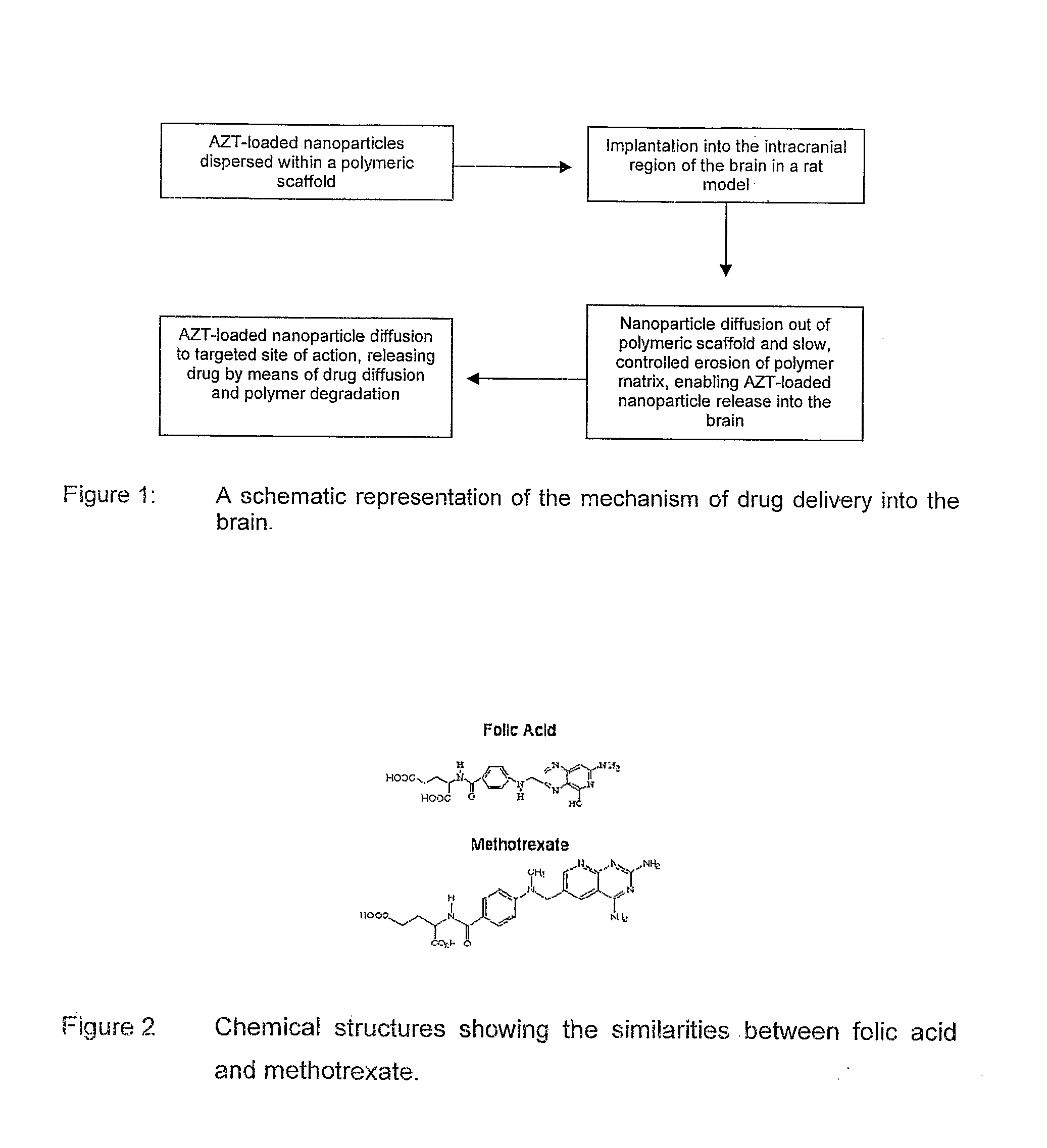
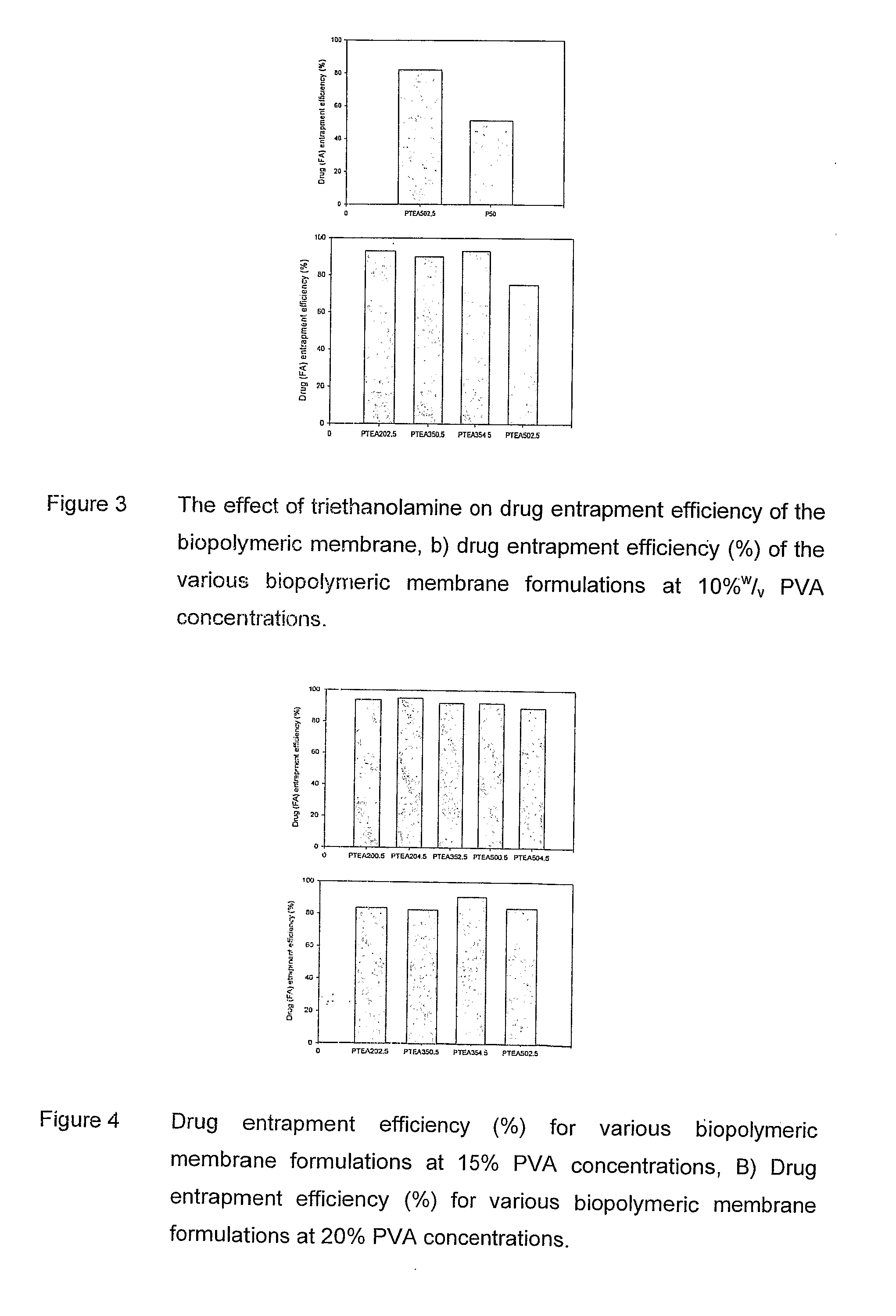
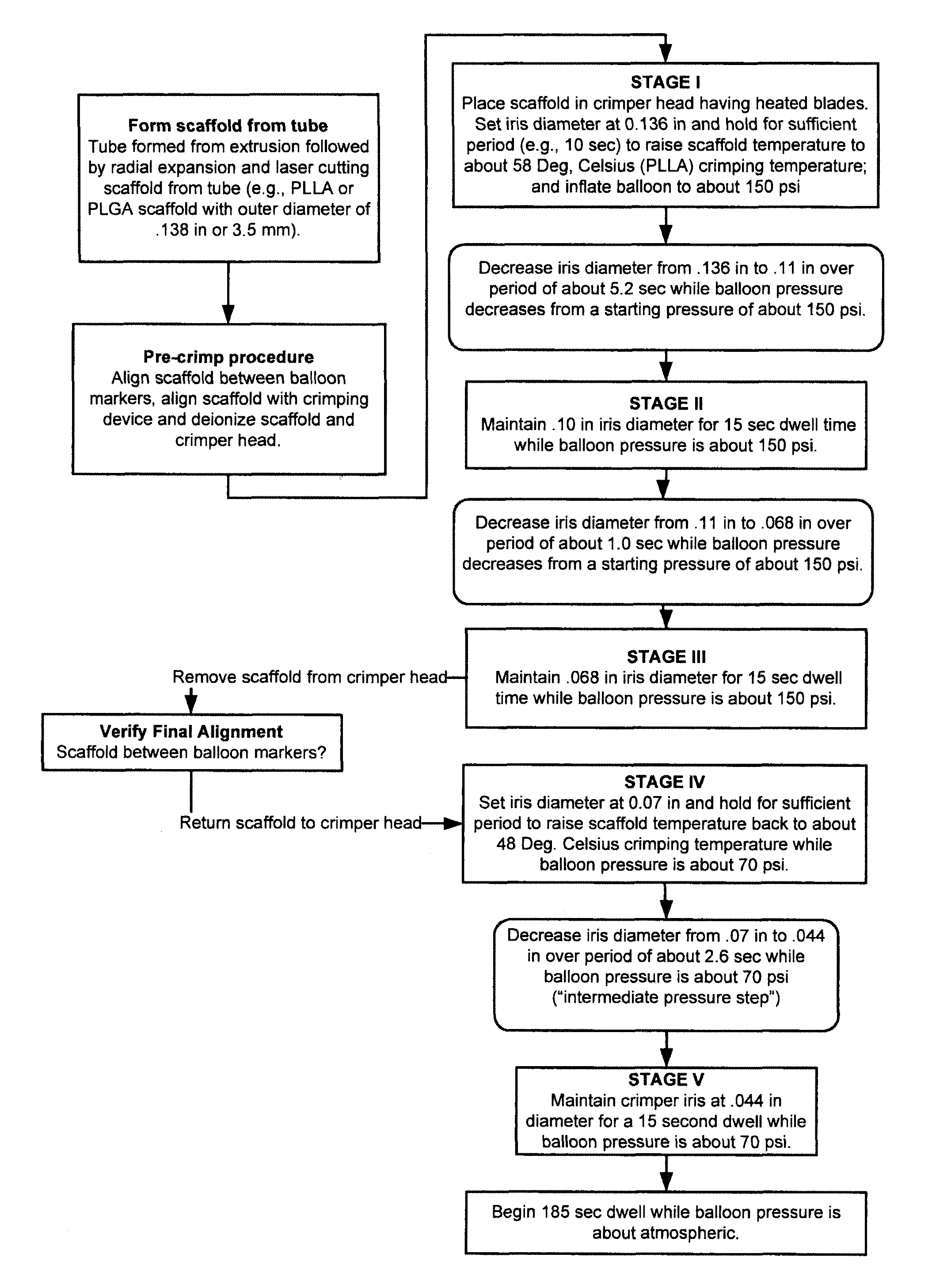
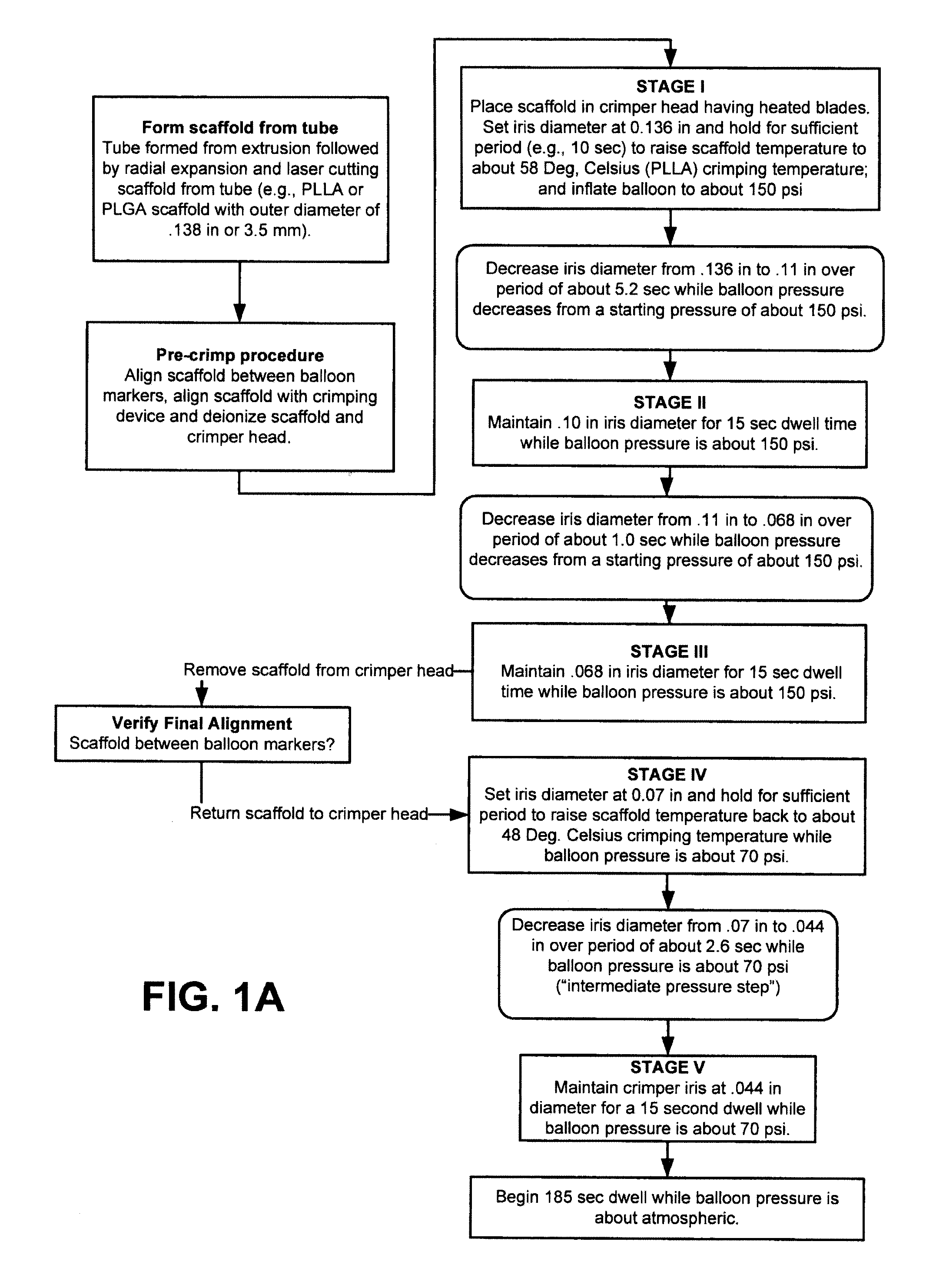
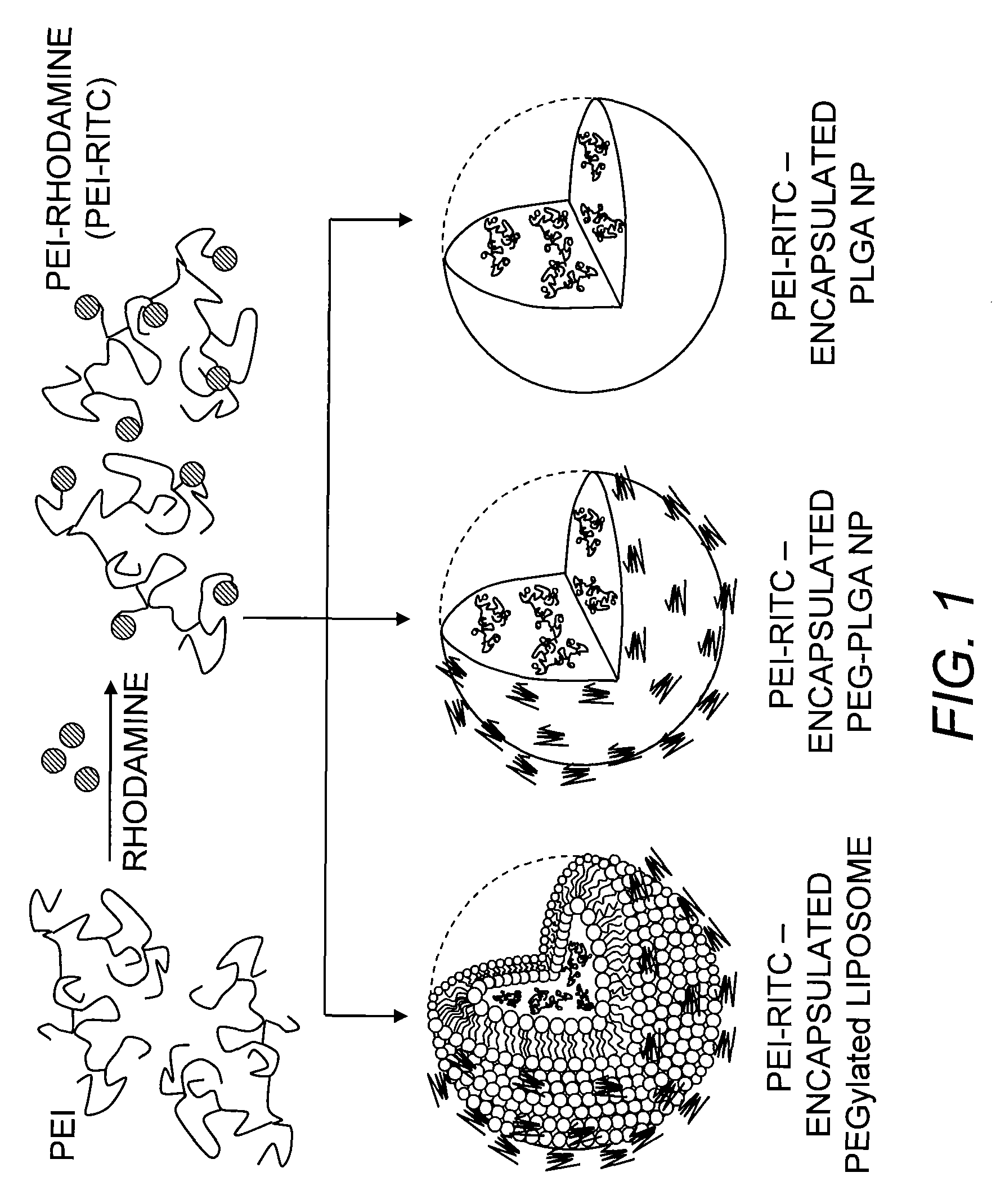
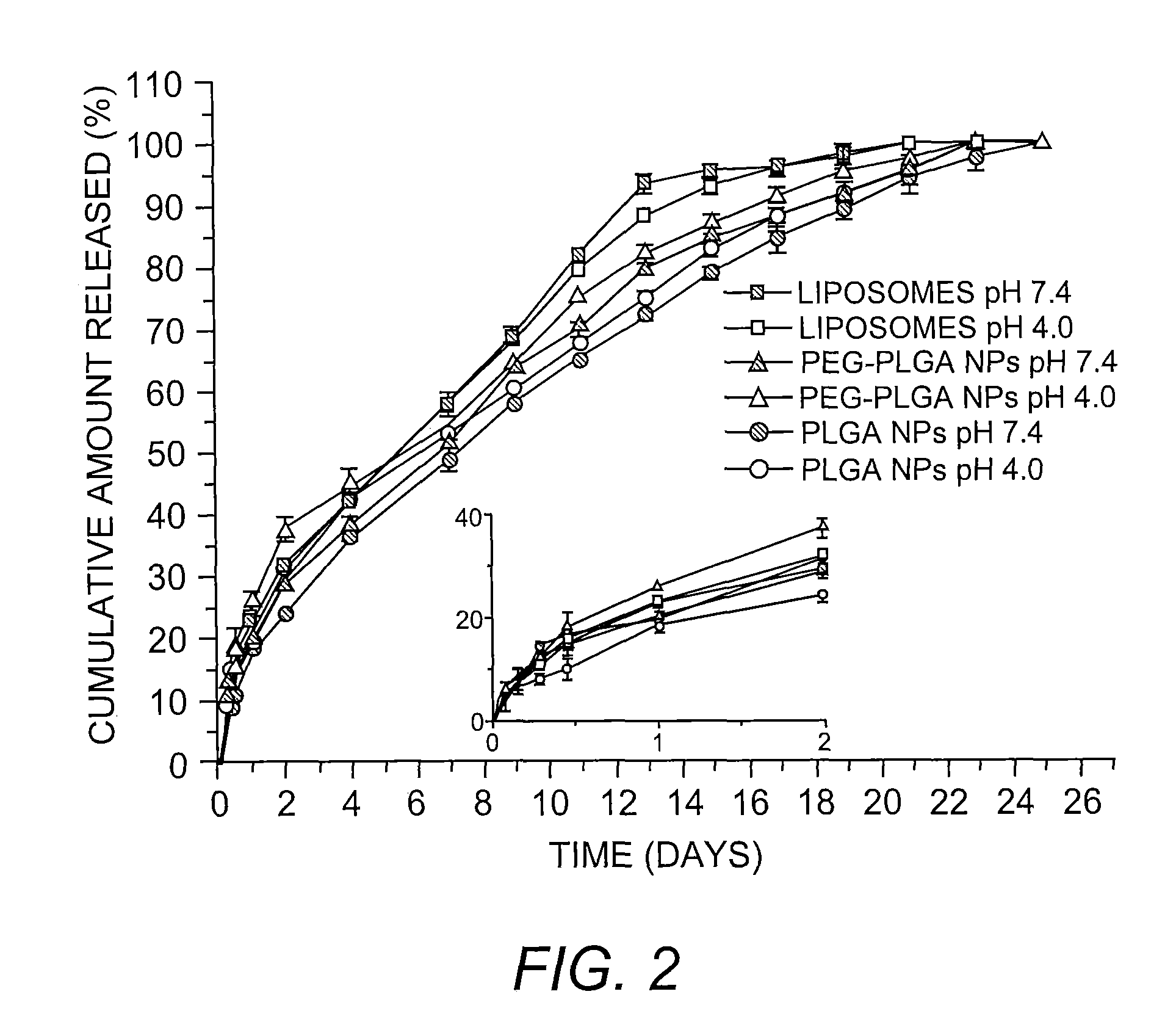
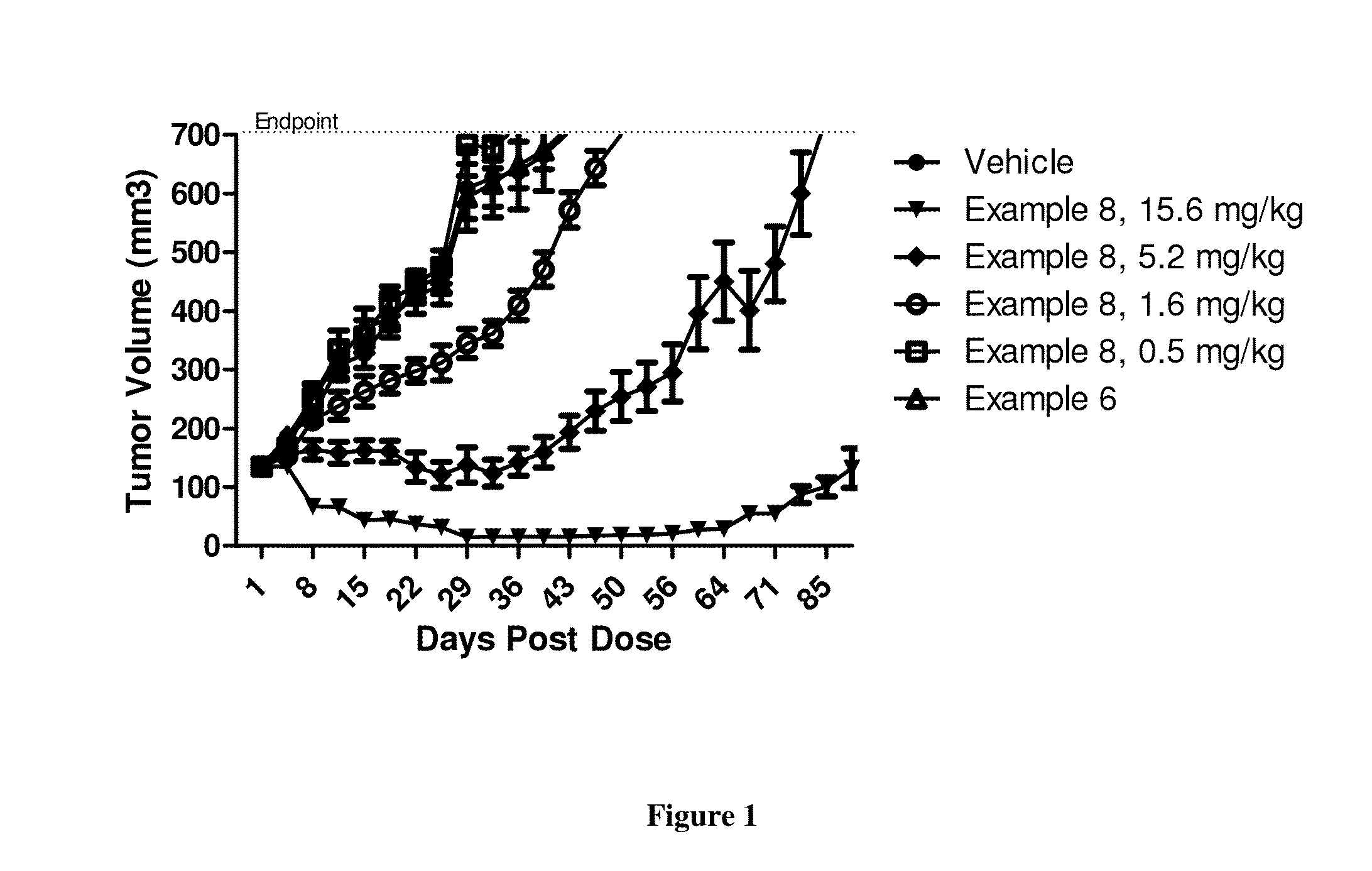
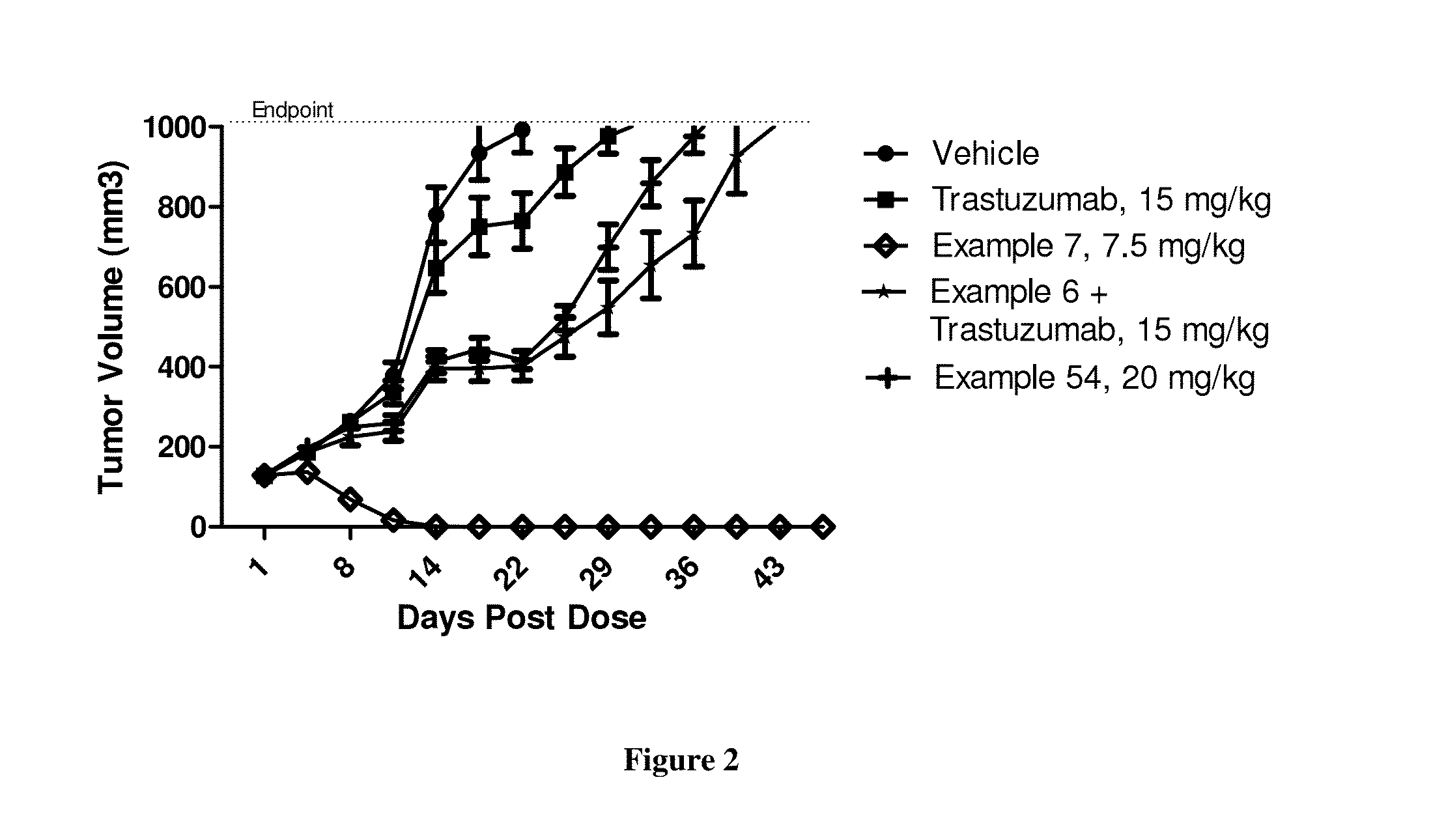
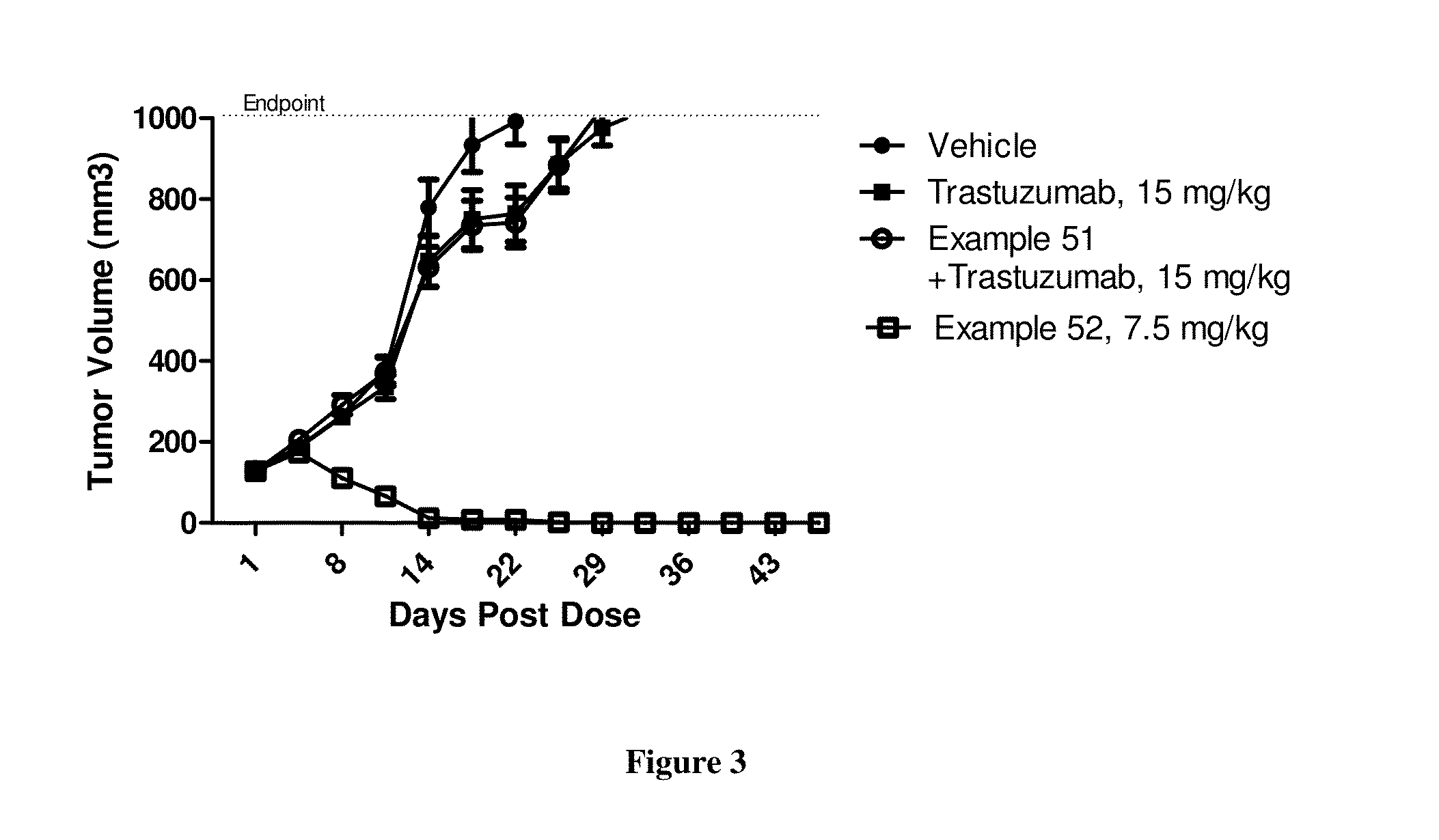
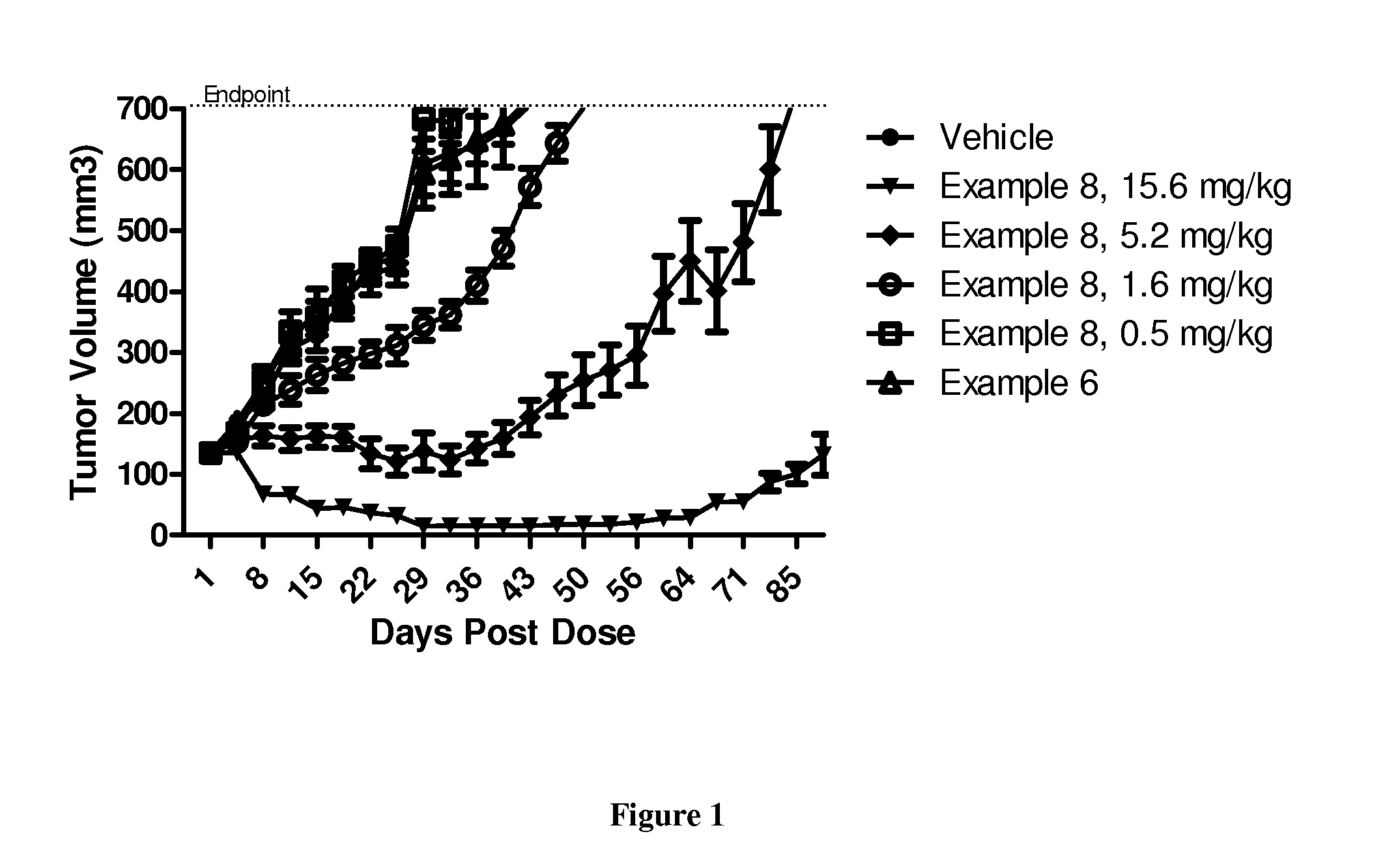
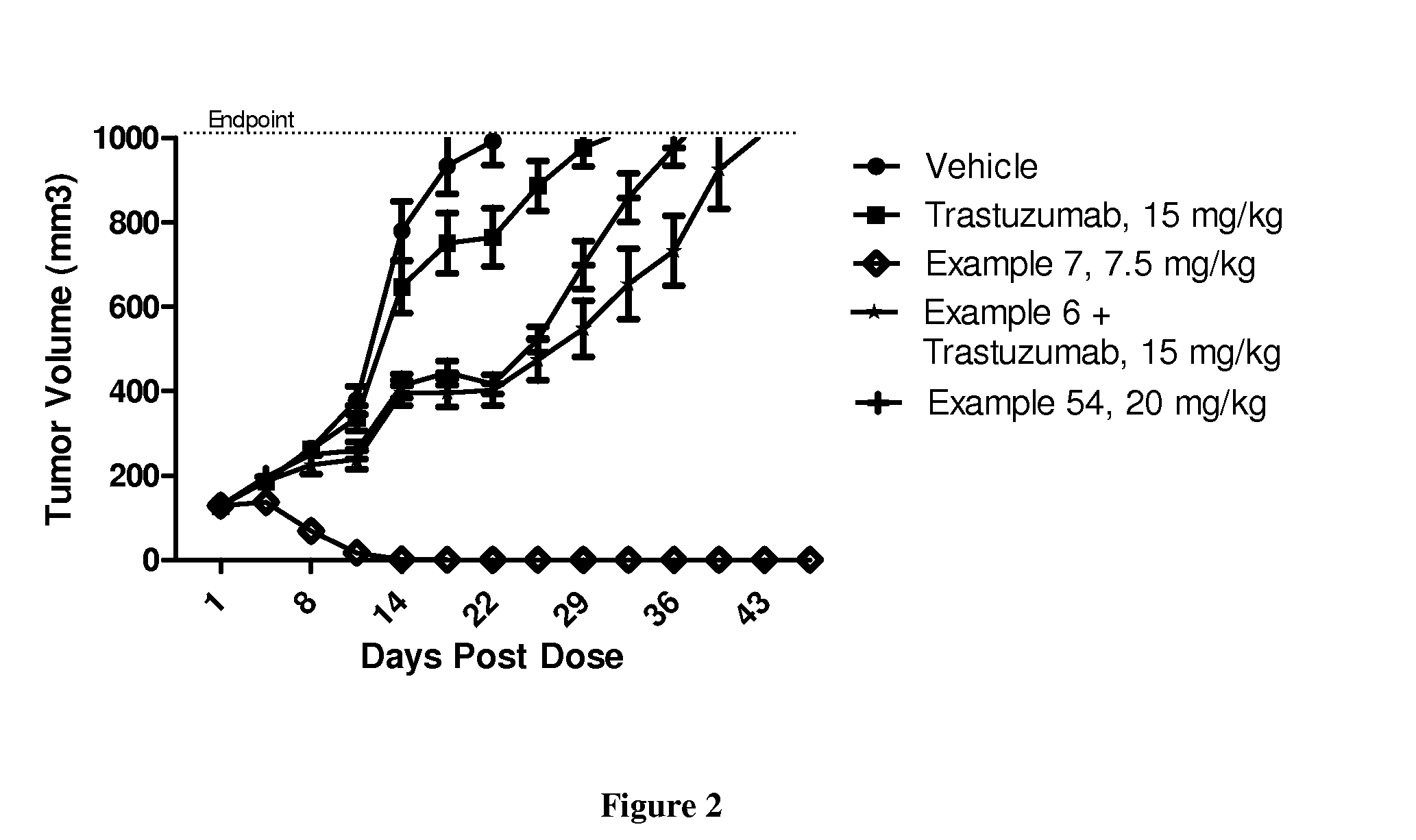
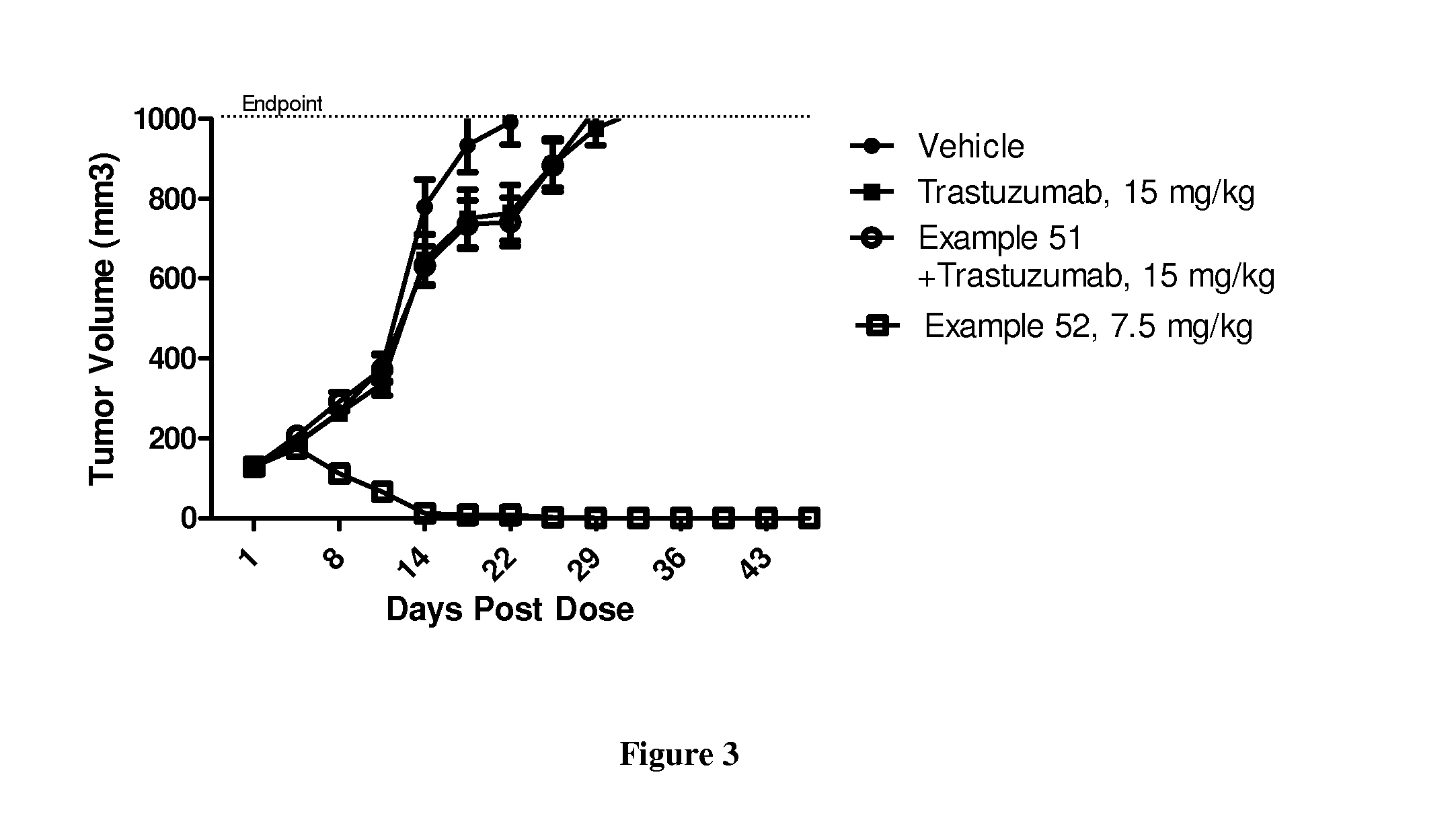
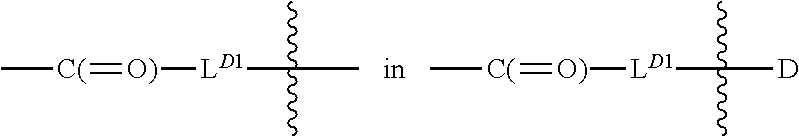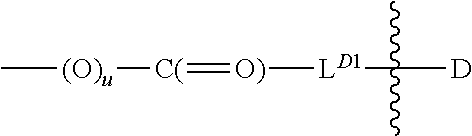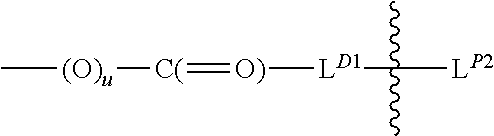Patents
Literature
63 results about "Polymeric scaffold" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Protein-Polymer-Drug Conjugates
ActiveUS20130101546A1Improve drug bioavailabilityImprove bioavailabilityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSynthetic polymeric active ingredientsDrug conjugationPharmaceutical drug
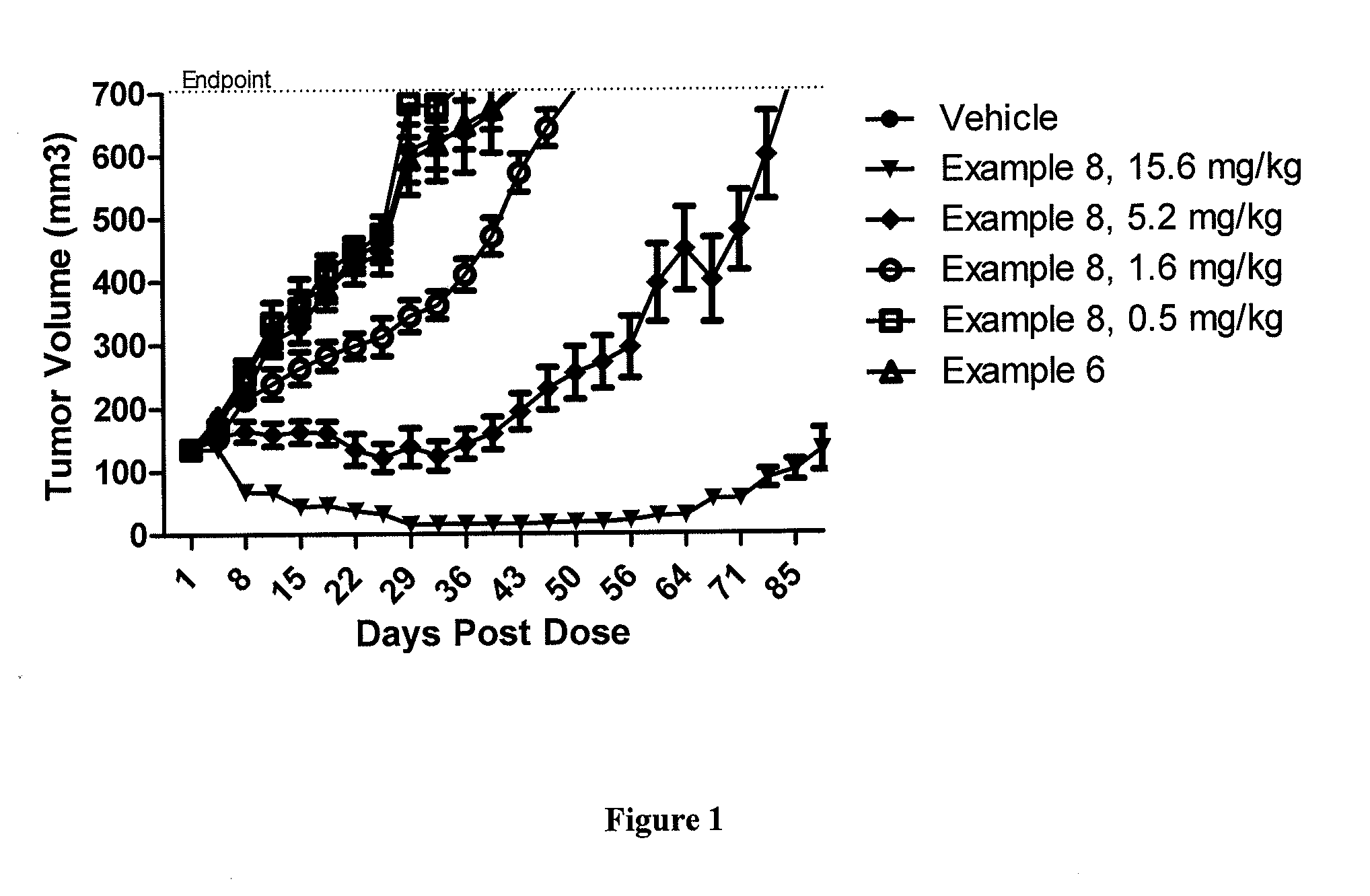
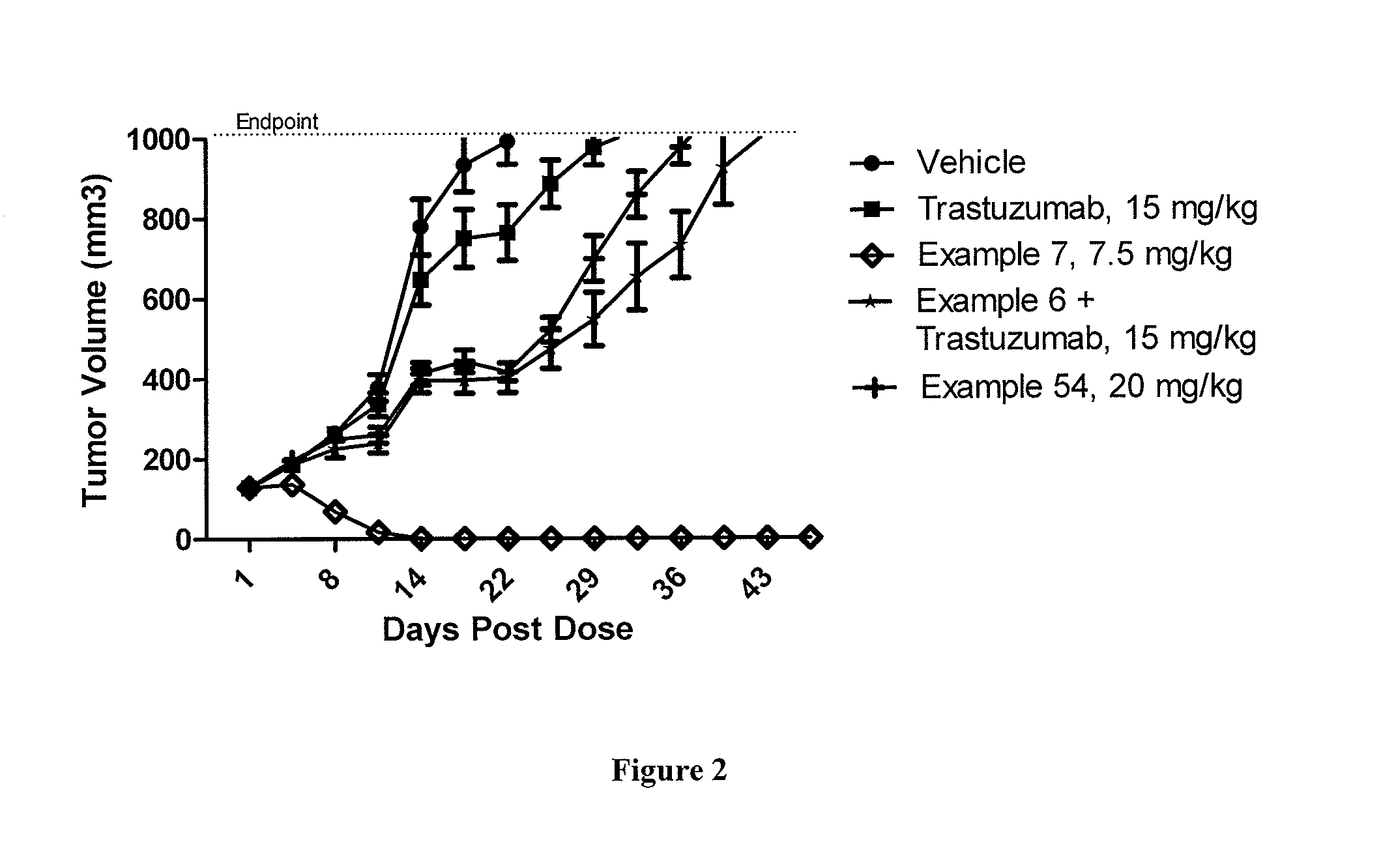
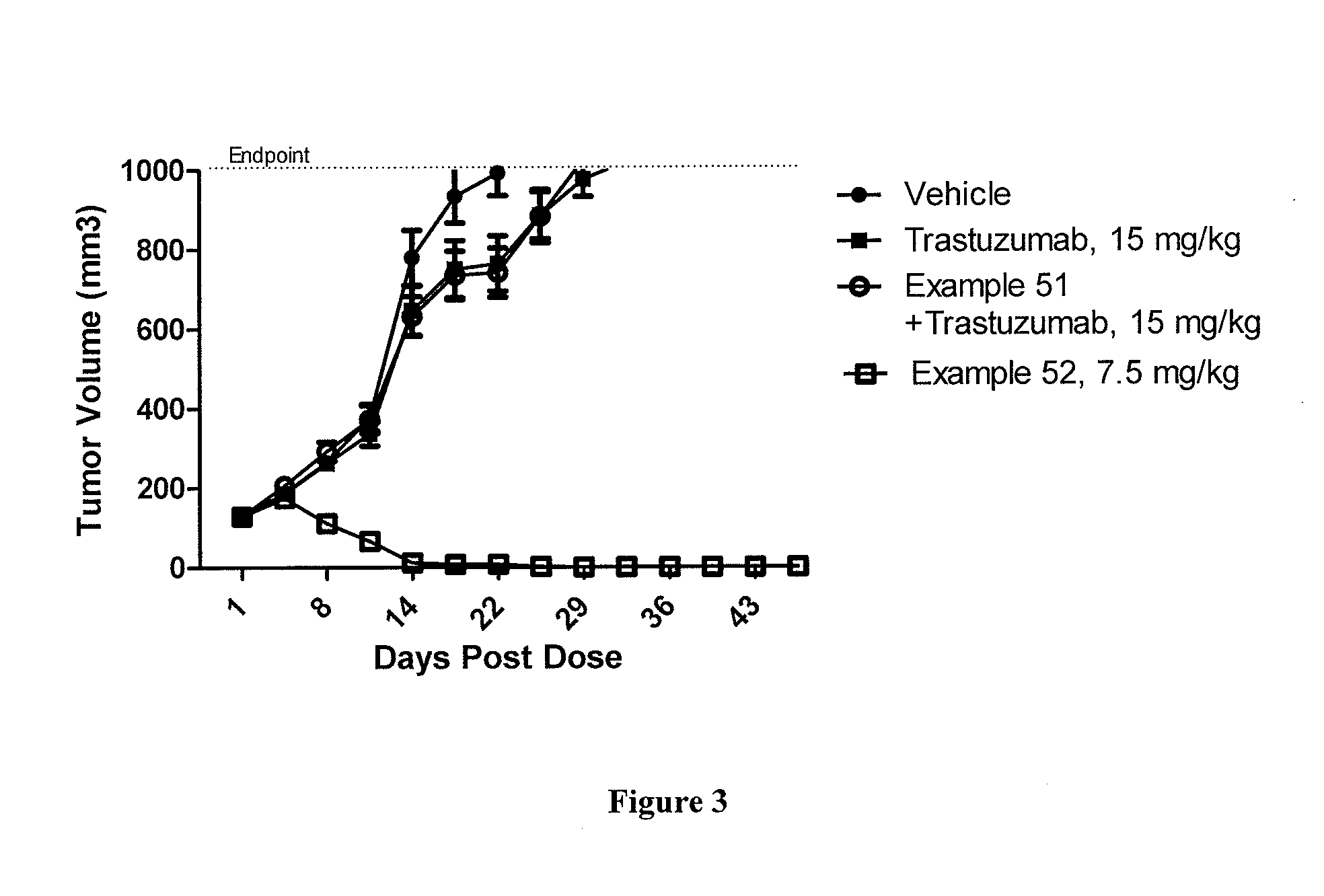
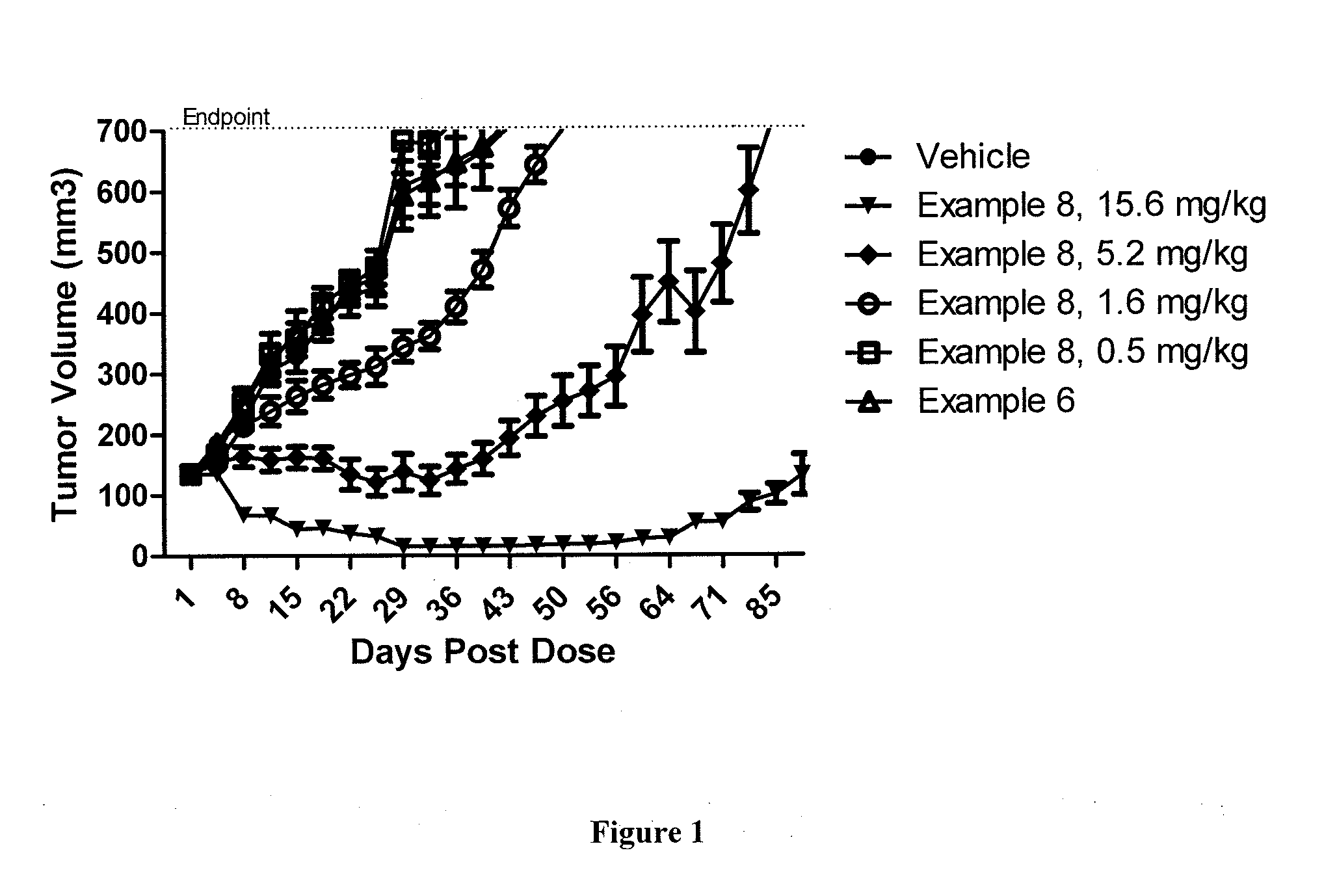
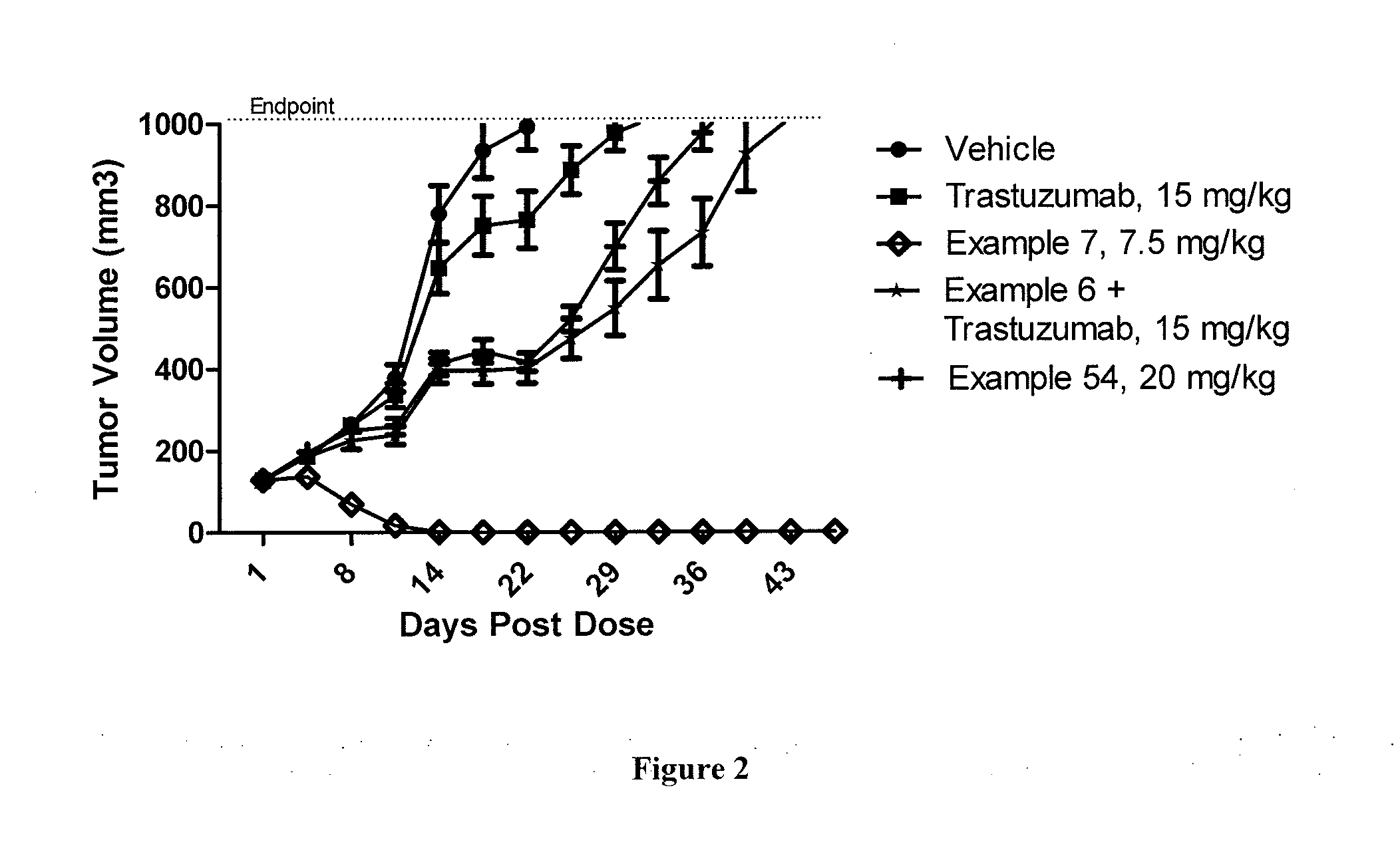
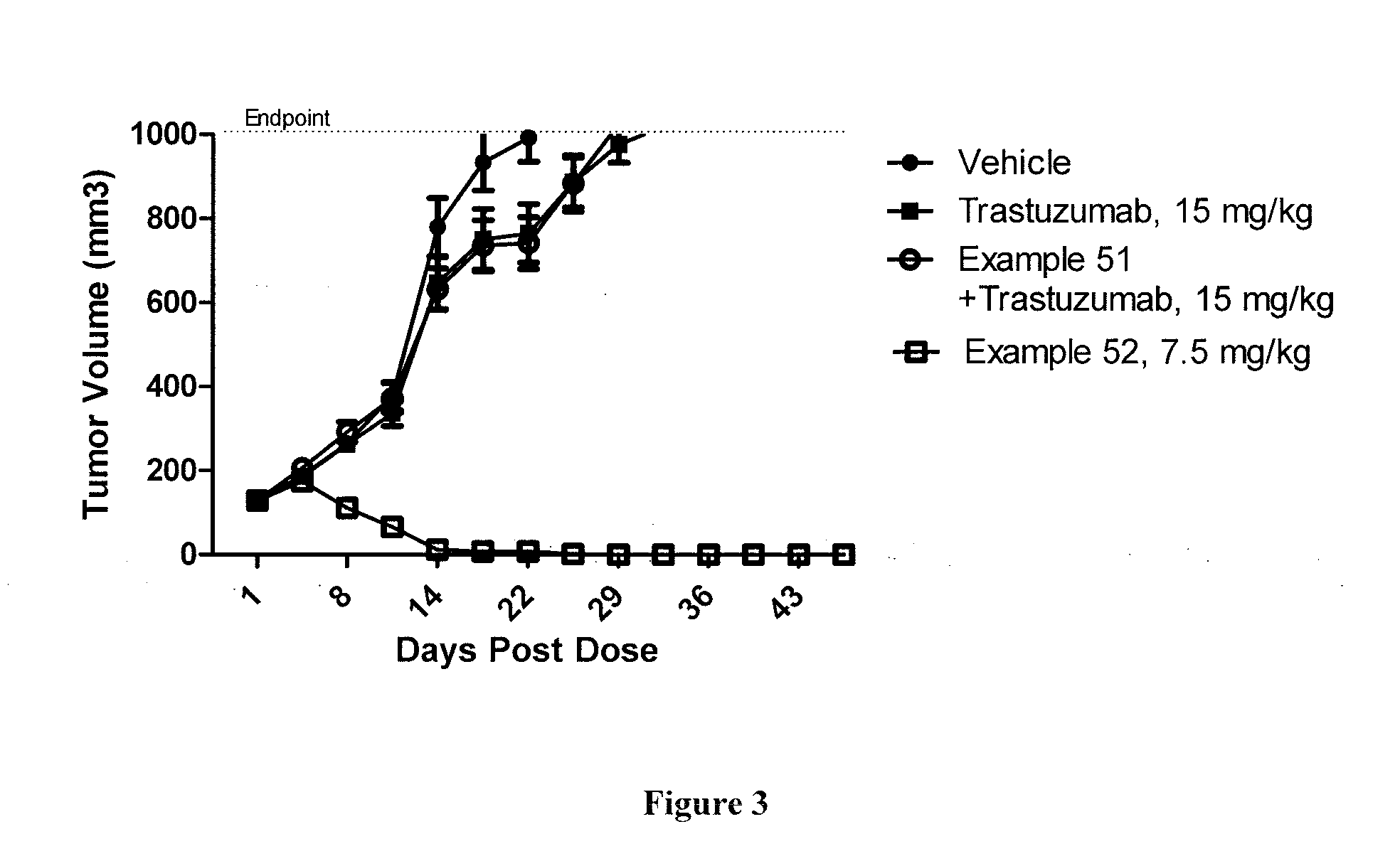
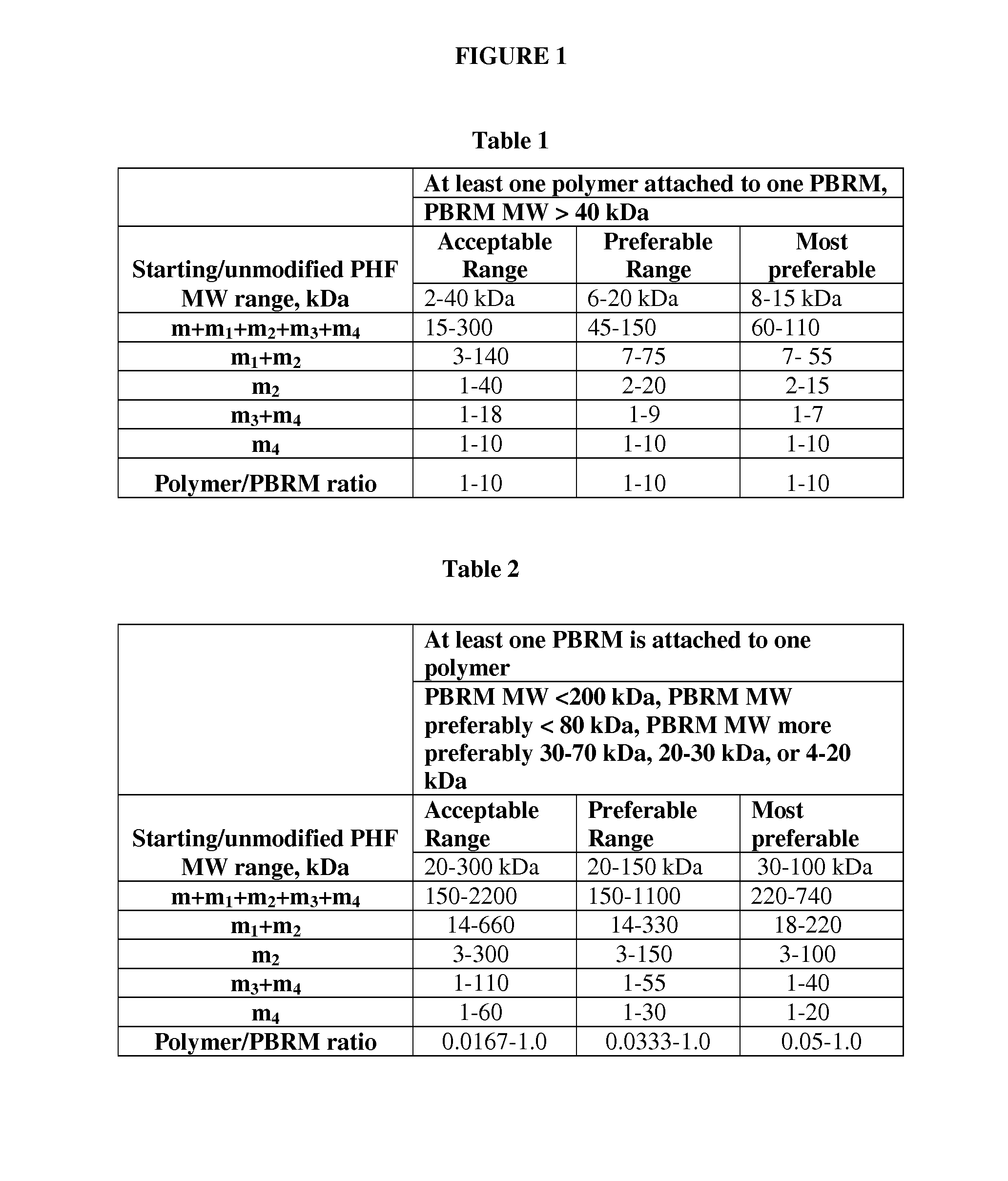
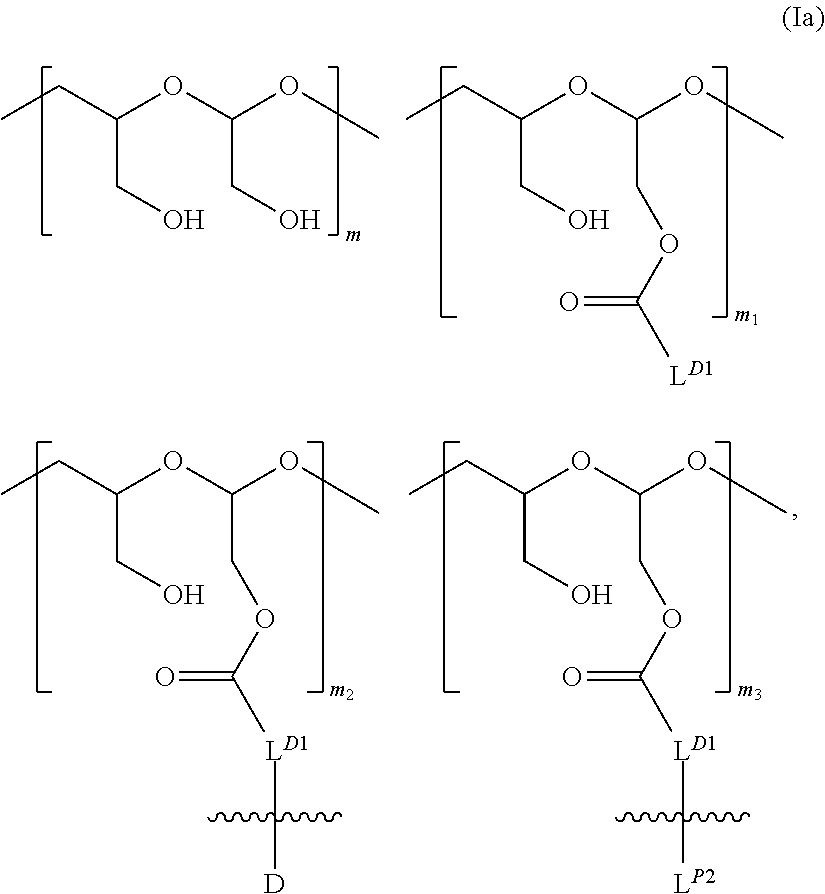
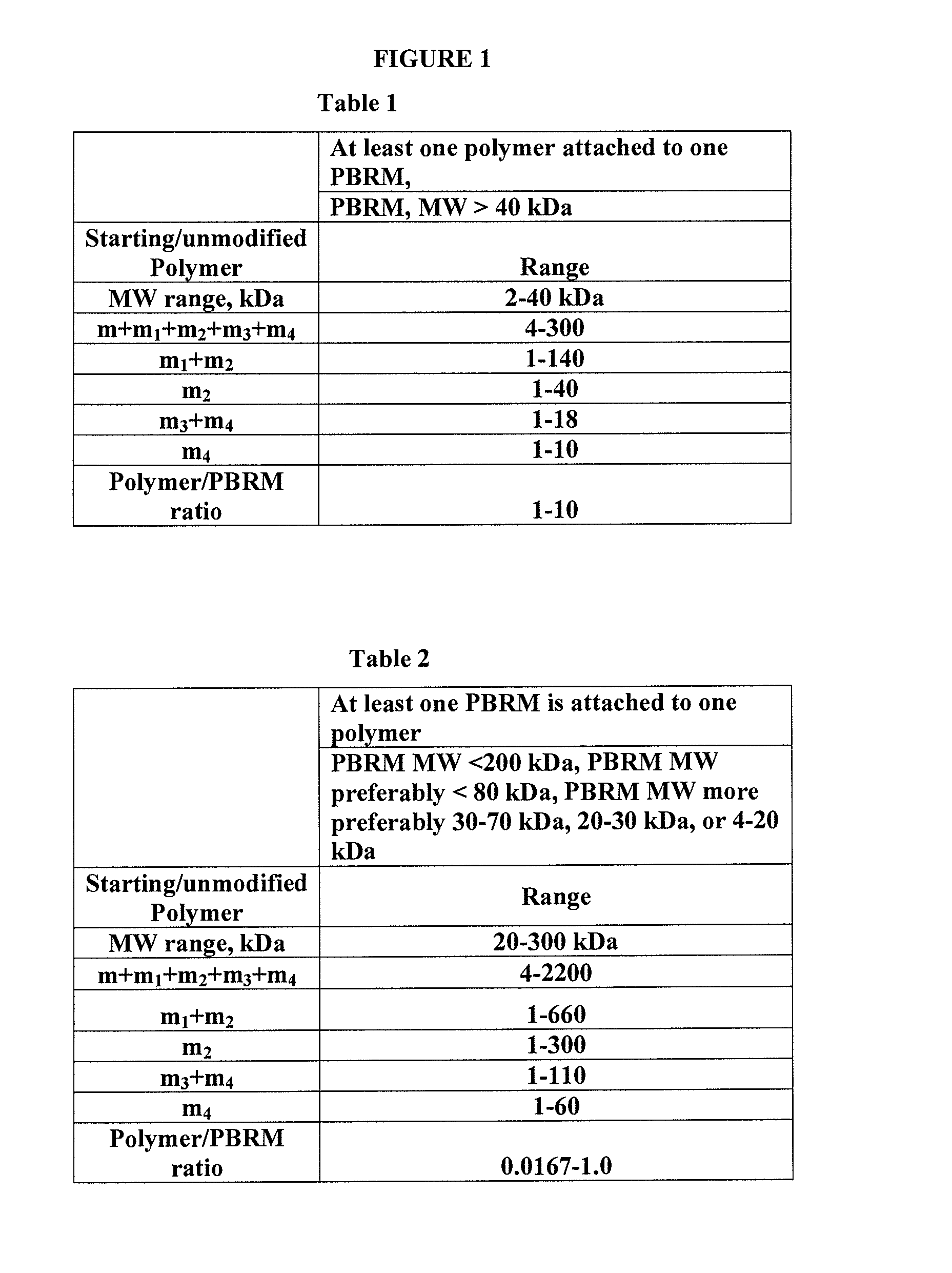
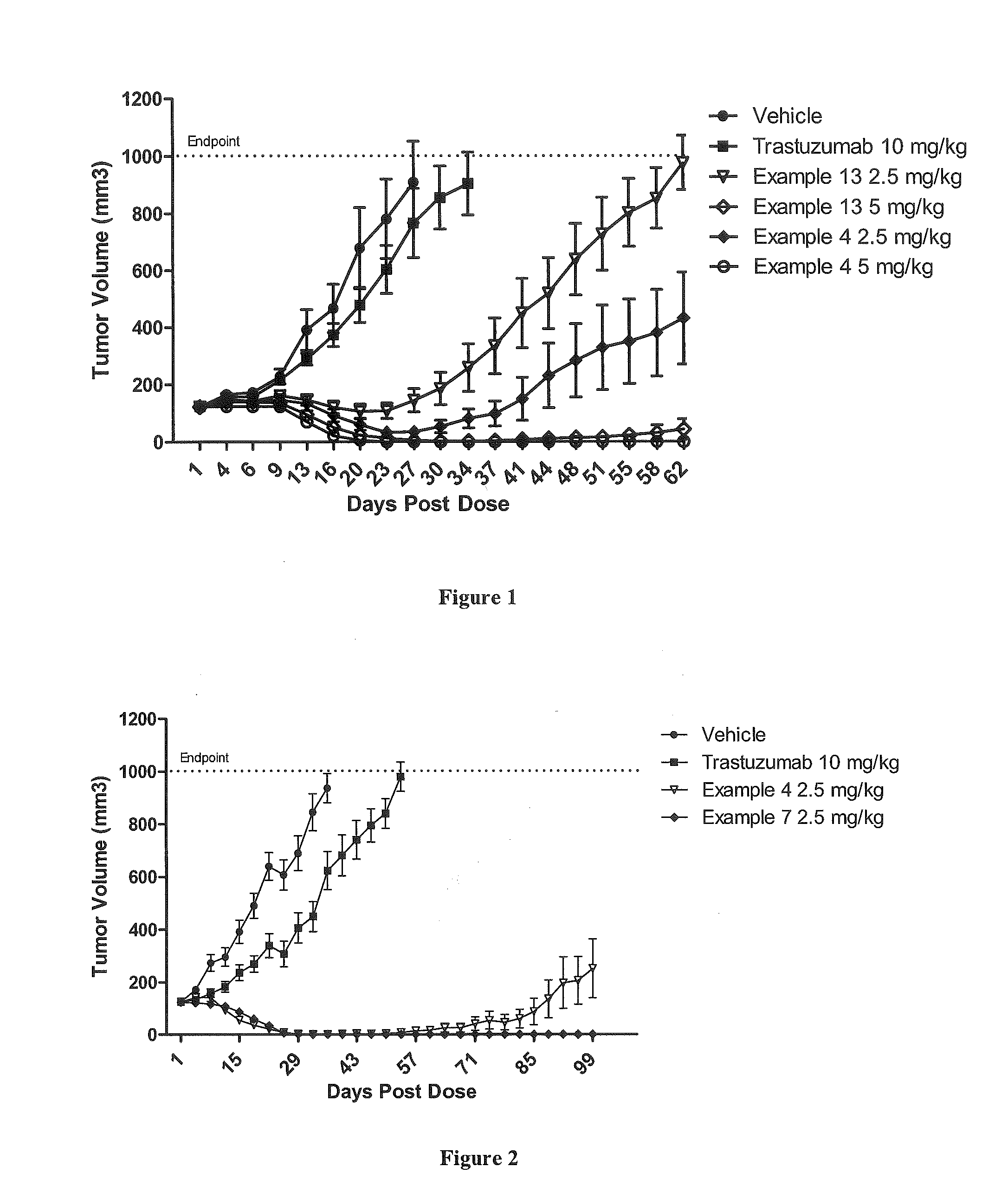
A drug conjugate is provided herein. The conjugate comprises a protein based recognition-molecule (PBRM) and a polymeric carrier substituted with one or more -LD-D, the protein based recognition-molecule being connected to the polymeric carrier by LP. Each occurrence of D is independently a therapeutic agent having a molecular weight≦5 kDa. LD and LP are linkers connecting the therapeutic agent and PBRM to the polymeric carrier respectively. Also disclosed are polymeric scaffolds useful for conjugating with a PBRM to form a polymer-drug-PBRM conjugate described herein, compositions comprising the conjugates, methods of their preparation, and methods of treating various disorders with the conjugates or their compositions.
Owner:MERSANA THERAPEUTICS INC
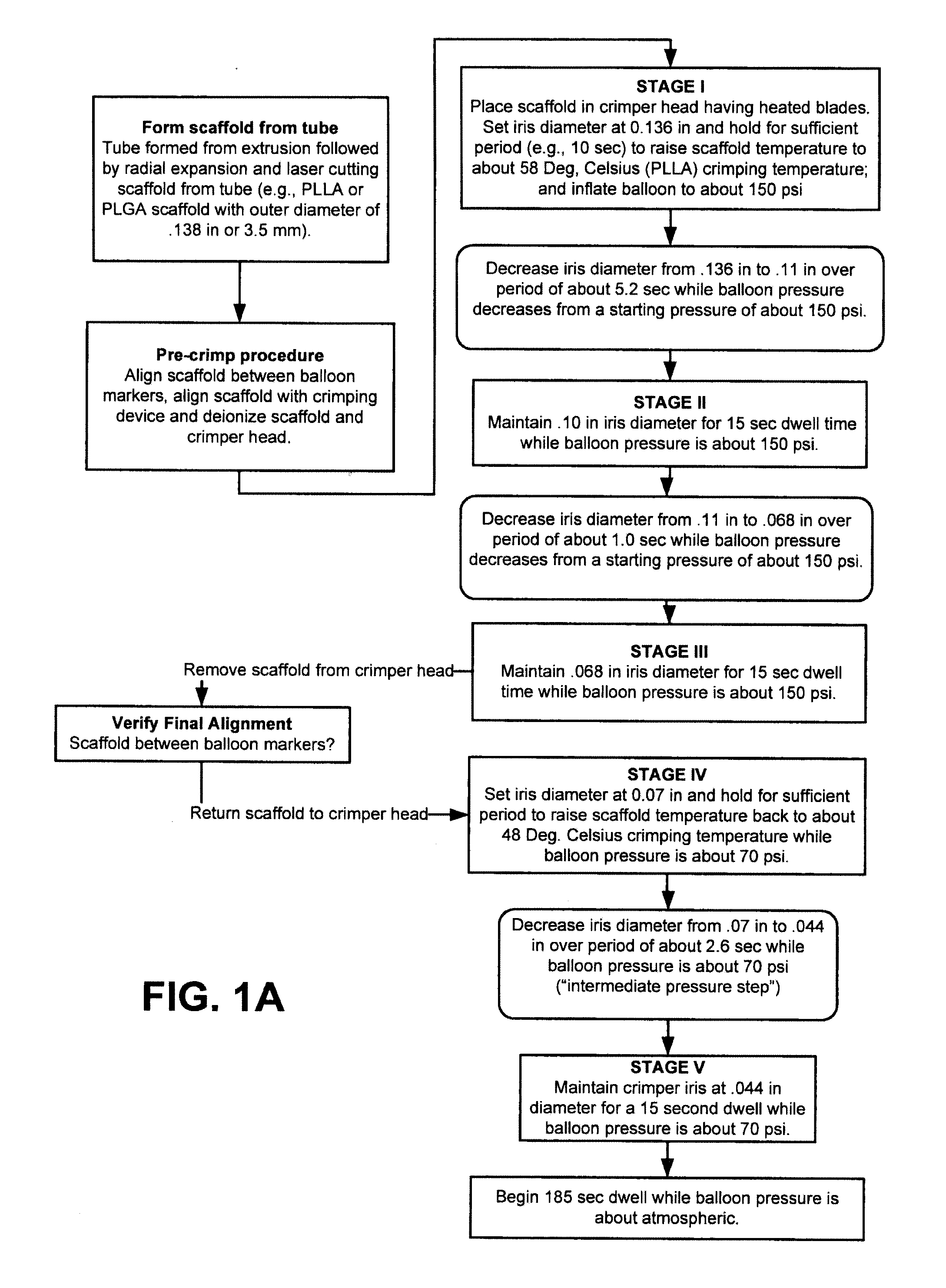
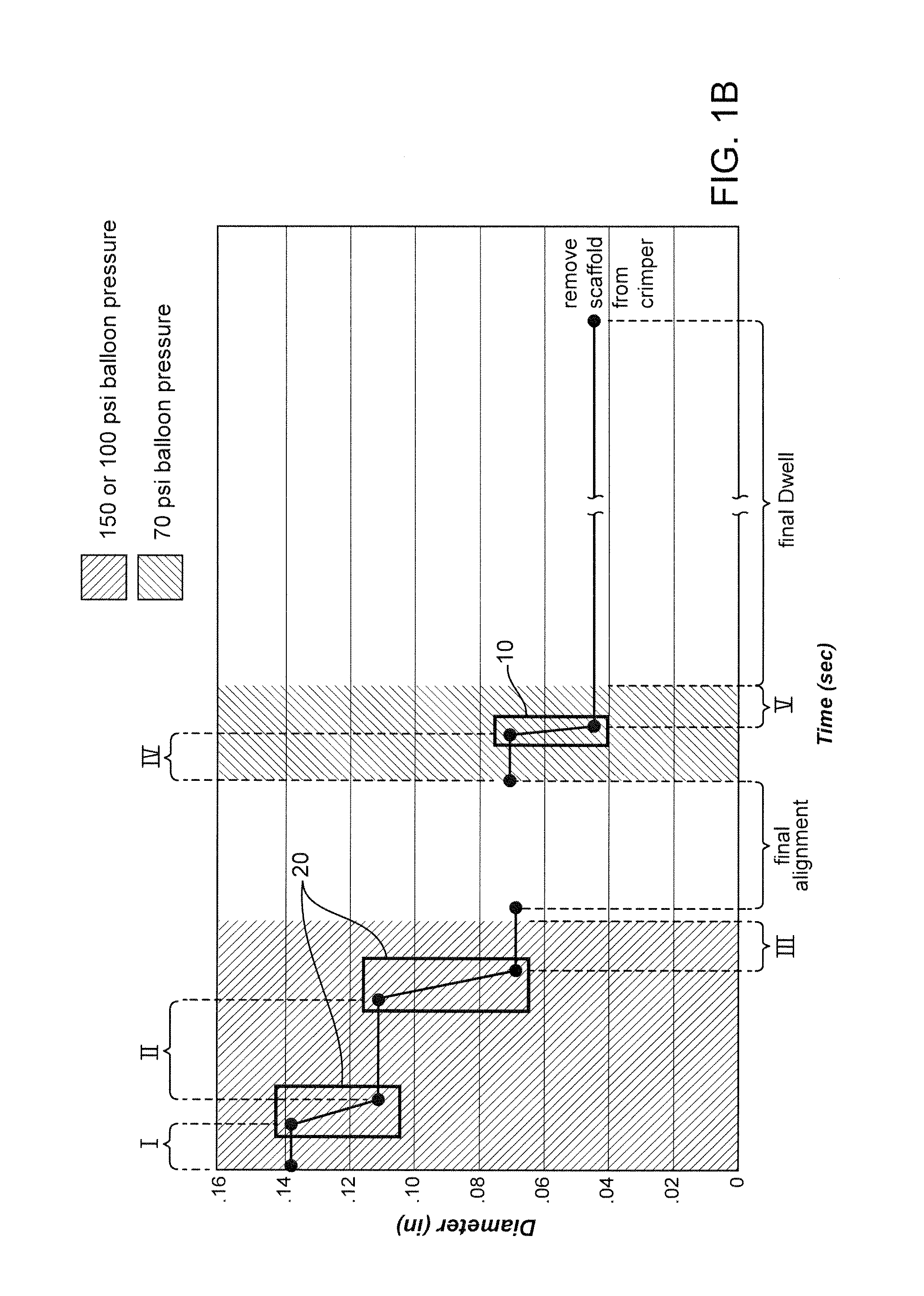
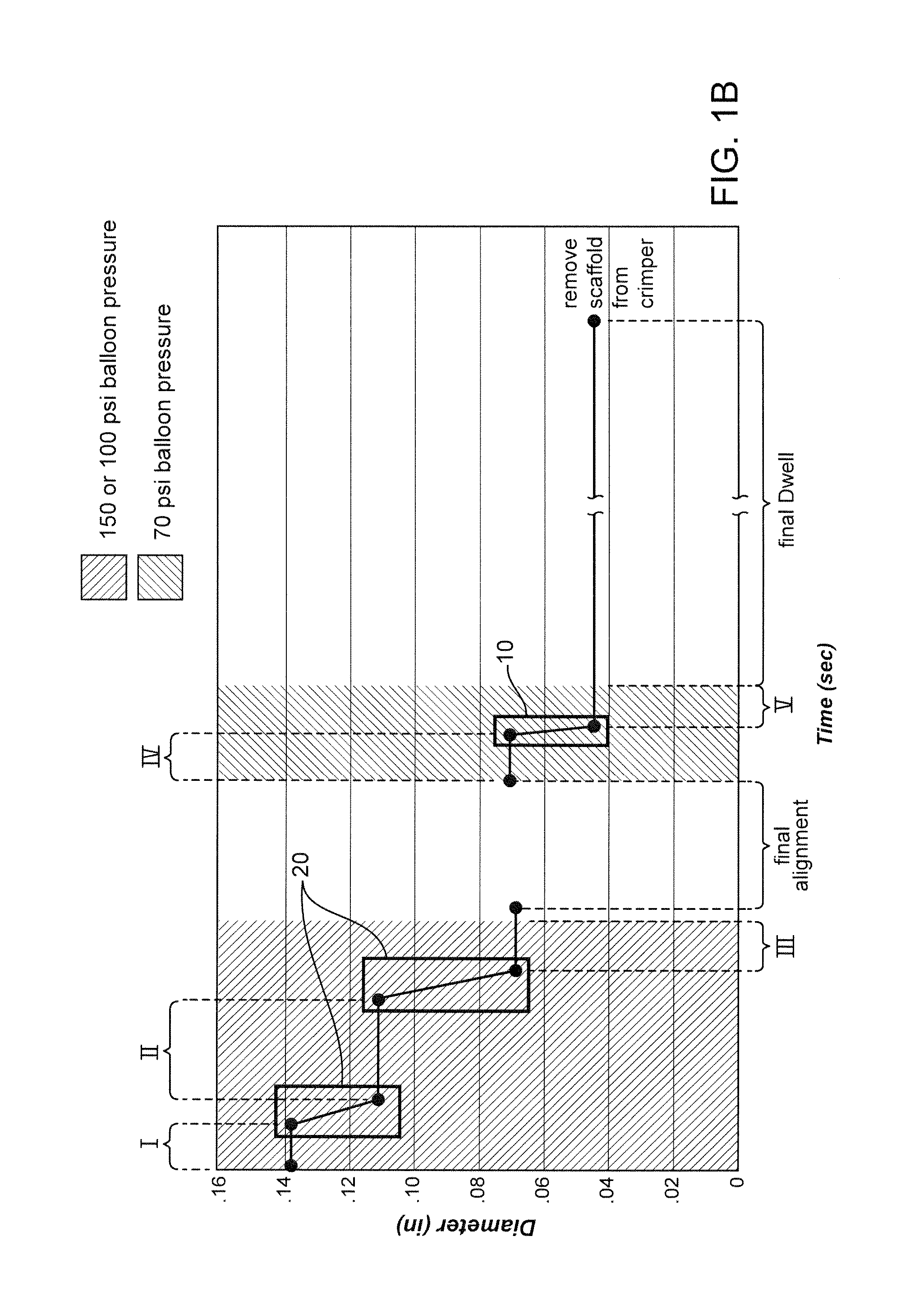
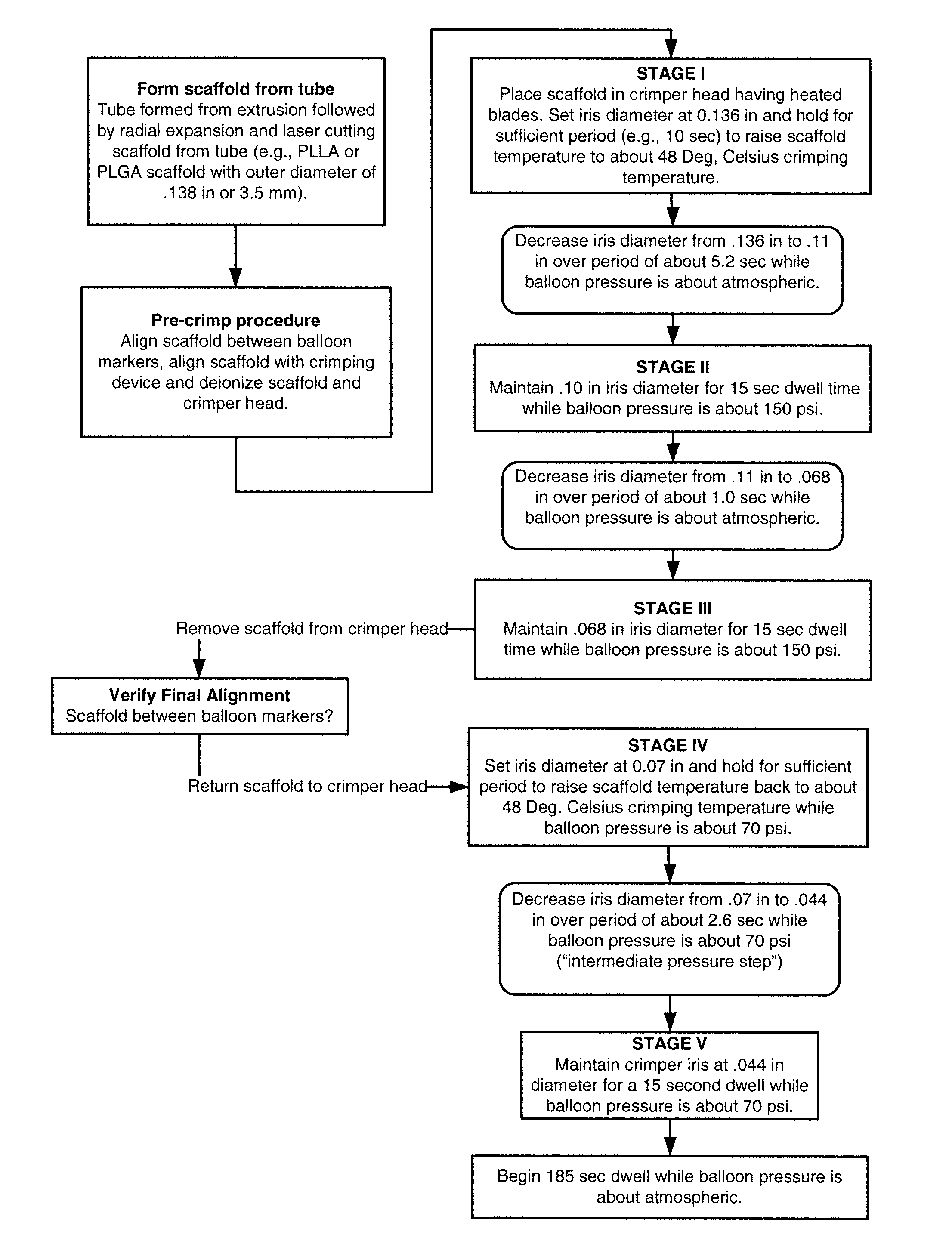
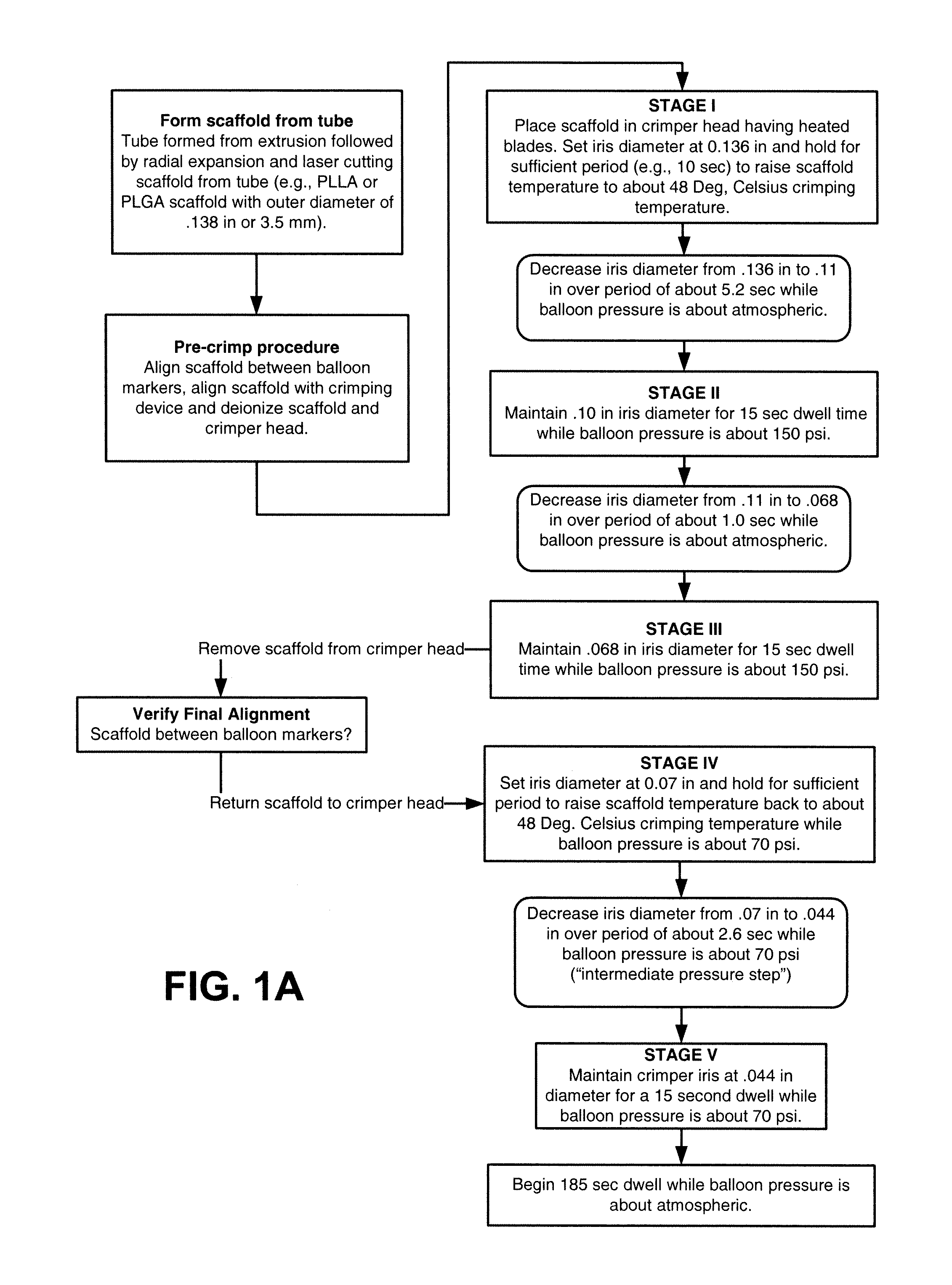
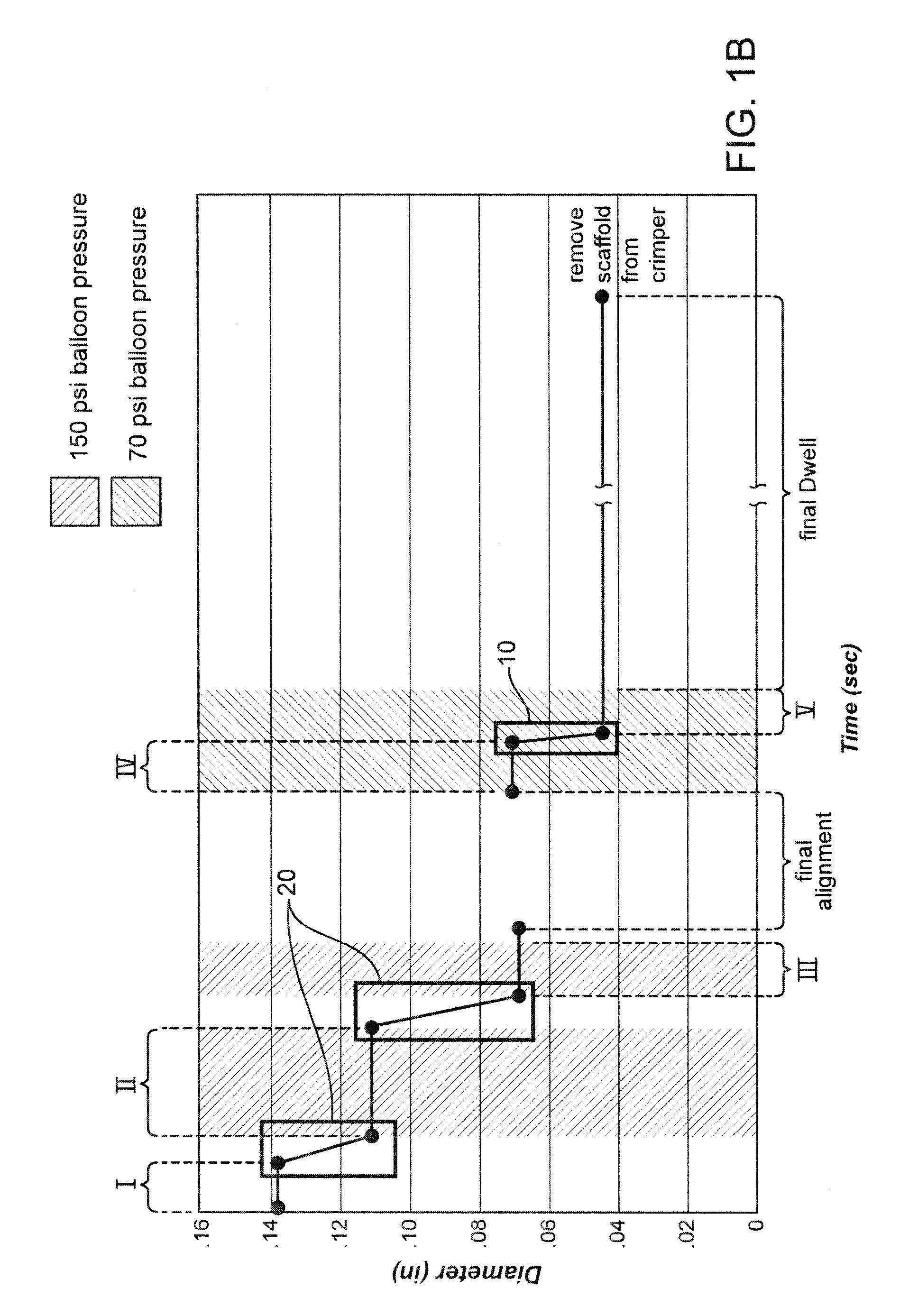
Methods for Crimping a Polymeric Scaffold to a Delivery Balloon and Achieving Stable Mechanical Properties in the Scaffold After Crimping
InactiveUS20120285609A1Reduce the overall diameterShorten the overall cycleStentsLabelling non-rigid containersVitrificationGlass transition
A medical device-includes a polymer scaffold crimped to a catheter having an expansion balloon. The scaffold is crimped to the balloon by a process that includes inflating the delivery balloon during a diameter reduction to improve scaffold retention. A crimping temperature is maintained at about the onset of glass transition of the polymer material to facilitate more rapid stabilization of mechanical properties in the scaffold following crimping.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Protein-polymer-drug conjugates
ActiveUS20150104407A1Improve drug bioavailabilityImprove bioavailabilityOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDrug conjugationPharmaceutical drug
A polymeric scaffold useful for conjugating with a protein based recognition-molecule (PBRM) to form a PBRM-polymer-drug conjugate is described herein. The scaffold includes one or more terminal maleimido groups. Also disclosed is a PBRM-polymer-drug conjugate prepared from the scaffold. Compositions comprising the conjugates, methods of their preparation, and methods of treating various disorders with the conjugates or their compositions are also described.
Owner:MERSANA THERAPEUTICS INC
Protein-Polymer-Drug Conjugates
ActiveUS20120321583A1High drug loadingImprove bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody ingredientsDrug conjugationPharmaceutical drug
A drug conjugate is provided herein. The conjugate comprises a protein based recognition-molecule (PBRM) and a polymeric carrier substituted with one or more -LD-D, the protein based recognition-molecule being connected to the polymeric carrier by LP. Each occurrence of D is independently a therapeutic agent having a molecular weight ≦5 kDa. LD and LP are linkers connecting the therapeutic agent and PBRM to the polymeric carrier respectively. Also disclosed are polymeric scaffolds useful for conjugating with a PBRM to form a polymer-drug-PBRM conjugate described herein, compositions comprising the conjugates, methods of their preparation, and methods of treating various disorders with the conjugates or their compositions.
Owner:MERSANA THERAPEUTICS INC
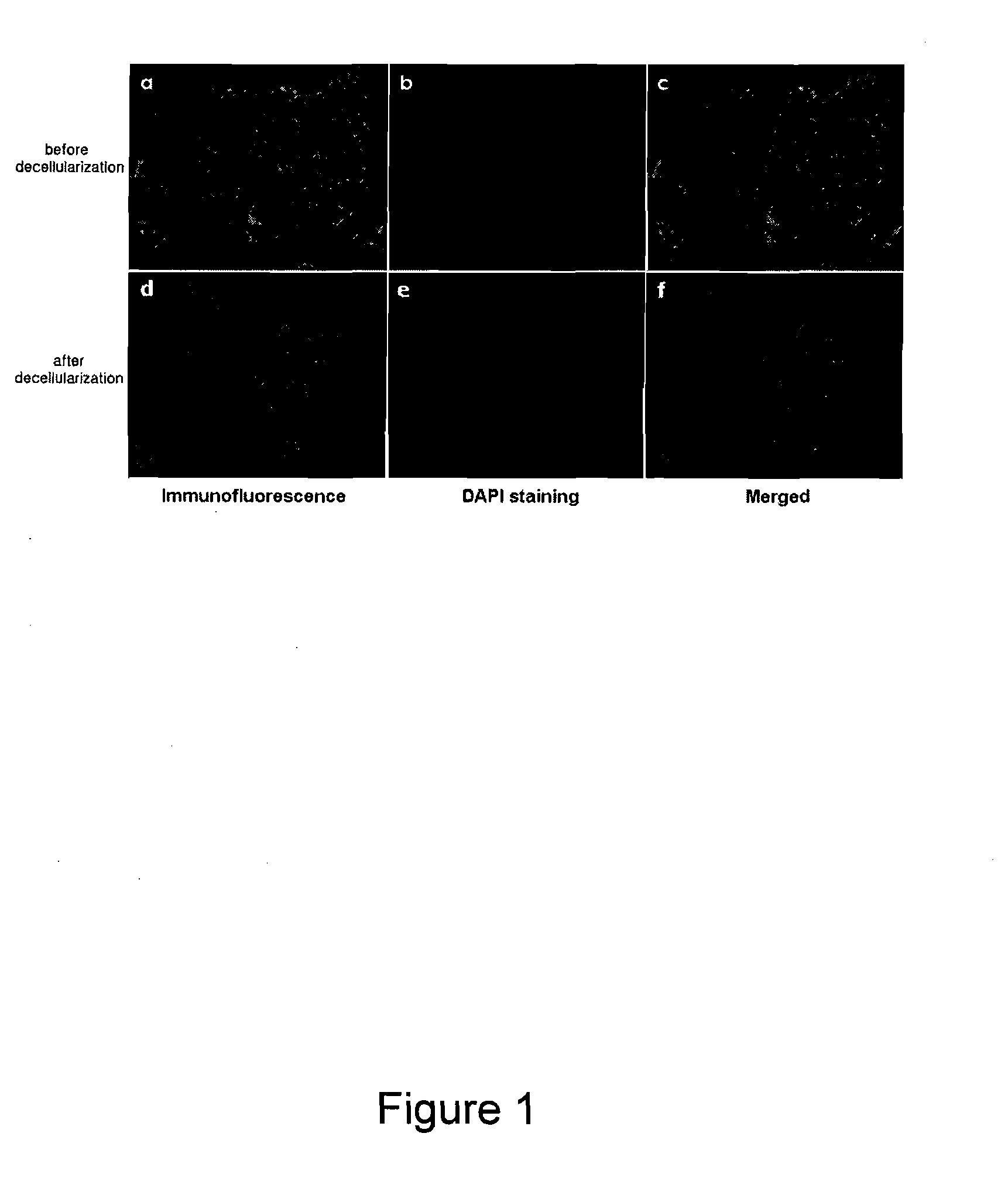
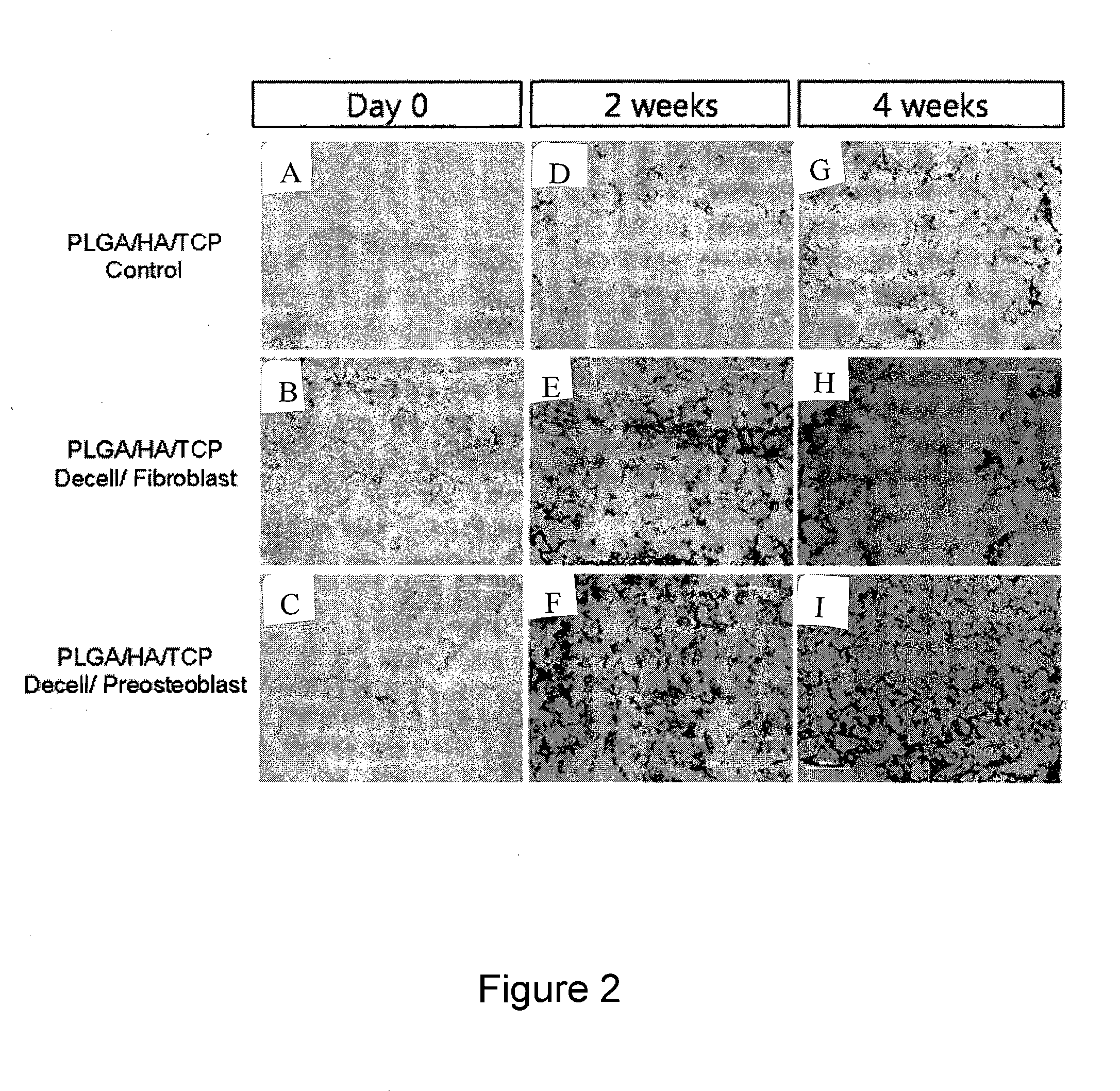
Method for Surface Modification of Polymeric Scaffold for Stem Cell Transplantation Using Decellularized Extracellular Matrix
InactiveUS20100267143A1Easy to stickArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
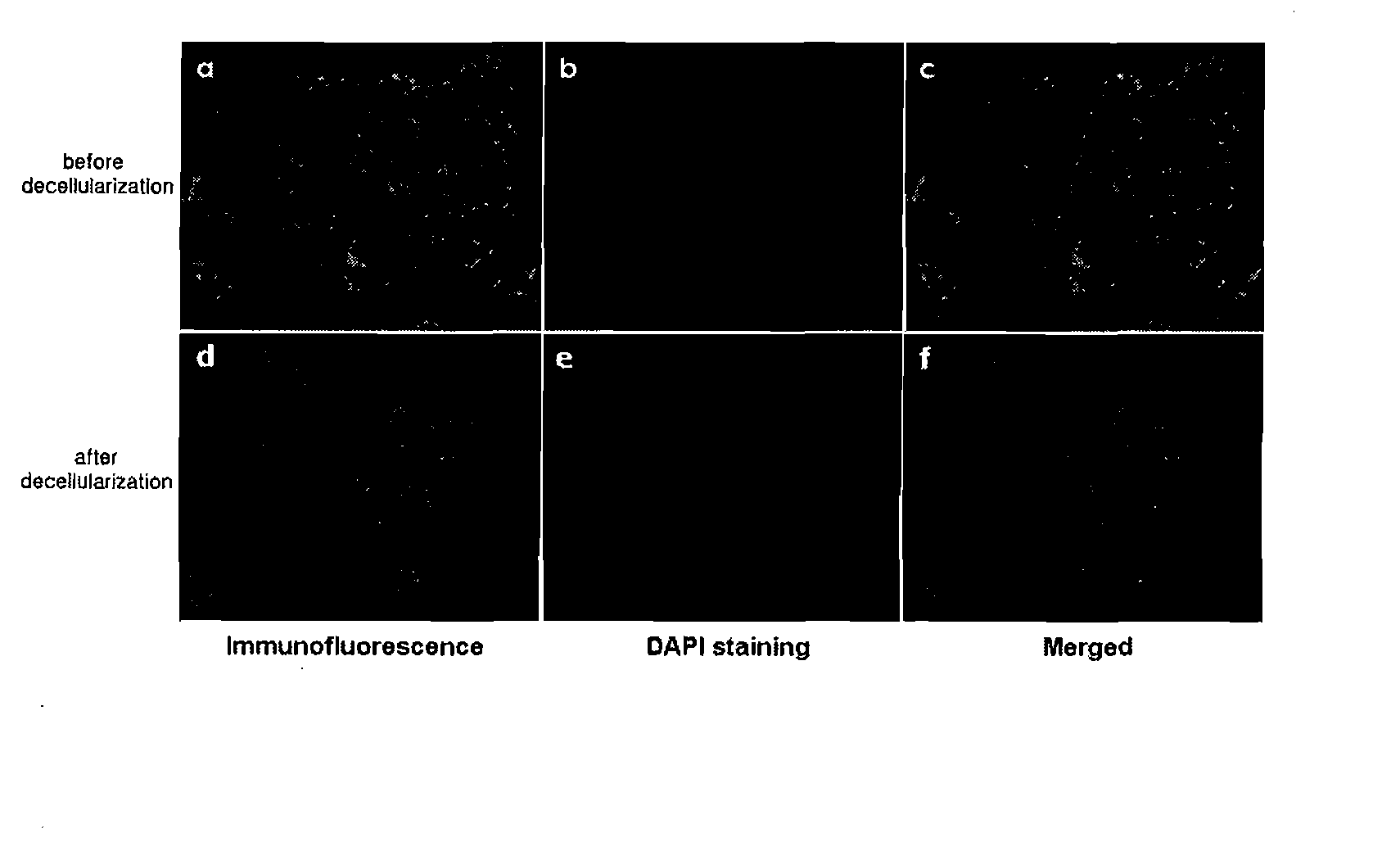
The present invention relates to a method for the surface modification of a polymeric scaffold for stem cell transplantation using a decellularized extracellular matrix. The method for the surface modification of the polymeric scaffold according to the present invention can embody a biomimetic surface environment that is effective for initial cell attachment, cell growth and differentiation of stem cells by modifying the surface of the polymeric scaffold using the decellularized extracellular matrix directly derived from specific tissue cells.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
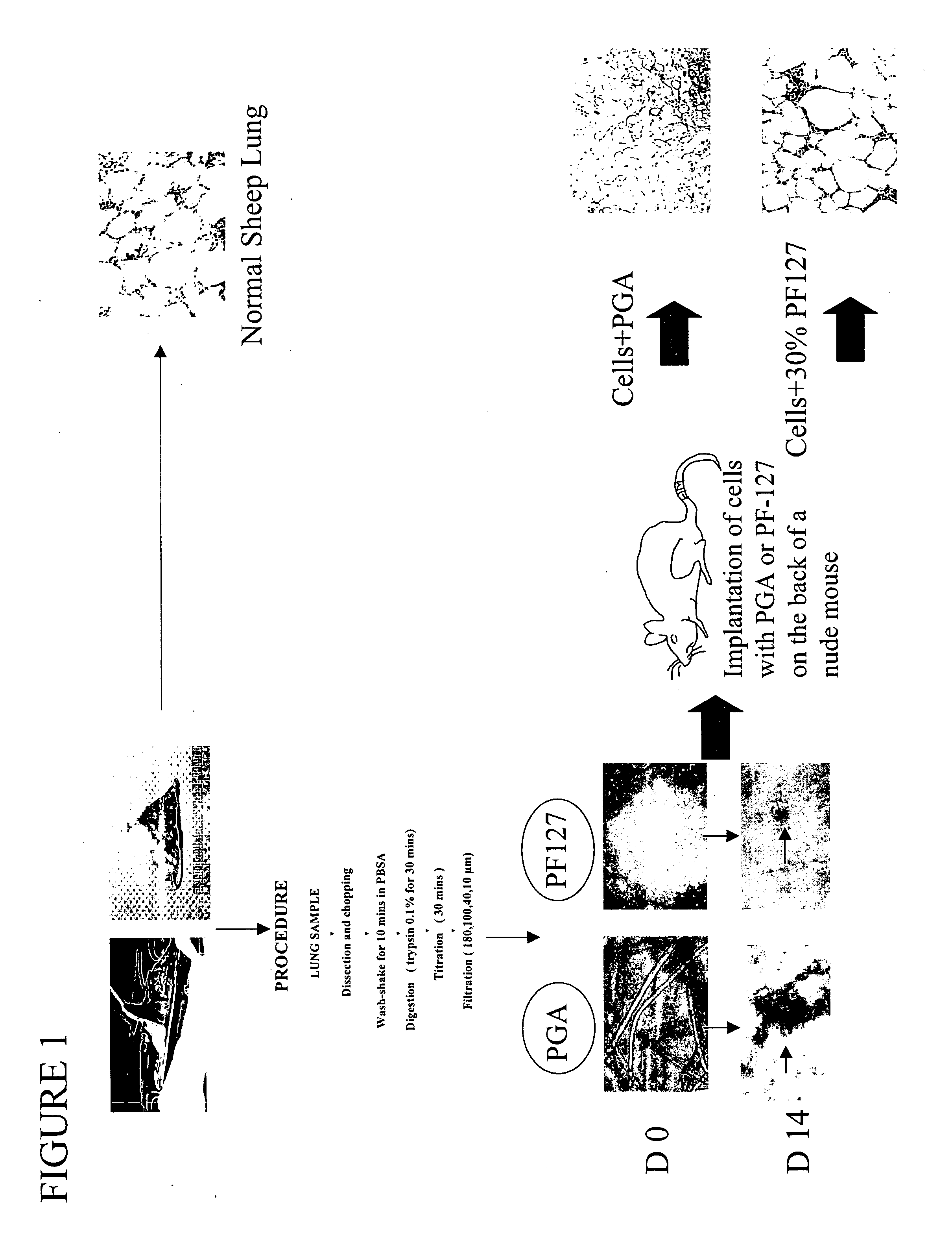
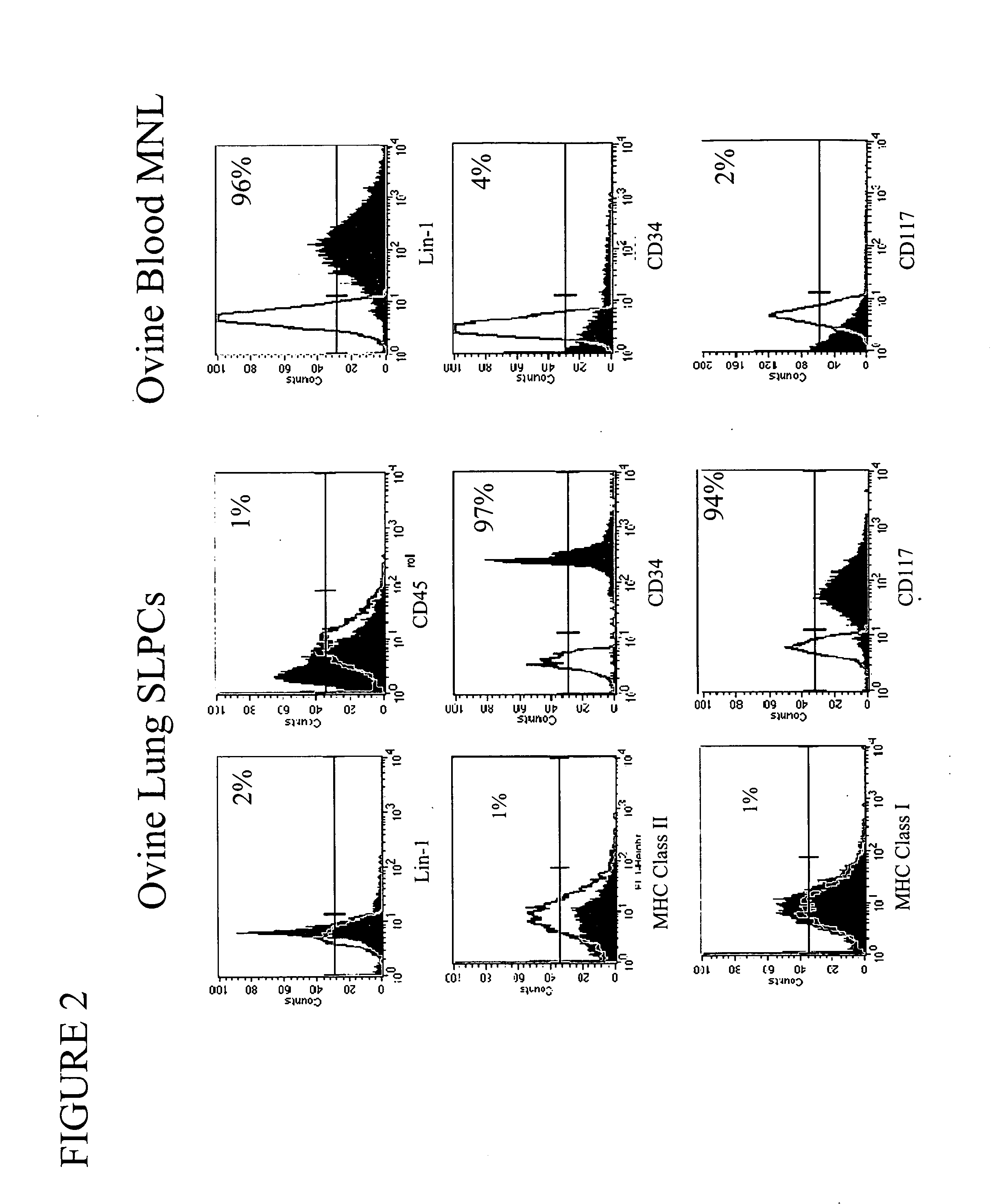
Engineered lung tissue, hydrogel/somatic lung progenitor cell constructs to support tissue growth, and method for making and using same
Somatic lung progenitor cell / polymer constructs are disclosed along with methods for isolating somatic lung progenitor cells from adult mammals, seeding the cells onto or into polymeric scaffolds and allowing the cells to differentiate and proliferate into functional lung tissue / polymer implants. A method for treating lung disease, disorders or injuries is also disclosed.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Preparing porous biodegradable polymeric scaffolds for tissue engineering using effervescent salts
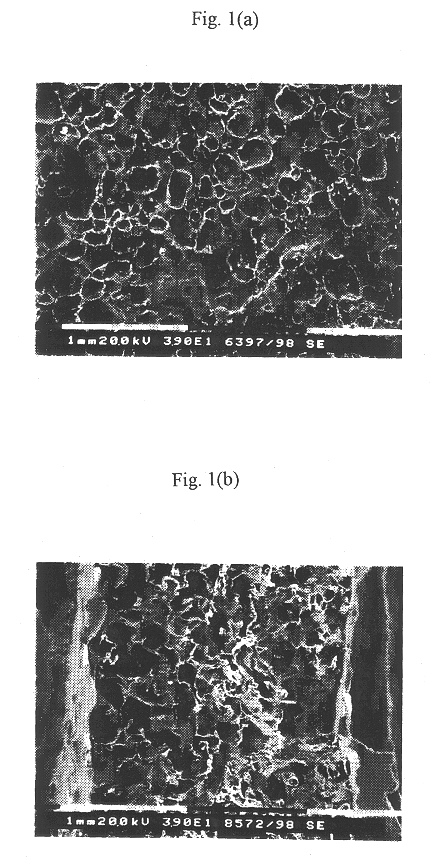
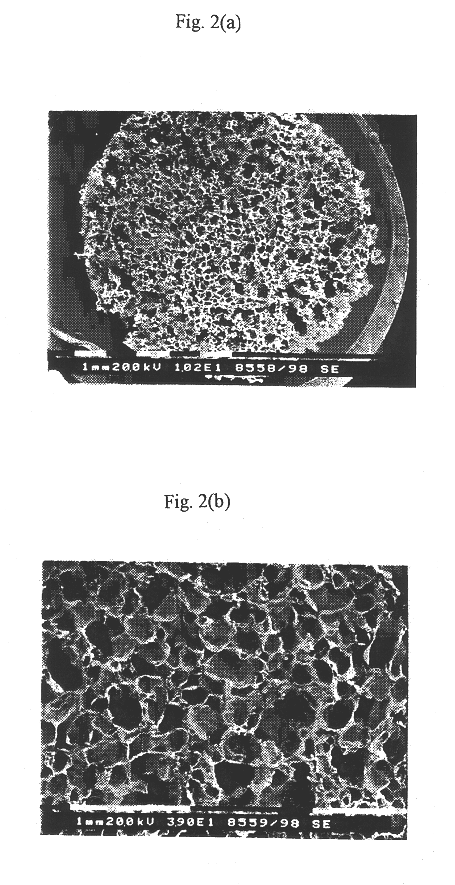
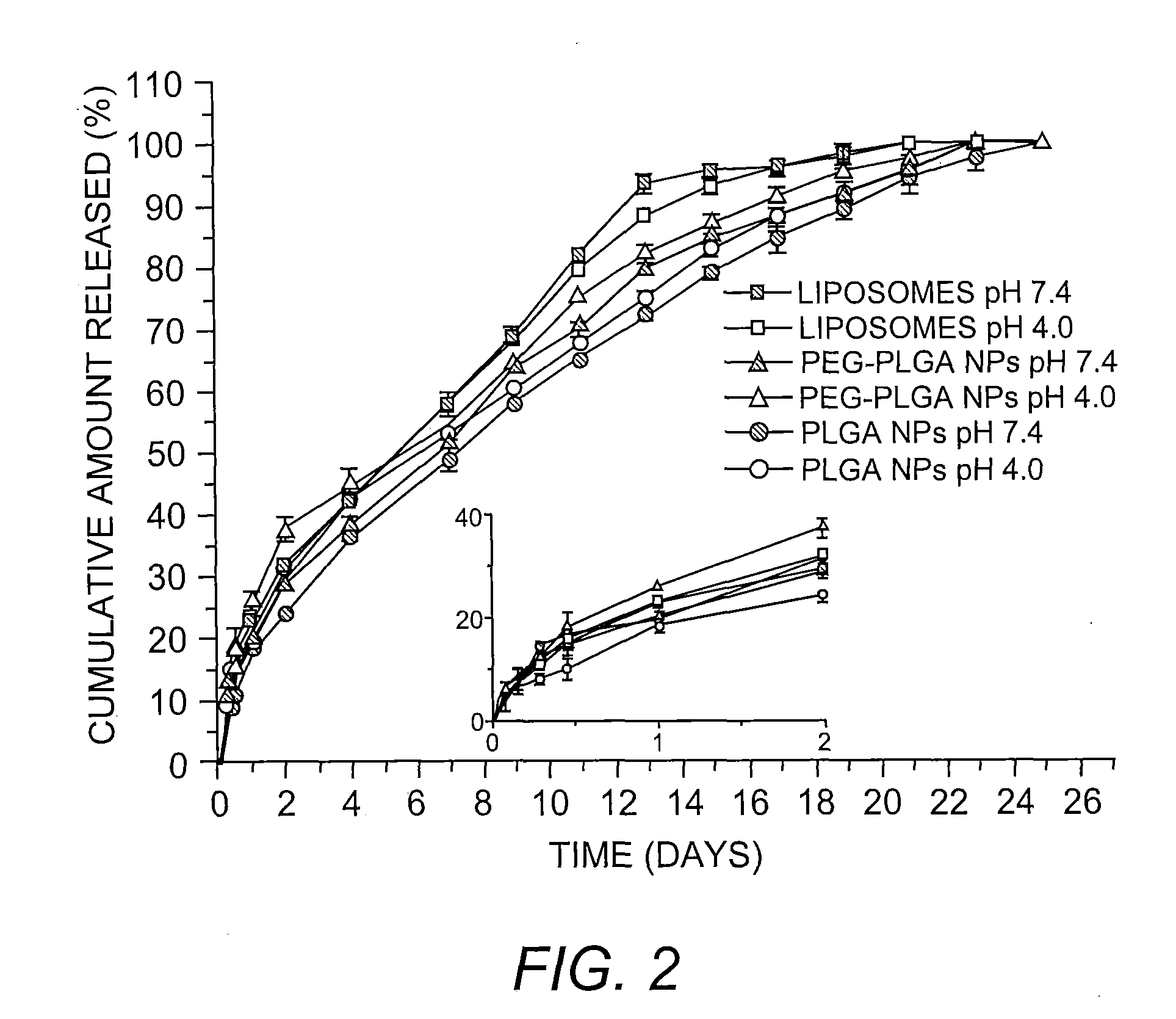
Three-dimensional porous biodegradable and biocompatible, polymeric scaffolds for tissue engineering are prepared by a method involving effervescing of an effervescent salt in a gel to result in a porous structure. A polymer is dissolved in an organic solvent to prepare a polymer solution of high viscosity. Optionally, the polymer solution is mixed with an organic solvent that does not dissolve the polymer to concentrate the solution. An effervescent salt is homogeneously mixed with the polymer solution to give a polymer / salt / organic solvent mixed gel. The organic solvent is removed from the mixed gel to produce an organic solvent-free polymer / salt gel slurry. The gel slurry is submerged in a hot aqueous solution or acidic solution to cause the salt to effervesce at room temperature to form a porous three-dimensional polymeric structure. The polymeric structure is washed with distilled water and freeze-dried to yield a scaffold that is suitable for cell or tissue culture. Pore size and porosity of the scaffold can be easily controlled by controlling the size and amount of the effervescent salt and concentration of the acidic solution.
Owner:INNOTECH MEDICAL
Nano-Hybrid Delivery System for Sequential Utilization of Passive and Active Targeting
ActiveUS20130121918A1Improve the immunityImprove mechanical stabilityPowder deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsDiseaseNano hybrid
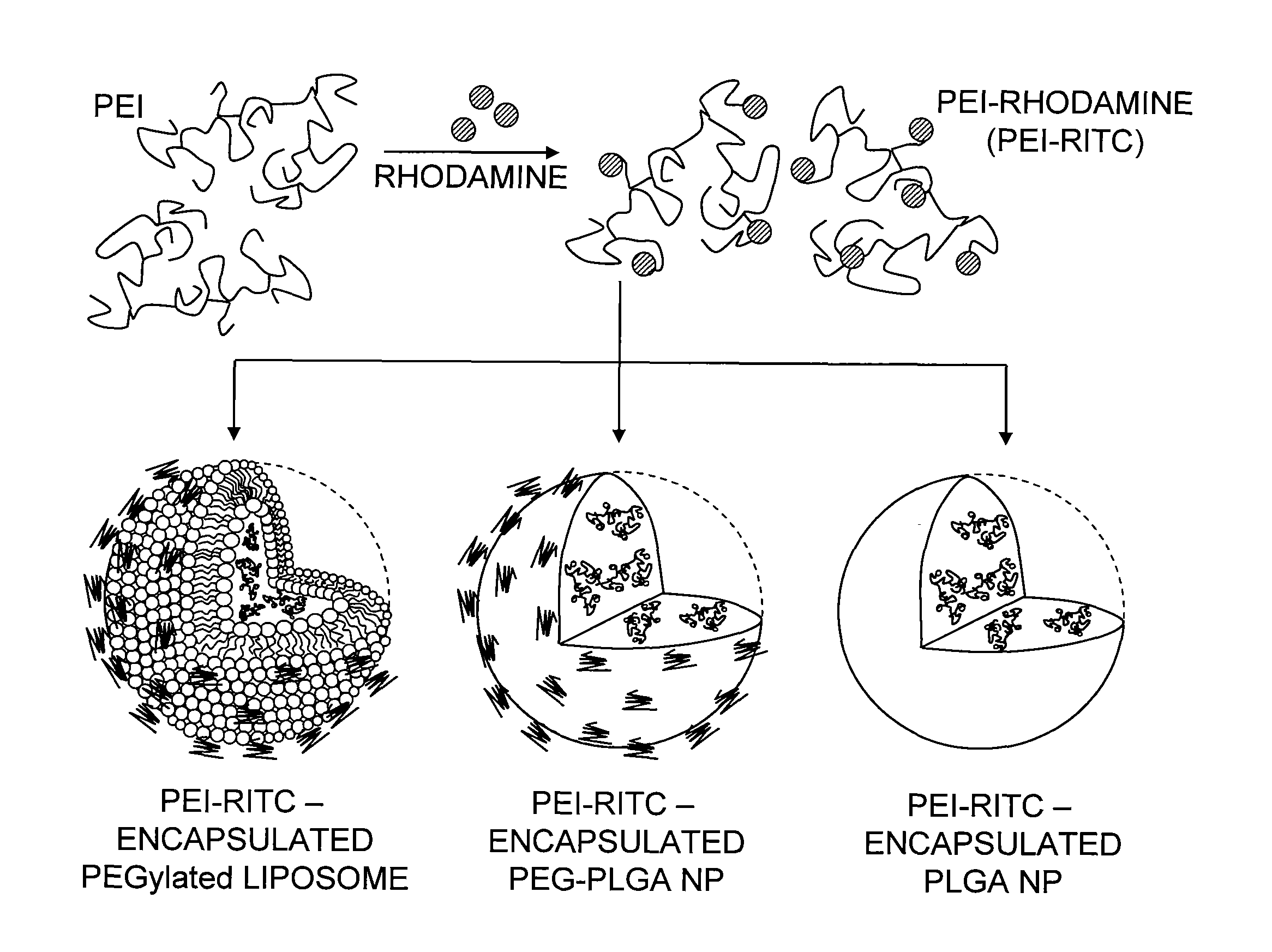
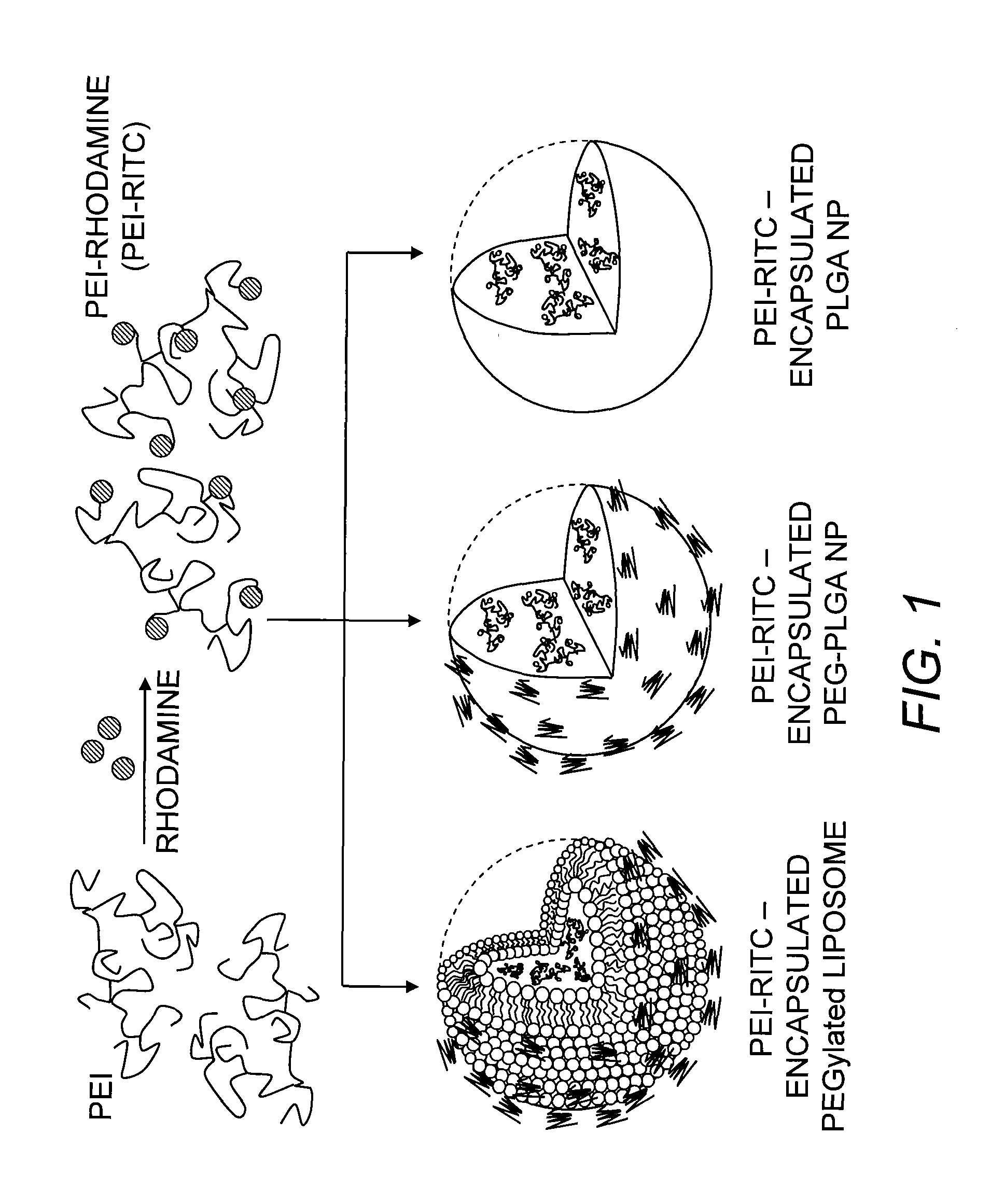
The present invention features nanohybrid drug delivery composition which combines both passive and active targeting for the prevention and treatment of disease. The composition is shell-encapsulated multivalent polymeric scaffold with a therapeutic agent and targeting agent attached thereto.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Strain sensors, methods of making same, and applications of same
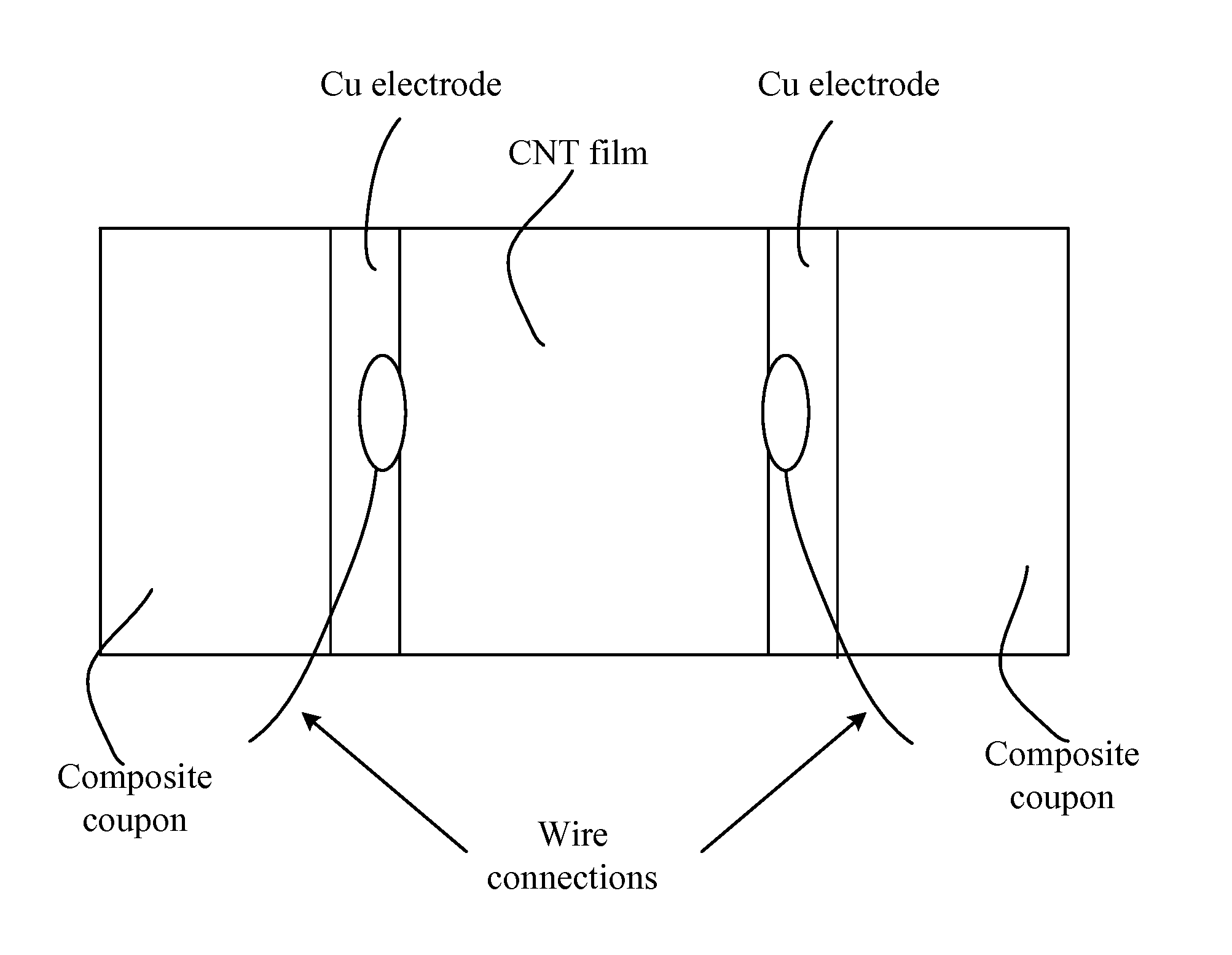
InactiveUS20130104665A1Improve conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyNitrogen compoundsElectrical resistance and conductanceYarn
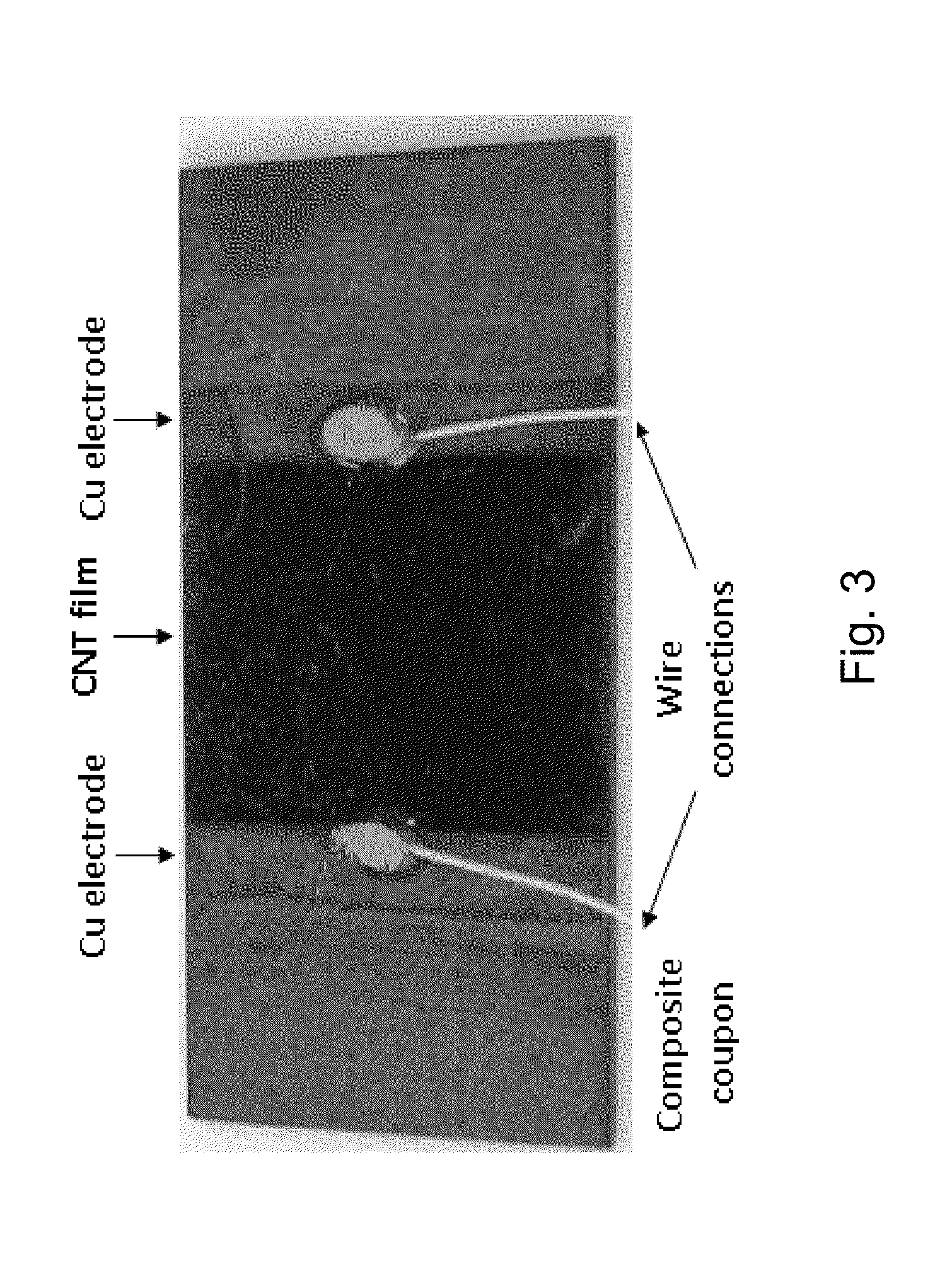
In one aspect, the present invention relates to a layered structure usable in a strain sensor. In one embodiment, the layered structure has a substrate with a first surface and an opposite, second surface defining a body portion therebetween; and a film of carbon nanotubes deposited on the first surface of the substrate, wherein the film of carbon nanotubes is conductive and characterized with an electrical resistance. In one embodiment, the carbon nanotubes are aligned in a preferential direction. In one embodiment, the carbon nanotubes are formed in a yarn such that any mechanical stress increases their electrical response. In one embodiment, the carbon nanotubes are incorporated into a polymeric scaffold that is attached to the surface of the substrate. In one embodiment, the surfaces of the carbon nanotubes are functionalized such that its electrical conductivity is increased.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Tissue Engineered Cartilage, Method of Making Same, Therapeutic and Cosmetic Surgical Applications Using Same
InactiveUS20100061962A1Uniform diameterDiameter is limitedBiocideCosmeticsReconstructive surgeryBioreactor
Cartilage has been constructed using biodegradable electrospun polymeric scaffolds seeded with chondrocytes or adult mesenchymal stem cells. More particularly engineered cartilage has been prepared where the cartilage has a biodegradable and biocompatible nanofibrous polymer support prepared by electrospinning and a plurality of chondocytes or mesenchymal stem cells dispersed in the pores of the support. The tissue engineered cartilages of the invention possess compressive strength properties similar to natural cartilage. Methods of preparing engineered tissues, including tissue engineered cartilages, are provided in which an electrospun nanofibrous polymer support is provided, the support is treated with a cell solution and the polymer-cell mixture cultured in a rotating bioreactor to generate the cartilage. The invention provides for the use of the tissue engineered cartilages in the treatment of cartilage degenerative diseases, reconstructive surgery, and cosmetic surgery.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Scaffold
InactiveUS20120015331A1Effective treatmentLow costAntibacterial agentsBiocideWound healingTissue repair
The present invention provides a polymeric scaffold containing an antibacterial photoactive drug and optionally comprising seeded cells such as stem cells. The invention also includes methods of using the scaffold for tissue regeneration, prevention or reduction of infection whilst tissue regeneration occurs, methods for improving graft or implant survival, promoting scaffold integration and tissue repair and wound healing.
Owner:WOOD SIMON +4
Polymeric pharmaceutical dosage form in sustained release
This invention relates to a polymeric pharmaceutical dosage form for the delivery, in use, of at least one pharmaceutical composition in a rate-modulated and site-specific manner. The dosage form comprises a biodegradable, polymeric, scaffold incorporating loaded with at least one active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). The polymer or polymers making up the scaffold degrade in a human or animal body in response to or in the absence of specific biological stimuli and, on degradation, release the API or APIs in an area where said stimuli are encountered. Preferably the polymeric scaffold is formed from poly (D1L-lactide) (PLA) and polymethacrylate (Eudragit S100 / ES100) polymers.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF THE WITWATERSRAND
Methods for crimping a polymeric scaffold to a delivery balloon and achieving stable mechanical properties in the scaffold after crimping
InactiveUS8752265B2Reduce the overall diameterShorten the overall cycleStentsLabelling non-rigid containersMedicineCatheter
A medical device-includes a polymer scaffold crimped to a catheter having an expansion balloon. The scaffold is crimped to the balloon by a process that includes inflating the delivery balloon during a diameter reduction to improve scaffold retention. A crimping temperature is maintained at about the onset of glass transition of the polymer material to facilitate more rapid stabilization of mechanical properties in the scaffold following crimping.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Protein-polymer-drug conjugates and methods of using same
InactiveUS20150366982A1Improve drug bioavailabilityImprove bioavailabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody ingredientsHer2 expressionMedicine
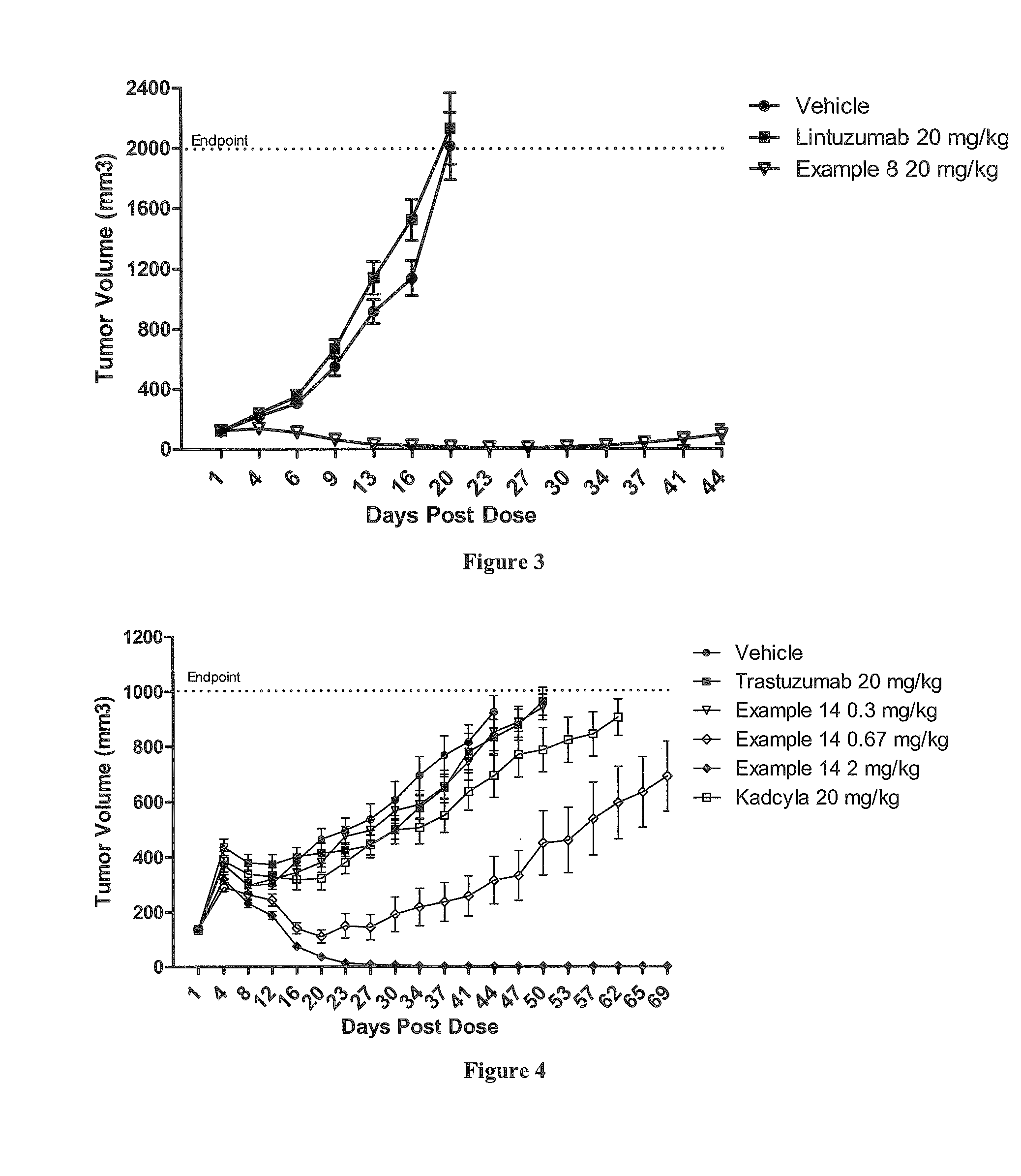
A polymeric scaffold useful for conjugating with a protein based recognition-molecule (PBRM) to form a PBRM-polymer-drug conjugate is described herein. The scaffold includes one or more terminal maleimido groups. Also disclosed is a PBRM-polymer-drug conjugate prepared from the scaffold. Compositions comprising the conjugates, methods of their preparation, and methods of treating various disorders, such as cancer in a subject having low HER2 expression with the conjugates or their compositions are also described.
Owner:MERSANA THERAPEUTICS INC
Tubulysin compounds and conjugates thereof
InactiveUS20160022829A1Improve drug bioavailabilityImprove bioavailabilityDipeptide ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismChemical compoundCombinatorial chemistry
A tubulysin compound conjugate is provided herein. The conjugate comprises a protein based recognition-molecule (PBRM) and a polymeric carrier substituted with one or more -LD-D, the protein based recognition-molecule being connected to the polymeric carrier by LP. Each occurrence of D is independently a tubulysin compound having a molecular weight≦5 kDa. LD and LP are distinct linkers connecting the tubulysin compound and PBRM to the polymeric carrier respectively. Also disclosed are polymeric scaffolds useful for conjugating with a PBRM to form a polymer-tubulysin compound-PBRM conjugate described herein, compositions comprising the conjugates, methods of their preparation, and methods of treating various disorders with the conjugates or their compositions.
Owner:MERSANA THERAPEUTICS INC
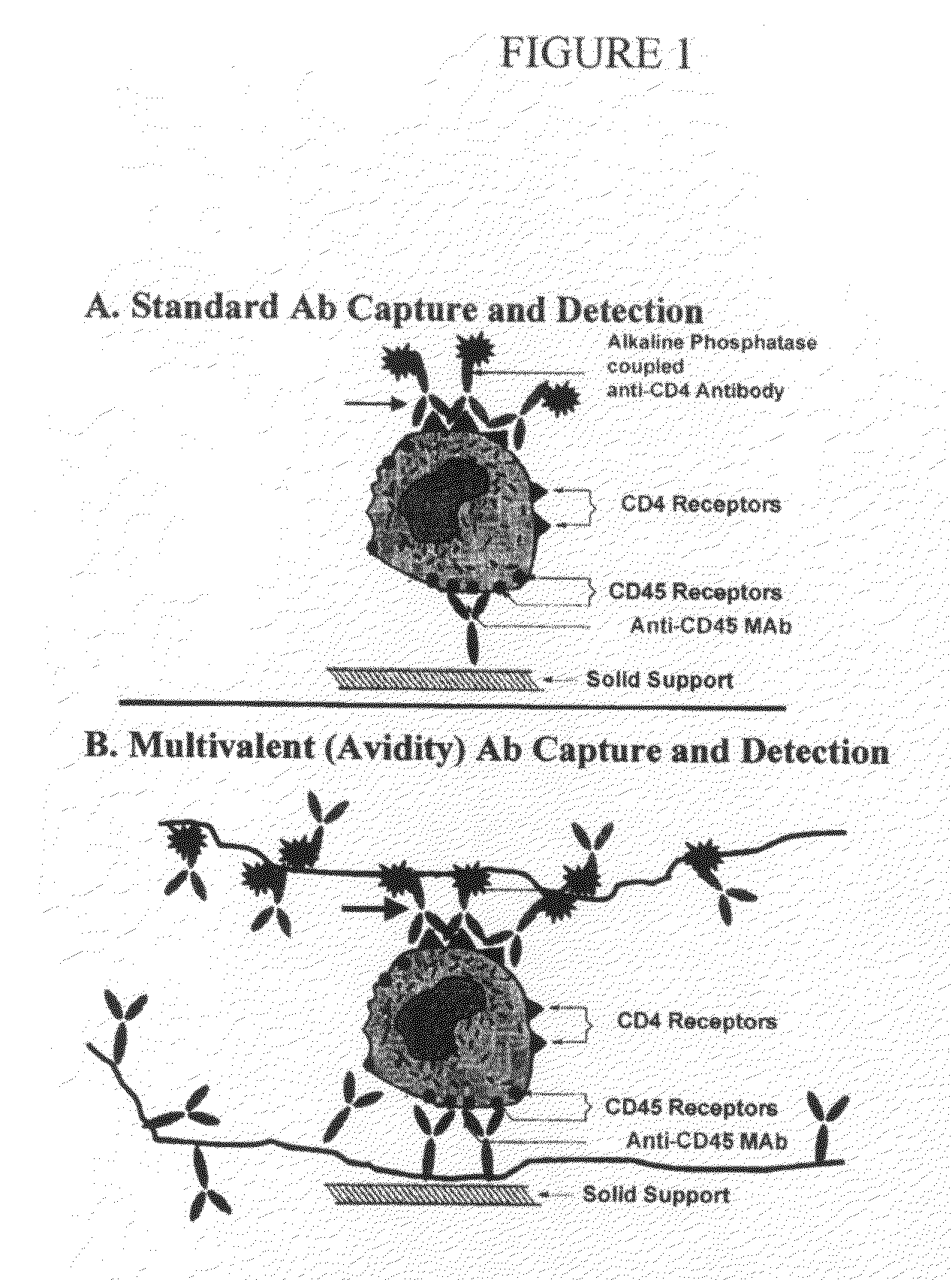
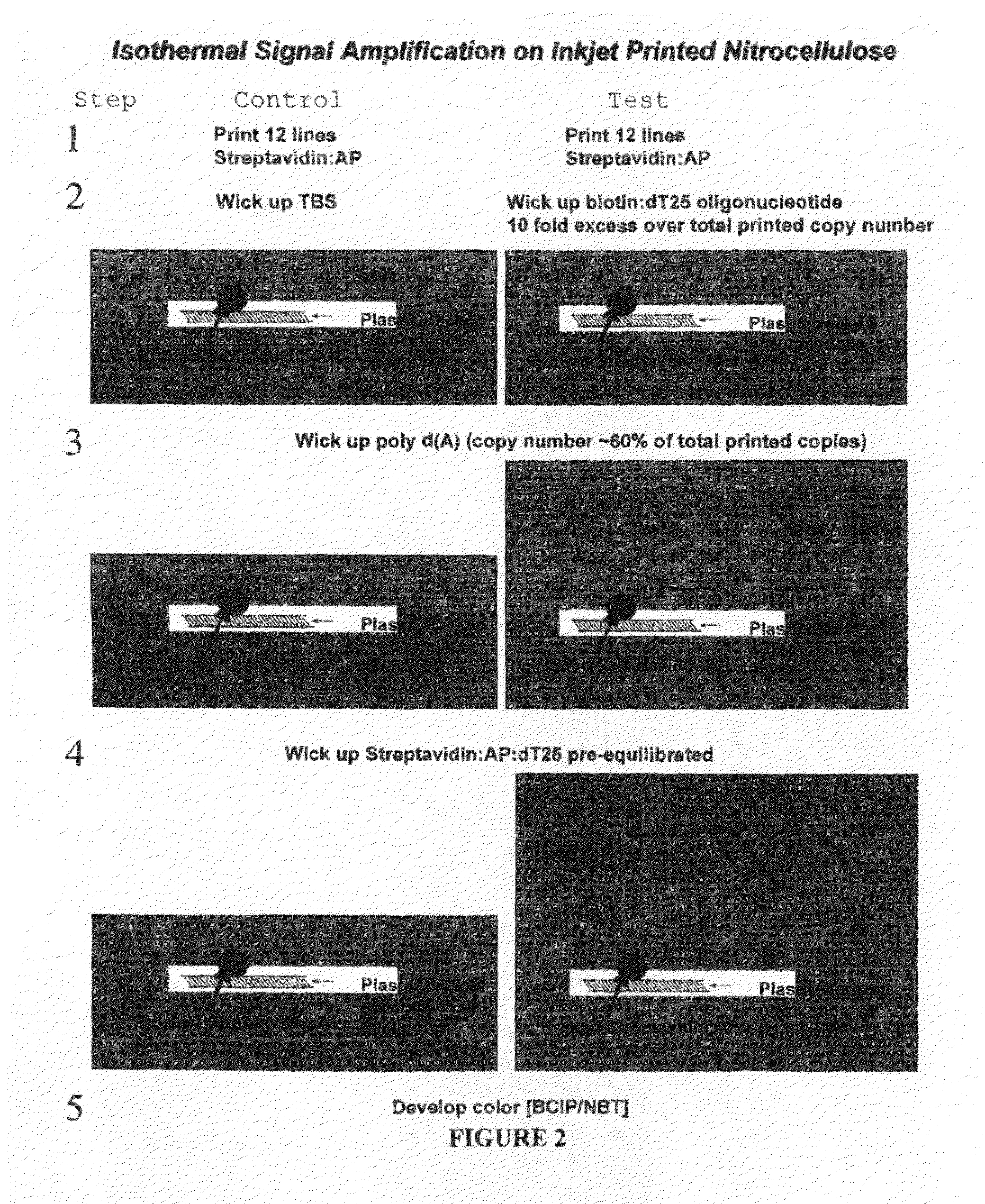
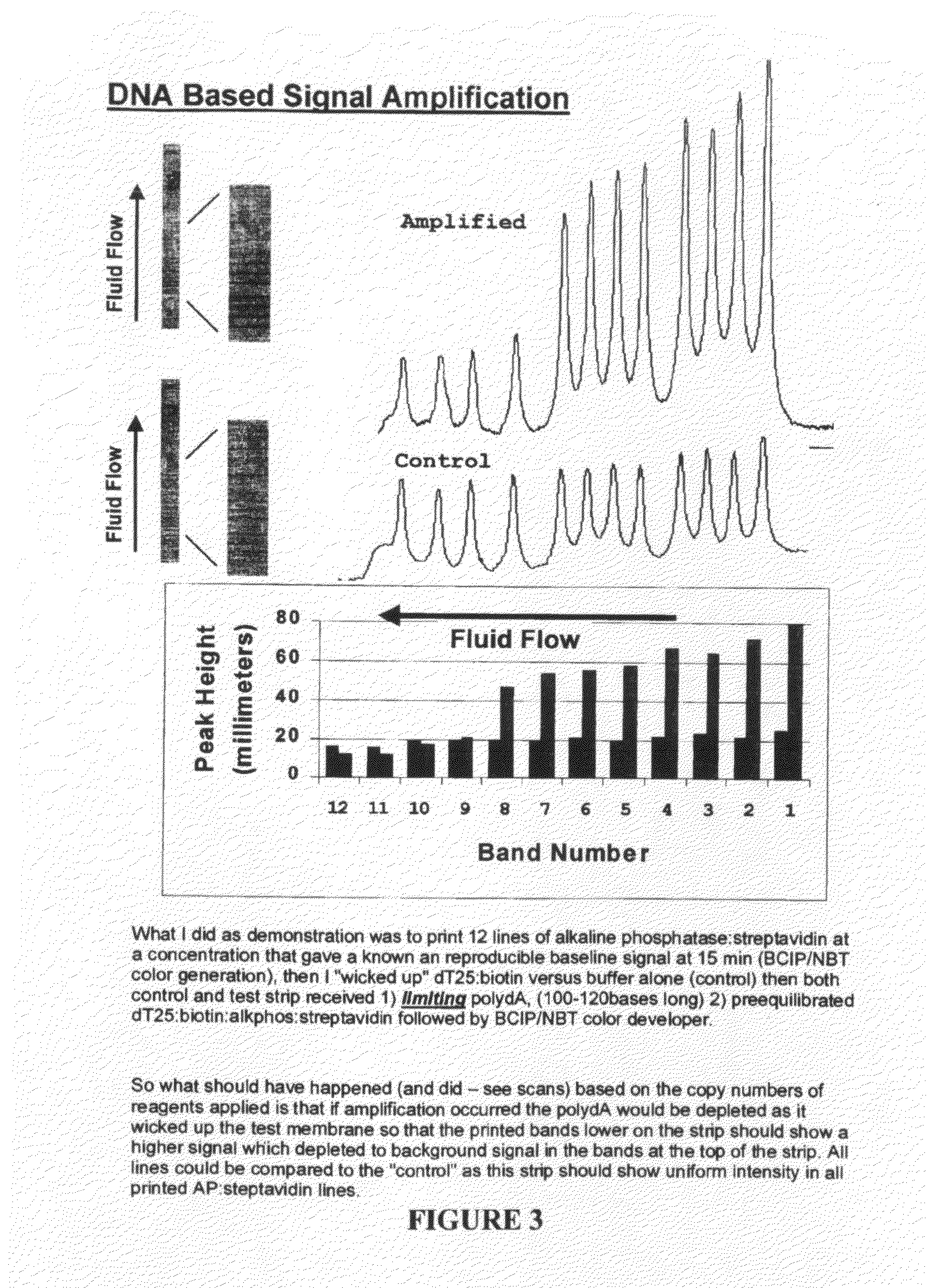
Methods and compositions for multivalent binding and methods for manufacture of rapid diagnostic tests
InactiveUS20100143905A1High affinityConstant gainMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresRapid screening testMultivalent binding
The invention provides reagents and methods for multivalent binding and quantitative capture of components in a sample. In one aspect, reagents and methods for diagnostic assay for antigen, ligand, binding agent, or antibody are provided. Compositions of a non-natural or deliberately constructed nucleic acid-like polymeric scaffold are provided, to which multiple antibodies, peptides or other binding agents can be affixed by hybridization of a oligonucleotide: binding agent complex such that the nucleic acid: binding agent construction displays multivalent behavior when interacting with a multivalent analyte. Methods for constructing and using the scaffolds are described. Such compositions may include assembly of mixed specificity binding agents such that the composition displays multivalent binding behavior against a target containing mixed analytes which can be bound by the construct to effect a binding affinity increase such as is observed in avidity reagents against single analytes expressed multiply on the target analyte. A manufacturing method for producing rapid diagnostic assays in a decentralized manner is also described. The method generates net economic advantages over conventional diagnostic manufacturing practices.
Owner:LANE MICHAEL J +2
Hydroxyl-polymer-drug-protein conjugates
ActiveUS20150306240A1Improve drug bioavailabilityImprove bioavailabilityOrganic active ingredientsDipeptide ingredientsDrug conjugationPharmaceutical drug
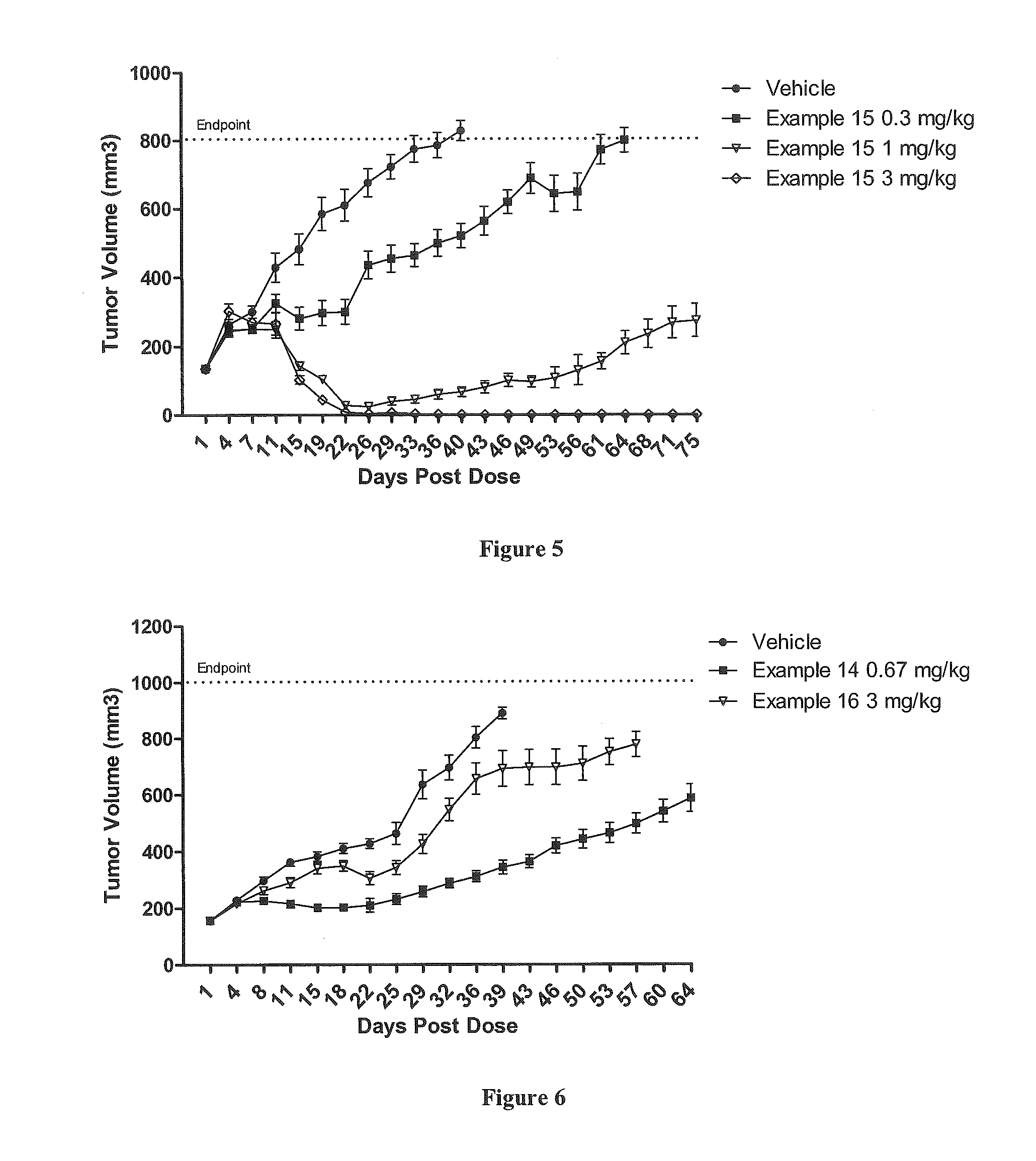
A drug conjugate is provided herein. The conjugate comprises a protein based recognition-molecule (PBRM) and a polymeric scaffold having one or more -LD-D, the PBRM being connected to the polymeric scaffold by Lp, wherein the polymeric scaffold comprises a linear, branched or cyclic polymer having four or more —OH groups. Each occurrence of D is independently a therapeutic agent having a molecular weight <5 kDa. LD and Lp are linkers connecting the therapeutic agent and PBRM to the polymeric scaffold respectively. Also disclosed are polymeric scaffolds useful for conjugating with a PBRM to form a polymer-drug-PBRM conjugate described herein, compositions comprising the conjugates, methods of their preparation, and methods of treating various disorders with the conjugates or their compositions.
Owner:MERSANA THERAPEUTICS INC
Post deployment radial force recovery of biodegradable scaffolds
ActiveUS20180116837A1Maintain mechanical propertiesImproves exhibited chronic radial forceStentsProsthesisBiodegradable scaffoldCatheter
Post deployment radial force recovery of biodegradable scaffolds are described where a high molecular weight polymer may be formed into a high molecular weight scaffold by solution casting into a tubular substrate such that the scaffold retains its mechanical properties through processing. The tubular substrate is laser cut and subsequently crimped onto a catheter for deployment into a body lumen. The polymeric scaffold may retain its mechanical properties and result in increased radial strength post-deployment in a saline environment, e.g., within a body lumen. This scaffold enhancement may be attributable at least in part to entanglement of high molecular weight polymer chains as one factor that effects radial force recovery and also to the design or geometry of the scaffold as another factor that effects radial force recovery after deployment.
Owner:RAZMODICS LLC
Protein-polymer-drug conjugates
ActiveUS20150125474A1Improve drug bioavailabilityImprove bioavailabilityOrganic active ingredientsDipeptide ingredientsDrug conjugationPharmaceutical drug
A polymeric scaffold useful for conjugating with a protein based recognition-molecule (PBRM) to form a PBRM-polymer-drug conjugate is described herein. The scaffold includes one or more terminal maleimido groups. Also disclosed is a PBRM-polymer-drug conjugate prepared from the scaffold. Compositions comprising the conjugates, methods of their preparation, and methods of treating various disorders with the conjugates or their compositions are also described.
Owner:ASANA BIOSCI
Device and Method for Gingival Attachment Associated with Endosseous Implants
A gingival attachment device associated with an endosseous implant, which comprises a cervically located component of a dental implant coated on a gingival facing surface thereof with a biocompatible and non-degradable polymeric scaffold, to which epithelial and connective tissue cells of the gingiva are attachable. The polymeric scaffold may be polyvinylpyrronidole mixed with butyl-methylmethacrylate, silk fibroin fibrous protein polymer mixed with chitosan or with derivatives of chitosan, and polyHEMA and may be coated on all gingival facing surfaces of the cervically located component.
Owner:MEDINTAL
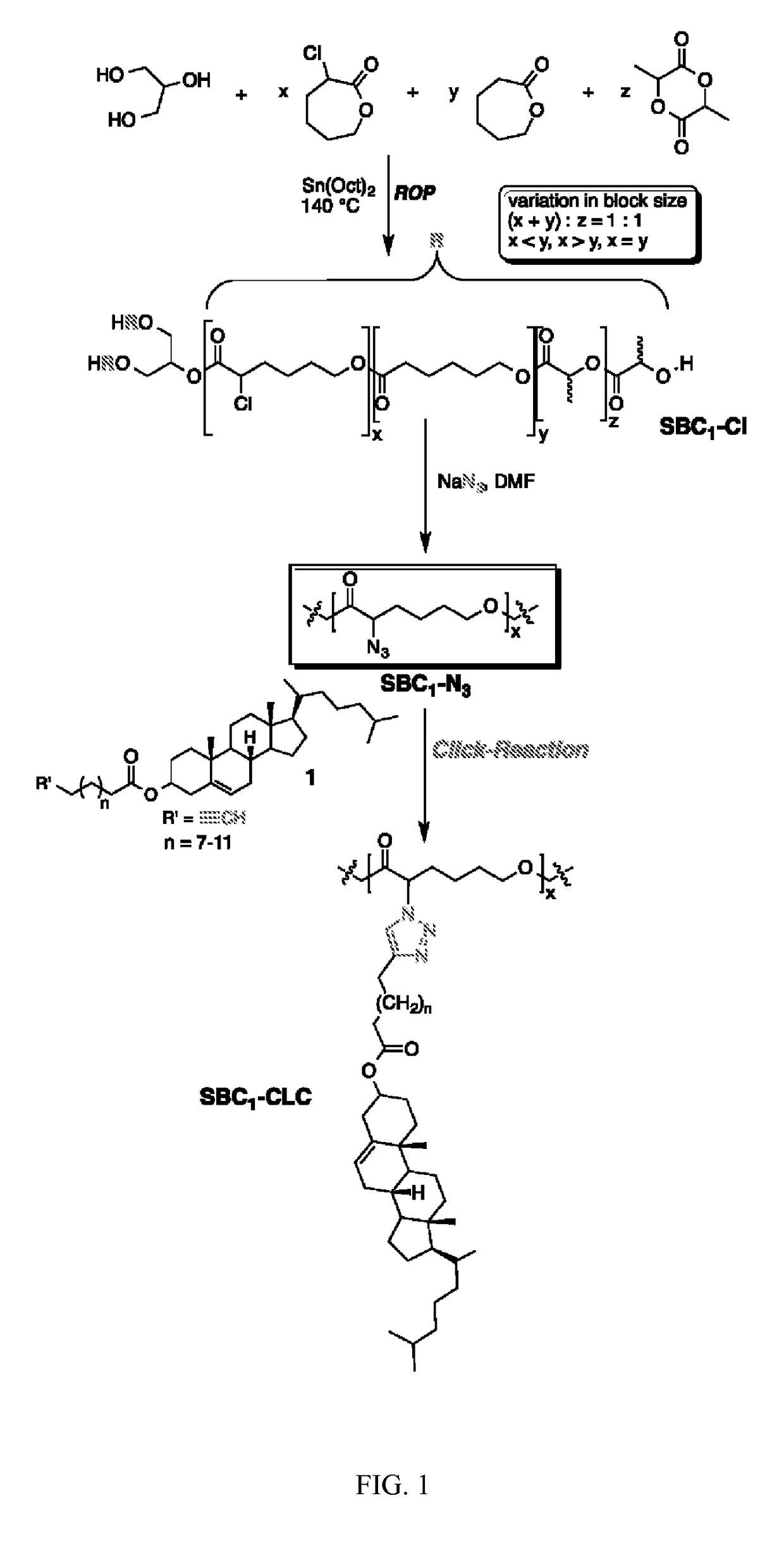
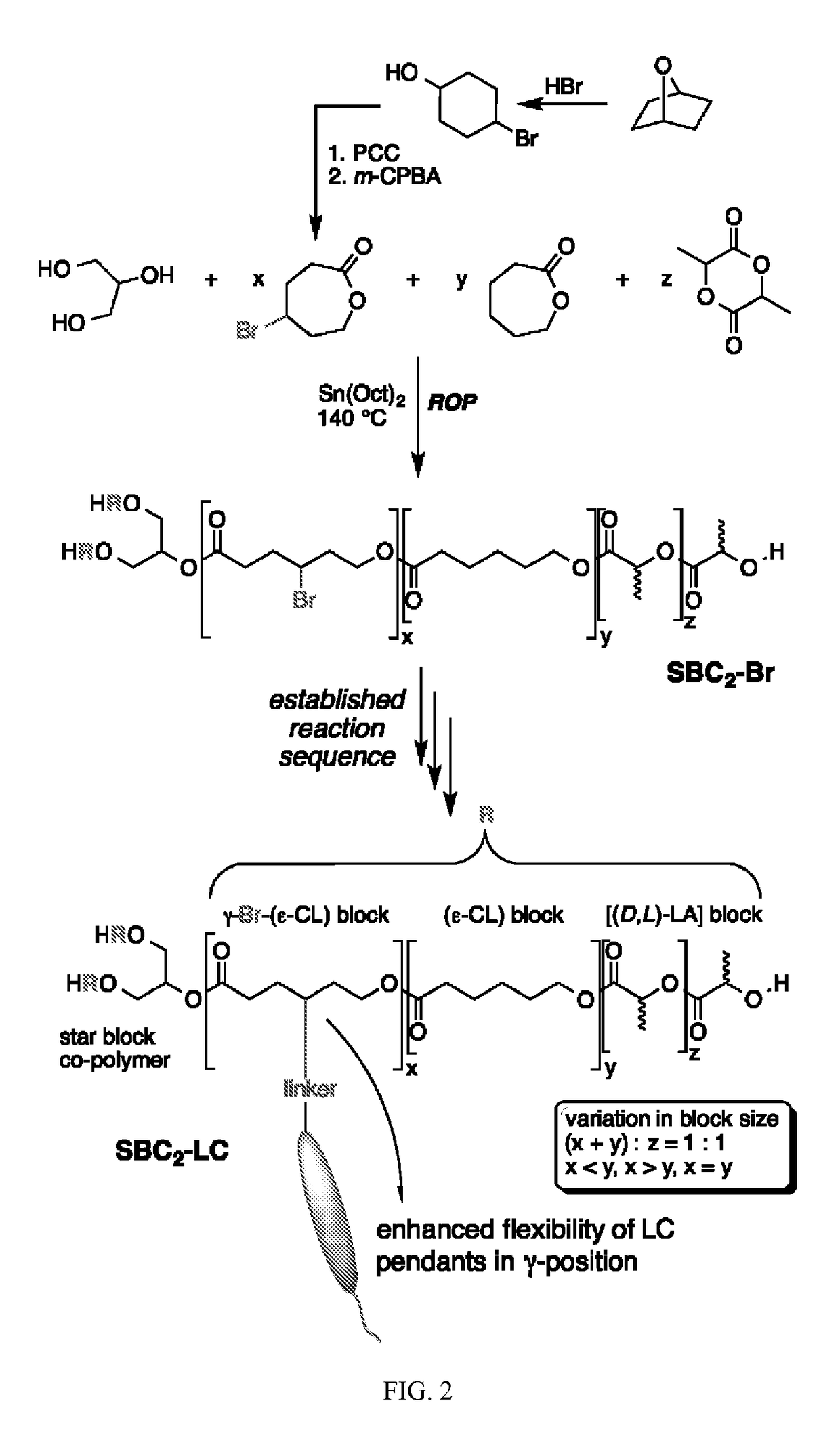
Biodegradable side chain liquid crystal elastomers: smart responsive scaffolds (SRS) for tissue regeneration
ActiveUS20160046761A1Improve orderEasy to liftLiquid crystal compositionsSurgeryPorosityCrystallography
Controlled biodegradable smart responsive scaffold (SRS) materials enhance attachment and viability of cells, i.e. actively guiding their expansion, proliferation and in some cases differentiation, while increasing their biomechanical functionality is an important key issue for tissue regeneration. Chemically build-in functionality in these biodegradable SRS materials is achieved by varying structural functionalization with biocompatible liquid crystal motifs and general polymer composition allowing for regulation and alteration of tensile strength, surface ordering, bioadhesion and biodegradability, bulk liquid crystal phase behavior, porosity, and cell response to external stimuli. Liquid crystal modification of such polymeric scaffolds is an ideal tool to induce macroscopic ordering events through external stimuli. None of these approaches have been demonstrated in prior art, and the use of biocompatible scaffolds that respond to a variety of external stimuli resulting in a macroscopic ordering event is a novel aspect of the present invention.
Owner:KENT STATE UNIV
Methods for increasing a retention force between a polymeric scaffold and a delivery balloon
ActiveUS8961848B2Reduce the overall diameterImprove retentionStentsSurgeryPolymer scaffoldMedical device
A medical device-includes a scaffold crimped to a catheter having an expansion balloon. The scaffold is crimped to the balloon by a process that includes inflating the delivery balloon during a diameter reduction to improve scaffold retention and maintaining an inflated balloon during the diameter reduction and prior and subsequent dwell periods.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
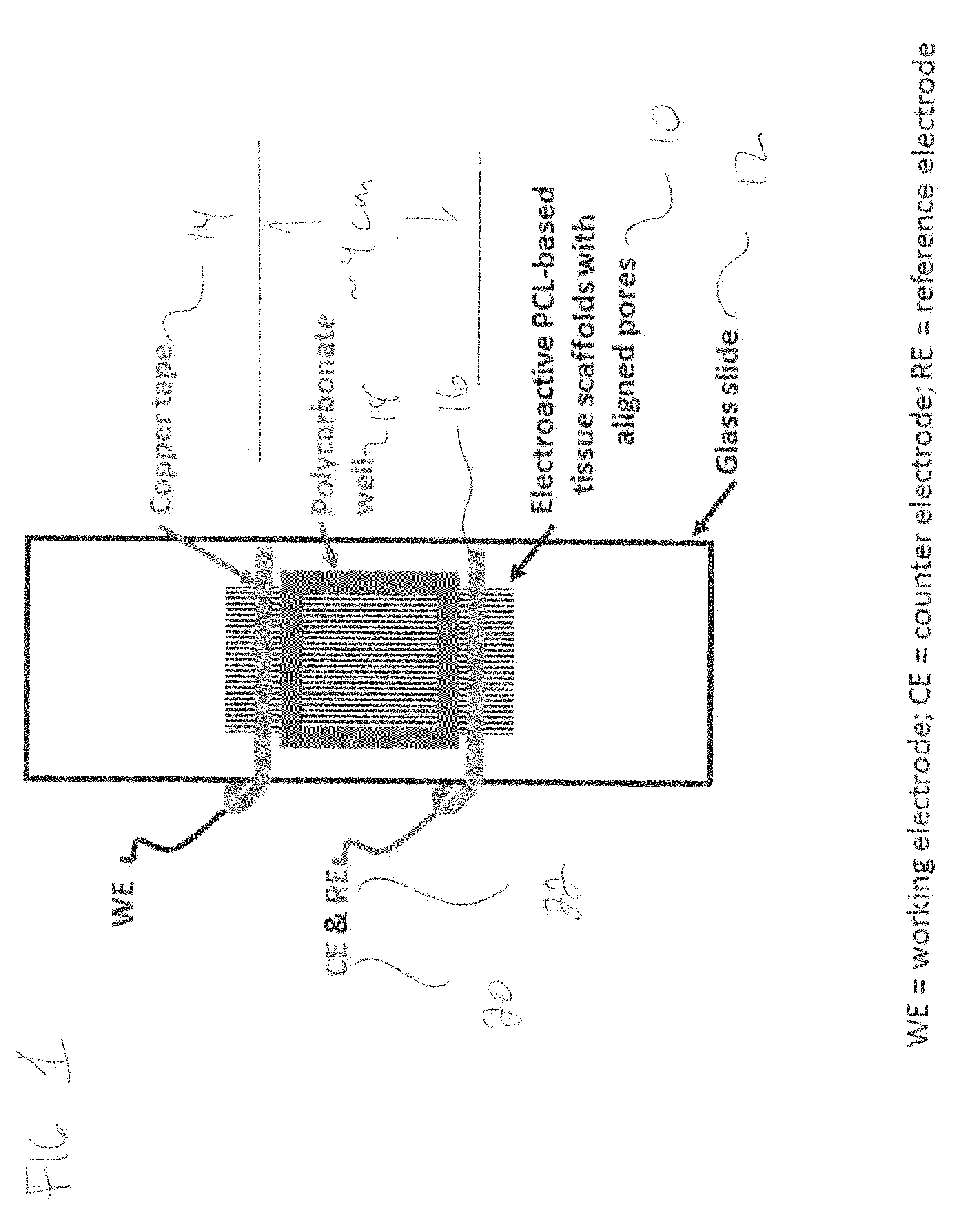
Electroactive polymeric scaffolds and method for delivering nerve growth factor to nerve tissue
ActiveUS20160083692A1Nervous system cellsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPolycaprolactonePolymerization
A polymerizable unit that yields an electrochemically responsive polymer (advantageously pyrrole) is anchored by polymerization within a polycaprolactone matrix to form an electroactive scaffold upon which cells can be cultured and in which the micro- and nano-topological features of the polycaprolactone matrix are preserved. A scaffold manufactured in accordance with the preferred embodiment can support Schwann cells, which produce nerve growth factor when electrically stimulated. Nerve growth factor has been demonstrated to promote the regeneration of nerve tissue. By implanting the scaffold on which Schwann cells have been cultured into damaged nerve tissue and applying a voltage across the scaffold, nerve growth factor is produced, thereby promoting repair of the damaged nerve tissue.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Tissue engineered cartilage, method of making same, therapeutic and cosmetic surgical applications using same
InactiveUS8202551B2Uniform diameterDiameter is limitedBiocideCosmeticsReconstructive surgeryBioreactor
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Nano-hybrid delivery system for sequential utilization of passive and active targeting
The present invention features nanohybrid drug delivery composition which combines both passive and active targeting for the prevention and treatment of disease. The composition is shell-encapsulated multivalent polymeric scaffold with a therapeutic agent and targeting agent attached thereto.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Protein-Polymer-Drug Conjugates
ActiveUS20140134127A1Improve drug bioavailabilityImprove bioavailabilityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSynthetic polymeric active ingredientsDrug conjugationPharmaceutical drug
A drug conjugate is provided herein. The conjugate comprises a protein based recognition-molecule (PBRM) and a polymeric carrier substituted with one or more -LD-D, the protein based recognition-molecule being connected to the polymeric carrier by LP. Each occurrence of D is independently a therapeutic agent having a molecular weight ≦5 kDa. LD and LP are linkers connecting the therapeutic agent and PBRM to the polymeric carrier respectively. Also disclosed are polymeric scaffolds useful for conjugating with a PBRM to form a polymer-drug-PBRM conjugate described herein, compositions comprising the conjugates, methods of their preparation, and methods of treating various disorders with the conjugates or their compositions.
Owner:MERSANA THERAPEUTICS INC
Auristatin Compounds and Conjugates Thereof
ActiveUS20130309192A1Improve drug bioavailabilityImprove bioavailabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody ingredientsChemical compoundPharmaceutical drug
Auristatin compounds and conjugates thereof are provided herein. The conjugate comprises a protein based recognition-molecule (PBRM) and a polymeric carrier substituted with one or more -LD-D, the protein based recognition-molecule being connected to the polymeric carrier by LP. Each occurrence of D is independently an Auristatin compound. LD and LP are linkers connecting the therapeutic agent and PBRM to the polymeric carrier respectively. Also disclosed are polymeric scaffolds useful for conjugating with a PBRM to form a polymer-drug-PBRM conjugate described herein, compositions comprising the conjugates, methods of their preparation, and methods of treating various disorders with the conjugates or their compositions.
Owner:MERSANA THERAPEUTICS INC
Strain sensors, methods of making same, and applications of same
InactiveUS9068283B2Improve conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyConductive materialYarnElectrical resistance and conductance
In one aspect, the present invention relates to a layered structure usable in a strain sensor. In one embodiment, the layered structure has a substrate with a first surface and an opposite, second surface defining a body portion therebetween; and a film of carbon nanotubes deposited on the first surface of the substrate, wherein the film of carbon nanotubes is conductive and characterized with an electrical resistance. In one embodiment, the carbon nanotubes are aligned in a preferential direction. In one embodiment, the carbon nanotubes are formed in a yarn such that any mechanical stress increases their electrical response. In one embodiment, the carbon nanotubes are incorporated into a polymeric scaffold that is attached to the surface of the substrate. In one embodiment, the surfaces of the carbon nanotubes are functionalized such that its electrical conductivity is increased.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com