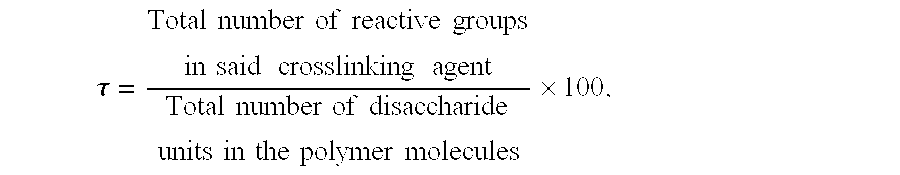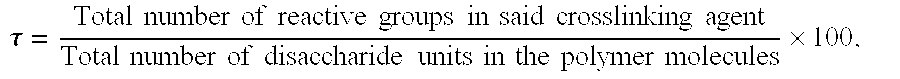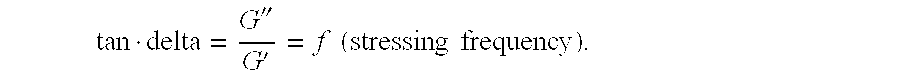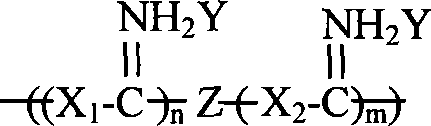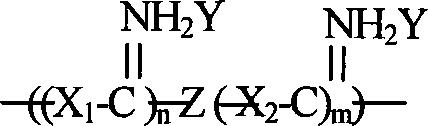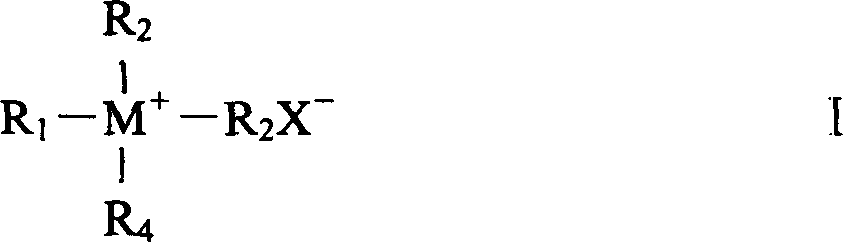Patents
Literature
521 results about "High molecular weight polymer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
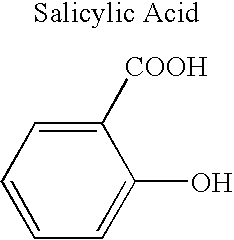
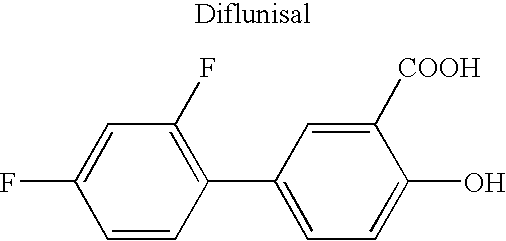
UHMW is ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene. It is a type of thermoplastic polymer. This polymer compound contains extremely long polymer chains having high molecular weights (around 5-9 million amu). Therefore, UHMW has the highest molecular density.
Polymerization catalysts for producing high molecular weight polymers with low levels of long chain branching
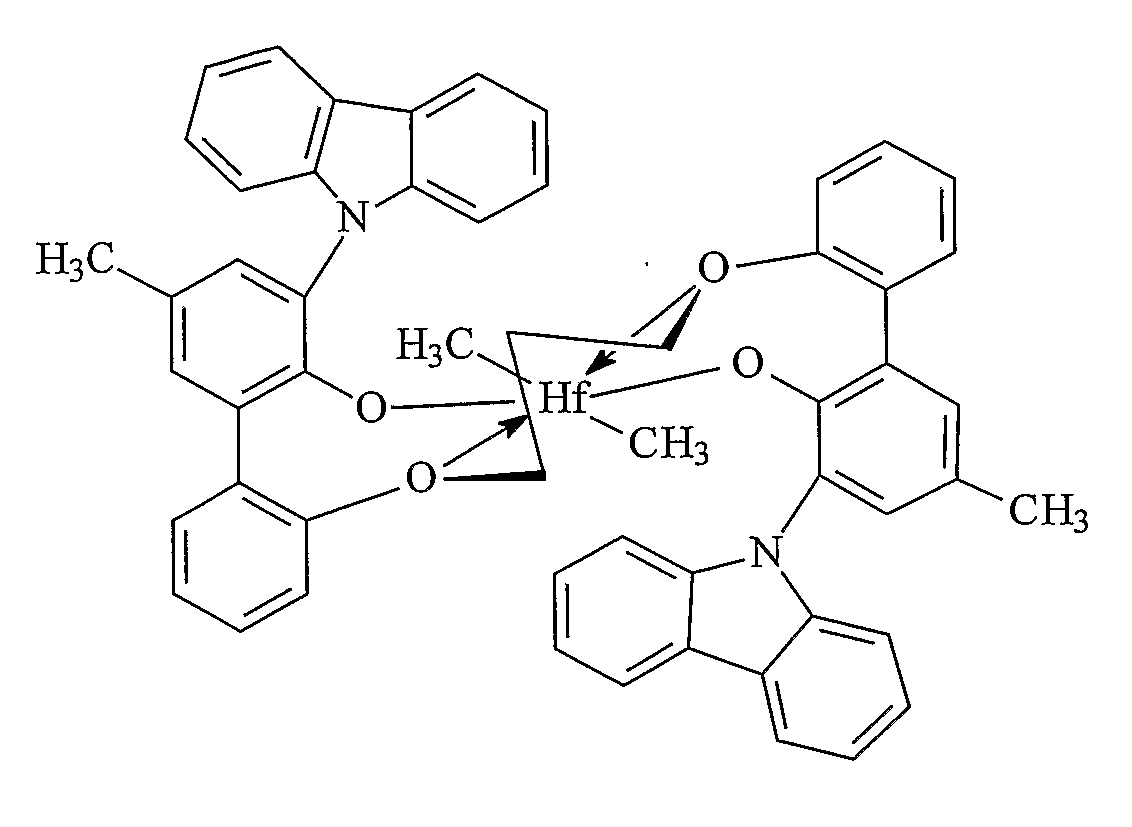
ActiveUS7517939B2High catalytic activityHigh activityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsHigh molecular massEthylene Polymers
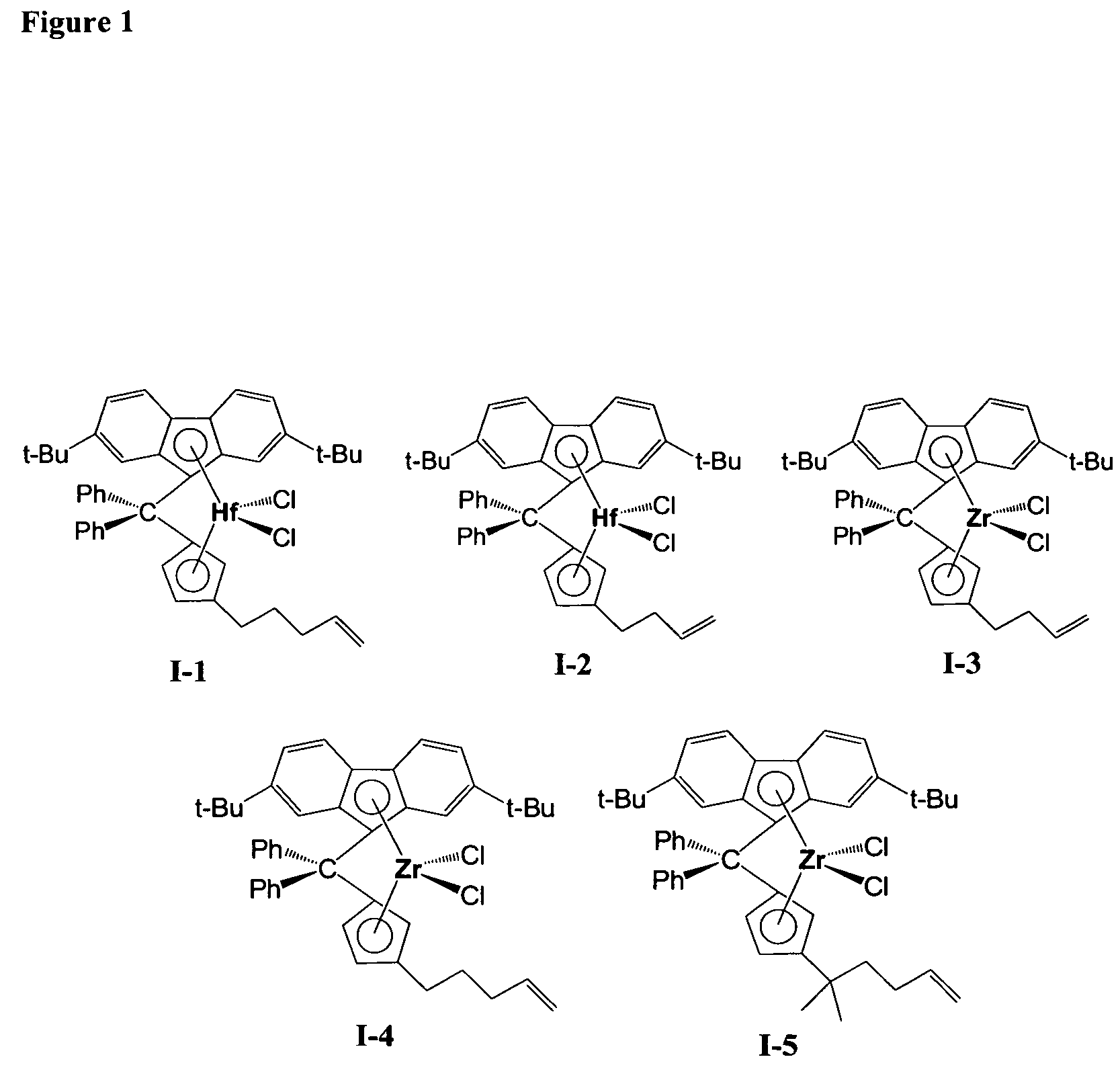
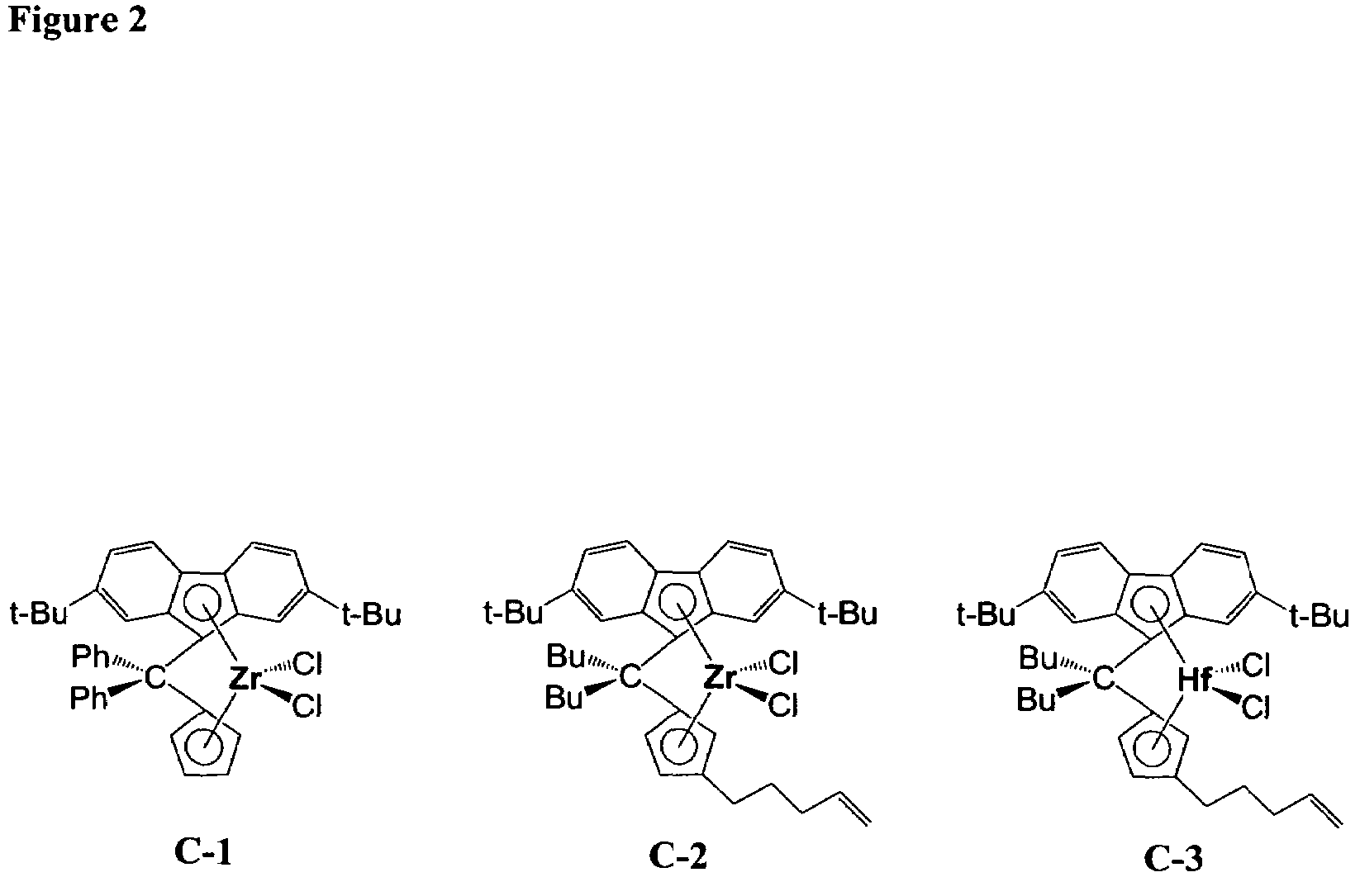
This invention relates to catalyst compositions, methods, and polymers encompassing at least one Group 4 metallocene compound comprising bridging η5-cyclopentadienyl-type ligands, typically in combination with at least one cocatalyst, and at least one activator. The compositions and methods disclosed herein provide ethylene polymers with low levels of long chain branching.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
High molecular wegiht polymers, devices and method for making and using same
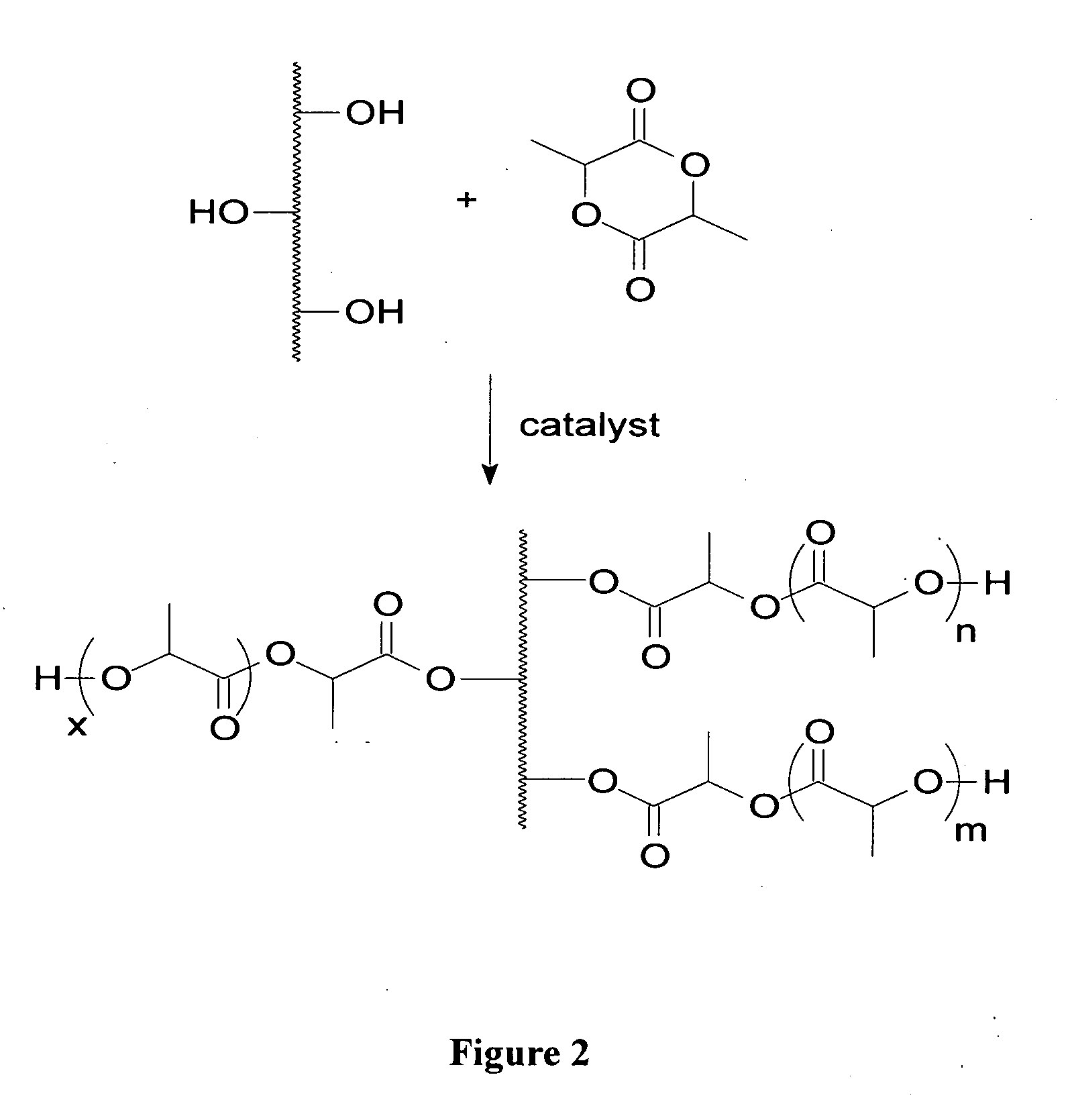
Anhydride polymers that release active or activatable agent(s) have pre-selected properties such as molecular weight, flexibility, hardness, adhesiveness, and other valuable properties. The polymers are suitable for use in compositions, formulations, coatings, devices, and the like that benefit from the controlled release of an agent(s) over a period of time. The polymers are prepared by a process involving various alternative and sequential steps that allow the design a priori of products with specific characteristics. The polymers are suitable as delivery systems, either by themselves, as compositions, formulations or devices.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
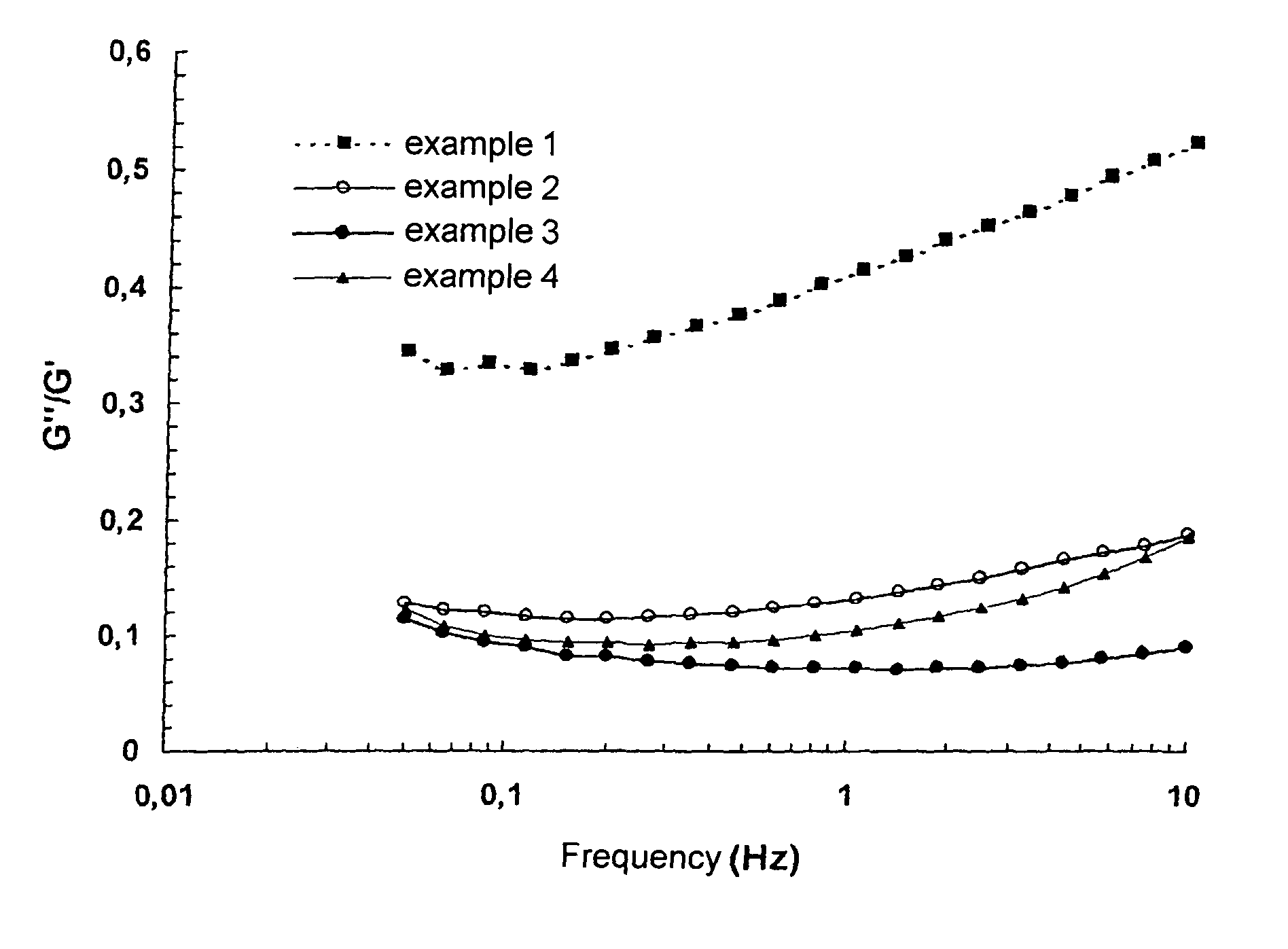
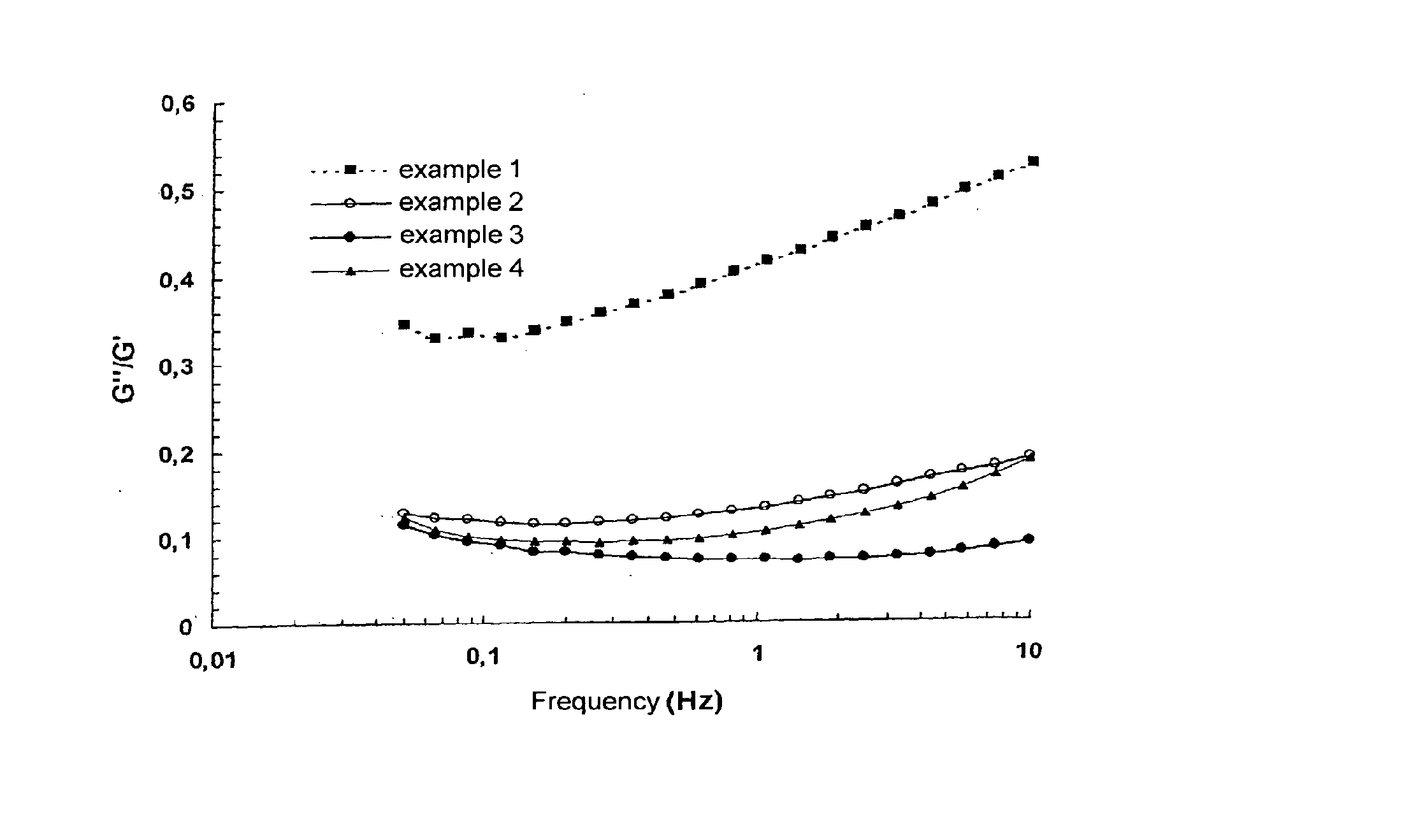
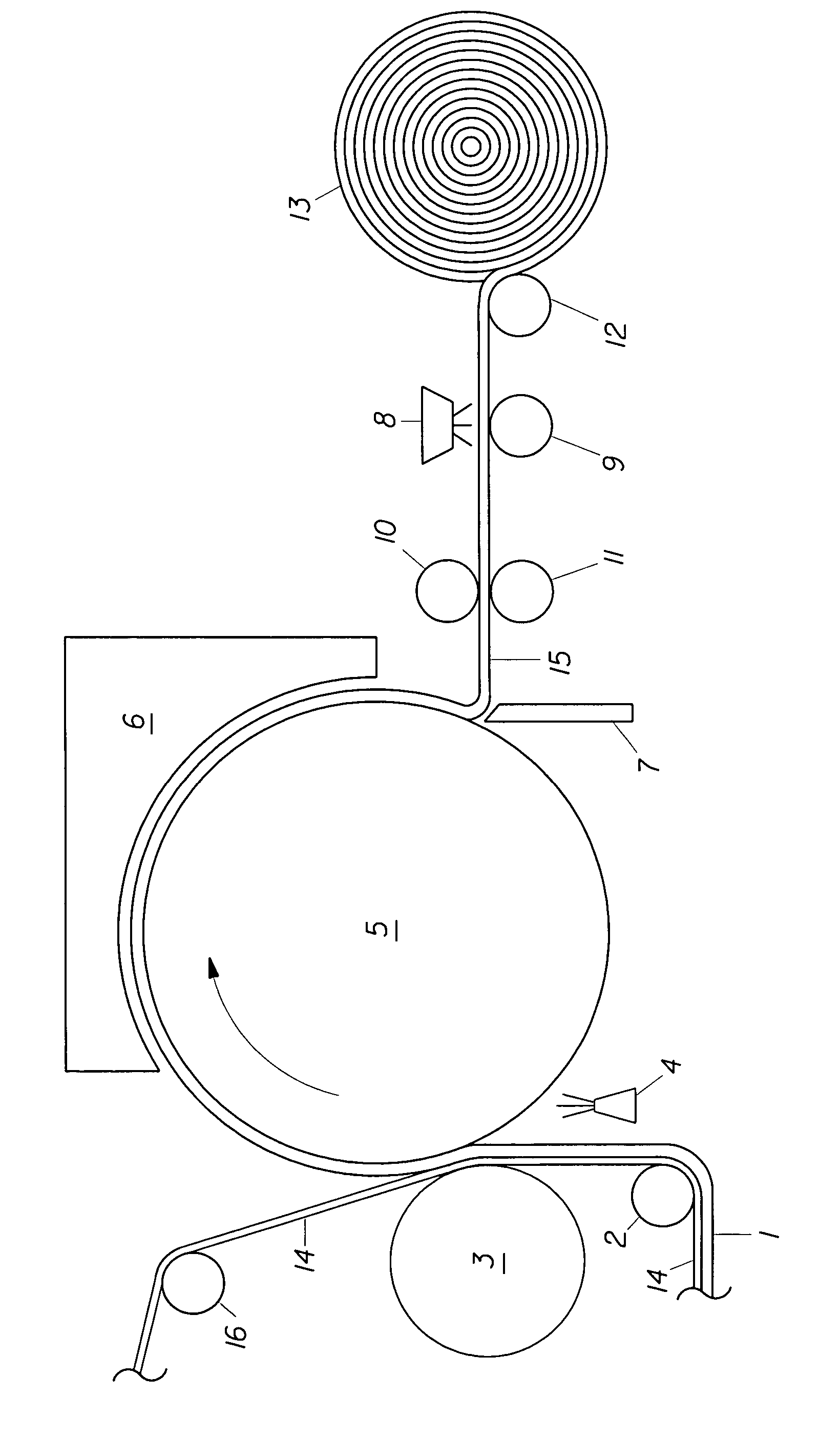
Cross-linking of low and high molecular weight polysaccharides preparation of injectable monophase hydrogels and polysaccharides and hydrogels thus obtained
A process for the crosslinking of at least one polymer selected from polysaccharides and derivatives thereof, which is carried out in an aqueous solvent by the action of an effective and non-excessive amount of at least one crosslinking agent, characterized in that it is carried out on a mixture containing at least one low-molecular weight polymer and at least one high-molecular weight polymer. A process for the preparation of an injectable monophase hydrogel of at least one crosslinked polymer selected from polysaccharides and derivatives thereof is also disclosed. Crosslinked polymers and injectable monophase hydrogels, respectively, are obtainable by each of said processes.
Owner:ALLERGAN IND
Cross-linking of low-molecular weight and high-molecular weight polysaccharides, preparation of injectable monophase hydrogels, polysaccharides and hydrogels obtained
ActiveUS20100226988A1Good curative effectImproved mechanical and remanence propertyPowder deliveryBiocidePolymer scienceCrosslinked polymers
A process for the crosslinking of at least one polymer selected from polysaccharides and derivatives thereof, which is carried out in an aqueous solvent by the action of an effective and non-excessive amount of at least one crosslinking agent, characterized in that it is carried out on a mixture containing at least one low-molecular weight polymer and at least one high-molecular weight polymer. A process for the preparation of an injectable monophase hydrogel of at least one crosslinked polymer selected from polysaccharides and derivatives thereof. Crosslinked polymers and injectable monophase hydrogels respectively obtainable by each of said processes.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Method for reducing the polymer and bentonite requirement in papermaking
The present invention relates to a method for reducing the polymer and bentonite requirement in papermaking wherein medium and high molecular weight polymers are reacted with bentonite. Further, mechanical shearing of the furnish after polymer addition is not required.
Owner:BASF CORP
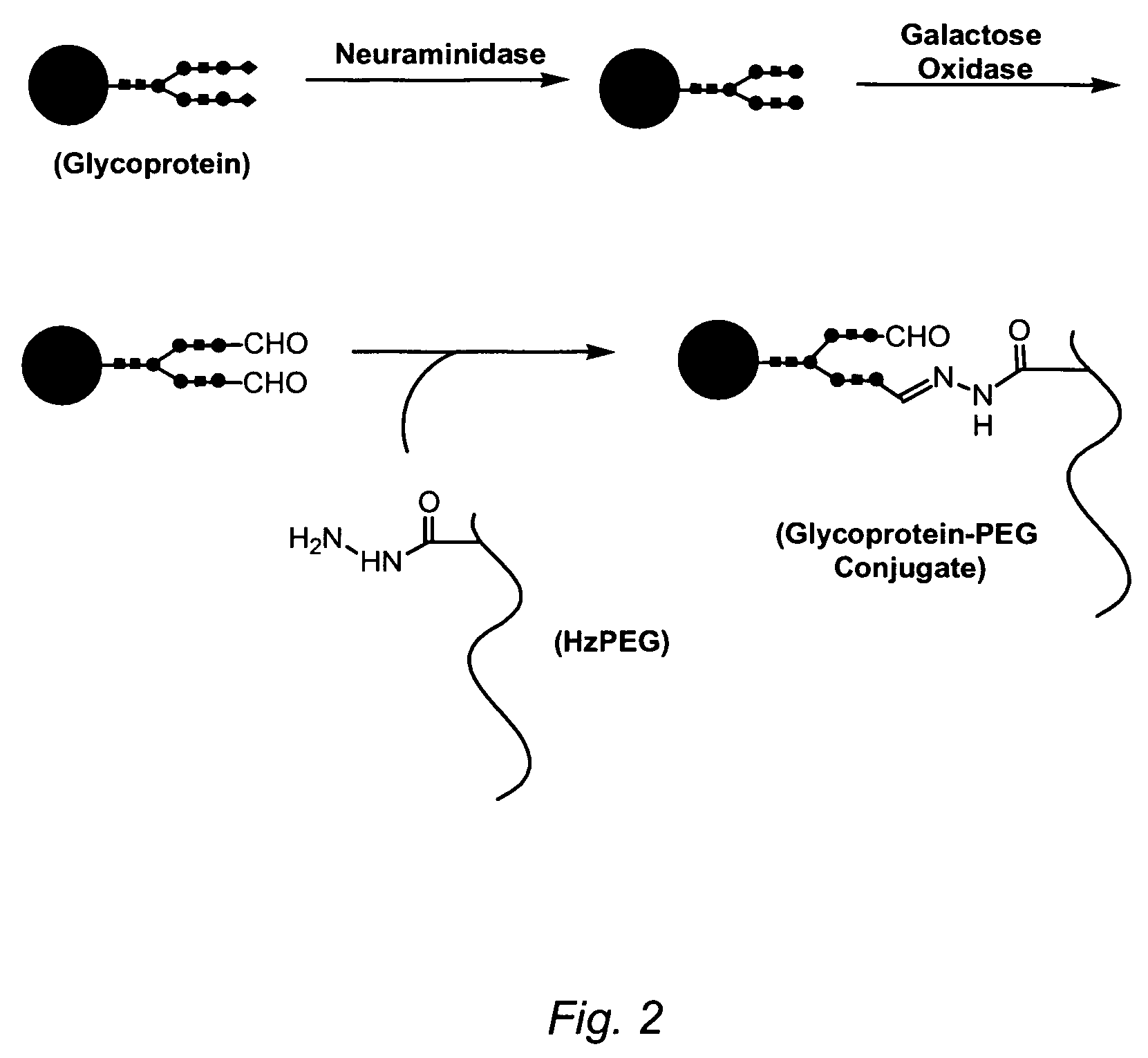
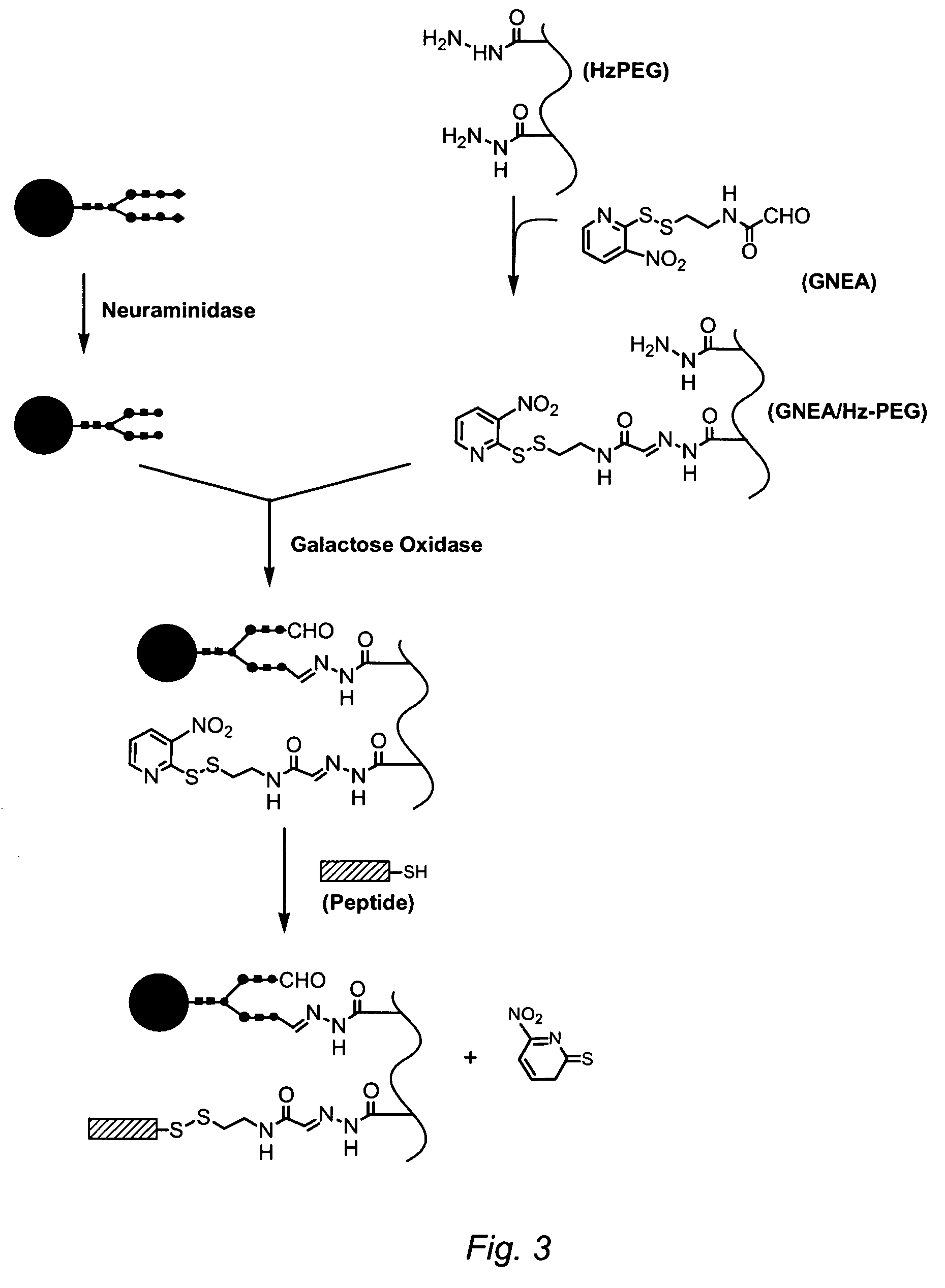
Targeting of glycoprotein therapeutics
Methods of making ligand-decorated polymer conjugates of therapeutic glycoproteins are described. Improved targeting of glycoproteins to specific tissues is achieved by masking the natural carbohydrate and other surface determinants with high molecular weight polymers, such as, e.g., PEG, polysialic acid, etc., which in turn are decorated with target-specific ligands. In some embodiments, acid-labile linkages in such conjugates or rapidly degradable masking groups allow for the intracellular release of the polymer from the glycoprotein, for example, under conditions found in lysosomes.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Polymerization catalysts for producing high molecular weight polymers with low levels of long chain branching
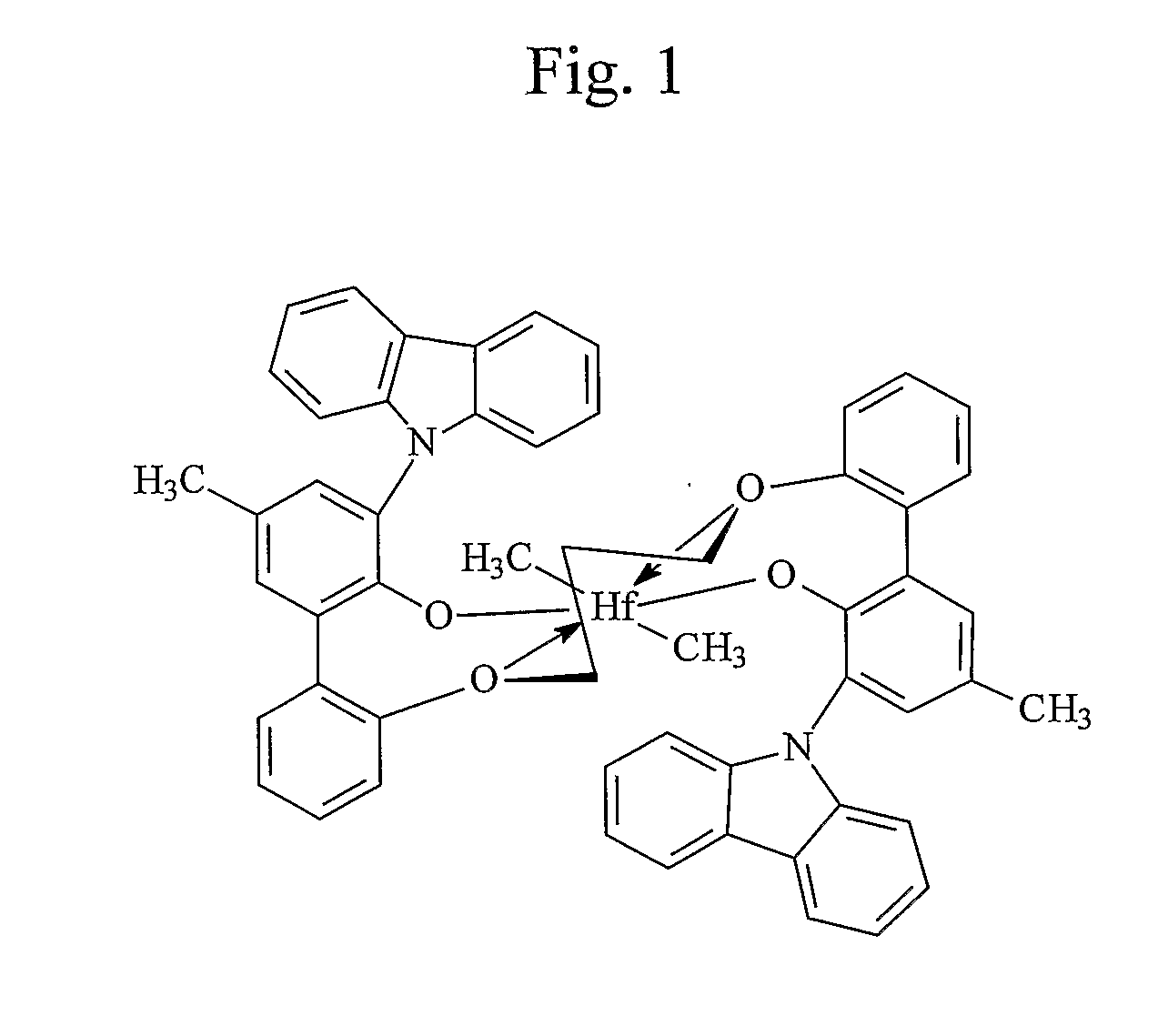
ActiveUS20070179044A1High catalytic activityHigh activityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsPolymer scienceEthylene Polymers
This invention relates to catalyst compositions, methods, and polymers encompassing at least one Group 4 metallocene compound comprising bridging η5-cyclopentadienyl-type ligands, typically in combination with at least one cocatalyst, and at least one activator. The compositions and methods disclosed herein provide ethylene polymers with low levels of long chain branching.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
Process for the fractionation of polymers
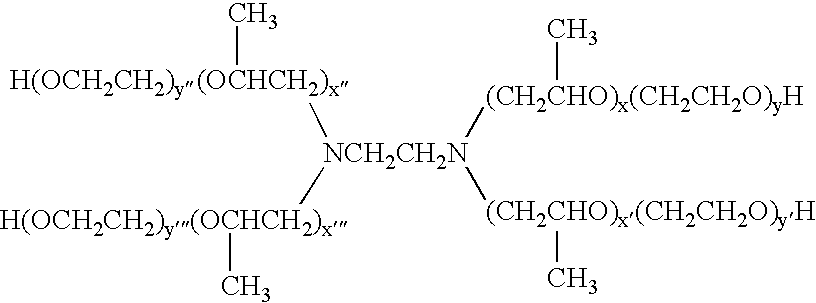
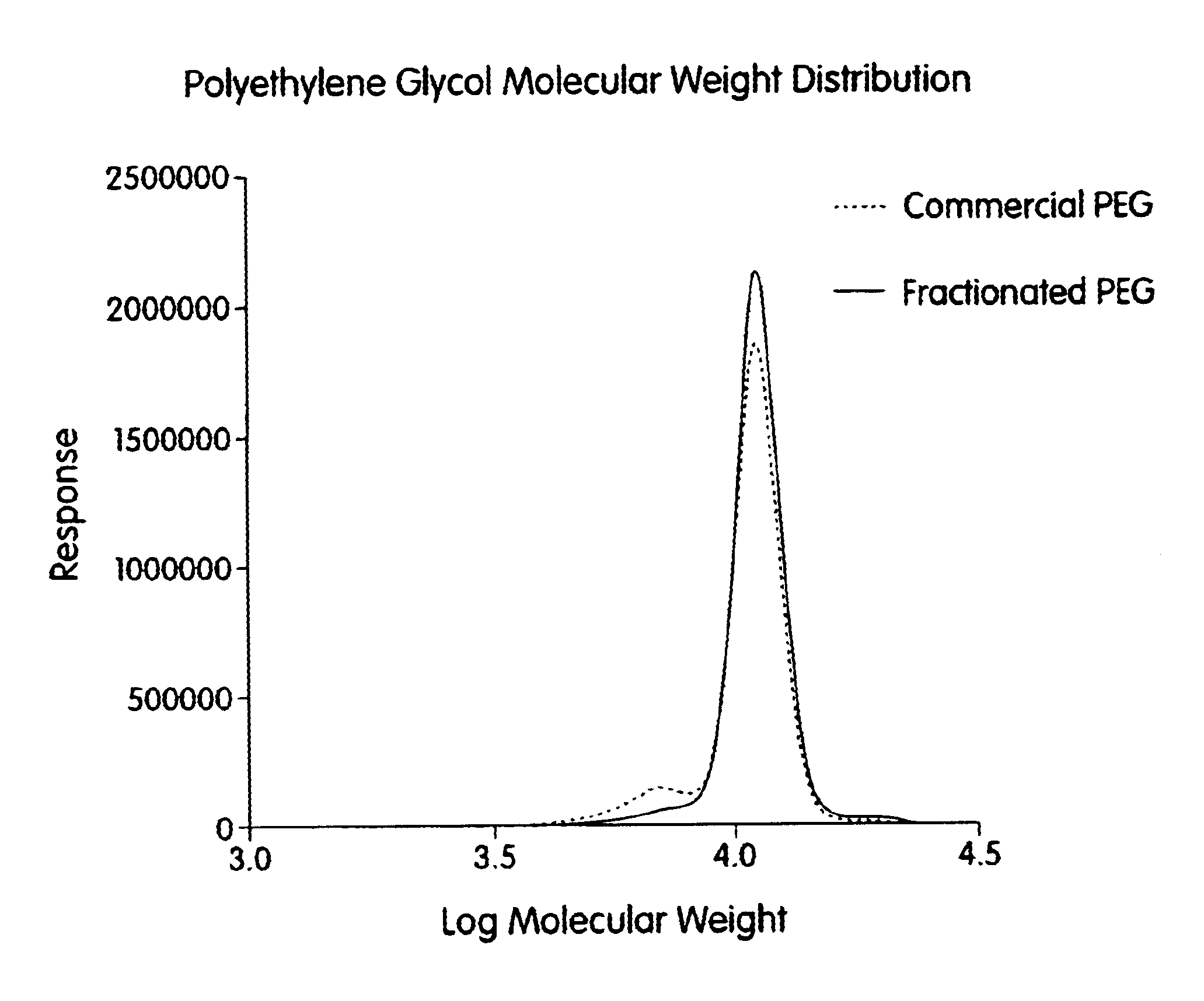
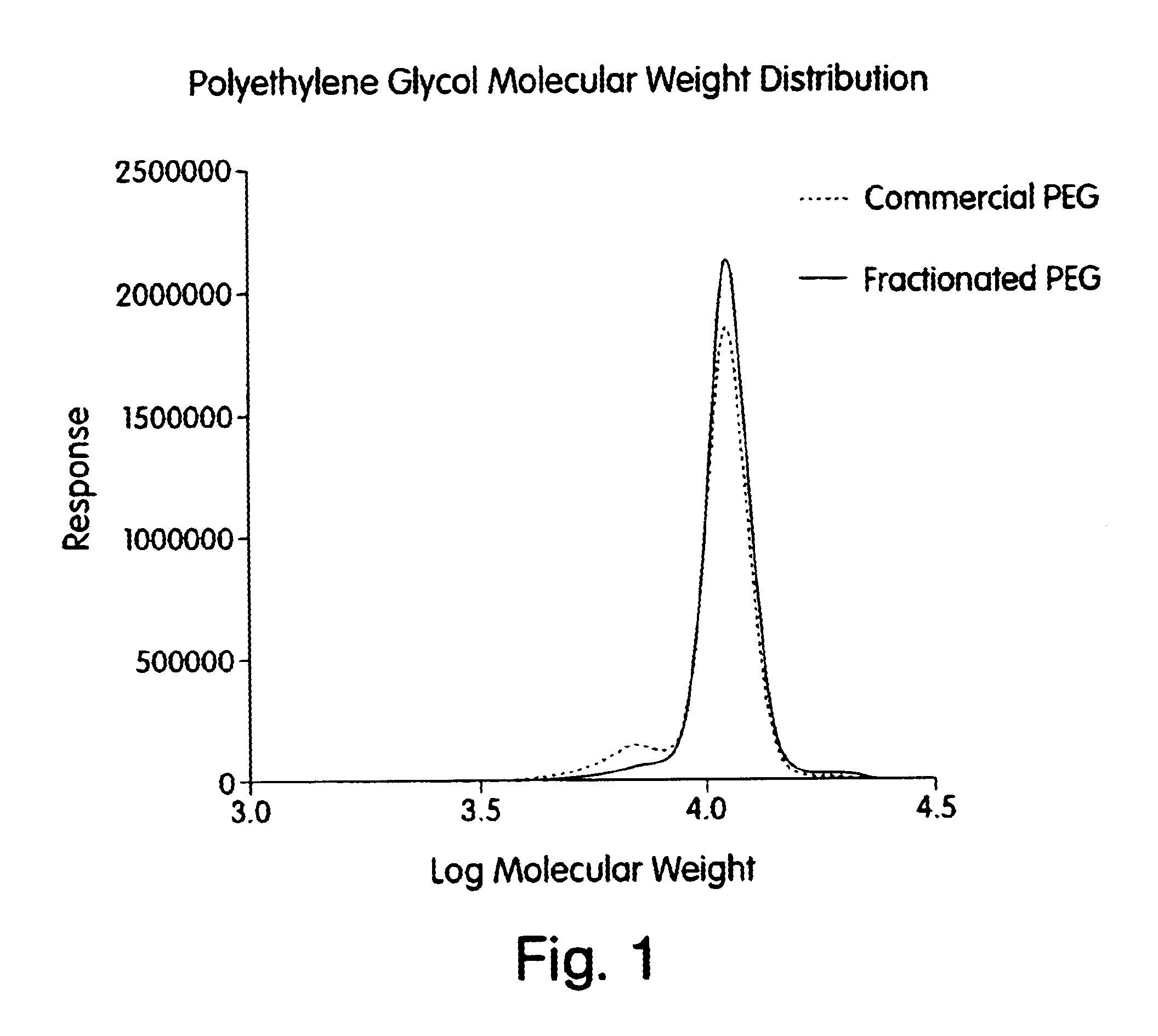
A process for the purification or fractionation of aqueous soluble polymers using an aqueous two-phase system is described. The concentrations of the polymer to be fractionated and of an aqueous soluble salt, and the temperature of the aqueous fractionation medium are adjusted so that two phases form, the lower molecular weight polymer molecules partition into the high salt concentration phase, and the higher molecular weight polymer molecules partition into the low salt concentration phase. The resulting high molecular weight polymers are characterized by a higher average molecular weight and a narrower molecular weight distribution and decreased unsaturation than the unfractionated polymers. After being subjected to the fractionation process, polyol polymers that form hydrogels in aqueous solution exhibited higher viscosities and a liquid to gel transition over a narrower temperature range than the unfractionated polyol polymers.
Owner:HINSBERG MICHAEL G +1
Targeting of glycoprotein therapeutics
Methods of making ligand-decorated polymer conjugates of therapeutic glycoproteins are described. Improved targeting of glycoproteins to specific tissues is achieved by masking the natural carbohydrate and other surface determinants with high molecular weight polymers, such as, e.g., PEG, polysialic acid, etc., which in turn are decorated with target-specific ligands. In some embodiments, acid-labile linkages in such conjugates or rapidly degradable masking groups allow for the intracellular release of the polymer from the glycoprotein, for example, under conditions found in lysosomes.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
High modulus polymer composites and methods of making the same
InactiveUS20060235113A1Improve polymerizationIncrease ratingsThin material handlingPolymer compositesHigh molecular weight polymer
The invention provides methods of producing composite polymers by combining fillers with polymers in the presence of preformed high molecular weight polymer. Monomer polymerization can be initiated through the addition of initiators or by reactive chemical groups on the surface of the fibers. The composite materials formed possess superior mechanical properties compared to similar polymer composites made by either purely mechanical mixing or solely polymerization of monomers in the presence of the fillers.
Owner:COLORADO SCHOOL OF MINES
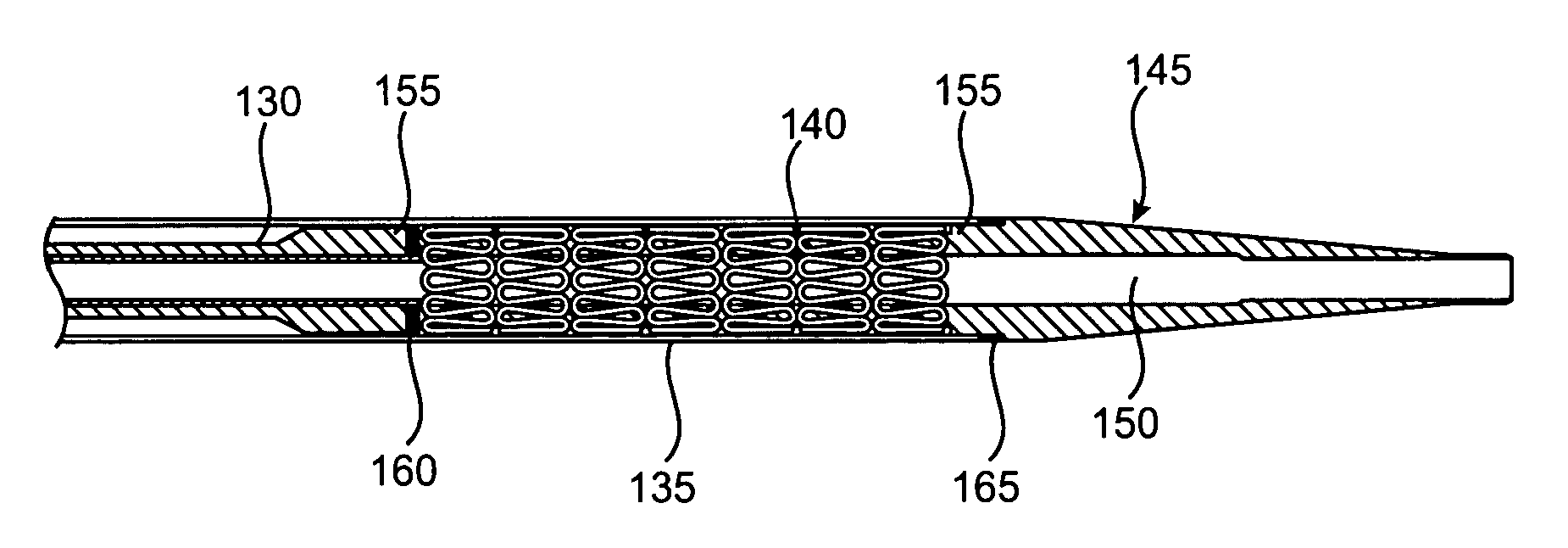
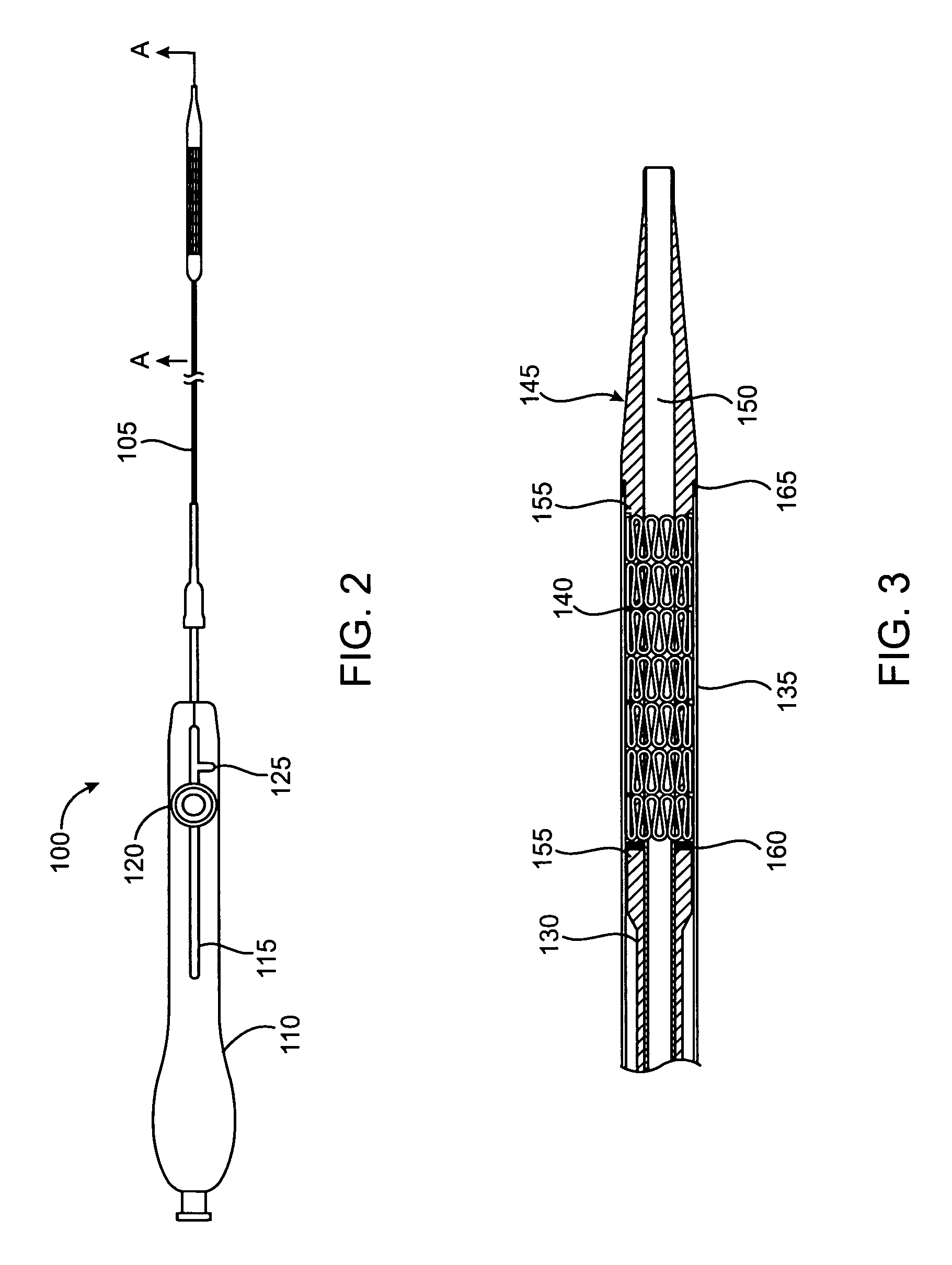
Stent Made From An Ultra High Molecular Weight Bioabsorbable Polymer With High Fatigue And Fracture Resistance
A stent made from an ultra high molecular weight bioabsorbable polymer is disclosed herein. The bioabsorbable polymer can have a Mw greater than 1 million g / mole or greater than 2 million g / mole. Methods of making the ultra high molecular weight polymer stent without degrading the molecular weight are further disclosed.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
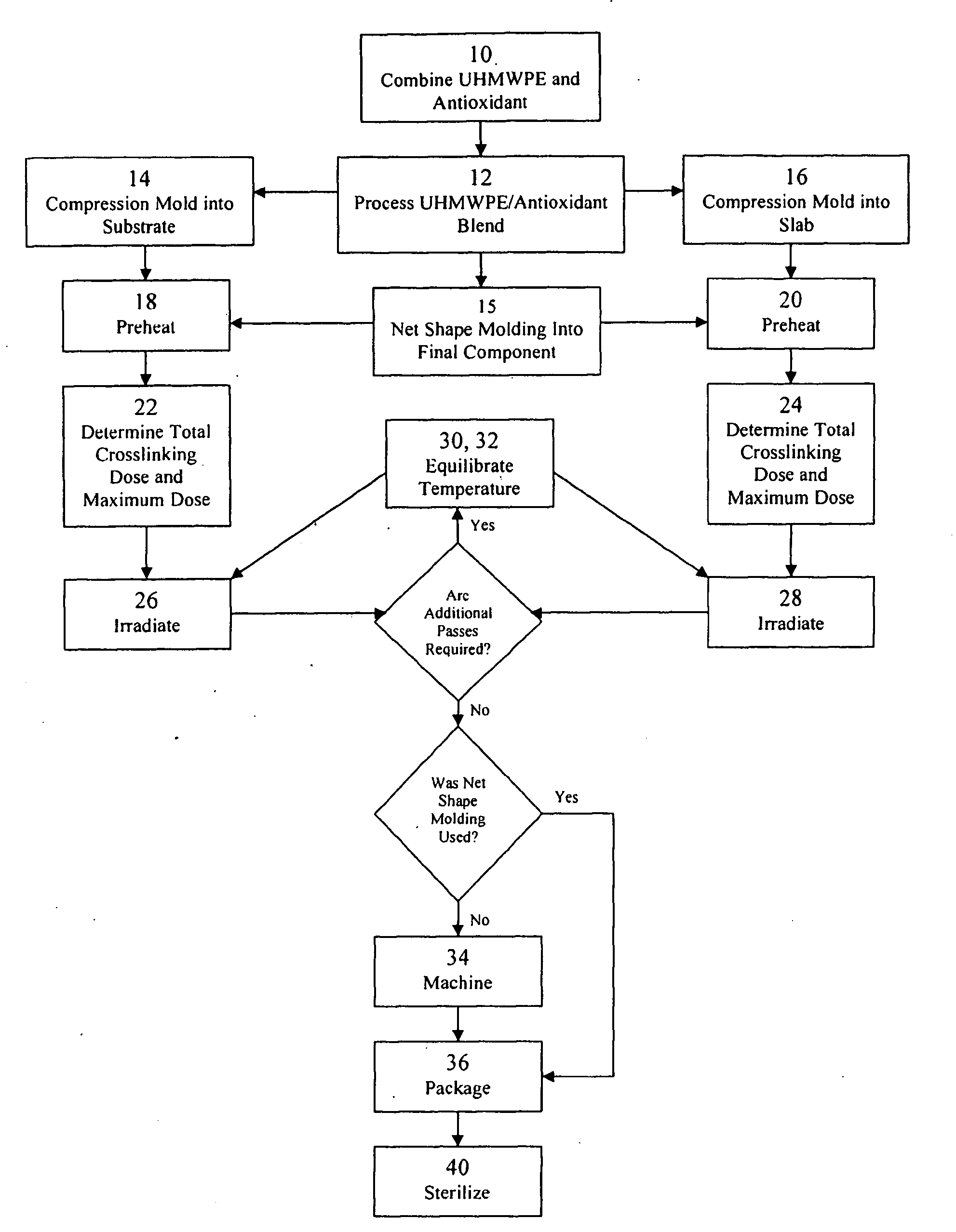
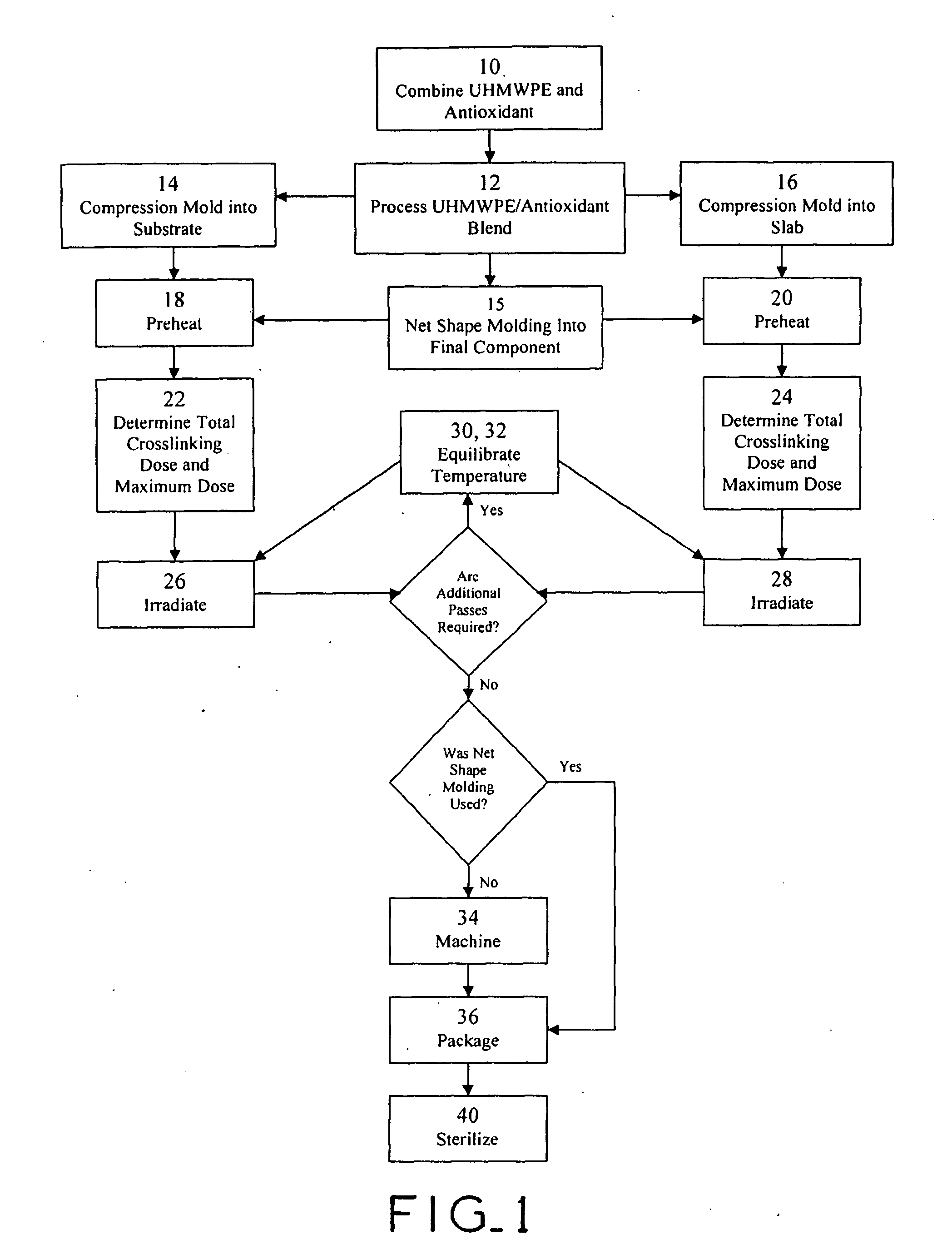
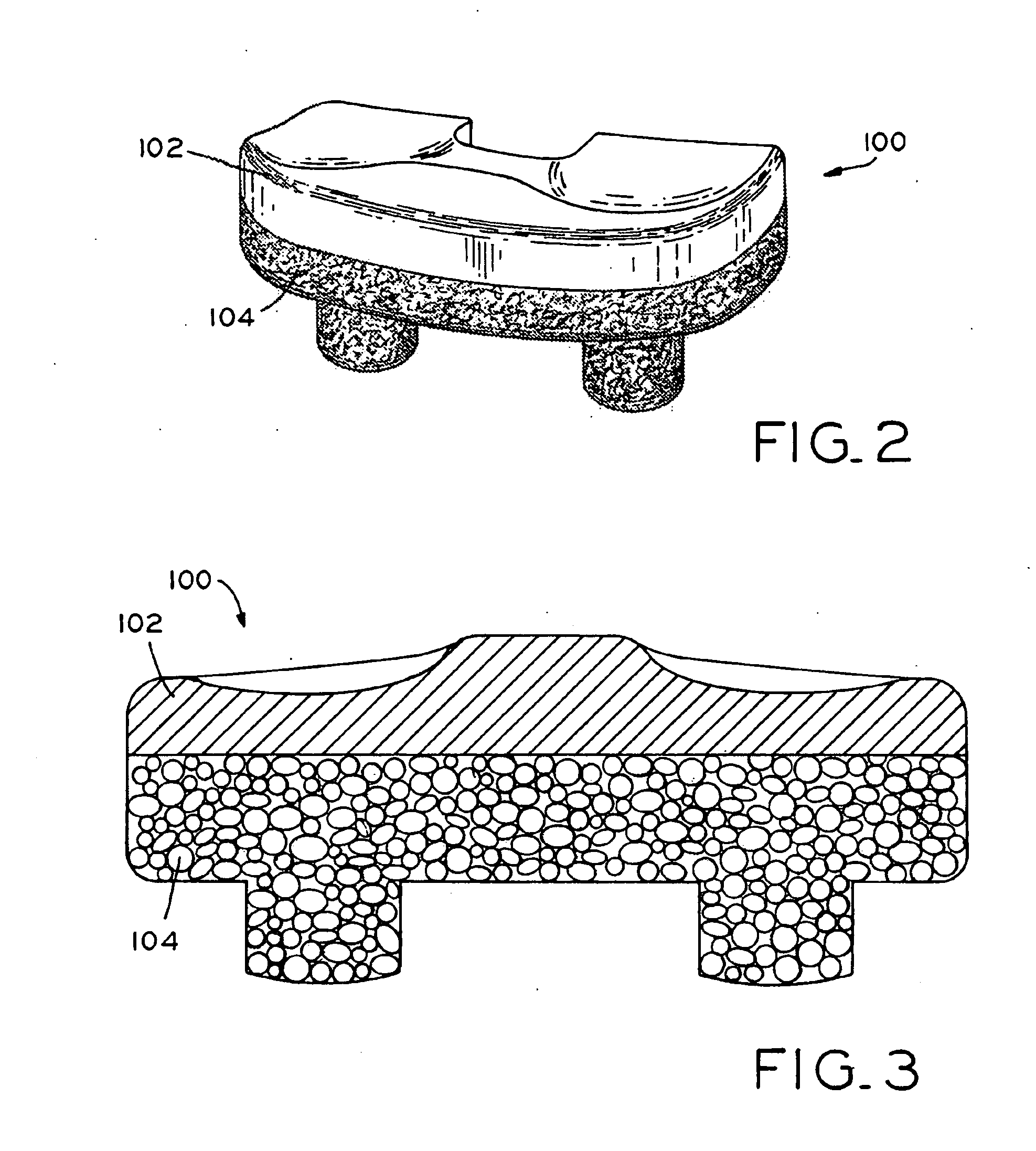
Antioxidant stabilized crosslinked ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene for medical device applications
InactiveUS20080319137A1Avoid mass meltingEncourage mobilityLavatory sanitoryDeodrantsAntioxidantOxidation resistant
An antioxidant combined with UHMWPE prior to subjecting the UHMWPE to crosslinking irradiation. In one exemplary embodiment, the antioxidant is tocopherol. After the antioxidant is combined with the UHMWPE, the resulting blend may be formed into slabs, bar stock, and / or incorporated into a substrate, such as a metal, for example. The resulting product may then be subjected to crosslinking irradiation. In one exemplary embodiment, the UHMWPE blend is preheated prior to subjecting the same to crosslinking irradiation. Once irradiated, the UHMWPE blended product may be machined, packaged, and sterilized in accordance with conventional techniques.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Galactomannan based well treating fluids
ActiveUS20050272612A1Low polymer contentHigh molecular weightFluid removalFlushingPolymer scienceFracturing fluid
A well fracturing fluid is shown which includes an aqueous base fluid, a hydratable polymer, such as a guar gum, and a suitable crosslinking agent for crosslinking the hydratable polymer to form a polymer gel. The hydratable polymer has a higher molecular weight which is achieved by improvements in the processing of the guar split. The higher molecular weight polymer provides improved performance in well fracturing operations.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Alkali Metal-Sulfur Secondary Battery Containing a Polymer-Encapsulated Sulfur Cathode and Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20180294475A1Inhibited DiffusionReduce and eliminate effectFinal product manufacturePositive electrodesConductive polymerElectrical battery
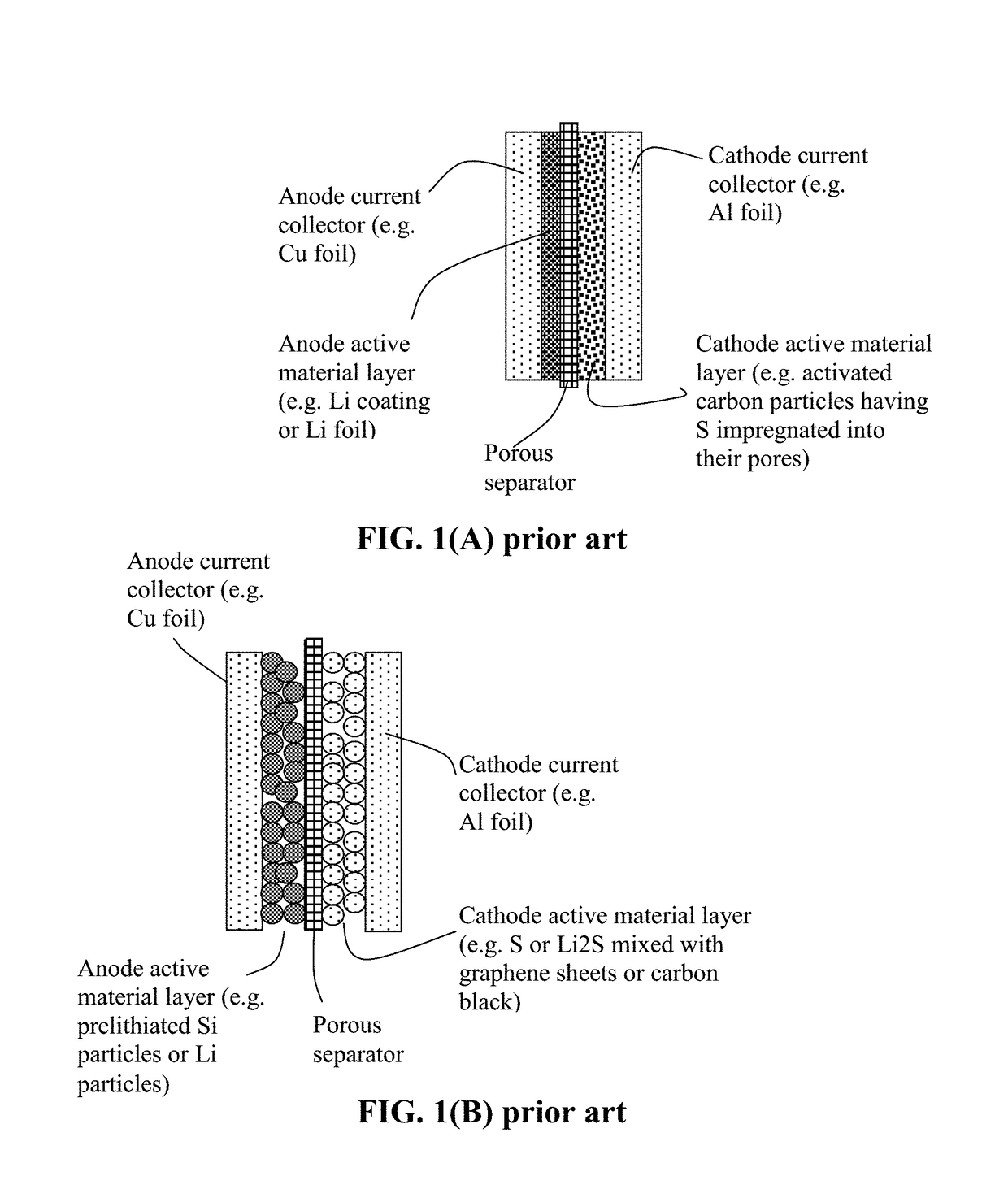
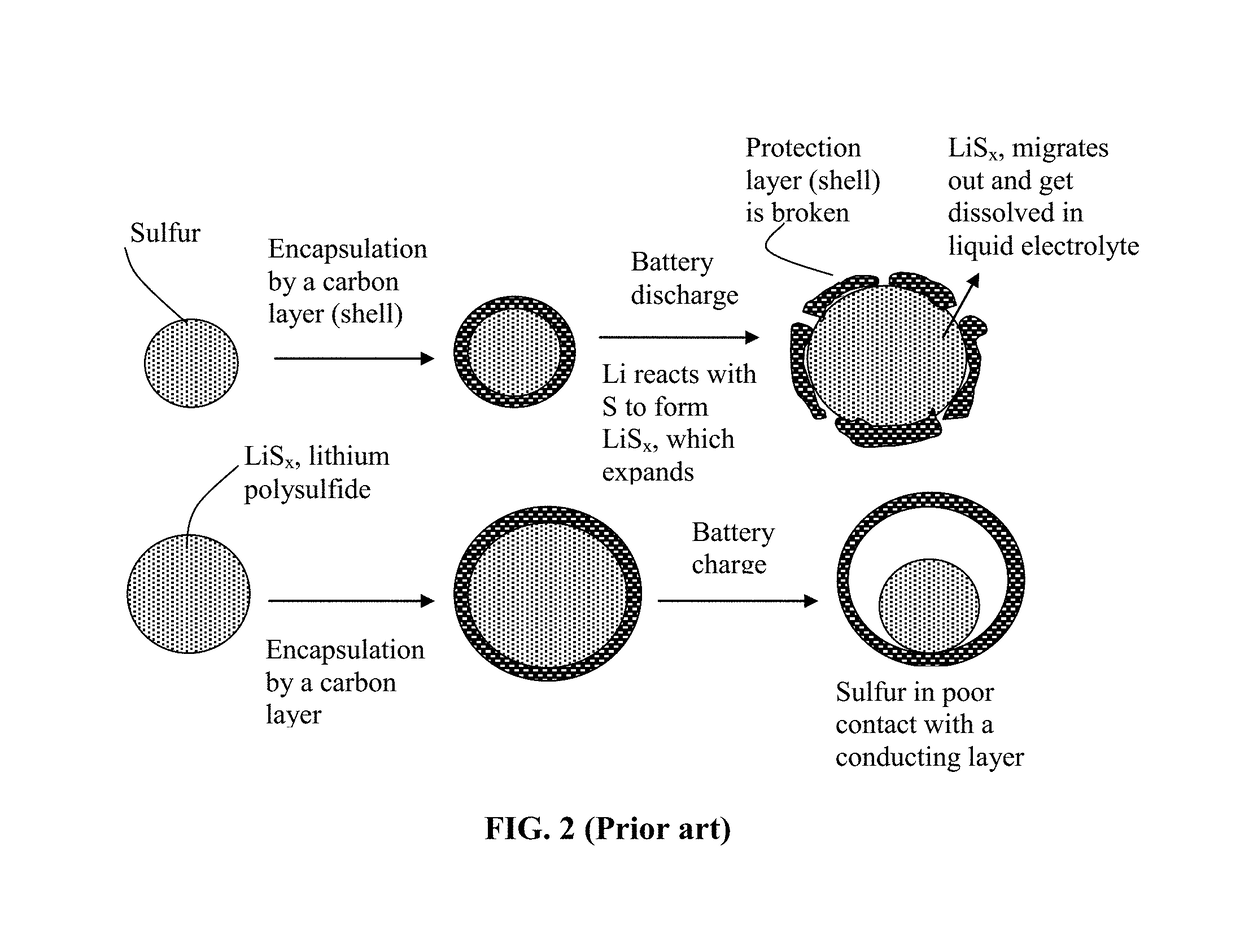
Provided is a rechargeable alkali metal-sulfur cell comprising an anode active material layer, an electrolyte, and a cathode active material layer containing multiple particulates of a sulfur-containing material selected from a sulfur-carbon hybrid, sulfur-graphite hybrid, sulfur-graphene hybrid, conducting polymer-sulfur hybrid, metal sulfide, sulfur compound, or a combination thereof and wherein at least one of the particulates is composed of one or a plurality of sulfur-containing material particles being embraced or encapsulated by a thin layer of a high-elasticity ultra-high molecular weight polymer having a recoverable tensile strain no less than 2%, a lithium ion conductivity no less than 10−6 S / cm at room temperature, and a thickness from 0.5 nm to 10 μm This battery exhibits an excellent combination of high sulfur content, high sulfur utilization efficiency, high energy density, and long cycle life.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Polymer blends
Owner:NOVA CHEM (INT) SA
Bi-axial oriented sheath
A sheath and method of forming is disclosed for a bi-axial oriented made of high molecular weight polymers. The high molecular weight polymers provide a bi-axial oriented sheath with a high hoop stress and a thin wall thickness. A device and method of use is also disclosed for a device for delivery of a self-expanding prosthesis covered by a bi-axial oriented sheath made of high molecular weight polymers. The bi-axial oriented sheath may be moved from a first position constraining the self-expanding prosthesis to a second position releasing the self-expanding prosthesis. During delivery, the device is inserted into the vascular system of the patient, with the self-expanding prosthesis positioned at the location to be treated. The self-expanding prosthesis is then released by moving the bi-axial oriented sheath from the first to second positions, releasing the self-expanding prosthesis.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Cross-linking of low-molecular weight and hih-molecular weight polysaccharides, preparation of injectable monphase hydrogels, polysaccharides and hydrogels obtained
InactiveUS20120295870A1Good curative effectImproved mechanical and remanence propertyOrganic active ingredientsBiocidePolymer scienceCrosslinked polymers
A process for the crosslinking of at least one polymer selected from polysaccharides and derivatives thereof, which is carried out in an aqueous solvent by the action of an effective and non-excessive amount of at least one crosslinking agent, characterized in that it is carried out on a mixture containing at least one low-molecular weight polymer and at least one high-molecular weight polymer. A process for the preparation of an injectable monophase hydrogel of at least one crosslinked polymer selected from polysaccharides and derivatives thereof. Crosslinked polymers and injectable monophase hydrogels respectively obtainable by each of said processes.
Owner:ALLERGAN IND SAS
Paper softening compositions containing low levels of high molecular weight polymers and soft tissue paper products comprising said compositions
Disclosed is a composition suitable for atomizing without excessive aerosolization in the form of an oil-in-water emulsion comprising: a) a continuous aqueous phase, and b) a discontinuous oil phase wherein the rheology of the aqueous phase is modified by the addition of a water-in-oil emulsion comprising: i) a high molecular weight polymer in a discontinuous aqueous phase, and ii) a continuous organic solvent phase. Preferred embodiments of the present invention relate to compositions for softening an absorbent paper tissue comprising a) a quaternary ammonium softening active ingredient; b) an electrolyte; c) a high molecular weight polymer emulsion comprising: i) from about 20% to about 40% by weight of the premix of a high molecular weight polymer; ii) from about 40% to about 60% of water; and iii) from about 20% to about 40% of an organic solvent; and d) a vehicle in which said softening active ingredient is dispersed.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Pultrusion method for thermoplastic composite material and forming die thereof
InactiveCN1730270AImprove impregnation effectImprove mechanical propertiesPolymer scienceFiber bundle
The invention relates to a pultrusion method for thermoplastic composite, which takes fortifying fiber and matrix fiber as raw material, including the following steps: a. placing matrix fiber and fortifying fiber on the creel in the weight ratio of 95-20:5-80; b. loading the fortifying fiber and matrix fiber to demand scale into the preheat chamber by the thread wire and board and preheating them; c. loading the preheated mixed fiber tuft into the preforming die, so the tuft near to the entrance shape of the forming die; d. loading the preformed mixed fiber into the forming die. Certainly the performing die and forming die can be diad, with performing segment and forming segment in one die; e. after loading out from the forming die the section bar cooling and shaping to get products. The invention overcomes the socking problem of high molecular polymer, improving the socking effects of thermoplastic composites, and the mechanical property enhances dramatically.
Owner:SINOMA SCI & TECH
Polymerization process and control of polymer composition properties
Methods of controlling the flow index and / or molecular weight split of a polymer composition are disclosed. The method of producing a polymer composition in one embodiment comprises incorporating a high molecular weight polymer into a low molecular weight polymer to form the polymer composition in a single polymerization reactor in the presence of polymerizable monomers, a bimetallic catalyst composition and at least one control agent; wherein the control agent is added in an amount sufficient to control the level of incorporation of the high molecular weight polymer, the level of low molecular weight polymer, or both. Examples of control agents include alcohols, ethers, amines and oxygen.
Owner:UNIVATION TECH LLC
Solid state deformation processing of crosslinked high molecular weight polymeric materials
InactiveUS20080140196A1Joint implantsElectric/magnetic/electromagnetic heatingPolymer scienceAccelerated aging
Solid-state deformation processing of crosslinked high molecular weight polymers such as UHMWPE, for example by extrusion below the melt transition, produces materials with a combination of high tensile strength and high oxidative stability. The materials are especially suitable for use as bearing components in artificial hip and other implants. Treated bulk materials are anisotropic, with enhanced strength oriented along the axial direction. The material is oxidatively stable even after four weeks of accelerated aging in a pressure vessel containing five atmospheres of oxygen (ASTM F2003). Because of its oxidative stability, the deformation processed material is a suitable candidate for air-permeable packaging and gas sterilization, which has thus far been reserved for remelted crosslinked UHMWPE.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
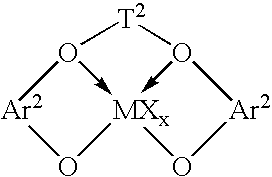
Supported Bis(Hydroxylarylaryloxy) Catalysts For Manufacture Of Polymers
InactiveUS20080051537A1Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalytic reactionsCompound (substance)Solid particle
A supported, heterogeneous catalyst composition for use in polymerization of addition polymerizable monomers to form high molecular weight polymers, comprising: 1) a substrate comprising a solid, particulated, high surface area, surface modified, inorganic oxide compound, 2) a Group 4 metal complex of a bis(hydroxyarylaryloxy) ligand; and optionally 3) an activating cocatalyst for the metal complex.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method for the production of a polypropylene blend
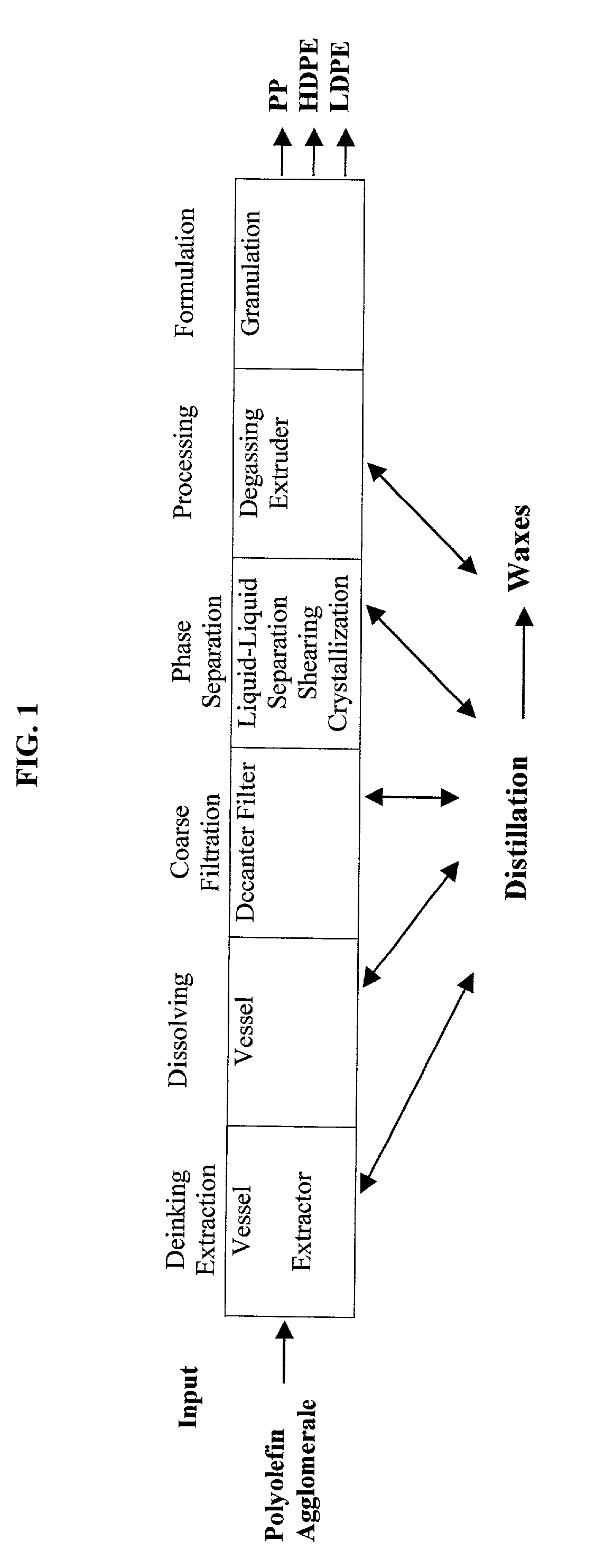
InactiveUS20020128394A1Faster cycle timeMechanical characteristicPlastic recyclingPolymer recoveryOrganic solventPlastic packaging
A method for producing a polypropylene blend from a plastic packaging materials containing high molecular weight polypropylene, other high molecular weight polymers such as polyethylene, low molecular weight polymers and other contaminants. The method includes extraction, solid-liquid separation and liquid-liquid phase separation using various organic solvents. The polypropylene blend has a purity of 95% and has favorable melt flow characteristics, while retaining satisfactory mechanical properties.
Owner:DER GRUNE PUNKT DUALES SYST DEUTLAND
Process for the production of paper
InactiveUS6100322AImprove performanceHigh retention ratePaper/cardboardInorganic compound additionInorganic saltsPolymer science
The invention relates to a process for the production of paper from a suspension of cellulose containing fibers, and optional fillers, comprising adding to the suspension a low molecular weight cationic organic polymer, a high molecular weight cationic or amphoteric polymer and anionic inorganic particles, forming and draining the suspension on a wire, wherein the low molecular weight polymer has a molecular weight below 700,000 and the high molecular weight polymer has a molecular weight above 1,000,000, said polymers being simultaneously added to the suspension. The invention further relates to a polymer mixture in the form of an aqueous dispersion comprising at least one high molecular weight cationic or amphoteric acrylamide-based polymer having a molecular weight above 1,000,000, at least one low molecular weight cationic organic polymer having a molecular weight below 700,000 and at least one water-soluble inorganic salt, the weight ratio of said high molecular weight polymer to said low molecular weight polymer being within the range of from 9:1 to 1:2.
Owner:EKA CHEM AC LTD
High molecular weight guanidine salt and polyamine antimicrobial polymeric compounds, producing method and application of the same
InactiveCN101173041AModulation of antimicrobial propertiesSolve the problem of difficult to obtain higher molecular weight polymersFibre treatmentPaper/cardboardFiberAntibiosis
The invention discloses a high molecular weight guanidine salt and polybasic amine antibiosis type polymer and a preparation method and the application thereof. The polymer comprises a repeated unit structure as right, wherein, X1 and X2 are the same or different polybasic amines; Y is Cl<->, NO3<->, HCO3<-> or H2PO4<->; Z is polyprotic acid, polyprotic acid anhydride or multielement ester. When in preparation, the mixture of polynary amine and guanidine salt is heated for reaction, and then polyprotic acid, polyprotic acid anhydride or multielement ester is added, and the temperature is continuously raised for reaction. The invention solves the problem that the polybasic amine and the guanidine salt react through a main body, thereby being difficulty to obtain a higher molecular weight polymer. In lower reaction temperature and shorter reaction time, by the chain expanding reaction to a polynary amine and guanidine salt prepolymer by the polyfunctionality substance, the high molecular weight guanidine salt and polybasic amine antibiosis polymer is formed. The polymer can be used as the anti fungus agent of the fiber product, the paper product, the non-weaving product and the tissue, etc.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Group IVB transition metal compounds
ActiveUS7569646B1Silicon organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPolymer scienceOlefin polymerization
The invention is a Group IVB transition metal compound which may be employed in the polymerization of olefins to produce high molecular weight polymers.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Sustained intraocular delivery of drugs from biodegradable polymeric microparticles
ActiveUS20100261646A1Lower eye pressureSustained releaseHormone peptidesBiocideMicrosphereActive agent
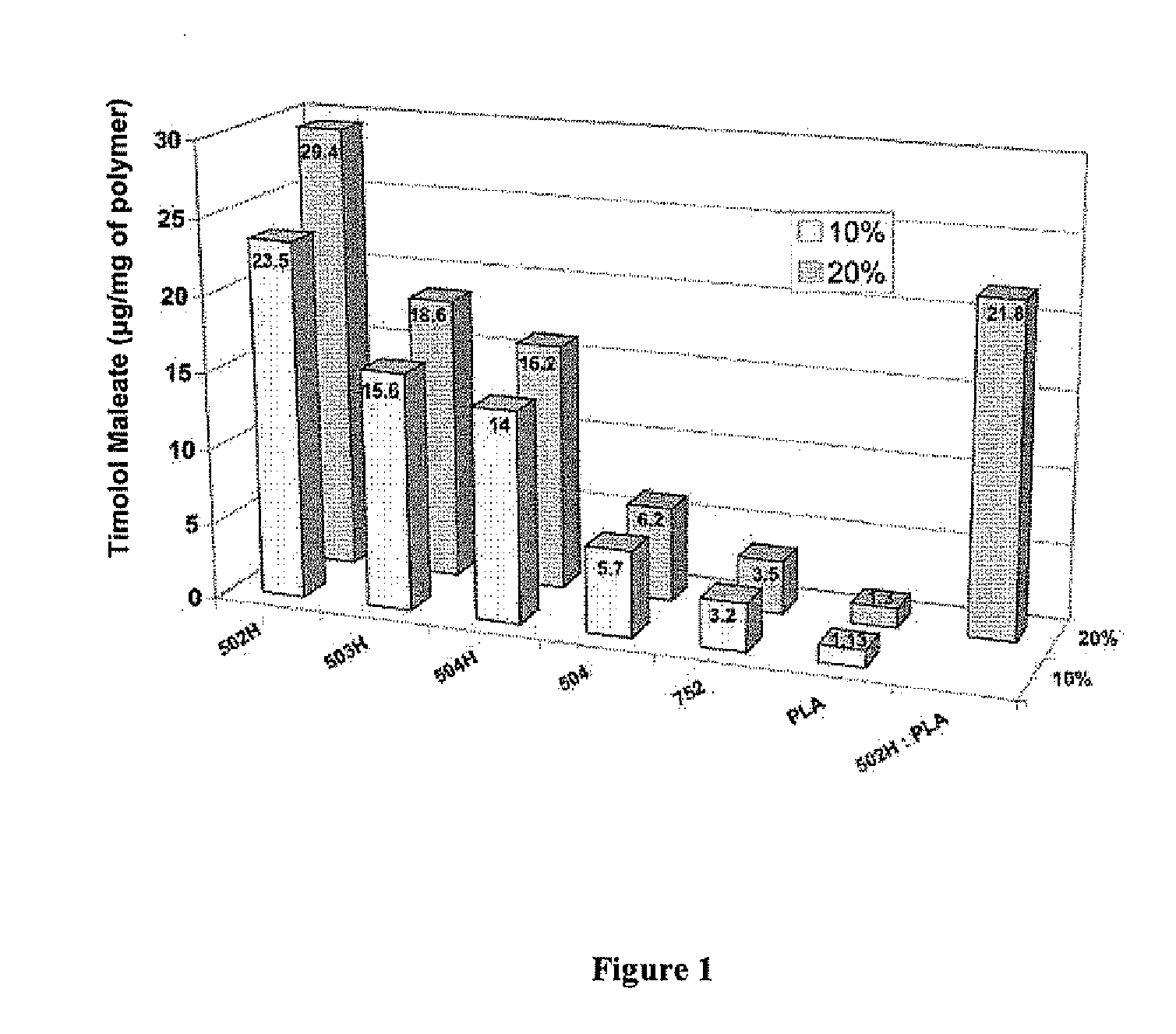
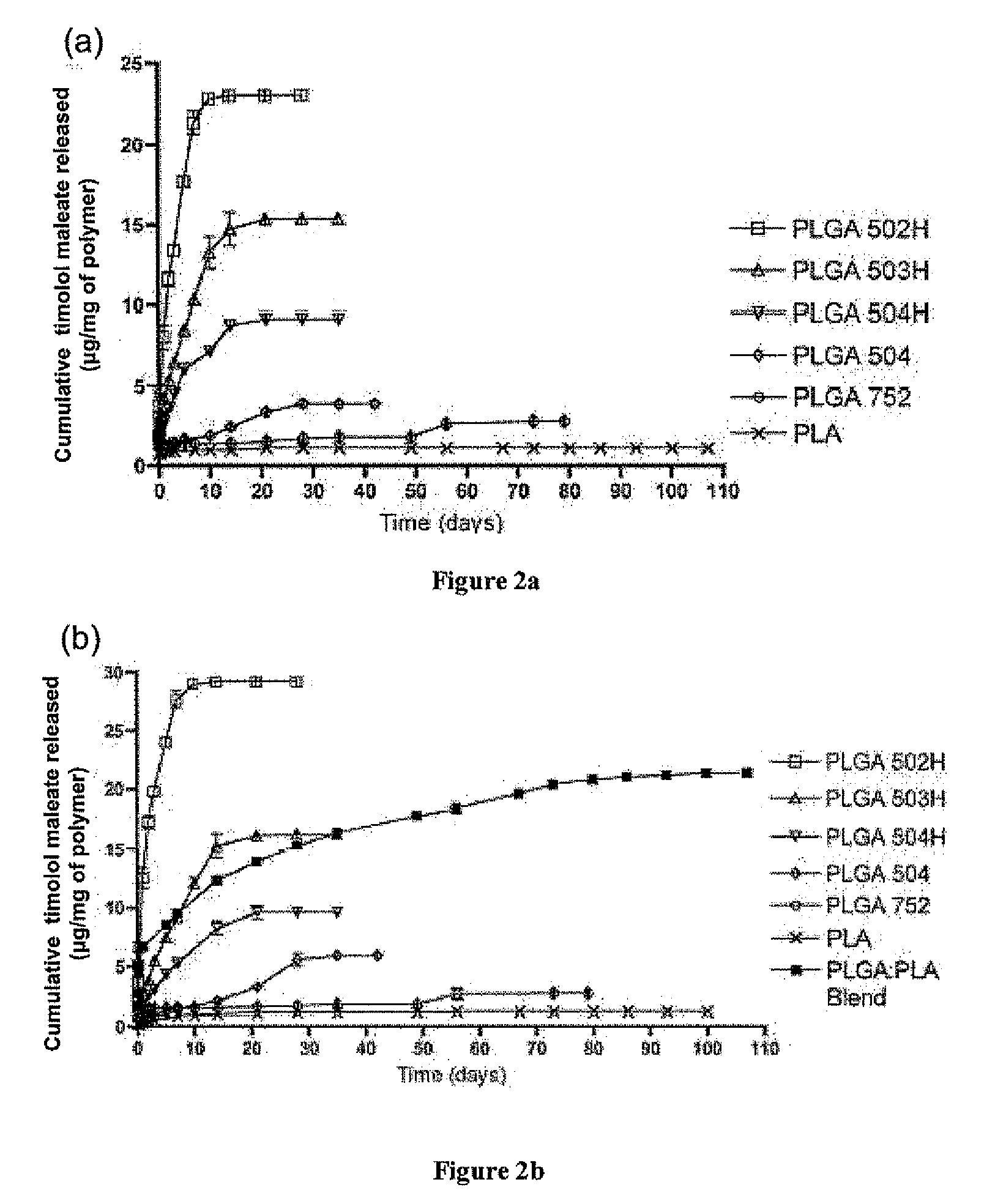
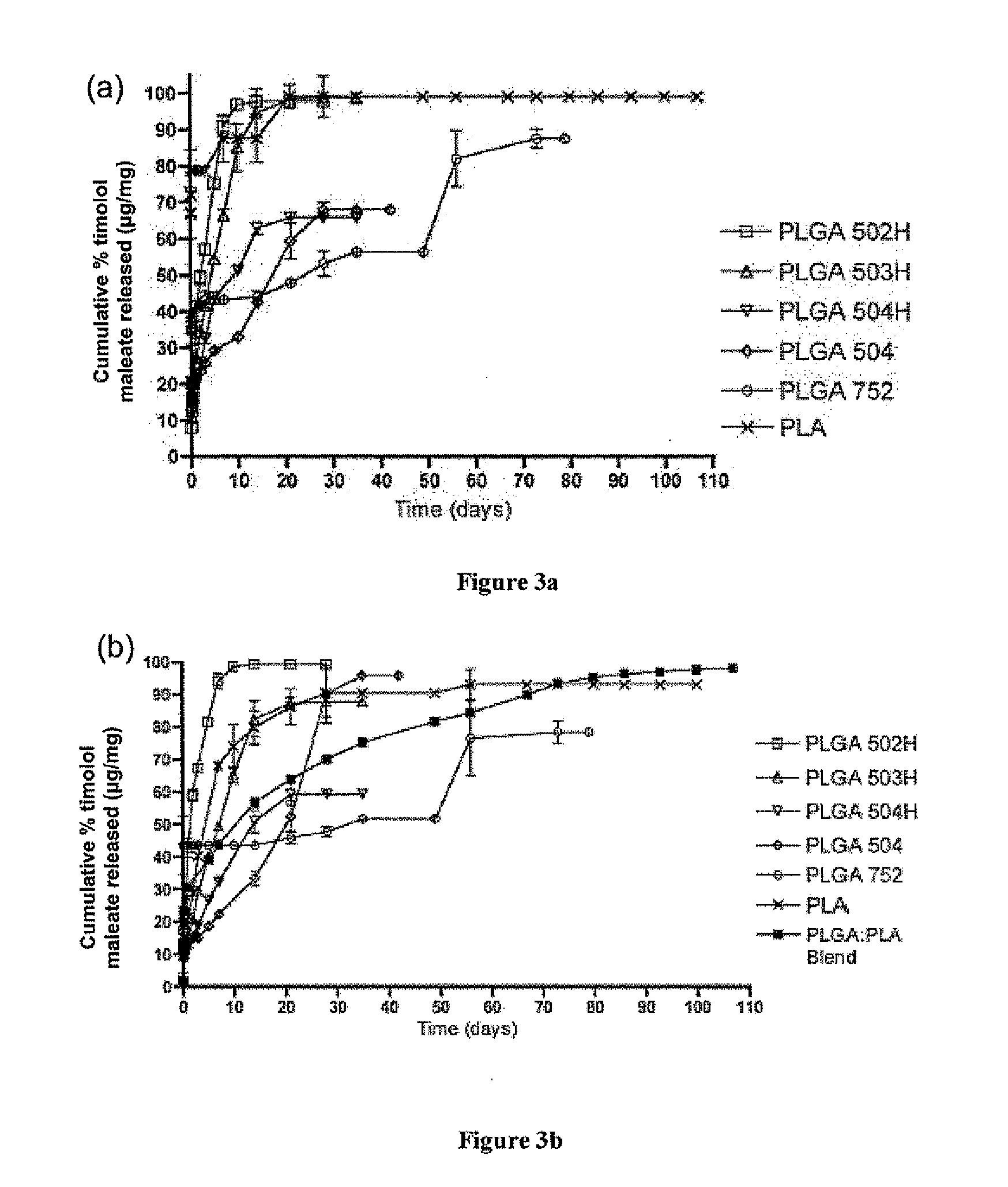
Biodegradable polymeric microparticle compositions containing one or more active agents, especially those useful for treating or preventing or one or more diseases or disorders of the eye, and methods of making and using thereof, are described. The microsphere compositions release an effective amount of the one or more active agents for a period greater than 14 days in vivo, preferably greater than 60 days in vivo, more preferably up to 73 days in vivo, more preferably greater than 90 days in vivo, even more preferably over 100 days in vivo, and most preferably greater than 107 days in vivo. In a preferred embodiment, the microparticle compositions contain one or more active agents useful for managing elevated intraocular pressure (TOP) in the eye. In one embodiment, the microspheres are formed from polylactide-co-glycolide (“PLGA”); in another embodiment, the microspheres are formed from a blend PLGA and poly lactic acid (“PLA”). Relatively hydrophilic, and preferably carboxylated, polymeric materials such as PLGA are used for a drug such as timolol maleate, which is relatively water soluble, to increase drug loading. Higher molecular weight polymers, as well as the ratio of LA (which has a longer degradation time, up to one to two years) to GA (which has a short degradation time, as short as a few days to a week), are used to provide release over a longer period of time. The combination of drug loading and release rate, as well as the minimization of initial burst release, result in prolonged release of a higher amount of drug.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
Preparation method of thermotropic liquid crystal polyarylester fiber
InactiveCN104389045AEasy to operateReaction condition controlArtificial filament heat treatmentMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentFiberAcetic anhydride
The invention discloses a preparation method of a thermotropic liquid crystal polyarylester fiber, relates to a preparation method of thermotropic liquid crystal polyarylester, and aims to solve the problems that the existing method for preparing the thermotropic liquid crystal polyarylester is complex and the polyarylester fiber is low in tensile strength. The preparation method of the thermotropic liquid crystal polyarylester fiber comprises the following steps: step one, adding p-hydroxybenzonic acid, 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-5-carboxylbenzimidazole, acetic anhydride, 4-diethylaminopyridine and an antioxidant into a polymerization kettle for carrying out melt condensation polymerization to prepare a pre-polymer of thermotropic liquid crystal polyarylester; step two, putting the pre-polymer in a rotary kiln under the condition with nitrogen protection for carrying out solid phase polycondensation reaction to obtain high-molecular-weight polymer powder; step three, mixing the high-molecular-weight polymer powder, then cooling and drawing to prepare primary polyarylester fiber; and step four, carrying out heat treatment on the primary polyarylester fiber. The preparation method of the thermotropic liquid crystal polyarylester fiber is simple to operate; the tensile strength of the polyarylester fiber which is finally obtained can reach 4.0-4.5GPa.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG JUXIANG TECH DEV CO LTD
Spectrum-controllable reflective polarizers having electrically-switchable modes of operation
InactiveUS6633354B2High bandwidthLiquid crystal compositionsSolar heating energyPolymer networkPolarizer
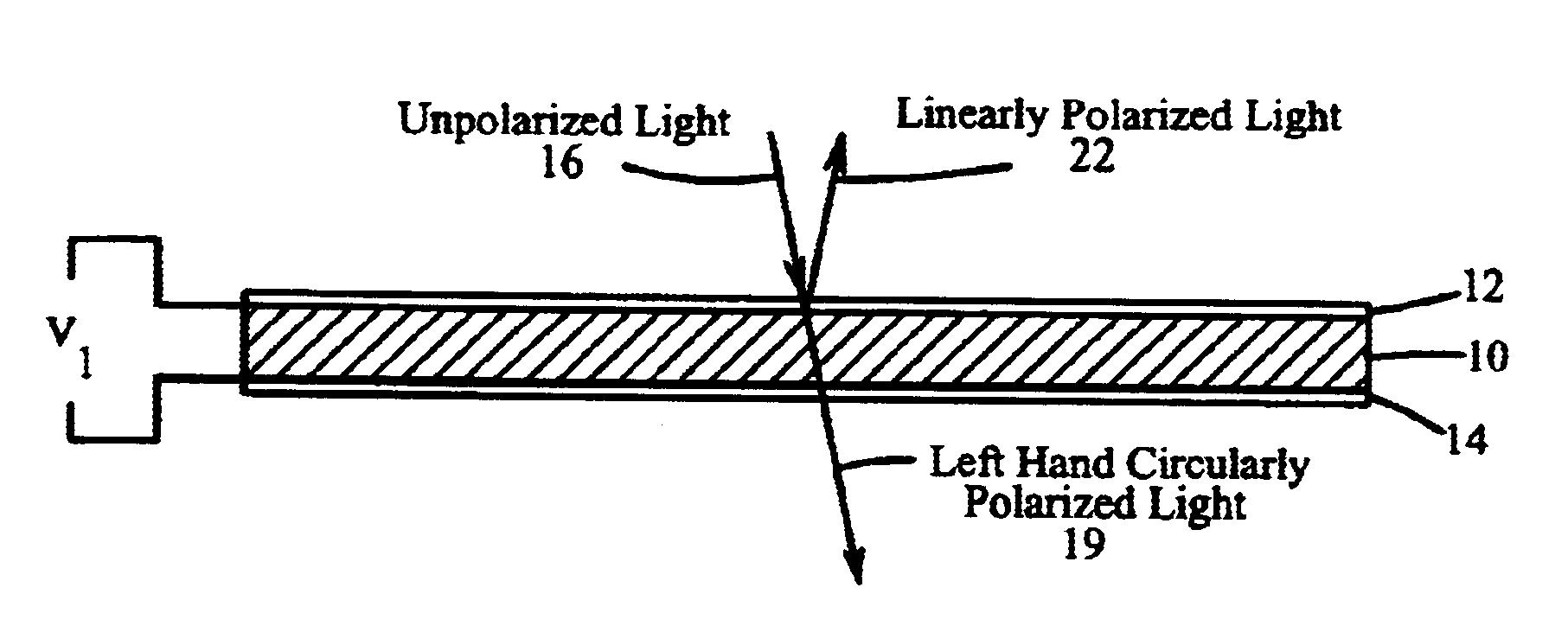
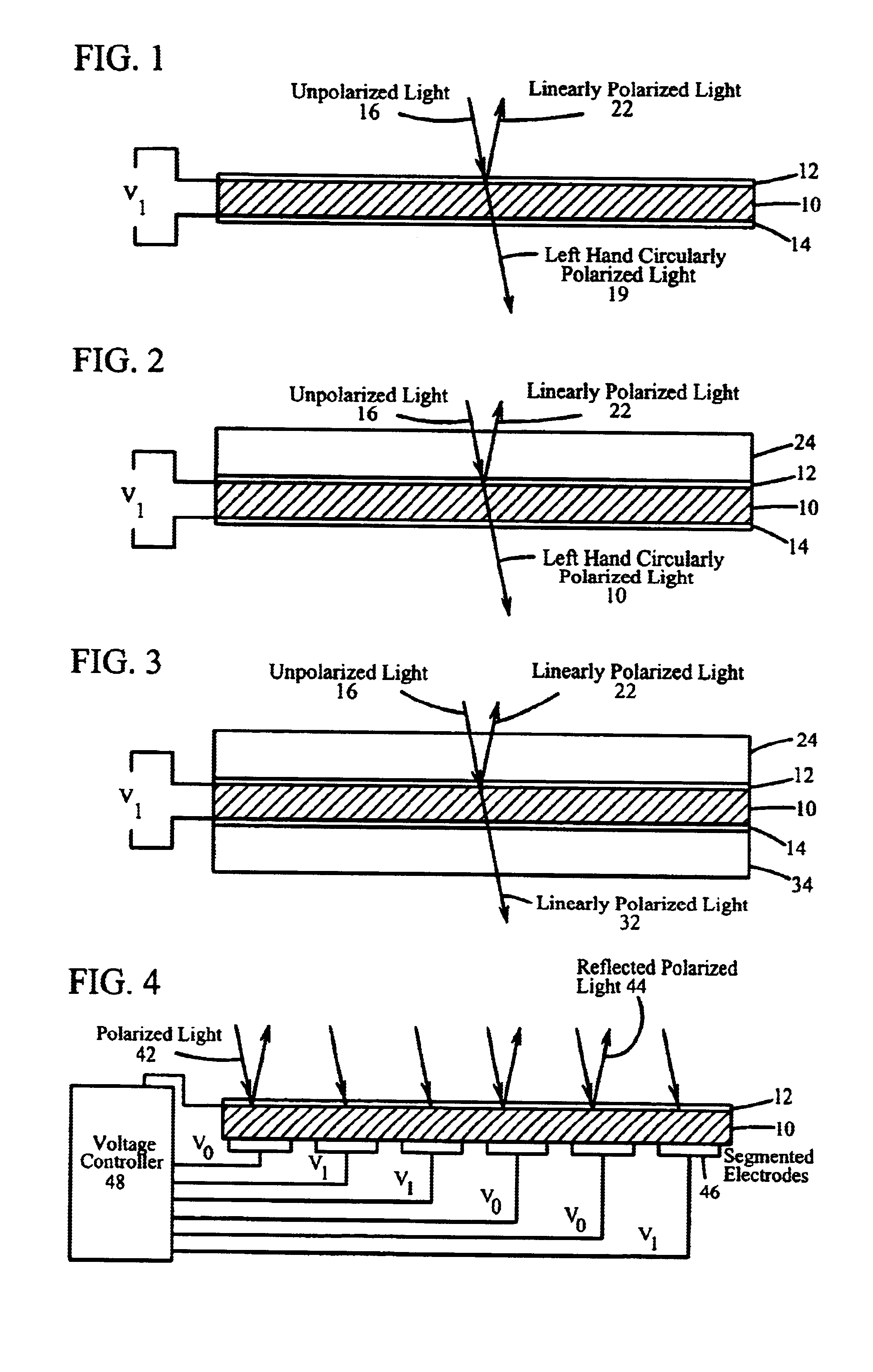
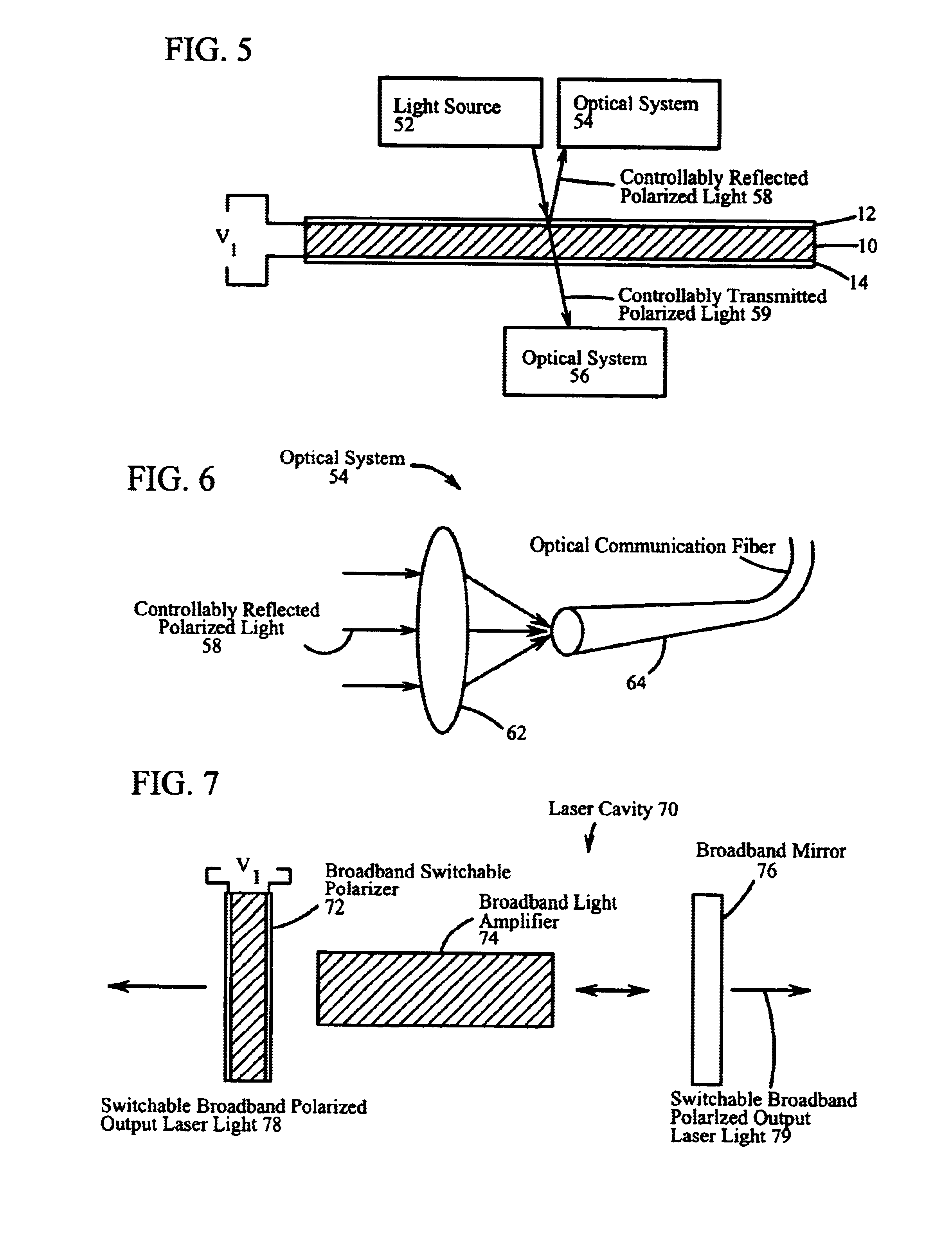
A light controlling film is disclosed, comprising a polymerized polymer network varying spatially in a direction normal to the film surface, where the polymerized polymer network is a crosslinked high molecular weight polymeric material mixed with a low molecular weight nematic material exhibiting cholesteric liquid crystal (CLC) order, wherein an electric field impressed in the film controls the reflection bandwidth of circularly polarized light.< / PTEXT>
Owner:REVEO
Preparation for water soluble high-molecular weight cationic polymer
A water-soluble, high molecular weight cationic polymer is prepared with polyphyletic composite oxidation-reduction triggering system by: adding multiple aid reagent, triggering methylpropyleneacyloxyethyltrimethyl ammonium chloride, or propyleneamide- propyleneacyloxyethyltrimethyl ammonium chloride, together with propyleneamide water solution to copolymer. The obtained products are water-soluble cationic polymer powder state, viscidity number 13.4-23.4dl / g, METMACS or AETMAC in polymer mol percent content is 0.5% -99.5%, residual monomers content is is less than or equal to 0.1 wt%. This invention has the features of that it adopts domestic industrial grade monomers as raw materials directly, without refine, the obtained products' cationic value is 50-99.5. The products can be used as clay stabilizer, reverse emulsion breaker, slow corrosion agent in petroleum engineering, intensifier, treating agent for wastewater in paper-making industry, water-treating agent and silt dewatering agent in environment protection etc.
Owner:HAISO TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com