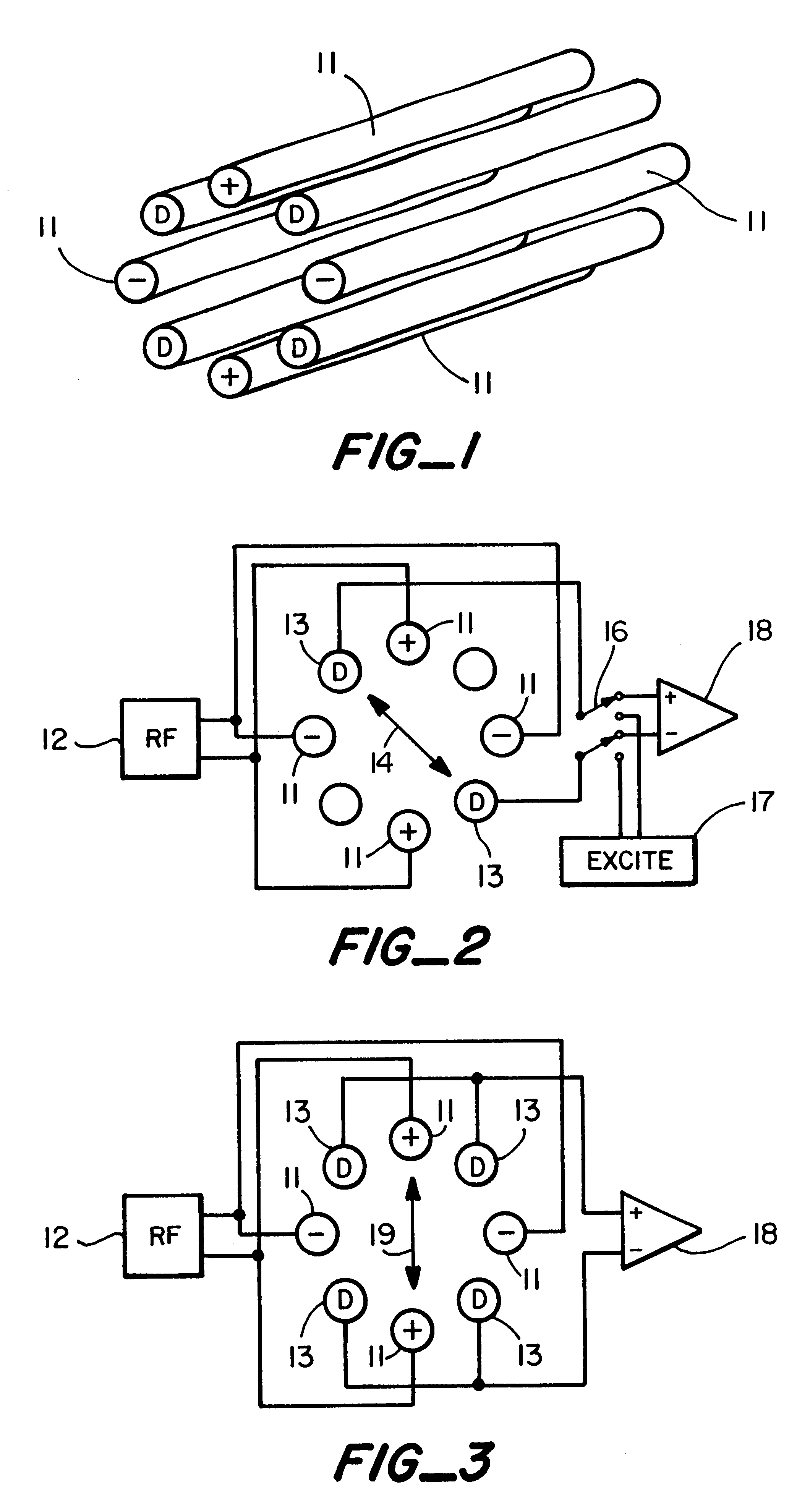
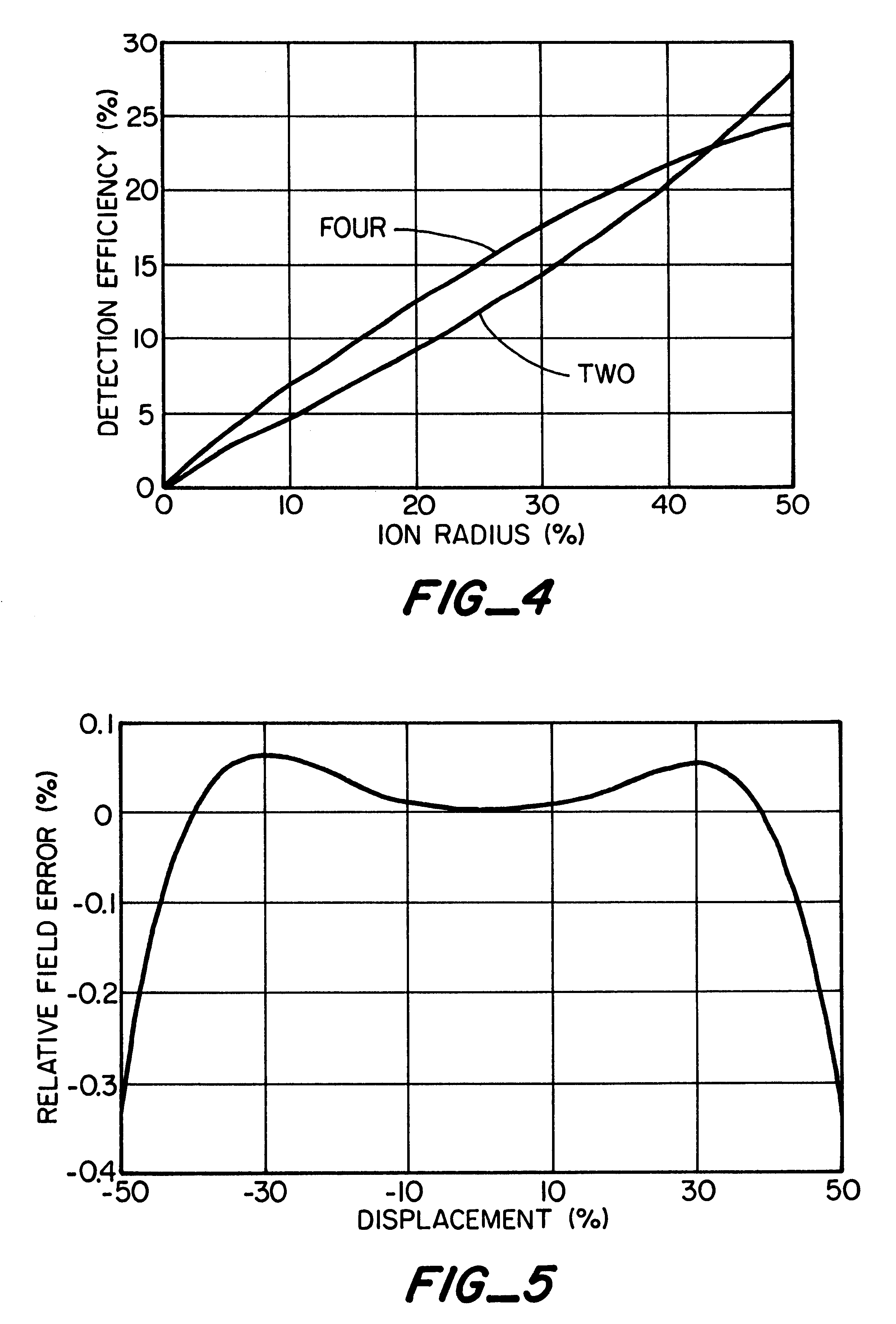
Patents
Literature
66 results about "Quadrupole ion trap" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A quadrupole ion trap is a type of ion trap that uses dynamic electric fields to trap charged particles. They are also called radio frequency (RF) traps or Paul traps in honor of Wolfgang Paul, who invented the device and shared the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1989 for this work. It is used as a component of a mass spectrometer or a trapped ion quantum computer.
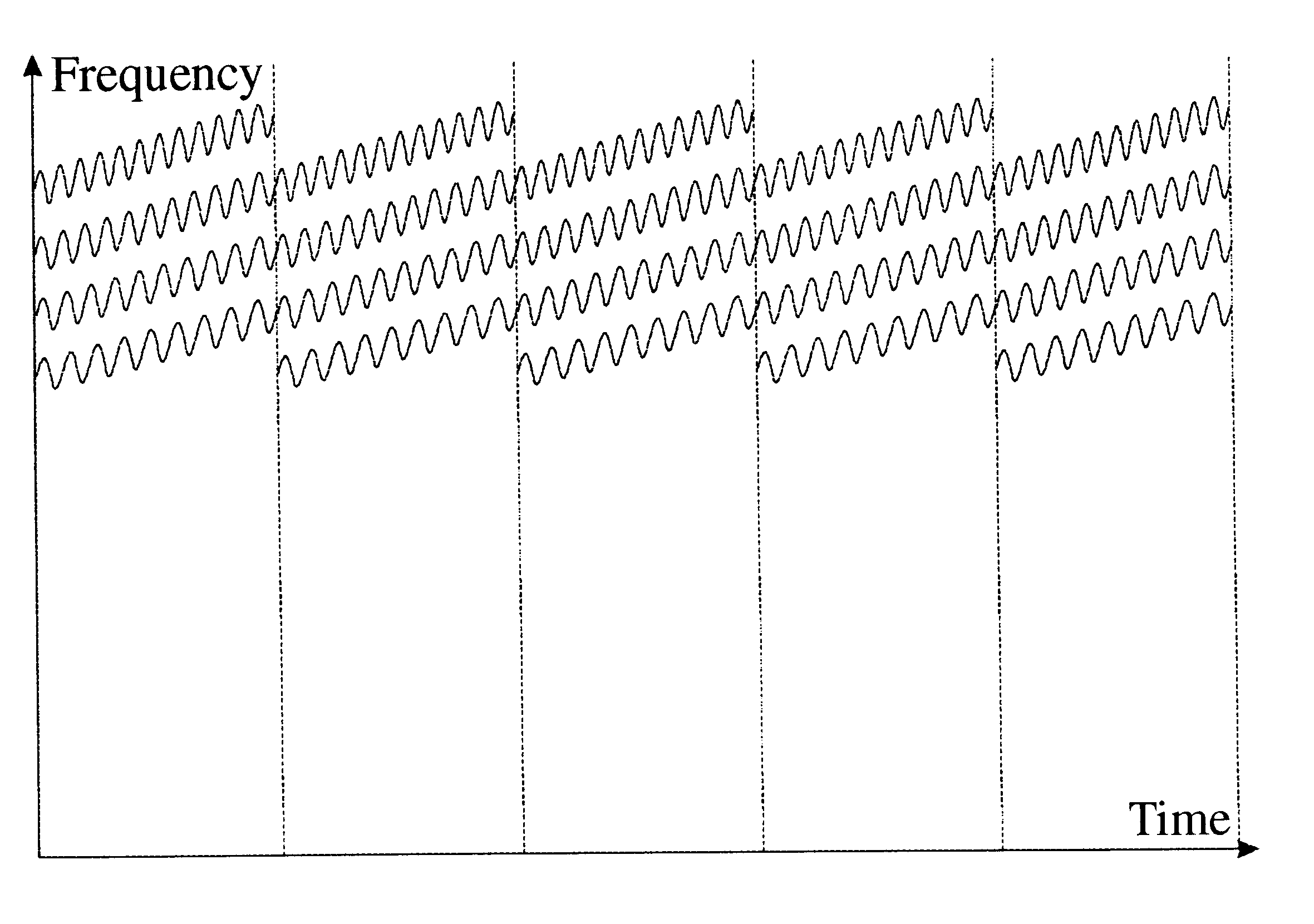
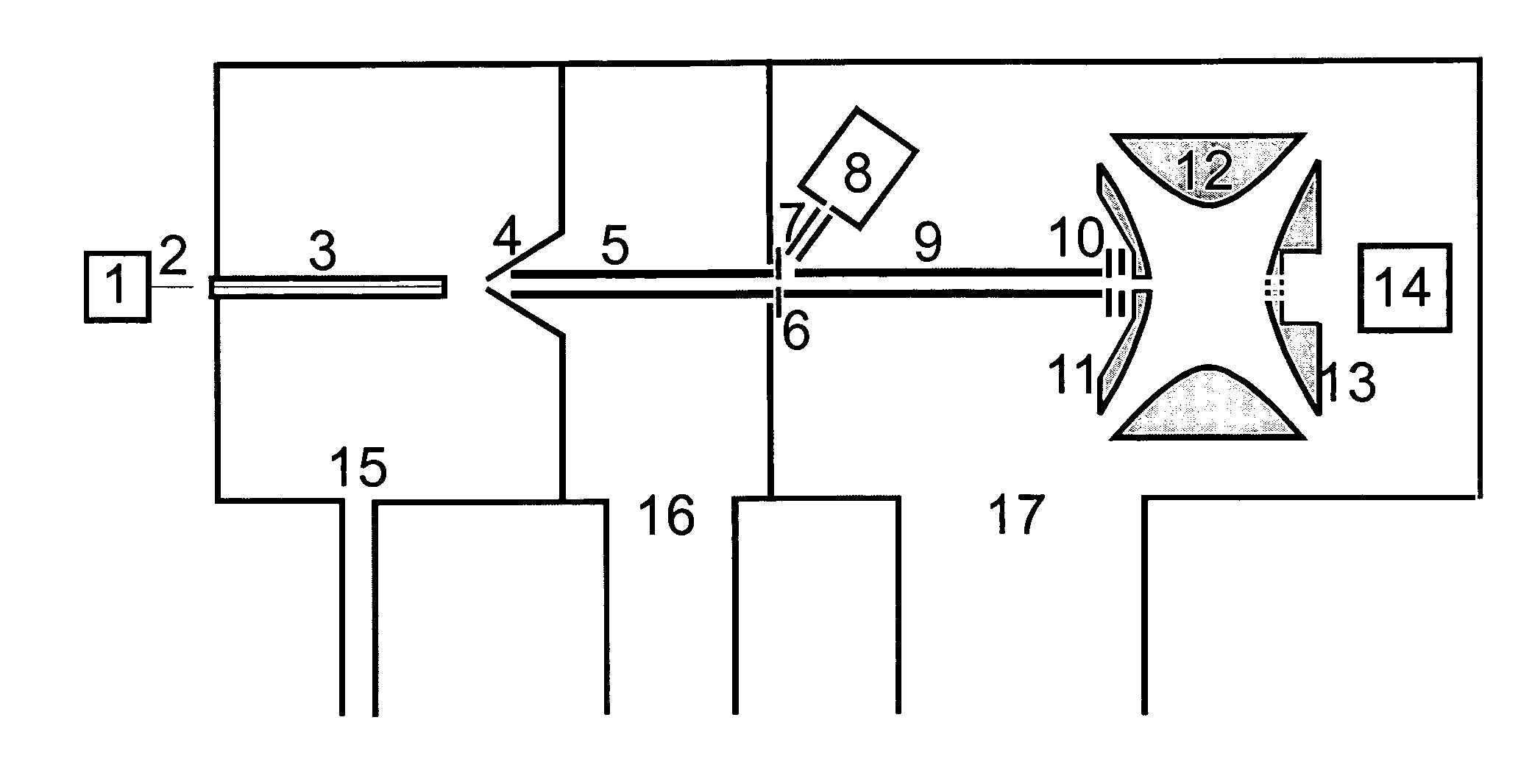
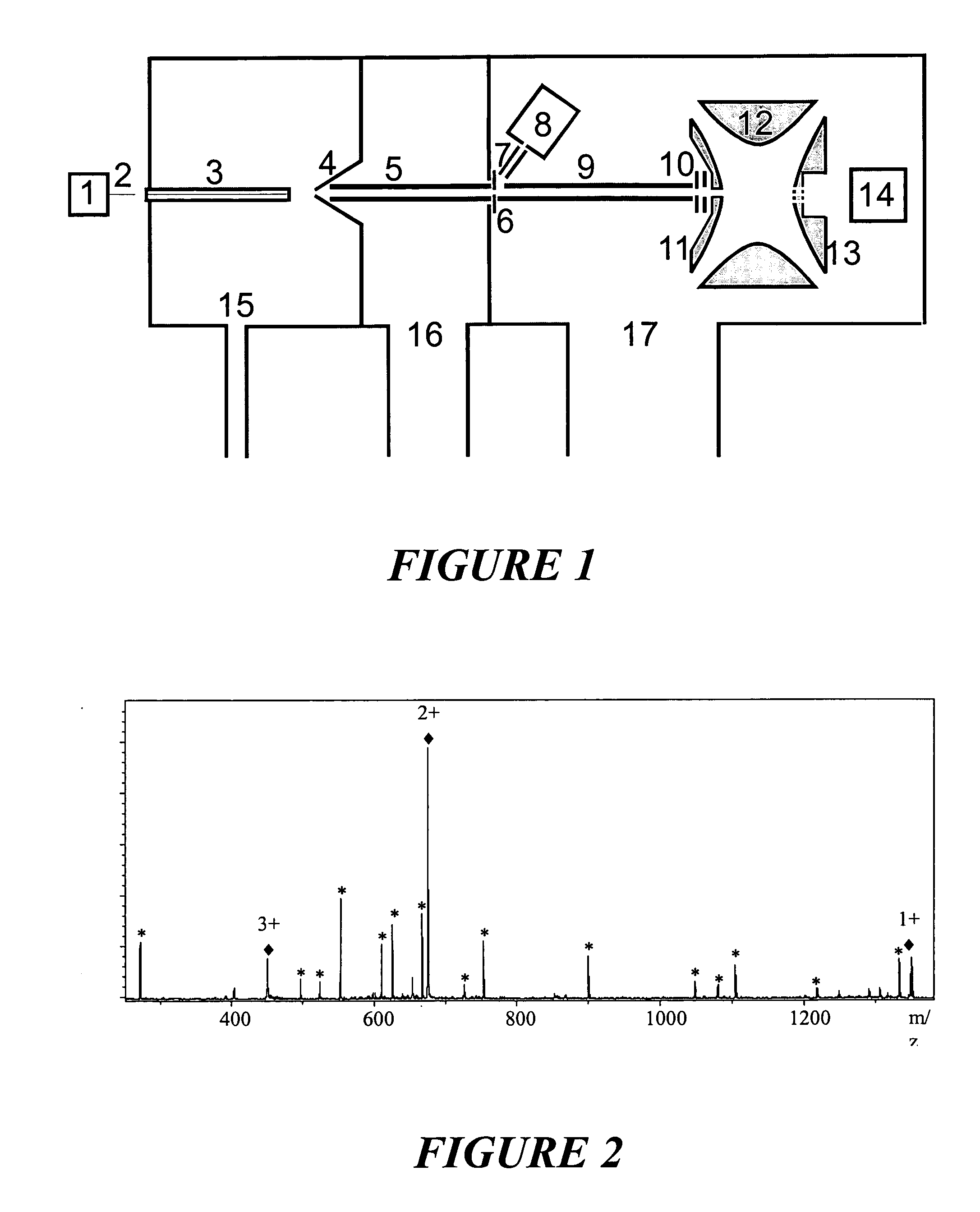
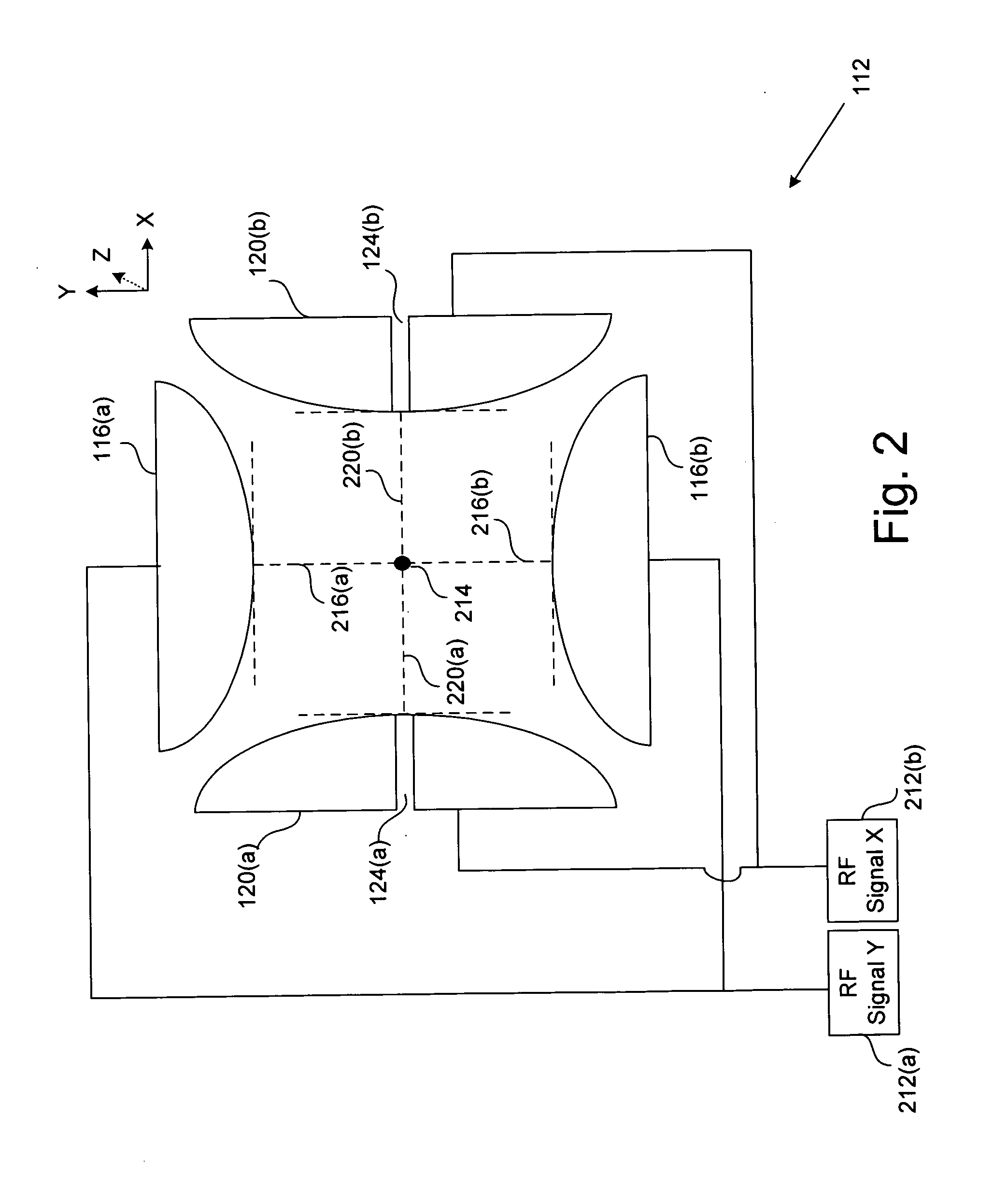
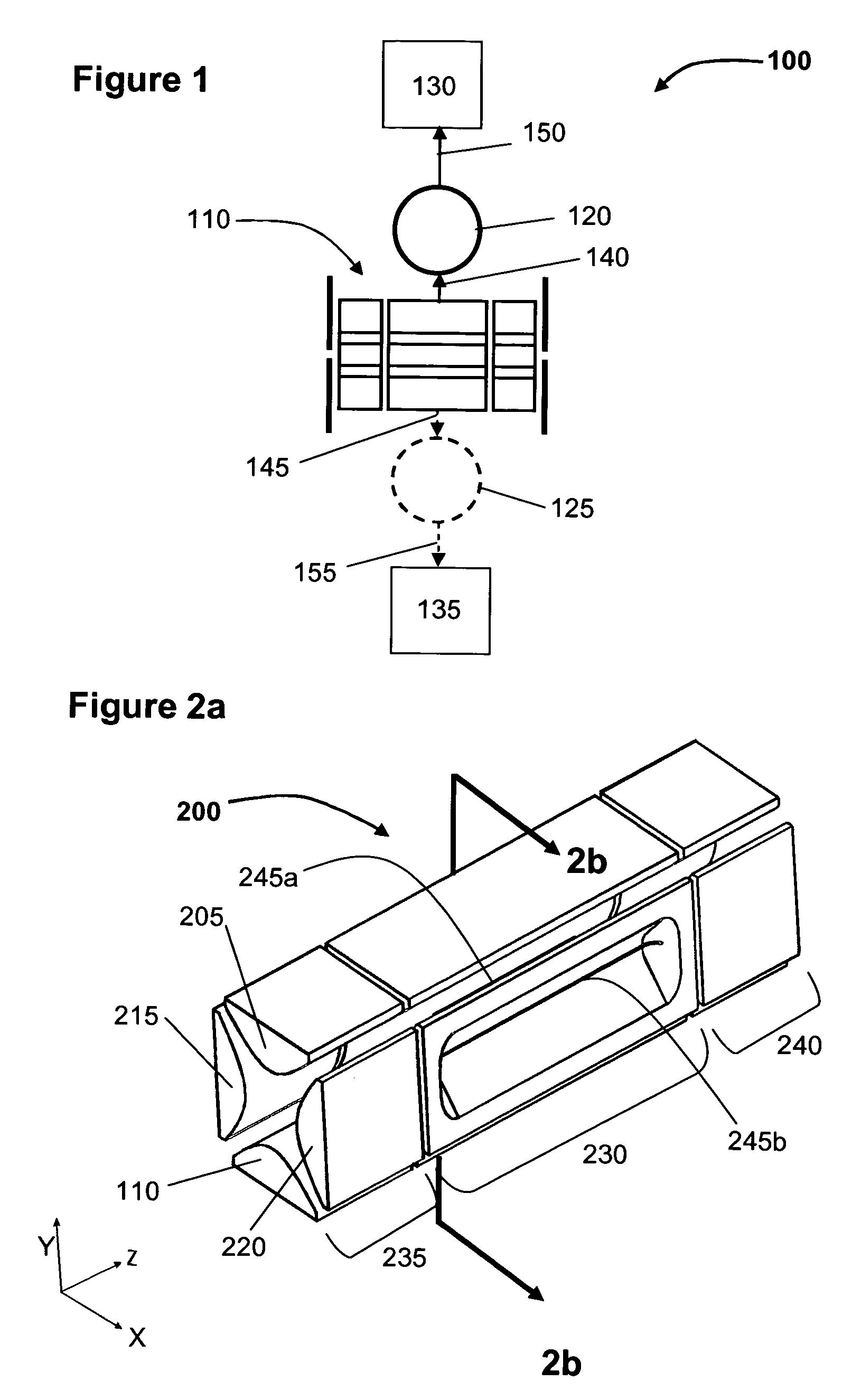
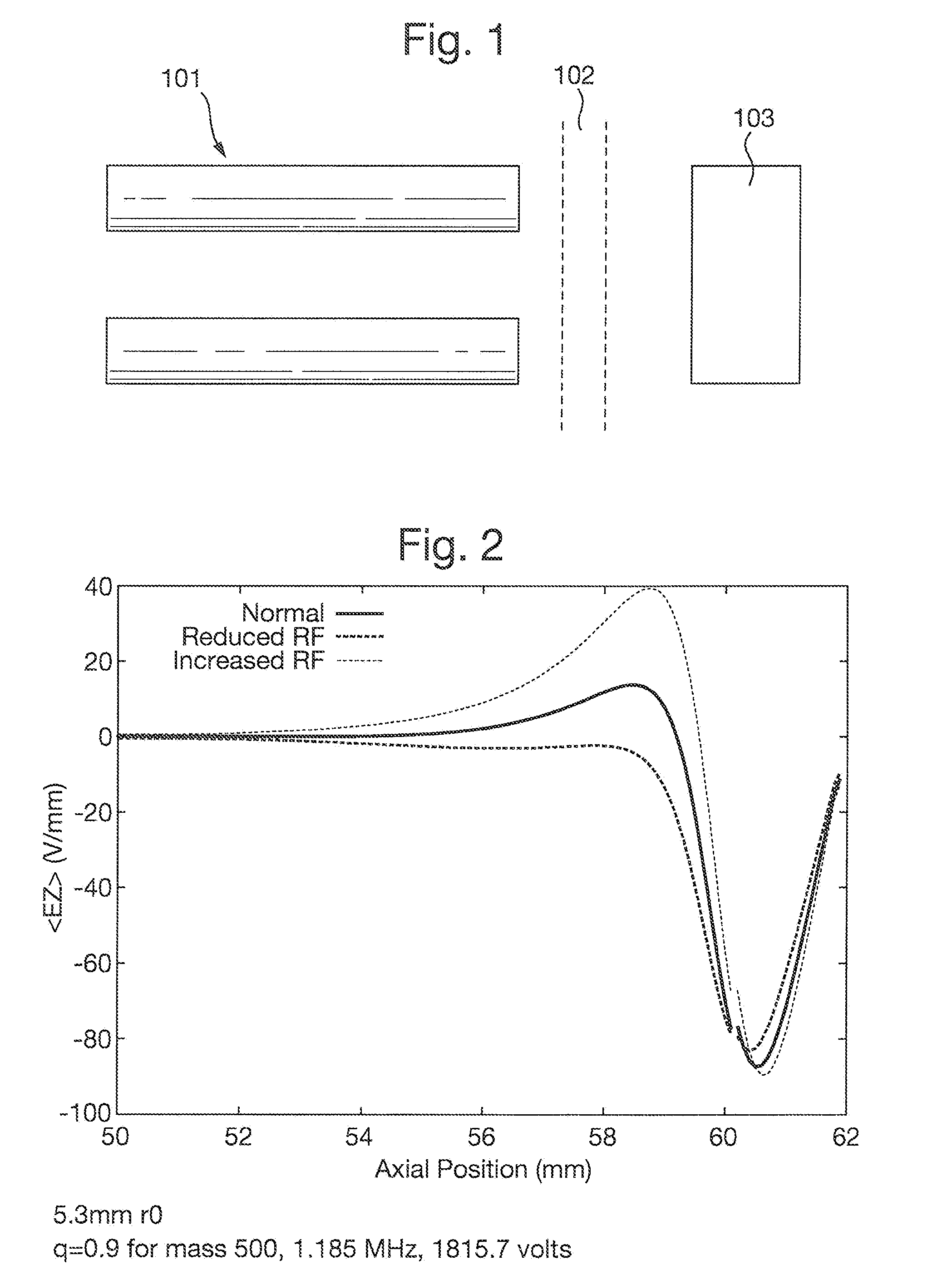
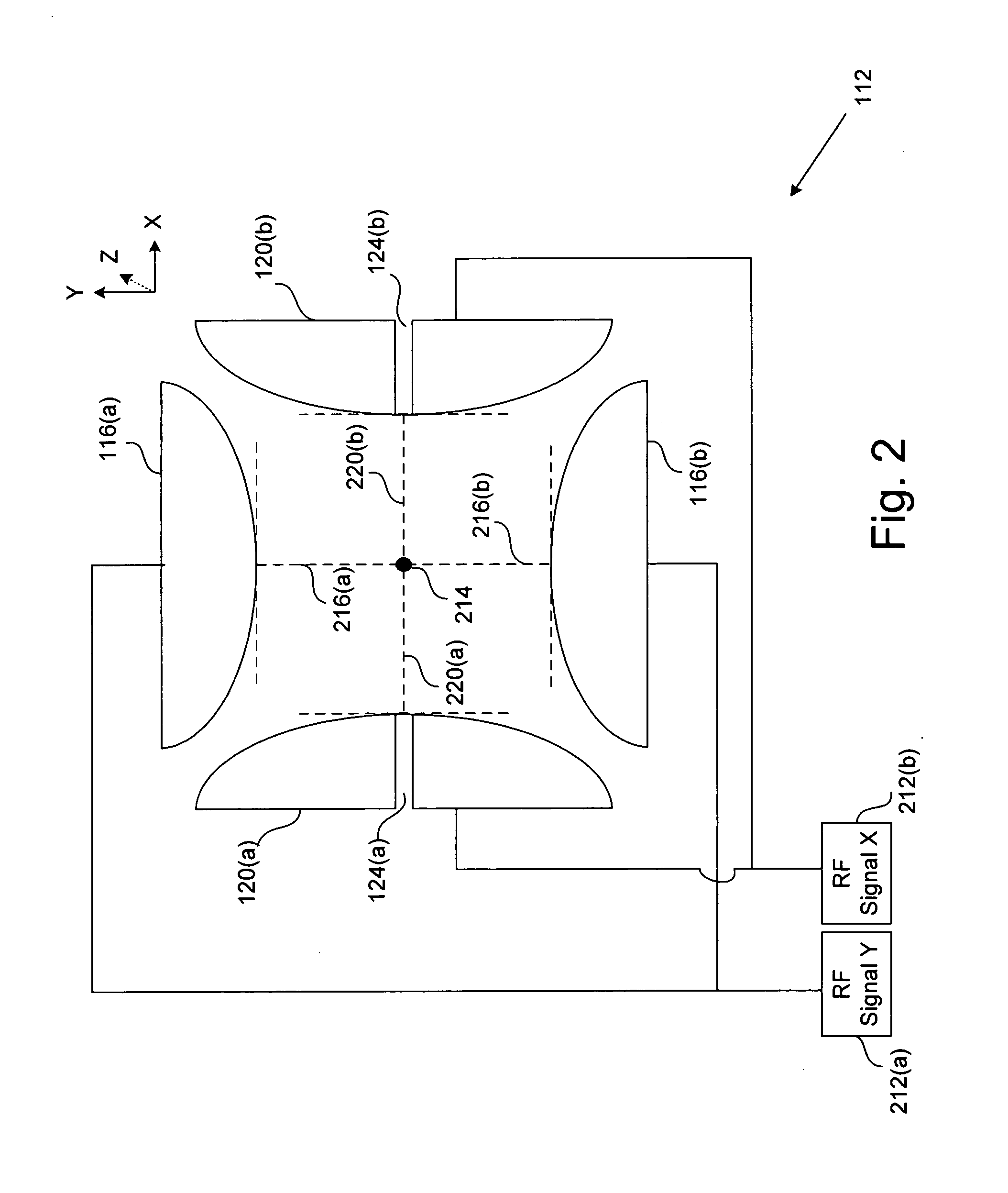
Two-dimensional quadrupole ion trap operated as a mass spectrometer
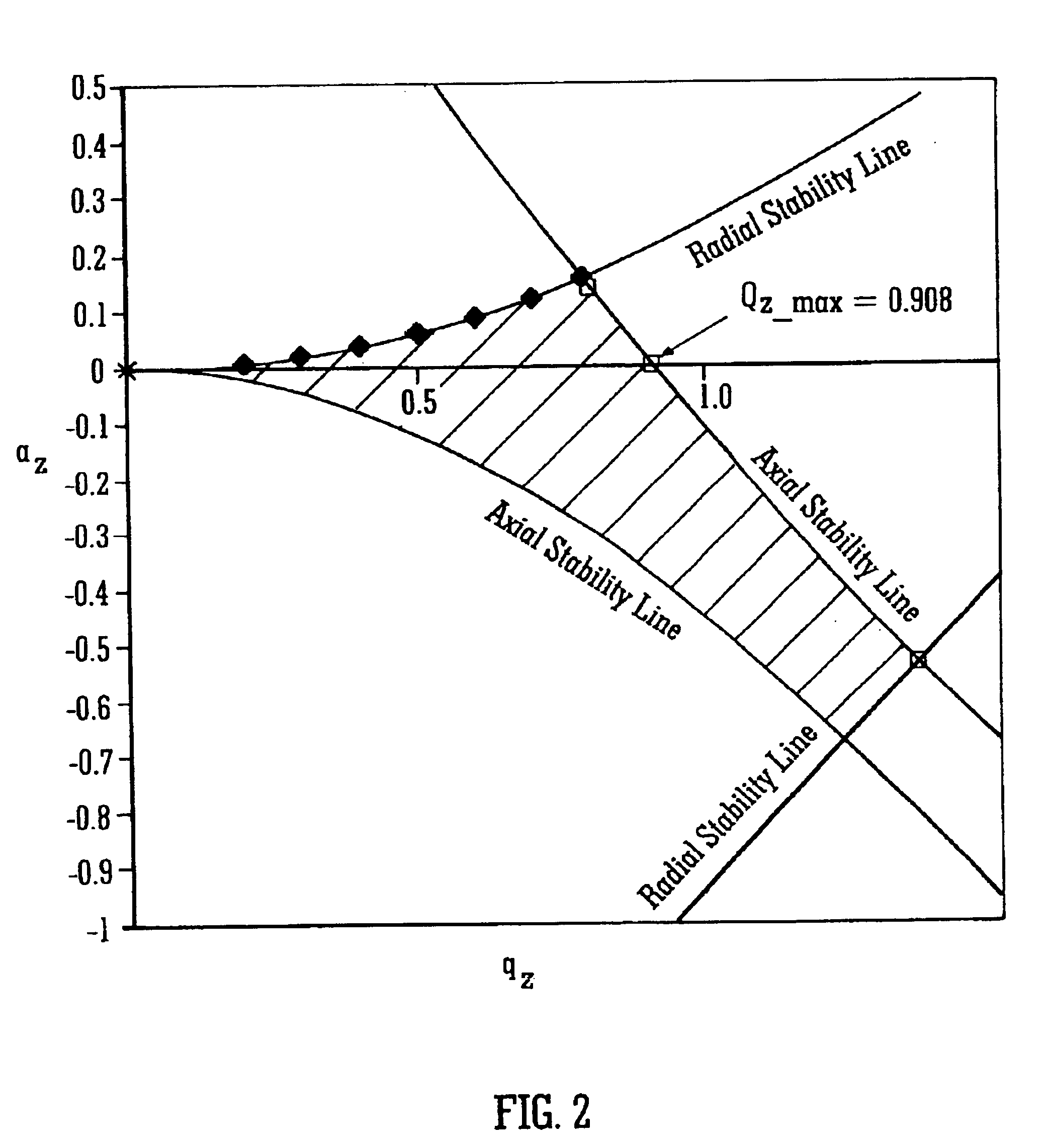
InactiveUS6797950B2Improve trapping efficiencyImprove capture abilityStability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationIon trap mass spectrometryImage resolution
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Linear quadrupole mass spectrometer
InactiveUS6403955B1Minimize feedbackLarge useful ion trapping volumeStability-of-path spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsTrappingLinear element
A quadrupole ion trap mass analyzer in which the trapping volume is defined by spaced linear rods in which linear elements located between the spaced linear rods produce image currents produced by motion of ions in the trapping volume.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Mass spectrometer
InactiveUS6875980B2Increases ion trapping volumeIncrease capacityStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersIon trap mass spectrometryMass analyzer
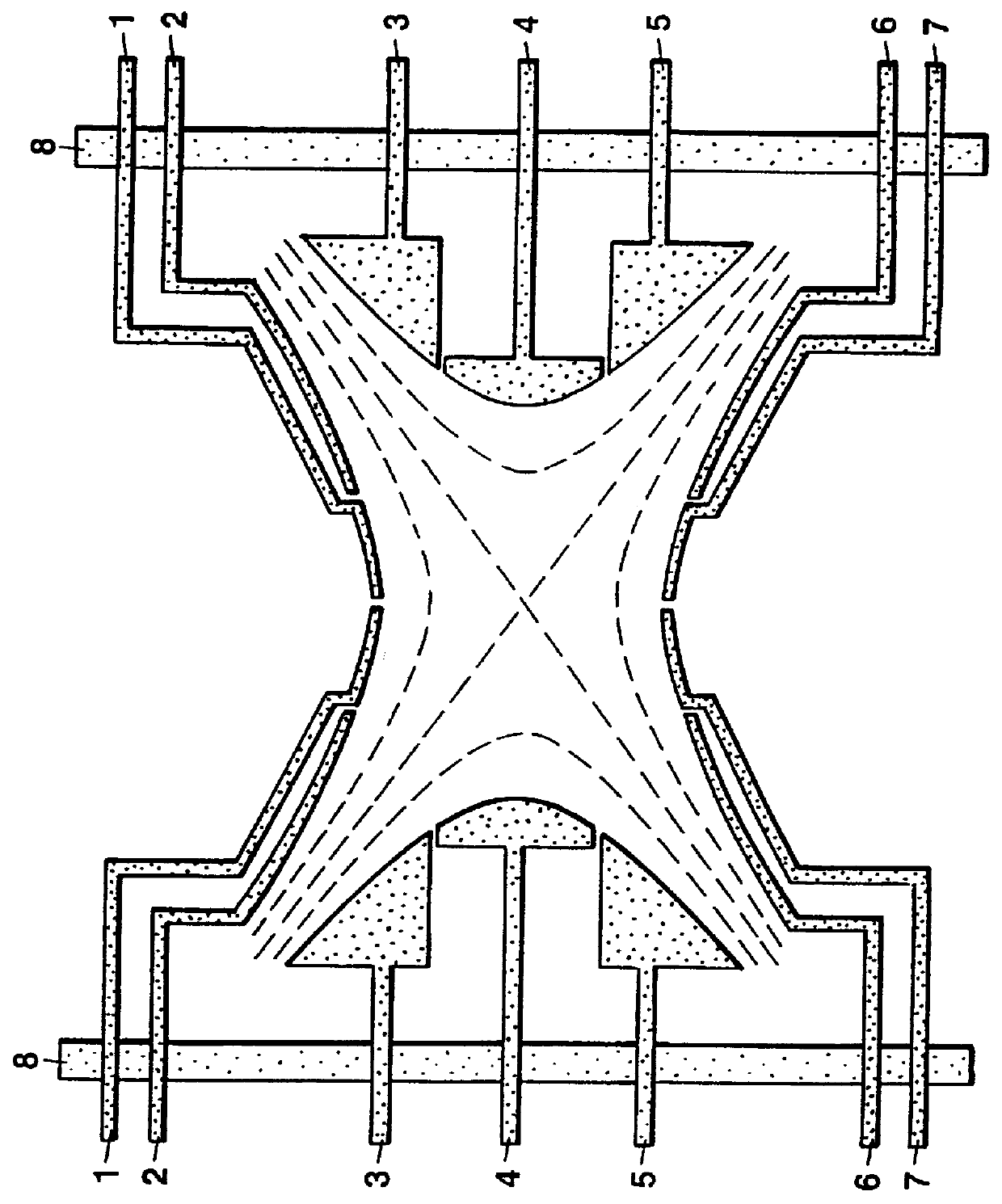
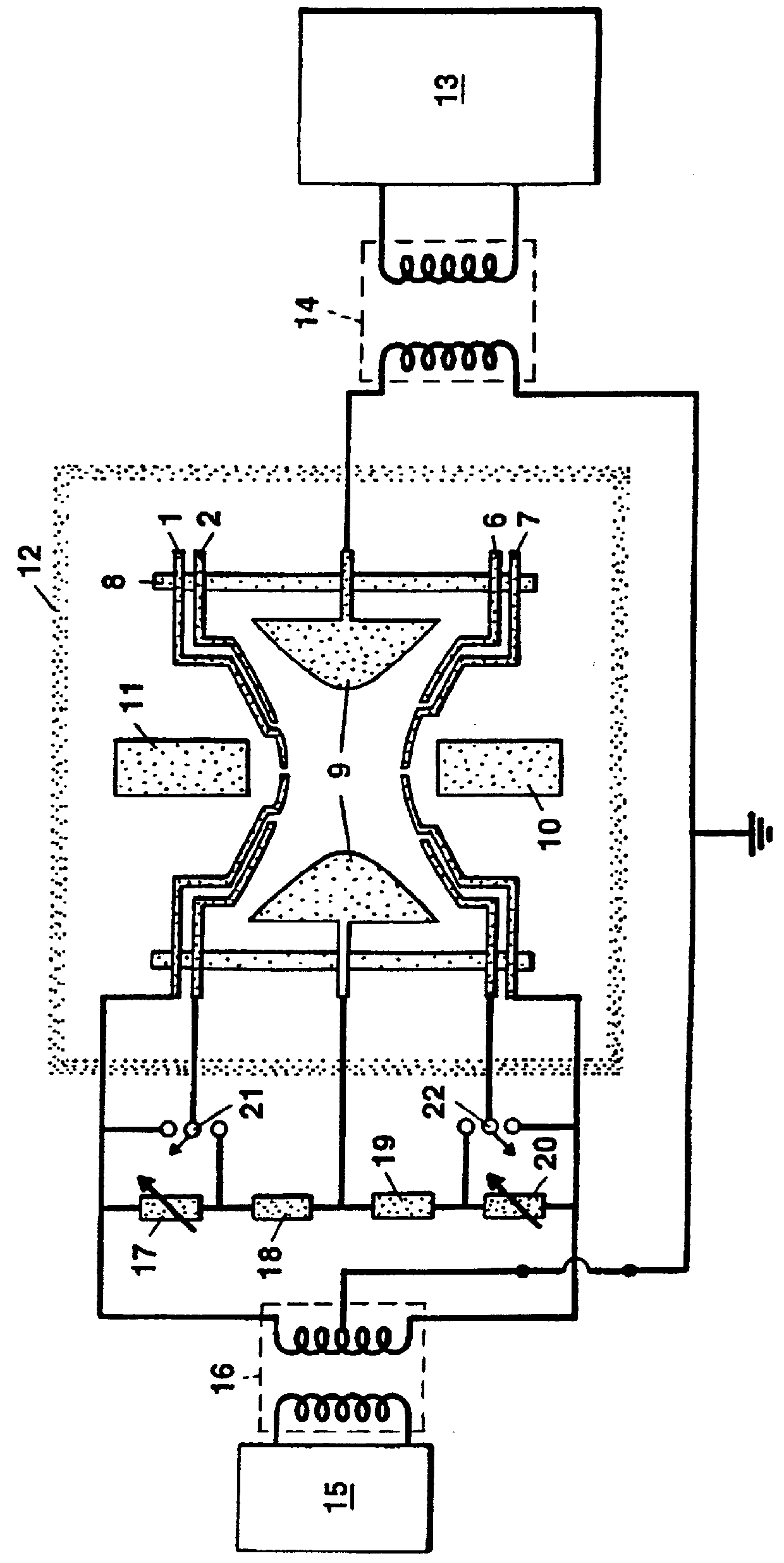
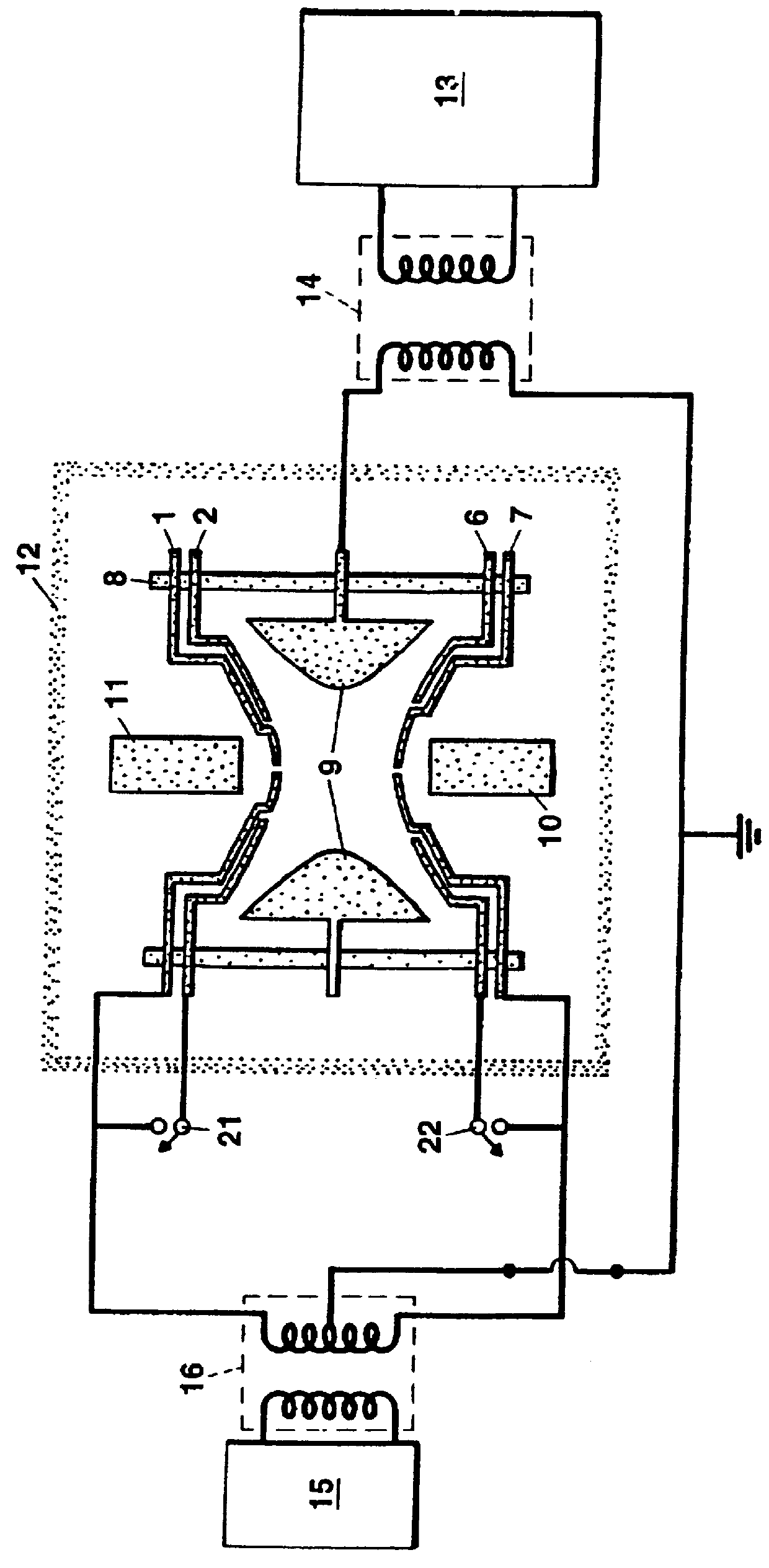
A mass spectrometer is disclosed wherein a relatively energetic pulse of ions having a relatively narrow spread of mass to charge ratios are ejected from a quadrupole ion trap and received in an ion trap upstream of a Time of Flight mass analyser. The ions are collisionally cooled within the ion trap and are pulsed out of the ion trap and into an extraction region of the Time of Flight mass analyser without substantially exciting the ions. This enables improved operation with the Time of Flight mass analyser. According to another embodiment, parent ions are fragmented and the resulting fragment ions are stored in two ion traps having different low mass cut-offs. The trapping system enables MS / MS experiments to be performed with a very high duty cycle.
Owner:MICROMASS UK LTD
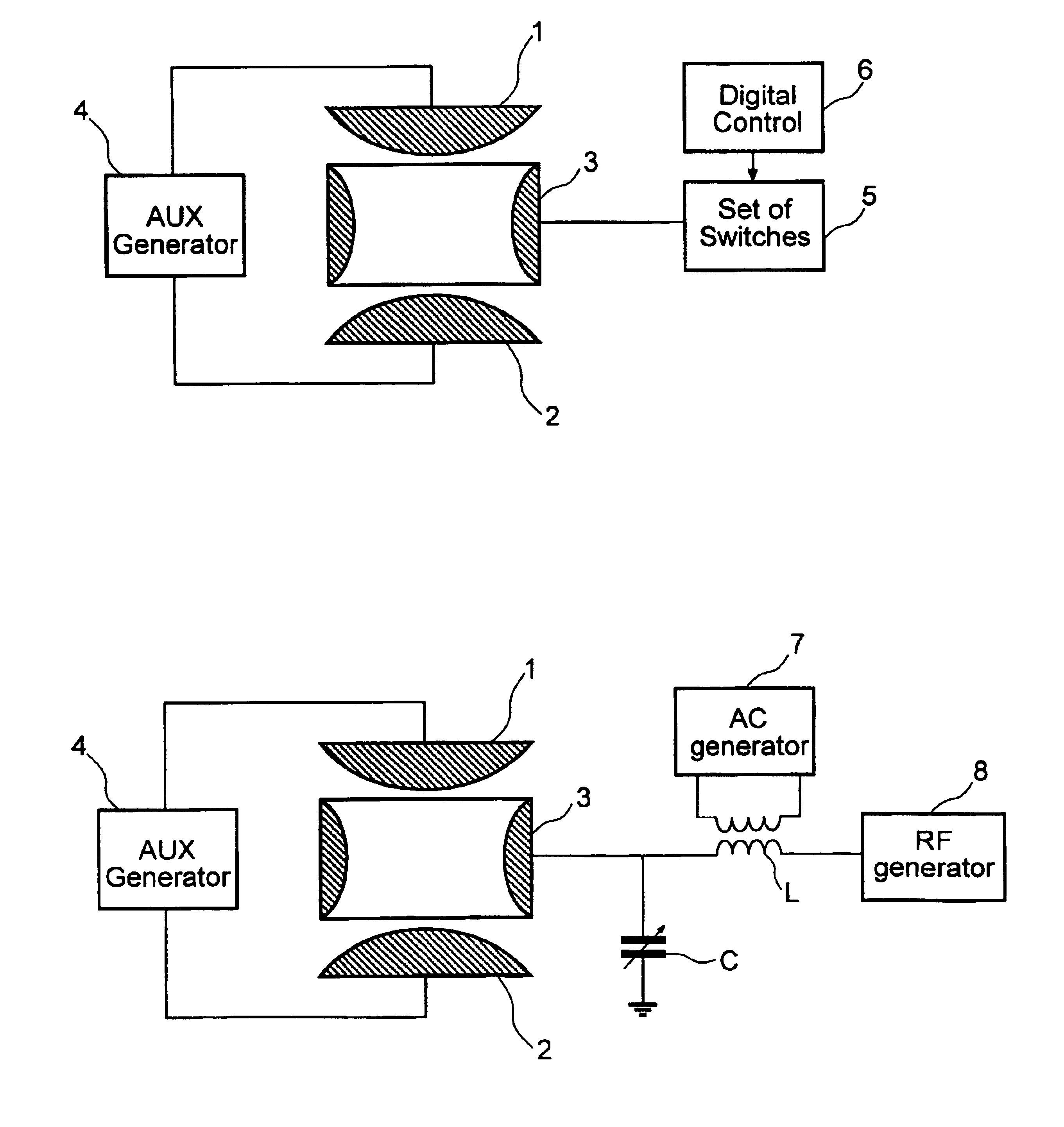
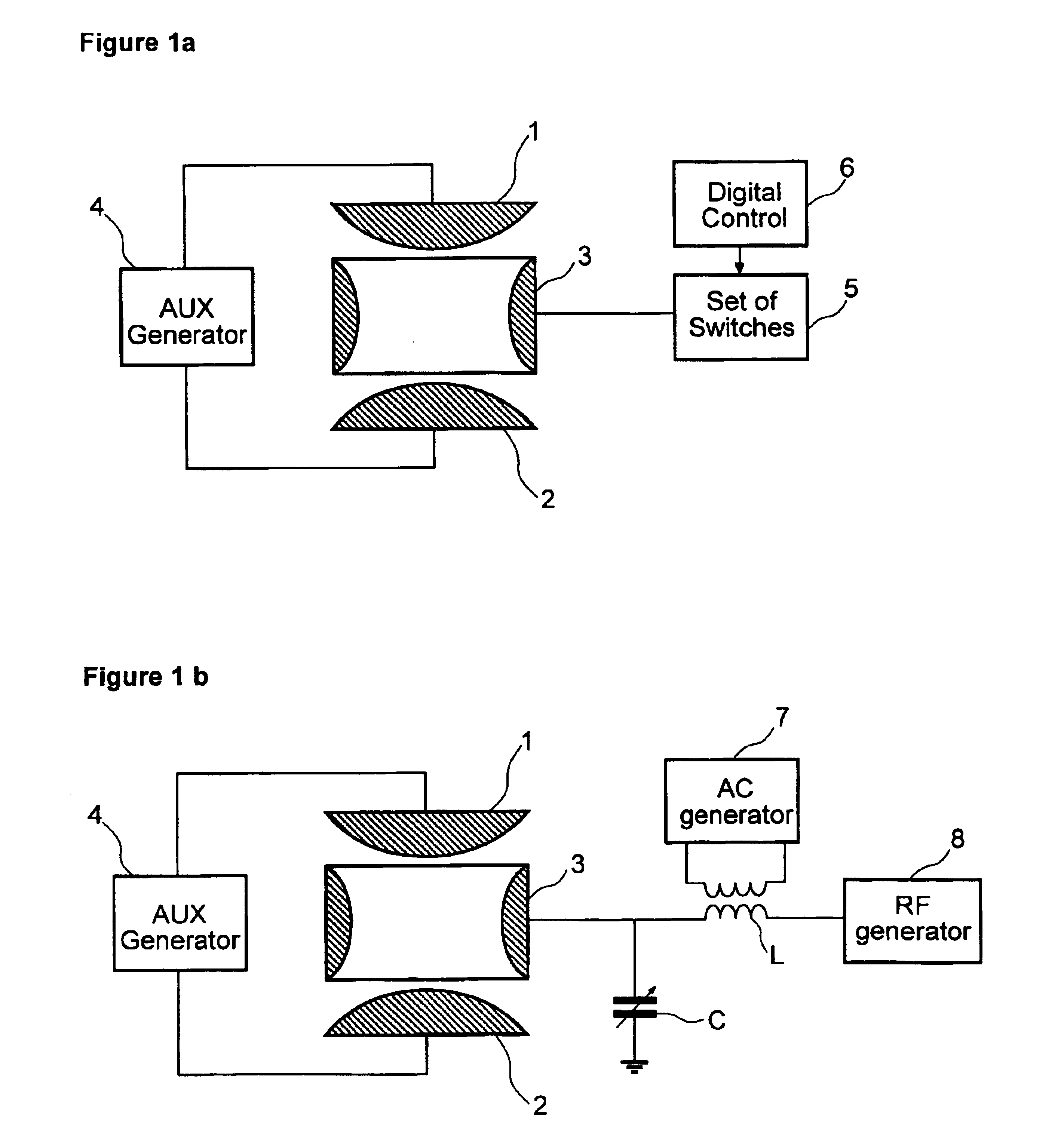
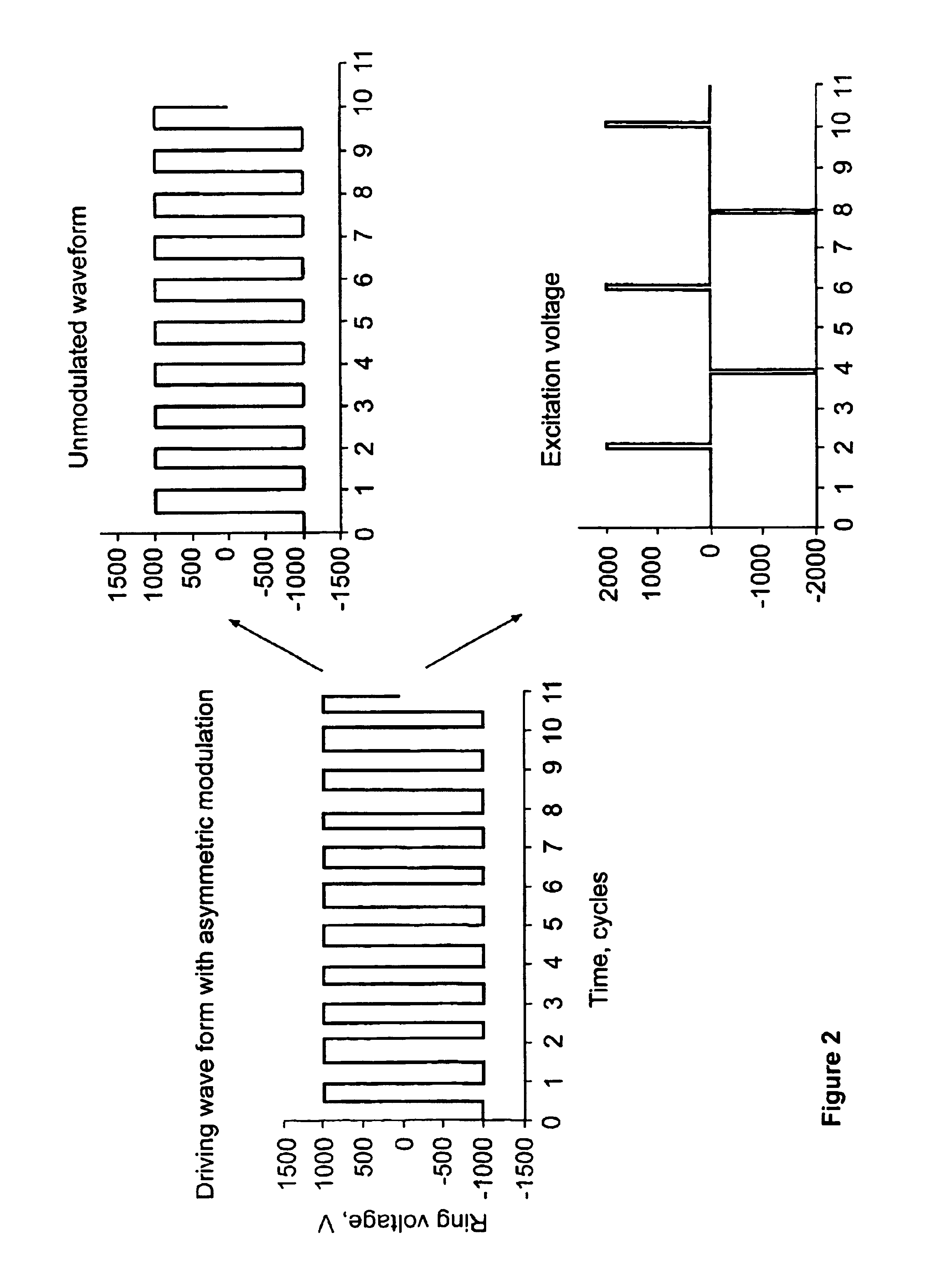
Methods and apparatus for driving a quadrupole ion trap device
InactiveUS7193207B1Spectrometer circuit arrangementsStability-of-path spectrometersLow voltageDipole excitation
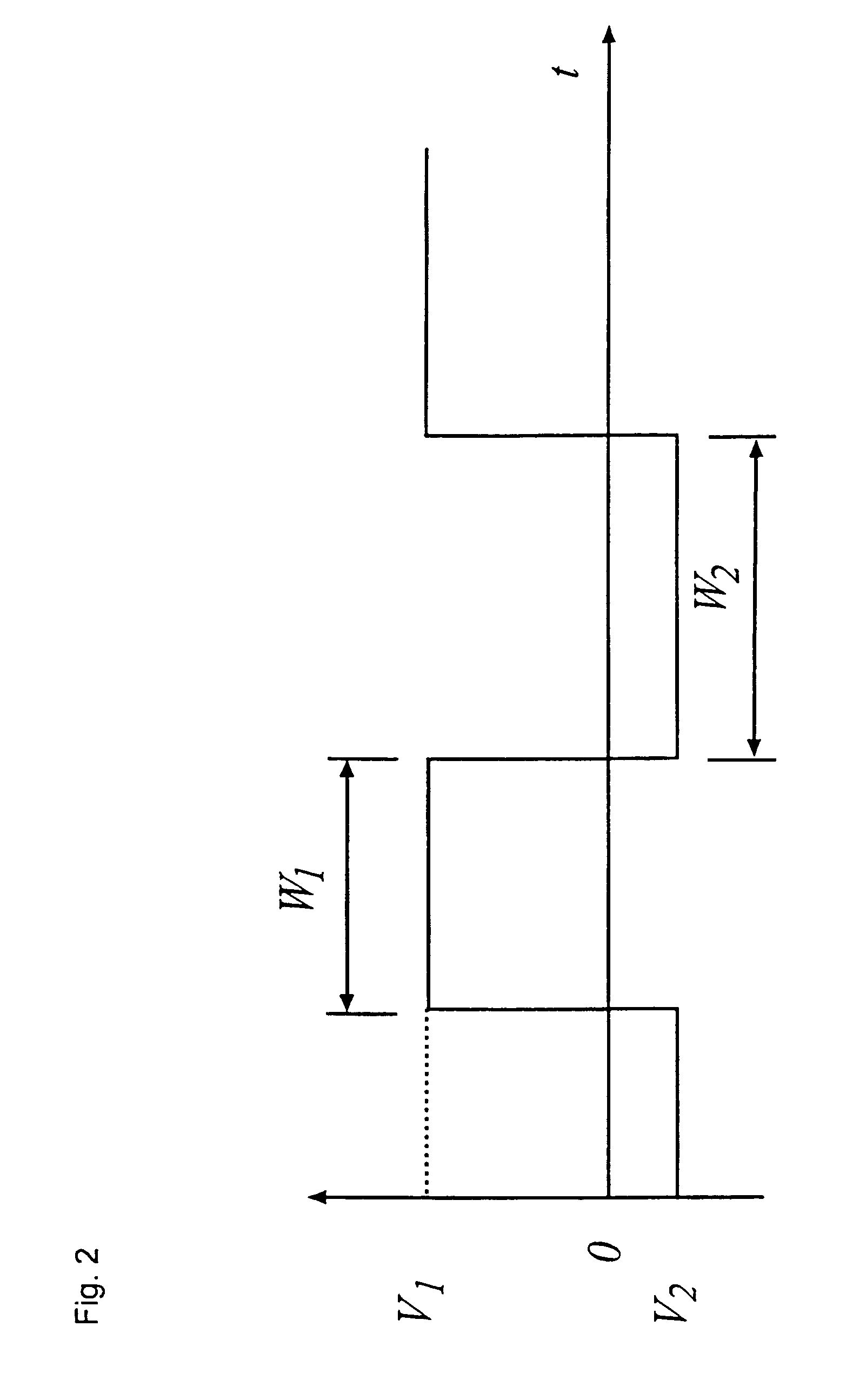
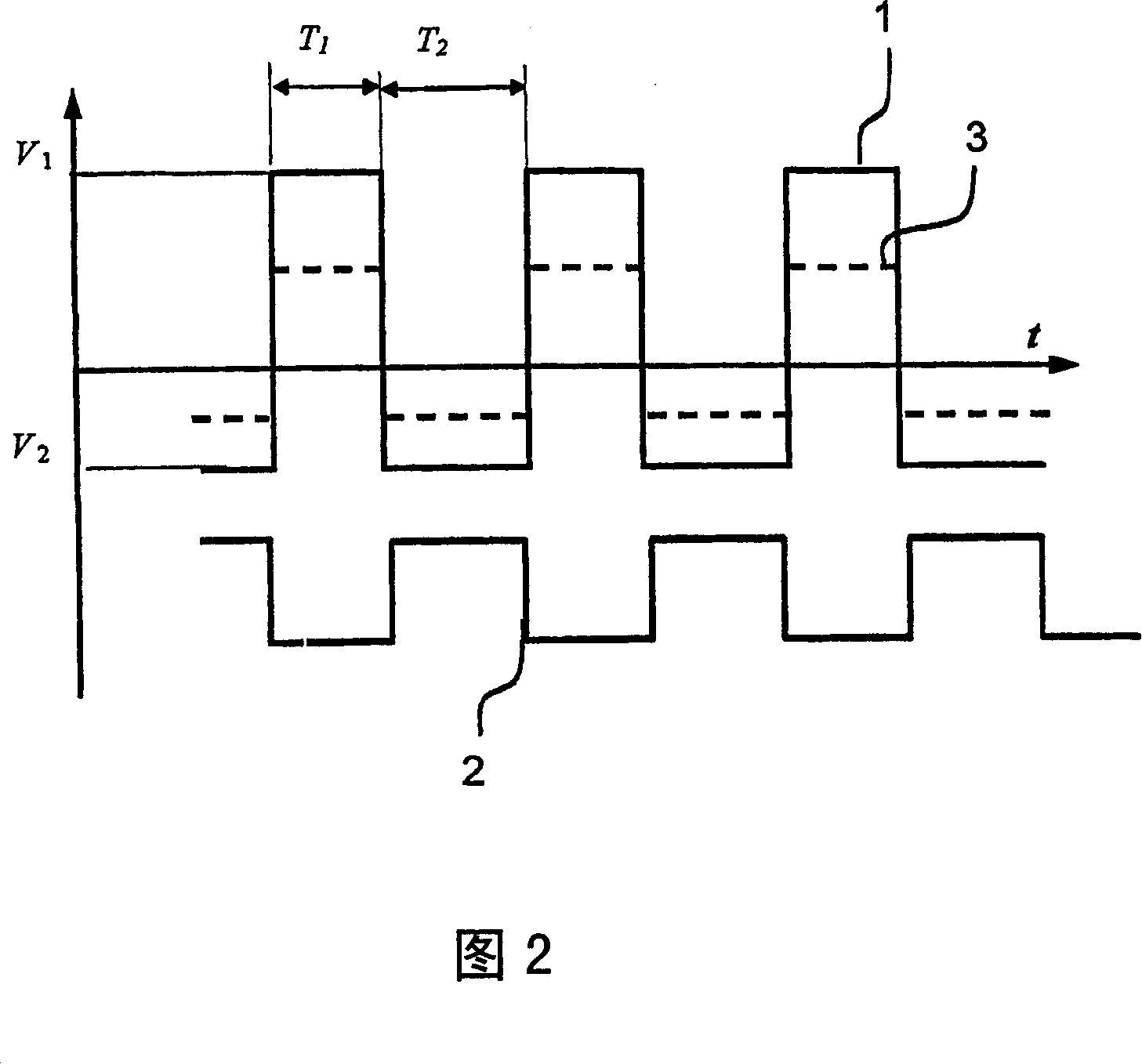
A digital drive apparatus (FIG. 3) for quadrupole device such as a quadrupole ion trap has a digital signal generator (11, 13, 14; 24, 25, 26) and a switching arrangement (16, 17) which alternately switches between high and low voltage levels (V1, V2) to generate a rectangular wave drive voltage. A dipole excitation voltage is also supplied to the quadrupole device to excite resonant oscillatory motion of ions.
Owner:SHIMADZU RES LAB EURO
Fragmentation in quadrupole ion trap mass spectrometers
InactiveUS6410913B1Improve distributionExtension of timeStability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationSpectrometerAtomic physics
The invention relates to the fragmentation of ions in ion traps filled with collision gas by exciting their axial oscillations in a dipole-shaped excitation field with a frequency mixture which covers the frequency of ion oscillations. The invention consists of ramping up the voltages of the frequency mixture for the dipolar excitation field, as a result of which, surprisingly, approximately the same fragmentation results are obtained for ions of different structures in the same fragmentation times as at a structurally specific optimal voltage applied at a constant level.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH
Methods for the isolation and analysis of cellular protein content
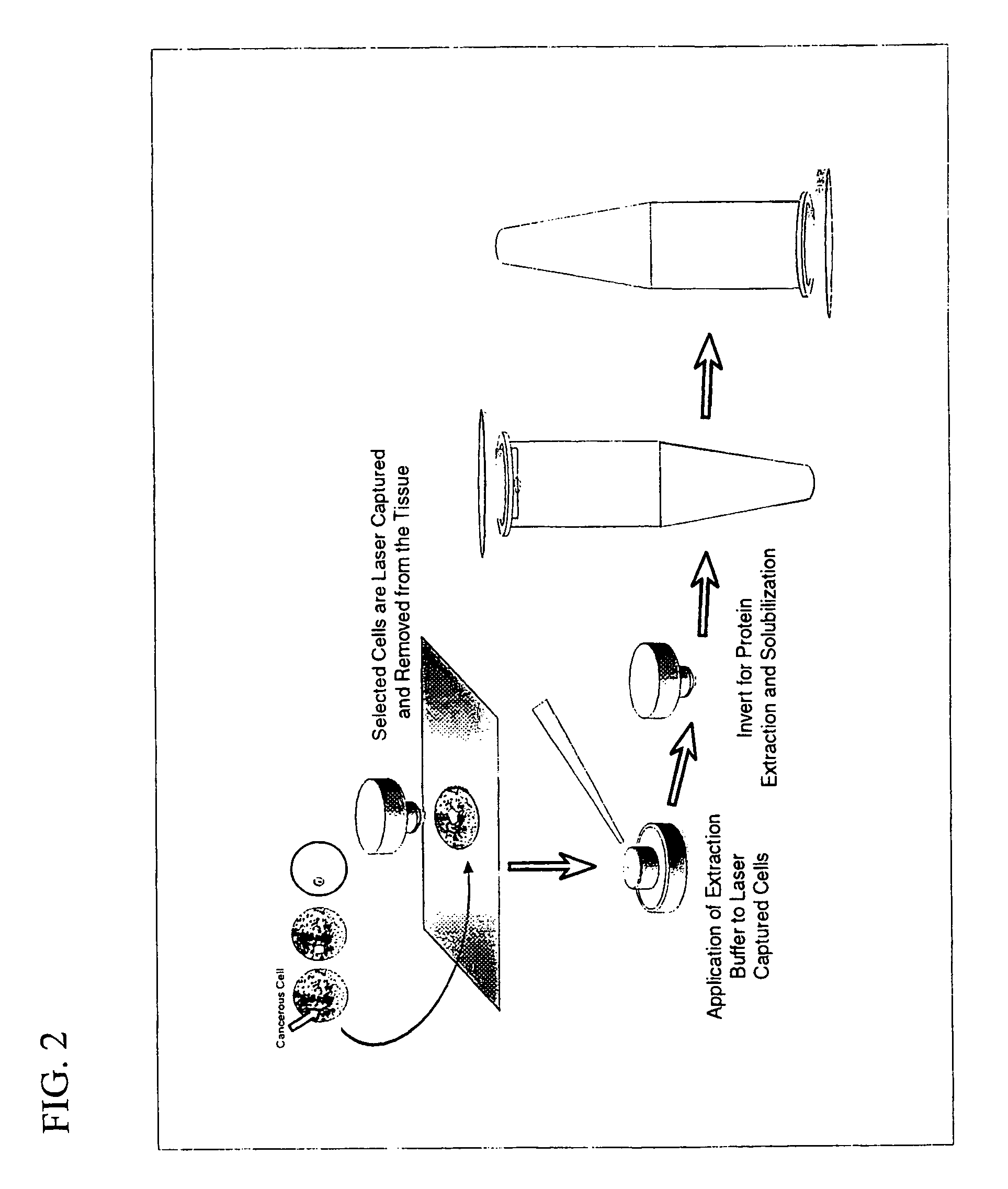
InactiveUS6969614B1Rapid and reliable to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementWithdrawing sample devicesLymphatic SpreadPresent method
The present invention describes devices and methods for performing protein analysis on laser capture microdissected cells, which permits proteomic analysis on cells of different populations. Particular disclosed examples are analysis of normal versus malignant cells, or a comparison of differential protein expression in cells that are progressing from normal to malignant. The protein content of the microdissected cells may be analyzed using techniques such as immunoassays, 1D and 2D gel electrophoresis characterization, Western blotting, liquid chromatography quadrapole ion trap electrospray (LCQ-MS), Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization / Time of Flight (MALDI / TOF), and Surface Enhanced Laser Desorption Ionization Spectroscopy (SELDI). In addition to permitting direct comparison of qualitative and quantitative protein content of tumor cells and normal cells from the same tissue sample, the methods also allow for investigation of protein characteristics of tumor cells, such as binding ability and amino acid sequence, and differential expression of proteins in particular cell populations in response to drug treatment. The present methods also provide, through the use of protein fingerprinting, a rapid and reliable way to identify the source tissue of a tumor metastasis.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Ion fragmentation by electron transfer in ion traps
The invention relates to a method and instrument for the fragmentation of large molecular analyte ions, preferably biopolymer ions, by reactions between multiply charged positive analyte ions and negative reactant ions in RF quadrupole ion traps. Some of these reactions involve electron transfer reactions with subsequent dissociation of the biopolymer analyte ions, and some involve the loss of a proton, leading to stable product ions. The invention can use any type of ion traps, particularly three-dimensional RF quadrupole ion traps, for the reactions between positive and negative ions. The fragmentation yield can be increased because ions that remain stable as radical cations after transfer of an electron are further fragmented by collisionally induced fragmentation, forming fragment ions that are typical of electron transfer, and not those typical of collisionally induced fragmentation. The invention preferentially introduces positive ions and negative ions into the ion trap sequentially through the same aperture.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Ion fragmentation by electron transfer in ion traps
ActiveUS20060186331A1Isotope separationParticle separator tube detailsIon trap mass spectrometryAnalyte
The invention relates to a method and instrument for the fragmentation of large molecular analyte ions, preferably biopolymer ions, by reactions between multiply charged positive analyte ions and negative reactant ions in RF quadrupole ion traps. Some of these reactions involve electron transfer reactions with subsequent dissociation of the biopolymer analyte ions, and some involve the loss of a proton, leading to stable product ions. The invention can use any type of ion traps, particularly three-dimensional RF quadrupole ion traps, for the reactions between positive and negative ions. The fragmentation yield can be increased because ions that remain stable as radical cations after transfer of an electron are further fragmented by collisionally induced fragmentation, forming fragment ions that are typical of electron transfer, and not those typical of collisionally induced fragmentation. The invention preferentially introduces positive ions and negative ions into the ion trap sequentially through the same aperture.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
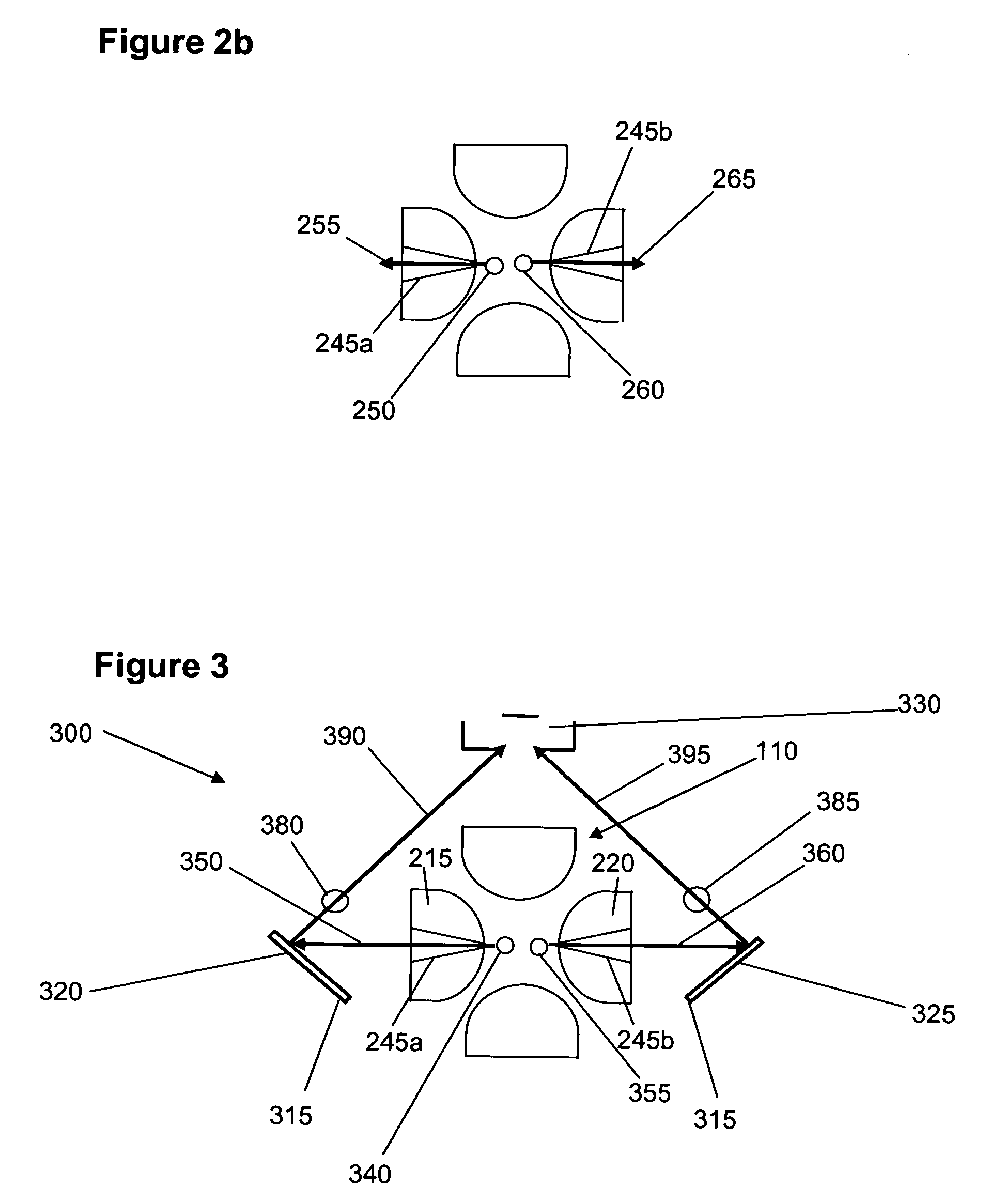
Quadrupole ion trap device and methods of operating a quadrupole ion trap device
ActiveUS7285773B2Improve efficiencyHigh resolutionStability-of-path spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsImage resolutionTrapping region
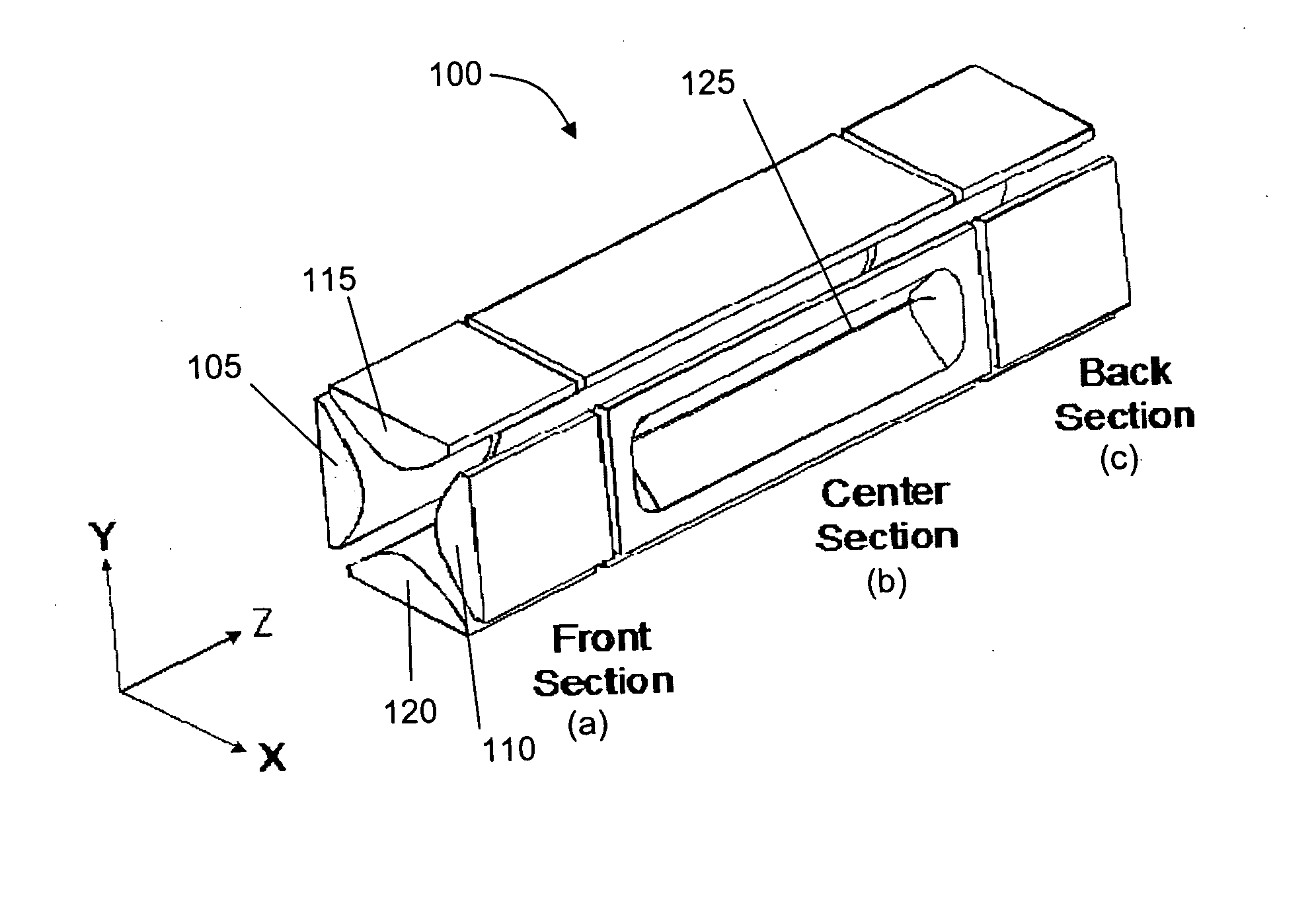
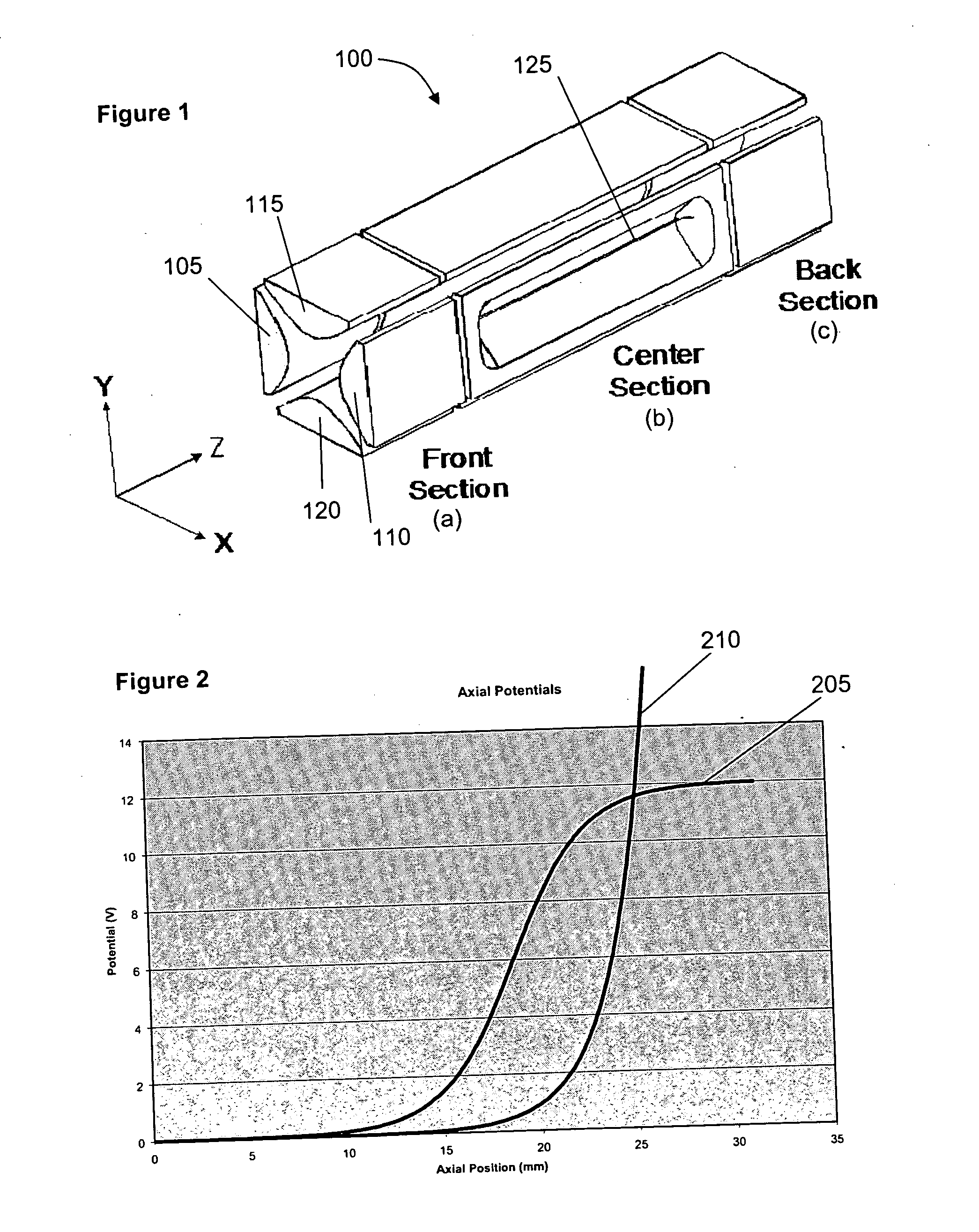
A quadrupole ion trap device has a field adjusting electrode located outside the trapping region adjacent the aperture in the entrance end cap electrode, and optionally adjacent the aperture in the exit end cap electrode. The field adjusting electrode(s) controls field distortion in the vicinity of the apertures. By appropriately setting the voltages on the field adjusting electrodes the efficiency and resolution of operational processes such as ion introduction, precursor ion isolation and mass scanning can be improved.
Owner:SHIMADZU RES LAB EURO
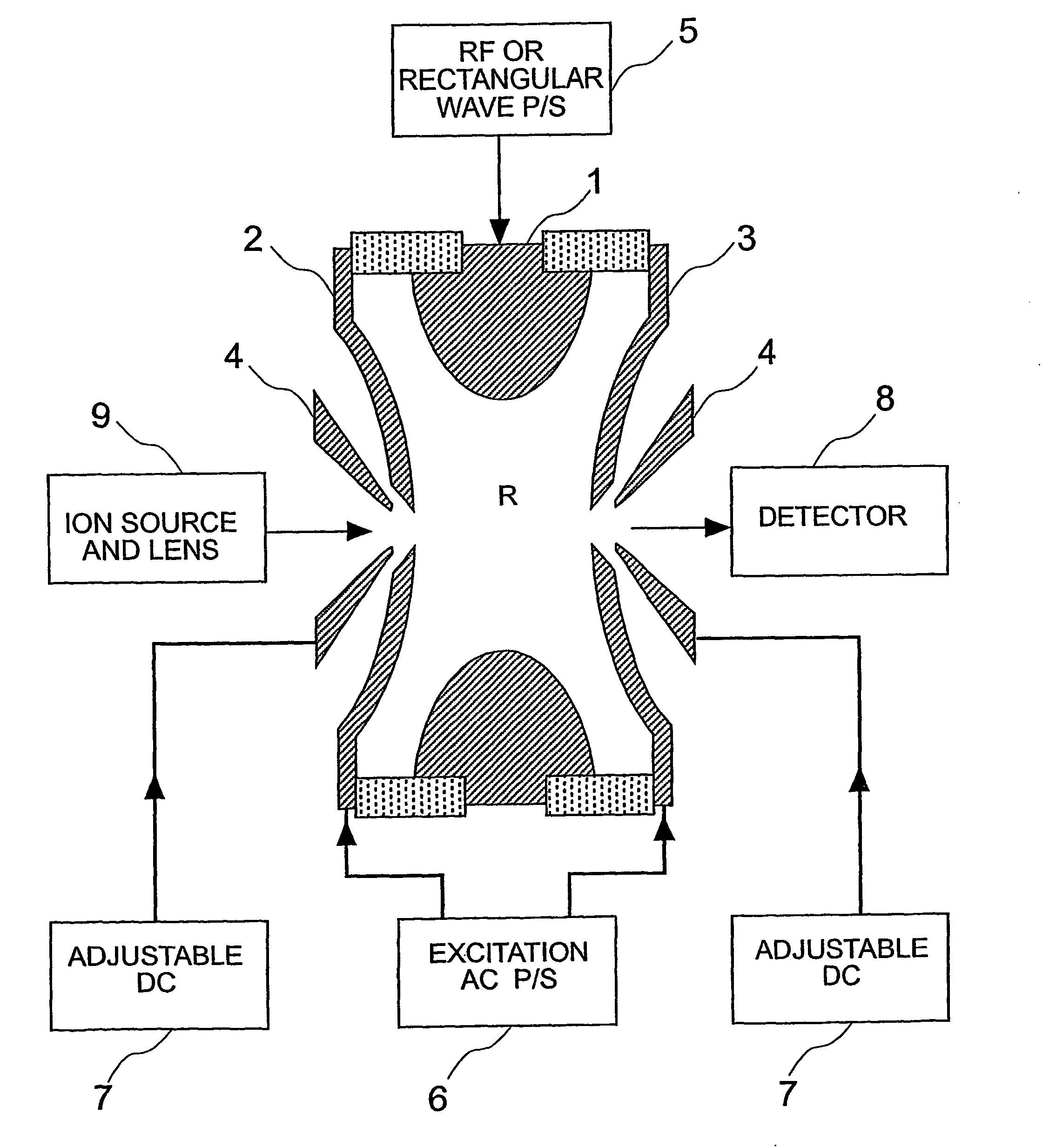
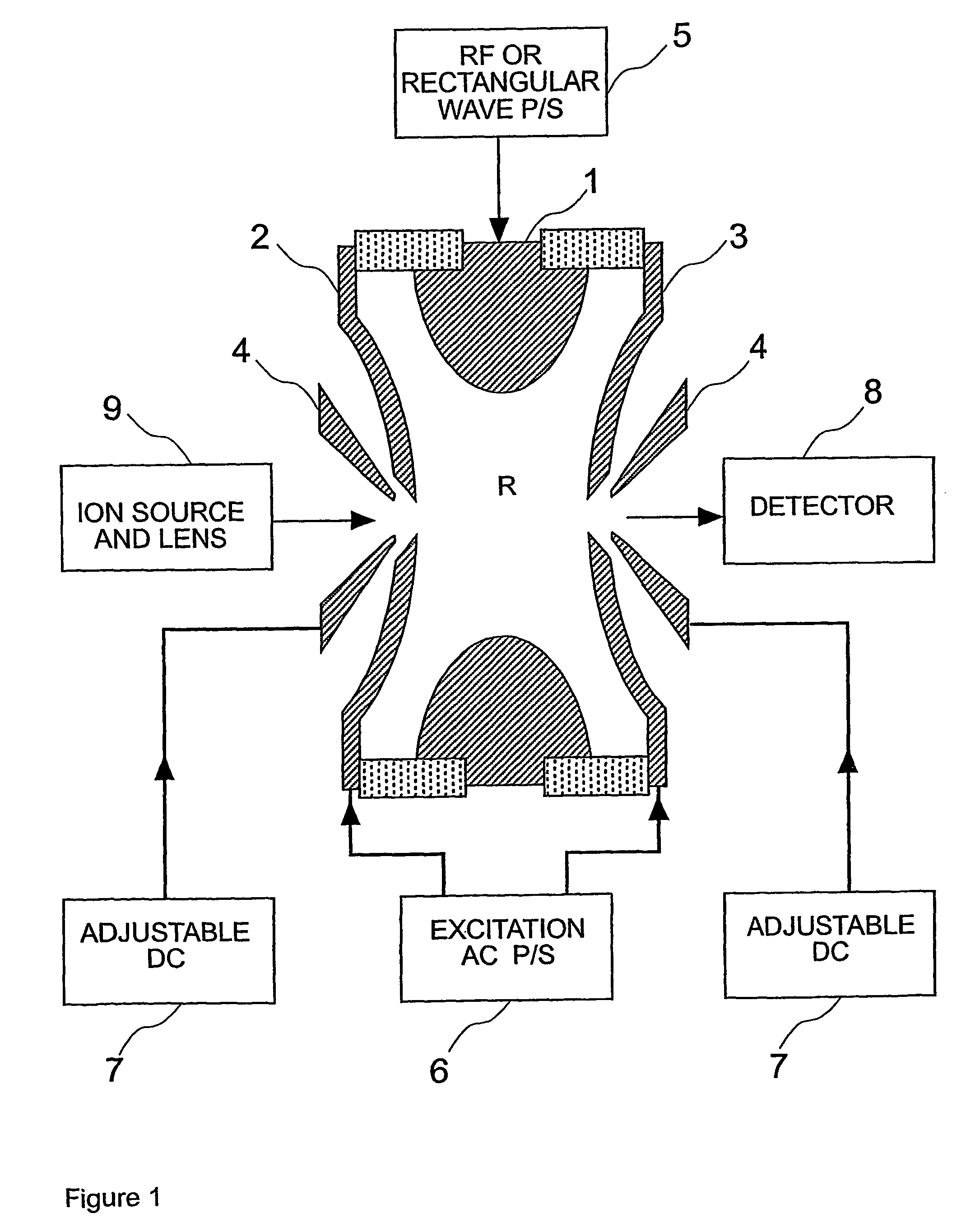
Quadrupole ion trap with switchable multipole fractions
InactiveUSRE36906E1Great massSwitch over the various operating states quicklyStability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationIon trap mass spectrometrySymmetrical components
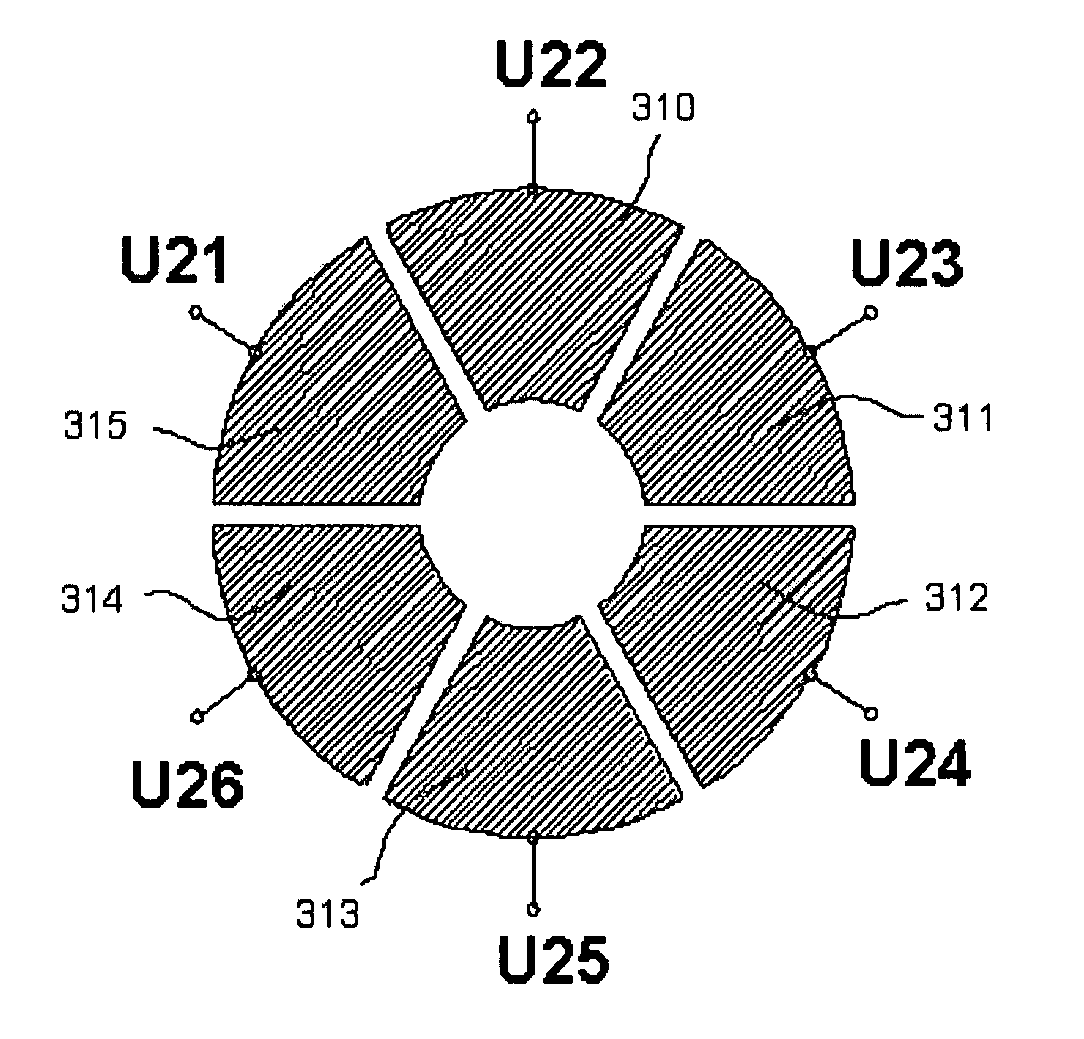
An ion trap is provided in which higher multipole field fractions can be switched on and off and, in addition, can be electrically tuned. Specifically, the electrodes of an ideally shaped ion trap are divided into rotationally symmetrical component electrodes positioned facing the interior of the ion trap on a hyperboloidal surface with rotationally symmetry.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH
Ion trap
InactiveUS6911651B2Stability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationIon trap mass spectrometryElectron injection
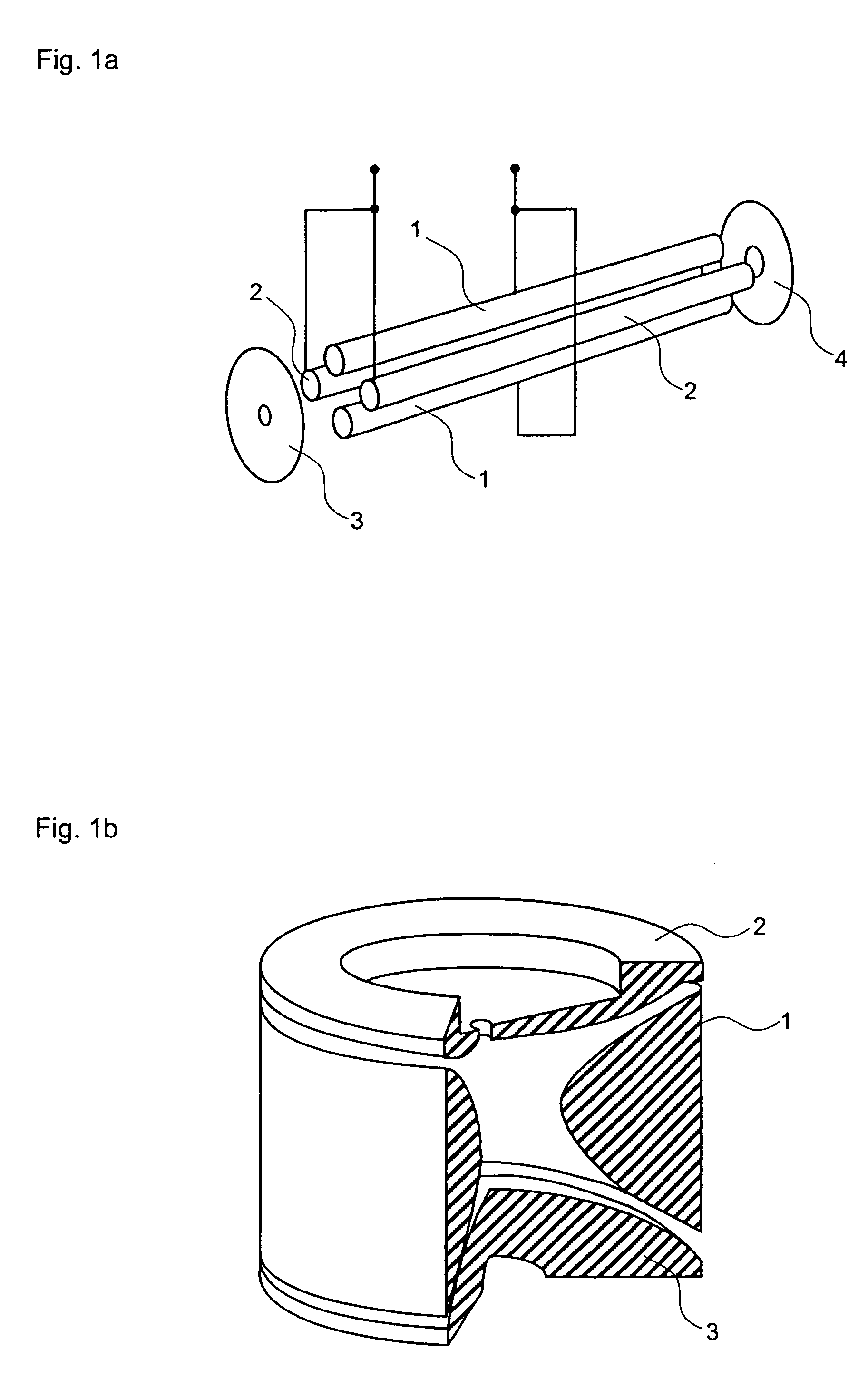
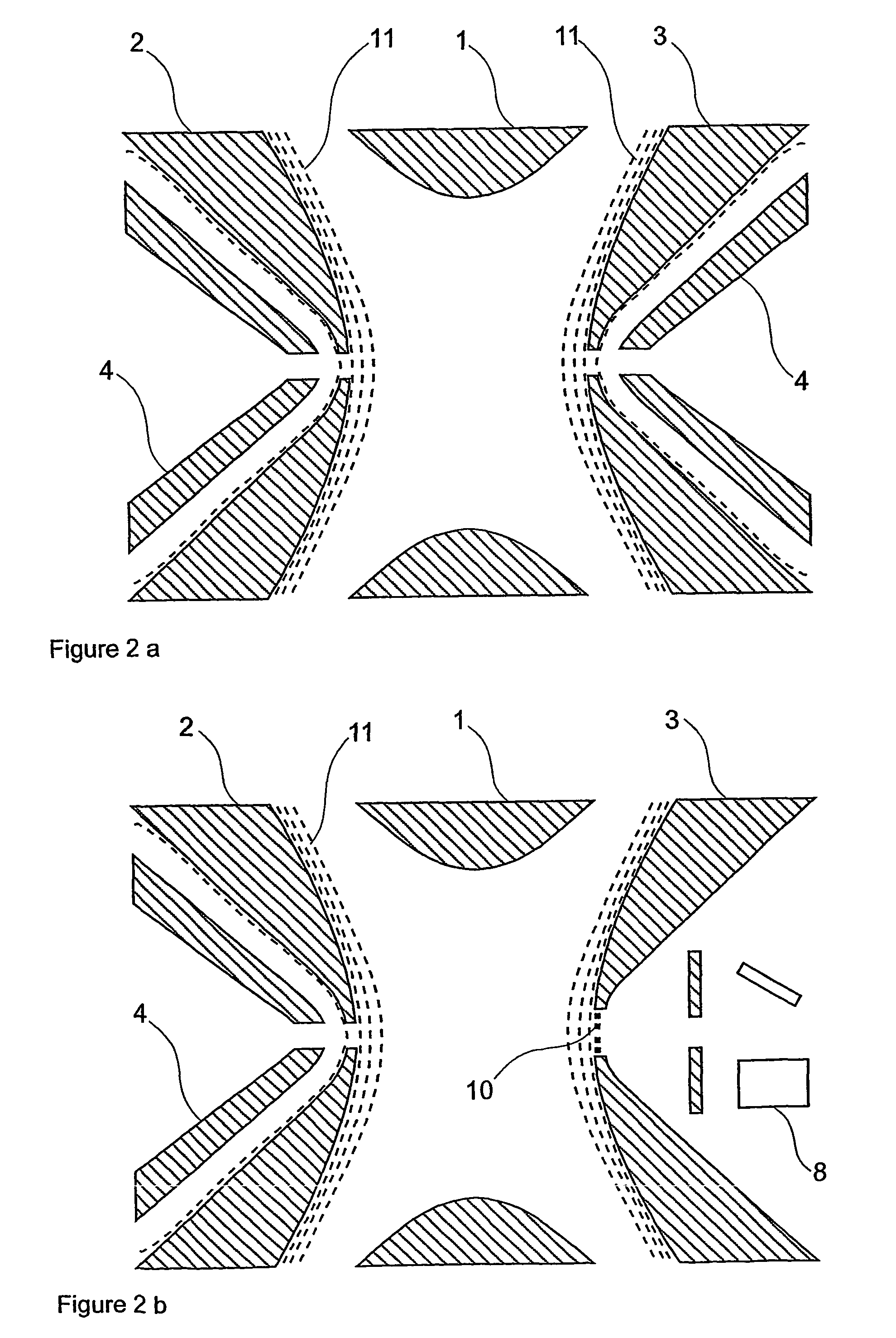
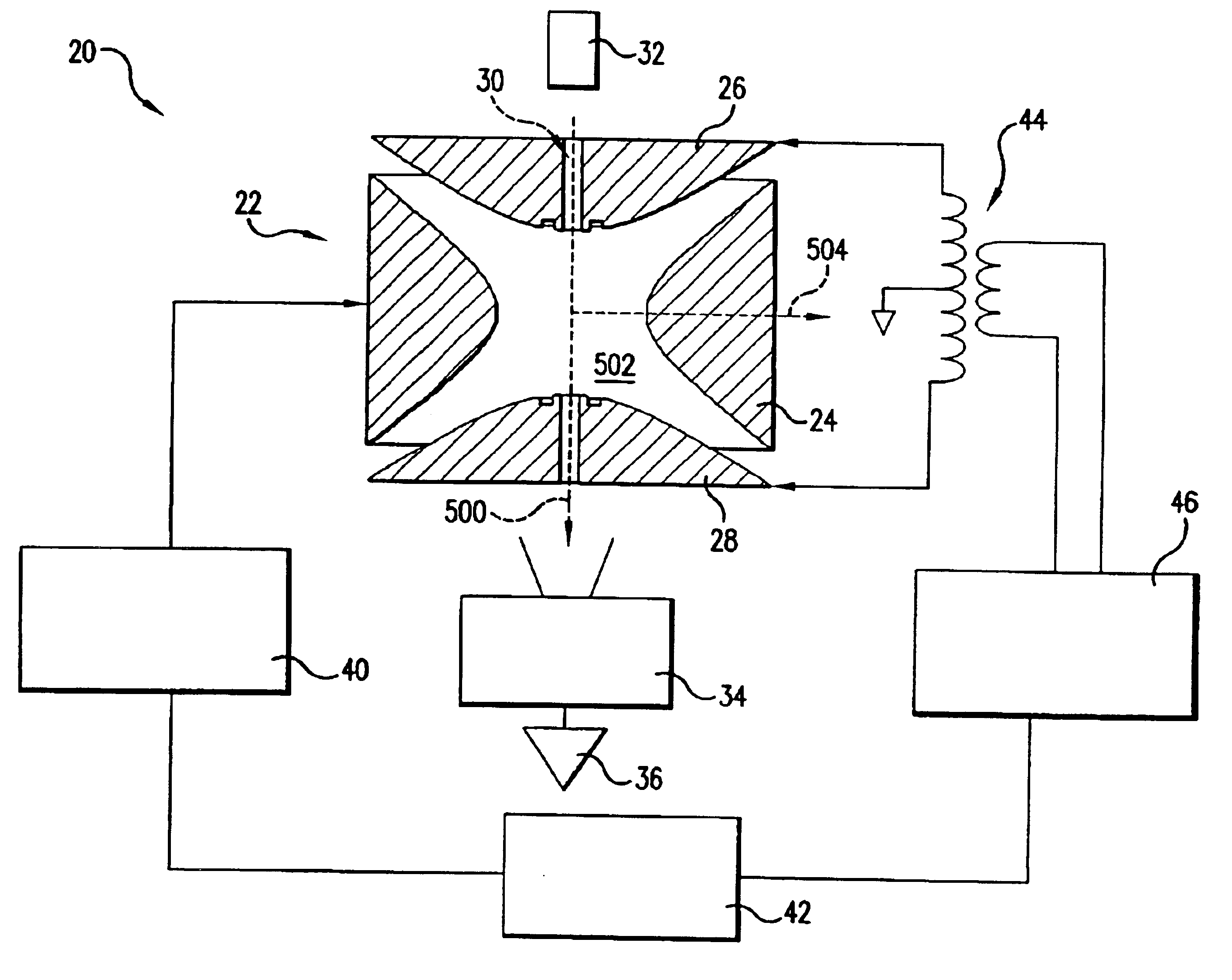
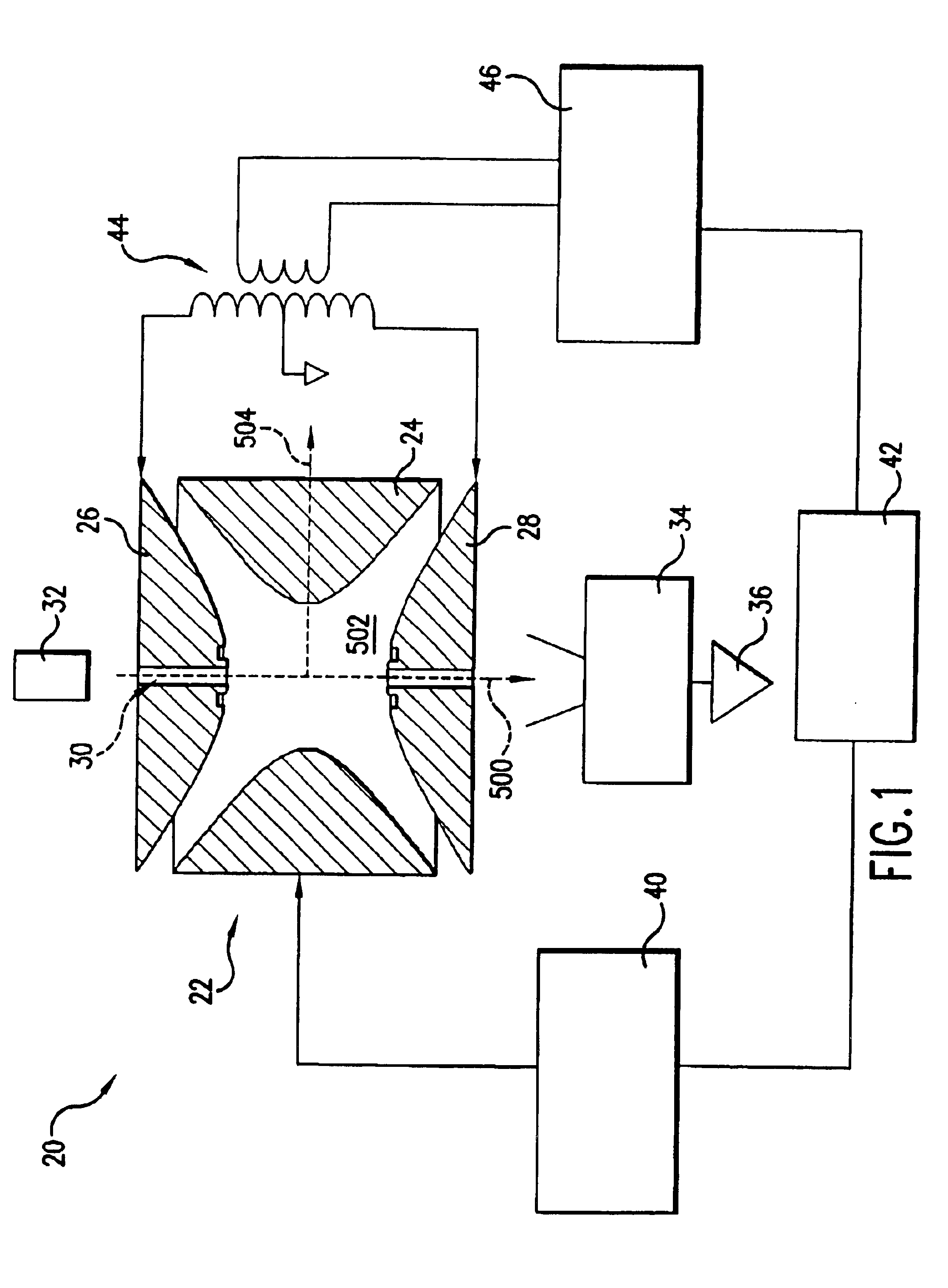
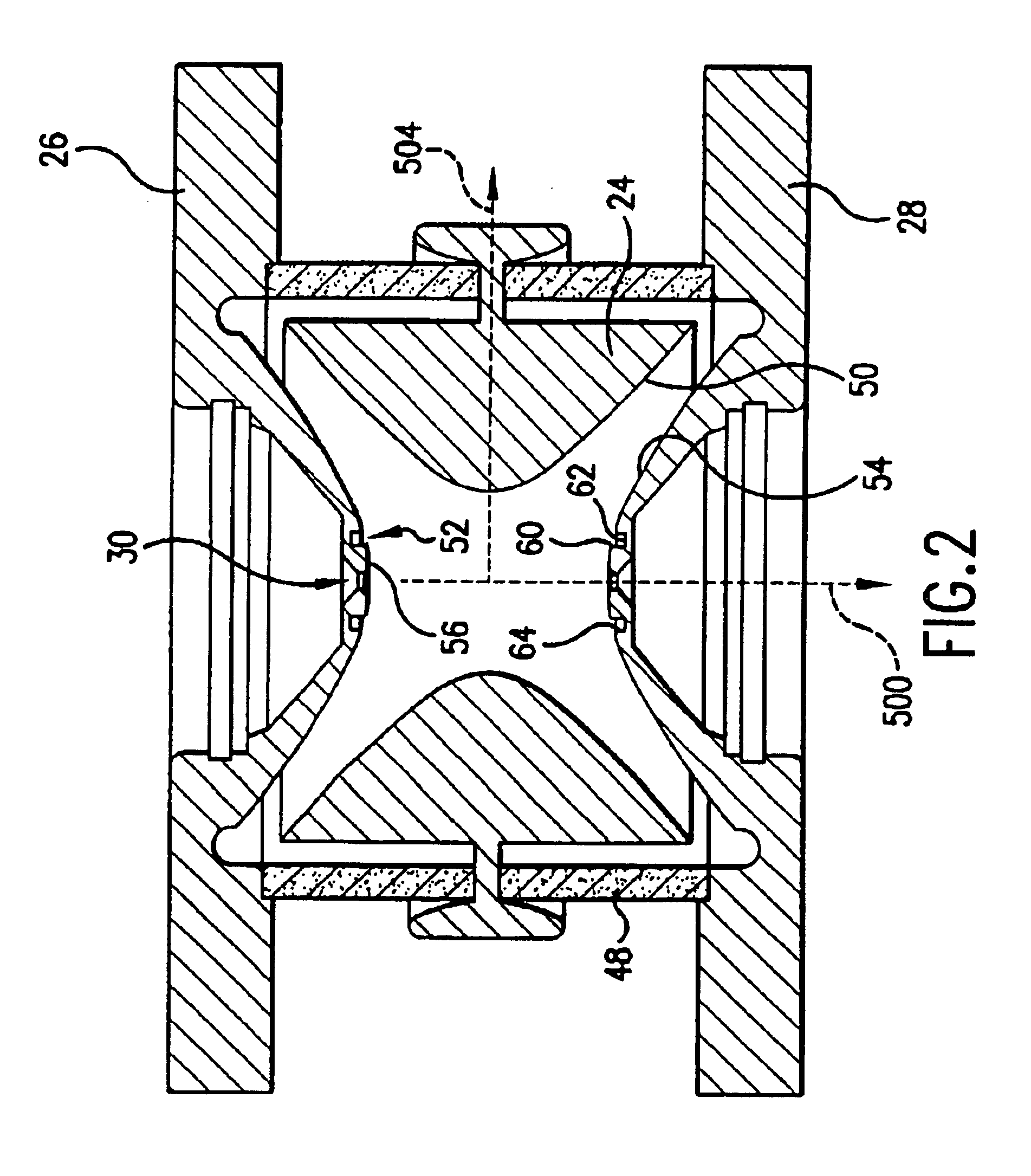
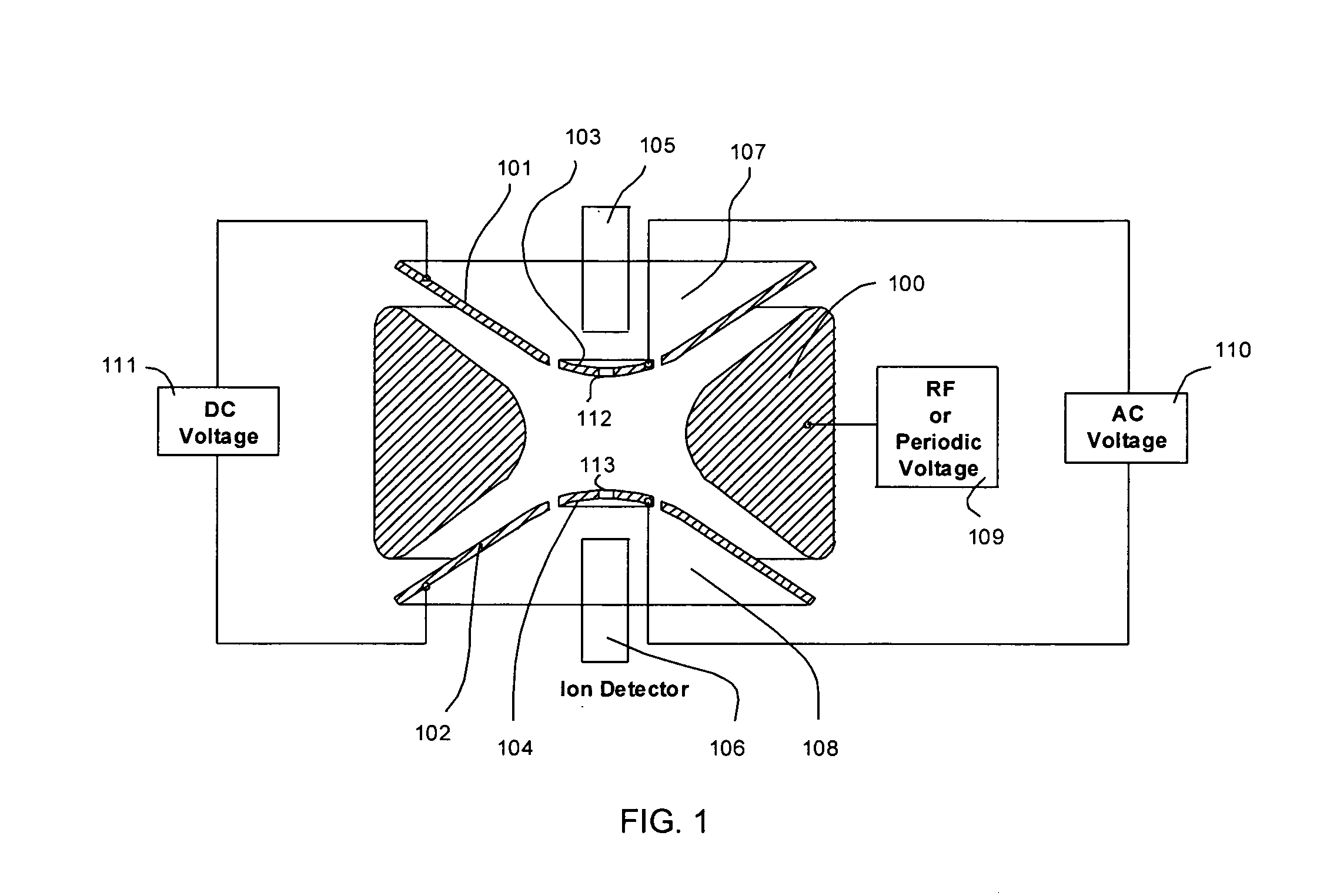
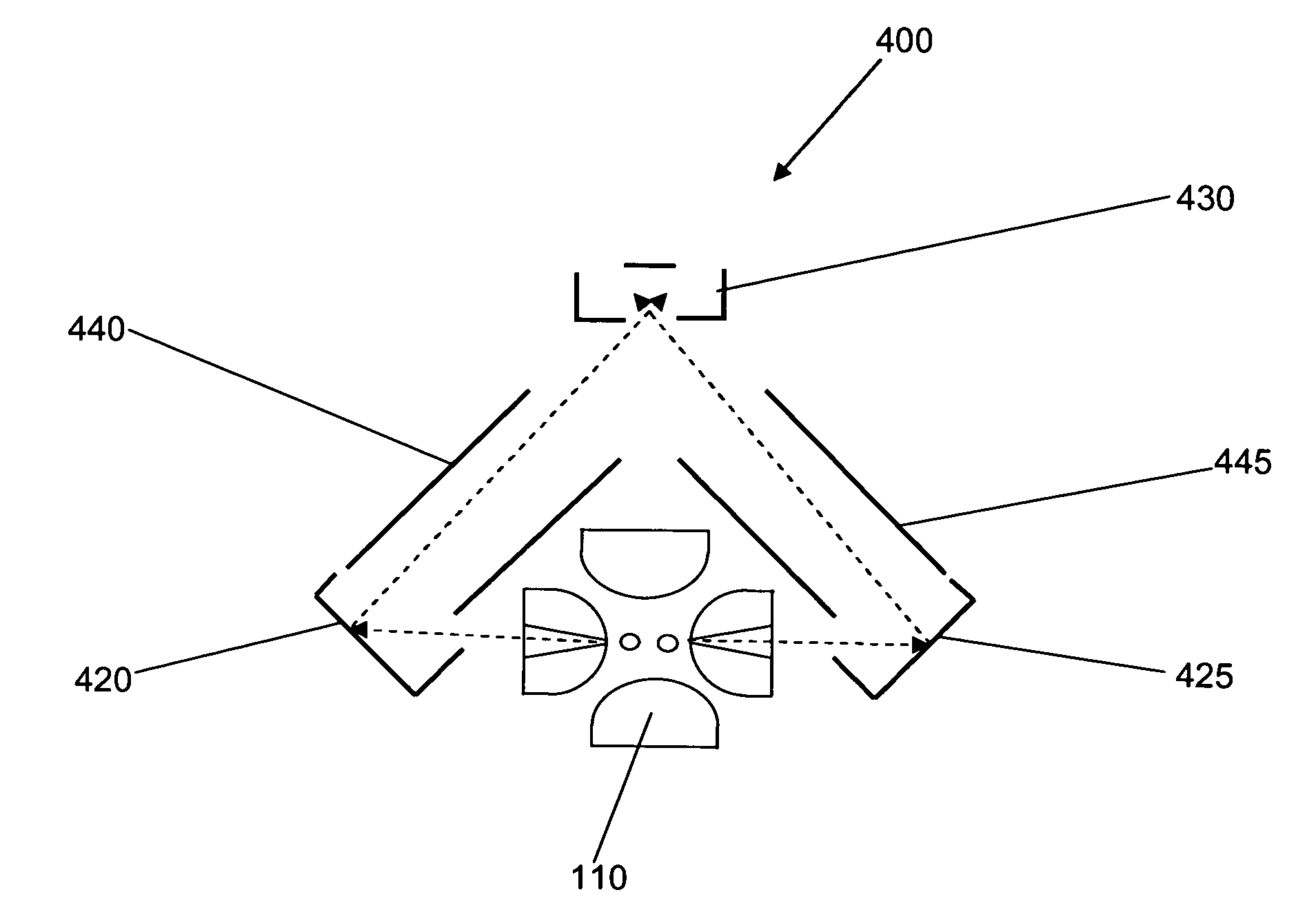
There is provided a quadruple ion trap (22) of the type including a ring electrode (24) and first and second end cap electrodes (26, 28), which define a trapping volume. The end cap electrodes (26, 28) include central apertures (30) for the injection of ions or electrons into the trapping volume and for the ejection of stored ions during the analysis of a sample. Field faults in the RF trapping field are compensated by addition of a concentric recess or depression in the surface of at least one end cap (26, 28) around the aperture (30). There is also provided an ion trap mass spectrometer employing the ion trap.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
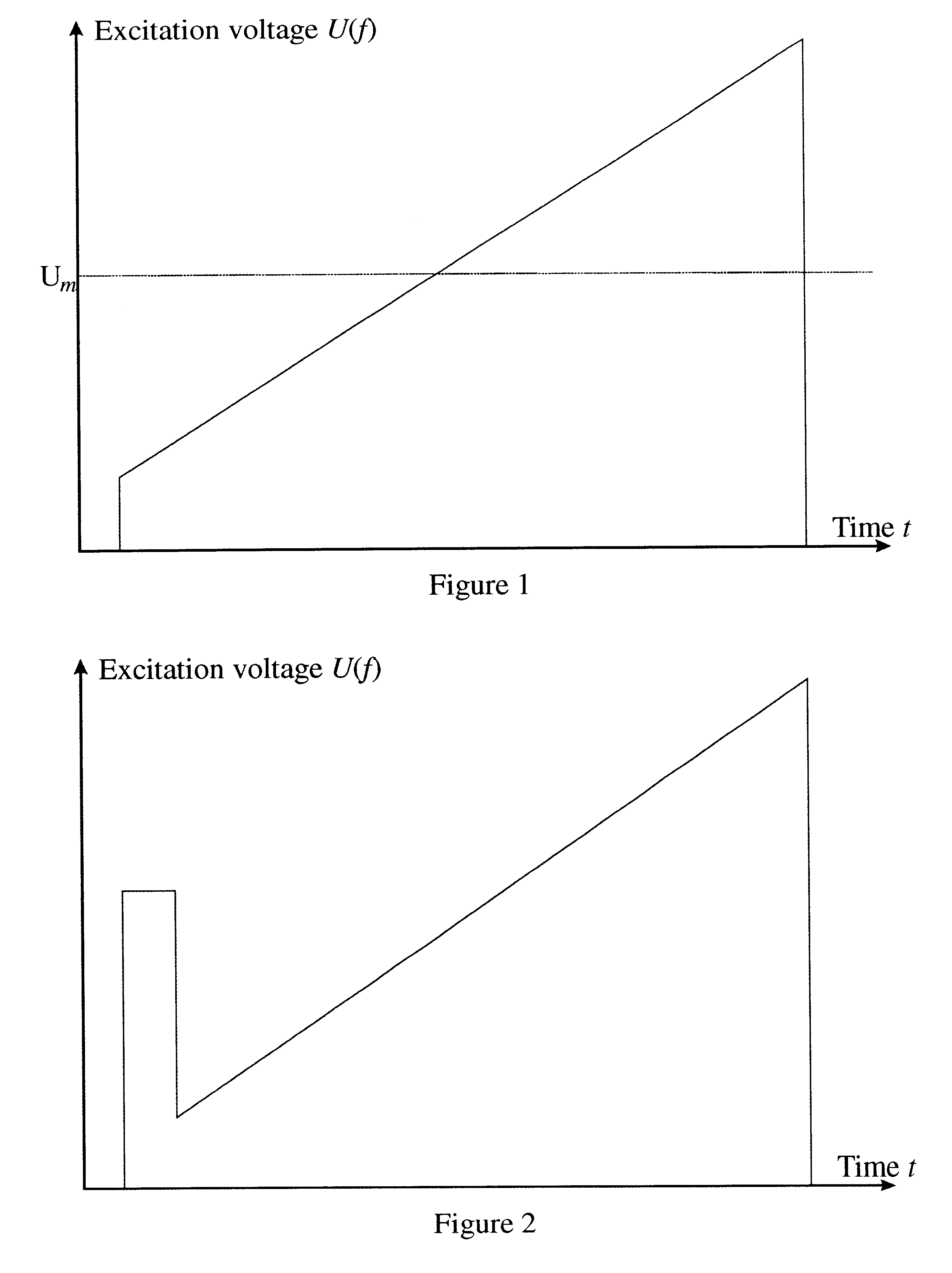
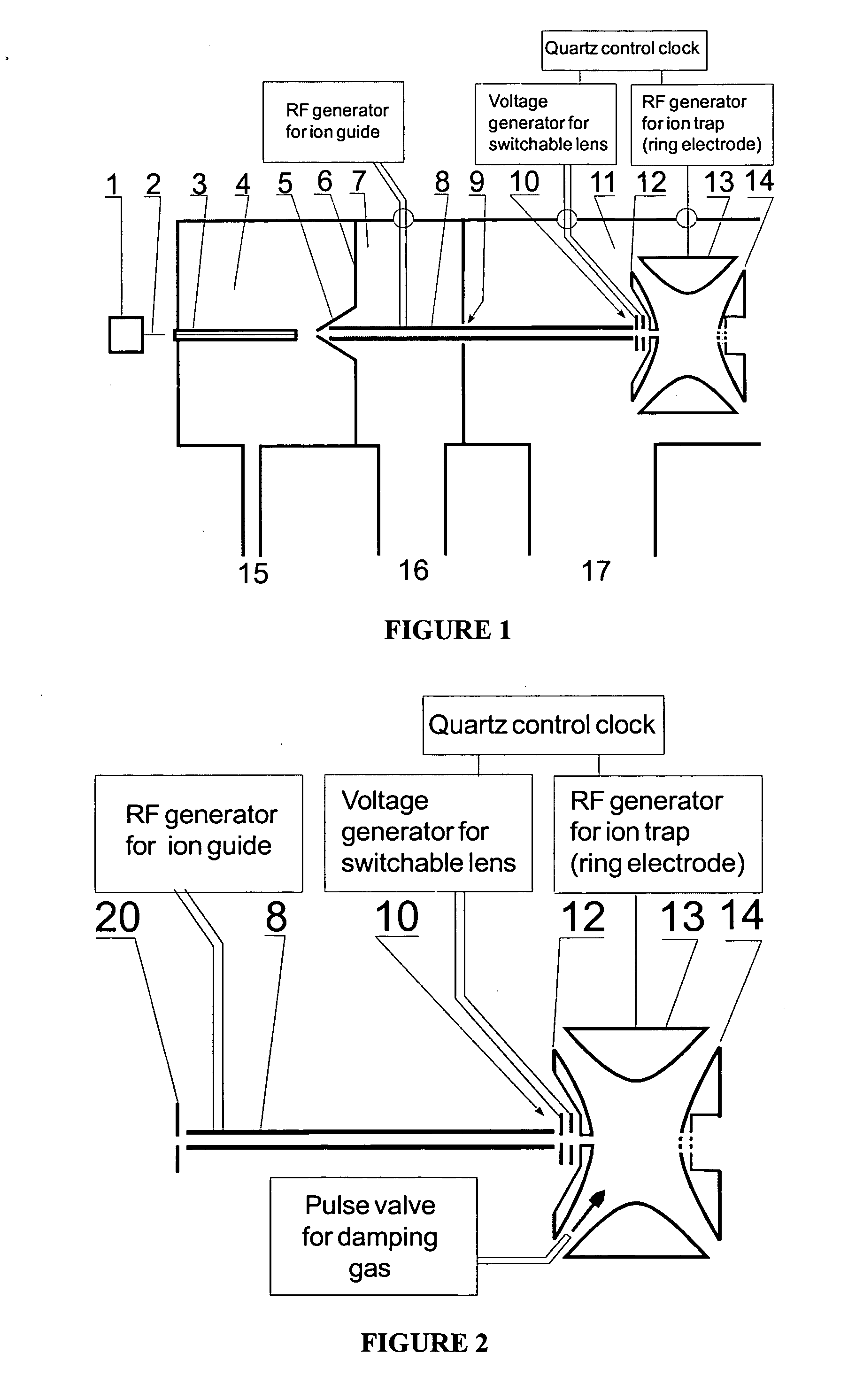
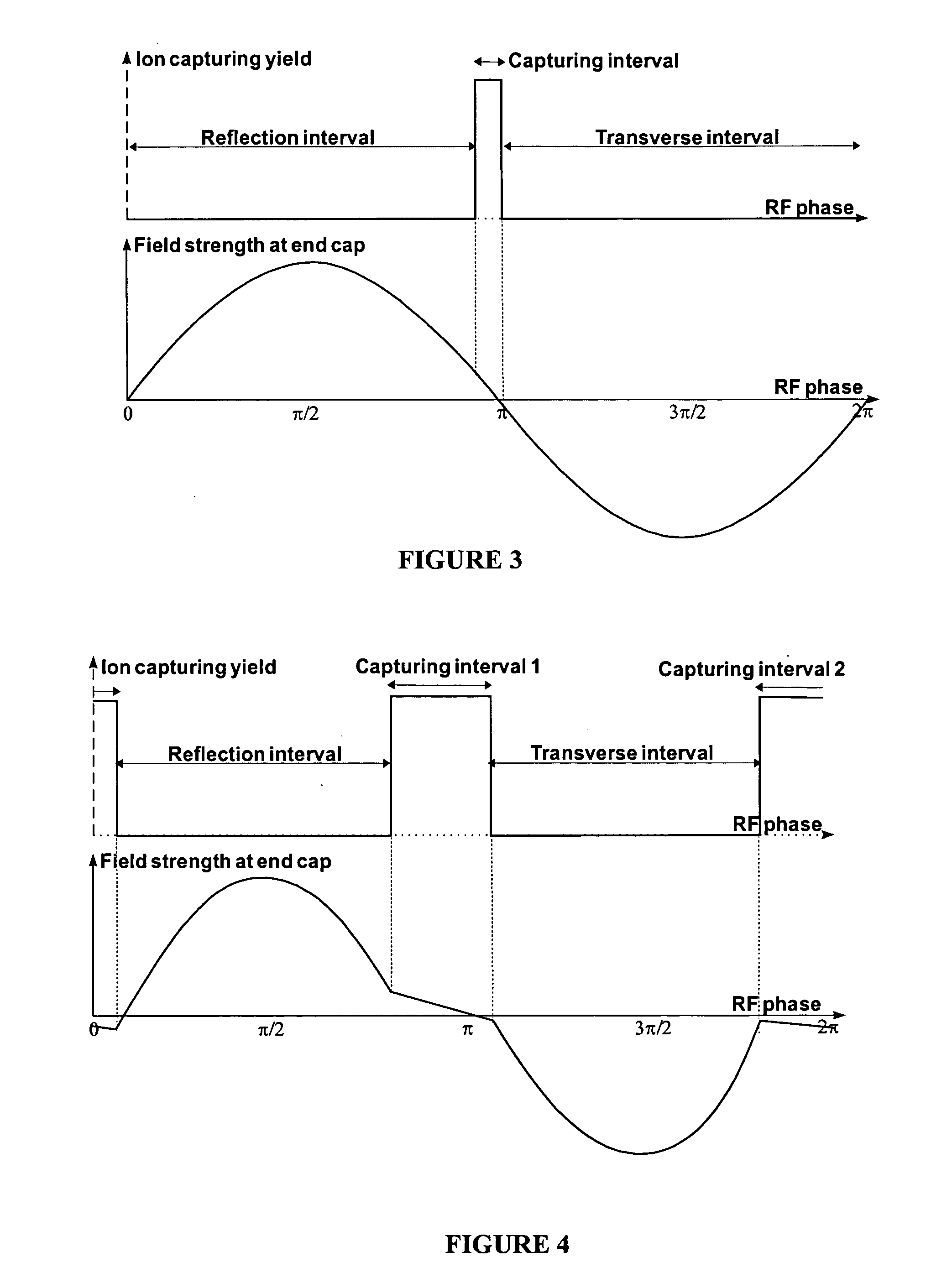
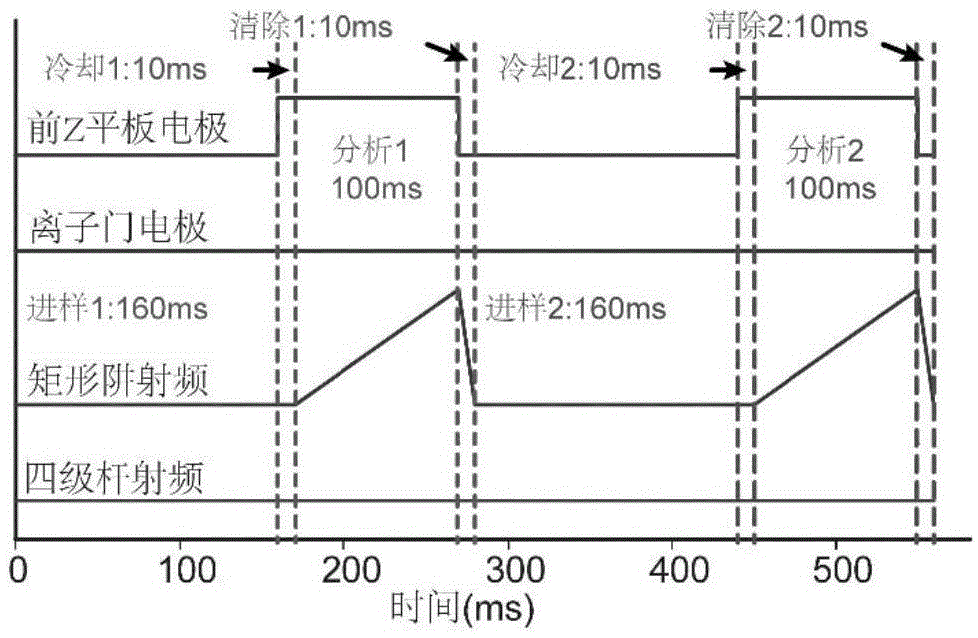
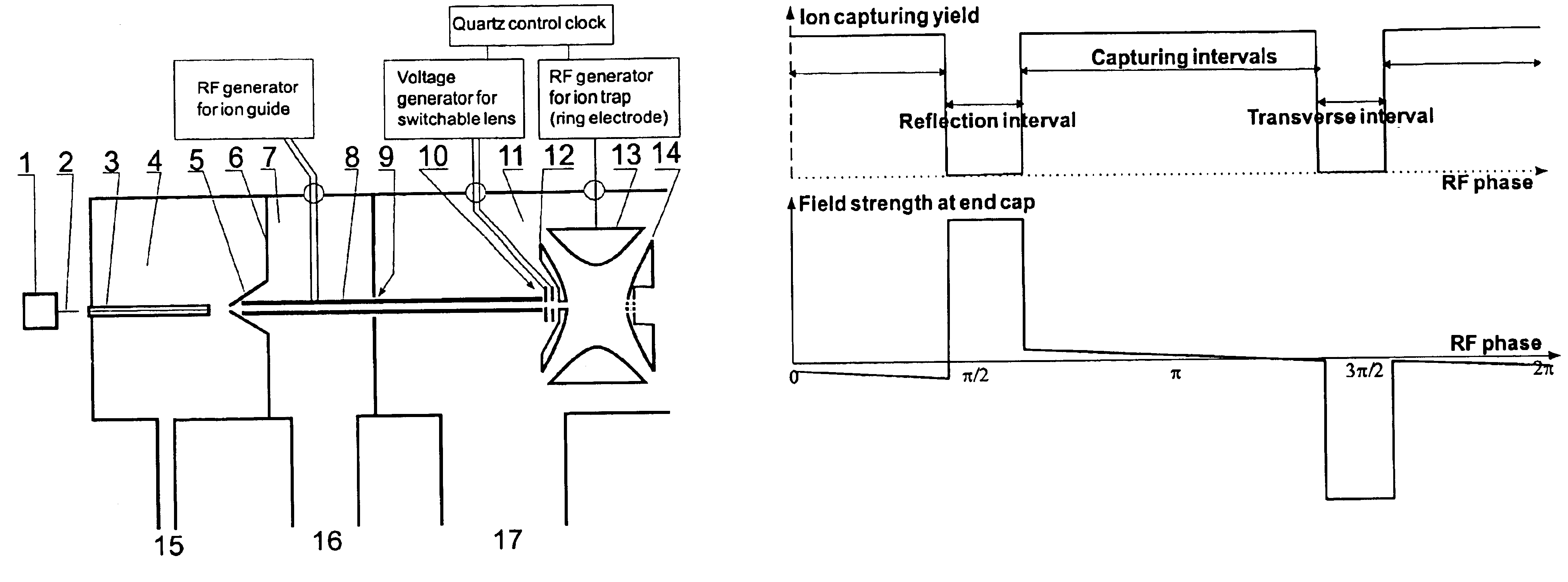
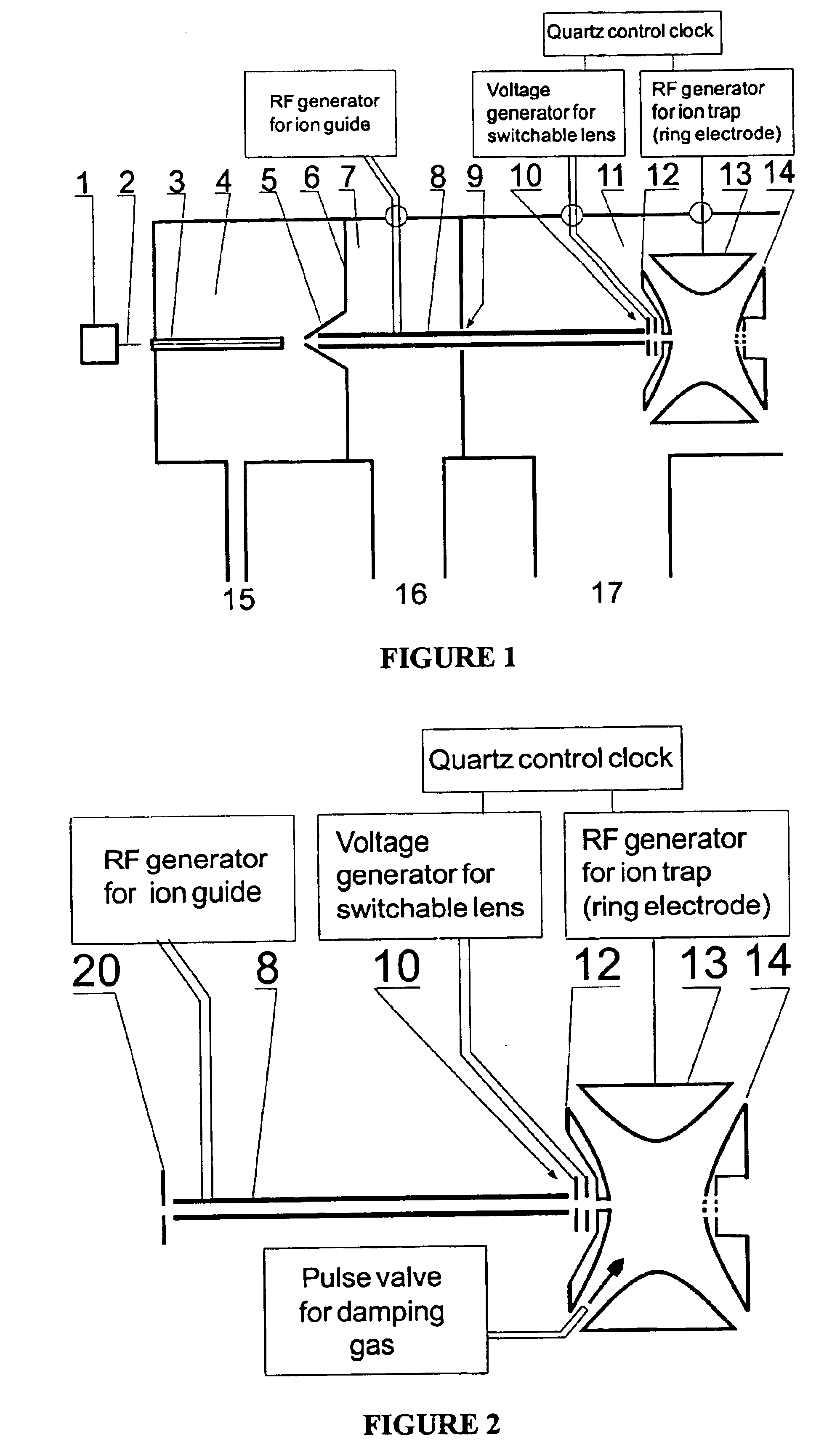
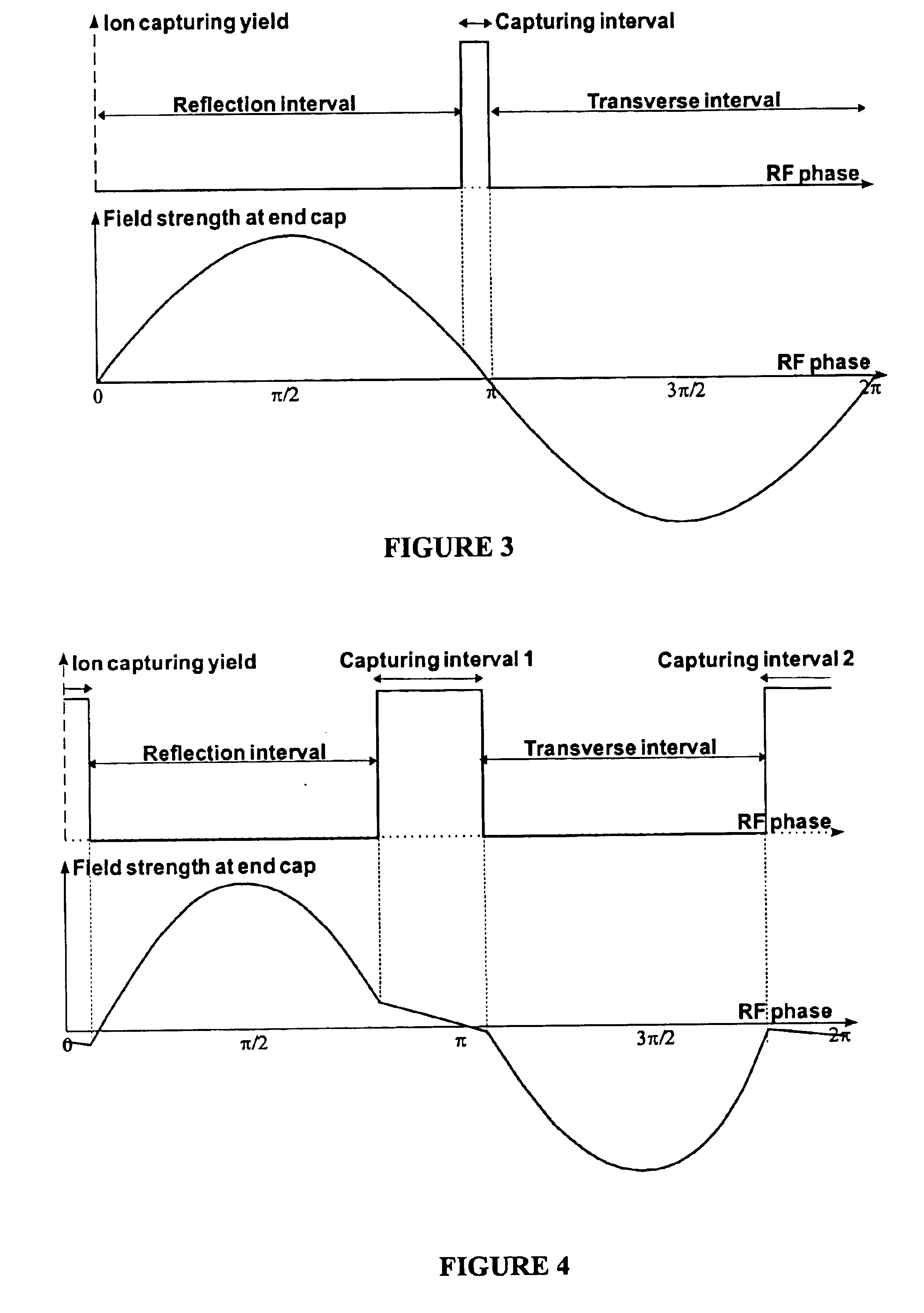
Method and device for the capture of ions in quadrupole ion traps
ActiveUS20050023461A1Increase productionWeaken energyStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAtomic physicsVoltage
The invention relates to methods and devices for the effective capturing of externally generated ions in an RF operated quadrupole ion trap. The invention involves applying a voltage consisting of positive and negative pulses, instead of a sinusoidal RF voltage, during the capturing process, with capturing intervals between each pulse in which the voltage is low.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
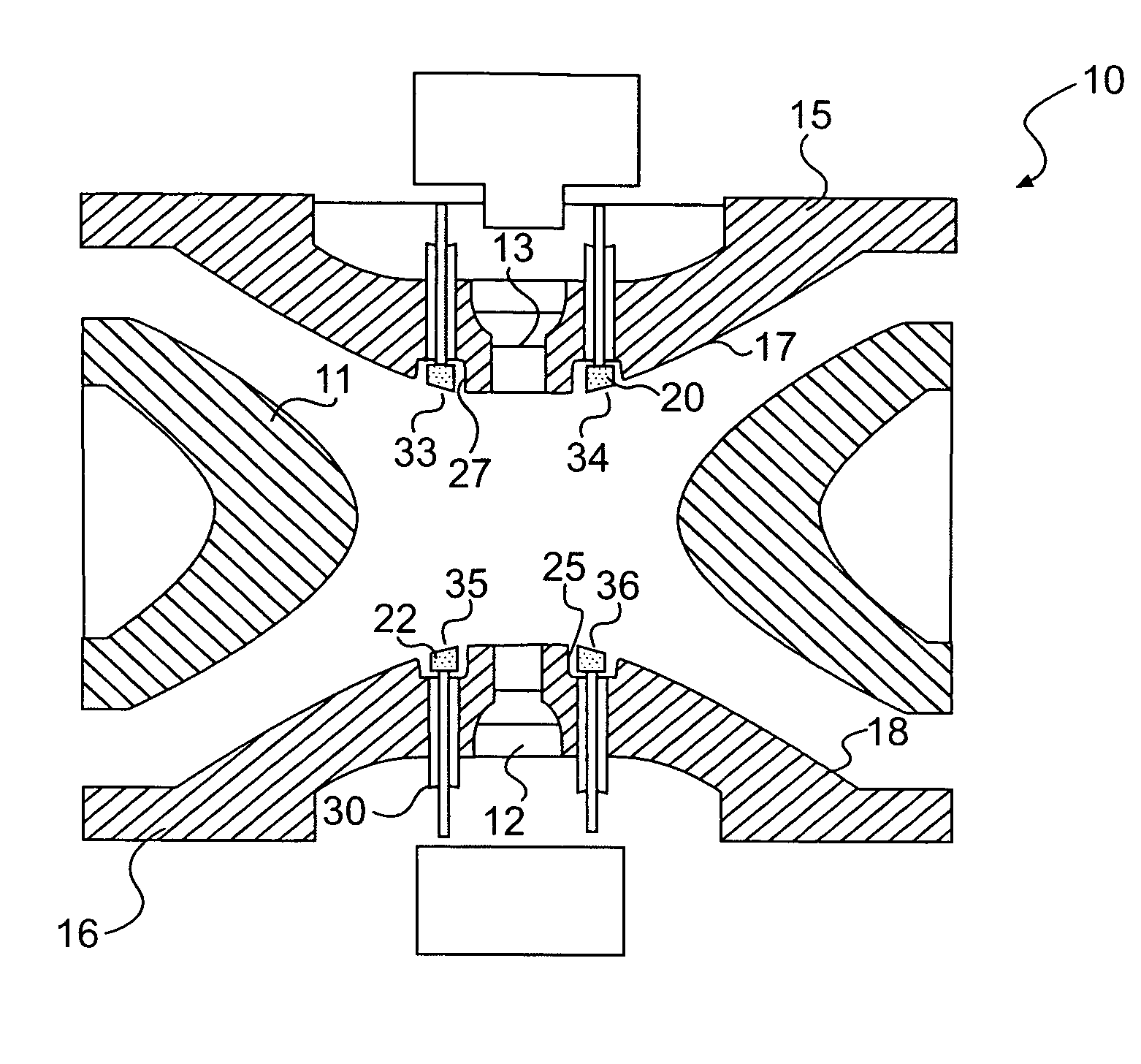
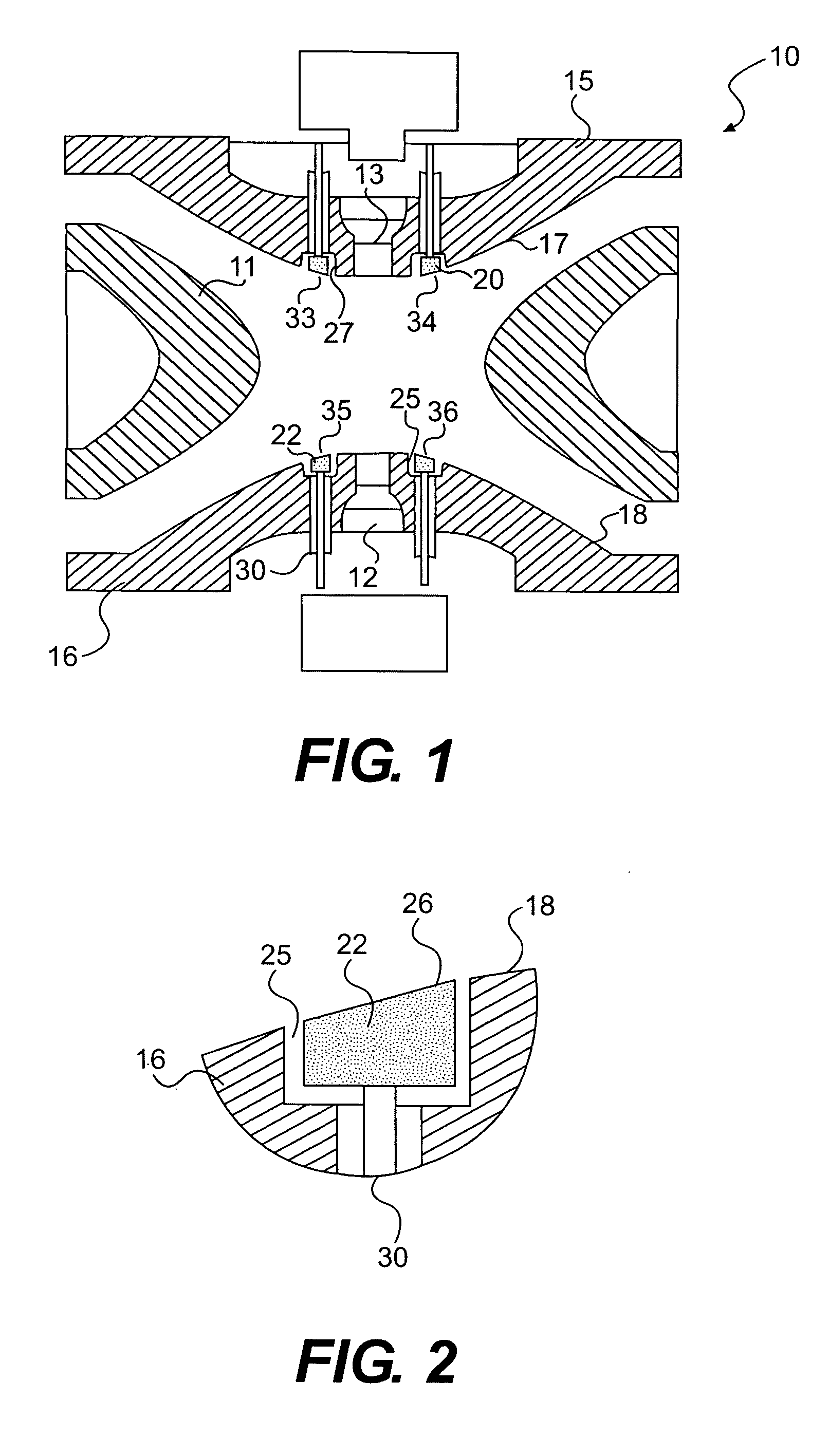
Ion trap with built-in field-modifying electrodes and method of operation
ActiveUS7279681B2Stability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationIon trap mass spectrometryQuadrupole field
An apparatus and method for correcting deviations in a quadrupole field in a quadrupole ion trap is provided. More specifically the invention provides for correction electrodes positioned in at least one primary quadrupole electrode and a method of using the correction electrodes to provide a field correction potential.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
An ion trap and a method for dissociating ions in an ion trap
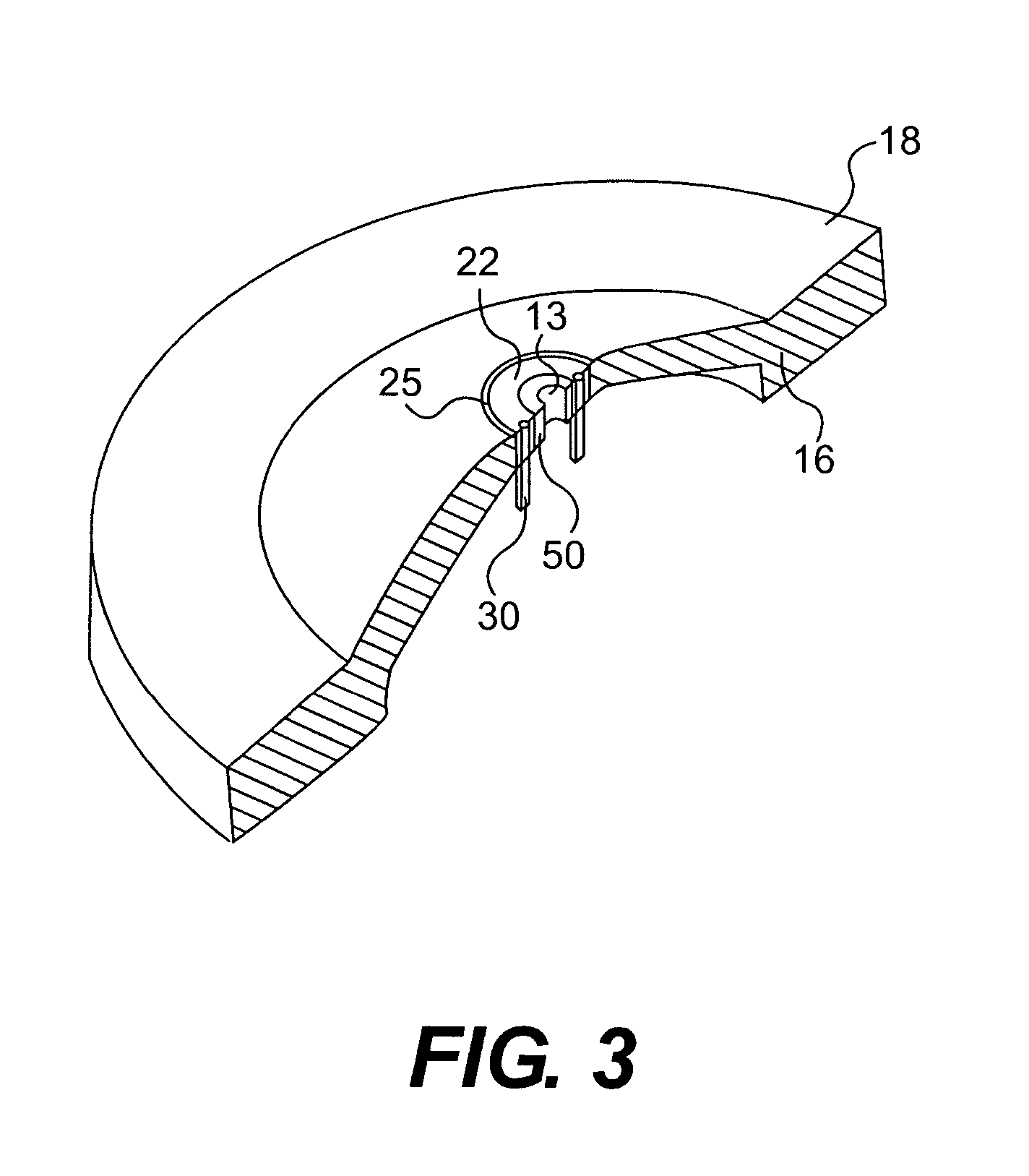
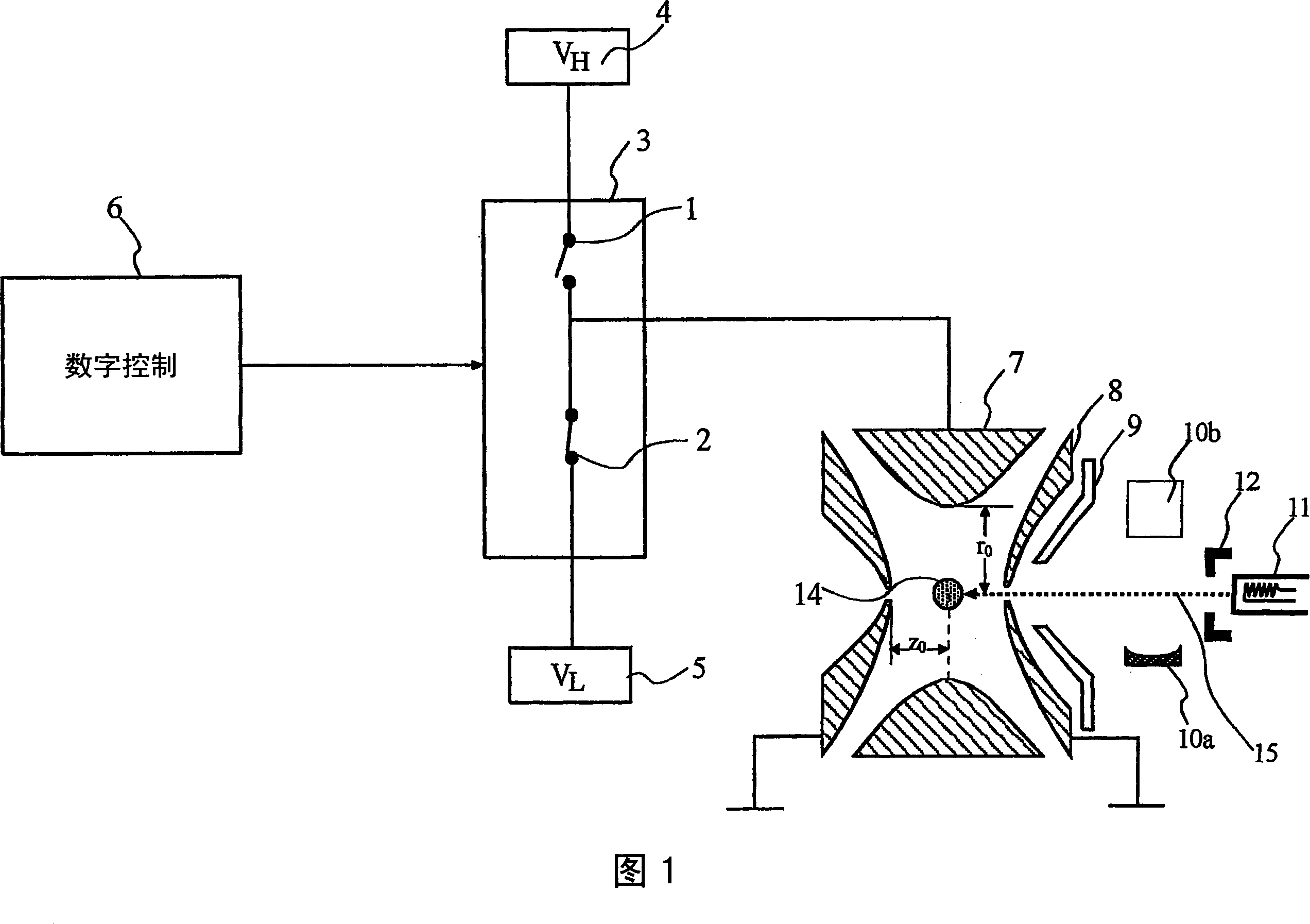
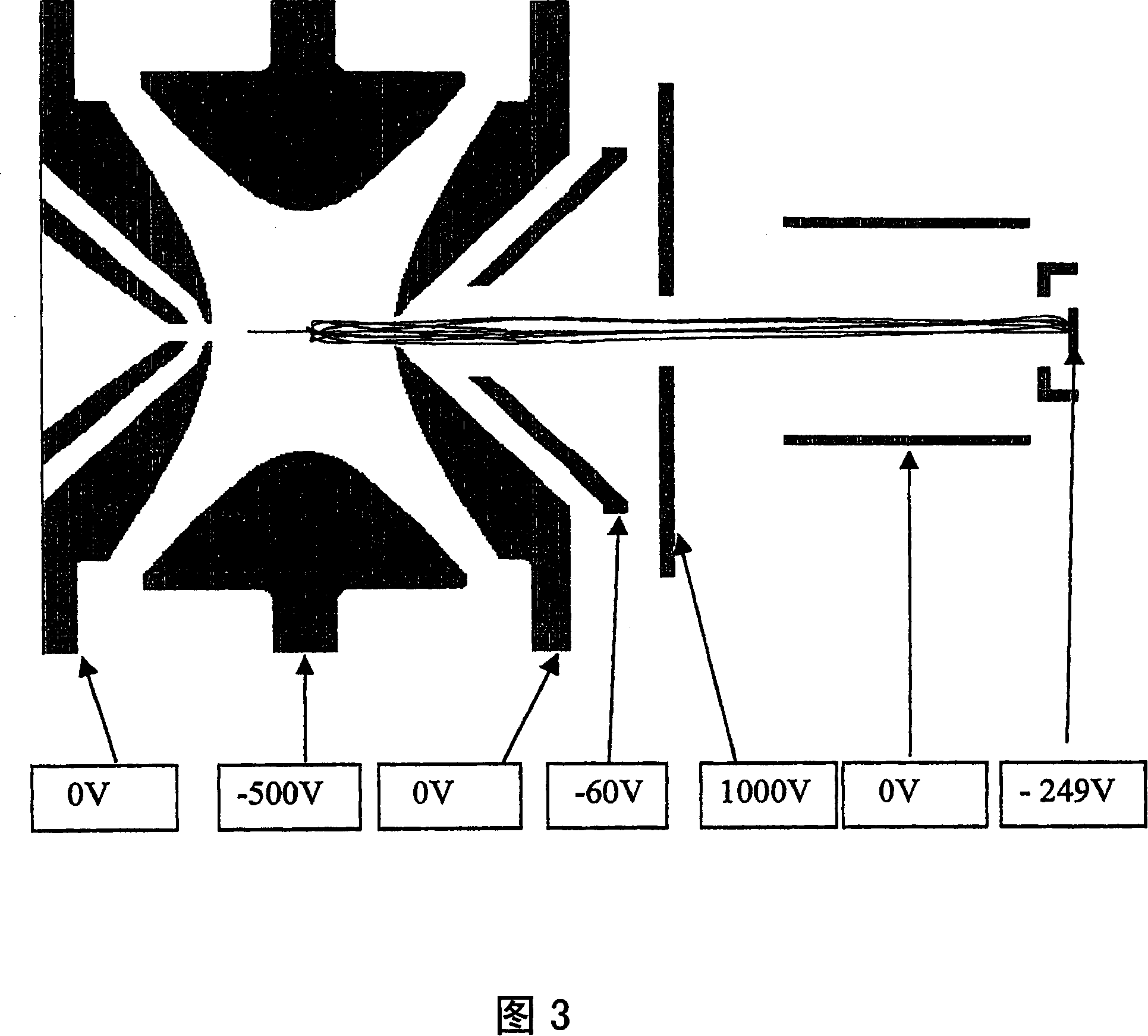
ActiveCN1922711AReduce electric field strengthRelieve pressureStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersIon trap mass spectrometryElectron injection
A quadrupole ion trap includes a switch (3) for switching a trapping voltage between discrete voltage levels VH, VL. This creates a digital trapping field for trapping precursor ions and product ions in a trapping region of the ion trap. A gating voltage is applied to a gate electrode (12) to control injection of source electrons into the ion trap. Application of the gating voltage is synchronised with the switching so that electrons are injected into the trapping region while the trapping voltage is at a selected one of the voltage levels and can reach the trapping region with a kinetic energy suitable for electron capture dissociation to take place.
Owner:岛津欧州研究所
Method for dissociating ions using a quadrupole ion trap device
InactiveUS6965106B2Stability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIon trap mass spectrometryQuadrupole
A method of trapping ions using a quadrupole ion trap device includes applying quadrupole excitation to trapped precursor ions causing them to be driven into the ring electrode where they undergo surface induced dissociation. The resultant product ions are then trapped within the ion trap device.
Owner:SHIMADZU RES LAB EURO
Mass spectrometer
InactiveUS7102126B2Increase capacityIncrease volumeTime-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationIon trap mass spectrometryTrapping
A mass spectrometer is disclosed wherein a relatively energetic pulse of ions having a relatively narrow spread of mass to charge ratios are ejected from a quadrupole ion trap and received in an ion trap upstream of a Time of Flight mass analyser. The ions are collisionally cooled within the ion trap and are pulsed out of the ion trap and into an extraction region of the Time of Flight mass analyser without substantially exciting the ions. This enables improved operation with the Time of Flight mass analyser. According to another embodiment, parent ions are fragmented and the resulting fragment ions are stored in two ion traps having different low mass cut-offs. The trapping system enables MS / MS experiments to be performed with a very high duty cycle.
Owner:MICROMASS UK LTD
Mass spectrometric system
ActiveUS20110315868A1Improve throughputImprove signal-to-noise ratioStability-of-path spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsData informationMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
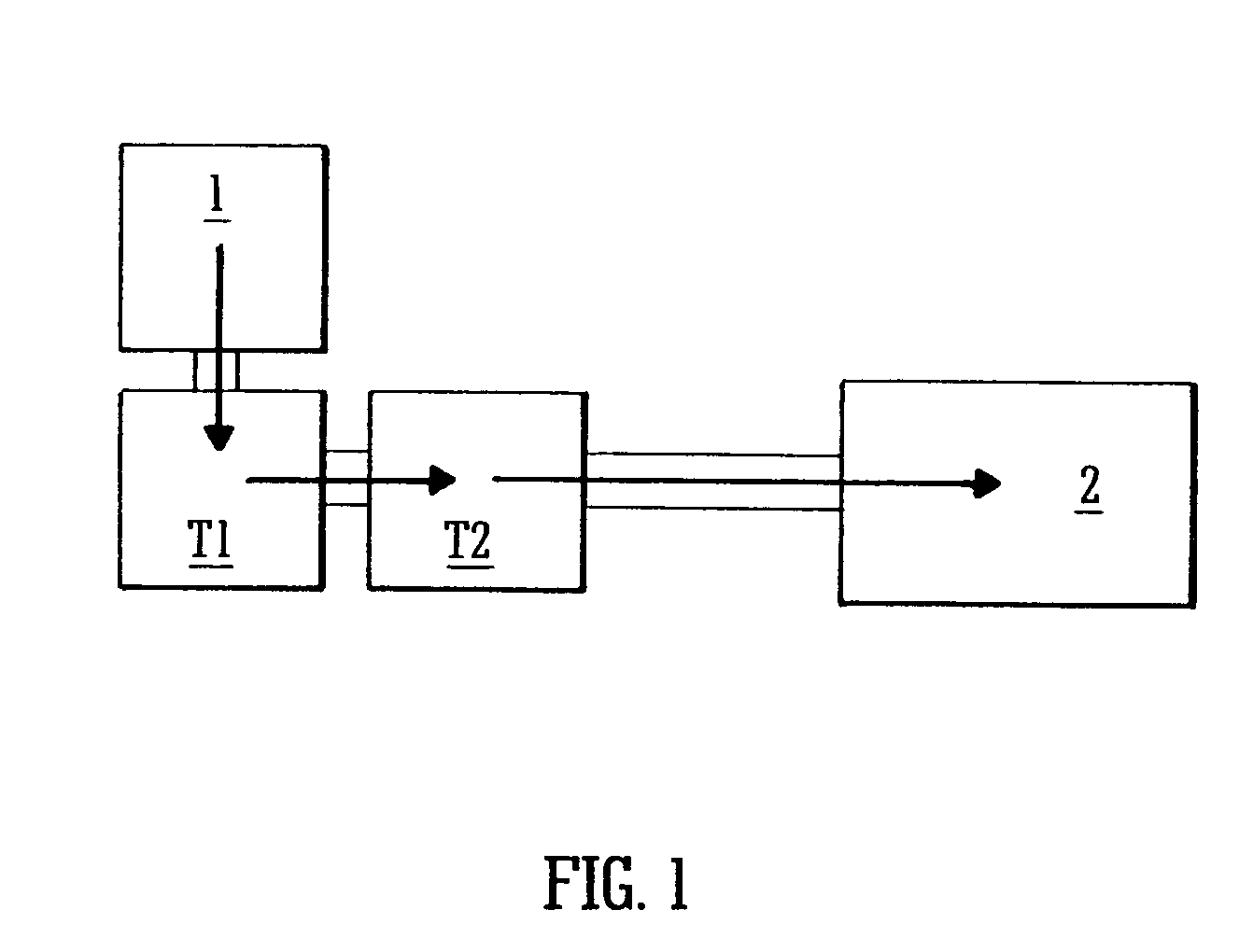
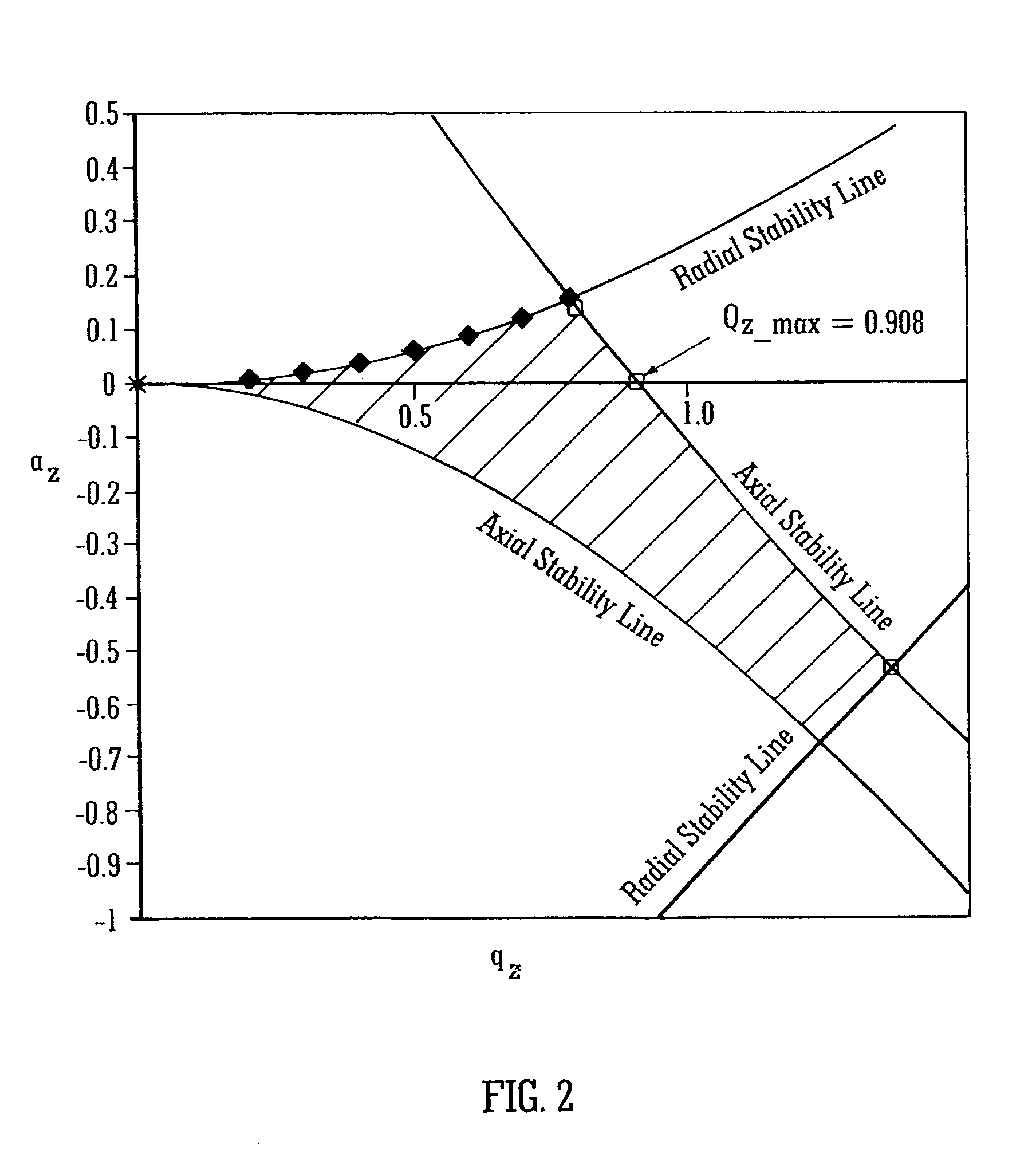
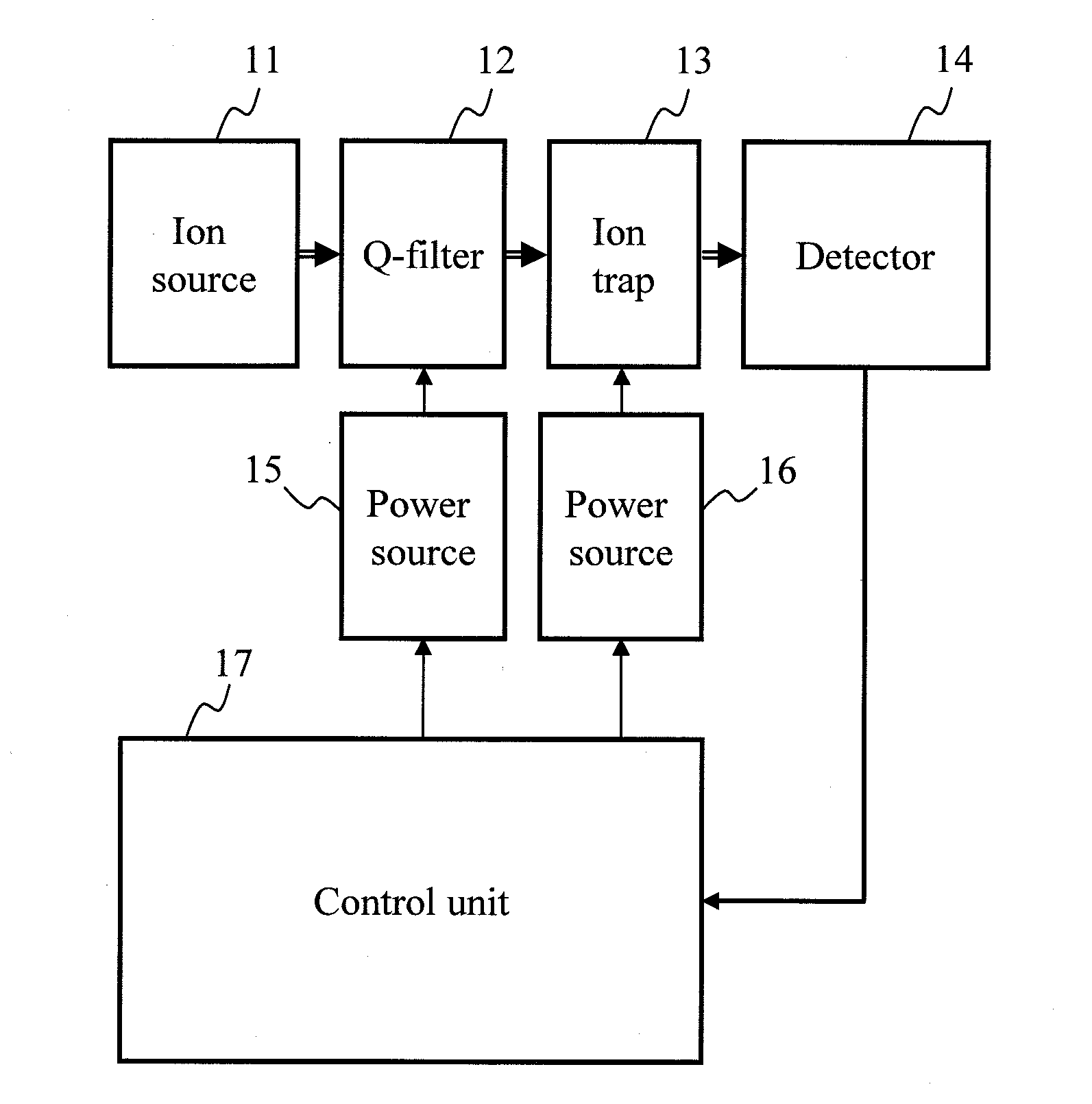
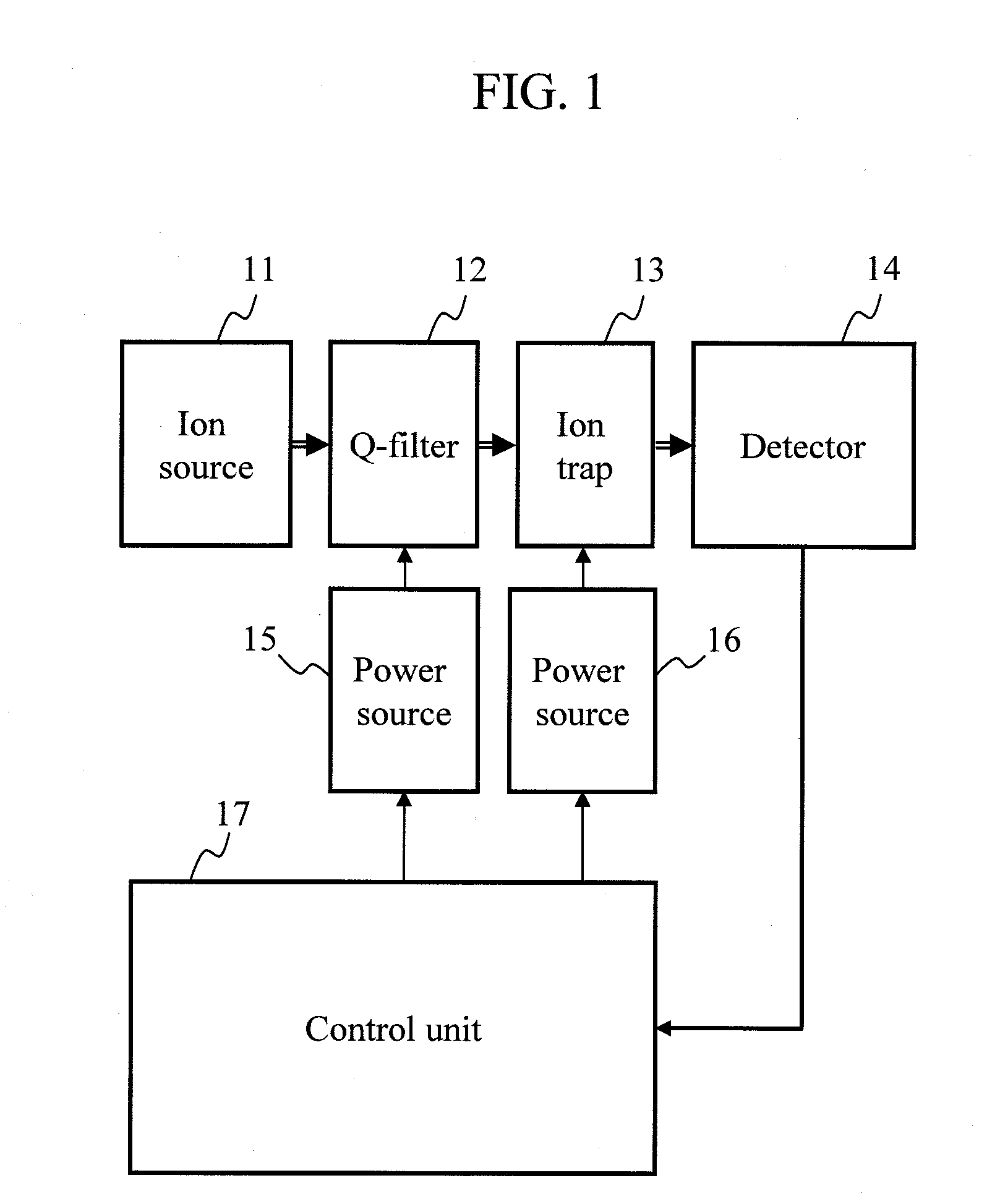
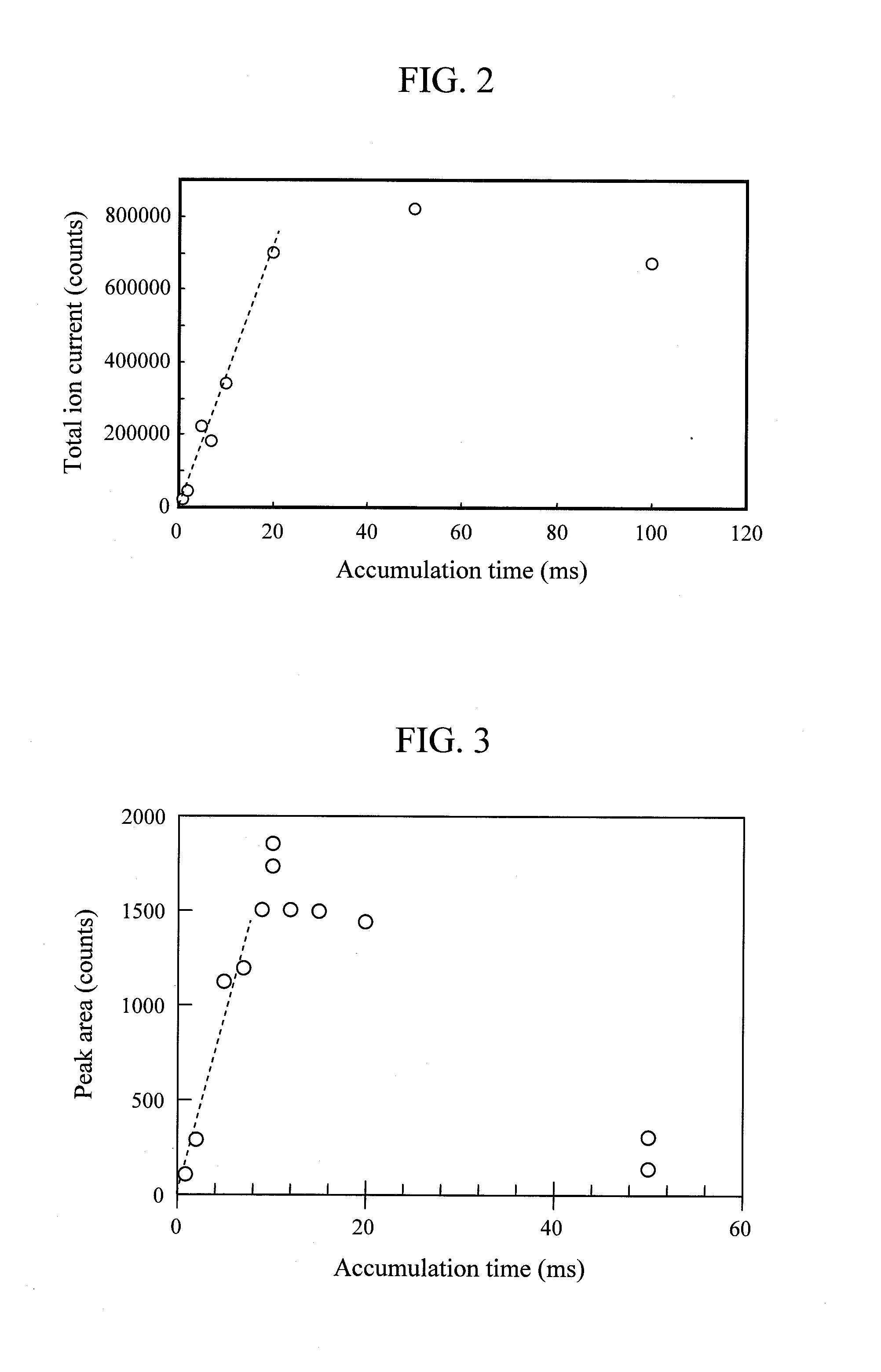
A mass spectrometric device of the present invention includes a quadrupole filter (12) located upstream of a quadrupole ion trap (13) and configured to transmit ions in a predetermined filter range, and determines the filter range of the quadrupole filter (12) such that accumulation time for the ions in the quadrupole ion trap (13) is maximized. The accumulation time for the ions is determined based on mass spectrometry data information. With this configuration, the present invention produces advantageous effects of improving analysis throughput and an S / N ratio in an analysis of a minor sample component mixed in various accompanying components by using the mass spectrometric device using the quadrupole ion trap.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Ion fragmentation in RF ion traps by electron capture with magnetic field
InactiveUS20050017165A1Prevent ionizationStability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationIon trap mass spectrometryElectron capture
The invention relates to a method and device for the fragmentation of macromolecules, preferably biomolecules, by electron capture in RF quadrupole ion trap mass spectrometers according to Wolfgang Paul. The invention comprises steering a beam of low energy electrons through a magnetic guide field exactly into an ion cloud in the center of the ion trap.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH
Methods and apparatus for switching ion trap to operate between three-dimensional and two-dimensional mode
InactiveUS6998610B2Stability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersPhysicsQuadrupole ion trap
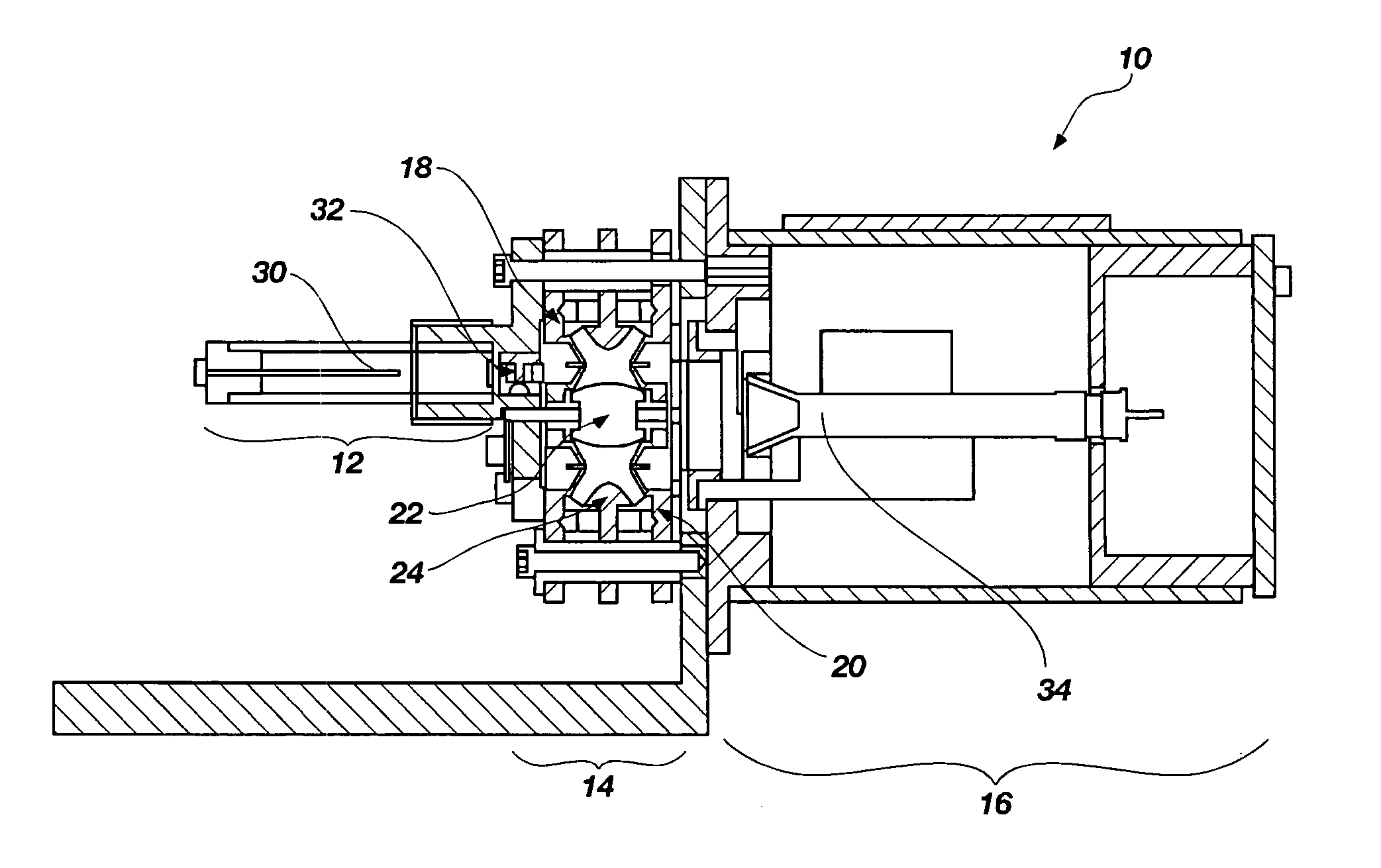
An ion trap comprises a three-dimensional rotationally symmetric ring electrode and two cap electrodes, the ring electrode is divided, in parallel to its central axis, into a plurality of even number, equal or larger than four, of component electrodes. The component electrodes are electrically isolated from each other, the surfaces of the two cap electrodes face toward the inside of the ion trap. A mechanism is constructed and arranged for switching the ion trap to operate between a three-dimensional quadrupole ion trap mode and a two-dimensional linear ion trap mode.
Owner:WANG YANG
Miniature toroidal radio frequency ion trap mass analyzer
ActiveUS20120267523A1Easily interfaceSamples introduction/extractionMiniaturised spectrometersTrappingElectron multiplier
A scaled down version of a toroidal radio frequency (RF) ion trap mass analyzer operating with RF trapping voltages on the order of 1 kVp-p yet despite the reduced dimensions, retains roughly the same ion trapping volume as conventional 3D quadrupole ion traps, wherein the curved geometry enables construction of a compact mass analyzer and easy interface with conventional electron multipliers.
Owner:BRIGHAM YOUNG UNIV
System and method for implementing balanced RF fields in an ion trap device
ActiveUS20080067363A1Reduces non-linear field componentMinimalStability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationRf fieldDistortion
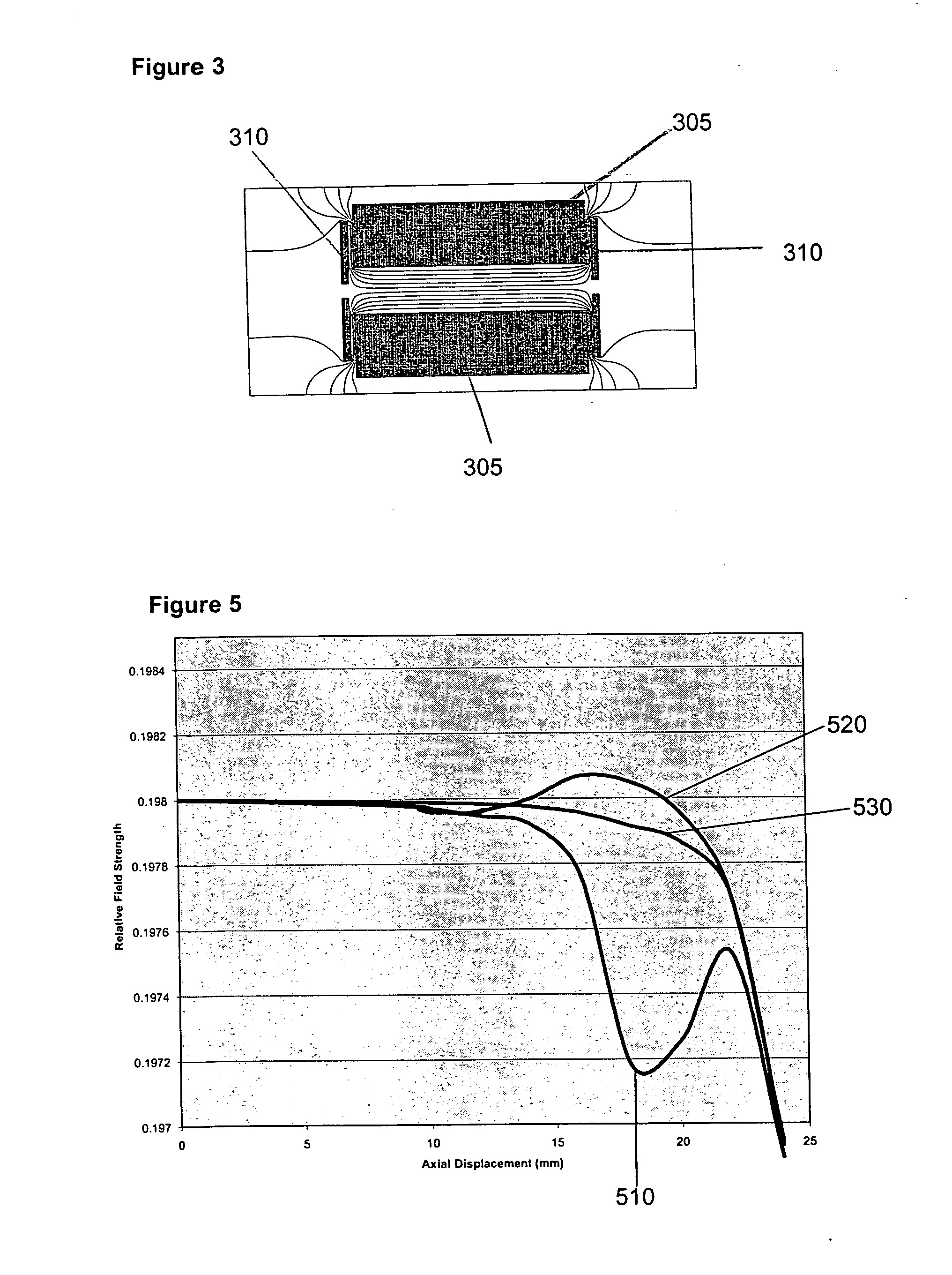
A system and method are disclosed for effectively compensating for non-linear field components created by a field distortion feature in a quadrupolar ion trap, compensation provided by a geometric surface shaping which reduces the non-linear field components and creates a minimal centerline radio-frequency potential in the ion trap. The ion trap includes a centerline that passes longitudinally through a trapping volume inside of the ion trap, a pair of Y electrodes with inner Y electrode surfaces that are approximately parallel to the centerline, and a pair of X electrodes with inner X electrode surfaces that are approximately parallel to the centerline. The X electrodes have one or more ejection slots through which trapped ions are ejected from said ion trap. The inner Y electrode surfaces each have a Y radius of curvature, and the inner X electrode surfaces each have an X radius of curvature. The X radius of curvature is selected to be smaller than the Y radius of curvature. A balanced centerline potential is provided at the centerline of the ion trap.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
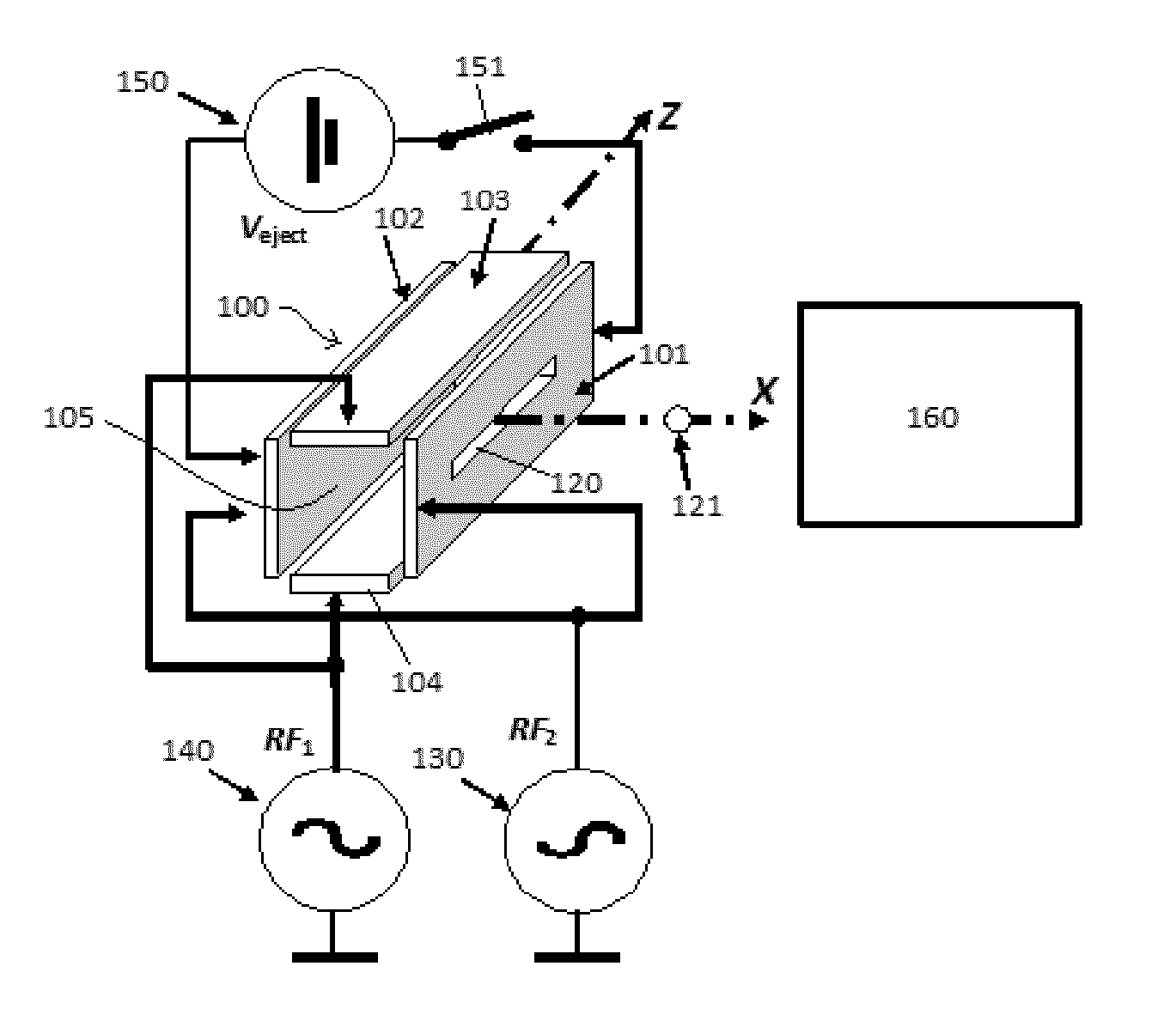
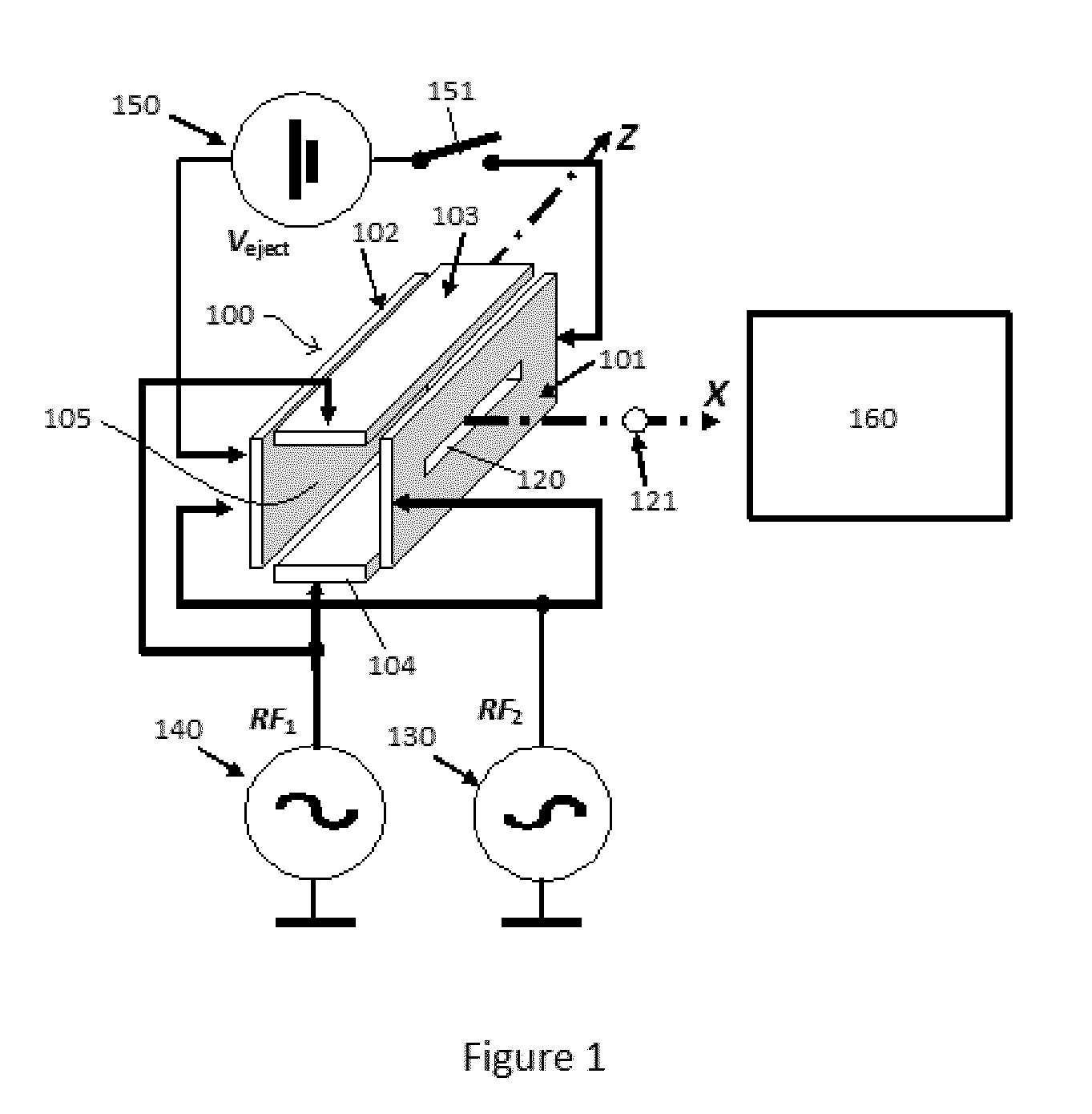
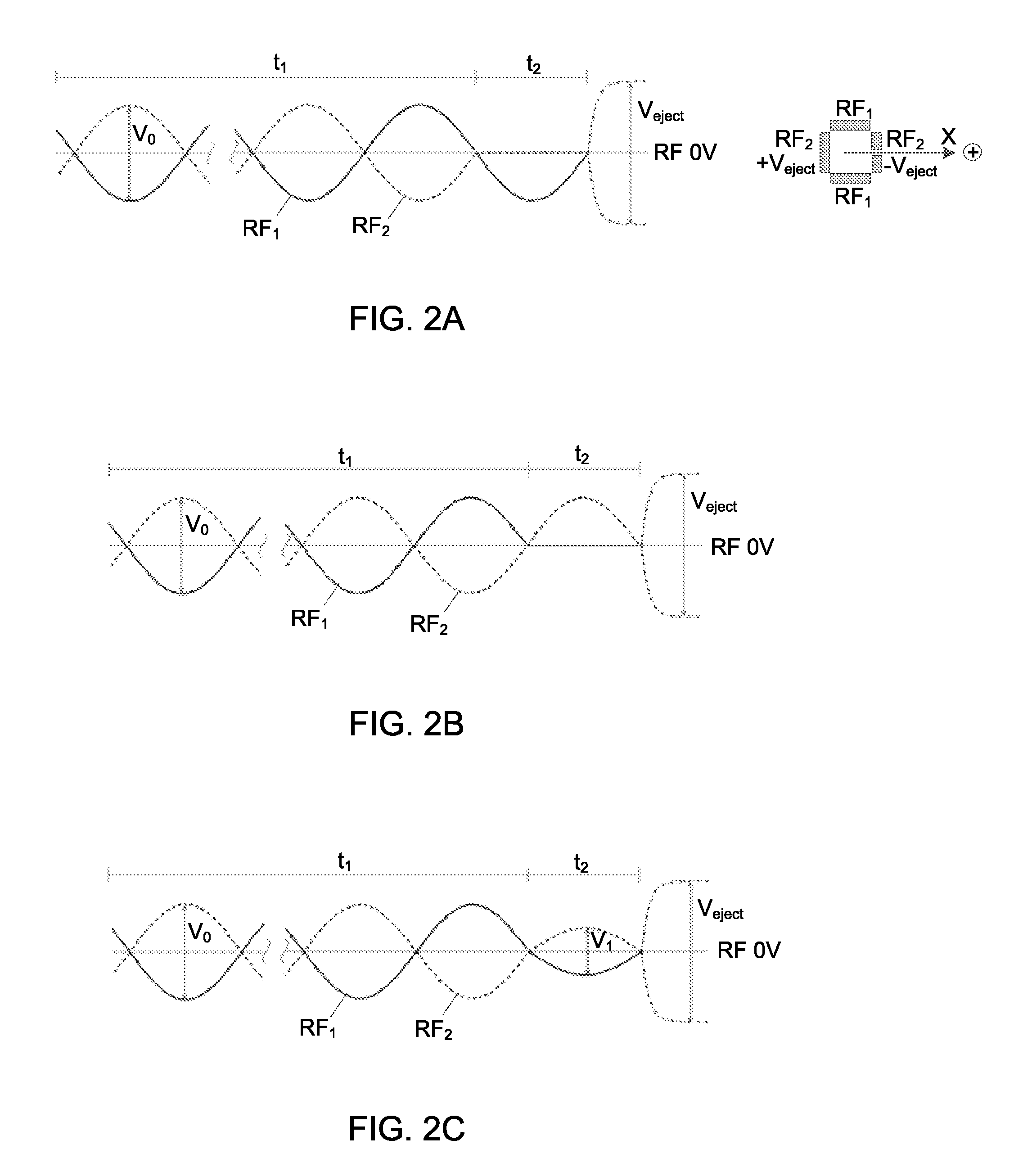
Ion ejection from a quadrupole ion trap
ActiveUS9312114B2Minimises velocity spreadStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersAtomic physicsIon
A method of ejecting ions to be analyzed from a quadrupole ion trap in which a trapping field is created by one or more RF voltages applied to one or more electrodes of the trap, the method comprising the steps of cooling the ions to be analyzed within the quadrupole ion trap until the ions are thermalized, reducing the amplitude of one or more RF voltages applied to the quadrupole ion trap and applying the reduced amplitude RF voltages for one half cycle after the one or more RF voltages have reached a zero crossing point, turning off the RF voltages applied to the quadrupole ion trap, and ejecting the ions to be analyzed from the quadrupole ion trap.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BREMEN
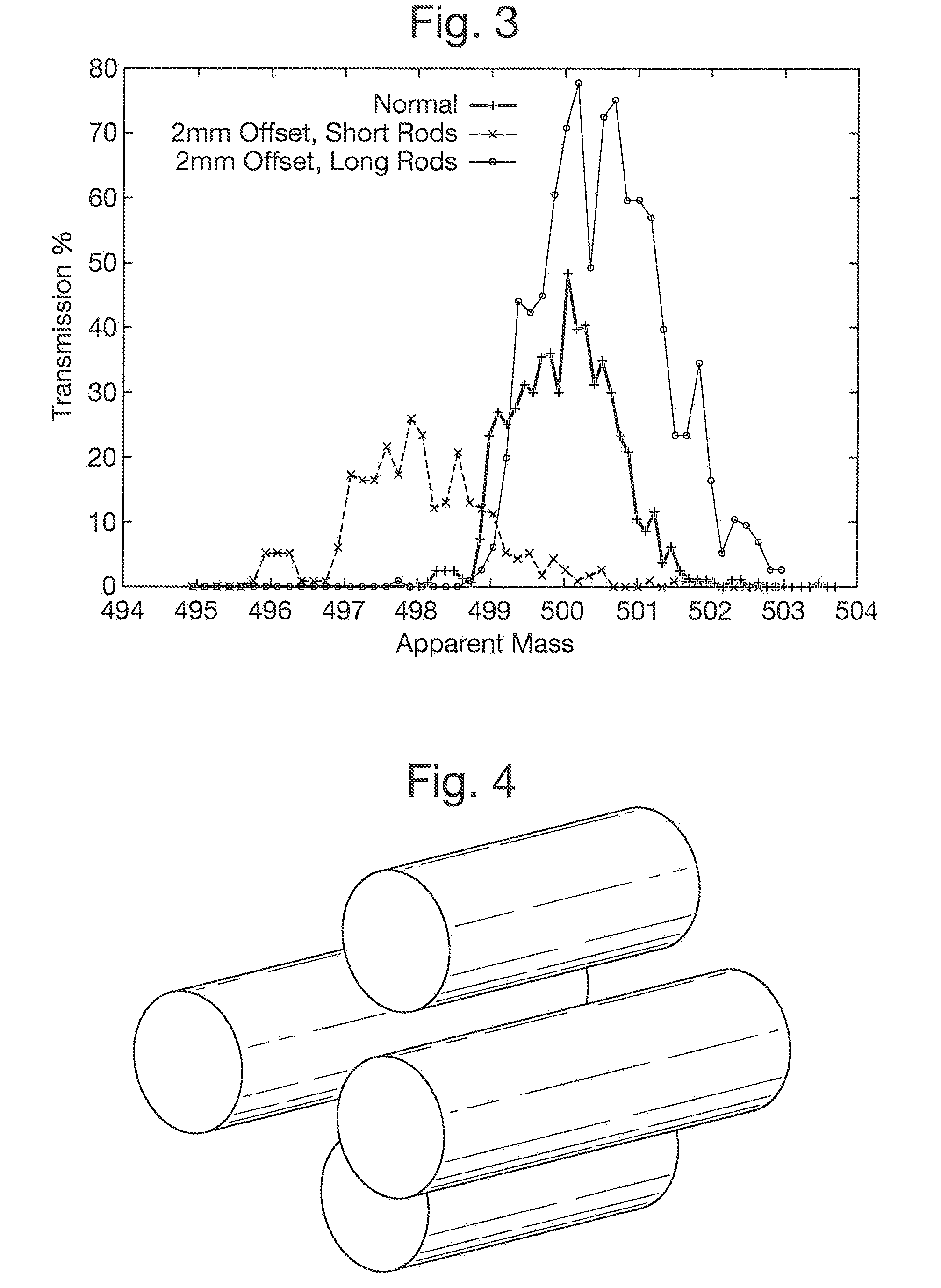
Two-dimensional quadrupole ion trap
ActiveUS20070029476A1Reduce complexityLess axial field inhomogeneityParticle separator tubesIsotope separationIon trap mass spectrometryTrapping
An aperture design for a linear ion trap is provided in which the aperture is optimized to minimize possible axial field inhomogeneities whilst preserving the structural integrity of the quadrupole rods. In general, the invention provides a linear ion trap for trapping and subsequently ejecting ions. The linear ion trap comprises a plurality of rods which define an interior trapping volume which has an axis extending longitudinally. One or more of the rods includes an aperture which extends both radially through the rod and longitudinally along the rod. The aperture being configured such that the ions can pass from the interior trapping volume through the aperture to a region outside the interior trapping volume. At least one recess is disposed adjacent the aperture, extending longitudinally along the rod and facing the interior trapping volume, the recess not extending radially through the rod.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
Efficient detection for ion traps
InactiveUS7456398B2Efficient detectionLow costSpectrometer detectorsPositive/negative analyte ion analysis/introduction/generationIon trap mass spectrometryDynode
An apparatus and method are disclosed for efficient detection of ions ejected from a quadrupolar ion trap, in which the ions are ejected as first and second groups of ions having different directions. The first and second groups of ions are received by a conversion dynode structure, which responsively emits secondary particles that are directed to a shared detector, such as an electron multiplier. The conversion dynode structure may be implemented as a common dynode or as two dynodes (or sets of dynodes), with each dynode positioned to receive one of the groups of ions.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
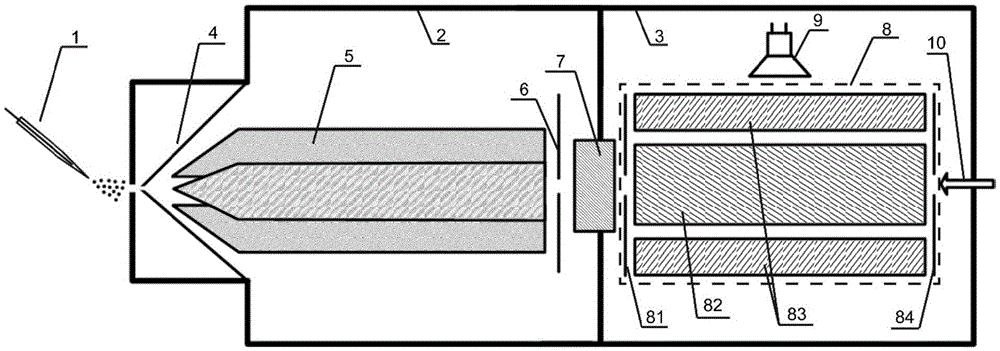
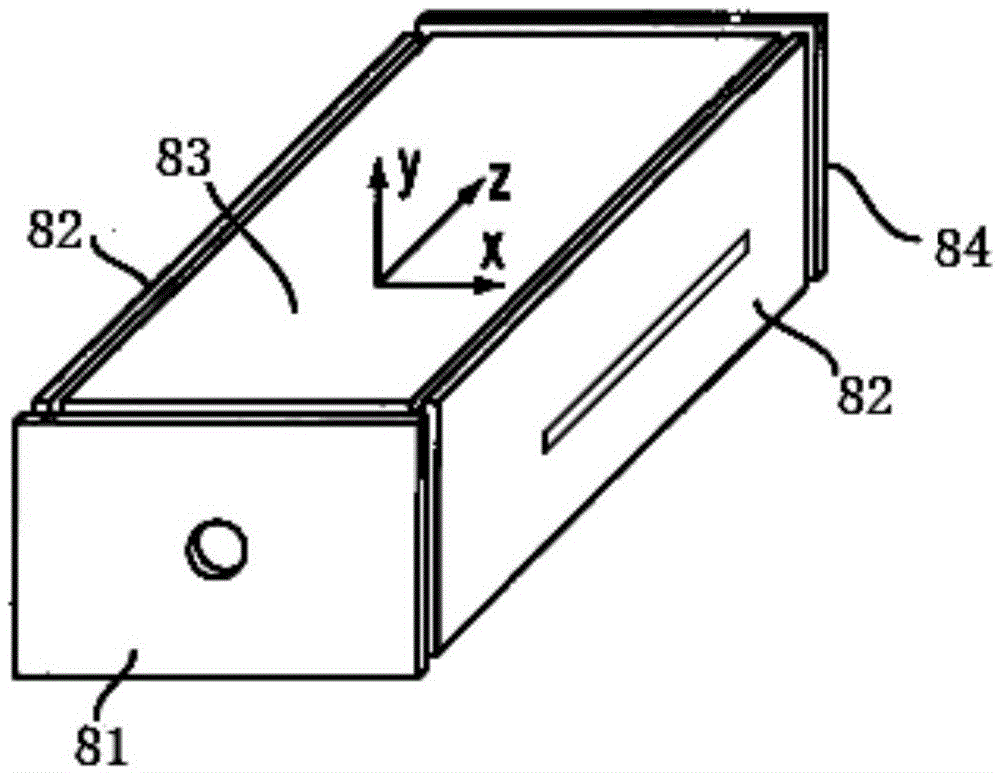
Small two-stage vacuum rectangular ion trap mass spectrometer and detection method thereof
ActiveCN105655224AIncrease profitReduce the number of ionsStability-of-path spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionSpot analysisSpectrometer
The invention provides a small two-stage vacuum rectangular ion trap mass spectrometer and a detection method thereof. The mass spectrometer comprises two stages of vacuum cavities. The first-stage vacuum cavity is internally provided with an atmospheric pressure interface sampling cone, a quadrupole rod and an ion gate electrode which form a quadrupole ion trap. The second-stage vacuum cavity is internally provided with a rectangular ion trap, an ion detector and a capillary tube. An ion optical element is arranged between the two stages of vacuum cavities. The detection method includes the steps that the quadrupole ion trap in the first-stage cavity is controlled to be in an ion trap storage mode and an ion trap synchronous analysis mode so that sensitivity of mass spectra can be improved, the quantitation limit is reduced, analysis flux is increased, influences of the space charge effect are reduced, and the resolution is increased. The quadrupole rod does not need high resolution and is low in processing precision requirement. Besides, the rectangular trap is easy to process and assemble, so that miniaturization is facilitated. Meanwhile, the detection method can guarantee good analysis performance and has wide application prospects in the field of on-site analysis and detection.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and device for the capture of ions in quadrupole ion traps
ActiveUS6989534B2Increase productionWeaken energyStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAtomic physicsVoltage
The invention relates to methods and devices for the effective capturing of externally generated ions in an RF operated quadrupole ion trap. The invention involves applying a voltage consisting of positive and negative pulses, instead of a sinusoidal RF voltage, during the capturing process, with capturing intervals between each pulse in which the voltage is low.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
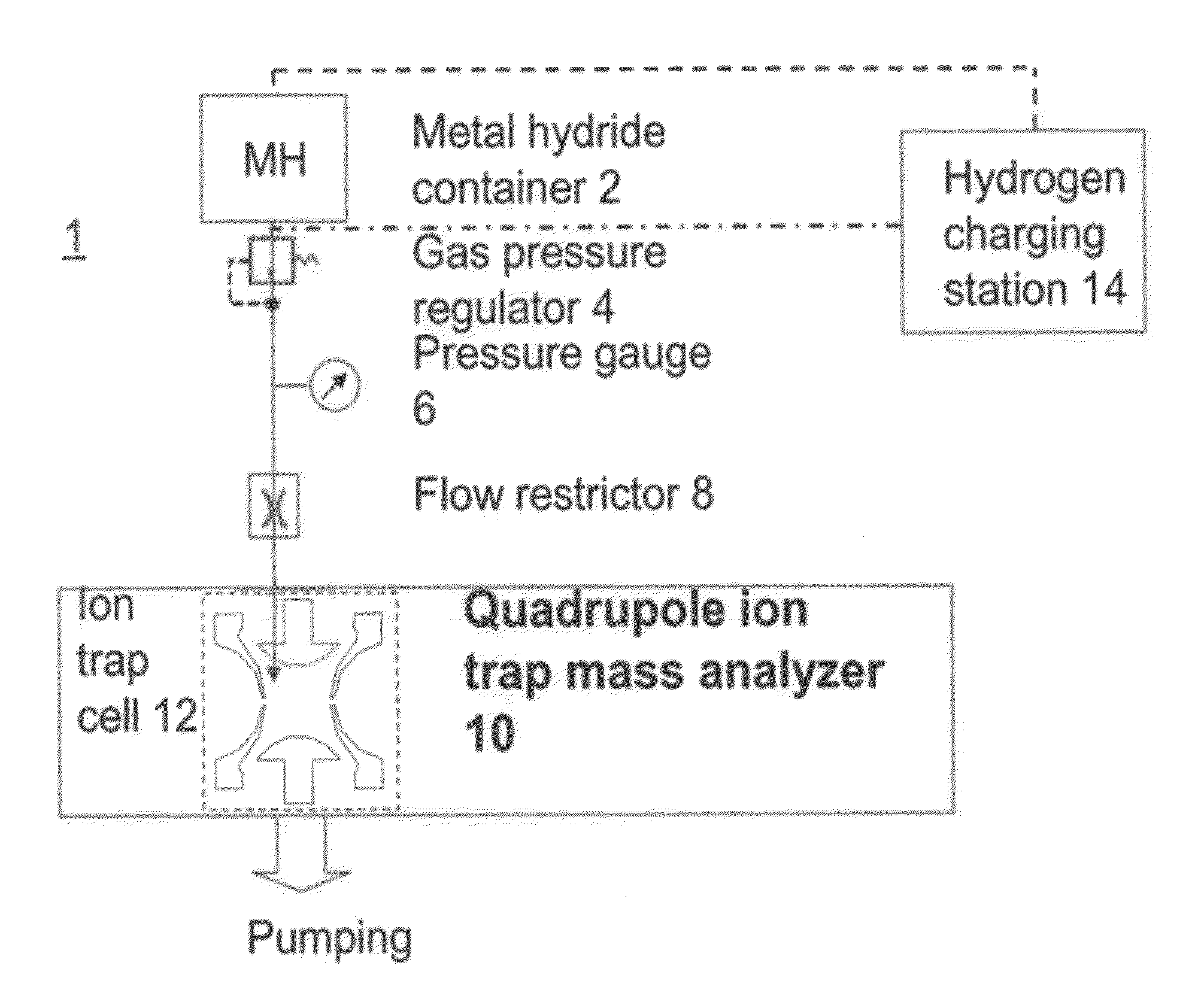
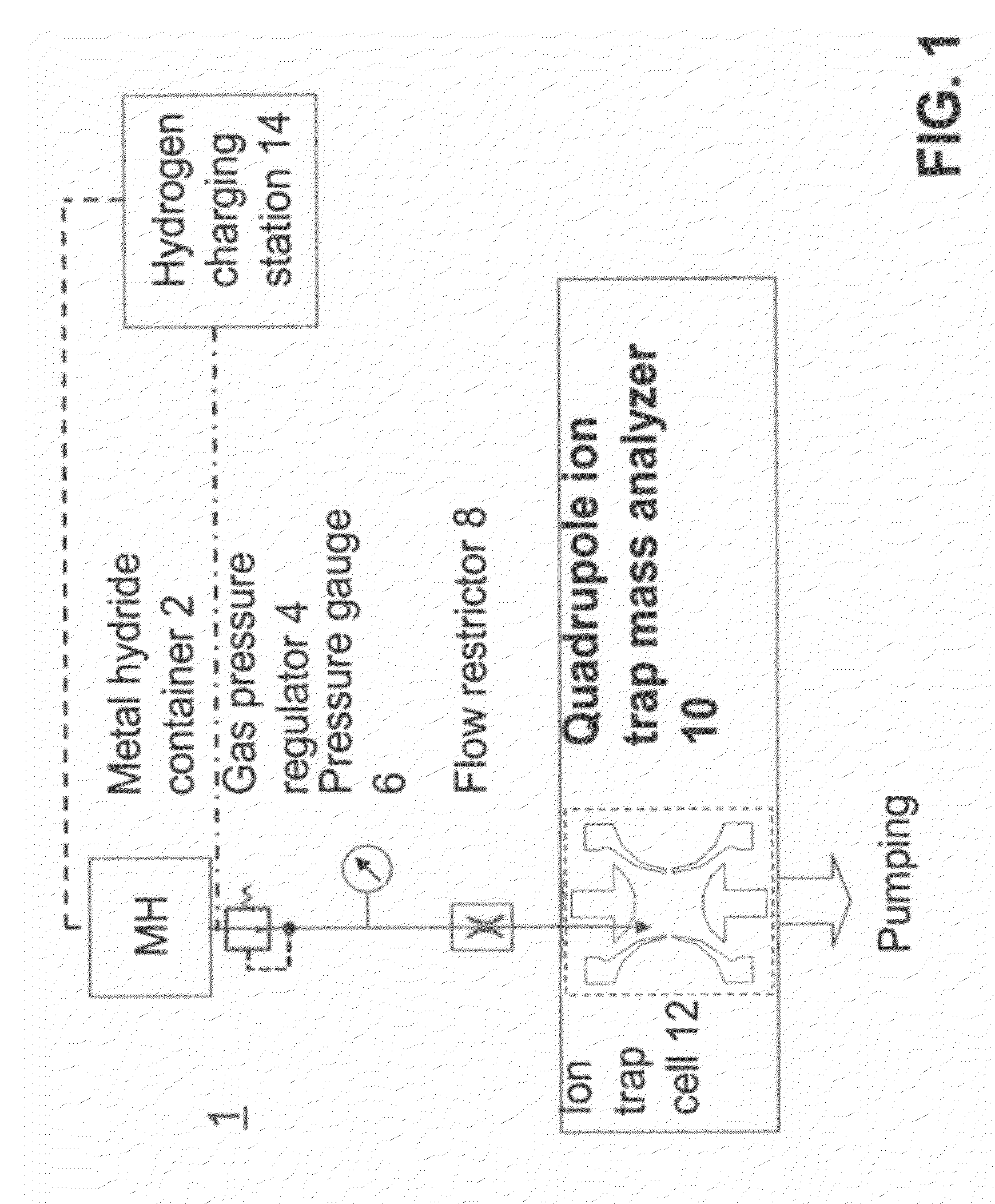
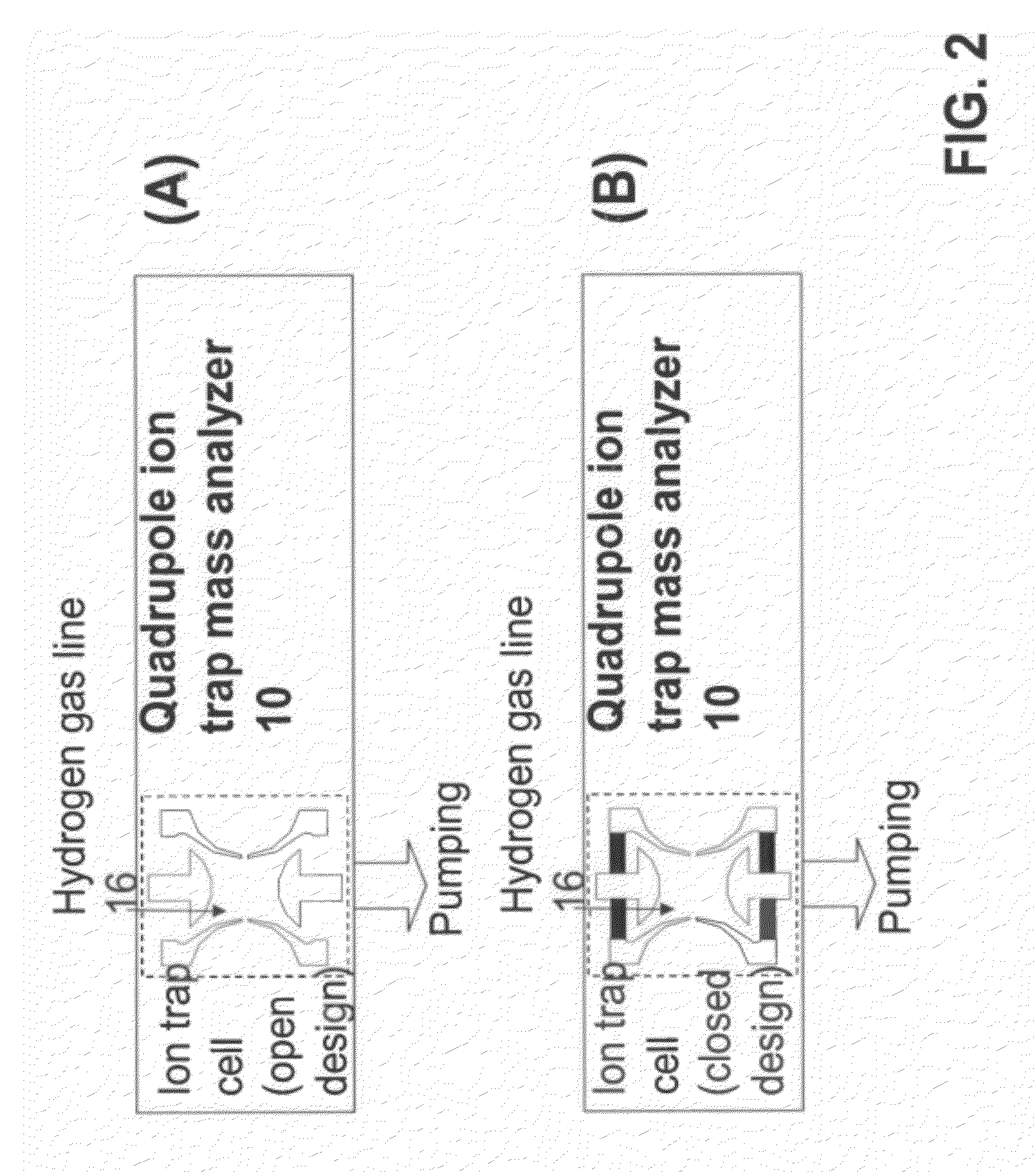
Portable ion trap mass spectrometer with metal hydride container as source of hydrogen buffer gas
ActiveUS20120326026A1Dynamic spectrometersMiniaturised spectrometersIon trap mass spectrometryTrapping
A mass spectrometry (MS) method which includes generating in a vicinity of the quadrupole ion trap hydrogen molecules, directing at least part of the hydrogen molecules into the quadrupole ion trap cell, applying AC and DC voltages to quadrupole ion trap cell electrodes to create a combined AC / DC trapping field, placing sample ions inside the quadrupole ion trap cell, cooling at least part of said ions using said hydrogen molecules as a buffer gas, changing the combined AC / DC trapping field to eject the ions from the quadrupole ion trap cell, and detecting the ejected ions
Owner:SCI & ENG SERVICES
Performance Improvements for RF-Only Quadrupole Mass Filters and Linear Quadrupole Ion Traps With Axial Ejection
InactiveUS20140284469A1Improve performanceStability-of-path spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsParticle physicsAtomic physics
A RF only quadrupole rod set mass filter or mass analyser and a linear quadrupole ion trap with axial ejection are disclosed comprising a first pair of rod electrodes, a second pair of rod electrodes and an energy filter. The first pair of rod electrodes is longer than the second pair of rod electrodes. Ions having desired mass to charge ratios experience fringing fields at an exit region which results in the ions possessing sufficient axial kinetic energy to be transmitted by the energy filter. Other ions possess insufficient axial kinetic energy to be transmitted by the energy filter and are attenuated.
Owner:MICROMASS UK LTD
System and method for implementing balanced RF fields in an ion trap device
ActiveUS20080067364A1Minimize non-linear field componentLinear characteristicStability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationIon trap mass spectrometryRadio frequency
A system and method are disclosed for effectively compensating for an unbalanced or non-zero centerline radio-frequency potential in a quadrupolar ion trap, the unbalanced centerline potential created by a compensation feature that minimizes non-linear field components created by one or more ejection slots in the ion trap. The ion trap includes a centerline that passes longitudinally through a trapping volume inside of the ion trap, a pair of Y electrodes with inner Y electrode surfaces that are approximately parallel to the centerline, and a pair of X electrodes with inner X electrode surfaces that are approximately parallel to the centerline. The X electrodes have ejection slots through which trapped ions are ejected from the ion trap. A Y signal with a Y signal amplitude is coupled to both of the Y electrodes. An X signal with an X signal amplitude is coupled to both of the X electrodes. The X signal amplitude is selected to be greater than the Y signal amplitude to thereby create a balanced centerline potential at the centerline of the ion trap device.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
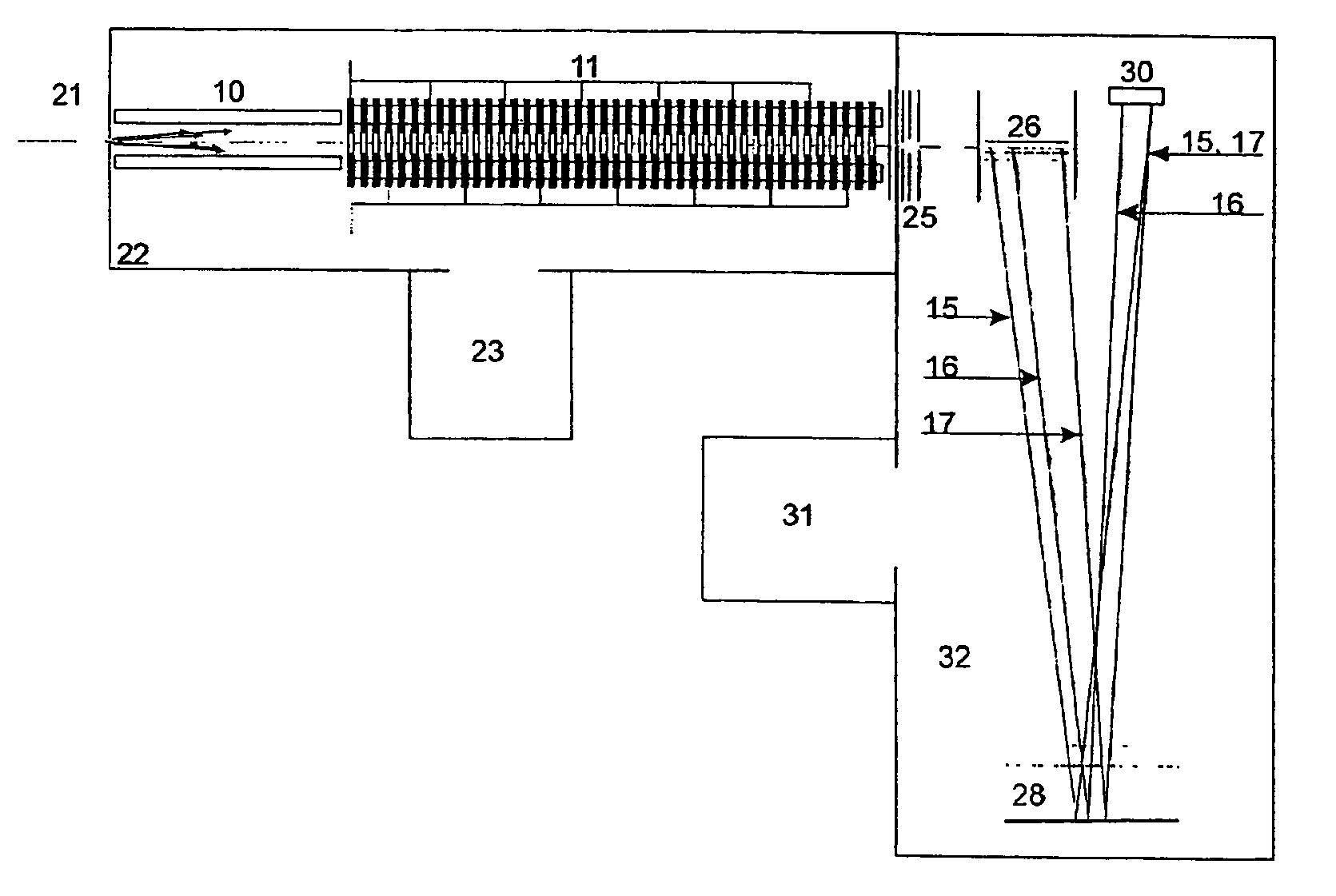
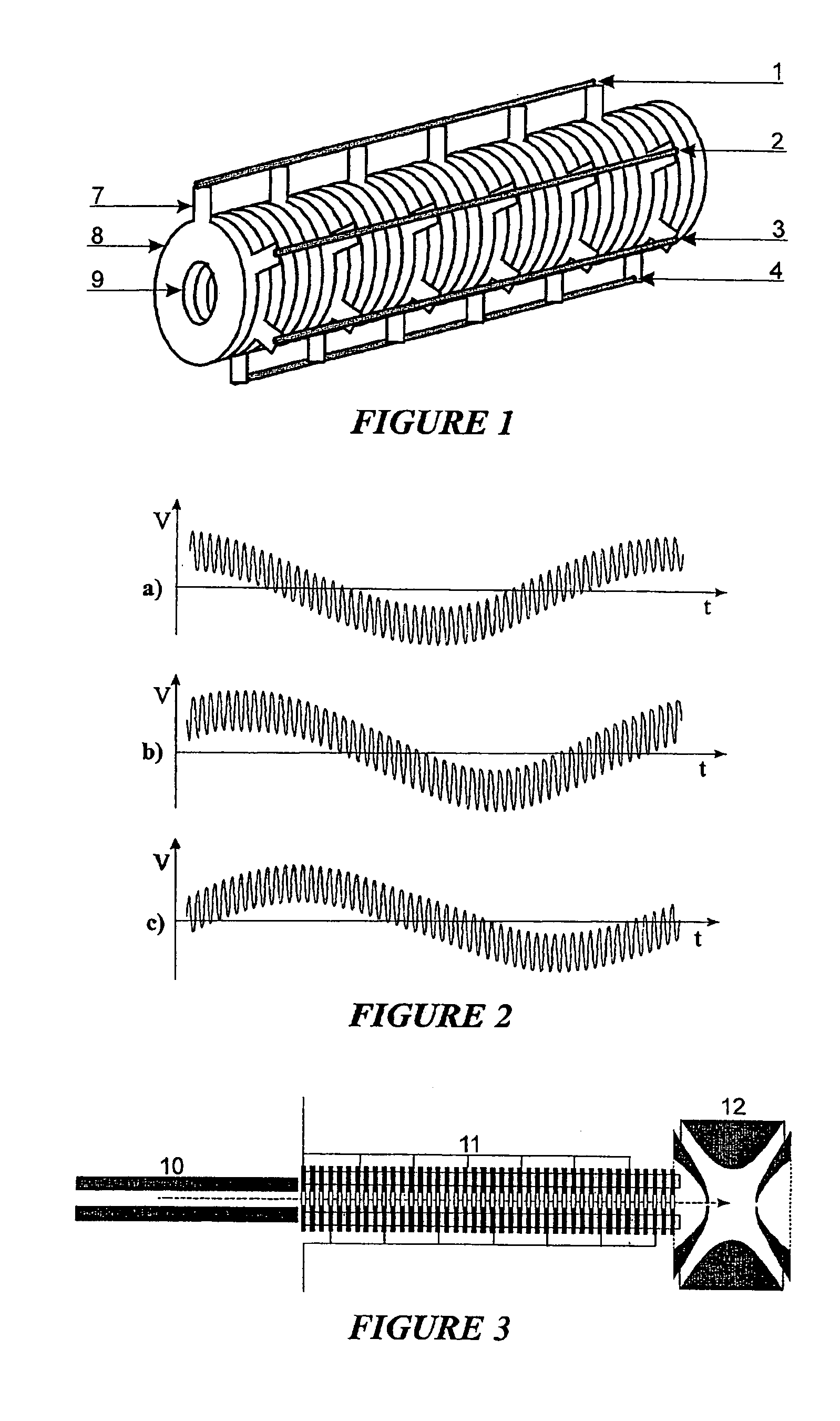
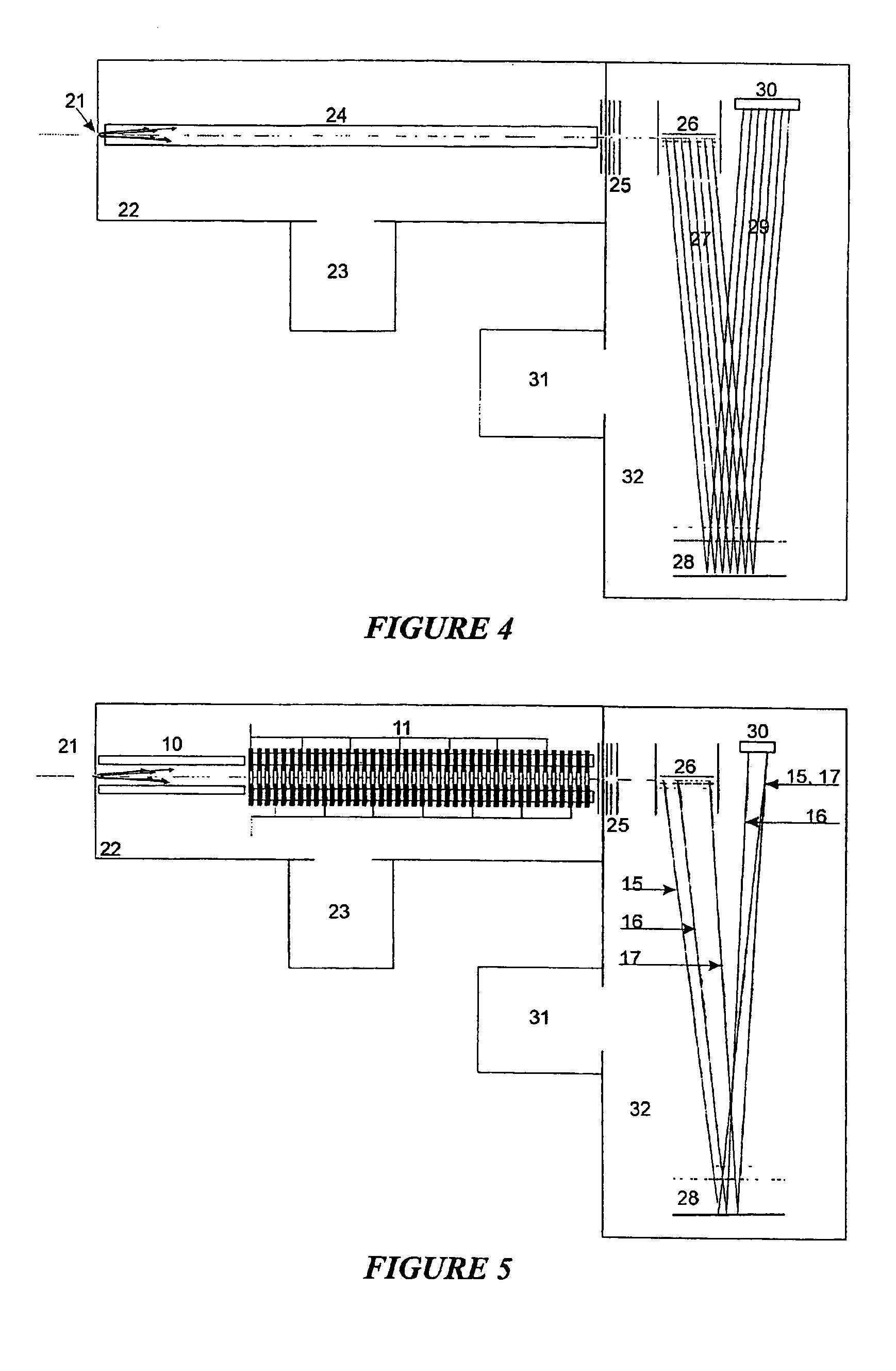
Travelling field for packaging ion beams
InactiveUS7151255B2Stability-of-path spectrometersMechanical apparatusIon trap mass spectrometryIon beam
The invention relates to a device and a method for producing, from any previously configured ion beams, precisely localized small packages of ions which all fly at the same velocity. The invention consists of damping the ions in a damping-gas filled series of apertured diaphragms (which are firstly subjected alternately to the two phases of an RF voltage and secondly to a multiphase low-frequency travelling field voltage) into the axis of the apertured diaphragm arrangement and packaging the ions in bundles which are propelled axially at the same velocity for ions of different specific masses. These ion packages, which are restricted both in an axial and a radial direction, can be used to advantage for injection into different types of mass spectrometer, both storage ion-trap mass spectrometers, such as cyclotron resonance mass spectrometers or quadrupole ion traps and, especially, for time-of-flight mass spectrometers with orthogonal injection. The arrangement of a damping-gas filled series of apertured diaphragms can also be used for ion fragmentation.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com