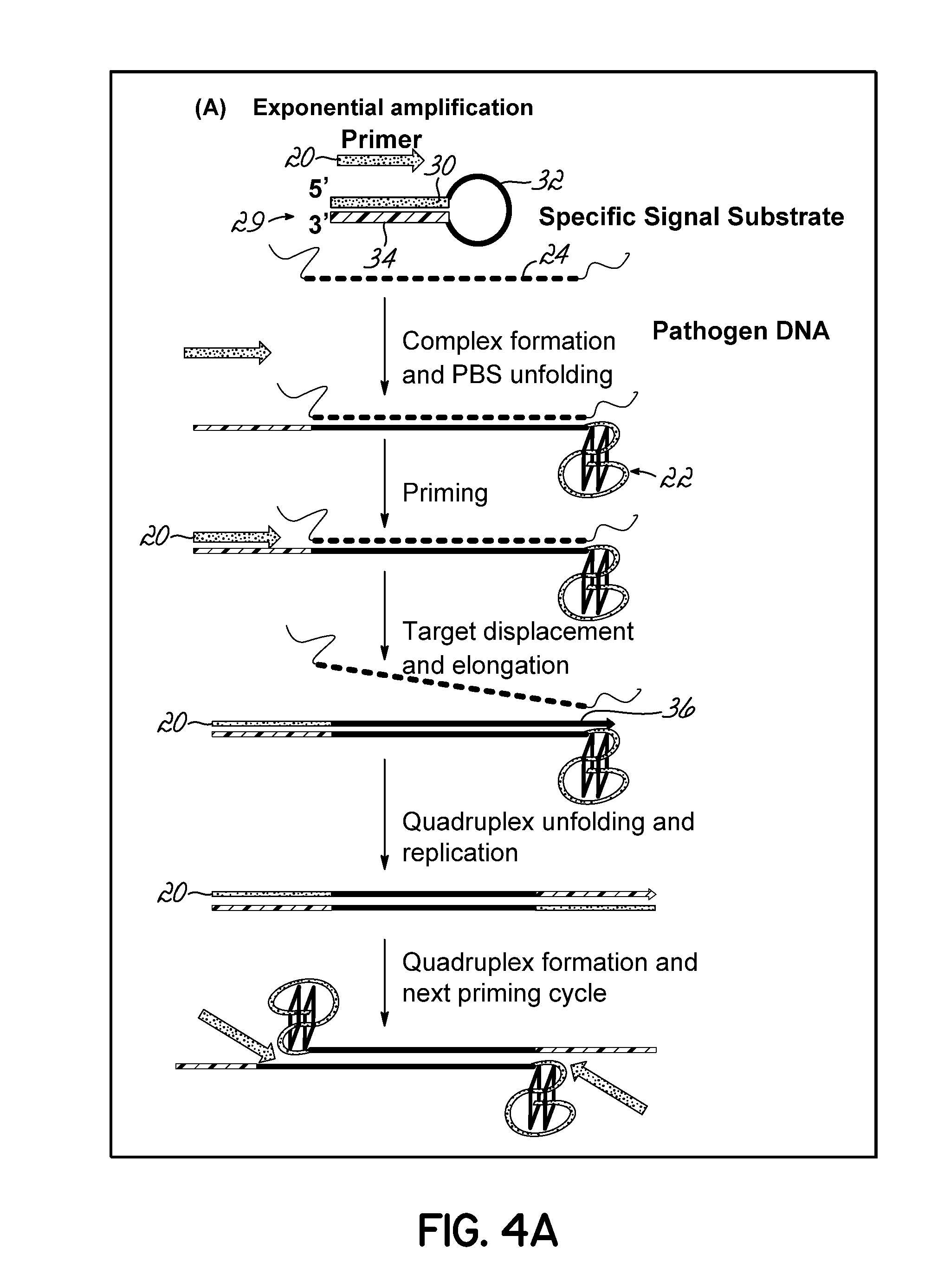
InactiveUS20160108468A1Reduces and eliminates shortcomingLittle useMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningLibrary preparationComputational biology
An amplification system that provides methods and reaction components that allow for isothermal amplification for detection of target nucleic acid 24; allow non-enzymatic amplification for detection of target nucleic acid 24; can be used to identify amplicons without having to create separate individual probes for each target nucleic acid 24, and can be used to improve sequencing processes.
Owner:OHIO STATE INNOVATION FOUND
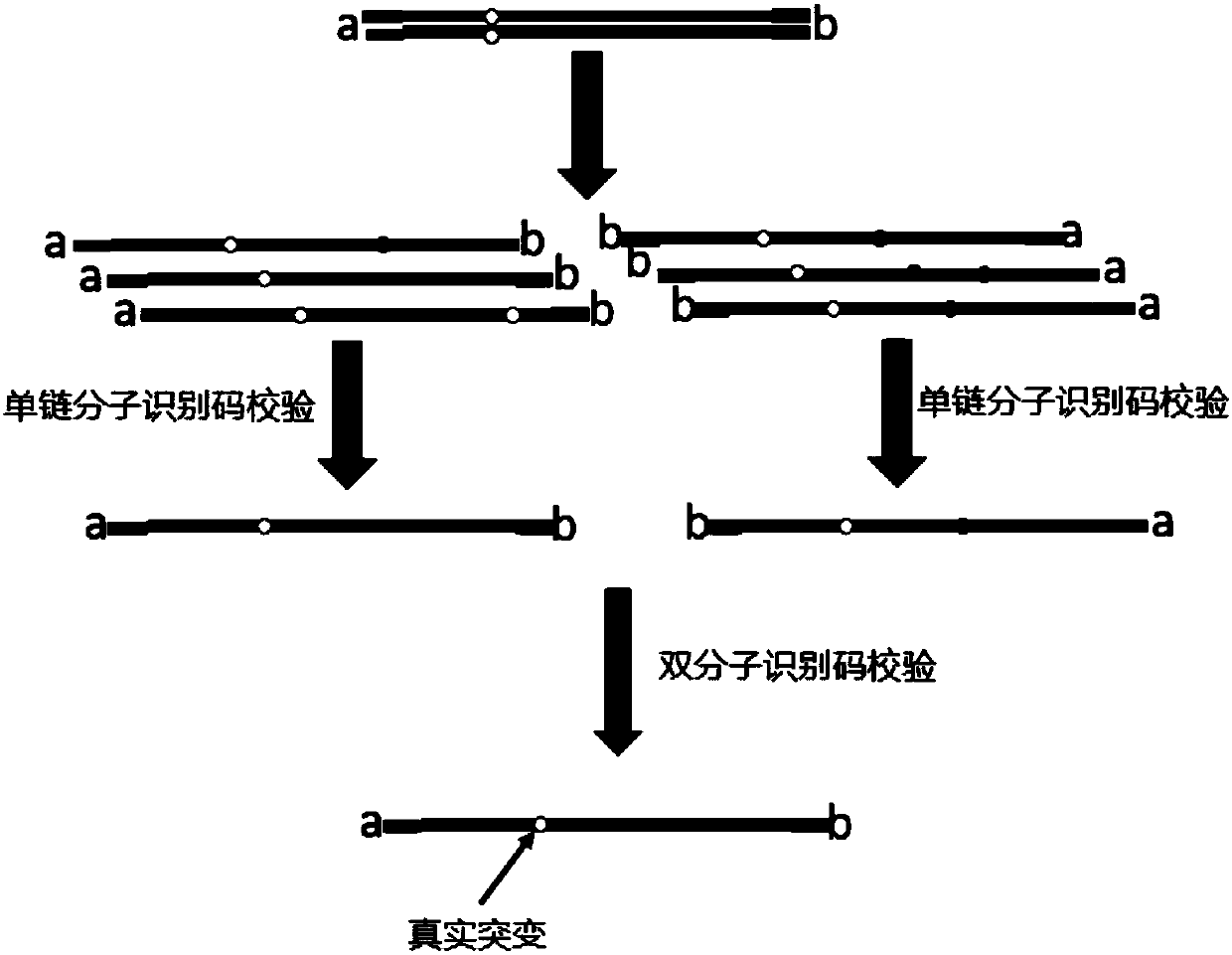
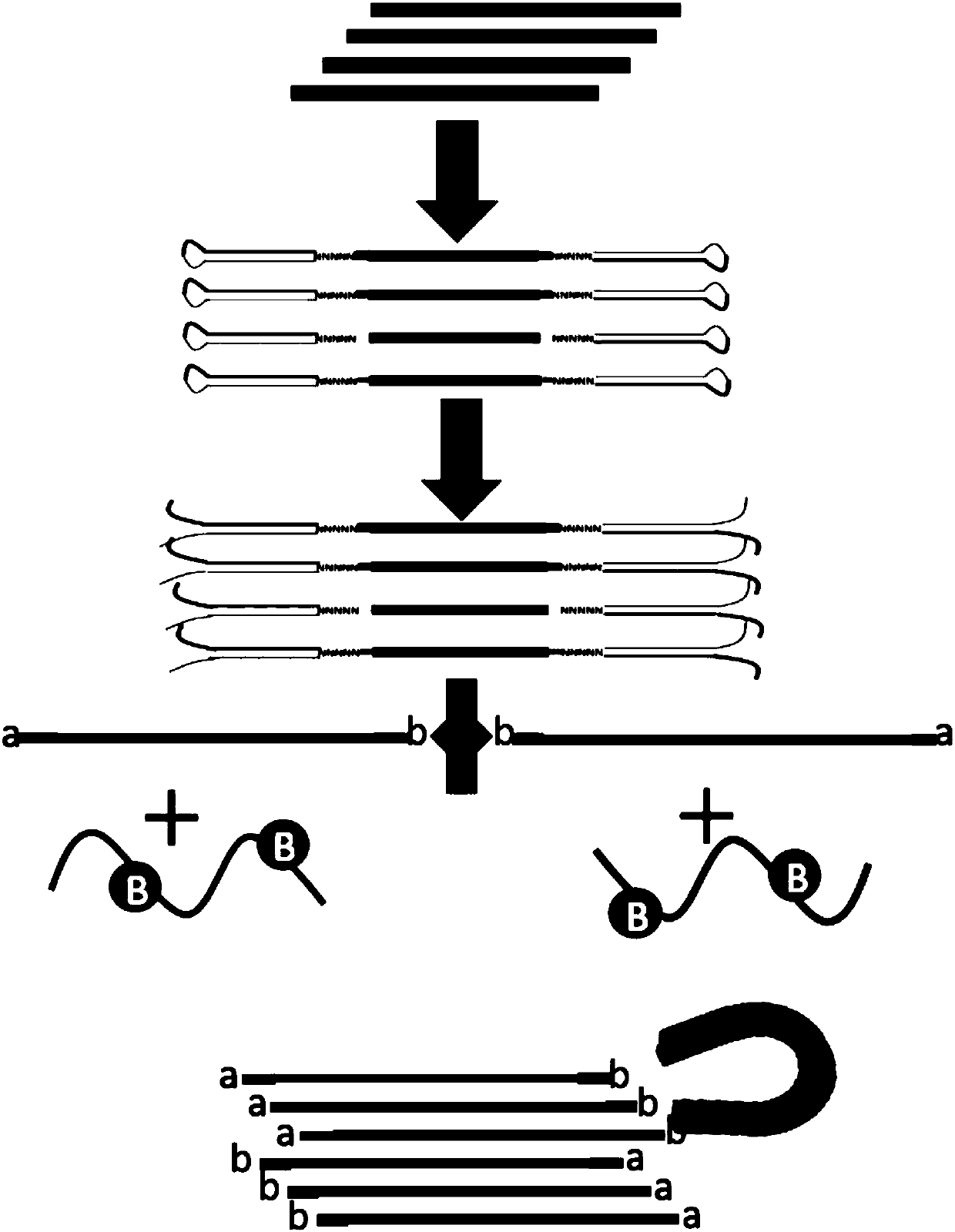
Second-generation sequencing method for dimolecular self-checking library preparation and hybrid capture used for trace DNA ultralow frequency mutation detection
ActiveCN107604046AIncrease profitHigh yieldNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary preparationData error
The invention discloses a second-generation sequencing method for dimolecular self-checking library preparation and hybrid capture used for trace DNA ultralow frequency mutation detection. The methodcomprises the following steps: extracting plasma free DNA, performing DNA chemical error repair, preparing a self-checking dimolecular identification code hairpin type joint, repairing plasma free DNA, connecting DNA with the joint, and performing Pre-PCR amplification, excessive hybrid capture, Post-PCR amplification, computer sequencing, data error correction, and mutation analysis and annotation. The method disclosed by the invention can efficiently realize low frequency mutation detection of plasma free DNA. DNA error repair and dual redundancy checking technology can enable the method tohave ultralow false positive rate and high sensitity while detecting trace samples, thus avoiding defects of existing plasma circulating free DNA detection methods, not only realizing cancer mutationdetection and targeted medication guidance, but also realizing early screening of genetic and birth defects of fetus.
Owner:SHANGHAI DYNASTYGENE CO
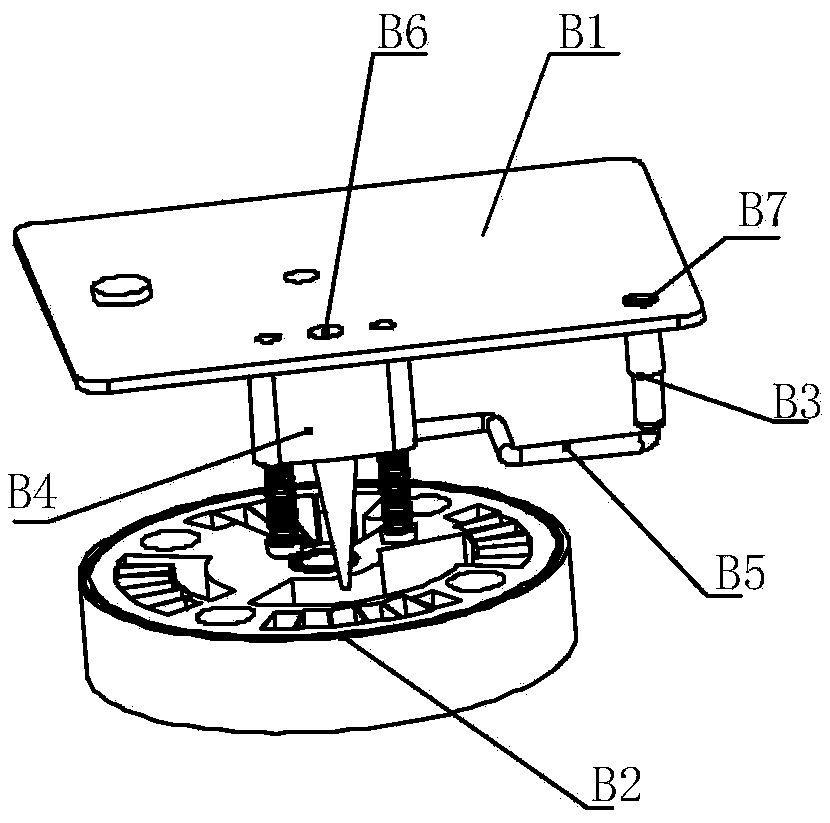
Closed sequencing library preparation card box
PendingCN110331075AEasy to moveAvoid potential risksBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLibrary preparationEngineering
The invention discloses a closed sequencing library preparation card box including a shell, a circular base plate and an injection unit; the shell is internally provided with a shaft extending downwards from the top wall of the shell; the circular base plate is provided with a plurality of accommodating grooves distributed at intervals in the circumference; the center of the circular base plate isprovided with a through hole for the shaft to pass through, so that the circular base plate can rotate in the shell around the shaft; the injection unit is located in the shell, and includes an injection main body connected with the shell and an injection head in fluid communication with the injection main body. The shell is provided with a first orifice for a driving mechanism to enter so as tooperate the injection main body, and the injection head can carry out lifting movement in the shell to inject and suck fluid of the accommodating grooves under the action of the injection main body. By replacing manual operation with the injection unit, the card box can greatly improve the operation efficiency, reduce the probability of occurrence of error and avoid the experimental error caused by artificial reagent addition and the potential risk generated to an operator.
Owner:上海思路迪医学检验所有限公司
Constructing method of maternal plasma free DNA library and typing method of parental alleles
ActiveCN107119046AIncrease success rateGuaranteed coverageMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationLibrary preparationGenomic DNA
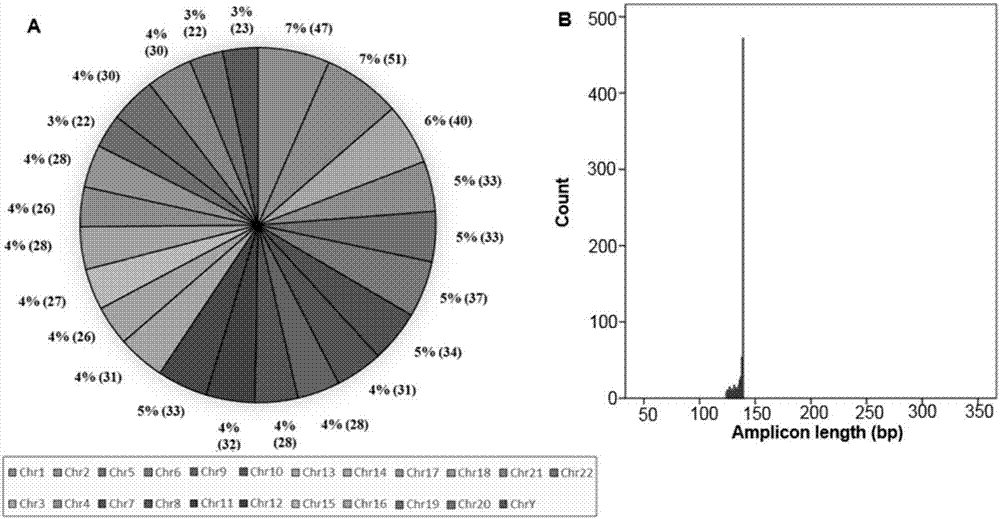
The invention discloses a constructing method of a maternal plasma free DNA library and a typing method of parental alleles. Firstly, a group of specific primers for amplifying SNP in maternal plasma free DNA is designed, and comprises 720 pairs of primers, and the sequences of upstream and downstream primers are shown as SEQ ID NO:1-1440. Then, peripheral blood of pregnant women of 9-20 weeks is acquired for the extraction of the plasma free DNA, and a multiple composite PCR amplification technology is applied to the construction of the free DNA library; after the library is purified and quantified, computer sequencing is performed on an Ion TorrentTM platform. The same method is used for performing library preparation and sequencing on corresponding maternal cells and fetal tissue genomic DNA. According to sequencing results, the maternal cells are selected as homozygous SNP sites, the percentage concentrations of non-parental alleles of the free DNA in maternal plasma at the corresponding sites are analyzed, and the purpose of determining a paternal allele in the free DNA is achieved.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
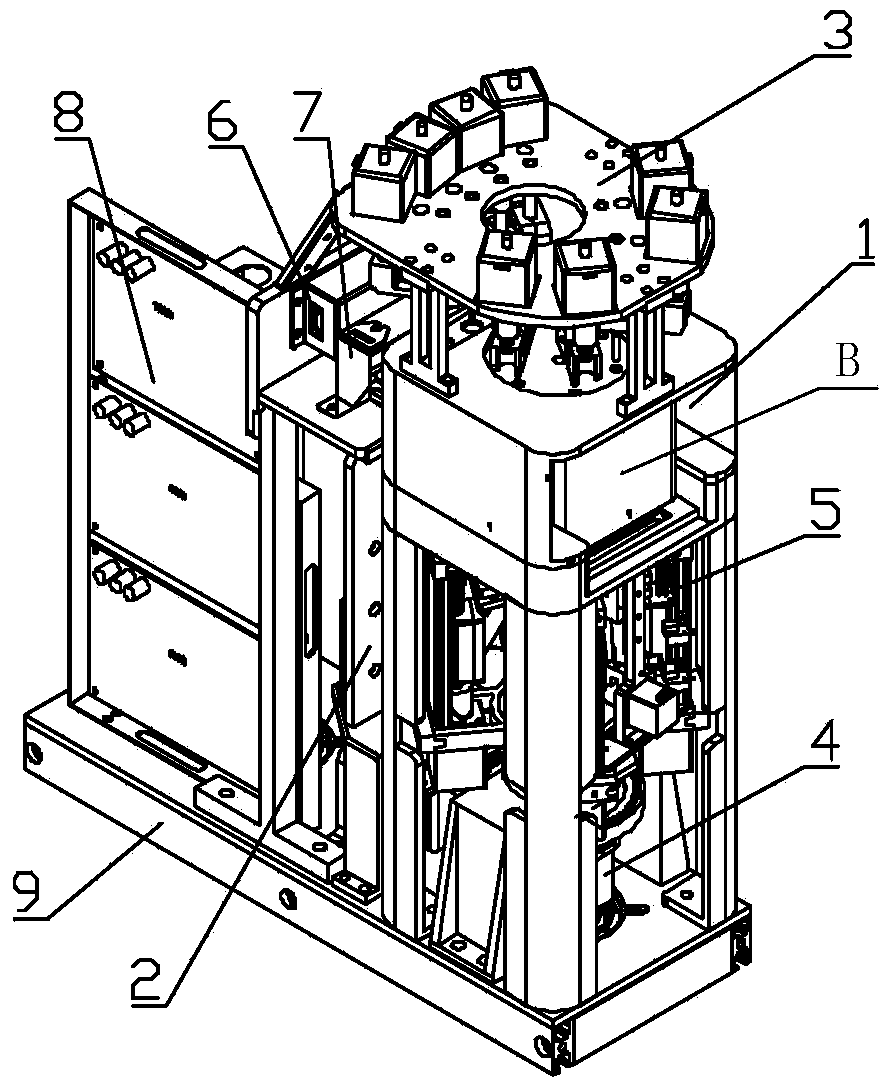
Gene sequencing library preparation device
ActiveCN109468215AEasy to moveAvoid potential risksBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLibrary preparationEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene sequencing and particularly discloses a gene sequencing library preparation device. The device comprises a card case holding unit, a card case locking unit, a liquid supply drive unit, a card case rotation drive unit and a controller, wherein the card case holding unit comprises a holding support and a holding groove located on the holding rackand used for holding a card case; the card case locking unit is used for locking the card case in the holding groove; the liquid supply driving unit comprises a first drive mechanism for driving an injection body of an injection unit of the card case and a second drive mechanism for driving of injection head communicated with the fluid of the injection body to rise and fall, so that the injectionbody performs injection and suction operation on accommodating grooves in a circular base plate of the card case; the card case rotation drive unit is used for driving the circular base plate of the card case to rotate around the axis, and the injection head can perform injection and suction operation on multiple accommodating grooves in the circular base plate; the controller controls the workingstates of the card case holding unit, the card case locking unit, the liquid supply drive unit and the card case rotation drive unit. The gene sequencing library preparation device can realize automation of library preparation.
Owner:3D BIOMEDICINE SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method for non-invasive preimplantation hereditary detection of embryos
ActiveCN111440857AHigh amplification yieldThe result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementGranular leucocyteLibrary preparation
The invention discloses a method for non-invasive preimplantation hereditary detection of embryos, and belongs to the technical field of biological detection. The method comprises the following steps:carrying out whole genome amplification on a blastocyst culture solution sample by using a kit, carrying out short tandem repeat sequence analysis on an amplification product and DNA samples of parents to detect maternal pollution, carrying out library preparation and next-generation sequencing detection on the amplification product to determine whether the number of chromosomes is abnormal or not; and optimizing a pre-amplification mixed solution and an amplification mixed solution by the provided kit. According to the method provided by the invention, the blastocyst culture solution can besubjected to parent source pollution detection, so that whether the chromosome aneuploidy detection result of the culture solution is accurate and reliable or not is judged. The invention provides a detection method for judging whether granular cells are completely removed or not, and the inhibition effect of components in the culture solution on amplification is effectively avoided through optimization of the kit, so that amplification uniformity is good, and the single cell amplification yield is high. The detection method is simple, the result is accurate, and data quality is improved.
Owner:阿吉安(福州)基因医学检验实验室有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com