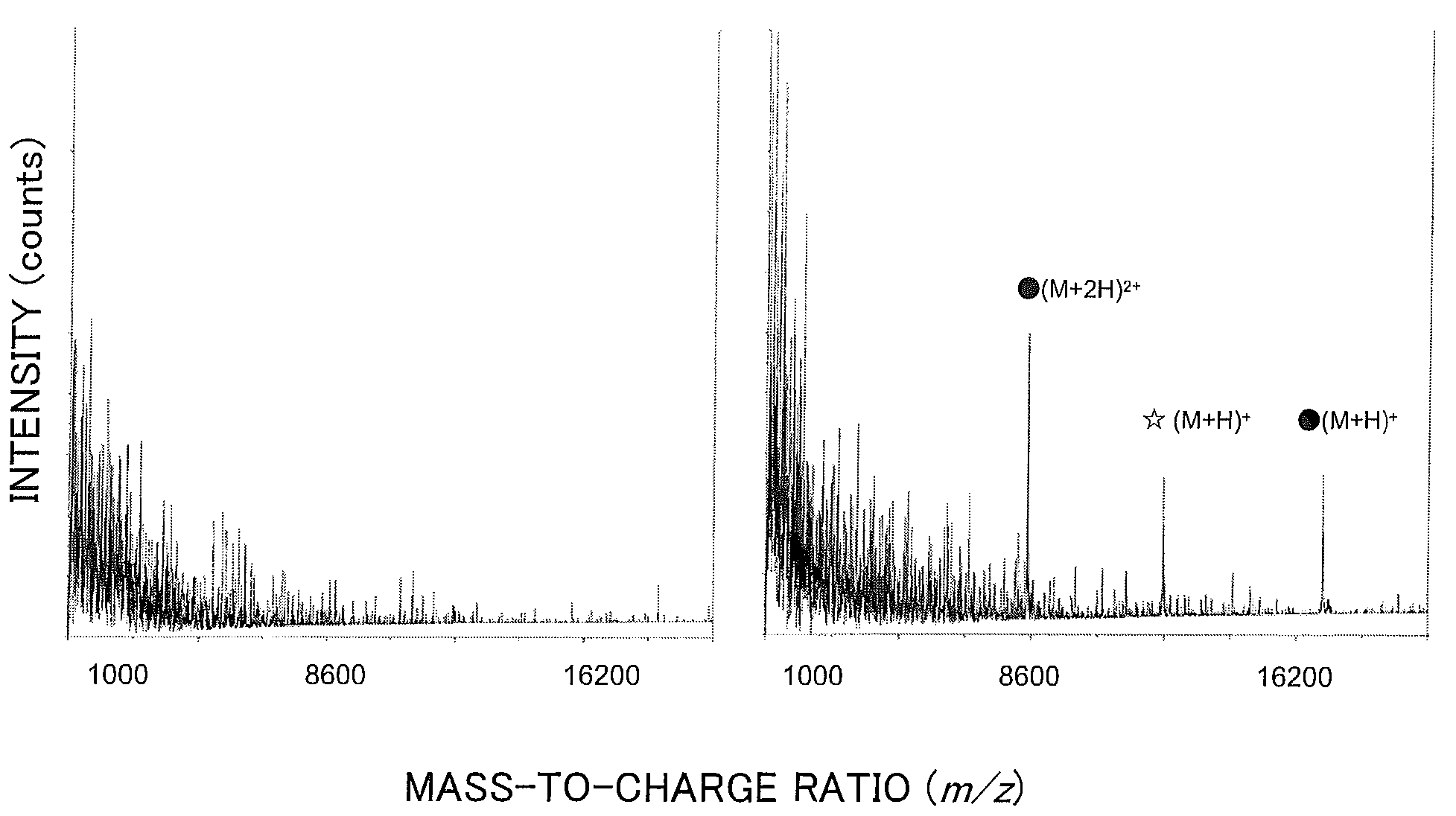
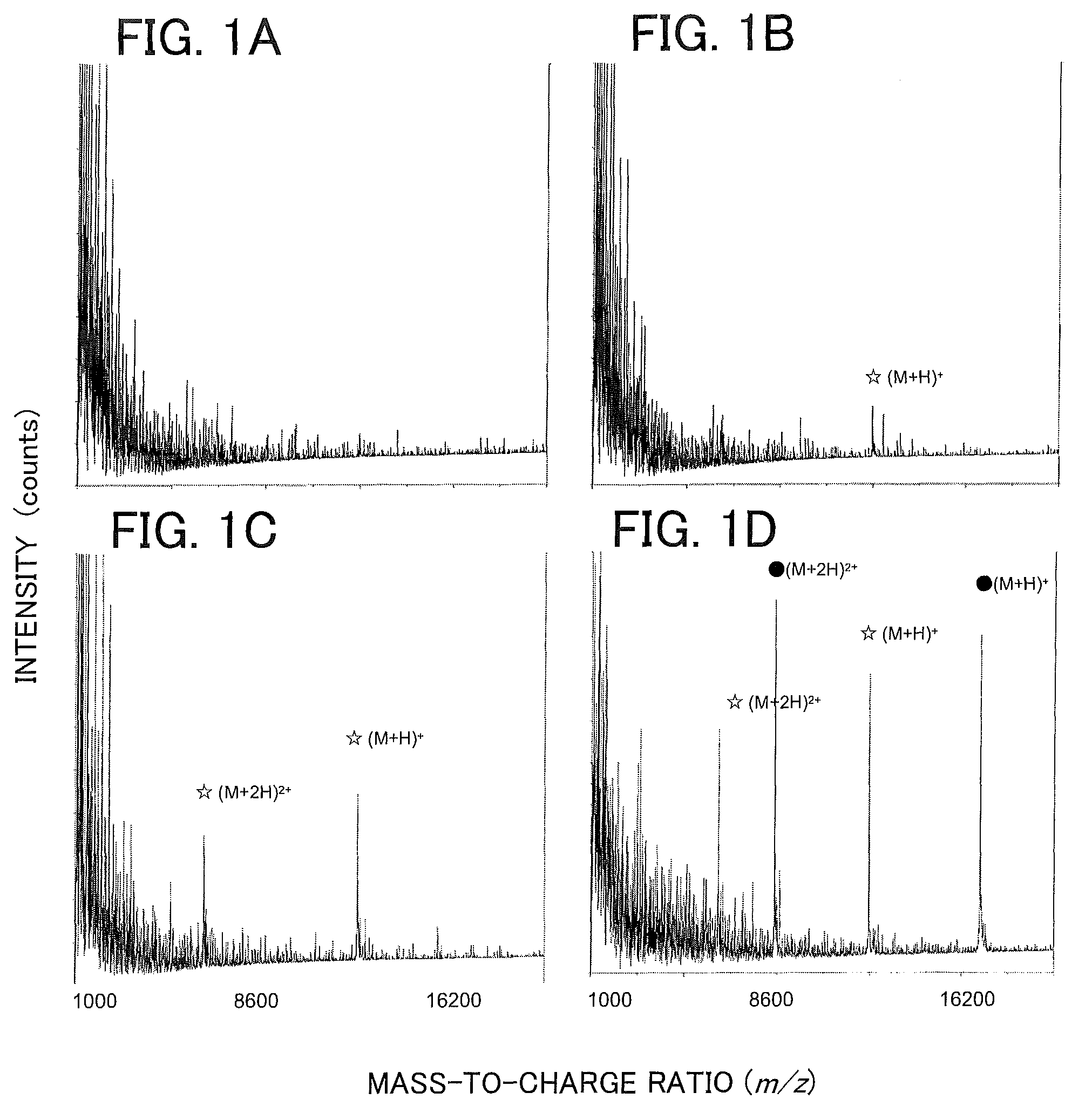
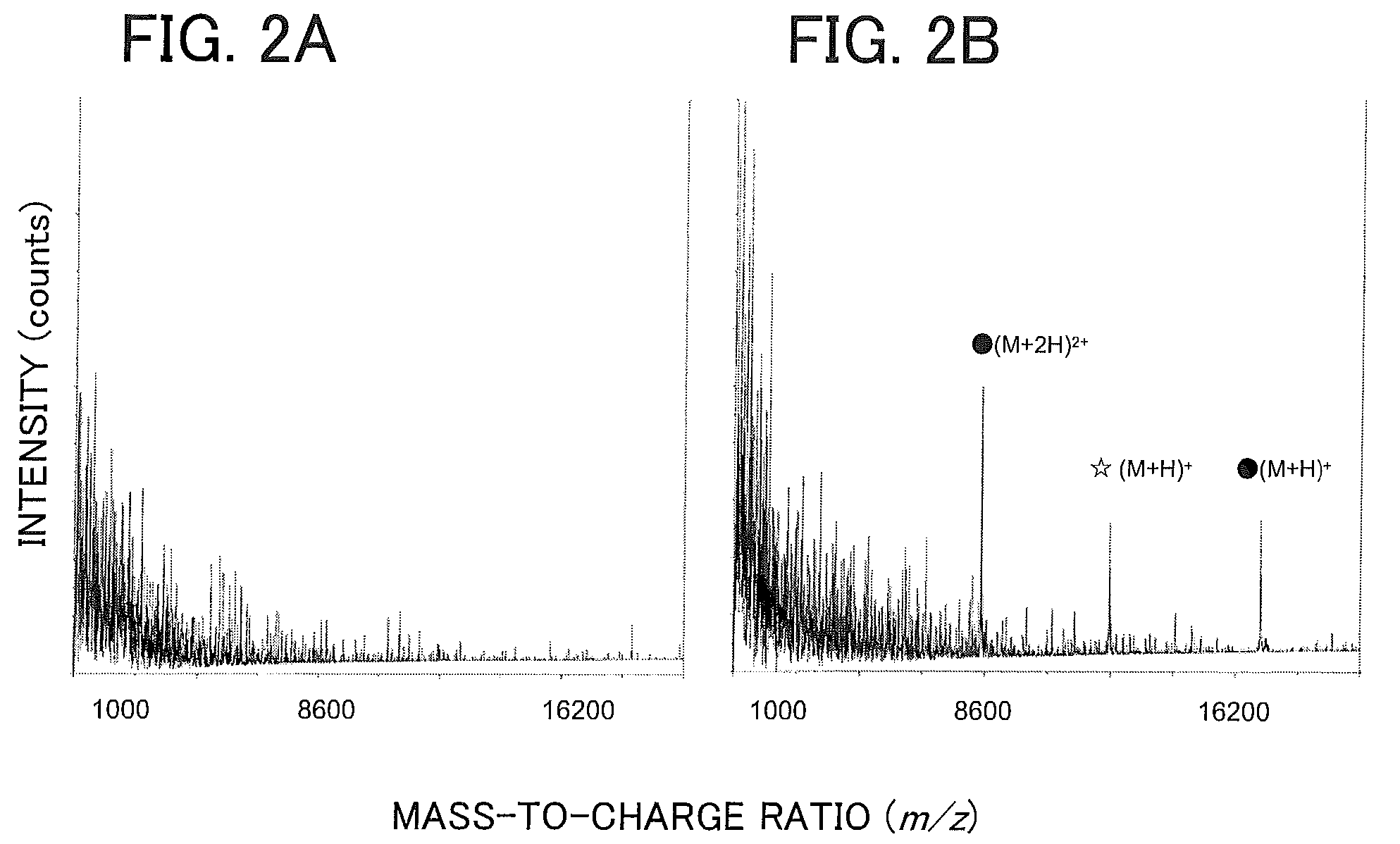
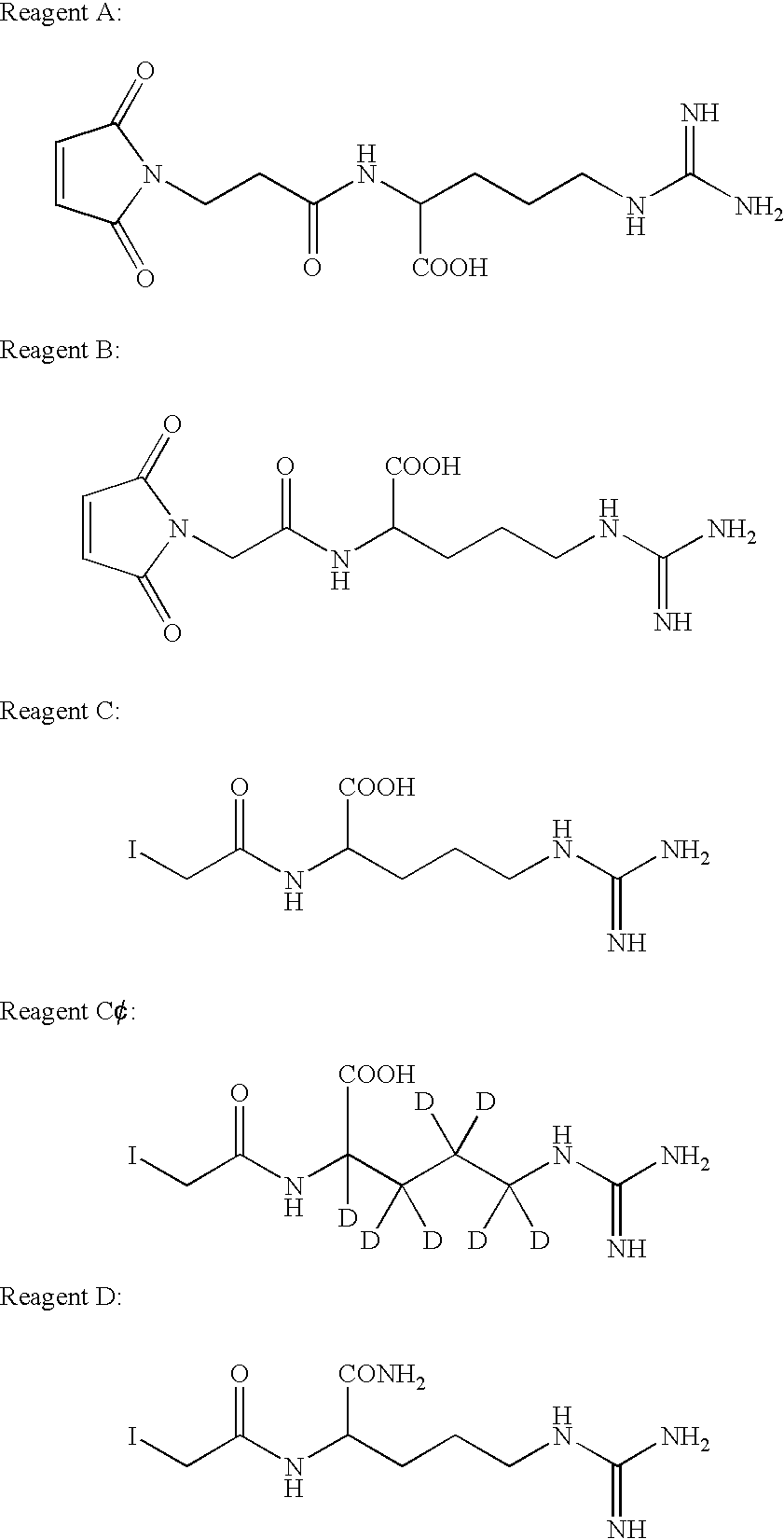
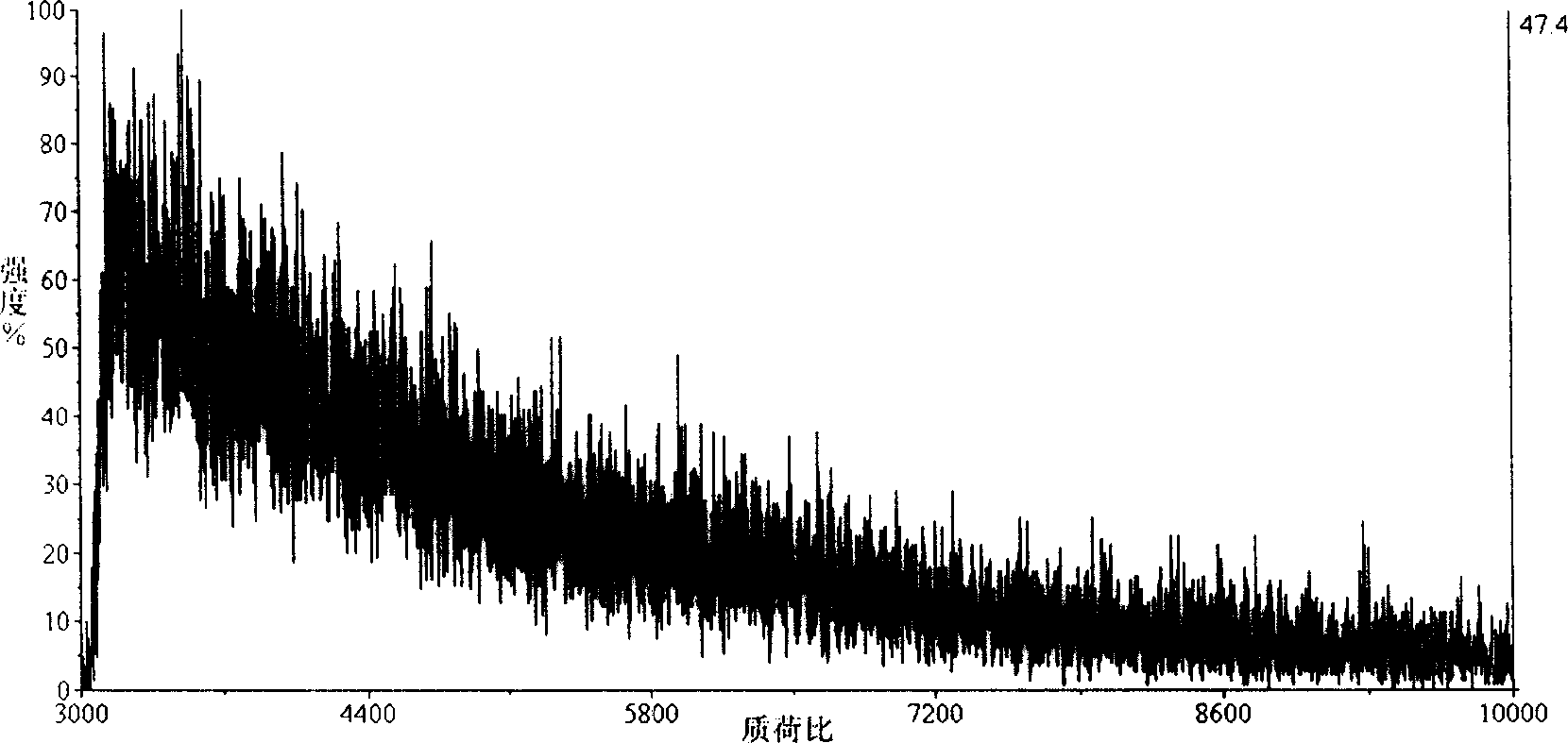
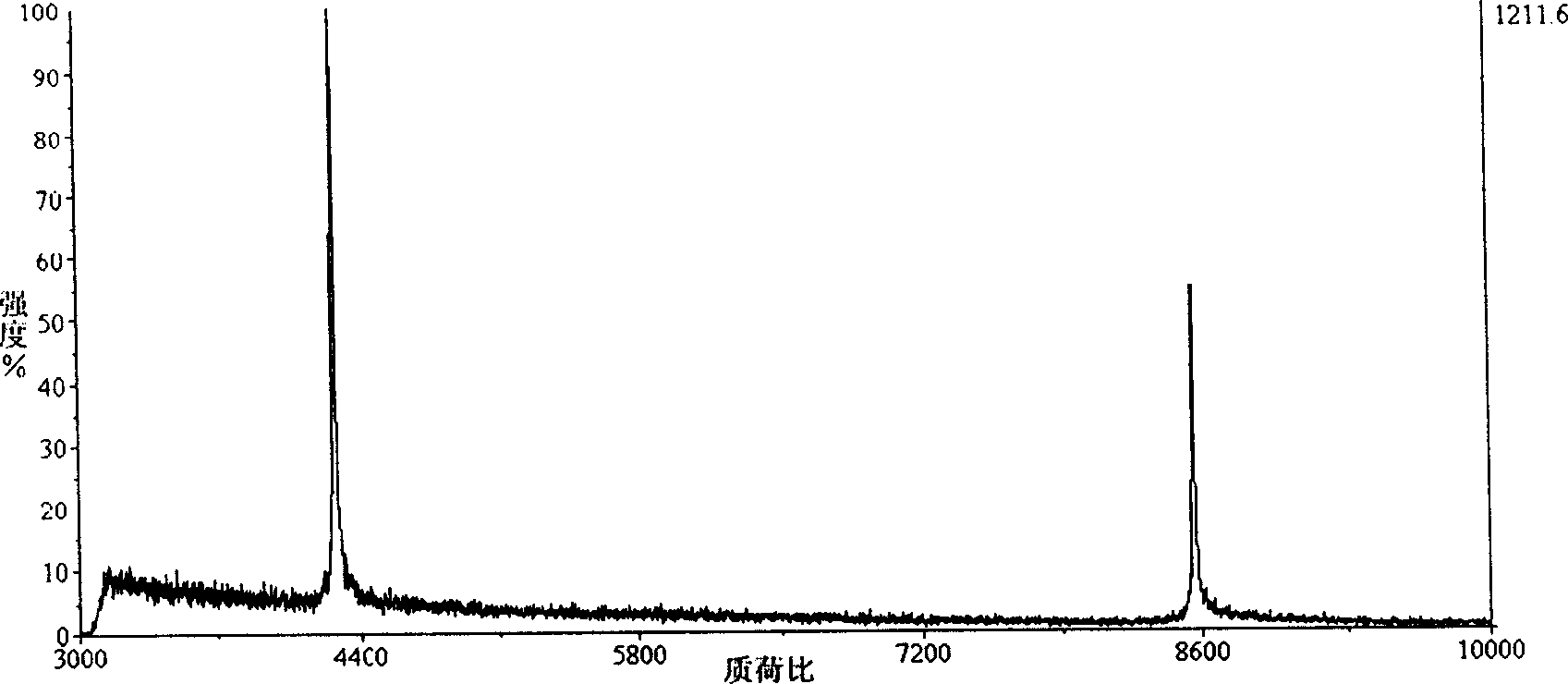
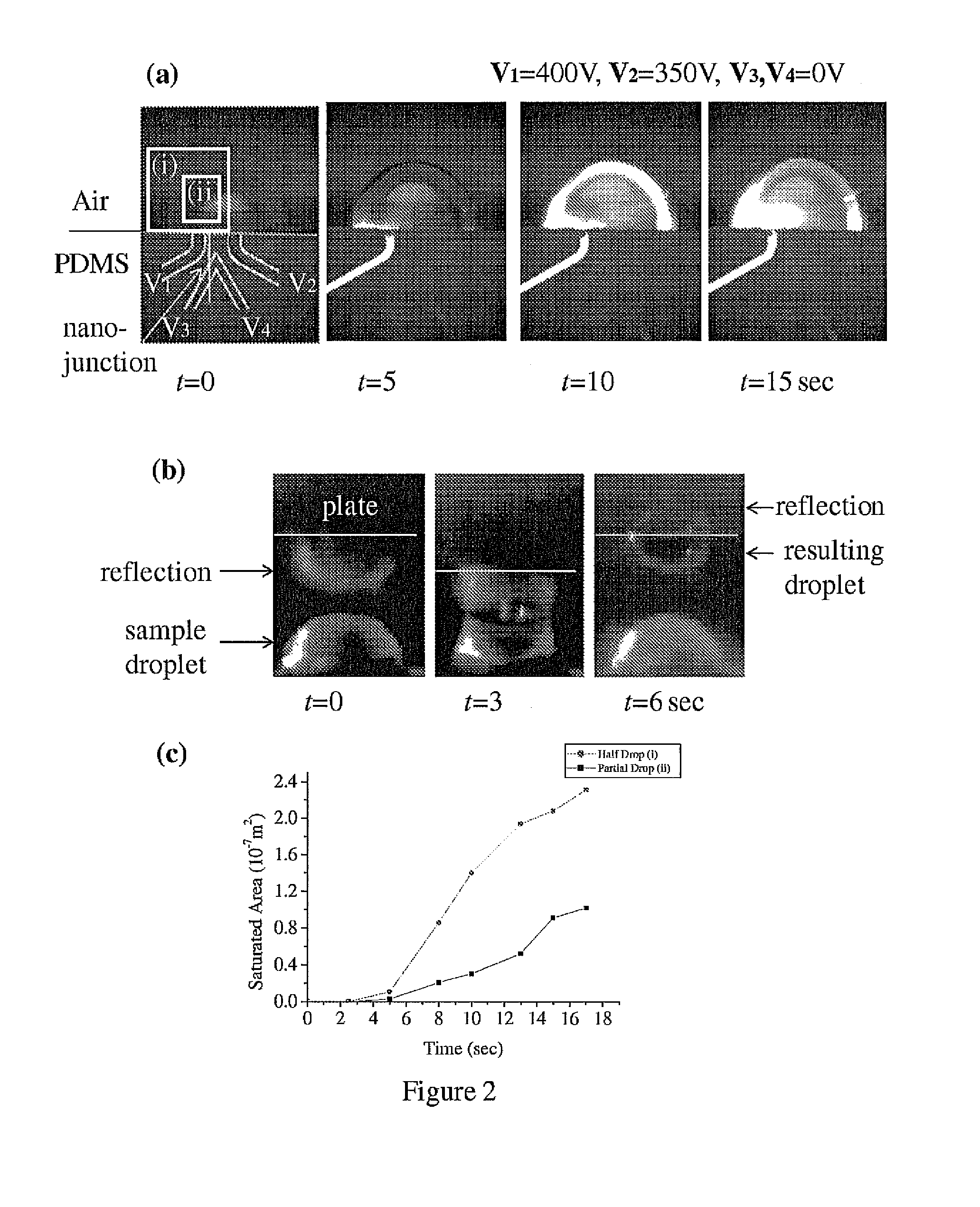
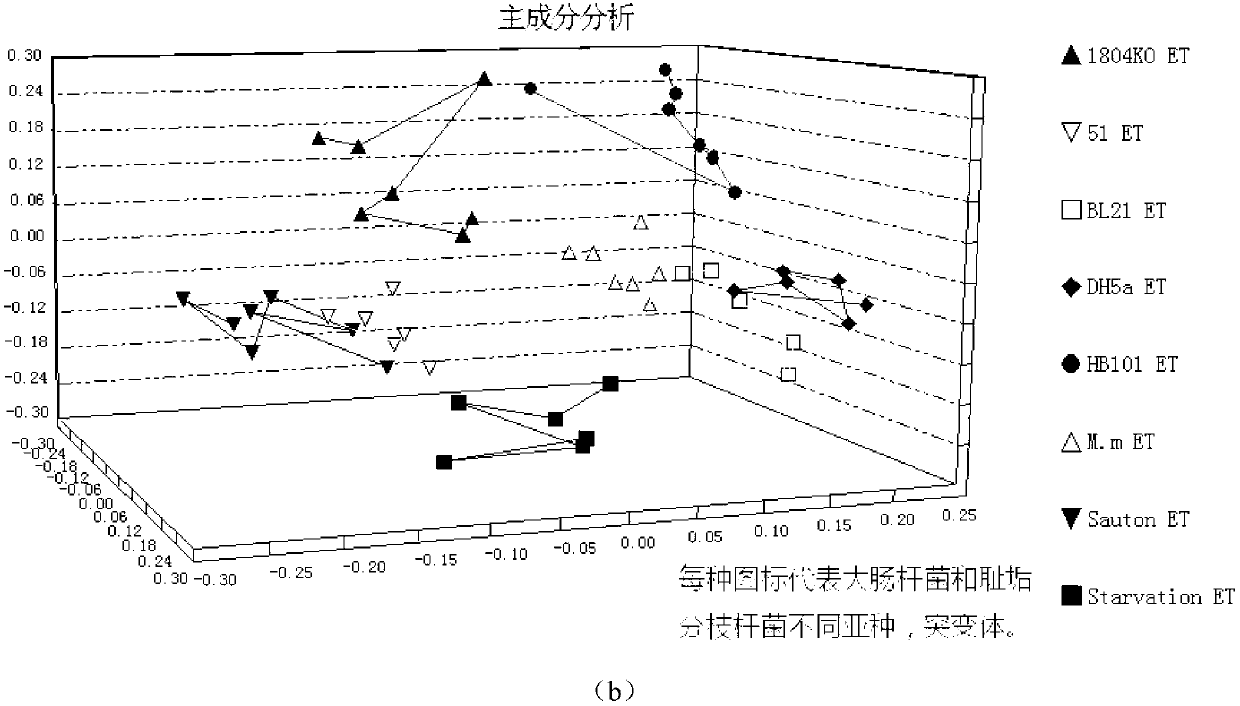
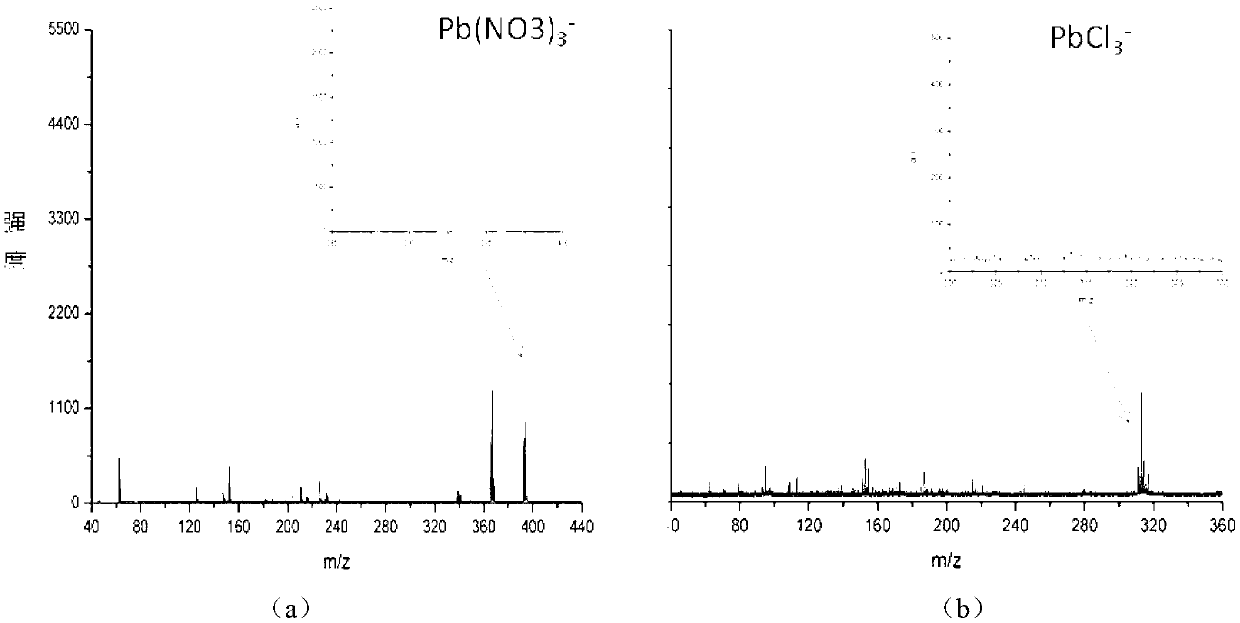
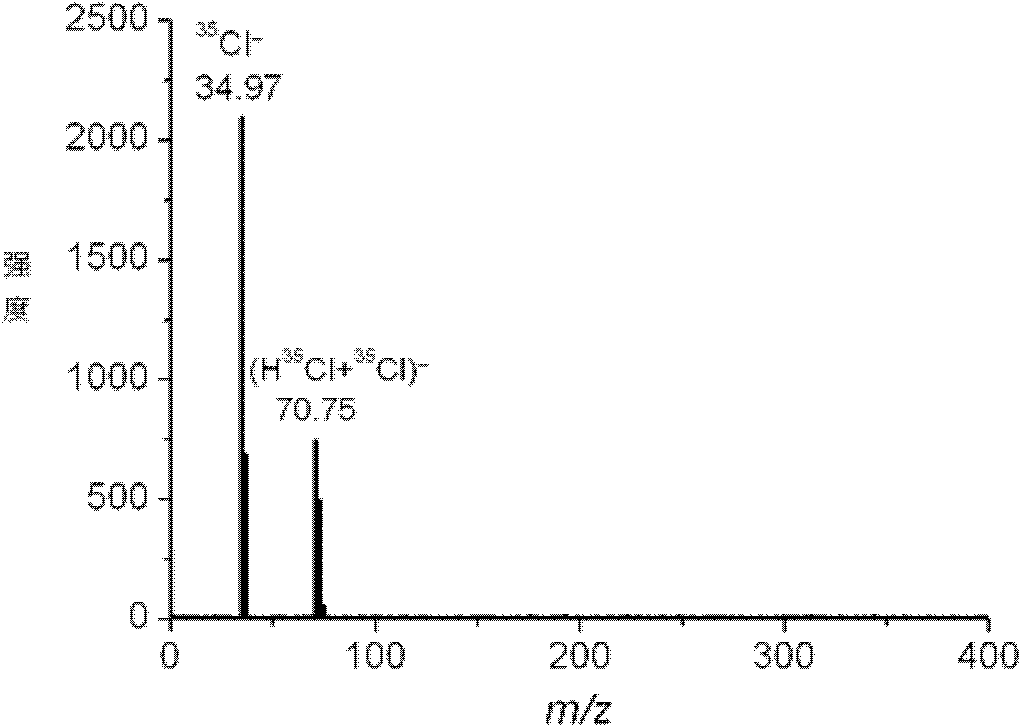
Patents
Literature
86 results about "Maldi ms" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
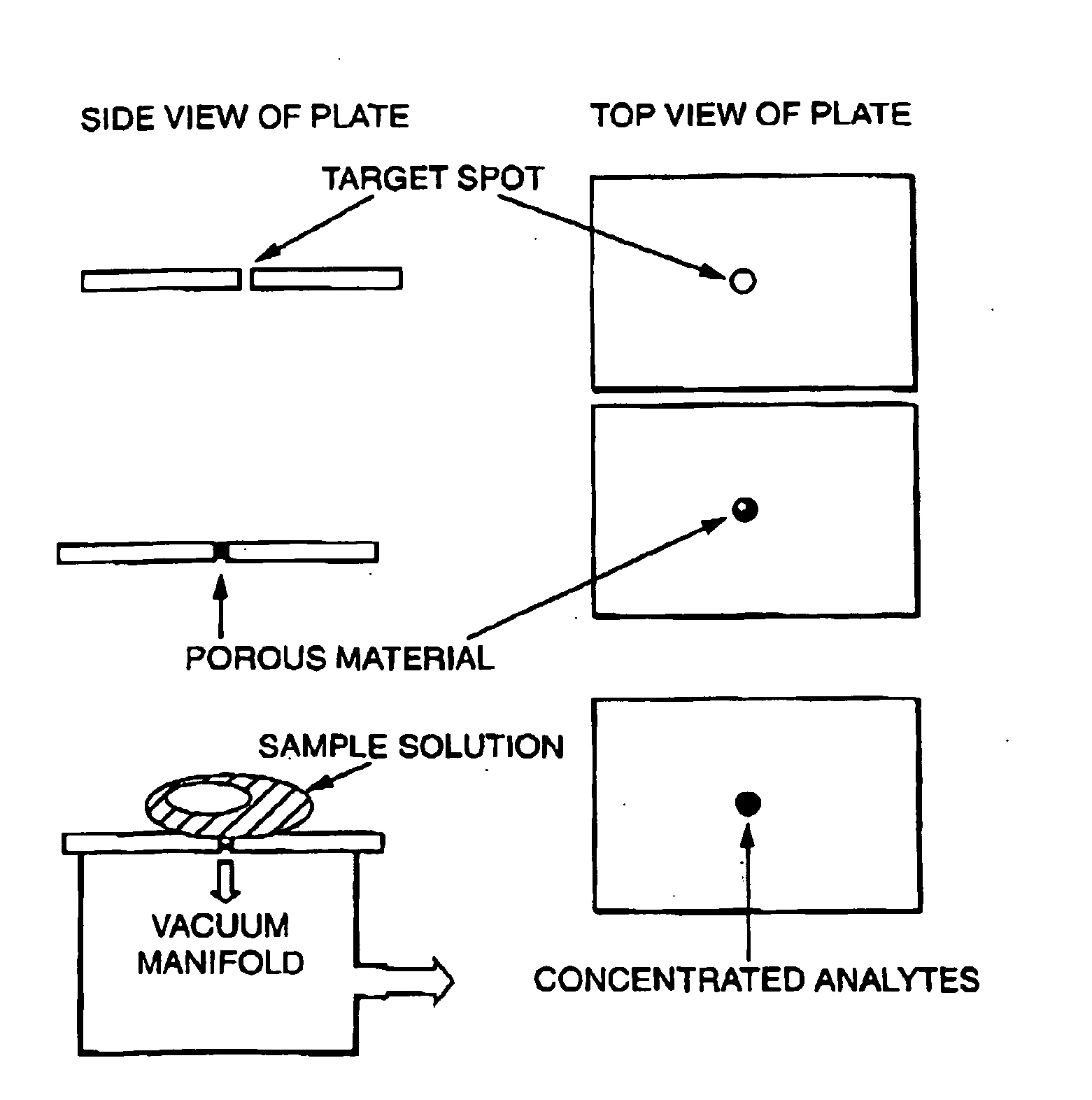
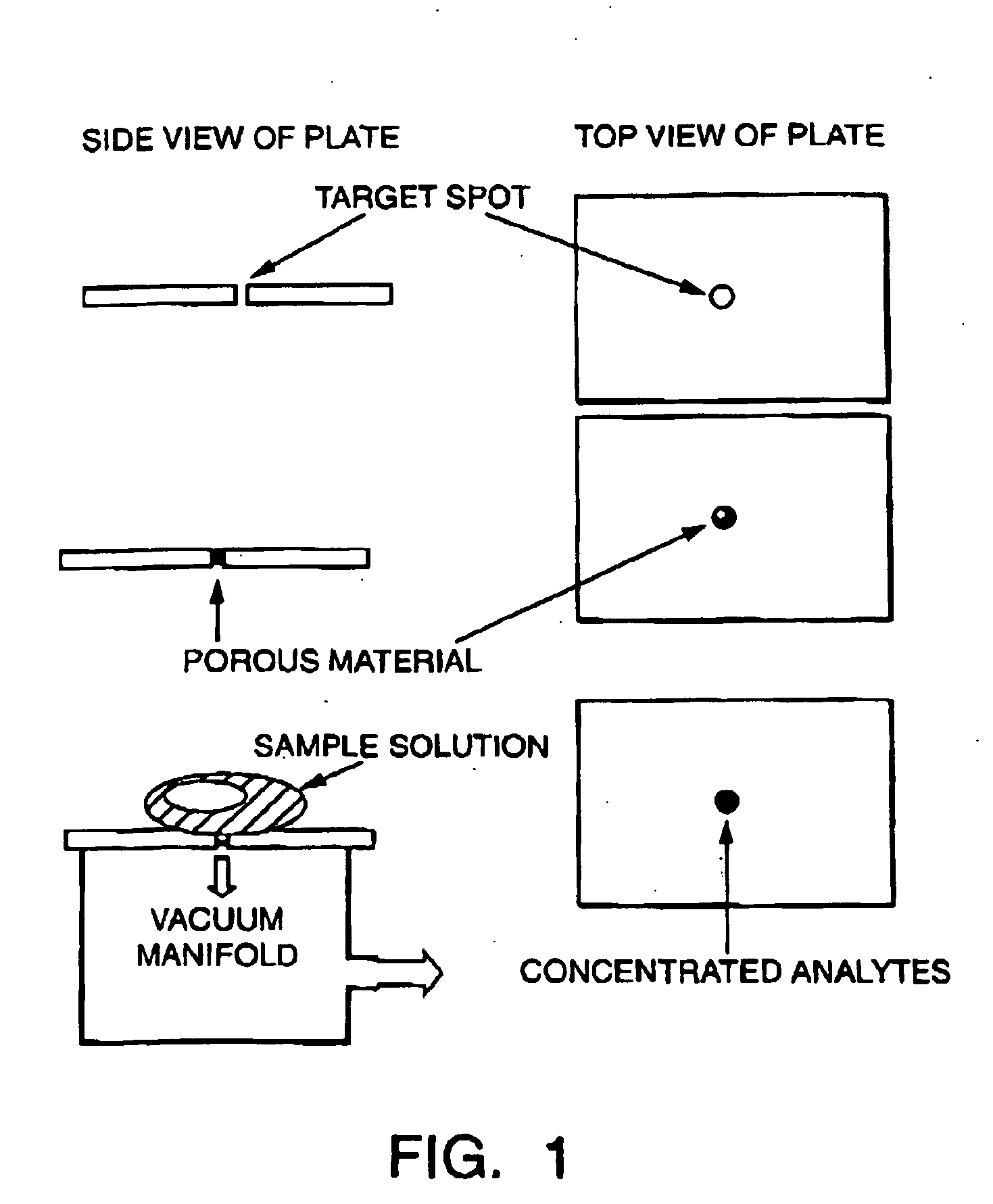
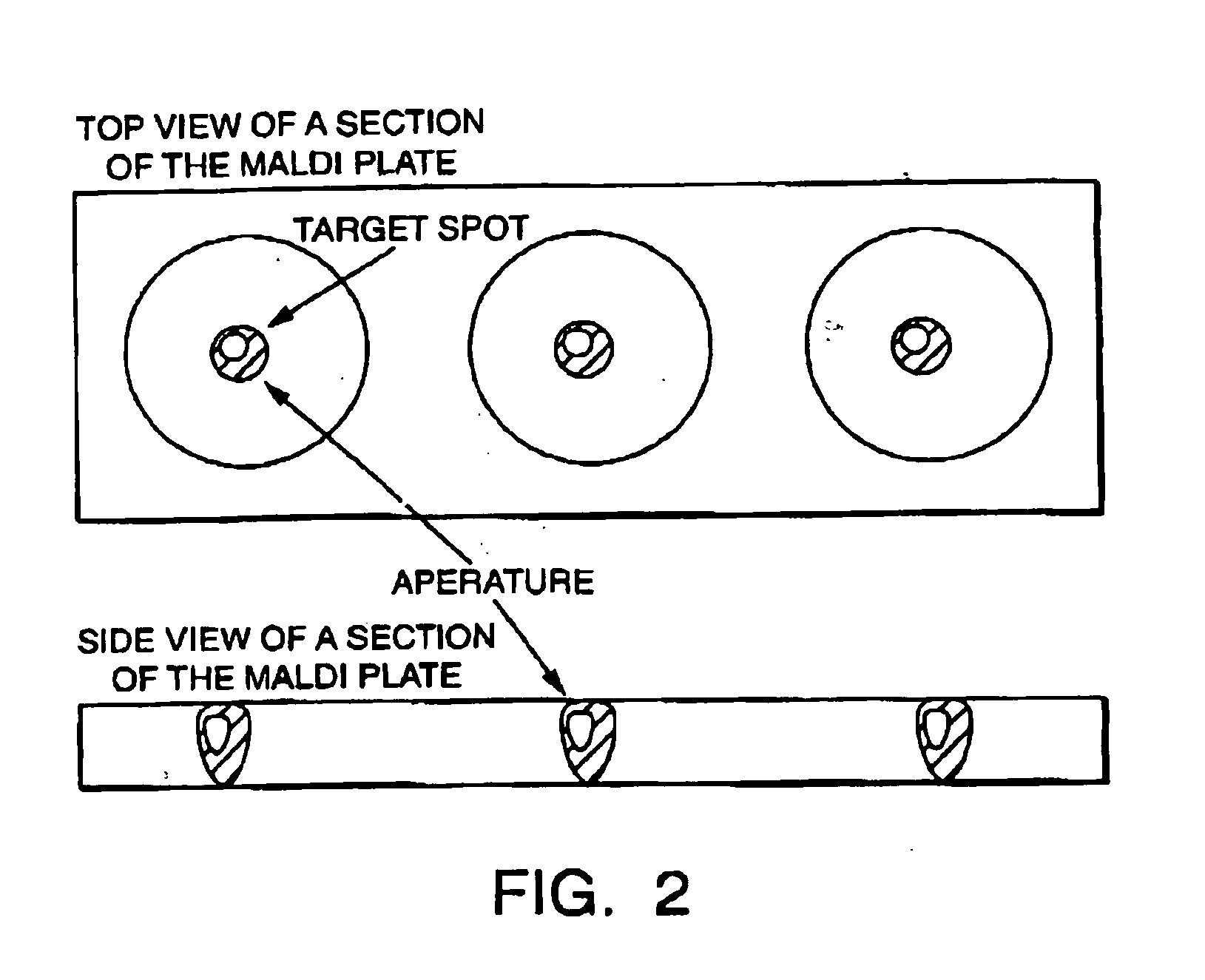
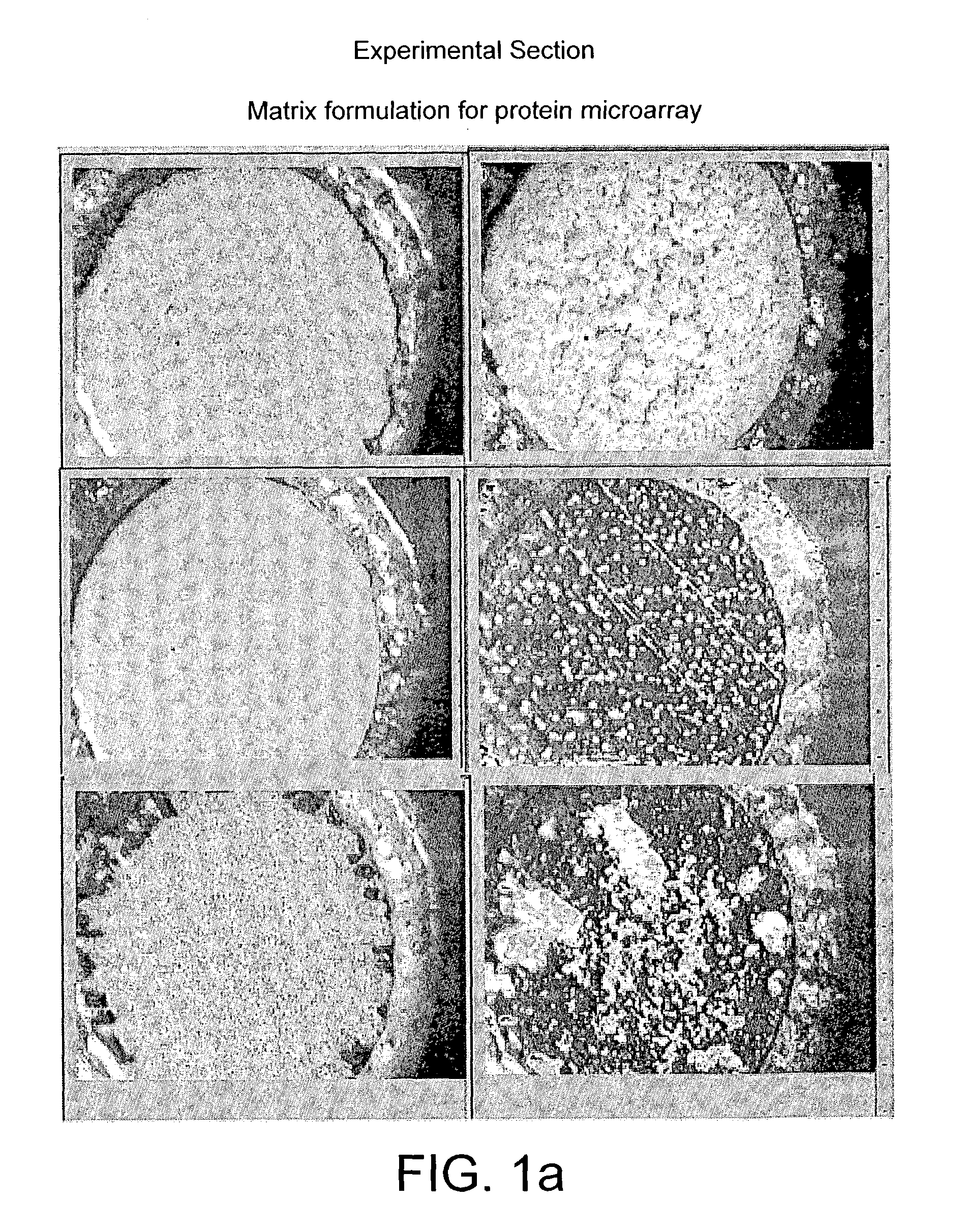
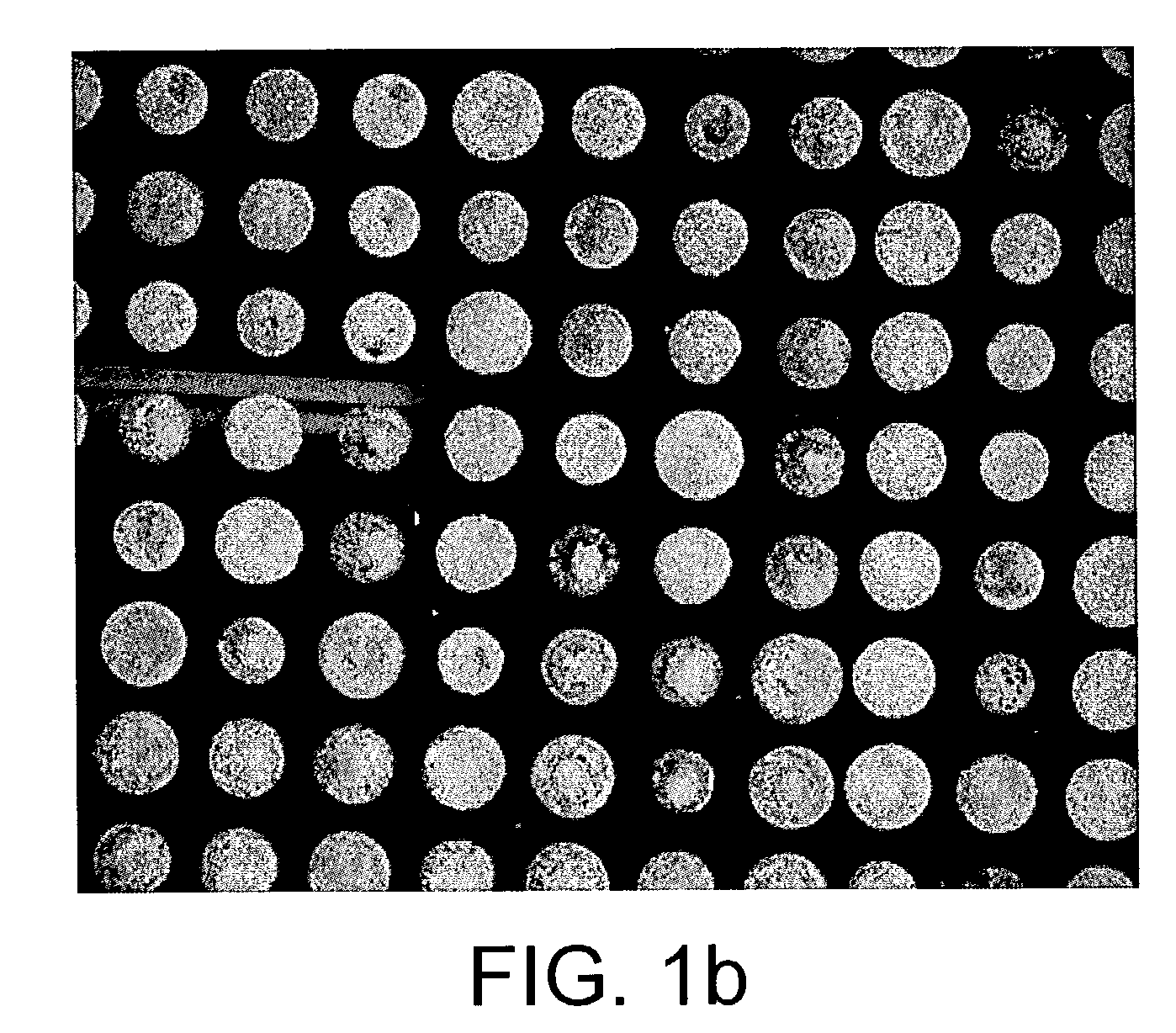
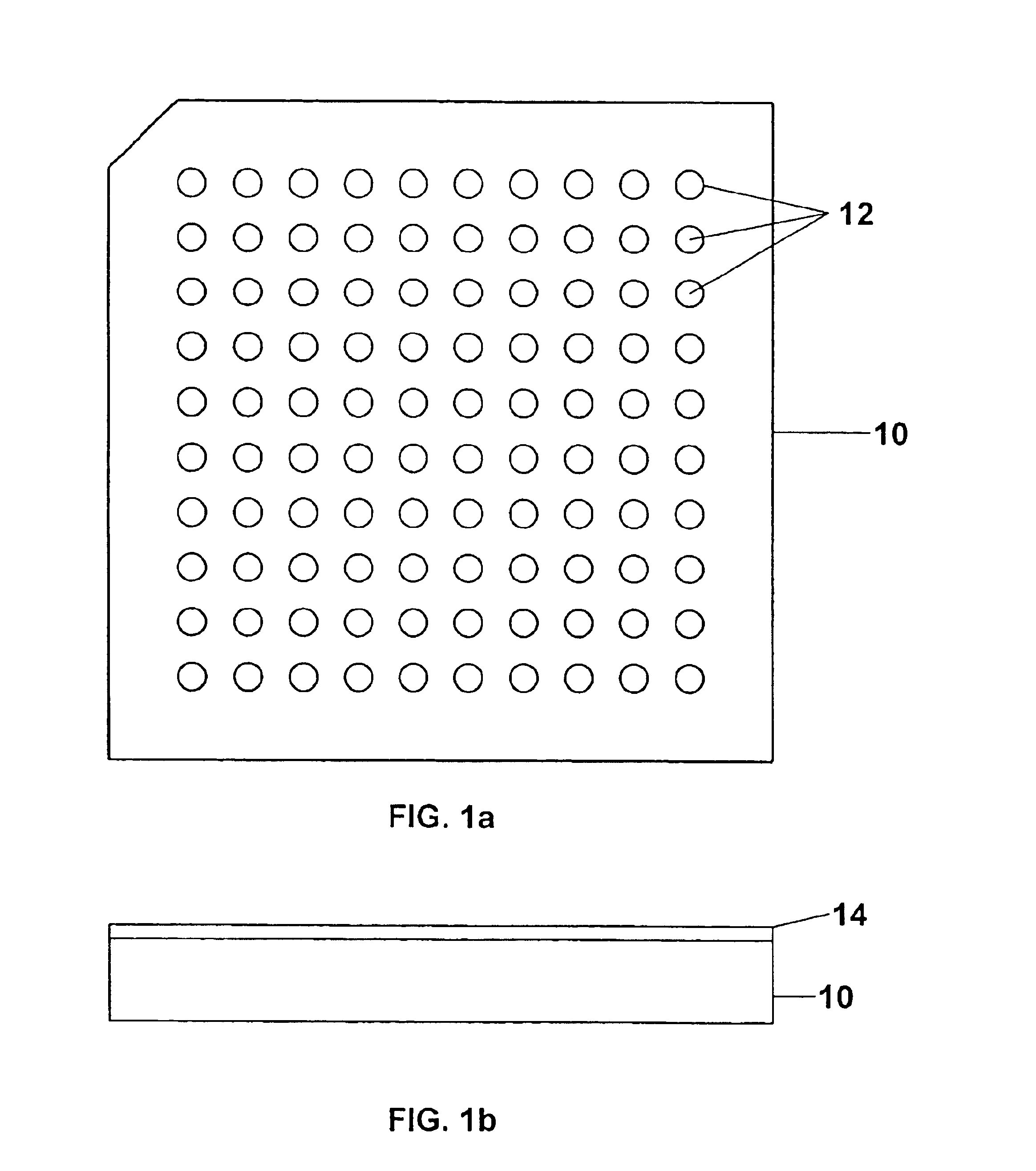
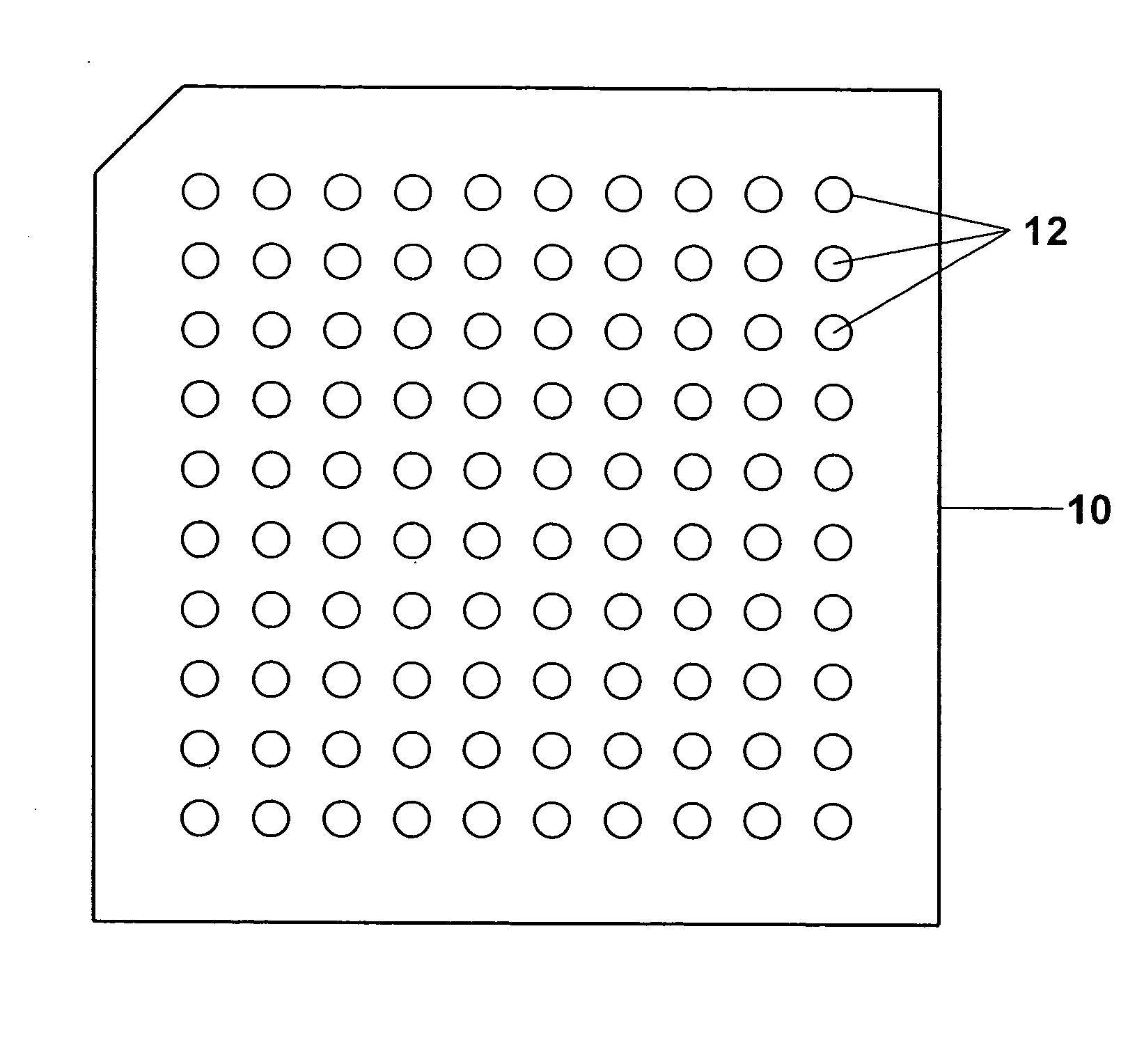
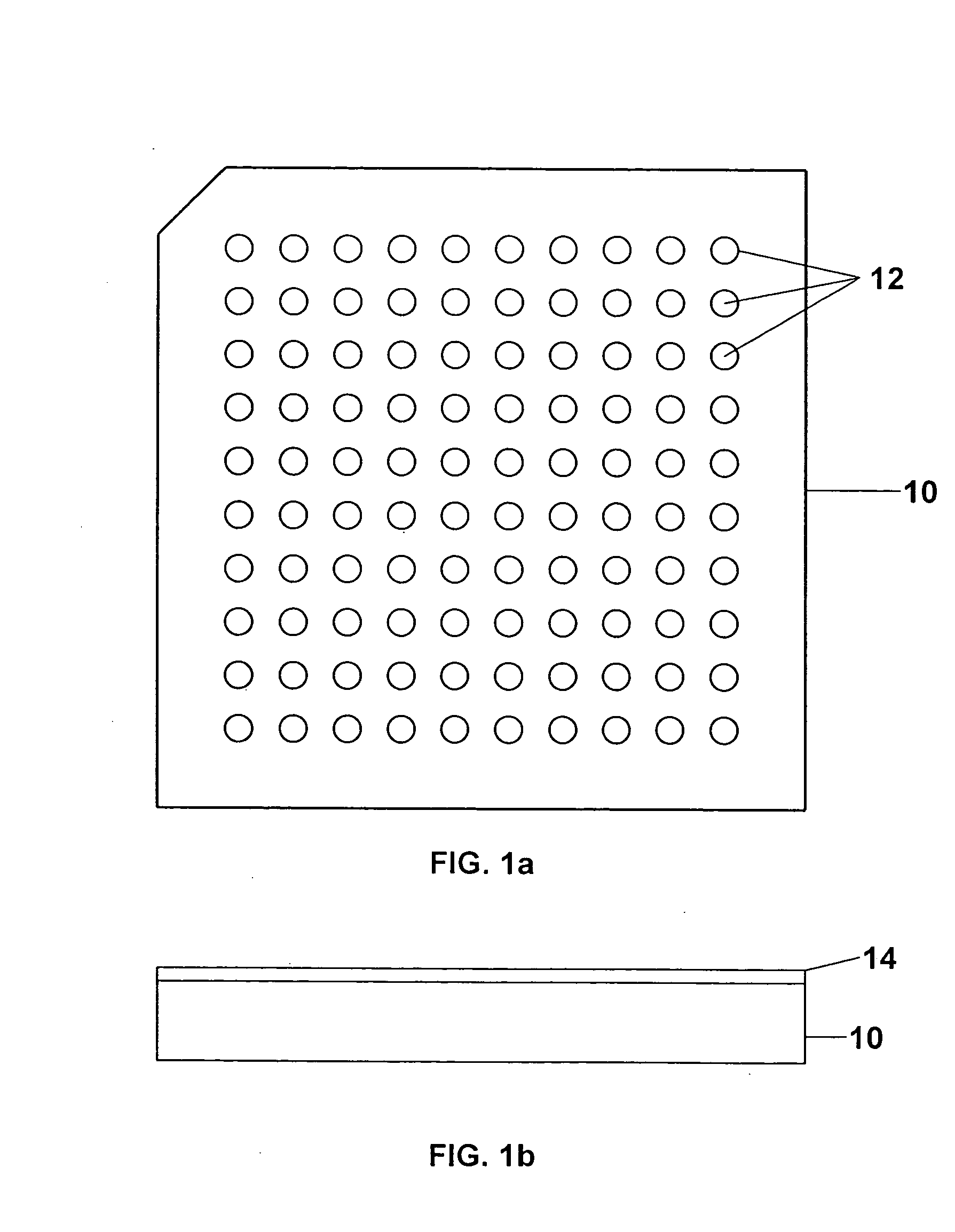
Sample concentration maldi plates for maldi mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20050130222A1Simple methodWide rangeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLaser desorption ionization mass spectrometryAnalyte
A novel Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption / Ionization Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-MS) sample support plate is described. The plate comprises a top sample presentation surface and a lower surface, wherein the top sample presentation surface comprises at least one aperture for receiving a sample. The aperture extends through and between the top sample presentation surface and the bottom surface, and contains a porous material that retains and concentrates at the target spot analyte and matrix molecules contained in the sample on the surface of the aperture. Methods for making and using the sample support plate in conventional and automated MALDI-MS are also described.
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
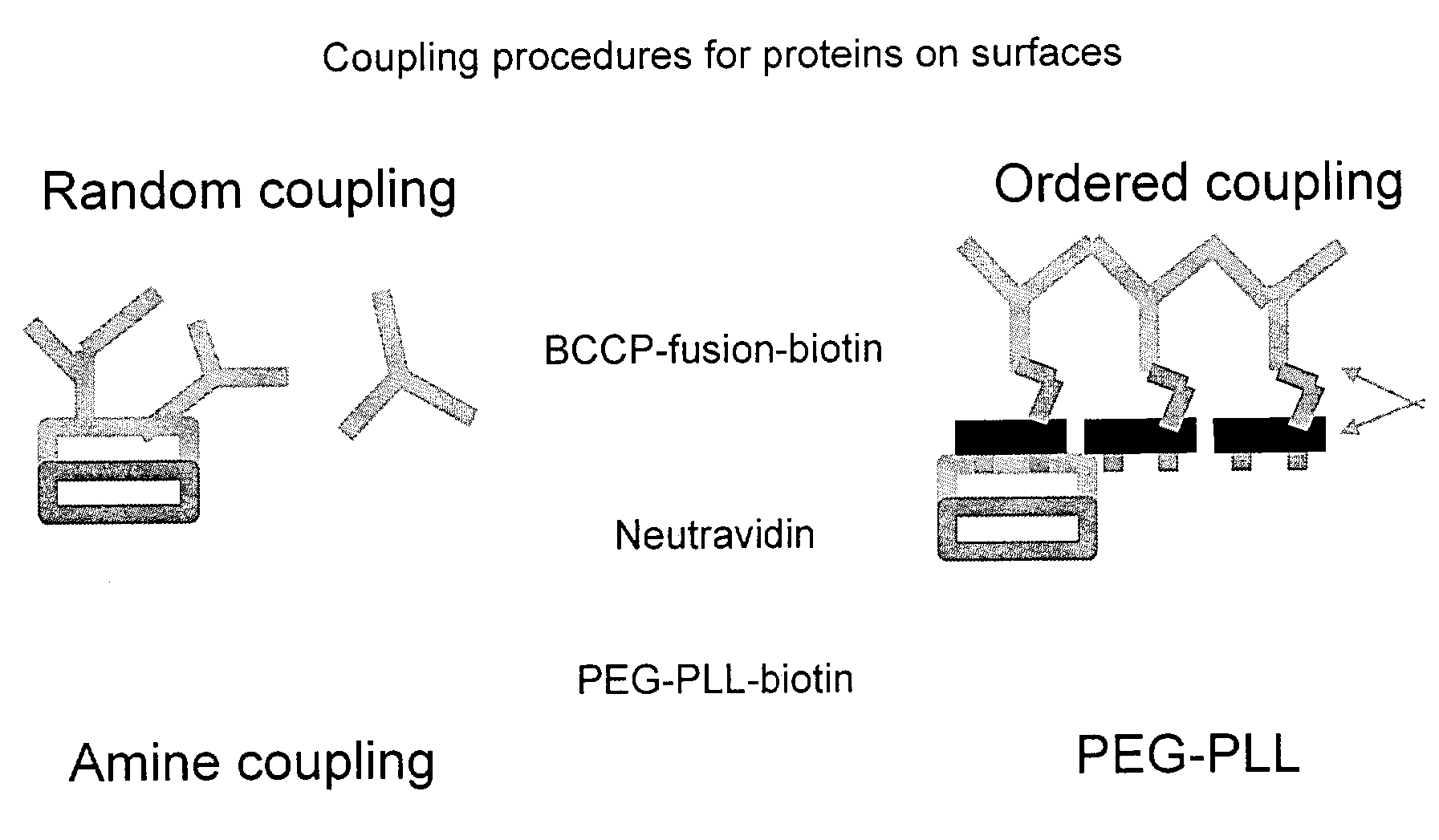
Probe for mass spectrometry
InactiveUS7057165B2High affinitySignificant biological activityMaterial nanotechnologySamples introduction/extractionTarget surfaceAnalyte
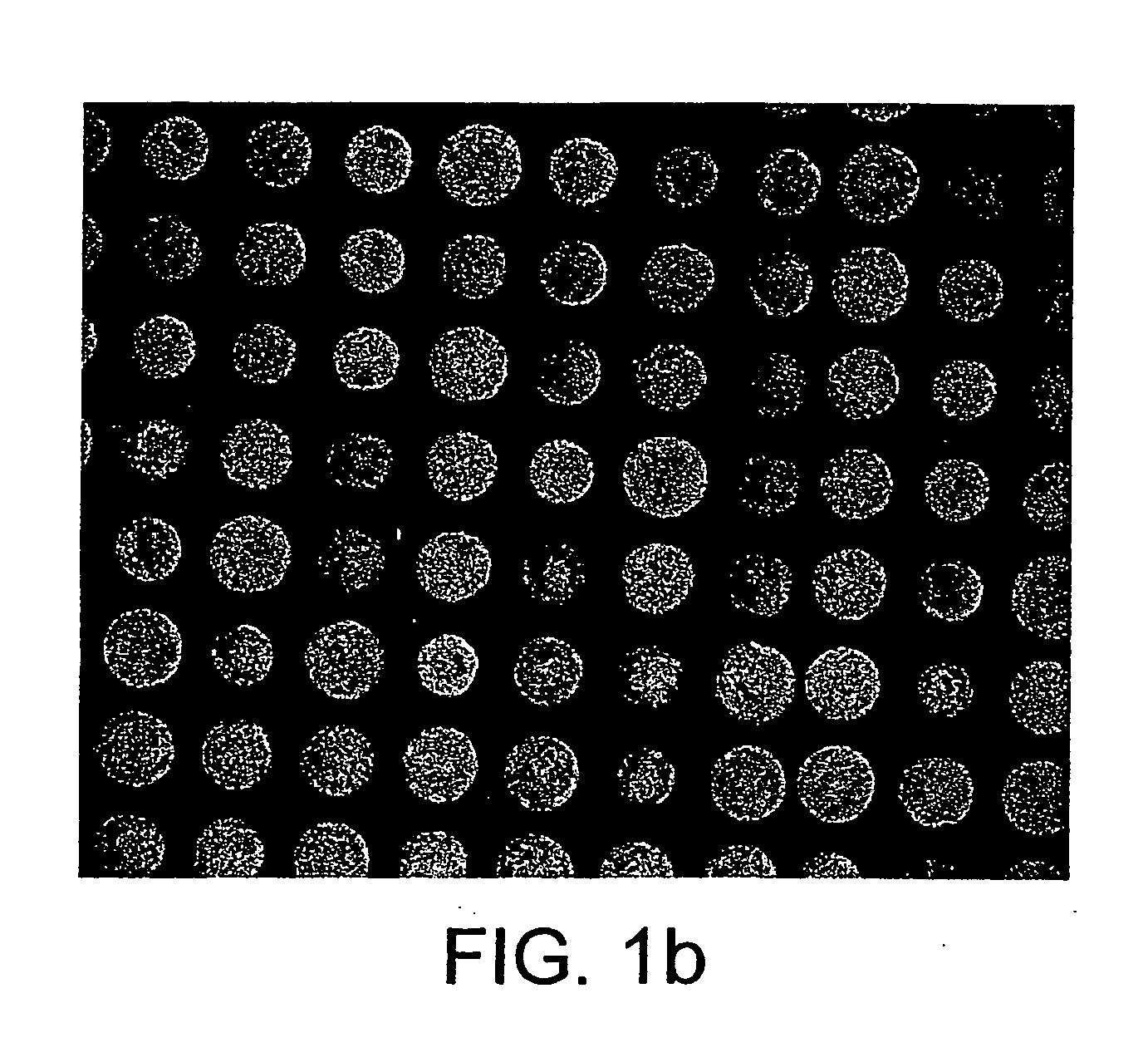
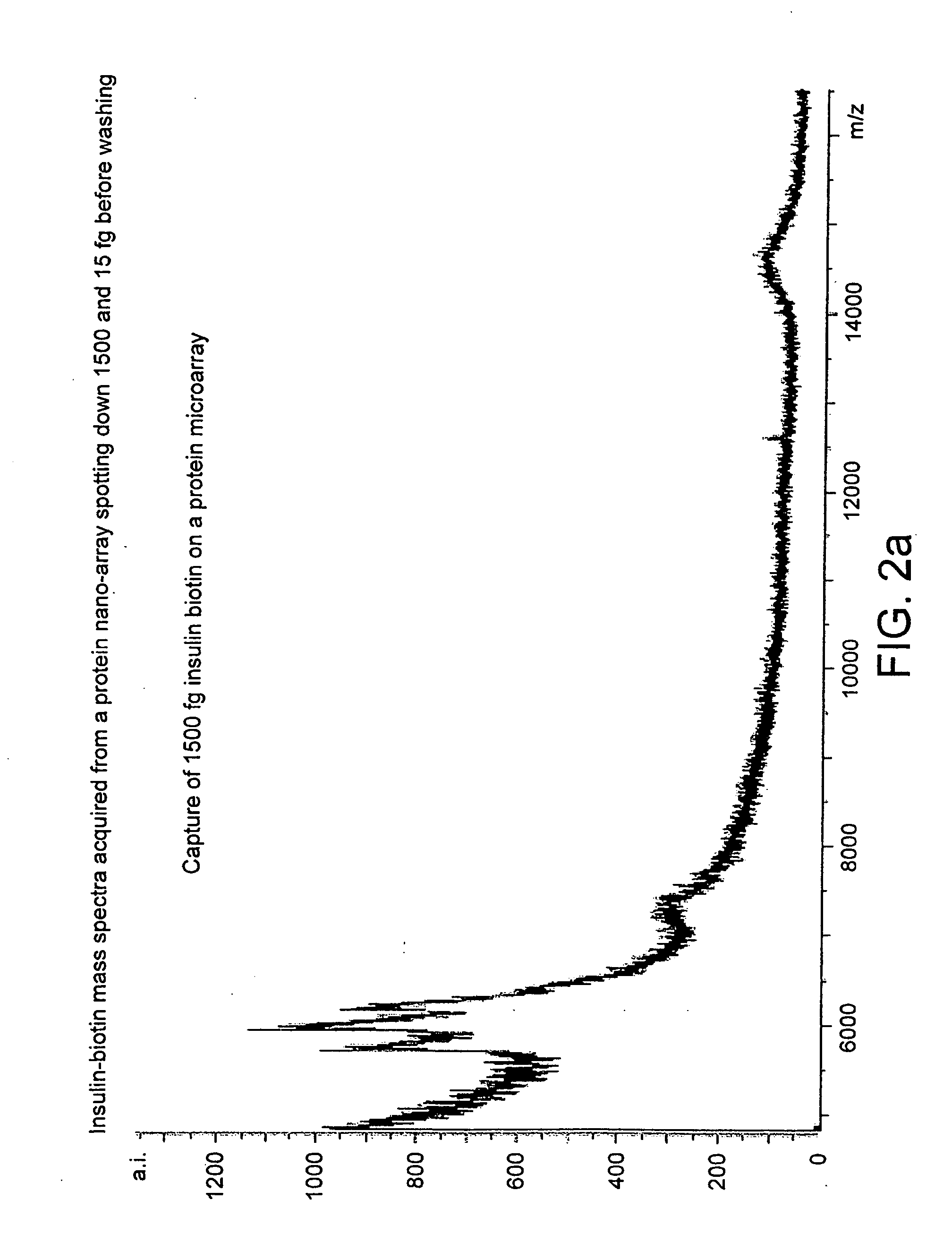
The present invention relates to a probe for the analysis of one or more analytes, particularly proteins or compounds capable of binding or otherwise interacting therewith, by laser desorption / ionization mass spectrometry, more particularly MALDI MS. It also relates to a protein microarray, a method of producing a protein microarray and a method of analyzing a protein microarray. The probe comprises a support having an electroconductive target surface thereon characterized in that the target surface comprises a micro array having a plurality of discrete target areas presenting one or more analyte capture moieties. Each discrete target area has an area of less than 1000 μm2, more preferably still less than 500 μm2, and more preferably still less than 100 μm2.
Owner:SENSE PROTEOMIC LTD
Silicon-based gold nano bowl array chip, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107515242ARealize detection and analysisEfficient use ofMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaldi msSilicon chip
The invention discloses a silicon-based gold nano bowl array chip, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The silicon-based gold nano bowl array chip comprises a gold nano bowl array and a sulfhydryl modified silicon slice; the gold nano bowl array is spread on the sulfhydryl modified silicon slice, and Au-S bond connection is formed between the gold nano bowl array and the sulfhydryl modified silicon slice. The silicon-based gold nano bowl array chip is applied in MALDI-MS detection of biomolecules. The method for MALDI-MS detection of the biomolecules comprises the following steps: dropwise adding a mixed liquid of a biomolecule sample and a matrix on the silicon-based gold nano bowl array chip, drying and crystallizing, attaching the treated silicon-based gold nano bowl array chip onto an MALDI-MS target plate, and then carrying out MALDI-MS detection. The silicon-based gold nano bowl array chip has the advantages of high sensitivity, good reproducibility, simple operation and low cost.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
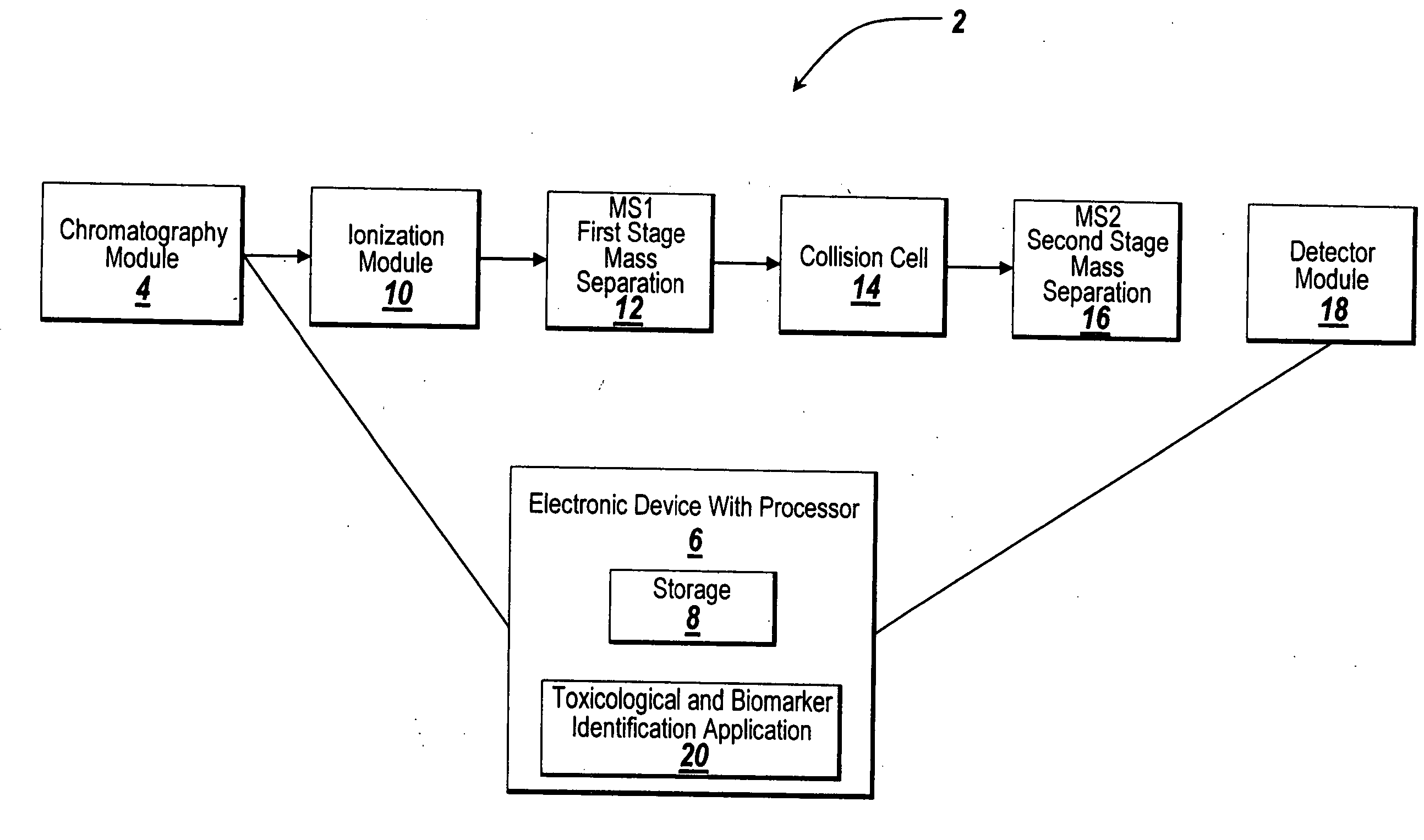
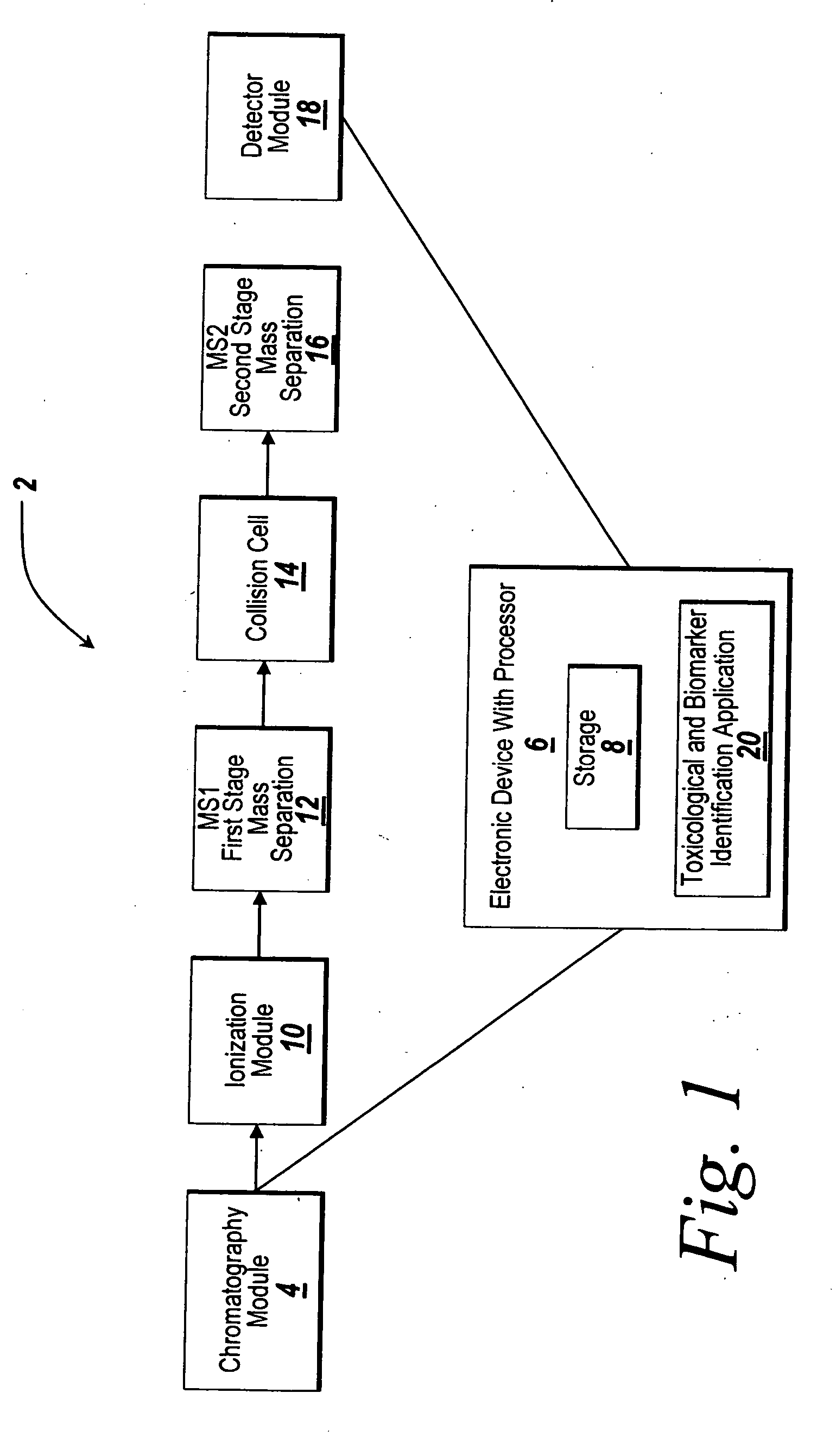
System and method for metabonomics directed processing of LC-MS or LC-MS/MS data
InactiveUS20060151688A1Reduce settingsParticle separator tubesComponent separationRetention timeLiquid chromatography mass spectroscopy
A method of programmatically reducing a set of collected LC-MS or LC-MS / MS data such that true chromatographic and MS peaks are identified for use in Metabonomics is disclosed. The identified peaks are used to create a list of LC / MS, GC / MS, DIOS-MS or MALDI-MS signals and responses for a batch of samples which appear in a Master Entity List. The samples in the Master Entity List are then subjected to isotope de-clustering and adduct removal prior to chemometrics being applied to automatically identify biomarkers. An LC-MS / MS or LC / MS, GC / MS, DIOS-MS or MALDI-MS acquisition list is generated for the signals identified as responsible for the PLS-DA or PCA separation. The LC or GC retention time, exact mass and MS / MS spectrum may be compared to databases of known compounds and identified compounds associated with biological parameters may be stored in a new compound database.
Owner:MICROMASSS UK LTD
Carbon nanotubes and their derivatives as matrix elements for the matrix-assisted laser desorption mass spectrometry of biomolecules and sequencing using associated fragmentation
InactiveUS20050277201A1Analysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionBiological testingAnalyteSpectroscopy
The present invention is directed toward novel matrix elements, generally comprising functionalized carbon nanotubes, for matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI)-mass spectroscopy (MS), methods of making such matrix elements, and to methods of using such matrix elements in MALDI-MS applications, particularly for the analysis of biological molecules. In some embodiments, by carefully tuning the absorption characteristics of the matrix element, biomolecular analytes can be sequenced.
Owner:RICE UNIV
High performance low cost MALDI MS-MS
InactiveUS7667195B2Rapidly and accurately ratioRapidly and accurately intensityTime-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationPhysical chemistryIonization
The invention comprises apparatus and methods for rapidly and accurately determining mass-to-charge ratios of molecular ions produced by a pulsed ionization source, and for fragmenting all of the molecular ions produced and rapidly and accurately determining the intensities and mass-to-charge ratios of the fragments produced from each molecular ion.
Owner:VIRGIN INSTR CORP
Method and Apparatus for Identification of Biological Material
InactiveUS20110204220A1Improve efficiencyEliminate needSamples introduction/extractionPreparing sample for investigationDesorptionSpectroscopy
Biological material is detected in a sample using a MALDI-MS technique (Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption and Ionization-Mass Spectroscopy). A liquid comprising the sample and a MALDI matrix material is prepared and used to form a continuous stream of the liquid. The stream is separated into successive parts to form drops, which are launched into flight, or the stream is launched into flight and then separated into drops. Drop forming techniques may be used that are known from ink jet printers. Material from the drops is ionized while in flight. Mass spectra from the ionized material of respective drops are measured. Preferably, before the drops are formed the liquid is diluted to a level where the majority of drops at most one micro-organism is present per drop.
Owner:DEEM CONSULTING BV
Quality control method for array manufacture
InactiveUS20050186580A1Simple methodSequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementQuality controlMaldi ms
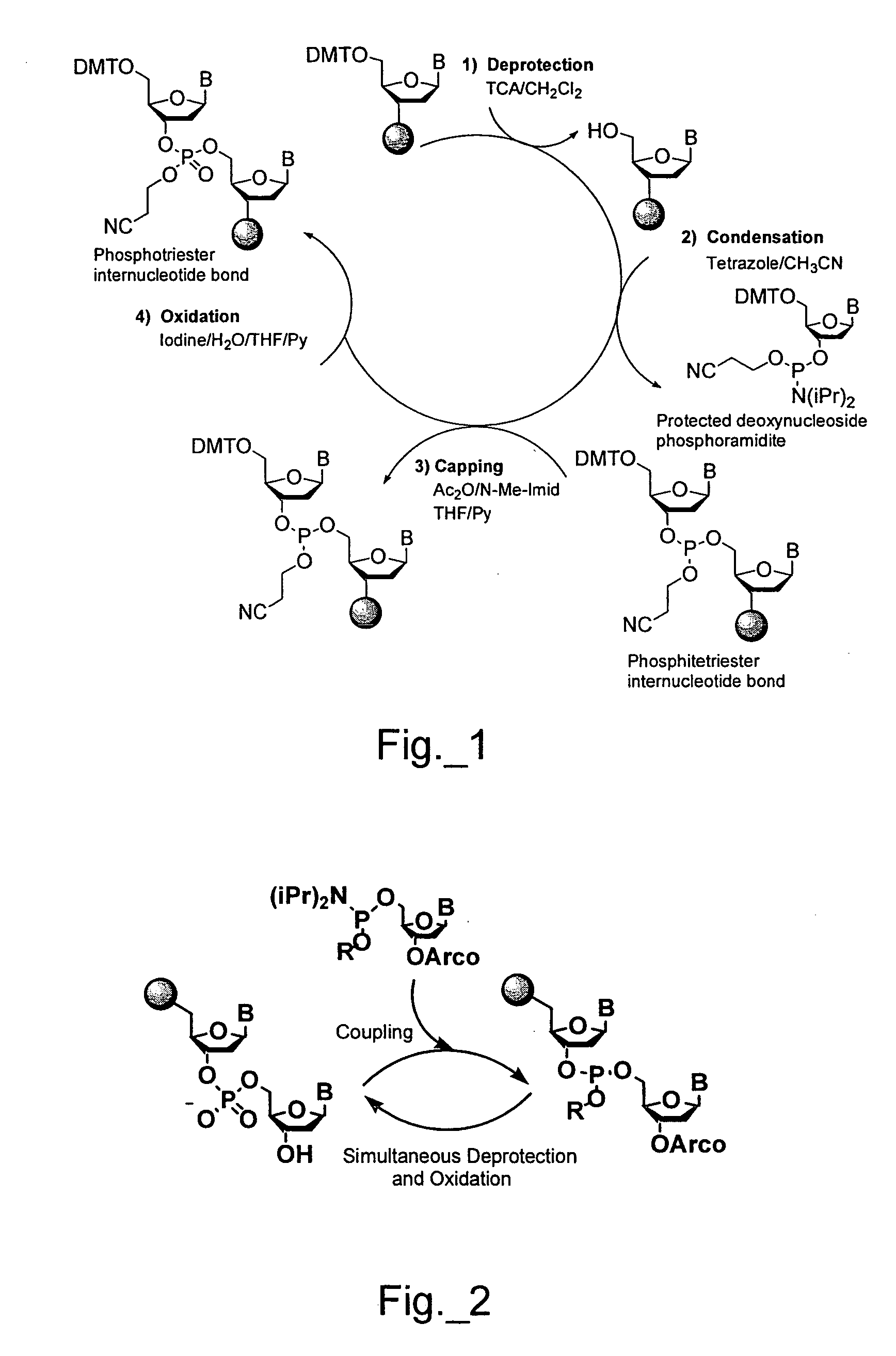
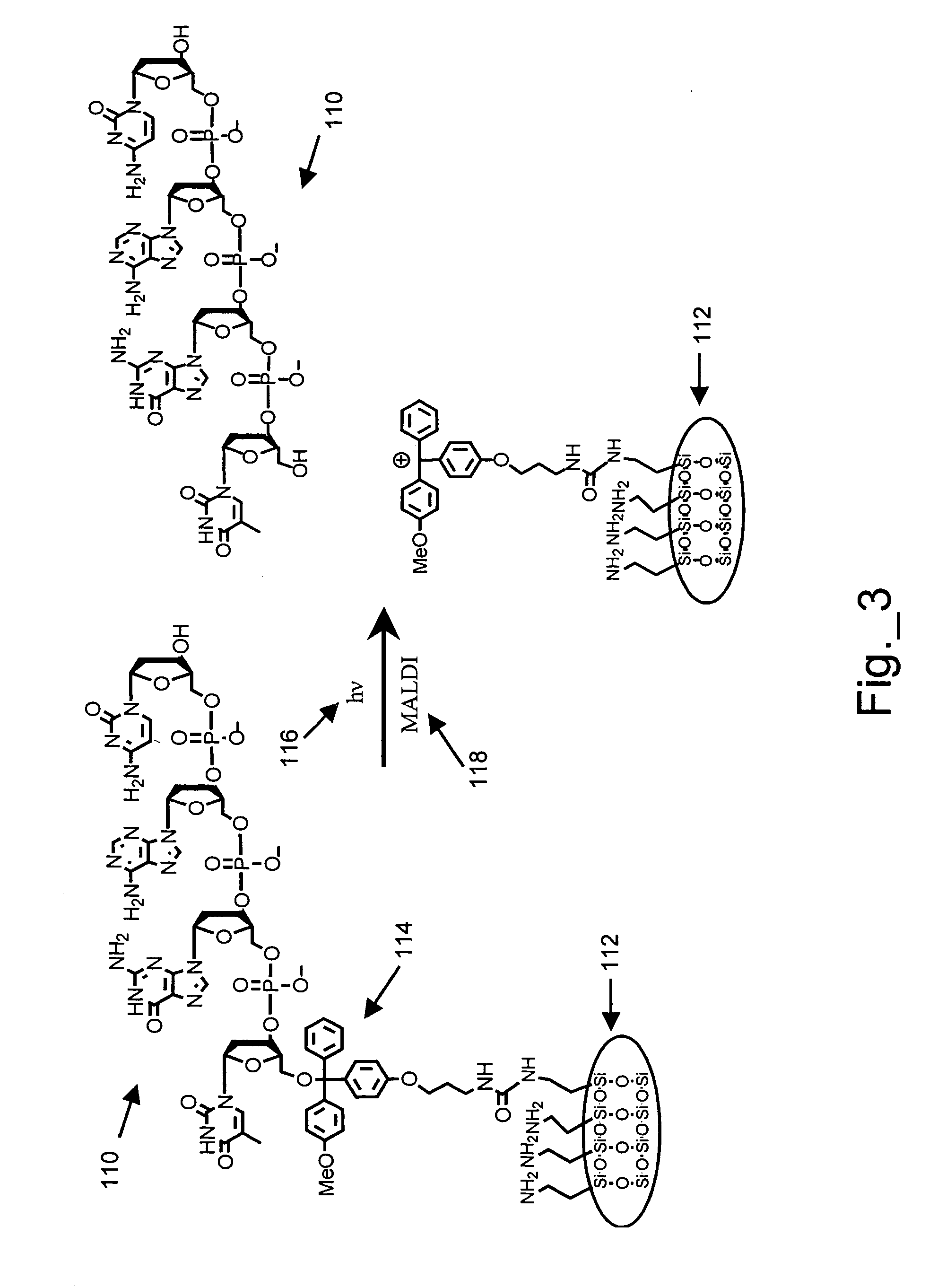
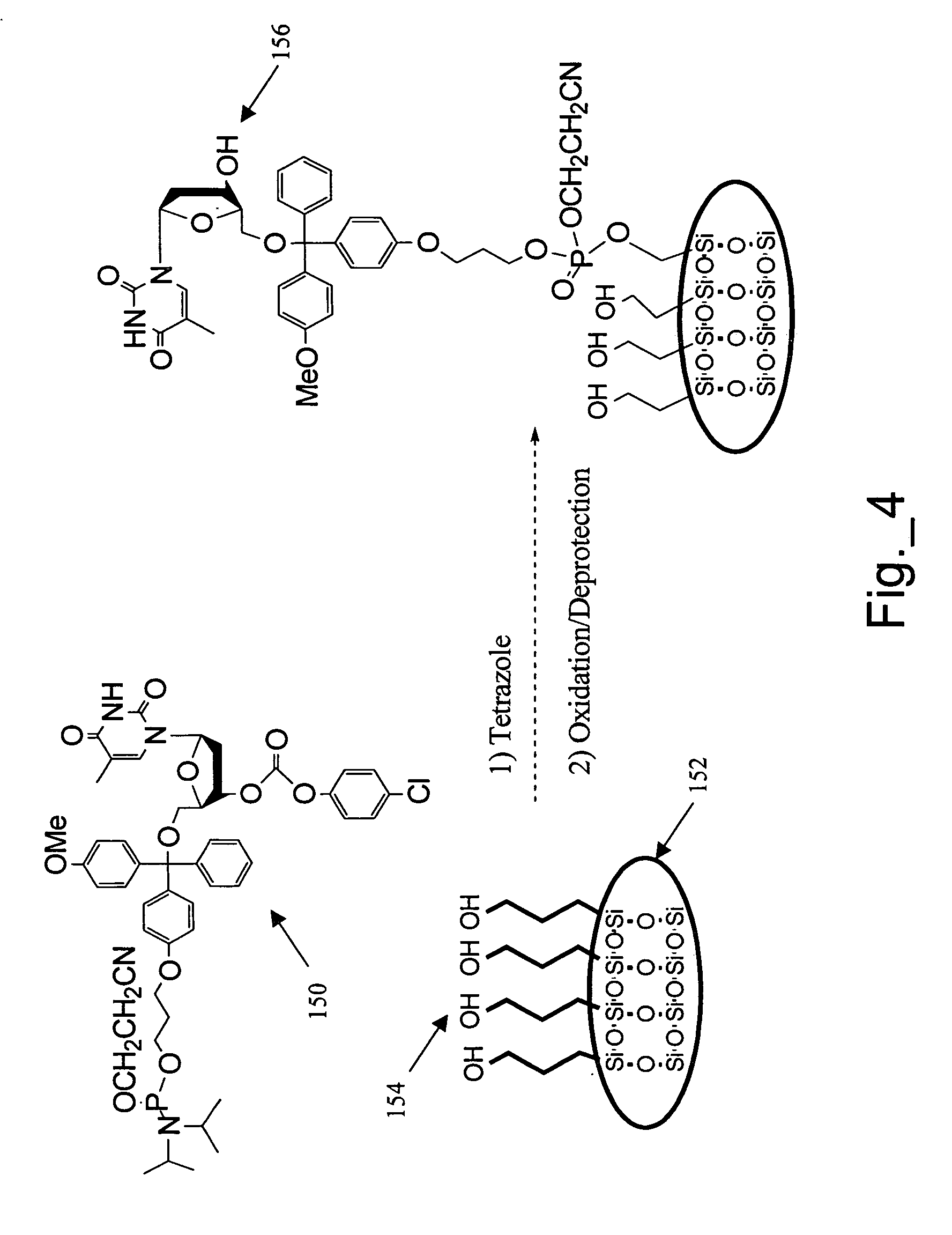
A method of analyzing an array during and / or after fabrication to obtain information relating to the quality of the array manufacturing process is described. The method includes providing an array of features on a substrate, wherein each feature has one or more polynucleotides bound to the substrate. At least one of the features of the provided array is a cleavable feature. The cleavable feature has one or more polynucleotides bound to the substrate via a cleavable linker. The cleavable feature is then contacted with a matrix material, and a MALDI-MS protocol is used to obtain information about the one or more polynucleotides of the cleavable feature. This information may then be used to evaluate the manufacturing process.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
MALDI plate and process for making a MALDI plate
InactiveUS6900061B2Creating and restoring surface hydrophobicityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLipid formationWax
A sample plate for a MALDI process is provided which comprises an electrically conductive substrate having a hydrophobic coating whose thickness and hydrophobic character can be modified by changing the coating substrate and / or the concentration of the substrate. Different coating substances that have provided optimal performance of the sample plate for reproducible deposition and analysis by MALDI-MS and MALDI-MS / MS processes of analyte mixtures include synthetic waxes such as paraffin compositions, lipids, organic acids, silicon-containing compounds, silica polymers and natural waxes. Metal polishes that have been used to clean and regenerate plate surfaces have also provided a sample plate that has optimal performance for reproducible deposition and analysis by MALDI-MS and MALDI-MS / MS processes of analyte mixtures.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC +1
Methods of preparing samples for MALDI mass spectrometry and reagent compositions for the same
InactiveUS7928367B2Quality improvementQuick measurementParticle separator tubesIsotope separationMicroparticleMaldi ms
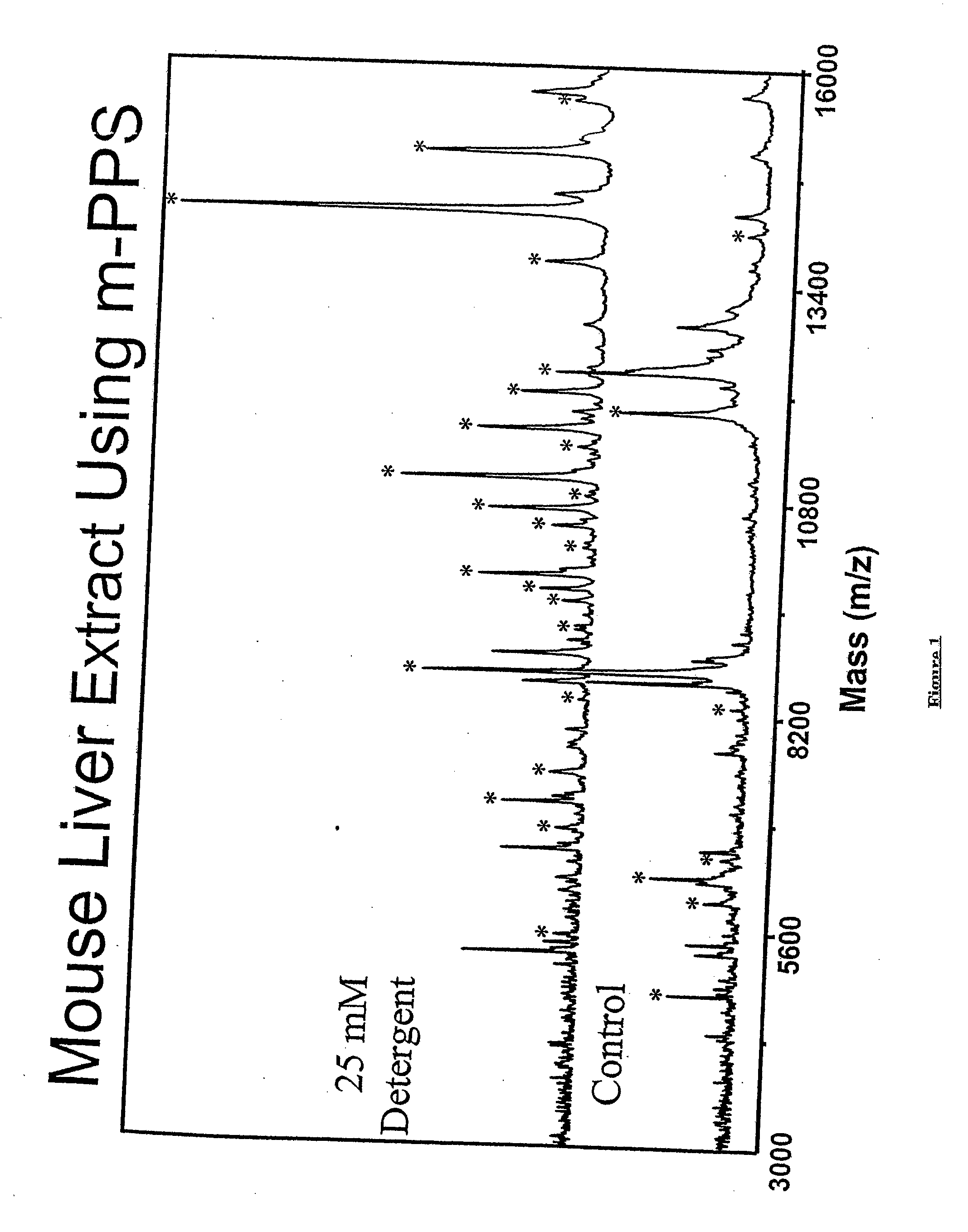
A simple and efficient method of preparing a sample in the measurement according to matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS) capable of inhibiting any ion suppression by impurities, such as inorganic salts and surfactants, contained in the sample. An analyte and matrix molecules are co-crystallized in the presence of porous microparticles. Preferably, this co-crystallization is carried out by bringing the analyte, matrix molecules and porous microparticles into contact with each other on a target plate and thereafter drying the mixture. The porous microparticles consist of an ion exchanger having an average particle diameter of not more than 50 μm, preferably a strongly basic anion exchanger.
Owner:RIKEN
Isotope-coded ionization-enhancing reagents (ICIER) for high-throughput protein identification and quantitation using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry
InactiveUS6905879B2Quantitative precisionReduce disulfide bondSamplingComponent separationLaser desorption ionization mass spectrometryArginine
Arginine-containing cysteine-modifying compounds useful for MALDI-MS analysis of proteins are provided. These compounds termed isotope-coded ionization enhancement reagents (ICIER) can provide ionization enhancement in MALDI-MS, relative quantitation, and additional database searching constraints at the same time without any extra sample manipulation. More specifically, ICIER increase the ionization efficiency of cysteine-containing peptides by attachment of a guanidino functional group. ICIER also increase the overall hydrophilicity of these peptides due to the hydrophilic nature of ICIER and thus increase the percentage of recovery of these peptides during sample handling and processing such as in-gel digestion or liquid chromatography. Finally, a combination of both light and heavy ICIER provides an accurate way to obtain relative quantitation of proteins by MALDI-MS and additional database searching constraints (number of cysteine residues in every single peptide peak) to increase the confidence of protein identification by peptide mass mapping.
Owner:GENETICS INST INC
Method for simultanuously enriching desalting and appraising micro protein or polypeptide solution
InactiveCN1821777AImprove adsorption capacityEfficient desalination abilityOther chemical processesComponent separationHigh concentrationSorbent
This invention relates to a method for synchronously enriching and desalting minim albumens or polypeptide solution and verifying them directly, which takes SiO nm particles as the sorbent to adsorb proteins and their enzyme polypeptides efficiently and overcomes interference of high concentration salt.Since SiO nm particles are compatible with MALDI-MS very well and MALDI-TOF / MS analysis can be done directly to the adsorbed samples without elution to avoid the loss.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
MALDI-MS analysis of nucleic acids bound to a surface
InactiveUS20050186579A1Microbiological testing/measurementLaser desorption ionization mass spectrometryNucleotide
A method of analyzing a polynucleotide using matrix assisted laser desorption / ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS) is described. The method includes obtaining the polynucleotide bound to a substrate via a linker moiety having a triaryl methyl linker group. The polynucleotide bound to the substrate is then contacted with a matrix material and analyzed by MALDI-MS. During the MALDI-MS analysis, laser radiation is directed at the matrix material, thereby exciting the matrix material and causing cleavage of the linker moiety. Ions generated as a result of this excitation and cleavage process are then analyzed to provide information about the polynucleotide.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Reduction of matrix interference for MALDI mass spectrometry analysis
ActiveUS6995363B2Samples introduction/extractionSynthetic resin layered productsThin layerMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
A MALDI plate suitable for MS or MS-MS analysis provided with a composite coating that comprises a hydrophobic coating and a thin layer coating of a mixture of a MALDI matrix material and an intercalating agent such as a polymer is disclosed. A MALDI plate produced in accordance with the present teachings is useful for suppression of matrix ions in the low mass region (<1,000 daltons) of a MALDI-MS spectrum.
Owner:MDS INC THROUGH ITS MDS SCIEX DIV
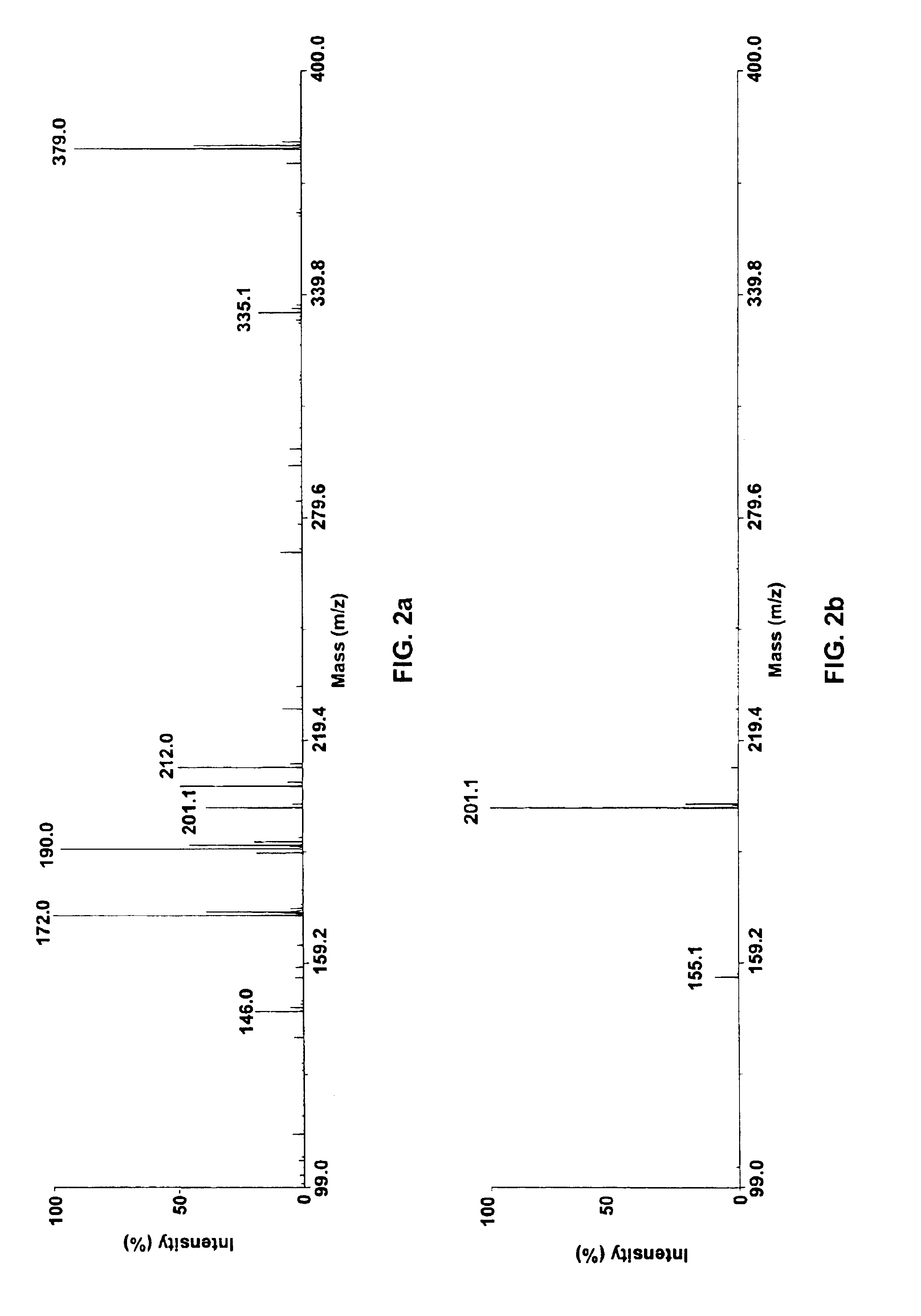
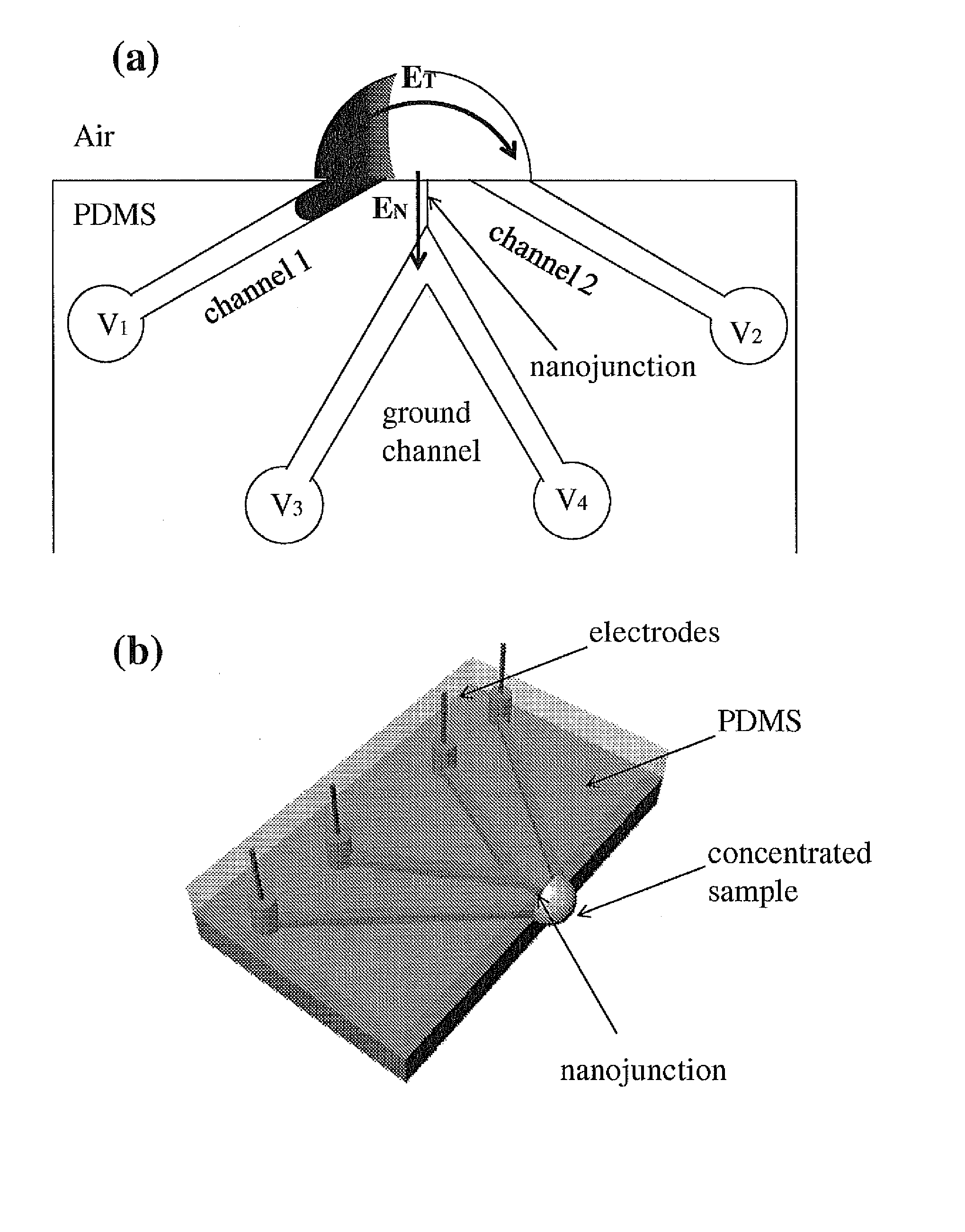
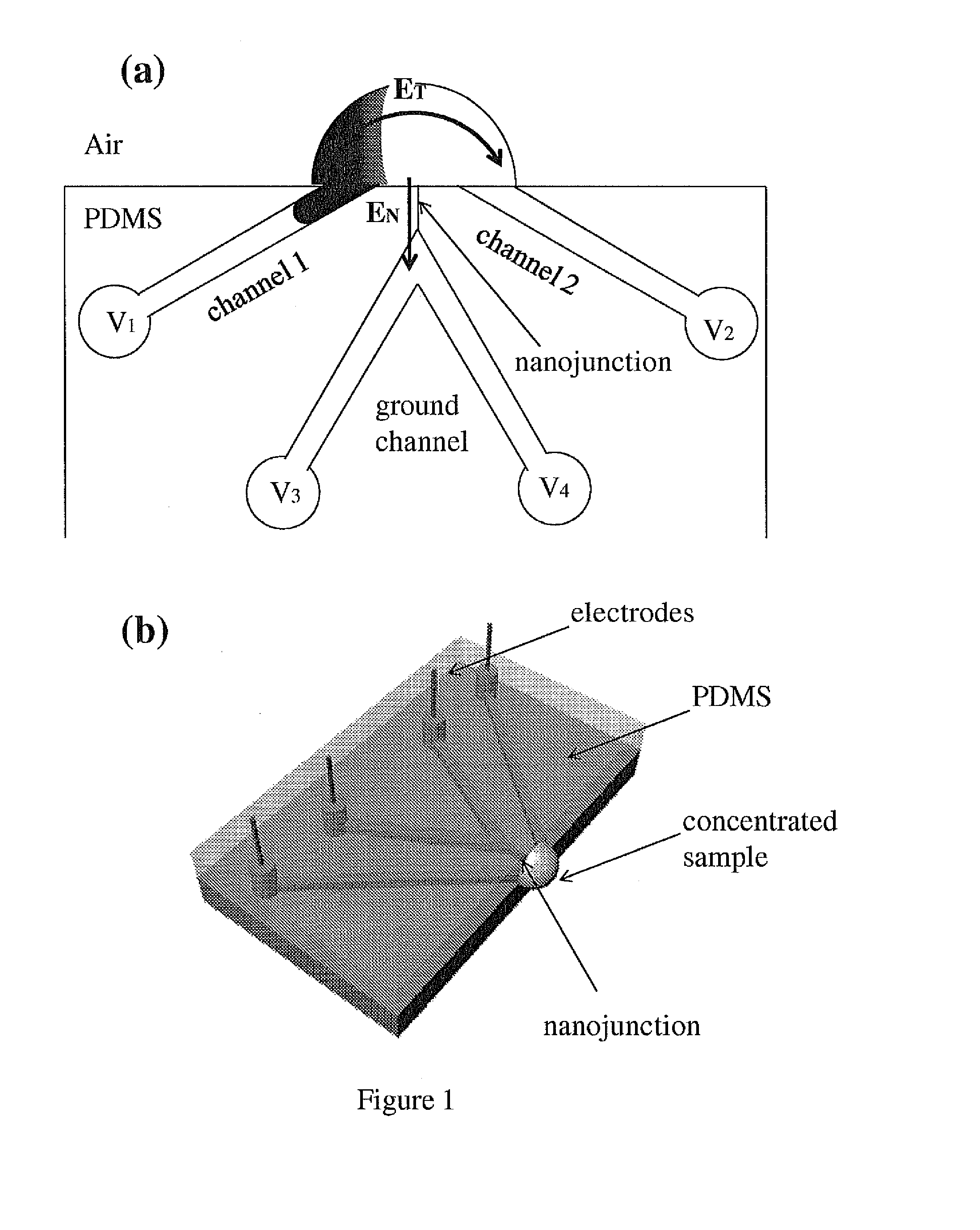
Nanofluidic preconcentration device in an open environment
InactiveUS8329115B2Proven can be successfulEasy to operateSludge treatmentCircuit elementsMeasurement deviceEngineering
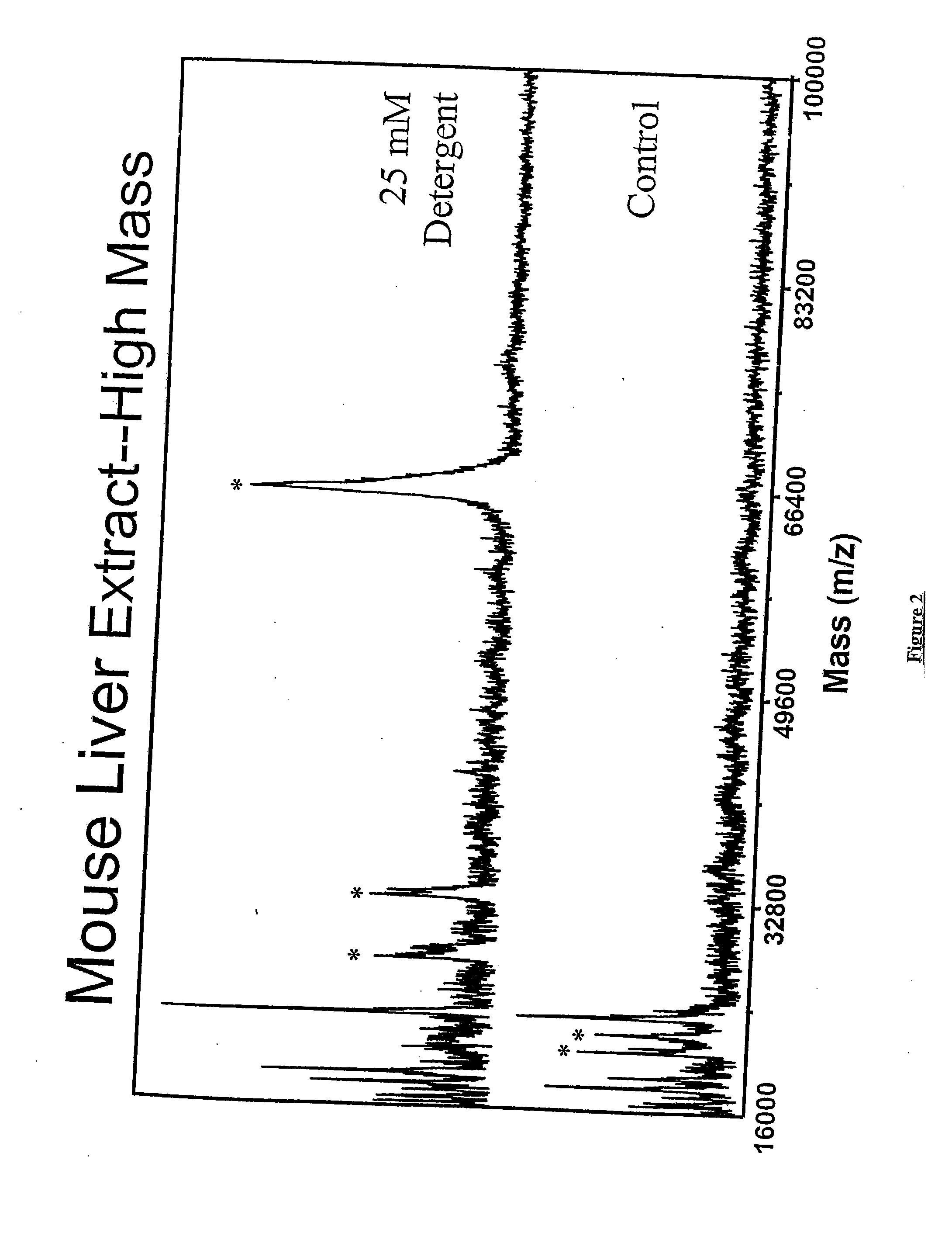
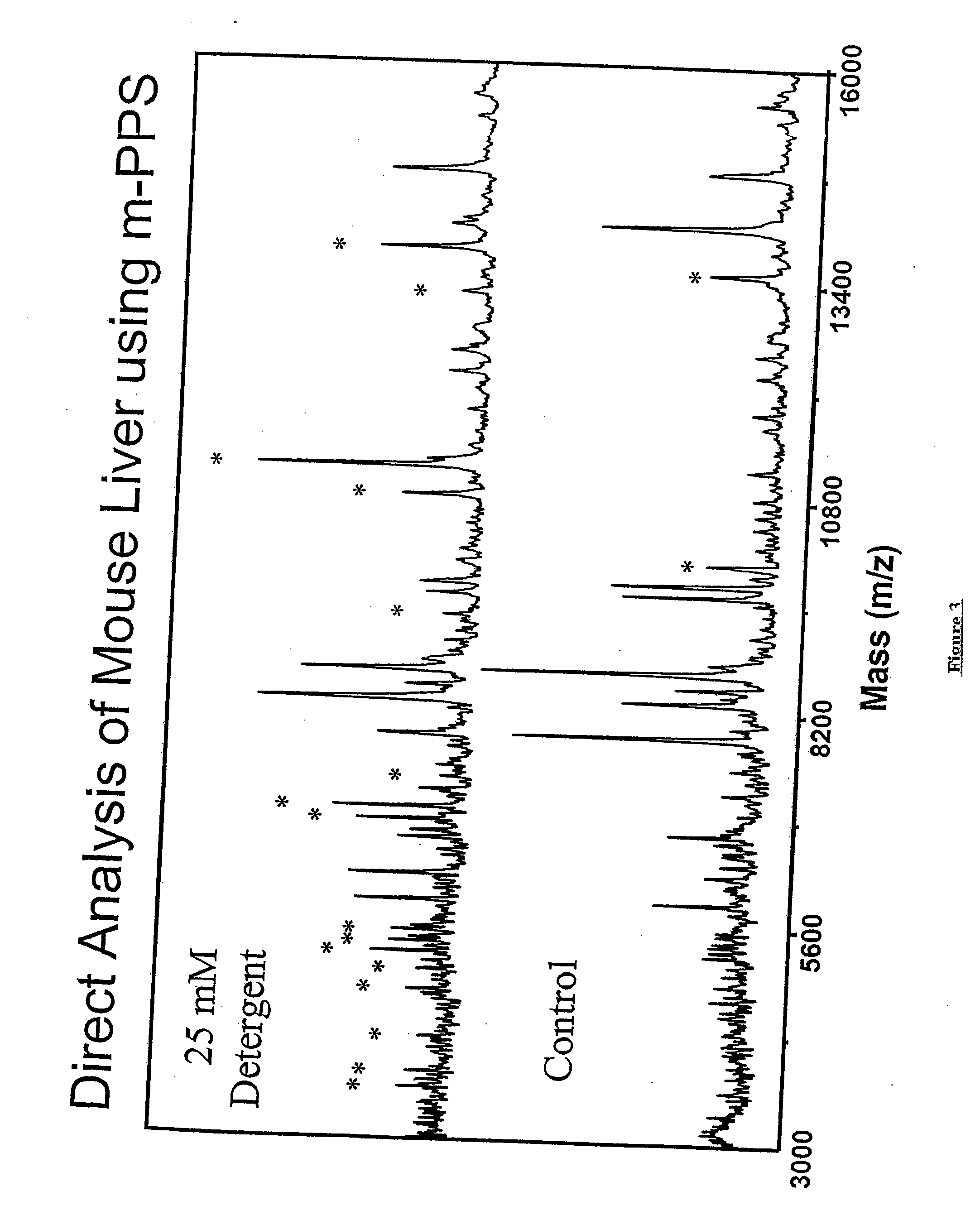
This invention provides a device and methods for increasing the concentration of a charged species in solution, wherein the solution containing the concentrated species is exposed to the environment. Such solution can be formed on a surface or on a tip of a measurement device. The open-environment concentration technique overcomes the disadvantages of in-channel concentration devices, especially by eliminating flow-induced delivery processes that lead to concentration losses. Combined with direct contact dispensing, methods of this invention can be used for various applications such as immunoassay and MALDI-MS.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Application of naphthylethylenediamine inorganic acid salt or Naphthylethylenediamine organic acid salt as matrix in MALDI MS (matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry)
ActiveCN102706952AReduce processing requirementsImprove compatibilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaser desorption ionization mass spectrometryPhosphate
The invention discloses application of naphthylethylenediamine inorganic acid salt or naphthylethylenediamine organic acid salt as a matrix in MALDI MS (matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization mass spectrometry). In the application, the MALDI MS is MALDI-TOF MS (matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization - time-of-flight mass spectrometry); the naphthylethylenediamine inorganic acid salt is naphthylethylenediamine hydrochloride, naphthylethylenediamine nitrate, naphthylethylenediamine phosphate or naphthylethylenediamine sulfate; and the naphthylethylenediamine organic acid salt is naphthylethylenediamine trifluoroacetate, naphthylethylenediamine acetate, naphthylethylenediamine formate, naphthylethylenediamine citrate or naphthylethylenediamine oxalate. The invention technically overcomes the defect that small-molecule samples cannot be effectively analyzed because serious matrix background interference is apt to be caused in a low molecular weight zone when organic small-molecule matrices are commonly used. The matrix used by the invention is not required to be added with ionizing reagent and the requirements on sample treatment are reduced; and since background interference hardly exists within a testing range (m / z: 0-1000), kinds of complex mixed systems can also be analyzed by using the matrix.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cleavable surfactants and methods of use thereof
Owner:CAPRIOLI RICHARD M +2
Nanofluidic preconcentration device in an open environment
InactiveUS20100187112A1Proven can be successfulEasy to operateSludge treatmentCircuit elementsMeasurement deviceEngineering
This invention provides a device and methods for increasing the concentration of a charged species in solution, wherein the solution containing the concentrated species is exposed to the environment. Such solution can be formed on a surface or on a tip of a measurement device. The open-environment concentration technique overcomes the disadvantages of in-channel concentration devices, especially by eliminating flow-induced delivery processes that lead to concentration losses. Combined with direct contact dispensing, methods of this invention can be used for various applications such as immunoassay and MALDI-MS.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
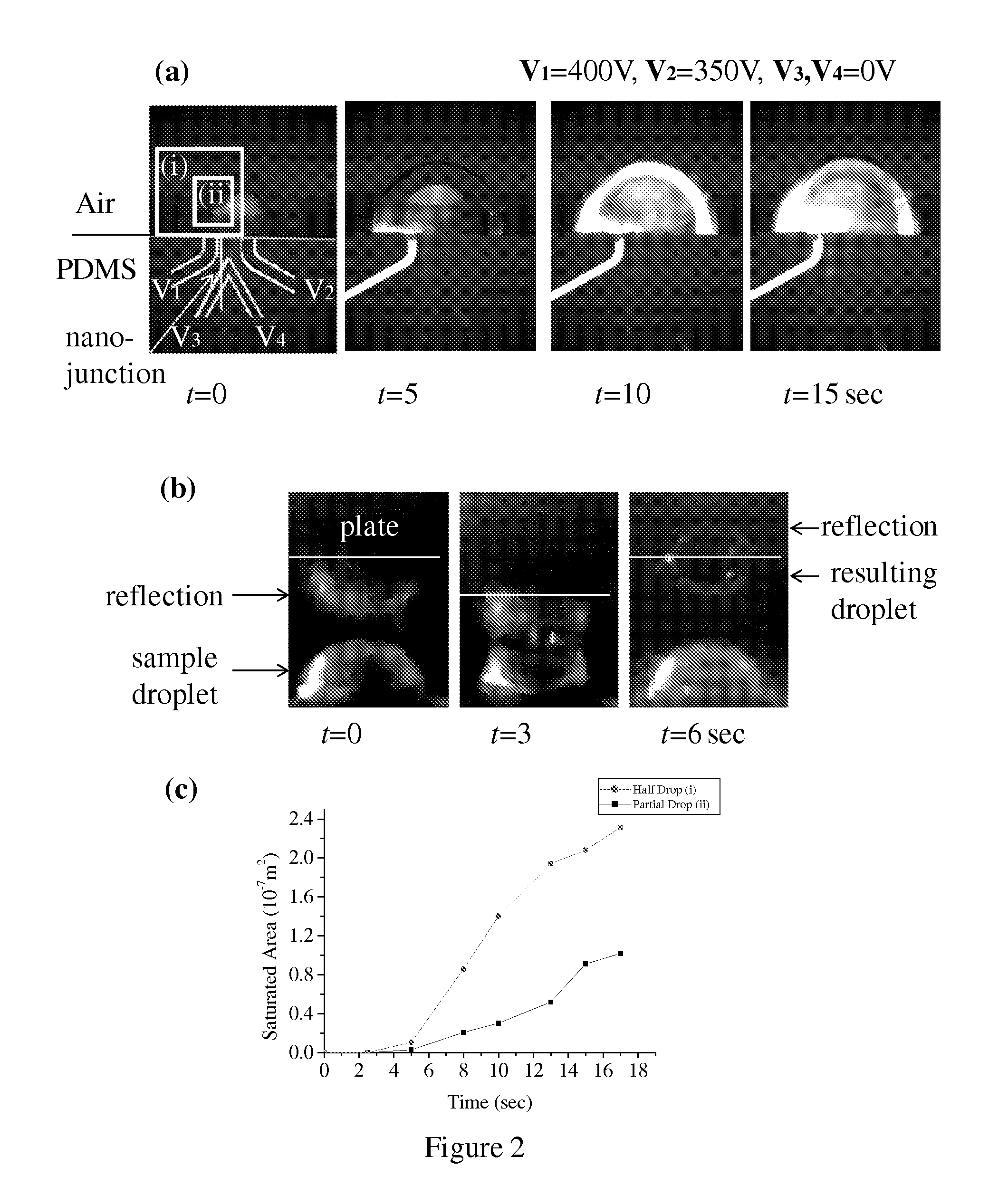
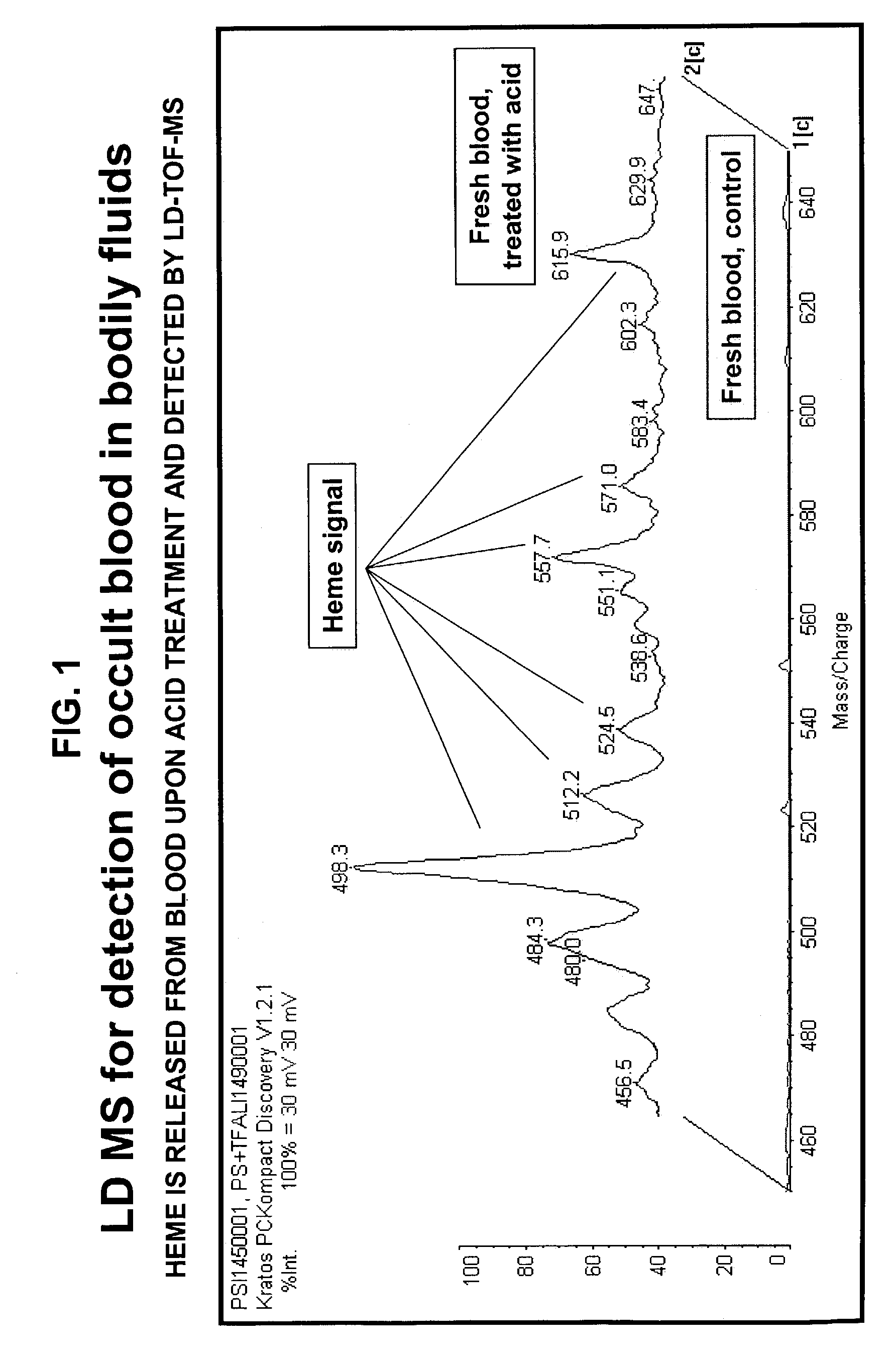
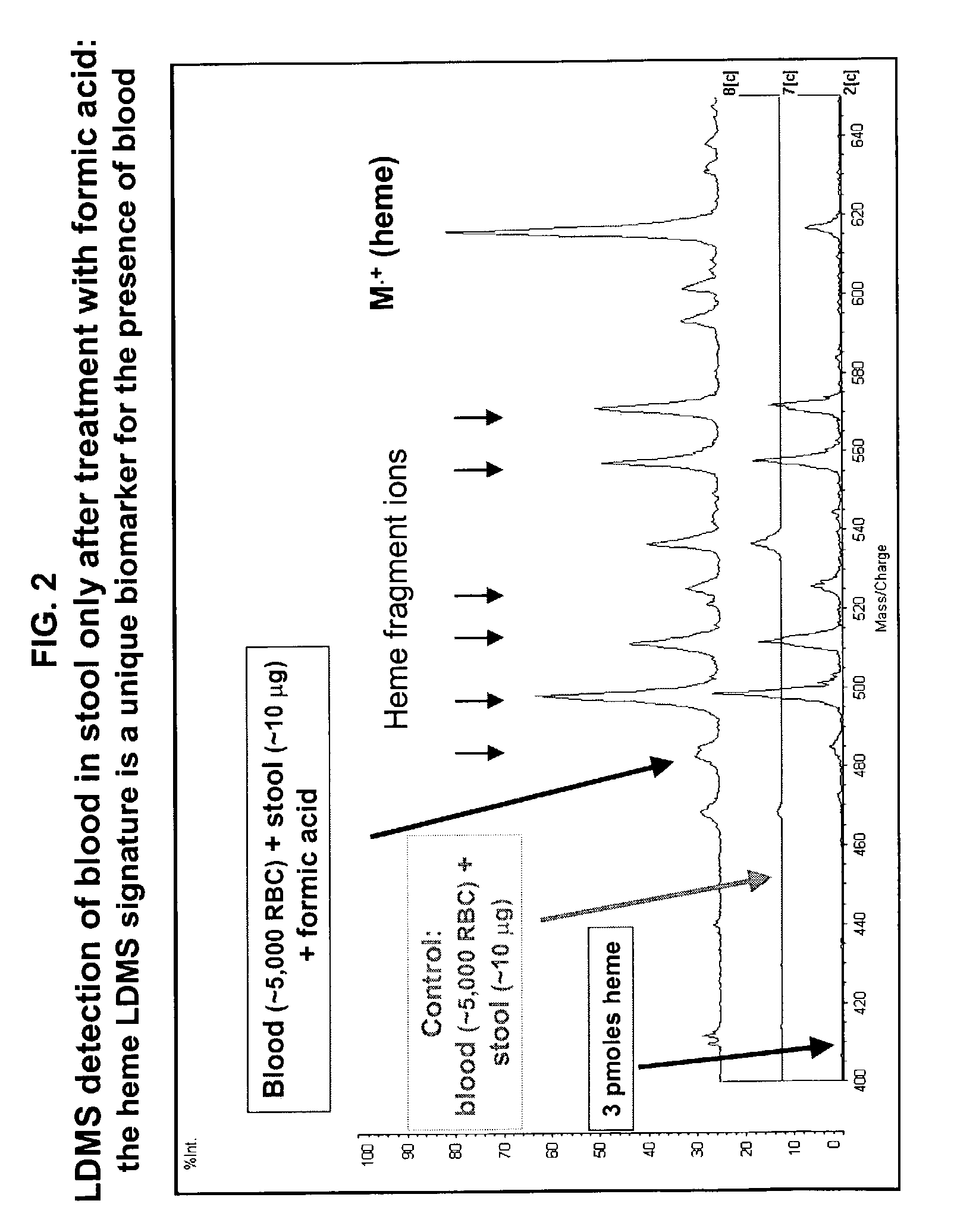
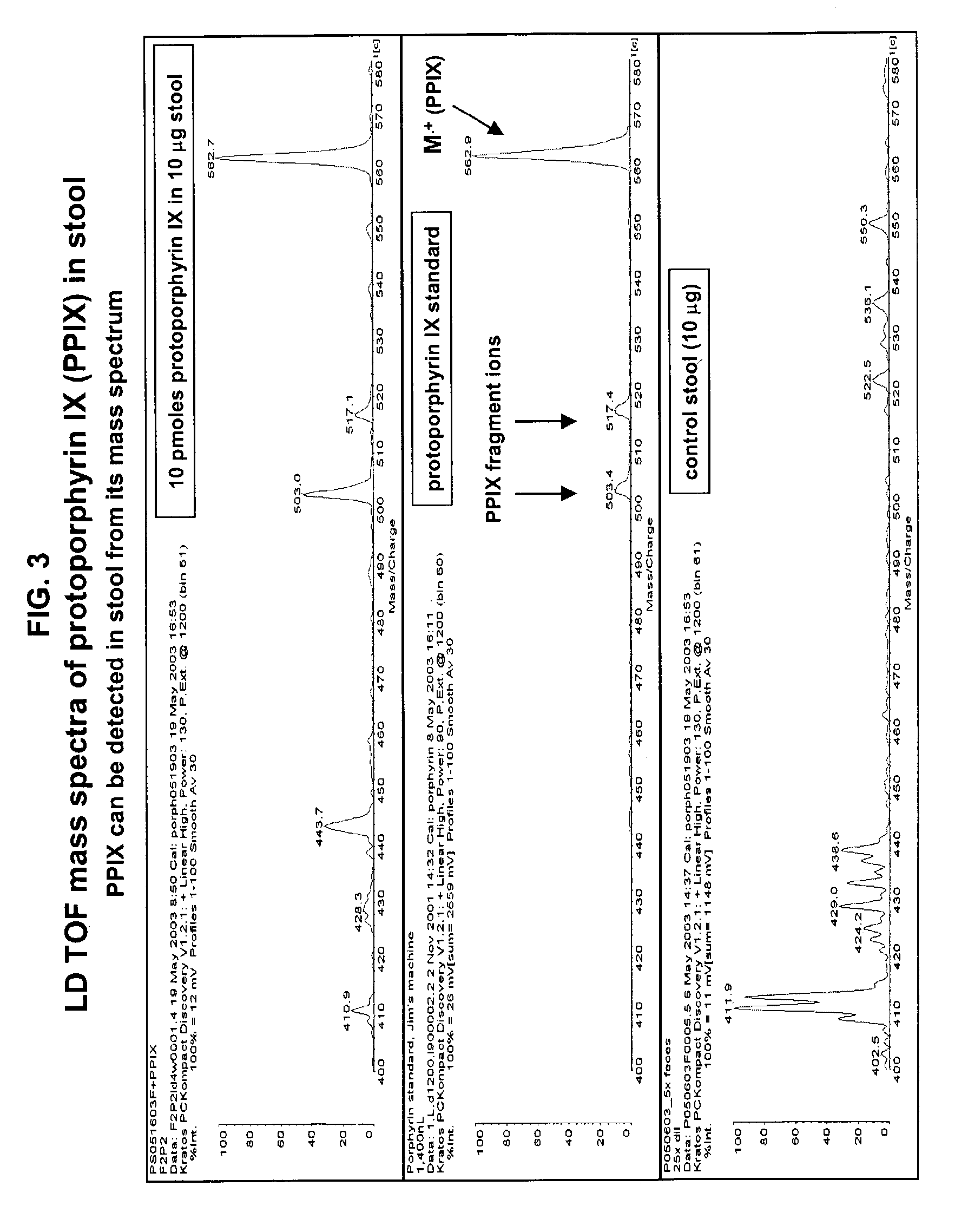
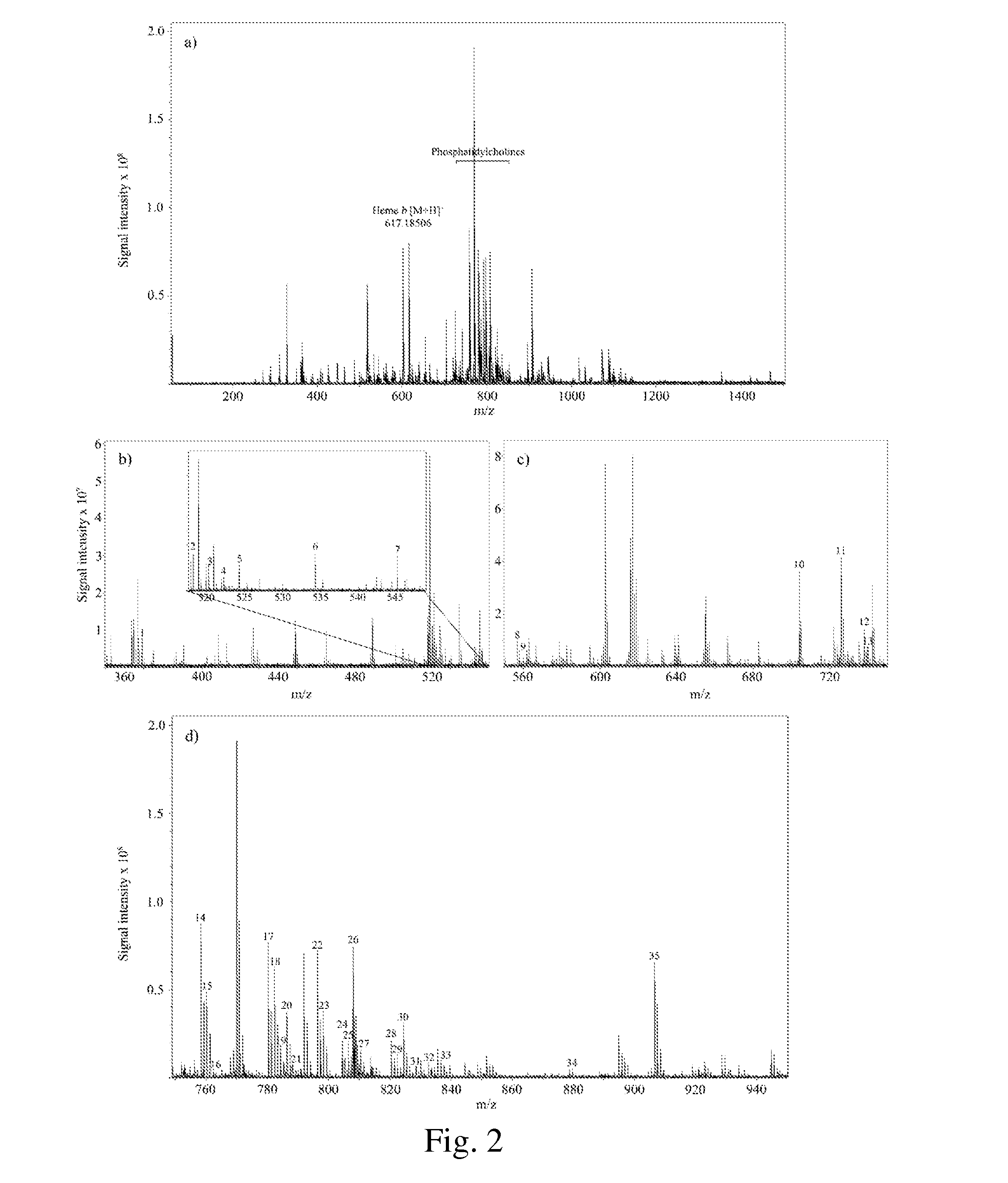
Occult blood detection in biological samples by laser desorption and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry for biomedical applications
Methods are described for detecting and quantifying occult blood in a biological sample using laser desorption mass spectrometry (LD MS). Biological samples that can be analyzed using various embodiments of the present invention include stool (fecal occult blood, FOB), and any bodily fluid including urine, cerebrospinal fluid and other bodily fluids. If the heme or heme metabolite is bound to protein, the sample is treated with acid before analysis to release the porphyrin. Some of the methods use LD MS with a time of flight analyzer (TOF) to detect and measure unbound heme, other hemoglobin metabolites and other molecules that have a porphyrin-based structure, e.g., bilirubin, biliverdin, protoporphyrin IX, and Zinc protoporphyrin in the biological sample. In other methods, matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI MS) is used to detect and quantify the individual α- and β-polypeptide chains of hemoglobin.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Reduction of matrix interference for MALDI mass spectrometry analysis
ActiveUS20050040328A1Easy to analyze and useSamples introduction/extractionSynthetic resin layered productsMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryThin layer
A MALDI plate suitable for MS or MS-MS analysis provided with a composite coating that comprises a hydrophobic coating and a thin layer coating of a mixture of a MALDI matrix material and an intercalating agent such as a polymer is disclosed. A MALDI plate produced in accordance with the present teachings is useful for suppression of matrix ions in the low mass region (<1,000 daltons) of a MALDI-MS spectrum.
Owner:MDS INC THROUGH ITS MDS SCIEX DIV
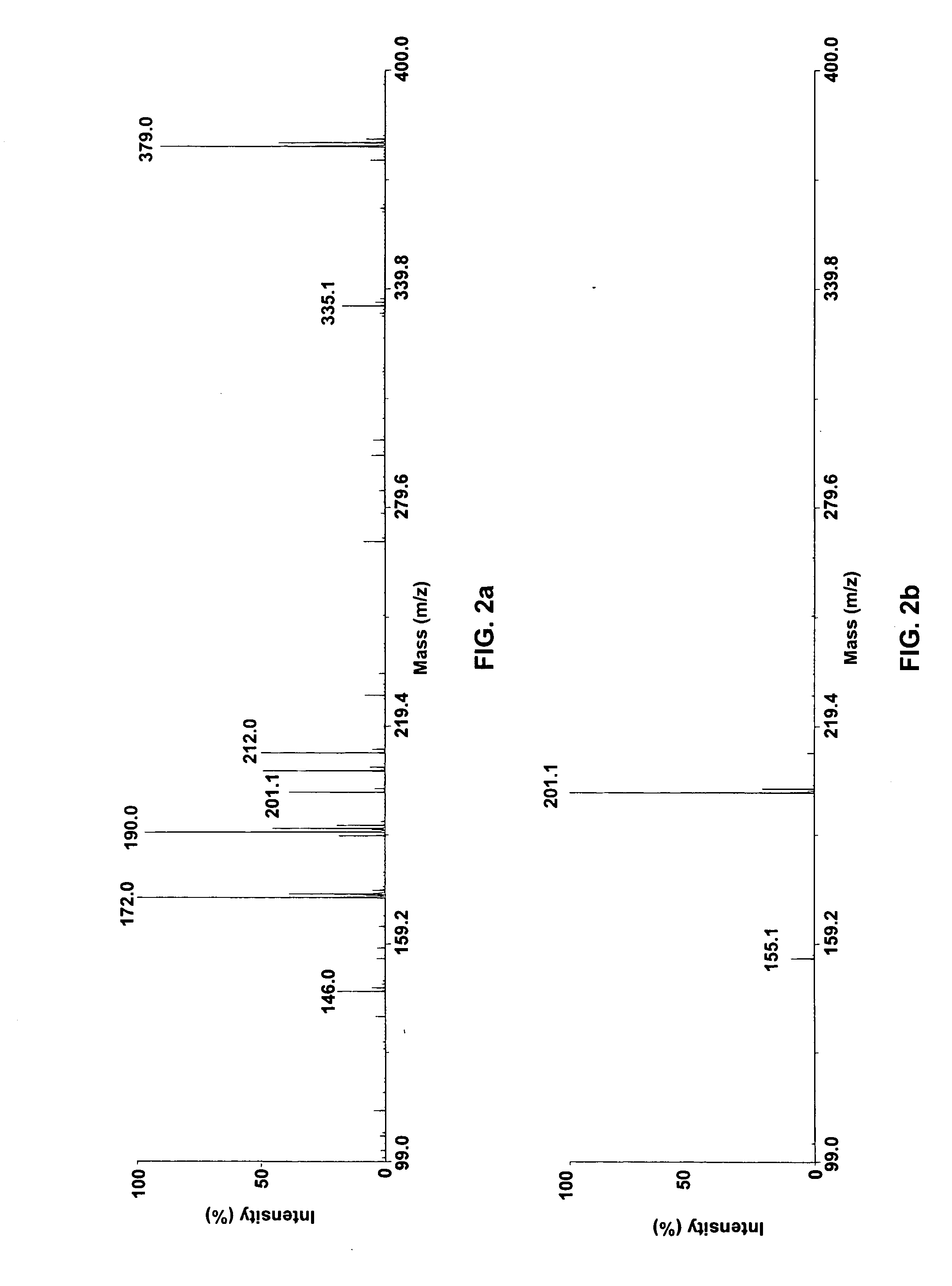
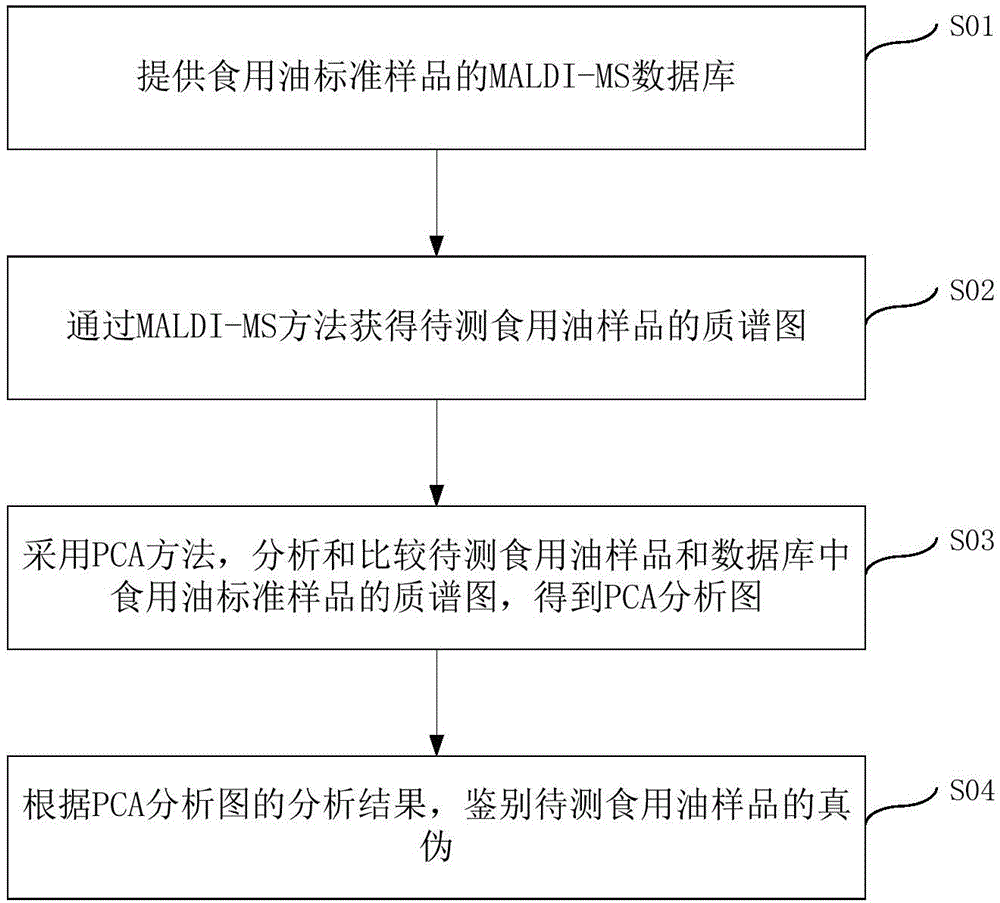
Method for distinguishing edible oil
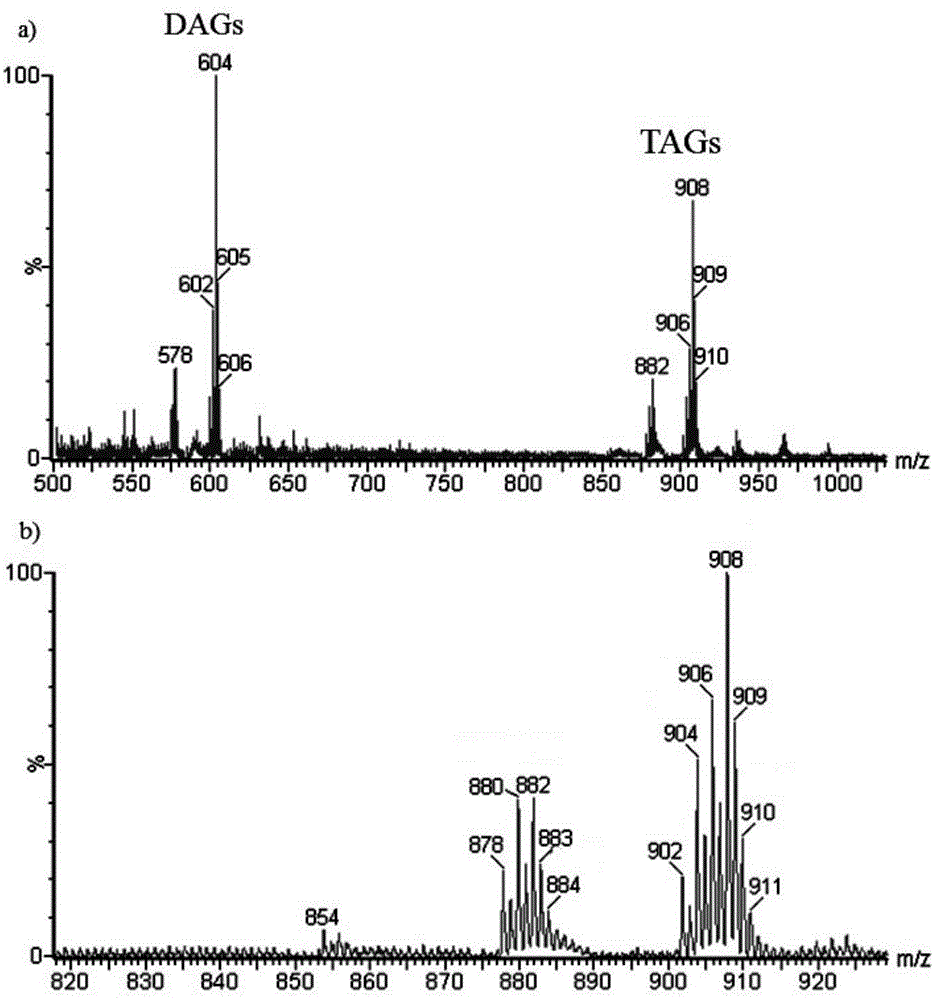
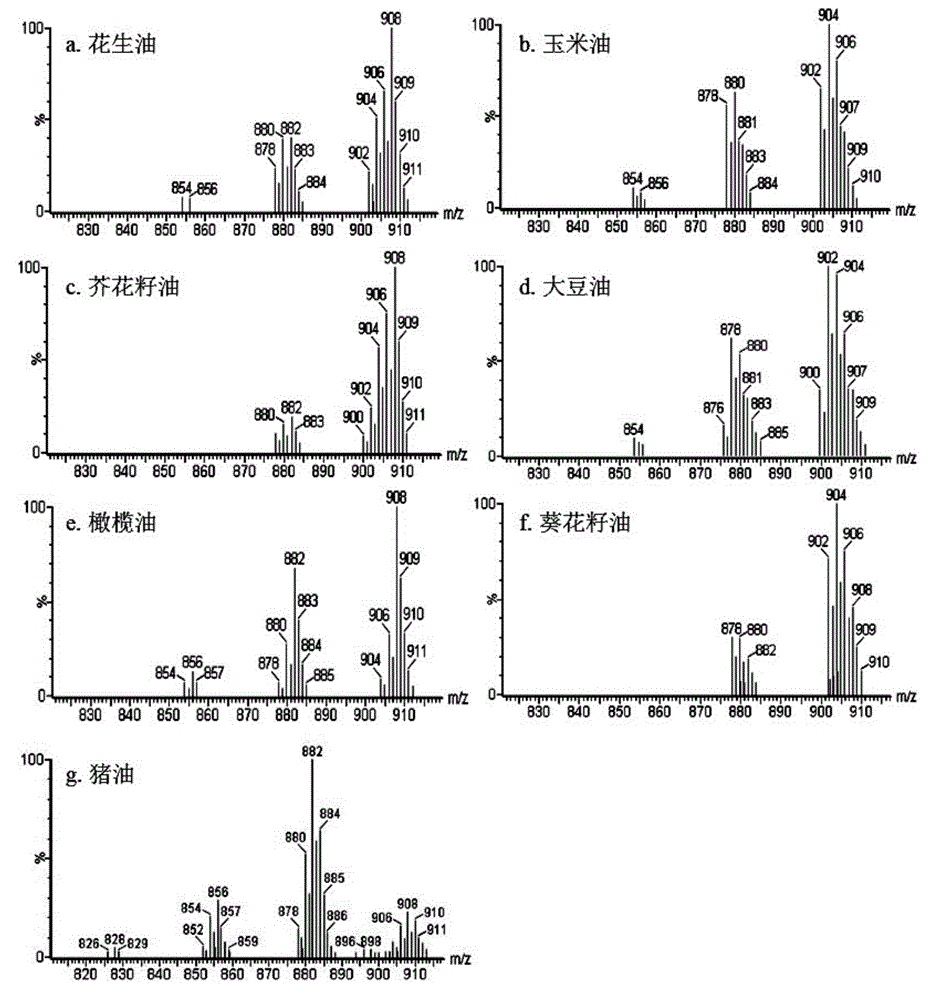
ActiveCN105486744AAccurate identificationPrevent cheatingMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaldi msEdible oil
The invention provides a method for distinguishing edible oil. The method comprises the following steps: providing a MALDI-MS database of an edible oil standard sample; through a MALDI-MS method, obtaining a mass spectrogram of the edible oil sample to-be-detected; employing a PCA method, analyzing and comparing the mass spectrogram of the edible oil sample to-be-detected and the edible oil standard sample in the MALDI-MS database, obtaining a PCA analysis graph; distinguishing authenticity of the edible oil sample to-be-detected through the PCA analysis graph, and distinguishing the edible oil sample to-be-detected as the edible oil standard sample, a counterfeit edible oil, an adulterated edible oil or a recovered edible oil. The invention establishes the preparation method of the novel MALDI-MS sample of the edible oil, by combing the PCA method, authenticity of the edible oil can be distinguished in a rapid, simple and accurate mode.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV SHENZHEN RES INST
Method for enriching, desalting protein or polypeptide in minute quantities, and carrying out analysis directly
InactiveCN1873407AEfficient desalinationImprove desalination performanceComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationProtein insertionSorbent
The invention relates to a method to directly take substrate assistant laser MALDI / MS analysis to trace protein and the protein enzymolysis sample desalination enrichment that adopts silicon oxide nanometer particle as adsorbent. It conquers the disturbance from high thickness salt and has good adsorbing effect to protein and protein enzymolysis polypeptide. The method has good desalination function. The silicon oxide has good compatibility with MALDI-MS, so it could take directly analysis and easy to operate, avoid the sample consumption. It could take identification to the protein enzymolysis sample of the thickness 10-10M, and conquers the disturbance from 4M sodium chloride or 8M urea to mass spectrum. The enrichment efficiency could reach 100 times.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
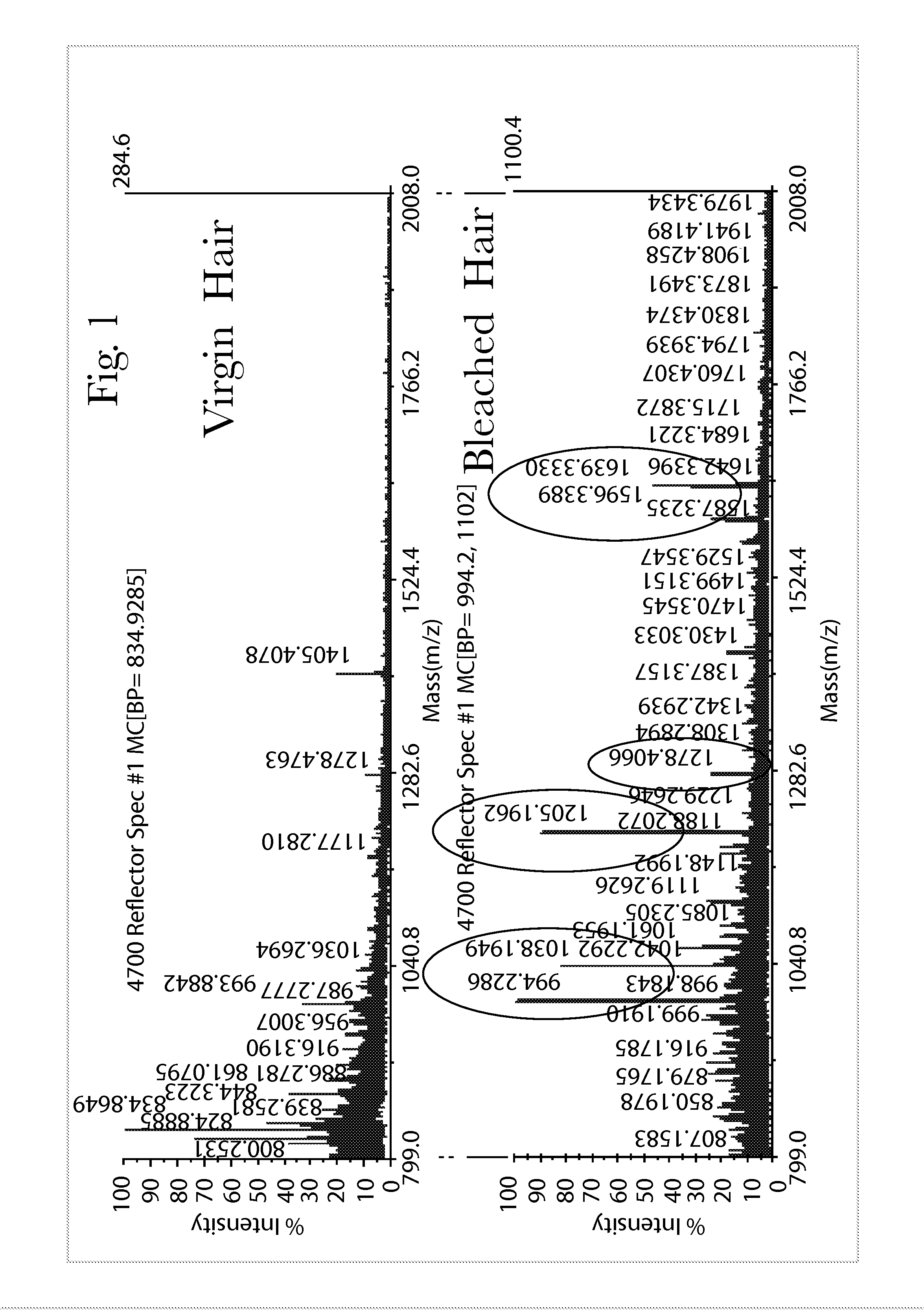
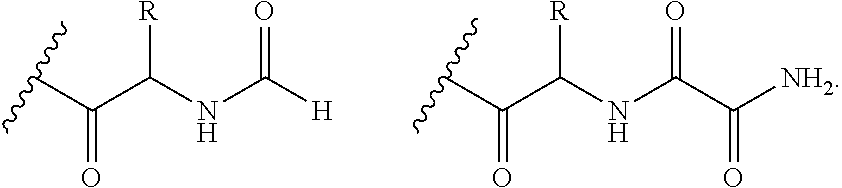
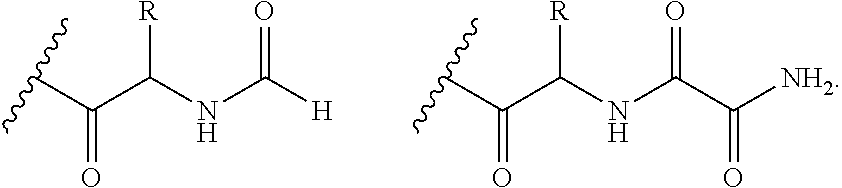
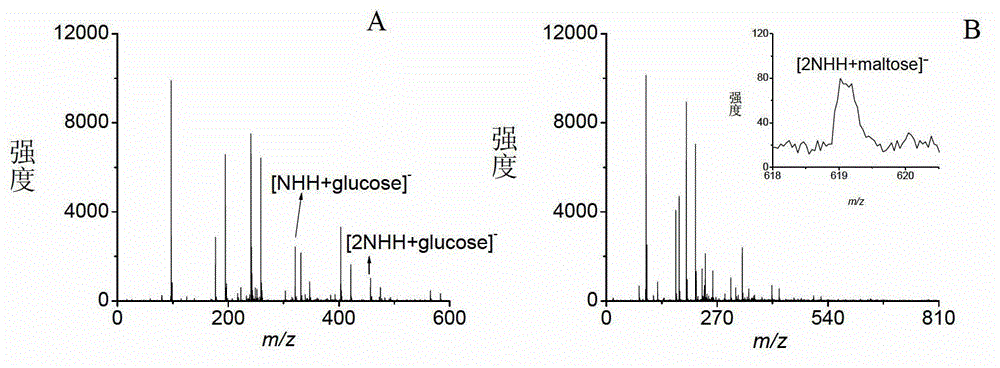
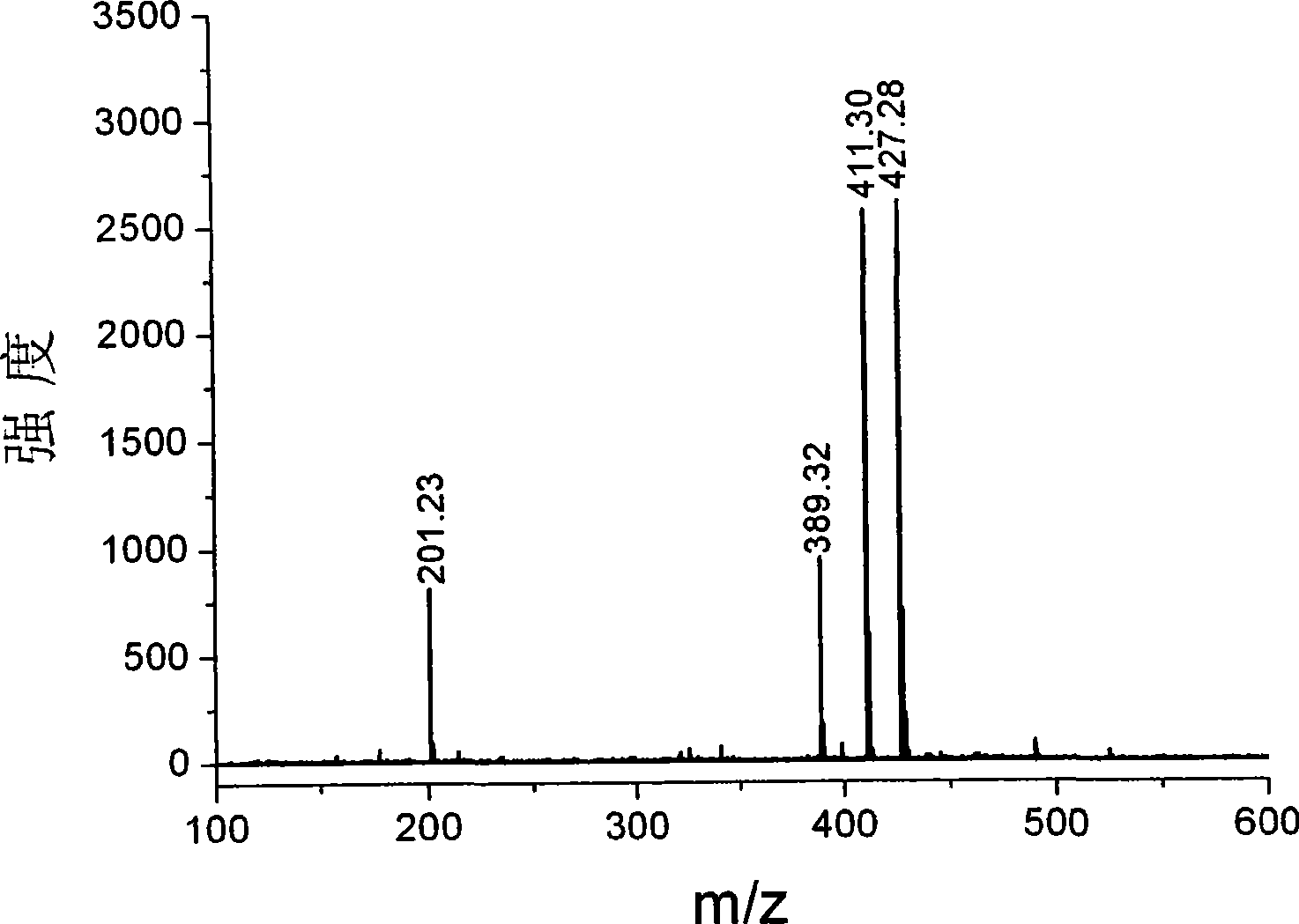
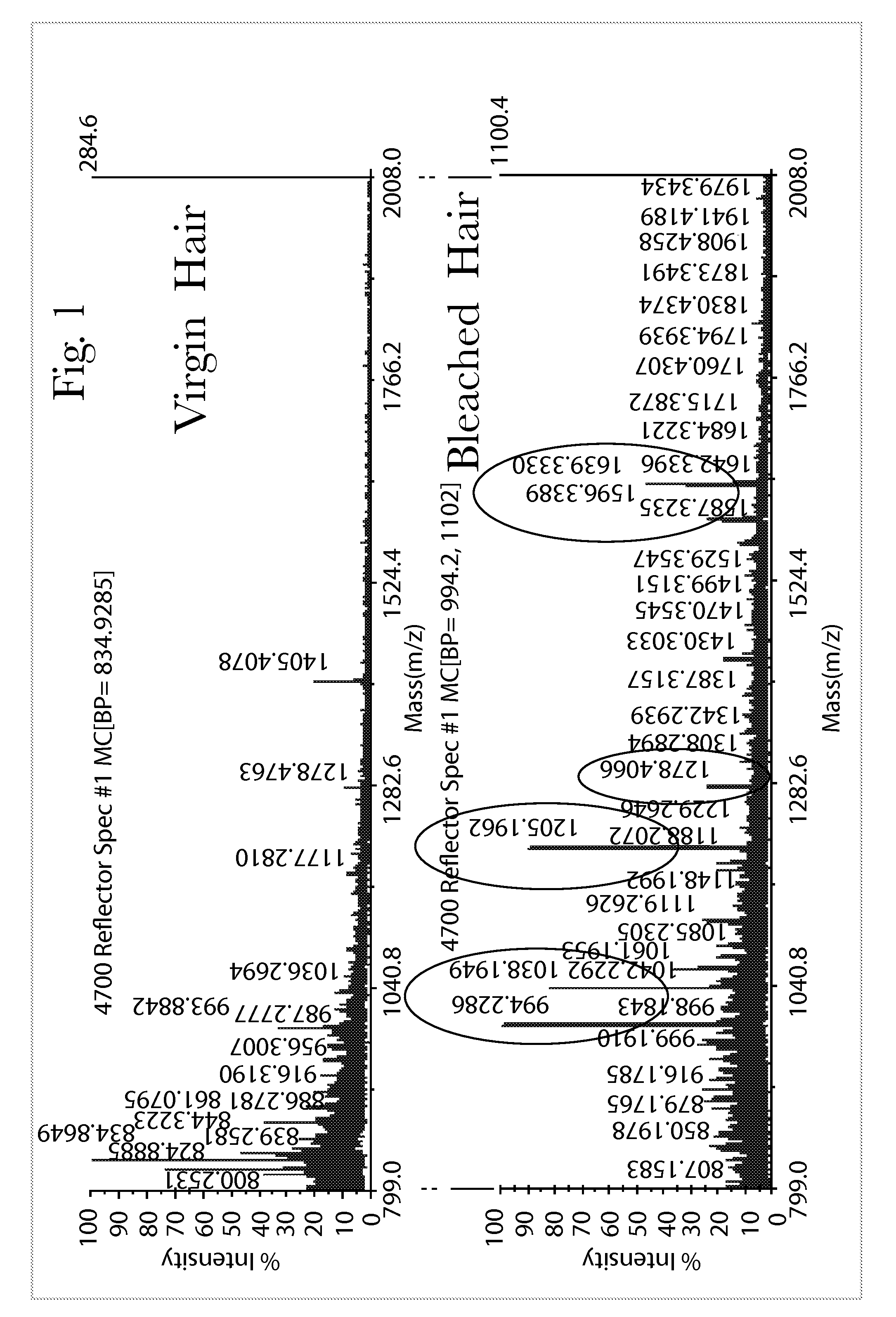
Systems and Methods of Detecting and Demonstrating Hair Damage Via Evaluation of Protein Fragments
Embodiments of a method for demonstrating type and / or source of hair damage comprises extracting protein fragments from a hair sample with an aqueous solution, testing the resulting protein fragments with the MALDI-MS test, and then either comparing the results between a damaged sample and an undamaged sample or comparing the results between a damaged sample and a list of known marker protein fragments to identify the type and / or source of the damage.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
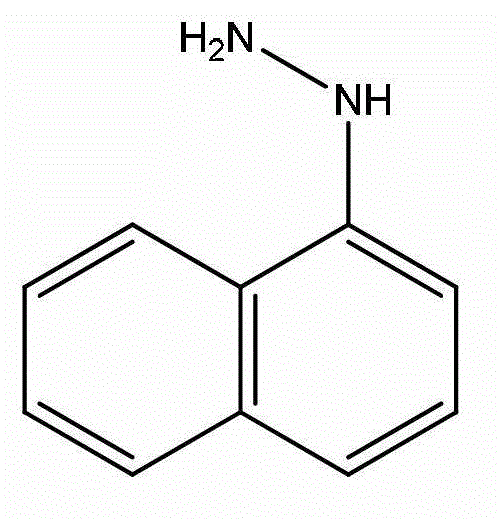
Application of naphthylhydrazine inorganic acid salt or Naphthylhydrazine organic acid salt as matrix in MALDI MS (matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry)
ActiveCN103063730AReduce processing requirementsImprove compatibilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaser desorption ionization mass spectrometryFormate
The invention discloses application of naphthylhydrazine inorganic acid salt or naphthylhydrazine organic acid salt as a matrix in MALDI MS (matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization mass spectrometry). The MALDI MS is MALDI-TOF MS (matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization - time-of-flight mass spectrometry); the naphthylhydrazine inorganic acid salt is naphthylhydrazine hydrochloride, naphthylhydrazine nitrate, naphthylhydrazine phosphate or naphthylhydrazine sulfate; and the naphthylhydrazine organic acid salt is naphthylhydrazine trifluoroacetate, naphthylhydrazine acetate, naphthylhydrazine formate, naphthylhydrazine citrate or naphthylhydrazine oxalate; and hydrazine radicals on the naphthylhydrazine inorganic acid salt or naphthylhydrazine organic acid salt are all 1-substituted or 2-substituted. The application technically overcomes the defect that small-molecule samples cannot be effectively analyzed because serious matrix background interference is apt to be caused in a low molecular weight zone when organic small-molecule matrices are commonly used. The matrix used by the invention is not required to be added with ionizing reagent and the requirements on sample treatment are reduced; and since background interference hardly exists when m / z is smaller than 500, various complex mixed systems can also be analyzed by using the matrix.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Use of rare earth fluoride nano material in MALDI-MS
InactiveCN101504387AEasy to prepareHigh yieldMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCeriumTrifluoride
The invention relates to a matrix material for MALDI, in particular to application of fluoride nanometer materials as a matrix in MALDI-MS. The fluoride nanometer materials are nano-particles with various shapes of ytterbium trifluoride, lanthanum trifluoride, cerium trifluoride, praseodymium trifluoride, neodymium trifluoride, samarium trifluoride, europium trifluoride, gadolinium trifluoride, terbium trifluoride, dysprosium trifluoride, holmium trifluoride, erbium trifluoride, thulium trifluoride, ytterbium trifluoride or lutetium trifluoride, or nano-particles of trifluorides compounded byany two or more of ytterbium, lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium or lutetium in any proportion. The invention takes rare earth fluoride nanometer materials as the matrix of the MALDI-MS for the first time, develops the matrix of the MALDI-MS with simple and convenient operation and strong universality, and realizes the quick and accurate analysis of the MALDI-MS.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
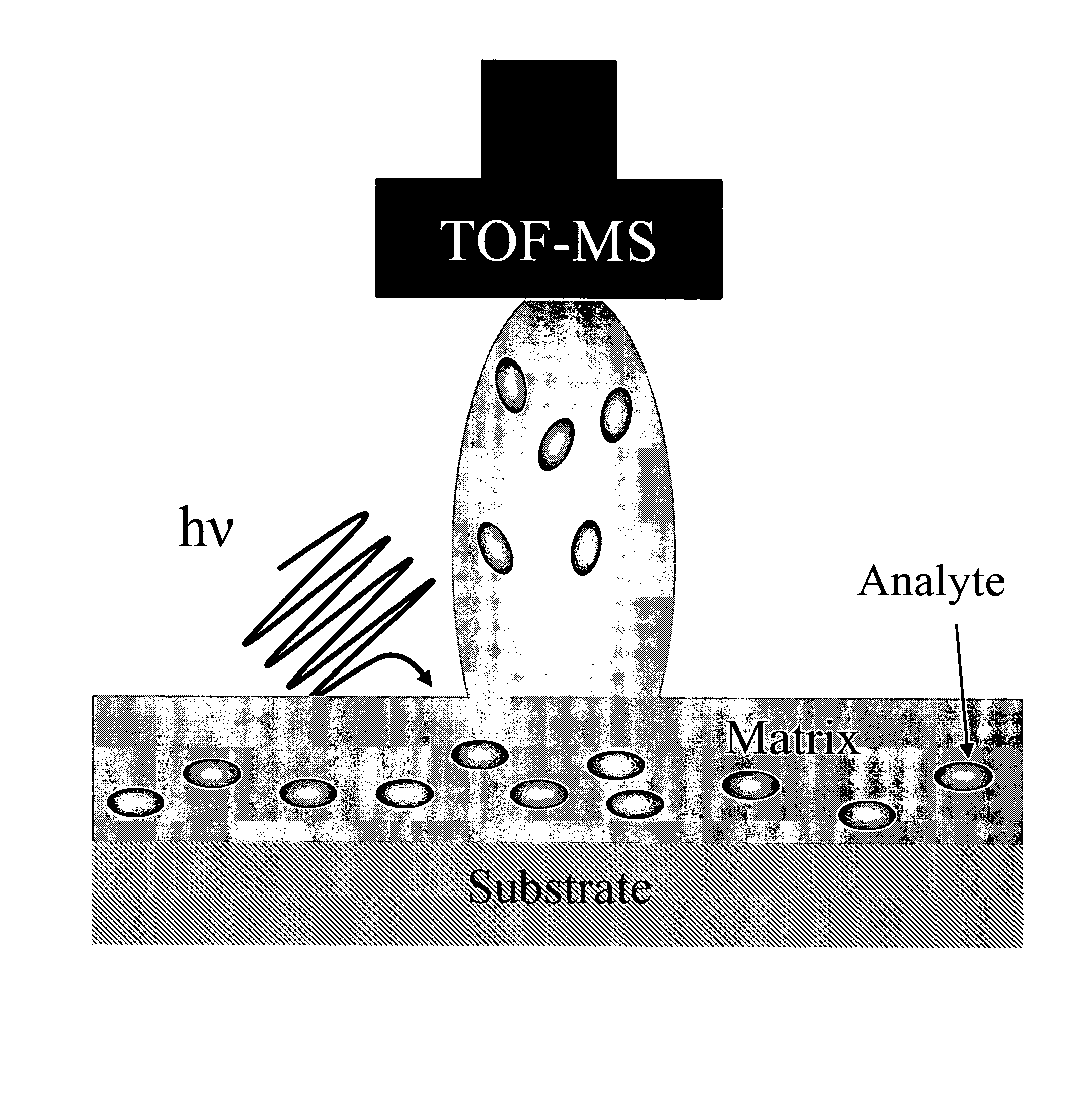
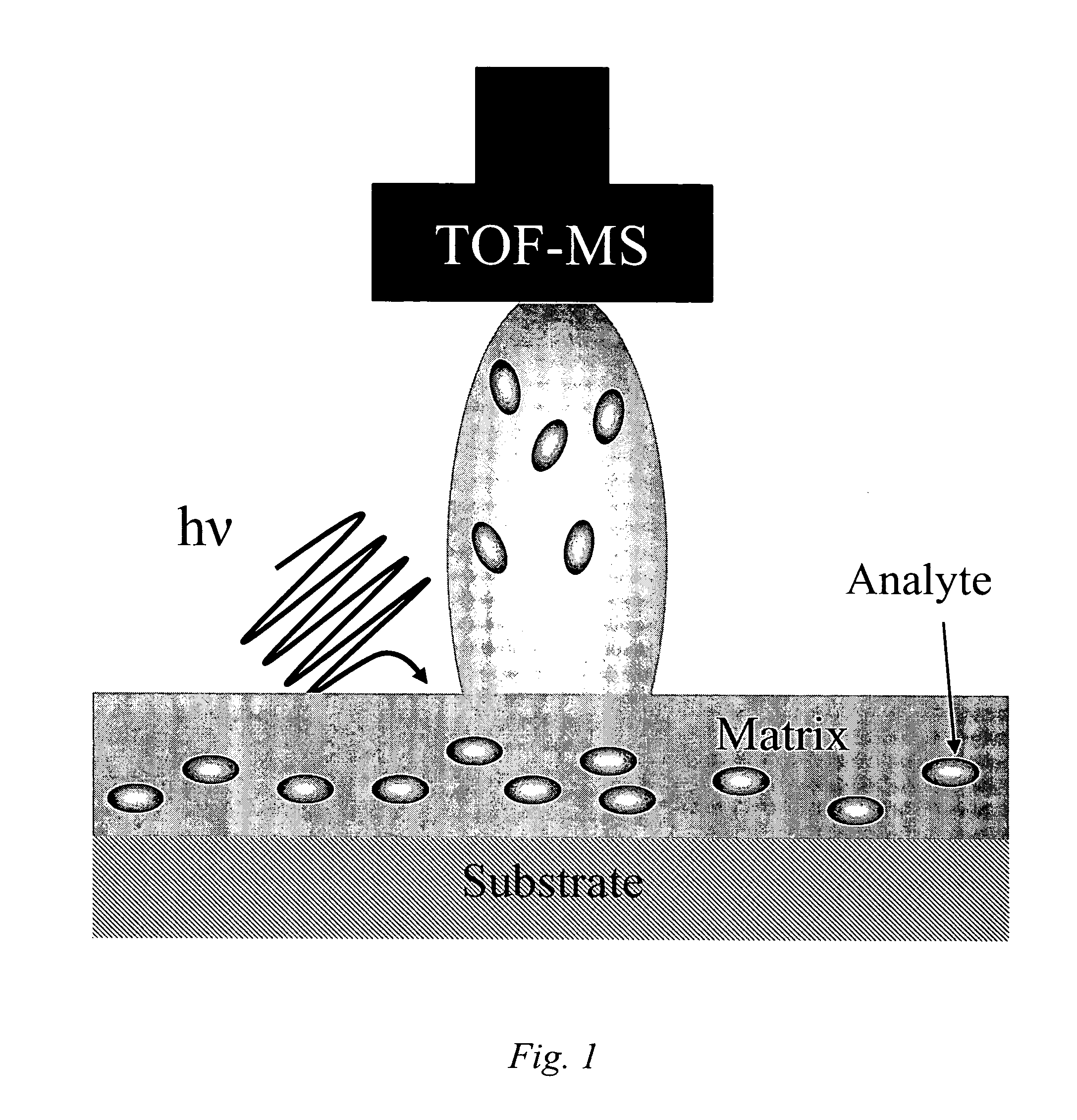
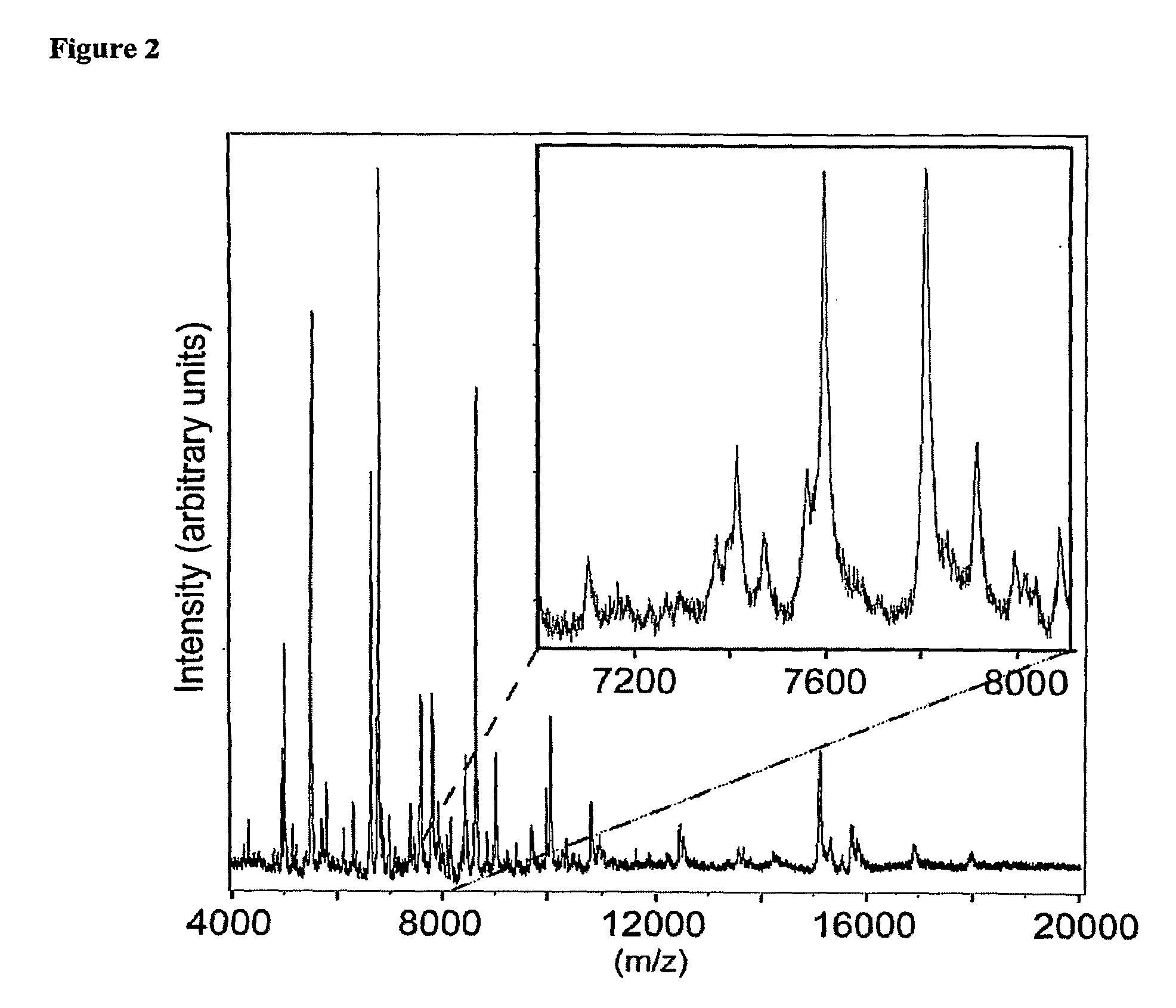
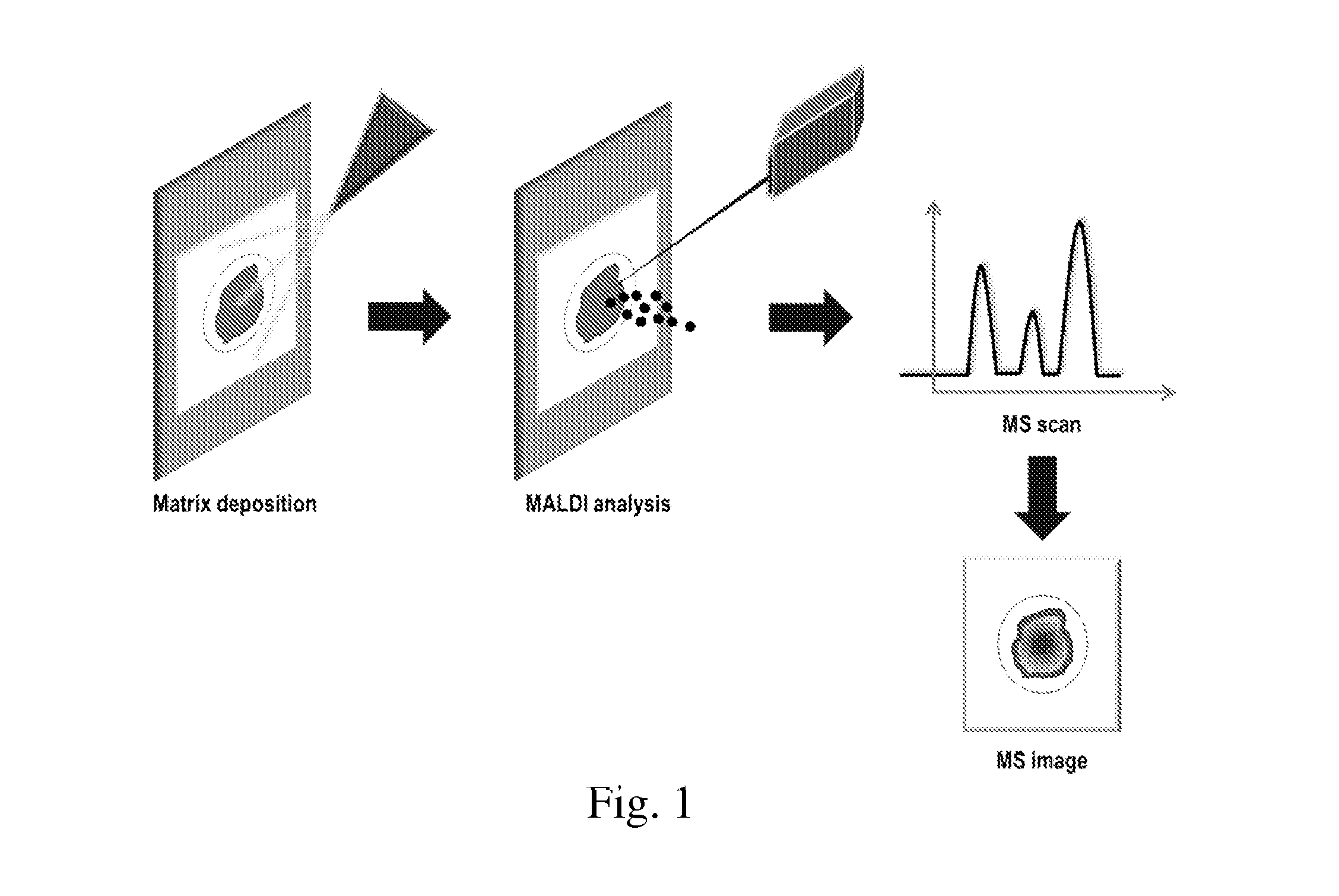
Tissue Sample Preparation and MALDI MS Imaging Thereof
InactiveUS20090325222A1Increase spaceQuality improvementPreparing sample for investigationImaging particle spectrometryLipid formationWhole Organism
Aspects of the present invention relate to a method for the preparation of samples for MALDI MS imaging. Certain embodiments relate to a method of matrix deposition for samples, wherein tissue sections are prepared via a synergistic combination of fixation with matrix. In certain embodiments, tissue is fixed with cold solvent, according to well-established histology protocols, and in the presence of matrix, allowing for high resolution spatial mapping of protein, lipid, sugar, and / or nucleic acid distribution. In certain embodiments, the present invention relates to fixation with matrix of whole organisms. In certain embodiments, animals are perfused with fixation and matrix mixtures, which allows for direct mass spectrometry analysis.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Systems and methods of detecting and demonstrating hair damage via evaluation of protein fragments
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Quantitative, high-throughput screening method for protein stability
InactiveUS20070099305A1Improve completenessImprove stabilityDisease diagnosisBiological testingLaser desorption ionization mass spectrometryHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
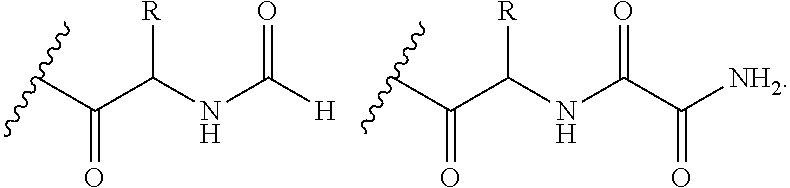
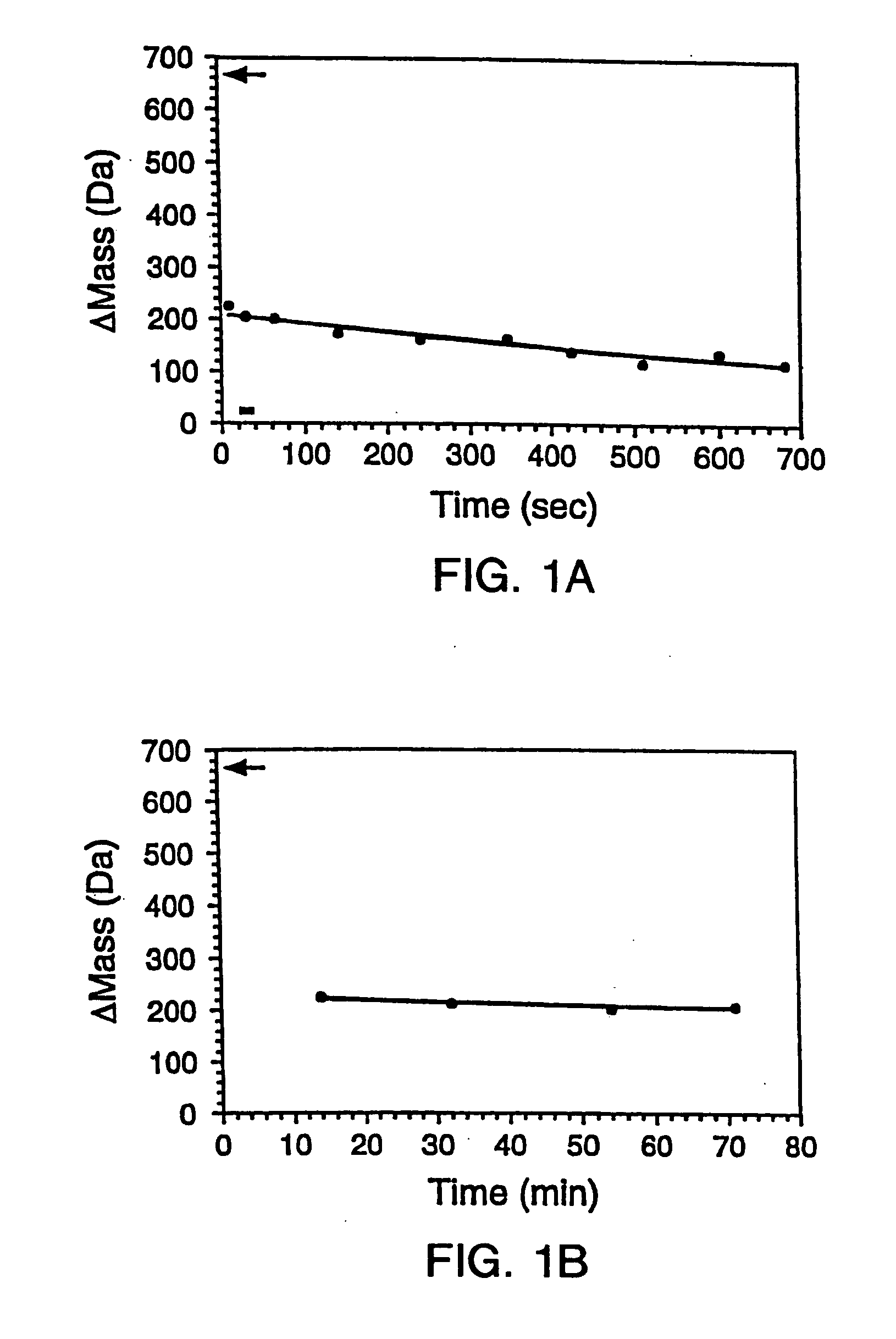
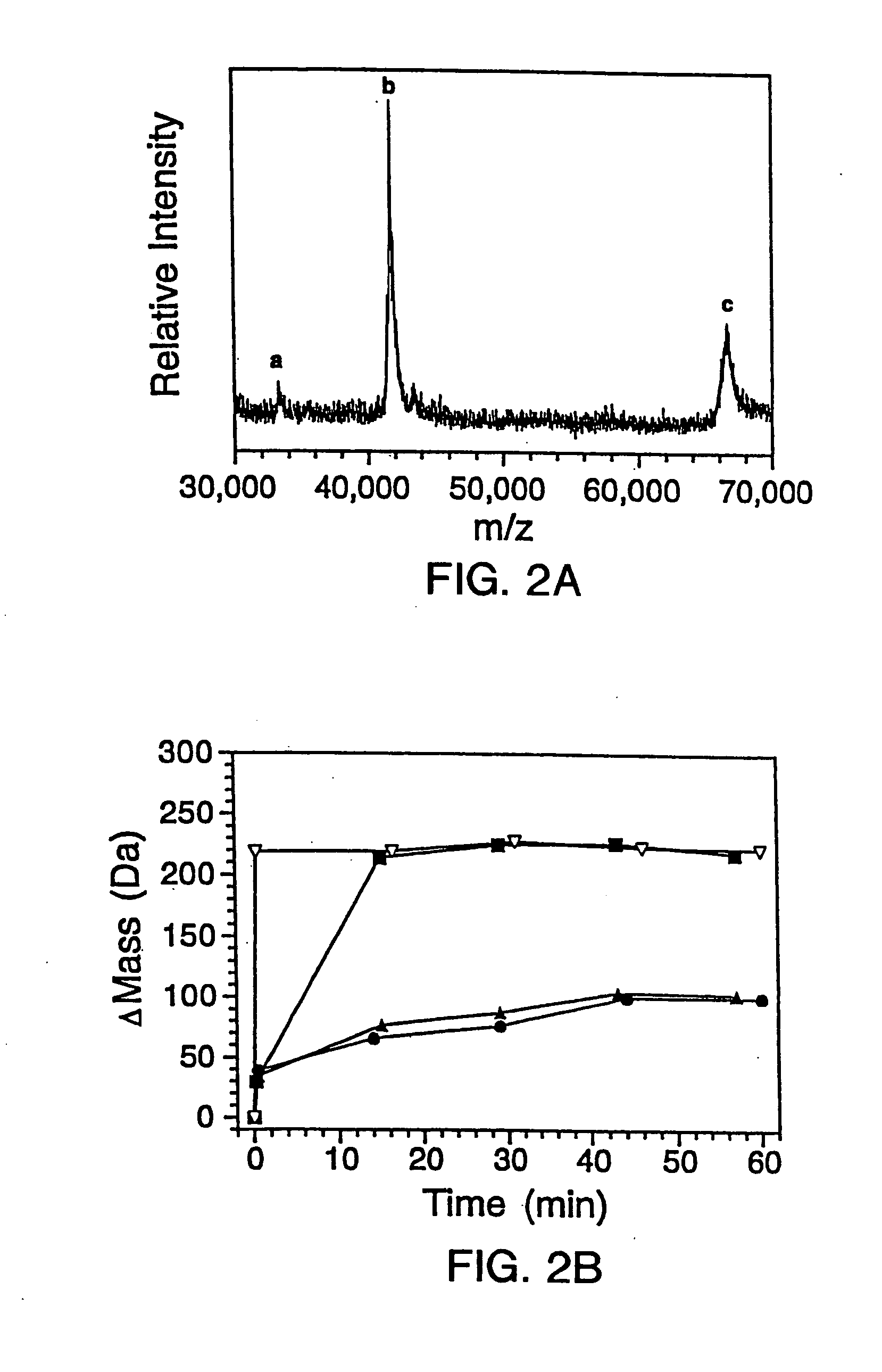
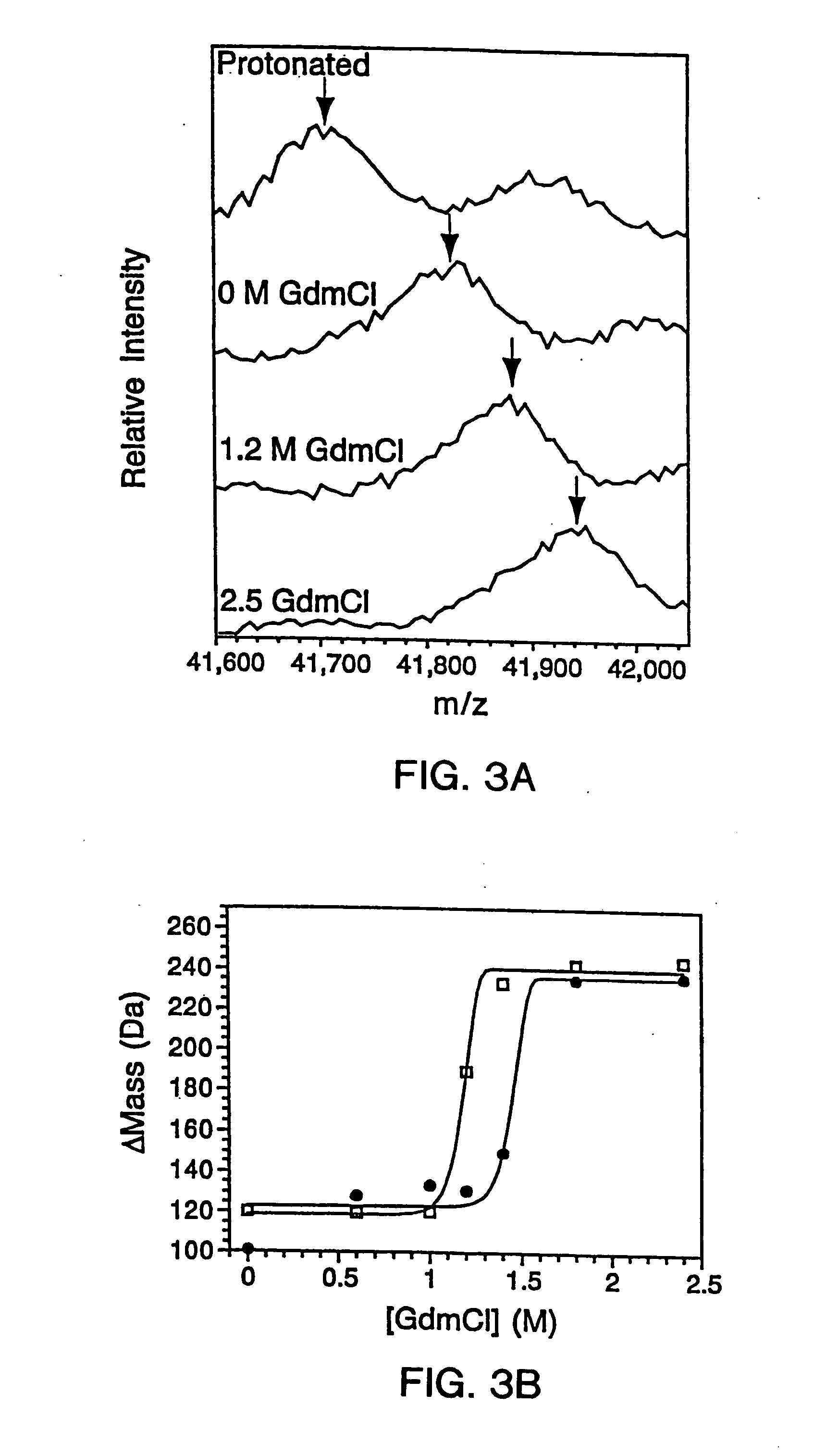
In proteomic research, it is often necessary to screen a large number of polypeptides for the presence of stable structure. Described herein are methods (referred to as MALDI MS-HX and SUPREX) for measuring the stability of proteins in a rapid, high-throughput fashion. The method employs hydrogen exchange to estimate the stability of quantities of unpurified protein extracts, using matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry. A method of quantitatively determining the stability of a test protein under native conditions is disclosed. The method includes the steps (a) providing a test protein; (b) contacting the protein with an exchange buffer comprising a denaturant and deuterium, the exchange buffer having a denaturant concentration; (c) contacting the test protein with a mass spectrometry matrix medium; (d) determining a change in mass of the test protein by mass spectrometry; (e) varying the denaturant concentration of the exchange buffer; (f) repeating steps (a)-(e) a desired number of times; and (g) quantitatively determining protein stability based on the change in mass of the test protein as a function of denaturant concentration, whereby the stability of a test protein under native conditions is quantitatively determined.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
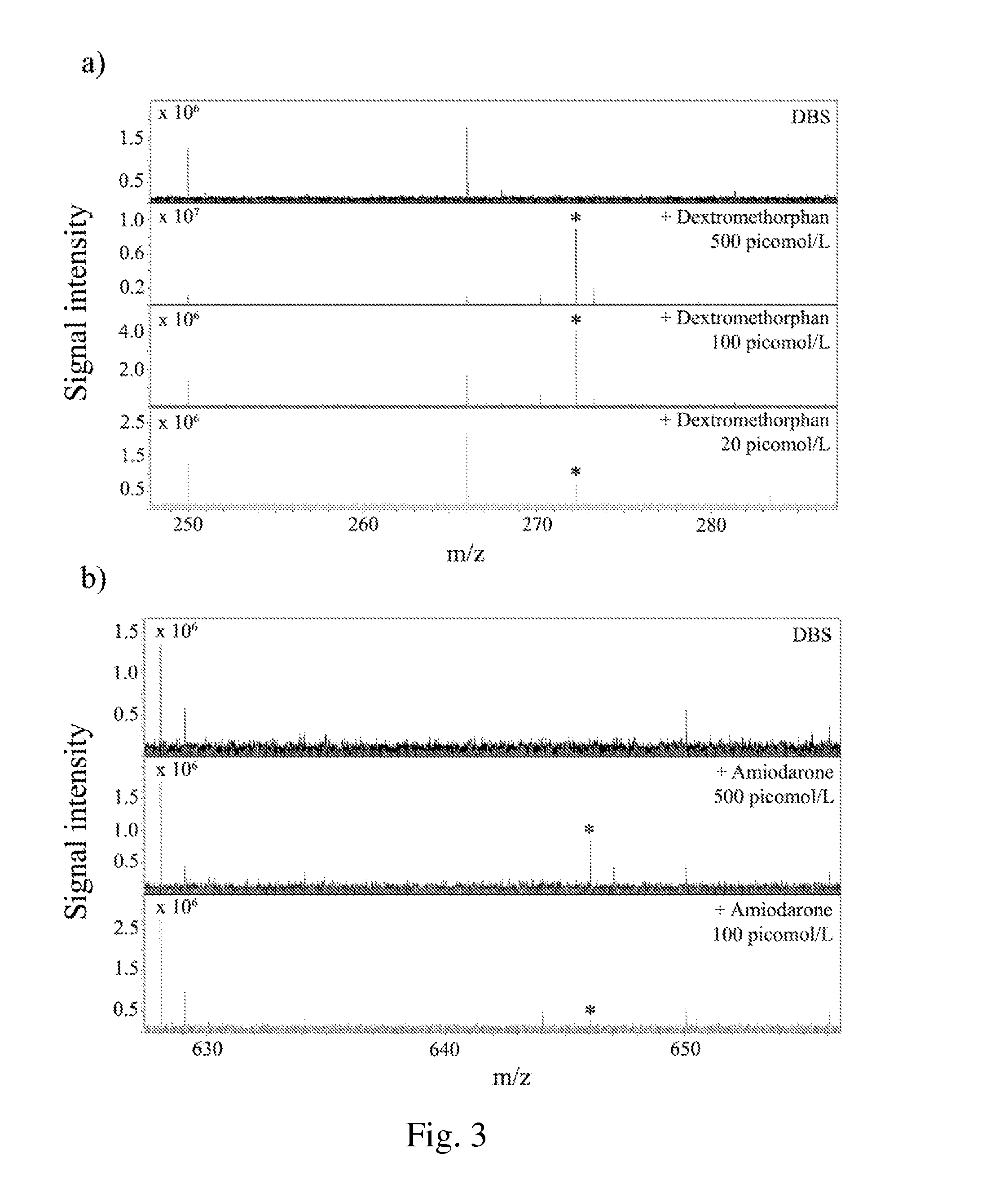
Detection of compounds in a dried fluid spot by direct maldi/ms
ActiveUS20160047799A1Fast and reliable detection and visualizationRapidly and easily analyzedParticle spectrometer methodsMass spectrometric analysisDigestionMaldi ms
It is provided a method for detection and / or quantification of at least one molecule presents in blood by a MALDI-MS analysis of a dried fluid spot without the presence of any digestion step or liquid extraction step, which permits to further analyse the physical distribution of at least one molecule within a dried fluid spot.
Owner:ZENTECH
Probe for mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20050196791A1Accurate measurementHigh affinityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyTarget surfaceLaser desorption ionization mass spectrometry
The present invention relates to a probe for the analysis of one or more analytes, particularly proteins or compounds capable of binding or otherwise interacting therewith, by laser desorption / ionisation mass spectrometry, more particularly MALDI MS. It also relates to a protein microarray, a method of producing a protein microarray and a method of analysing a protein microarray. The probe comprises a support having an electroconductive target surface thereon characterized in that the target surface comprises a micro array having a plurality of discrete target areas presenting one or more analyte capture moieties. Each discrete target area has an area of less than 1000 μm2, more preferably still less than 500 μm2, and more preferably still less than 100 μm2.
Owner:KOOPMAN JENS OLIVER +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com