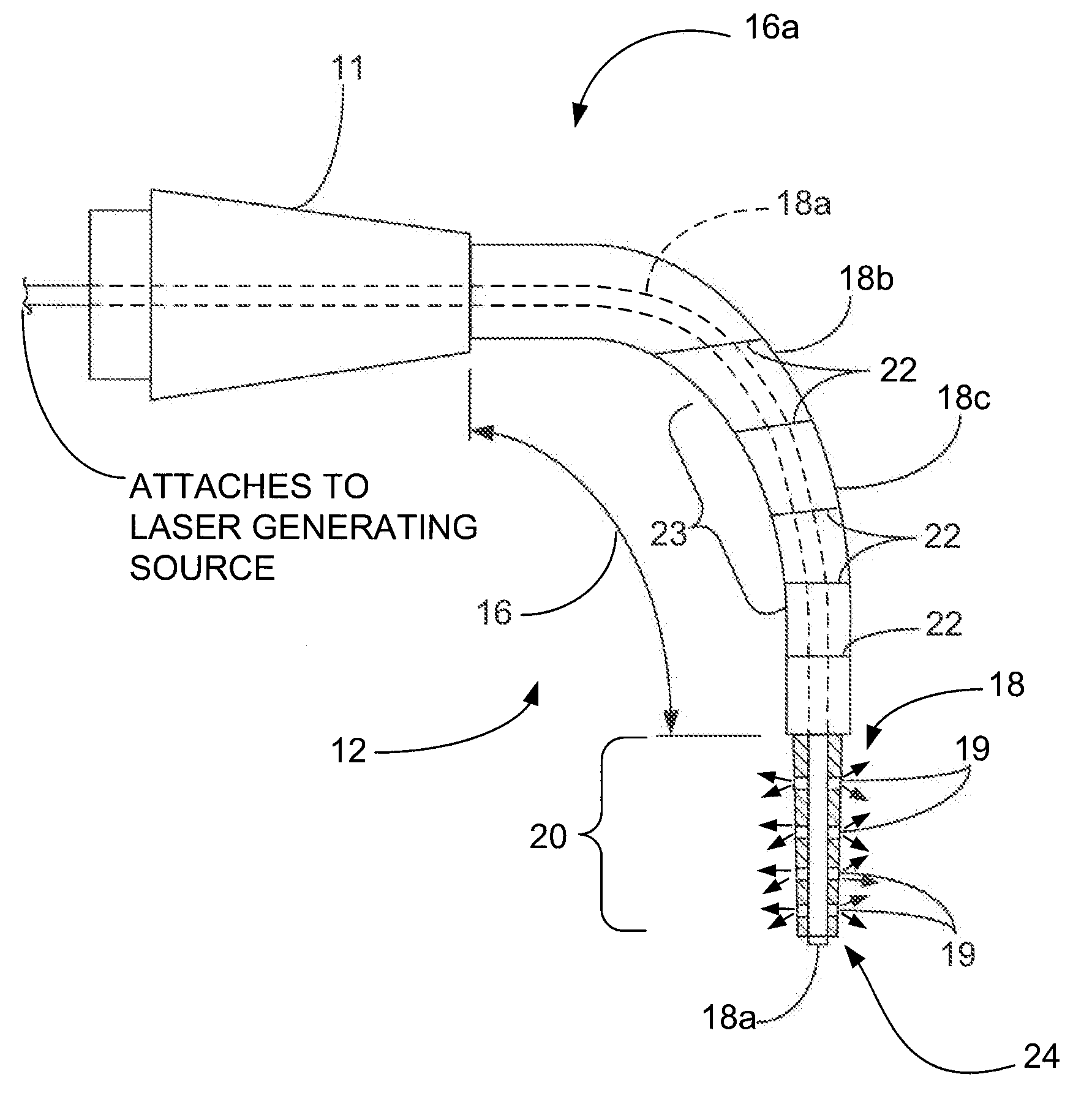
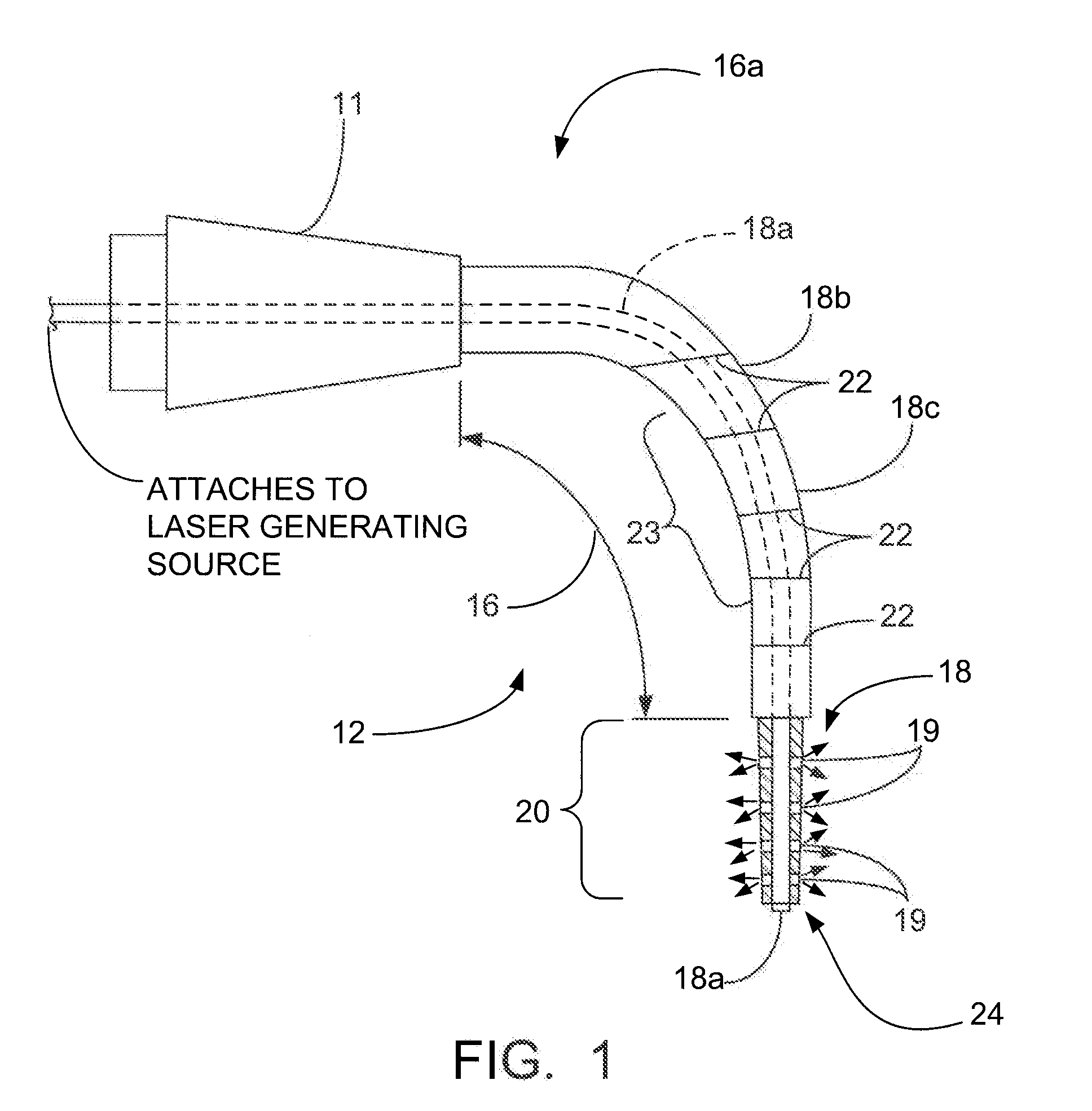
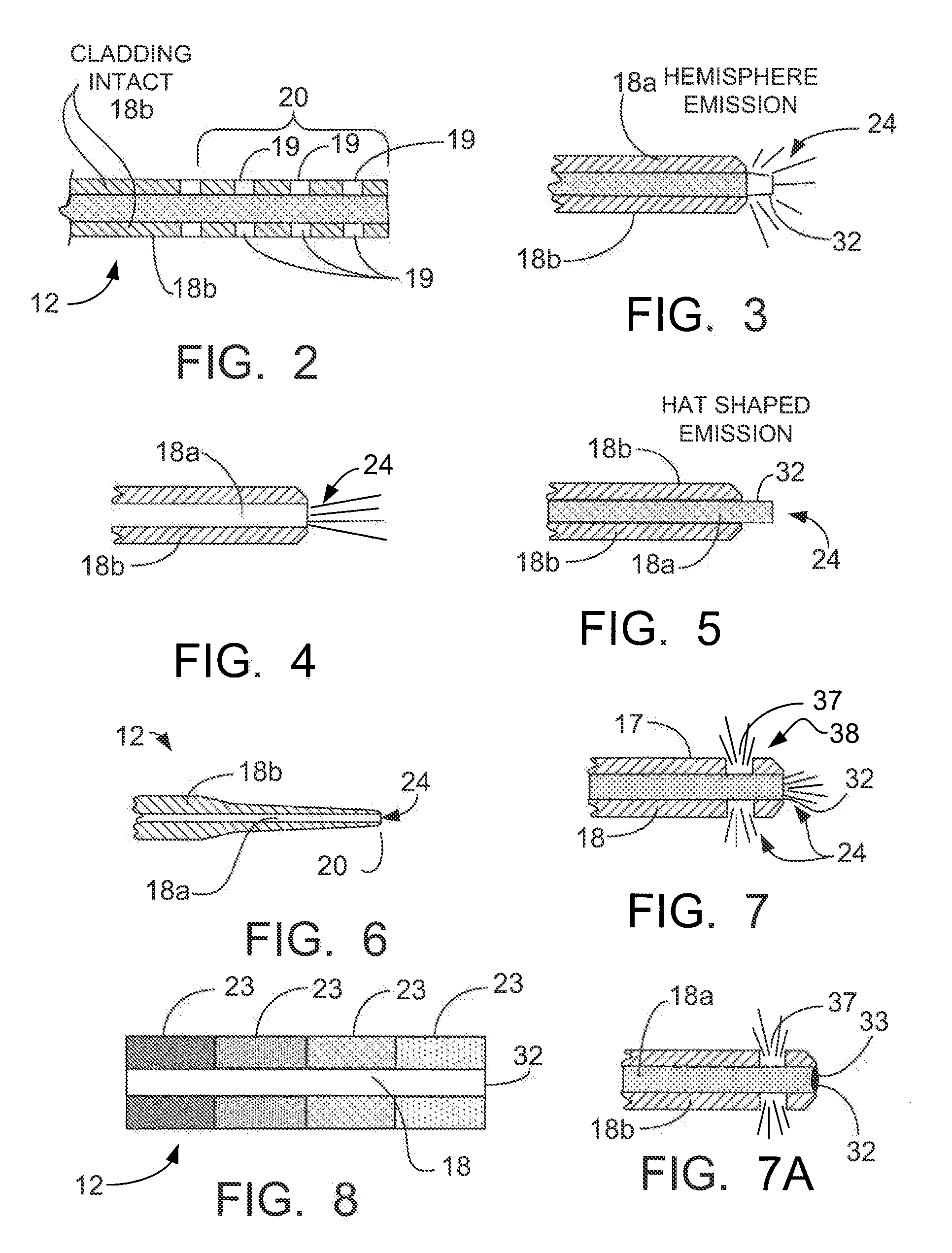
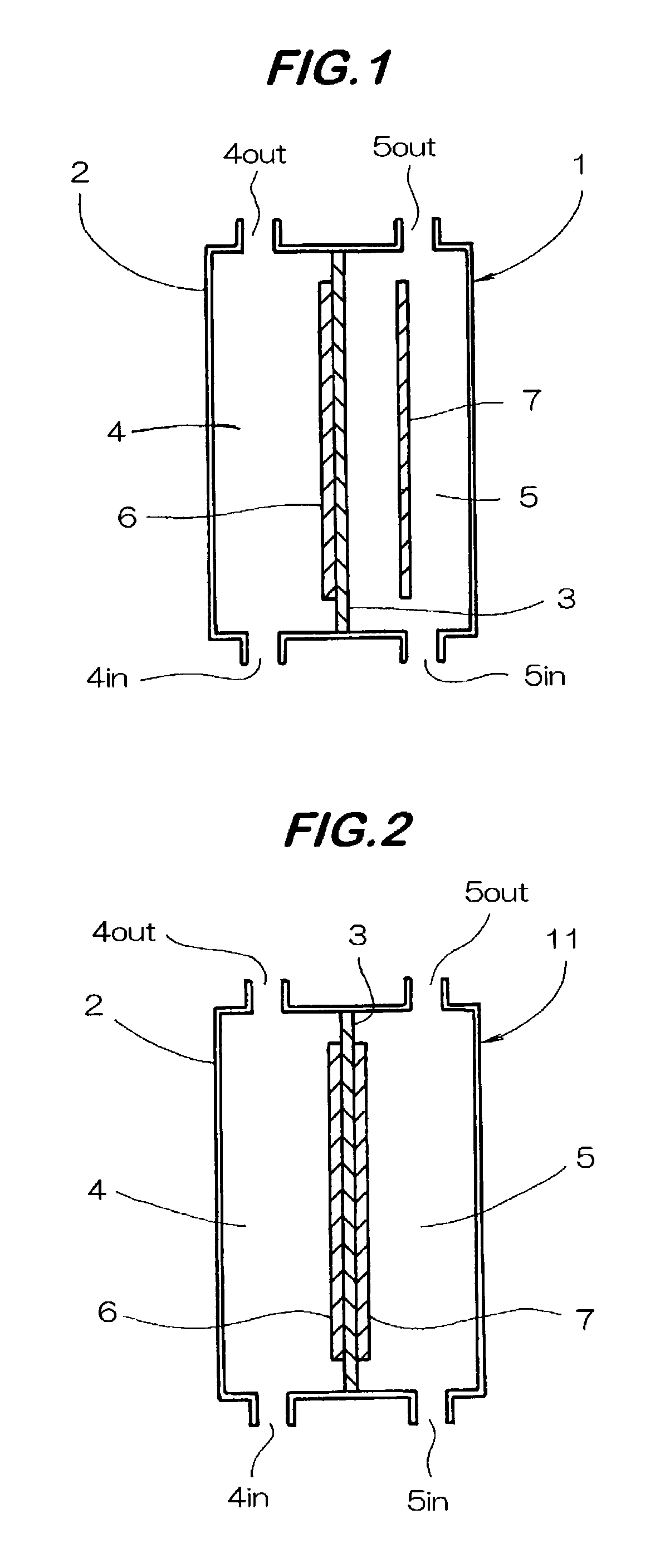
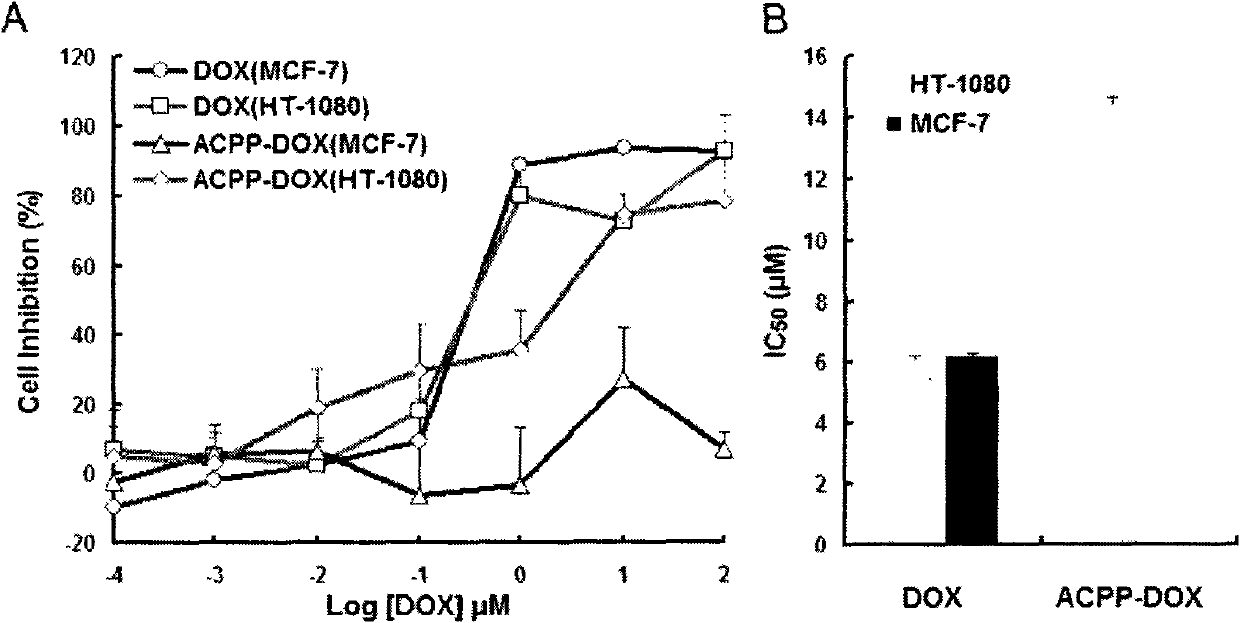
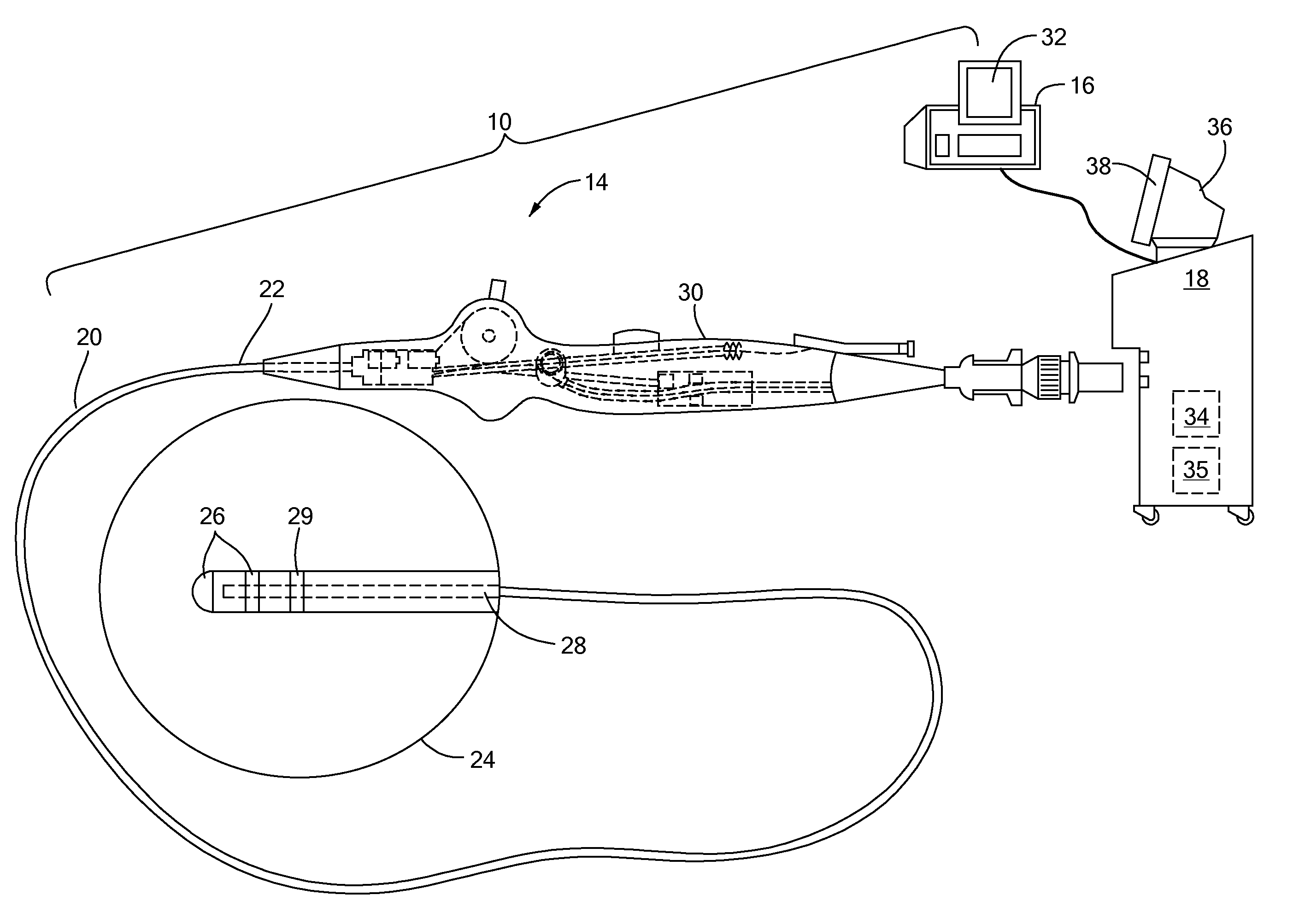
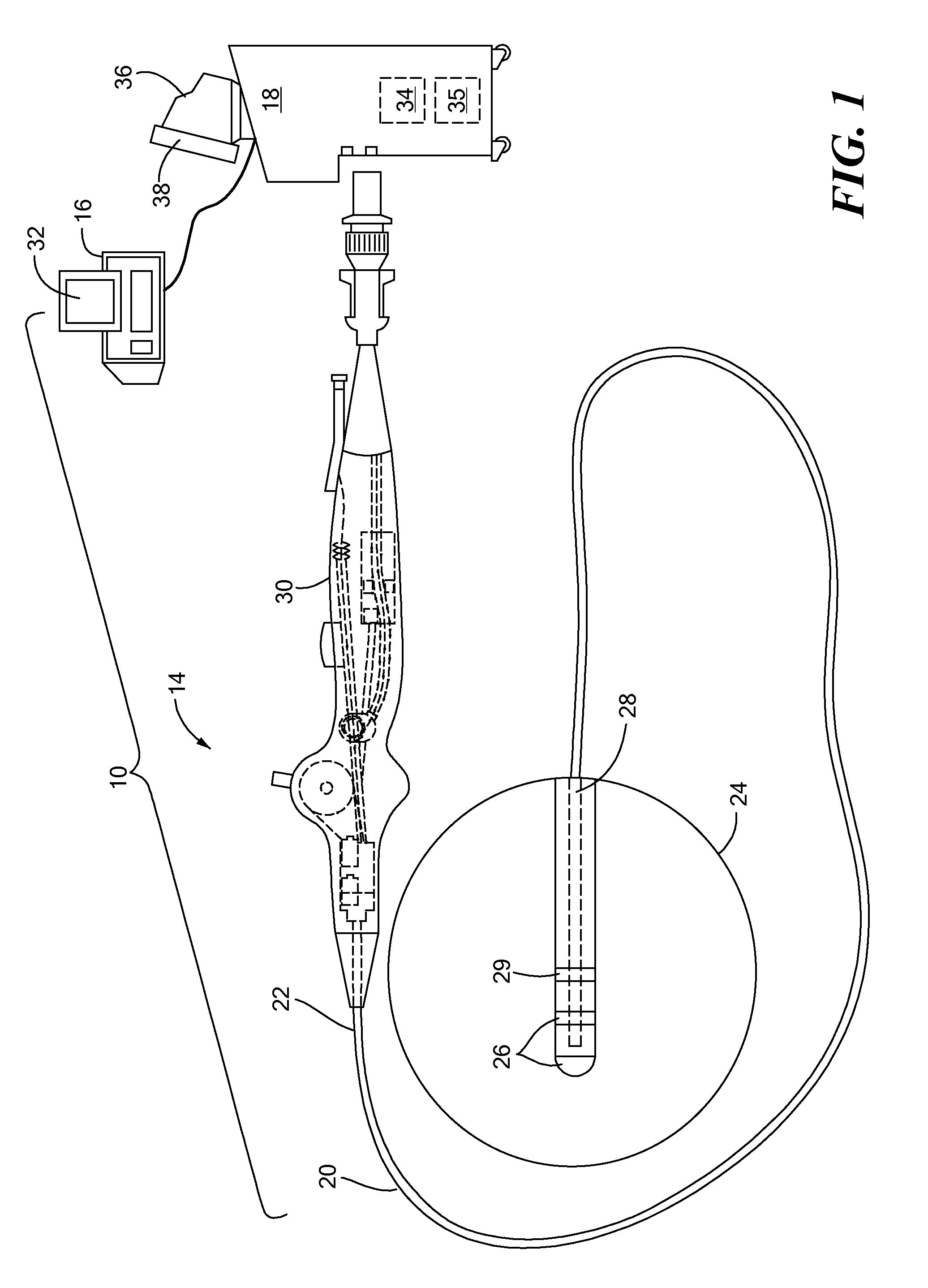
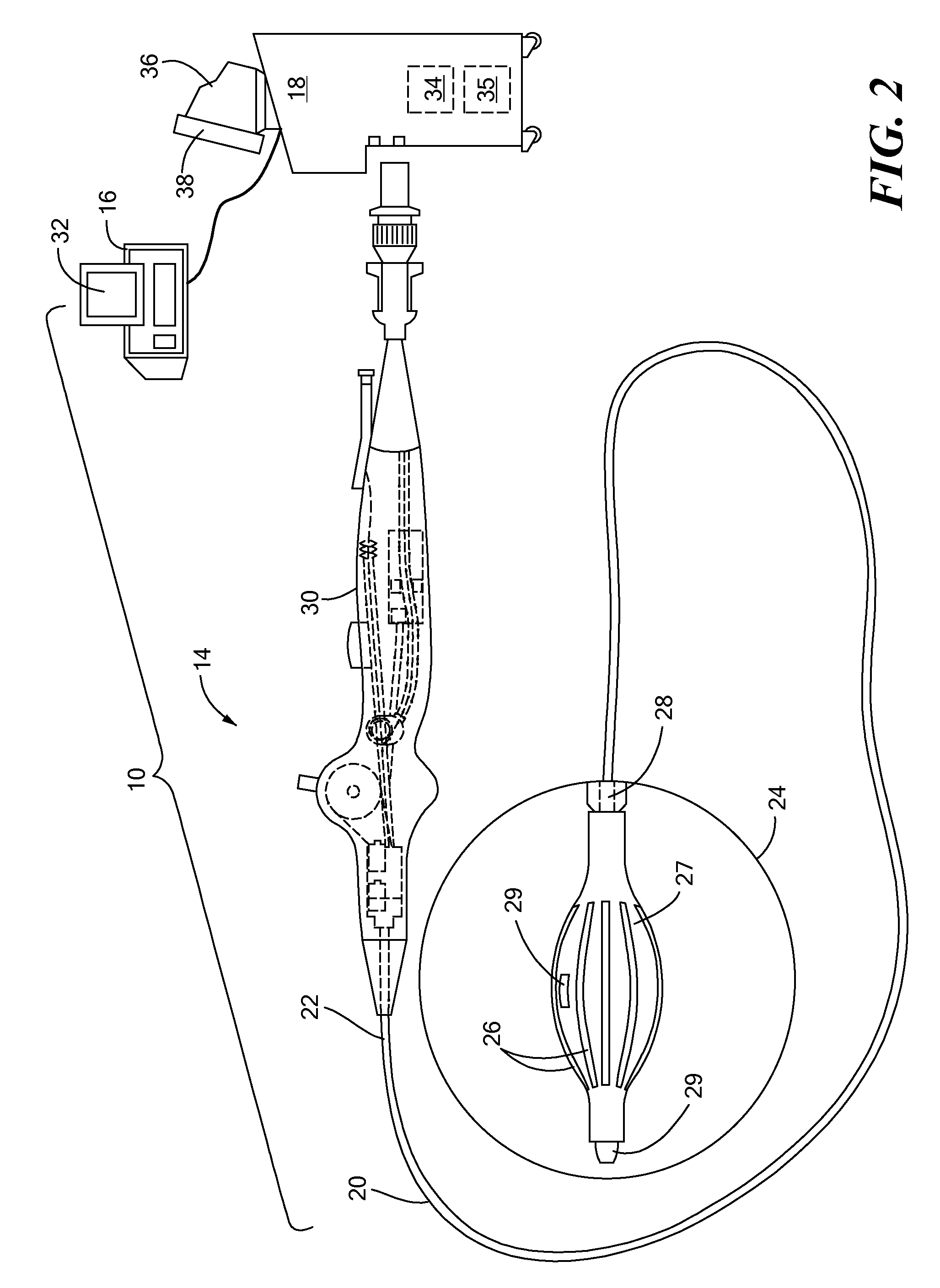
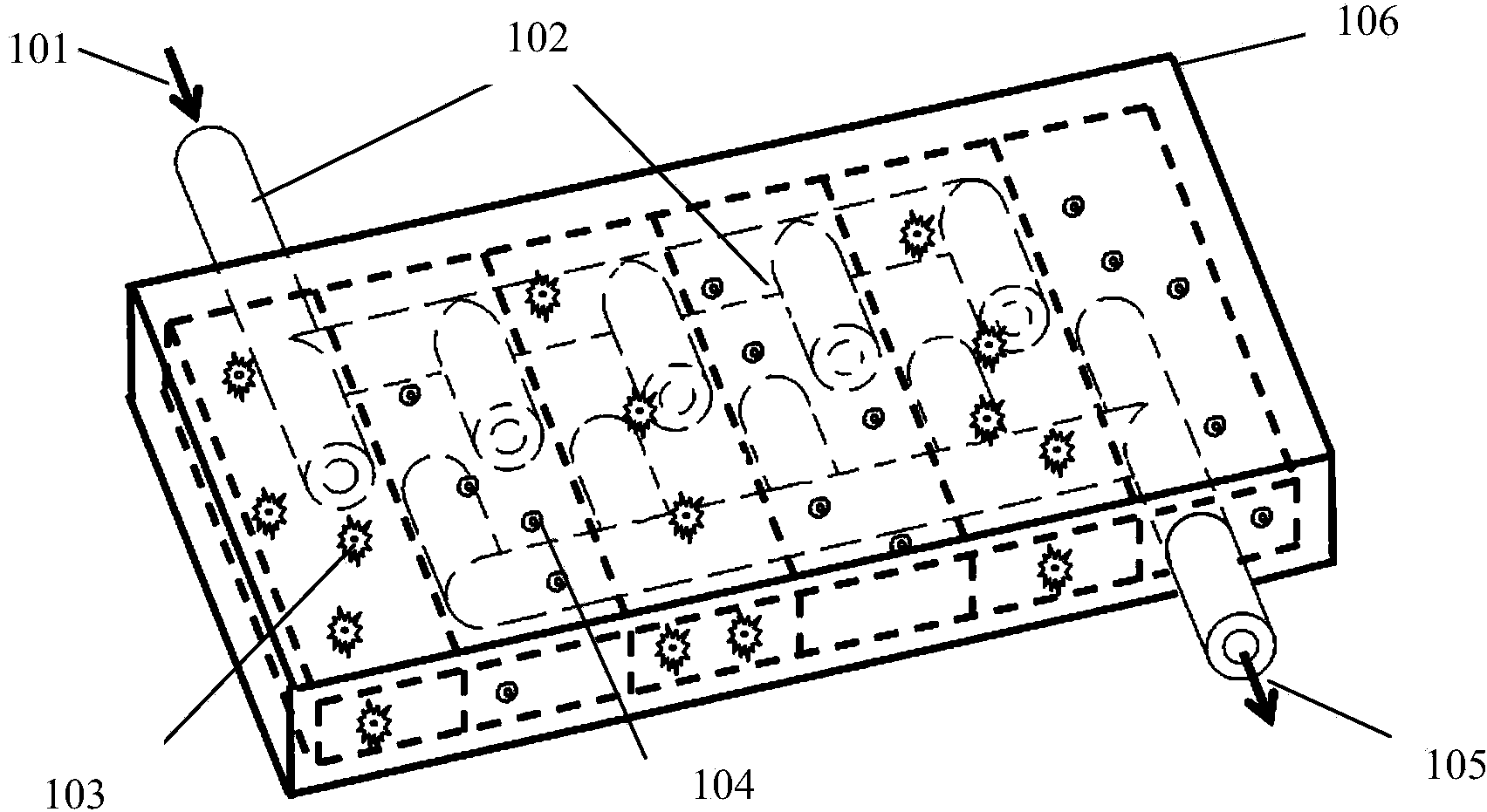
Patents
Literature
916 results about "Tissue cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tissue is a group of cells that have similar structure and that function together as a unit. A nonliving material, called the intercellular matrix, fills the spaces between the cells. ... Muscle tissue is composed of cells that have the special ability to shorten or contract in order to produce movement of the body parts. The tissue is highly cellular and is well supplied with blood vessels.
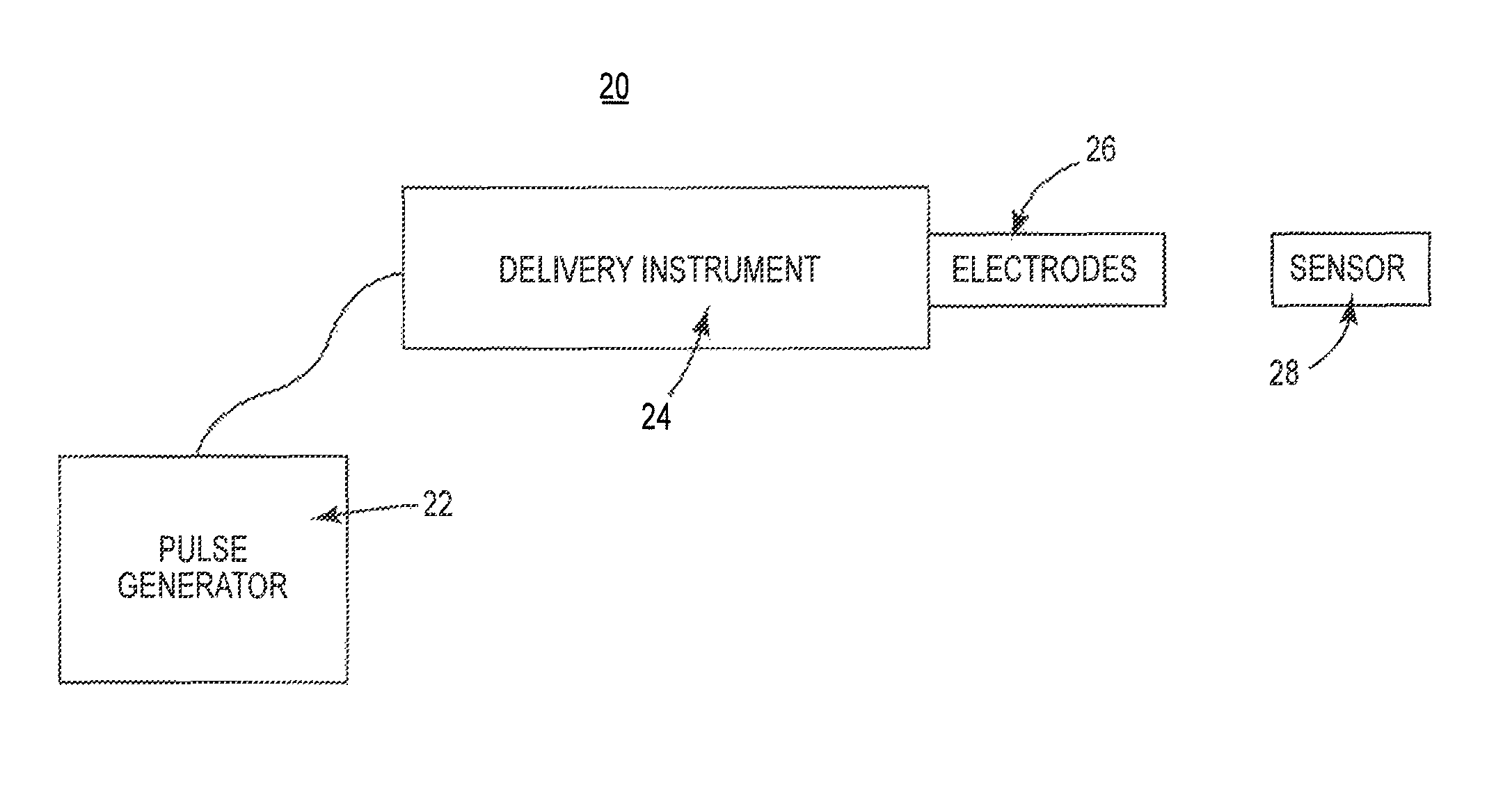
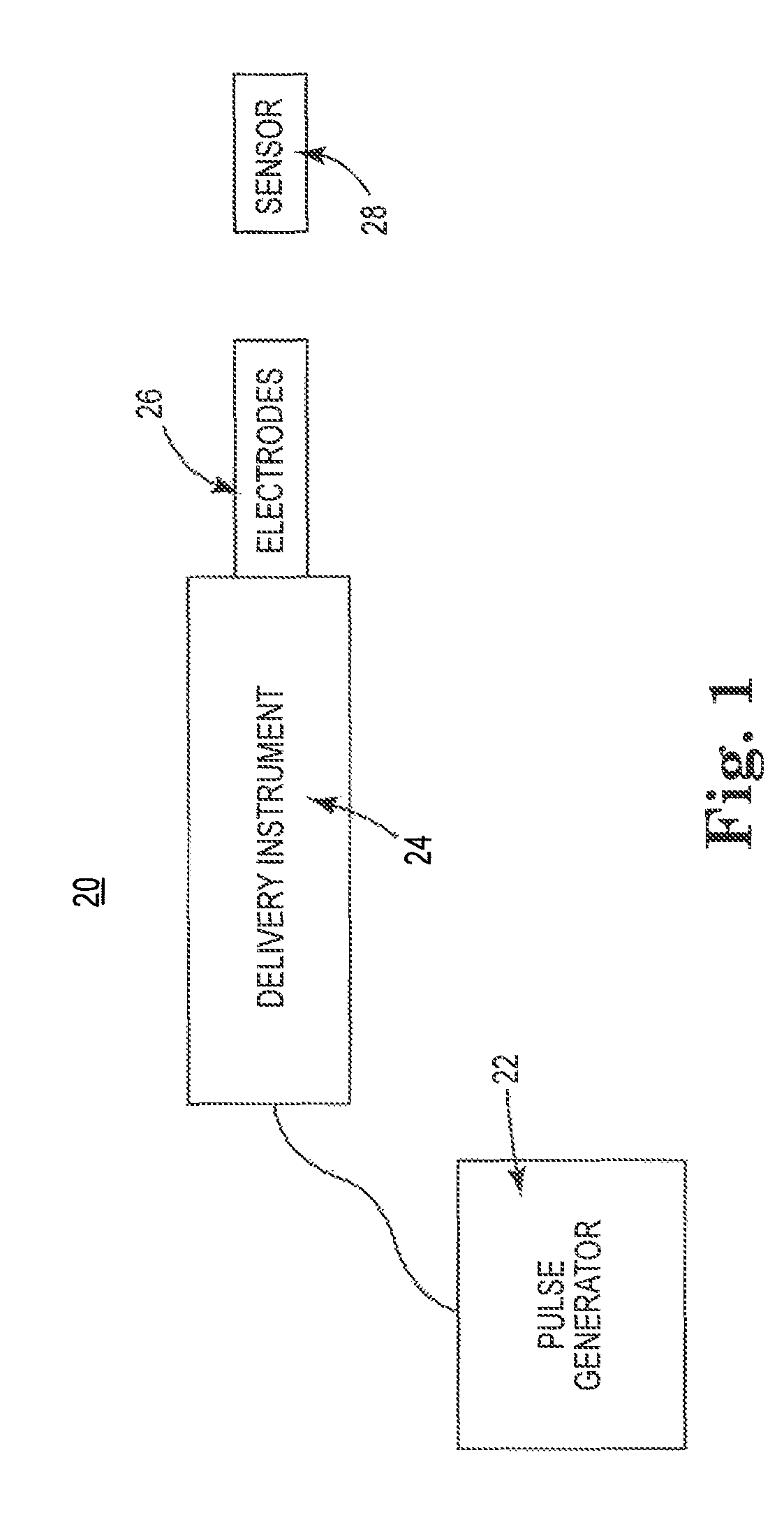
Systems and methods for cardiac tissue electroporation ablation
ActiveUS8221411B2Surgical instruments for aspiration of substancesSurgical forcepsCirculatory timeHigh pressure
Cardiac electroporation ablation systems and methods in which pulsed, high voltage energy is delivered to induce electroporation of cells of cardiac tissue followed by cell rupturing. In some embodiments, the delivered energy is biphasic, having a cycle time of not more than 500 microseconds.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method of destroying tissue cells by eletroporation
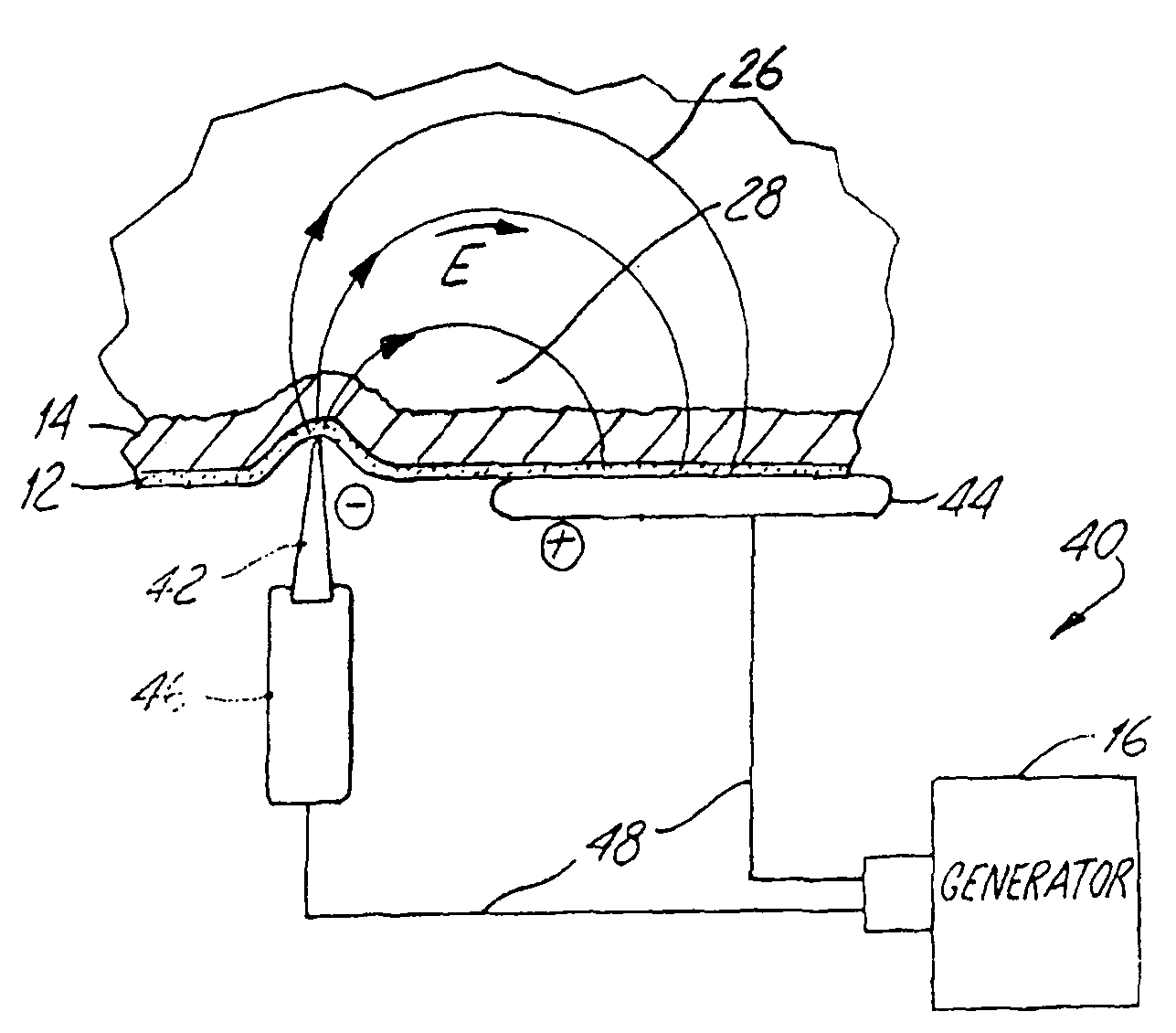
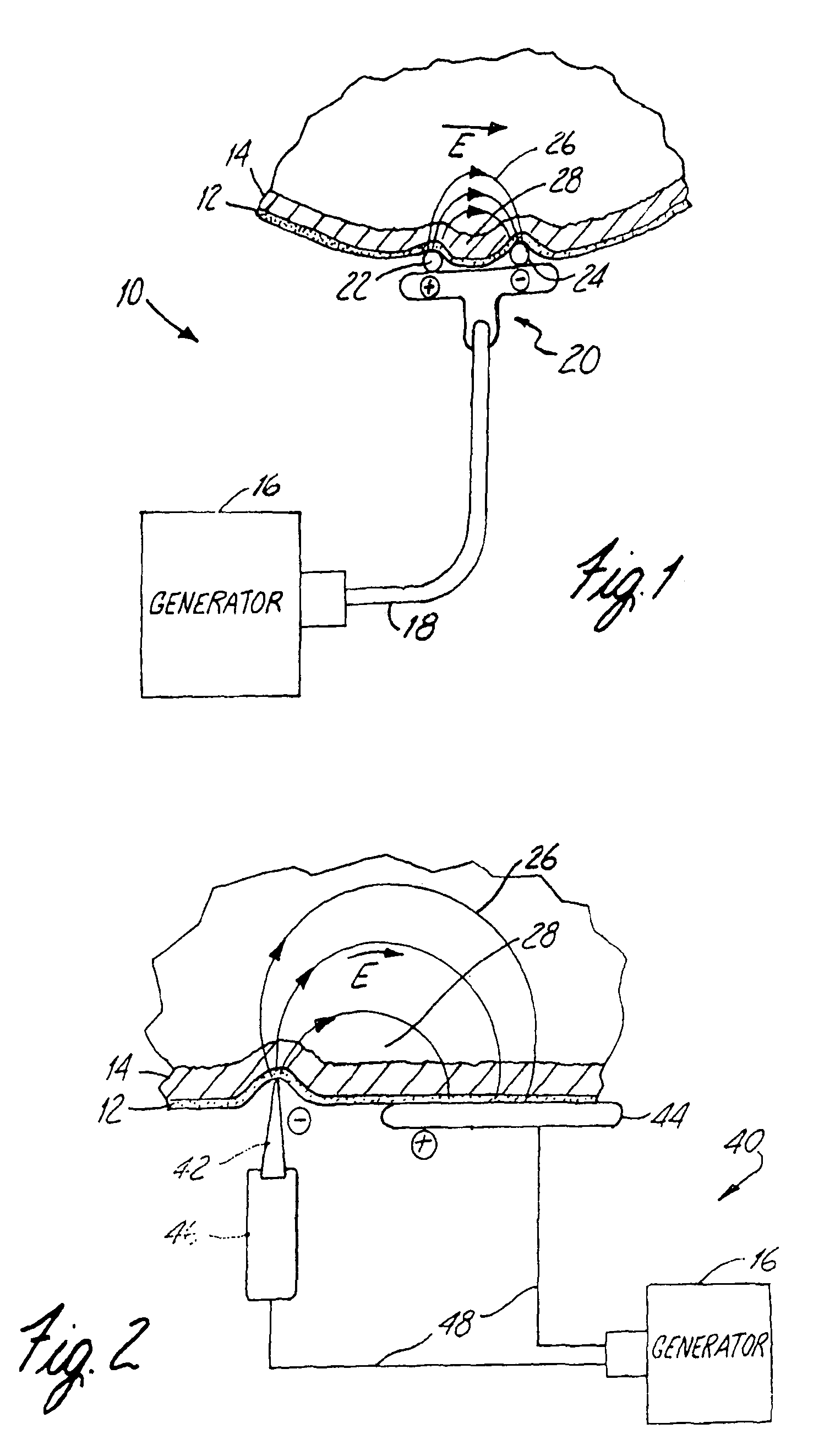
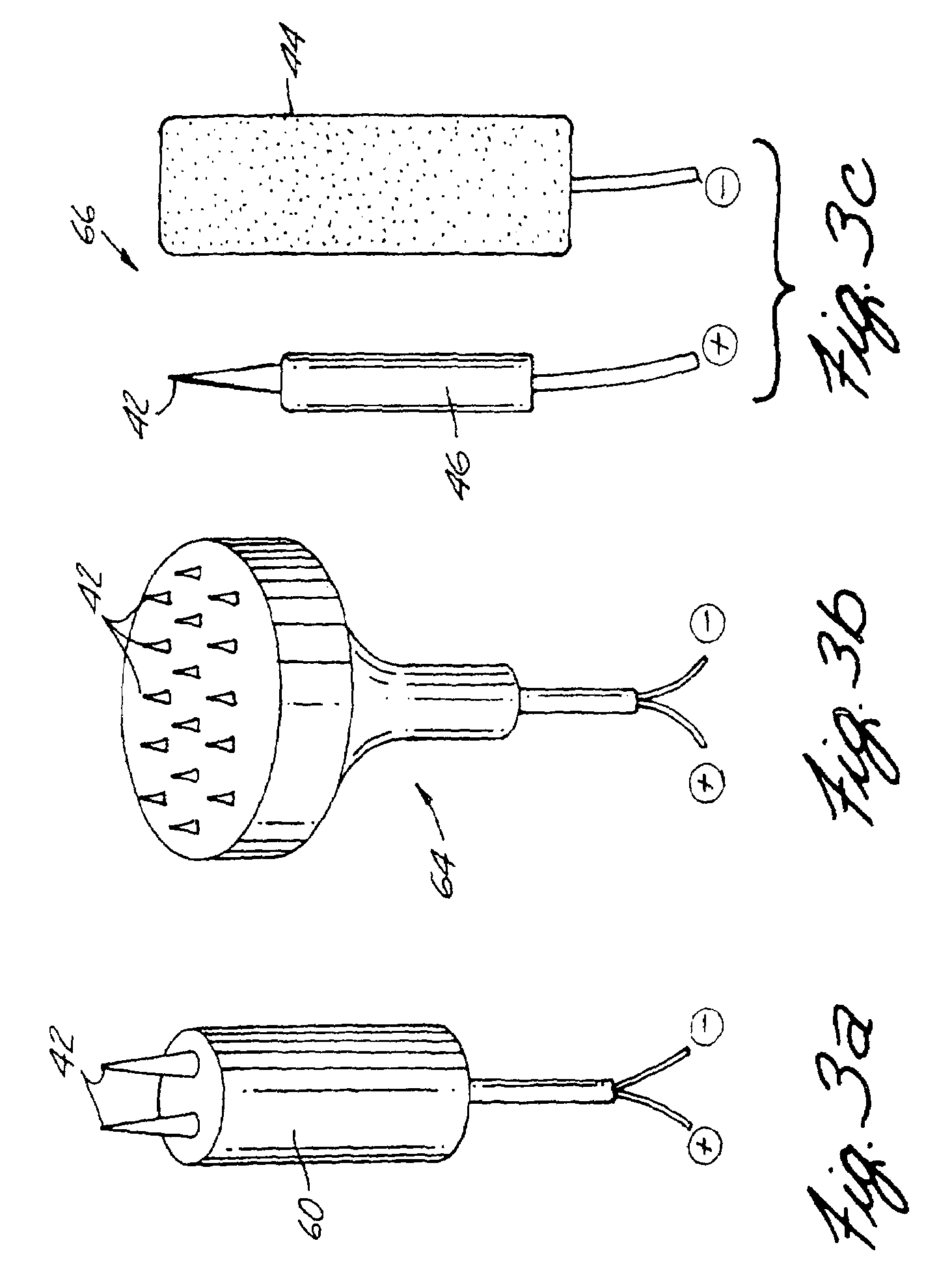
An apparatus and method for performing non-invasive treatment of the human face and body by electroporation in lieu of cosmetic surgery is provided. The apparatus comprises a high voltage pulse generator and an applicator having two or more electrodes in close mechanical and electrical contact with the patient's skin for applying the pulses to the patient's skin. The applicator may consist of two pieces with one electrode having a sharp tip and another having a flat surface. High voltage pulses delivered to the electrodes create at the tip of the sharp electrode an electric field high enough to cause death of relatively large subcutaneous fat cells by electroporation. Moving the electrode tip along the skin creates a line of necrotic subcutaneous fat cells, which later are metabolized by the body. Multiple applications of the electrode along predetermined lines on the face or neck create shrinkage of the skin and the subcutaneous fat volume underlying the treated area.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Generation of human embryonc stem-like cells using intronic RNA
ActiveUS20080293143A1Stable and relatively long-term effectDelivery stabilityOther foreign material introduction processesElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentReprogrammingMammal
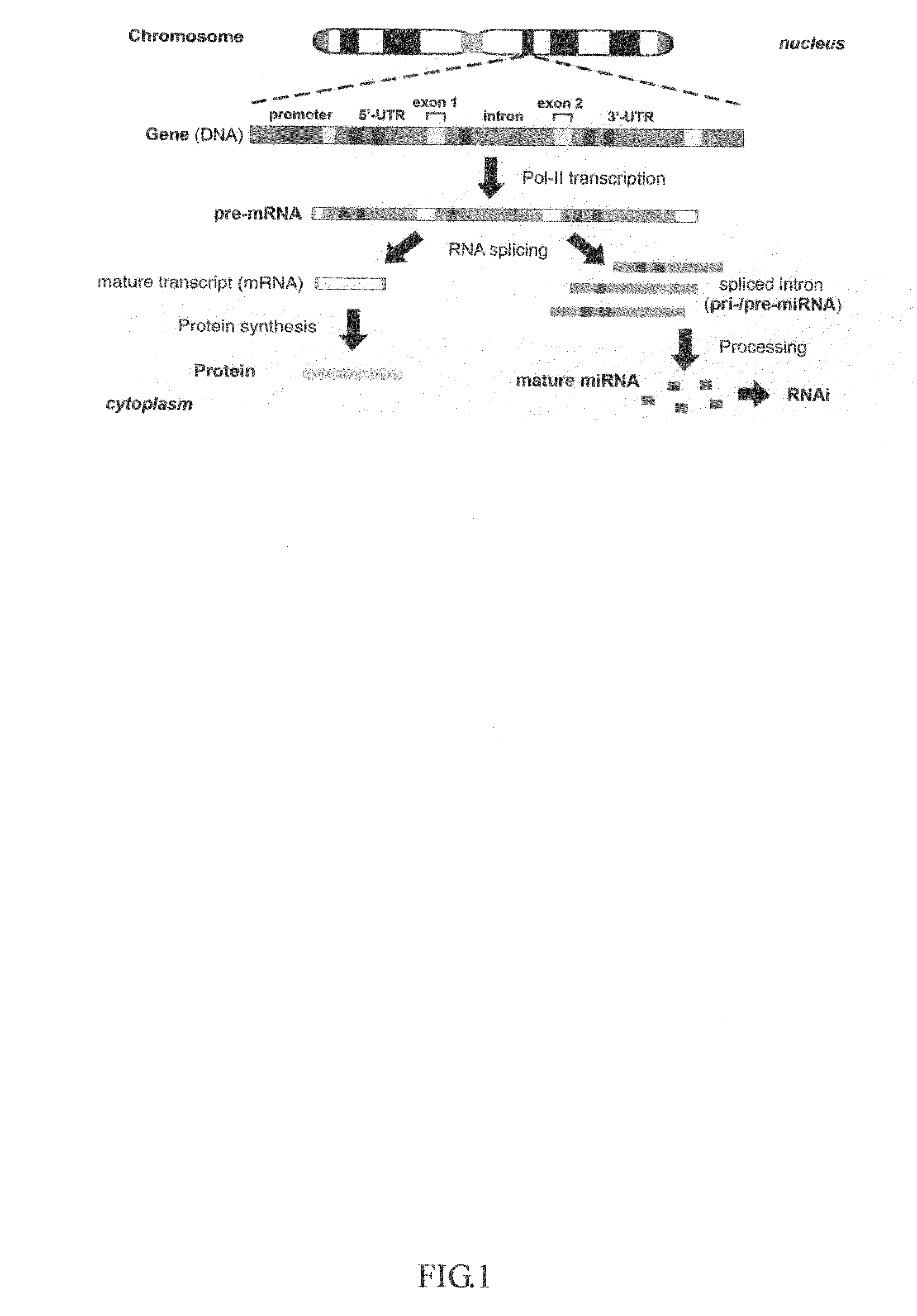
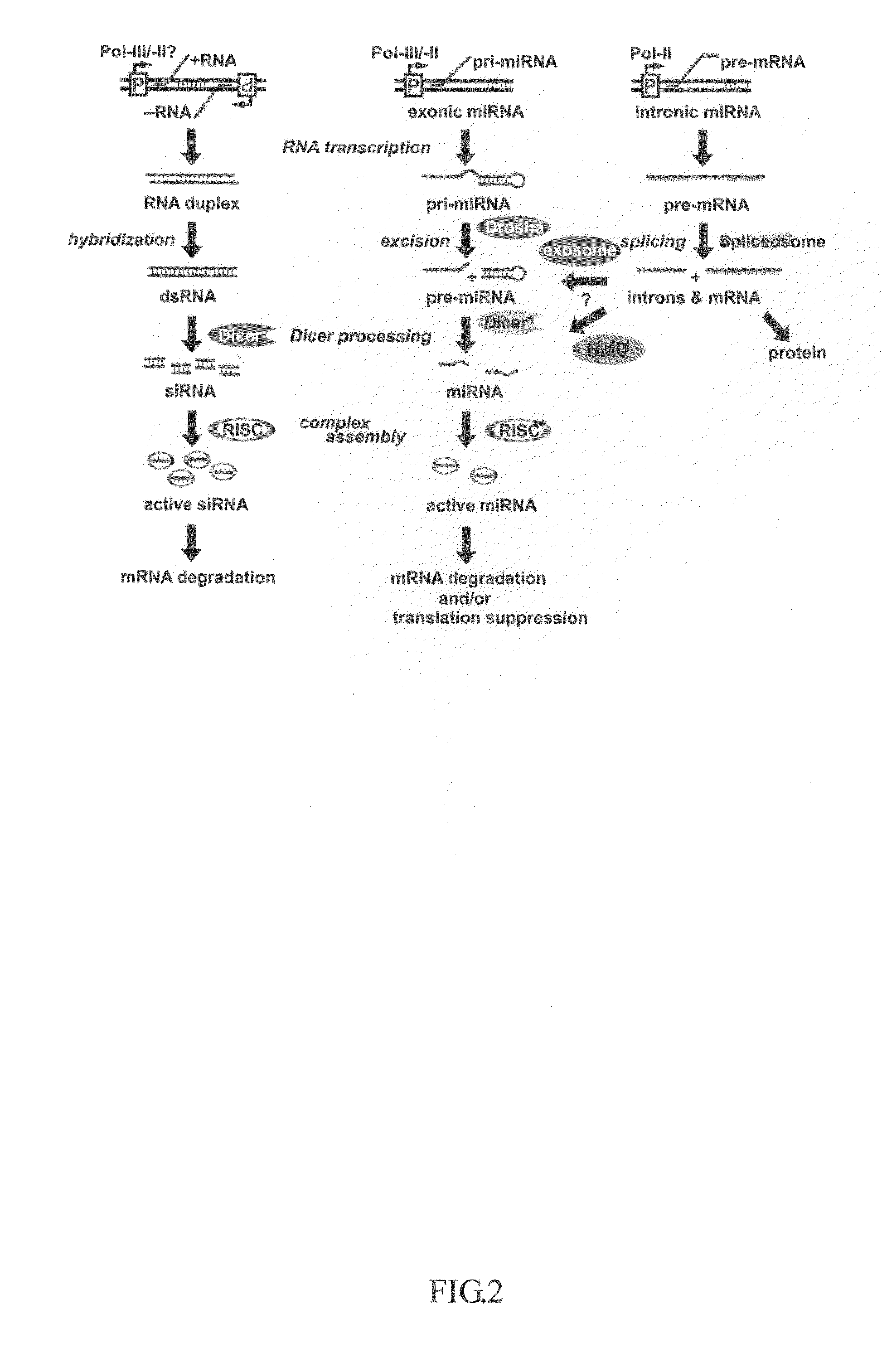
This invention generally relates to a method for developing, generating and selecting human embryonic stem (hES)-like pluripotent cells using transgenic expression of intronic microRNA-like RNA agents. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method and composition for generating a non-naturally occurring intron and its intronic components capable of being processed into mir-302-like RNA molecules in mammalian cells and thus inducing certain specific gene silencing effects on differentiation-related and fate-determinant genes of the cells, resulting in reprogramming the cells into a pluripotent embryonic stem (ES)-cell-like state. The ES-like cells so obtained are strongly express hES cell markers, such as Oct3 / 4, SSEA-3 and SSEA-4, and can be guided into various tissue cell types by treating certain hormones and / or growth factors under a feeder-free cell culture condition in vitro, which may be used for transplantation and gene therapies. Therefore, the present invention offers a simple, effective and safe gene manipulation approach for not only reprogramming somatic cells into ES-like pluripotent cells but also facilitating the maintenance of pluripotent and renewal properties of ES cells under a feeder-free cell culture condition, preventing the tedious retroviral insertion of four large transcription factor genes into one single cell as used in the previous iPS methods.
Owner:MELLO BIOTECH +1
System and method for increasing a target zone for electrical ablation
System for increasing a target zone for electrical ablation includes a treatment control module executable by a processor. The control module directs a pulse generator to apply pre-conditioning pulses to subject tissue cells in a pre-conditioning zone to electroporation, the pre-conditioning zone being smaller than a target ablation zone. After the pre-conditioning pulses have been applied, the control module directs the pulse generator to apply treatment pulses to electrically ablate the tissue cells in the target ablation zone. The pre-conditioning pulses cause the pre-conditioning zone to have a much higher conductivity so that the zone acts as a larger electrode area when the treatment pulses are applied, which results in a much larger target ablation zone than otherwise possible.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
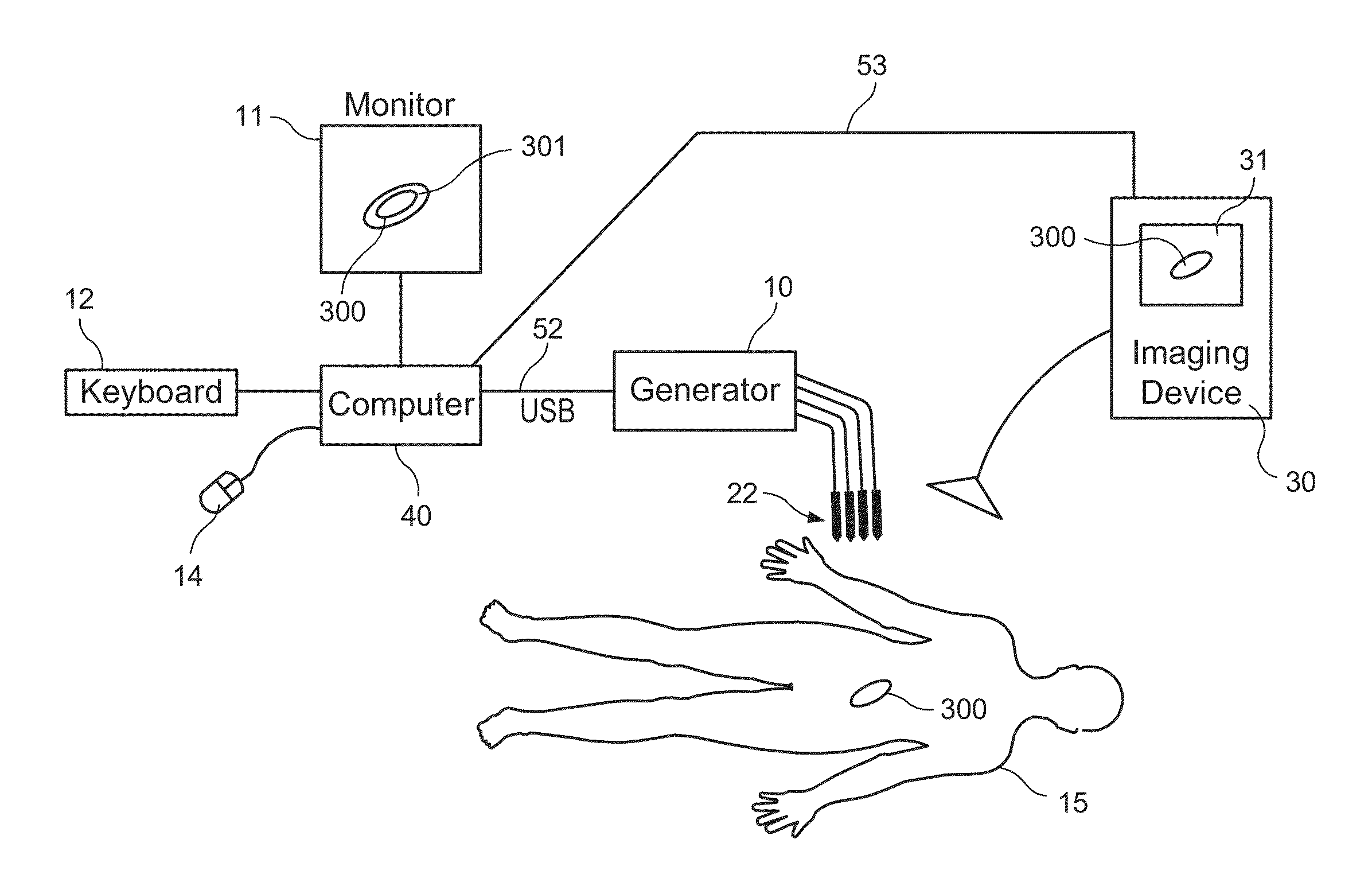
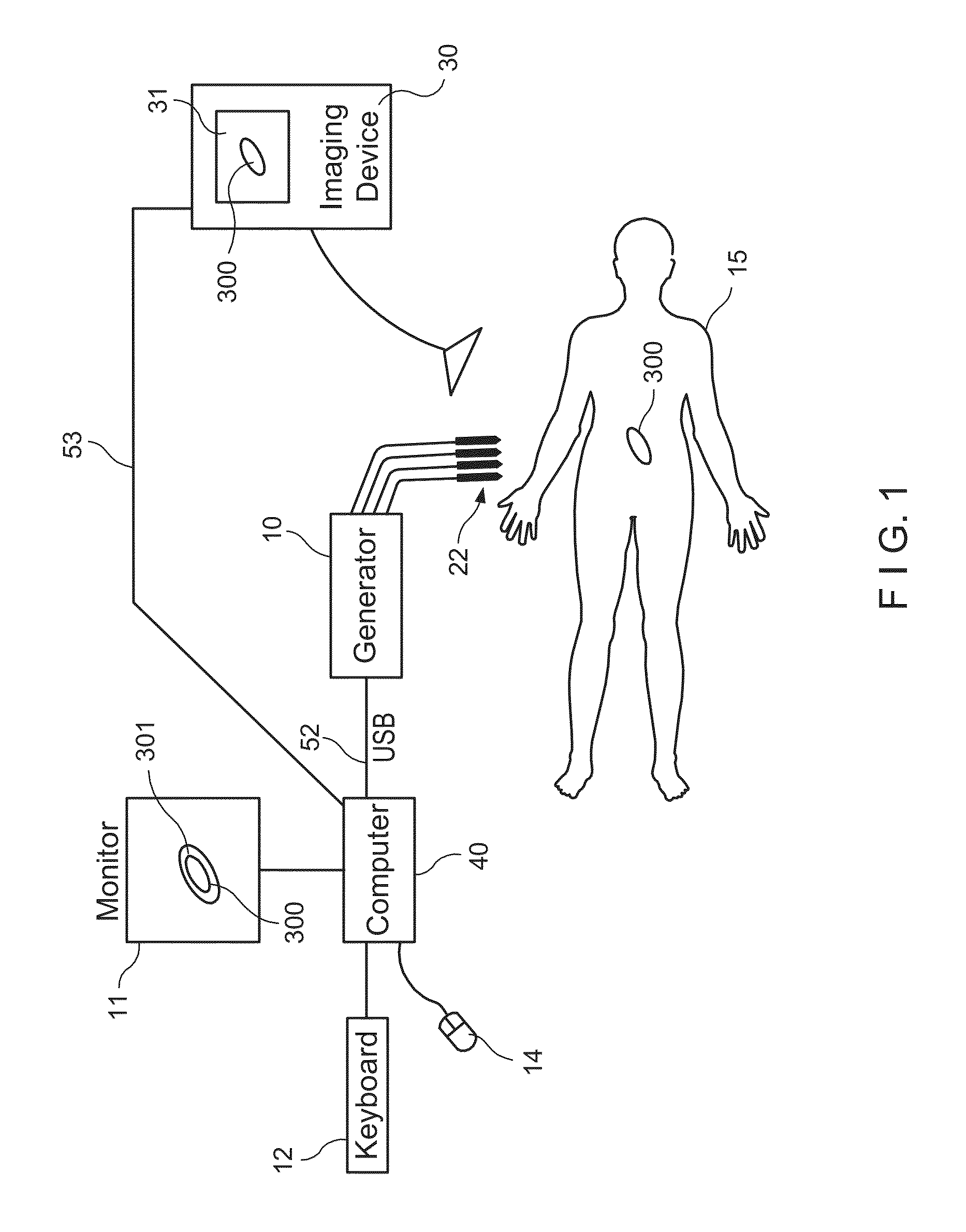
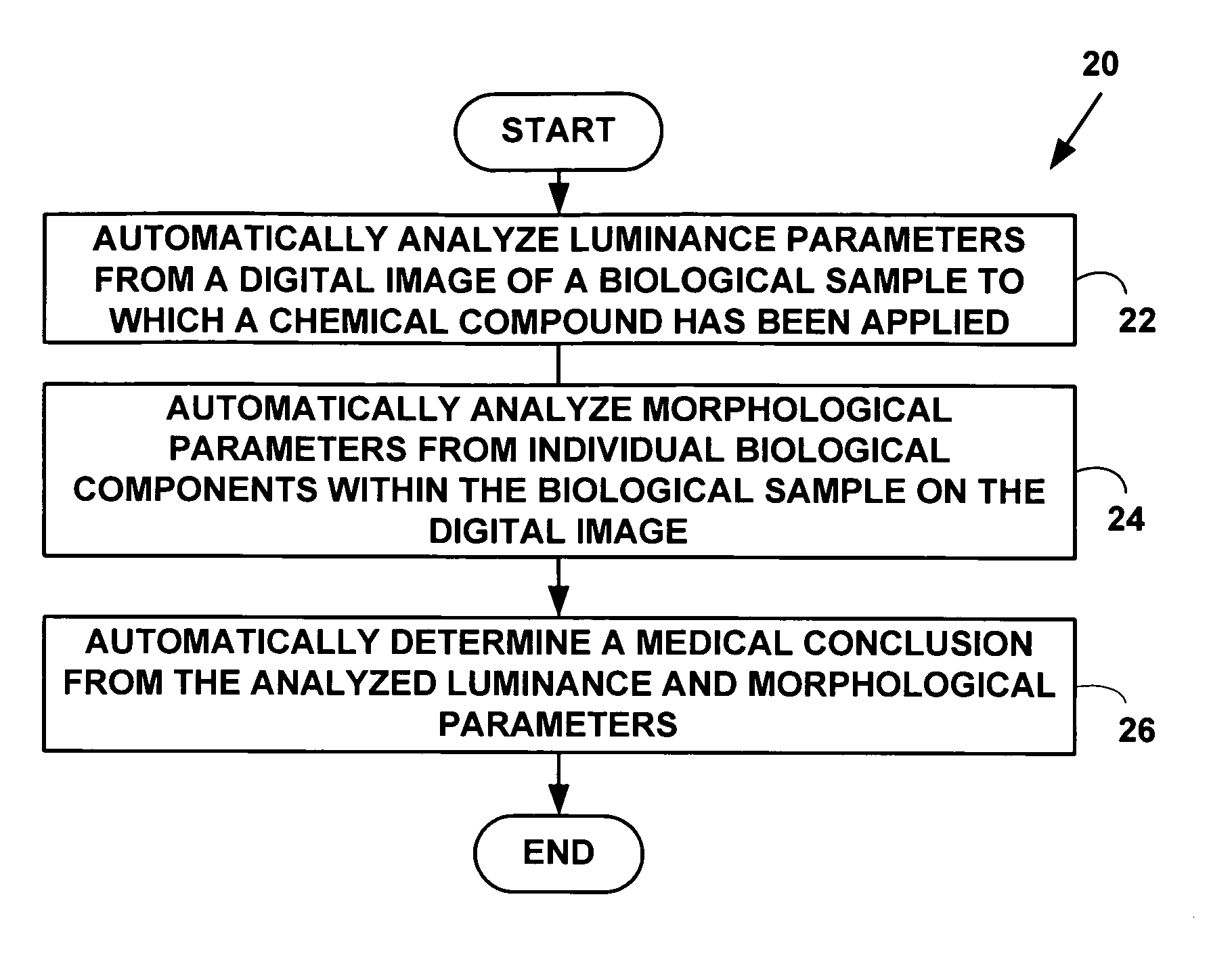
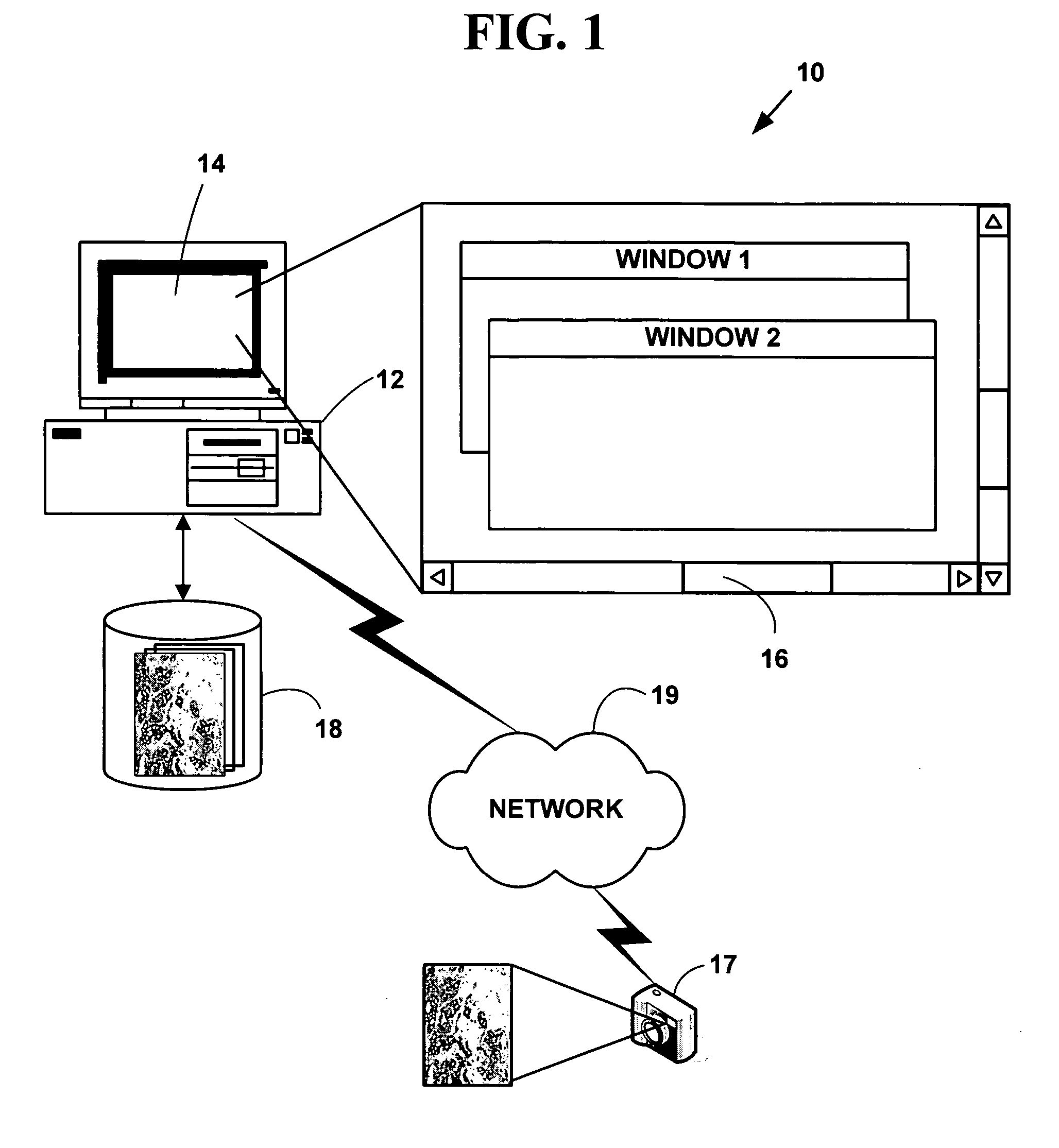
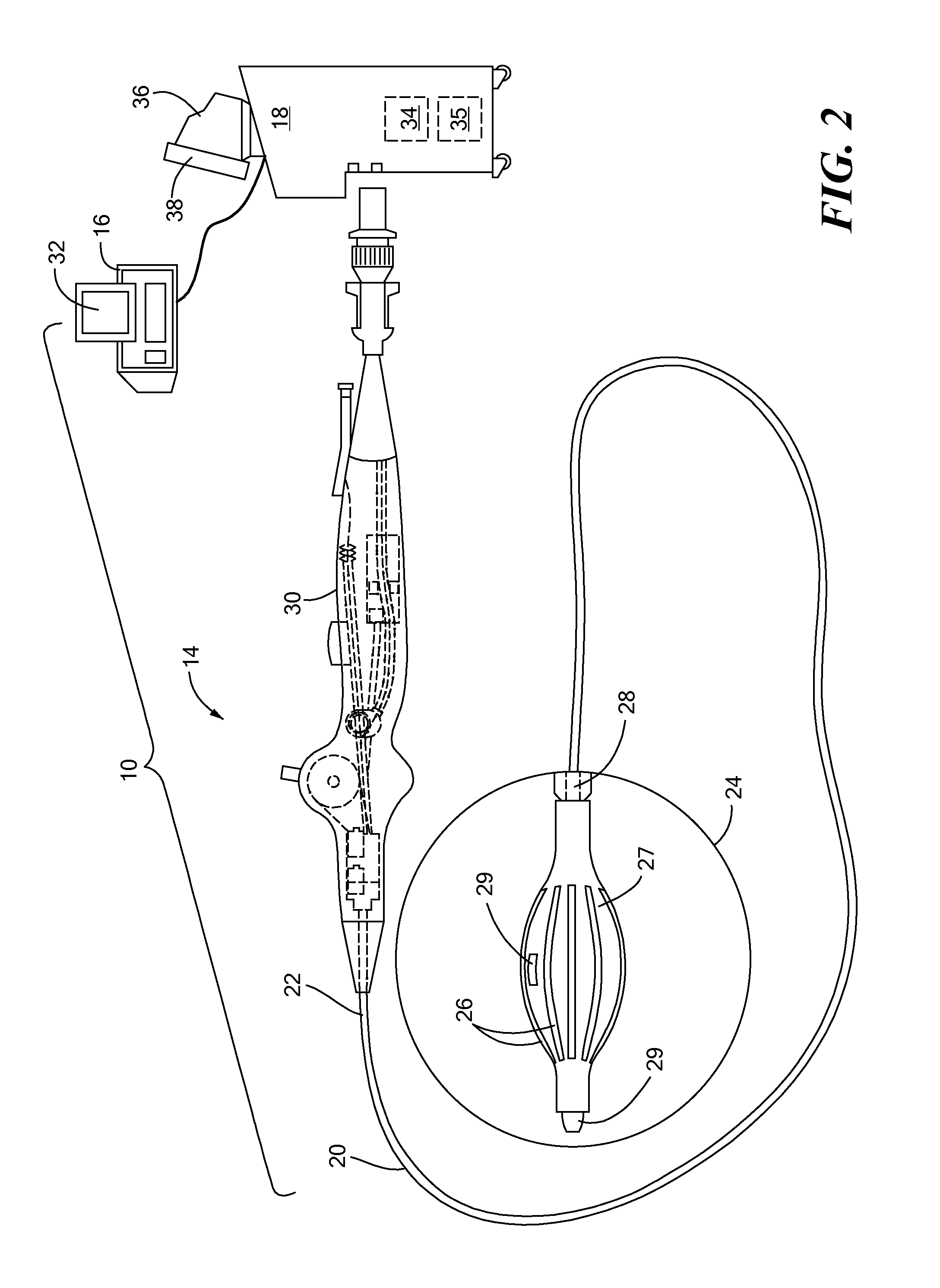
Method and system for automatically determining diagnostic saliency of digital images
InactiveUS20050136549A1Facilitates automated analysisImage enhancementImage analysisChemical compoundCell membrane
A method and system for automatically determining diagnostic saliency of digital images for medical and / or pathological purposes. Luminance parameters (e.g. intensity, etc.) from a digital image of a biological sample (e.g., tissue cells) to which a chemical compound (e.g., a marker dye) has been applied are automatically analyzed and automatically corrected if necessary. Morphological parameters (e.g., cell membrane, cell nucleus, mitotic cells, etc.) from individual components within the biological sample are automatically analyzed on the digital image. A medical conclusion (e.g., a medical diagnosis or prognosis) is automatically determined from the analyzed luminance and morphological parameters.
Owner:BIOIMAGENE
Acellular matrix repairing gel and new method for preparing the same
ActiveCN104971380ARetain biological activityImprove securityProsthesisCell-Extracellular MatrixClinical value
The invention relates to the field of bio-materials, and especially relates to an acellular matrix repairing gel and a new method for preparing the same. The invention discloses the acellular matrix repairing gel and the method for preparing the same, wherein the method includes steps of acellular treatment and gelatinization treatment on tissue and organs from mammal animals to prepare the acellular matrix repairing gel. The acellular matrix repairing gel is eliminated in immunogenicity of heterologous and foreign tissue, so that activity of extracellular matrix components of the tissue is maintained as more as possible. The gel can specially repair damaged tissue and organs of human body, is strong in applicability, is suitable for requirements of various irregular-shaped repair zones and different position environments in body and has a huge clinical value.
Owner:山东隽秀生物科技股份有限公司
Application of a therapeutic substance to a tissue location using an expandable medical device
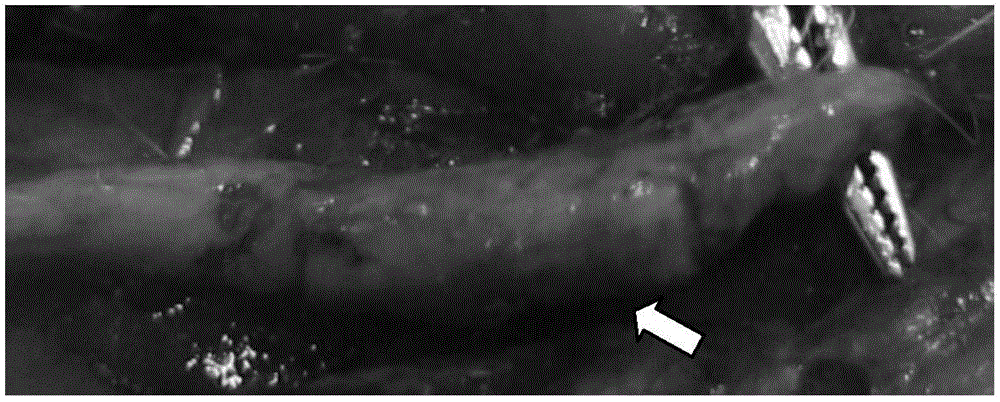
A non-polymeric or biological coating applied to radially expandable medical delivery device provides uniform drug distribution and permeation of the coating and any therapeutic agents mixed therewith into a targeted treatment area within the body. The delivery device is expanded using the pressure of an inflation fluid. After expanding the delivery device to a pre-determined size and shape, the inflation fluid weeps through the porous surface of the delivery device. The coating releases the delivery device and floats on the inflation fluid until bonding to the tissue due to its affinity for the tissue. Once the coating bonds or affixes to the tissue, through an absorption mechanism by the tissue cells of the coating material, the coating and any therapeutics contained therein are delivered to the tissue. The fluid can contain a therapeutic agent, or can be otherwise biocompatible and / or inert.
Owner:ATRIUM MEDICAL
Method and Apparatus for Disinfecting or Sterilizing a Root Canal System Using Lasers Targeting Water
InactiveUS20090130622A1Sufficient deliveryEnhanced light absorptionSurgical instrument detailsDental toolsDiseaseEnergy absorption
Method and apparatus for disinfecting and / or sterilizing a root canal system by targeting the water content of disease and debris in the canals. The laser technique of employs a frequency of the wavelength emissions between about 930 to about 1065 nanometers with an optimum of 980 nm. This range of wavelengths targets the water content of tissue cells and pathogens as well as any residual organic debris in water within the root canal system after its preparation while being poorly absorbed by the surrounding dentin. The selection of the optimum wavelength produces significant effects generating and advancing treatment to the targeted aqueous environments. This is due to the rapid energy absorption by the water and the subsequent creation of gas bubbles, liberation of heat and subsequent propulsion of waves of heat and gas that impact along the canal walls and ramifications resulting in an enhanced bacterial kill and cleaning of the canal walls and ramifications. No dyes or other additives are necessary to enhance the effectiveness of the laser kill of bacteria, etc.
Owner:BOLLINGER JAMES EDWIN +2
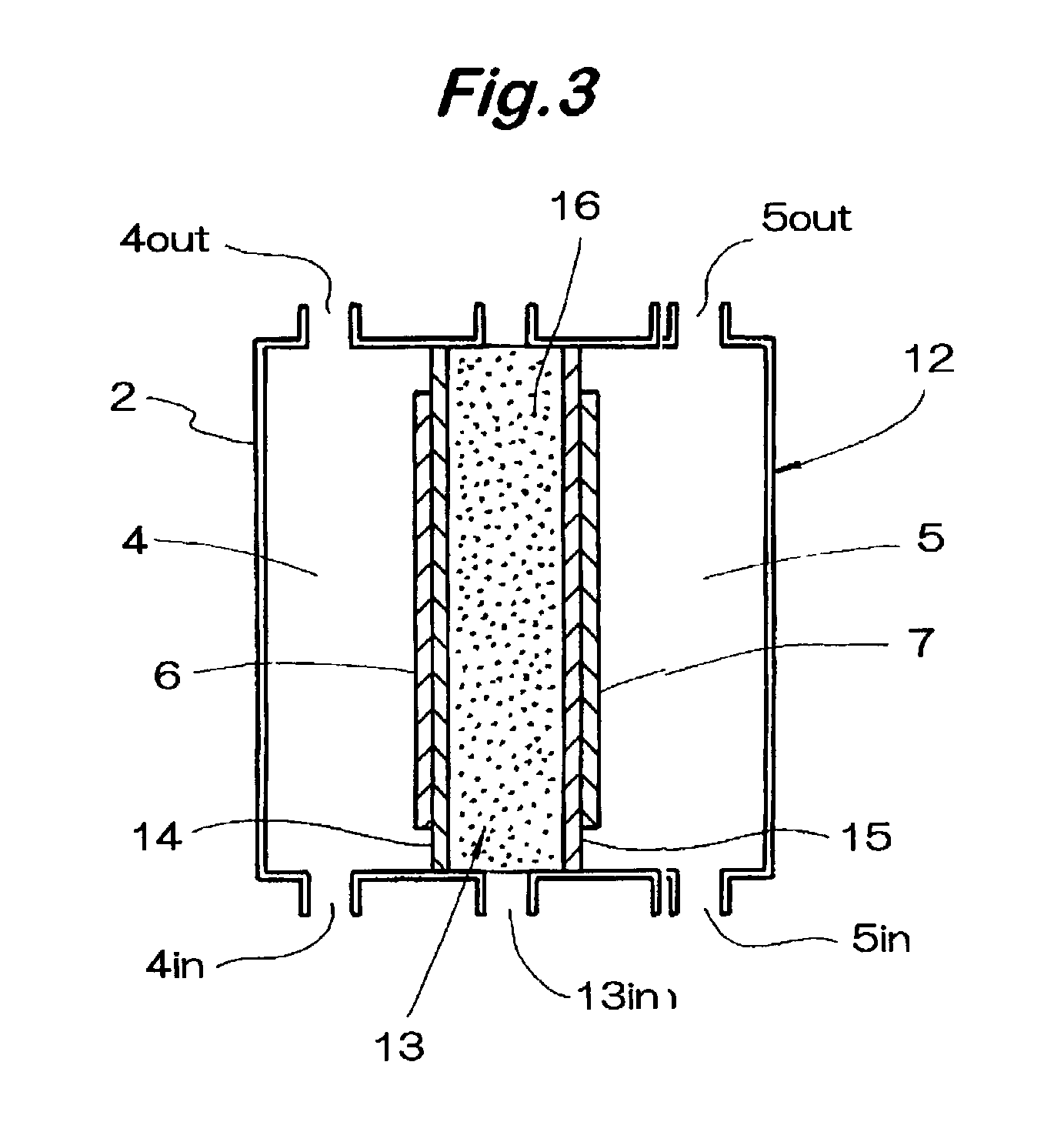
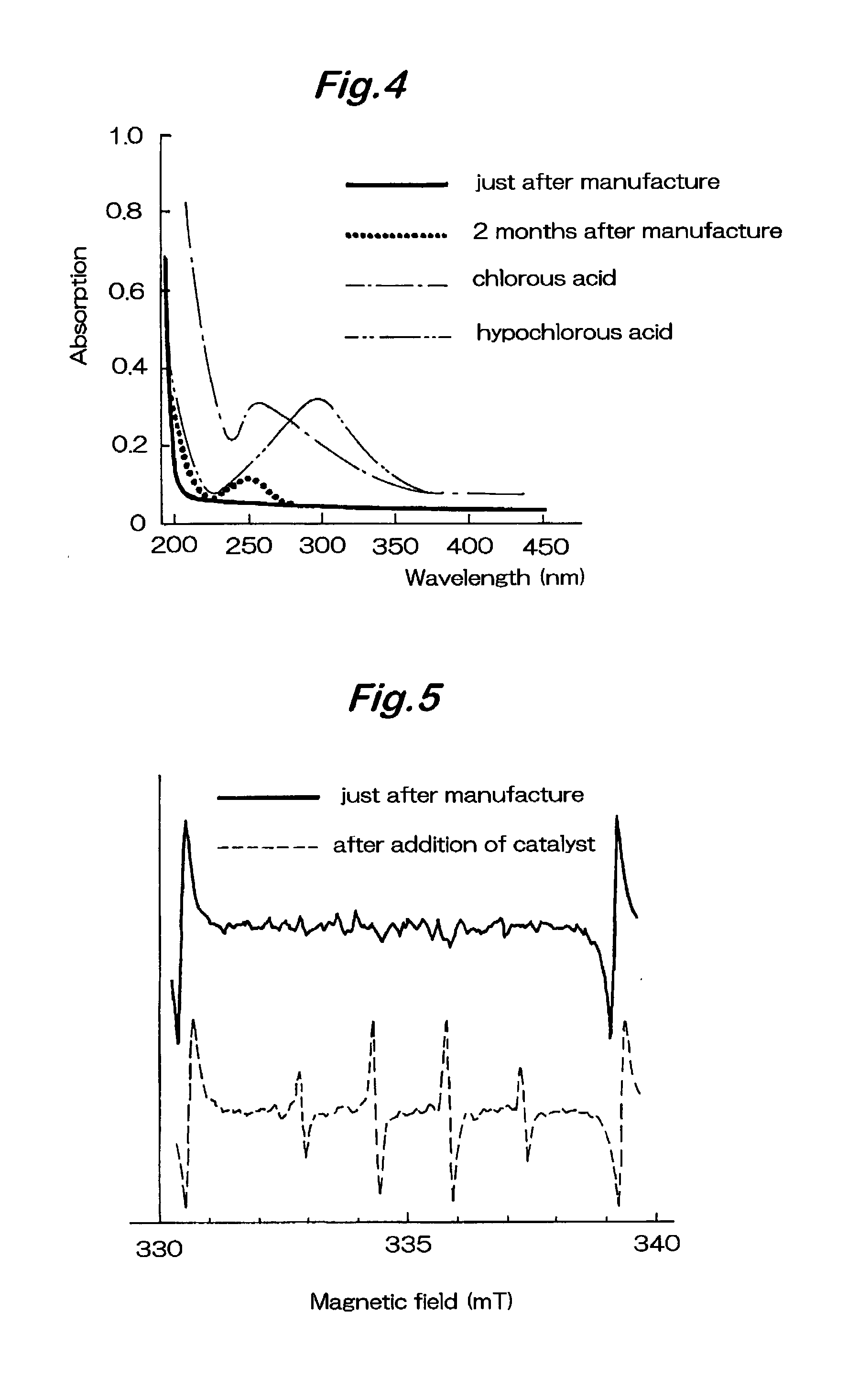
Solution for promoting growth of tissue cells at wound sites and production process therefor
InactiveUS20020160053A1Promote growthWound can be promotedBiocidePhotography auxillary processesGrowth promotingNeutrophil granulocyte
A tissue cell growth-promoting solution produced by this invention comprising water containing at least 1 to 500 ppm of active oxygen, when applied to a wound, supplies active oxygen originating from outside the biobody to supplement the active oxygen produced by the biobody's own protective system cells such as neutrophils and macrophages which gather at the wound site, thus increasing the concentration of active oxygen at the site of the wound, mimicking a state in which a large quantity of such bio-signals is secreted by the biobody itself, to promote the reconstruction of tissues, the action corresponding to the last of the four main steps involved in wound healing biochemical processes of "blood vessel reaction", "blood vessel coagulation", "inflammation", "reconstruction of tissues" and which would otherwise have to rely on the natural healing power of the biobody itself.
Owner:SONOMA PHARMA INC
Ablation device and method for electroporating tissue cells
A method and system for producing deep lesions without the production of high heat. The method generally includes ablating target tissue cells with a device in communication with an energy generator programmable to ablate tissue using heat energy, electroporation, or a combination thereof. The system generally includes a medical device having a plurality of electrodes at a distal end, and an energy generator in communication with the plurality of electrodes, the generator programmable to deliver alternating current energy between approximately 100 volts RMS and approximately 2000 volts RMS or greater. The generator is further programmable to deliver energy in unipolar mode, bipolar mode, and a combination thereof.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ABLATION FRONTIERS
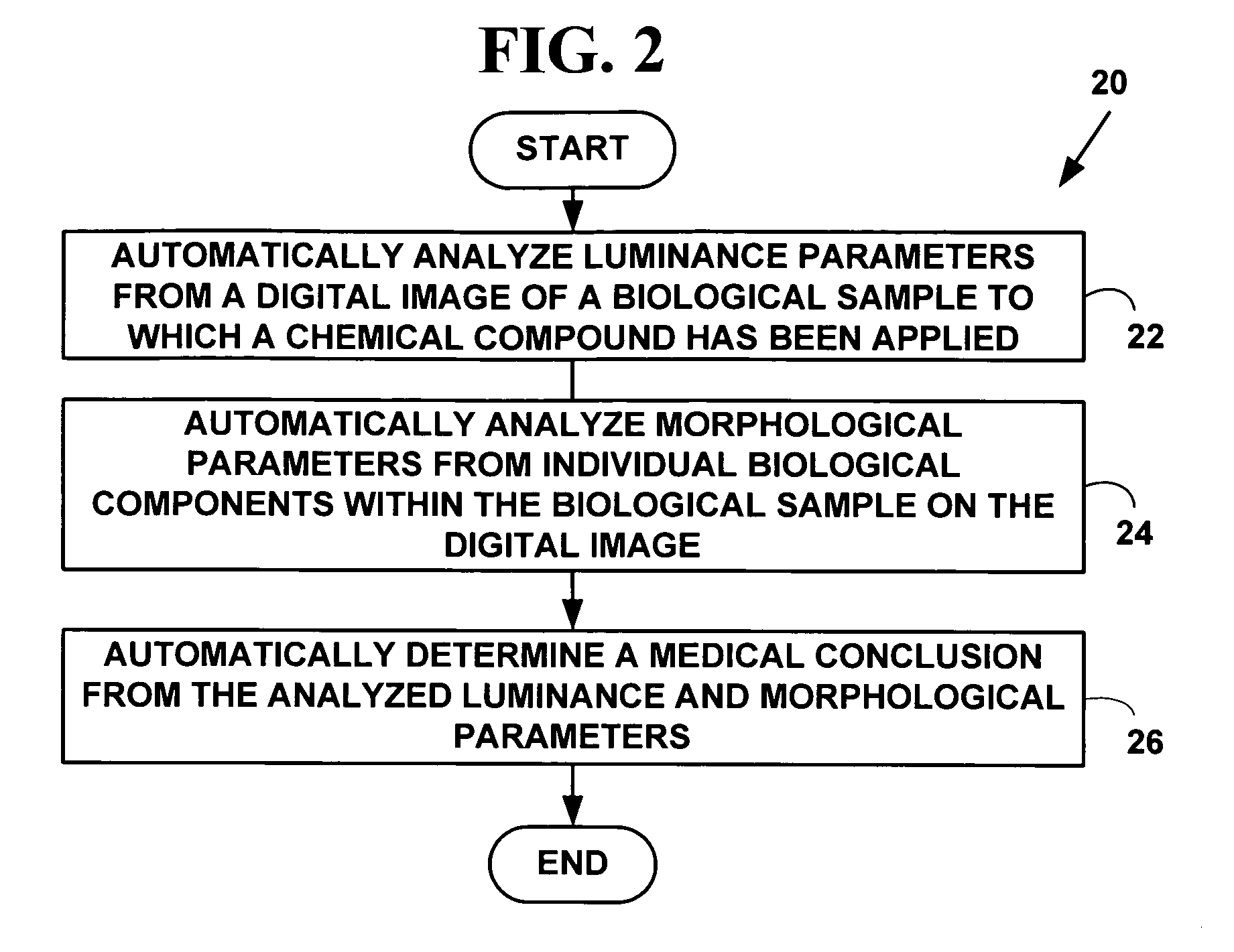
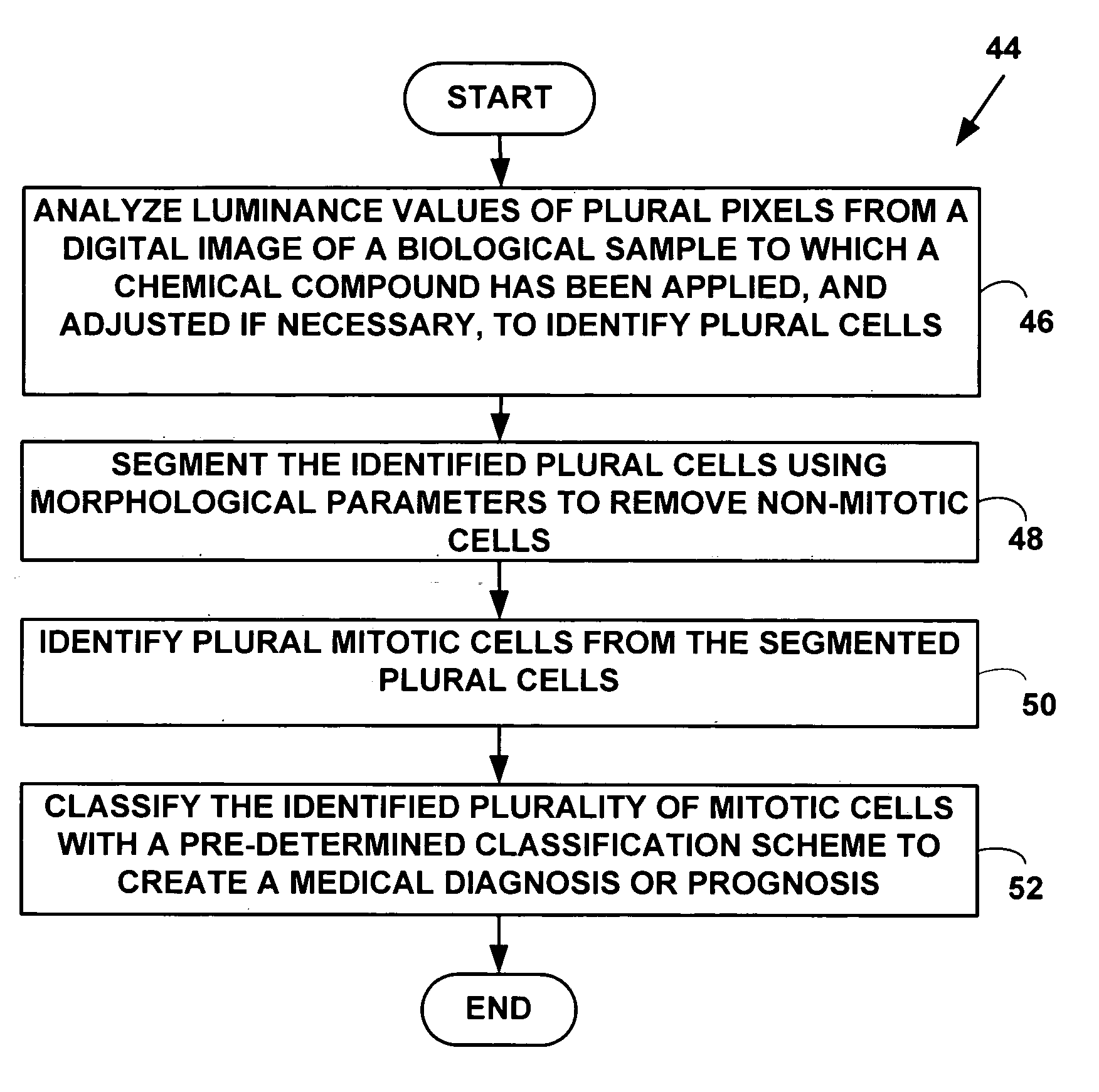
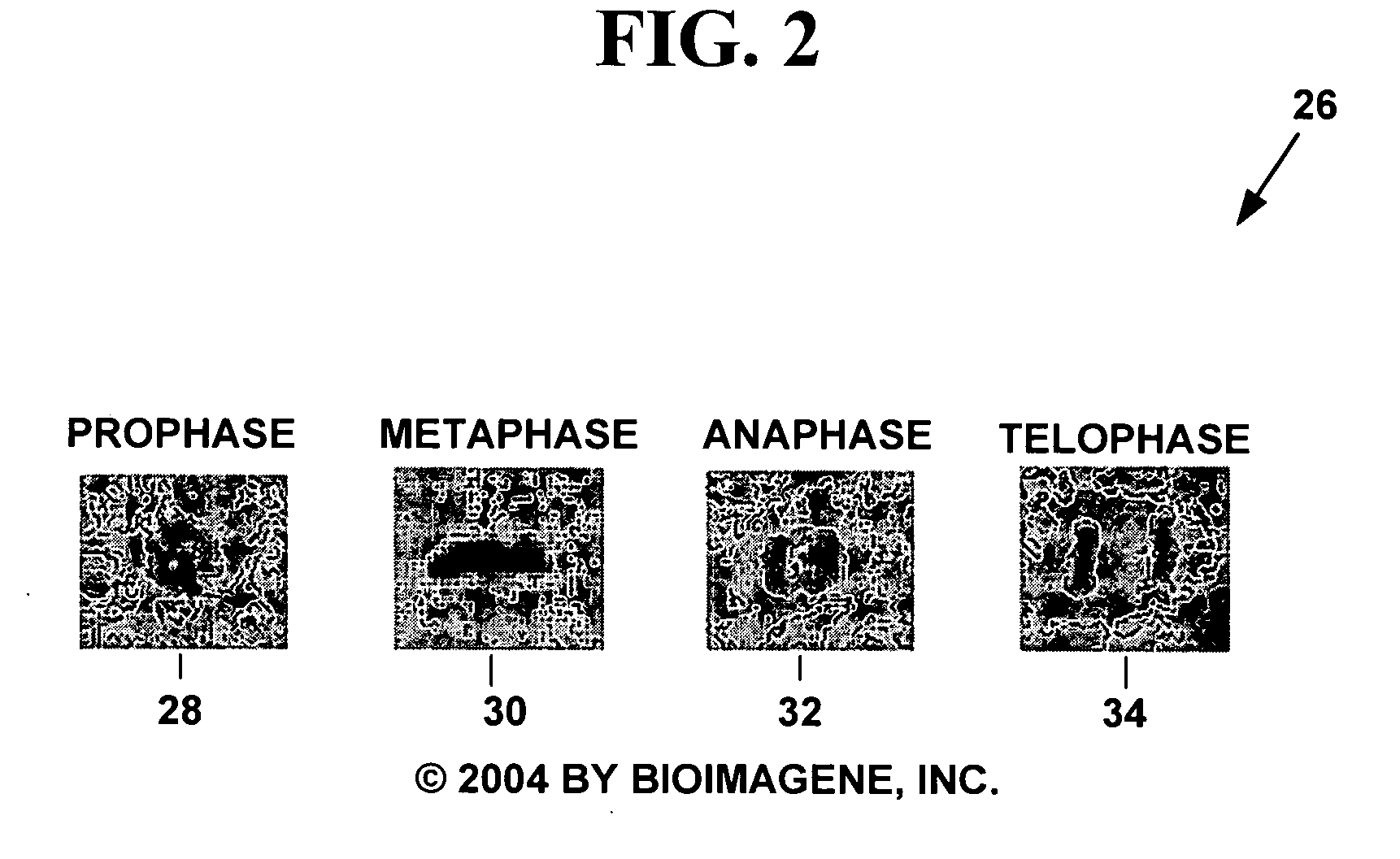
Method and system for morphology based mitosis identification and classification of digital images
ActiveUS20050266395A1Improved prognosisExpand selectionImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionChemical compound
A method and system for morphology based mitosis identification and classification of digital images. Luminance parameters such as intensity, etc. from a digital image of a biological sample (e.g., tissue cells) to which a chemical compound (e.g., a marker dye) has been applied are analyzed and corrected if necessary. Morphological parameters (e.g., size, elongation ratio, parallelism, boundary roughness, convex hull shape, etc.) from individual components within the biological sample are analyzed. A medical conclusion (e.g., type and count of mitotic cells) or a life science and biotechnology experiment conclusion is determined from the analyzed luminance and morphological parameters. The method and system may be used to develop applications for automatically obtaining a medical diagnosis (e.g., a carcinoma diagnosis).
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
System and methods for image-guided thermal treatment of tissue
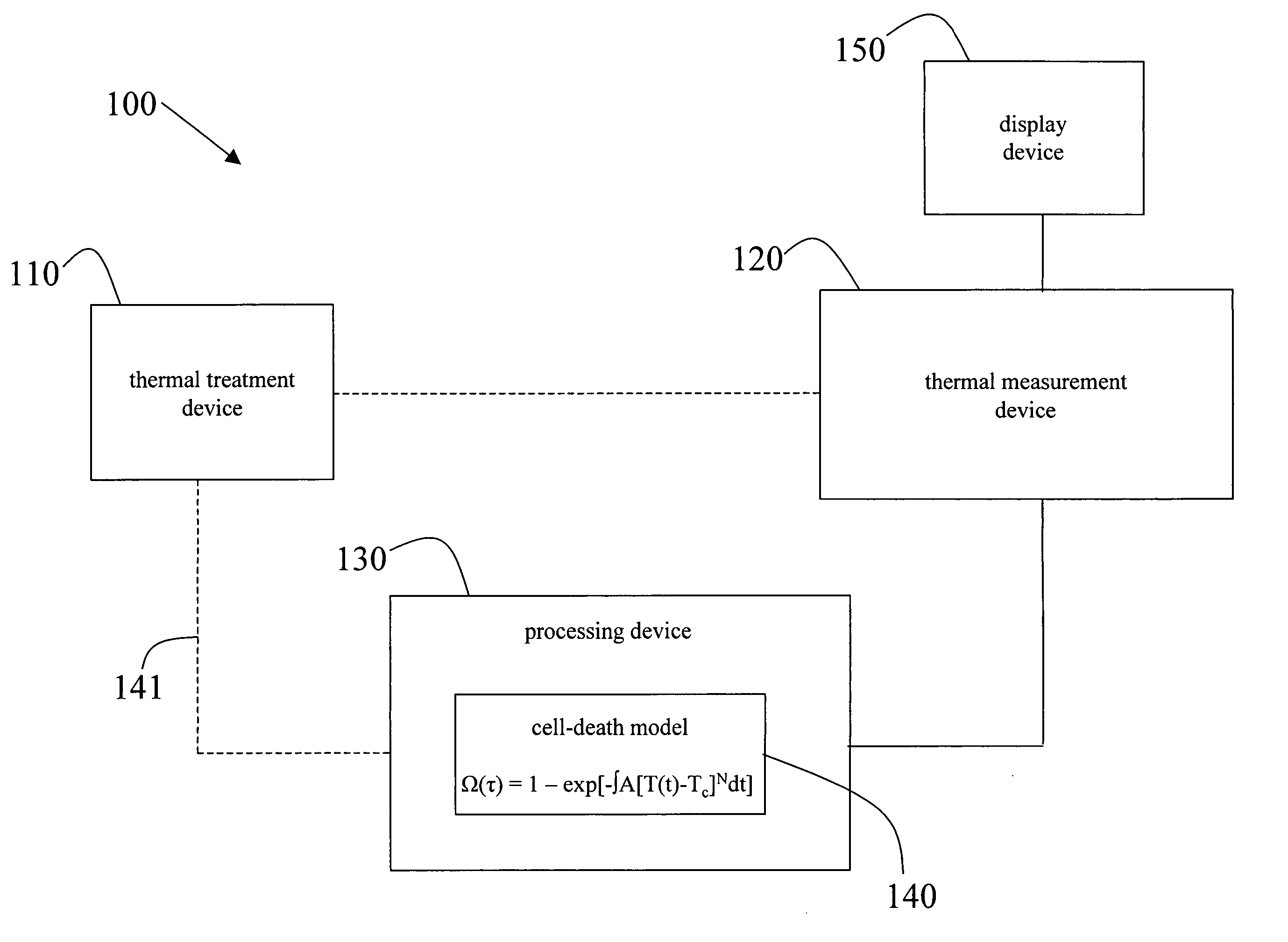
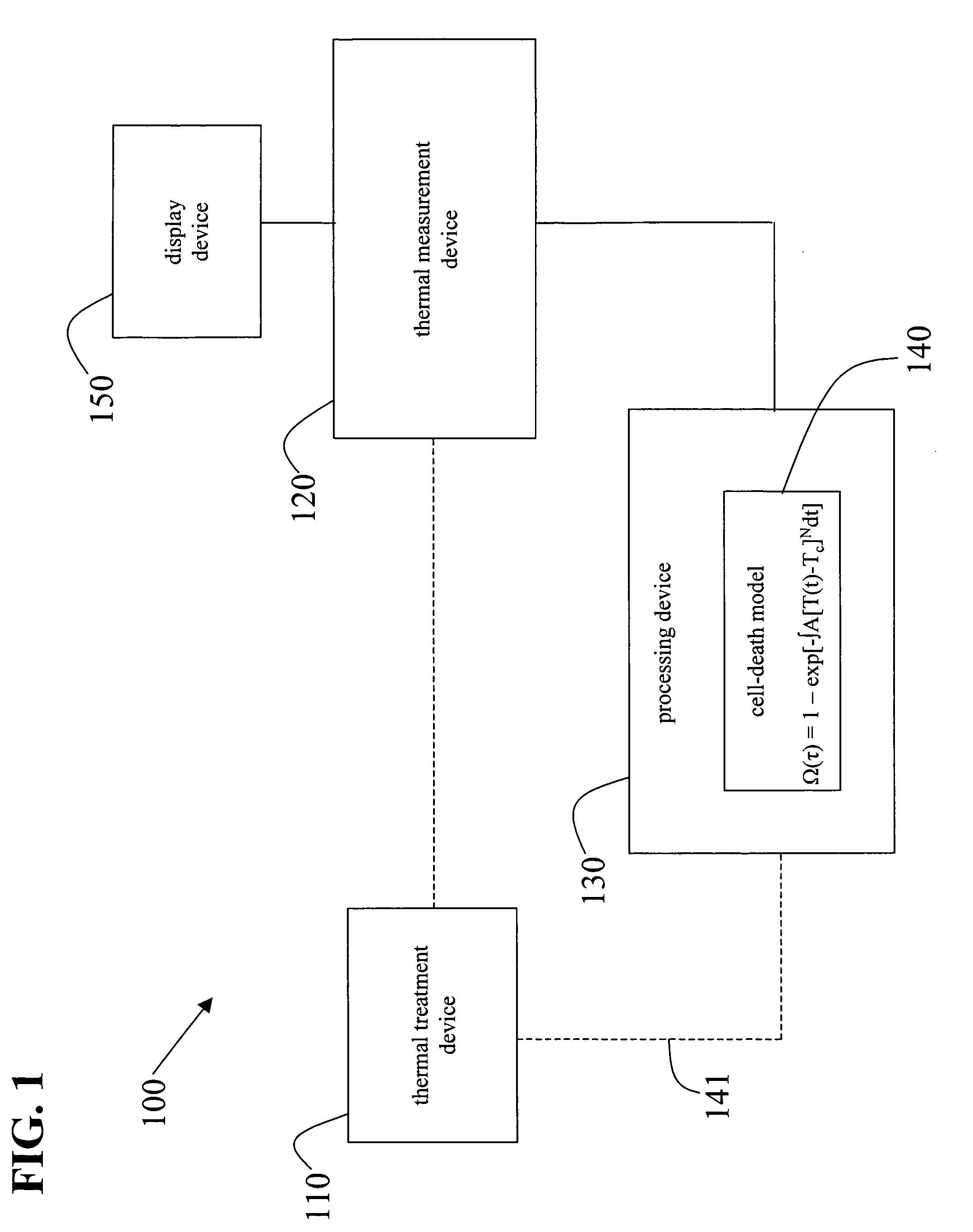
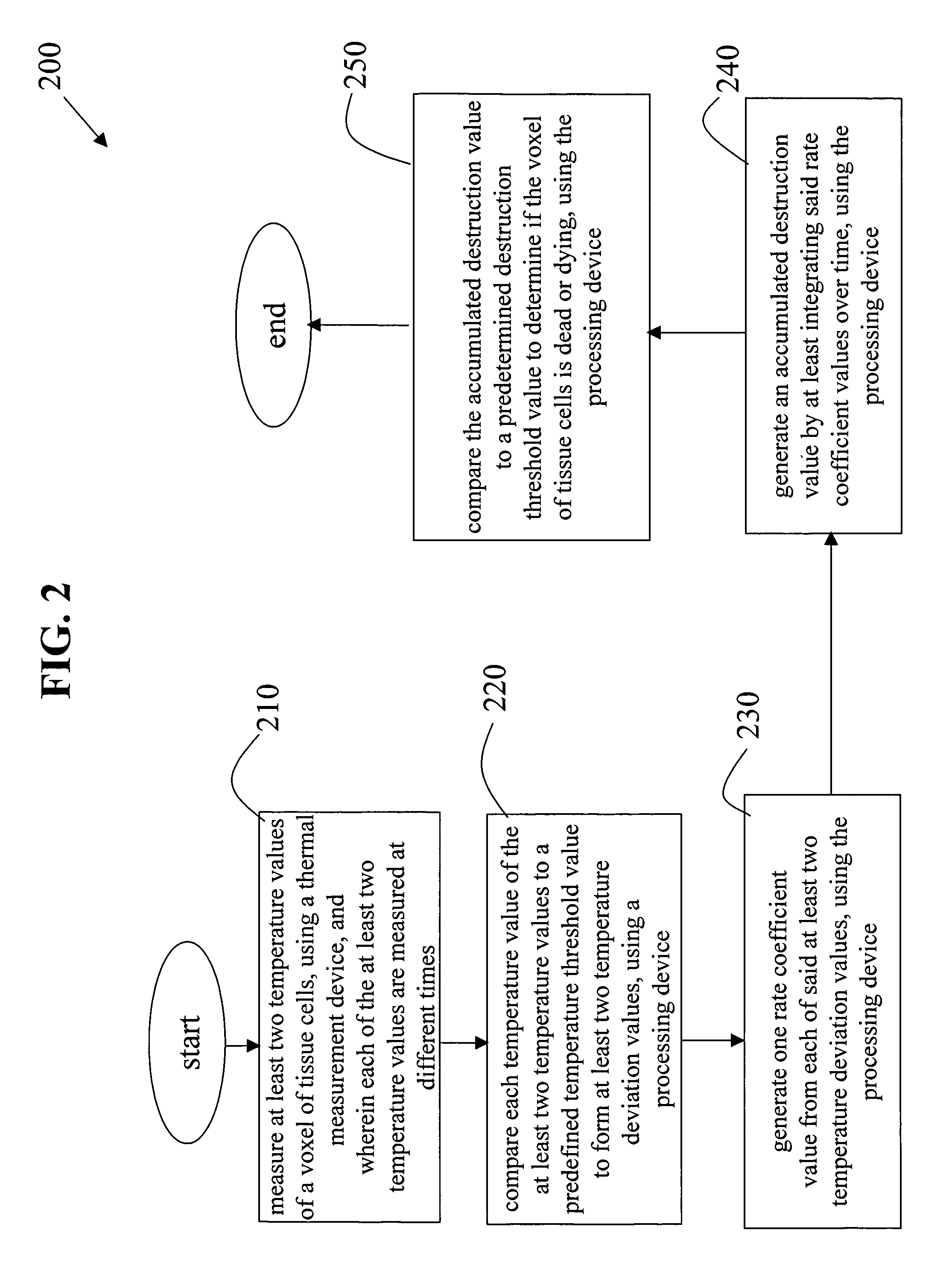
A system and methods for modeling the death of tissue cells that are thermally treated using thermal treatment devices is disclosed. A cell-death model accurately predicts, in real-time, which voxels of cells are dead or are about to die as the thermal treatment is applied to these cells. The effects of thermal treatment are monitored by a thermal measurement device which feeds thermal information to the cell-death model. The cell-death model accounts for the temperature of each voxel of tissue cells with respect to a temperature threshold value and the duration over which the thermal treatment is applied. When the thermal measurement device is an imaging device, the results of the thermal treatment may be displayed to the user in real-time. As a result, a user of the thermal treatment device can determine, in real-time, which target voxels of cells he has killed and which still need to be killed. The user can also more easily avoid inadvertently killing healthy tissue that he does not intend to kill. The cell-death model may be implemented in software on the thermal measurement device, on the thermal treatment device, or on a separate processing device which interfaces to and communicates with at least one of the thermal measurement device and the thermal treatment device.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Separation method of buffering stem cell in human placenta
InactiveCN1548529AMicrobiological testing/measurementSkeletal/connective tissue cellsAnatomical structuresCord blood stem cell
The present invention discloses the separation method of mesenchymal stem cell in human placenta. On the basis of past separation of tissue cell, the present inventor separates from placenta mesenchymal stem cell with high purity via perfusion process based on the special anatomical structure of placenta. Identification result shows that the mesenchymal stem cell separated from placenta has the biological characteristic and polydirectional differentiation capacity as the reported mesenchymal stem cell of marrow. Owing to the infantile cell component and wide source of placenta, like cord blood, the present invention will have wide clinical application foreground.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
System and Method for Increasing a Target Zone for Electrical Ablation
System for increasing a target zone for electrical ablation includes a treatment control module executable by a processor. The control module directs a pulse generator to apply pre-conditioning pulses to subject tissue cells in a pre-conditioning zone to electroporation, the pre-conditioning zone being smaller than a target ablation zone. After the pre-conditioning pulses have been applied, the control module directs the pulse generator to apply treatment pulses to electrically ablate the tissue cells in the target ablation zone. The pre-conditioning pulses cause the pre-conditioning zone to have a much higher conductivity so that the zone acts as a larger electrode area when the treatment pulses are applied, which results in a much larger target ablation zone than otherwise possible.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
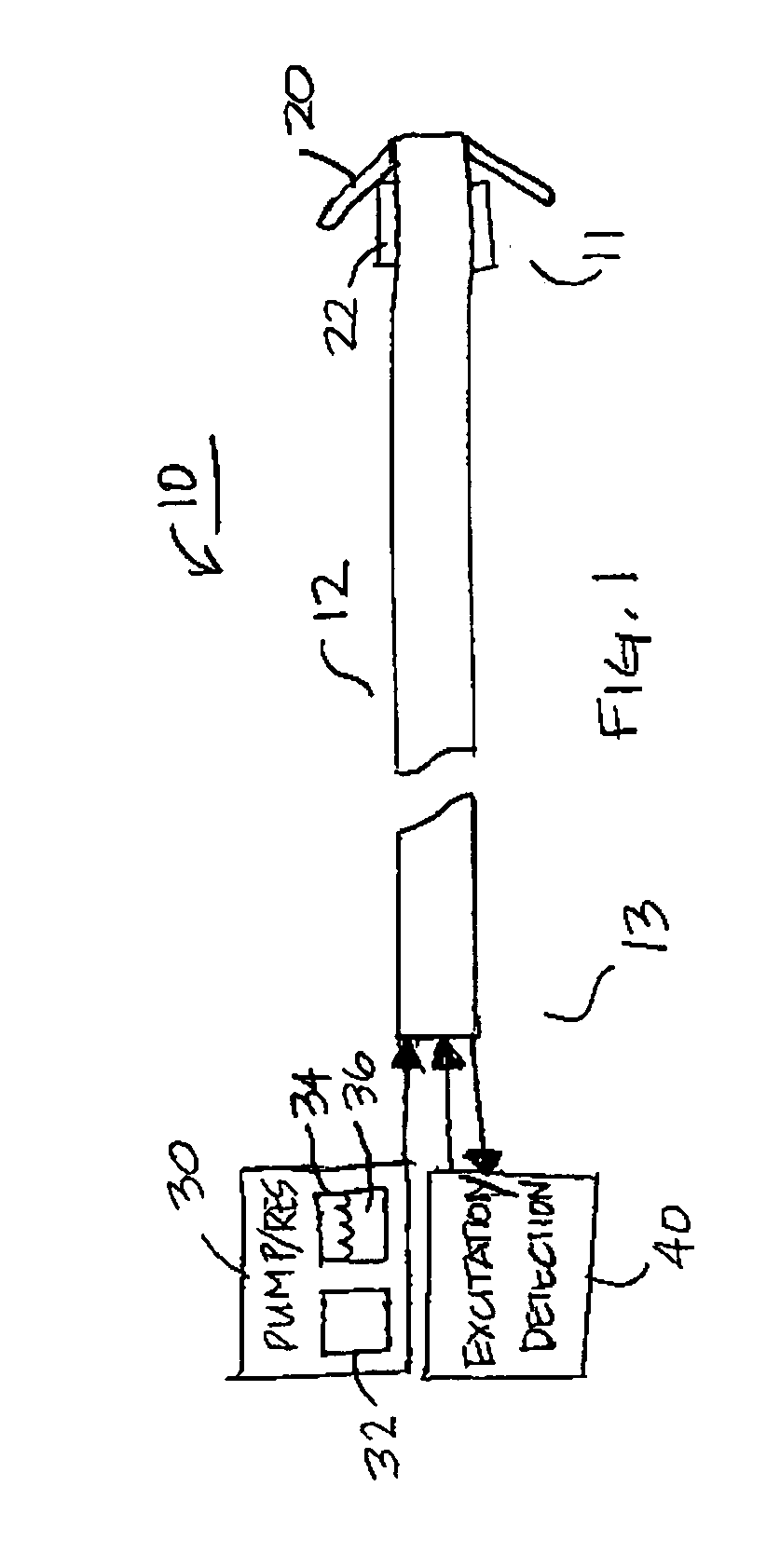
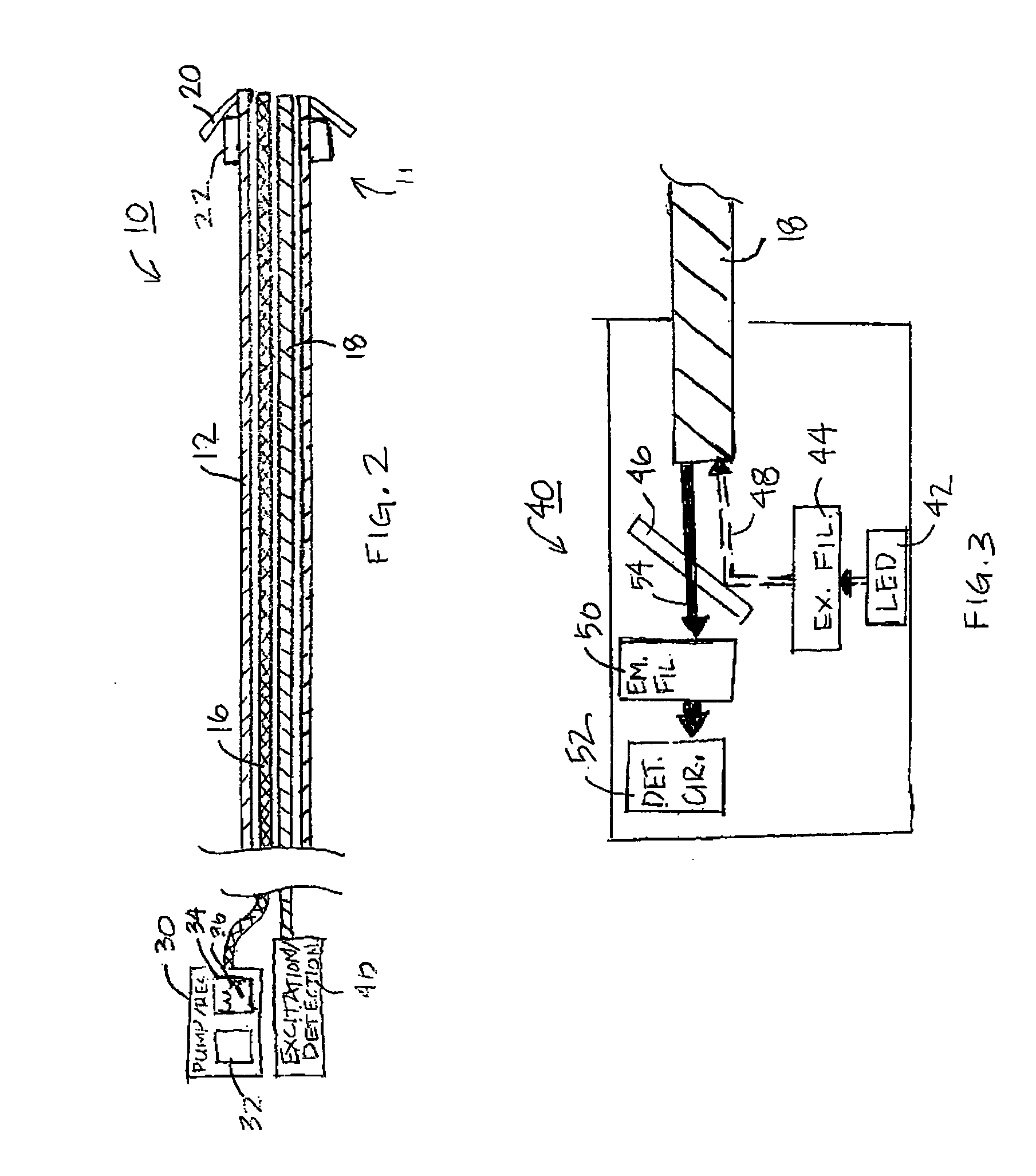
Implantable medical device having optical fiber for sensing electrical activity
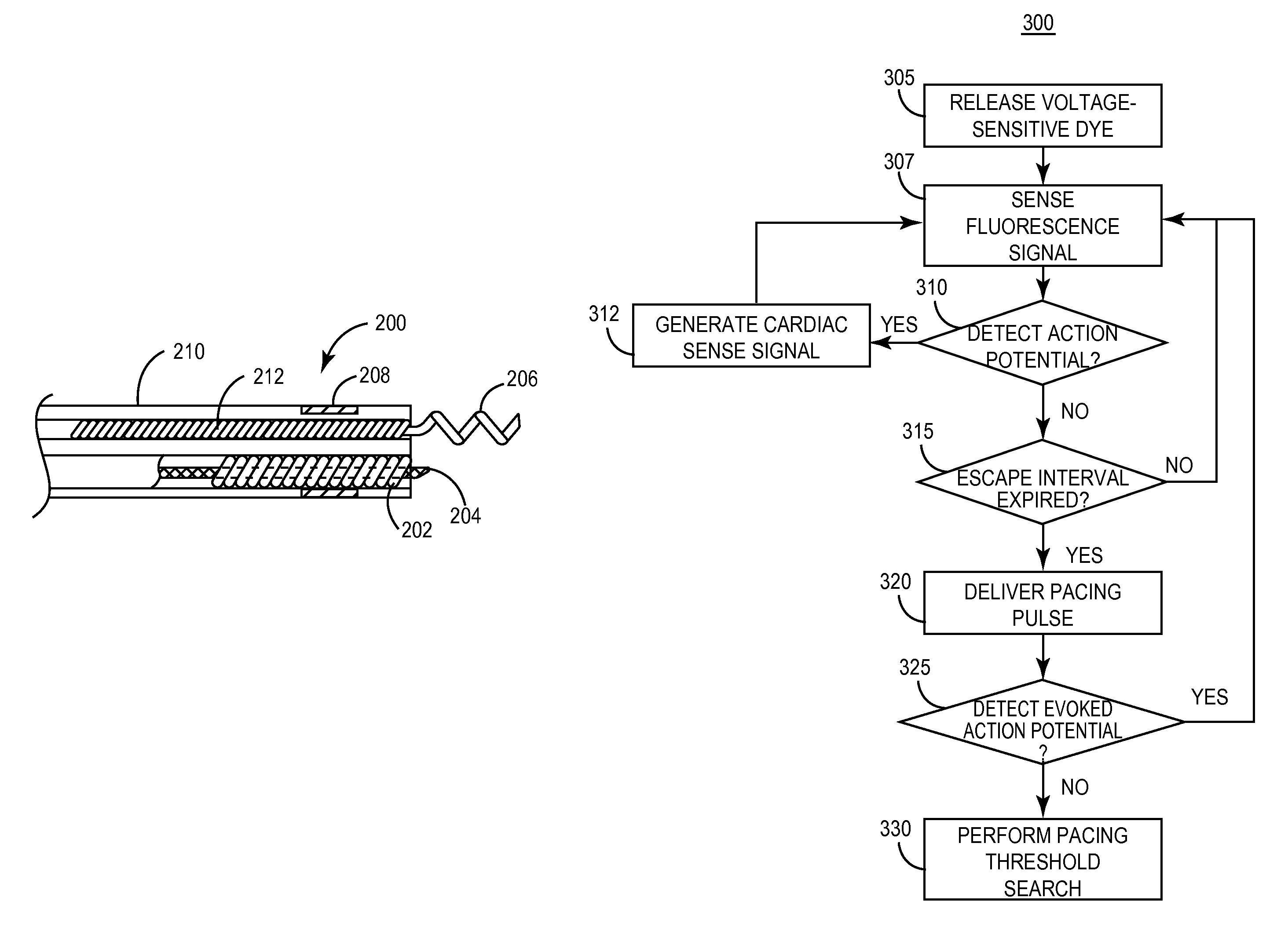
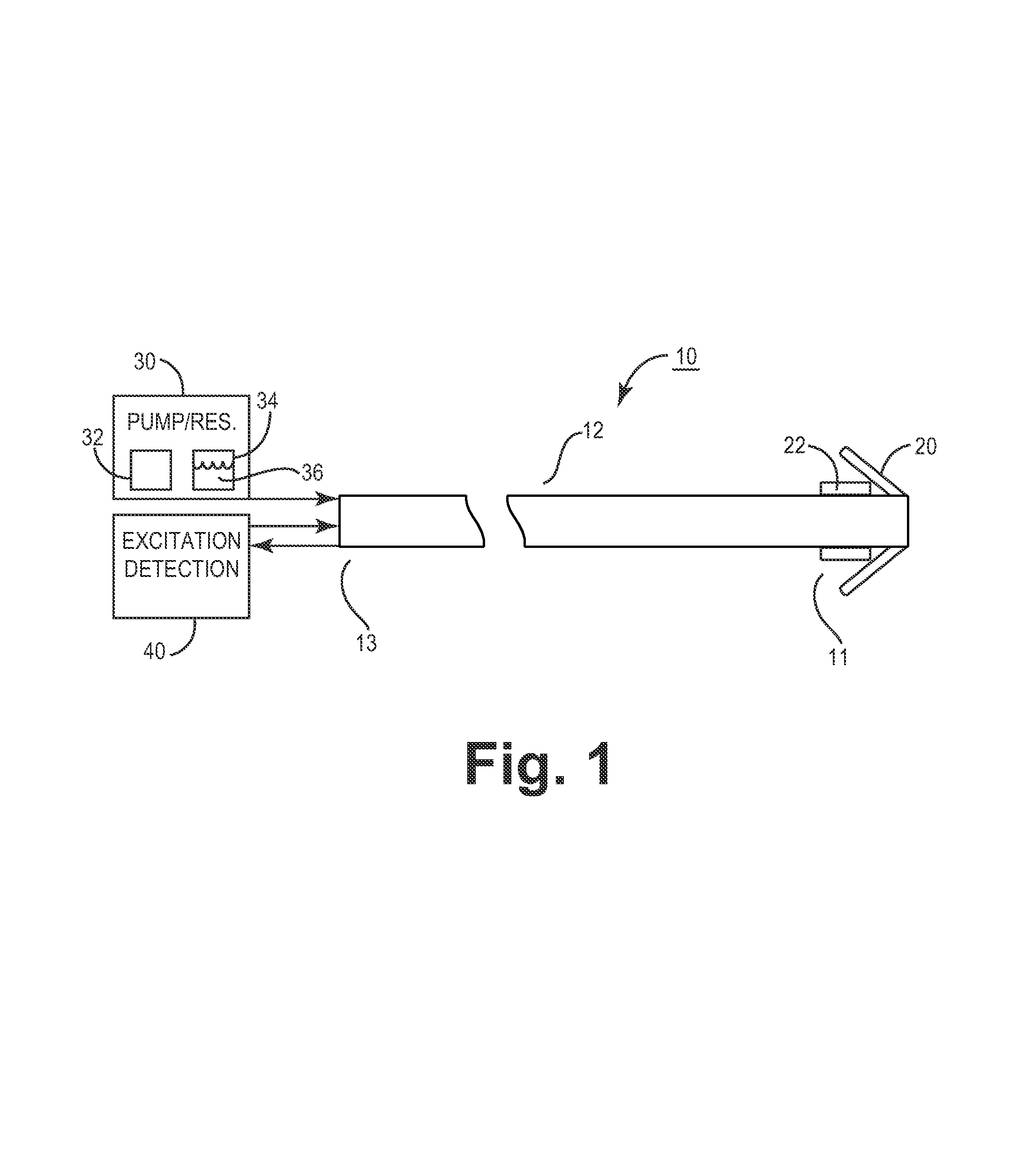
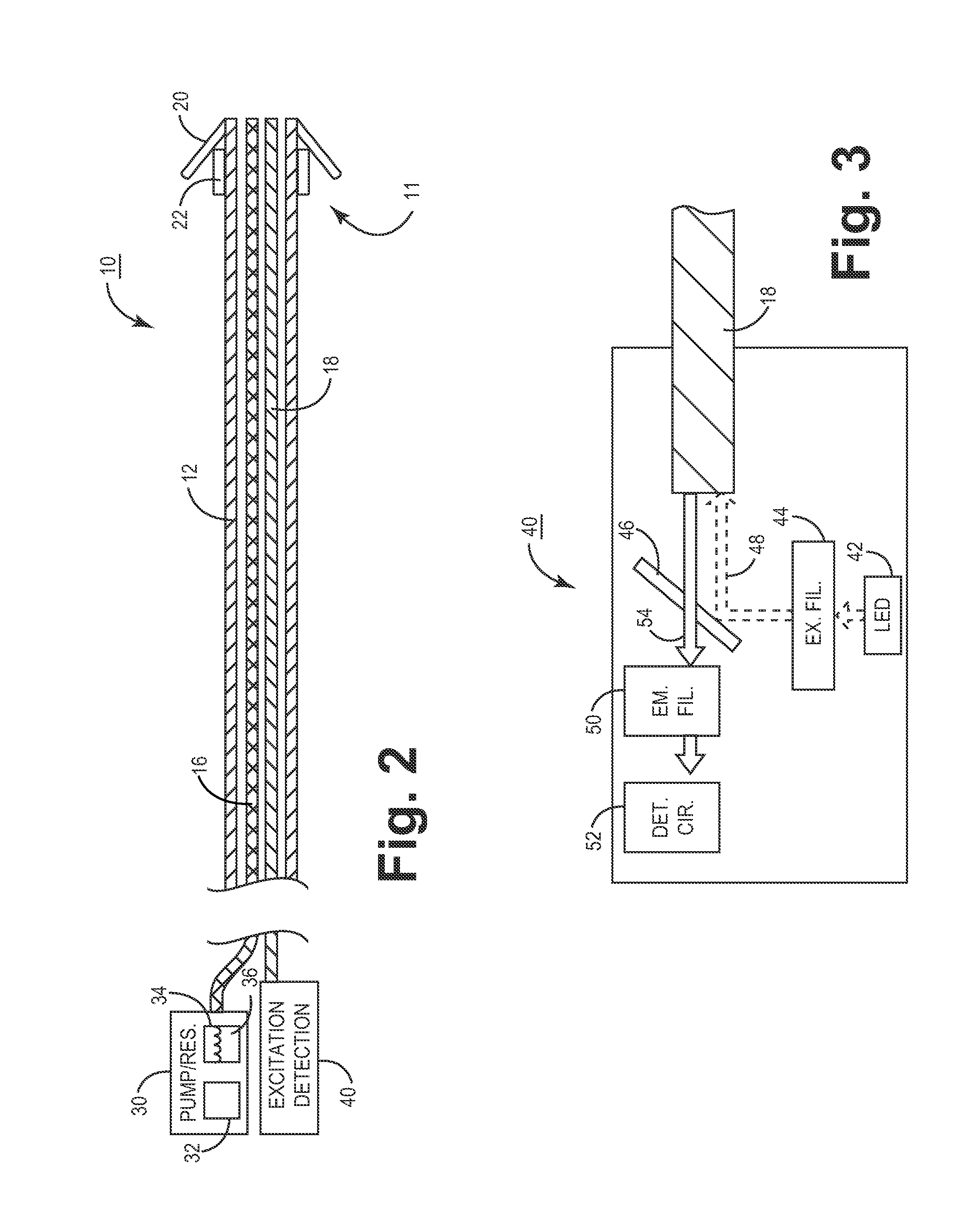
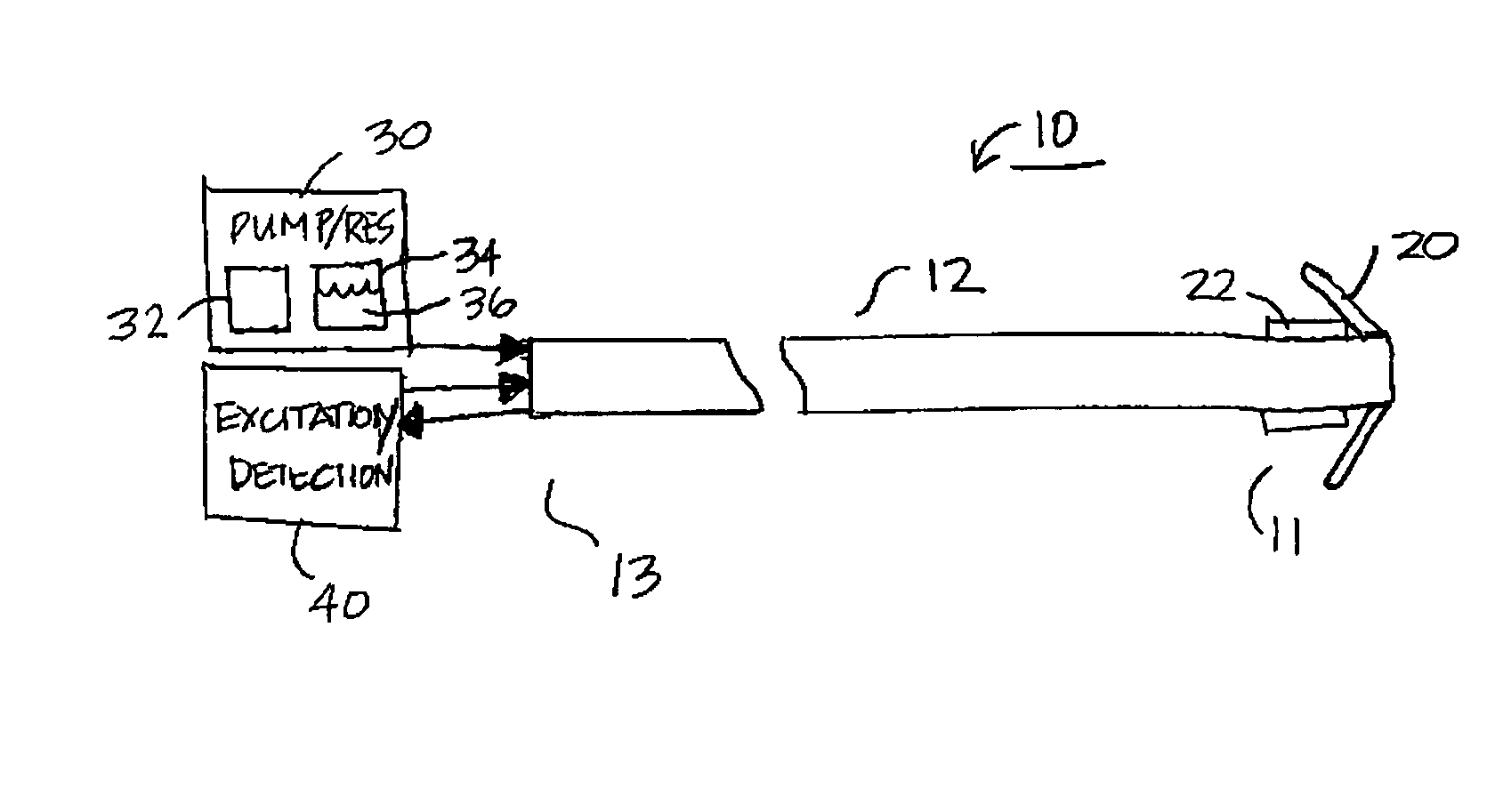
An implantable medical device for optically sensing action potential signals in excitable body tissue. The device includes an elongated tubular lead body carrying an optical fiber extending from a proximal lead end to a distal lead end to position the optical fiber at a target site. The lead body additionally carries a conduit for dispensing a voltage-sensitive fluorescent dye into tissue surrounding the target site. The optical fiber transmits excitation light to the fluorescent dye to cause the dye to fluoresce with varying intensity as the transmembrane potentials of local tissue cells vary due to passing depolarization wavefronts. The optical fiber transmits the fluorescence signal to the device to generate an action potential signal or fiducial points of an action potential signal for use in accurately measuring and characterizing electrical activity of excitable tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Implantable medical device having optical fiber for sensing electrical activity
An implantable medical device for optically sensing action potential signals in excitable body tissue. The device includes an elongated tubular lead body carrying an optical fiber extending from a proximal lead end to a distal lead end to position the optical fiber at a target site. The lead body additionally carries a conduit for dispensing a voltage-sensitive fluorescent dye into tissue surrounding the target site. The optical fiber transmits excitation light to the fluorescent dye to cause the dye to fluoresce with varying intensity as the transmembrane potentials of local tissue cells vary due to passing depolarization wavefronts. The optical fiber transmits the fluorescence signal to the device to generate an action potential signal or fiducial points of an action potential signal for use in accurately measuring and characterizing electrical activity of excitable tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Tissue-derived tissugenic implants, and methods of fabricating and using same
The disclosure provides implants containing a plurality of particles containing at least one population of viable tissuegenic cells adherent to and resident in the growth-conductive matrix or at least viable population of tissuegenic cells caused to be in contact with the growth-conductive matrix; methods to fabricate implants; methods of fabricating the implants; and use of the implants in tissue repair.
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT FOUND INC
Three-dimensional bioresorbable scaffolds for tissue engineering applications
InactiveUS8071007B1Biocompatibility hardHard integrationAdditive manufacturing apparatusCeramic shaping apparatusBiocompatibility TestingHard tissue
The invention relates to the use of Fused Deposition Modeling to construct three-dimensional (3D) bioresorbable scaffolds from bioresorbable polymers such as polycaprolactone (PCL), or from composites of bioresorbable polymers and ceramics, such as polycaprolactone / hydroxyapatite (PCL / HA). Incorporation of a bioresorbable ceramic to produce a hybrid / composite material support provides the desired degradation and resorption kinetics. Such a composite material improves the biocompatibility and hard tissue integration and allows for increased initial flash spread of serum proteins. The basic resorption products of the composite also avoids the formation of an unfavorable environment for hard tissue cells due to a decreased pH. The scaffolds have applications in tissue engineering, e.g., in tissue engineering bone and cartilage.
Owner:OSTEOPORE INT PTE
Novelmultifunctional ready-to-useaerogel composite for whole blood component protection and preparation method of novelmultifunctional ready-to-useaerogel composite
InactiveCN106832439ALow thermal conductivityImprove thermal conductivityChemical industryPullulanAntioxidant
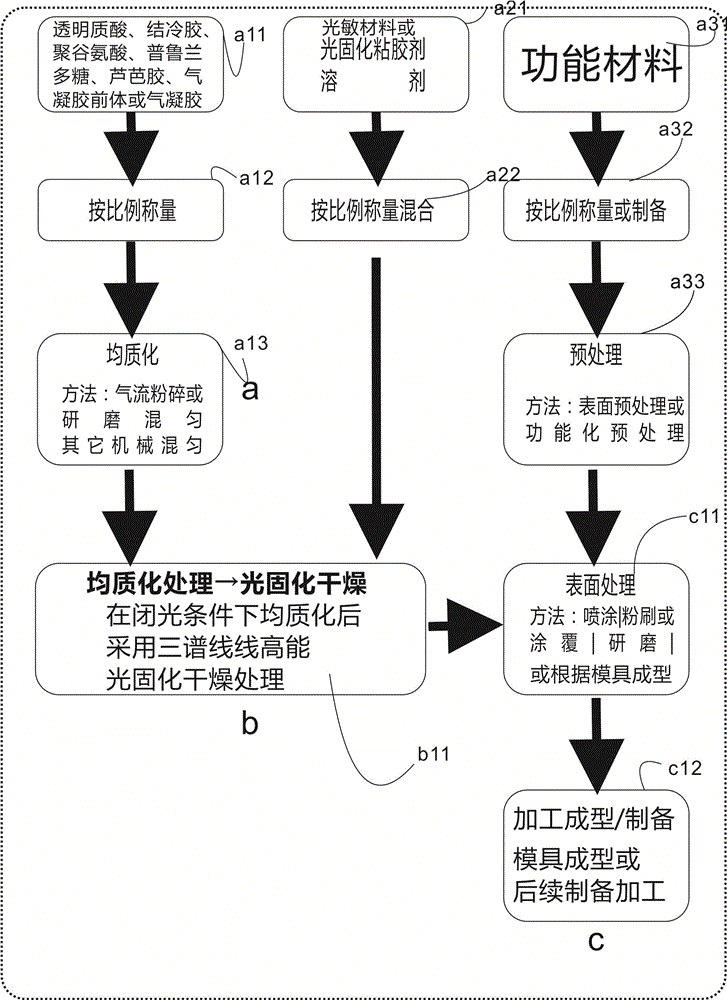
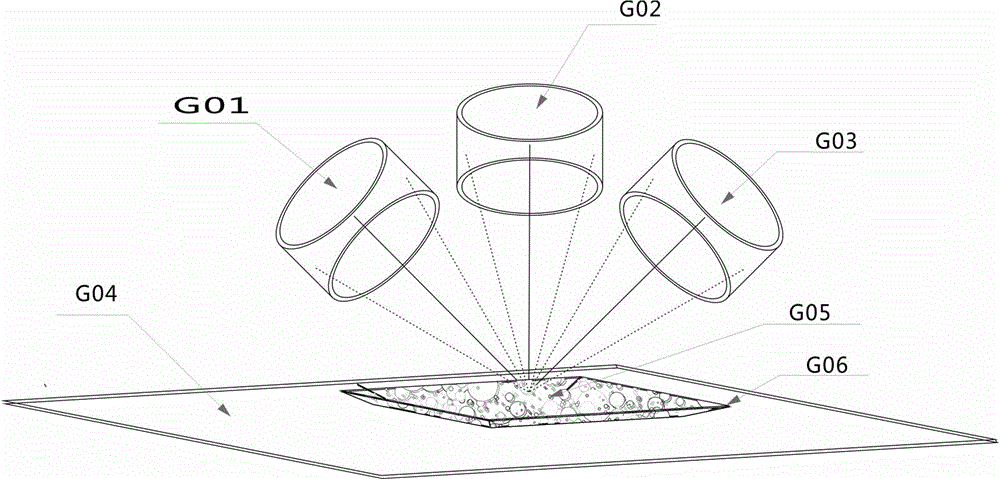
The invention provides a multifunctional aerogel material for blood component protection and a preparation method of the multifunctional aerogel material. Gellan gum, hyaluronic acid, Pullulan, Lubrajel CG andpoly(gamma-glutamic acid), derivatives or a mixture thereof are taken as a skeleton to act with a novellight-sensitive material, aerogel or a precursor for preparation of the ready-to-useaerogel material, and then multifunctional ready-to-useaerogel composite is prepared from the ready-to-useaerogel material as well as raw materials includingglucose, a novel solvent, a novel fixing agent, a buffering agent, a stabilizer, a novel preservative, a surfactant, a high-molecular compound, essential oil, an antioxidant and the likewith a three-spectral-line high-energy photocuring method by utilizing a high polymer material such as hyaluronic acid and the like as the skeleton. The material has the characteristics of being convenient to use, green, environment-friendly and the like, the whole blood component treated with the material keeps good cellular morphology, is stored for a long time, reducesbatch-to-batch difference and is an ideal additive for a whole blood controlling product and other products, and the material can also be applied to collection, storage and transfer of tissue cells as well as fields of cosmetics, food, drugs and the like.
Owner:广州市芯检康生物科技有限公司
Two-phase oxygenated solution and method of use
A two-phase mixture is provided having a dissolved gas and a suspension of bubbles in a liquid. Methods for making, maintaining, and using the two-phase mixture are also provided. The gas molecules may be introduced into the liquid at a high velocity under elevated pressure to form a supersaturated solution that retains the dissolved gas concentration in solution when the solution is exposed to ambient conditions. The mixture may be used in a number of applications where high concentrations of gas must be retained in solution during prolonged exposure to ambient conditions. An example of use is the treatment of wounds to non-surgically remove dead, devitalized, contaminated and foreign matter from tissue cells. The mixture may be combined with a plastic to encapsulate the suspension of bubbles to minimize liberation of the gas bubbles from the mixture.
Owner:ECKERT C EDWARD
Method for enhancing targeting selectivity of administration system by modifying cell penetrating peptide
InactiveCN102552929AEliminate or reduce transmembrane effectAvoid damageIn-vivo radioactive preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsCell membraneEnzyme system
The invention relates to modification of a cell penetrating peptide for realizing a low-toxicity administration system with a positive targeting selecting function. A shielding peptide, an enzymolysis substrate peptide and a cell-penetrating peptide are connected in sequence, so that an activatable cell penetrating peptide is formed; and a medicament and / or a tracer and / or a medicament carrier is connected or embedded or adsorbed to the cell penetrating peptide, so that an administration system is constructed. According to a shielding peptide sequence, positive charges carried on the surface of the administration system can be reduced or completely neutralized, the cell penetrating capability of the cell penetrating peptide is shielded, and the toxicity of the administration system on normal cells of an organism is lowered; and an enzymolysis substrate peptide sequence can be identified by enzyme systems secreted specifically by different pathological change tissue cells and fractured by enzyme hydrolysis, so that a cell penetrating peptide is released and is used for carrying a medicament and / or a medicament carrier through a cell membrane, and the medicament enters cells and is brought into play. The invention aims to actively convey an antitumor medicament to tumor tissues in a targeted way and make the antitumor medicament enter tumor cells to a larger extent by using the administration system which can be used for activating a cell penetrating function, so that the toxicity at a non-tumor position is lowered while the antitumor effect of the medicament is enhanced.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Ablation device and method for electroporating tissue cells
A method and system for producing deep lesions without the production of high heat. The method generally includes ablating target tissue cells with a device in communication with an energy generator programmable to ablate tissue using heat energy, electroporation, or a combination thereof. The system generally includes a medical device having a plurality of electrodes at a distal end, and an energy generator in communication with the plurality of electrodes, the generator programmable to deliver alternating current energy between approximately 100 volts RMS and approximately 2000 volts RMS or greater. The generator is further programmable to deliver energy in unipolar mode, bipolar mode, and a combination thereof.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ABLATION FRONTIERS
Methods for identifying conditions affecting a cell state
InactiveUS20060035211A1Fast wayMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingCell stateTissue cell
The present invention is directed to methods for identifying agents which affect cell state. The instant invention provides rapid and efficient methods for identifying agents which affect cell state. Methods are directed toward the screening of complex combinations of agents for their ability to affect cell state. In one embodiment, cells are incubated under suitable conditions and subjected to different agents. After an appropriate amount of time, the cells are assayed to determine what, if any, characteristics they possess. Cell characteristics can be organized in a manner such that different and novel cell states can be identified.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
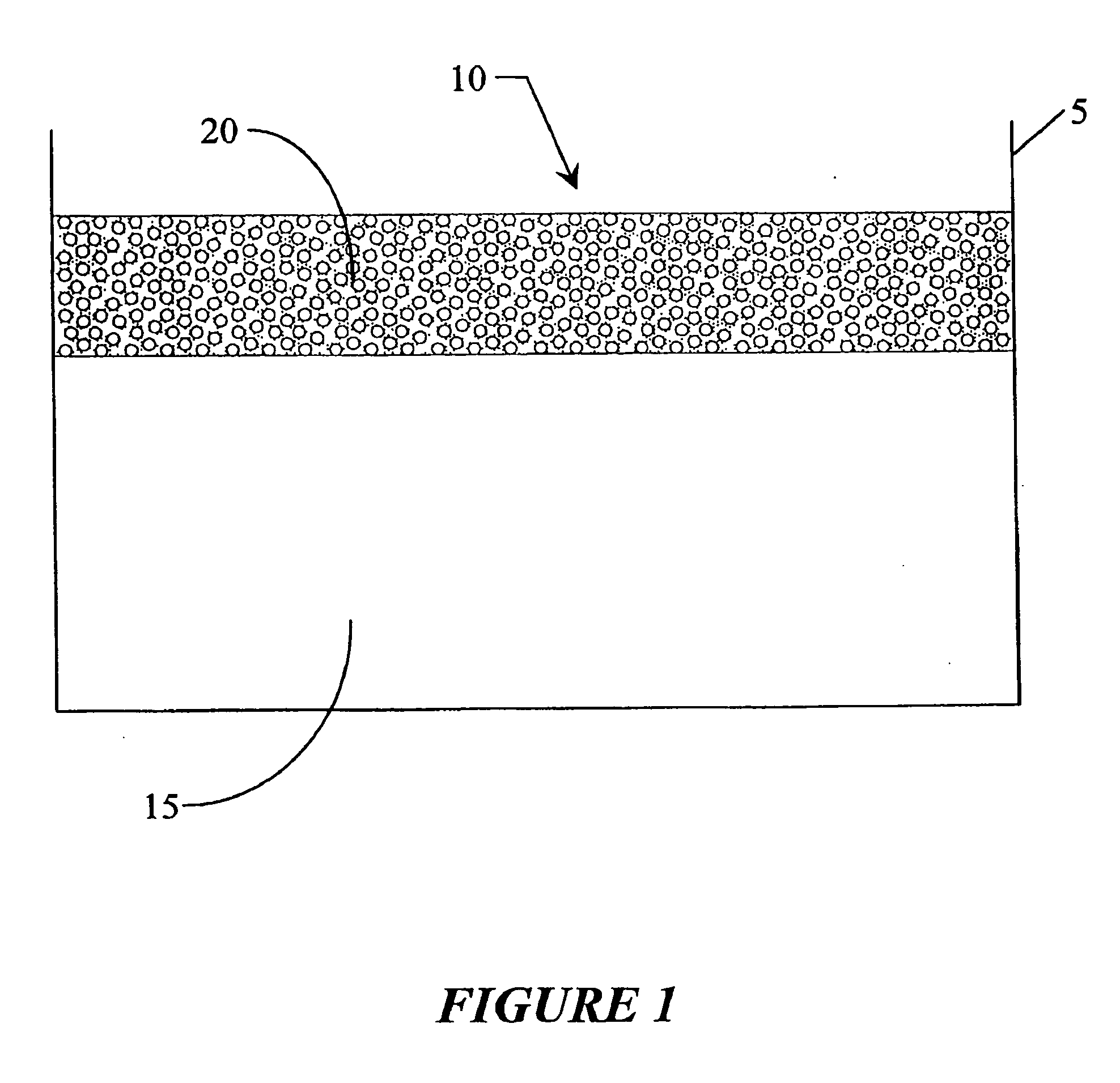
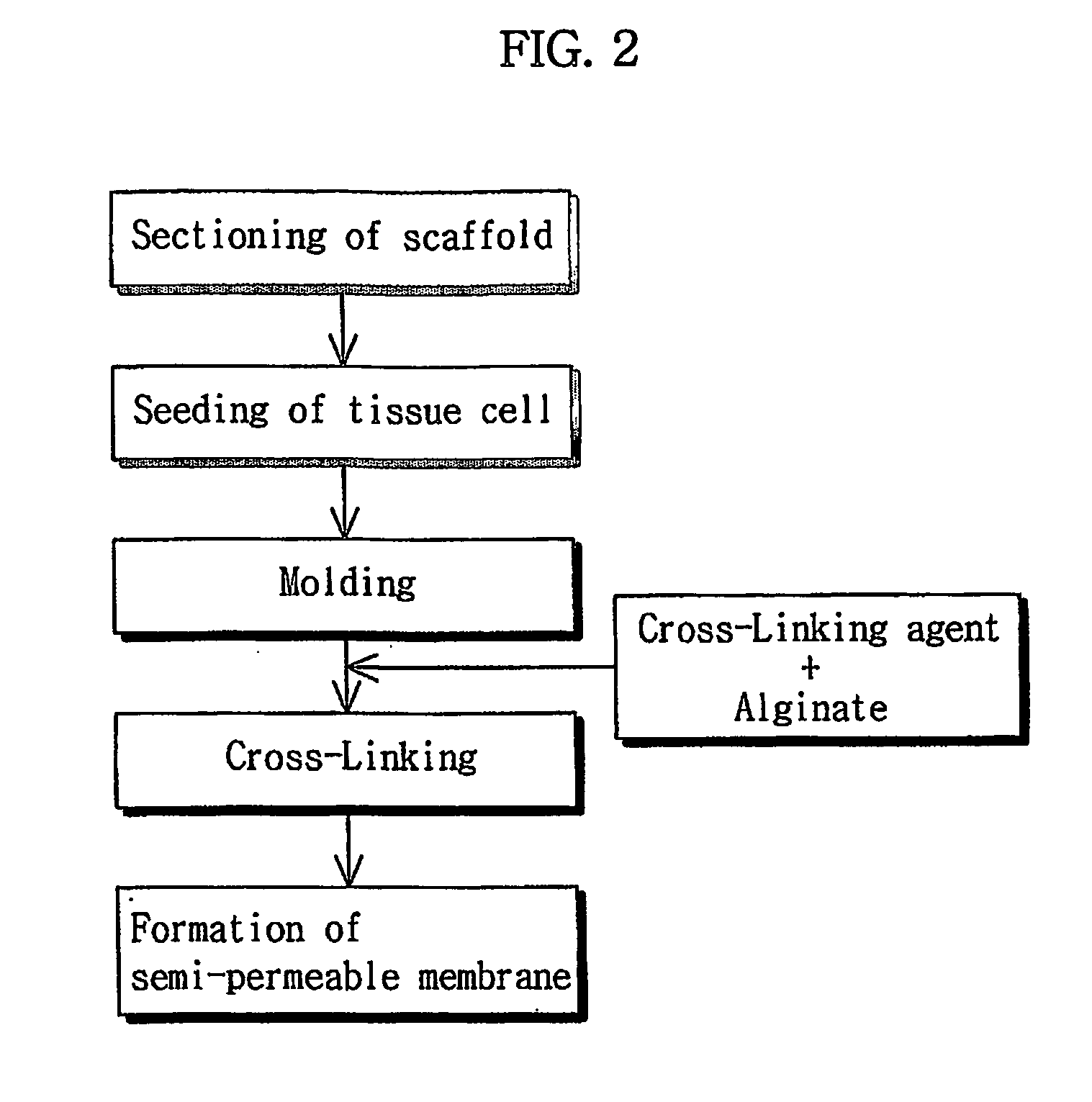
Biodegradable dual porous scaffold wrapped with semi-permeable membrane and tissue cell culture using thereof
InactiveUS20060147486A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCross-linkSemipermeable membrane
Disclosed is a scaffold including a semi-permeable membrane on an outer surface thereof. The present invention also discloses a method of preparing a scaffold covered with a semi-permeable membrane, including loading one or more scaffolds into a mold with a predetermined form and size; and adding a semi-permeable agent and a cross-linking agent to the mold and cross-linking the semi-permeable agent to form the semi-permeable membrane on the outer surface of each of the scaffolds. The scaffold covered with the semi-permeable membrane selectively introduces nutrients into the scaffold by allowing penetration of only external nutrients into the scaffold and excreting metabolic wastes generated by tissue cells to the outside of the scaffold. In addition, the scaffold has the morphology of a biological tissue of interest by cross-linking the small-sized scaffolds, thereby allowing uniform proliferation of tissue cells throughout the whole scaffold.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
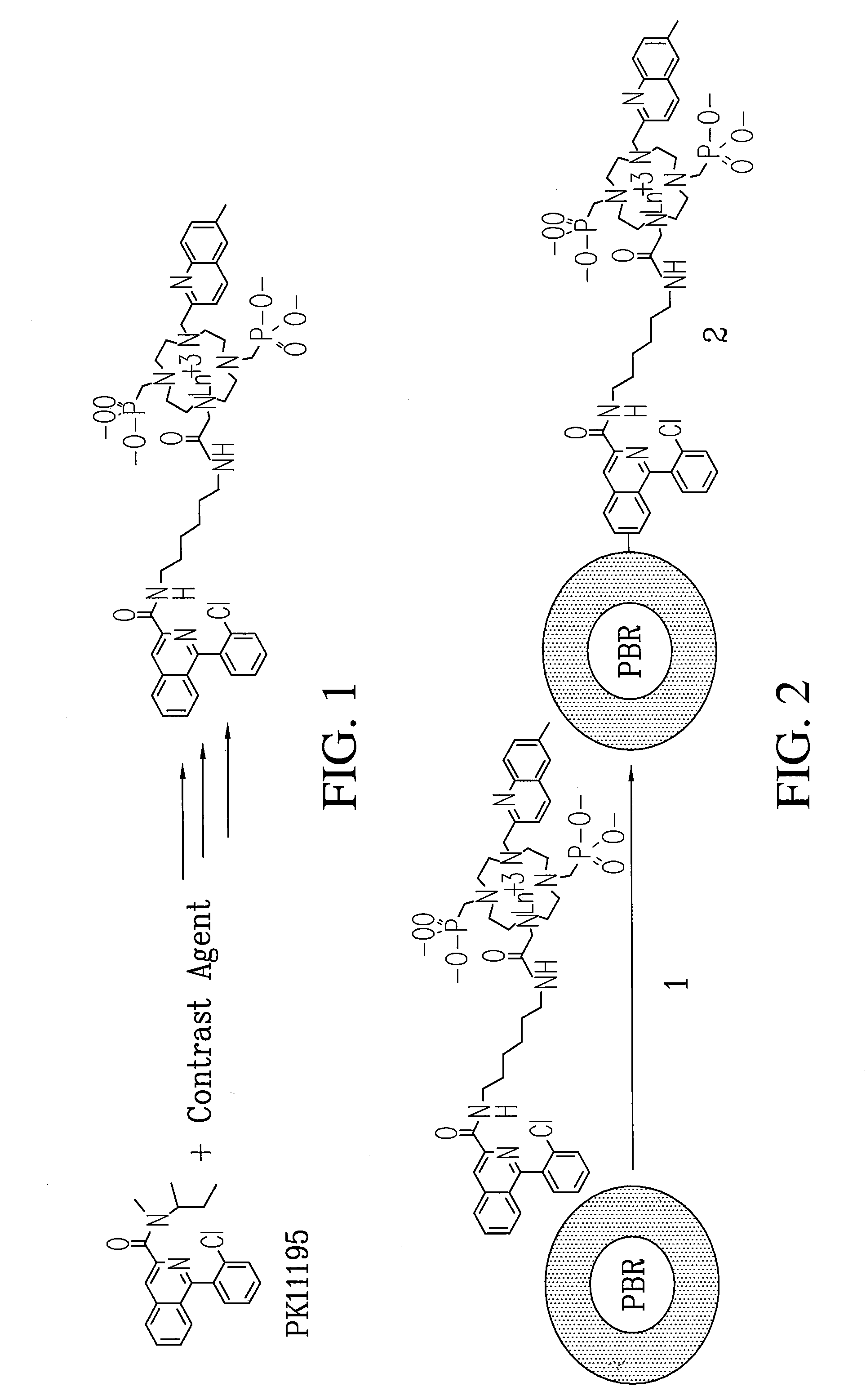
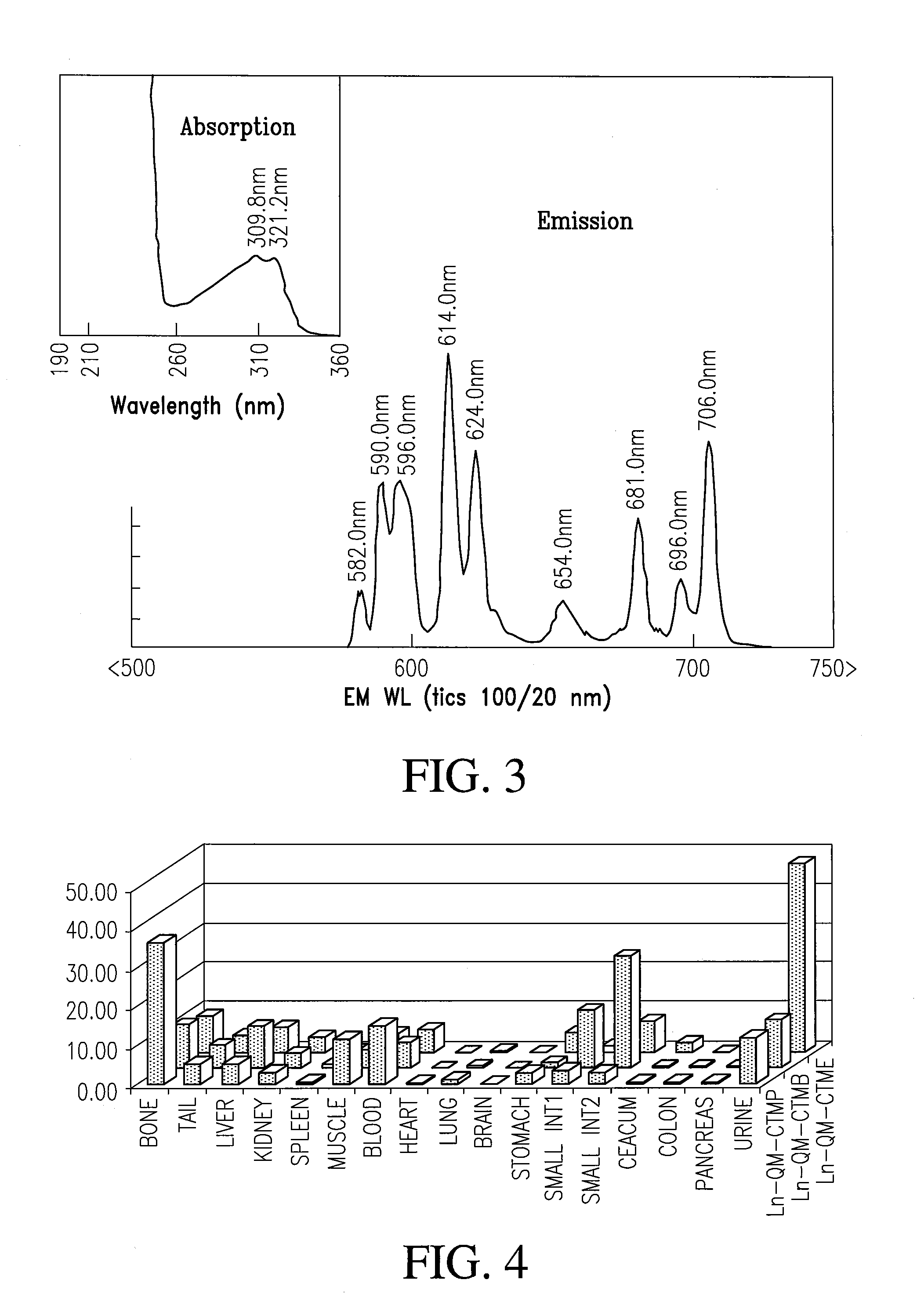
Multi-use multimodal imaging chelates
InactiveUS7338651B2Improve discriminationEasy to detectUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic active ingredientsCancer cellFluorescence
Cyclen-based chelates can be used as contrast agents for multi-modal imaging of tissue cells. The cyclen-based chelates are preferably polyazamacrocyclic molecules formed from 1,4,7,10 tetraazacyclododecane (“cyclen”) having varying chelating ions, phosphoester chains, and light harvesting moieties. By changing the chelating ion, phosphoester chain length and / or the light harvesting moiety different imaging techniques, such as MRI, CT, fluorescence and absorption, x-ray and NIR, may be employed to image the tissue cells. Additionally, the cyclen-based chelates may be conjugated to provide for site-specific delivery of the cyclen-based chelate to the desired tissue cells. The cyclen-based chelates may also be delivered to the tissue cells by attaching the cyclen-based chelates to a polymeric delivery vehicle. Although these cyclen-based chelates have a wide variety of application, the preferred use is for imaging of cancer cells, such as brain cancer, for improving resection of a cancerous tissue.
Owner:TEXAS TECH UNIV SYST +1
Method for Surface Modification of Polymeric Scaffold for Stem Cell Transplantation Using Decellularized Extracellular Matrix
InactiveUS20100267143A1Easy to stickArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
The present invention relates to a method for the surface modification of a polymeric scaffold for stem cell transplantation using a decellularized extracellular matrix. The method for the surface modification of the polymeric scaffold according to the present invention can embody a biomimetic surface environment that is effective for initial cell attachment, cell growth and differentiation of stem cells by modifying the surface of the polymeric scaffold using the decellularized extracellular matrix directly derived from specific tissue cells.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Personalized bionic composite structure as well as preparation method of composite structure and method for drug screening by using composite structure
InactiveCN103756955AUseful for drug screeningFully formedMicrobiological testing/measurementVertebrate cellsCross-linkVascular tissue
The invention discloses a personalized bionic composite structure as well as a preparation method of the composite structure and a method for drug screening by using the composite structure, and relates to a bionic composite structure based on a composite multi-nozzle three-dimensional printing technology and a preparation method thereof. The bionic composite structure comprises a polymer shell, a branched vascular stent, a functional tissue area, a vascular tissue area and polymer isolating layers, wherein the functional tissue area is a hydrogel layer containing tissue cells; the vascular tissue area is a hydrogel layer containing vascular seed cells; the functional tissue area and the vascular tissue area are alternately arranged in space; the polymer isolating layers are alternately distributed in the functional tissue area and the vascular tissue area, and divide the functional tissue area and the vascular tissue area into a plurality of small regions; the branched vascular stent includes two parts, i.e., artery blood vessel and vein blood vessel. According to the invention, the tissue / organ bionic structure with the branched blood vessel is prepared through the composite multi-nozzle 3D printing technology; the hydrogel structures are not cross-linked or polymerized; in vivo vascularized tissue and blood vessel states are simulated to the greatest extent, thus providing a reference for vascularized organ and tissue.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for preparing evoked pluripotent stem cell
InactiveCN101250502APotential for differentiationImprove efficiencyMammal material medical ingredientsImmunological disordersInduced pluripotent stem cellTissue cell
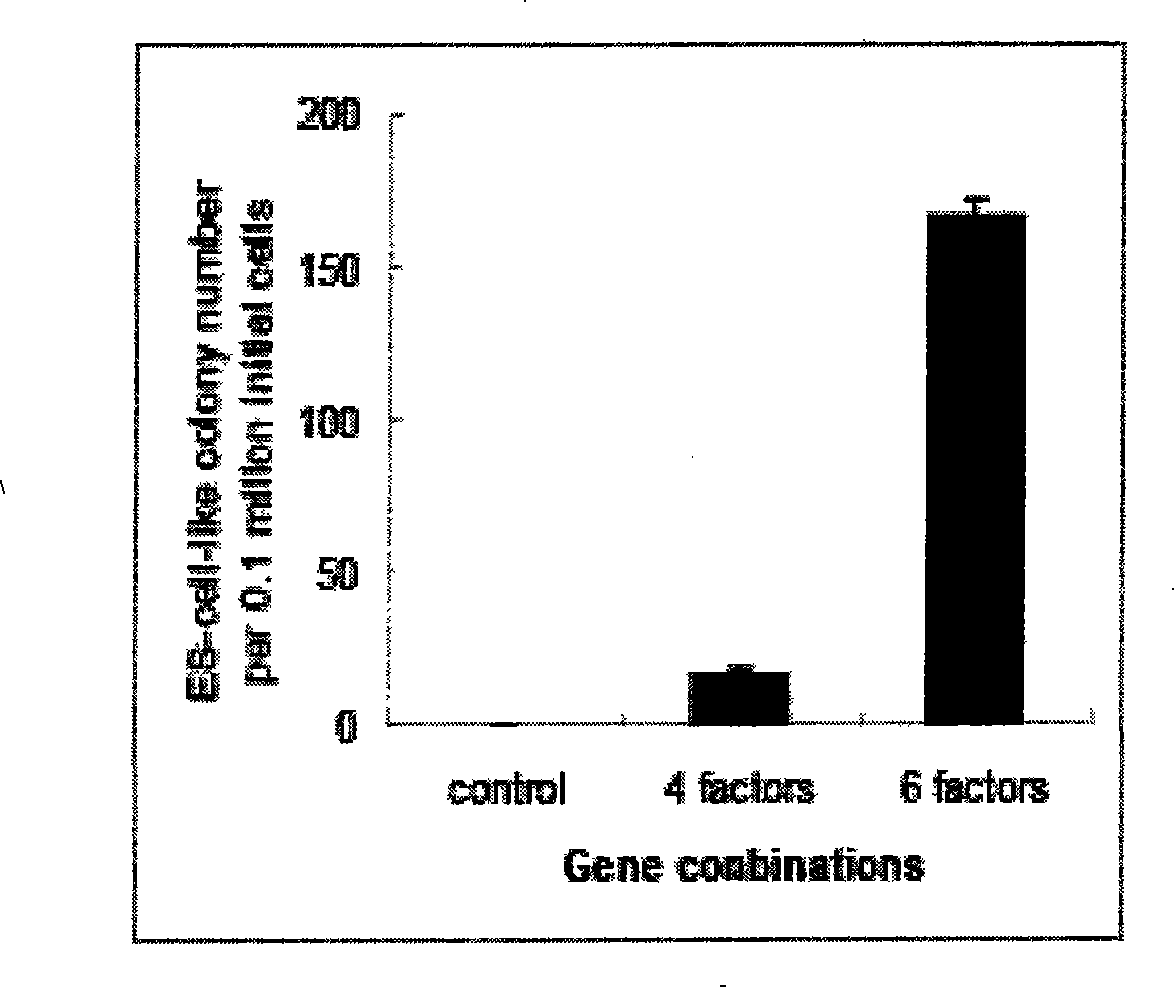
The invention provides a method for preparing induced embryonic stem cells, which comprises following steps: firstly, introducing six transcription factors into adult cells, secondly, culturing the adult cells under the condition for culturing the embryonic stem cells, and enabling the adult cells to form cells with the form of embryonic stem cells. The method of the invention also comprises: cloning the six transcription factors into a carrier and then transforming the six transcription factors into the adult cells. When the method of the invention is adopted to prepare the embryonic stem cells, the efficiency is high, the acute rejection can be avoided, the embryonic stem cells can be differentiated into different tissue cells under special conditions, and the method of the invention has wide applying prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Tissue material and matrix
InactiveUS20060153797A1Organic active ingredientsNervous disorderCell-Extracellular MatrixTissue material
The present invention relates generally to a tissue preparation including tissue cells and extracts thereof useful for promoting or facilitating the growth, development and differentiation of cells and tissues. More particularly, the present invention provides muscle-derived material comprising intact or extracted extracellular matrix and / or cells as well as cytokines, growth factors and other components. The muscle preparations of the present invention resemble basement membrane and are derived from cellular-based material. The muscle preparation may be used in vitro or in vivo as inter alia, a cellular scaffold in various tissue engineering applications and in other cell culture systems for nurturing and enriching a range of cell types including, but not limited to, precursor and stem cells such as pre-adipogenic cells. The muscle preparation is also useful as a base for creams, such as in the cosmetic and topical therapeutic industries and as a matrix or additive in the food industry.
Owner:VICTORIAN TISSUE ENG CENT
Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles Based on Iron Oxides with Modified Surface, Method of Their Preparation and Application
InactiveUS20090309597A1Less loadImprove abilitiesPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyArginineDextran
The subject of the invention is superparamagnetic nanoparticle probes based on iron oxides, to advantage magnetite or maghemite, with modified surface, coated with mono-, di- or polysaccharides from the group including D-arabinose, D-glucose, D-galactose, D-mannose, lactose, maltose, dextrans and dextrins, or with amino acids or poly(amino acid)s from the group including alanine, glycine, glutamine, asparagine, histidine, arginine, L-lysine, aspartic and glutamic acid or with synthetic polymers based on (meth)acrylic acid and their derivatives selected from the group containing poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide), poly(N,N-dimethylmethacrylamide), poly(N,N-diethylacrylamide), poly(N,N-diethylmethacrylamide), poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), poly(N-isopropylmethacrylamide), which form a colloid consisting of particles with narrow distribution with polydispersity index smaller than 1.3, the average size of which amounts to 0.5-30 nm, to advantage 1-10 nm, the iron content is 70-99.9 wt. %, to advantage 90 wt. %, the modification agent content 0.1-30 wt. %, to advantage 10 wt. %.The particles of size smaller than 2 nm with polydispersity index smaller than 1.1 can be obtained by a modified method of preparation.Superparamagnetic nanoparticle probes according to the invention are prepared by pre-precipitation of colloidal Fe(OH)3 by the treatment of aqueous 0.1-0.2M solution of Fe(III) salt, to advantage FeCl3, with less than an equimolar amount of NH4OH, at 21° C., under sonication, to which a solution of a Fe(II) salt, to advantage FeCl2, is added in the mole ratio Fe(III) / Fe(II)=2 under sonication and the mixture is poured into five- to tenfold, to advantage eightfold, molar excess of 0.5M NH4OH. The mixture is left aging for 0-30 min, to advantage 15 min, and then the precipitate is repeatedly, to advantage 7-10 times, magnetically separated and washed with deionized water. Then 1-3 fold amount, to advantage 1.5 fold amount, relative to the amount of magnetite, of 0.1 M aqueous solution of sodium citrate is added and then, dropwise, 1-3 fold amount, to advantage 1.5 fold amount, relative to the amount of magnetite, of 0.7 M aqueous solution of sodium hypochlorite. The precipitate is repeatedly, to advantage 7-10 times, washed with deionized water under the formation of colloidal maghemite to which, after dilution, is added dropwise, to advantage under 5-min sonication, an aqueous solution of a modification agent, in the weight ratio modification agent / iron oxide=0.1-10, to advantage 0.2 for amino acids and poly(amino acid)s and 5 for saccharides.The particles smaller than 2 nm with polydispersity index smaller than 1.1 are prepared by mixing at 21° C. 1 volume part of 10-60 wt. %, to advantage 50 wt. %, of an aqueous solution of a saccharide, disaccharide or polysaccharide, such as D-arabinose, D-glucose, D-galactose, D-mannose, lactose, maltose, dextran and dextrins, and 1 volume part of aqueous solution of a Fe(II) and Fe(III) salt, to advantage FeCl2 and FeCl3, where the molar ratio Fe(III) / Fe(II)=2. A 5-15%, to advantage 7.5%, solution of NH4OH is added until pH 12 is attained and the mixture is heated at 60° C. for 15 min. The mixture is then sonicated at 350 W for 5 min and then washed for 24 h by dialysis in water using a membrane with molecular weight cut-off 14,000 until pH 7 is reached. The volume of solution is reduced by evaporation so that the final dry matter content is 50-100 mg / ml, to advantage 80 mg per 1 ml.Superparamagnetic nanoparticle probes according to the invention can be used for labelling cells used in magnetic resonance imaging for monitoring their movement, localization, survival and differentiation especially in detection of pathologies with cell dysfunction and of tissue regeneration and also for labelling and monitoring cells administered for cell therapy purposes, in particular embryonal stem cells, fetal stem cells, stem cells of an adult human including bone marrow stem cells, olfactory glial cells, fat tissue cells, in the recipient organism by magnetic resonance.The preparation of labelled cells proceeds by adding to the complete culture medium 5-20 μl, to advantage 10 μl, of a colloid containing 0.05-45 mg iron oxide per ml, to advantage 1-5 mg iron oxide per ml of the medium, and culturing the cells for a period of 1-7 days, to advantage for 1-3 days, at 37° C. and 5% of CO2.
Owner:INST OF MACROMOLECULAR CHEM ASCR V V I +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com