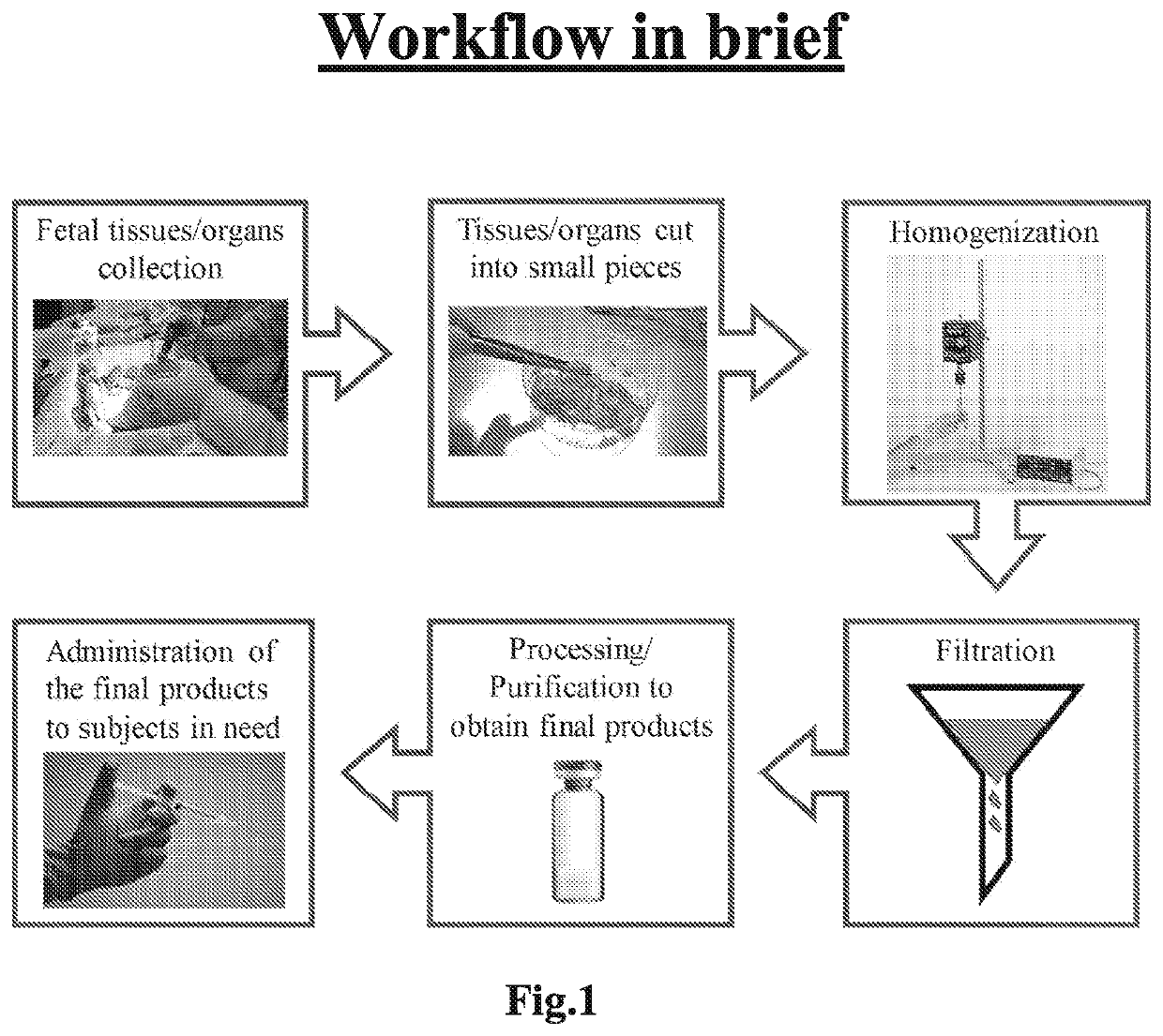
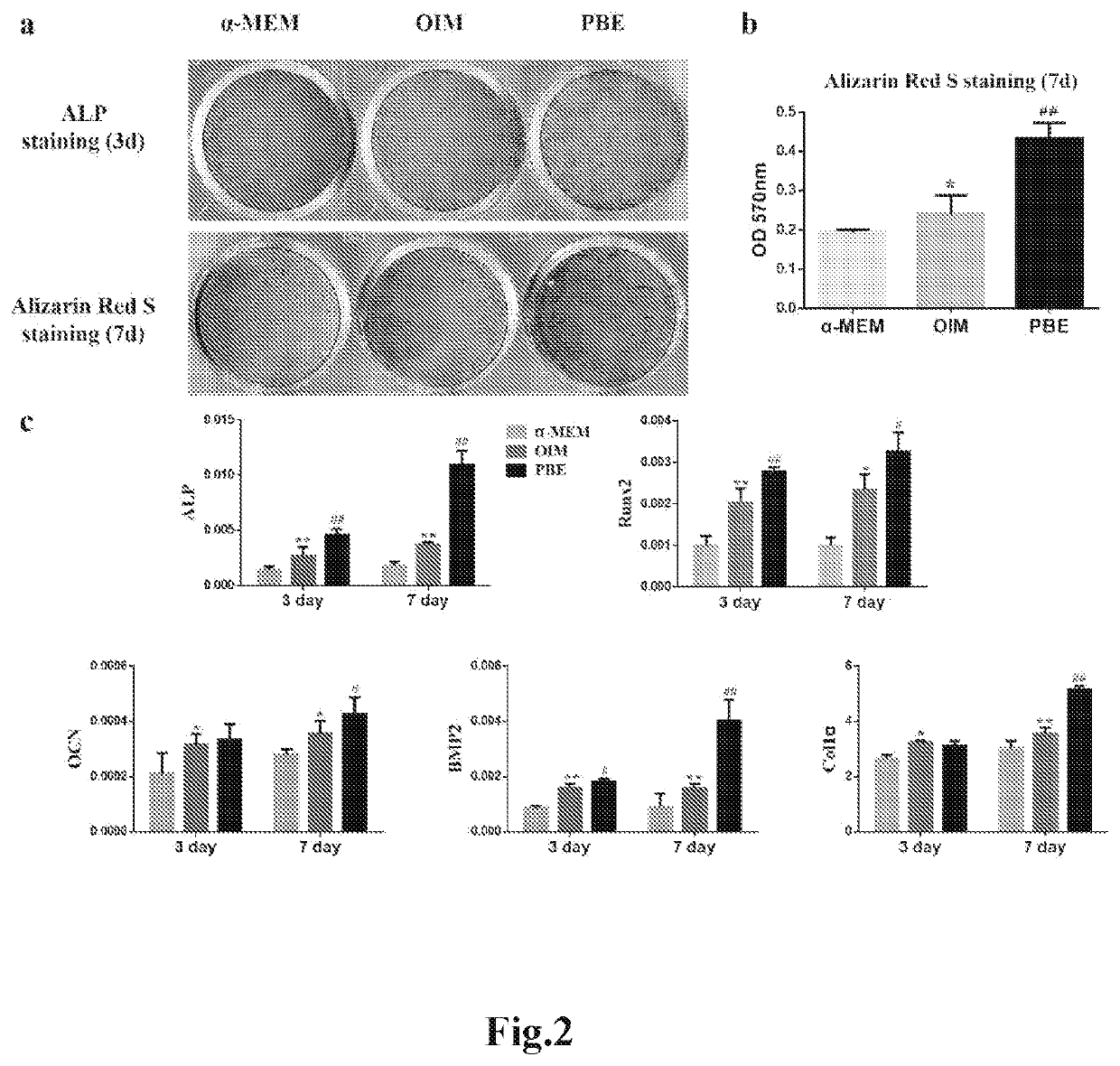
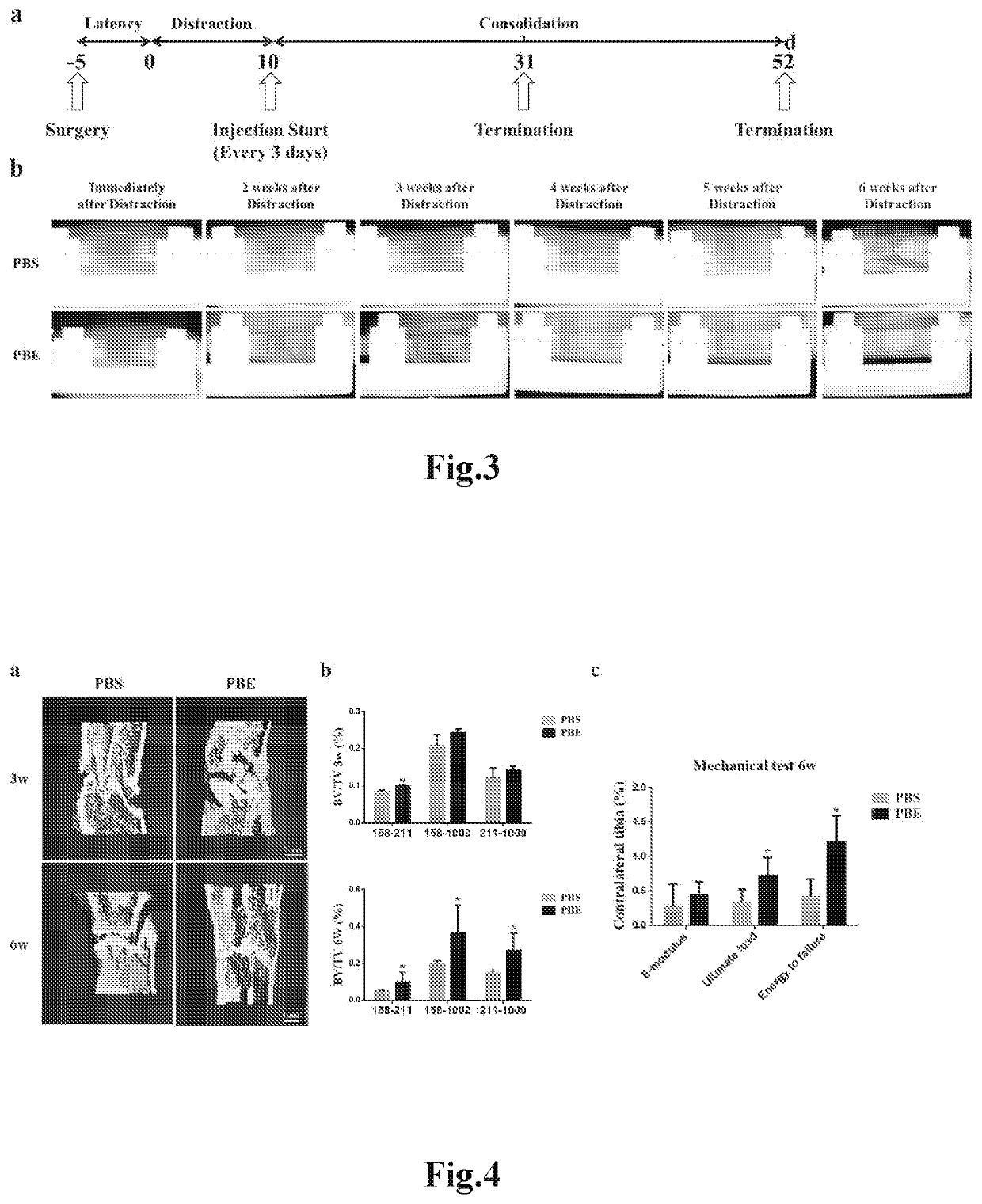
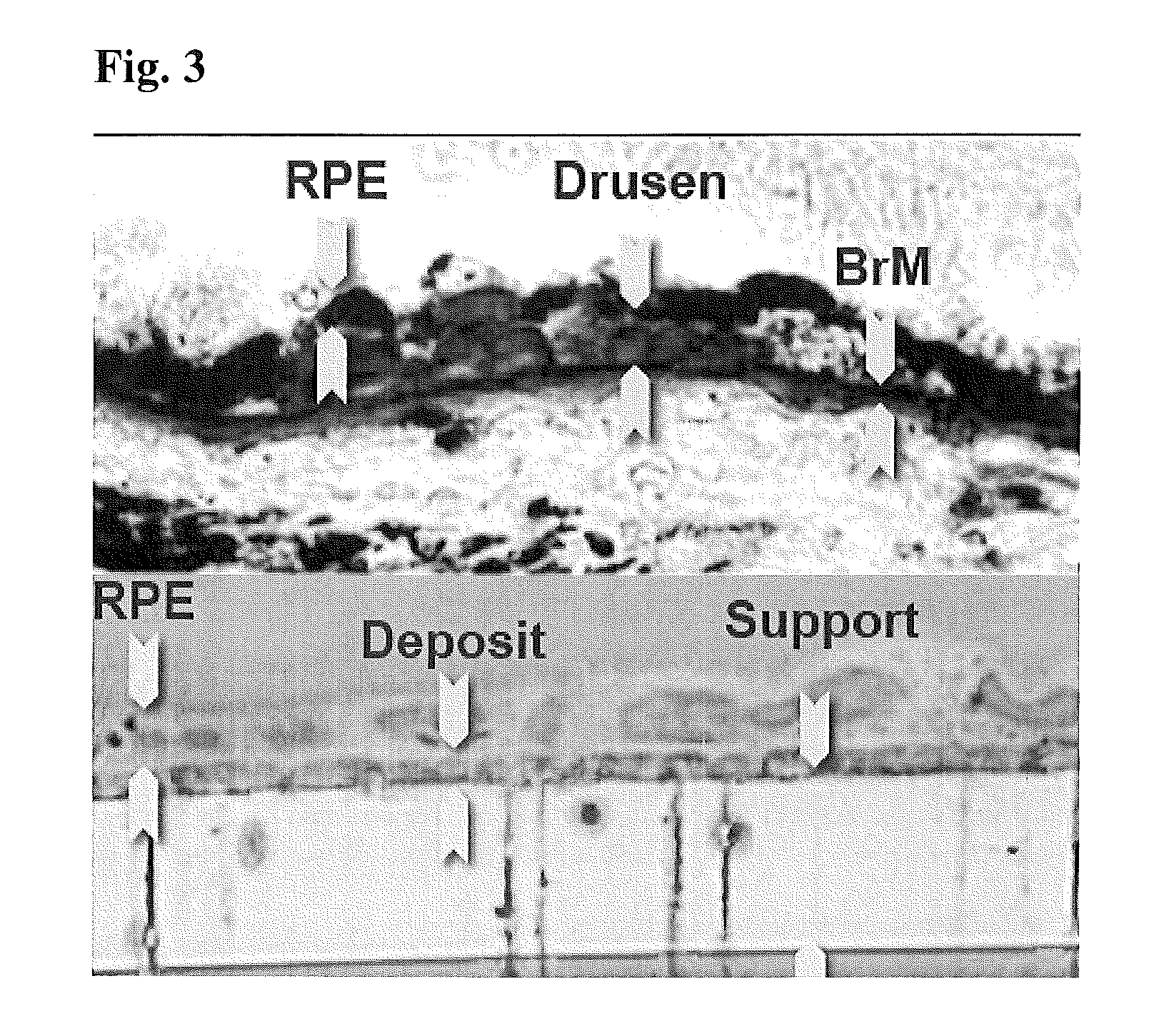
Patents
Literature
36 results about "Fetal tissue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Definition of Fetal tissue Fetal tissue means any body part, organ, or cell of an unborn human child. Fetal tissue means cells, or groups of cells with a specific function, obtained from an aborted human embryo or fetus. Fetal tissue means cells, or groups of cells with a specific function, obtained from an aborted human embryo or fetus.
Pluripotent stem cells derived without the use of embryos or fetal tissue
InactiveUS20030113910A1New breed animal cellsArtificial cell constructsPluripotential stem cellGerm layer
Owner:STEMA
EB Matrix Production from Fetal Tissues and its Use for Tissue Repair
InactiveUS20020146393A1Reducing biological propertyPreserve strengthBiocideHepatocytesCross-linkTissue repair
<heading lvl="0">Abstract of Disclosure< / heading> A method of forming and preserving a bioremodelable, biopolymer scaffold material by subjecting animal tissue, particularly fetal or neo-natal tissue, to chemical and mechanical processing. The process includes, but is not limited t, harvesting the tissue, optionally extracting growth and differentiation factors from the tissue, inactivating infective agents of the tissue, mechanically expressig undesirable components frm the tissue, delipidizing the tissue, washing the tissue, optionally drying the tissue, and optionally cross-linking the tissue not necessarily in the order described. The resulting product, EBM, is characterized by its microbial, fungal, viral and prion inactivated state. EBM is storng, bioremodelable, drapable and does not undergo calicification. EBM supplants previous inventions because of its unique method of preparation and broad applicability in tissue reengineering
Owner:TEI BIOSCI
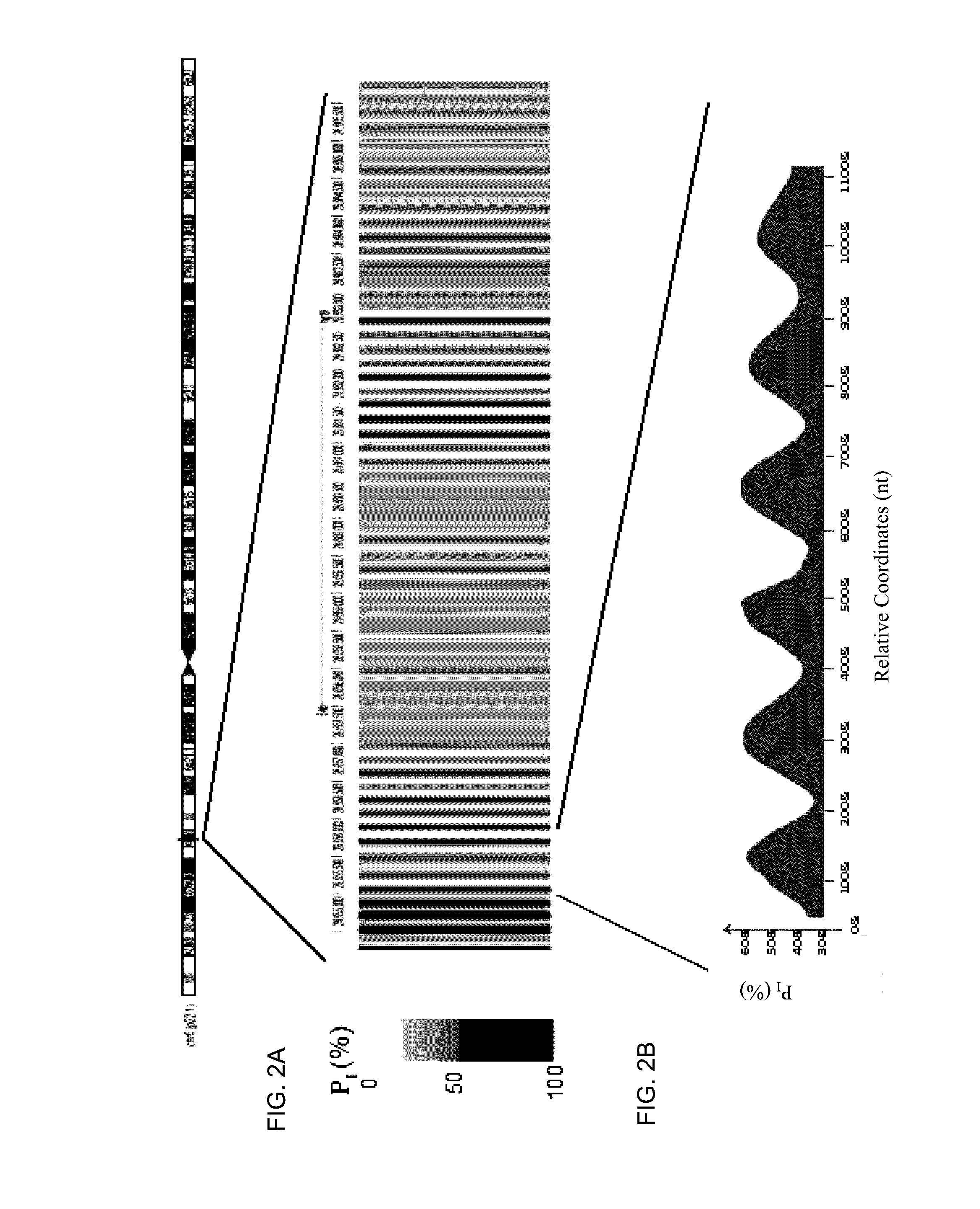
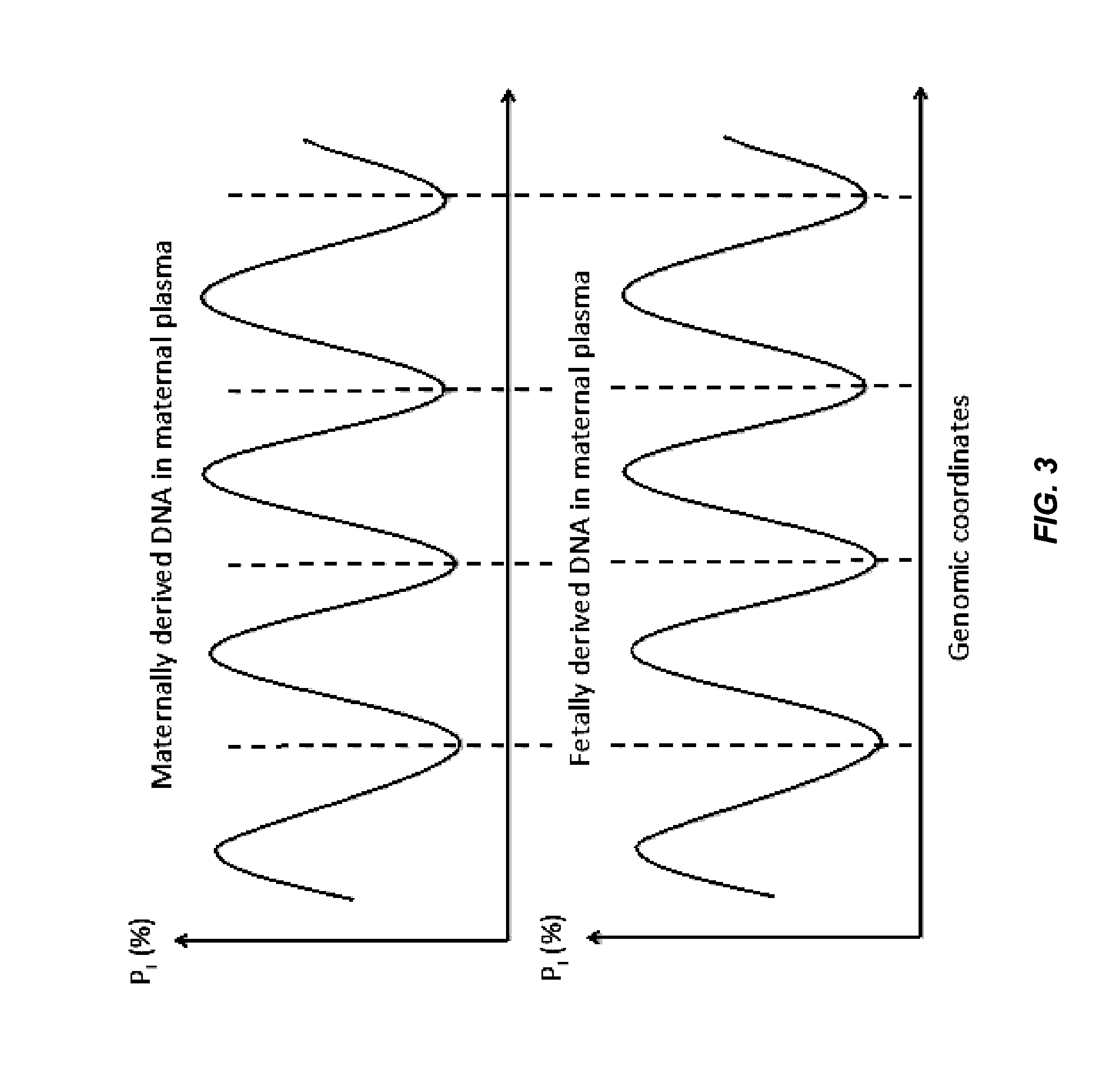
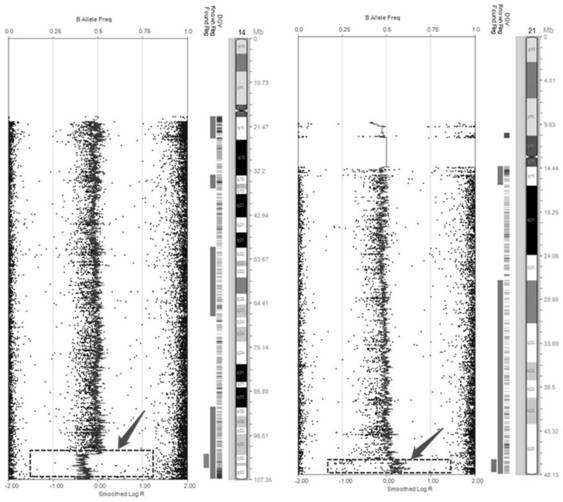
Analysis of fragmentation patterns of cell-free DNA
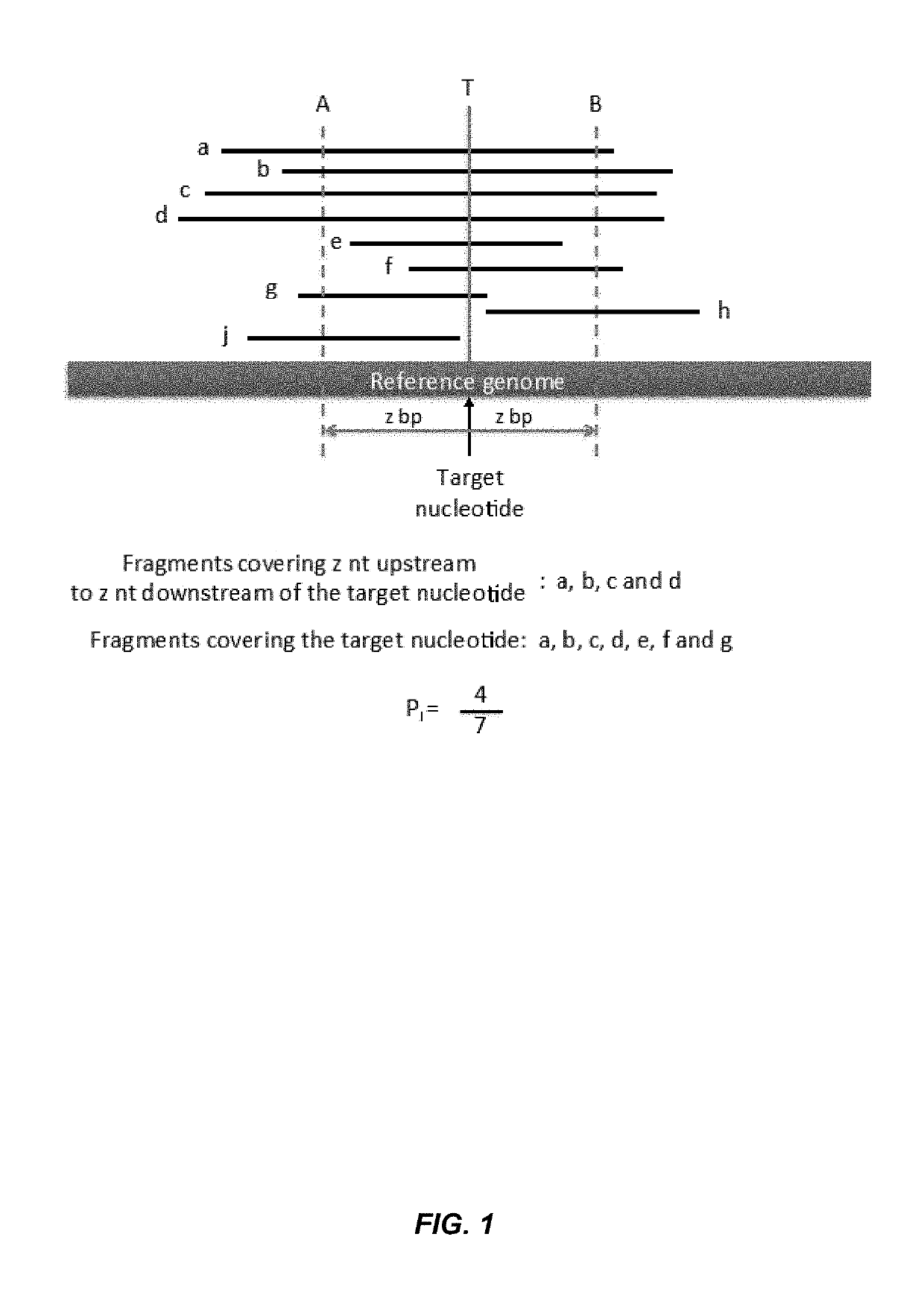
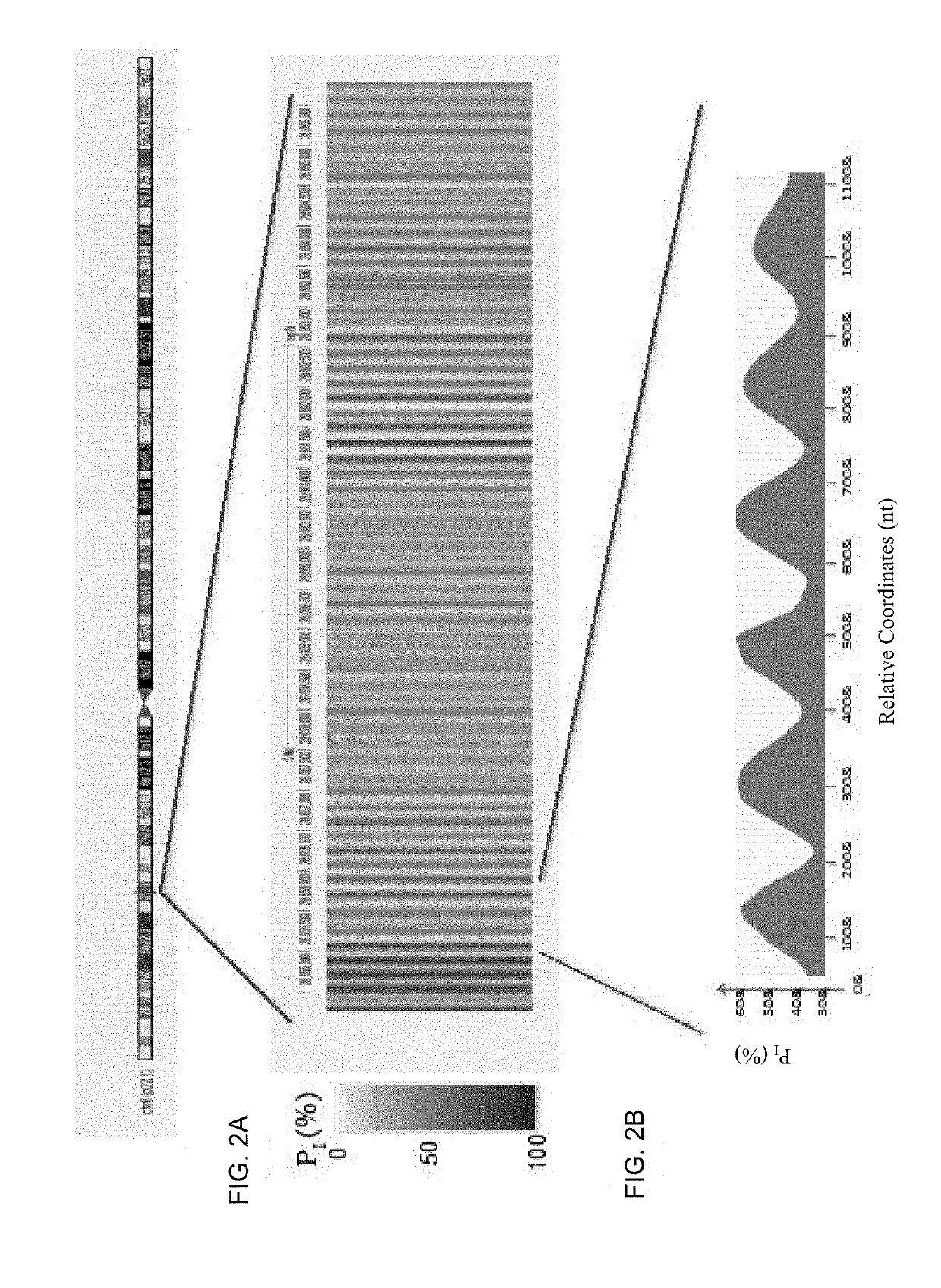
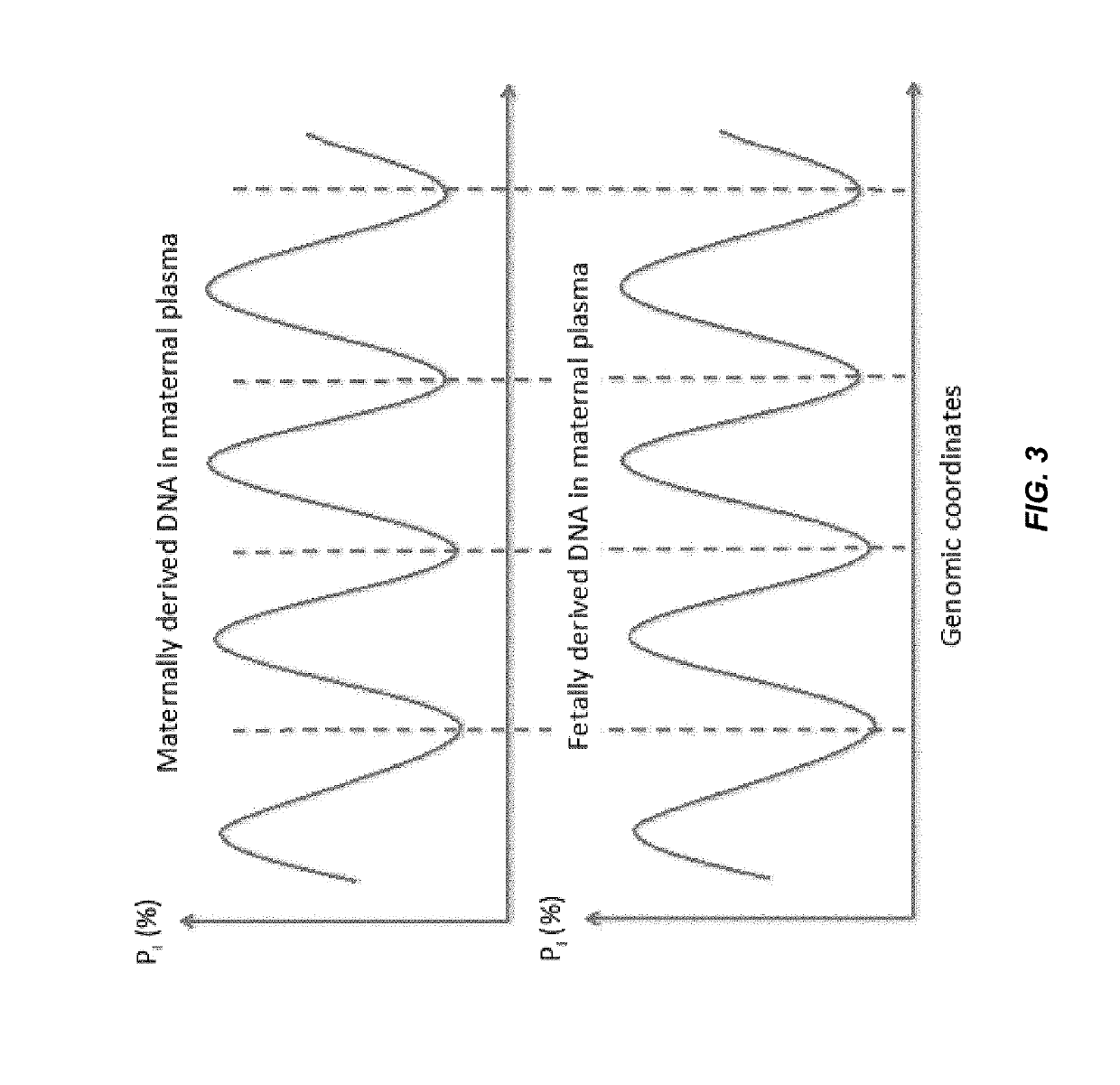
Factors affecting the fragmentation pattern of cell-free DNA (e.g., plasma DNA) and the applications, including those in molecular diagnostics, of the analysis of cell-free DNA fragmentation patterns are described. Various applications can use a property of a fragmentation pattern to determine a proportional contribution of a particular tissue type, to determine a genotype of a particular tissue type (e.g., fetal tissue in a maternal sample or tumor tissue in a sample from a cancer patient), and / or to identify preferred ending positions for a particular tissue type, which may then be used to determine a proportional contribution of a particular tissue type.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Method of isolation and use of cells derived from first trimester umbilical cord tissue
A method of isolating a pluripotent cell from human umbilical cord is described herein. The method involves collecting a sample of umbilical cord from fetal tissue obtained at less than 20 weeks of gestation, for example a first trimester umbilical cord. The sample is treated to obtain isolated umbilical cord cells, after which the isolated umbilical cord cells are incubated. Stem cells obtained in this way can be differentiated for use in therapeutic applications.
Owner:LIBRACH CLIFFORD L +2
EB matrix production from fetal tissues and its use for tissue repair
A method of forming and preserving a bioremodelable, biopolymer scaffold material by subjecting animal tissue to chemical and mechanical processing. In addition to skin tissue, another source of EBM is a blood vessel. EBM may be used for hernia repair, colon, rectal, vaginal and or urethral prolapse treatment; pelvic floor reconstruction; muscle flap reinforcement; lung tissue support; rotator cuff repair or replacement; periosteum replacement; dura repair; pericardial membrane repair; soft tissue augmentation; intervertebral disk repair; and periodontal repair. EBM may also be used as a urethral sling, laminectomy barrier or spinal fusion device.
Owner:TEI BIOSCI
Prenatal enzyme replacement therapy
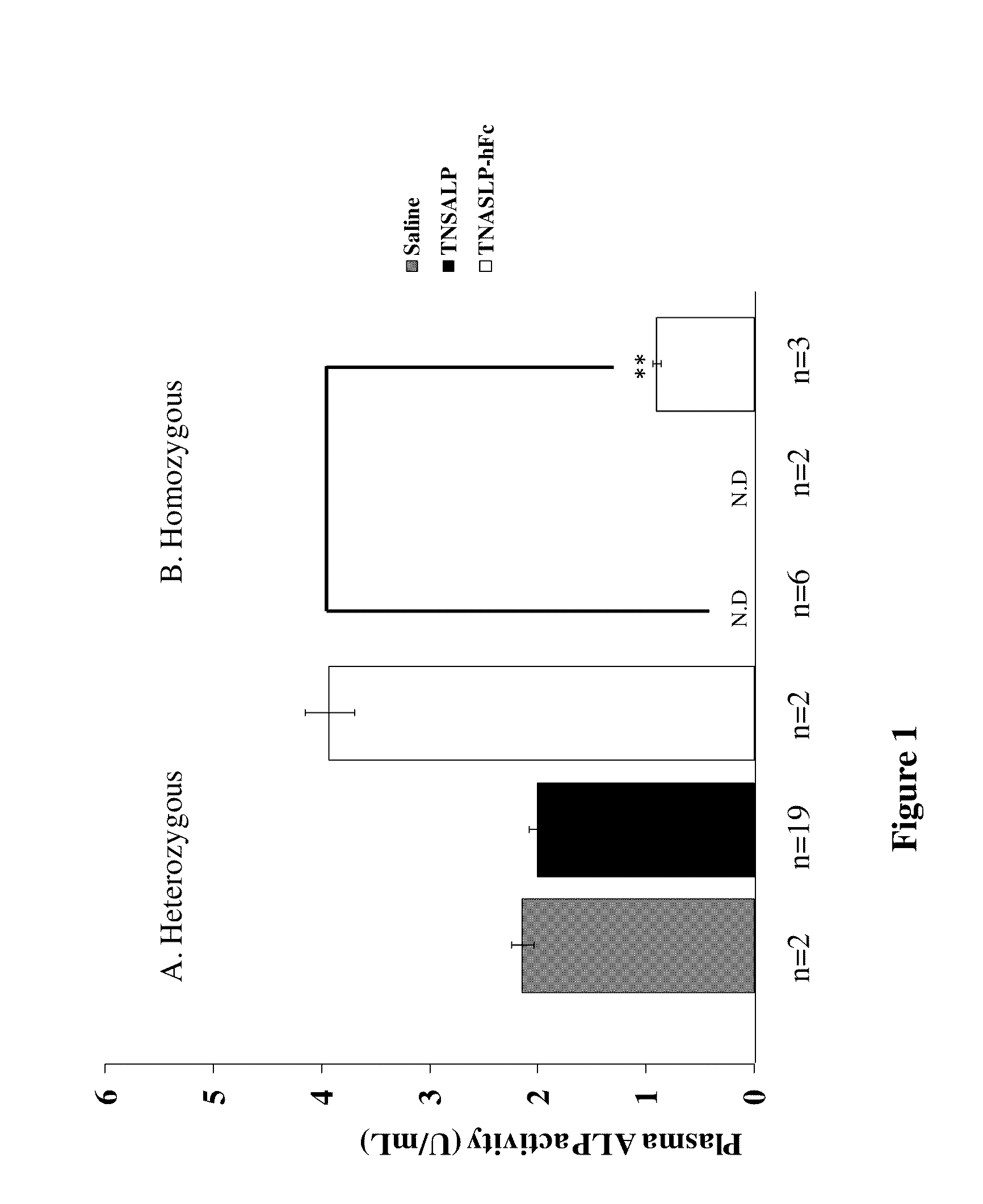
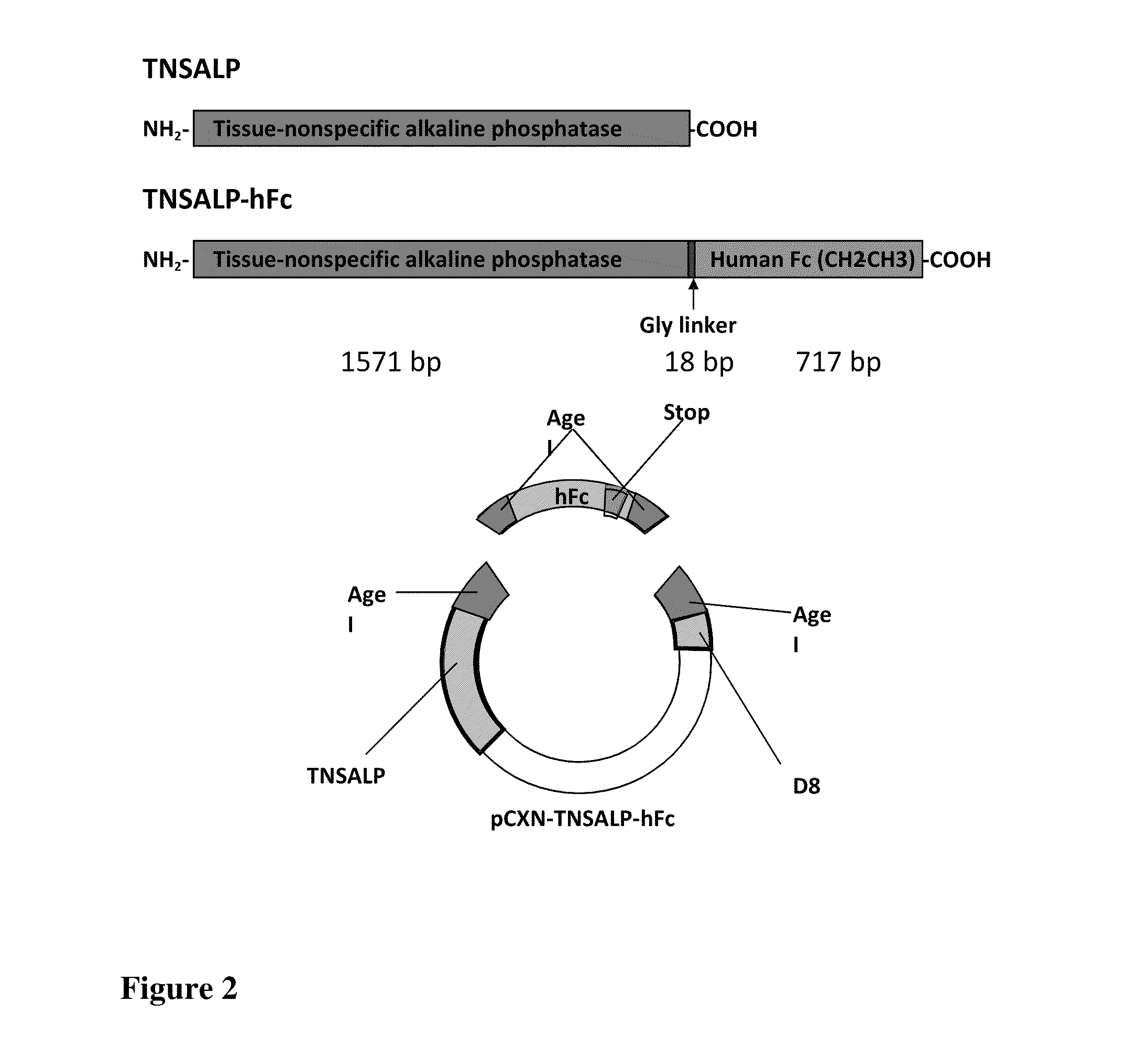
The invention contemplates transplacental enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) for deficiency of a polypeptide such as a tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNSALP) by administering a before-described pharmaceutical composition to a pregnant animal whose fetus or embryo is in need of such therapy. The fusion protein of such a composition comprises a water-soluble TNSALP portion, e.g., C-terminus-truncated TNSALP peptide-bonded to an IgG1 antibody Fc portion.The invention also contemplates a method for treating a metabolic disorder, such as HPP, in a fetus or embryo were a protein is administered to a pregnant mother. The fusion protein comprises a Fc fragment of an IgG1 antibody peptide-bonded to TNSALP. The protein crosses the placenta of the mother and enters the fetal blood stream. The protein is taken up into fetal tissue such that the TNSALP restores normal metabolic activity in the fetus.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
EB Matrix production from fetal tissue and its use for tissue repair
InactiveUS20050013802A1Improve suppression propertiesTissue strength is preservedBiocideHepatocytesCross-linkTissue repair
A method of forming and preserving a bioremodelable, biopolymer scaffold material by subjecting animal tissue, particularly fetal or neo-natal tissue, to chemical and mechanical processing. The process includes, but is not limited to, harvesting the tissue, optionally extracting growth and differentiation factors from the tissue, inactivating infective agents of the tissue, mechanically expressing undesirable components from the tissue, delipidizing the tissue, washing the tissue, optionally drying the tissue, optionally cross-linking the tissue not necessarily in the order described. The resulting product, EBM, is characterized by its microbial, fungal, viral and prion inactivated state. EBM is strong, bioremodelable, drapable and does not undergo calcification. EBM supplants previous inventions because of its unique method of preparation and broad applicability in tissue reengineering.
Owner:TEI BIOSCI
EB matrix production from fetal tissues and its use for tissue repair
InactiveUS20050008708A1Improve abilitiesImprove propertiesPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderTissue repairUrethral Sling
A method of forming and preserving a bioremodelable, biopolymer scaffold material by subjecting animal tissue to chemical and mechanical processing. In addition to skin tissue, another source of EBM is a blood vessel. EBM may be used for hernia repair, colon, rectal, vaginal and or urethral prolapse treatment; pelvic floor reconstruction; muscle flap reinforcement; lung tissue support; rotator cuff repair or replacement; periosteum replacement; dura repair; pericardial membrane repair; soft tissue augmentation; intervertebral disk repair; and periodontal repair. EBM may also be used as a urethral sling, laminectomy barrier or spinal fusion device.
Owner:TEI BIOSCI
Pluripotent mammalian cells
InactiveUS20050210537A1Enhance chromatin remodellingStably integratedNew breed animal cellsGenetic material ingredientsReprogrammingCell type specific
The invention relates to a method of making pluripotent stem cells that does not involve the formation of early preimplantation embryos or fetal tissue. The method has general utility in the production of pluripotent stem cells from many mammalian species but has particular application in man where pluripotent stem cell production can be customized to particular human individual. The method involves the fusion of donor somatic or stem cells (or their karyoplasts) with cytoplasmic, membrane-delimited fragments of mammalian oocytes or zygotes. After the initial genomic reprogramming occurs, the cells can proliferate and thus multiply in vitro yielding a large number of autologous cells for cell therapy application. The result of this process is a cell population genomically identical to the somatic, differentiated cells derived from an individual patient. However, these cells are pluripotent in that upon application of specific growth factors, the cells are capable of differentiating into specific cell types as required by the sought clinical indication.
Owner:DOMINKO TANJA +4
Analysis of fragmentation patterns of cell-free DNA
Factors affecting the fragmentation pattern of cell-free DNA (e.g., plasma DNA) and the applications, including those in molecular diagnostics, of the analysis of cell-free DNA fragmentation patterns are described. Various applications can use a property of a fragmentation pattern to determine a proportional contribution of a particular tissue type, to determine a genotype of a particular tissue type (e.g., fetal tissue in a maternal sample or tumor tissue in a sample from a cancer patient), and / or to identify preferred ending positions for a particular tissue type, which may then be used to determine a proportional contribution of a particular tissue type.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Reference product for non-invasive prenatal detection of fetal aneuploid chromosomes
ActiveCN109112209AEasy to makeQuantitatively accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationReference productQuality control
The present invention provides a reference product for non-invasive prenatal detection of fetal aneuploid chromosomes. The reference product comprises: a first fragmented nucleic acid derived from thetissue of a maternal body having normal chromosome ploidy or the cultured cell line genome, and a second fragmented nucleic acid derived from the tissue or the cultured cell line genome of a fetus with positive chromosome aneuploidy, wherein the first fragmented nucleic acid is genetically related to the second fragmented nucleic acid, the first fragmented nucleic acid at least accounts for 70% of the total nucleic acid amount of the reference product, and the second fragmented nucleic acid accounts for 5-30% of the total nucleic acid amount of the reference product. According to the presentinvention, the reference product is easy to prepare, meets clinical practical demands, is used for the research and development and quality control on non-invasive prenatal detection related products,and has important application prospects.
Owner:国家卫生健康委科学技术研究所 +1
Method for separating, purifying, culturing and proliferating totipotent stem cell from tissue of early aborted fetus of human being
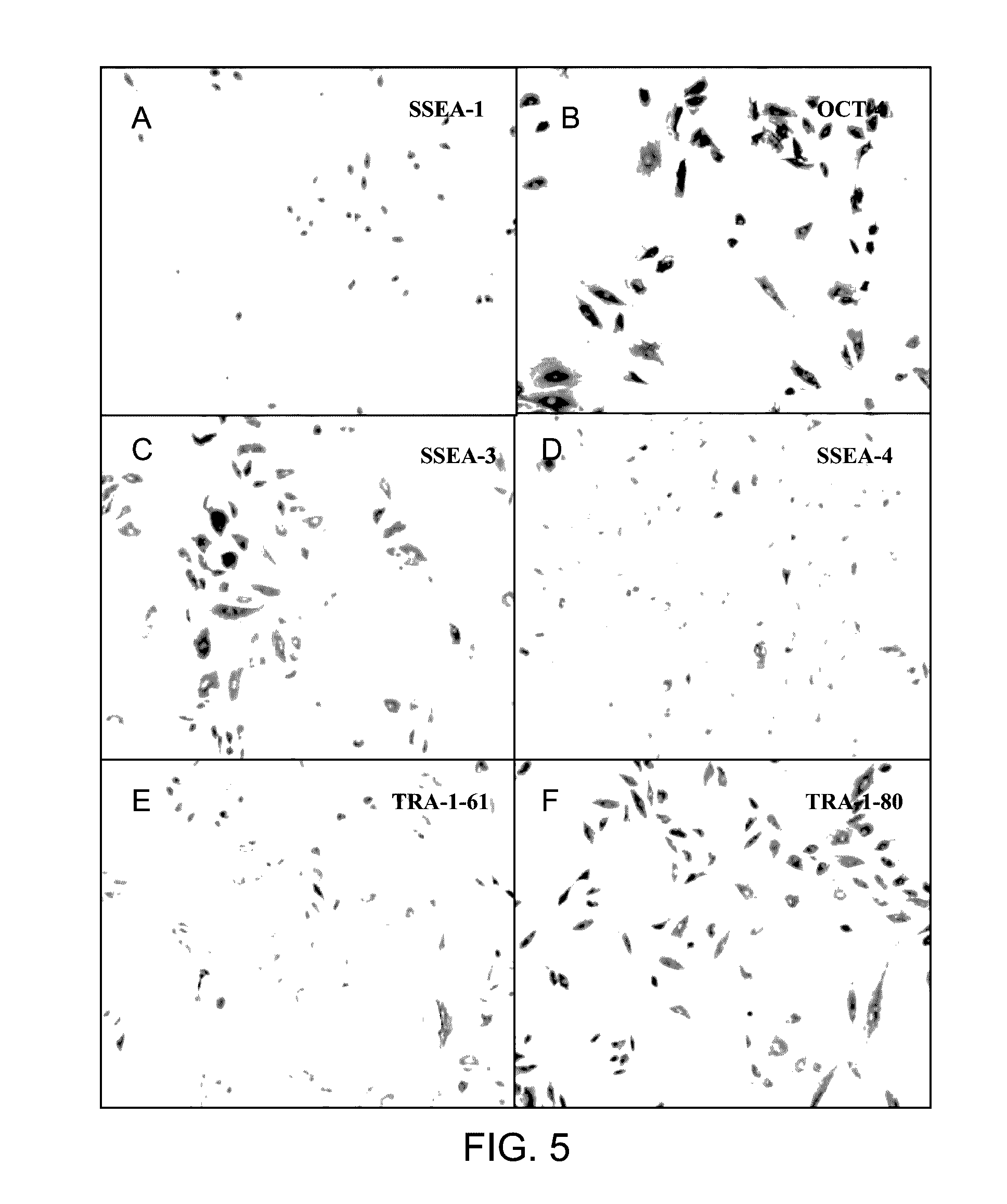
The invention discloses a method for separating and purifying totipotent stem cells from the tissues of early aborted fetuses of human beings, including the steps: a. a sample of the placenta tissue of the aborted fetus after the first pregnancy period is collected; b. the umbilical cord tissue or the intestine tissue of the fetus is obtained from the sample gained in the step a; c. cells are obtained from the umbilical cord tissue or the intestine tissue of the fetus gained in the step b; and d. markers of the embryonic stem cell, such as OCT-4, Nanog, SSEA-3, SSEA-4, TRA-1-60, TRA-1-81, and the like which are obtained from the cells of the umbilical cord tissue or the intestine tissue of the fetus, are separated, purified and expressed, and can form the stem cell of an embryoid body. The cells obtained by the method of the invention are always in the state of undifferentiation. The invention also discloses the application of the stem cells in forming different human cells, such as cardiac muscles, nerves and islet beta cells or osseus cells. The method avoids the dispute over ethnics which needs to be faced with during the operation of obtaining the totipotent stem cells from the embryo, and more stem cells can be obtained than from blastocyst.
Owner:叶尚勉
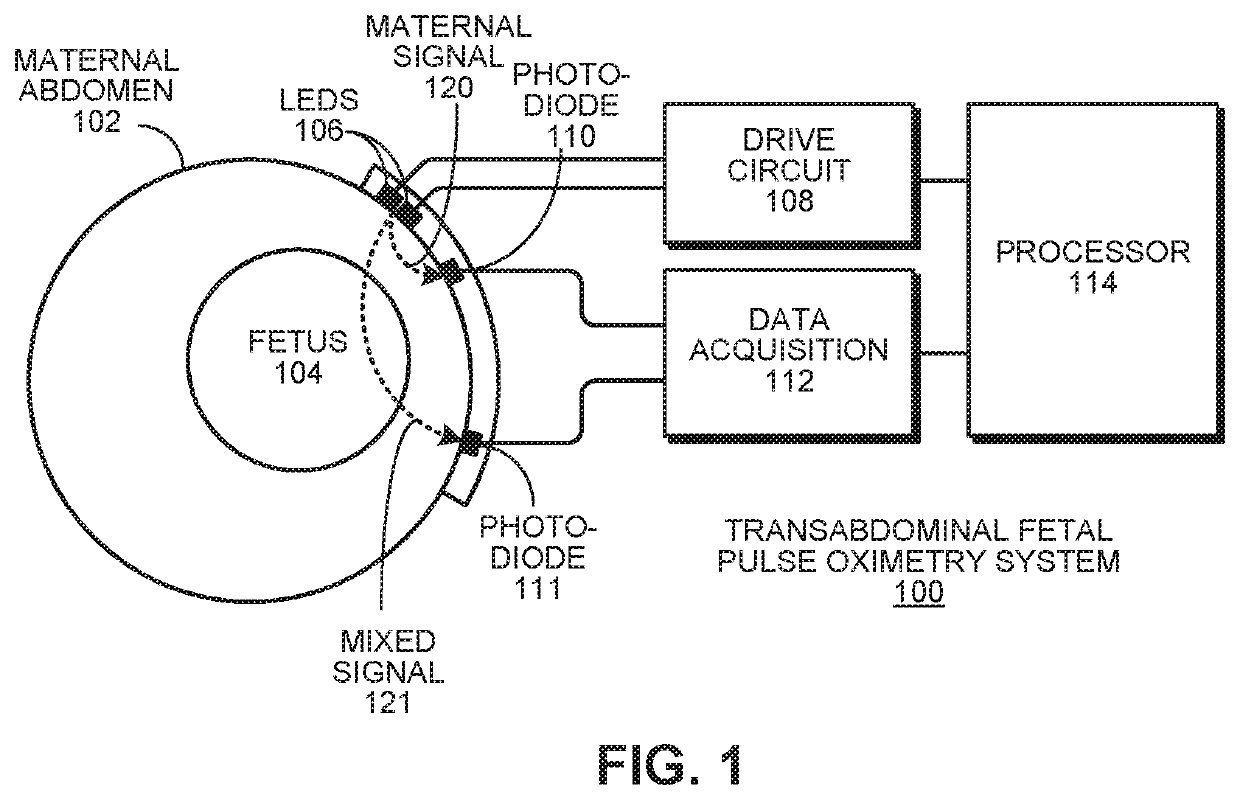
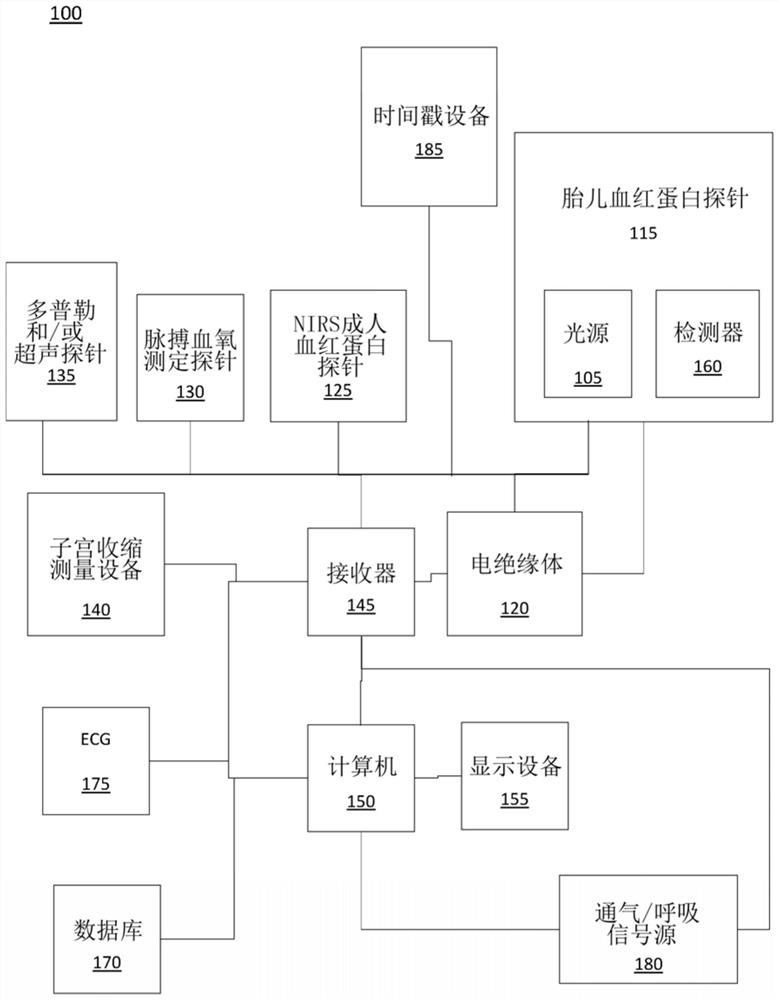
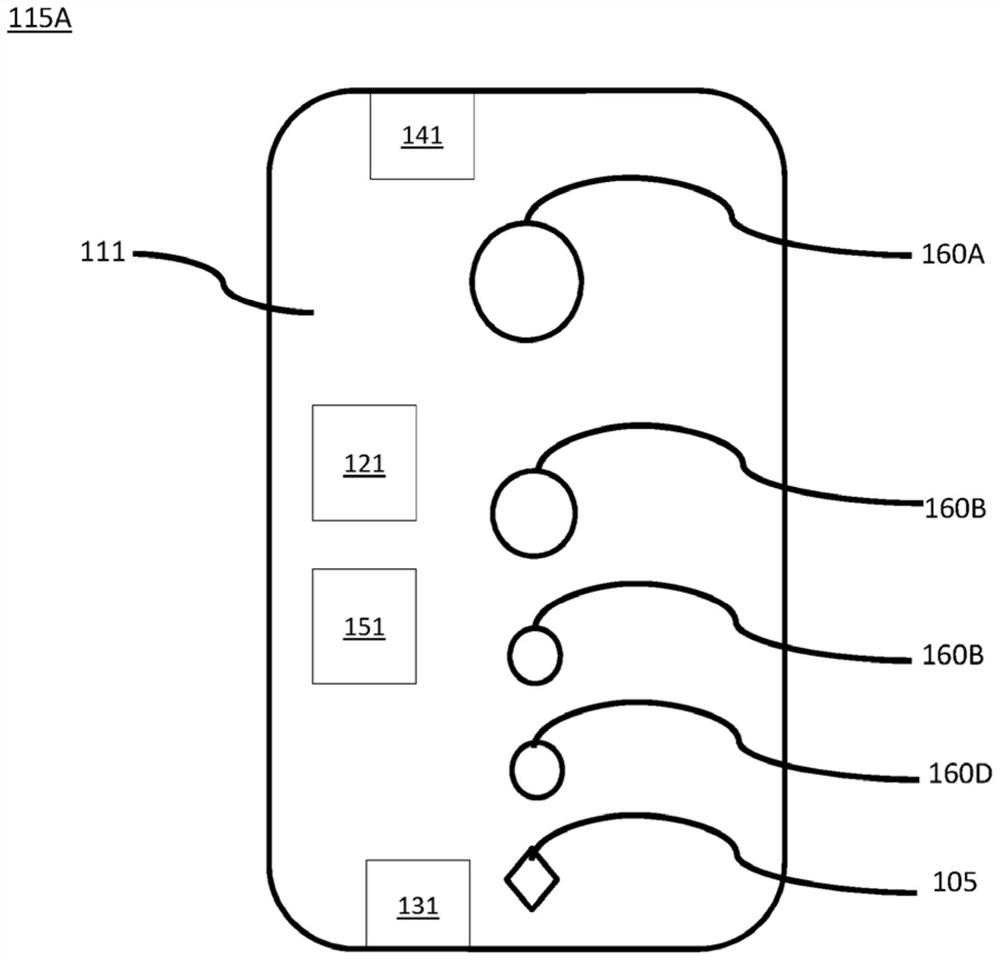
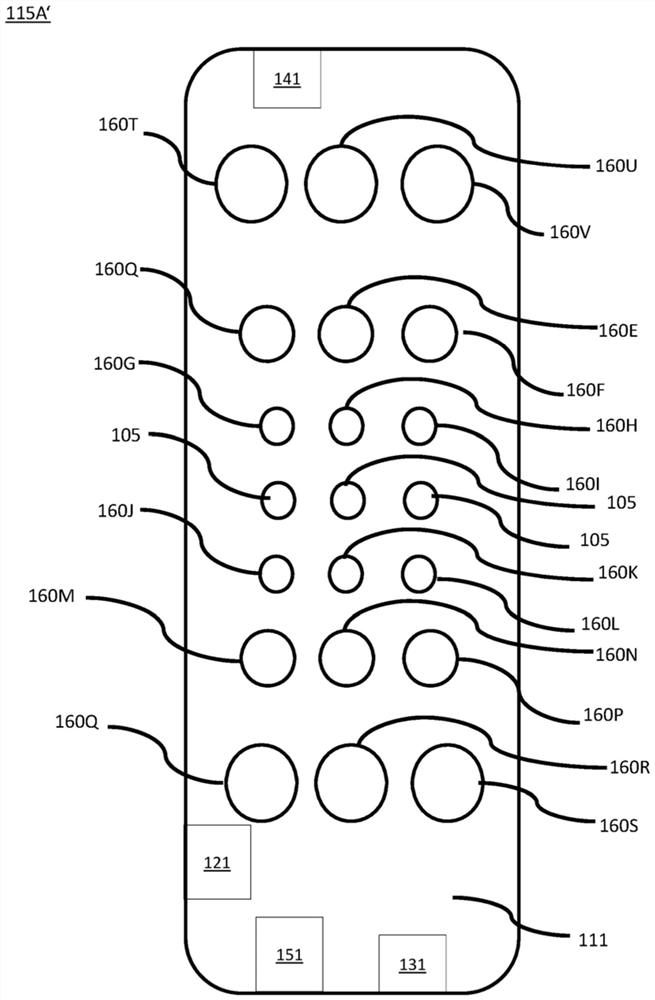
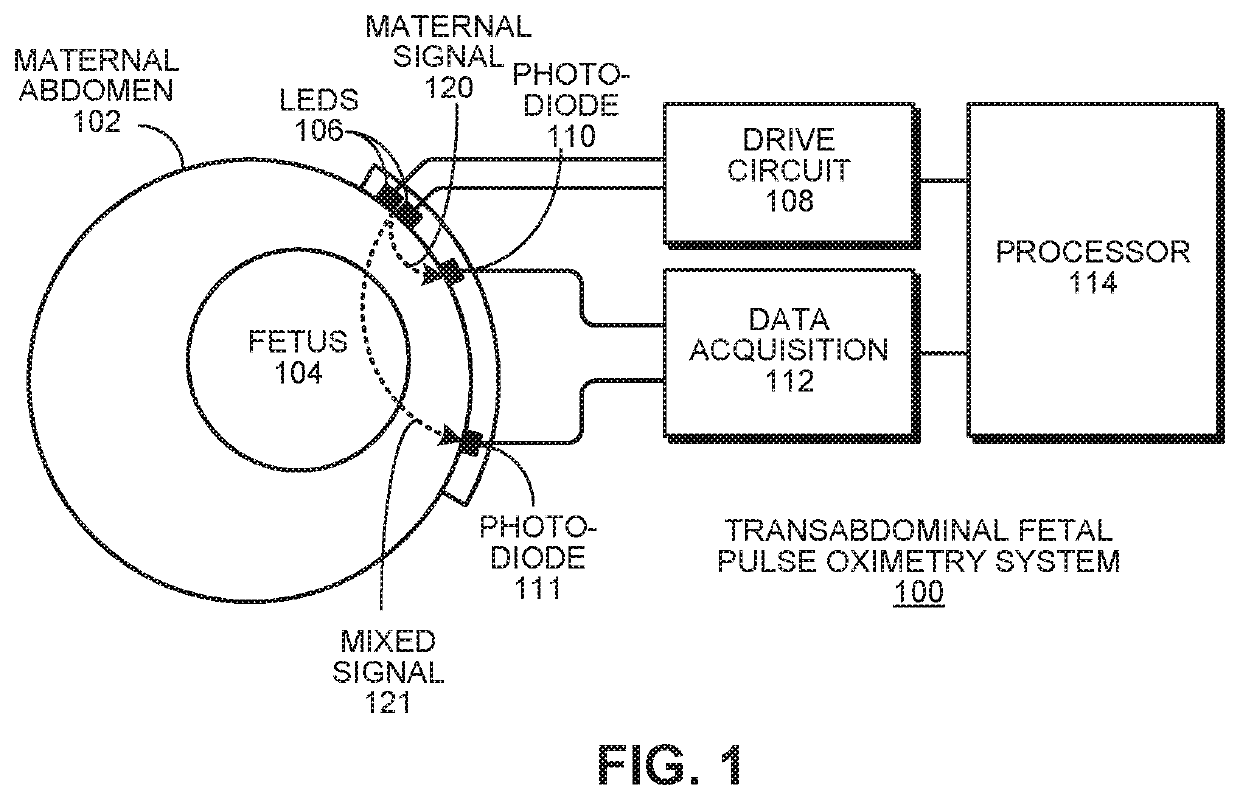
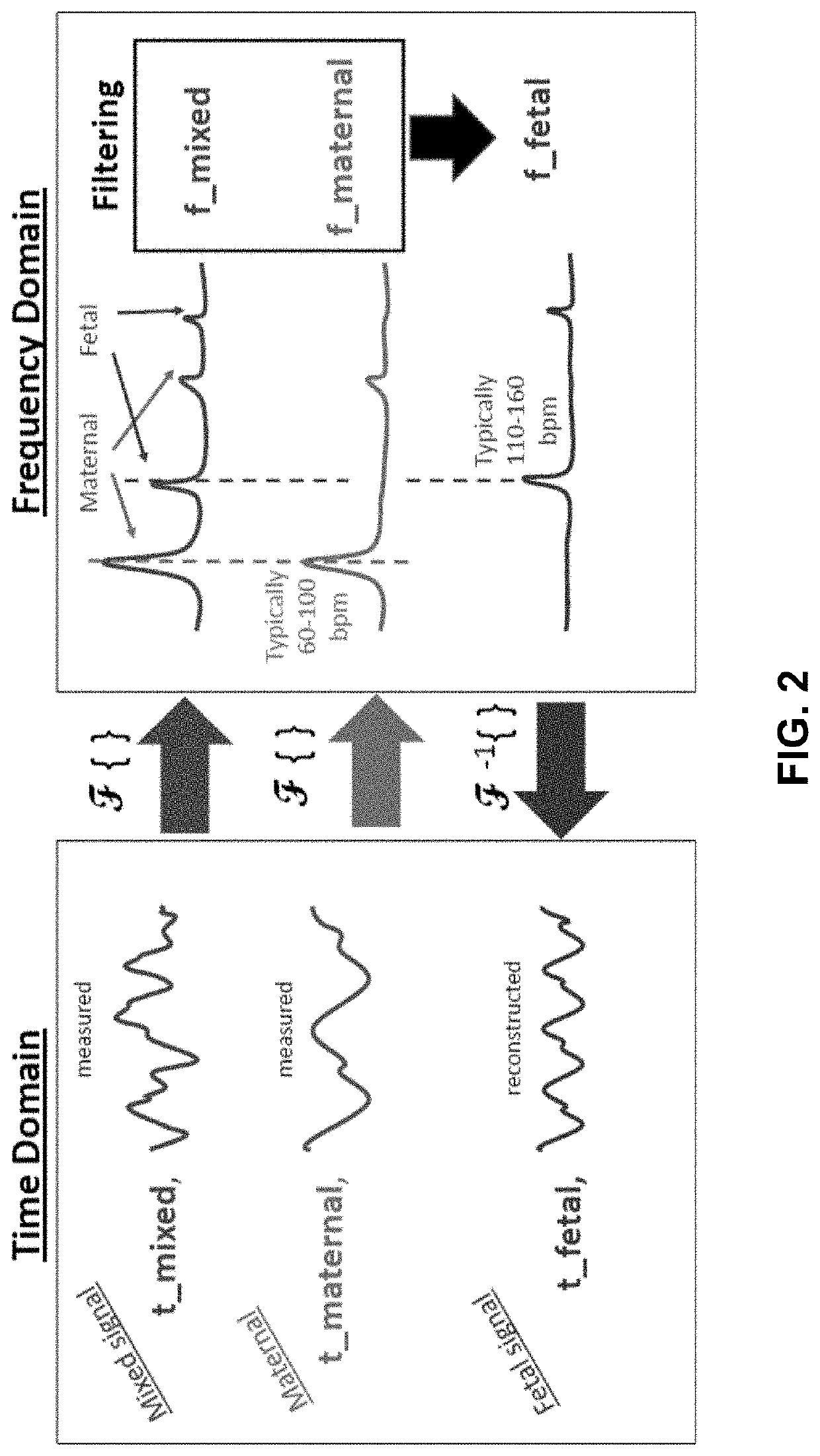
Robust, clinical-grade transabdominal fetal pulse oximetry
ActiveUS20200245879A1Enhanced signalSensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateObstetricsPhotovoltaic detectors
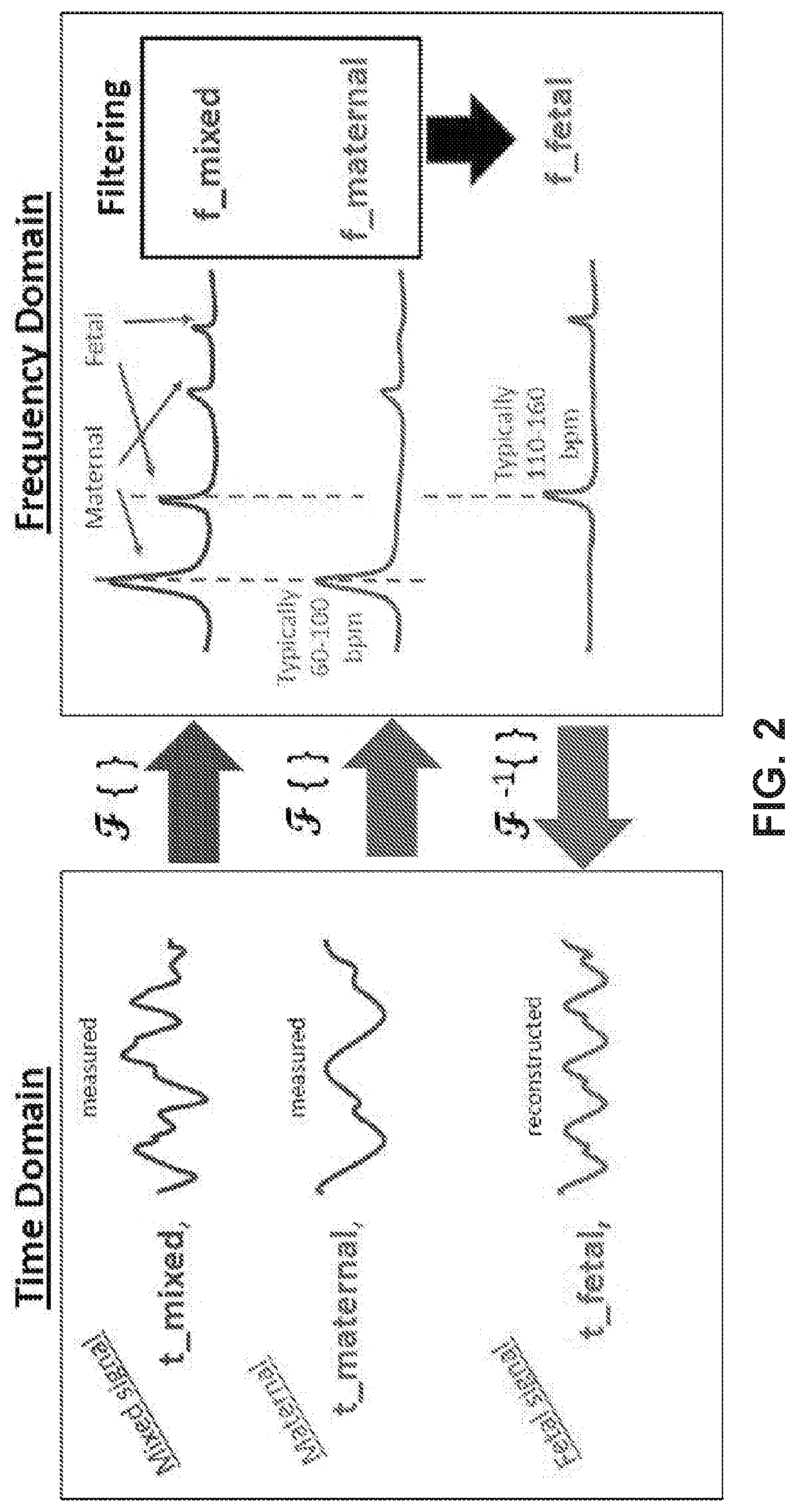
The system determines a fetal blood oxygenation level by activating two or more light sources, having different wavelengths, which are positioned on the maternal abdomen of a pregnant mammal to direct light into a maternal abdomen toward a fetus. The system then receives a maternal signal from a first photodetector, which is positioned on the maternal abdomen to receive reflected light that traverses maternal tissue. The system also receives a mixed signal from a second photodetector, which is positioned on the maternal abdomen to receive reflected light that traverses both maternal and fetal tissue. The system performs a filtering operation that removes maternal signal components from the mixed signal to produce a fetal signal. The system determines the fetal blood oxygenation level by performing a pulse-oximetry computation on the fetal signal. The system dynamically adjusts operational parameters in the face of changing variables, such as fetus position and depth.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Animal model for toxicology and dose prediction
InactiveCN1655671ARestore or improve effectivenessReduce incidenceCompounds screening/testingBiocideHuman animalEmbryo
Owner:RAVEN BIOTECHNOLOGIES INC
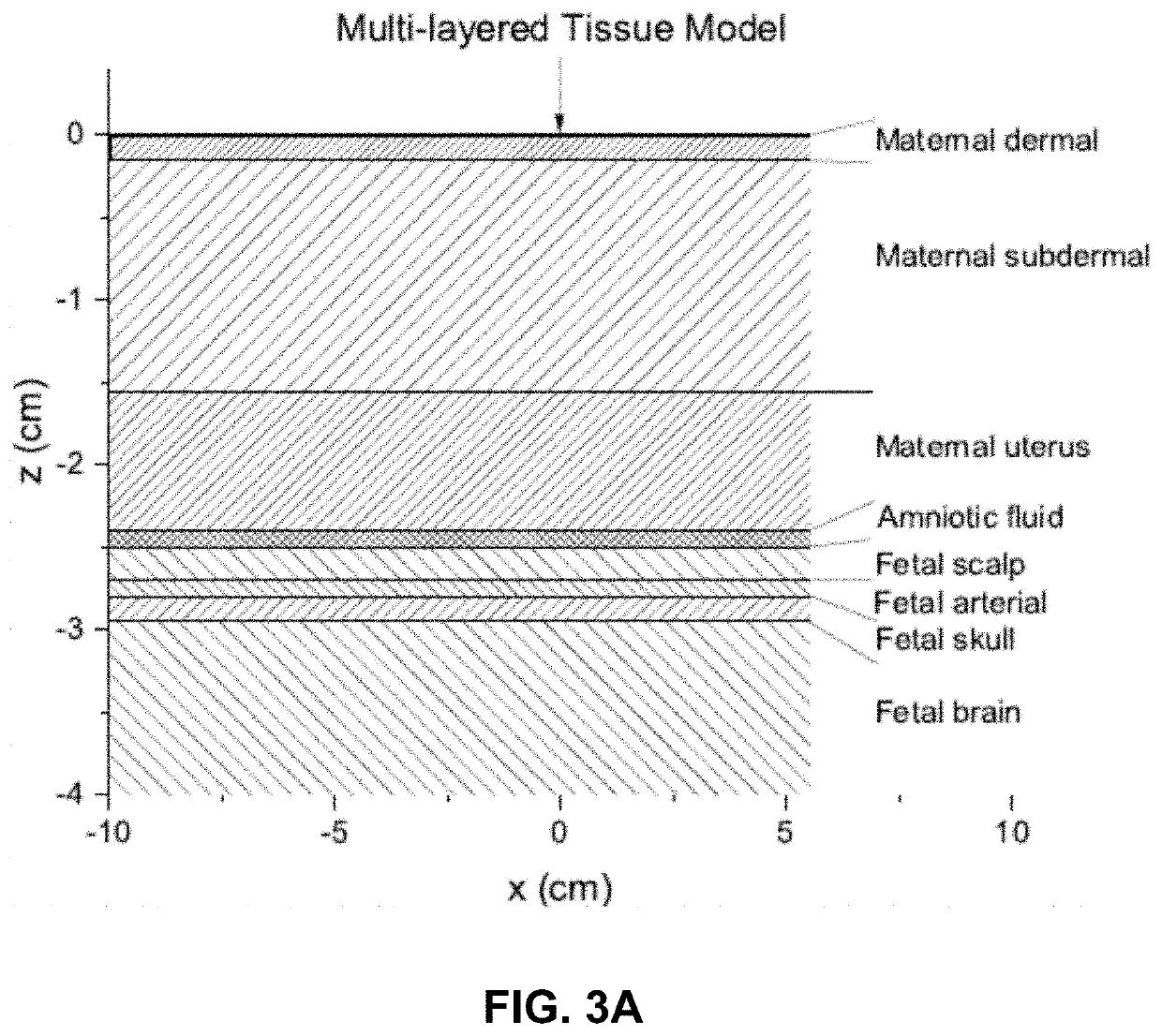
Performing trans-abdominal fetal oxymetry by using optical tomography
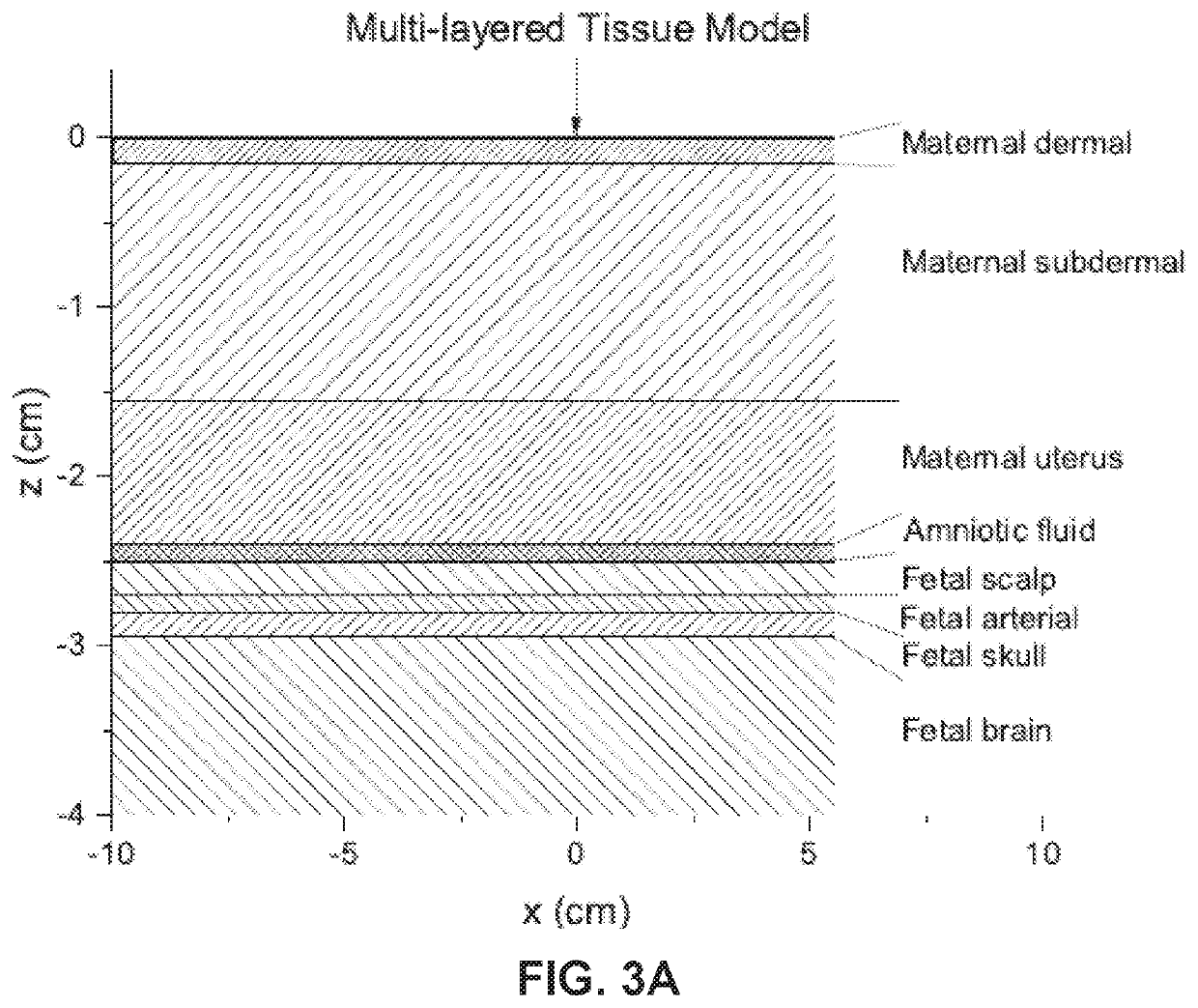
Fetal tissue oxygenation may be performed transabdominally by, for example, receiving a plurality of detected electronic signals that correspond to light emitted from a pregnant mammal's abdomen and afetus contained therein that has been detected by the detector and converted into the detected electronic signal. An indication of a depth of the fetus within the pregnant mammal's abdomen may be received, and a portion of the detected electronic signals that correspond to light that was incident upon the fetus may be isolated responsively to the indication of the depth of the fetus by using, forexample, time of flight of photons that correspond to the detected electronic signals. A fetal tissue oxygen saturation level may then be determined by using the isolated portion of the detected electronic signals that correspond to light that was incident upon the fetus.
Owner:雷迪安特血氧测定公司
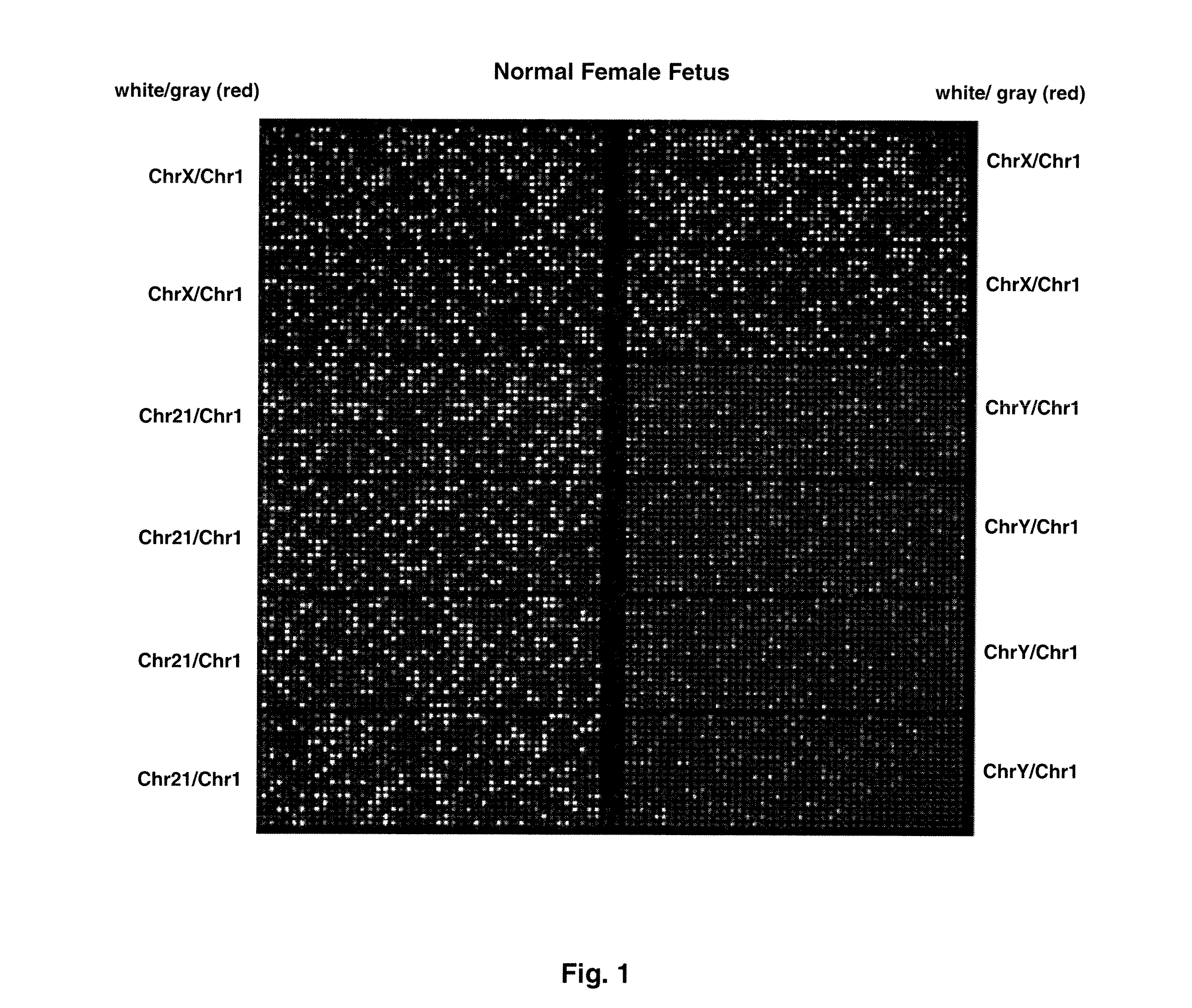
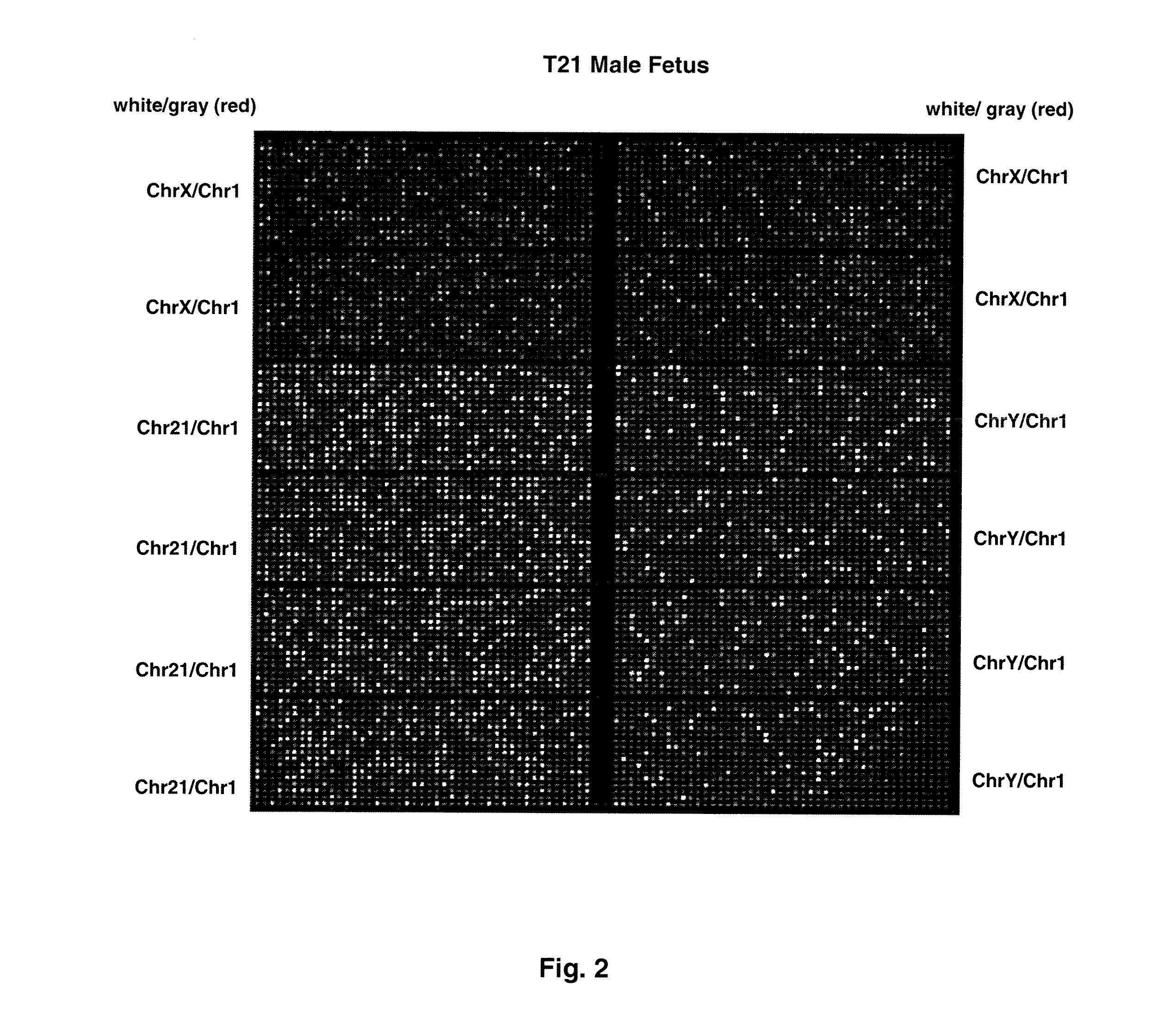
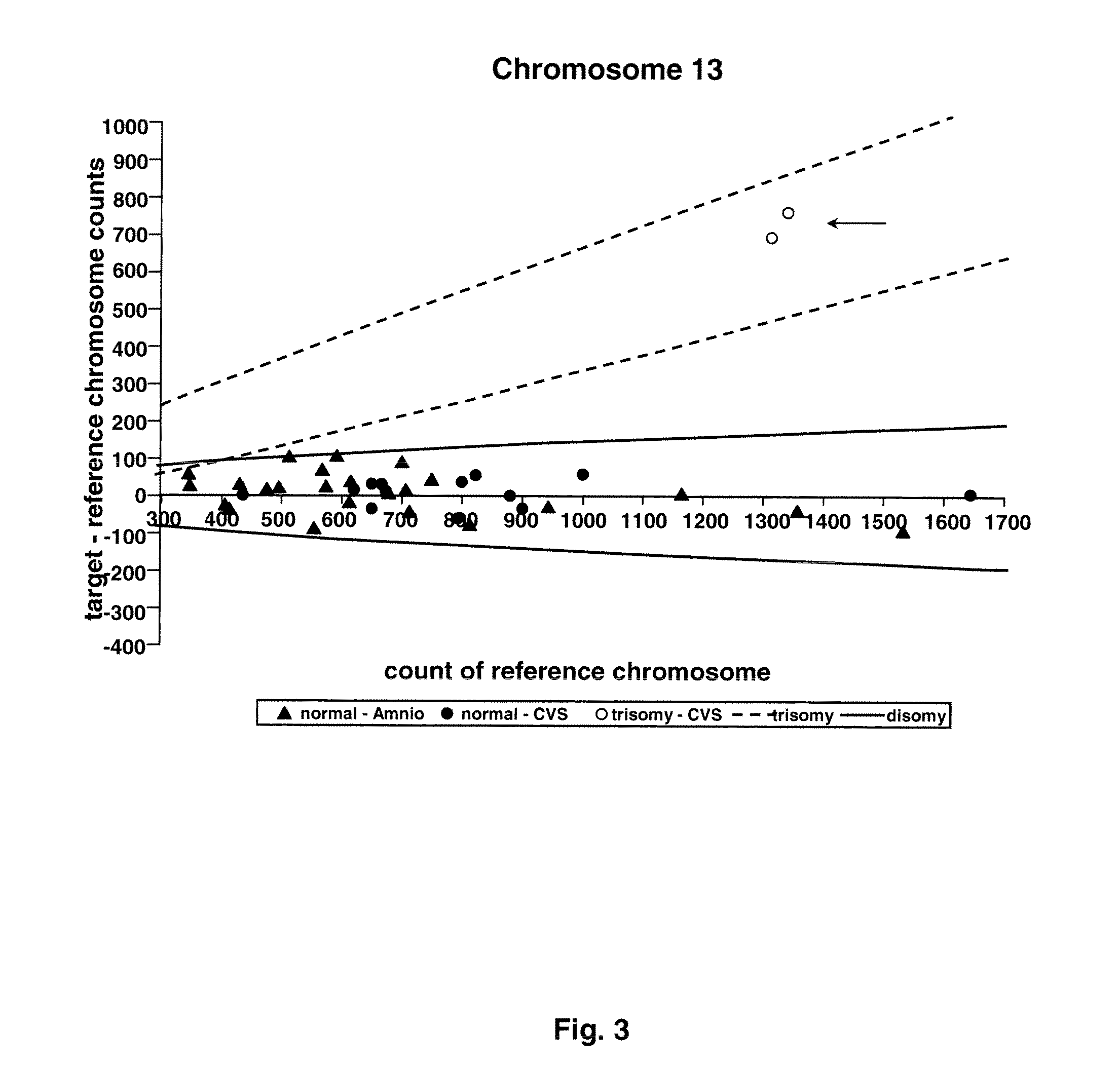
Direct molecular diagnosis of fetal aneuploidy
ActiveUS8574842B2Addressing slow performanceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecific chromosomeChromosomal region
Methods and materials for detection of aneuploidy and other chromosomal abnormalities using fetal tissue are disclosed. Results can be obtained rapidly, without cell culture. The method uses digital PCR for amplification and detection of single target sequences, allowing an accurate count of a specific chromosome or chromosomal region. Specific polynucleic acid primers and probes are disclosed for chromosomes 1, 13, 18, 21, X and Y. These polynucleic acid sequences are chosen to be essentially invariant between individuals, so the test is not dependent on sequence differences between fetus and mother.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Use of cells derived from first trimester umbilical cord tissue
ActiveUS20160354412A1Mammal material medical ingredientsDead animal preservationSpinal cord lesionUmbilical cord tissue
A method of isolating a pluripotent cell from human umbilical cord is described herein. The method involves collecting a sample of umbilical cord from fetal tissue obtained at less than 13 weeks of gestation, for example a first trimester umbilical cord. The sample is treated to obtain isolated umbilical cord cells, after which the isolated umbilical cord cells are incubated. Cells obtained in this way can be differentiated for use in treating conditions of cell damage, by supplanting the function of a damaged cell in a condition such as spinal cord injury, cardiovascular injury or heart disease.
Owner:REPROBIOGEN INC
Robust, clinical-grade transabdominal fetal pulse oximetry
ActiveUS11116412B2Enhanced signalSensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateObstetricsPhotovoltaic detectors
The system determines a fetal blood oxygenation level by activating two or more light sources, having different wavelengths, which are positioned on the maternal abdomen of a pregnant mammal to direct light into a maternal abdomen toward a fetus. The system then receives a maternal signal from a first photodetector, which is positioned on the maternal abdomen to receive reflected light that traverses maternal tissue. The system also receives a mixed signal from a second photodetector, which is positioned on the maternal abdomen to receive reflected light that traverses both maternal and fetal tissue. The system performs a filtering operation that removes maternal signal components from the mixed signal to produce a fetal signal. The system determines the fetal blood oxygenation level by performing a pulse-oximetry computation on the fetal signal. The system dynamically adjusts operational parameters in the face of changing variables, such as fetus position and depth.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
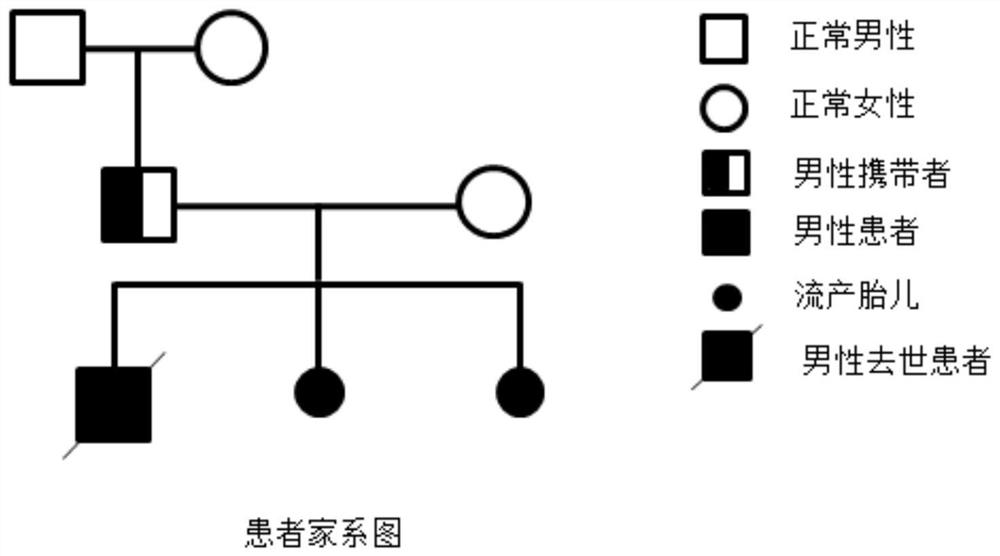
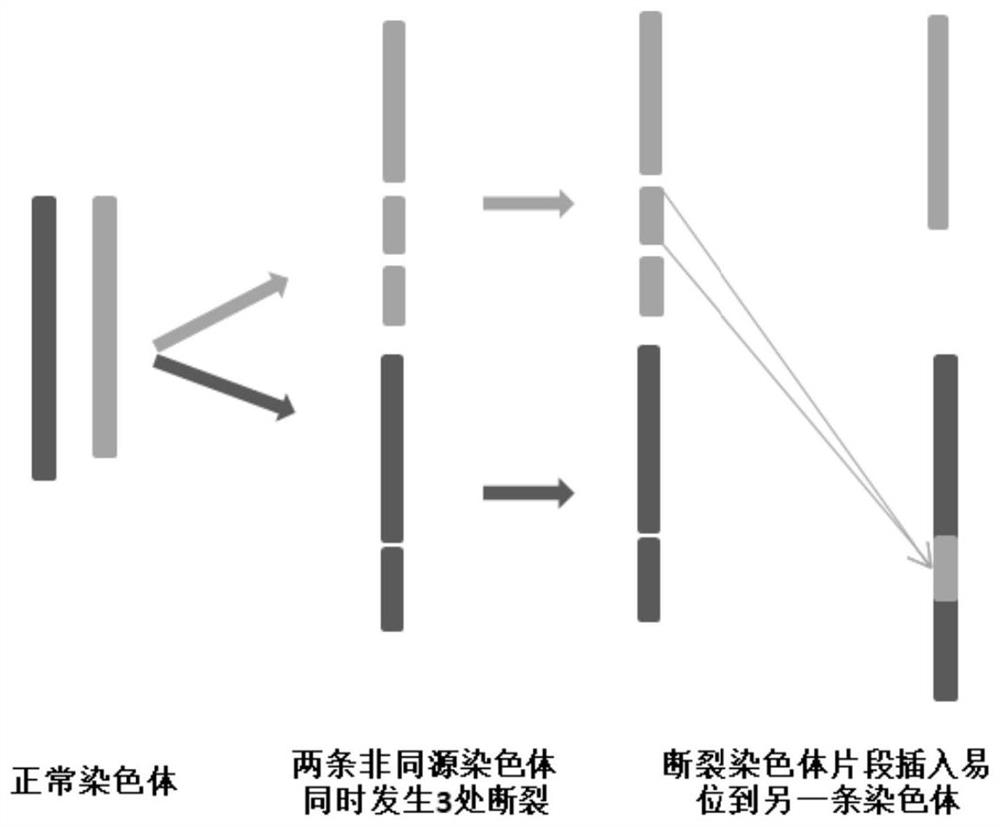
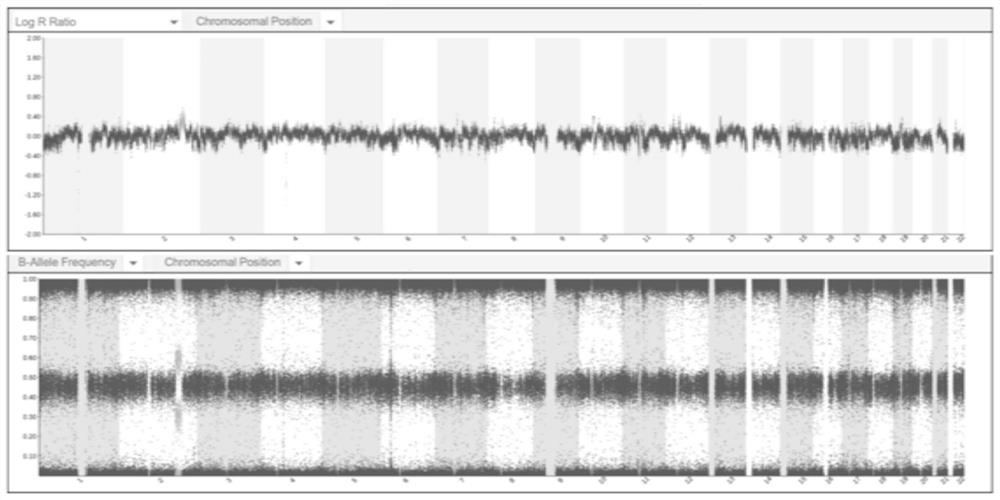
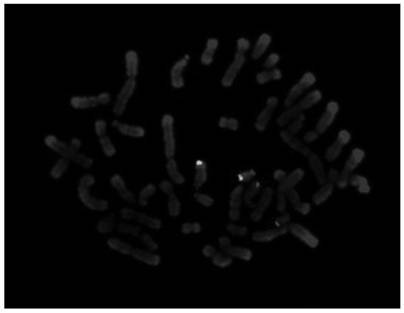
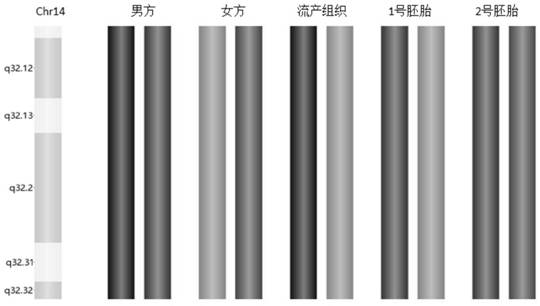
Method for identifying chromosome insertion translocation carried embryo and normal embryo
PendingCN114480609ASolve fertility problemsAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementEmbryo transplantationChromosomal Insertion
The invention relates to a method for identifying a chromosome insertion translocation carried embryo and a normal embryo, belongs to the field of genetic diagnosis and human assisted reproduction, and particularly relates to an embryo pre-implantation detection technology (PGT). According to the method disclosed by the invention, family haplotype linkage analysis is carried out on a patient with chromosome balance insertion translocation and a partner thereof, an embryo after in-vitro insemination, relatives of a translocation carrier or fetal tissues with abnormal insertion fragments or chromosomes of an embryo with abnormal insertion fragments; the method can quickly, simply and accurately distinguish embryos with chromosomes inserted and translocated from embryos with normal chromosomes and screen chromosome aneuploidy of the embryos at the same time, so that diseased embryos and non-diseased embryos are detected in time before embryo transplantation, and defective children are prevented from birth; and the genetic transmission from chromosome insertion translocation to the next generation is blocked in time before embryo transplantation. The development and progress of a human assisted reproduction technology are promoted to a certain extent.
Owner:THE OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV +1
Method for detecting translocation fragment monomer or trisome in latent balance translocation carrier embryo
The invention belongs to the field of genetic diagnosis and human assisted reproduction, and particularly relates to a genetic detection technology (PGT) before embryo implantation. According to the method disclosed by the invention, family haplotype linkage analysis is carried out on a patient with the occult balance translocation of the chromosome, a partner of the patient, an embryo after in-vitro insemination, relatives of a translocation carrier or fetal tissues with abnormal translocation fragments, so that a translocation fragment monomer or trisome in the embryo of the occult balance translocation carrier can be simply, conveniently and accurately detected; the method has important clinical significance on embryo detection and birth defect prevention, and promotes the development and progress of human assisted reproduction technology to a certain extent.
Owner:THE OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV +1
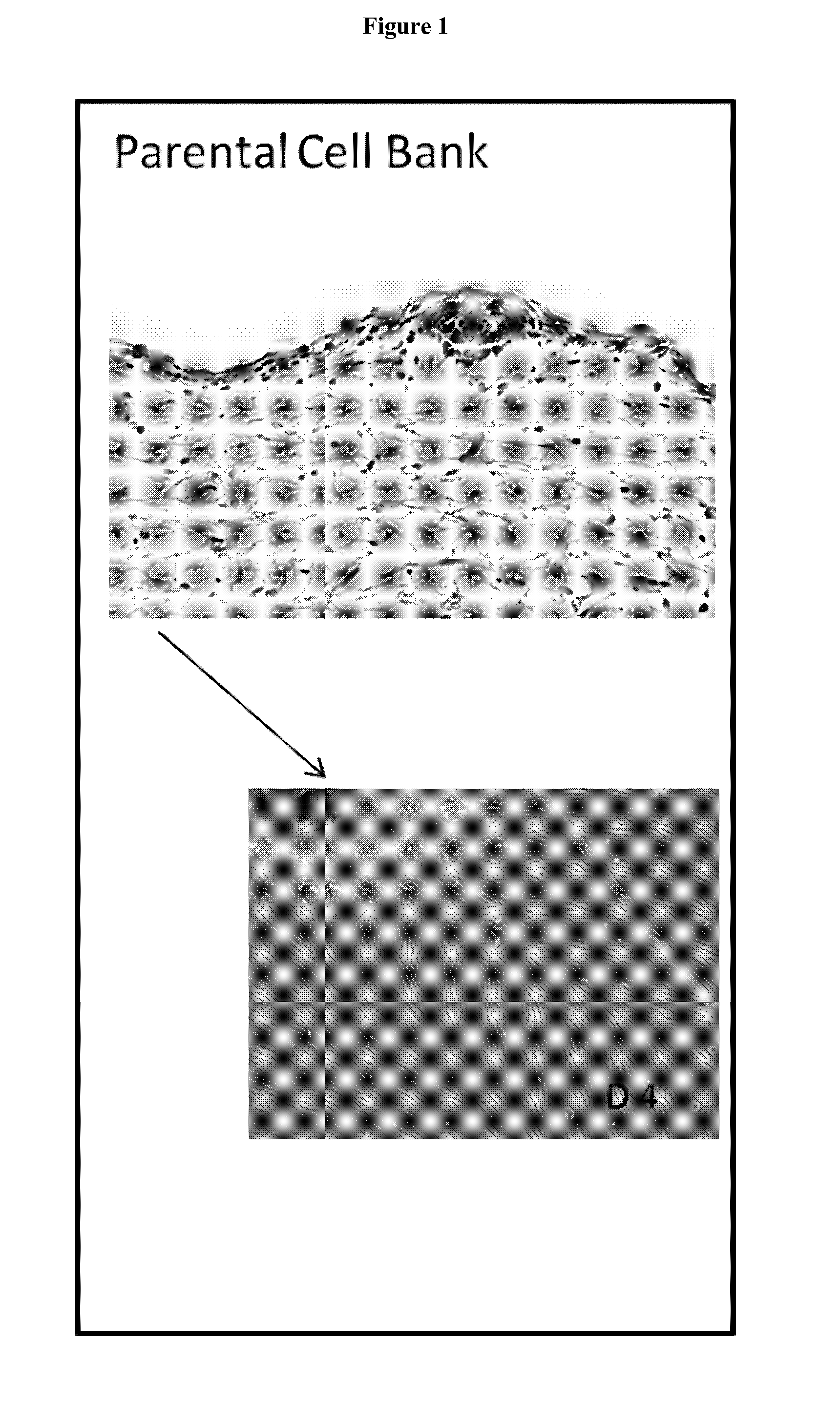
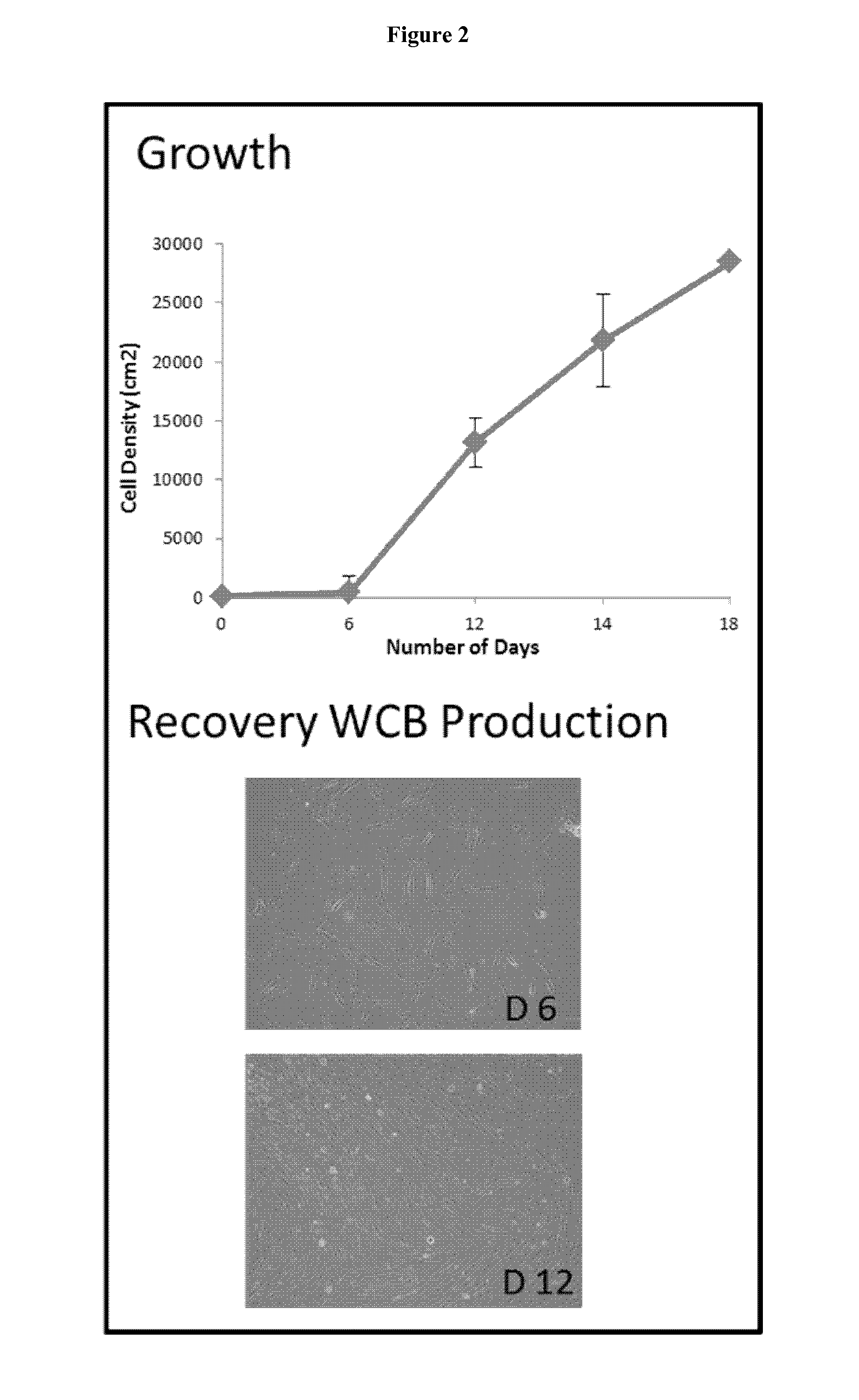
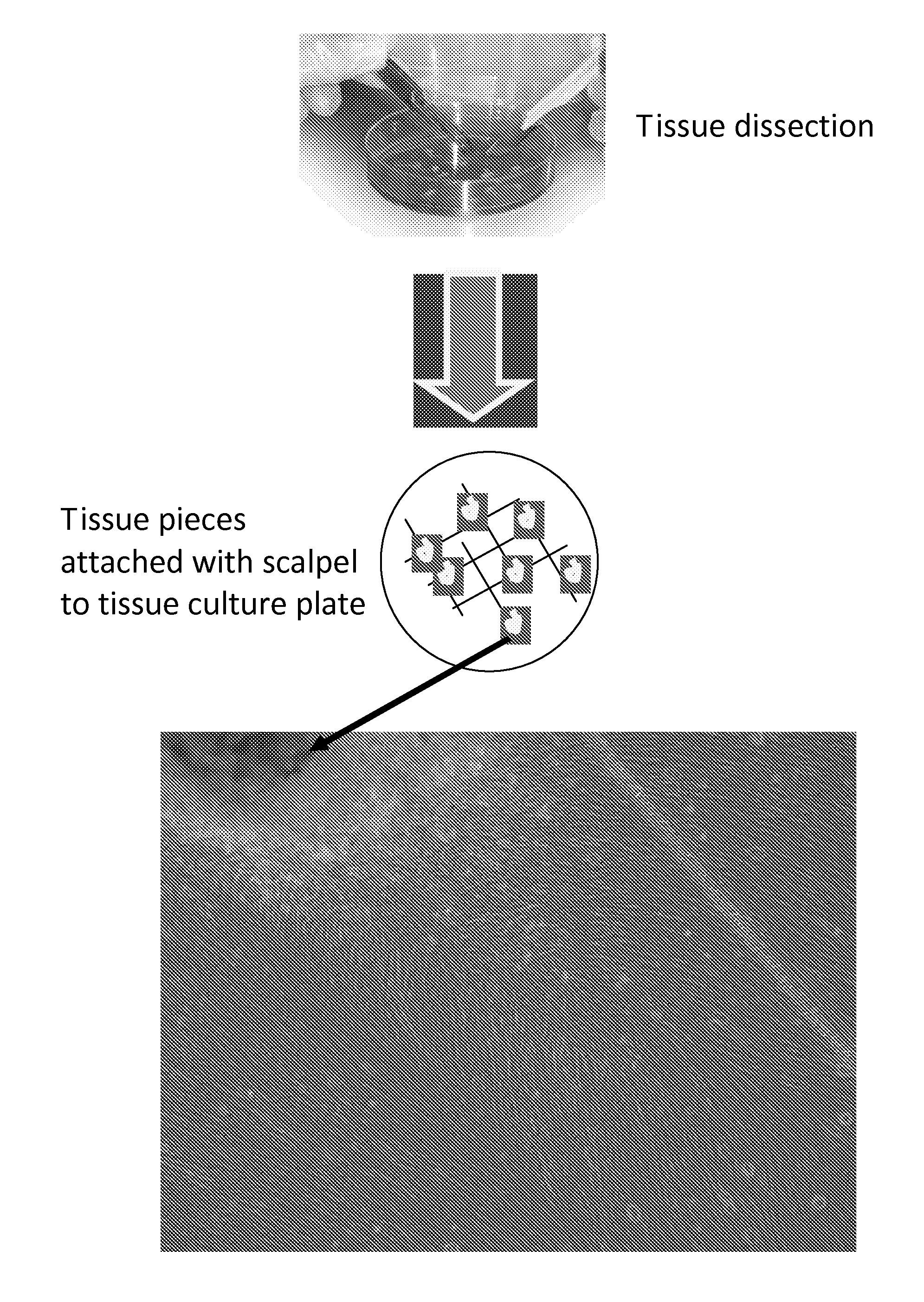
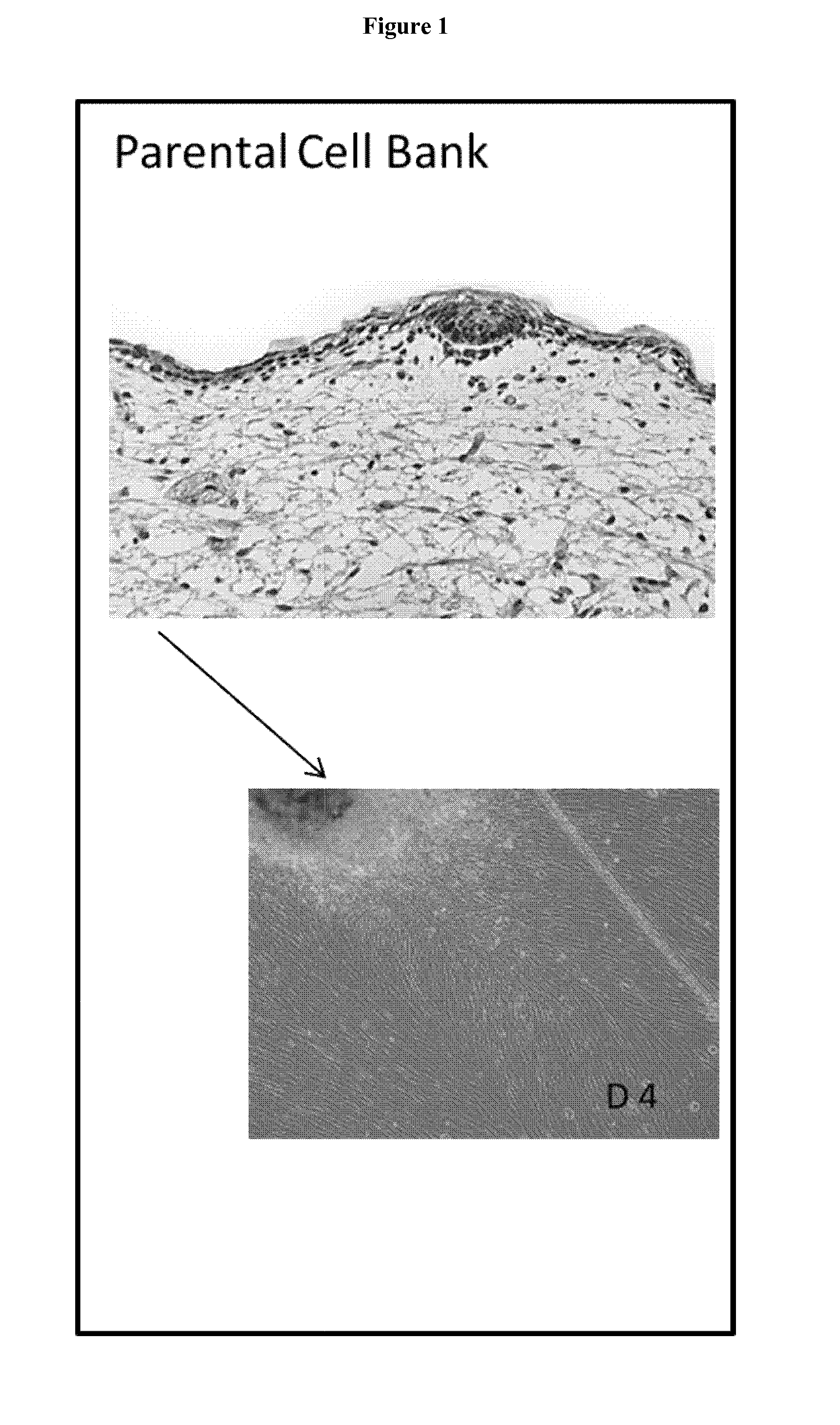
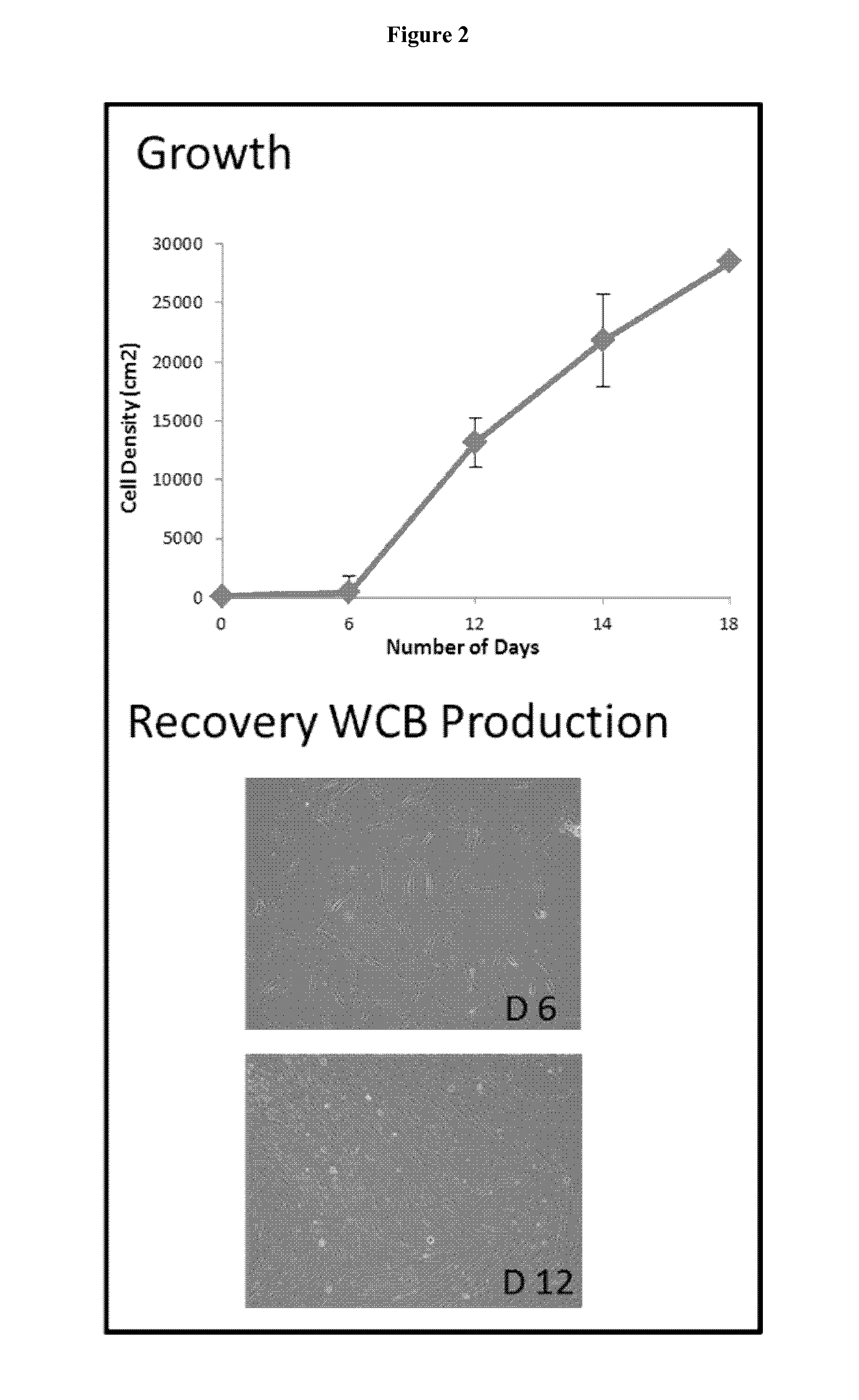
Preparation of parental cell bank from foetal tissue
The present invention relates to methods of in vitro preparation of a parental cell bank (PCB) from foetal tissue consisting of foetal epiphyseal tissue, foetal Achilles tendon tissue and foetal skin tissue, using a rapid mechanical primary cell culture selection of cell type to be used in methods for wound and tissue repair.
Owner:CENT HOSPITALIER UNIV VAUDOIS C H U V
A method of callus induction and tissue culture seedling rapid propagation
ActiveCN105028208BIncrease the number of budsReduce the cost of trainingHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureGrowth coefficientEcological environment
The invention discloses a callus induction and tissue culture seedling rapid propagation method of rhizoma ardisiae gigantifoliae. According to the callus induction and tissue culture seedling rapid propagation method, rhizoma ardisiae gigantifoliae seeds are sterilely sowed to obtain sterile plants, and stems and buds of the sterile plants are subjected to callus induction; and a lot of buds can be rapidly obtained through a manner of differentiating calluses into the buds, so that the defect that the growth coefficients of cluster buds at a tissue culture phase of some plants are low is made up. With the adoption of the method disclosed by the invention, the quantity of the buds of rhizoma ardisiae gigantifoliae can be rapidly increased at the differentiating phase of the calluses, and a lot of rhizoma ardisiae gigantifoliae tissue culture seedlings can be obtained in short time, so that the culture cost is reduced and energy consumption is saved. The method disclosed by the invention is simple to operate and has low production cost, and can be used for producing germchits of rhizoma ardisiae gigantifoliae in a factory-like manner, so that a foundation is laid for sustainable utilization of rhizoma ardisiae gigantifoliae and protection of diversity of ecological environments.
Owner:广西华泰药业有限公司
Use of cells derived from first trimester umbilical cord tissue
ActiveUS10925903B2Dead animal preservationMammal material medical ingredientsSpinal cord lesionUmbilical cord tissue
A method of isolating a pluripotent cell from human umbilical cord is described herein. The method involves collecting a sample of umbilical cord from fetal tissue obtained at less than 13 weeks of gestation, for example a first trimester umbilical cord. The sample is treated to obtain isolated umbilical cord cells, after which the isolated umbilical cord cells are incubated. Cells obtained in this way can be differentiated for use in treating conditions of cell damage, by supplanting the function of a damaged cell in a condition such as spinal cord injury, cardiovascular injury or heart disease.
Owner:REPROBIOGEN INC
Method for rapidly and efficiently extracting macromolecular compound from sheep embryonic cells
InactiveCN113621561AIncrease contentImprove extraction efficiencyCell dissociation methodsCosmetic preparationsHistiocyteBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention relates to a method for quickly and efficiently extracting a macromolecular compound from sheep embryonic cells. The method mainly comprises two parts of contents. The core technical content I is that: fetal tissue cells are quick-frozen by liquid nitrogen, the obtained product is dried, and the obtained product is subjected to primary treatment by using a low-temperature ultrafine grinder; and the core technical content II is that: tissue cell precipitates and molecular complexes are gradually separated by using a method of carrying out centrifugation with different centrifugal speeds, and molecular peptide substances in cells are released to the maximum extent by combining ultrahigh-pressure cell crusher and low-temperature ultrasonic cell crusher treatment technologies. By the method, compound sheep placenta containing macromolecular and micromolecular peptides and the like can be obtained, natural active ingredients in the sheep embryonic cells are reserved to the maximum extent, the whole operation needs short time and is carried out under a low-temperature condition, the influence of temperature and time on the active ingredients such as the micromolecular peptide and the like in the extraction process is guaranteed to the maximum extent, and no any chemical reagent is added in the extraction process, so that the product obtained in the invention has better biological functions than a product obtained in the prior art.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Fetal tissue extract, methods for producing the extract, and the use thereof
InactiveUS20210369786A1Effectively prevent or treat bone disordersMetabolism disorderSkeletal disorderDiseaseHistiocyte
Provided are fetal tissue cells or a fetal tissue extract which can effectively prevent or treat bone disorders or diseases.
Owner:ALIS PHARMA LTD
Retinal pigment epithelial primary cell culture system producing subcellular deposits
The present invention provides a retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) primary cell culture system on a material surface seeded at a high density that produces a layer of subcellular deposits, wherein the RPE primary cells are harvested from non-fetal tissue. The present invention additionally provides methods of making and using the PRE primary cell culture system.
Owner:CURCIO CHRISTINE A +1
Xenogenic normal tissue-derived vaccines for breaking the immune tolerance to tumor-associated, antigens
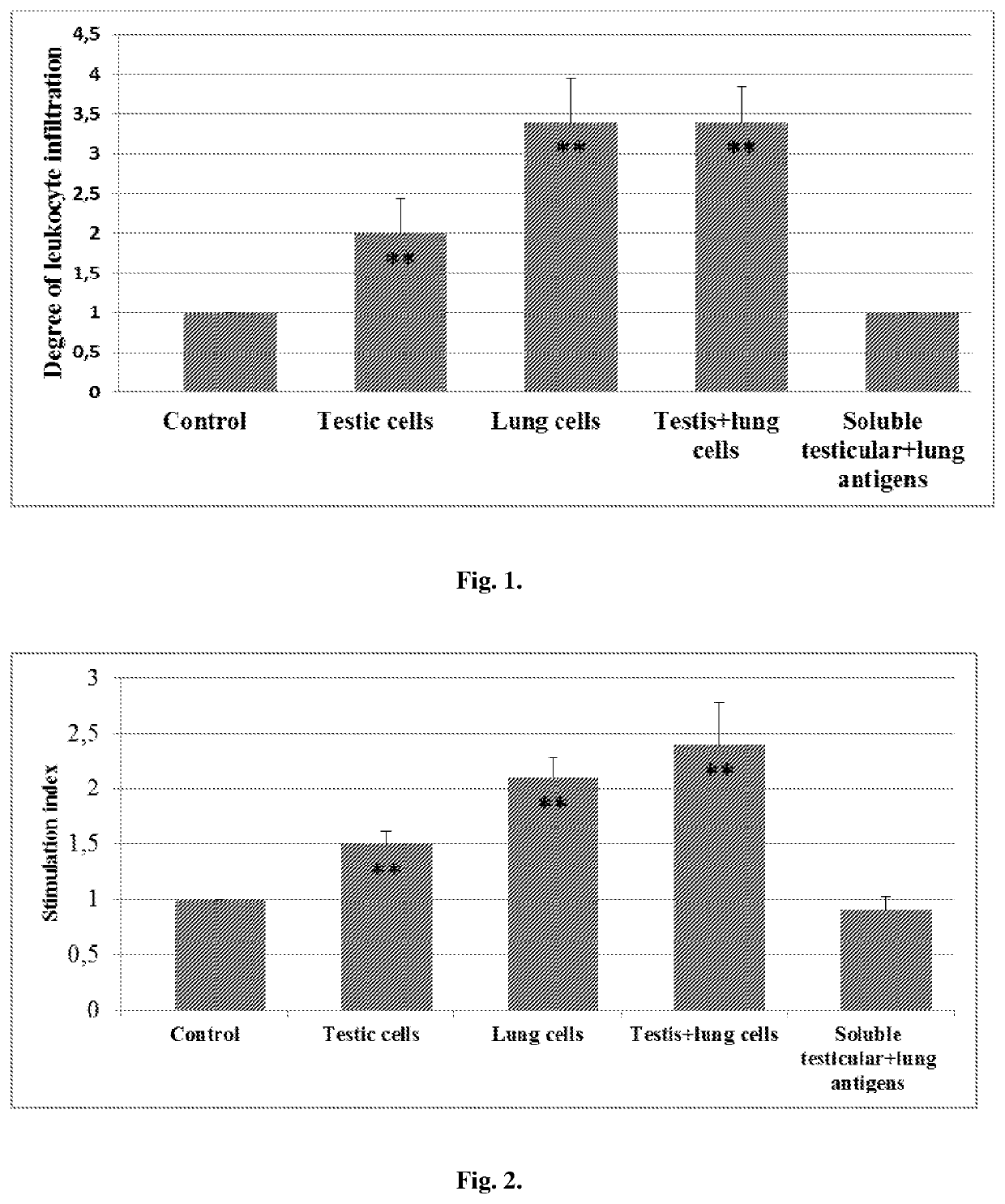
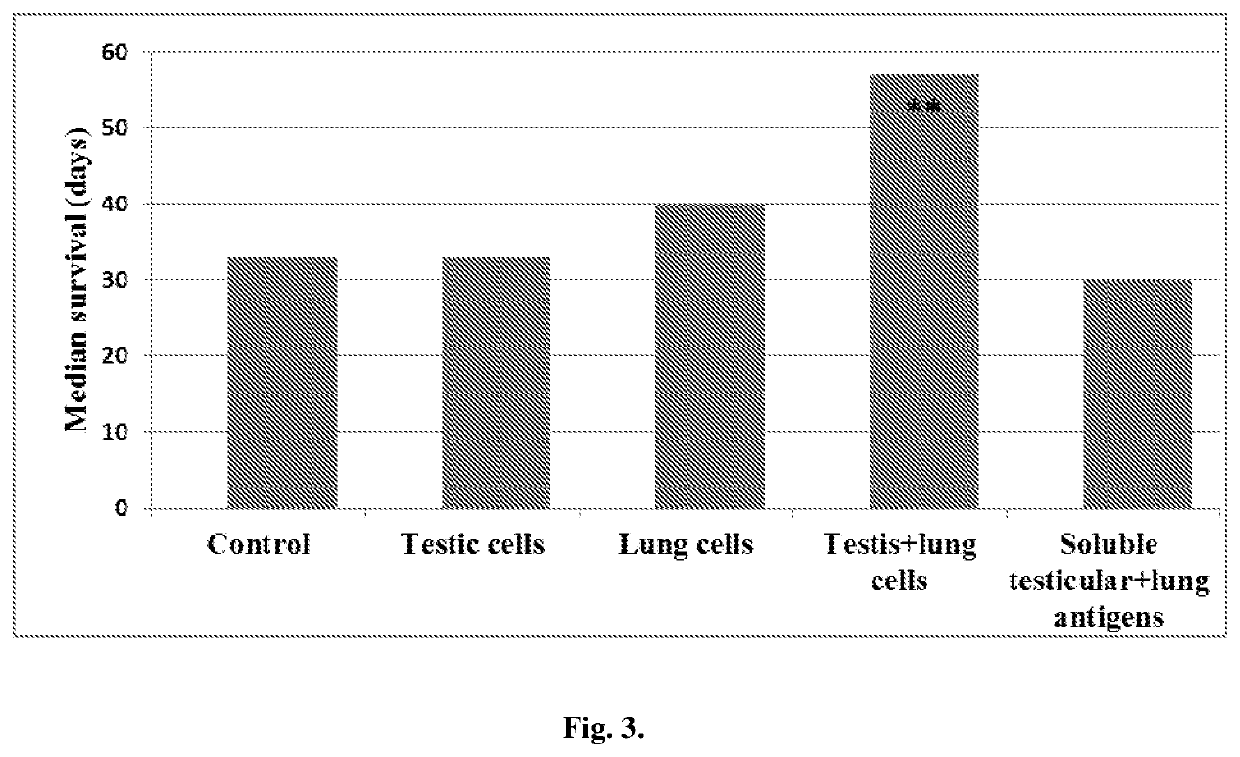
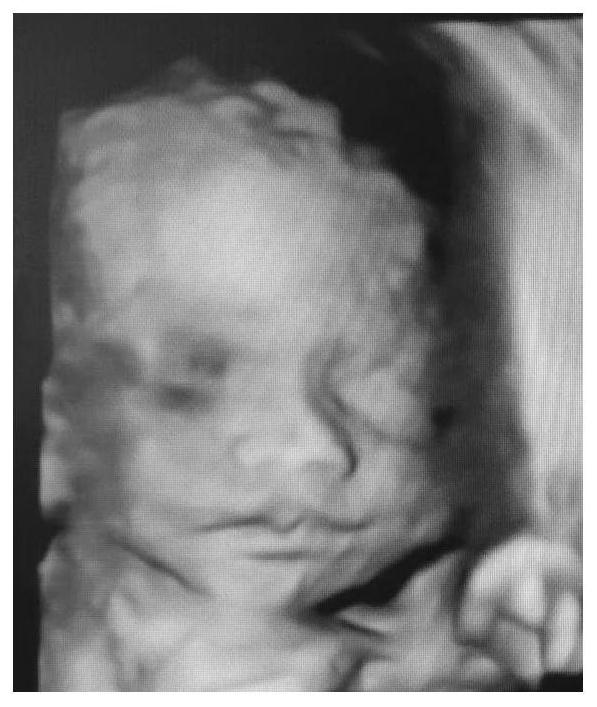
Disclosed is an antitumor vaccine including testicular and fetal tissue-derived components. Cell preparations are prepared from normal tissues harvested directly from animals. Such vaccines may be used in the treatment and prevention of different cancers. For example, a vaccine consisting of glutaraldehyde-treated cells prepared from sheep testis and fetal lung has been found to be effective in inducing antitumor cell-mediated responses, as well as in prolonging the survival of mice with lung cancer.
Owner:UAB INNOVITA RES
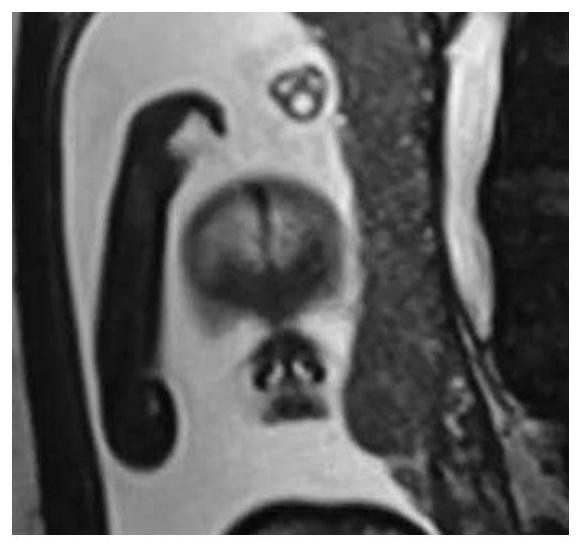
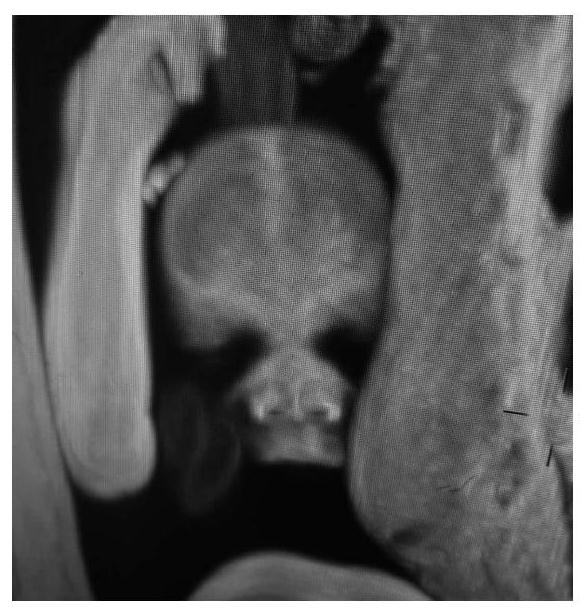
Three-dimensional imaging method for visualization of fetal body surface structure based on magnetic resonance scanning
InactiveCN108133512BDiagnosis meetsImprove image qualityDetails involving processing stepsDiagnostic signal processing3d imageFetal mri
The invention discloses a three-dimensional imaging method for fetal body surface structure visualization based on magnetic resonance scanning. The projection method completes the volume rendering display, so as to calculate the color value at the pixel point on the screen. The present invention utilizes the real steady-state free precession gradient echo sequence and the existing magnetic resonance imaging hardware facilities to collect three-dimensional data of the tissue structure of the fetal region of interest, and generates new data containing fetal histological characteristics through data processing. The processing software performs surface reconstruction on the new data to obtain a three-dimensional image of the fetal body surface structure.
Owner:肖连祥
Preparation of parental cell bank from foetal tissue
The present invention relates to methods of in vitro preparation of a parental cell bank (PCB) from foetal tissue consisting of foetal epiphyseal tissue, foetal Achilles tendon tissue and foetal skin tissue, using a rapid mechanical primary cell culture selection of cell type to be used in methods for wound and tissue repair.
Owner:CENT HOSPITALIER UNIV VAUDOIS C H U V
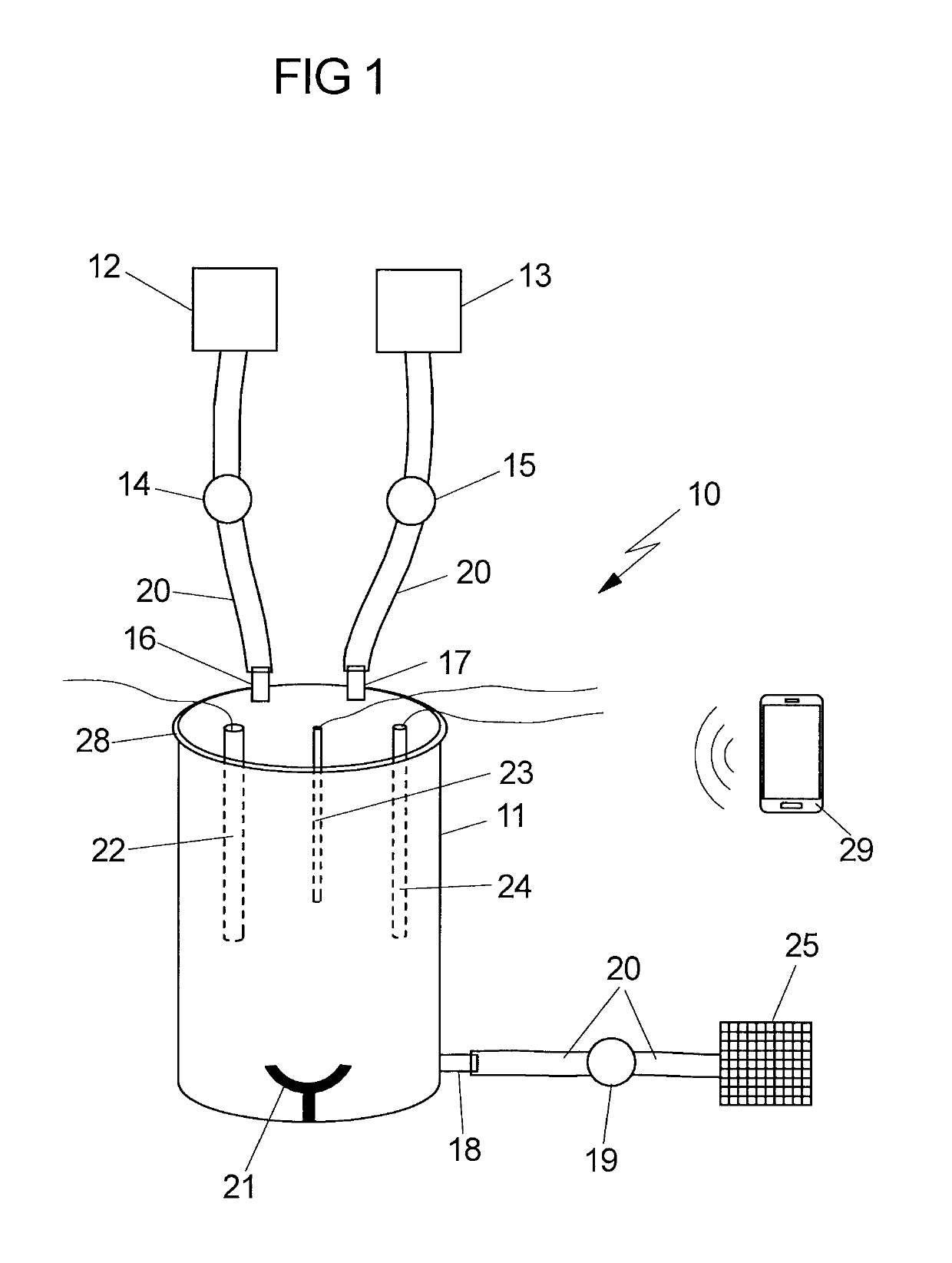
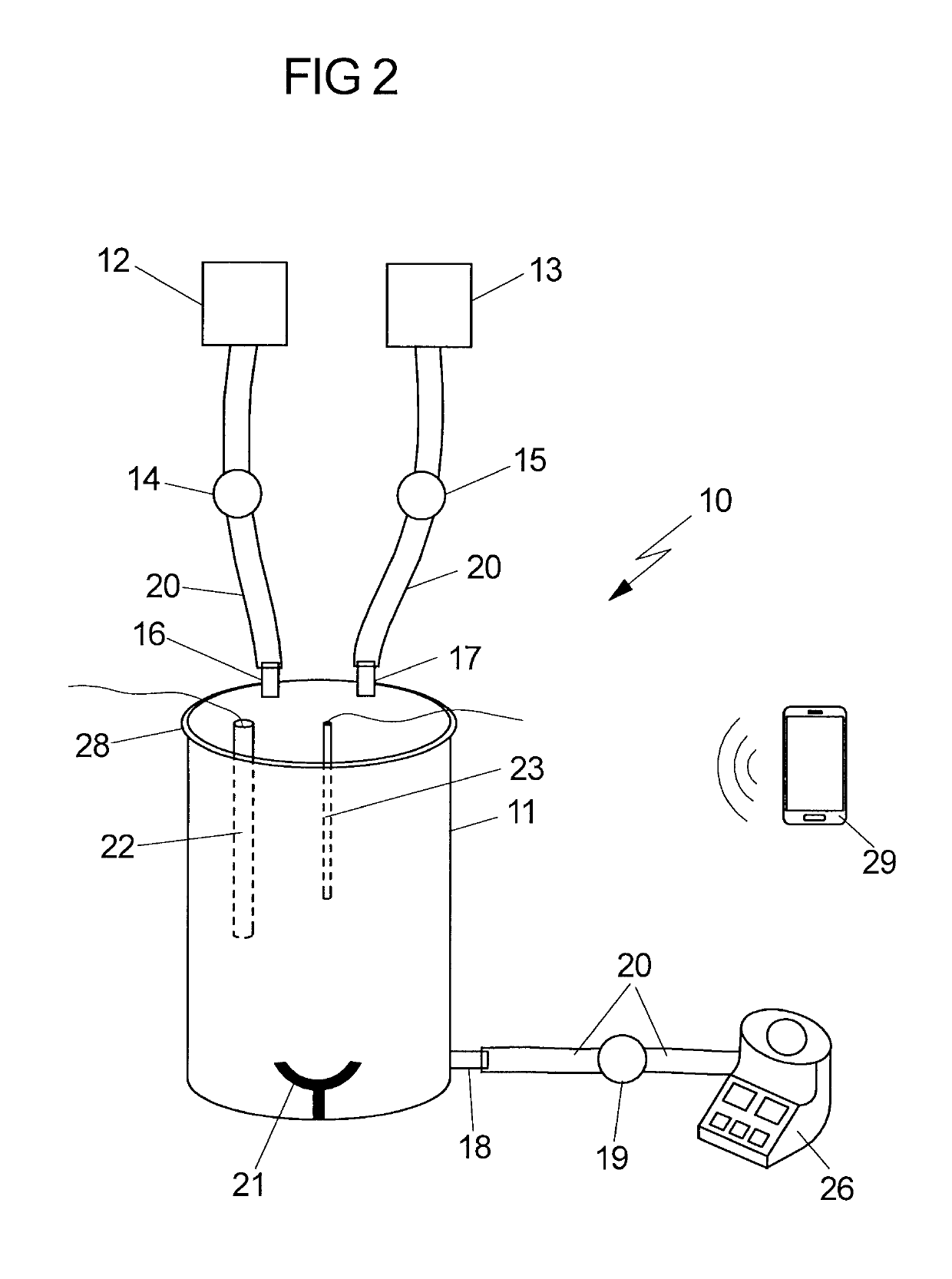
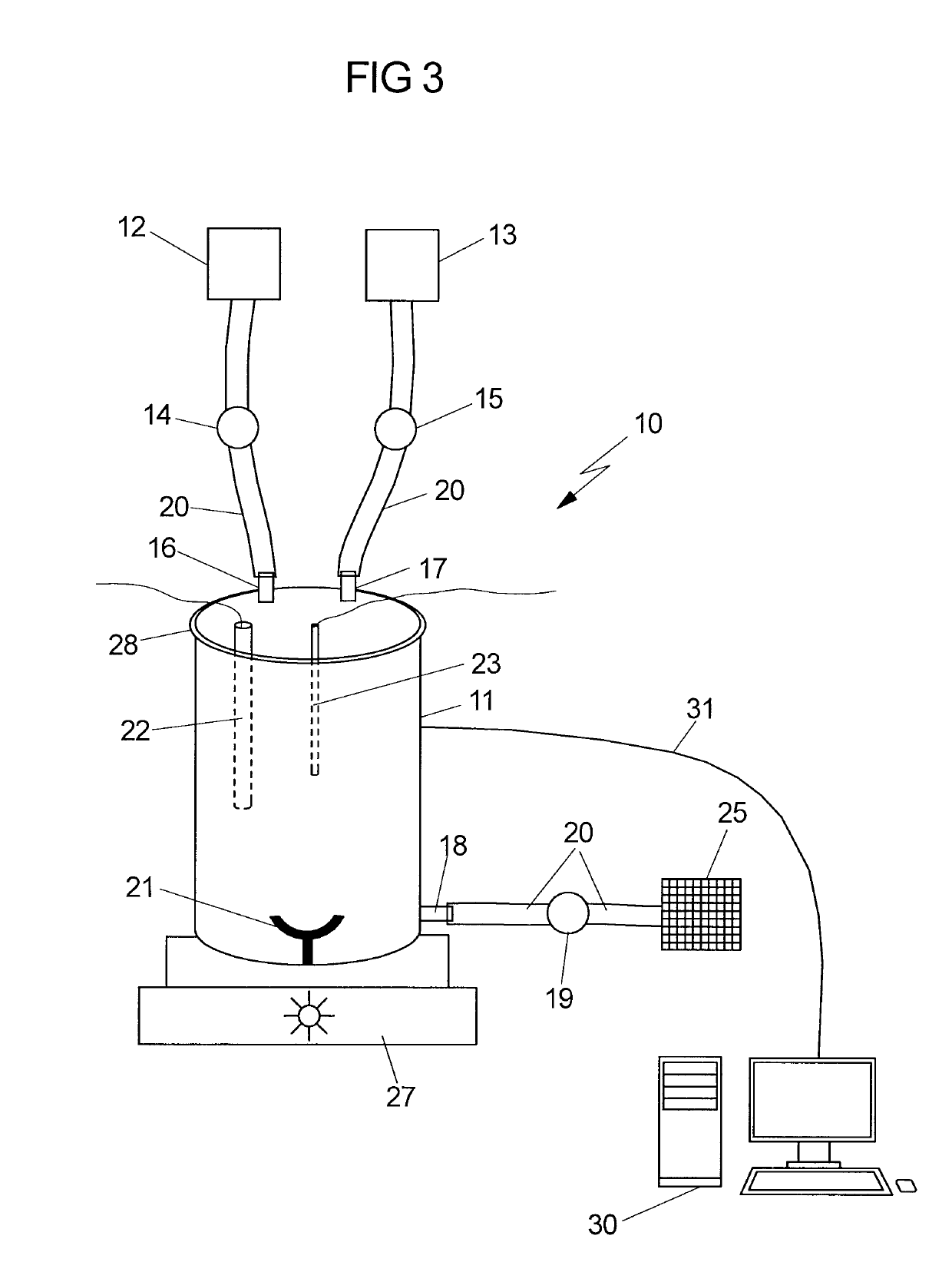
Device for isolating stem cells from fetal tissues
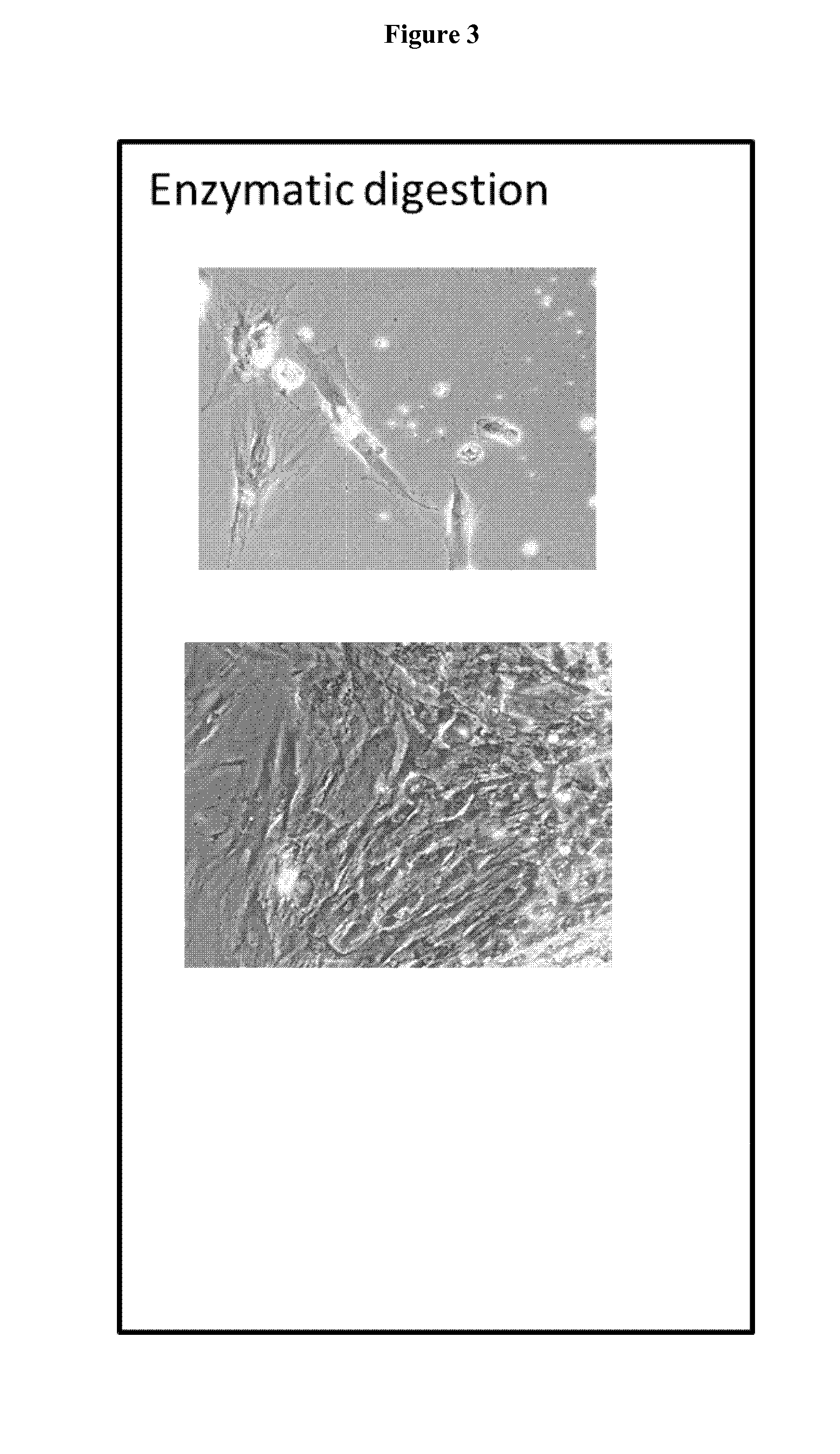
ActiveUS20190185809A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFetal lungEnzymatic digestion
The invention relates to a device for isolating stem cells from fetal tissues, which device has an incubation chamber, at least one pump, at least one reservoir for a tissue break-down solution, at least one reservoir for a rinsing solution, optionally a control unit, optionally a means for removing contaminants, and optionally a means for expansion of the isolated stem cells. The invention further relates to a method for isolating stem cells from fetal tissue, which method comprises, among other things, the mechanical dissociation and the enzymatic digestion of the fetal tissue and optionally density gradient centrifugation for removing contaminants. The device and the method according to the invention are particularly suitable for isolating mesenchymal stem cells from fetal tissues, such as umbilical cord tissue, placenta tissue, or fetal lung tissue.
Owner:MDTB CELL MFG GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com