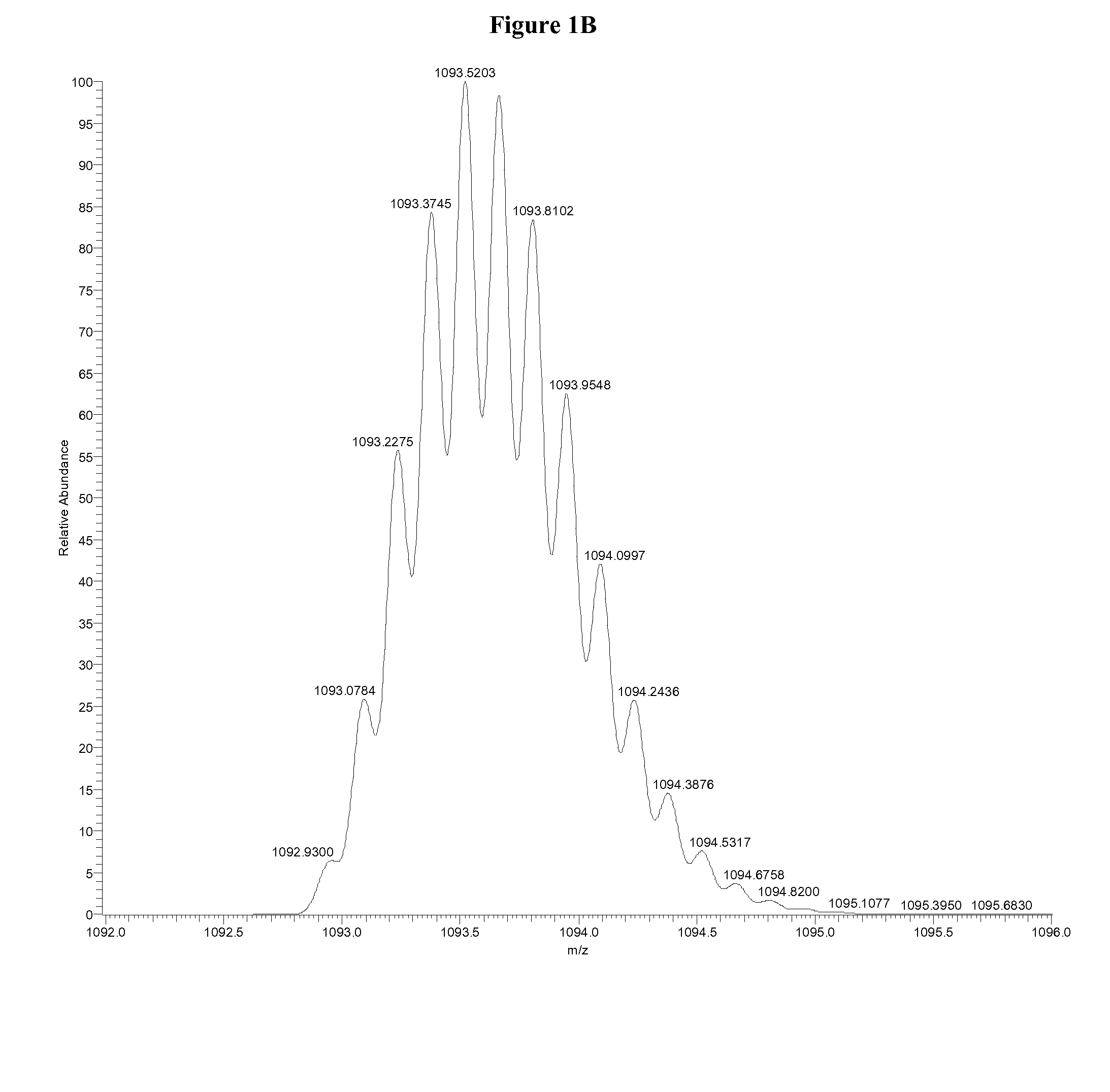
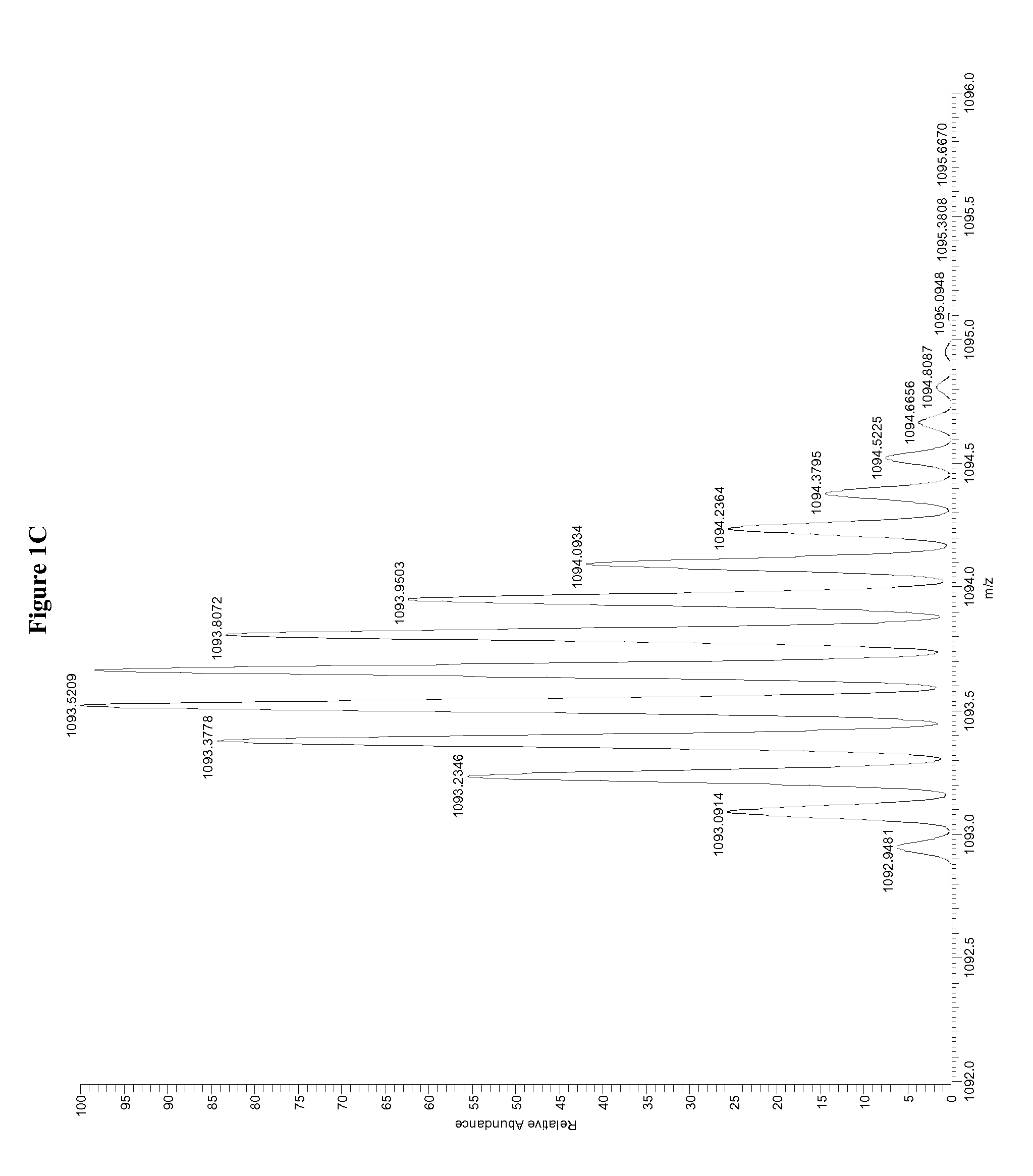
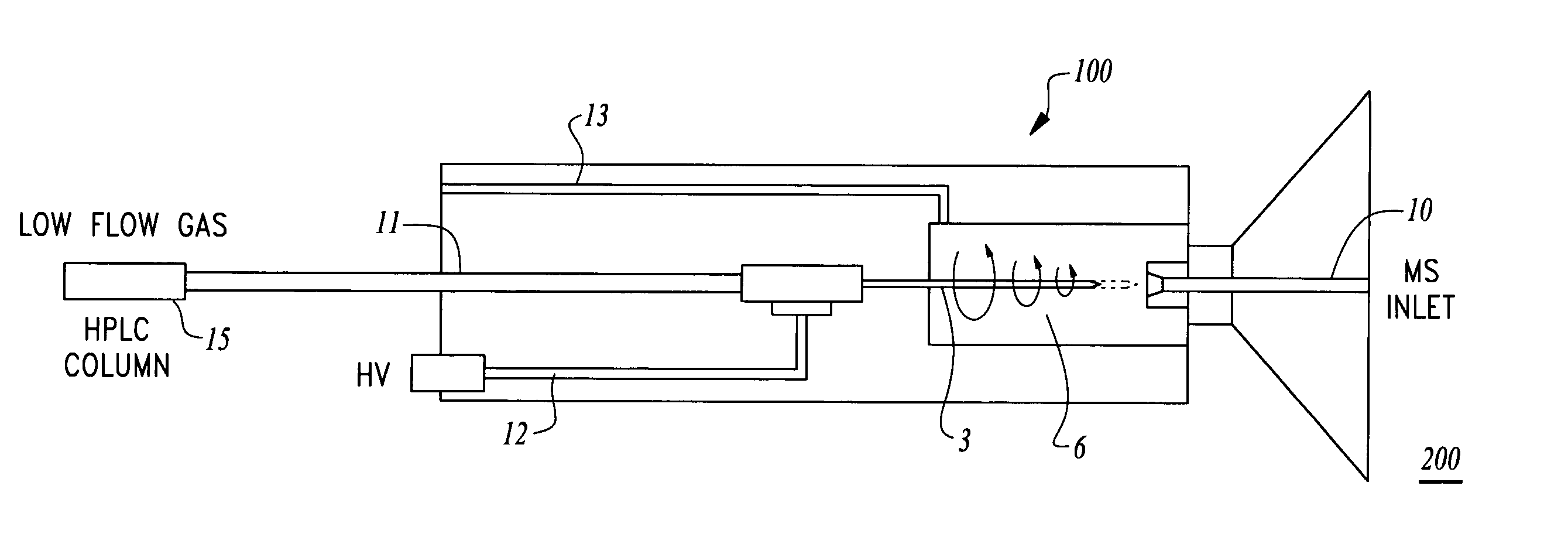
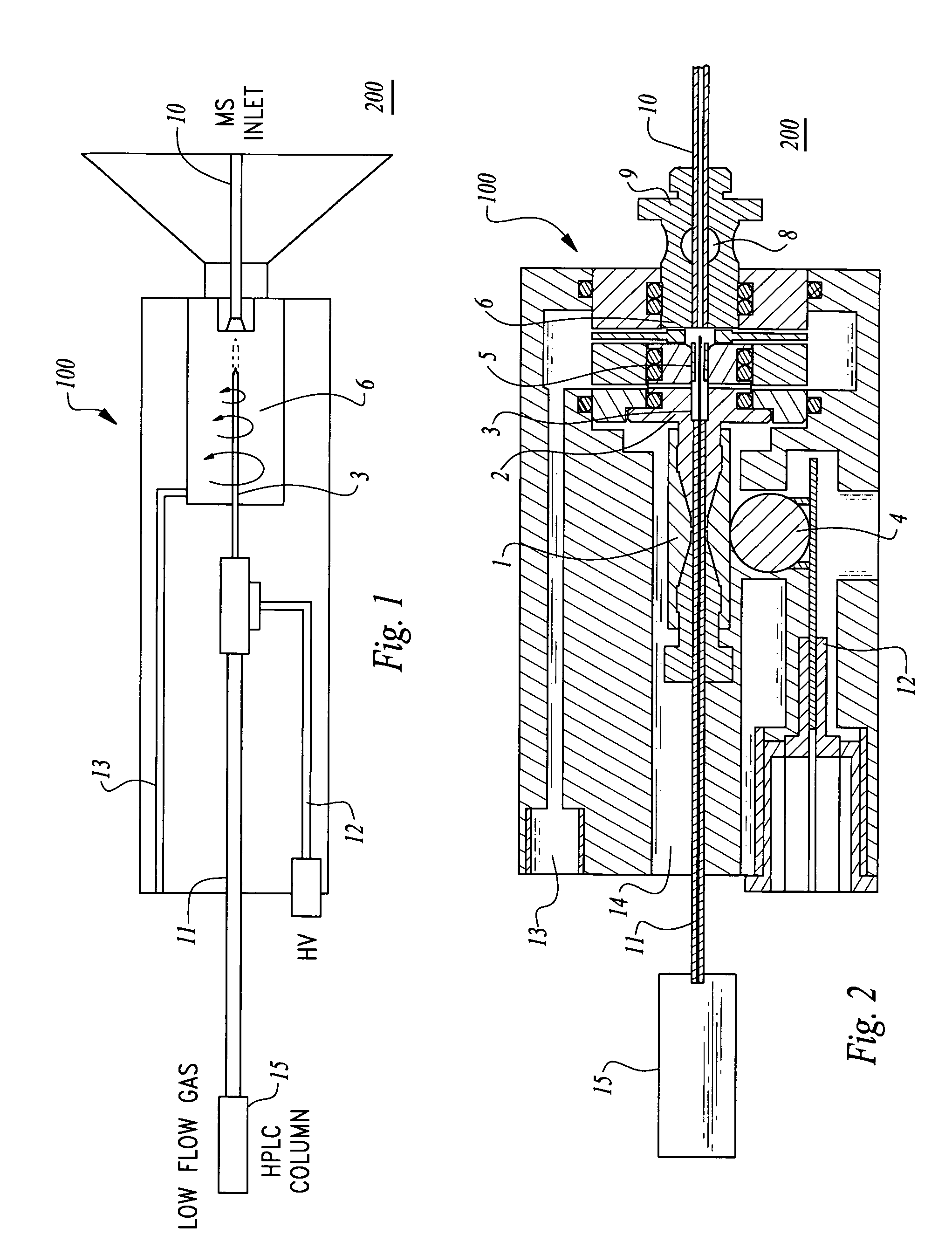
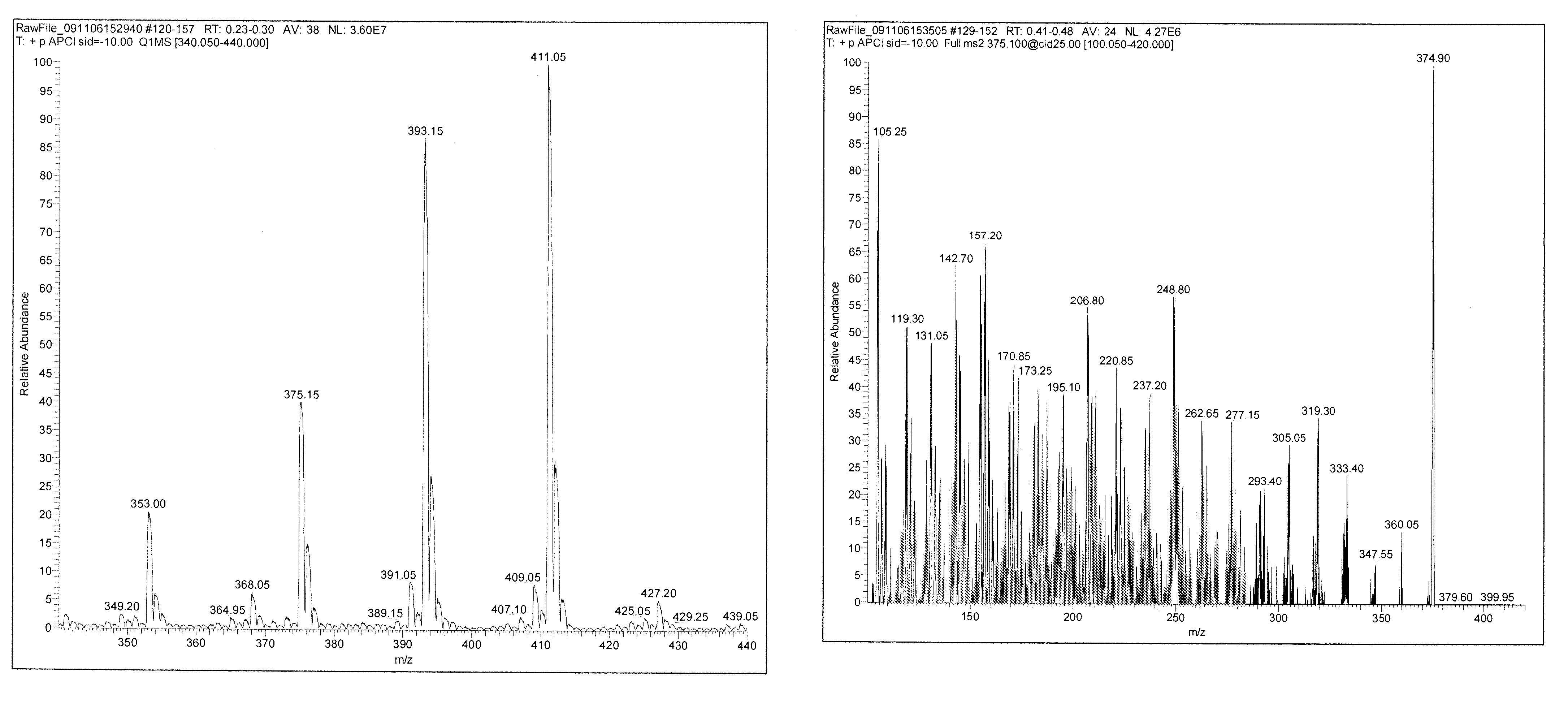
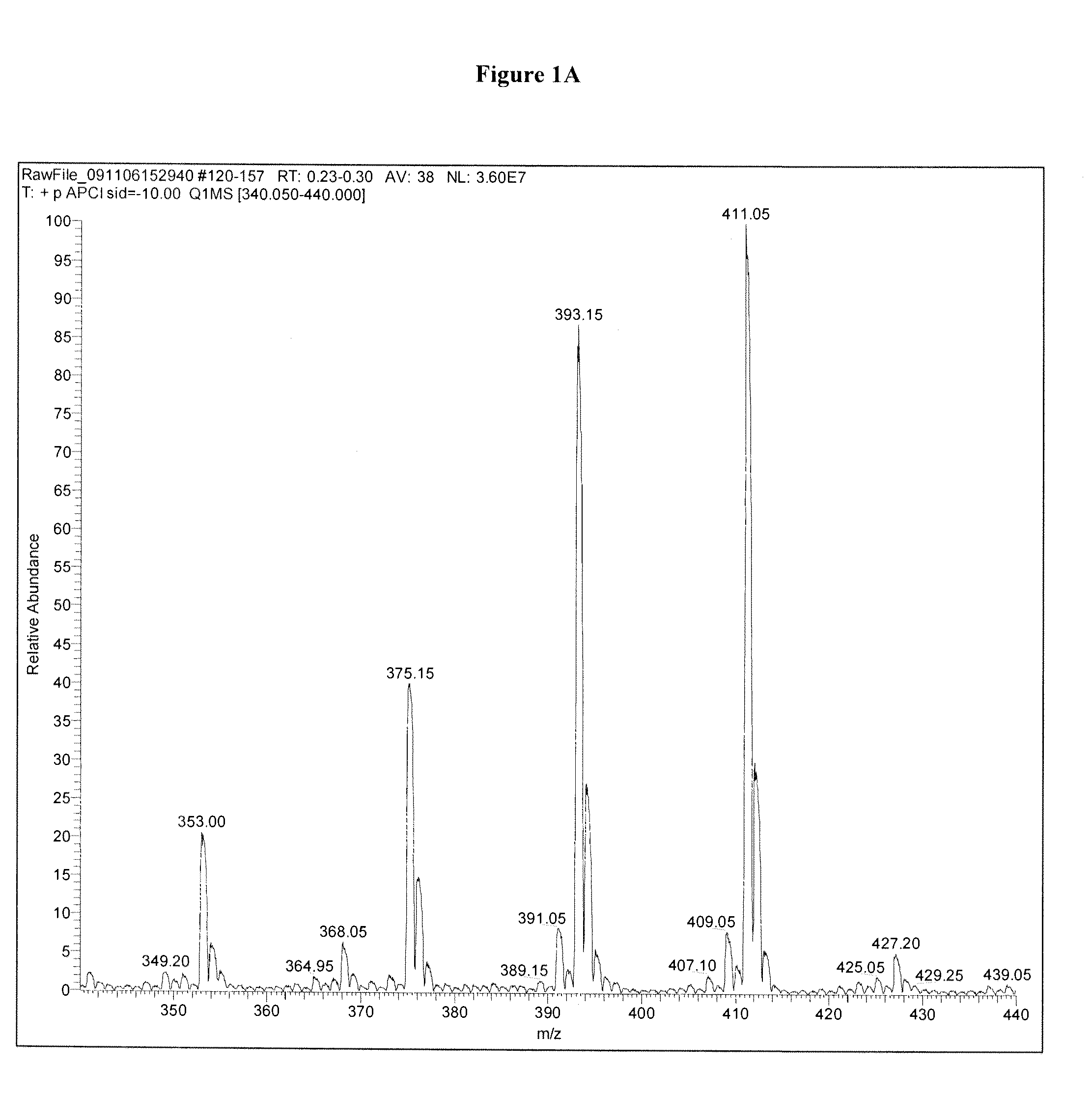
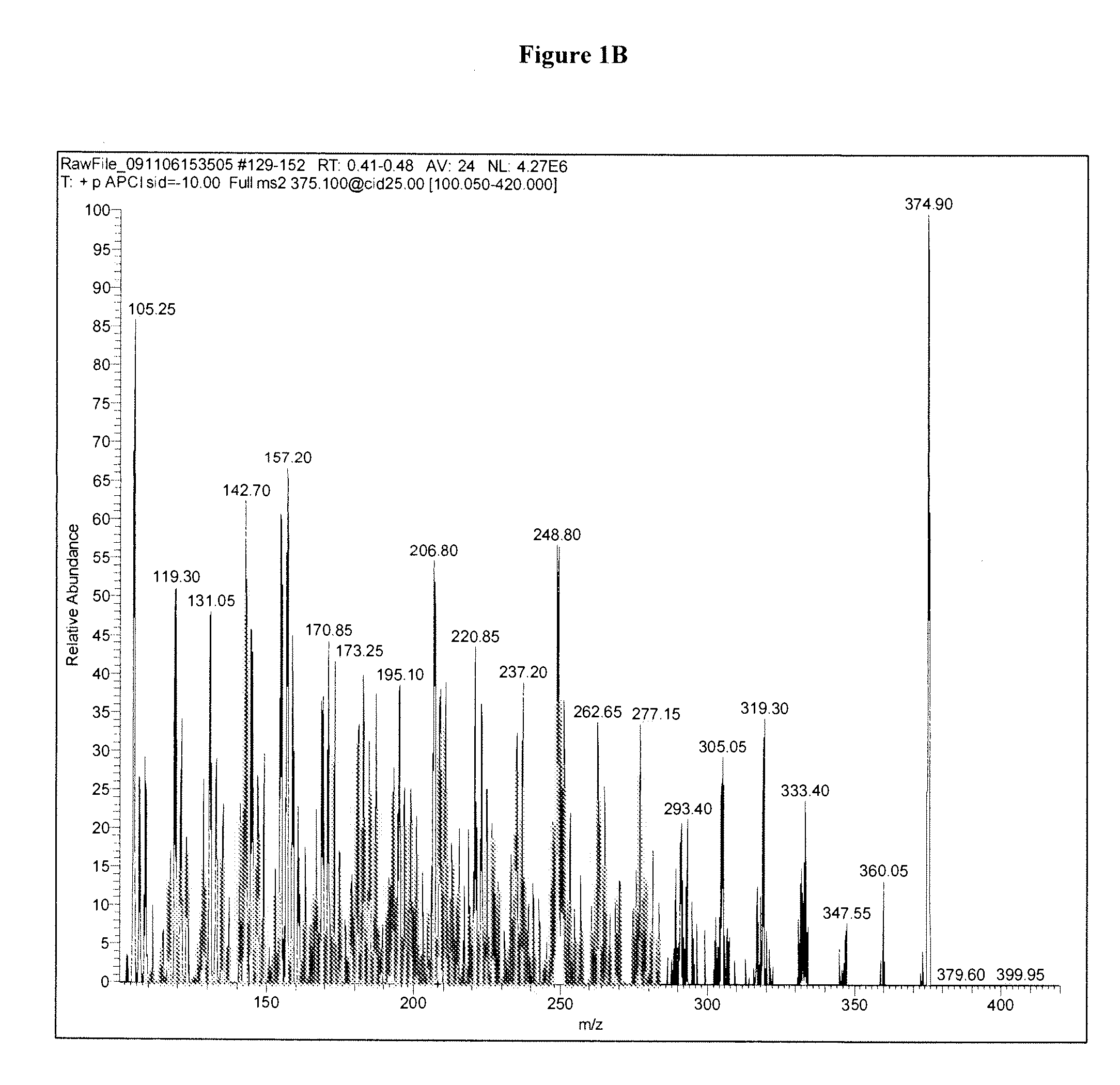
Patents
Literature
778 results about "Mass spectrometry imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
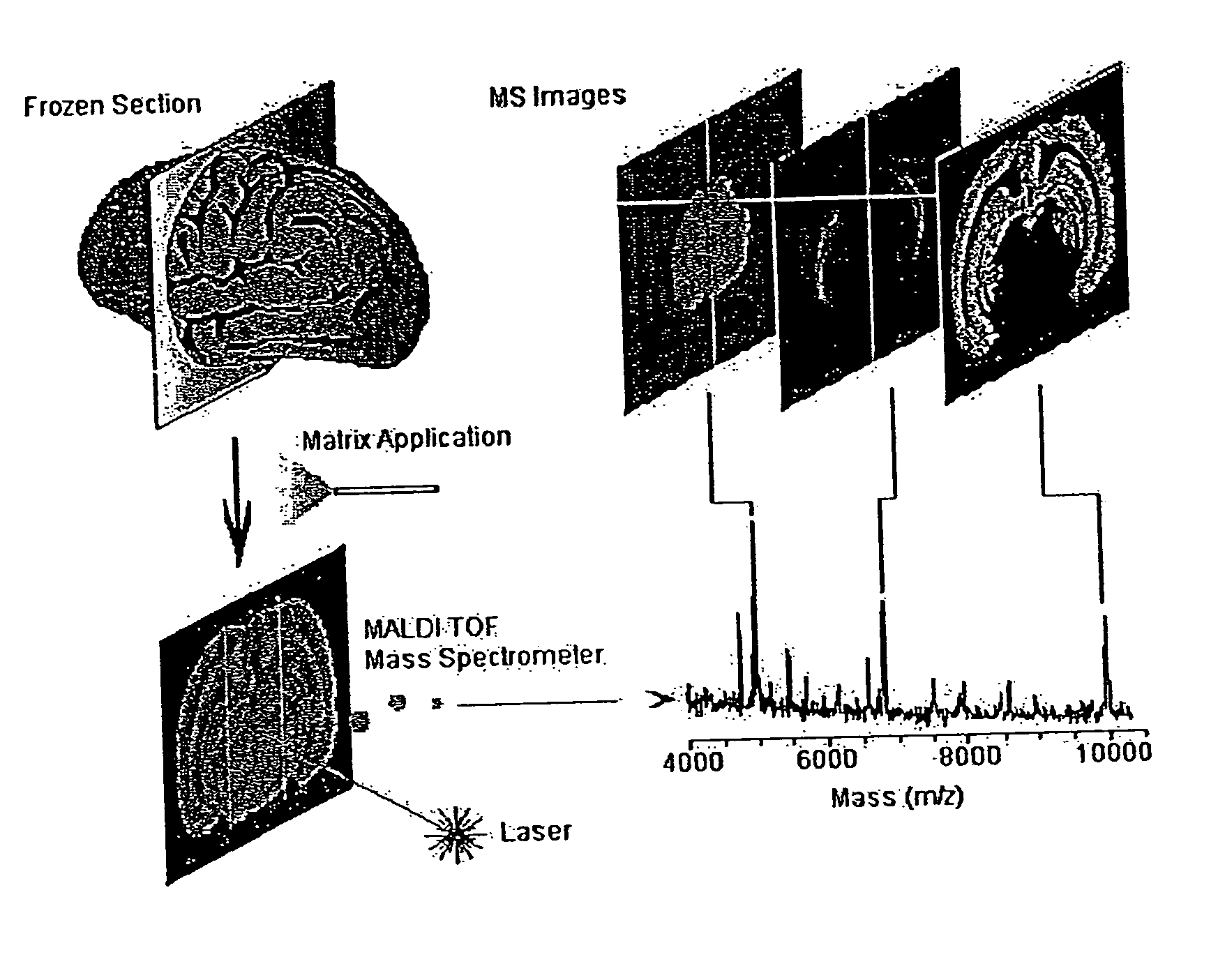
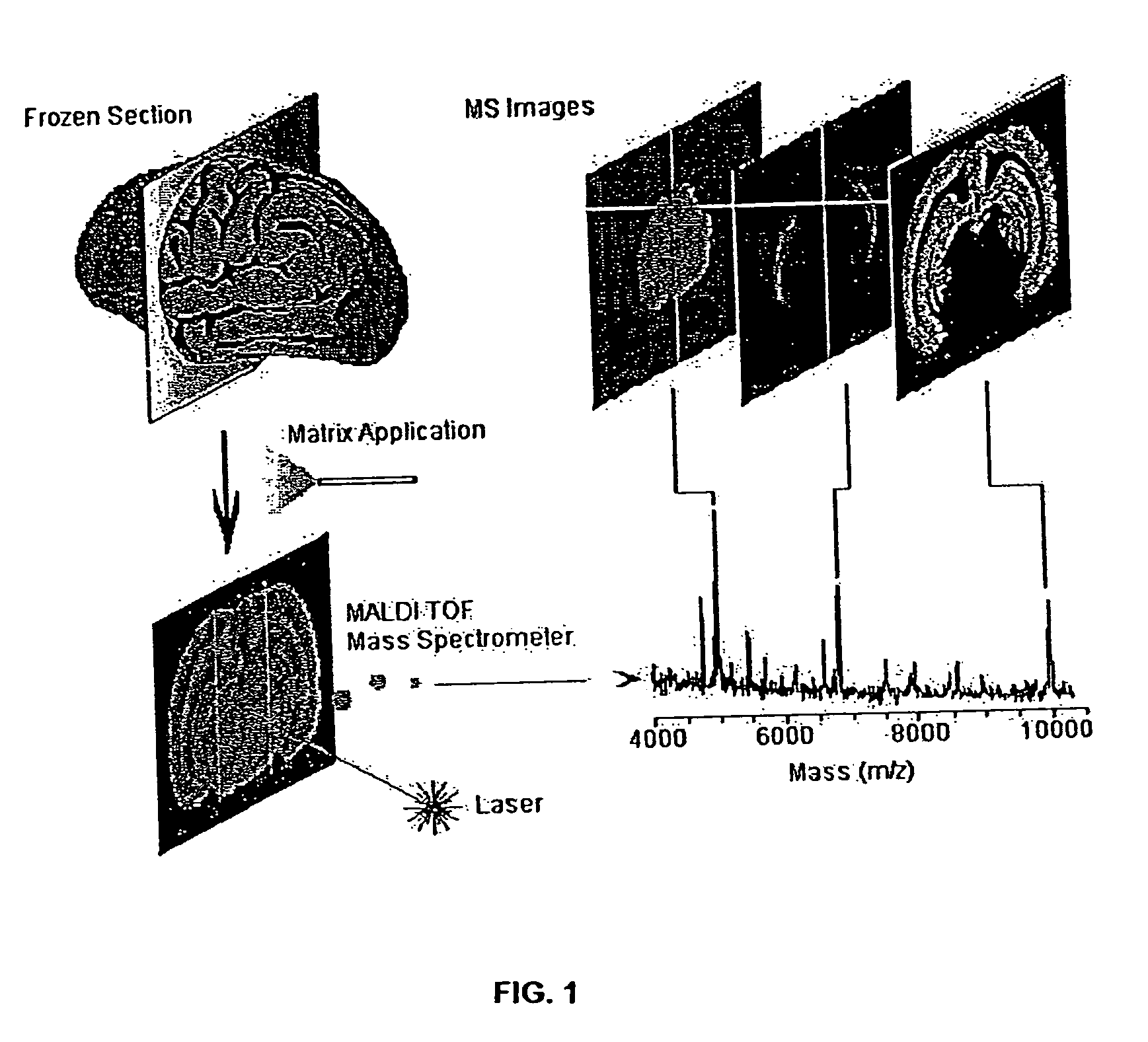
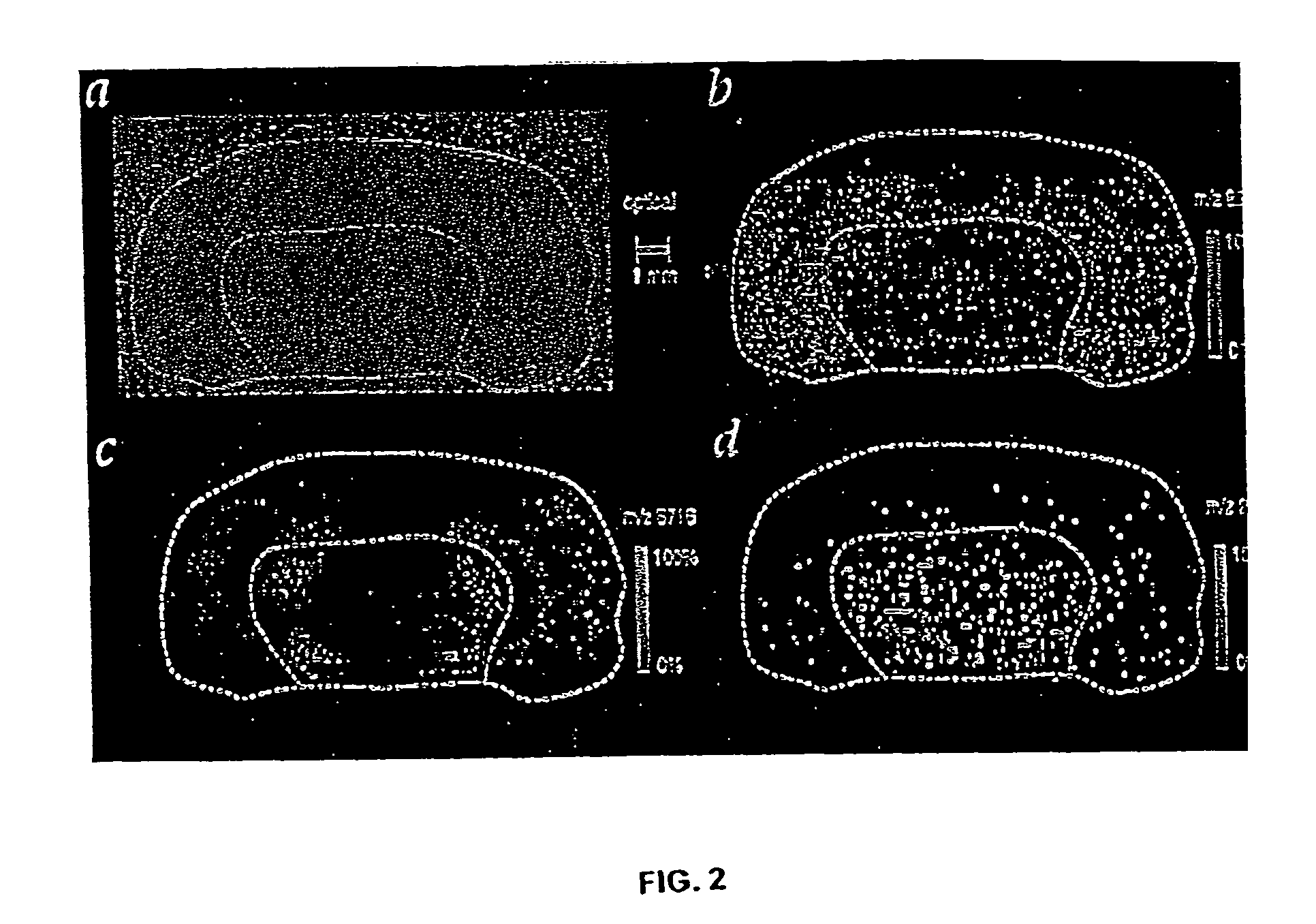
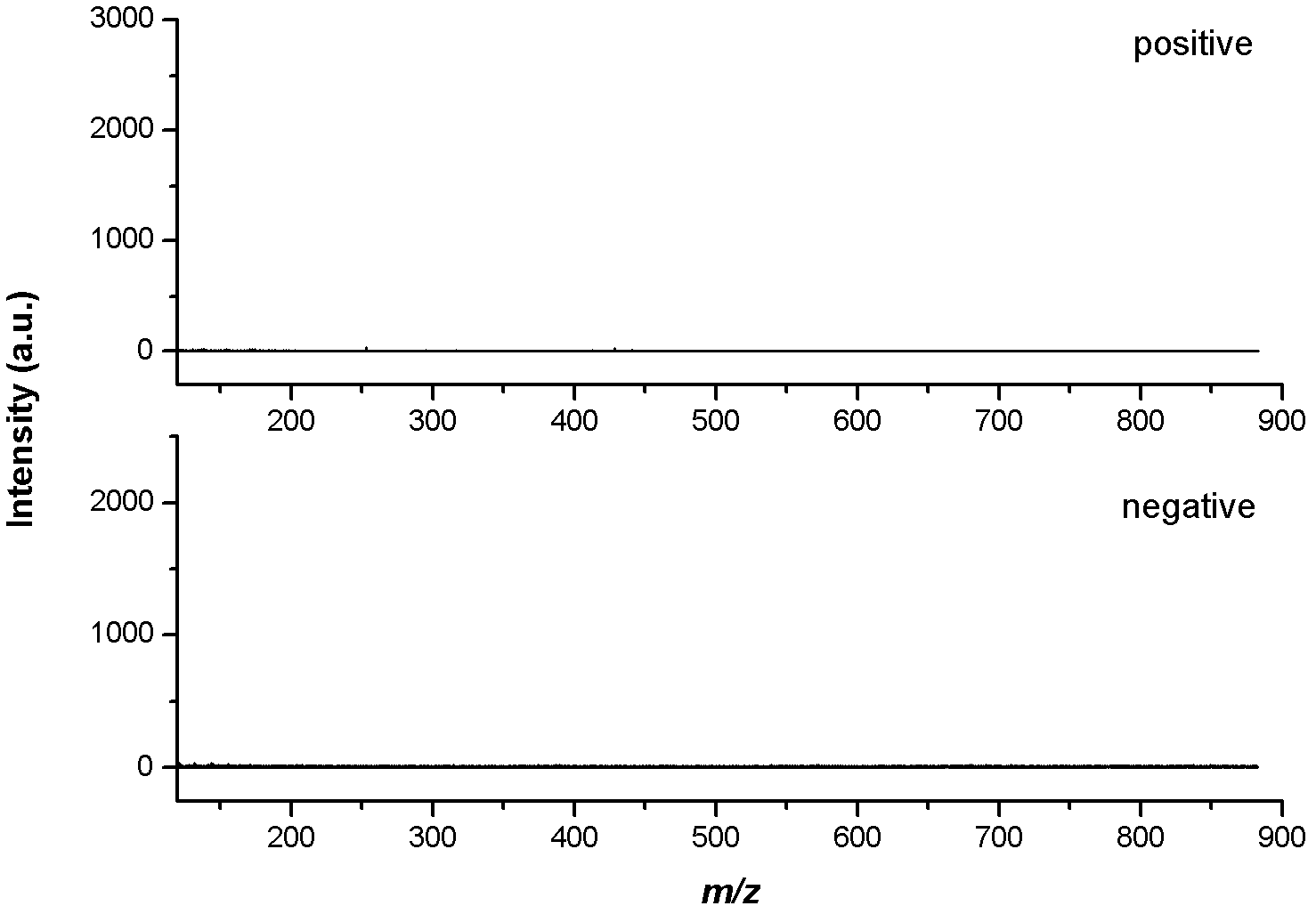
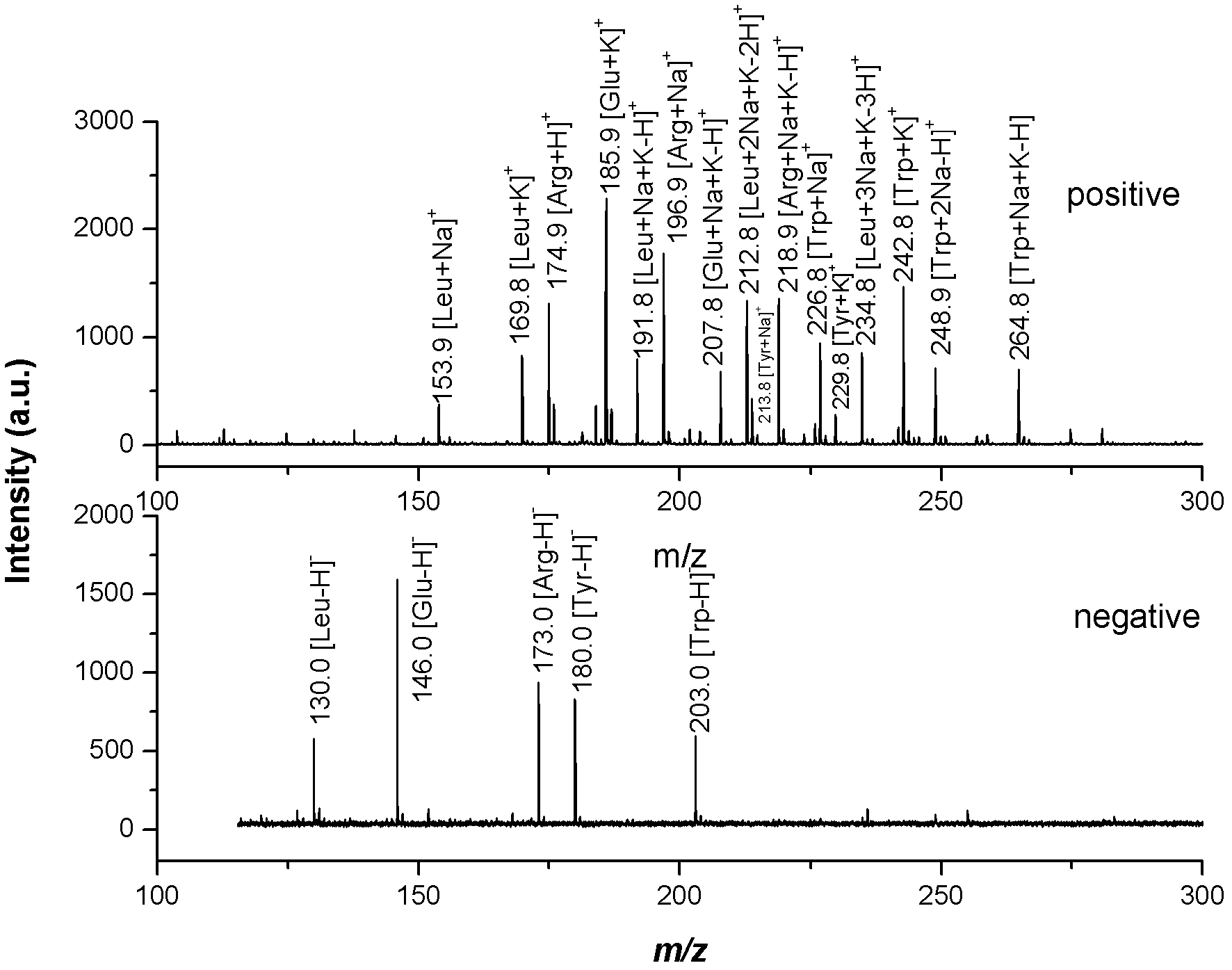
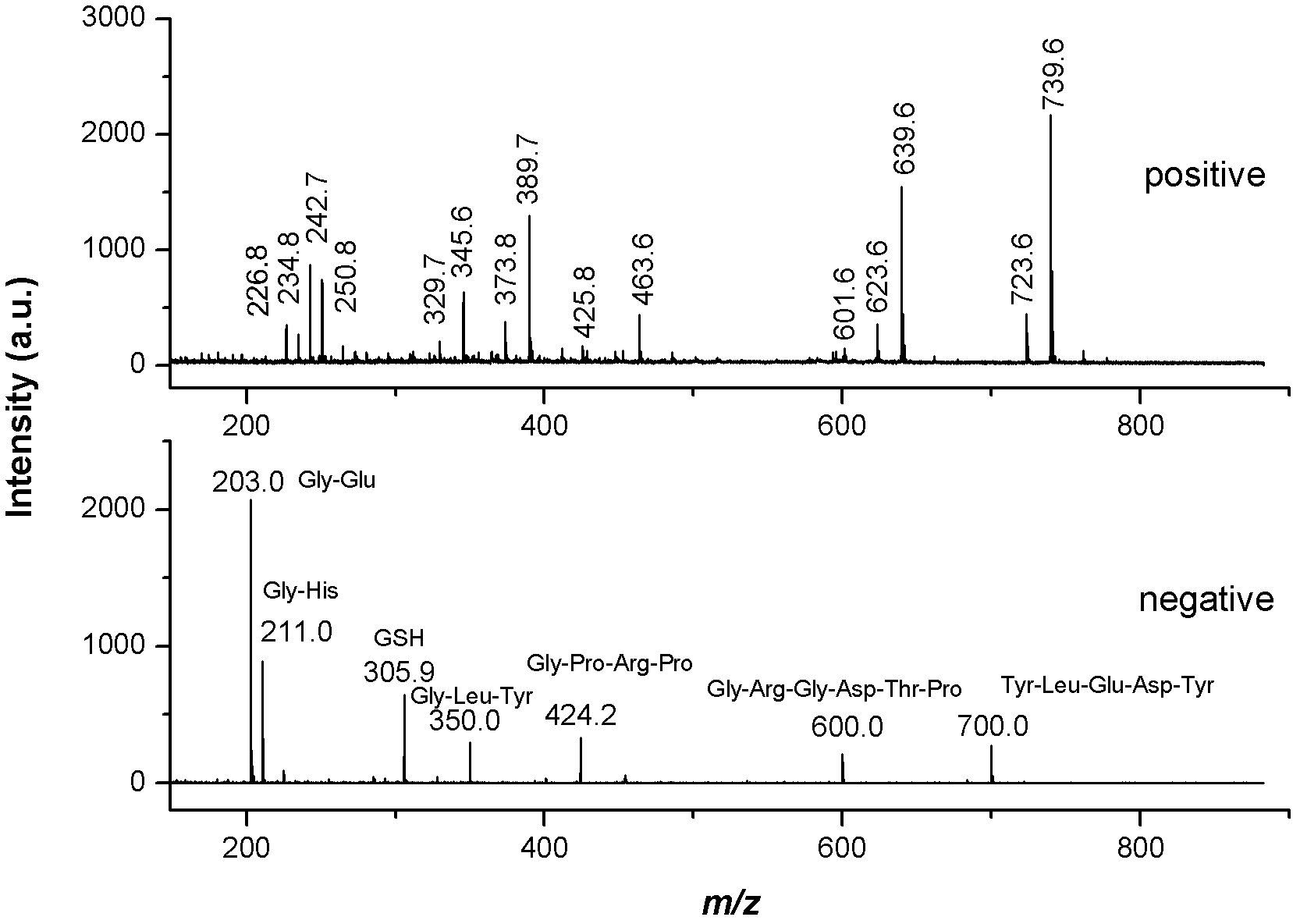
Mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) is a technique used in mass spectrometry to visualize the spatial distribution of molecules, as biomarkers, metabolites, peptides or proteins by their molecular masses. After collecting a mass spectrum at one spot, the sample is moved to reach another region, and so on, until the entire sample is scanned. By choosing a peak in the resulting spectra that corresponds to the compound of interest, the MS data is used to map its distribution across the sample. This results in pictures of the spatially resolved distribution of a compound pixel by pixel. Each data set contains a veritable gallery of pictures because any peak in each spectrum can be spatially mapped. Despite the fact that MSI has been generally considered a qualitative method, the signal generated by this technique is proportional to the relative abundance of the analyte. Therefore, quantification is possible, when its challenges are overcome. Although widely used traditional methodologies like radiochemistry and immunohistochemistry achieve the same goal as MSI, they are limited in their abilities to analyze multiple samples at once, and can prove to be lacking if researchers do not have prior knowledge of the samples being studied. Most common ionization technologies in the field of MSI are DESI imaging, MALDI imaging and secondary ion mass spectrometry imaging (SIMS imaging).
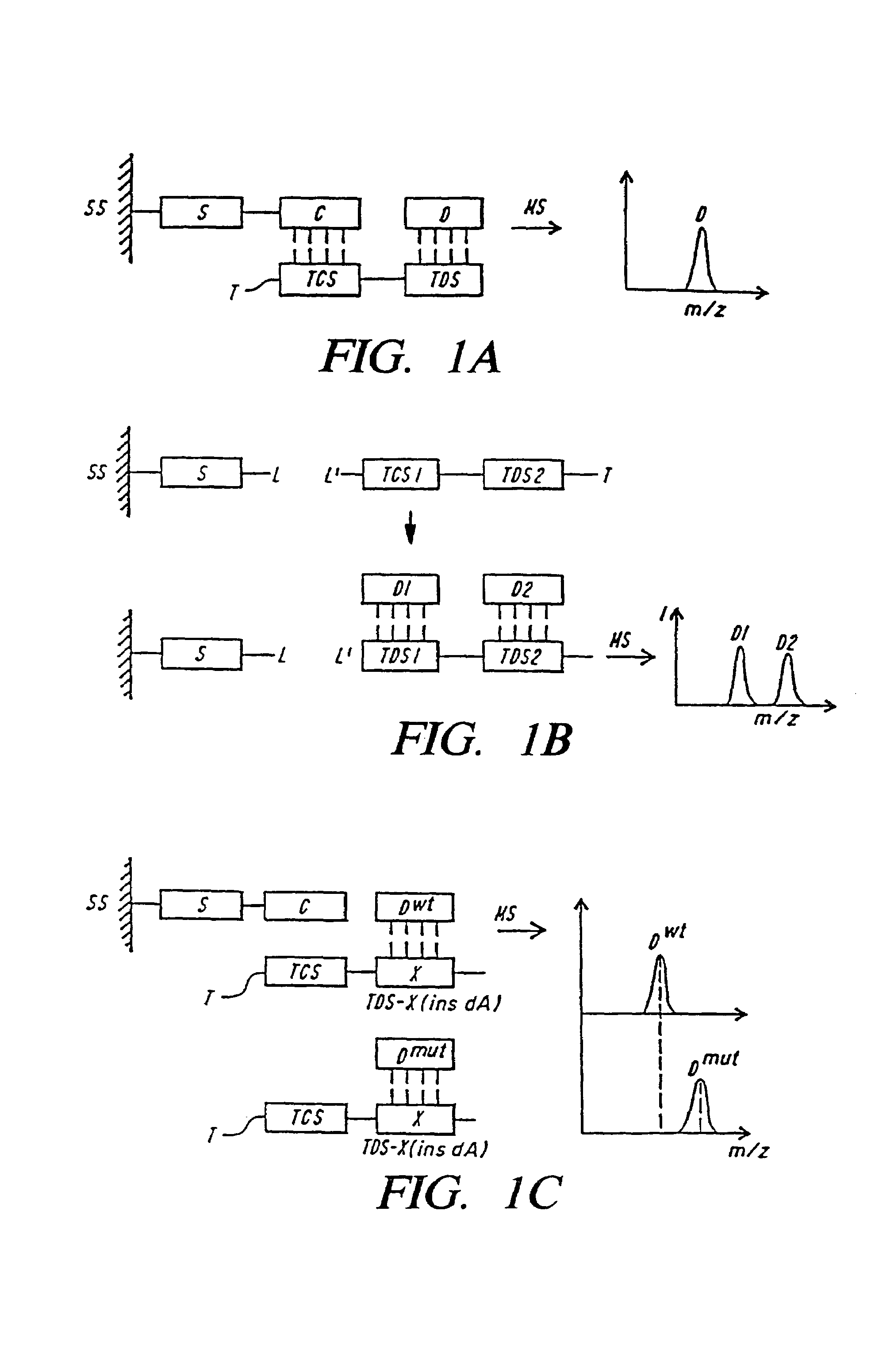
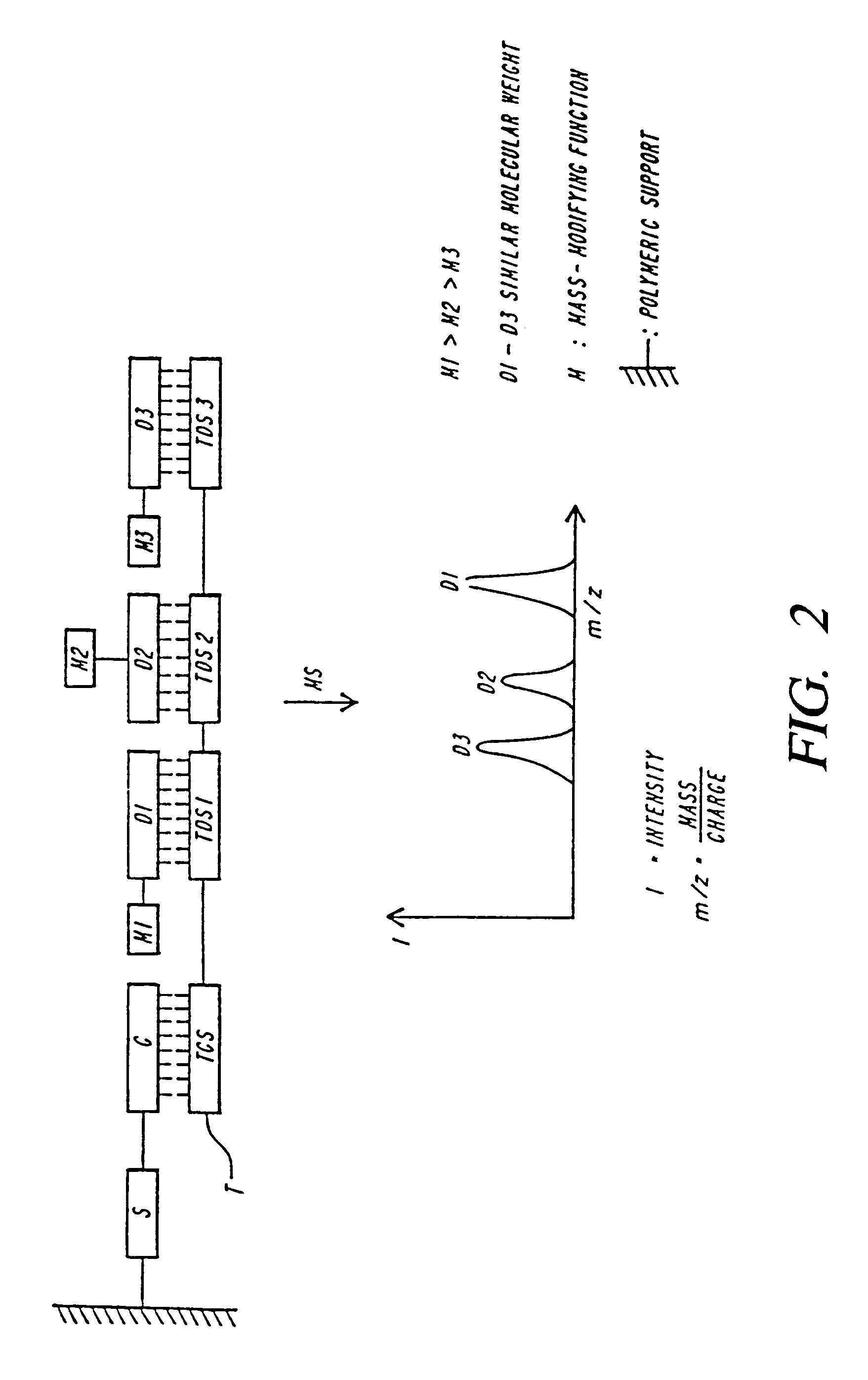
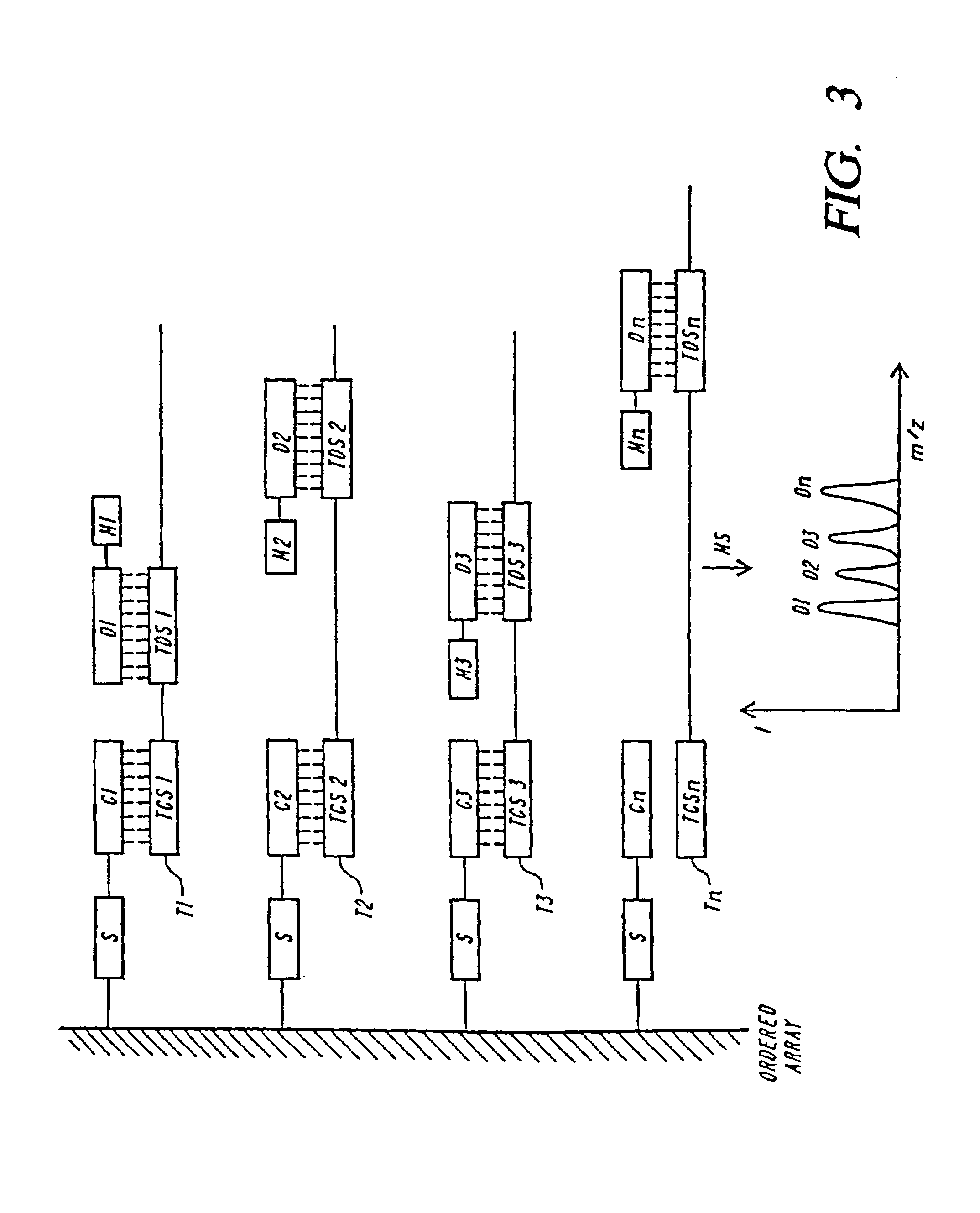
DNA diagnostics based on mass spectrometry
InactiveUS7198893B1Increase mass resolution massIncrease mass mass accuracyPeptide librariesSequential/parallel process reactionsMass spectrometry imagingOrganism
Fast and highly accurate mass spectrometry-based processes for detecting a particular nucleic acid sequence in a biological sample are provided. Depending on the sequence to be detected, the processes can be used, for example, to diagnose a genetic disease or chromosomal abnormality; a predisposition to a disease or condition, infection by a pathogenic organism, or for determining identity or heredity.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
Laser ablation flowing atmospheric-pressure afterglow for ambient mass spectrometry
ActiveUS20090272893A1Time-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMass analyzer
Disclosed is an apparatus for performing mass spectrometry and a method of analyzing a sample through mass spectrometry. In particular, the disclosure relates to an apparatus capable of ambient mass spectrometry and mass spectral imaging and a method for the same. The apparatus couples laser ablation, flowing atmospheric-pressure afterglow ionization, and a mass spectrometer.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
High sensitivity quantitation of peptides by mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20040072251A1Loss of substantial specific binding capacityReduce complexitySamplingComponent separationChemical structureProtein target
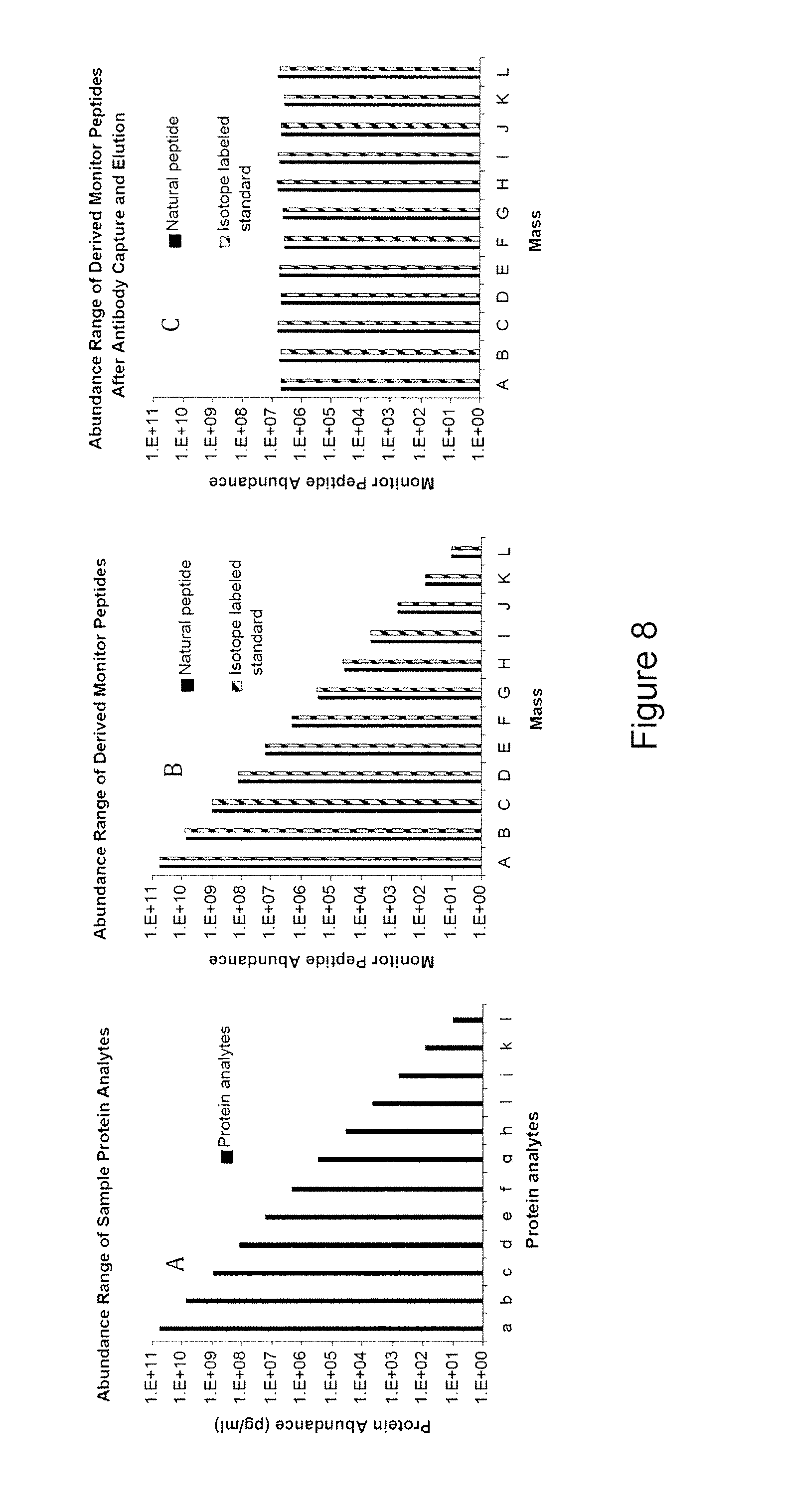
The instant invention provides an economical flow-through method for determining amount of target proteins in a sample. An antibody preparation (whether polyclonal or monoclonal, or any equivalent specific binding agent) is used to capture and thus enrich a specific monitor peptide (a specific peptide fragment of a protein to be quantitated in a proteolytic digest of a complex protein sample) and an internal standard peptide (the same chemical structure but including stable isotope labels). Upon elution into a suitable mass spectrometer, the natural (sample derived) and internal standard (isotope labeled) peptides are quantitated, and their measured abundance ratio used to calculate the abundance of the monitor peptide, and its parent protein, in the initial sample
Owner:ANDERSON FORSCHUNG GROUP
Mass spectrometry of antibody conjugates
ActiveUS20050232929A1High resolutionAvoid interferenceHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsMetaboliteAntibody conjugate
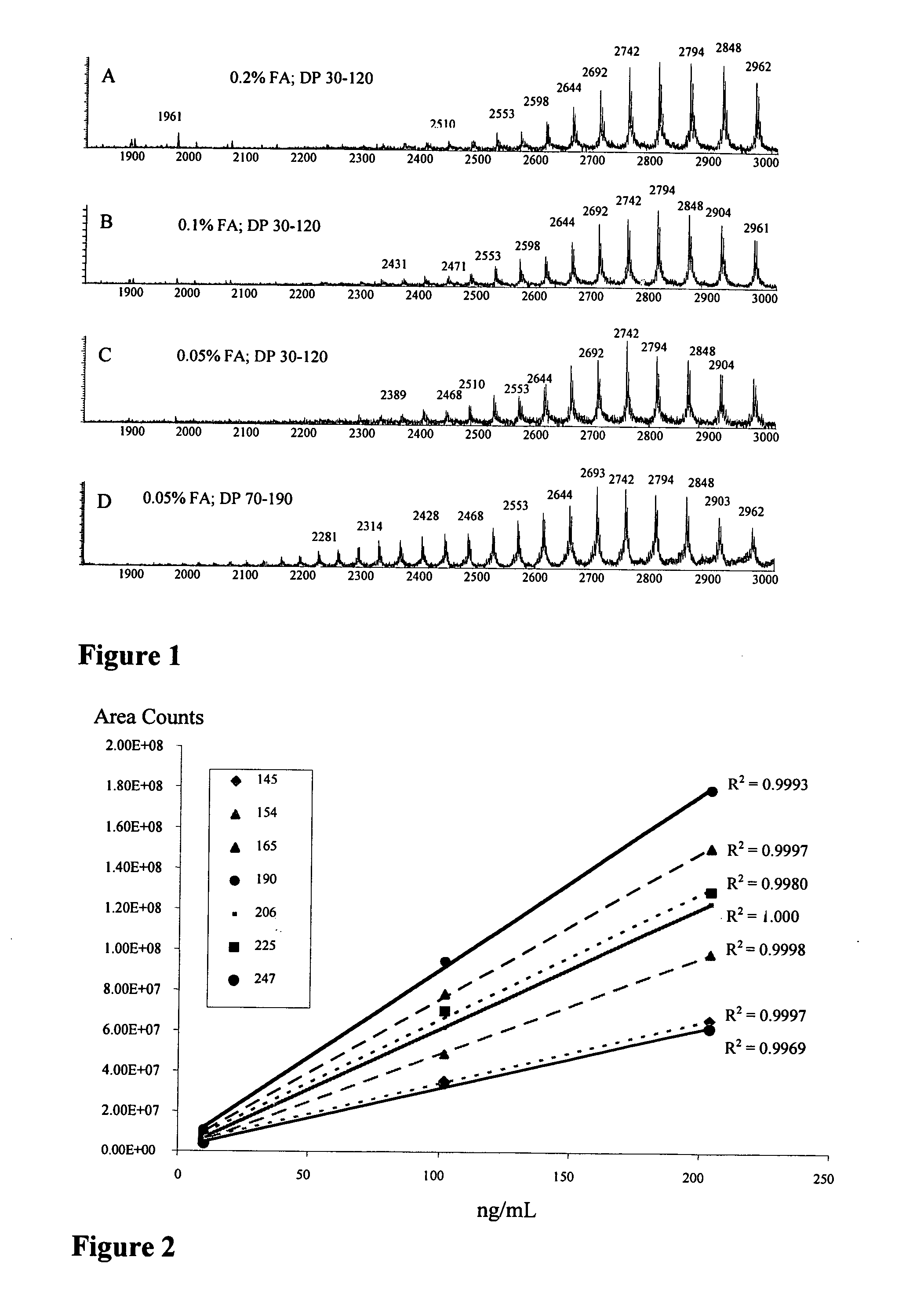
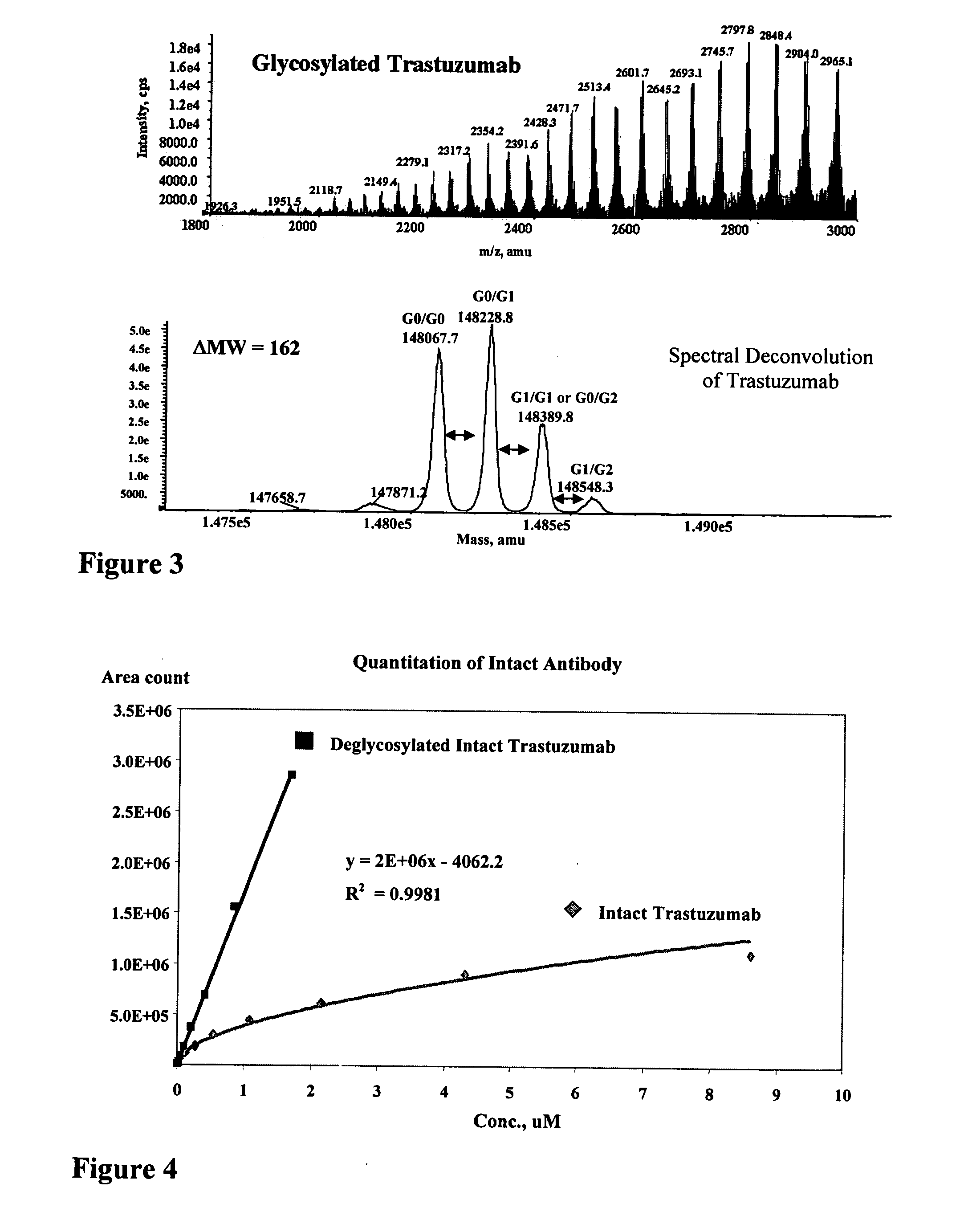
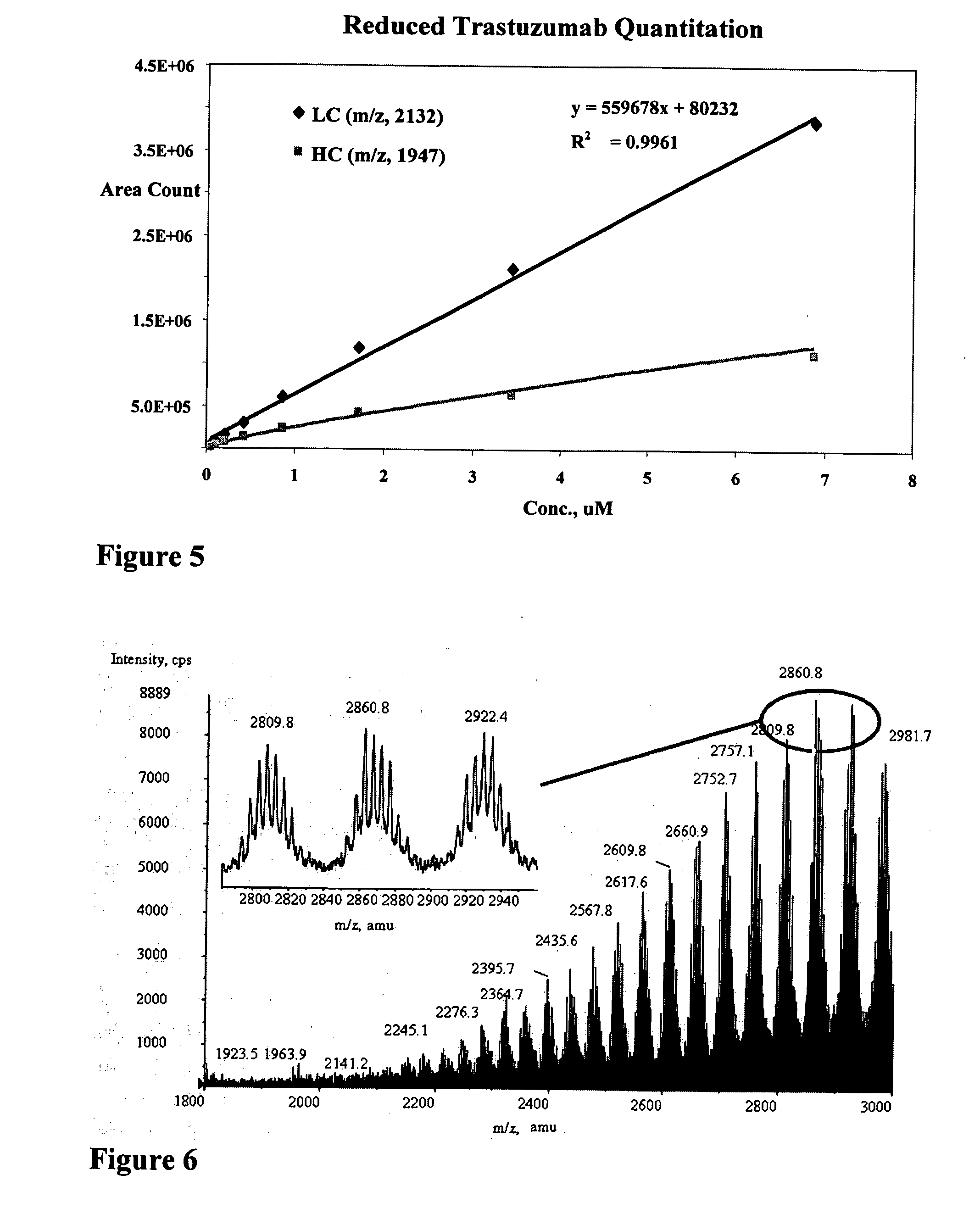
Methods to detect, screen, and quantitate biological samples after administration of antibody conjugates, antibody-drug conjugates of Formula I, antibodies, and fragments and metabolites thereof, by affinity separation, chromatography, and mass spectrometry are disclosed. Ab-(L-D)p I wherein Ab is an antibody; D is a drug moiety; L is a linker covalently attached to Ab, and covalently attached to D; and p is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, or 8;
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Method for separation, characterization and/or identification of microorganisms using mass spectrometry
ActiveUS20100120085A1Rapid diagnosisRapid characterizationParticle separator tubesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismLysis
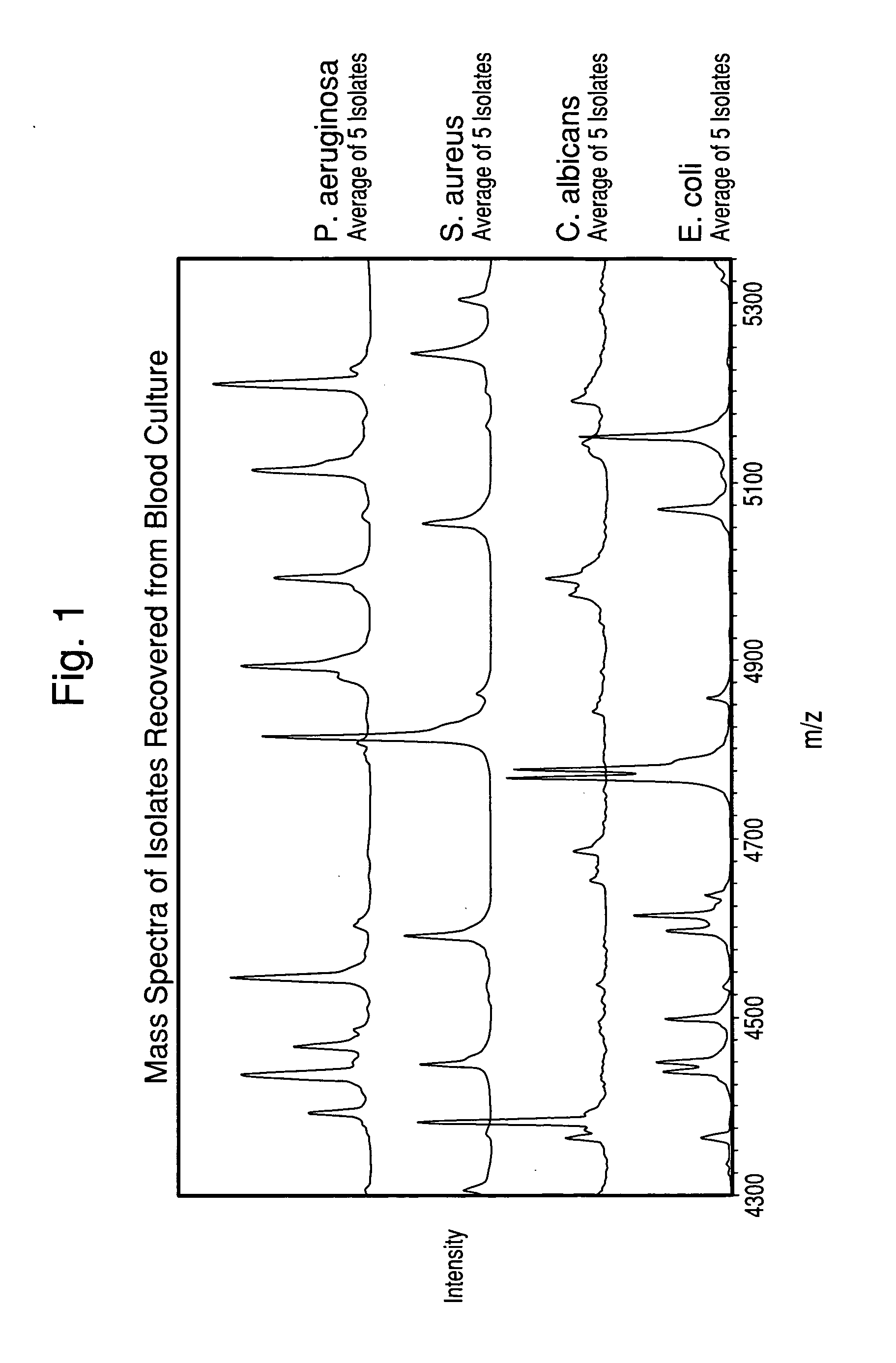
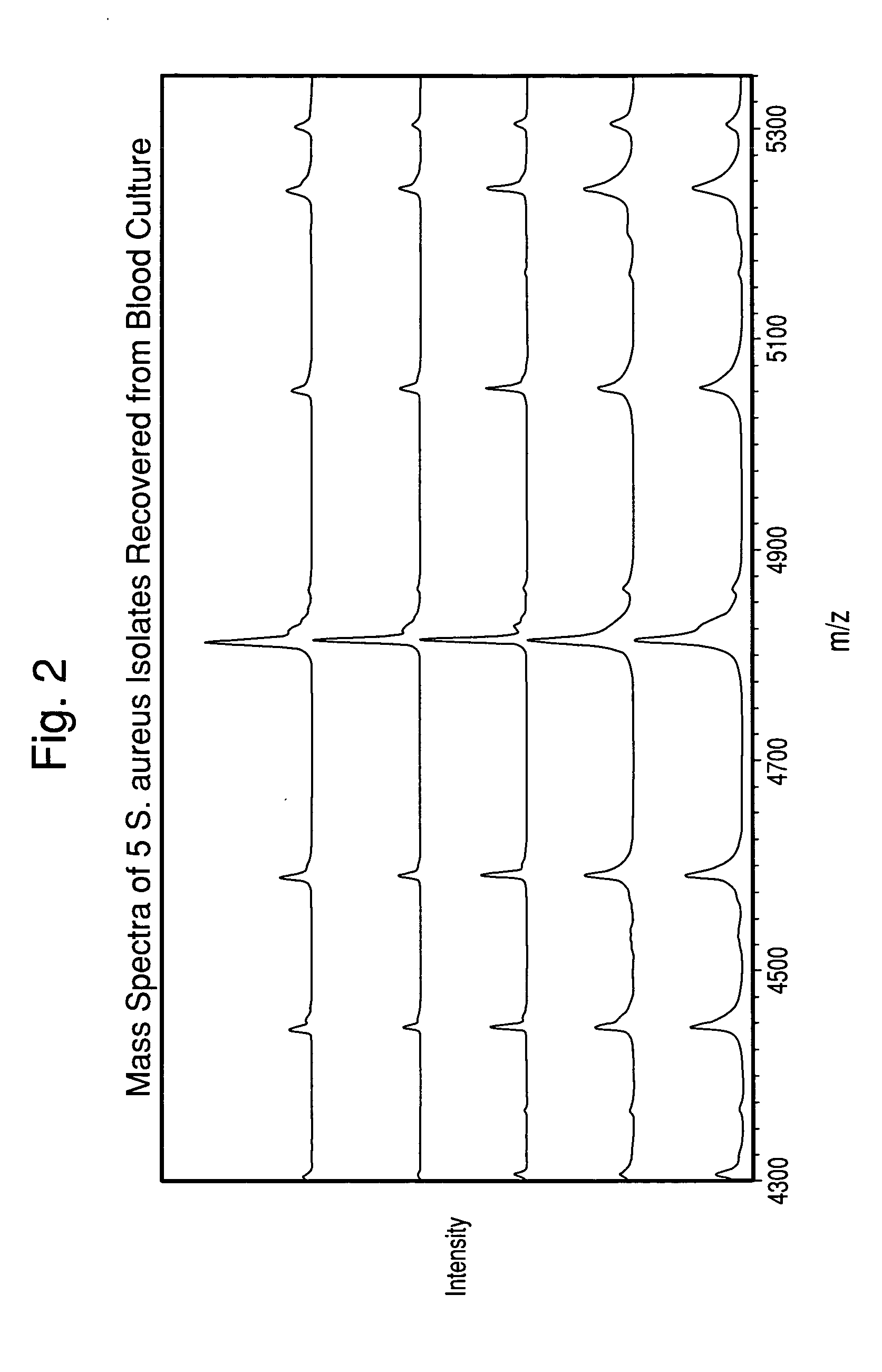
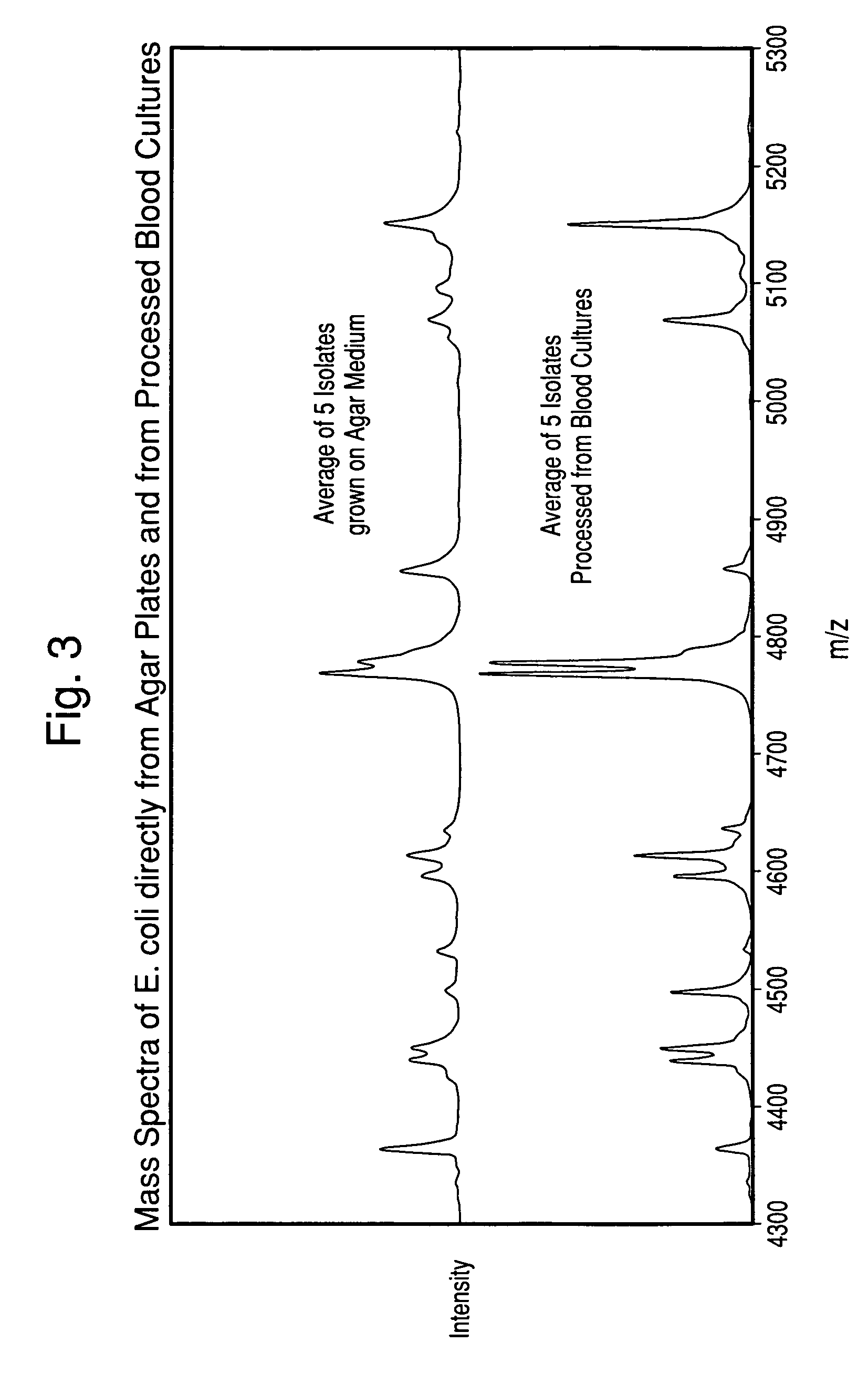
The present invention is directed to a method for separating, characterizing and / or identifying microorganisms in a test sample. The method of the invention comprises an optional lysis step for lysing non-microorganism cells that may be present in a test sample, followed by a subsequent separation step. The method may be useful for the separation, characterization and / or identification of microorganisms from complex samples such as blood-containing culture media. The invention further provides for interrogation of the separated microorganism sample by mass spectrometry to produce a mass spectrum of the microorganism and characterizing and / or identifying the microorganism in the sample using the mass spectrum obtained.
Owner:BIOMERIEUX INC
Fragmentation methods for mass spectrometry
InactiveUS6919562B1Shorten speedMinimizing velocityIsotope separationMass spectrometersMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMass analyzer
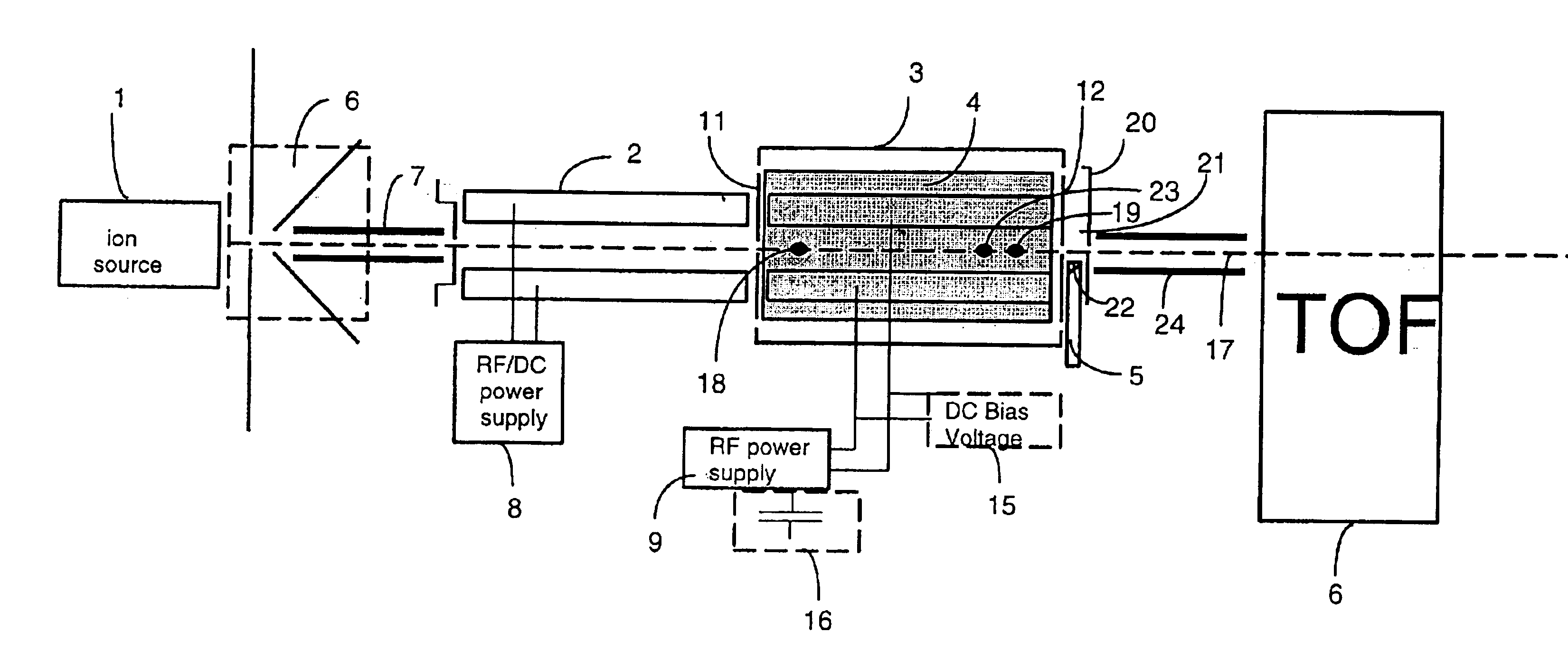
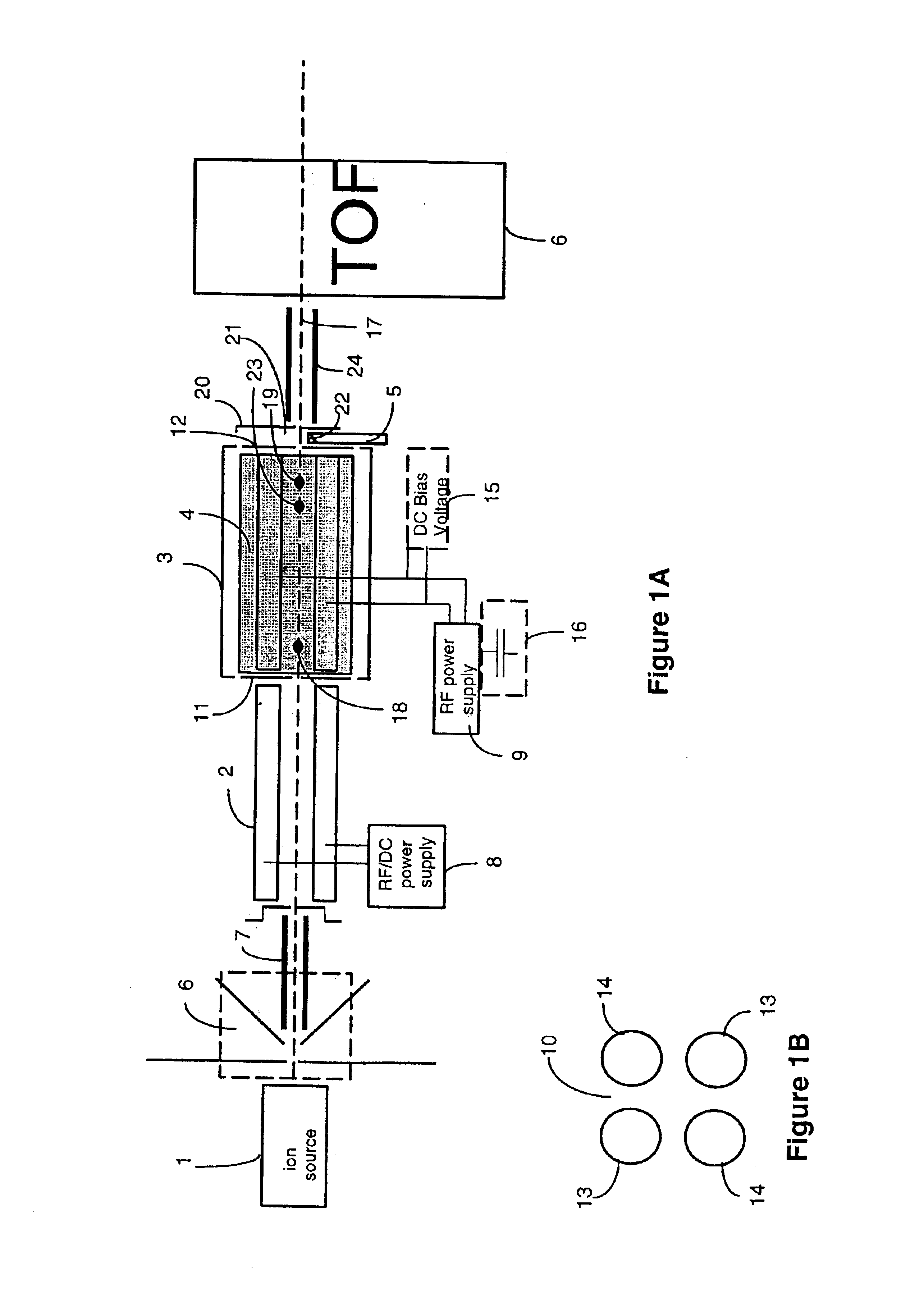
Apparatus and methods are provided that enable the interaction of low-energy electrons and positrons with sample ions to facilitate electron capture dissociation (ECD) and positron capture dissociation (PCD), respectively, within multipole ion guide structures. It has recently been discovered that fragmentation of protonated ions of many biomolecules via ECD often proceeds along fragmentation pathways not accessed by other dissociation methods, leading to molecular structure information not otherwise easily obtainable. However, such analyses have been limited to expensive Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance (FTICR) mass spectrometers; the implementation of ECD within commonly-used multipole ion guide structures is problematic due to the disturbing effects of RF fields within such devices. The apparatus and methods described herein successfully overcome such difficulties, and allow ECD (and PCD) to be performed within multipole ion guides, either alone, or in combination with conventional ion fragmentation methods. Therefore, improved analytical performance and functionality of mass spectrometers that utilize multipole ion guides are provided.
Owner:PERKINELMER U S LLC
Mutation analysis using mass spectrometry
InactiveUS6503710B2Rapid and economic sample preparationAccurate massSamplingSugar derivativesChemical treatmentFree form
The invention presents a method for examining genetic material (deoxyribonucleic acid, DNA) to detect the presence of pre-known mutations, especially single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), using mass spectrometry with ionization by matrix-assisted laser desorption (MALDI). The invention uses nucleoside triphosphates with modified sites for the method of primer extension in a duplicating, enzymatic reaction and at least partially removal of primers from the extension product, in combination with product neutralization by chemical treatment of the modified sites, so that the resulting DNA products can be, by using special matrix materials, preferredly ionized in an adduct-free form over other constituents in the reaction solution without any further cleaning. The method is particularly suitable for simultaneous identification of several mutations by multiplexing.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH
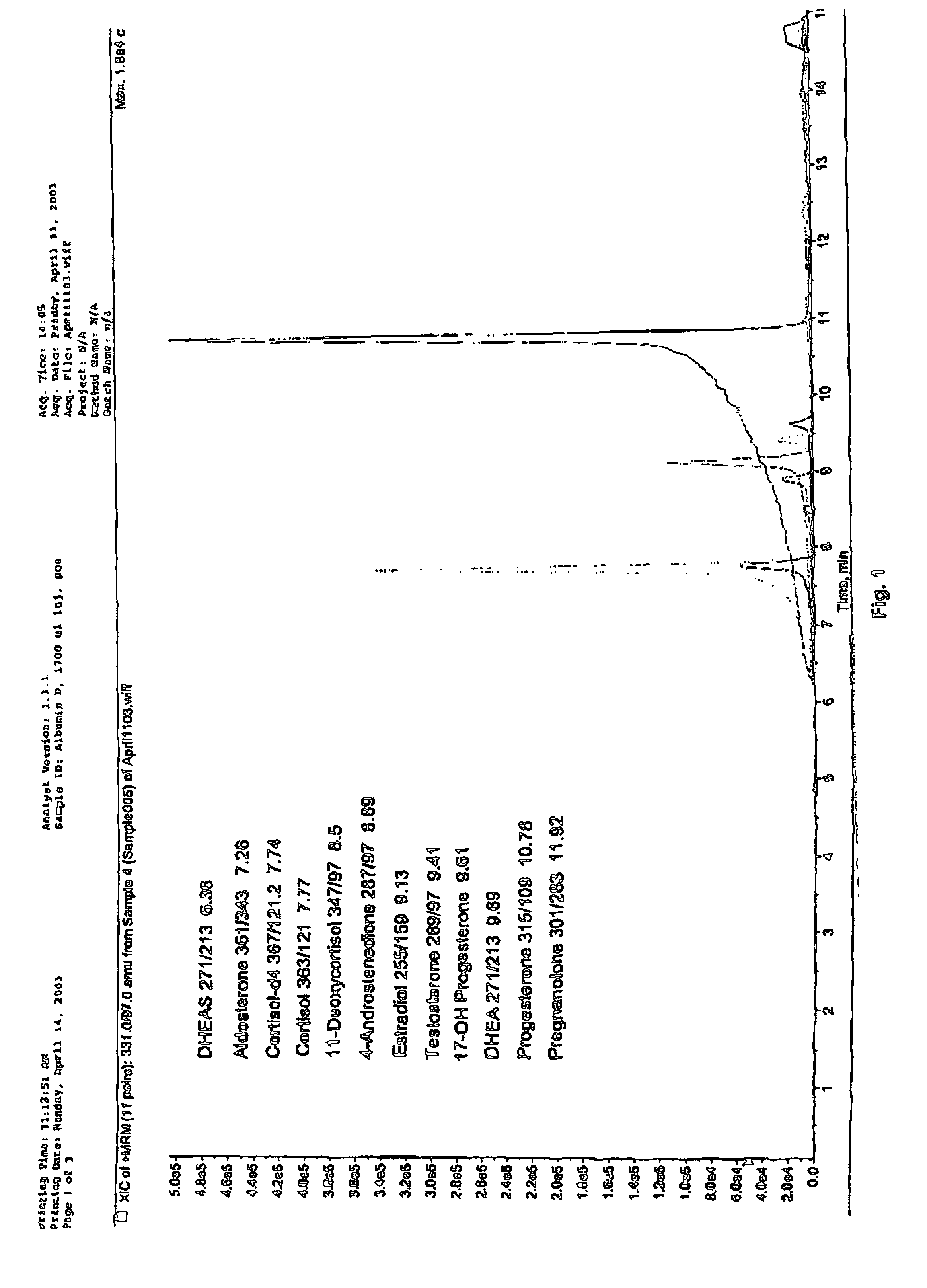
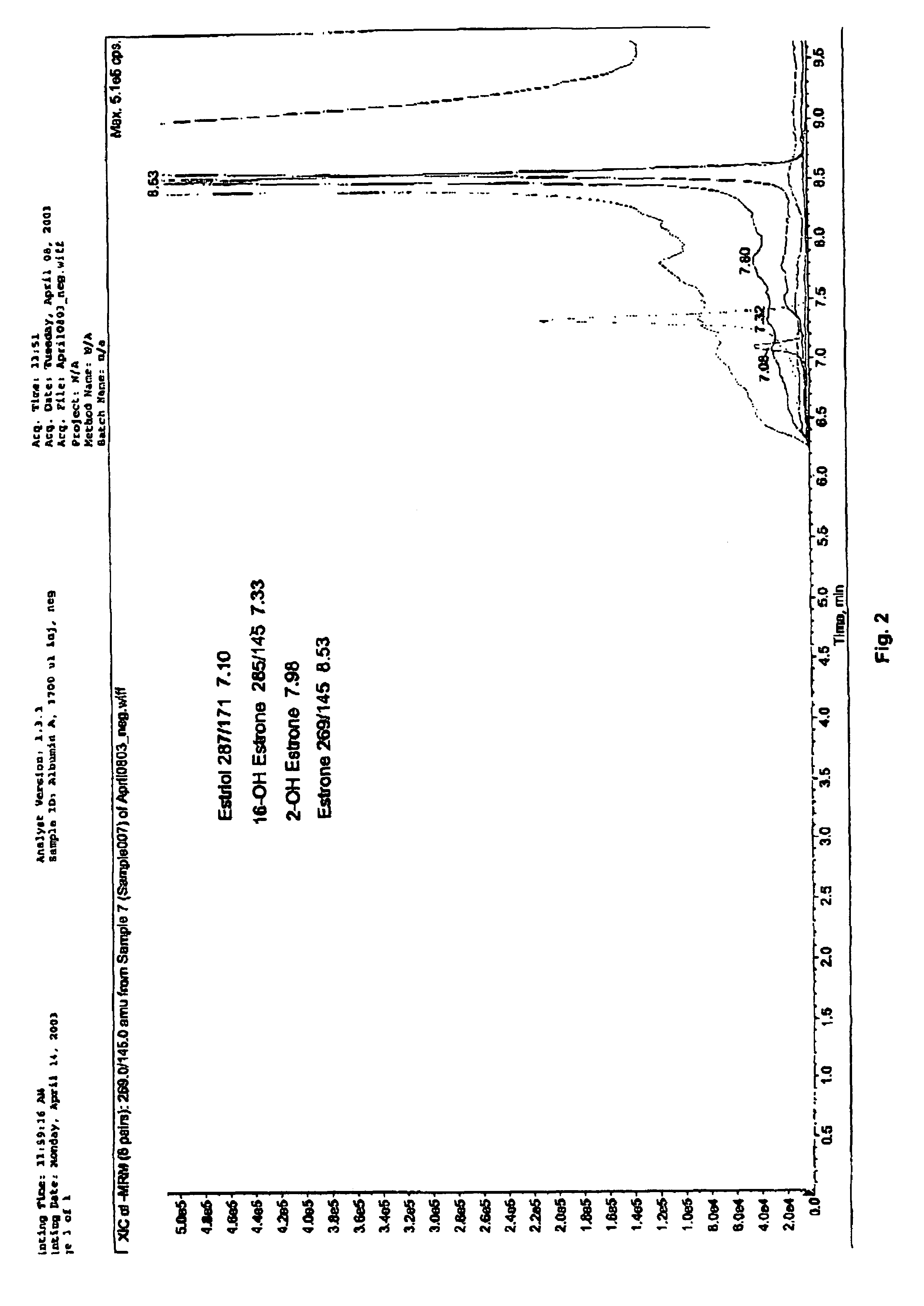
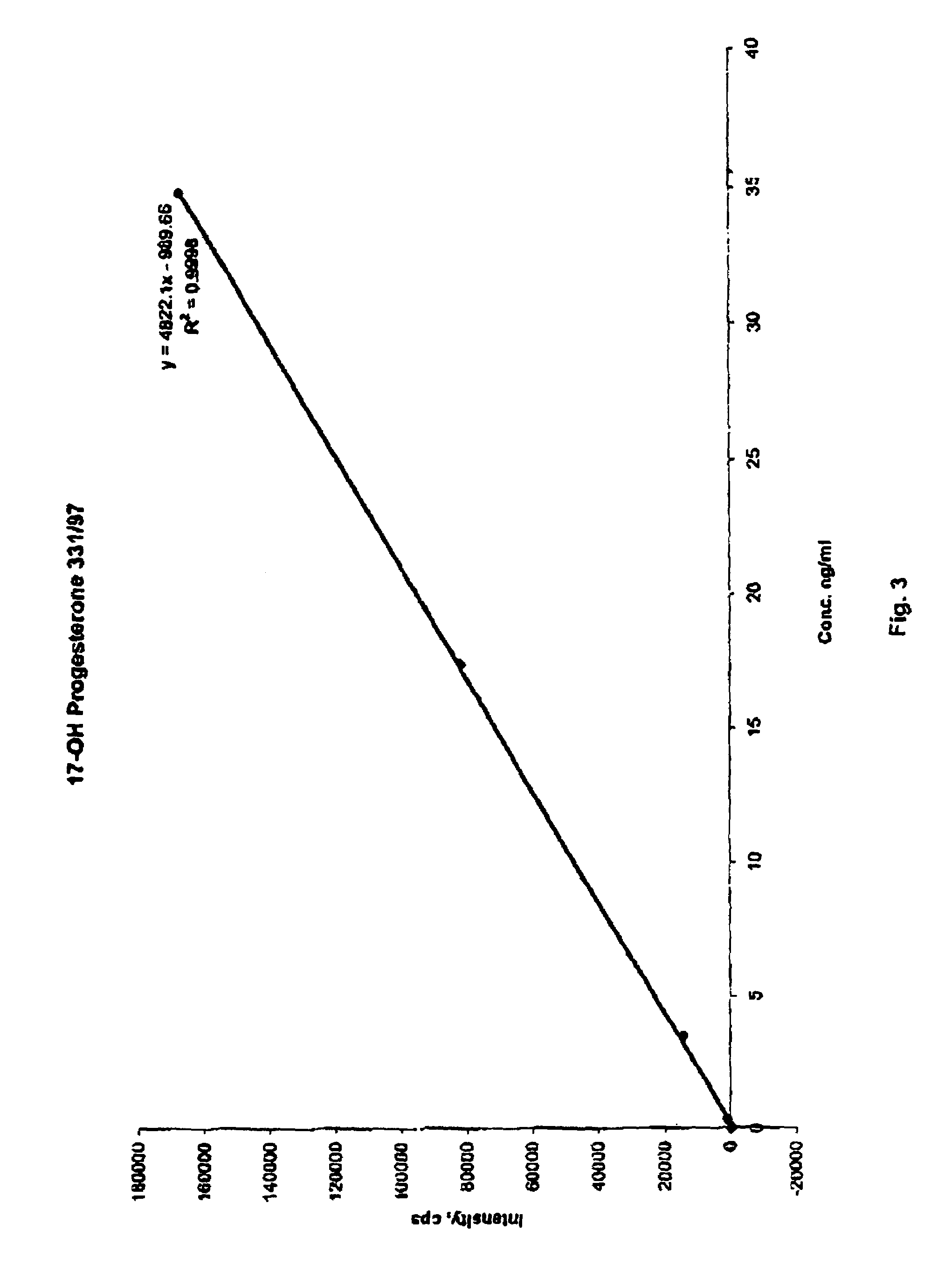
Steroid hormone analysis by mass spectrometry
ActiveUS7473560B2Fast and accurate methodFast and accurate of and quantificationParticle separator tubesComponent separationMedicineMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
Methods, systems and kits for the simultaneous or sequential analysis of a multitude of steroid hormones by mass spectrometry are disclosed. The methods require minimal sample size and minimal preparation time. The methods include ionizing the hormones and analyzing the hormones by mass spectrometry. In addition, methods, systems and kits for the simultaneous or sequential analysis of steroid hormones are disclosed including ionization of the steroid hormones by photoionization.
Owner:GEORGETOWN UNIV
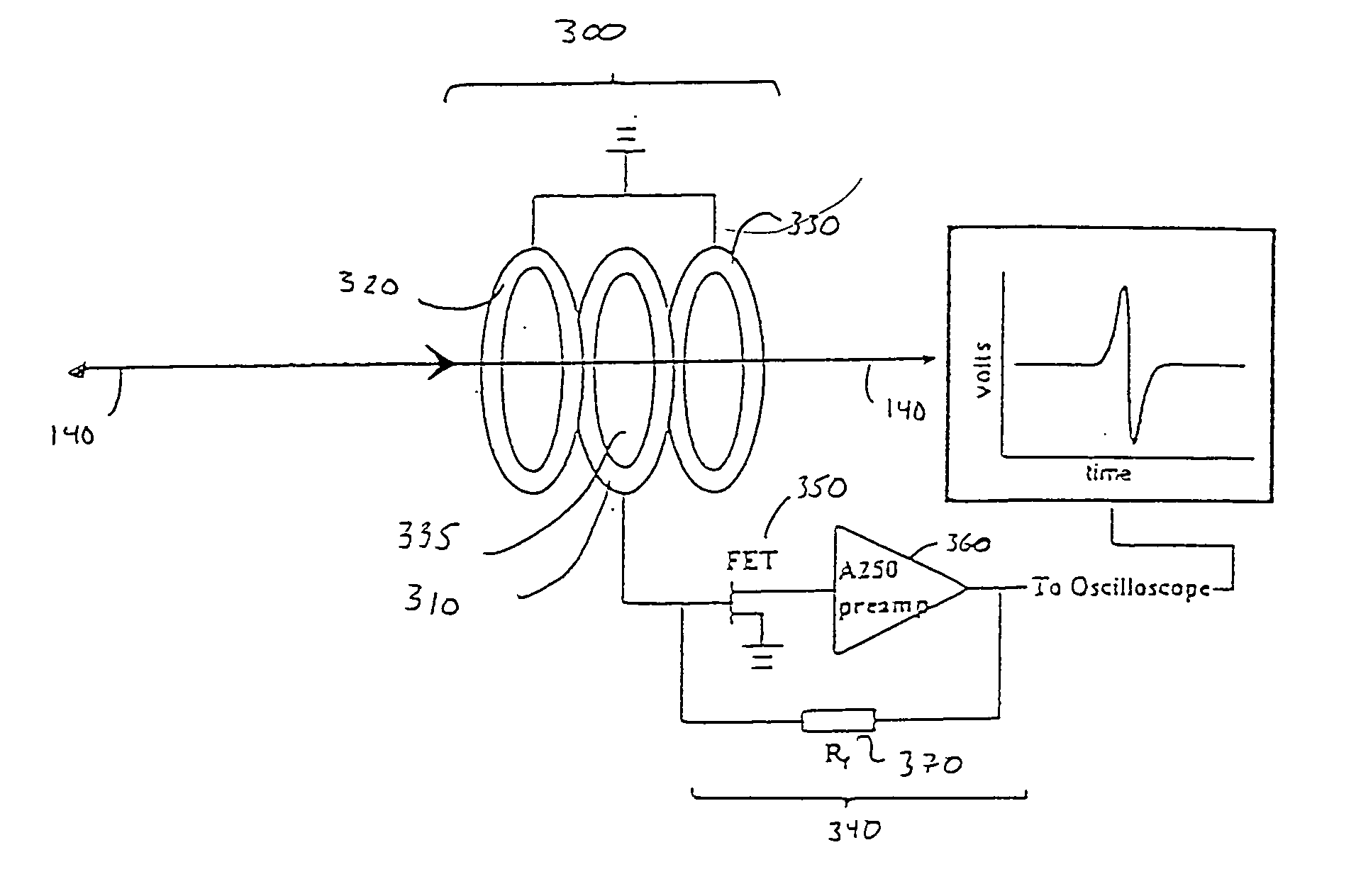
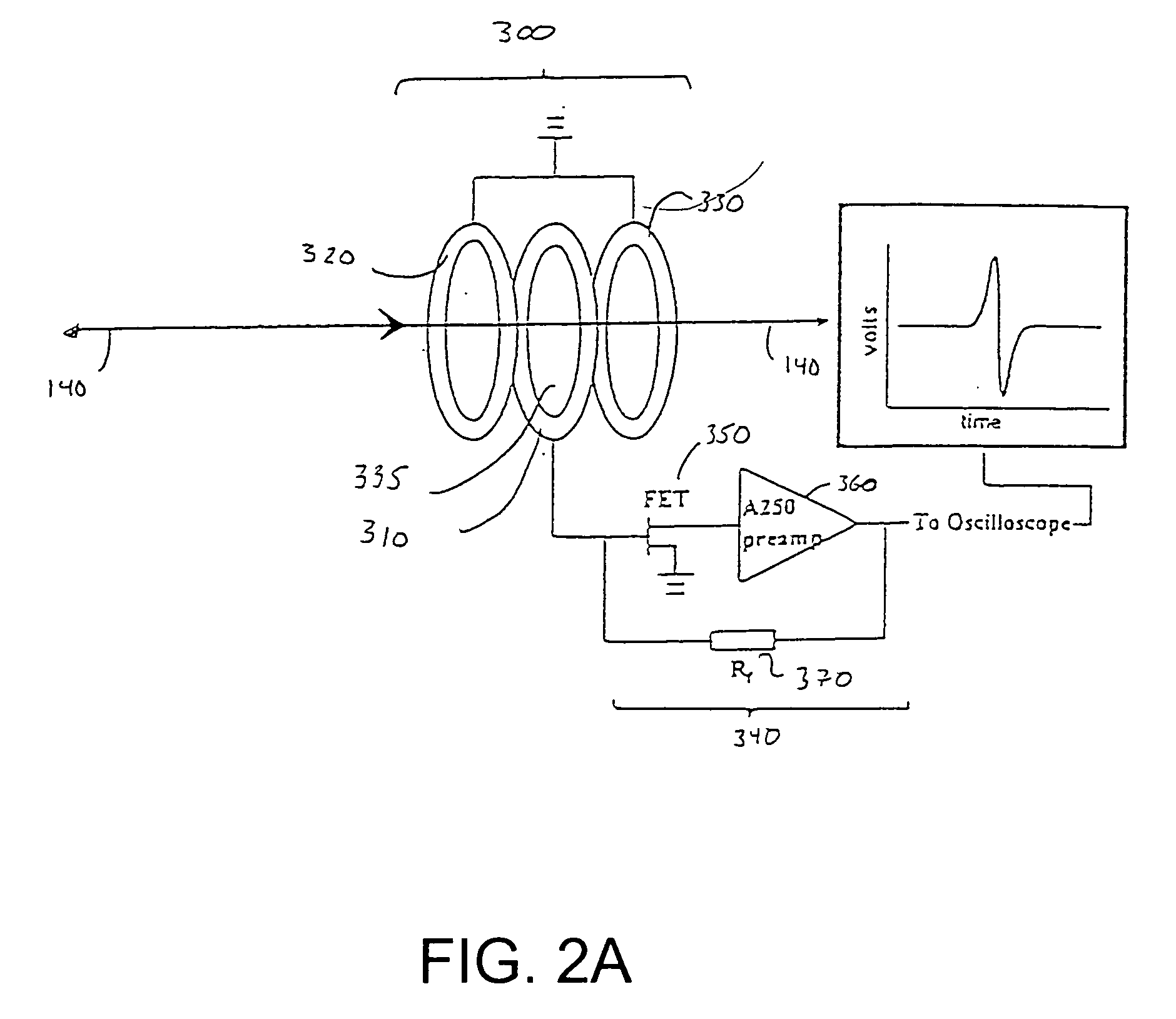
Inductive detection for mass spectrometry
ActiveUS20040169137A1Improve accuracyHigh resolutionTime-of-flight spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsGas phaseBiopolymer
The invention provides devices, device configurations and methods for improved sensitivity, resolution and efficiency in mass spectrometry, particularly as applied to biological molecules, including biological polymers, such as proteins and nucleic acids. More particularly, the invention provides methods and devices for analyzing and detecting electrically charged particles, especially suitable for gas phase ions generated from high molecular weight compounds. In one aspect, the invention provides devices and methods for determining the velocity, charged state or both of electrically charged particles and packets of electrically charged particles. In another aspect, the invention provides methods and devices for the time-of-flight analysis of electrically charged particles comprising spatially collimated sources. In another aspect, the invention relates to multiple detection using inductive detectors, improved methods of signal averaging and charged particle detection in coincidence.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
High sensitivity quantitation of peptides by mass spectrometry
InactiveUS7632686B2Reduce complexityOverwhelm resolutionSamplingComponent separationChemical structureProtein target
The instant invention provides an economical flow-through method for determining amount of target proteins in a sample. An antibody preparation (whether polyclonal or monoclonal, or any equivalent specific binding agent) is used to capture and thus enrich a specific monitor peptide (a specific peptide fragment of a protein to be quantitated in a proteolytic digest of a complex protein sample) and an internal standard peptide (the same chemical structure but including stable isotope labels). Upon elution into a suitable mass spectrometer, the natural (sample derived) and internal standard (isotope labeled) peptides are quantitated, and their measured abundance ratio used to calculate the abundance of the monitor peptide, and its parent protein, in the initial sample.
Owner:ANDERSON FORSCHUNG GROUP
Methods for operating mass spectrometry (MS) instrument systems
InactiveUS6983213B2Improve accuracyQuality improvementTesting/calibration apparatusParticle separator tubesClustered dataMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
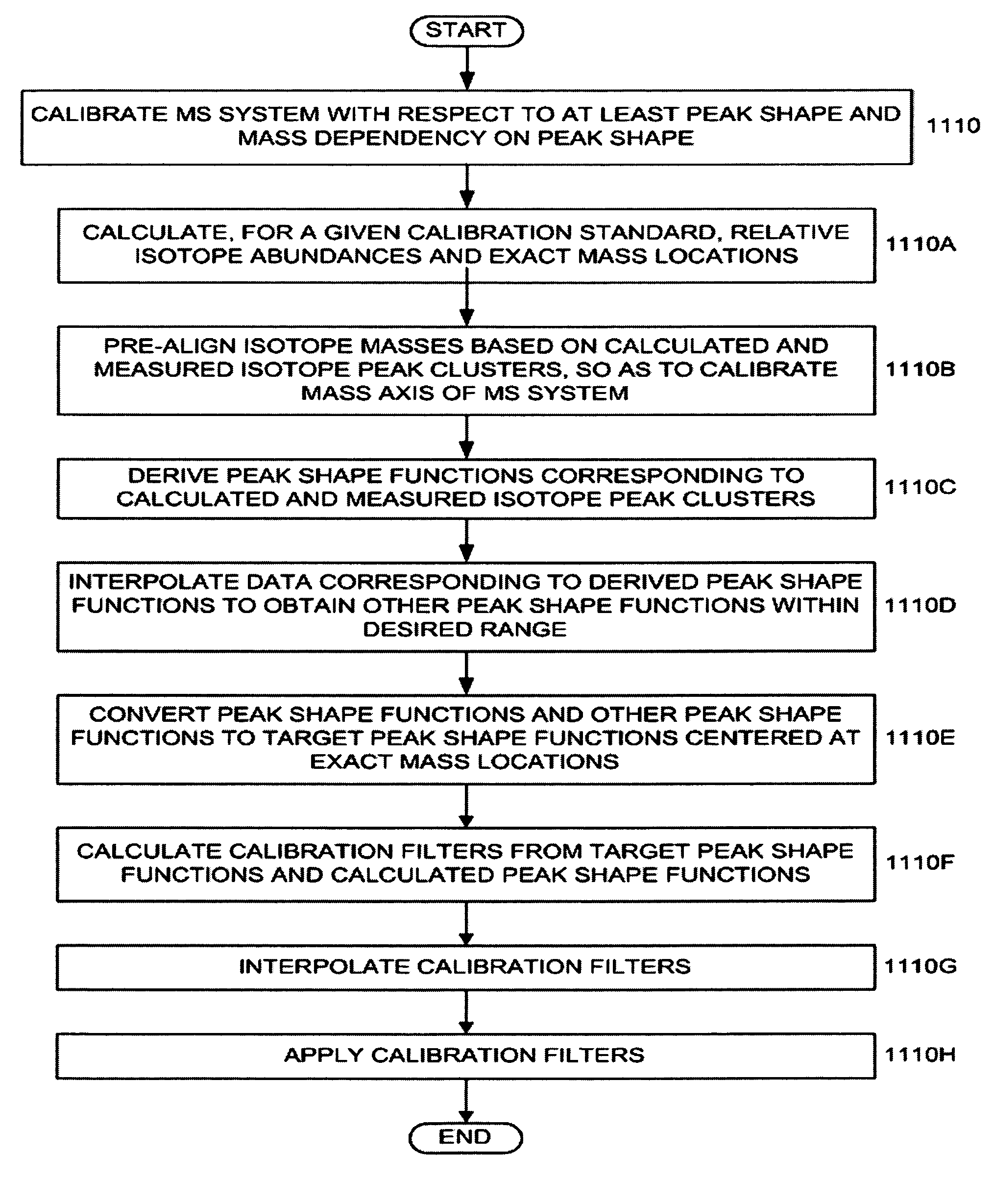
There is provided a method for obtaining at least one calibration filter for a Mass Spectrometry (MS) instrument system. Measured isotope peak cluster data in a mass spectral range is obtained for a given calibration standard. Relative isotope abundances and actual mass locations of isotopes corresponding thereto are calculated for the given calibration standard. Mass spectral target peak shape functions centered within respective mass spectral ranges are specified. Convolution operations are performed between the calculated relative isotope abundances and the mass spectral target peak shape functions to form calculated isotope peak cluster data. A deconvolution operation is performed between the measured isotope peak cluster data and the calculated isotope peak cluster data after the convolution operations to obtain the at least one calibration filter.
Owner:CERNO BIOSCI
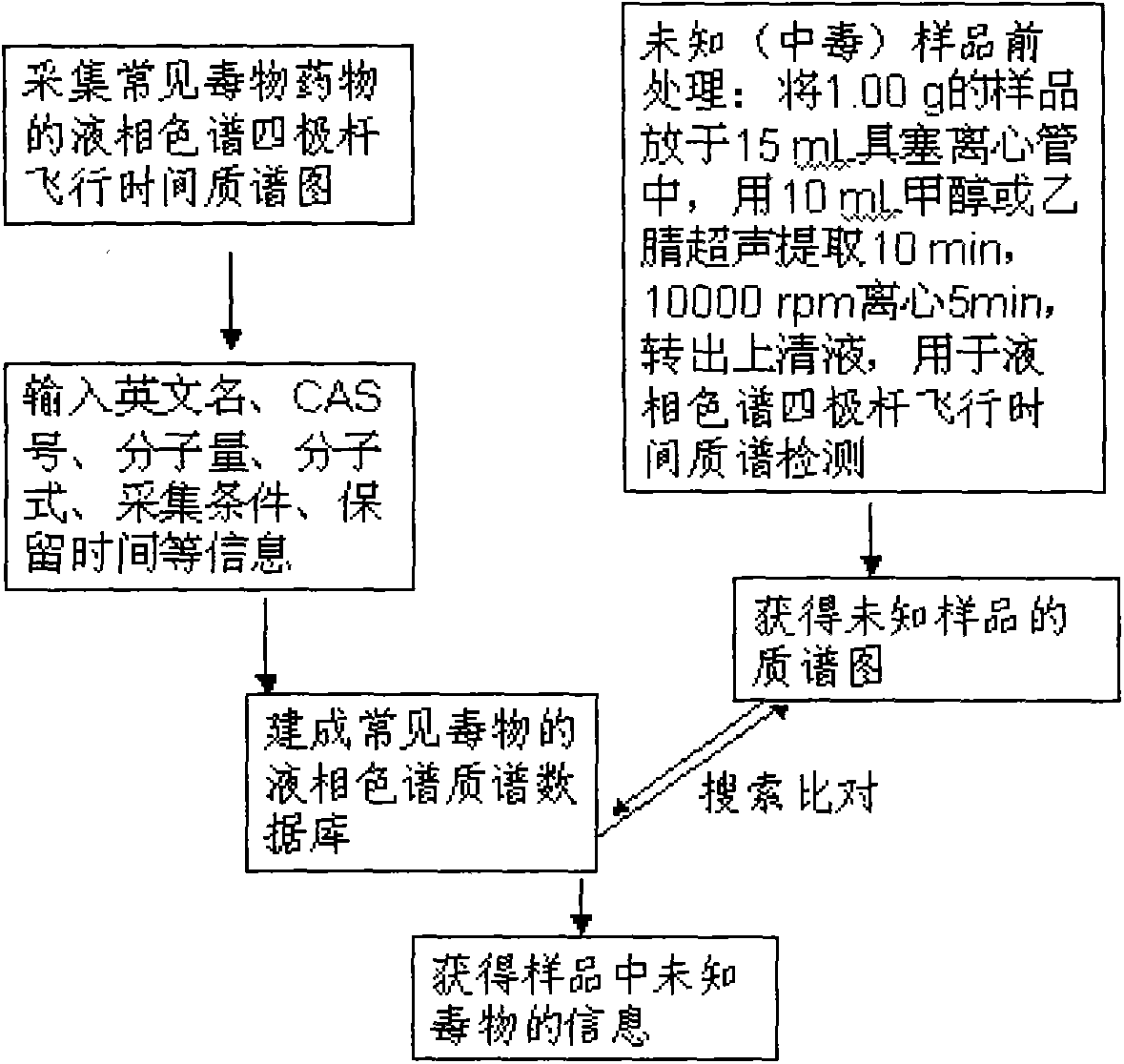
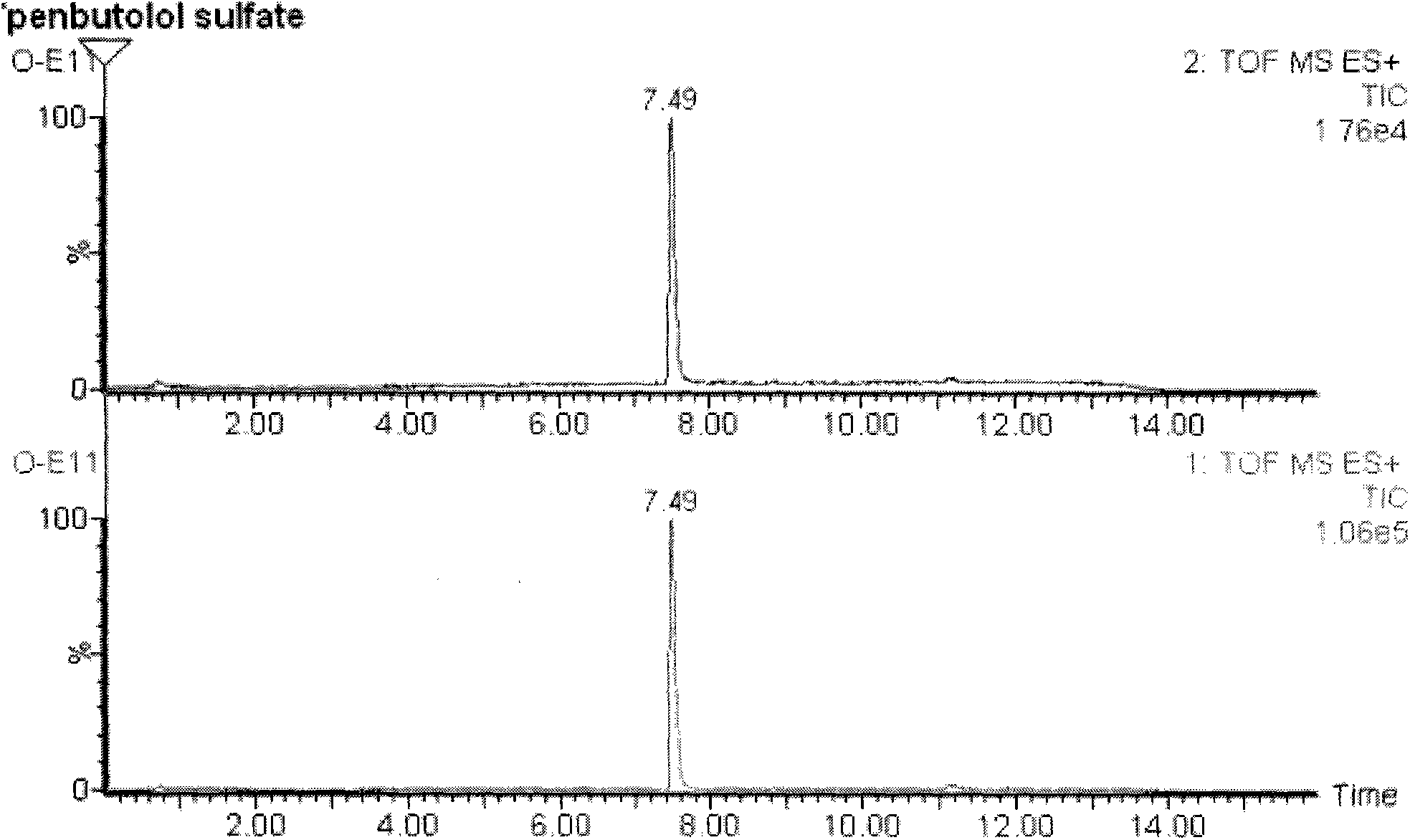
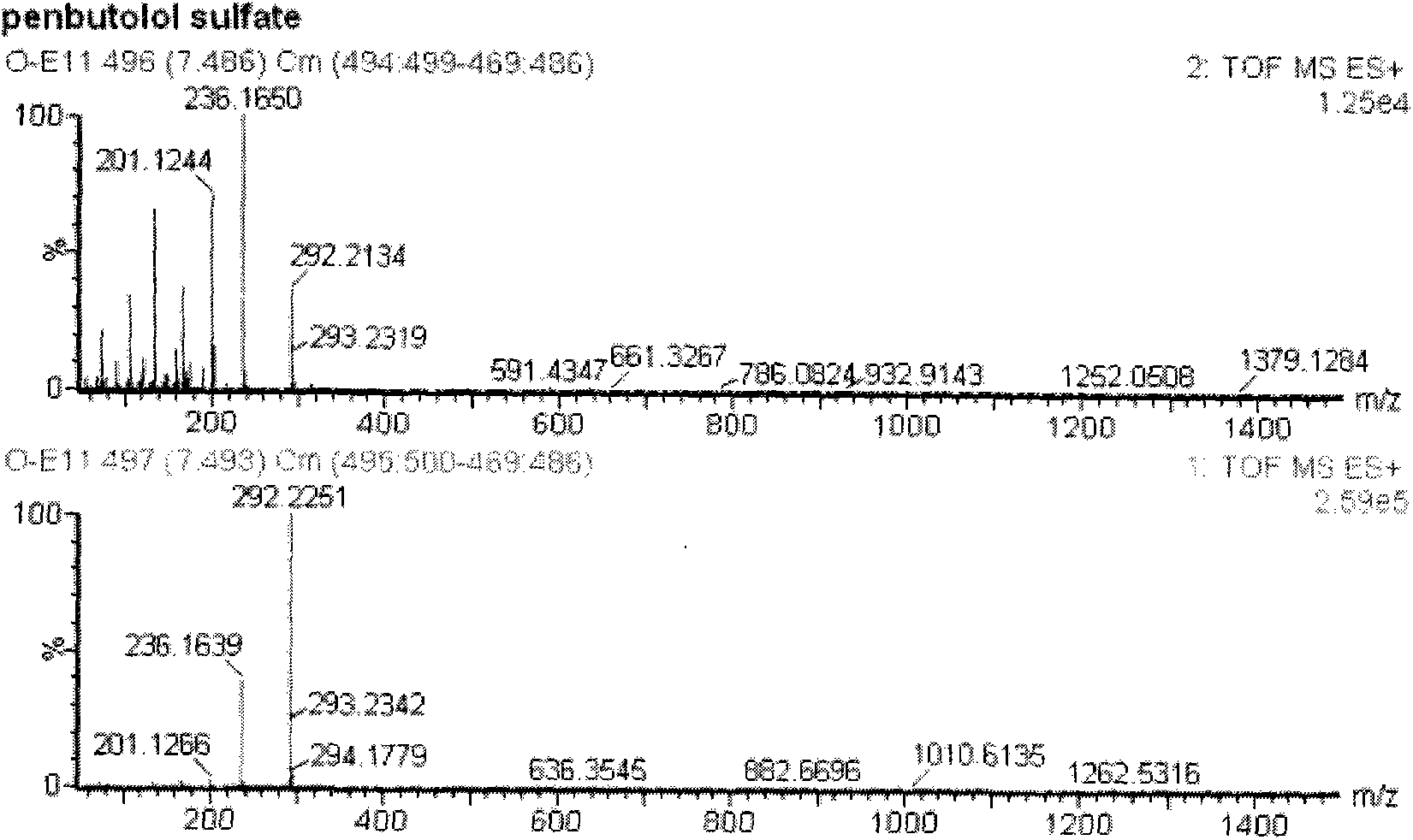
Method for detecting unknown poison by establishing liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry database
ActiveCN103823008AShorten detection timeReduce processing timeComponent separationMass spectrometry measurementToxicant
The invention relates to a method for detecting unknown poison by establishing a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry database, in particular to a method used for detecting unknown poison during food poisoning. According to the method, firstly, an ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry method is used for establishing a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry database of common poison; then, a sample is subjected to supersonic extraction with methyl alcohol or acetonitrile, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry data of an extracting solution are measured similarly and searched and compared in the liquid chromatogram-mass spectrometry database of common poison according to the retention time of the sample and mass spectrometry fragments, and the variety of the unknown poison in the sample is judged; and the unknown poisoning sample is simply extracted and directly measured and compared, and a screening result can be acquired in one hour, so that the detecting and treating time of the sample is greatly shortened, the detecting efficiency is improved, and technical support is provided for related events such as food poisoning and the like caused by unknown reasons.
Owner:BEIJING CENT FOR DISEASE PREVENTION & CONTROL
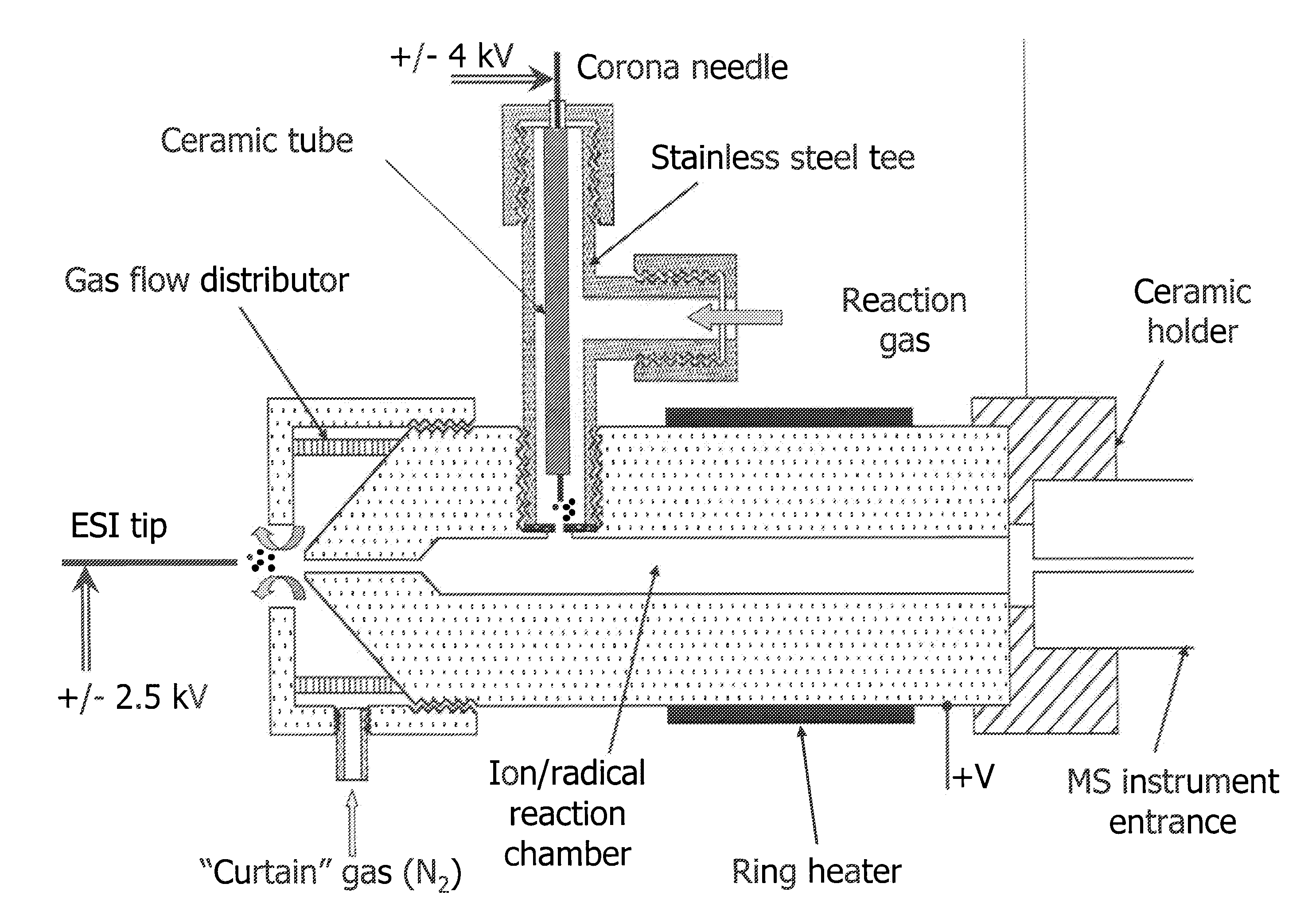
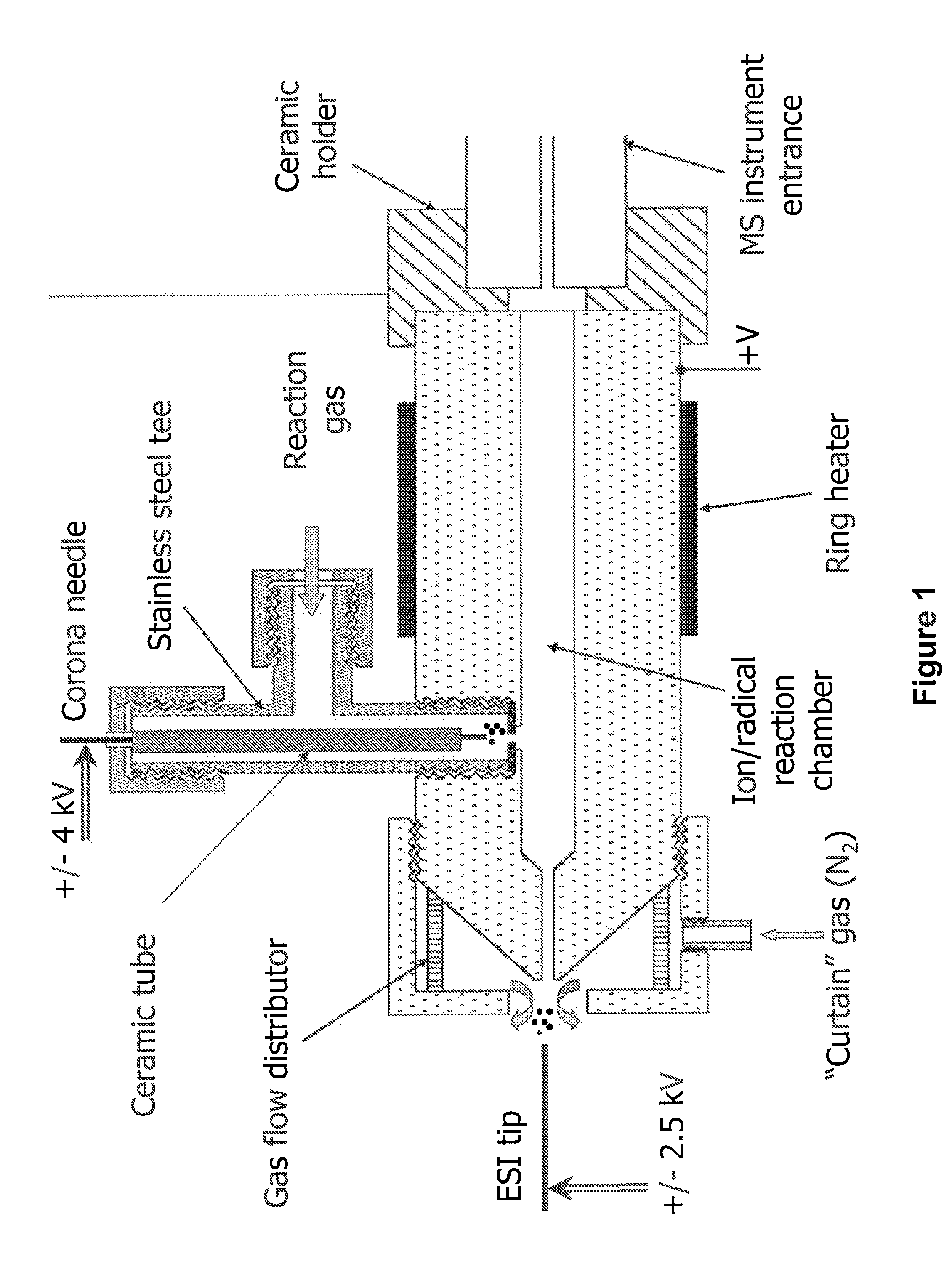
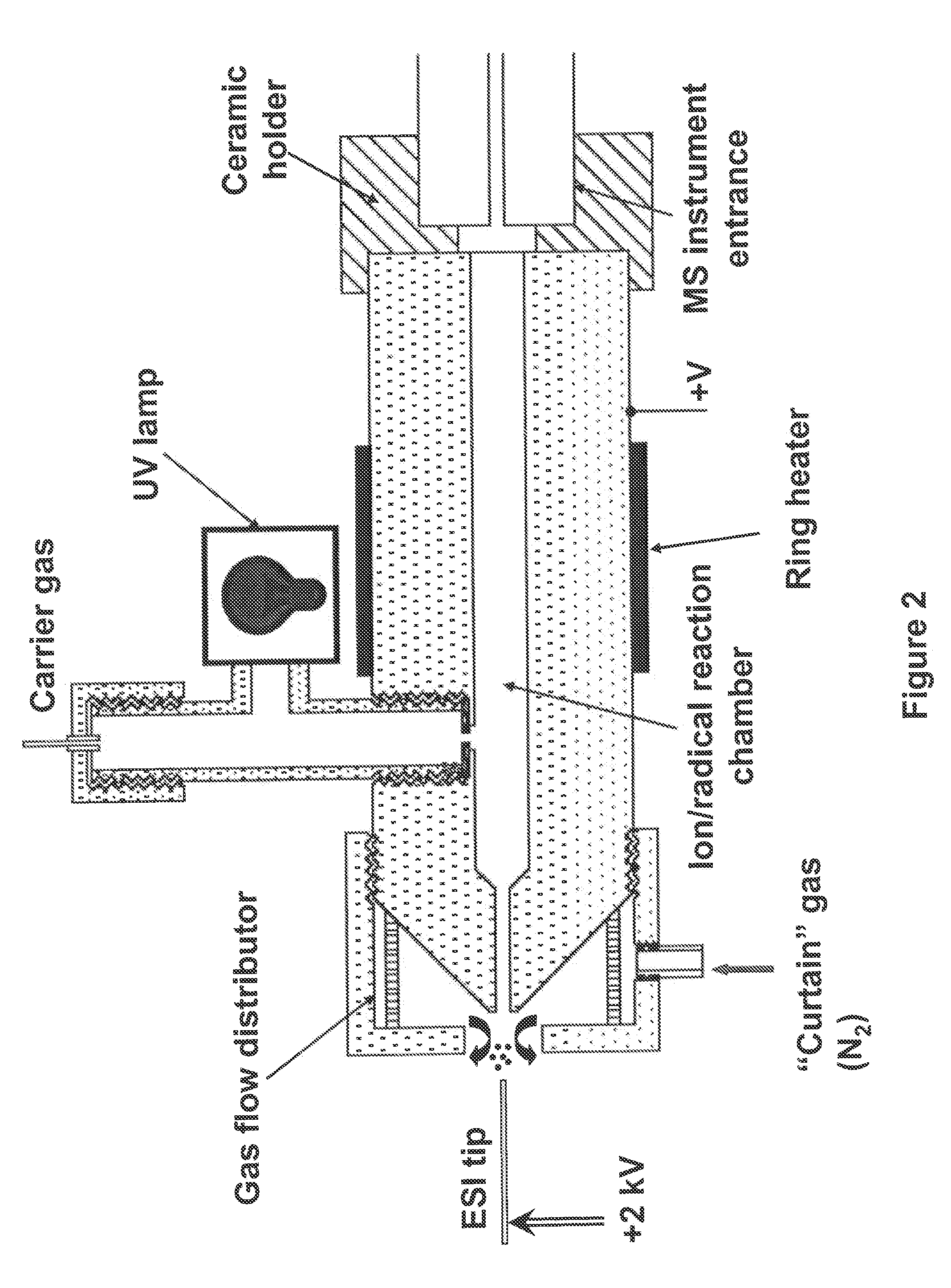
Method and apparatus for ion fragmentation in mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20090152458A1Time-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by optical meansAnalyteGas phase
A method for fragmentation of analyte ions for mass spectroscopy and a system for mass spectroscopy. The method produces gas-phase analyte ions, produces gas-phase radical species separately from the analyte ions, and mixes the gas-phase analyte ions and the radical species at substantially atmospheric pressure conditions to produce fragment ions prior to introduction into a mass spectrometer. The system includes a gas-phase analyte ion source, a gas-phase radical species source separate from the gas-phase analyte ion source, a mixing region where the gas-phase analyte ions and the radical species are mixed at substantially atmospheric pressure to produce fragment ions of the analyte ions, a mass spectrometer having an entrance where at least a portion of the fragment ions are introduced into a vacuum of the mass spectrometer, and a detector in the mass spectrometer which determines a mass to charge ratio analysis of the fragment ions.
Owner:SCI & ENG SERVICES
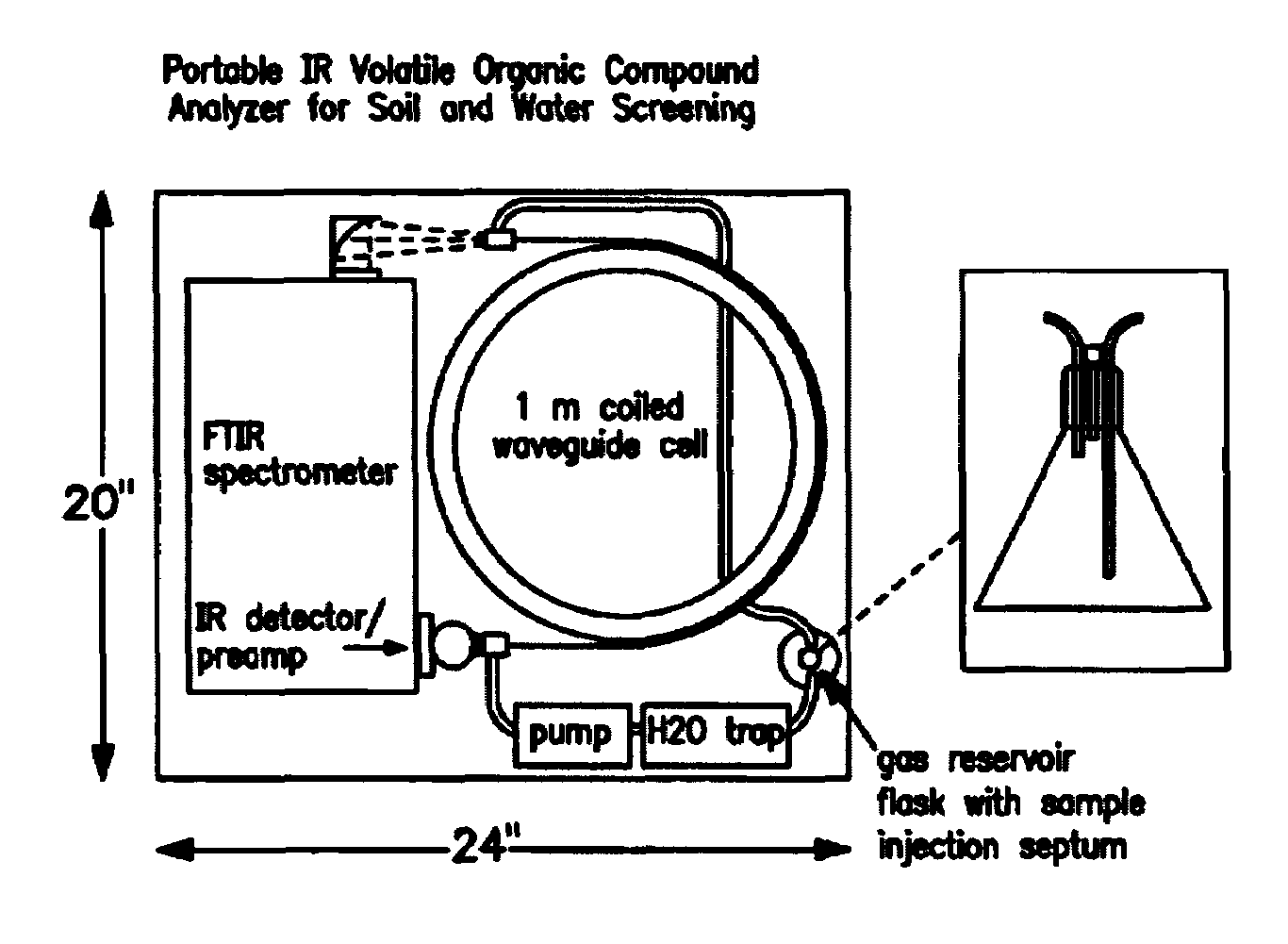
Thermoelectrically cooled water trap
InactiveUS7000490B1Low detection sensitivityEasy to removeWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationThermoelectric coolingWater vapor
A water trap system based on a thermoelectric cooling device is employed to remove a major fraction of the water from air samples, prior to analysis of these samples for chemical composition, by a variety of analytical techniques where water vapor interferes with the measurement process. These analytical techniques include infrared spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, ion mobility spectrometry and gas chromatography. The thermoelectric system for trapping water present in air samples can substantially improve detection sensitivity in these analytical techniques when it is necessary to measure trace analytes with concentrations in the ppm (parts per million) or ppb (parts per billion) partial pressure range. The thermoelectric trap design is compact and amenable to use in a portable gas monitoring instrumentation.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Increasing ionization efficiency in mass spectrometry
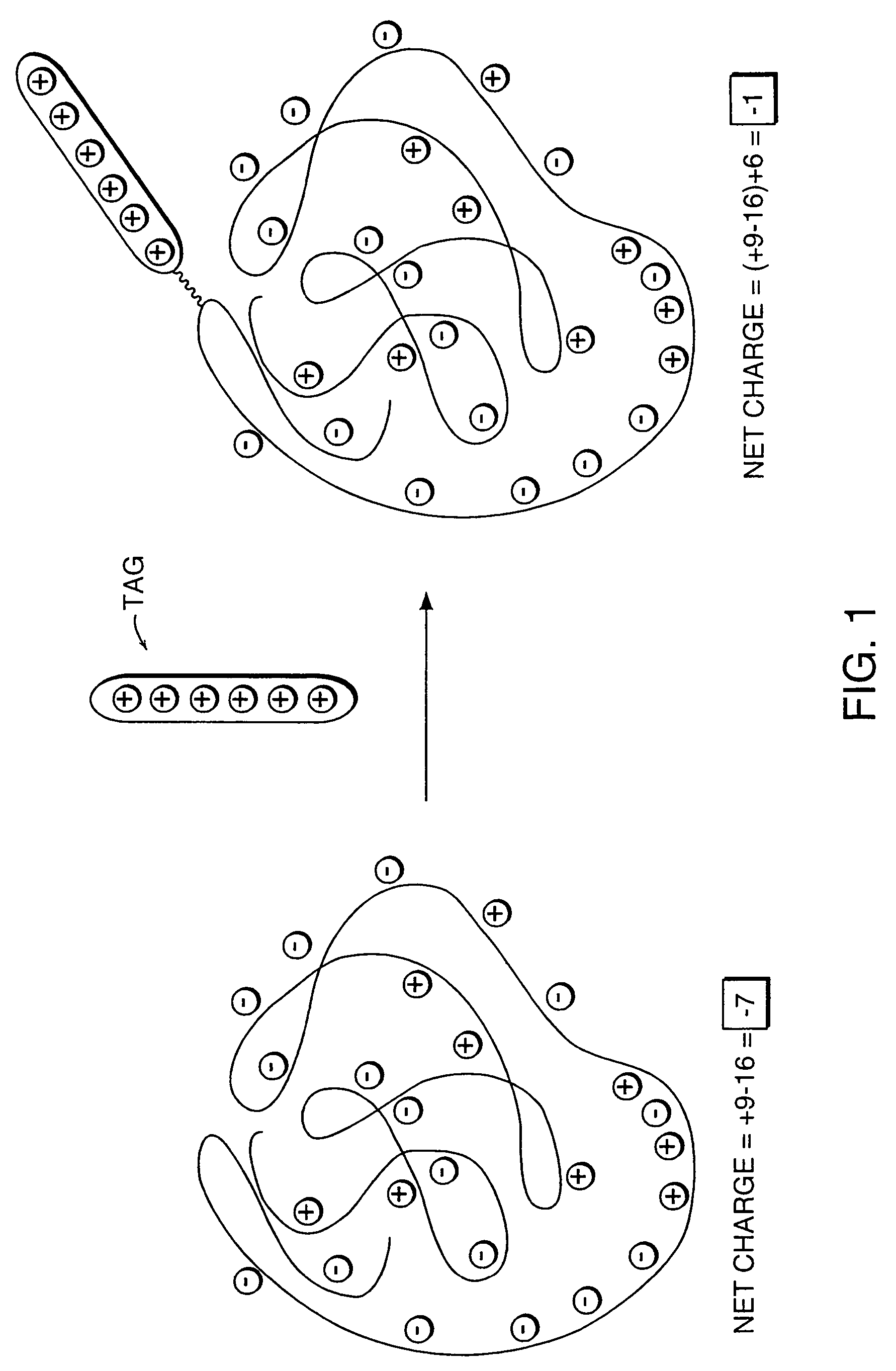
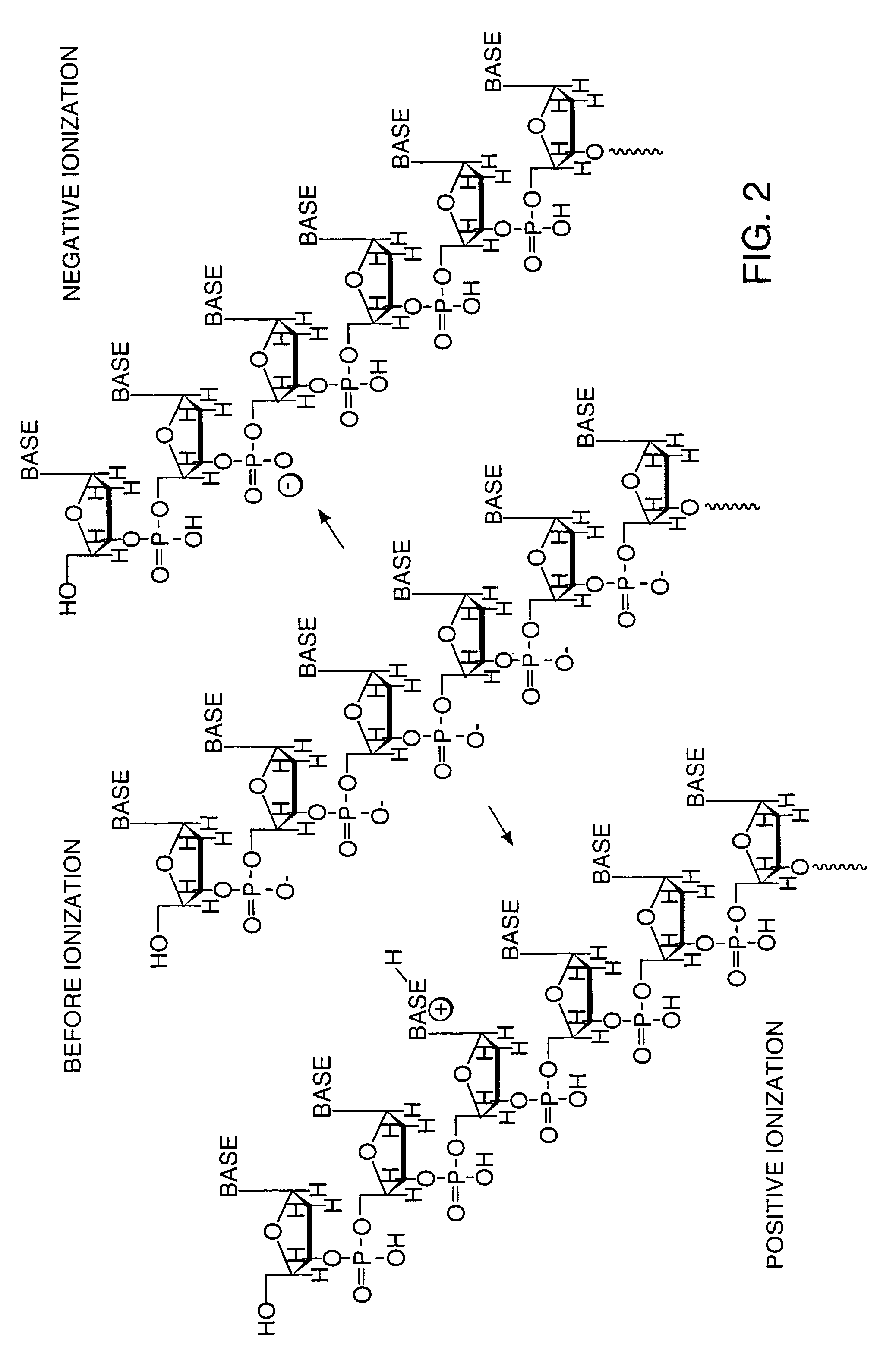
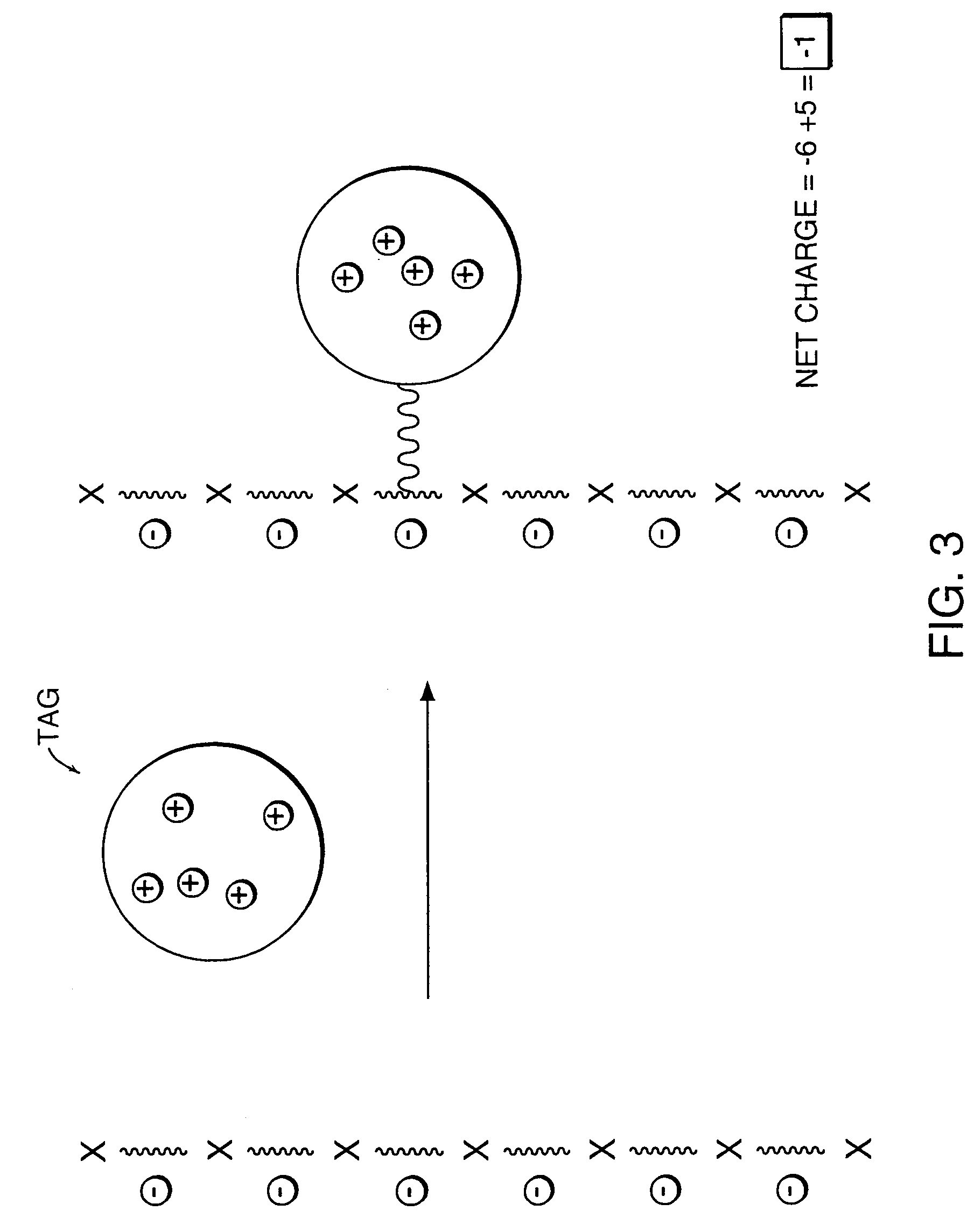
InactiveUS7276378B2Improve ionization efficiencyLess fragmentationTime-of-flight spectrometersSamplingAnalyteMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
A system for the analysis of polyionic molecules by mass spectrometry is provided. The polyionic molecule is attached to a charged tag which neutralizes some of the charge on the polyionic analyte. The formed adduct with a reduced net charge is then analyzed by mass spectrometry, and the determined molecular weight of the adduct can be used to calculate the molecular weight of the analyte. Mass spectrometric analyses of polynucleotides and proteins are particularly amenable to this method.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
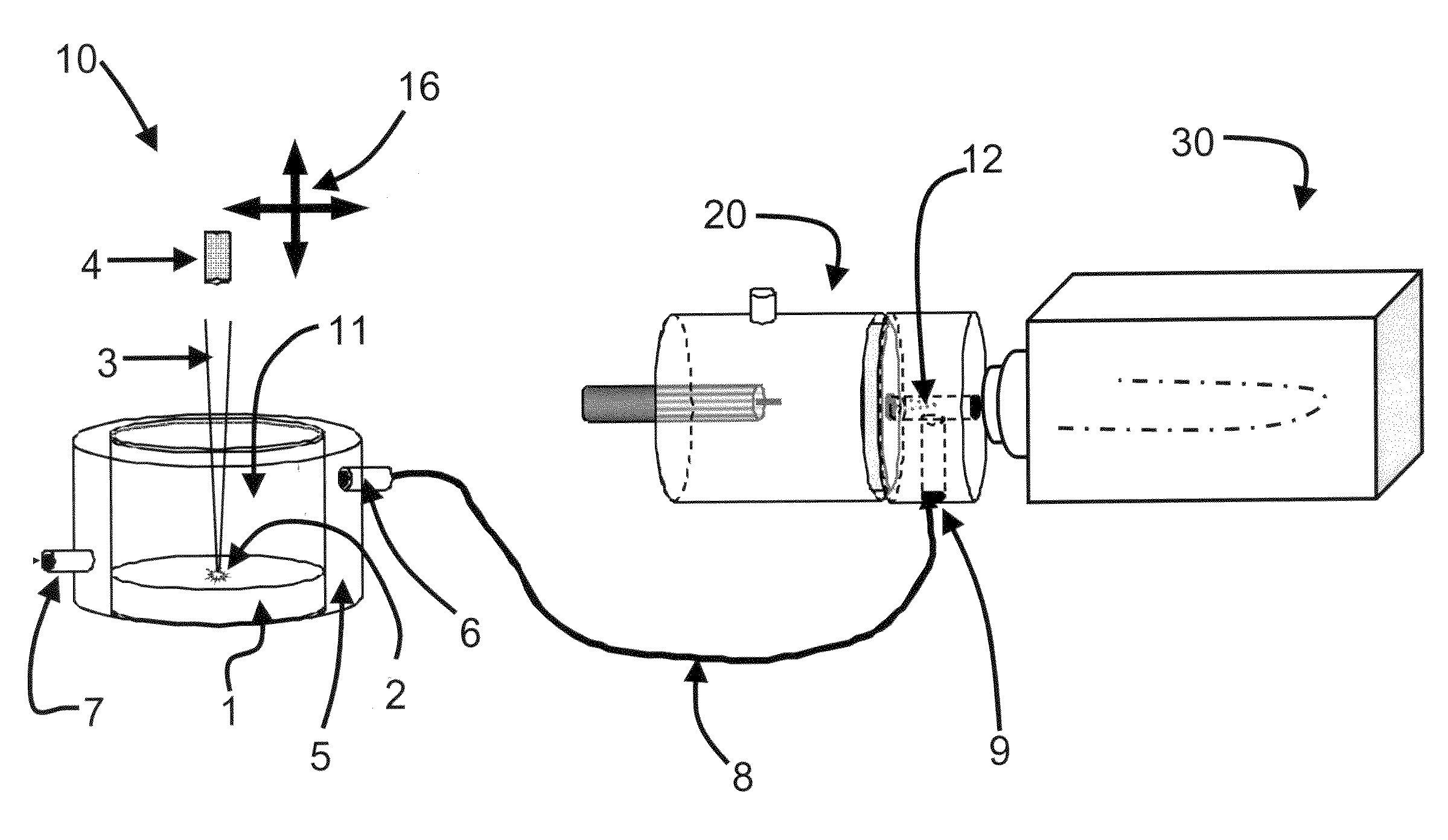
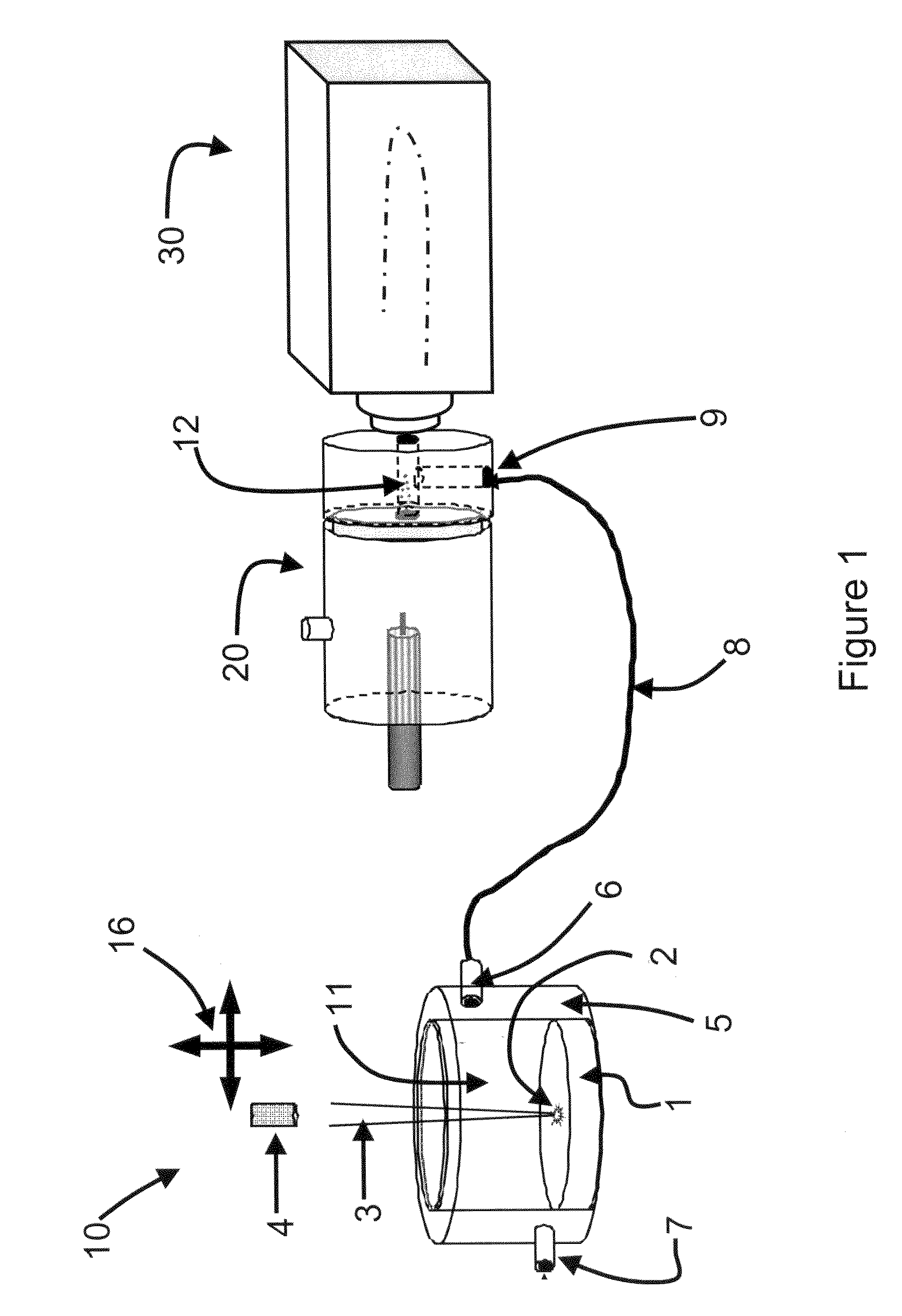
System and method for analyzing tissue intra-operatively using mass spectrometry
A system and method for ample analysis including acquiring a tissue sample, preparing the tissue sample for mass spectrometry imaging, conducting a mass spectrometry procedure on the tissue sample to produce an image, analyzing the image to determine the presence or absence of a biomarker; and generating a report indicating a presence or absence of cancer.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
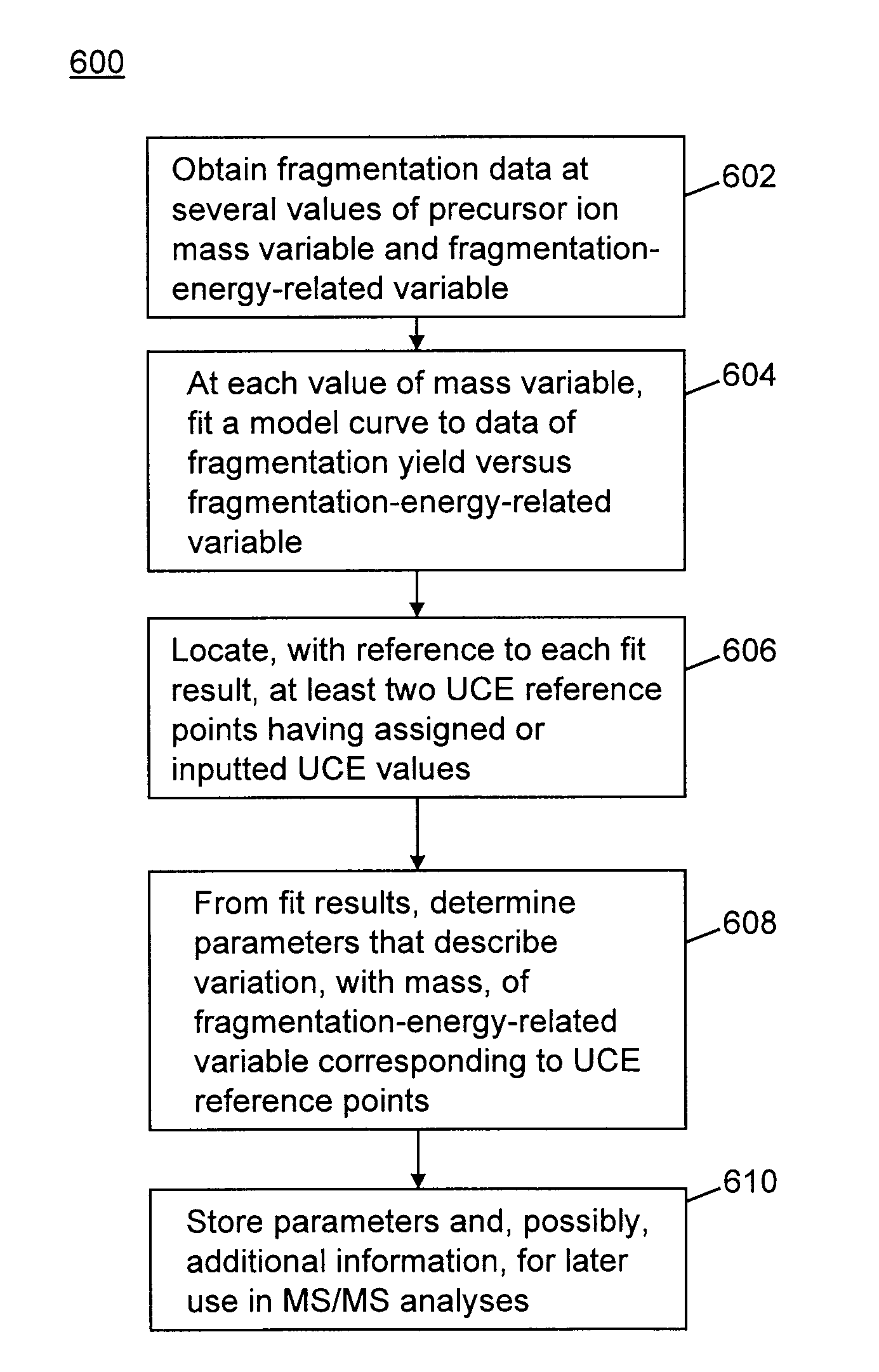
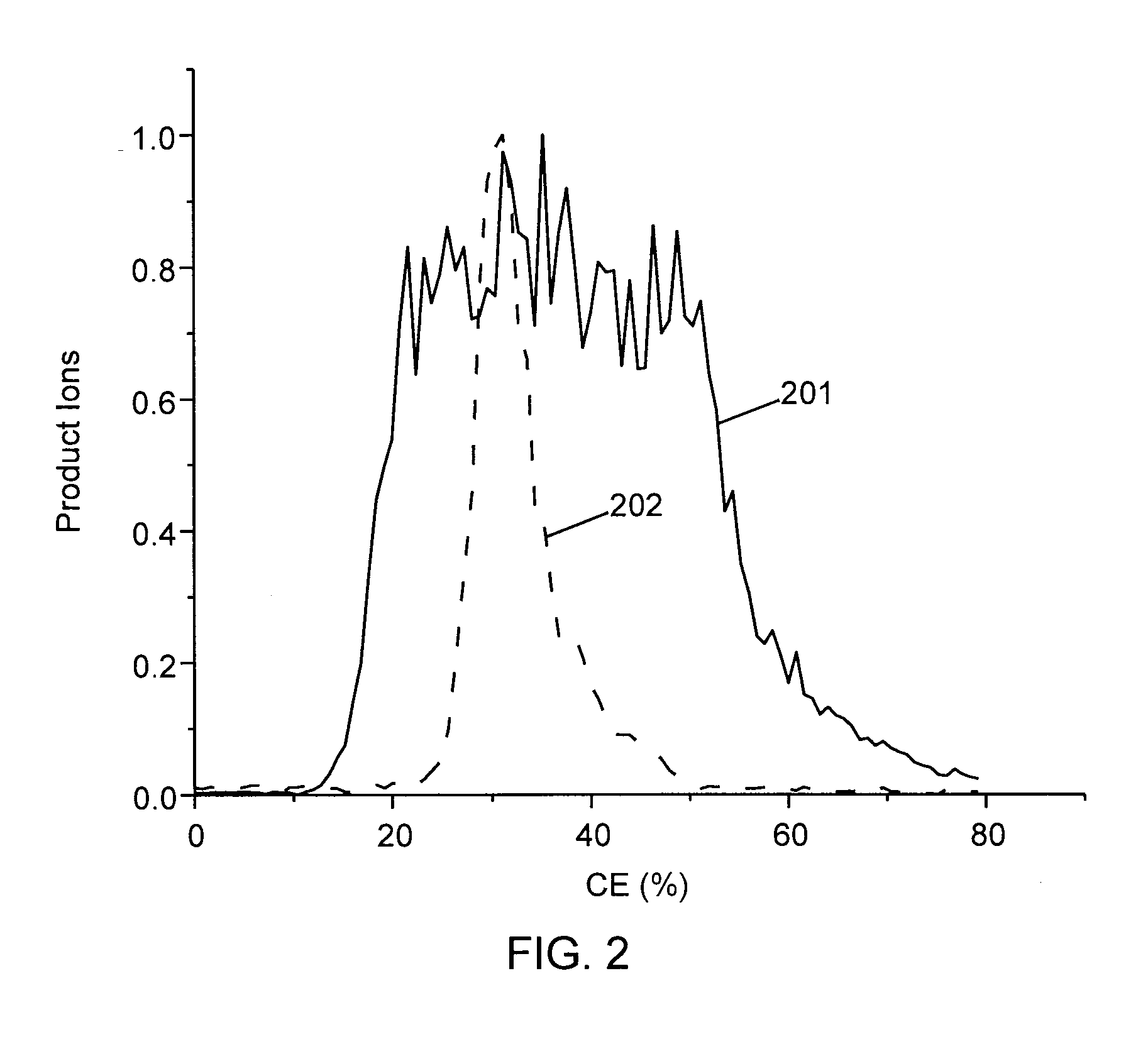
Methods for calibration of usable fragmentation energy in mass spectrometry
ActiveUS8278620B2Isotope separationCalibration apparatusMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMass analyzer
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Method and Apparatus for Analyzing Biomolecules Using Raman Spectroscopy
ActiveUS20150192590A1Highly accurate excellent analyzerReduce variationComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopyBinding site
The present invention provides an apparatus having a sample separation unit, a Raman spectroscopy unit, and a mass spectrometry unit. The present invention further provides a method for specifying a biomolecule and a method for identifying the binding site of the biomolecule and the low-molecular-weight compound, comprising a combination of Raman spectroscopy and mass spectrometry. The present invention further provides a surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy method with improved sensitivity.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Detection and quantification of biomolecules using mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20110160093A1Reduce processing stepsReduce rateSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesPolymerase LMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
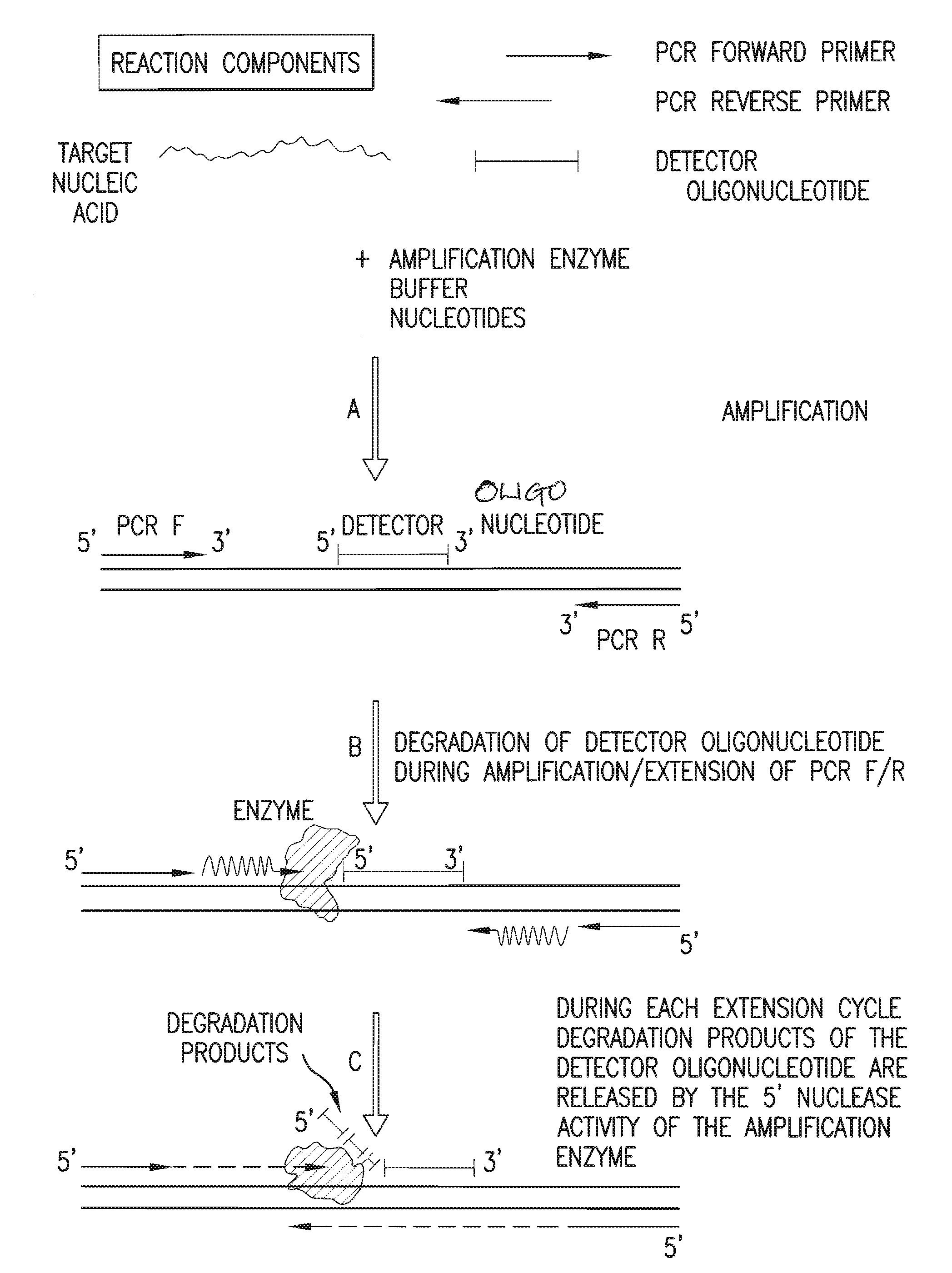
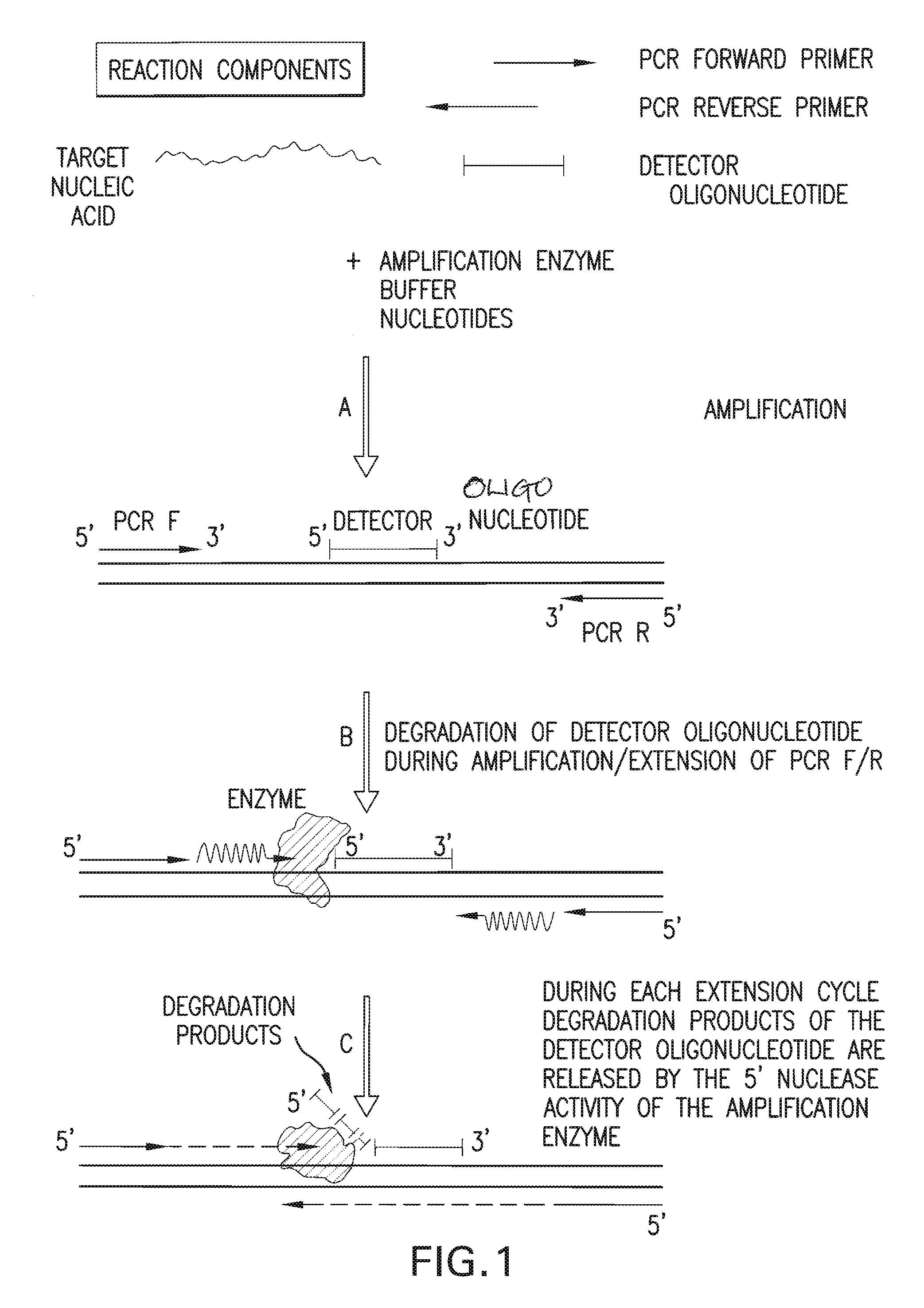
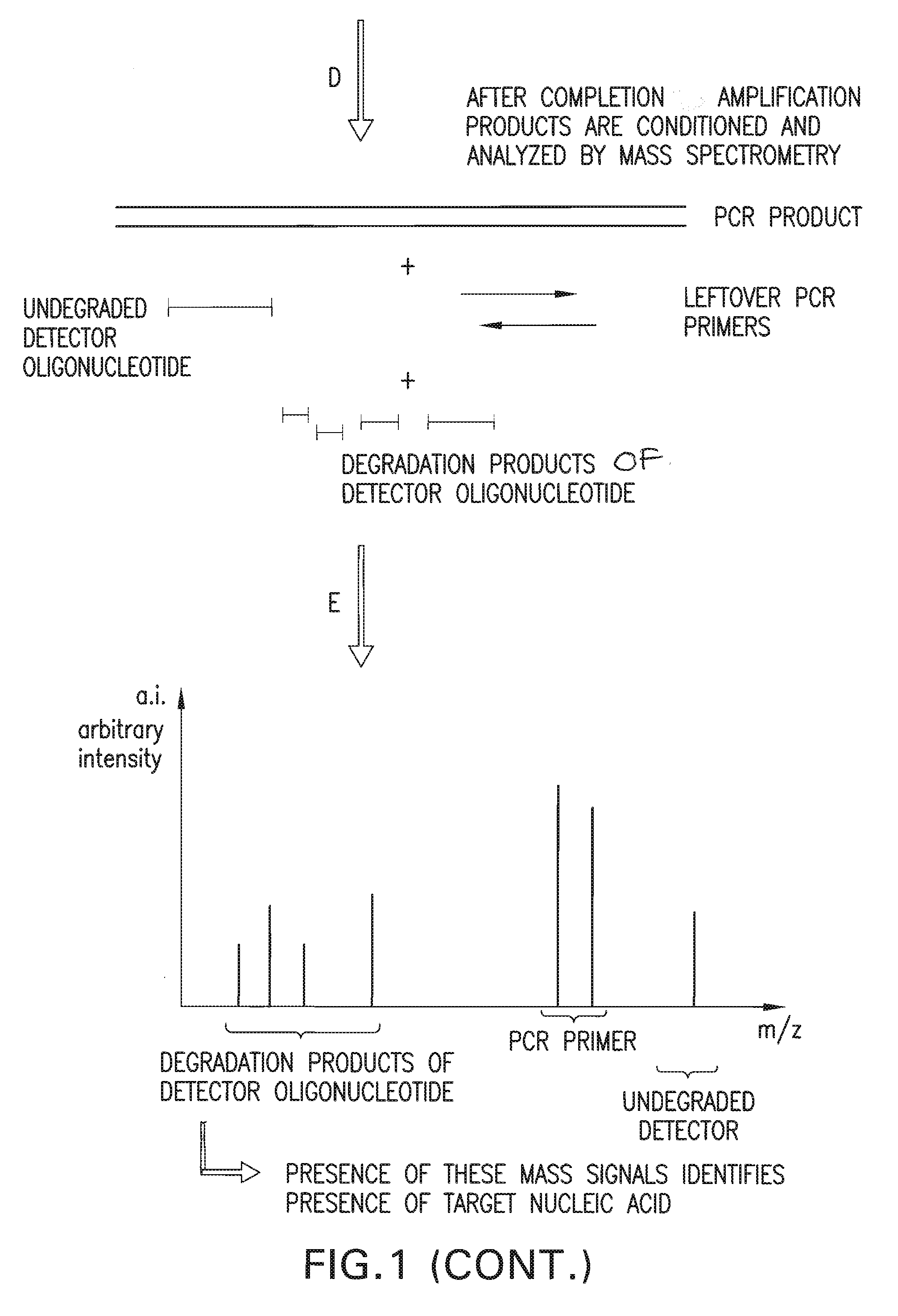
The present invention is directed in part to a method for detecting a target nucleic acid using detector oligonucleotides detectable by mass spectrometry. This method takes advantage of the 5′ to 3′ nuclease activity of a nucleic acid polymerase to cleave annealed oligonucleotide probes from hybridized duplexes and releases labels for detection by mass spectrometry. This process is easily incorporated into a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification assay. The method also includes embodiments directed to quantitative analysis of target nucleic acids.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCIENCE INC
Mass spectrometer and method of mass spectrometry
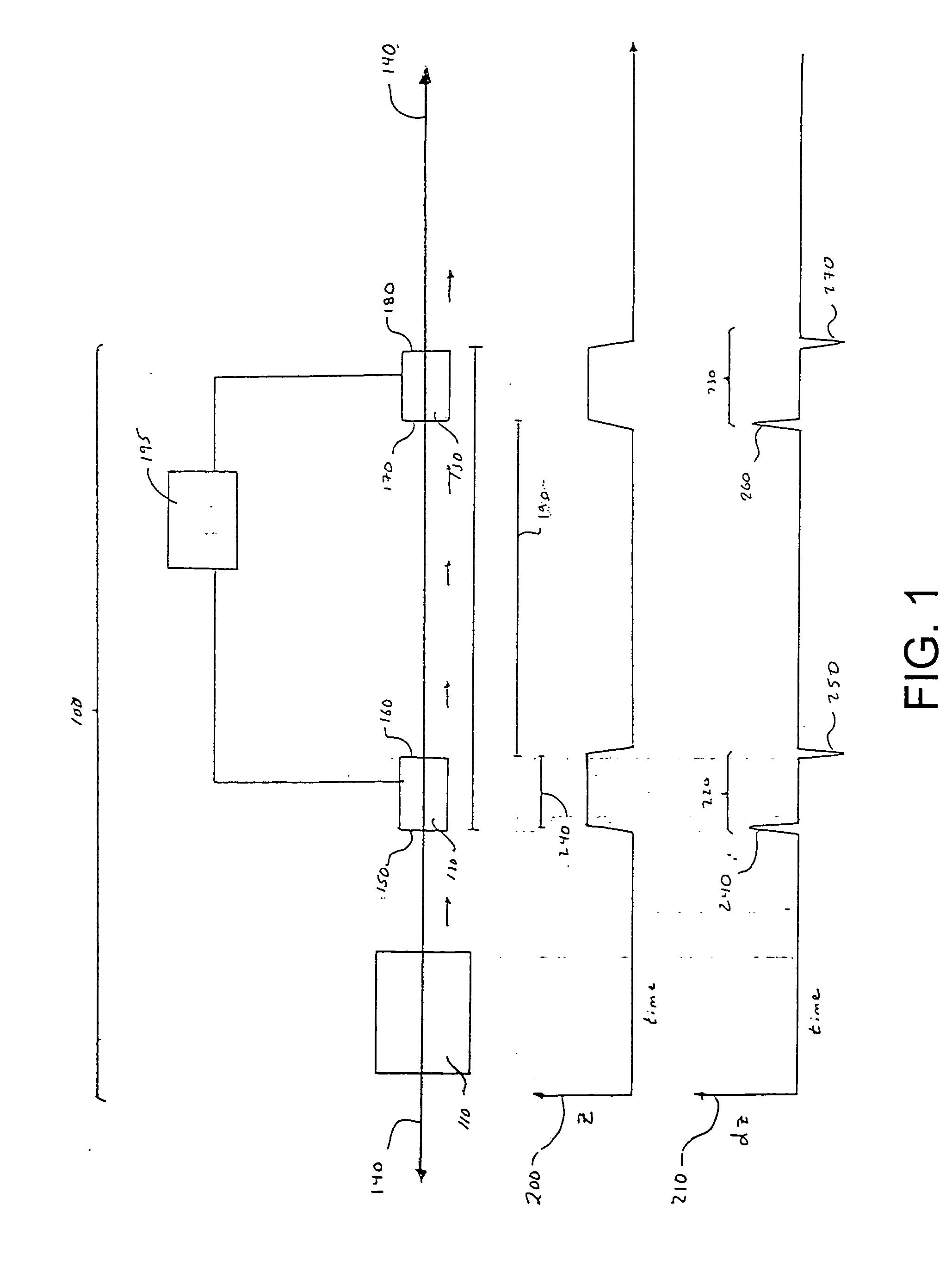
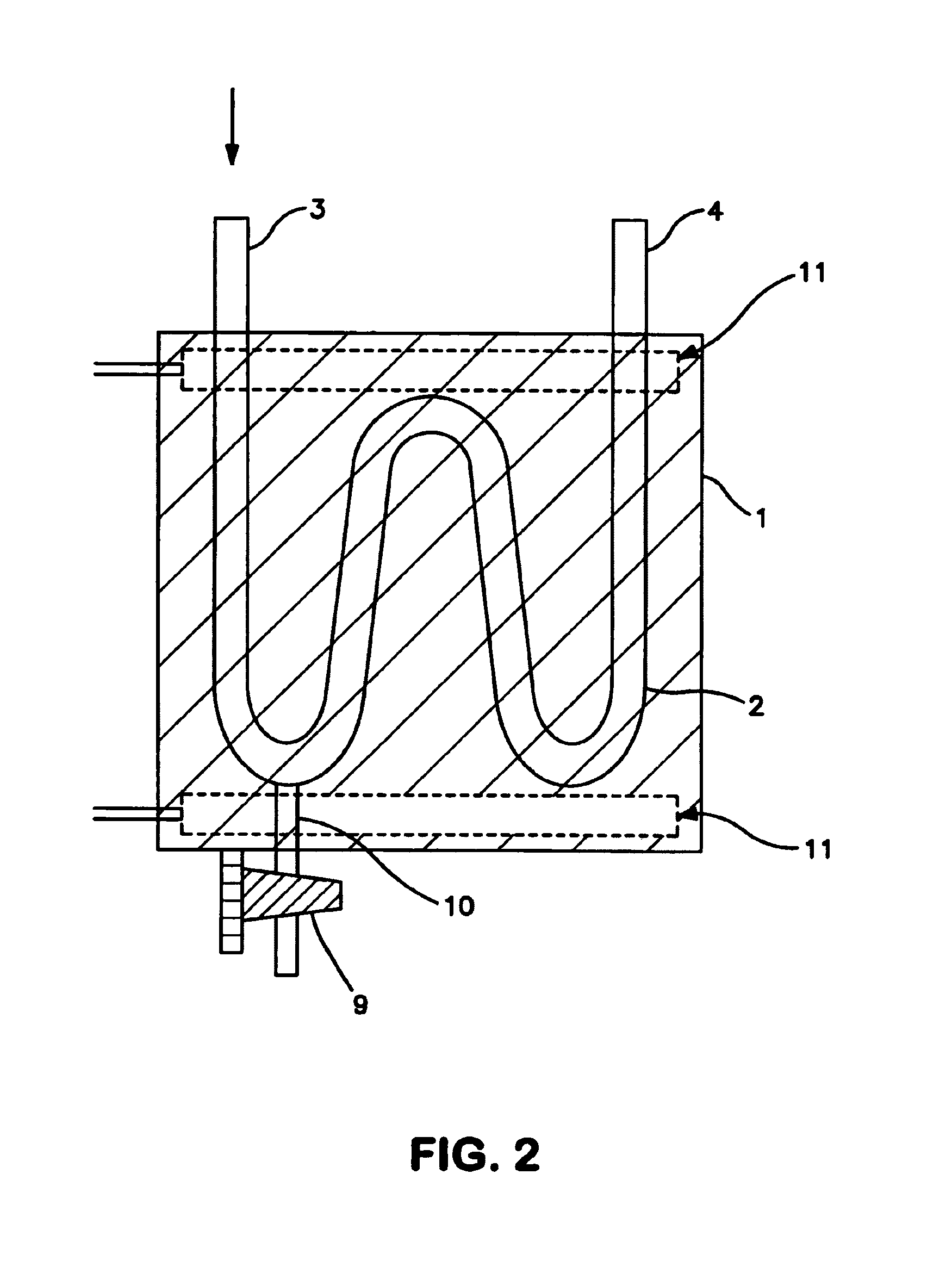
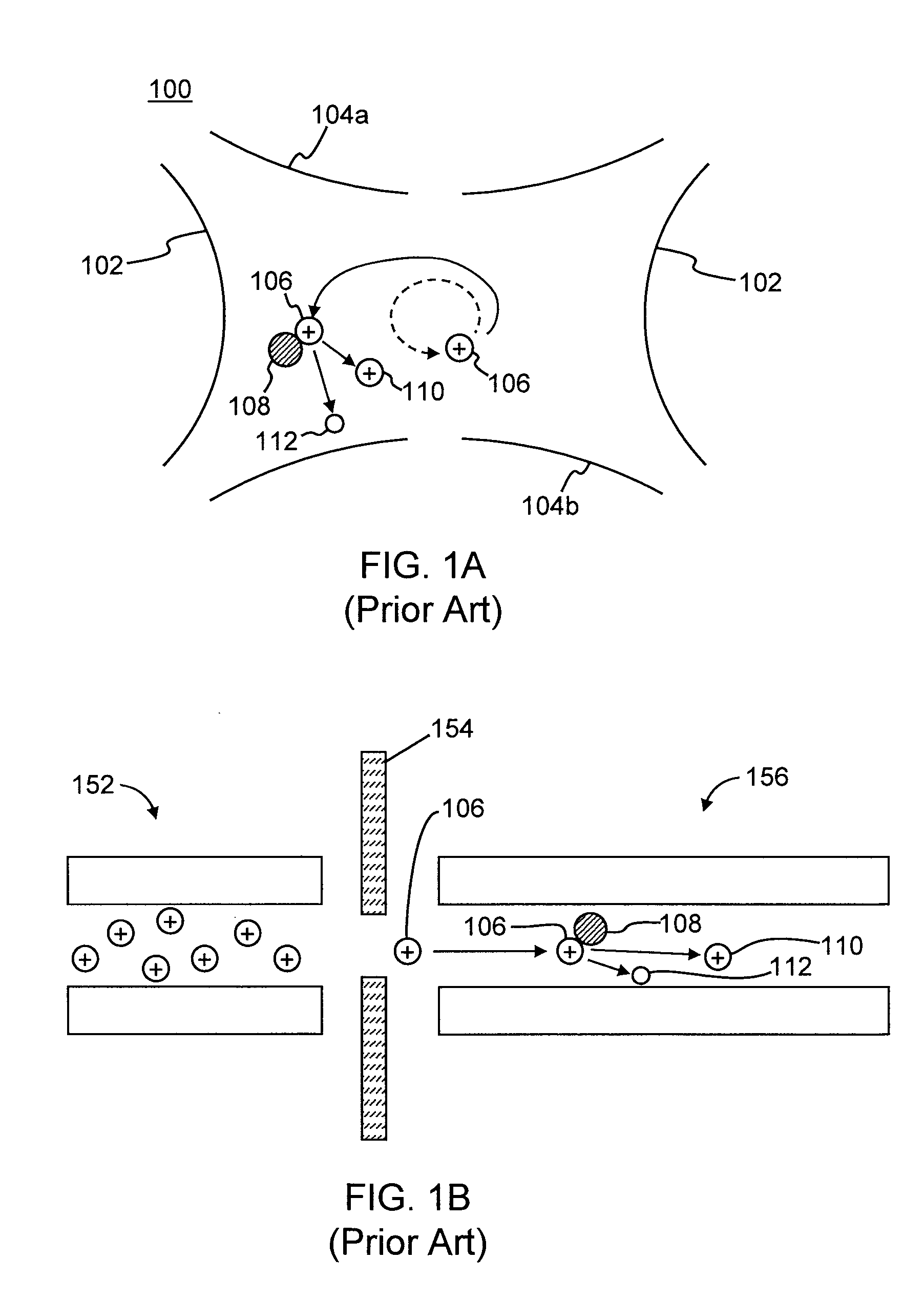
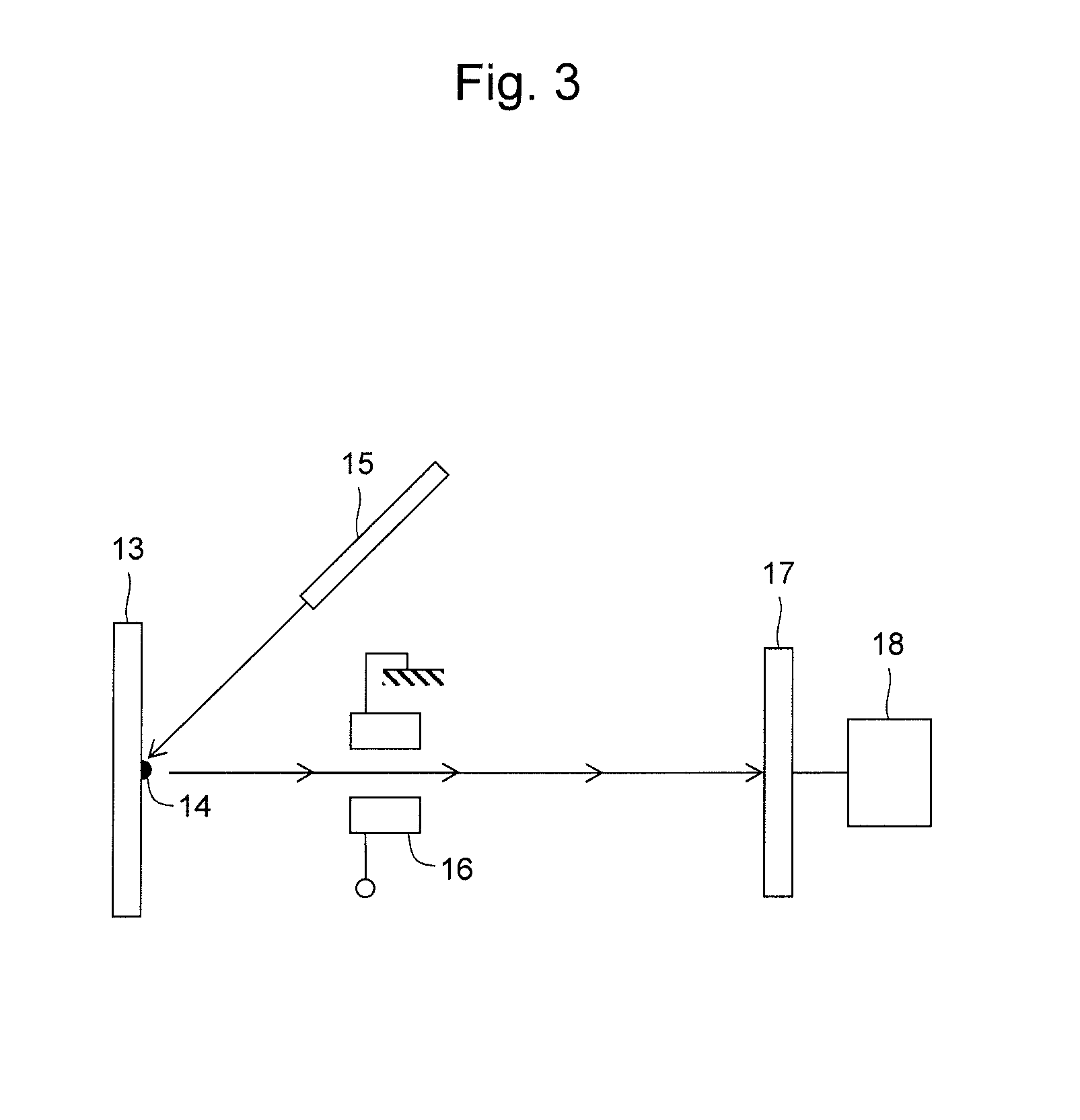
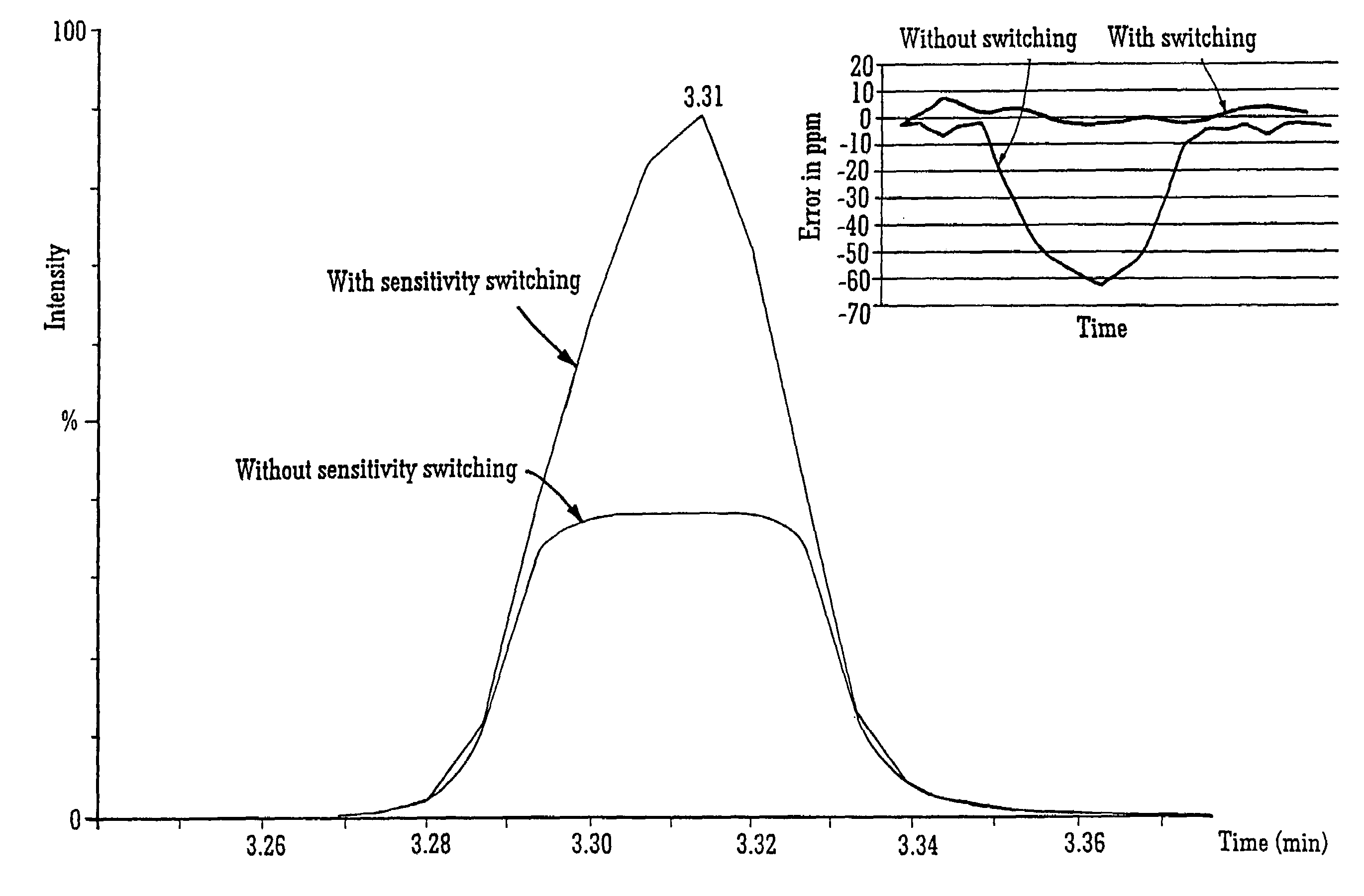
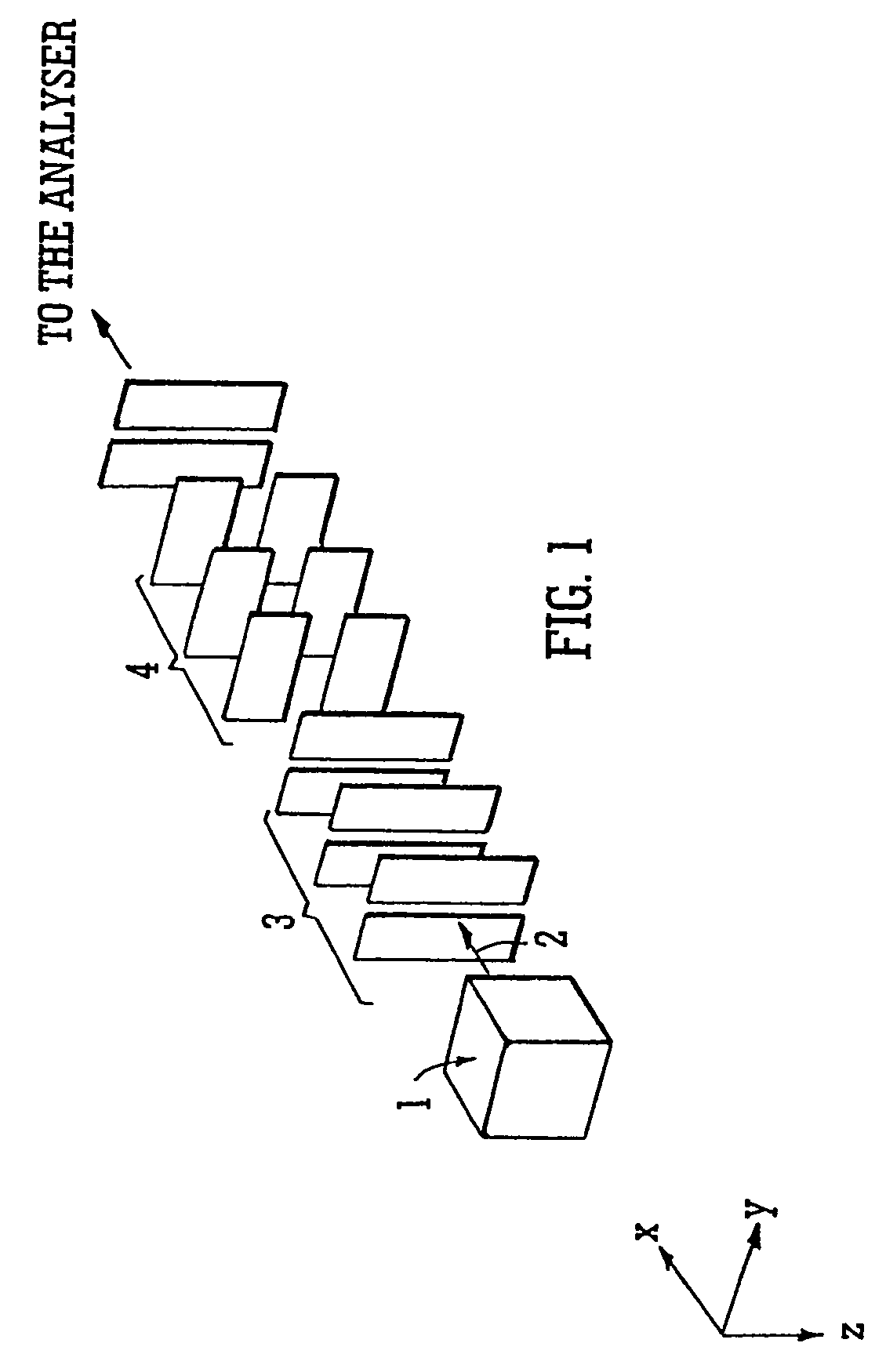
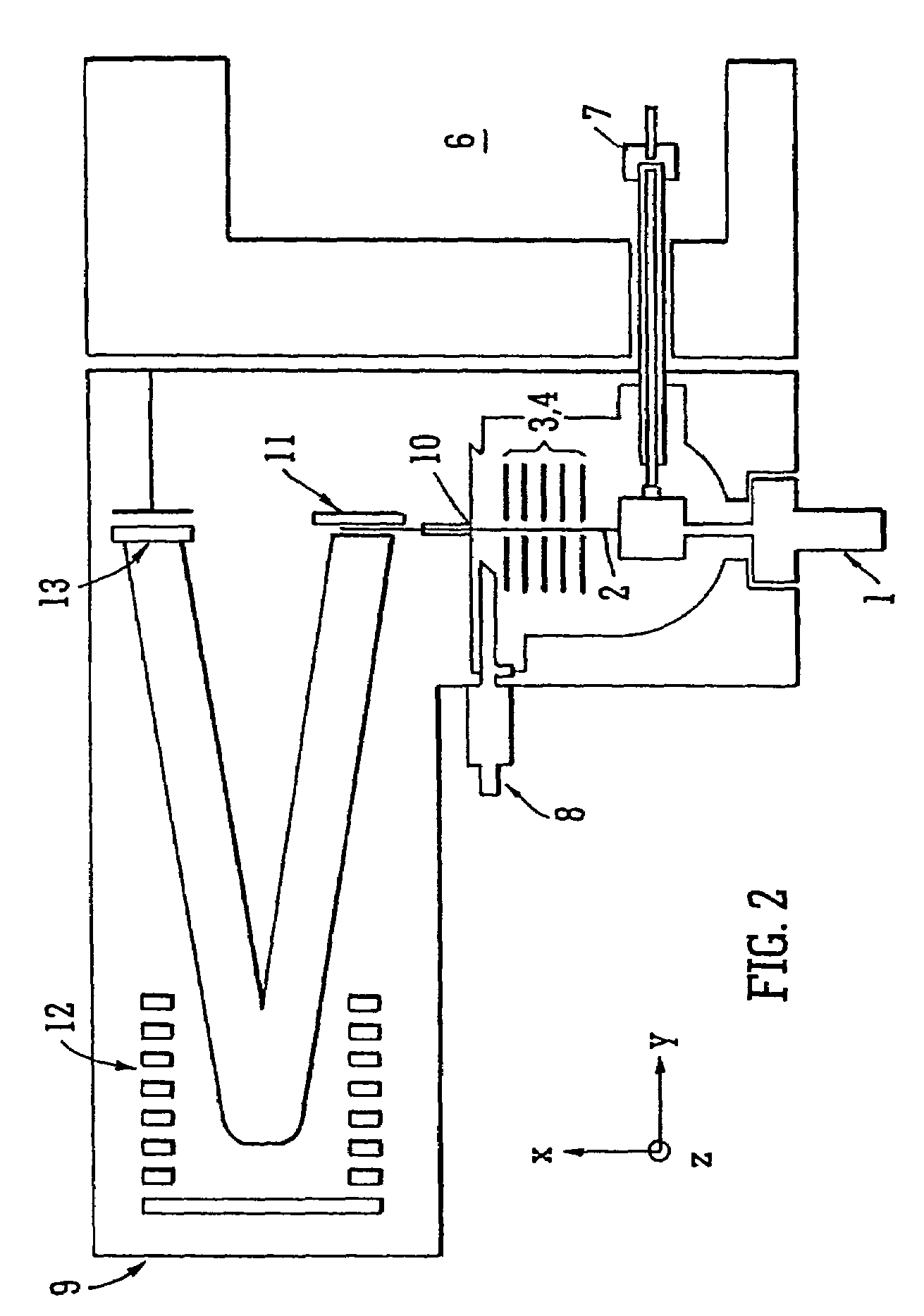
InactiveUS7038197B2Reducing pressure/flowEfficient ionizationThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersMass analyzerMass spectrometry imaging
A mass spectrometer is disclosed wherein a z-lens upstream of an orthogonal acceleration Time of Flight mass analyser is repeatedly switched between a first mode wherein ions are transmitted to the mass analyser for subsequent mass analysis with a relatively high transmission and a second mode wherein ions are transmitted with a relatively low transmission. If it is determined that mass spectral data obtained when the mass analyser is in the first mode is suffering from saturation, then suitably scaled mass spectral data obtained when the mass analyser is in the second mode is used instead. If the saturation is severe then the mass spectral data obtained in the first mode may be replaced in its entirety with mass spectral data obtained in the second mode.
Owner:MICROMASS UK LTD
Quantitation of insulin by mass spectrometry
ActiveUS20120164741A1Improve accuracyBiological material analysisBiological testingPurification methodsMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
Methods are described for determining the amount of insulin in a sample. More specifically, mass spectrometric methods are described for detecting and quantifying insulin in a biological sample utilizing purification methods coupled with tandem mass spectrometric or high resolution / high accuracy mass spectrometric techniques.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
Method and apparatus for nano-capillary/micro electrospray for use in liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
ActiveUS8227750B1Good adhesionReduce setup timeParticle separator tubesComponent separationAtmospheric airEngineering
An ion injection spray apparatus and method are provided for coupling a liquid chromatograph or other liquid flow device to a mass spectrometer. The ion injection spray assembly is composed in part of a chamber for voltage and gas input, a metal union for a liquid voltage junction, a gas distribution assembly, a vacuum seal and an ion spray needle. The position of the ion spray needle within this assembly is directly coupled to the outlet of the upstream liquid flow device through the metal union. The vacuum of the mass spectrometer pulls gas at atmospheric pressure though the gas distribution assembly to focus the sample liquid at the spray needle outlet and create a centrifugal gas funnel which helps to desolvate the sample ions and sweep them into the mass spectrometer over a wide range of flow rates.
Owner:BRUKER SCI LLC +1
Inductive detection for mass spectrometry
InactiveUS7078679B2Improve accuracyHigh resolutionTime-of-flight spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsGas phaseBiopolymer
The invention provides devices, device configurations and methods for improved sensitivity, resolution and efficiency in mass spectrometry, particularly as applied to biological molecules, including biological polymers, such as proteins and nucleic acids. More particularly, the invention provides methods and devices for analyzing and detecting electrically charged particles, especially suitable for gas phase ions generated from high molecular weight compounds. In one aspect, the invention provides devices and methods for determining the velocity, charged state or both of electrically charged particles and packets of electrically charged particles. In another aspect, the invention provides methods and devices for the time-of-flight analysis of electrically charged particles comprising spatially collimated sources. In another aspect, the invention relates to multiple detection using inductive detectors, improved methods of signal averaging and charged particle detection in coincidence.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
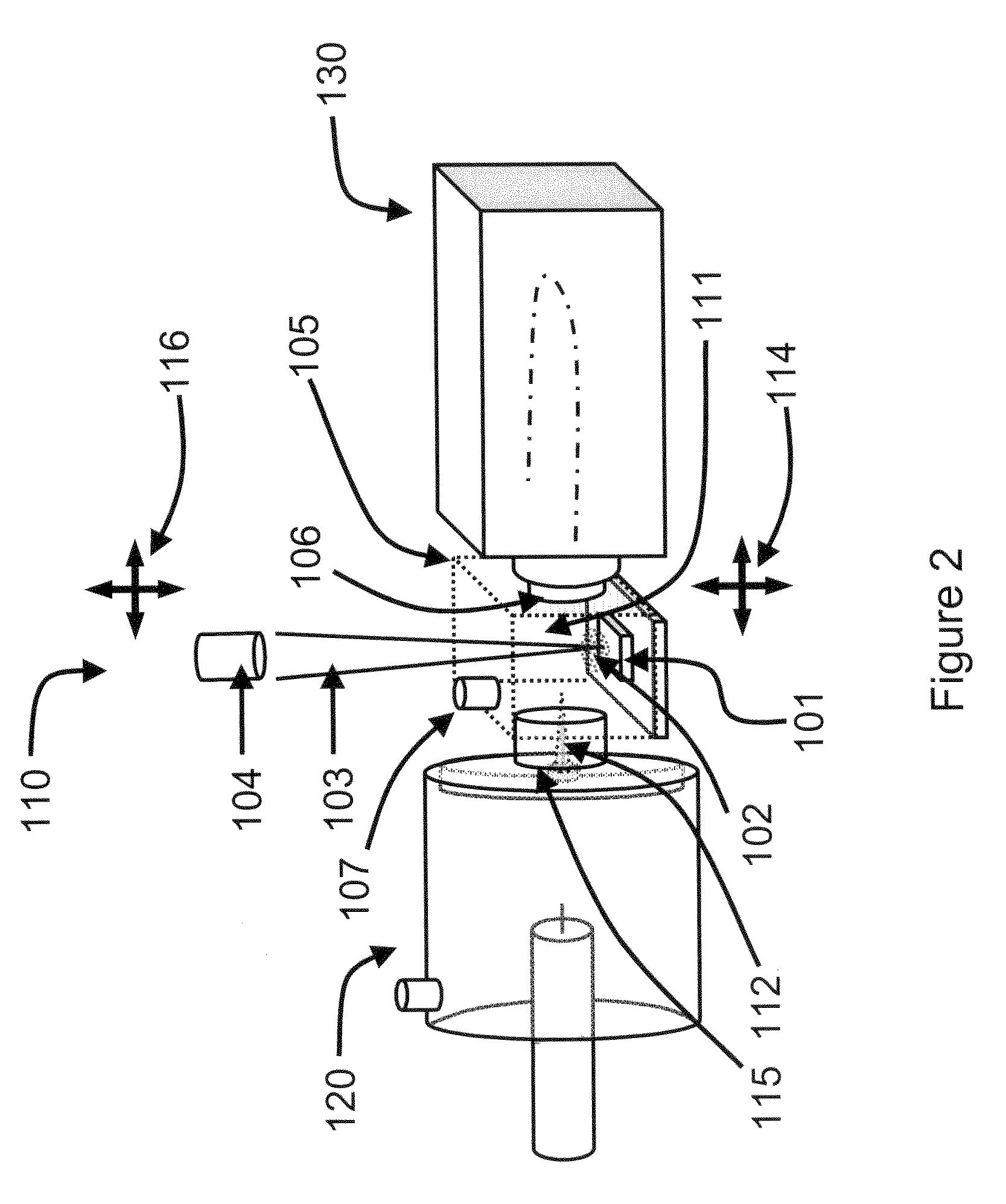
Methods and apparatuses for analyzing biological samples by mass spectrometry
InactiveUS8778695B2Particle separator tubesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDiseaseMass spectrometry imaging
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
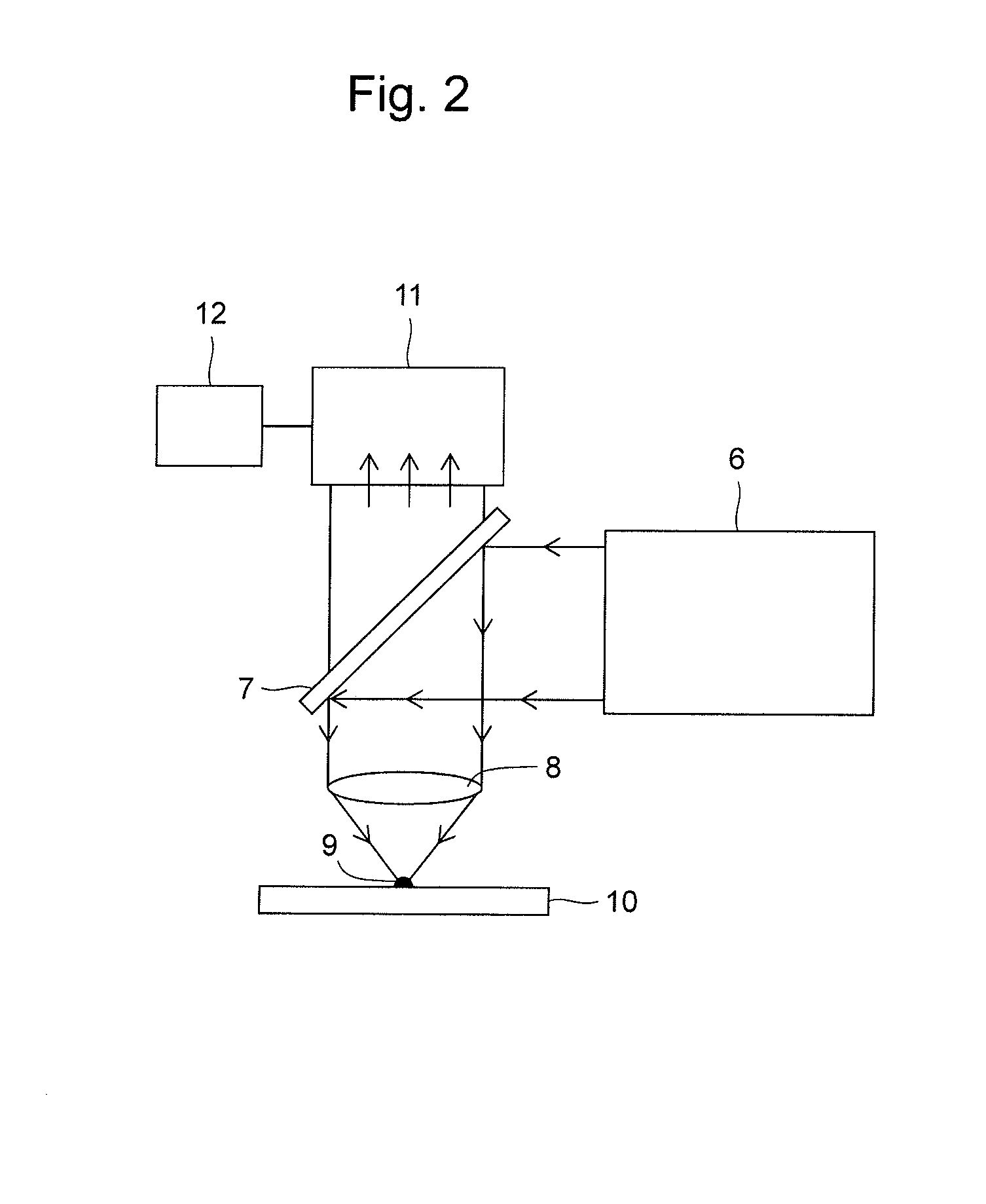
Application for analyzing micromolecules with irradiating nanometer carbon spots serving as matrix assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) matrix
InactiveCN102645481AOvercoming the inability to efficiently analyze small molecule samplesReduce processing requirementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSpectroscopyBiomarker discovery
The invention discloses application for analyzing micromolecules with irradiating nanometer carbon spots serving as a matrix assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) matrix. The carbon spots serve as an analysis method of the MALDI matrix and are suitable to mass spectrum analysis for the micromolecules with the m / z between 150-1000. Suitable molecule types comprise amino acid, polypeptide, beta-exhilarant, fatty acid, polymer and the like. When the method is used for detecting the molecule with the m / z between 150-1000, background peaks hardly exist to produce background interference. The method can be effectively used in the fields of organic and biomass spectrometry, spectrometry imaging, protein spectroscopy, metabonomics, biomarker discovery, environment analysis and the like.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Reduction of scan time in imaging mass spectrometry
ActiveUS7655476B2Raise the possibilityBig spaceCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging particle spectrometryImage resolutionTissue sample
Techniques are disclosed for reducing scan times in mass spectral tissue imaging studies. According to a first technique, a tissue imaging boundary is defined that closely approximates the edges of a tissue sample. According to a second technique, a low-resolution scan is performed to identify one or more areas of interest within the tissue sample, and the identified areas of interest are subsequently scanned at higher resolution.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
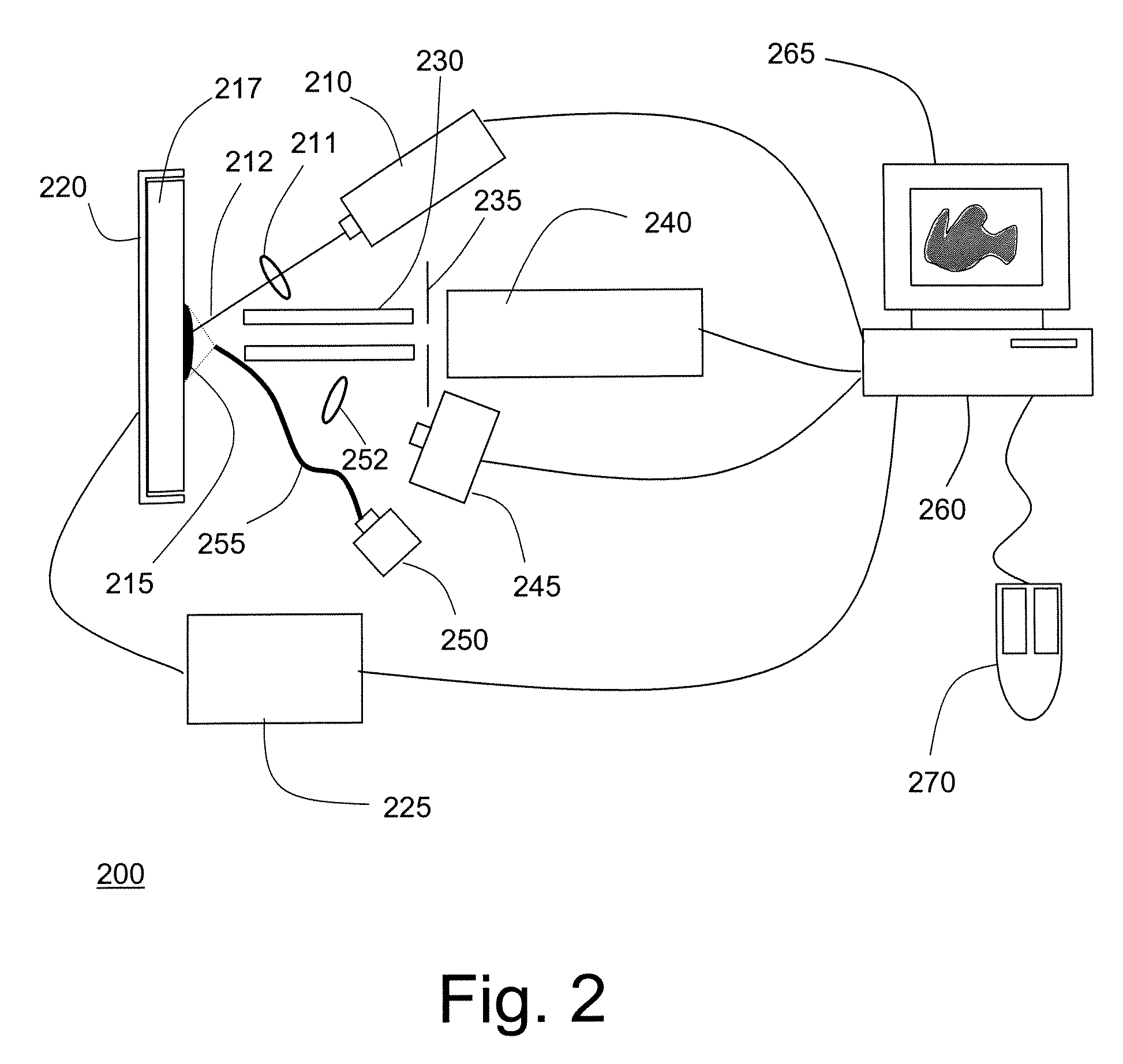
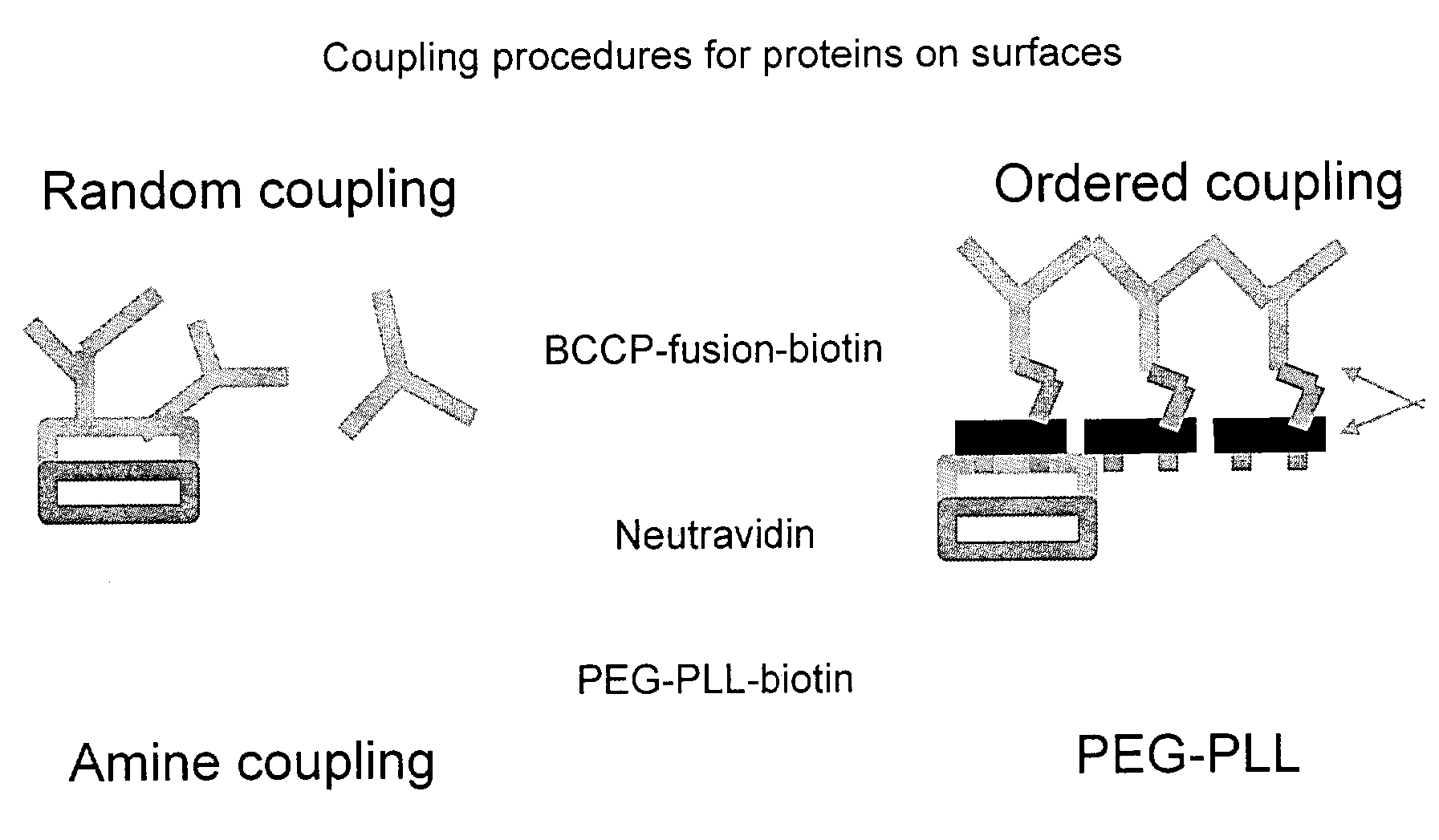
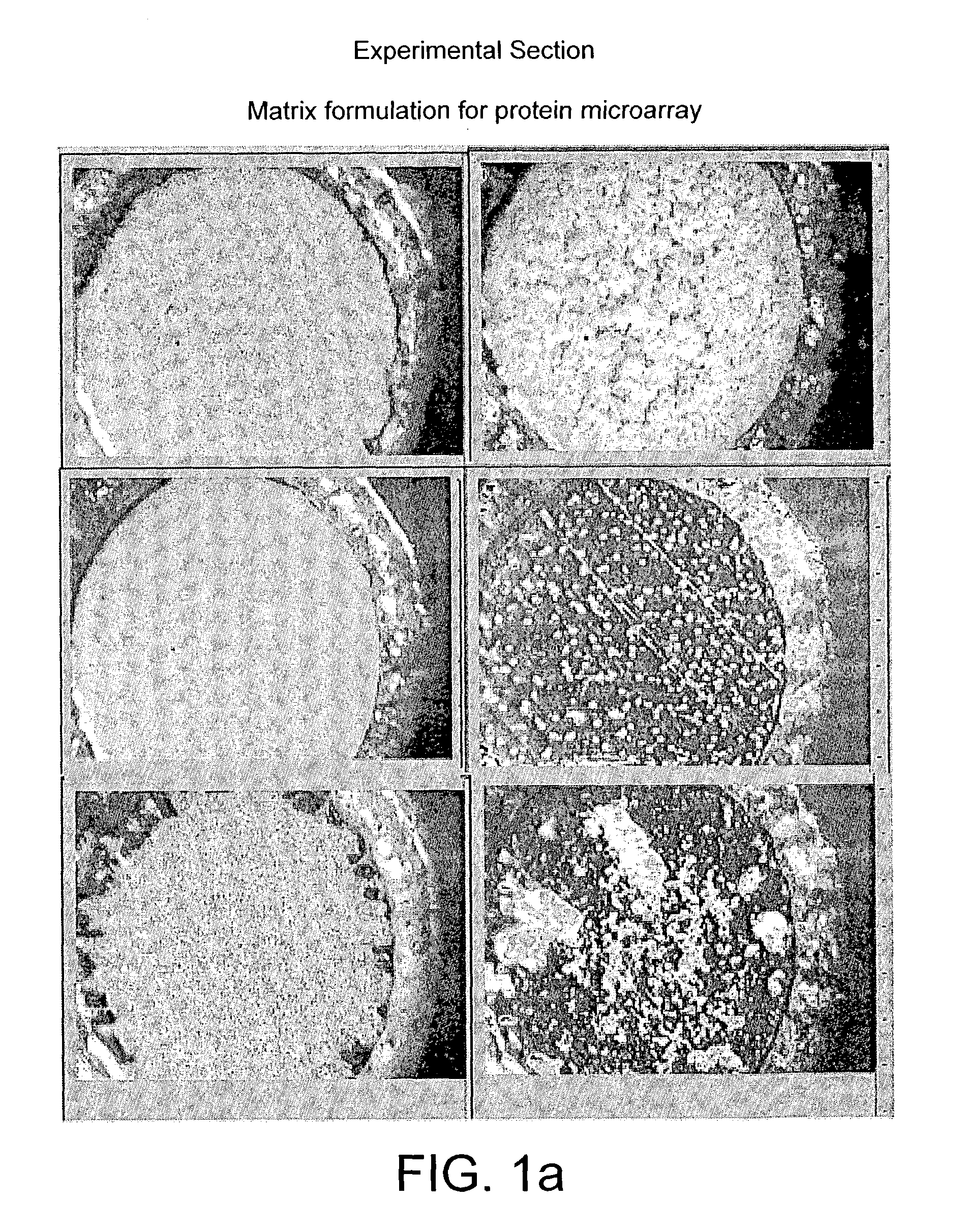
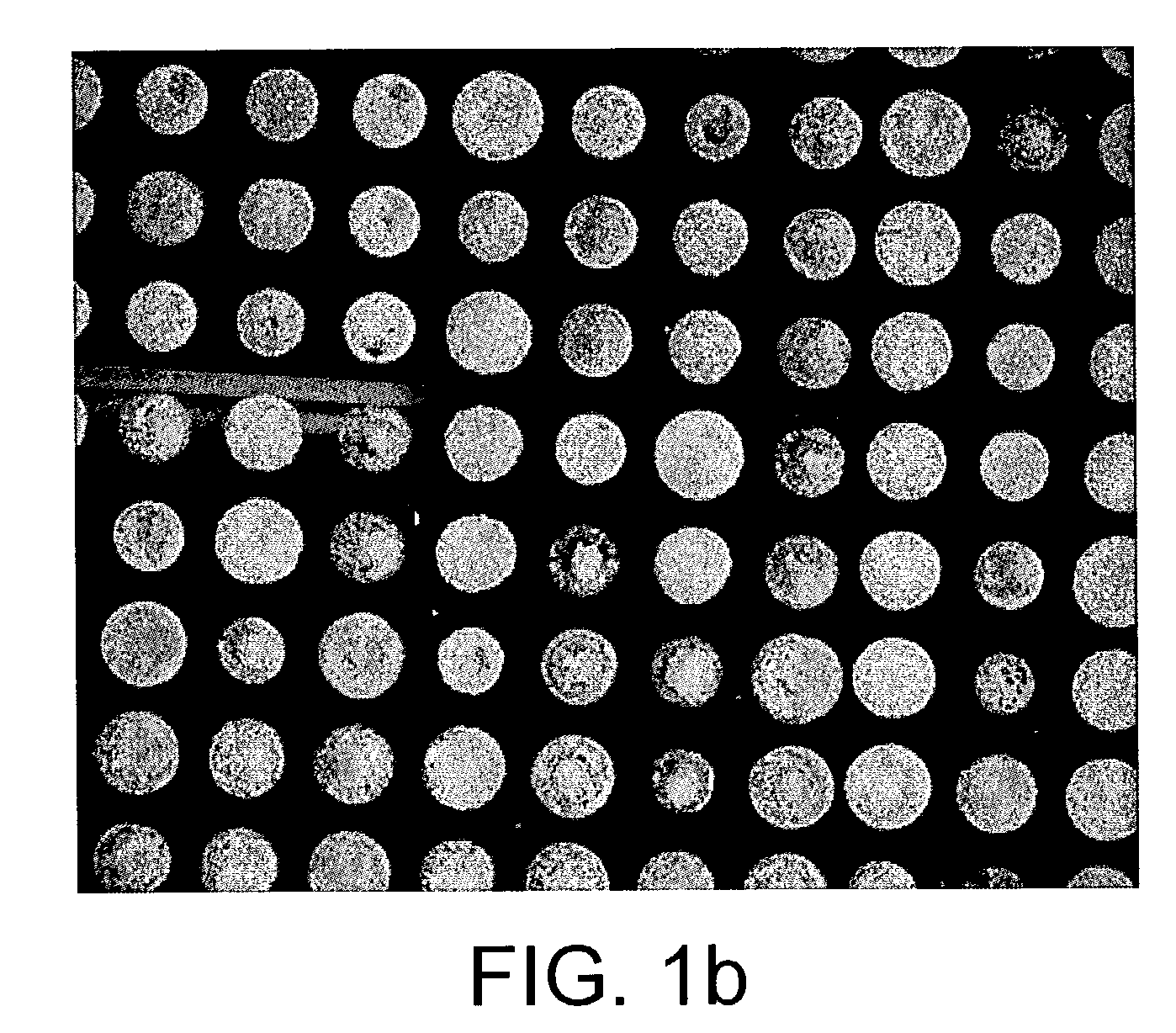
Probe for mass spectrometry
InactiveUS7057165B2High affinitySignificant biological activityMaterial nanotechnologySamples introduction/extractionTarget surfaceAnalyte
The present invention relates to a probe for the analysis of one or more analytes, particularly proteins or compounds capable of binding or otherwise interacting therewith, by laser desorption / ionization mass spectrometry, more particularly MALDI MS. It also relates to a protein microarray, a method of producing a protein microarray and a method of analyzing a protein microarray. The probe comprises a support having an electroconductive target surface thereon characterized in that the target surface comprises a micro array having a plurality of discrete target areas presenting one or more analyte capture moieties. Each discrete target area has an area of less than 1000 μm2, more preferably still less than 500 μm2, and more preferably still less than 100 μm2.
Owner:SENSE PROTEOMIC LTD
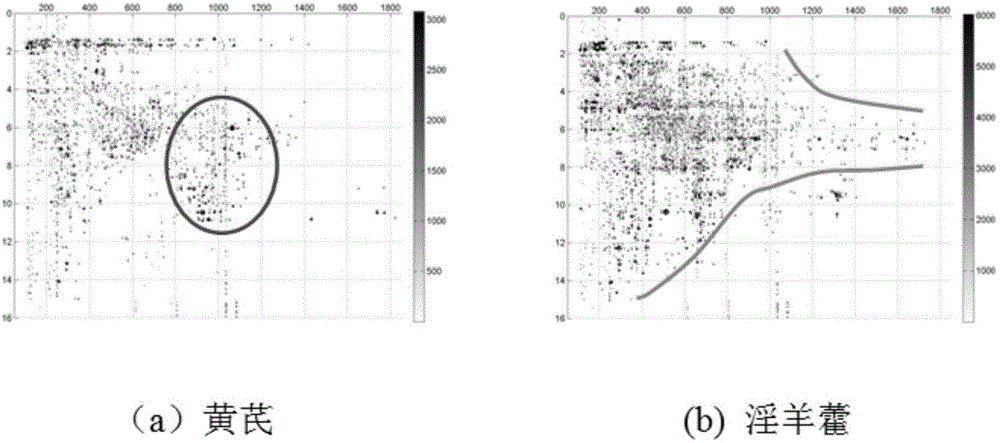
Mass spectrometry information-based biological characteristic image identification method
ActiveCN105574474AEasy to identifyEasy to extract featuresMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCharacter and pattern recognitionClustered dataMass spectrometry imaging
The invention provides a mass spectrometry information-based biological characteristic image identification method. The method comprises the steps as follows: firstly, chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis is carried out on a sample, and m / z, t and I of compounds in the sample are obtained; with m / z and t as coordinates, the mass spectrometry signal intensity of the compounds is represented by chromatic values of points; a generated m / z-t-I image is suitable for identification of the sample; biological characteristics in the sample are converted into spatial characteristics by extracting overall spatial information and local spatial information, for example, outlines, textures or colority from the image; the sample in which the composition or abundance of each compound is different displays specific spatial information; and closely clustered data points are selected, the characteristic region of the image is found out; and similarity analysis is carried out for sample identification and nature judgment. The mass spectrometry information-based biological characteristic image identification method breaks through a method for identifying the sample by mass spectrometry signal intensity or a method for identifying the sample by only mass spectrometry information of a few of index compounds and greatly improves the mass spectrometry-based complicated sample identification ability.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cascade mass spectrometry method performed in ion trap mass analyzer
ActiveCN103413751AAchieve dissociationSimplify the experimental processStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansHigh energyMass analyzer
The invention belongs to the technical field of mass spectrometry and particularly relates to a cascade mass spectrometry method performed in an ion trap mass analyzer. The cascade mass spectrometry method performed in the ion trap mass analyzer specifically comprises three stages of ion selective segregation, collision induction dissociation and mass scanning and analyzing. According to the cascade mass spectrometry method performed in the ion trap mass analyzer, in the stage of collision induction dissociation, by changing the period of a radio frequency signal, namely changing the frequency of radio-frequency voltage loaded on an ion trap, parent ions with a certain mass-to-charge ratio undergo resonance excitation so as to obtain energy. The high-energy ions which undergo resonance excitation collide with neutral molecules in the ion trap and are dissociated, outcome ions are generated, and the cascade mass spectrometry is achieved. The cascade mass spectrometry method performed in the ion trap mass analyzer has the advantages that only arrangement of software can be used for changing the scanning period of the stage of collision induction dissociation in order to achieve collision induction dissociation, and thus, an experiment device and a method of cascade mass spectrometry can be obviously simplified.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Methods for detecting dihydroxyvitamin D metabolites by mass spectrometry
ActiveUS8084269B2Facilitate desorptionGood removal effectParticle separator tubesIsotope separationMetaboliteMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
Provided are methods of detecting the presence or amount of a dihydroxyvitamin D metabolite in a sample using mass spectrometry. The methods generally comprise ionizing a dihydroxyvitamin D metabolite in a sample and detecting the amount of the ion to determine the presence or amount of the vitamin D metabolite in the sample. In certain preferred embodiments the methods include immunopurifying the dihydroxyvitamin D metabolites prior to mass spectrometry. Also provided are methods to detect the presence or amount of two or more dihydroxyvitamin D metabolites in a single assay.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com