Patents
Literature
77results about "Dynamic spectrometers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
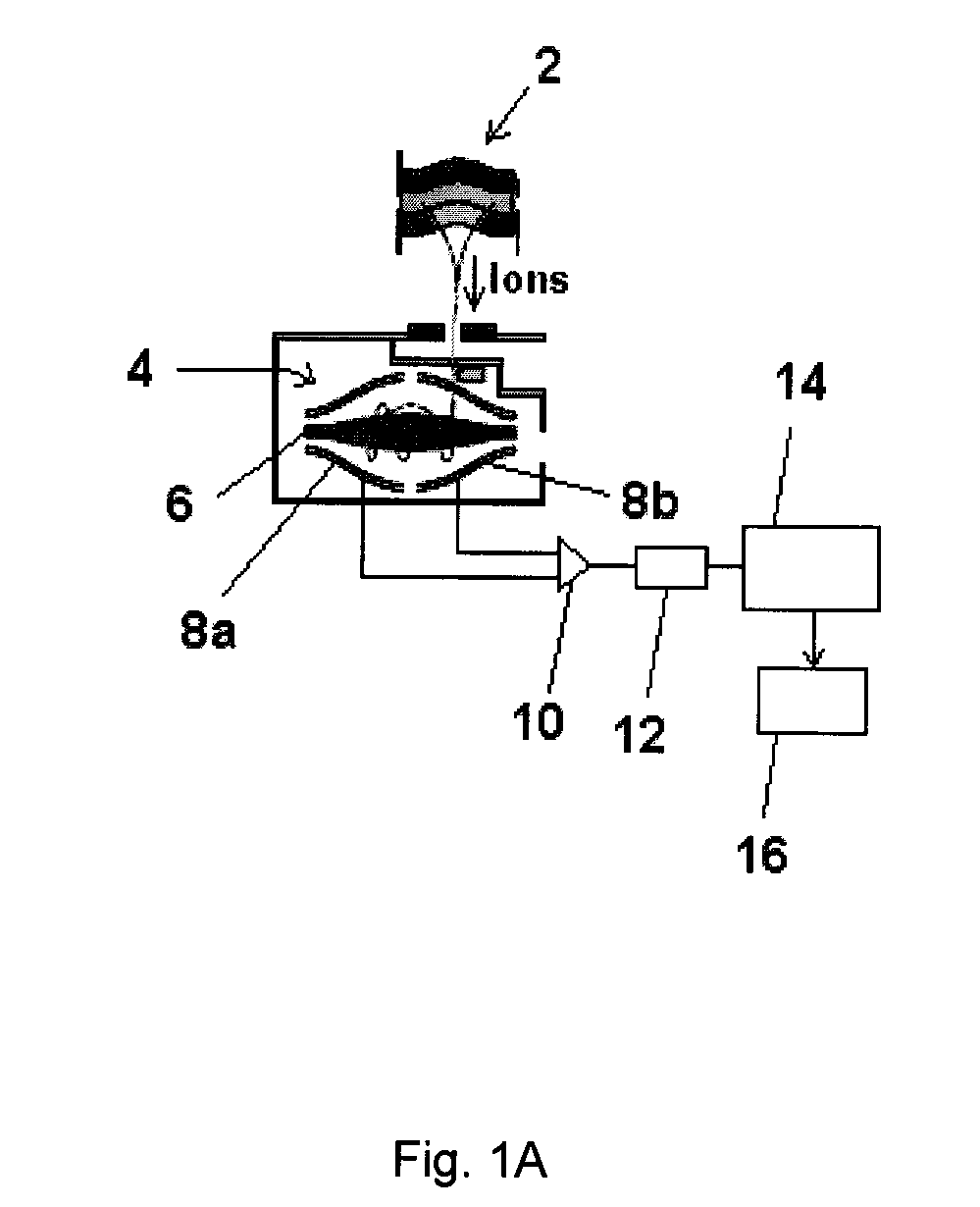
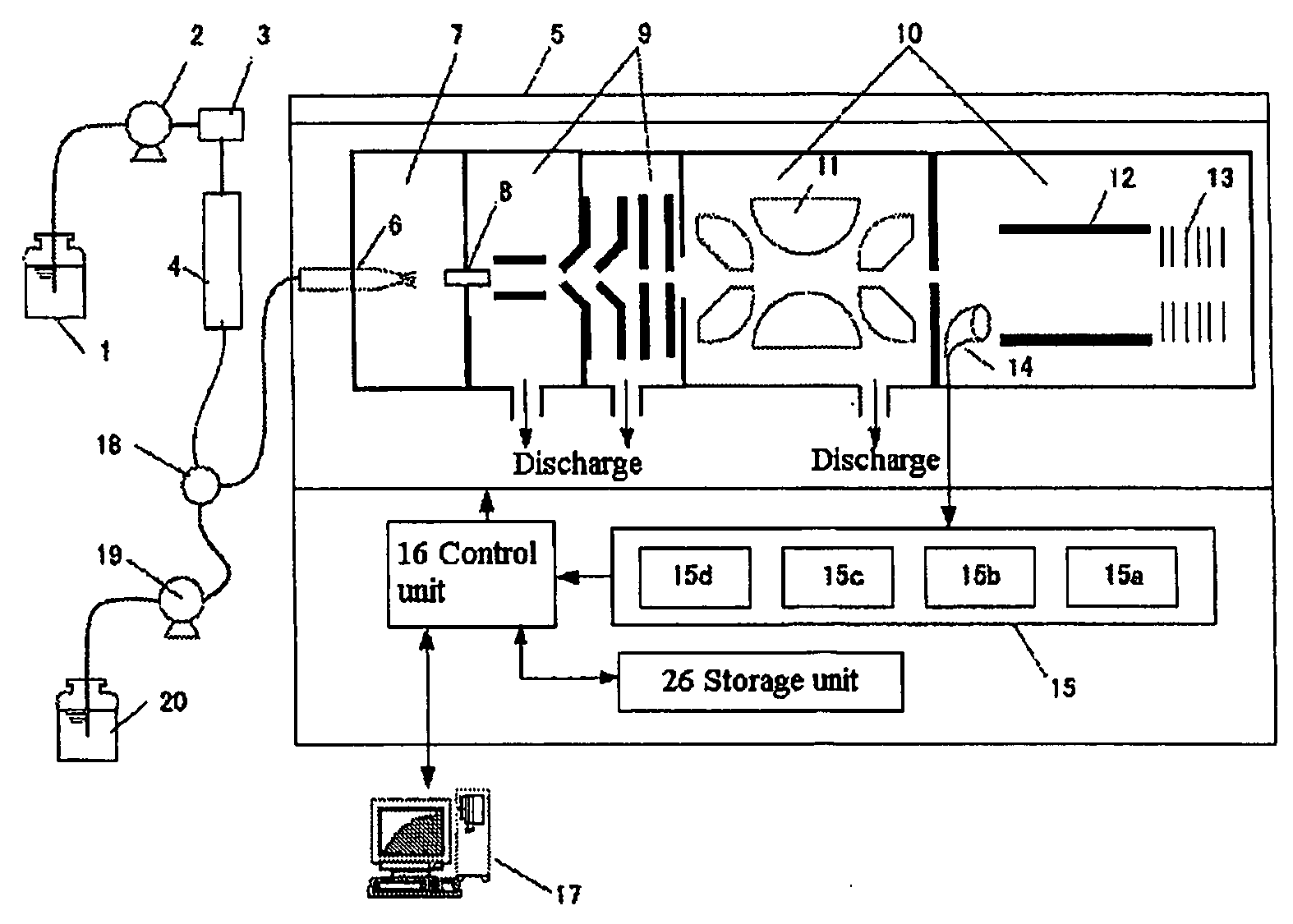
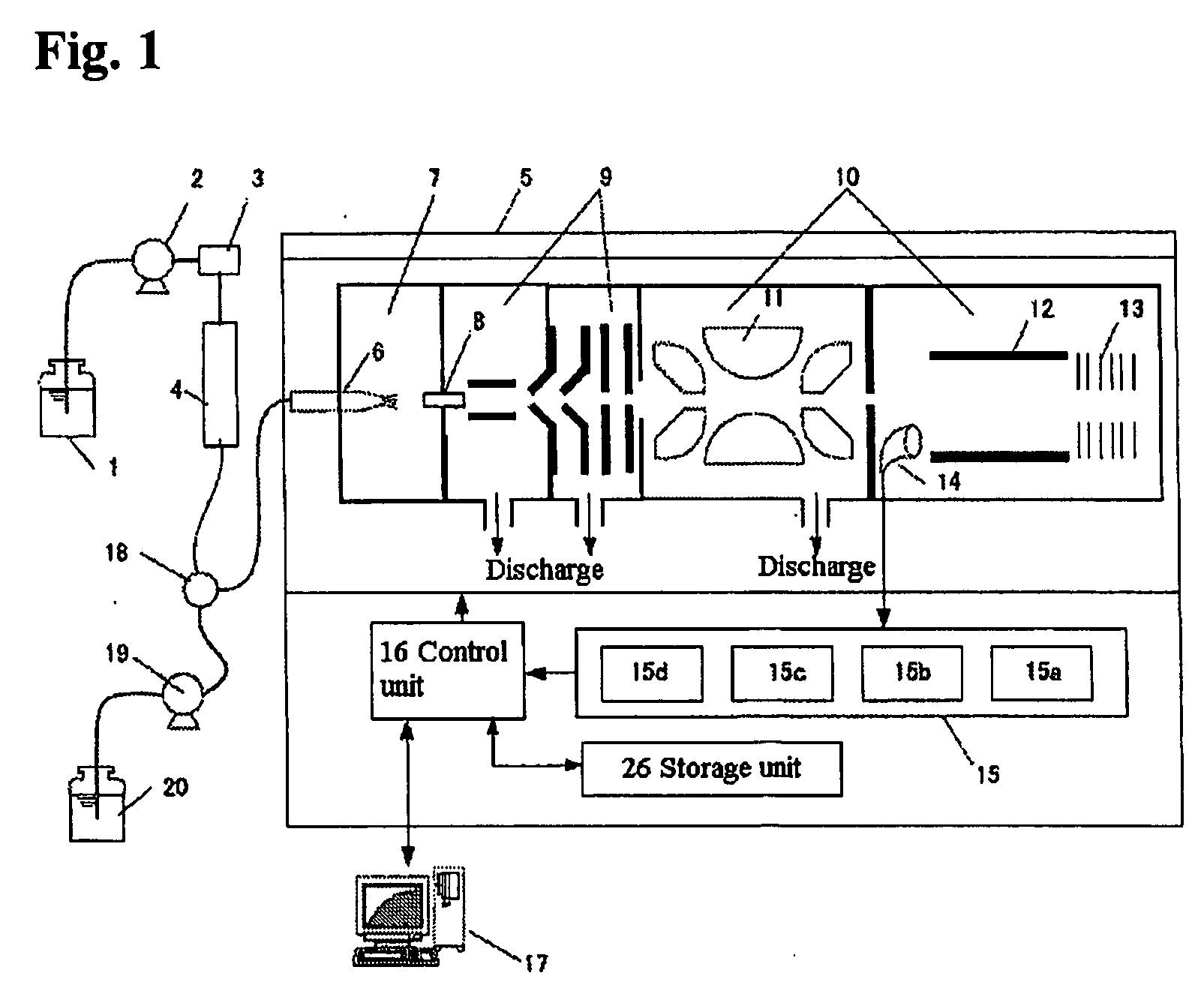
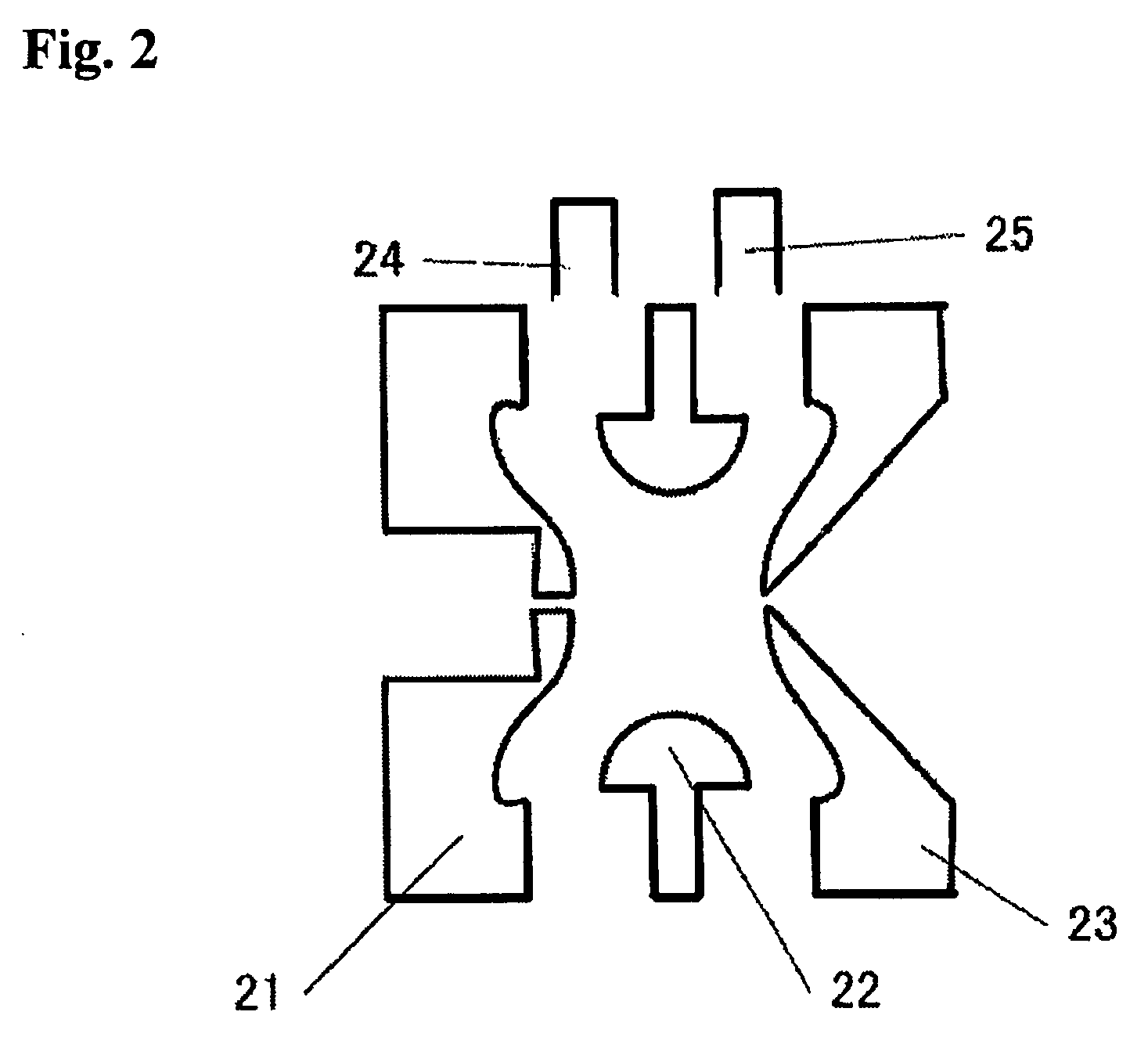
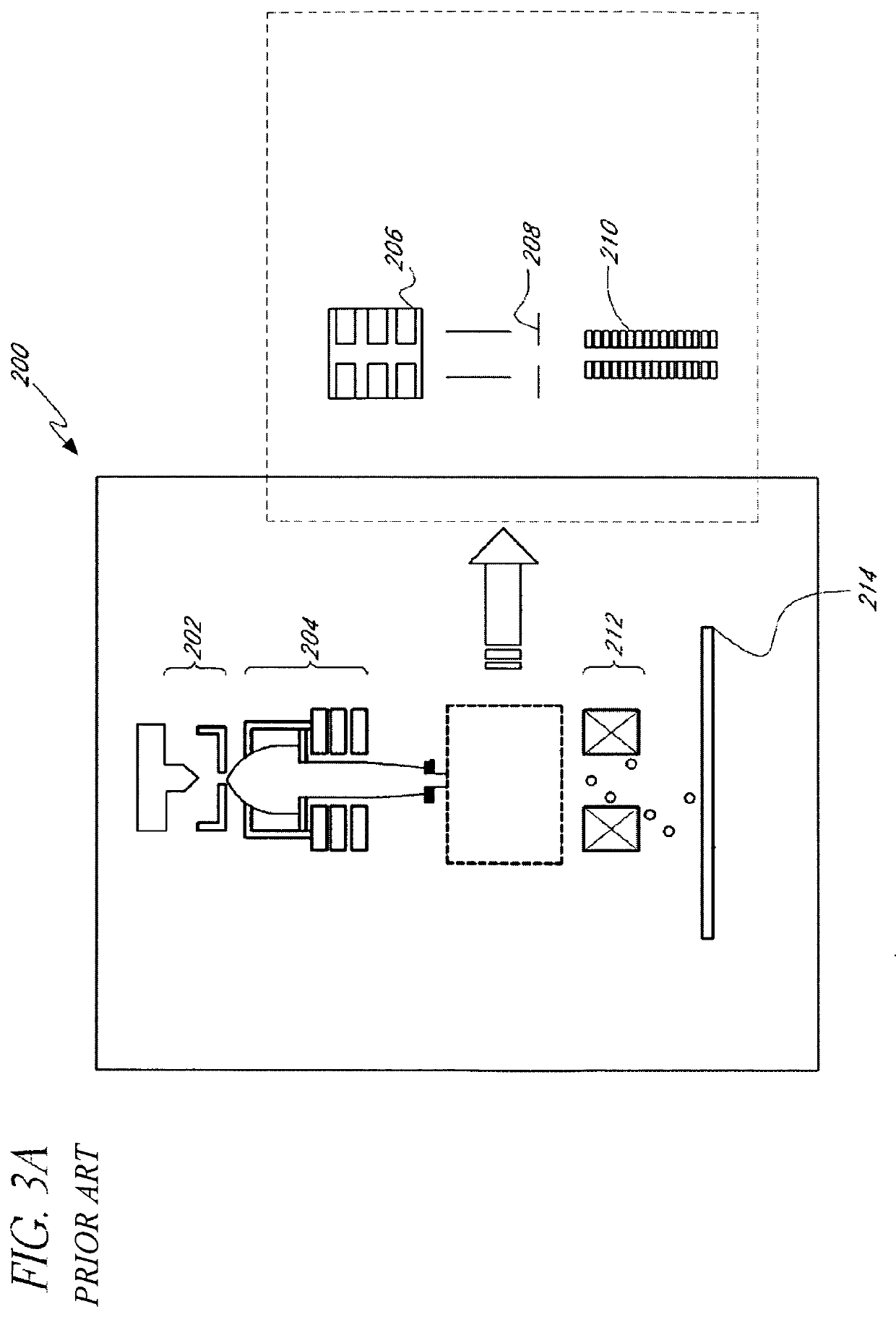
Mass spectrometer and method for using same
ActiveUS8395112B1Prolongs time of whole analysisImprove detection limitDynamic spectrometersMicrobiological testing/measurementControl signalMass analyzer
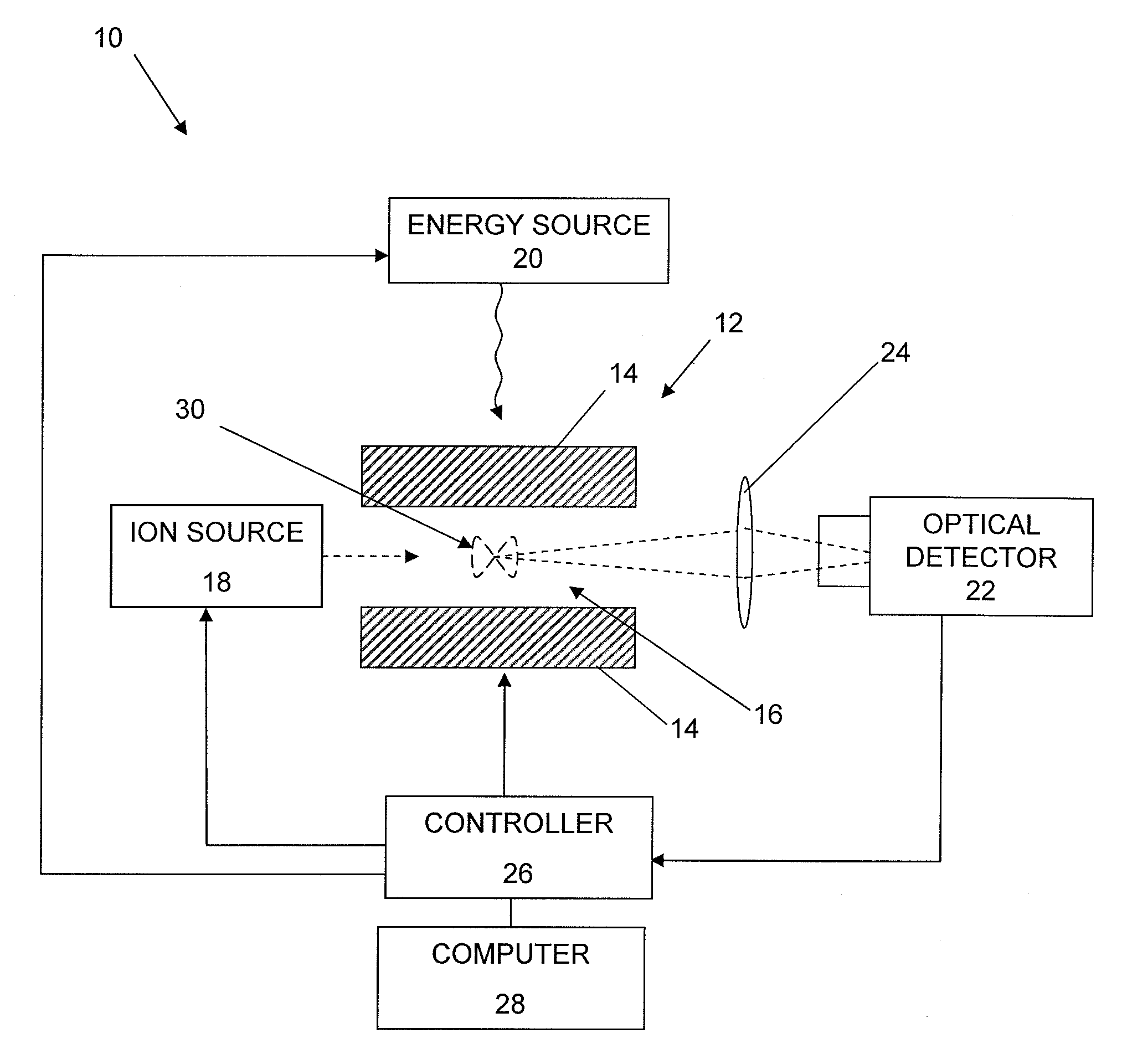
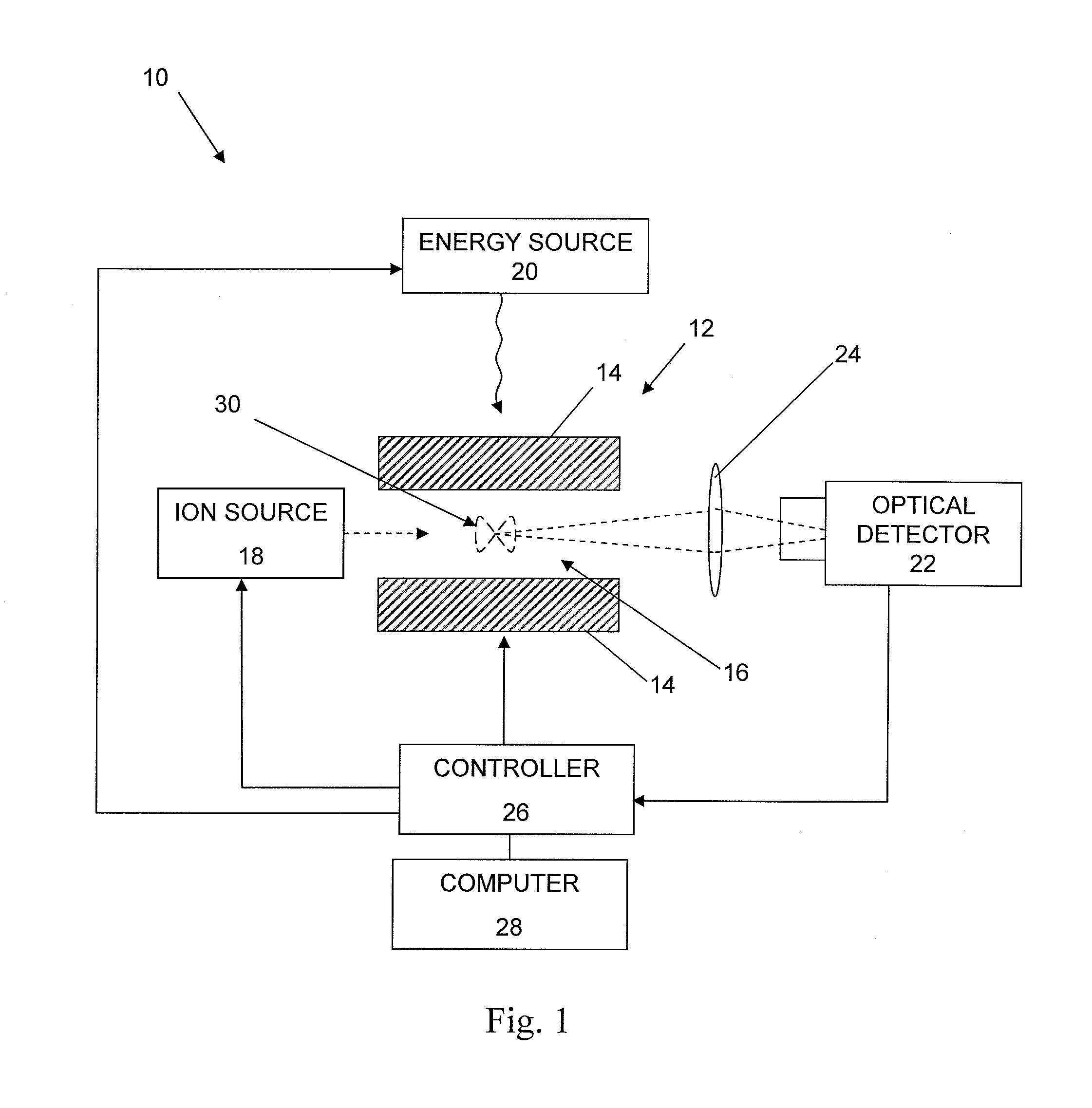
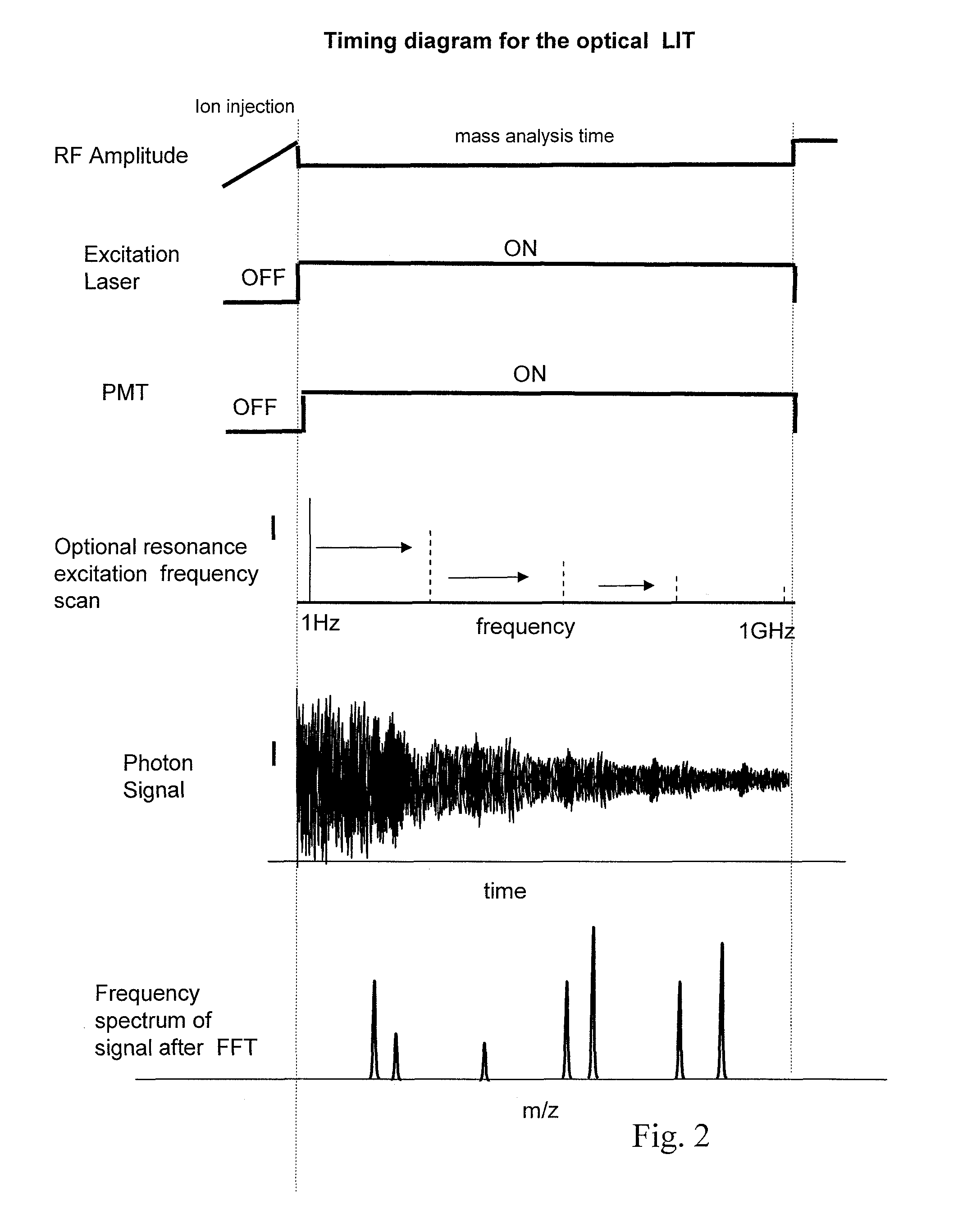
Apparatus including an ion trap, a controller connected to the ion trap, wherein the controller includes a memory containing computer readable instructions which, when executed, cause the controller to send control signals to the ion trap so that the ion trap produce and maintain a trapping field in the ion trap, a waveform generator to change the trapping field so that ions of a predetermined mass in the trapping chamber are selectively moved; a secondary waveform generator to change the orbits of the ions; an energy source to excite ions to emit photons, an optical detector to detect the emitted photons, and a processor which can apply fast-Fourier transform analysis of the time-domain signal of the detected emitted photons to generate a frequency or mass spectrum related to mass-to-charge ratio of the ions.
Owner:BIER MARK E
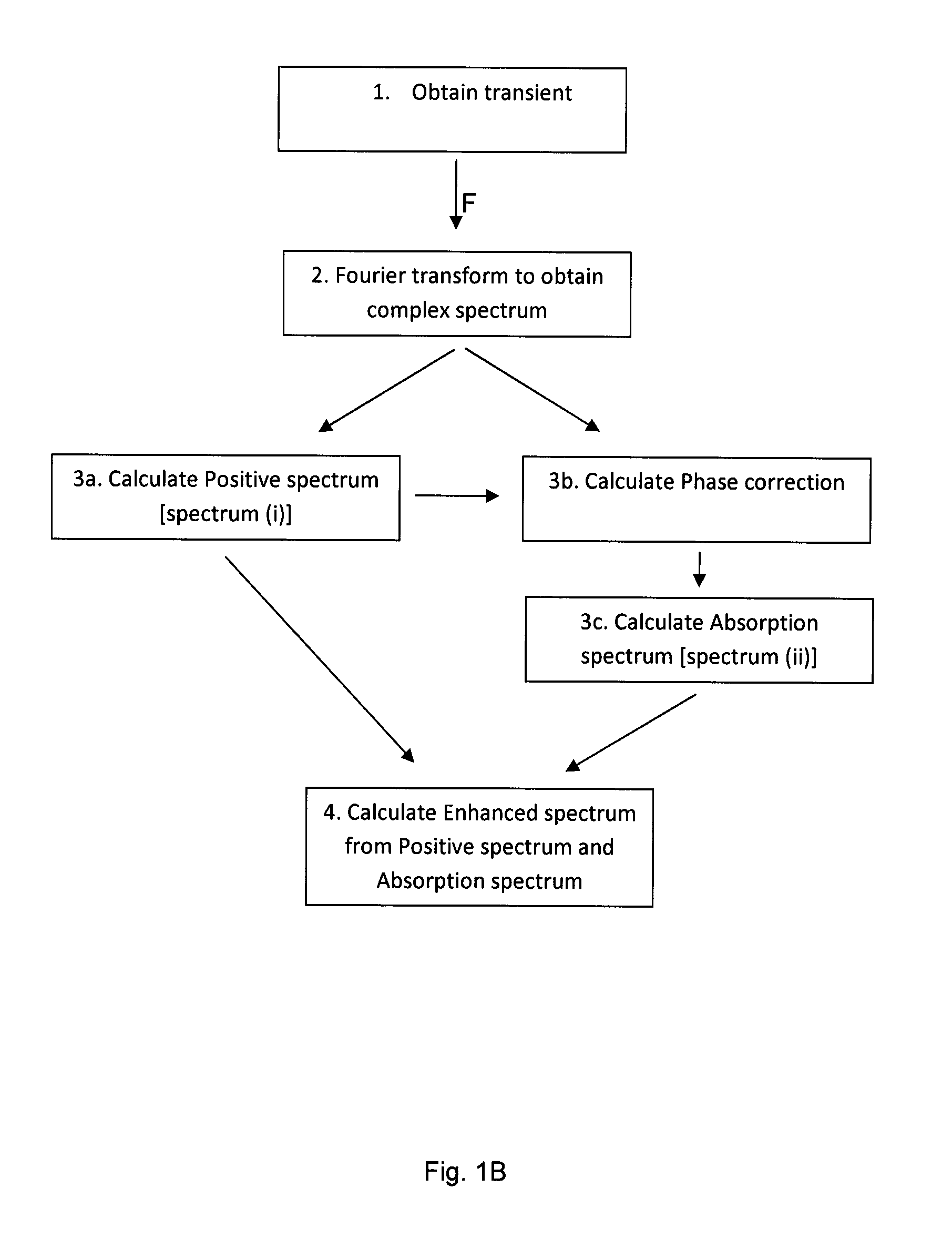
Methods and Apparatus for Producing a Mass Spectrum
ActiveUS20110240841A1High resolutionIncrease speedDynamic spectrometersIon sources/gunsPhase correctionFourier transform on finite groups
The invention provides a method of producing a mass spectrum, comprising:obtaining a transient from the oscillation of ions in a mass analyser;Fourier transforming the transient to obtain a complex spectrum having a real component and an imaginary component; andcalculating an enhanced spectrum which comprises a combination of (i) and (ii) wherein(i) comprises a Positive spectrum; and(ii) comprises an Absorption spectrum.Also provided are an apparatus for producing a mass spectrum suitable for carrying out the method as well as a method of determining a phase correction for a complex spectrum obtained by Fourier transformation from a detected transient obtained from a mass analyser.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BREMEN
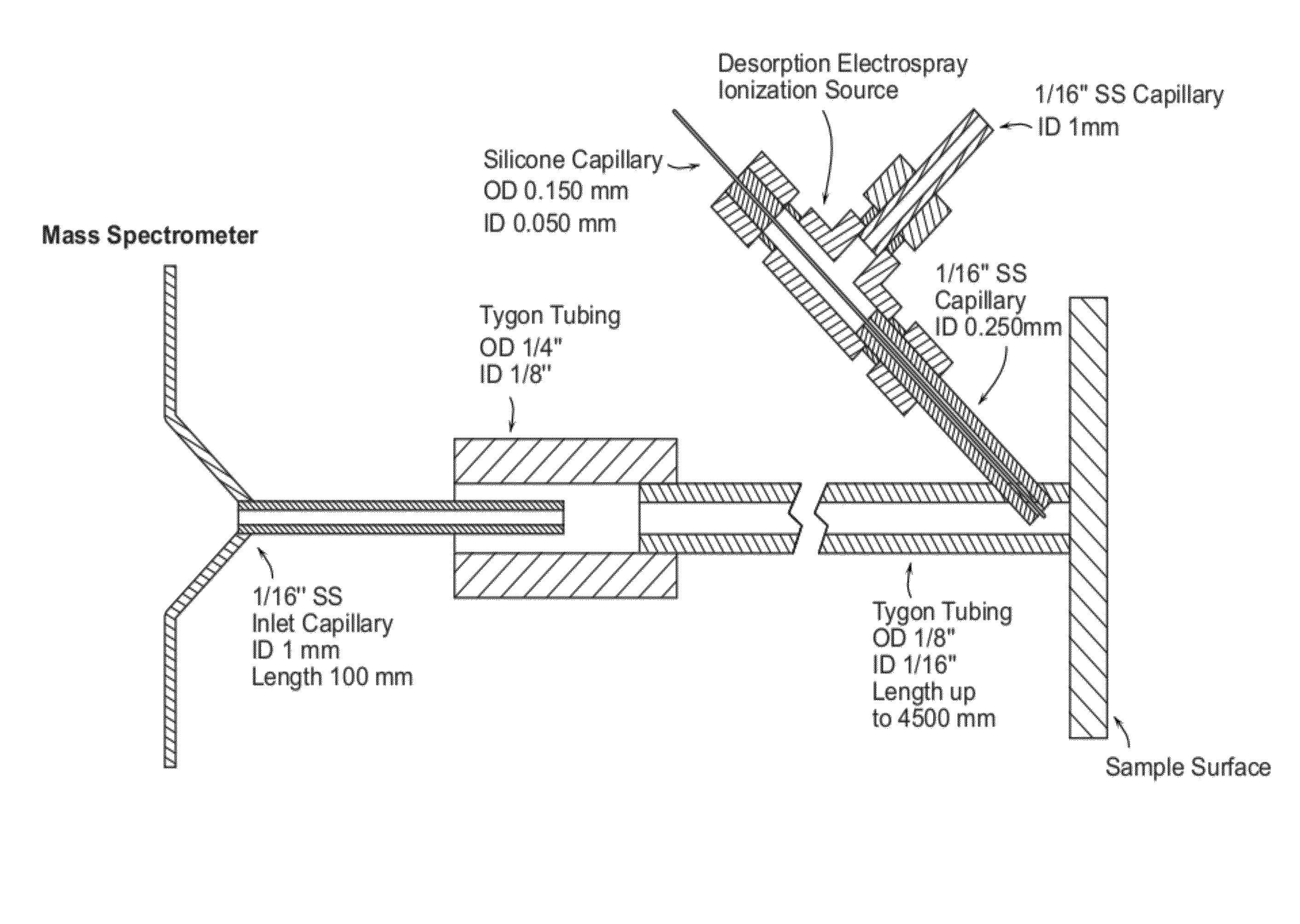
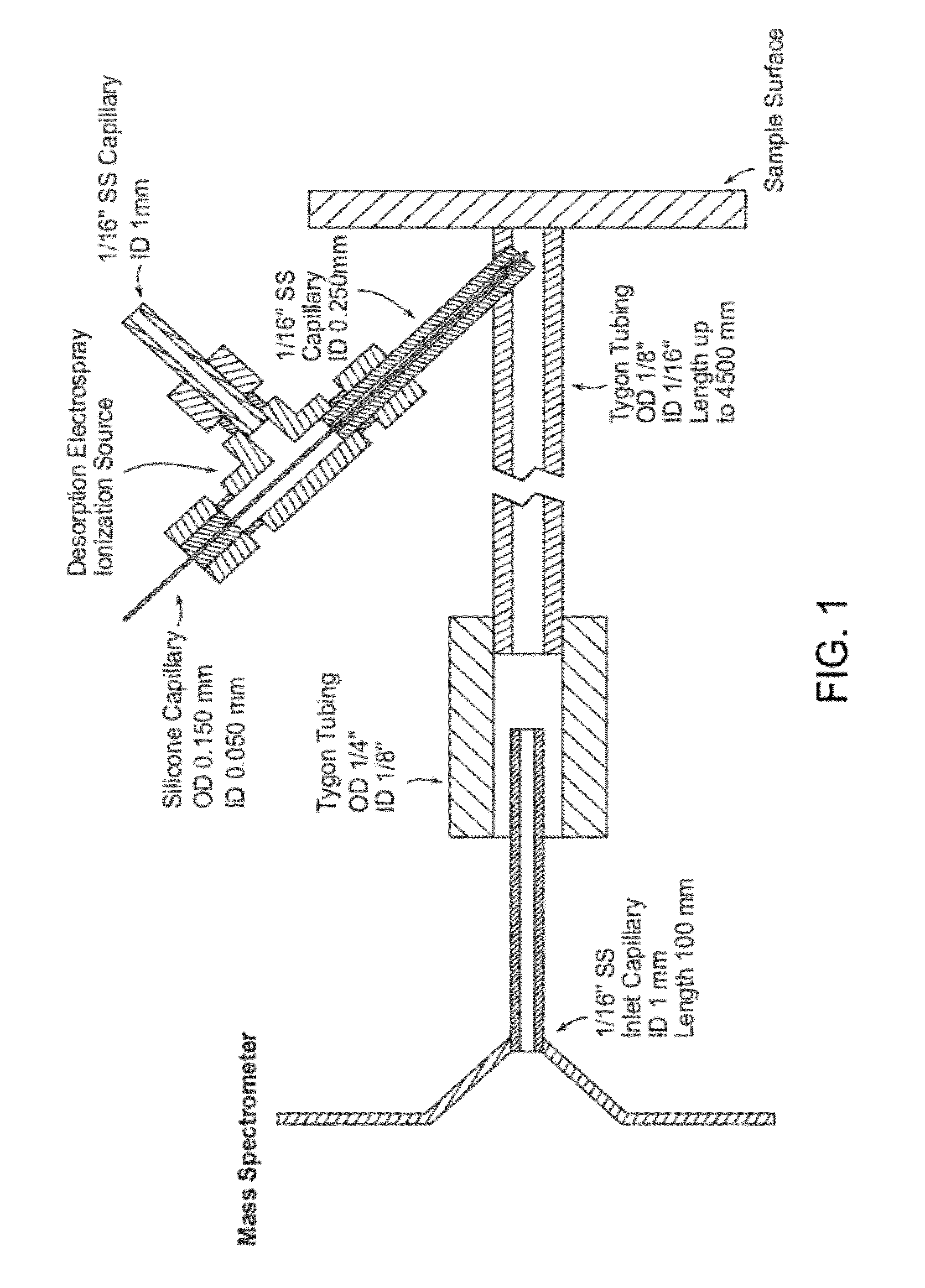
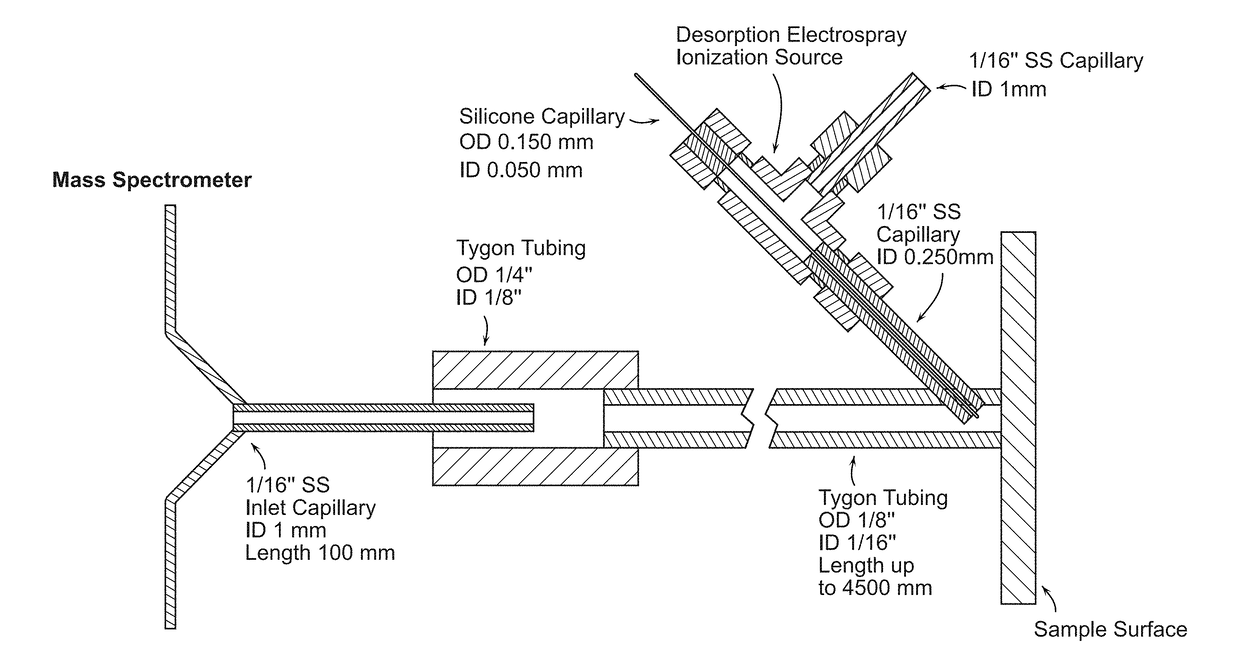
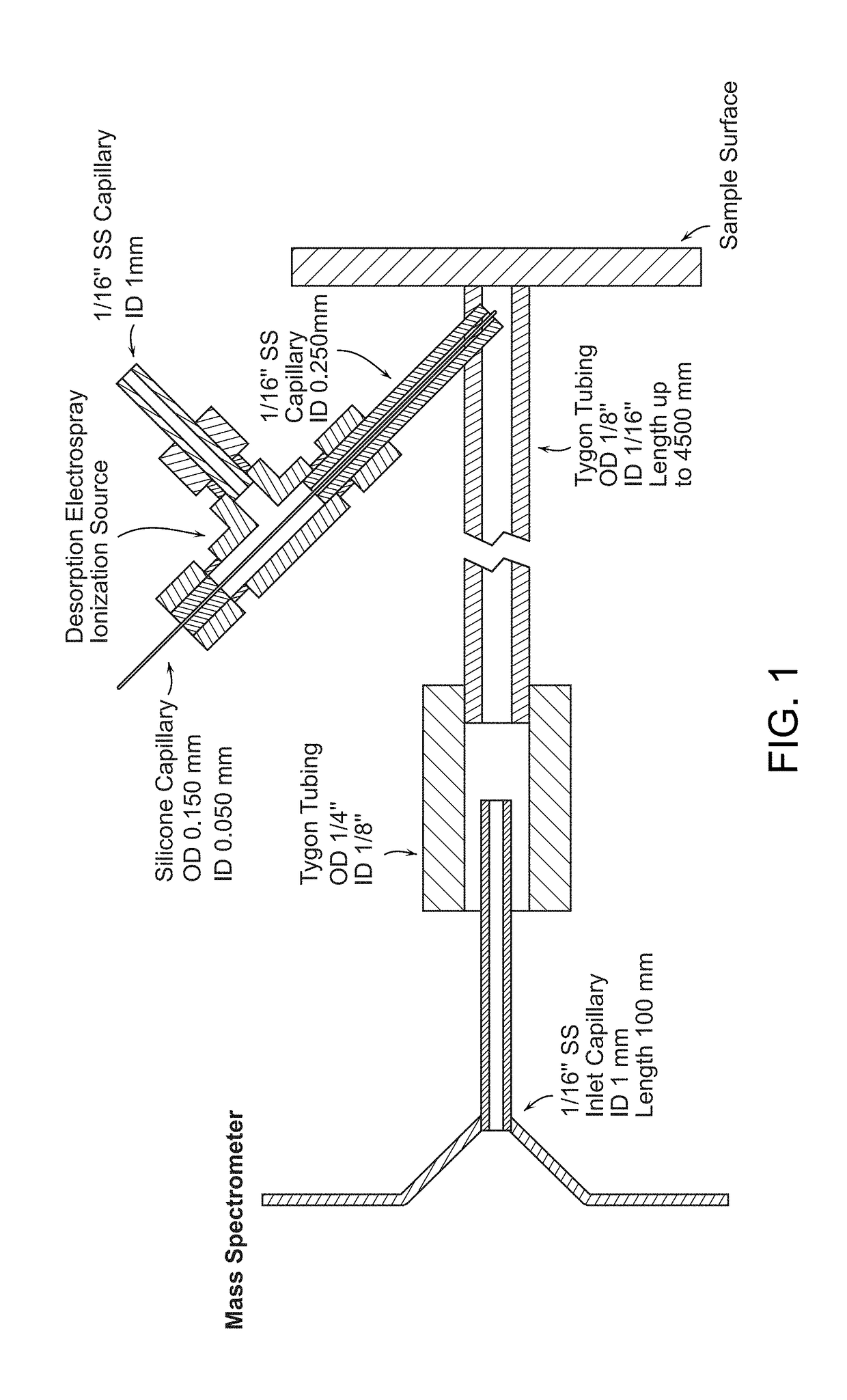
Enclosed desorption electrospray ionization probes and method of use thereof
The invention generally relates to enclosed desorption electrospray ionization probes, systems, and methods. In certain embodiments, the invention provides a source of DESI-active spray, in which a distal portion of the source is enclosed within a transfer member such that the DESI-active spray is produced within the transfer member.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Auxiliary frequency parametric excitation of quadrupole mass spectrometers
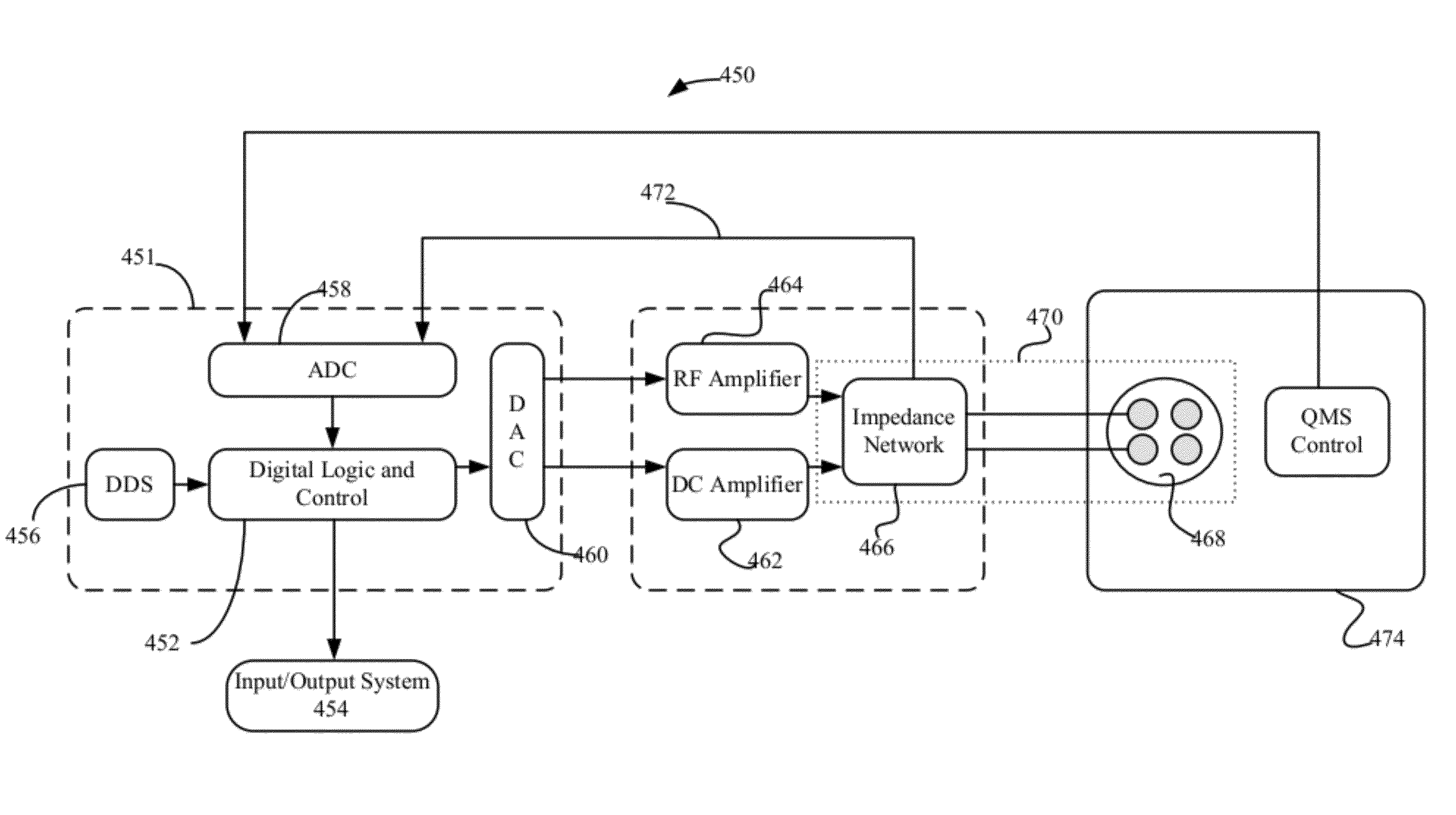
ActiveUS20120145892A1Improve dynamic rangeImprove power efficiencySpectrometer circuit arrangementsDynamic spectrometersFundamental frequencySpectrometer
The apparatus introduces a second adjustable resonant point in a QMS at a frequency that is close to a multiple of the fundamental frequency by adjusting driving point impedance characteristics of the QMS. The apparatus measures the first and second resonant point of the QMS to account for changes in the operational characteristics of the QMS.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Mass spectrum VUV (Vacuum Ultraviolet) photoionization source device for in-source collision induced dissociation
ActiveCN102117728AQuick analysisQuick Qualitative AnalysisDynamic spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIon accelerationCollision-induced dissociation
The invention relates to a mass spectrum analyzer, in particular to a mass spectrum VUV (Vacuum Ultraviolet) photoionization source device for in-source collision induced dissociation, which comprises a sample injecting capillary tube, an ion repelling electrode, an ion accelerating electrode, a vacuum ultraviolet lamp, a side pumping valve and an ionization source cavity, wherein the ion repelling electrode and the ion accelerating electrode are placed in the ionization source cavity at interval in parallel, the sample injecting capillary tube passes through the outer wall of the ionization source cavity, and one end of the sample injecting capillary tube is arranged in a central small hole of the ion repelling electrodes; a light emitting window of the vacuum ultraviolet lamp is placed opposite to a gap between the ion repelling electrode and the ion accelerating electrode; and an air outlet is arranged on the side wall of the ionization source cavity, and the side pumping valve is connected with the air outlet through a pipeline. The mass spectrum VUV photoionization source device can be used together with any types of quality analyzers, can simultaneously obtain the molecular weight and the structural information of a matter to be analyzed and also be used for rapidly distinguishing isomerides by utilizing in-source collision induced dissociation.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Single molecule mass spectroscopy enabled by nanoelectromechanical systems (nems-ms)
The present invention relates to an apparatus for measuring a mass of a sample, using a nanoelectromechanical system (NEMS) arranged to receive the sample added onto a resonator of the NEMS and a microfluidic sample delivery and sample ionization system. The nanoelectromechanical system is located at an output of the ionization system. The nanoelectromechanical resonator system is highly sensitive and is capable of detecting masses in the single Dalton range.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
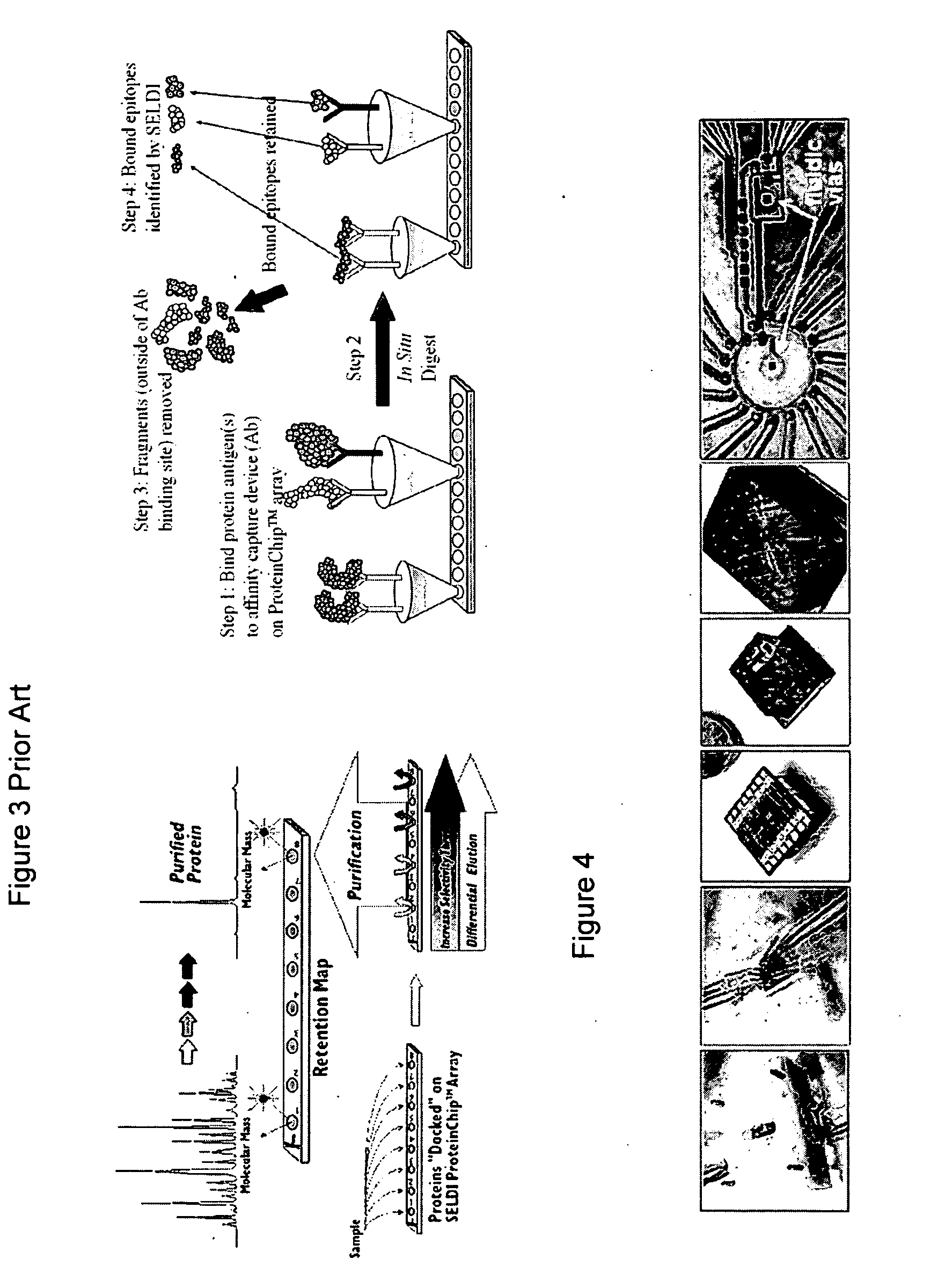
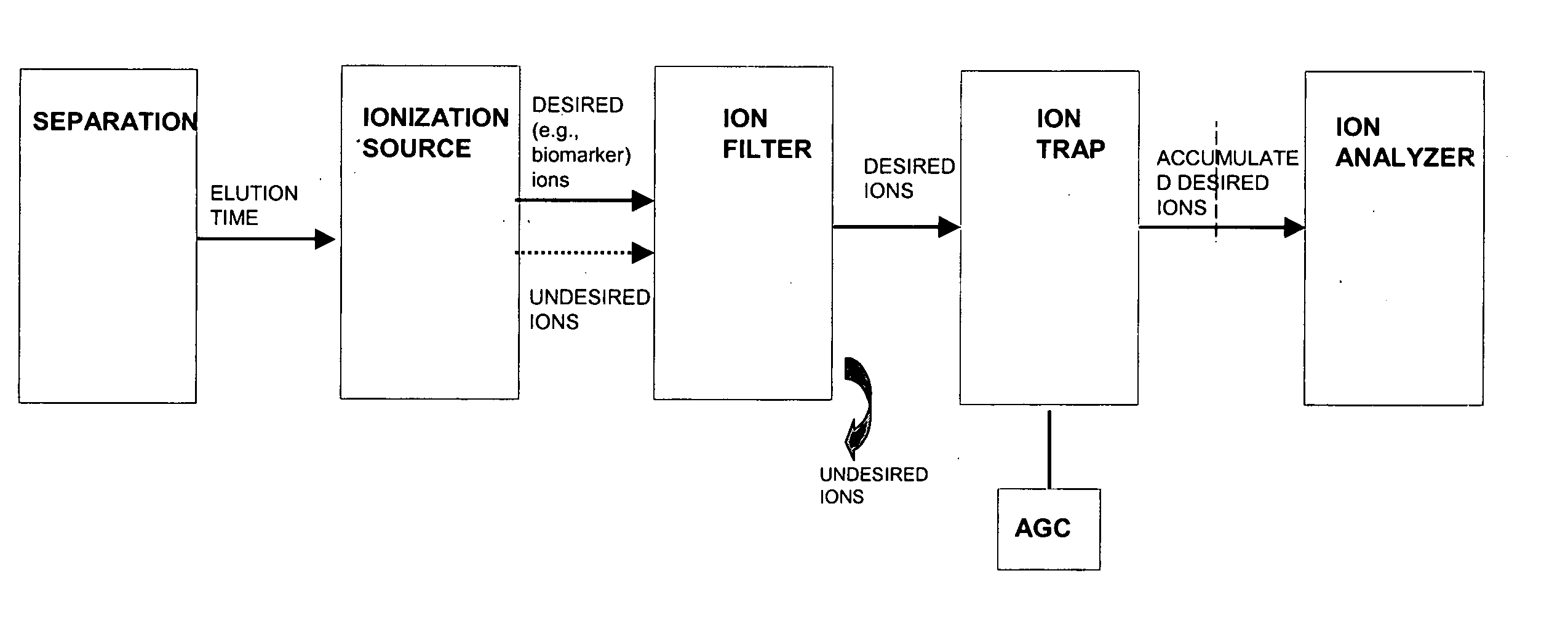
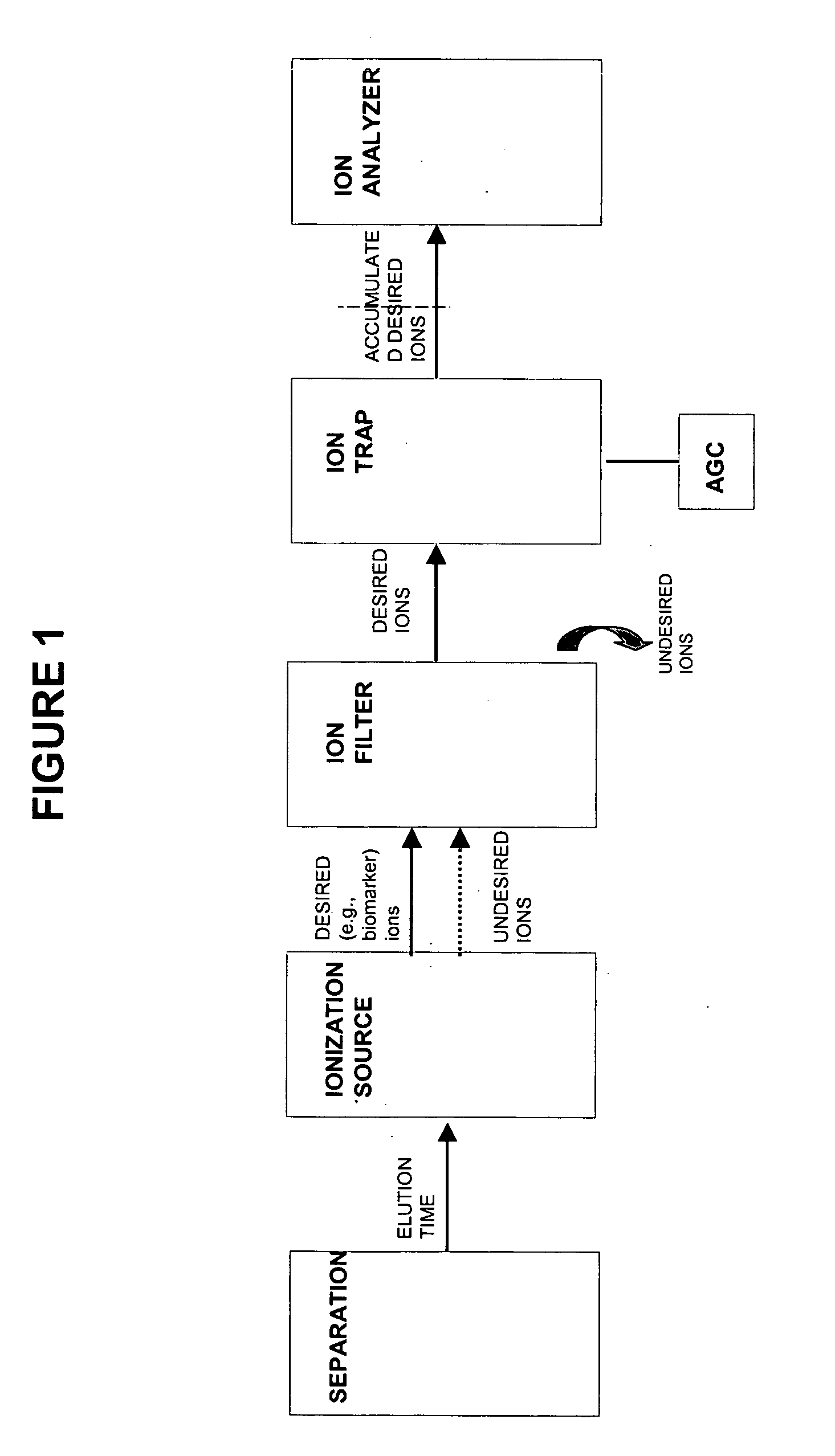
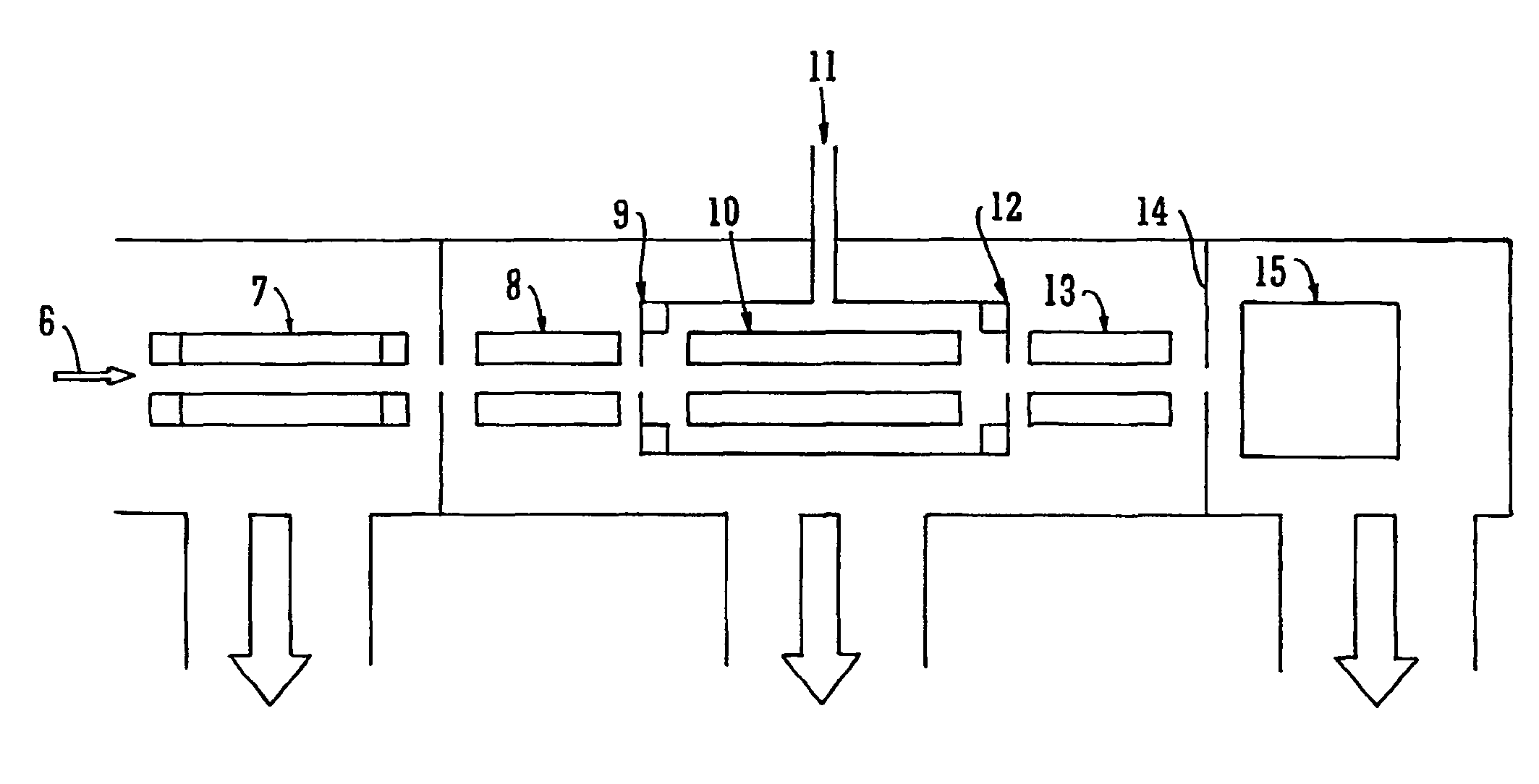
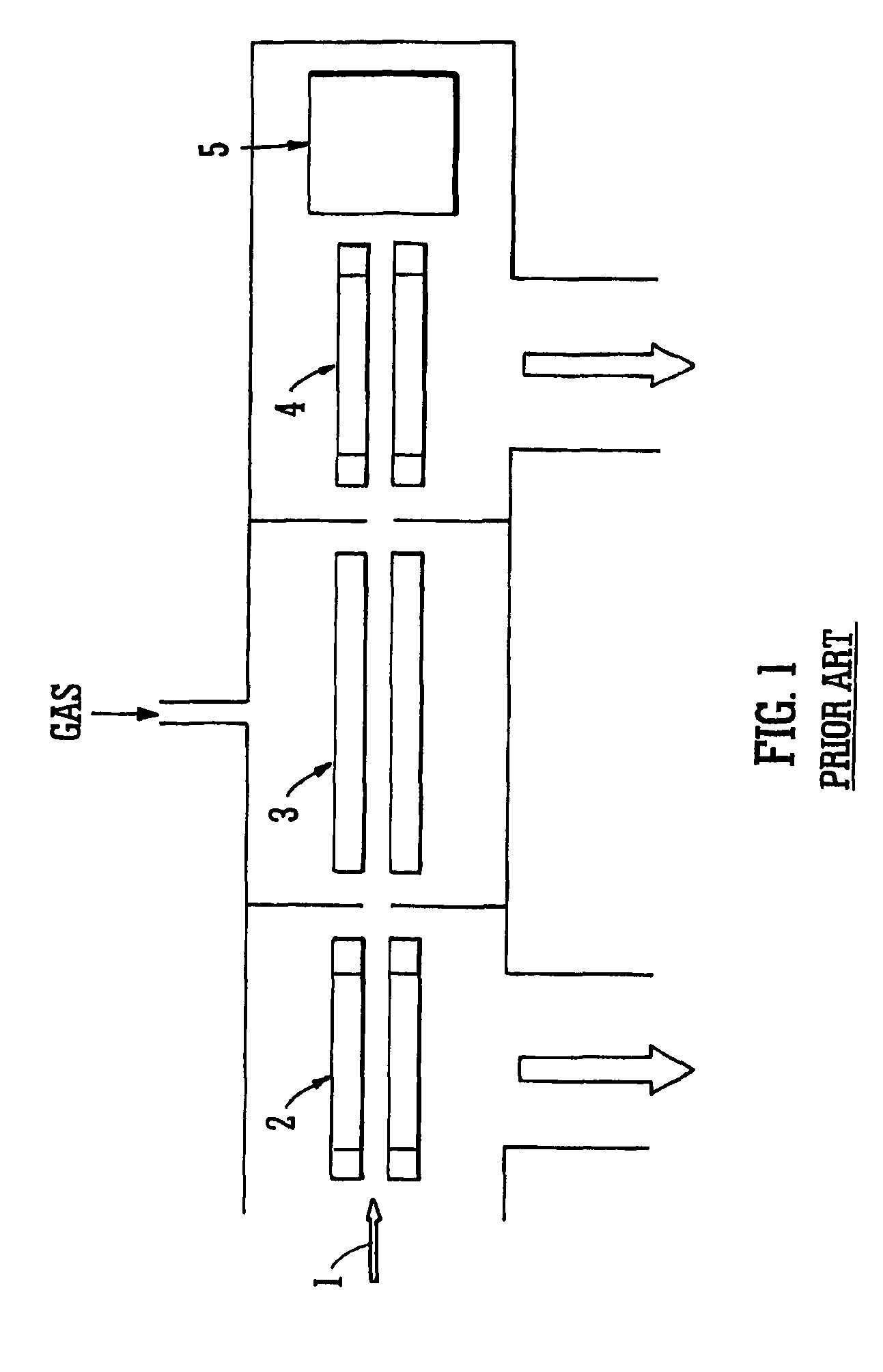
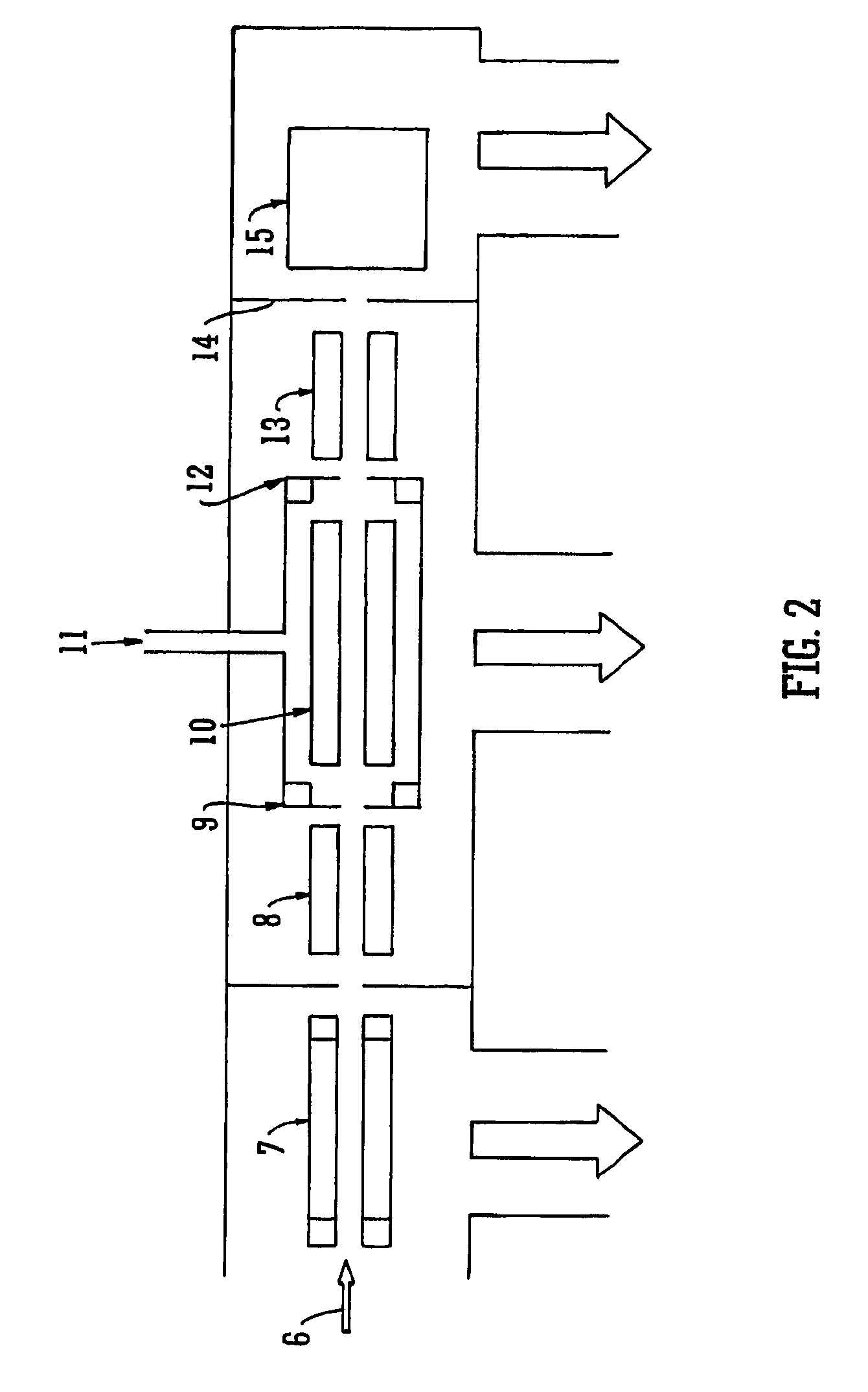
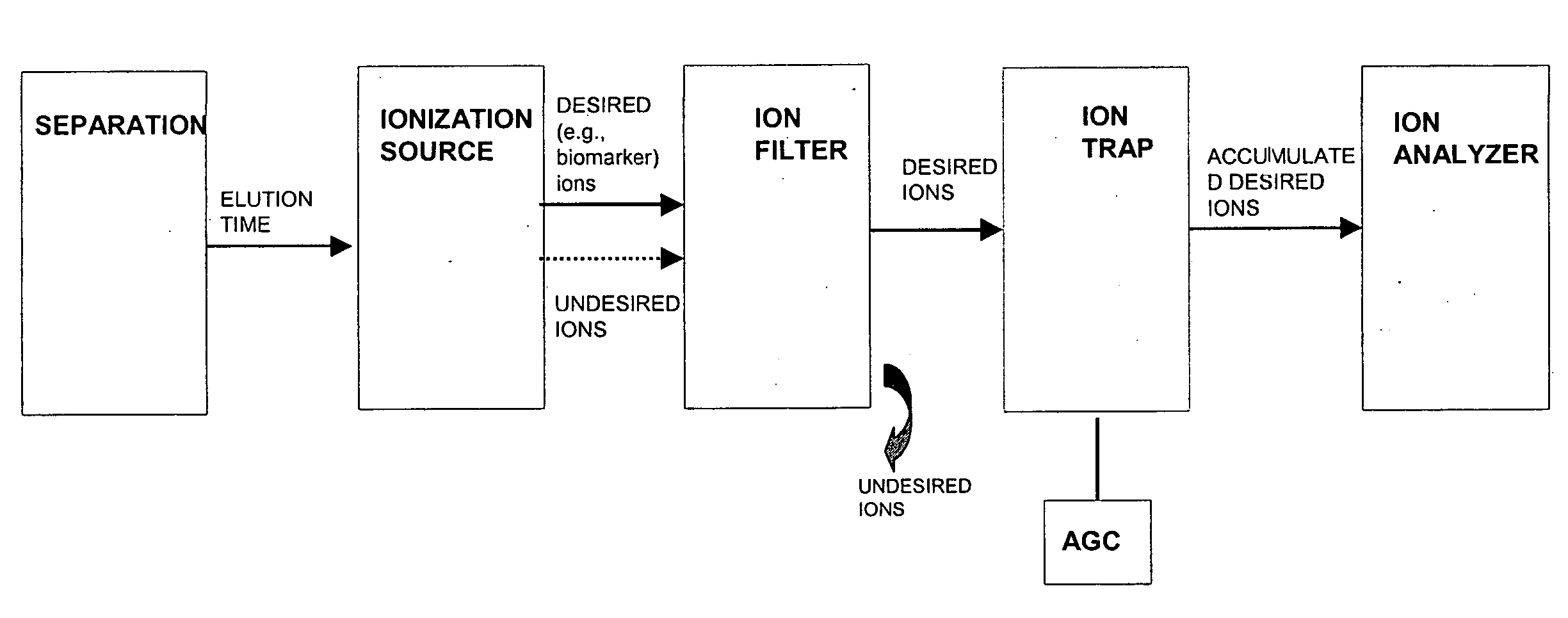
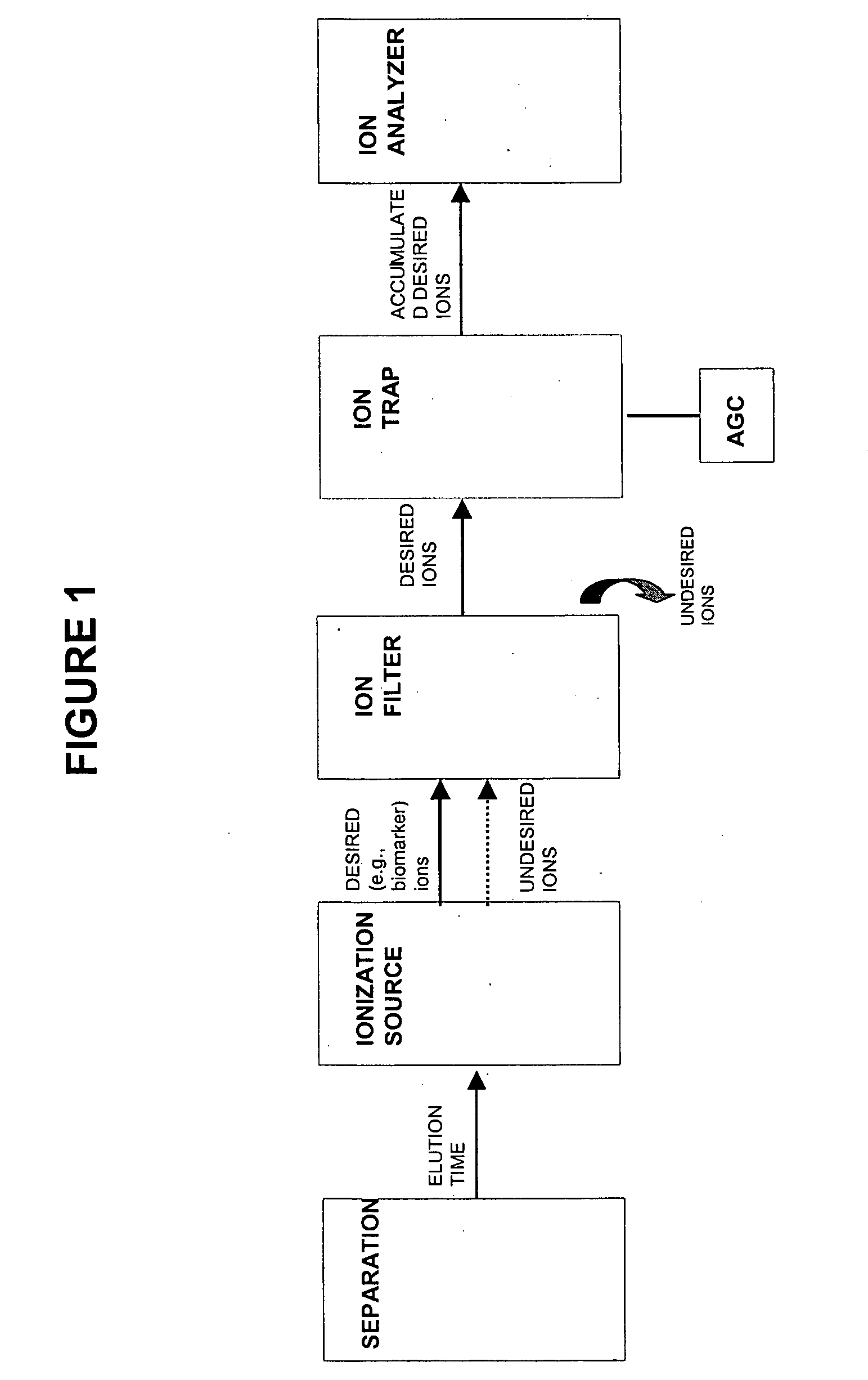
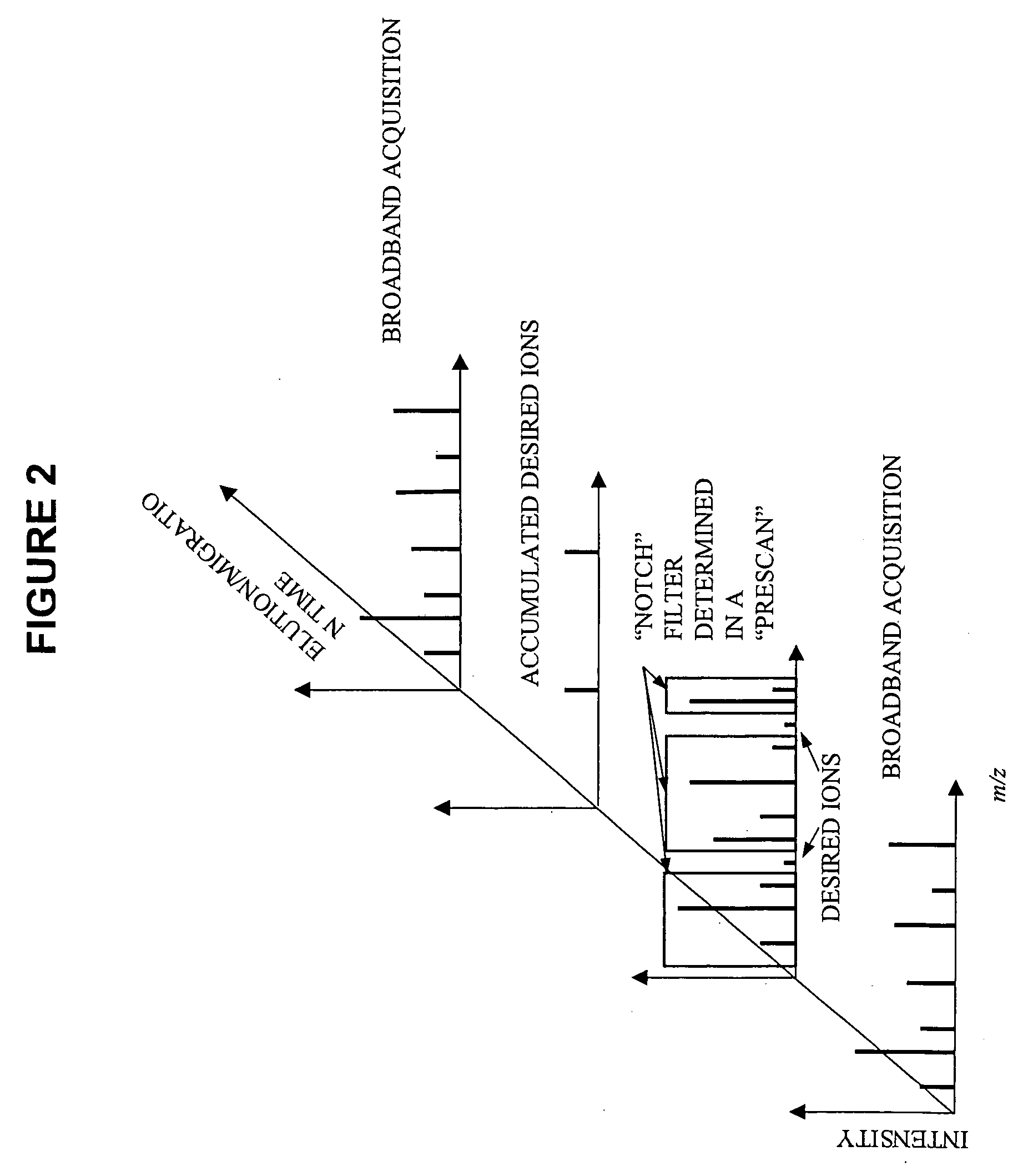
A-priori biomarker knowledge based mass filtering for enhanced biomarker detection
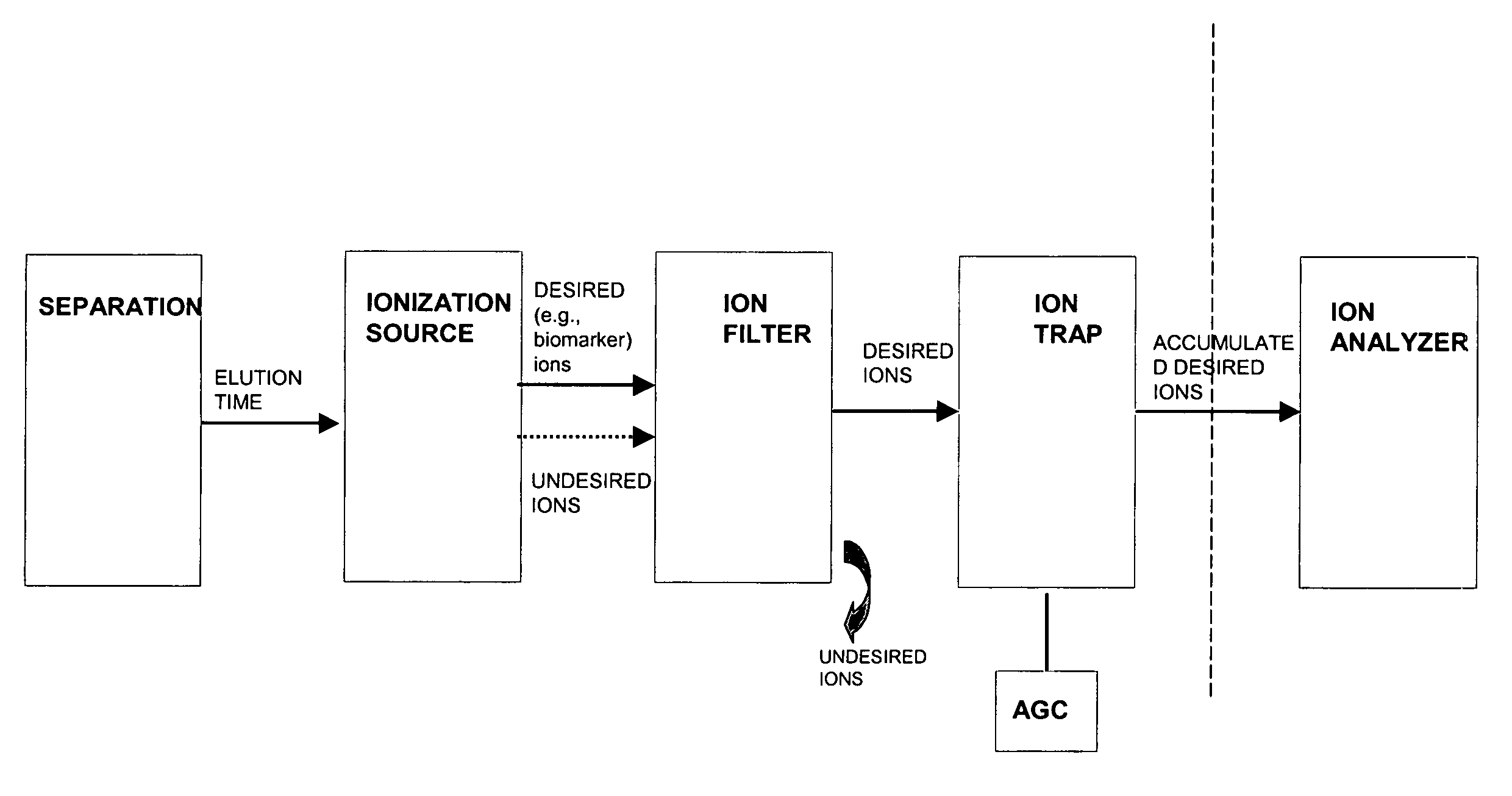
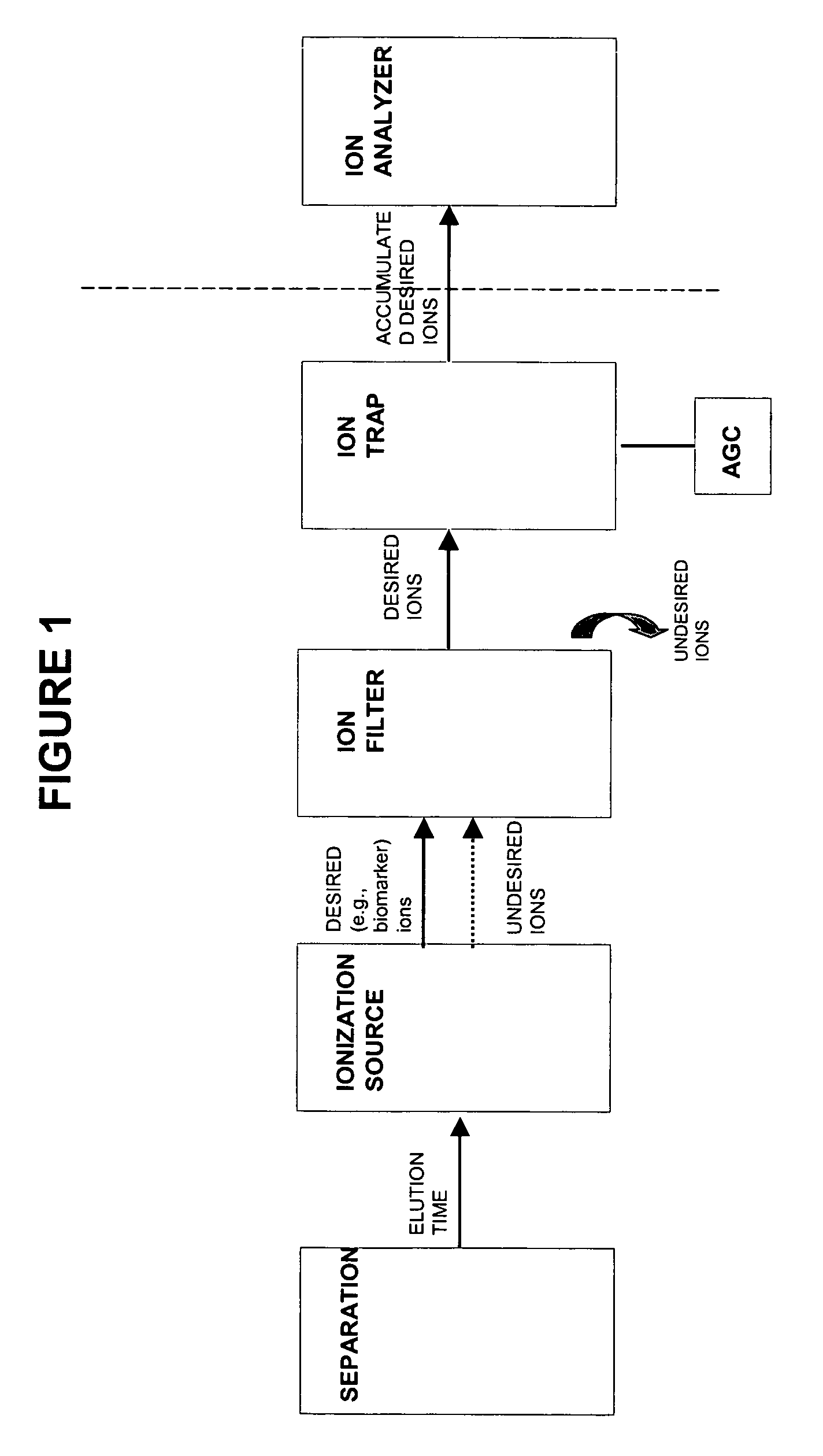
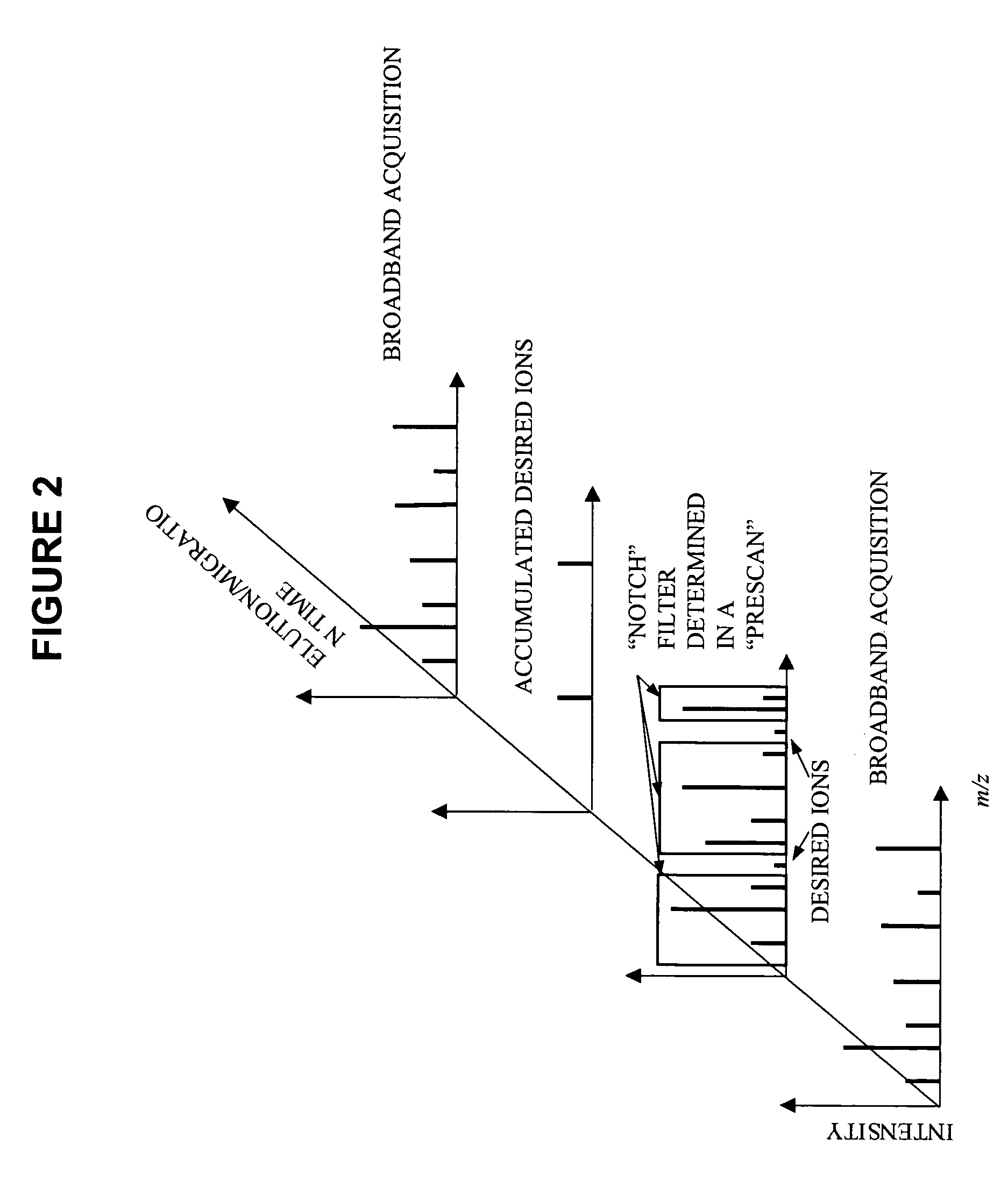
InactiveUS20050211891A1High sensitivityImprove dynamic rangeDynamic spectrometersComponent separationElutionOrganism
Methods and apparatus for mass filtering based on a-priori biomarker knowledge and elution time intervals for selected ion species from a separation device. A sample may be screened for biomarker patterns based on distinct elutions times for selected ions or peptides. A mass spectrum for species of interest can be tailored by filtering out undesired ions by measuring corresponding elution times and determining a priori selected elution time intervals for desired ion species only. The invention assists in the identification of biomarkers having known mass spectral peaks corresponding to known proteins or ions of interest that are known to elute from a separation device within a pre-defined elution time window.
Owner:NORVIEL VERN
Aerosol mass spectrometer with particle size selection
InactiveCN103426712AReduce storageReduce the difficulty of analysisDynamic spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionSynchronous motorParticle beam
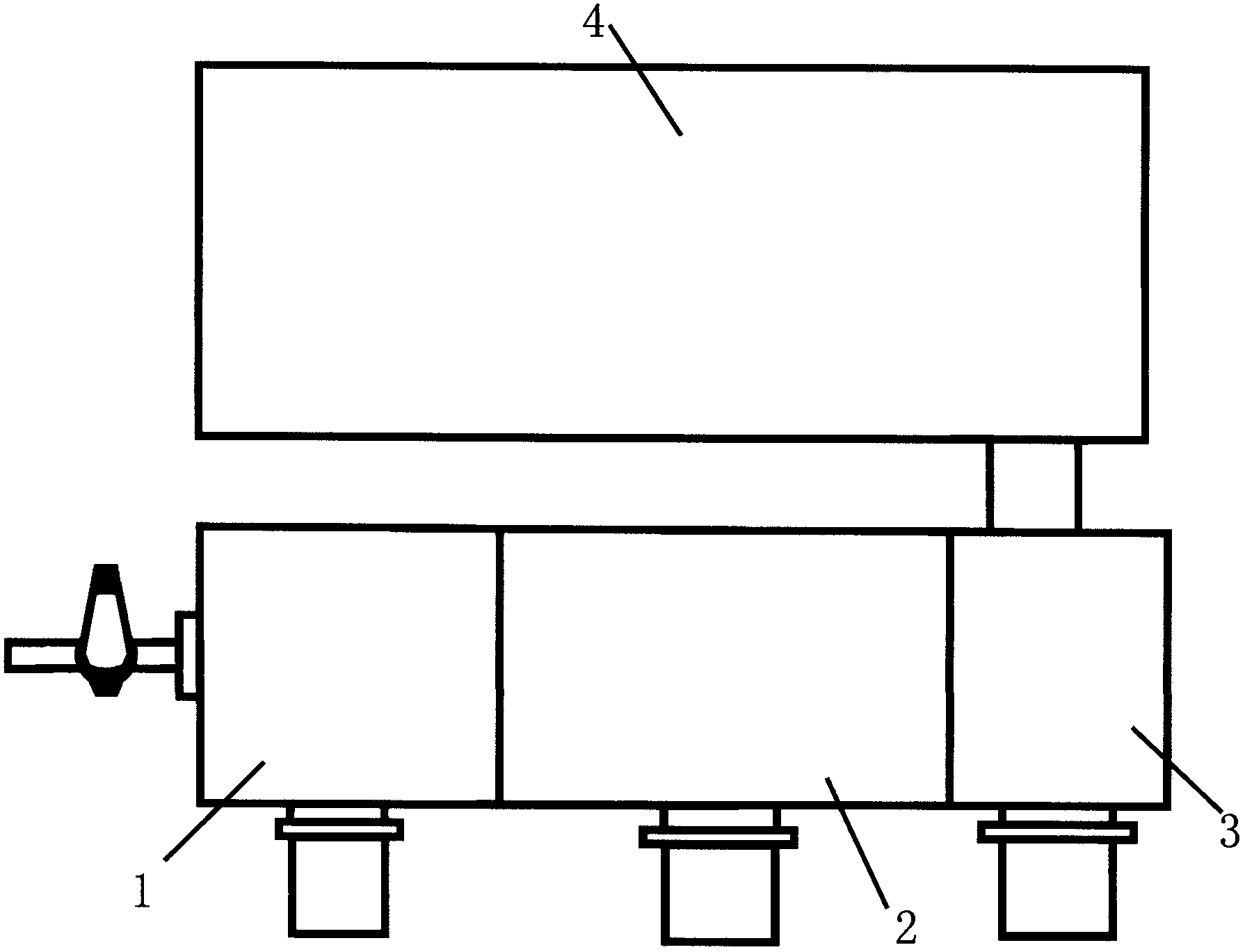
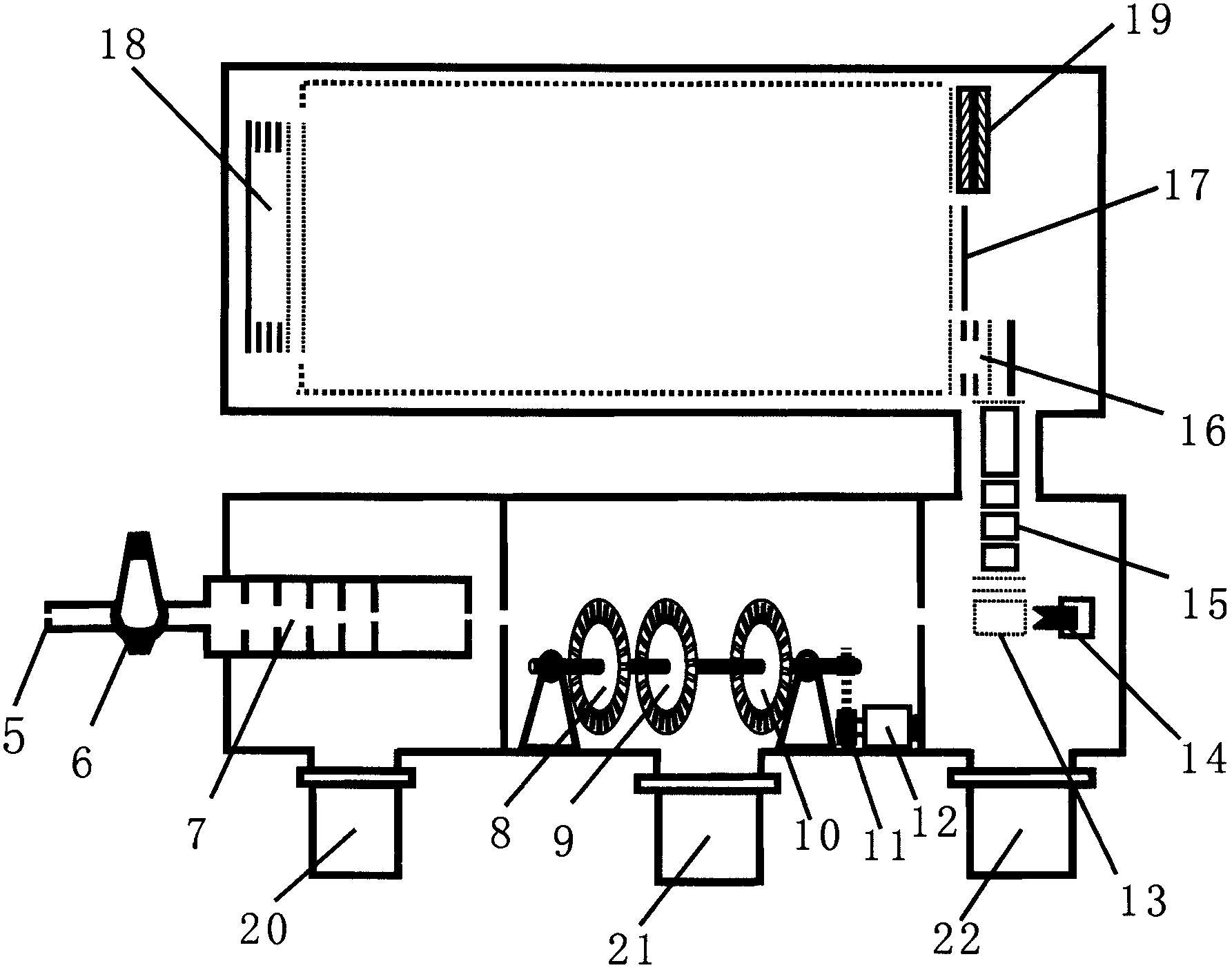
The invention applies for an aerosol mass spectrometer with particle size selection, wherein the aerosol mass spectrometer can simultaneously select the particle size, the concentration and the chemical component of the atmospheric aerosol. The aerosol mass spectrometer uses a sampling hole with the diameter of 100 micrometers to carry out direct sampling on an aerosol in a natural environment; aerosol particles are focused into a particle beam flow with the 0.5-milimeter diameter by a pneumatic focusing lens; the aerosol particles are selected by a particle size selector that is formed by three coaxial rotating plates with slits, wherein the rotating plates of the particle size selector are driven by a synchronous motor and the frequency of the synchronous motor power supply can be adjusted continuously; an aerosol particle that is selected by the particle size selector is gasified by a gasifier with the high temperature from 600 to 700 degrees; gas after gasification is ionized by an electron collision ionizer; a generated ion is detected by a W type reflection type mass spectrum apparatus so as to obtain the mass spectrum of the aerosol. Therefore, information including the particle size, the concentration and the chemical composition of the organic aerosol can be obtained by analyzing the sampling rate, the frequency of the synchronous motor power supply and the obtained mass spectrum.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A-priori biomarker knowledge based mass filtering for enhanced biomarker detection
Methods and apparatus for mass filtering based on a-priori biomarker knowledge and elution time intervals for selected ion species from a separation device. A sample may be screened for biomarker patterns based on distinct elutions times for selected ions or peptides. A mass spectrum for species of interest can be tailored by filtering out undesired ions by measuring corresponding elution times and determining a priori selected elution time intervals for desired ion species only. The invention assists in the identification of biomarkers having known mass spectral peaks corresponding to known proteins or ions of interest that are known to elute from a separation device within a pre-defined elution time window.
Owner:NORVIEL VERN
Chromatograph mass spectrometer
InactiveUS20070284520A1Easy to measurePrecise shiftDynamic spectrometersComponent separationMass numberComputational physics
An exact centroid spectrum with a mass number corrected is determined from a profile spectrum adjacent to a plurality of peaks. Regarding a profile spectrum determined by a mass spectrometer, overlapping with adjacent peaks occurs, and compounds having a plurality of peaks with different overlapping degrees is measured, a correction function is created from a relationship between an overlapping degrees with respect to the plurality of peaks and a shift of the mass number, and a centroid peak is corrected by the correction function when the profile spectrum is converted into the centroid spectrum.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Mass spectrometer
ActiveUS9012840B2Loss of sensitivityWithout any loss in duty cycle and sensitivitySpectrometer circuit arrangementsTime-of-flight spectrometersMass spectrometricSpectrometer
A mass spectrometer is disclosed comprising a first quadrupole rod set mass filter, a collision cell, an ion mobility spectrometer or separator, an ion guide or collision cell arranged downstream of the ion mobility spectrometer or separator, a second quadrupole rod set mass filter and an ion detector.
Owner:MICROMASS UK LTD
A-priori biomarker knowledge based mass filtering for enhanced biomarker detection
Methods and apparatus for mass filtering based on a-priori biomarker knowledge and elution time intervals for selected ion species from a separation device. A sample may be screened for biomarker patterns based on distinct elutions times for selected ions or peptides. A mass spectrum for species of interest can be tailored by filtering out undesired ions by measuring corresponding elution times and determining a priori selected elution time intervals for desired ion species only. The invention assists in the identification of biomarkers having known mass spectral peaks corresponding to known proteins or ions of interest that are known to elute from a separation device within a pre-defined elution time window.
Owner:BELOV MIKHAIL +1
Single molecule mass spectroscopy enabled by nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS-MS)
The present invention relates to an apparatus for measuring a mass of a sample, using a nanoelectromechanical system (NEMS) arranged to receive the sample added onto a resonator of the NEMS and a microfluidic sample delivery and sample ionization system. The nanoelectromechanical system is located at an output of the ionization system. The nanoelectromechanical resonator system is highly sensitive and is capable of detecting masses in the single Dalton range.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
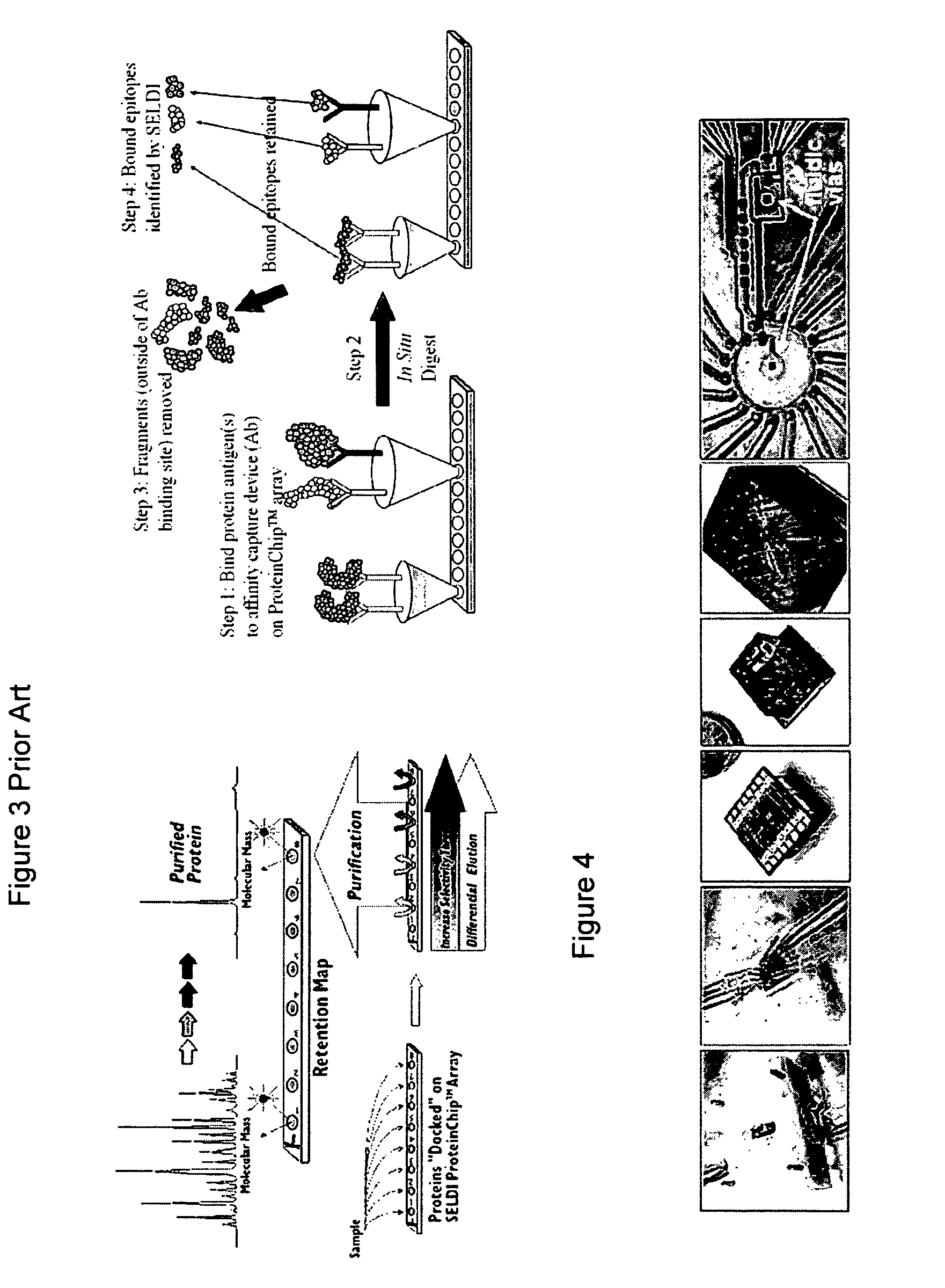
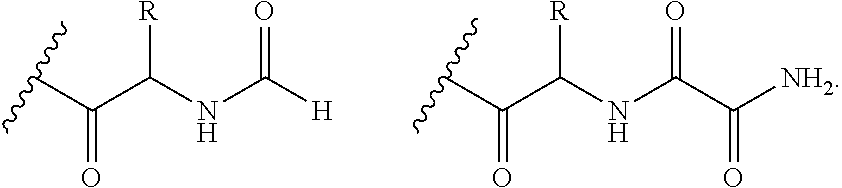
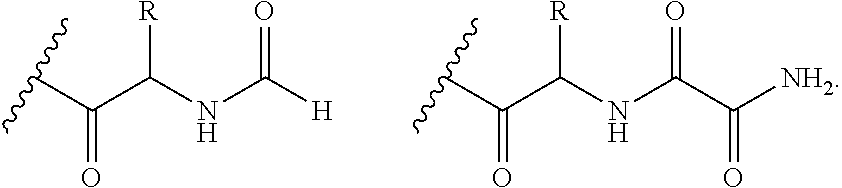
Systems and Methods of Detecting and Demonstrating Hair Damage Via Evaluation of Protein Fragments
Embodiments of a method for demonstrating type and / or source of hair damage comprises extracting protein fragments from a hair sample with an aqueous solution, testing the resulting protein fragments with the MALDI-MS test, and then either comparing the results between a damaged sample and an undamaged sample or comparing the results between a damaged sample and a list of known marker protein fragments to identify the type and / or source of the damage.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
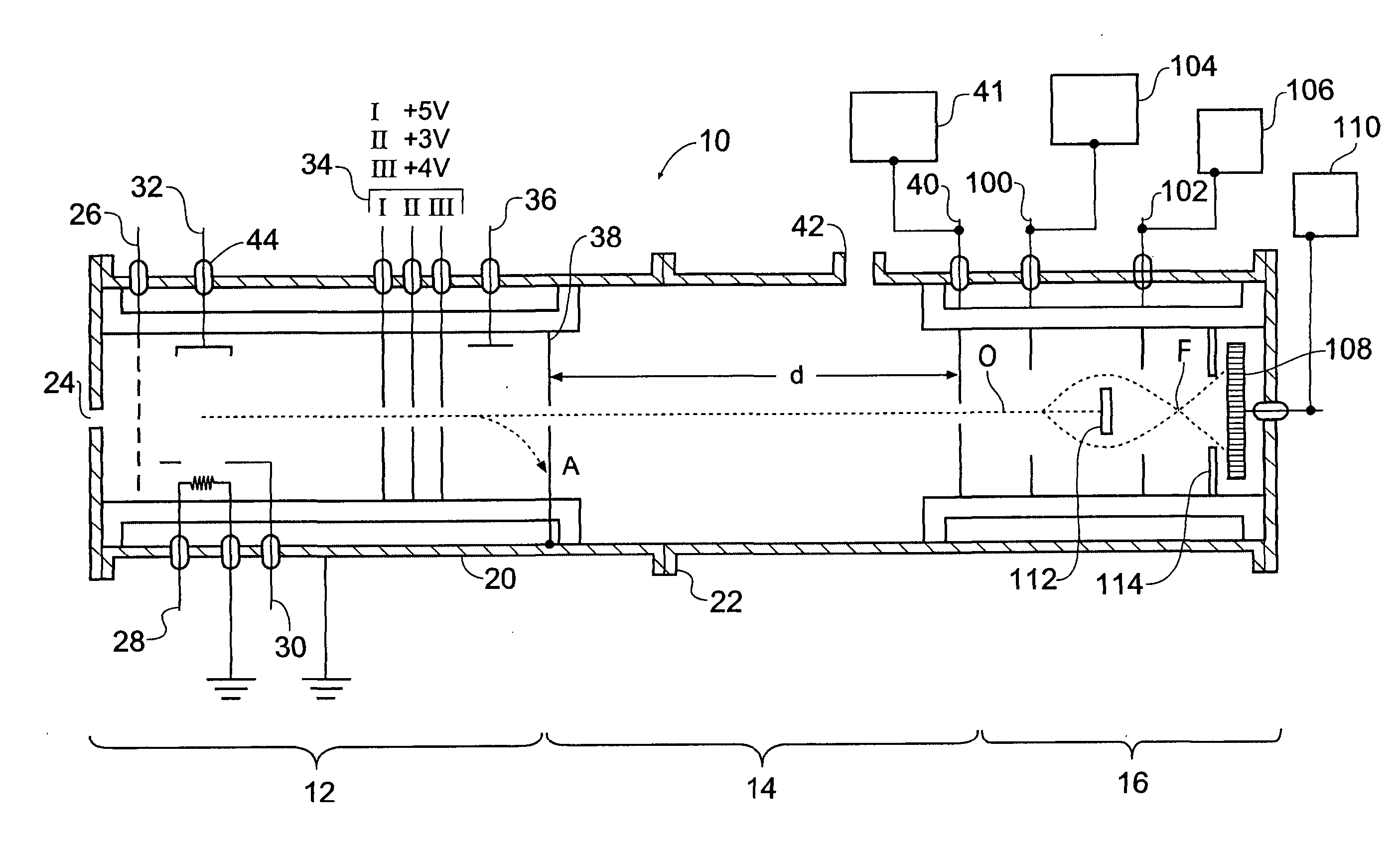
Ion trap device
ActiveUS9245725B2Dynamic spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsRf fieldIon trap mass spectrometry
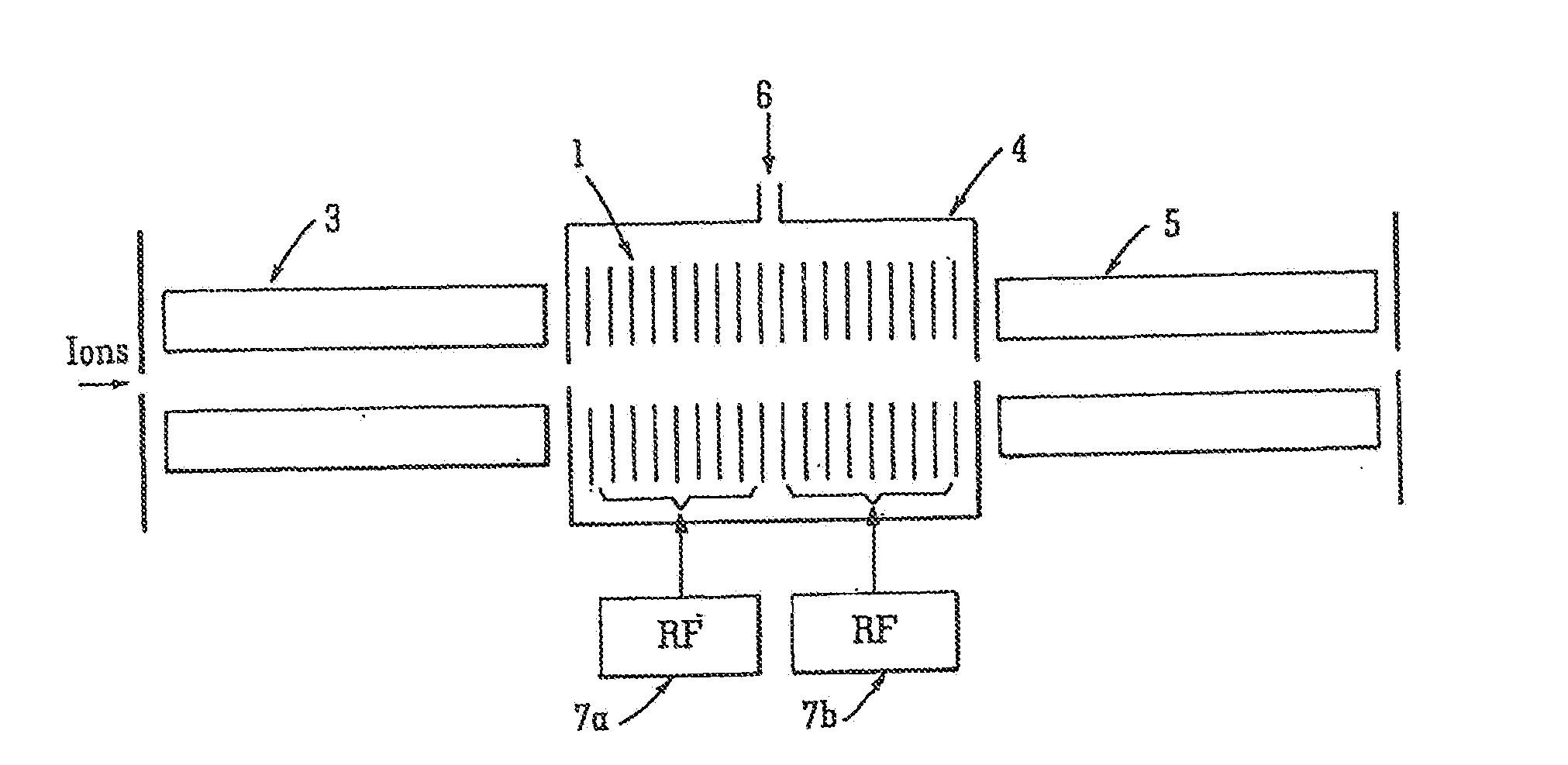
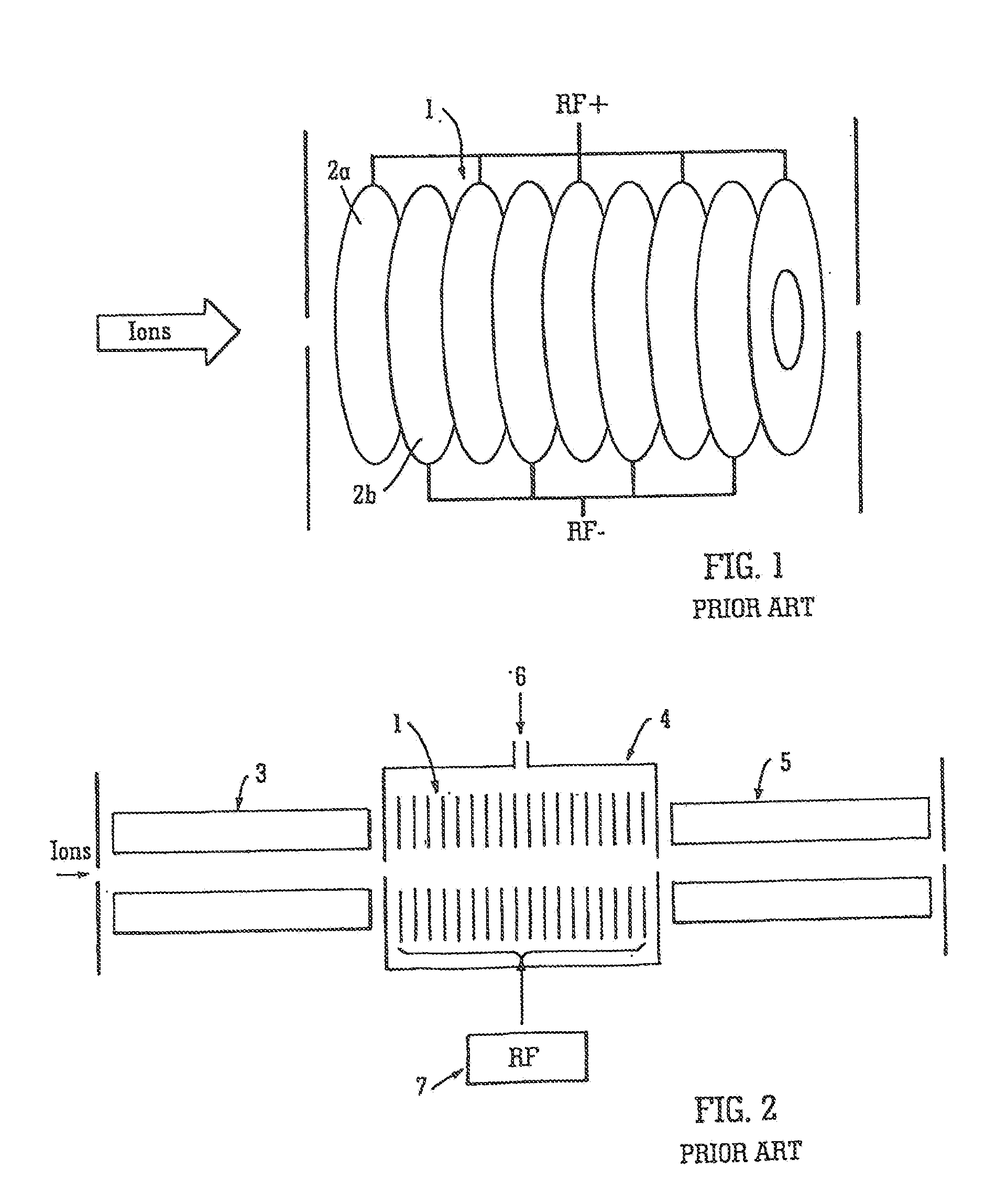
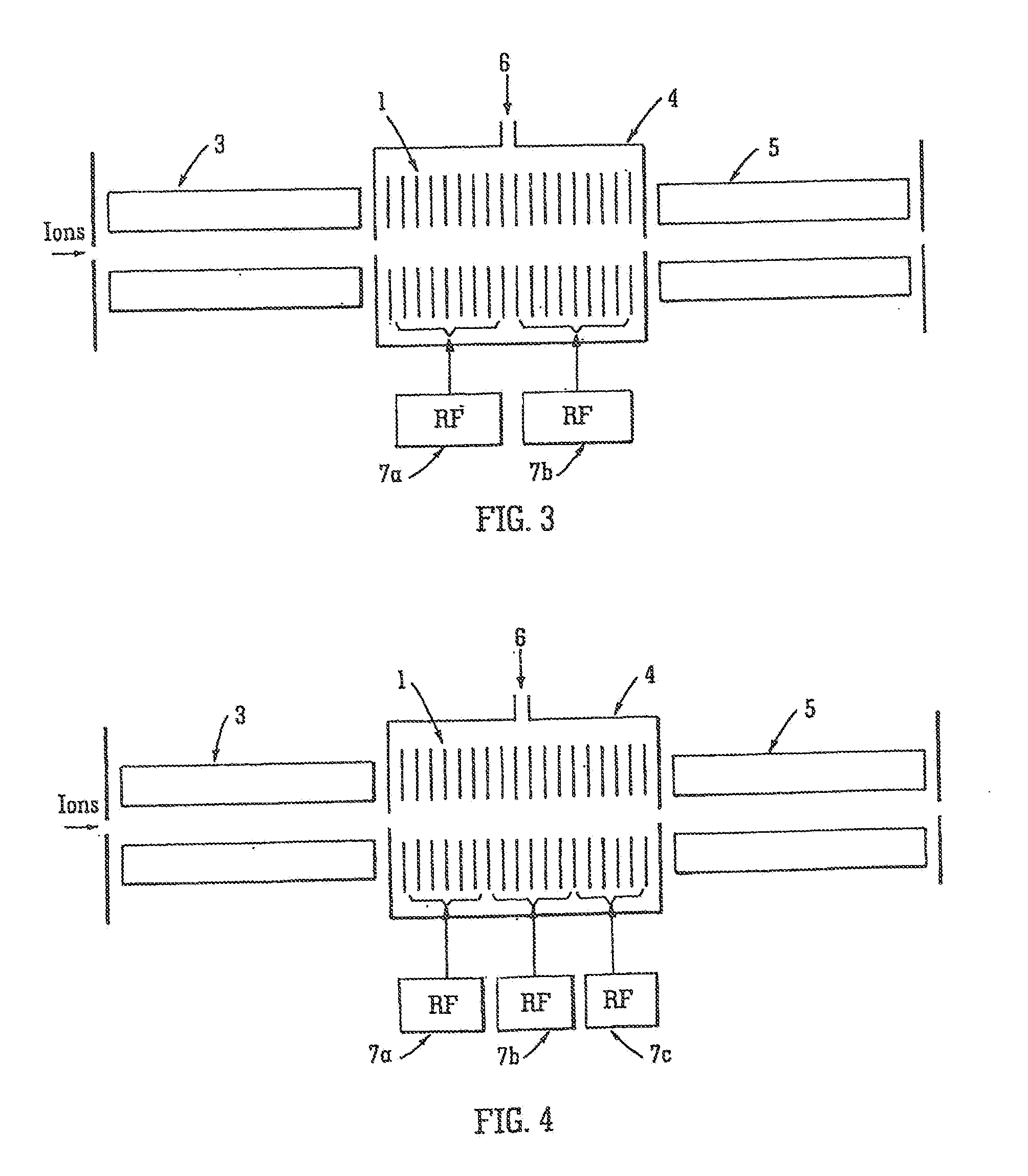
An ion trap device is disclosed. The device includes a series of electrodes that define an ion flow path. A radio frequency (RF) field is applied to the series of electrodes such that each electrode is phase shifted approximately 180 degrees from an adjacent electrode. A DC voltage is superimposed with the RF field to create a DC gradient to drive ions in the direction of the gradient. A second RF field or DC voltage is applied to selectively trap and release the ions from the device. Further, the device may be gridless and utilized at high pressure.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Measuring the mobility of mass selected ions
ActiveUS8022359B2High mobility resolutionReduced measurement timeSpectrometer circuit arrangementsDynamic spectrometersModulation functionIon current
In an ion mobility spectrometer (IMS) coupled to a mass spectrometer (MS), the ion current from a suitable ion source is modulated with an analog modulation having a smooth modulation function, whose instantaneous frequency varies with time over a wide frequency range. The modulated ion current is continuously fed through a mobility drift region into the mass spectrometer, where the temporally varying ion current profile of at least one ion species is measured. The mobility spectrum of the ion species is then generated by correlating its ion current time profile with the modulation function.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Mass spectrometry apparatus and methods
InactiveUS20120318972A1Easy to synthesizeHigh voltageDynamic spectrometersIsotope separationMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMass analyzer
A mass spectrometer having a mass filter which applies a transient voltage profile to accelerate ion packets. The voltage profile is chosen to have a functional form which imparts each ion species with a kinetic energy which is larger the larger the mass-to- charge ratio and a velocity which is smaller the larger the mass-to-charge ratio. The ions are detected in an ion detector which discriminates between different ion species based on their kinetic energy and taking account of the functional form of the voltage profile. Suitable voltage profiles include periodic functions such as sinusoids, triangles and sawtooths, which allow the amplification of drive pulses in the mass filter to be carried out with narrow band amplification stages, which are simple and inexpensive to construct.
Owner:ILIKA TECH
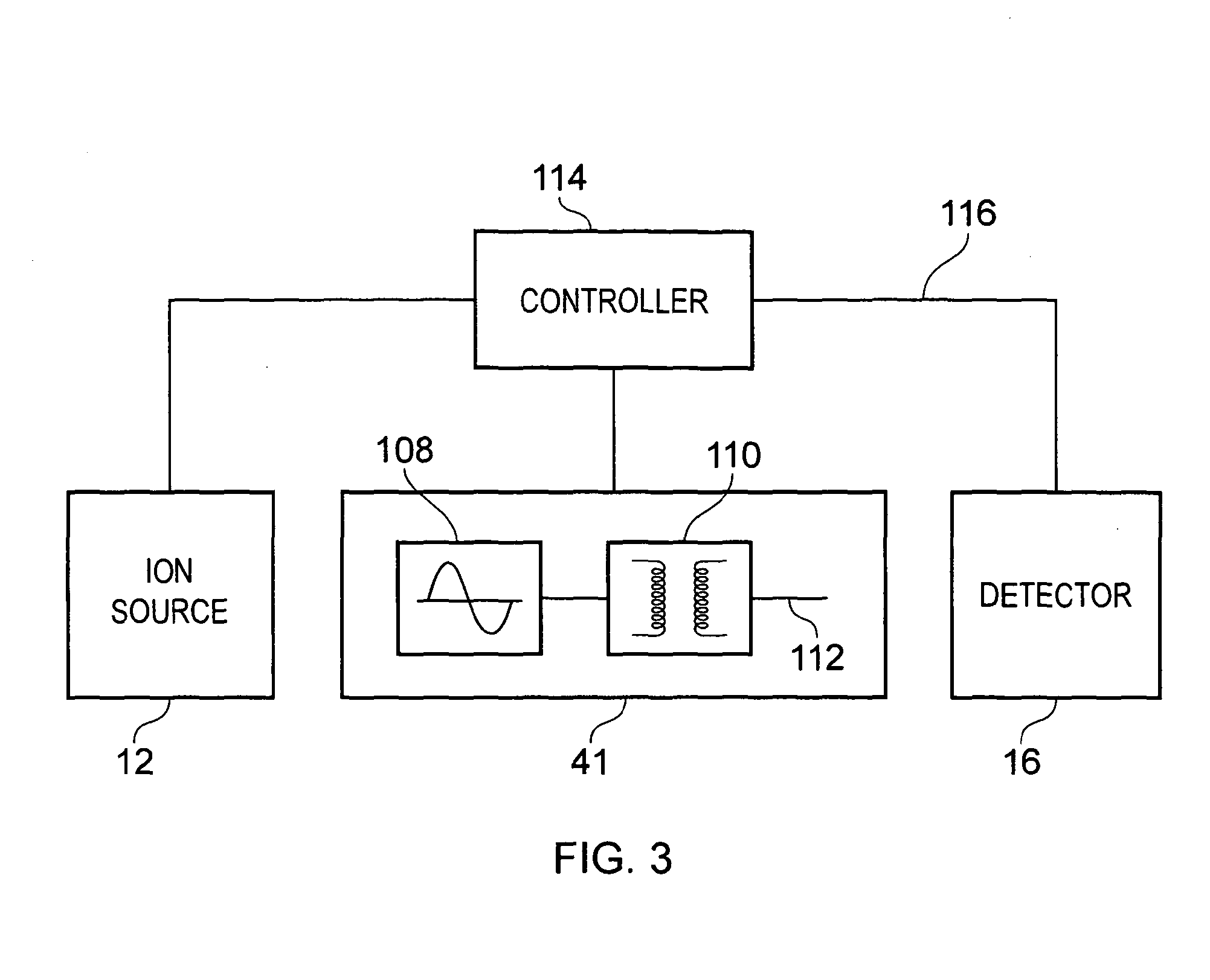
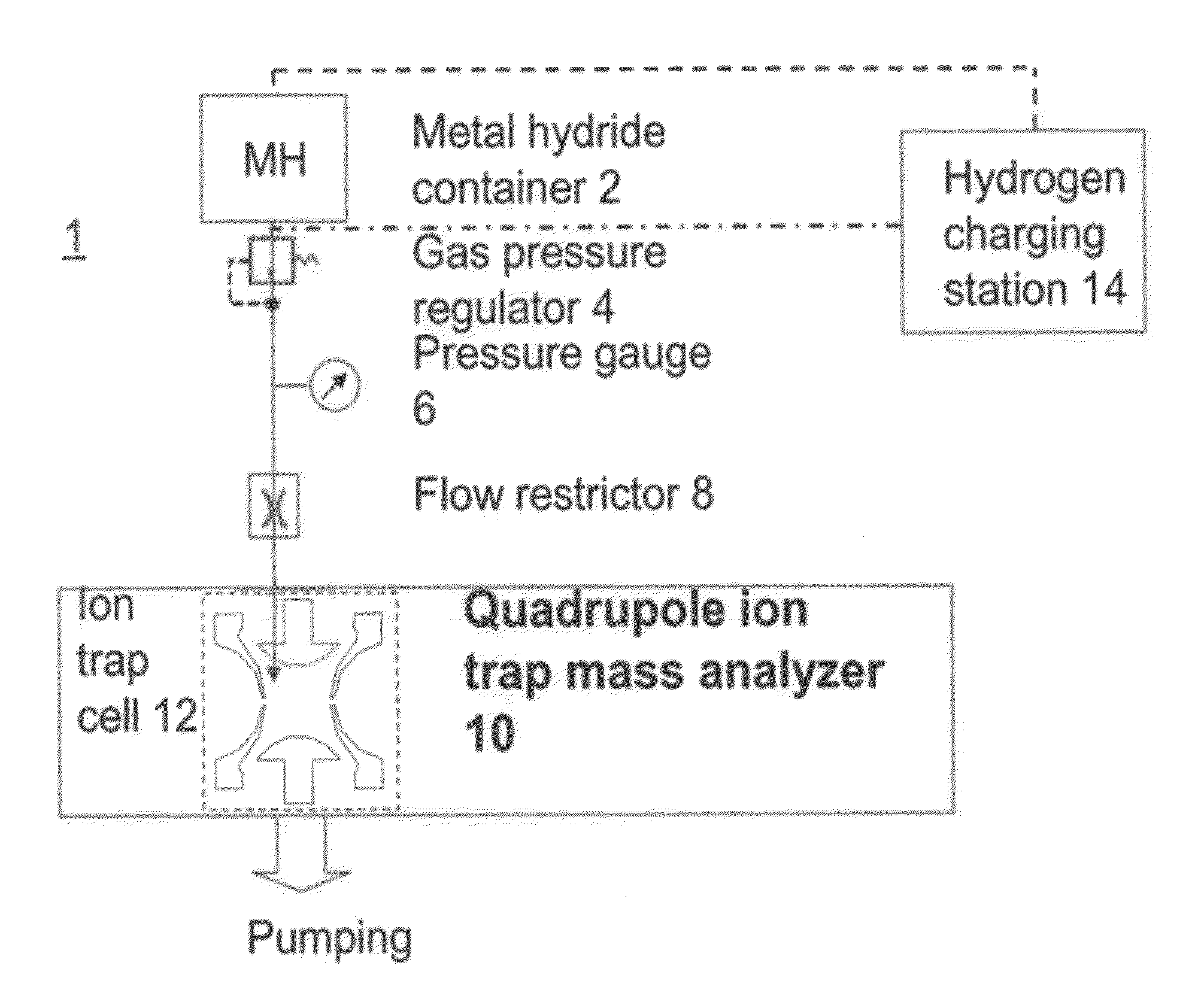
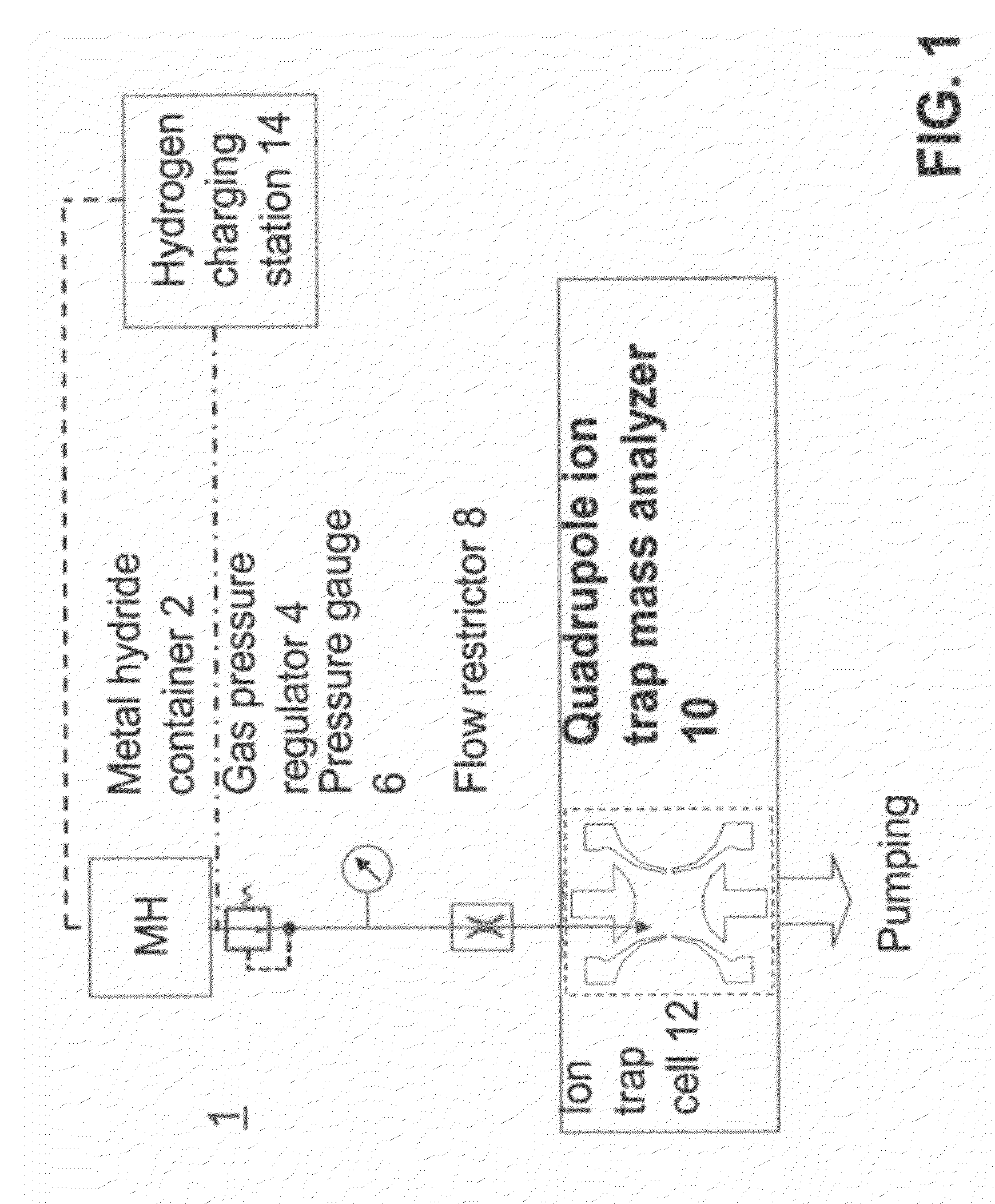
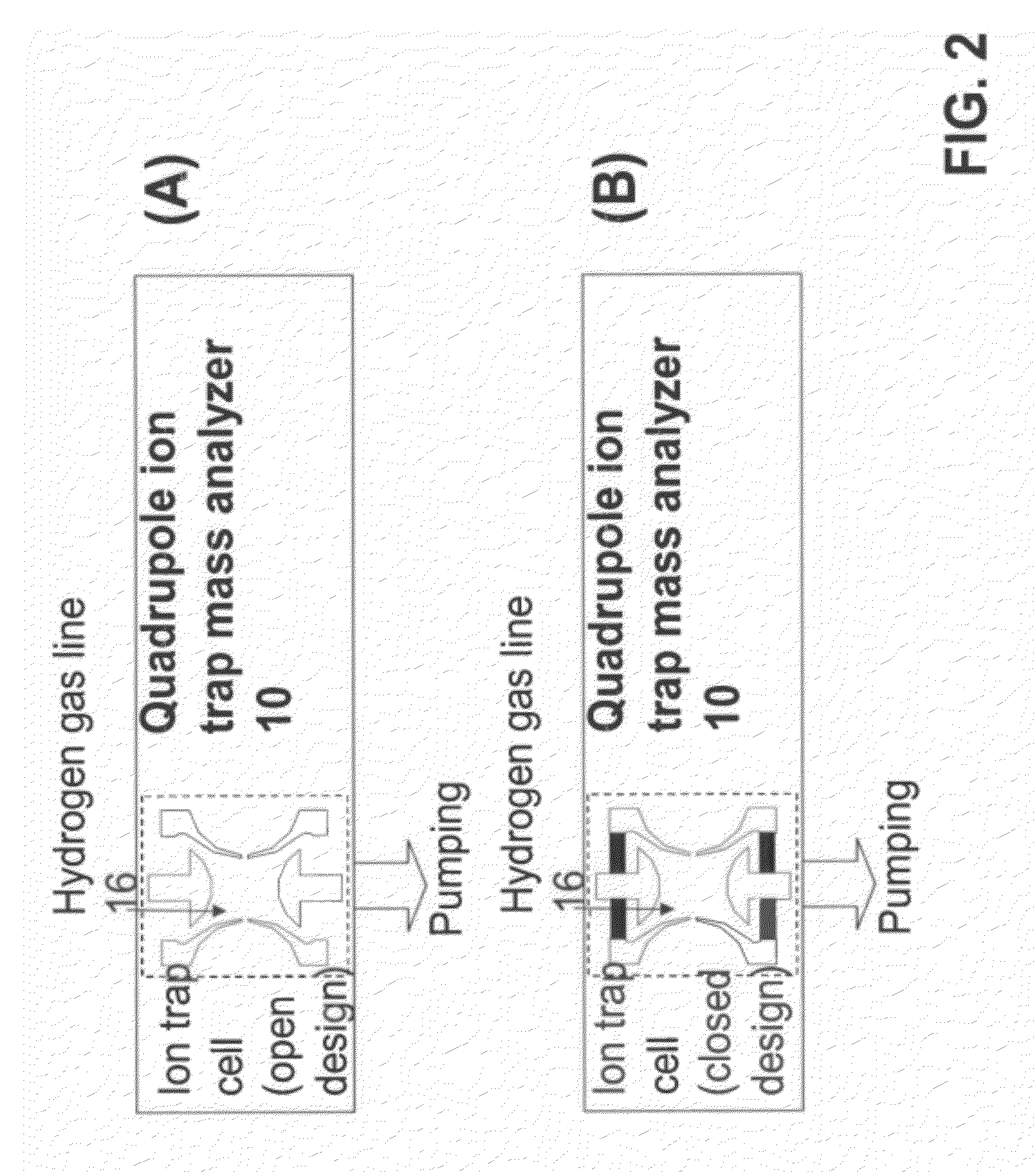
Portable ion trap mass spectrometer with metal hydride container as source of hydrogen buffer gas
ActiveUS20120326026A1Dynamic spectrometersMiniaturised spectrometersIon trap mass spectrometryTrapping
A mass spectrometry (MS) method which includes generating in a vicinity of the quadrupole ion trap hydrogen molecules, directing at least part of the hydrogen molecules into the quadrupole ion trap cell, applying AC and DC voltages to quadrupole ion trap cell electrodes to create a combined AC / DC trapping field, placing sample ions inside the quadrupole ion trap cell, cooling at least part of said ions using said hydrogen molecules as a buffer gas, changing the combined AC / DC trapping field to eject the ions from the quadrupole ion trap cell, and detecting the ejected ions
Owner:SCI & ENG SERVICES
Enclosed desorption electrospray ionization probes and method of use thereof
The invention generally relates to enclosed desorption electrospray ionization probes, systems, and methods. In certain embodiments, the invention provides a source of DESI-active spray, in which a distal portion of the source is enclosed within a transfer member such that the DESI-active spray is produced within the transfer member.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Mass spectrometers and methods of ion separation and detection
InactiveUS20120312982A1Instrument is often sensitiveIsotope separationMass spectrometersLight beamDetector array
A mass spectrometer operating according to the iso-tach principle in which a mass filter accelerates ions to nominally equal velocities irrespective of their mass-to-charge ratios. The mass spectrometer is provided with an improved detector based on an electrostatic lens arrangement made of a concave lens followed in the beam path by a convex lens. These lenses deflect ions away from the beam axis by a distance from the beam axis that is inversely proportional to their mass-to-charge ratios. The mass-to-charge ratio of the ions can then be determined by a suitable detector array, such as a multi-channel plate placed in the beam path. This provides a compact and sensitive instrument.
Owner:ILIKA TECH
Method and device for spatial charged particle bunching
A charged particle buncher includes a series of spaced apart electrodes arranged to generate a shaped electric field. The series includes a first electrode, a last electrode and one or more intermediate electrodes. The charged particle buncher includes a waveform device attached to the electrodes and configured to apply a periodic potential waveform to each electrode independently in a manner so as to form a quasi-electrostatic time varying potential gradient between adjacent electrodes and to cause spatial distribution of charged particles that form a plurality of nodes and antinodes. The nodes have a charged particle density and the antinodes have substantially no charged particle density, and the nodes and the antinodes are formed from a charged particle beam with an energy less than or equal to 500 keV.
Owner:NEXGENSEMI HLDG INC
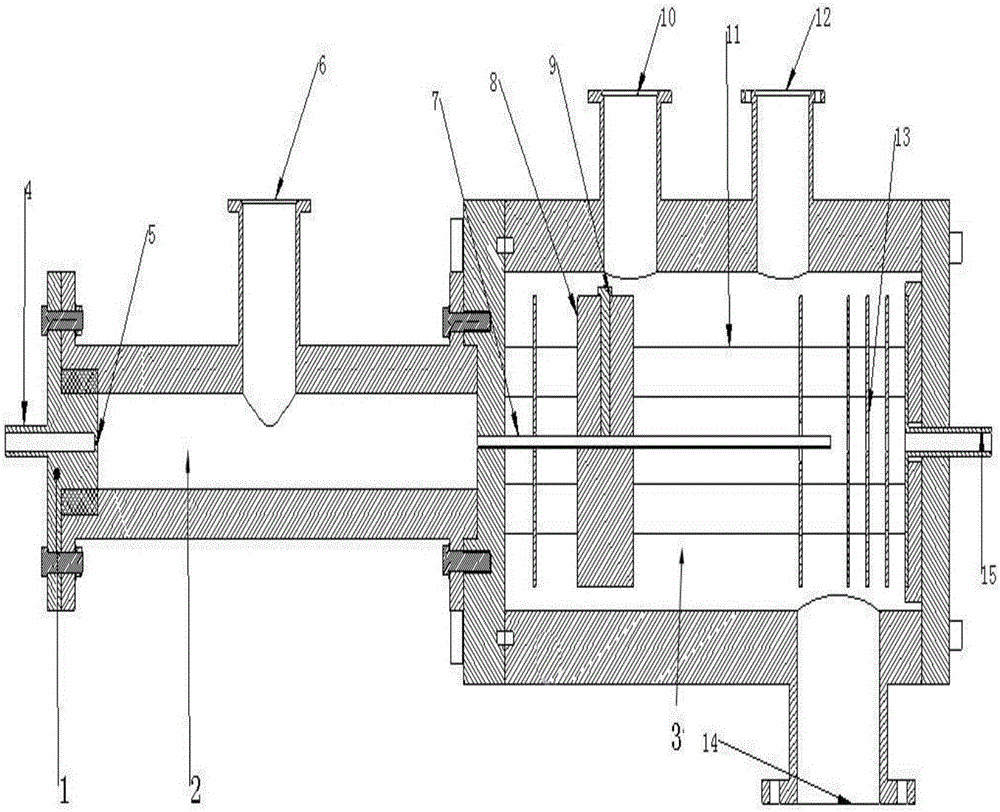
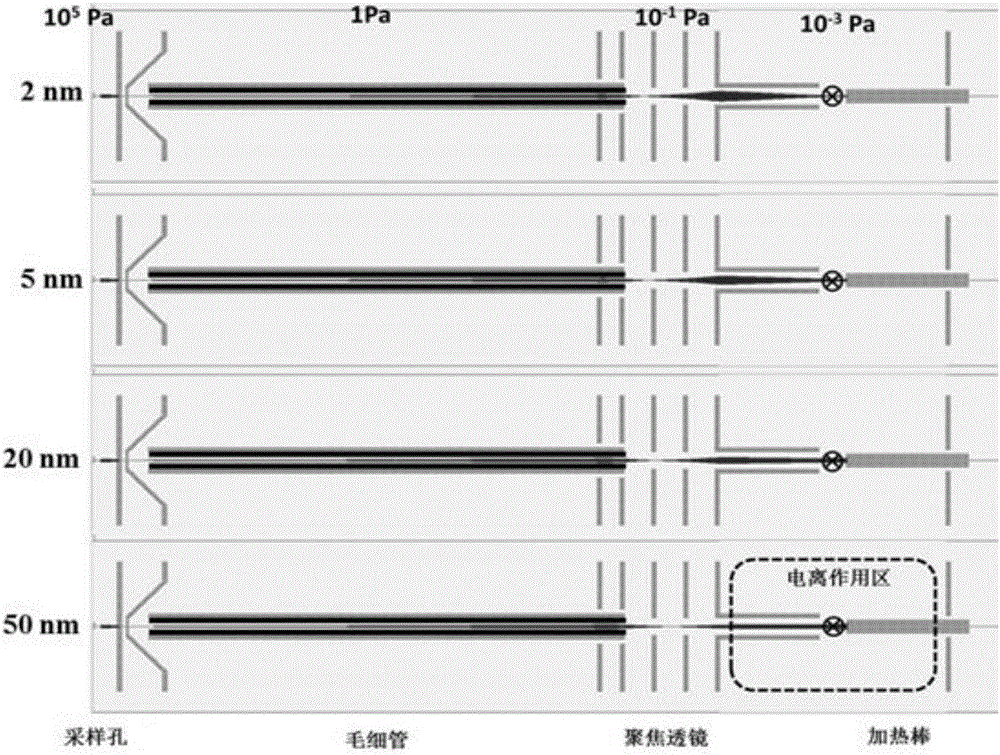
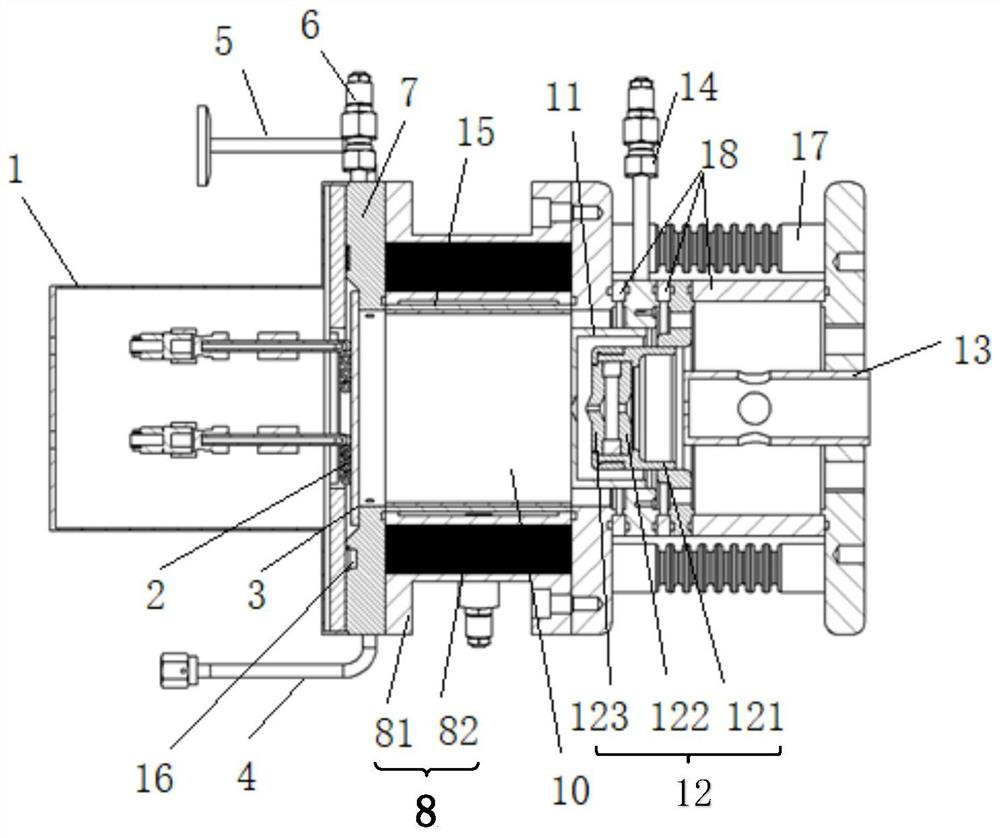
Capillary tube injection interface device for nanoparticle aerosol mass spectrometer
ActiveCN106449348AGuaranteed normal transmissionOvercoming Brownian motion effectsDynamic spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionCapillary TubingVacuum pump
The invention discloses a capillary tube injection interface device for a nanoparticle aerosol mass spectrometer. The device comprising a general-purpose connector, a buffer chamber, a capillary tube, a focusing lens and a differential chamber, wherein the general-purpose connector, the buffer chamber, the capillary tube, the focusing lens and the differential chamber are successively connected. The general-purpose connector is provided with an aerosol inlet and a current-limiting hole, wherein the aerosol inlet and the current-limiting hole are connected with an aerosol particle pretreatment instrument. The capillary tube which is connected with the buffer chamber, positioning ceramic, a positioning screw, the focusing lens on the rear side of the capillary tube, an insulation straight cylinder which fixes the focusing lens and the positioning ceramic, and a differential chamber outlet in the rear end of the focusing lens are arranged in the differential chamber. The positioning ceramic and the positioning screw are used for fixing the capillary tube. Voltage is applied on the surface of the capillary tube. The influence of Brownian motion in nanoparticle transport is compensated through the action of an electric field, so that charged nanoparticles can converge on the axis of the capillary tube. The gas accompanying matters of the charged nanoparticles can be removed by a vacuum pump which is connected with the differential chamber. The focusing lens can further converge the charged nanoparticles. Atmospheric pressure sample injection and high efficiency transmission of the nanoparticles are realized.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Radio frequency negative ion source for secondary ion mass spectrometer
ActiveCN111755317AHigh densityIncrease brightnessDynamic spectrometersNuclear energy generationIon beamMass analyzer
The invention discloses a radio frequency negative ion source for a secondary ion mass spectrometer. The radio frequency negative ion source comprises an ion source body, a radio frequency injection assembly and an ion beam lead-out system, wherein the ion source body comprises a discharge cavity and a packaging magnet disposed outside the discharge cavity, and the packaging magnet comprises a plasma confinement part and an offset magnetic field generation part which are distributed in the axial direction of the discharge cavity; the radio frequency injection assembly comprises a gas source supply part and a radio frequency injection part, the gas source supply part feeds working gas into the discharge cavity, and the radio frequency injection part is installed on the front end side of theion source body and emits radio frequency into the discharge cavity; the ion beam lead-out system comprises a plasma electrode, an extraction electrode and a ground electrode which are sequentially arranged from front to back; a first lead-out hole is formed in the plasma electrode, a second lead-out hole is formed in the extraction electrode and a third lead-out hole is formed in the ground electrode; the plasma electrode is used for modulating the state of plasma; the extraction electrode is used for preliminarily accelerating the led-out negative ion beam and adsorbing electrons; and the ground electrode is used for accelerating the negative ion beam to target energy.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Magnetically assisted electron impact ion source for mass spectrometry
ActiveCN107301944ADynamic spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsMass analyzerElectron bombardment
The invention relates to a mass spectrometer having an electron impact ionization source which comprises an ejector for forming a beam of sample gas being driven in a first direction through an interaction region; a magnet assembly configured and arranged such that its magnetic field lines pass through the interaction region substantially parallel to the first direction; an electron emitter assembly for directing electrons toward the interaction region in a second direction being aligned substantially opposite to the first direction, wherein the electrons propagate along and are confined about the magnetic field lines until reaching the interaction region and forming sample gas ions therein; and a mass analyzer located downstream from the interaction region to which the sample gas ions are guided for mass analysis.
Owner:BRUKER SCI LLC
Method for identification of the elemental composition of species of molecules
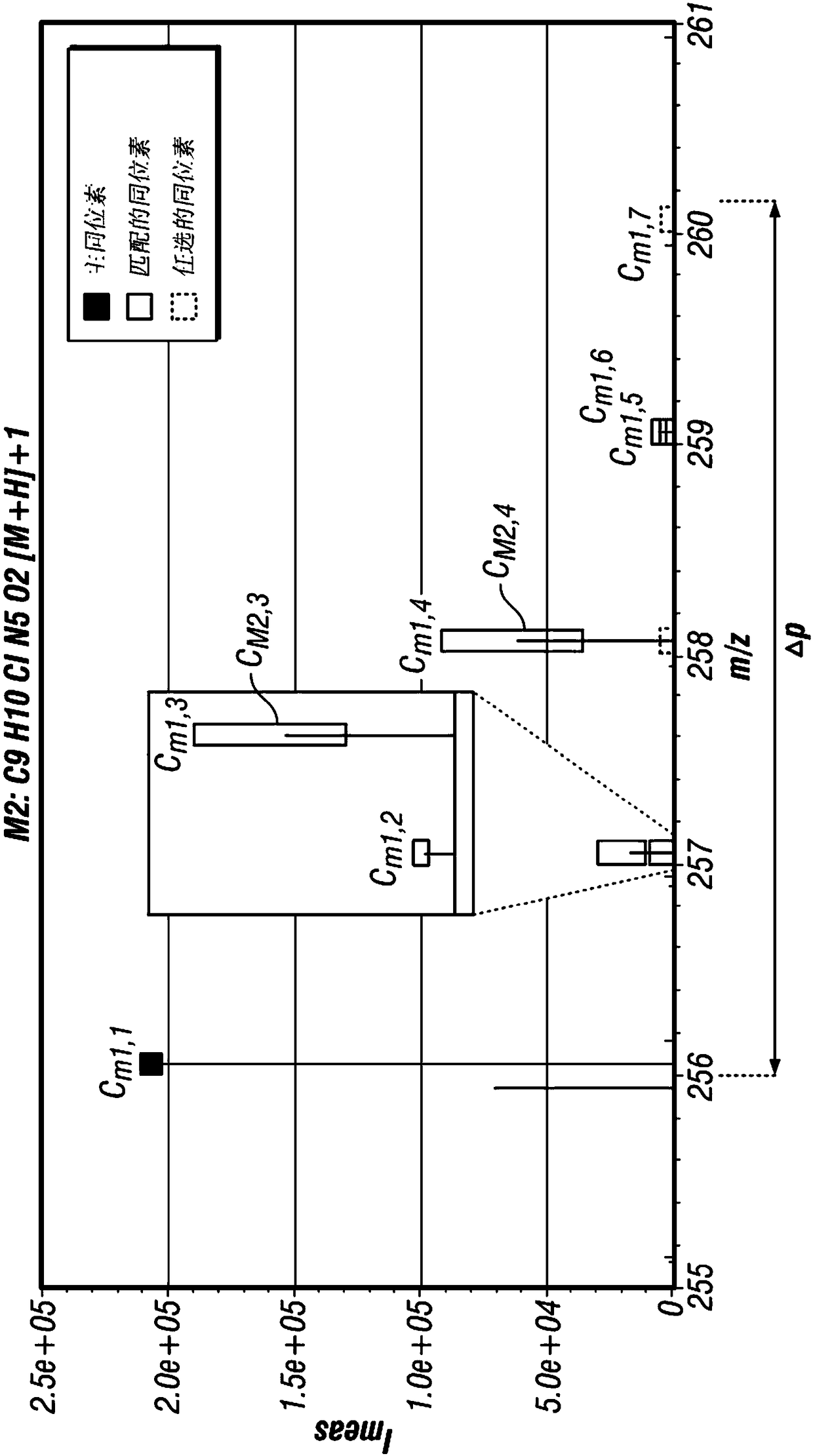
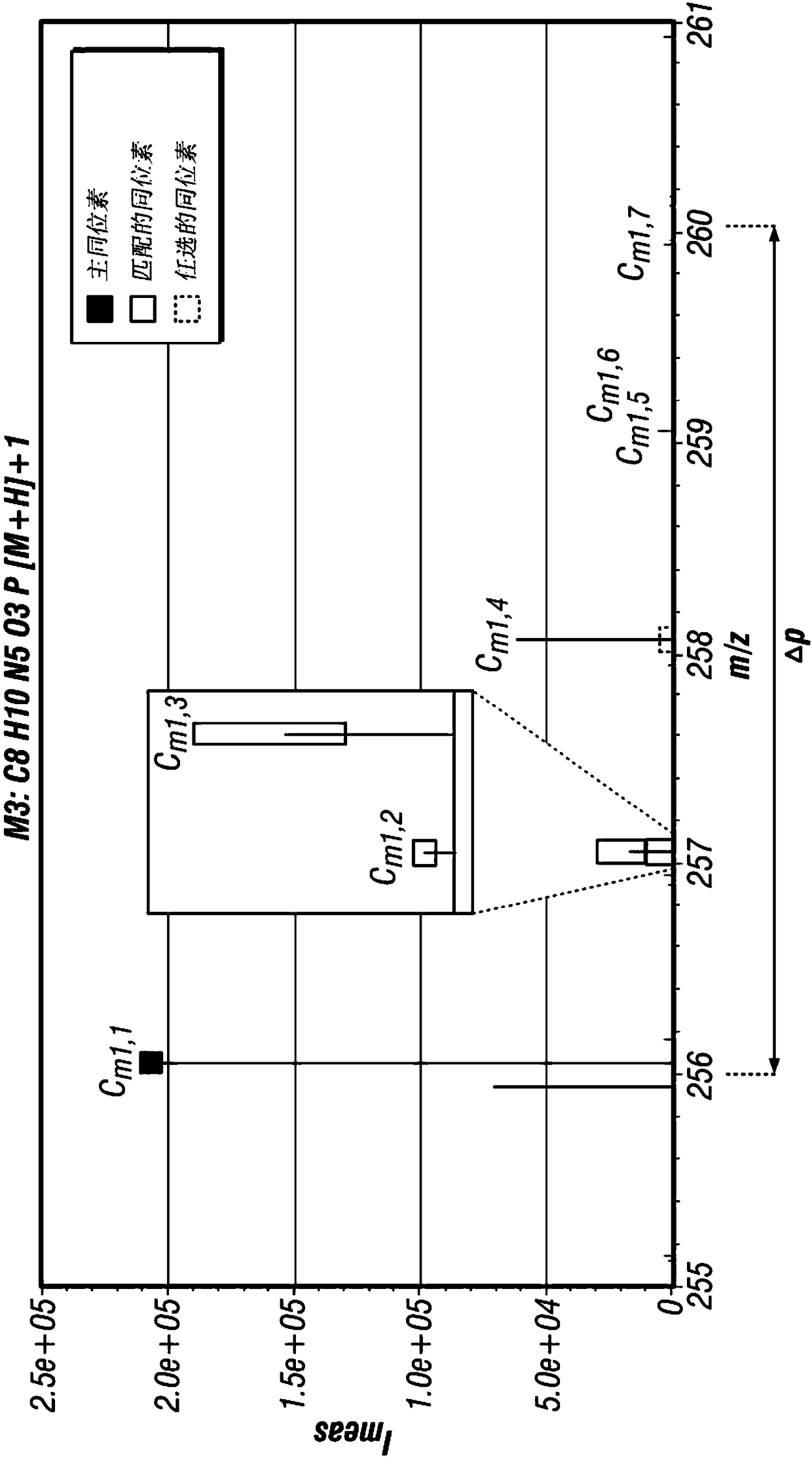
Methods of identification of at least one most likely elemental composition of at least one species of molecules contained in a sample and / or originated from a sample by at least one ionisation process are provided. The method includes measuring a mass spectrum of the sample and may include reducing the measured mass spectrum to a neutral mass spectrum. The method further includes determining fora peak of interest a set of candidate species of molecules which have an expected peak with a peak position within a peak position tolerance range in the corresponding measured mass spectrum or neutral mass spectrum. An identification mass spectrum is identified for each candidate species and a range of peak positions is determined of all isotopic peaks of the identification mass spectrum. Two subscores of candidate species are determined by comparing the identification spectra with the measured or neutral mass spectrum, and final scores are calculated from the subscores. An elemental composition of the candidate species is determined having calculated final scores of the highest values.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BREMEN
Mass Spectrometer
ActiveUS20140131566A1Improve performanceReduce kinetic energyDynamic spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsMass analyzerSpectrometer
Owner:MICROMASS UK LTD
Method and apparatus for chemical and biological sample separation
ActiveUS8217338B2High resolutionDynamic spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansImage resolutionGas phase
The present invention describes a method and apparatus for separating chemical and / or biological samples based on selective ion-molecular interactions in the gas phase. A chemical modifier is added to the drift gas that interacts selectively with a targeted molecule in at least one component of the sample in a drift tube. The component may be impurities and / or interferences in the sample whereby the chemical modifier enhances sample resolution by shifting the components drift times. In addition, reagents can be added to the sample prior to, during, or after ionization to form a complex with selected components in the sample. In addition, one or more internal and / or external standard can also be added to the sample as a calibration for the measurement.
Owner:EXCELLIMS CORP
Quality analysis method based on restricted theory of relativity and mass spectroscope
InactiveCN102592937AAccurate massNo calibration requiredDynamic spectrometersHigh pressureHigh voltage
The invention belongs to the technical field of quality analysis and particularly discloses a quality analysis method based on the restricted theory of relativity and a mass spectroscope. The method comprises the following steps of: introducing irons of an object to be measured into an iron source area; accelerating the irons to 3*105m / s or more by using an accelerating electric field; introducing the irons into a field-free flying area to freely fly; introducing the irons into an iron detector; and determining the static mass of the irons according to the flying time of the irons in the field-free flying area. The mass spectroscope based on the method comprises the iron source area, the accelerating electric field, a field-free drift tube and the iron detector, wherein the accelerating electric field consists of three or more pulsed high voltages; and the pulsed high voltages are provided by corresponding electrodes. Data measured by the method and the mass spectroscope is the real mass-to-charge ratio of the irons, so the mass is accurate and is not required to be corrected; the mass spectroscope is high in sensitivity and resolution; the quality detection up limit is only limited by the detector; and the mass spectroscope is high in analysis speed, does not require scanning and can realize full-spectrum analysis within tens of seconds.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for identification of the elemental composition of species of molecules
ActiveUS20180240659A1Increase valueImprove accuracyDynamic spectrometersComponent separationPosition toleranceElemental composition
Methods of identification of at least one most likely elemental composition of at least one species of molecules contained in a sample and / or originated from a sample by at least one ionisation process are provided. The method includes measuring a mass spectrum of the sample and may include reducing the measured mass spectrum to a neutral mass spectrum. The method further includes determining for a peak of interest a set of candidate species of molecules which have an expected peak with a peak position within a peak position tolerance range in the corresponding measured mass spectrum or neutral mass spectrum. An identification mass spectrum is identified for each candidate species and a range of peak positions is determined of all peaks of the identification mass spectrum. Two subscores of candidate species are determined by comparing the identification spectra with the measured or neutral mass spectrum and final scores are calculated from the subscores. An elemental composition of the candidate species is determined having calculated final scores of the highest values.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BREMEN
Electro-spray ionization mass spectrometry device based on conductive nano-material and method for realizing electro-spray ionization mass spectrometry
InactiveCN105575755ASimple methodLow costDynamic spectrometersParticle separator tube detailsAcute angleEngineering
The invention relates to an electro-spray ionization mass spectrometry device based on a conductive nano-material. The device comprises a sample introducing channel and an electro-spray generation base. The electro-spray generation base comprises a mass spectrometry high-voltage power supply and an electro-spray nozzle. The sample introducing channel is contacted with the electro-spray nozzle; the electro-spray nozzle is made of the conductive nano-material; the mass spectrometry high-voltage power supply is connected with the electro-spray nozzle through a high-voltage line; the front end of the electro-spray nozzle is of an acute-angle tip-end structure; and the front end of the electro-spray nozzle faces to a mass spectrometry entryway. The invention also discloses a method for realizing the electro-spray ionization mass spectrometry through the device. The electro-spray ionization mass spectrometry device has the advantages of not only meeting the requirement of mass spectrometry of a compound dissolved in an electro-spray-friendly solvent, but also meeting the requirement of mass spectrometry of compounds dissolved in the electro-spray-friendly solvent and an electro-spray-unfriendly solvent, such as a low polar solvent. The method is simple; the cost is low; adjustable parameters are few, ionization efficiency is high; introduction of extra auxiliary solvents is not need; and matrix interference of the extra solvents does not exist.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com