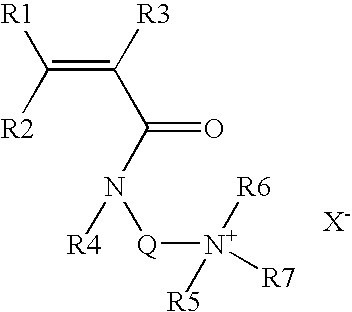
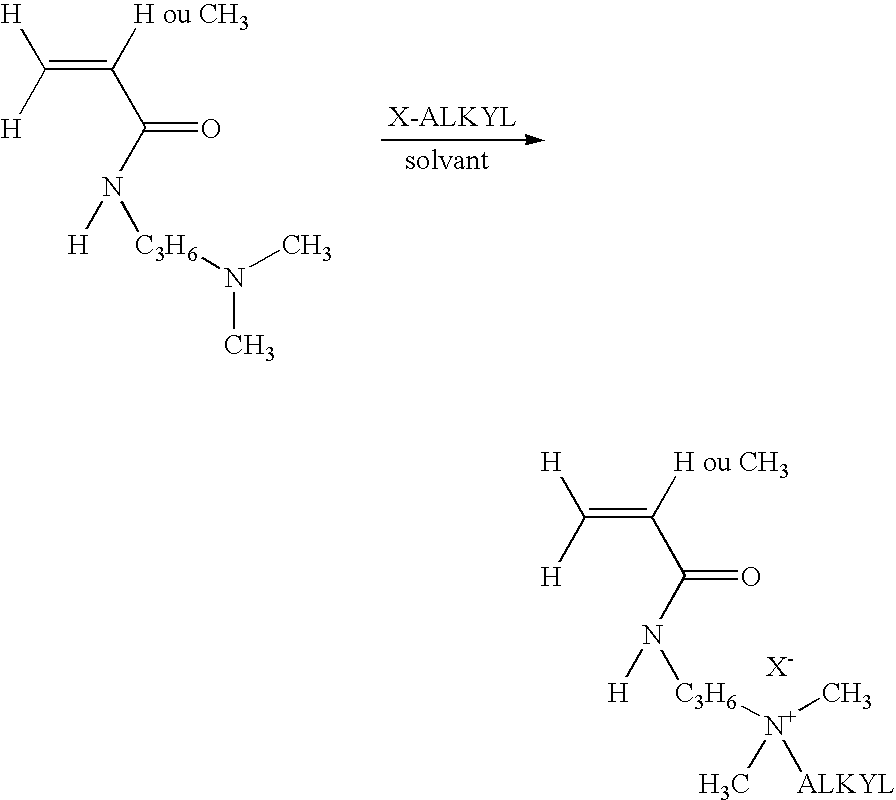
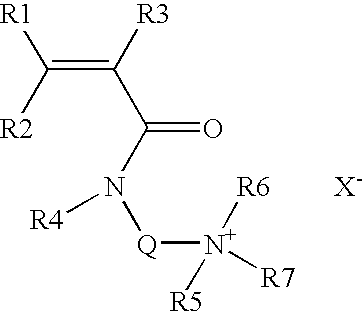
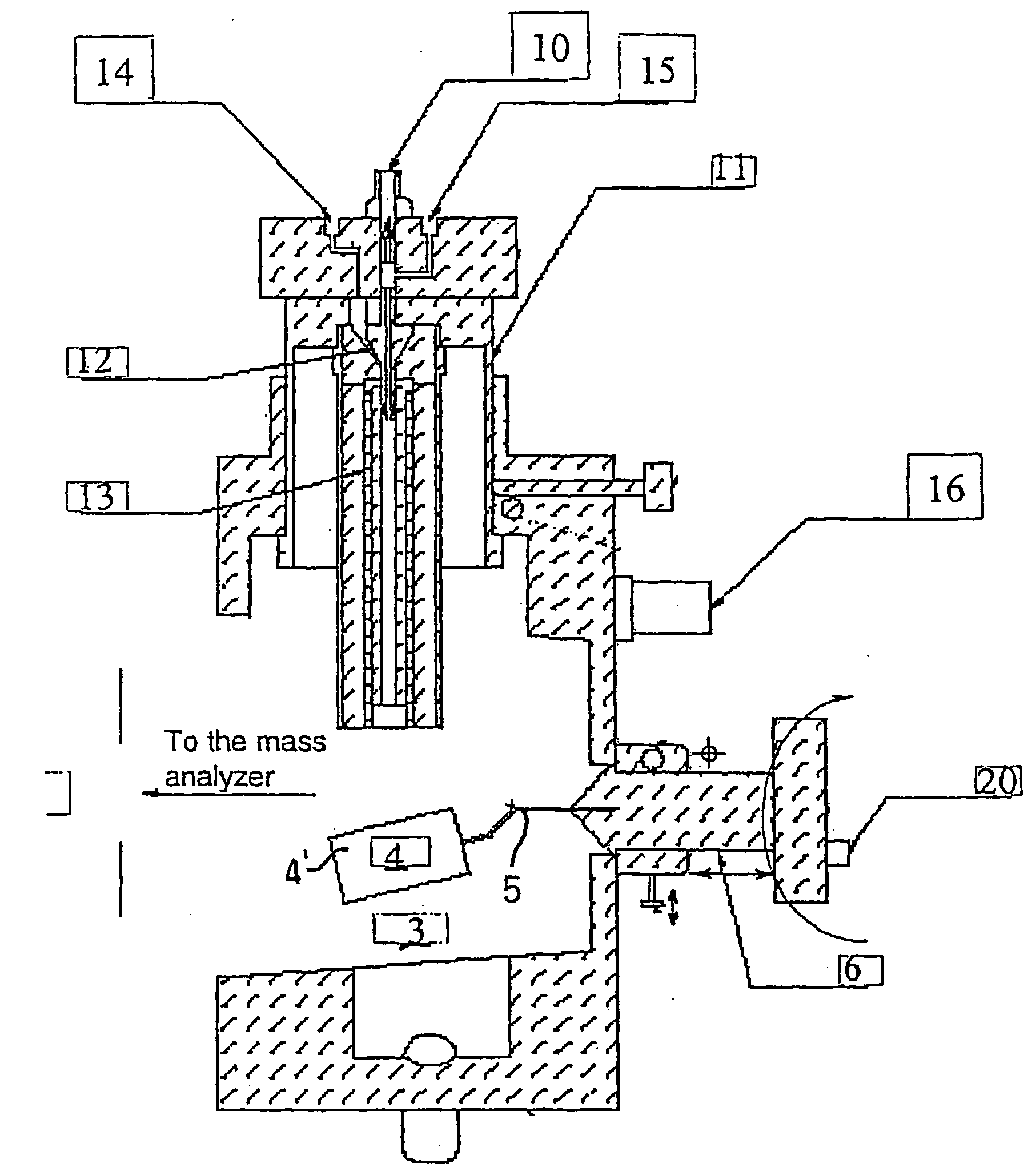
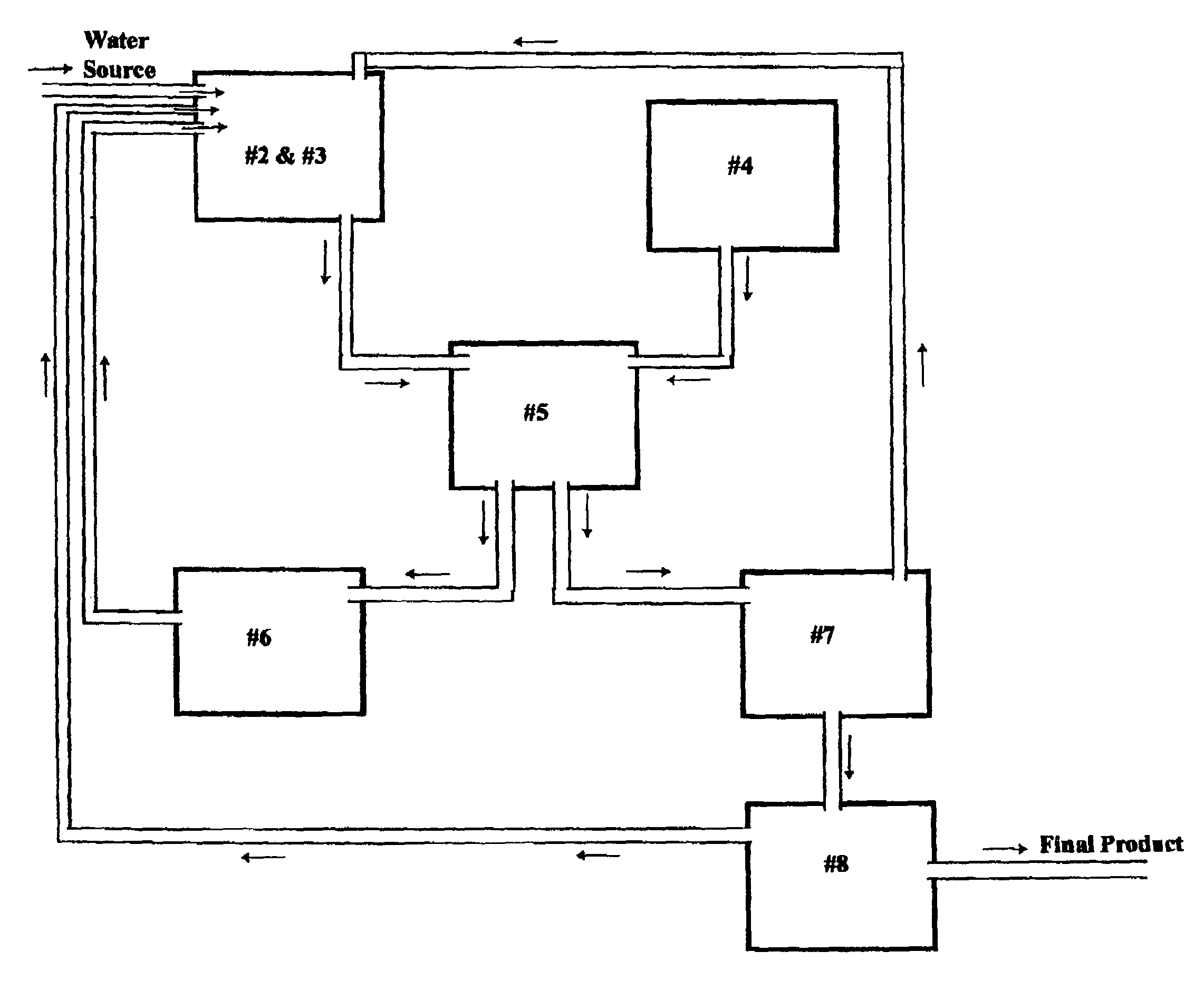
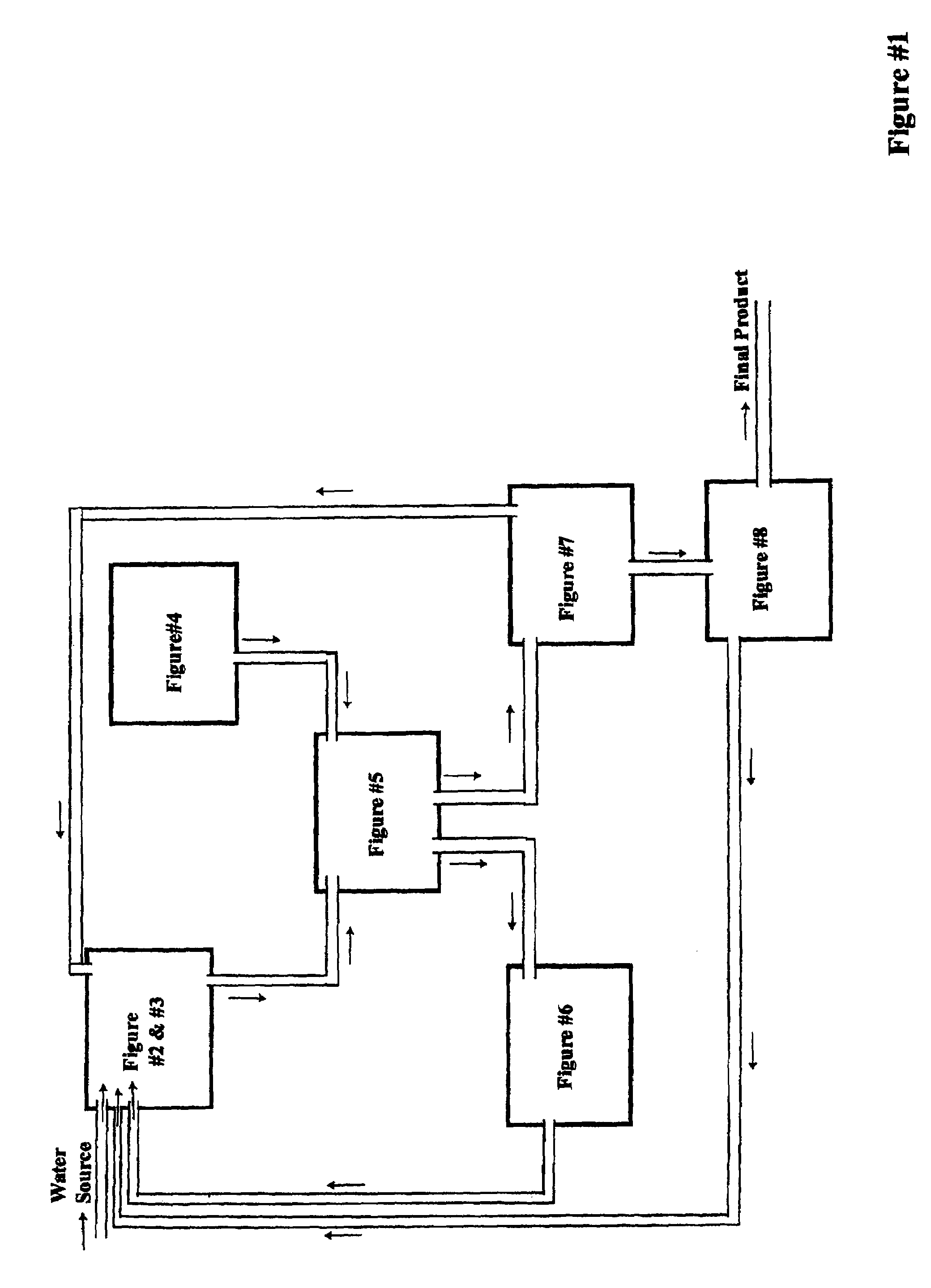
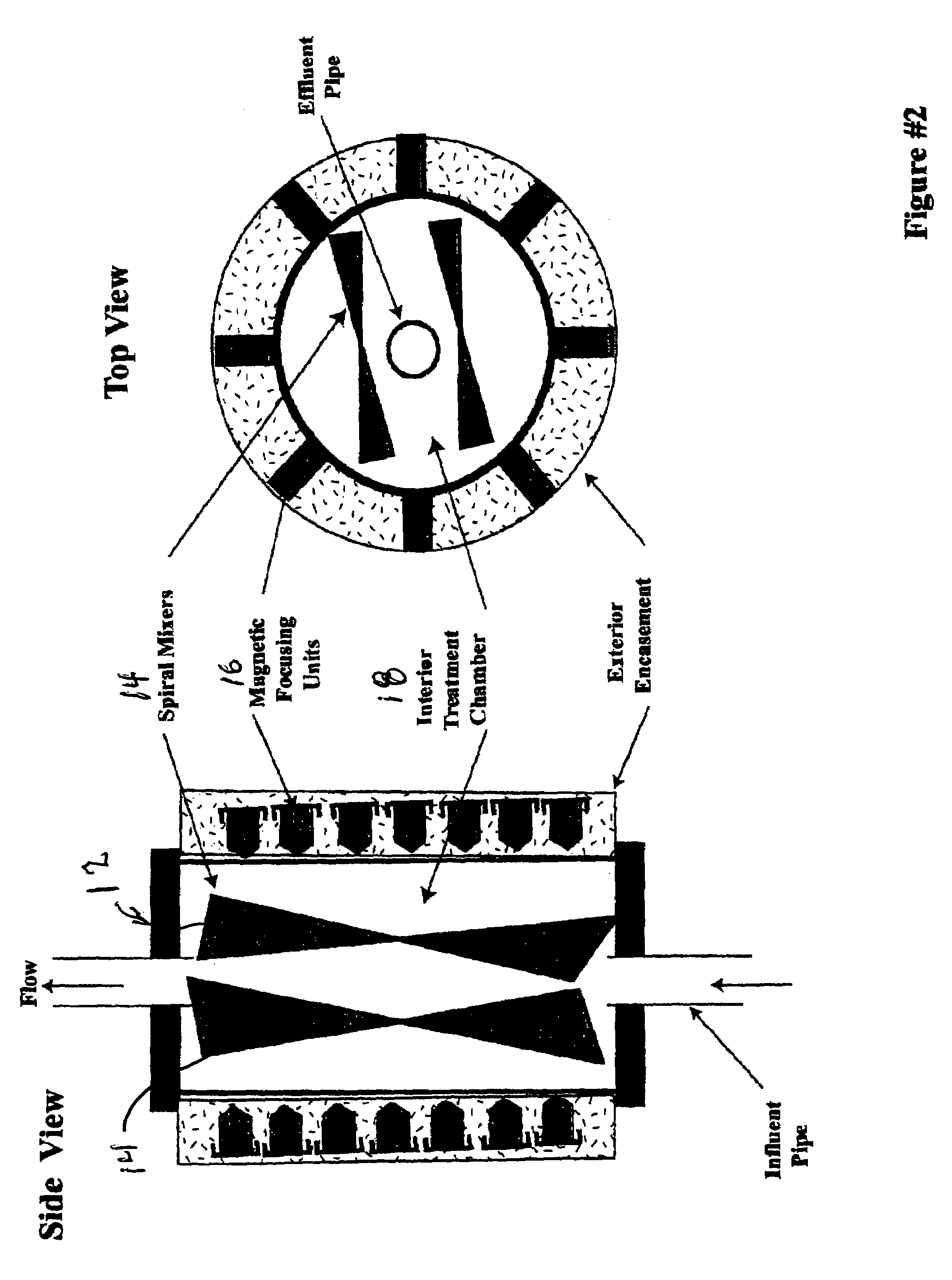
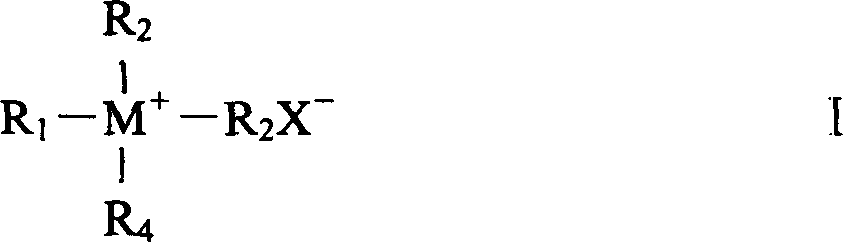Patents
Literature
590 results about "High molecular mass" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
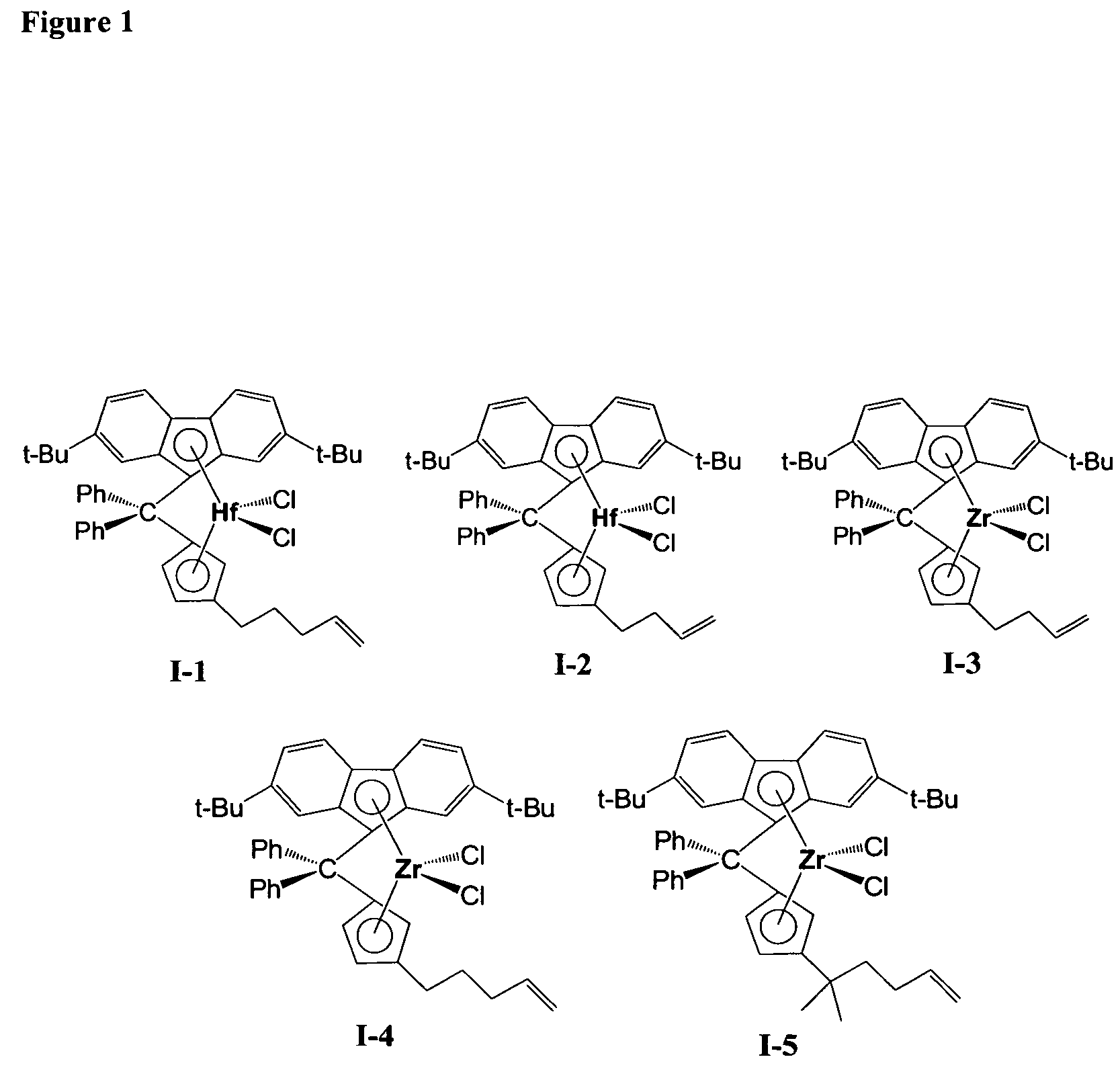
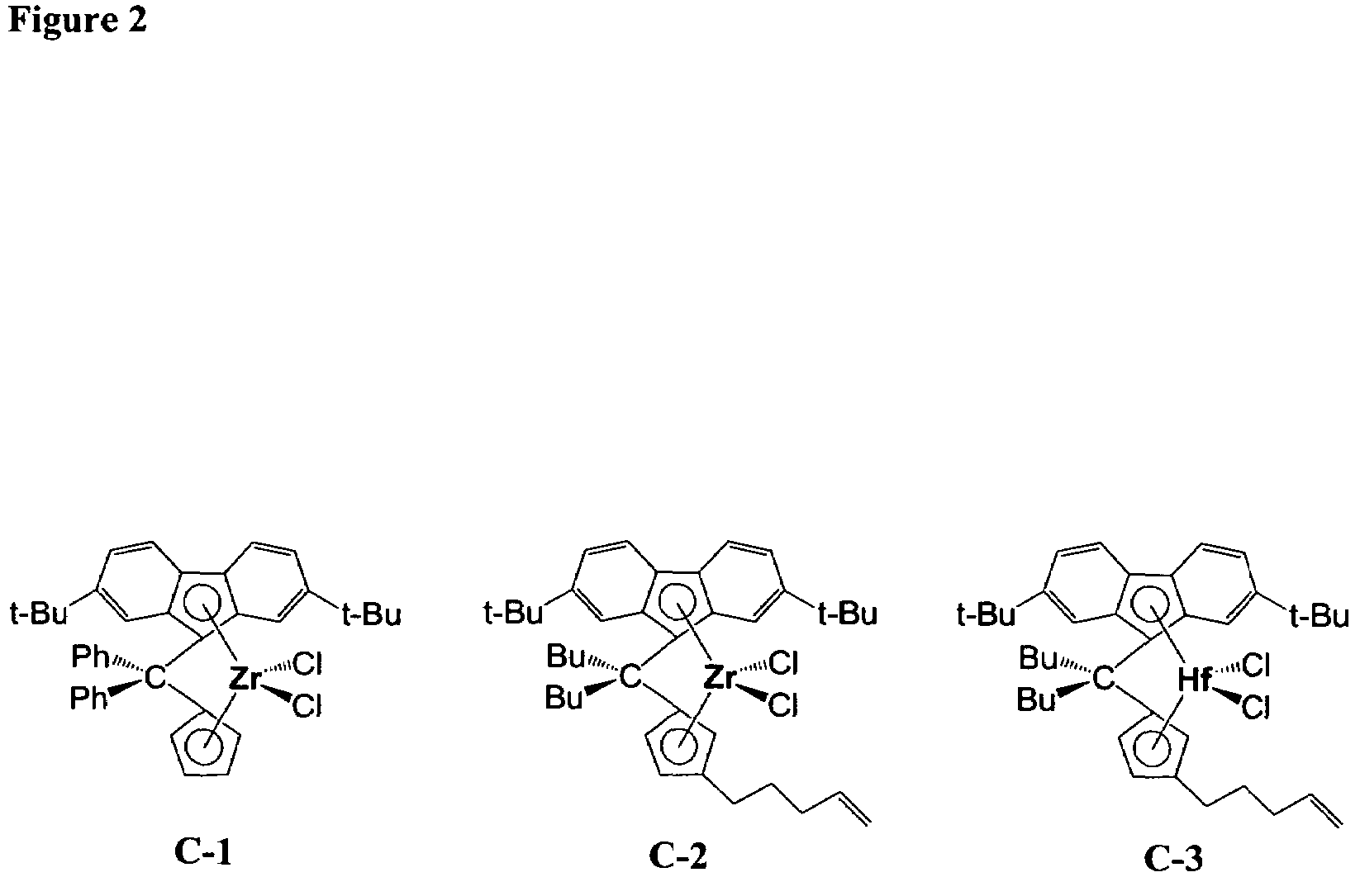
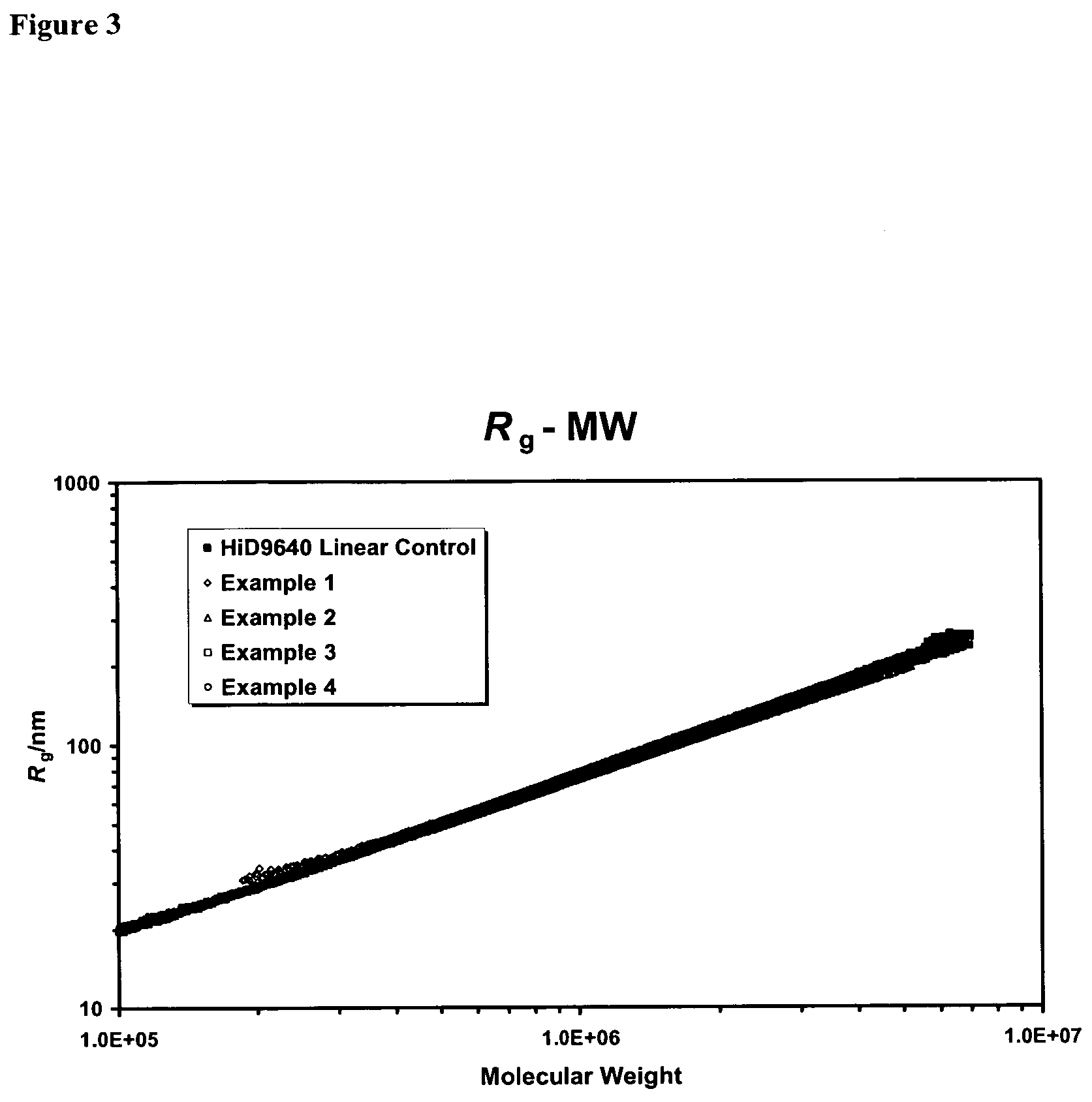
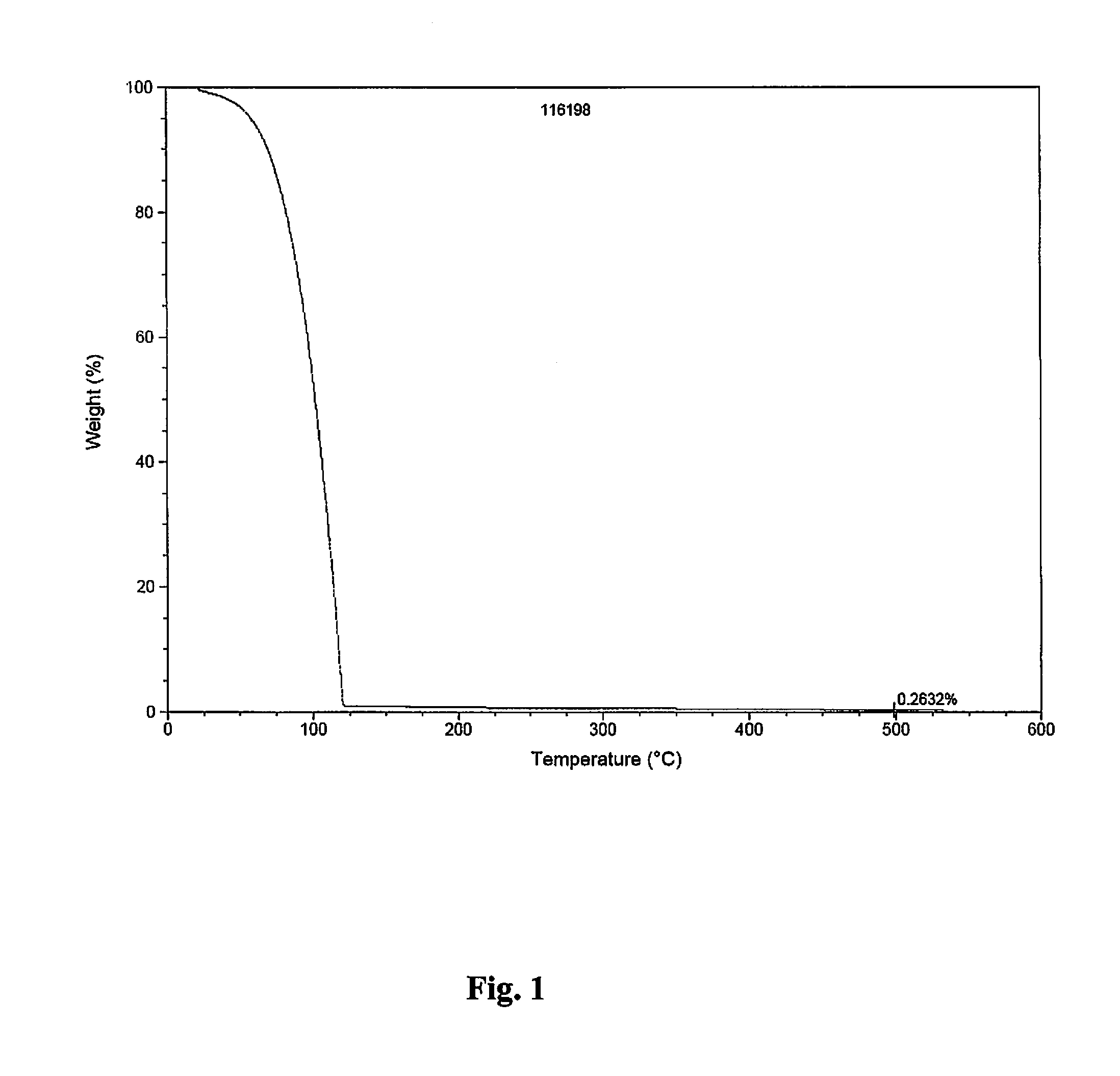
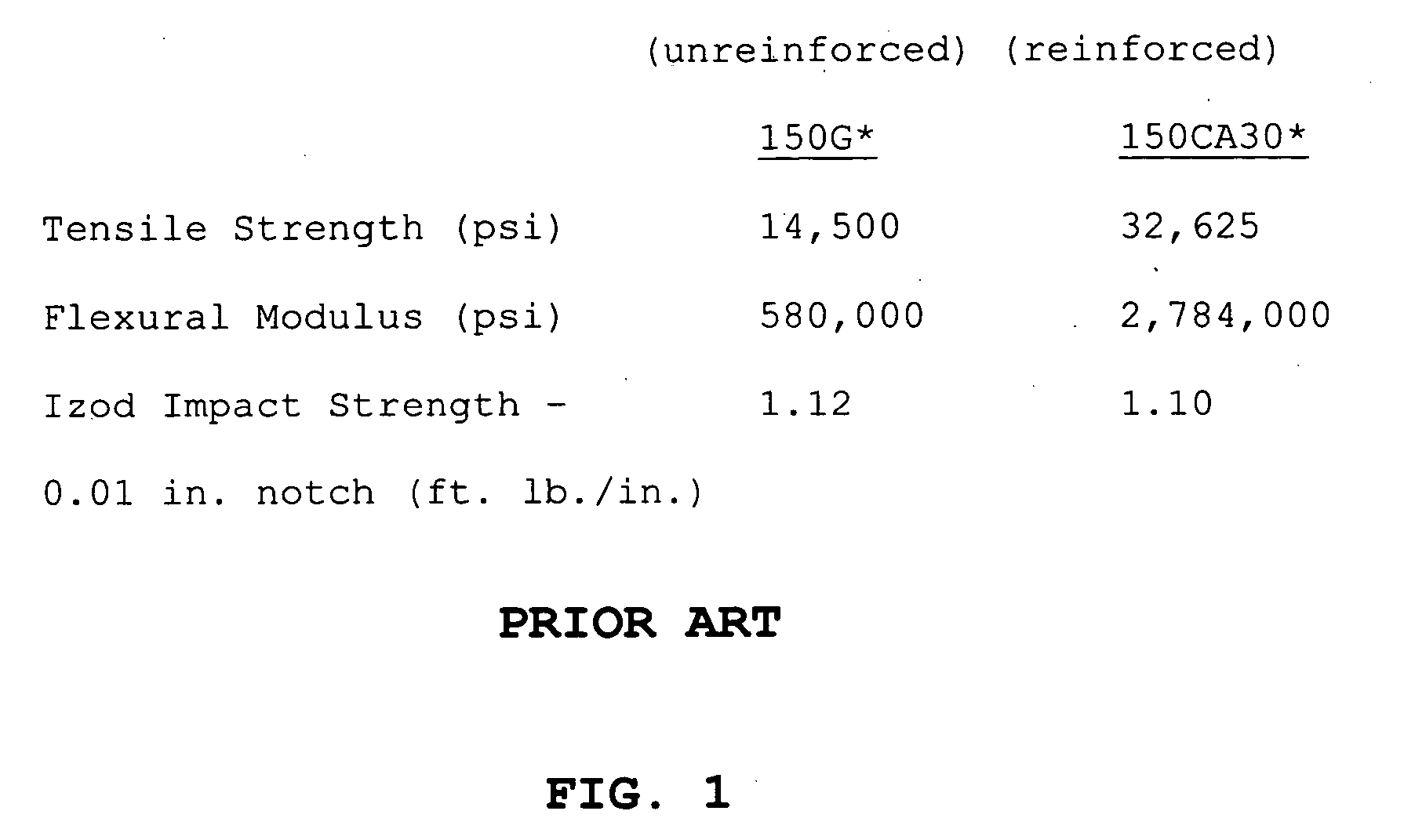
Polymerization catalysts for producing high molecular weight polymers with low levels of long chain branching
ActiveUS7517939B2High catalytic activityHigh activityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsHigh molecular massEthylene Polymers
This invention relates to catalyst compositions, methods, and polymers encompassing at least one Group 4 metallocene compound comprising bridging η5-cyclopentadienyl-type ligands, typically in combination with at least one cocatalyst, and at least one activator. The compositions and methods disclosed herein provide ethylene polymers with low levels of long chain branching.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
Process for medical implant of cross-linked ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene having improved balance of wear properties and oxidation resistance
A medical implant of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene having an improved balance of wear properties and oxidation resistance is prepared by irradiating a preform of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene, annealing the irradiated preform in the absence of oxygen to a temperature at or above the onset of melting temperature, and forming an implant from the stabilized cross-linked polymer. Implants prepared according to the process of the present invention have comparable oxidation resistance and superior wear performance compared to unirradiated ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene.
Owner:DEPUY ORTHOPAEDICS INC
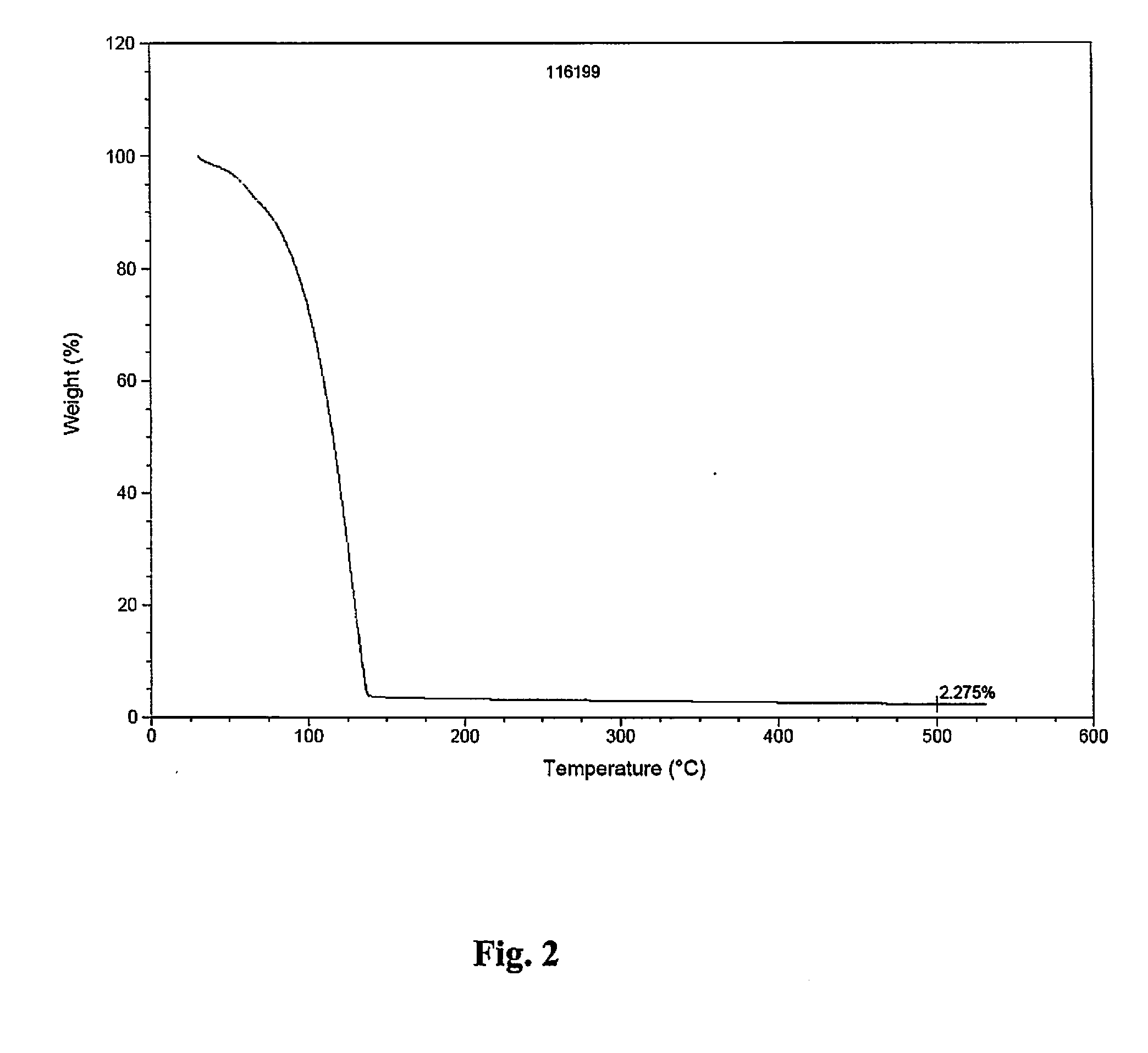
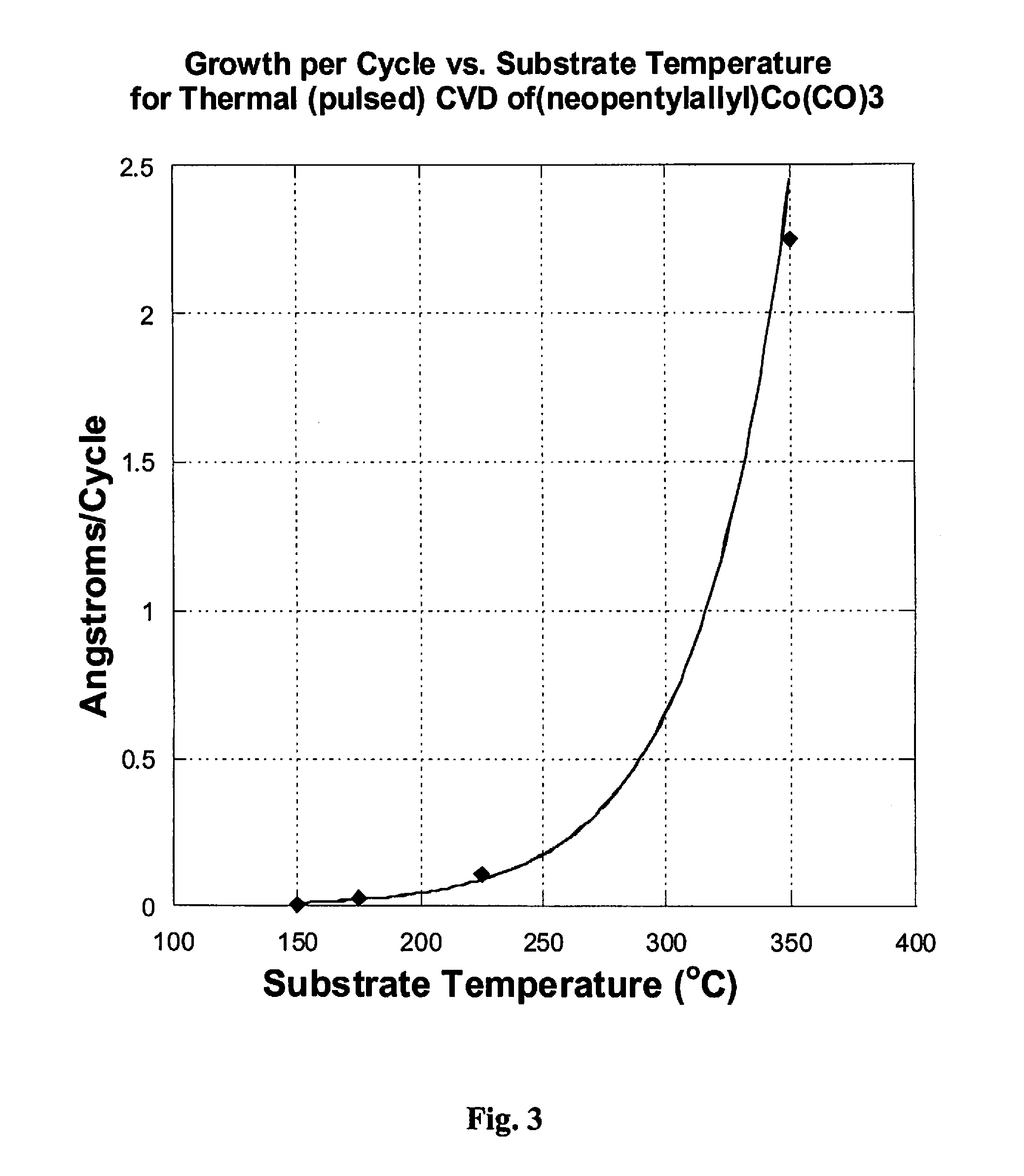
High molecular weight alkyl-allyl cobalttricarbonyl complexes and use thereof for preparing dielectric thin films
ActiveUS20120177845A1Easy to handleCobalt organic compoundsChemical vapor deposition coatingPolymer scienceThin membrane
A method for forming a cobalt-containing thin film by a vapor deposition process is provided. The method comprises using at least one precursor corresponding in structure to Formula (I); wherein R1 and R2 are independently C2-C8-alkyl; x is zero, 1 or 2; and y is zero or 1; wherein both x and y can not be zero simultaneously.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Mixture for Transdermal Delivery of Low and High Molecular Weight Compounds
InactiveUS20080154210A1Low and high molecular weightPromote recoveryOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsHigh molecular massDrug
Owner:ORIX +1
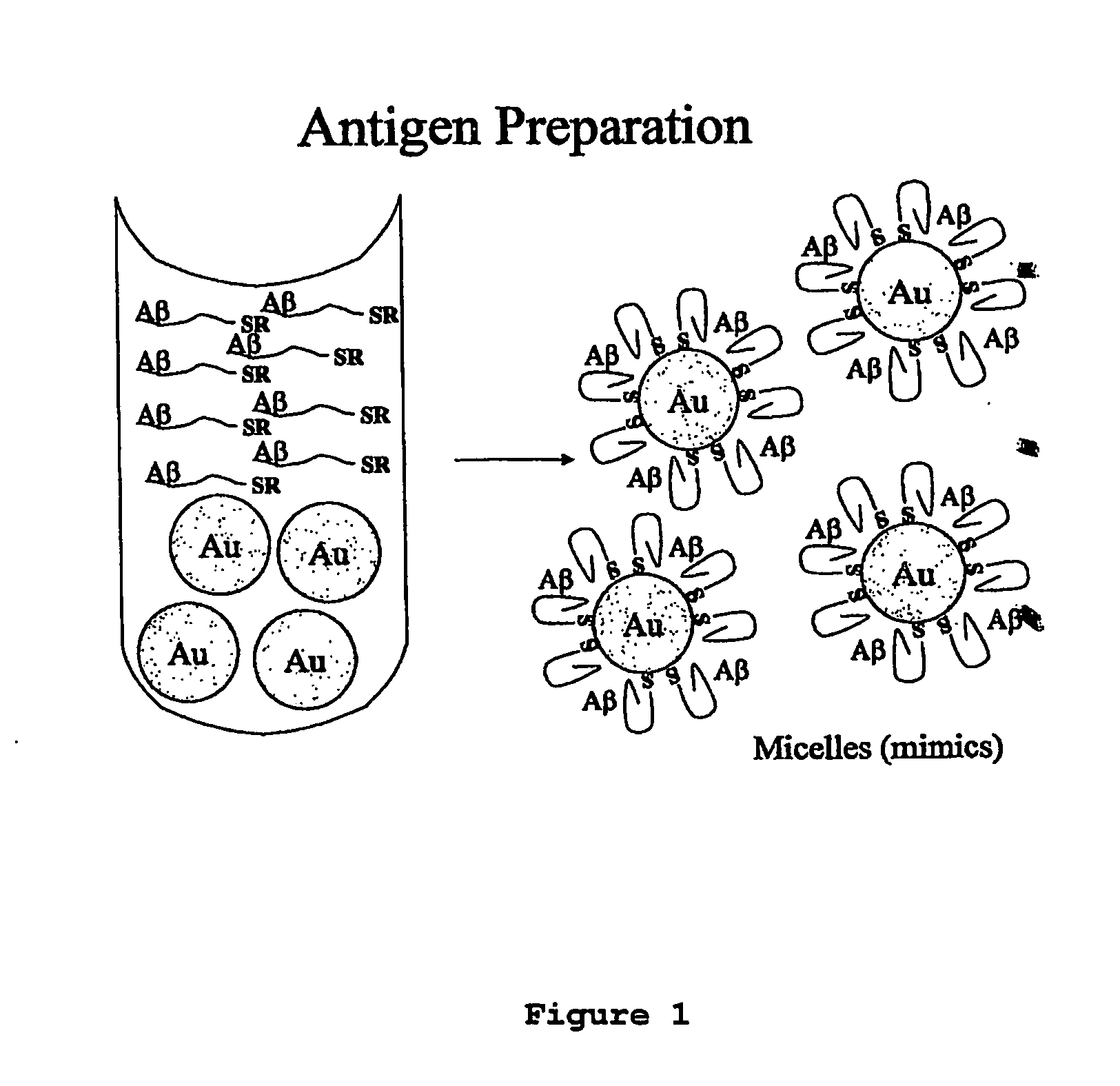
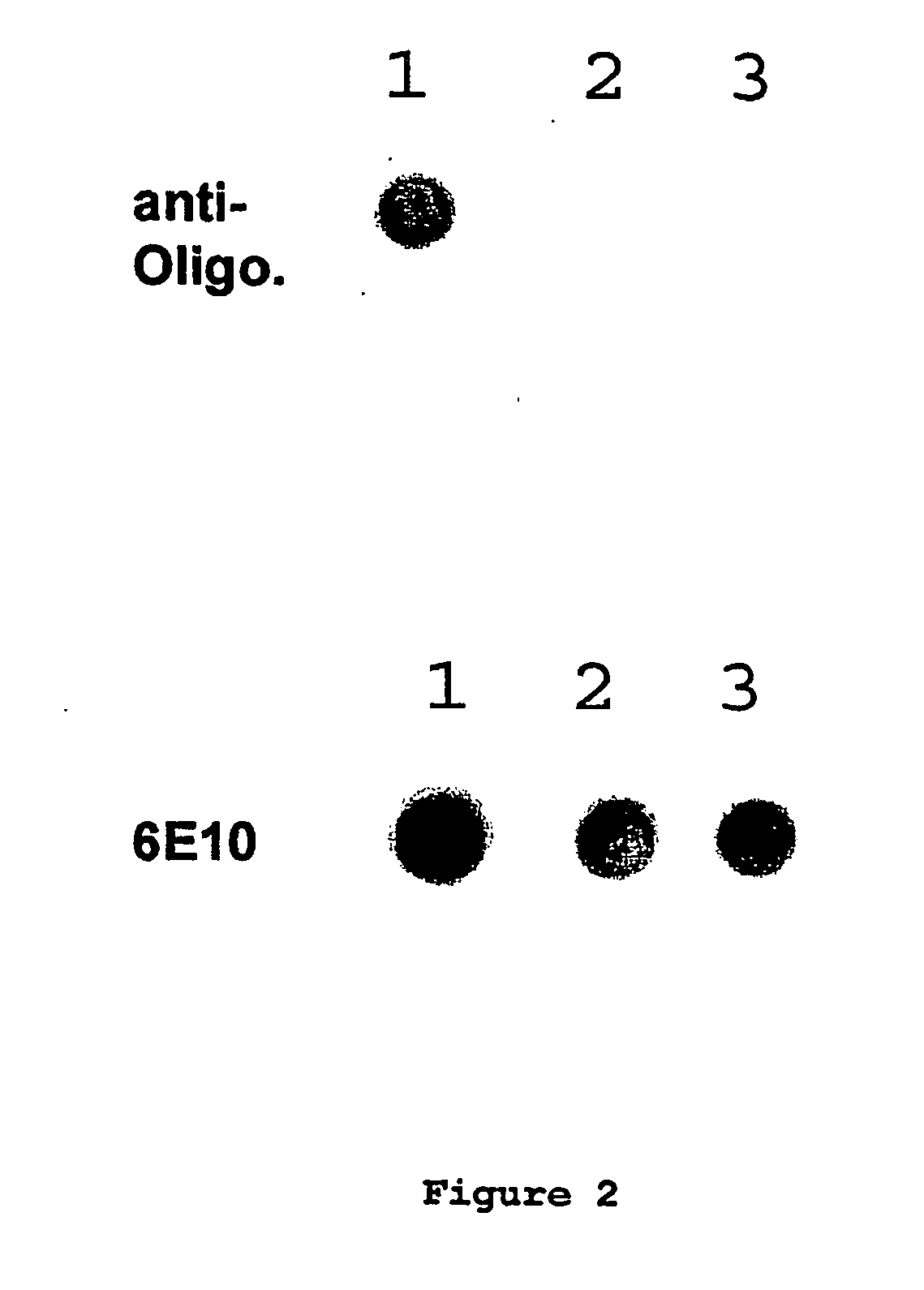
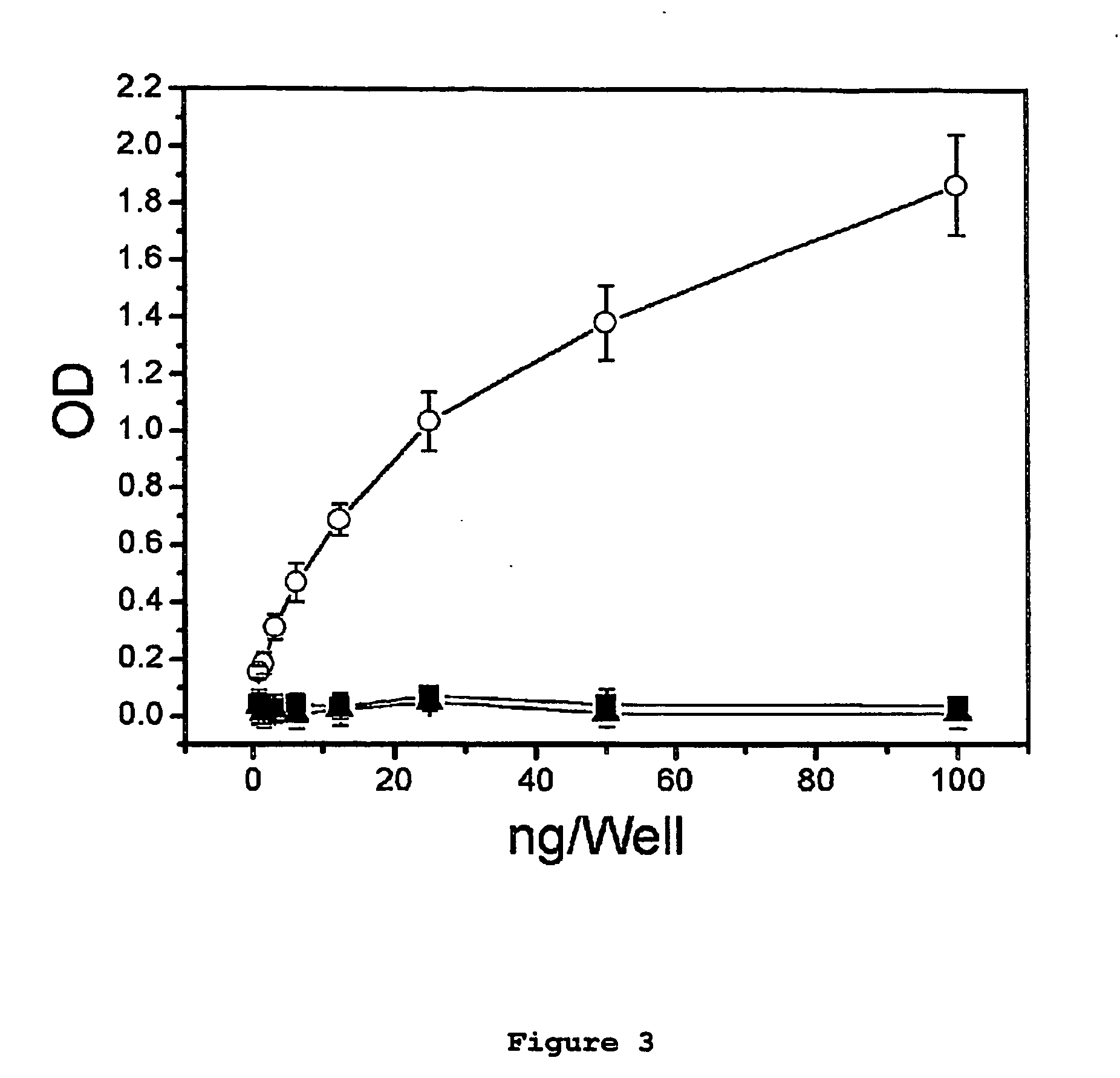
Immunogens and corresponding antibodies specific for high molecular weight aggregation intermediates common to amyloids formed from proteins of differing sequence
ActiveUS20060280733A1Low toxicityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsHigh molecular massAmyloid disease
Compositions of matter that comprise one or more conformational epitopes found on amyloid peptide aggregates, antibodies to such epitopes and methods for making and using the compositions, eptitopes and / or antibodies. The invention includes synthetic or isolated compositions that contain or consist of certain conformational epitopes that are found on peptide aggregates (e.g., toxic peptide aggregates) present in human or veterinary patients who suffer from, or who are likely to develop, amyloid diseases (e.g., Alzheimer's Disease). The invention includes methods for the detection, treatment and prevention of diseases in humans or animals, using such compositions. The invention further includes antibodies which bind to the conformational epitopes as well as methods for making such antibodies and methods for the detection, treatment and prevention of diseases and / or identification of potential therapies (e.g., drug screening) using such antibodies.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
High molecular weight poly(alpha-olefin) solutions and articles made therefrom
ActiveUS20070231572A1Improve productivityDry spinning methodsMonocomponent polyolefin artificial filamentPolymer scienceHigh molecular mass
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
High molecular weight associative amphoteric polymers and uses thereof
High molecular weight associative amphoteric polymers for increasing the viscosity of aqueous solutions, comprise: at lease one cationic monomer derived from acrylamide bearing at least one hydrophobic chain of 8 to 30 carbon atoms; 1 to 99.9 mole % of at least one anionic monomer; and 1 to 99 mole % of one or several non-ionic water-soluble monomers. Aqueous solutions containing said polymers find uses in industry, in particular the oil, paper, water treatment, mining, cosmetics, textile, detergency industries and generally in all industrial techniques using thickened solutions.
Owner:S P C M SA
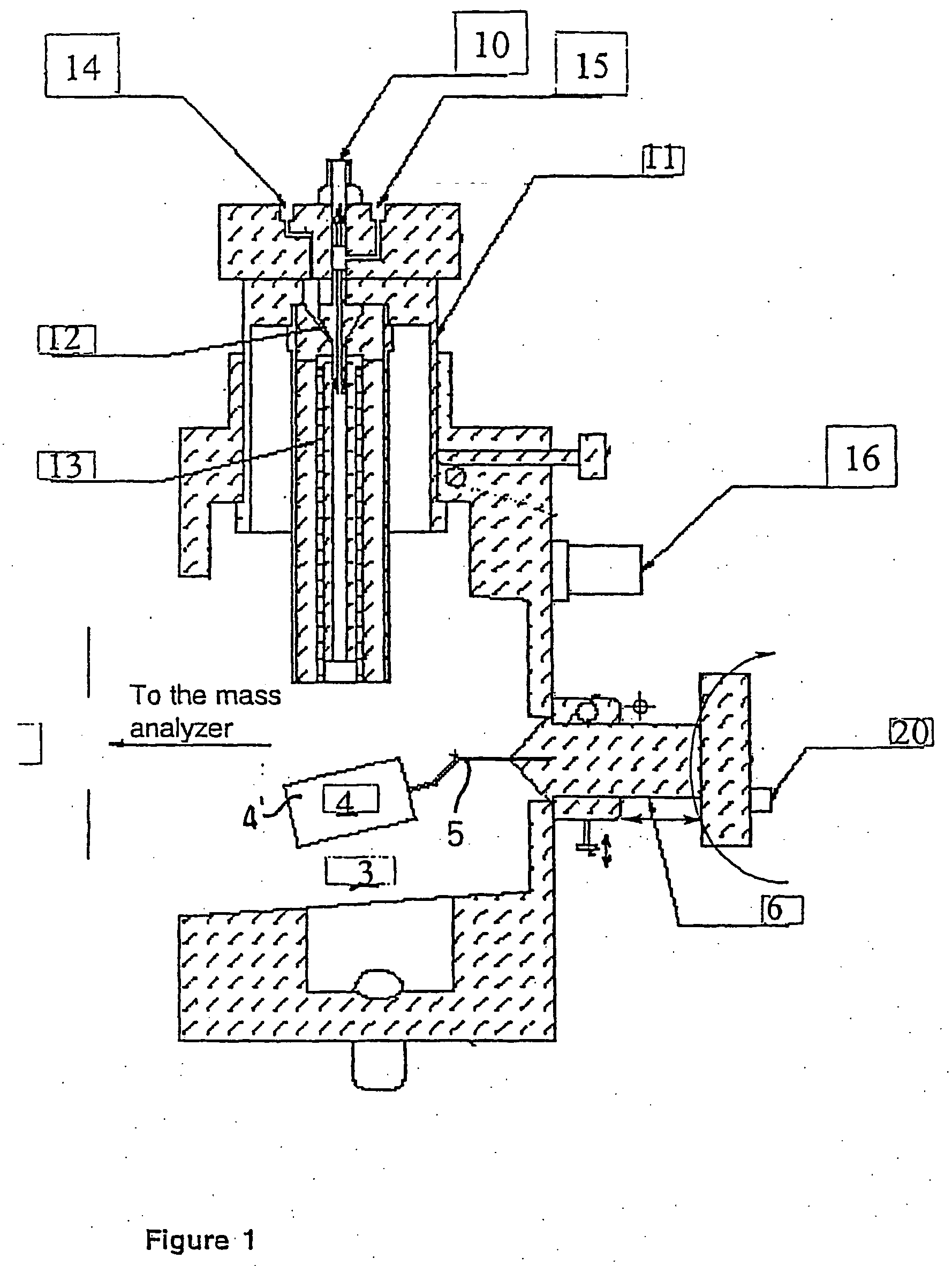
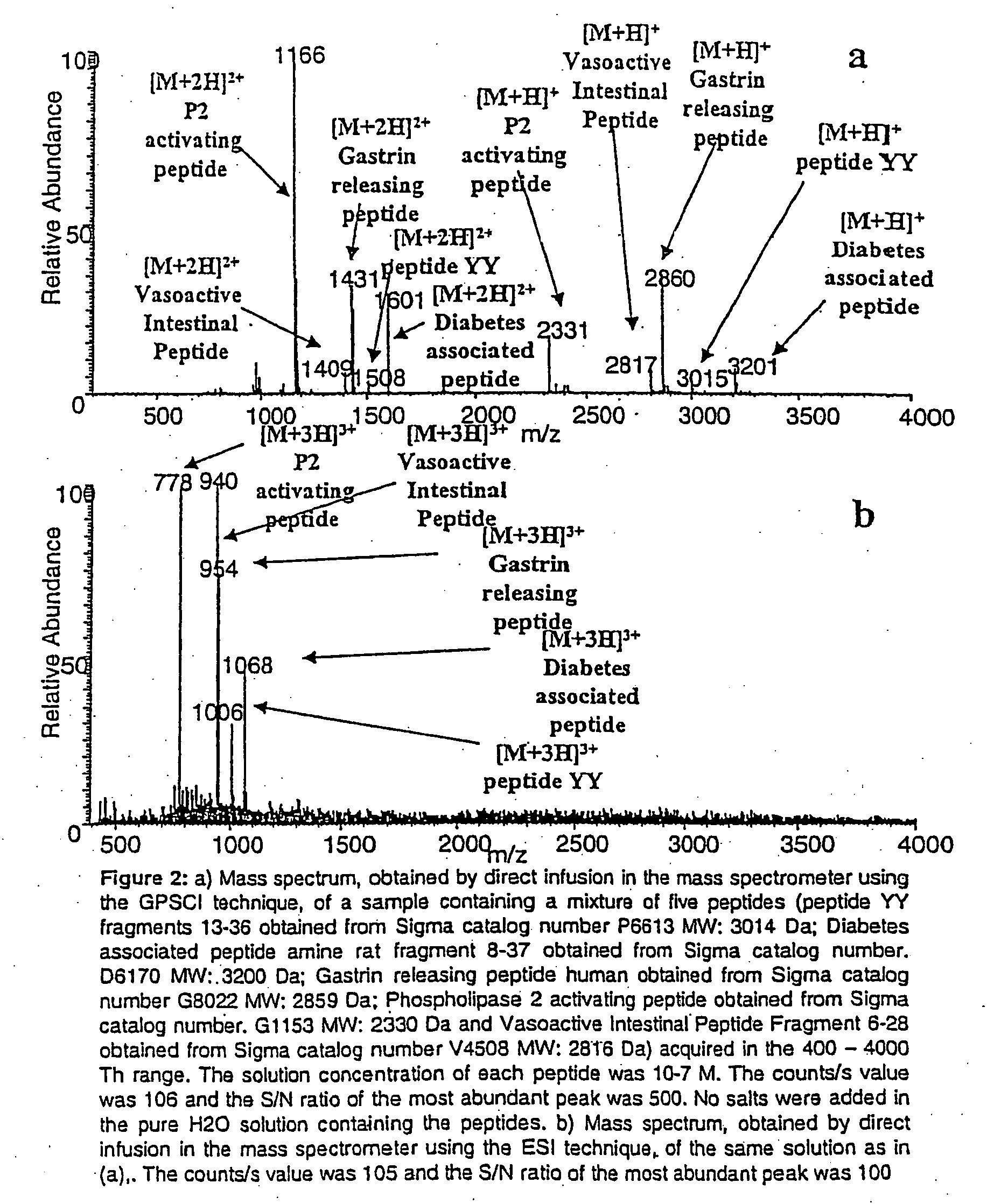
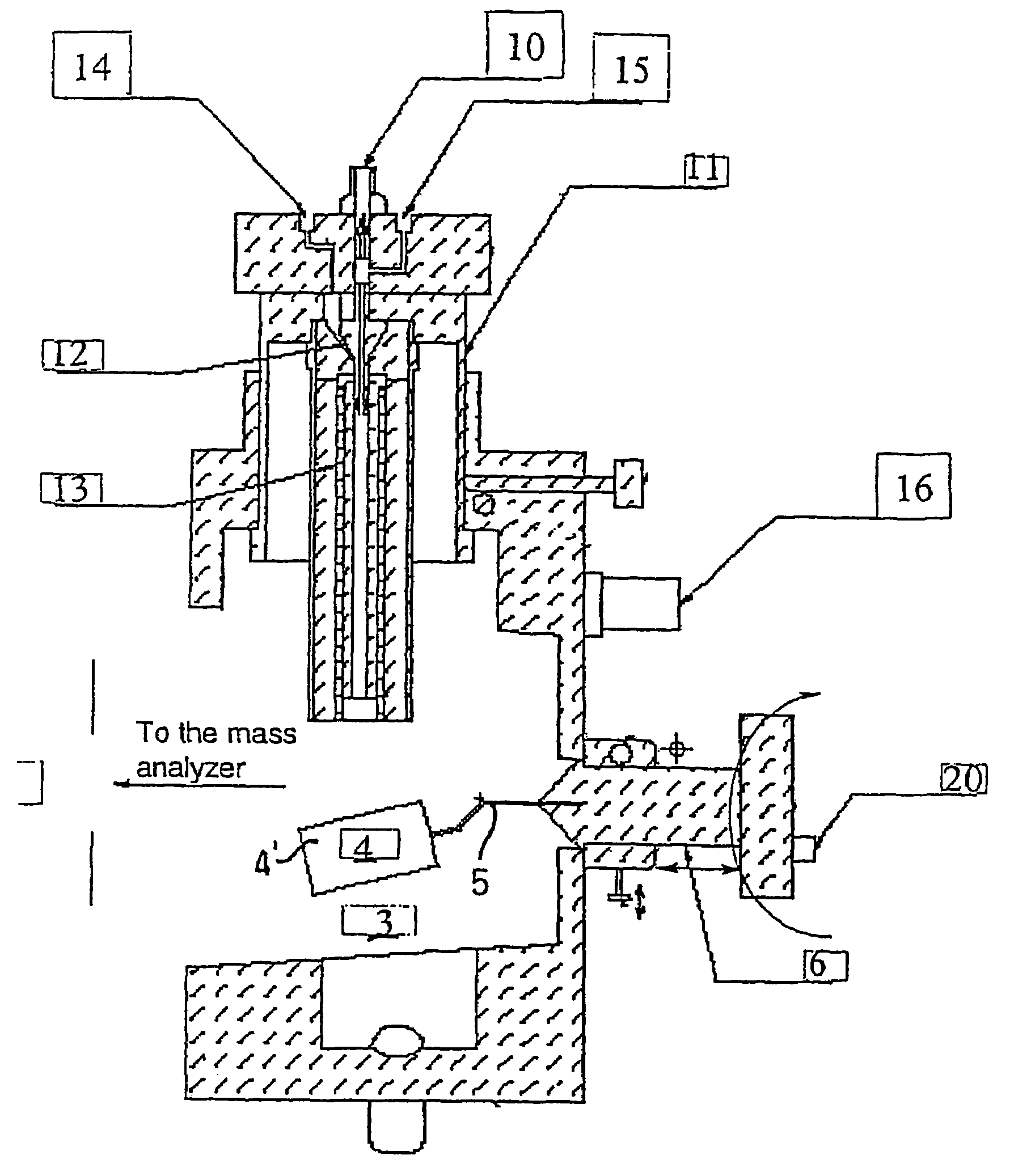
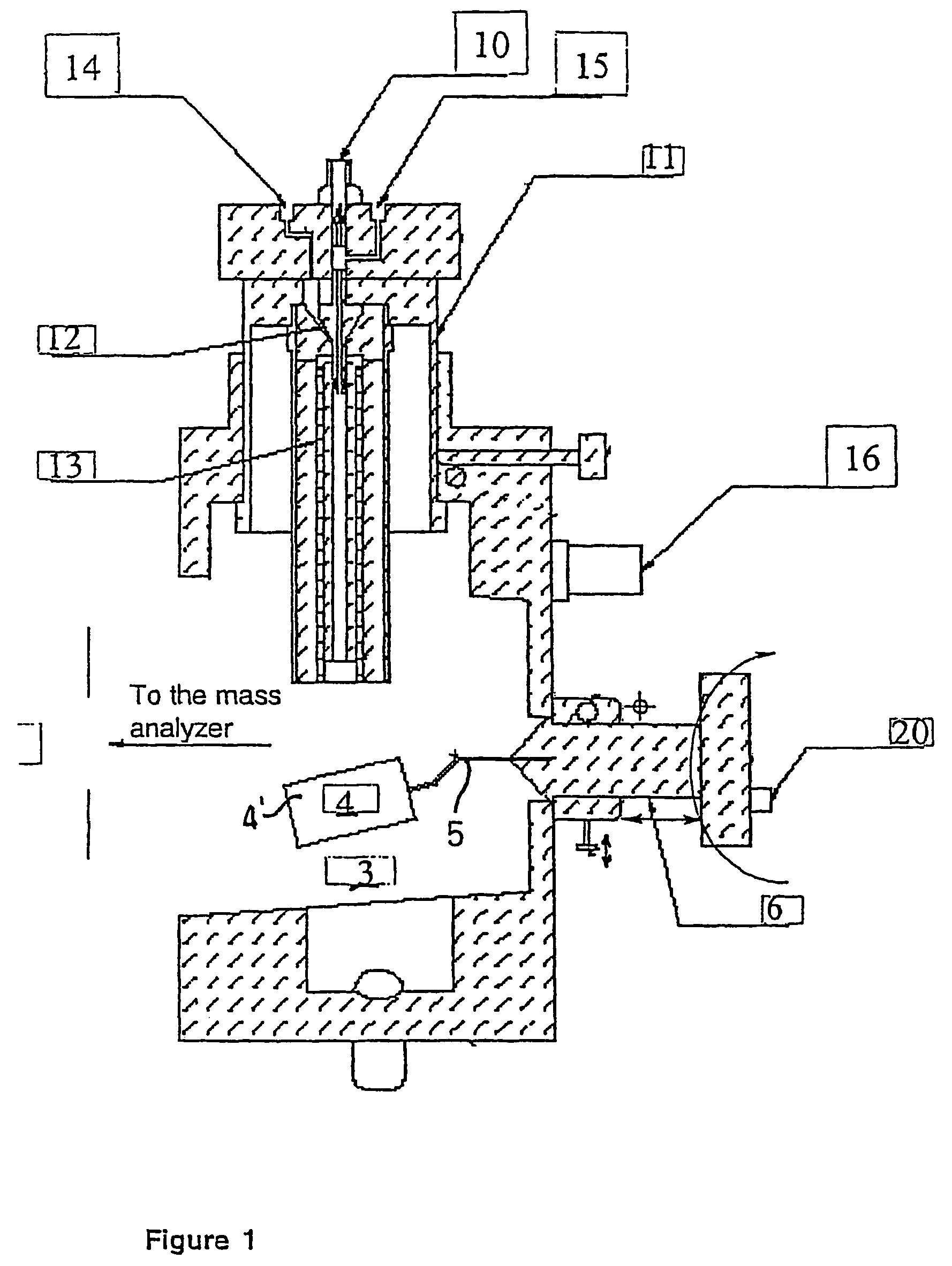
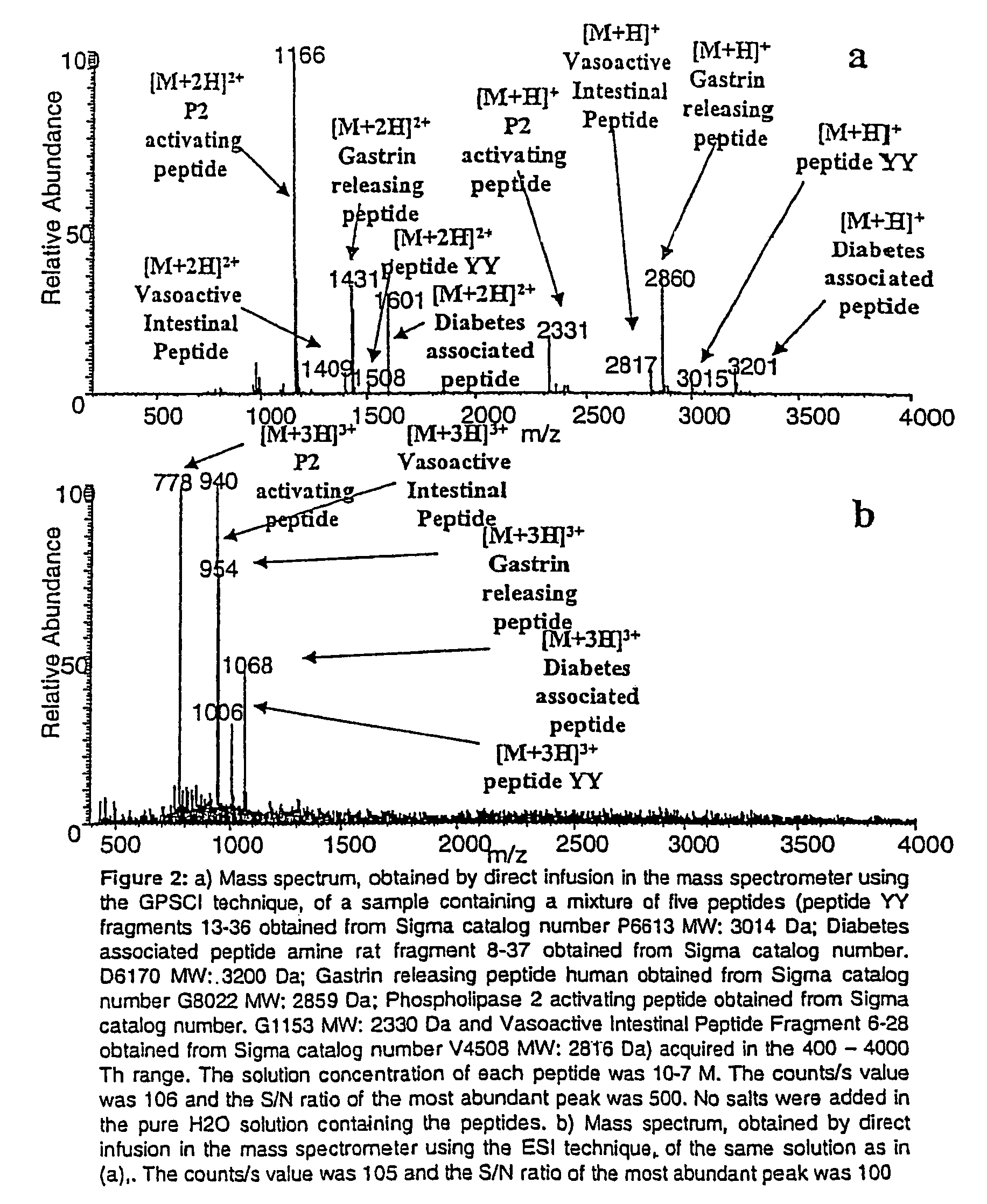
Ionization source for mass spectrometry analysis
ActiveUS20060145089A1Samples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by optical meansGas phaseMass analyzer
A new ionization source named Surface Activated Chemical Ionization (SACI) has been discovered and used to improve the sensitivity of the mass spectrometer. According to this invention the ionization chamber of a mass spectrometer is heated and contains a physical new surface to improve the ionization process. The analyte neutral molecules that are present in gas phase are ionized on this surface. The surface can be made of various materials and may also chemically modified so to bind different molecules. This new ionization source is able to generate ions with high molecular weight and low charge, an essential new key feature of the invention so to improve sensitivity and reduce noise. The new device can be especially used for the analysis of proteins, peptides and other macromolecules. The new invention overcomes some of the well known and critical limitations of the Electrospray (ESI) and Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometric techniques.
Owner:UNIV DELGI STUDI DI MILANO
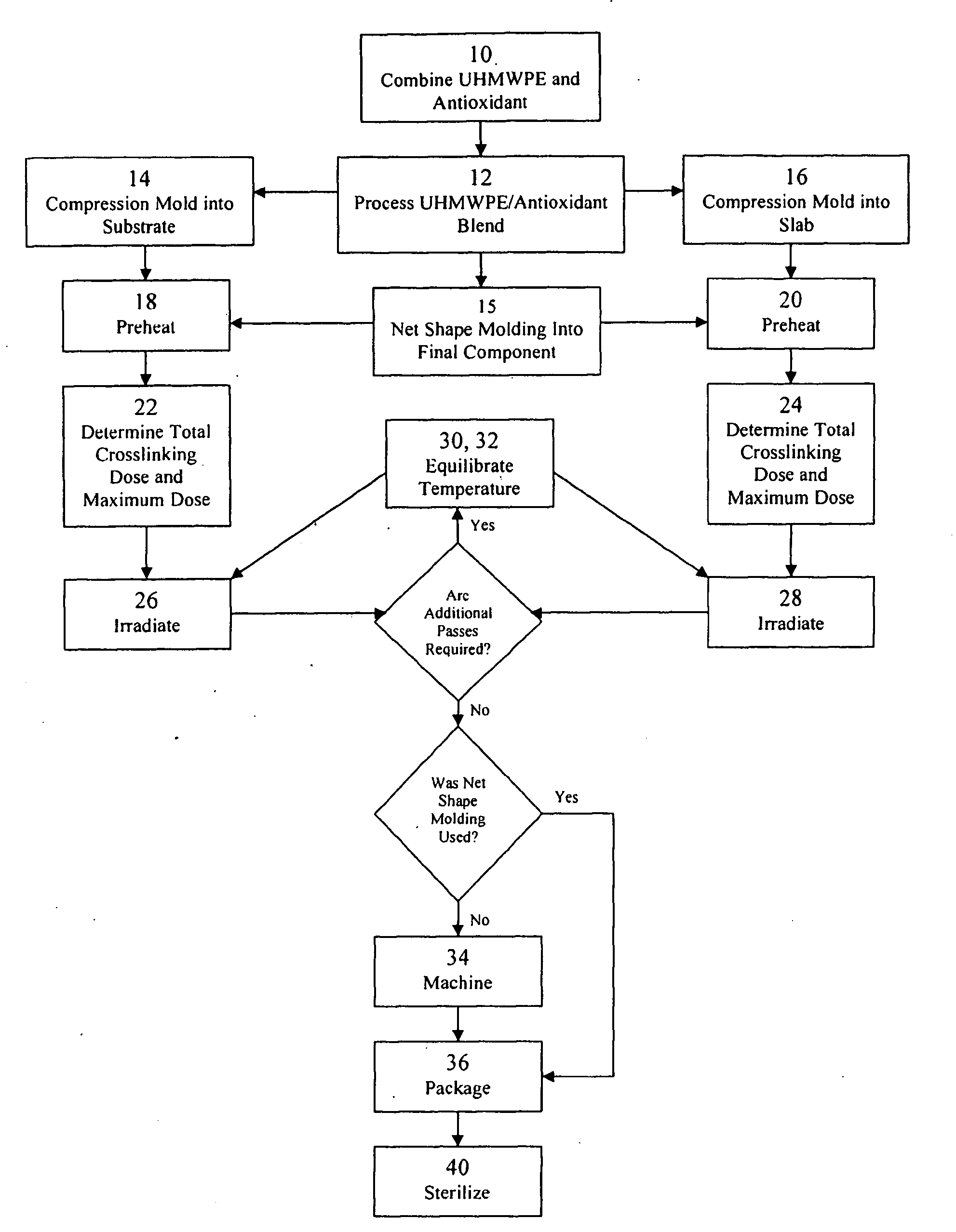
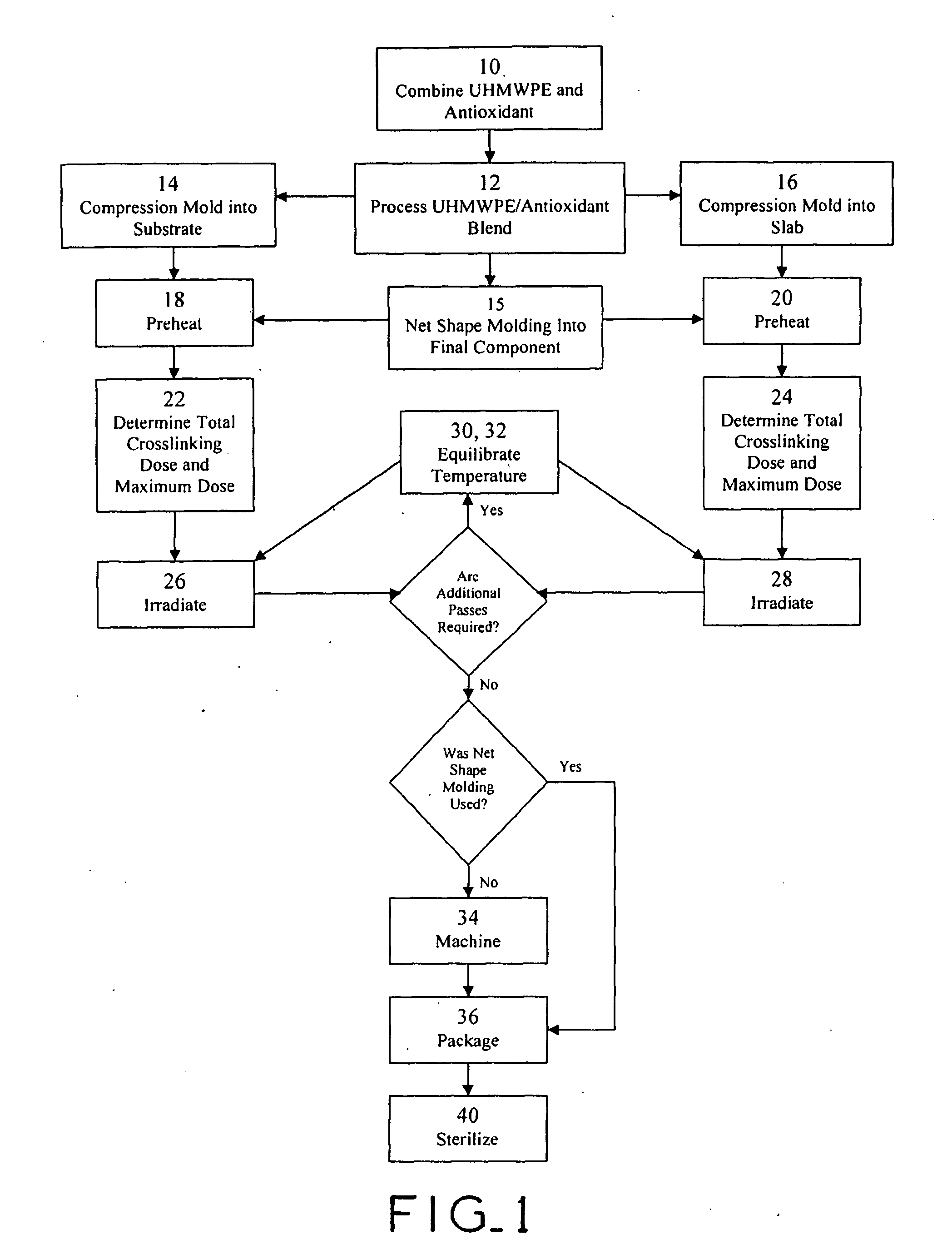
Antioxidant stabilized crosslinked ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene for medical device applications
InactiveUS20080319137A1Avoid mass meltingEncourage mobilityLavatory sanitoryDeodrantsAntioxidantOxidation resistant
An antioxidant combined with UHMWPE prior to subjecting the UHMWPE to crosslinking irradiation. In one exemplary embodiment, the antioxidant is tocopherol. After the antioxidant is combined with the UHMWPE, the resulting blend may be formed into slabs, bar stock, and / or incorporated into a substrate, such as a metal, for example. The resulting product may then be subjected to crosslinking irradiation. In one exemplary embodiment, the UHMWPE blend is preheated prior to subjecting the same to crosslinking irradiation. Once irradiated, the UHMWPE blended product may be machined, packaged, and sterilized in accordance with conventional techniques.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Method for producing medical and commercial grade poly-gamma-glutamic acid of high molecular weight
ActiveUS20050095679A1Reduce molecular weightHigh molecular weightBacteriaFermentationFiltrationHigh molecular mass
Methods for producing high molecular weight poly-gamma-glutamic acid (PGA). The PGA is produced by fermentation, and purified by use of tangential flow filtration, followed by diafiltration, as necessary, to yield a product of the desired purity. Product obtained may be of very high purity using all the prescribed purification steps. Product of this purity is suitable for in vivo medical applications. Other applications, such as food or agricultural, may utilize lower purity levels, and hence do not require all the purification steps specified.
Owner:CRESCENT INNOVATIONS
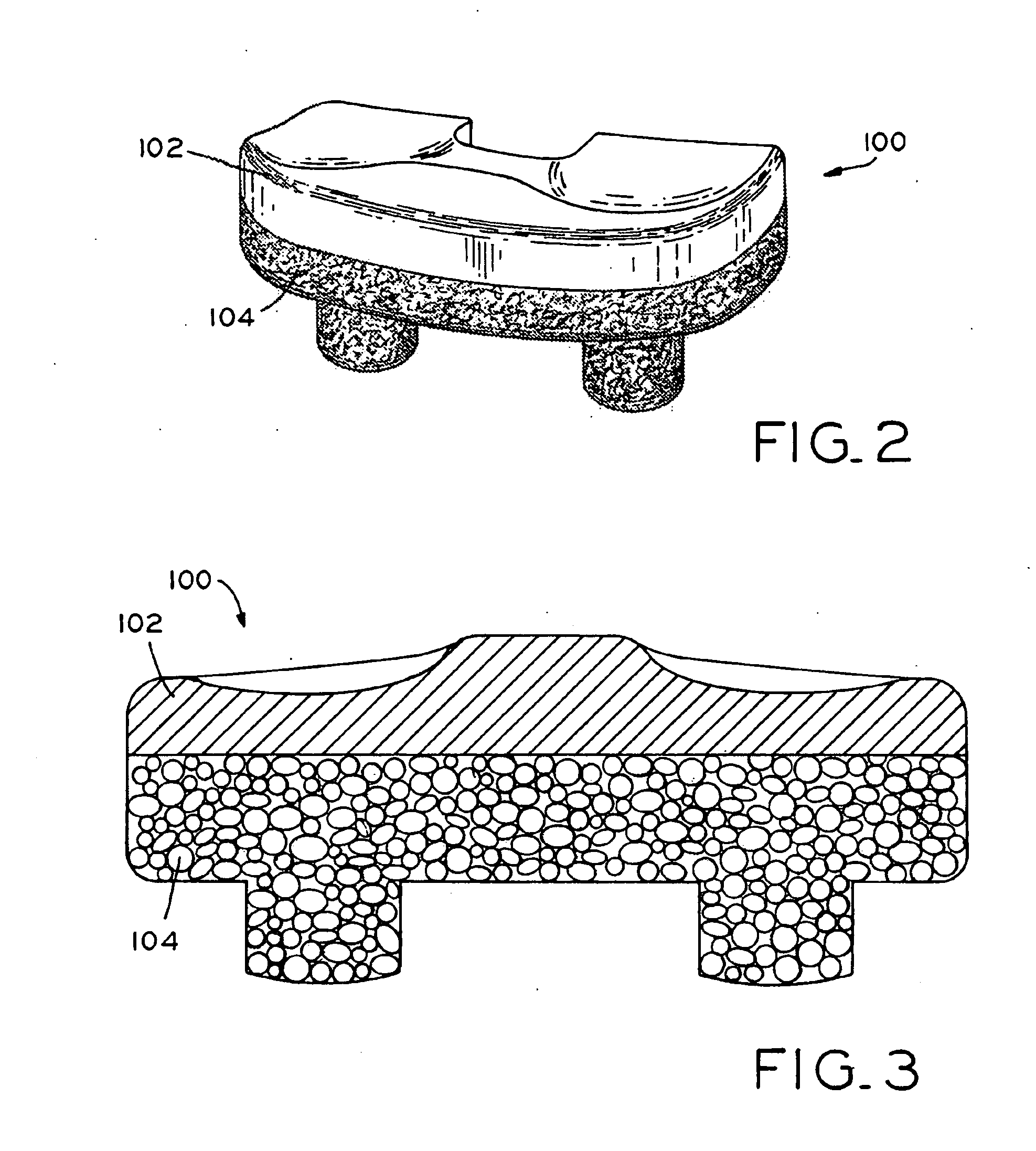
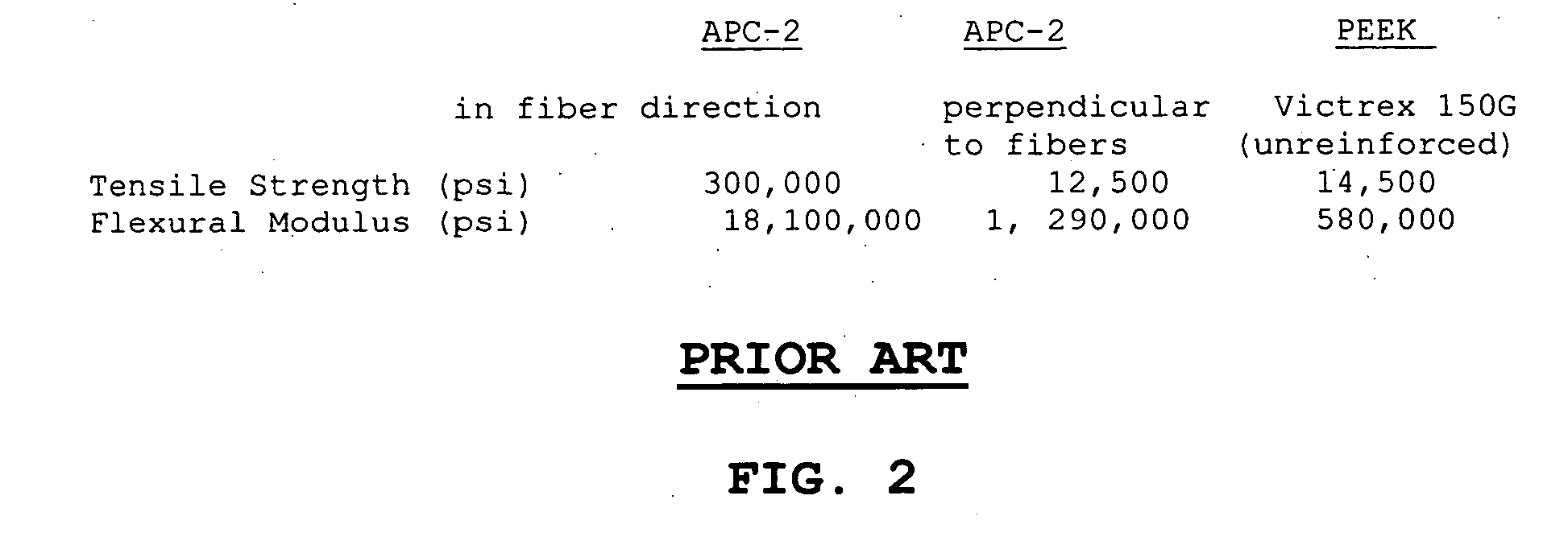
Composite material of continuous fiber and ultra high molecular weight polyethylene
InactiveUS20050287891A1Good physical propertiesImprove wear resistanceSynthetic resin layered productsWoven fabricsPolymer sciencePolyamide
A composite material composed of continuous high strength fibers such as carbon, aramid or glass, and ultra high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMW PE), wherein the UHMW PE comprises a continuous matrix among and surrounding the fibers. The resultant composite material exhibits extraordinarily high strength, stiffness and other fiber dominated properties in the directions parallel to the fibers and exhibits its lowest strength and stiffness in directions perpendicular to the fibers. It also exhibits superb abrasion resistance, good impact strength, excellent chemical resistance, a low coefficient of friction and other beneficial properties of UHMW PE.
Owner:PARK DAVID B
Super high molecular mass polythylene/carbon nano tube composite fiber used in jelly glue spinning and its preparation
InactiveCN1431342AImprove performanceAvoid damageMonocomponent polyolefin artificial filamentFiberRefractory
A gel-spinning ultrahigh-molecular-weight composite polyethene (UHMWPE) / carbon nanotube fibre is composed of UHMWPE and carbon nanotubes (0.01-5 wt.%) as modifier. It is prepared through purifying and organizing carbon nanotubes, preparing gel, and spinning. Its advantages are simple preparing process and high refractory and anticreep performance.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
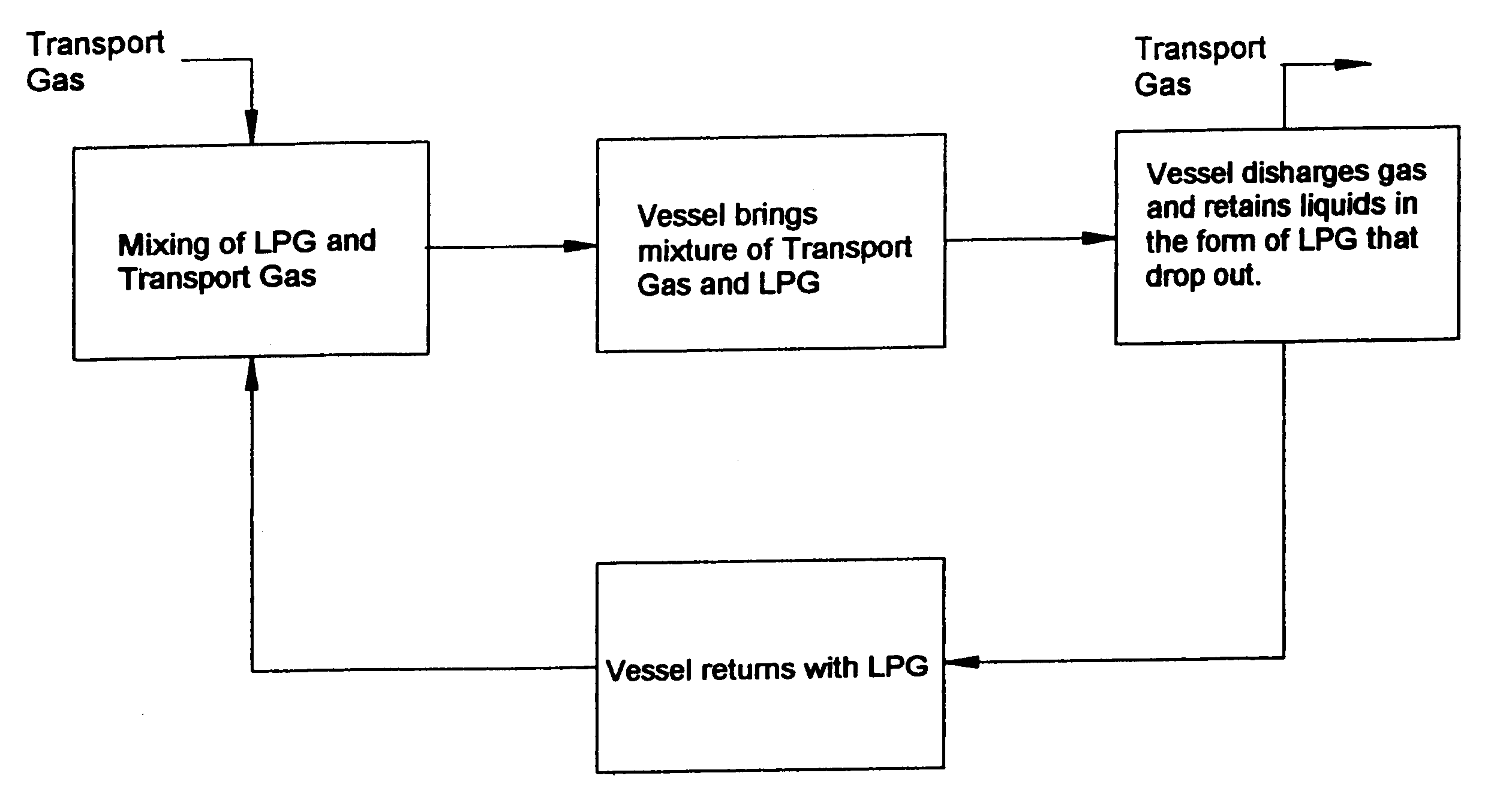
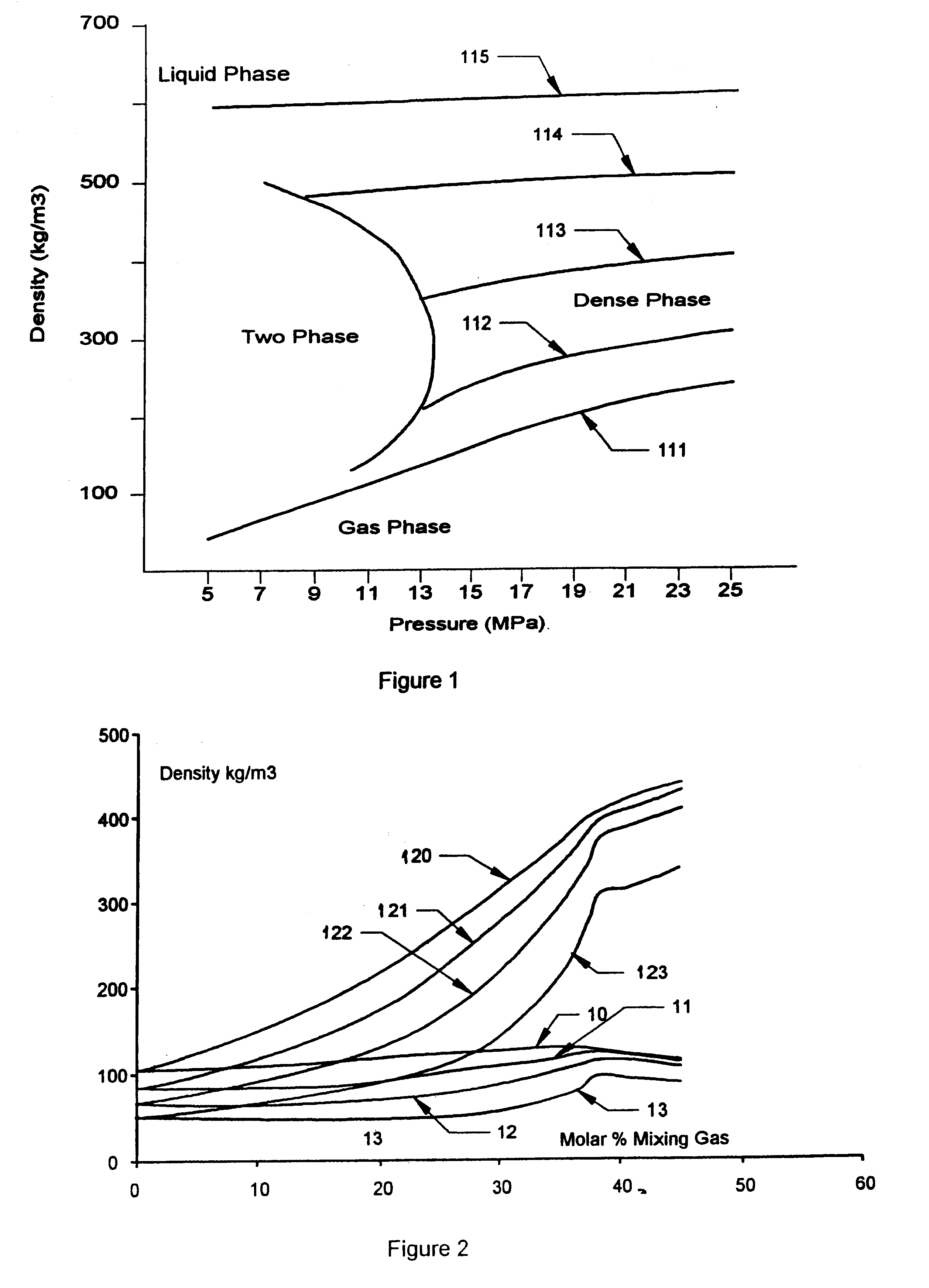
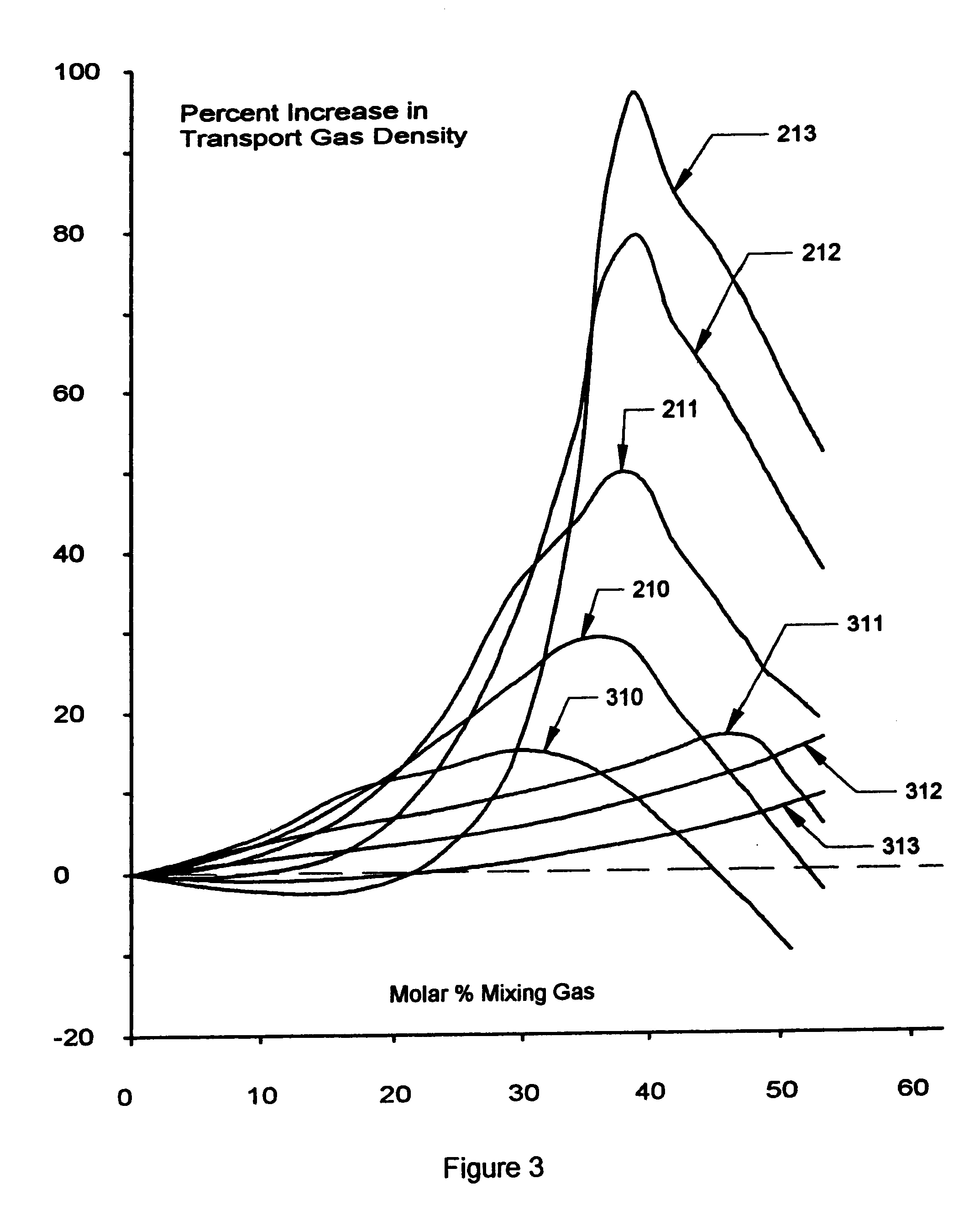
Method for transportation of low molecular weight hydrocarbons
InactiveUS6449961B1Vessel mounting detailsVessel geometry/arrangement/sizeHigh densityHigh molecular mass
A system achieving a high density of transported natural gas by compressing it to high pressures typically above 5 MPa to transport the gas in a modified composition that permits a very low compressibility factor at near ambient temperature either above or below. This reduces greatly the size of the cooling systems that are required. In some cases cooling of the compressed gas may be achieved in a simple heat exchanger cooled by air or water. The transport of the gas takes place in self propelled ships or non-self propelled barges fitted with a cargo containment system capable of storing the cargo at high pressures, typically above 5 MPa and usually not above 25 MPa. The transport vessel may carry a store of higher molecular weight gases (c2 through c7) that when mixed with the incoming cargo results in a molecular weight of the mixture of at least 22 and possibly as high as 28 or higher. The store of higher molecular weight cargo may be gained from gases that condense during discharge of the vessel at its destination due to the adiabatic cooling of the cargo during discharge. These liquids may be retained aboard and transported back to the origin. If insufficient quantities of heavy gases are available at the origin they may be loaded at the destination. If required, the composition of the heavy gases transported back to the origin may be changed through partial discharge or partial receipt of additional hydrocarbons or a combination thereof at the destination point.
Owner:KORSGAARD JENS
Method for preparing high molecular weight anion type polyacrylamide by ultralow-temperature initiation
The present invention provides a preparation method of anionic polyacrylamide with a high molecular weight by ultra-low-temperature initiation, a polynary initiator and a plurality of additives are added in the acrylamide water solution, and high-purity nitrogen is introduced for water solution polymerization. The colloids are carried out the hydrolysis by granulation, adding the hydrolytic agents, mixing and heating after a period of polymerization and aging, after that, the anionic polyacrylamide with a molecular weight of more than 25 million can be generated by granulation, drying, smashing and screening, the present invention has the advantages of smooth polymerization reaction, being conductive to the growth of a chain and the formation of the products with the high molecular weight, overcoming the shortcoming of slow temperature increase or uneven speed of temperature increase of a single azo initiator, low initiation temperature and so on.
Owner:东营顺通化工(集团)有限公司
Synthesis of high molecular weight iron-saccharidic complexes
A process for preparing parenteral iron-saccharidic complexes, and the complexes produced, comprising: (1) providing an aqueous solution or dispersion including (i) Fe(III) and (OH)− ions and (ii) at least one saccharide, to form a reaction mixture, where the molar ratio of (i): (ii) is about 30:1 to about 1:30; and the mixture temperature and pH are at or above the complex assembly point (CAP); and (2) maintaining temperature and pH at or above the CAP for a time sufficient to form an iron-saccharidic complex having a molecular weight of about 25,000 Daltons or more. Control of the temperature and pH efficiently produces a high molecular weight complex. The complex can be separated by precipitation, dialysis and / or column fractionation and, if desired, dried, e.g., lyophilized or spray dried. The process can controllably synthesize complexes of varying molecular weight and / or chemical composition, particularly sodium ferric gluconate and ferric hydroxide-sucrose.
Owner:CHROMACEUTICAL ADVANCED TECH
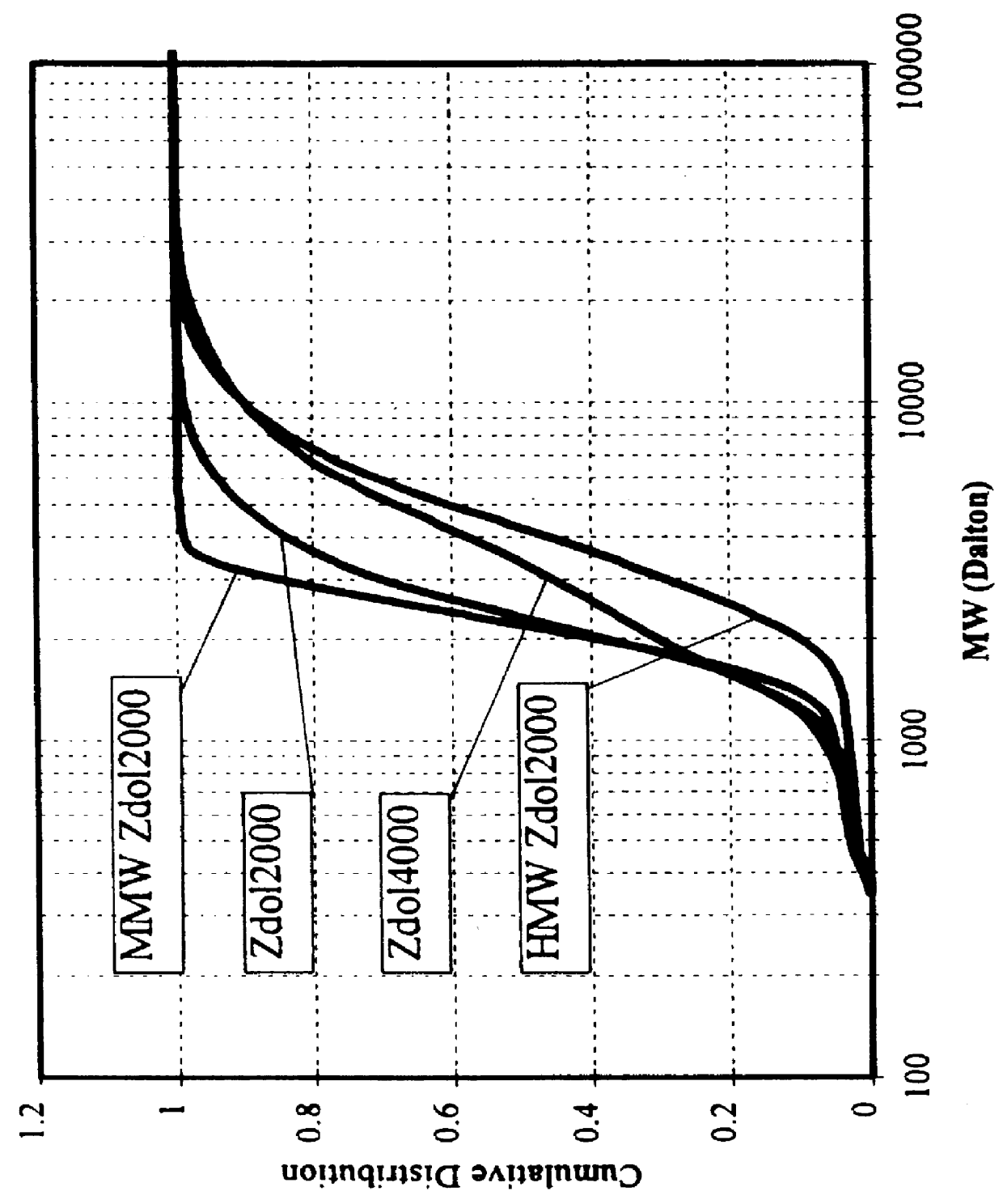
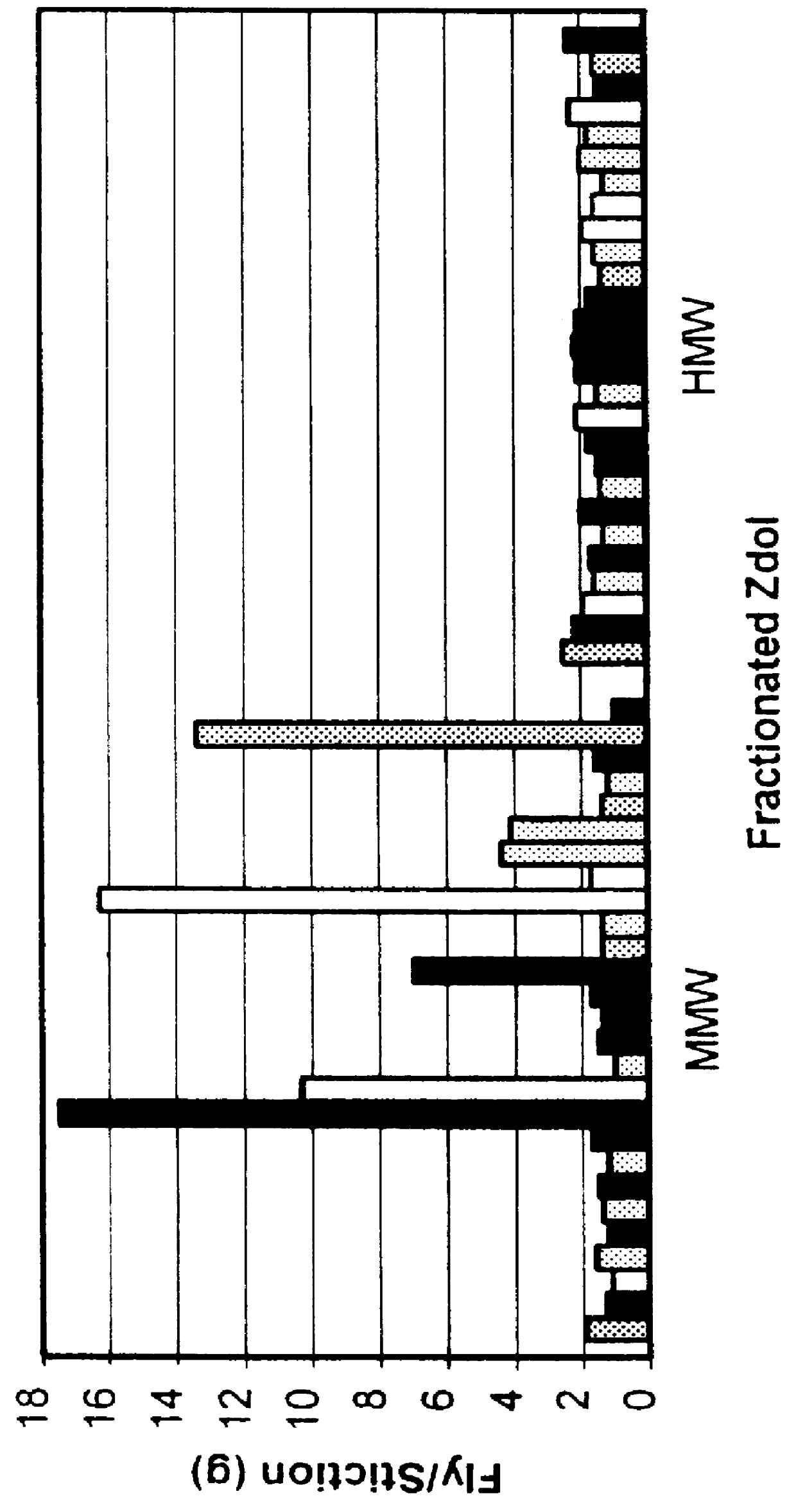
High molecular weight fractionated lubricant for use with thin film magnetic media
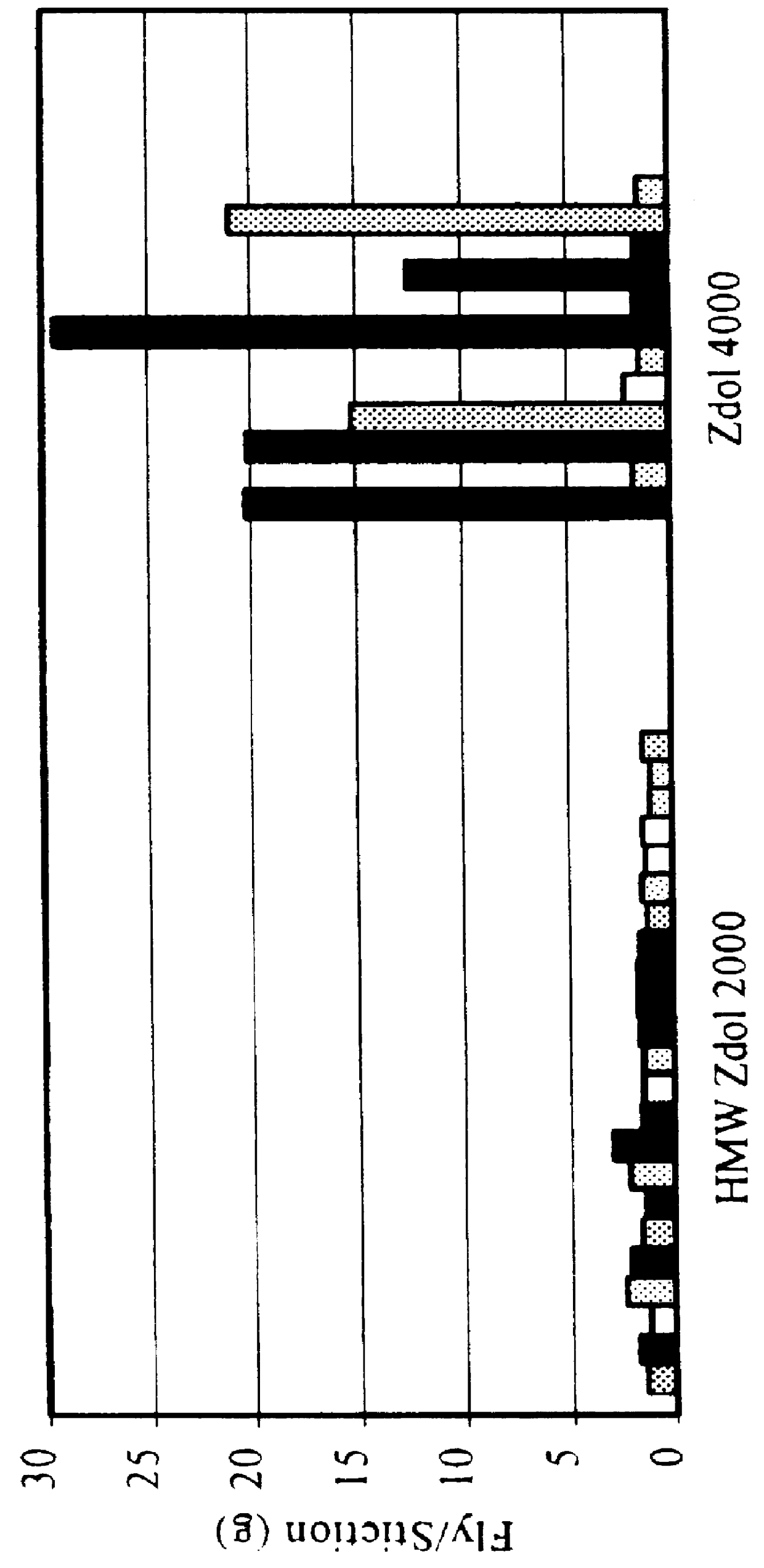
InactiveUS6099937AReduces fly/stictionReduce transferOrganic chemistryProtective coatings for layersRough surfaceAir bearing
Disclosed is a perfluoropolyether (PFPE) lubricant comprising less than about 10 percent PFPE molecules having a molecular weight lower than about 2000 Daltons, and wherein the average molecular weight of the lubricant is greater than about 5000 Daltons. Such a lubricant comprises less than about 15 percent PFPE molecules having a moleuclar weight greater than about 10,000 Daltons. Also disclosed is a thin film magnetic disc comprising a recording surface and a PFPE lubricant in contact with the recording surface. The recording surface of such a thin film magnetic disc can be adapted to magnetically record information via an air bearing read / write head. The recording surface can be smooth. The disc can further comprise a rough-surfaced landing zone inward of the recording surface, wherein the PFPE lubricant is in contact with the landing zone. Also disclosed is a method of lubricating a thin film magnetic disc. The method can comprise applying a narrow, high molecular weight fractionated PFPE lubricant to the disc. In addition, a method of preparing a PFPE lubricant for use with a thin film magnetic disc is disclosed. The method can comprise fractionating a PFPE lubricant to include less than about 10 percent PFPE molecules having a molecular weight lower than about 2000 Daltons. The average molecular weight of such a lubricant after fractionation is greater than about 5000 Daltons.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Preparation of high molecular weight instant cation polyacrylamide
The invention relates to a preparation method for instant cation polyacrylamide with a high molecular weight. The monomer of acrylamide and a cation type monomer are used as the main materials, firstly, the acrylamide and a comonomer are dissolved into deionized water; then a photoinitiator and / or a photosensitizer additive and a redox initiator are added in the solution to form a compound initiating system; the materials of the components are uniformly mixed in a viscous state, poured on a plane and paved into a sheet shape, introduced with high purity nitrogen, then ultraviolet light illumination is carried out to the materials paved into the sheet shape; after the materials of the viscous state are in a gel block, the materials are dried, broken, granulated and cracked to obtain a product of a dry powder shape. In the invention, the heat release and temperature rising of bulk adiabatic polymerization are avoided, while the polymerization and drying are carried out under a lower temperature; therefore, the reaction process is stable; the product has the advantages of higher molecular weight, better solubility, faster dissolving speed, simple technique and low cost; in addition, the processing after polymerization reduces the working procedure of breaking of bulk gel.
Owner:朱定洋
Non-fibrous high modulus ultra high molecular weight polyethylene tape for ballistic applications
A non-fibrous ultra high molecular weight polyethylene tape having a width of 1-inch or greater and a modulus of 1,400 grams per denier or greater. The non-fibrous UHMWPE tape is obtained by compression molding ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene powder at a temperature below its melting point and then drawing and stretching the entire resultant compression molded UHMWPE sheet, with no slitting or splitting of the sheet, at a draw ratio of at least 100:1. The UHMWPE tape can be produced in weights of 6,000 to 90,000 denier or greater. The UHMWPE tape of the present invention minimizes the effect of stress concentrators that are prevalent with fibers and thereby enables the tape to be drawn at much higher draw ratios than is possible with fibrous UHMWPE. When used in ballistics panels, the high modulus high molecular weight polyethylene tape of the present invention improves ballistic performance by providing enhanced dissipation of the impact energy of a projectile.
Owner:DUPONT SAFETY & CONSTR INC
Ionization source for mass spectrometry analysis
ActiveUS7368728B2Samples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by optical meansLaser desorption ionization mass spectrometryGas phase
A new ionization source named Surface Activated Chemical Ionization (SACI) has been discovered and used to improve the sensitivity of the mass spectrometer. According to this invention the ionization chamber of a mass spectrometer is heated and contains a physical new surface to improve the ionization process. The analyte neutral molecules that are present in gas phase are ionized on this surface. The surface can be made of various materials and may also chemically modified so to bind different molecules. This new ionization source is able to generate ions with high molecular weight and low charge, an essential new key feature of the invention so to improve sensitivity and reduce noise. The new device can be especially used for the analysis of proteins, peptides and other macromolecules. The new invention overcomes some of the well known and critical limitations of the Electrospray (ESI) and Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometric techniques.
Owner:UNIV DELGI STUDI DI MILANO
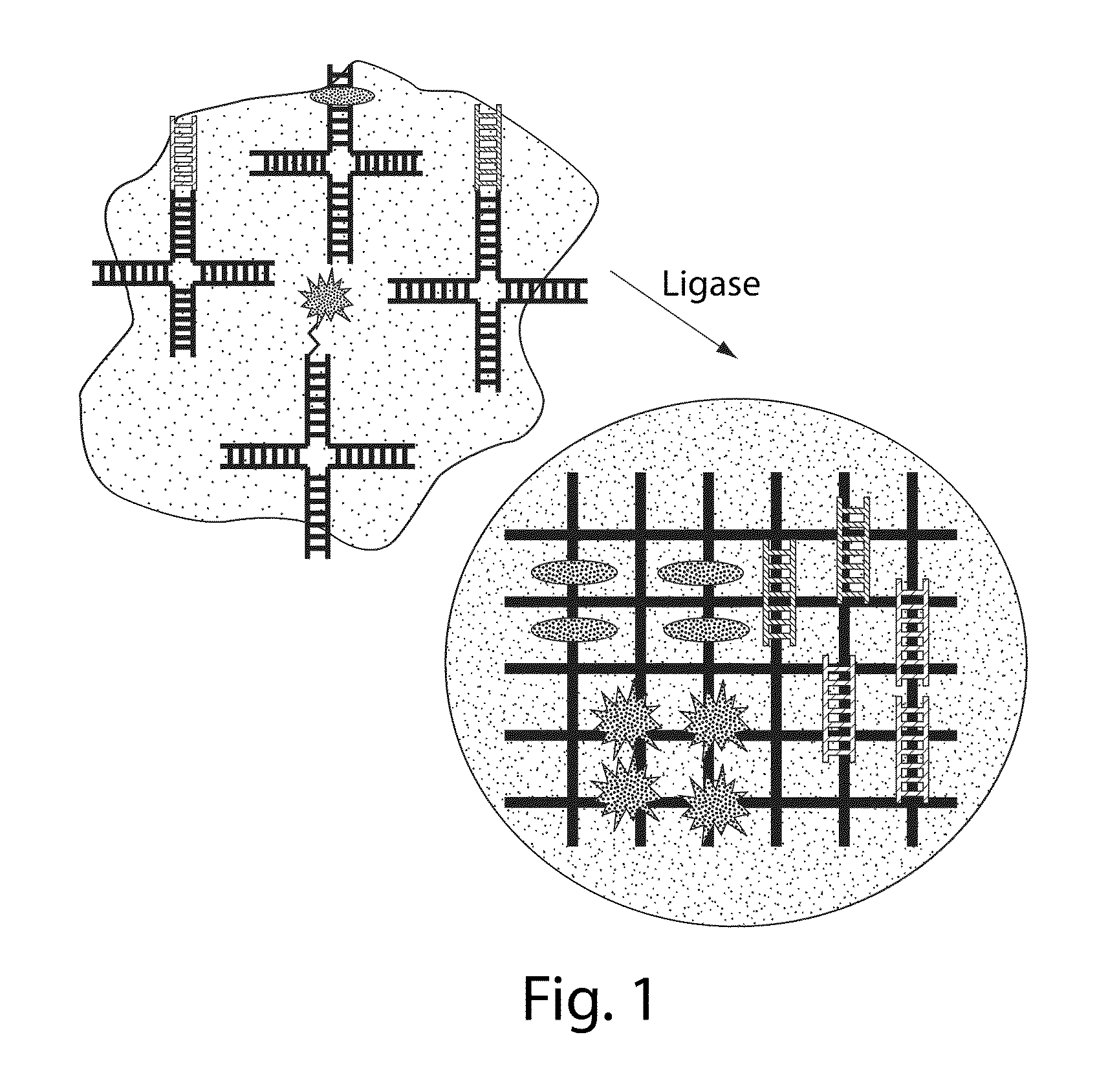
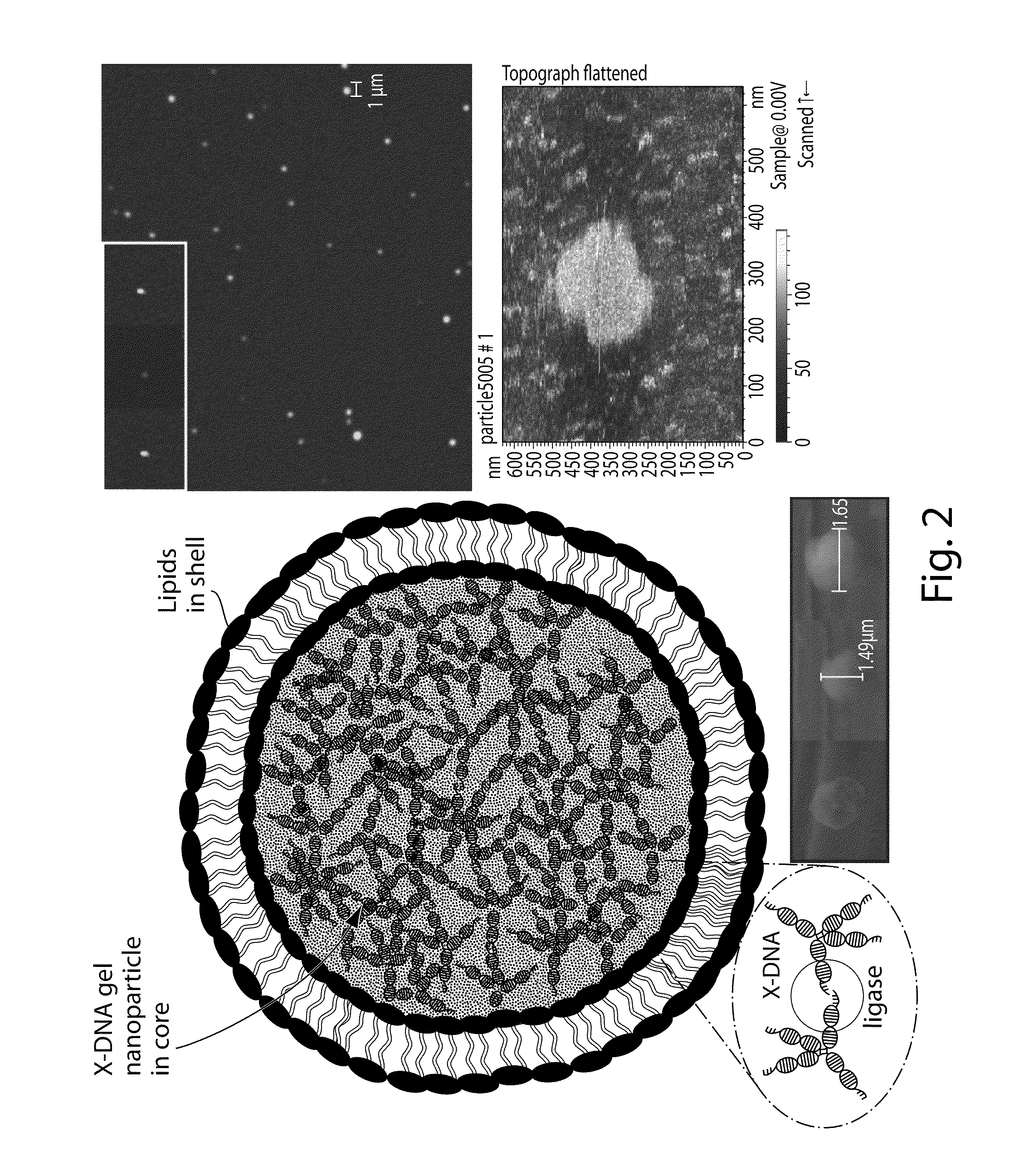
Branched DNA/RNA monomers and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100323018A1Activity of siRNA can be reducedInterfere with activityPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsLipid formationDiagnostic agent
The invention provides compositions and methods relating to delivery of agents in vivo or in vitro. More specifically, the invention provides nanoparticles synthesized from crosslinked nucleic acids, optionally having a lipid shell or coating, and may further comprise for example small molecule or high molecular weight compounds as therapeutic or diagnostic agents.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
High strength tape articles from ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
High molecular weight ionized water
ActiveUS7513987B1Increase oxidation potentialAvoid inclusionsPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsHydronium ionHigh molecular mass
A method for generating a multihydrated hydronium ion including the steps: agitating water to reduce cluster size, mixing sulfuric acid in the water, adding a solution containing Ca3+ ions, removing precipitated Ca sulfate, cooling the resultant liquid to a form a slush, filterin out ice from the slush, distilling free water from the remaining liquid wherein the remaining liquid is H9O4+.
Owner:MILLSTONE PROPERTIES
Method for preparing high molecular weight polyacrylamide dried powder
The preparation of high molecular weight polyacrylamide powder is one low temperature aqua polymerization process, and compared with available technology, the present invention is different in that it adopts the mixture of sodium bicarbonate and sodium carbonate as hydrolyzing agent, the added foaming agent, and trinary initiator system comprising high temperature initiator added before reaction and oxidation-reduction initiator added after the system temperature is controlled in 10-40 deg.c. The polyacrylamide product of the present invention has the advantages of high molecular sieve of 18-23 million, solid content of about 90 %, characteristic viscosity not lower than 23 dl / g, high water solubility, free monomer less than 0.03 % and hydrolysis degree of 20-30 %.
Owner:许振举
Preparation for water soluble high-molecular weight cationic polymer
A water-soluble, high molecular weight cationic polymer is prepared with polyphyletic composite oxidation-reduction triggering system by: adding multiple aid reagent, triggering methylpropyleneacyloxyethyltrimethyl ammonium chloride, or propyleneamide- propyleneacyloxyethyltrimethyl ammonium chloride, together with propyleneamide water solution to copolymer. The obtained products are water-soluble cationic polymer powder state, viscidity number 13.4-23.4dl / g, METMACS or AETMAC in polymer mol percent content is 0.5% -99.5%, residual monomers content is is less than or equal to 0.1 wt%. This invention has the features of that it adopts domestic industrial grade monomers as raw materials directly, without refine, the obtained products' cationic value is 50-99.5. The products can be used as clay stabilizer, reverse emulsion breaker, slow corrosion agent in petroleum engineering, intensifier, treating agent for wastewater in paper-making industry, water-treating agent and silt dewatering agent in environment protection etc.
Owner:HAISO TECH
Non-flaking capacitor material, capacitive substrate having an internal capacitor therein including said non-flaking capacitor material, and method of making a capacitor member for use in a capacitive substrate
InactiveUS20070177331A1Enhance circuitized substrate artLow costThin/thick film capacitorPrinted circuit aspectsEpoxyCapacitance
A capacitor material including a thermosetting resin (e.g., epoxy resin), a high molecular mass flexibilizer (e.g., phenoxy resin), and a quantity of nano-particles of a ferroelectric ceramic material (e.g., barium titanate), the capacitor material not including continuous or semi-continuous fibers (e.g., fiberglass) as part thereof. The material is adapted for being positioned in layer form on a first conductor member and heated to a predetermined temperature whereupon the material will not possess any substantial flaking characteristics. A second conductor member may then be positioned on the material to form a capacitor member, which then may be incorporated within a substrate to form a capacitive substrate. Electrical components may be positioned on the substrate and capacitively coupled to the internal capacitor.
Owner:I3 ELECTRONICS
Transdermal delivery system for dried particulate or lyophilized medications
InactiveUS20060233871A1Extended shelf lifeStability longElectrotherapyPeptide/protein ingredientsParticulatesActive agent
The present invention provides a system for transdermal delivery of dried or lyophilized pharmaceutical compositions and methods using thereof. The system comprises an apparatus for facilitating transdermal delivery of an agent that generates hydrophilic micro-channels, and a patch comprising a therapeutically active agent. The present invention is useful for transdermal delivery of hydrophilic agents, particularly of high molecular weight proteins.
Owner:SYNERON MEDICAL LTD
Super high molecular weight polyacrylamide industrialized production process
InactiveCN1865299AHigh molecular weightRealize large-scale industrial productionManufacturing technologyFunctional monomer
The invention discloses an industrial manufacturing technology of polyacrylamide (over 25,000 thousand molecular weights), which is characterized by the following: introducing functional monomer under insulation condition; finishing polymerization reaction through synergic action of three-segmented composite initiator; grinding; graining; hydrolyzing; drying; breaking; screening; improving polymerization molecular weight to polymerize block kettle-typed polyacrylamide; fitting for large scale producing; making the product quality, volume of production, energy consumption and using scope satisfy domestic leading level.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Polymer composition and process to manufacture high molecular weight-high density polyethylene and film therefrom
The present invention includes a multimodal polyethylene composition has (1) a density of at least about 0.940 g / cm3 as measured by ASTM Method D-1505; (2) a melt flow index (I5) of from about 0.2 to about 1.5 g / 10 min (as measured by ASTM D-1238, measured at 190° C. and 5 kilograms); (3) a melt flow index ratio (I21 / I5) of from about 20 to about 50; (4) a molecular weight distribution, Mw / Mn, of from about 20 to about 40; (5) a bubble stability measured on specified equipment according to specified conditions for a film of about 6×10−6 m thickness of at least about 1.22 m / s line speed, at least about 45 kg / hr (0.013 kg / sec) output rate, or at least about 0.5 lb / hr / rpm (0.0000011 kg / s / rps) specific output rate or a combination thereof; the composition comprising; and (6) a dart impact on 12.5 micron (1.25×10−5 m) film of at least 300 g; measured according to ASTM 1709, Method A; (A) a high molecular weight fraction which; (a) is present in an amount of from about 30 to about 70 weight percent (based on the total weight of the composition); (b) has a density of at least about 0.860 g / cm3 as measured by ASTM D-1505; (c) has a melt flow index (I21) of from about 0.01 to about 50 g / 10 min (as measured by ASTM D-1238, measured at 190° C. and 21.6 kilograms); and (d) a melt flow index ratio (I21 / I5) of from about 6 to about 12; and (B) a low molecular weight fraction which; (a) is present in an amount of from about 30 to about 70 weight percent (based on the total weight of the composition); (b) has a density of at least about 0.900 g / cm3 as measured by ASTM D-1505; (c) has a melt flow index (I2) of from about 0.5 to about 3000 g / 10 min (as measured by ASTM D-1238, measured at 190° C. and 2.16 kilograms); (d) a melt flow index ratio (I21 / I5) of from about 5 to about 15; and (e) is prepared using a mole ratio of alpha olefin to ethylene of less than or equal to about 0.001:1. The invention also include a process for producing a multimodal ethylene polymer, which process comprises the following steps: (1) contacting in a first gas phase fluidized bed reactor under polymerization conditions and at a temperature of from about 70° C. to about 110° C., a titanium magnesium catalyst precursor, cocatalyst, and a gaseous composition, the gaseous composition having; (i) a mole ratio of alpha-olefin to ethylene of from about 0.01:1 to about 0.8:1; and optionally (ii) a mole ratio of hydrogen to ethylene of from about 0.001:1 to about 0.3:1, to produce a high molecular weight polymer(HMW); and (2) transferring the HMW polymer from step 1 to a second gas phase fluidized bed reactor under polymerization conditions and at a temperature of from about 70° C. to about 110° C., with a gaseous composition having; (i) a mole ratio of alpha-olefin to ethylene of from about 0.0005:1 to about 0.01:1; and (ii) a mole ratio of hydrogen (if present) to ethylene of from about 0.01:1 to about 3:1 to form a polymer blend
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
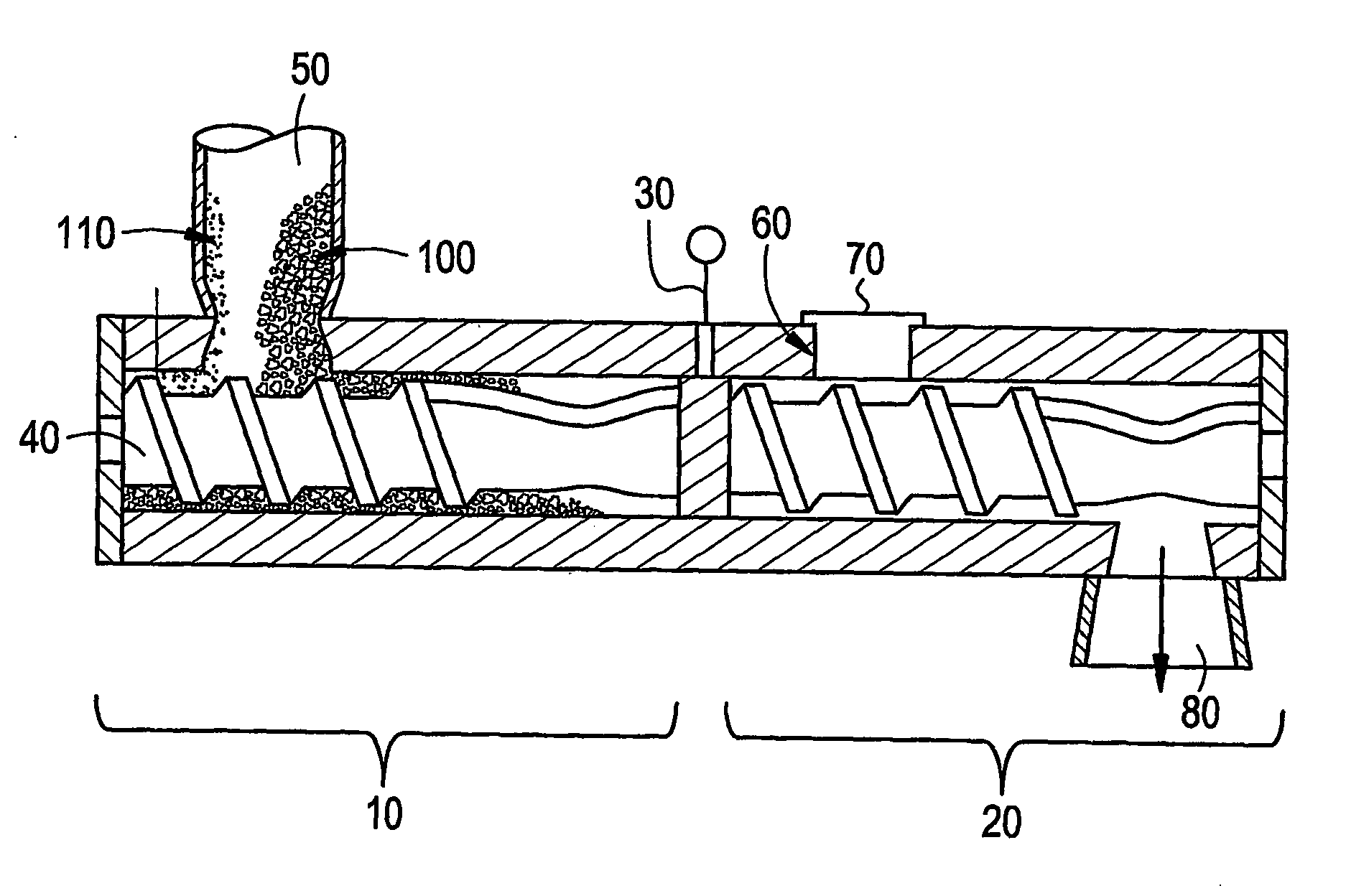
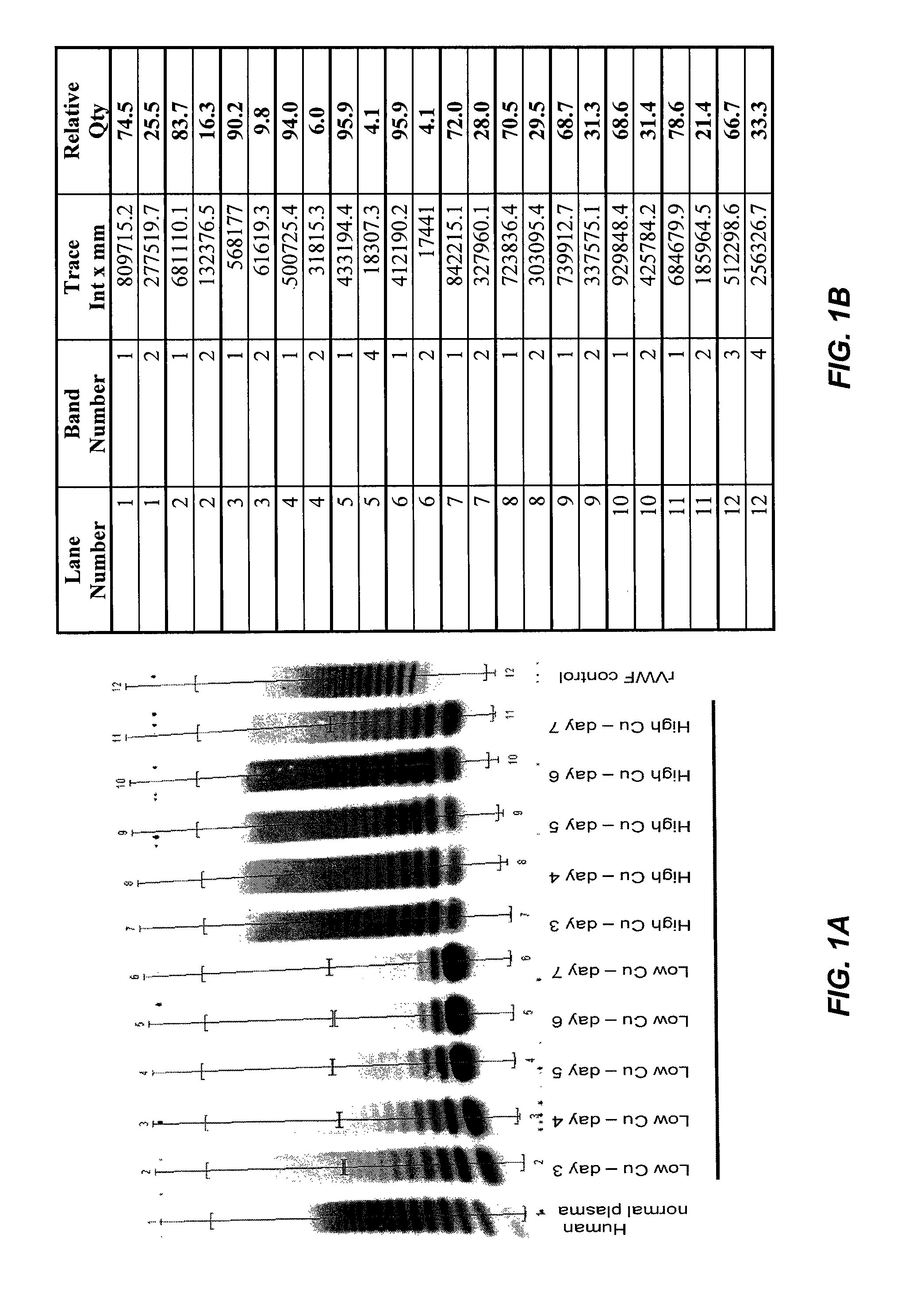
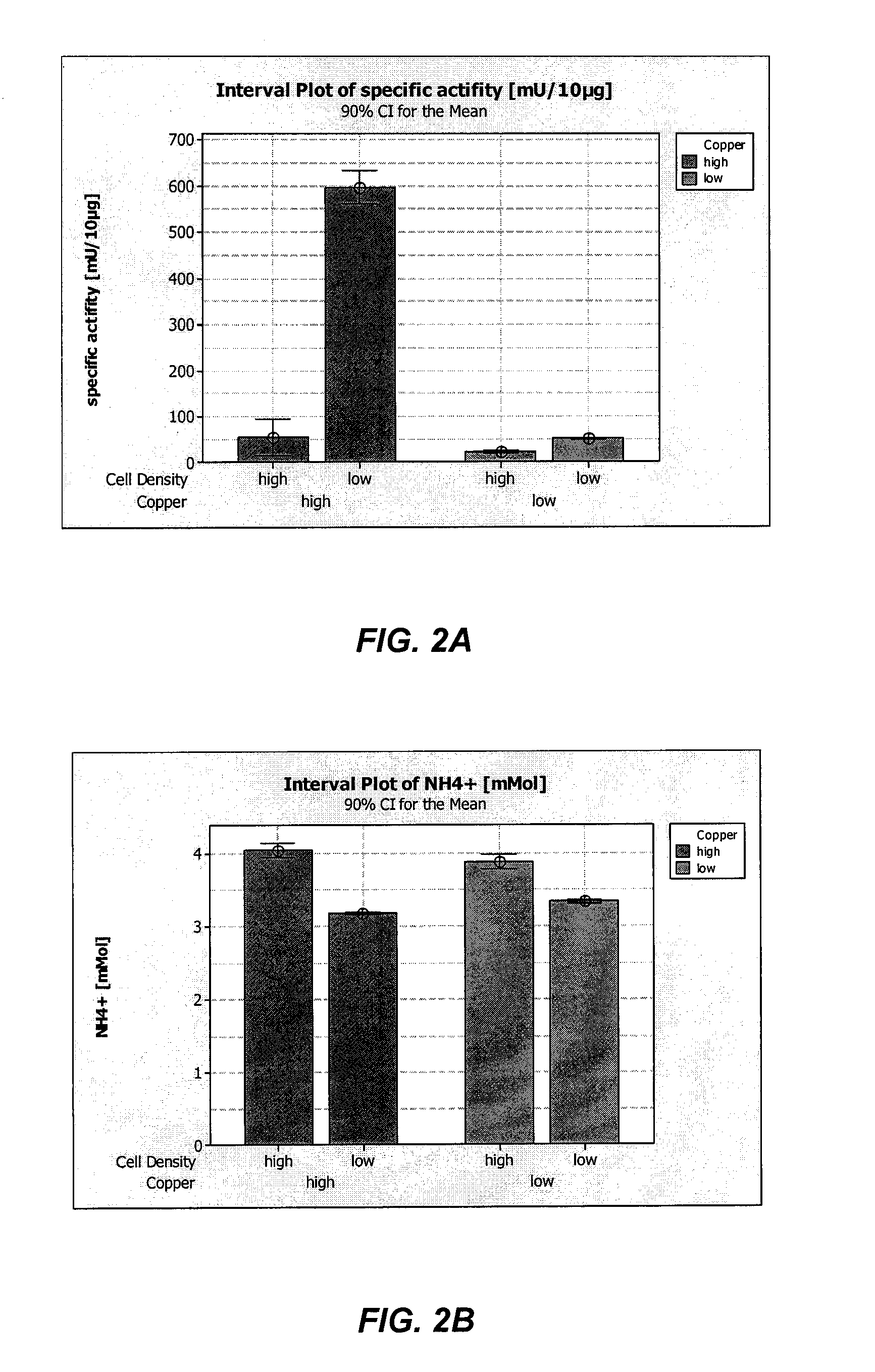
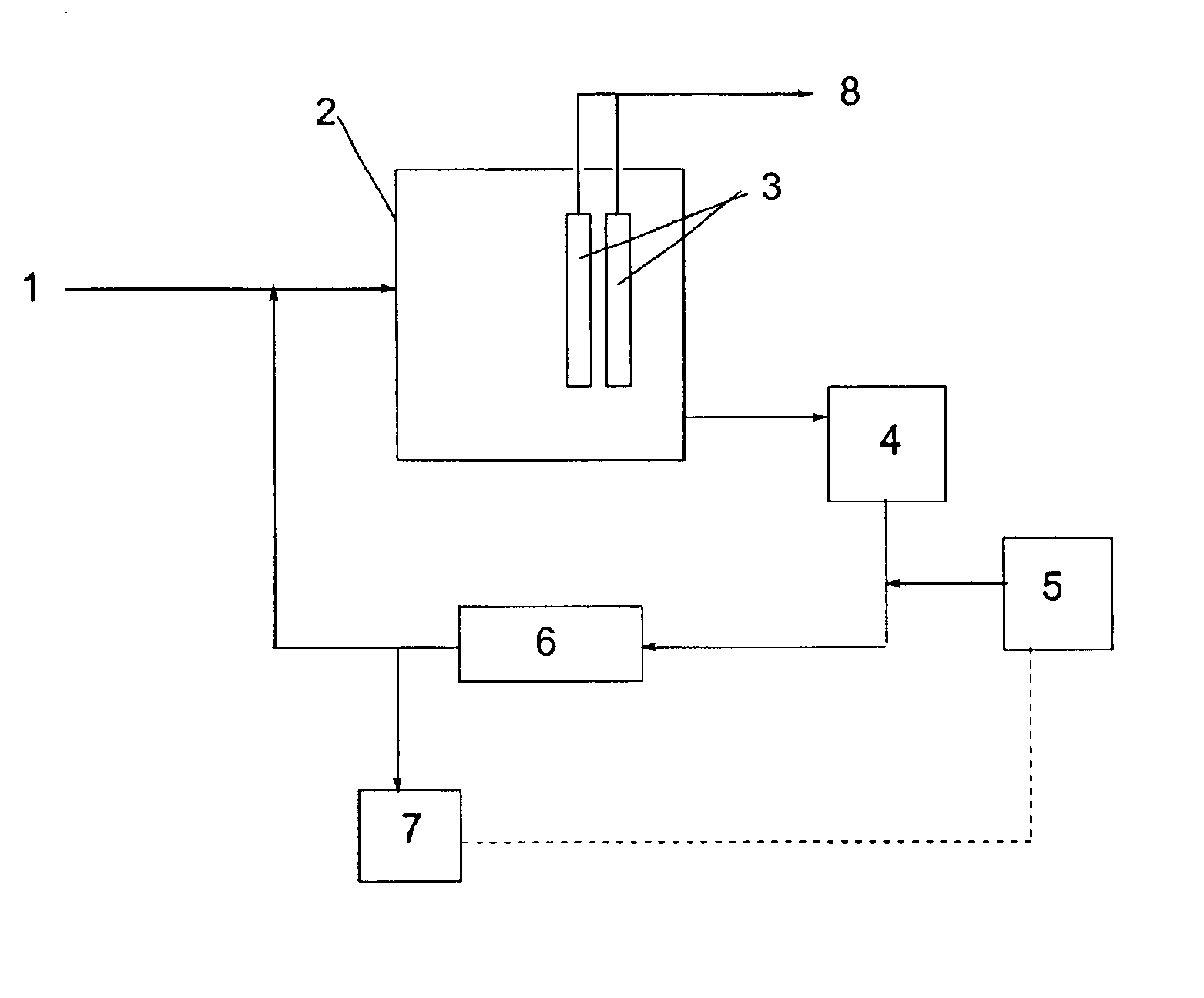
Method of producing recombinant high molecular weight vWF in cell culture
ActiveUS8852888B2High activityHigh expressionFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsCell culture mediaCell culture supernatant
Among other aspects, the present invention relates to cell culture conditions for producing high molecular weight vWF, in particular, highly multimericWF with a high specific activity and ADAMTS13 with a high specific activity. The cell culture conditions of the present invention can include, for example, a cell culture medium with an increased copper concentration and / or cell culture supernatant with a low ammonium (NH4+) concentration. The present invention also provides methods for cultivating cells in the cell culture conditions to express high molecular weight vWF and rA13 having high specific activities.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
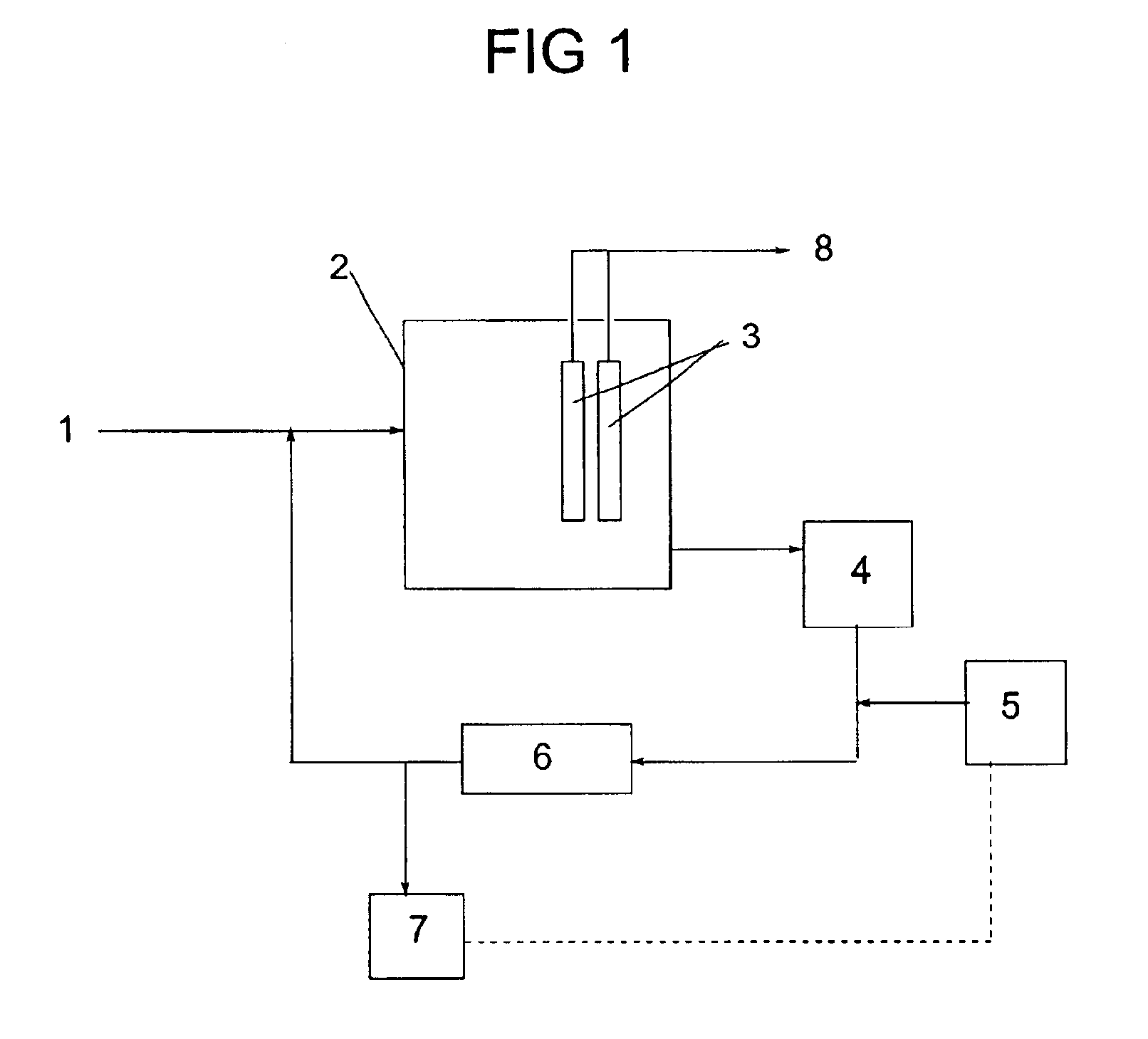
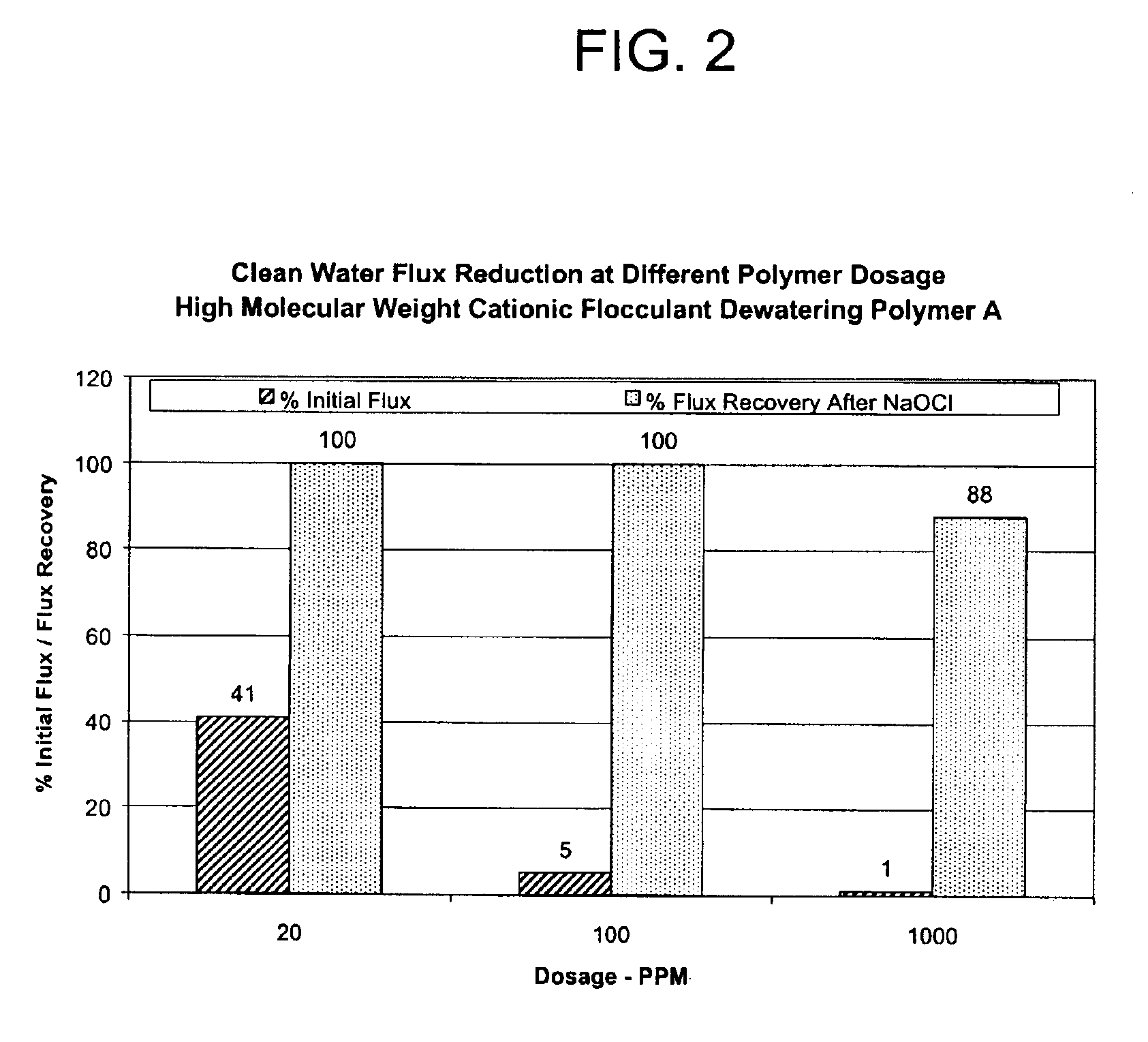
Method of using high molecular weight water soluble polymers in membrane bioreactor systems
InactiveUS6872312B1Semi-permeable membranesSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningActivated sludgeFluorescence
An activated sludge process for the clarification of wastewater comprising introducing the wastewater into a reactor where microorganisms consume organic material in the wastewater to form a mixed liquor comprising water, the microorganisms and an activated sludge; separating clarified water from the mixed liquor by filtration through a microfiltration or ultrafiltration membrane; separating the activated sludge from the mixed liquor; adding to the activated sludge at least one high molecular weight water soluble polymer to form a mixture of water and coagulated and flocculated solids; dewatering the coagulated and flocculated solids to form a mixture of dewatered solids and filtrate water; and recycling the filtrate water into the mixed liquor and a method of controlling polymer dosage, preferably using fluorescence emission spectroscopy.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com