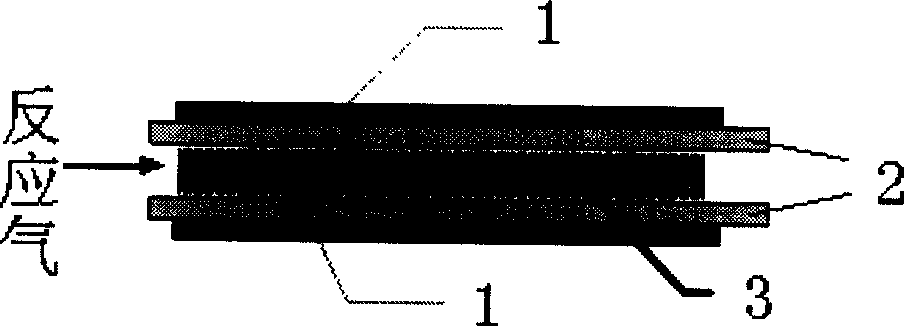
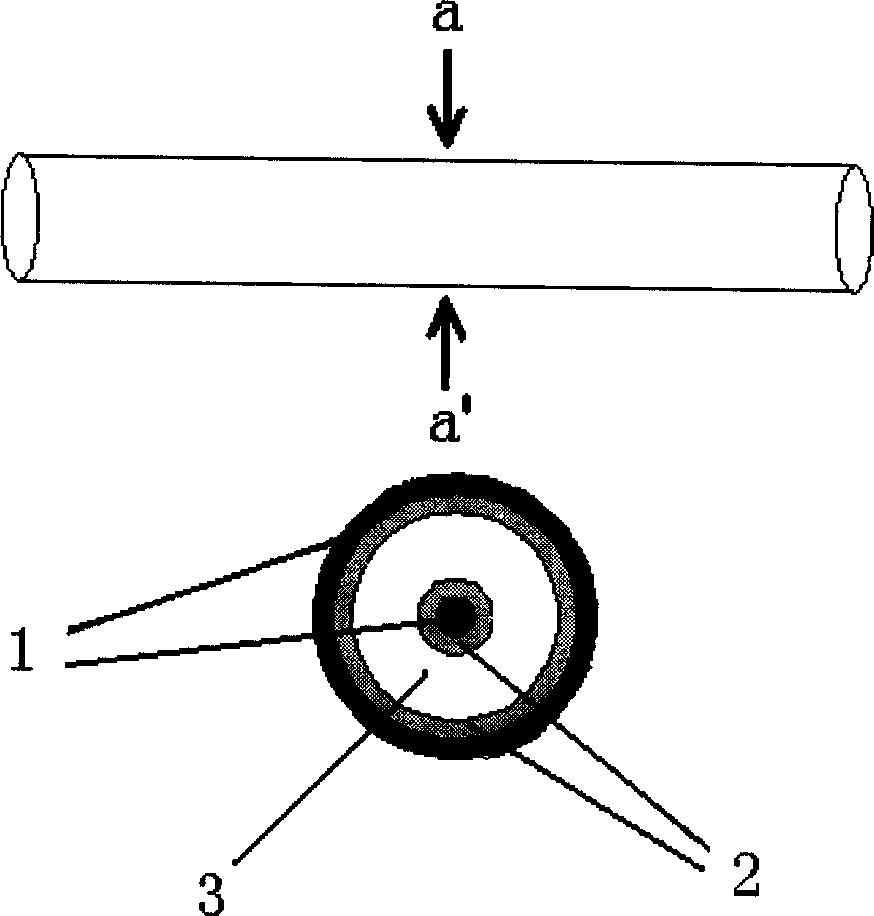
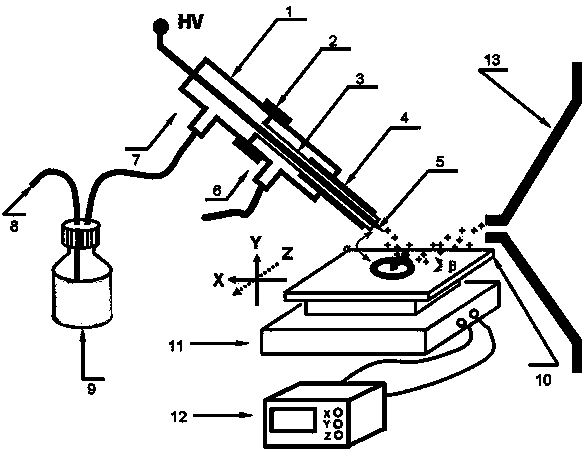
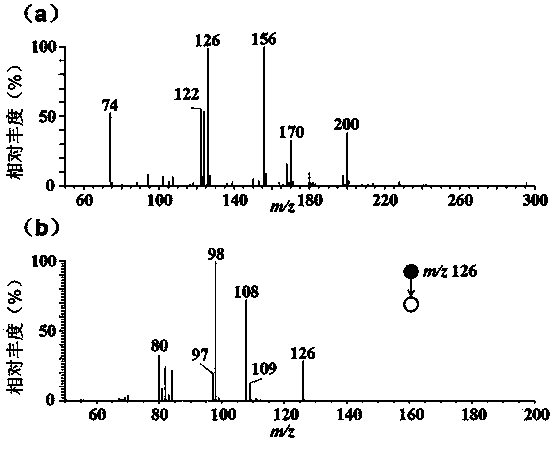
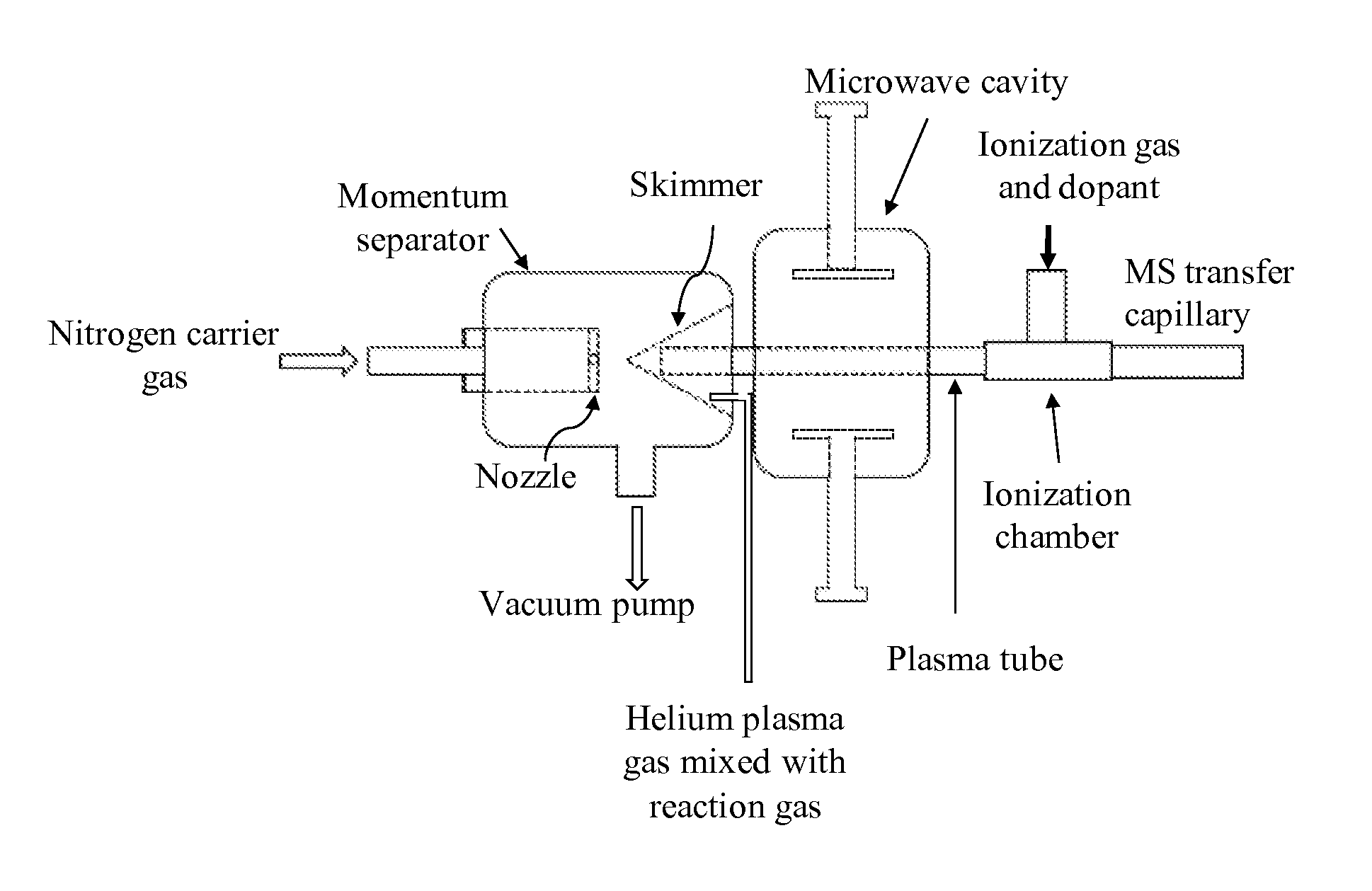
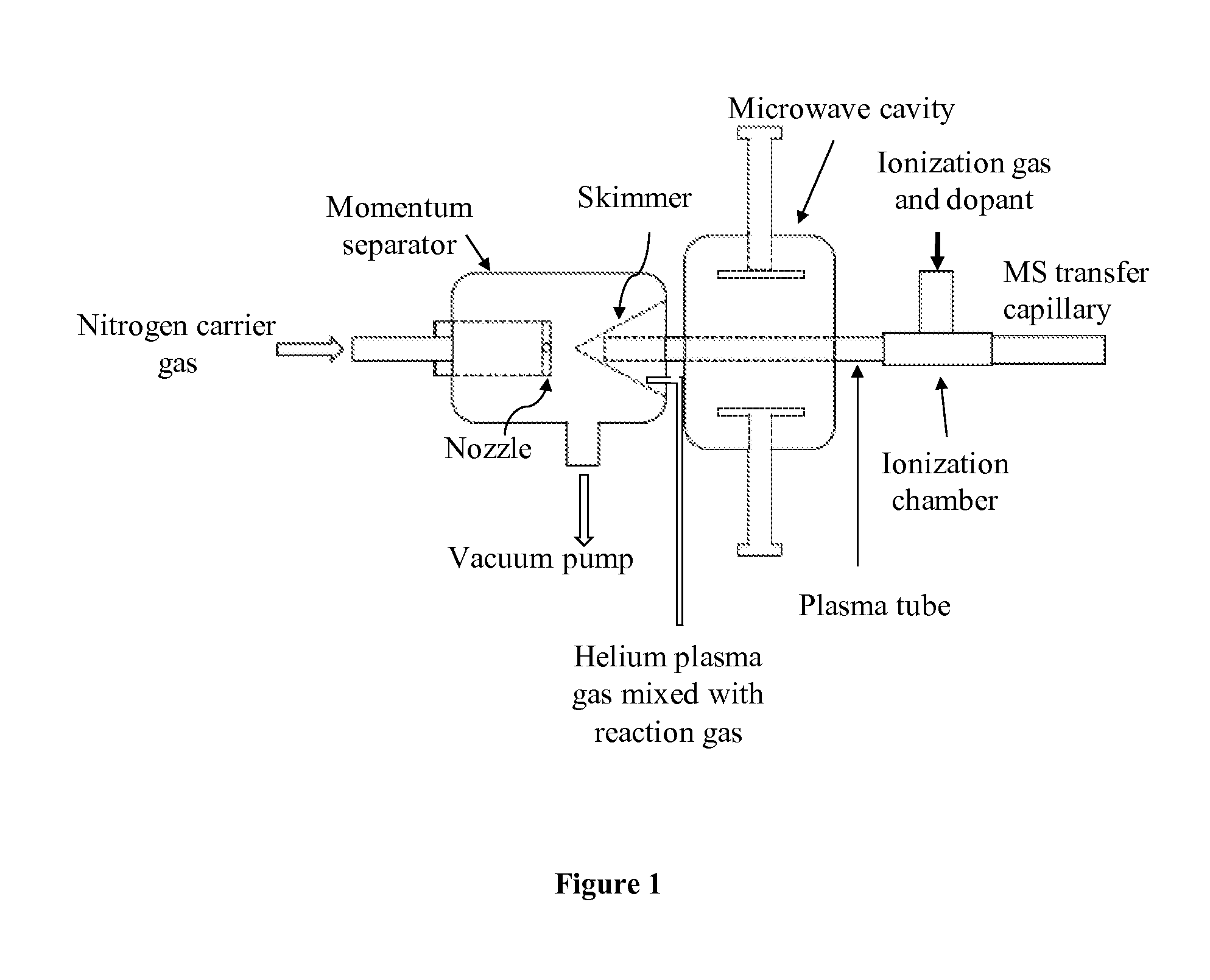
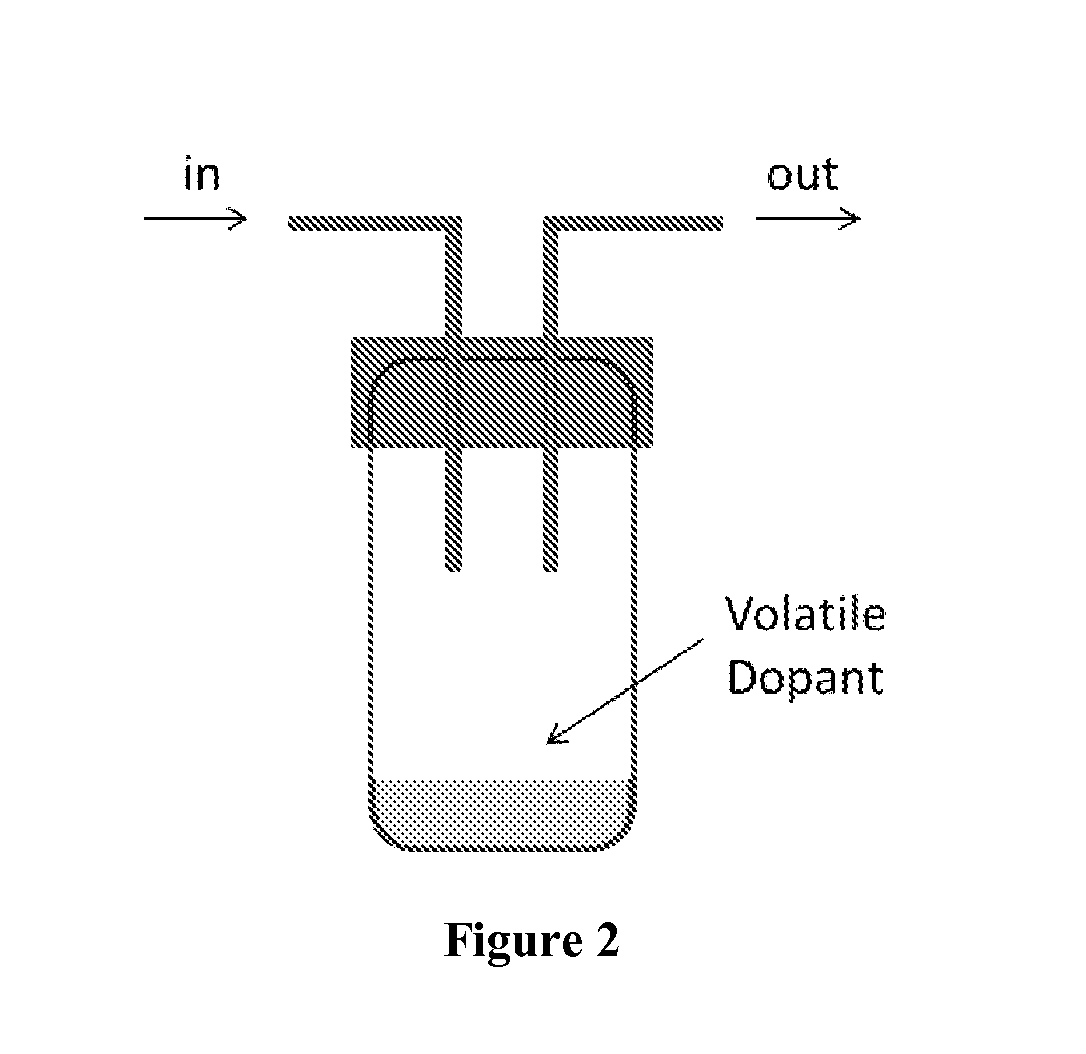
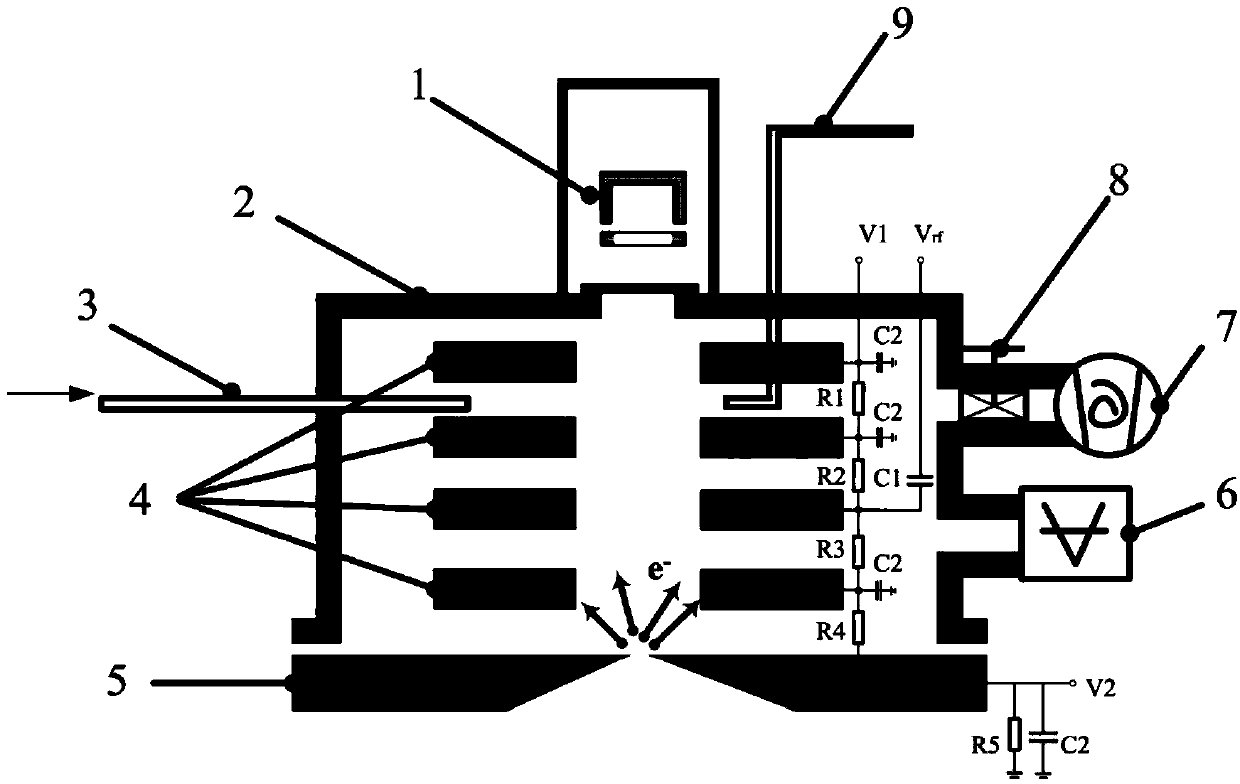
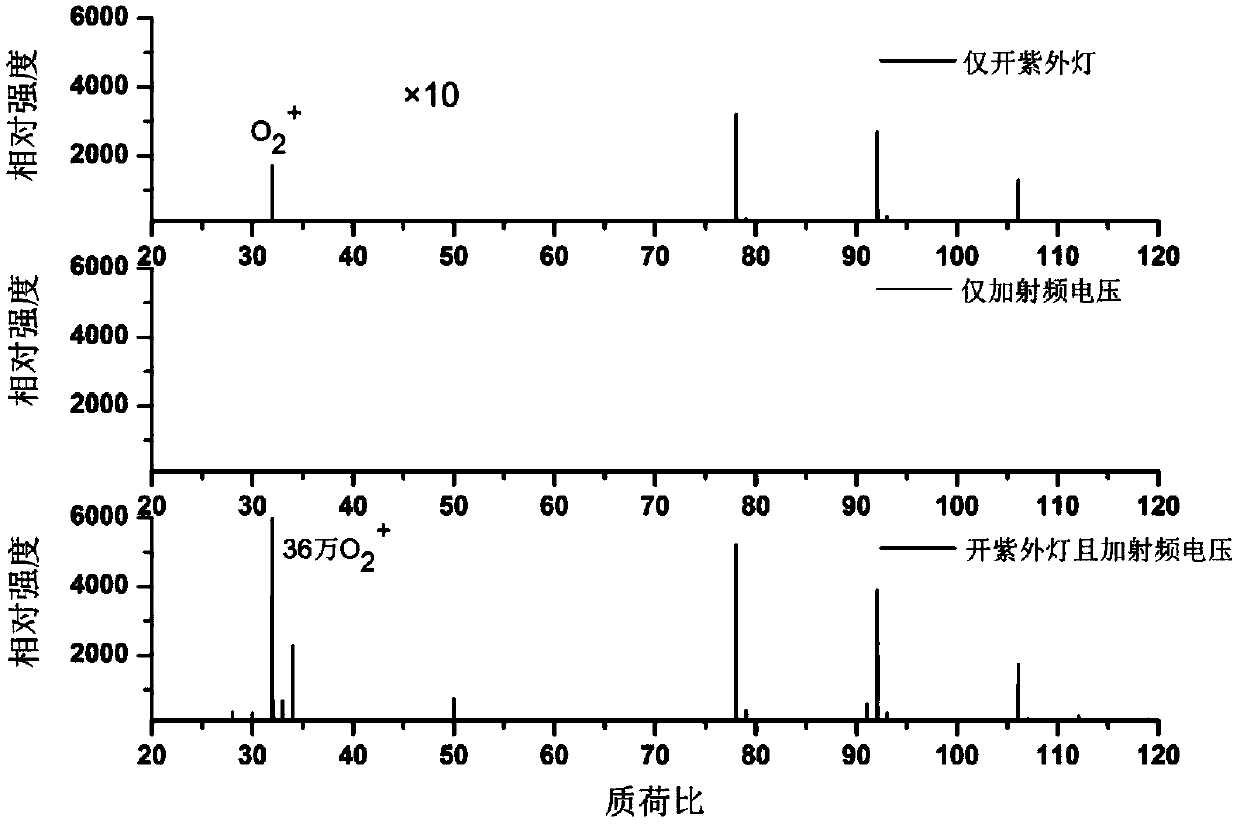
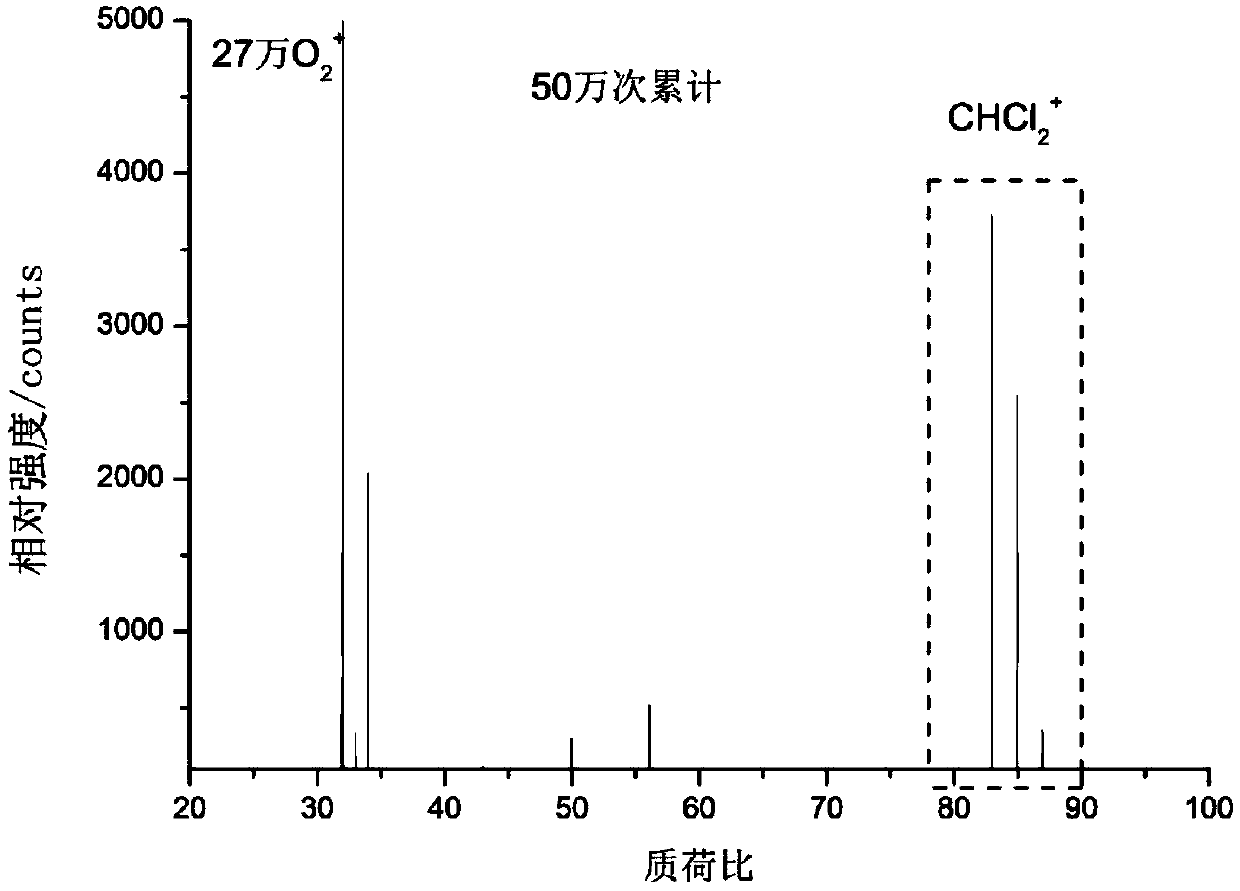
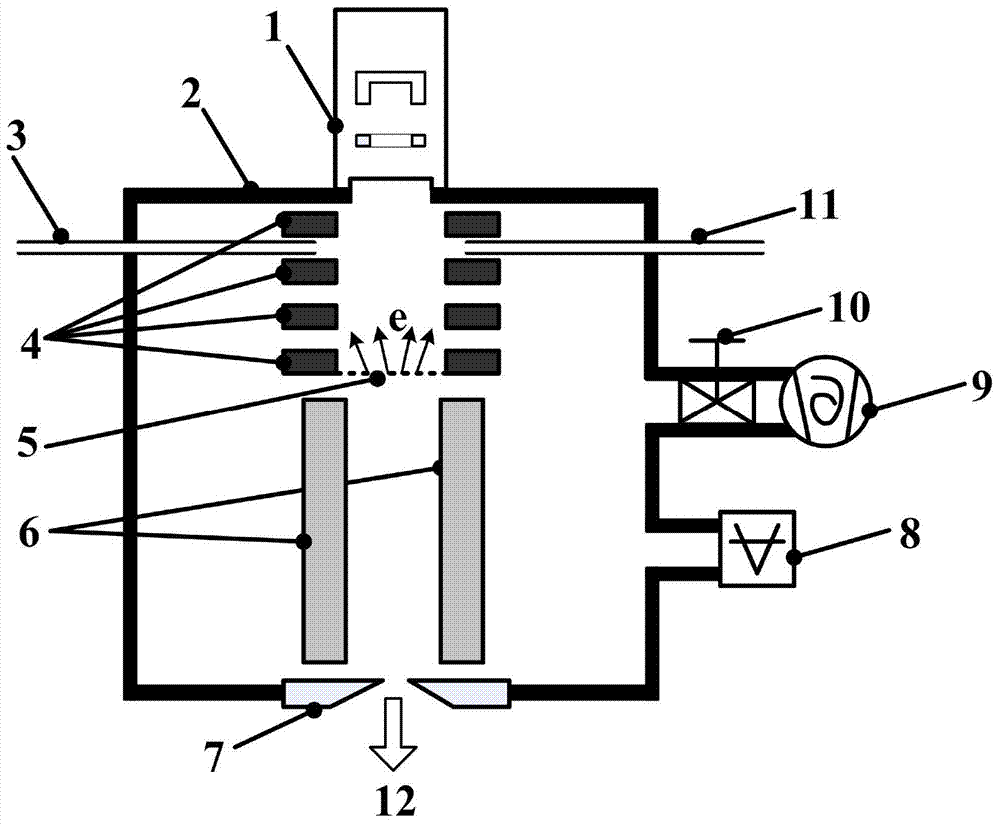
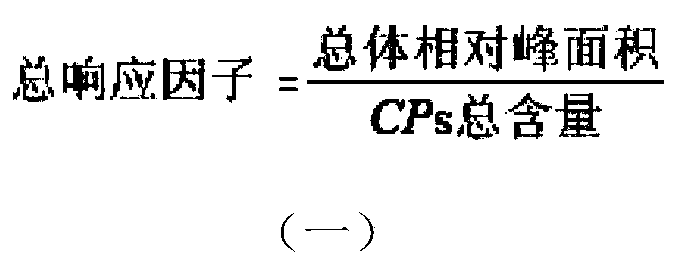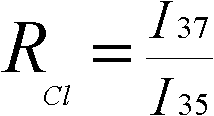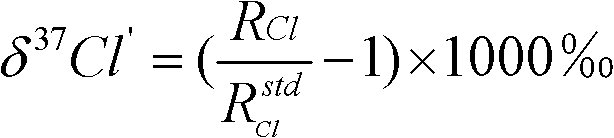Patents
Literature
142 results about "Chemical ionization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
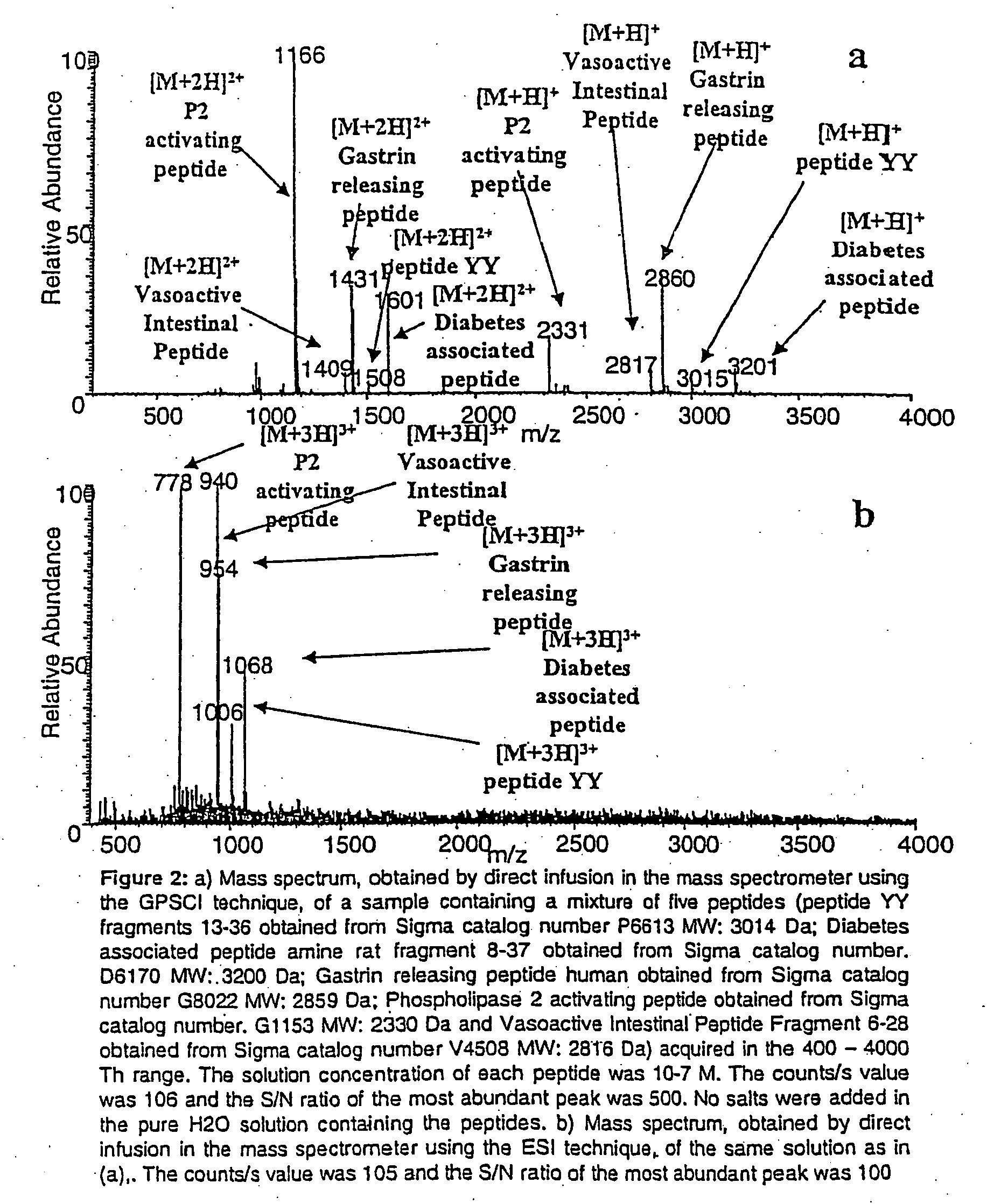
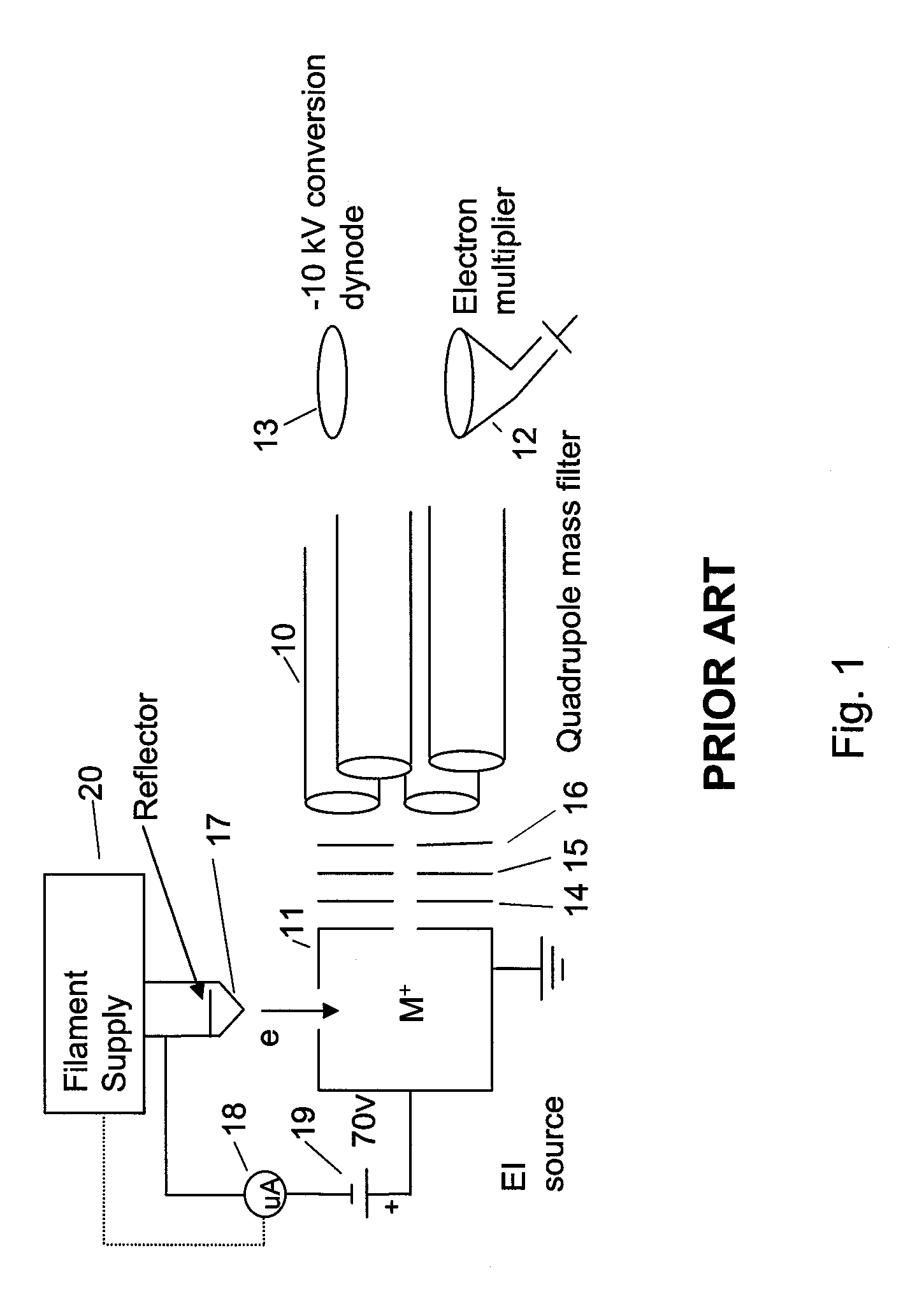
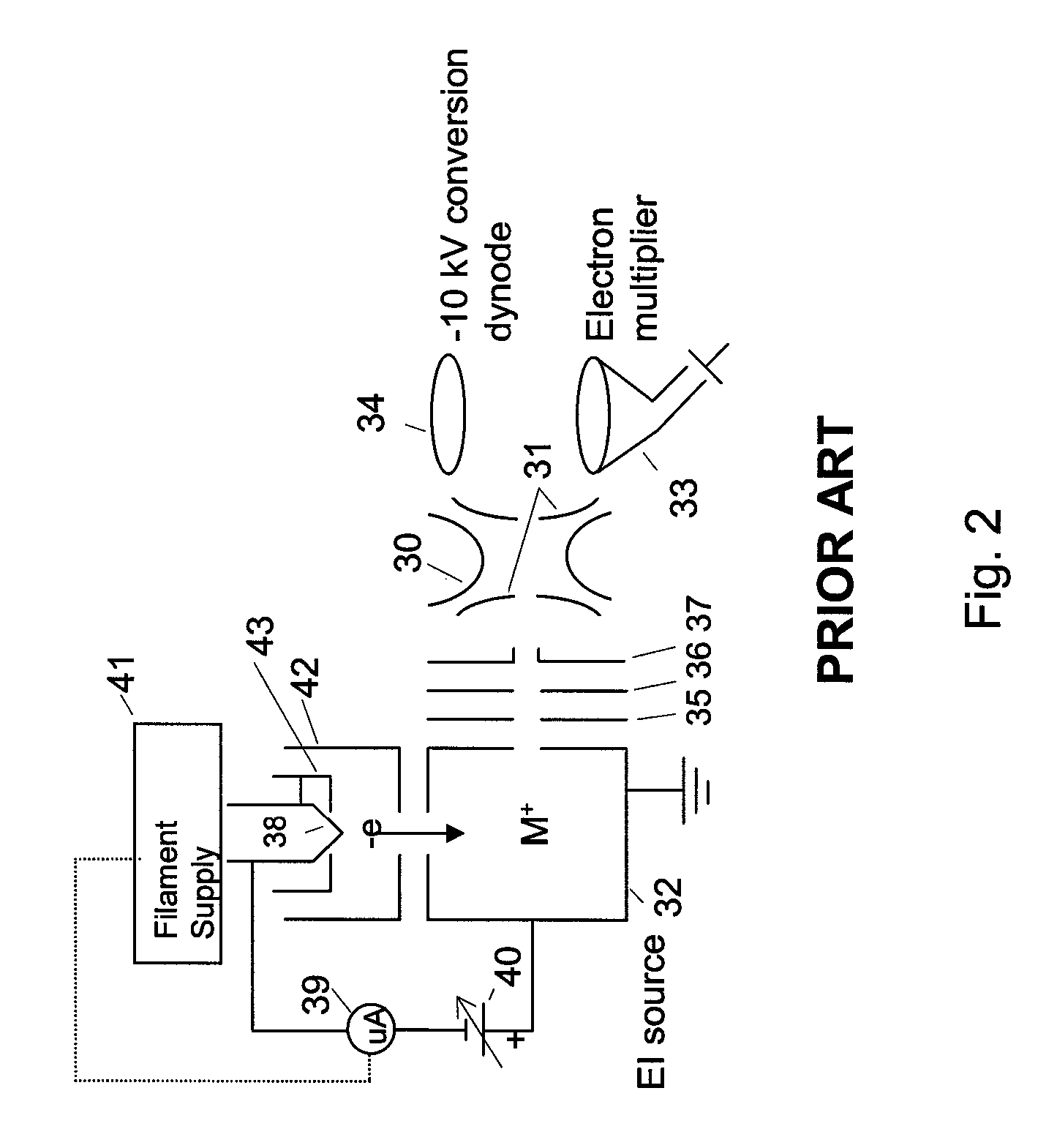
Chemical ionization (CI) is a soft ionization technique used in mass spectrometry. This was first introduced by Burnaby Munson and Frank H. Field in 1966. This technique is a branch of gaseous ion-molecule chemistry. Reagent gas molecules are ionized by electron ionization, which subsequently react with analyte molecules in the gas phase in order to achieve ionization. Negative chemical ionization (NCI), charge-exchange chemical ionization and atmospheric-pressure chemical ionization (APCI) are some of the common variations of this technique. CI has several important applications in identification, structure elucidation and quantitation of organic compounds. Beside the applications in analytical chemistry, the usefulness in chemical ionization extends toward biochemical, biological and medicinal fields as well.
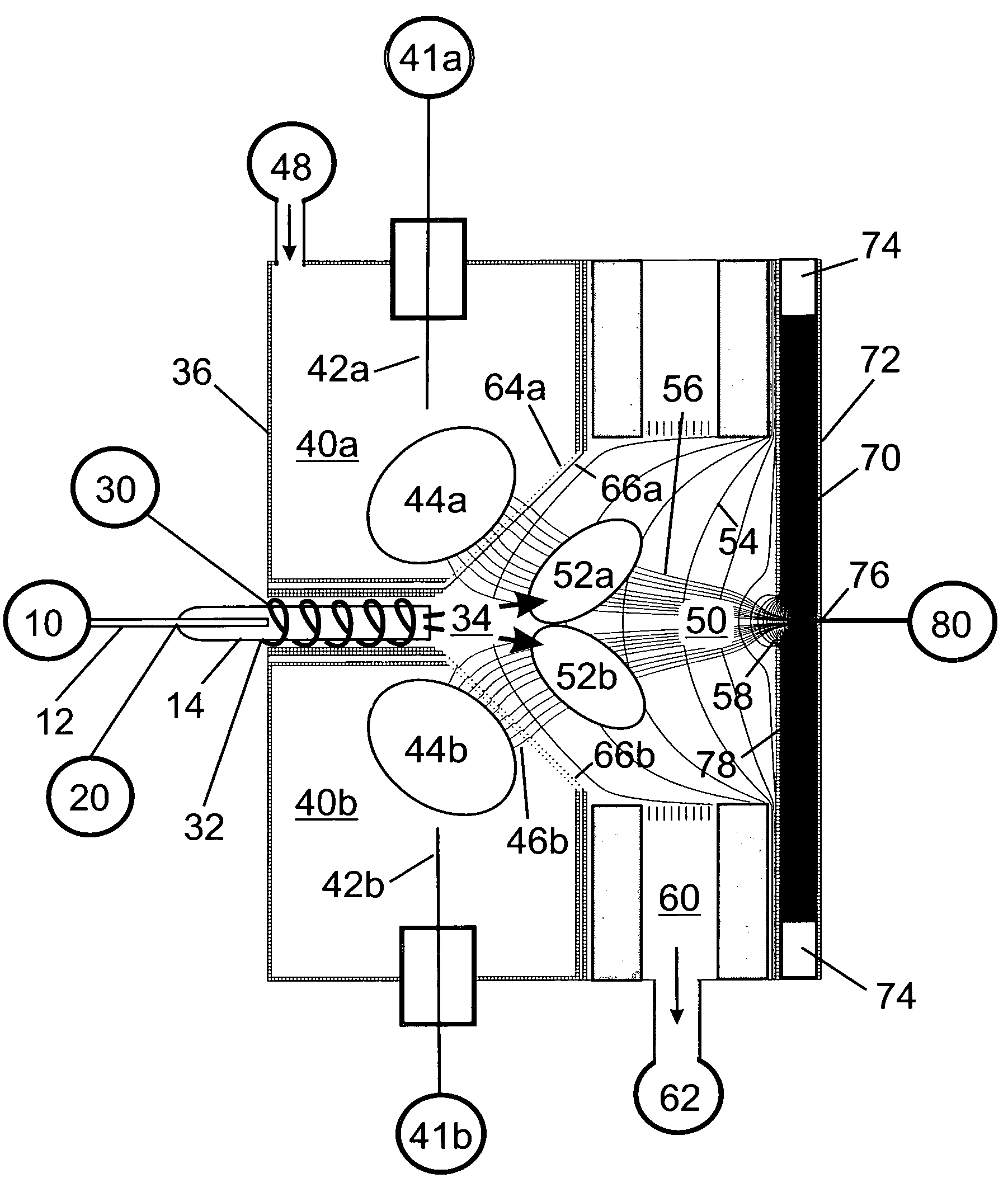
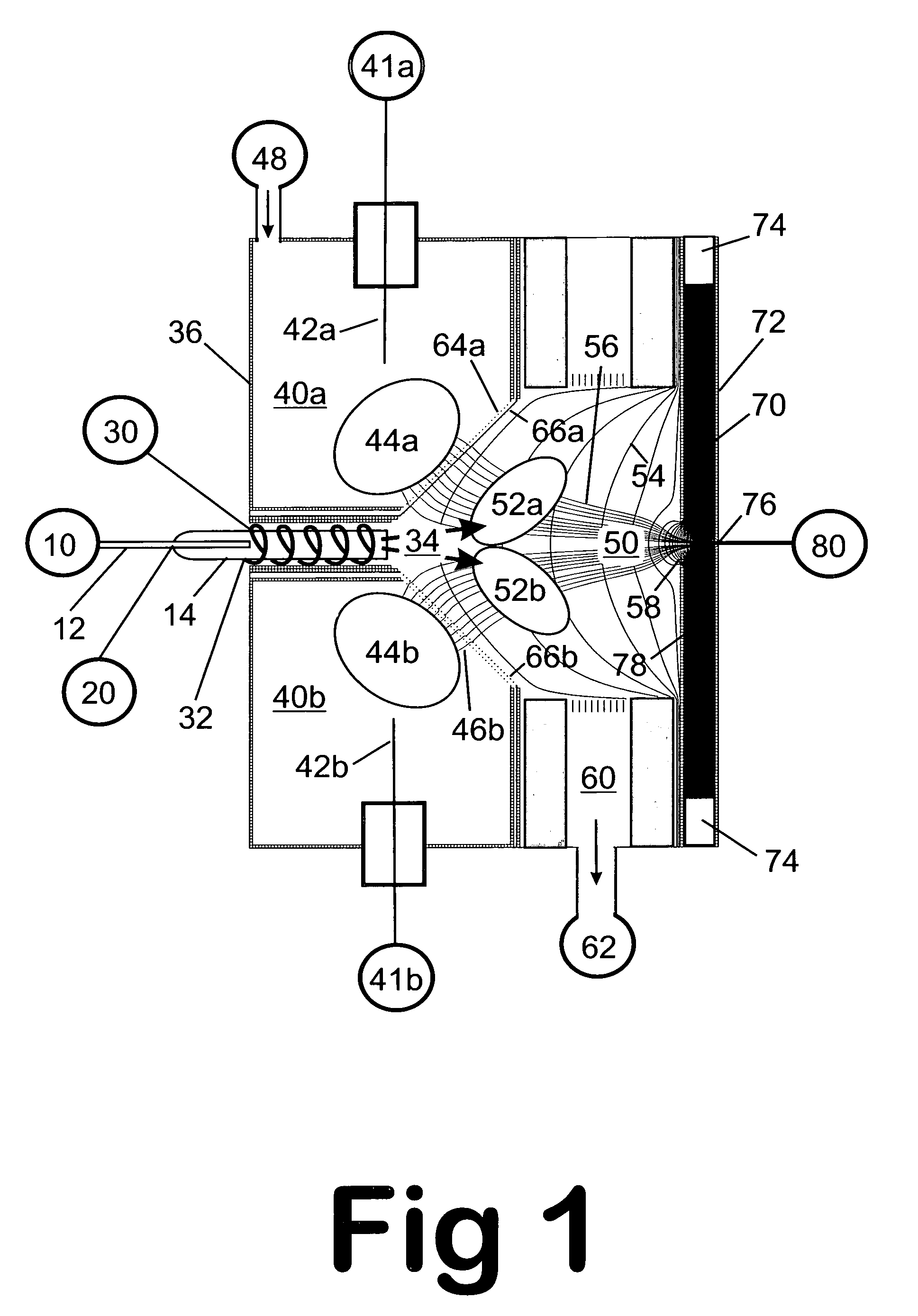
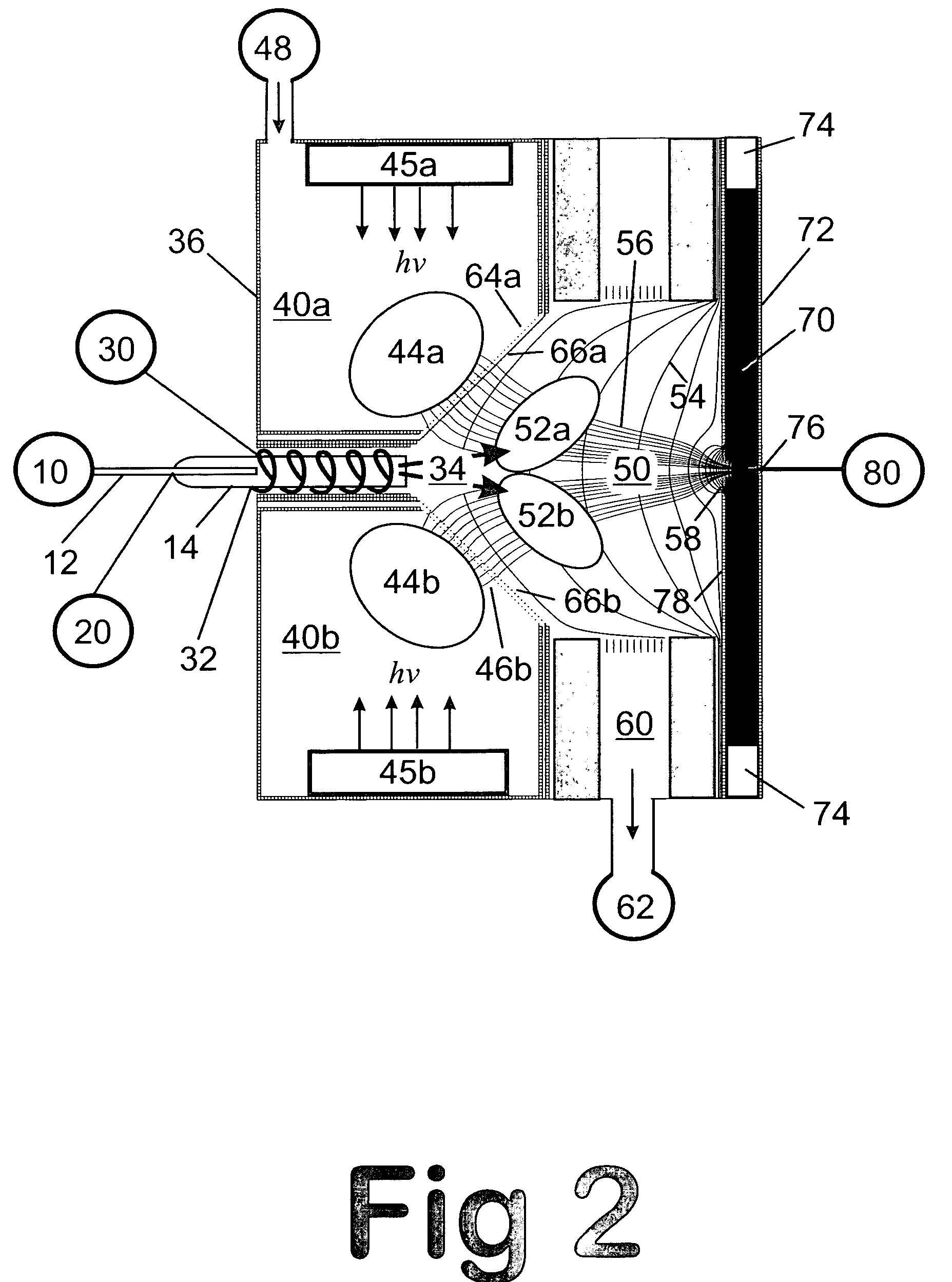
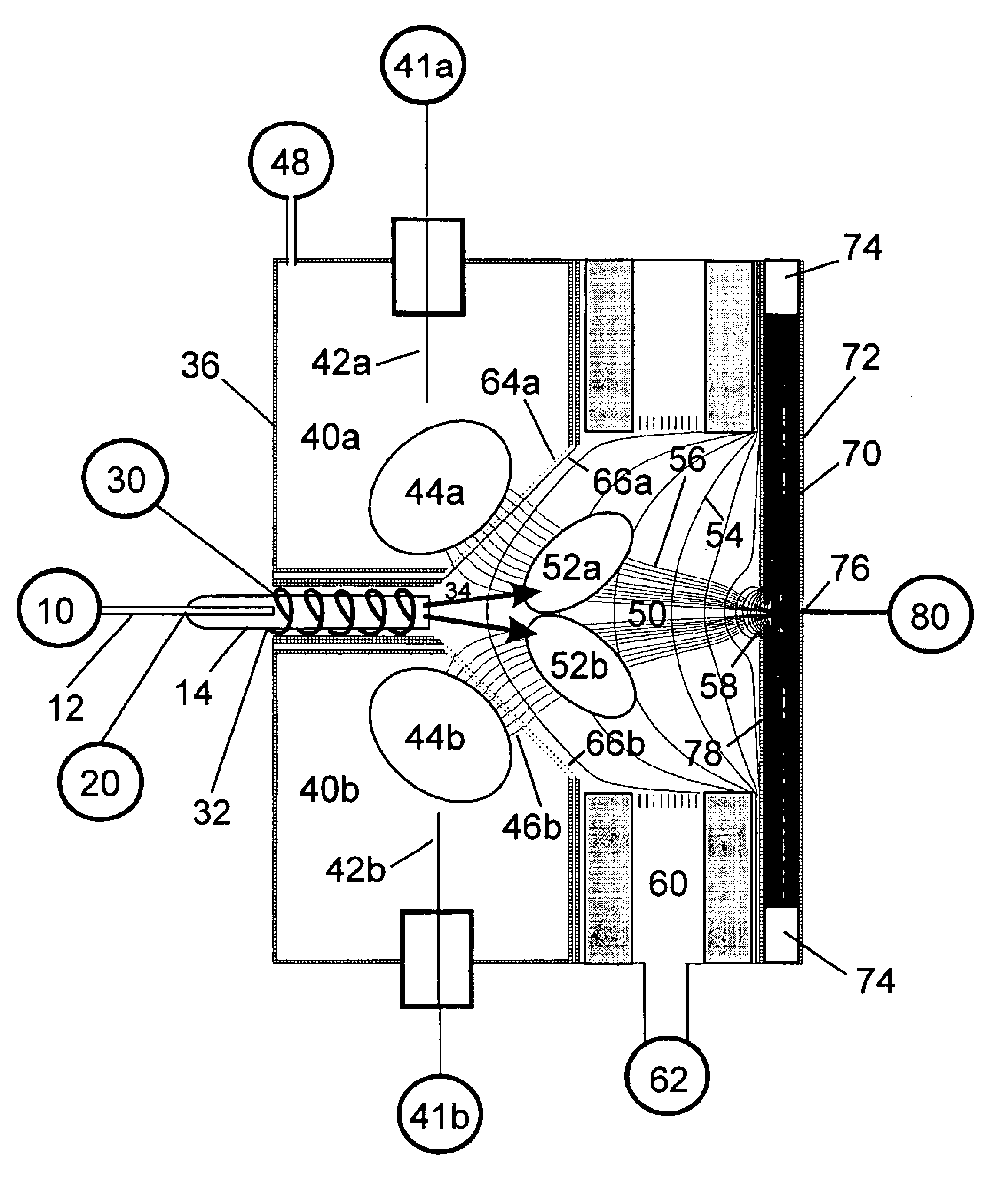
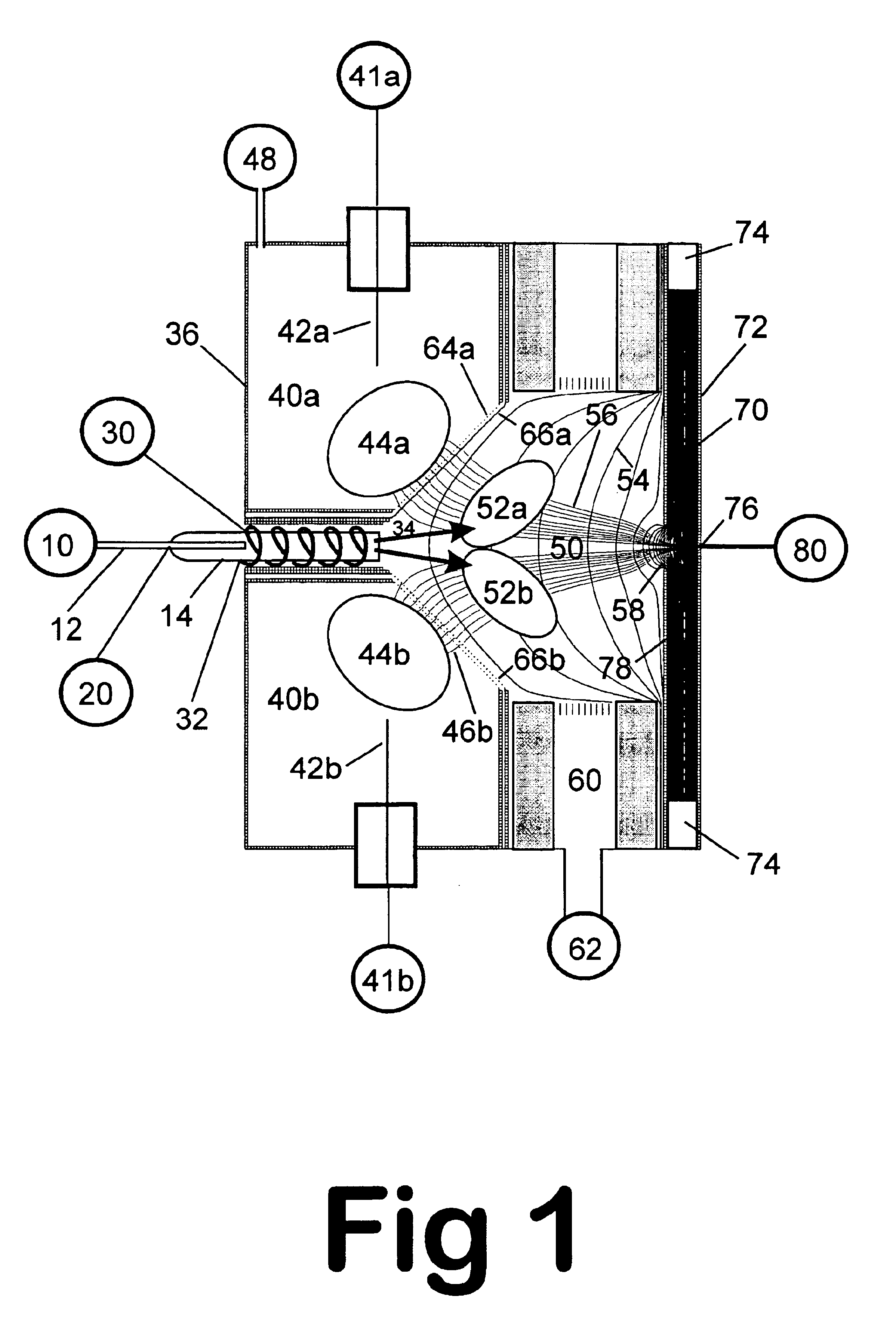
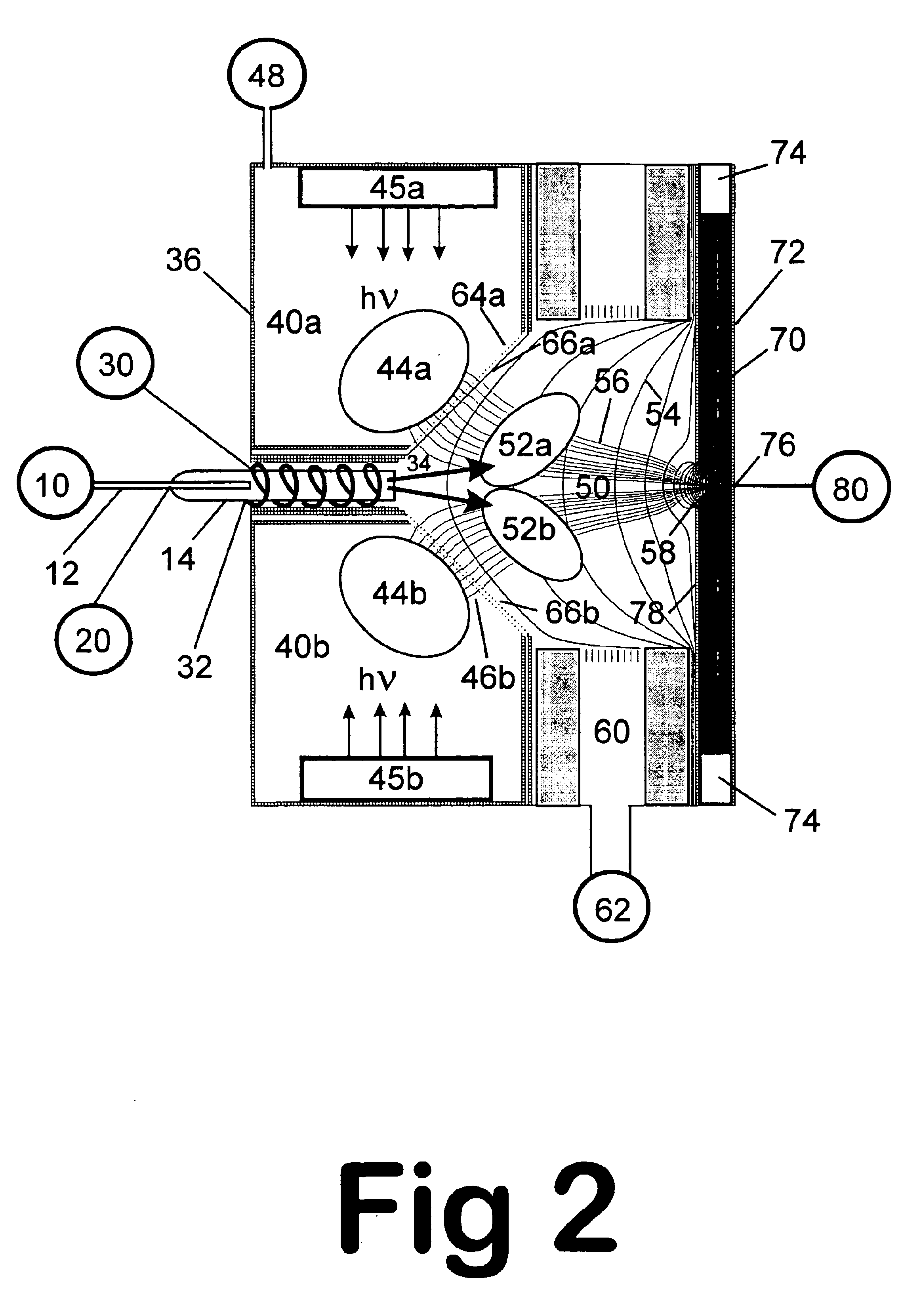
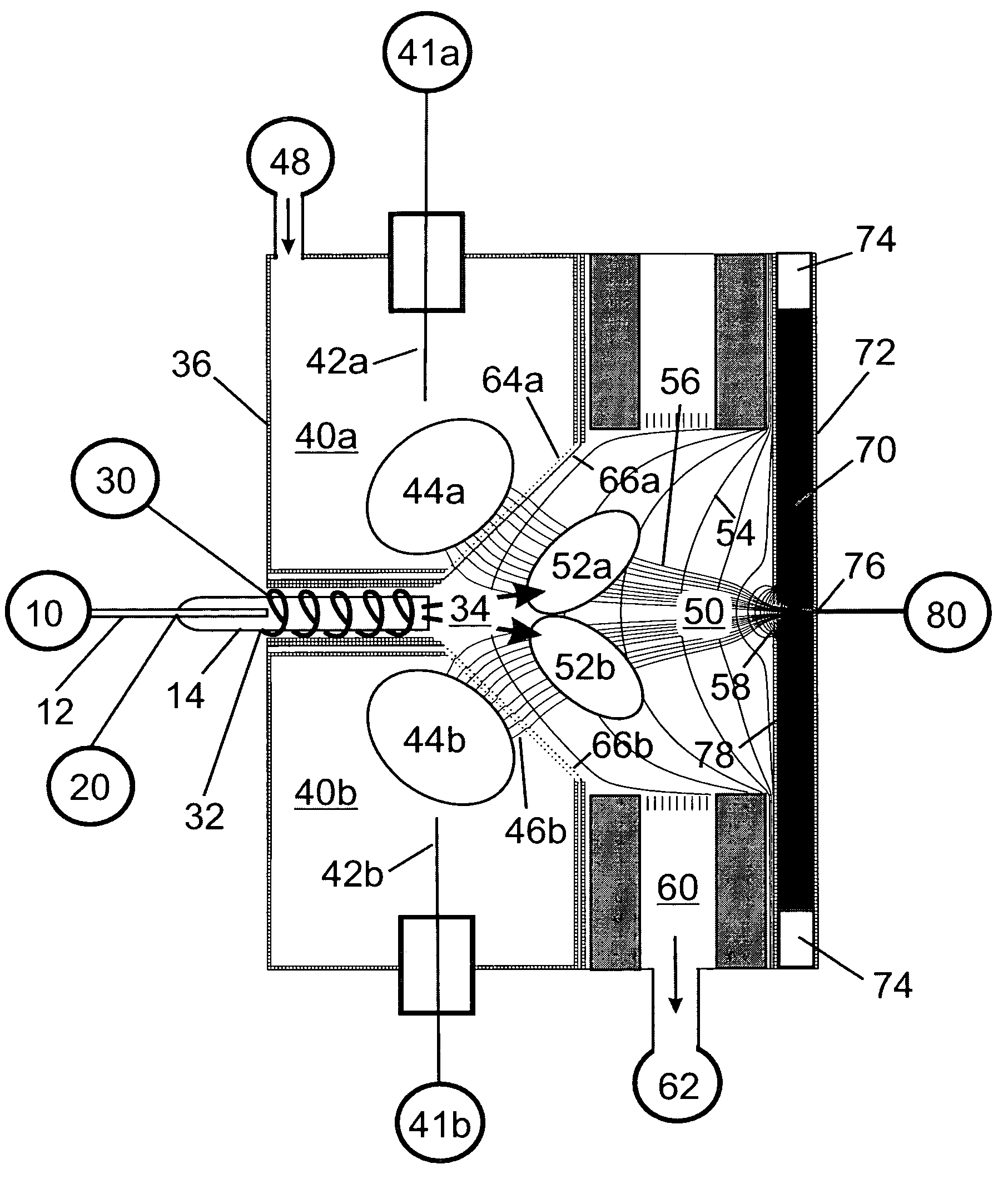
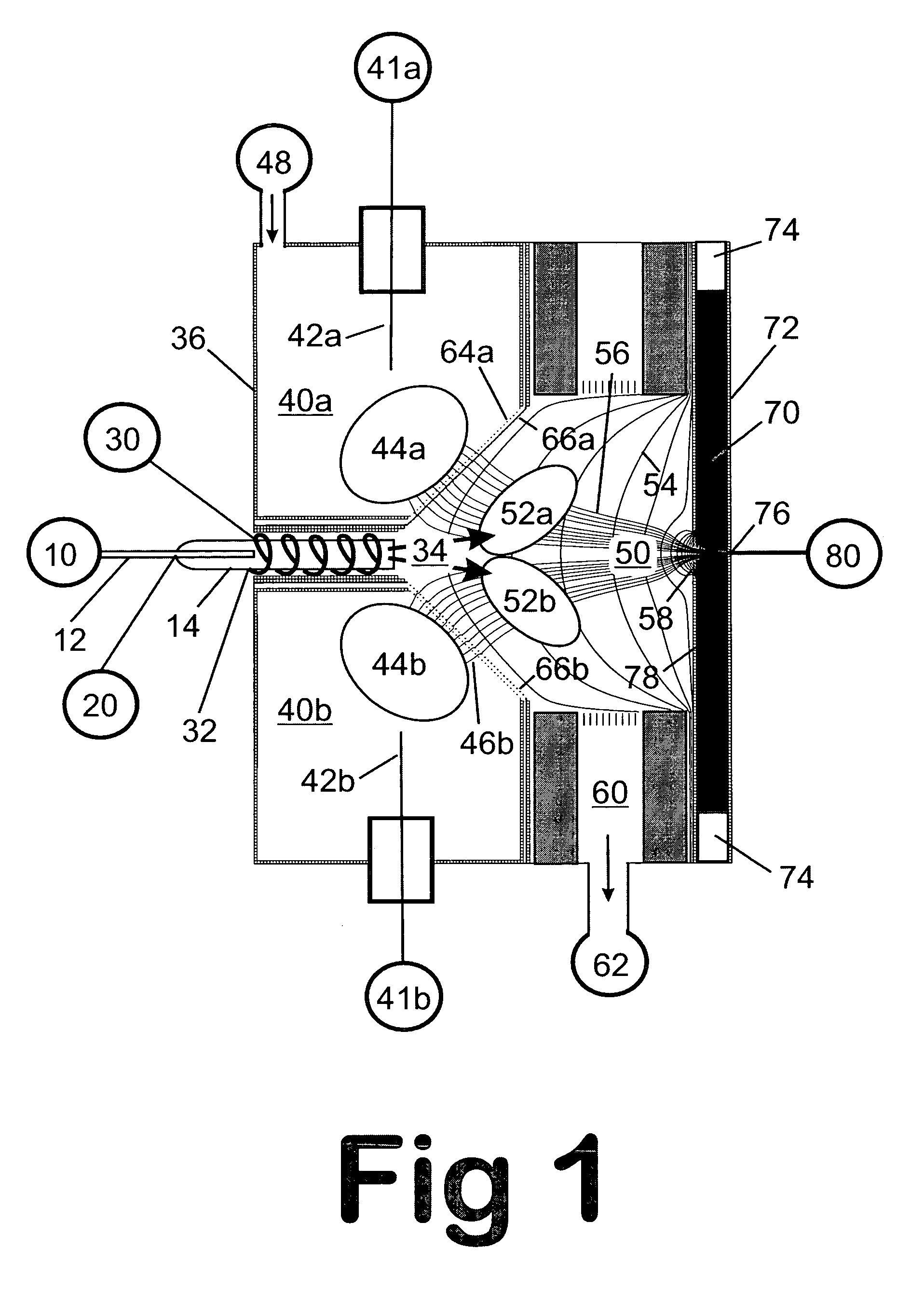
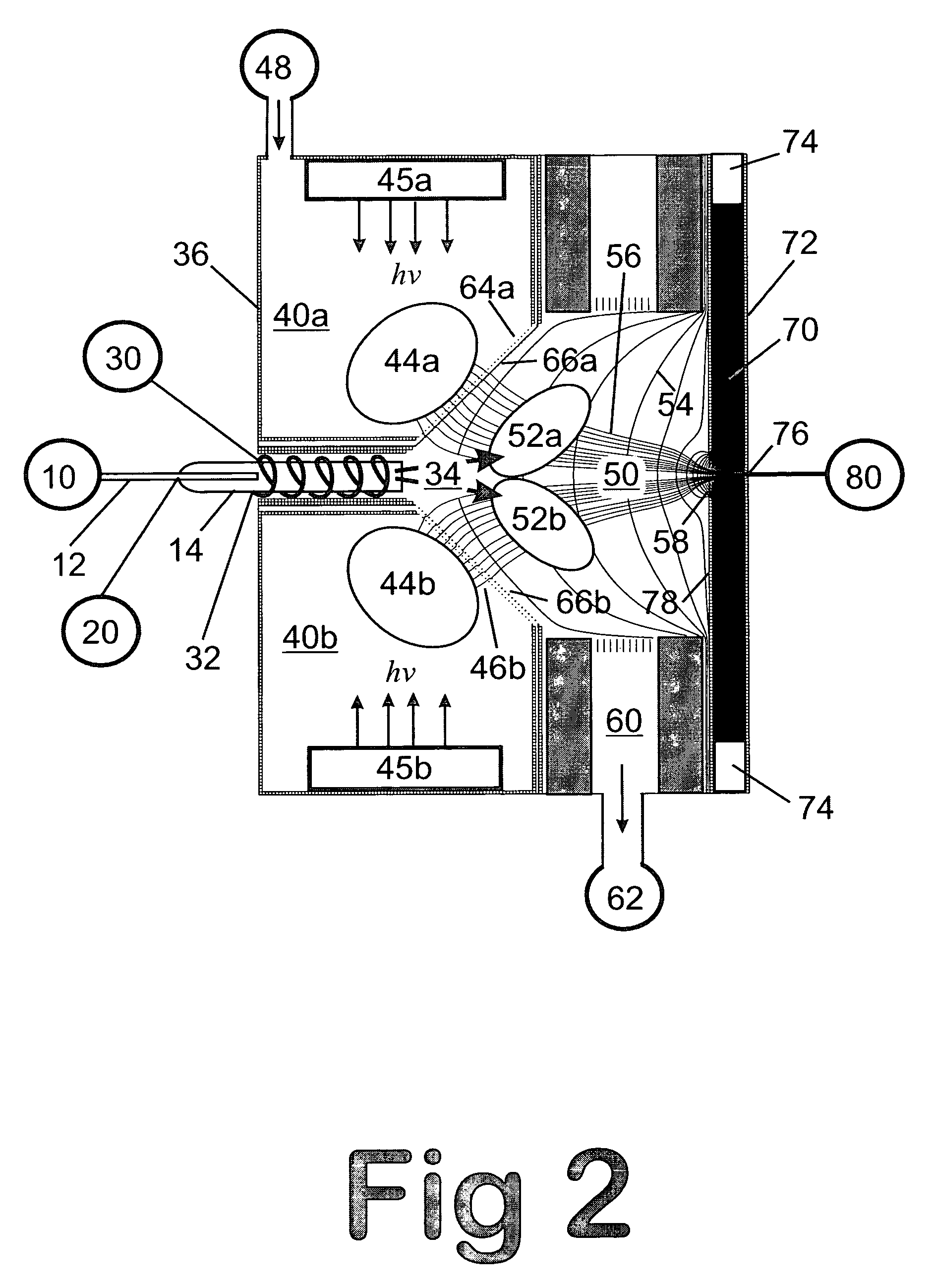
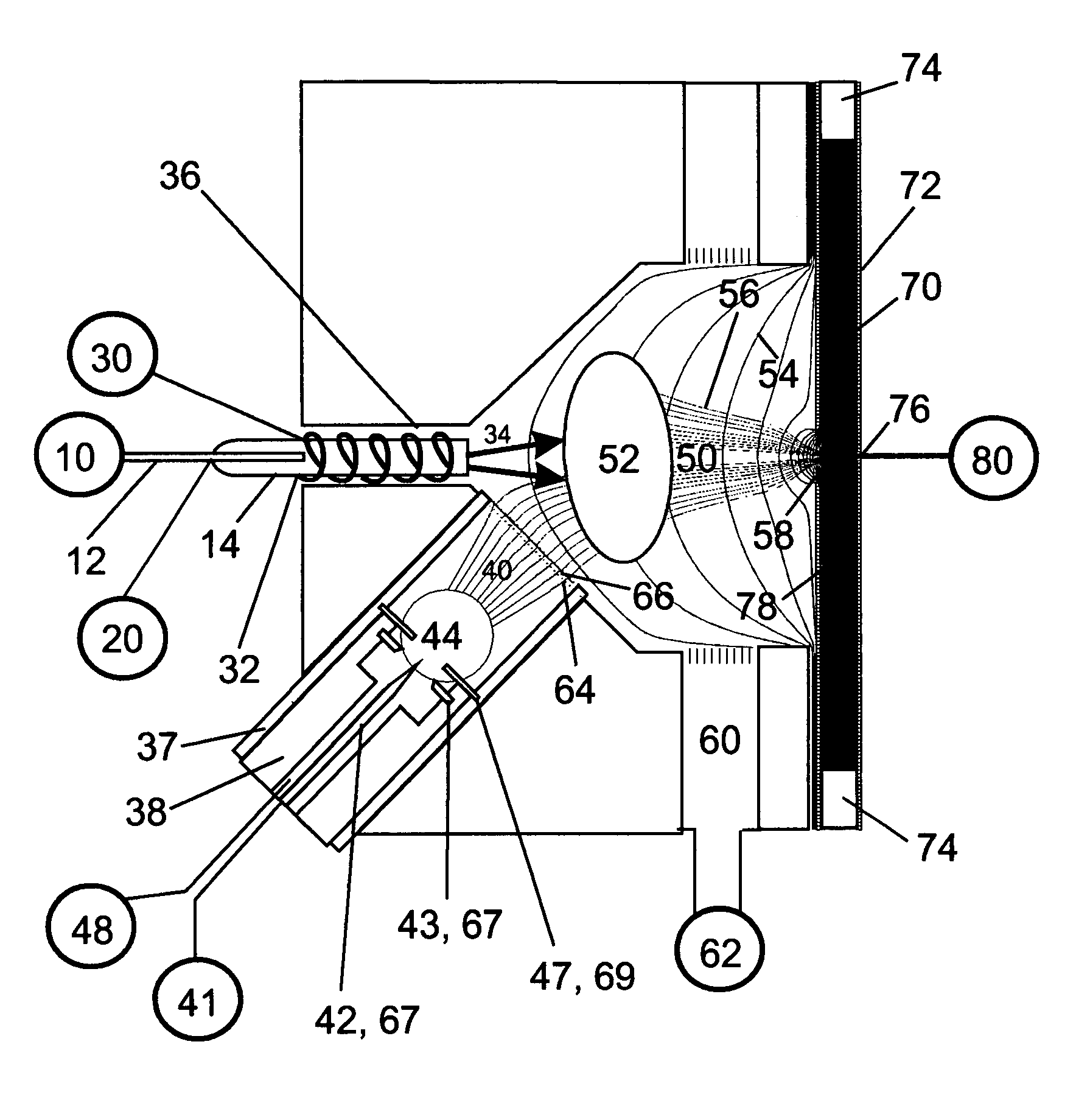
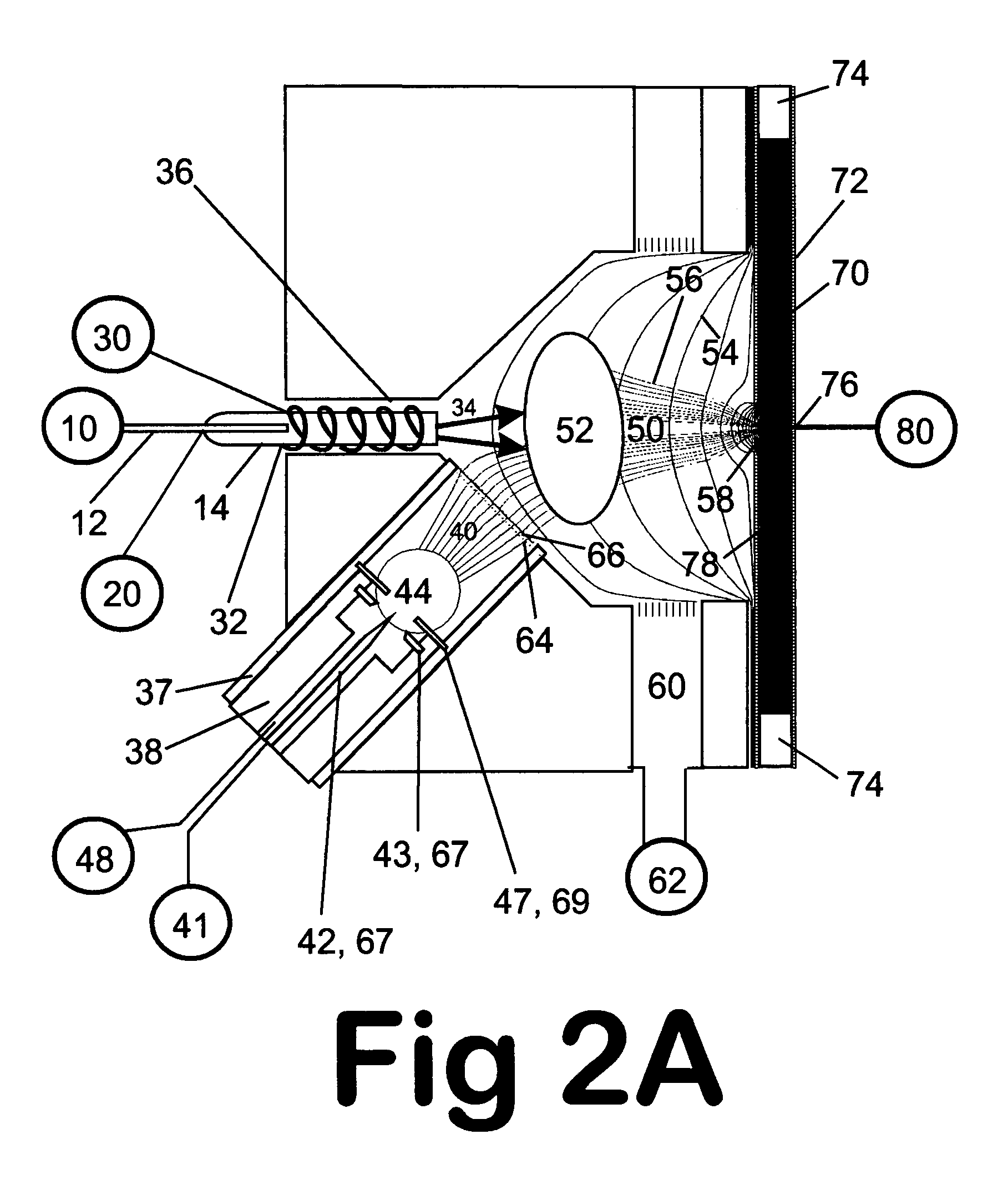
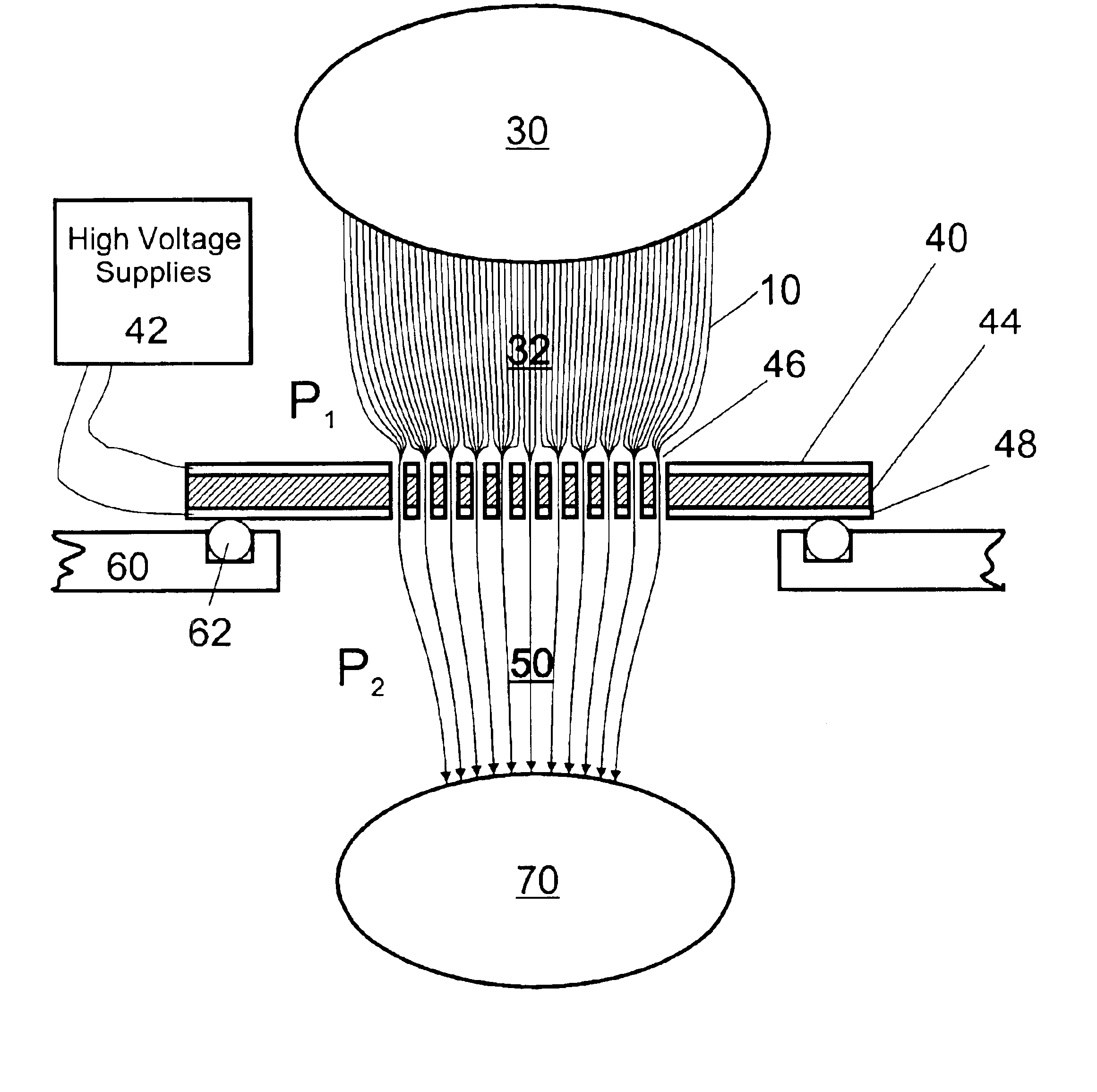
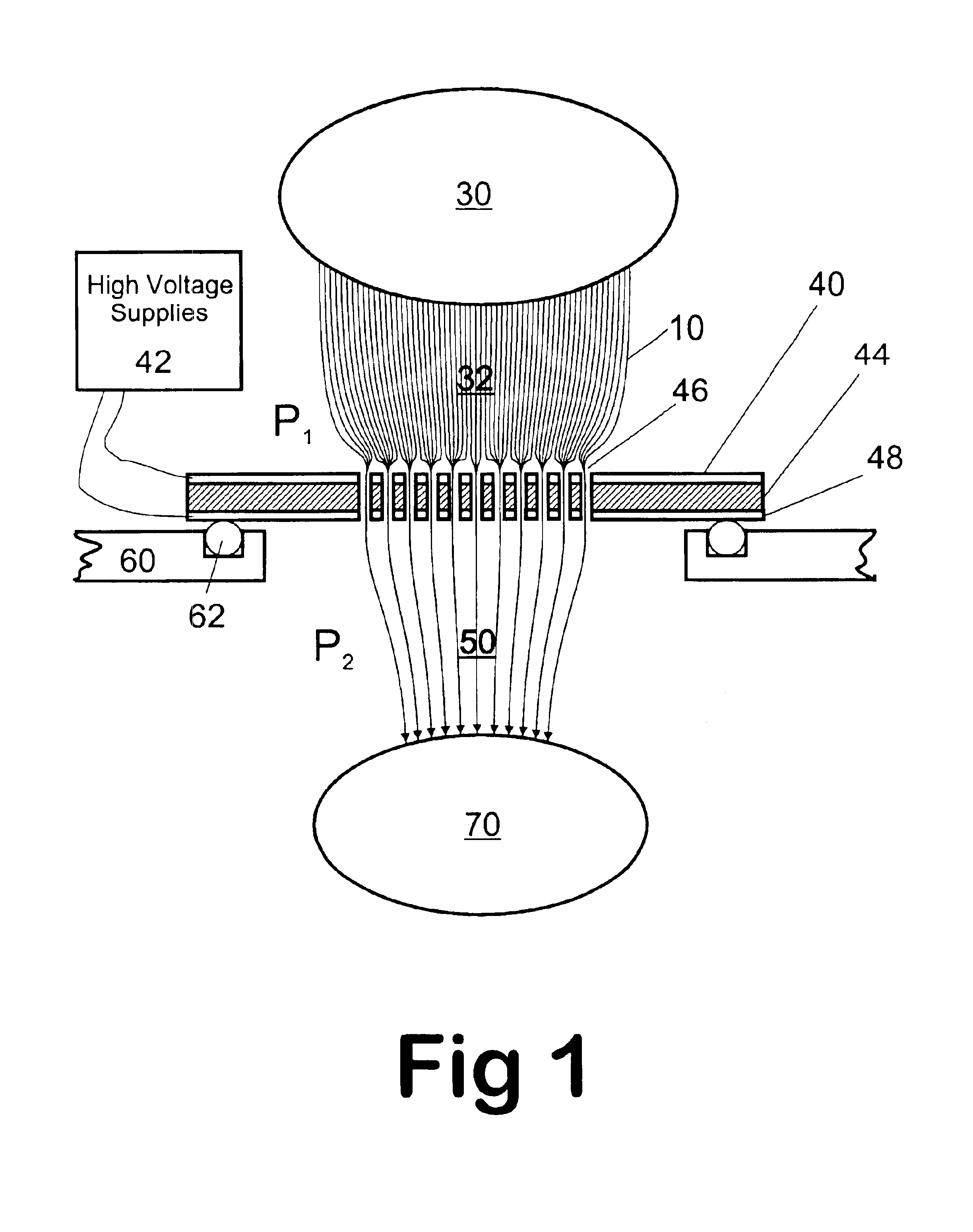
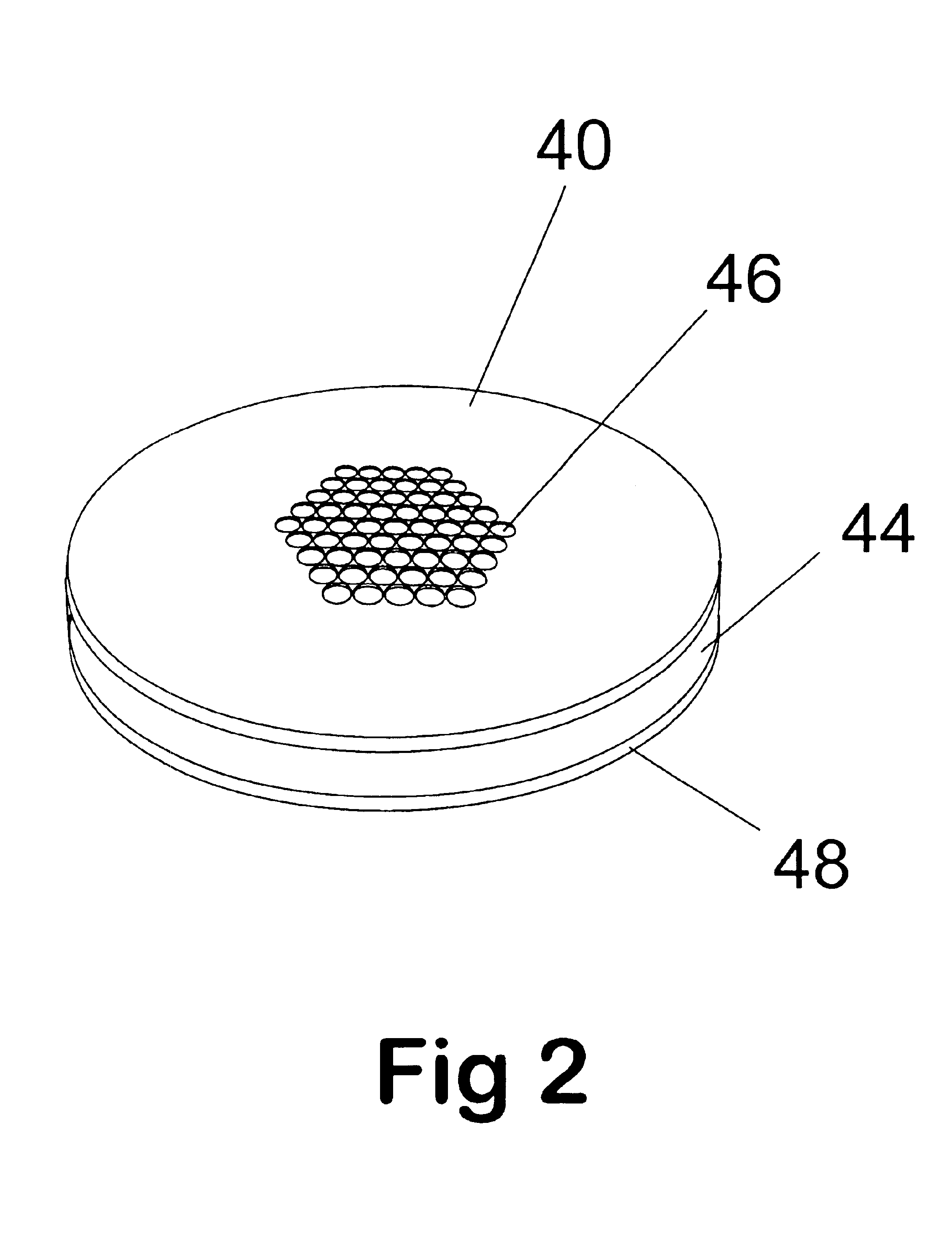
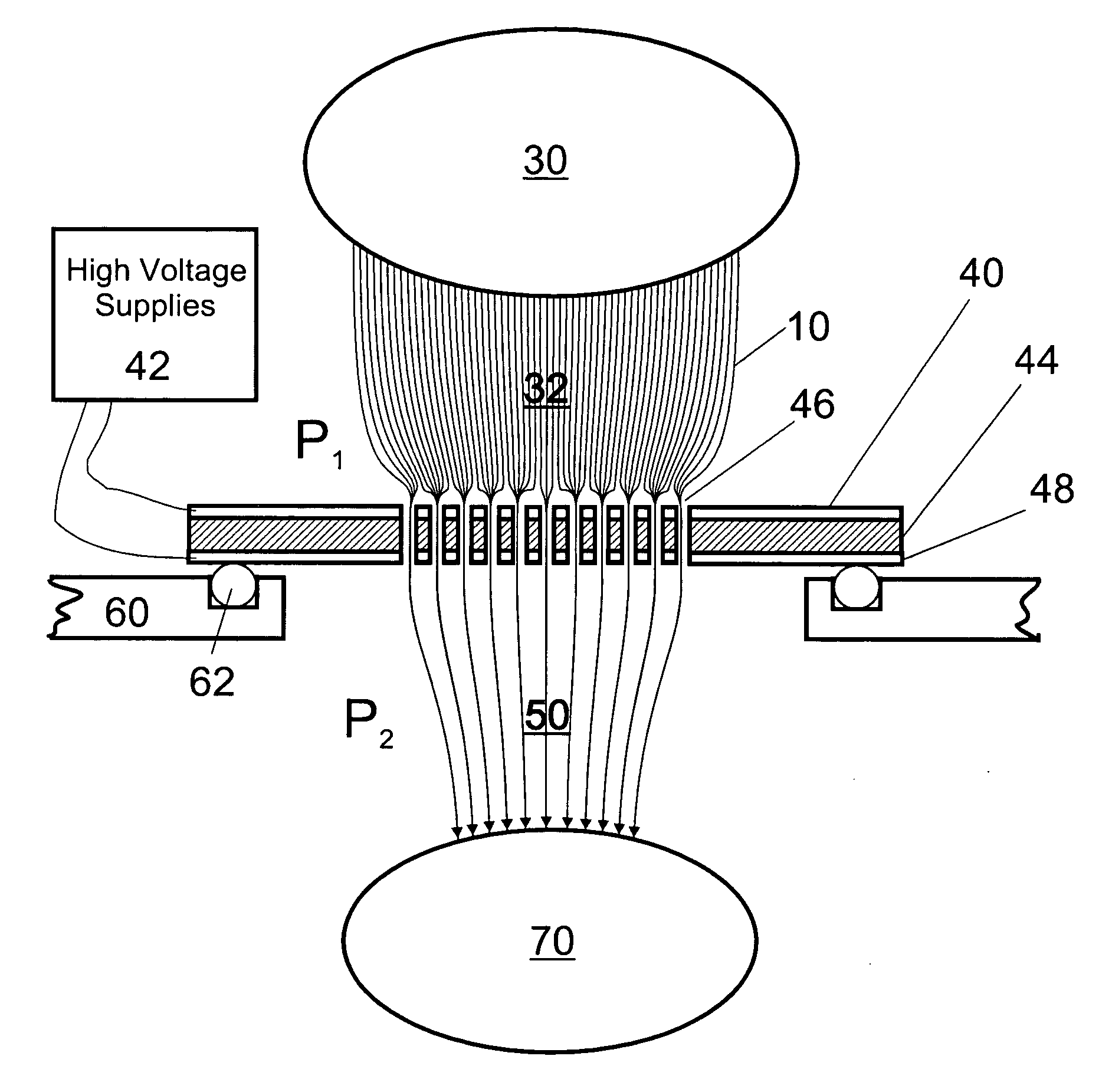
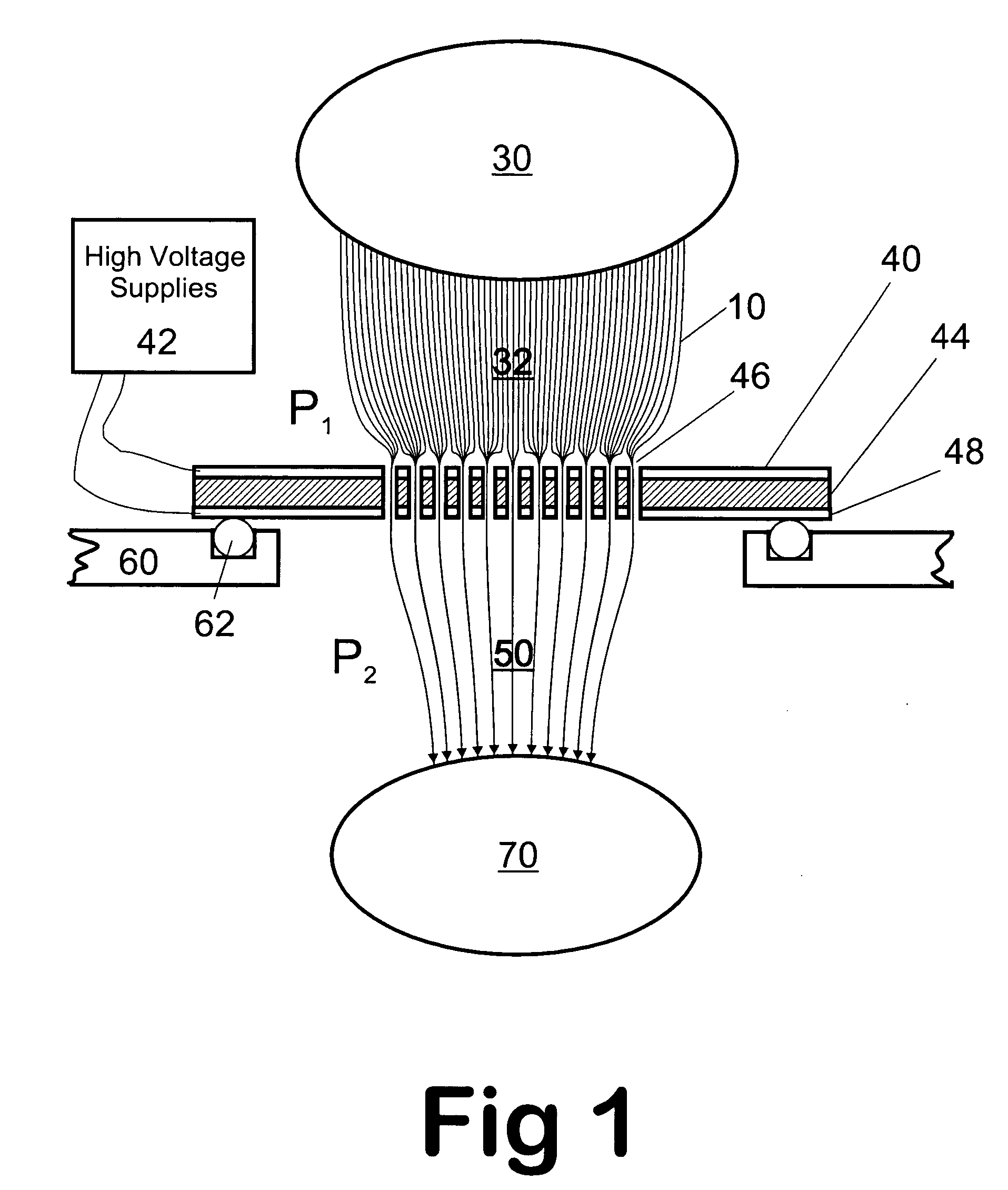
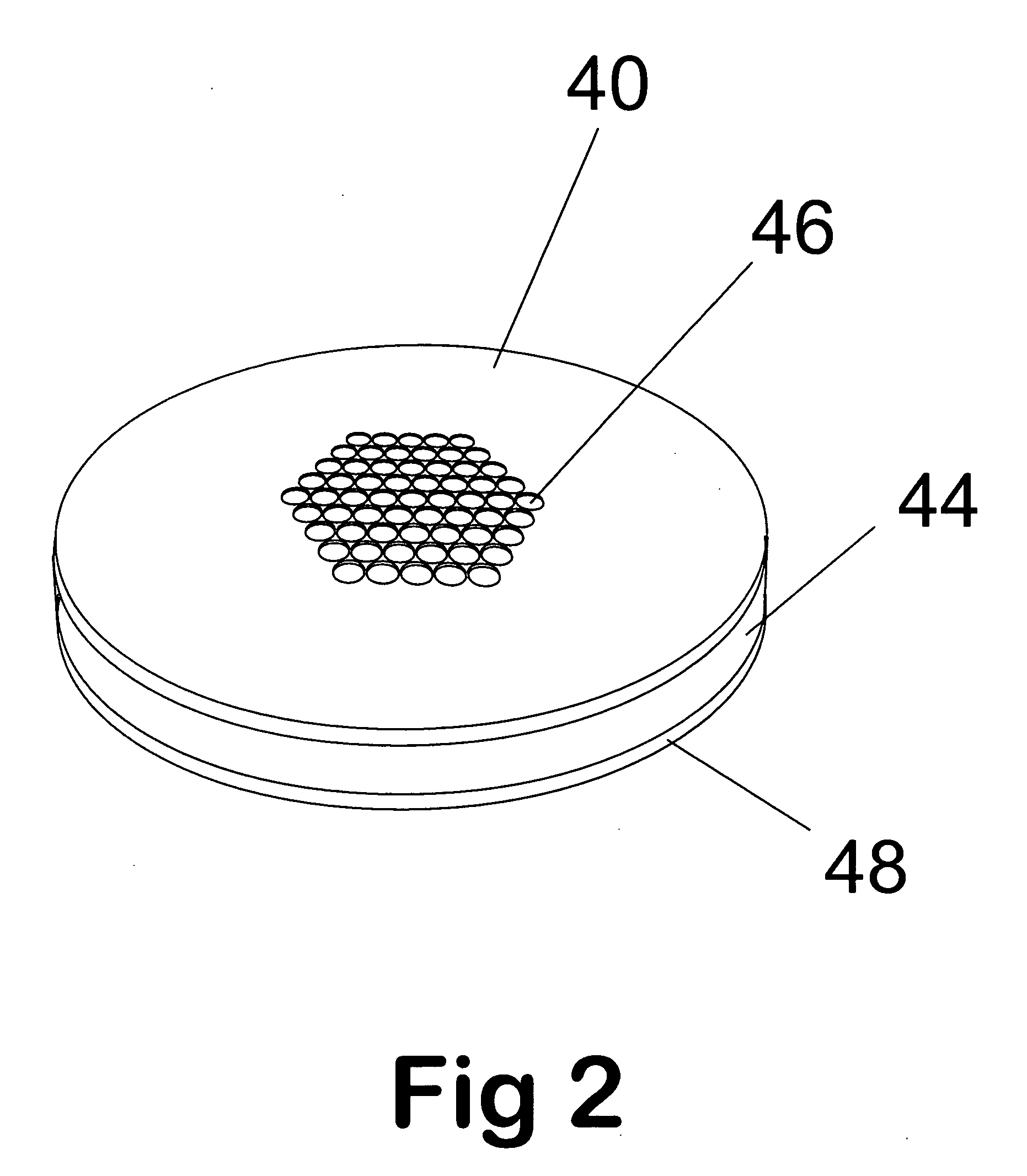
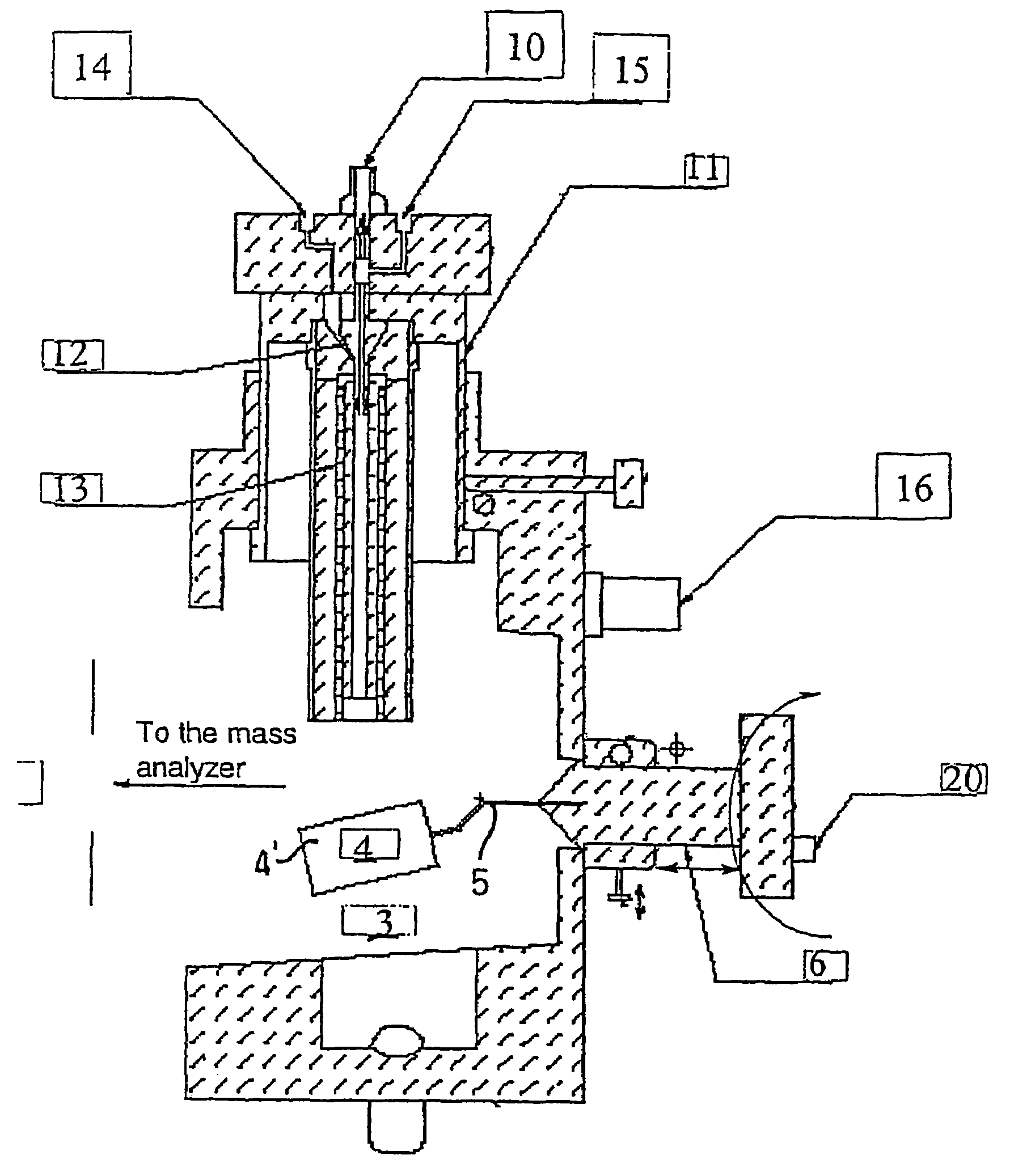
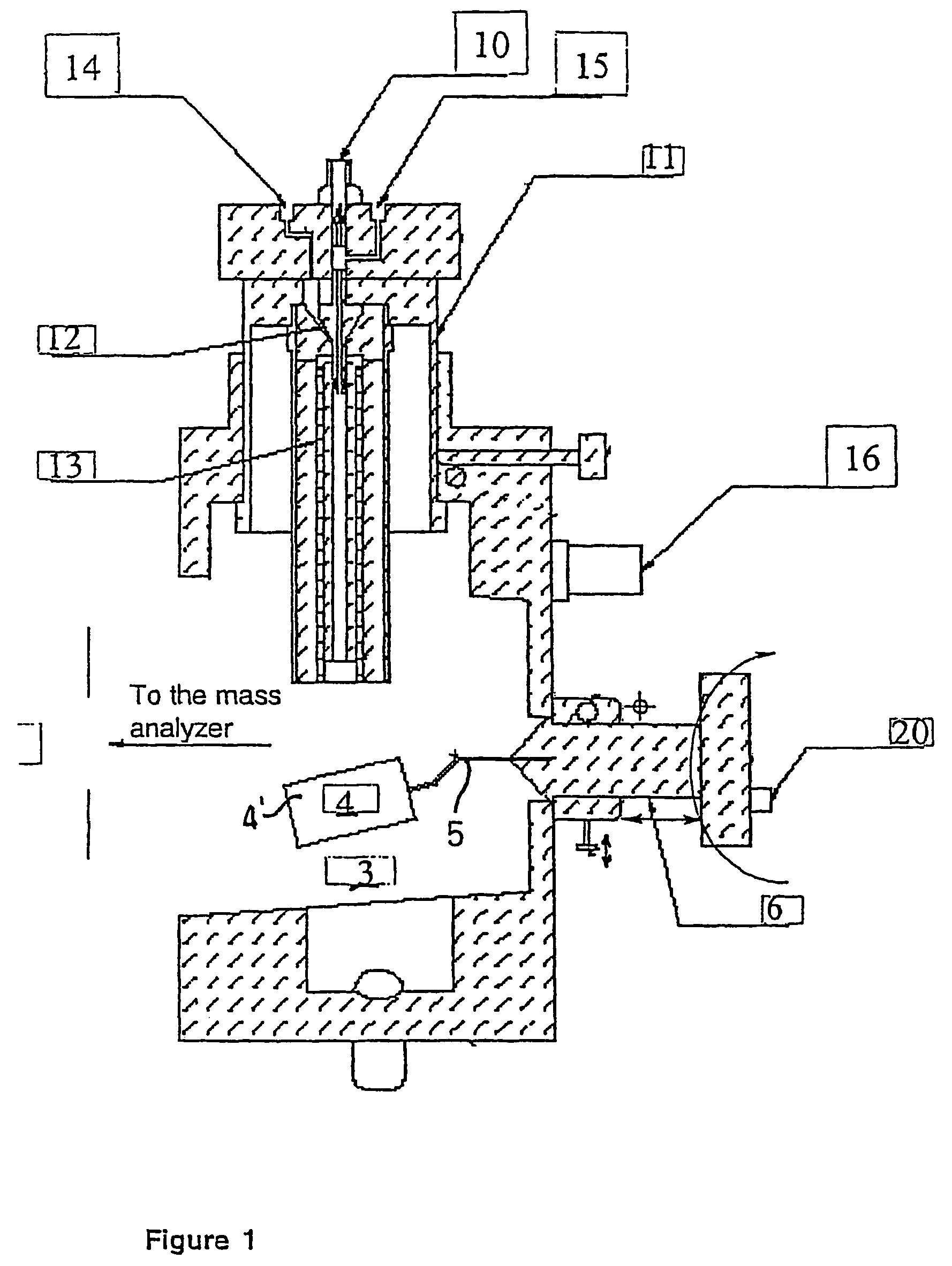
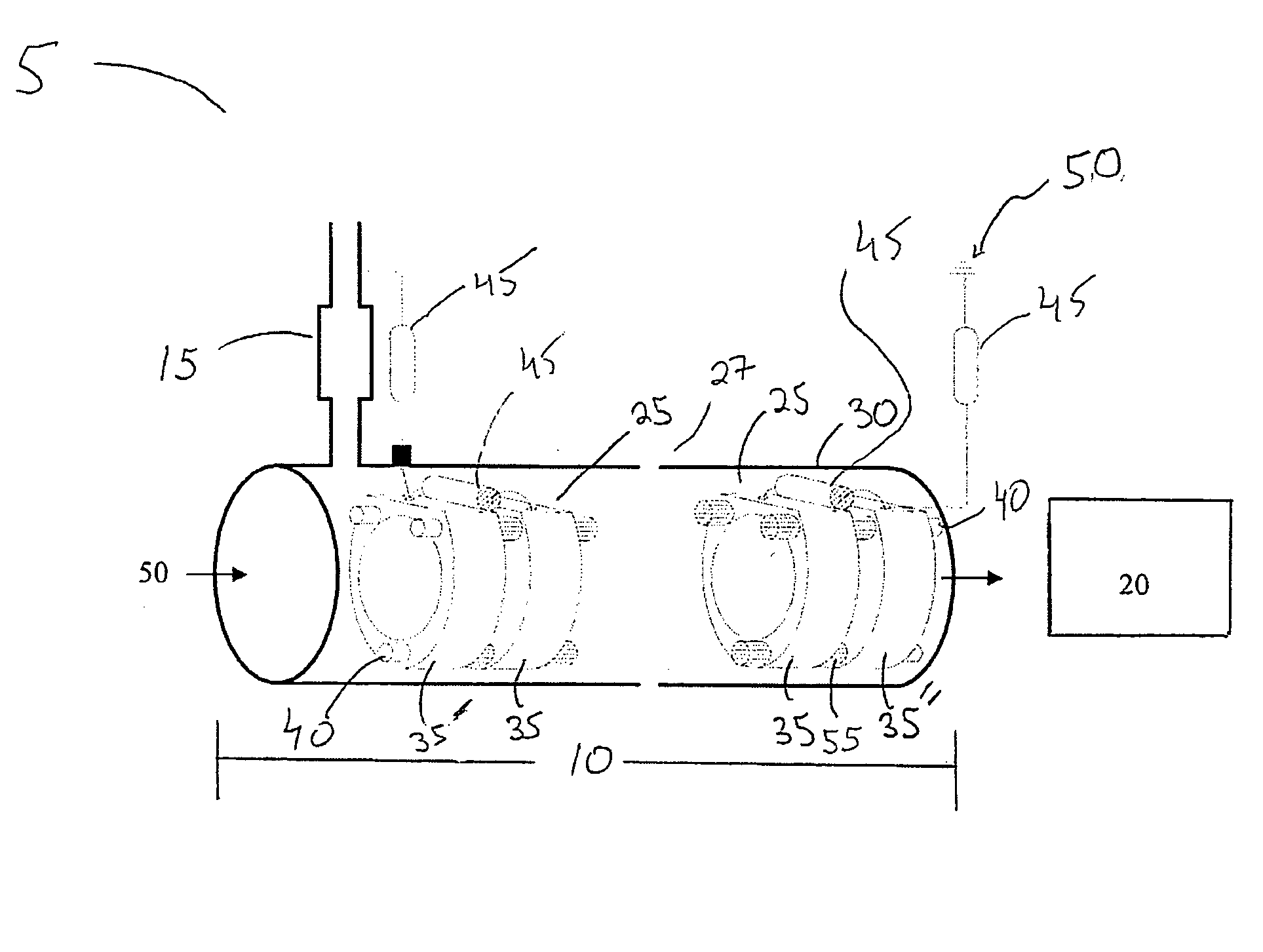
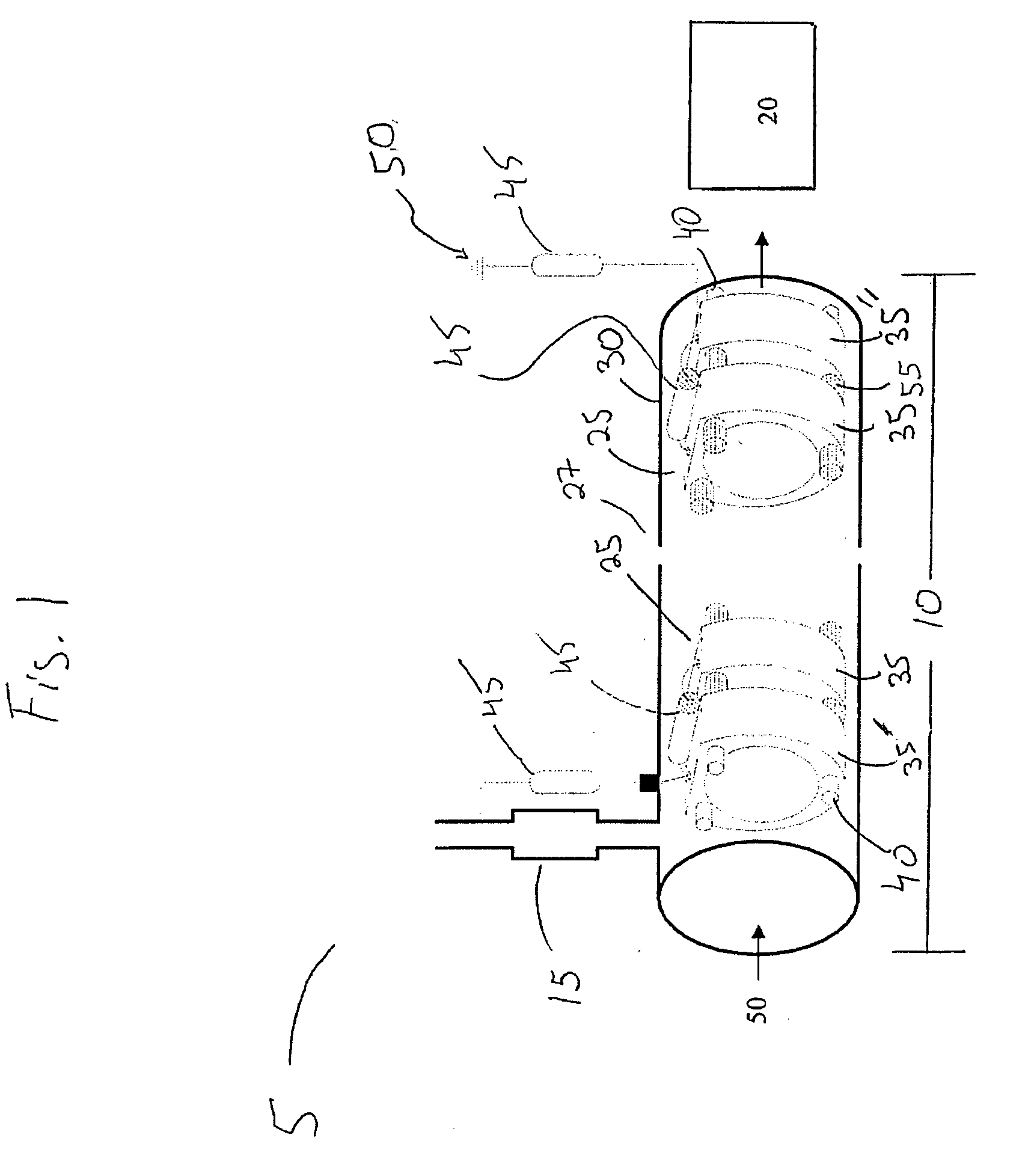
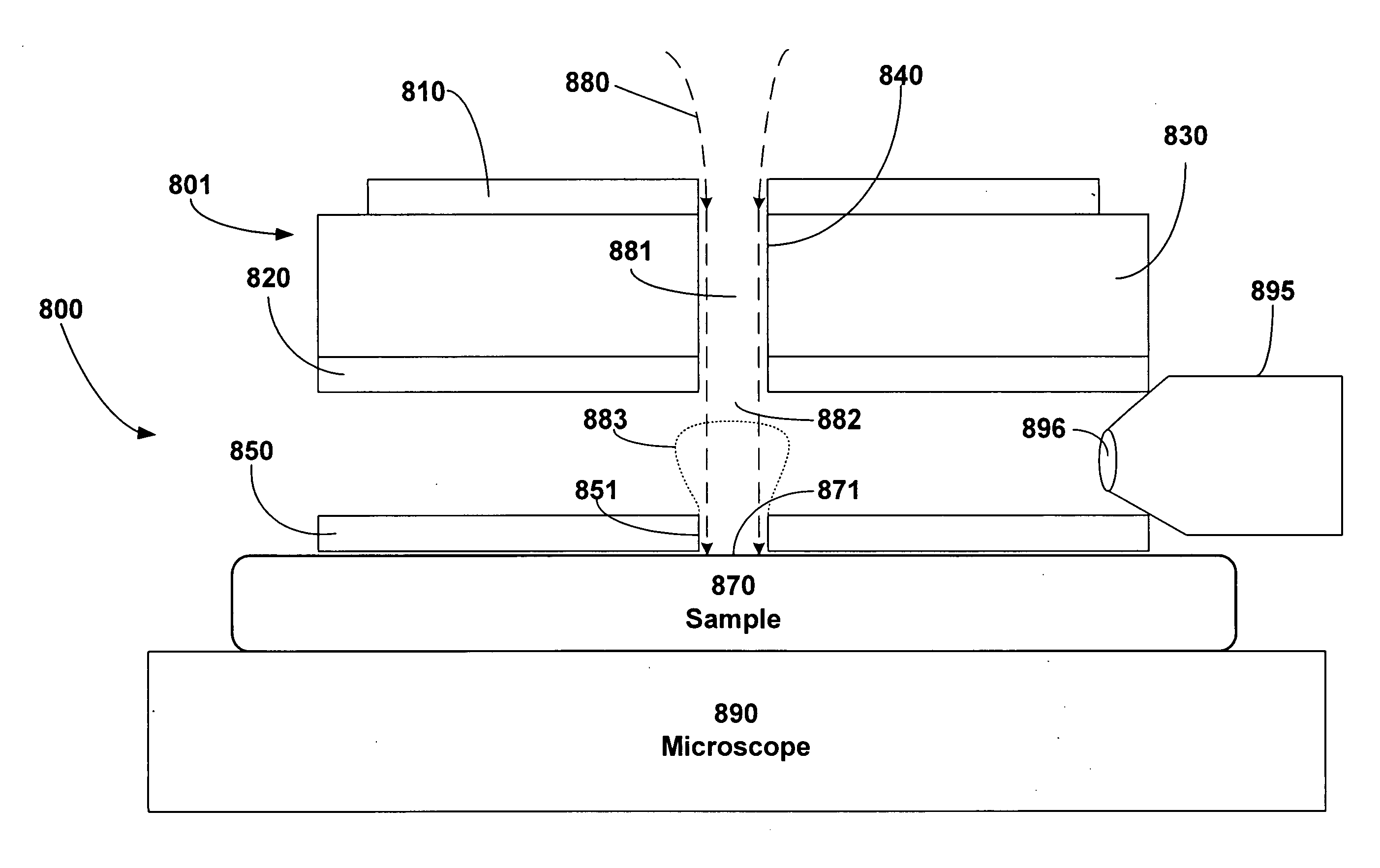
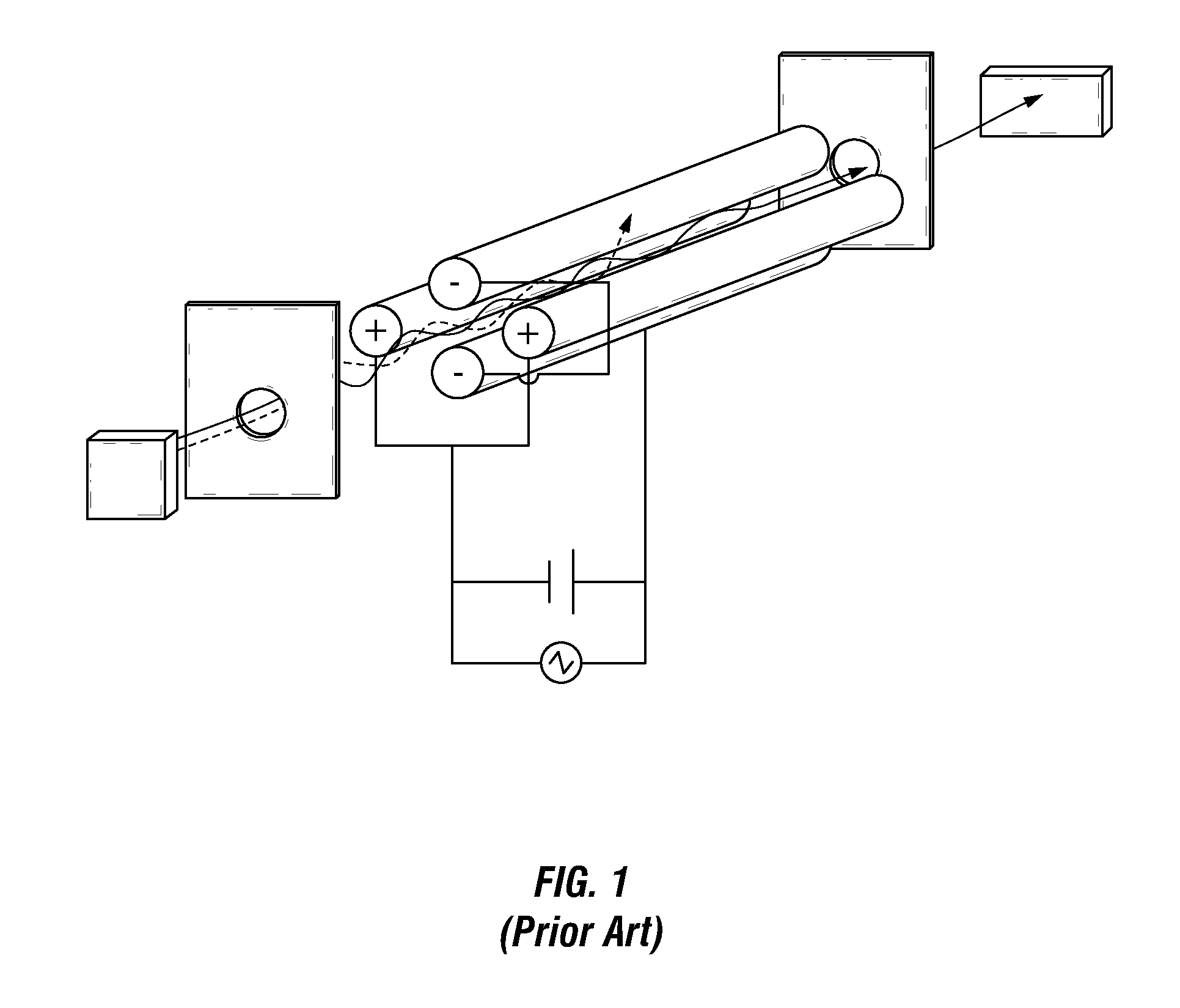
Remote reagent chemical ionization source
InactiveUS7095019B1Facilitate efficient sample ionizationEasy to collectTime-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationChromatographic separationGas phase
An improved ion source and portable analyzer for collecting and focusing dispersed gas-phase ions from a reagent source at atmospheric or intermediate pressure, having a remote source of reagent ions generated by direct or alternating currents, separated from a low-field sample ionization region by a stratified array of elements, each element populated with a plurality of openings, wherein DC potentials are applied to each element necessary for transferring reagent ions from the remote source into the low-field sample ionization region where the reagent ions react with neutral and / or ionic sample forming ionic species. The resulting ionic species are then introduced into the vacuum system of a mass spectrometer or ion mobility spectrometer. Embodiments of this invention are methods and devices for improving sensitivity of mass spectrometry when gas and liquid chromatographic separation techniques or probes containing samples are coupled to atmospheric and intermediate pressure photo-ionization, chemical ionization, and thermospray ionization sources.
Owner:CHEM SPACE ASSOCS
Remote reagent chemical ionization source
InactiveUS6888132B1Time-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationChromatographic separationGas phase
An improved ion source for collecting and focusing dispersed gas-phase ions from a reagent source at atmospheric or intermediate pressure, having a remote source of reagent ions separated from a low-field sample ionization region by a stratified array of elements, each element populated with a plurality of openings, wherein DC potentials are applied to each element necessary for transferring reagent ions from the remote source into the low-field sample ionization region where the reagent ions react with neutral and / or ionic sample forming ionic species. The resulting ionic species are then introduced into the vacuum system of a mass spectrometer or ion mobility spectrometer. Embodiments of this invention are methods and devices for improving sensitivity of mass spectrometry when gas and liquid chromatographic separation techniques are coupled to atmospheric and intermediate pressure photo-ionization, chemical ionization, and thermospray ionization sources.
Owner:CHEM SPACE ASSOIATES
Remote reagent chemical ionization source
InactiveUS7253406B1Improve collection efficiencyAccurate shapeTime-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationChromatographic separationGas phase
An improved ion source for collecting and focusing dispersed gas-phase ions from a reagent source at sub-atmospheric or intermediate pressure, having a remote source of reagent ions separated from a low-field sample ionization region by a barrier, comprised of alternating laminates of metal and insulator, populated with a plurality of openings, wherein DC potentials are applied to each metal laminate necessary for transferring reagent ions from the remote source into the low-field sample ionization region where the reagent ions react with neutral and / or ionic sample forming ionic species. The resulting ionic species are then introduced into the vacuum system of a mass spectrometer or ion mobility spectrometer. Embodiments of this invention are methods and devices for improving sensitivity of mass spectrometry when gas and liquid chromatographic separation techniques are coupled to sub-atmospheric and intermediate pressure photo-ionization, chemical ionization, and thermal-pneumatic ionization sources.
Owner:CHEM SPACE ASSOCS
Remote reagent ion generator
InactiveUS7569812B1Significant excessIncrease percentageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChromatographic separationGas phase
An improved ion source and means for collecting and focusing dispersed gas-phase ions from a remote reagent chemical ionization source (R2CIS) at atmospheric or intermediate pressure is described. The R2CIS is under electronic control and can produce positive, negative, or positive and negative reagent ions simultaneously. This remote source of reagent ions is separated from a low-field sample ionization region by a stratified array of elements, each element populated with a plurality of openings, wherein DC potentials are applied to each element necessary for transferring reagent ions from the R2CIS into the low-field sample ionization region where the reagent ions react with neutral and / or ionic sample forming sample ionic species. The resulting sample ionic species are then introduced into a mass spectrometer, ion mobility spectrometer or other sensor capable of detecting the sample ions. Embodiments of this invention are methods and devices for improving sensitivity of mass spectrometry when gas and liquid chromatographic separation techniques are coupled to atmospheric and intermediate pressure photo-ionization, chemical ionization, and thermospray ionization sources; and improving the sensitivity of chemical detectors or probes.
Owner:LEIDOS
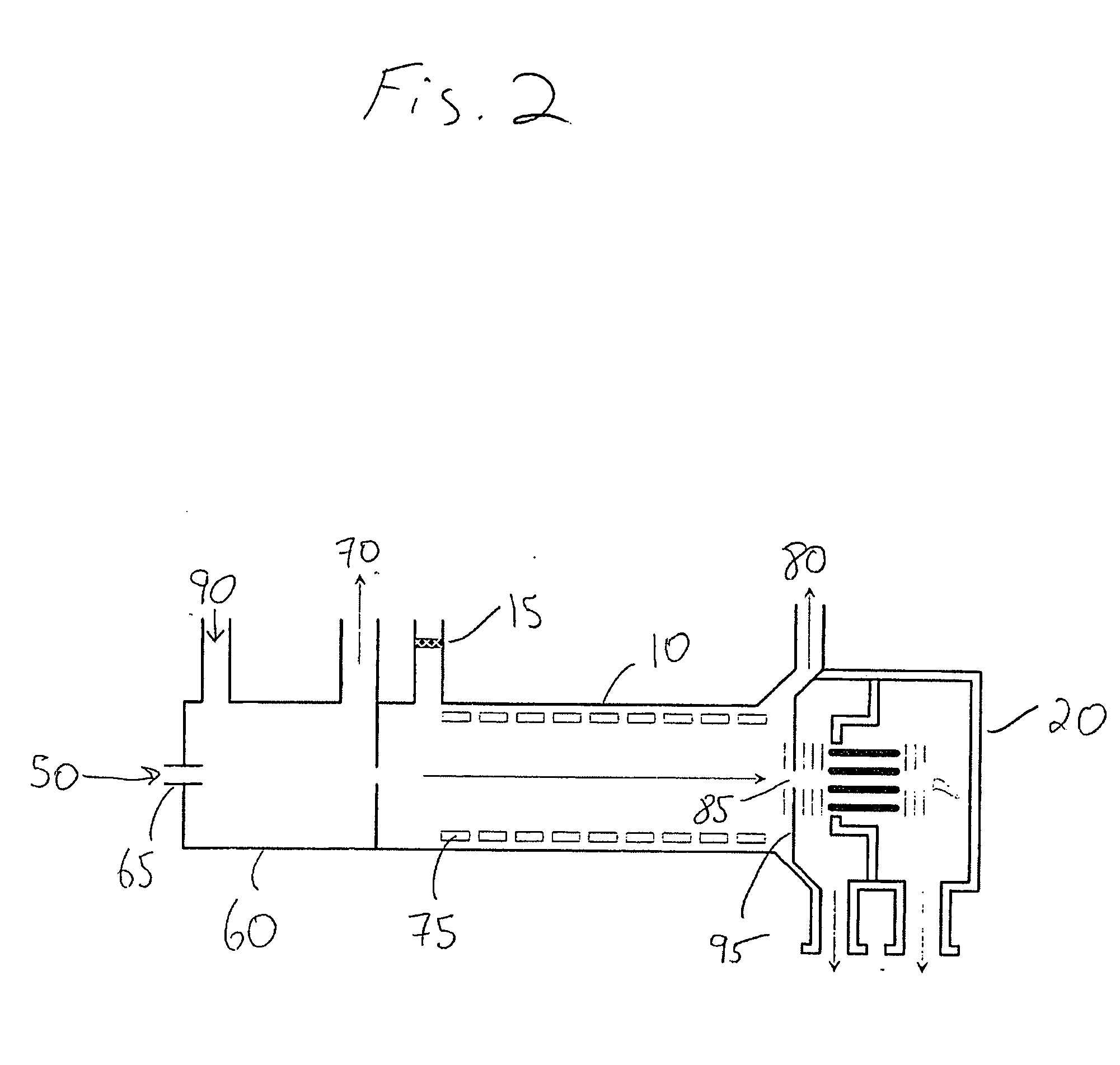
Ion enrichment aperture arrays
InactiveUS6914243B2Time-of-flight spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsAtmospheric pressure dischargeInductively coupled plasma
Improvements have been made for collecting, focusing, and directing of ions and / or charged particles generated at atmospheric or near atmospheric pressure sources, such as but not limited to, electrospray; atmospheric pressure discharge ionization, chemical ionization, photoionization, and matrix assisted laser desorption ionization; and inductively coupled plasma ionization. A multiple-aperture laminated structure is place at the interface of two pressure regions. Electric fields geometries and strengths across the laminated structure and diameters of the apertures; all of which act to optimize the transfer of the ions from the higher pressure region into the lower pressure region while reducing the gas-load on the lower pressure region. Embodiments of this invention are methods and devices for improving sensitivity of mass spectrometry when coupled to atmospheric, near atmospheric, or higher pressure ionization sources by reducing the gas-load on the vacuum system.
Owner:CHEM SPACE ASSOIATES
Ion enrichment aperture arrays
InactiveUS20040245458A1Maximizes transmission of ionImprove transmittanceTime-of-flight spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsAtmospheric pressure dischargeInductively coupled plasma
Improvements have been made for collecting, focusing, and directing of ions and / or charged particles generated at atmospheric or near atmospheric pressure sources, such as but not limited to, electrospray; atmospheric pressure discharge ionization, chemical ionization, photoionization, and matrix assisted laser desorption ionization; and inductively coupled plasma ionization. A multiple-aperture laminated structure is place at the interface of two pressure regions. Electric fields geometries and strengths across the laminated structure and diameters of the apertures; all of which act to optimize the transfer of the ions from the higher pressure region into the lower pressure region while reducing the gas-load on the lower pressure region. Embodiments of this invention are methods and devices for improving sensitivity of mass spectrometry when coupled to atmospheric, near atmospheric, or higher pressure ionization sources by reducing the gas-load on the vacuum system.
Owner:CHEM SPACE ASSOIATES
Ionization source for mass spectrometry analysis
ActiveUS20060145089A1Samples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by optical meansGas phaseMass analyzer
A new ionization source named Surface Activated Chemical Ionization (SACI) has been discovered and used to improve the sensitivity of the mass spectrometer. According to this invention the ionization chamber of a mass spectrometer is heated and contains a physical new surface to improve the ionization process. The analyte neutral molecules that are present in gas phase are ionized on this surface. The surface can be made of various materials and may also chemically modified so to bind different molecules. This new ionization source is able to generate ions with high molecular weight and low charge, an essential new key feature of the invention so to improve sensitivity and reduce noise. The new device can be especially used for the analysis of proteins, peptides and other macromolecules. The new invention overcomes some of the well known and critical limitations of the Electrospray (ESI) and Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometric techniques.
Owner:UNIV DELGI STUDI DI MILANO
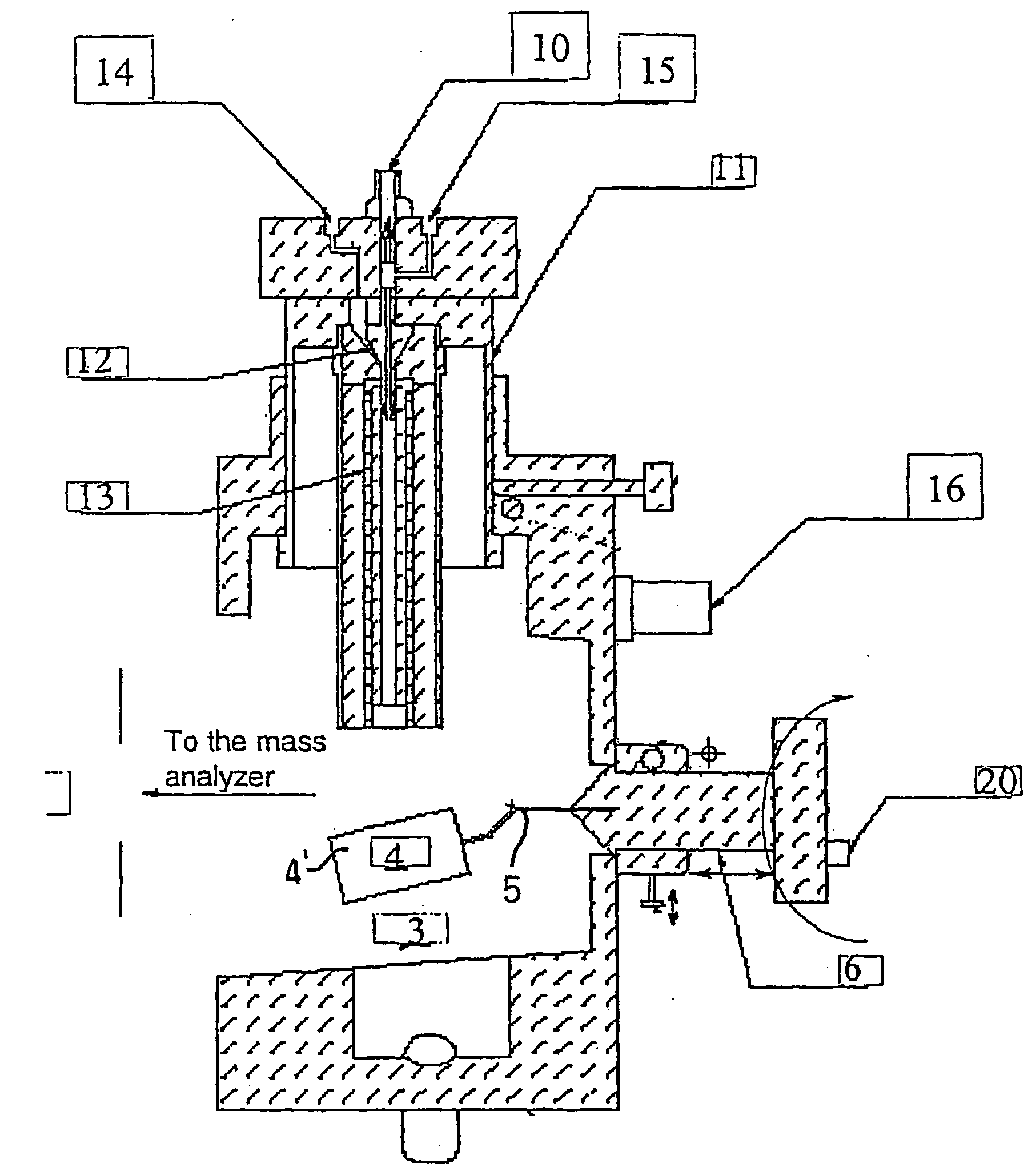
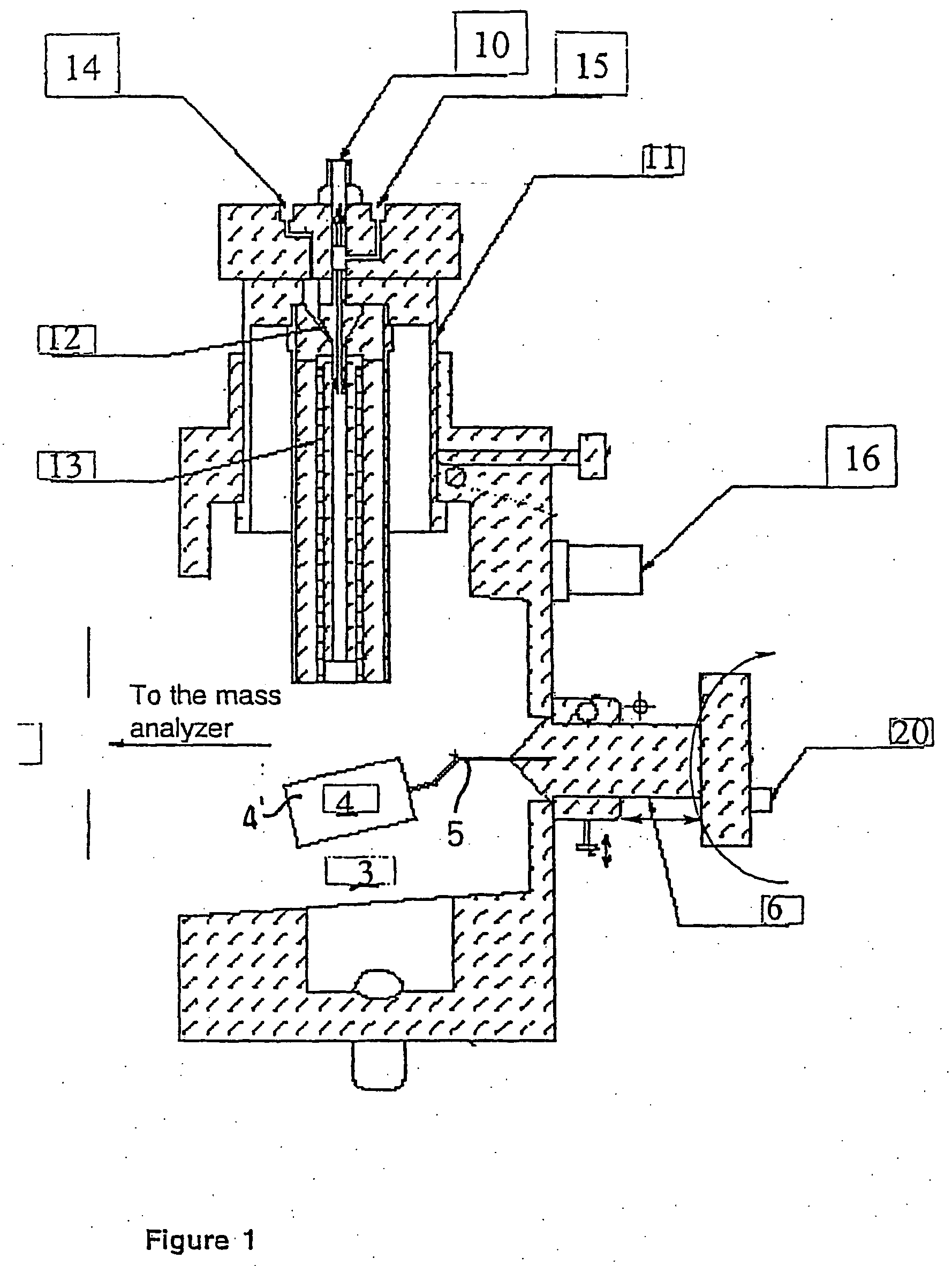
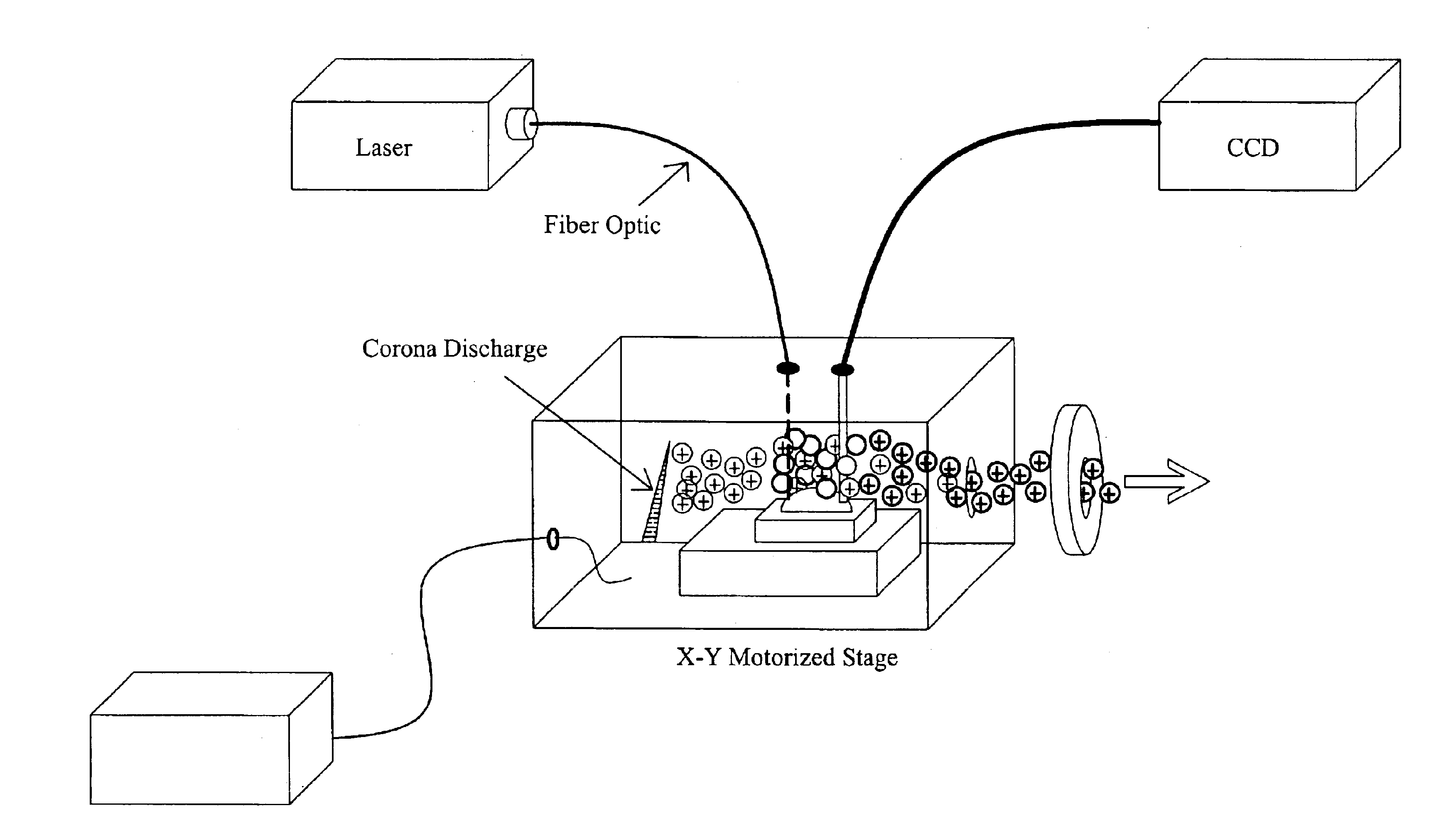
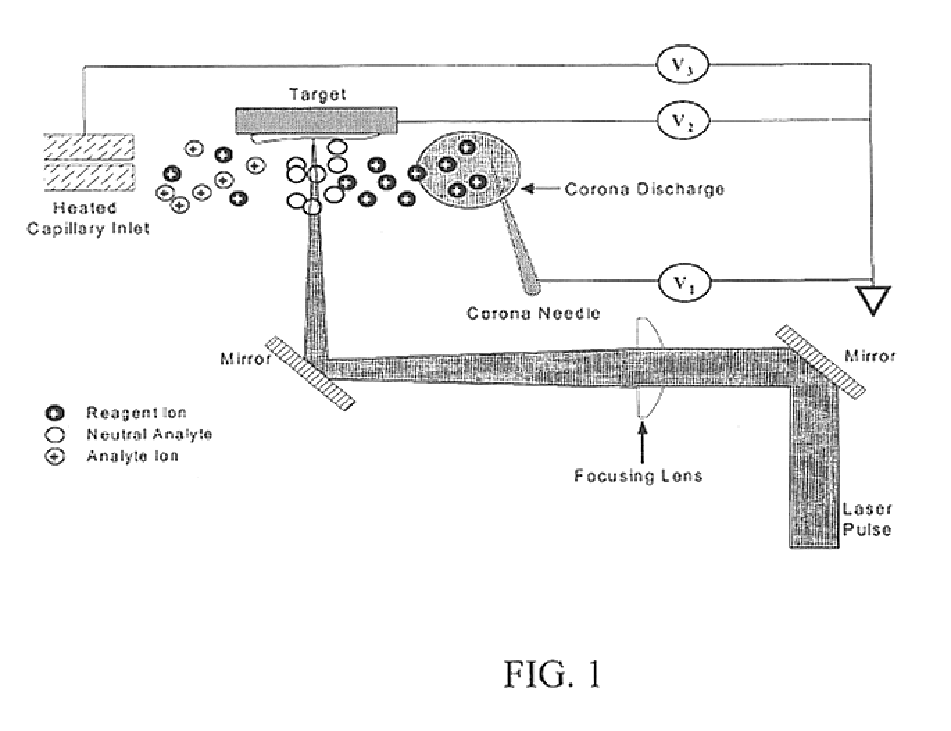
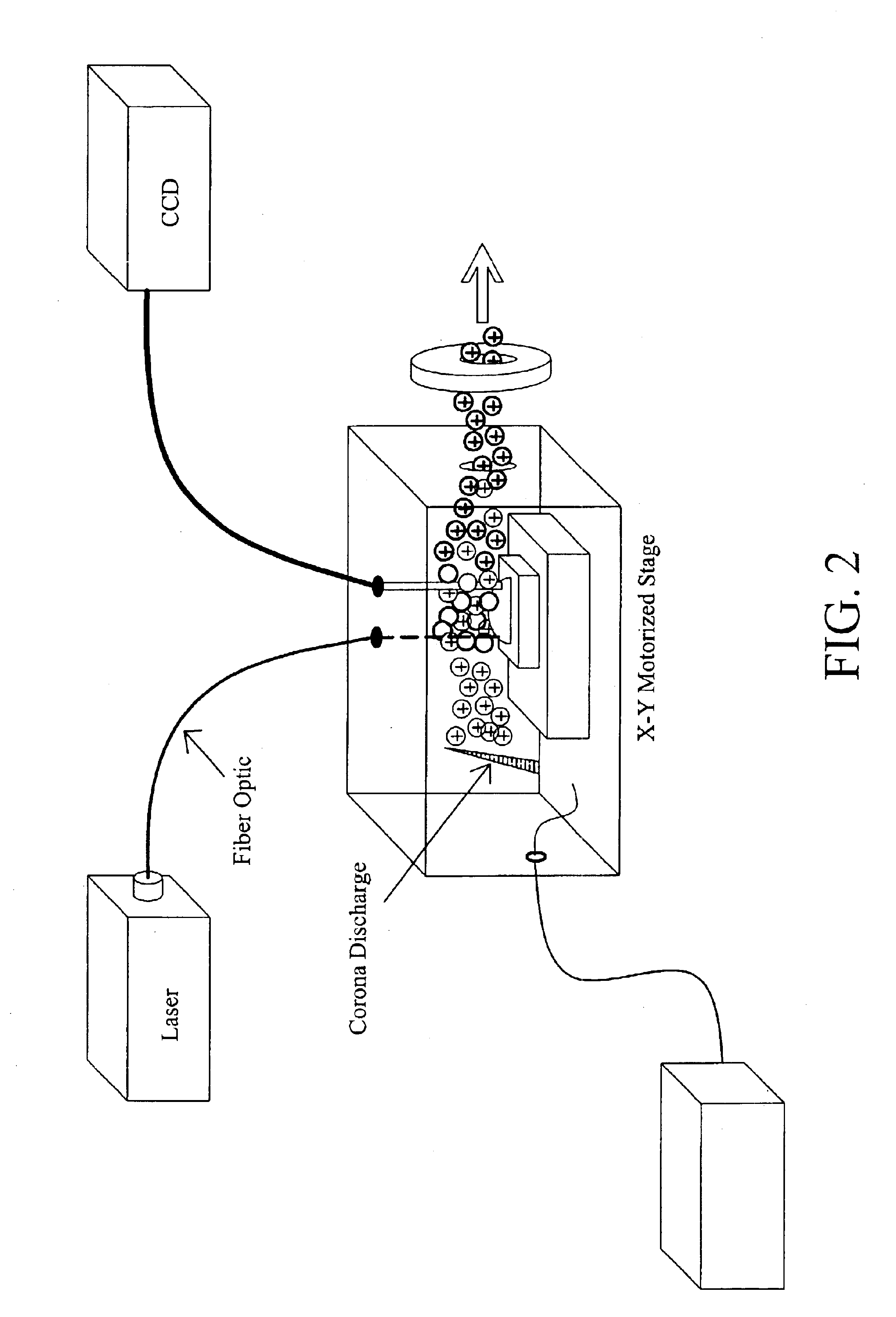
Methods and devices for laser desorption chemical ionization
InactiveUS6838663B2Growing populationSamples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by optical meansDesorptionGas phase
The subject invention pertains to a methods and devices for ionizing a sample material. The subject invention also relates to an ionization source and to a method of sampling gas-phase ions from a sample. An ionization source in accordance with the subject invention can be used in conjunction with mass spectrometry or other sampling techniques. The subject invention can utilize a means for desorbing gas-phase ions and neutral molecules from a sample and a means to generate reagent ions where the reagent ions ionize the desorbed neutral molecules so as to increase the population of gas-phase ions. The subject invention can incorporate laser radiation for desorbing gas-phase ions and neutral molecules from a sample. In a specific embodiment, the subject invention provides an ionization source that uses a pulsed laser for desorption, so as to produce a population of desorbed neutral molecules from a sample, as well as a number of gas-phase sample ions. In a further specific embodiment, the pulsed laser radiation can be adjusted such that neutral molecules are desorbed without the production of gas-phase sample ions by the laser radiation.
Owner:FLORIDA UNIV OF A FLORIDA
Detection method of phthalate plasticizer
InactiveCN101858897AImprove accuracySolve problems that cannot be accurately qualitative and quantitativeComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationOrganic solventThermal ionization mass spectrometry
The invention discloses a detection method of a phthalate plasticizer, comprising the following steps: 1. pretreatment: putting a sample to be detected into an organic solvent, and then dissolving and treating to obtain the solution to be detected in which the plasticizer is dissolved; and 2. content determination of the plasticizer: utilizing a gas chromatogram method and a chemical ionization mass spectrometry method to detect the type and the content of the plasticizer in the detected solution, wherein, the chemical ionization reagent used in the chemical ionization mass spectrometry method is composed of isobutane, methane or ammonia. The detection method of the phthalate plasticizer provided by the invention has high qualitative and quantitative accuracy and high quantitative detection sensitivity.
Owner:深圳出入境检验检疫局玩具检测技术中心
Ionization source for mass spectrometry analysis
ActiveUS7368728B2Samples introduction/extractionMaterial analysis by optical meansLaser desorption ionization mass spectrometryGas phase
A new ionization source named Surface Activated Chemical Ionization (SACI) has been discovered and used to improve the sensitivity of the mass spectrometer. According to this invention the ionization chamber of a mass spectrometer is heated and contains a physical new surface to improve the ionization process. The analyte neutral molecules that are present in gas phase are ionized on this surface. The surface can be made of various materials and may also chemically modified so to bind different molecules. This new ionization source is able to generate ions with high molecular weight and low charge, an essential new key feature of the invention so to improve sensitivity and reduce noise. The new device can be especially used for the analysis of proteins, peptides and other macromolecules. The new invention overcomes some of the well known and critical limitations of the Electrospray (ESI) and Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometric techniques.
Owner:UNIV DELGI STUDI DI MILANO
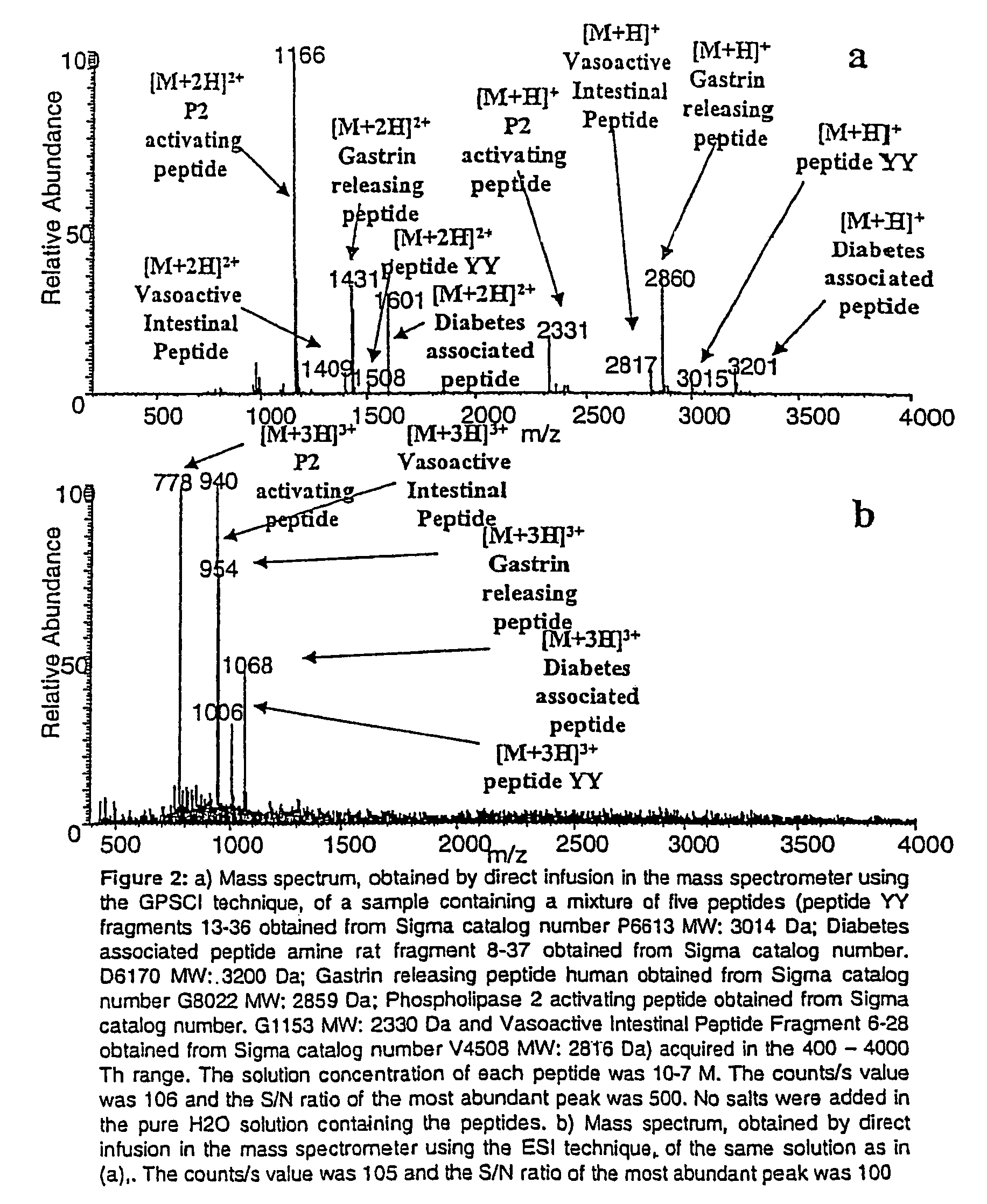
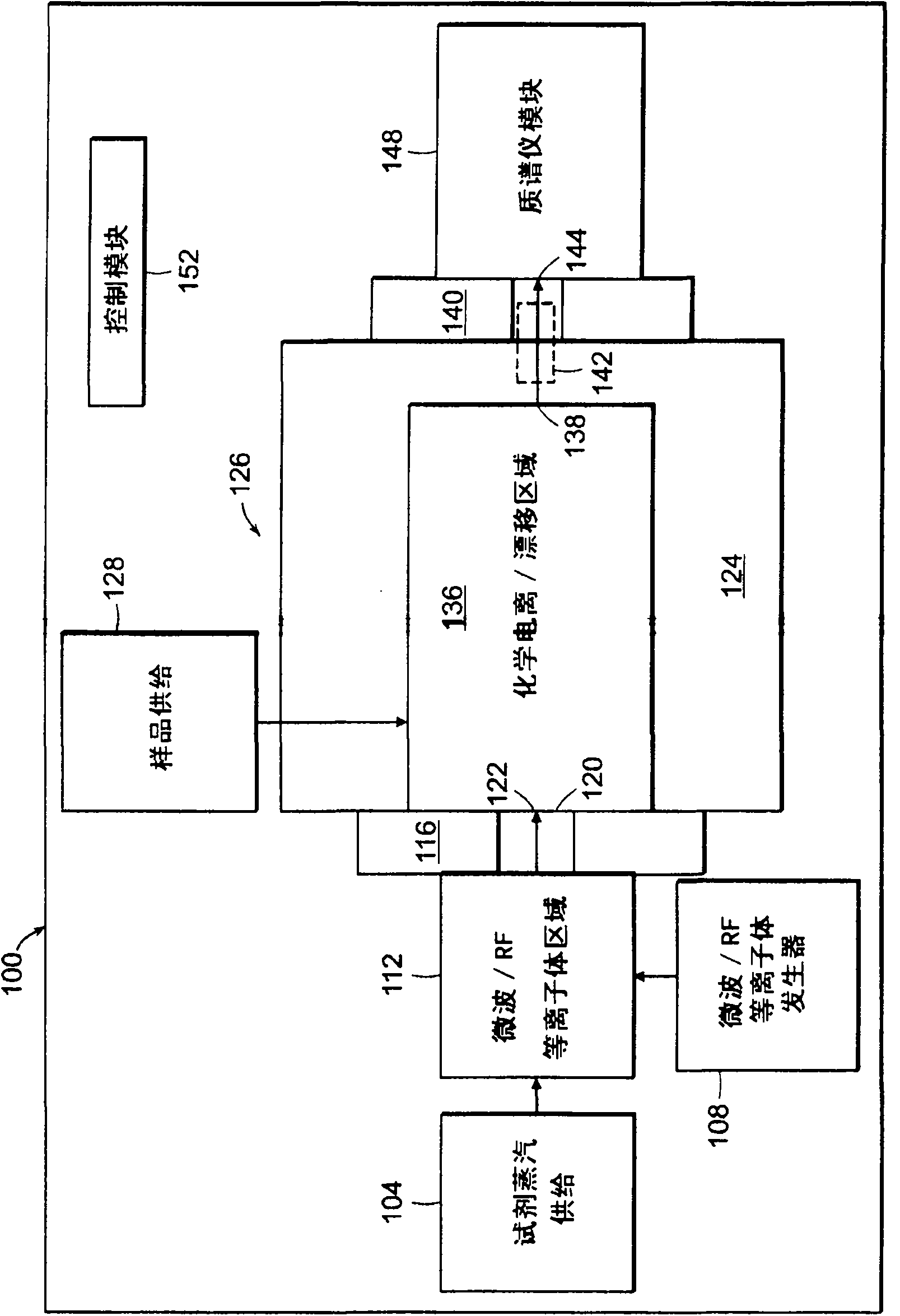
Chemical ionization reaction or proton transfer reaction mass spectrometry with a quadrupole or time-of-flight mass spectrometer
InactiveCN101855700AConvenient quantitative measurementFacilitate and/or identifyIon sources/gunsMass spectrometersPeak valueMass analyzer
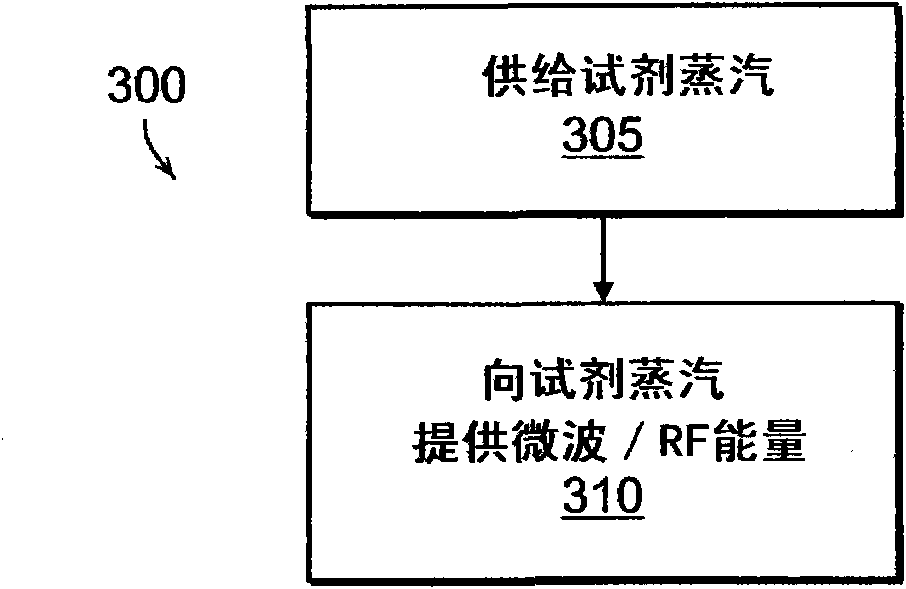
A system and methods are described for generating reagent ions and product ions for use in a mass spectrometry system. Applications for the system and method are also disclosed for detecting volatile organic compounds in trace concentrations. A microwave or high-frequency RF energy source ionizes particles of a reagent vapor to form reagent ions. The reagent ions enter a chamber, such as a drift chamber, to interact with a fluid sample. An electric field directs the reagent ions and facilitates an interaction with the fluid sample to form product ions. The reagent ions and product ions then exit the chamber under the influence of an electric field for detection by a mass spectrometer module. The system includes various control modules for setting values of system parameters and analysis modules for detection of mass and peak intensity values for ion species during spectrometry and faults within the system.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Detecting method for multiple kinds of poly brominated diphenyl ethers in aquatic product
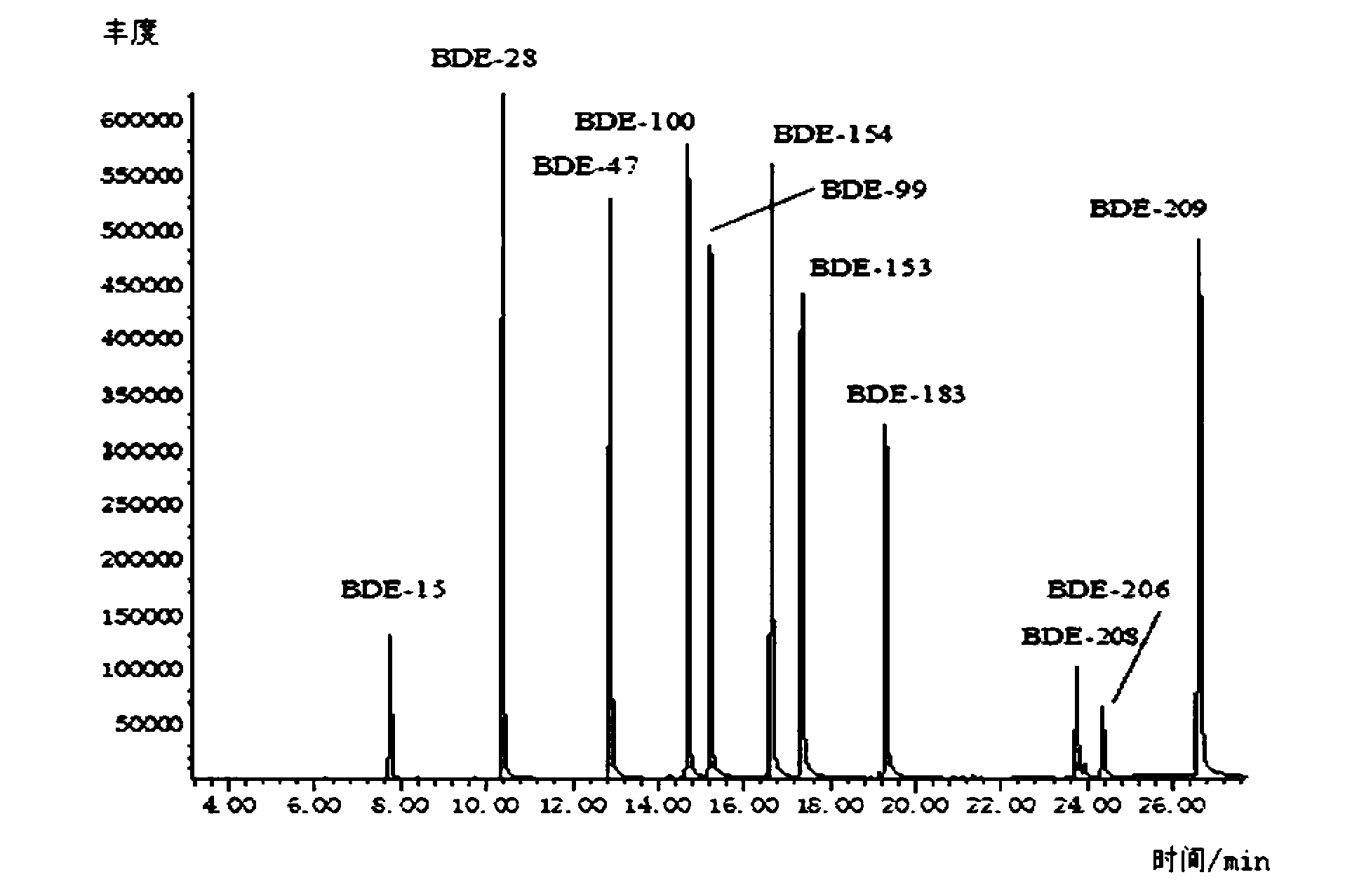
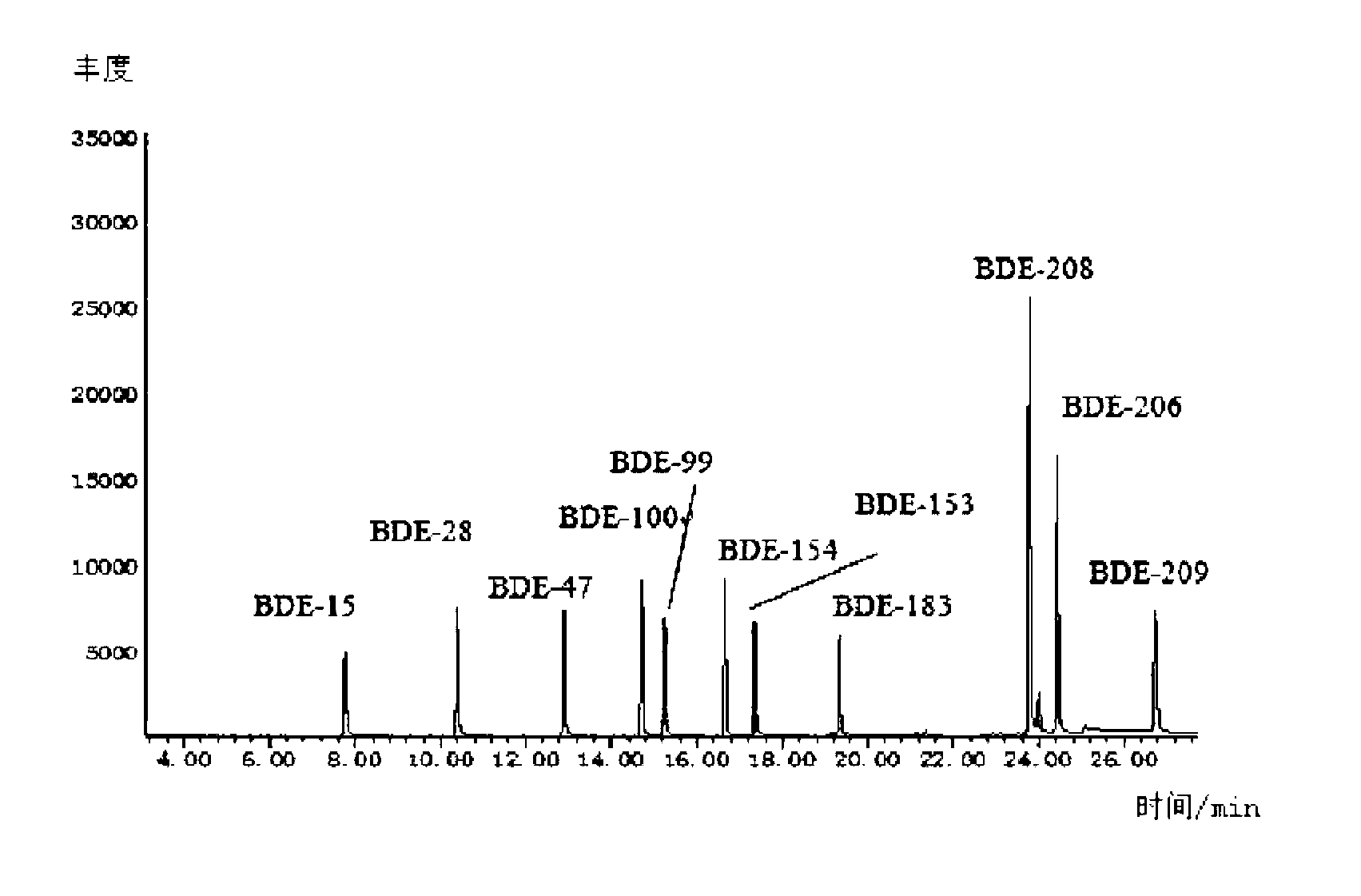
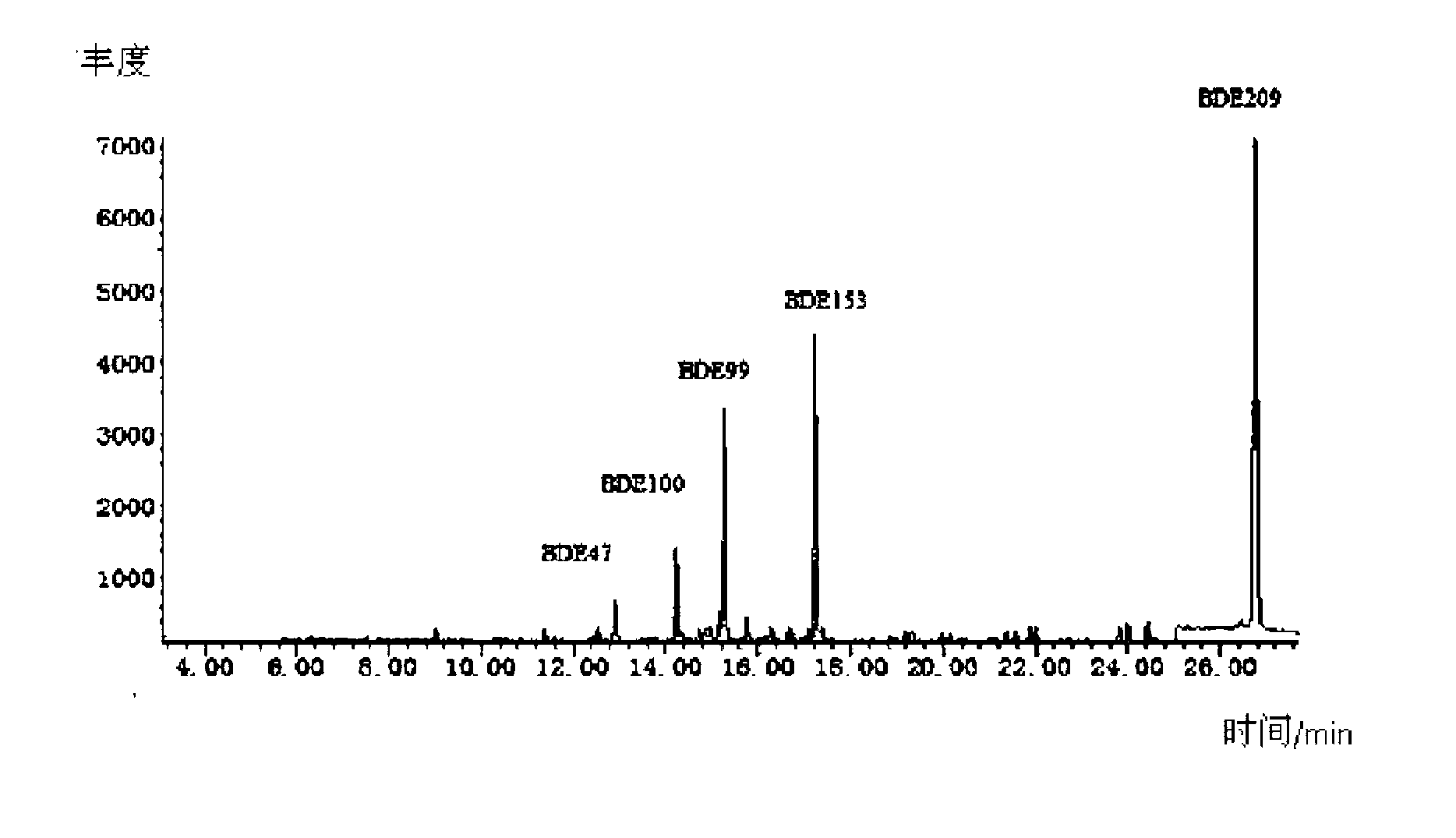
InactiveCN103235062AAchieve simultaneous separationEasy to separateComponent separationFood safetyMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The invention relates to a detecting method for multiple kinds of poly brominated diphenyl ethers in an aquatic product. The detecting method comprises the steps of carrying out extracting, degreasing, silicagel column purifying and concentrating on an aquatic product sample, and analyzing and detecting the aquatic product sample through gas chromatography-negative chemical ionization mass spectrometry. By adopting the treatment measures and proper technique parameters, the method is capable of simply, quickly and accurately measuring the contents of as much as 11 kinds of poly brominated diphenyl ethers in the aquatic product at the same time, and the method has the advantages of high detecting sensitivity, good stability, accurate result, and the like, thereby providing a reliable and quick detecting method for qualitatively and quantitatively detecting the residual poly brominated diphenyl ethers in the aquatic product and monitoring food safety.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
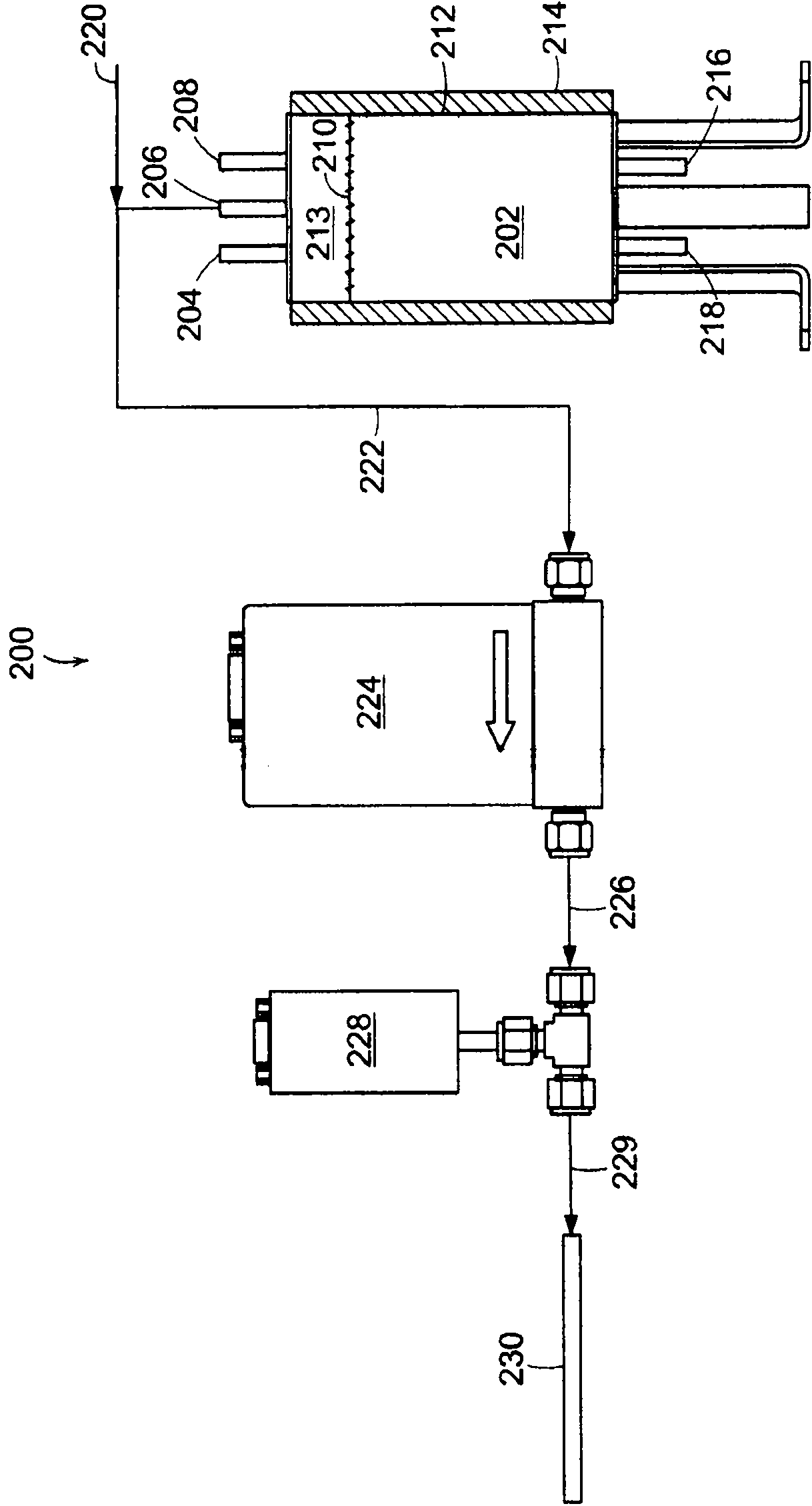
Ion drift-chemical ionization mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20060022132A1Particle separator tubesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansThermal ionization mass spectrometryMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
A method and apparatus for conducting mass spectrometry. The mass spectrometry may be accomplished by ion drift-chemical ionization mass spectrometry. One embodiment includes a chemical ionization mass spectrometer comprising an ion drift zone having an ion conductor that transports positive or negative ions. The chemical ionization mass spectrometer further comprises an ion source that produces the positive or negative ions and a mass spectrometer.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
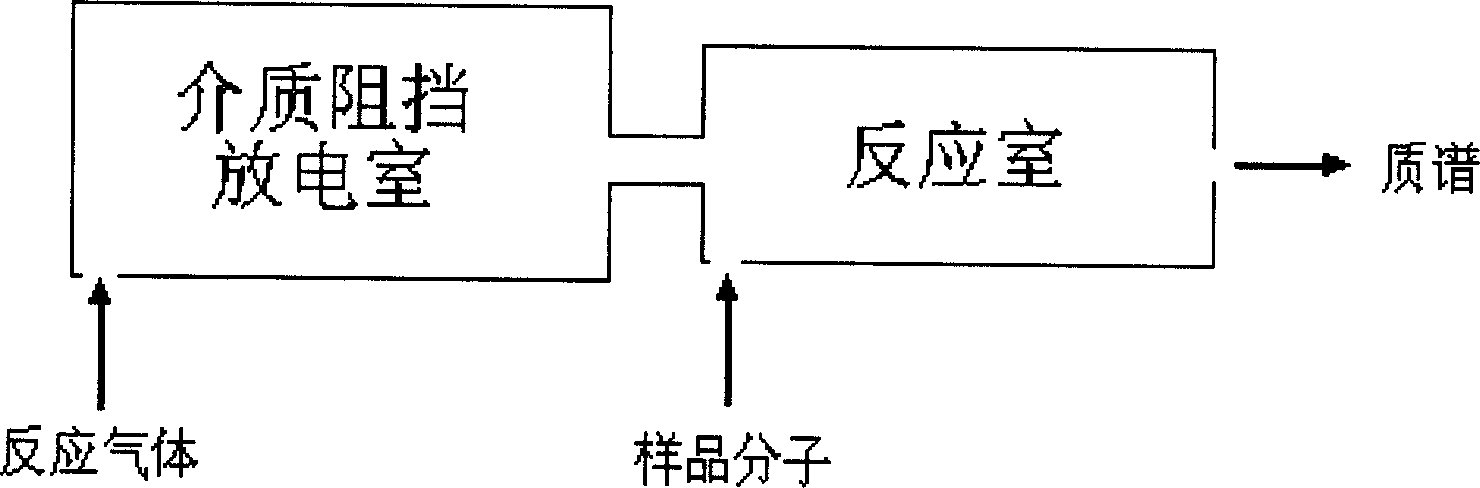
Chemical ioning method based on dielectric blocking discharge and mass ion source
InactiveCN1862760AReduce volumeReduce energy consumptionIon sources/gunsMass spectrometersCompound (substance)Mass spectrometry
This invention relates to chemical ionization base on medium resisting discharging and mass spectrum ion source, it belongs to chemical engineering technique field. It especially relates to active base group ionization to organic matter molecular based on medium resisting discharging technique and mass spectrum ion source used for organic matter detecting. The features are that the medium resisting discharging device is used to ionize the reaction gas that can be used to chemical ionization, the reaction gas is ionized to generate ion and the reaction ion is ion-molecular react with the measuring organic matter to make the organic matter ionization, so mass spectrum can be used t realize detecting. The discharging voltage is 220V-10000V, frequency is 50 Hz to 50MHz, and reaction gas flow velocity is 10ml / min-1000ml / min. The corresponding mass spectrum is also provided. The measuring organic matter can be ionized in this invention, and it can be realized in atmospheric pressure environment, the device volume is small, energy consumption is low.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
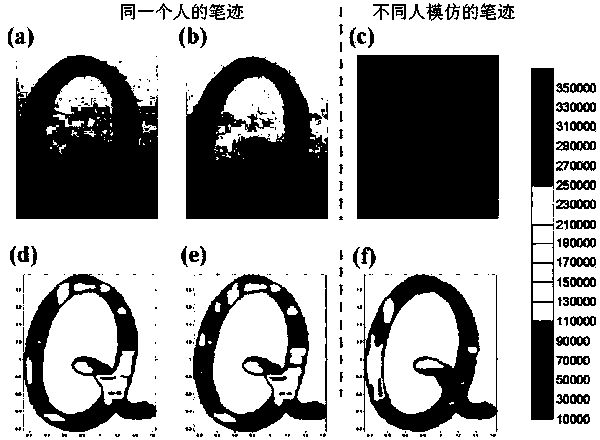
Mass spectrometry imaging method capable of rapidly identifying of handwriting authenticity
InactiveCN103389336ARapid identificationNo damageMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansHandwritingAutomatic control
The invention relates to a mass spectrometry imaging method capable of rapidly identifying of handwriting authenticity. According to the mass spectrometry imaging method, a surface desorption chemical ionization mass spectrometry is adopted in combination of a three-dimensional high-precision automatic control mobile system to carry out two-dimensional spectrum scan on the handwriting without pre-treating the sample, and mass spectrometry images of character compounds in the handwriting are obtained according to changes of ion signal intensities of the character compounds in the handwriting. The mass spectrometry imaging method can directly realize rapid identification of the handwriting authenticity of files at a molecular level under a normal temperature and a normal pressure without pre-treating the sample. The mass spectrometry imaging method has the advantages of simple operations, fast analysis speed, high precision, high sensitivity and no damage to the sample, overcomes the limits of low precision, low sensitivity and slow analysis speed in a conventional handwriting identification method and has enormous potential application prospects in the technical fields related to forensic analysis, archeology, finance, justice, etc.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
System and method for spatially-resolved chemical analysis using microplasma desorption and ionization of a sample
ActiveUS20090121127A1Damage to minimized eliminatedFragmentation and to minimized eliminatedParticle separator tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansNoble gasDesorption
A method and system for desorbing and ionizing molecules from a sample for mass spectrometry using a microplasma device is disclosed. The system and method relies upon a microplasma device, or array of such devices, to partially ionize a gas to form a microplasma. The ionized gas can be a mixture of a noble gas, such as neon or argon, and hydrogen (H2). The ionized gas can form a effluent stream directed onto the surface of a sample to desorb molecules from the remainder of the sample. The desorbed molecules can be ionized by the effluent stream as they leave the surface of the sample. The ionization process can include: photoionization, penning ionization, chemical ionization (proton transfer), and electron impact ionization. The ionized particles from the sample can be directed to a mass spectrometer for analysis. This can produce spatially-resolved mass spectral data, and can be conducted concurrently with another imaging system, such as a microscope.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Apparatus and methods for plasma-assisted reaction chemical ionization (PARCI) mass spectrometry
ActiveUS20160013037A1Eliminate lossComponent separationSamples introduction/extractionChemical reactionElemental analysis
Plasma-assisted reaction chemical ionization (PARCI) provides highly sensitive elemental analysis by producing positively and negatively charged ions. The PARCI apparatuses, kits, and methods described in this application relate to systems that comprise a chemical reaction interface (CRI) containing reactant gas plasma and an ionization chamber that is downstream from the CRI. The ionization chamber facilitates formation of ions from element-specific products of the CRI by an electron source or an ionization gas. In particular, PARCI provides a method for conducting highly sensitive mass spectrometric elemental analysis of analyte compounds with high ionization potential elements; for example, fluorine, chlorine, and bromine.
Owner:GEORGETOWN UNIV
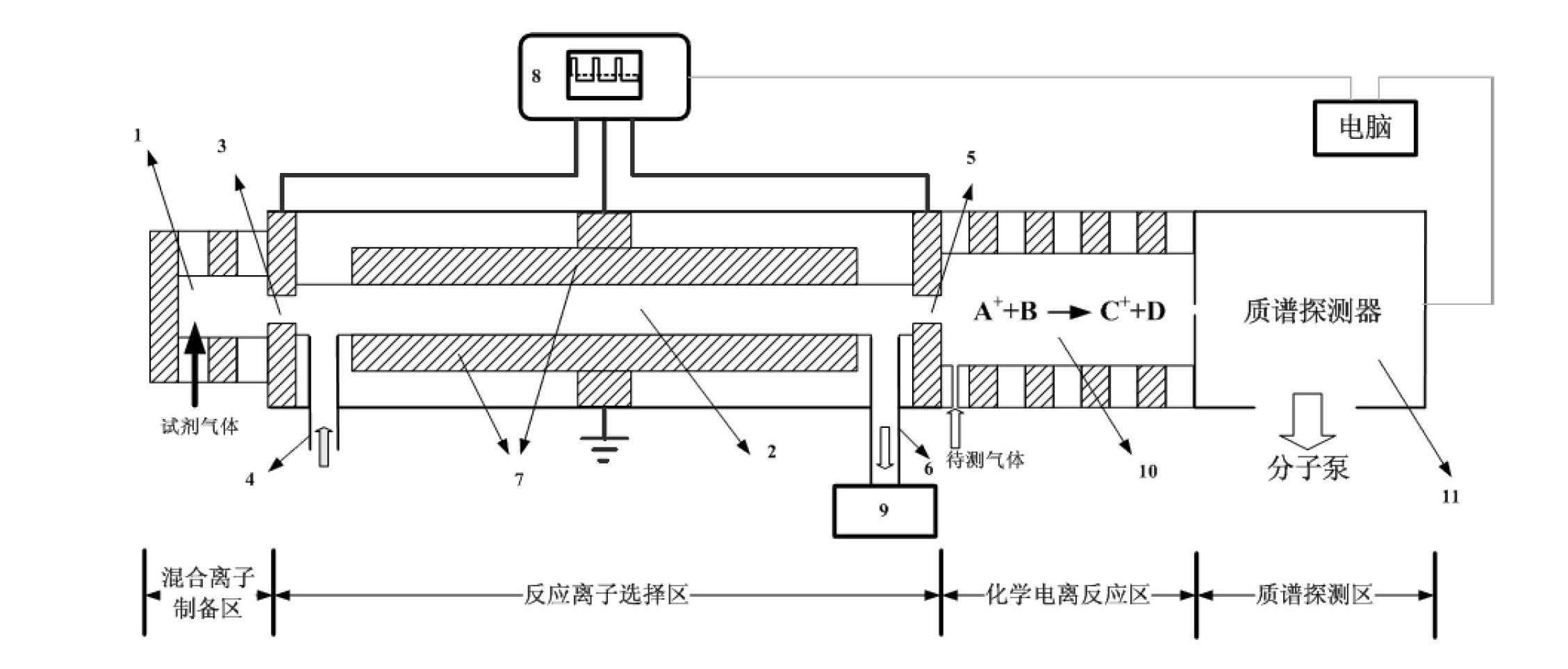
Chemical ionization mass spectrometer for selectively controlling reaction ions
ActiveCN102683151AReduce difficultyLow costElectron/ion optical arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansParallel plateAlternating current
The invention discloses a chemical ionization mass spectrometer for selectively controlling reaction ions, which comprises an ion source, a reaction ion selecting cavity, a chemical ionization reaction cavity and a mass spectrum detecting cavity, wherein the ion source is used for generating mixed ions; a certain ion in the mixed ions can selectively pass through the reaction ion selecting cavity; two parallel-plate electrodes are arranged in the reaction ion selecting cavity; and the parallel-plate electrodes are connected with a controllable radio-frequency power supply. According to the chemical ionization mass spectrometer provided by the invention, the mixed ions are separated by controlling radio-frequency voltage alternating current components loaded on the parallel-plate electrodes and a direct current component is utilized to select one ion, so as to realize the selective control on the passing of any ion; the ion enters the chemical ionization reaction cavity and is served as the reaction ion for chemical ionization, so as to realize the ionization on a to-be-detected object and detect in the mass spectrum detecting cavity; the chemical ionization mass spectrometer provided by the invention can work under atmosphere pressure and has the characteristics of simplicity in technology and low cost; various reaction ions are selectively controlled and the scope of materials detected by the chemical ionization mass spectrometer is expanded; and the identifying analytical capability of an instrument on unknown samples is increased.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for determination of short-chain chlorinated paraffins in plastic, rubber and textile materials
InactiveCN102288691AEffective interferenceEffectively remove interferenceComponent separationPurification methodsGas phase
The invention belongs to the field of analytical chemistry, and specifically relates to a method for determining short-chain chlorinated paraffins in plastics, rubber, and textile materials. (2) purification by sulfonation with concentrated sulfuric acid; and (3) detection step (2) using gas chromatography-electron capture detector or gas chromatography-negative chemical ionization (NCI) mass spectrometry detector The content of short-chain chlorinated paraffins in the obtained purified samples. Beneficial effects of the present invention: Utilize concentrated sulfuric acid sulfonation purification method, can effectively remove interference, use gas chromatography-electron capture detector and NCI mass spectrometry detector to detect medium and short-chain chlorinated paraffins in plastics, rubber, textile materials, can realize Accurate quantification; according to the specific mass spectrum of short-chain chlorinated paraffins, the interference of medium and long-chain chlorinated paraffins can be effectively eliminated, making the qualitative more accurate, the selectivity stronger, and the sensitivity higher.
Owner:SGS STANDARD TECHNICAL SERVICES SHANGHAI CO LTD
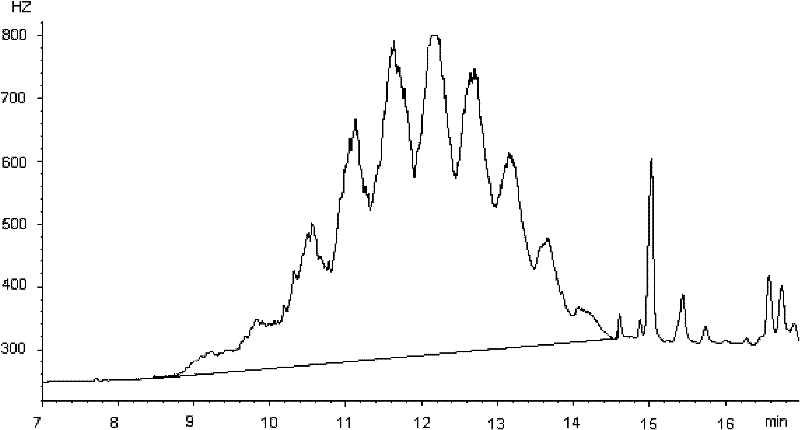
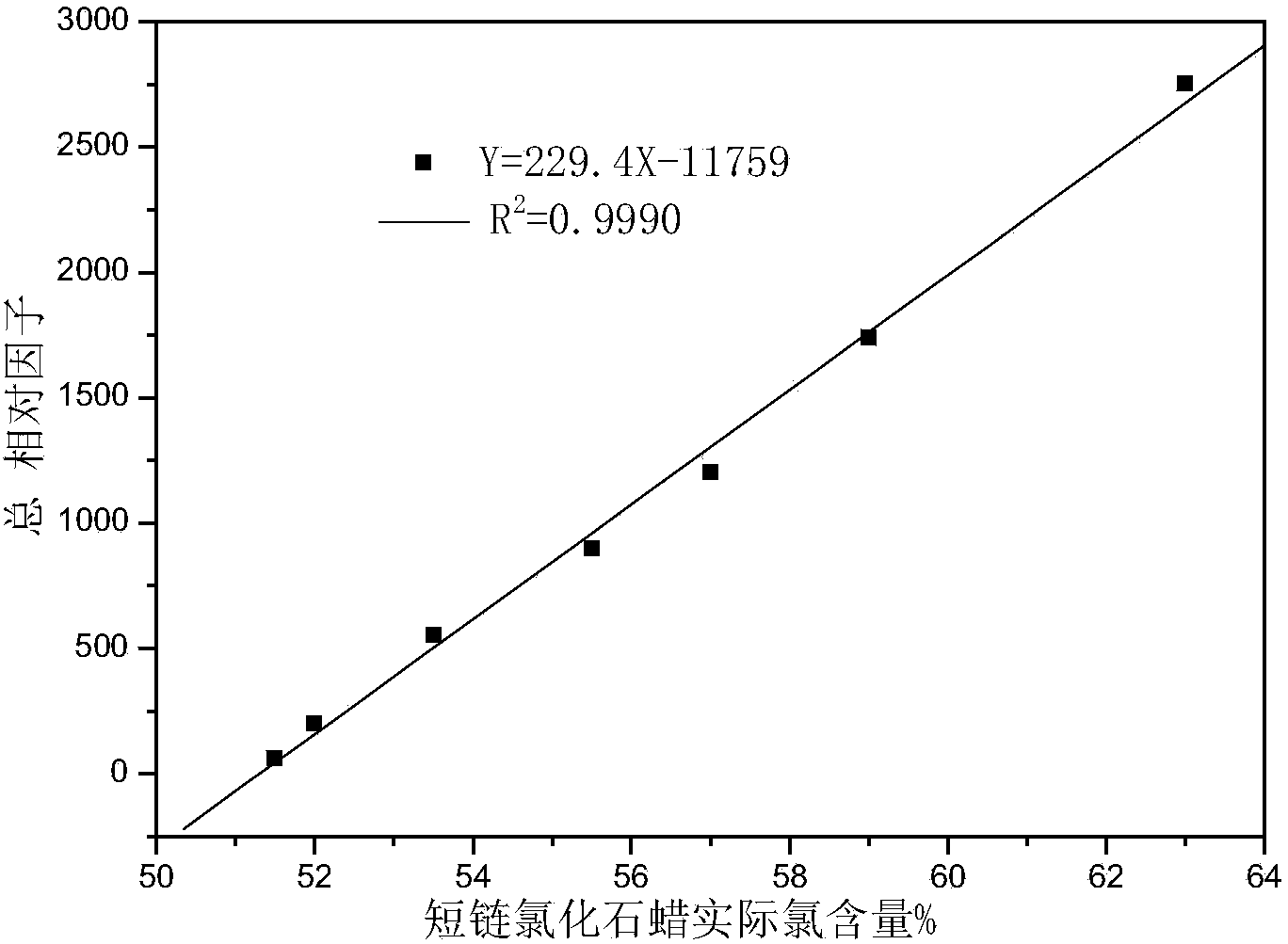
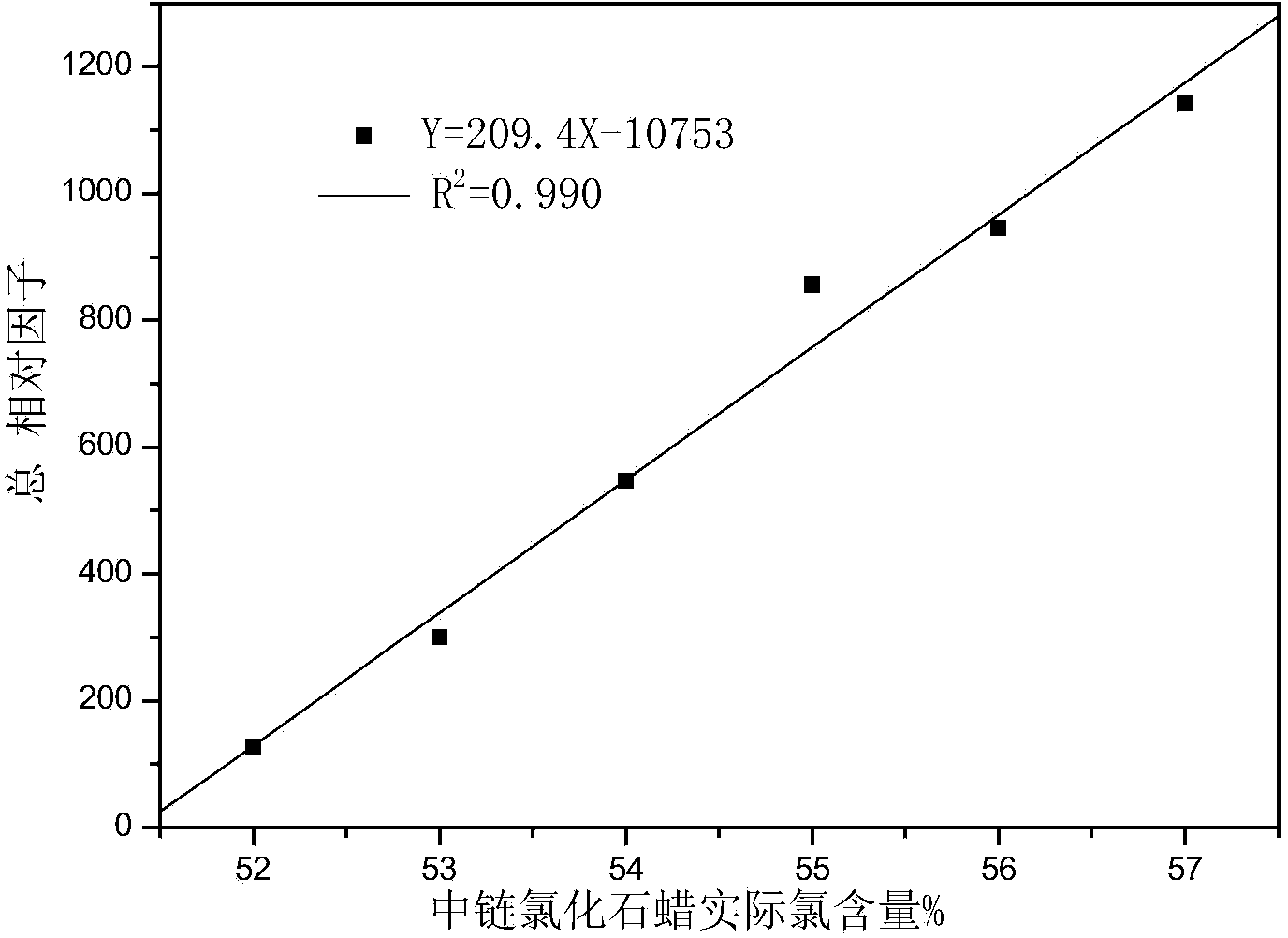
Method for detecting content of short-chain or medium-chain chlorinated paraffin in paint
ActiveCN103543233AEfficient separationReduce lossesComponent separationTotal responseLinear relationship
The invention discloses a method for detecting content of short-chain or medium-chain chlorinated paraffin in a paint. The method comprises the following steps: extracting the short-chain or medium-chain chlorinated paraffin in the paint, detecting with a gas chromatography-negative chemical ionization source mass spectrometry detector, using the internal standard method, performing linear association on a total response factor of a short-chain or medium-chain chlorinated paraffin standard sample on the NCI (negative chemical ionization) mass spectrometry detector with the chlorine content of a short-chain or medium-chain chlorinated paraffin standard solution, detecting the actually measured chlorine content of the sample by the gas chromatography-negative chemical ionization source mass spectrometry detector, corresponding the actually measured chlorine content with the a liner reaction expression of the total response factor and the chlorine content of the short-chain or medium-chain, to obtain the total response factor of the sample, and thus obtaining the content of the short-chain or medium-chain chlorinated paraffin in the paint. The analysis method disclosed by the invention is exact and fast, has small interfering, and can perform optimal separation and qualitative and quantitative detections on each component in the sample.
Owner:GUANGDONG TESTING INST OF PROD QUALITY SUPERVISION
Method for online-analyzing organic monomer chlorine or bromine isotope and based on chemical ionization
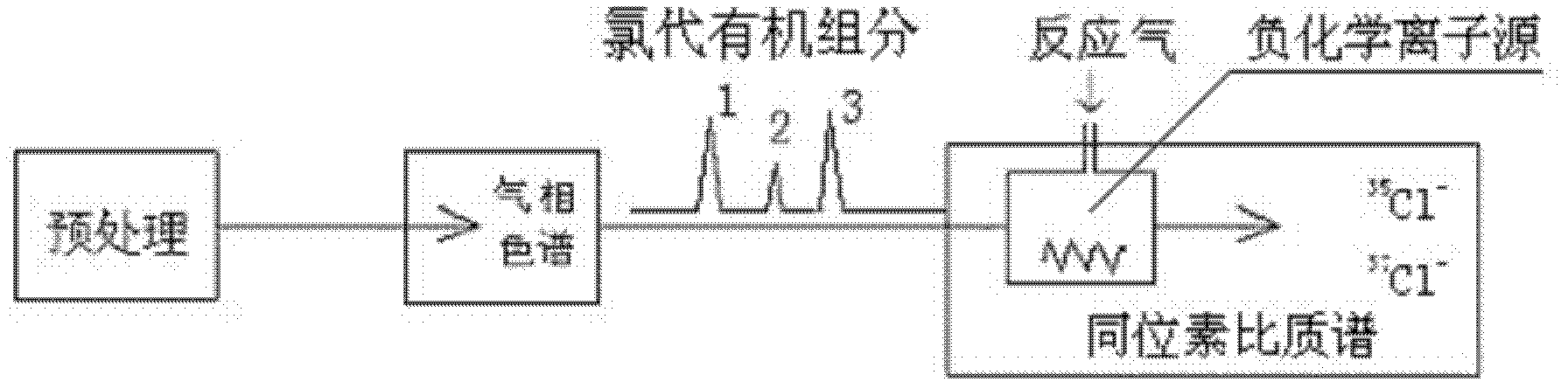
InactiveCN102590379AAvoid separationSimplify the process of online analysisComponent separationMass numberGas phase
The invention aims at providing a method for online-analyzing organic monomer chlorine or bromine isotope, which adopts a direct negative chemical ionization to replace an original complex organic monomer conversion process. The method is characterized by including the steps: A. gathering chlorine or bromine substitute; B. separating gas chromatography: placing the gathered chlorine or bromine substitute into the gas chromatography to be separated; C. conducting negative chemical ionization: components analyzed through chromatography directly flow into a negative chemical ion source through acapillary column, the negative chemical ion source replaces an original electron bombardment source configured on an isotope ratio mass spectrum to conduct the negative chemical ionization; D. mass spectrometric detecting: on a gas isotope ratio mass spectrum, selecting a faraday receiving cup corresponding to mass number of chlorine or bromine substitute directly, and receiving electronegative isotope fragment ions generated by the negative chemical ionization. The process is conducted under high vacuum state, and degree of vacuum is higher than 1.0*10<-3> Pa. The method greatly simplifies aprocess of online-analyzing organic monomer chlorine or bromine isotope and can form various special devices for detecting organic monomer isotope ratio.
Owner:INST OF HYDROGEOLOGY & ENVIRONMENTAL GEOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF GEOLOGICAL SCI
Hydrocarbon determination in presence of electron and chemical ionization
ActiveUS20110189778A1Earth material testingIsotope separationHydrocotyle bowlesioidesChemical ionization
Methods and apparatus for obtaining a mass spectrum of a sample and determining a concentration of a component of the sample by utilizing a model of chemical and electron ionization and the obtained mass spectrum.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Radio-frequency discharge VUV composite ionization source used for mass spectrometry
InactiveCN104716008AReduce volumeCompact structureIon sources/gunsChemical ionizationMass spectrometry imaging
The invention relates to an ionization source, in particular to a composite ionization source which comprises a VUV single-photon ionization source based on radio-frequency voltage discharge and a chemical ionization source obtained by utilizing photoelectron ionization reagent gas in the photoelectric effect. The composite ionization source comprises a radio-frequency VUV source, an ion transmission optical system and an ion source cavity. An ion repulsing electrode, an ion focusing electrode and a difference interface electrode plate are sequentially arranged in the VUV source emergent direction of radio-frequency discharge, the three electrodes are all round sheet electrodes with round holes in the centers, and the three electrodes are spaced through insulation pads and are coaxially arranged in parallel. The VUV light beam of the radio-frequency voltage discharge and coaxial light beams of all the round sheet electrodes penetrate through the center holes of all the electrodes in the axis direction, and finally the beams are irradiated on the surface of the difference interface electrode plate. Chemical ionization is acted on the photoelectrons after reagent gas is added. Soft ionization of sample molecules with ionization energy higher than the photon energy is achieved, the range of analyzable samples is enlarged, and the detection sensitivity of instruments is improved.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Radio-frequency electric field enhanced single photon and chemical ionization source
ActiveCN103972018AQuick switchMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIon sources/gunsUltravioletChemical ionization
The invention relates to a mass spectrometer ionization source, in particular to a radio-frequency electric field enhanced single photon and chemical ionization source comprising a vacuum ultraviolet source, an ion generation and transmission area and a vacuum chamber vacuum cavity. A plurality of transmission electrodes and vacuum differential perforated electrodes are disposed in parallel and at intervals in the ion generation and transmission area. Each electrode is axially provided with a through hole. Ultraviolet emitted by the vacuum ultraviolet source enters the perforated electrodes along the axes. Direct-current voltage is applied to all transmission electrodes and perforated electrodes; radio-frequency voltage is superposed to one transmission electrode. Two different ionization ways are switched by controlling start and stop of the radio-frequency voltage. The radio-frequency electric field enhanced single photon and chemical ionization source comprises the single photon ionization source, the chemical ionization source is obtained through photoelectron ionization reagent gas obtained by means of photoelectric effect, radio-frequency electric field is introduced to the ionization area to enhance chemical ionization triggered by photoelectrons, detection sensitivity is improved, soft ionization of sample molecules with ionization energy higher than the energy of ultraviolet photons can be achieved, and range of analyzable samples is widened.
Owner:SHENZHEN BREATHA BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Vacuum ultraviolet photoionization and chemical ionization compound ionization source based on radio frequency electric field enhancement of quadrupole rod
InactiveCN104716010AExtended stayImprove ionization efficiencyIon sources/gunsUltraviolet lightsMass spectrometry
The invention relates to a mass spectrum analysis instrument, in particular to a vacuum ultraviolet photoionization and chemical ionization compound ionization source based on radio frequency electric field enhancement of quadrupole rods. The vacuum ultraviolet photoionization and chemical ionization compound ionization source based on radio frequency electric field enhancement of the quadrupole rod comprises a vacuum ultraviolet light source and an ionization chamber cavity; a plurality of transmission electrodes, the quadrupole rods and vacuum differential hole electrodes are coaxially arranged in an ionization chamber in a spaced mode; a metal grid mesh is attached to the transmission electrode far away from an ultraviolet light inlet, ultraviolet light emitted by the vacuum ultraviolet light source is irradiated to the metal grid mesh and phoelectrons are generated; direct-current voltage and radio frequency voltage are applied to the quadrupole rods. On the basis of vacuum ultraviolet photoionization, the compound ionization source ionizes reagent gas through the phoelectrons generated through the photoelectric effect, and therefore chemical ionization happens to samples through reagent ions; through the radio frequency electric field of the quadrupole rods, ionization efficiency of chemical ionization caused by the phoelectrons can be improved; besides, chemical compounds with ionization higher than vacuum ultraviolet light photon energy can be ionized through chemical ionization, and the range of the chemical compounds capable of being ionized is widened.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
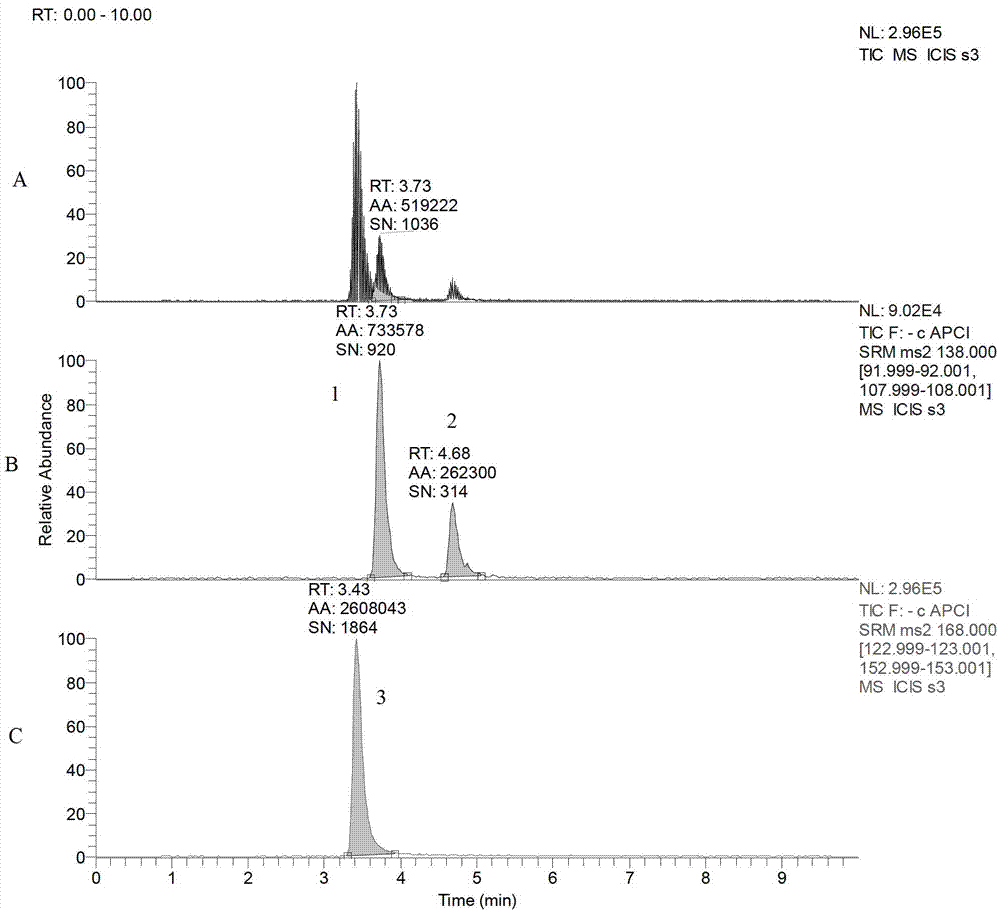
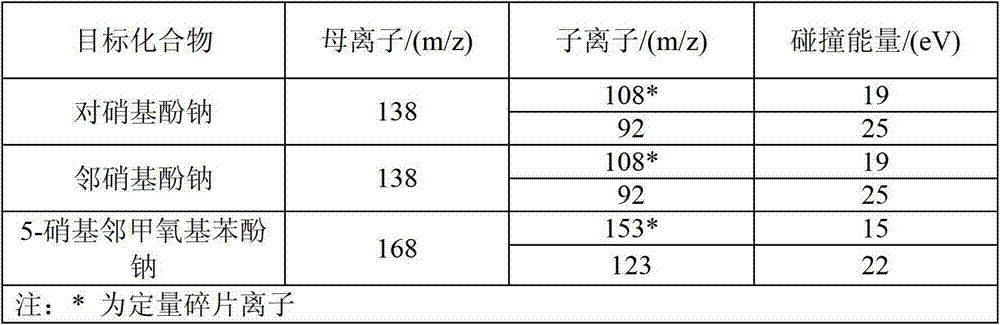
Method for detecting residual quantity of sodium nitrophenol in aquatic product
ActiveCN103091422AHigh sensitivityEasy to prepareComponent separationHazardous substancePhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a method for detecting residual quantity of sodium nitrophenol in an aquatic product and belongs to the technical field of detection of aquatic products. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting and purifying a sample; drawing a standard curve; and determining and quantifying apparatus conditions. According to the method disclosed by the invention, an APCI (Atmosphere Pressure Chemical Ionization) ion source is selected by a mass spectrometer, so that the sensitivity of sodium orotho-nitrophenolate is improved by dozens of times; neutral alumina is adopted for purifying, so that interfering substances such as fat in the sample can be effectively removed, and the concentration time is shortened; sodium hydroxide is added during the concentration process, so that the sodium orotho-nitrophenolate exits in the sample in the form of sodium salt, thereby enabling the recovery rate of the sodium orotho-nitrophenolate to be more than 70%. Phosphoric acid is added after the concentration for neutralizing the excessive sodium hydroxide, so that the pH of the purifying liquid kept at about 3, and the requirements of upper solid-phase extractor column can be satisfied. The method disclosed by the invention fills up the blank that no method is provided for detecting residual quantity of sodium nitrophenol in aquatic products and other animal foods at present, and has great significance in accurately and scientifically evaluating the quality safety of the aquatic products and making the novel standards of harmful substances in the aquatic products.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
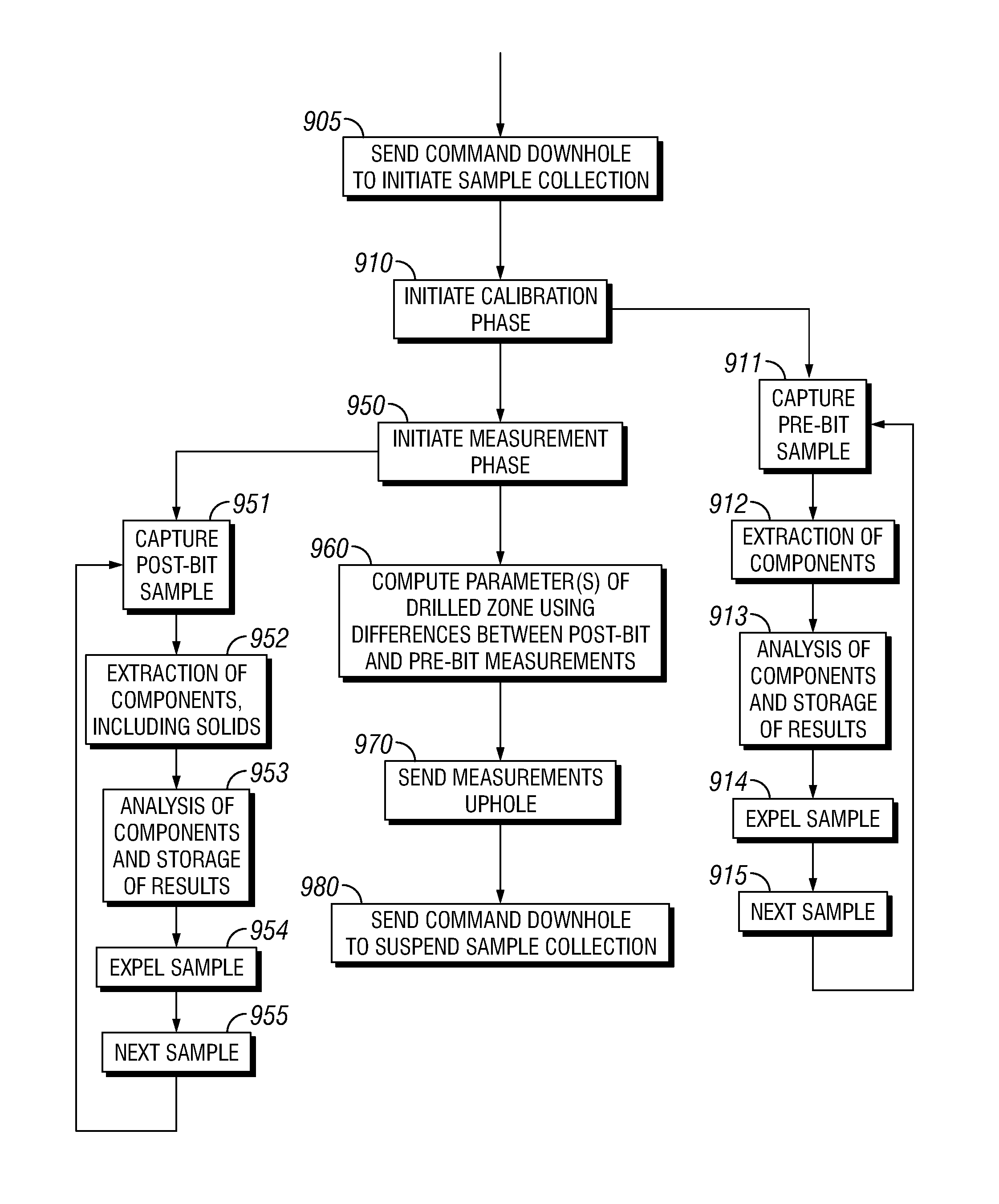
Downhole mass spectrometric hydrocarbon determination in presence of electron and chemical ionization
Methods and apparatus for obtaining a mass spectrum of a sample and determining a concentration of a component of the sample by utilizing a model of chemical and electron ionization and the obtained mass spectrum.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
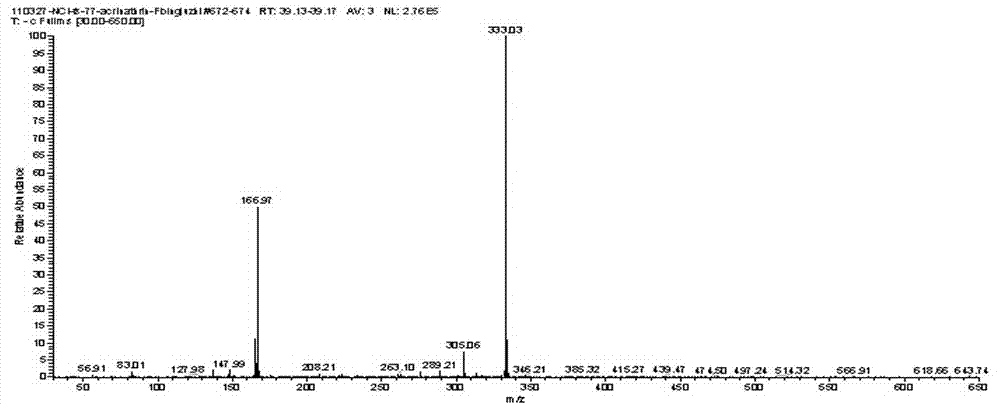
Direct chemical ionization mass spectrometry detection method for illegal cooking oil
InactiveCN102128875AQuick checkMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDesorptionStatistical analysis
The invention discloses a direct chemical ionization mass spectrometry detection method for illegal cooking oil, which is characterized by comprising: (1) setting a linear trap quadrupole mass spectrometry (LTQ-MS) in an anionic or cationic detection mode, regulating a spectrometric detection scanning range, an ionization voltage and a capillary temperature, and setting the parameters of a desorption atmospheric chemical ionization (DAPCI) source; and (2) directly dripping an oil sample on a glass slide, uniformly coating, processing all spectral data into a matrix X by using a mass to charge ratio as an independent variable and the absolute abundance of a mass spectrum peak as a dependent variable, importing the matrix X into data statistic analysis software, directly performing principal component analysis (PCA) computation, and inputting the result of the computation into SIGMAPLOT for graphic display. In the invention, the method which can quickly detect and identify illegal cooking oil without pretreating a sample to be detected overcomes the drawbacks of complex and time-consuming detection operation steps and the like.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV +1
Pulsed Ion Source for Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer and Method
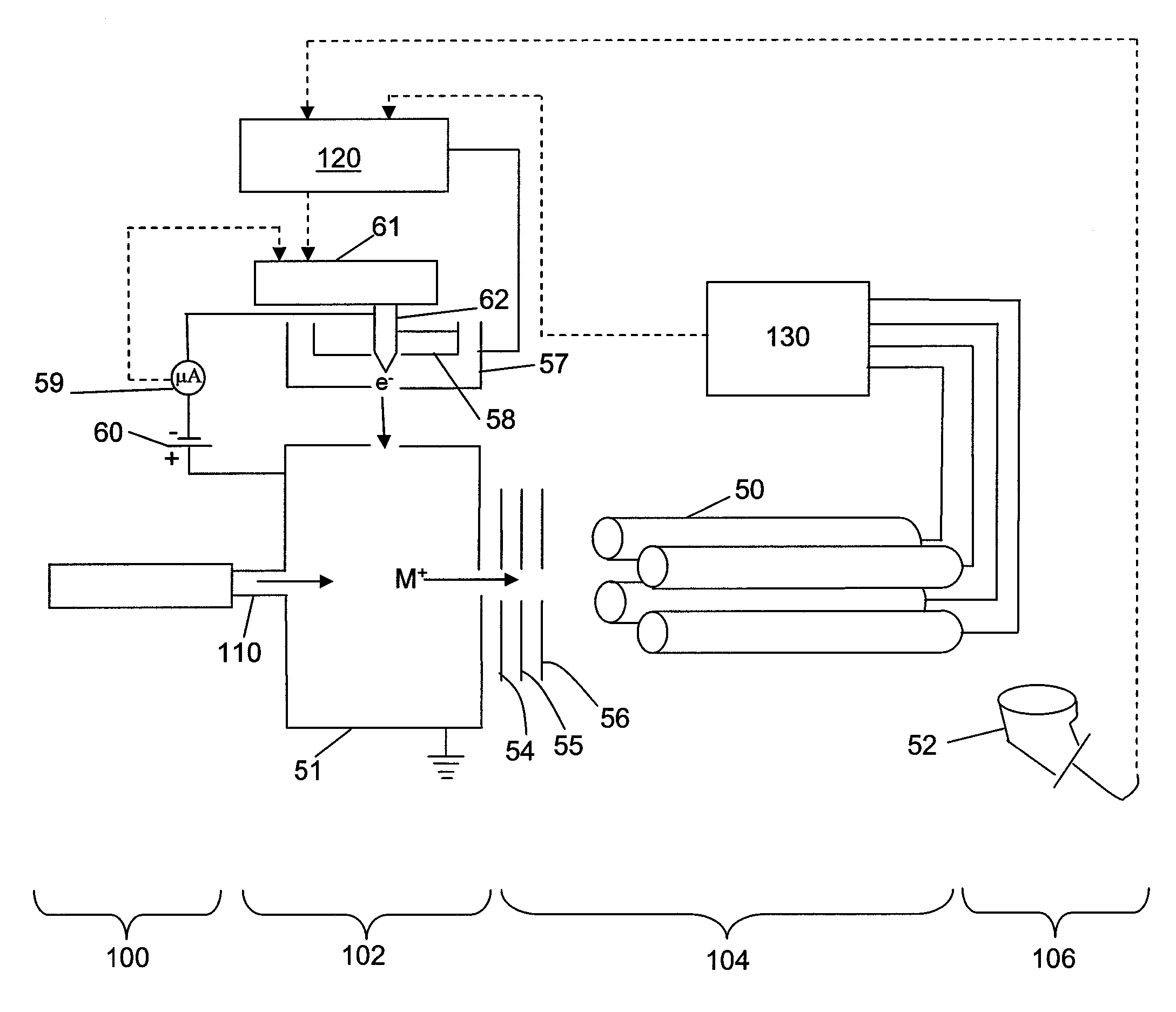
ActiveUS20080087816A1Preserve detection limitImprove dynamic rangeParticle separator tubesIsotope separationIonic strengthContinuous beam
A variable duty cycle ion source assembly is coupled to a continuous beam mass spectrometer. The duty cycle can be adjusted based on previous scan data or real time sampling of ion intensities during mass analysis. This provides the ability to control the total number of ions formed, mass analyzed and detected for each ion mass of interest. The frequency of the ion source can be sufficiently high (kHz range) so as to maintain accurate peak centroiding. The ion source assembly can be used for both electron ionization (EI) or chemical ionization (CI) modes of operation.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Method for detection of electronegative element containing pesticides by negative chemical ionization mass spectrum database
InactiveCN104764843AReduce distractionsEasy to useComponent separationPesticide residueGas liquid chromatographic
Owner:INTEGRATION TECH SERVICE CENT OF WEIFANG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com